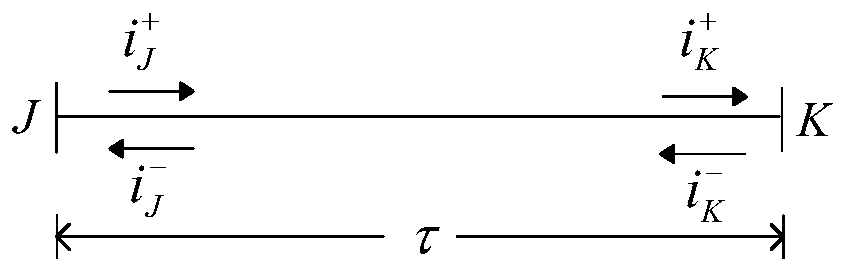Fault location method, device, equipment and medium based on traveling wave difference current
A technology of fault location and differential current, which can be used in measurement devices, fault locations, and fault detection according to conductor types, etc., and can solve the problems of high sampling rate identification and calibration of the traveling wave method.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
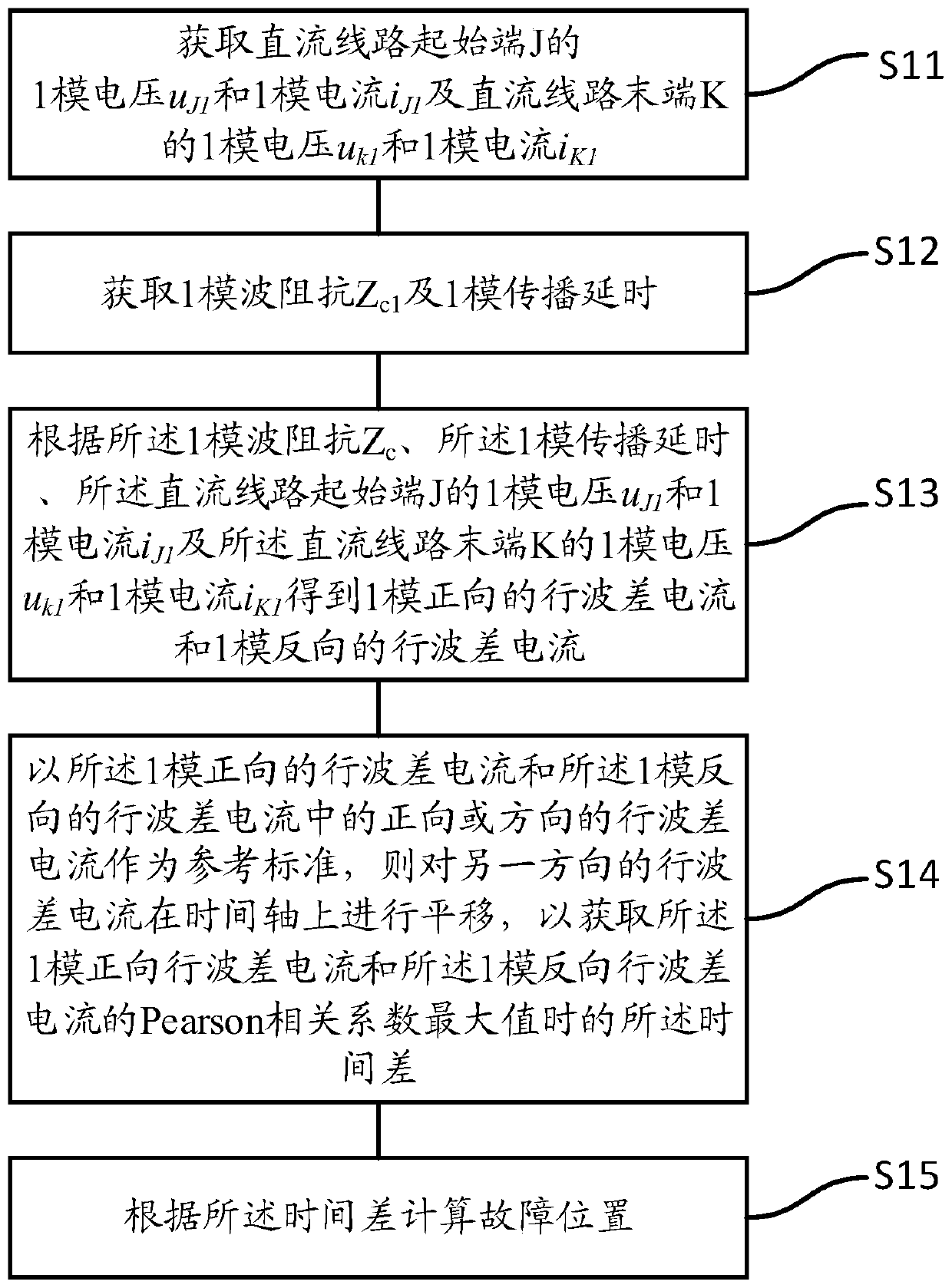
[0065] see figure 1 , a schematic flowchart of a fault location method based on traveling wave difference current provided in the first embodiment of the present invention;
[0066] S11. Acquiring the 1-mode voltage u of the starting end J of the DC line J1 and 1-mode current i J1 and the 1-mode voltage u at the terminal K of the DC line k1 and 1-mode current i K1 ;
[0067] Preferably, the acquisition of the 1-mode voltage u of the starting end J of the DC line J1 and 1-mode current i J1 and the 1-mode voltage u at the terminal K of the DC line k1 and 1-mode current i K1 include:
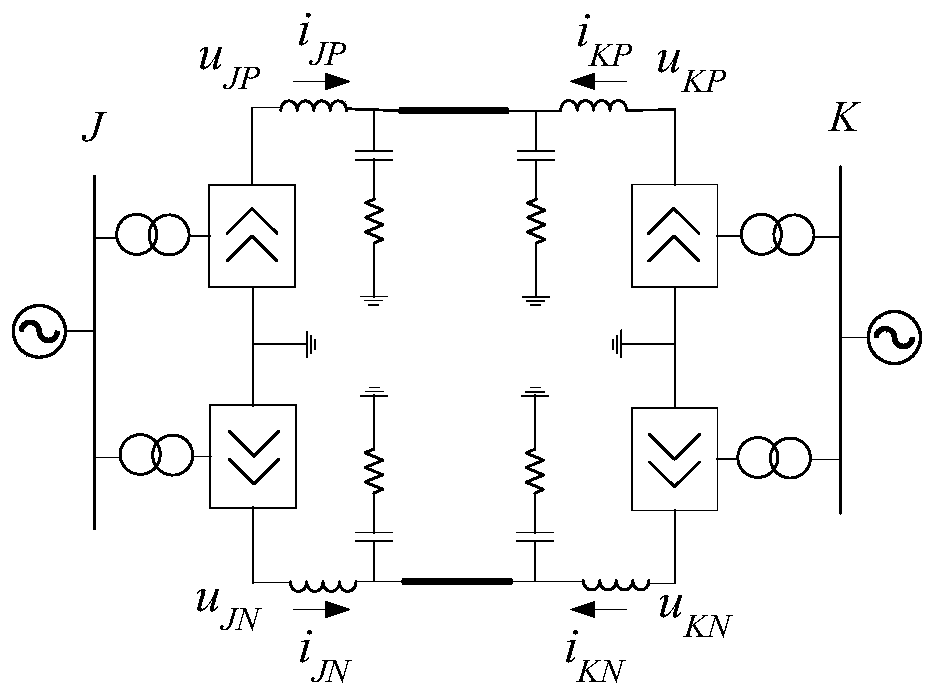
[0068] Obtain the positive voltage u of the starting terminal J of the DC line JP , Negative voltage u JN ;
[0069] Obtain the positive current i of the starting end J of the DC line JP , Negative current i JN ;
[0070] Obtain the positive voltage u of the starting end K of the DC line KP , Negative voltage u KN ;
[0071] Obtain the positive current i of the starting end K of th...
Embodiment 2
[0135] Embodiment two, on the basis of embodiment one, refer to Figure 5 It is a schematic flowchart of another fault location method based on traveling wave difference current provided by the second embodiment of the present invention; preferably, the traveling wave difference current with the 1-mode forward and the reverse traveling wave difference current of the 1-mode The positive or reverse traveling wave difference current in the middle is used as a reference standard, then the traveling wave difference current in the other direction is shifted on the time axis to obtain the 1-mode forward traveling wave difference current and the 1-mode reverse traveling wave difference current The time difference Δt at the time of the maximum value of the Pearson correlation coefficient includes:
[0136] S21. Select the time window after the fault as [t st ,t st +t w ] of the 1-mode reverse traveling wave difference current As a reference standard; where, the t w ≥2·τ 1 ...
Embodiment 3
[0147] Embodiment three, on the basis of embodiment one, refer to Image 6 It is a schematic flowchart of another fault location method based on traveling wave difference current provided by the third embodiment of the present invention;
[0148] Preferably, the traveling wave difference current in the 1-mode forward direction and the reverse traveling wave difference current of the 1-mode The positive or reverse traveling wave difference current in the middle is used as a reference standard, then the traveling wave difference current in the other direction is shifted on the time axis to obtain the 1-mode forward traveling wave difference current and the 1-mode reverse traveling wave difference current The time difference Δt at the time of the maximum value of the Pearson correlation coefficient includes:
[0149] S31, select the time window after the fault as [t st ,t st +t w ] of the 1-mode forward traveling wave difference current As a reference standard; where,...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com