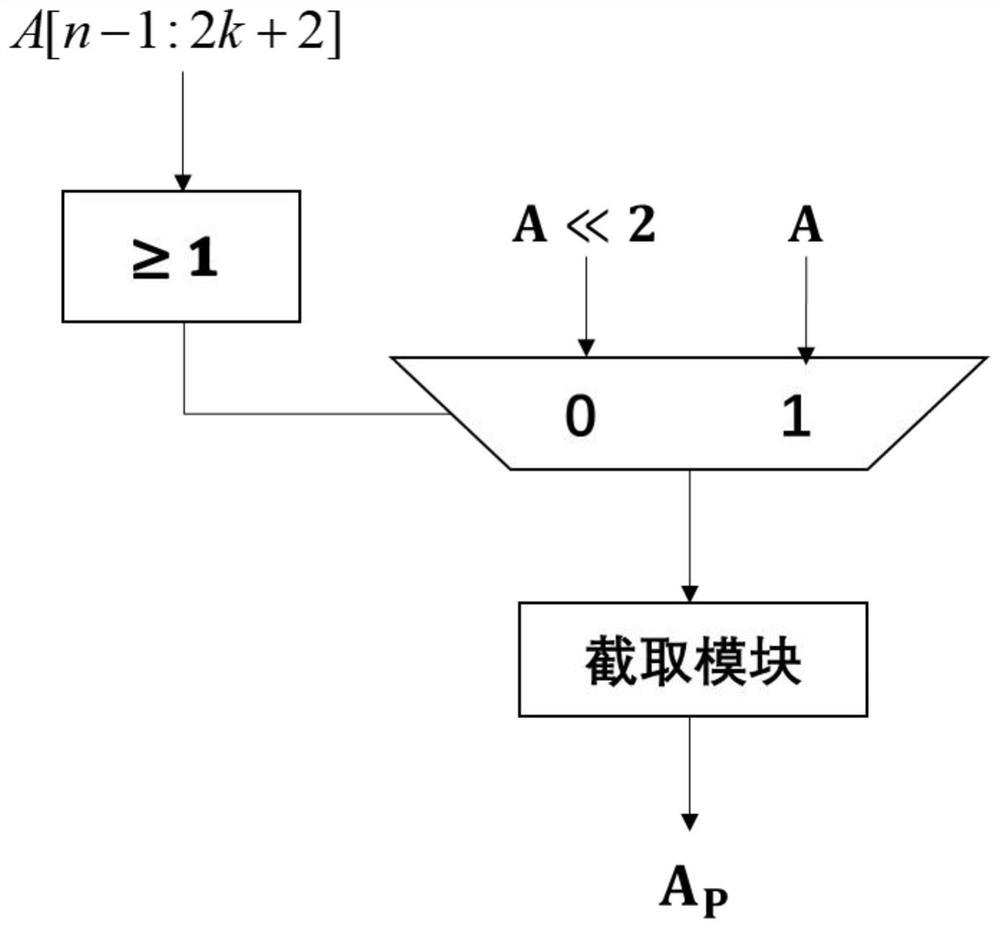
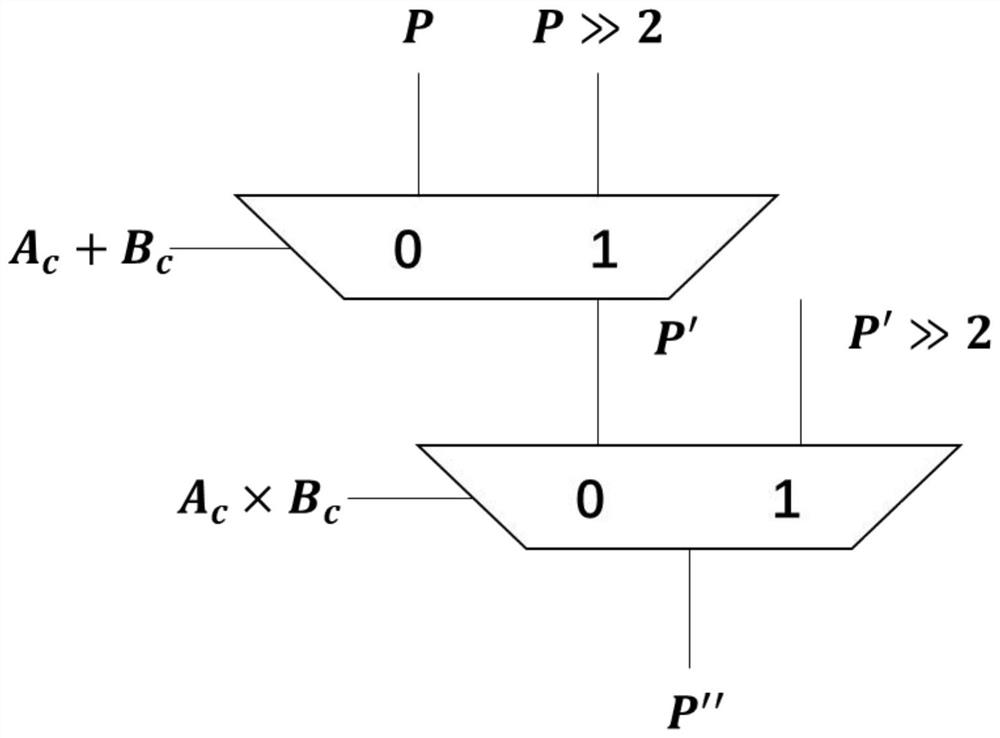
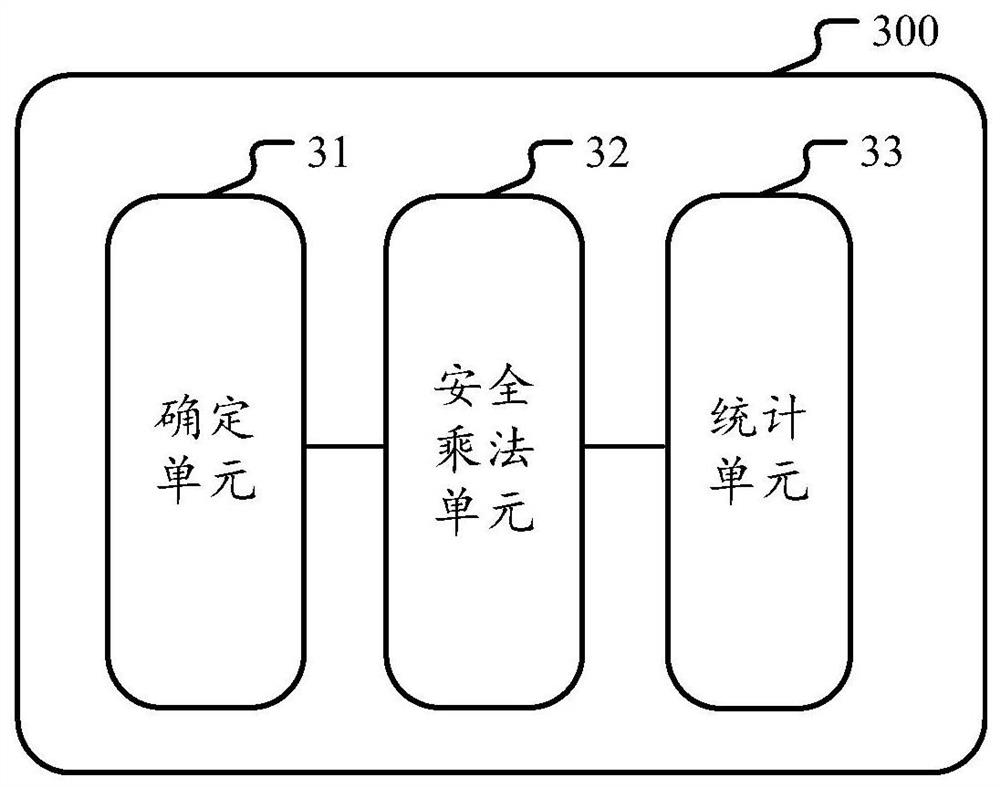
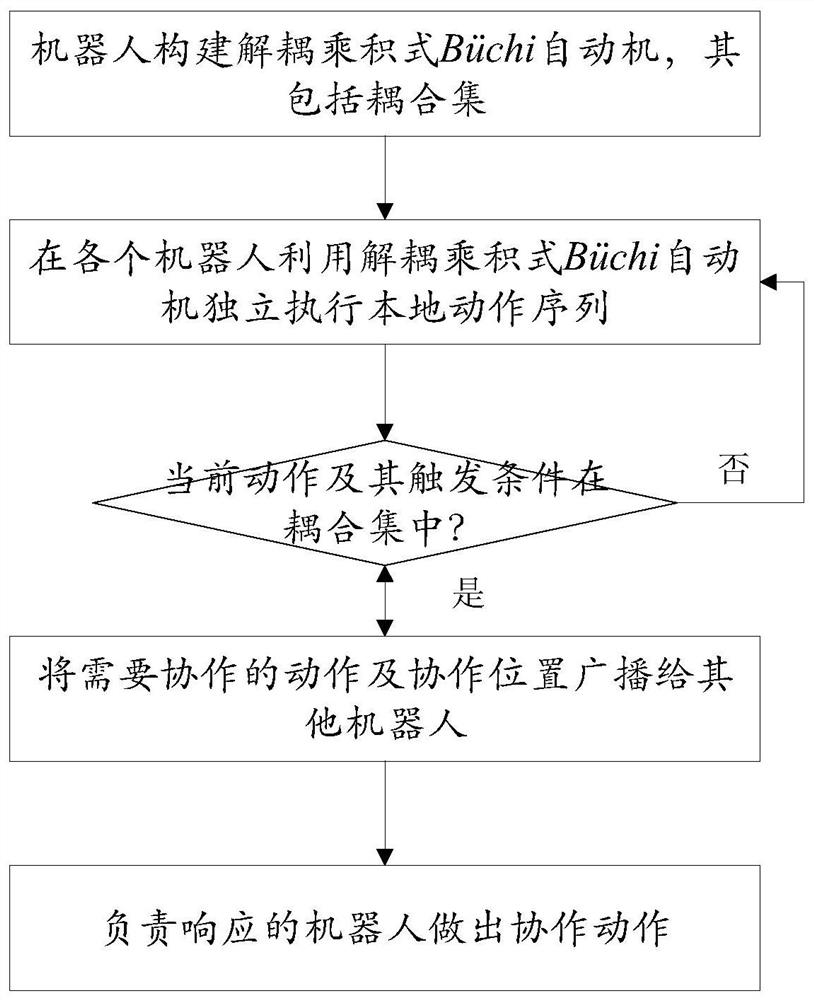
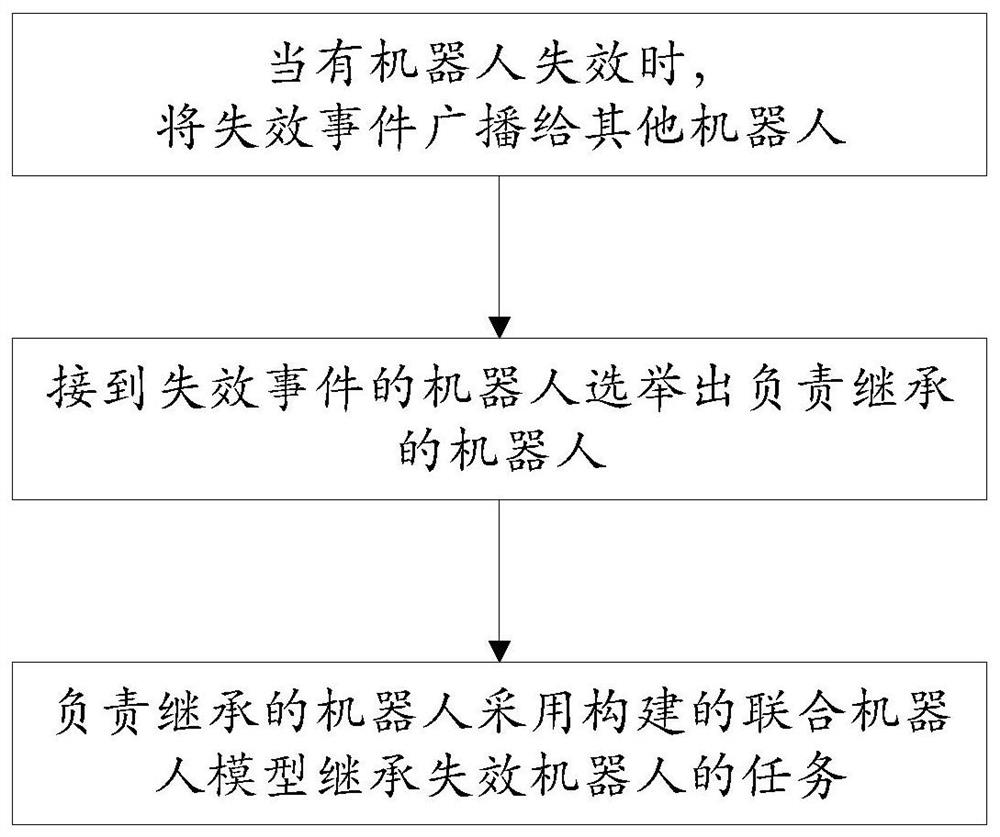
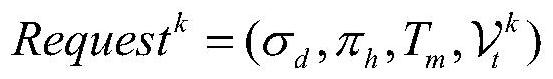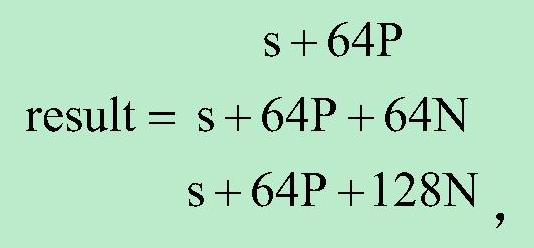Patents
Literature
41 results about "Multiplicative Product" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Method and system for quantization for a general beamforming matrix in feedback information
ActiveUS20070160011A1Radio/inductive link selection arrangementsRadio transmissionFormation matrixSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
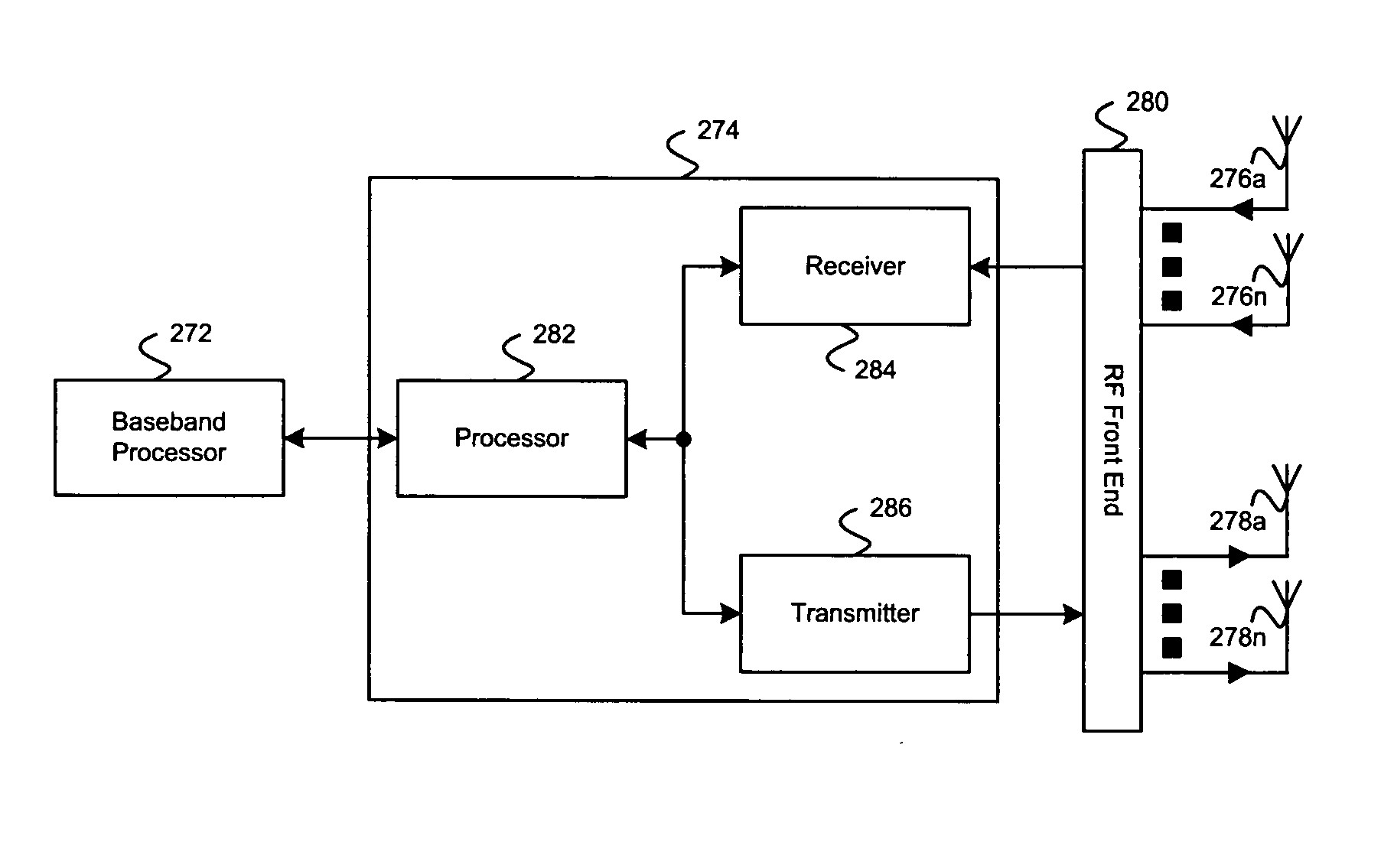
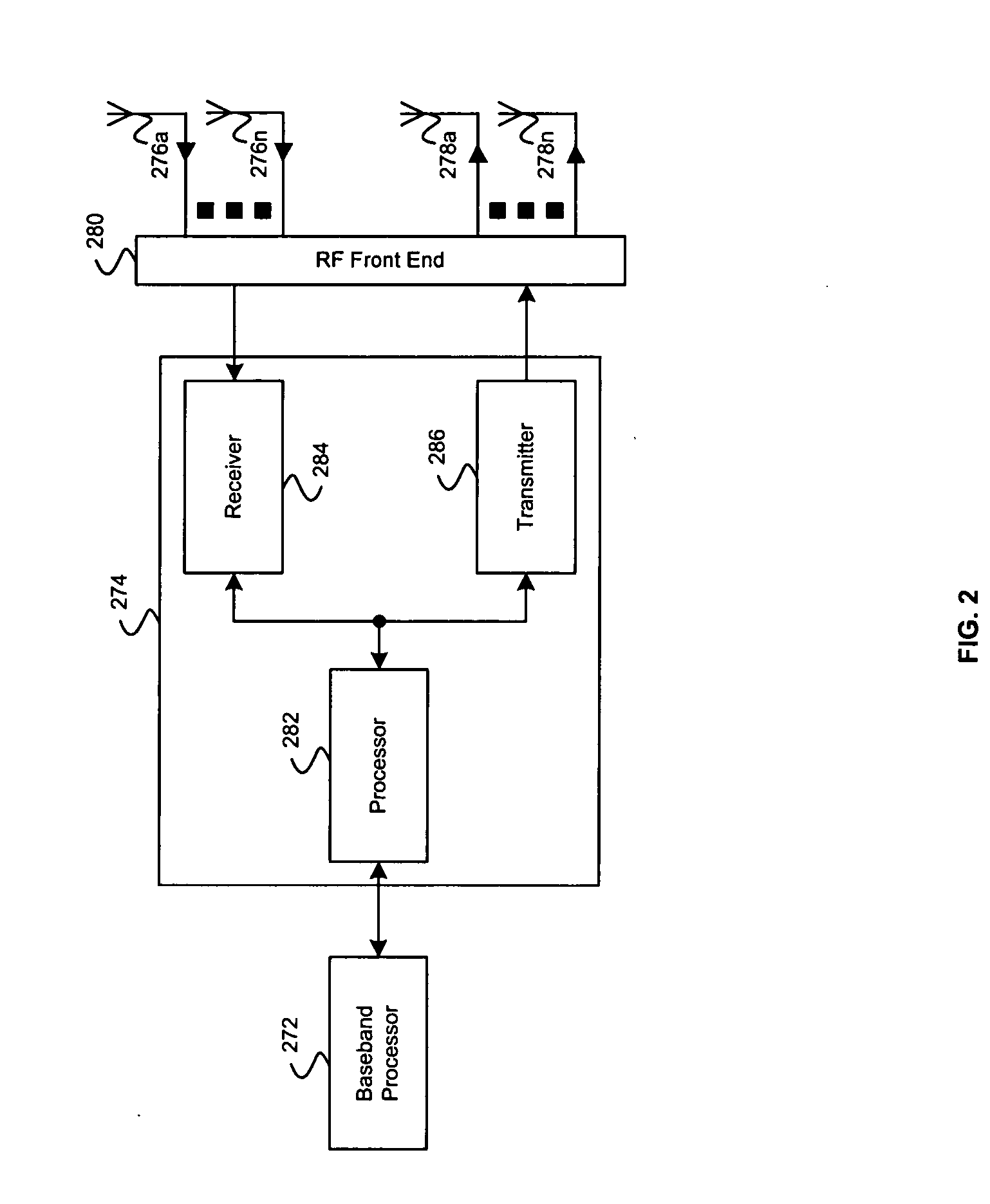
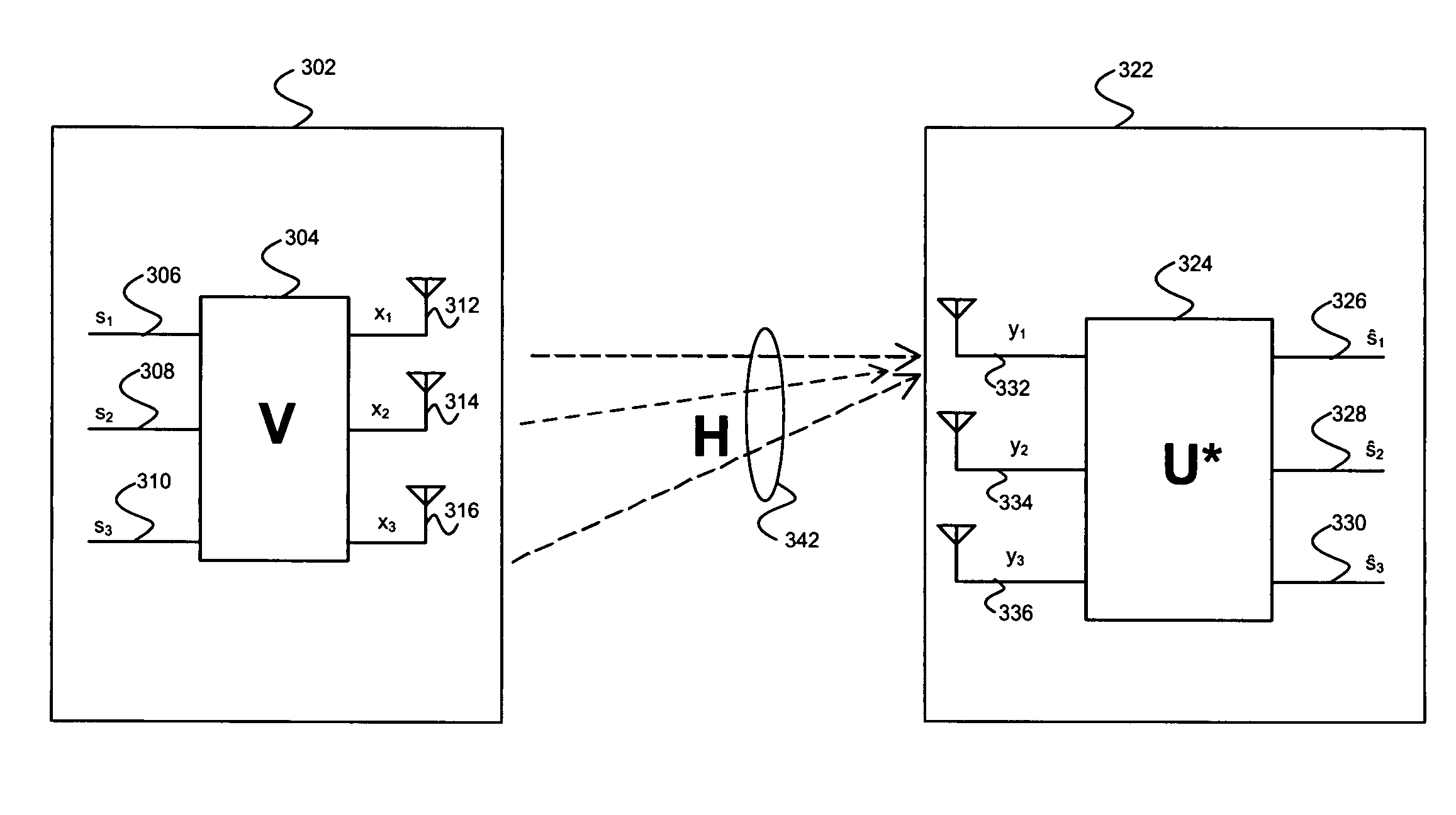
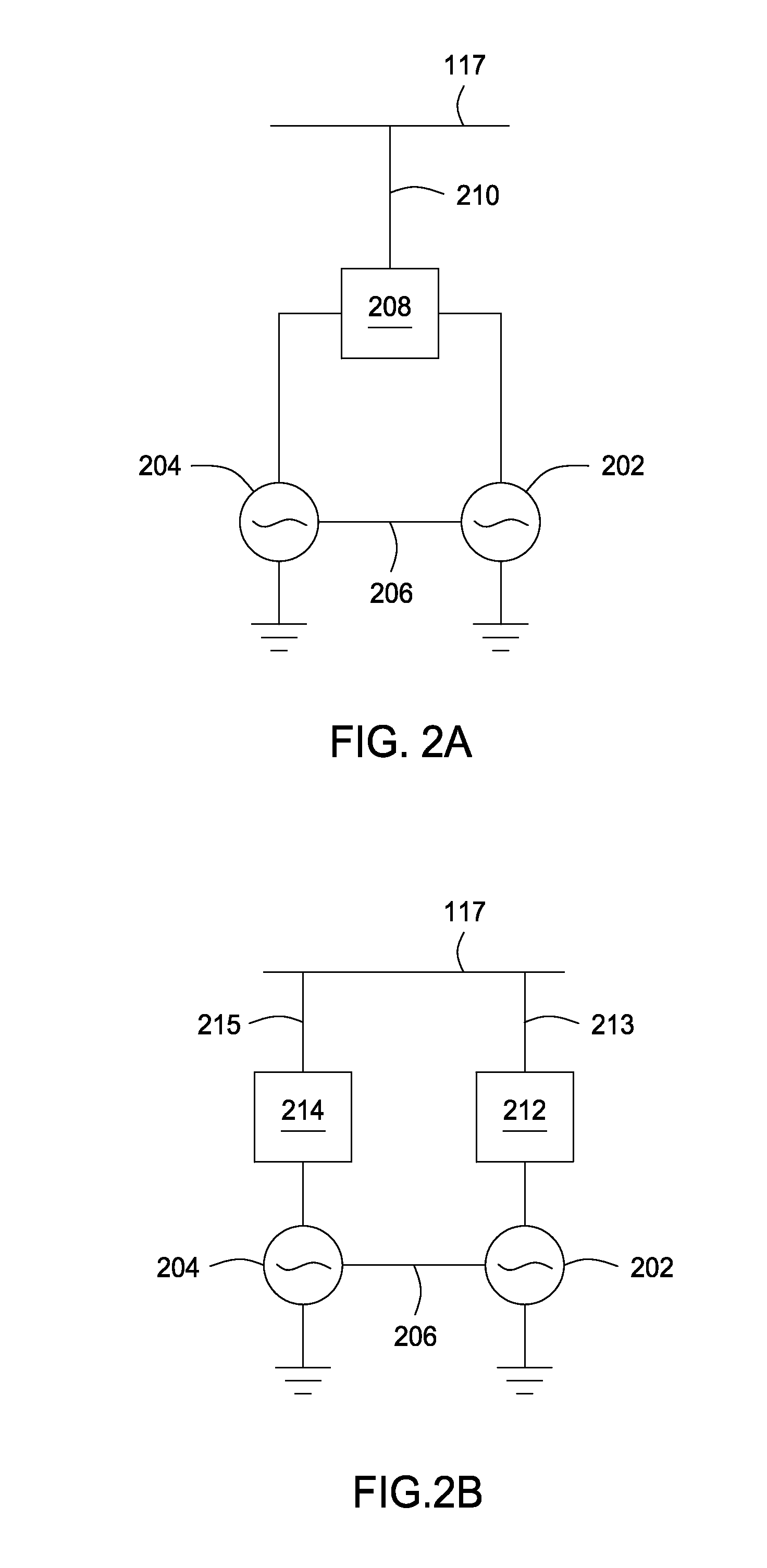
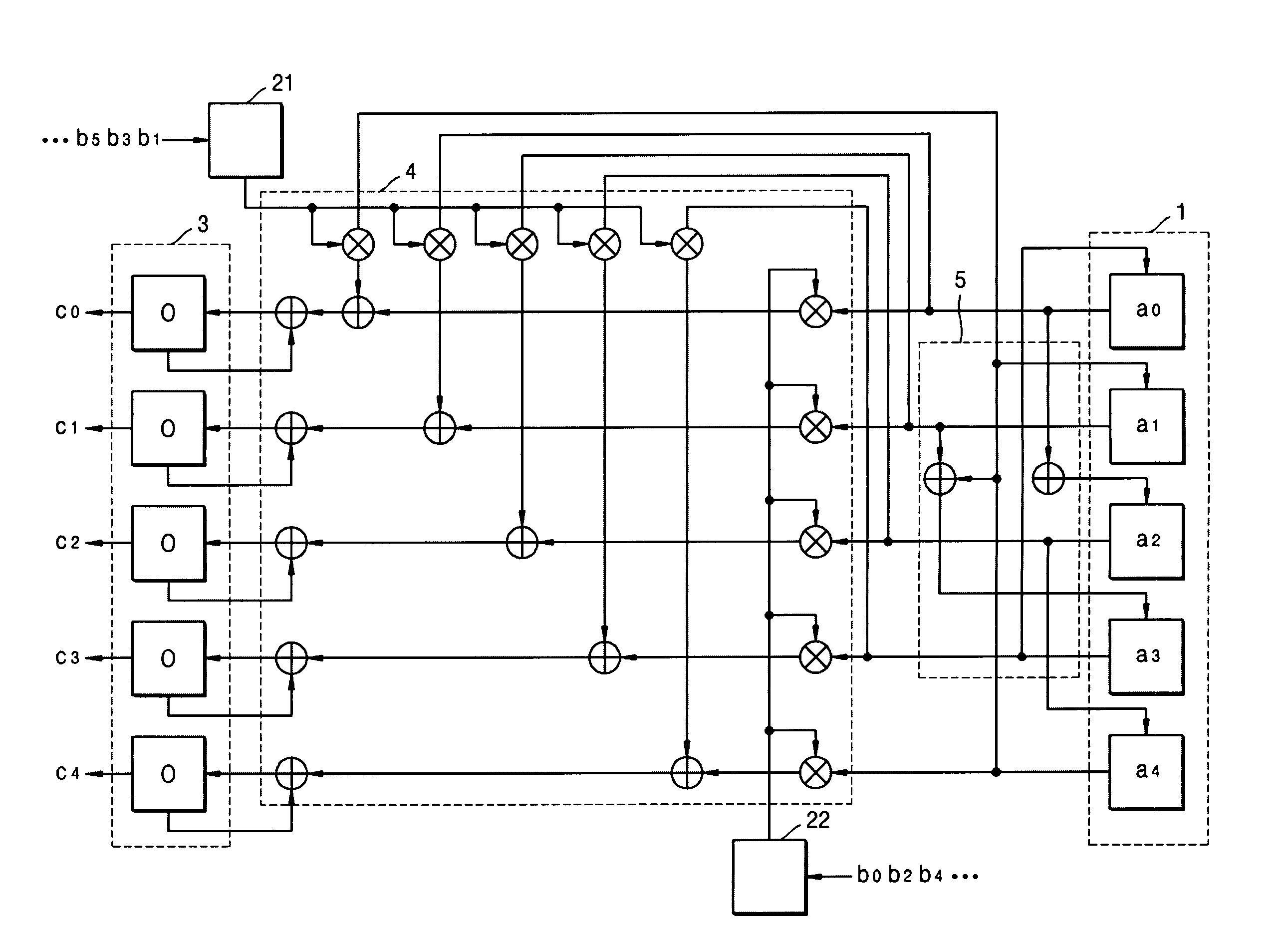
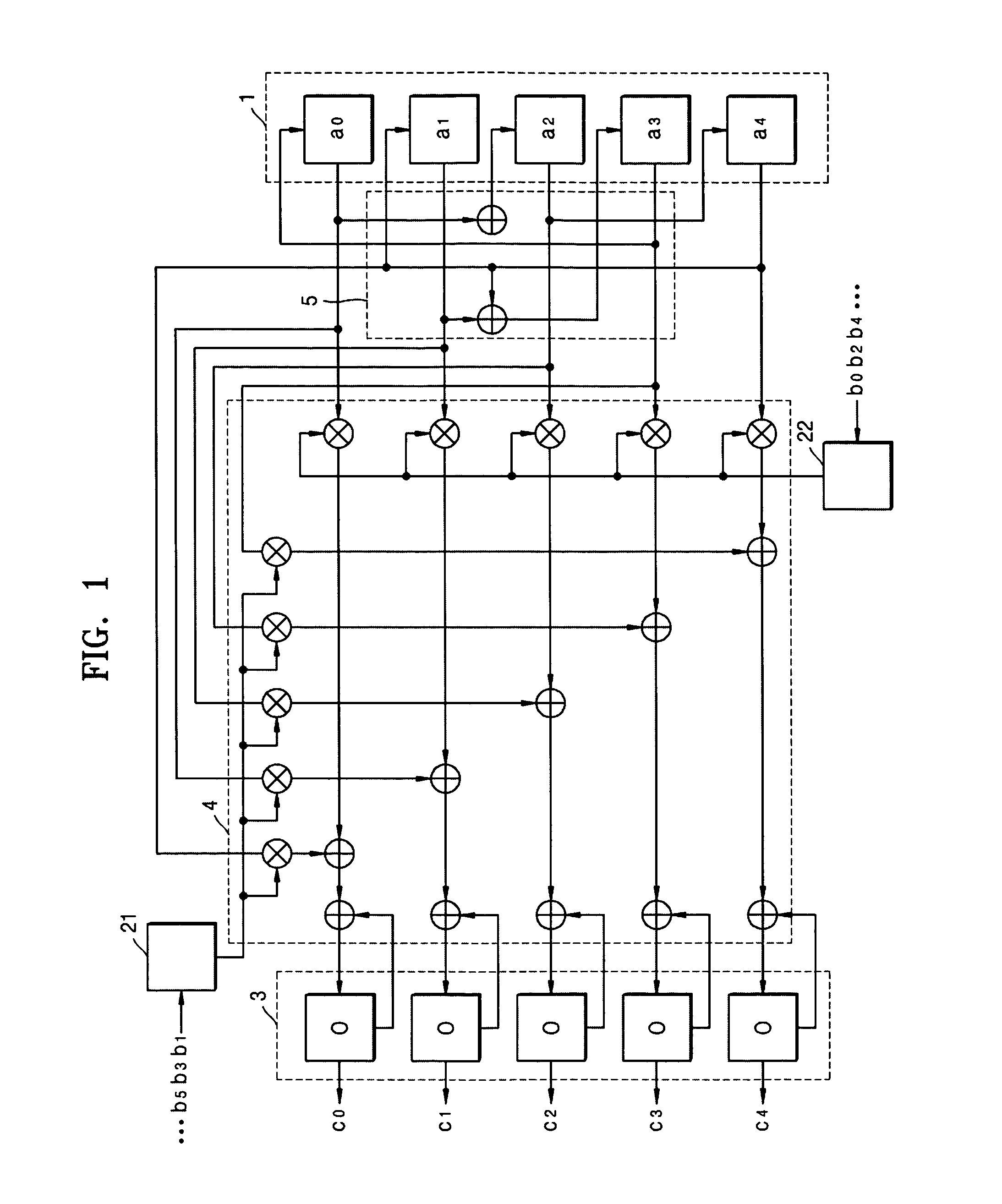
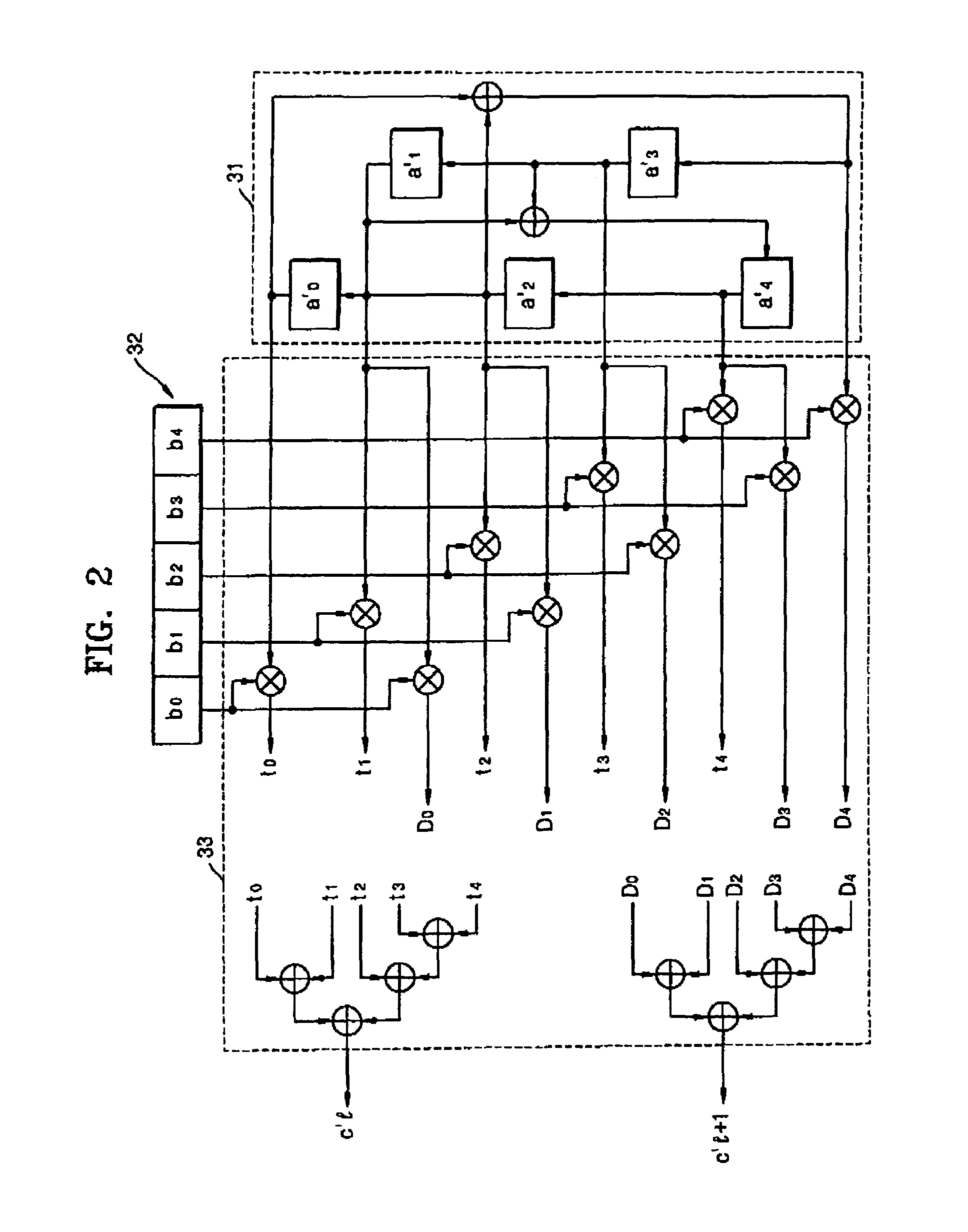
Aspects of a method and system for utilizing Givens rotation expressions for quantization for a general beamforming matrix in feedback information. In one aspect of the invention, feedback information is computed at the receiving MIMO wireless device based on a geometric mean decomposition (GMD) method. The feedback information may include a matrix that describes a wireless medium. The matrix may represent a multiplicative product of at least one rotation matrix and at least one diagonal phase rotation matrix. Each of the rotation matrices may include at least one matrix element whose value is based on Givens rotation angle. The transmitting MIMO wireless device may subsequently transmit a plurality of signals via the wireless medium based on the received matrix information. The signal strength and / or signal to noise ratio (SNR) measurement (as measured in decibels, for example) associated with each of the transmitted plurality of signals may be about equal.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Methods and apparatuses for performing Z-buffer granularity depth calibration in graphics displays of three-dimensional scenes
The weight given to each object in a scene in the computation of the z-buffer granularity is determined based upon a variable normalized risk parameter which may be supplied by the application. A recursive composite parent object process is invoked upon the two children of the scene object in order to allocate graphics resources to objects A and B. Primary and secondary hit value means corresponding to objects A and B are computed. The hit value means are the average sum of hit values recorded for all the leaf objects contained by the objects over a predetermined number of frames. The statistical variances of the primary hit value and secondary hit value are also computed over the previous predetermined number of frames in order facilitates the mapping of the normalized risk parameter to a non-normalized risk parameter indicating the optimal risk for objects A and object B. A quadratic parametric variance equation is solved for the optimal fraction of the remaining graphics resources to be allocated to object A. The optimal fraction is multiplied by the available graphics resources, resulting in the resources allocated to object A; the remaining graphics resources are to object B. If either object A or B is a composite parent object, the recursive parent object process is invoked on the two children of object A or B with the available graphics resources for the instantiation of the recursive parent object process set to the graphics resources allocated to object A or B. The resources allocated each object are then used as weighting factors in the computation of the z-buffer granularity. In an embodiment, the z-buffer midpoint depth is determined by dividing the sum of the multiplicative products of the distance from the observation point, the allocated resources, and the importance coefficient for each object by the sum of the products of the observation point and the allocated resources for each object.
Owner:XEROX CORP
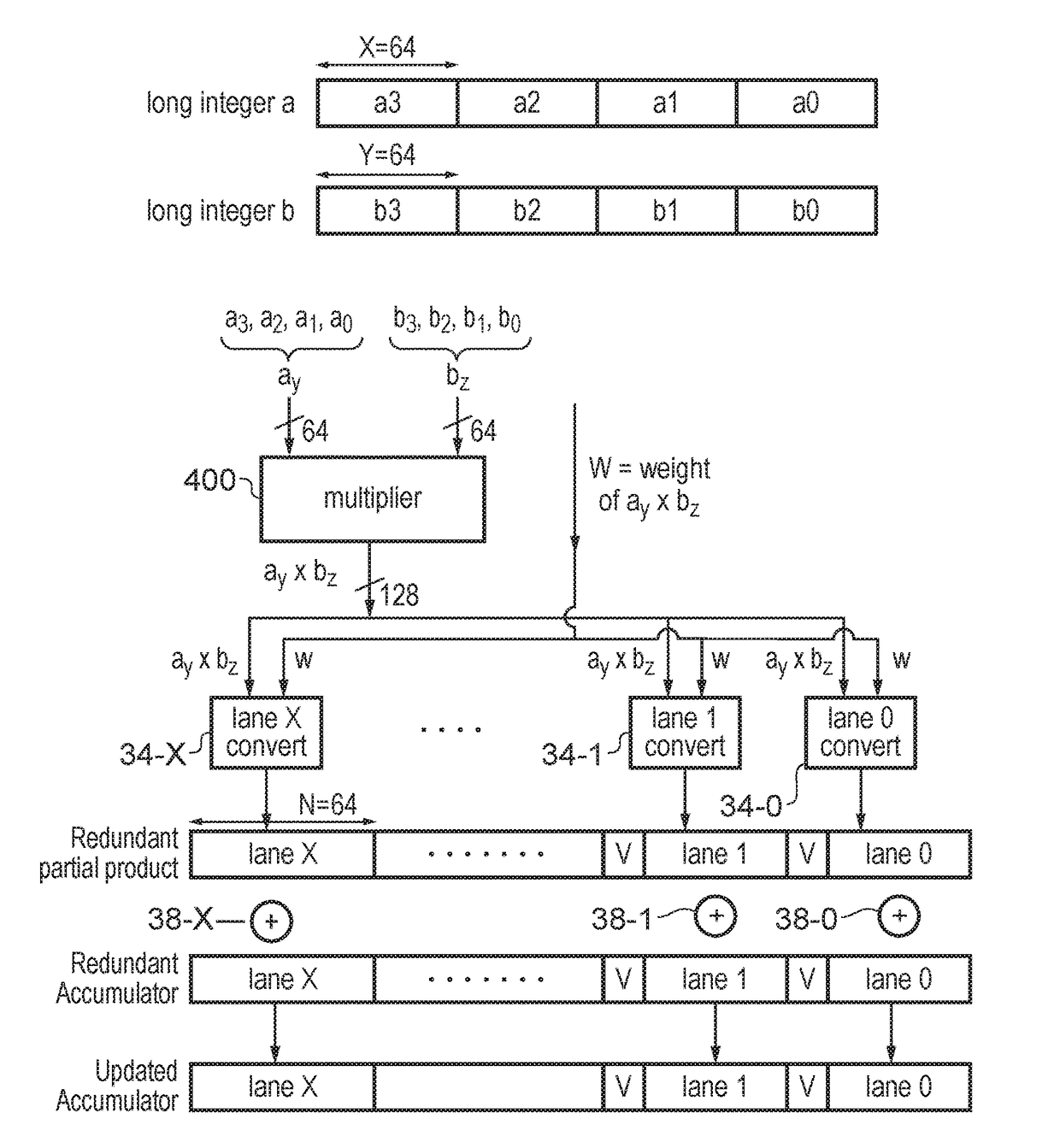
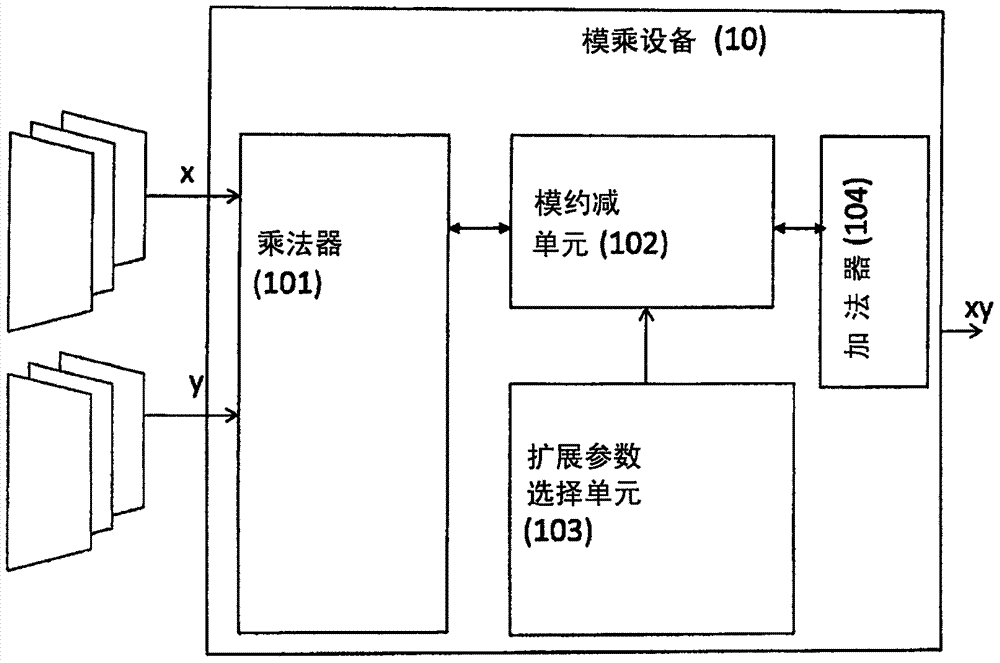
Multiplication of first and second operands using redundant representation
A method is provided for multiplying a first operand comprising at least two X-bit portions and a second operand comprising at least one Y-bit portion. At least two partial products are generated, each partial product comprising a product of a selected X-bit portion of the first operand and a selected Y-bit portion of the second operand. Each partial product is converted to a redundant representation in dependence on significance indicating information indicative of a significance of the partial product. In the redundant representation, the partial product is represented using a number of N-bit portions, and in a group of at least two adjacent N-bit portions, a number of overlap bits of a lower N-bit portion of the group have a same significance as some least significant bits of at least one upper N-bit portion of the group. The partial products are added while represented in the redundant representation.
Owner:ARM LTD
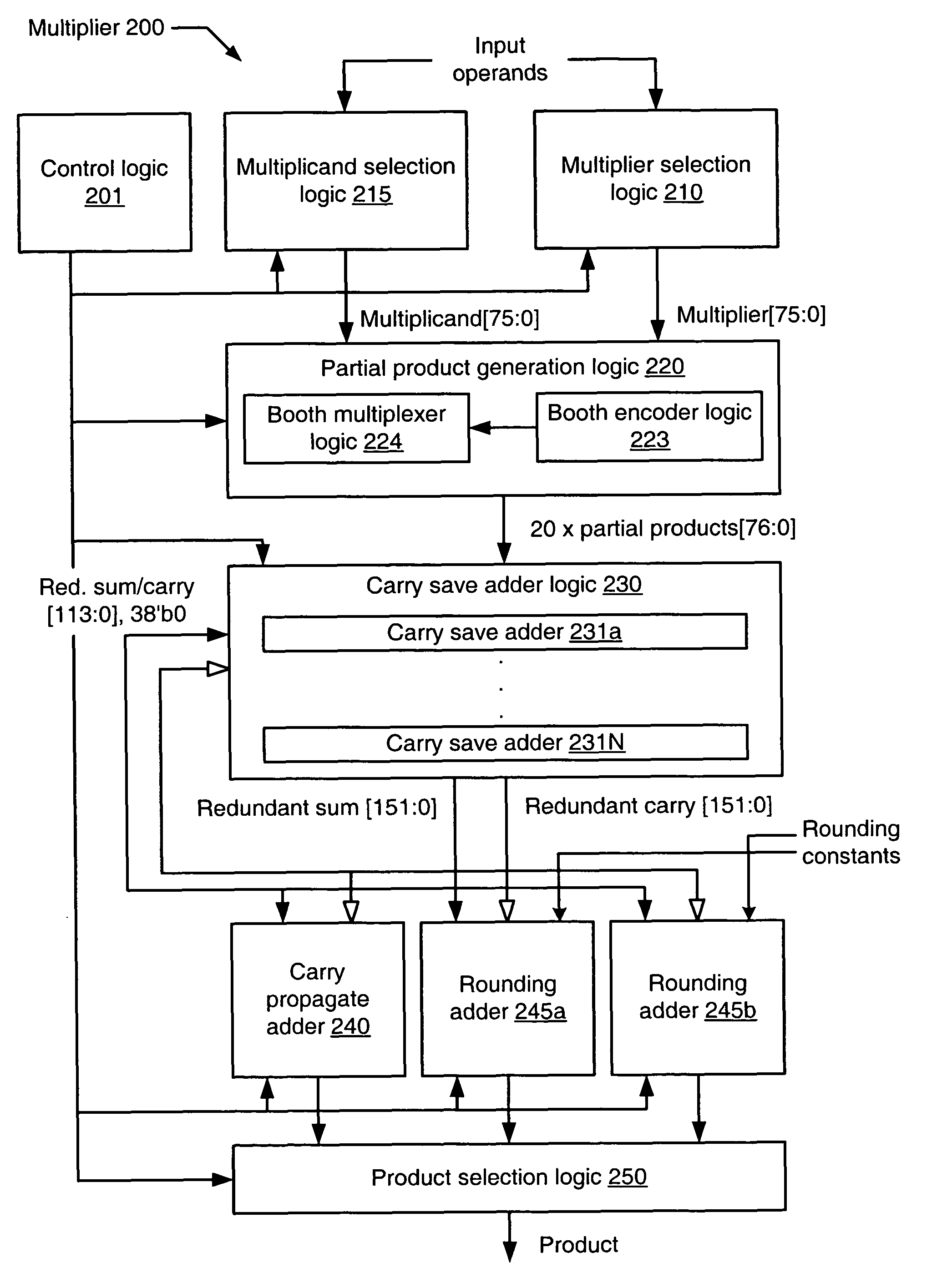
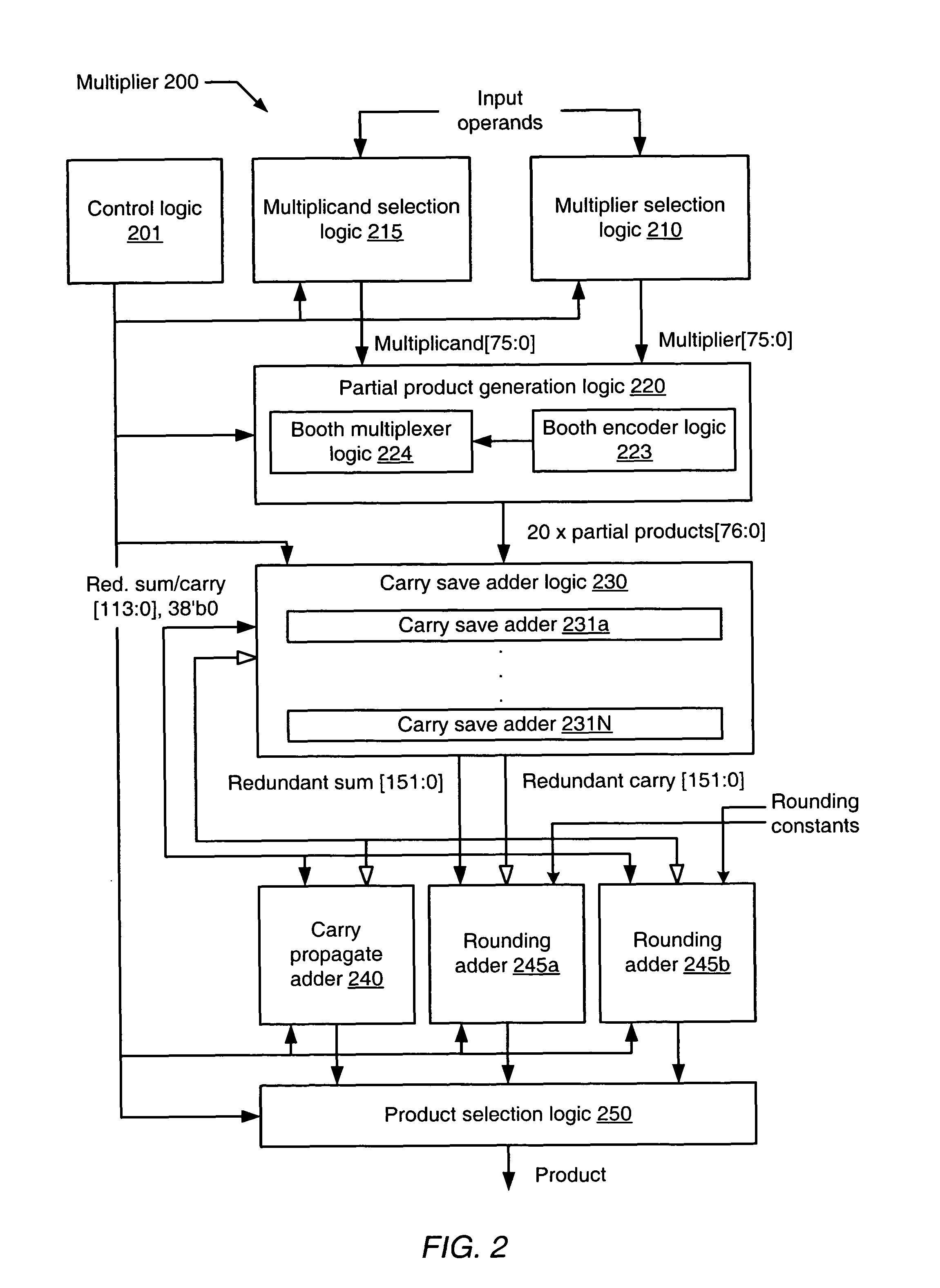
Apparatus and method for multiple pass extended precision floating point multiplication
InactiveUS8019805B1Computations using contact-making devicesComputation using non-contact making devicesComputational scienceCarry-save adder
A floating point multiplier circuit includes partial product generation logic configured to generate a plurality of partial products from multiplicand and multiplier values. The plurality of partial products corresponds to a first and second portion of the multiplier value during respective first and second partial product execution phases. The multiplier also includes a plurality of carry save adders configured to accumulate the plurality of partial products generated during the first and second partial product execution phases into a redundant product during respective first and second carry save adder execution phases. The multiplier further includes a first carry propagate adder coupled to the plurality of carry save adders and configured to reduce a first and second portion of the redundant product to a multiplicative product during respective first and second carry propagate adder phases. The first carry propagate adder phase begins after the second carry save adder execution phase completes.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
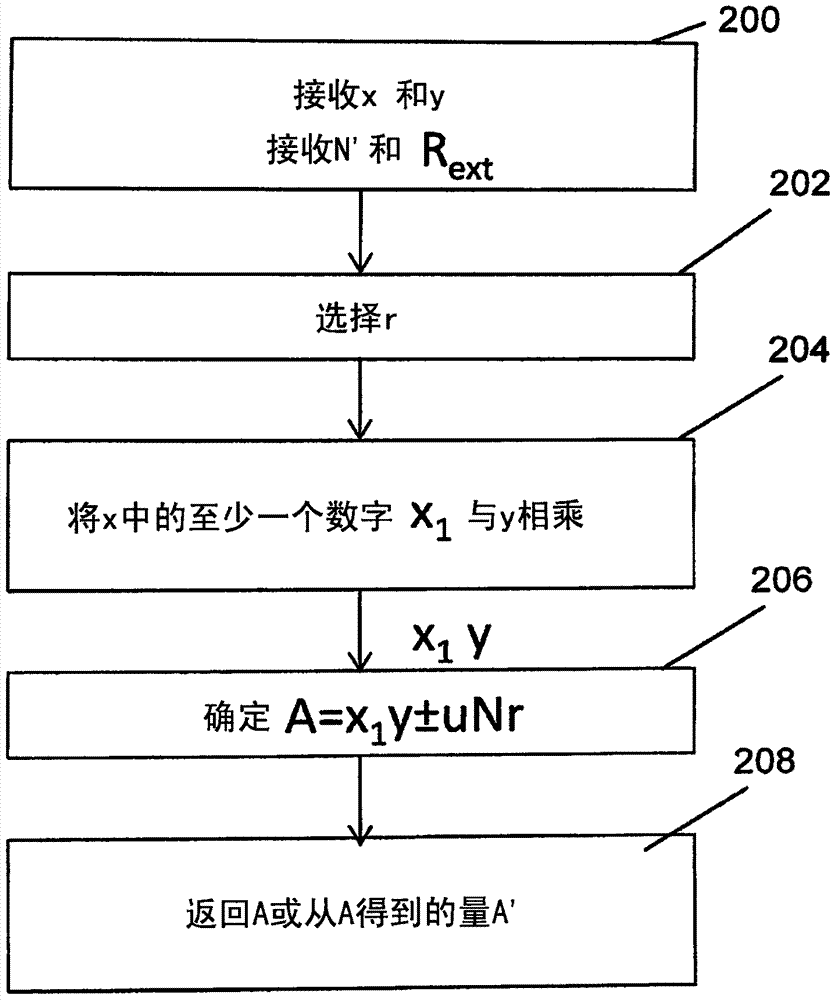
Generic modular multiplier using partial reduction
ActiveUS20030206628A1Public key for secure communicationDigital computer detailsBinary multiplierParallel computing
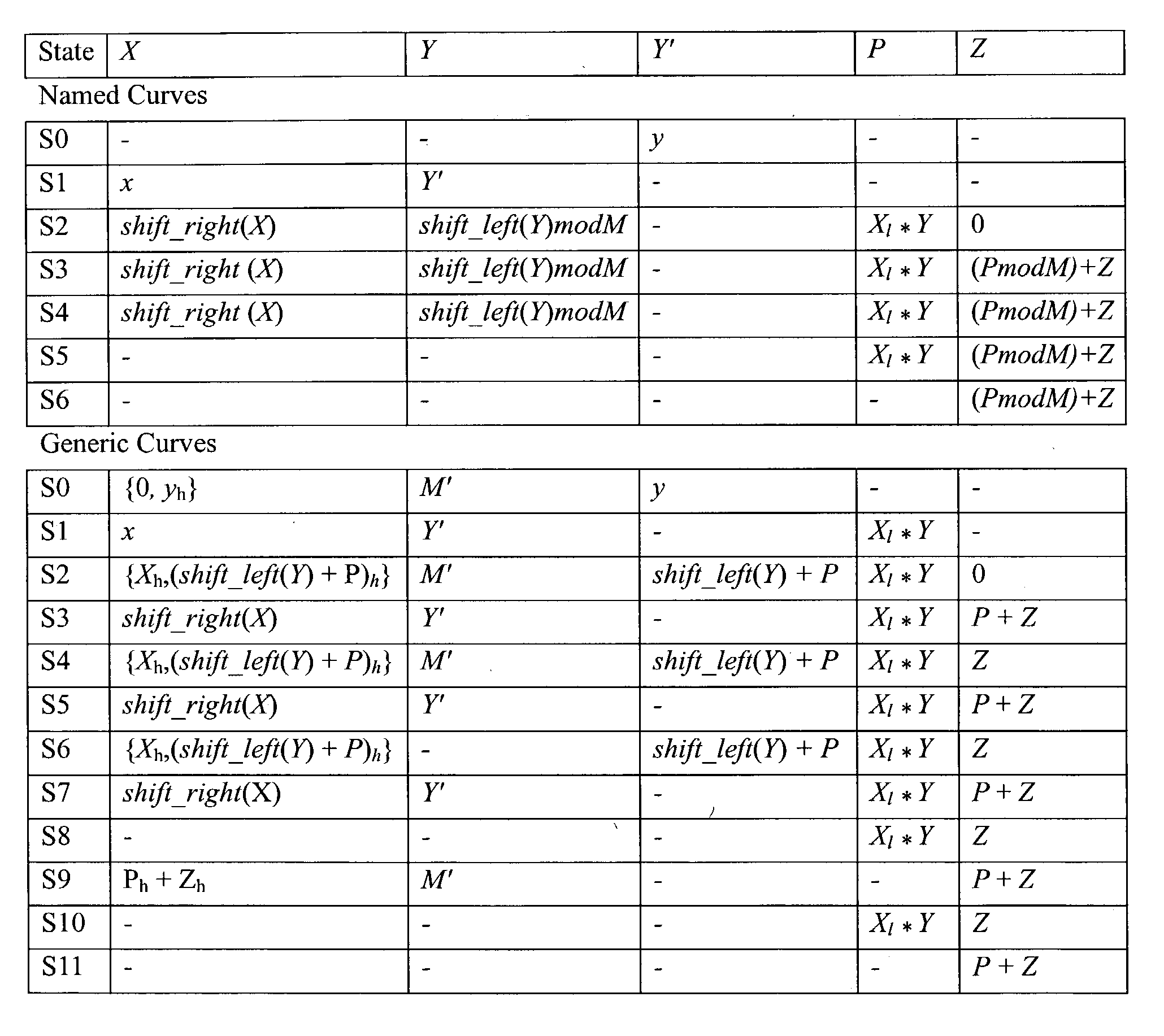
An apparatus multiplies a first and a second binary polynomial X(t) and Y(t) over GF(2), where an irreducible polynomial Mm(t)=t<m>+am-1t<m-1>+am-2t<m-2>t<m-2>+ . . . +a1t+a0, and where the coefficients ai are equal to either 1 or 0, and m is a field degree. The degree of X(t)<n, and the degree of Y(t)<n, and m<=n. The apparatus includes a digit serial modular multiplier circuit coupled to supply a multiplication result of degree >=m of a multiplication of the first and second binary polynomials. The digit serial modular multiplier circuit includes a first and second register, each being <=n bits. A partial product generator circuit multiplies a portion of digit size d of contents of the first register and contents of the second register. The partial product generator is also utilized as part of a reduction operation for at least one generic curve.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
One-Round Secure Multiparty Computation of Arithmetic Streams and Evaluation of Functions
InactiveUS20210167946A1Key distribution for secure communicationCommunication with homomorphic encryptionSecret shareTheoretical computer science
A method for performing, in a single round of communication and by a distributed computational system, Secure MultiParty Computation (SMPC) of an arithmetic function ƒ:pk→p represented as a multivariate polynomial over secret shares for a user, comprising the steps of sharing secrets among participants being distributed computerized systems, using multiplicative shares, the product of which is the secret, or additive shares, that sum up to the secret by partitioning secrets to sums or products of random elements of the field; implementing sequences of additions of secrets locally by addition of local shares or sequences of multiplications of secrets locally by multiplication of local shares; separately evaluating the monomials of ƒ by the participants; adding the monomials to obtain secret shares of ƒ.
Owner:B G NEGEV TECH & APPL LTD AT BEN GURION UNIV 907553
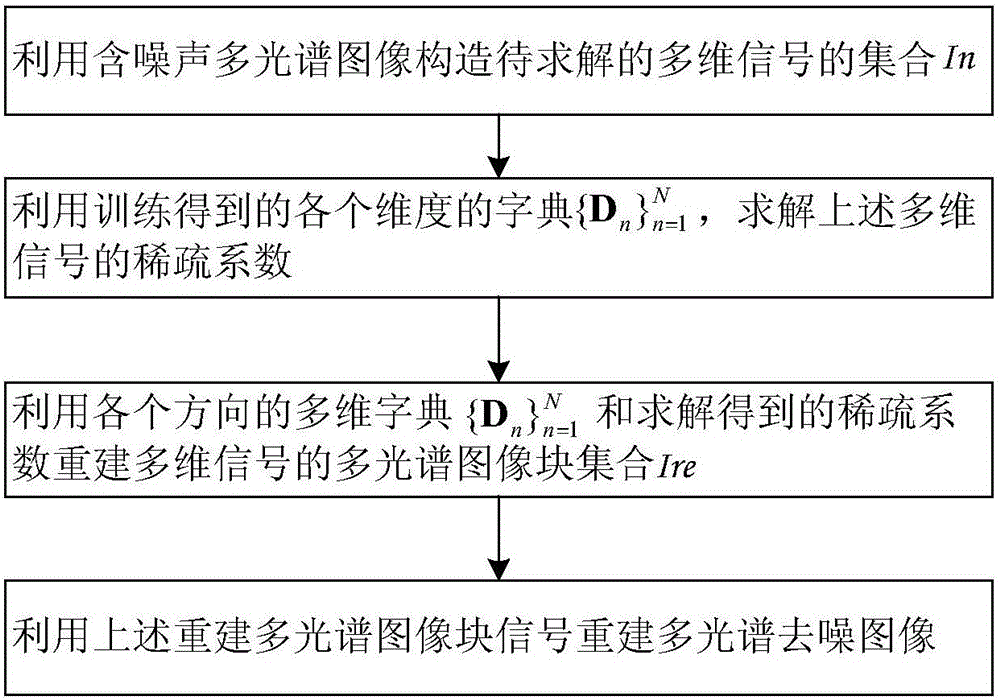
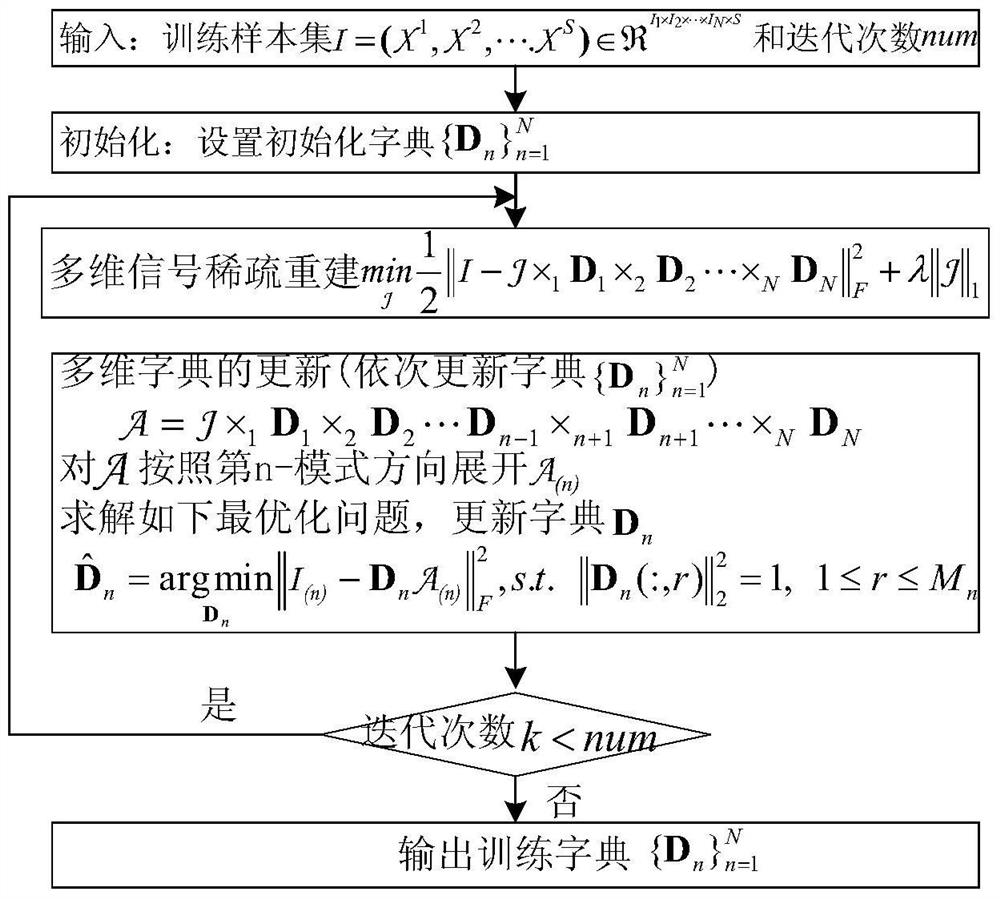
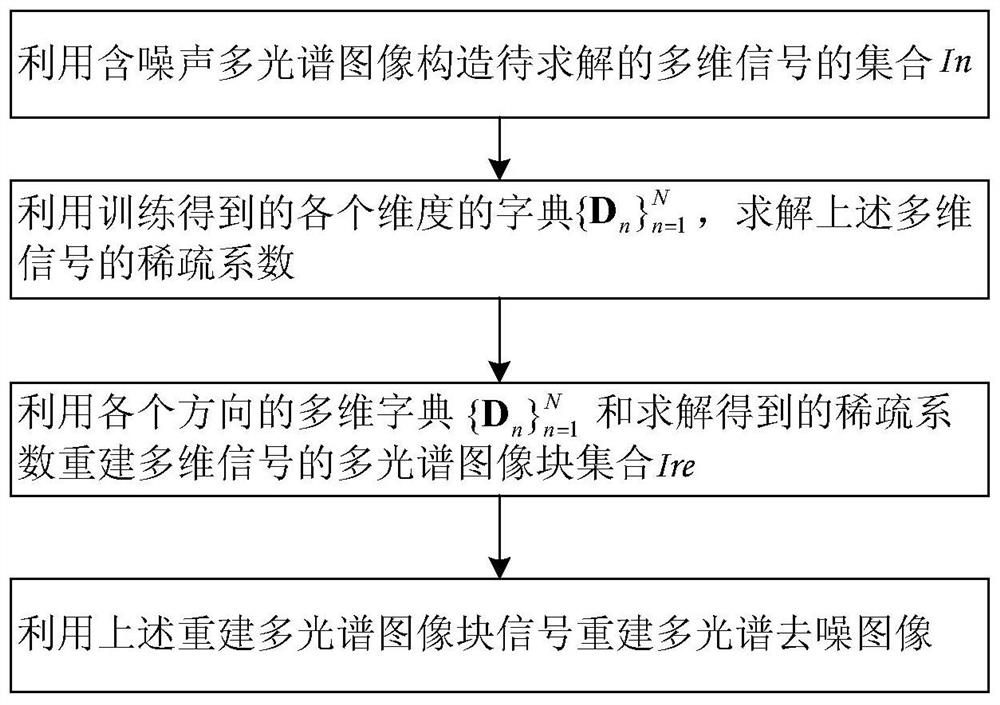
Sparse model of multi-directional signal, reconstruction method of sparse model and dictionary training method of reconstruction method
ActiveCN106097278AReduce complexityReduce storage spaceImage enhancementImage analysisSparse modelReconstruction method
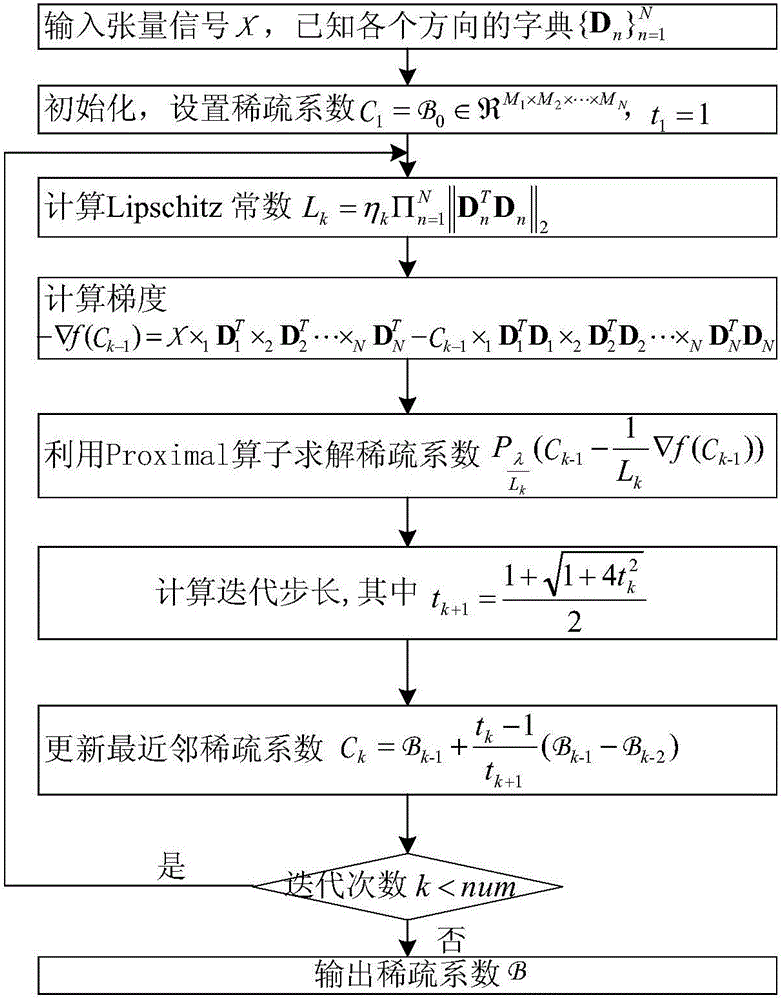
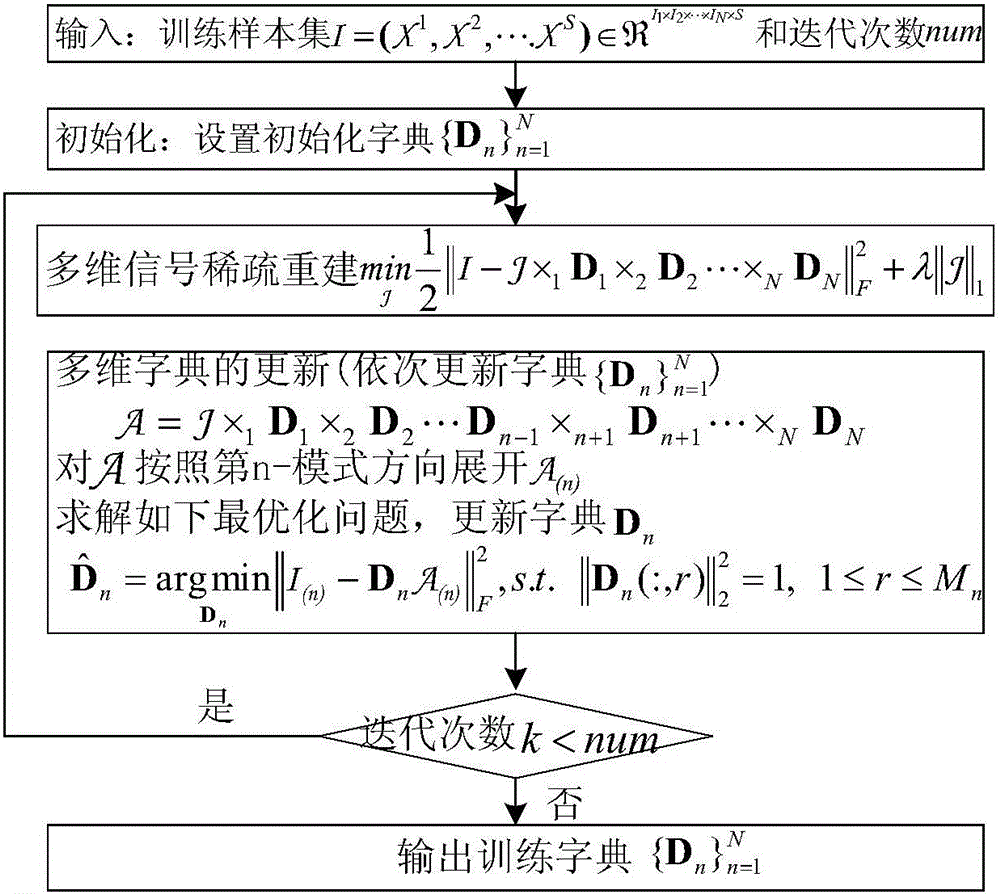
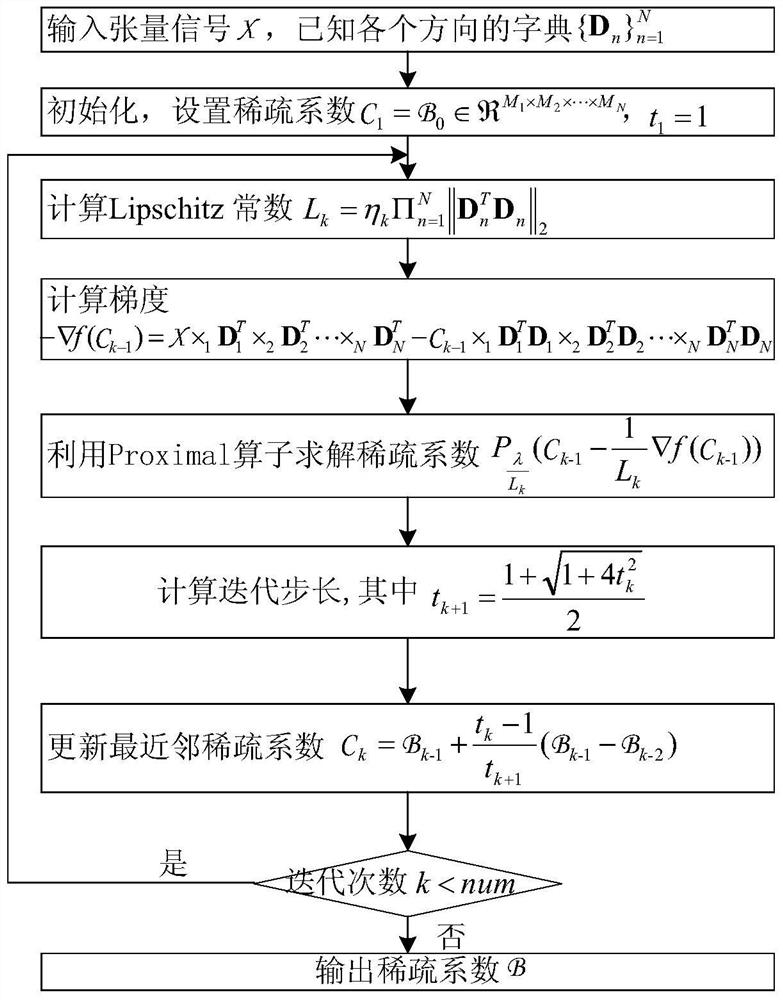
The invention discloses a sparse model of a multi-directional model, wherein the sparse model can ensure remarkable improvement on algorithm complexity and storage space without Kronecker product. The sparse model of the multi-directional model is represented by a formula x=B*1D1*2*D2...NDN, wherein ||B||<=K. In the formula, tension x represents a tension product between an N-directional sparse tension B which belongs to R<M1*M2*...*MN and a series of sparse dictionary Dn which belongs to R<In*Mn>, wherein In<=Mn, Dn is defined as the dictionary in an n-th direction, K is sparsity and is used for representing the number of non-zero elements in a sparse coefficient B. The invention furthermore provides a reconstruction method of the sparse model and a dictionary training method of the reconstruction method.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
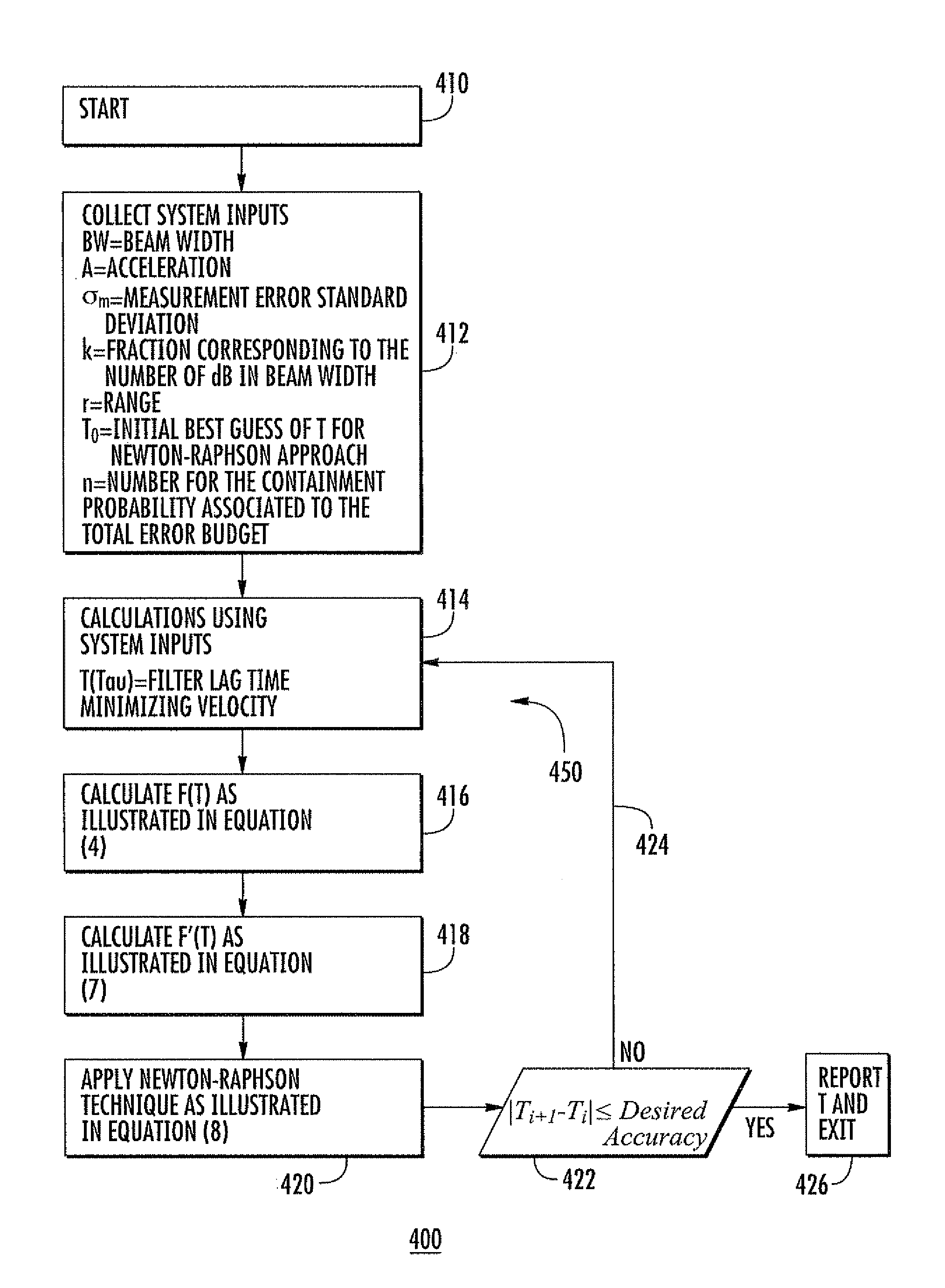
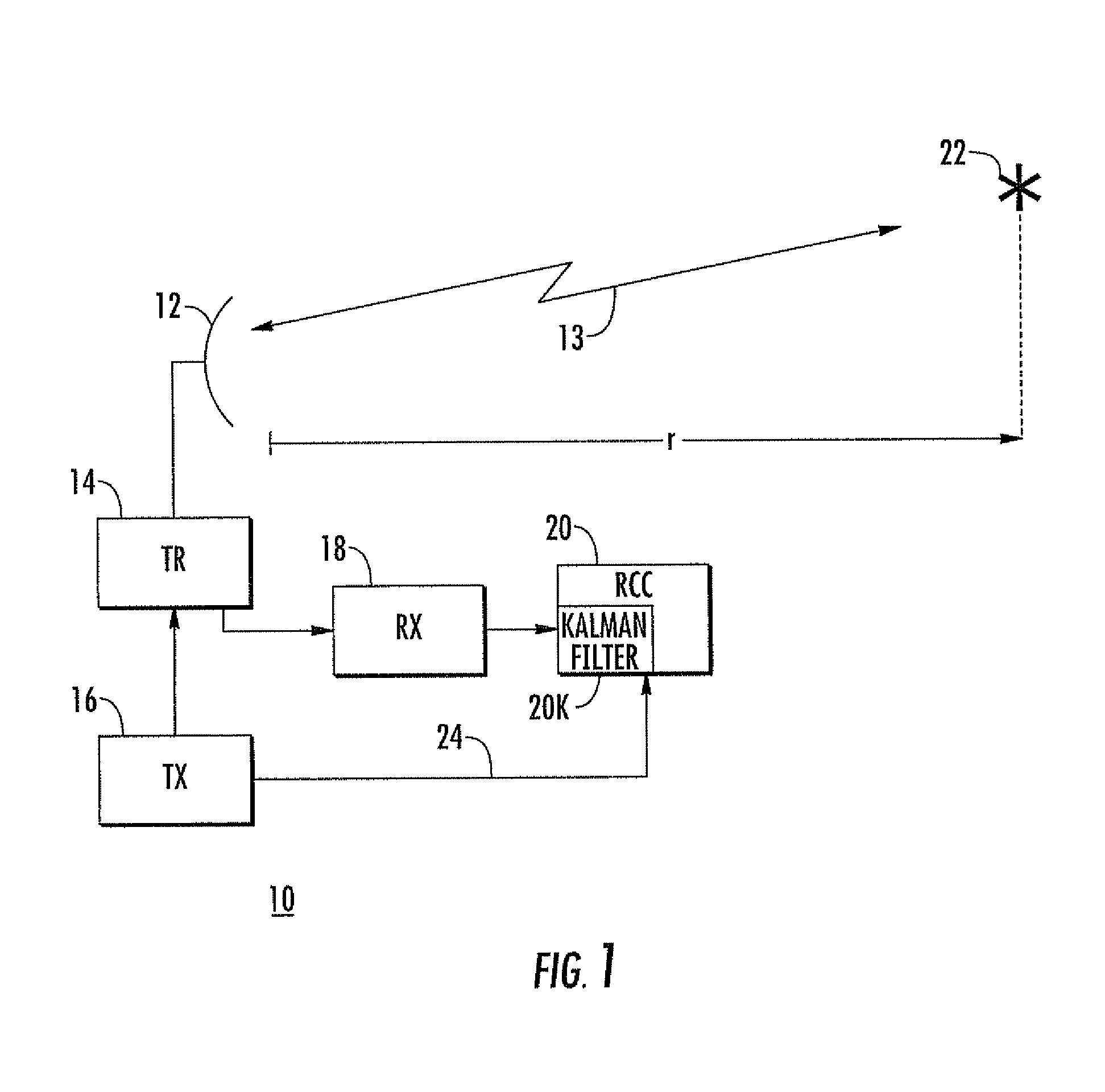
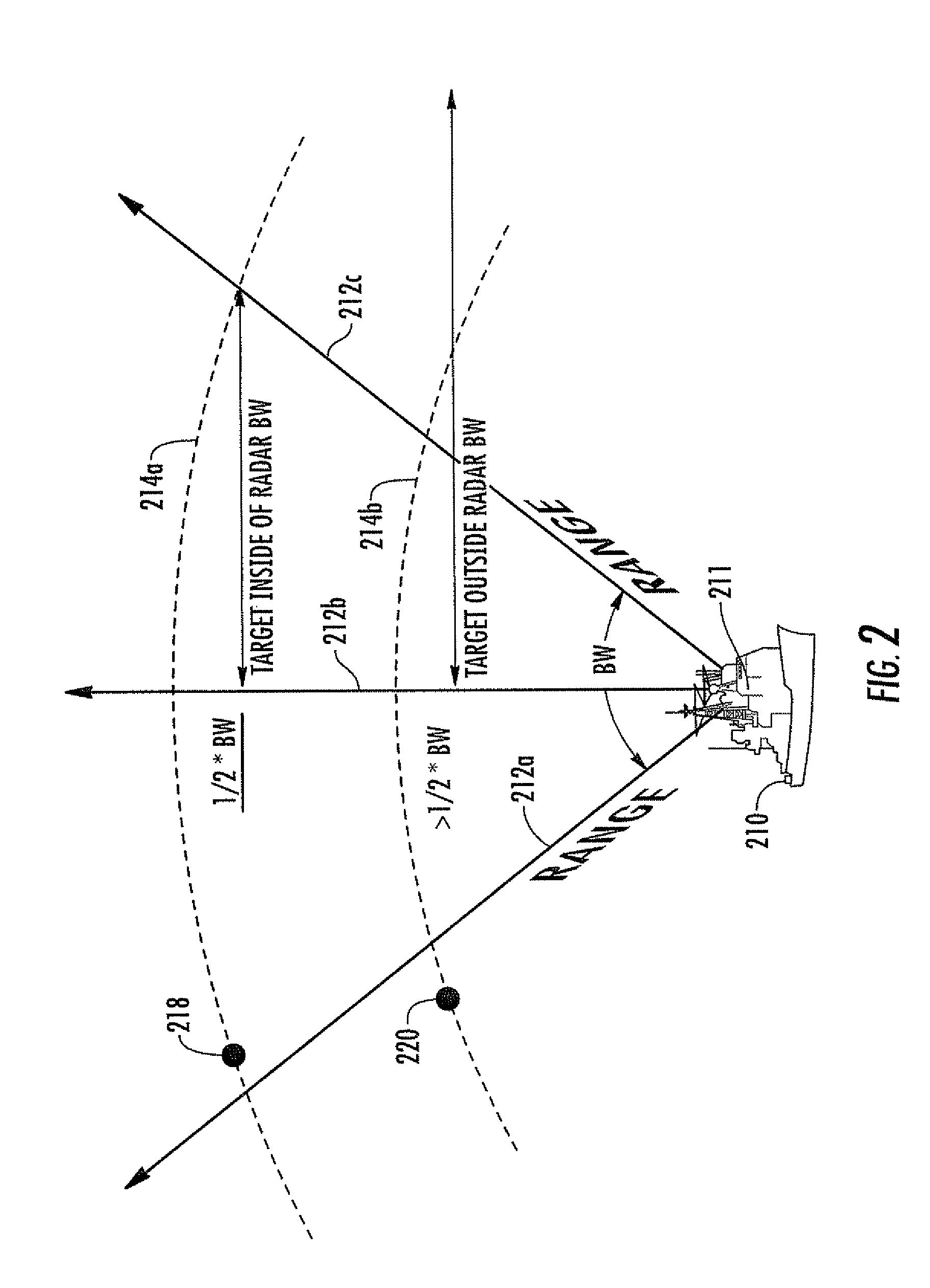
Optimization of radar resources
The radar tracking or pulse refresh rate is calculated for a target. The refresh rate is selected which makes a sum equal to a predetermined fraction of the radar beamwidth, where the sum is the sum of the bias error and a multiplicative product. The multiplicative product is the product of the random error multiplied by a number associated with the containment probability of the total error.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Method and system for quantization for a general beamforming matrix in feedback information
Aspects of a method and system for utilizing Givens rotation expressions for quantization for a general beamforming matrix in feedback information. In one aspect of the invention, feedback information is computed at the receiving MIMO wireless device based on a geometric mean decomposition (GMD) method. The feedback information may include a matrix that describes a wireless medium. The matrix may represent a multiplicative product of at least one rotation matrix and at least one diagonal phase rotation matrix. Each of the rotation matrices may include at least one matrix element whose value is based on Givens rotation angle. The transmitting MIMO wireless device may subsequently transmit a plurality of signals via the wireless medium based on the received matrix information. The signal strength and / or signal to noise ratio (SNR) measurement (as measured in decibels, for example) associated with each of the transmitted plurality of signals may be about equal.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Modular multiplication device and method
ActiveCN107040362AKey distribution for secure communicationMultiple keys/algorithms usageBinary multiplierAlgorithm
Owner:SECURE IC
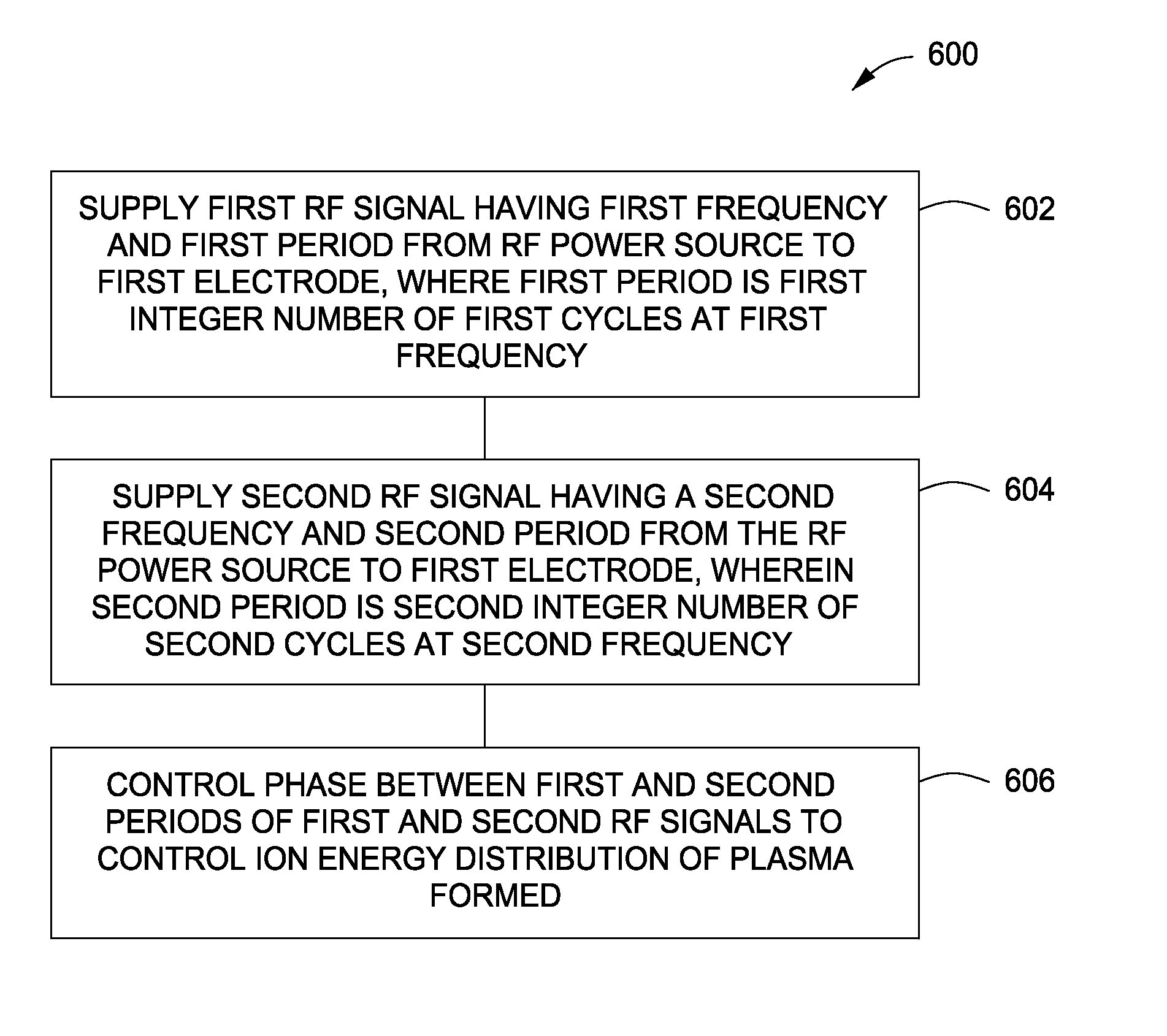
Methods and apparatus for controlling plasma in a process chamber
Methods and apparatus for controlling a plasma are provided herein. In some embodiments, a method may include supplying a first RF signal having a first frequency and a first period from an RF power source to a first electrode, wherein the first period is a first integer number of first cycles at the first frequency; supplying a second RF signal having a second frequency and a second period from the RF power source to the first electrode, wherein the second period is a second integer number of second cycles at the second frequency and wherein a first multiplicative product of the first frequency and the first integer number is equal to a second multiplicative product of the second frequency and the second integer number; and controlling the phase between the first and second periods to control an ion energy distribution of the plasma formed in a process chamber.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Method and apparatus for testing digital multiplier
ActiveCN103984519AImprove efficiencyCharacter width smallDigital data processing detailsNon-redundant fault processingBinary multiplierAlgorithm
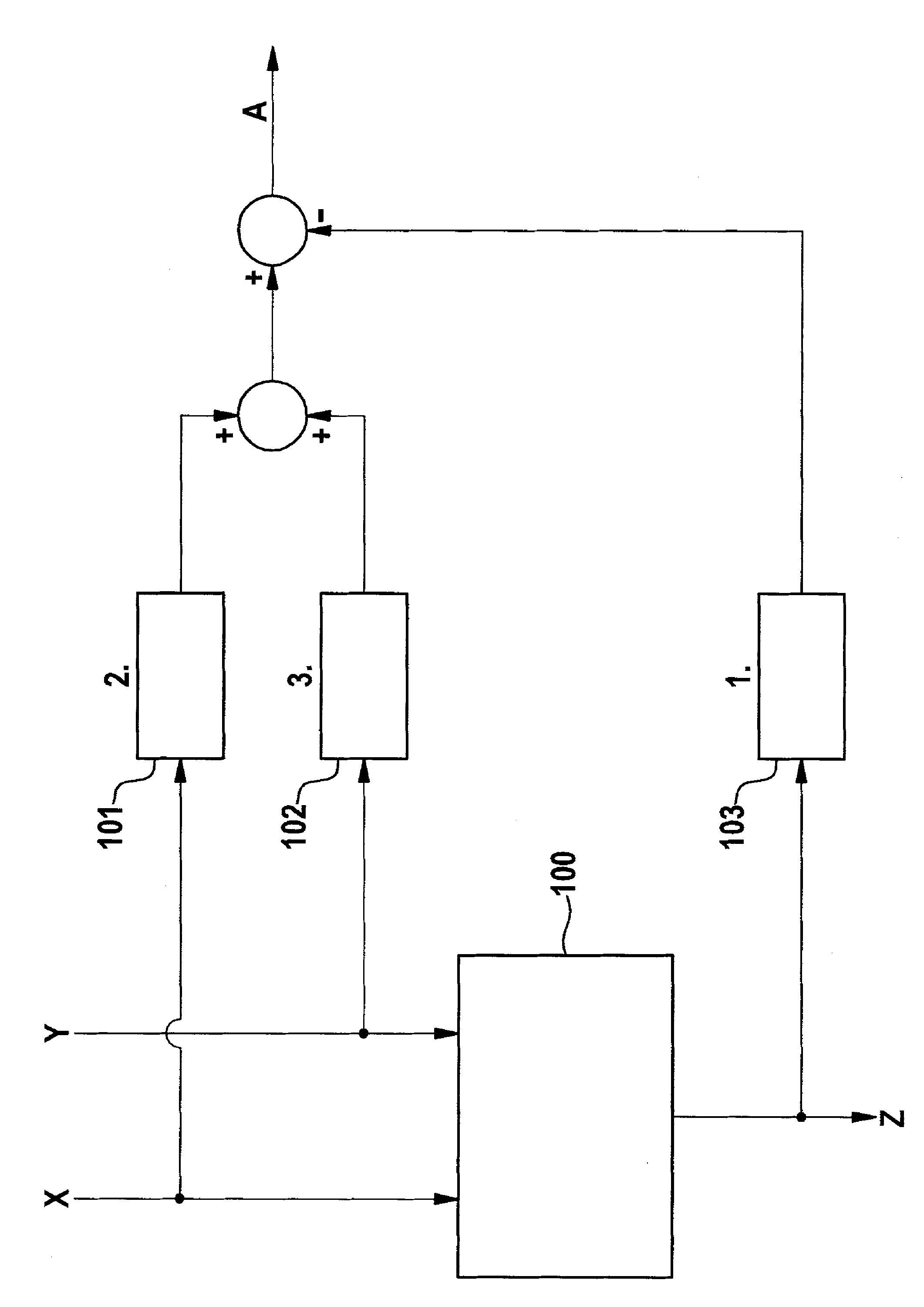
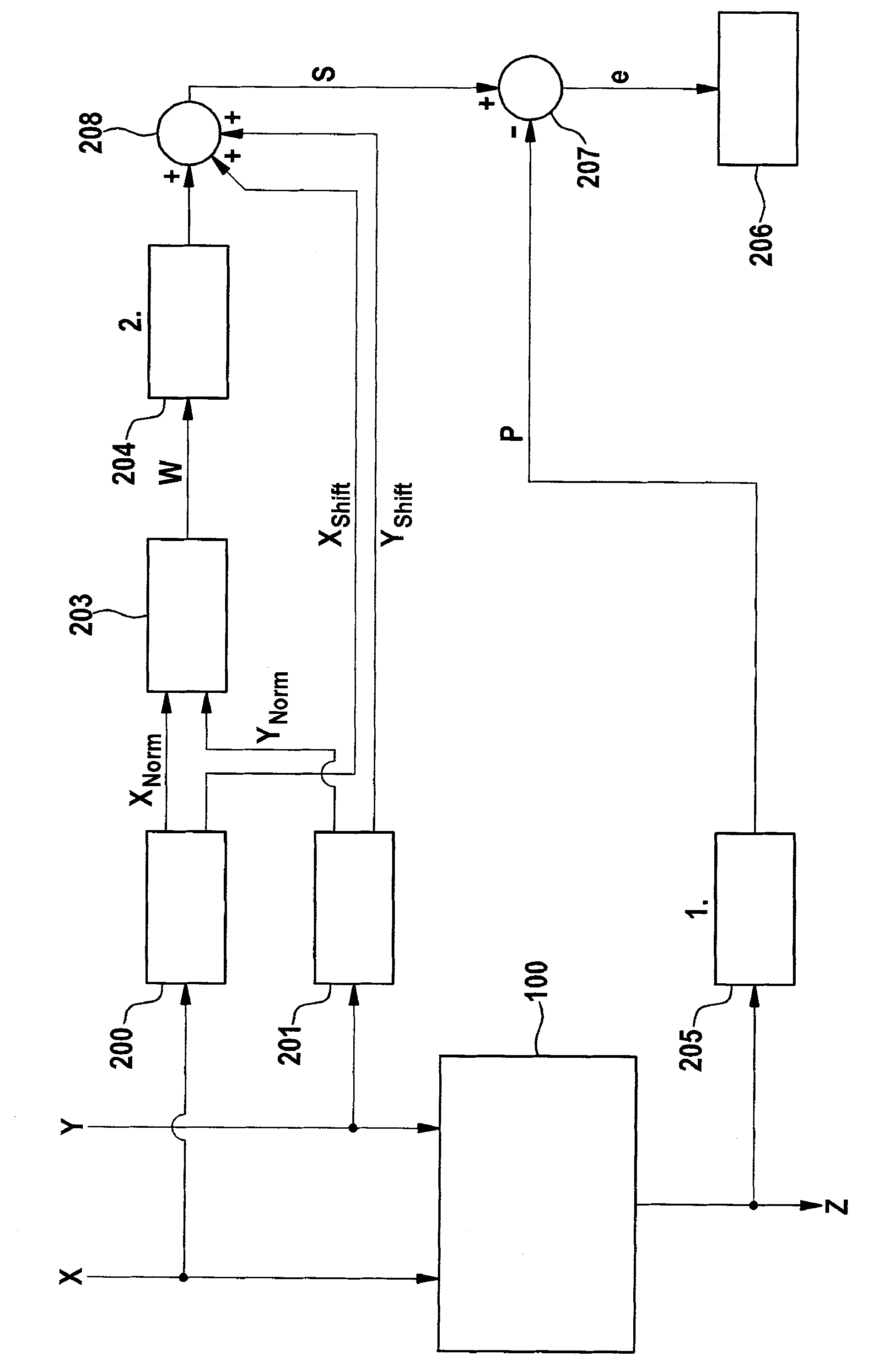
The invention relates to a method and apparatus for testing a digital multiplier. A method for calculating an error signal is disclosed, wherein the error signal is determined to be a difference between a sum logarithm and a product logarithm which is determined to be a logarithm of the absolute value of a product determined by a first multiplication device. The method is characterized in that the sum logarithm is determined to be the sum of a first exponent, a second exponent and a mantissa logarithm; the mantissa logarithm is determined to be a logarithm of the absolute value of a mantissa product; the mantissa product is determined to a product of a first approximate normalized mantissa and a second approximate normalized mantissa; the first approximate normalized mantissa is determined to be an approximation of a normalized mantissa of float point representation of a first divider relative to a base; the first exponent is an exponent of the base in the float point representation of the first divider; the second approximate normalized mantissa is determined to be an approximate normalized mantissa of float point representation of a second divider relative to the base; and the second exponent is an exponent of the base in the float point representation of the second divider.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
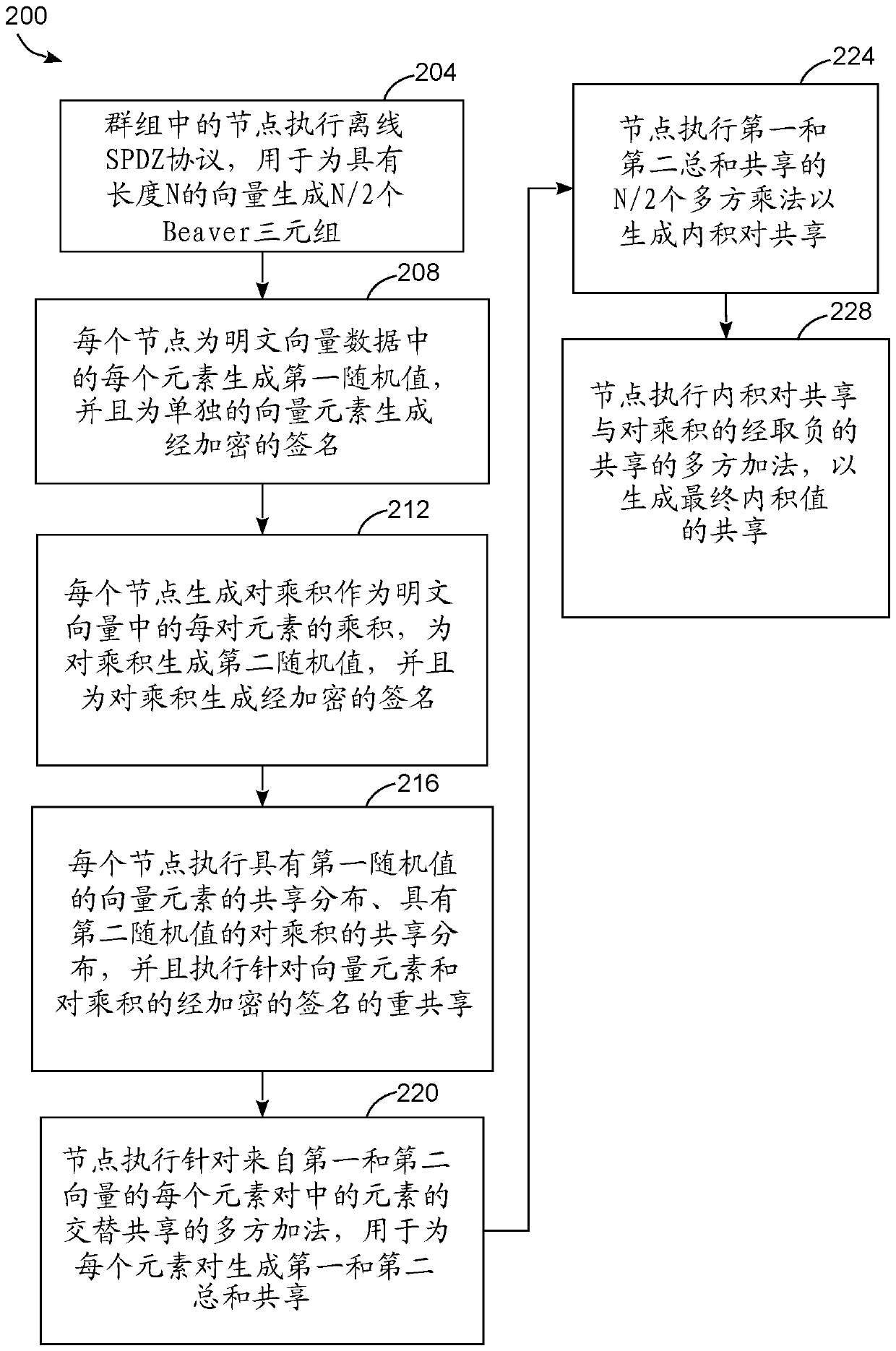
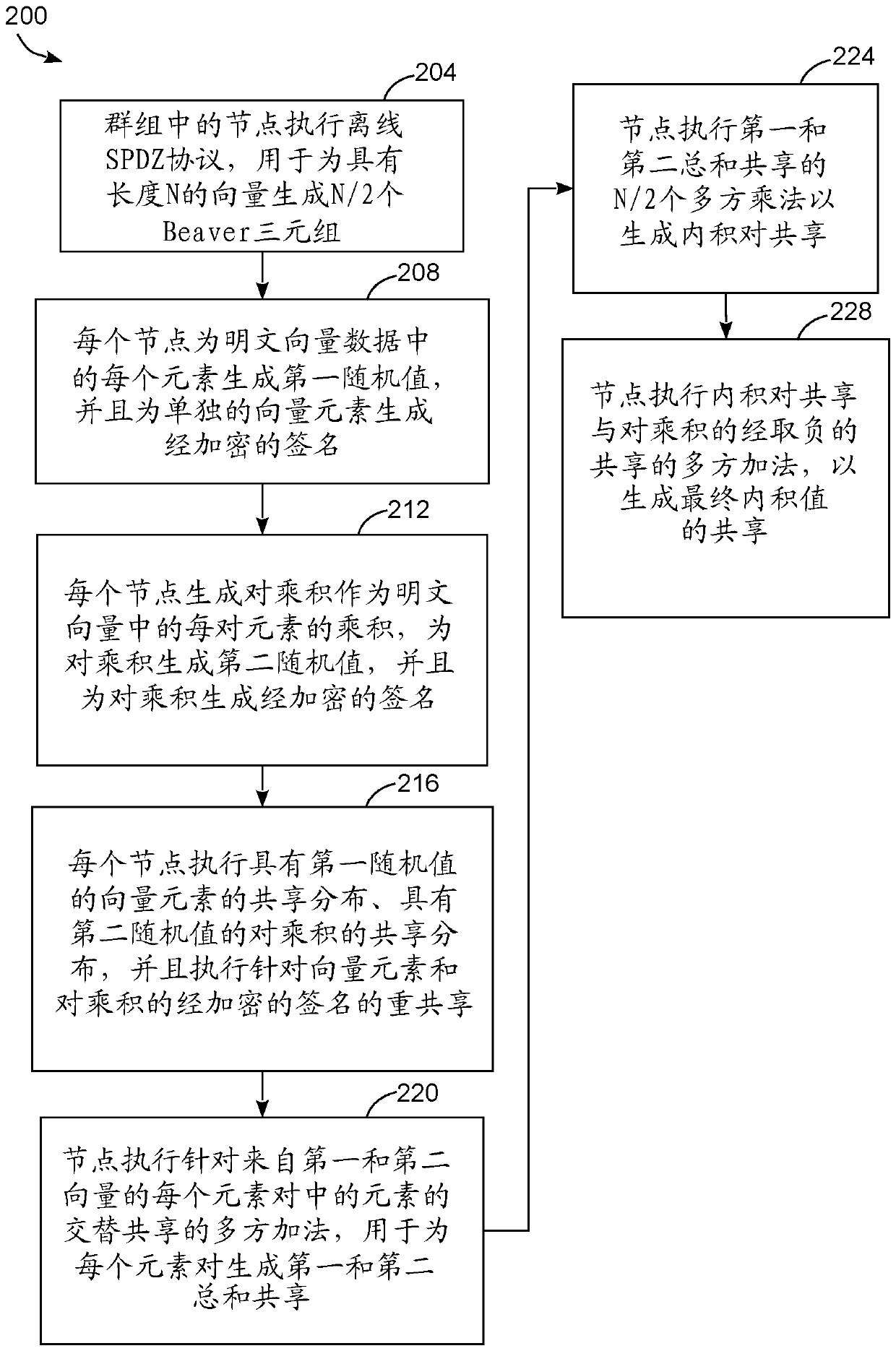
Method for Faster Secure Multiparty Inner Product Computation with SPDZ
PendingCN111133719ASecuring communicationComplex mathematical operationsAlgorithmTheoretical computer science
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Operation method and device based on multiplier and computer readable storage medium
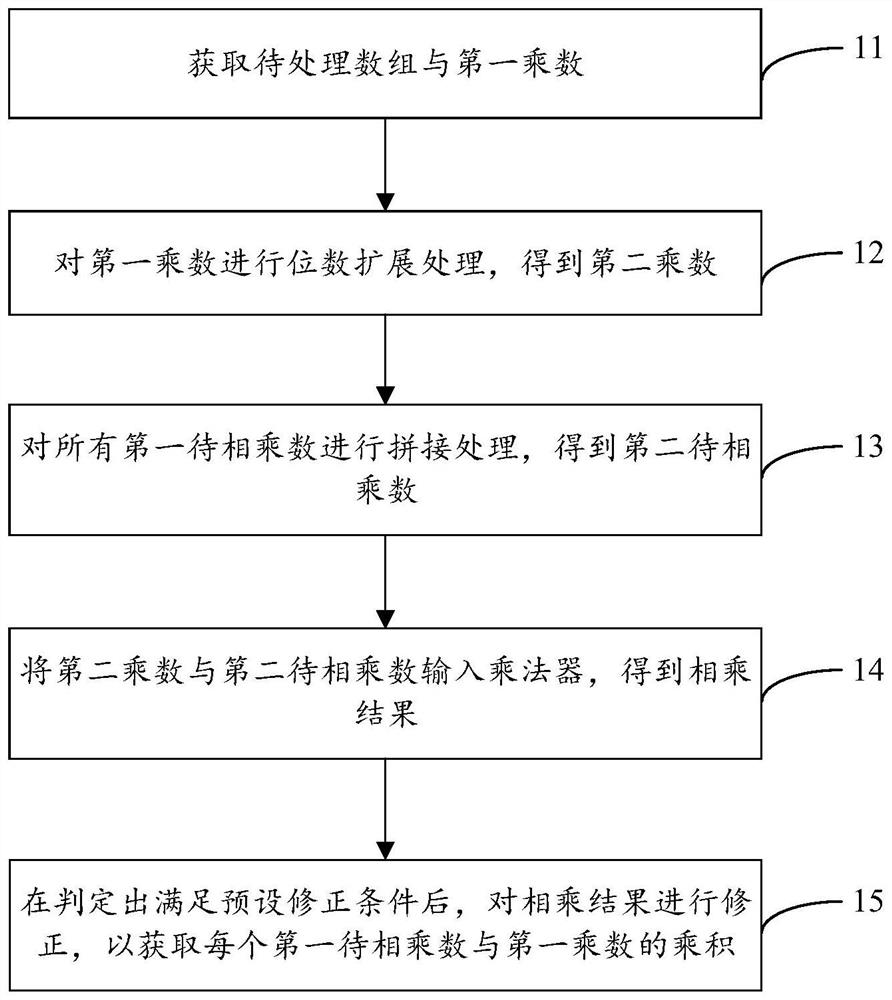
PendingCN114003194AImprove computing powerMake full use of computing resourcesDigital data processing detailsBinary multiplierComputer science
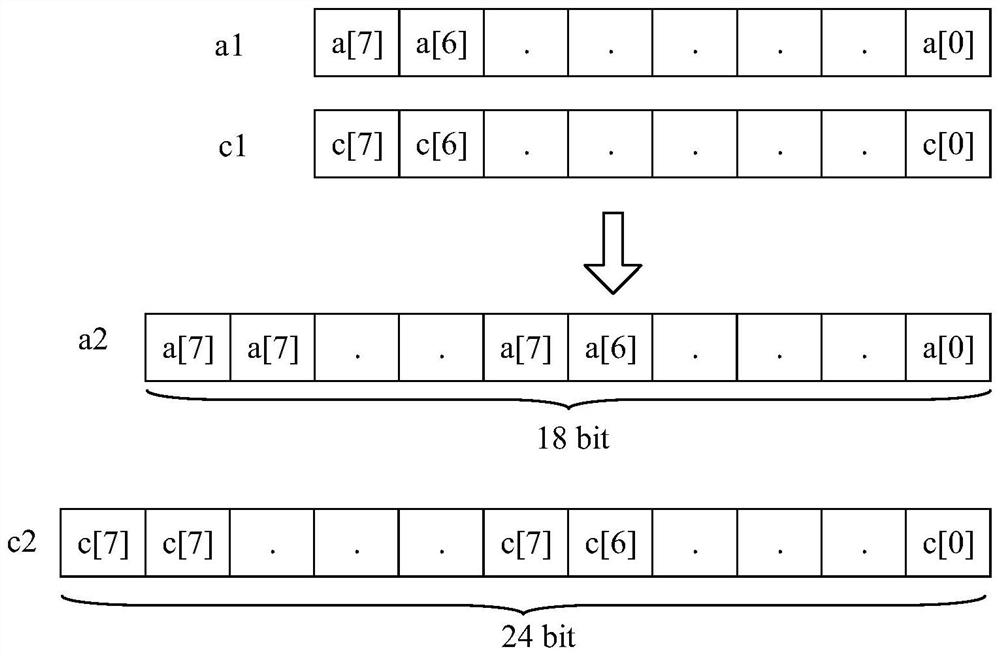
The invention discloses an operation method and device based on a multiplier and a computer readable storage medium, and the method comprises the steps: obtaining a to-be-processed array and a first multiplier, wherein the to-be-processed array comprises at least two first to-be-multiplied numbers; performing digit expansion processing on the first multiplier to obtain a second multiplier; splicing all the first to-be-multiplied numbers to obtain a second to-be-multiplied number; inputting the second multiplier and the second to-be-multiplied number into the multiplier to obtain a multiplication result; after it is judged that a preset correction condition is met, correcting the multiplication result to obtain a product of each first to-be-multiplied number and the first multiplier, the preset correction condition includes that an exclusive-or result of a value of a highest bit of the first to-be-multiplied number and a value of a highest bit of the first multiplier is a first value, and neither the first to-be-multiplied number nor the first multiplier is a second value. In this way, the computing power can be improved, and resources are fully utilized.
Owner:ZHEJIANG DAHUA TECH CO LTD
Multiply execution unit for performing integer and XOR multiplication
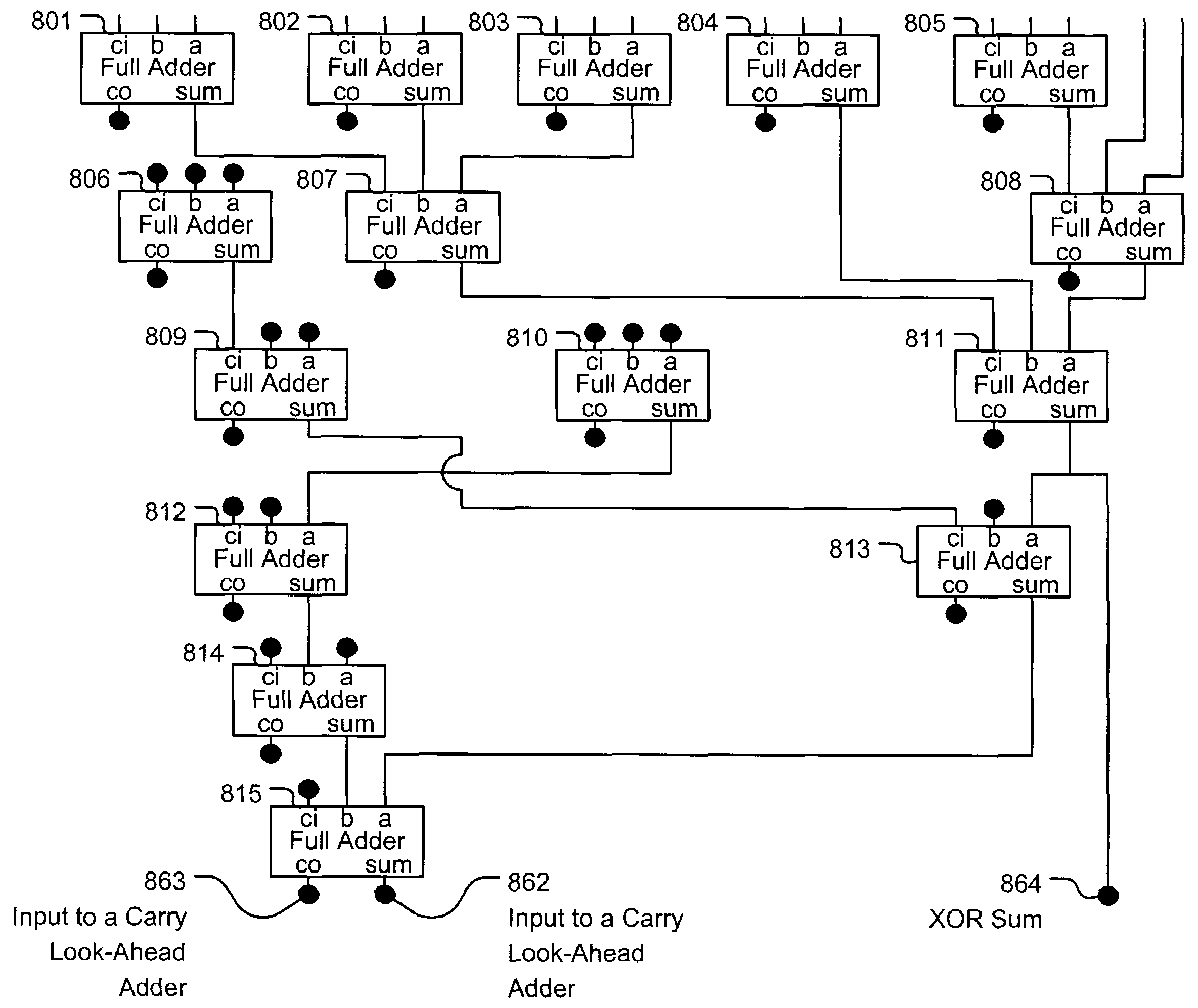
ActiveUS7139787B2Computation using non-contact making devicesDigital computer detailsAlgorithmExecution unit
A multiply execution unit that is operable to generate the integer product and the XOR product of a multiplicand and a multiplier. The multiply execution unit includes a summing circuit for summing a plurality of partial products. The partial products may be Booth encoded. The summing circuit can generate an integer sum of the plurality of partial products and can generate an XOR sum of the plurality of partial products. The summing circuit includes a first plurality of full adders. The first plurality of full adders each has three inputs, a carry output, and a sum output. The sum outputs of the first plurality of full adders are independent of the value of any carry output in the summing circuit. The summing circuit also includes a second plurality of full adders. The second plurality of full adders each has three inputs, a carry output, and a sum output. The XOR sum is dependent upon at least one of the sum outputs of the first plurality of full adders but is independent of the sum outputs of the second plurality of full adders. The integer sum is dependent upon the sum outputs of at least one of the first plurality of full adders and is also dependent on at least one of the sum outputs of the second plurality of full adders.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
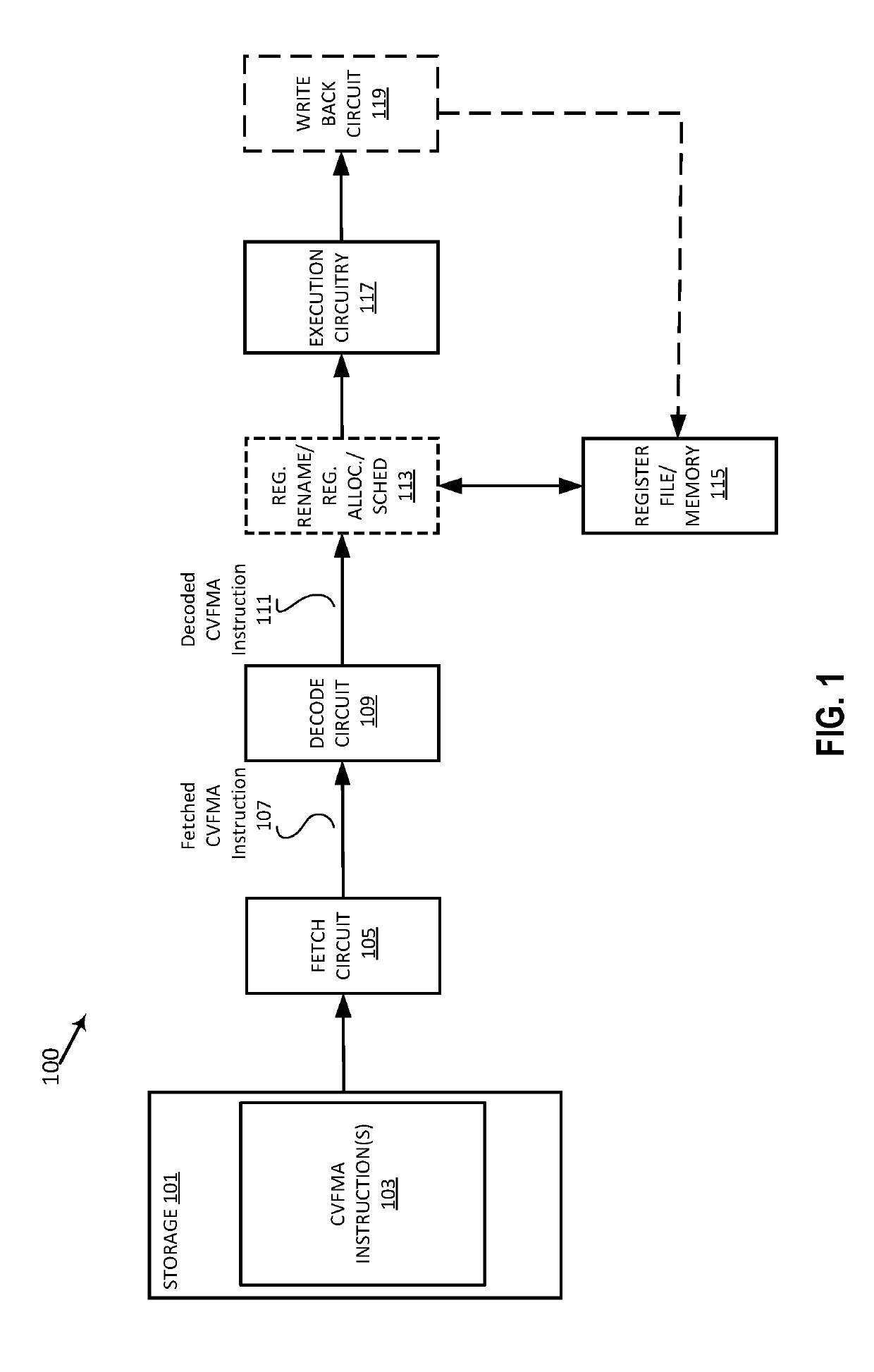
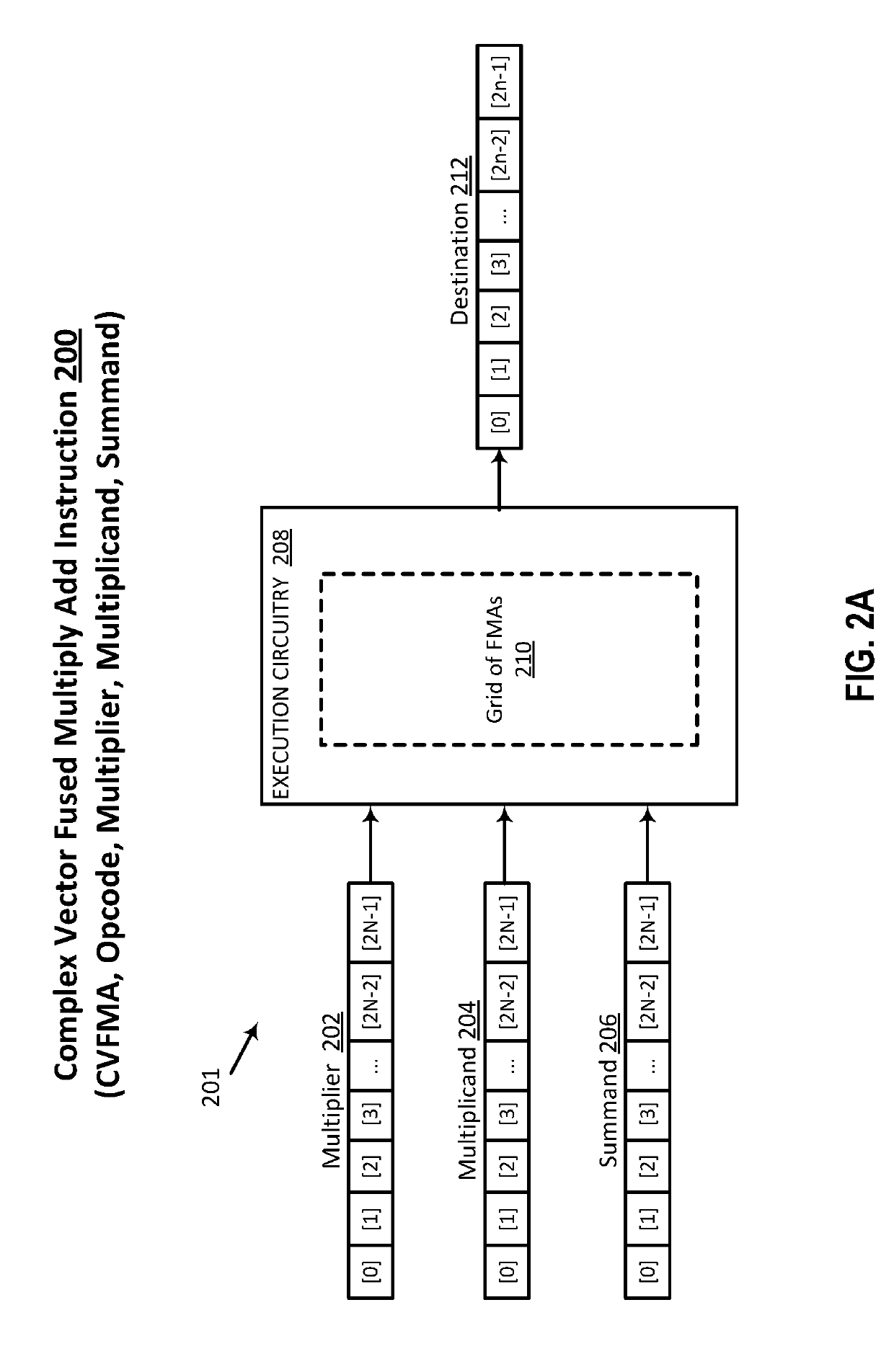
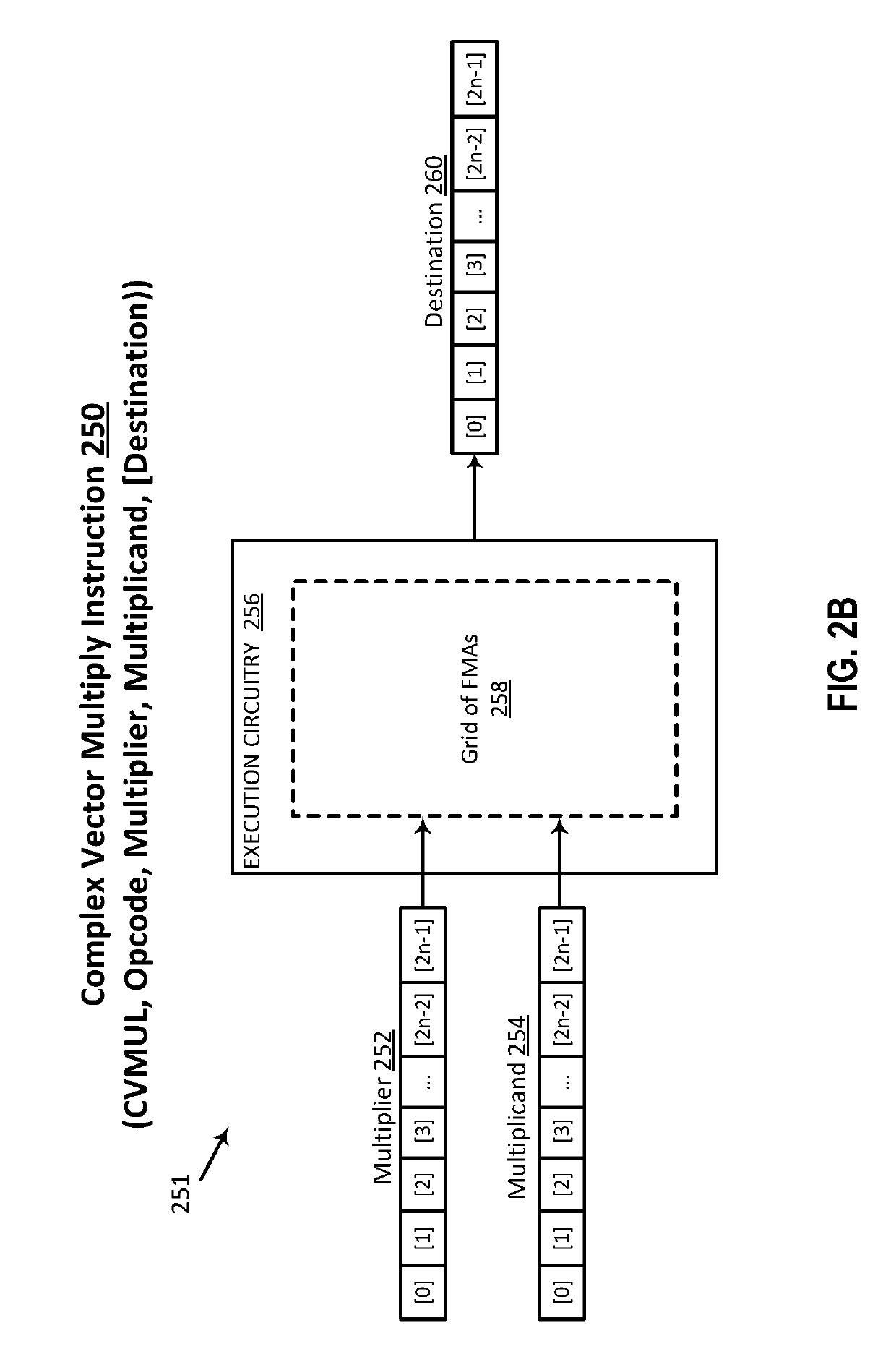
Efficient implementation of complex vector fused multiply add and complex vector multiply
ActiveUS20190303142A1Digital data processing detailsInstruction analysisTheoretical computer scienceAlgorithm
Owner:INTEL CORP
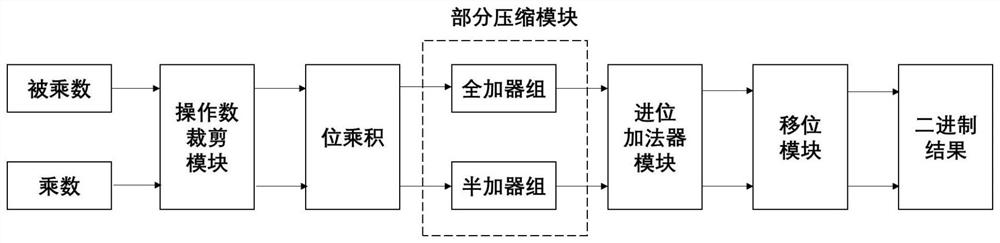
High-performance approximate multiplier based on operand cutting and calculation method thereof
PendingCN114691086AExcellent areaExcellent hardware costDigital data processing detailsBinary multiplierBinary outcome
The invention discloses a high-performance approximate multiplier based on operand cutting and a calculation method of the high-performance approximate multiplier. The approximate multiplier comprises a partial product generation module, a partial product tree compression module, a carry adder module and a shifting module. The partial product generation module comprises an operand cutting module and a bit product module, the operand cutting module performs cutting operation on a multiplier and a multiplicand to obtain an approximate operand, and the bit product module obtains a corresponding partial product; the partial product tree compression module is used for obtaining two final summed addend numbers; the carry adder module is used for finally adding two adders, and the shifting module is used for shifting the output of the carry adder module to obtain a solved binary result. According to the invention, the area, the delay and the power consumption of the multi-bit multiplier can be greatly reduced, and meanwhile, better accuracy can be kept.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
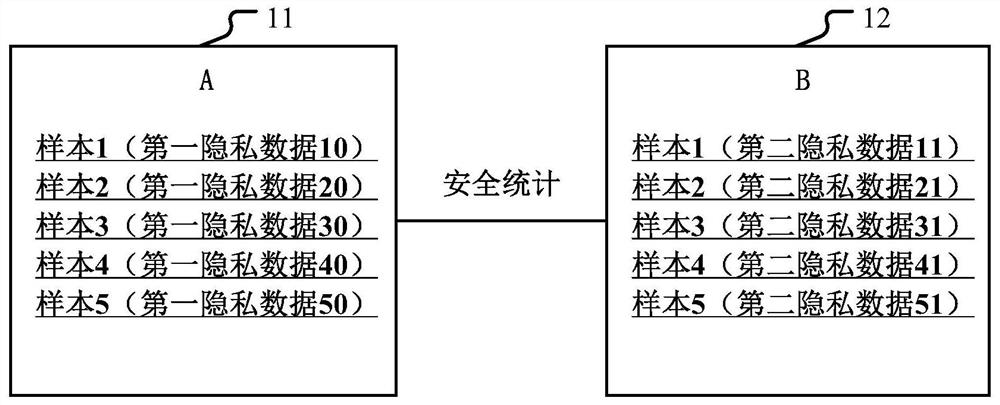
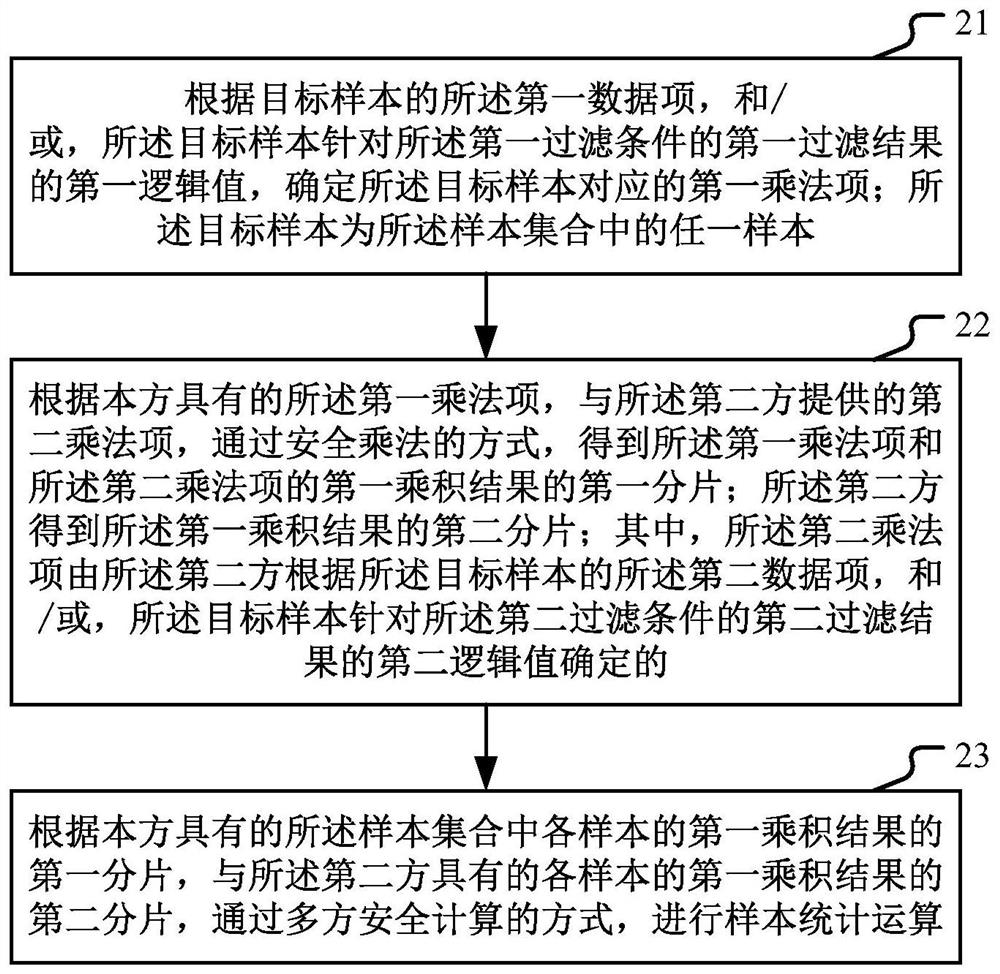
Multi-party joint security statistics method and device
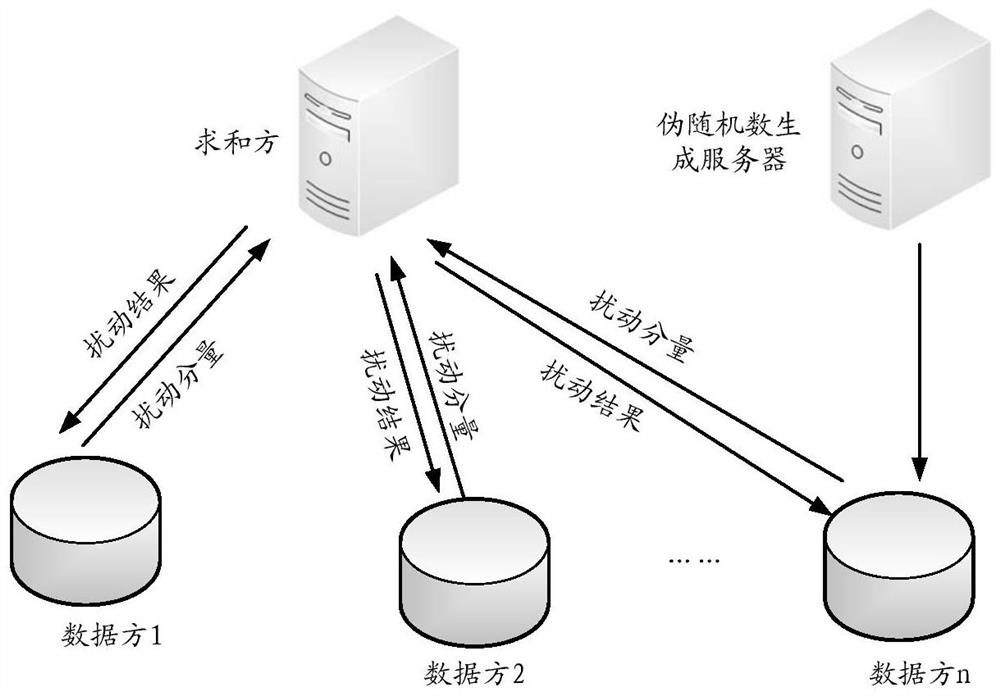
PendingCN112199639AReduce trafficWill not disclose private dataDigital data protectionComplex mathematical operationsAlgorithmReliability engineering
Owner:ALIPAY (HANGZHOU) INFORMATION TECH CO LTD
A distributed multi-agent task cooperation method based on linear temporal logic
ActiveCN111340348BReduce time complexityImprove COPResourcesLinear temporal logicCollaborative intelligence
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Multi-party secure multiplication
PendingCN114722435ADigital data processing detailsInternal/peripheral component protectionAlgorithmEngineering
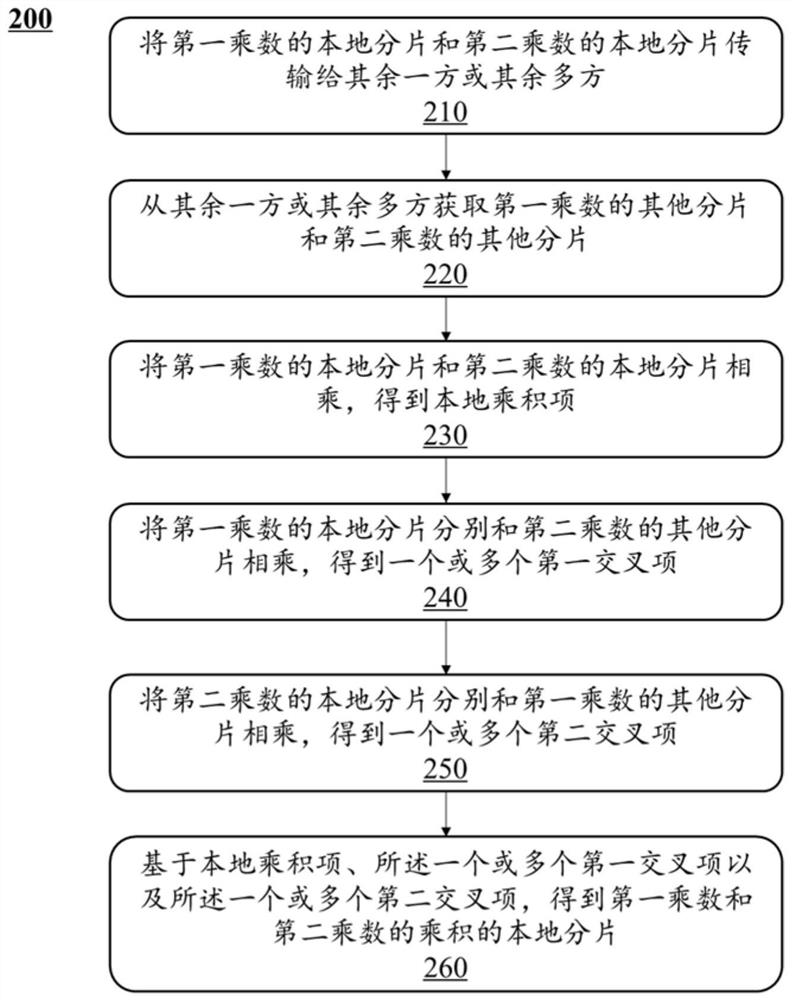
The embodiment of the invention discloses a multi-party safe multiplication, and relates to n parties, and n is a positive integer not less than 3. Each party holds fragments of two multipliers. Any calculation participant can transmit the local fragments of the two multipliers to the other party or the other multiple parties and obtain other fragments of the two multipliers from the other party or the other multiple parties, and the number of the other multiple parties is not larger than n-2. Furthermore, any calculation participant can multiply the local fragments of the two multipliers to obtain a local product term, multiply the local fragment of one multiplier with other fragments of the other multiplier to obtain one or more cross terms, and obtain the local fragment of the product of the two multipliers based on the local product term and the one or more cross terms.
Owner:ALIPAY (HANGZHOU) INFORMATION TECH CO LTD
Approximate multiplier design method based on optimal compensation and approximate multiplier
PendingCN111695312AMinimum mean square errorGuaranteed accuracyDigital data processing detailsCAD circuit designBinary multiplierMean square
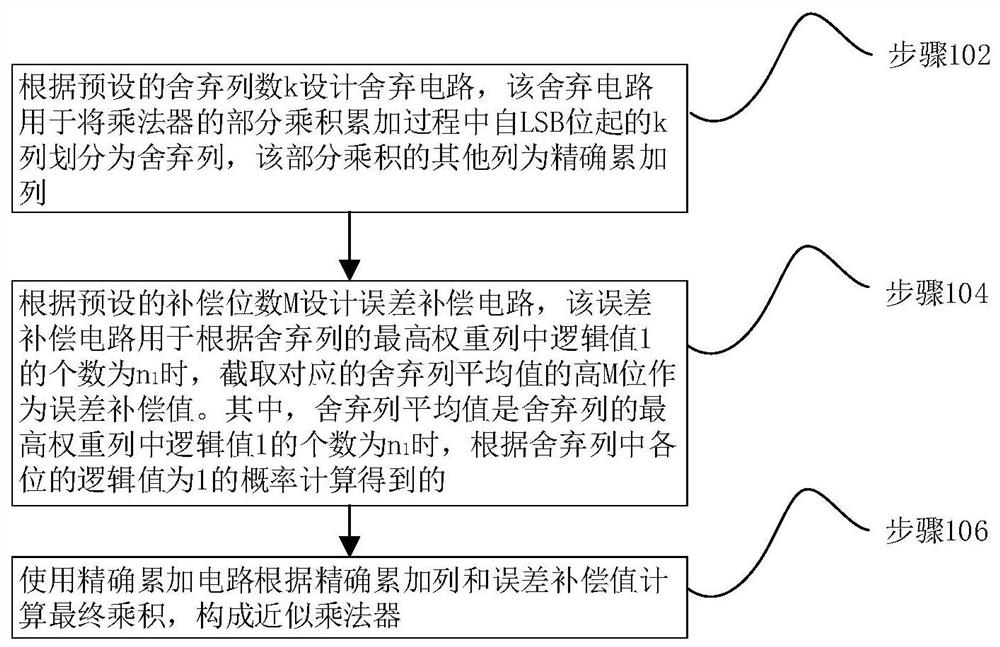
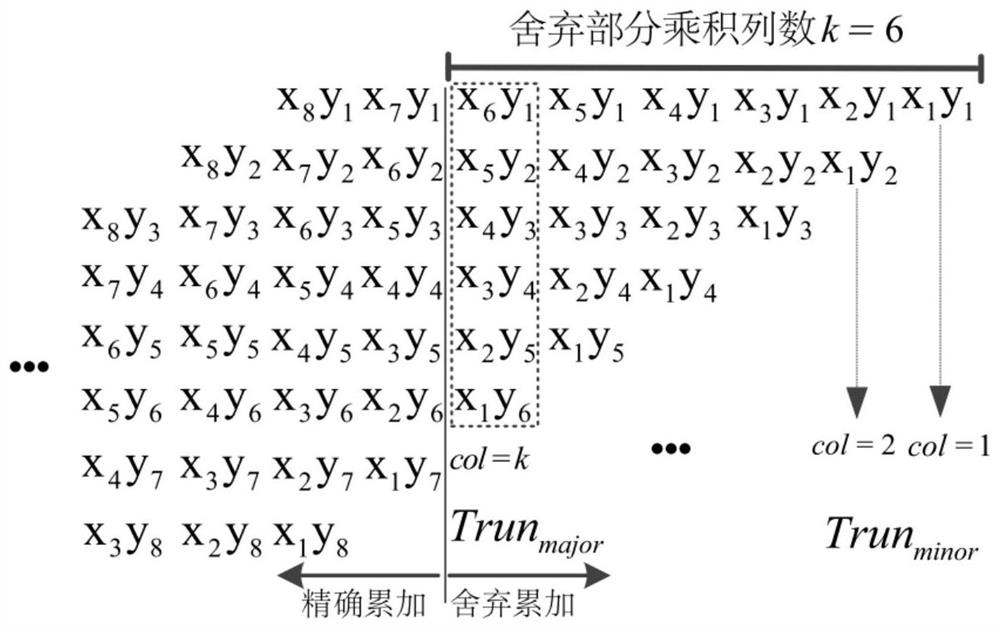
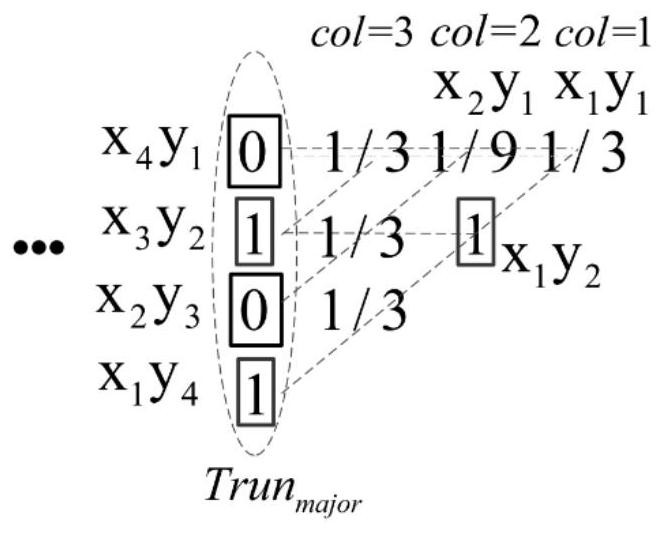
The invention relates to an approximate multiplier design method based on optimal compensation and an approximate multiplier. The method comprises the following steps: designing a discarding circuit according to a preset discarding column number k, dividing k columns starting from an LSB bit in a partial multiplication accumulation process of a multiplier into discarding columns, and taking othercolumns as accurate accumulation columns; and designing an error compensation circuit according to a preset compensation digit M, and calculating an average value of the abandoned columns of the M bits as an error compensation value according to the number n1 of the logic values 1 in the highest weight column of the abandoned columns and the probability that the logic value of each bit in the abandoned columns is 1; and calculating a final product by using an accurate accumulation circuit according to the accurate accumulation column and the error compensation value to form an approximate multiplier. By adopting the method, the final product result of the approximate multiplier has the minimum mean square error, and the calculation precision of the approximate multiplier is ensured.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Method and device for executing multi-party secure multiplication
PendingCN114489564AImprove computing efficiencyReduce data trafficRandom number generatorsAlgorithmOperations research
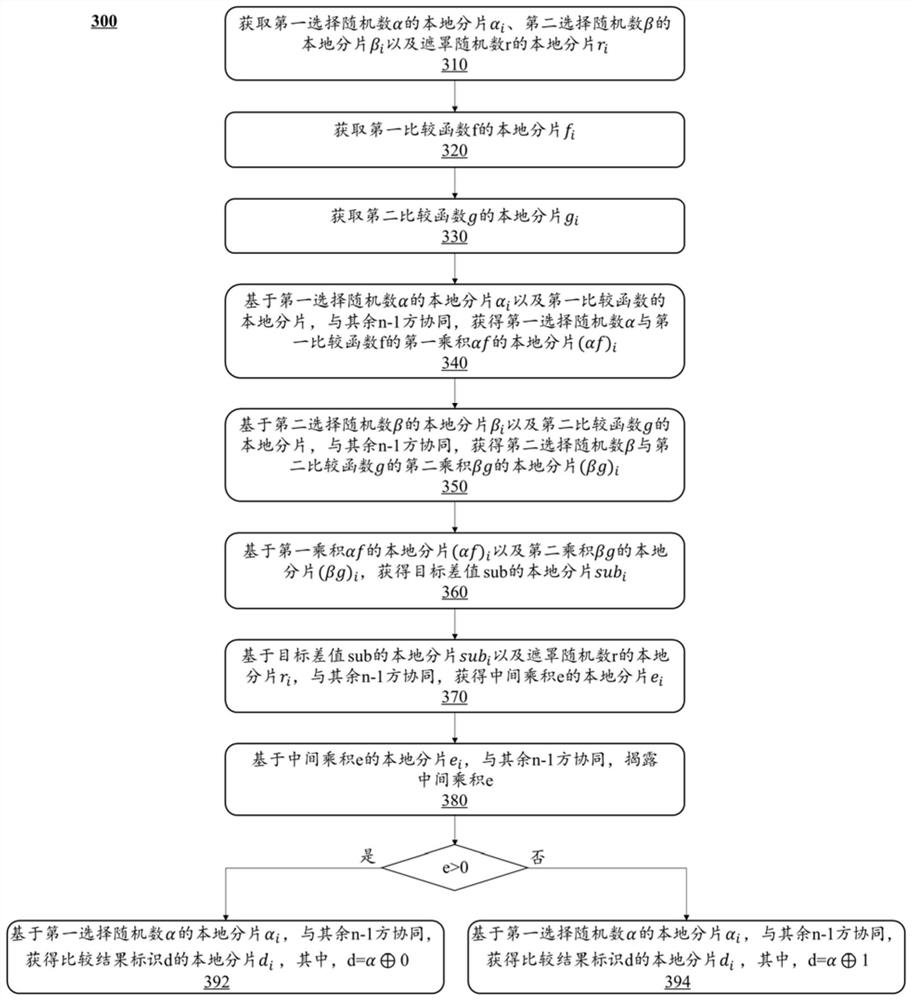
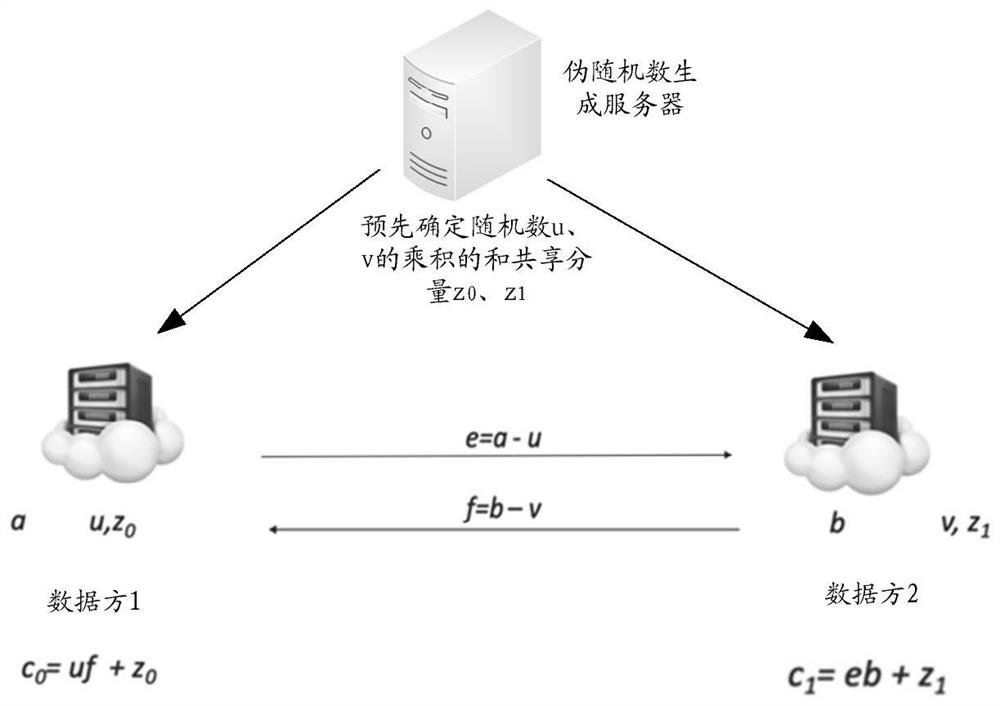
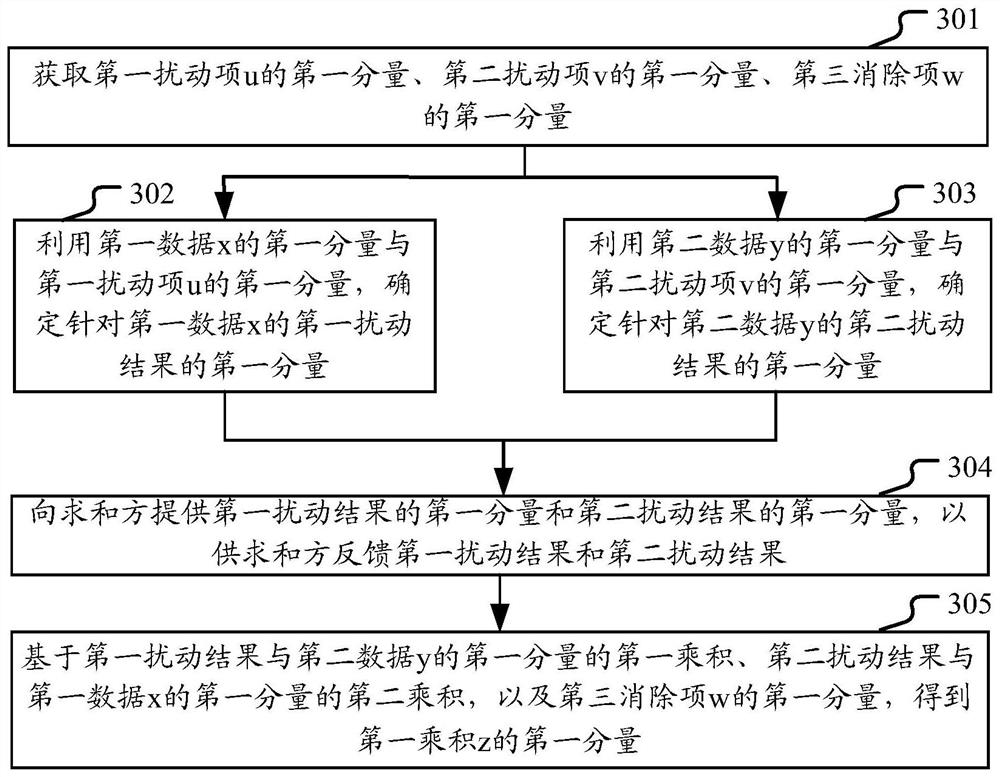
The embodiment of the invention provides a multi-party secure multiplication execution method and device which are used for determining a product z of first data x and second data y stored in n data parties in a sharing mode, and a first party in the n data parties holds a first component of x and a first component of y. A first party can obtain a first component of a first disturbance term u, a first component of a second disturbance term v and a first component of a third elimination term w, determine a first component of a first disturbance result dx for x by using the first component of x and the first component of u, determine a first component of a second disturbance result dy for y by using the first component of y and the first component of v, and determine a second disturbance result dx for y by using the first component of y and the first component of v. The first component of dx and the first component of dy are then provided to the summator for the summator to feed back dx and dy, thereby determining a first component of product z based on a first product of dx and the first component of y, a second product of dy and the first component of x, and the first component of w.
Owner:ANT BLOCKCHAIN TECH SHANGHAI CO LTD
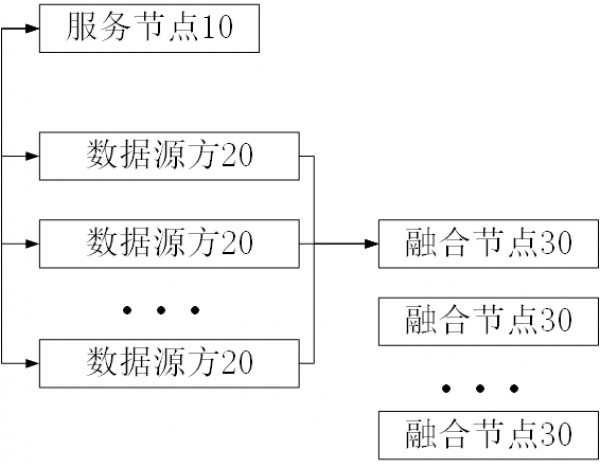
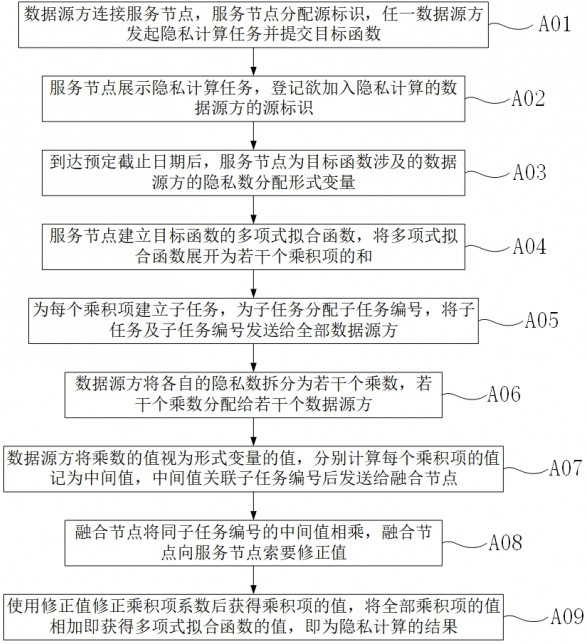
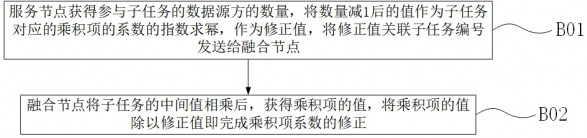
Multi-source data fusion platform based on privacy computing
PendingCN114048518AMeeting Privacy Computing NeedsImprove execution efficiencyDigital data processing detailsInternal/peripheral component protectionTheoretical computer scienceData source
The invention relates to the technical field of information, in particular to a multi-source data fusion platform based on privacy computing. The platform comprises a service node and a fusion node, wherein the service node displays a privacy computing task, registers source identifiers of data source parties to be added into privacy computing, and distributes formal variables for privacy numbers of the data source parties related to a target function; the service node establishes a polynomial fitting function of the target function, and expands the polynomial fitting function into the sum of a plurality of product terms; the data source parties split the privacy numbers into a plurality of multipliers and distribute the multipliers to a plurality of data source parties; the data source parties take values of the multipliers as values of the formal variables, calculate a value of each product term as an intermediate value, and send the intermediate values to the fusion node; and the fusion node multiplies the intermediate values of the same subtask number, corrects coefficients of the product terms by using a correction value to obtain values of the product terms, and adds the values of all the product terms to obtain a value of the polynomial fitting function. The invention has the substantive effects that wide privacy computing requirements can be met, and higher execution efficiency is achieved.
Owner:浙江数秦科技有限公司
Method and device for jointly generating data tuples for secure computing
ActiveCN113434886BGenerate efficientlyComputationally efficientDigital data protectionComplex mathematical operationsSecret shareAlgorithm
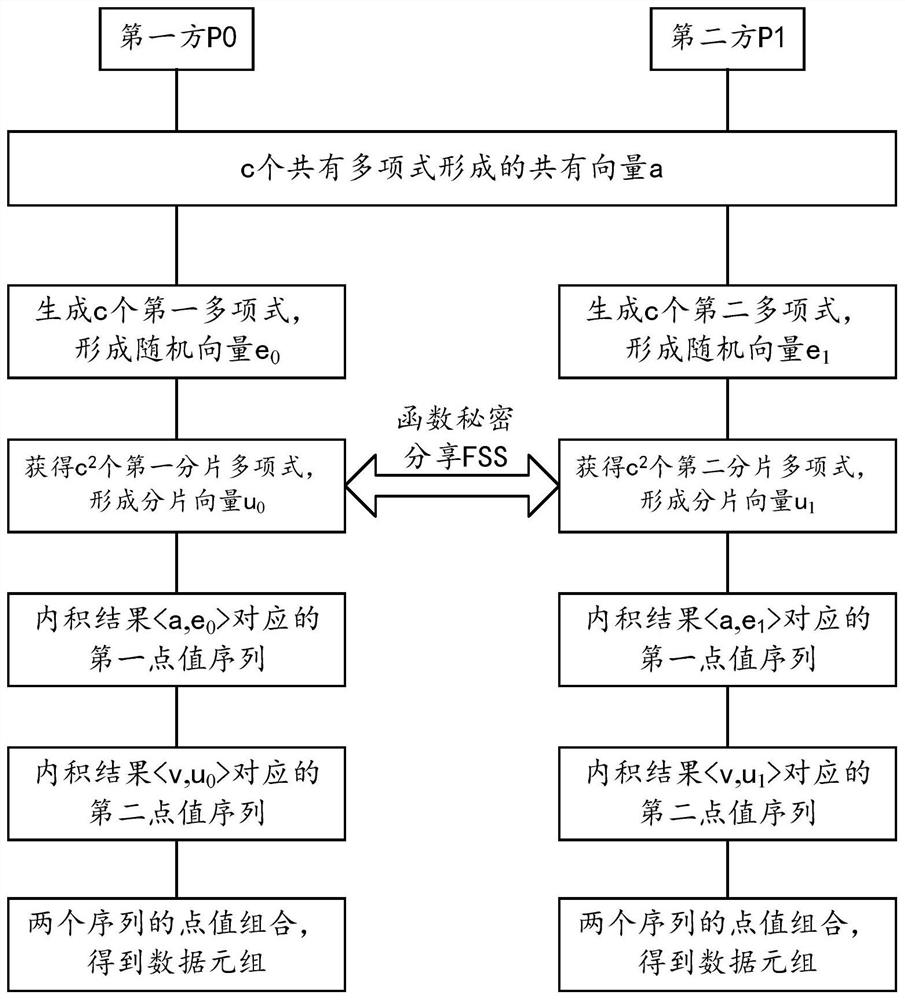
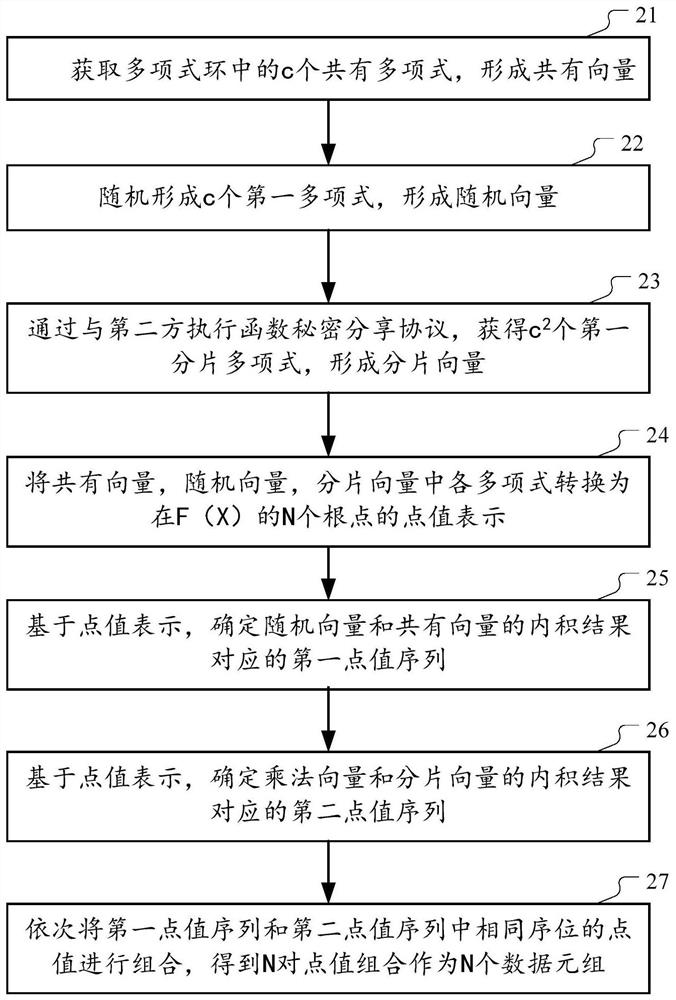
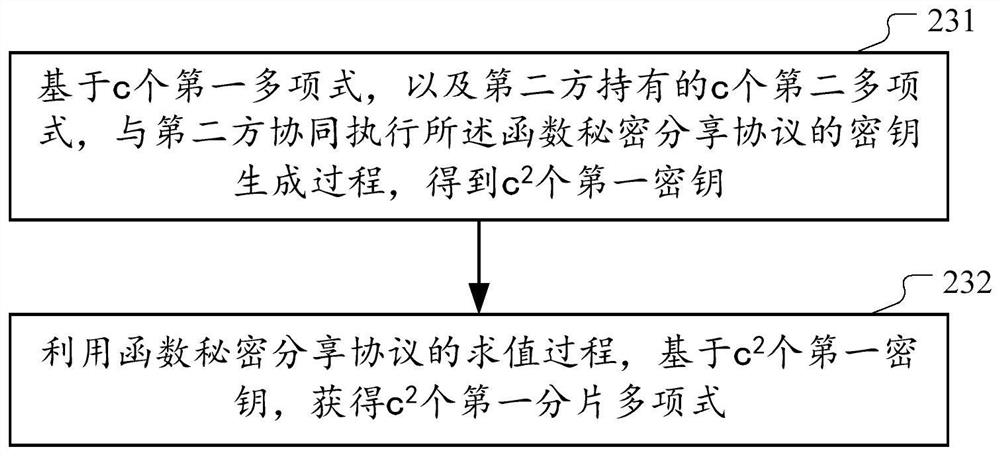
The embodiments of this specification provide a method and an apparatus for jointly generating data tuples for secure computing. According to this method, the first party obtains a common vector formed by c common polynomials in the polynomial ring, and randomly generates c first polynomials to form a random vector. Then, the first party and the second party execute the function secret sharing protocol, and obtain the fragmentation vector formed by c2 first fragmentation polynomials, and the sum of the corresponding fragmentation obtained by the second party and the c2 polynomials of both parties corresponds to c2 product polynomials. Each polynomial in each vector is then converted to a point-valued representation of the N root points of the modulo polynomial F(X) in the polynomial ring. Thus, the point value sequence corresponding to the inner product result of the random vector and the common vector, and the point value sequence corresponding to the inner product result of the multiplication vector and the slice vector obtained by performing tensor multiplication on the common vector itself are determined. Combine the point values of the two point value sequences in turn to obtain N data tuples.
Owner:ALIPAY (HANGZHOU) INFORMATION TECH CO LTD
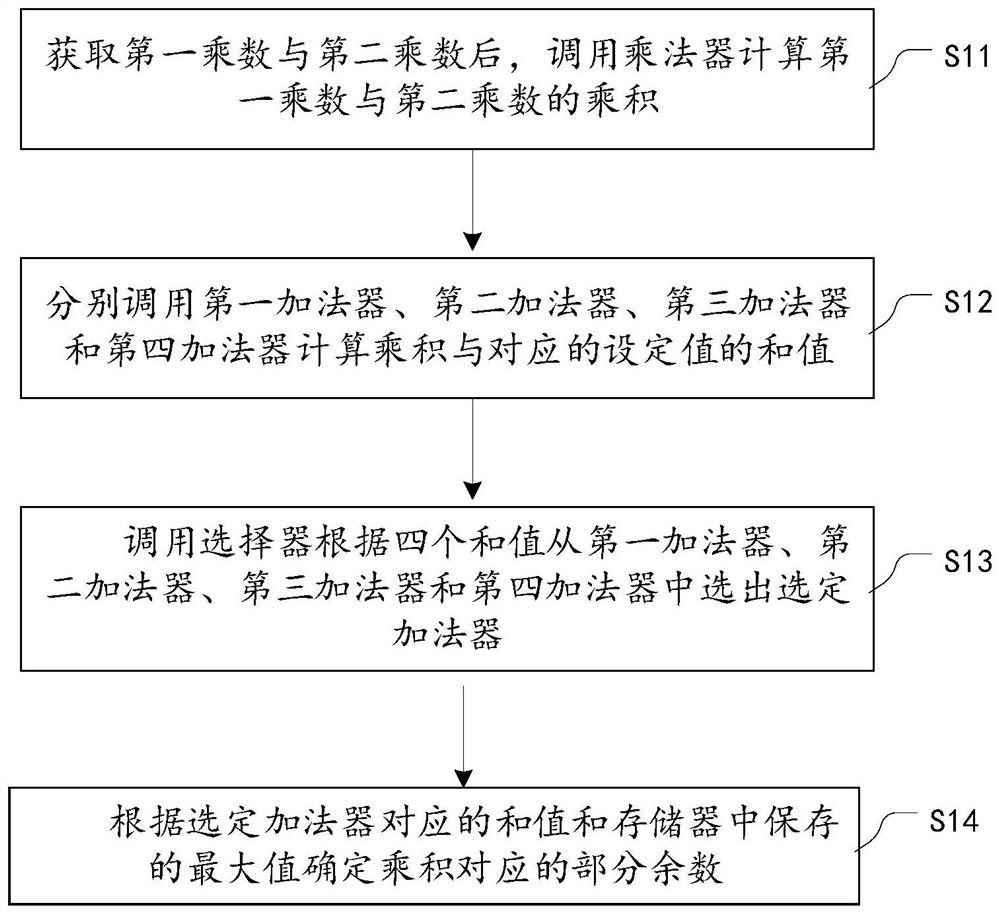
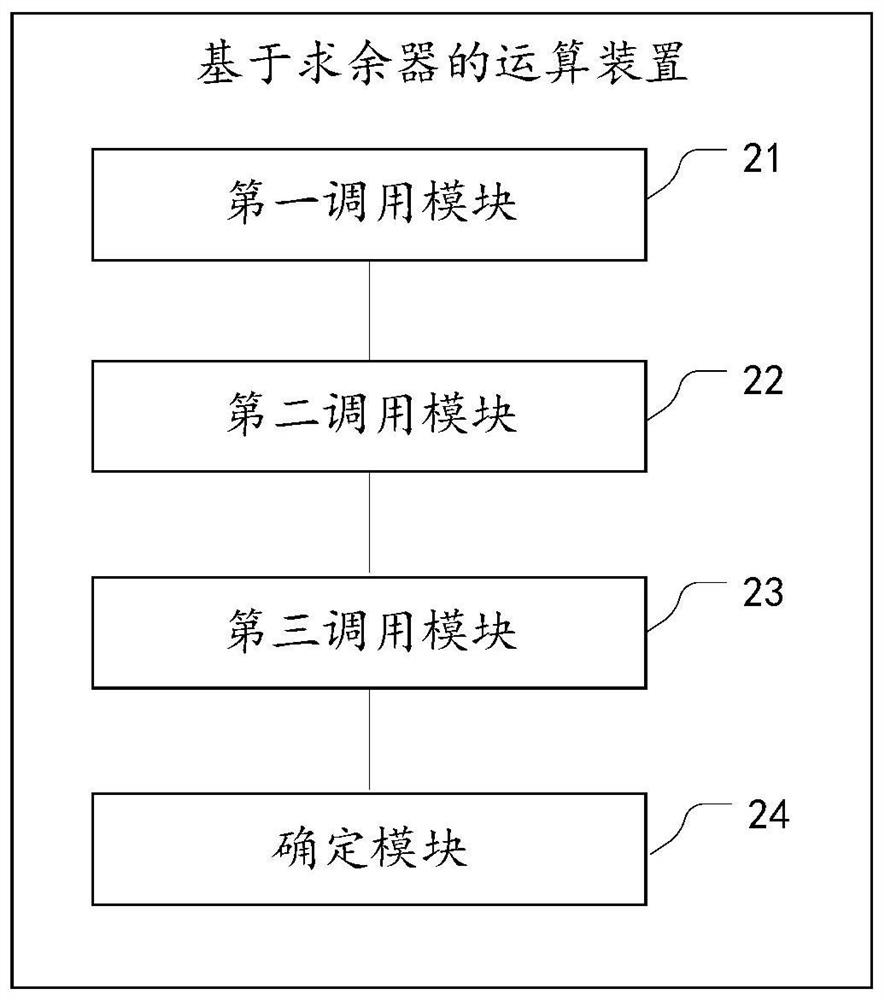
Calculation method and device based on remainder
ActiveCN109947393BReduce computing pressureImprove computing efficiencyComputation using non-contact making devicesBinary multiplierControl theory
Owner:AEROSPACE INFORMATION
Flexible accelerator for sparse tensor in convolutional neural network
The invention discloses a system with a multiplication circuit. The multiplication circuit is provided with a plurality of multipliers. Each multiplier of the plurality of multipliers is configured to receive the data value and the weight value to generate a product value in a convolution operation of the machine learning application. The system also includes an accumulator configured to receive the product value from each multiplier of the plurality of multipliers, and a register bank configured to store an output of the convolution operation. The accumulator is further configured to receive a portion of the values stored in the register bank and combine the received portion of the values with the product values to generate a combined value. The register bank is further configured to replace the portion of values with the combined values.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Method and system for high-speed multiplication
InactiveUS7191203B2Proceed very rapidlyComputation using non-contact making devicesBit pairingBinary multiplier
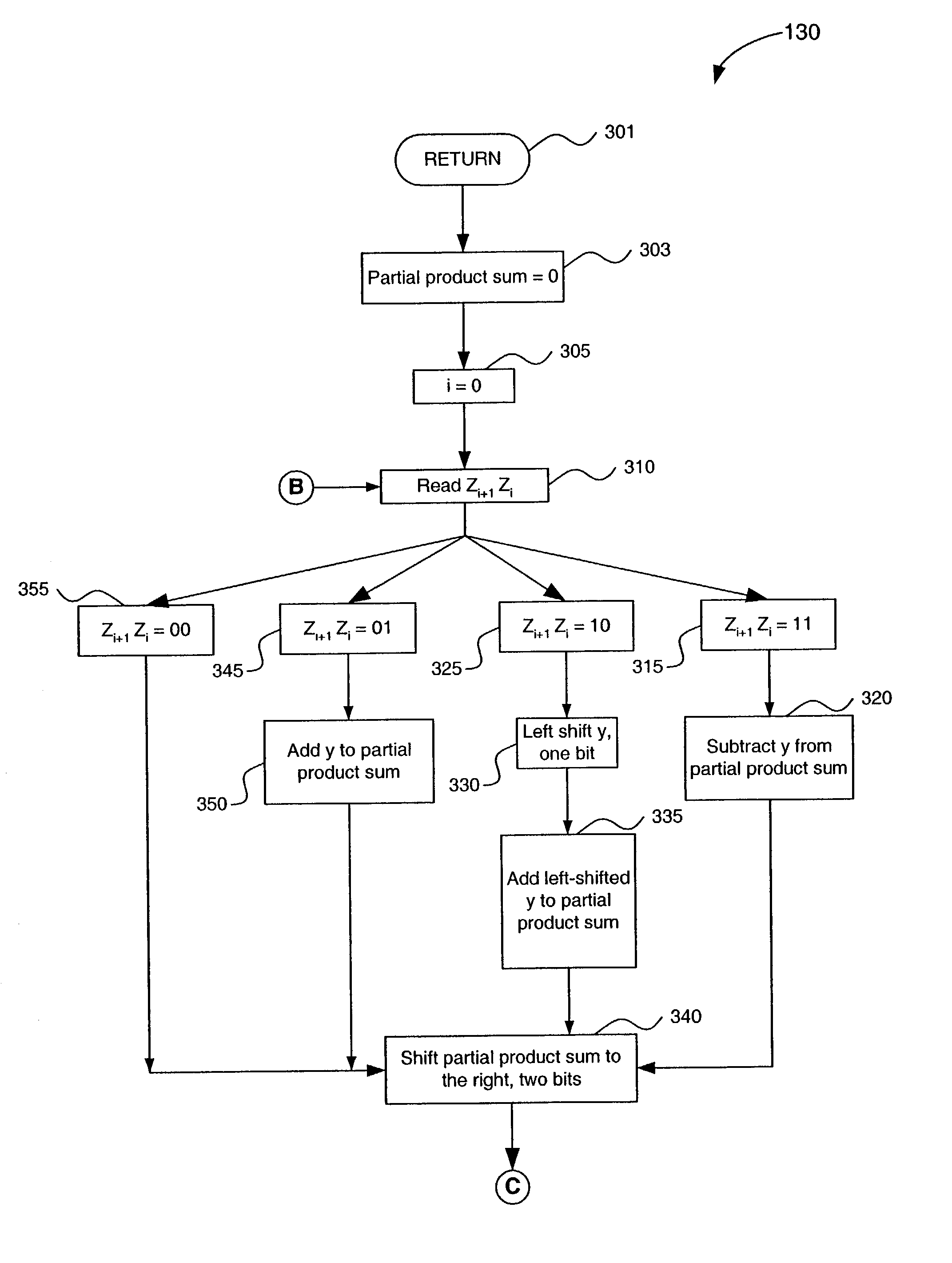
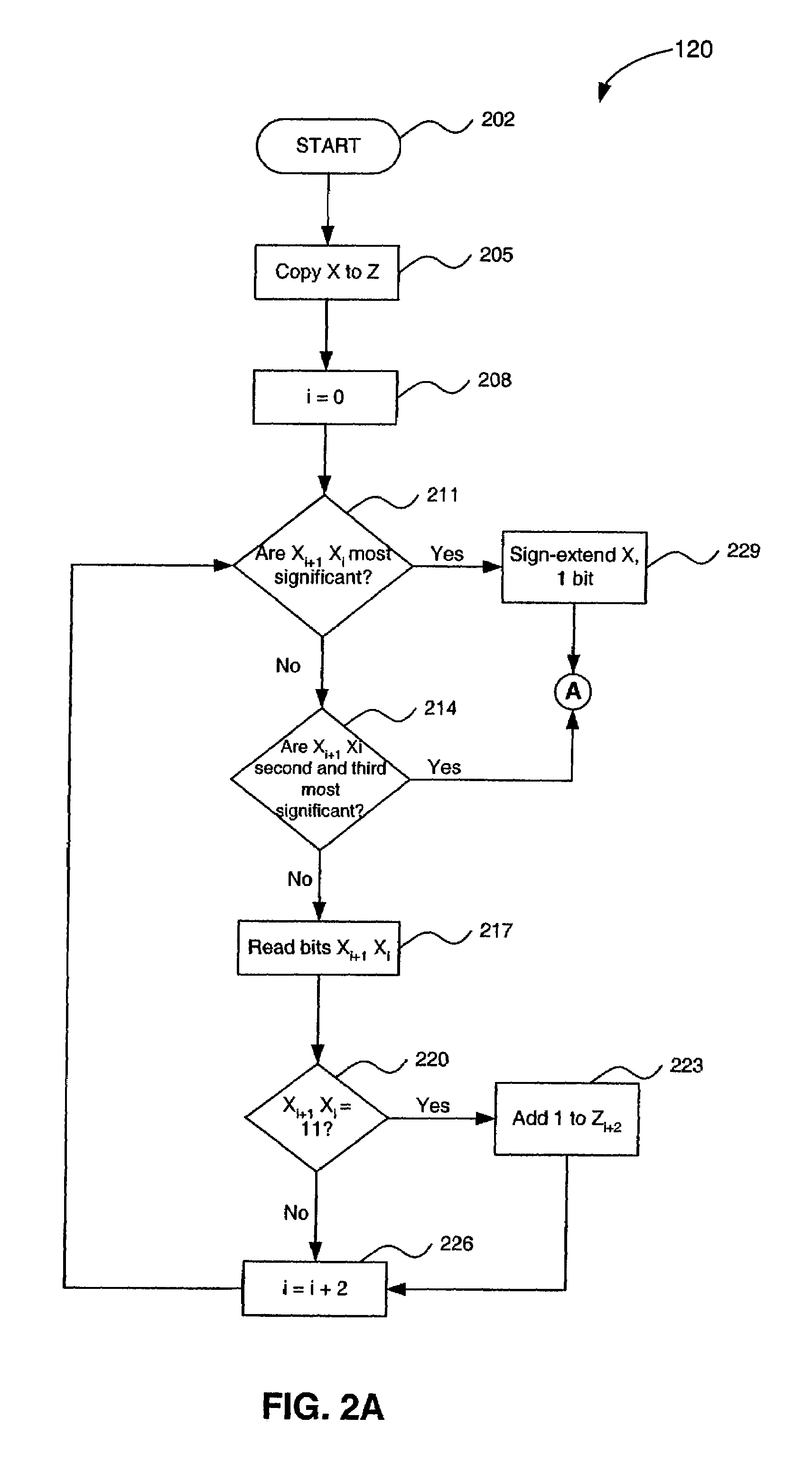
A system, method, and computer product for high-speed multiplication of binary numbers. A multiplier X is first encoded, and the encoded multiplier is then used in a multiplication process that yields the product. The encoding is performed in a manner that allows the actual multiplication process to proceed quickly. X is copied into a variable Z. Z is then manipulated to form the coded version of the multiplier. The bits of the multiplier X are read two at a time, starting with the least significant two bits. If the bit pair Xi+1Xi is equal to 11, then 1 is added to Zi+2. The process continues for successive non-overlapping pairs of bits, until the most significant three bits of X are reached. These last three bits are encoded using a table look-up process.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
Method and apparatus for performing multiplication in finite field GF(2n)
InactiveUS7539719B2Computation using non-contact making devicesDigital computer detailsComputational physicsMechanical engineering
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
A sparse model, reconstruction method and dictionary training method for multidimensional signals
ActiveCN106097278BReduce complexityReduce storage spaceImage enhancementImage analysisSparse modelRound complexity
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
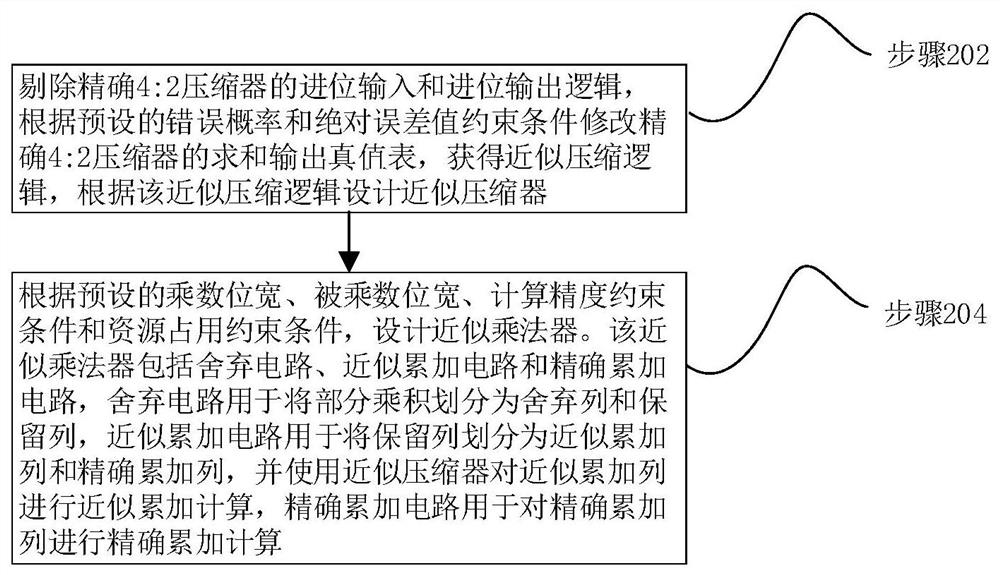
Approximate multiplier design method, approximate multiplier and FIR filter
PendingCN111695313AEnsure calculation accuracyEnsuring Resource Utilization EfficiencyDigital technique networkDigital data processing detailsBinary multiplierControl engineering
The invention relates to an approximate multiplier design method, an approximate multiplier and an FIR filter. The method comprises the following steps: eliminating carry input and carry output logicsof an accurate 4: 2 compressor, modifying a summation output truth table of the accurate 4: 2 compressor according to a preset average absolute error value constraint condition to obtain approximatecompression logics, and designing the approximate compressor according to the approximate compression logics; designing an approximate multiplier according to a preset multiplier bit width, a preset multiplicand bit width, a preset calculation precision constraint condition and a preset resource occupation constraint condition. According to the method, transmission delay in a partial product compression process is eliminated; an approximate compressor with error constraint is designed according to a preset average absolute error value constraint condition; based on the approximate compressor,the multiplier structure with the most balanced error performance and resource occupation performance is selected to design the approximate multiplier, and the calculation accuracy and resource utilization efficiency of the approximate multiplier based on compression calculation logic modification can be ensured.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com