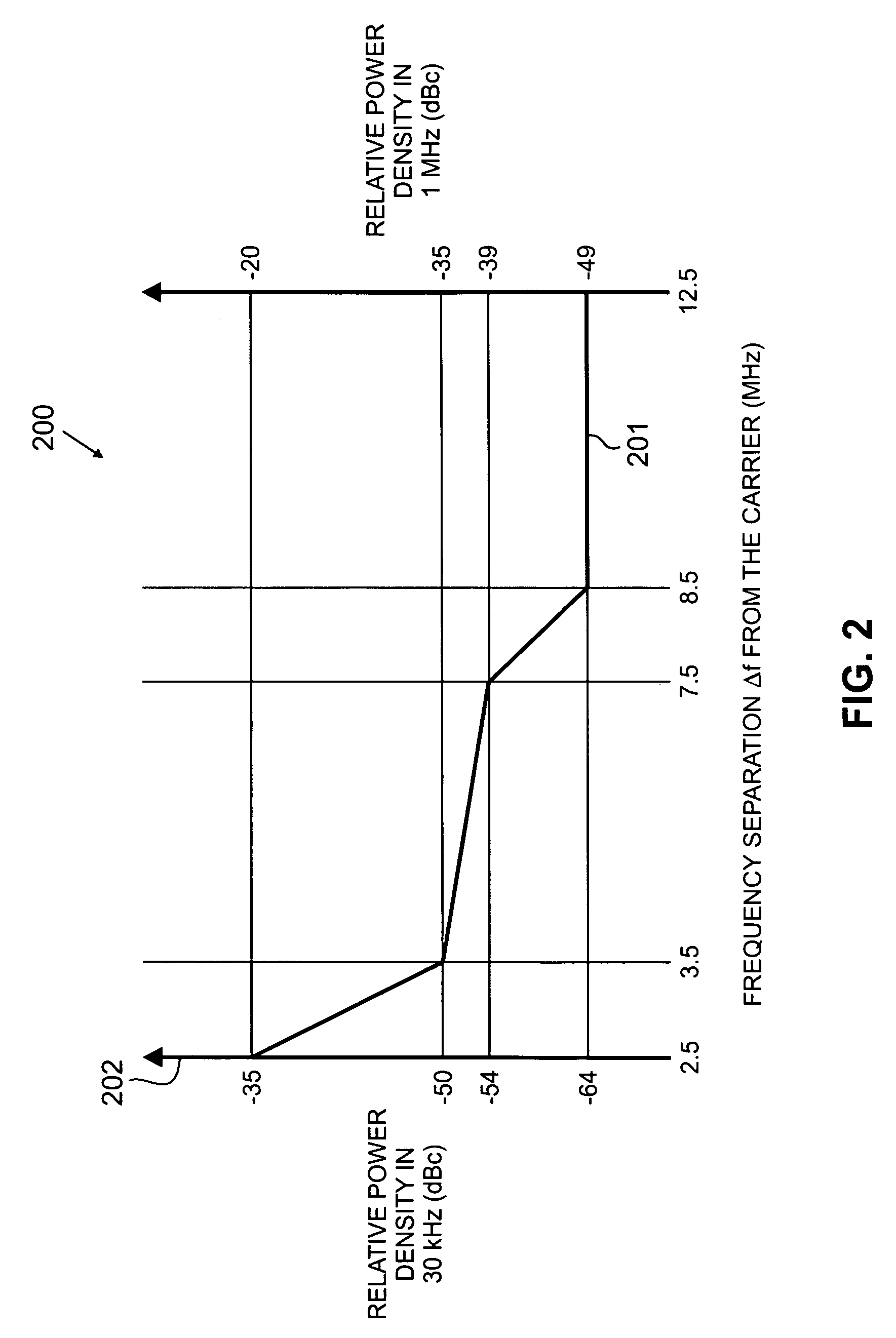
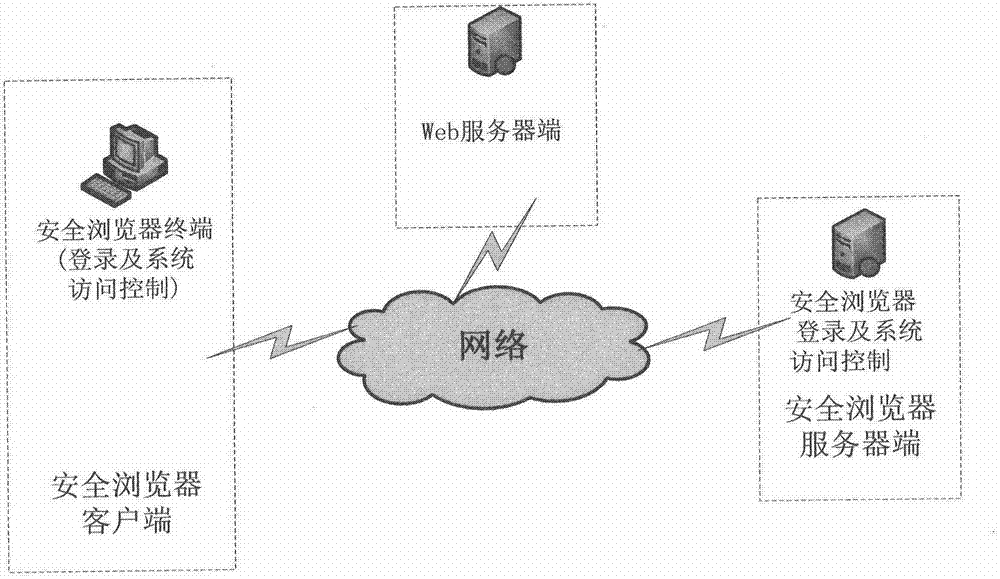
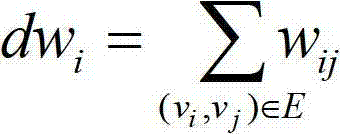Patents
Literature
47 results about "Instructions per second" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Instructions per second (IPS) is a measure of a computer's processor speed. For CISC computers different instructions take different amounts of time, so the value measured depends on the instruction mix; even for comparing processors in the same family the IPS measurement can be problematic. Many reported IPS values have represented "peak" execution rates on artificial instruction sequences with few branches and no cache contention, whereas realistic workloads typically lead to significantly lower IPS values. Memory hierarchy also greatly affects processor performance, an issue barely considered in IPS calculations. Because of these problems, synthetic benchmarks such as Dhrystone are now generally used to estimate computer performance in commonly used applications, and raw IPS has fallen into disuse.
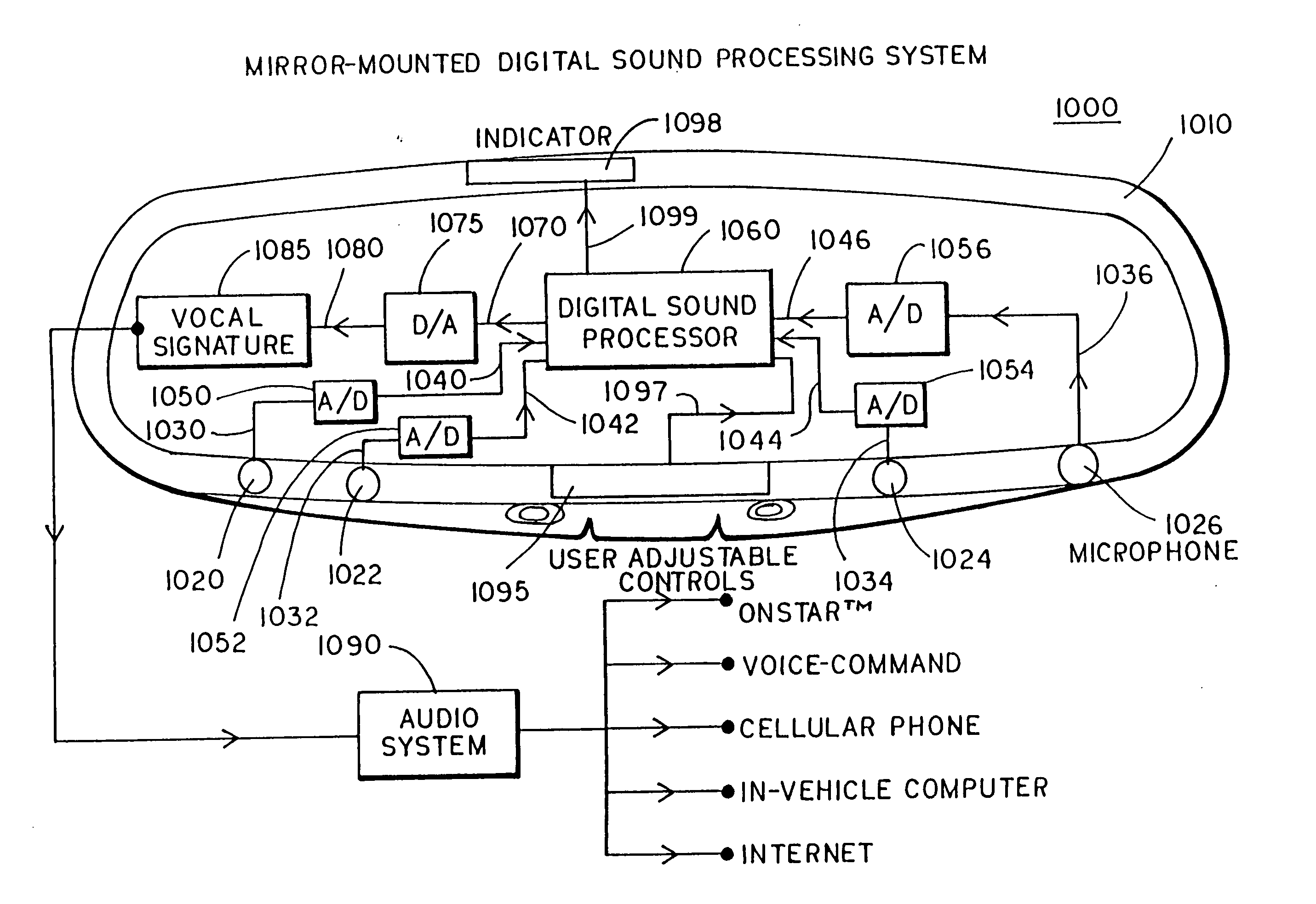
Digital sound processing system for a vehicle
InactiveUS20050156753A1Accurate receptionOptionally installed to the vehicle with easeOrganic chemistryEar treatmentInstructions per secondEngineering
A digital sound processing system suitable for use in a vehicle comprises an interior rearview mirror assembly that includes at least a first microphone and a second microphone. The first microphone generates a first signal indicative of a vocal input with vehicle cabin noise included therewith and the second microphone generates a second signal indicative of a vocal input with vehicle cabin noise included therewith. A digital signal processor is provided that processes the first signal and the second signal and that provides an output signal with reduced vehicle cabin noise. The digital signal processor preferably comprises a microprocessor executing at least one million instructions per second.
Owner:DONNELLY CORP
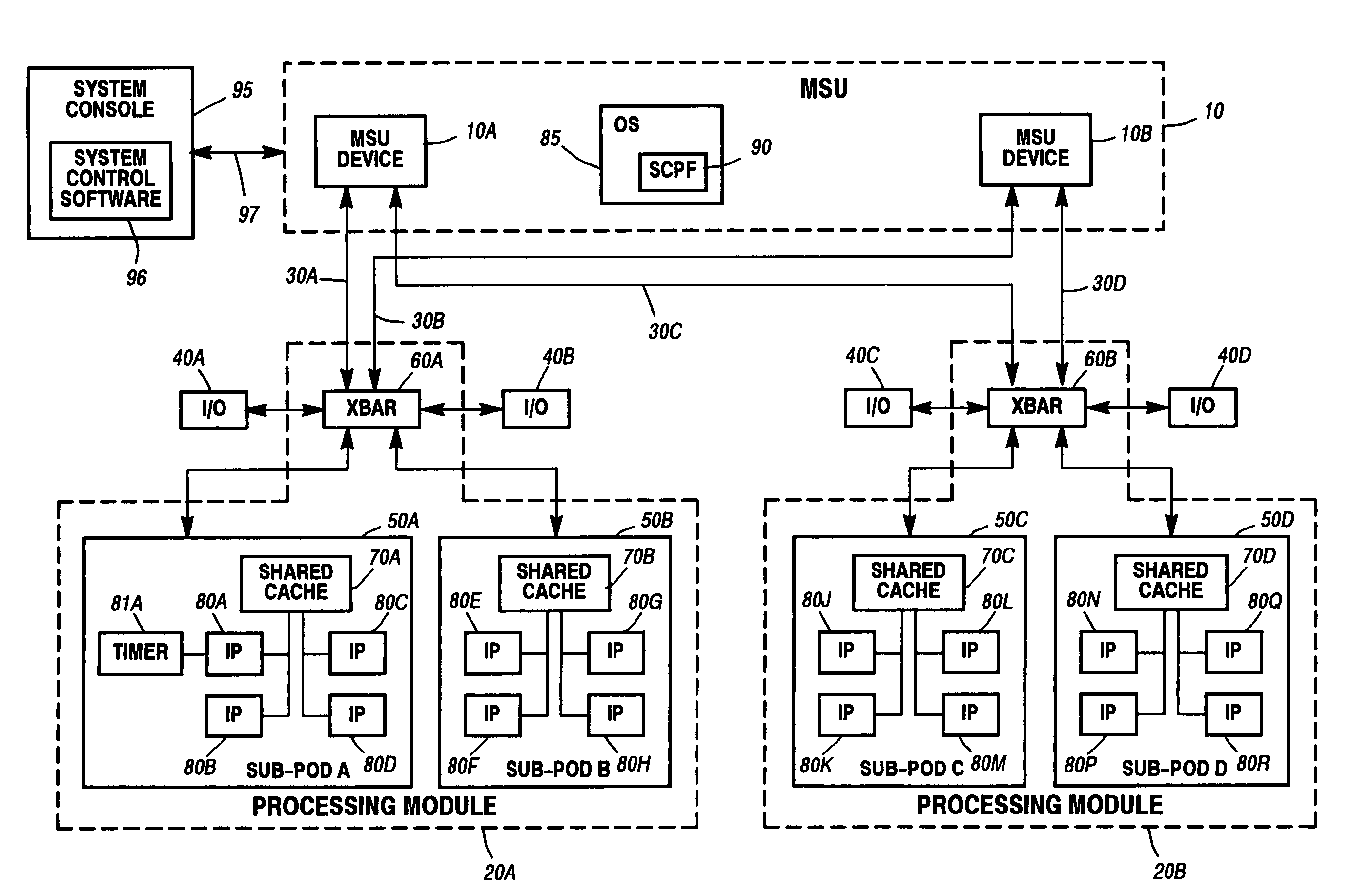
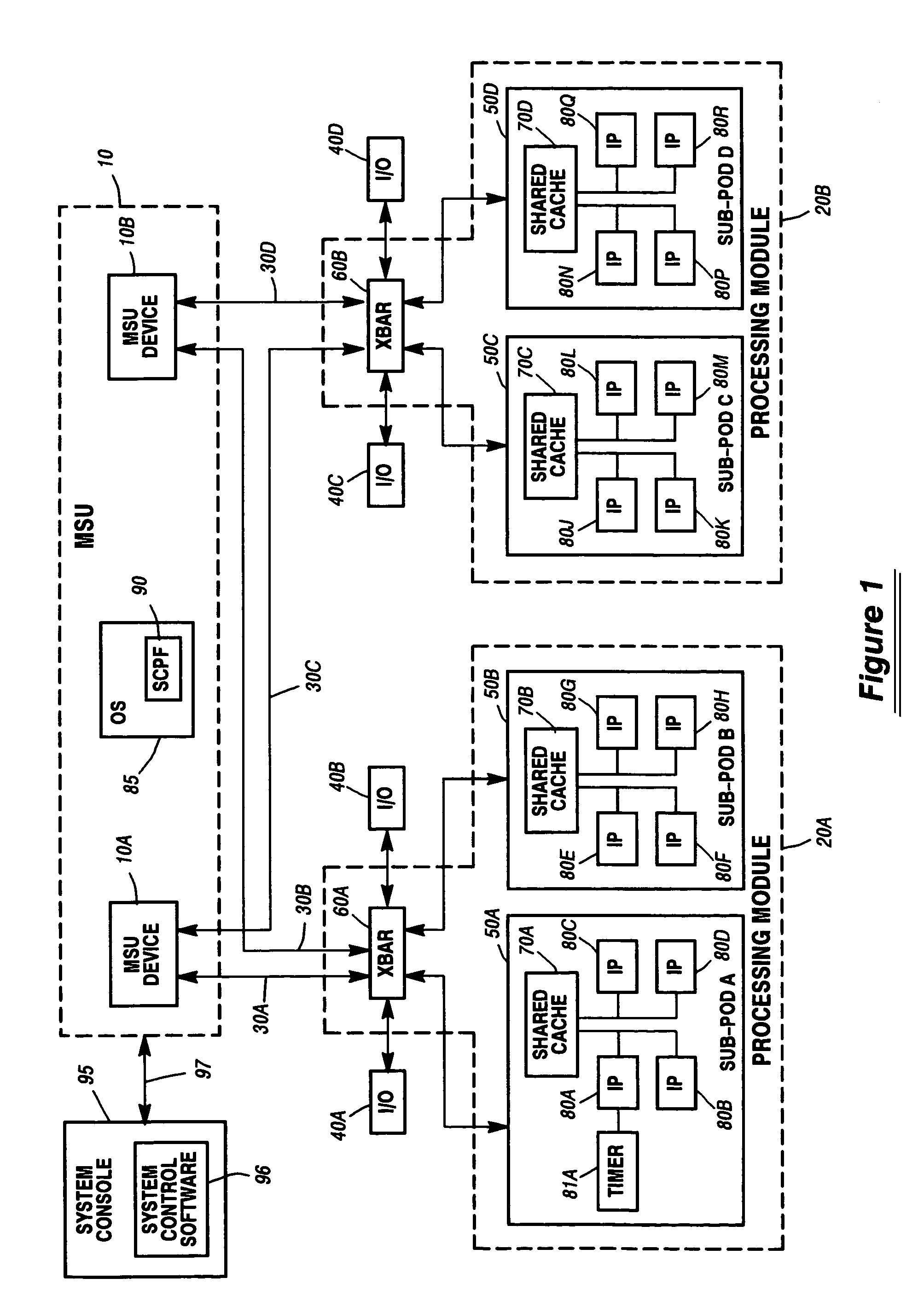
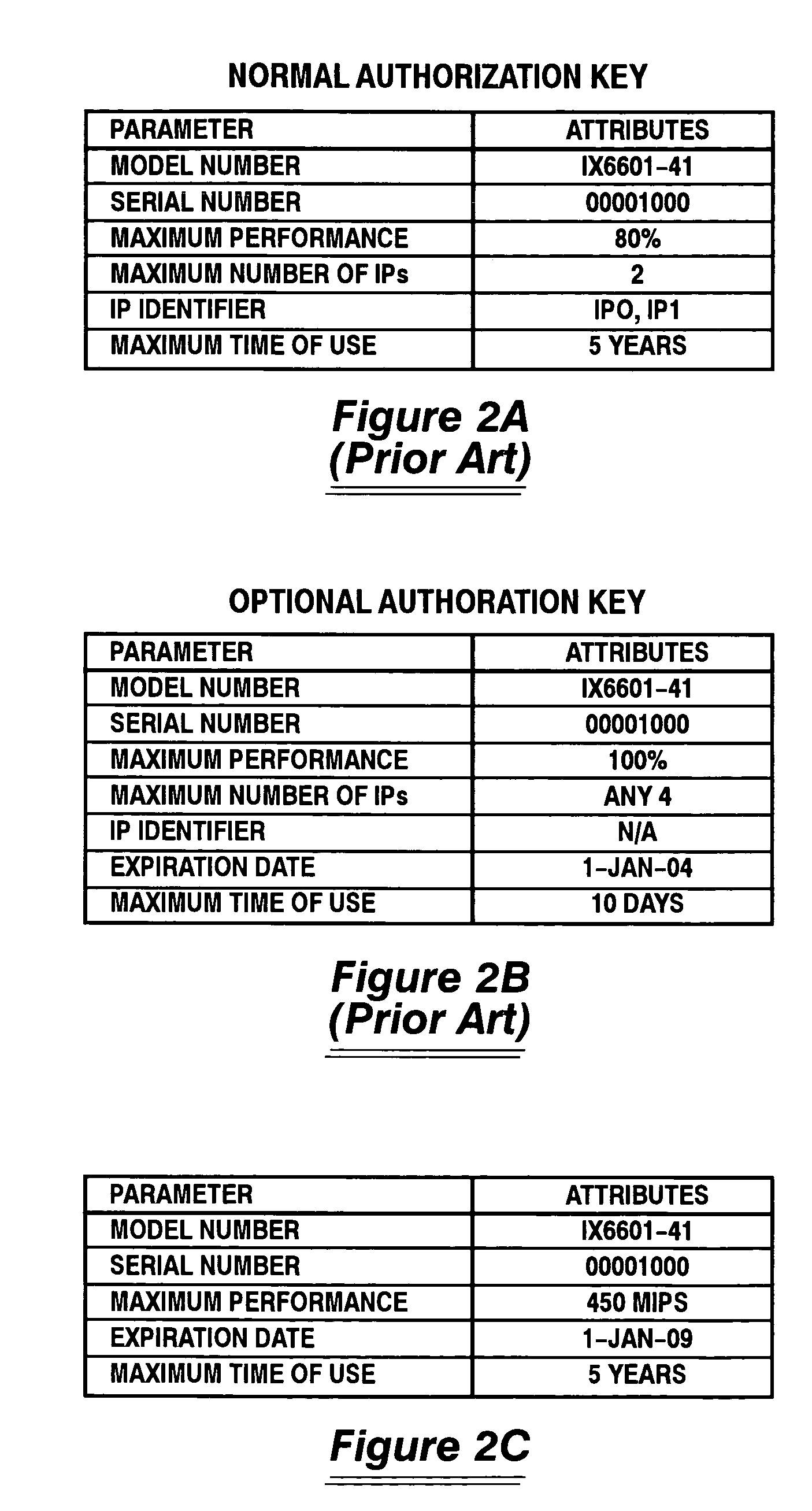
System and method for scaling performance of a data processing system
ActiveUS7421691B1Maximize throughputControl performanceMultiprogramming arrangementsInternal/peripheral component protectionData processing systemInstructions per second
A system and method for scaling the performance of a data processing system is disclosed. According to one method, a level of system performance is purchased for use with the data processing system. This purchased performance level is described in Millions of Instructions Per Second (MIPS) or a similar unit of measure. A system administrator selects which resources within the data processing system will be enabled, as well as how those resources will be configured. The enabled system resources will include one or more instruction processors. The performance of each of the enabled processors is then scaled to achieve the purchased system performance level. Performance scaling is performed in a manner that takes into account characteristics associated with the selected configuration as well as the system architecture.
Owner:UNISYS CORP
Method and apparatus for parallel multi-view point video capturing and compression
InactiveUS7035453B2Remove uncertaintyTelevision system detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesDigital videoInstructions per second
A method and apparatus for digital video capturing and compression supports multi-viewpoint interactive video applications. Multiple (typically hundreds of) video cameras centripetally placed in a three dimensional space acquire real-time visual pictures of the same 3D scene from multiple viewpoints at the rate of 20˜30 frames per second (fps). Parallel Multi-Viewpoint Video Capturing and Compression (PMVCC) supports the operation of the apparatus. In an exemplary realization, a Multi-DSP Array (MDA) architecture uses hundreds of high-performance digital signal processors (DSPs) working in parallel to obtain a sustained computation power of hundreds of GIPS (Giga Instructions Per Second).
Owner:REALITY COMMERCE CORP
Special ASIC (Application Specific Integrated Circuit) chip system for spaceflight
ActiveCN102929836AHigh degree of integrationReduce mass volume power consumptionGeneral purpose stored program computerArea networkAdvanced Microcontroller Bus Architecture
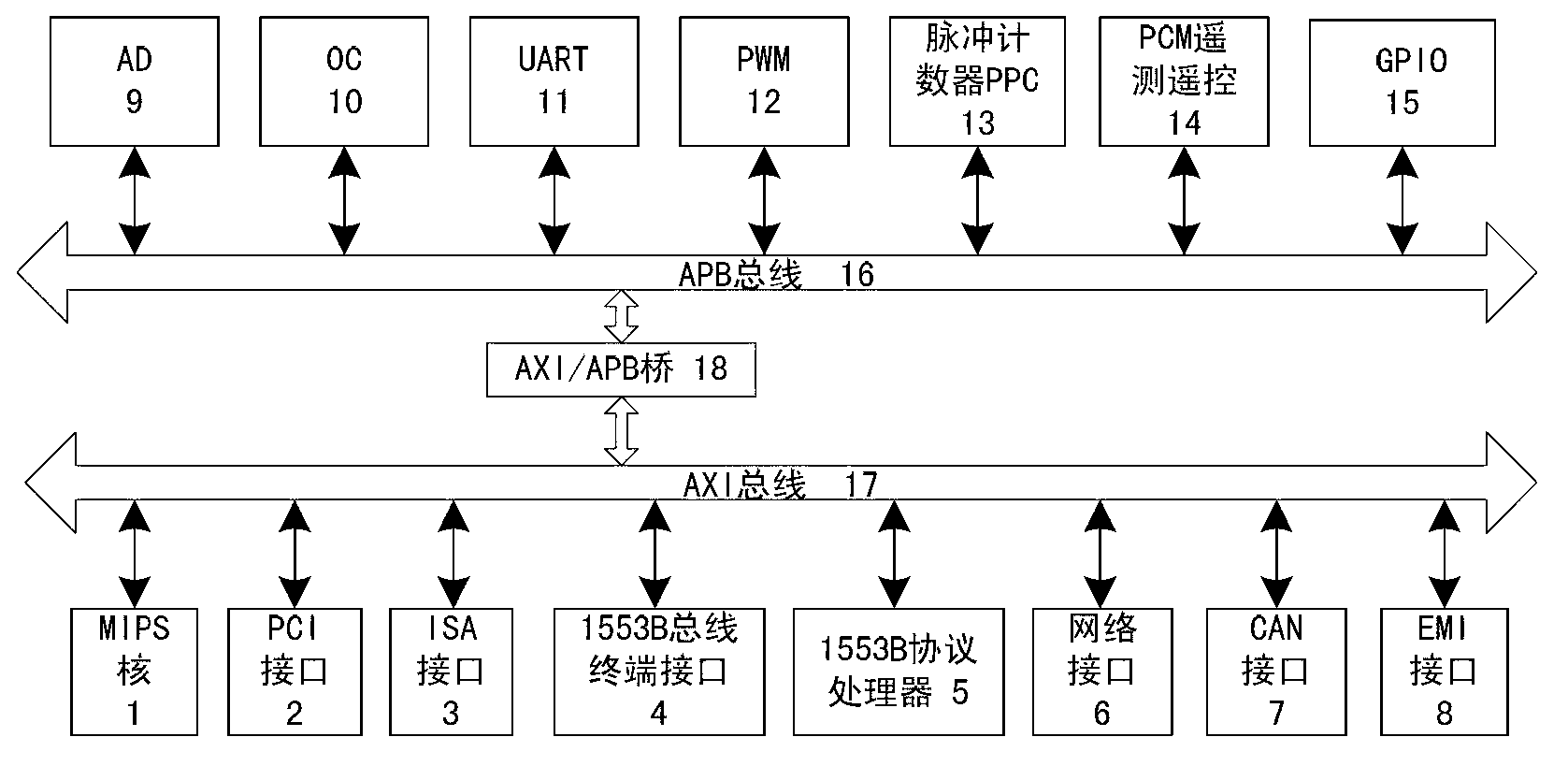
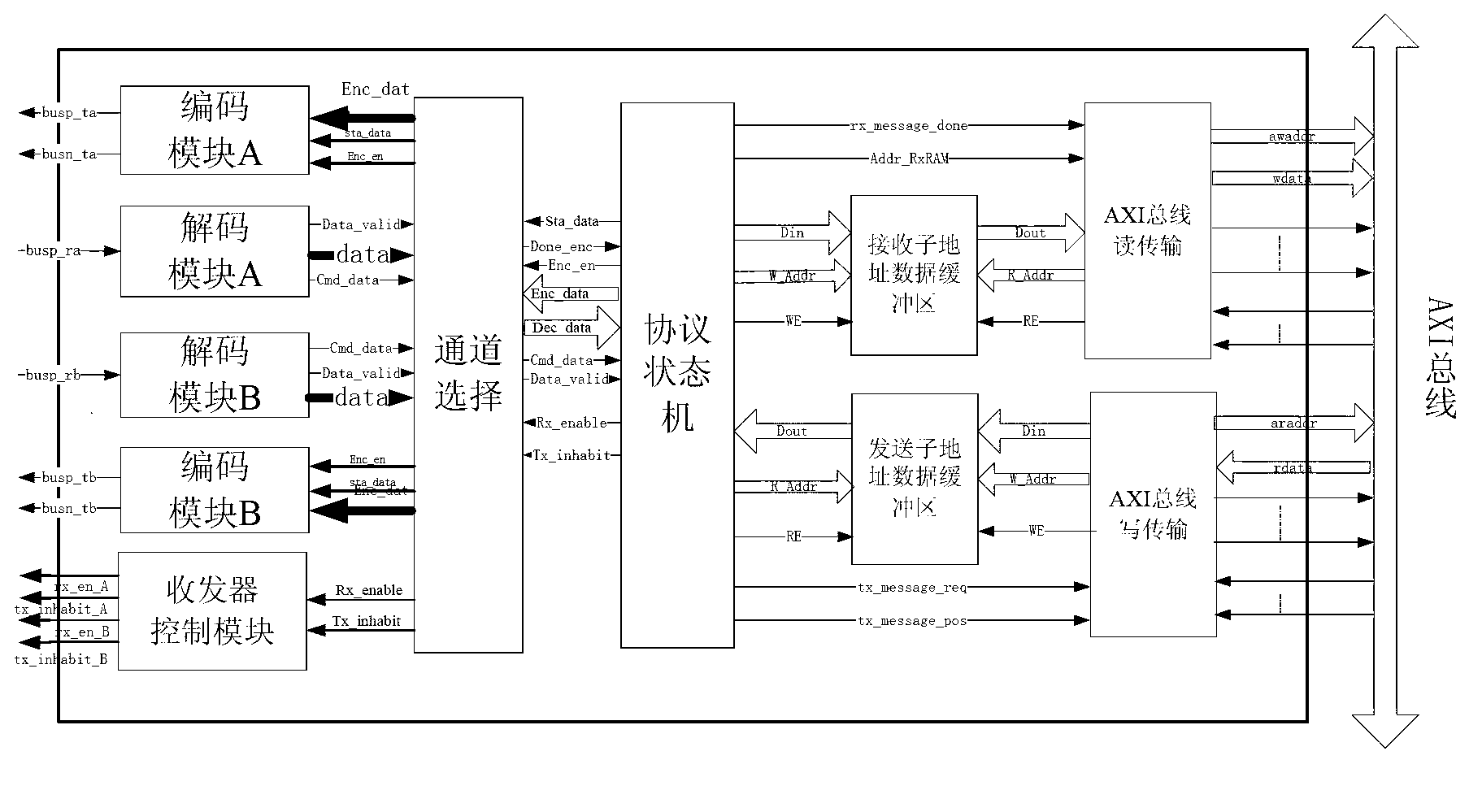
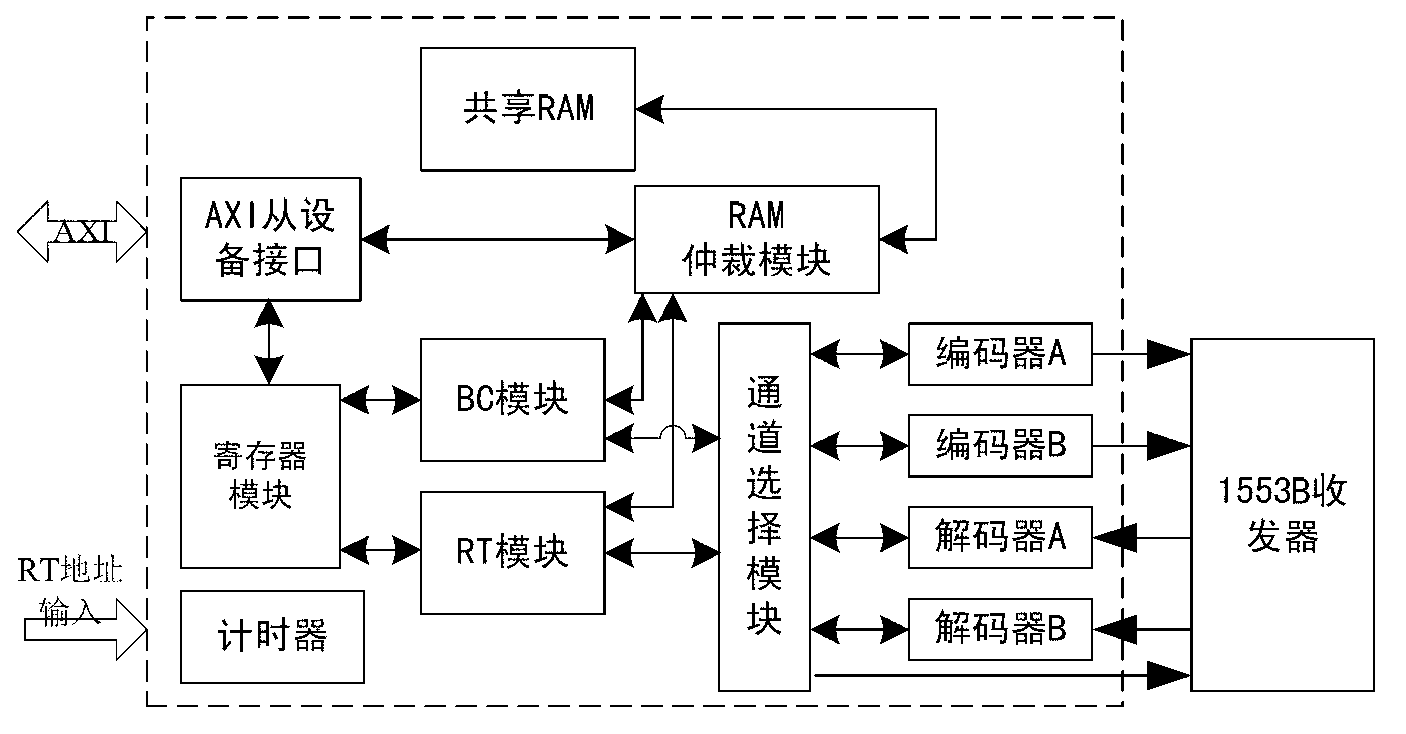
The invention relates to a special ASIC (Application Specific Integrated Circuit) chip system for spaceflight. The special ASIC chip system comprises a MIPS (Million Instructions Per Second) nucleus, a PCI (Programmable Communications Interface) bus interface, an ISA (Internet Security And Acceleration) bus interface, a 1553B bus terminal interface, a 1553B protocol processor, a network interface, a CAN (Controller Area Network) interface, an EMI (External Memory Interface), AD acquisition control logic, OC door control logic, UART (Universal Asynchronous Receiver / Transmitter) serial port, PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) interface, a pulse counter PPC, PCM (Pulse Code Modulation) telemetry remote control module and a general input / output module, wherein the MIPS nucleus, the PCI bus interface, the ISA bus interface, the 1553B bus terminal interface, the 1553B protocol processor, a network interface, the CAN interface and the EMI are connected to an AMBA AXI (Advanced Microcontroller Bus Architecture Advanced eXtensible Interface) bus; and the AD acquisition control logic, the OC door control logic, the UART serial port, the PWM interface, the pulse counter PPC, the PCM telemetry remote control module and the general input / output module are connected to an AMBA APB (All Points Bulletin) bus; and the AMBA AXI bus is connected with the AMBA APB bus through an AXI / APB bridge.
Owner:NAT SPACE SCI CENT CAS
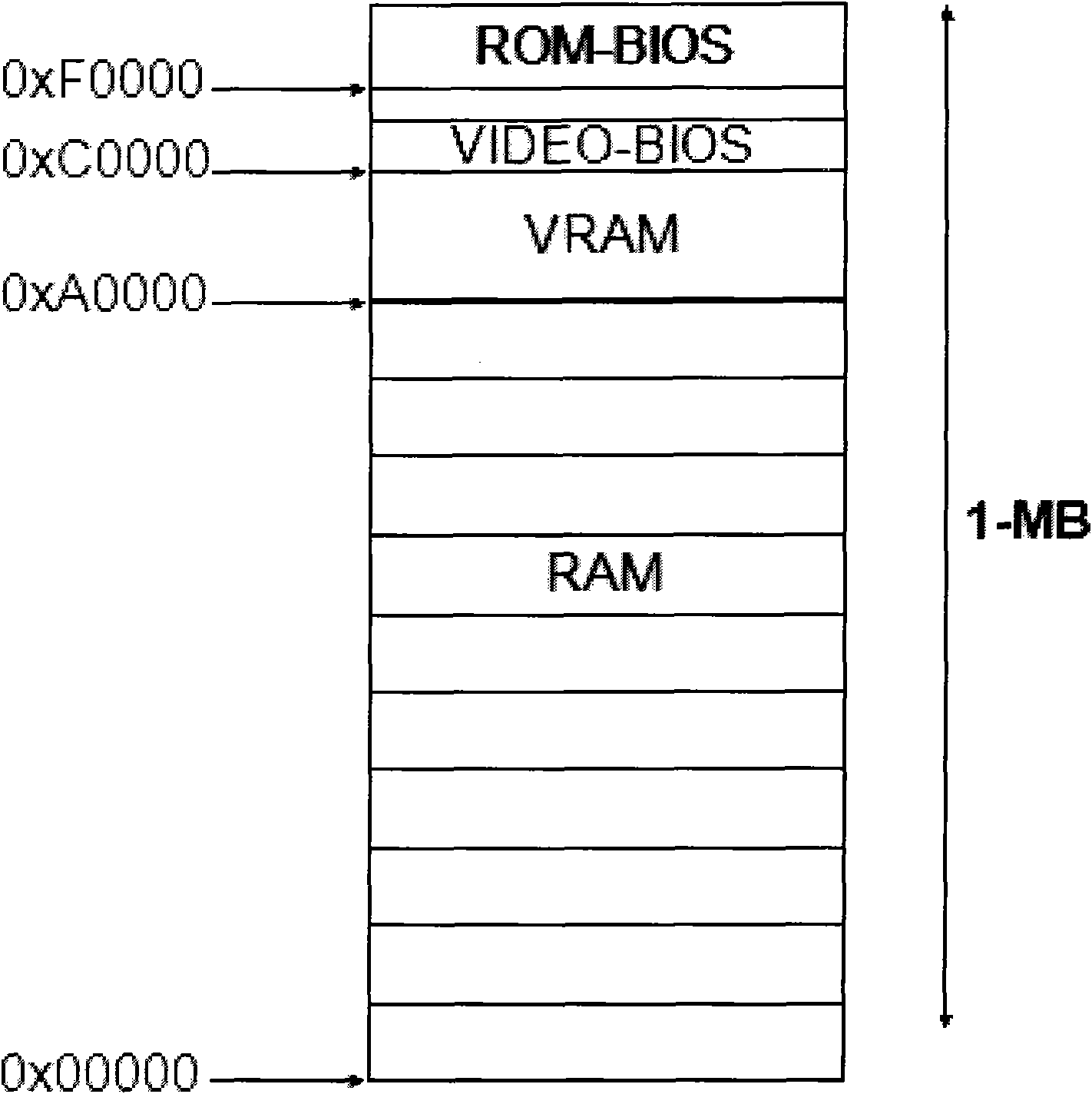
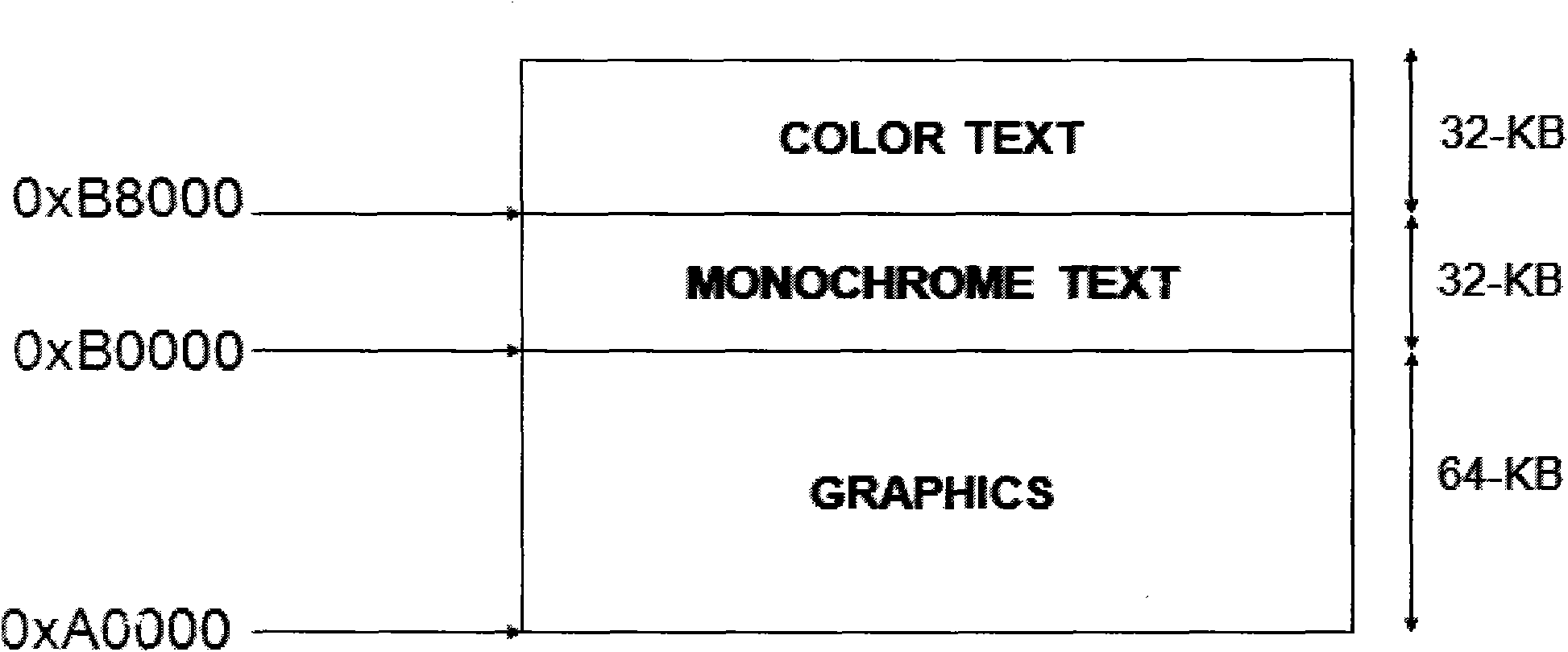
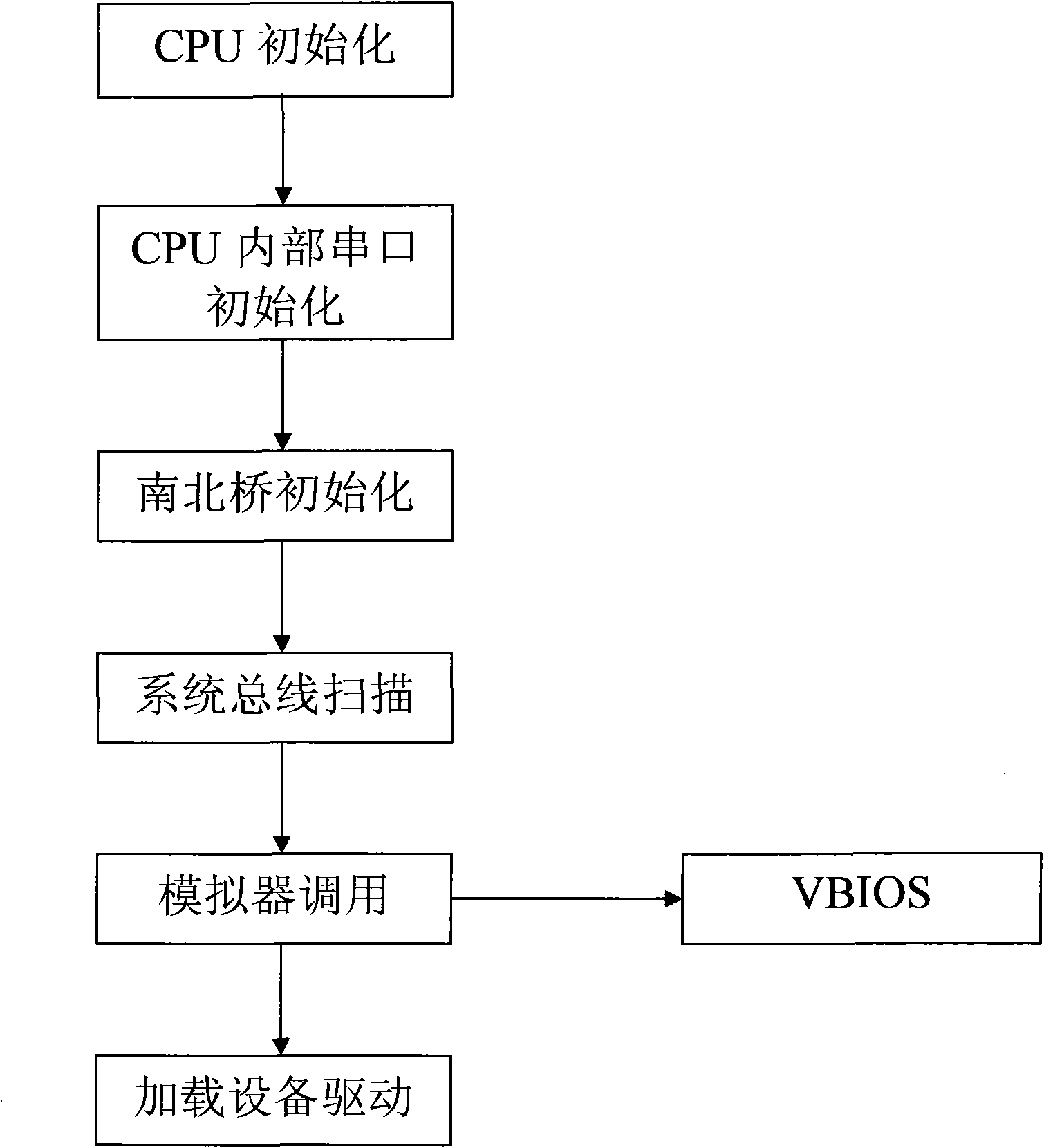
Method for realizing operation of X86 VBIOS (video-bios) on MIPS (million instruction per second) framework
InactiveCN102023889AAddress the disadvantages of non-disclosureFlexible designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationVideo memoryInstructions per second
The invention provides a method for realizing operation of an X86 VBIOS (video-bios) on an MIPS (million instructions per second) framework. The method comprises the following steps: a vga_bios_init (void) function reads video-bios and sends the video-bios into an X86 simulator; the X86 simulator simulates a local video memory address 0xa0000; the X86 simulator simulates a video card bios address 0xc0000; the X86 simulator simulates an X86 CPU (central processing unit) register and instructions; the X86 simulator simulates an INT10 interrupt vector; and the X86 simulator simulates sys bios. Through the invention, the display requirements of a Loongson blade are met.
Owner:SUGON INFORMATION IND
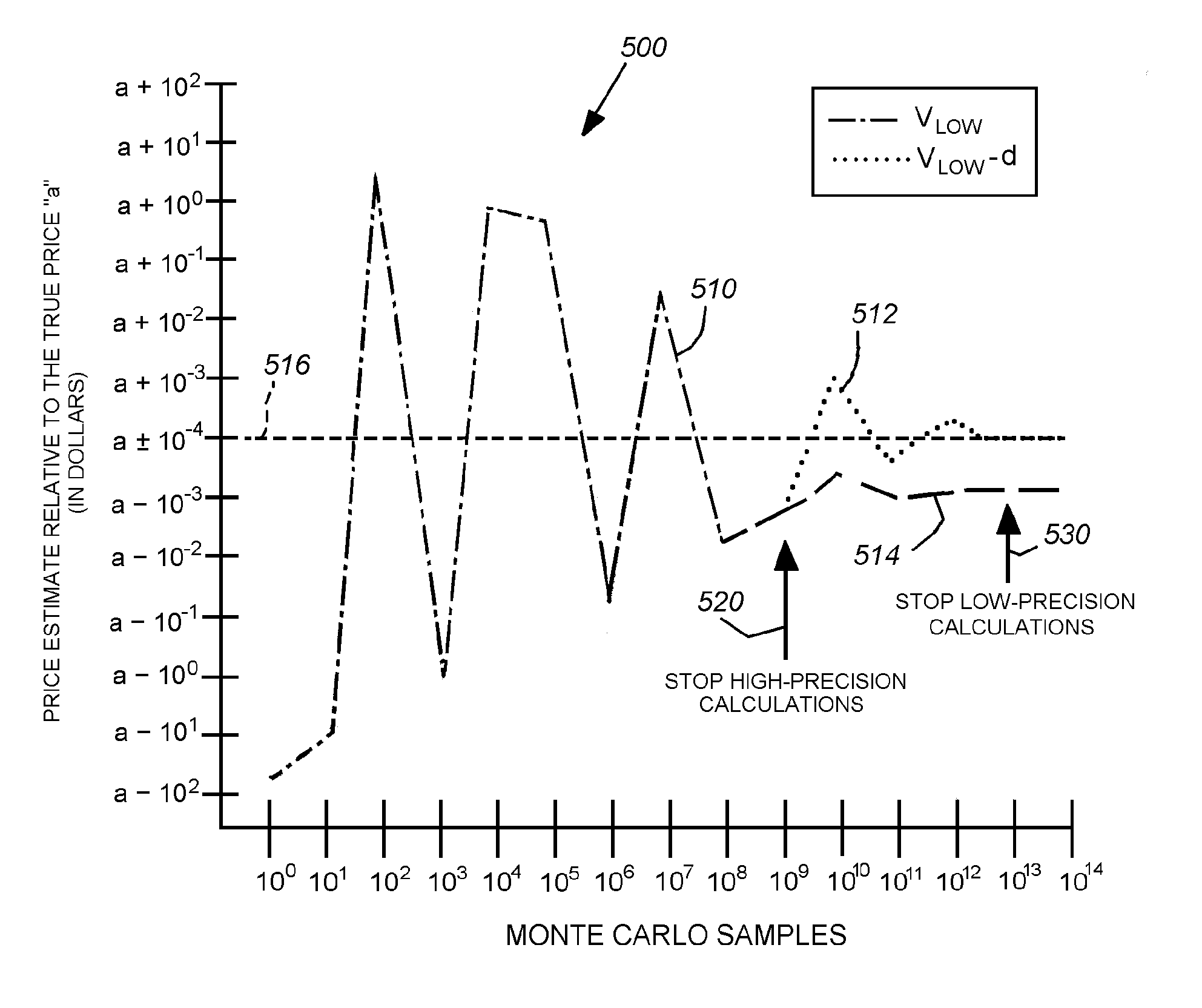
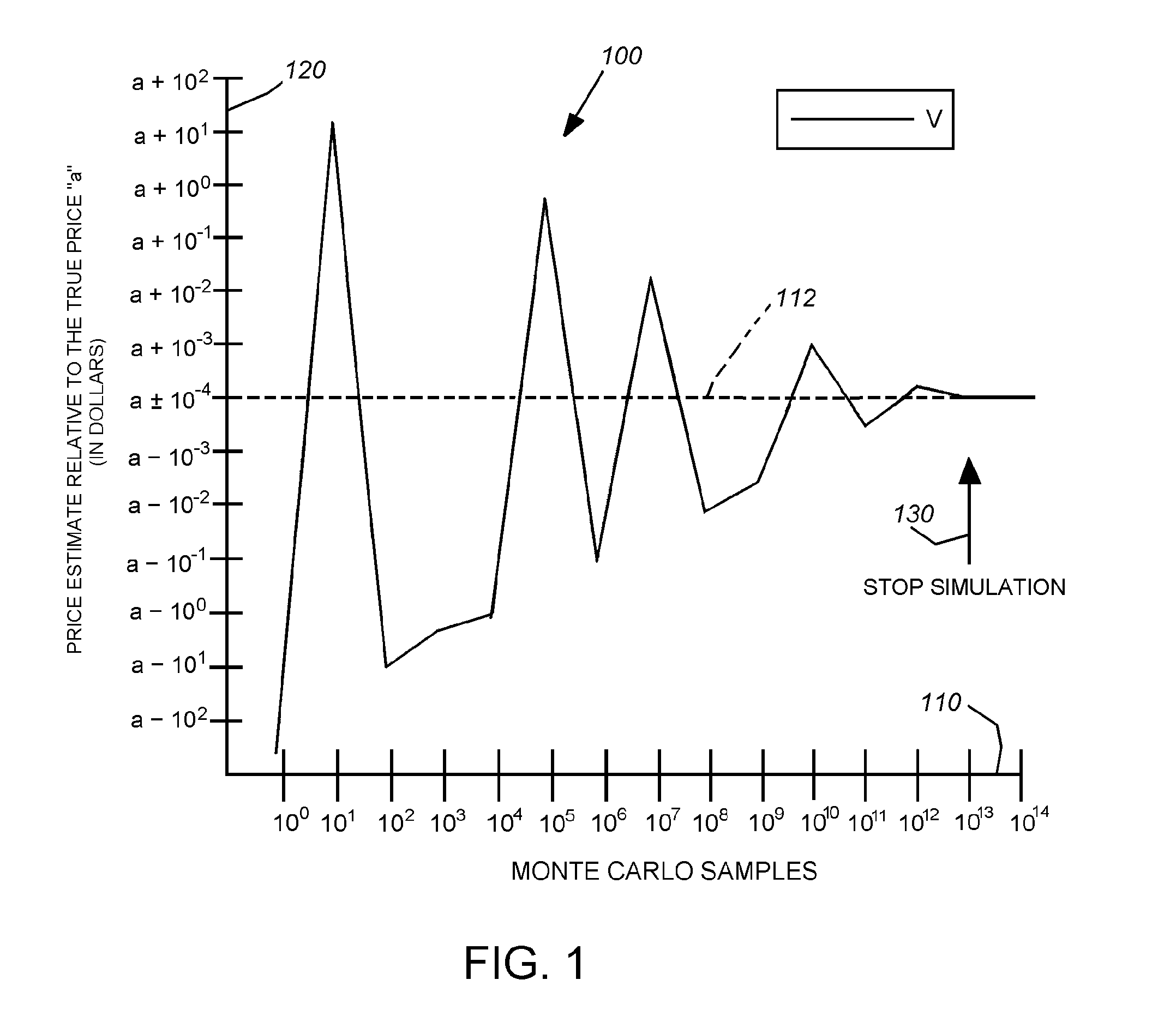
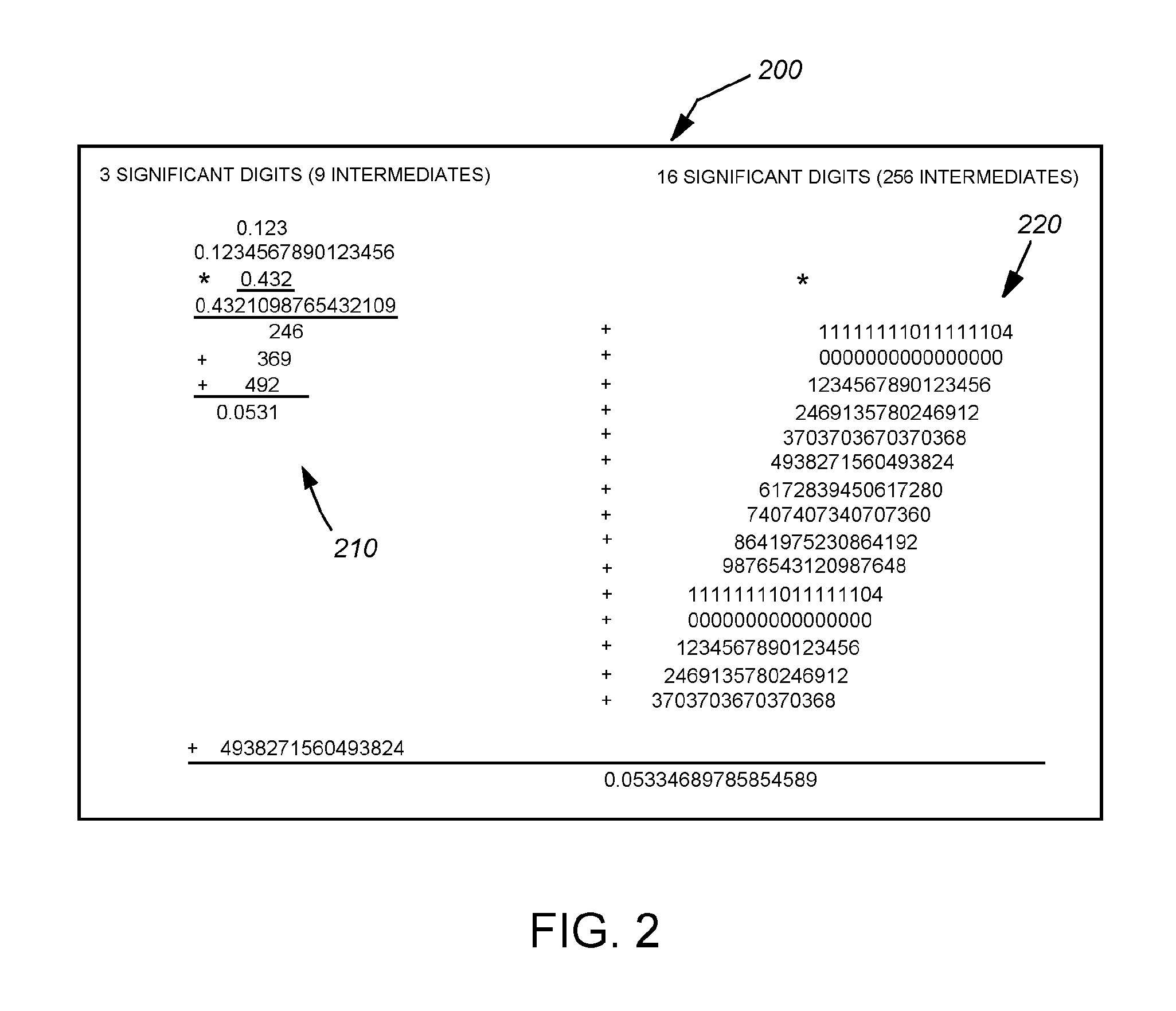
System and method for achieving improved accuracy from efficient computer architectures
ActiveUS8209597B2Reduce errorsSame precisionError preventionFinanceInstructions per secondProgram instruction
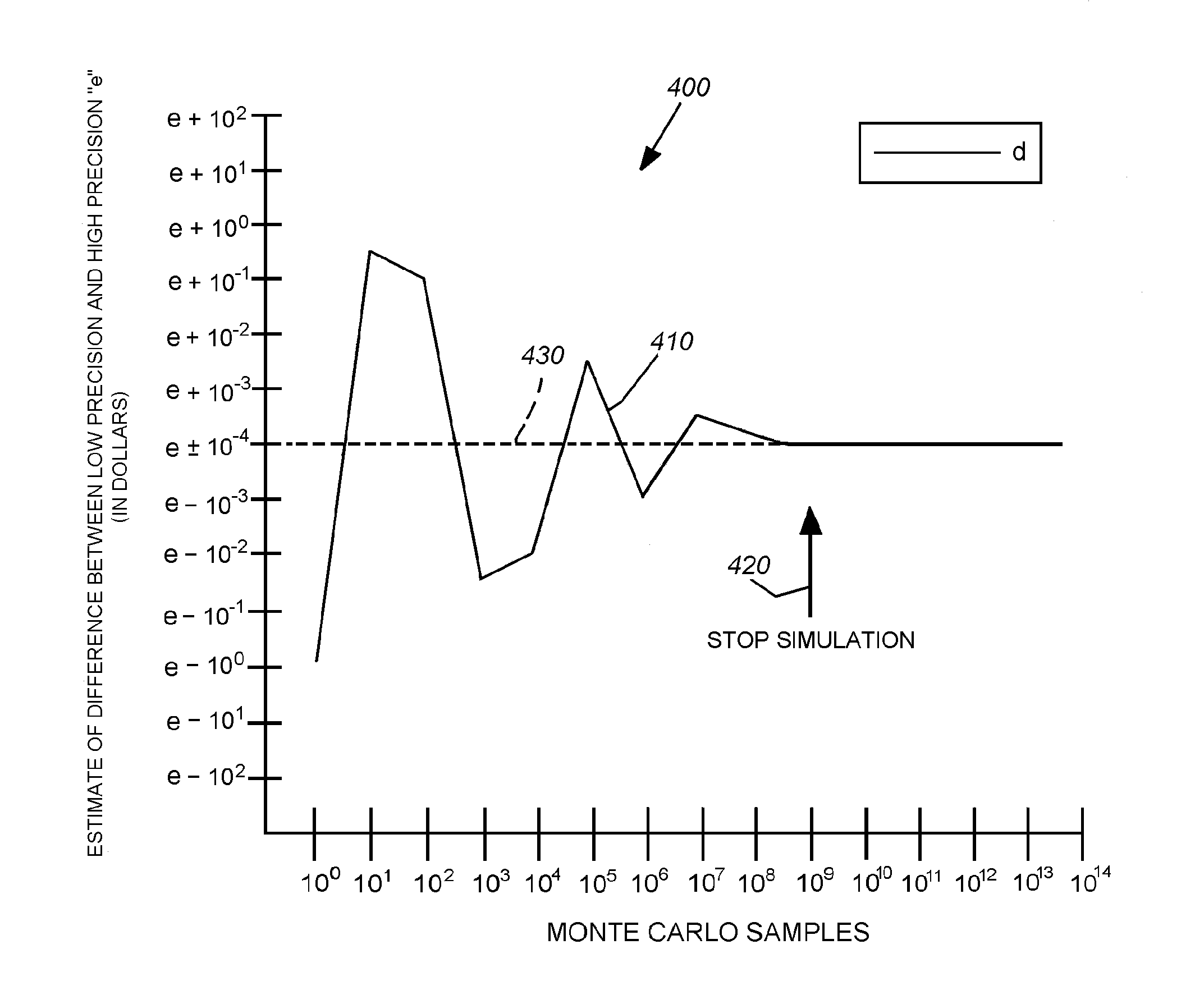
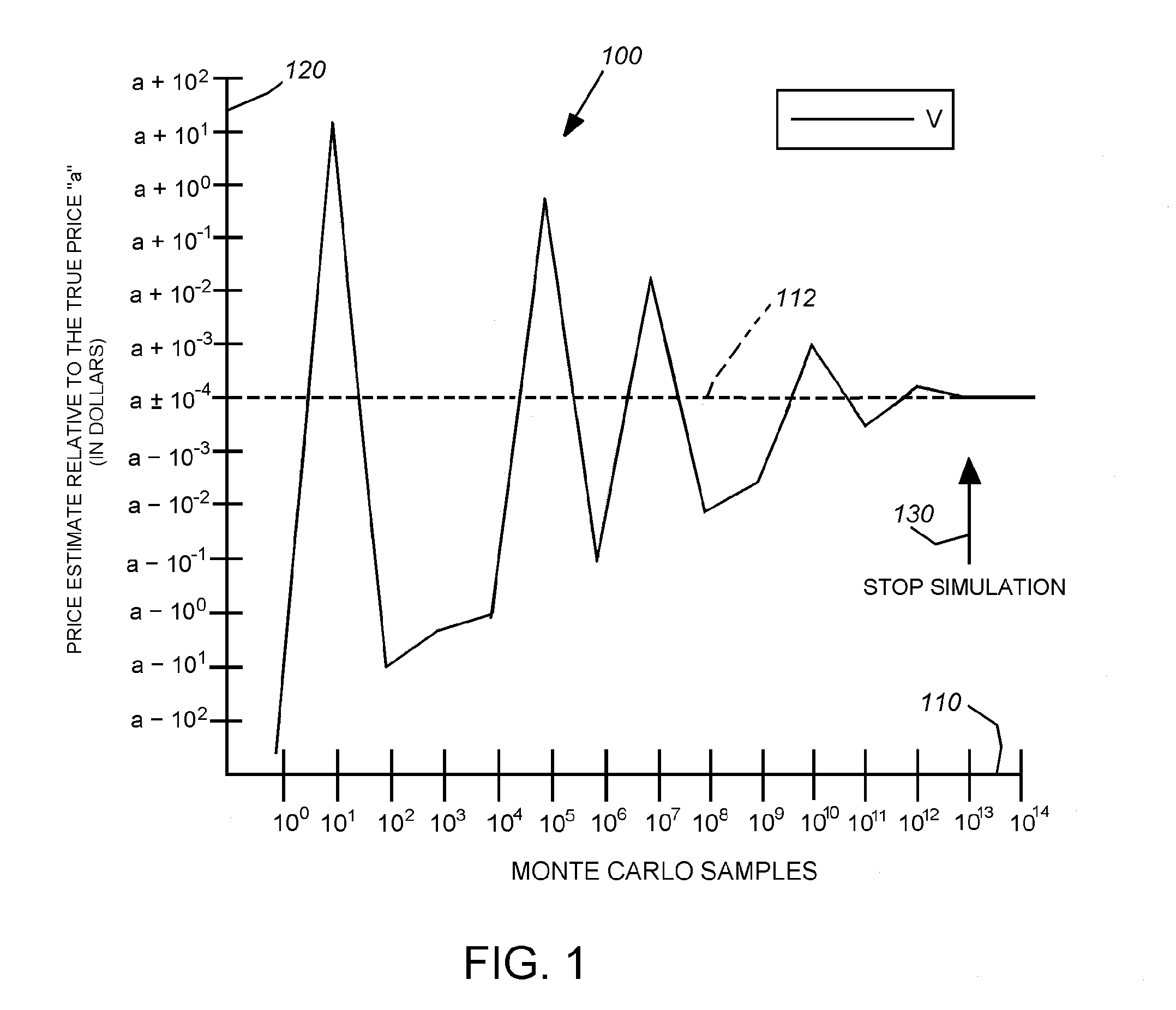
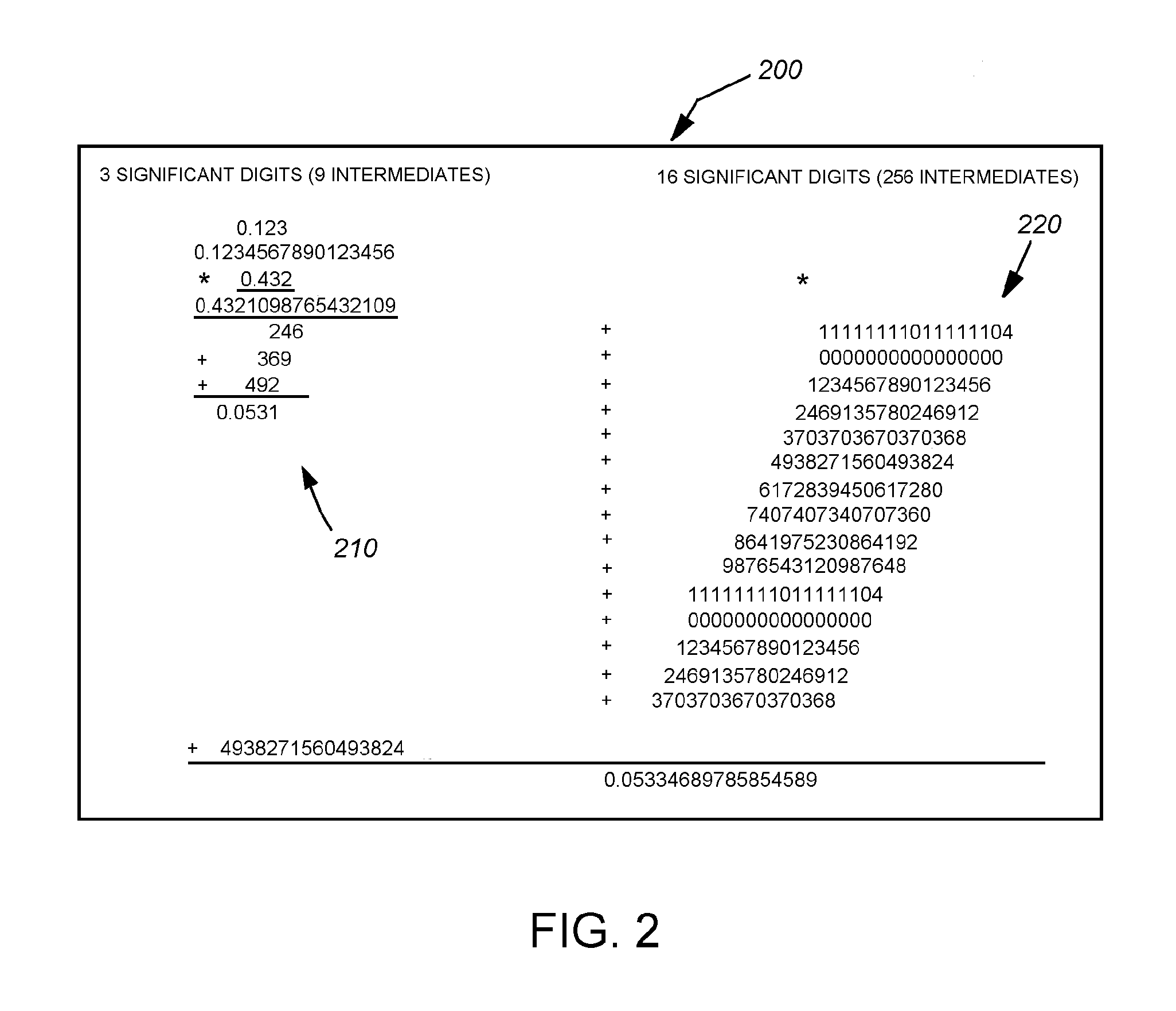
This invention provides a system and method that can employ a low-instruction-per-second (lower-power), highly parallel processor architecture to perform the low-precision computations. These are aggregated at high-precision by an aggregator. Either a high-precision processor arrangement, or a low-precision processor arrangement, employing soft-ware-based high-precision program instructions performs the less-frequent, generally slower high-precision computations of the aggregated, more-frequent low-precision computations. One final aggregator totals all low-precision computations and another high-precision aggregator totals all high-precision computations. An equal number of low precision computations are used to generate the error value that is subtracted from the low-precision average. A plurality of lower-power processors can be arrayed to provide the low-precision computation function. Alternatively a plurality of SIMD can be used to alternately conduct low-precision computations for a predetermined number of operations and high-precision operations on a fewer number of operations. In an embodiment, aggregation can include summing values within predetermined ranges of orders of magnitude, via an adding tree arrangement, so that significant digits therebetween are preserved.
Owner:GRANGER RICHARD
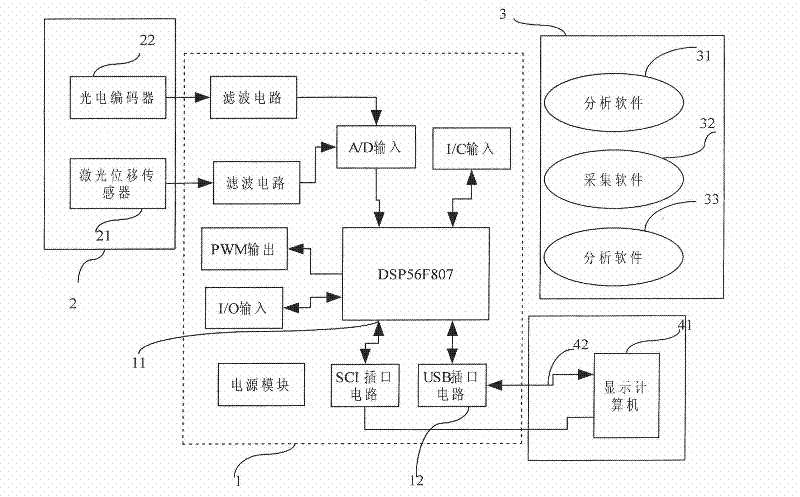
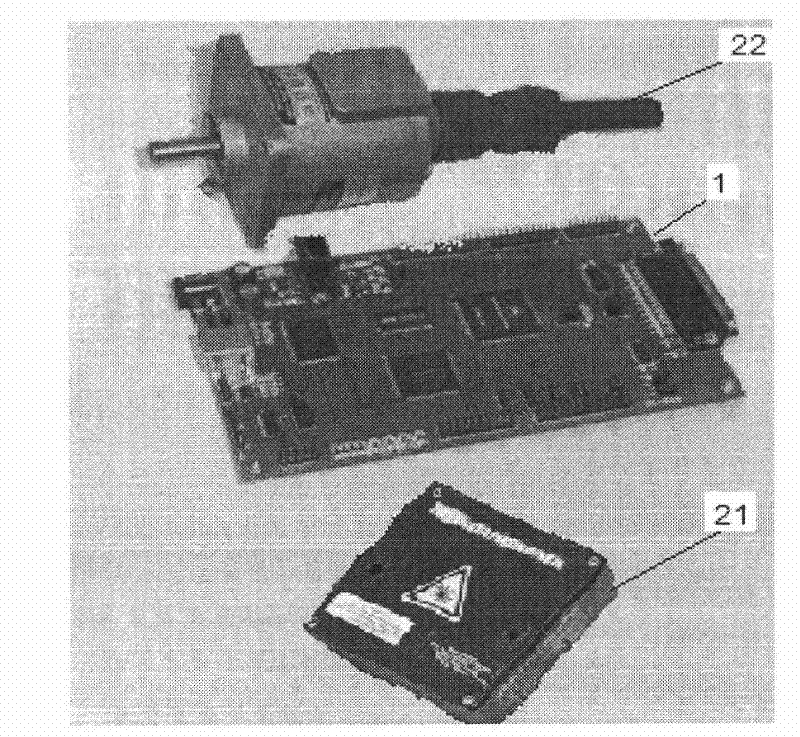
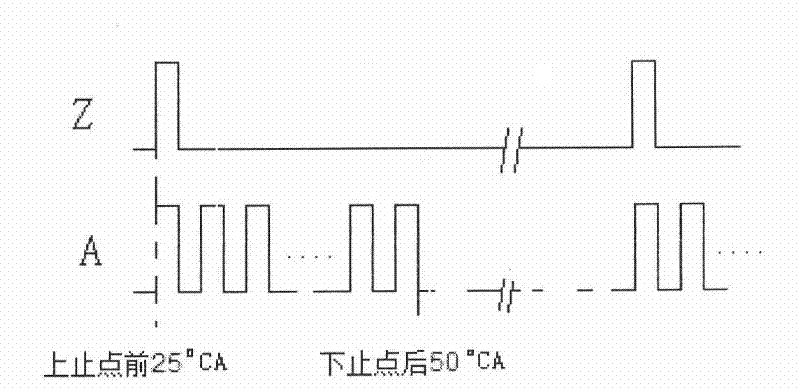
Automatic tester for valve lift and timing phase of engine
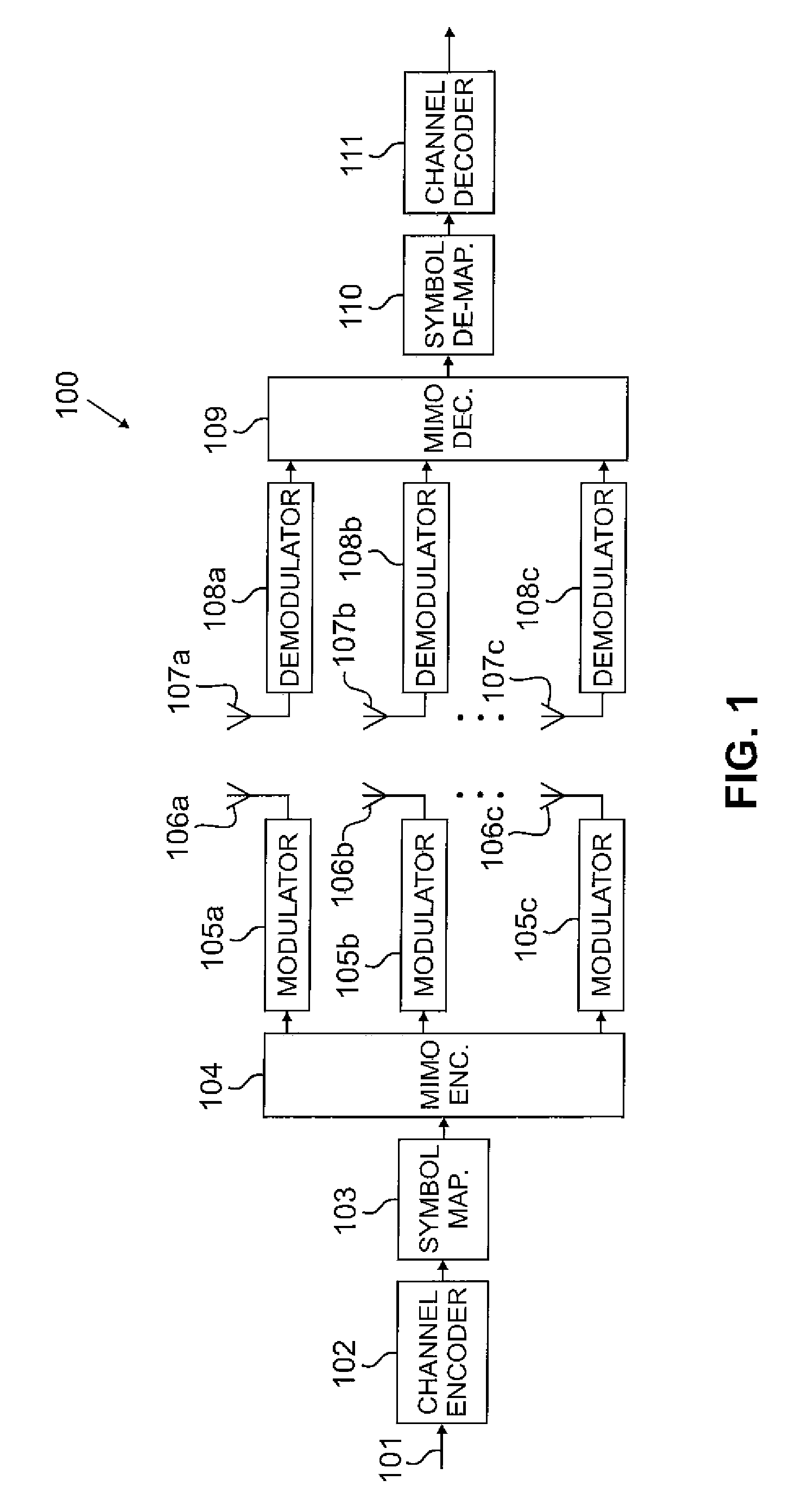
The invention provides an automatic tester for valve lift and timing phase of an engine, consisting of a laser displacement sensor, a photoelectric encoder, a digital signal processor and a display computer, as shown in Figure 1. A newly-designed local raster area of the photoelectric encoder triggers a pulse signal to realize the work timing sequence for time-share data collecting and data processing for the digital signal processor. The integrated laser displacement sensor directly outputs voltage quantity, so that a signal converting circuit of the tester is reduced. The single-channel analog to digital converter (ADC) 200K acquisition accuracy and the instruction execution speed 400 billion instructions / S MIPS (million instructions per second) of the digital signal processor can realize the high-speed acquisition of the valve lift and the complex data process. A double-data communication mode of asynchronous serial communication interface (SCI) and high speed data transmission universal serial bus (USB) is used in a multi-parameter transmission monitor mode and a single-parameter multi-data transmission test mode respectively. After the laser displacement sensor and digital signal processor-based automatic tester for valve lift and timing phase is used, the automatic test and the data process of the valve lift and the timing phase can be completed.
Owner:ACADEMY OF ARMORED FORCES ENG PLA
MIMO transceiver with pooled adaptive digital filtering
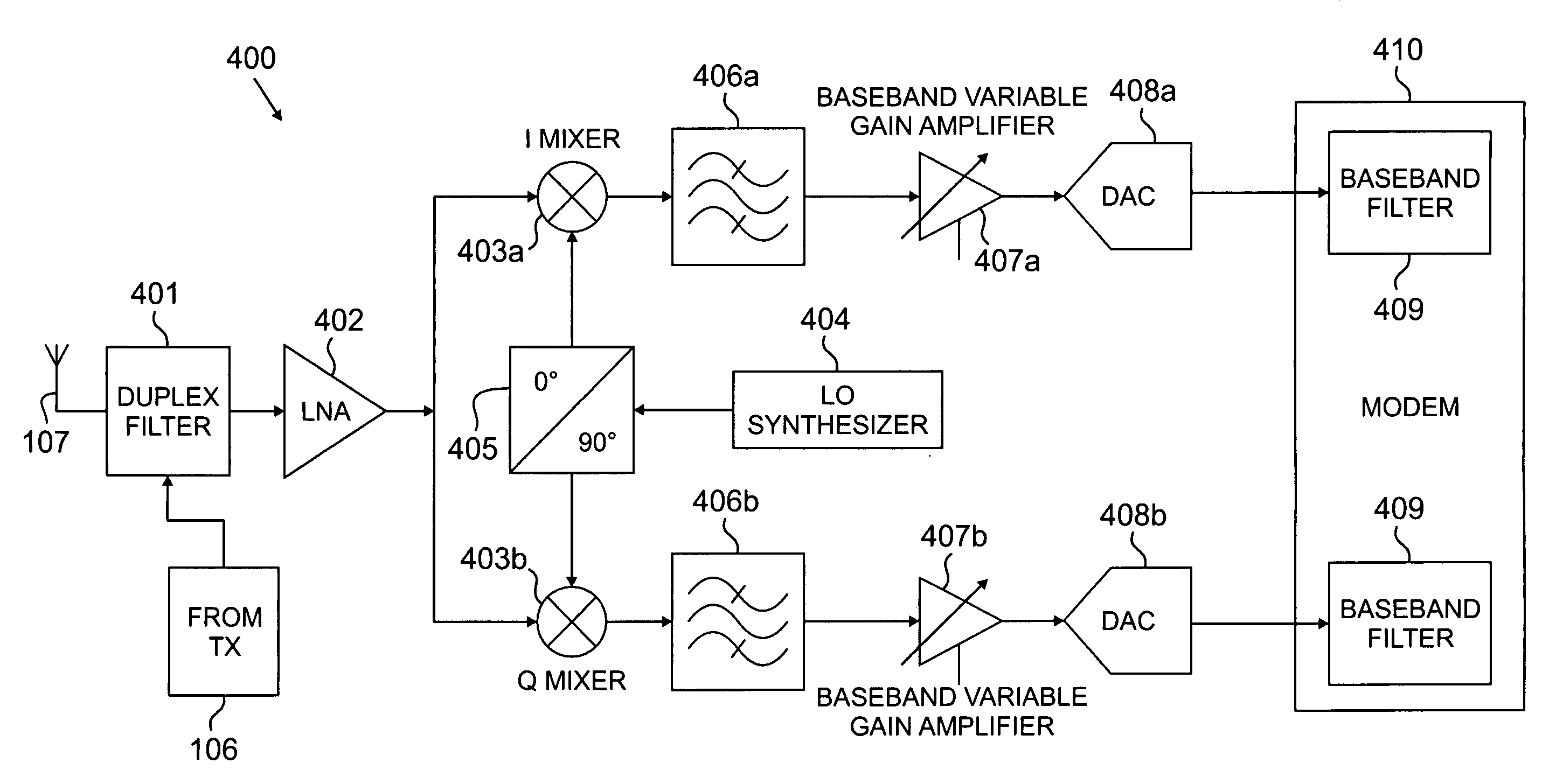
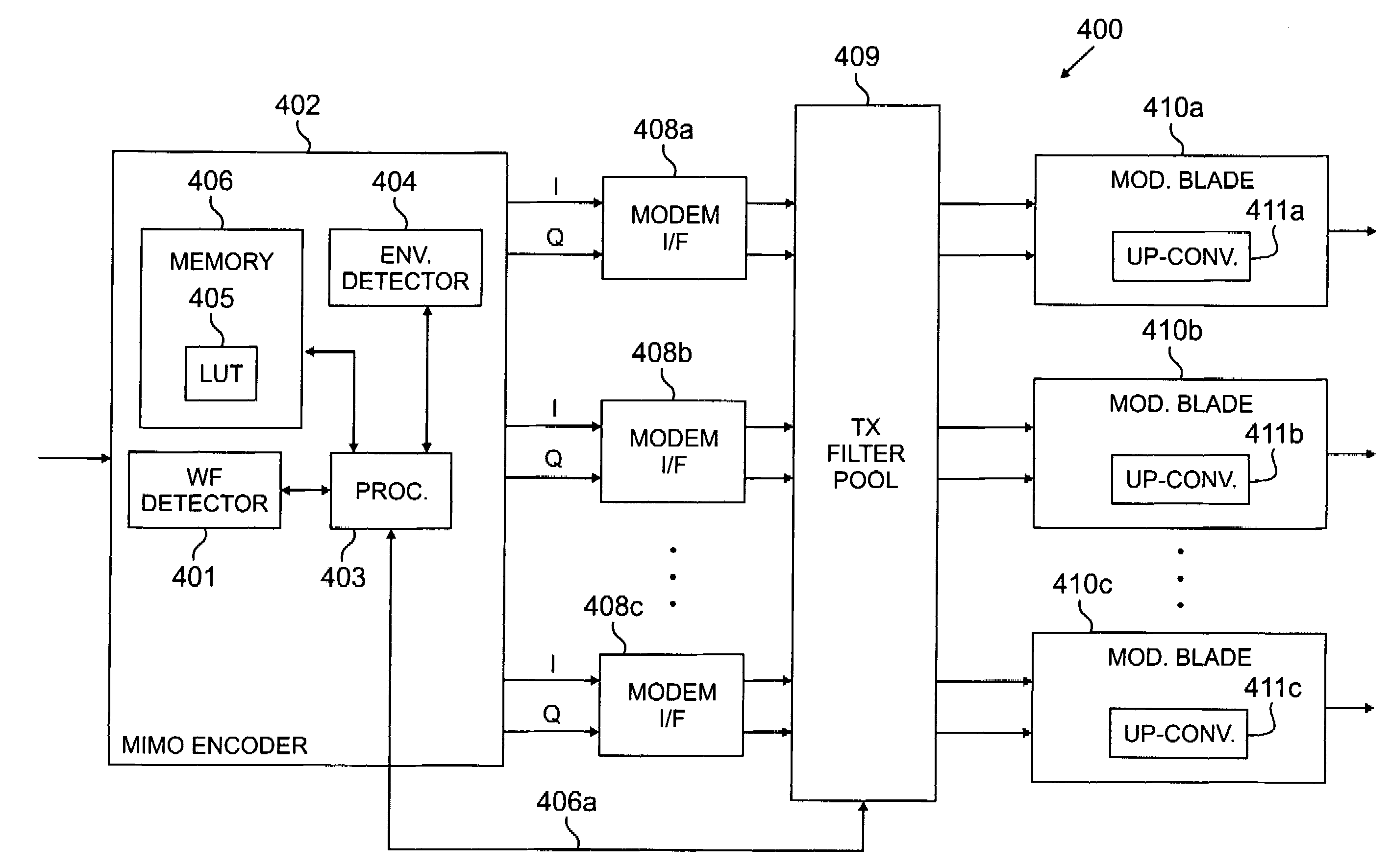
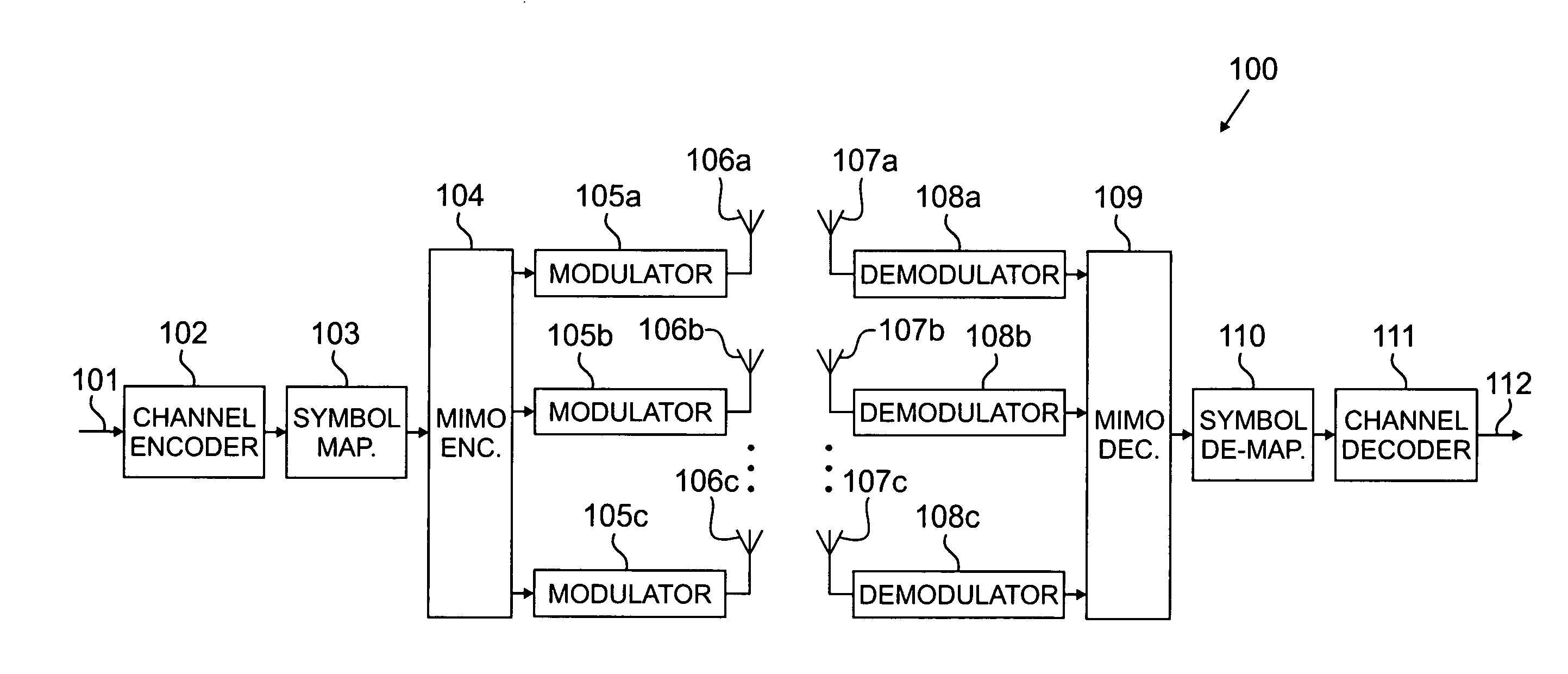
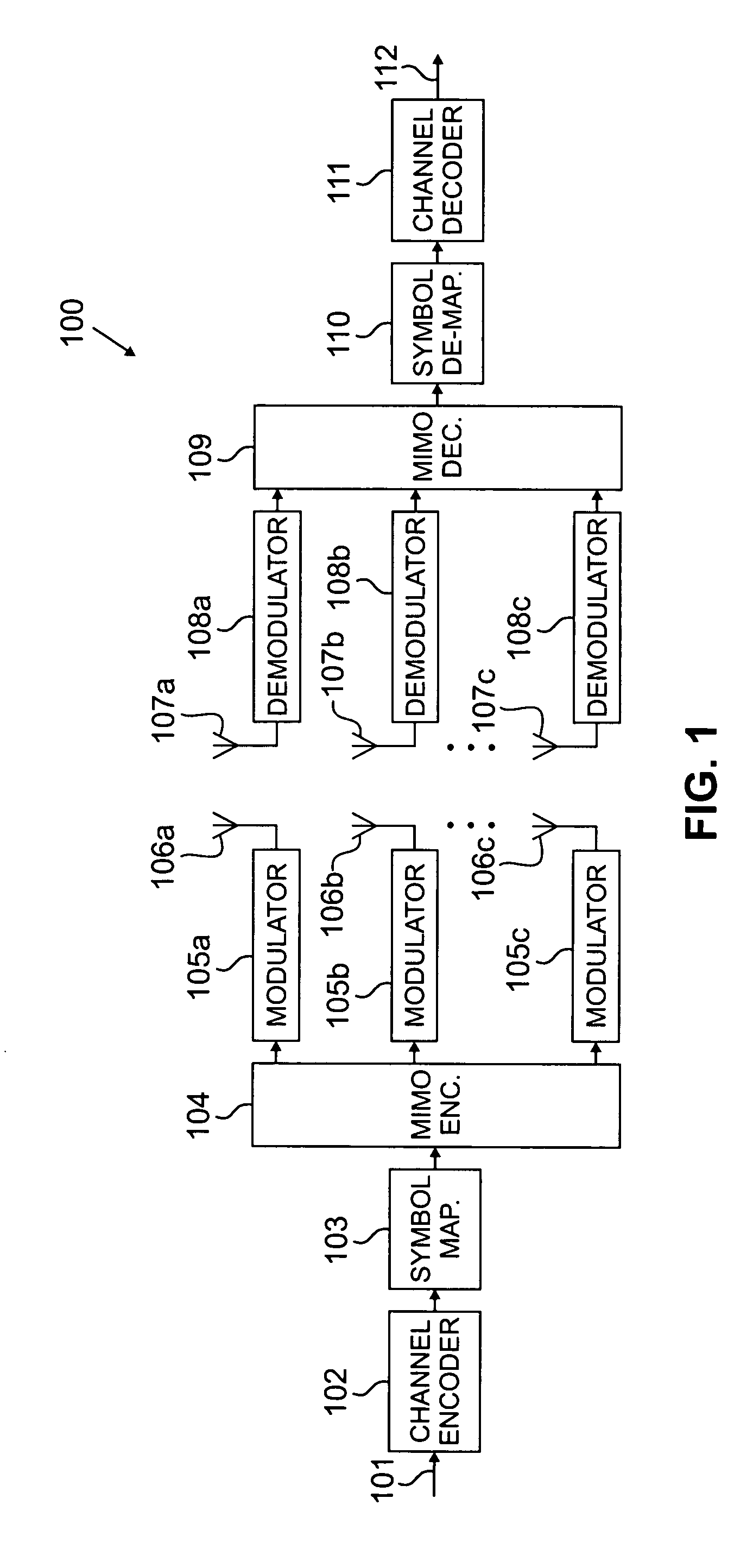
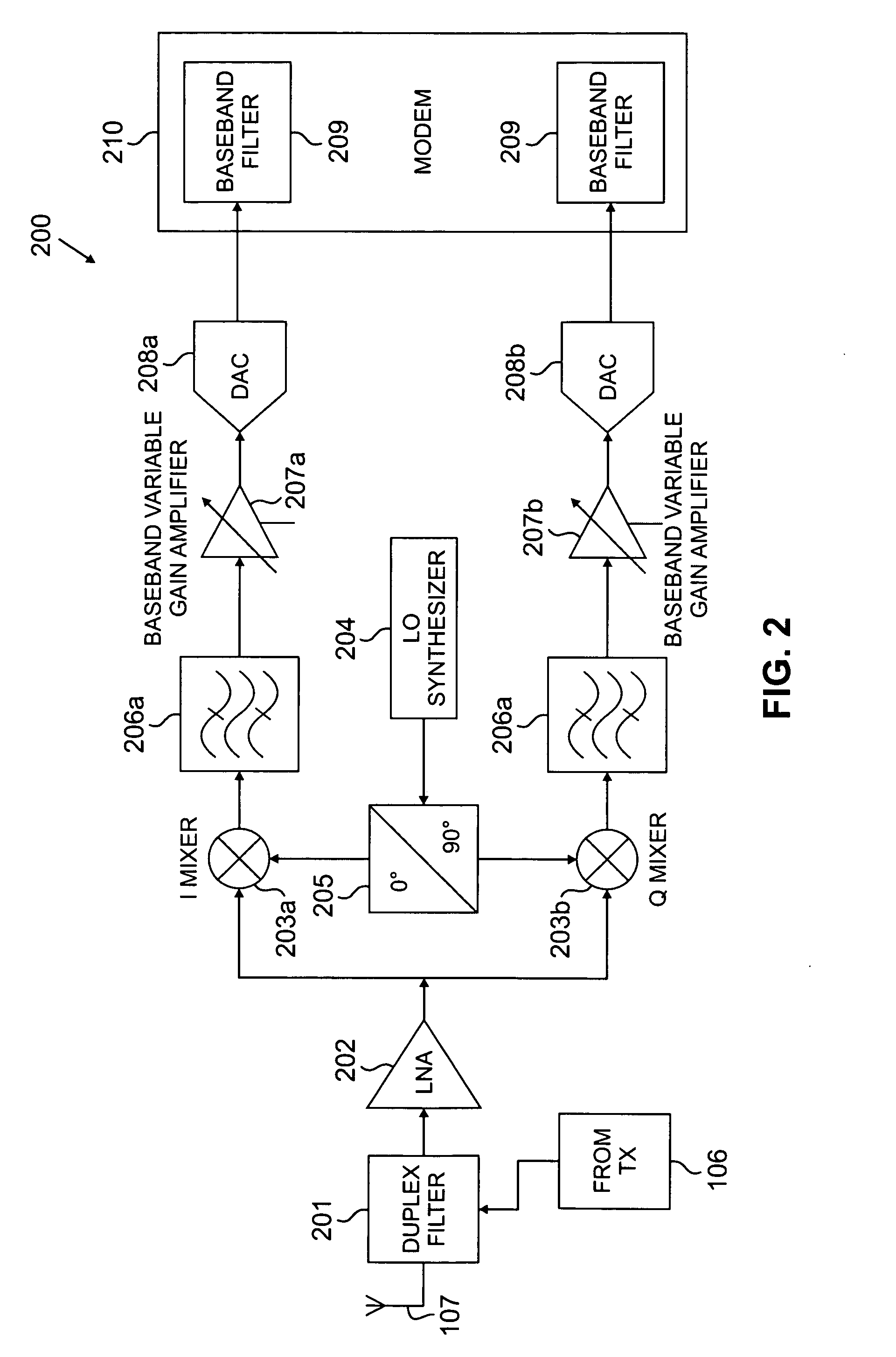
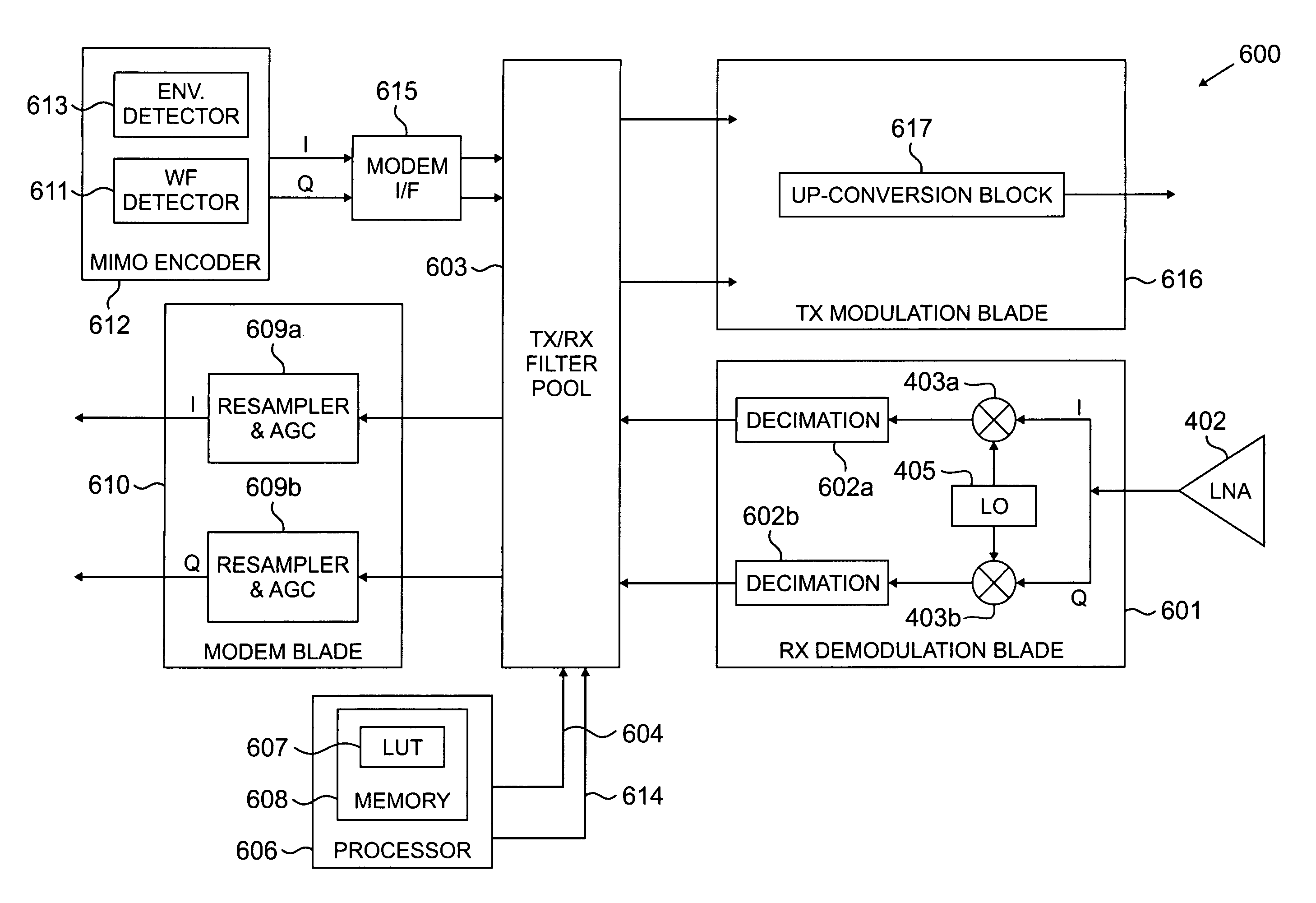
InactiveUS20080112470A1Reduced signaling processMultiple-port networksDelay line applicationsTransceiverInstructions per second
MIMO transceiver with a reconfigurable pooled digital filter is disclosed. A processor sets parameters of the filter to minimize the number of instructions per second and the amount of power required by the filter to perform, while matching the filter to at least one of: a transmitter filter and a receiver filter. The processor uses an algorithm or a lookup table stored in memory to select the combination of filter parameters. The parameters may be selected from at least one of: a number of taps, a filter length, a word length, a coefficient quantization, a sampling rate, bits per sample, a sampling bit, a tap delay and a coefficient length. After selecting a combination of filter parameters, the processor sends a control signal to the adaptive filter. The pooled adaptive filter reconfigures itself in accordance with the selected filter parameters.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
MIMO transmitter with pooled adaptive digital filtering
InactiveUS20070258544A1Reduced signaling processSpatial transmit diversityModulated-carrier systemsInstructions per secondAdaptive filter
MIMO transmitter with a reconfigurable pooled digital filter is disclosed. A processor uses the output of an envelope detector to set parameters of the filter to minimize the number of instructions per second and the amount of power required by the filter to perform. The processor uses an algorithm or a lookup table stored in memory to select the combination of filter parameters. The parameters may be selected from at least one of: a number of taps, a filter length, a word length, a coefficient quantization, a sampling rate, bits per sample, a sampling bit, a tap delay and a coefficient length. After selecting a combination of filter parameters, the processor sends a control signal to the adaptive filter. The pooled adaptive filter reconfigures itself in accordance with the selected filter parameters.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Vehicle failure diagnostic apparatus
InactiveCN102063120AReduce power consumptionHigh precisionElectric testing/monitoringMicrocontrollerData acquisition
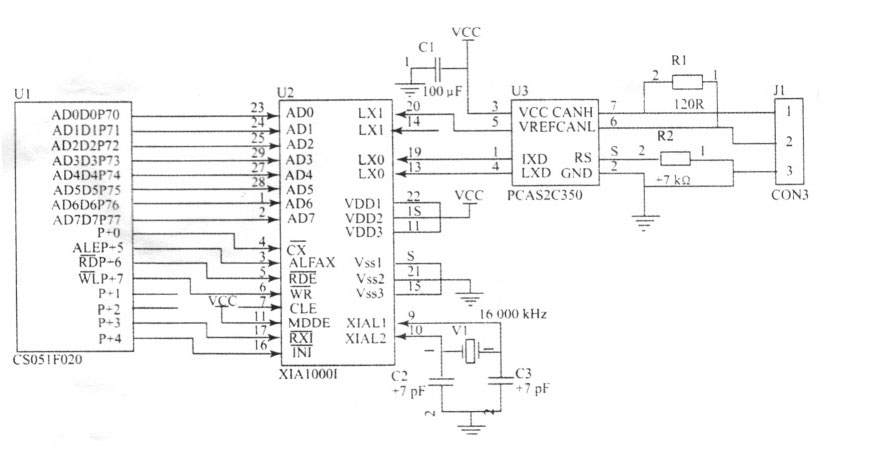
The invention provides a singlechip vehicle failure diagnostic apparatus which is mainly characterized in that a C8051F020 singlechip is selected as a CPU, a CIP-51 microprocessor core completely compatible with an MCS-51 command set is adopted in the CPU, and the peak valve reaches 2MIPS (Million Instructions Per Second). Meanwhile, nearly all analog and digital peripheries and other function parts including a PGA (Professional Graphics Adapter), an ADC (Analog to Digital Converter), a DAC (Digital to Analog Converter), a voltage comparer, a voltage inference, a temperature sensor, an SMBus / I2C, an UART (Universal Asynchronous Receiver Transmitter), an SPI (Serial Peripheral Interface), a timer, a programmable counter and a timer array required by a singlechip data acquisition or control system are integrated in one chip. The invention has the advantages of being capable of realizing that parameters of different electric control systems are measured, reading failure codes of a vehicle-mounted computer, and testing an executer, and has the characteristics of low power consumption, high accuracy, convenience of carrying, and the like.
Owner:王学生
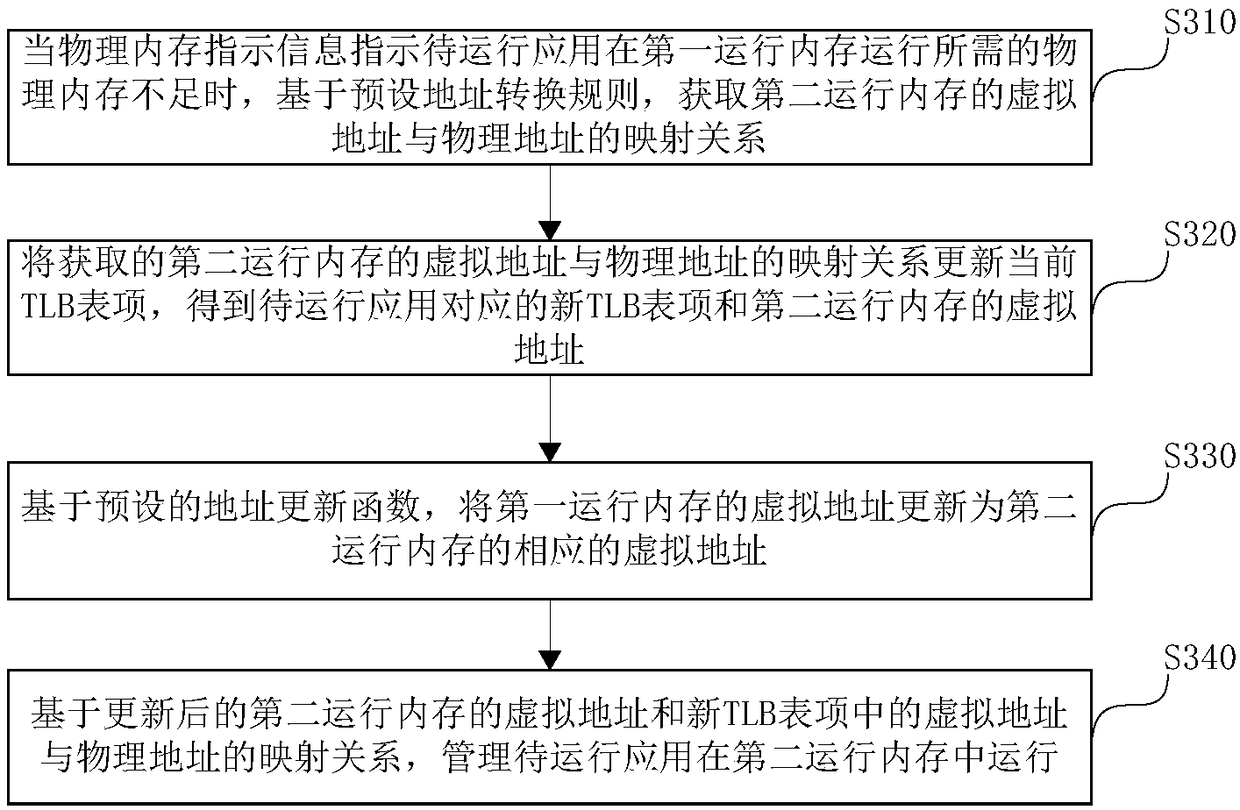
Physical memory management method and device for embedded real-time system
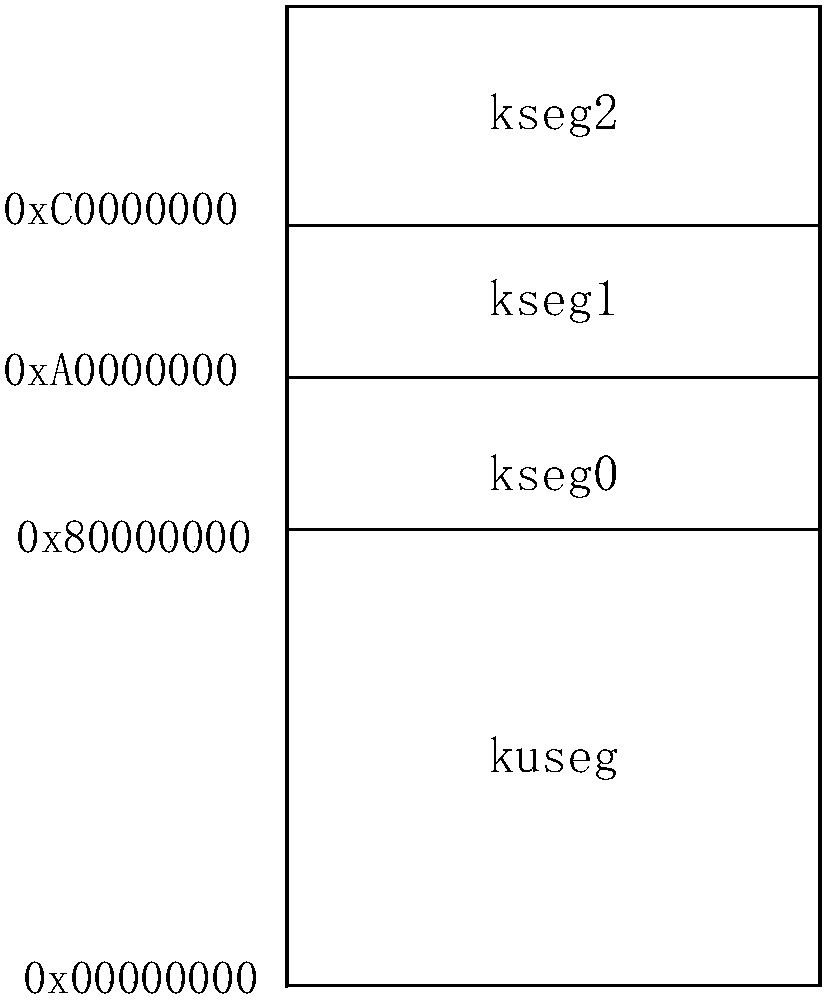
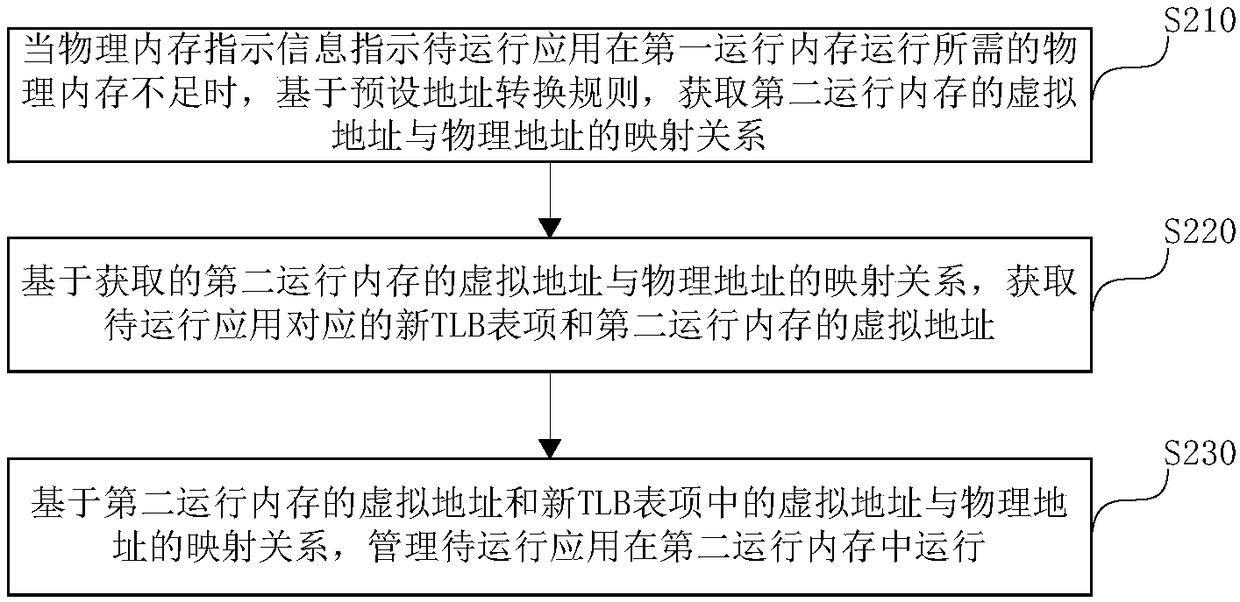
The embodiment of the invention discloses a physical memory management method and device for an embedded real-time system. The method comprises the following steps that: when physical memory indication information which indicates the insufficient physical memory of an application to be operated is obtained, on the basis of a preset address conversion rule, obtaining a mapping relationship betweenthe virtual address and the physical address of a second operation memory, wherein the physical memory indication information is to operate the application to be applied in a first operation memory; and on the basis of the obtained mapping relationship between the virtual address and the physical address of the second operation memory, obtaining a new TLB (Translation Lookaside Buffer) corresponding to the application to be operated and the virtual address of the second operation memory so as to manage the operation of the application to be operated in the second operation memory. Obviously, under the kernel mode of an MIPS (Million Instructions Per Second) framework, the method carries out address mapping relationship conversion on the second operation memory and carries out address update on the current operation address of the application to be operated, a large physical space is managed under the kernel mode, and the problem in the prior art that only a small memory space can be accessed is overcome.
Owner:KYLAND TECH CO LTD +1
System and method for achieving improved accuracy from efficient computer architectures
ActiveUS20100241938A1Reduce errorsSame precisionError preventionFinanceInstructions per secondProgram instruction
This invention provides a system and method that can employ a low-instruction-per-second (lower-power), highly parallel processor architecture to perform the low-precision computations. These are aggregated at high-precision by an aggregator. Either a high-precision processor arrangement, or a low-precision processor arrangement, employing soft-ware-based high-precision program instructions performs the less-frequent, generally slower high-precision computations of the aggregated, more-frequent low-precision computations. One final aggregator totals all low-precision computations and another high-precision aggregator totals all high-precision computations. An equal number of low precision computations are used to generate the error value that is subtracted from the low-precision average. A plurality of lower-power processors can be arrayed to provide the low-precision computation function. Alternatively a plurality of SIMD can be used to alternately conduct low-precision computations for a predetermined number of operations and high-precision operations on a fewer number of operations. In an embodiment, aggregation can include summing values within predetermined ranges of orders of magnitude, via an adding tree arrangement, so that significant digits therebetween are preserved.
Owner:GRANGER RICHARD
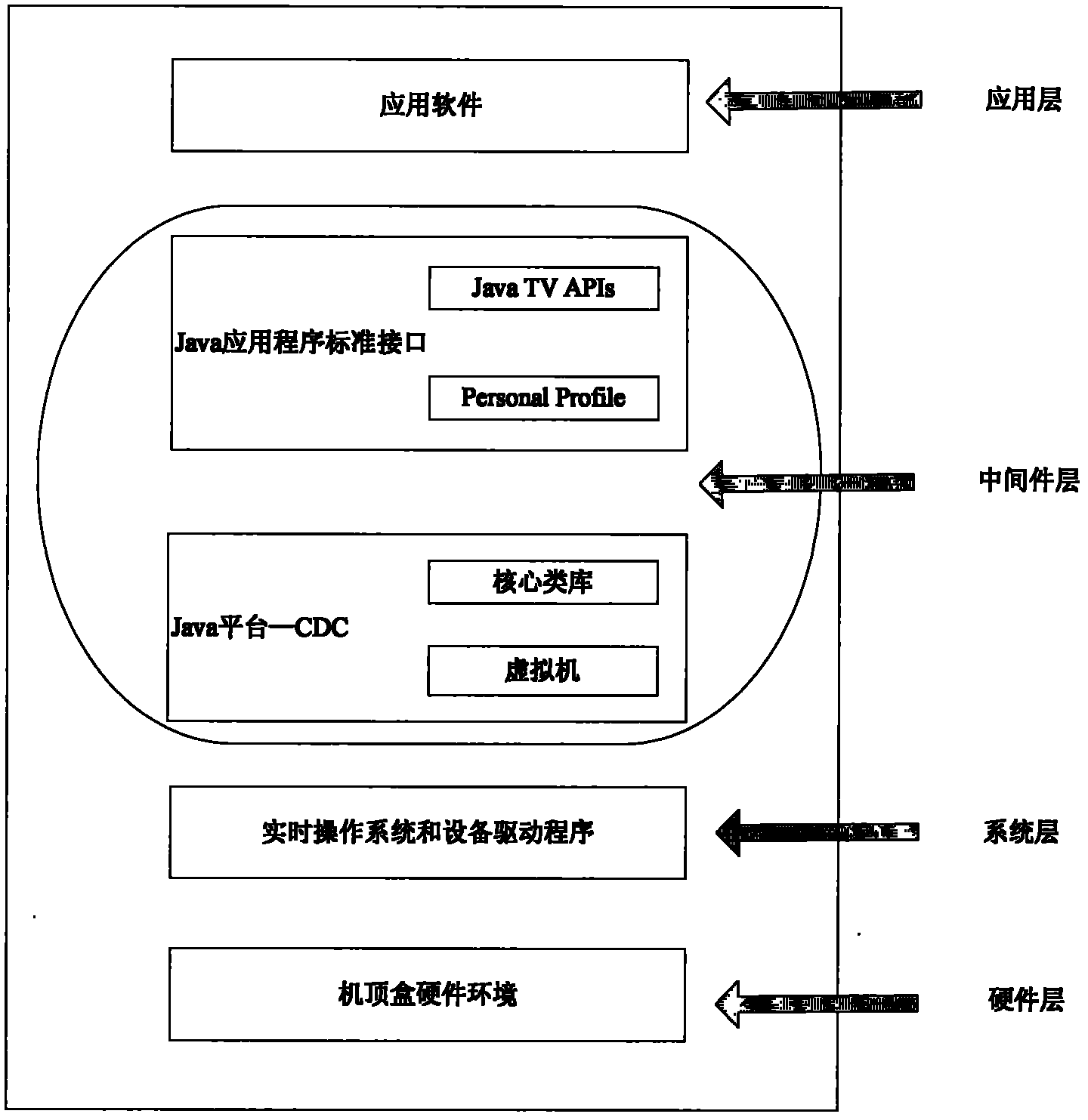
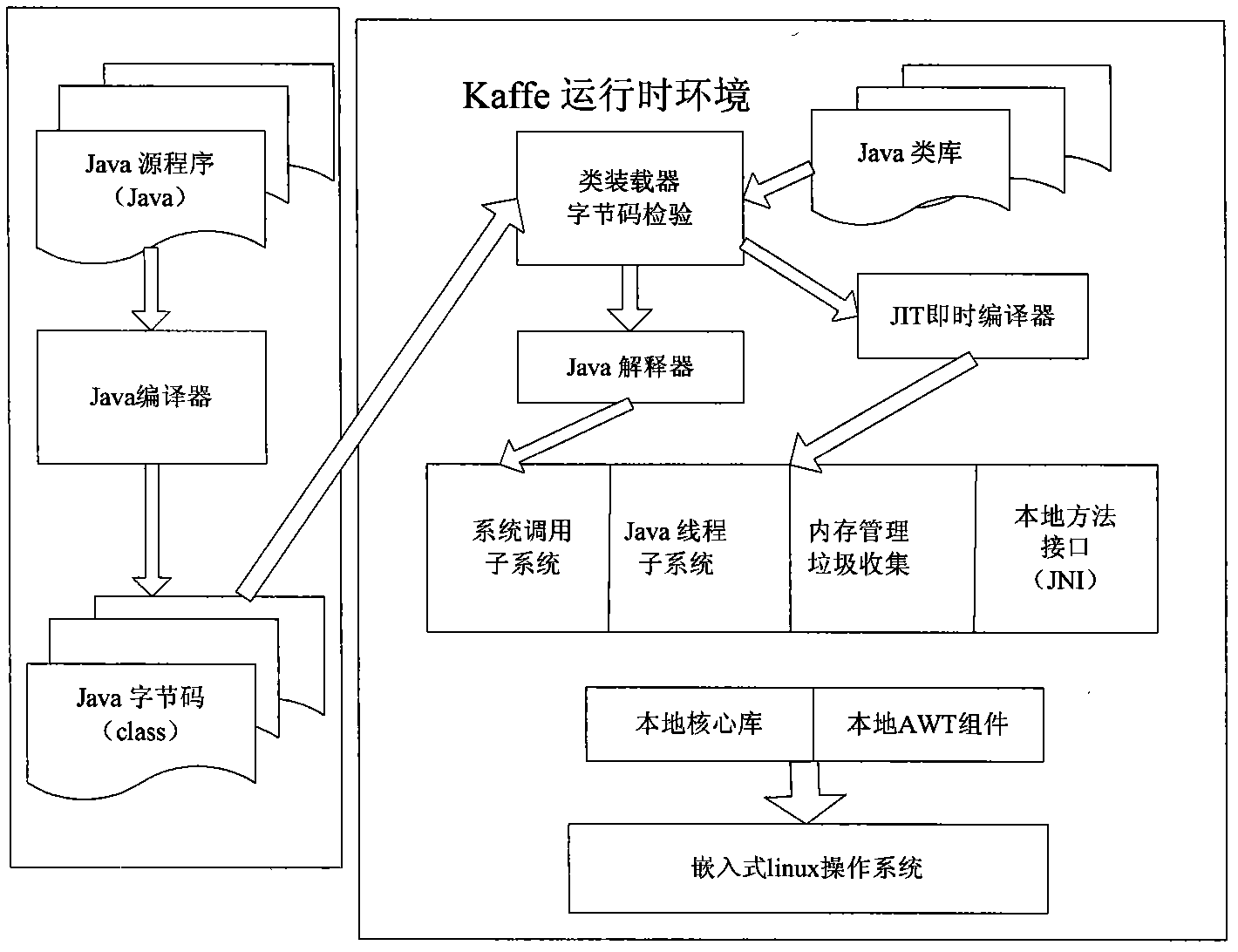
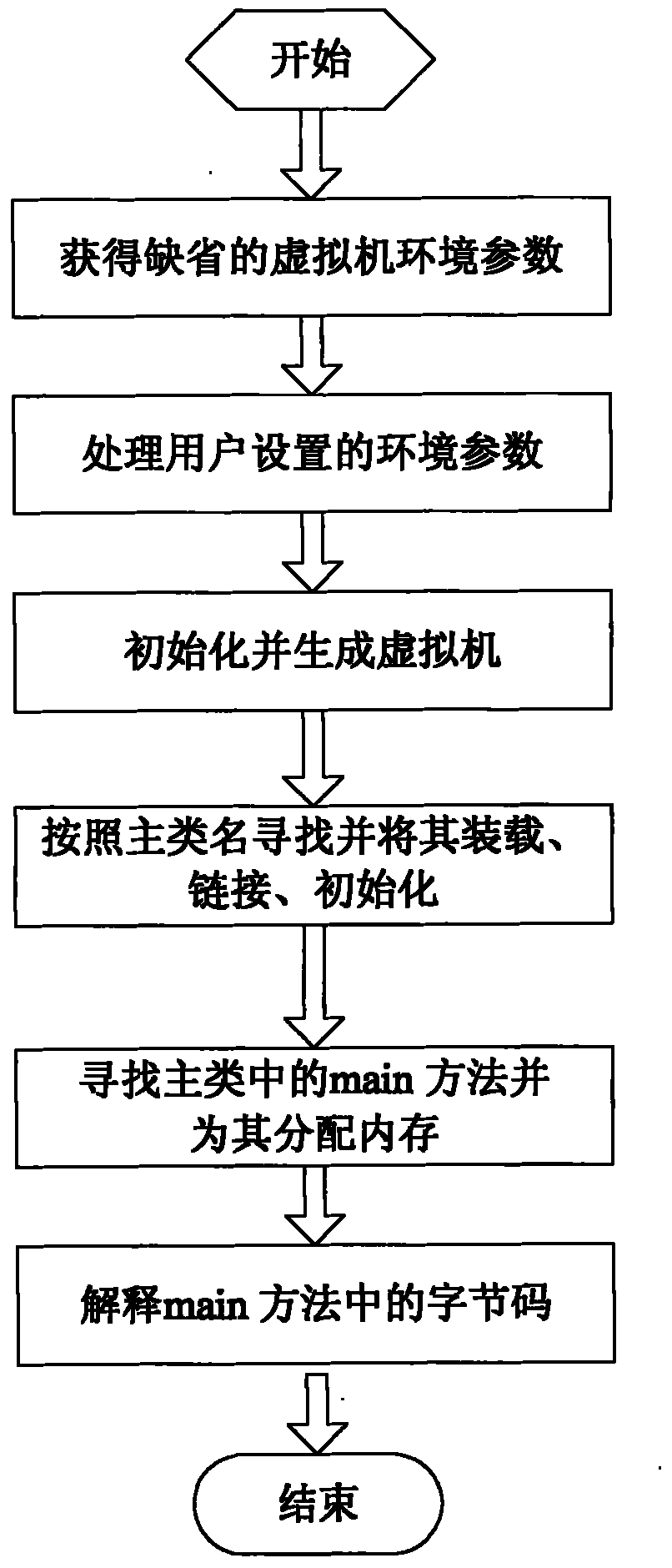
Virtual machine system and implementing method thereof
InactiveCN102096598AImprove portabilityEasy to transplantSelective content distributionSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationInstructions per secondLocal method
The invention discloses a kaffe virtual machine system and an implementing method thereof. The system is positioned in a sub-middleware layer of a set-top box. The system consists of a plurality of independent subsystems, namely a class manager, a byte code verifier, a kaffe virtual machine execution engine, a system call subsystem, a storage management subsystem and a local method interface subsystem, wherein the class manager takes charge in loading classes, initializing the classes and the like; the byte code verifier ensures the correctness of a class file format; and the kaffe virtual machine execution engine comprises an interpreter and a just-time compiler. The kaffe virtual machine system has an OpenSource characteristic, a small kernel and high portability, and supports the application of an embedded system in a Linux / million instructions per second (MipS) system.
Owner:GUANGDONG TRI SUN ELECTRONICS TECH
Timekeeping method using mixed clock source
ActiveCN102707765AAccurate timingAchieve precise timingGenerating/distributing signalsInstructions per secondHigh Precision Event Timer
The invention discloses a timekeeping method using a mixed clock source. The method includes a hardware clock source selection and a software initialization operation. The hardware clock source selection includes that an internal clock source selects a million instructions per second (MIPS) clock source and is used for Clock Event of a non-zero central processing unit (CPU) in a tickless timekeeping mode, and an external clock source selects a high precision event timer (HPET) clock source and is used for Clock Event and Clock Source in a periodic timekeeping mode, Clock Event of a zero CPU in the tickless timekeeping mode and Clock Source in the tickless timekeeping mode. The software initialization operation includes the steps that 1) CPU initialization is performed; 2) the MIPS clock source is registered as Clock Event by each of CPU cores; 3) the MIPS clock source is registered as Clock Source; 4) system device initialization is performed; 5) the HPET clock source is registered as Clock Event by a non-zero core; 6) the HPET clock source is registered as Clock Source; and 7) dynamic core regulation and automatic frequency conversion mechanisms are started. The method simultaneously supports traditional periodic timekeeping modes and recent tickless timekeeping modes.
Owner:JIANGSU LEMOTE TECH CORP
MIMO receiver with pooled adaptive digital filtering
InactiveUS20070258600A1Reduced signaling processSpatial transmit diversityReceivers monitoringInstructions per secondControl signal
MIMO receiver with a reconfigurable pooled digital filter is disclosed. A processor sets parameters of the filter to minimize the number of instructions per second and the amount of power required by the filter to perform, while matching the filter to a transmitter filter. The processor uses an algorithm or a lookup table stored in memory to select the combination of filter parameters. The parameters may be selected from at least one of: a number of taps, a filter length, a word length, a coefficient quantization, a sampling rate, bits per sample, a sampling bit, a tap delay and a coefficient length. After selecting a combination of filter parameters, the processor sends a control signal to the adaptive filter. The pooled adaptive filter reconfigures itself in accordance with the selected filter parameters.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Universal blockiness correction
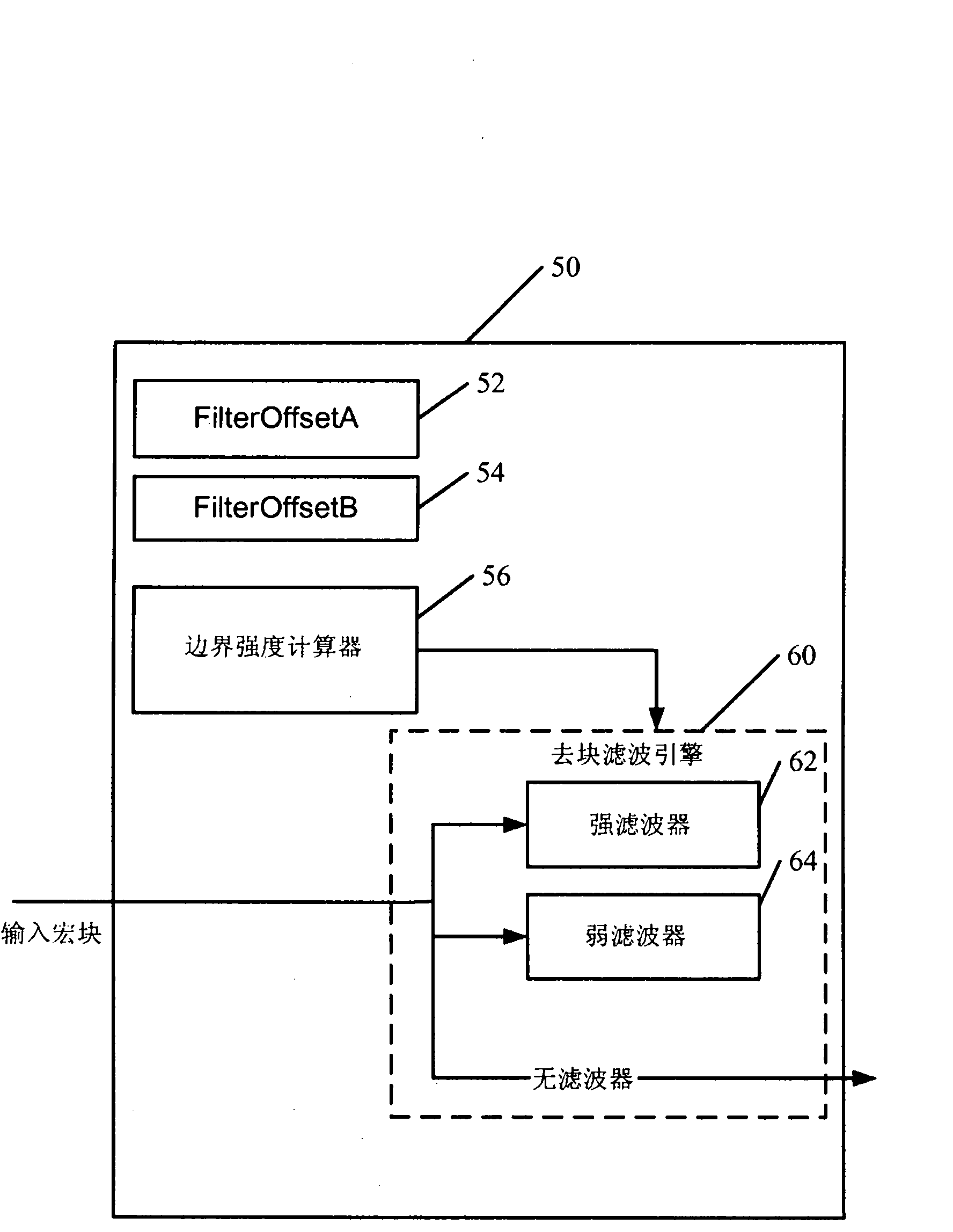
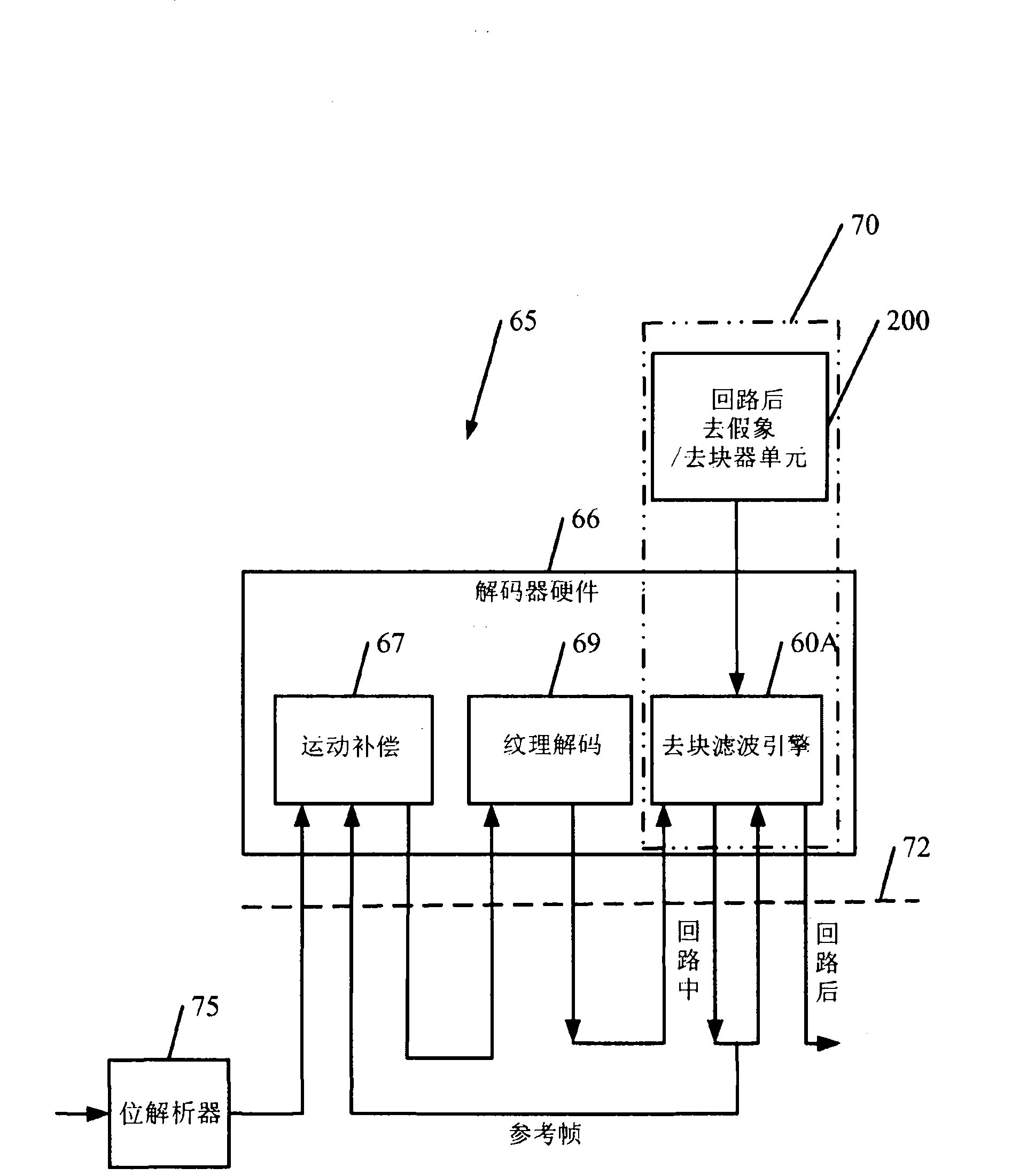
ActiveCN101822054ATelevision systemsDigital video signal modificationInstructions per secondDeblocking filter
Techniques to remove inherited blockiness with a low million instructions per second (MIPs) are provided. In one configuration, a device comprises a processor operative to implement a set of instructions to universally correct blockiness. The processor commandeers the in-loop deblocking filtering engine and universally corrects blockiness, including inherited blockiness, using the in-loop deblocking filtering engine.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
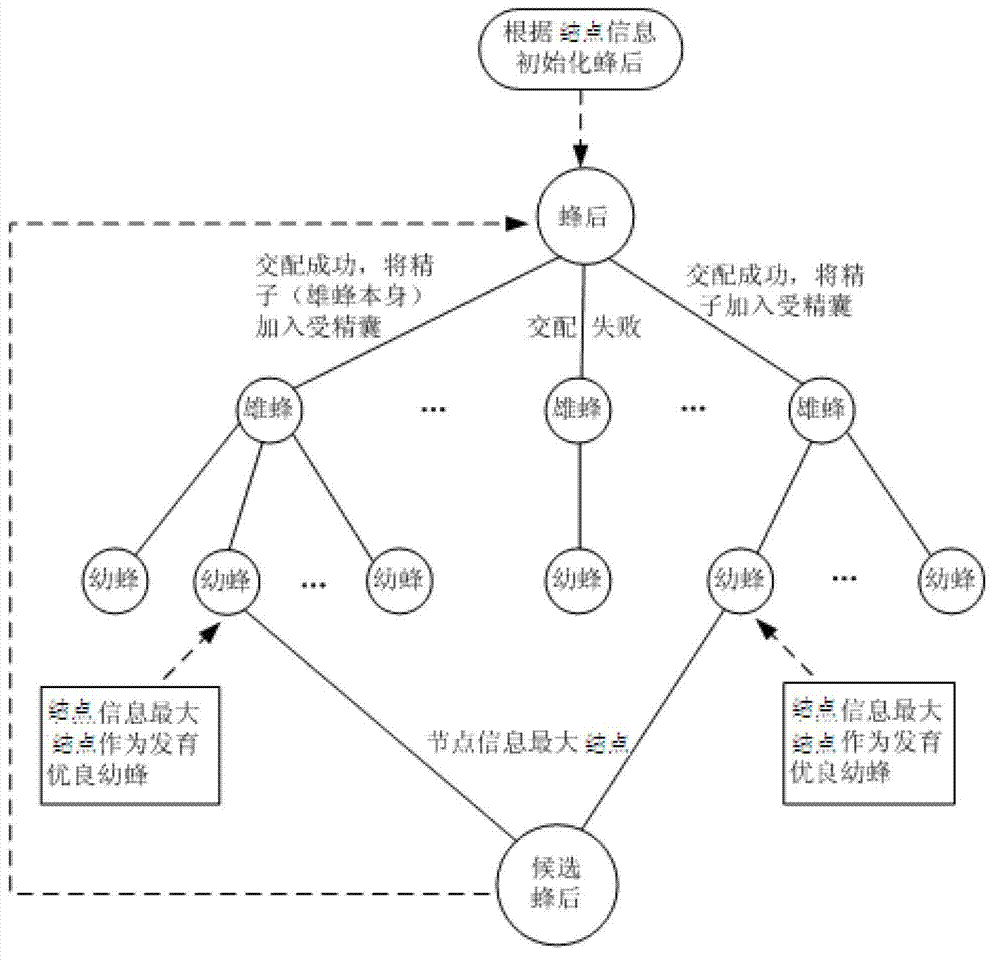
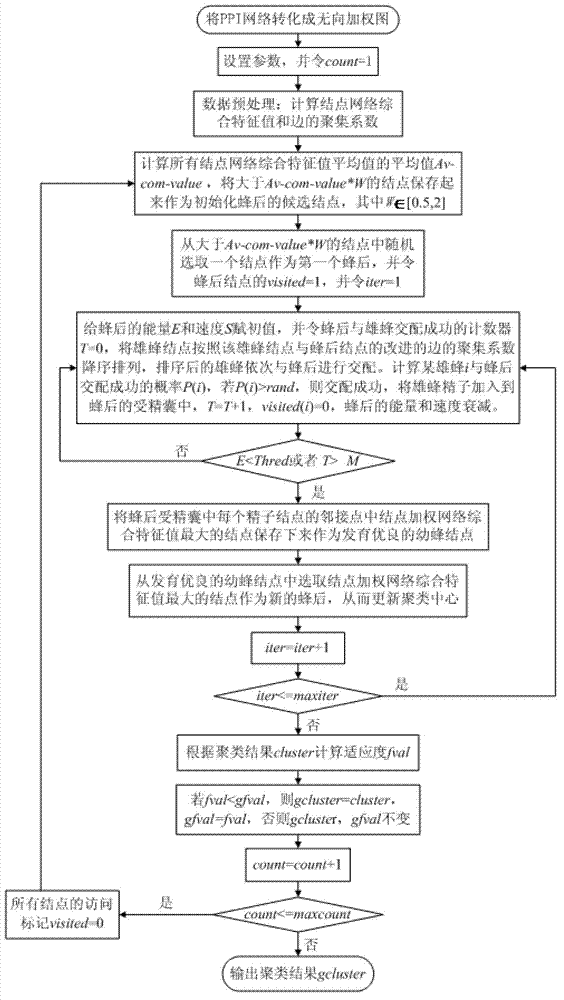
PPI (Point-Point Interaction) network clustering method based on artificial swarm reproduction mechanism
InactiveCN102779241AAvoid subjectivityImprove clustering effectSpecial data processing applicationsTime complexityQueen bee
The invention discloses a PPI (Point-Point Interaction) network clustering method based on an artificial swarm reproduction mechanism, comprising specific steps of: converting a PPI network into an undirected weighted graph; setting parameters; pre-treating each knot and each edge of the PPI network; calculating a weighted network comprehensive characteristic value of all the knots; initializing queen bees; carrying out a mating flight process; partially searching young bees; optimally selecting the queen bees; and selecting the current fitness and comparing until a global optimum clustering result is output. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the clustering quantity does not be pre-set and can be automatically obtained in a clustering process, so that the subjectivity of artificially setting the clustering quantity is avoided, and the time complexity is obviously reduced. An MIPS (Million Instructions Per Second) database is used for carrying out experiment simulation, a result is closer to a standard database, and indexes including the accuracy, the recall ratio, the operation time and the like are better. Compared with the other clustering methods, the method can automatically determine the clustering quantity by adopting the artificial swarm reproduction mechanism based on the reproduction mechanism, so that the clustering process is realized, and the clustering effect and the calculation efficiency are effectively improved.
Owner:SHAANXI NORMAL UNIV
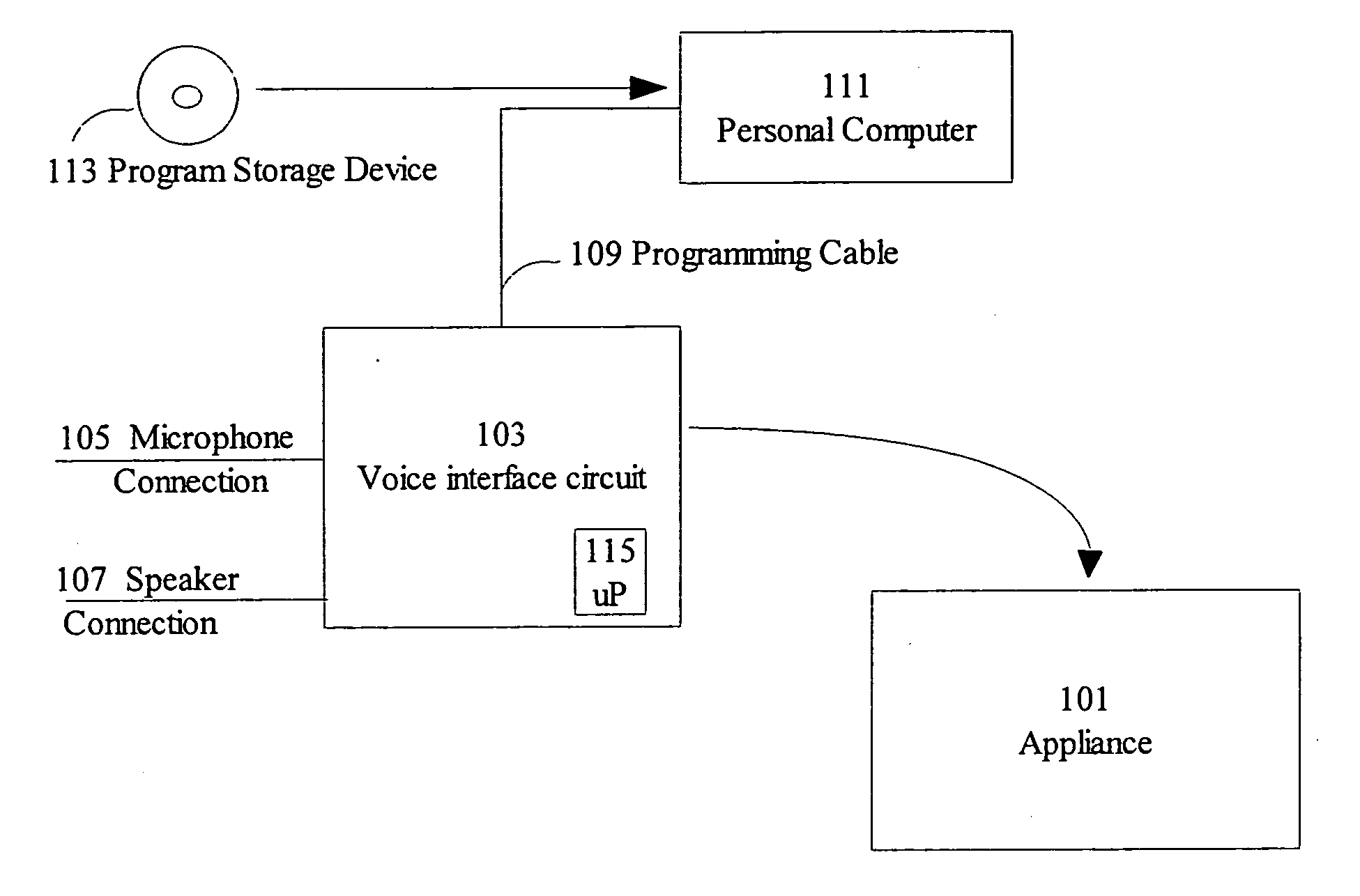
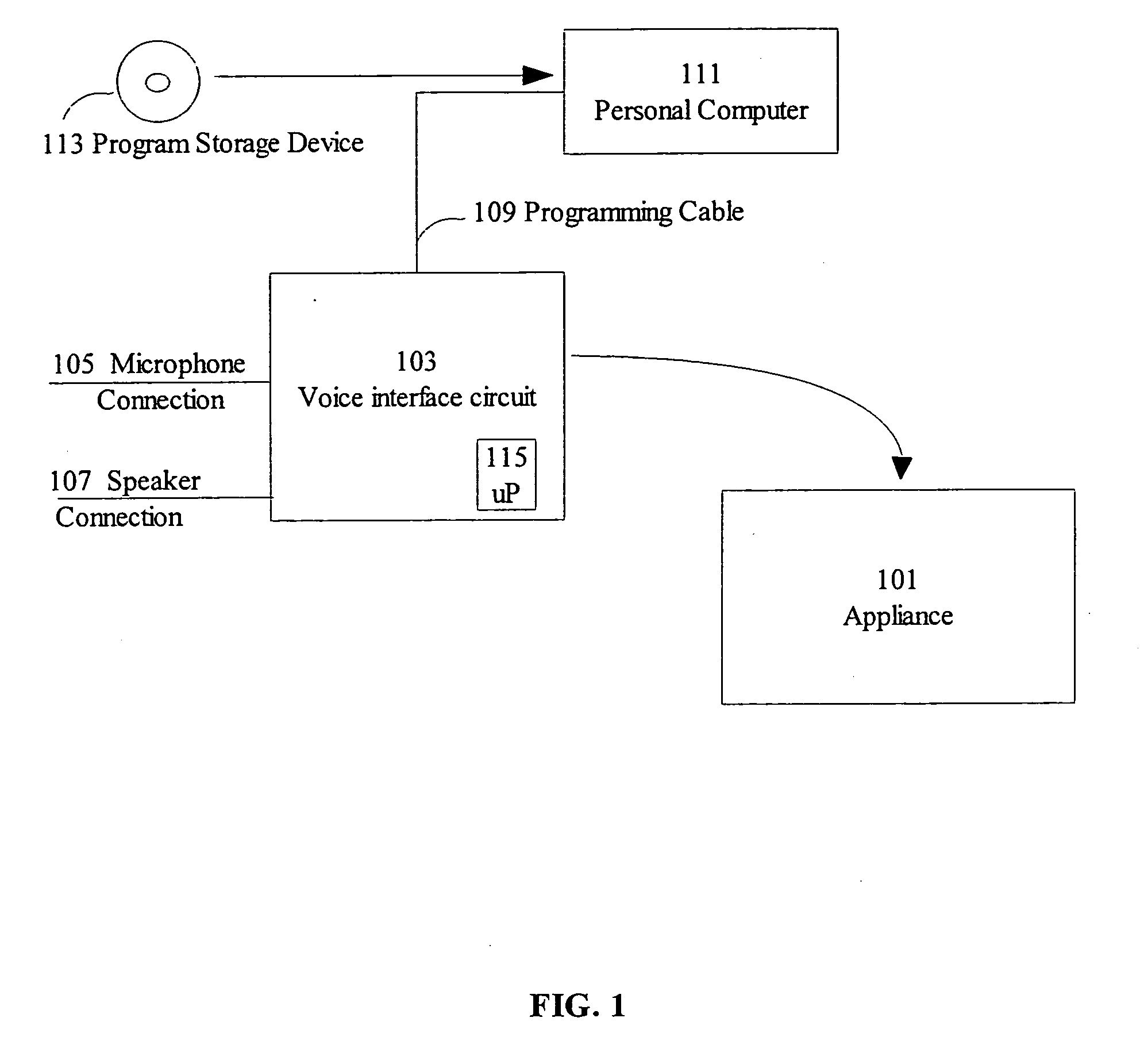
Voice interface for consumer products
A method for generating voice interface for appliances which may be performed by a manufacturer of the appliance. The manufacturer selects a programmable device for controlling the appliance, the programmable device having resources of less than 9 kilobytes of random access memory and capable of less than 41 million instructions per second. The manufacturer is further provided with an application development kit for building an application for the voice interface including a speech recognition module. The manufacturer programs the programmable device with the application. Preferably, while programming and running the application, the application includes multiple stages and for each stage a different set of open words are recognizable by the speech recognition module. Preferably, the open words are recognized by the speech recognition module, solely in response to a previously stored question posed to a user of the appliance.
Owner:CARMIEL YISHAY +1
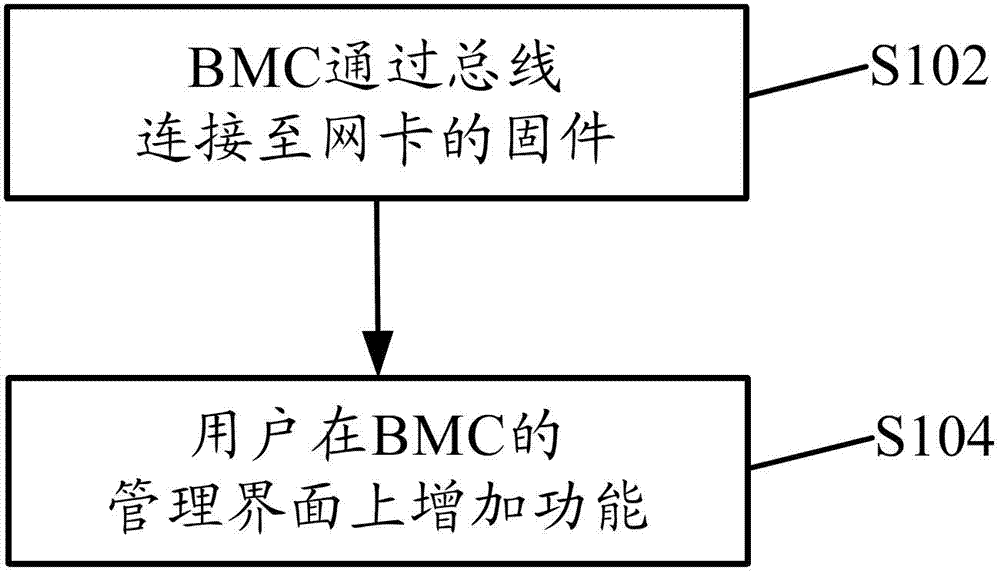
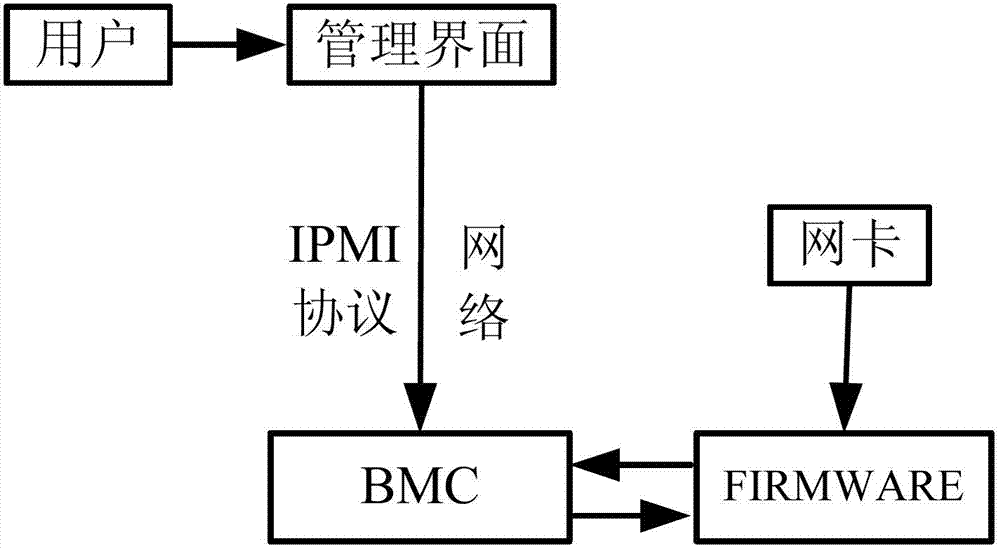
Method and system for adding network card function to MIPS frame server based on BMC
ActiveCN102789388AImprove usabilityProgram loading/initiatingInstructions per secondMillion instruction per second
The invention discloses a method and system for adding the network card function to an MIPS (million instructions per second) frame server based on a baseboard management controller (BMC). The method comprises the following steps of: connecting the BMC to a network card firmware, and enabling a user to add functions on the management interface of the BMC. With the technical scheme disclosed by the invention, the operations (such as network card MAC address burning and network card upgrading) can be performed on the MIPS frame server, so as to improve the usability of products.
Owner:DAWNING INFORMATION IND BEIJING +1
Encryption transmission method for MIPS (Million Instructions Per Second) platform on basis of HTTP (Hyper Text Transfer Protocol)
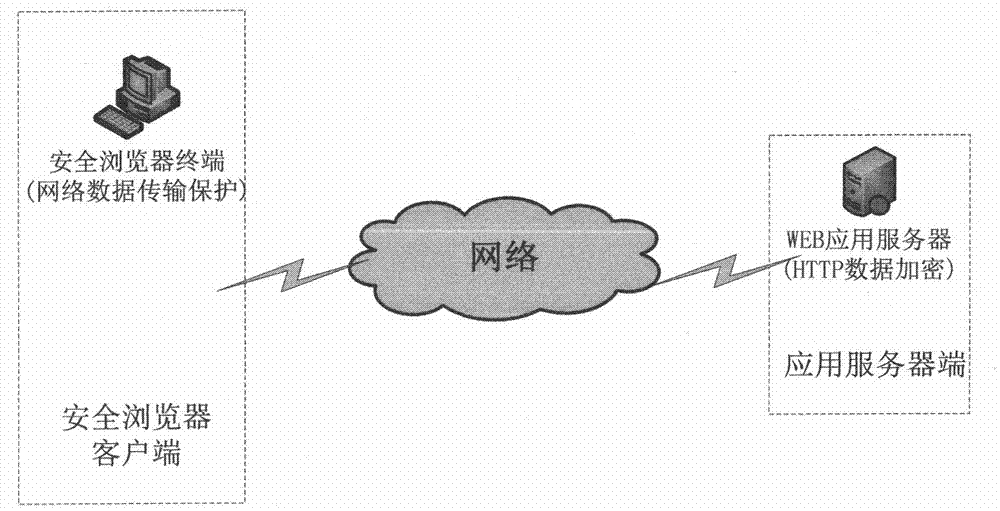
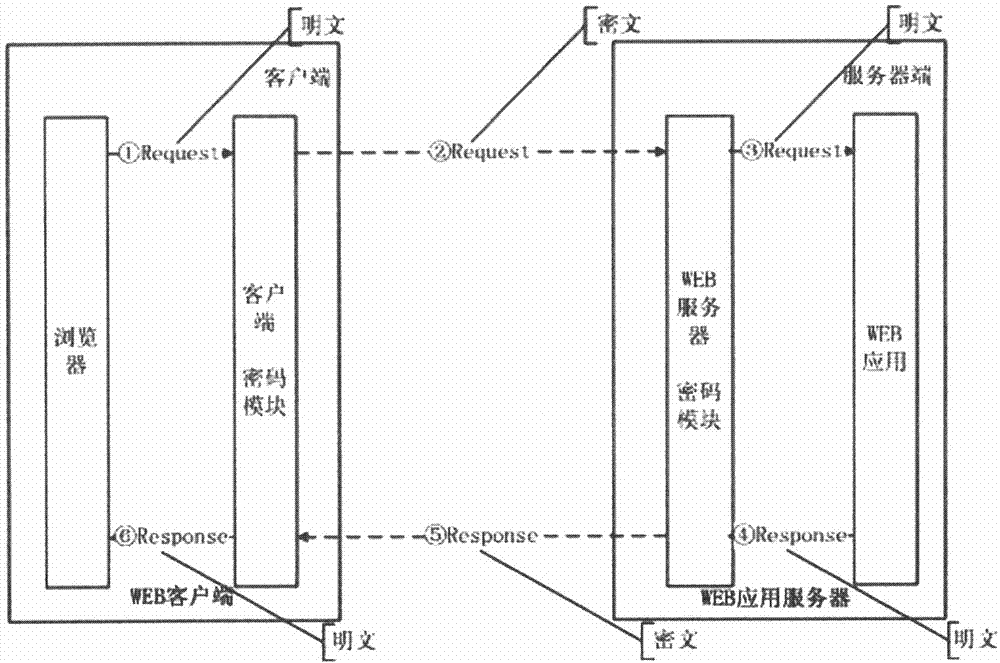
InactiveCN104506517AImplement encryption protectionWeb data retrievalTransmissionPlaintextInstructions per second
The invention discloses an encryption transmission method for an MIPS (Million Instructions Per Second) platform on the basis of an HTTP (Hyper Text Transfer Protocol). By simultaneously carrying out encryption and decryption transformation on a browser side and a WEB server side, data transmitted by the HTTP is enabled to be in a ciphertext form. The encryption transmission method has the advantage of implementing encryption protection on plaintext data transmitted between a browser and a WEB server on the basis of the HTTP.
Owner:中软信息系统工程有限公司
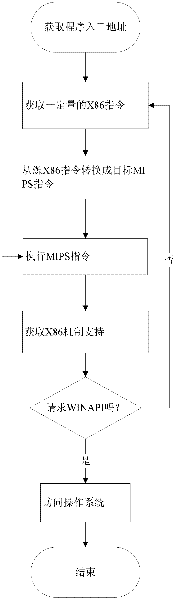
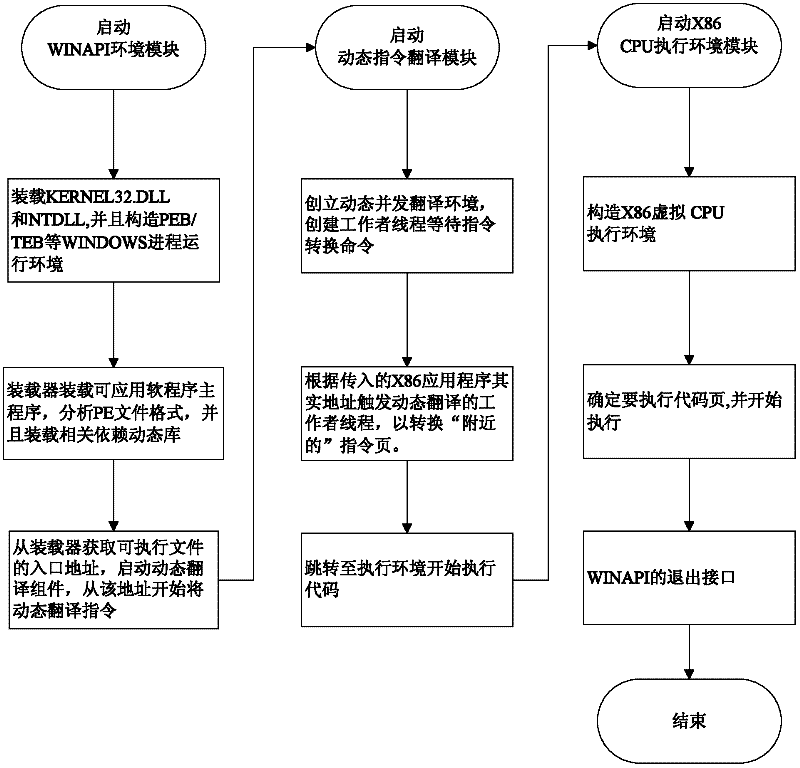
Method for operating Windows application software on Linux operating system of million instructions per second (MIPS) version
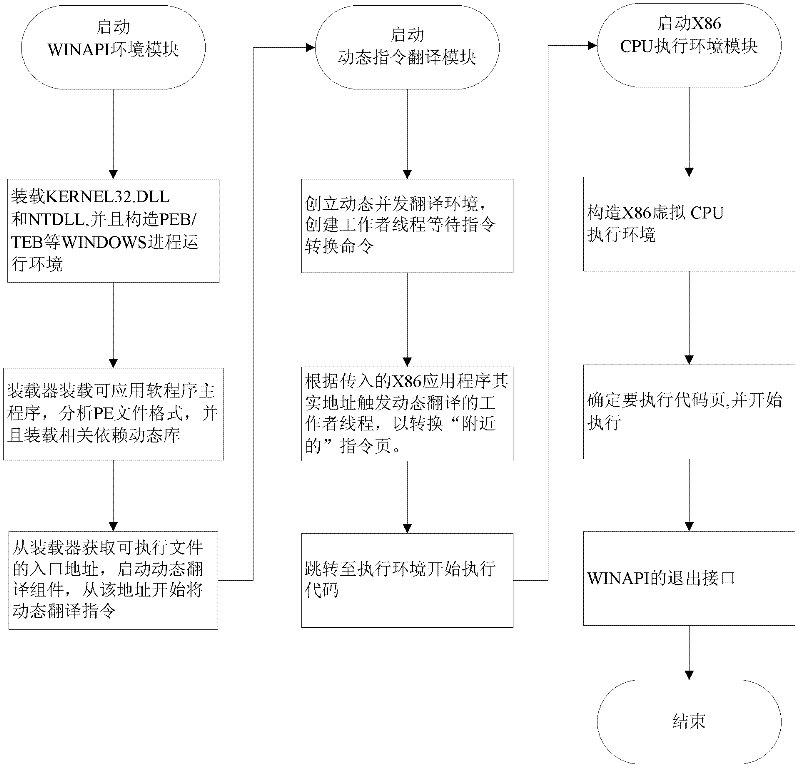
ActiveCN102455938ALow costImprove efficiencyMultiprogramming arrangementsInstructions per secondGNU/Linux
The invention discloses a method for operating Windows application software on a Linux operating system of a million instructions per second (MIPS) version. The Windows application software can be directly operated on the Linux operating system of the MIPS version by using a high-speed X86 instruction simulation method, a central processing unit (CPU) environment management method, a Windows application programming interface (API) environment management method and the like, a Windows operating system is not required, and revising of source codes of Windows software is not required. With tool software which is designed by using the method, a user can use software, which can be only operated on a Windows platform, on a computer of an MIPS framework as randomly as on an X86 computer in spiteof difference between a bottom-layer hardware platform and an operating system, so that a supporting range of application software by the computer of the MIPS framework is expanded, and the method has a high practical value.
Owner:CHINA STANDARD SOFTWARE
Multiple input multiple output (MIMO) transceiver with pooled adaptive digital filtering
InactiveUS7864885B2Reduced signaling processMultiple-port networksDelay line applicationsTransceiverAdaptive filter
A multiple input, multiple output (MIMO) transceiver includes a reconfigurable pooled digital filter. A processor sets parameters of the filter to minimize the number of instructions per second and the amount of power required by the filter to perform, while matching the filter to at least one of: a transmitter filter and a receiver filter. The processor uses an algorithm or a lookup table stored in memory to select the combination of filter parameters. The parameters may be selected from at least one of: a number of taps, a filter length, a word length, a coefficient quantization, a sampling rate, bits per sample, a sampling bit, a tap delay and a coefficient length. After selecting a combination of filter parameters, the processor sends a control signal to the adaptive filter. The pooled adaptive filter reconfigures itself in accordance with the selected filter parameters.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
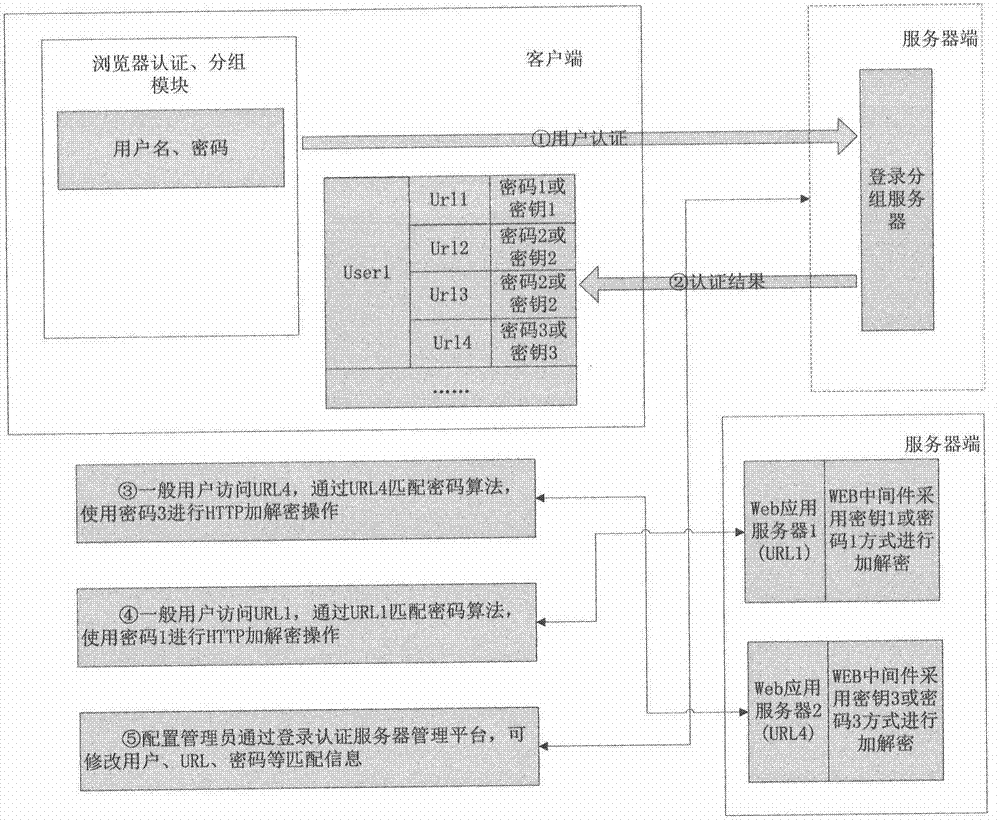
Identity authentication method for access control of MIPS (Million Instructions Per Second) platform network system
The invention discloses an identity authentication method for access control of an MIPS (Million Instructions Per Second) platform network system. The identity authentication method adopts a mechanism of providing a login identity authentication of a browser and using different encryption algorithms to provide protection for HTTP (Hyper Text Transfer Protocol) transmission data according to an identity of a login user when the user accesses different URLs. The identity authentication method has the advantages that confirmation of identity authentication can be carried out on access of the MIPS platform network system and control of access permission can be carried out according to personal identities.
Owner:中软信息系统工程有限公司
Multi-emulex device based on 1U design
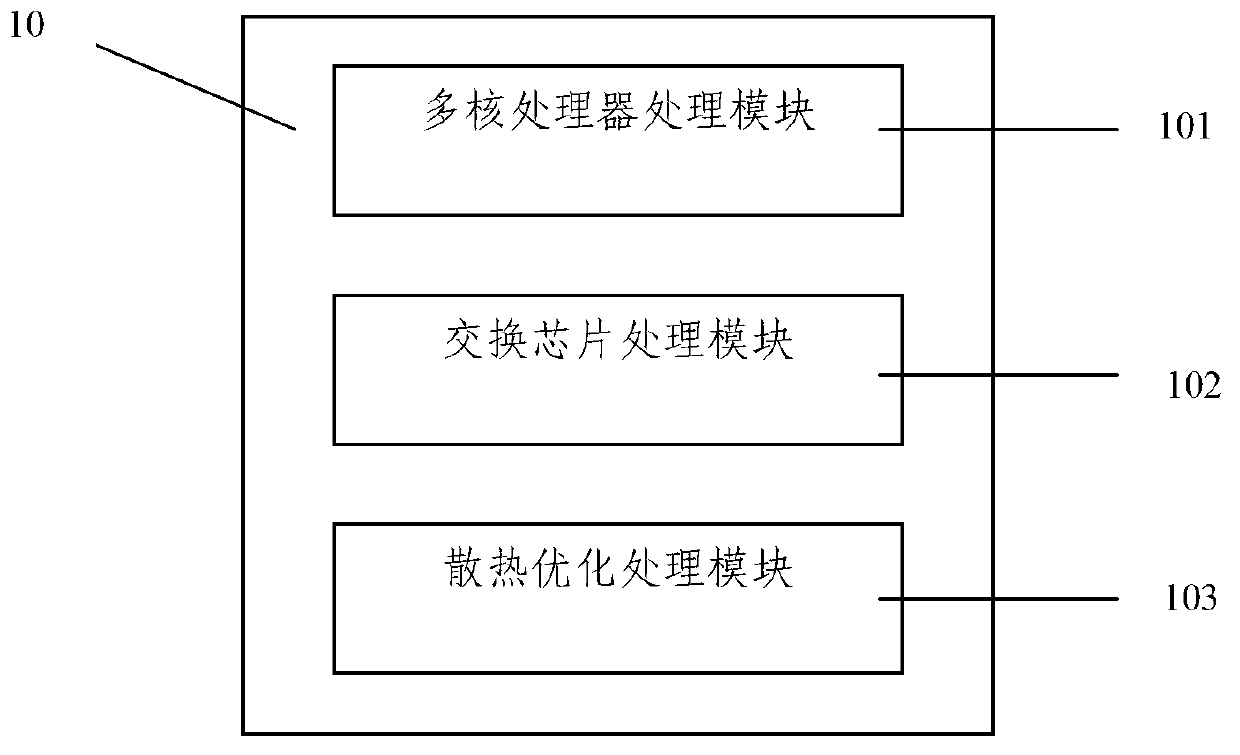
InactiveCN103002600AMeet collectionIncrease costEnergy efficient ICTTransmissionInstructions per secondData acquisition
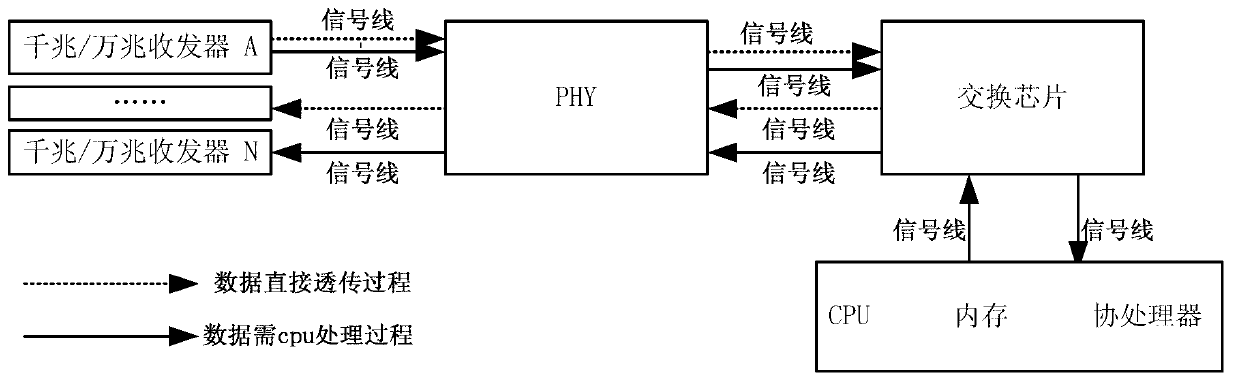
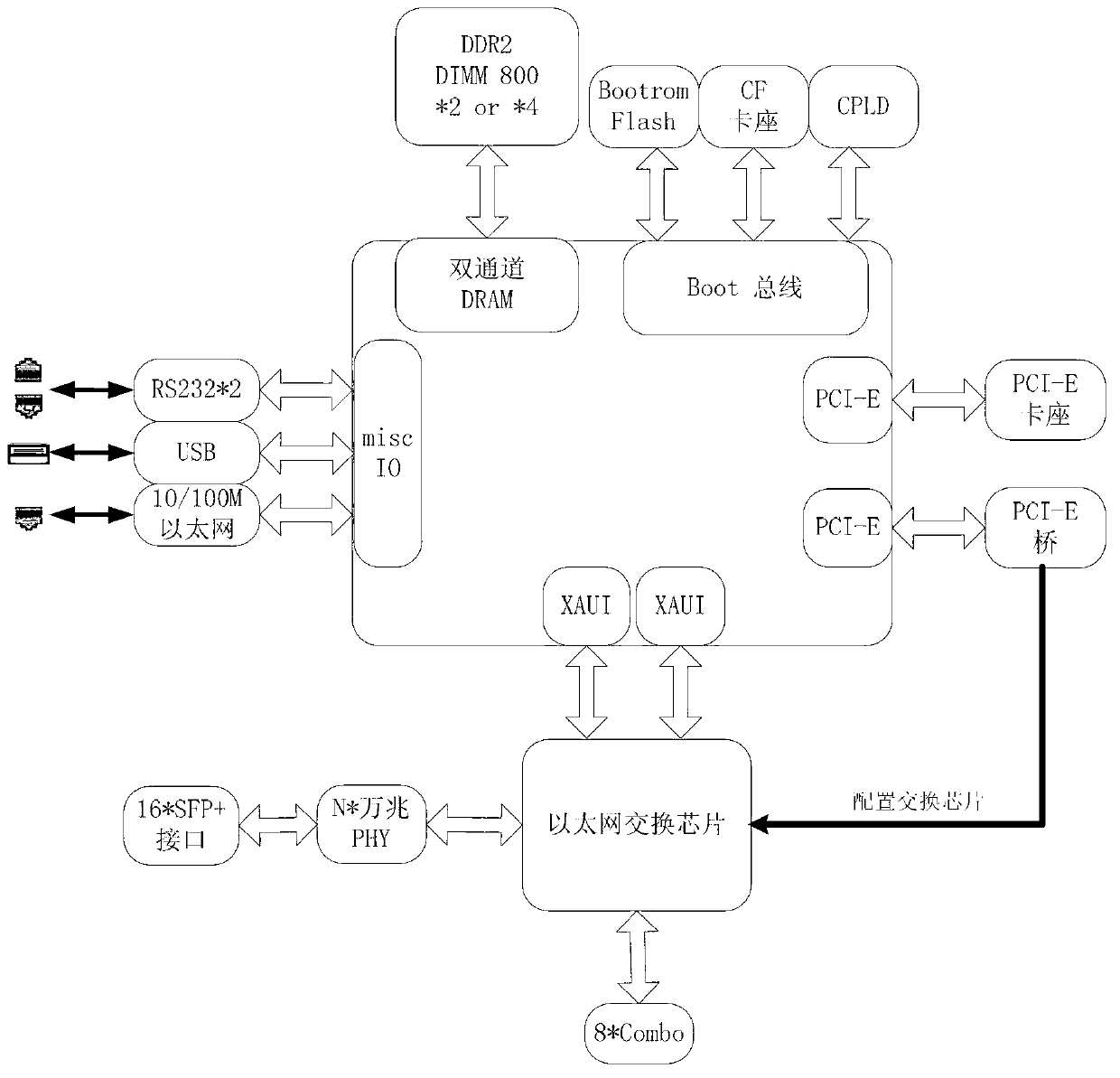
The invention discloses a multi-emulex device based on 1U design. The multix-emulex device is designed based on multi-core millon instructions per second (MIPS) framework and comprises the following modules: a multi-core processor processing module, an exchange chip processing module and a radiating optimizing processing module. The multi-core processor processing module is used for processing 12 internuclear parallel synchronous computing, and each core can reach the 64-bit computing power; the exchange chip processing module is used for providing 240-G access capability indicators and providing 16-emulex small form pluggable (SFP)+interface+8 kilomega Combo interface combination and has great advantages in interface density and handling capacity; and the radiating optimizing processing module is used for radiating heat of important chips and power sources of a printed circuit board (PCB) of an integral machine system, and power consumption is reduced. The multi-emulex device can well solve the problem that the data collection in the prior art is not flexible, occupies space of an operator and increases project cost and can totally meet the on-the-spot link collection with the 16-emulex+8-kilomega state.
Owner:BEIJING ZHONGCHUANG TELECOM TEST
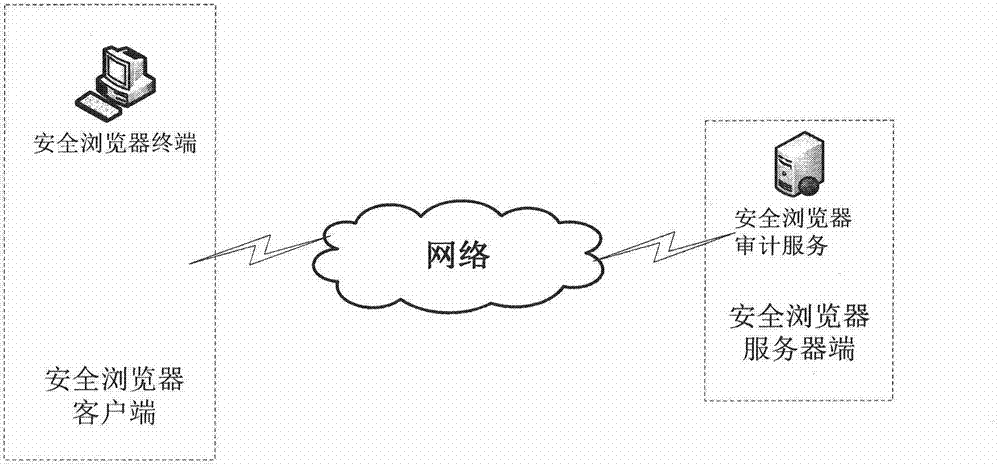
Web site access security audit method for MIPS (Million Instructions Per Second) platform
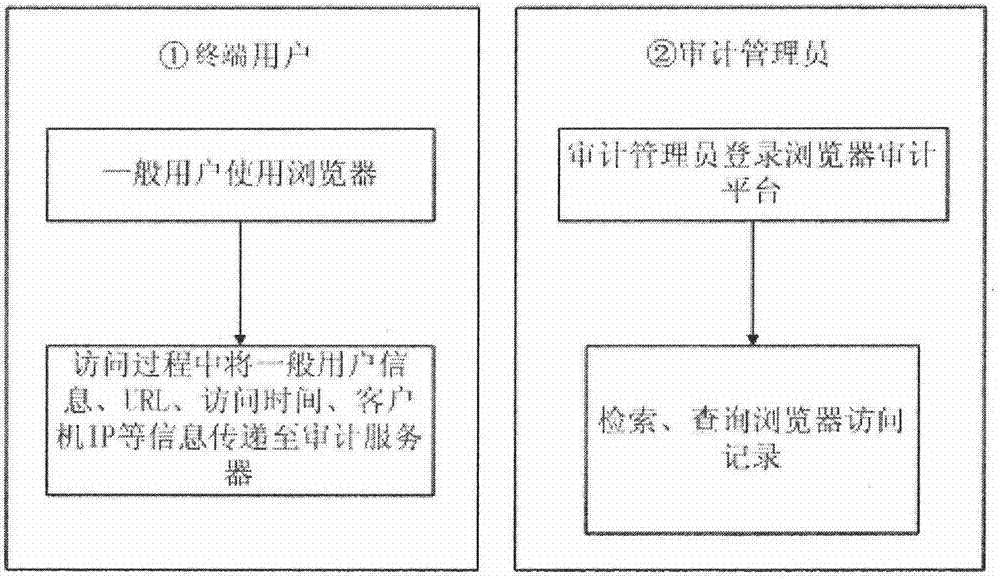
InactiveCN104506519AImplement Security AuditTimely detection of abnormal operationsWeb data retrievalData switching networksInstructions per secondAccess time
The invention discloses a web site access security audit method for an MIPS (Million Instructions Per Second) platform. Every time when URL (Uniform Resource Locator) access is carried out, a URL access address, a user name, access time, IP (Internet Protocol) address information of an accessor and the like are automatically submitted to an audit server on a background by a browser; meanwhile, an audit viewing system is provided, so that an audit administrator can find safety risks by timely analyzing audit information. The web site access security audit method for the MIPS platform has the advantages that a security audit on access record of a user to a Web site in the MIPS platform is implemented; individual behaviors can be monitored; individuals who carry out illegal operations are timely found. By analyzing audit data, various abnormal operations, such as hacker attack, in a network can be timely found.
Owner:中软信息系统工程有限公司
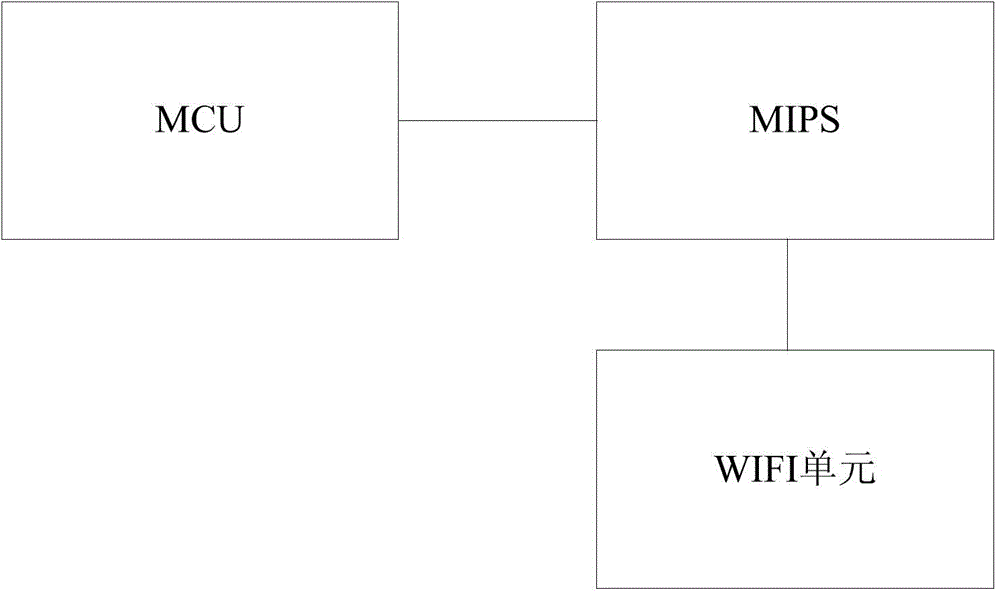
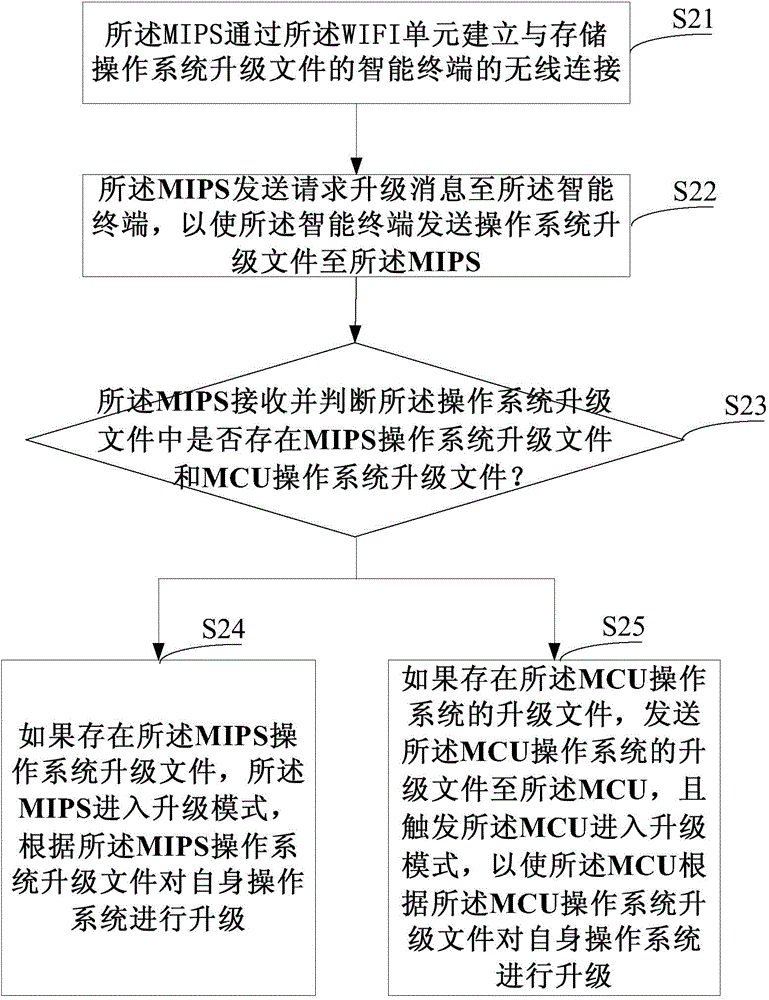
WIFI (Wireless-Fidelity) upgrading method and apparatus for operation system of vehicle-mounted terminal
ActiveCN105700905AReduce transfer timeProgram loading/initiatingTransmissionInstructions per secondOperational system
The invention discloses a WIFI (Wireless Fidelity) upgrading method and apparatus for an operation system of a vehicle-mounted terminal. The upgrading method comprises the steps that an MIPS (Million Instructions Per Second) establishes a wireless connection with an intelligent terminal storing operation system upgrading files through a WIFI unit; the MIPS sends an upgrading request message to the intelligent terminal for enabling the intelligent terminal to send the operation system upgrading files to the MIPS; the MIPS receives and judges whether an operation system upgrading file for the MIPS and an operation system upgrading file for an MCU (Micro Control Unit) exist in the operation system upgrading files or not; if the operation system upgrading file for the MIPS exists, the MIPS enters an upgrading mode and an operation system of the MIPS is upgraded according to the operation system upgrading file for the MIPS; and if the operation system upgrading file for the MCU exists, the operation system upgrading file for the MCU is sent to the MCU and the MCU is triggered to enter the upgrading mode for enabling the MCU to upgrade an operation system of the MCU according to the operation system upgrading file for the MCU.
Owner:NEW SINGULARITY INT TECHN DEV
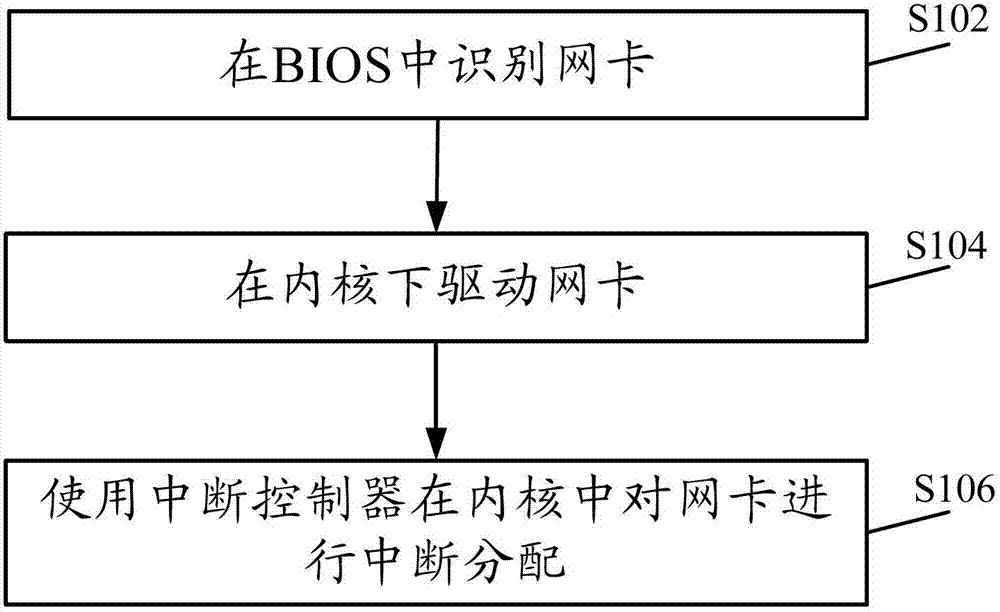
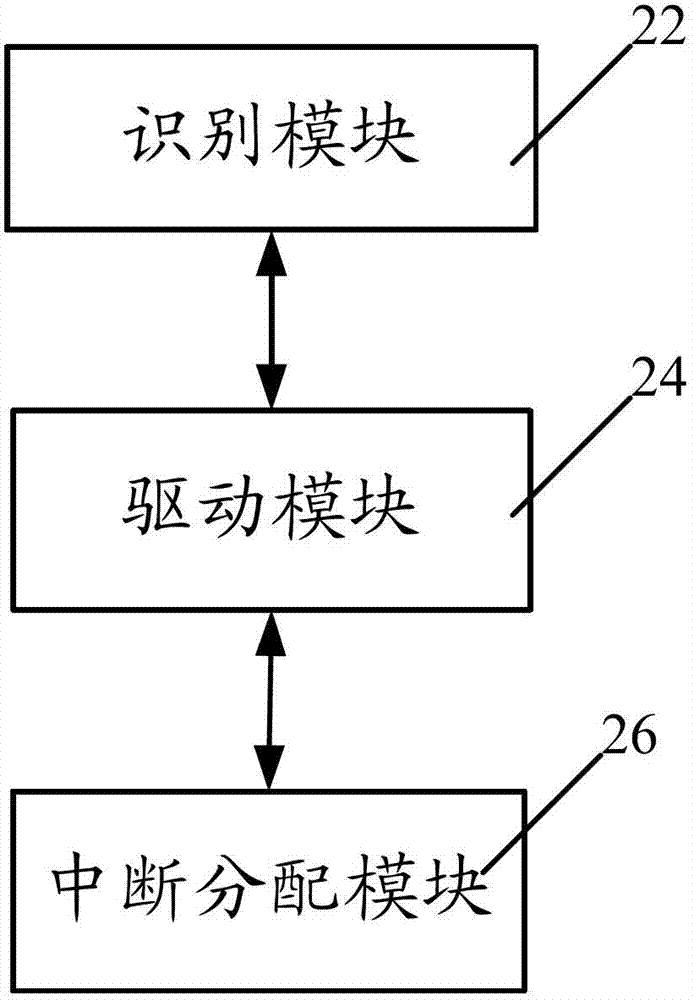
Method and system for realizing network card in MIPS (Million Instructions Per Second) framework server
InactiveCN102779052AWork lessProgram loading/initiatingInstructions per secondMillion instruction per second
The invention discloses a method and a system for realizing a network card in an MIPS (Million Instructions Per Second) framework server. The method comprises the following steps of: identifying the network card in a BIOS (Basic Input Output System); driving the network card under an inner core; and carrying out interrupt distribution on the network card in the inner core by using an interrupt controller. With the adoption of the method and the system provided by the invention, the network card can normally work on the MIPS framework server.
Owner:DAWNING INFORMATION IND BEIJING
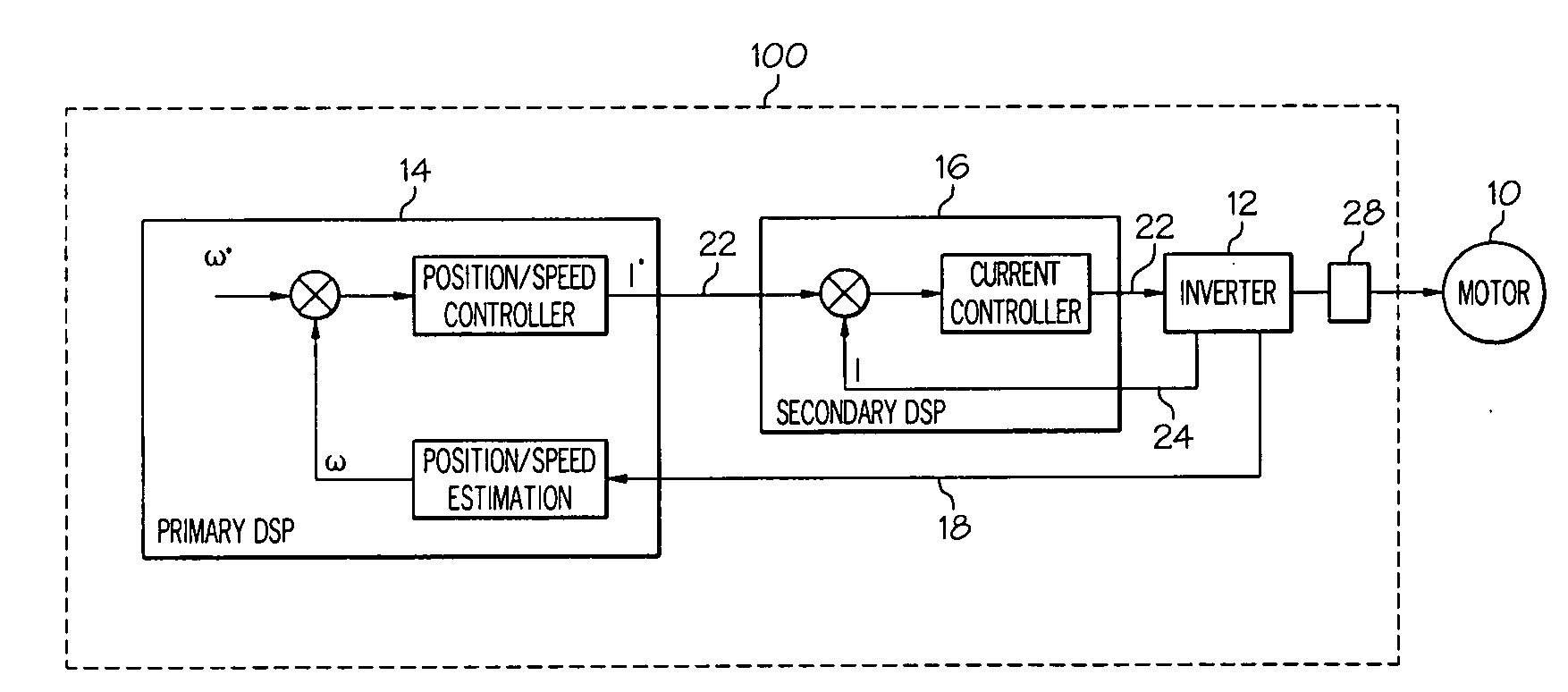
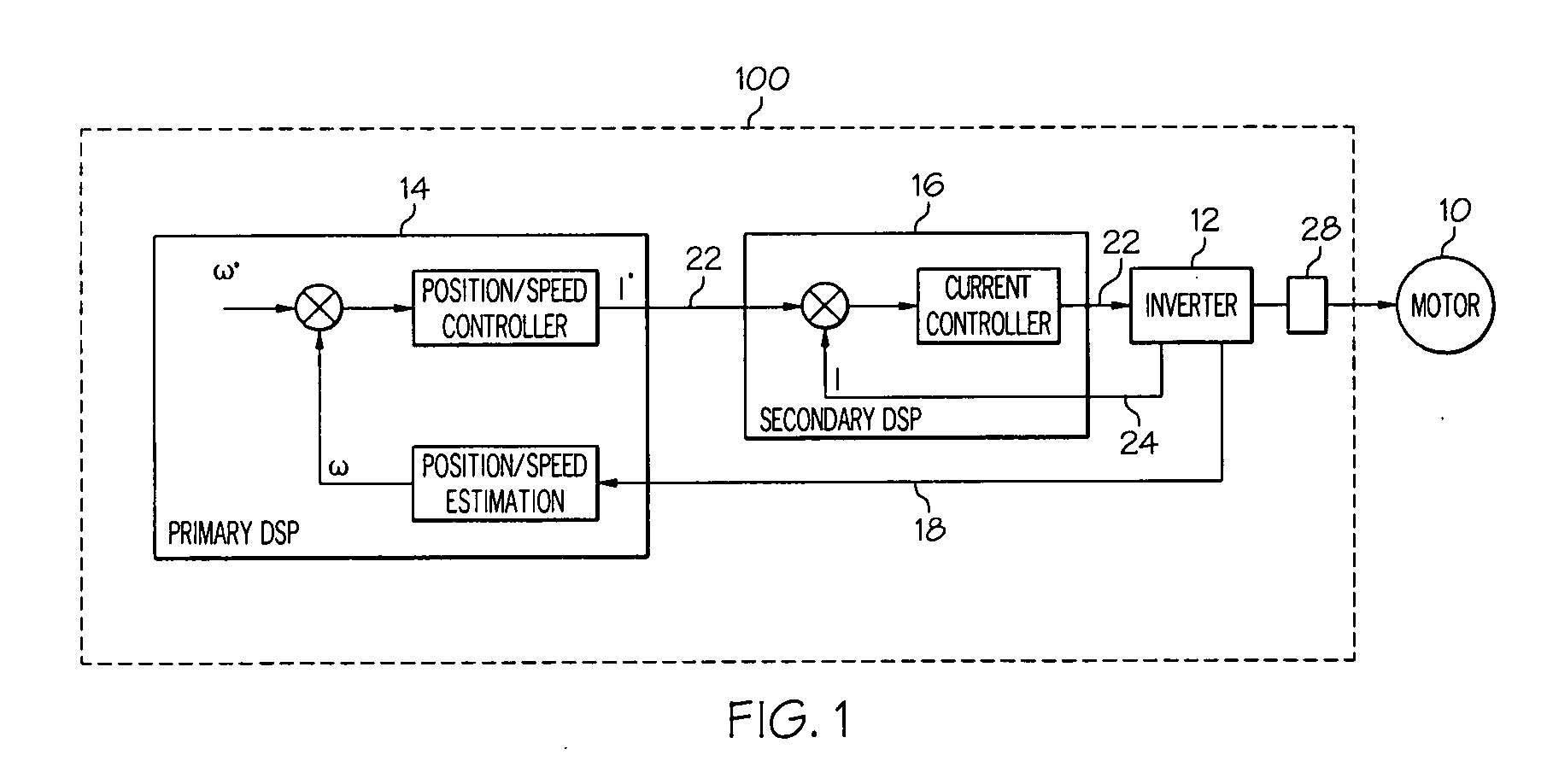
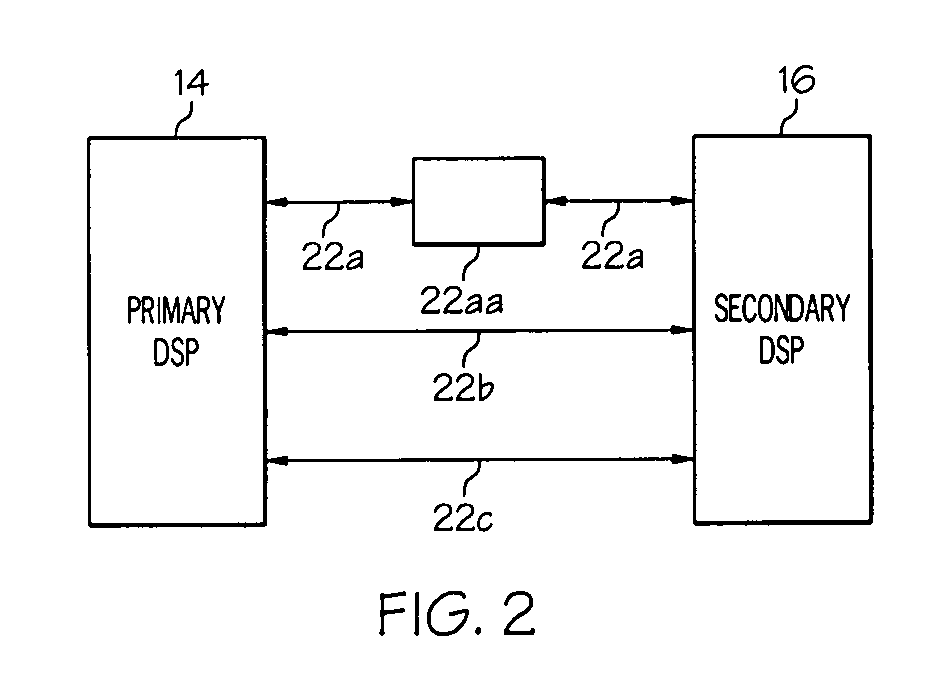
Control bandwidth for cost effective ac motor drives in aerospace applications using two DSP devices with dissimilar redundant inter-processor communication link
InactiveUS20080203953A1Motor/generator/converter stoppersDC motor speed/torque controlTelecommunications linkCommunication link
A digital control system for an electric motor uses two motor-control DSP's operated in parallel to provide high bandwidth motor control. Each of the two DSP's individually may have a limited processing rate (e.g. about 150 million instructions per second [MIPS]). Parallel operation of the DSP's with efficient cross-communication may facilitate motor control at a high sampling frequency. The high sampling frequency may require processing at a rate greater than the limited processing rate (e.g. greater than 150 MIPS), but the combined DSP's may provide the requisite processing speed.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
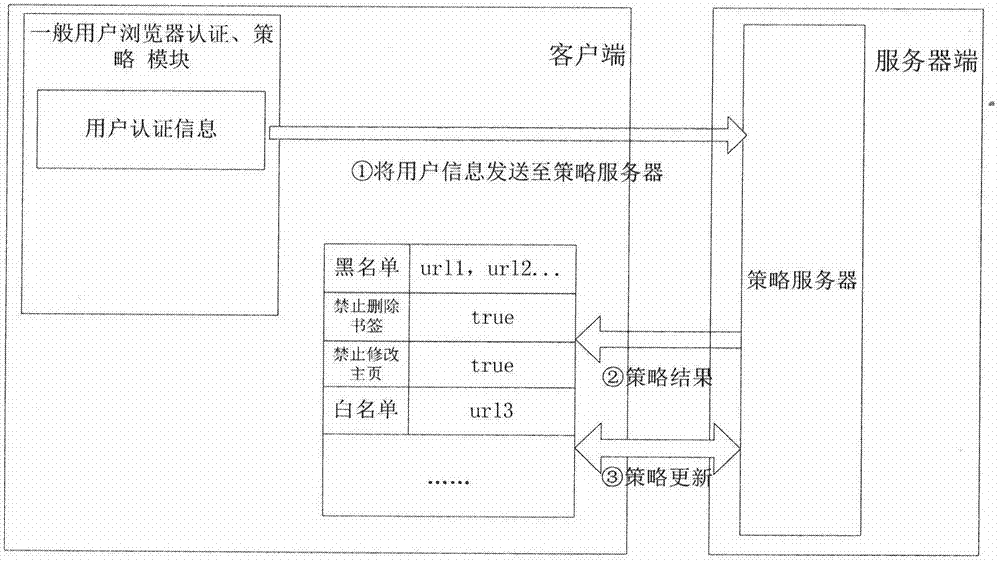
MIPS (Million Instructions Per Second) platform Web access strategy control method
InactiveCN104506520AAvoid visitingAvoid Malicious ModificationsPlatform integrity maintainanceTransmissionInstructions per secondHome page
The invention discloses an MIPS (Million Instructions Per Second) platform Web access strategy control method. According to the MIPS platform Web access strategy control method, strategy setting of users of a client browser is uniformly managed and controlled in a centralized manner by a strategy server; the browser requests for the strategy server at certain time intervals; the strategy server manages strategy information of the users and returns the strategy information of the users to the client browser; the browser implements corresponding control according to the related strategy information. The MIPS platform Web access strategy control method has the advantages that control on an MIPS platform Web access strategy, functions of URL (Uniform Resource Locator) access blacklist control, URL access white list control and a forced home page address setting strategy, a function that whether a bookmark is editable, a function of installing a blacklist on an extension and functions of a download directory setting strategy, a plug-in URL white list, a plug-in URL blacklist and the like of the browser, are implemented, so that a local terminal can be protected and the users are prevented from accessing malicious websites, operating malicious plug-ins, installing malicious extensions, maliciously modifying a home page of the browser and the like.
Owner:中软信息系统工程有限公司
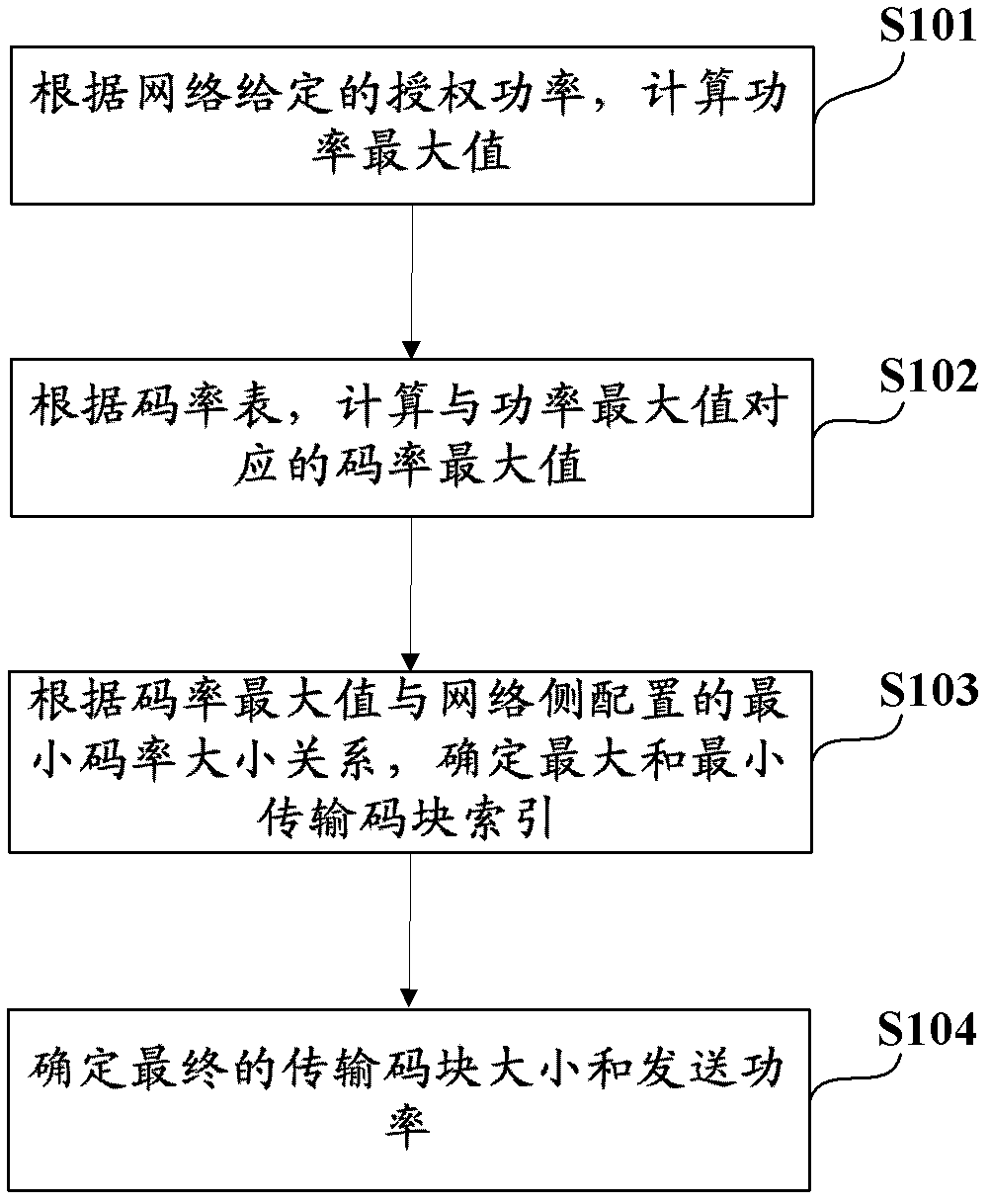
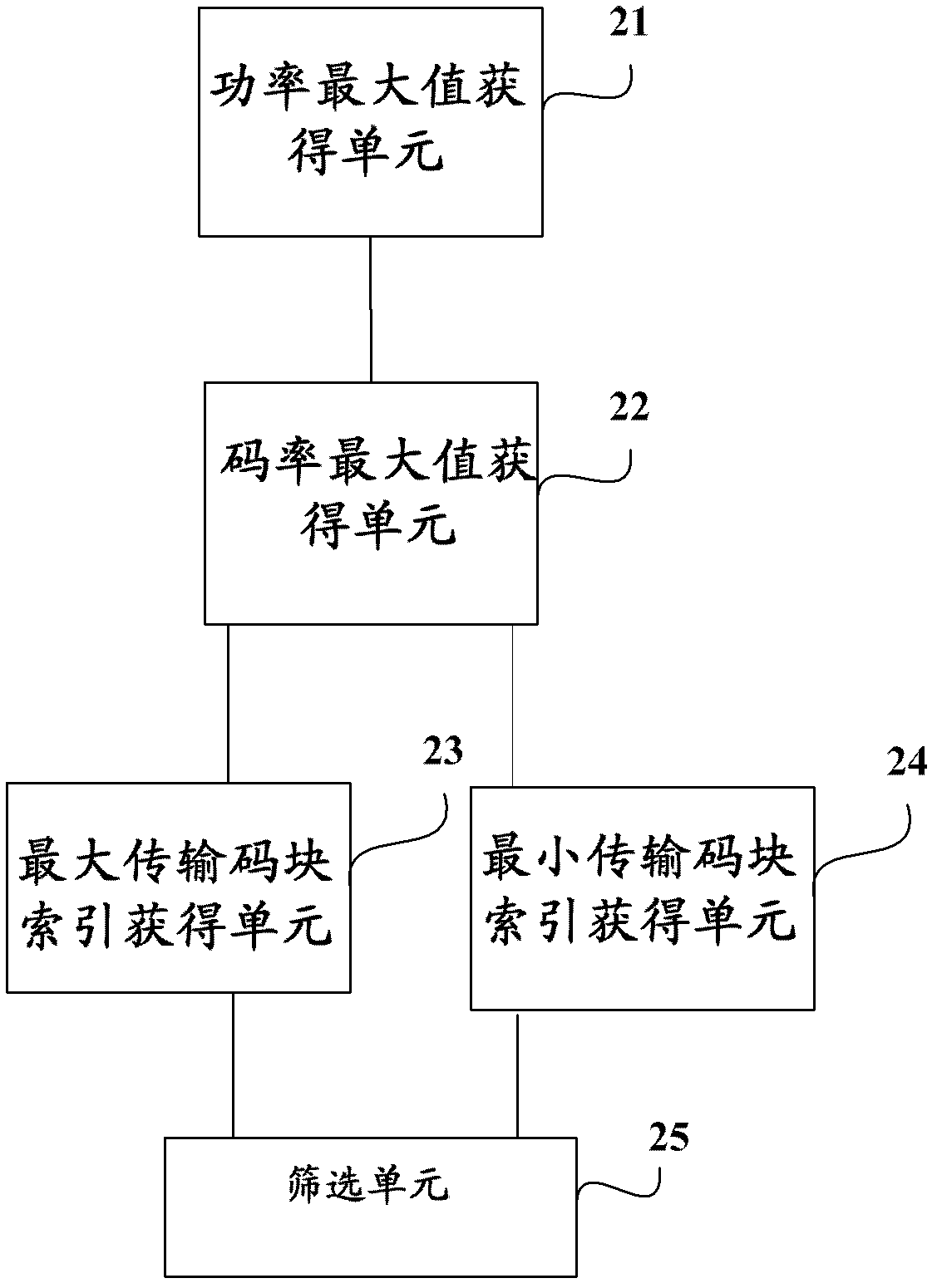
E-DCH transport format combination (E-TFC) selection method and system
ActiveCN103188776AReduce consumptionReduce time complexityPower managementHigh level techniquesCoding blockInstructions per second
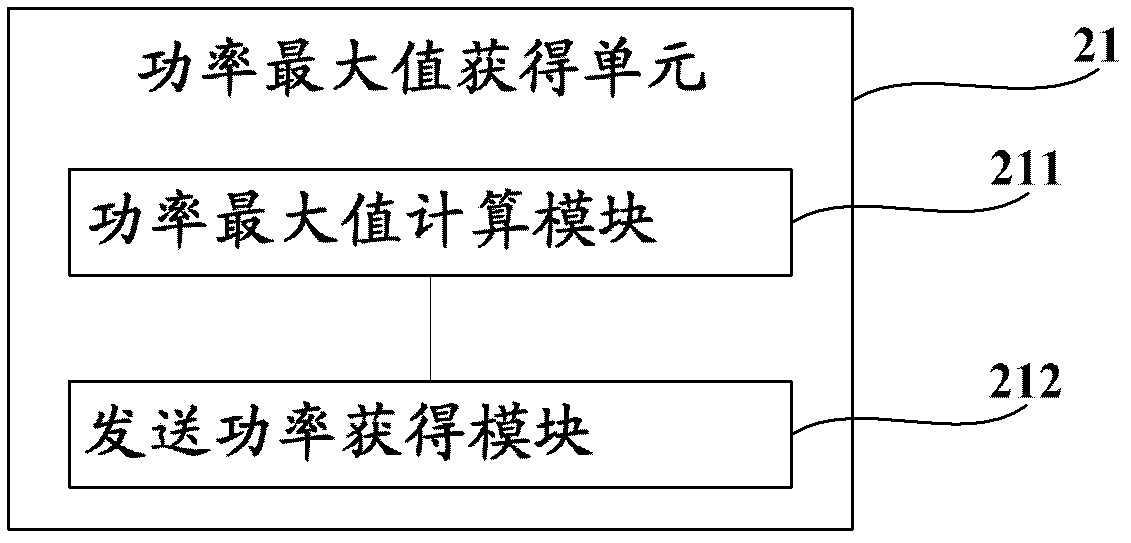
The invention discloses an E-DCH transport format combination (E-TFC) selection method and a system. The method comprises the steps: calculating a power maximum value beta 0, e-max according to an authorized power Parant given by a network; calculating a code rate maximum value lambada 0, e-max corresponding to the power maximum value beta 0; comparing the code rate maximum value lambada 0, e-max with a minimum code rate lambada n w-min configured by a network side, and confirming a maximum transmission code block index TB index and a minimum transmission code block index TB index according to a comparative result; and confirming size and sending power of a final transmission code block. The E-TFC selection method and the system optimize existing E-TFC selection, effectively reduce time complexity of correlation calculations, and reduce million instructions per second (MIPS) consumption in an E-TFC selection process.
Owner:SPREADTRUM COMM (SHANGHAI) CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com