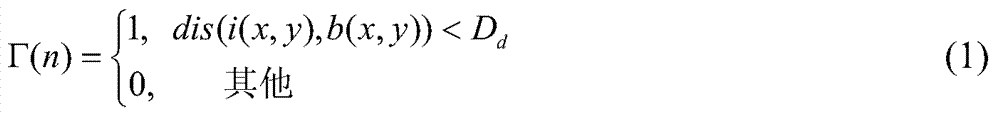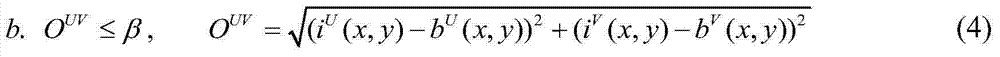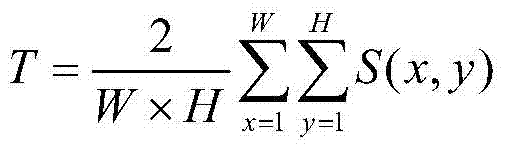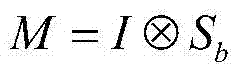Patents
Literature
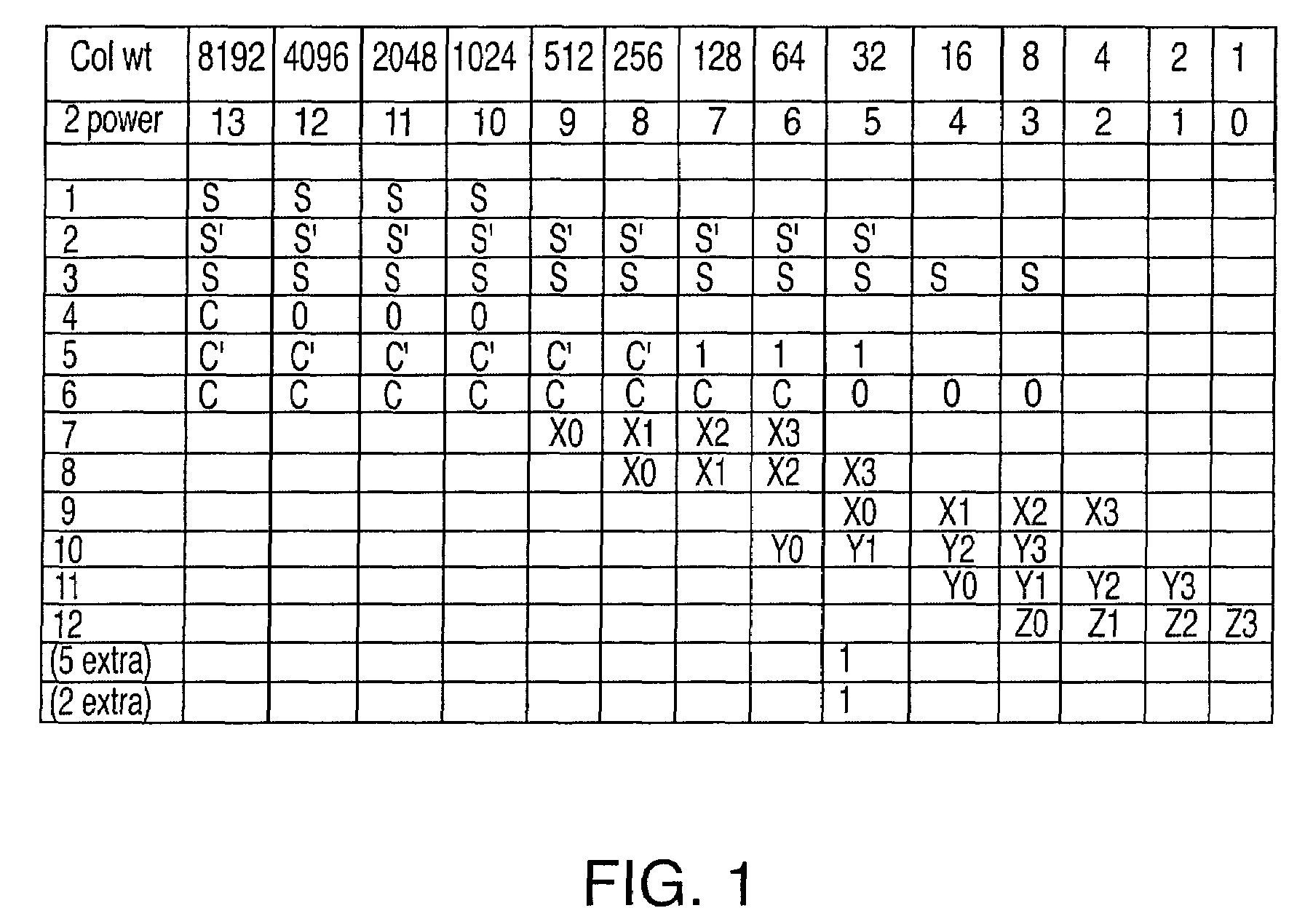
43 results about "Significant figures" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
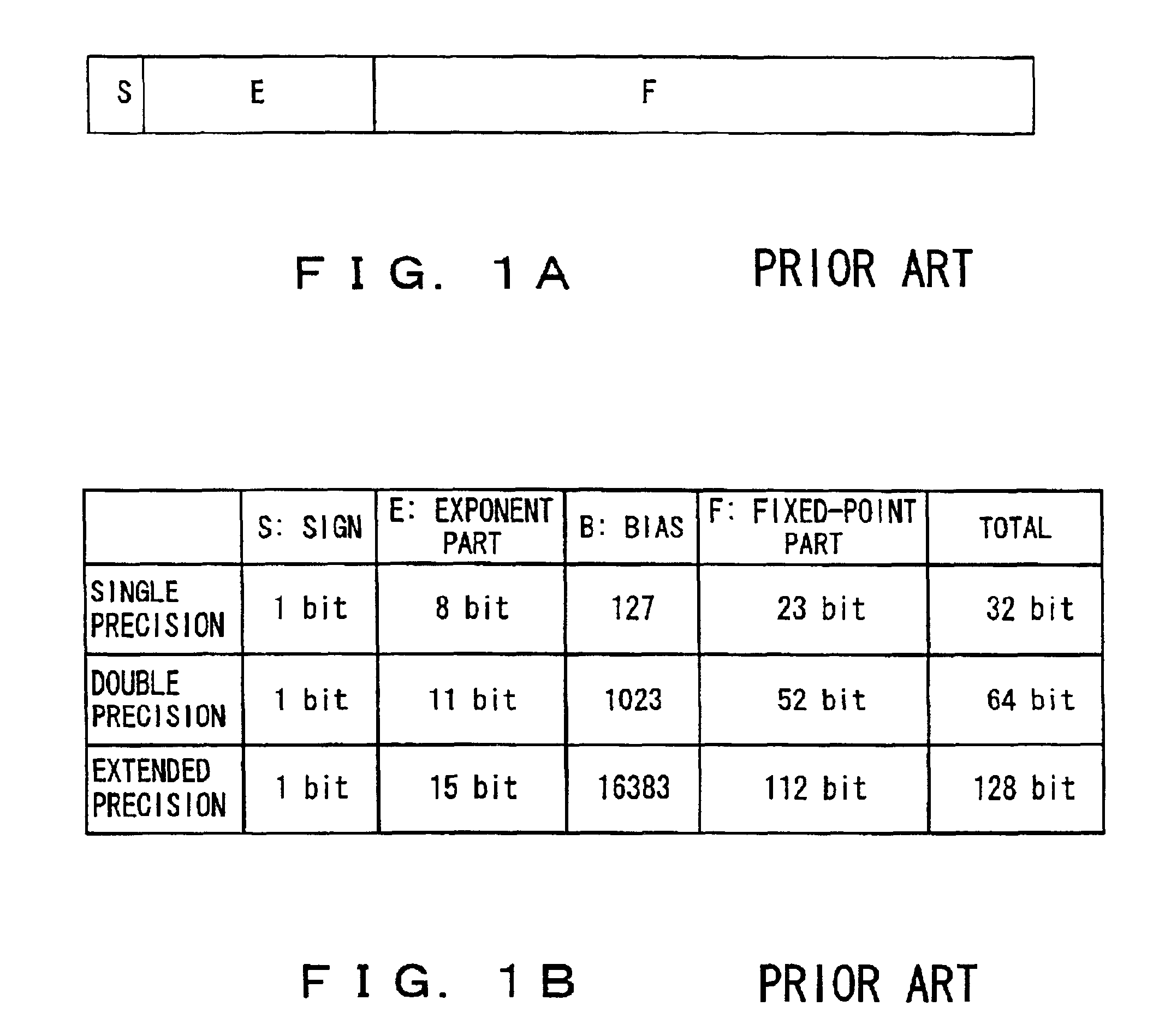
The significant figures (also known as the significant digits and decimal places) of a number are precision|measurement resolution. Significance arithmetic is a set of approximate rules for roughly maintaining significance throughout a computation. The more sophisticated scientific rules are known as propagation of uncertainty.
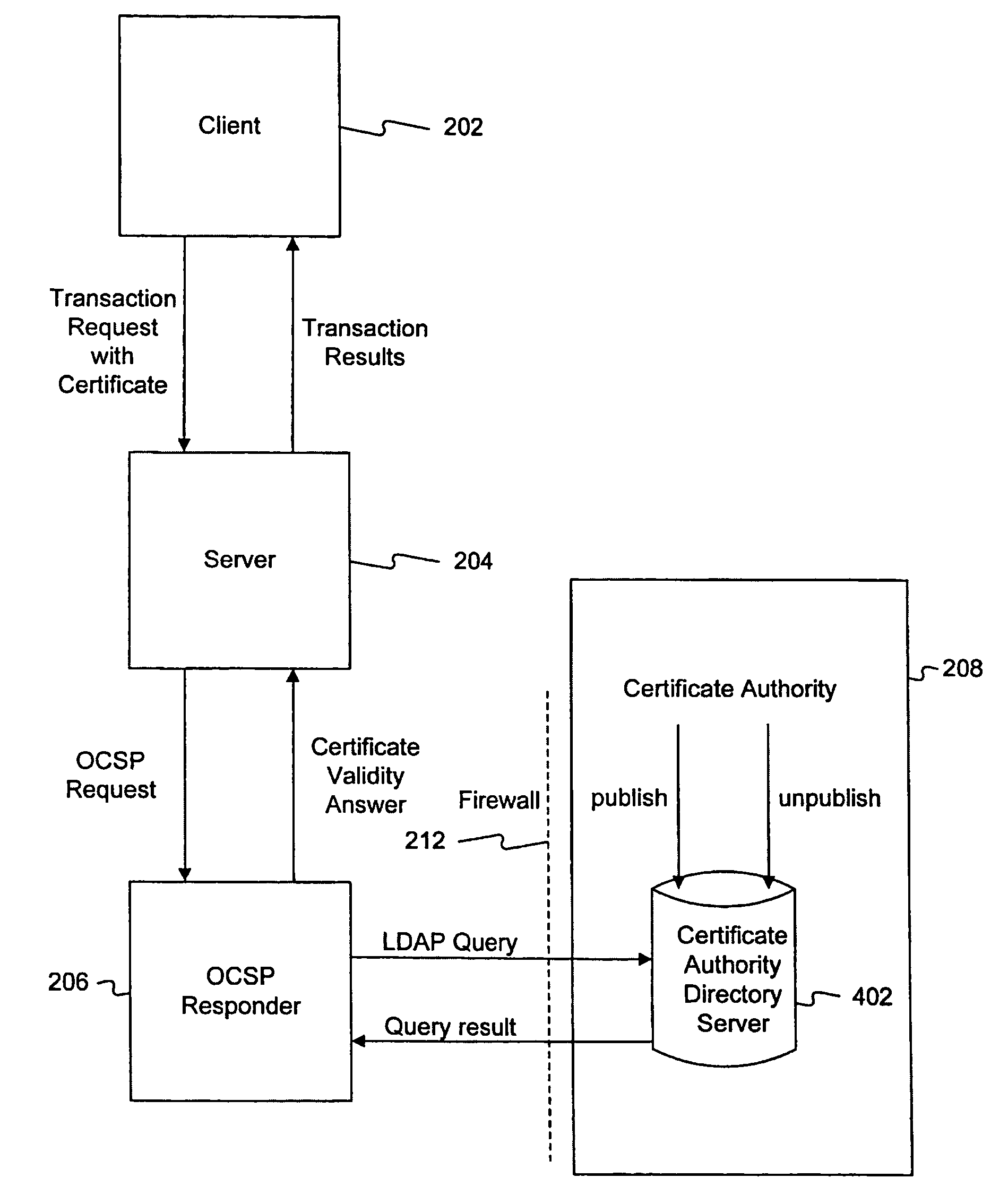
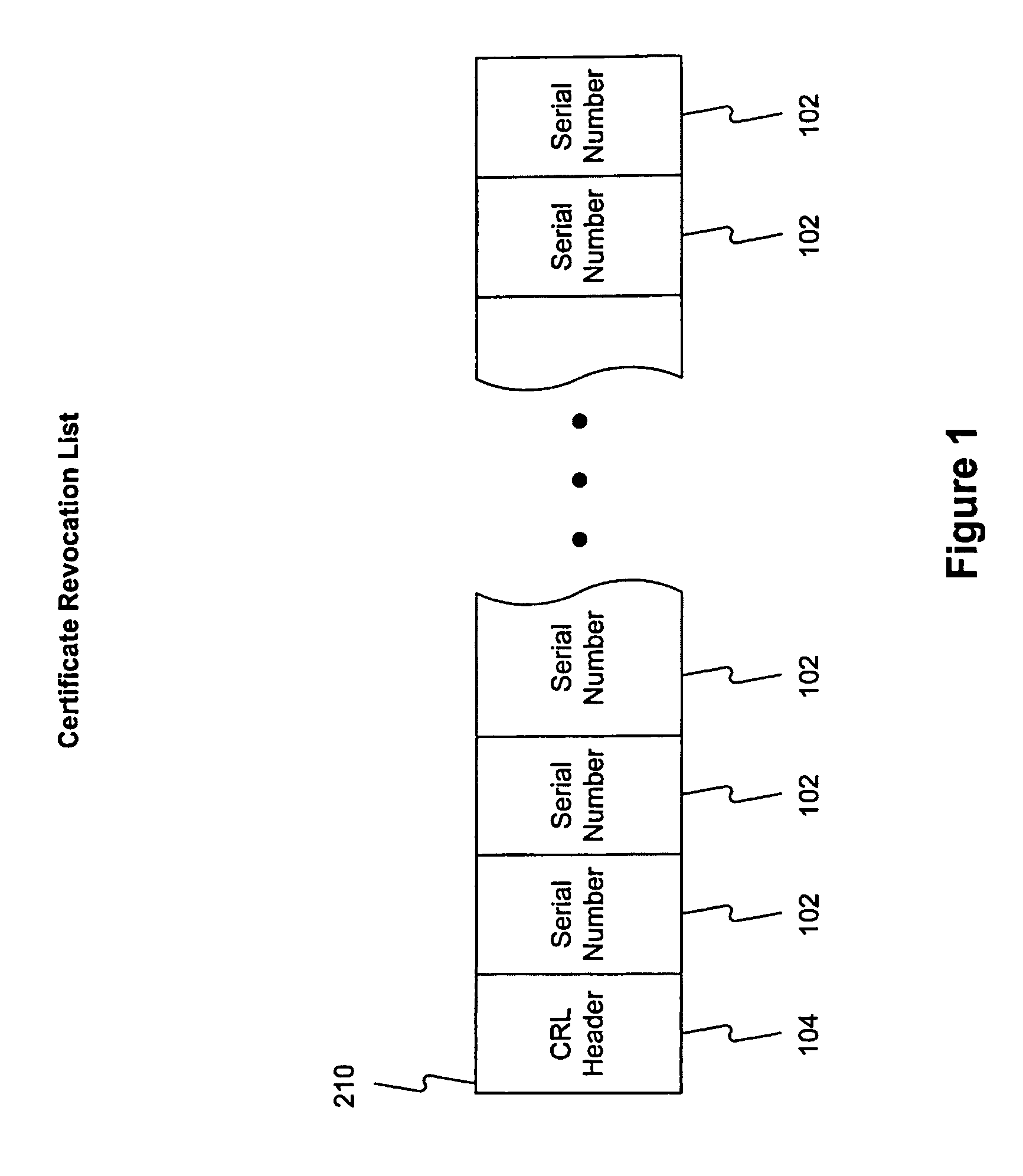
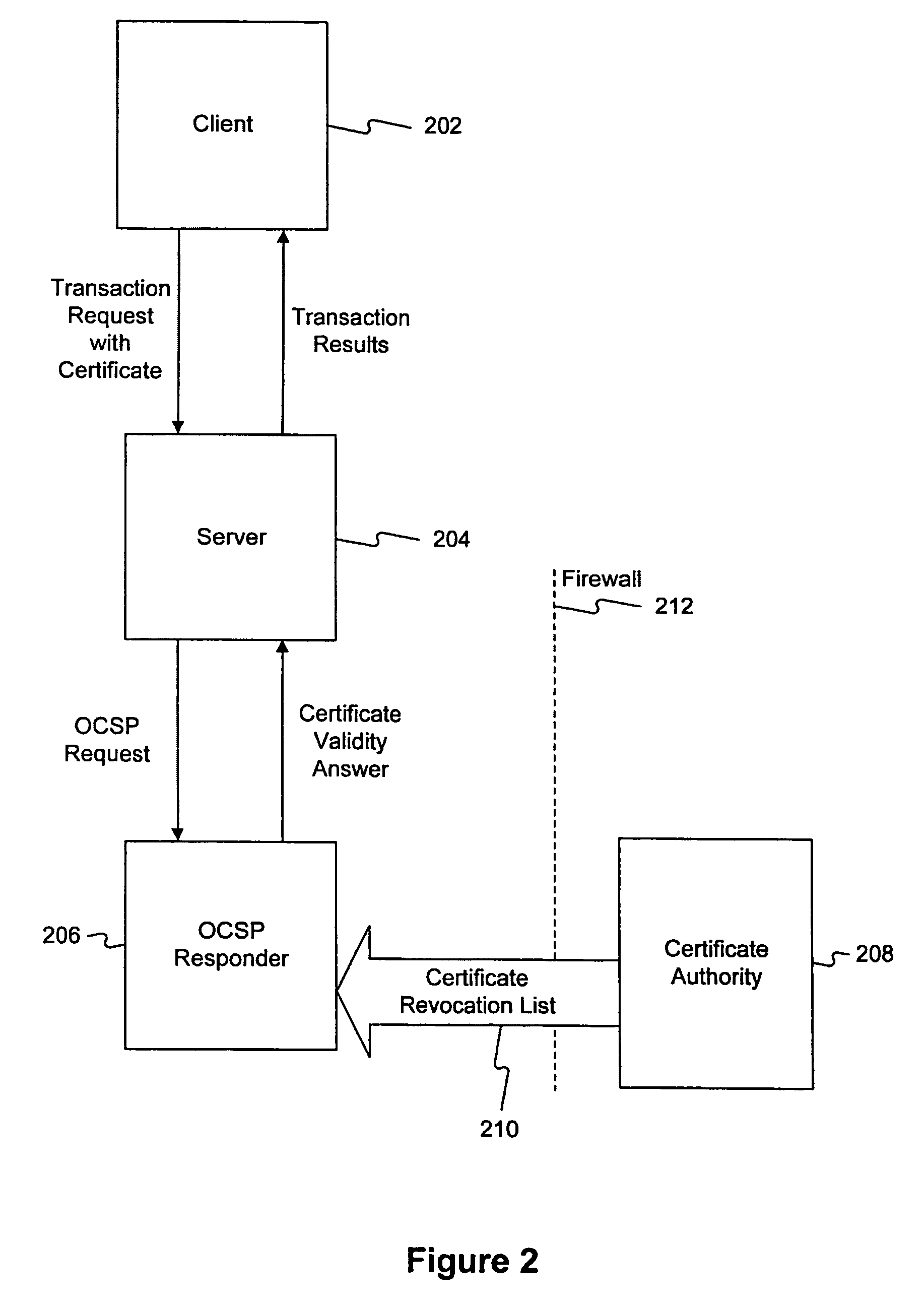
Method and system for answering online certificate status protocol (OCSP) requests without certificate revocation lists (CRL)
InactiveUS6970862B2Digital data protectionElectronic credentialsDirectory Access ProtocolClient-side
Methods and systems in accordance with the present invention efficiently validate digital certificates by answering Online Certificate Status Protocol (“OCSP”) requests without Certificate Revocation Lists (“CRL”). During validation of digital certificates, these methods and systems speed transmission, reduce required bandwidth and reduce required data storage by eliminating the need for the transmission of lengthy CRLs from a Certificate Authority (“CA”) when verifying a digital certificate from a client. In one implementation, they send a Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (“LDAP”) database query to a CA directory server to determine and pinpoint the existence of a valid digital certificate and check its validity without receiving a long list of data, such as a CRL, from a CA. The CA directory server returns the query result, and the database query in the CA directory server is performed faster than using an entire CRL, and furthermore, the transmission of the database query result is a small piece of information and does not require the large amounts of data transmission bandwidth and storage as required with transmitting CRL's.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
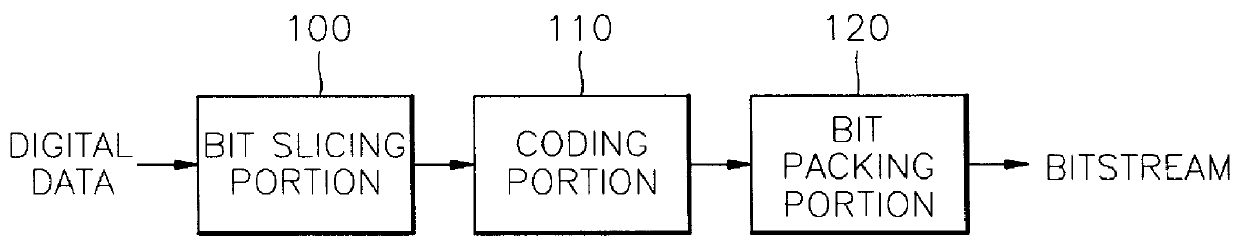
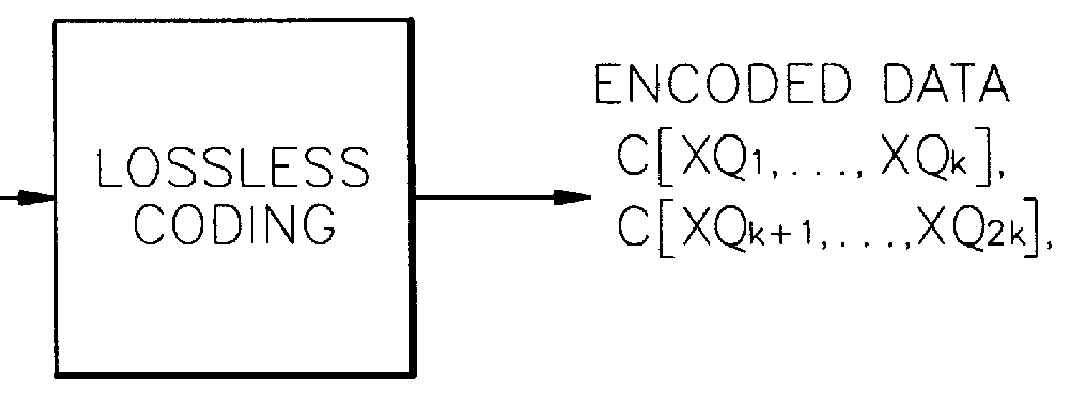
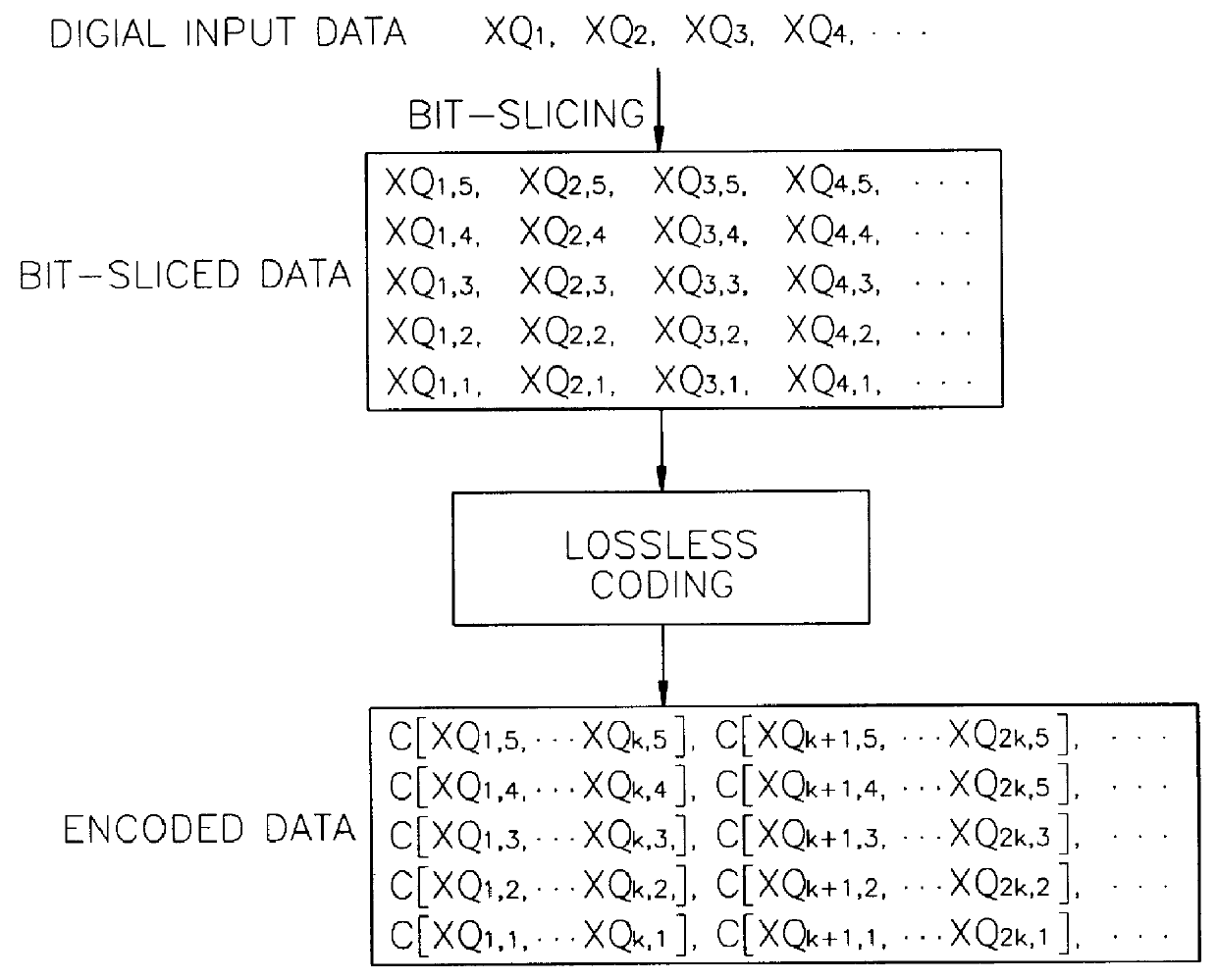
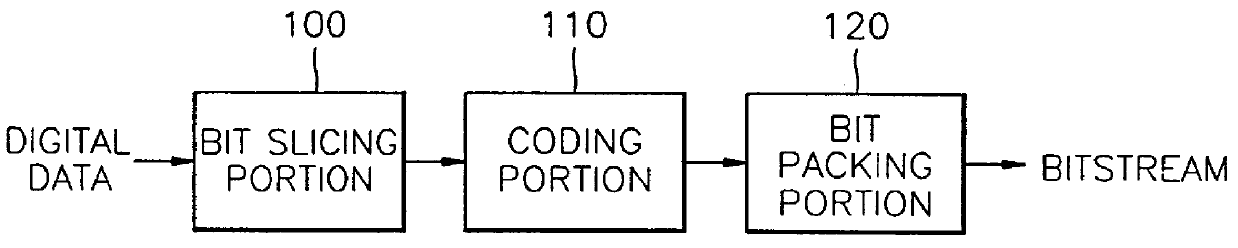
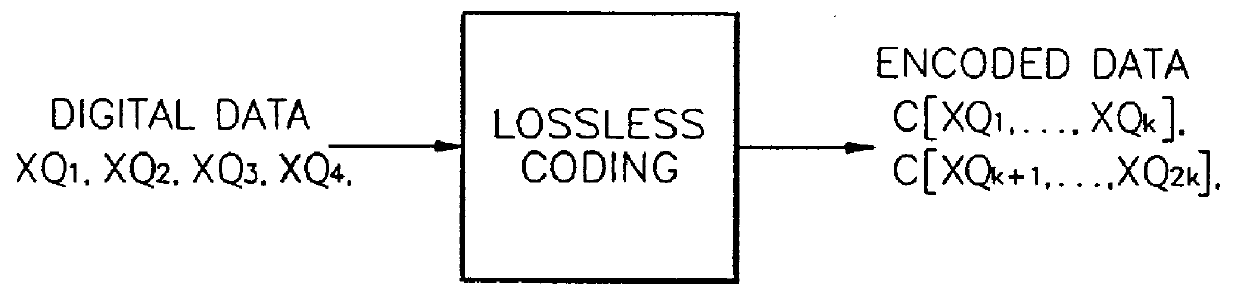
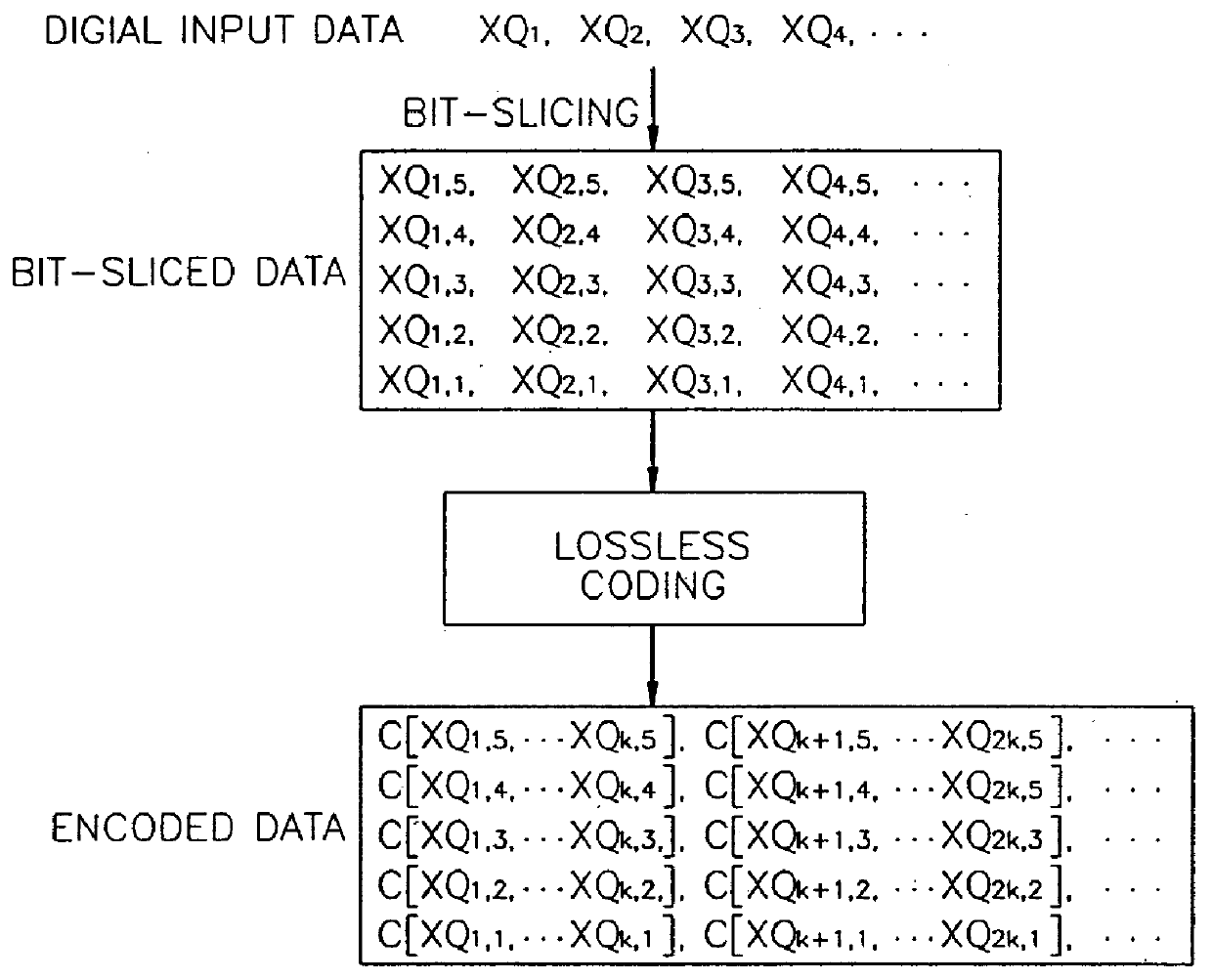
Digital data coding/decoding method and apparatus
A digital data coding / decoding method and apparatus are provided. The coding method includes the steps of representing respective digital data by digits of a predetermined same number, and coding the digital data represented by digits of the same number by a predetermined coding method from the uppermost significant digit sequence to the least significant digit sequence. The method for decoding digital data coded in the order of significance by rating the significance of digits of the digital data, includes the steps of analyzing significance of coded digital data, and decoding the analyzed digital data from upper significant digits to lower significant digits by a predetermined decoding method. Even if some bitstreams are lost or damaged by coding important information first, deterioration in audio quality can be reduced.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
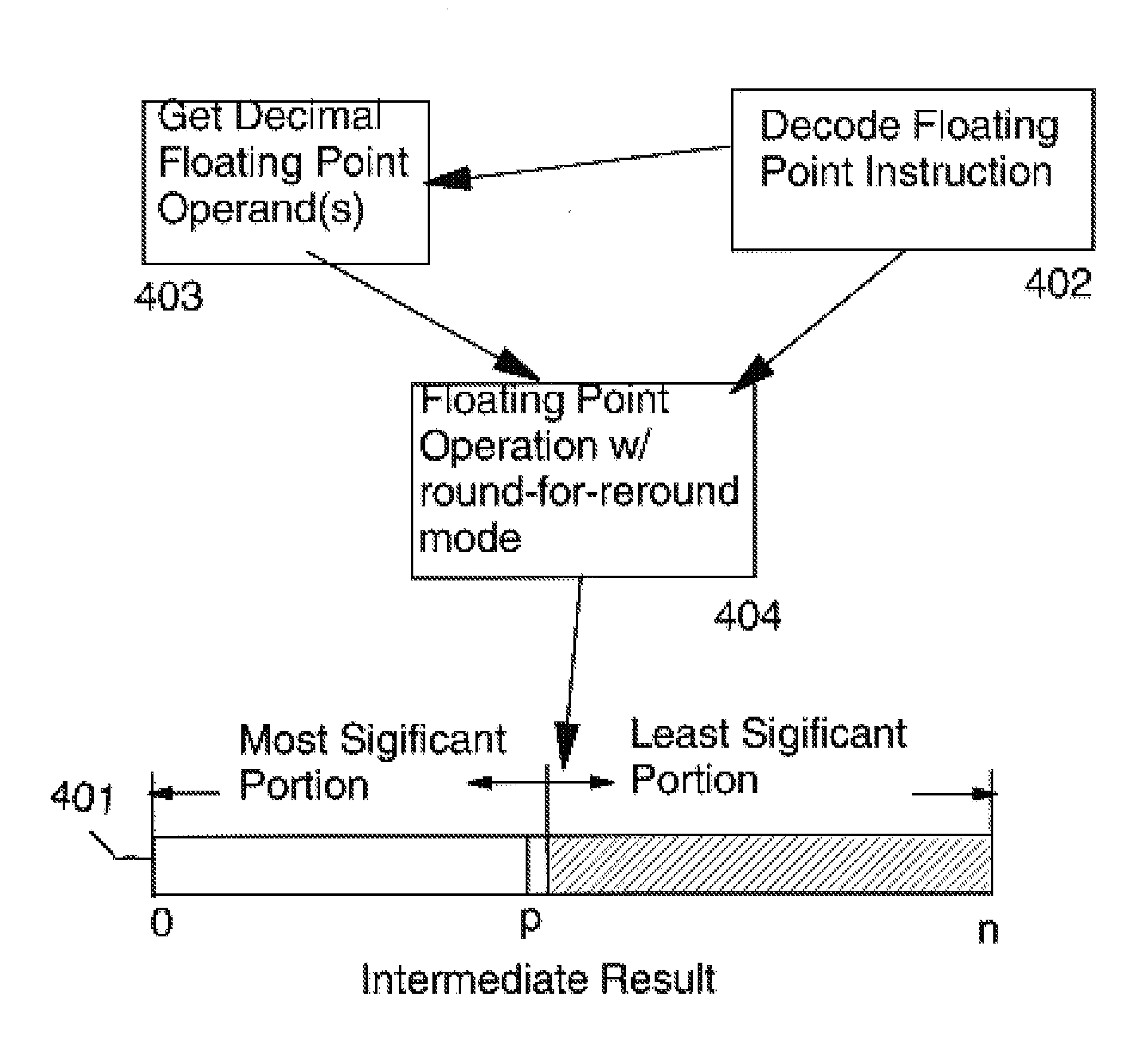
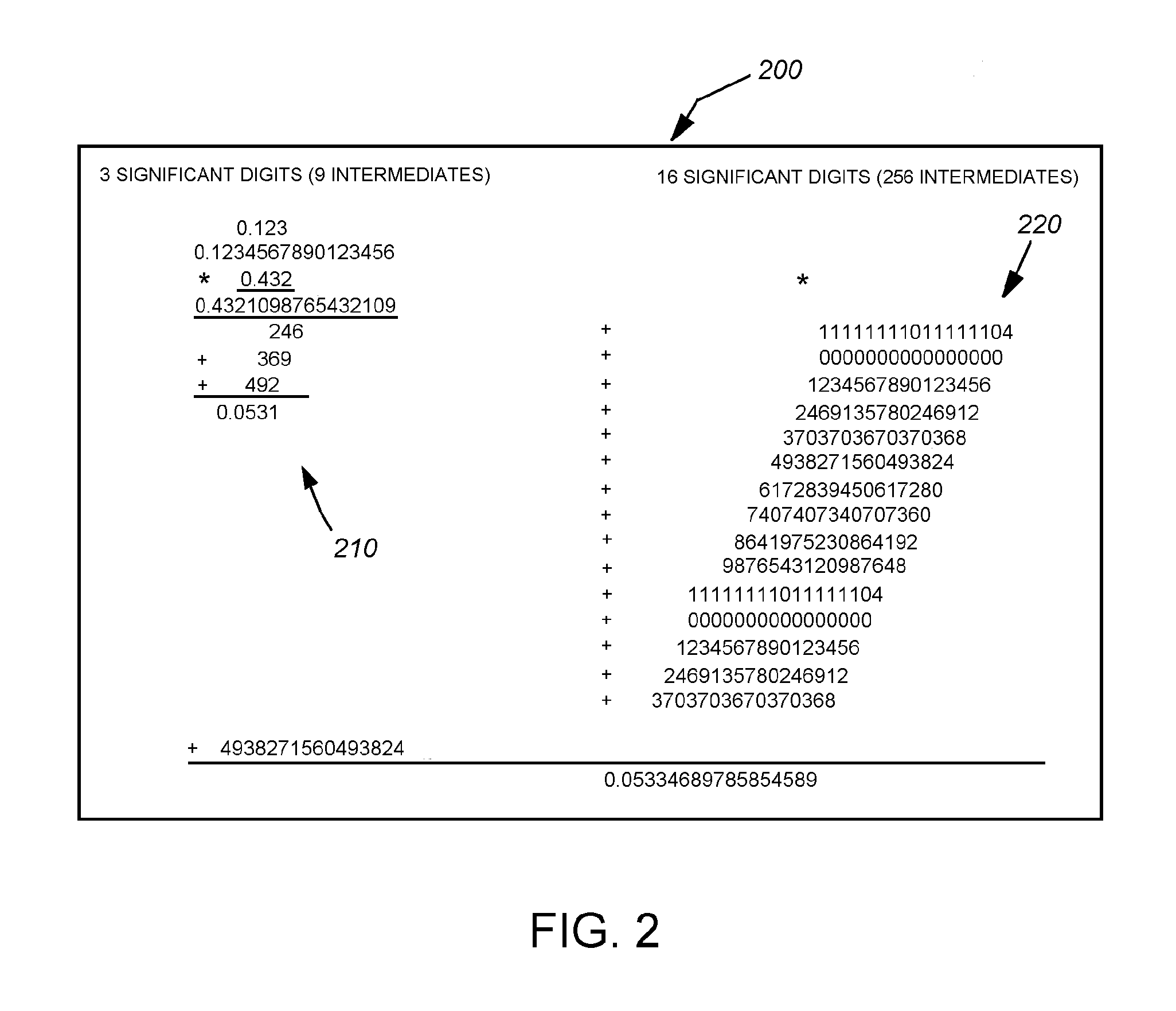
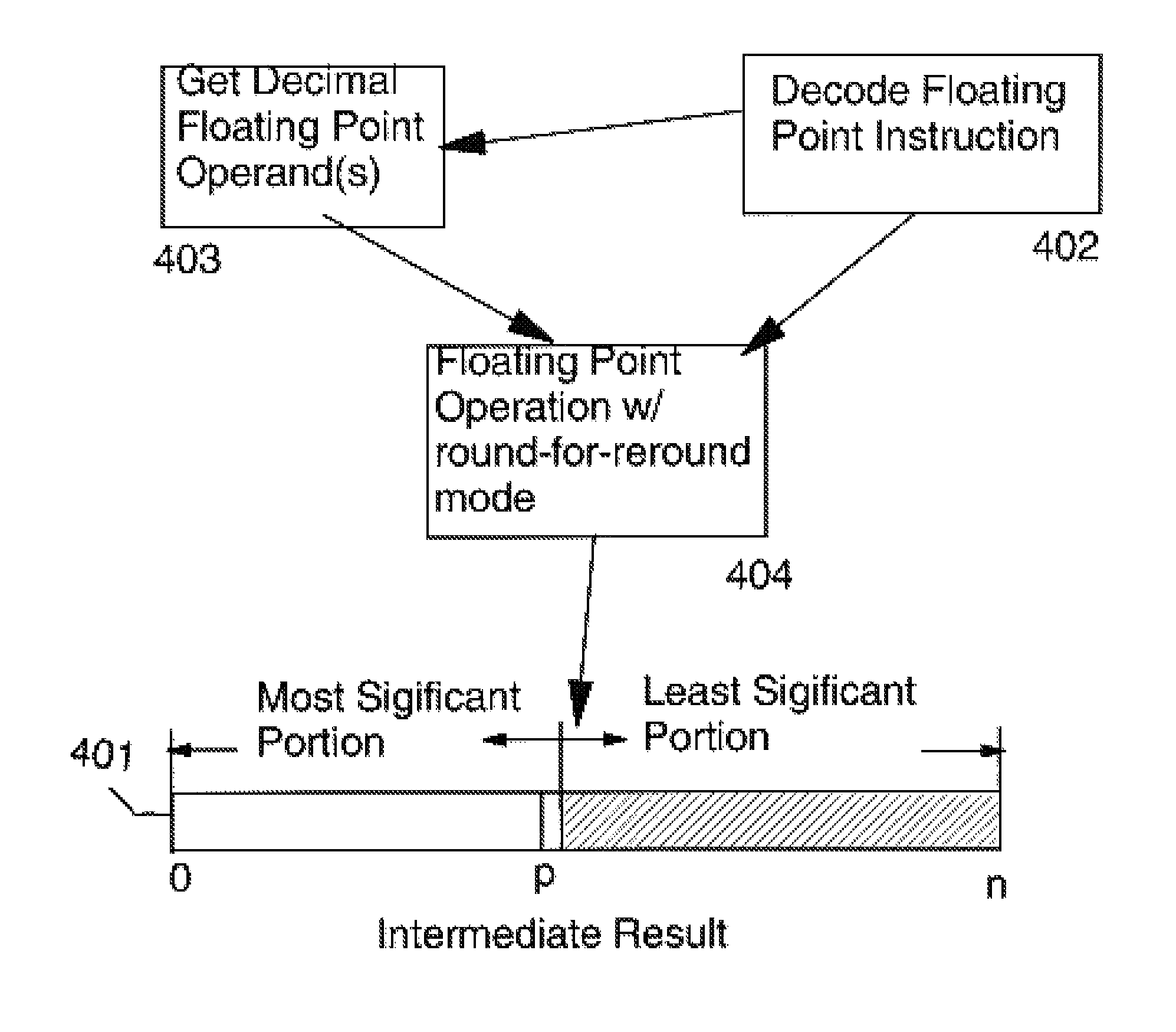
Round for Reround Mode in a Decimal Floating Point Instruction
ActiveUS20080215659A1Computations using magnetic elementsProgram controlParallel computingFloating point
a round-far-reround mode (preferably in a BID encoded Decimal format) of a floating point instruction prepares a result for later rounding to a variable number of digits by detecting that the least significant digit may be a 0, and if so changing it to 1 when the trailing digits are not all 0. A subsequent reround instruction is then able to round the result to any number of digits at least 2 fewer than the number of digits of the result. An optional embodiment saves a tag indicating the fact that the low order digit of the result is 0 or 5 if the trailing bits are non-zero in a tag field rather than modify the result. Another optional embodiment also saves a half-way-and-above indicator when the trailing digits represent a decimal with a most significant digit having a value of 5. An optional subsequent rewound instruction is able to round the result to any number of digits fewer or equal, to the number of digits of the result using the saved tags.
Owner:IBM CORP
Digital data coding/decoding method and apparatus
A digital data coding / decoding method and apparatus are provided. The coding method includes the steps of representing respective digital data by digits of a predetermined same number, and coding the digital data represented by digits of the same number by a predetermined coding method from the uppermost significant digit sequence to the least significant digit sequence. The method for decoding digital data coded in the order of significance by rating the significance of digits of the digital data, includes the steps of analyzing significance of coded digital data, and decoding the analyzed digital data from upper significant digits to lower significant digits by a predetermined decoding method. Even if some bitstreams are lost or damaged by coding important information first, deterioration in audio quality can be reduced.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
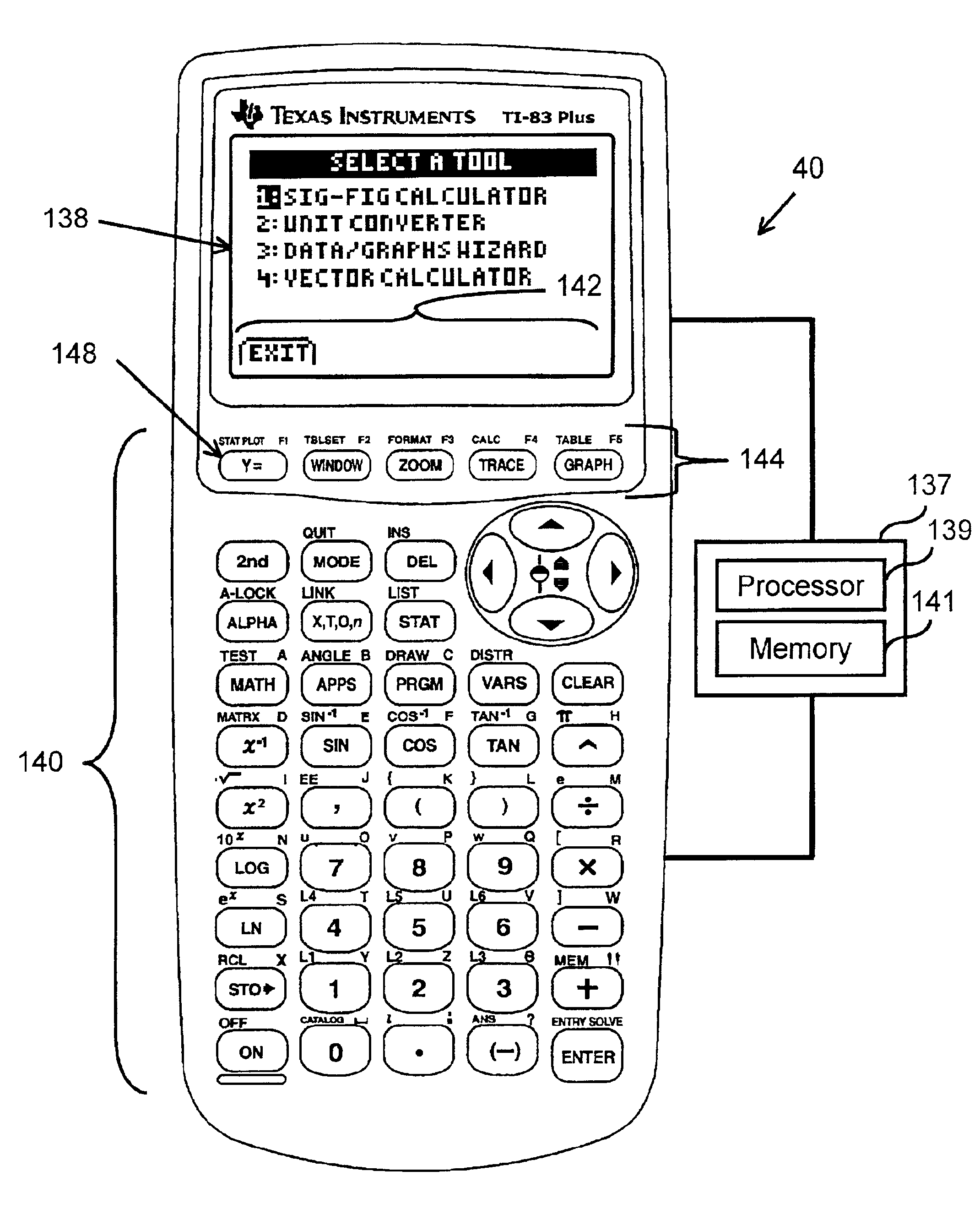
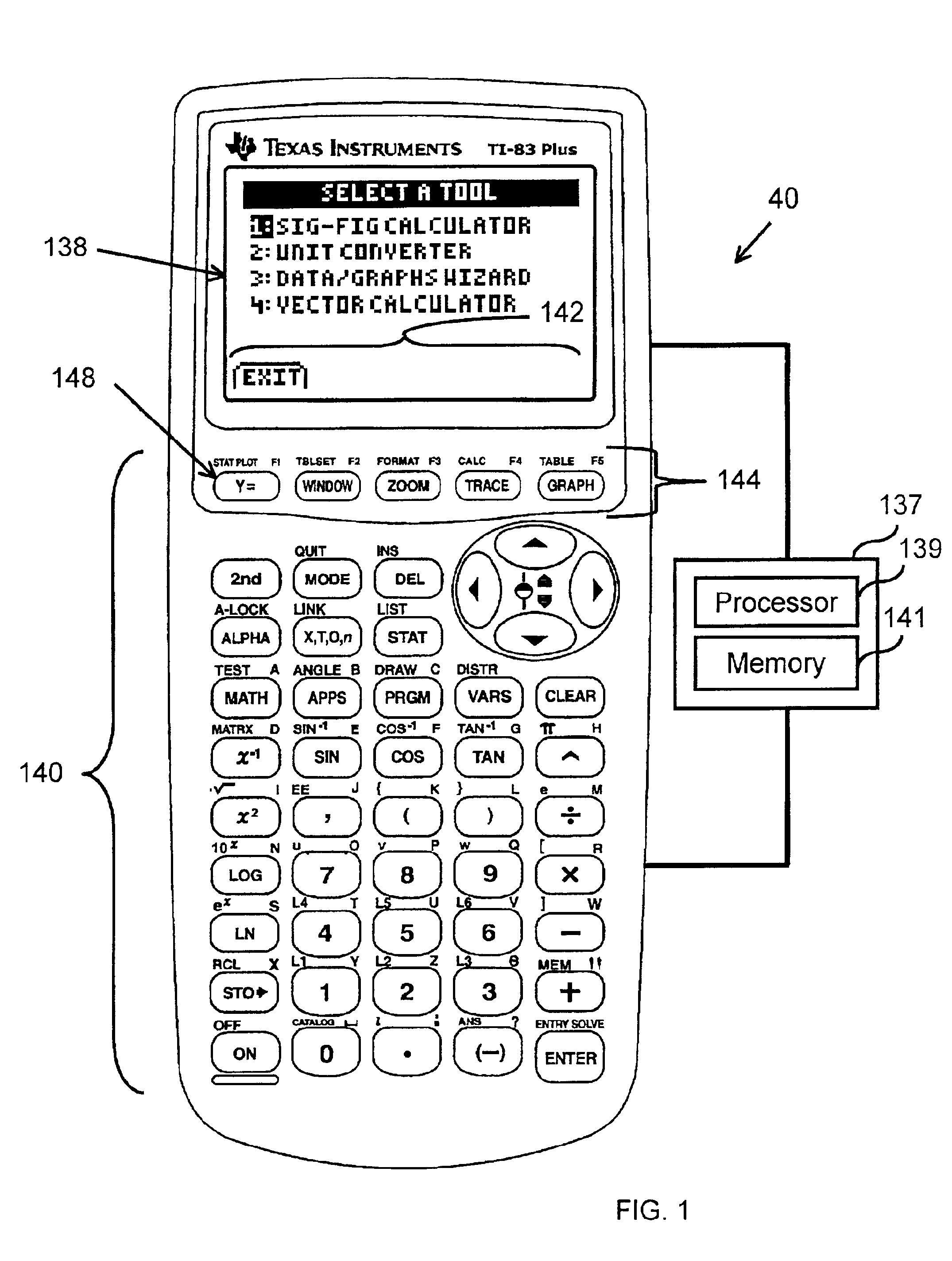
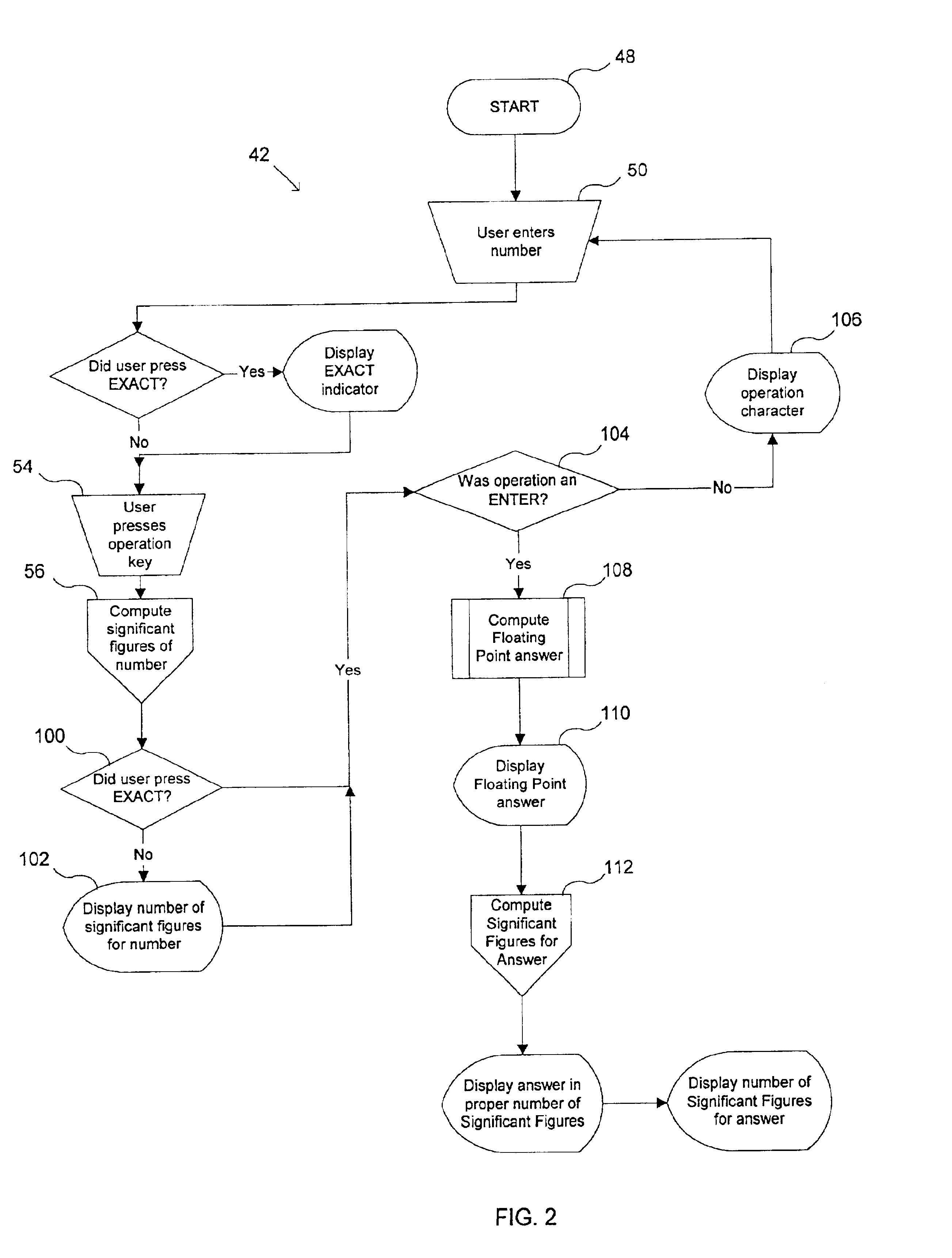
Apparatus and method for simultaneously displaying a number along with its number of significant figures
InactiveUS6854001B2Digital output to display deviceComputation using denominational number representationElectricityParallel computing
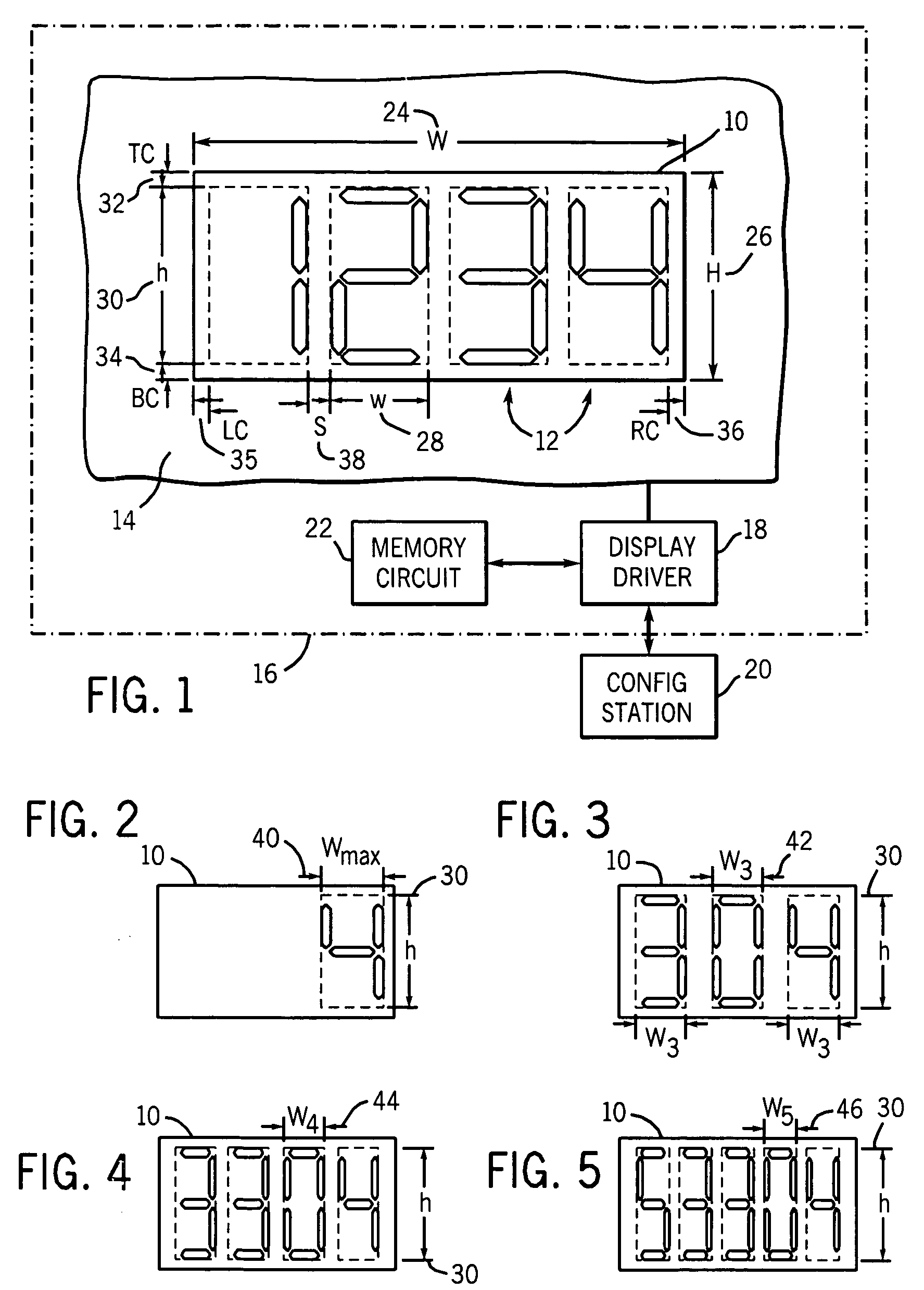
A computing device (40) comprises an electrical circuit and a software application. A display screen (138) and an input device (140) are electrically coupled to the electrical circuit. The software application provides instructions to determine the number of significant figures for a number entered via the input device, and simultaneously display on the display screen the entered number along with the number of significant figures for the entered number, and / or the software application provides instructions to calculate a floating point answer for a mathematical operation entered for one or more numbers entered into the computing device, round the floating point answer to the proper precision or to the proper number of significant figures, determine the number of significant figures for the rounded answer, and simultaneously display on the display the rounded answer and its number of significant figures.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
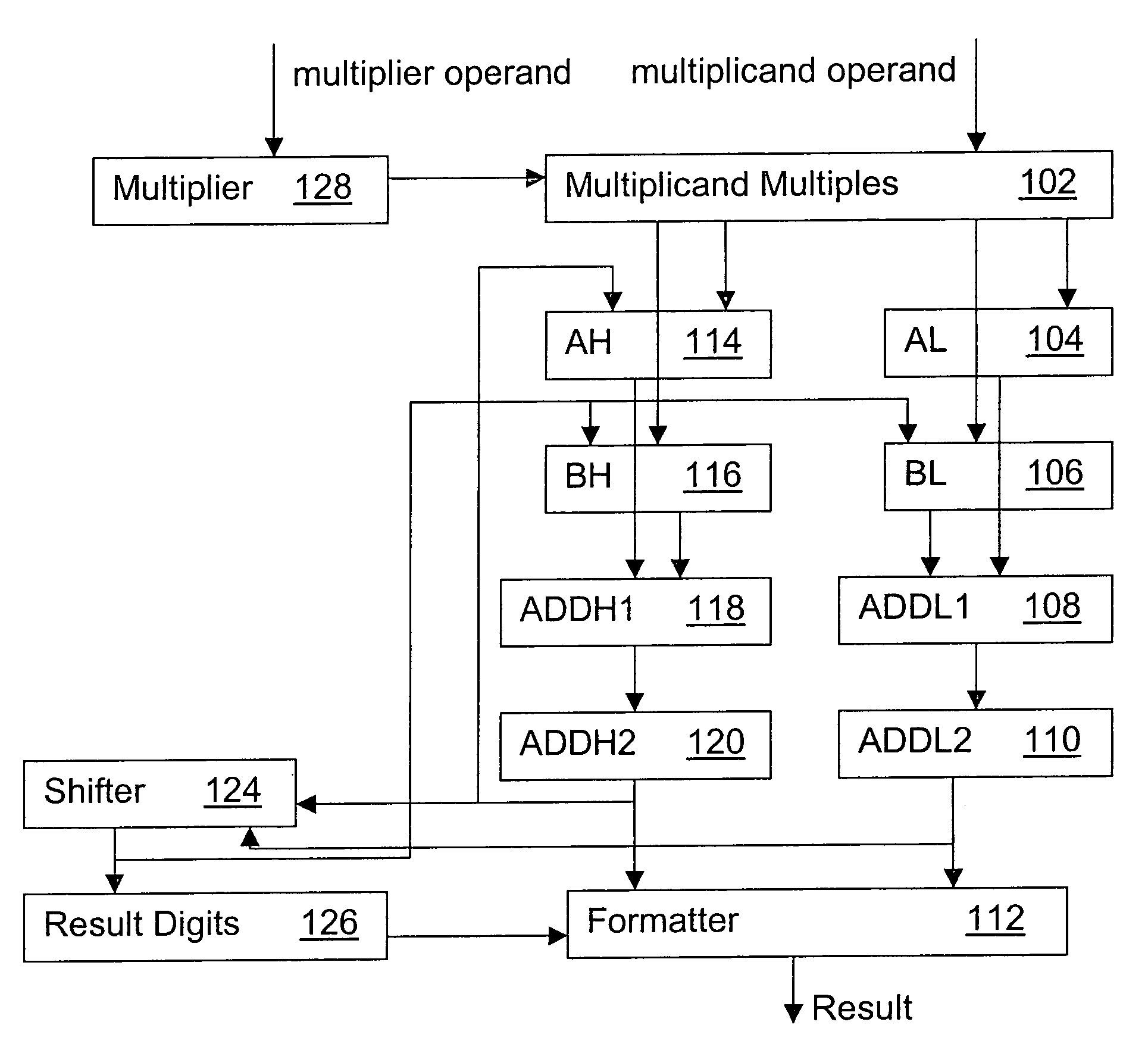
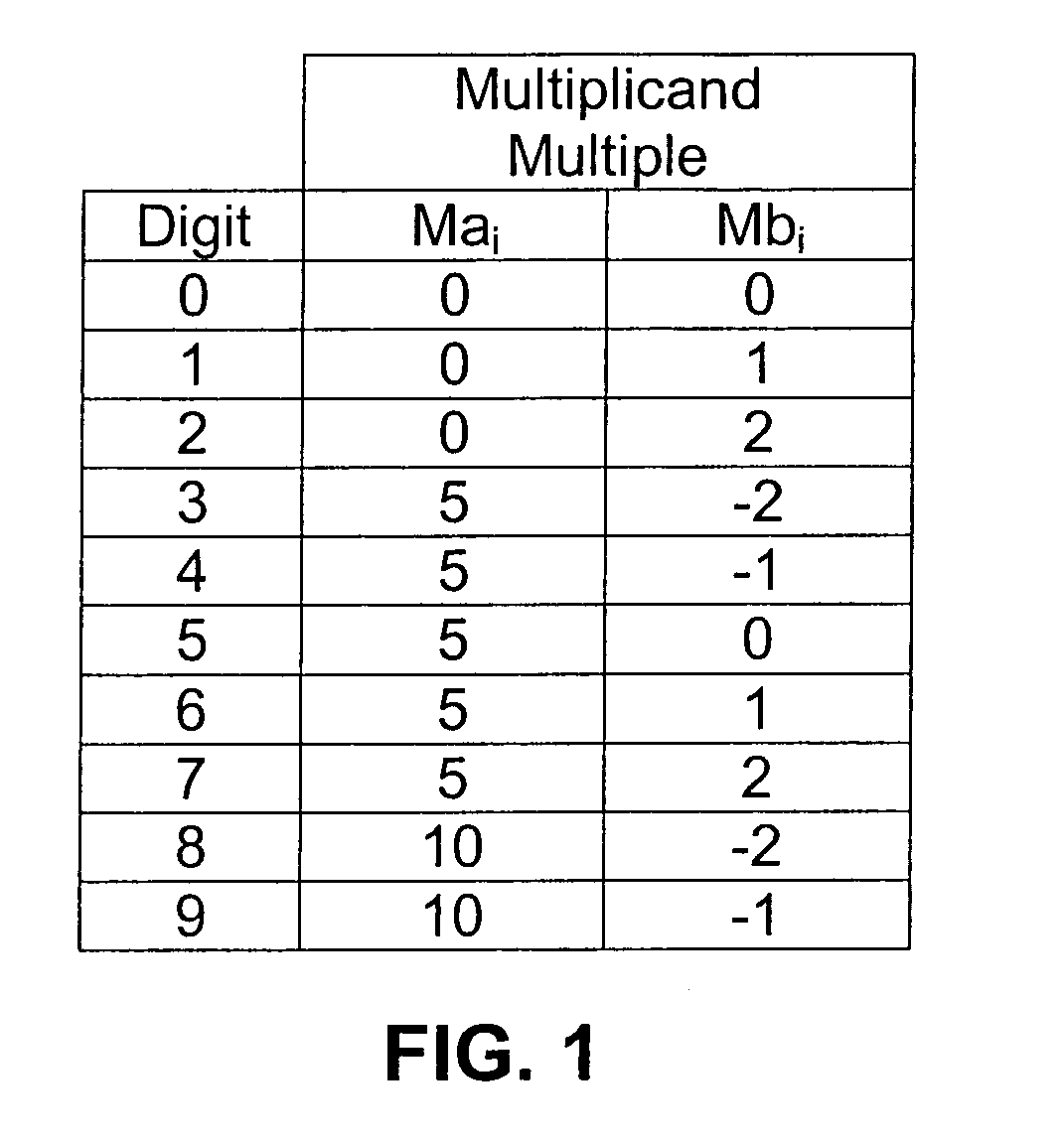
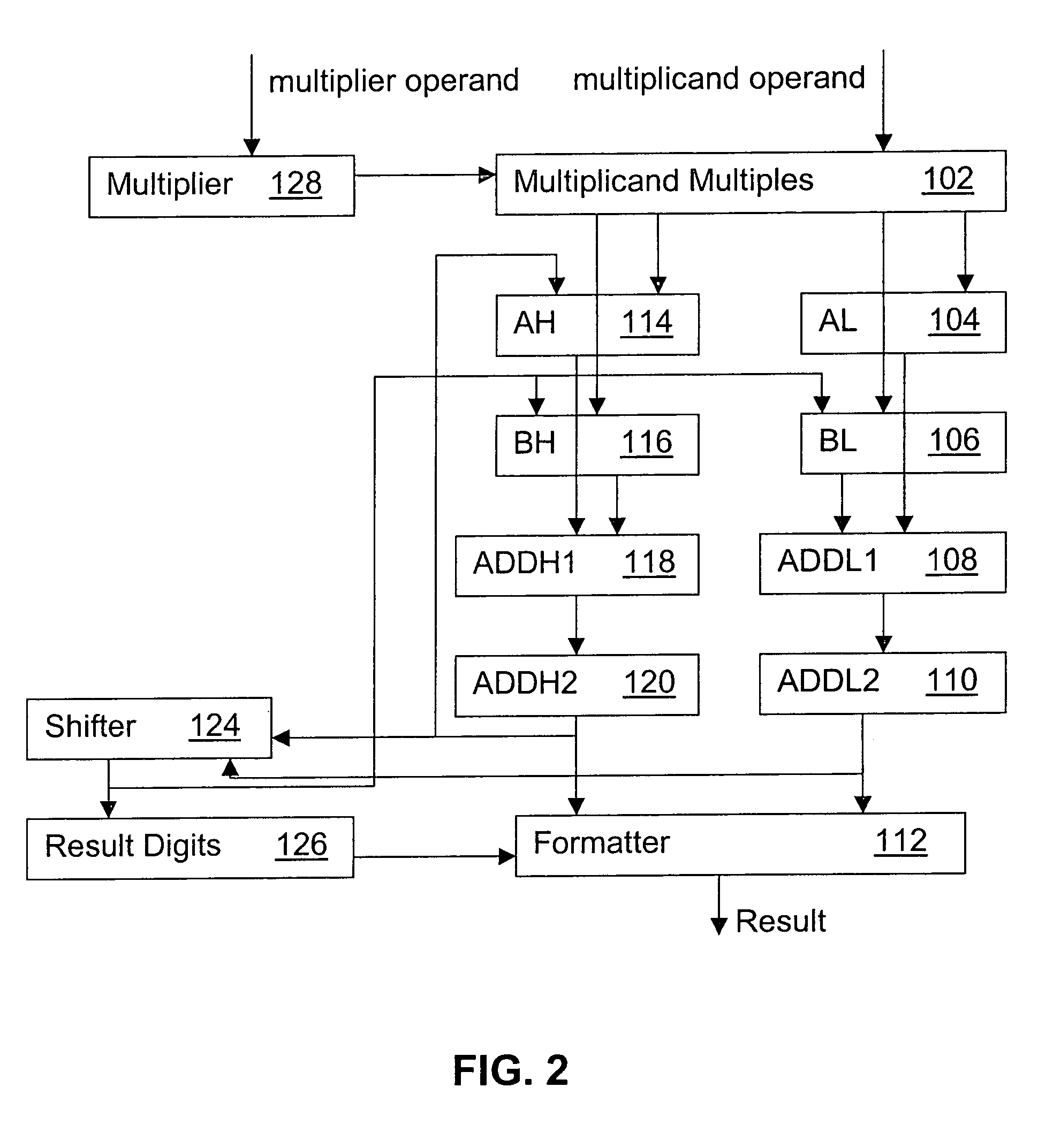
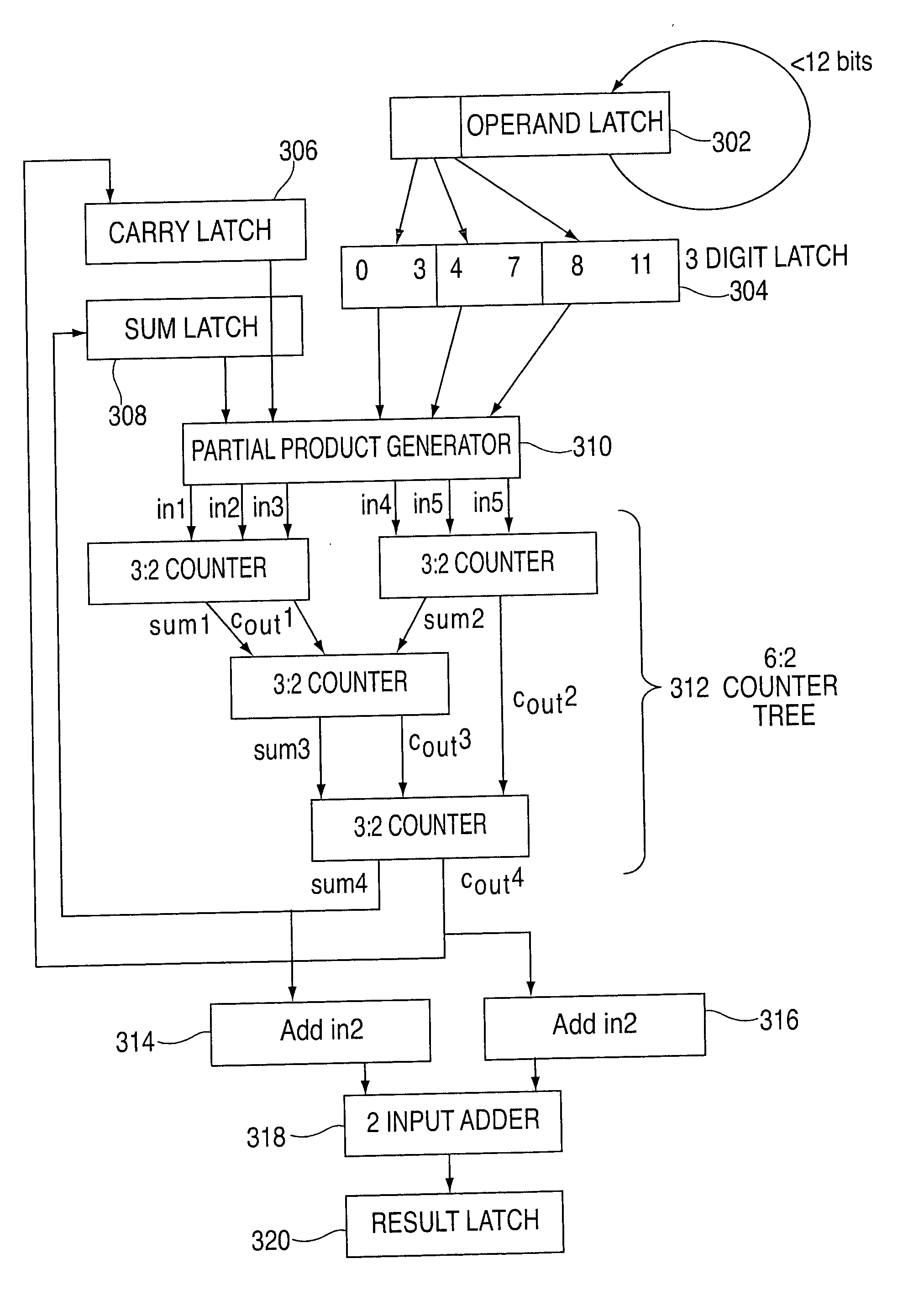
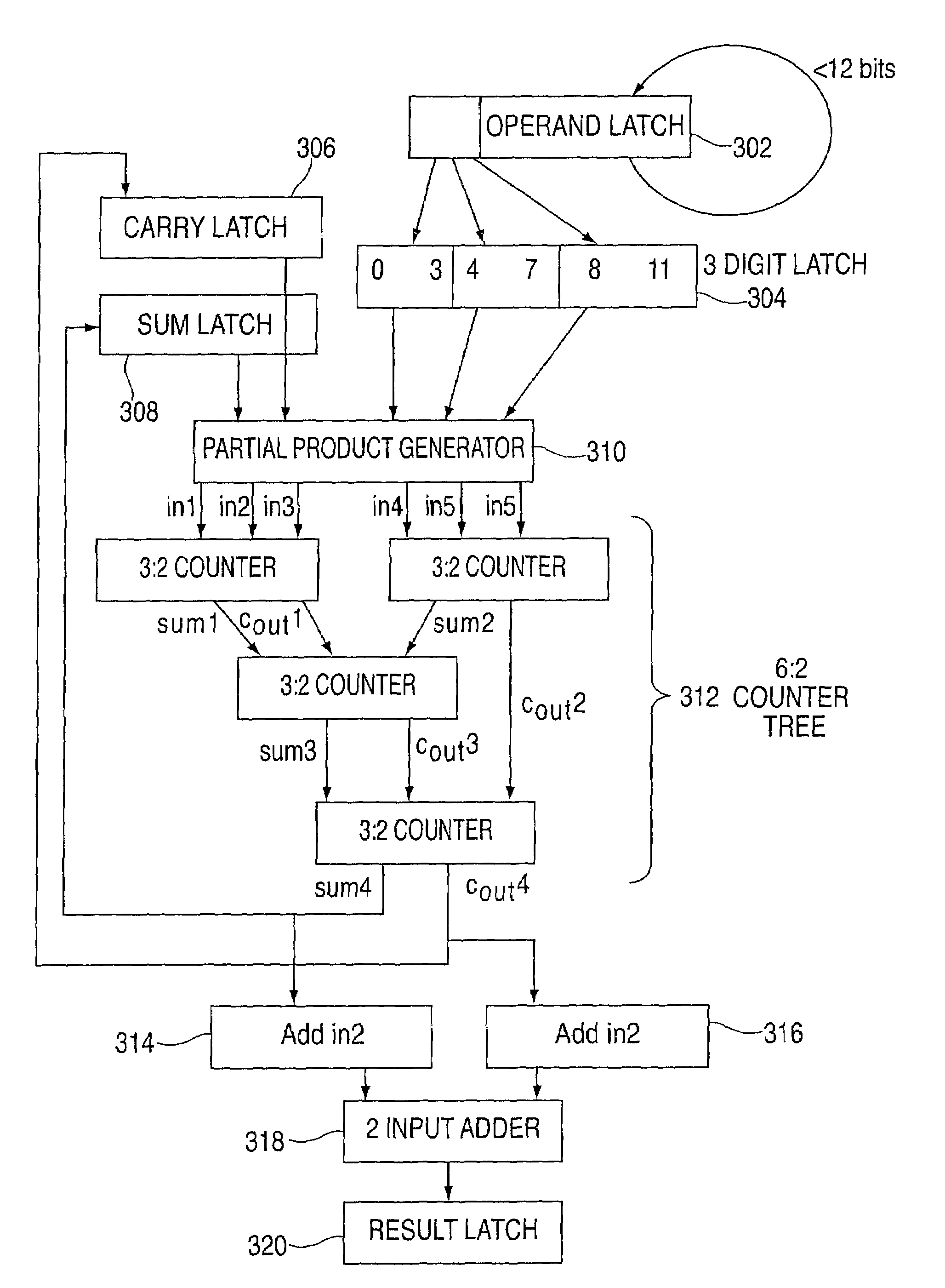
System and method for providing a decimal multiply algorithm using a double adder
InactiveUS7519647B2Computation using non-contact making devicesBinary multiplierTheoretical computer science
A system for performing decimal multiplication including input registers for inputting a multiplier and a multiplicand. The multiplier includes one or more digits. The system also includes one or more two cycle adders and mechanism. The mechanism receives the multiplier and the multiplicand into the input registers. A running sum is reset to zero. The mechanism also performs for each of the digits in the multiplier in order from least significant digit to most significant digit: creating a partial product of the digit and the multiplicand; and adding the partial product to the running sum using the two cycle adders. When the loop is completed for each of the digits in the multiplier, the mechanism outputs the running sum as the result.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
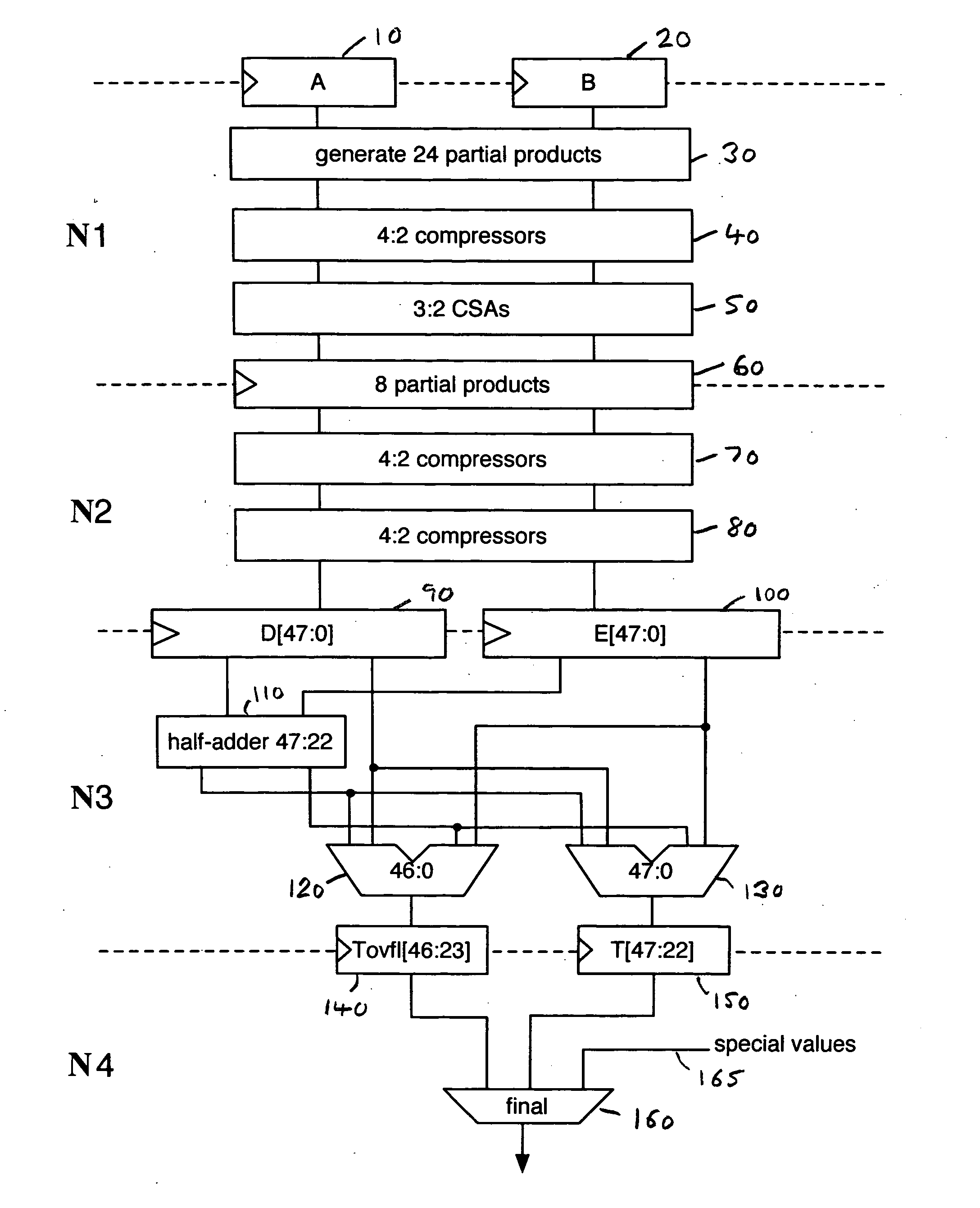
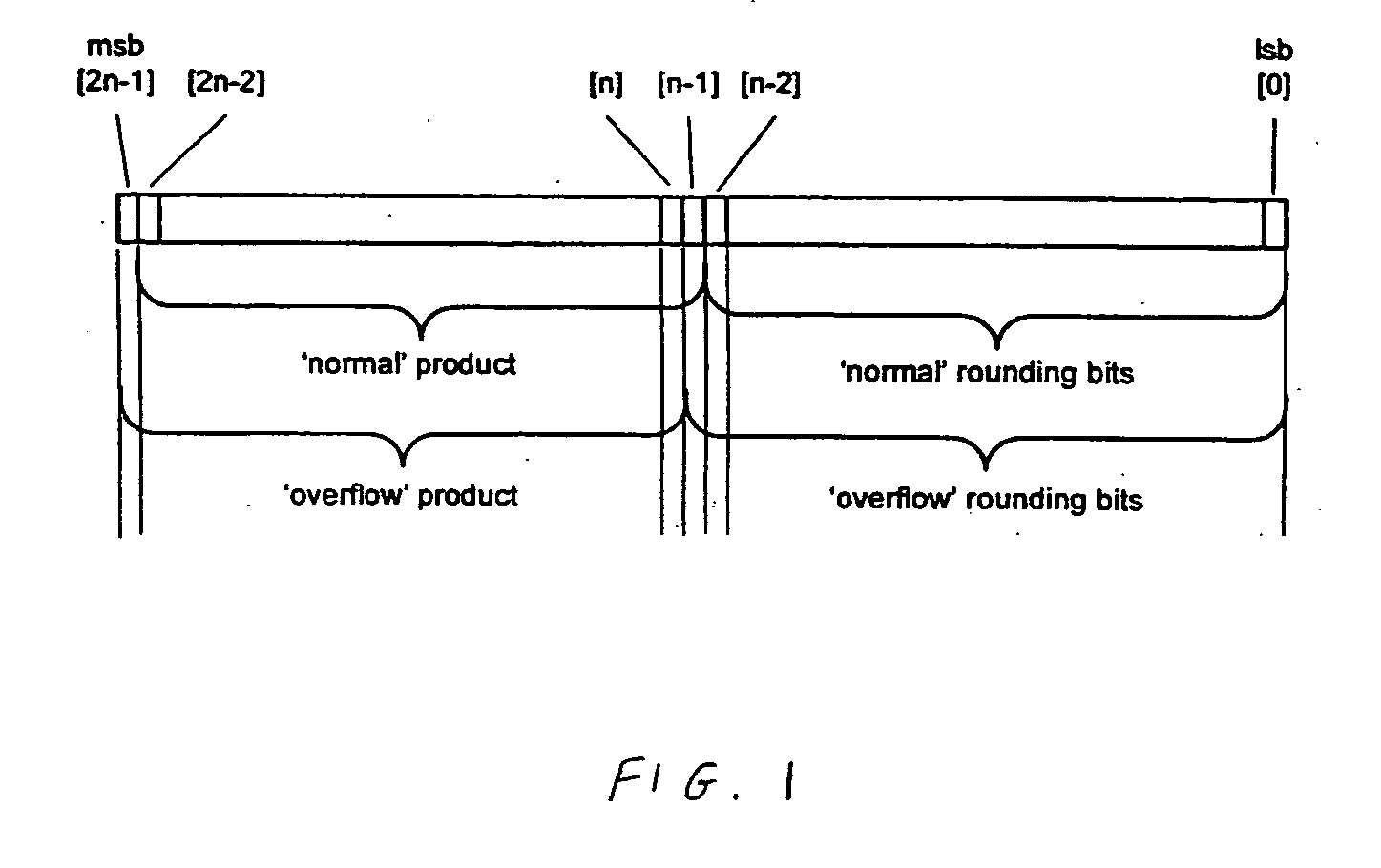
Data processing apparatus and method for performing floating point multiplication
ActiveUS20060117080A1Avoid the needComputation using non-contact making devicesBinary multiplierLeast significant bit
A data processing apparatus and method are provided for multiplying first and second n-bit significands of first and second floating point operands to produce an n-bit result. The data processing apparatus comprises multiplier logic operable to multiply the first and second n-bit significands to produce a pair of 2n-bit vectors. Half adder logic is then arranged to produce a plurality of carry and sum bits representing a corresponding plurality of most significant bits of the pair of 2n-bit vectors. The first adder logic then performs a first sum operation in order to generate a first rounded result equivalent to the addition of the pair of 2n-bit vectors with a rounding increment injected at a first predetermined rounding position appropriate for a non-overflow condition. To achieve this, the first adder logic uses as the m most significant bits of the pair of 2n-bit vectors the corresponding m carry and sum bits, the least significant of the m carry bits being replaced with a rounding increment value prior to the first adder logic performing the first sum operation. Second adder logic is arranged to perform a second sum operation in order to generate a second rounded result equivalent to the addition of the pair of 2n-bit vectors with a rounding increment injected at a second predetermined rounding position appropriate for an overflow condition. To achieve this, the second adder logic uses as the m-1 most significant bits of the pair of 2n-bit vectors the corresponding m−1 carry and sum bits, with the least significant of the m−1 carry bits being replaced with the rounding increment value prior to the second adder logic performing the second sum operation. The required n-bit result is then derived from either the first rounded result or the second rounded result. The data processing apparatus takes advantage of a property of the half adder form to enable a rounding increment value to be injected prior to performance of the first and second sum operations without requiring full adders to be used to inject the rounding increment value.
Owner:ARM LTD
Visible light and infrared detection result integration based moving target detection method
InactiveCN104123734AEffectively deal with the technical problems of poor target detection effectTo achieve the effect of all-weather detectionImage analysisComputer visionExtraction methods
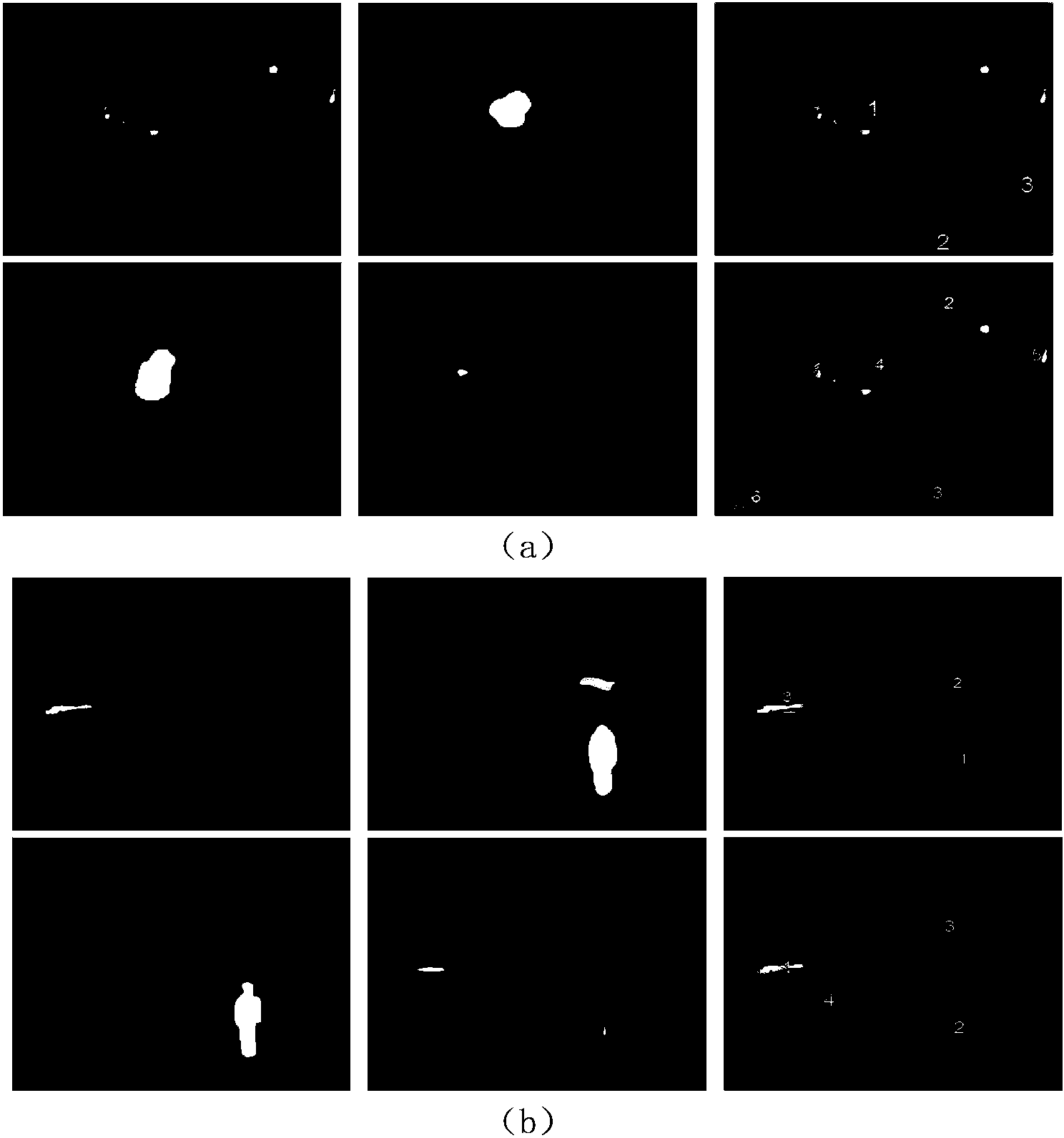
The invention discloses a visible light and infrared detection result integration based moving target detection method which is used for solving the technical problem that the existing moving target detection method is poor in detection effect. According to the technical scheme, the visible light and infrared detection result integration based moving target detection method comprises extracting a foreground picture of a visible light image by a ViBe background extraction method; converting the foreground picture to an LUV space for shadow judgment after the foreground picture is obtained; extracting a significant figure of an infrared image by a significance detection method; integrating two detection results and extracting a final moving target. According to the visible light and infrared detection result integration based moving target detection method, the technical problem of the poor target detection effect caused by shadows and illumination intensity environment changes can be effectively solved and the all-weather detection effect can be achieved.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Orthogonal frequency division multiplexing receiver system and its automatic gain control method
InactiveCN101257472AEasy to detectIncrease success rateMulti-frequency code systemsComputation complexityBand-pass filter
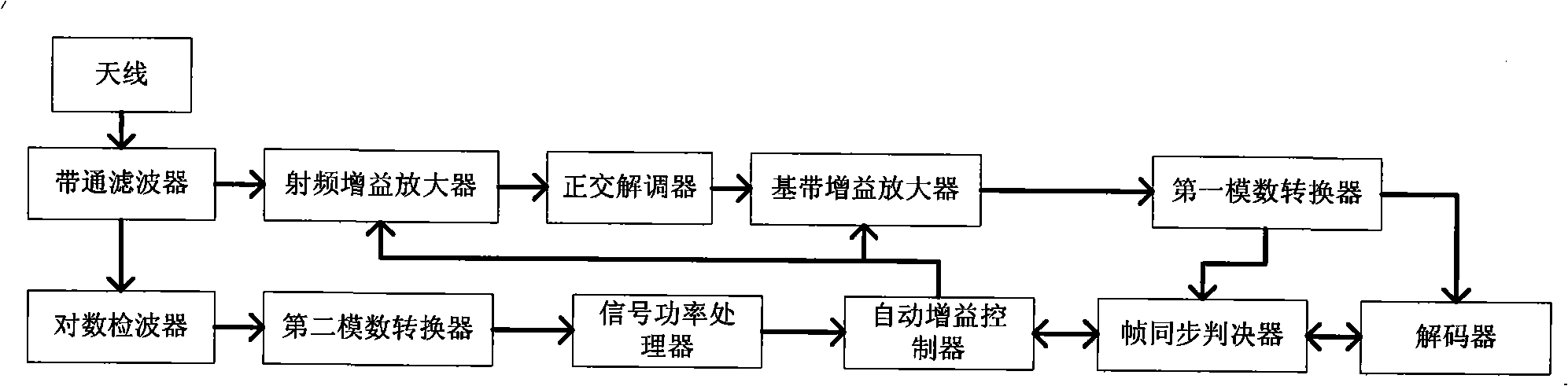
The invention provides an orthogonal frequency division multiplexing receiving system and an automatic gain control method. The antenna of the system is connected with a band-pass filter, a radio frequency gain amplifier, an orthogonal demodulator, a baseband gain amplifier, a first digital-to-analog converter, a decoder, a frame alignement judging device, an automatic gain controller, a signal power processor, a second digital-to-analog converter, a ogarithmic detector, a band-pass filter in turn, wherein the automatic gain controller is respectively connected with the baseband gain amplifier, the radio frequency gain amplifier, while the first digital-to-analog converter is connected with the frame alignement judging device. The gain control method is that the receiver carries the logarithm demodulation on the received signals, to control the system gain according to the power detecting result and the state of the two modules of frame synchronization and the decoder, to reach the aim of correctly adjusting the system gain. The invention has high detecting precision, small computation complexity, short response time, which is suitable to orthogonal frequency division multiplexing receiving system and can effectively increase the significant figure of the analog-to-digital converter.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
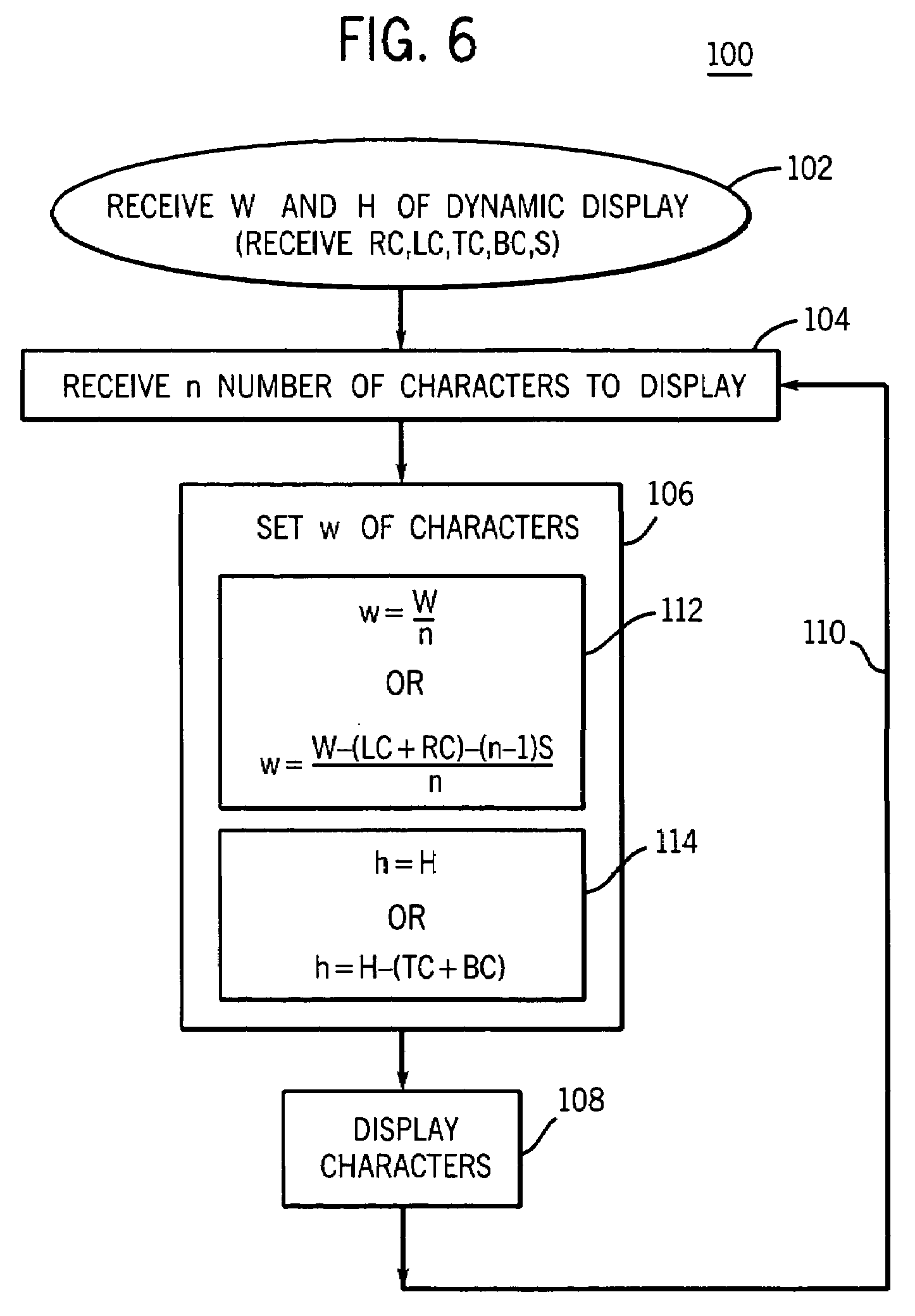
Digital numeric display with adaptive character width
ActiveUS20080082913A12D-image generationCathode-ray tube indicatorsHuman–machine interfaceDisplay device
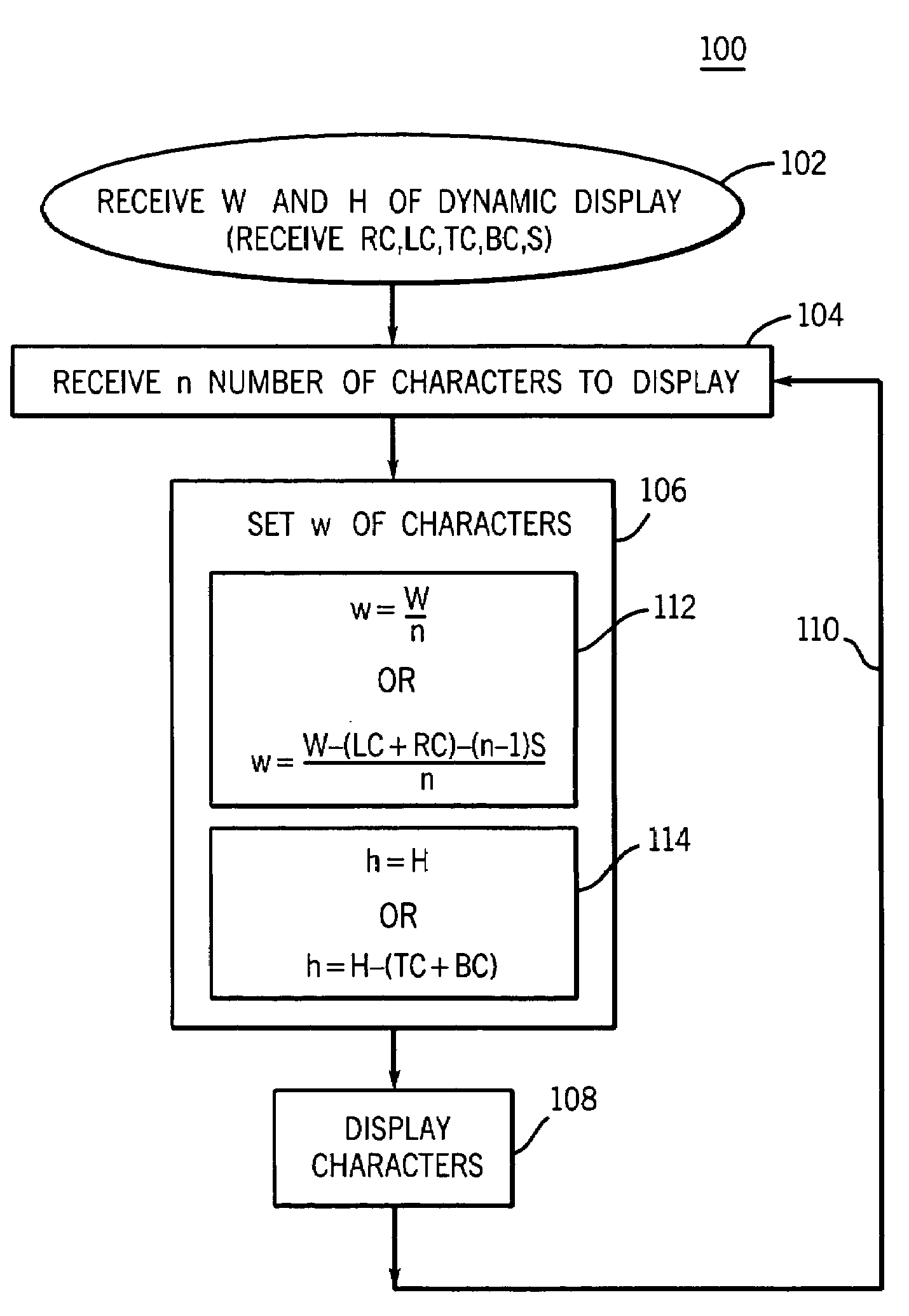
A technique is disclosed for dynamically adjusting dimensions of characters, such as digits, displayed on a configurable display, such as in a human-machine interface. The height of the characters is fixed and the width is altered depending upon the number of characters to be displayed, resulting in changing aspect ratios for the characters. The width may be set to a predetermined maximum character width if all characters to be displayed will fit within the available space, or the width may be reduced to accommodate more characters. The technique may take into account cushion spaces for borders or frames, as well as spaces between characters. The resulting display allows for a change in the number of significant digits in a displayed numeral, while maintaining excellent readability.
Owner:ROCKWELL AUTOMATION TECH
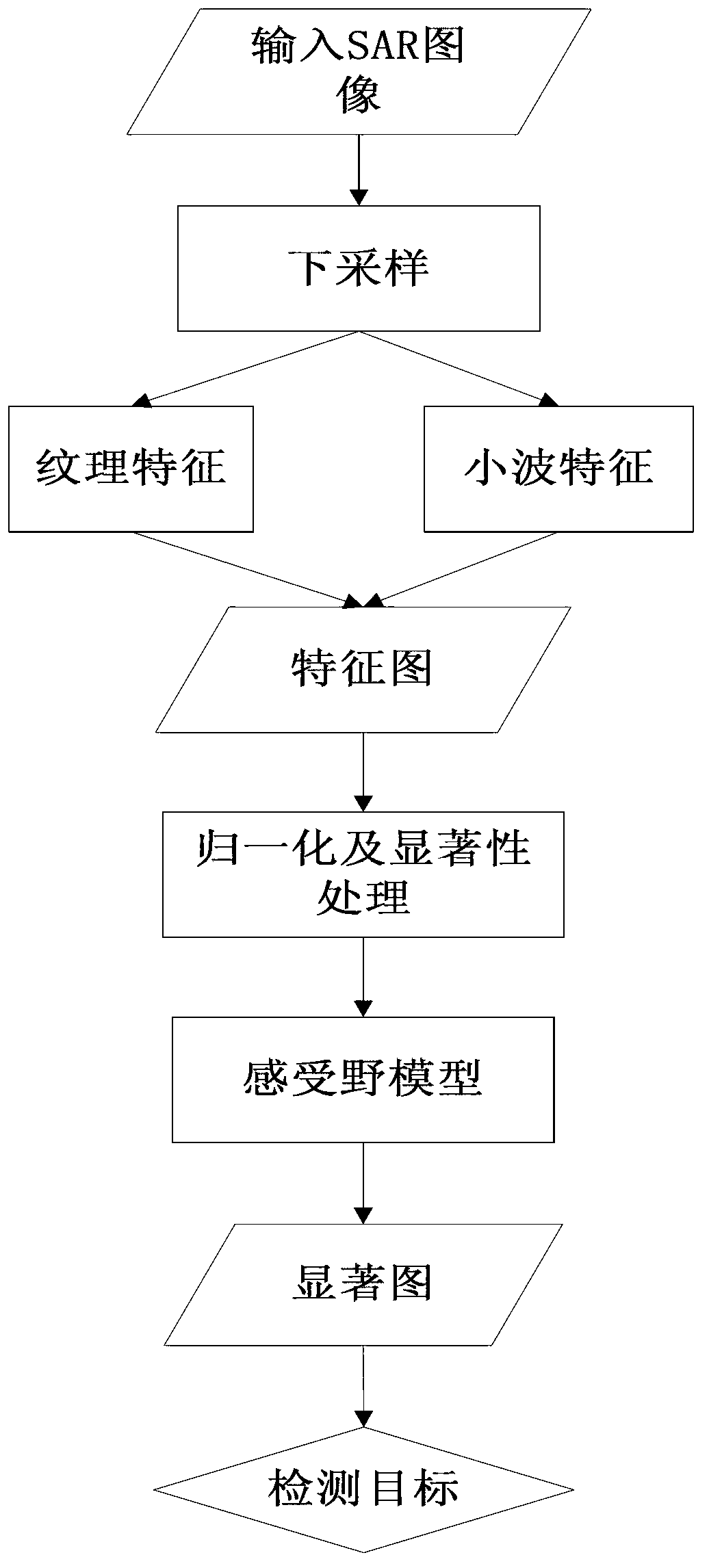
Synthetic aperture radar (SAR) target detection method based on improved visual attention model
InactiveCN102999909AIntegrity guaranteedClear outlineImage analysisImaging processingSynthetic aperture radar
The invention discloses a synthetic aperture radar (SAR) target detection method based on an improved visual attention model and belongs to the technical field of image processing. The SAR target detection method mainly solves the problem of failure of a traditional visual attention model in the aspect of SAR image processing. The SAR target detection method includes: under-sampling is performed on an SRA image to be detected, texture features and wavelet features are extracted from the sampled image, linear superposition is performed on the features, and normalization and significance processing is performed on the features to obtain an initial significant figure; visual receptive field template filtering is performed on the initial significant figure to obtain a final significant figure; at last the final significant figure adopts bilinear interpolation to be the same as the size of an original SAR image, and a light area in the interpolated significant figure is used as a target area. The SAR target detection method based on the improved visual attention model has the advantages of being rapid in calculating speed, remarkable in detection effect, accurate in positioning and capable of being used for early detection of an SAR image target.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
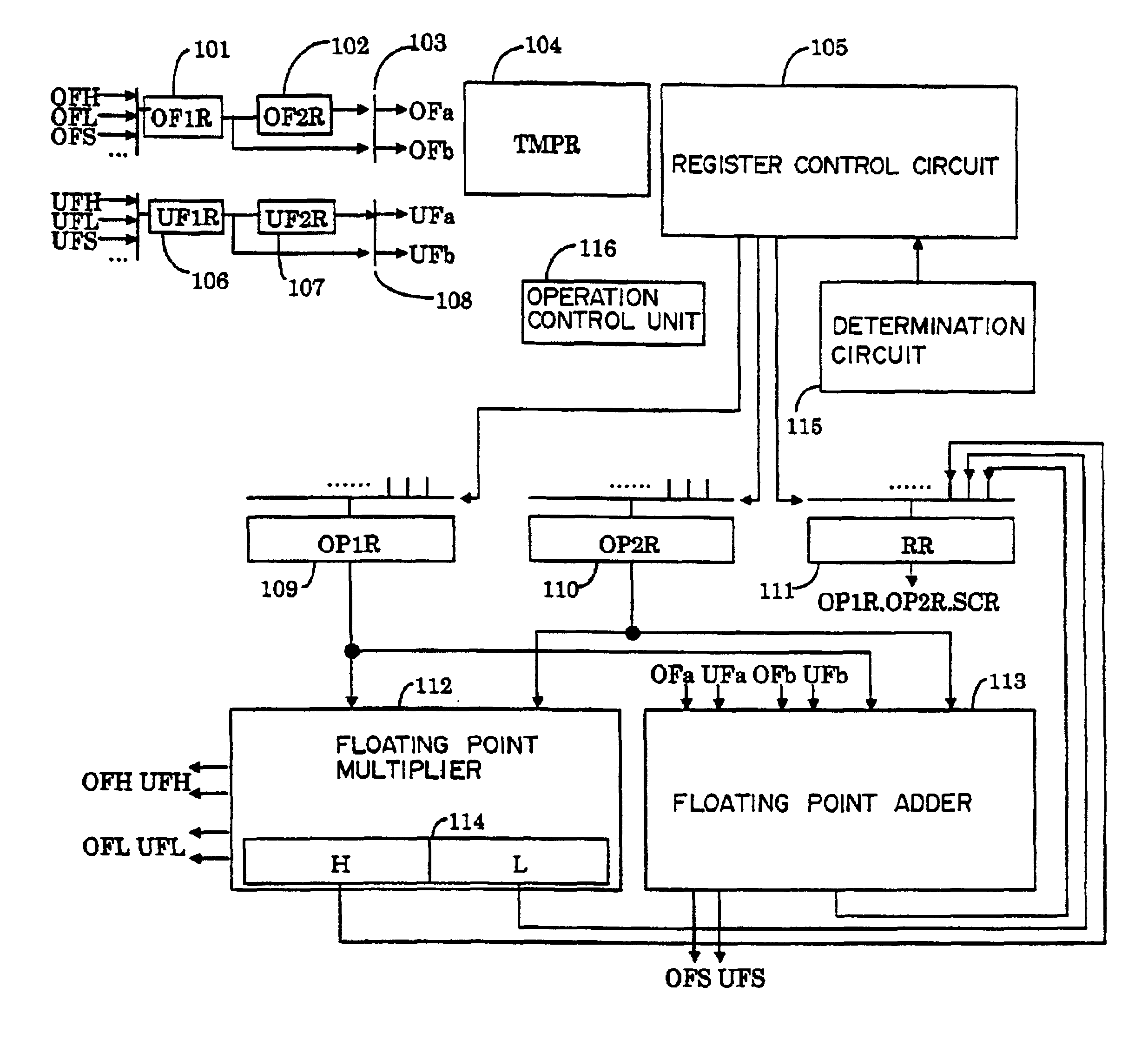
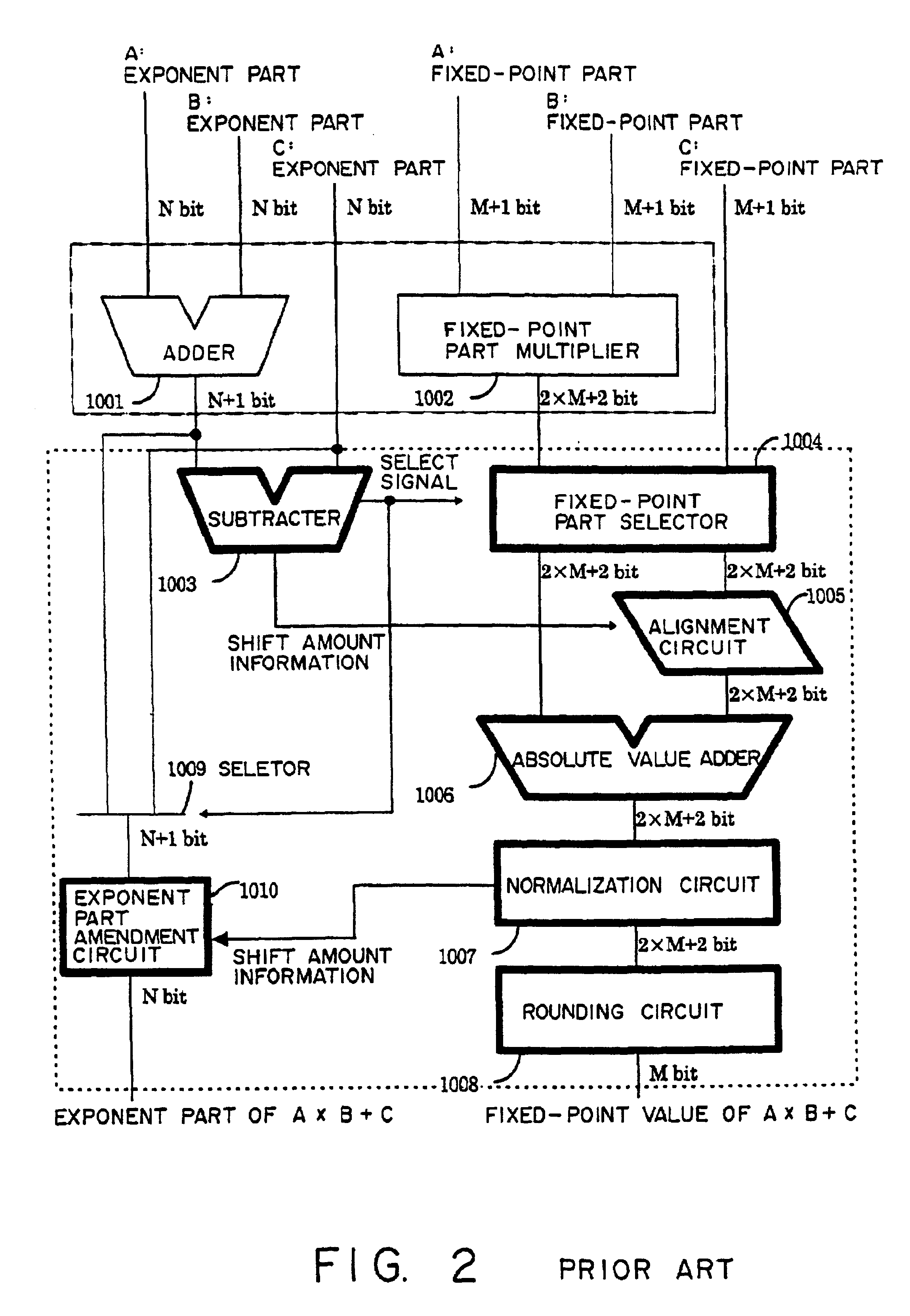
Apparatus and method of performing product-sum operation
InactiveUS6895423B2Reduce circuit sizeSmall circuitComputation using non-contact making devicesComplex mathematical operationsTheoretical computer scienceFloating point multiplier
To perform a product-sum operation by adding third data to a product of first data and second data, a floating point multiplier first multiplies the first data by the second data, and a bit string representing a fixed-point part in the multiplication result is divided into a portion representing more significant digits in the fixed-point part and a portion representing less significant digits in the fixed-point part. Then, a floating point adder first adds less significant multiplication result data having a bit string representing the less significant digits as a fixed-point part to the third data, and then adds the addition result to more significant multiplication result data having a bit string representing the more significant digits as a fixed-point part. A rounding process is performed on the two addition results to obtain a result of the product-sum operation.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
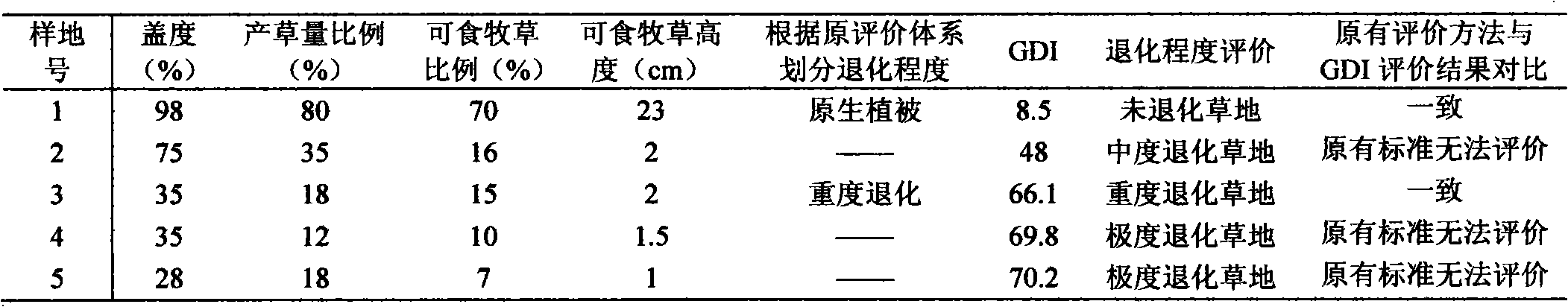
Method for evaluating degradation degree of alpine grassland based on visual vegetation indexes
InactiveCN102323974AEasy accessEasy to acceptHorticulture methodsSpecial data processing applicationsPlant communityVegetation Index
The invention discloses a method for evaluating degradation degree of alpine grassland based on visual vegetation indexes by using a grassland degradation index. The grassland degradation index (GDI) comprises an integer bit and a significant figure behind the decimal point and has a structure that GDI=(100-C)*28 percent+(100-P)*39 percent+(70-E)*26 percent+(25-H)*7 percent, wherein C is a cover degree, P is a grass yield, E is an edible grass proportion, and H is an edible grass height. During actual application, the cover degree, the biomass liveweight, the edible grass quantity and the edible grass height of a plant community are only determined, so that the GDI can be calculated. The degradation degree of the alpine grassland is judged according to the GDI, when the GDI is less than 13.9, the grassland is non-degraded grassland; when the GDI is 13.9-33.5, the grassland is lightly-degraded grassland; when the GDI is 33.5-52.4, the grassland is medium-degraded grassland; when the GDI is 52.4-68.4, the grassland is seriously-degraded grassland; and when the GDI is more than 68.4, the grassland is extremely-degraded grassland. According to the invention, the degradation condition information of the grassland can be completely expressed, and the degradation degree of the alpine grassland is quantitatively and qualitatively evaluated.
Owner:BEIJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Three-dimensional picture quality objective evaluation method based on three-dimensional visual attention
ActiveCN103200420AIncrease reflectionImprove reliabilityTelevision systemsSteroscopic systemsSubjective perceptionVisual perception
The invention discloses a three-dimensional picture quality objective evaluation method based on three-dimensional visual attention. The method comprises the steps of respectively calculating an original undistorted three-dimensional picture one-eyed figure and an one-eyed figure of an anamorphic three-dimensional picture to be evaluated; calculating significant figures of the two one-eyed figures and an off-centering figure, a foreground figure and a background figure of the original undistorted three-dimensional picture one-eyed figure; obtaining a three-dimensional visual attention image, and merging objective evaluation metric values of all pixel points in the one-eyed figure of the anamorphic three-dimensional picture to be evaluated, and obtaining a picture quality objective evaluation predicted value of the anamorphic three-dimensional picture to be evaluated. The three-dimensional picture quality objective evaluation method based on the three-dimensional visual attention has the advantages that the obtained three-dimensional visual attention image can well reflect influence of space three-dimensional vision information to attention, and an objective evaluation result can be better fit with human vision, so that relevancy of the objective evaluation result and subjective perception is effectively improved.
Owner:深圳市点维文化传播有限公司
System and method for achieving improved accuracy from efficient computer architectures
ActiveUS20100241938A1Reduce errorsSame precisionError preventionFinanceInstructions per secondProgram instruction
This invention provides a system and method that can employ a low-instruction-per-second (lower-power), highly parallel processor architecture to perform the low-precision computations. These are aggregated at high-precision by an aggregator. Either a high-precision processor arrangement, or a low-precision processor arrangement, employing soft-ware-based high-precision program instructions performs the less-frequent, generally slower high-precision computations of the aggregated, more-frequent low-precision computations. One final aggregator totals all low-precision computations and another high-precision aggregator totals all high-precision computations. An equal number of low precision computations are used to generate the error value that is subtracted from the low-precision average. A plurality of lower-power processors can be arrayed to provide the low-precision computation function. Alternatively a plurality of SIMD can be used to alternately conduct low-precision computations for a predetermined number of operations and high-precision operations on a fewer number of operations. In an embodiment, aggregation can include summing values within predetermined ranges of orders of magnitude, via an adding tree arrangement, so that significant digits therebetween are preserved.
Owner:GRANGER RICHARD
Round for reround mode in a decimal floating point instruction
ActiveUS8443029B2Computations using magnetic elementsProgram controlParallel computingFloating point
A round-far-reround mode (preferably in a BID encoded Decimal format) of a floating point instruction prepares a result for later rounding to a variable number of digits by detecting that the least significant digit may be a 0, and if so changing it to 1 when the trailing digits are not all 0. A subsequent reround instruction is then able to round the result to any number of digits at least 2 fewer than the number of digits of the result. An optional embodiment saves a tag indicating the fact that the low order digit of the result is 0 or 5 if the trailing bits are non-zero in a tag field rather than modify the result. Another optional embodiment also saves a half-way-and-above indicator when the trailing digits represent a decimal with a most significant digit having a value of 5. An optional subsequent rewound instruction is able to round the result to any number of digits fewer or equal, to the number of digits of the result using the saved tags.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Low-light-level image target detection method based on texture significance
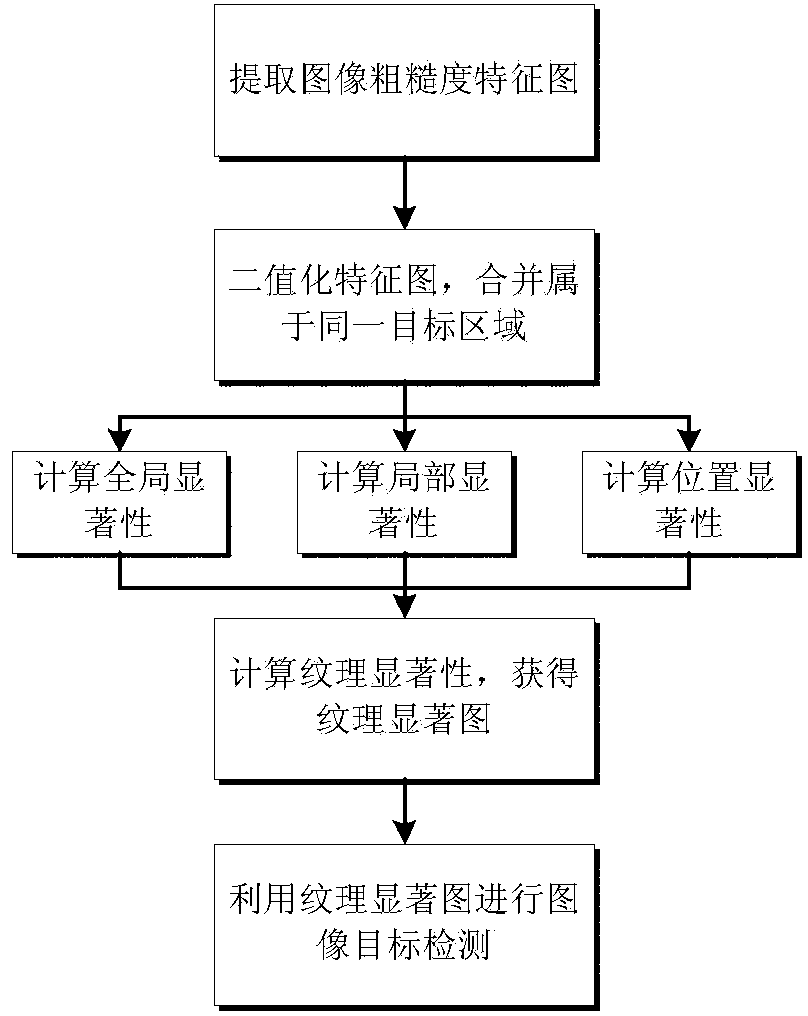
ActiveCN104346800AHigh target hit rateReduce false alarm rateImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionComputer science
The invention relates to a low-light-level image target detection method based on texture significance. The method comprises the steps of: firstly, extracting an image roughness characteristic figure, performing binaryzation characteristic treatment, merging regions belonging to the same target, respectively calculating global significance, local significance and position significance, so as to calculate the texture significance and obtain a texture significant figure, and finally, performing image target detection by utilizing the texture significant figure. The method is characterized in that the target detection is performed through the texture significance by utilizing the characteristic of larger difference between low-light-level image target texture and the background. When the method is used for detecting a low-light-level image target, the target contour is good, and the hit rate is high.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
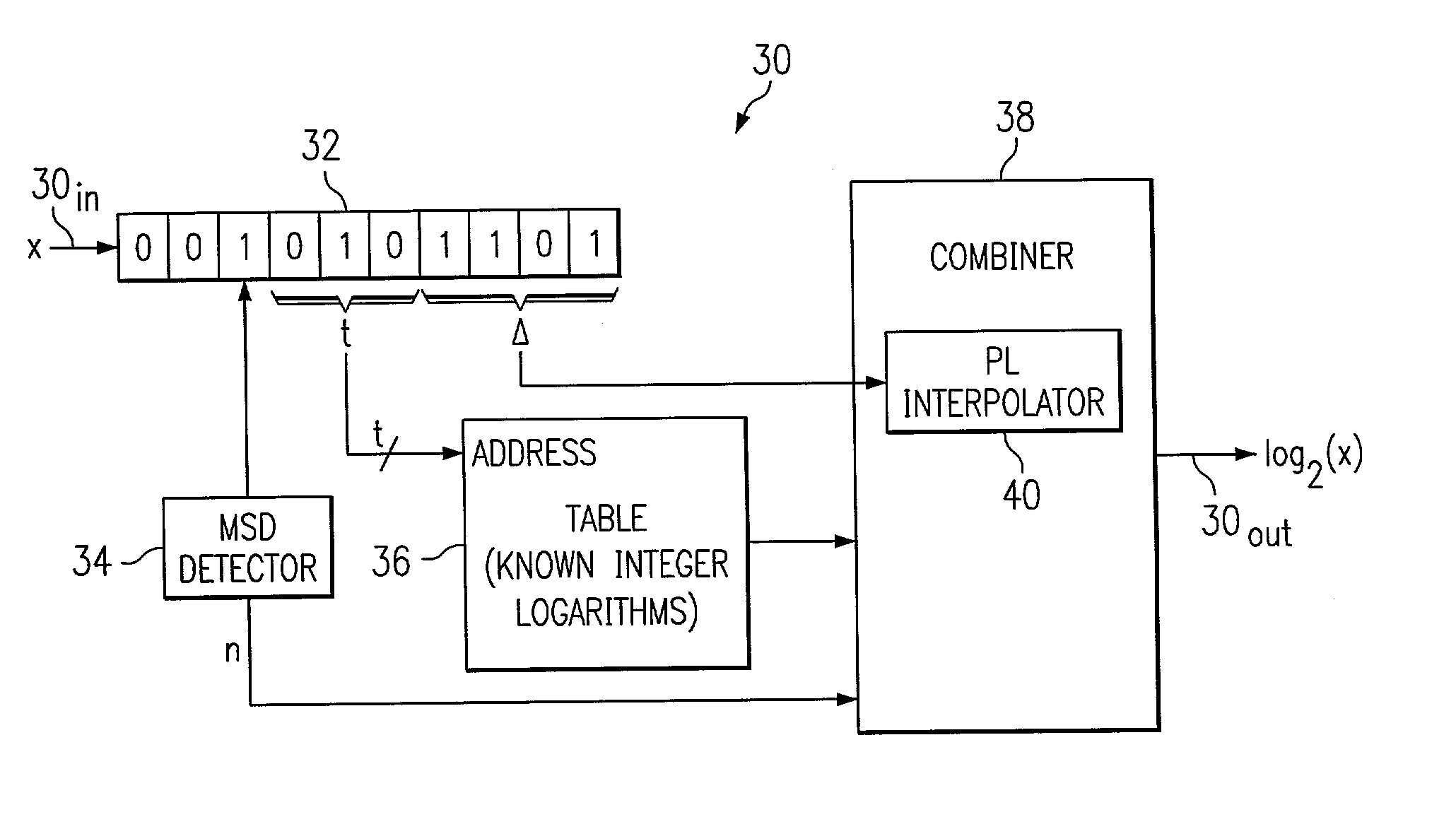
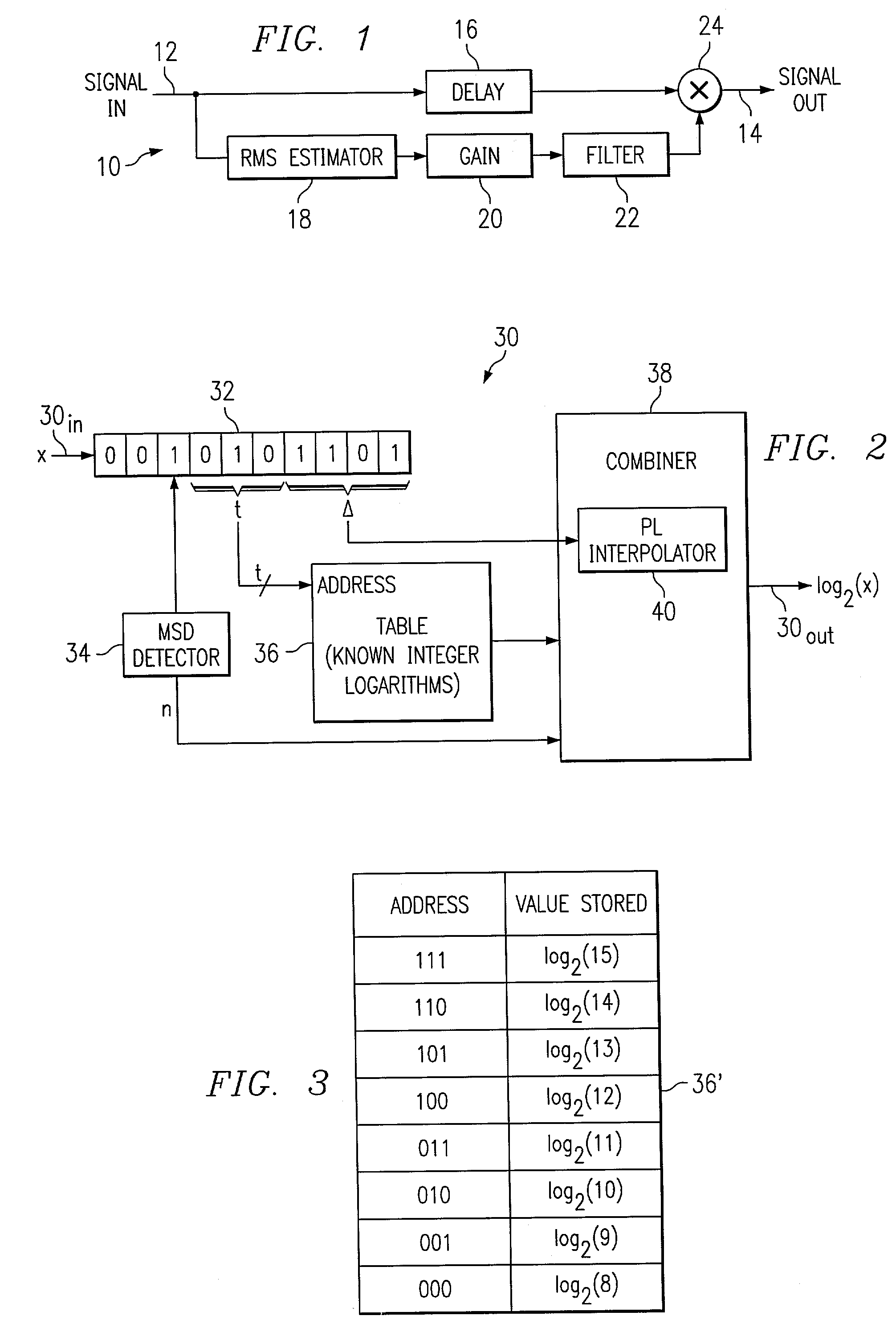
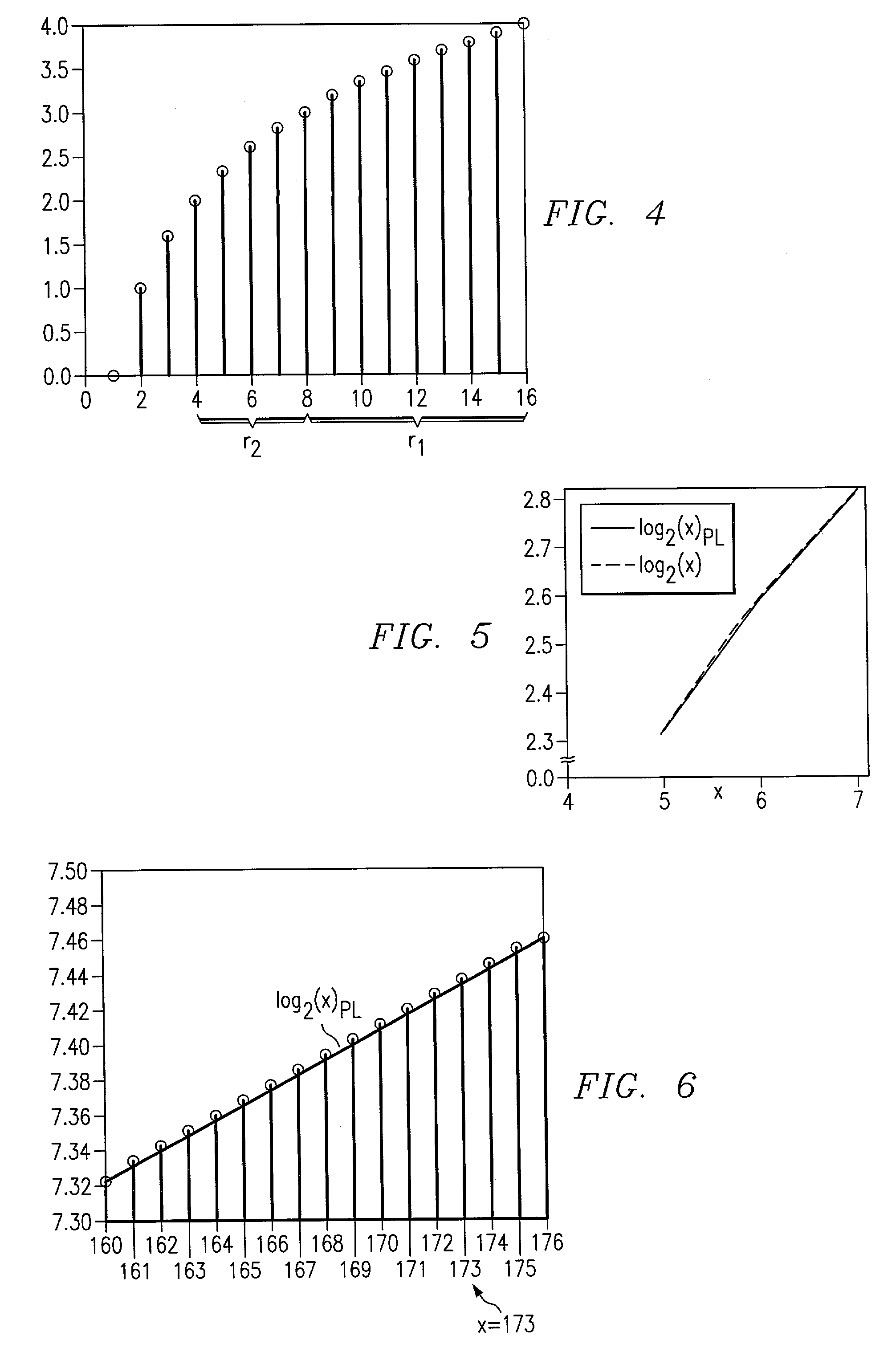
Circuits, systems, and methods implementing approximations for logarithm, inverse logarithm, and reciprocal
A digital signal system (30) for determining an approximate logarithm of a value of x having a base b is described. The system comprises circuitry for storing x as a digital representation, identifying a most significant digit (MSD) of the digital representation, a table for storing a set of predetermined logarithms having the base b, circuitry for addressing the table in response to a first bit group (t) of the set of bits in respective lesser significant bit locations and for outputting a one of the predetermined logarithms corresponding to a first number (la) in the set of numbers, and circuitry for outputting the approximate logarithm of the value of x in response to the one of the predetermined logarithms and in response to a function estimation between logarithms at a first and second endpoint.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
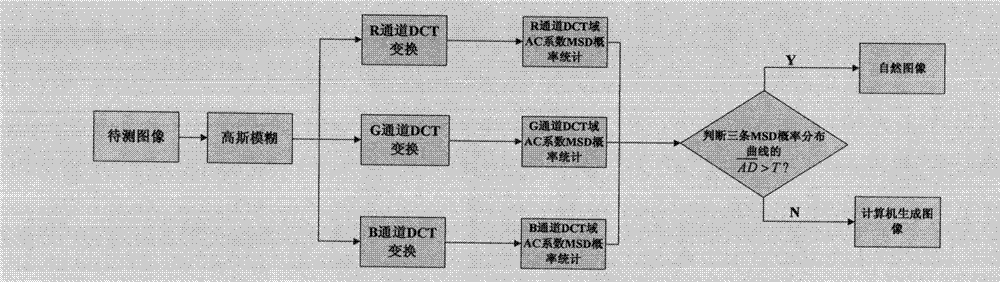
Method for identifying natural image and computer generated image based on DCT (Discrete Cosine Transformation)-domain statistic characteristics
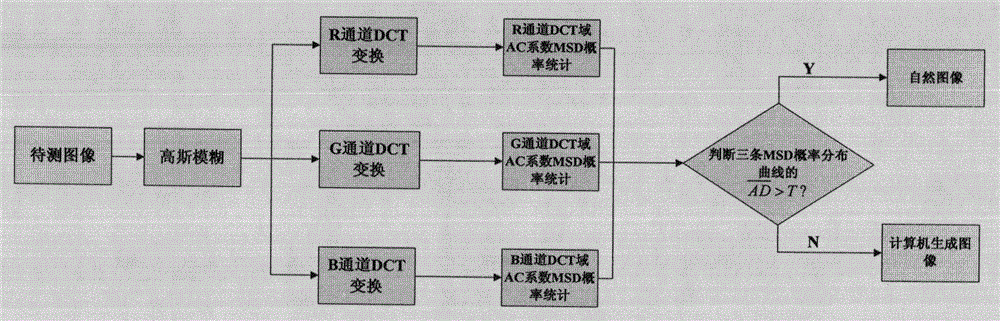
InactiveCN102968793AHigh identification accuracyImprove recognition rateImage analysisAc coefficientMean difference
The invention discloses a method for identifying a natural image and a computer generated image based on DCT (Discrete Cosine Transformation)-domain statistic characteristics. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps of (1) firstly, carrying out gaussian fuzzy processing and dimension reduction processing on an image to be detected, carrying out 8*8 no-repeat DCT on3 channels R, G and B of the image to obtain a 8*8 partitioning DCT coefficient matrix; (2) carrying out statistics on the distribution of a first significant figure of the DCT-domain AC coefficient of each channel to obtain three probability distribution curves; and (3) calculating an average absolute differential of the three probability distribution curves, if the average absolute differential is greater than a set threshold T to prove that the overlapping degree of the three curves is not sufficient, judging the image to be detected as the natural image, otherwise, judging the image to be detected as the computer generated image. Experimental results show that due to the algorithm, the identification accuracy rate of the natural image and the computer generated image is increased. Compared with the existing algorithm, the method has the advantages that the identification rate is higher, the calculating amount is small, the implementation is easy, and the identification accuracy rate reaches 95.22%.
Owner:BAINIAN JINHAI SCI & TECH +1
Method, base station and user equipment for reducing a cognitive pilot channel bandwidth
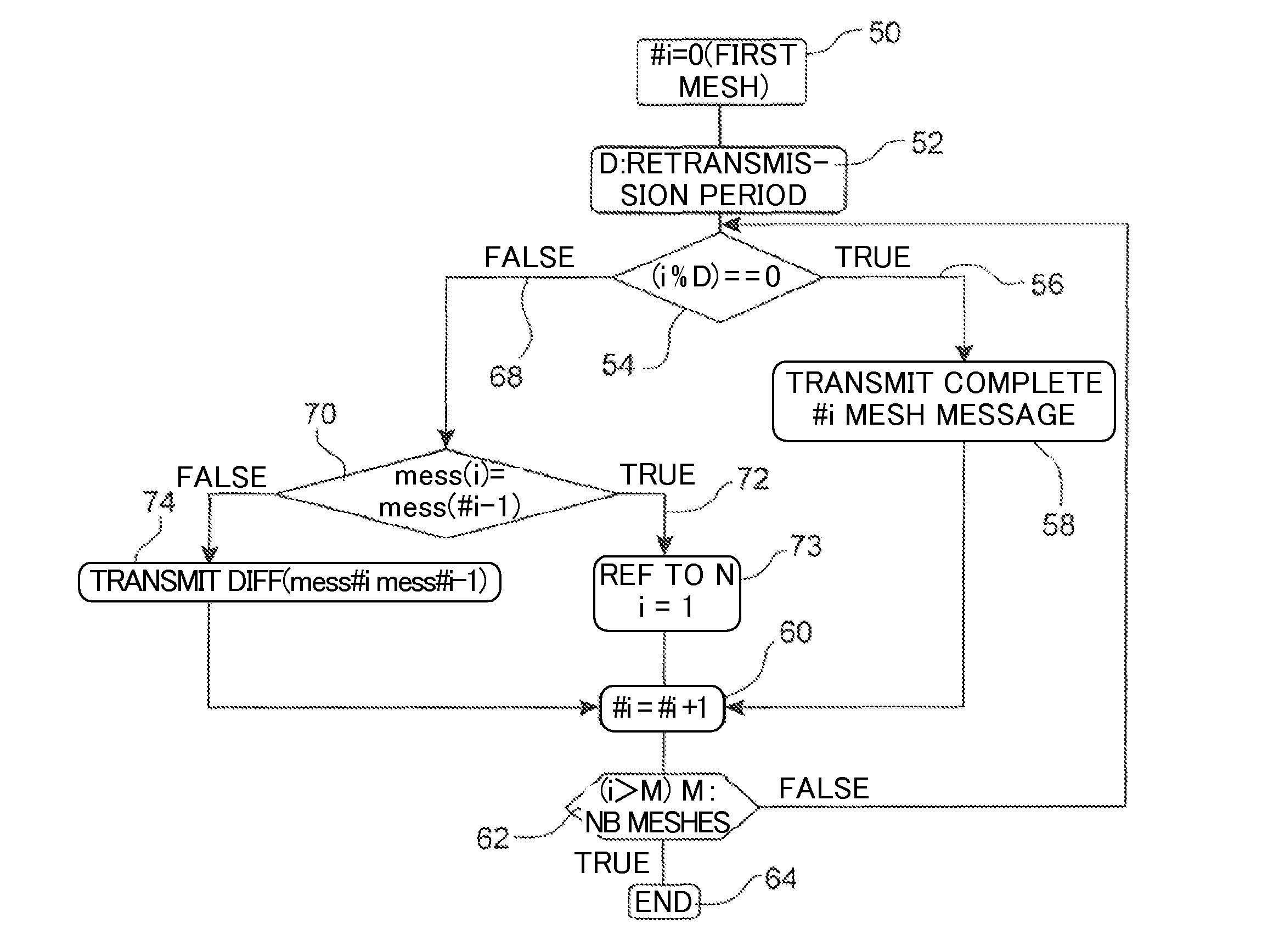
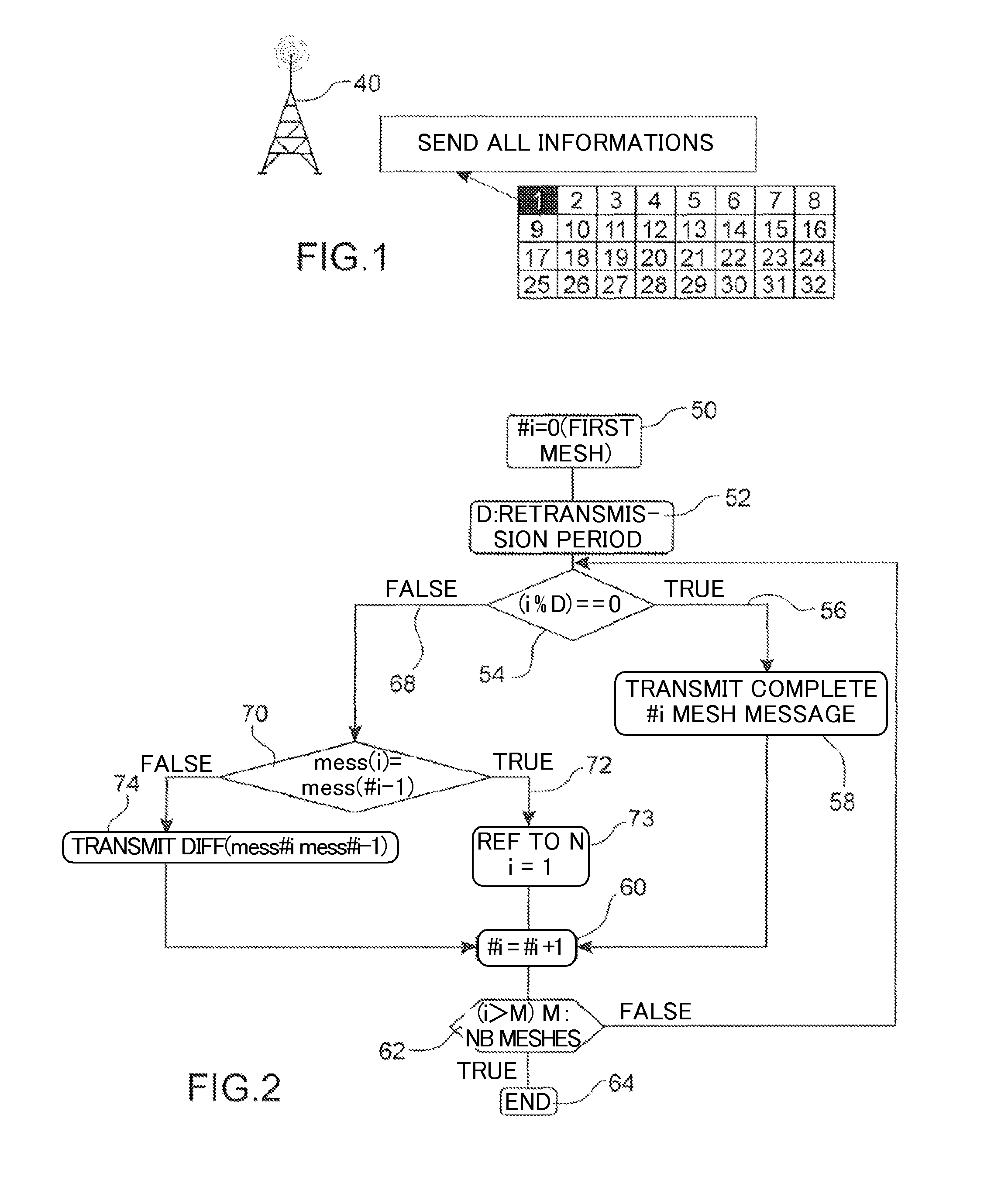
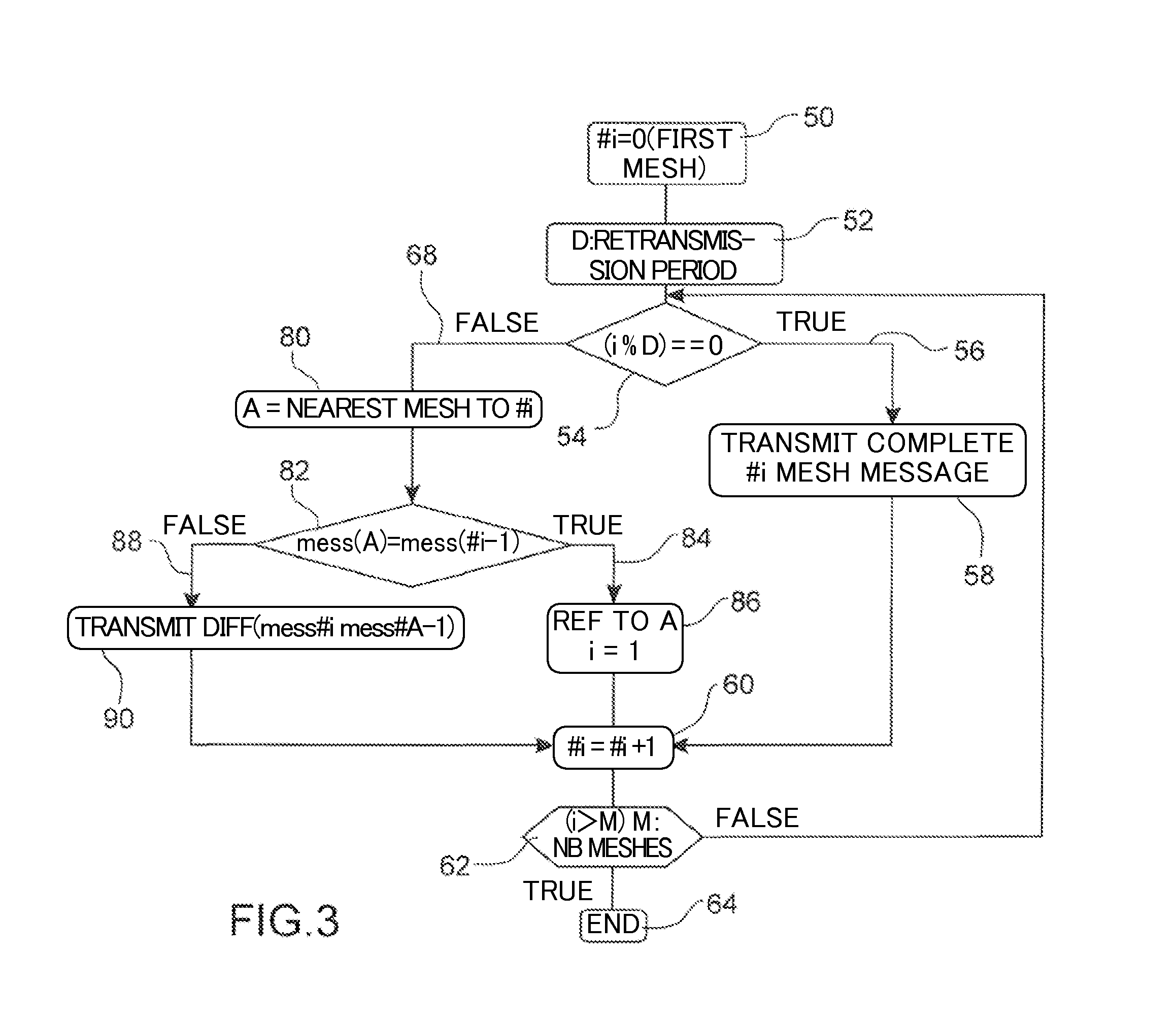
ActiveUS20120108247A1Reducing CPC data rateReduce CPC message lengthWireless communicationAccess technologyReference mesh
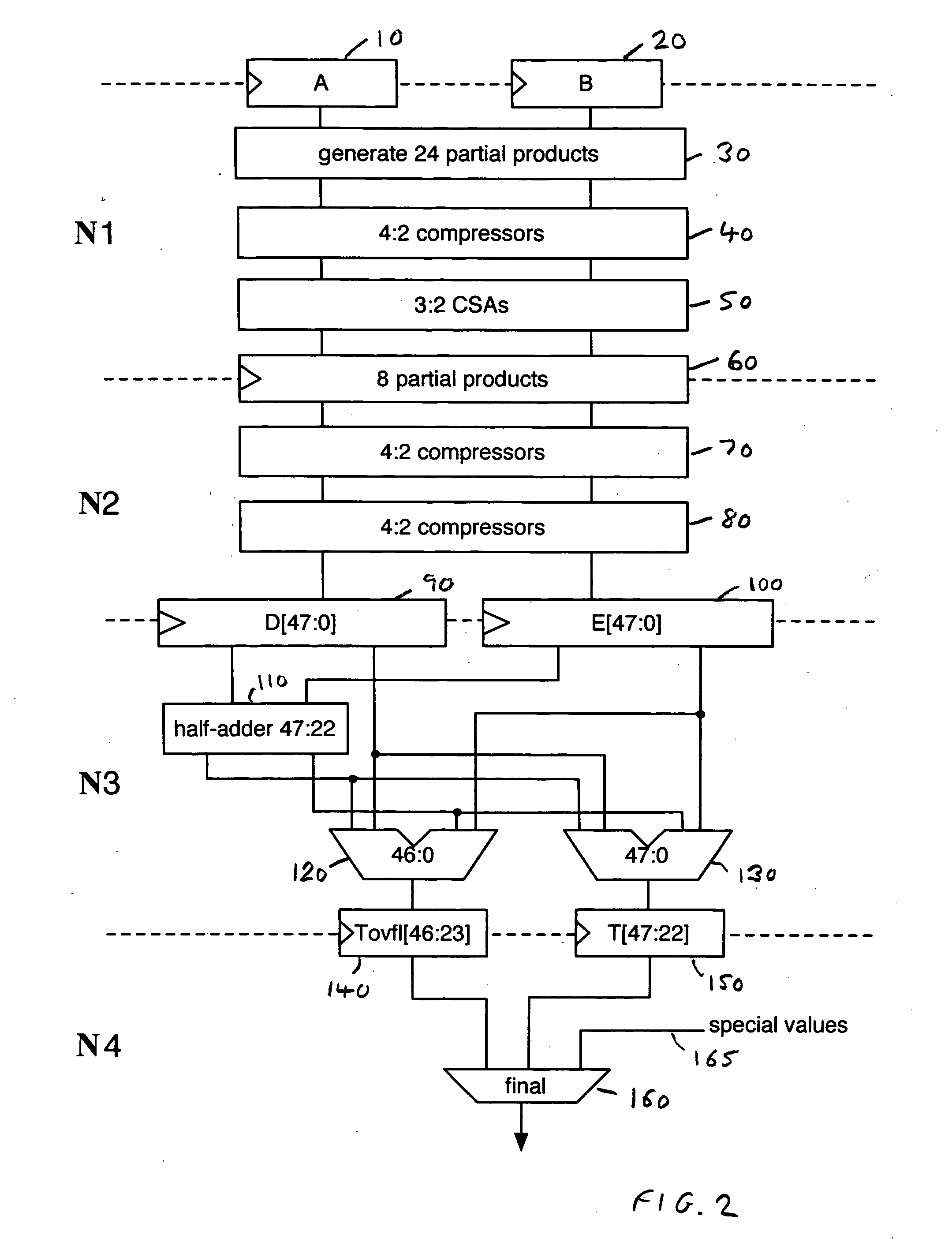
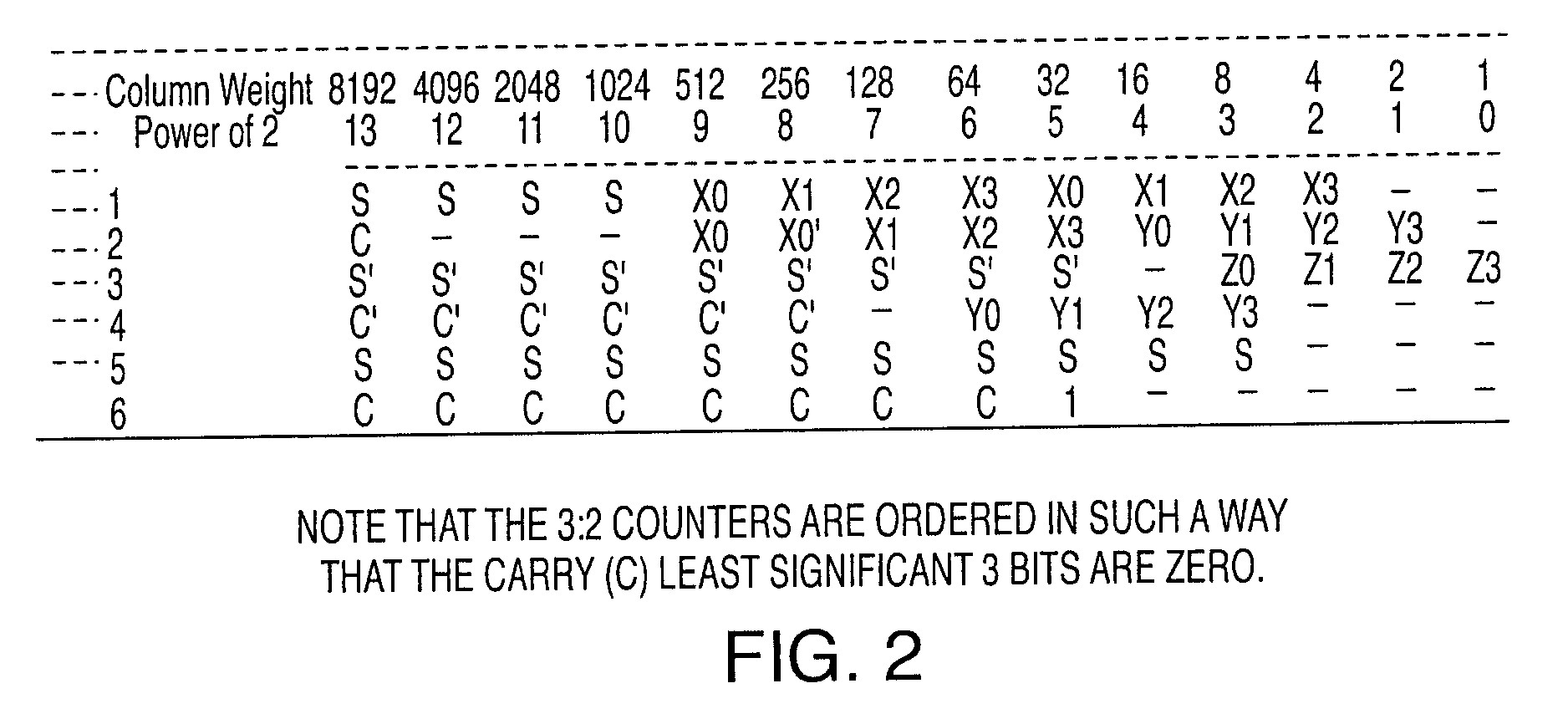
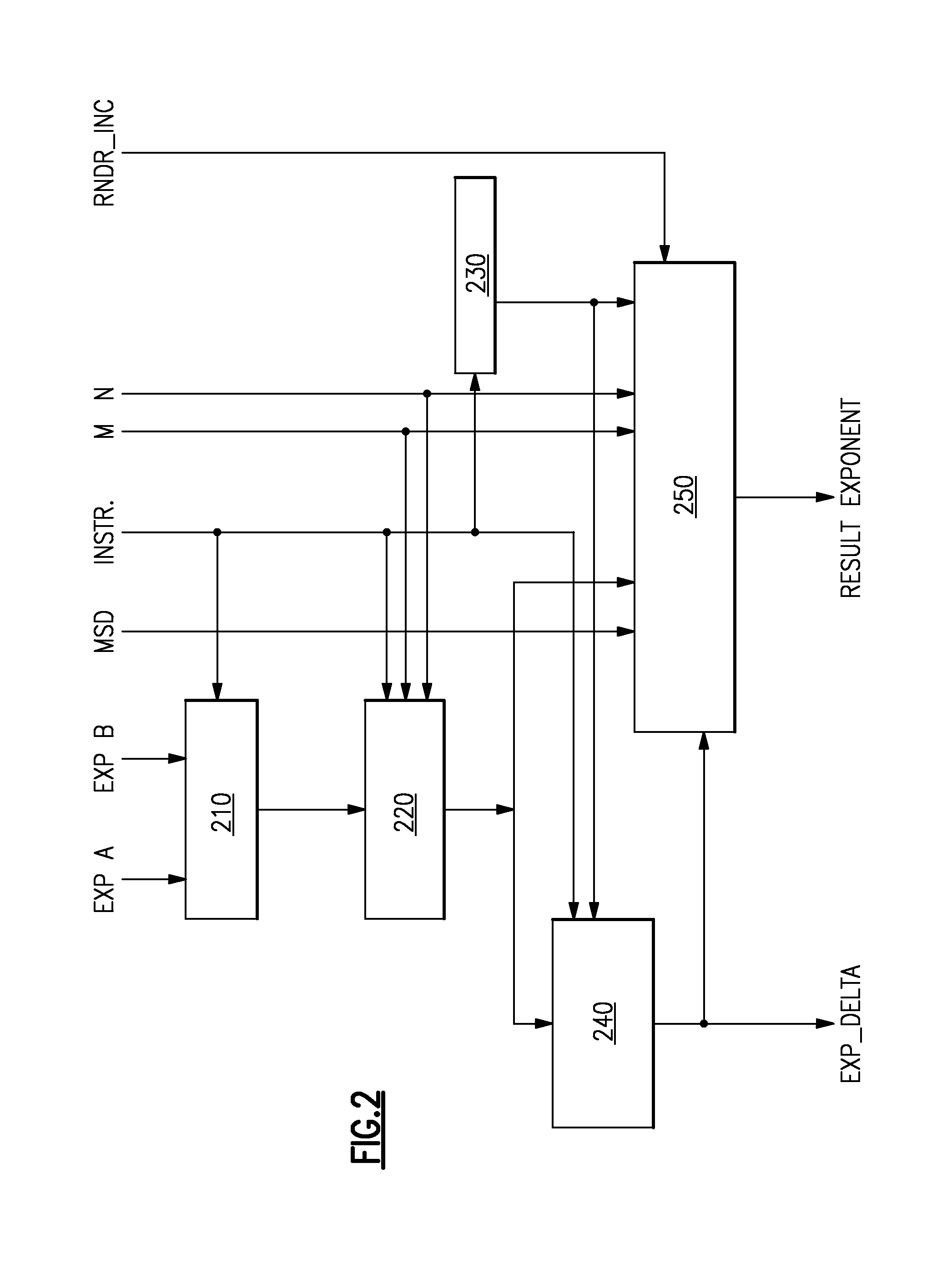
The invention relates to a method for reducing a Cognitive Pilot Channel (CPC) bandwidth used for transmitting lists of information to a plurality of meshes of a geographical area comprising at least one base station (4) covering n meshes to allow a User Equipment camping on a given mesh among said plurality of meshes to select an operator and / or an access technology and / or a communication frequency available in said given mesh.According to the invention, for a given mesh #i (i=2 to n), the base station transmits to said mesh #i an identifier of a predetermined reference mesh and the difference between the list of information intended for said given mesh and the list of information intended for said reference mesh.Significant Figure: FIG. 2
Owner:NEC CORP
System and method for performing decimal to binary conversion
Owner:TWITTER INC
Intelligent selection and representation method for significant digits of significant figure operational result
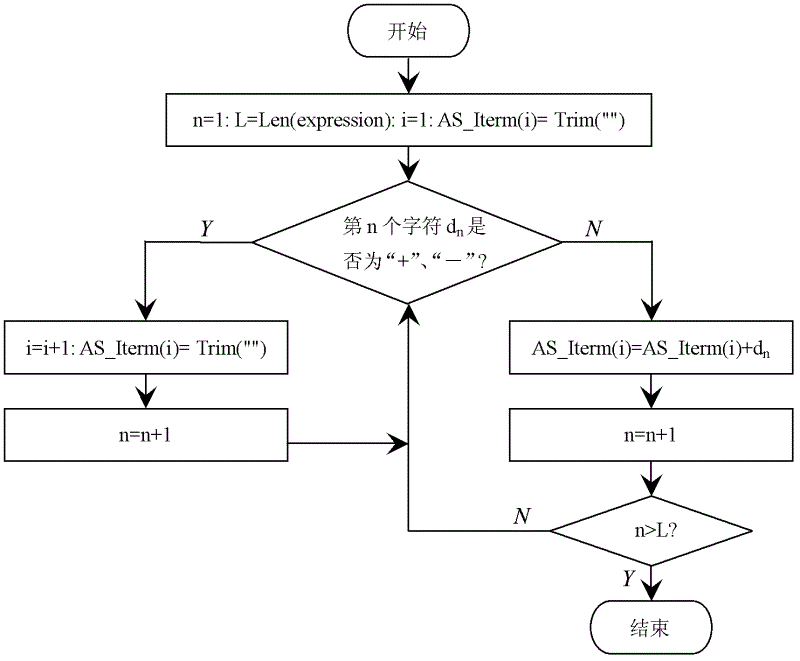
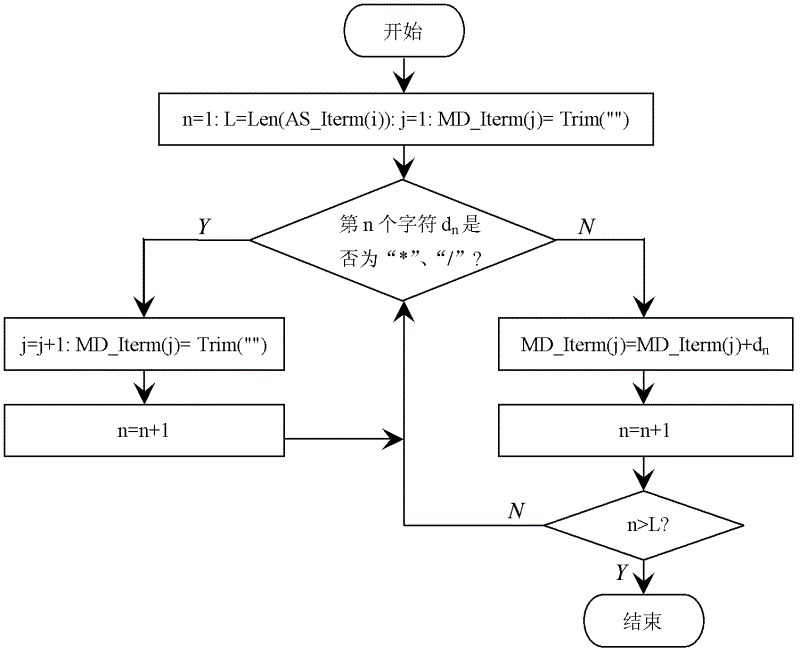
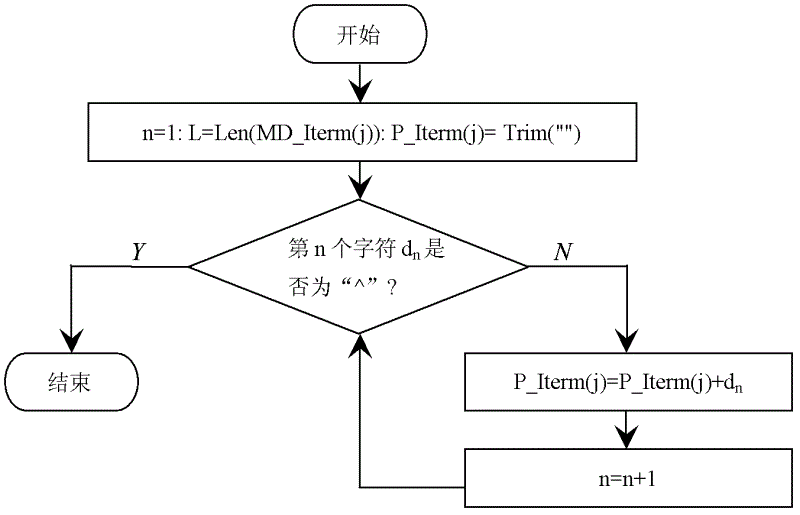
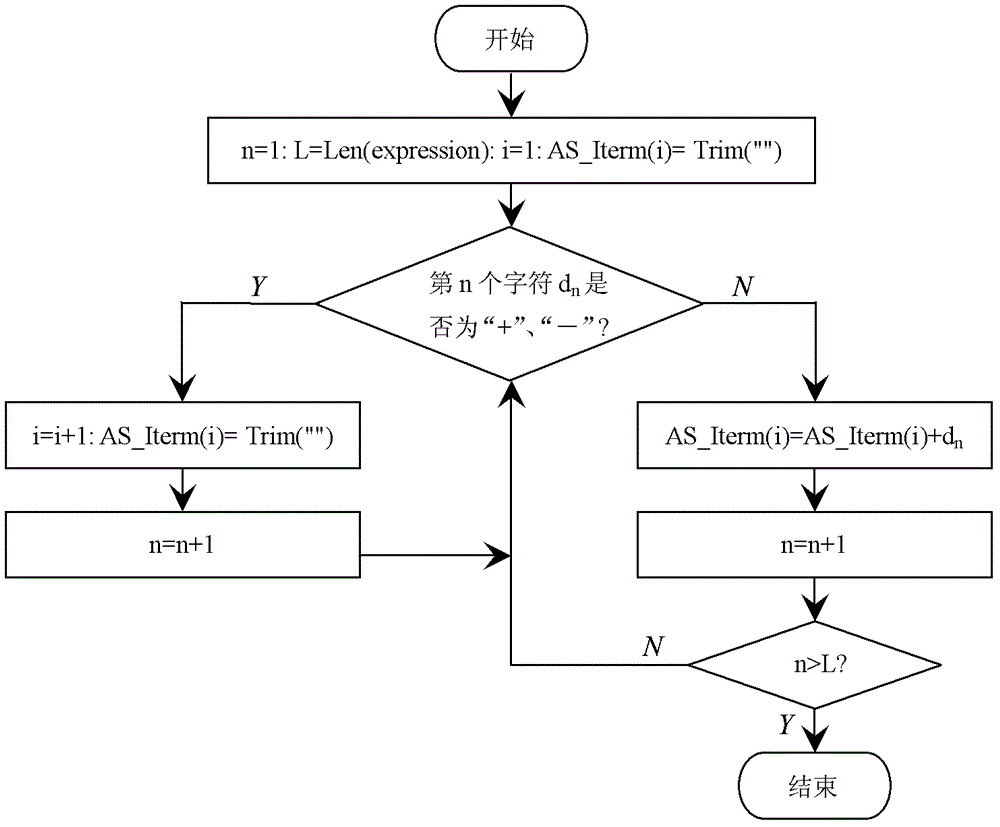
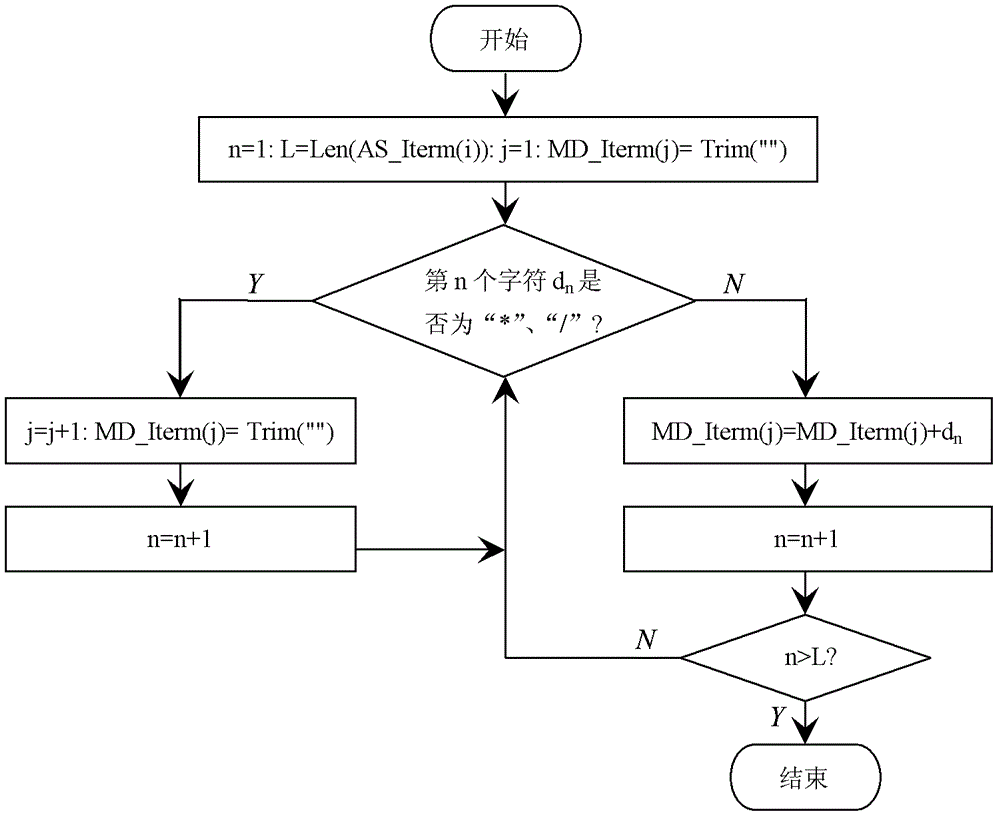
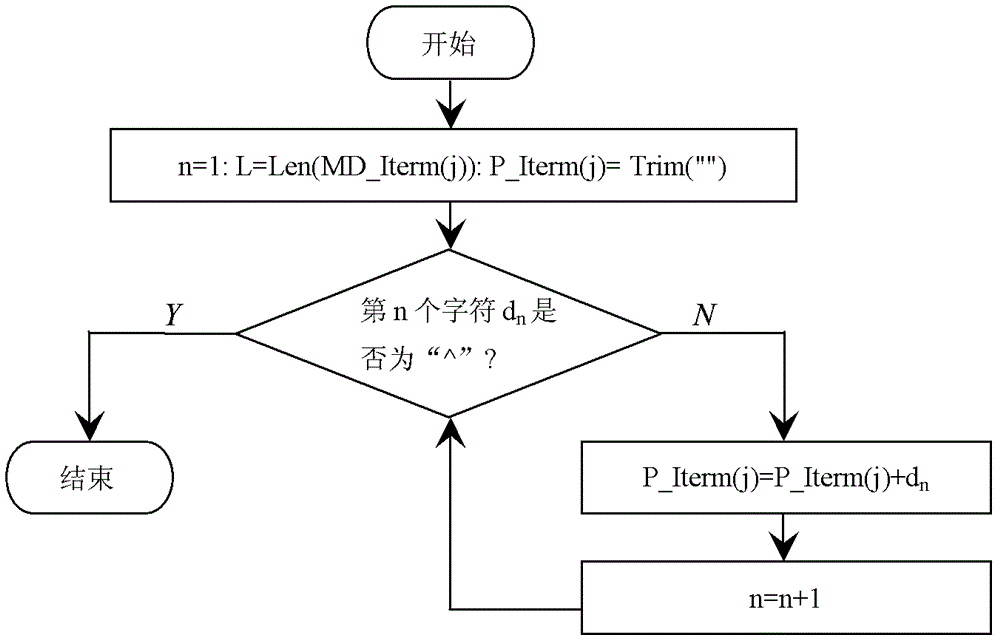
ActiveCN102622202AEffective application of treatmentEffectively applicable to random occasionsData selectionExponential formComputer science
An intelligent selection and representation method for significant digits of a significant figure operational result includes the steps: firstly, searching each character in a numeric expression from left to right, acquiring adding and subtracting items with '+' or '-' serving as a breakpoint, acquiring multiplying and dividing items in each adding and subtracting item with '*' or ' / ' serving as a breakpoint, and acquiring power base items of each multiplying and dividing item with '^' serving as a breakpoint; secondly, performing trigonometric function and logarithm operation, selecting the significant digits of the operational result, and utilizing a selection result to substitute for an original trigonometric function or logarithm function expression; thirdly, counting significant digits of multiplying and dividing data and power base data in each adding and subtracting item, wherein the minimum digits are the significant digits of a result of the data after multiplication, division and power operation, and the operational expression only including addition and subtraction is obtained after multiplication, division and power operation; and fourthly, unifying the exponential form of scientific notation of all the adding and subtracting data, counting error digits of all the data, and obtaining error digits of significant figures. The intelligent selection and representation method adopts intelligent selection, is effectively applicable to occasions for processing massive data and with random digits, and is high in applicability.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
System and method for performing decimal to binary conversion
ActiveUS7660838B2Digital data processing detailsCode conversionBinary outcomeBi-quinary coded decimal
Owner:TWITTER INC
A Optic Disc Localization Method Combining GBVS Model and Phase Consistency
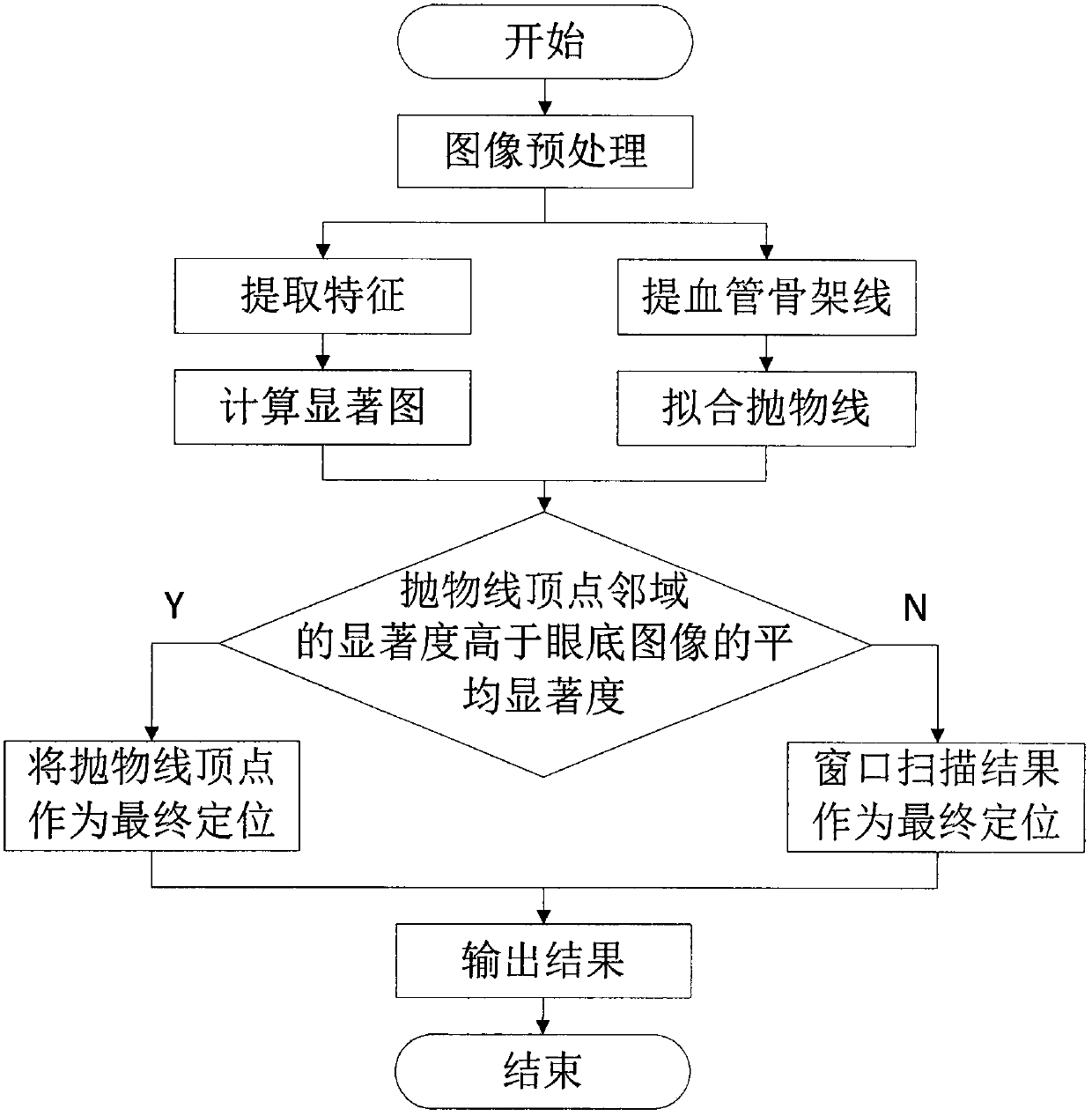
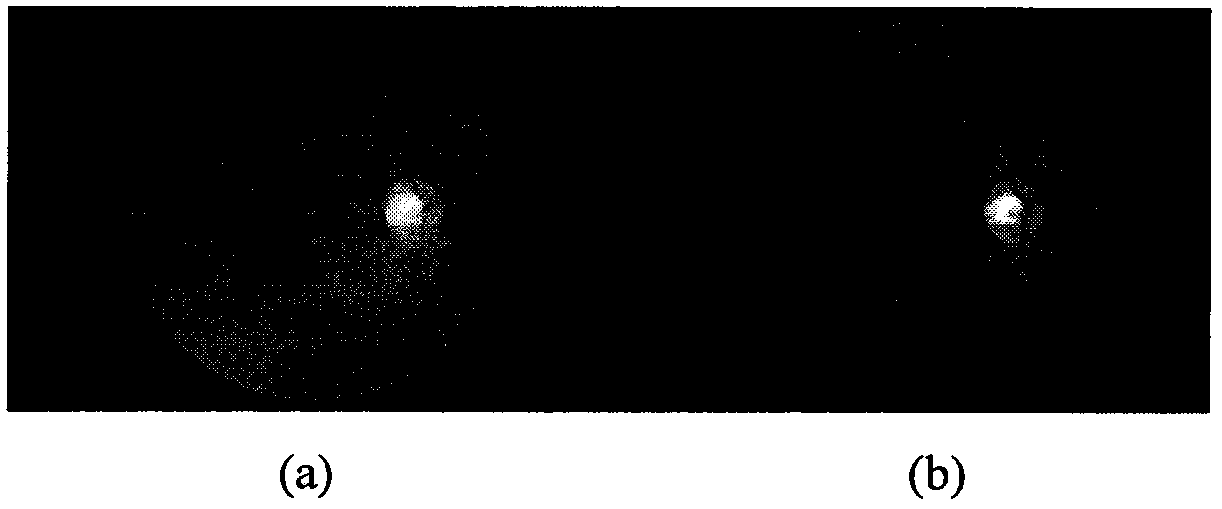
ActiveCN106204555BPrecise positioningInaccurate positioningImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionVenous blood
The invention discloses an optic disk positioning method combining Gbvs model and phase consistency. The implementation process is: (1) extracting the green channel of the color fundus image; (2) obtaining the mask image of the fundus image to obtain the Region of Interest (ROI) of the fundus image; (3) extracting brightness, Three types of features: brightness contrast and phase consistency; (4) Construct a saliency map with an improved graph-based visual saliency model (Gbvs); (5) Extract the skeleton line of veins and blood vessels from the fundus image, and use the least squares method Parabola fitting; (6) comparing the significance in the neighborhood of the apex of the parabola with the average significance of the entire fundus image to determine the position of the optic disc. In the process of calculating the saliency map, according to the characteristics of the optic disc in the fundus image, three types of features, brightness, brightness contrast, and phase consistency are extracted, and the saliency model based on the map is improved, and the structural characteristics of the veins are used when locating the optic disc. Aids in precise positioning. The experiment proves that the method in this paper works well.
Owner:TIANJIN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Accuracy verification program for model parameter computation using a quantifier elimination method
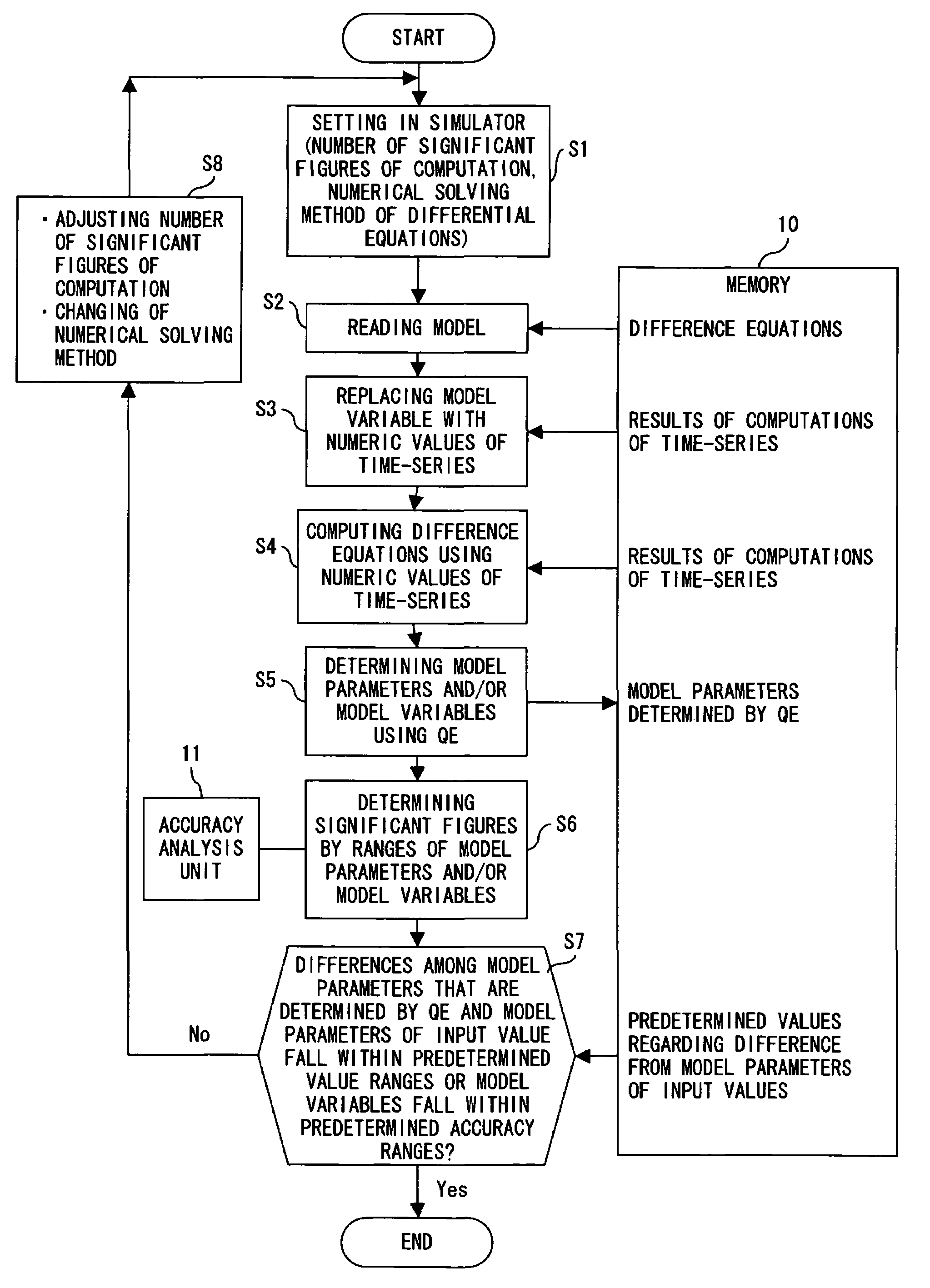
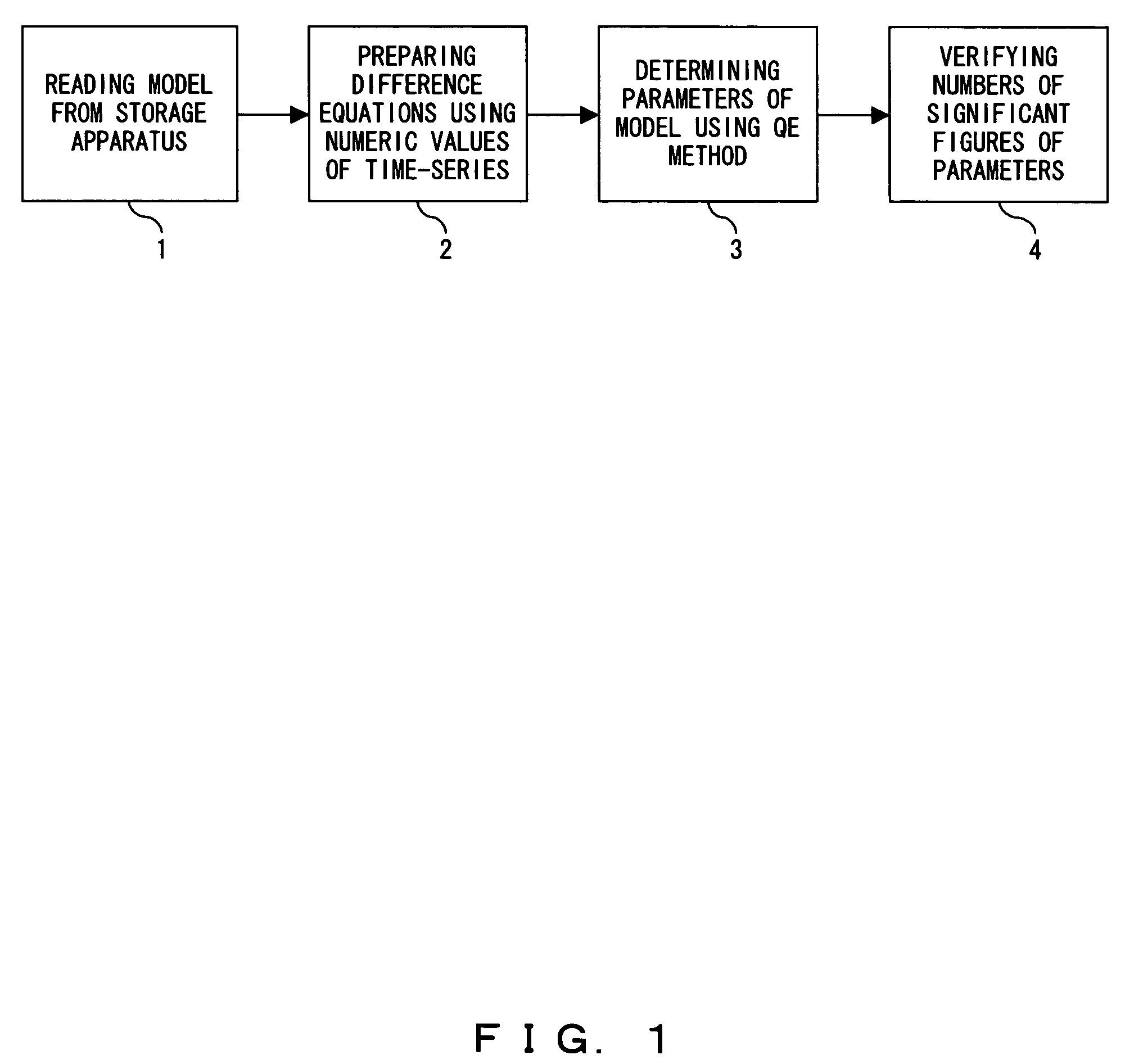
ActiveUS7711528B2Improve approximationAccuracy controllableComputation using non-denominational number representationSystems biologyAlgorithmModel parameters
A program causes a computer to perform a step 1 of reading a model from a storage apparatus; a step 2 of computing difference equations by replacing variables with numeric values of a time-series that are stored in the storage apparatus; a step 3 of determining ranges of parameters of the model using a quantifier elimination method and a step 4 of verifying numbers of significant figures that show an accuracy of a computation by the determined ranges of parameters of the model.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Decimal Floating Point Mechanism and Process of Multiplication without Resultant Leading Zero Detection
InactiveUS20110320512A1Simplifies and reduces number of cycleNot easy to make mistakesComputations using contact-making devicesComputation using non-contact making devicesFloating pointLeading zero
A decimal multiplication mechanism for fixed and floating point computation in a computer having a coefficient mechanism without resulting leading zero detection (LZD) and process which assumes that the final product will be M+N digits in length and performs all calculations based on this assumption. Least significant digits that would be truncated are no longer stored, but retained as sticky information which is used to finalize the result product. Once the computation of the product is complete, a final check based on the examination of key bits observed during partial product accumulation is used to determine if the final product is truly M+N digits in length, or M+N−1 digits. If the latter is true, then corrective final product shifting is employed to obtain the proper result. This eliminates the need for dedicated leading zero detection hardware used to determine the number of significant digits in the final product. The corrective final product shifting also incorporates adjustments to the coefficient of the product when the product's exponent is at its extremes and the final product must be brought to be within the precision and range of a given format.
Owner:IBM CORP
An Intelligent Selection and Representation Method of Significant Digits of Significant Figure Operation Results
A method for intelligently selecting and representing effective digits of effective digit calculation results, searching for each character in a numerical calculation formula from left to right, using "+" or "-" as a breakpoint to obtain addition and subtraction items, and "* " or " / " as a breakpoint to obtain the multiplication and division items in each addition and subtraction item, and use "^" as a breakpoint to obtain the power bottom item in each multiplication and division item. Perform trigonometric functions and logarithmic operations first, select the effective digits of the operation results, and replace the original trigonometric or logarithmic expressions with the selected results. Count the effective digits of multiplication and division data and exponentiation data in each addition and subtraction item, and the least number of digits is the effective digits of the result of these data multiplication and division exponentiation operations. Unify the exponential form of scientific notation for each addition and subtraction data, count the error bits of each data, and obtain the error bits of the effective figures. The invention adopts intelligent selection, is effectively applicable to the occasions of processing massive data and random digits, and has good applicability.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Discrimination method between natural image and computer-generated image based on statistical properties of dct domain
InactiveCN102968793BHigh identification accuracyImprove recognition rateImage analysisAc coefficientMean difference
The invention discloses a method for identifying a natural image and a computer generated image based on DCT (Discrete Cosine Transformation)-domain statistic characteristics. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps of (1) firstly, carrying out gaussian fuzzy processing and dimension reduction processing on an image to be detected, carrying out 8*8 no-repeat DCT on3 channels R, G and B of the image to obtain a 8*8 partitioning DCT coefficient matrix; (2) carrying out statistics on the distribution of a first significant figure of the DCT-domain AC coefficient of each channel to obtain three probability distribution curves; and (3) calculating an average absolute differential of the three probability distribution curves, if the average absolute differential is greater than a set threshold T to prove that the overlapping degree of the three curves is not sufficient, judging the image to be detected as the natural image, otherwise, judging the image to be detected as the computer generated image. Experimental results show that due to the algorithm, the identification accuracy rate of the natural image and the computer generated image is increased. Compared with the existing algorithm, the method has the advantages that the identification rate is higher, the calculating amount is small, the implementation is easy, and the identification accuracy rate reaches 95.22%.
Owner:BAINIAN JINHAI SCI & TECH +1
Image real-time processing method
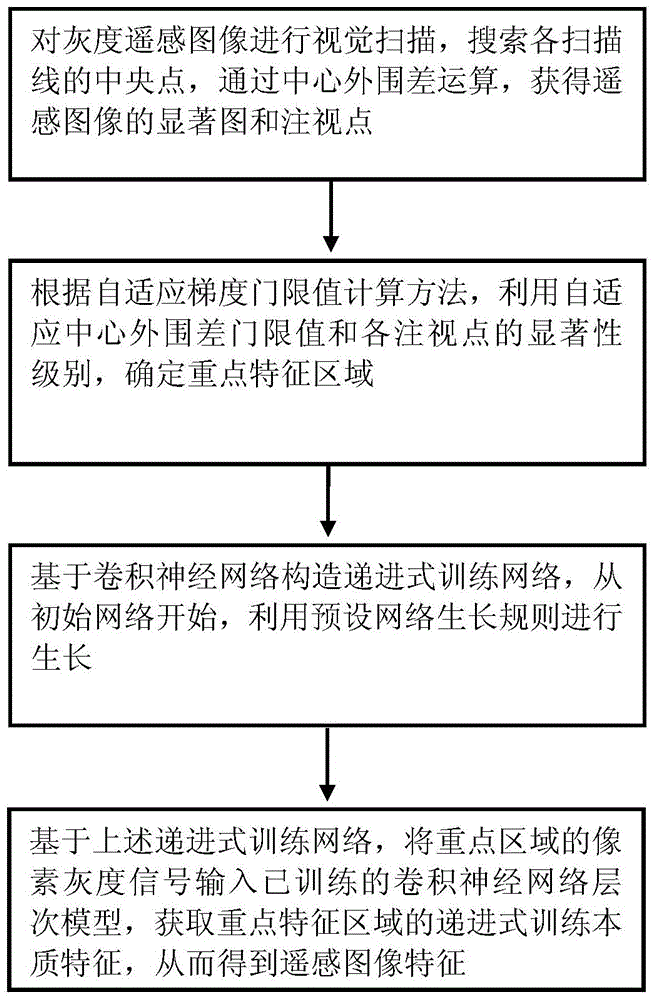
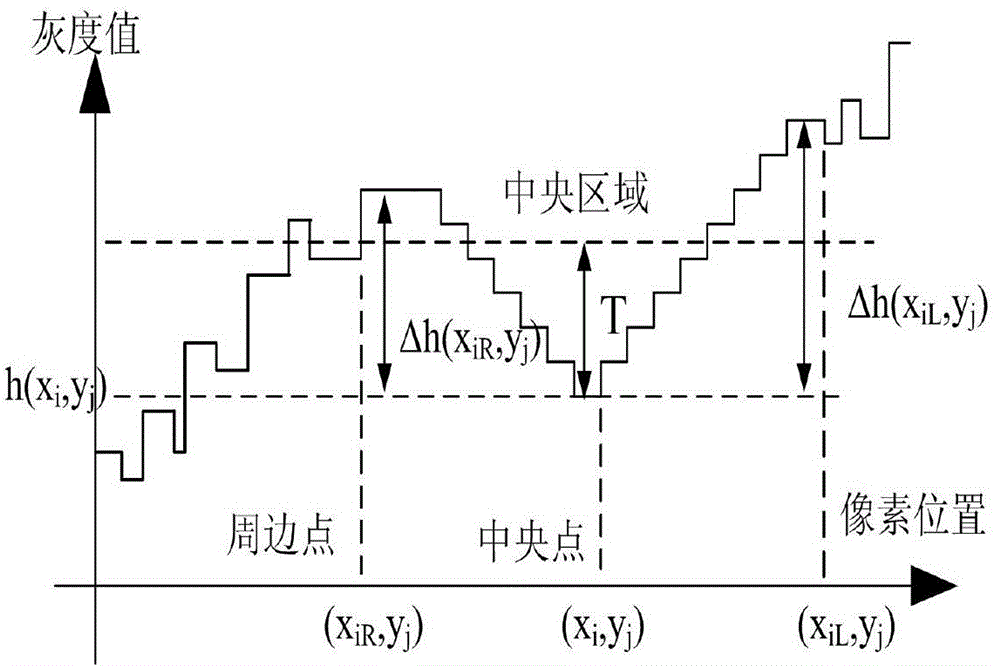
ActiveCN104103033BReduce processingReduce distractionsProcessor architectures/configurationPattern recognitionFixation point
The invention provides an image real-time processing method, which is used for recognizing features in images and comprises the steps of visual scanning, center periphery difference operation, gray significant figure obtaining, fixation point searching and key region determination; progressive training is adopted for directly passing pixel grey scale signals in a key region through a trained network hierarchical model; essential features of a key feature region are obtained; and the recognition is directly carried out. The image real-time processing method has the advantages that image targets are serially selected and recognized according to the intensity sequence of visual saliency; the efficiency and the accuracy of the image analysis and recognition are improved; the adaptability is high; and the universality is good.
Owner:广州国米科技有限公司
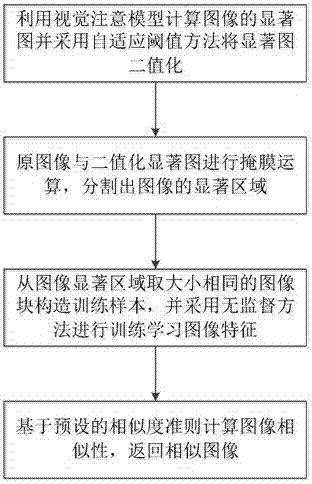
A remote sensing image retrieval method and system based on unsupervised feature learning
ActiveCN104462494BOptimize search resultsFits visual attentionStill image data retrievalCharacter and pattern recognitionFeature extractionFeature learning
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com