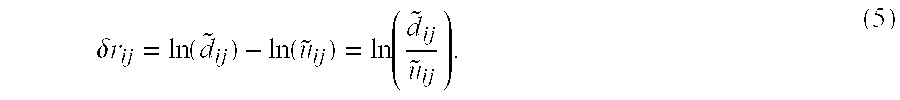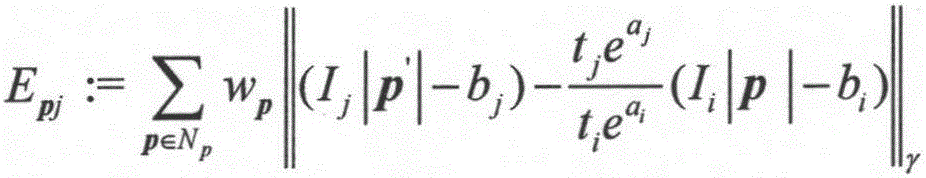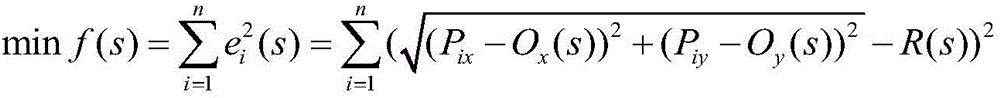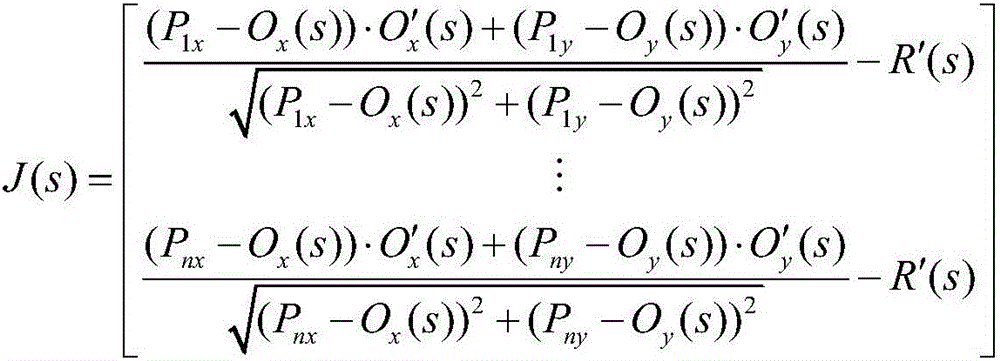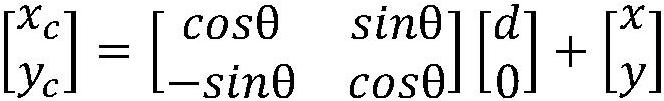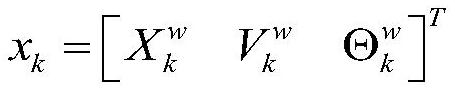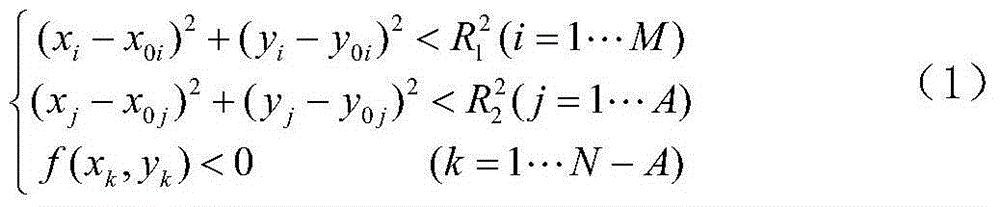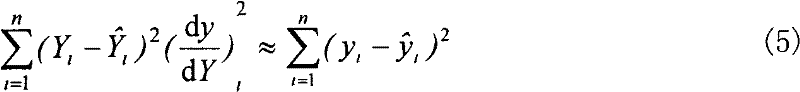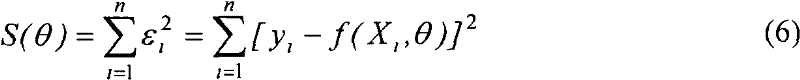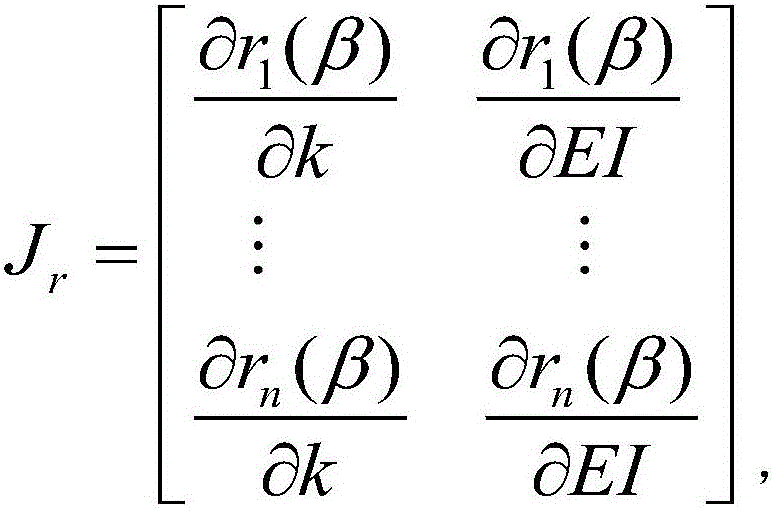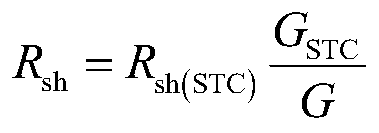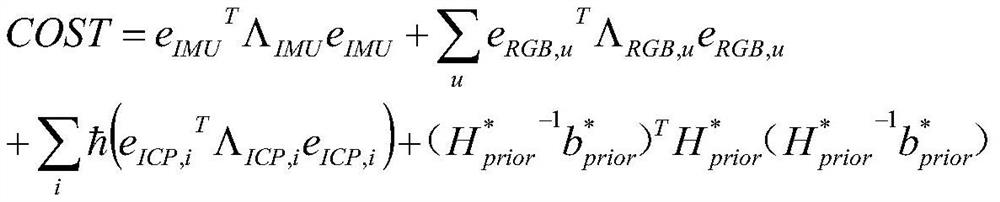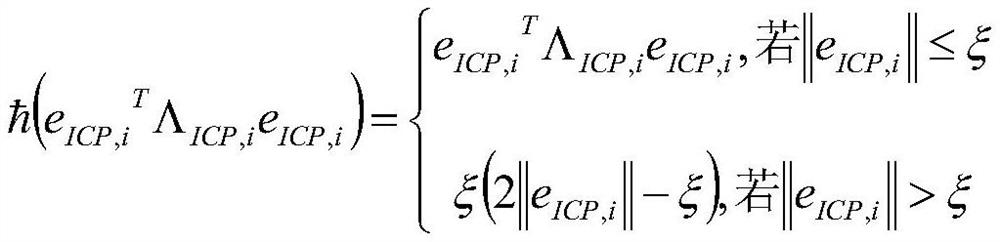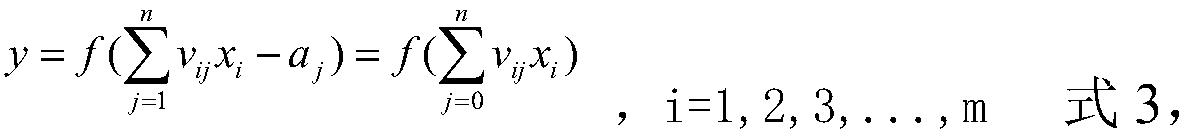Patents
Literature
56 results about "Gauss newton method" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The Gauss-Newton method is an iterative algorithm to solve nonlinear least squares problems. “Iterative” means it uses a series of calculations (based on guesses for x-values) to find the solution. It is a modification of Newton’s method, which finds x-intercepts (minimums) in calculus.
Guidance method based on 3D-2D pose estimation and 3D-CT registration with application to live bronchoscopy
ActiveUS7756563B2Maximizing costEasy to useRadiation diagnostic clinical applicationsSurgical navigation systemsGauss newton methodEndoscopic Procedure
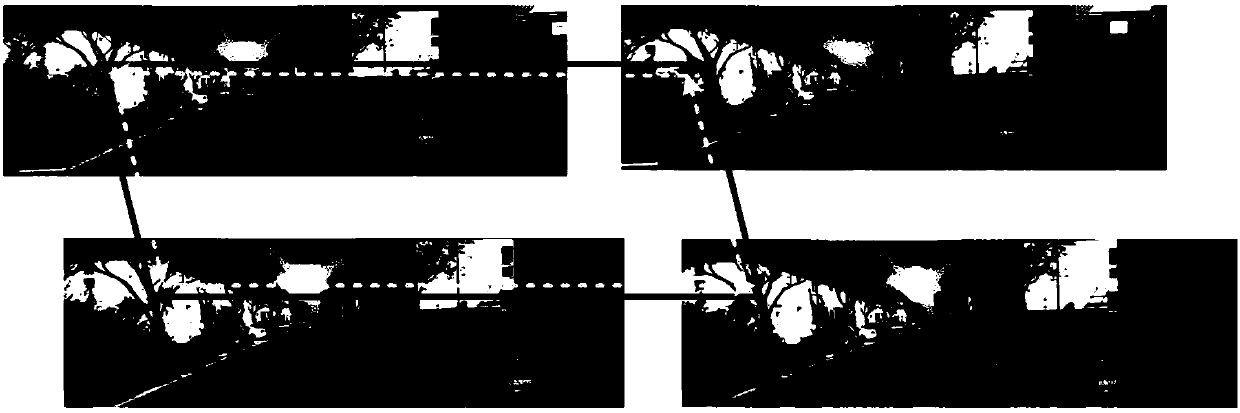
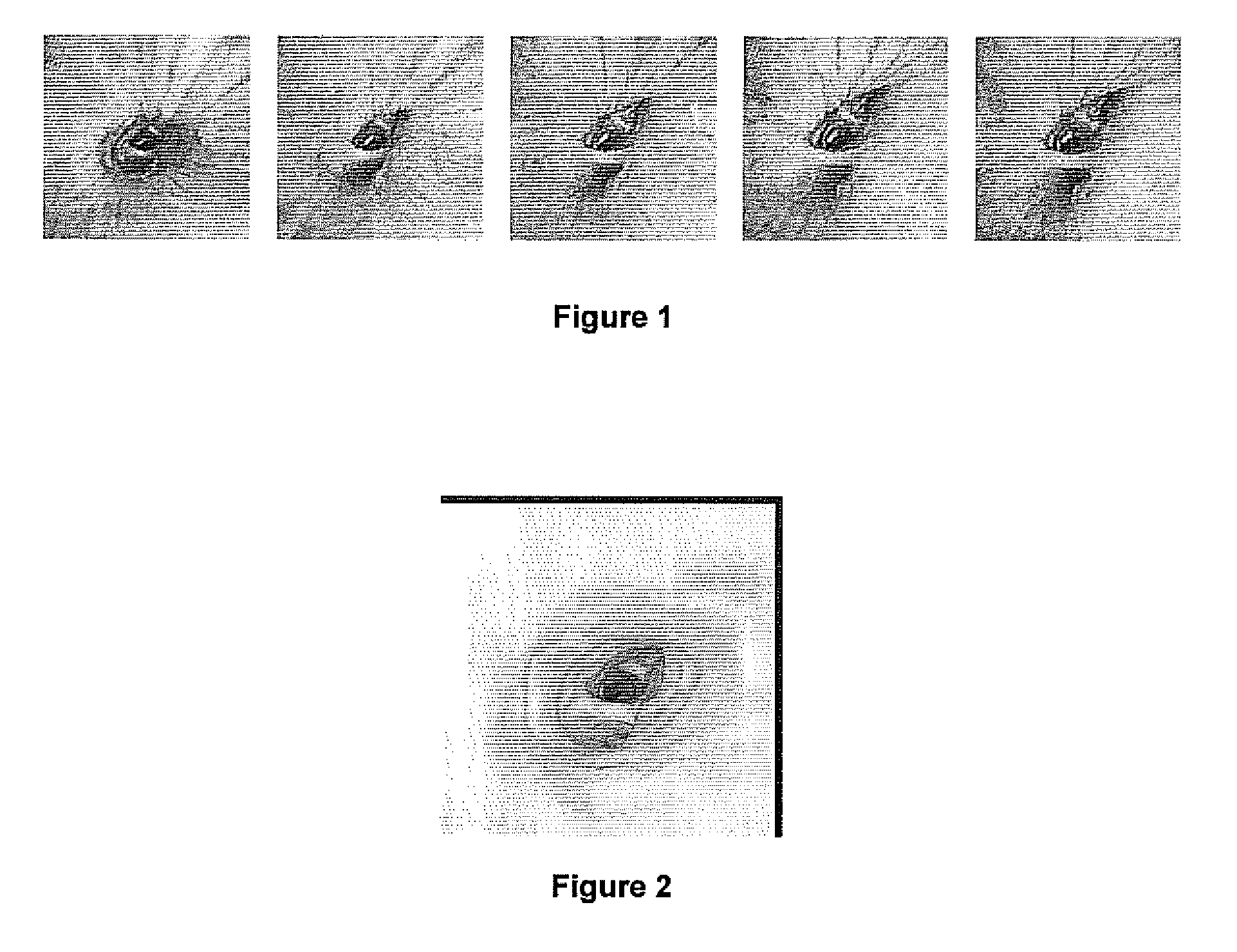
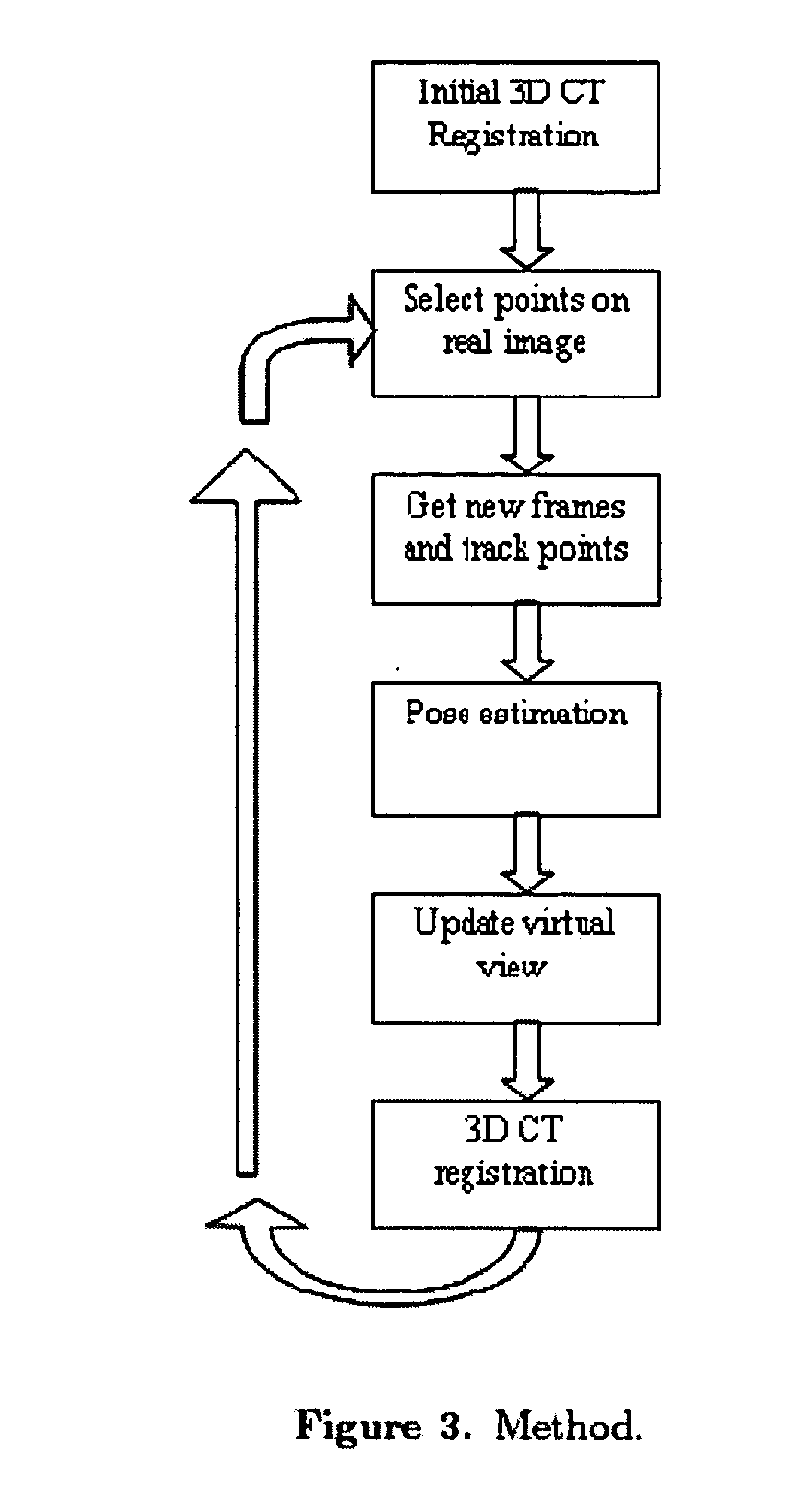
A method provides guidance to the physician during a live bronchoscopy or other endoscopic procedures. The 3D motion of the bronchoscope is estimated using a fast coarse tracking step followed by a fine registration step. The tracking is based on finding a set of corresponding feature points across a plurality of consecutive bronchoscopic video frames, then estimating for the new pose of the bronchoscope. In the preferred embodiment the pose estimation is based on linearization of the rotation matrix. By giving a set of corresponding points across the current bronchoscopic video image, and the CT-based virtual image as an input, the same method can also be used for manual registration. The fine registration step is preferably a gradient-based Gauss-Newton method that maximizes the correlation between the bronchoscopic video image and the CT-based virtual image. The continuous guidance is provided by estimating the 3D motion of the bronchoscope in a loop. Since depth-map information is available, tracking can be done by solving a 3D-2D pose estimation problem. A 3D-2D pose estimation problem is more constrained than a 2D-2D pose estimation problem and does not suffer from the limitations associated with computing an essential matrix. The use of correlation-based cost, instead of mutual information as a registration cost, makes it simpler to use gradient-based methods for registration.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
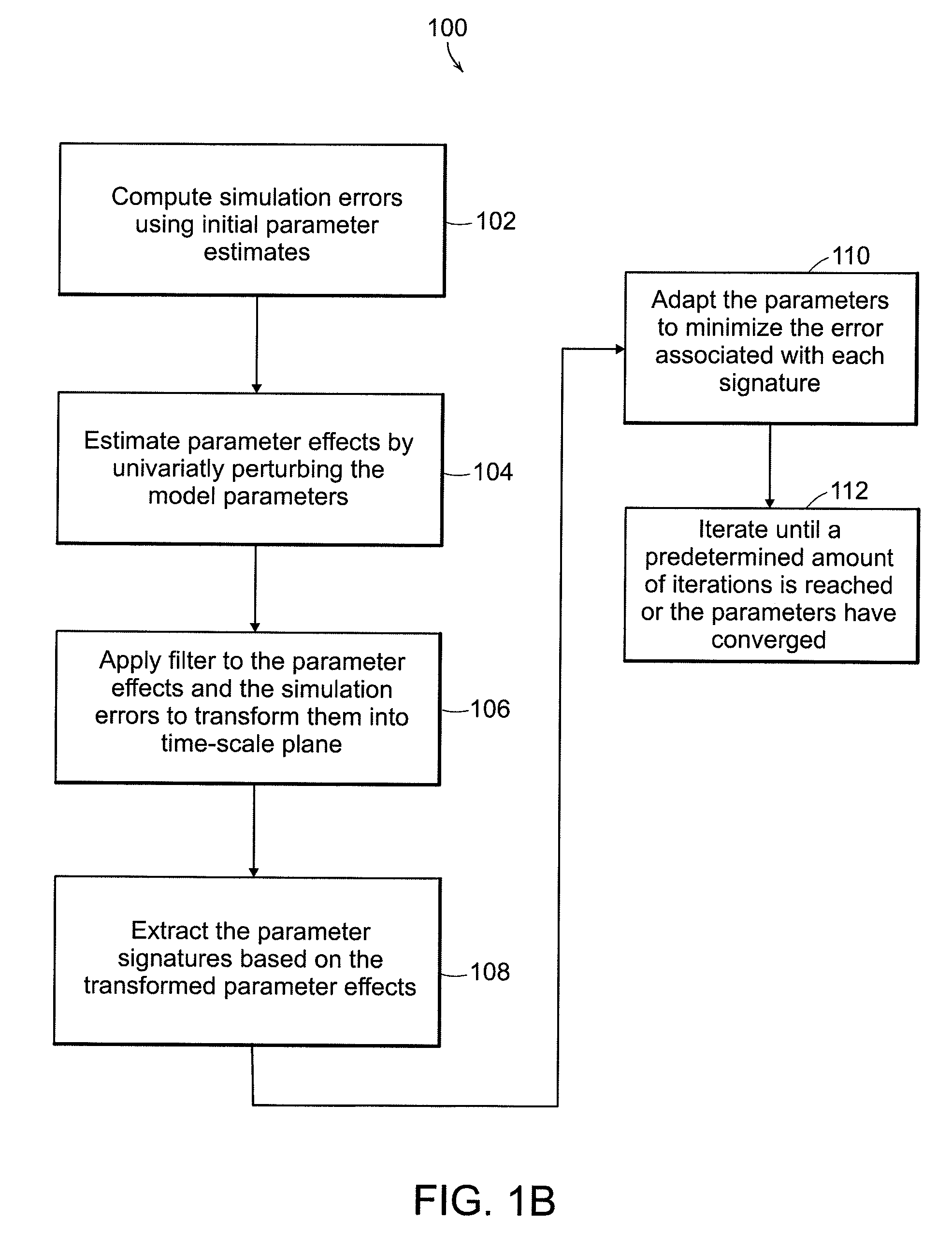
Systems and methods for parameter adaptation
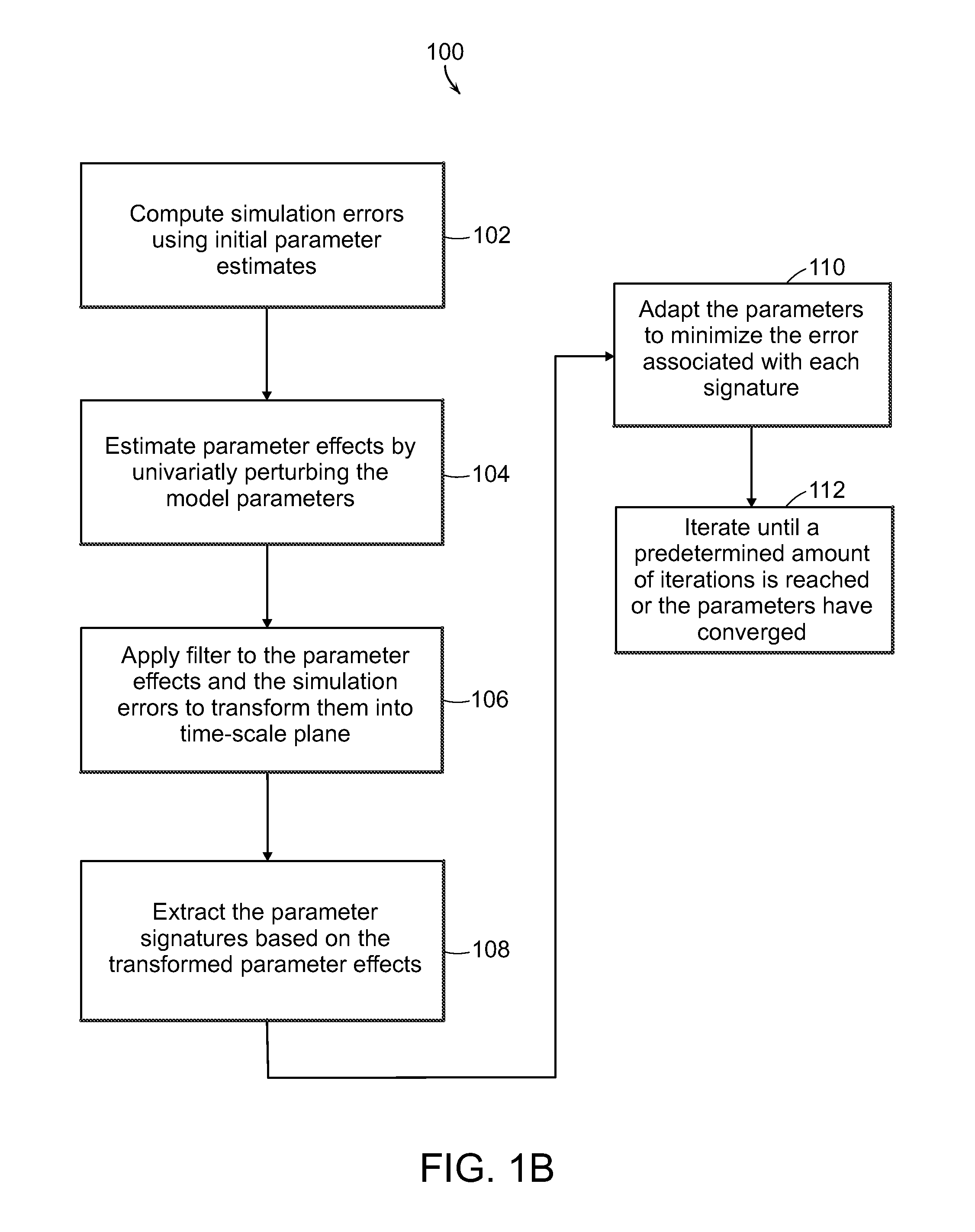
InactiveUS20110167025A1Accurate representationAccurate modelingSimulator controlDigital computer detailsAlgorithmGauss newton method
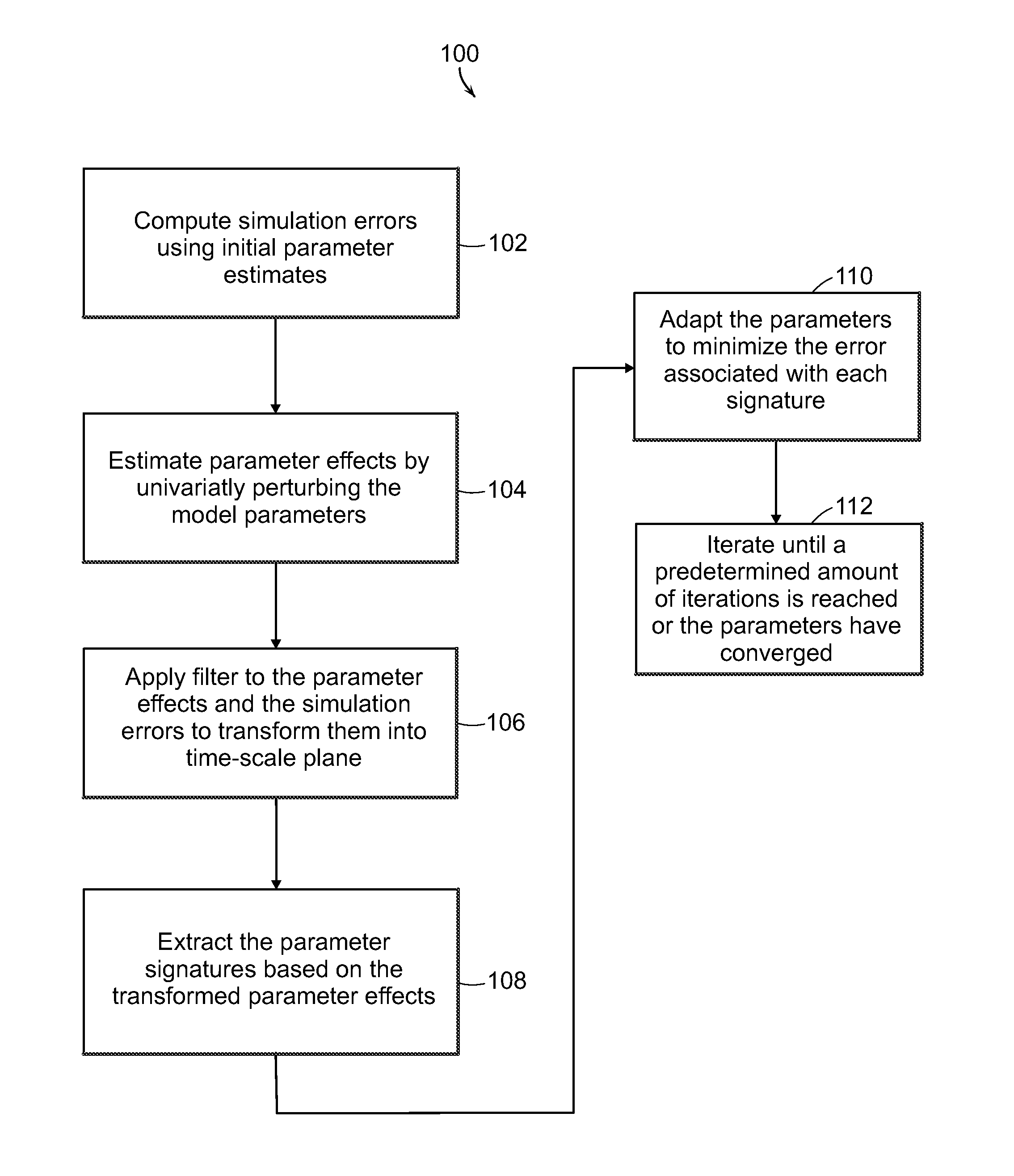
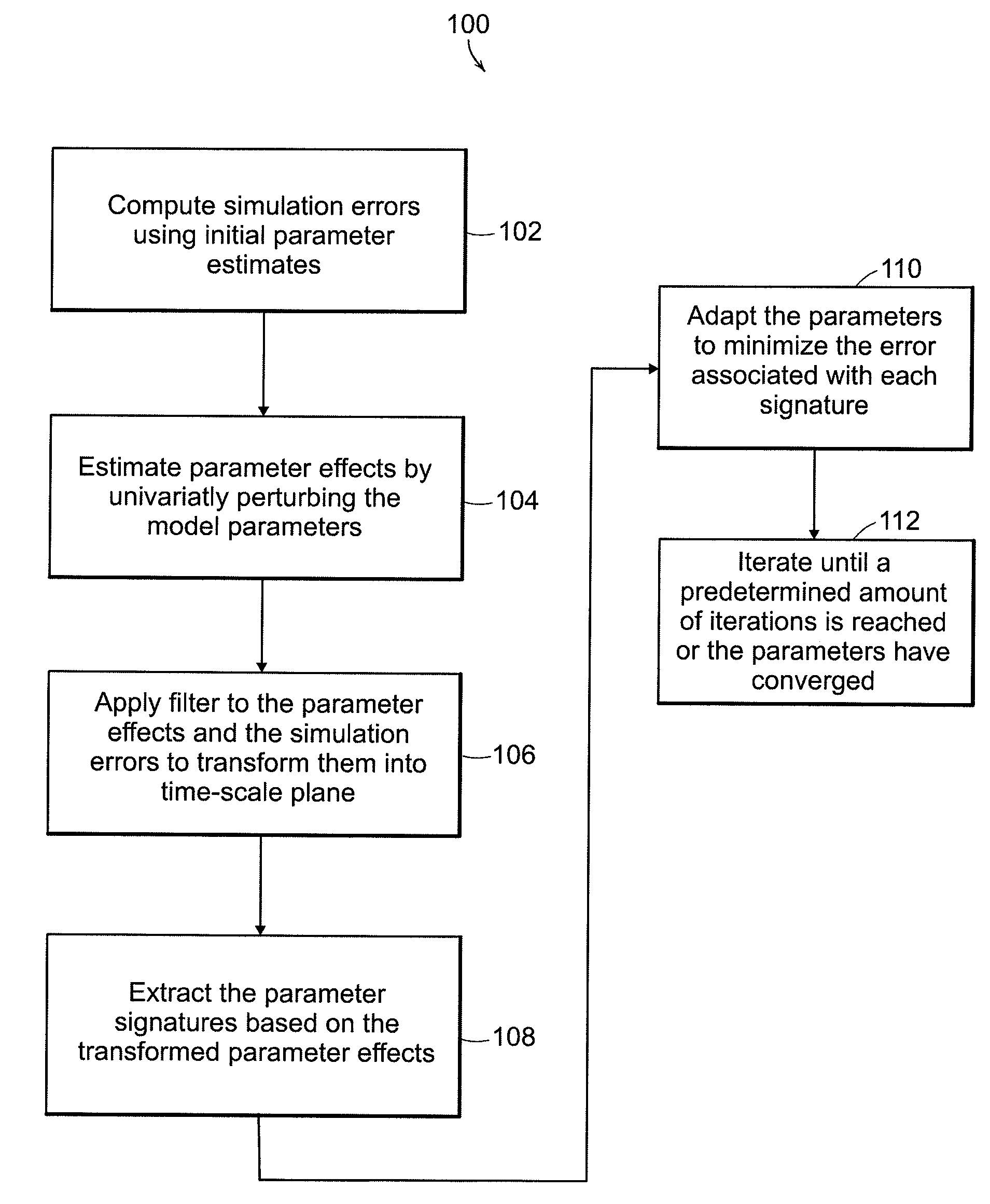
A method of parameter adaptation is used to modify the parameters of a model to improve model performance. The model separately estimates the contribution of each model parameter to the prediction error. It achieves this by transforming to the time-scale plane the vectors of output sensitivities with respect to model parameters and then identifying the regions within the time-scale plane at which the dynamic effect of individual model parameters is dominant on the output. The method then attributes the prediction error in these regions to the deviation of a single parameter from its true value as the basis of estimating individual parametric errors. The proposed Signature Isolation Method (PARSIM) then uses these estimates to adapt individual model parameters independently of the others, implementing, in effect, concurrent adaptation of individual parameters by the Newton-Raphson method in the time-scale plane. The Signature Isolation Method has been found to have an adaptation precision comparable to that of the Gauss-Newton method for noise-free cases. However, it surpasses the Gauss-Newton method in precision when the output is contaminated with noise or when the measurements are generated by inadequate excitation.
Owner:UNIV OF MASSACHUSETTS
Guidance method based on 3D-2D pose estimation and 3D-CT registration with application to live bronchoscopy
ActiveUS20070015997A1Maximizing costEasy to useRadiation diagnostic clinical applicationsSurgical navigation systemsGauss newton methodEndoscopic Procedure
A method provides guidance to the physician during a live bronchoscopy or other endoscopic procedures. The 3D motion of the bronchoscope is estimated using a fast coarse tracking step followed by a fine registration step. The tracking is based on finding a set of corresponding feature points across a plurality of consecutive bronchoscopic video frames, then estimating for the new pose of the bronchoscope. In the preferred embodiment the pose estimation is based on linearization of the rotation matrix. By giving a set of corresponding points across the current bronchoscopic video image, and the CT-based virtual image as an input, the same method can also be used for manual registration. The fine registration step is preferably a gradient-based Gauss-Newton method that maximizes the correlation between the bronchoscopic video image and the CT-based virtual image. The continuous guidance is provided by estimating the 3D motion of the bronchoscope in a loop. Since depth-map information is available, tracking can be done by solving a 3D-2D pose estimation problem. A 3D-2D pose estimation problem is more constrained than a 2D-2D pose estimation problem and does not suffer from the limitations associated with computing an essential matrix. The use of correlation-based cost, instead of mutual information as a registration cost, makes it simpler to use gradient-based methods for registration.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
Apparatus and method for seismic imaging using waveform inversion solved by conjugate gradient least squares method
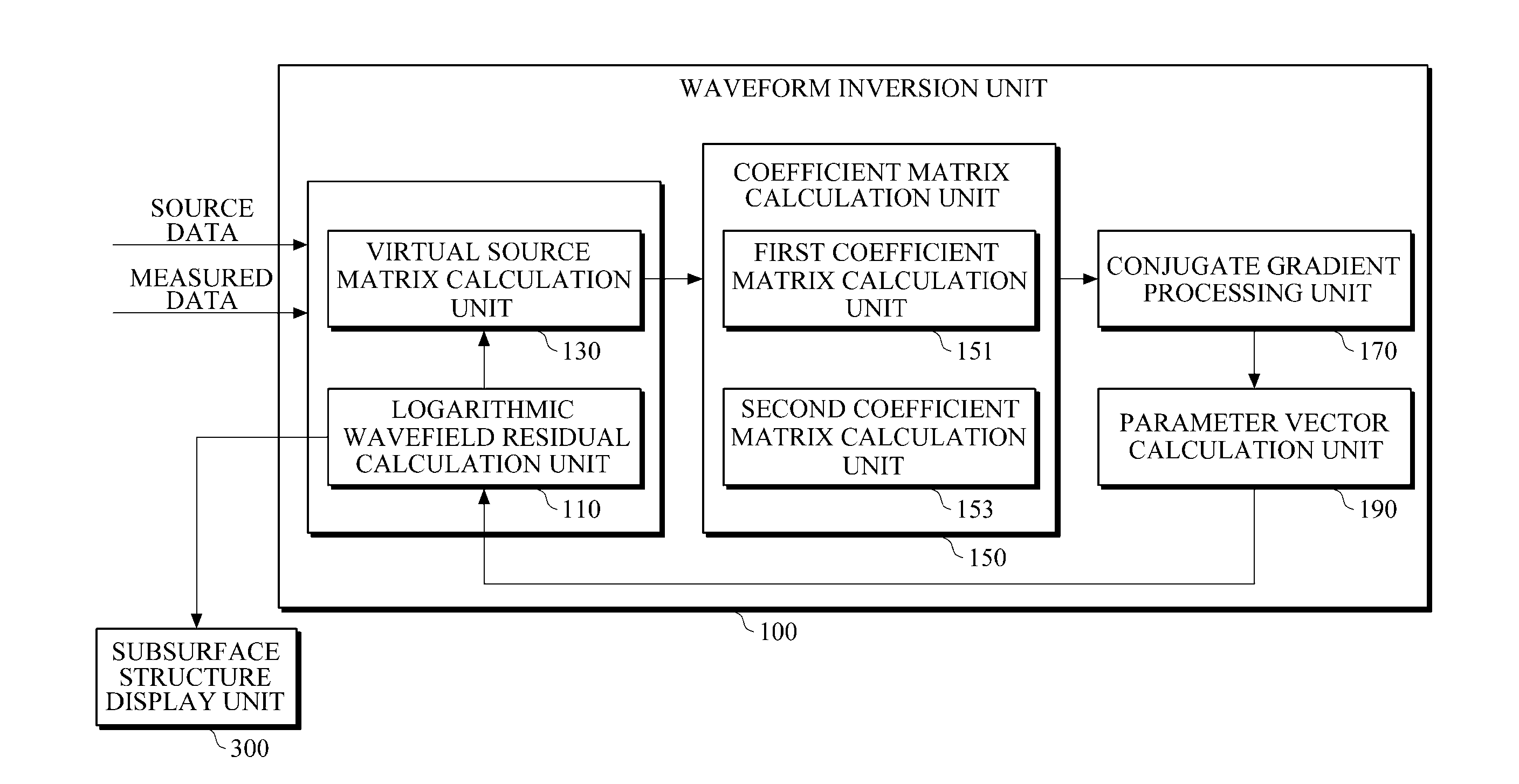
InactiveUS20110267923A1Seismic signal processingSeismology for water-loggingGauss newton methodWave field
Provided is an apparatus for seismic imaging by using waveform inversion in the frequency domain. The seismic imaging apparatus includes: a waveform inversion unit obtaining an equation by applying a Gauss-Newton method to an objective function consisting of residuals of logarithmic wavefields in frequency-domain waveform inversion and then obtaining a parameter vector, which minimizes the objective function, by solving the equation using a conjugate gradient method; and a subsurface structure display unit generating subsurface structure information using the parameter vector obtained by the waveform inversion unit and displaying the generated subsurface structure information.
Owner:SEOUL NAT UNIV R&DB FOUND
VSLAM method based on multi-characteristic visual odometer and graph optimization model
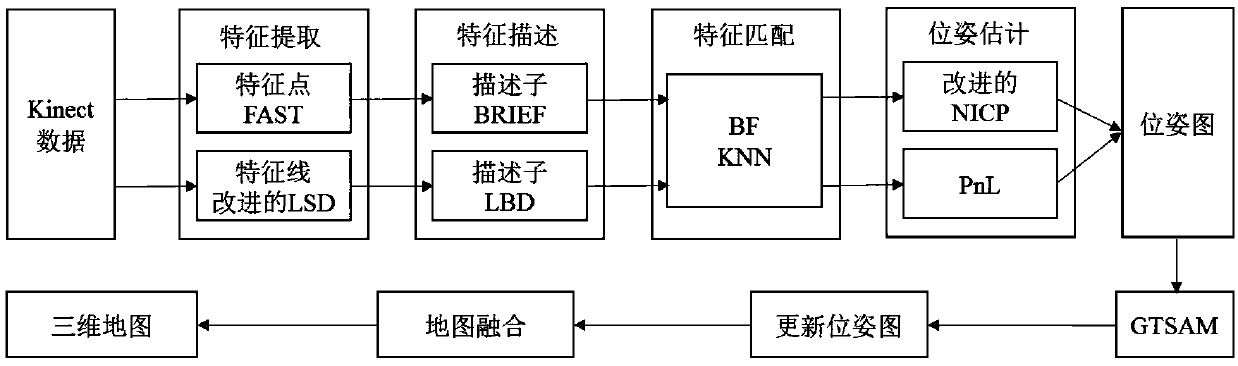
The invention discloses a VSLAM method based on a multi-characteristic visual odometer and a graph optimization model, and belongs to the robot SLAM field; the method comprises the following steps: firstly using a FAST (features from accelerated segment test) and an improved LSD algorithm to extract point and line features in a color image; further using different descriptors to describe characteristics; then carrying out characteristic matching; finally using an improved NICP (normal iterative closest point) algorithm and a PnL (perspective n line) algorithm to estimate a robot initial posture. The method can extract image line features so as to enlarge algorithm application scenes, can obtain a well robot initial posture, uses a Bayes network to express a multi-characteristic visual odometer, obtains a factor graph on the basis of the Bayes network, uses a maximum posterior probability to estimate a robot global posture in the factor graph, and uses a Gauss-Newton method to solve themaximum posterior probability to obtain the updated posture graph; finally, the posture graph and three dimensional points of corresponding frames are fused to obtain a reconstructed three dimensional map.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Monocular infrared video three-dimensional reconstruction method based on visual odometer
InactiveCN106846417AIncrease the sense of spaceRealize 3D reconstructionImage enhancementImage analysisDirect computationSparse methods
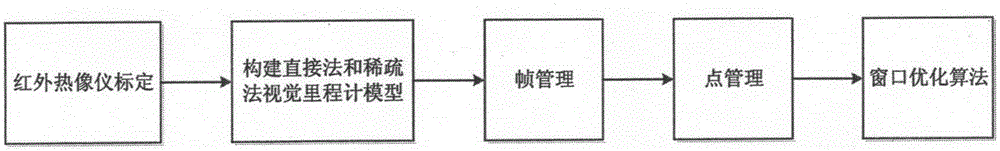
The invention provides a monocular infrared video three-dimensional reconstruction method based on a visual odometer. Firstly, a thermal infrared imager is calibrated; then, a direct method and sparse method visual odometer model is constructed; then, frames are managed, a key frame is generated from a continuous infrared image sequence to be processed, and the key frame is marginalized; point management is conducted on the pixel on the key frame; finally, sliding window optimization is conducted on the key frame, a photometric error of the direct method and sparse method visual odometer model is minimized, the reverse depths of thermal infrared imager pose, internal references and spatial points are solved in an iterative algorithm by a gauss-newton method, and finally, three-dimensional point cloud of a scene is obtained. According to the monocular infrared video three-dimensional reconstruction method based on the visual odometer, the direct method is applied to photometric error minimization, traditional feature point detection and matching are skipped, through direction operation on a grey value of the pixel, all variables which the photometric error to be optimized depend on is calculated directly, and therefore three-dimensional reconstruction of a night vision scene is achieved, the real-time capability of the three-dimensional reconstruction is ensured, and the spaciousness of the scene is enhanced.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Quaternion-based attitude resolving method for extended Kalman filter algorithm
ActiveCN108225308ASolve problems such as unknown calculationsImprove estimation accuracyNavigational calculation instrumentsNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsProcess noiseAccelerometer
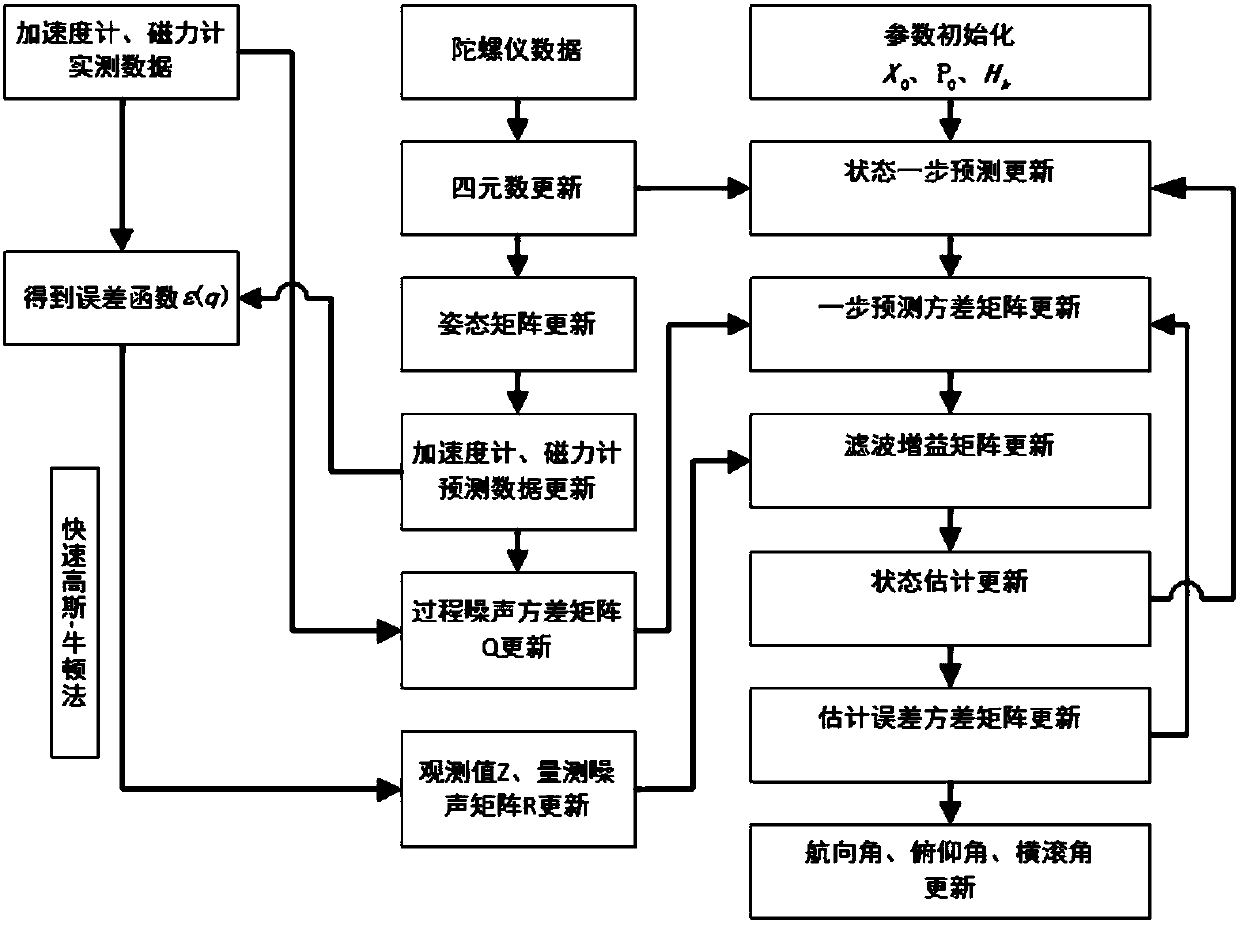
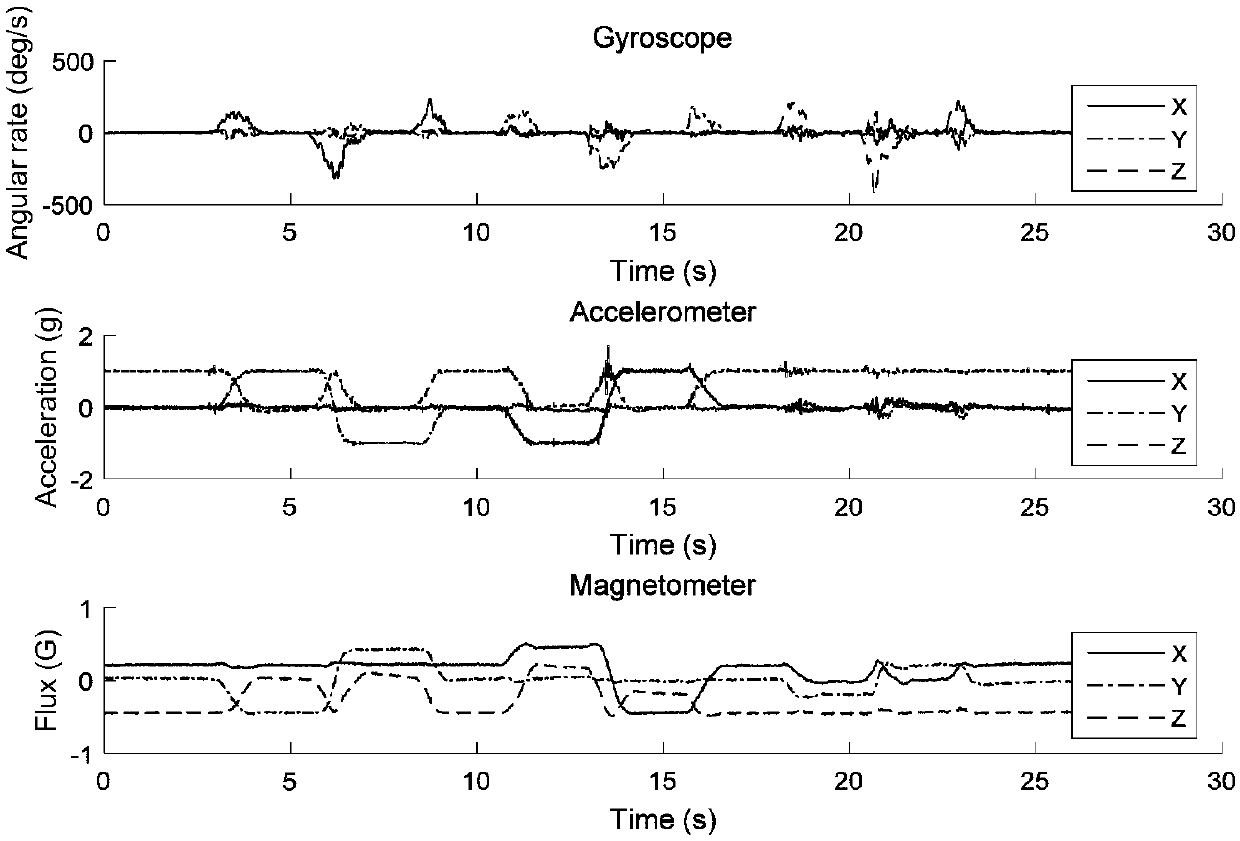
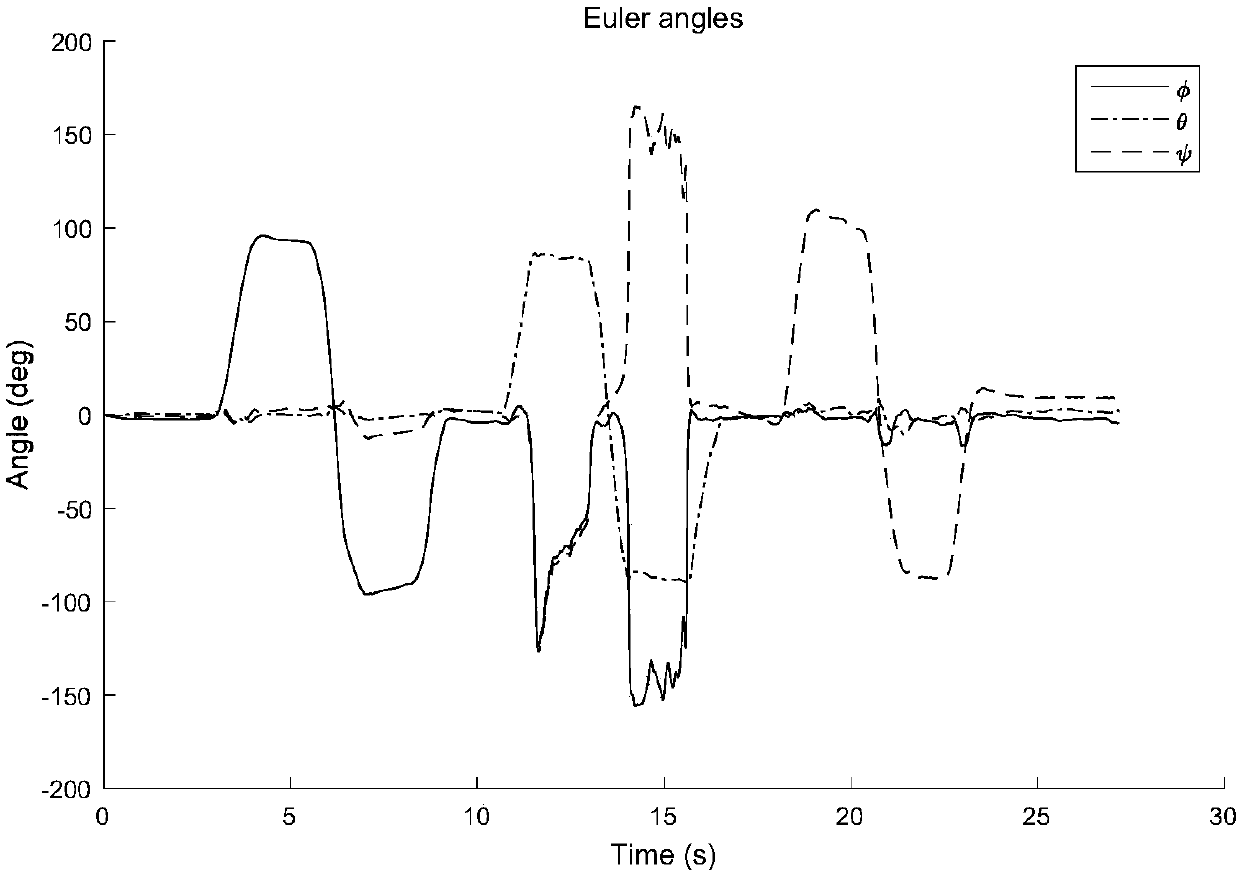
The invention discloses a quaternion-based attitude resolving method for an extended Kalman filter algorithm. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring multisensor data of a vector in a fixed coordinate system; filtering data acquired by an accelerometer and a magnetometer, and subjecting the data acquired by the two sensors to normalization processing; constructing a state equation of avector system according to a quaternion differential equation and an attitude matrix, and determining a process noise variance matrix of the system; constructing a systematic observation model by using a rapid Gauss-Newton method, and determining a system measured noise variance matrix; constructing a Kalman filtering recurrence equation according to the constructed system state equation and theobservation model; resolving three attitude angles of the vector by using an optimal quaternion obtained through recurrence. According to the method, the computing capacity can be greatly simplified,and the existing problem that parameters are unclear in computing is solved.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Systems and methods for parameter adaptation
InactiveUS20100023464A1Accurate representationAccurate modelingSimulator controlDigital computer detailsGauss newton methodModel parameters
A method of parameter adaptation is used to modify the parameters of a model to improve model performance. The model separately estimates the contribution of each model parameter to the prediction error. It achieves this by transforming to the time-scale plane the vectors of output sensitivities with respect to model parameters and then identifying the regions within the time-scale plane at which the dynamic effect of individual model parameters is dominant on the output. The method then attributes the prediction error in these regions to the deviation of a single parameter from its true value as the basis of estimating individual parametric errors. The proposed Signature Isolation Method (PARSIM) then uses these estimates to adapt individual model parameters independently of the others, implementing, in effect, concurrent adaptation of individual parameters by the Newton-Raphson method in the time-scale plane. The Signature Isolation Method has been found to have an adaptation precision comparable to that of the Gauss-Newton method for noise-free cases. However, it surpasses the Gauss-Newton method in precision when the output is contaminated with noise or when the measurements are generated by inadequate excitation.
Owner:UNIV OF MASSACHUSETTS
Mean-line-based blade front and back edge fitting and section line smooth reconstruction method
InactiveCN106021782AImprove calculation accuracyFast convergenceGeometric CADSpecial data processing applicationsMeasurement pointGauss newton method
The invention discloses a mean-line-based blade front and back edge fitting and section line smooth reconstruction method. The method is used for solving the technical problem that an existing method is poor in practicability. According to the technical scheme, on the basis of a fitting problem of front and back edge measuring points, a restrained least square fitting method is built for fitting of front and back edges meeting the design requirement. Different from unrestraint least square method front and back edge fitting, the method adopts a mean line as constraint conditions for front and back edge fitting, the restrained least square method is built, a Gauss-Newton method is used for iterative solving, finally, a fitting front and back edge curve approximating the designed front and back edges is obtained, front edge radius errors are lowered to 0.007% from original 0.670%, and the back edge radius errors are lowered to 0.062% from original 1.018%. The fitting front and back edge and the blade back and blade basin achieve smooth connection, and the smooth section line curve is built. The method has the advantages of being high in calculation precision, high in convergence rate and effective in constraint.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
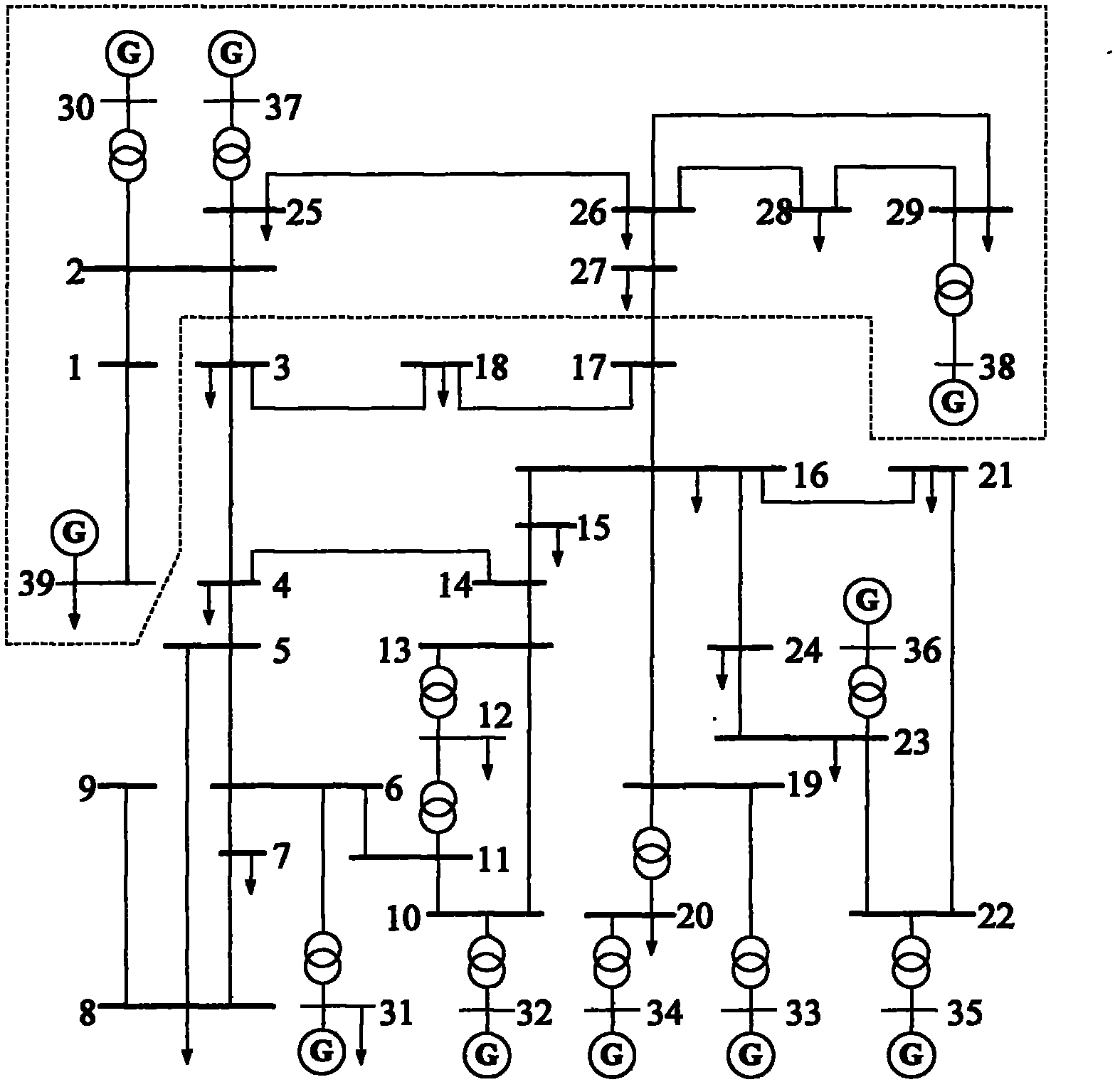
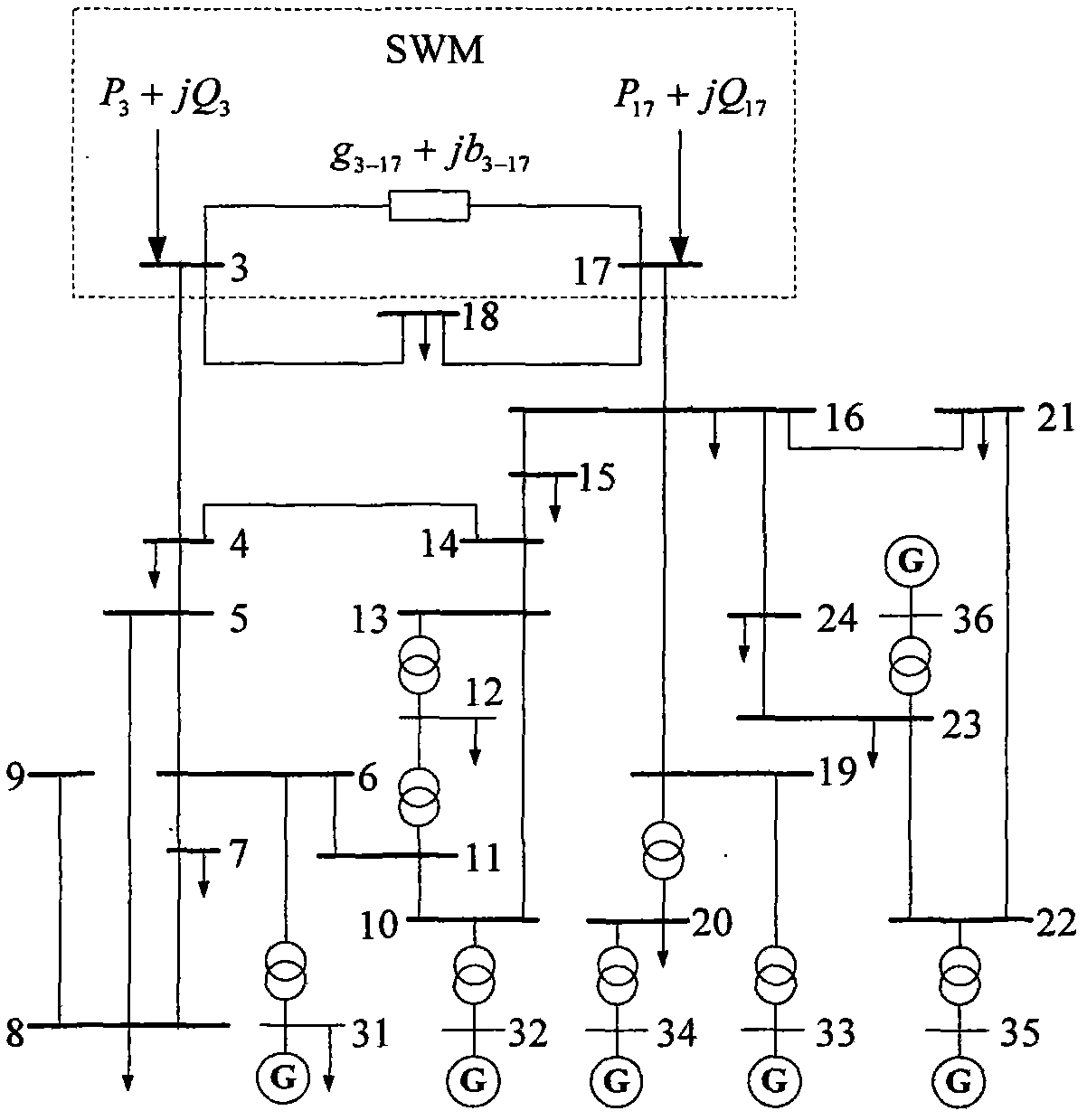
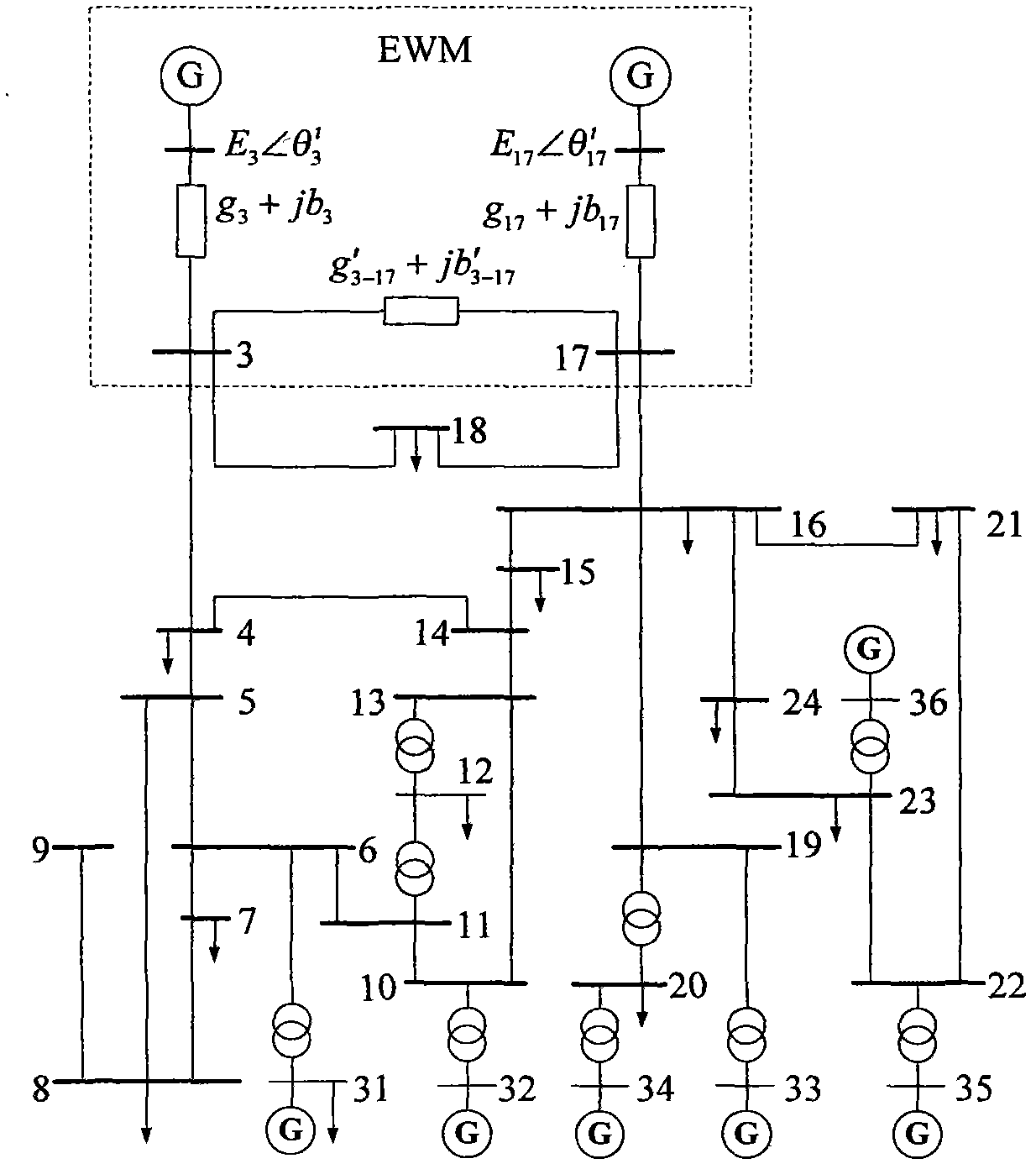
Internal network actual information based method for external network static equivalents of two ports
InactiveCN102005758ASolve the static equivalence problemAdaptableAc network circuit arrangementsNODALGauss newton method
The invention provides an internal network actual information based method for external network static equivalents of two ports, which comprises the following steps of: (1) establishing a simplified Ward equivalent circuit (SWM for short) of an external network; (2) establishing a multiperiod least-squares estimation model of an SWM equivalent parameter according to boundary nodes and state information of an internal network in multiple periods, and solving the SWM equivalent parameter by using Gauss-Newton method; (3) establishing a Ward equivalent circuit of an expanded voltage source branch (EWM for short) of the same external network; (4) establishing a multiperiod least-squares estimation model of an EWM equivalent parameter according to the constrain relation between the SWM parameter and the EWM parameter, the boundary nodes and the state information of the internal network in multiple periods, and solving the EWM equivalent parameter by using a Gauss-Newton method, wherein the obtained EWM is the final equivalent circuit of the external network. The method has the advantages of no need of any information of the external network, high engineering adaptability and very high equivalent accuracy no matter the tidal current of the internal network changes greatly or slightly.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
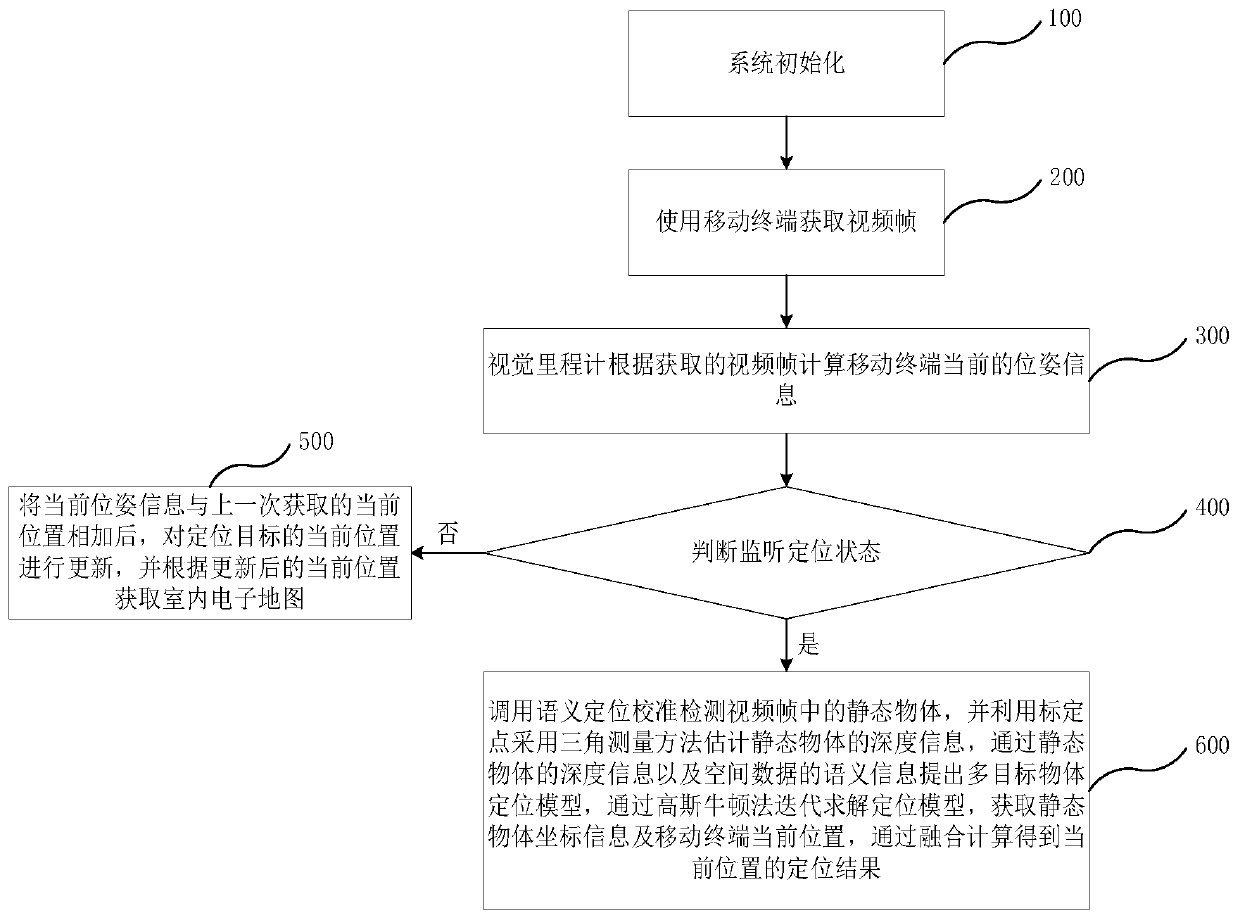
Mobile side vision fusion positioning method and system, electronic equipment
ActiveCN110375739AAccurate locationAccurate positioning methodNavigational calculation instrumentsGauss newton methodMobile end
The application relates to a mobile side vision fusion positioning method and system, and electronic equipment. The method comprises the following steps: step a, acquiring an initial location of a mobile terminal as the current location of a positioning target based on the calibrated starting location and sensor information; step b, acquiring a video frame by using the mobile terminal; and step c,detecting a static object in the video frame, acquiring geographic coordinate information of the static object through a BIM space database, and substituting the coordinate information of the staticobject into a multi-target object positioning model, iteratively solving the positioning model through a Gaussian newton method, acquiring the current location of the mobile terminal, and combining the current location of the mobile terminal and the coordinate information of the static object to obtain a positioning result of the positioning target. Through the positioning method disclosed by theapplication, the more convenient, precise and cheaper positioning method can be realized.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
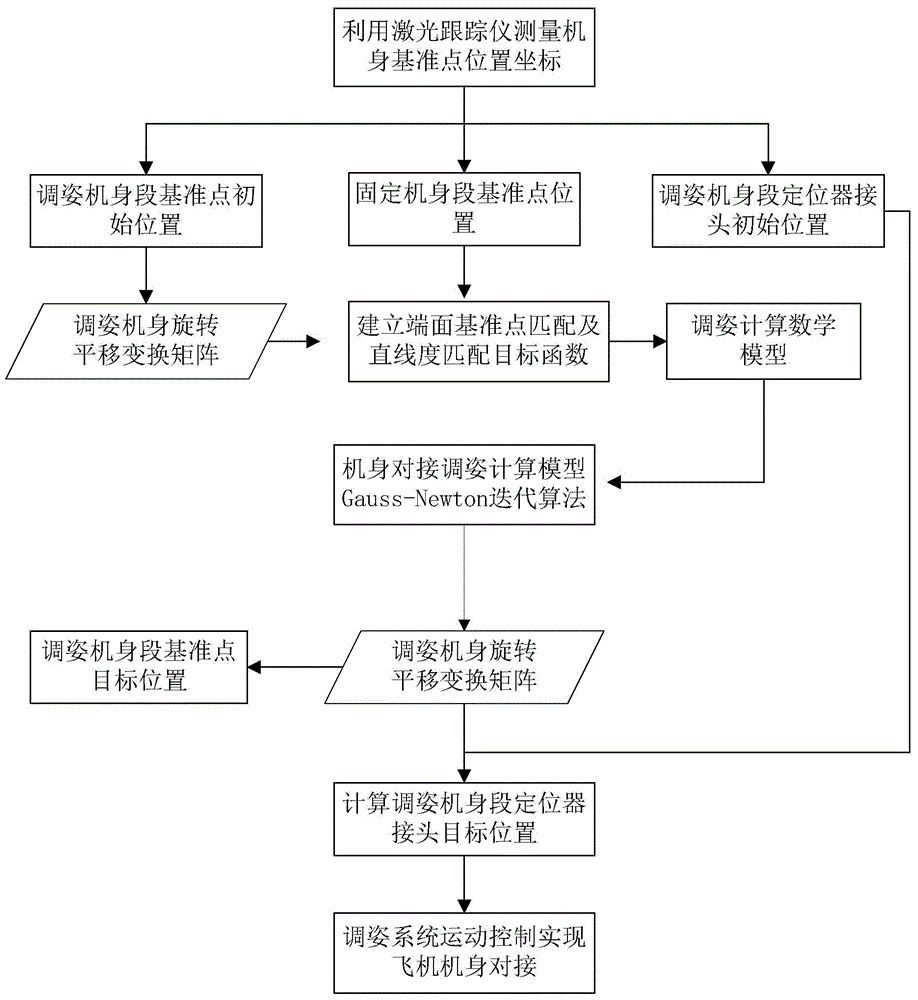
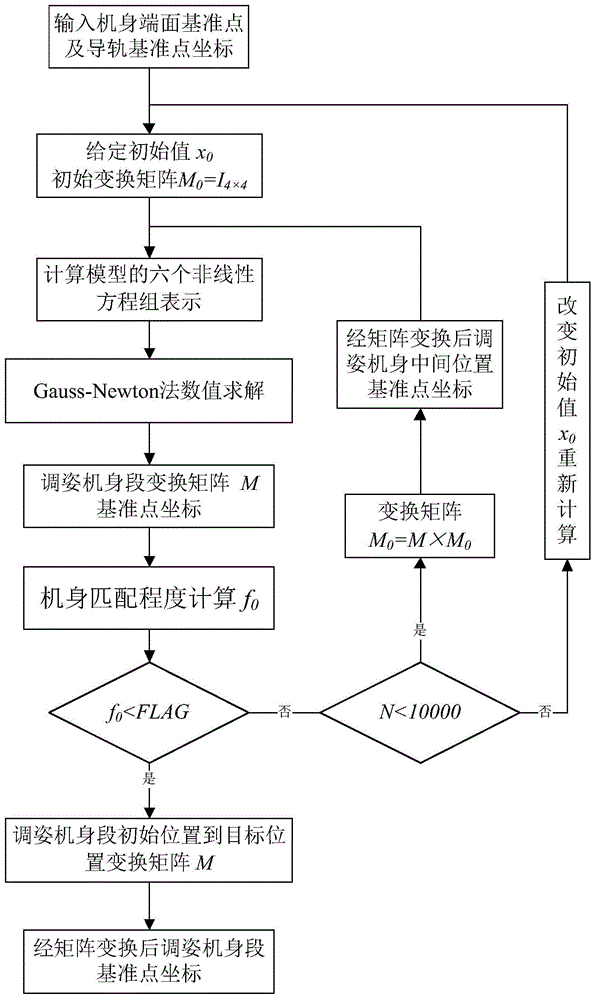
Airframe butt joint attitude-adjusting method meeting stringer reference alignment and straightness requirements
ActiveCN104477402ASolve the problem of not being able to consider the straightness of the aircraft fuselageImprove guidanceAircraft assemblyMathematical modelGauss newton method
An airframe butt joint attitude-adjusting method meeting stringer reference alignment and straightness requirements includes the steps: measuring end face reference points and linear guide rail reference points of a fixed airframe section and an attitude-adjusting airframe section and coordinates of the position of an attitude-adjusting system three-dimensional positioner connector connected with the attitude-adjusting airframe section by a laser tracker; building airframe end face reference point matching and straightness matching target functions, and accordingly building a mathematic model for airframe butt joint attitude-adjusting calculation; performing iterative calculation for the airframe butt attitude-adjusting model by a Gauss-Newton method to obtain coordinates of optimal butt joint positions of the attitude-adjusting airframe section and the fixed airframe section and obtain a transformational matrix from an initial position to a target position; calculating the coordinates of the target position of an attitude-adjusting system three-dimensional positioner connector connected with the attitude-adjusting airframe section according to the obtained transformational matrix, and butting the attitude-adjusting airframe section and the fixed airframe section by controlling movement of the attitude-adjusting system three-dimensional positioner from the initial position to the target position.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
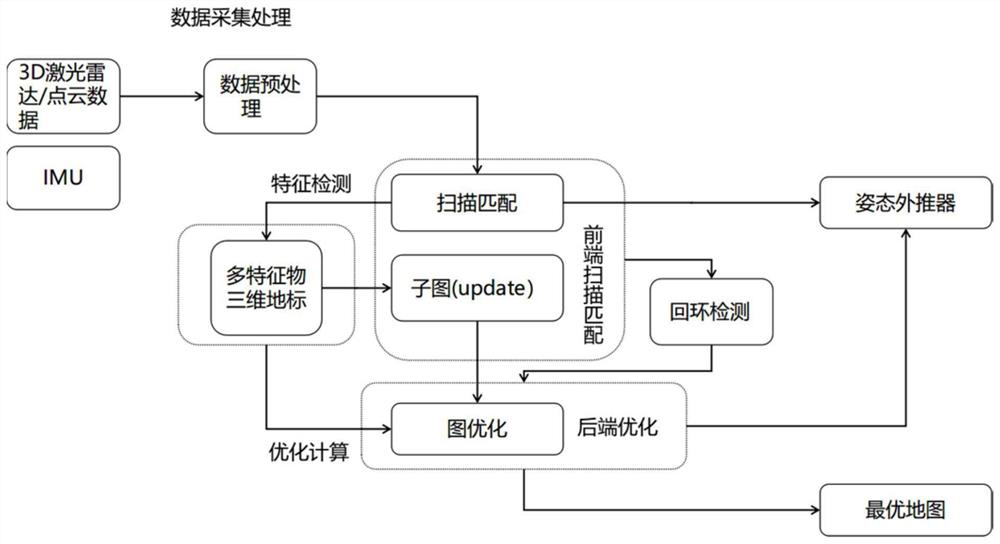
Multi-feature fusion IGV positioning and mapping method based on 3D laser radar
PendingCN113409410AQuick solveStable and fast operationImage enhancementImage analysisData acquisitionGauss newton method
The invention discloses a multi-feature fusion IGV positioning and mapping method based on a 3D laser radar. The method mainly comprises four processes of data acquisition processing, scanning matching and local map construction, back-end optimization and loopback detection. Data acquisition processing is data processing of the 3D laser radar sensor; according to the scanning matching and local map construction, a frame-subgraph matching mode is adopted for processed laser point cloud data, a three-dimensional landmark with multi-feature information such as angle, distance and reflection intensity is used for resolving an initial pose, and a local optimal subgraph is constructed by occupying a grid map; according to back-end optimization, for continuously iterated sub-graphs, a graph optimization strategy is adopted, an optimization problem is solved by using a Gaussian Newton method, and a solving process is accelerated by using a three-dimensional landmark, so that accumulated errors are eliminated; all tracks are stored in loopback detection, a multi-resolution map is adopted, calculation is accelerated through a branch and bound method, and closed-loop detection is completed. Finally, high-precision positioning and mapping of the AGV are realized.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
Passive sensor error registering method and apparatus based on maximum likelihood estimation
The invention provides a passive sensor error registering method and apparatus based on maximum likelihood estimation. When an observed point is positioned, coordinates of the observed point and three observation points under the same coordinate system, azimuth measurement values between the observation points and the observed point and random measurement deviations are obtained. By use of the maximum likelihood estimation and a Gauss-Newton method, system deviations and random deviations in an observation process are processed, and positioning results satisfying precision requirements are obtained by use of an iteration method. Compared to a positioning method in the prior art, the method brought forward by the invention takes system deviations between the observation points into consideration and improves the positioning precision of a passive sensor.
Owner:NAVAL AERONAUTICAL & ASTRONAUTICAL UNIV PLA
Method for determining rainfall intensity formula with functional rainfall attenuation index
InactiveCN102663256AImprove computing efficiencyImprove fitting accuracyComplex mathematical operationsUltrasound attenuationTotal Formula
The invention relates to a method for determining a rainfall intensity formula with a functional rainfall attenuation index, and belongs to the technical field of the municipal engineering. The method comprises the following steps of: according to relation values of a return period P, a rainfall intensity i and the duration t, firstly, determining parameters of each single return period subformula by adopting a Gauss-Newton method; secondly, selecting a rainfall attenuation index n and the return period P to form a semi-logarithmic or power-functional correlative relation by regression calculation, using the relation with a larger correlation index R2 as the adopted relation of n and P, simultaneously carrying out regression calculation on parameters in a relation of a rain force A and the return period P, using obtained parameter values as initial values of corresponding parameters in each return period total formula and for a parameter b, using an average value of all the single return periods as an initial value of b in the total formula; and then determining parameters of the total formula with the functional rainfall attenuation index n by adopting the Gauss-Newton method so as to obtain the rainfall intensity formula. The formula is the basic foundation of determining the rainwater design flow in the urban drainage work design.
Owner:JIANGSU VOCATIONAL INST OF ARCHITECTURAL TECH
Bionic polarization synchronous localization and mapping method based on factor graph optimization
ActiveCN112697138AImprove environmental adaptabilityImprove anti-interference abilityInternal combustion piston enginesNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsRadarGauss newton method
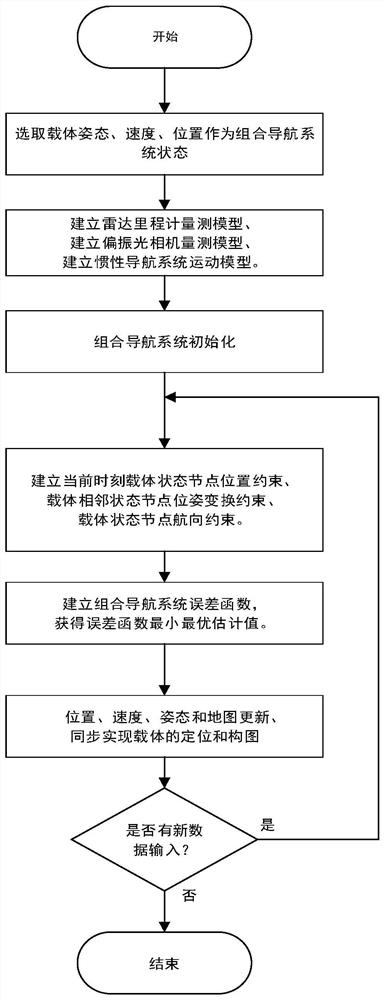
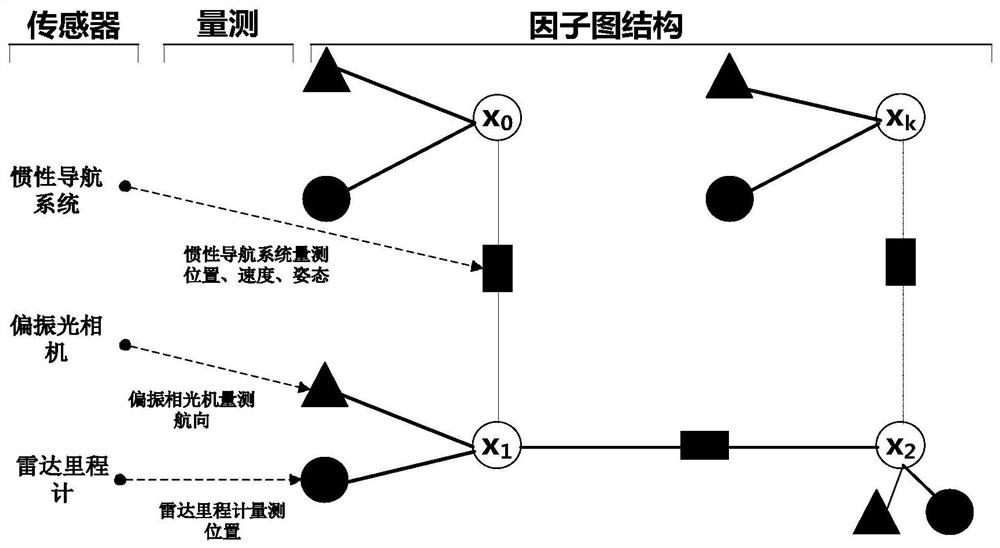
The invention discloses a bionic polarization synchronous localization and mapping method based on factor graph optimization. The method comprises the steps of: selecting the state of an integrated navigation system, building a radar odometer and polarized light camera measurement model and an inertial navigation system motion model, and initializing the integrated navigation system; according to the state node position constraint, the adjacent state node pose transformation constraint and the state node heading constraint of a carrier at the current moment, establishing an integrated navigation system state and measurement node error function to obtain a to-be-optimized factor graph; optimizing the to-be-optimized factor graph by using a Gauss-Newton method to obtain optimal estimated values of the position, the speed and the attitude of the carrier under the world coordinate system with the minimum error function; and updating and synchronizing the optimal estimated values and the map to realize localization and mapping of the carrier. Inertia, polarization and radar odometer multi-source information are fused and complemented, and the method has the characteristic of being free of external interference; and due to the characteristics of the historical information of factor graph optimization measurement and state, the environment adaptability is good, the anti-interference performance is high, and the localization and mapping precision is high.
Owner:NORTH CHINA UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
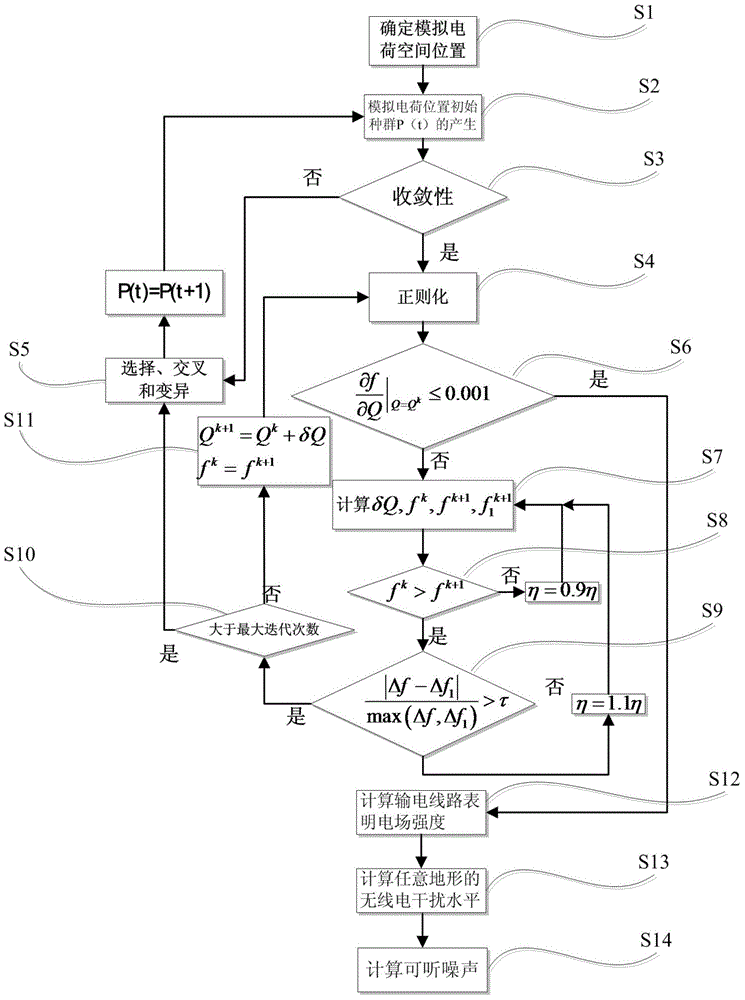
Method for calculating direct-current transmission line electric field intensity and radio interference
ActiveCN104573219ASolve the ill-posed problem of the legacy original equationImprove test efficiencyData processing applicationsGenetic modelsElectrical field strengthGauss newton method
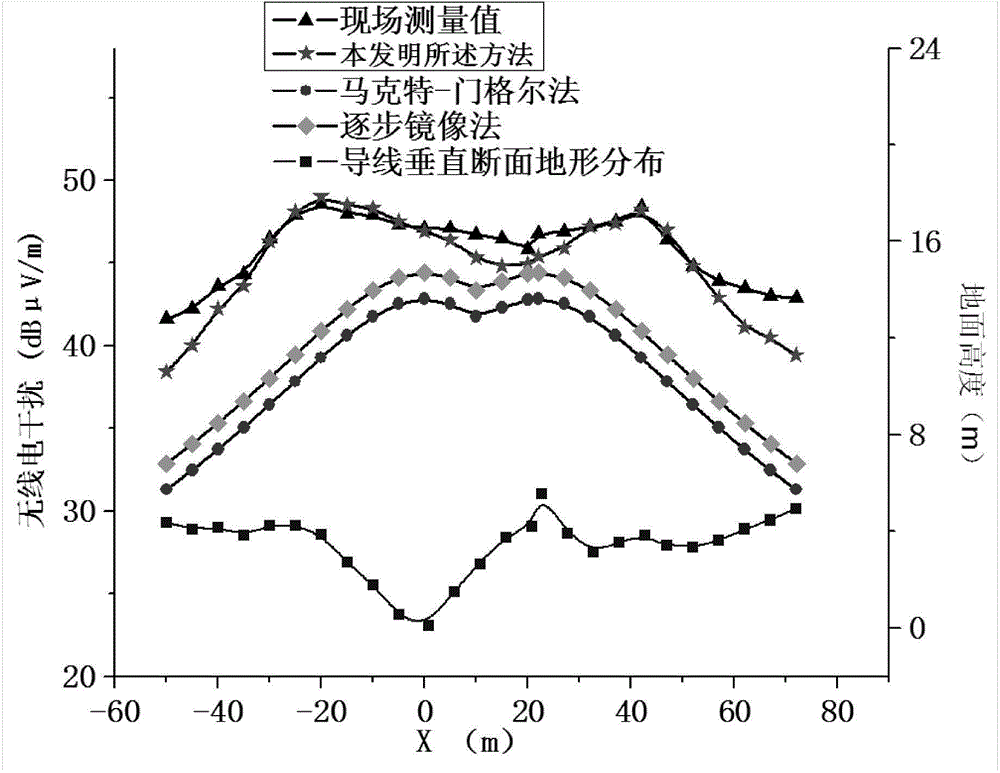
The invention discloses a method for calculating direct-current transmission line electric field intensity and radio interference. The method solves the problems that in the prior art and a traditional method, a transmission line lead section has waved relief, so that lead mirror image charge cannot be directly set, and ill-posed problems of an original equation can be solved when a direct-current transmission line adopts linear equations such as a Gauss-Newton method. Compared with a traditional partial discharge method, experimental efficiency is improved, and the method has practicability and feasibility through experimental verification.
Owner:YUNNAN POWER GRID CO LTD ELECTRIC POWER RES INST
Method for fitting power function type stage-discharge relation
InactiveCN102693215AComputational methods are easy to implementGood effectComplex mathematical operationsGauss newton methodWater resources
The invention relates to a method for fitting a power function type stage-discharge relation, and belongs to the technical field of hydrology and water resources. The method includes utilizing a larger group of relation values and a smaller group of relation values in n groups of relation values to determine initial values theta (0)=[beta 0(0), beta (0)]' of parameters to be estimated in a power function type stage-discharge relation formula according to a stage-discharge relation value (Ze1, Q1) to be fit in a certain hydrometric station, or solving a nonlinear regression coefficient as initial values of the parameters beta 0 and beta to be estimated by a traditional method of converting nonlinear regression to linear regression; and determining regression coefficients beta 0 and beta by a Gauss-Newton method. An i ranges from 1 to n. The stage-discharge relation is one of important contents for reorganizing hydrologic data, and is one of important references for water-conservancy and water-power engineering planning programming, hydrological forecasting and reservoir regulation.
Owner:JIANGSU VOCATIONAL INST OF ARCHITECTURAL TECH
Transient electromagnetic inversion method for sharp boundary model
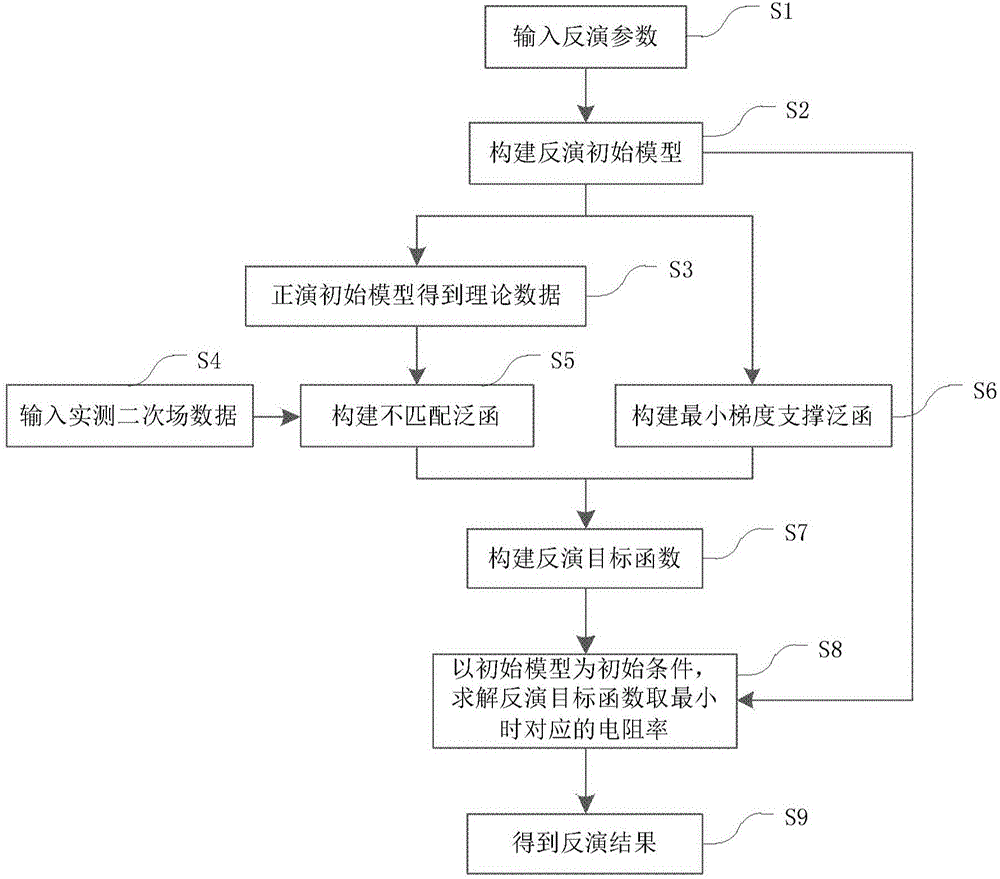
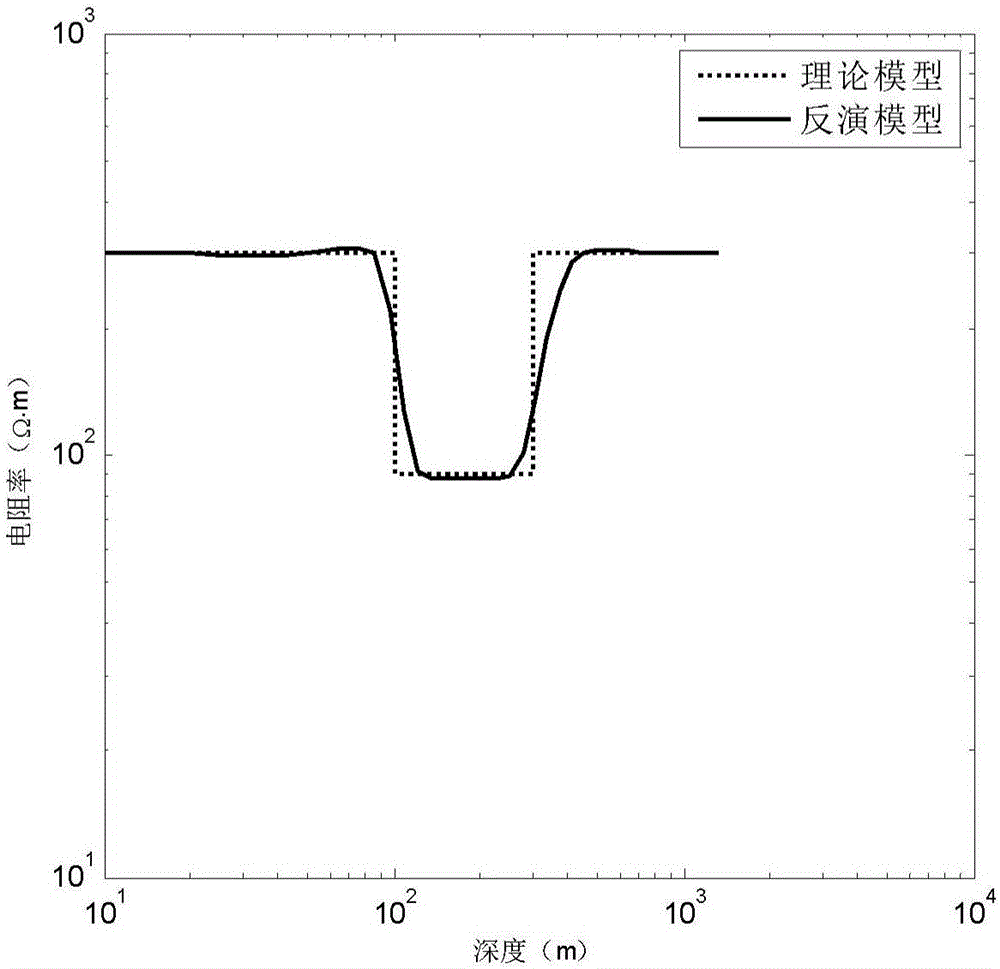
InactiveCN106646625AFind the global optimumMake up for the deficiencies that are not reflected clearlyElectric/magnetic detectionAcoustic wave reradiationGeneral functionImage resolution
The invention discloses a transient electromagnetic inversion method for a sharp boundary model. The method comprises the following steps: secondary field data observed via a transient electromagnetic method is input, inversion parameters are input and an inversion initial model is built; a mismatch general function between observed data and forward modeling theory data is built, a minimum gradient support general function used for restraining resistivity change is built, an inversion object function is built via the mismatch general function and the minimum gradient support general function, the initial model is used as initial conditions, a Gauss-Newton method is used for solving resistivity corresponding to a minimum target function, and an inversion result is obtained. Via the inversion method, a resolution of a underground resistivity abrupt change surface, a defect of unclear electrical interface reflection in an Occam inversion algorithm can be compensated, characteristics of stability and simplicity of the Occam inversion algorithm are kept in the transient electromagnetic inversion method, and the transient electromagnetic inversion method is of great significance for transient electromagnetic data inversion and late stage data interpretation.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Electrical impedance imaging method based on movable deformation component, device and system
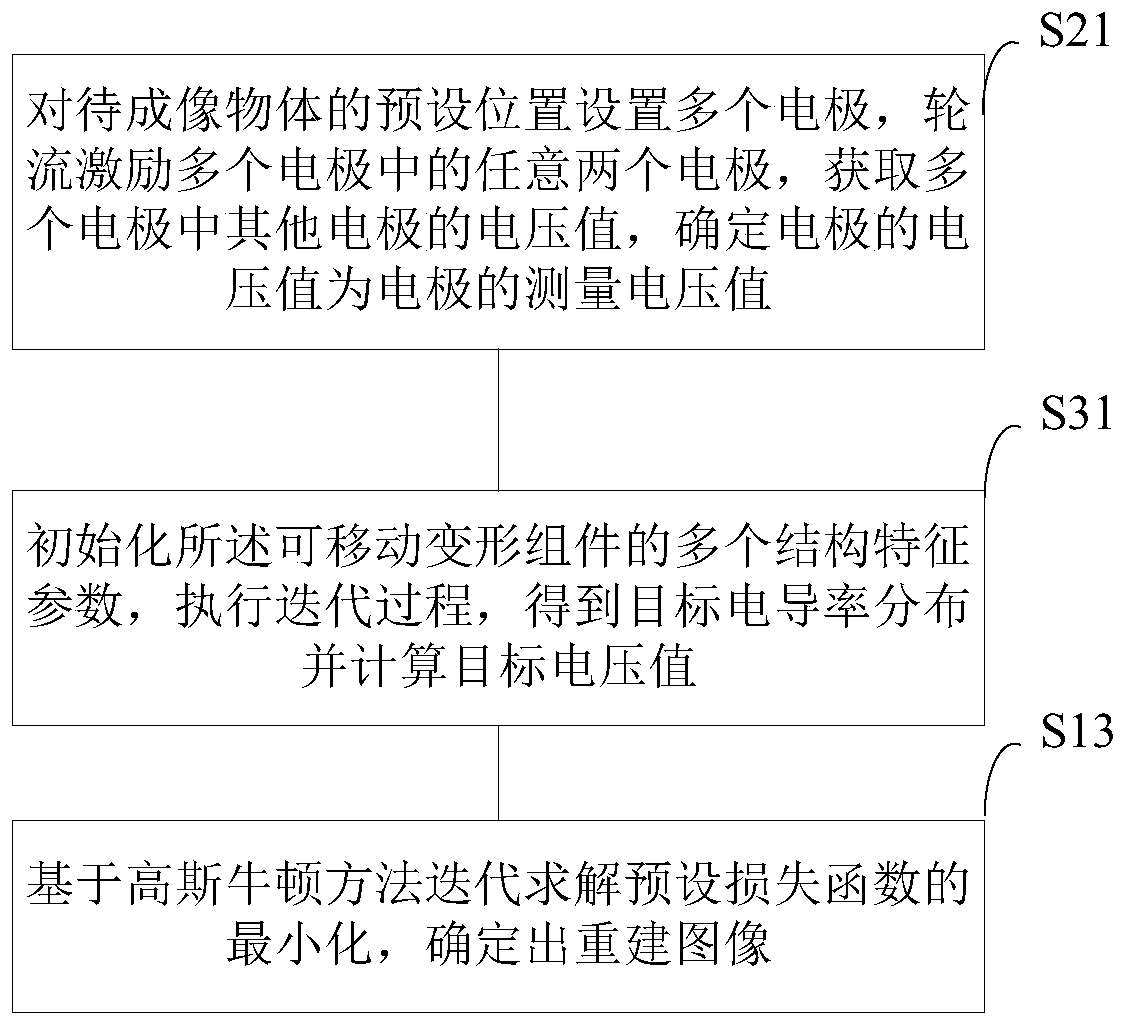
ActiveCN110251130AHigh resolutionImproving Imaging AccuracyDiagnostic signal processingSensorsElectrical resistance and conductanceImage resolution
The invention provides an electrical impedance imaging method based on a movable deformation component, a device and a system. The electrical impedance imaging method first establishes a finite element electrode model for a target field and acquires a measured voltage value of each electrode corresponding to an object to-be-imaged; a plurality of movable deformation components are initially placed for each object to-be-imaged as an initial value of a Gauss-Newton iteration method, an iterative process is performed, a target conductivity distribution is obtained, and a target voltage value is calculated; and the reconstructed image is determined by iteratively solving the minimization of the preset loss function based on the Gauss-Newton method. The scheme is based on the movable deformation component for image reconstruction, and utilizes the flexibility control of the movable deformation component in structural topology optimization, and the resolution and imaging precision of the electrical impedance reconstruction image can be improved.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Bridge cable monitoring method based on optimized tensioning string model and bridge cable monitoring system thereof
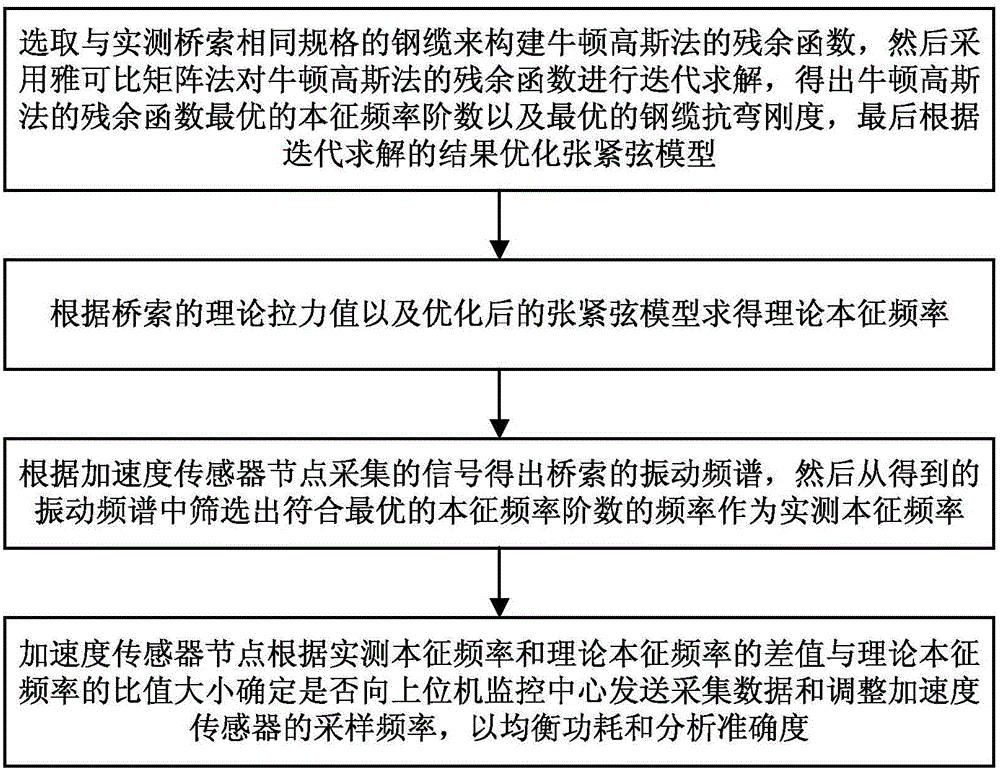
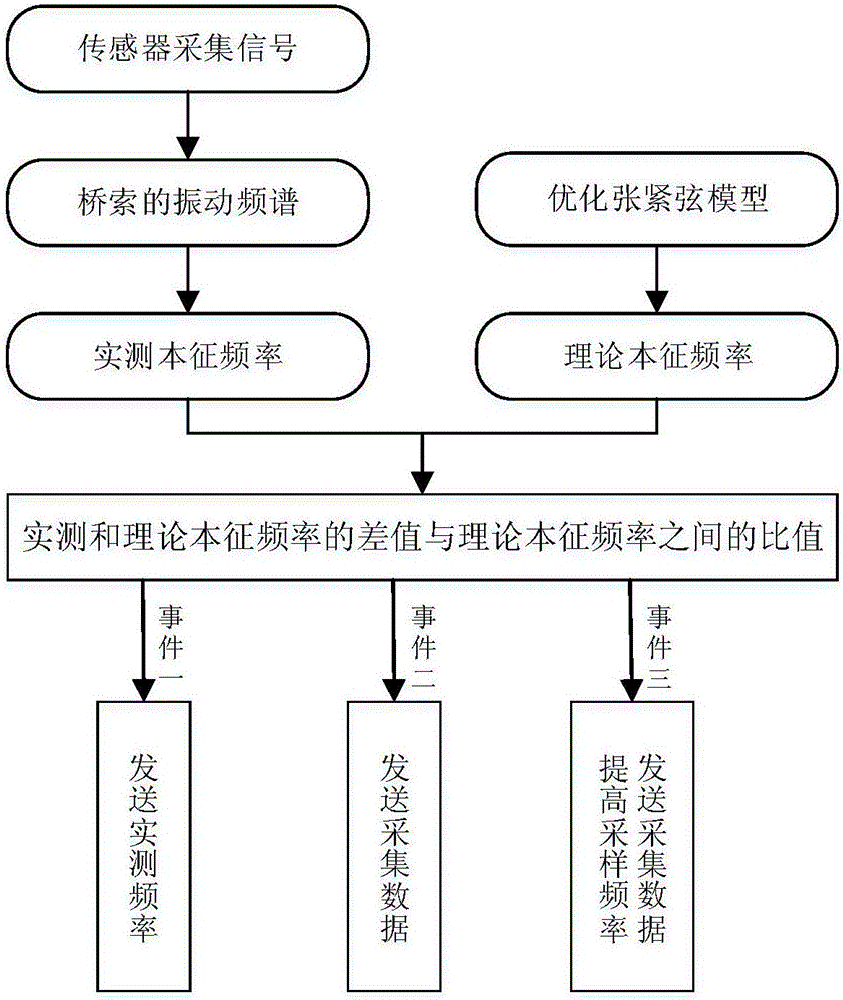
ActiveCN106197970AThe bending stiffness is accurately derived fromReduce mistakesMachine part testingTension measurementFrequency spectrumEigen frequency
The invention discloses a bridge cable monitoring method based on an optimized tensioning string model and a bridge cable monitoring system thereof. The method comprises the steps that a steel cable having the same specification with the actually measured bridge cable is selected to construct the residual function of the Gauss-Newton method, then iterative solving is performed on the residual function of the Gauss-Newton method and the optimal eigen-frequency order number and the optimal steel cable flexural rigidity of the residual function of the Gauss-Newton method are obtained, and finally the tensioning string model is optimized according to the result of iterative solving; the theoretical eigen-frequency is solved; the vibration spectrum of the bridge cable is obtained, and then the frequency meeting the optimal eigen-frequency order number is selected from the obtained vibration spectrum to act as the actually measured eigen-frequency through screening; and an acceleration sensor node determines transmitting of acquisition data and sampling frequency for adjusting the acceleration sensor to an upper computer monitoring center according to the size of the ratio of the difference value of the actually measured eigen-frequency and the theoretical eigen-frequency to the theoretical eigen-frequency. The bridge cable monitoring method is low in error and considers analysis of both accuracy and power consumption so that the bridge cable monitoring method can be widely applied to the field of bridge monitoring.
Owner:深圳市智能机器人研究院
Maximum power estimation method for photovoltaic power generation system
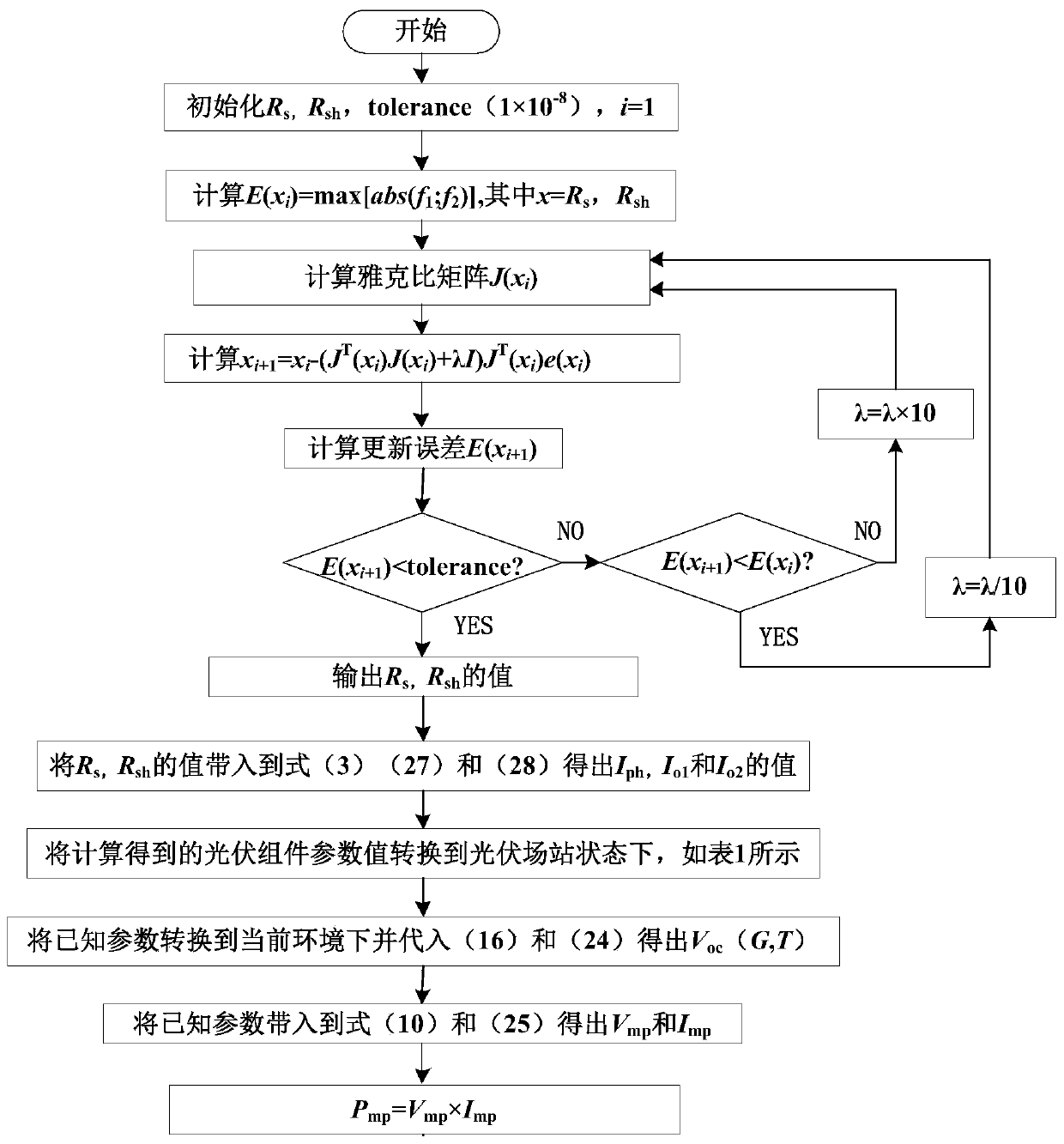
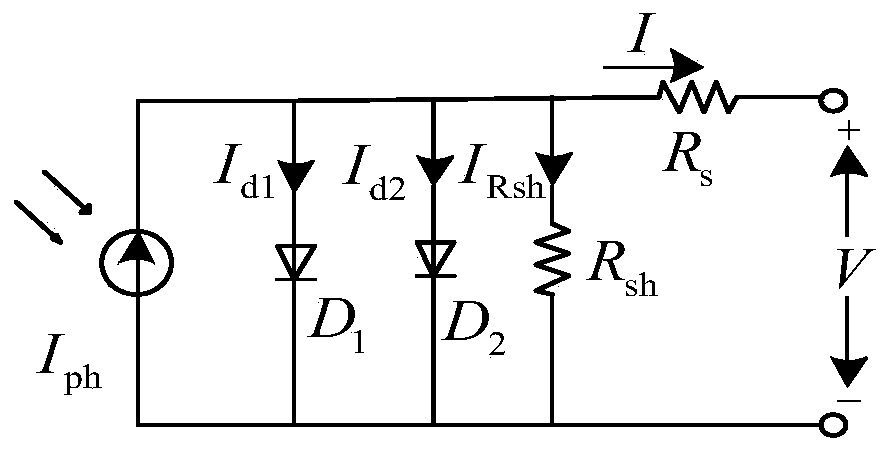
PendingCN111446732ASelect a small impactFast convergenceSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsPhotovoltaic energy generationGauss newton methodComputational physics
The invention provides a maximum power estimation method for a photovoltaic power generation system. The maximum power estimation method comprises the steps of establishing a double-diode 7 parametermodel of a photovoltaic cell, and realizing conversion calculation from environmental parameters to standard conditions by adopting open-circuit voltage and short-circuit current parameters; and usingan L-M algorithm controlled by parameters, so that the algorithm shows the characteristics of a gradient descent method and a Gauss-Newton method in sections, and the advantages of the two methods are fully combined. Photovoltaic double-diode model parameter calculation based on the L-M algorithm is less affected by iterative initial value selection, and convergence speed and precision are increased. The maximum power value is obtained based on an open-circuit voltage approximation method. The process of one-time iteration is omitted, and the calculation speed is increased.
Owner:STATE GRID GASU ELECTRIC POWER RES INST +2
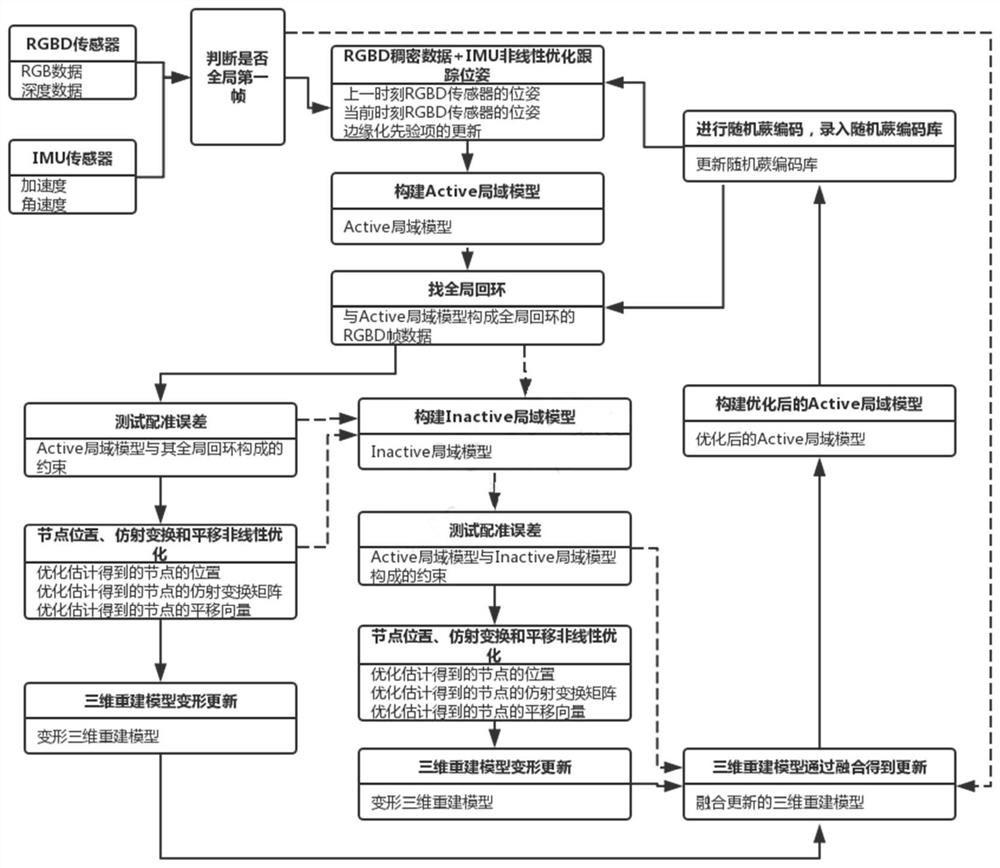
Three-dimensional reconstruction method based on optimized IMU tight coupling dense direct RGBD
PendingCN111862316AEnhancing Global ConsistencyImprove robustnessImage enhancementDetails involving processing stepsAlgorithmOriginal data
The invention discloses a three-dimensional reconstruction method based on optimized IMU tight coupling dense direct RGBD, and the method comprises the steps: (1) collecting optimized RGB data and optimized depth data from a local model reconstructed at the last moment, and obtaining original RGB data, original depth data and IMU data; (2) constructing a nonlinear cost function according to the inertial navigation error, the dense luminosity error and the ICP error, forming a nonlinear optimization problem by taking minimization of the nonlinear cost function as a target, and solving the nonlinear optimization problem by using a Gauss-Newton method so as to estimate an RGBD sensor optimization pose; (3) carrying out real-time three-dimensional reconstruction by utilizing the original RGB data and the original depth data at the current moment under the optimized pose of the RGBD sensor, and deforming the three-dimensional reconstruction model by using the nodes under the condition of finding the loopback constraint so as to ensure the global consistency. According to the method, the accuracy and efficiency of three-dimensional reconstruction are improved.
Owner:杭州深瞳科技有限公司
A phasor measurement device laboratory calibrator and a phasor measurement method thereof
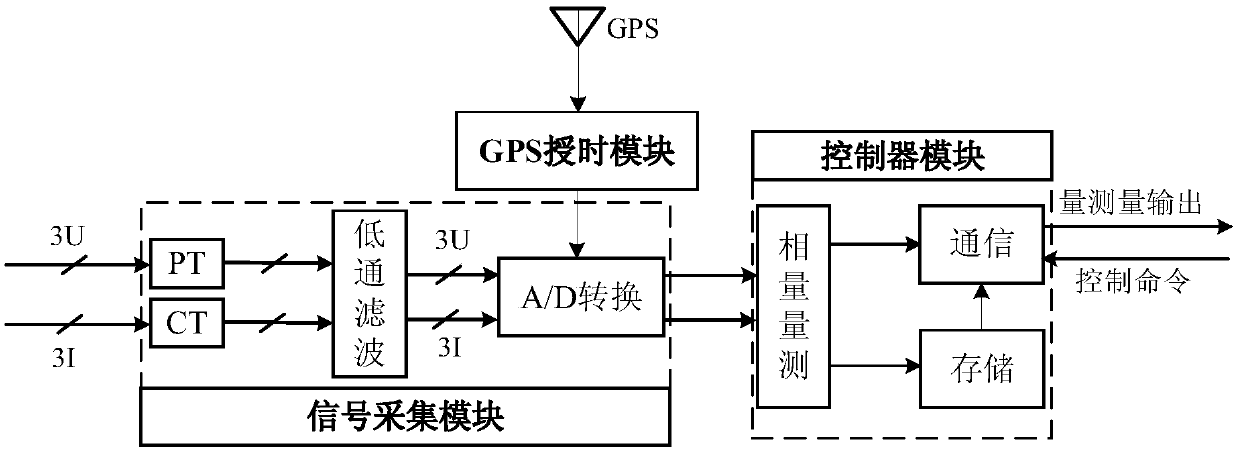
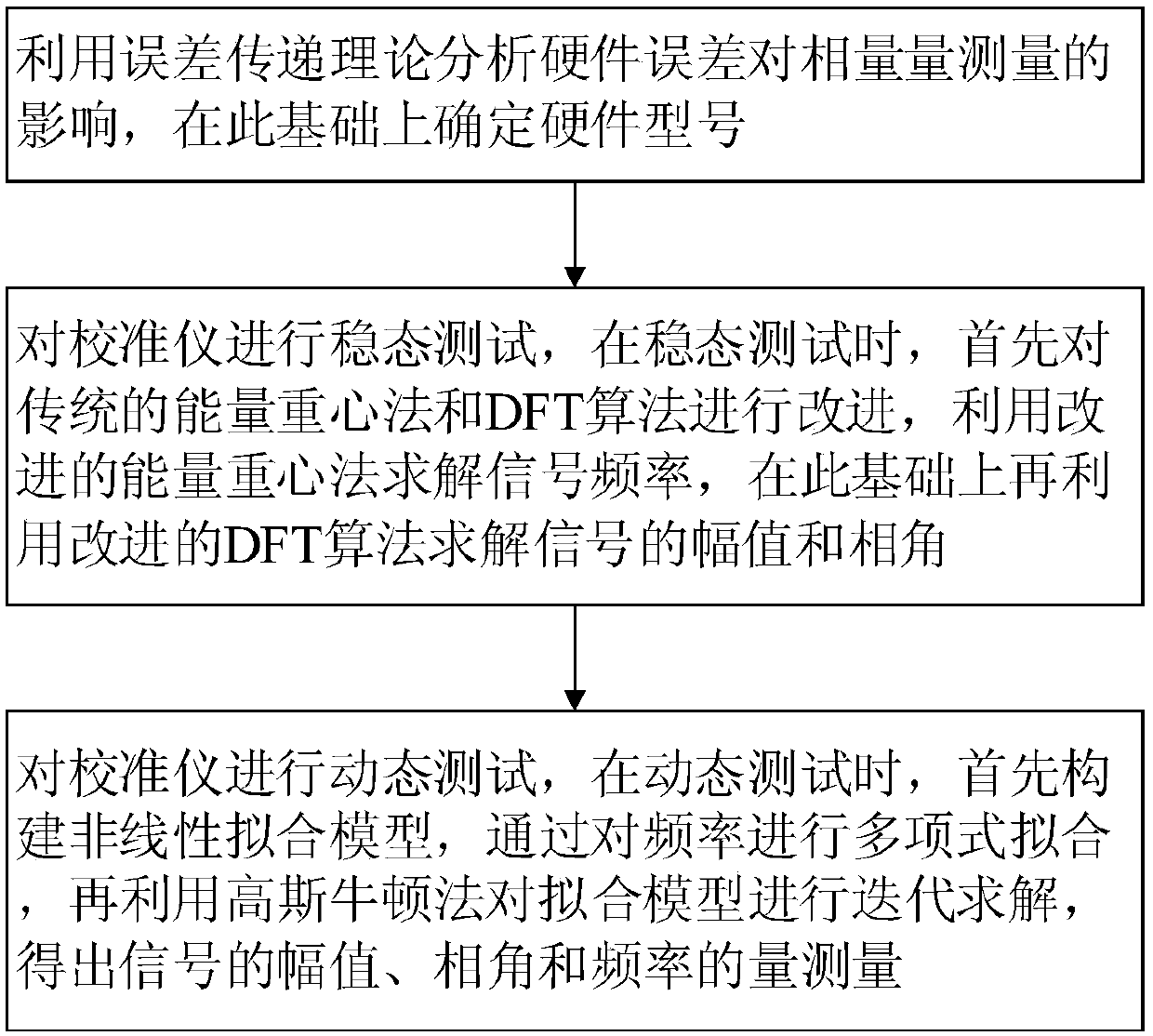
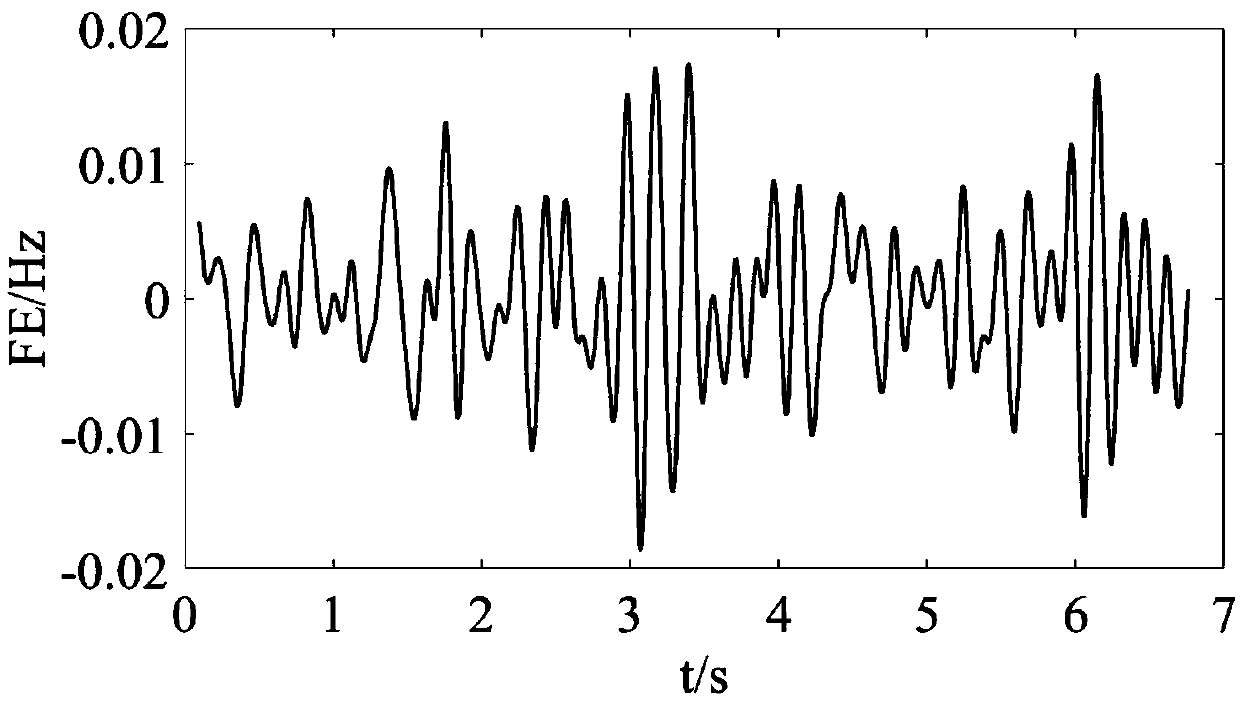
ActiveCN108896944AWork reliablyHigh precisionSpectral/fourier analysisVoltage-current phase angleMeasurement deviceModel selection
The invention provides a phasor measurement device laboratory calibrator and a phasor measurement method thereof which belongs to the technical field of phasor measurement and phasor measurement device test. The system includes a GPS synchronous time service module, a signal collection module and a controller module; the measurement method includes: model selection is performed on a hardware, influence of hardware error to phasor measurement is disclosed by utilizing an error transmission theory; measurement is performed by utilizing an improved energy center of gravity method and an improvedDFT algorithm during stable state test, a non-linear fitting model is constructed during dynamic test, solving is performed by utilizing a Gauss-Newton method, polynomial fitting is adopted for solving a frequency change rate of static and dynamic test signals. The calibrator can work reliably, and can limit influence on phasor measurement precision by a collection system within a small range andprovide a high precision reference value for error analysis. The measurement method makes the phasor measurement accuracy more than four times higher than an error standard, and has a good inhibitioneffect on harmonic wave and inter-harmonics interference.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING) +1
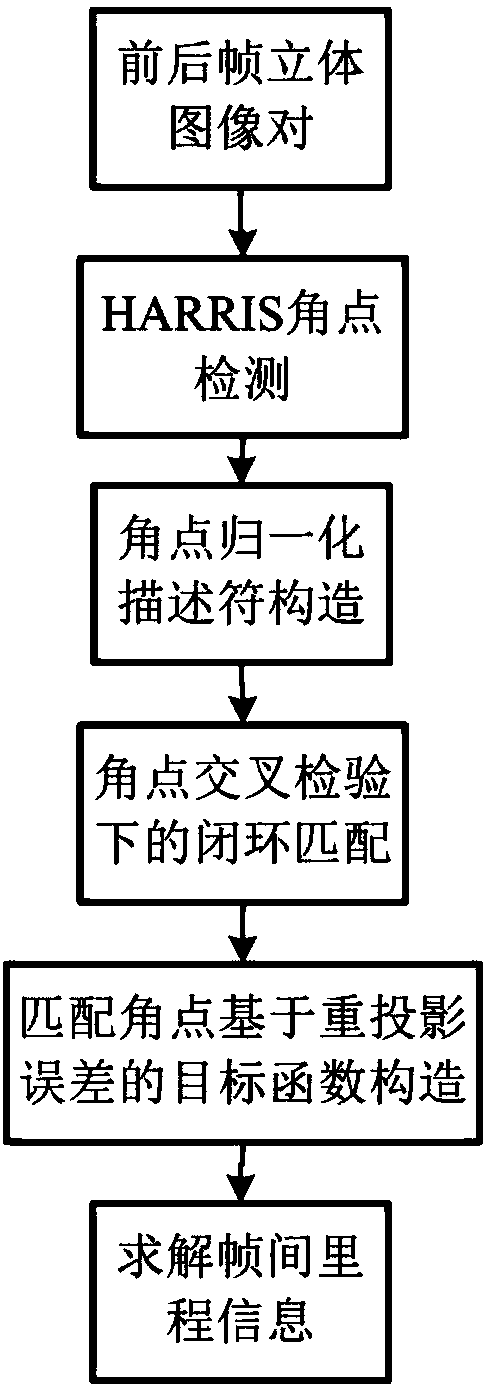
Real-time high-precision visual mileage calculation method
The invention relates to a real-time high-precision visual mileage calculation method. According to the method, the mileage information of a system is acquired in real time by means of a closed-loop corner matching strategy under cross-check and the objective function weight setting based on a corner life cycle. The method comprises the following steps: (1) obtaining corner positions in stereo image pairs by partitioning HARRIS corner detection; (2) obtaining a normalized descriptor of corners according to pixel information around the corners; (3) carrying out corner cross-check matching on stereo image pairs, and then performing closed-loop detection on the corners between the stereo image pairs and the front and back image pairs so as to obtain a matching corner set; (4) constructing anobjective function based on the re-projection error of the matching corner set, and setting a weight according to the corner life cycle; (5) solving the mileage information by means of a RANSAC algorithm and a Gauss Newton method. The method provided by the invention has the advantages that the high-accuracy matching corner set is obtained, the interior point selection time of the RANSAC algorithmis shortened, and the real-time mileage information calculation can be realized.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
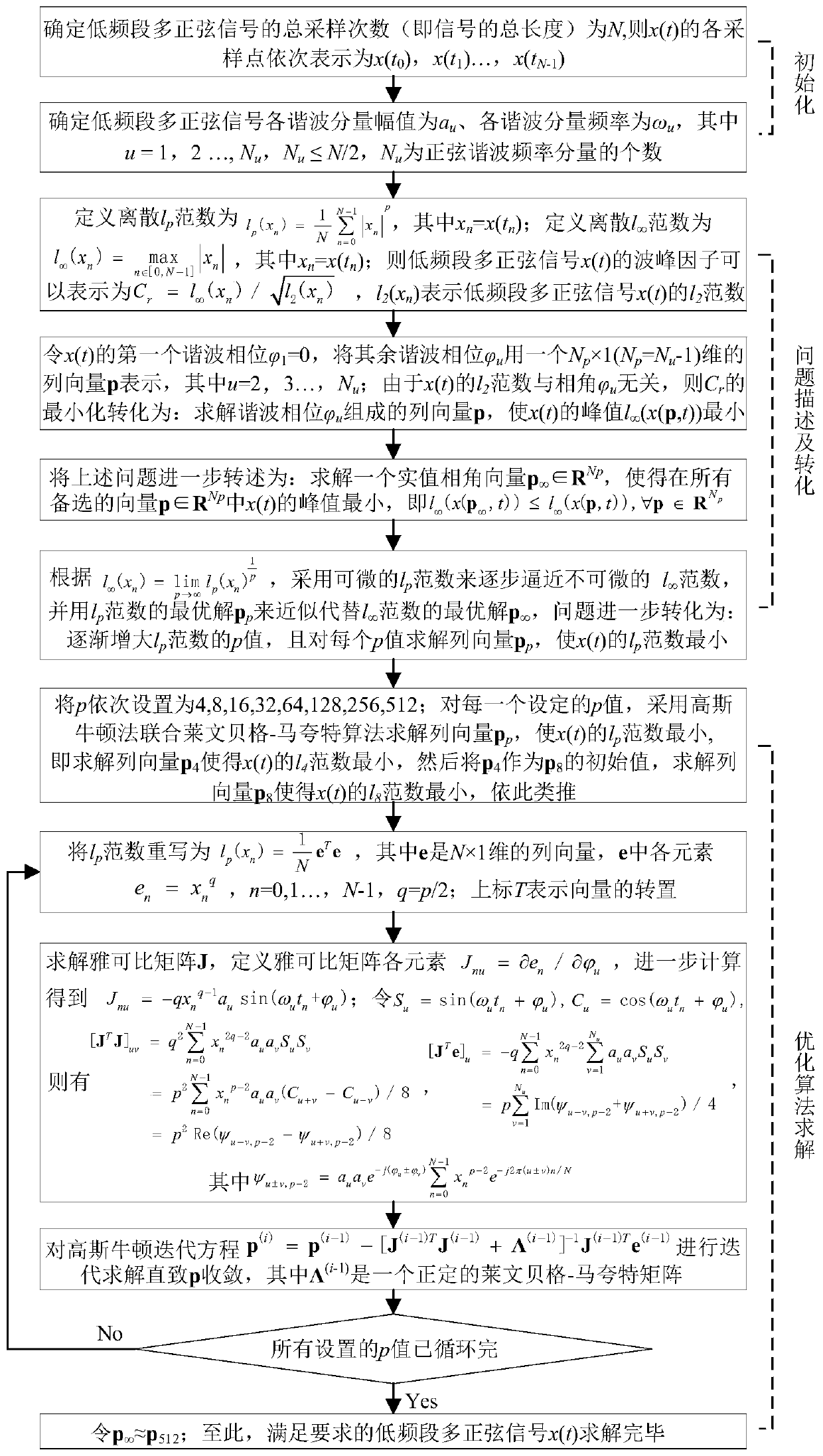
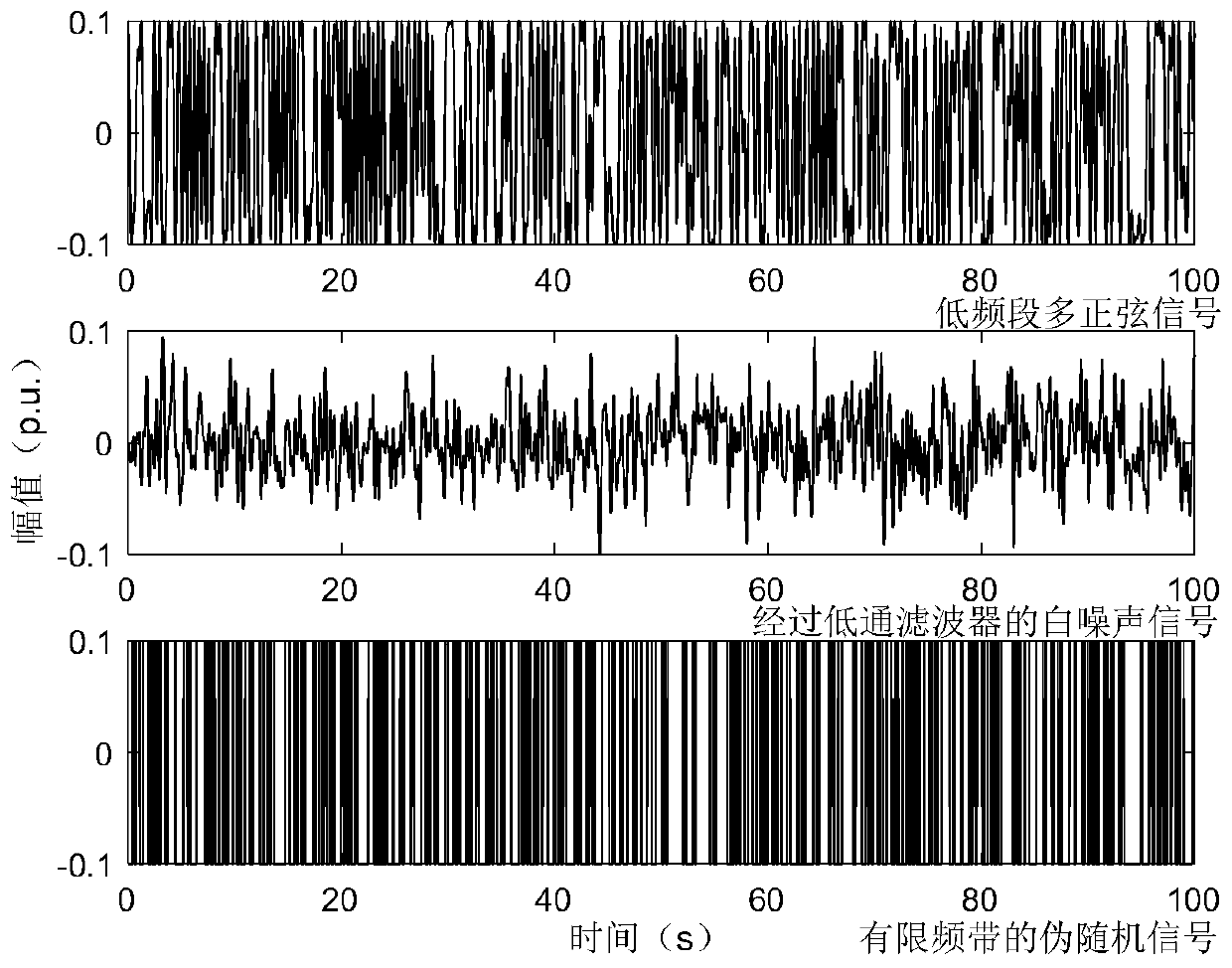
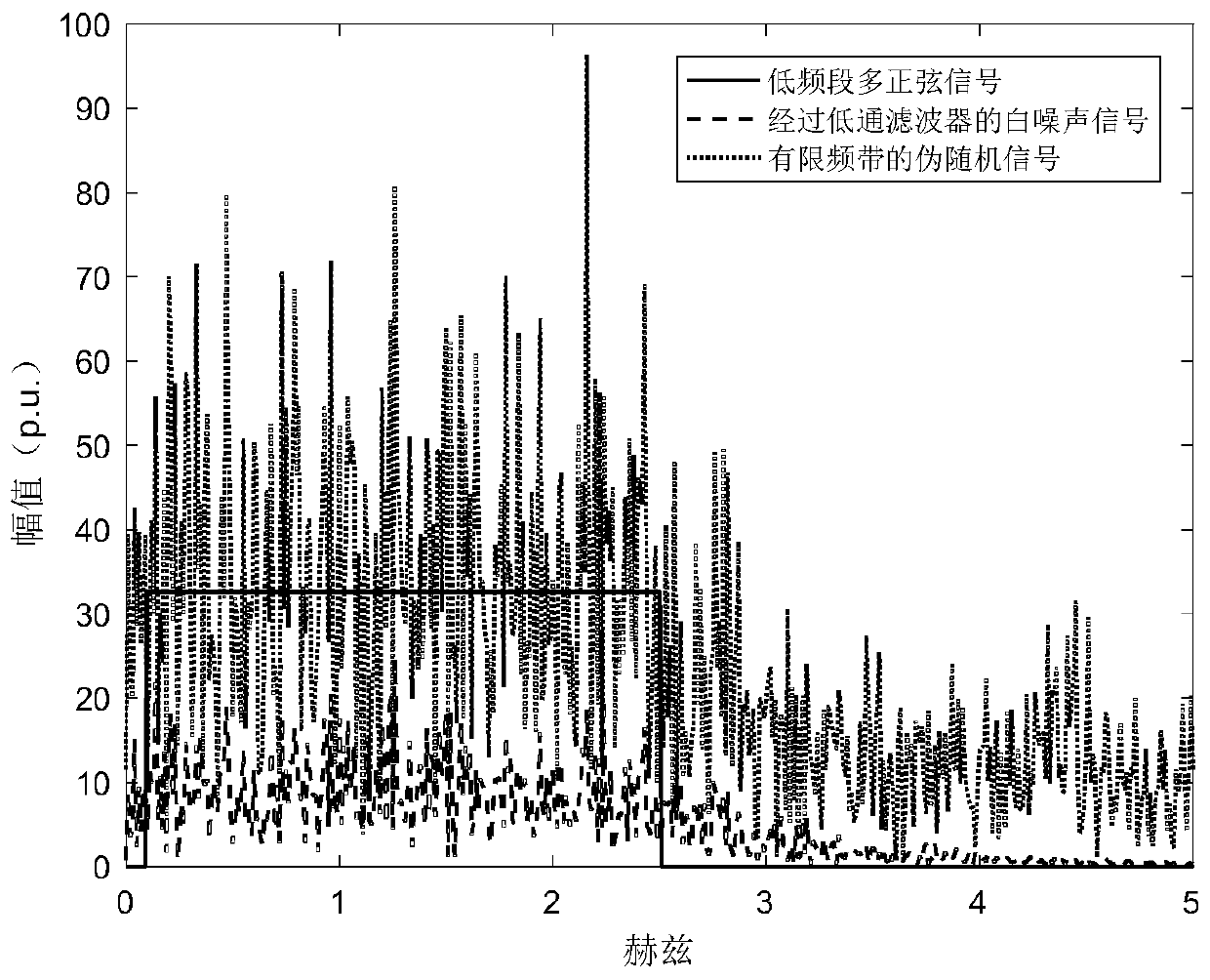
A low-frequency band multi-sine signal design method for electric power system state space model identification
ActiveCN109726490AMeet the time-domain amplitude limit requirementsSolve the low signal-to-noise ratioSpecial data processing applicationsLevenberg–Marquardt algorithmElectric power system
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
A water supply pipe burst time prediction method and device based on a neural network
PendingCN109558900AFast convergenceShort training timeForecastingCharacter and pattern recognitionGauss newton methodNetwork model
The invention discloses a water supply pipe burst time prediction method and device based on a neural network, which relates to the technical field of artificial intelligence, solves the influence ofthe environment on damage of a water supply pipeline by taking the environment where the water supply pipeline is located as an attribute and using the improved BP neural network algorithm and the least square method model, greatly optimizes the defects of the BP neural network algorithm, and has the advantages of a Gaussian Newton method and a gradient method. According to the present invention,the BP neural network model is optimized, so that the network has higher convergence speed and shorter training time, the operation speed is accelerated, and the water supply pipeline rupture time canbe obtained more efficiently and quickly. Resources are reasonably utilized, waste is avoided, unnecessary damage to residents and the society is avoided, after the breaking time of the water supplypipeline is known, the water supply pipeline can be replaced before being broken, and management by municipal staff is facilitated.
Owner:FOSHAN UNIVERSITY
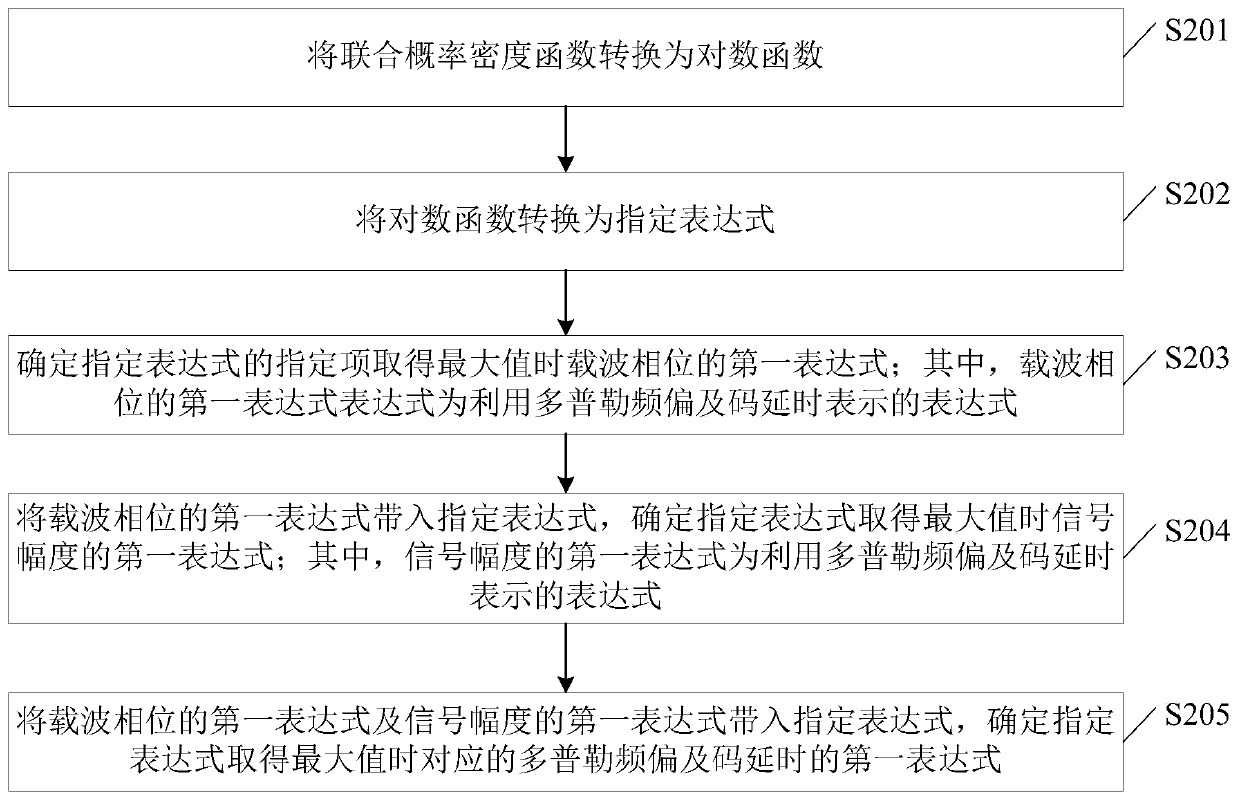
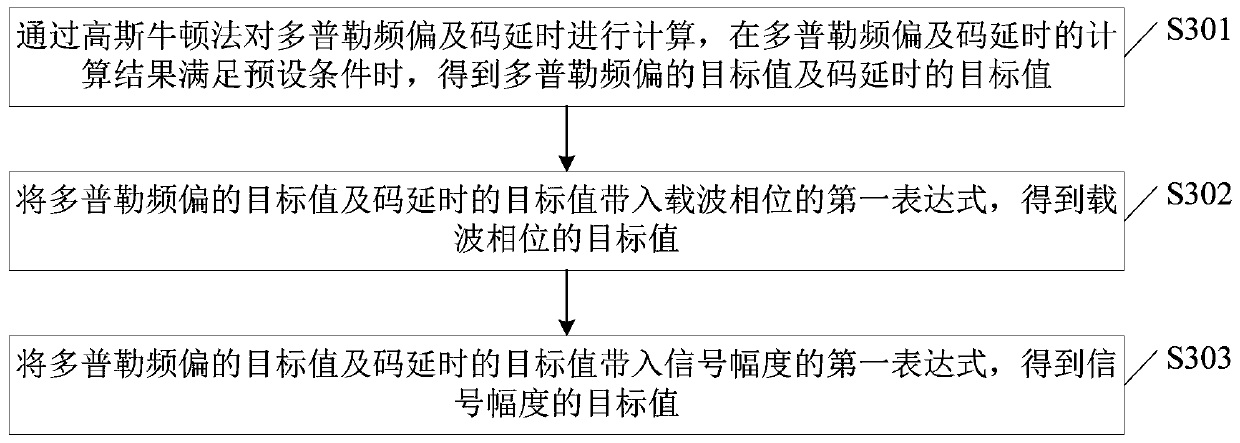
Signal determination method and device, electronic equipment and storage medium
ActiveCN110113287AStable trackingFast convergenceMulti-frequency code systemsNormal densityGauss newton method
The embodiment of the invention provides a signal determination method and device, electronic equipment and a storage medium. The method comprises the steps of acquiring a sample signal and a currentreceiving signal; determining a joint probability density function of the sample signal and the current received signal with respect to each parameter to be estimated; determining an expression corresponding to the parameter to be estimated when the joint probability density function obtains a maximum value through a maximum likelihood estimation algorithm; calculating doppler frequency offset andcode delay through a Gauss Newton method, and obtaining a target value of the Doppler frequency offset, a target value of the code delay, a target value of a carrier phase and a target value of a signal amplitude according to an expression corresponding to a parameter to be estimated when a calculation result of the Doppler frequency offset and the code delay meets preset conditions, wherein thetarget value of the Doppler frequency offset, the target value of the code delay, the target value of the carrier phase and the target value of the signal amplitude represent the current received signal. According to the invention, stable tracking of a signal with a small duty ratio is realized.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
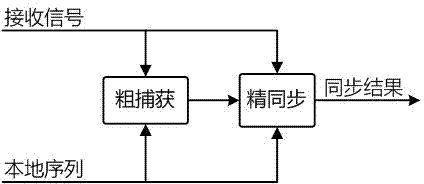
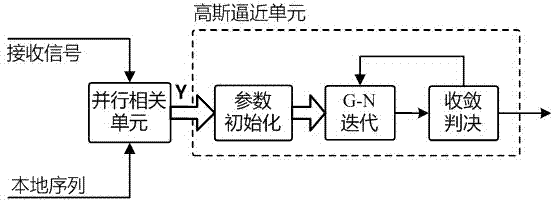
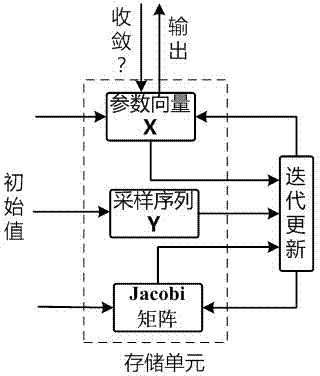
High-precision fine synchronization device and method
ActiveCN104123267AHigh precisionExtract directlyComplex mathematical operationsGauss newton methodSample sequence
The invention discloses a high-precision fine synchronization device and method. The method comprises the steps that (S1) course capture of a synchronization sequence is carried out; (S2) multipath parallel correlation units are adopted for carrying out correlation operation in a chip before a peak value of the course capture and in a chip after the peak value of the course capture to obtain a sample sequence Y of a correlation function; (S3) the correlation function is approximated by means of the Gaussian function, the Gaussian function is initialized with the help of the sample sequence Y, and Gaussian function parameters are iterated through a Gaussian-Newton method; (S4) after iteration is finished, the parameter b of the Gaussian function is extracted, and the estimated value of the peak value position is obtained directly. According to the high-precision fine synchronization device and method, the shape features of the correlation function are utilized fully, the correlation function is approximated by means of the Gaussian function, the parameters are iterated through the Gauss-Newton method, synchronization results are extracted from the parameters, and the precision of precision synchronization is improved; the convergence sped is high, and parameter extraction is direct; achievement complexity is low, calculated amount is not increased greatly compared with a parallel correlation method under an equivalent sampling rate, and the device and the method are less influenced by noise, and are convenient to apply in reality.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Ground transient electromagnetic method inversion method and device based on emission current full waveform
PendingCN114779355AImprove processing interpretation precisionSimple designElectric/magnetic detectionAcoustic wave reradiationWave shapeGauss newton method
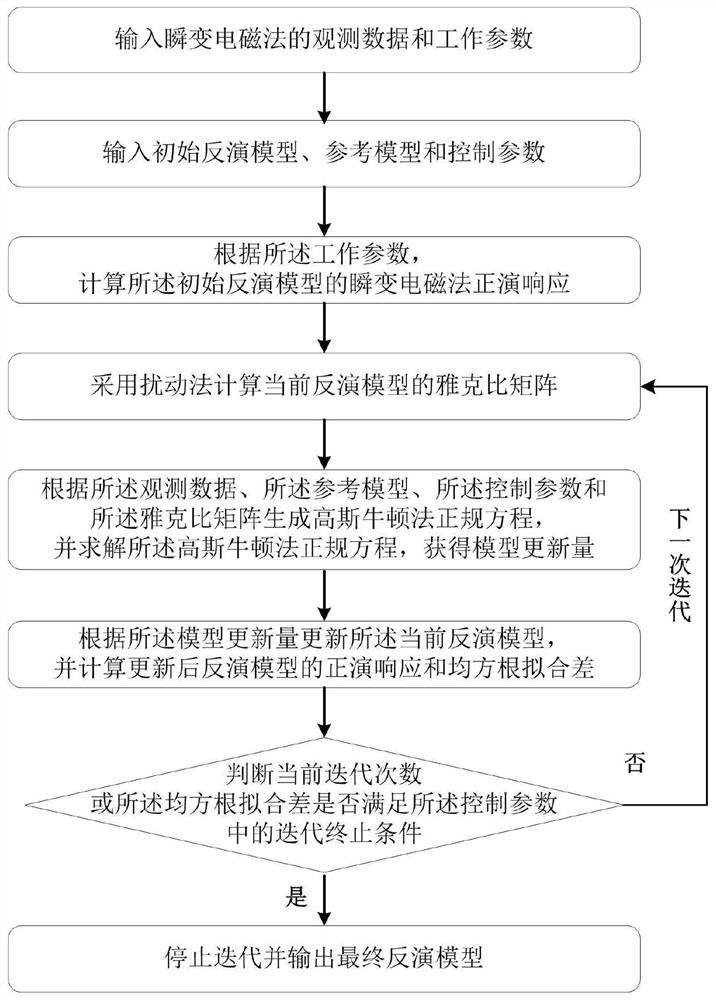
The invention provides a ground transient electromagnetic method inversion method and device based on emission current full waveforms, and the method comprises the following steps: constructing a one-dimensional inversion target function based on a Tikhonov regularization mode, carrying out the optimization of the inversion target function through employing a Gaussian Newton method, and outputting a final inversion model. In a process of optimizing an inversion objective function, an emission current basic waveform used for one-dimensional inversion of a ground transient electromagnetic method is expanded from a slope step waveform to an emission current full waveform containing starting time, stabilization time, turn-off time and a duty ratio, and a cycle number parameter is included in the emission current basic waveform. The strategy is not only helpful for improving the interpretation precision of data processing, but also helpful for perfecting the design of instrument parameters.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF GEOSCIENCES (WUHAN)
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com