Patents
Literature
107 results about "Row-major order" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In computing, row-major order and column-major order are methods for storing multidimensional arrays in linear storage such as random access memory. The difference between the orders lies in which elements of an array are contiguous in memory. In a row-major order, the consecutive elements of a row reside next to each other, whereas the same holds true for consecutive elements of a column in a column-major order. While the terms allude to the rows and columns of a two-dimensional array, i.e. a matrix, the orders can be generalized to arrays of any dimension by noting that the terms row-major and column-major are equivalent to lexicographic and colexicographic orders, respectively.
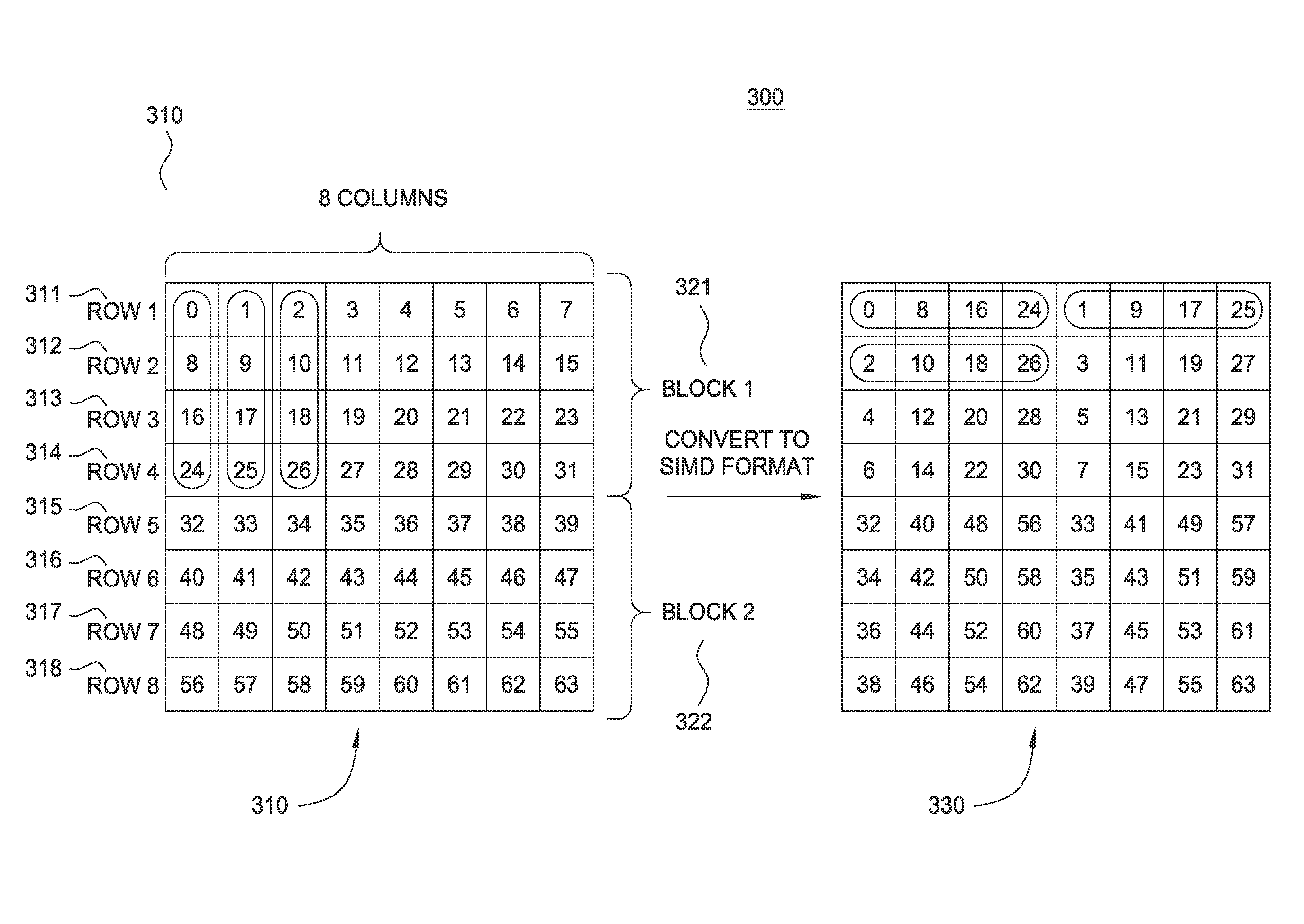
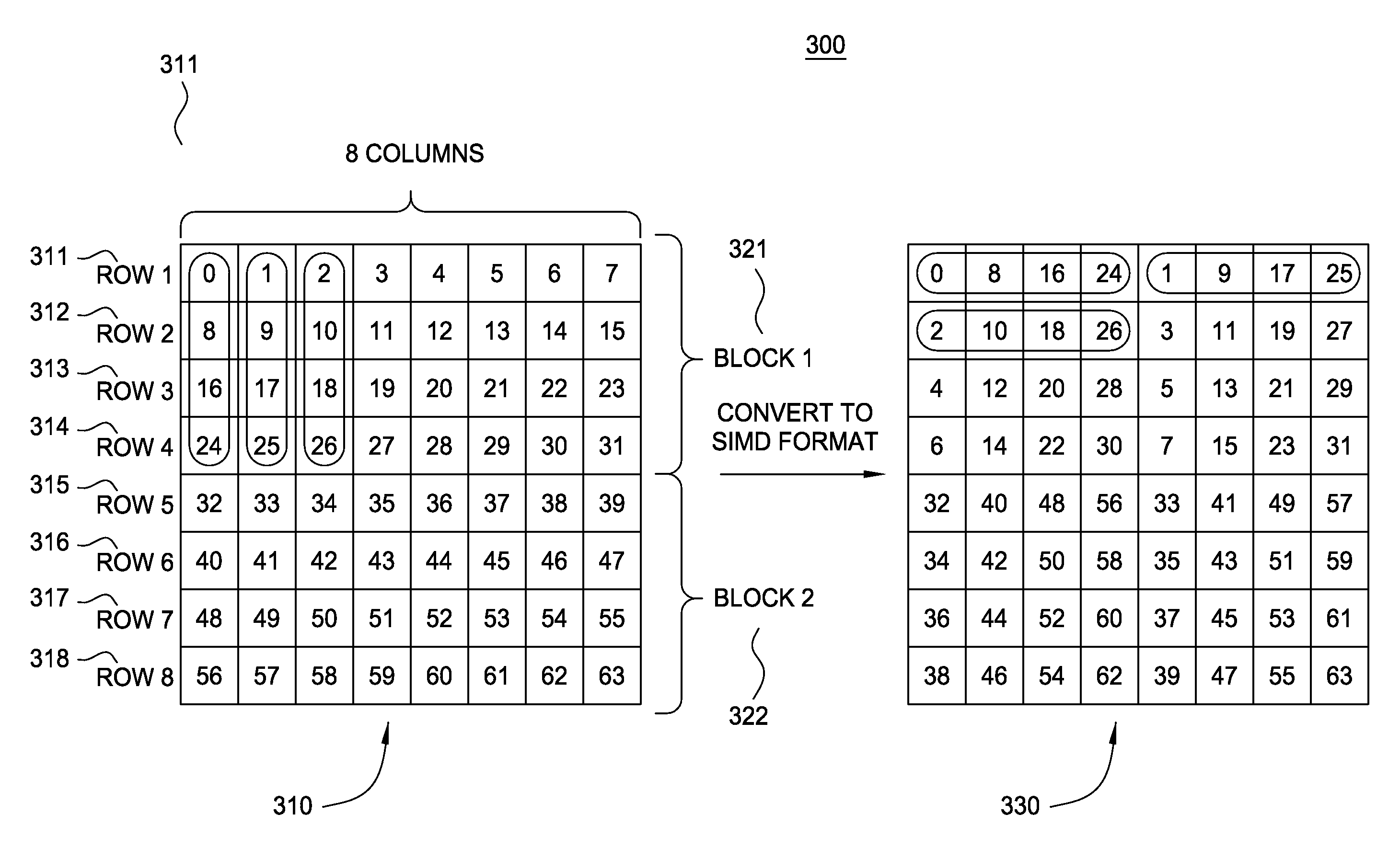
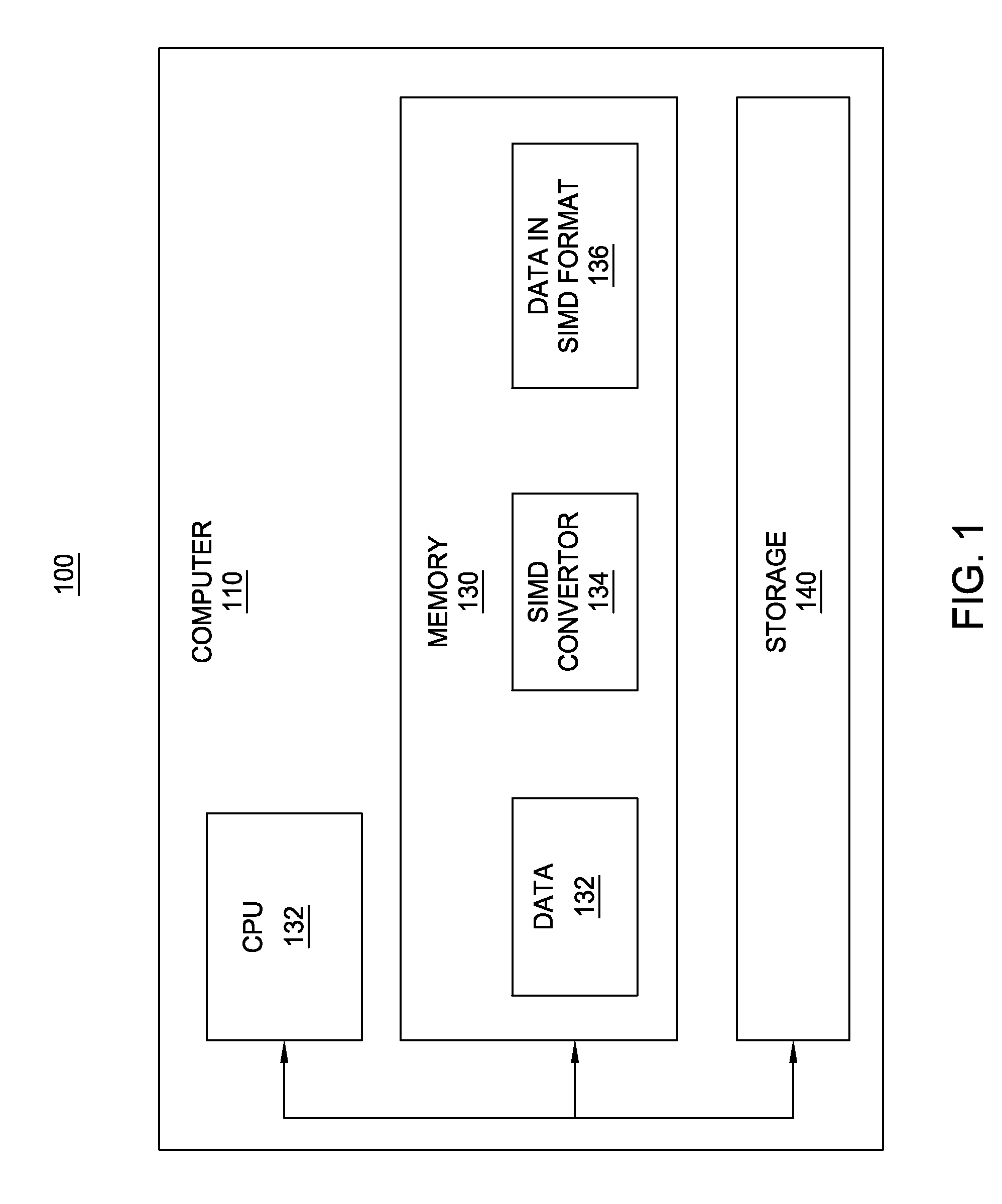
Processing array data on SIMD multi-core processor architectures
InactiveUS8484276B2Program control using stored programsGeneral purpose stored program computerFast Fourier transformFourier transform on finite groups
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
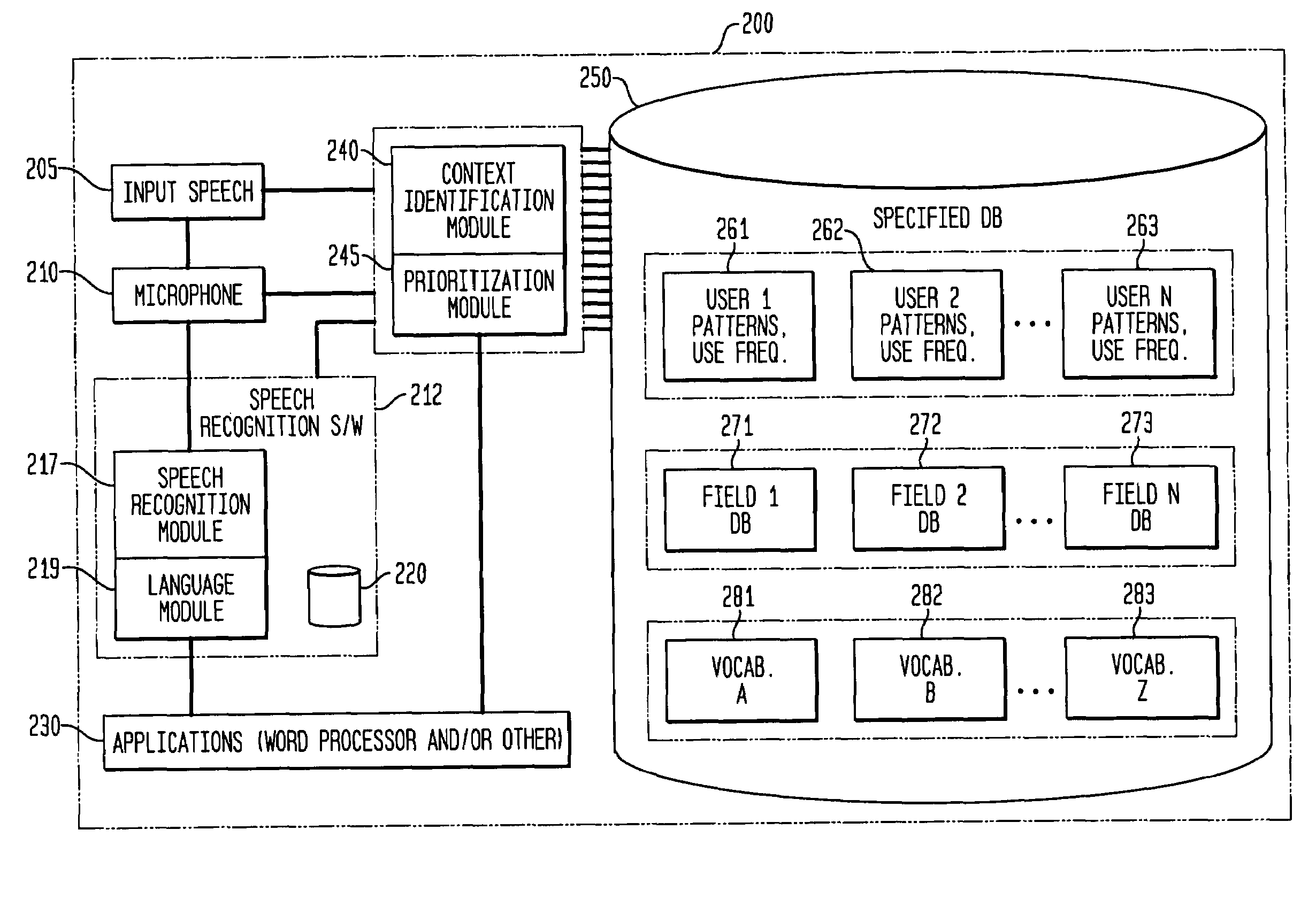
Method and apparatus for improving the transcription accuracy of speech recognition software
ActiveUS7426468B2Improve accuracyImprove speech recognition performanceSpeech recognitionSpeech identificationSpeech input
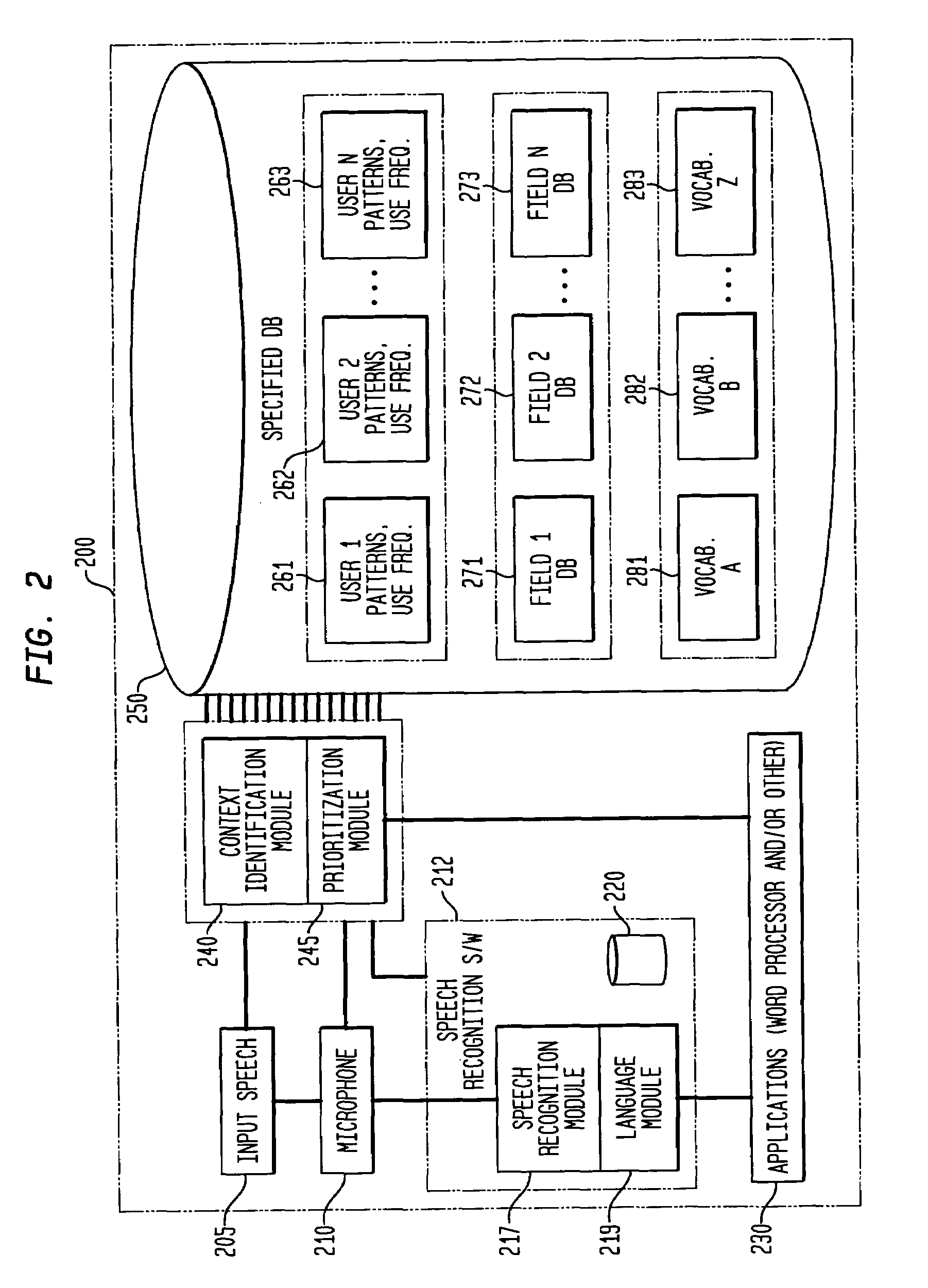
The present invention involves the dynamic loading and unloading of relatively small text-string vocabularies within a speech recognition system. In one embodiment, sub-databases of high likelihood text strings are created and prioritized such that those text strings are made available within definable portions of computer-transcribed dictations as a first-pass vocabulary for text matches. Failing a match within the first-pass vocabulary, the voice recognition software attempts to match the speech input to text strings within a more general vocabulary. In another embodiment, the first-pass text string vocabularies are organized and prioritized and loaded in relation to specific fields within an electronic form, specific users of the system and / or other general context-based, interrelationships of the data that provide a higher probability of text string matches then those otherwise provided by commercially available speech recognition systems and their general vocabulary databases.
Owner:COIFMAN ROBERT E +1
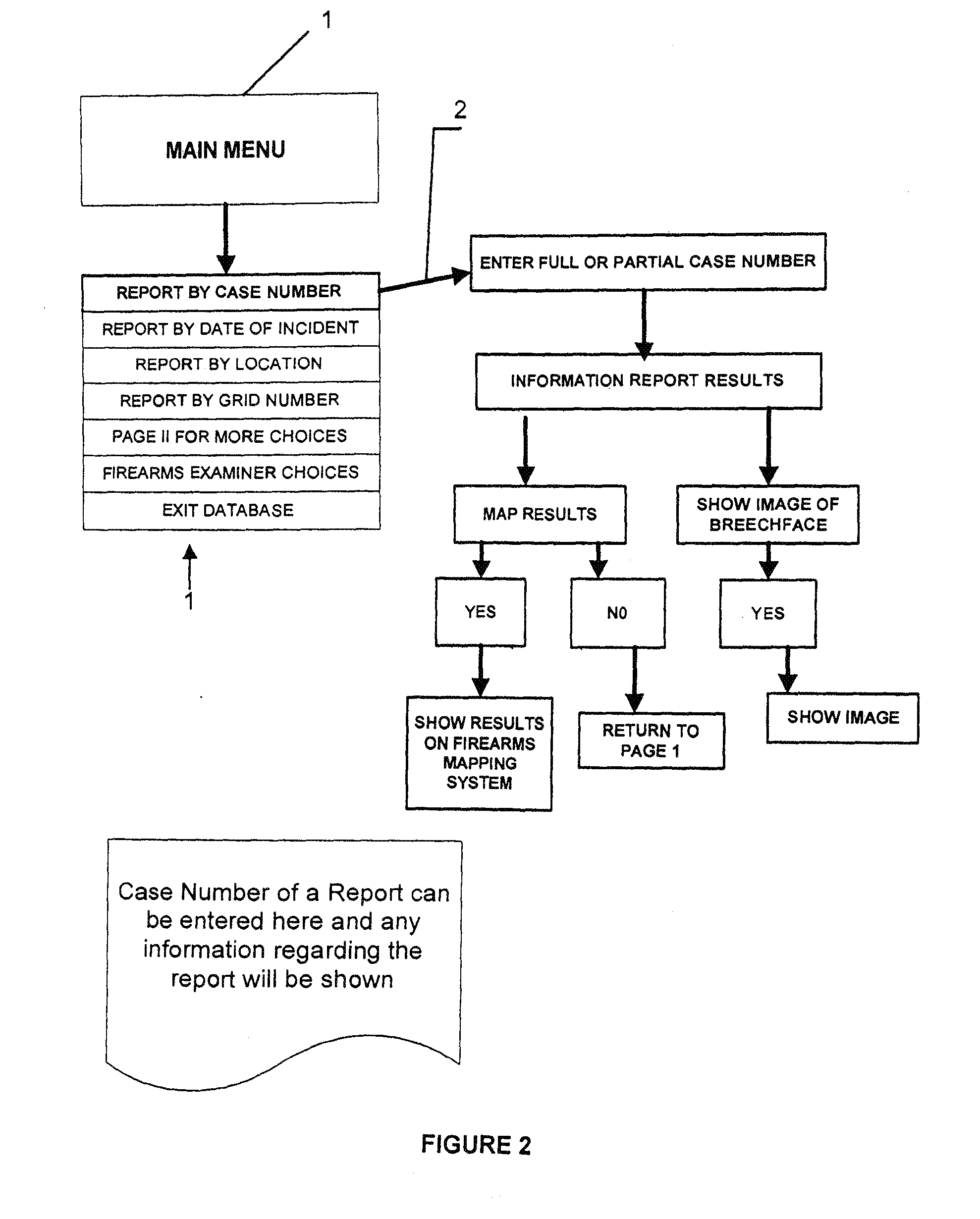
System and Methods for Linking Multiple Events Involving Firearms and Gang Related Activities
InactiveUS20110225198A1Data processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsEvent typeGeolocation
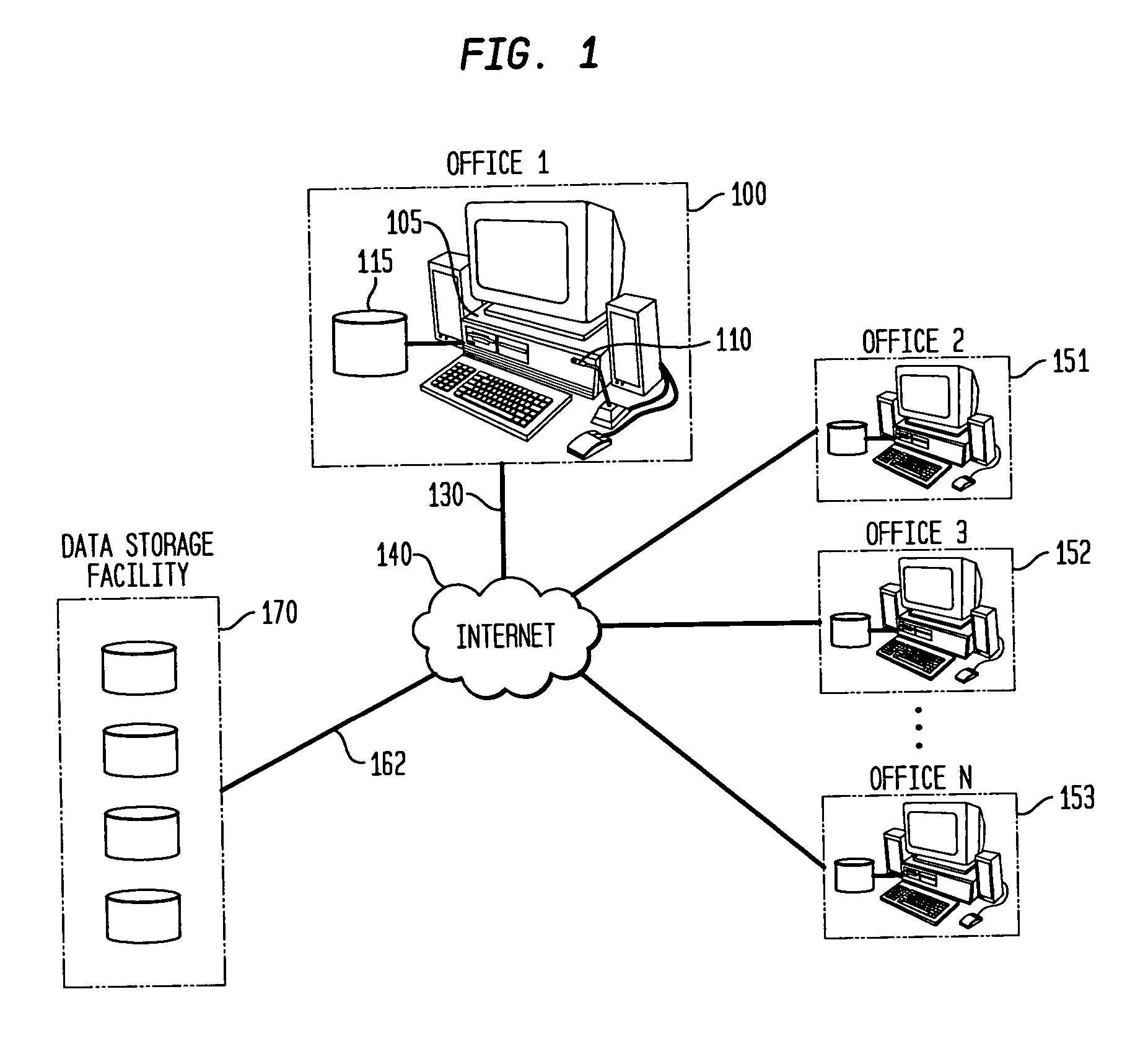
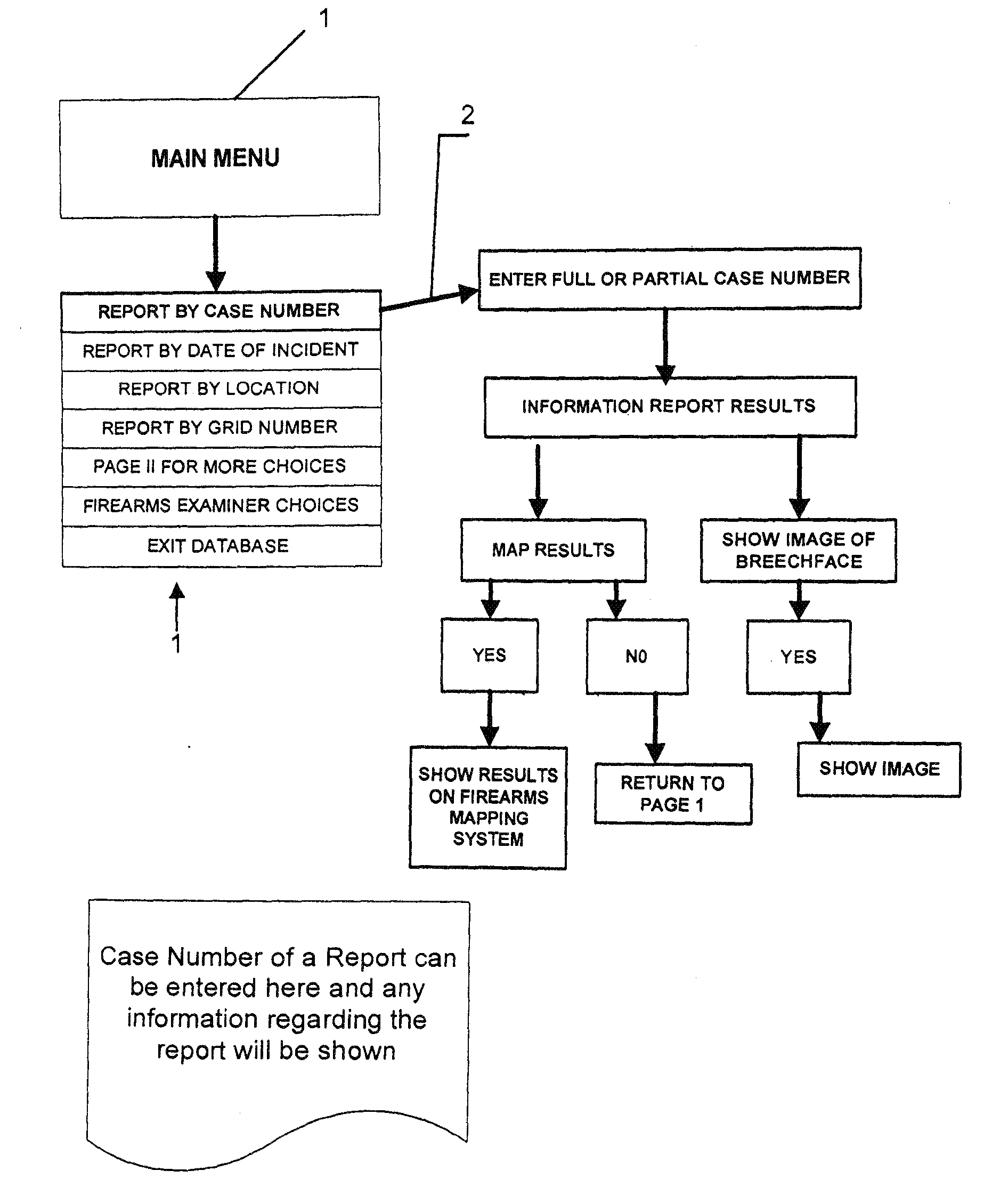
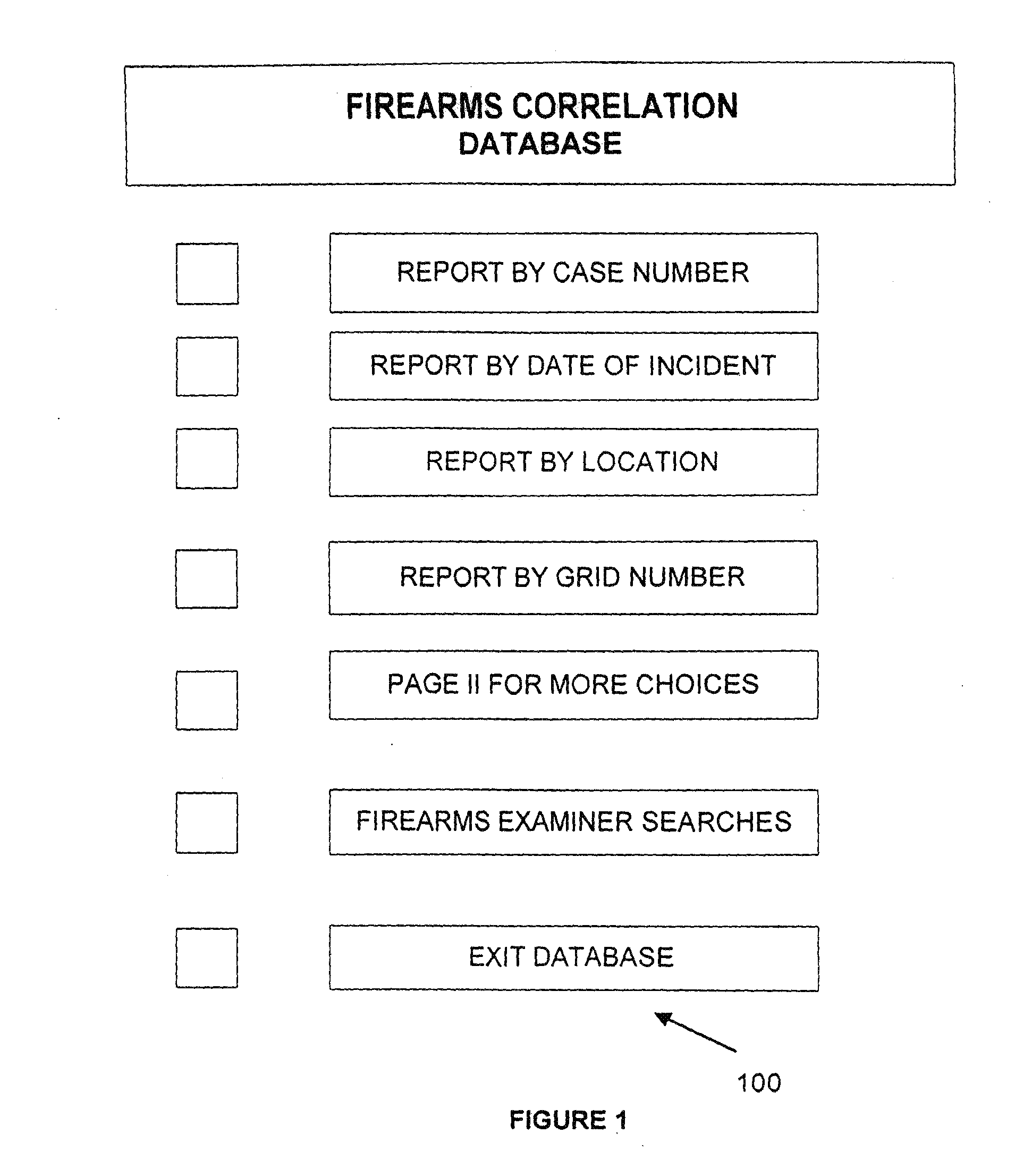
Methods for linking multiple events involving firearms submit event information data and firearms information data to a system that includes a database for multiple firearms events and generate a query map that correlates data in the system database with a preselected geographical grid based upon one or more preselected matching criteria to one or more data entries for a selected event. The map is used to generate a request for a possible link analysis which may be initiated by a firearms examiner and is then performed to determine if there is a link. The event information data can include a case number, a geographical location data entry, a date entry, a crime type, a weapon involved and a suspect information data field based upon input from an investigating officer while the firearms information data can include a weapon data entry and a bullet data entry based upon input from a person with firearms examiner training. The methodology can be used to prioritize multiple requests for a possible link analysis based upon information obtained in one or more query responses and the query response can display at least some of its information in a query map that correlates data in the system database with a preselected geographical grid. One or more gang database modules allow users to execute searches of a gang database and plot incidents on a geographic grid with each incident being represented by a unique icon related to a class of crime or type of incident.
Owner:EDWARDS ROCKY L +1
Intelligent positioning of items in a tree map visualization
Displaying data from a data set in a tree map visualization is provided by prioritizing the data in the data set so as to associate a priority with respective elements of the data in the data set. A tree map visualization is generated based on the data set where a location of bounding boxes in the tree map is based on the priority associated with the corresponding element. Tree maps having locations of bounding boxes that are based on a priority associated with the bounding boxes are also provided.
Owner:ACTIVISION PUBLISHING
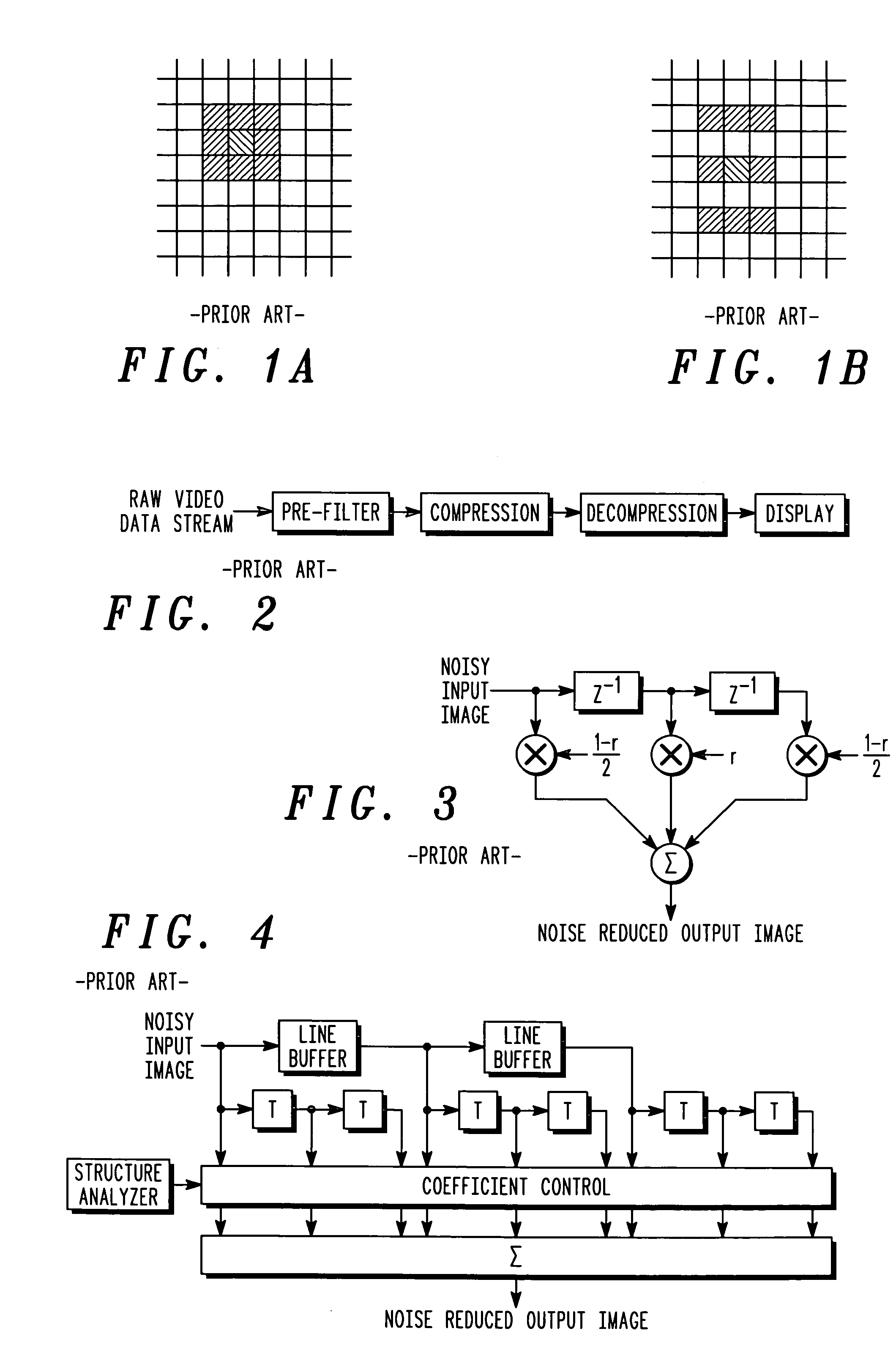
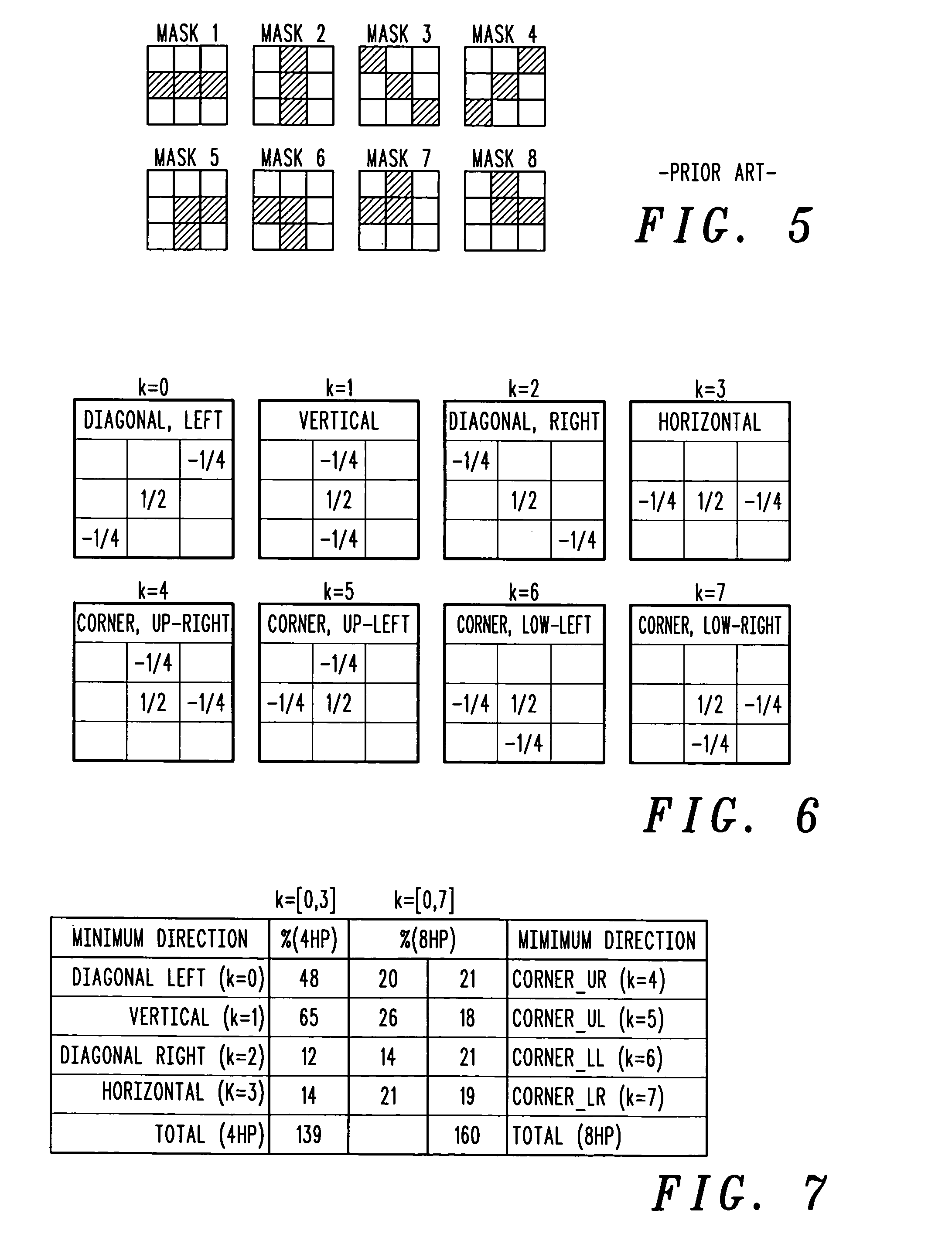
Directional spatial video noise reduction
InactiveUS20050135700A1Quality improvementLighten the computational burdenImage enhancementTelevision system detailsPattern recognitionSpatial noise
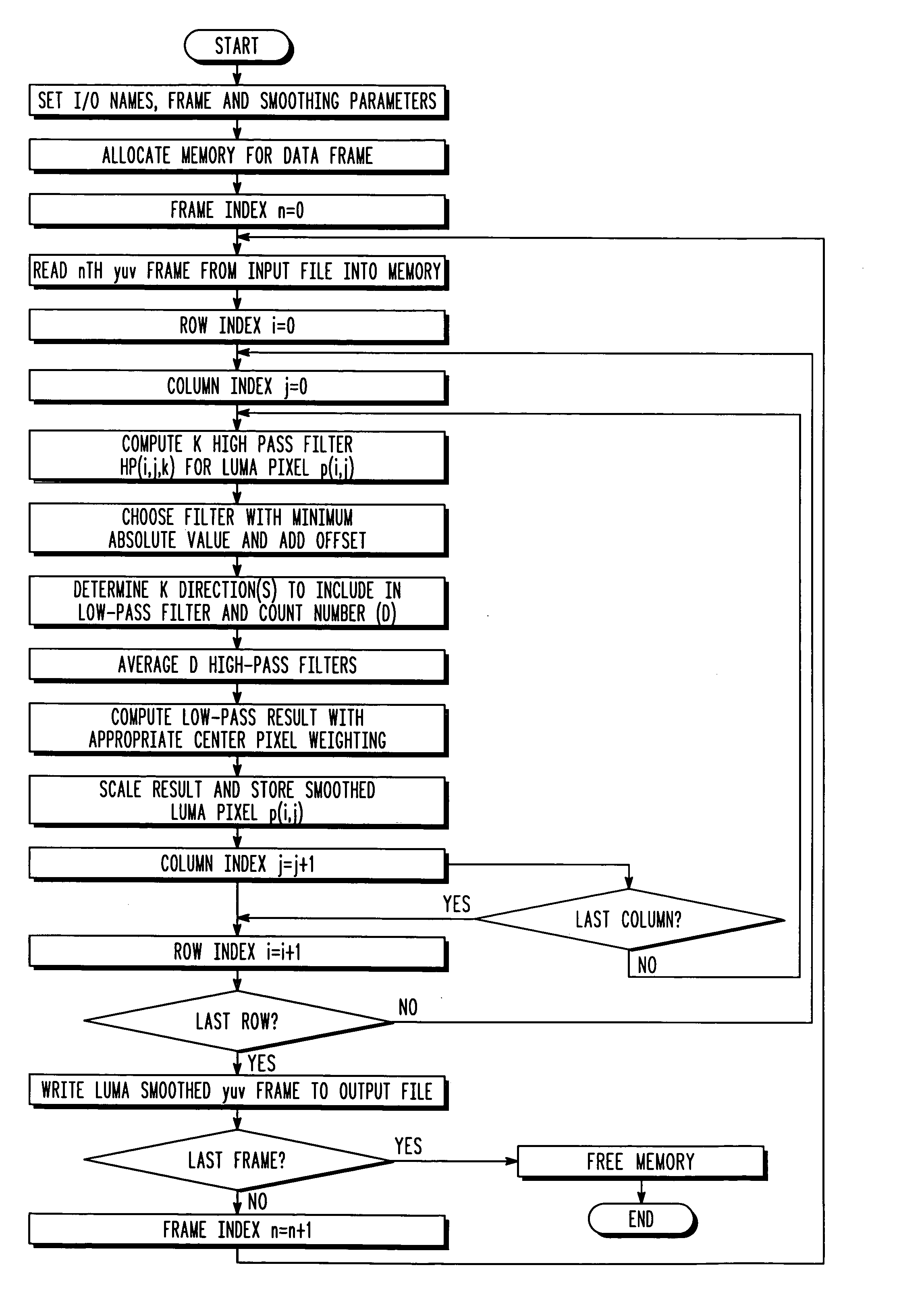
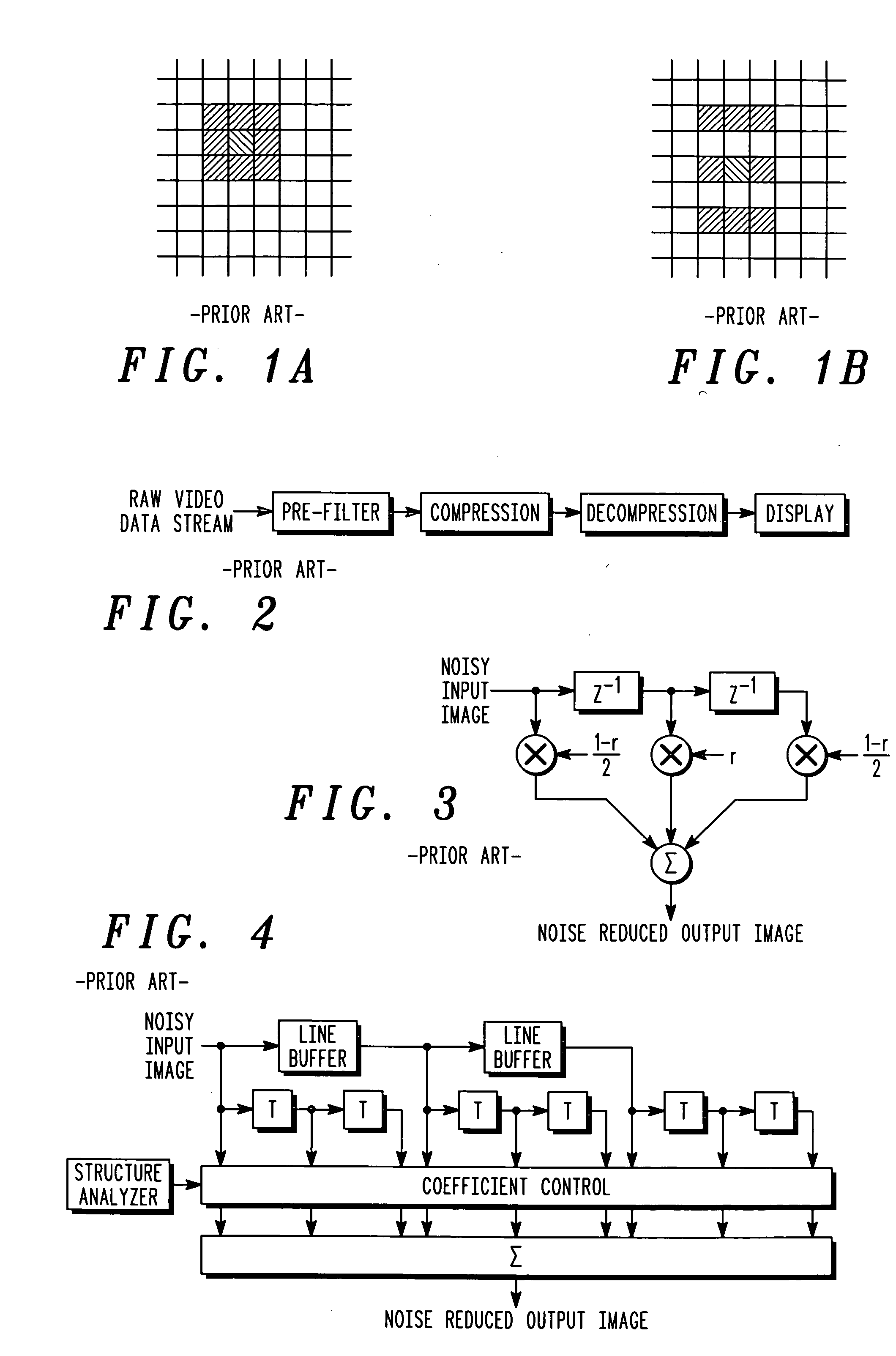
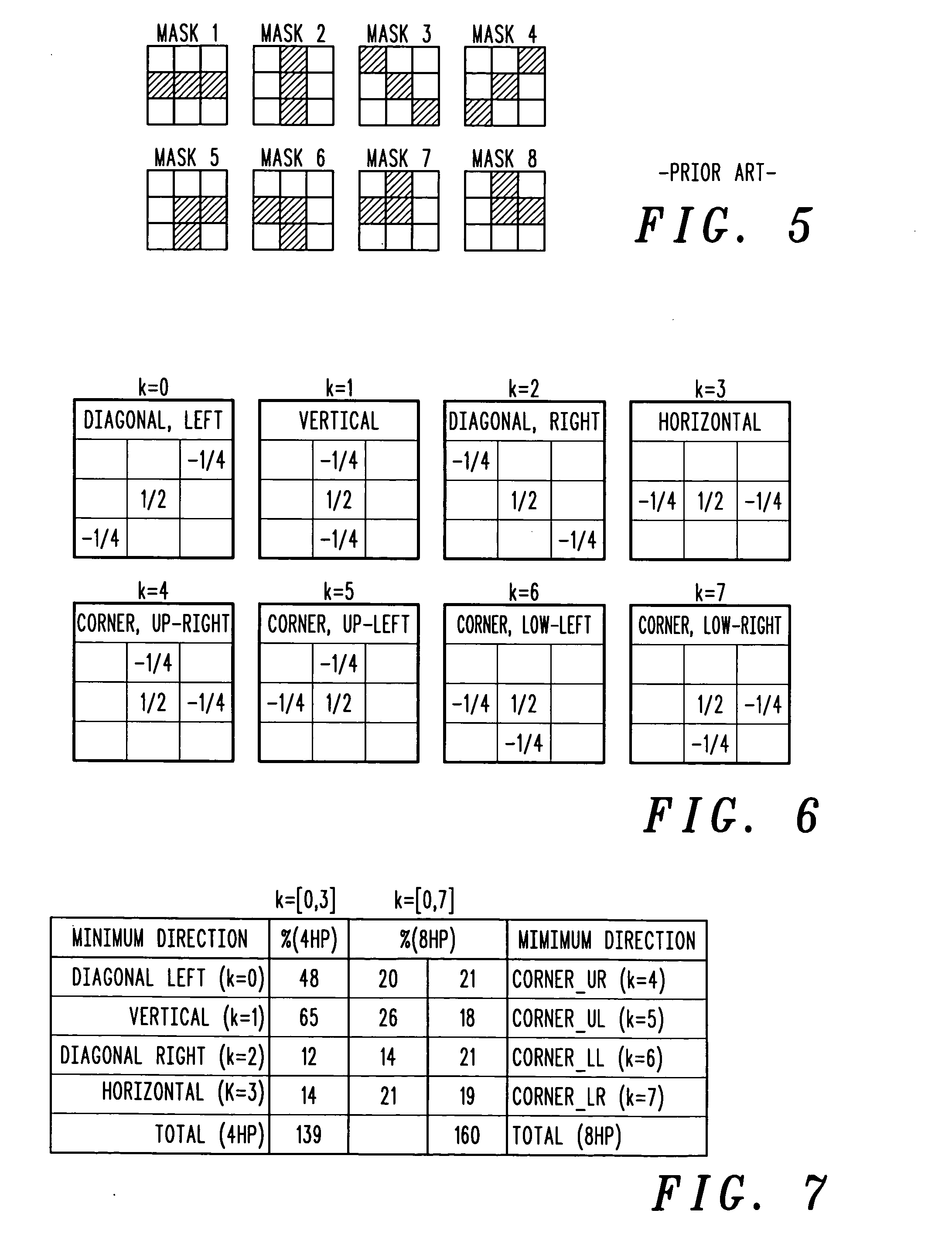
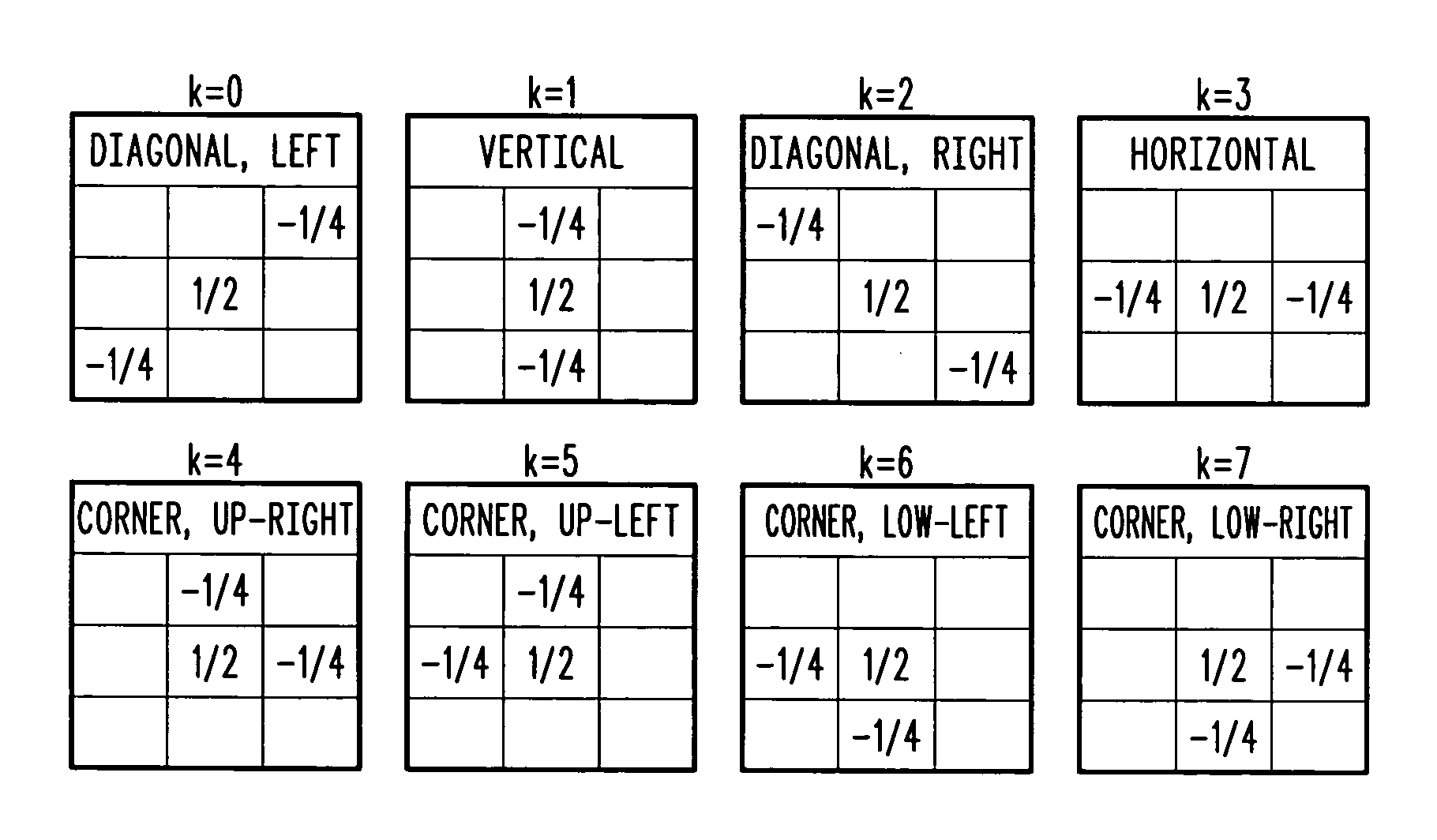
A method of reducing spatial noise in an image. Low-pass (smoothing) filters are calculated simultaneously from three successive image rows. Three blocks (m1, m2, m3) are associated with the three successive image rows, and the blocks are processed in row-major order. This implementation is applicable to both luminance and chrominance. The number of smoothing parameters is reduced to one. The technique is applicable to both luminance and chrominance. Directional mapping is used. Extension of the technique to spatial filtering using a 5×5 neighborhood (using five successive image rows) is described. Embodiments of the method using the MMX instruction set are described.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
Directional spatial video noise reduction
InactiveUS7437013B2Quality improvementLighten the computational burdenImage enhancementTelevision system detailsPattern recognitionSpatial noise
A method of reducing spatial noise in an image. Low-pass (smoothing) filters are calculated simultaneously from three successive image rows. Three blocks (m1, m2, m3) are associated with the three successive image rows, and the blocks are processed in row-major order. This implementation is applicable to both luminance and chrominance. The number of smoothing parameters is reduced to one. The technique is applicable to both luminance and chrominance. Directional mapping is used. Extension of the technique to spatial filtering using a 5×5 neighborhood (using five successive image rows) is described. Embodiments of the method using the MMX instruction set are described.
Owner:GOOGLE TECHNOLOGY HOLDINGS LLC
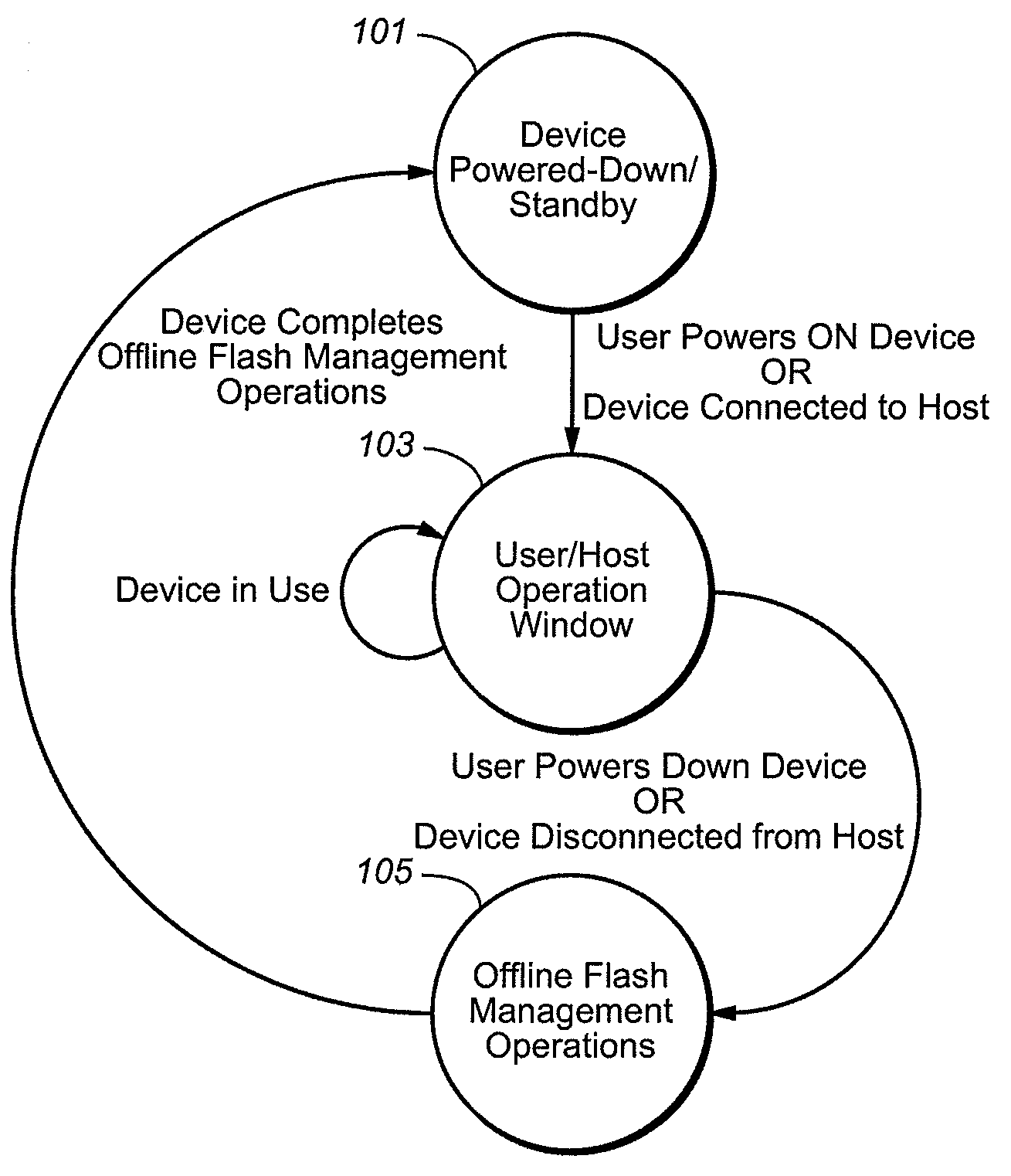
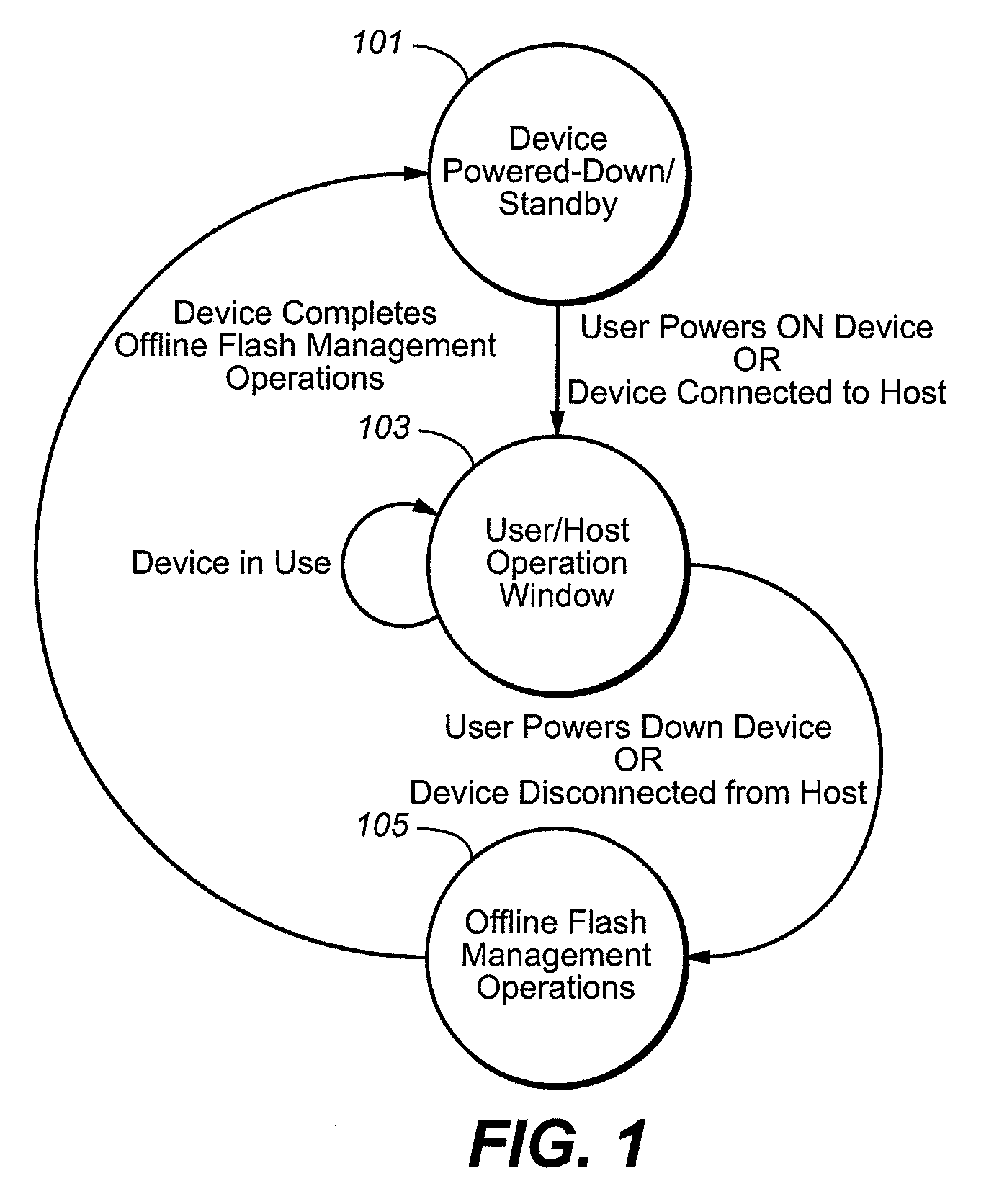
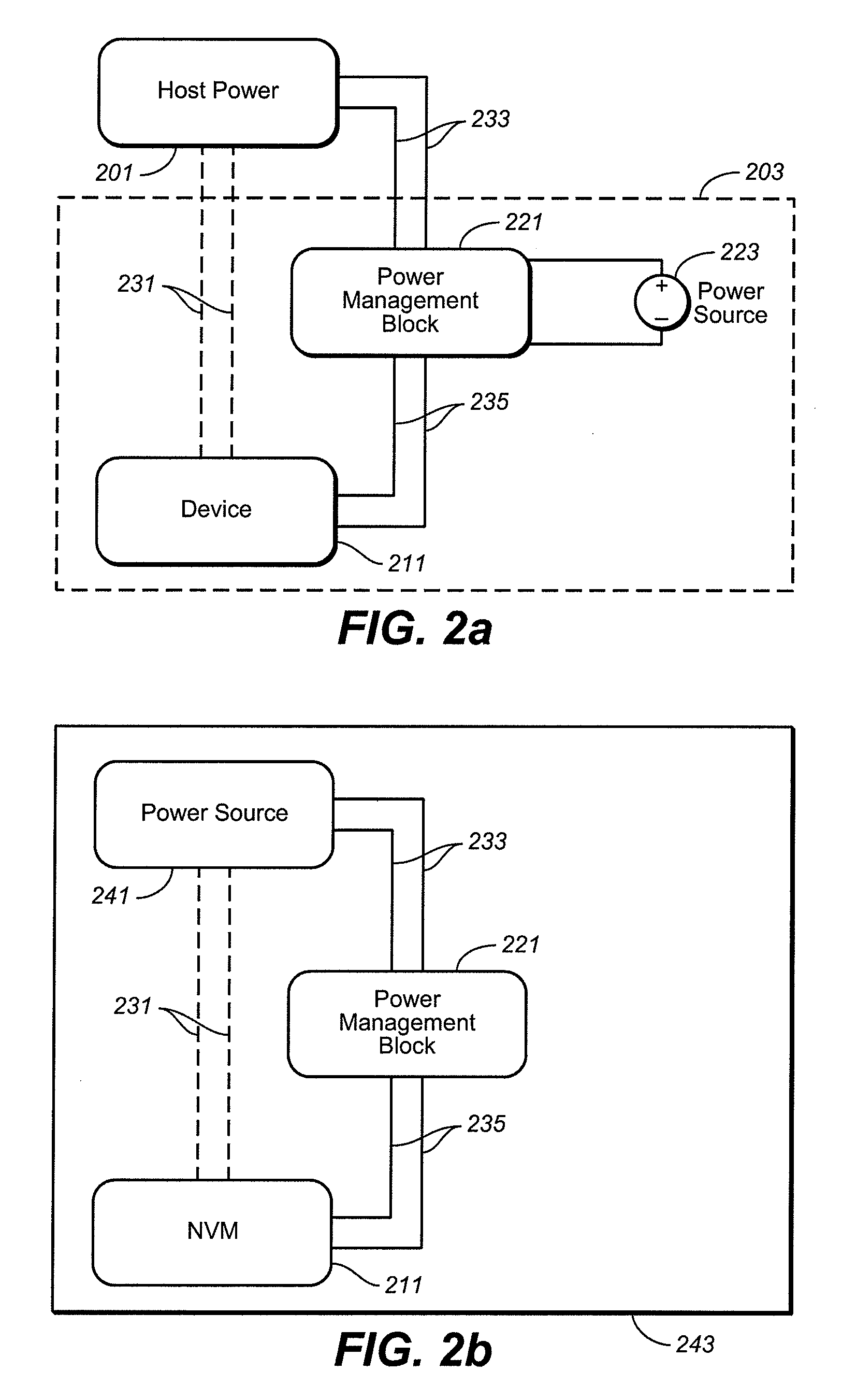
Leveraging Portable System Power to Enhance Memory Management and Enable Application Level Features
ActiveUS20090089481A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationDigital data processing detailsStandby powerData management
A memory device and techniques for its operation are presented. After operating on power received from a host, the memory device determines that it is no longer receiving host power and, in response, activates a power source on the memory device itself. Using this reserve power, the memory device can then perform data management operations. The techniques can also be applied to a digital appliance having a non-volatile memory. The memory device or digital appliance can prioritize its memory management operation during the host / user operating window based on the ability to perform these operations outside of the host / user operating window. Additionally, in a data write operations, where the memory device receives data from a host, stores the data in volatile memory, and then writes the data into the non-volatile memory, the memory device sends the host an acknowledgment of the data having been written into the non-volatile memory after it has been store in the volatile memory, but before the write into the non-volatile memory is complete.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
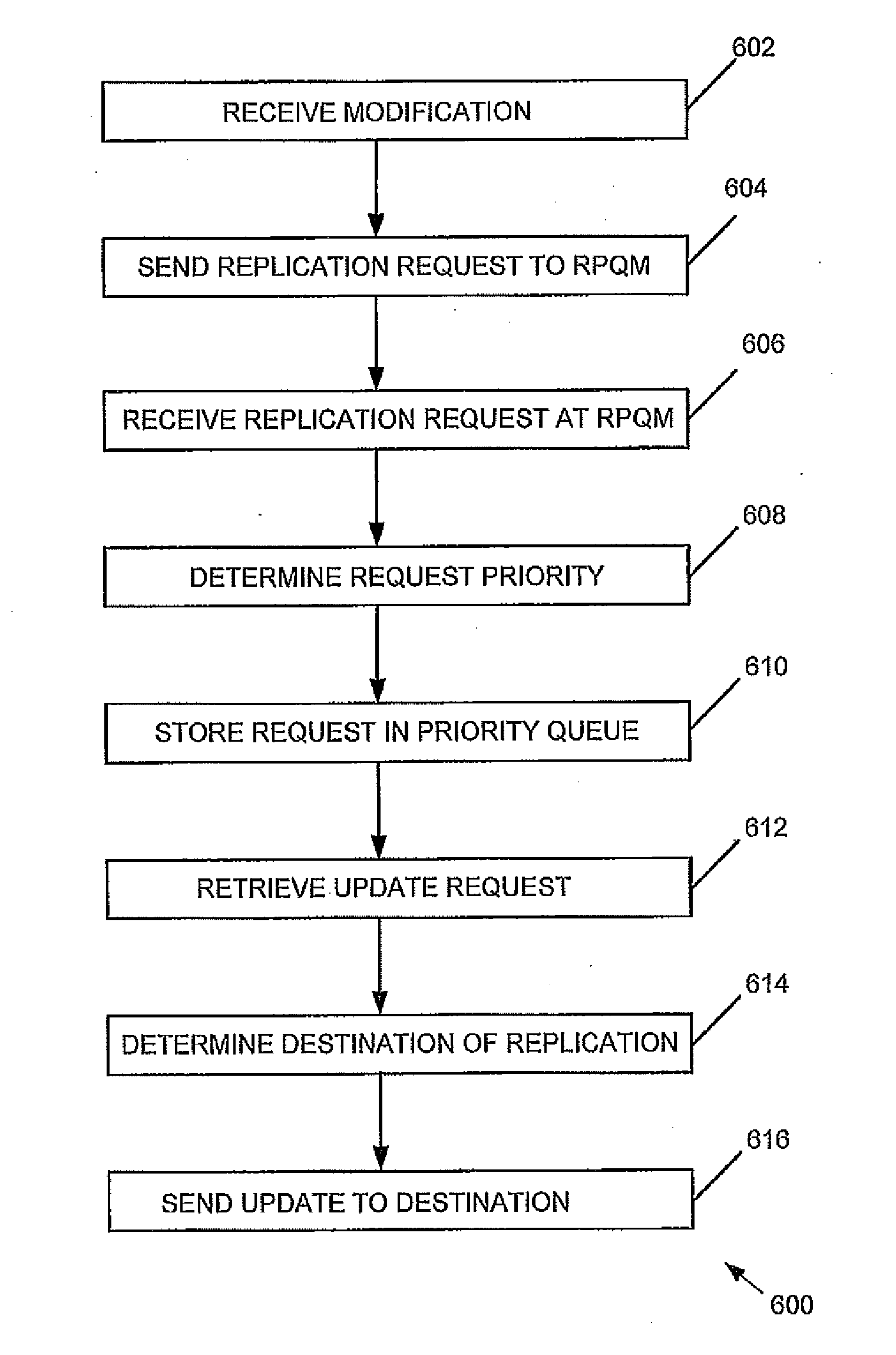
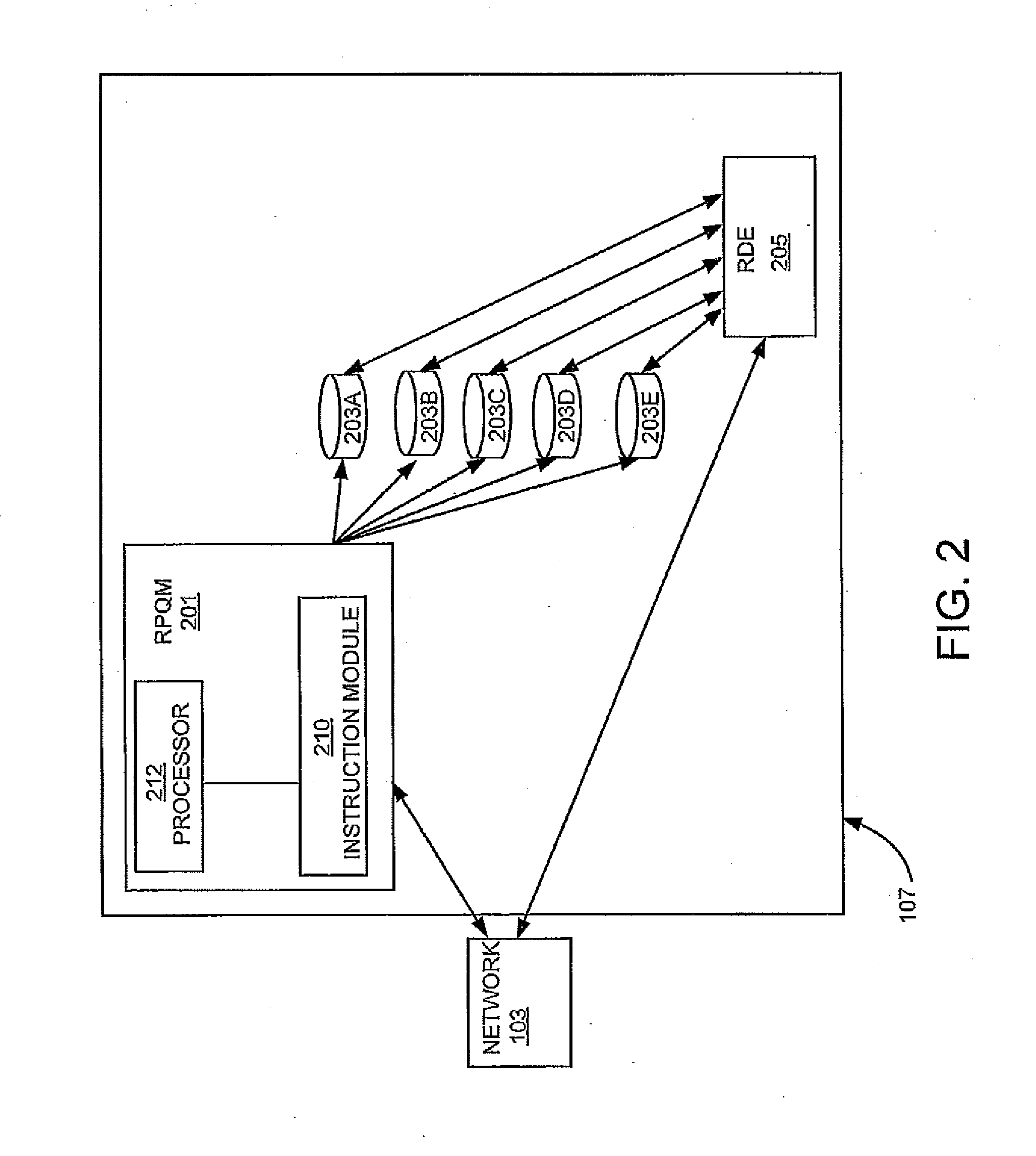
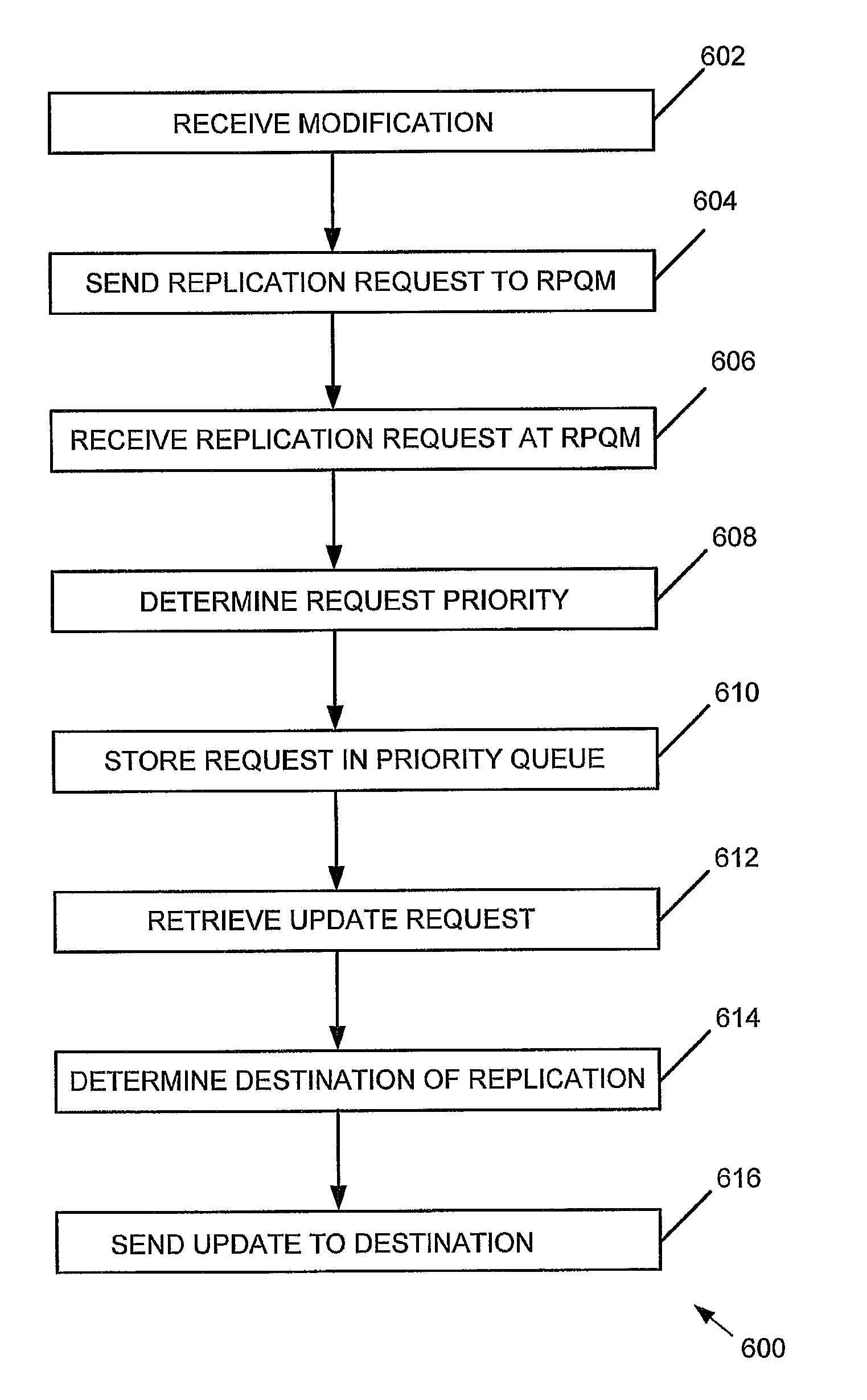
LDAP Replication Priority Queuing Mechanism
A replication priority queuing system prioritizes replication requests in accordance with a predetermined scheme. An exemplary system includes a Replication Priority Queue Manager that receives update requests and assigns a priority based upon business rules and stores the requests in associated storage means. A Replication Decision Engine retrieves the requests from storage and determines a destination for the update based upon predetermined replication rules, and sends the update to the destination.
Owner:CINGULAR WIRELESS II LLC
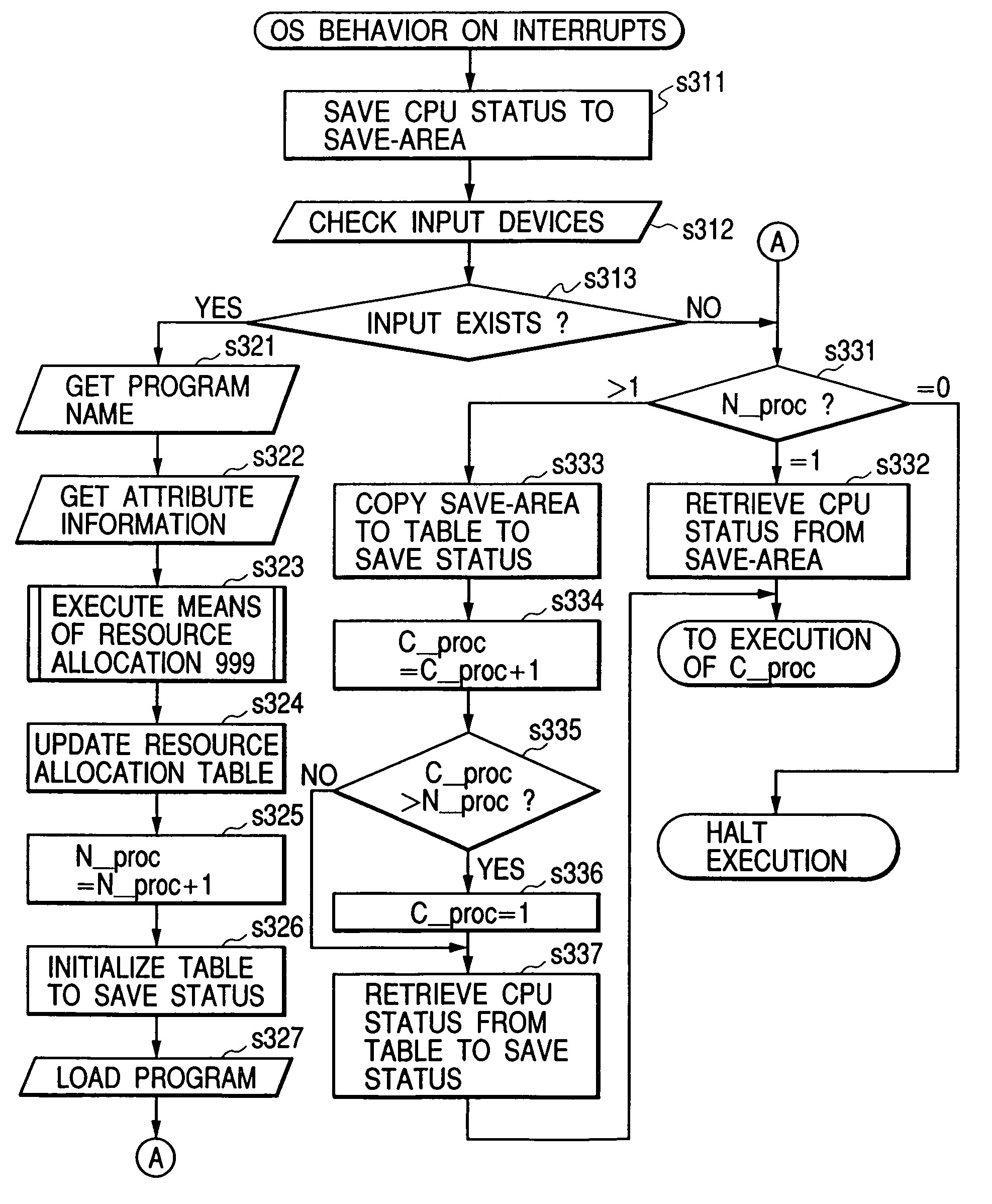
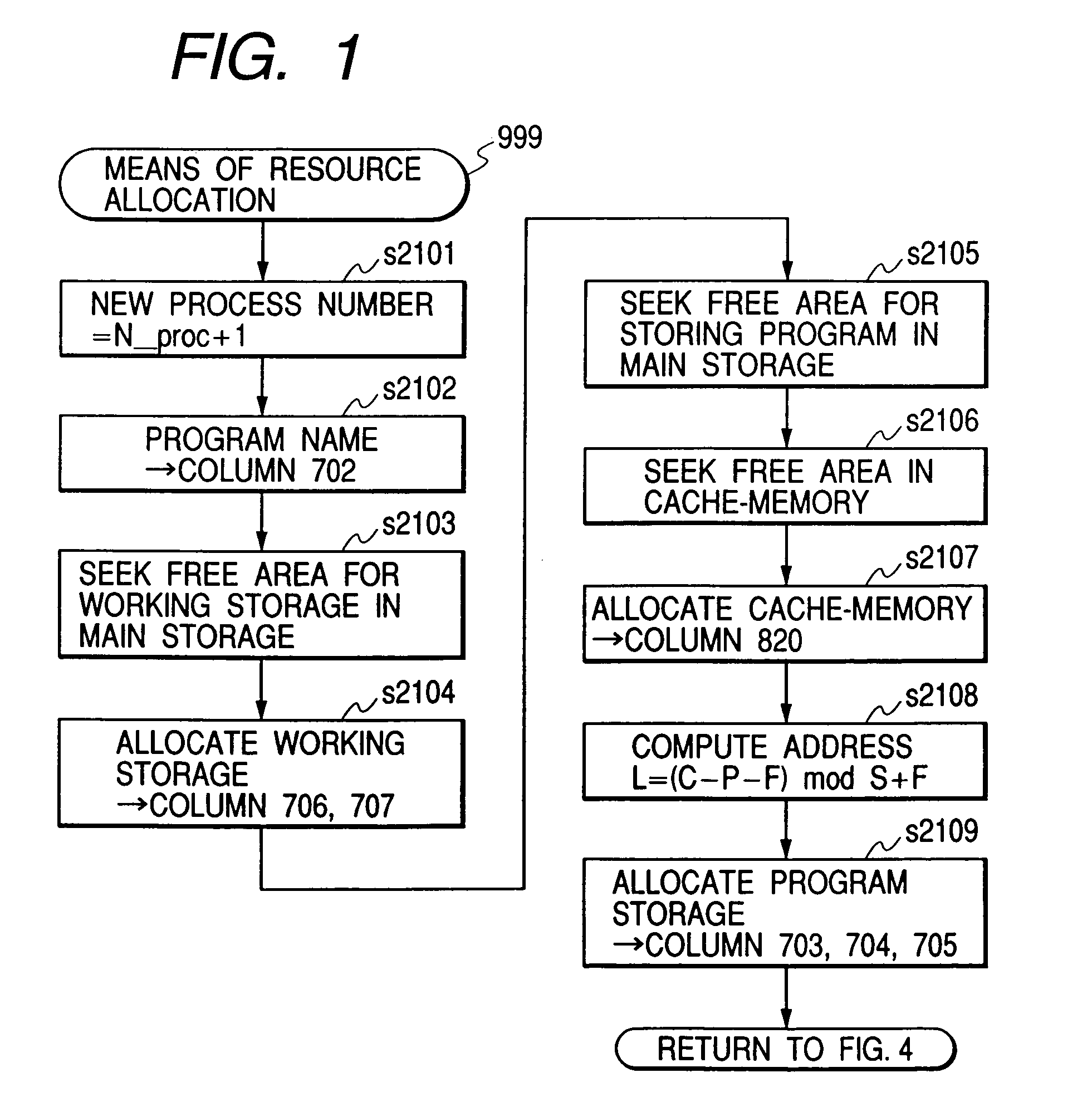
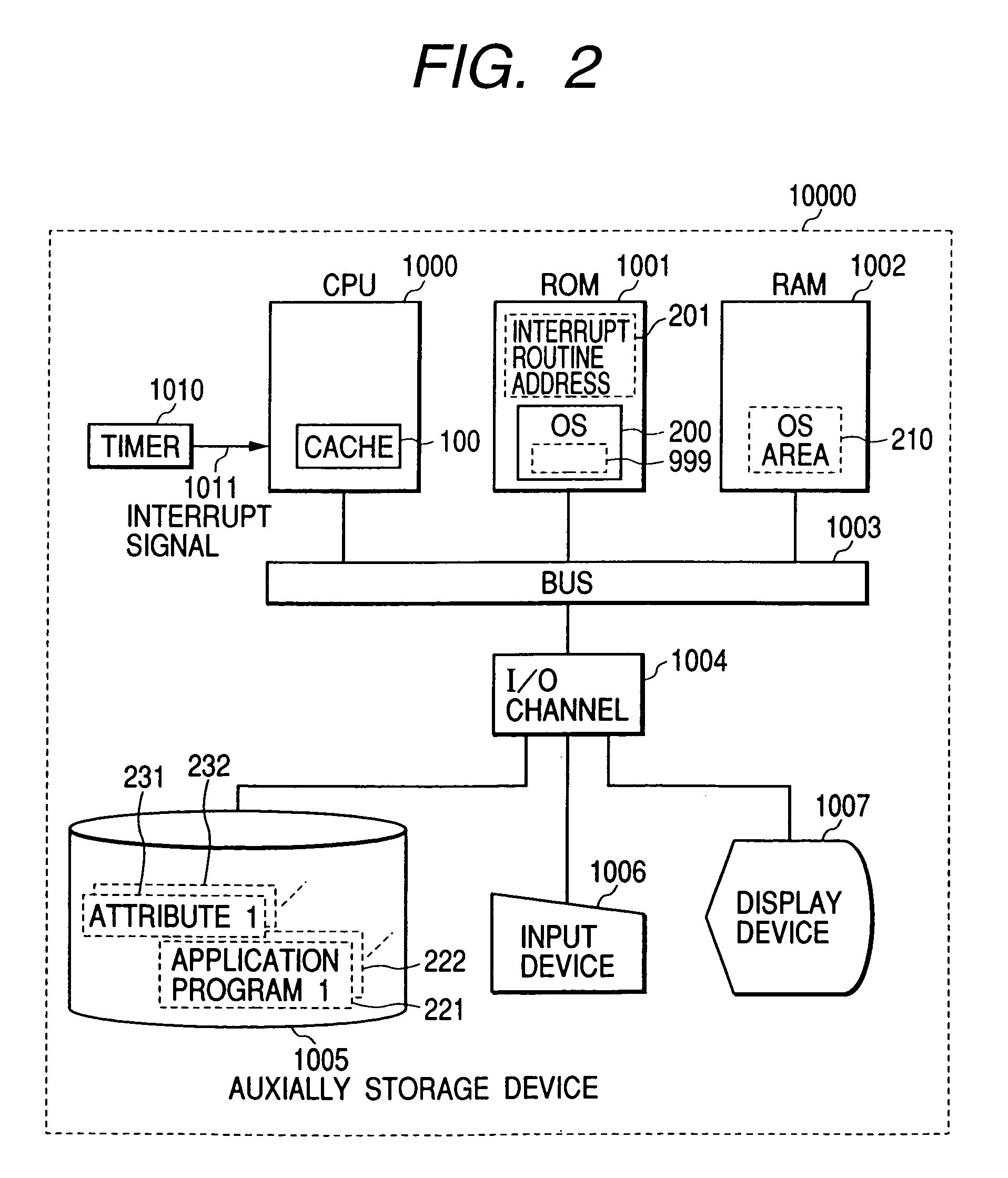
Cache memory allocation method
InactiveUS7000072B1Effective preventive measureAvoid bumpingMemory architecture accessing/allocationData processing applicationsDistribution methodComputerized system
To assure the multiprocessing performance of CPU on a microprocessor, the invention provides a method of memory mapping for multiple concurrent processes, thus minimizing cache thrashing. An OS maintains a management (mapping) table for controlling the cache occupancy status. When a process is activated, the OS receives from the process the positional information for a specific part (principal part) to be executed most frequently in the process and coordinates addressing of a storage area where the process is loaded by referring to the management table, ensuring that the cache address assigned for the principal part of the process differs from that for any other existing process. Taking cache memory capacity, configuration scheme, and process execution priority into account when executing the above coordination, a computer system is designed such that a highest priority process can have a first priority in using the cache.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
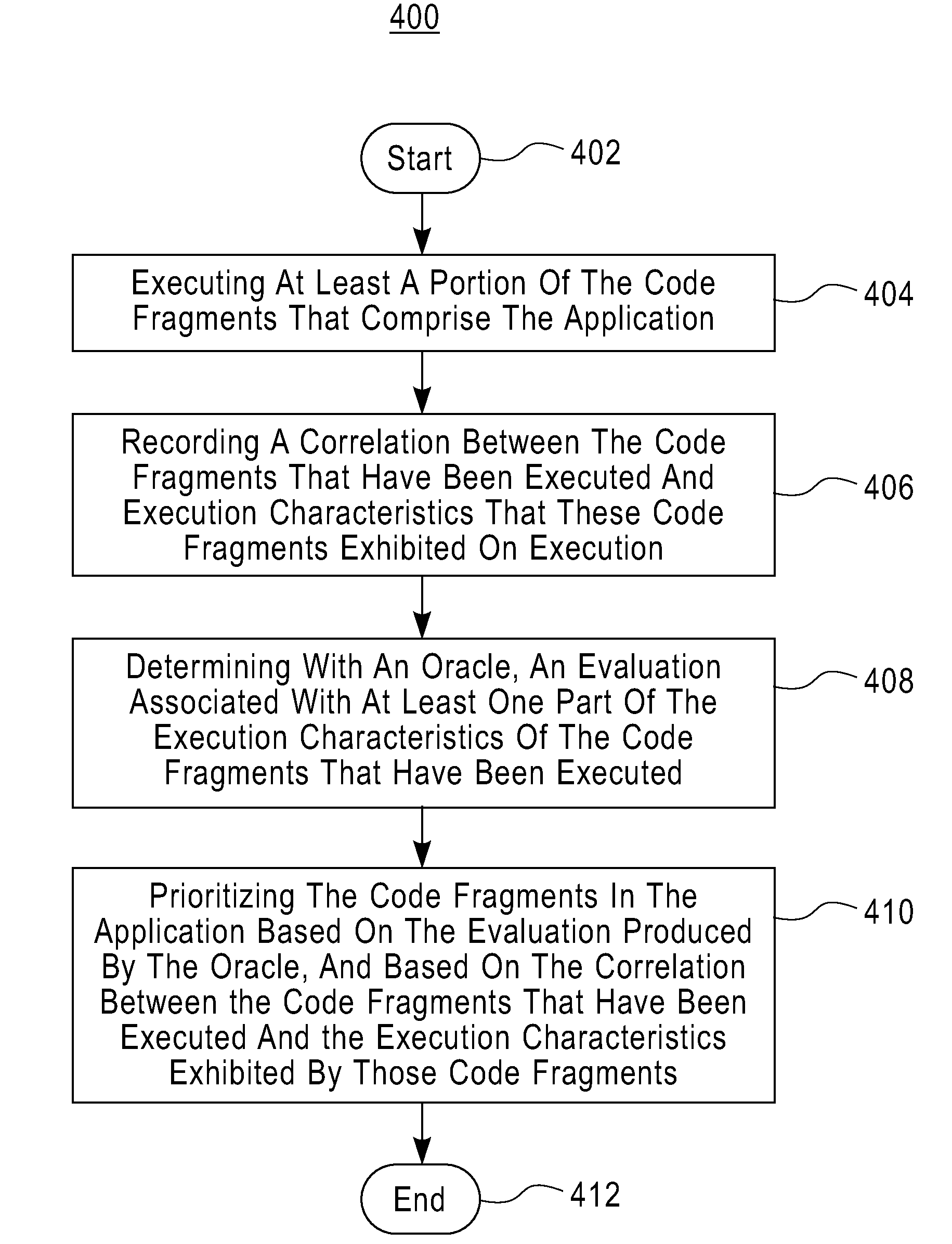
Fault detection and localization in dynamic software applications requiring user inputs and persistent states
InactiveUS20110016457A1Automatically user interactionImprove efficiencyMemory loss protectionError detection/correctionUser inputConcolic testing
The present invention provides a system, computer program product and a computer implemented method for prioritizing code fragments based on the use of a software oracle and on a correlation between the executed code fragments and the output they produce. Also described is a computer-implemented method generates additional user inputs based on execution information associated with path constraints and based on information from the oracle. Advantageously, the embodiment is useful in a test generation tool that generated many similar inputs when a failure-inducing input is found, in order to enhance fault localization. Further, described is a computer-implemented flow for extending the existing idea of concolic testing to applications that interact with persistent state.
Owner:IBM CORP +1
LDAP replication priority queuing mechanism
A replication priority queuing system prioritizes replication requests in accordance with a predetermined scheme. An exemplary system includes a Replication Priority Queue Manager that receives update requests and assigns a priority based upon business rules and stores the requests in associated storage means. A Replication Decision Engine retrieves the requests from storage and determines a destination for the update based upon predetermined replication rules, and sends the update to the destination.
Owner:CINGULAR WIRELESS II LLC
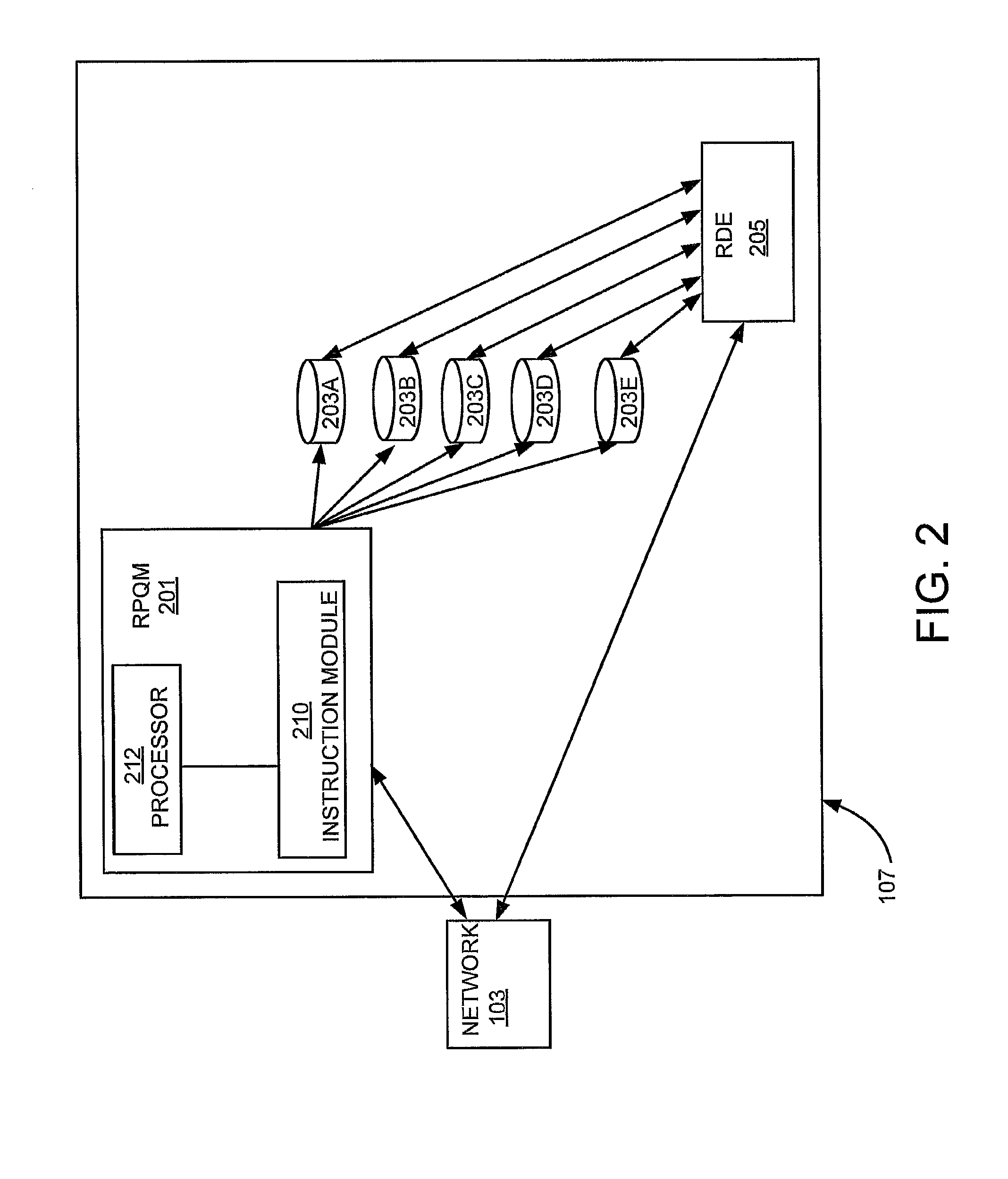
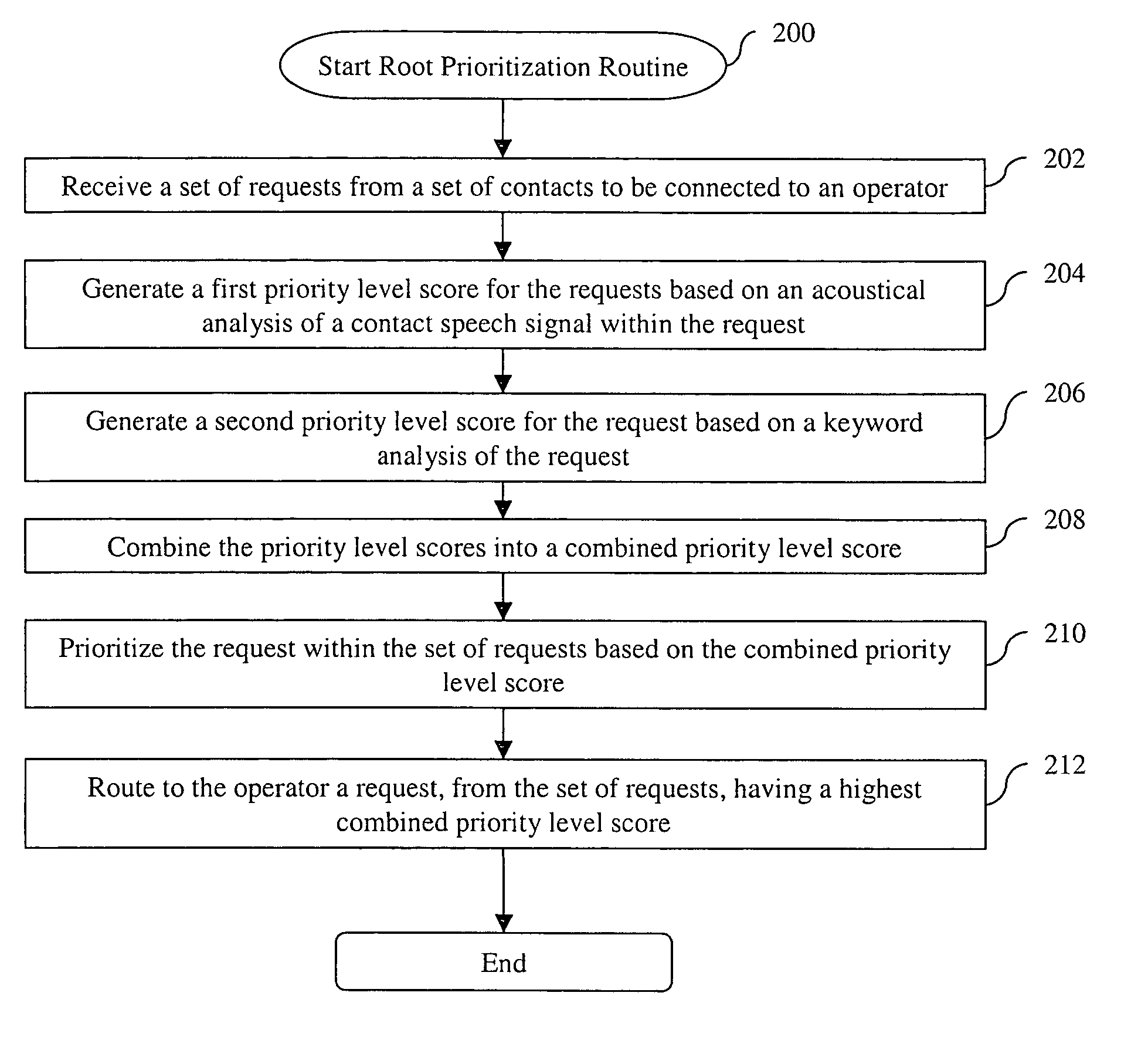
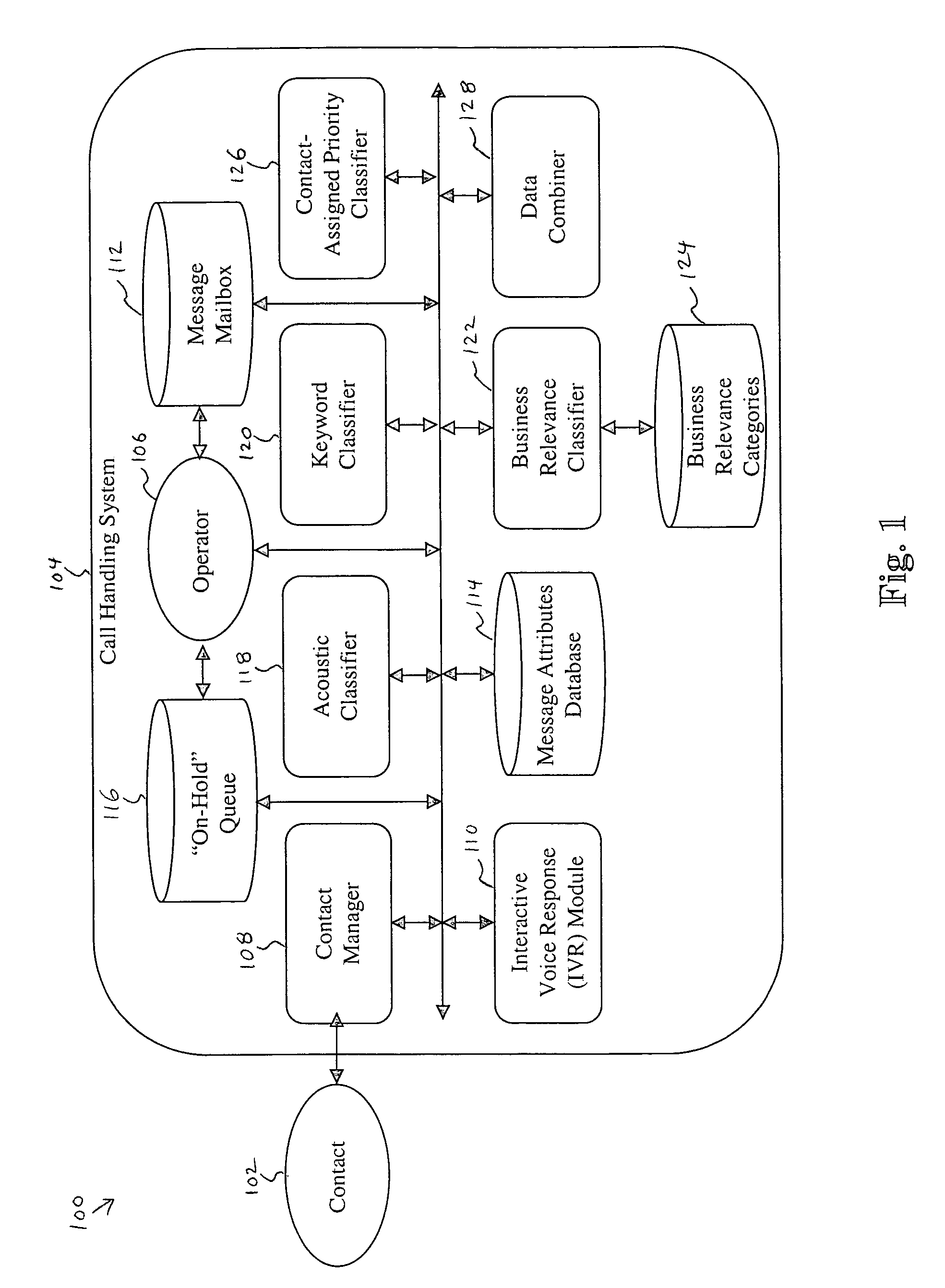
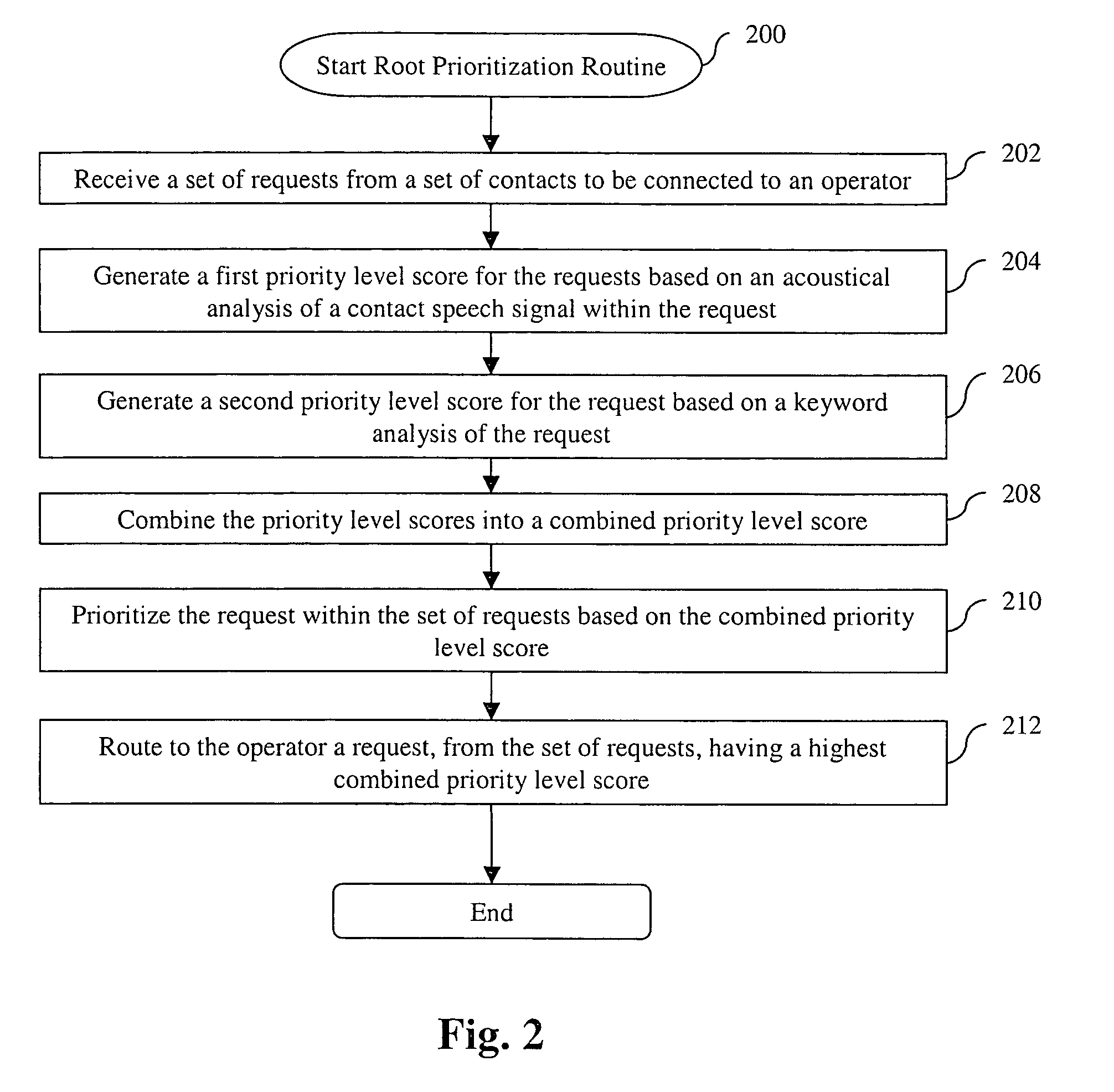
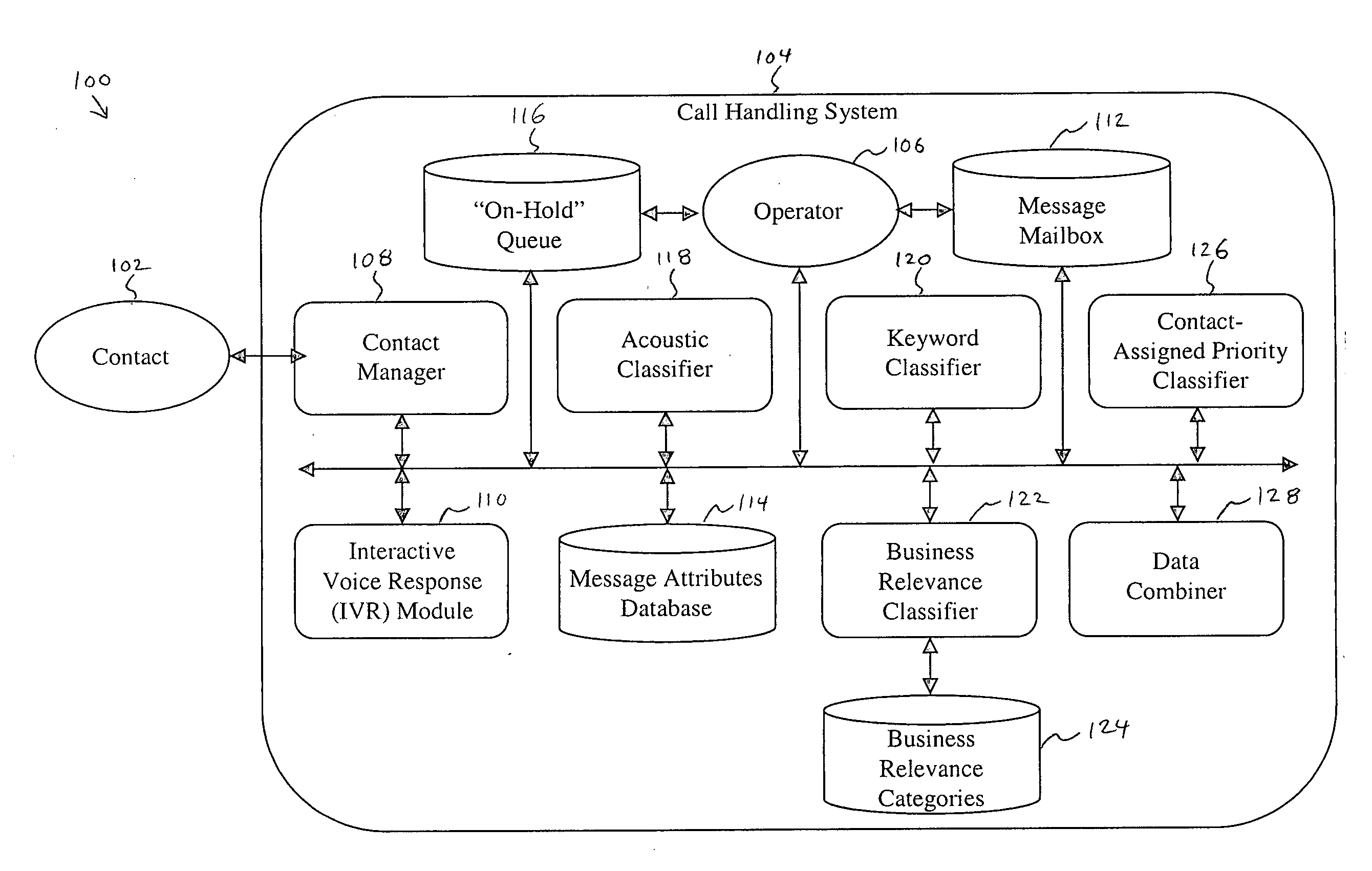
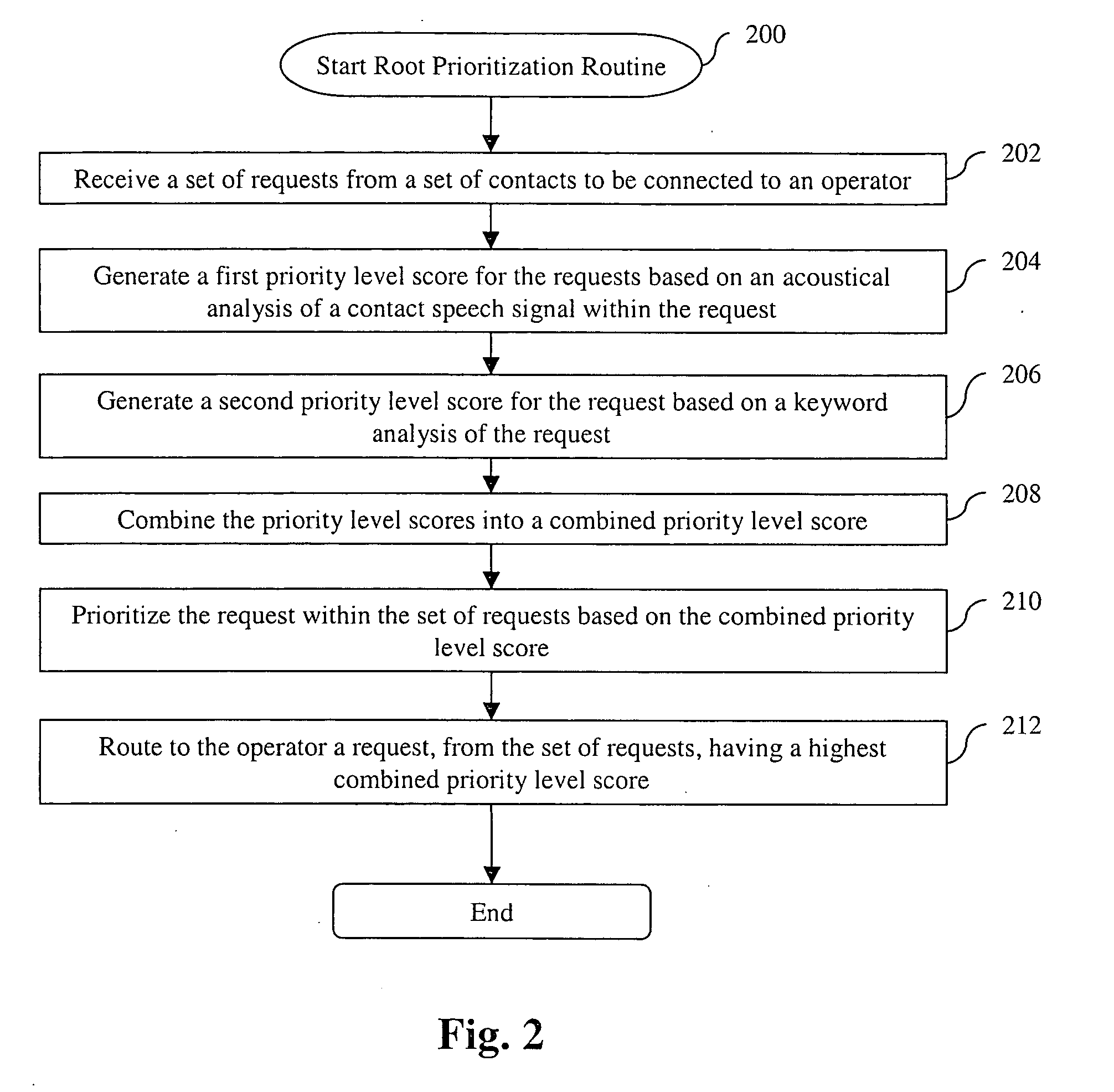
System and method for prioritizing contacts
A system and method for prioritizing contacts is disclosed. The method discloses: receiving a set of requests from a set of contacts to be connected to a recipient; generating a first priority level score for each request based on an acoustical analysis of a contact speech signal within the request; generating a second priority level score for each request based on a keyword analysis of the request; combining the priority level scores for each request into a combined priority level score; prioritizing the requests within the set of requests based on their respective combined priority level scores; and routing to the recipient that request, from the set of requests, having a highest combined priority level score. The system of the present invention includes all means and mediums for implementing the method.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
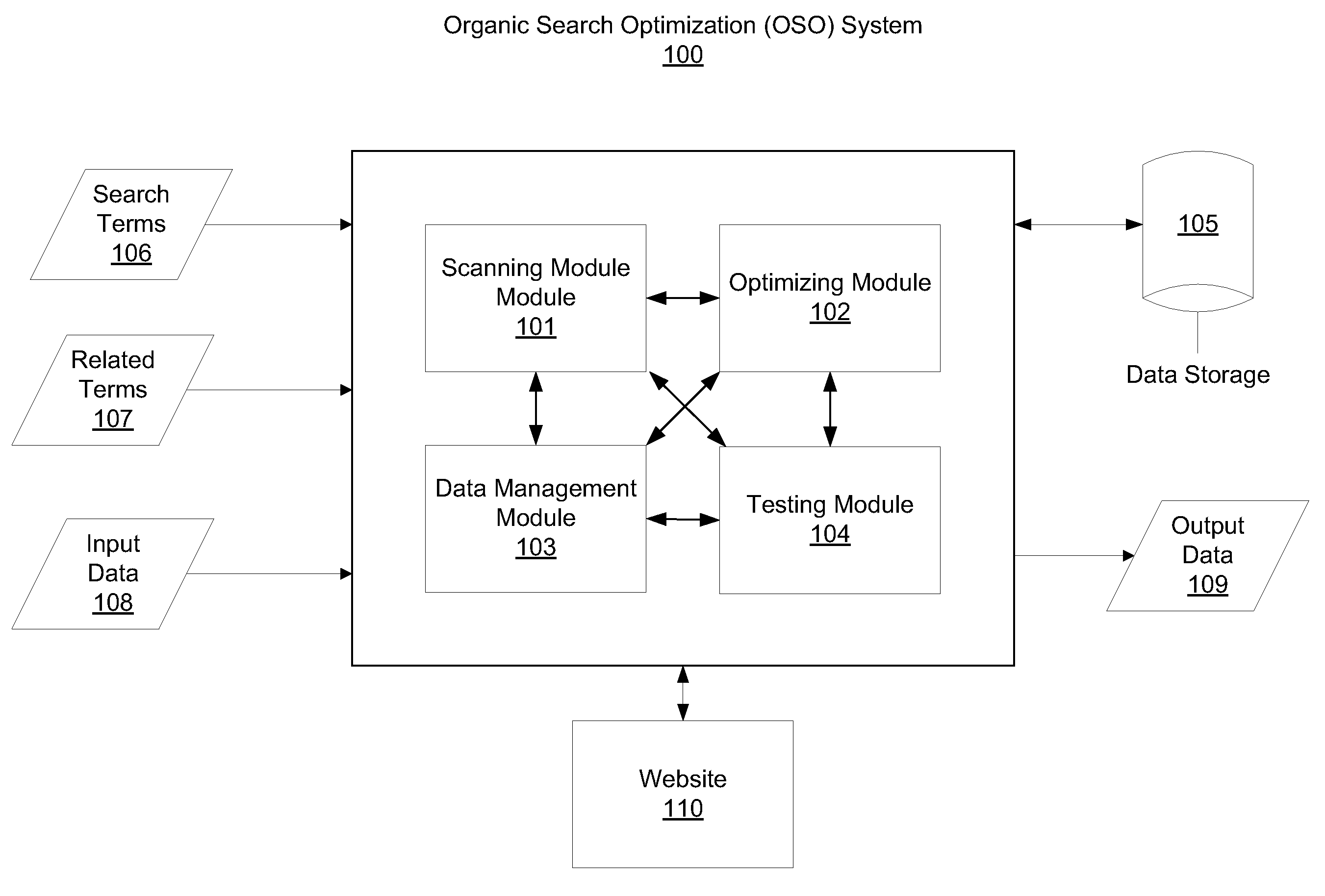
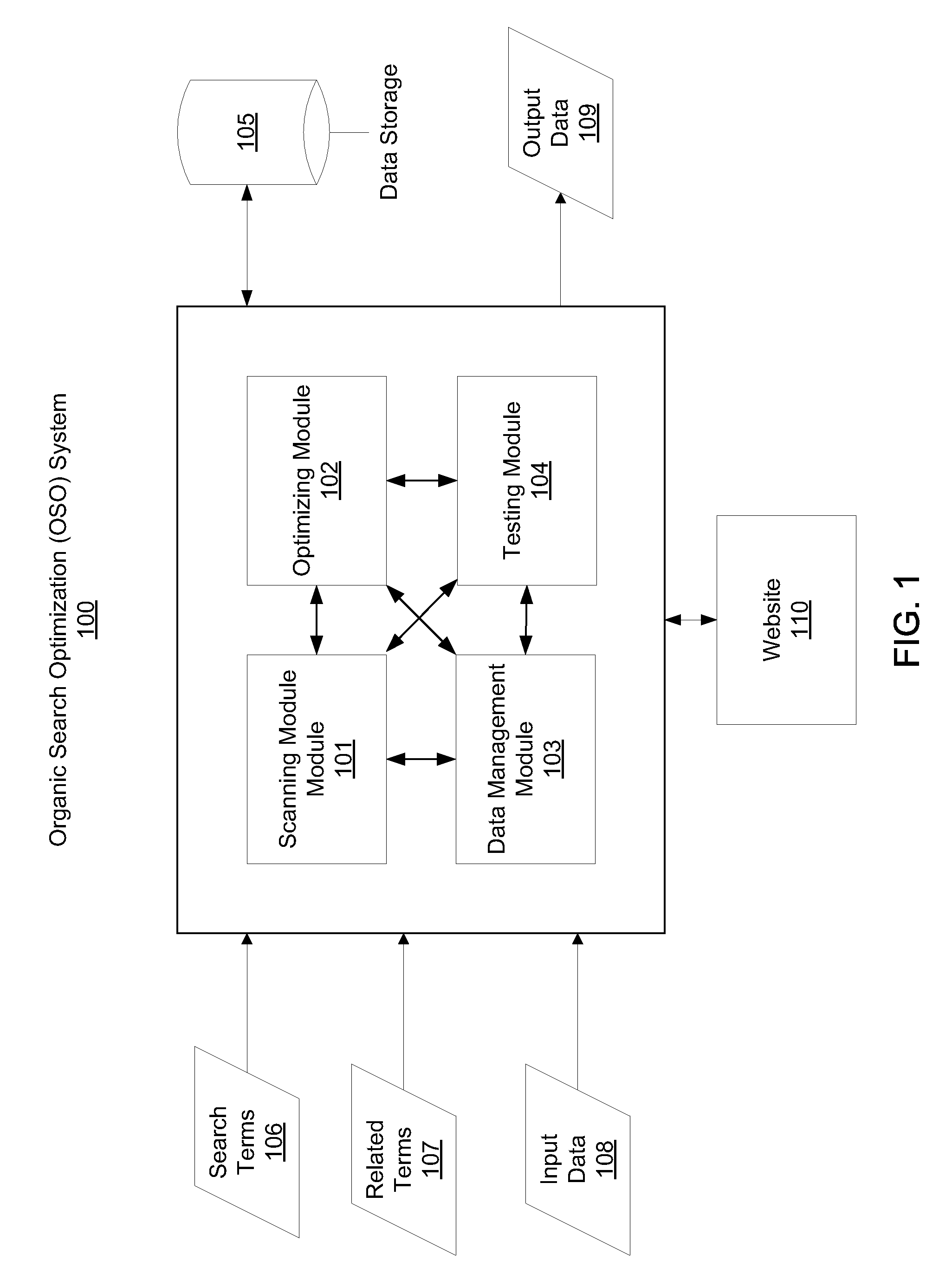
System to modify websites for organic search optimization
A system is configured to modify a website to optimize the website for an organic search of a topic. The system includes a data management module configured to receive search terms for the topic, receive related terms to the search terms for the topic, and receive website input data. The system also includes a scanning module configured to scan and index web pages and web objects in the website and identify a subset of web pages and web objects associated with the search terms and the related terms. The system also includes an optimizing module configured to process the subset of web pages and web objects from the website by prioritizing the subset of web pages and web objects or measuring a metric with respect to the subset of web pages and web objects. The search terms and related terms are deployed into the subset of web pages and web objects on the website based on the processing.
Owner:ACCENTURE GLOBAL SERVICES LTD
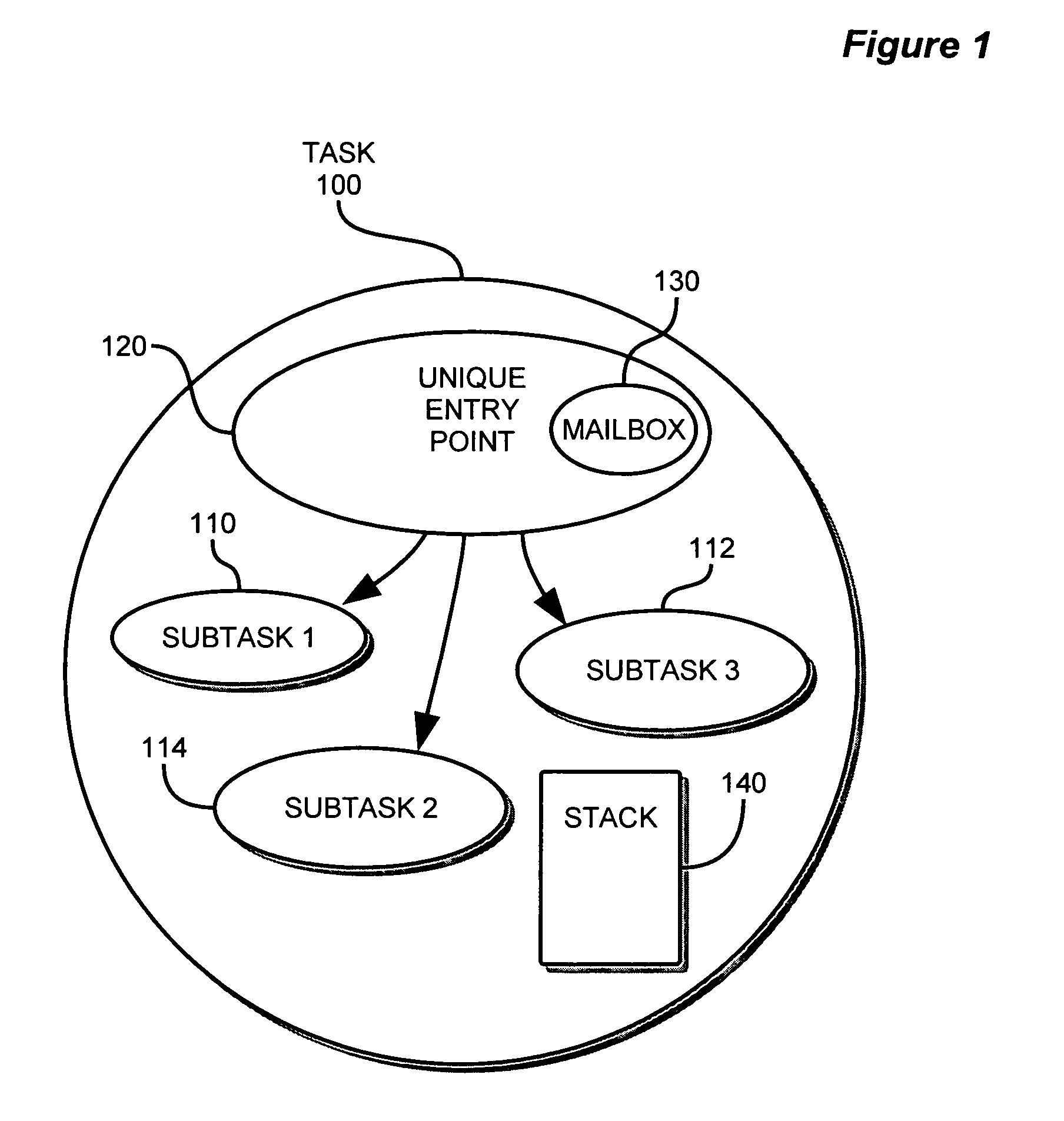
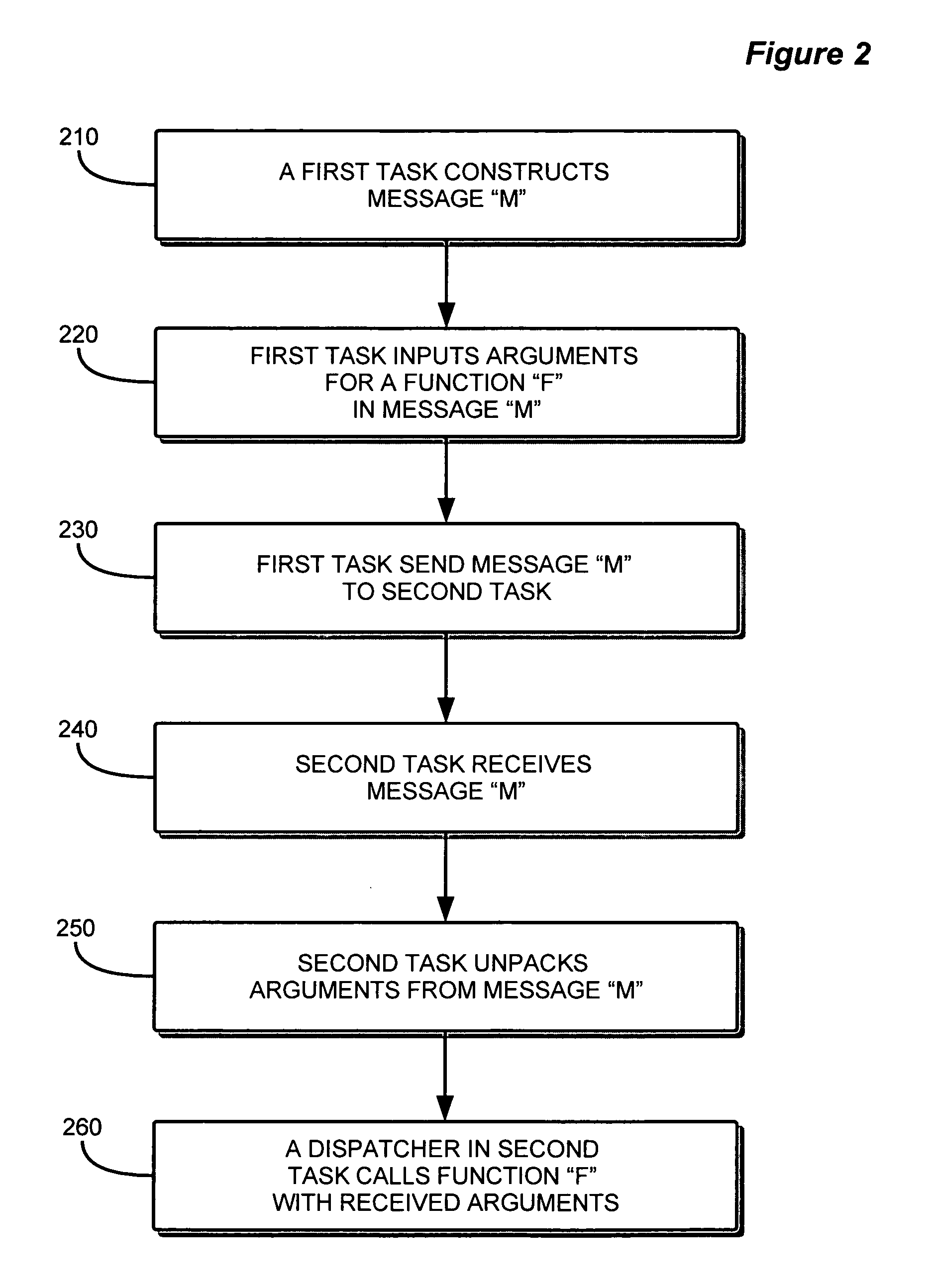
Method and apparatus for implementing task management of computer operations
InactiveUS20060107268A1Easily includedImprove performanceMultiprogramming arrangementsSpecific program execution arrangementsOperational systemPre processor
A development and runtime framework for applications that execute in real-time operating systems. Application development is enhanced through simple instructions that allow a programmer to declare functions and sets of functions as tasks and supertasks, respectively, and manage the execution of functions, tasks and supertasks with priorities. A compiler or pre-processor provides tools for generating the code for tasks and supertasks, and the management code for managing execution. Function calls may be made directly to functions within supertasks via respective entrypoints, and the tasks are managed based on the functions being invoked. Within a supertask, a higher priority function may be runnable while a lower priority function of that supertask is suspended. A cookie is used to recognize when a register update for a supertask may be omitted, enabling more efficient context switching.
Owner:SOFTWARE WIRELESS
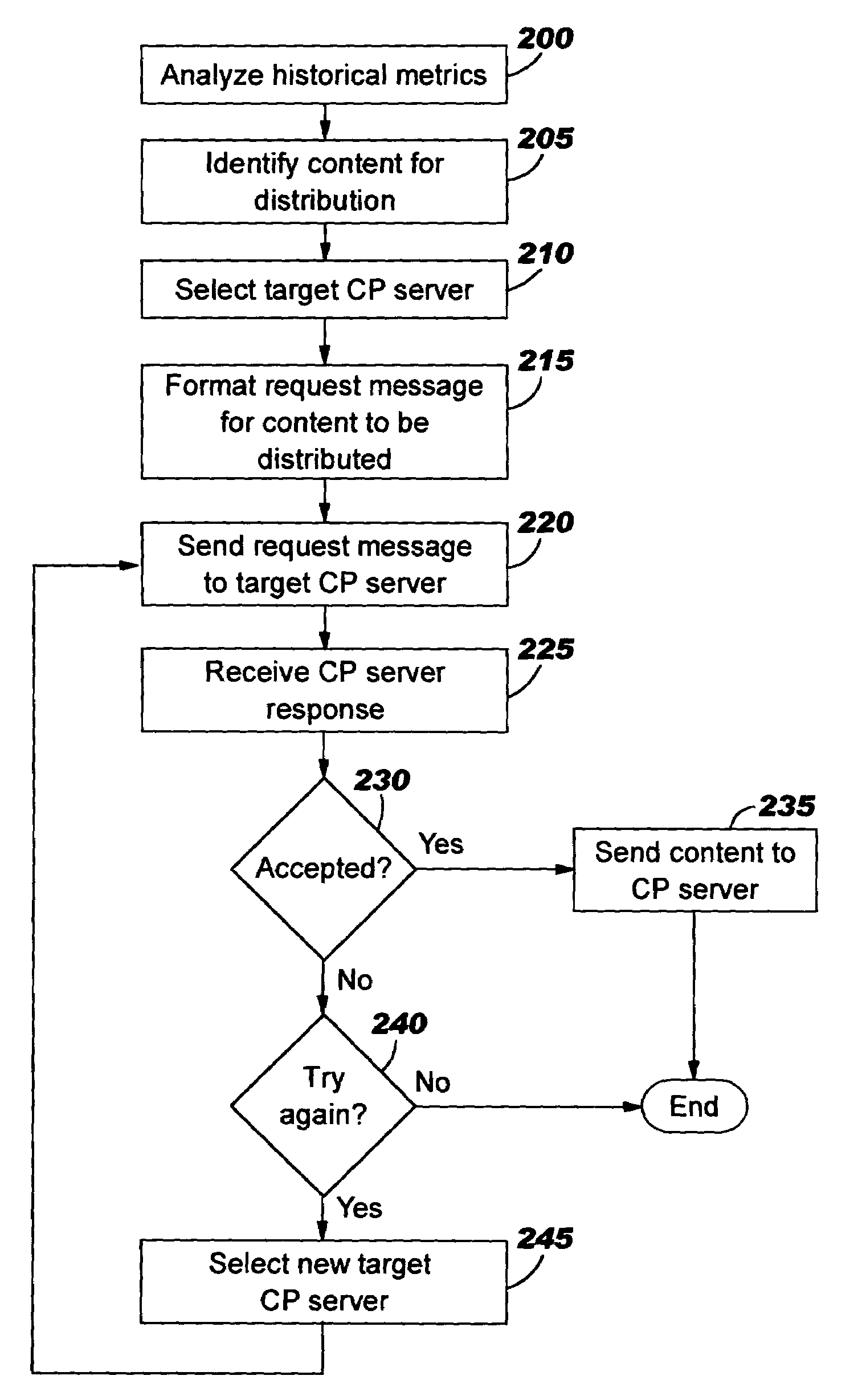
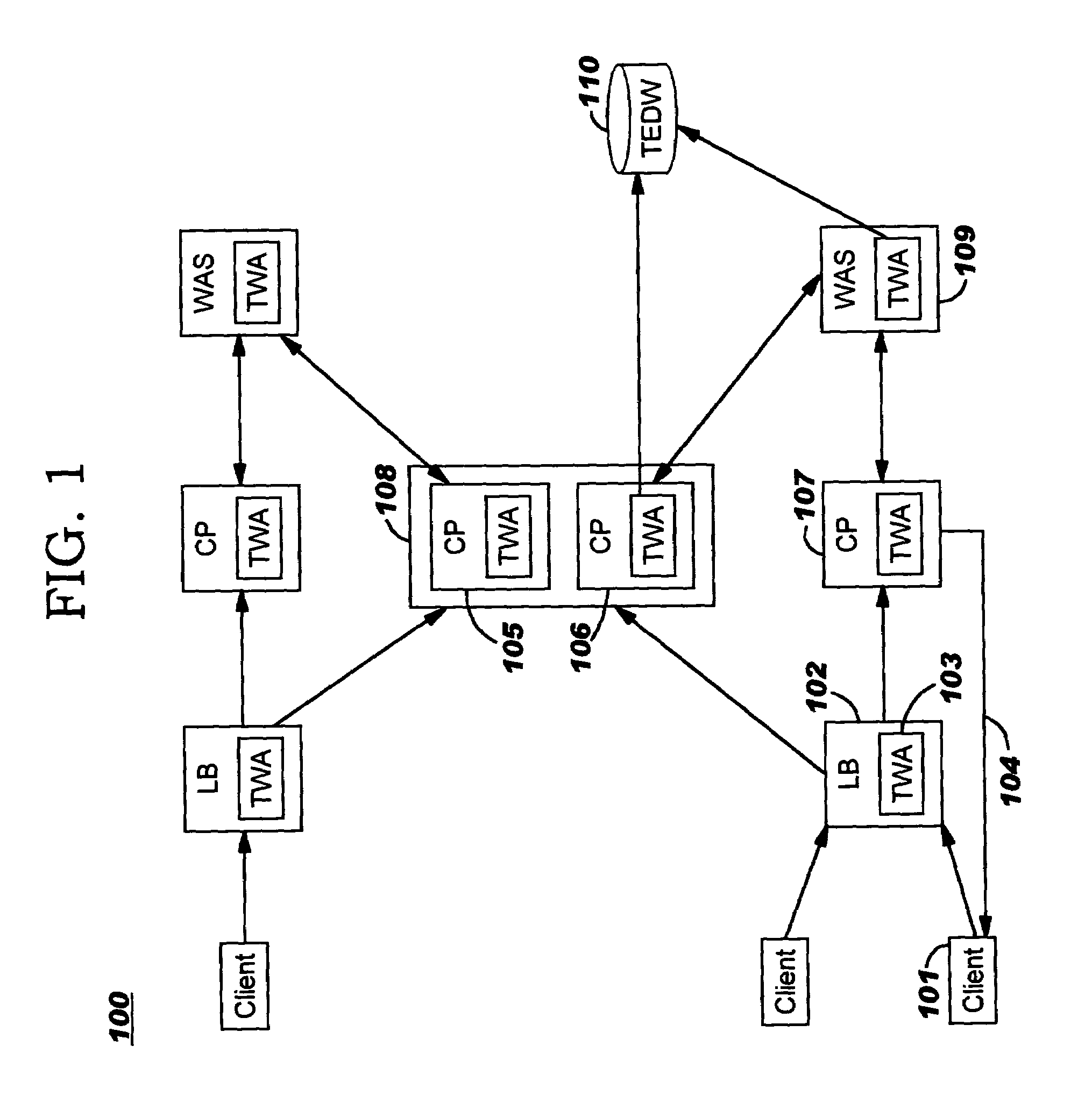
Negotiated distribution of cache content
ActiveUS7085893B2Digital data information retrievalMultiple digital computer combinationsContent distributionWeb service
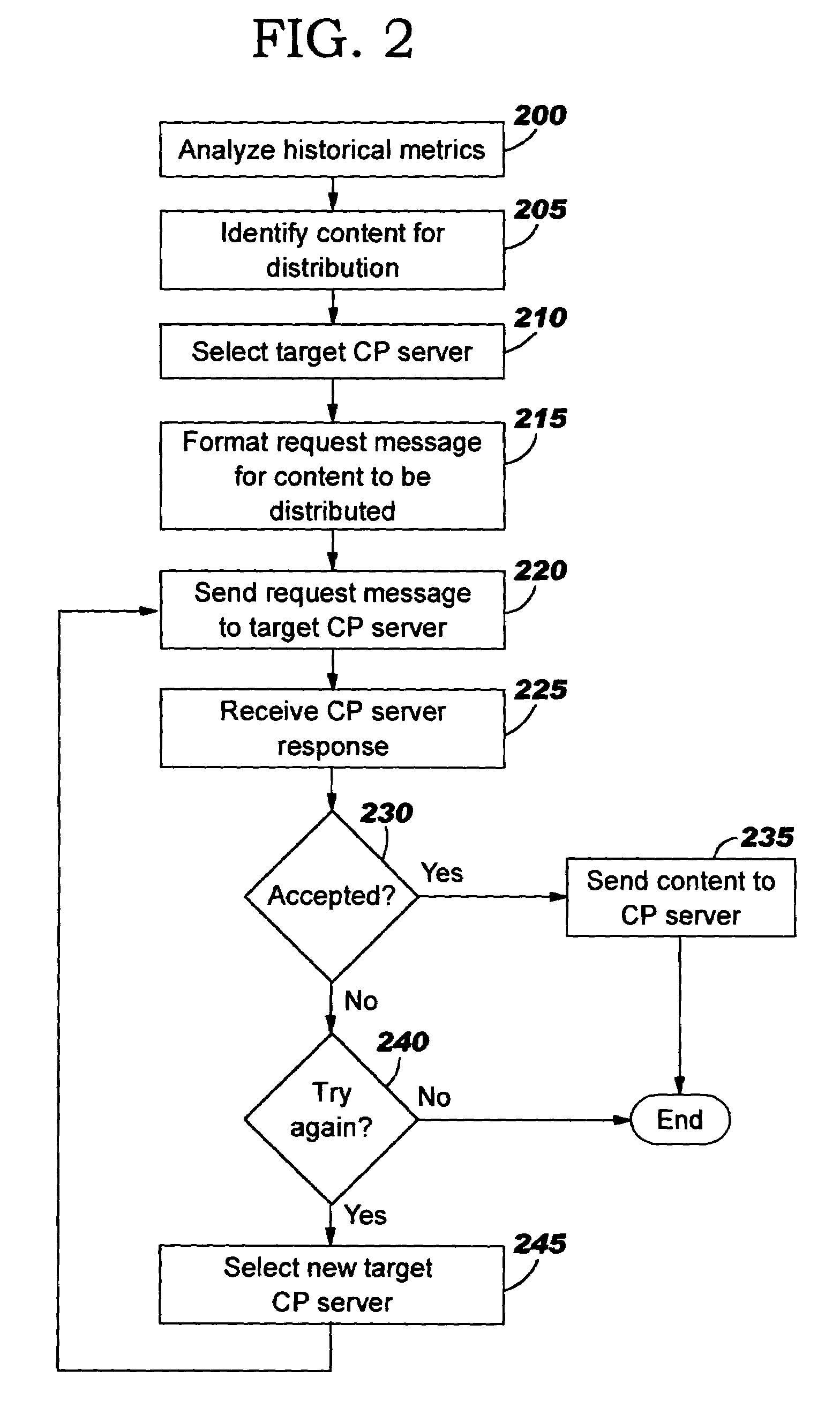
Improved caching of content at caching proxy (“CP”) servers is disclosed. In one aspect, negotiations occur before content is dynamically distributed, whereby an entity such as a Web server selects content and at least one target CP server, and sends a content distribution request to each target, describing the content to be distributed. Preferably, the selection is made by dynamically prioritizing content based on historical metrics. In another aspect, a CP server that receives a content distribution request during these negotiations determines its response to the distribution request. Preferably, content priority of already-cached content is compared to priority of the content described by the content distribution request when making the determination. In yet another aspect, a CP server selectively determines whether to cache content during cache miss processing. Preferably, this comprises comparing content priority of already-cached content to priority of content delivered to the CP server during the cache miss.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Methods and arrangements for identifying objects
ActiveUS9224184B2Improve checkout speedEasy to detectImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionRow-major orderDigital watermarking
The present disclosure relates generally to digital watermarking and grocery / retail store checkout. One claim recites a system comprising: a 2D camera for capturing imagery of packaged items, the packaged items including digital watermarking printed on product packaging; one or more processors programmed for: prioritizing at least some image areas from within at least one captured imagery frame for digital watermark detection based on: i) area brightness, and on ii) area frame location; and detecting digital watermarks from one or more image areas prioritized from the prioritizing image areas, in which the detecting digital watermarks analyzes image areas in order of prioritization. Of course, other features, combinations and claims are also provided.
Owner:DIGIMARC CORP
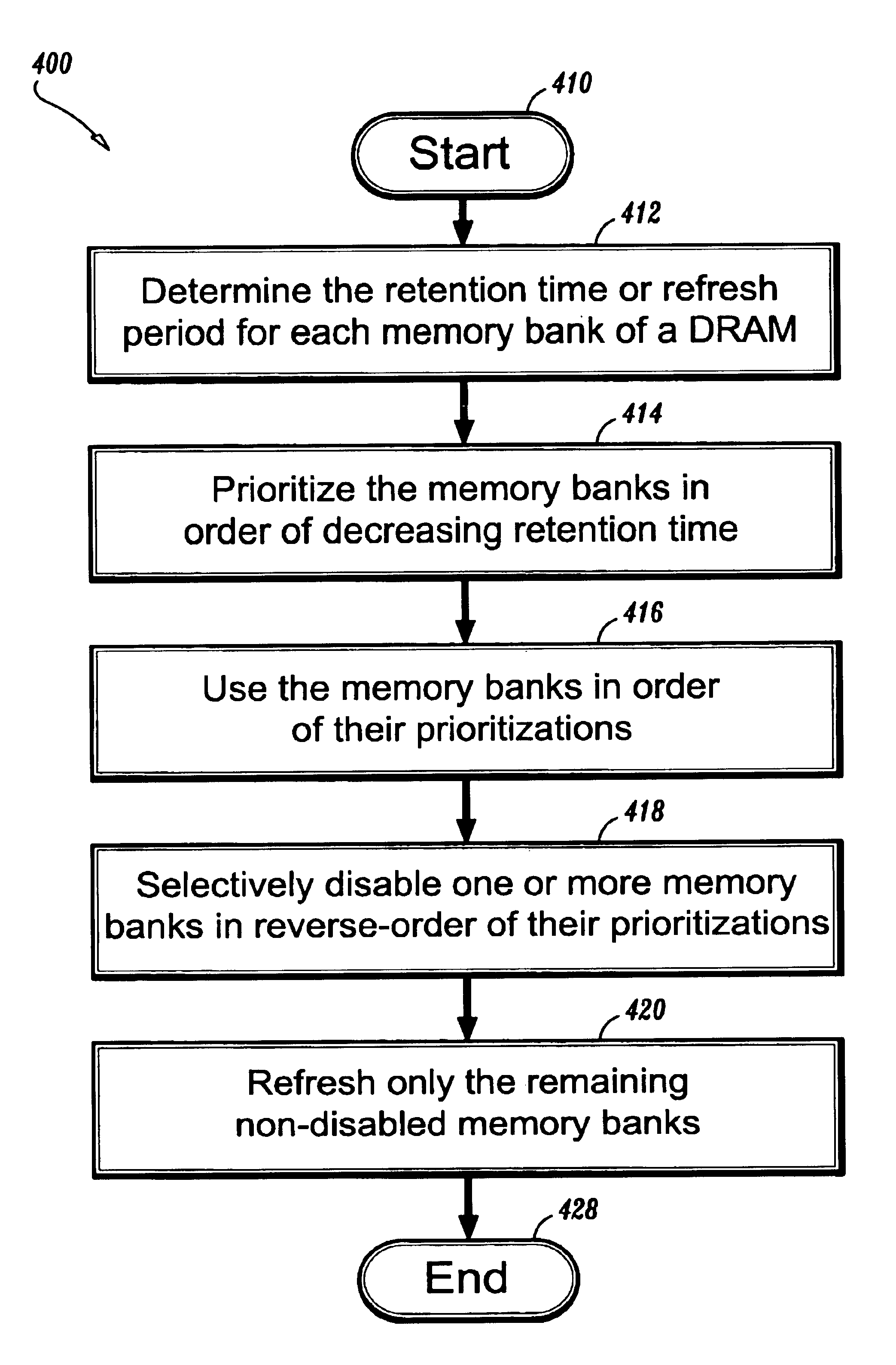
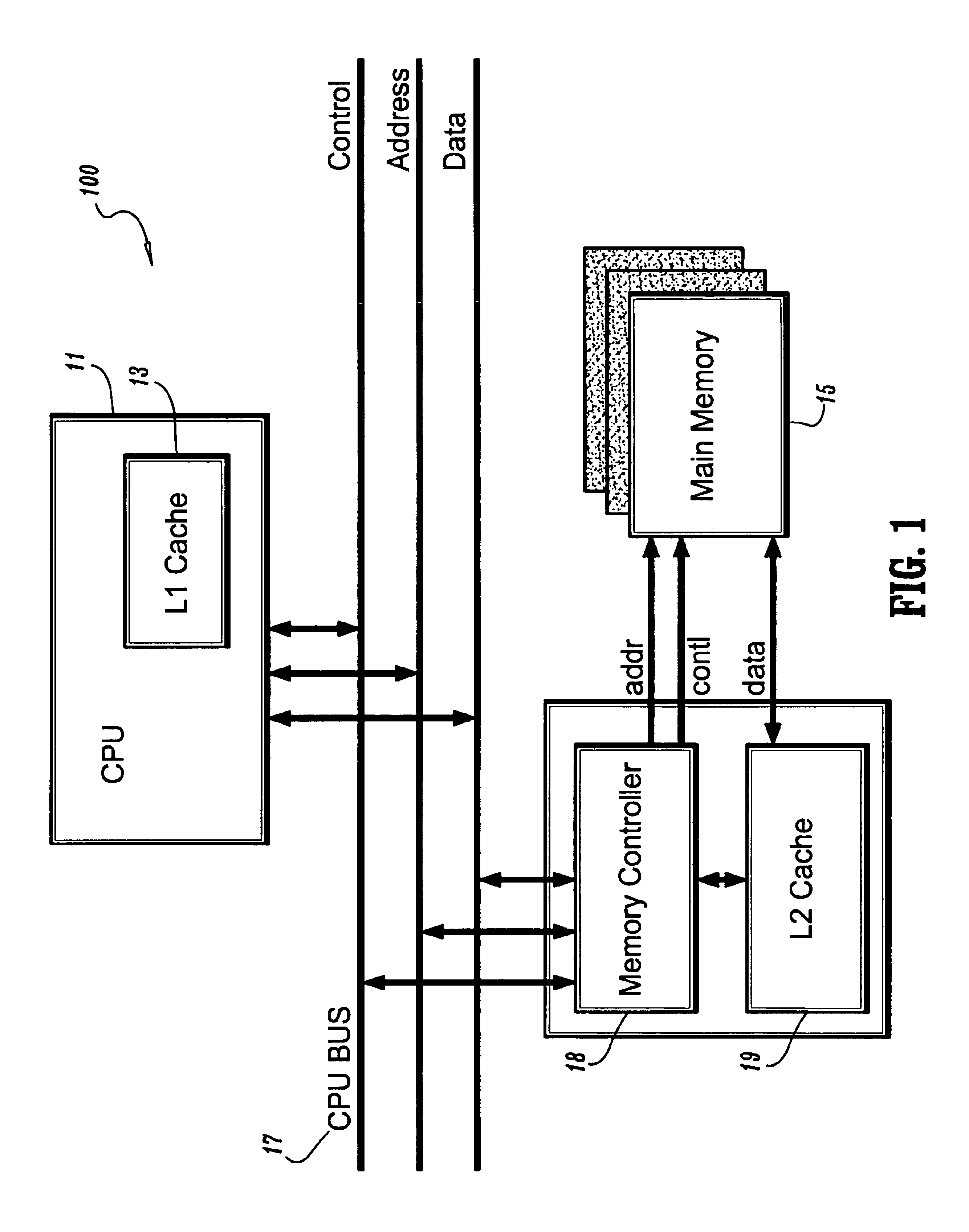
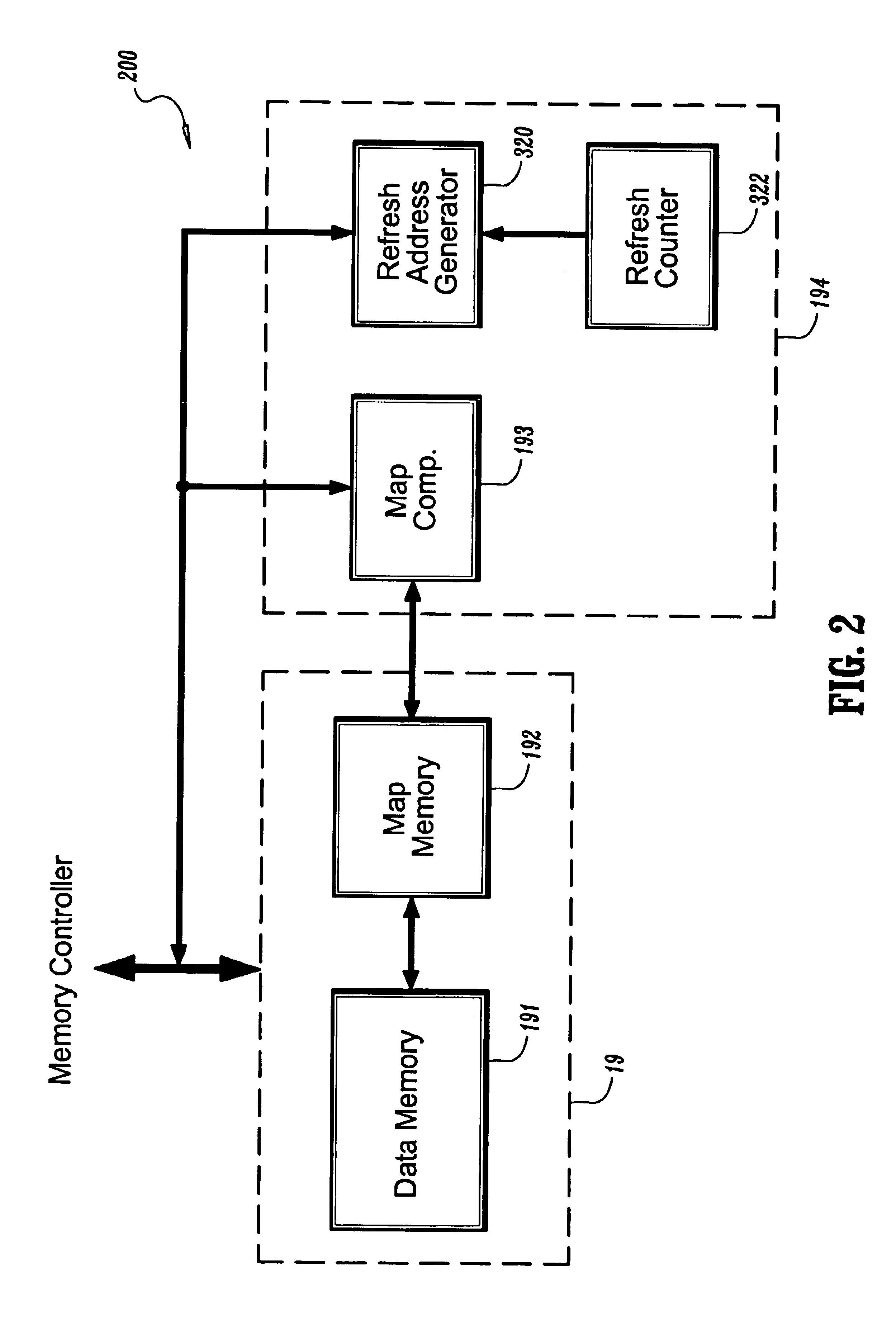
Bank address mapping according to bank retention time in dynamic random access memories
InactiveUS6920523B2Memory architecture accessing/allocationEnergy efficient ICTStatic random-access memoryRetention time
A system and method for refreshing data in a dynamic random access memory (“DRAM”) is provided, where the system includes a data memory having a plurality of memory banks, a map memory in signal communication with the data memory for translating an internal address of each of the plurality of memory banks into a corresponding external address, a map comparator in signal communication with the map memory for selectively enabling a memory bank in accordance with its external address, a refresh address generator in signal communication with the map comparator for selectively refreshing the enabled memory bank in accordance with its external address, and a refresh counter in signal communication with the refresh address generator for signaling a refresh in accordance with the maximum required refresh time of the enabled memory bank; and where the corresponding method includes determining the maximum required refresh period for each of the memory banks, respectively, prioritizing the memory banks in accordance with their respective refresh periods, utilizing the memory banks in order of their respective prioritizations, selectively disabling at least one of the memory banks in reverse-order of their respective prioritizations, and refreshing only the remaining non-disabled memory banks.
Owner:POLARIS INNOVATIONS LTD
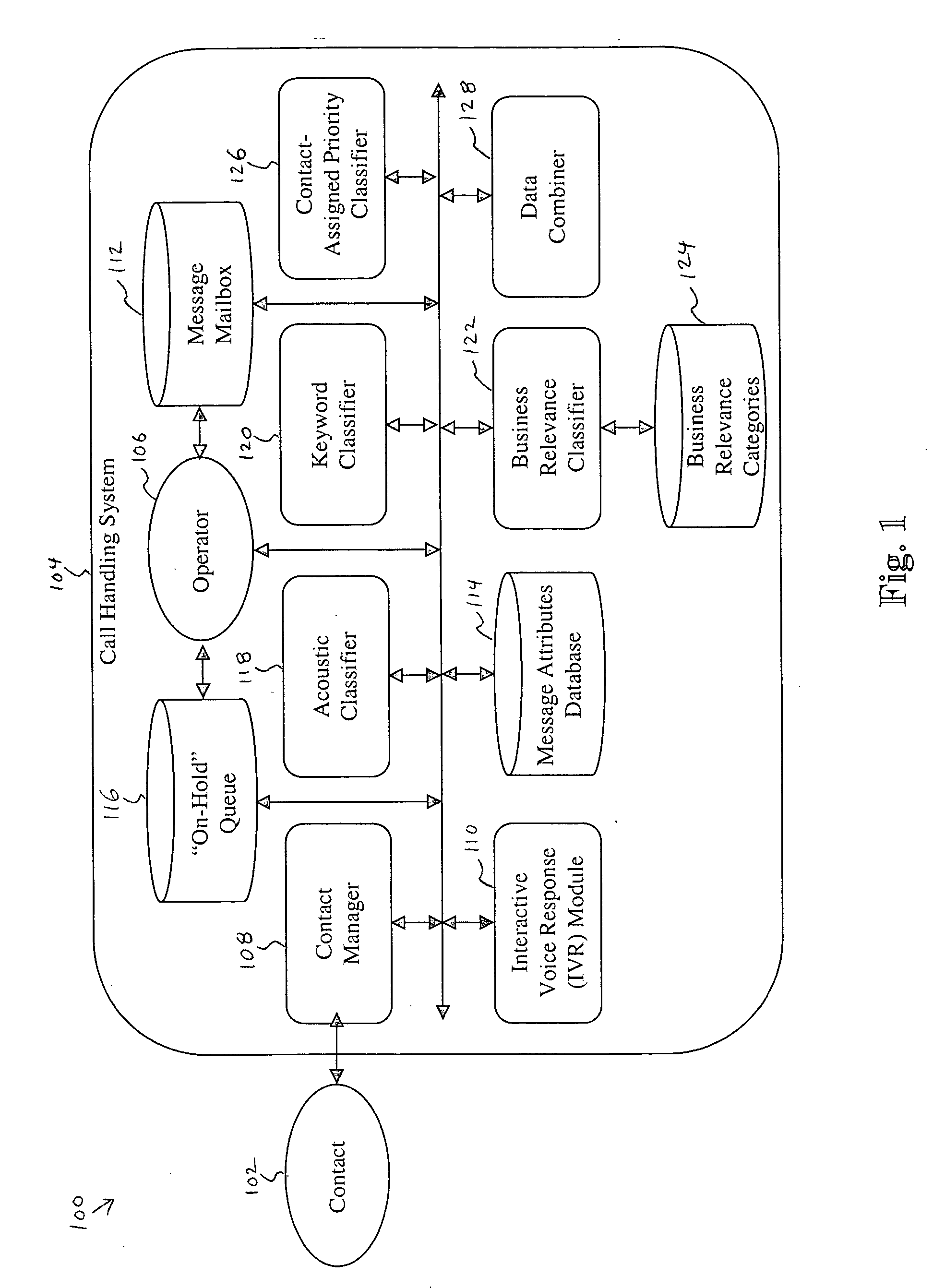
System and method for prioritizing contacts
A system and method for prioritizing contacts is disclosed. The method discloses: receiving a set of requests from a set of contacts to be connected to a recipient; generating a first priority level score for each request based on an acoustical analysis of a contact speech signal within the request; generating a second priority level score for each request based on a keyword analysis of the request; combining the priority level scores for each request into a combined priority level score; prioritizing the requests within the set of requests based on their respective combined priority level scores; and routing to the recipient that request, from the set of requests, having a highest combined priority level score. The system of the present invention includes all means and mediums for implementing the method.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
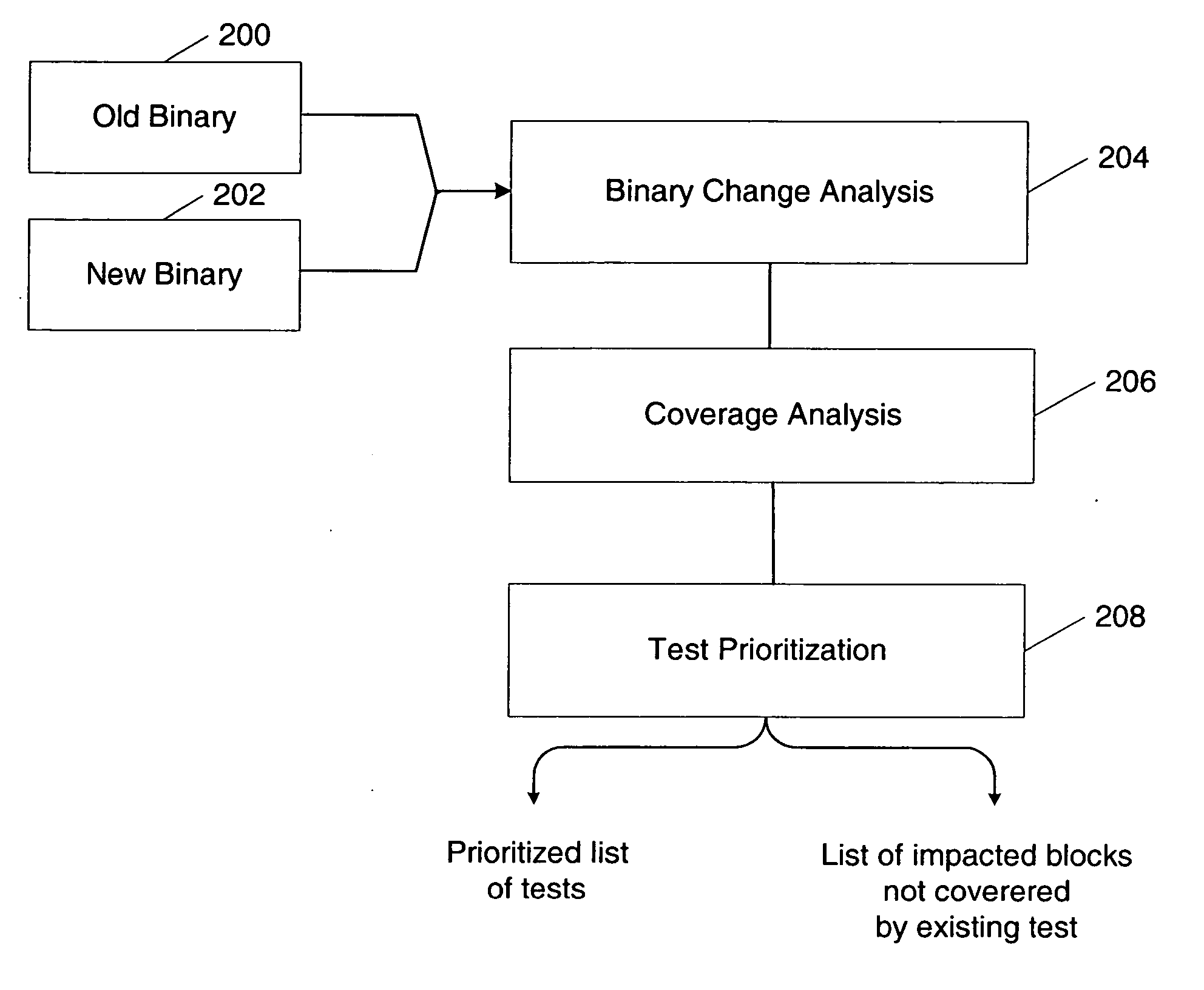
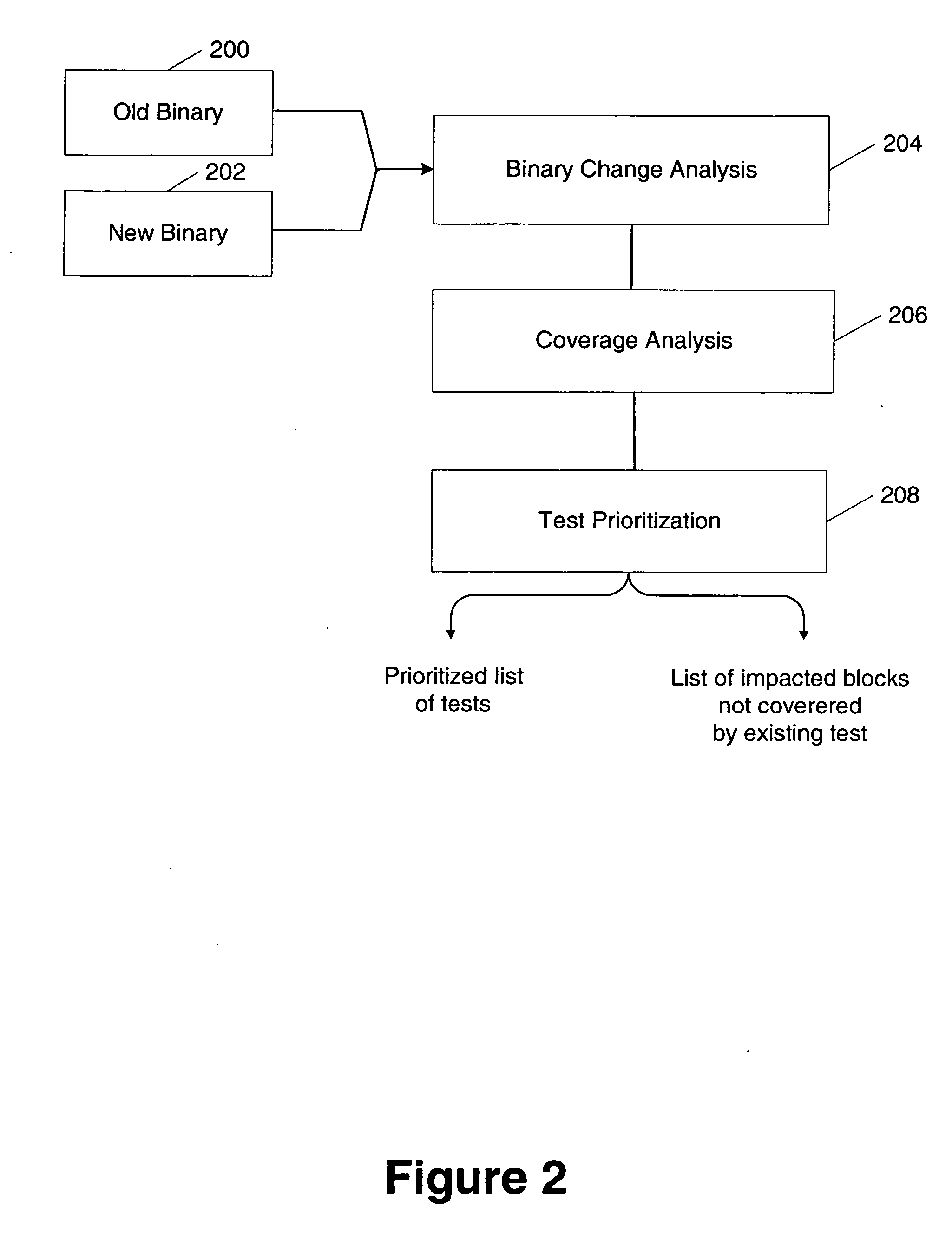
Method and apparatus for prioritizing software tests
InactiveUS20060129994A1Raise priorityHighly prioritizedSoftware testing/debuggingSpecific program execution arrangementsComputerized systemRow-major order
A computer system and method is provided for prioritizing software tests. Software tests are prioritized based on coverage indicators for the software tests and an indication of impacted areas of the software. Each of the coverage indicators indicates which portions of the software are executed for a respective one of the software tests. The portions of the software include at least one of a plurality of blocks. The indication of impacted areas of the software indicates ones of the plurality of blocks that are modified or new with respect to a previous version of the software. A prioritized list of software tests is output. The prioritized list includes at least one test sequence.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Internet search engine with browser tools
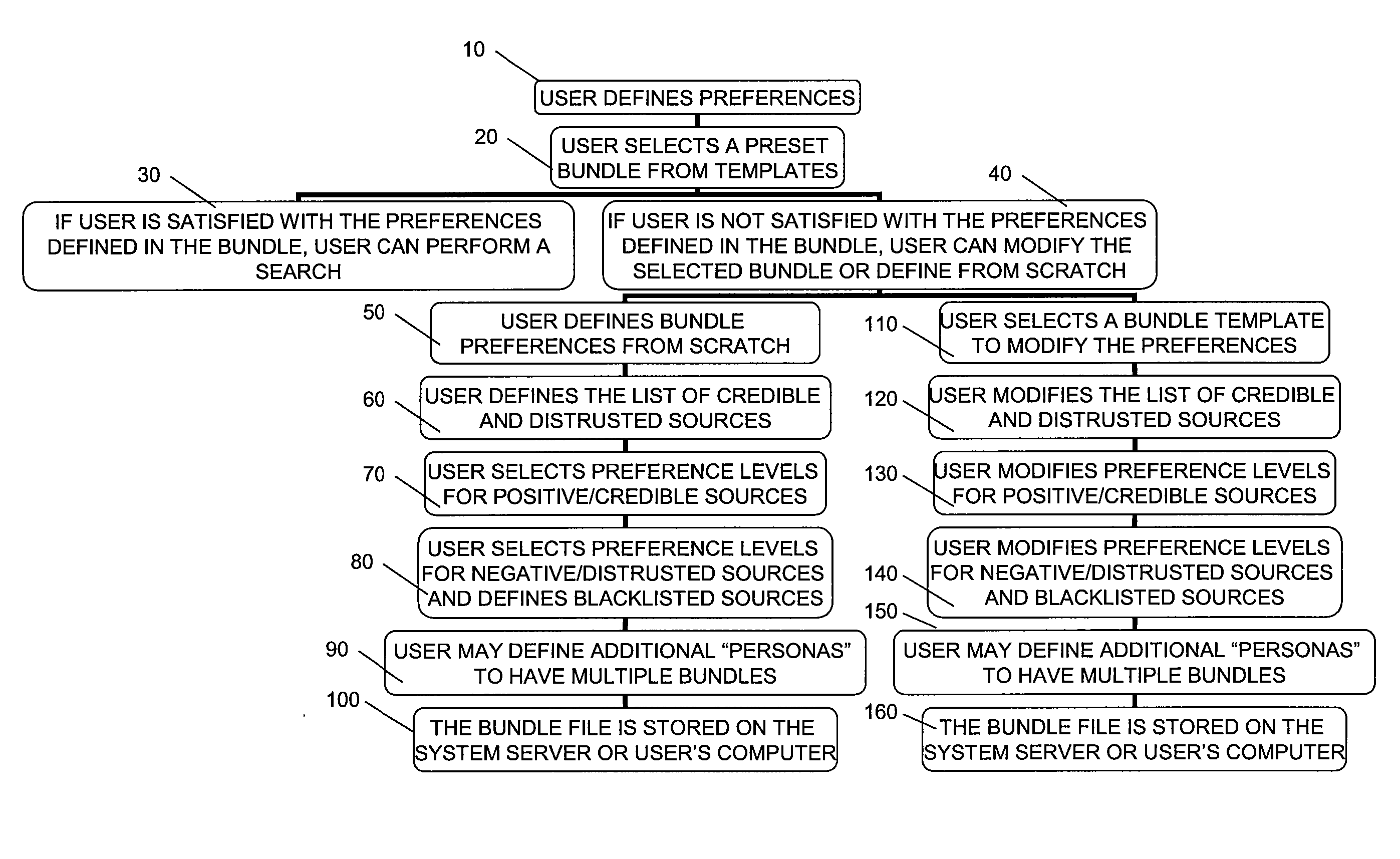
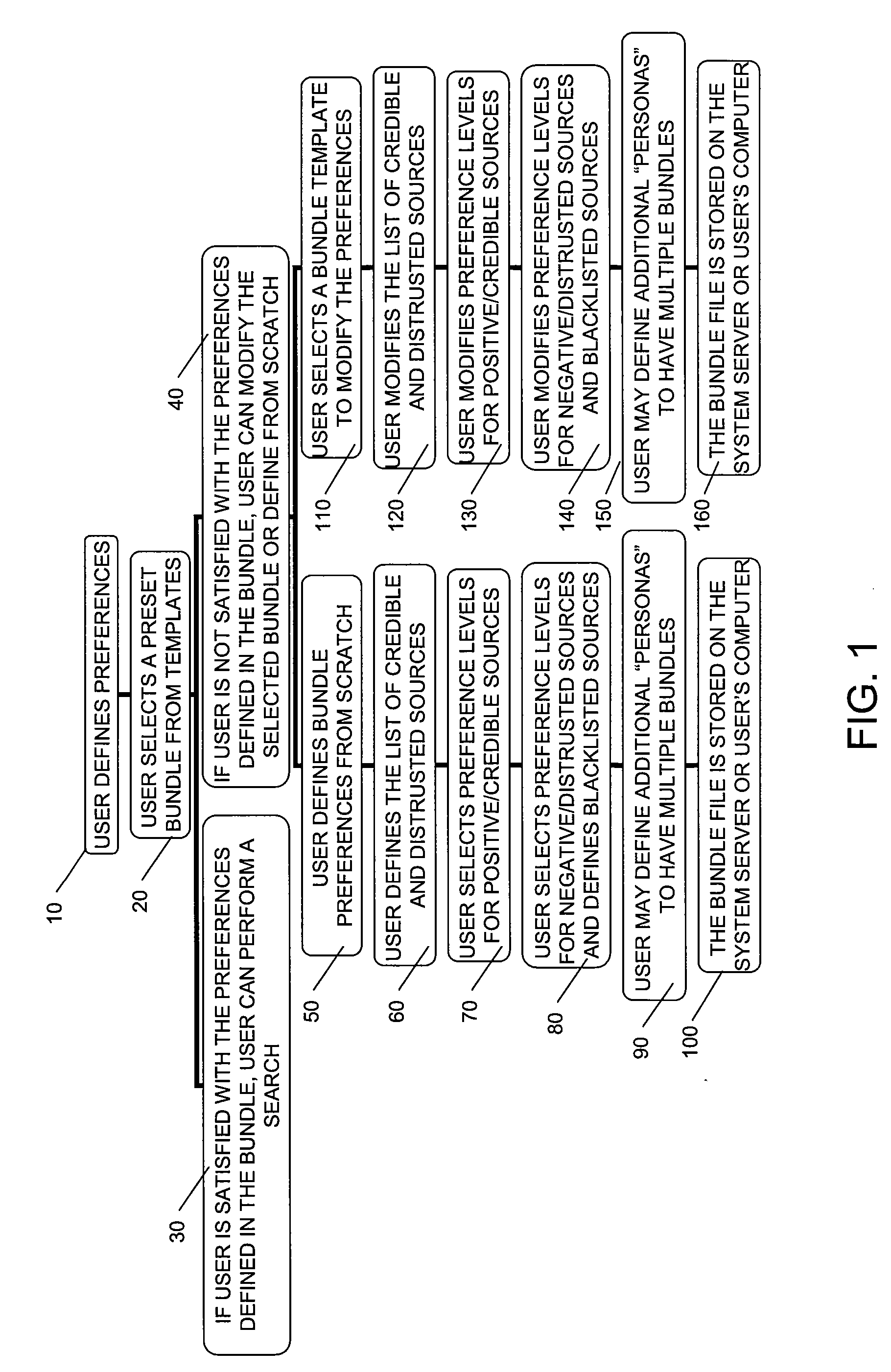
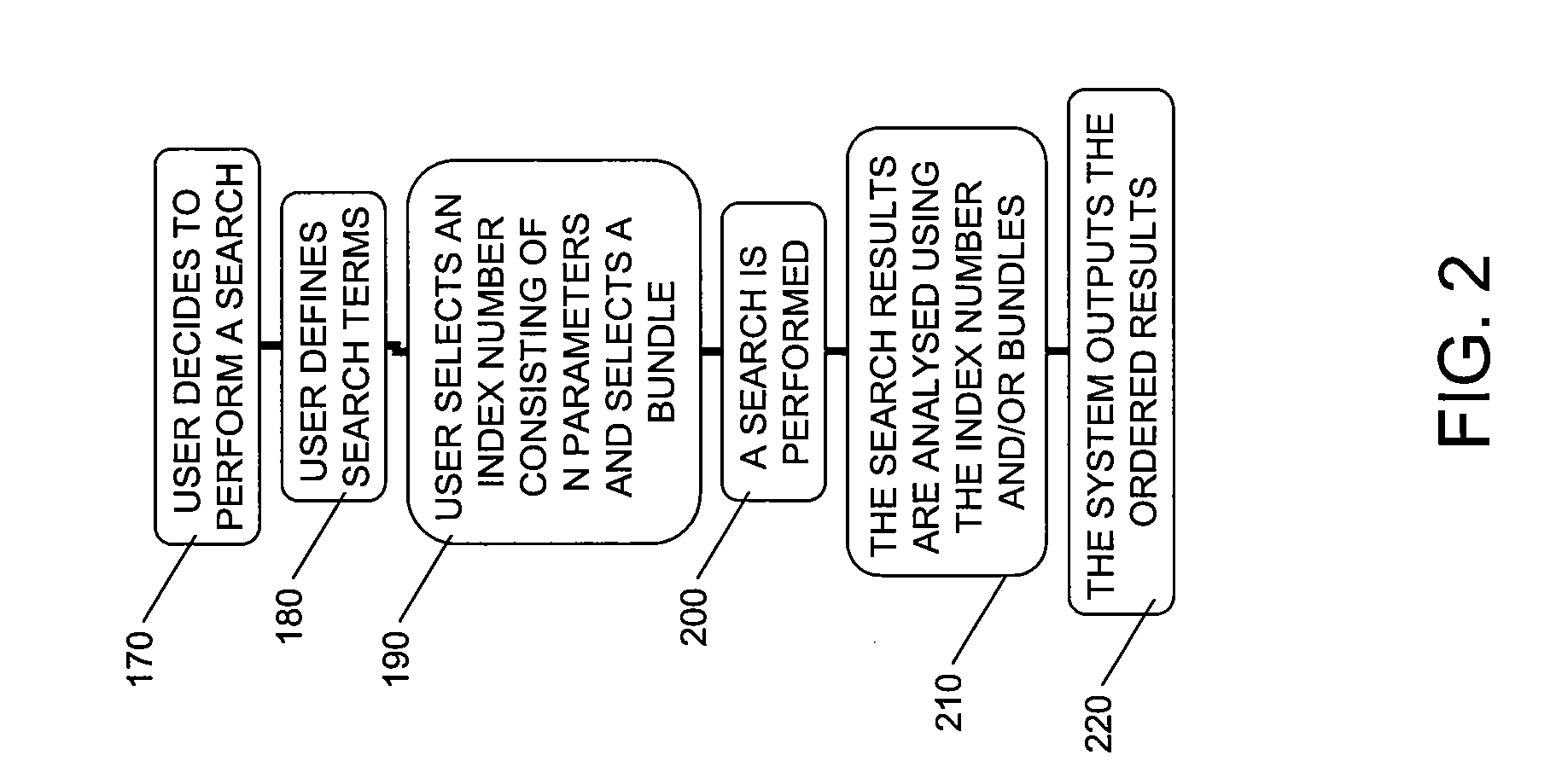
A system and method for searching the Internet is presented wherein the search results are ordered and selected using one or more preference tools. One such tool consists of the user defining a reference index number that is employed to prioritize and re-rank at least some of the sites obtained by the search, comparing each site's parameters to the reference index number. Each index number includes several parameters in a preset order, each parameter being assigned a quantized relevance based on particular search criteria. Another tool makes use of at least one bundle of websites having particular user-settings designating credibility or trustworthiness. Websites from the search results are then accepted or ordered based on the contents of the bundles. Other tools adjust search criteria based on a desired number of search results and separate browser cookies into (1) those personally trusted and (2) all other cookies that are routinely purged.
Owner:ABRAMS DANIEL L
Packet transmission scheduling in a data communication network
InactiveUS20020126690A1Easy to handleRadio transmissionNetworks interconnectionHeap (data structure)Fair queuing
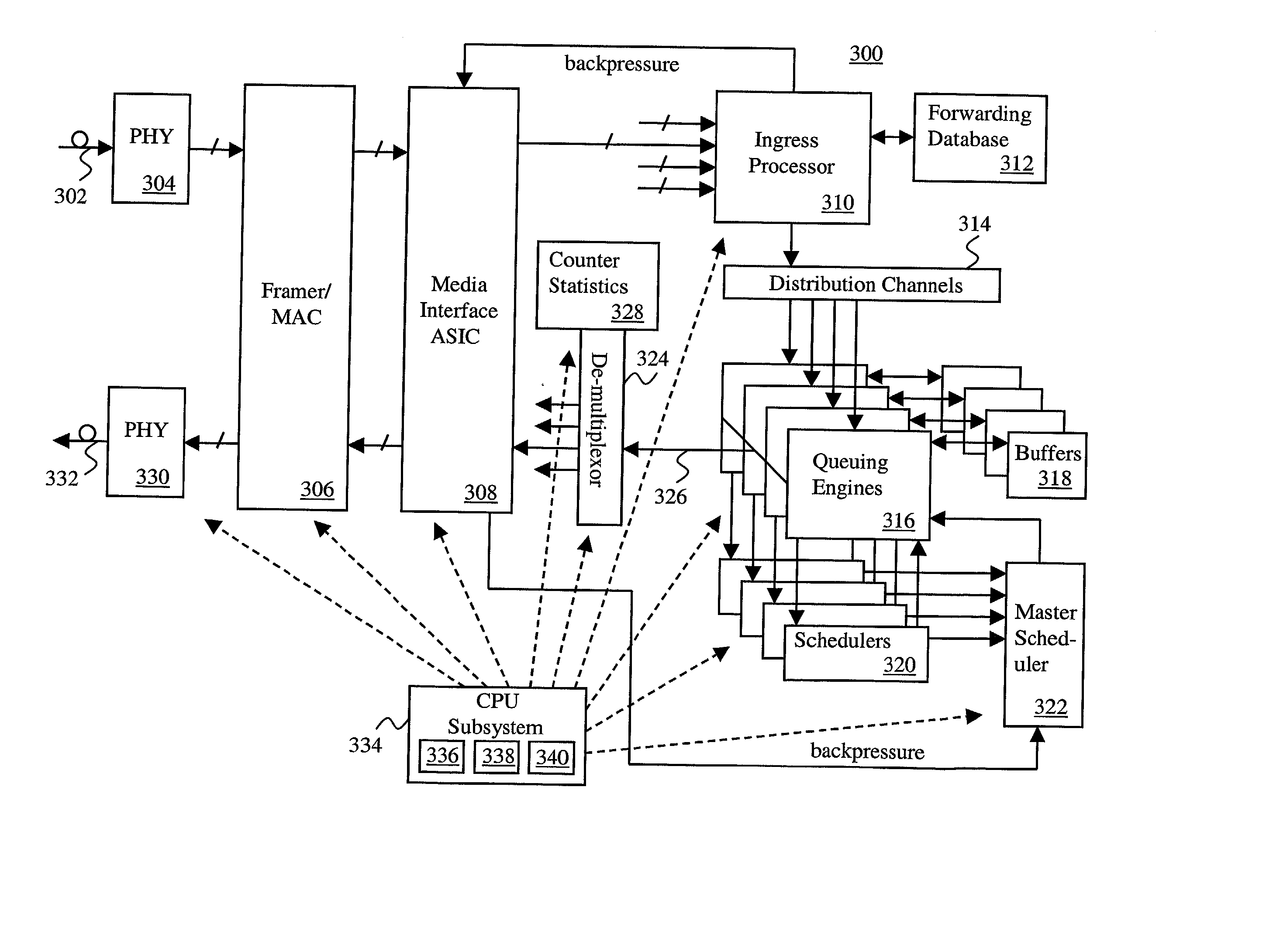
The present invention is directed toward methods and apparatus for packet transmission scheduling in a data communication network. In one aspect, received data packets are assigned to an appropriate one of a plurality of scheduling heap data structures. Each scheduling heap data structure is percolated to identify a most eligible data packet in each heap data structure. A highest-priority one of the most-eligible data packets is identifying by prioritizing among the most-eligible data packets. This is useful because the scheduling tasks may be distributed among the hierarchy of schedulers to efficiently handle data packet scheduling. Another aspect provides a technique for combining priority schemes, such as strict priority and weighted fair queuing. This is useful because packets may have equal priorities or no priorities, such as in the case of certain legacy equipment.
Owner:MAPLE OPTICAL SYST
Method and system for prioritizing data values for robust data representation
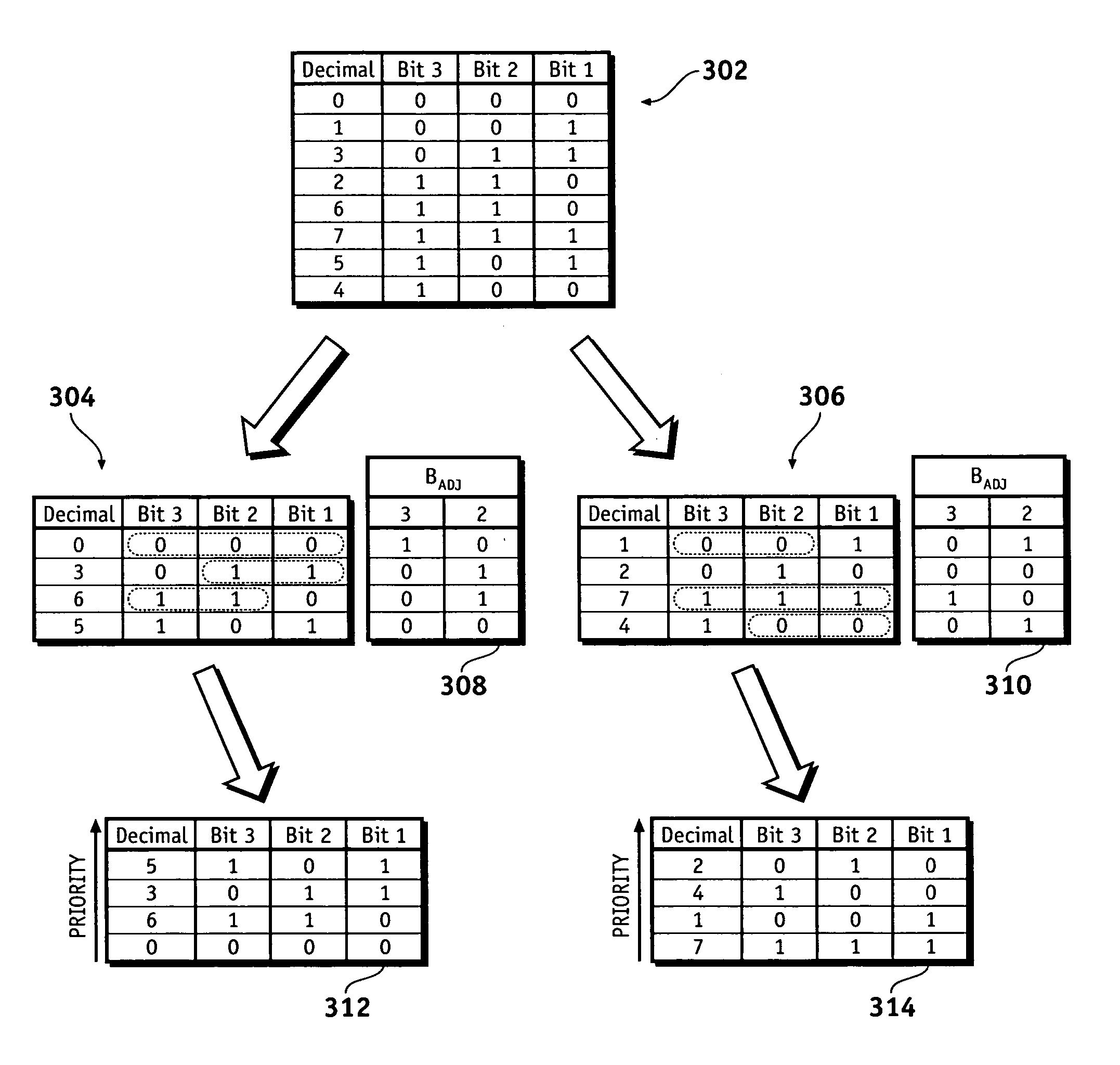
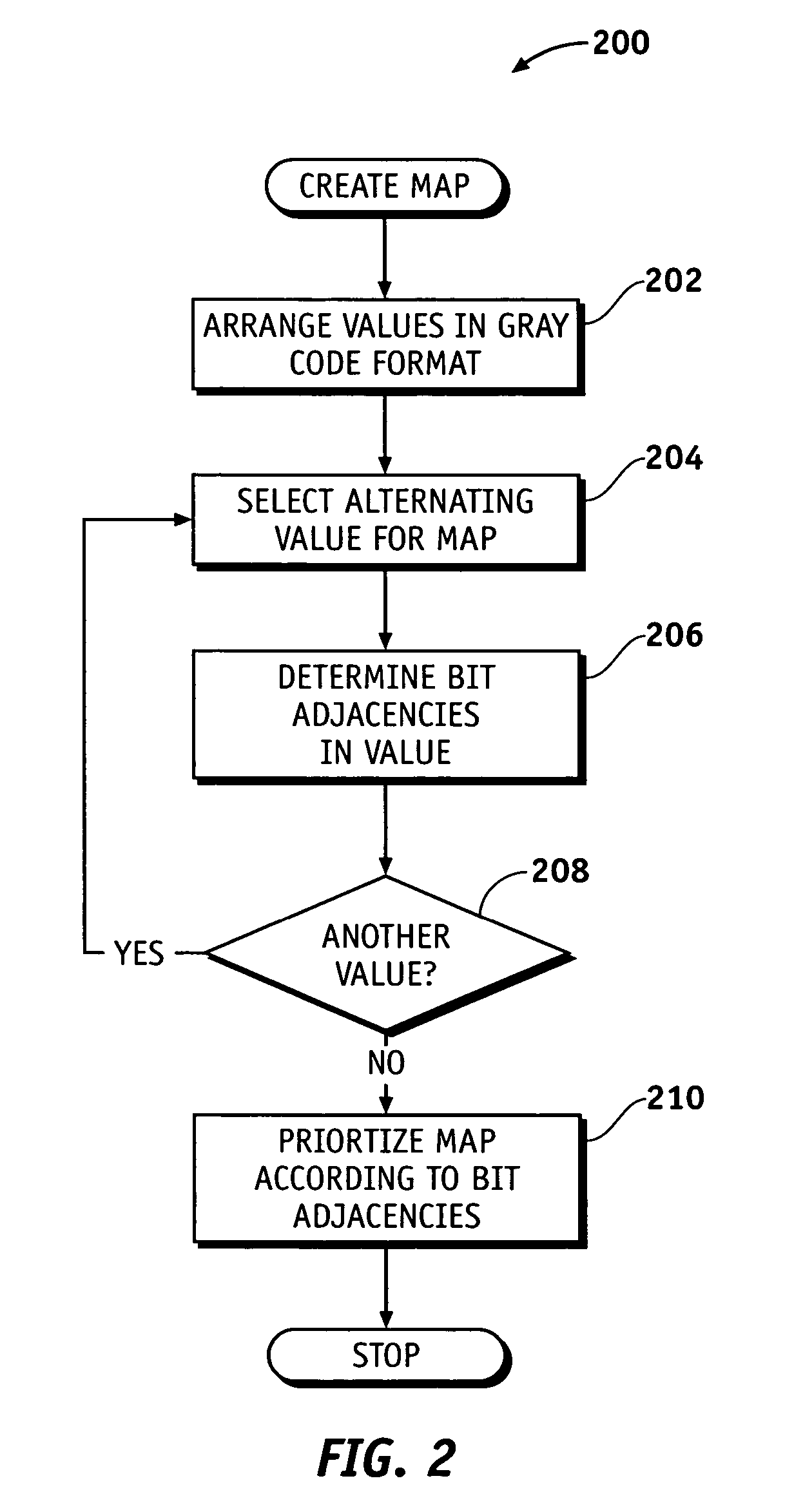
InactiveUS7242329B2Reduce needReduce sensitivityDigital data processing detailsCode conversionTheoretical computer scienceRow-major order
Methods, systems and data structures select prioritized robust data values from a plurality of available data values formed by a plurality of data bits, each capable of exhibiting a bit value. Available data values are arranged into a gray code format, and alternate values of gray code format are selected to form a value map. An optional complementary value map may also be formed from the remaining data values. The value map is then prioritized according to bit adjacencies, wherein bit adjacencies are defined by contiguous bits within one of the data values that exhibit a common bit value. Priority may be given to data values having shortest and / or fewest bit adjacencies.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Method and apparatus with dynamic graphics surface memory allocation
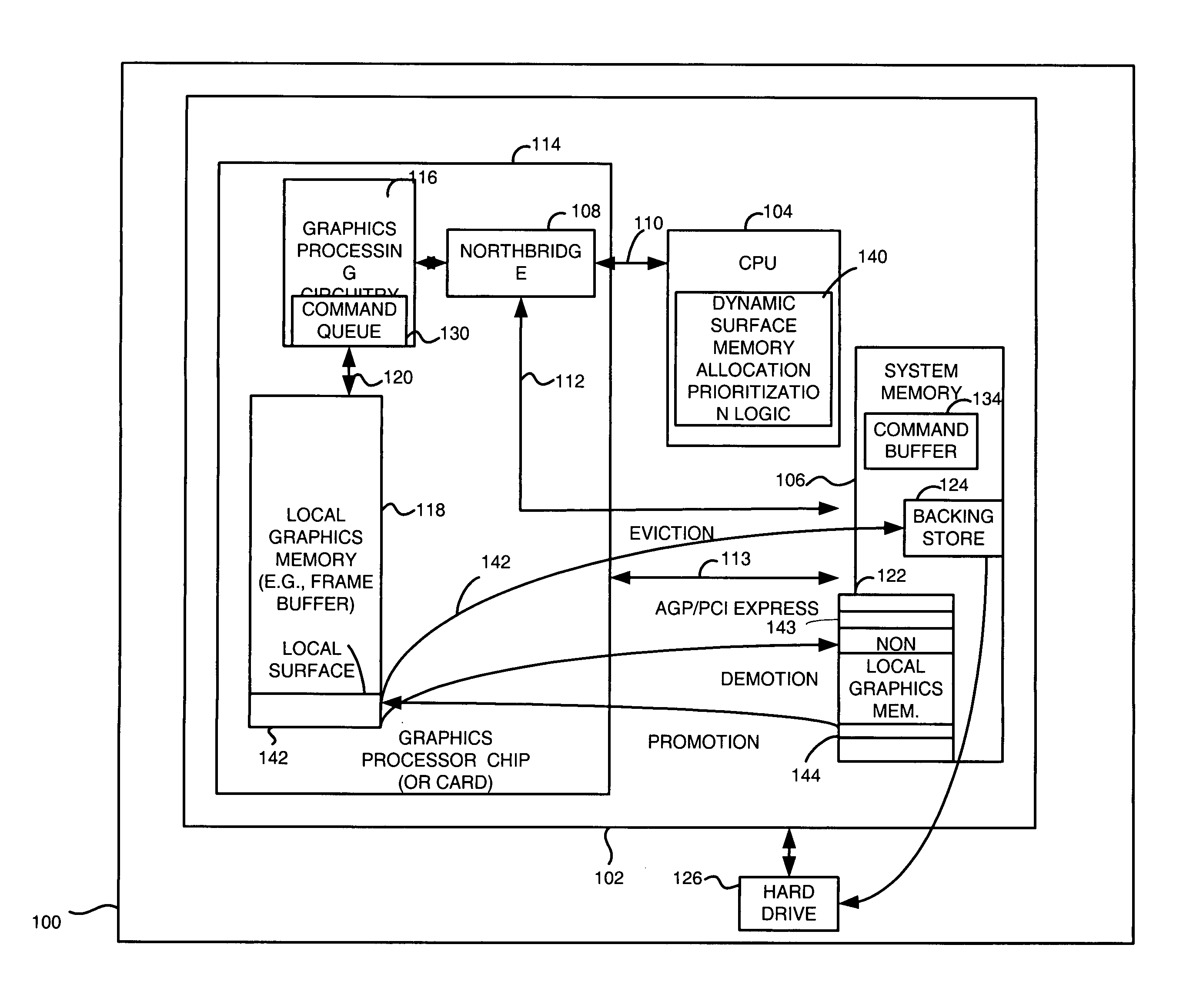
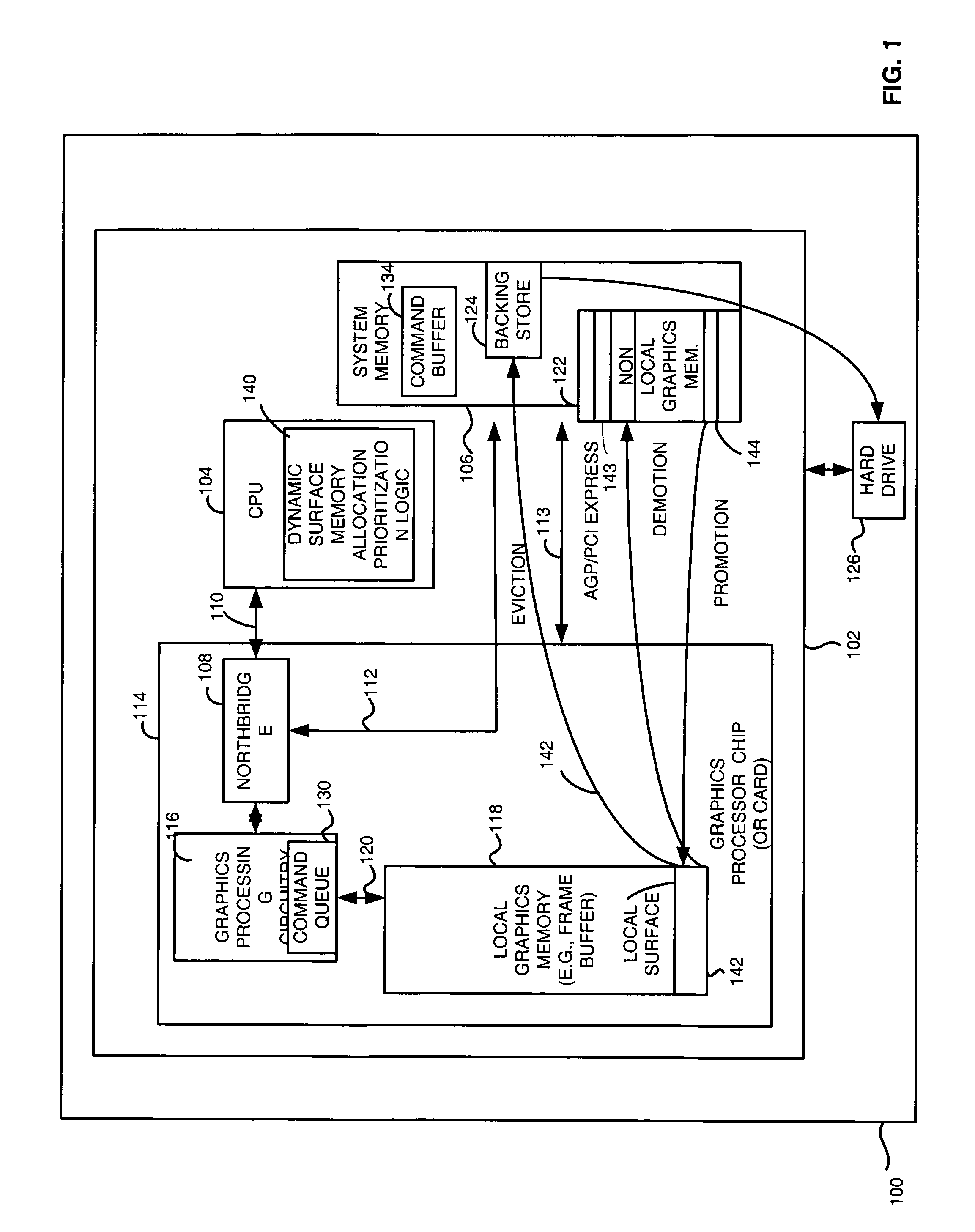
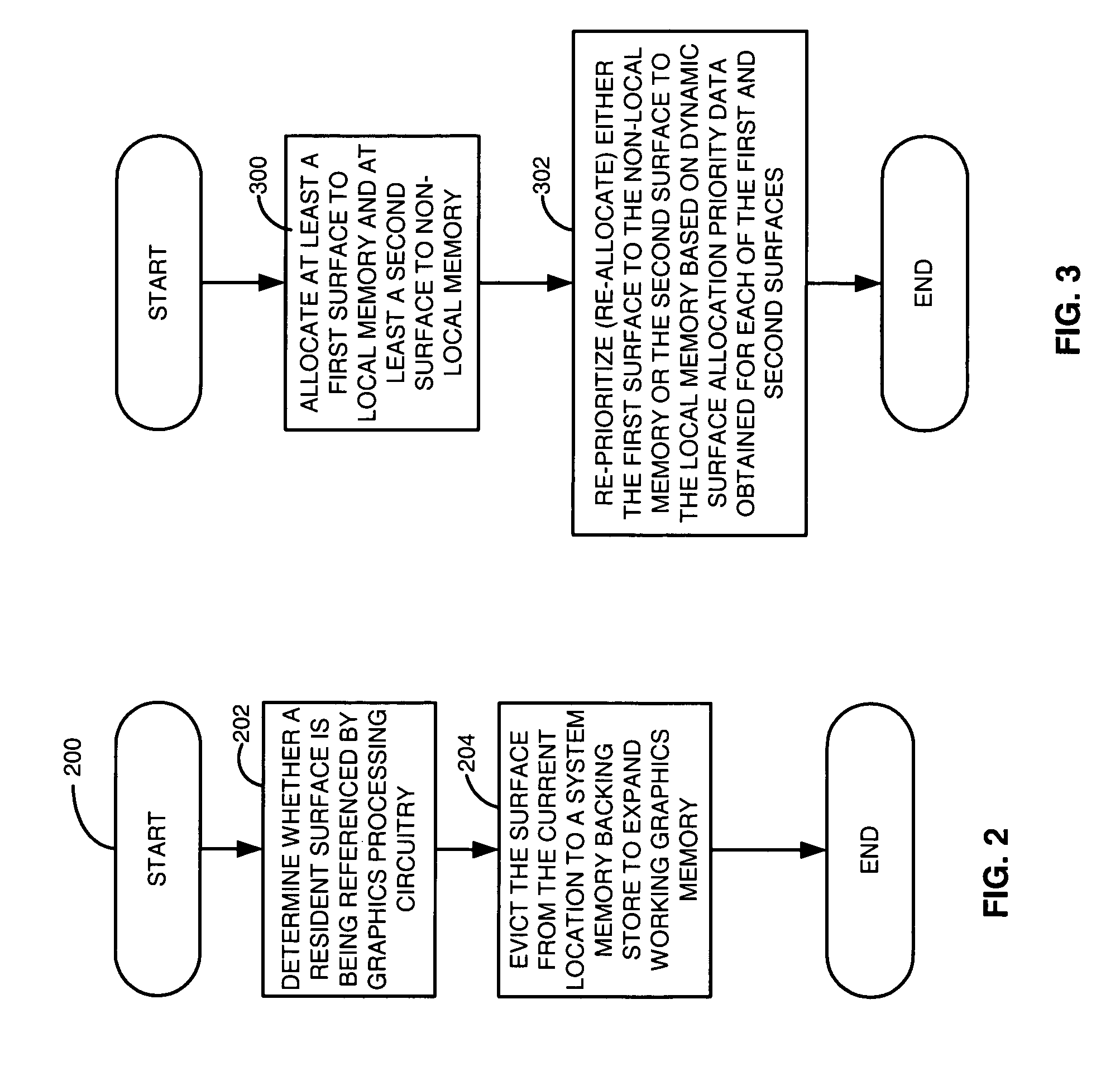
An apparatus and method utilizes system memory as backing stores so that local graphics memory may be oversubscribed. Surfaces may be paged in and out of system memory based on the amount of usage of the surfaces. The apparatus and method also prioritizes surfaces among different tiers of local memory (e.g. frame buffer), non-local memory (e.g. page locked system memory), and system memory backing stores (e.g. pageable system memory) locations based on predefined criteria and runtime statistics relating to the surfaces. As such, local memory may be, for example, expanded without extra memory costs such as adding a frame buffer memory to allow graphics applications to effectively use more memory and run faster.
Owner:ATI TECH INC
Management of data cartridges in multiple-cartridge cells in an automated data storage library
InactiveUS20070211366A1Raise priorityRecord information storageAutomatic cassette changing arrangementsMagnetic tapeRow-major order
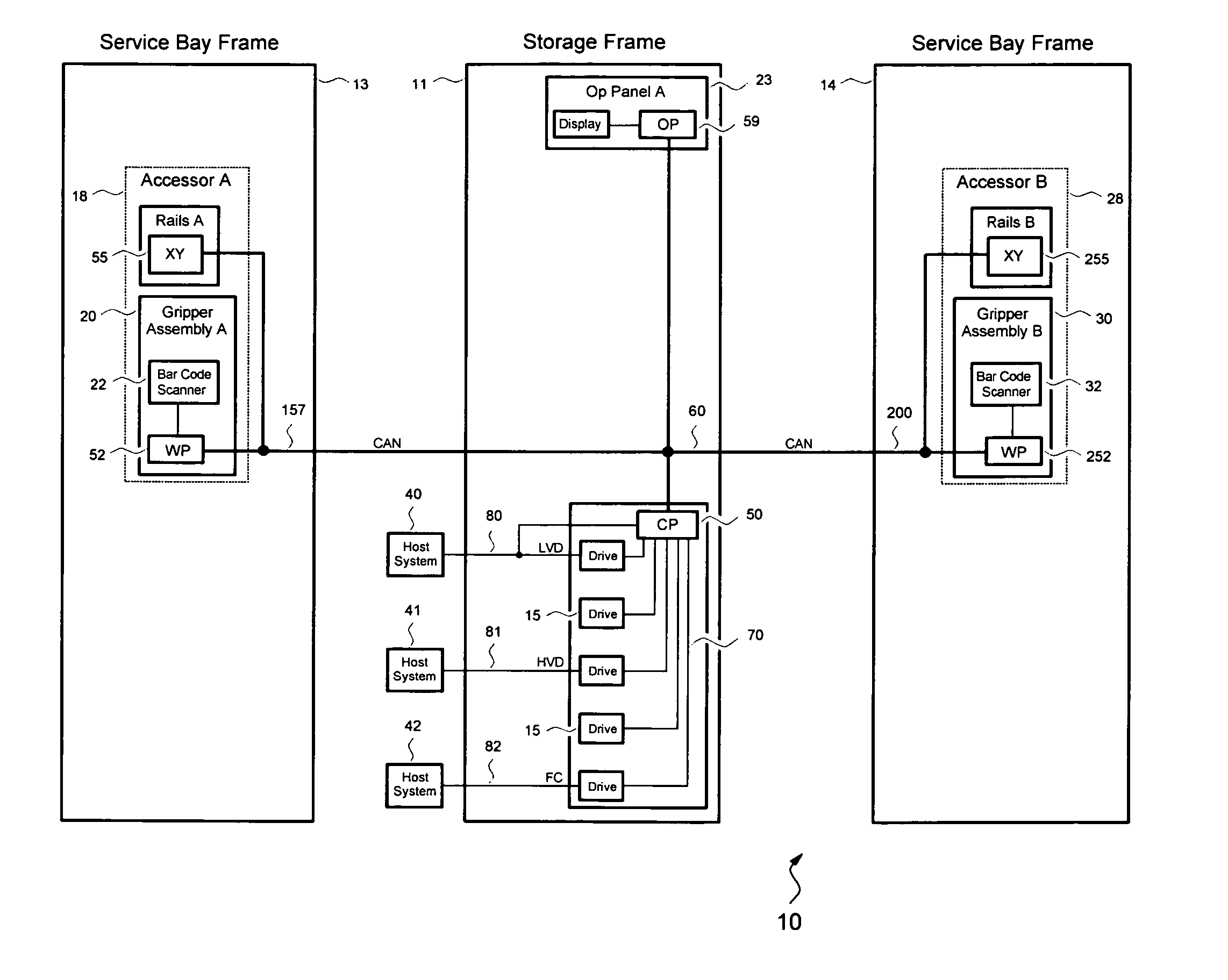
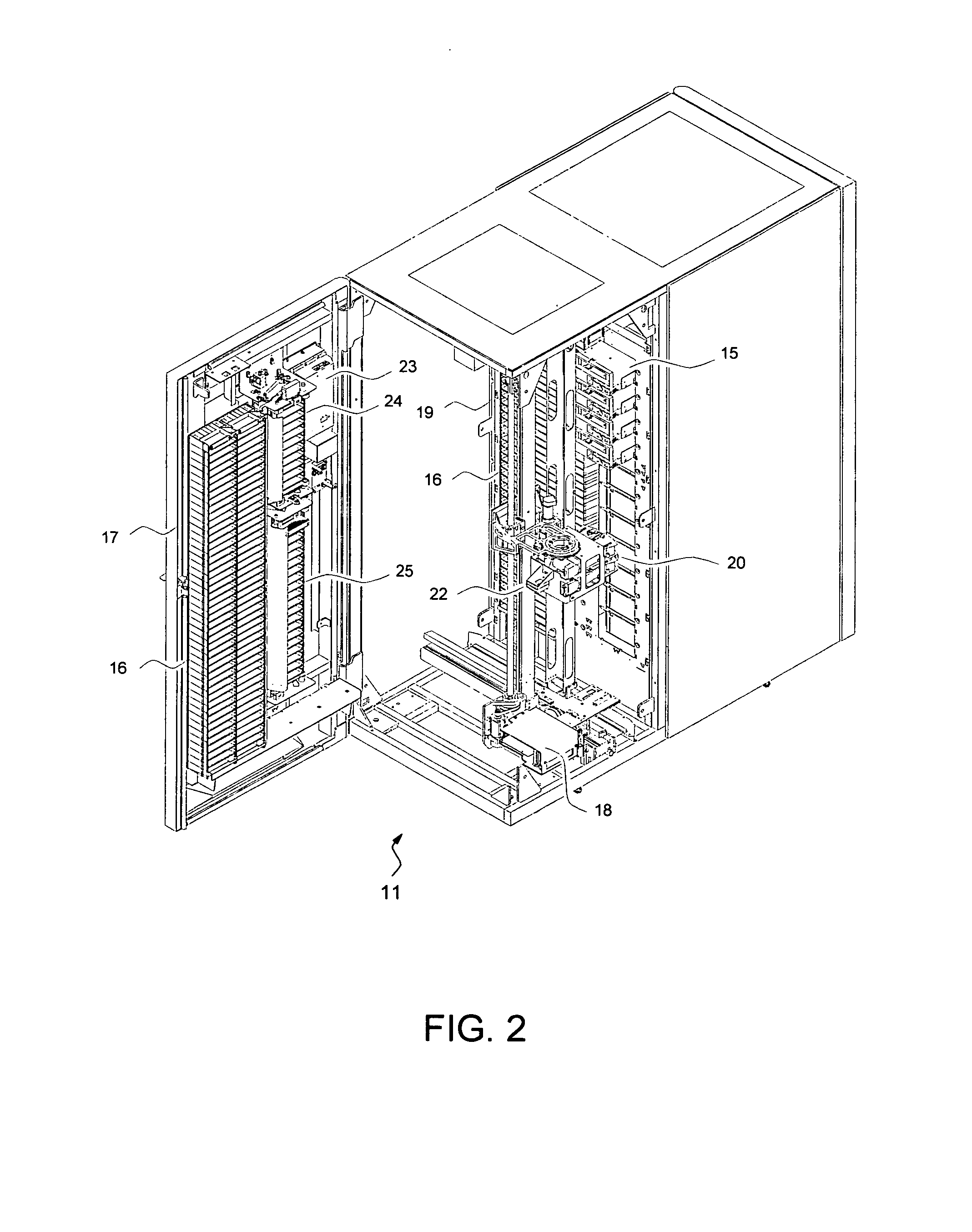
In an automated library, data cartridges, such as magnetic tape cartridges, are stored in storage cells and accessed by data storage drives. An accessor with a gripper transports cartridges between storage cells and storage drives. Cartridges are prioritized according to their relative importance. A processor manages the placement of the cartridges in cells by having higher priority cartridges stored closer to the front of multi-cartridge cells than cartridges with a lower priority. Cartridges with a higher priority may also be stored closer to a storage drive than cartridges with a lower priority. A pusher may be used to push cartridges towards the front of multi-cartridge cells with an empty position to enable the gripper to reach the front cartridge.
Owner:IBM CORP
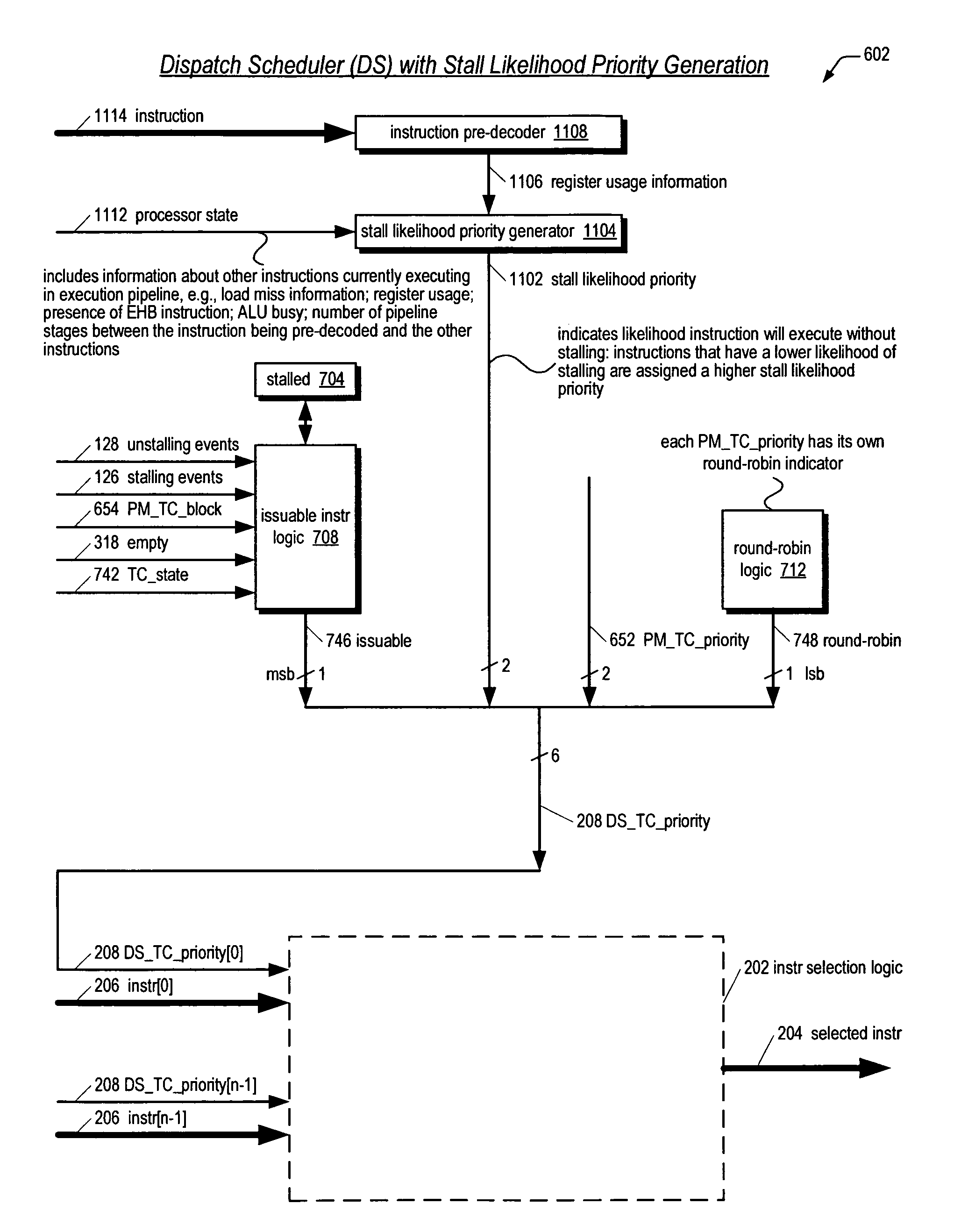
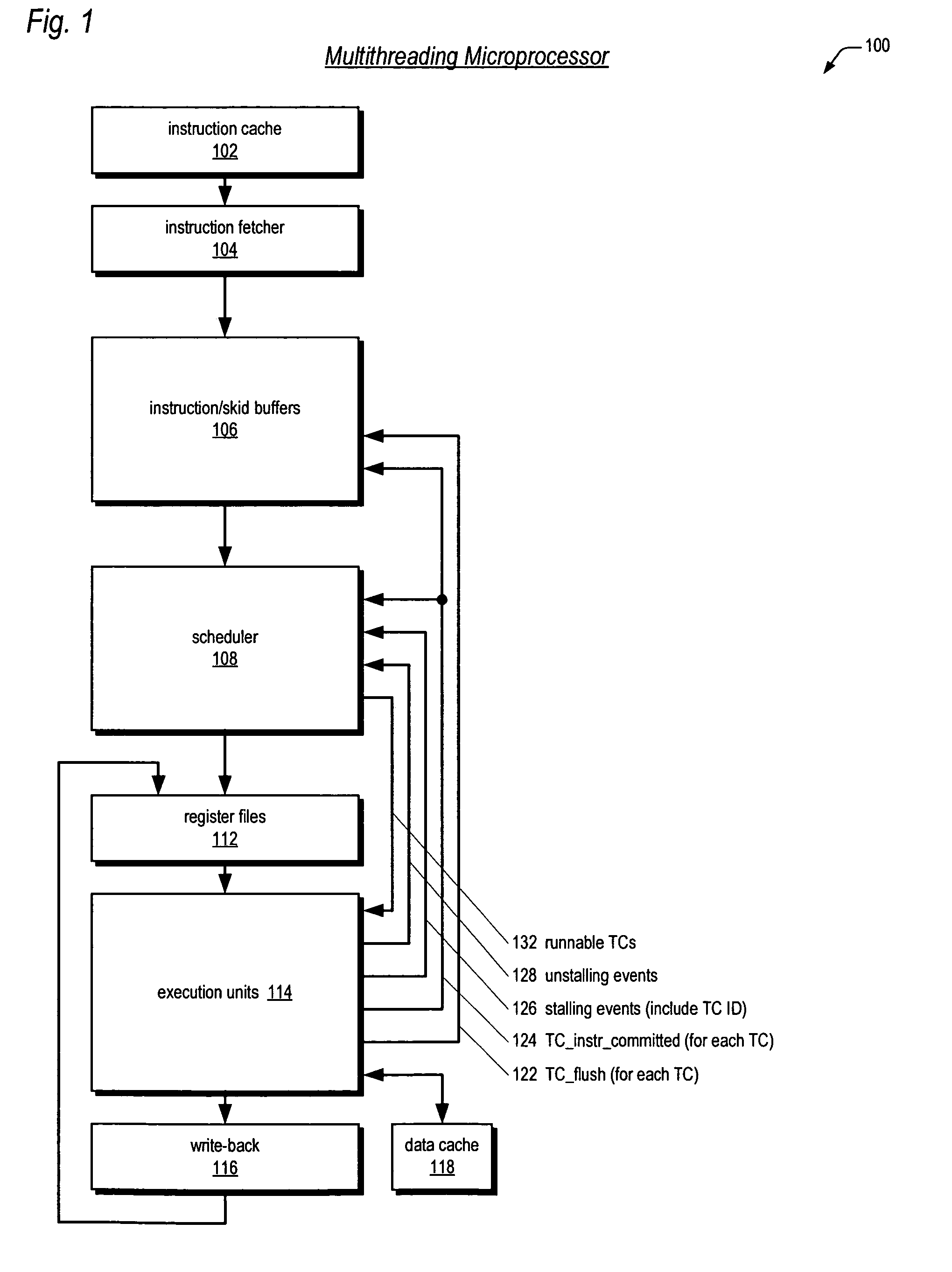
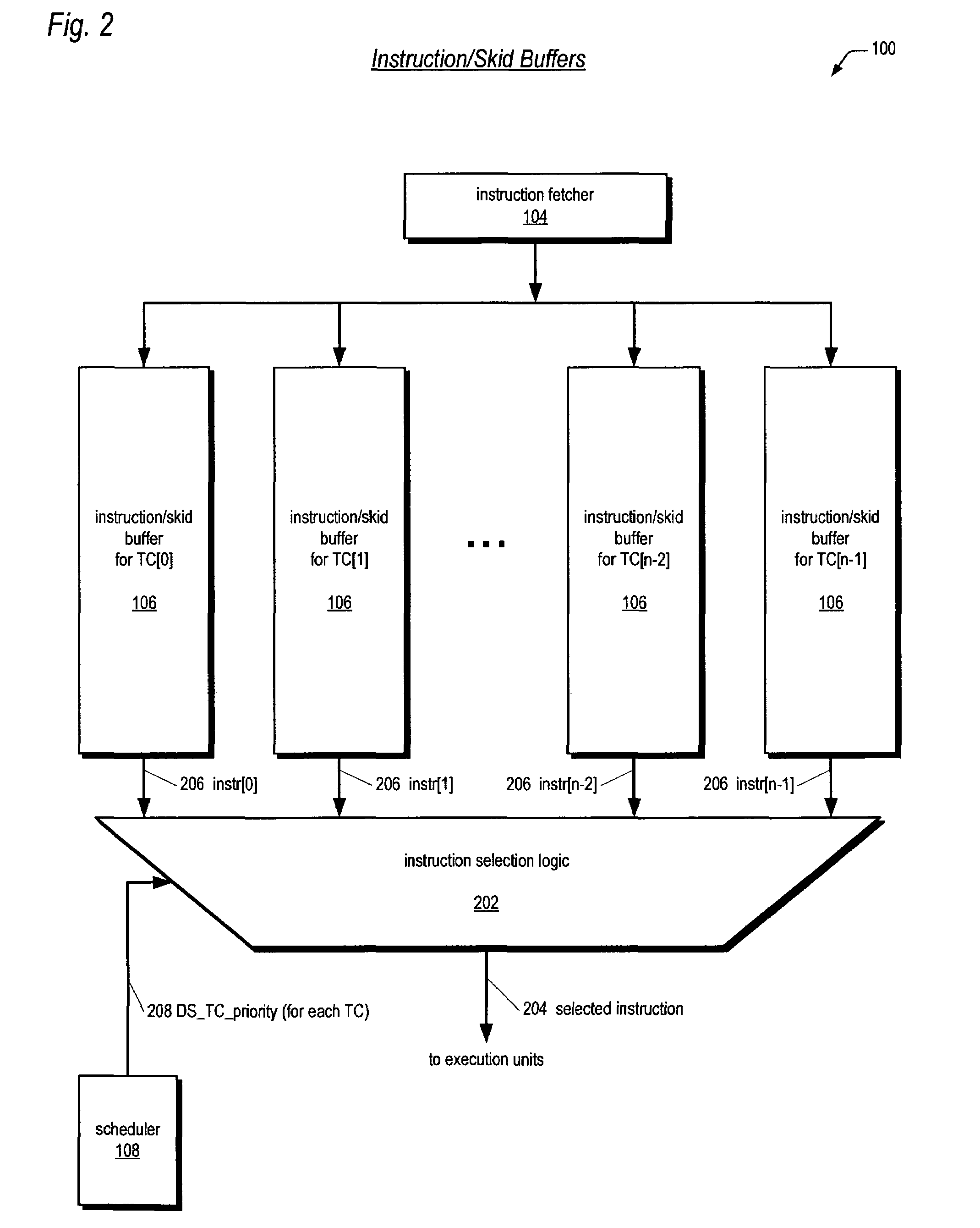
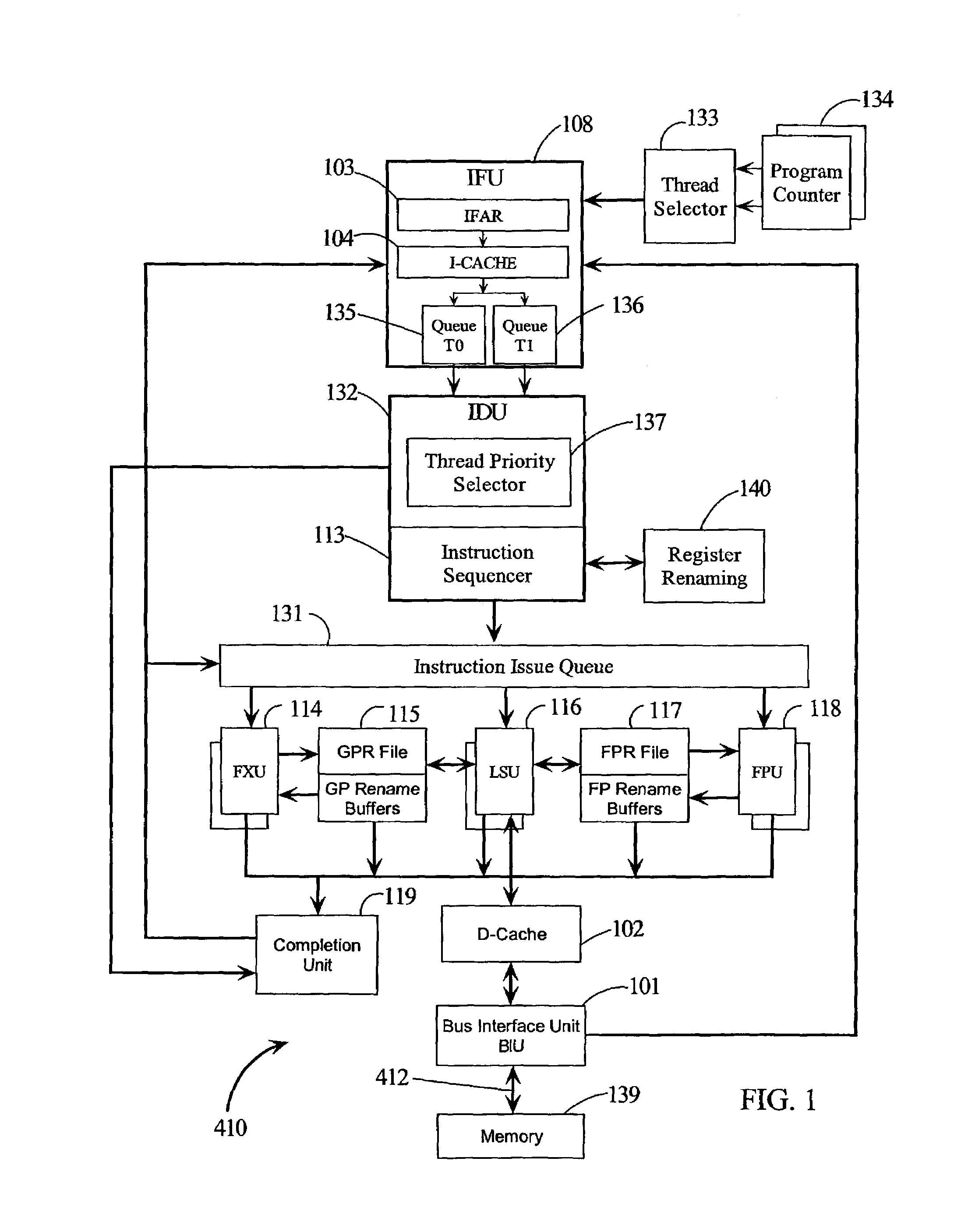
Prioritizing thread selection partly based on stall likelihood providing status information of instruction operand register usage at pipeline stages
ActiveUS7664936B2Improve efficiencyReduce in quantityResource allocationDigital computer detailsLoad instructionProcessor register
Owner:ARM FINANCE OVERSEAS LTD
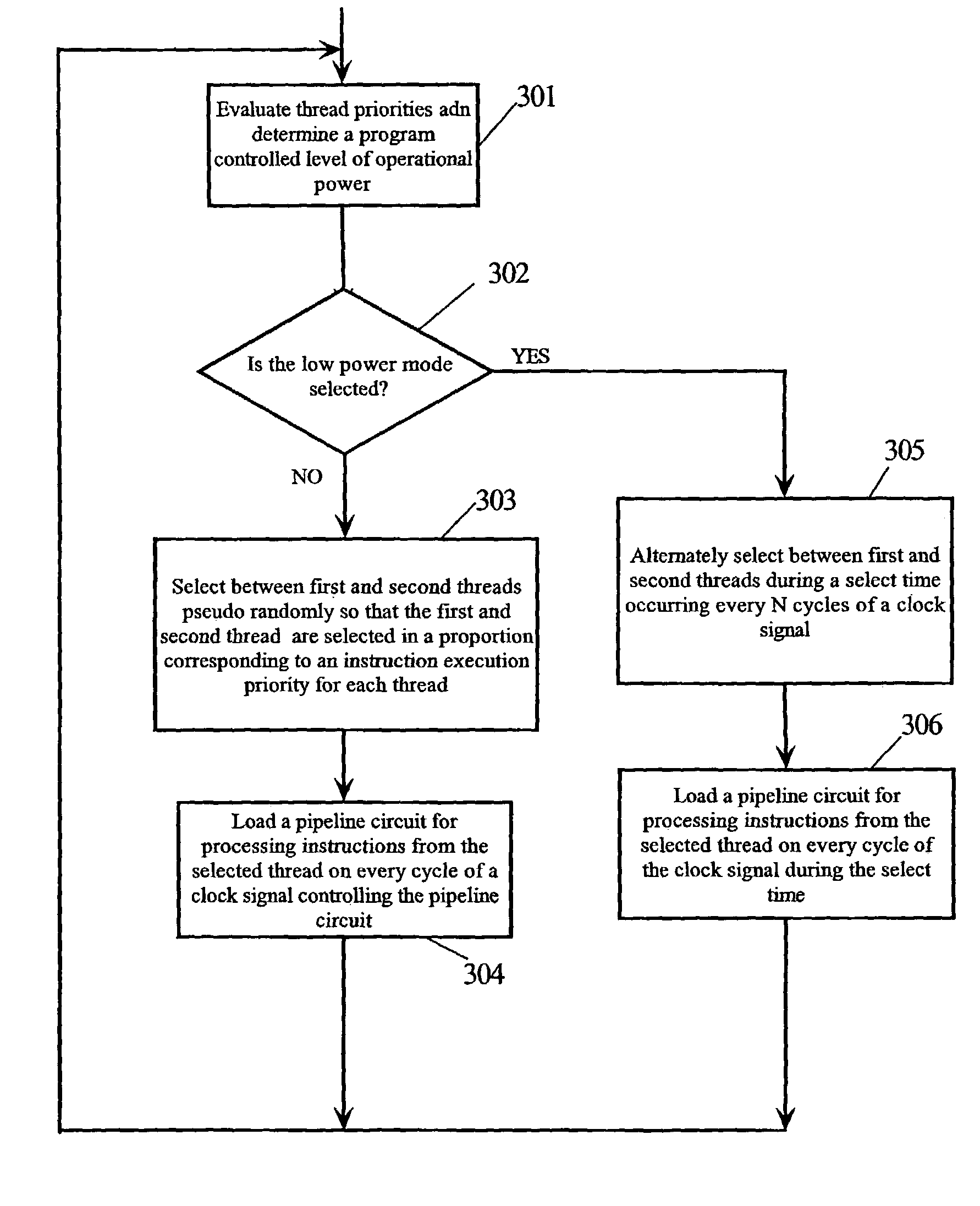
Method for managing power in a simultaneous multithread processor by loading instructions into pipeline circuit during select times based on clock signal frequency and selected power mode
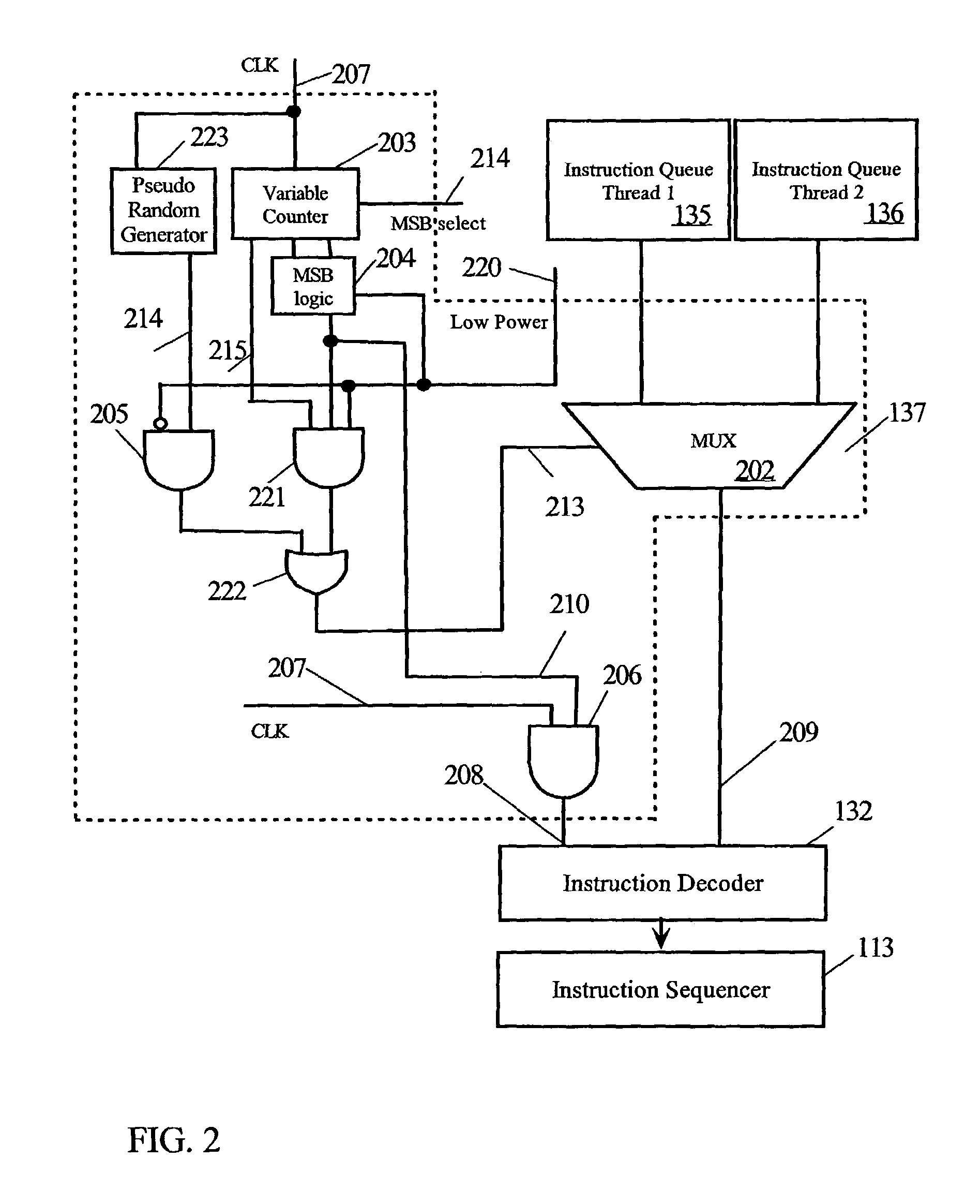
ActiveUS7013400B2Save powerVolume/mass flow measurementDigital computer detailsPower modeLoad instruction
A register in the control unit of the CPU that is used to keep track of the address of the current or next instruction is called a program counter. In an SMT system having two threads, the CPU has program counters for both threads and means for alternately selecting between program counters to determine which thread supplies an instruction to the instruction fetch unit (IFU). The software for the SMT assigns a priority to threads entering the code stream. Instructions from the threads are read from the instruction queues pseudo-randomly and proportional to their execution priorities in the normal power mode. If both threads have a lowest priority, a low power mode is set generating a gated select time every N clock cycles of a clock when valid instructions are loaded. N may be adjusted to vary the amount of power savings and the gated select time.
Owner:IBM CORP
Mark reader configured to prioritize images
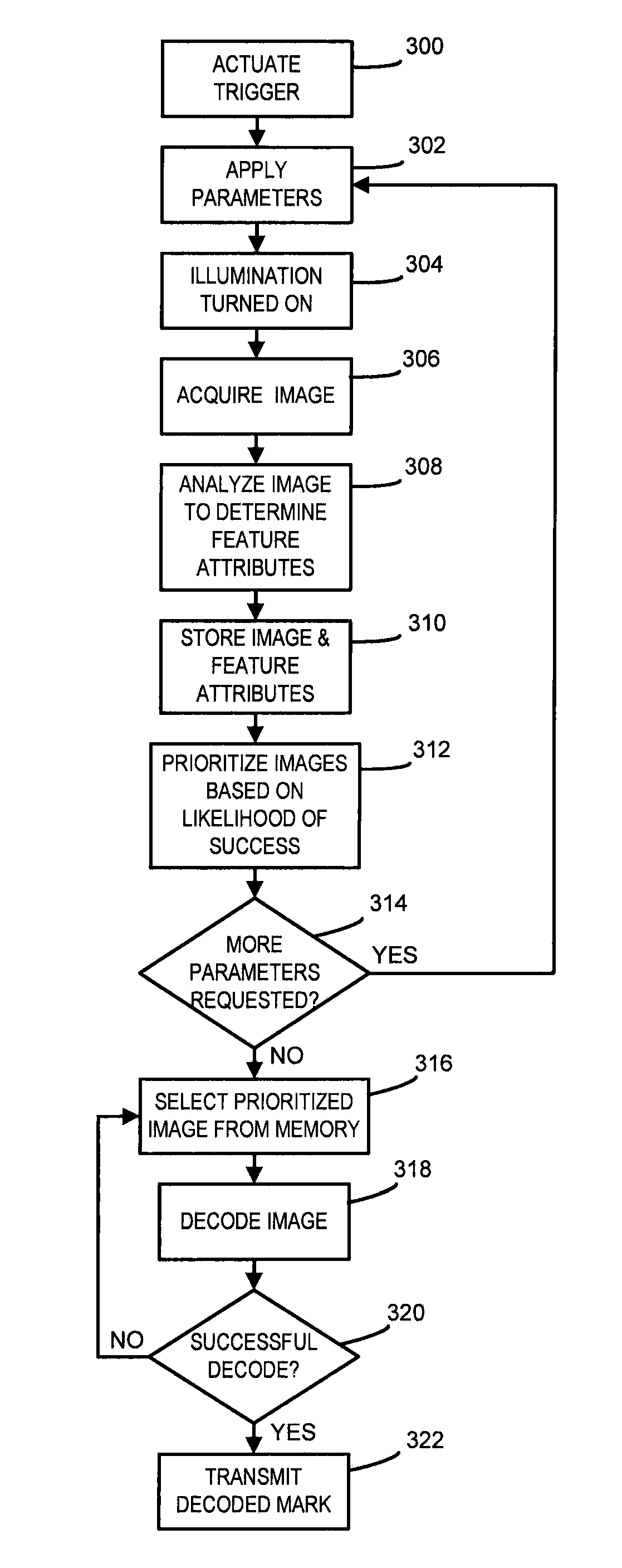
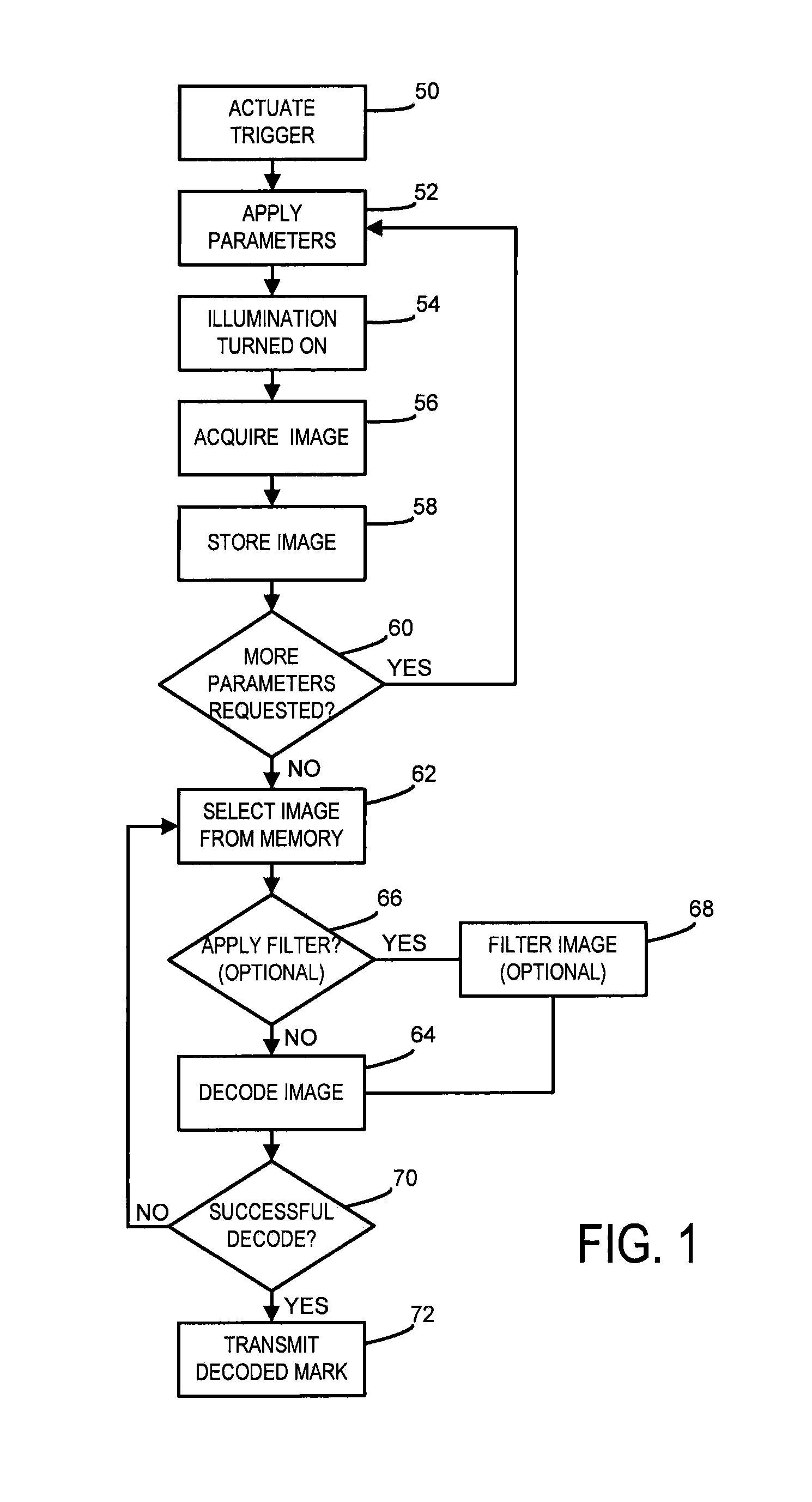
ActiveUS8542930B1Short response timeOvercome disadvantagesCharacter and pattern recognitionSensing by electromagnetic radiationPattern recognitionImaging Feature
Systems and methods for use with a mark reader that reduce the trigger-to-decode response time by prioritizing images to be decoded based on the likelihood of a successful decode are provided. A reader attempts to decode a priority image(s) first to avoid attempting to decode images that are less likely than other images to be successfully decoded. Images are rated based on feature attributes, and then prioritized for decoding. Image feature attributes are correlated with parameter groups, and the parameter groups are prioritized for use in subsequent image acquisitions.
Owner:COGNEX CORP
Processing array data on simd multi-core processor architectures
InactiveUS20100241824A1Program control using stored programsGeneral purpose stored program computerFast Fourier transformFourier transform on finite groups
Techniques are disclosed for converting data into a format tailored for efficient multidimensional fast Fourier transforms (FFTS) on single instruction, multiple data (SIMD) multi-core processor architectures. The technique includes converting data from a multidimensional array stored in a conventional row-major order into SIMD format. Converted data in SIMD format consists of a sequence of blocks, where each block interleaves s rows such that SIMD vector processors may operate on s rows simultaneously. As a result, the converted data in SIMD format enables smaller-sized 1D FFTs to be optimized in SIMD multi-core processor architectures.
Owner:IBM CORP
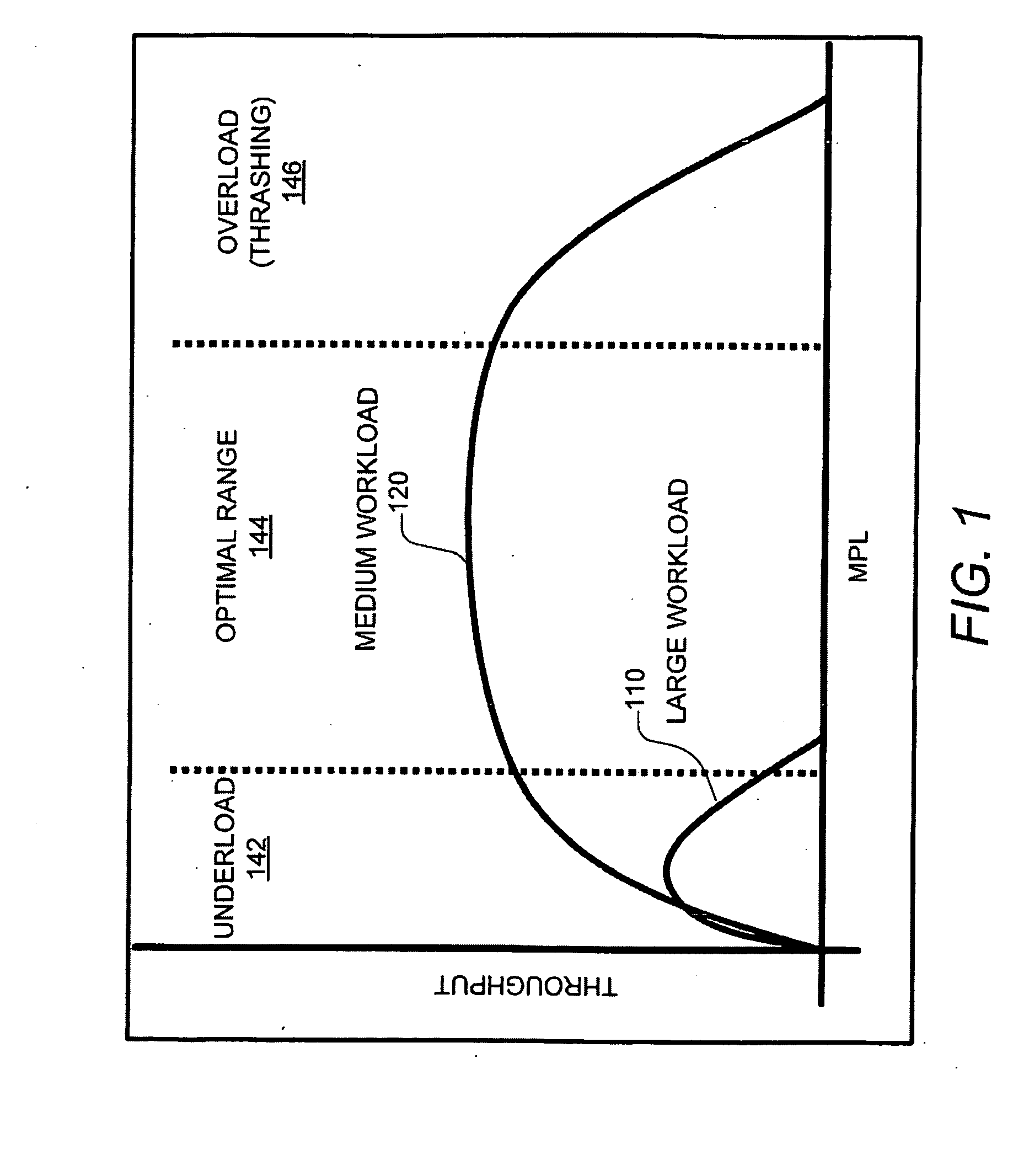
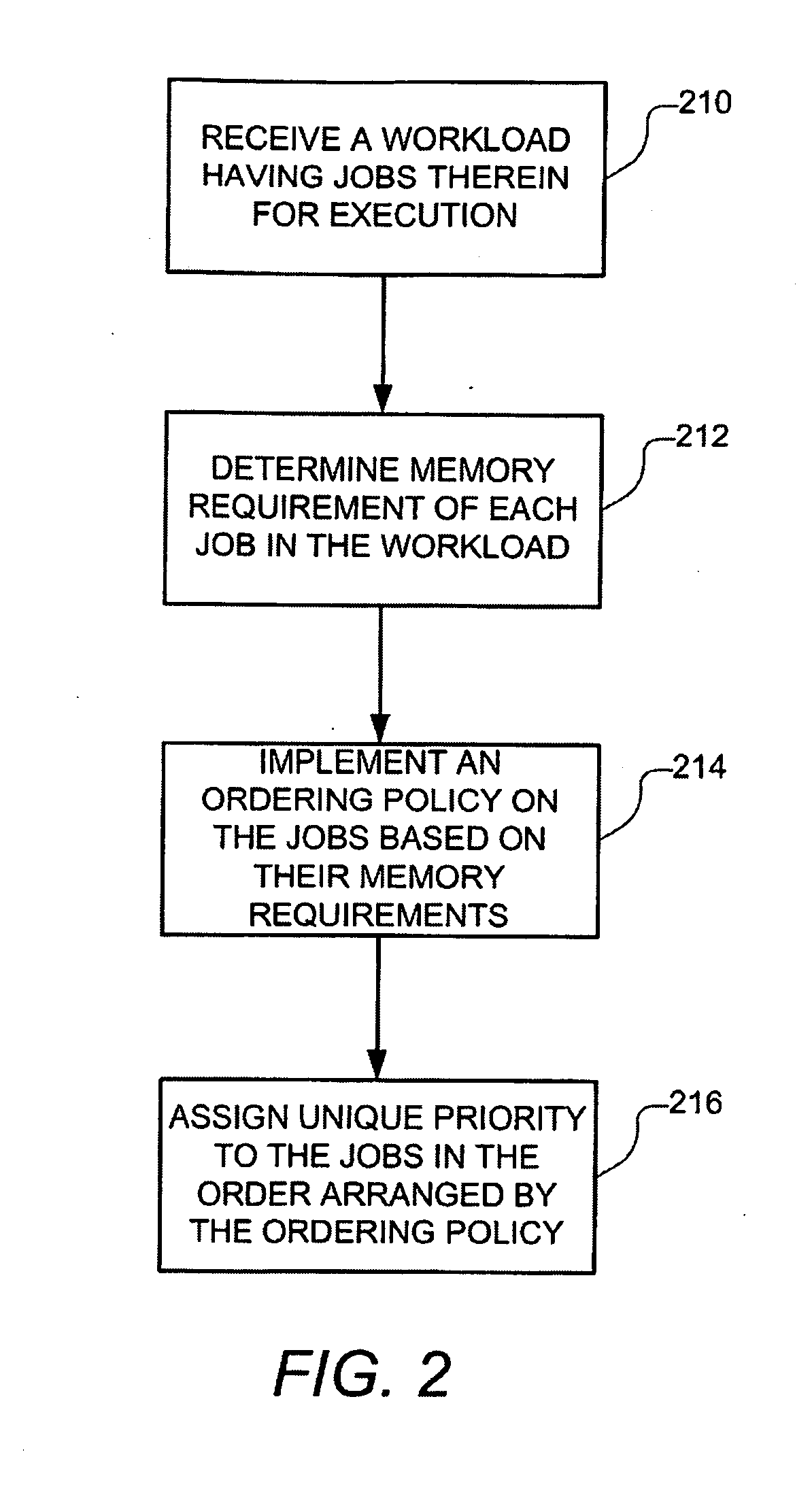
Scheduling Memory Usage Of A Workload
Described herein is a method for scheduling memory usage of a workload, the method comprising: receiving the workload, wherein the workload includes a plurality of jobs; determining a memory requirement to execute each of the plurality of jobs; arranging the plurality of jobs in an order of the memory requirements of the plurality of jobs such that the job with the largest memory requirement is at one end of the order and the job with the smallest memory requirement is at the other end of the order; assigning in order a unique priority to each of the plurality of jobs in accordance with the arranged order such that the job with the largest memory requirement is assigned the highest priority for execution and the job with the smallest memory requirement is assigned the lowest priority for execution; and executing the workload by concurrently executing the jobs in the workload in accordance with the arranged order of the plurality of jobs and the unique priority assigned to each of the plurality of jobs.
Owner:MICRO FOCUS LLC
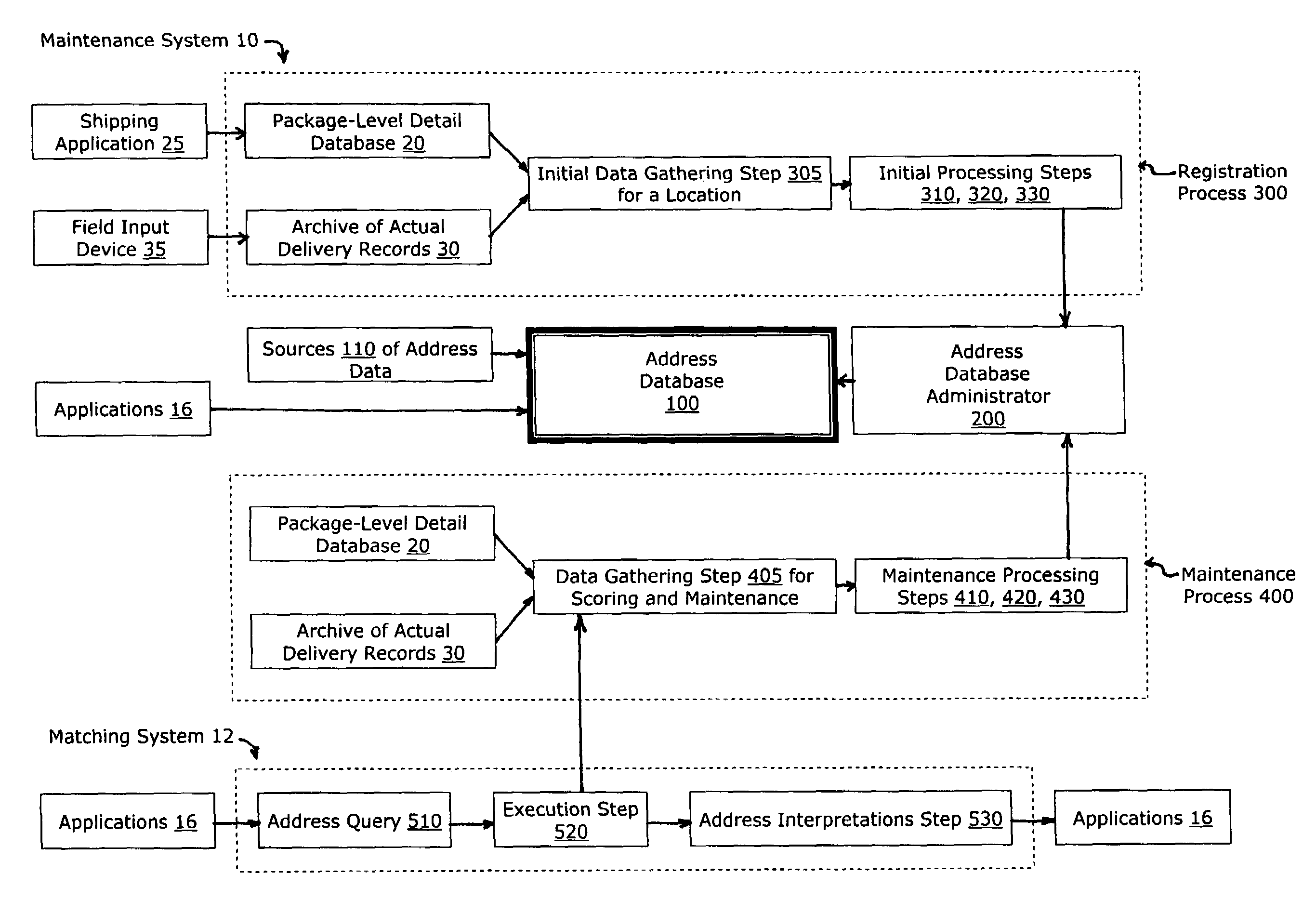
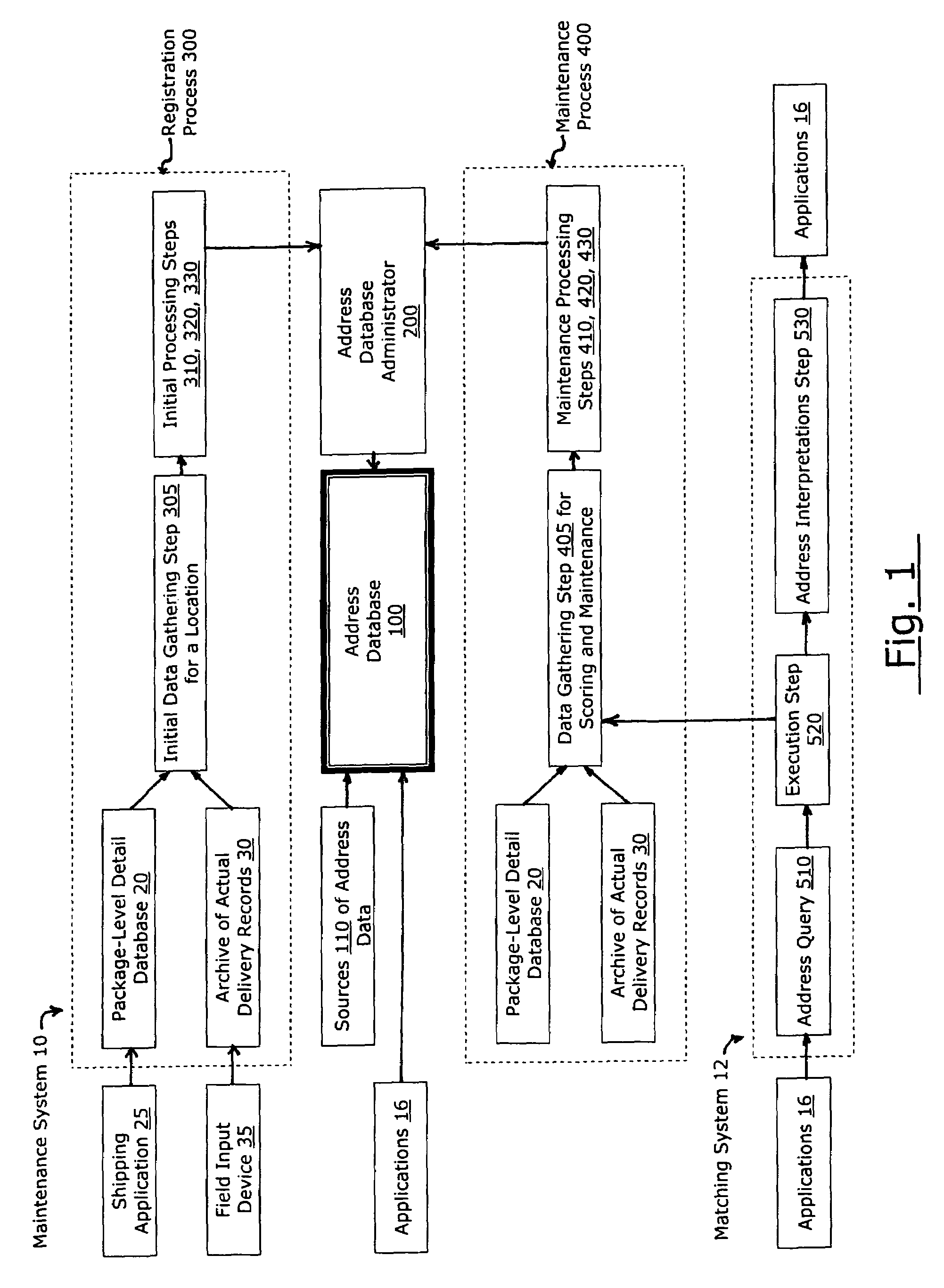
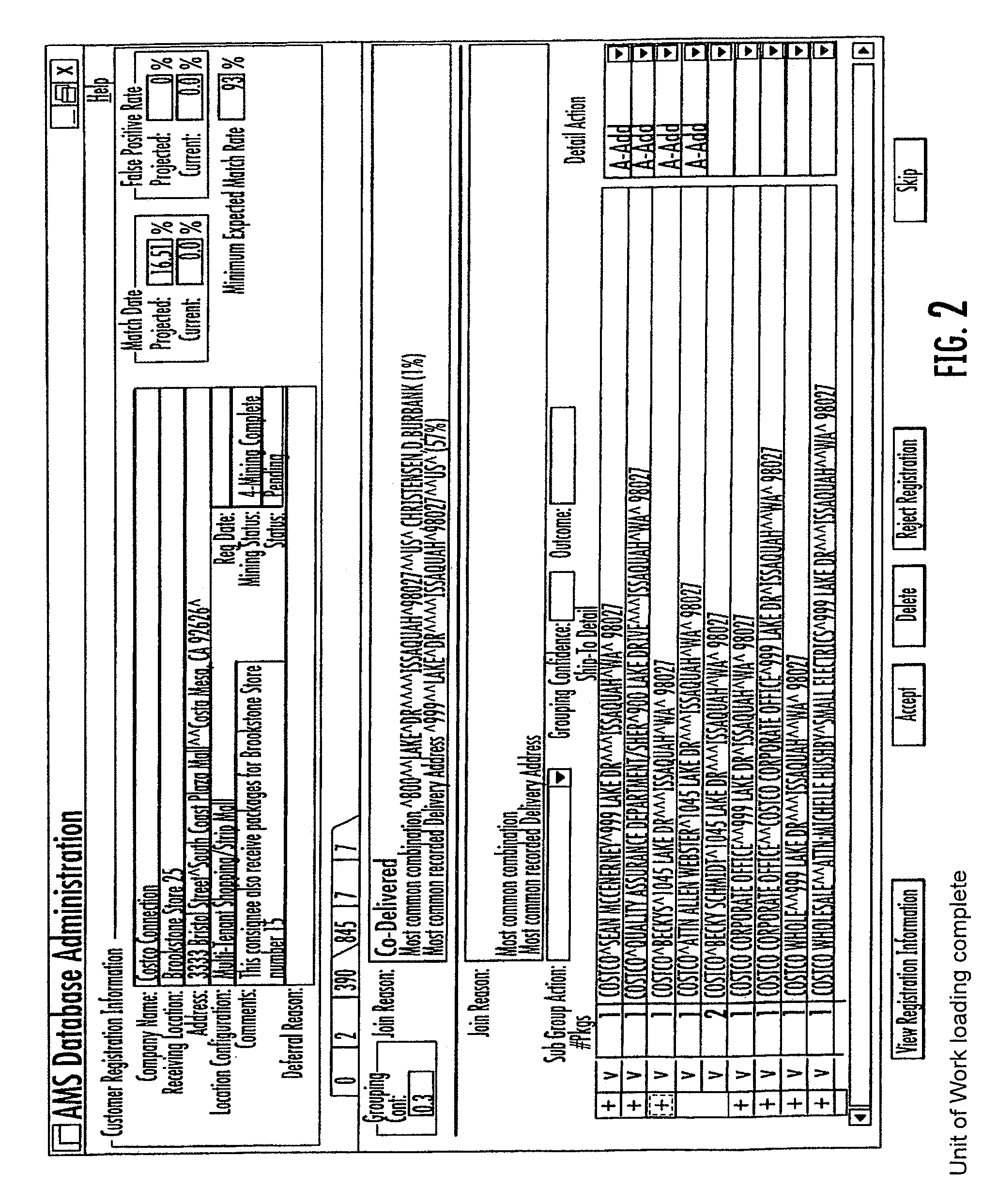
Registration and maintenance of address data for each service point in a territory
A computer system and method is disclosed for mining current and archived address data in order to identify a preferred address for each service point in a territory. The data mining system may start in response to the presentation of a candidate address for matching. The set of mined data may be prioritized by clustering like characteristics, building similarity matrices, and by constructing dendrograms with nodes joined according to common characteristics. A computer system and method for maintaining a central database of preferred addresses is also disclosed. Selected address data gathered in a queue may be scored by characteristic, grouped by consignee location, and staged for processing. The scored queue of data may be prioritized by clustering like characteristics, building similarity matrices, and by constructing dendrograms.
Owner:UNITED PARCEL SERVICE OF AMERICAN INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com