Current differential protection method based on fault component current amplitudes and phase differences
A technology of fault component and current amplitude, applied in the direction of automatic disconnection emergency protection device, emergency protection circuit device, electrical components, etc., can solve the problems of performance improvement, achieve small differential current, improve sensitivity, brake The effect of small current
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0027] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and embodiments.
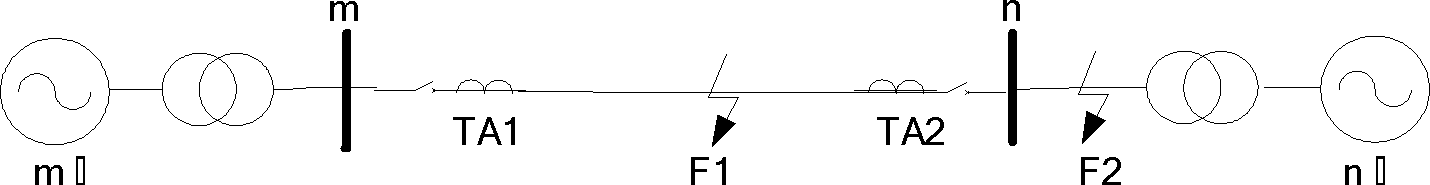
[0028] 1. Performance Analysis of Current Differential Protection Criterion for Internal Faults
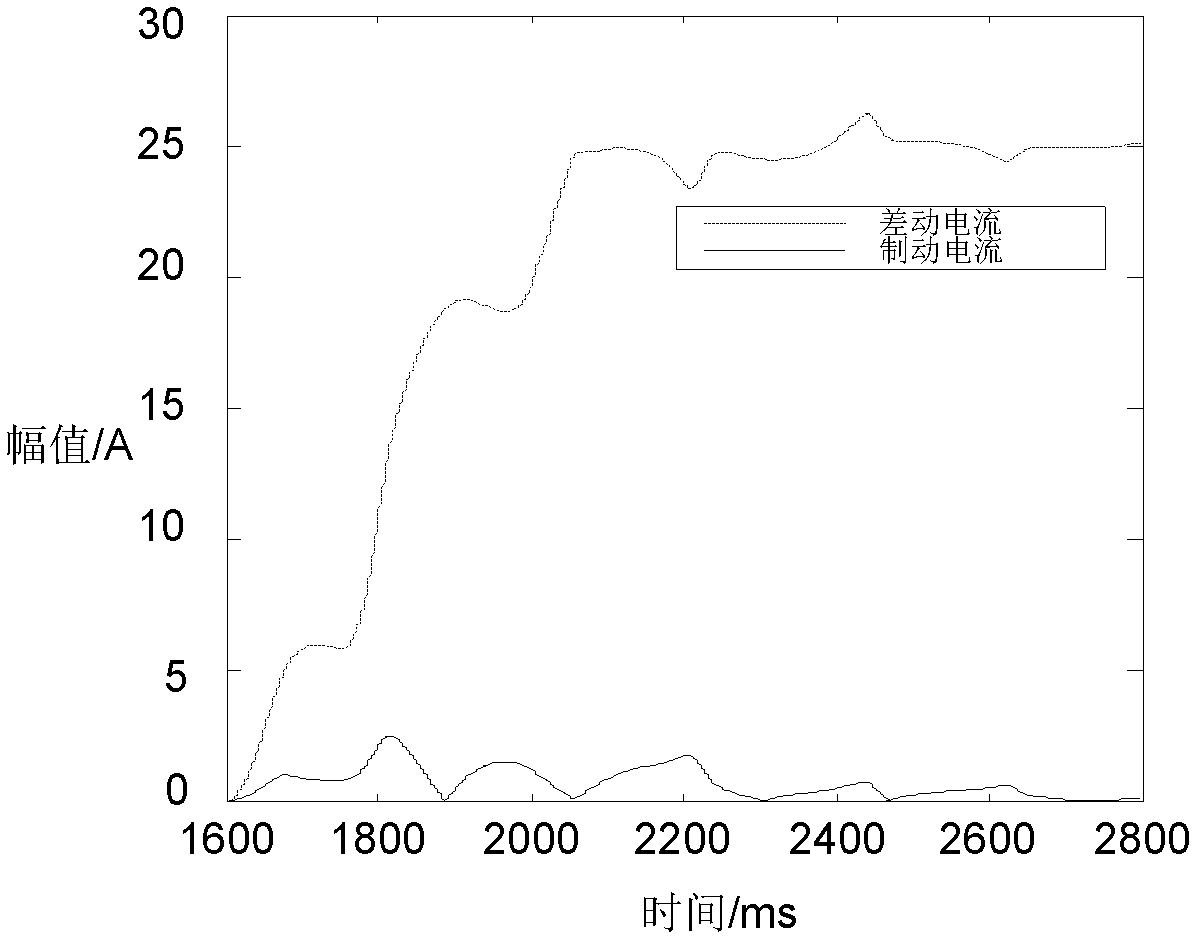
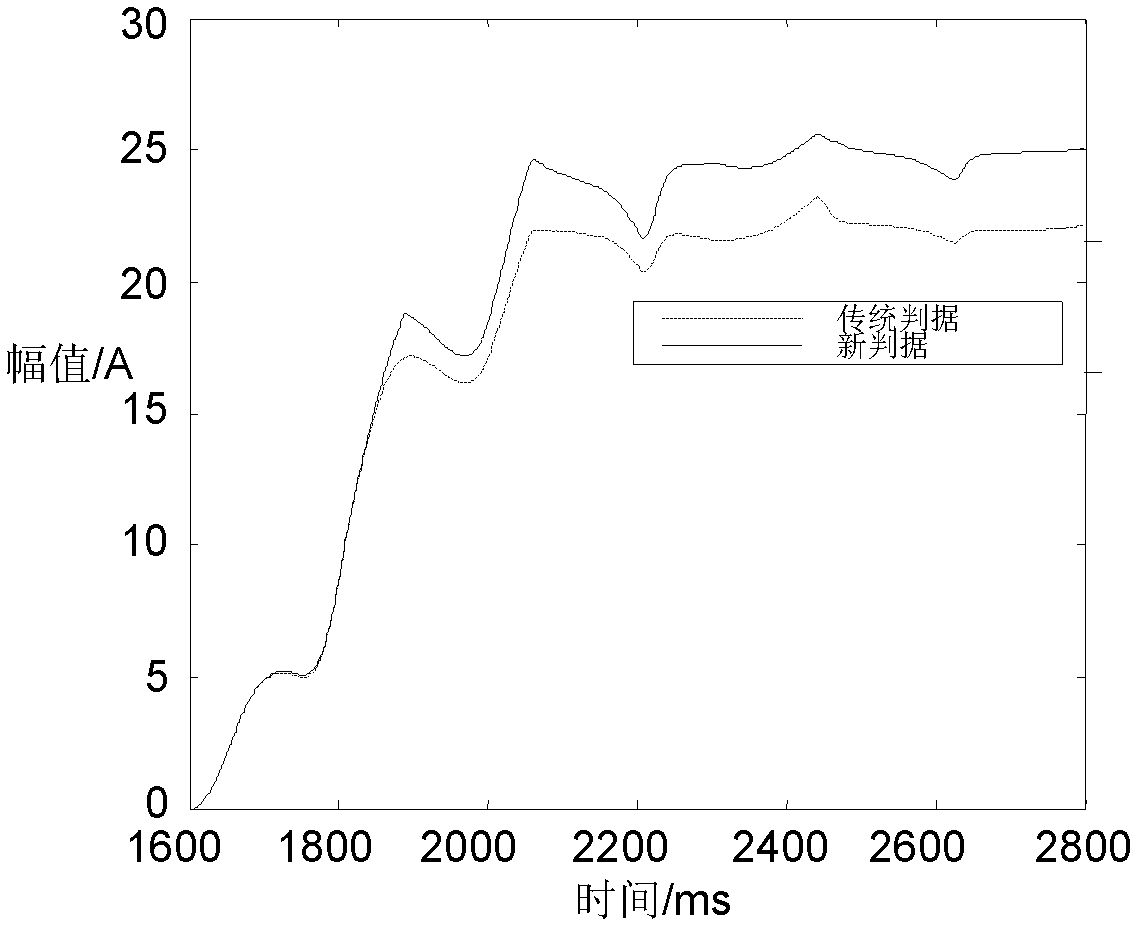
[0029] exist figure 1 In the shown double-terminal power supply power system model, the A-phase metallic grounding fault is set at point F1 in the protection zone, and the differential and braking current curves obtained are obtained according to the differential current and braking current calculation method designed in the present invention Such as figure 2 , where the solid line represents the braking current, and the dashed line represents the differential current. In the event of an internal fault, the differential current is much greater than the braking current. In order to illustrate the superiority of the criterion of the present invention, it is compared with the current commonly used differential criterion (traditional criterion) performance....
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com