Data processing apparatus and method for multiplying floating point operands
A data processing device and operand technology, applied in the direction of electrical digital data processing, digital data processing components, data transformation, etc., can solve problems such as affecting performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
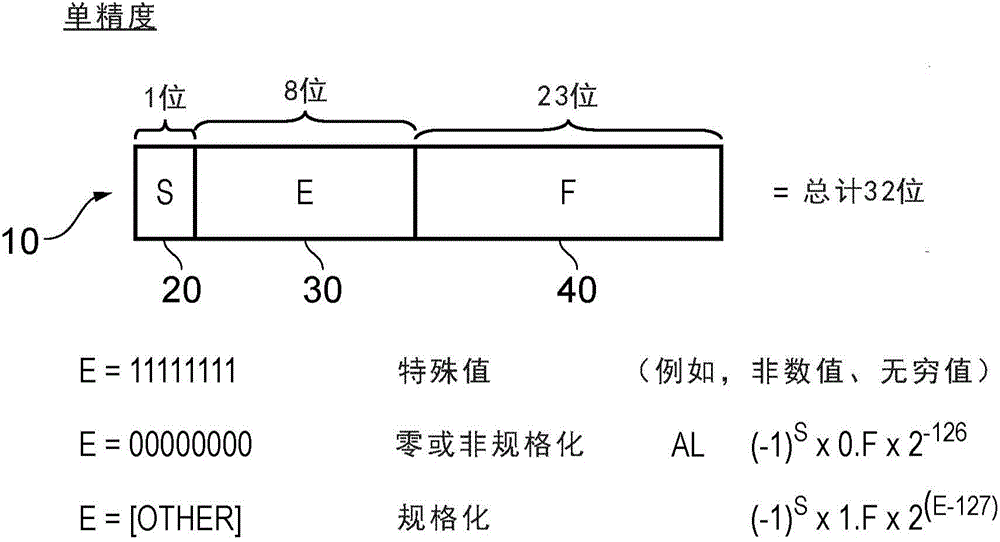
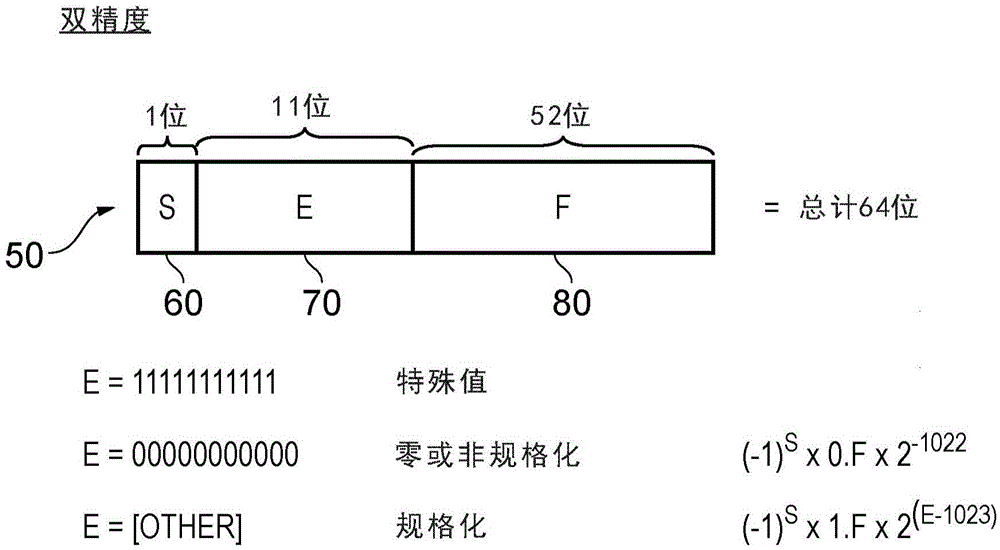
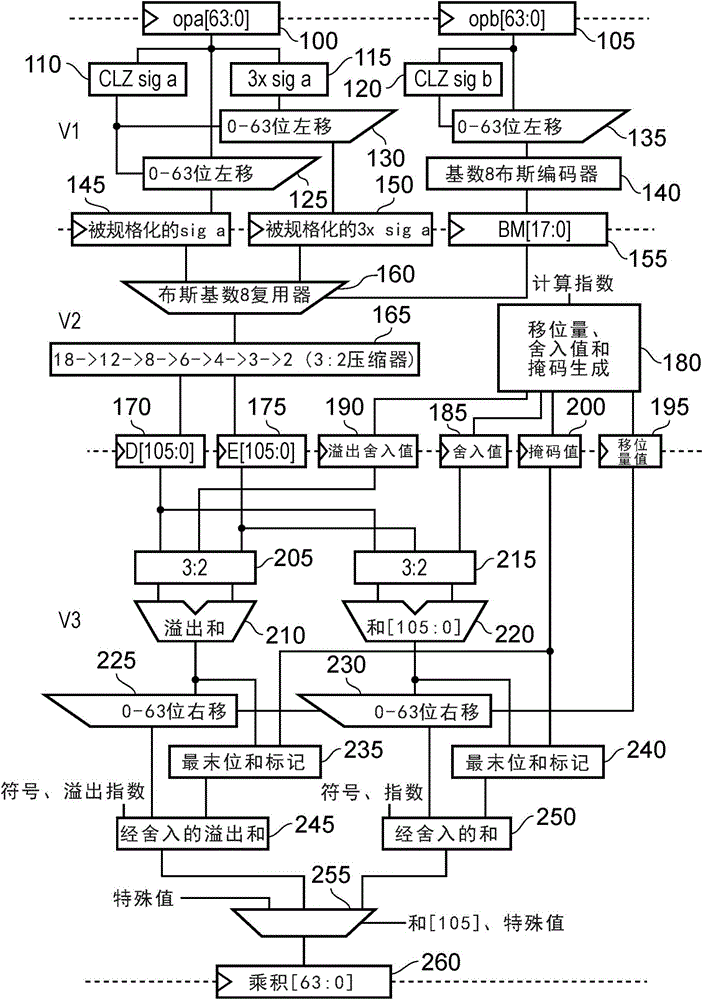
[0028] In floating-point notation, numbers are represented by using a sign bit, an exponent bit E, and a fraction bit F. Significant figures are the numbers 1.F or 0.F, depending on the value of the exponent E, i.e. if E is zero, it is 0.F, otherwise it is 1.F. The integer part of the significand (0. or 1.) is not explicitly stored in the IEEE-754 standard, but is required for multiplication. The sign bit indicates whether the floating-point number is positive or negative, the significand indicates the number of significant digits of the floating-point number, and the exponent indicates the position of the decimal point (also known as the binary point) relative to the significand. By changing the value of the exponent, the decimal point can be "floated" left and right within the significand. This means that for a predetermined number of bits, floating-point representation is capable of representing a wider range of numbers than fixed-point representation (where the decimal po...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com