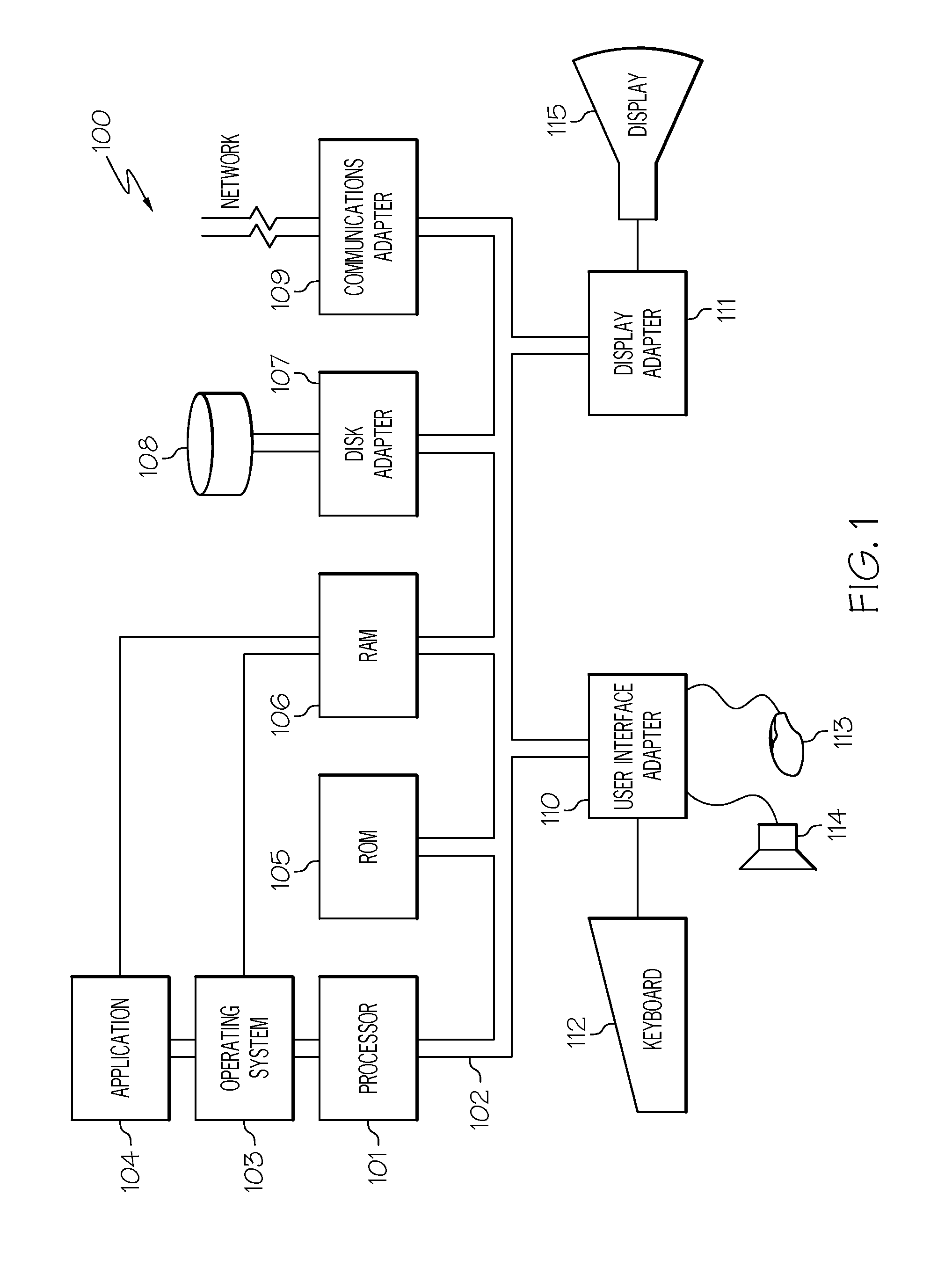
Patents
Literature
67 results about "Significand" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
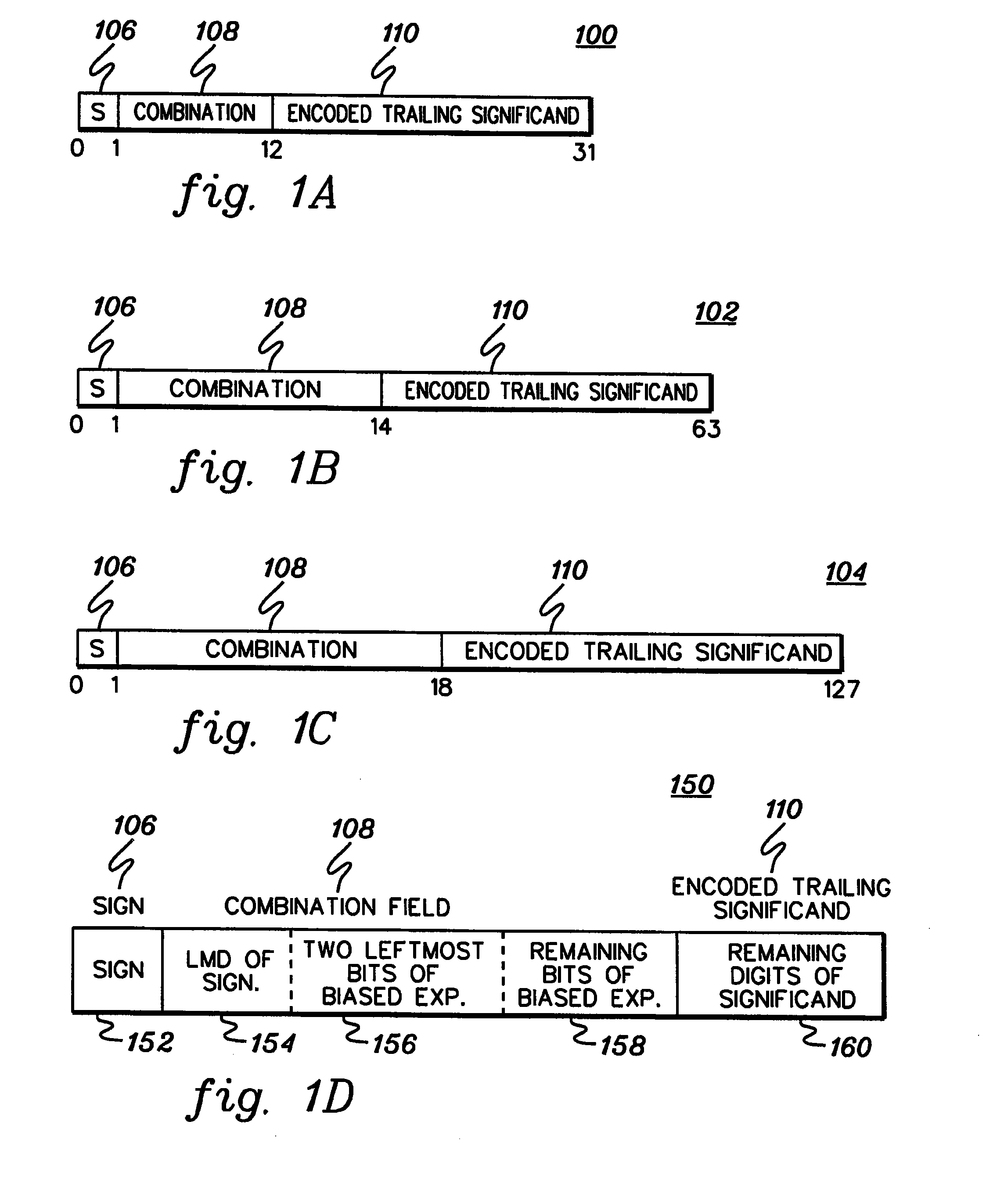
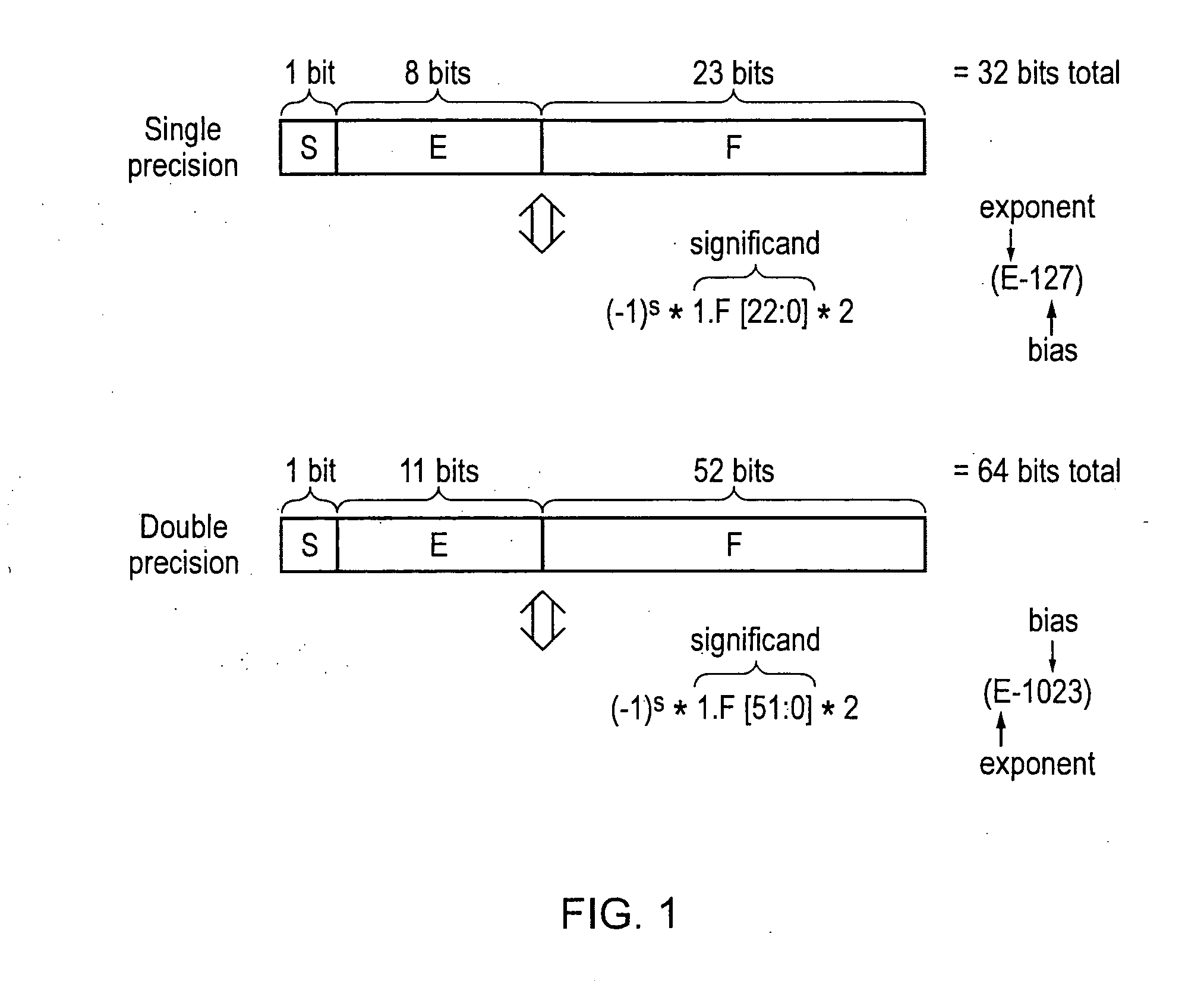
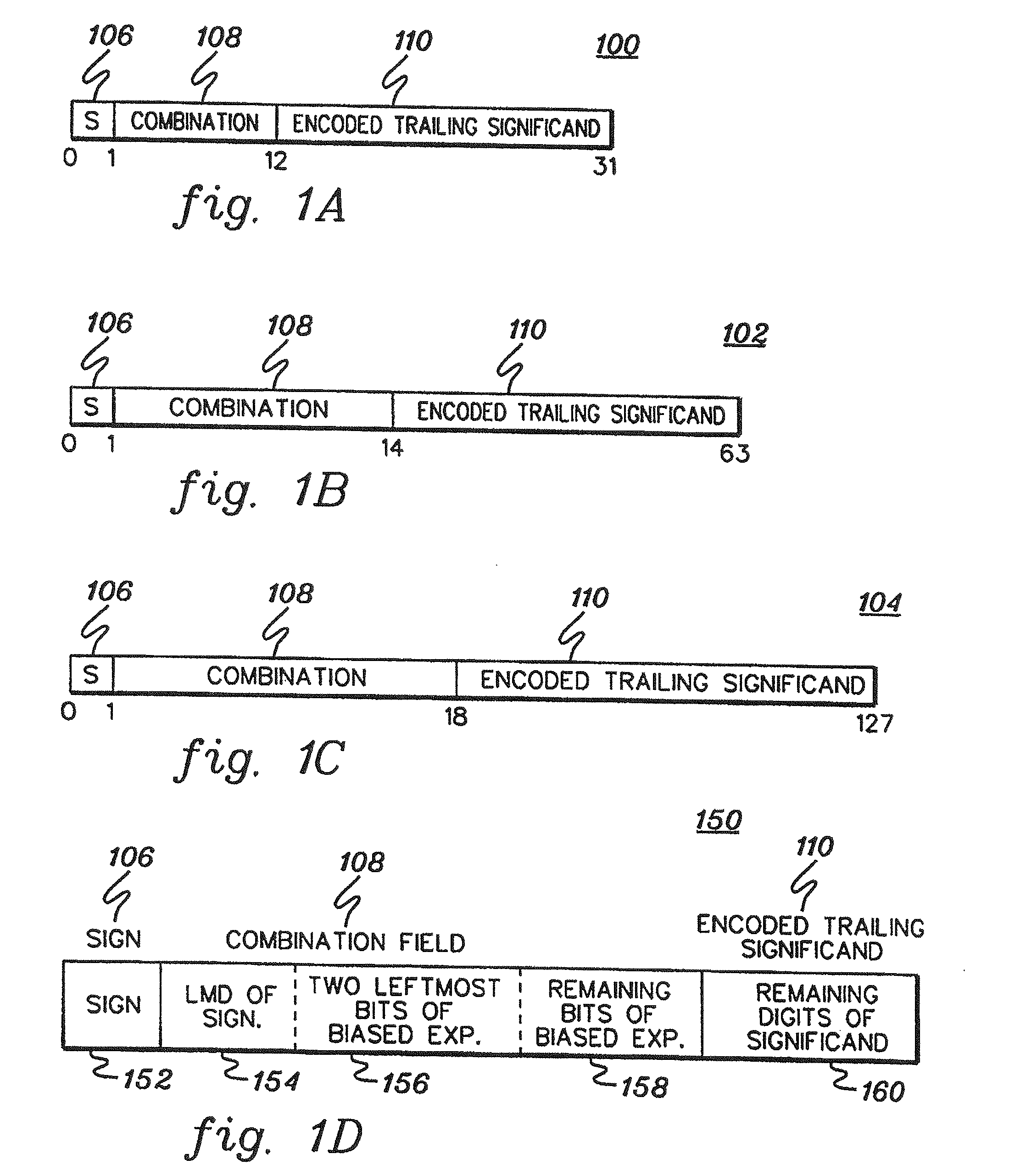
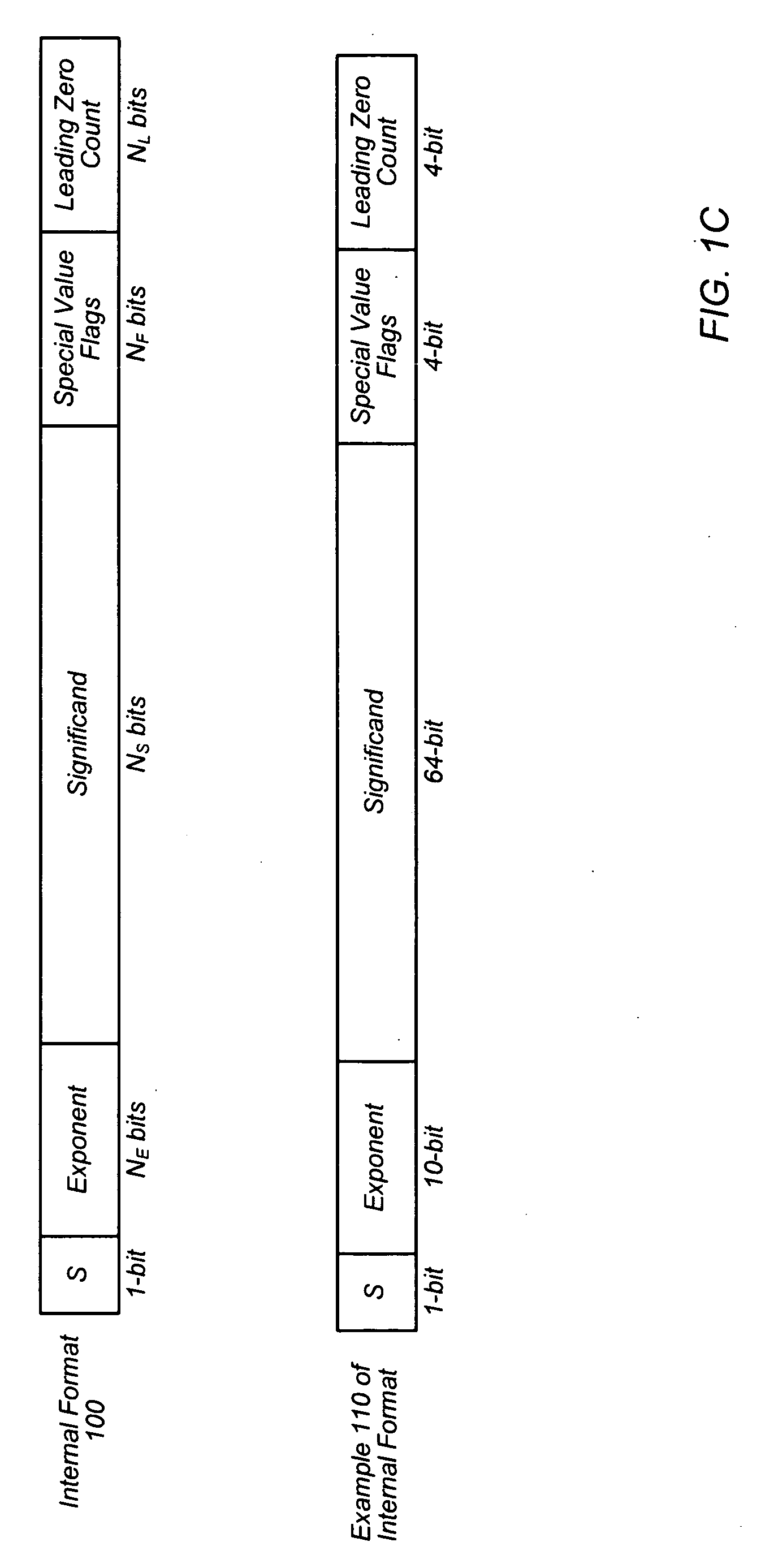
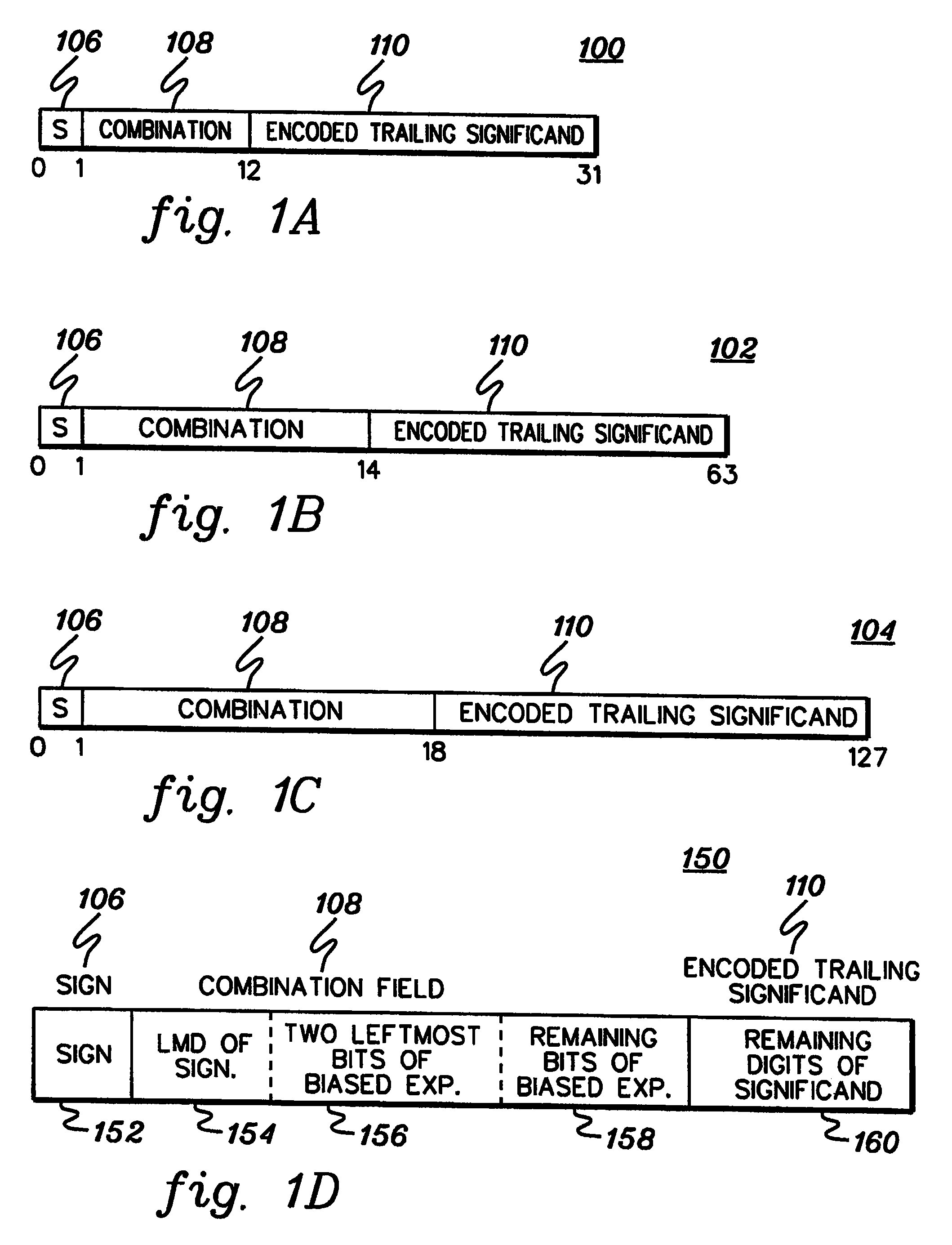
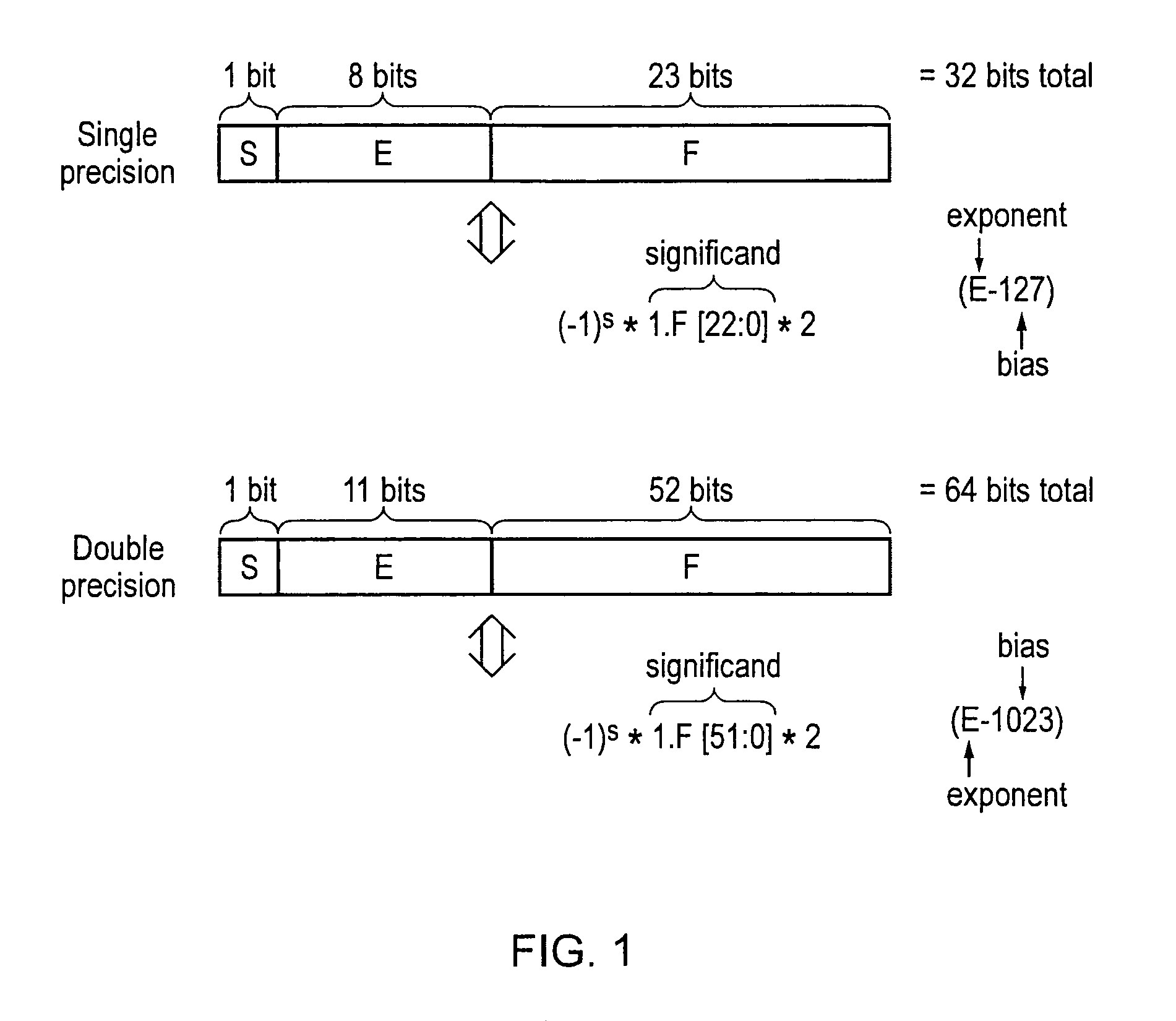
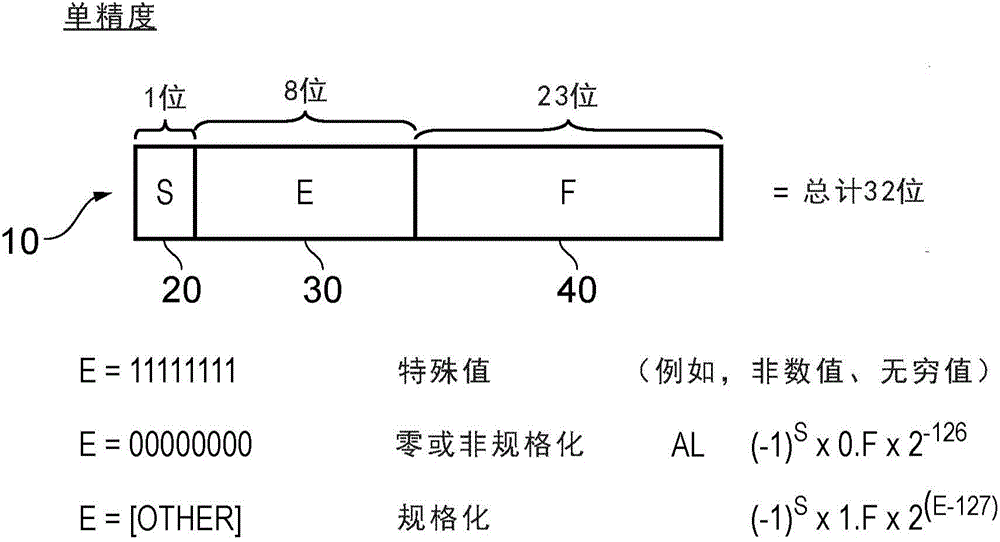
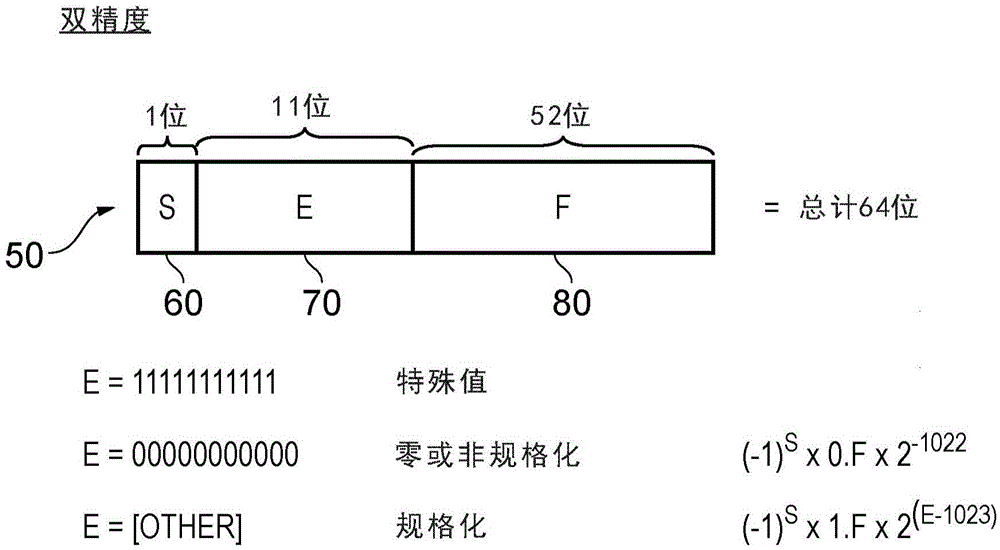
The significand (also mantissa or coefficient, sometimes also argument or fraction) is part of a number in scientific notation or a floating-point number, consisting of its significant digits. Depending on the interpretation of the exponent, the significand may represent an integer or a fraction. The word mantissa seems to have been introduced by Arthur Burks in 1946 writing for the Institute for Advanced Study at Princeton, although this use of the word is discouraged by the IEEE floating-point standard committee as well as some professionals such as the creator of the standard, William Kahan, and also the prominent computer programmer and author of The Art of Computer Programming, Donald E. Knuth.
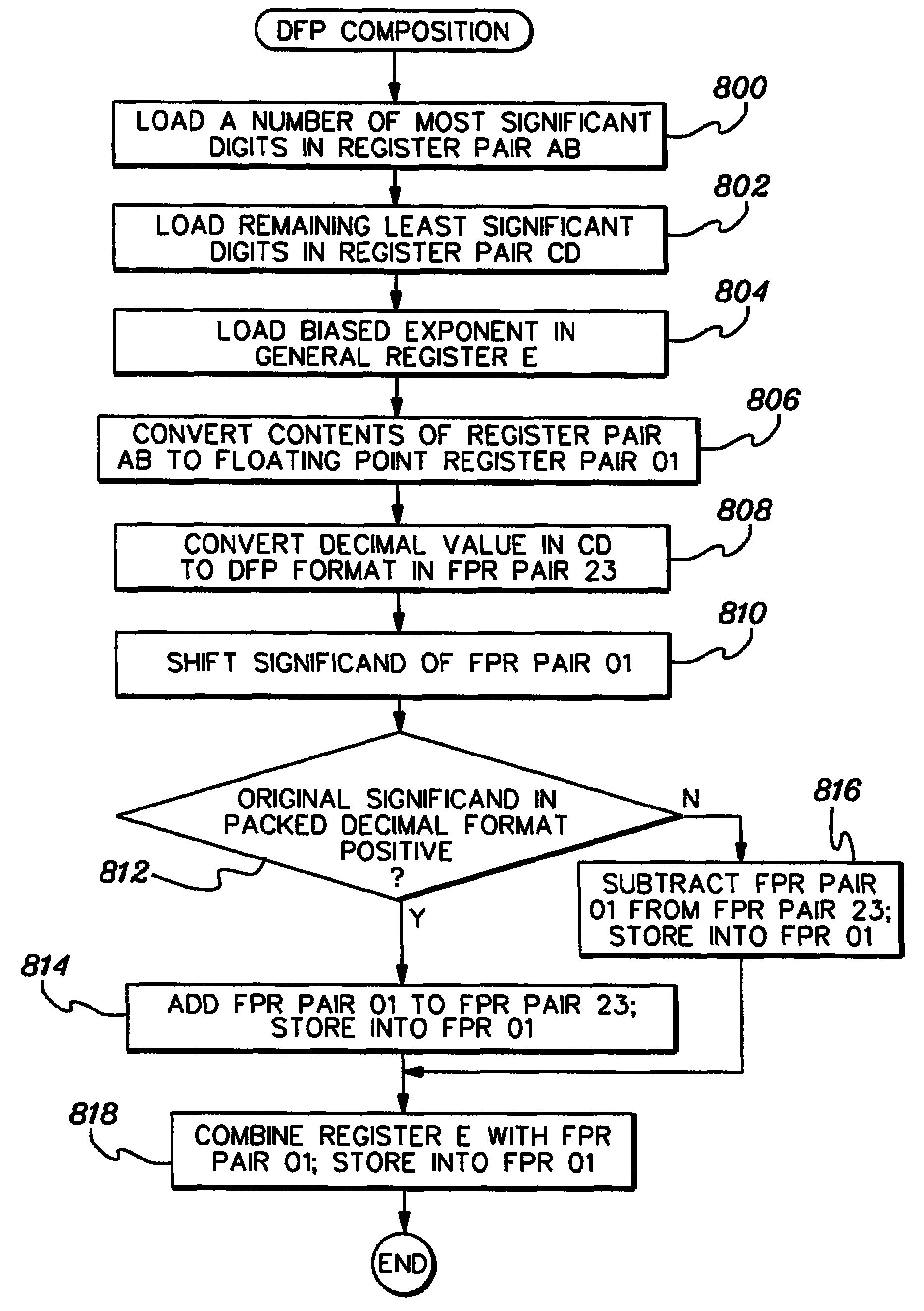
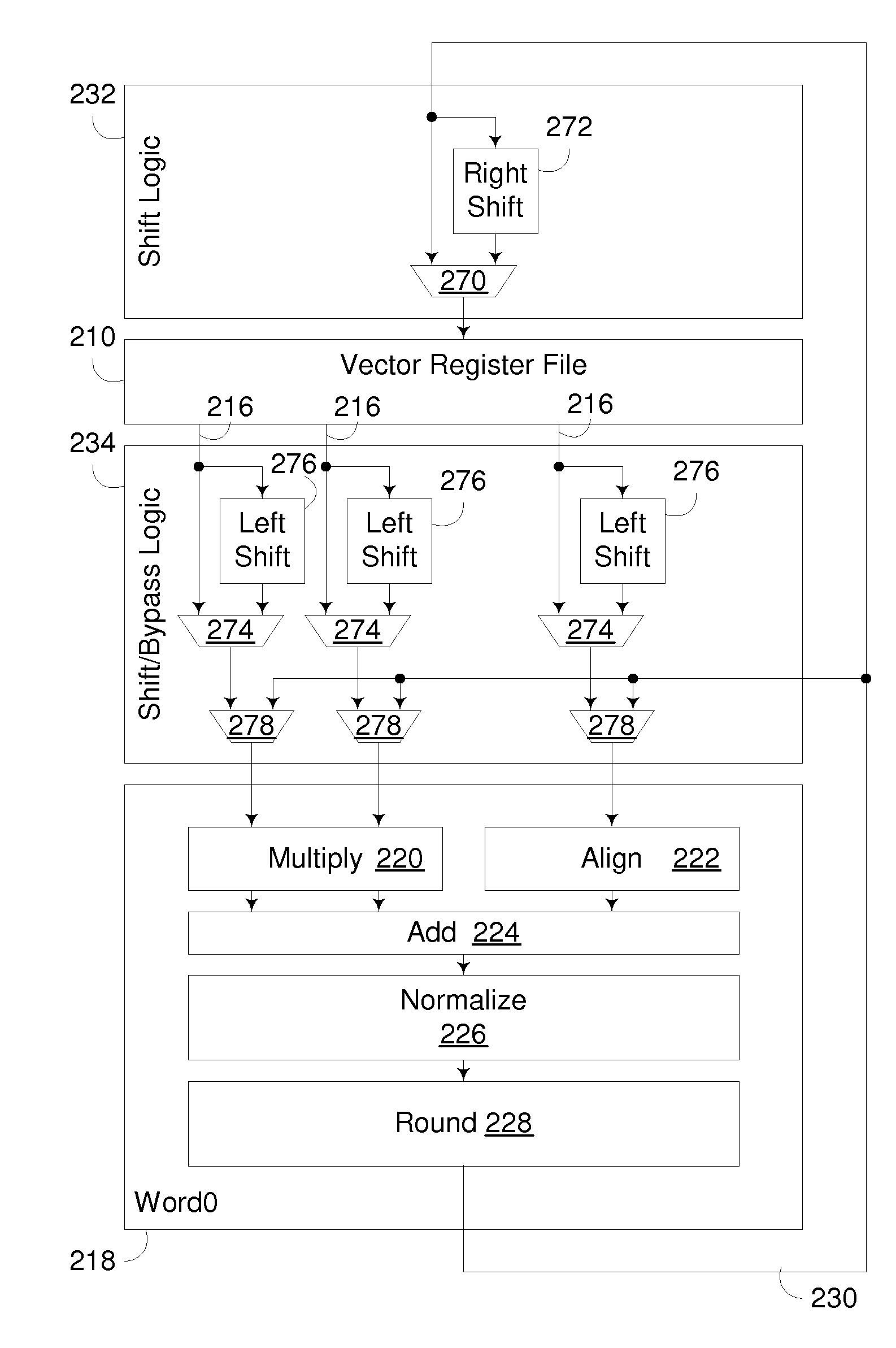
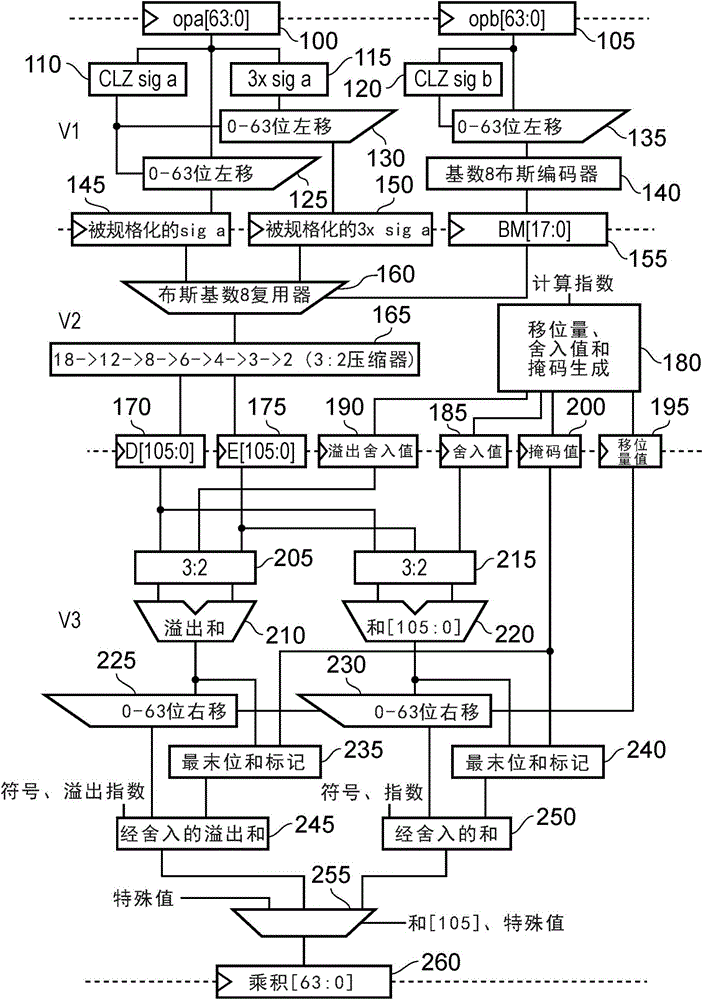
Shift significand of decimal floating point data
ActiveUS20080270756A1Digital data processing detailsDigital computer detailsParallel computingSialic acid synthase
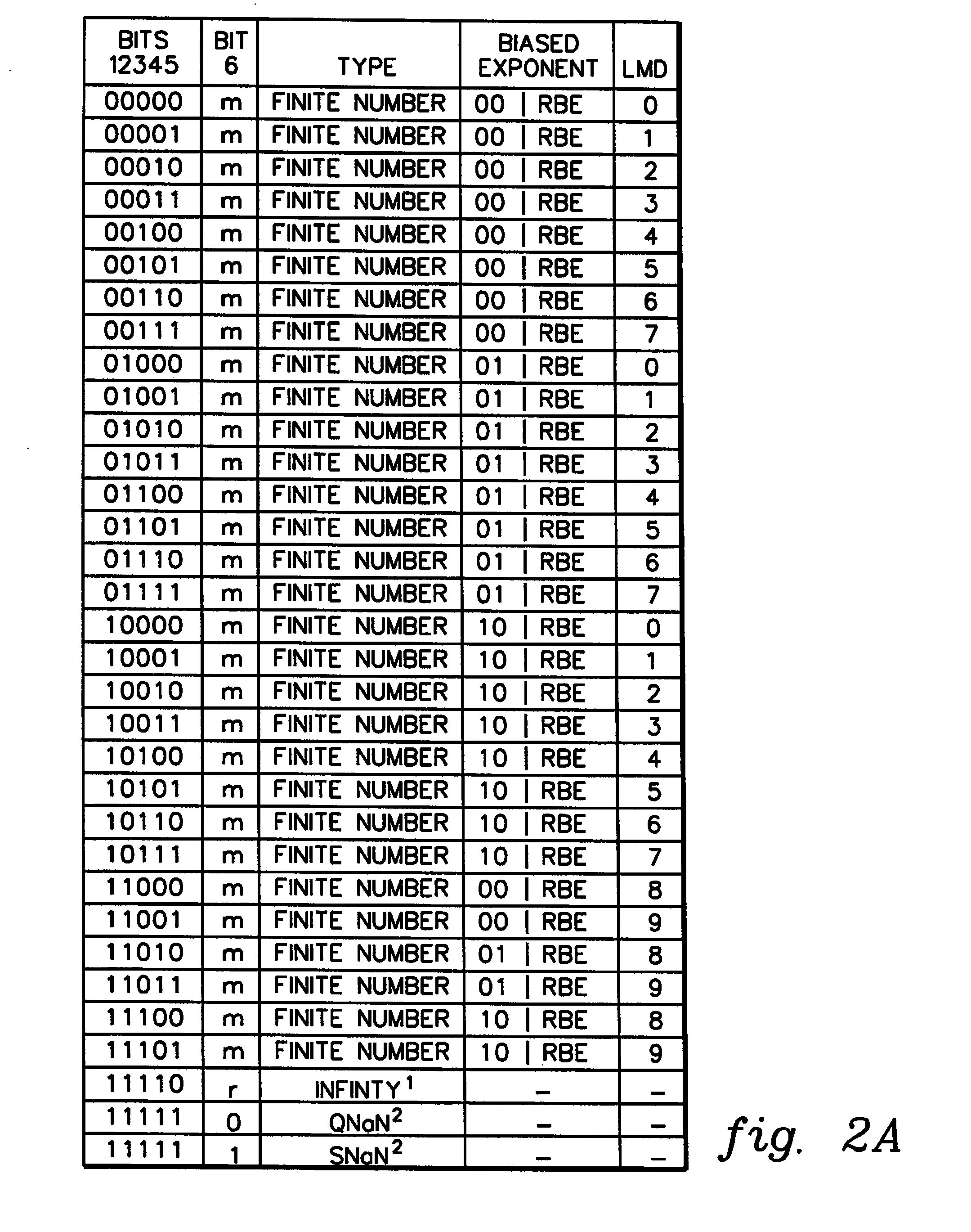
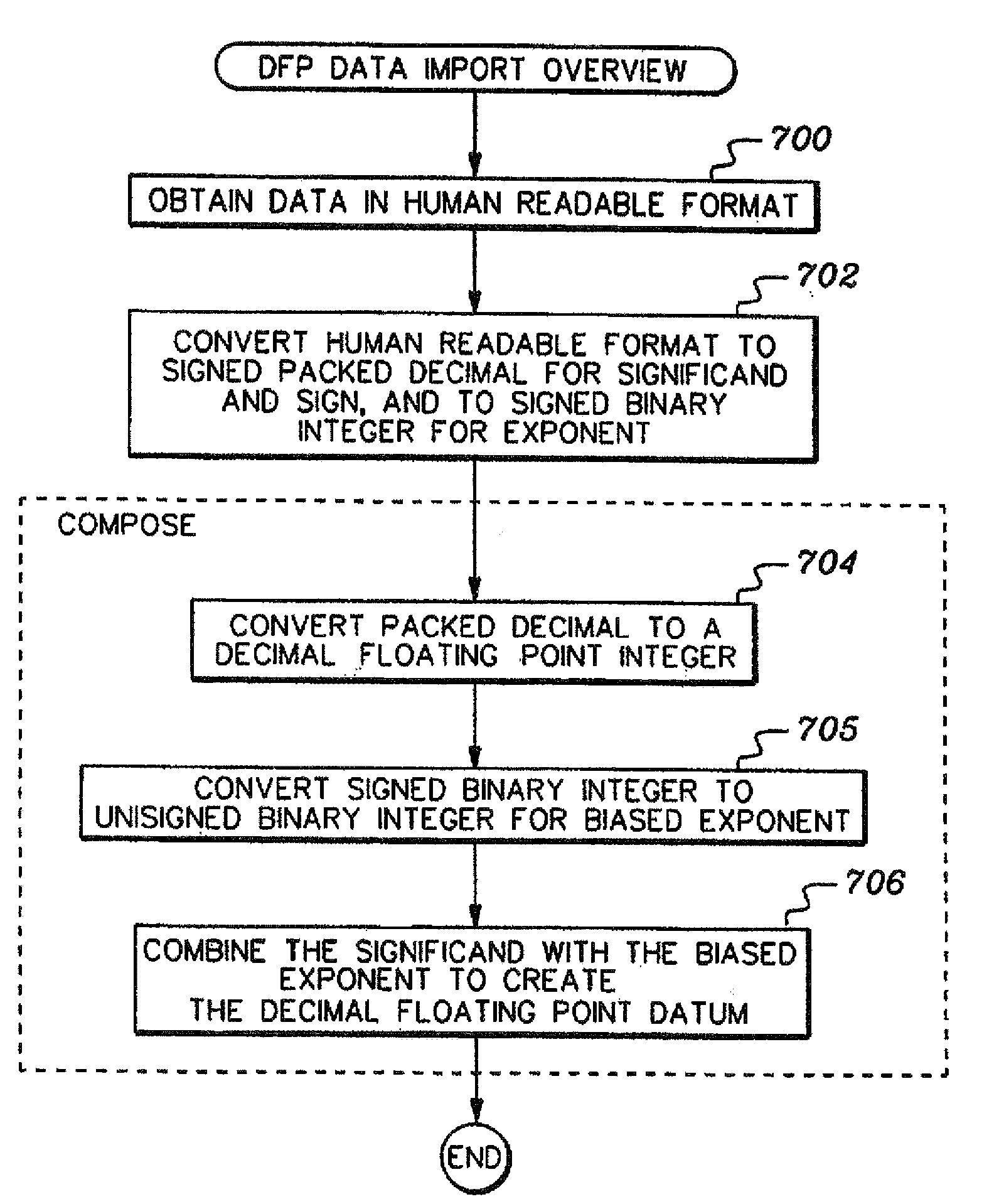
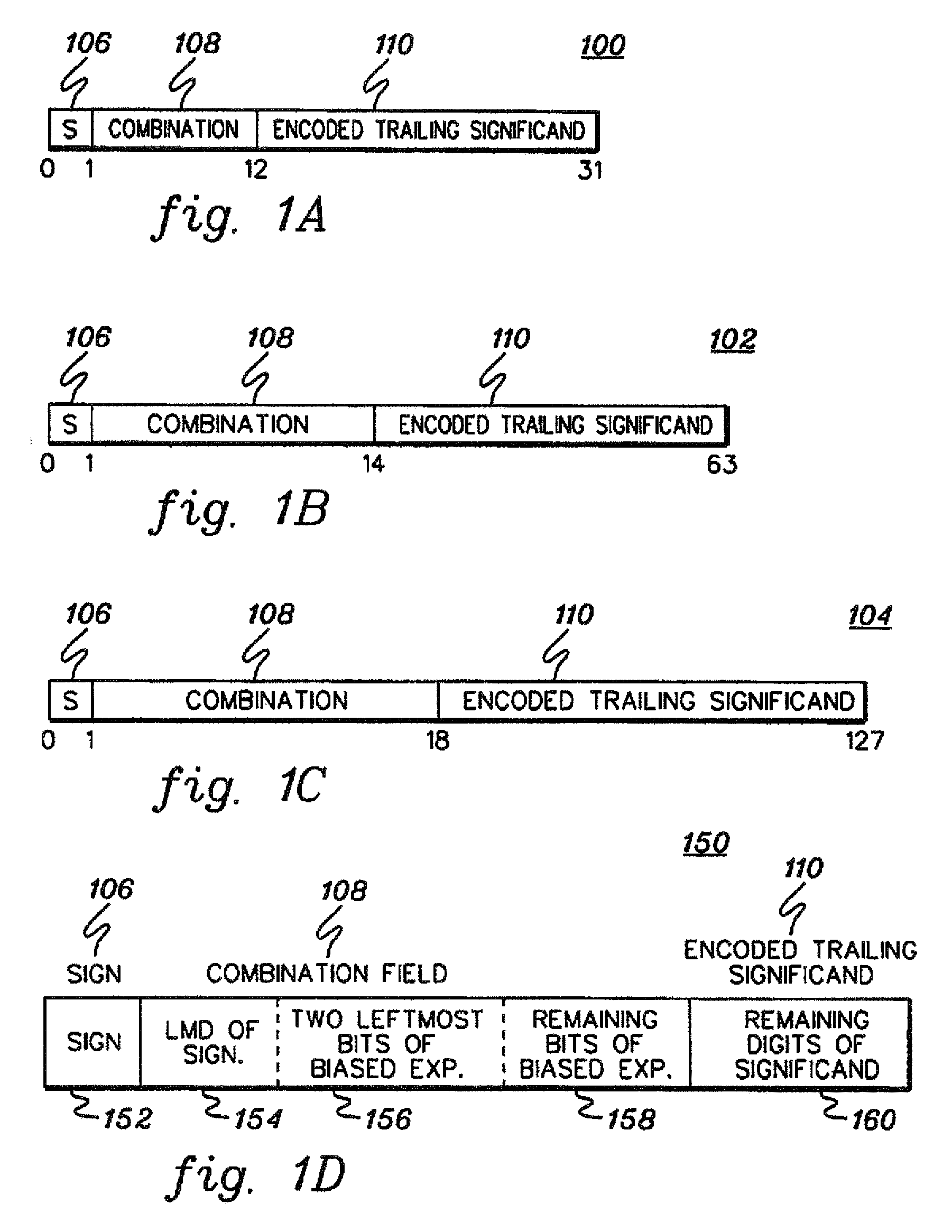
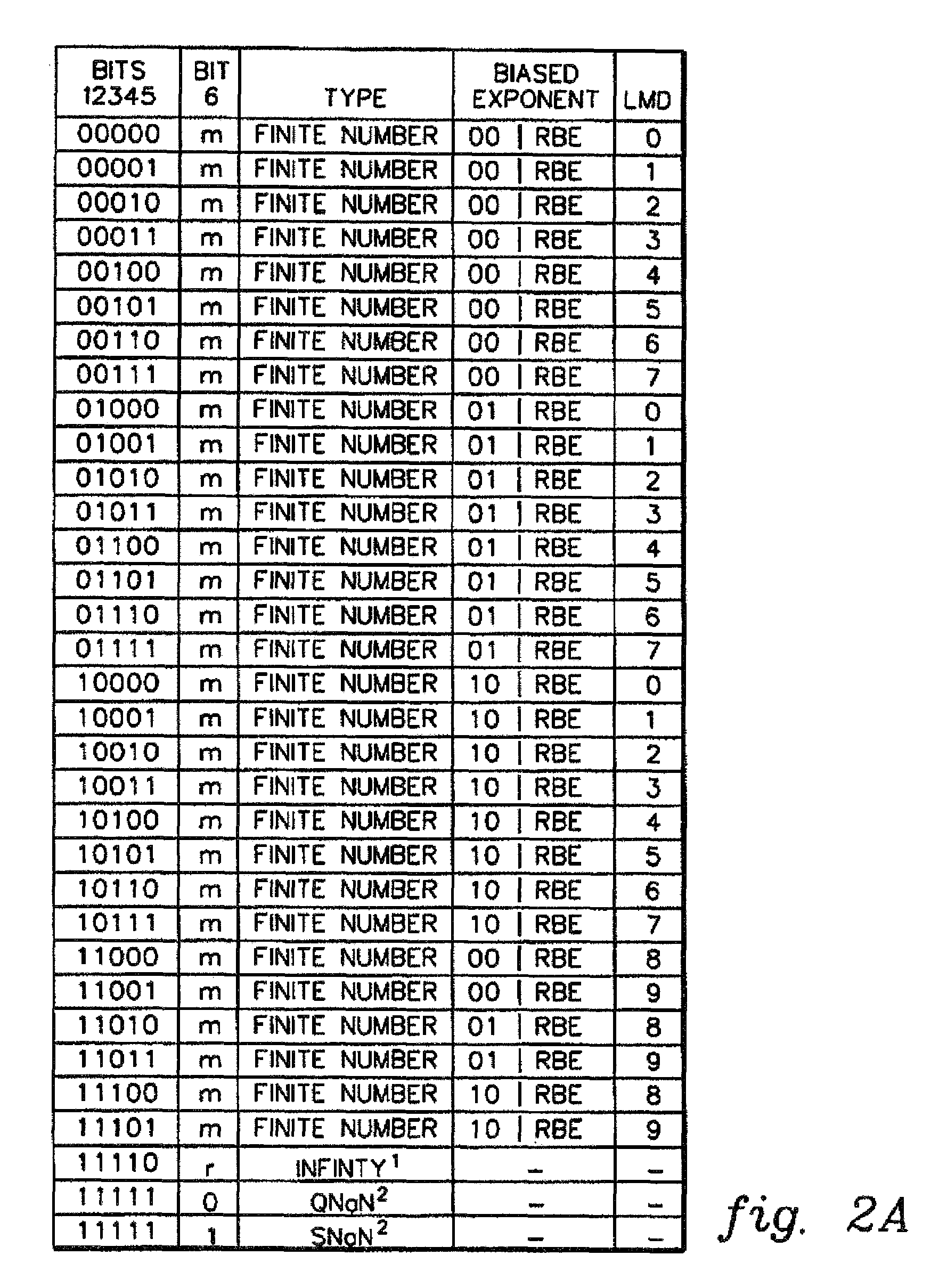
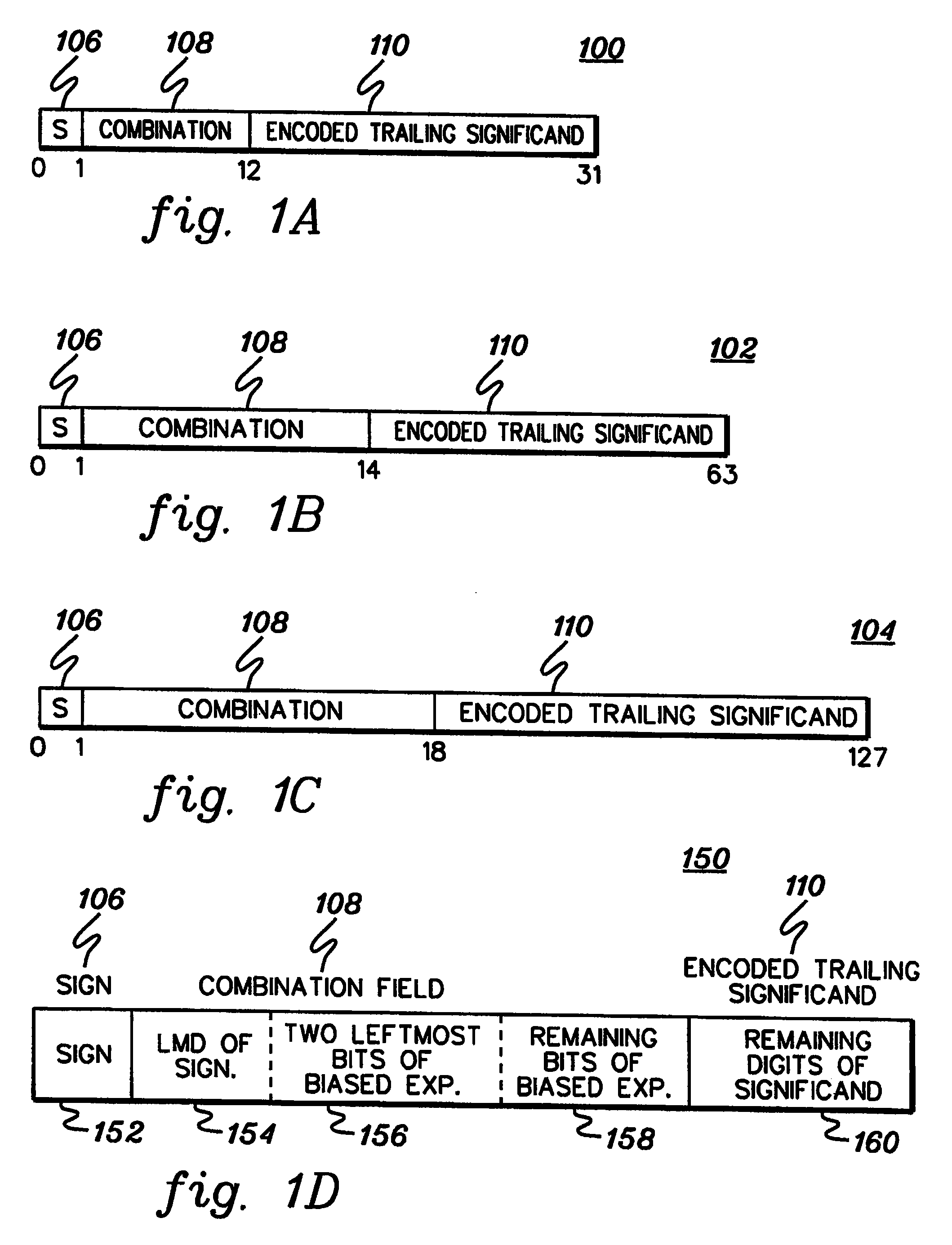
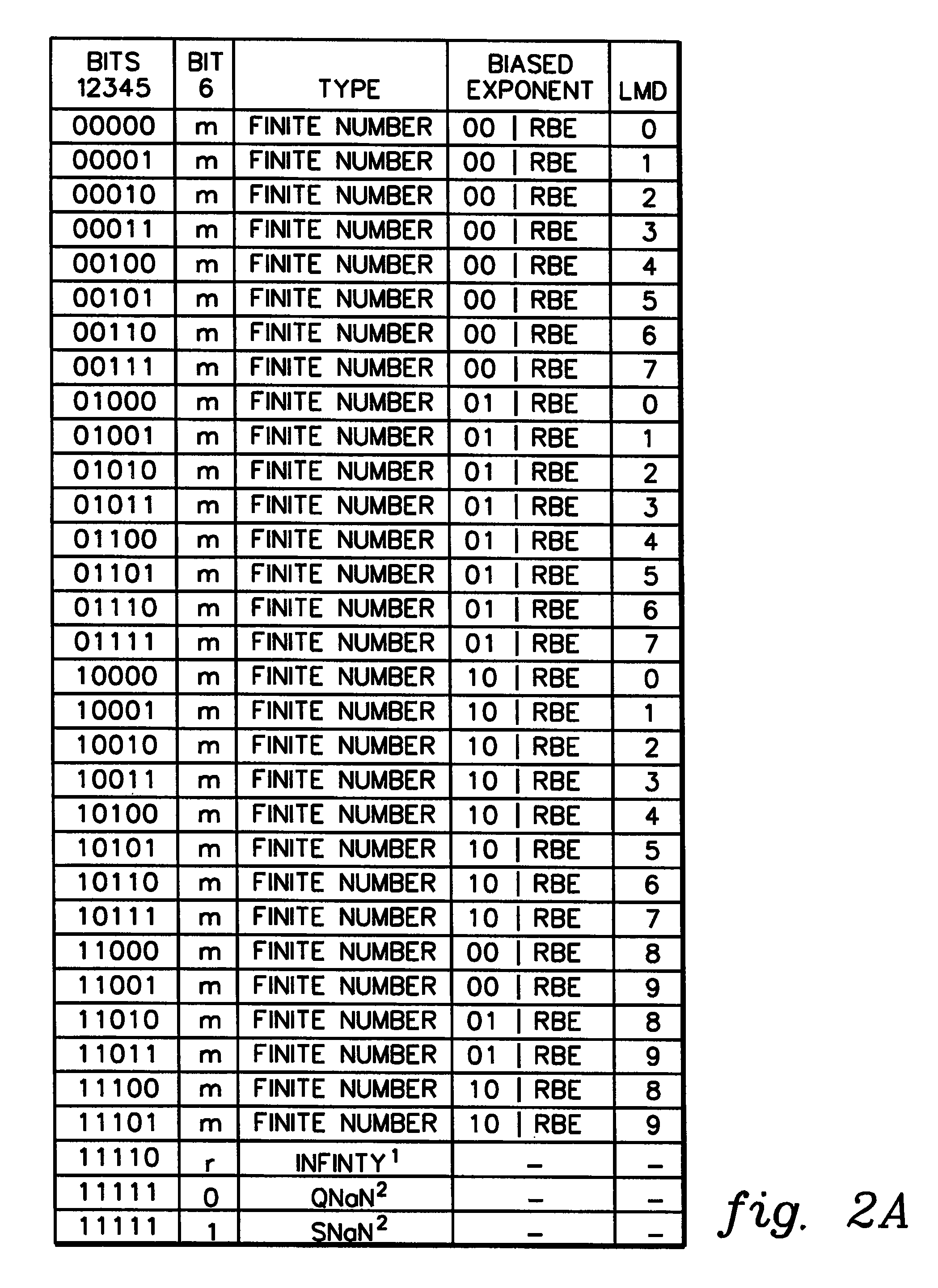
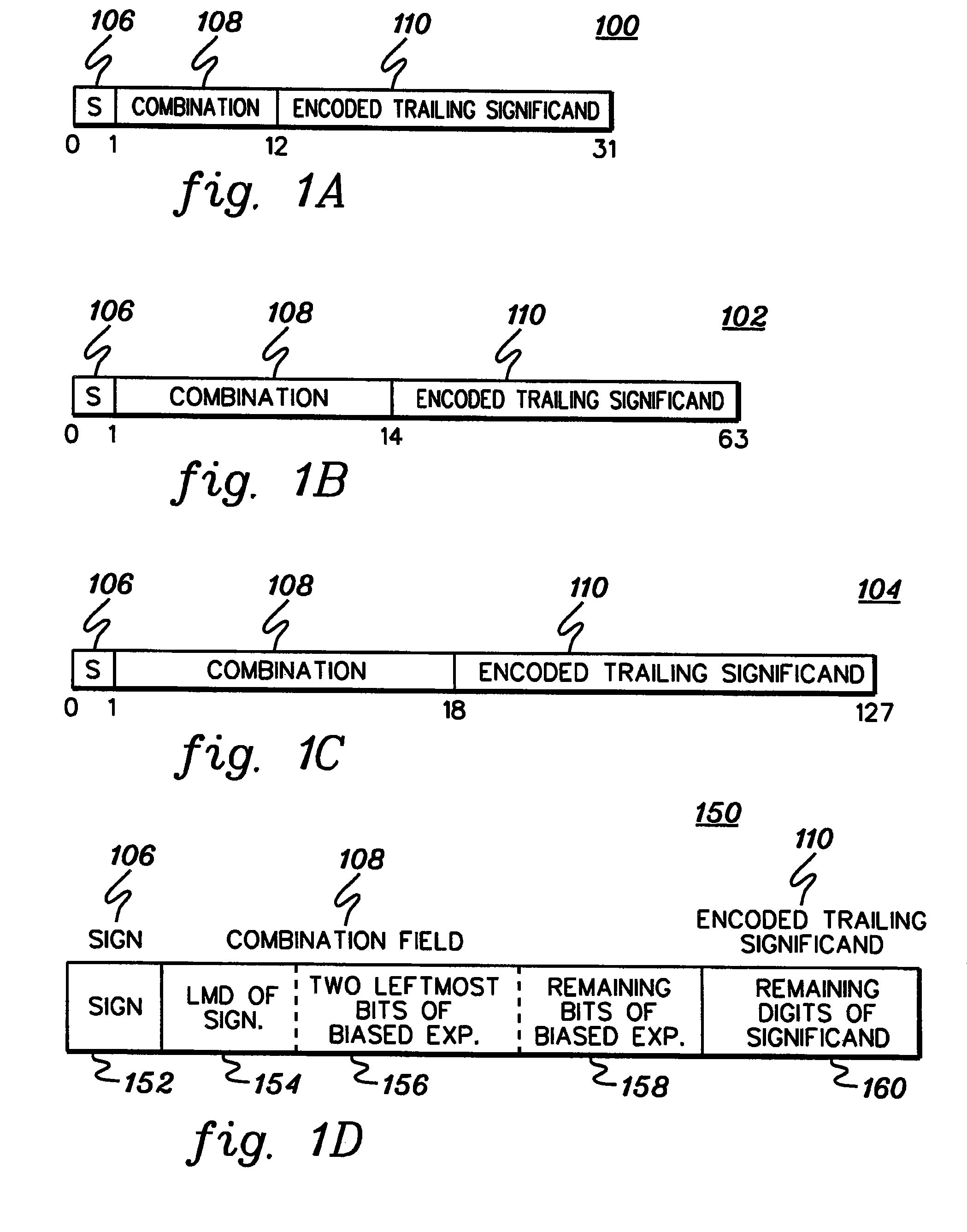
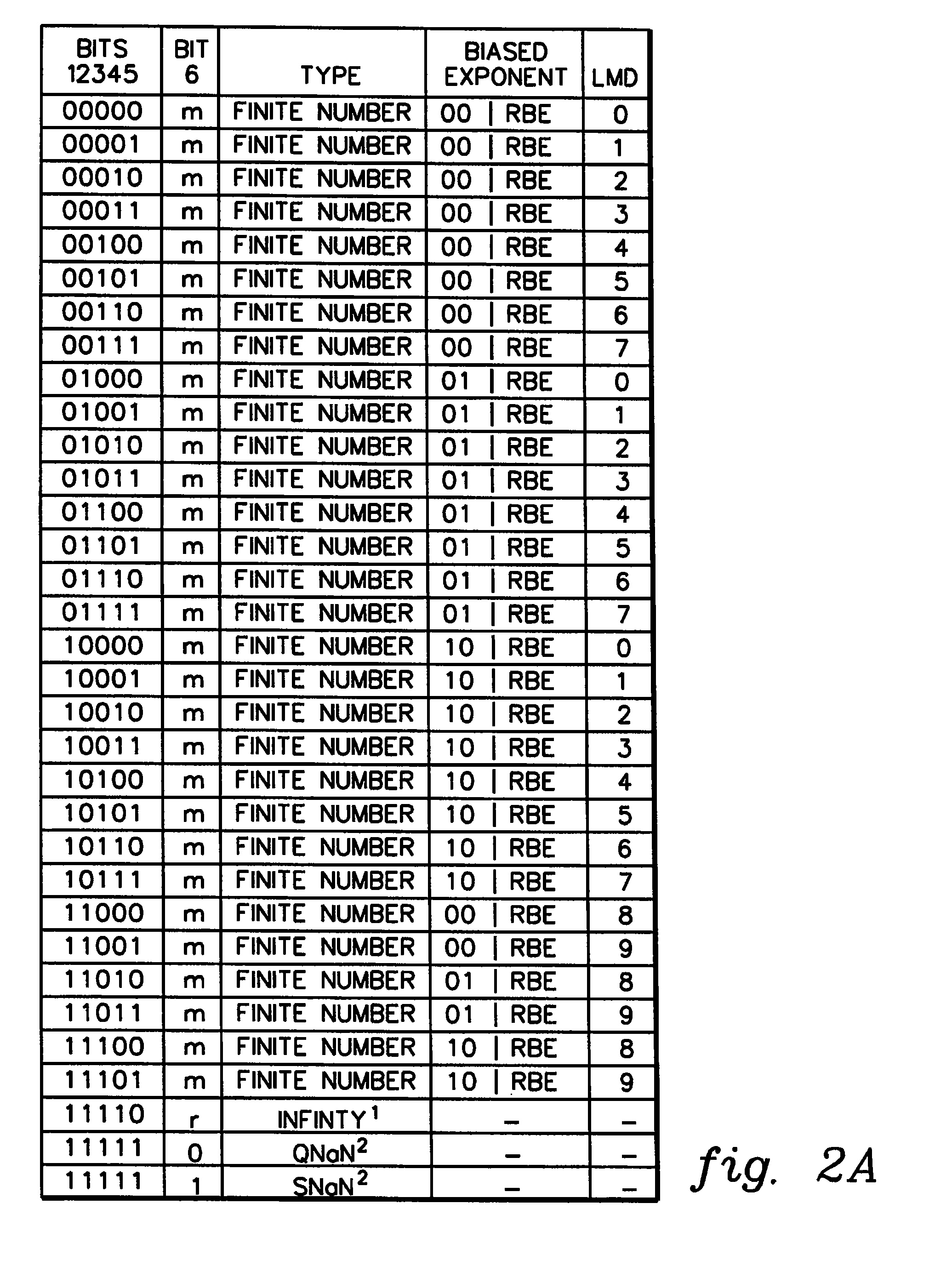
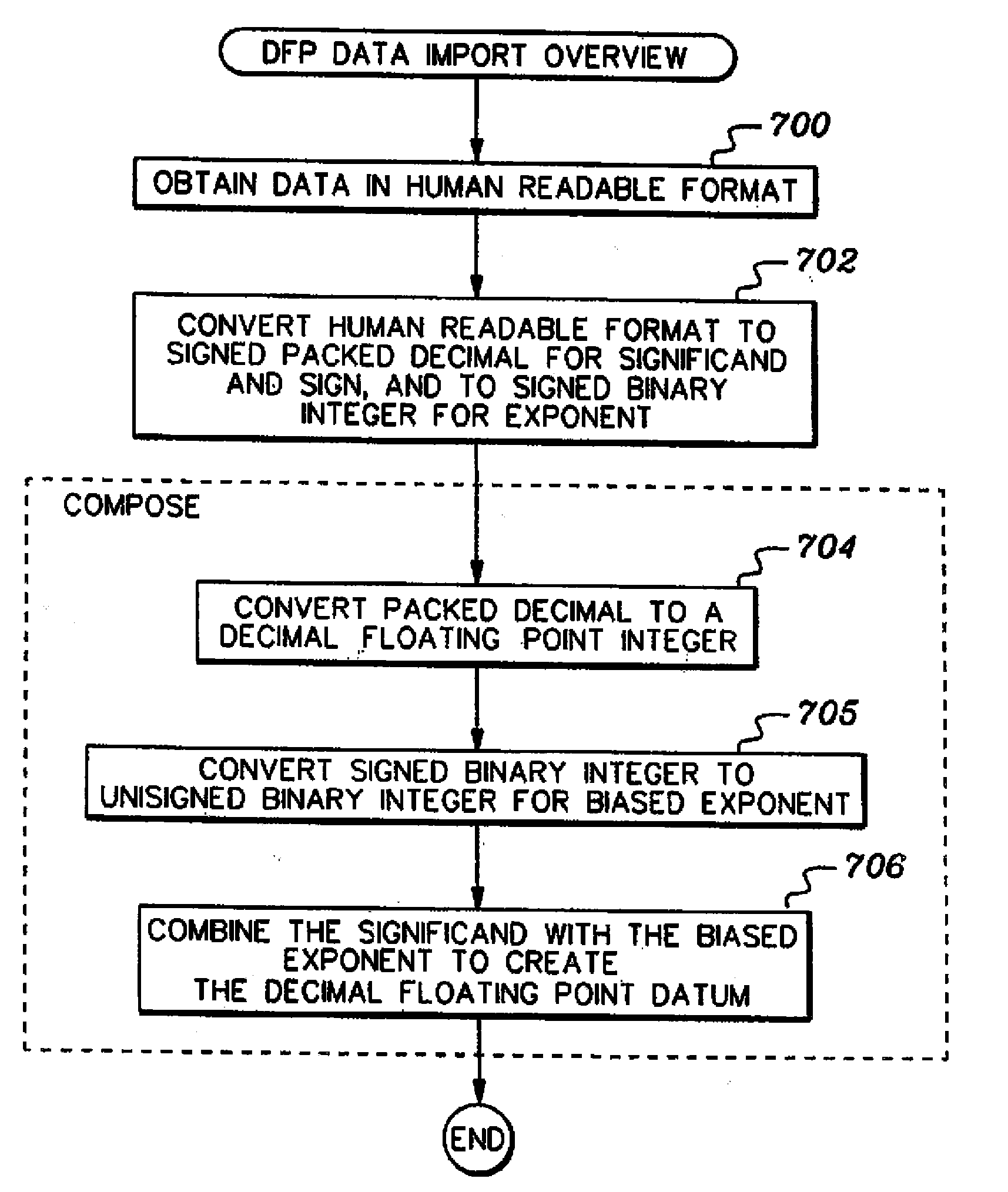
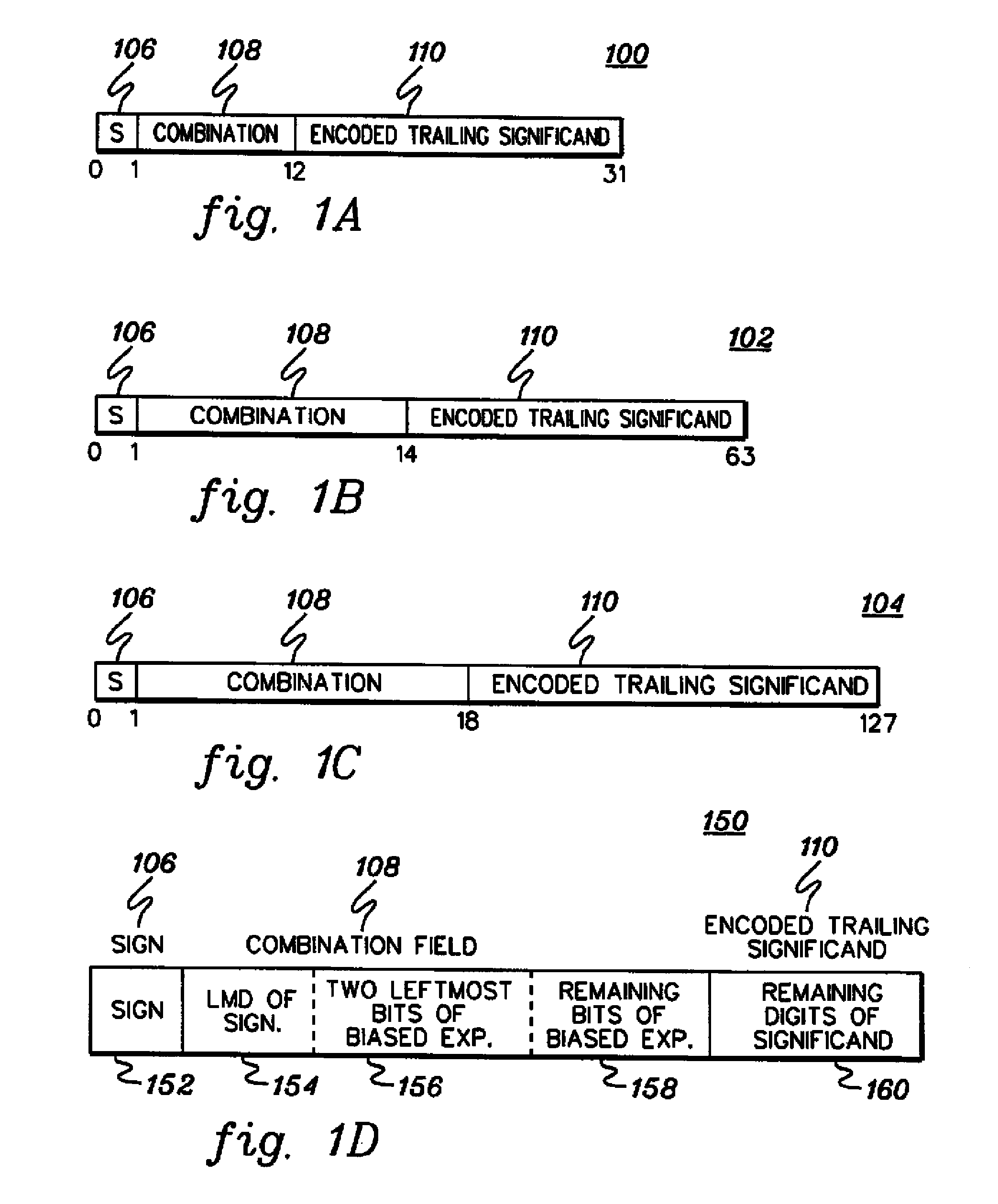
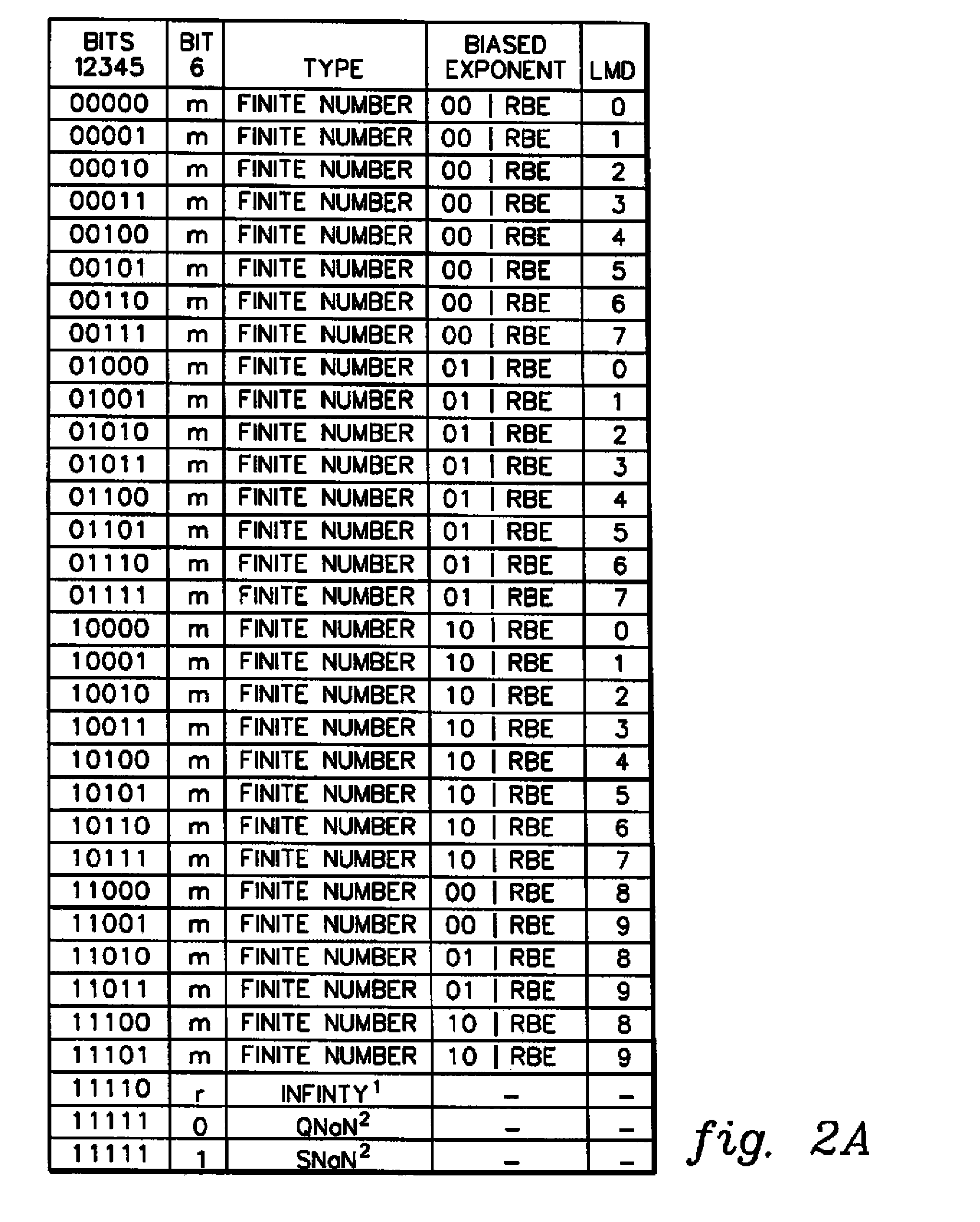
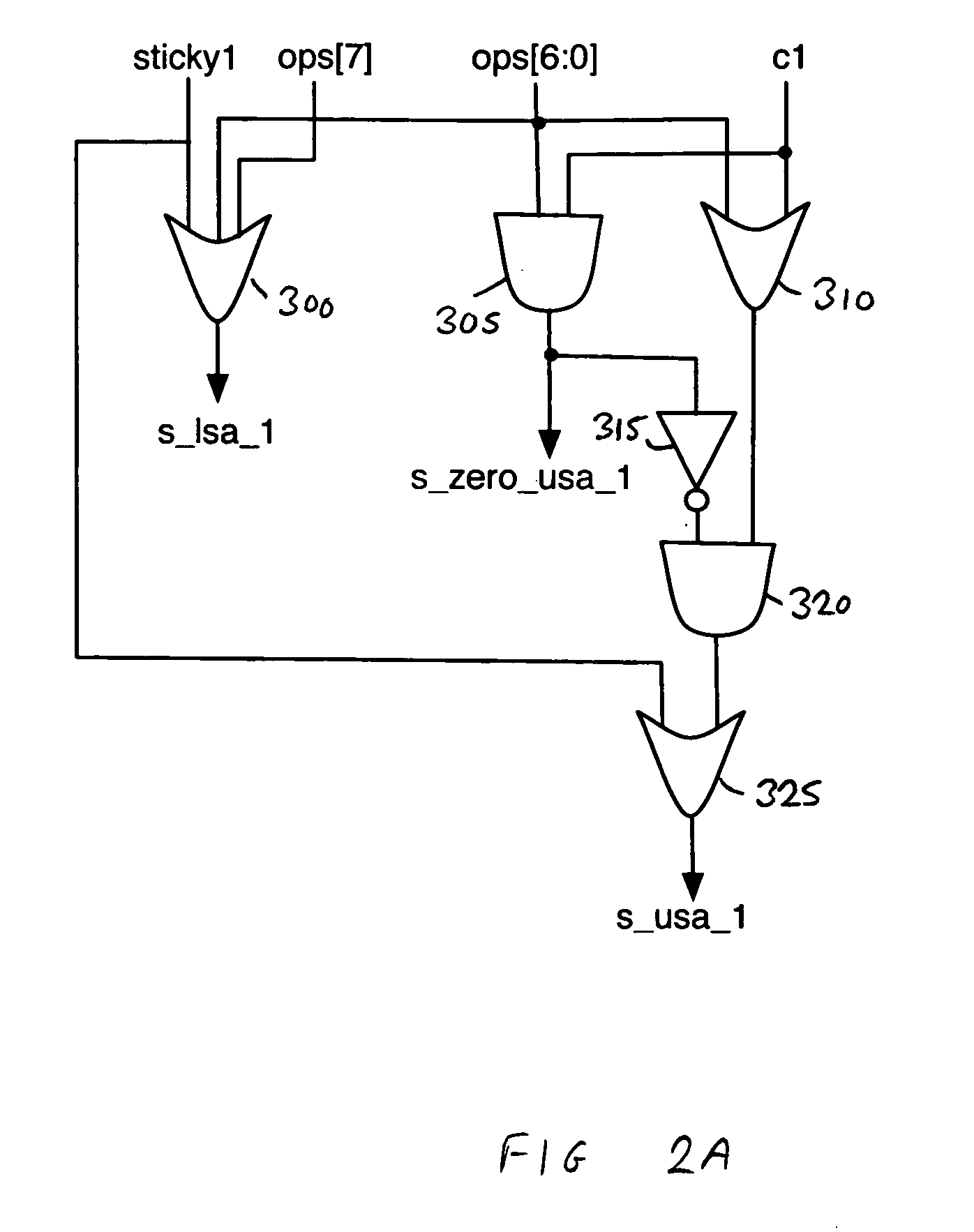
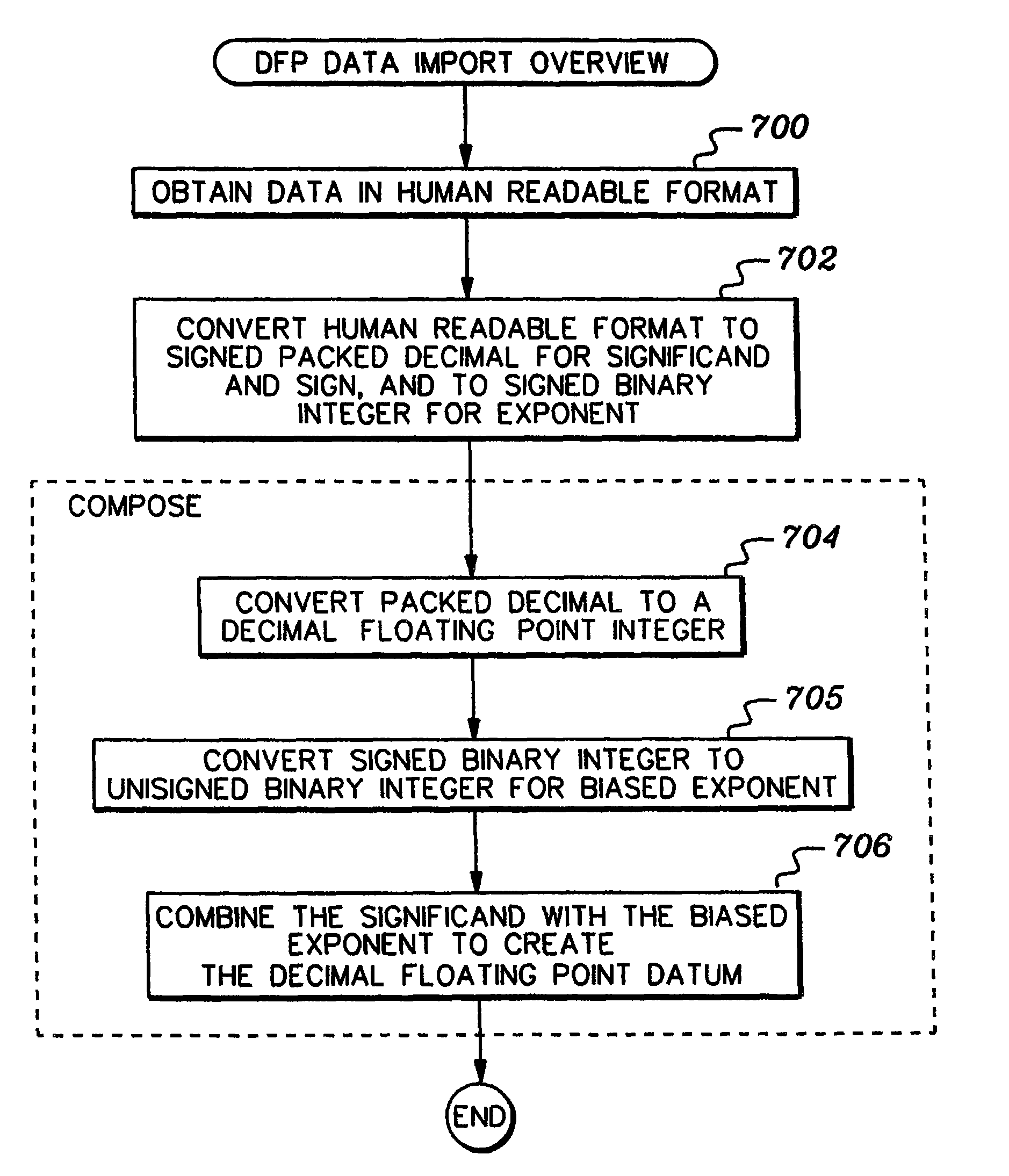
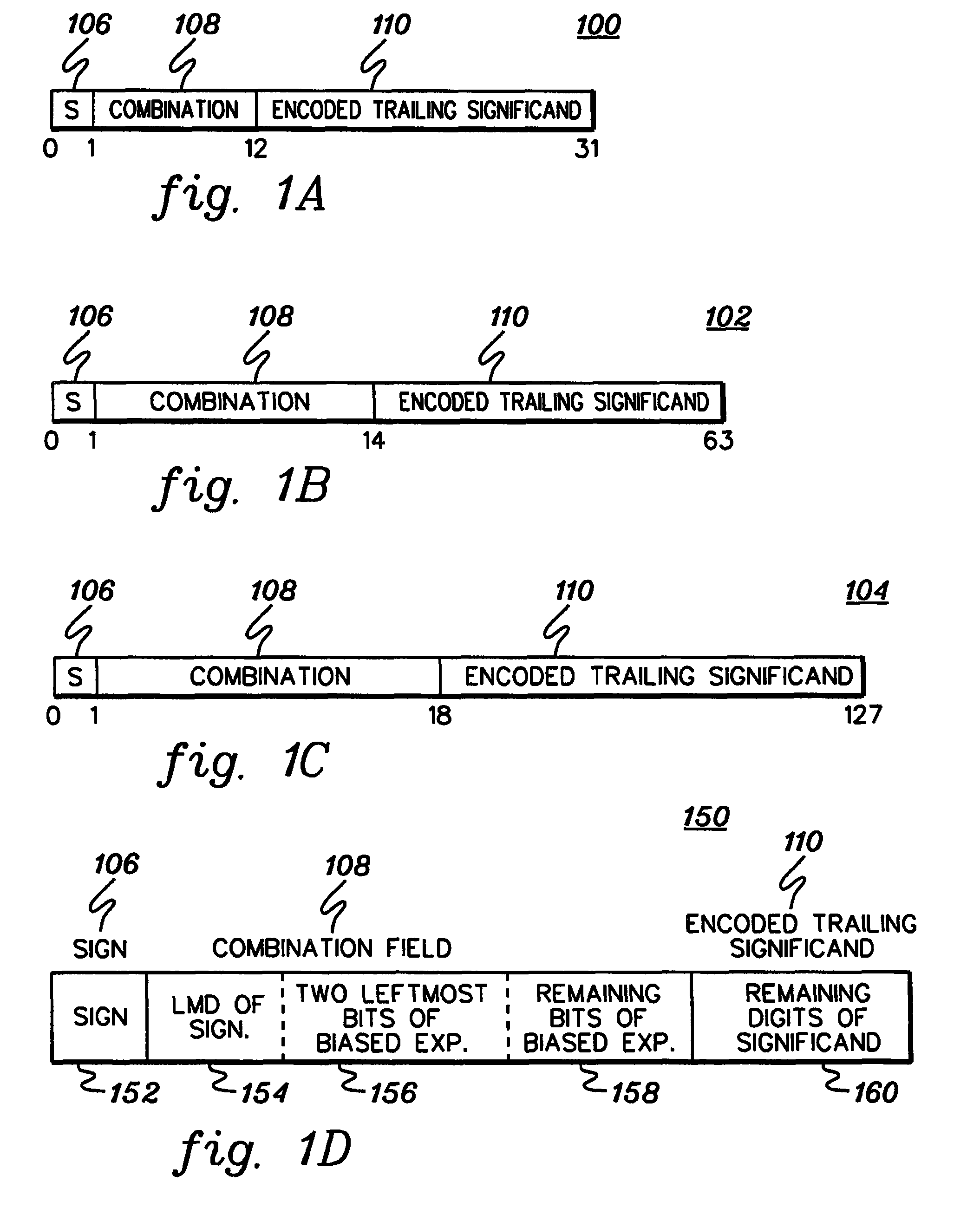
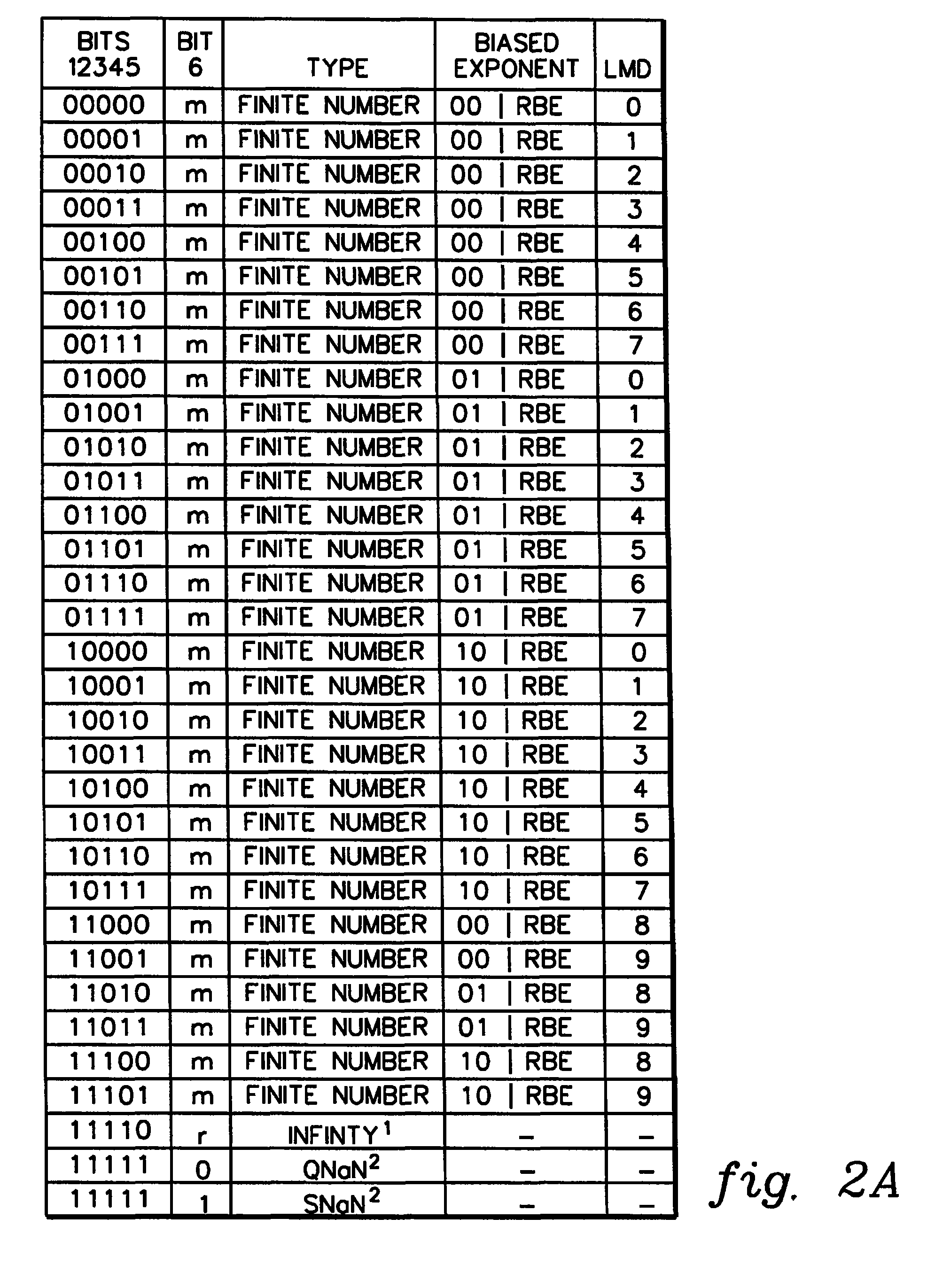
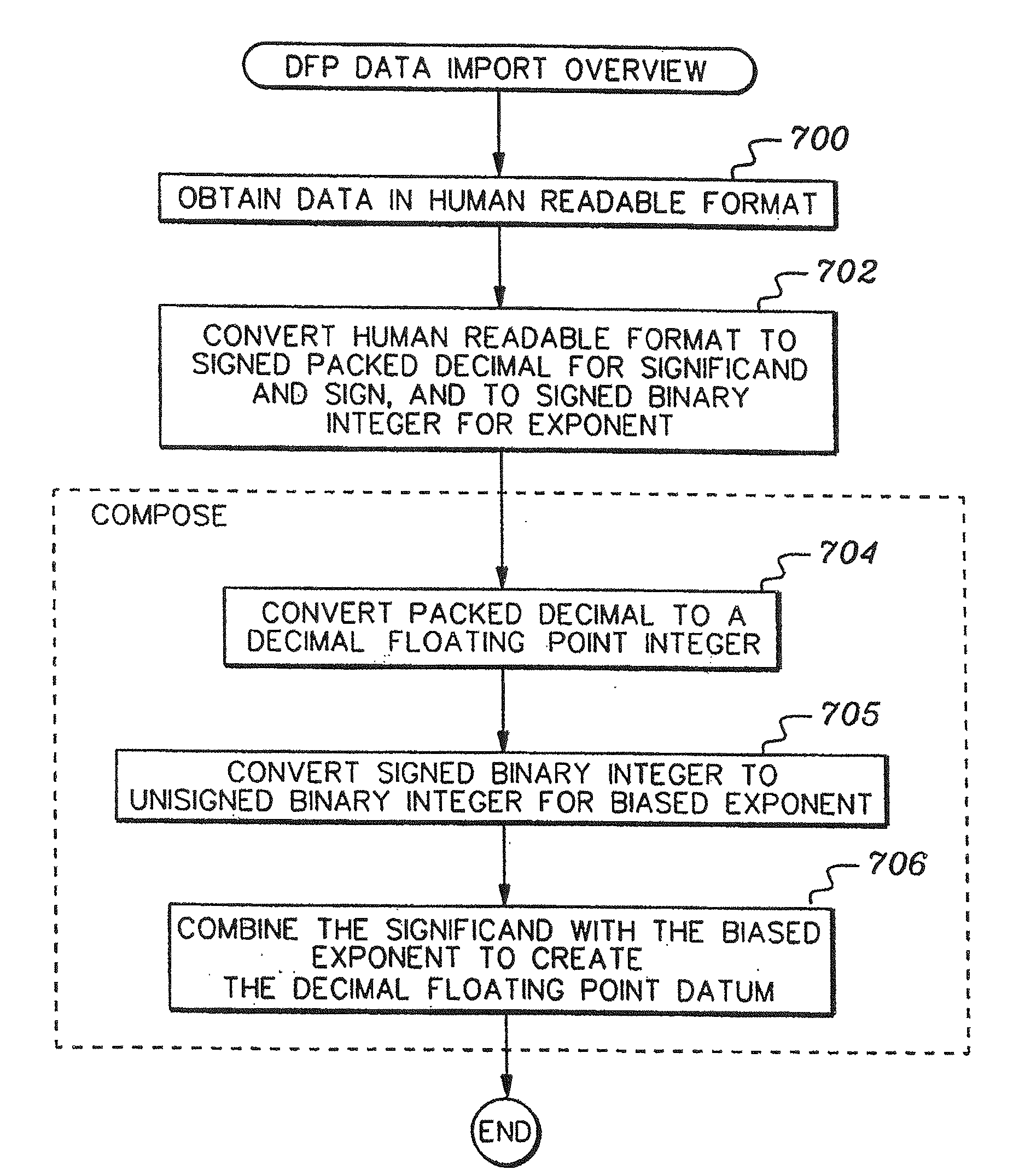
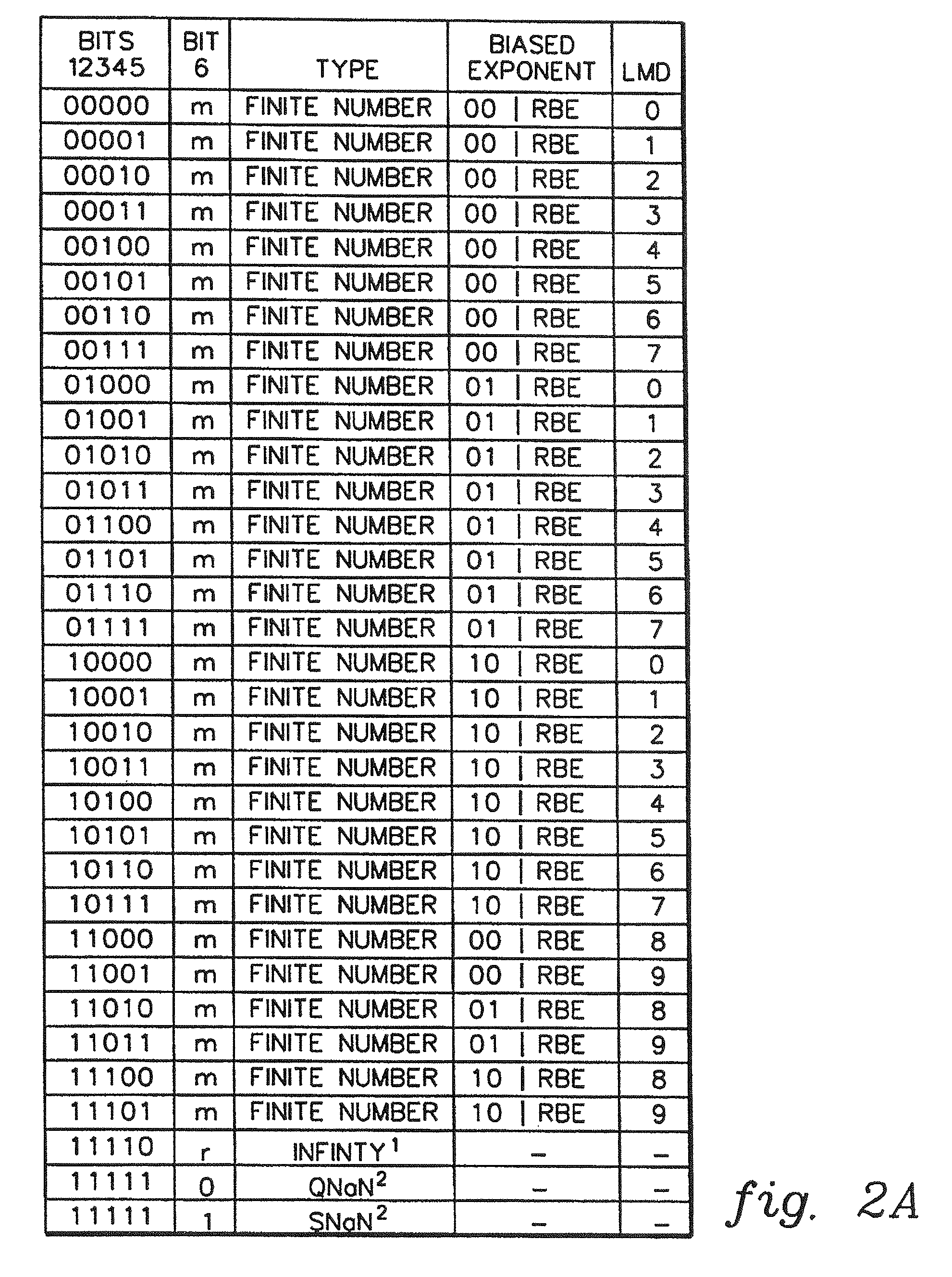
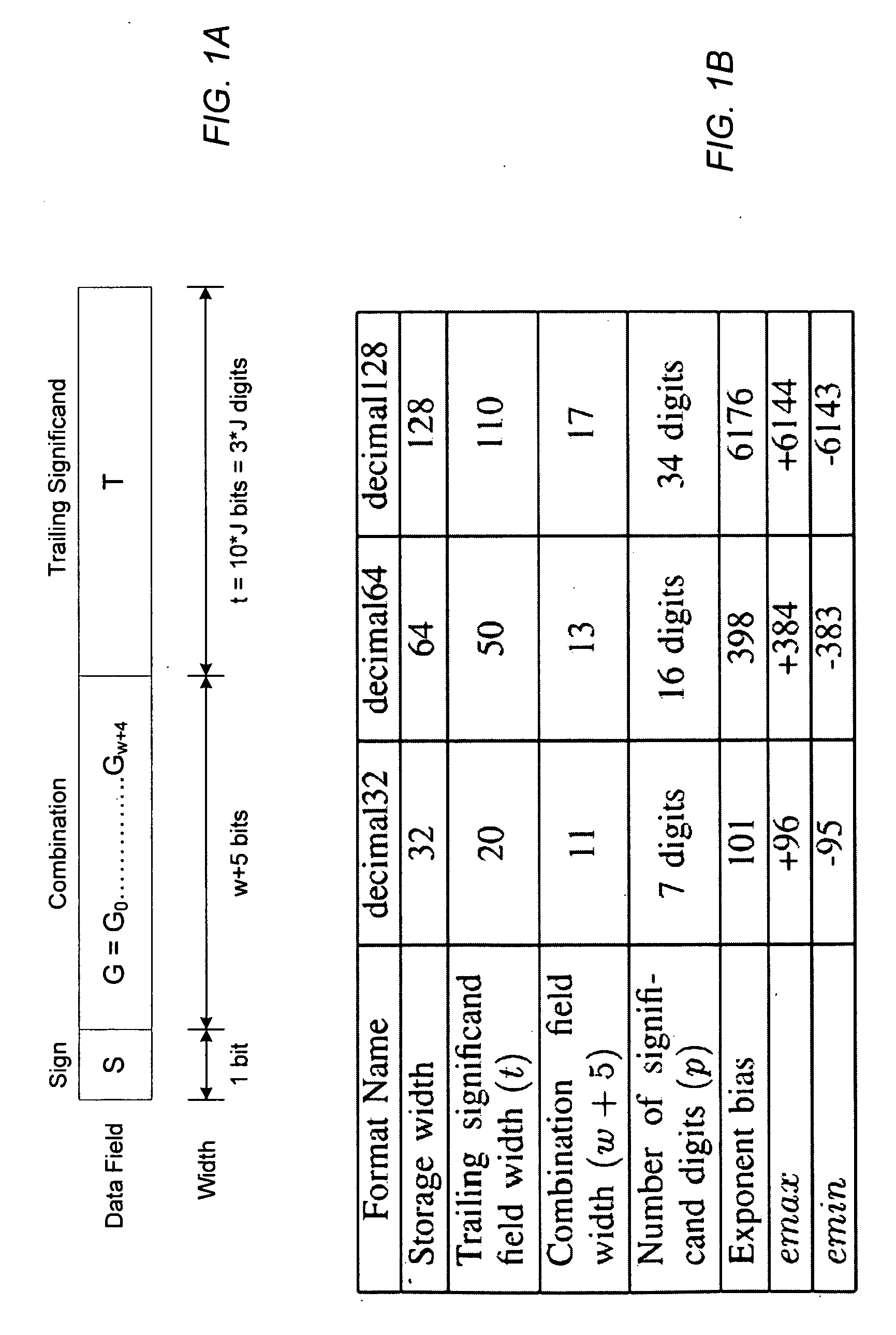
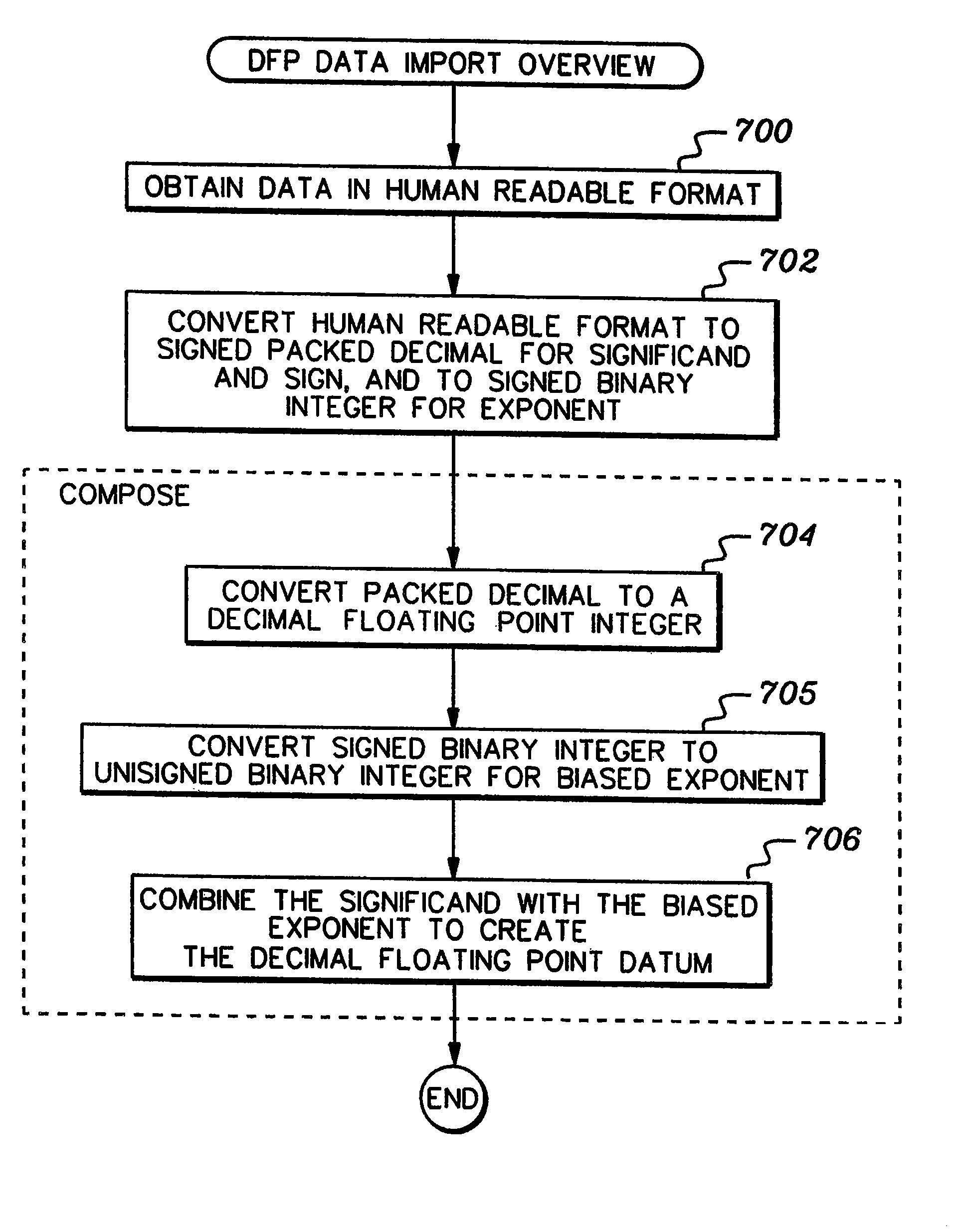
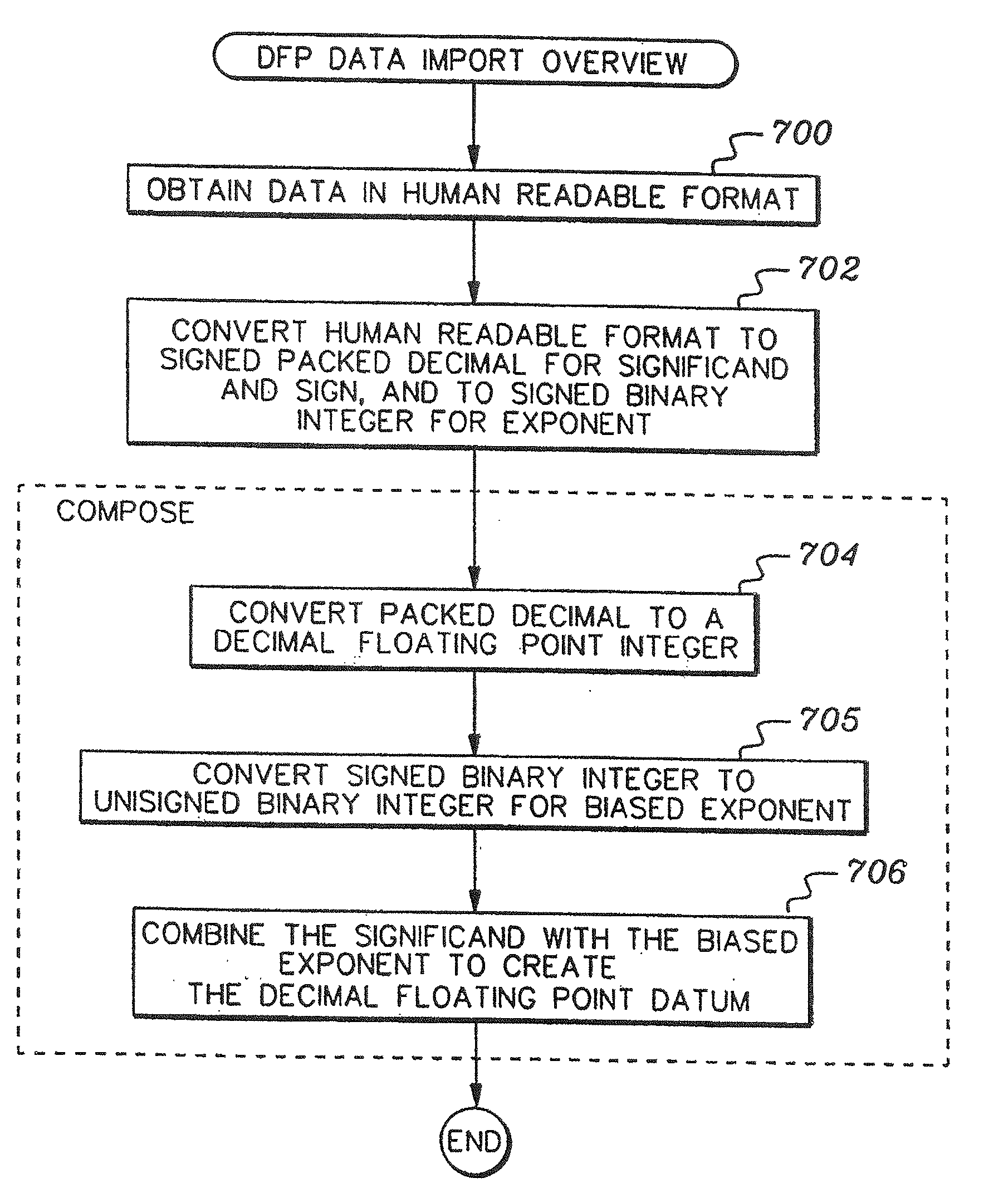
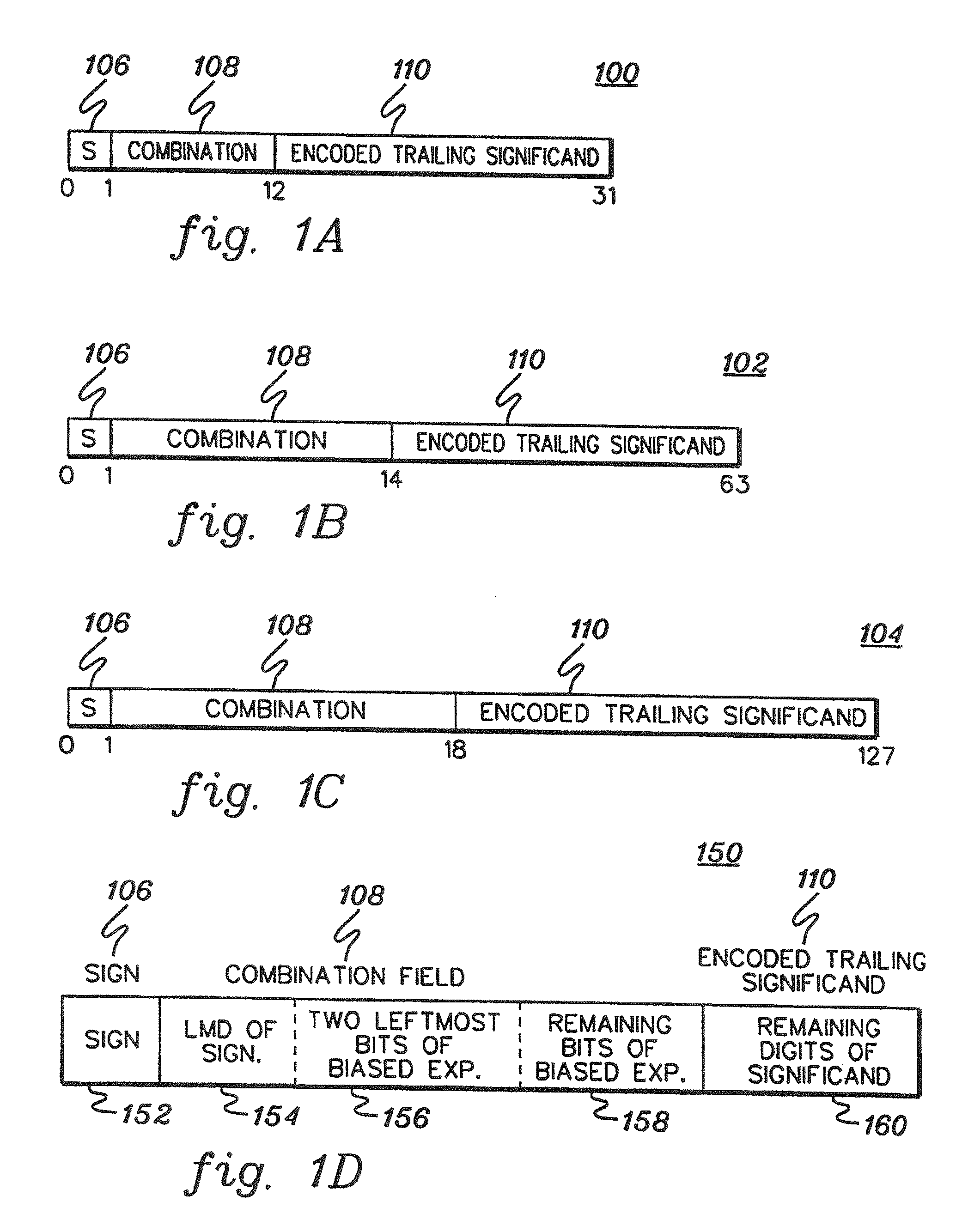
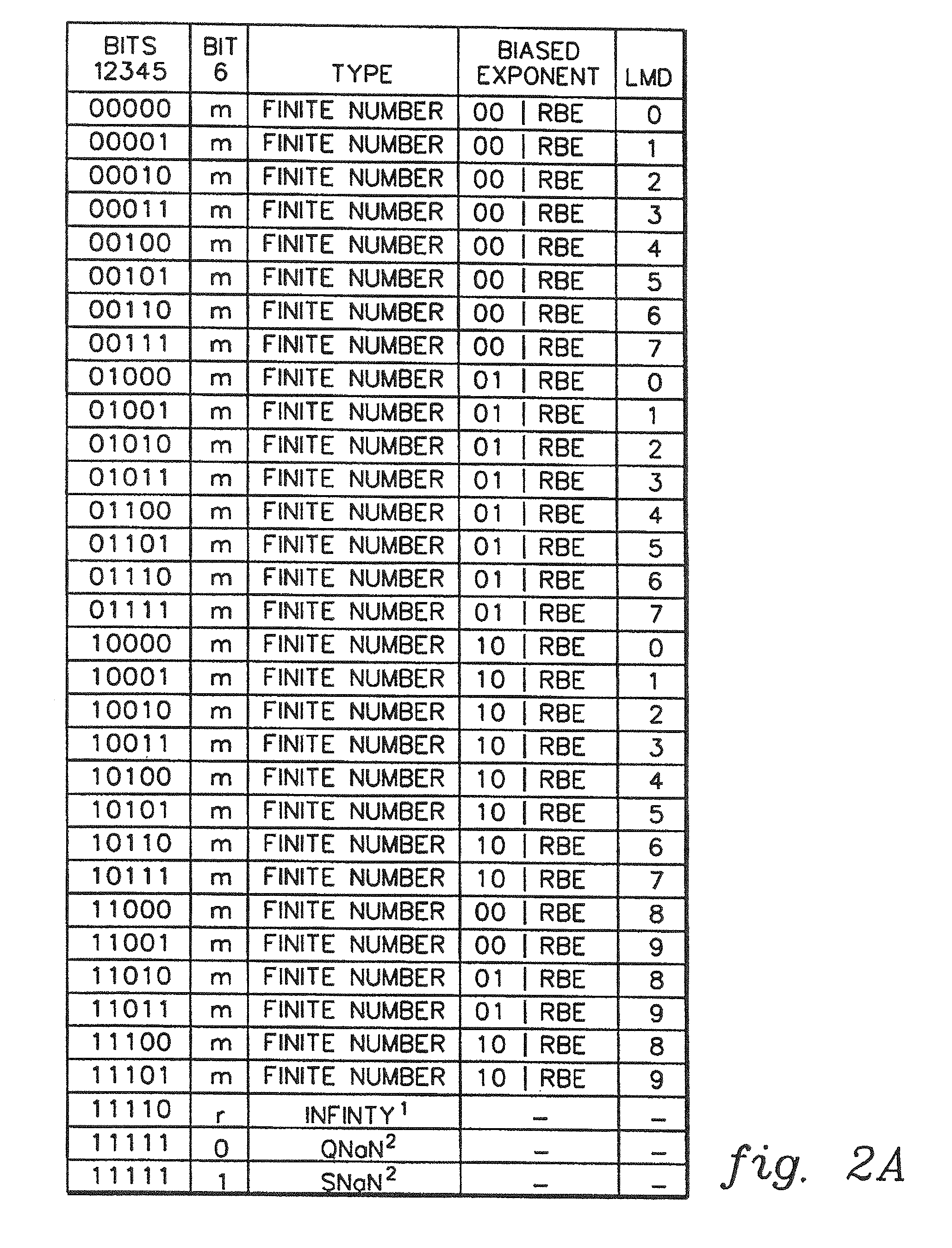
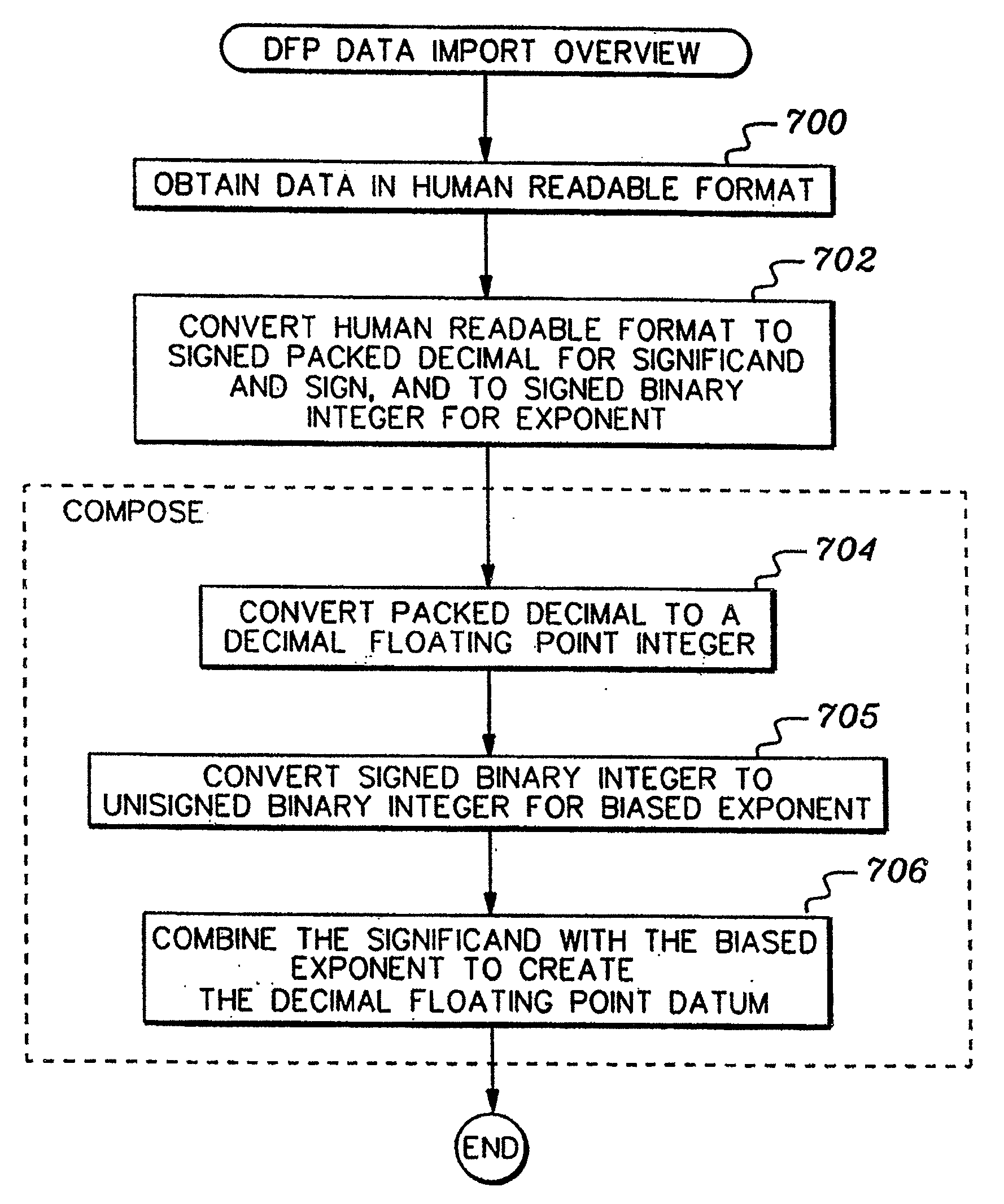
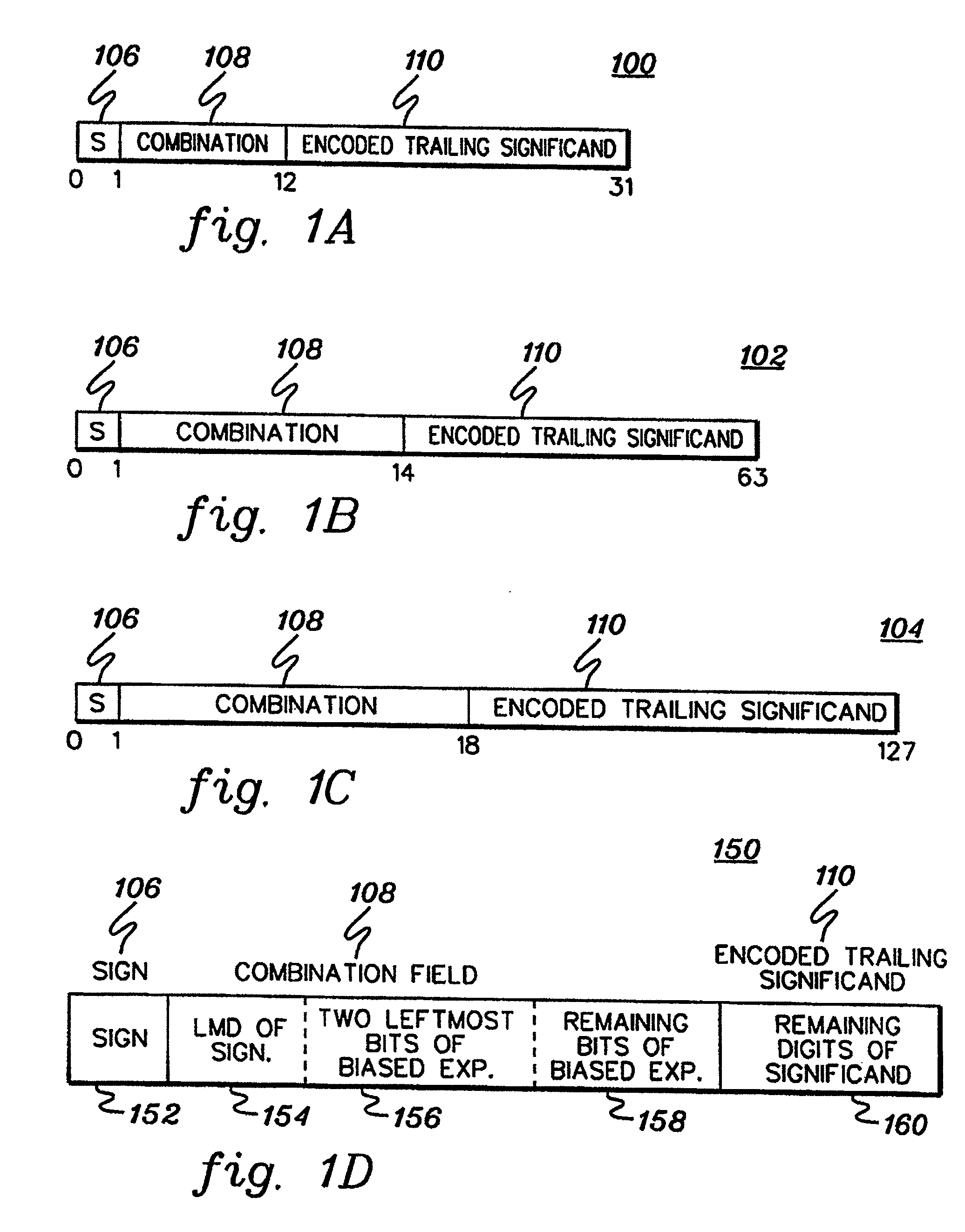
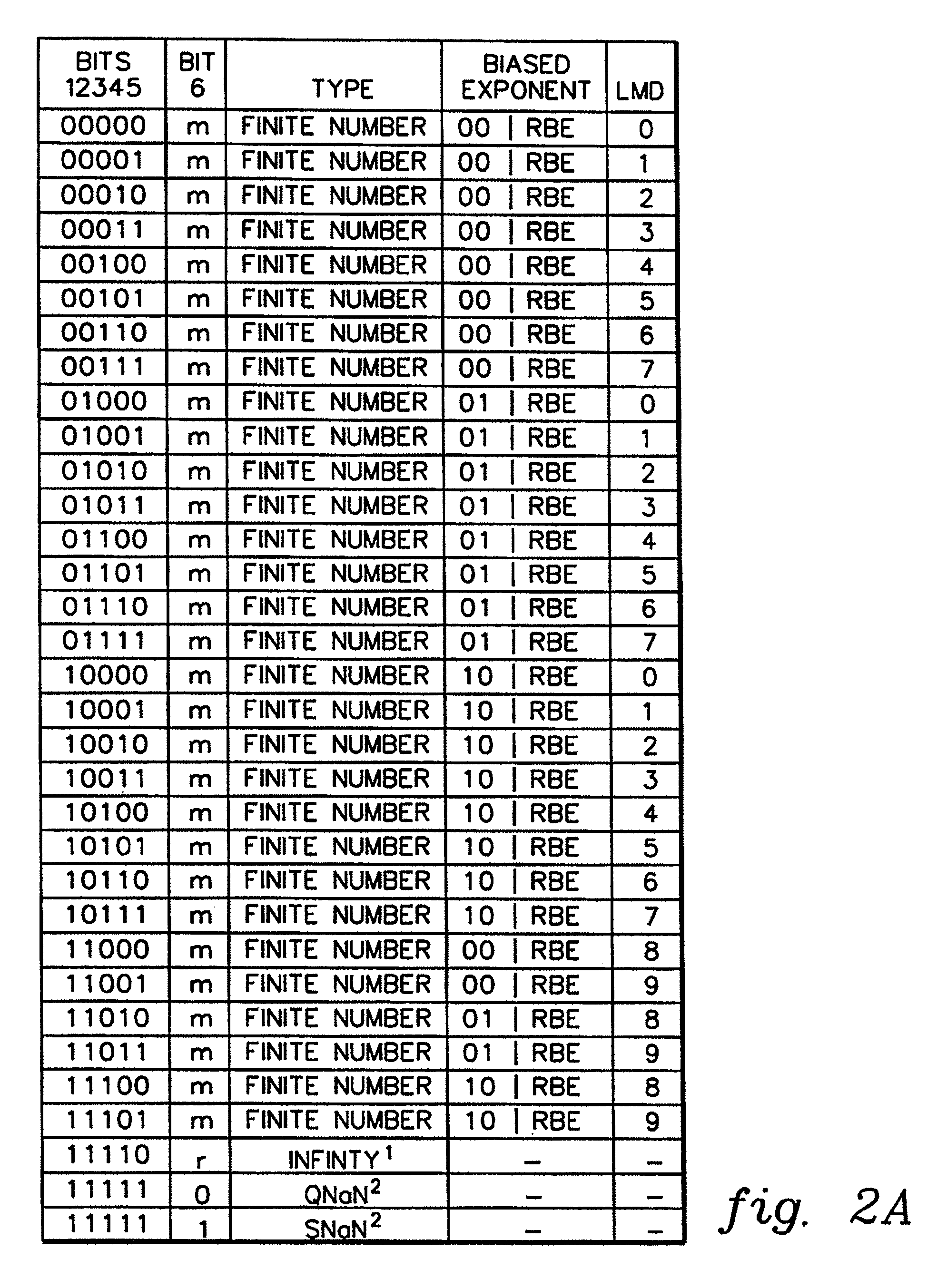
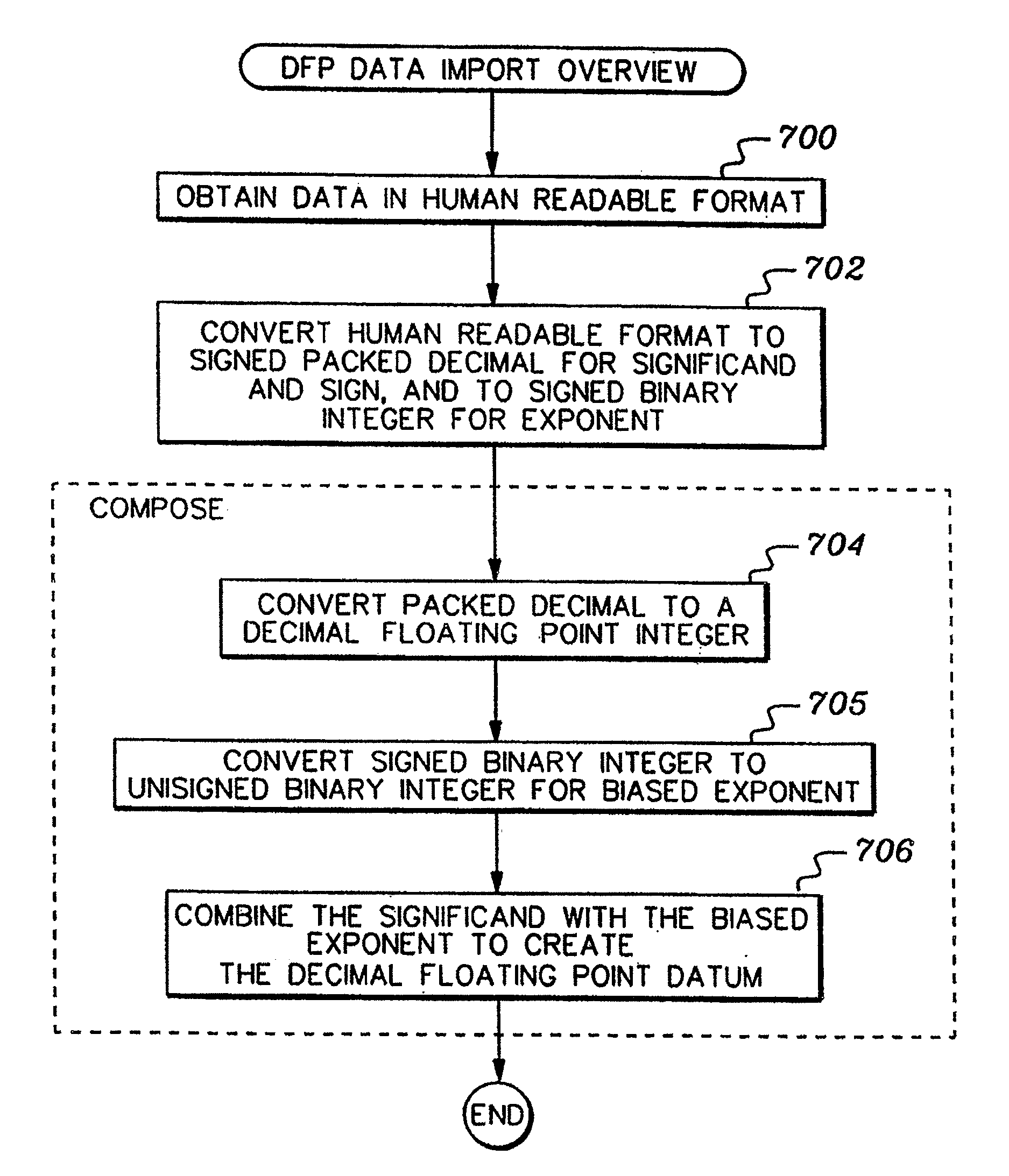
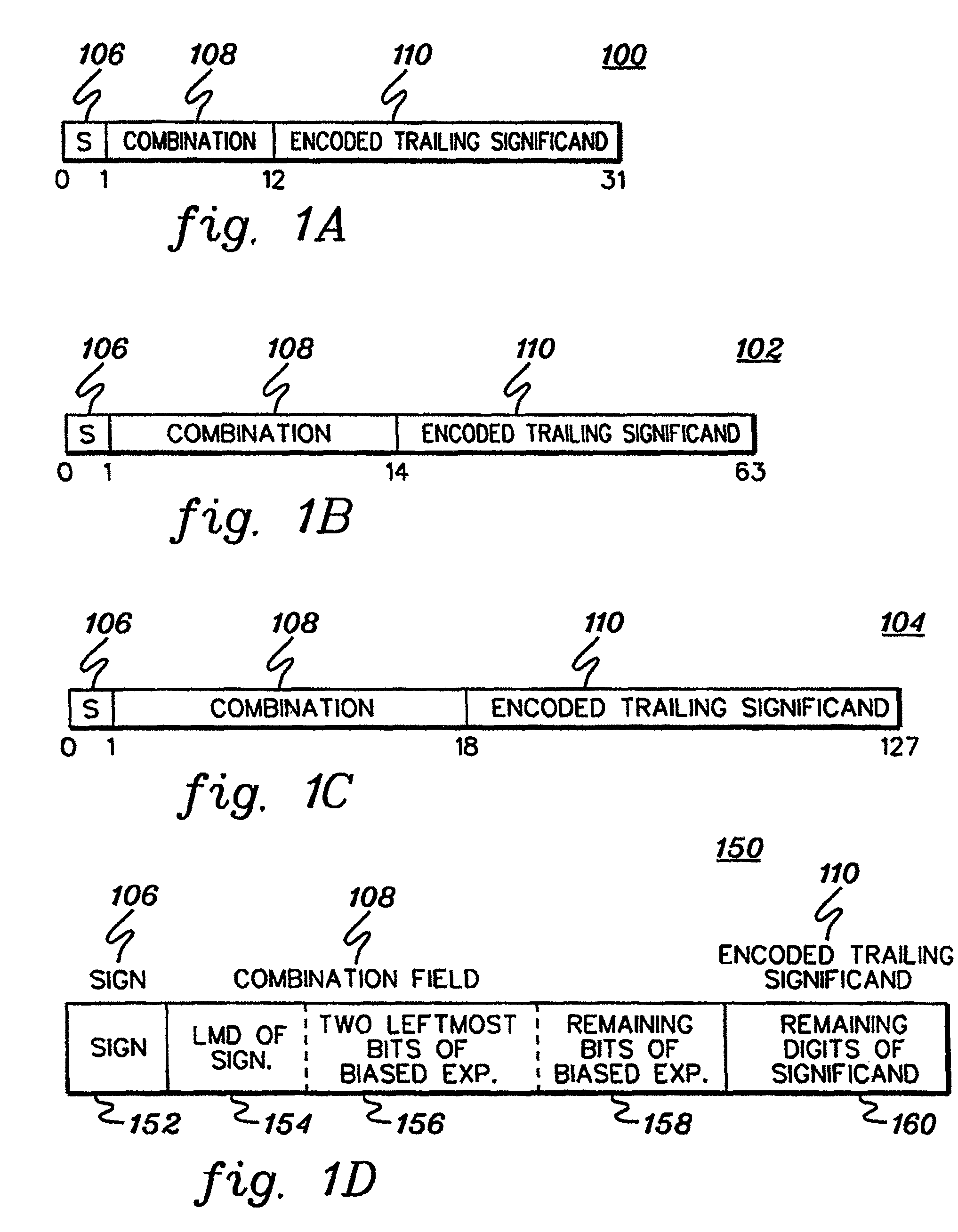
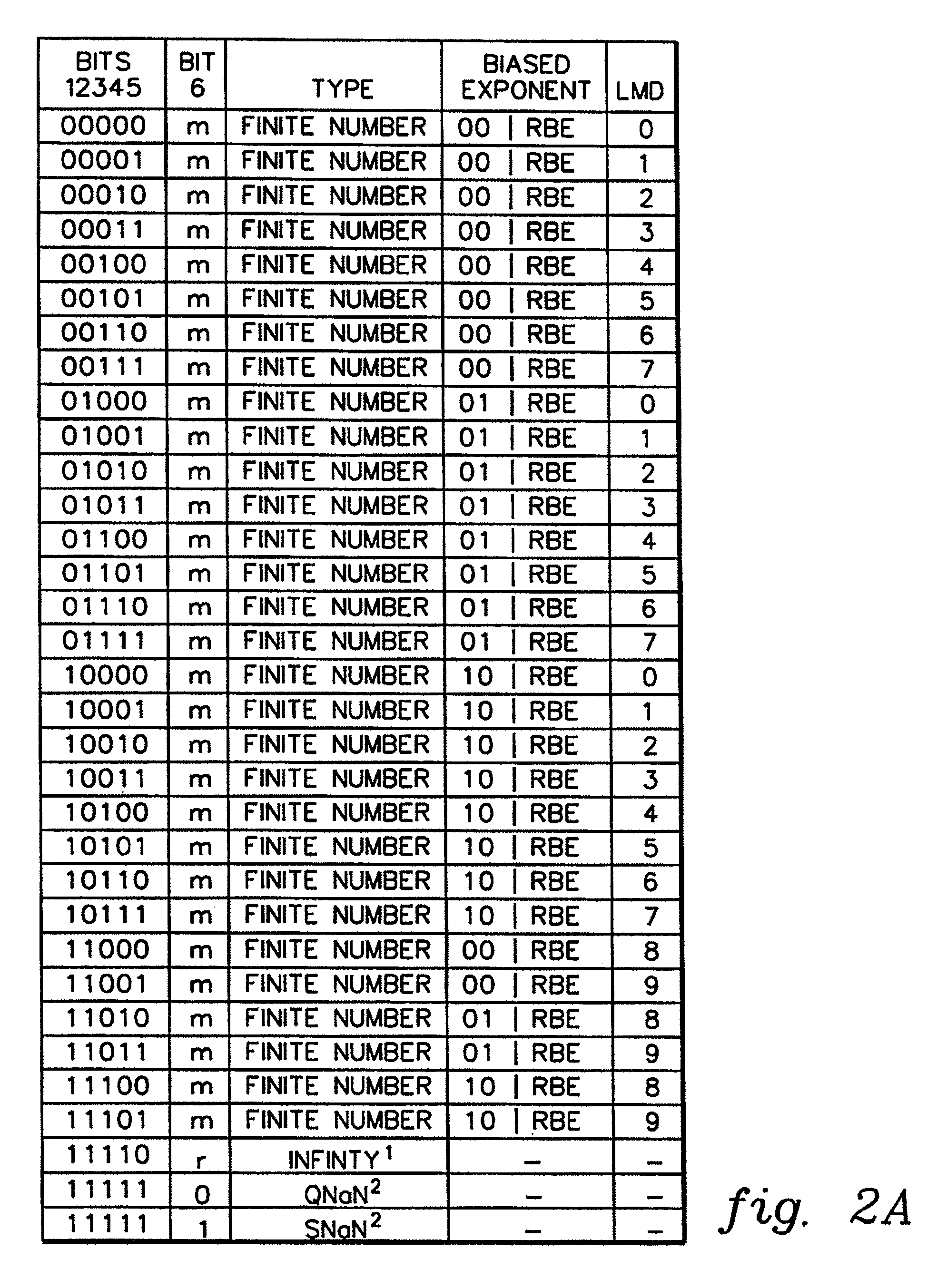
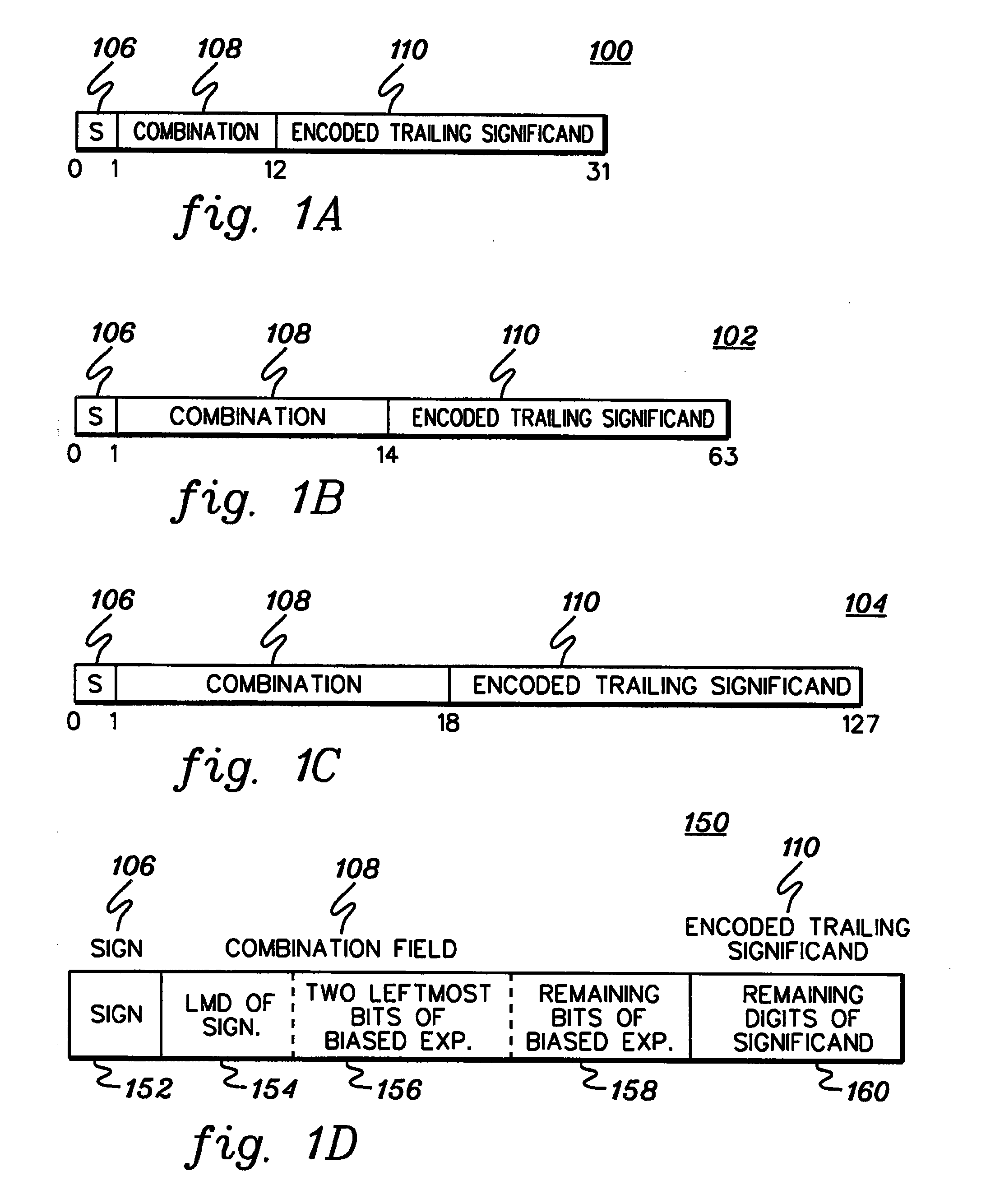
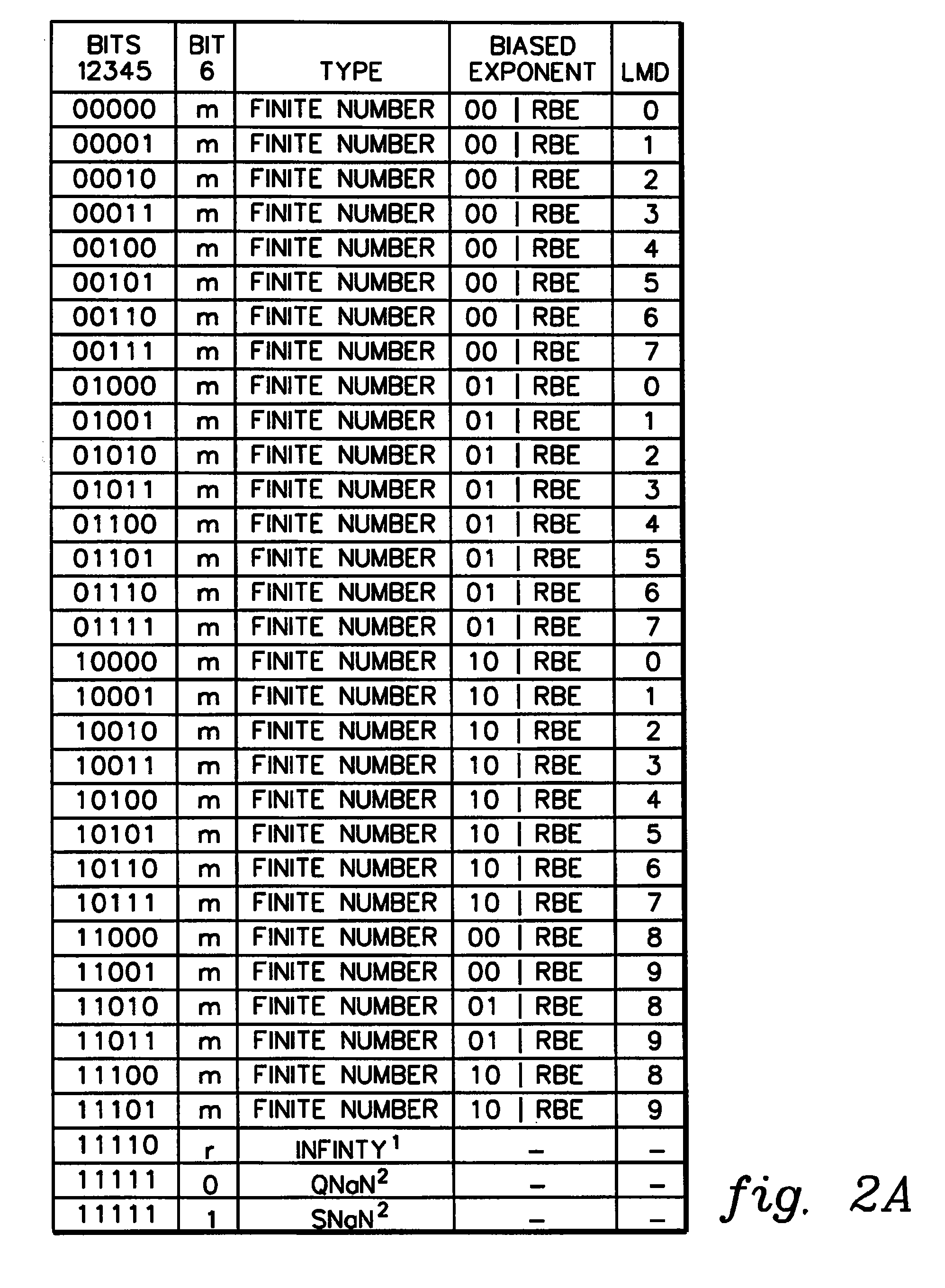
A decimal floating point finite number in a decimal floating point format is composed from the number in a different format. A decimal floating point format includes fields to hold information relating to the sign, exponent and significand of the decimal floating point finite number. Other decimal floating point data, including infinities and NaNs (not a number), are also composed. Decimal floating point data are also decomposed from the decimal floating point format to a different format. For composition and decomposition, one or more instructions may be employed, including a shift significand instruction.
Owner:IBM CORP
Apparatus and method for performing floating point addition
ActiveUS20120215823A1Small and simpleSignificant comprehensive benefitsComputations using contact-making devicesDigital computer detailsOperandLeading zero
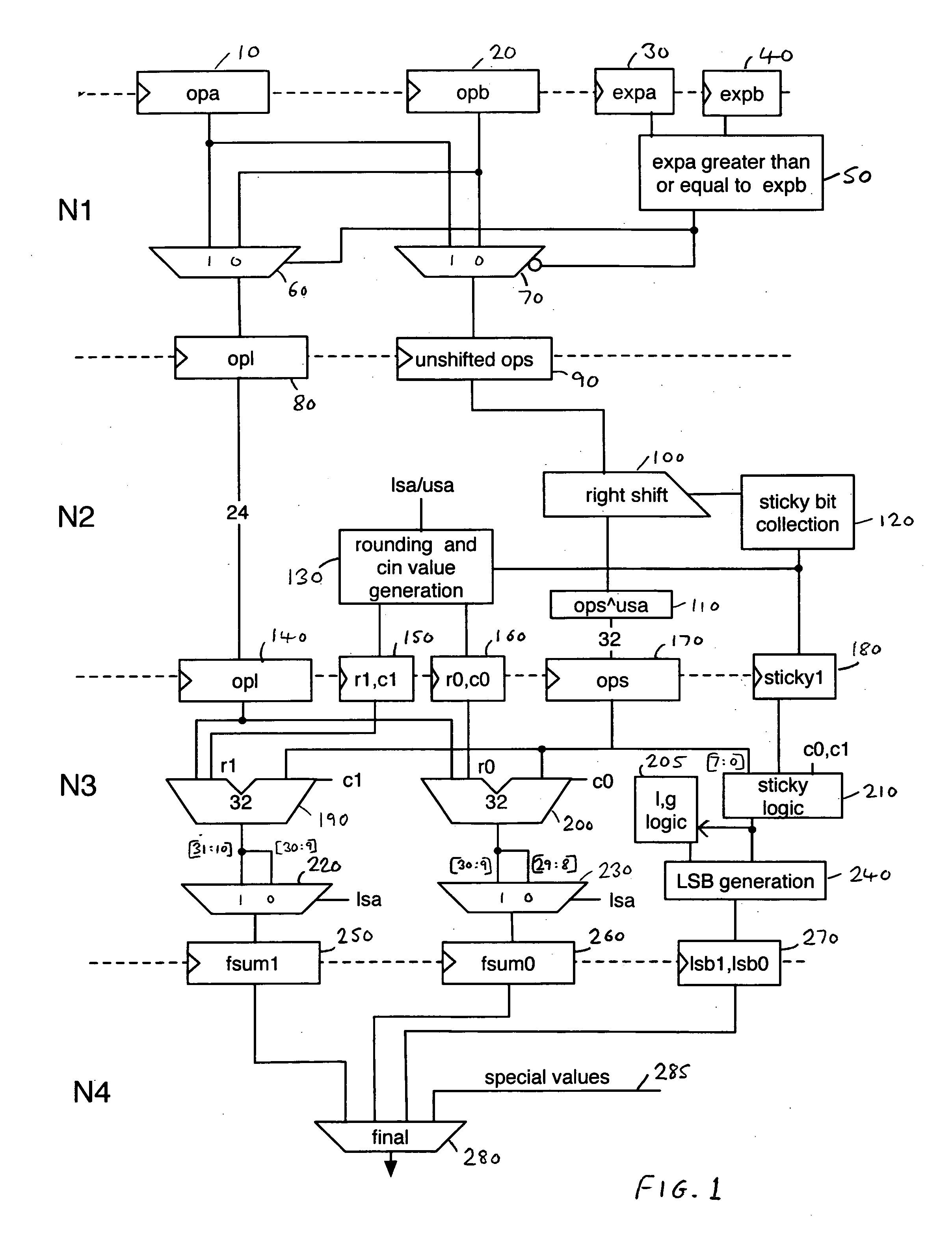
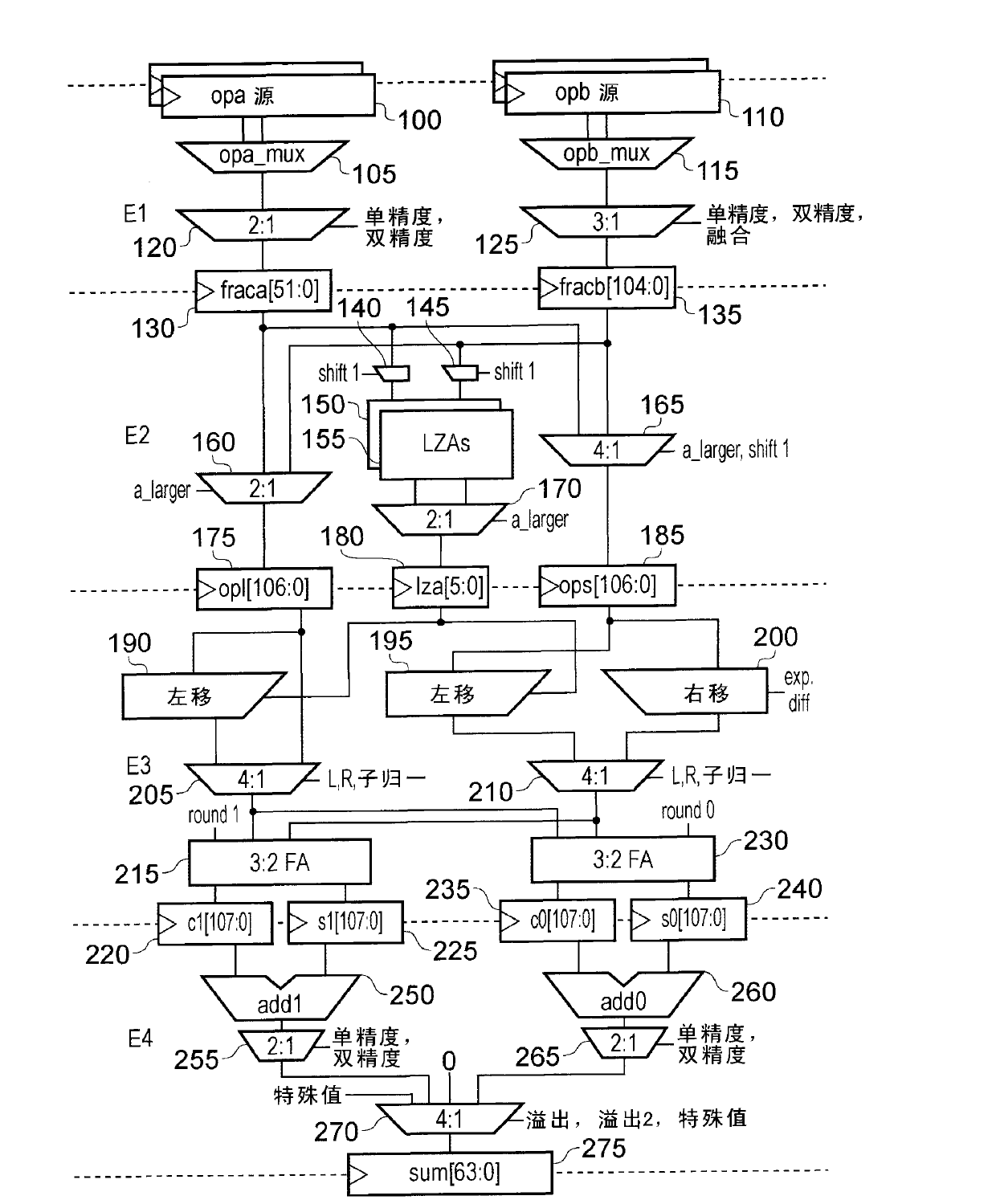
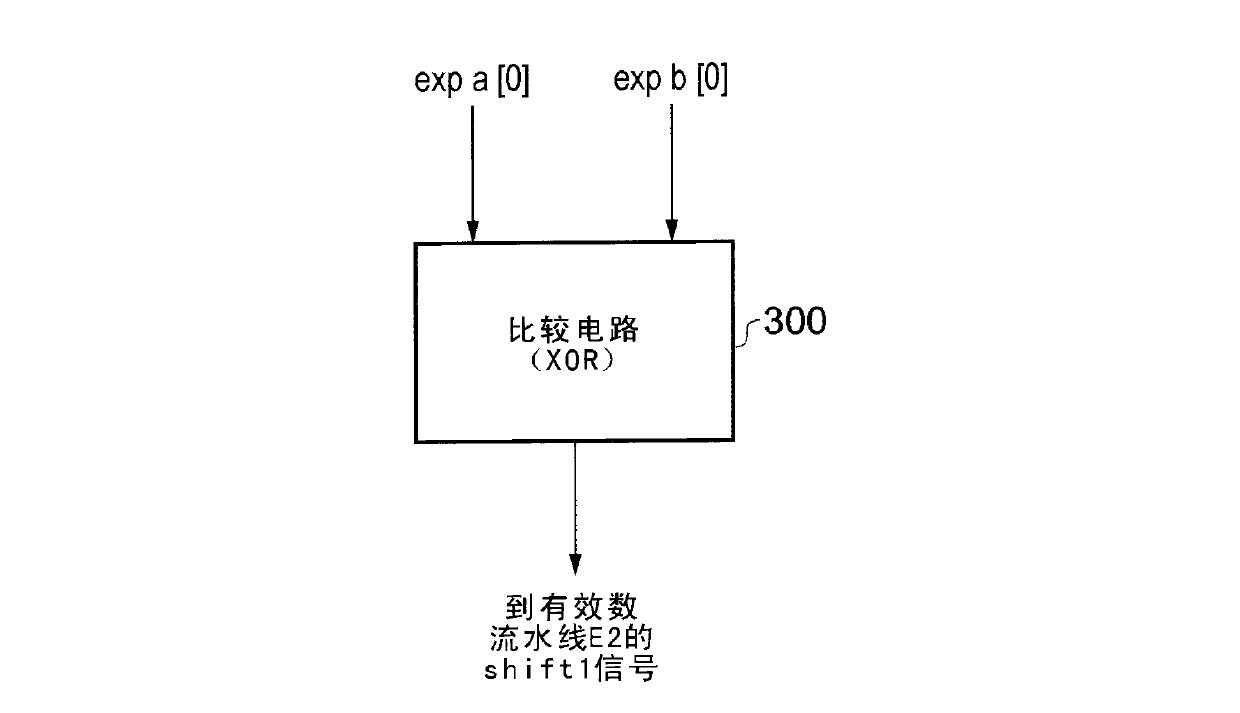
An apparatus and method are provided for performing an addition operation on operands A and B in order to produce a result R, the operands A and B and the result R being floating point values each having a significand and an exponent. The apparatus comprises prediction circuitry for generating a shift indication based on a prediction of the number of leading zeros that would be present in an output produced by subjecting the operands A and B to an unlike signed addition. Further, result pre-normalization circuitry performs a shift operation on the significands of both operand A and operand B prior to addition of the significands, this serving to discard a number of most significant bits of the significands of both operands as determined by the shift indication in order to produce modified significands for operands A and B. Operand analysis circuitry detects, with reference to the exponents of operands A and B, the presence of a leading bit cancellation condition, and addition circuitry is configured, in the presence of the leading bit cancellation condition, to perform an addition of the modified significands for operands A and B, in order to produce the significand of the result R. Such an approach provides a particularly simple and efficient apparatus for performing addition operations.
Owner:ARM LTD
Convert significand of decimal floating point data from packed decimal format
A decimal floating point finite number in a decimal floating point format is composed from the number in a different format. A decimal floating point format includes fields to hold information relating to the sign, exponent and significand of the decimal floating point finite number. Other decimal floating point data, including infinities and NaNs (not a number), are also composed. Decimal floating point data are also decomposed from the decimal floating point format to a different format. For composition and decomposition, one or more instructions may be employed, including one or more convert instructions.
Owner:IBM CORP
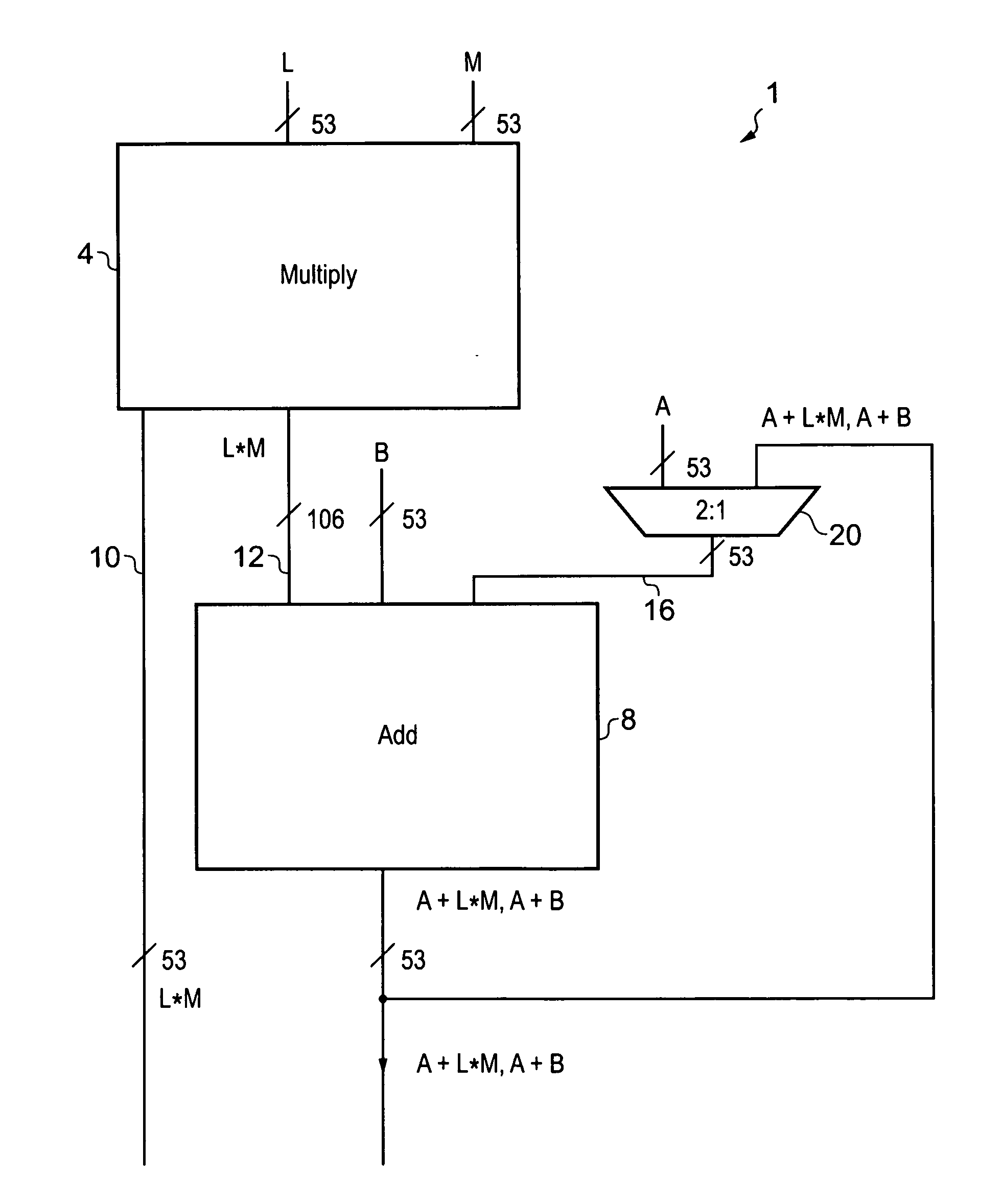
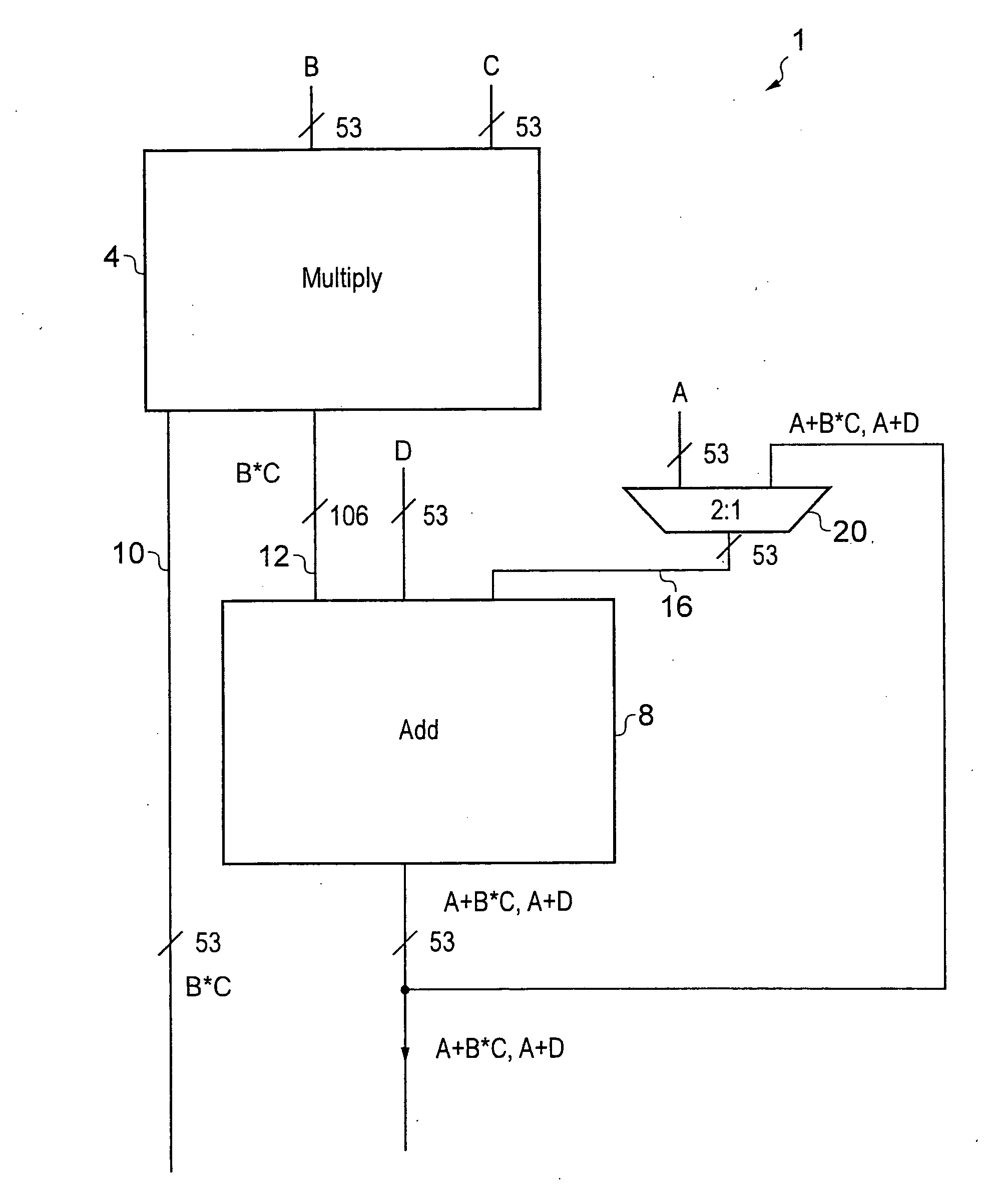
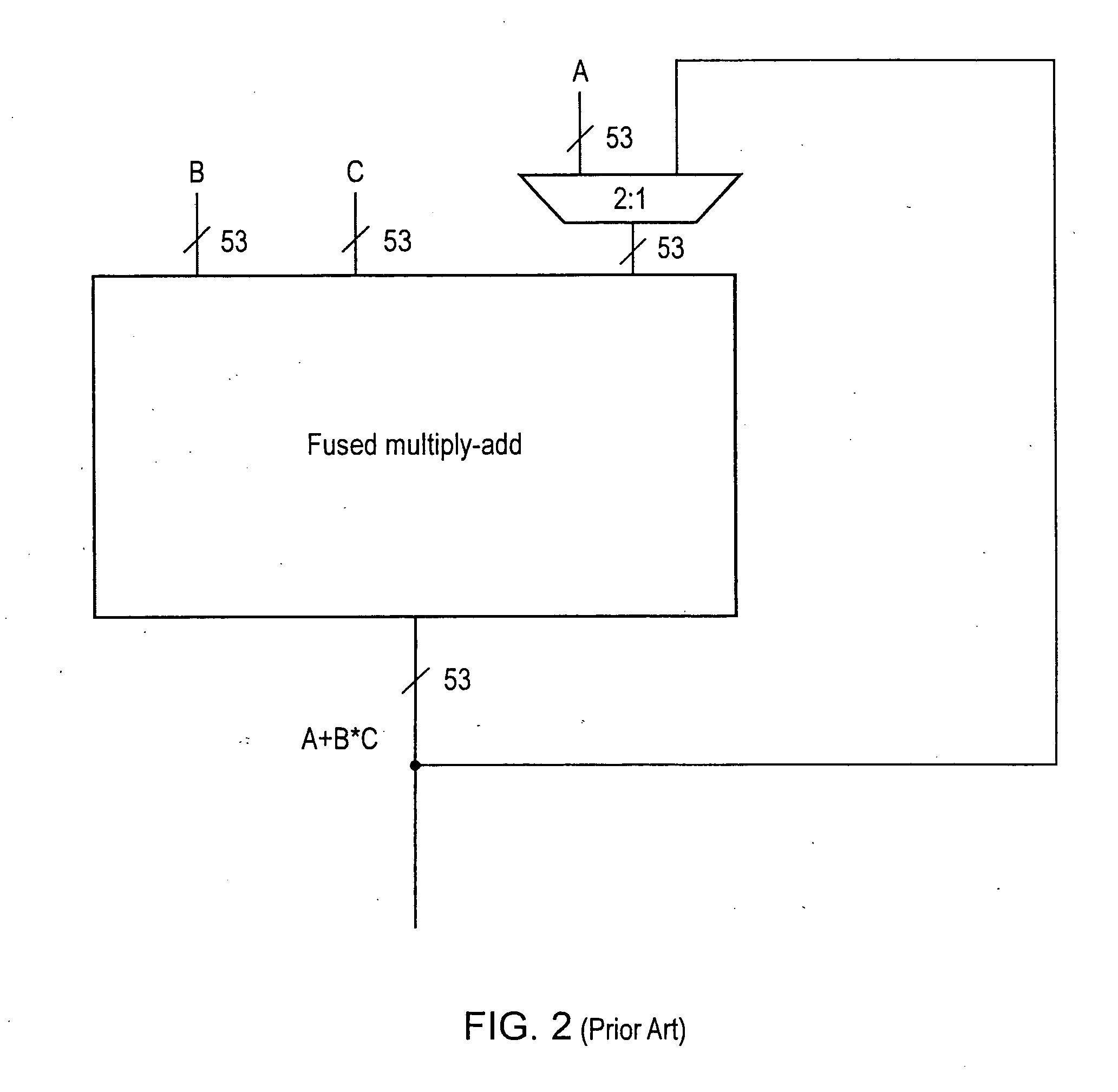
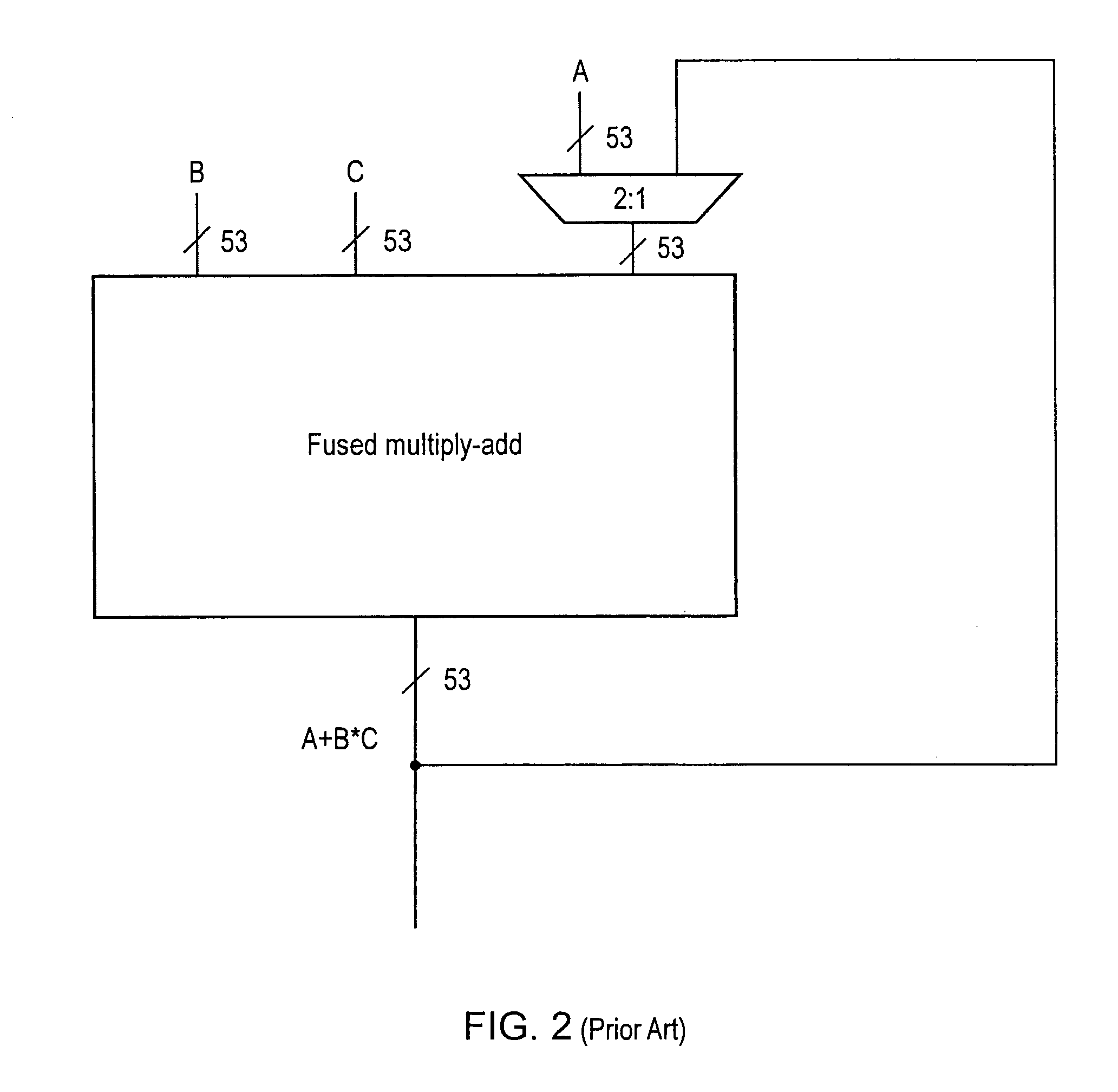
Apparatus and method for performing fused multiply add floating point operation
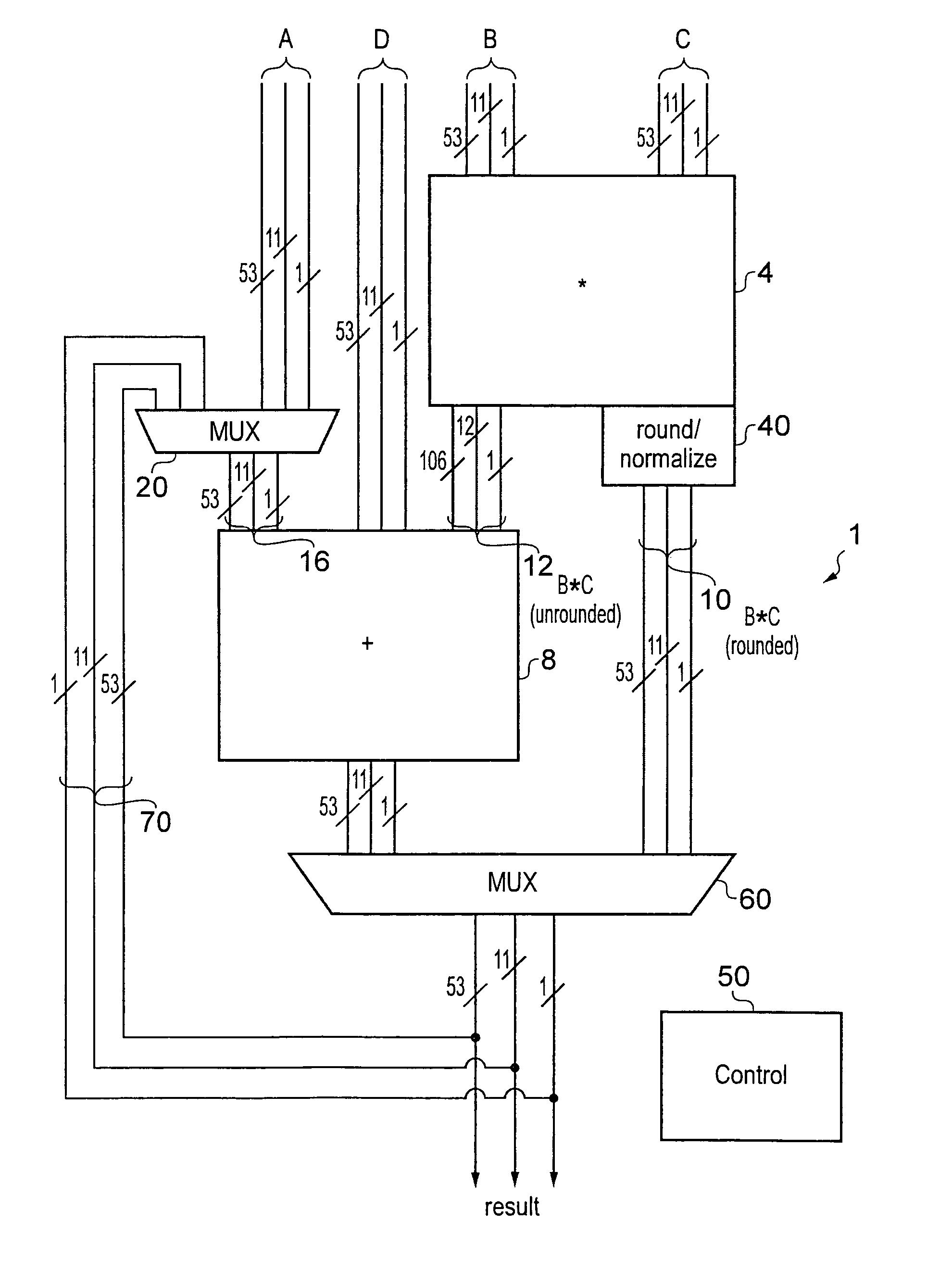
ActiveUS20110072066A1Precise cuttingImprove final accuracyComputation using denominational number representationComputer architectureFloating-point unit
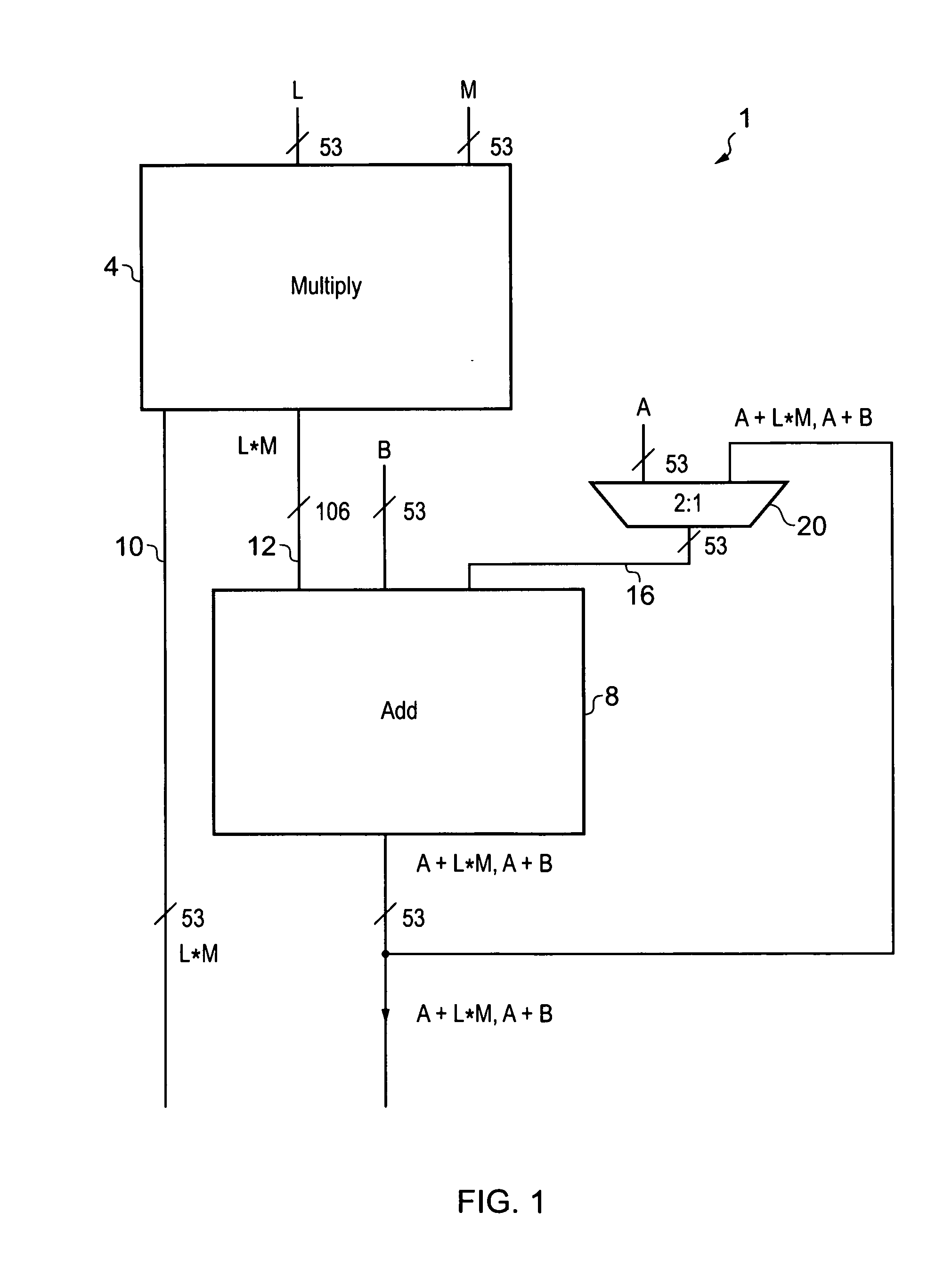
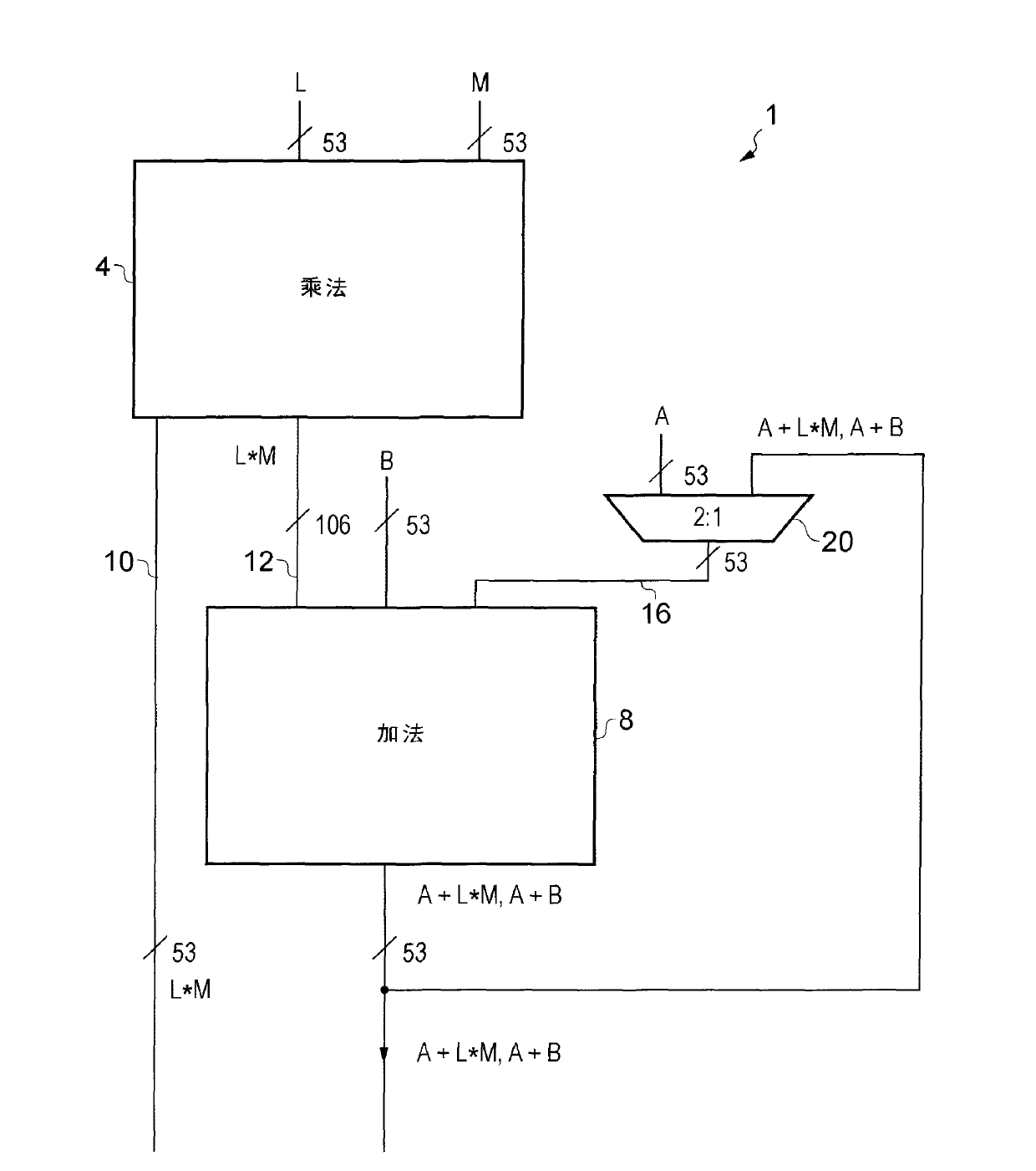
A fused multiply add floating point unit 1 includes multiplying circuitry 4 and adding circuitry 8. The multiply circuitry 4 multiplies operands B and C having N-bit significands to generate an unrounded product B*C. The unrounded product B*C has an M-bit significand, where M>N. The adding circuitry 8 receives an operand A that is input at a later processing cycle than a processing cycle at which the multiplying circuitry 4 receives operands B and C. The adding circuitry 8 commences processing of the operand A after the unrounded product B*C is generated by the multiplying circuitry 4. The adding circuitry 8 adds the operand A to the unrounded product B*C and outputs a rounded result A+B*C.
Owner:ARM LTD
Dynamic Range Adjusting Floating Point Execution Unit
A floating point execution unit is capable of selectively repurposing a subset of the significand bits in a floating point value for use as additional exponent bits to dynamically provide an extended range for floating point calculations. A significand field of a floating point operand may be considered to include first and second portions, with the first portion capable of being concatenated with the second portion to represent the significand for a floating point value, or, to provide an extended range, being concatenated with the exponent field of the floating point operand to represent the exponent for a floating point value.
Owner:IBM CORP
Composition/decomposition of decimal floating point data
A decimal floating point finite number in a decimal floating point format is composed from the number in a different format. A decimal floating point format includes fields to hold information relating to the sign, exponent and significand of the decimal floating point finite number. Other decimal floating point data, including infinities and NaNs (not a number), are also composed. Decimal floating point data are also decomposed from the decimal floating point format to a different format.
Owner:IBM CORP
Insert/extract biased exponent of decimal floating point data
InactiveUS20080270495A1Digital computer detailsSpecific program execution arrangementsParallel computingSialic acid synthase
A decimal floating point finite number in a decimal floating point format is composed from the number in a different format. A decimal floating point format includes fields to hold information relating to the sign, exponent and significand of the decimal floating point finite number. Other decimal floating point data, including infinities and NaNs (not a number), are also composed. Decimal floating point data are also decomposed from the decimal floating point format to a different format. For composition and decomposition, one or more instructions may be employed, including an insert biased exponent or extract biased exponent instruction.
Owner:IBM CORP
Extract biased exponent of decimal floating point data
A decimal floating point finite number in a decimal floating point format is composed from the number in a different format. A decimal floating point format includes fields to hold information relating to the sign, exponent and significand of the decimal floating point finite number. Other decimal floating point data, including infinities and NaNs (not a number), are also composed. Decimal floating point data are also decomposed from the decimal floating point format to a different format. For composition and decomposition, one or more instructions may be employed, including an insert biased exponent or extract biased exponent instruction.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method for setting a bit associated with each component of packed floating-pint operand that is normalized in SIMD operations
InactiveUS6321327B1Improve processor performanceEliminate needGeneral purpose stored program computerSpecific program execution arrangementsProcessor registerOperand
A method is provided for loading a packed floating-point operand into a register file entry having one or more associated implicit bits. The packed floating point operand includes multiple component operands. Significand and exponent bits for each component operand are copied to corresponding fields of the register entry, and the exponent bits are tested to determine whether the component operand is normalized. An implicit bit corresponding to the component operand is set when the component operand is normalized.
Owner:INTEL CORP
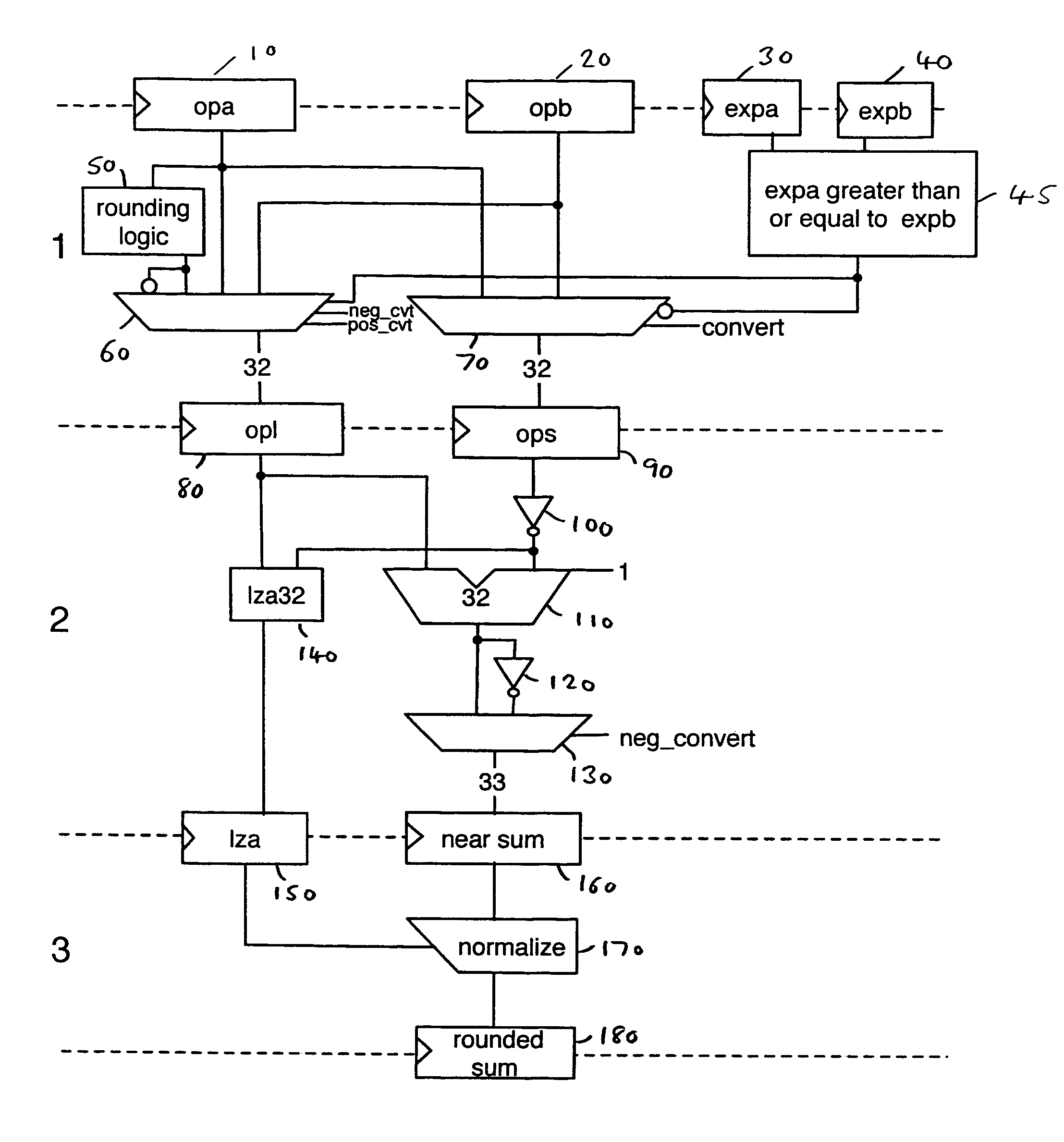
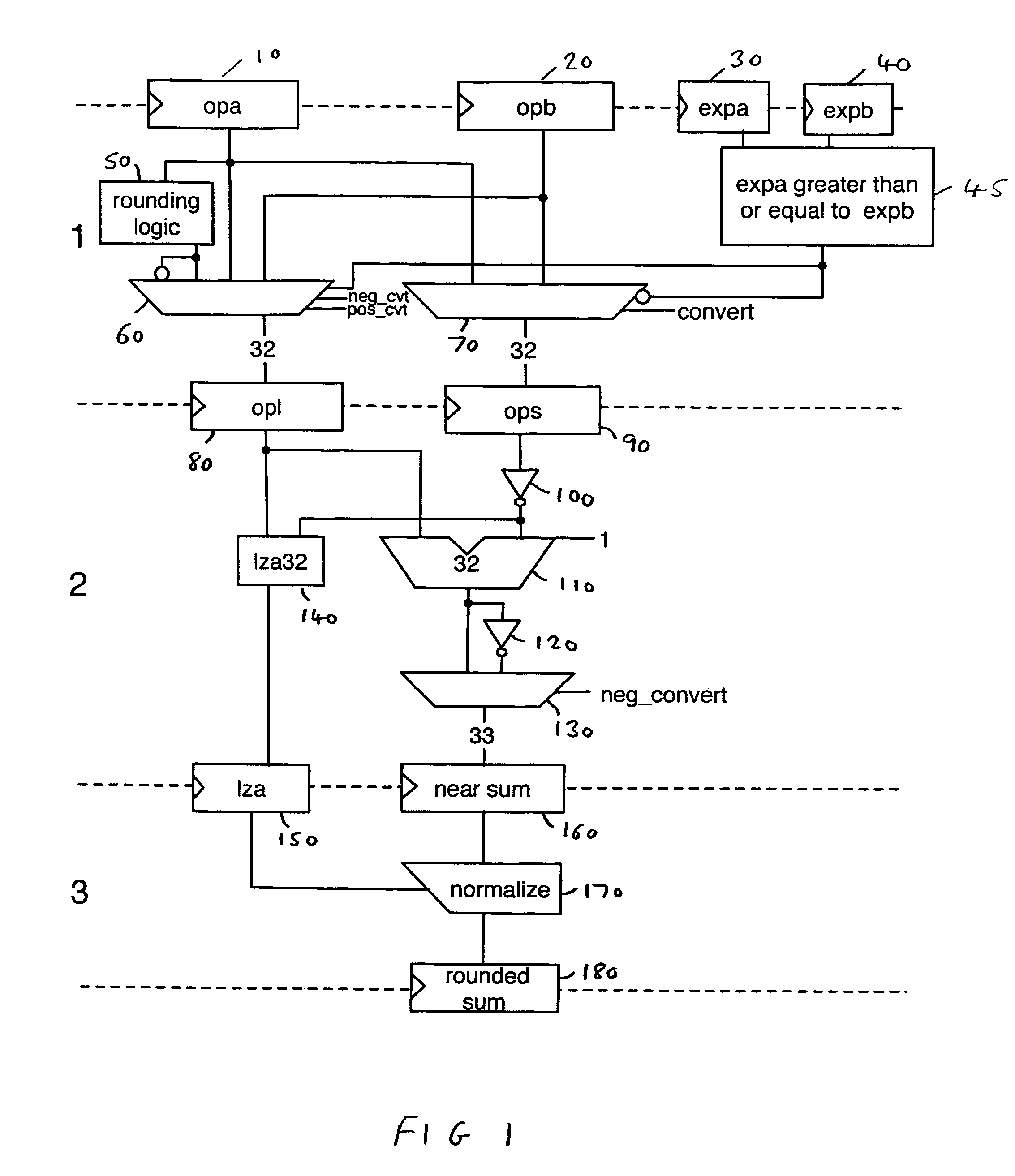
Data processing apparatus and method for performing floating point addition
ActiveUS20060136543A1Reduce logicLow costComputations using contact-making devicesComputation using non-contact making devicesSingle levelOperand
A data processing apparatus and method are provided for adding n-bit significands of first and second floating point operands to produce an n-bit result. The data processing apparatus comprises determination logic operable to determine the larger operand of the first and second operands, and alignment logic operable to align the n-bit significand of the smaller operand with the n-bit significand of the larger operand. First adder logic is then operable to perform a first sum operation in order to generate a first rounded result in non-redundant form equivalent to the addition of the aligned significands with a rounding increment injected at a first predetermined rounding position appropriate for a non-overflow condition, the first adder logic comprising a single level of adder logic. Further, second adder logic is provided to perform a second sum operation in order to generate a second rounded result in non-redundant form equivalent to the addition of the aligned significands with a rounding increment injected at a second predetermined rounding position appropriate for an overflow condition, the second adder logic also comprising a single level of adder logic. Selector logic is then used to derive the n-bit result from either the first rounded result or the second rounded result.
Owner:ARM LTD
Employing a mask field of an instruction to encode a sign of a result of the instruction
A decimal floating point finite number in a decimal floating point format is composed from the number in a different format. A decimal floating point format includes fields to hold information relating to the sign, exponent and significand of the decimal floating point finite number. Other decimal floating point data, including infinities and NaNs (not a number), are also composed. Decimal floating point data are also decomposed from the decimal floating point format to a different format. For composition and decomposition, one or more instructions may be employed, including one or more convert instructions.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Decomposition of decimal floating point data, and methods therefor
ActiveUS20080270507A1Computations using contact-making devicesCode conversionDecompositionParallel computing
A decimal floating point finite number in a decimal floating point format is composed from the number in a different format. A decimal floating point format includes fields to hold information relating to the sign, exponent and significand of the decimal floating point finite number. Other decimal floating point data, including infinities and NaNs (not a number), are also composed. Decimal floating point data are also decomposed from the decimal floating point format to a different format.
Owner:IBM CORP
Decimal Floating-Point Adder with Leading Zero Anticipation
ActiveUS20100312812A1Computations using contact-making devicesDigital computer detailsOperandLeading zero
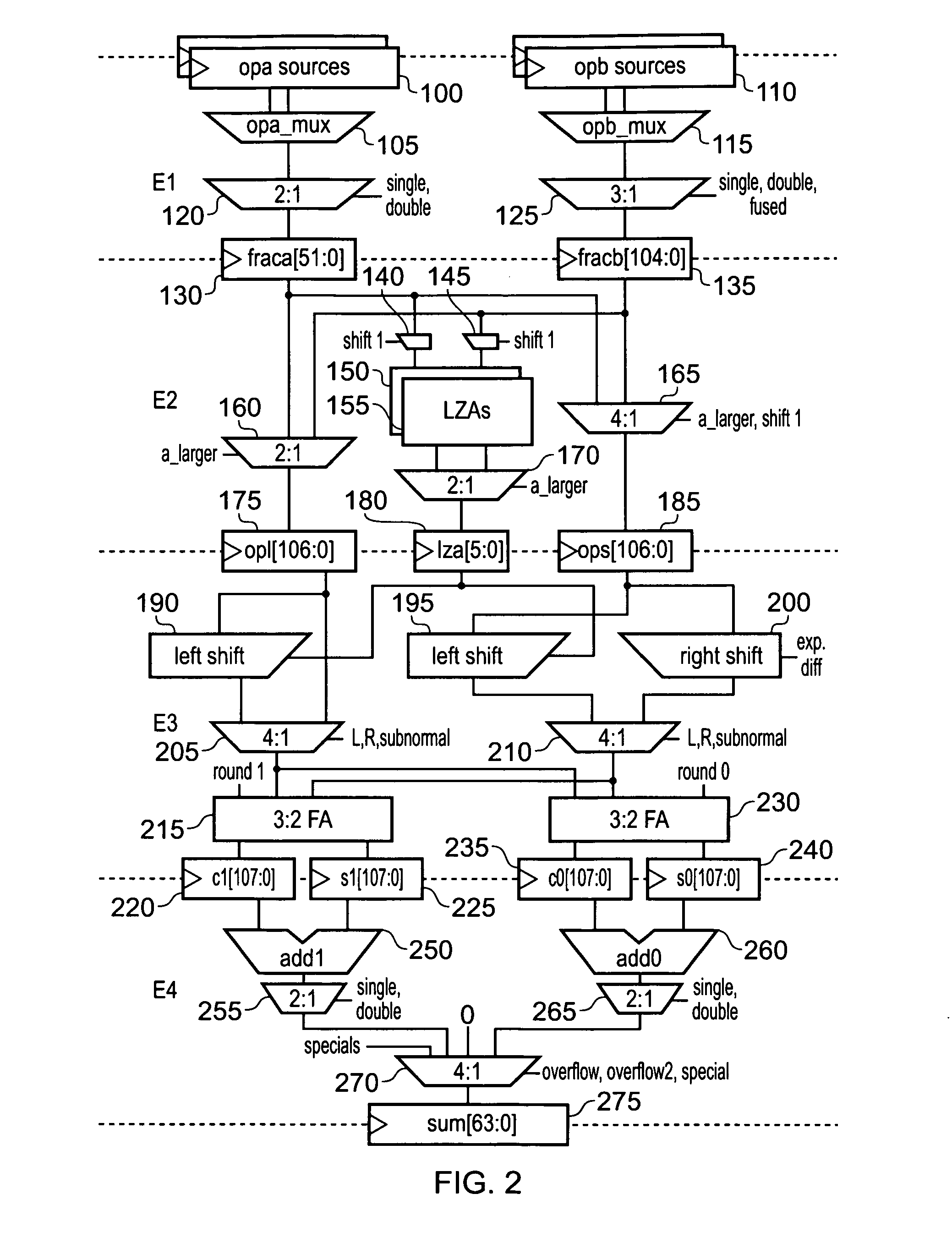
A decimal floating-point (DFP) adder includes a decimal leading-zero anticipator (LZA). The DFP adder receives DFP operands. Each operand includes a significand, an exponent, a sign bit and a leading zero count for the significand. The DFP adder adds or subtracts the DFP operands to obtain a DFP result. The LZA determines the leading zero count associated with the significand of the DFP result. The LZA operates at least partially in parallel with circuitry (in the DFP adder) that computes the DFP result. The LZA does not wait for that circuitry to finish computation of the DFP result. Instead it “anticipates” the number of leading zeros that the result's significand will contain.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
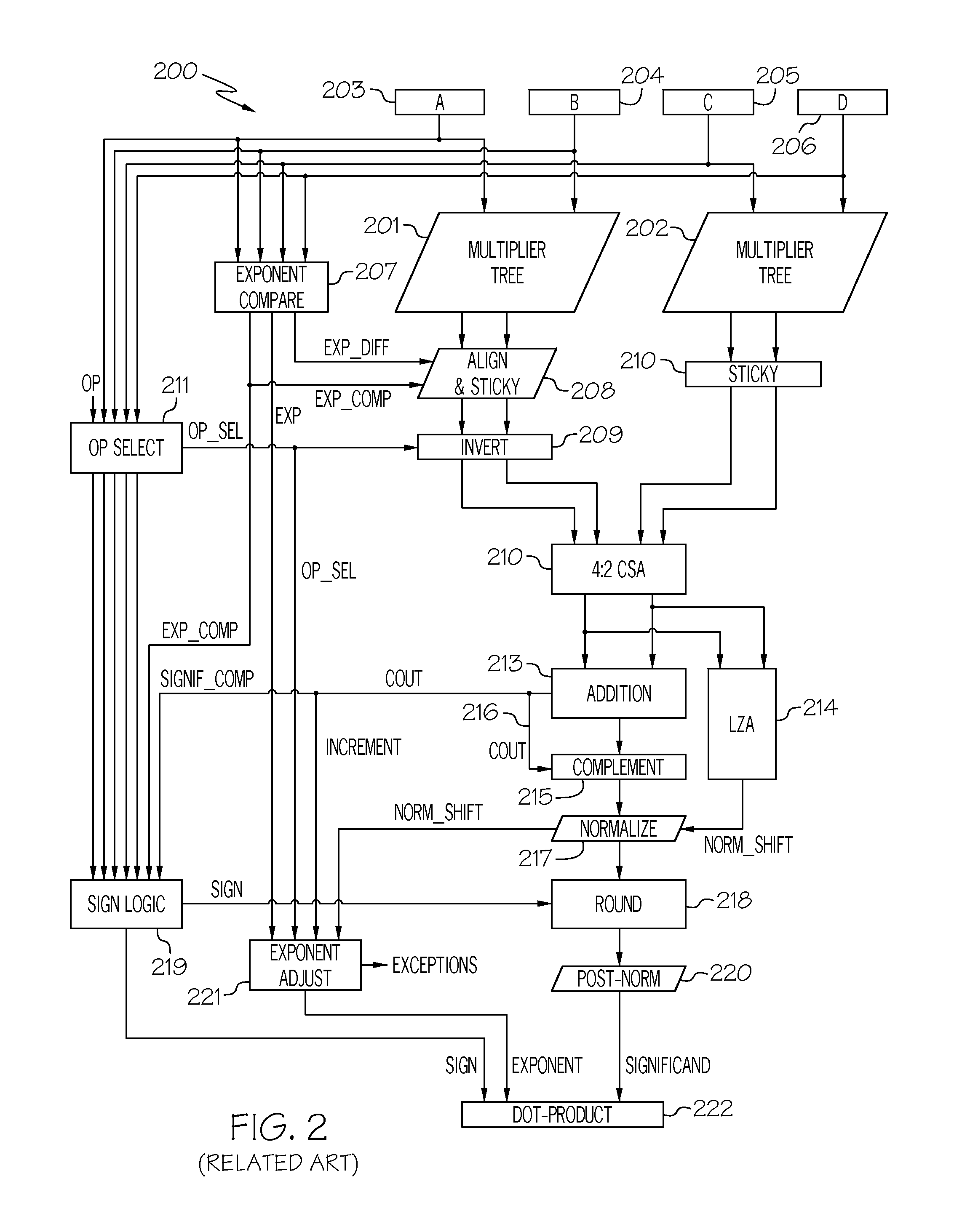
Dual-path fused floating-point two-term dot product unit
InactiveUS8626813B1Shorten the lengthComputation using denominational number representationLeading zeroComputer science
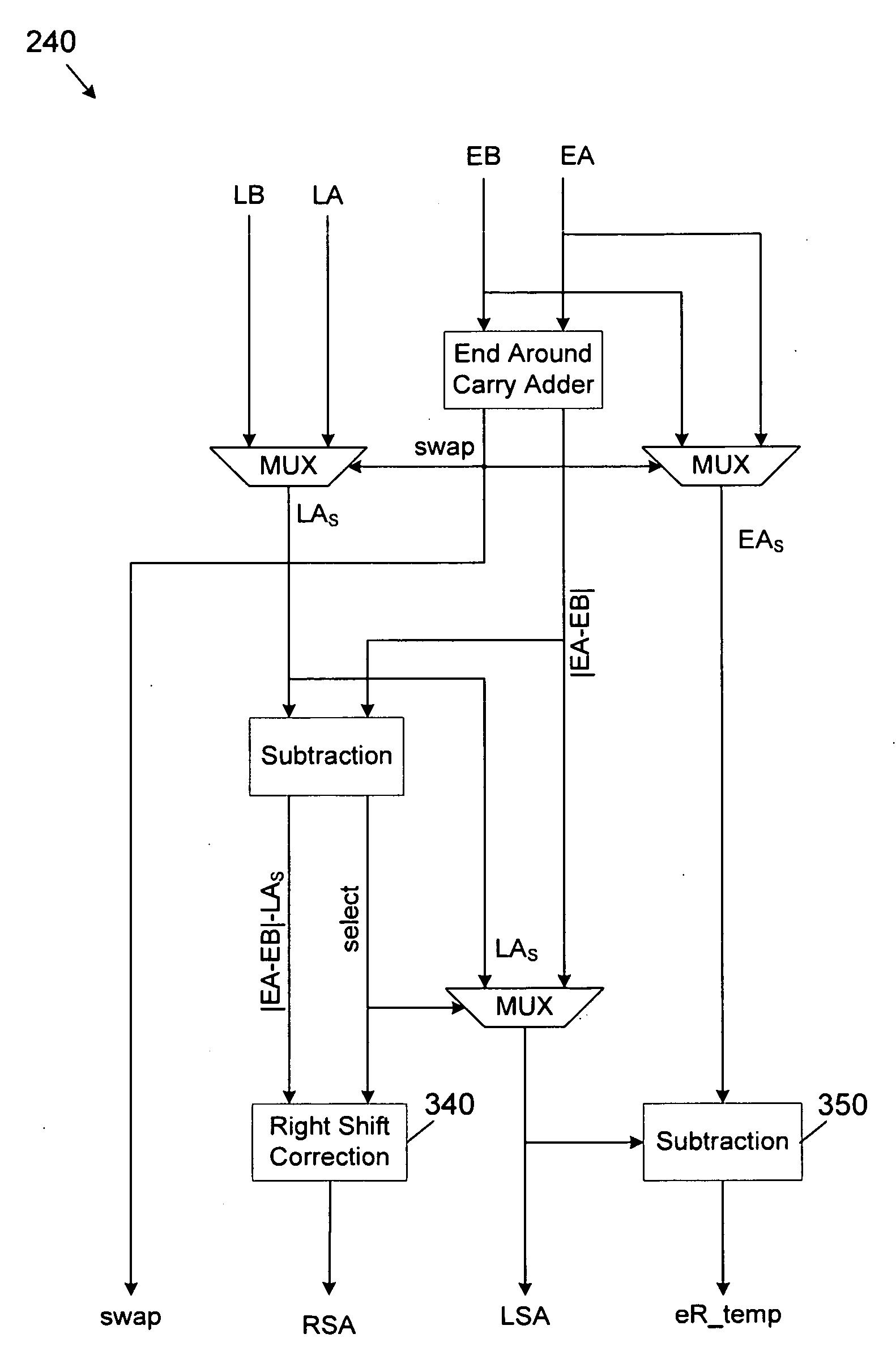
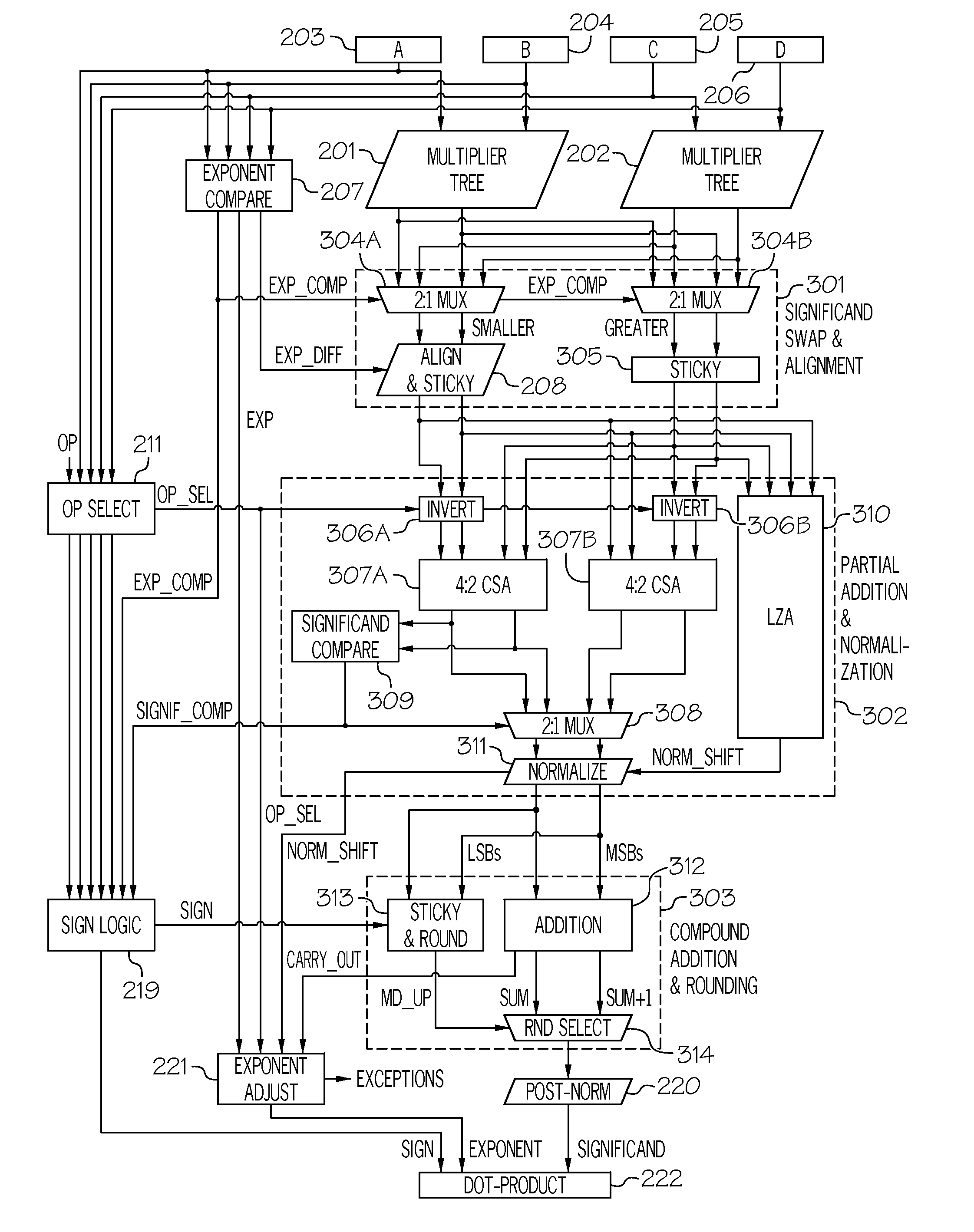
A fused floating-point dot product unit. The fused dot product unit includes an improved alignment scheme that generates smaller significand pairs compared to the traditional alignment due to the reduced shift amount and sticky logic. Furthermore, the fused dot product unit implements early normalization and a fast rounding scheme. By normalizing the significands prior to the significand addition, the length of the adder can be reduced and the round logic can be performed in parallel. Additionally, the fused dot product unit implements a four-input leading zero anticipation unit thereby reducing the overhead of the reduction tree by encoding the four inputs at once. The fused floating-point dot product unit may also employ a dual-path (a far path and a close path) algorithm to improve performance. Pipelining may also be applied to the dual-path fused dot product unit to increase the throughput.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Composition of decimal floating point data
ActiveUS8051118B2Code conversionDigital computer detailsDecimal128 floating-point formatParallel computing
A decimal floating point finite number in a decimal floating point format is composed from the number in a different format. A decimal floating point format includes fields to hold information relating to the sign, exponent and significand of the decimal floating point finite number. Other decimal floating point data, including infinities and NaNs (not a number), are also composed. Decimal floating point data are also decomposed from the decimal floating point format to a different format.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Floating point format converter
ActiveUS8719322B2Small amount of memoryMore accurateComputations using contact-making devicesDigital computer detailsComputer scienceComputer program
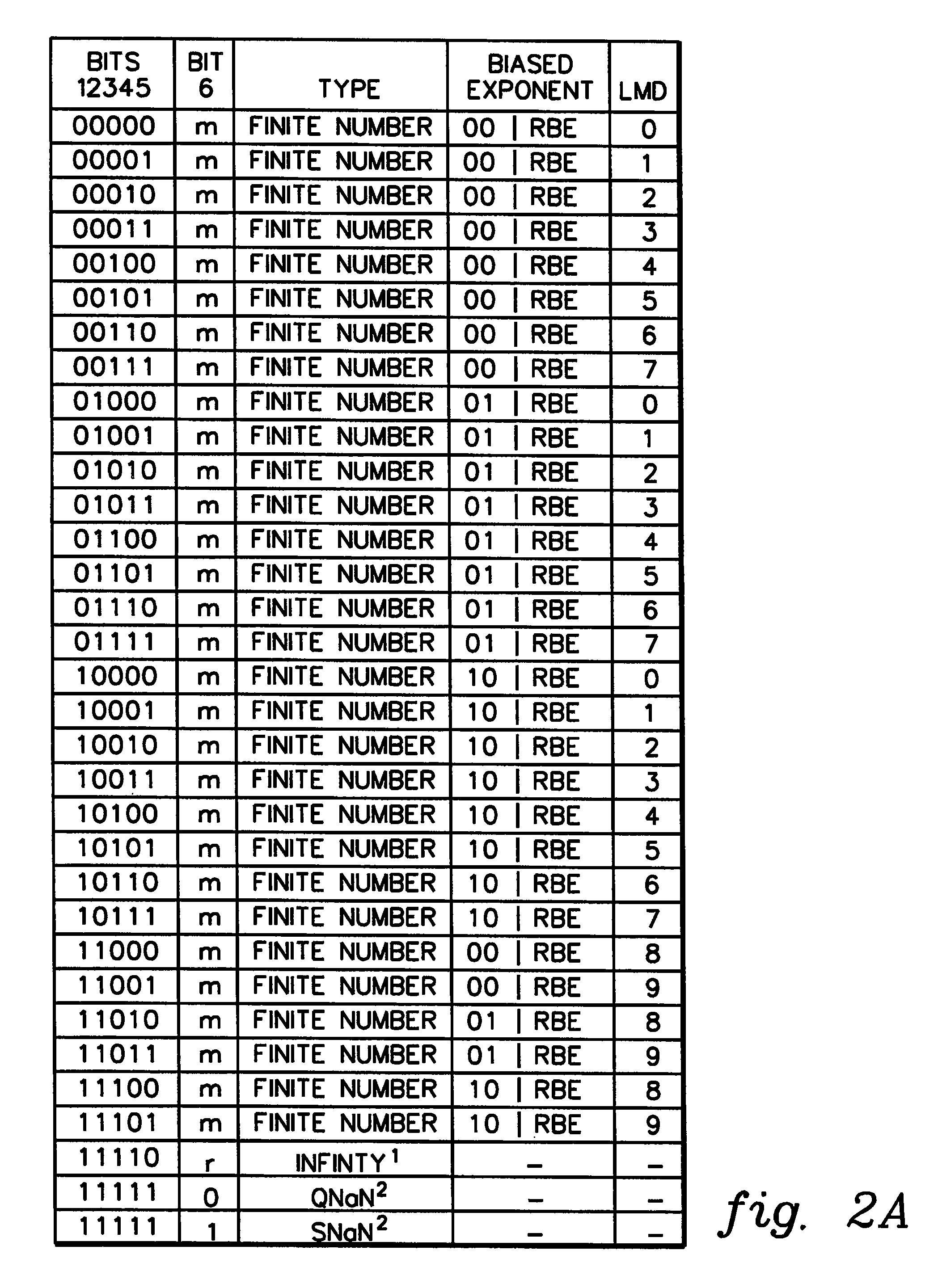
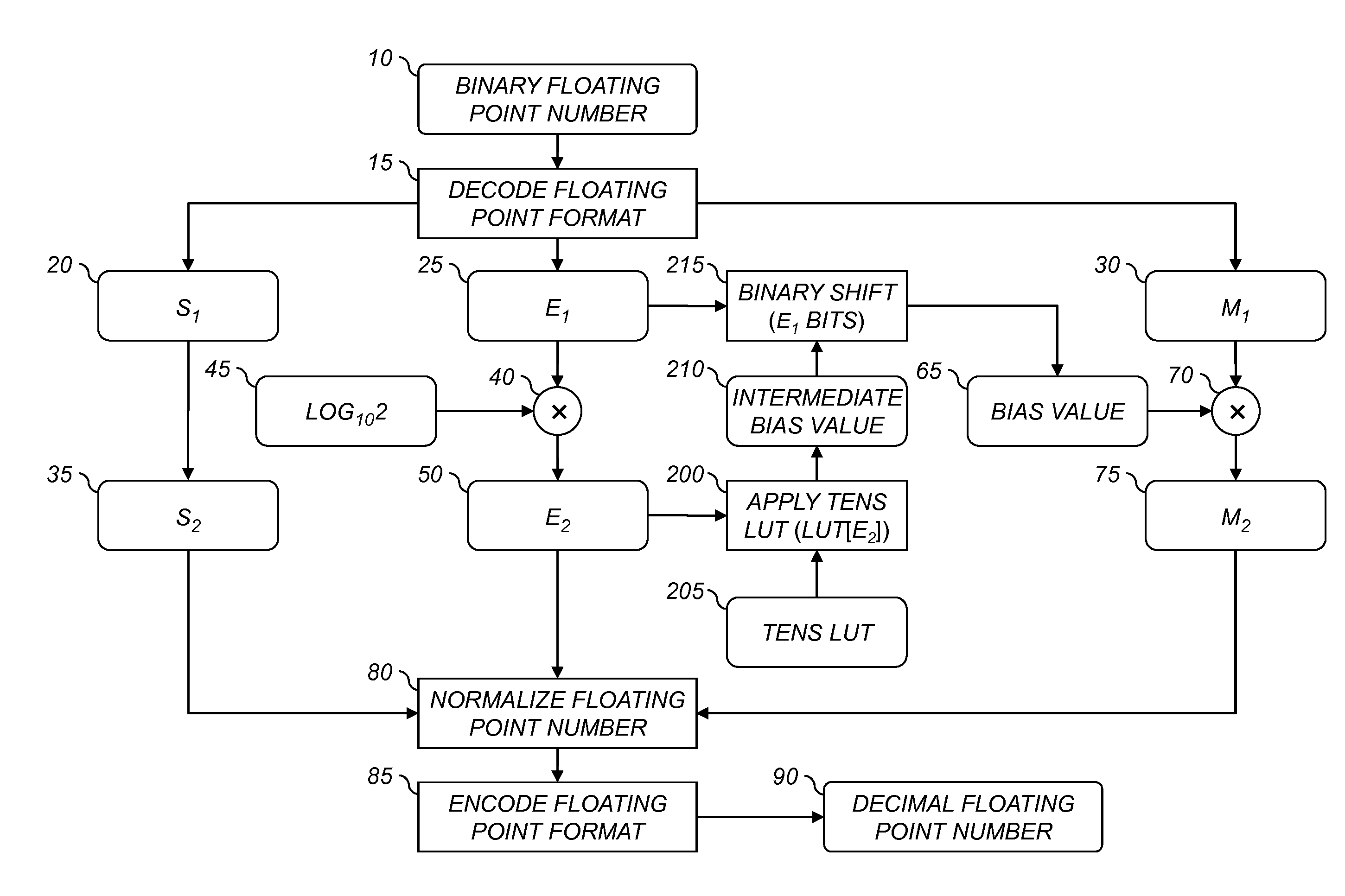
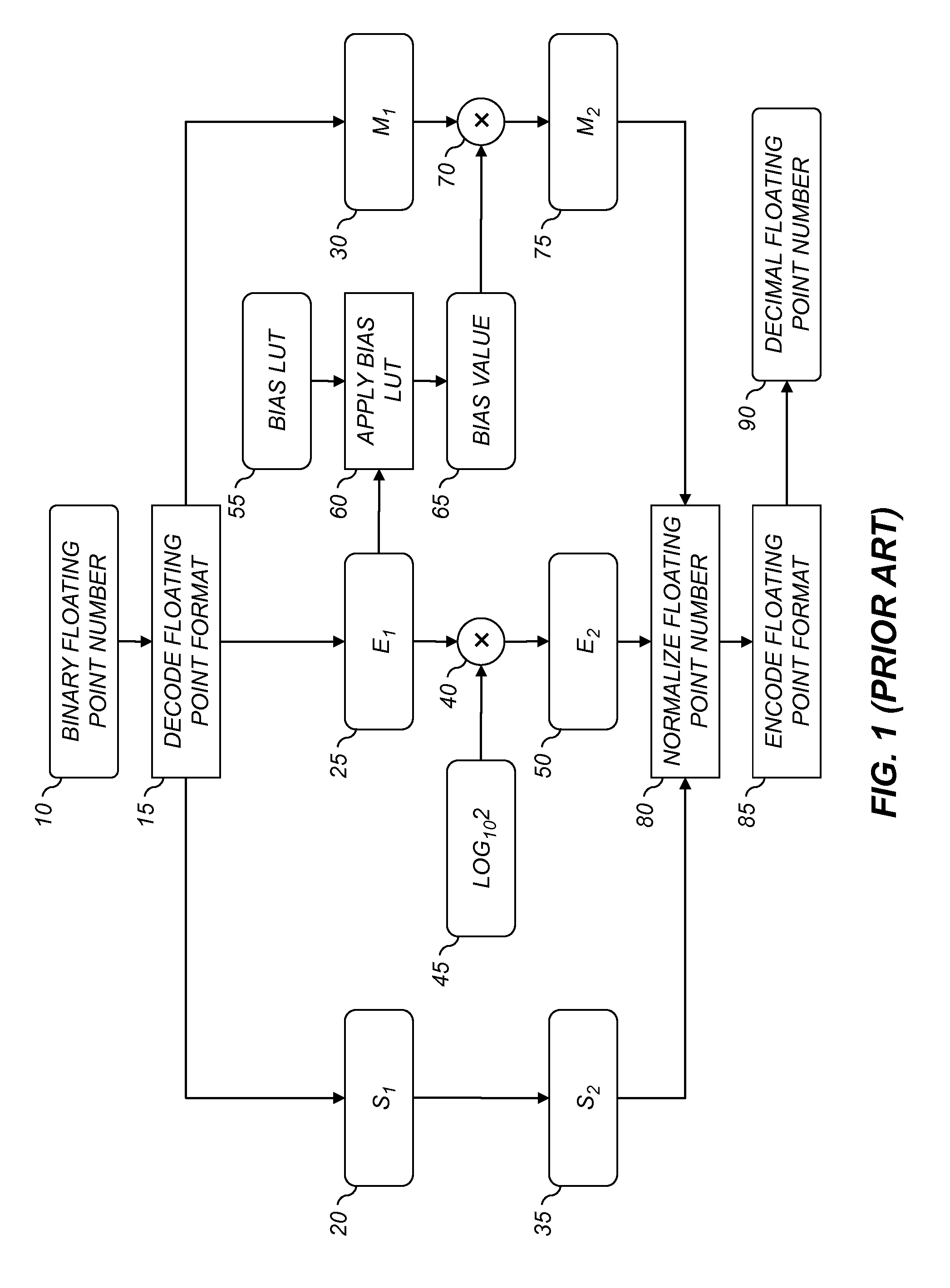
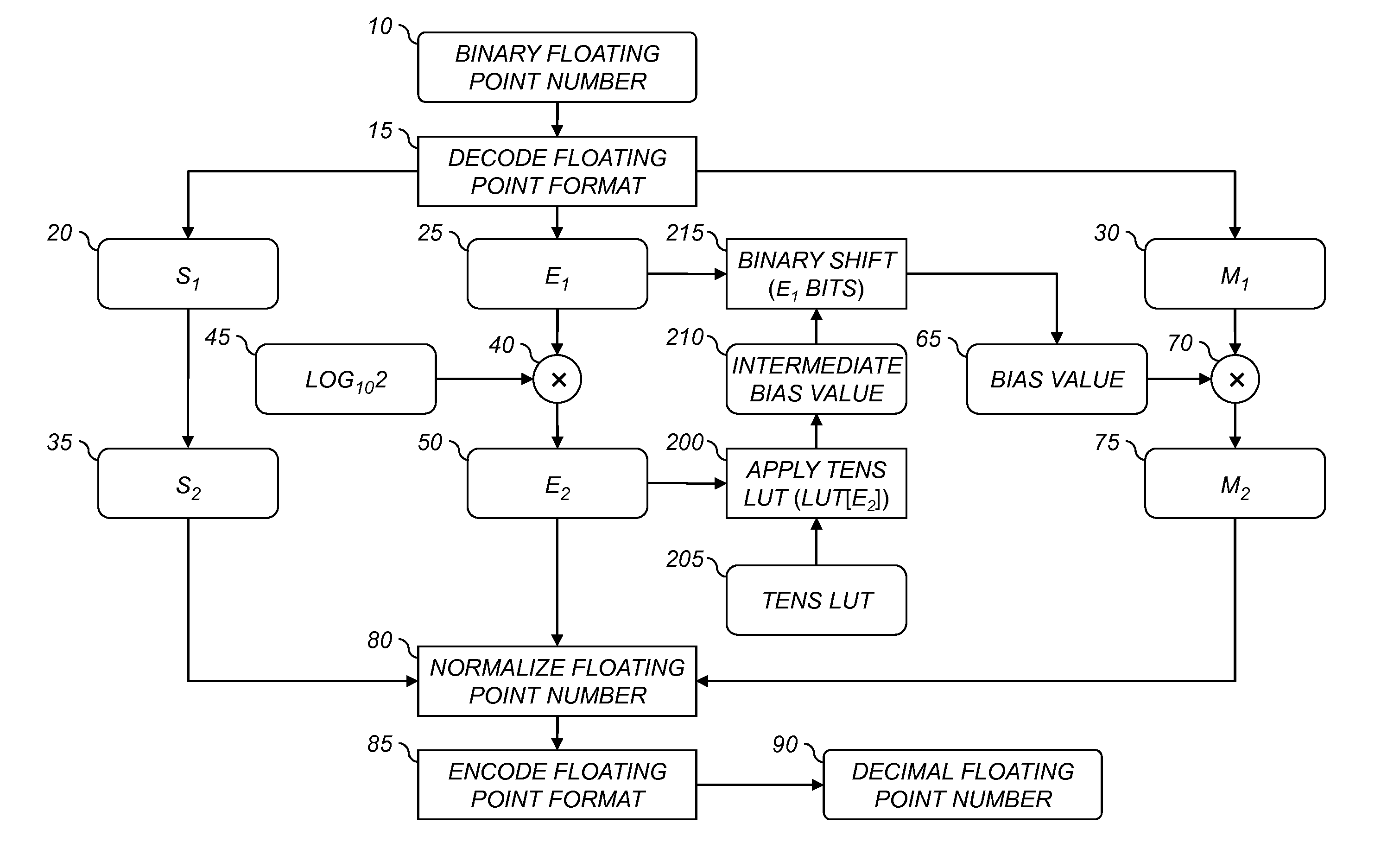
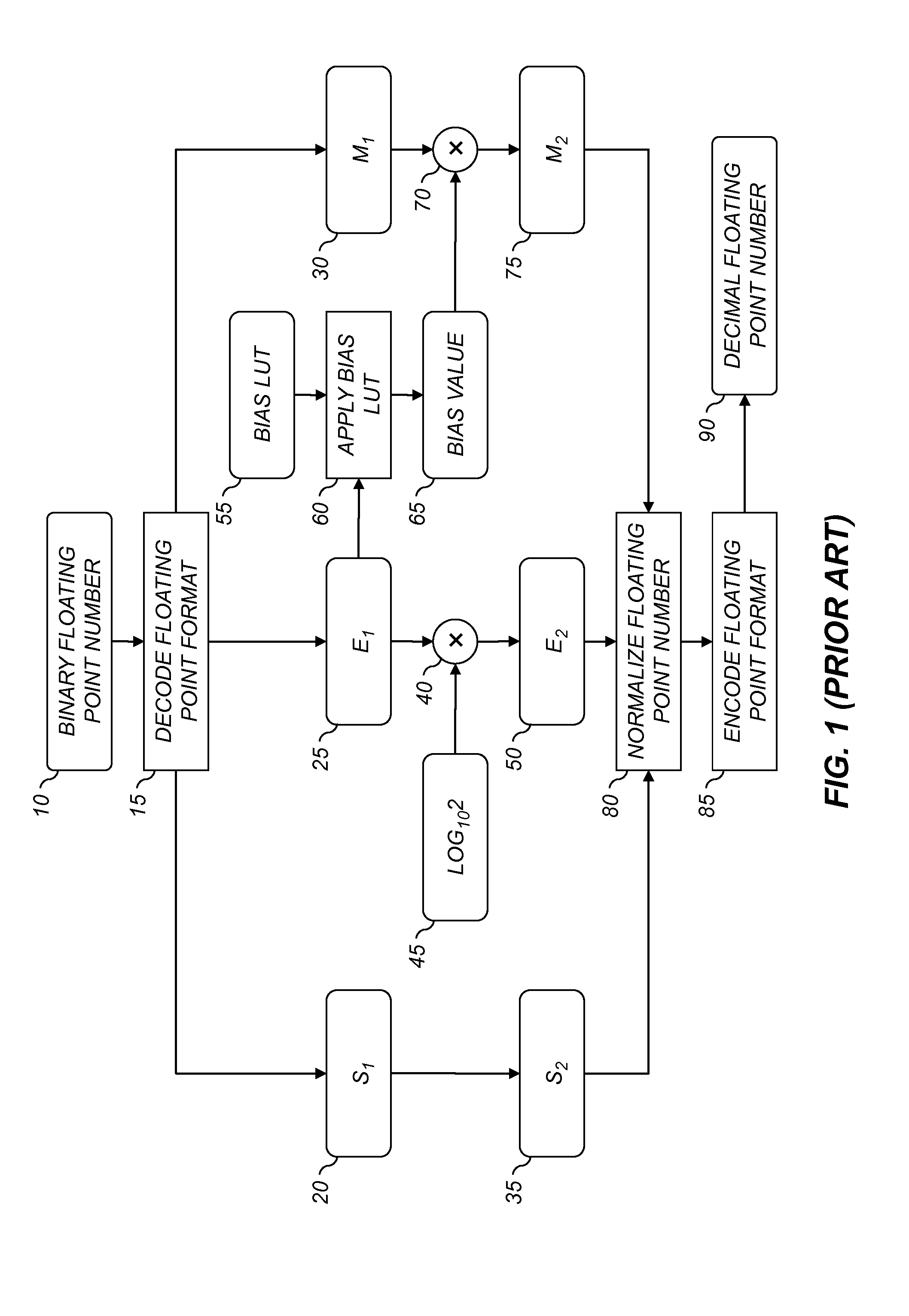
A computer program product for converting from a first floating point format to a second floating point format, each floating point format having an associated base value and being represented by a significand value and a exponent value, comprising an executable algorithm to perform the steps of: determining the second exponent value by multiplying the first exponent value by a predefined constant and taking the integer portion of the result, the predefined constant being substantially equivalent to the logarithm of the first base value divided by the logarithm of the second base value; determining a bias value substantially equivalent to the second base value raised to the second exponent value divided by the first base value raised to the first exponent value; and determining the second significand value by multiplying the first significand value by the bias value.
Owner:KODAK ALARIS INC
Composition of decimal floating point data, and methods therefor
A decimal floating point finite number in a decimal floating point format is composed from the number in a different format. A decimal floating point format includes fields to hold information relating to the sign, exponent and significand of the decimal floating point finite number. Other decimal floating point data, including infinities and NaNs (not a number), are also composed. Decimal floating point data are also decomposed from the decimal floating point format to a different format.
Owner:IBM CORP
Decomposition of decimal floating point data
ActiveUS20080270499A1Digital data processing detailsDigital computer detailsParallel computingSialic acid synthase
A decimal floating point finite number in a decimal floating point format is composed from the number in a different format. A decimal floating point format includes fields to hold information relating to the sign, exponent and significand of the decimal floating point finite number. Other decimal floating point data, including infinities and NaNs (not a number), are also composed. Decimal floating point data are also decomposed from the decimal floating point format to a different format.
Owner:IBM CORP
Decomposition of decimal floating point data
ActiveUS8051119B2Digital data processing detailsCode conversionDecimal128 floating-point formatParallel computing
A decimal floating point finite number in a decimal floating point format is composed from the number in a different format. A decimal floating point format includes fields to hold information relating to the sign, exponent and significand of the decimal floating point finite number. Other decimal floating point data, including infinities and NaNs (not a number), are also composed. Decimal floating point data are also decomposed from the decimal floating point format to a different format.
Owner:IBM CORP
Convert significand of decimal floating point data to packed decimal format
A decimal floating point finite number in a decimal floating point format is composed from the number in a different format. A decimal floating point format includes fields to hold information relating to the sign, exponent and significand of the decimal floating point finite number. Other decimal floating point data, including infinities and NaNs (not a number), are also composed. Decimal floating point data are also decomposed from the decimal floating point format to a different format. For composition and decomposition, one or more instructions may be employed, including one or more convert instructions.
Owner:IBM CORP
Floating point format converter
ActiveUS20120259904A1Small amount of memoryMore accurateComputations using contact-making devicesCode conversionComputer scienceComputer program
A computer program product for converting from a first floating point format to a second floating point format, each floating point format having an associated base value and being represented by a significand value and a exponent value, comprising an executable algorithm to perform the steps of: determining the second exponent value by multiplying the first exponent value by a predefined constant and taking the integer portion of the result, the predefined constant being substantially equivalent to the logarithm of the first base value divided by the logarithm of the second base value; determining a bias value substantially equivalent to the second base value raised to the second exponent value divided by the first base value raised to the first exponent value; and determining the second significand value by multiplying the first significand value by the bias value.
Owner:KODAK ALARIS INC
Apparatus and method for performing fused multiply add floating point operation
ActiveUS8990282B2Improve throughputImprove processing throughputComputation using denominational number representationComputer architectureFloating-point unit
A fused multiply add floating point unit 1 includes multiplying circuitry 4 and adding circuitry 8. The multiply circuitry 4 multiplies operands B and C having N-bit significands to generate an unrounded product B*C. The unrounded product B*C has an M-bit significand, where M>N. The adding circuitry 8 receives an operand A that is input at a later processing cycle than a processing cycle at which the multiplying circuitry 4 receives operands B and C. The adding circuitry 8 commences processing of the operand A after the unrounded product B*C is generated by the multiplying circuitry 4. The adding circuitry 8 adds the operand A to the unrounded product B*C and outputs a rounded result A+B*C.
Owner:ARM LTD
Data processing apparatus and method for converting a fixed point number to a floating point number
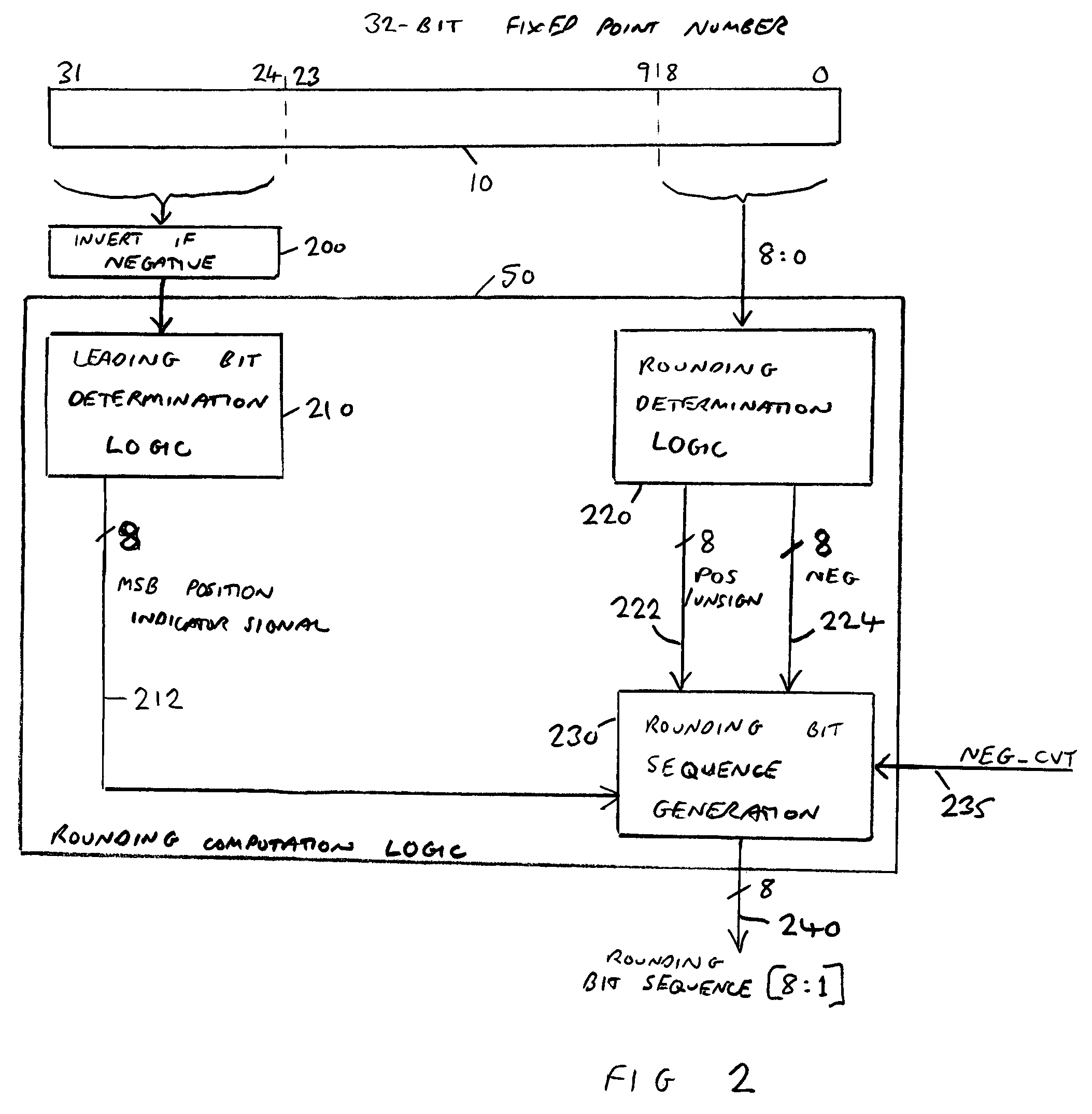
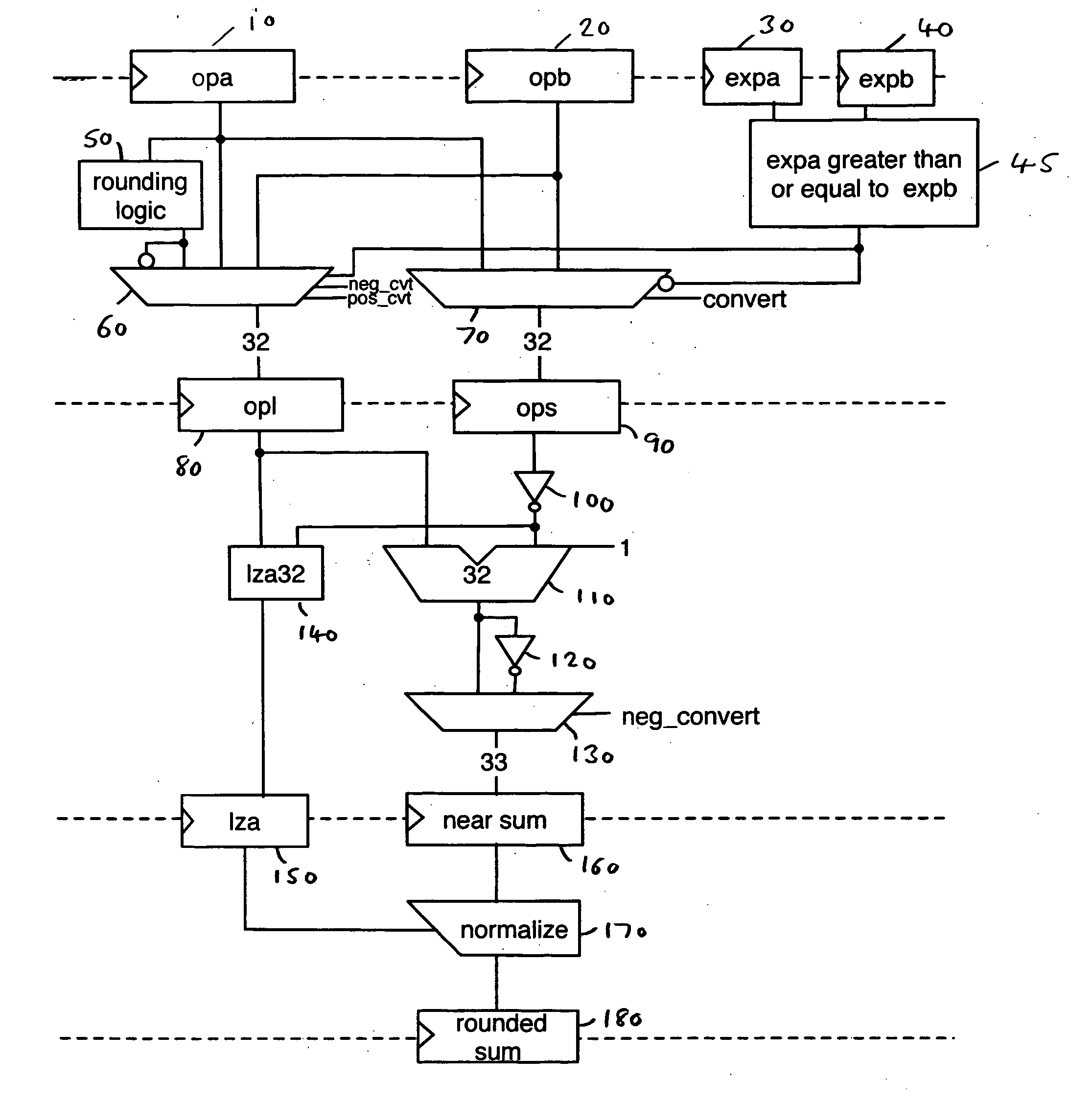
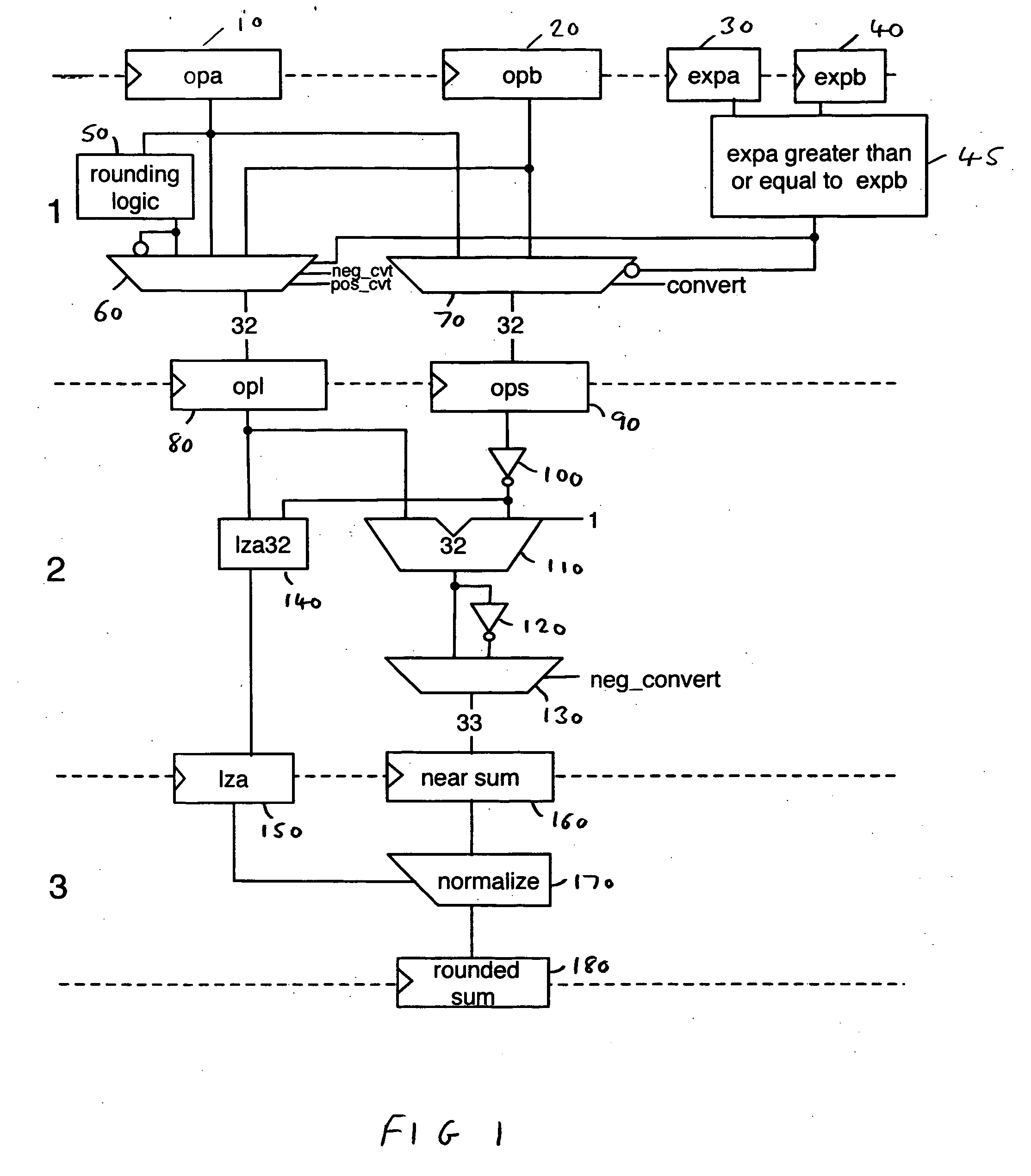
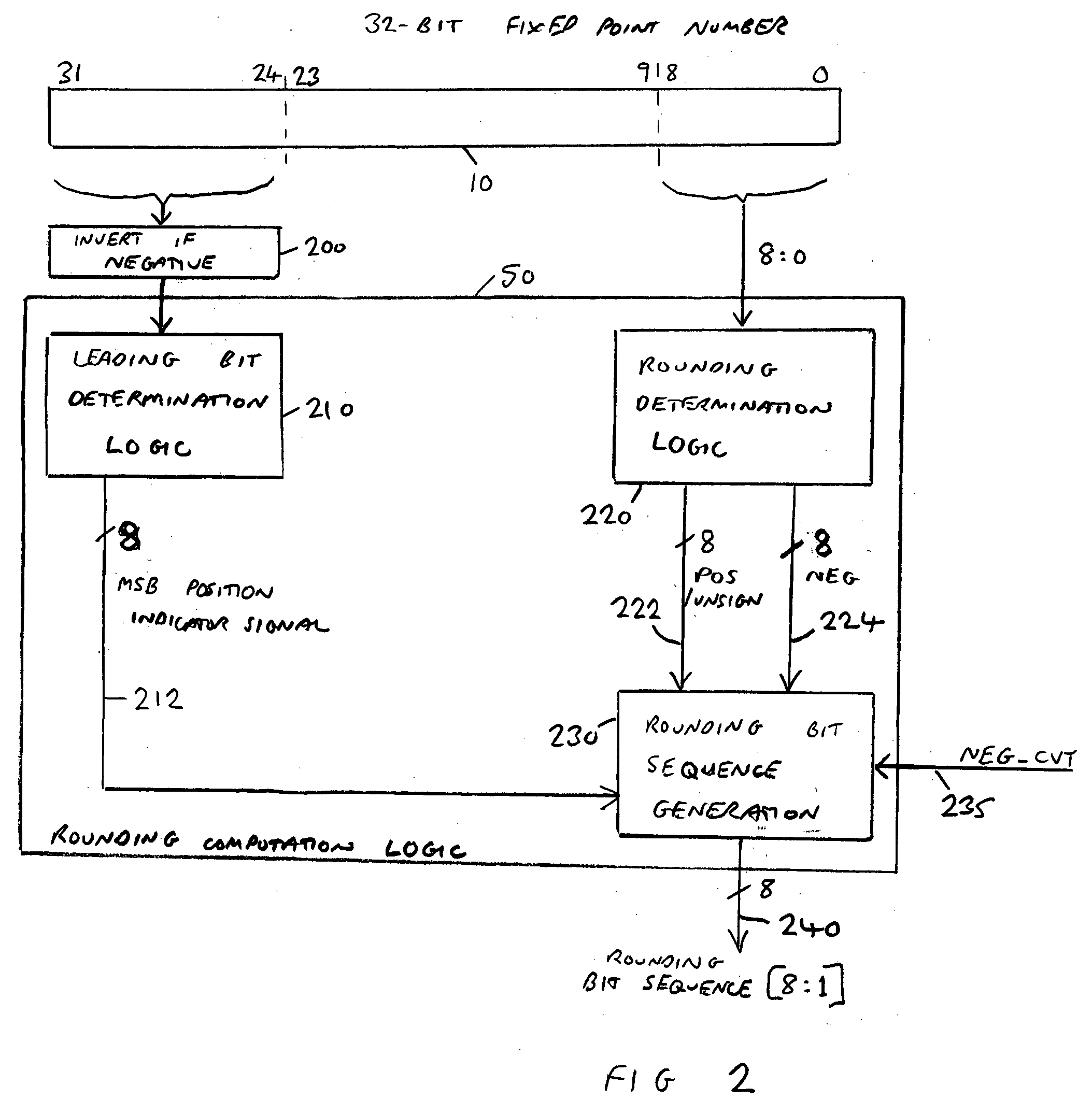
ActiveUS7401107B2Sequencing is requiredDigital data processing detailsDigital computer detailsFixation pointLeast significant bit
A data processing apparatus and method are provided for converting an m-bit fixed point number to a rounded floating point number having an n-bit significand, where n is less than m. The data processing apparatus comprises determination logic for determining the bit location of the most significant bit of the value expressed within the m-bit fixed point number, and low order bit analysis logic for determining from a selected number of least significant bits of the m-bit fixed point number a rounding signal indicating whether a rounding increment is required in order to generate the n-bit significand. Generation logic is then arranged in response to the rounding signal to generate a rounding bit sequence appropriate having regard to the bit location determined by the determination logic. Adder logic then adds the rounding bit sequence to the m-bit fixed point number to generate an intermediate result, whereafter normalisation logic shifts the intermediate result to generate the n-bit significand. At this point, due to the incorporation of the rounding information prior to the addition, the generated n-bit significand is correctly rounded.
Owner:ARM LTD
Pulse width measuring device with automatic range setting function
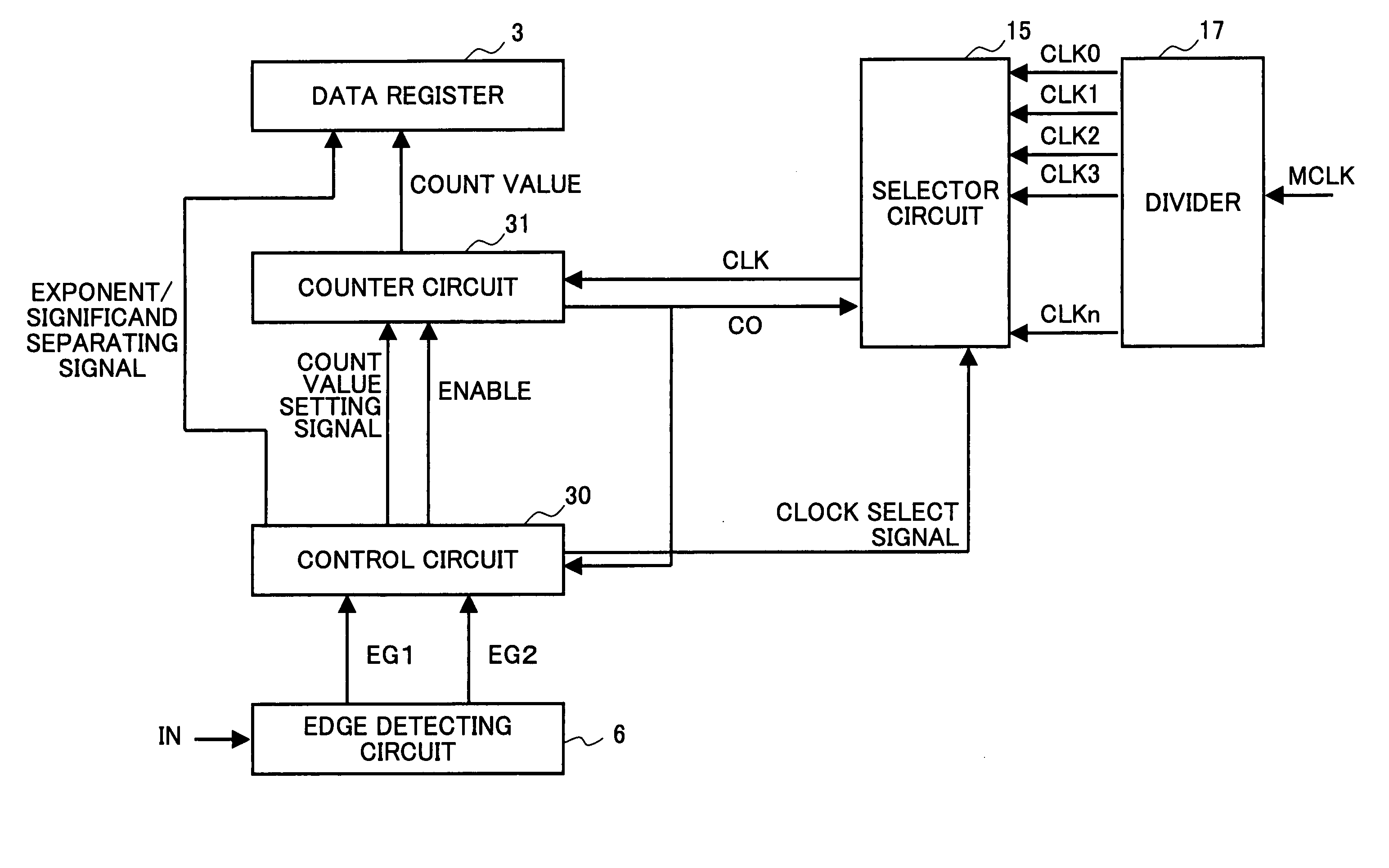
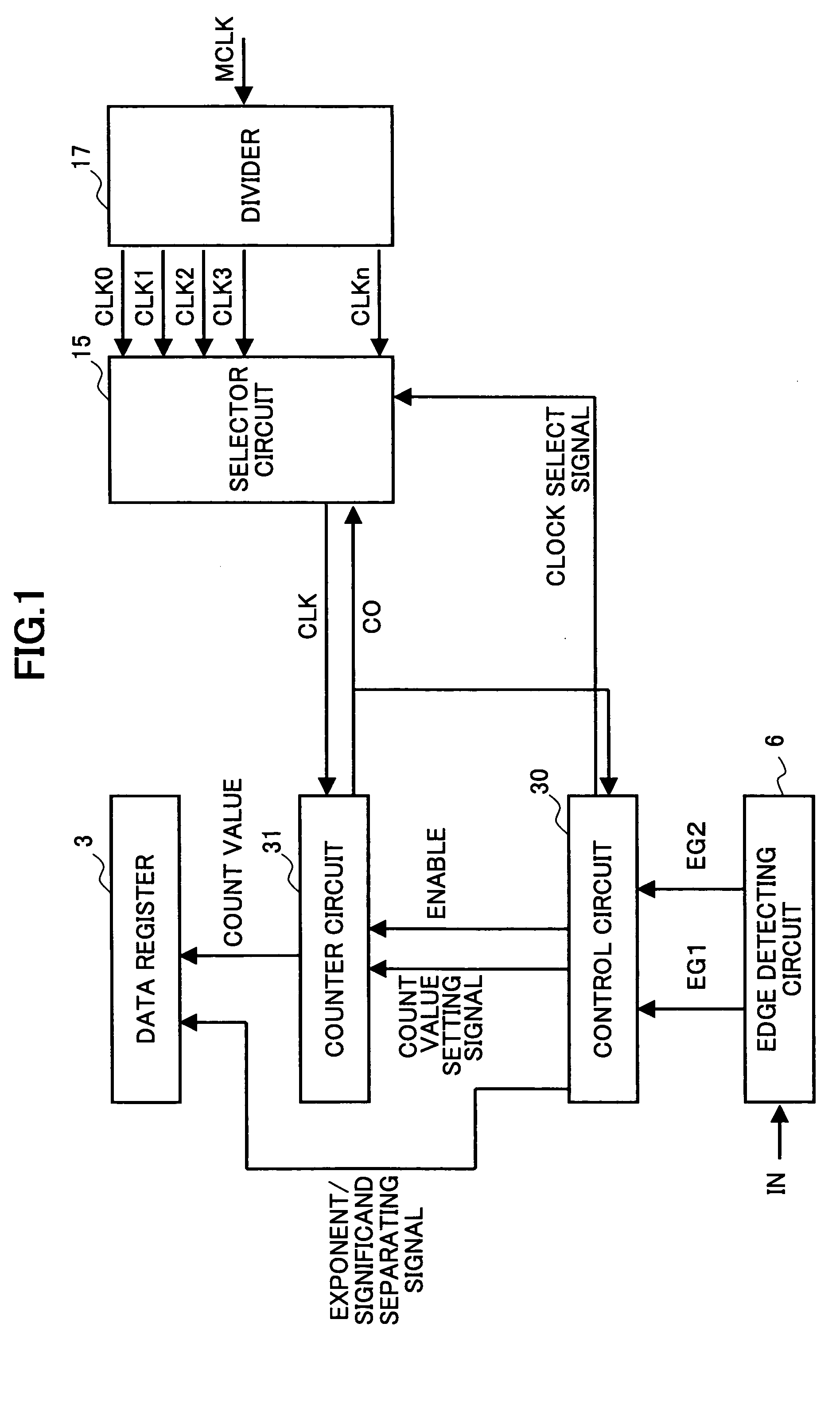
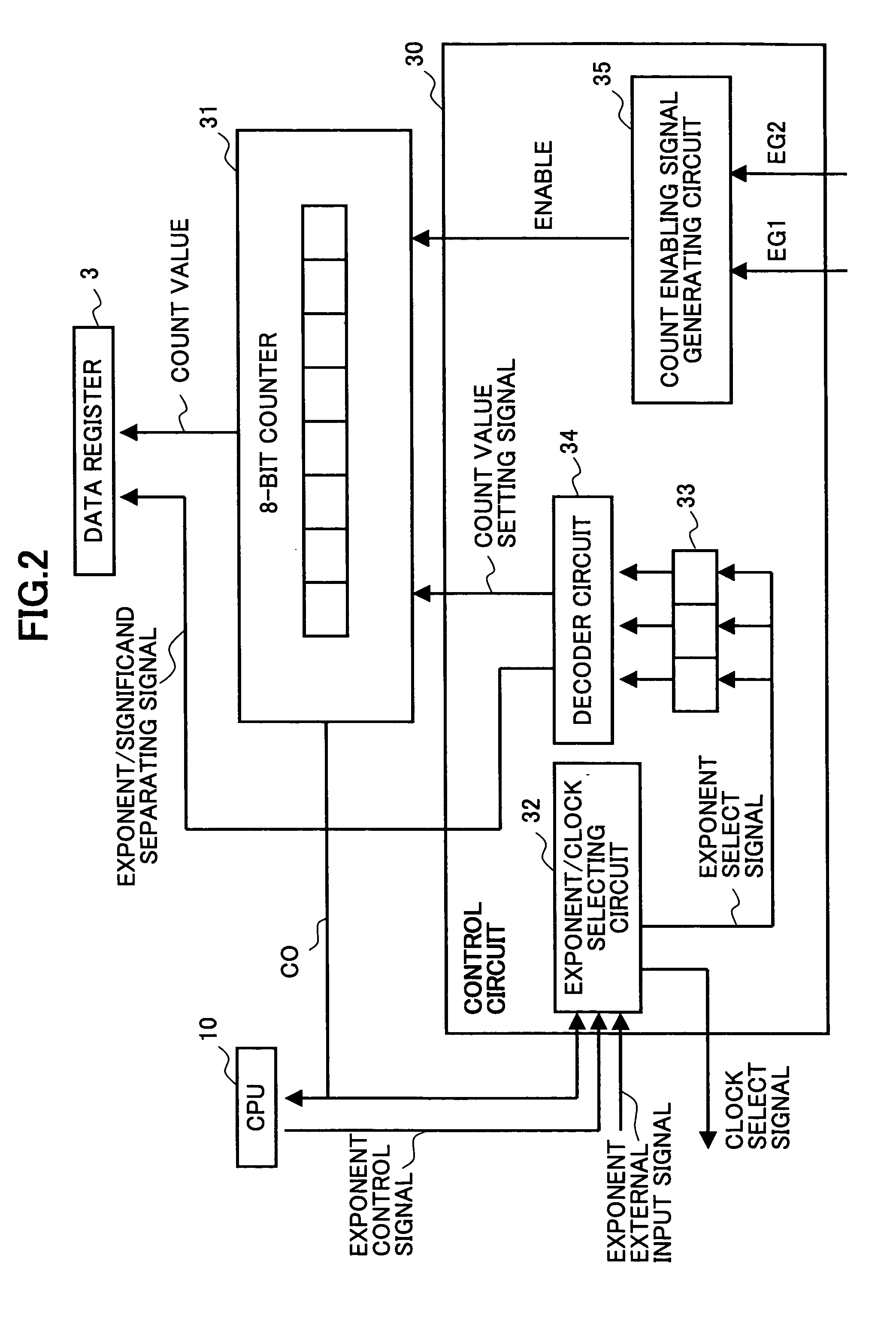
InactiveUS20050165569A1Reduce circuit sizeIncrease blockingVolume/mass flow measurementElectrical testingValue setMeasurement device
A pulse width measuring device is disclosed that calculates the pulse width of a signal to be measured, based on a count value and a count clock signal. In the pulse width measuring device, the counter circuit has a plurality of bits that are divided into an exponent and a significand. The control unit of the pulse width measuring device includes: an exponent storing unit that stores an exponent setting value that represents the number of bits of the exponent of the counter circuit; and a decoder unit that generates a count value setting signal for rewriting the count value of the counter circuit, based on the exponent setting value stored in the exponent storing unit, when the count value overflows in the counter circuit, the decoder unit then outputting the count value setting signal to the counter circuit.
Owner:CYPRESS SEMICON CORP
Leading zero prediction in floating point addition
An apparatus and method are provided for performing an addition operation on operands A and B in order to produce a result R, the operands A and B and the result R being floating point values each having a significand and an exponent. The apparatus comprises prediction circuitry for generating a shift indication based on a prediction of the number of leading zeros that would be present in an output produced by subjecting the operands A and B to an unlike signed addition. Further, result pre-normalization circuitry performs a shift operation on the significands of both operand A and operand B prior to addition of the significands, this serving to discard a number of most significant bits of the significands of both operands as determined by the shift indication in order to produce modified significands for operands A and B. Operand analysis circuitry detects, with reference to the exponents of operands A and B, the presence of a leading bit cancellation condition, and addition circuitry is configured, in the presence of the leading bit cancellation condition, to perform an addition of the modified significands for operands A and B, in order to produce the significand of the result R. Such an approach provides a particularly simple and efficient apparatus for performing addition operations.
Owner:ARM LTD +1
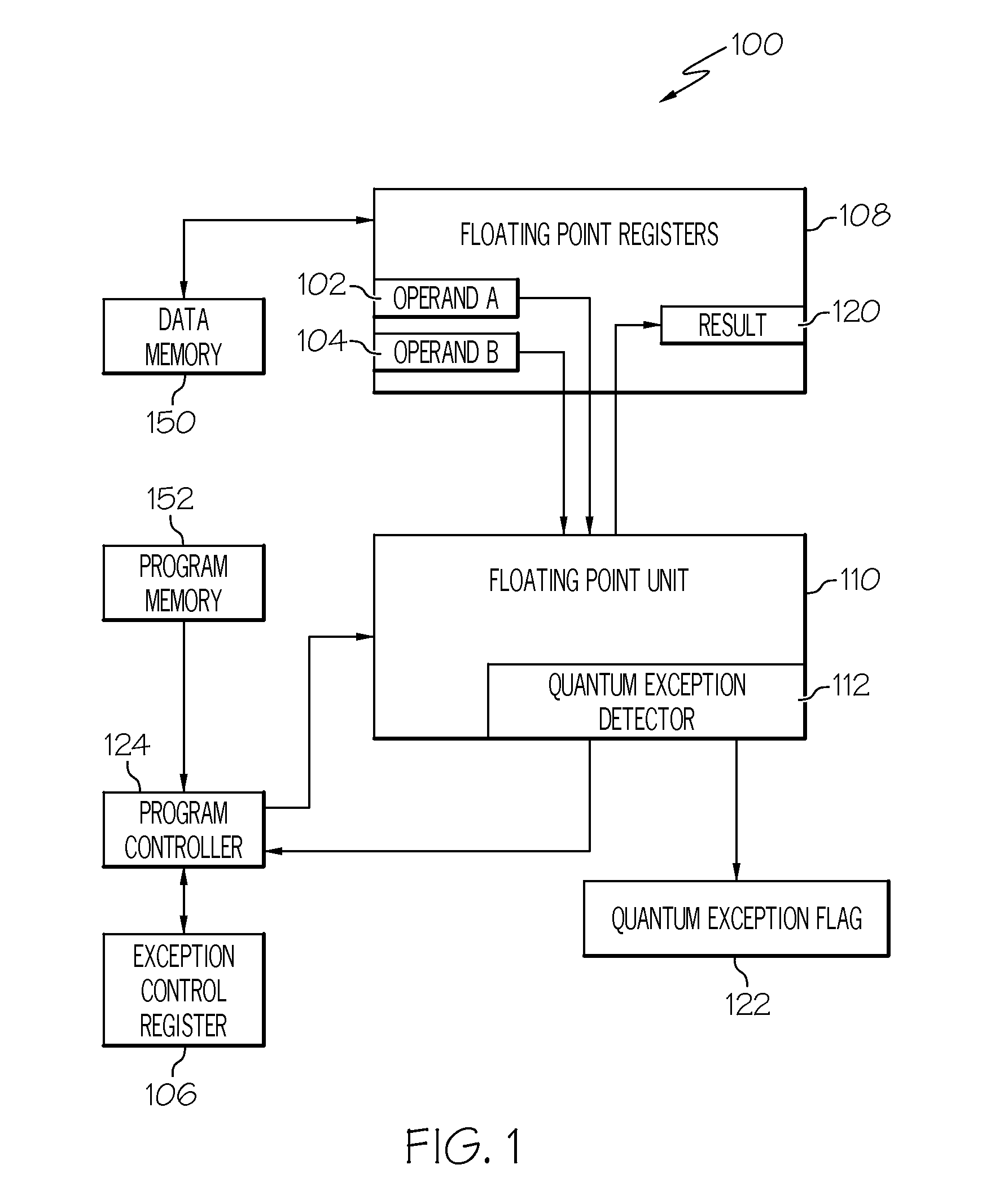
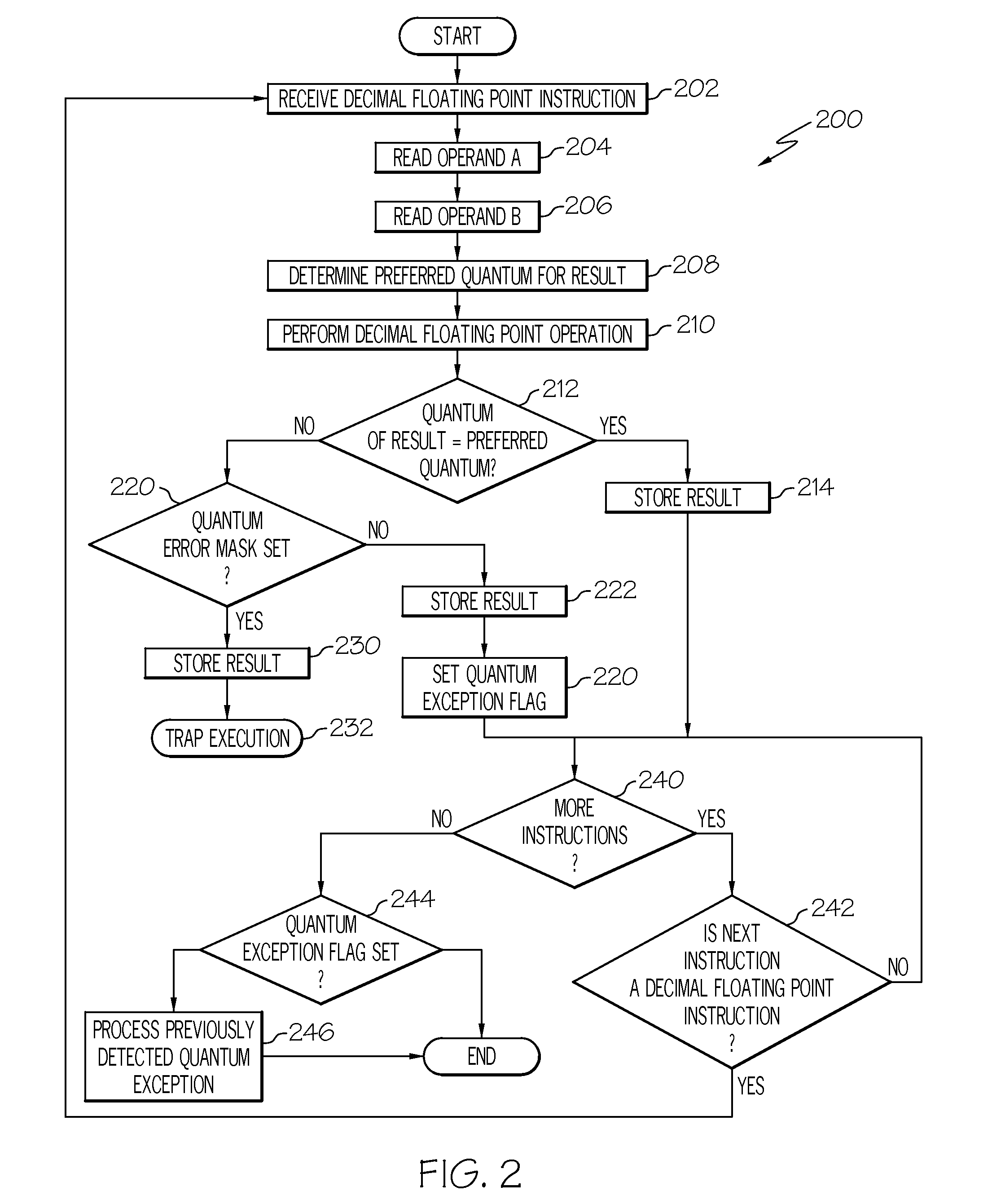
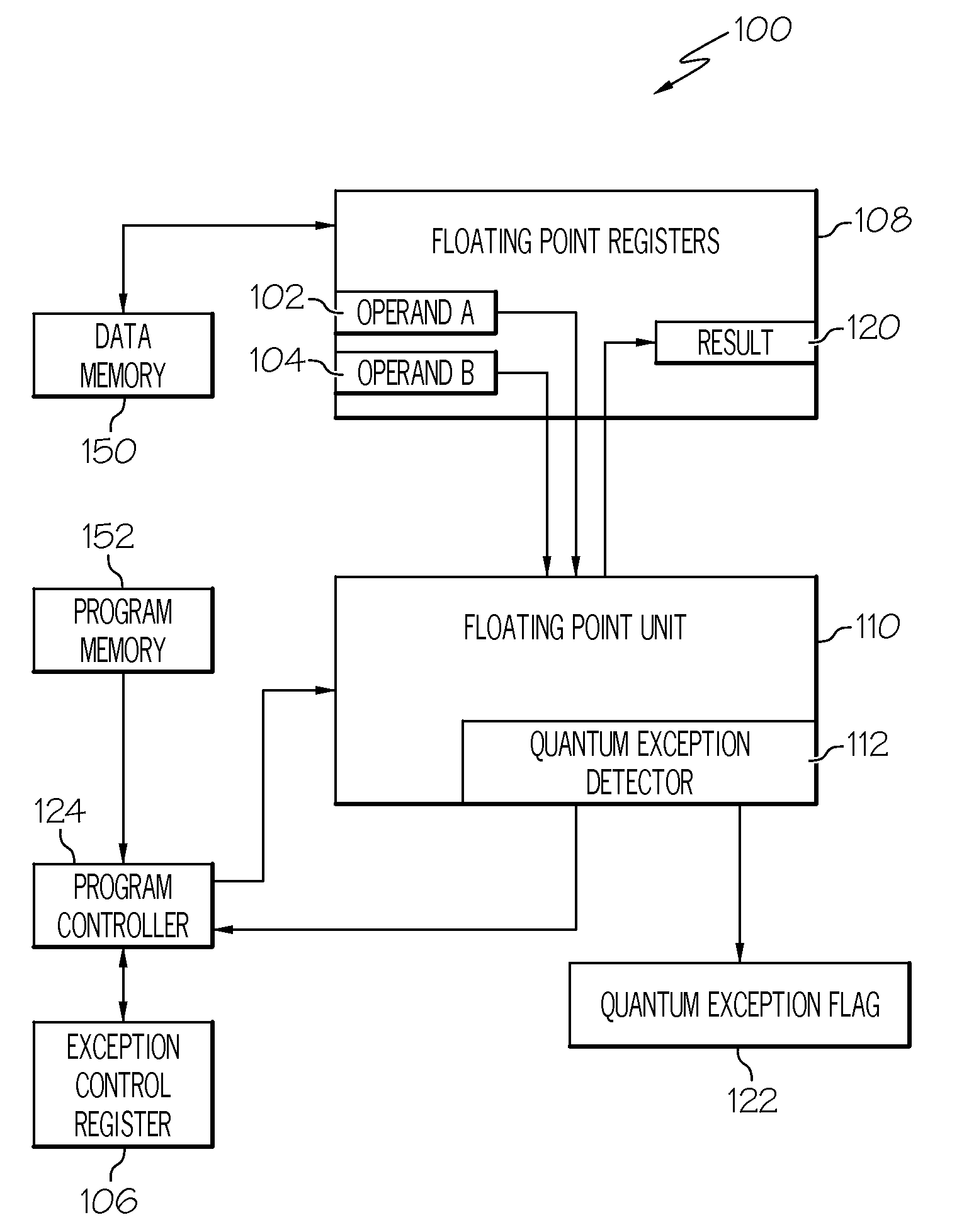
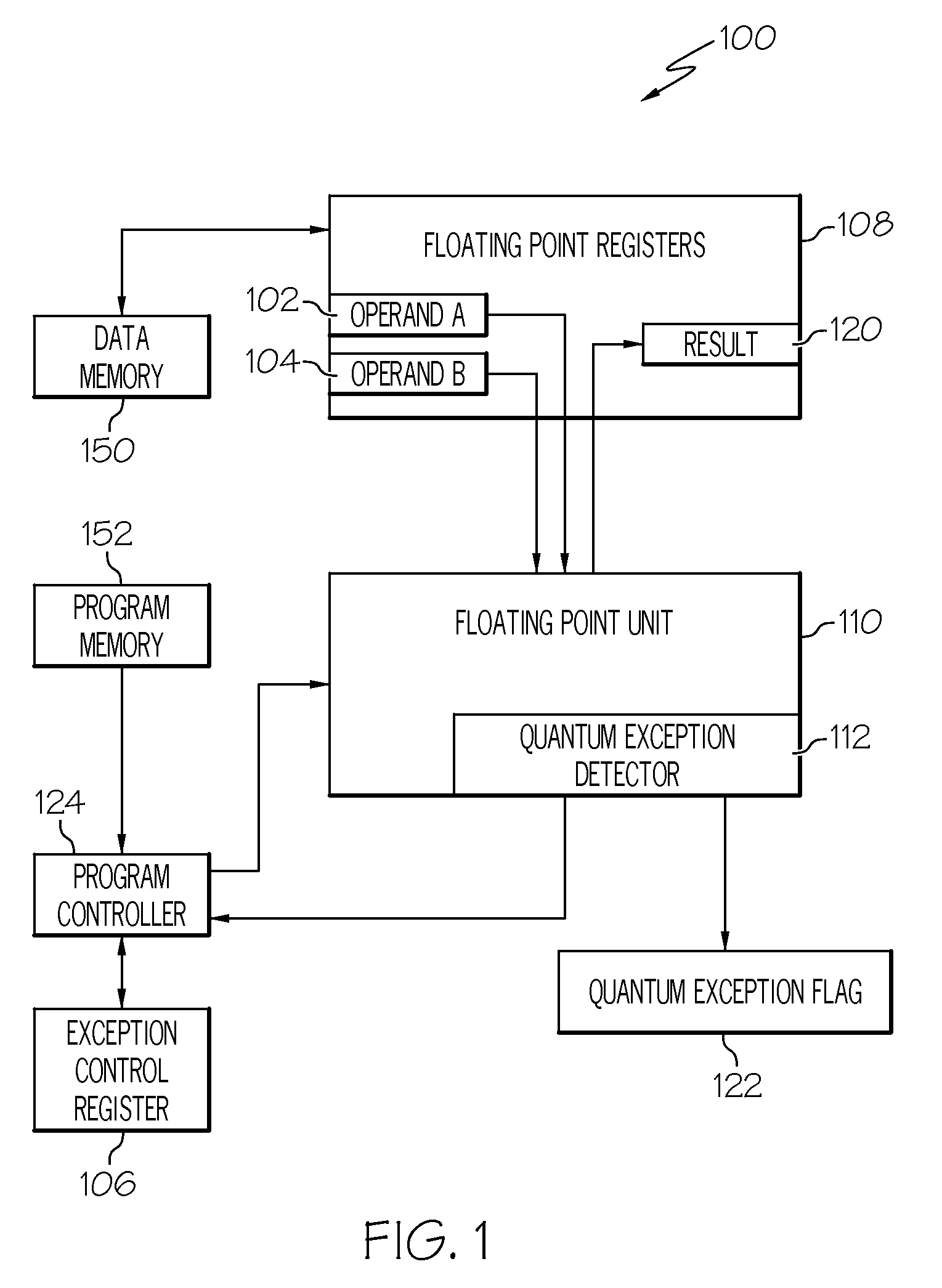
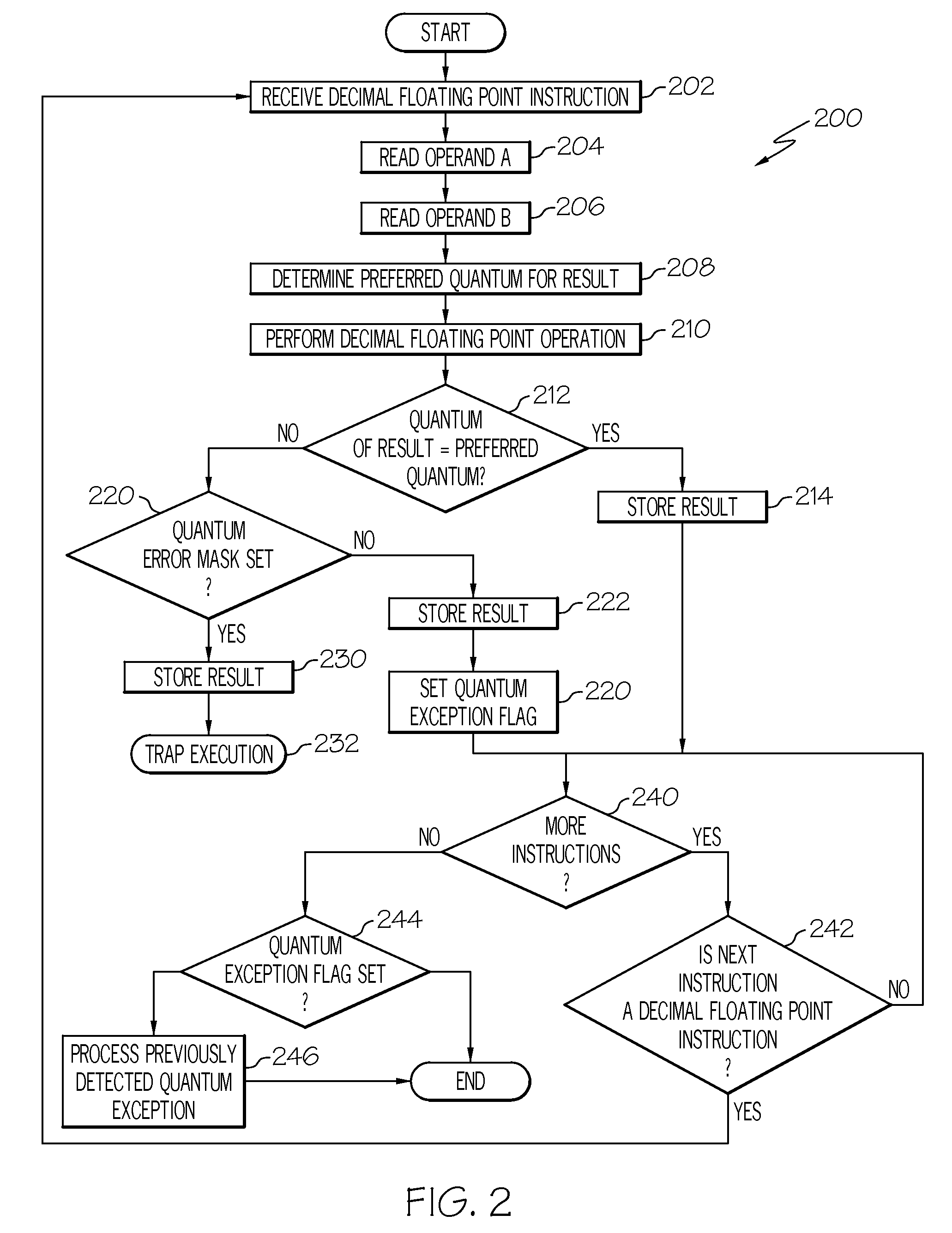
Decimal floating-pointing quantum exception detection
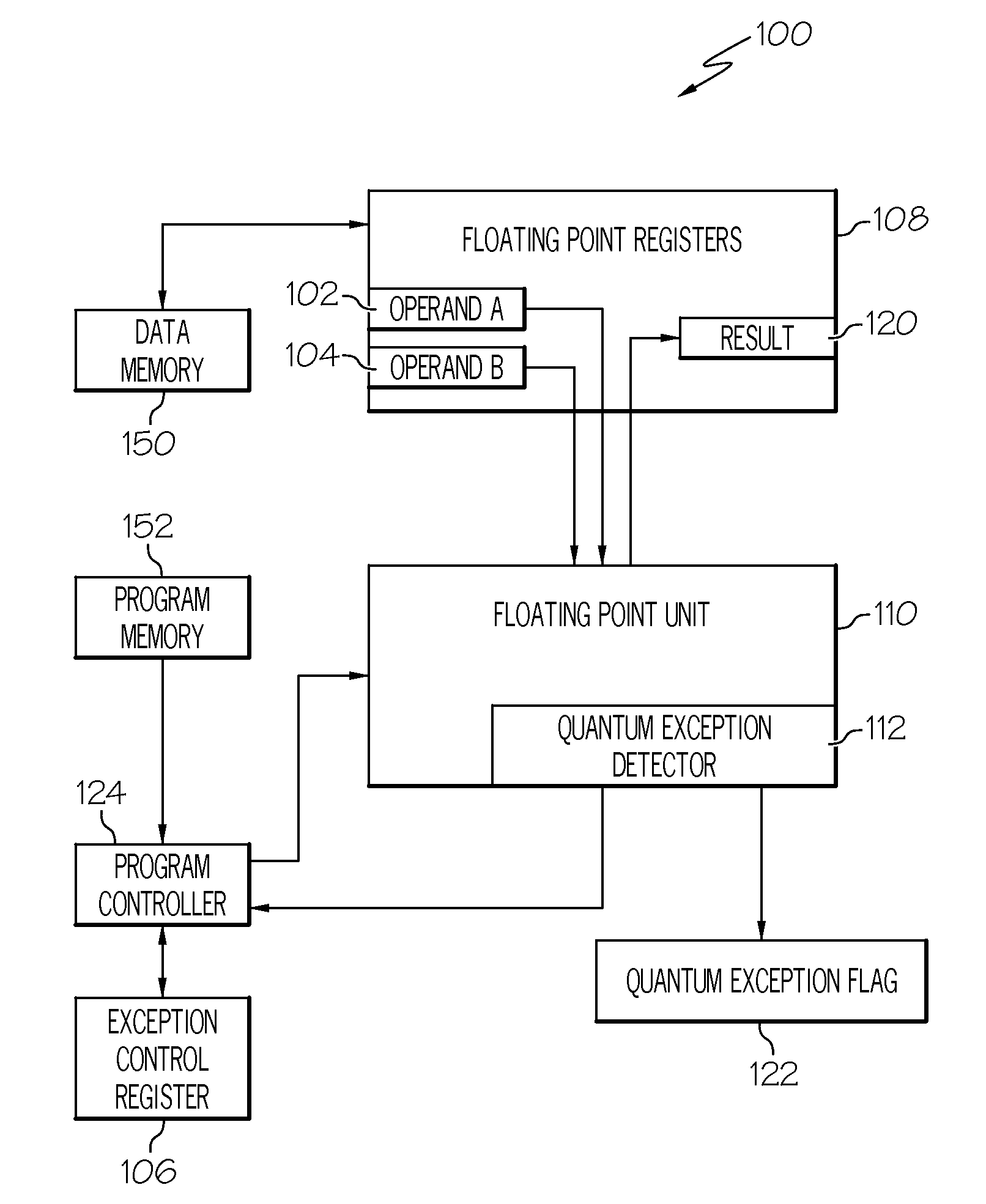
A system and method for detecting decimal floating point data processing exceptions. A processor accepts at least one decimal floating point operand and performs a decimal floating point operation on the at least one decimal floating point operand to produce a decimal floating point result. A determination is made as to whether the decimal floating point result fails to maintain a preferred quantum. The preferred quantum indicates a value represented by a least significant digit of a significand of the decimal floating point result. An output is provided, in response to the determining that the decimal floating point result fails to maintain the preferred quantum, indicating an occurrence of a quantum exception. A maskable exception can be generated that is immediately trapped or later detected to control conditional processing.
Owner:IBM CORP
Data processing apparatus and method for multiplying floating point operands
A data processing apparatus and method are provided for multiplying first and second normalised floating point operands in order to generate a result, each normalised floating point operand comprising a significand and an exponent. Exponent determination circuitry is used to compute a result exponent for a normalised version of the result, and rounding value generation circuitry then generates a rounding value by shifting a rounding constant in a first direction by a shift amount that is dependent on the result exponent. Partial product generation circuitry multiplies the significands of the first and second normalised floating point operands to generate the first and second partial products, and the first and second partial products are then added together, along with the rounding value, in order to generate a normalised result significand. Thereafter, the normalised result significand is shifted in a second direction opposite to the first direction, by the shift amount, in order to generate a rounded result significand. This provides a particularly efficient mechanism for multiplying floating point numbers, whilst correctly rounding the result in situations where the result is subnormal.
Owner:ARM LTD
Decimal floating-pointing quantum exception detection
ActiveUS8219605B2Conditional code generationError detection/correctionAnomaly detectionLeast significant bit
A system and method for detecting decimal floating point data processing exceptions. A processor accepts at least one decimal floating point operand and performs a decimal floating point operation on the at least one decimal floating point operand to produce a decimal floating point result. A determination is made as to whether the decimal floating point result fails to maintain a preferred quantum. The preferred quantum indicates a value represented by a least significant digit of a significand of the decimal floating point result. An output is provided, in response to the determining that the decimal floating point result fails to maintain the preferred quantum, indicating an occurrence of a quantum exception. A maskable exception can be generated that is immediately trapped or later detected to control conditional processing.
Owner:IBM CORP
Floating-point arithmetic device
InactiveUS6571264B1Computation using non-contact making devicesDigital computer detailsLeading zeroComputer science
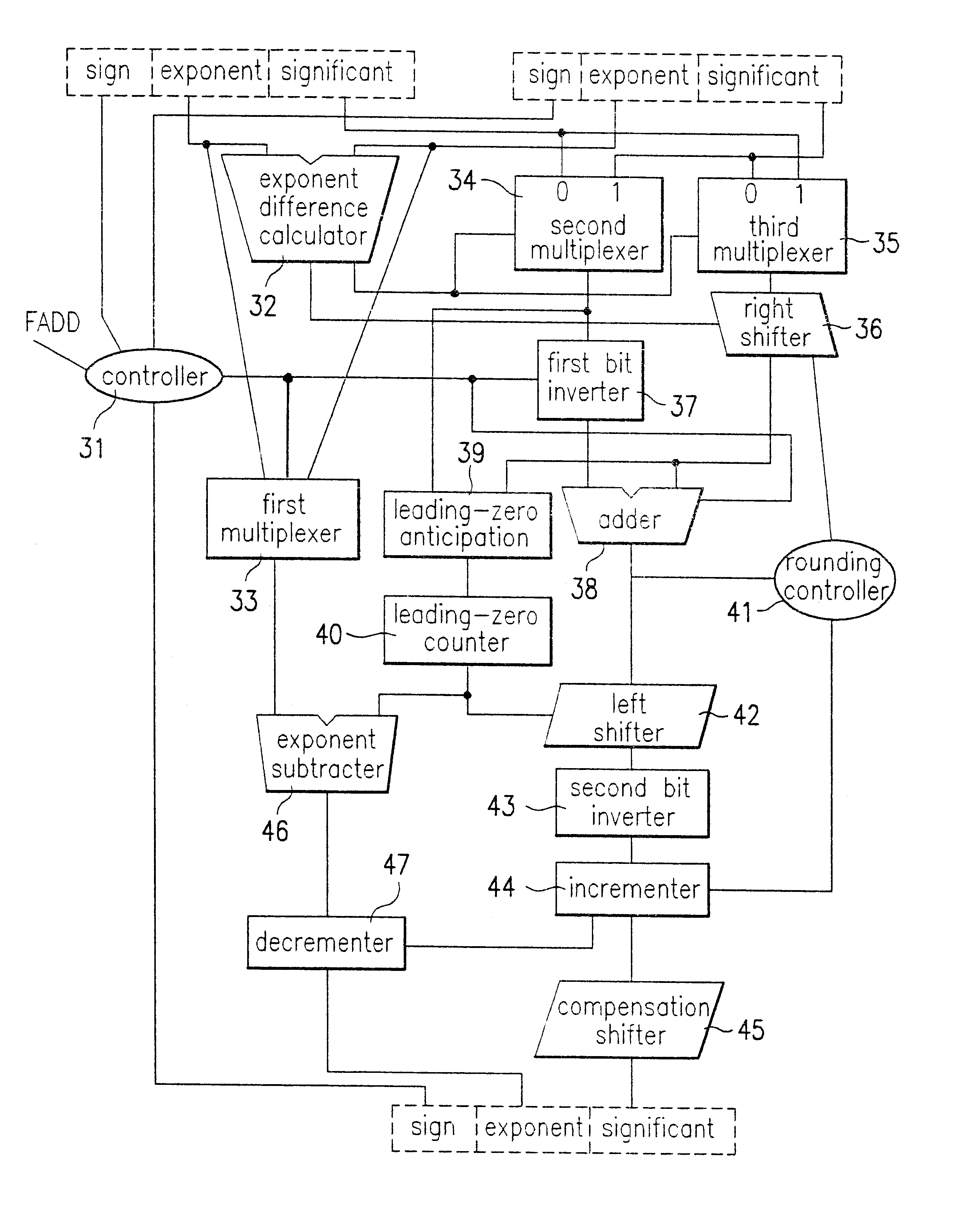
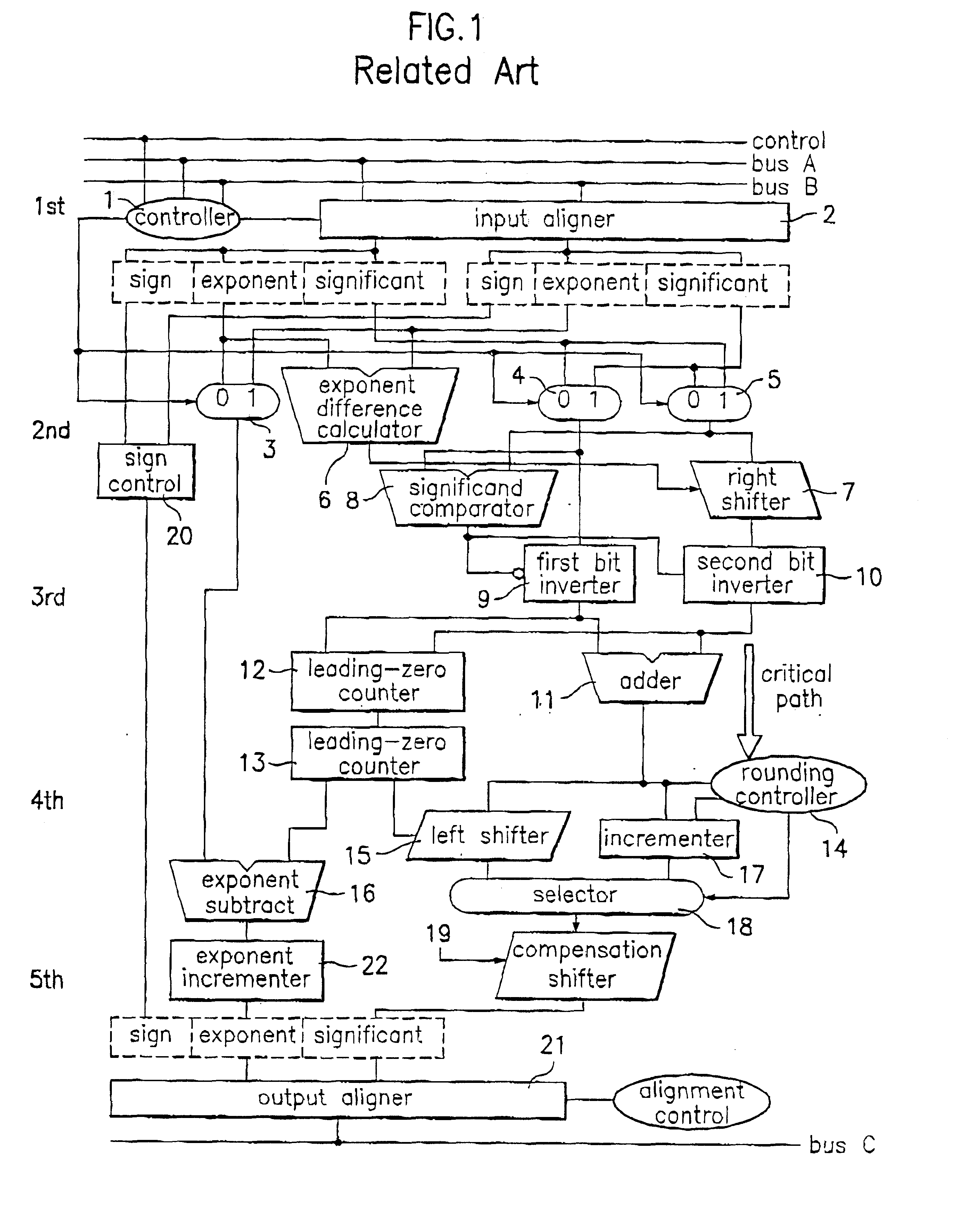
A floating-point arithmetic device, including a significand output circuit for calculating a difference between exponents, outputting a first significand with a larger exponent, and shifting the remaining significand by the calculated exponent difference, a first bit inverter, an adder, a leading-zero anticipation circuit for anticipating the consecutiveness of leading zeros from the significands, a leading-zero counter for counting the anticipated number of leading zeros, a left shifter for shifting an output value from the adder, a second bit inverter for taking two's complement of an output value from the left shifter, an incrementer for incrementing an output value from the second bit inverter by one, a compensation shifter for shifting an output value from the incrementer, an exponent subtracter for subtracting the number counted by the leading-zero counter from the larger exponent, and a decrementer for decrementing an output exponent from the exponent subtracter by one.
Owner:MAGNACHIP SEMICONDUCTOR LTD
Data processing apparatus and method for converting a fixed point number to a floating point number
ActiveUS20060136536A1Sequencing is requiredDigital data processing detailsDigital computer detailsLeast significant bitFixed-point arithmetic
A data processing apparatus and method are provided for converting an m-bit fixed point number to a rounded floating point number having an n-bit significand, where n is less than m. The data processing apparatus comprises determination logic for determining the bit location of the most significant bit of the value expressed within the m-bit fixed point number, and low order bit analysis logic for determining from a selected number of least significant bits of the m-bit fixed point number a rounding signal indicating whether a rounding increment is required in order to generate the n-bit significand. Generation logic is then arranged in response to the rounding signal to generate a rounding bit sequence appropriate having regard to the bit location determined by the determination logic. Adder logic then adds the rounding bit sequence to the m-bit fixed point number to generate an intermediate result, whereafter normalisation logic shifts the intermediate result to generate the n-bit significand. At this point, due to the incorporation of the rounding information prior to the addition, the generated n-bit significand is correctly rounded.
Owner:ARM LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com