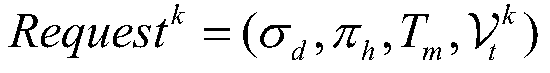Patents
Literature
39 results about "Collaborative intelligence" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Collaborative intelligence characterizes multi-agent, distributed systems where each agent, human, or machine is uniquely positioned with autonomy to contribute to a problem-solving network. Collaborative autonomy of organisms in their ecosystems makes evolution possible. Natural ecosystems, where each organism's unique signature is derived from its genetics, circumstances, behavior and position in its ecosystem, offer principles for design of next generation social networks to support collaborative intelligence, crowd-sourcing individual expertise, preferences, and unique contributions in a problem-solving process.
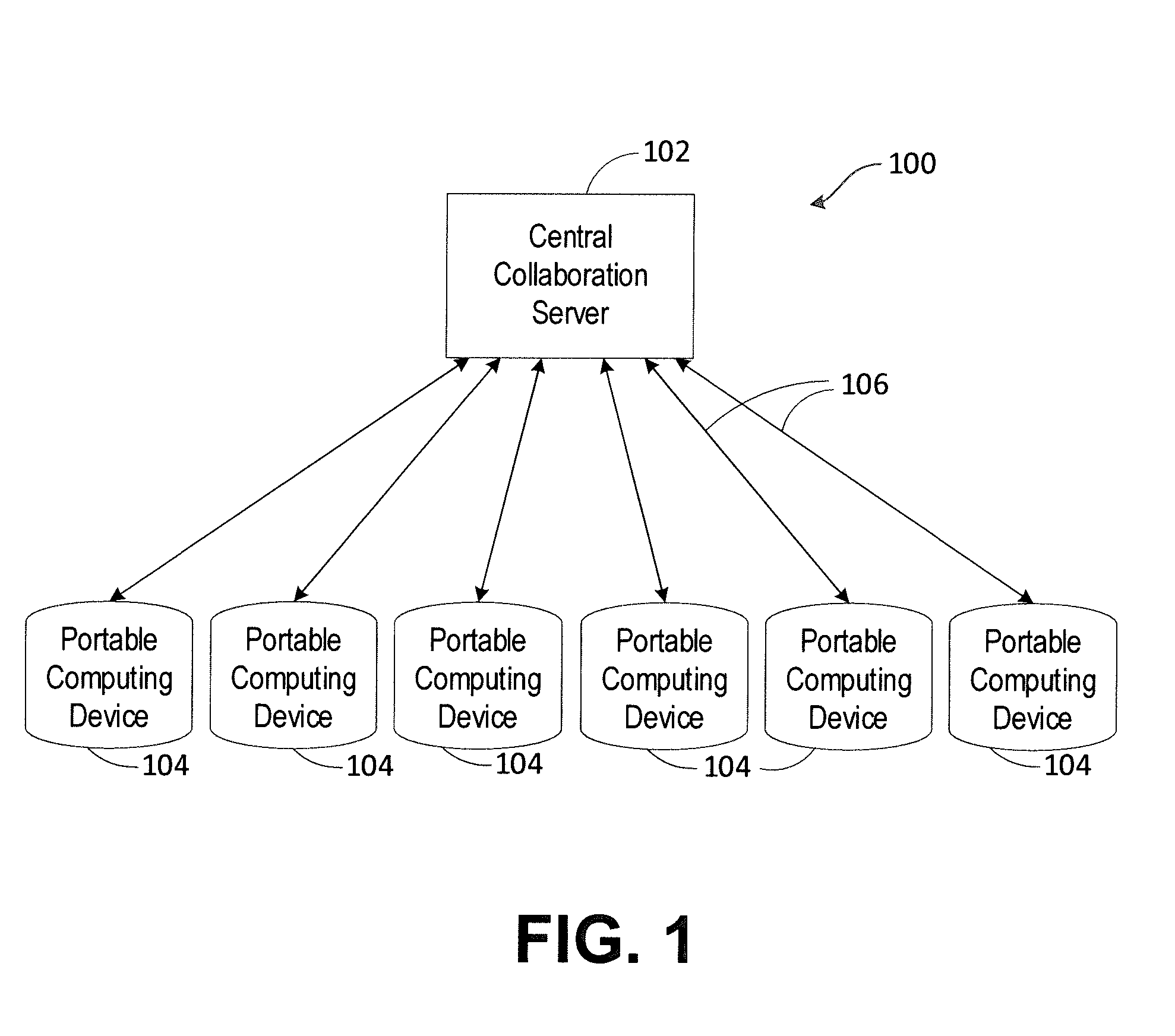
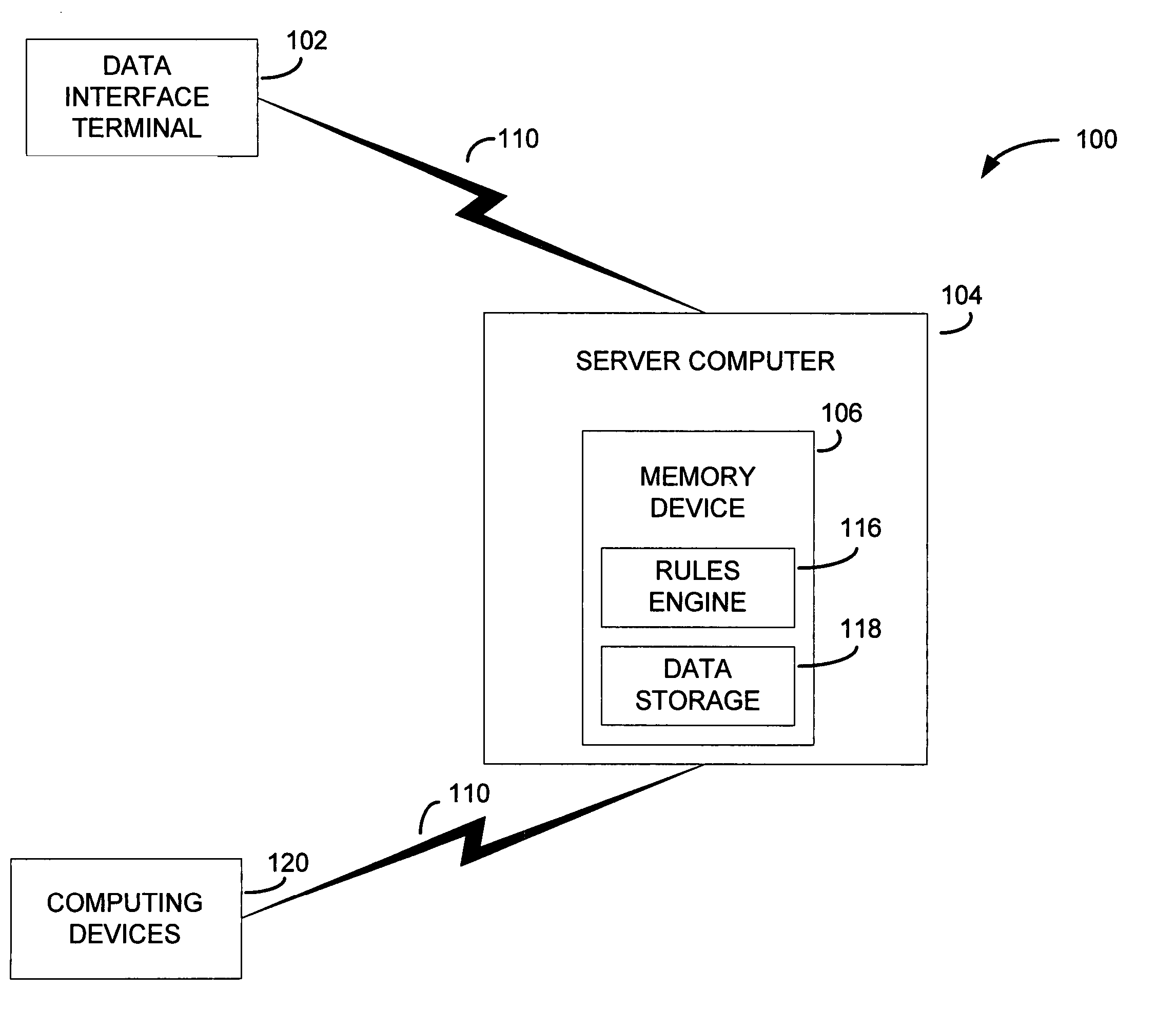
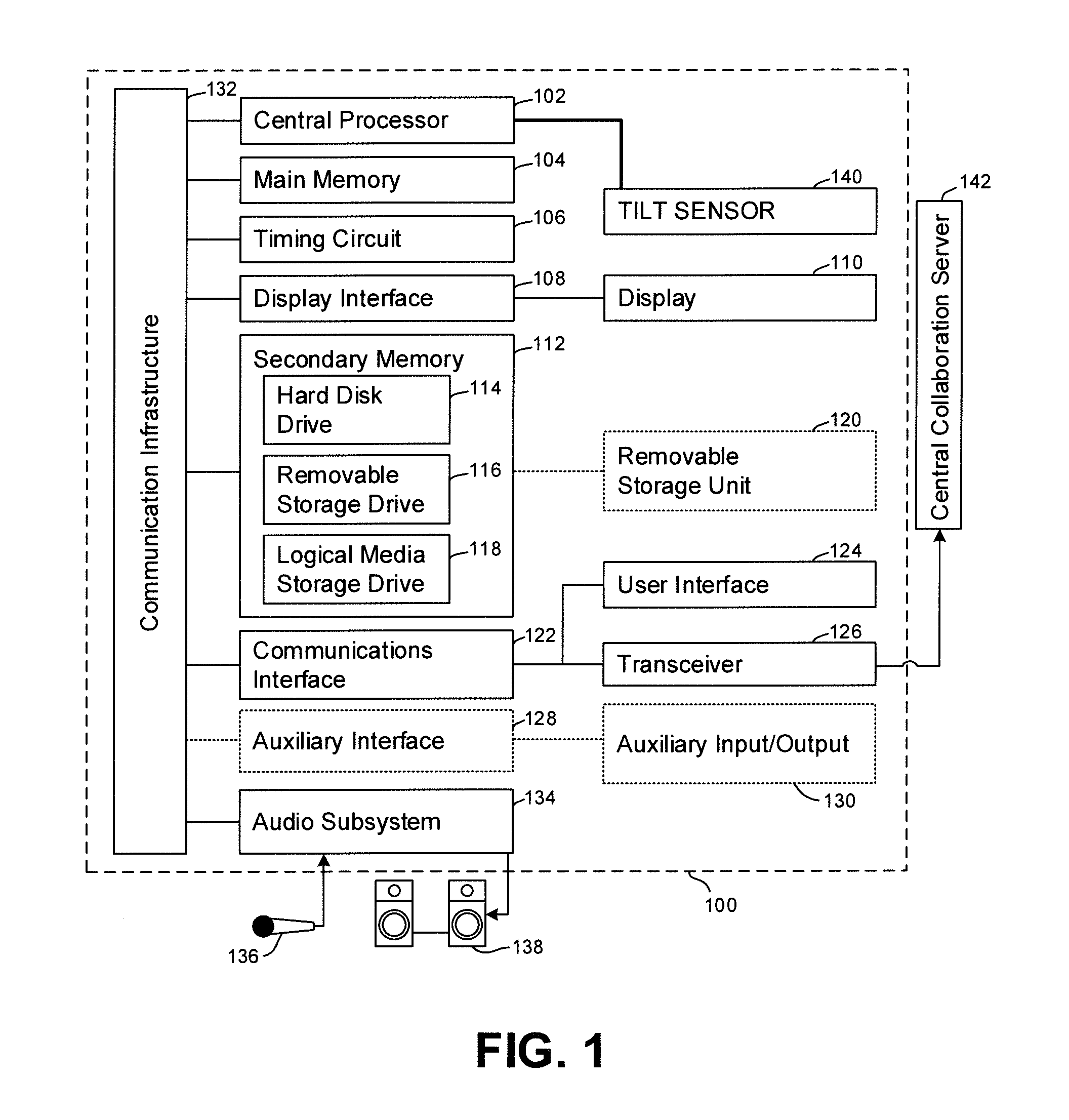
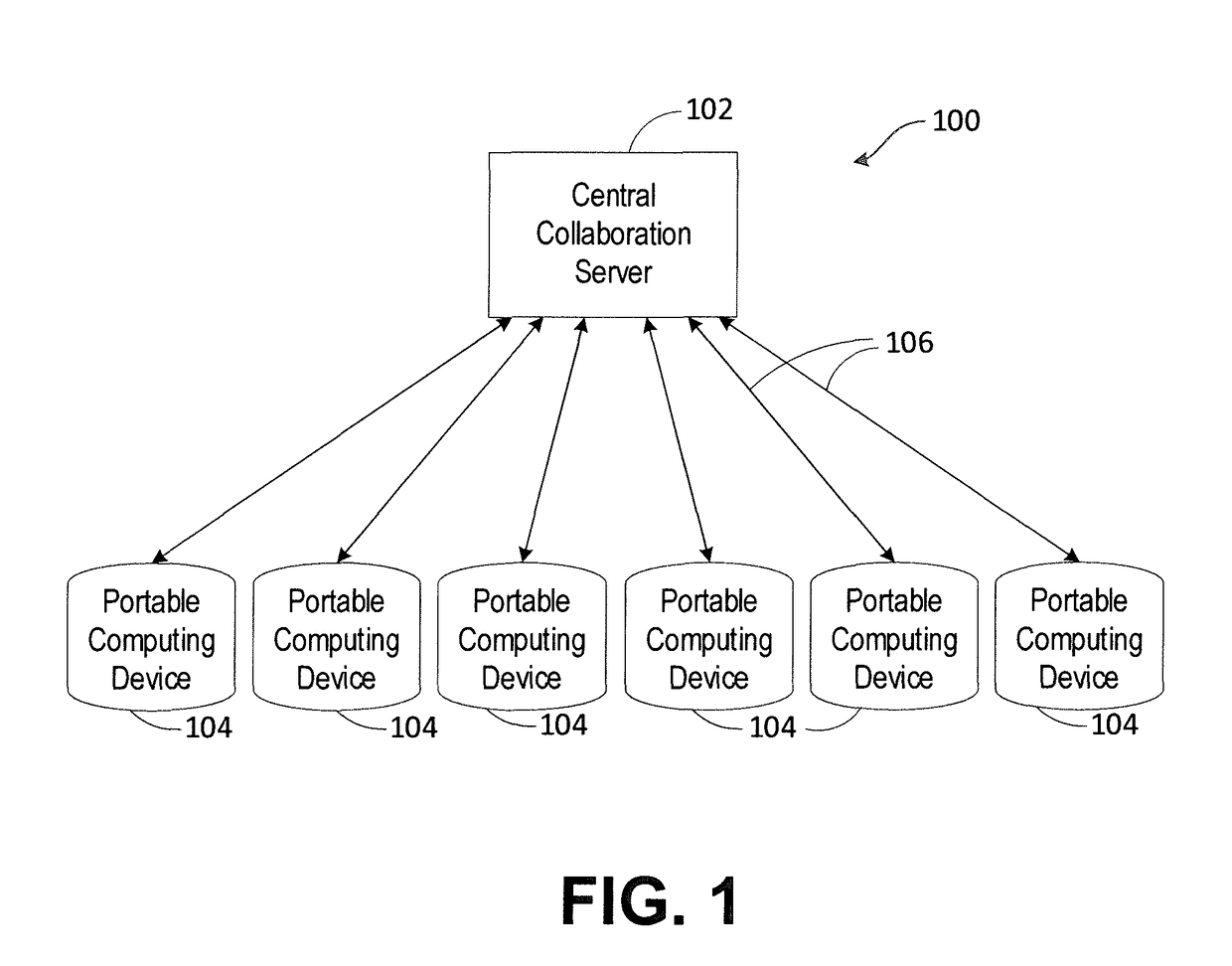
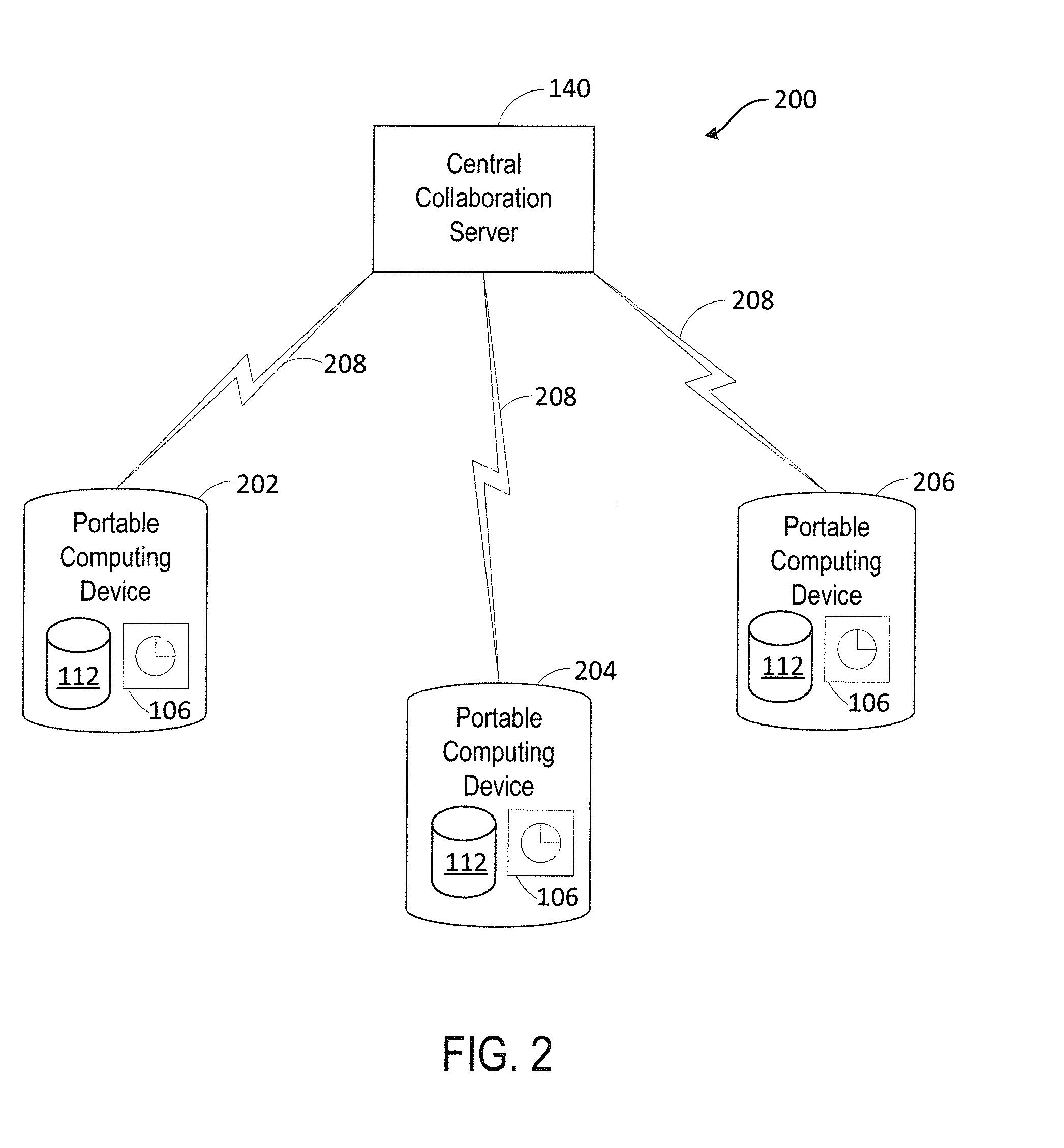
Communications network management
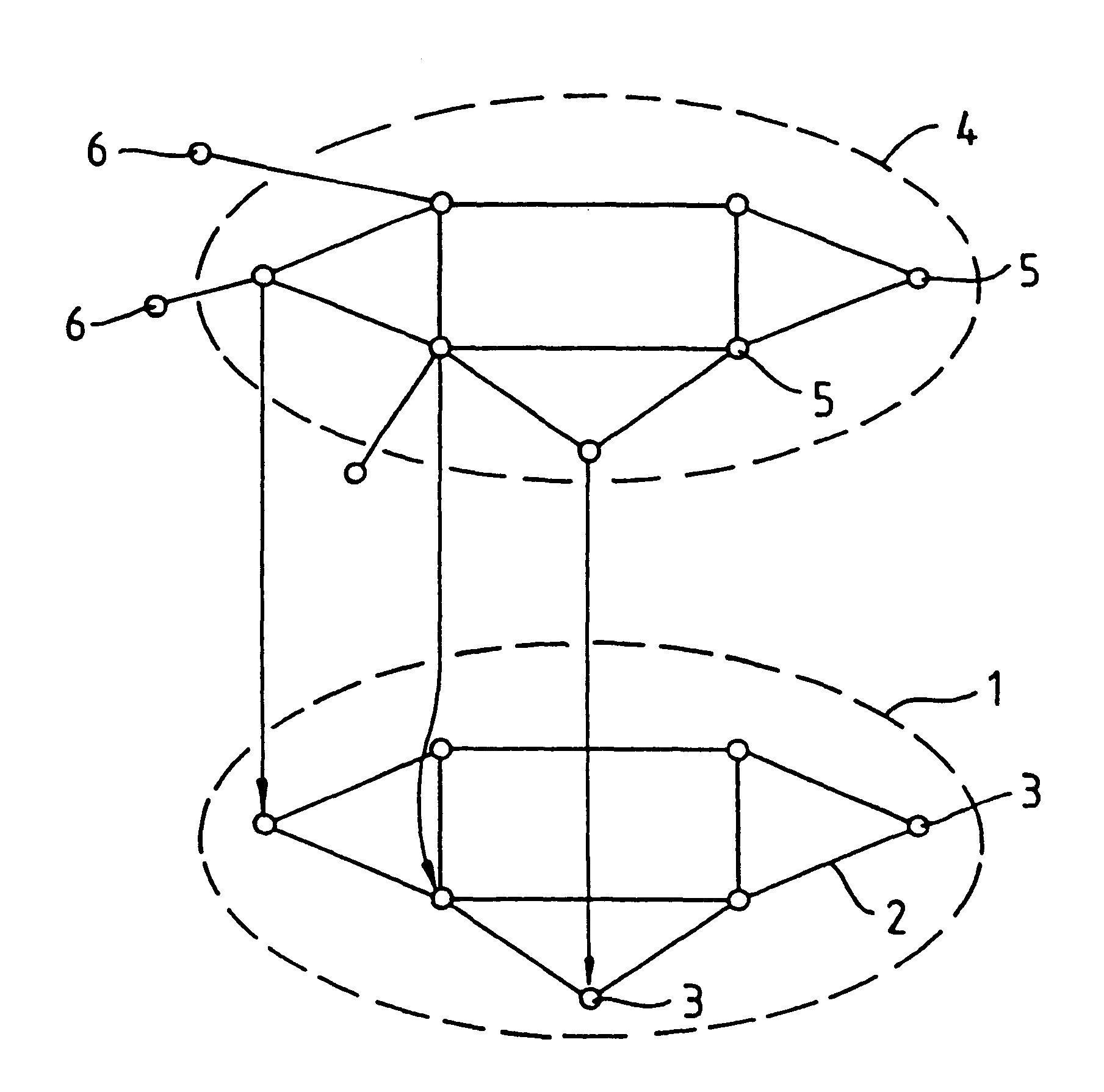
InactiveUS6226273B1Minimize consequencesCarry-out quicklyMultiplex system selection arrangementsSpecial service provision for substationNetwork managementService networks
A communications network such as a Global Multi Service Network is provided with a management system which includes a distributed control system. The distributed control system is an open community of co-operation intelligent software agents which individually have control, or responsibility for managing, one or more nodes of the communications network. There are software agents of more than one type and the service management agents which have control over nodes of the network enter a negotiation process with customer agents in the provision of new services, so as to meet the constraints of both customer requirements and the interest of the relevant service provider. In the event of agent failure, the service management agents initiate a bidding process to reallocate the responsibilities of a failed agent.
Owner:BRITISH TELECOMM PLC
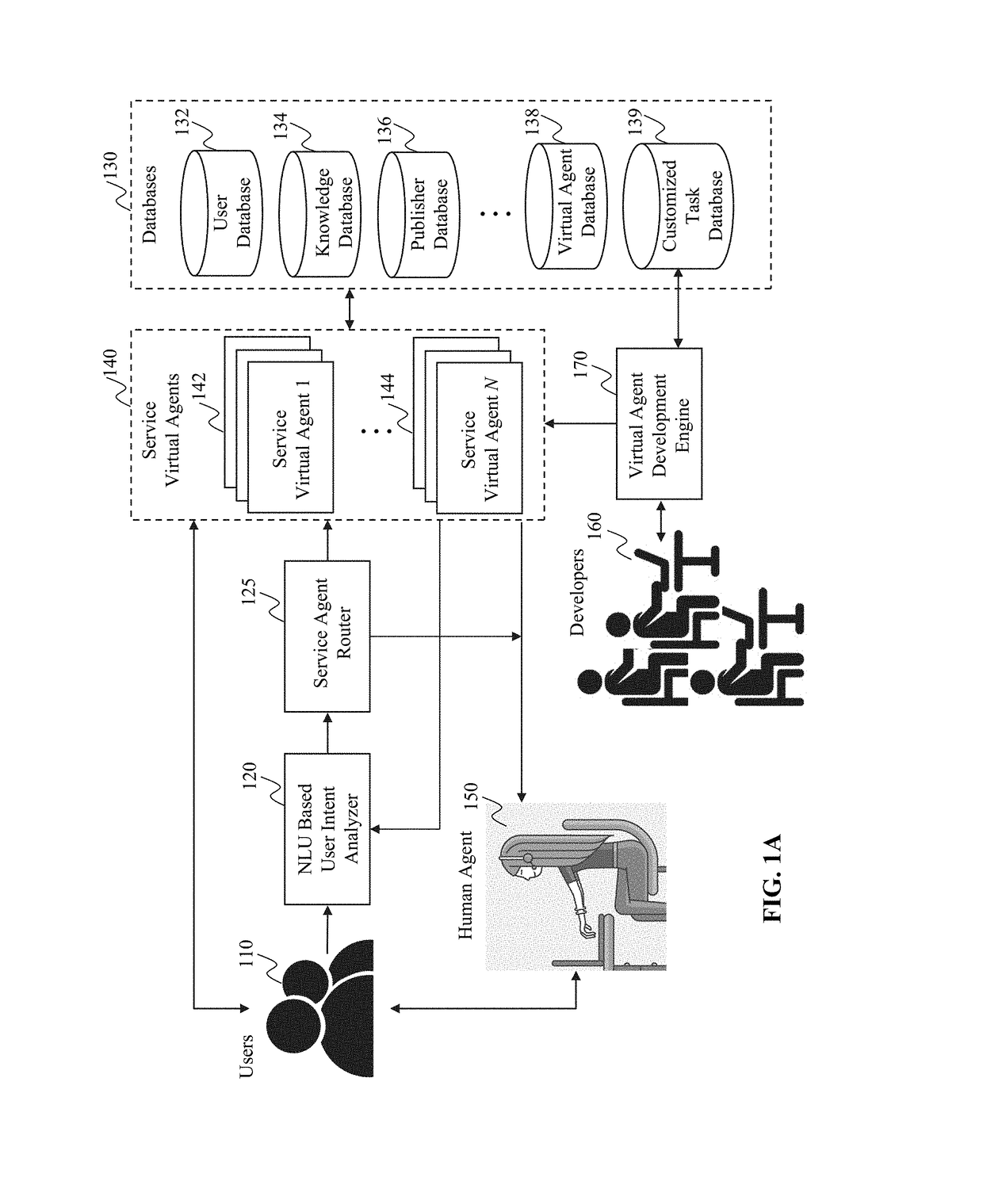
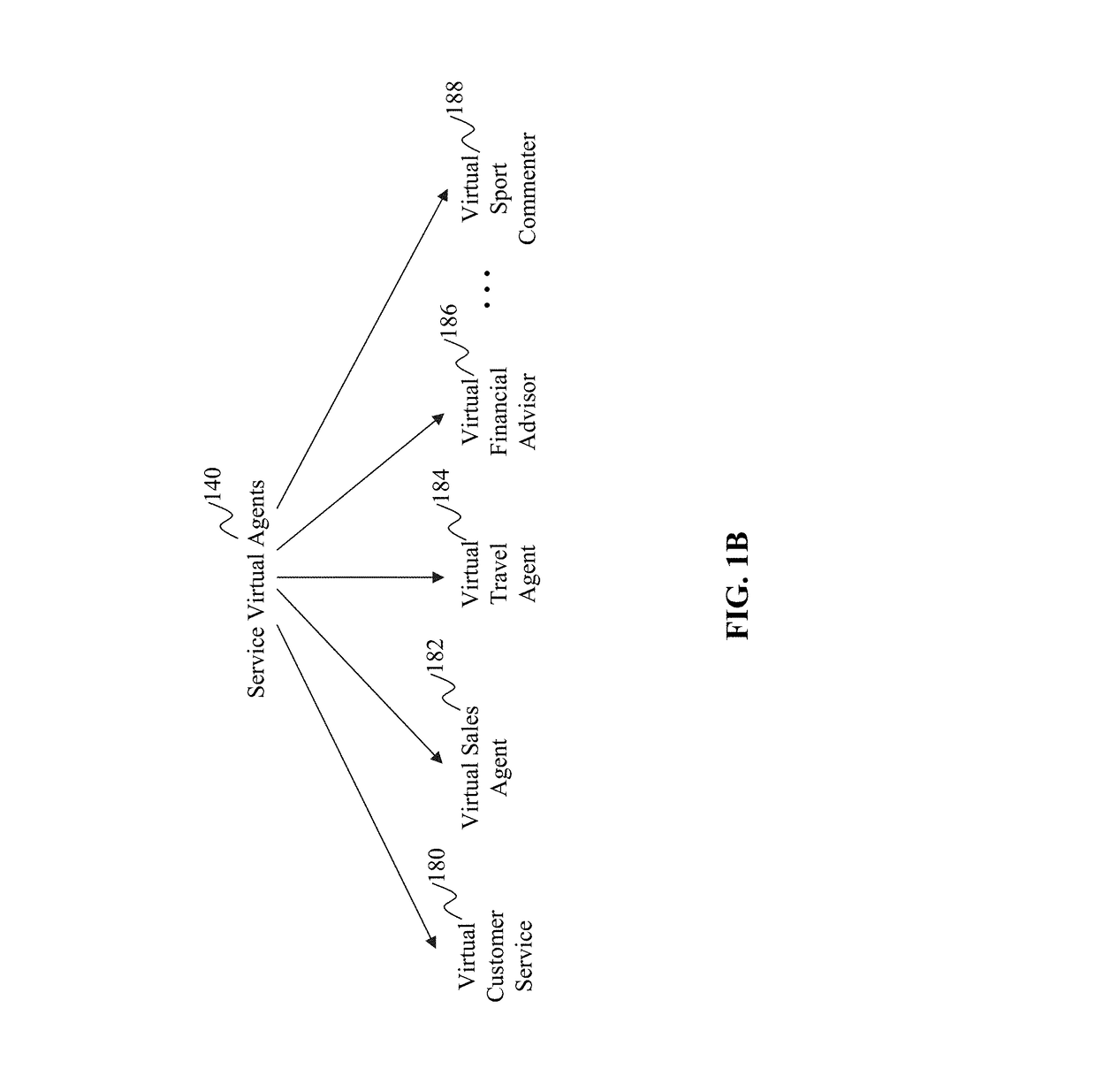
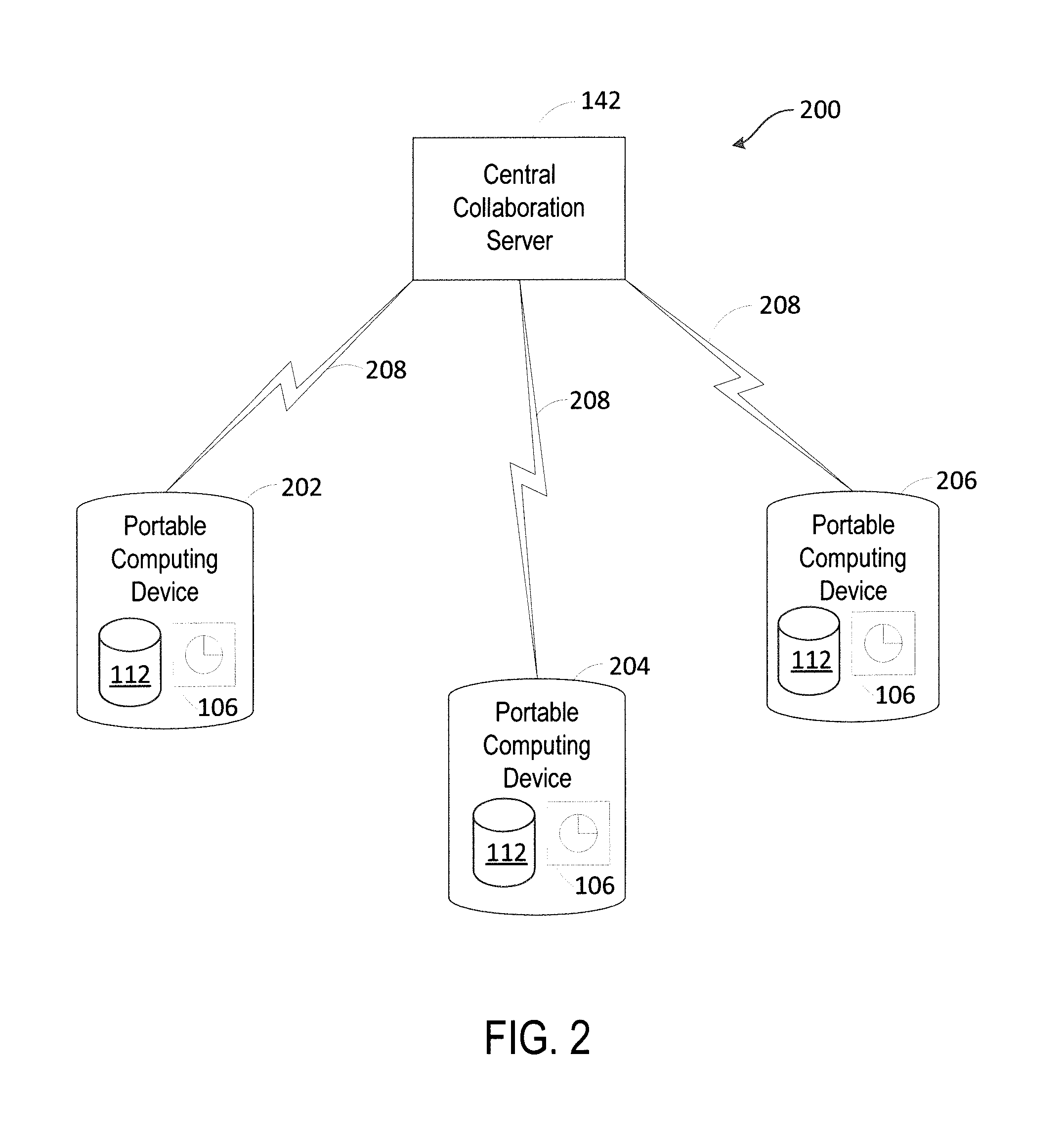
Method and system for collaborative intelligent virtual agents
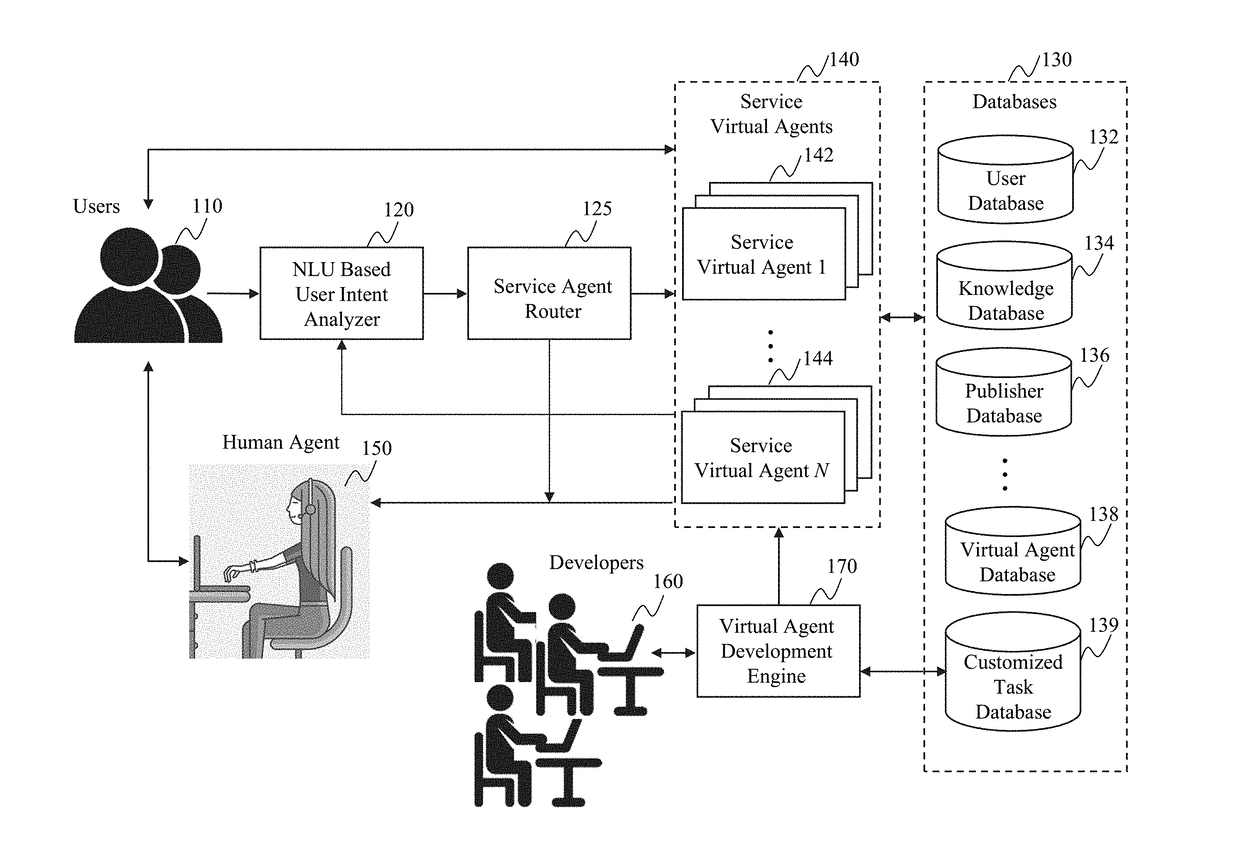
The present teaching relates to method, system, and medium of automatic re-routing a chat user in a dialog. A request is first received for re-routing the chat user, currently engaged in a dialog involving a first agent, to a second agent. The request comprises relevant information and context of the dialog that gives rise to the re-routing request. Based on the relevant information and the context of the dialog, a re-routing strategy is automatically determined in accordance with re-routing configurations. A second agent to which the chat user is to be re-routed to is then selected based on the re-routing strategy. The chat user is then re-routed to the second agent to continue the dialog.
Owner:RULAI INC
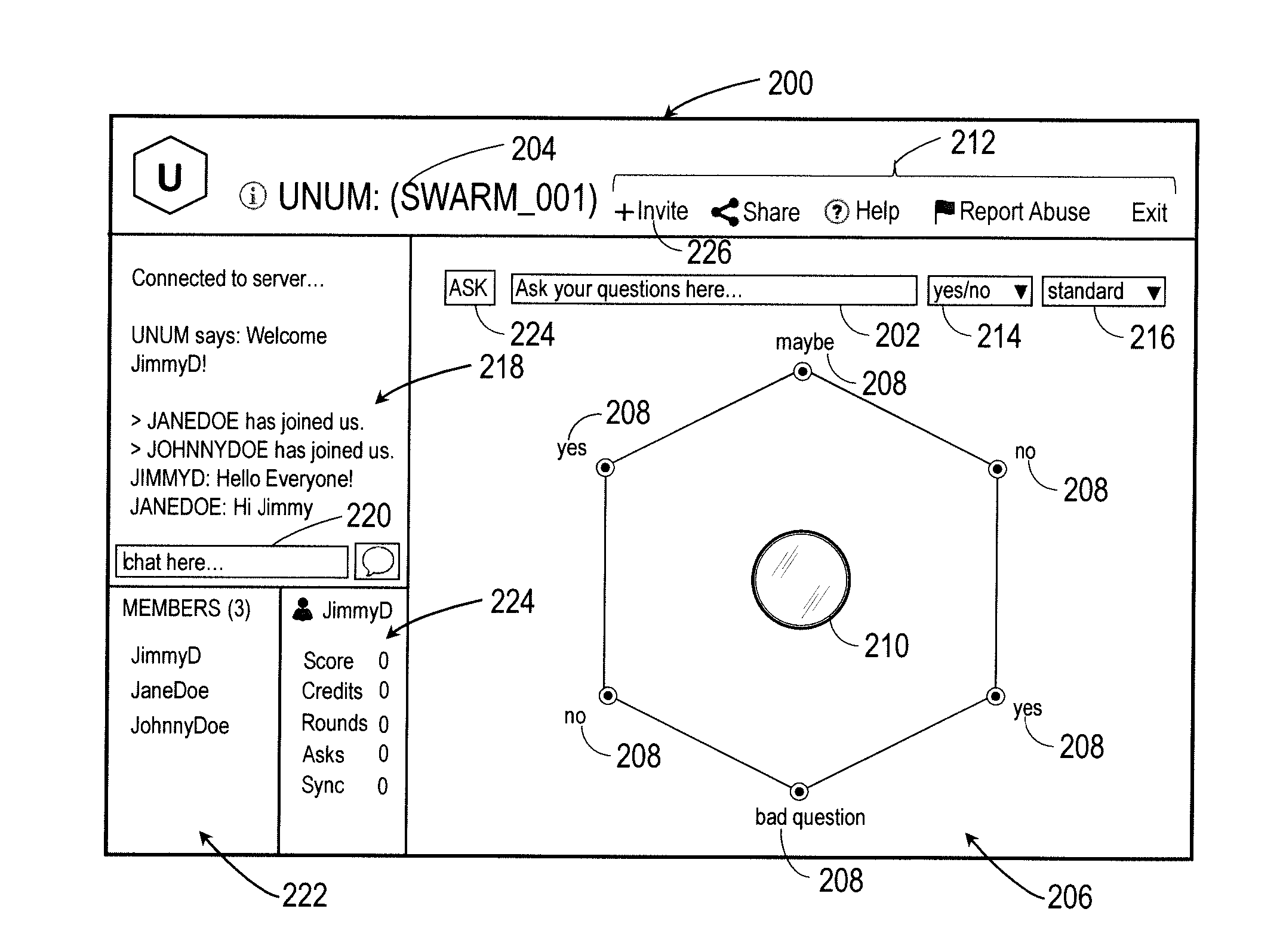
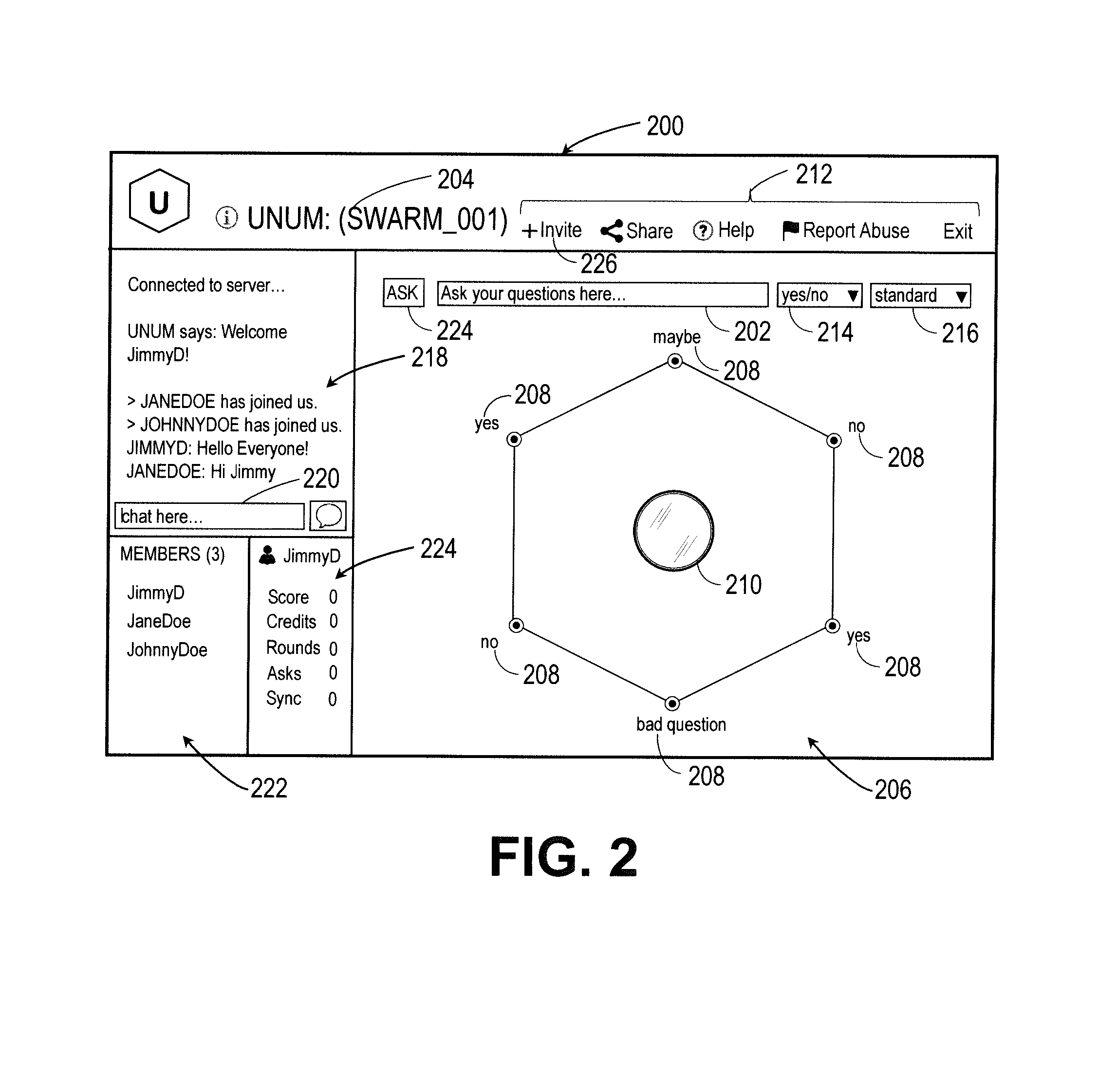
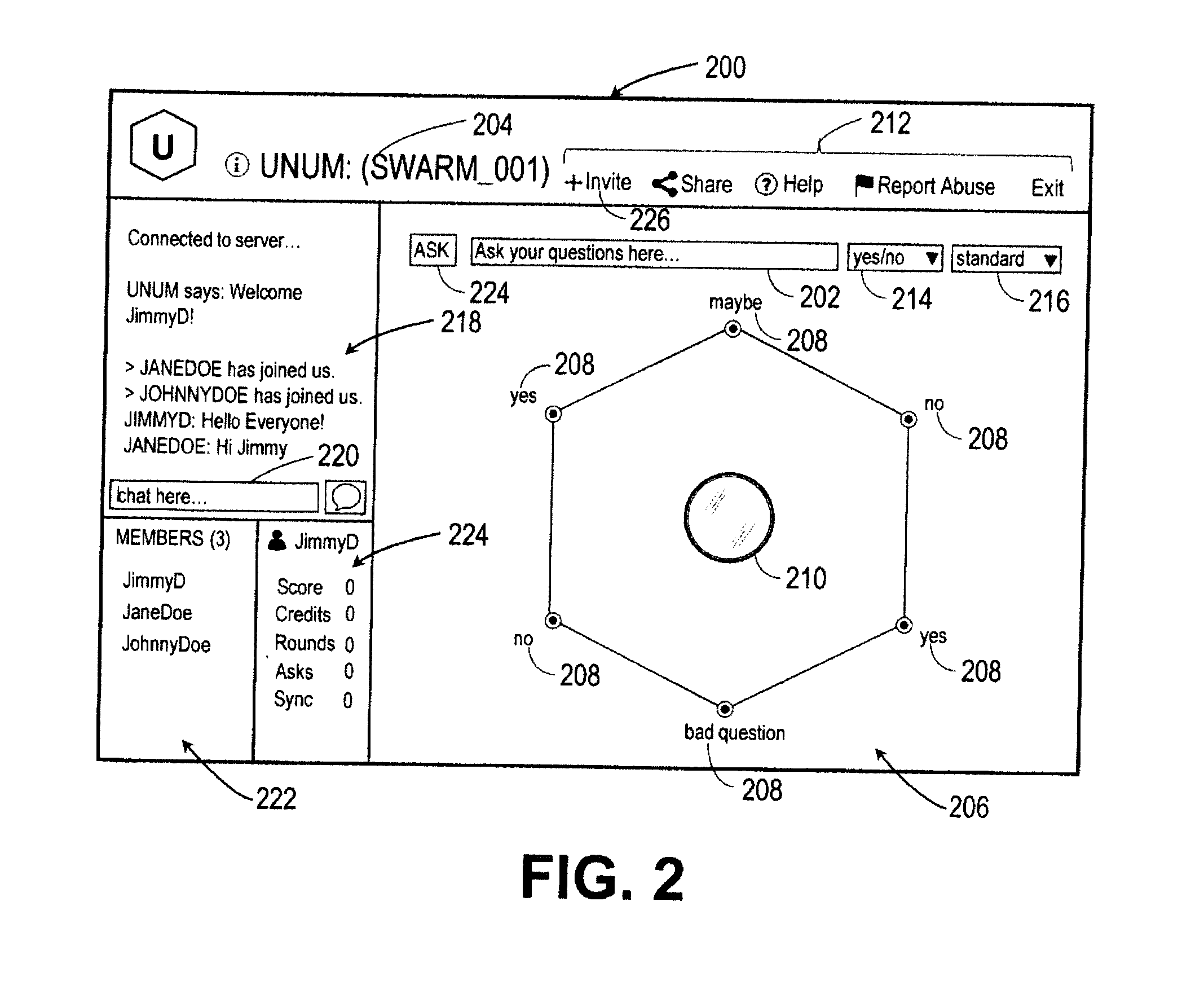
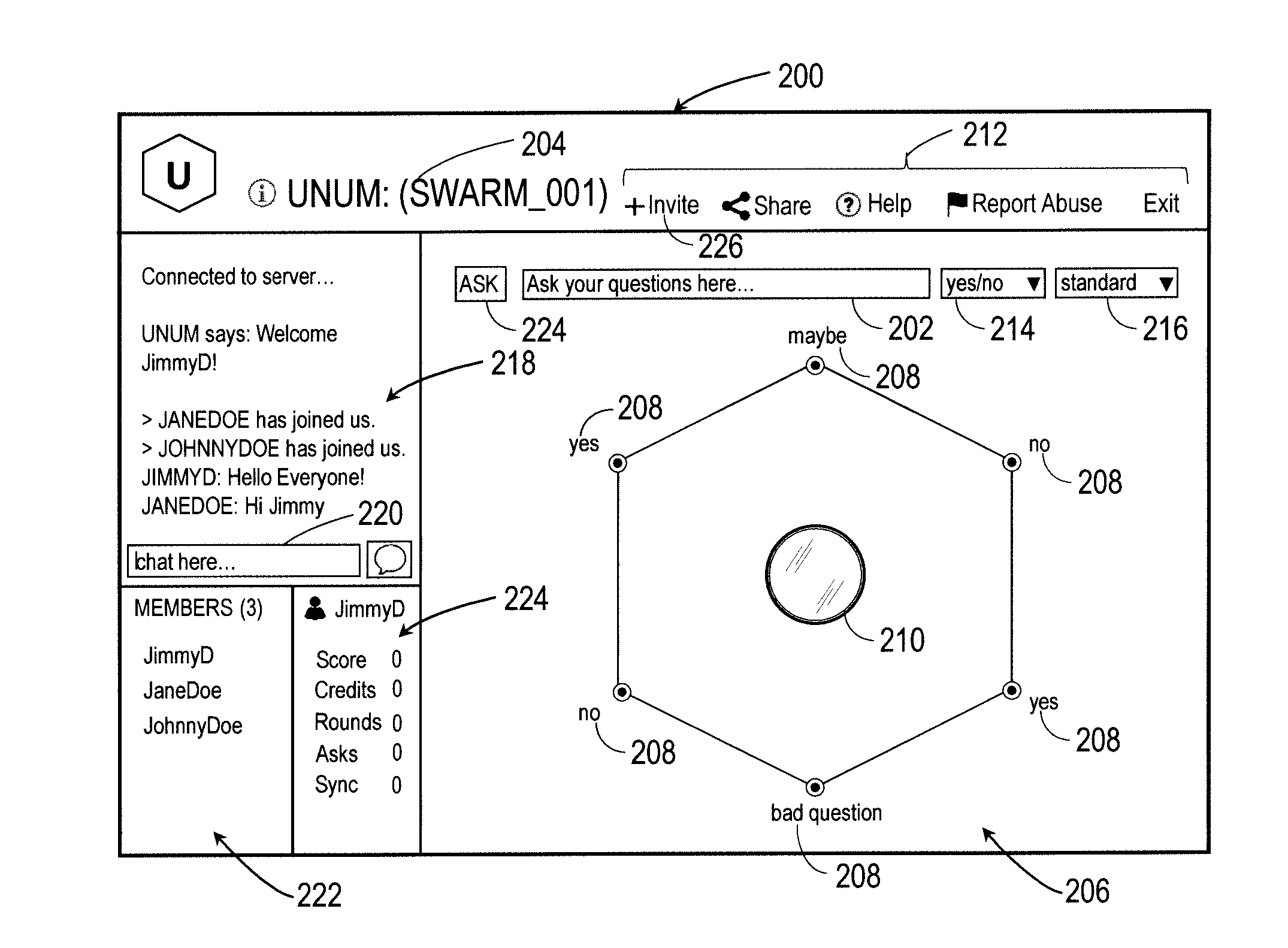
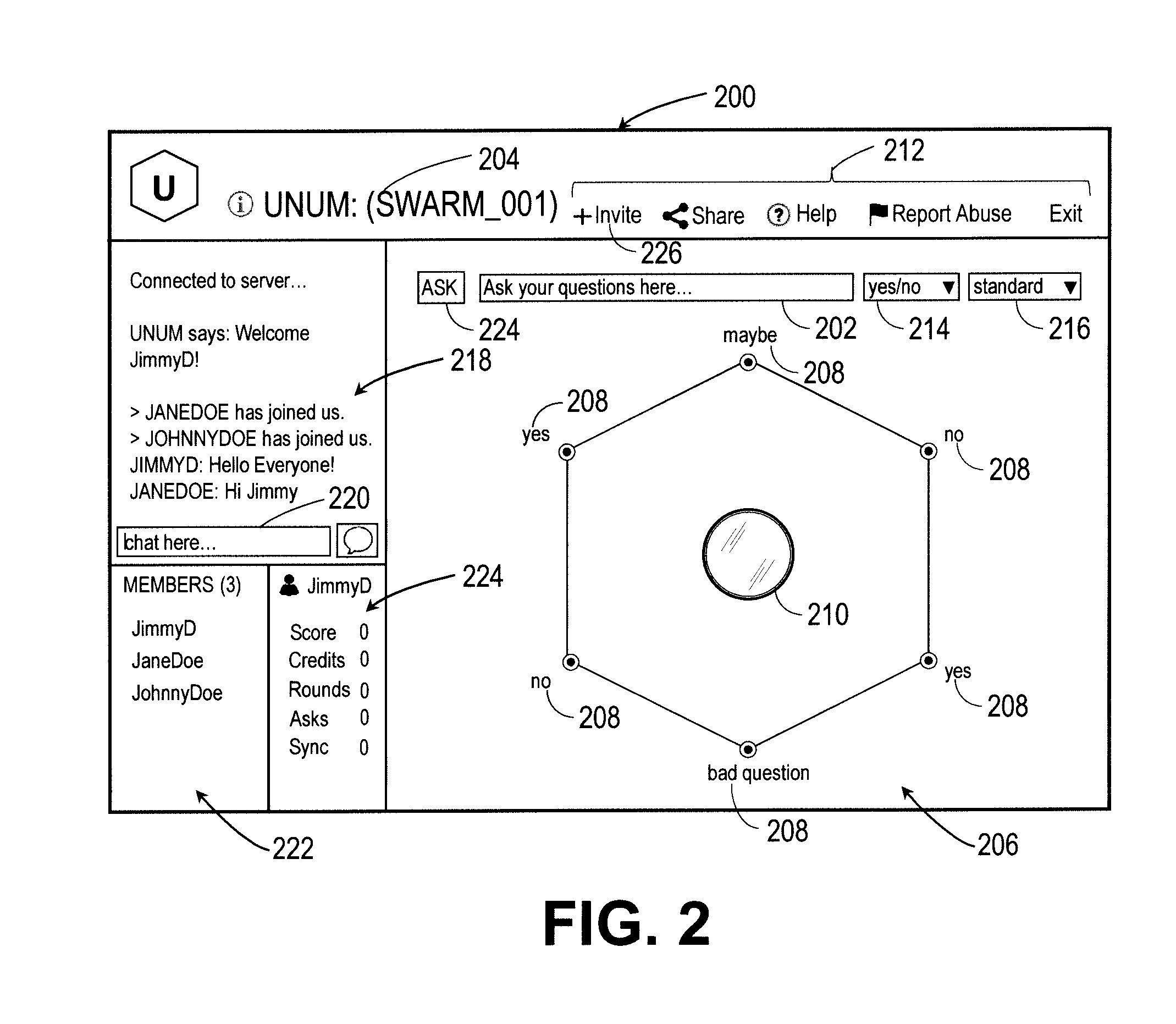
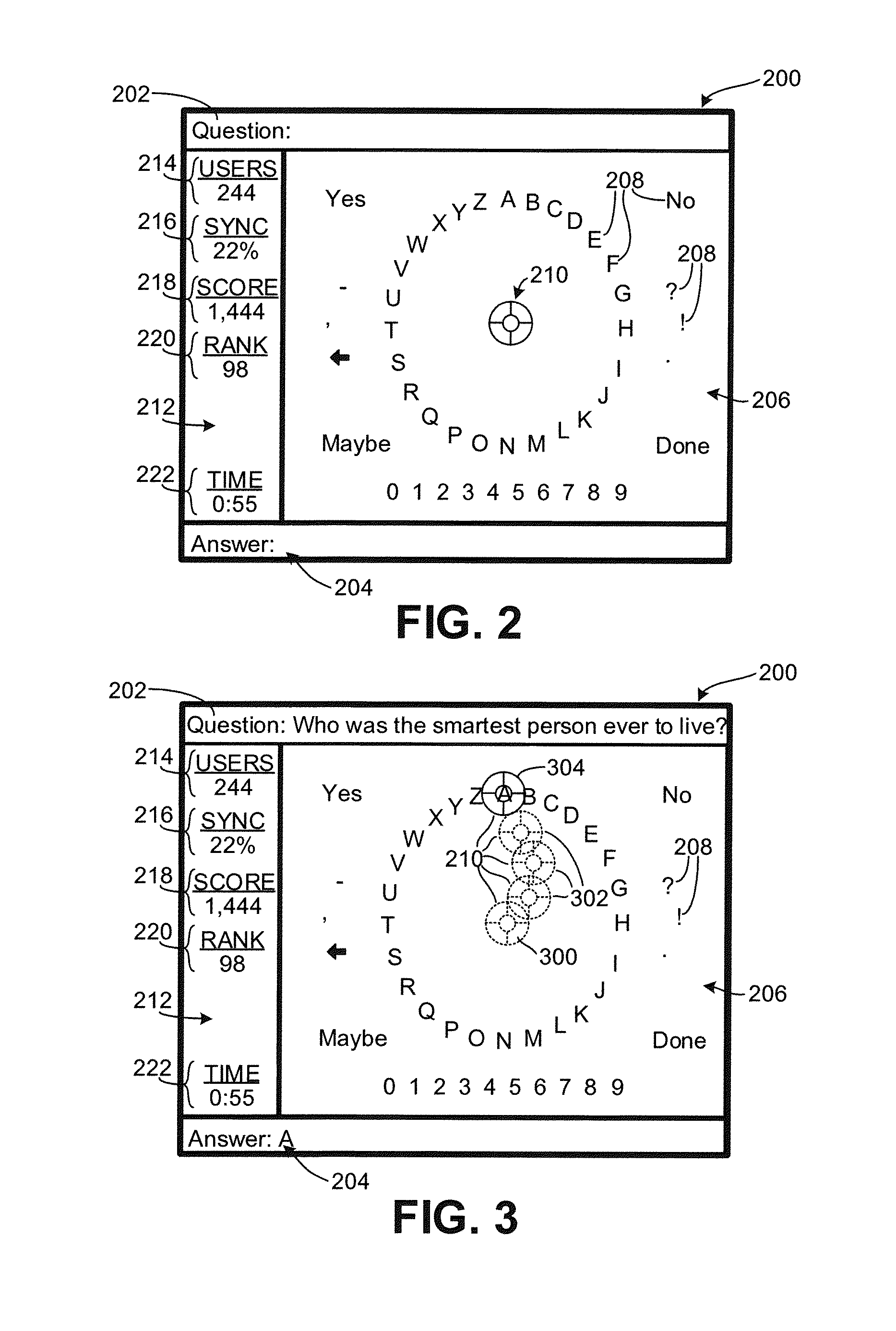
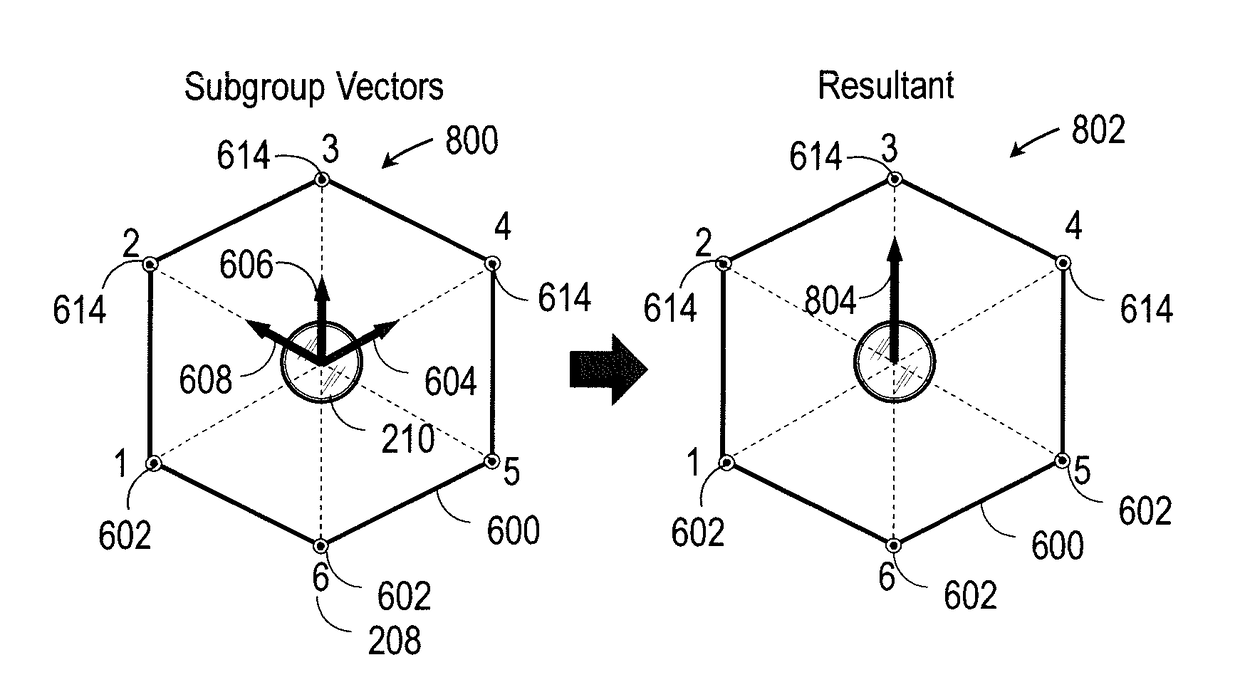
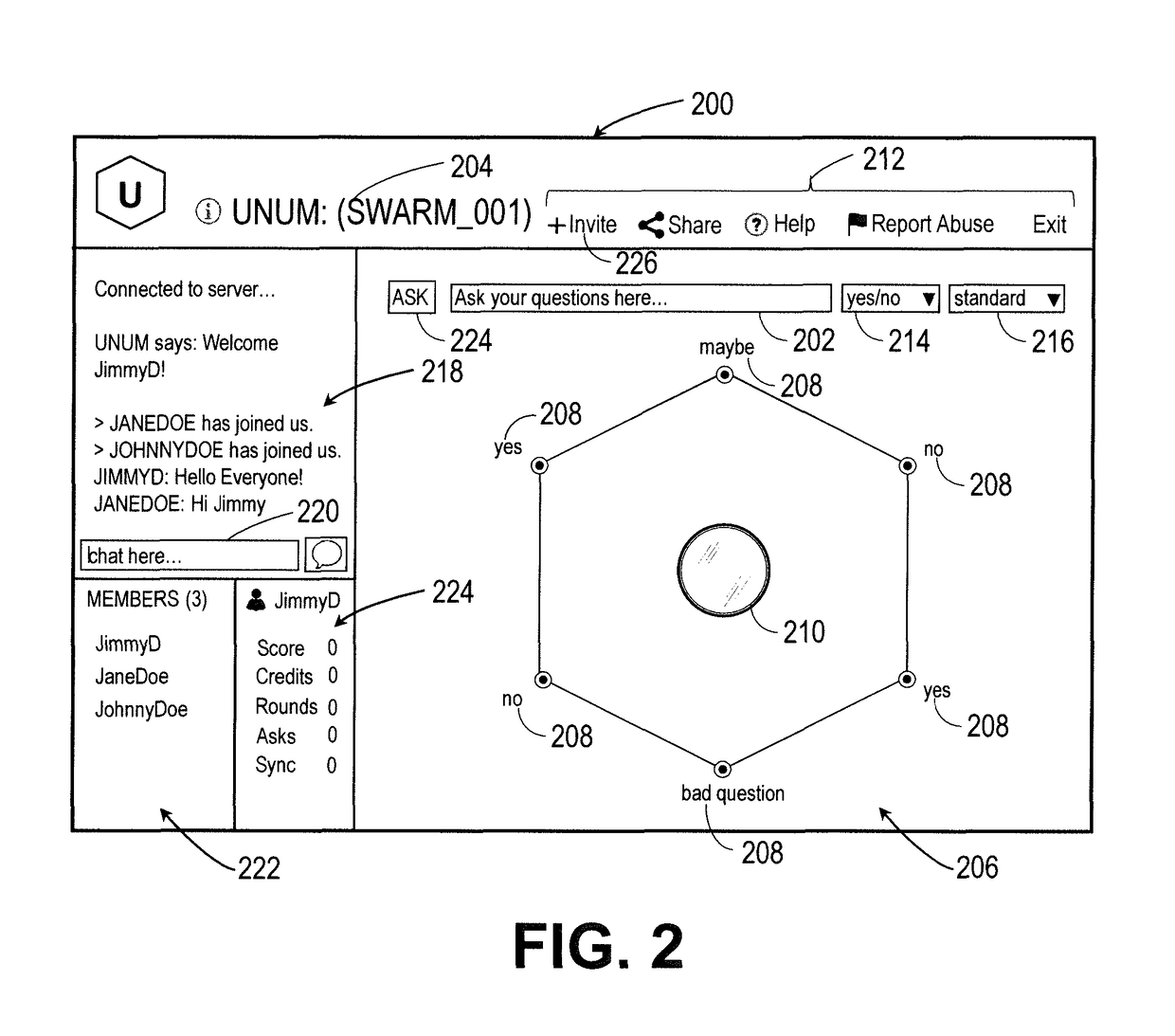
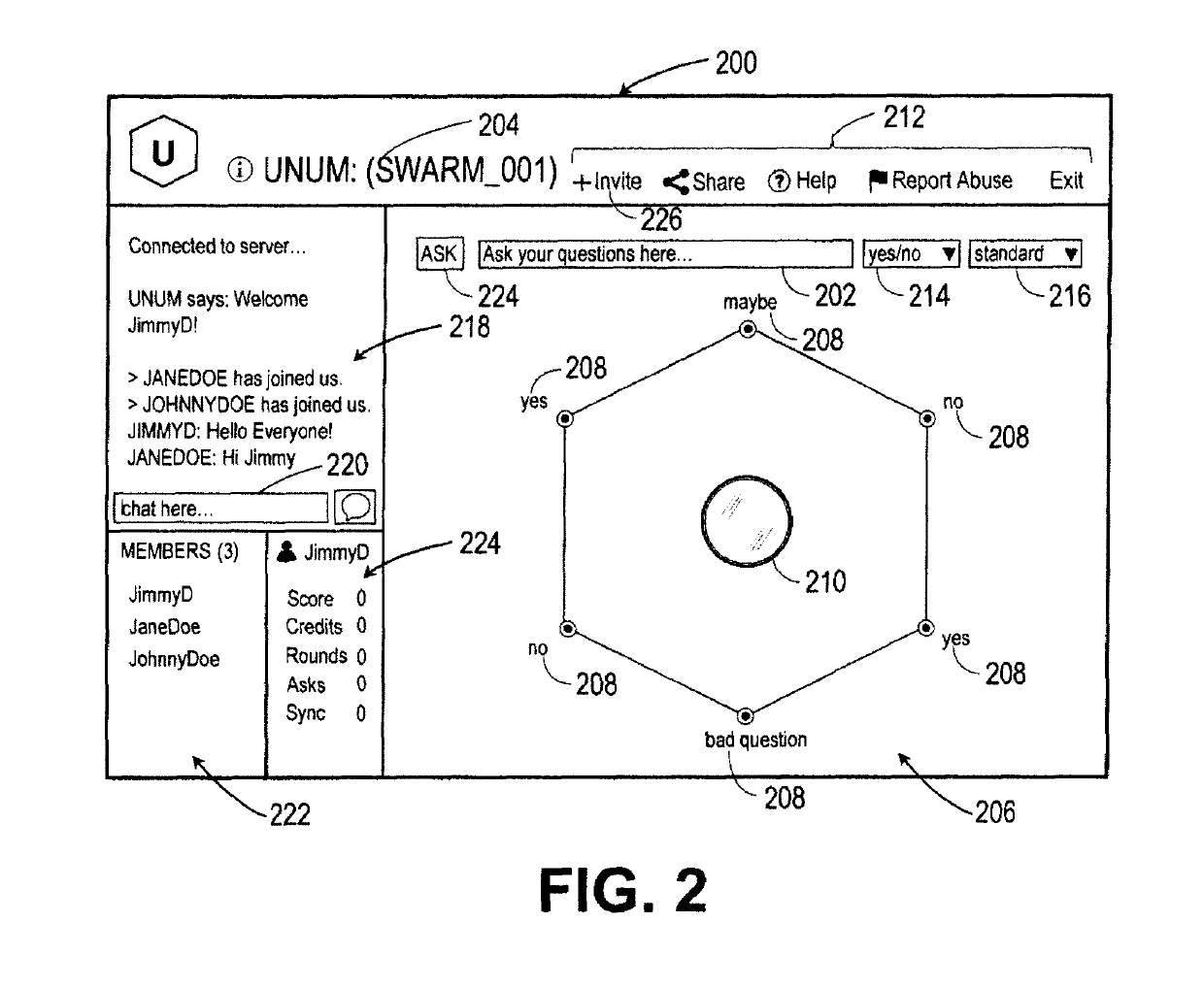
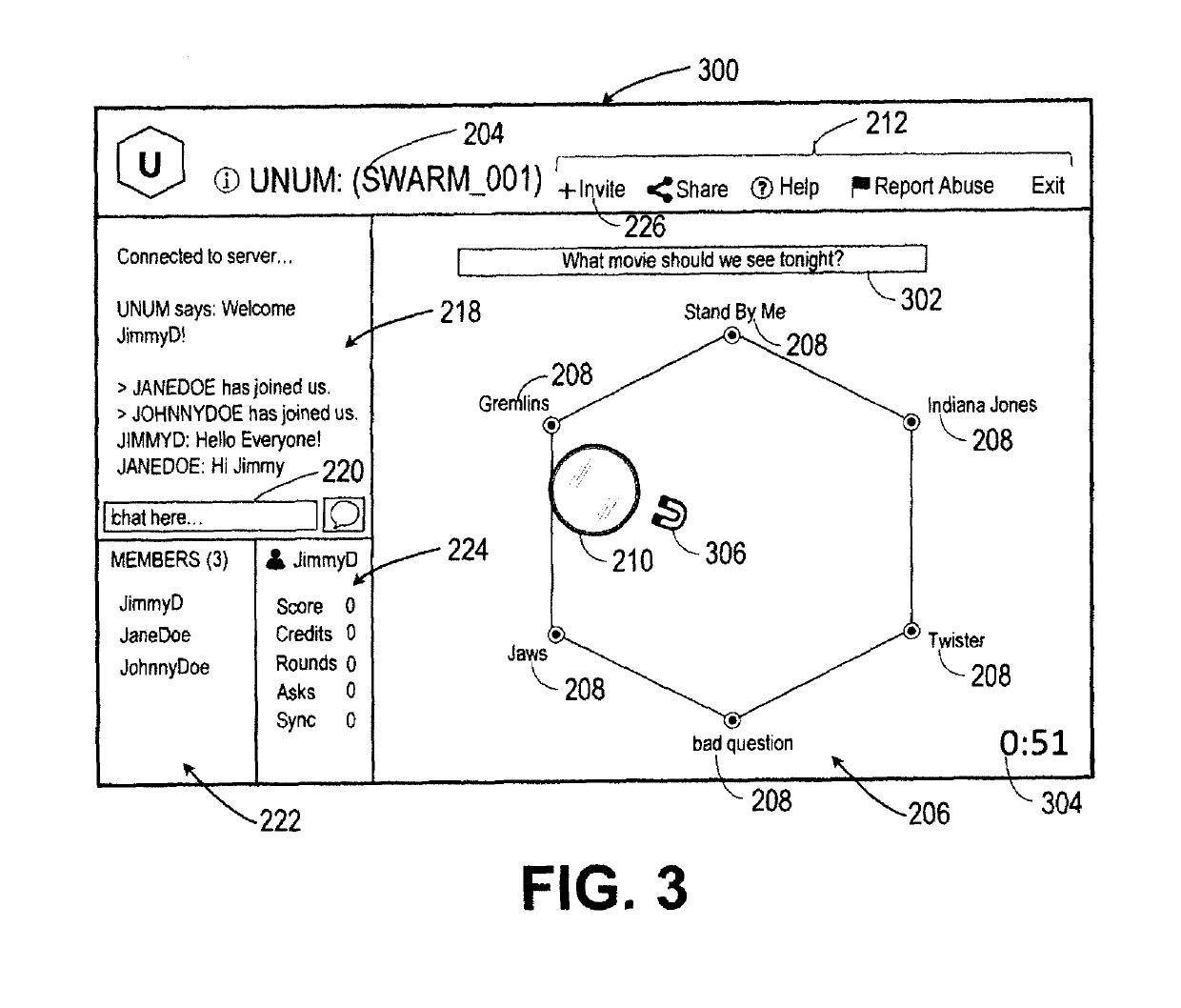
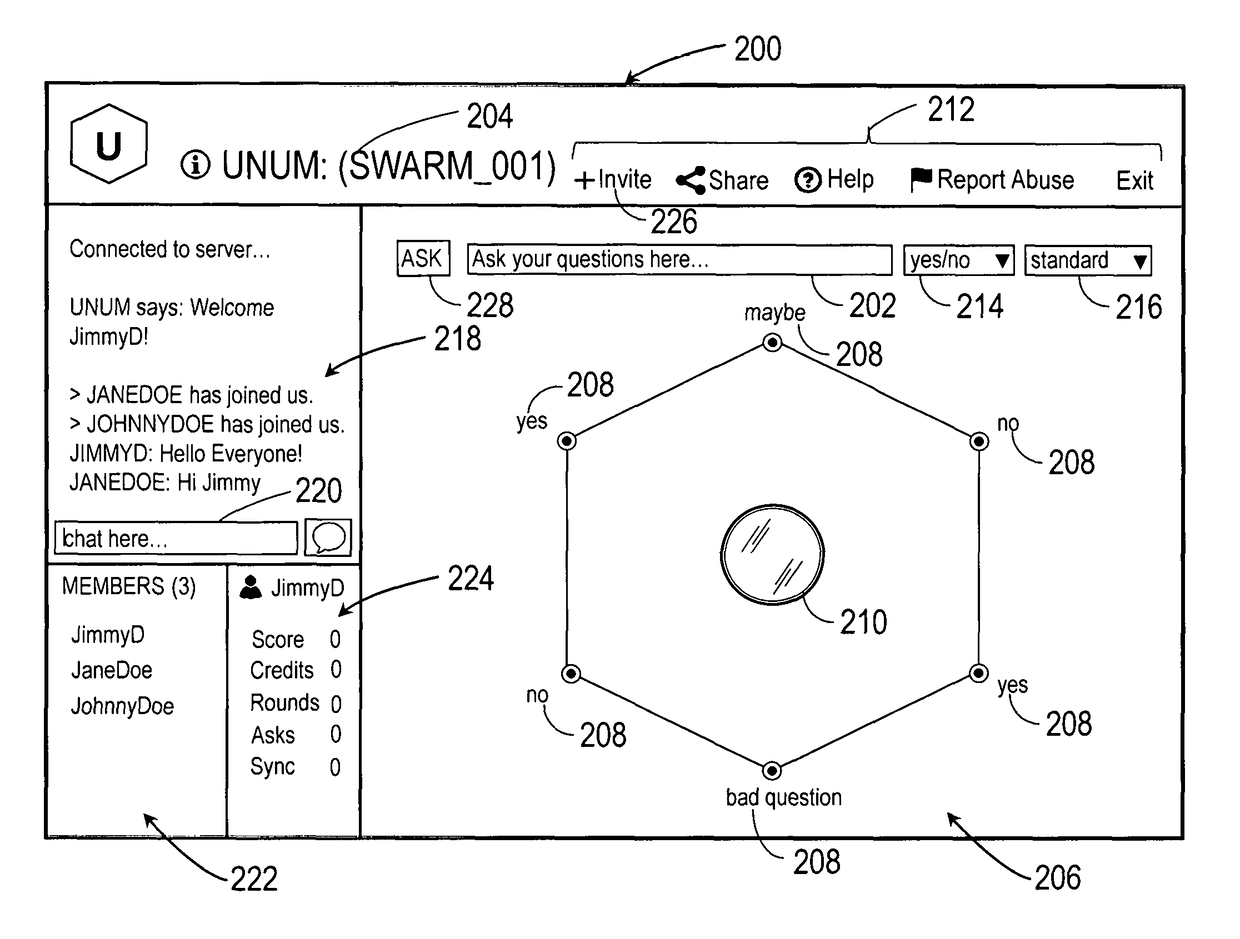
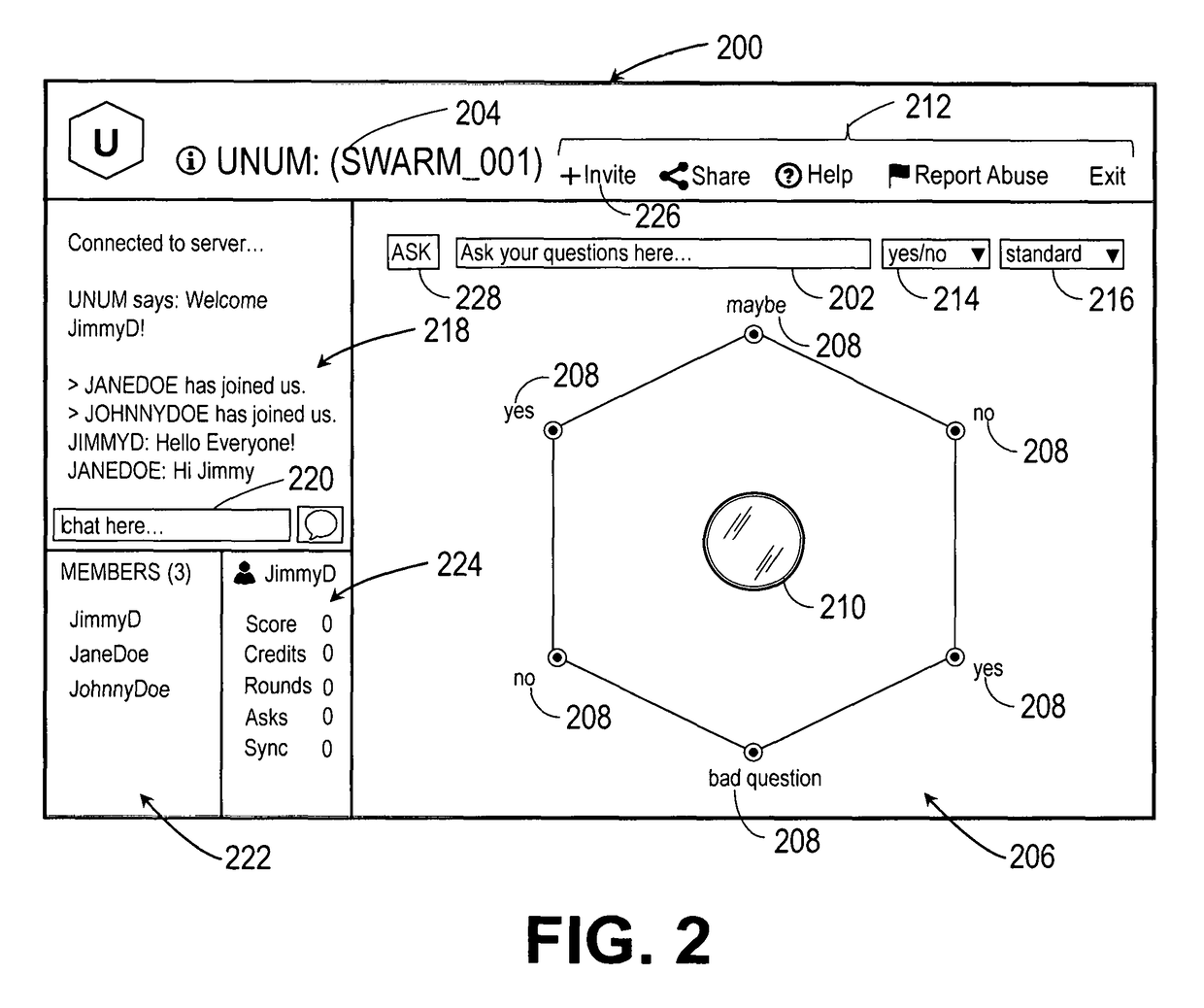
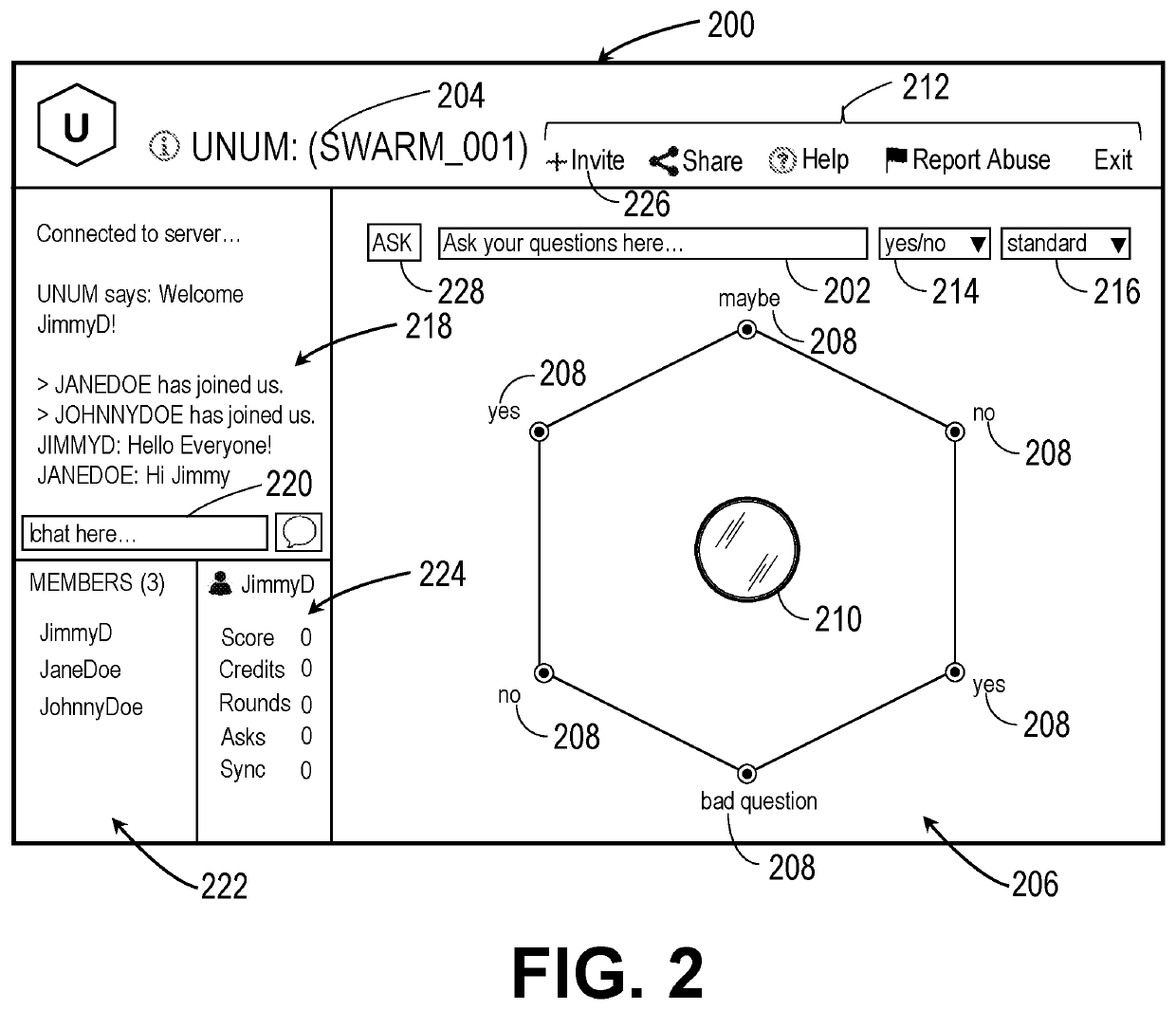
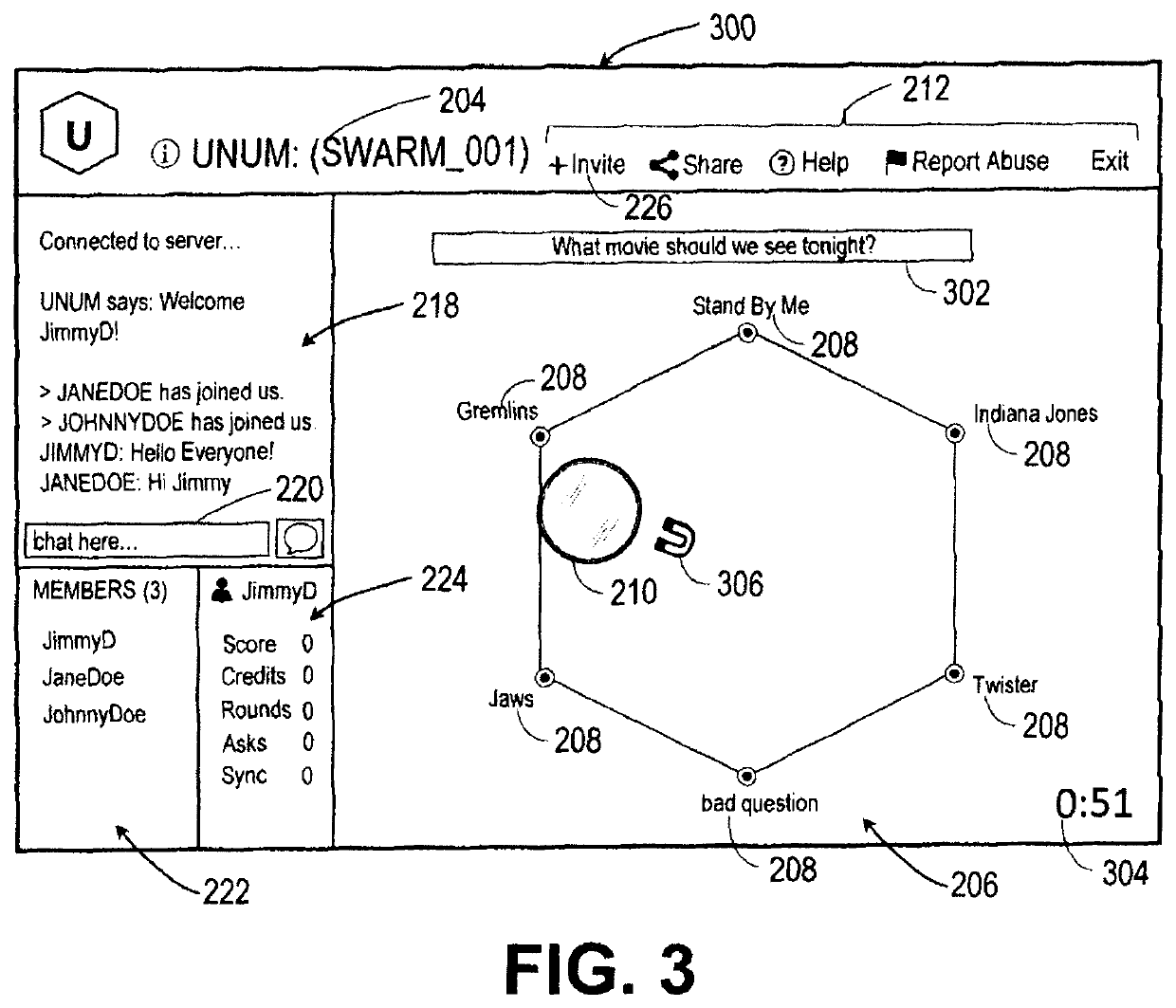
Intuitive interfaces for real-time collaborative intelligence
Systems and methods for user interfaces for use on a computing device of a real-time collaborative computing system. A collaborative application runs on the computing device and displays information and data regarding the collaboration system and also receives user input via the user interface. The display interface arrangement may vary based on a type of collaborative session. Graphical user interfaces include a user interface based on a magnetic force model.
Owner:UNANIMOUS A I
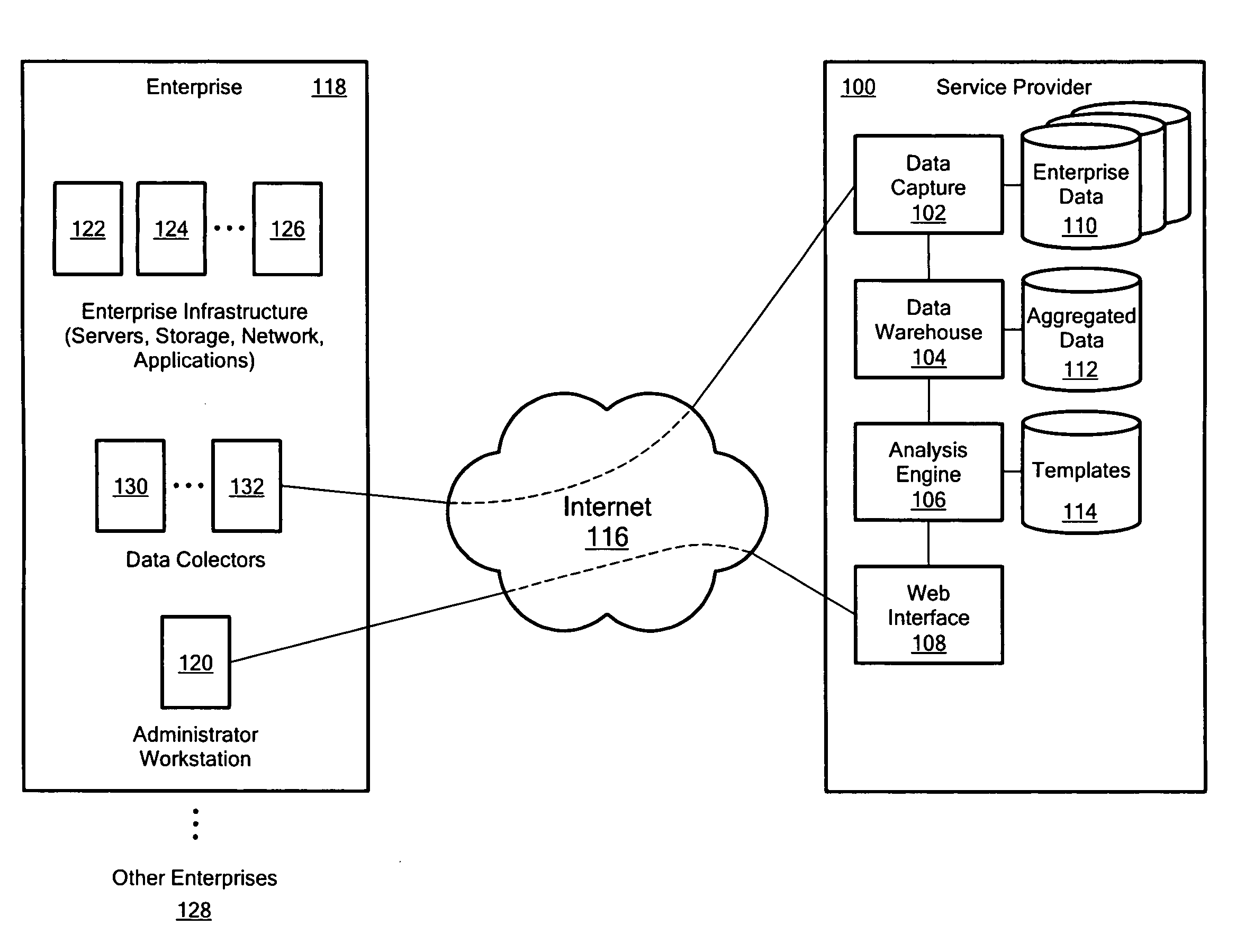
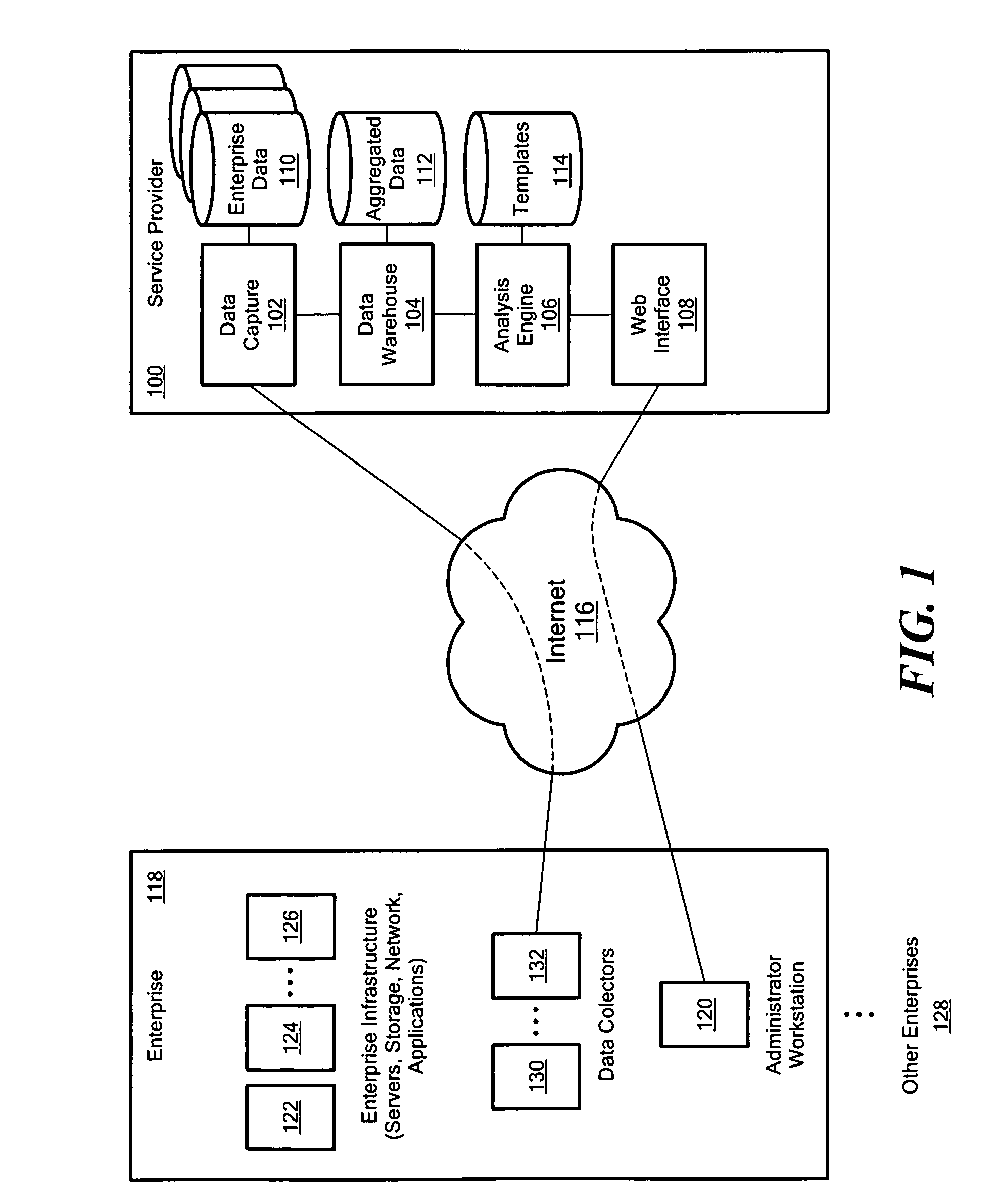
Systems and Methods for Analyzing Information Technology Systems Using Collaborative Intelligence
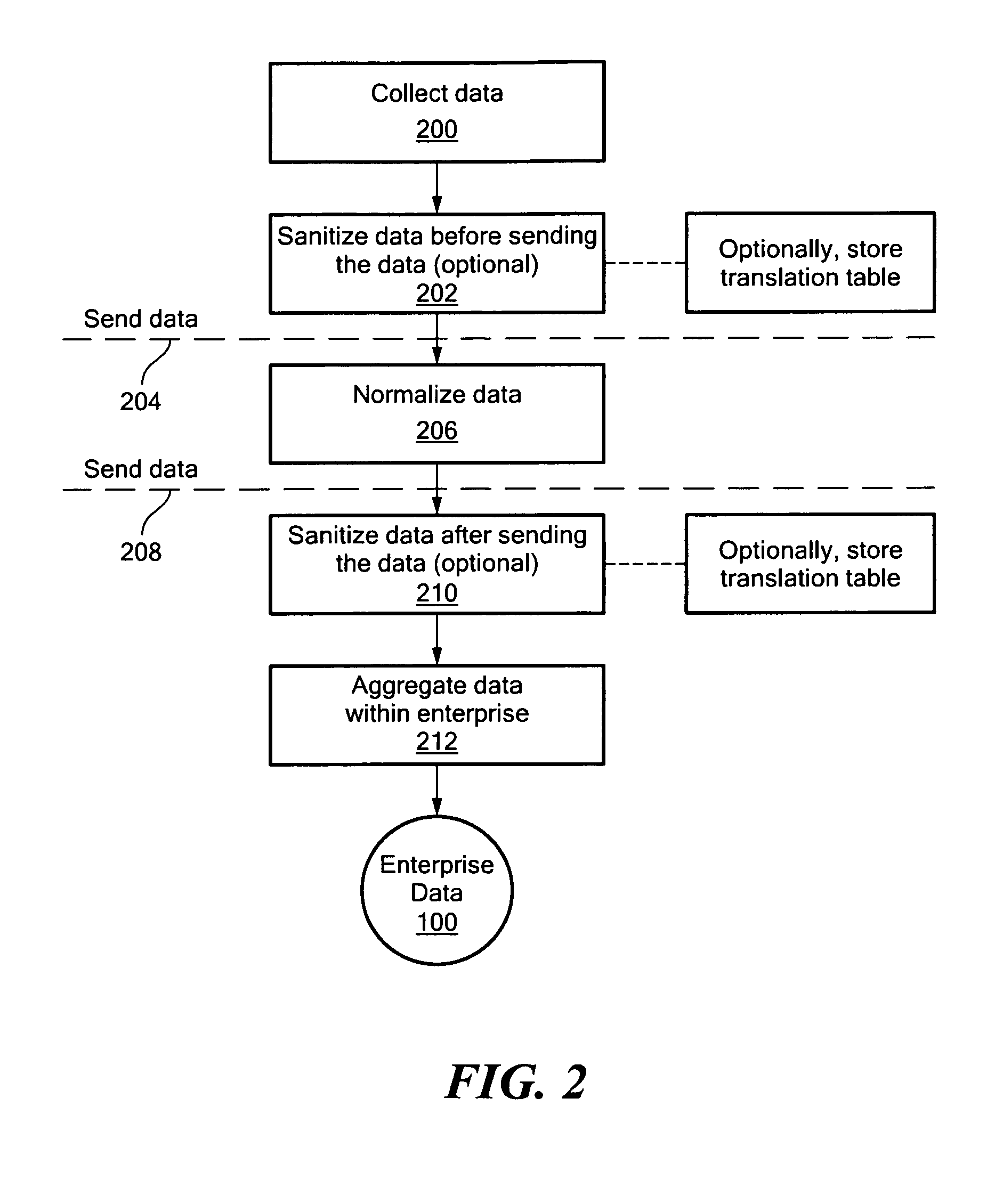
An information technology (IT) system of interest is analyzed using collaborative, community-based sharing of expert knowledge, analysis and advice through user-submitted analysis rules and / or user-submitted report templates. Users may submit rules that have been found to be useful in analyzing or managing IT systems. A rule may analyze a particular item of configuration data or performance data according to a predetermined criterion. Other users may apply these rules to their own systems' data and, thereby, utilize the collective expertise of the people who submitted the rules. Performance and configuration data from IT systems or components of the systems in various enterprises is collected and then sanitized by removing or masking identifying information before storing the sanitized data in a data warehouse. An IT manager may compare data from his / her IT system to historical data from the system or to data from IT systems having similar workloads, configurations, problems or according to other matching criteria, without obtaining confidential information about the comparison systems. Such comparisons may use the user-submitted rules. Reports are generated from these analyses and comparisons according to predefined and / or user-submitted report templates and report component templates for items such as text blocks, tables, graphs, charts and block diagrams.
Owner:TIMMINS SOFTWARE CORP
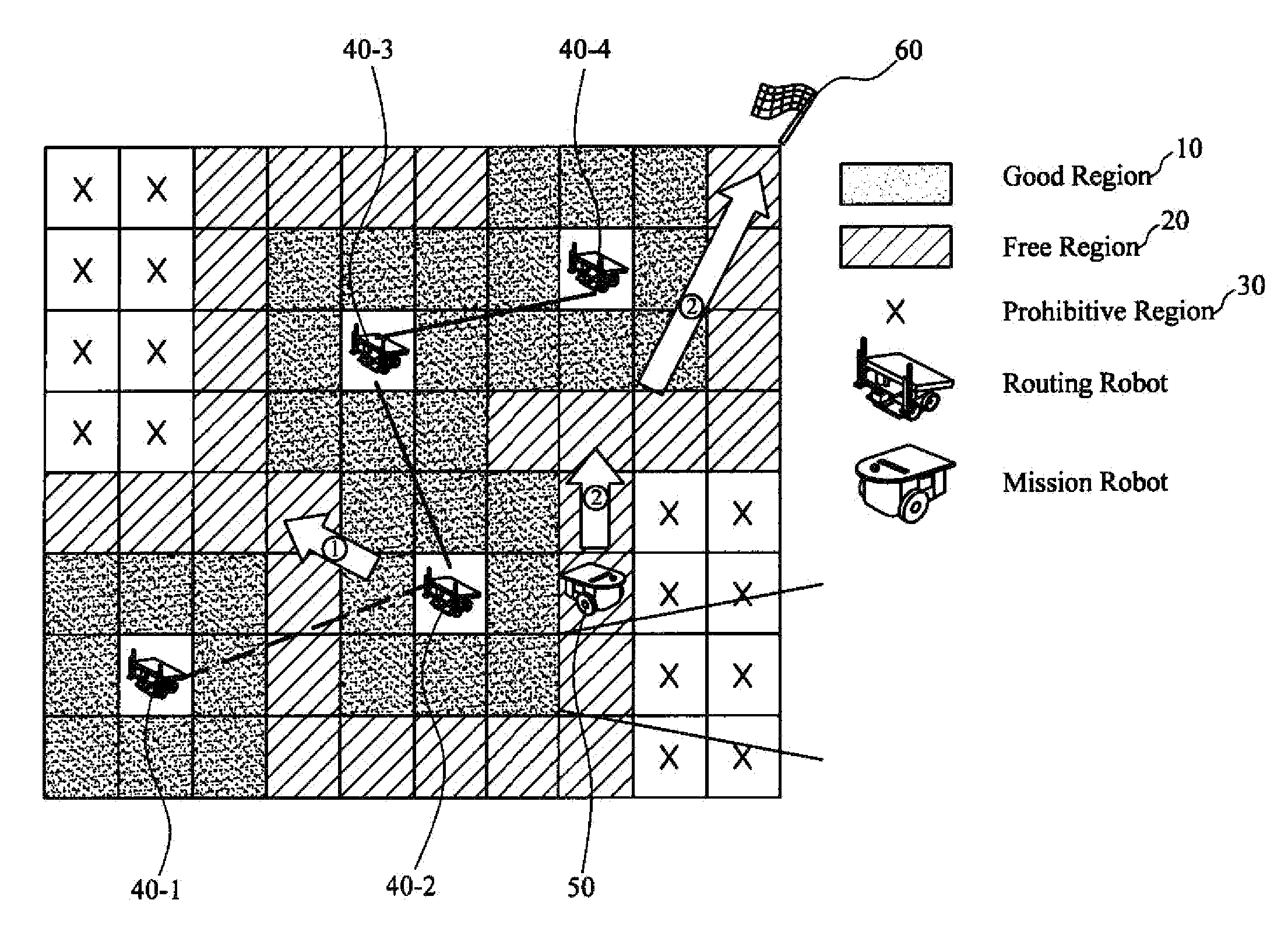
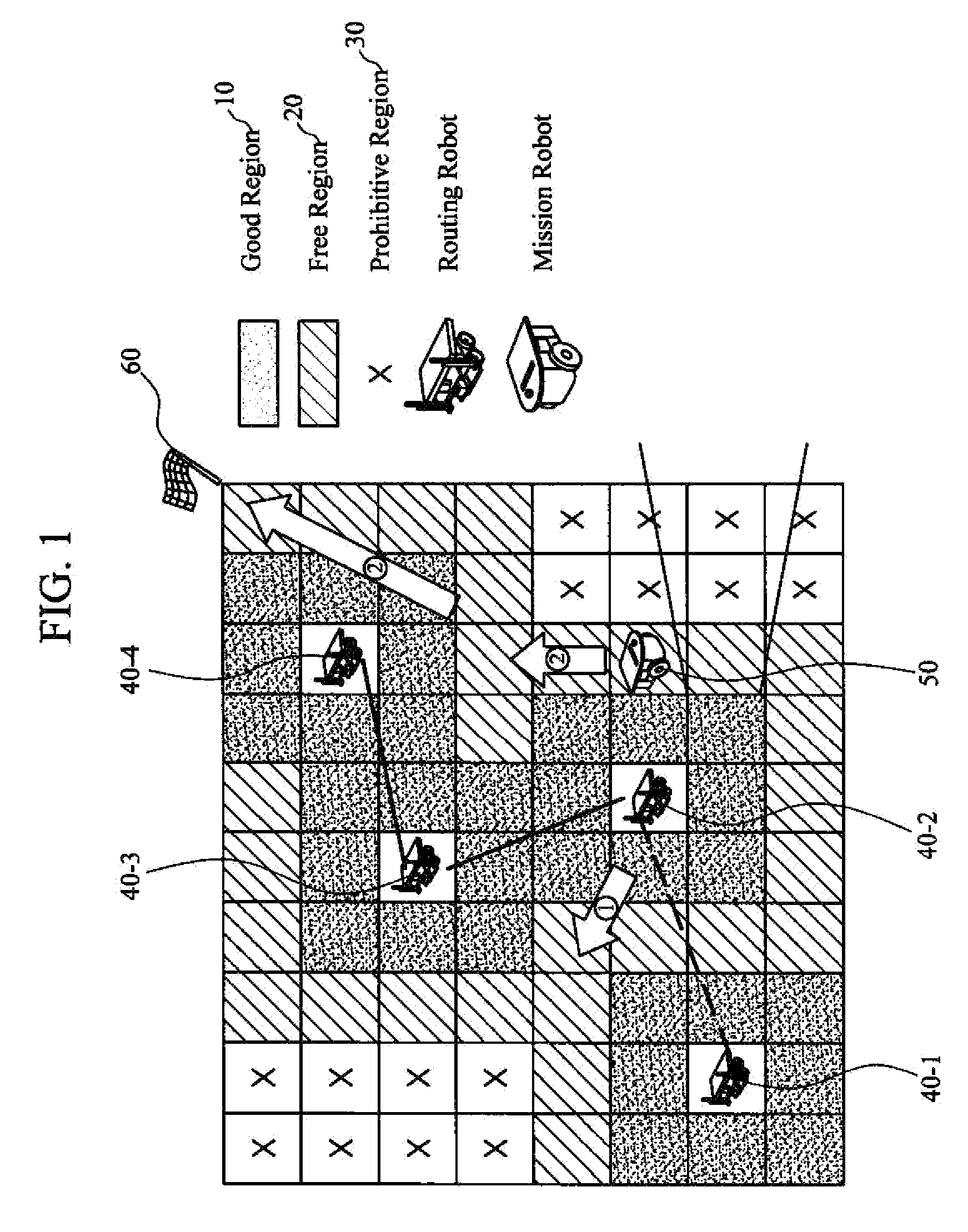
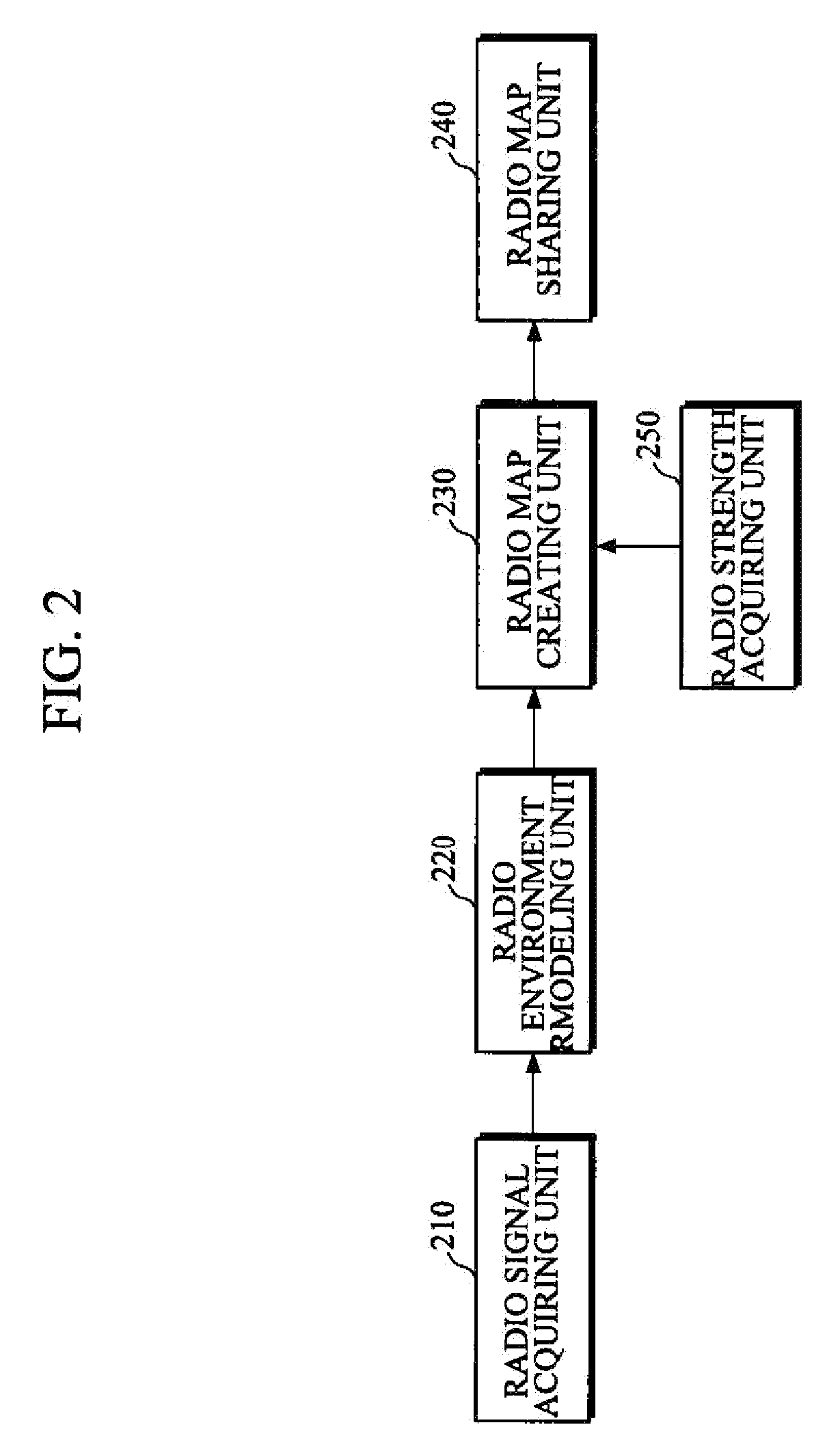
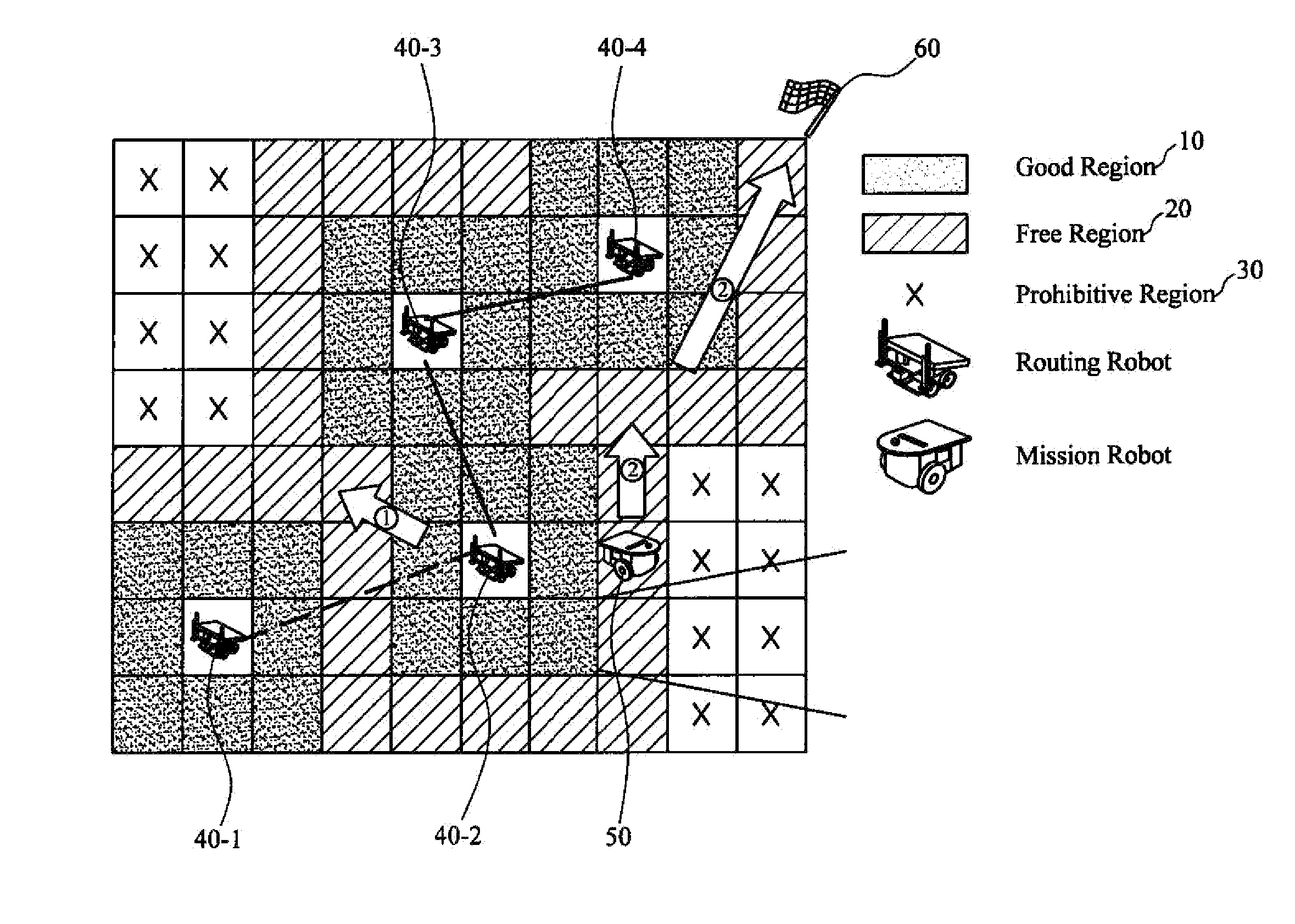
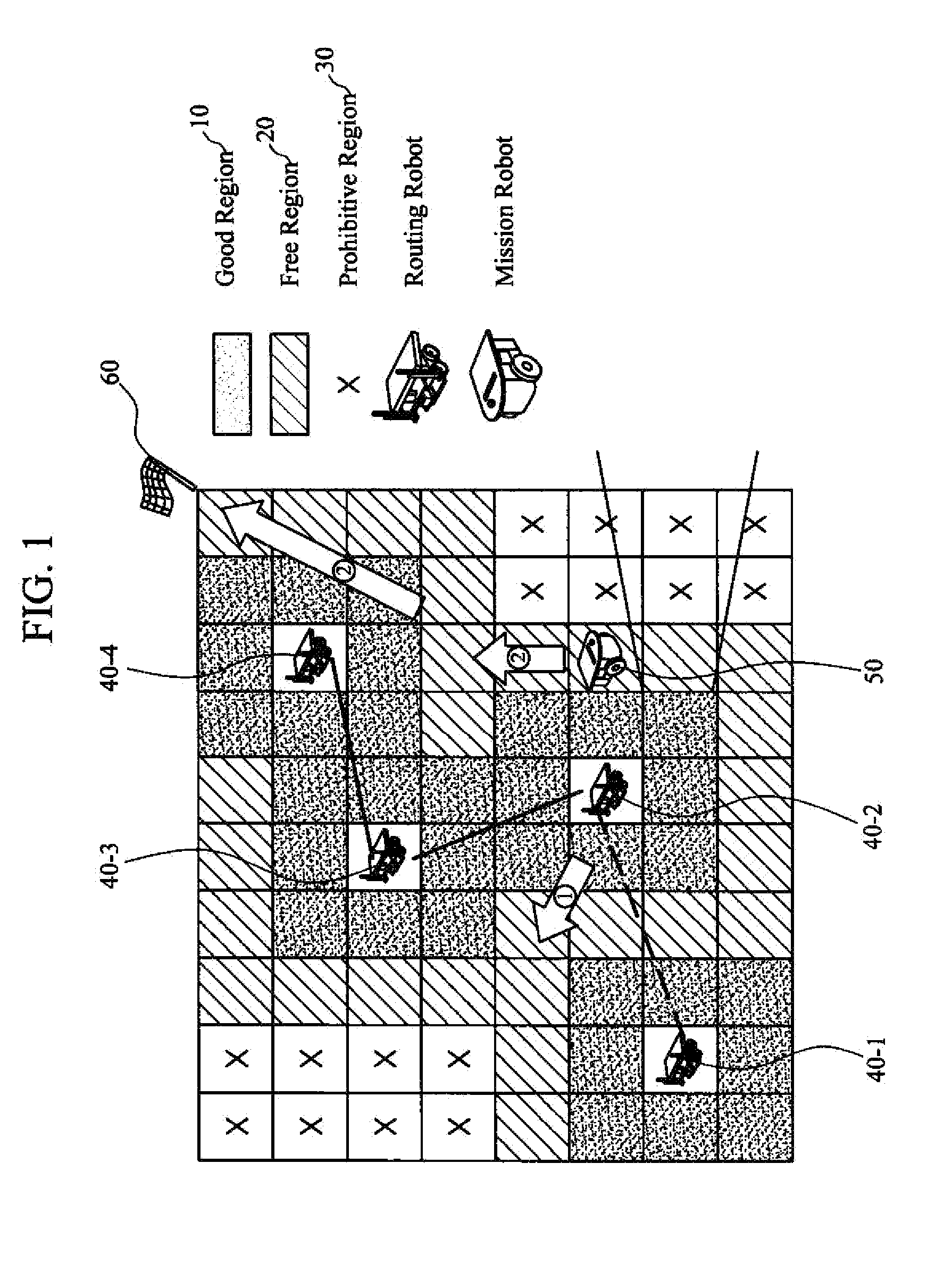
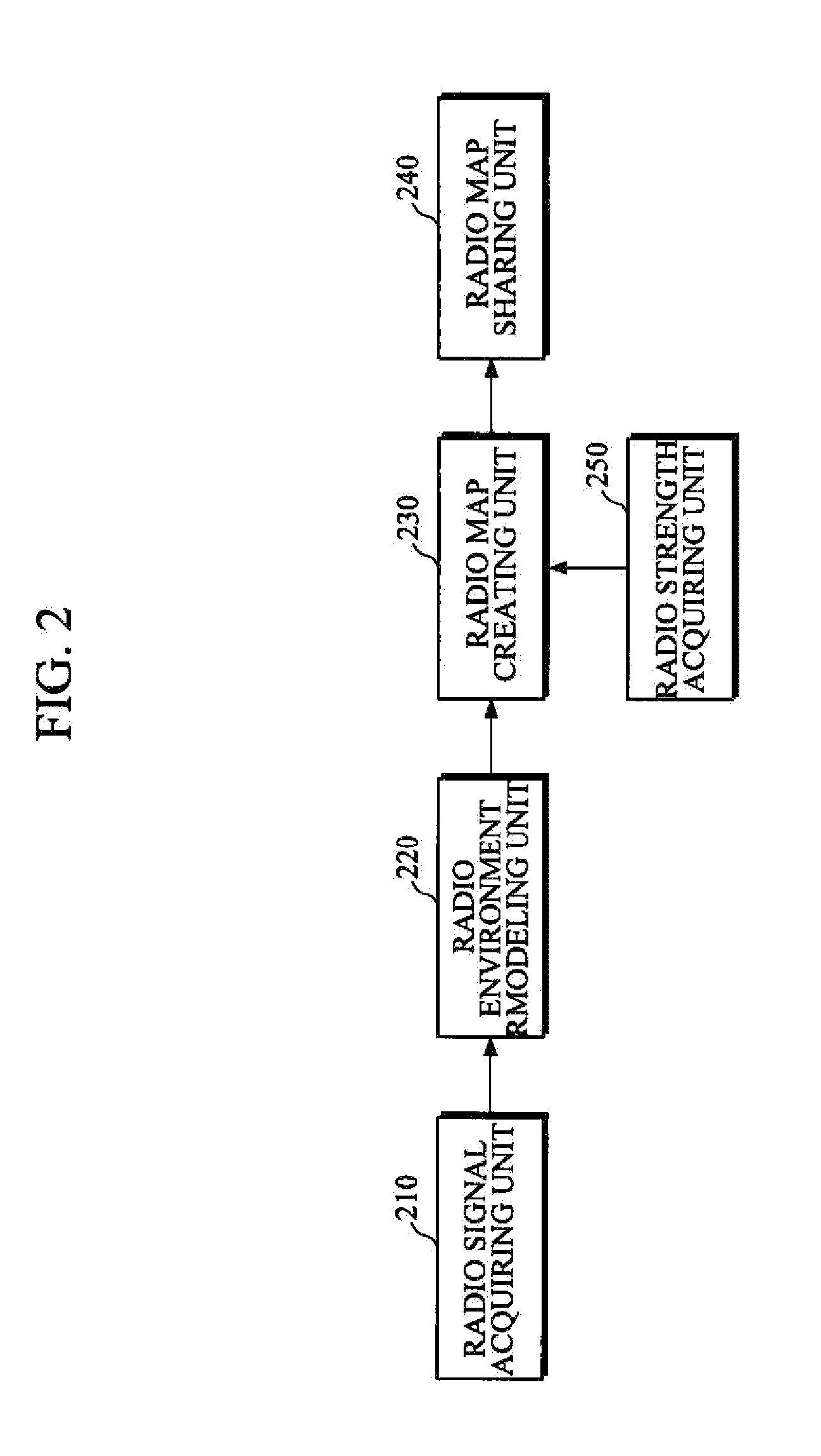
Apparatus and method for creating probability-based radio map for cooperative intelligent robots
An apparatus for creating a radio map includes a radio signal acquiring unit that acquires information on radio signals between one or more cooperative intelligent robots, a radio environment modeling unit that estimates radio strength for each cell configuring the radio map from the information on radio signals acquired by the radio signal acquiring unit, and a radio map creating unit that classifies a communication region of each cell and models the radio map according to the radio strength for each cell estimated by the radio environment modeling unit.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
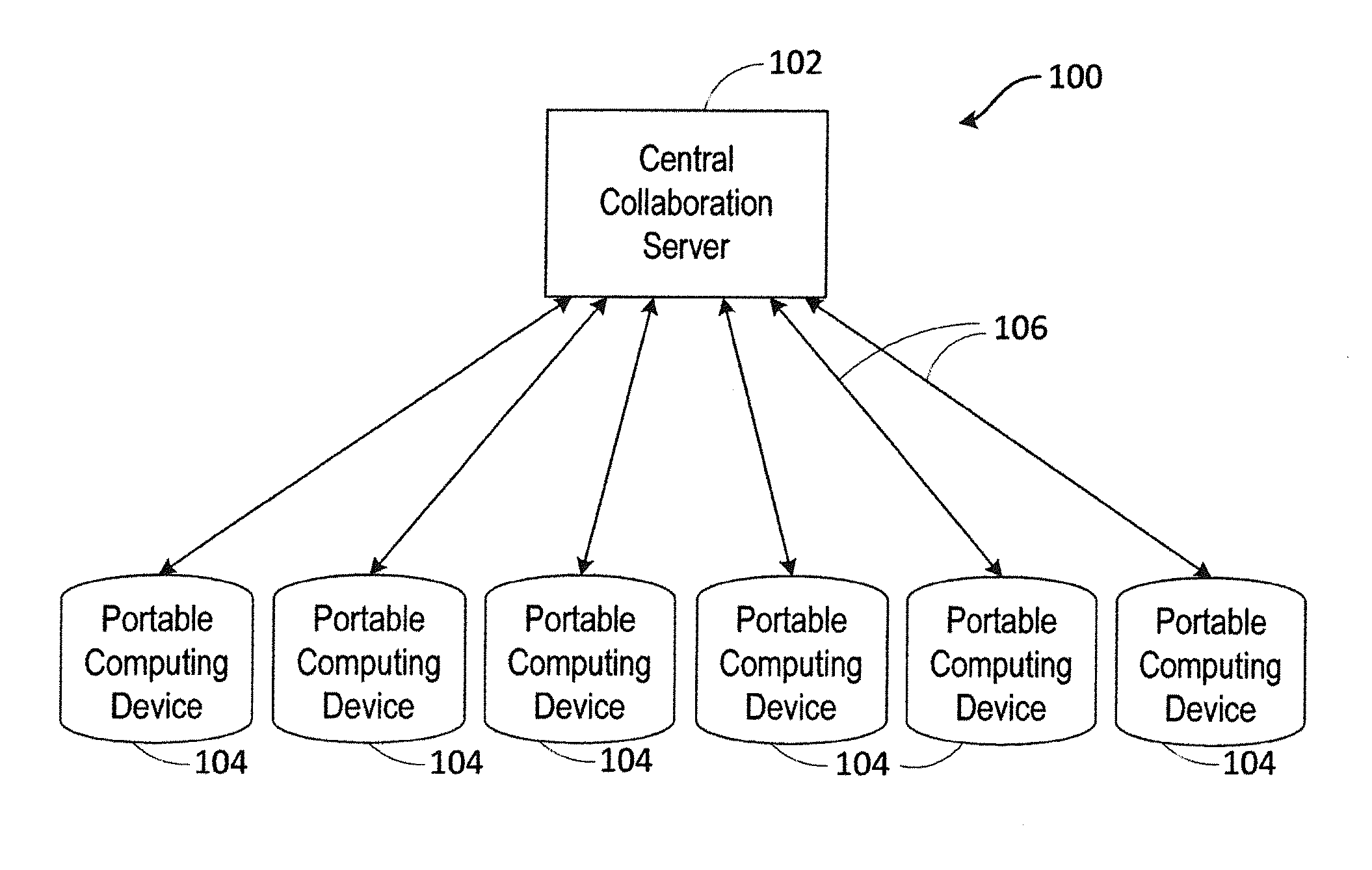
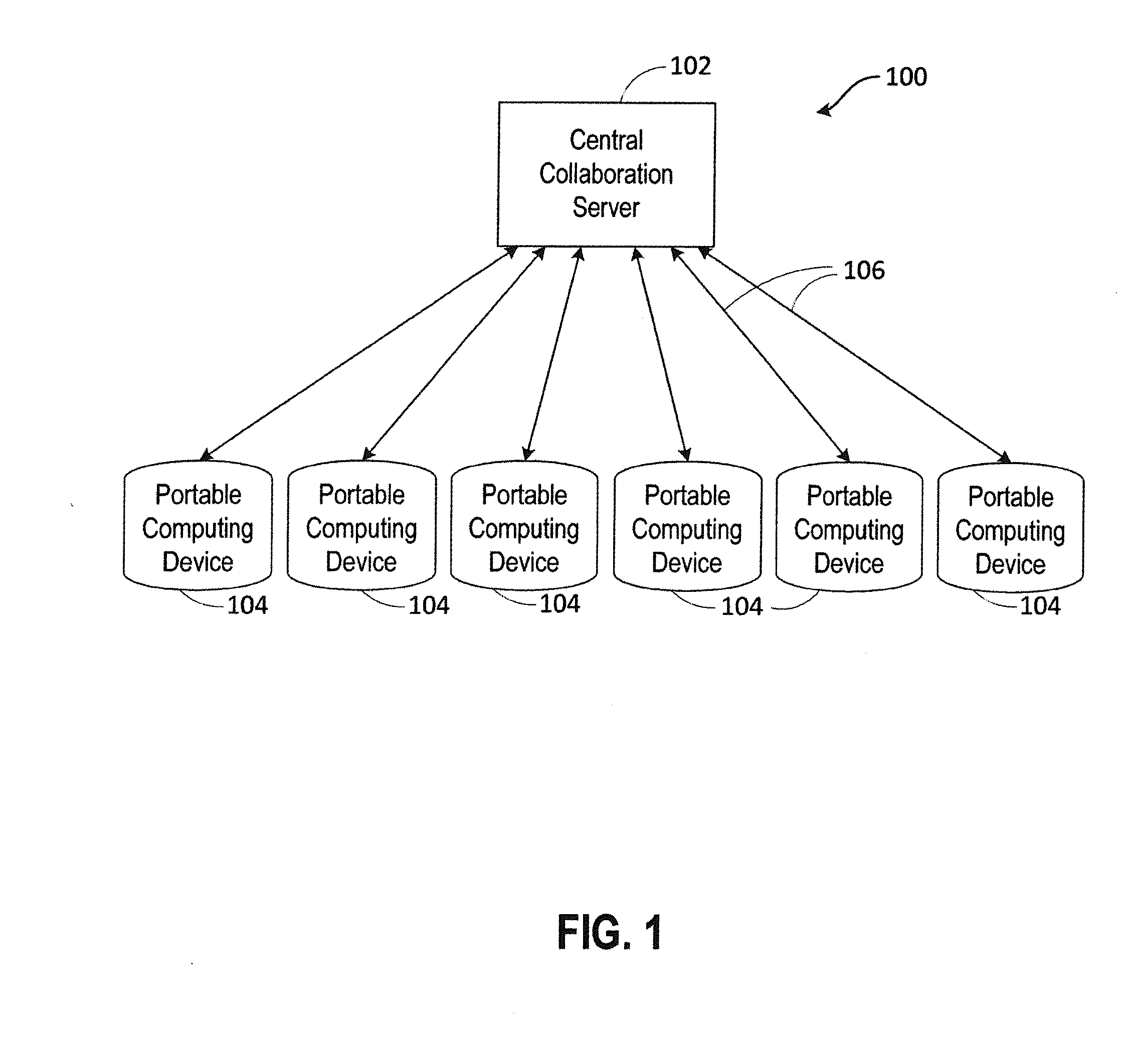
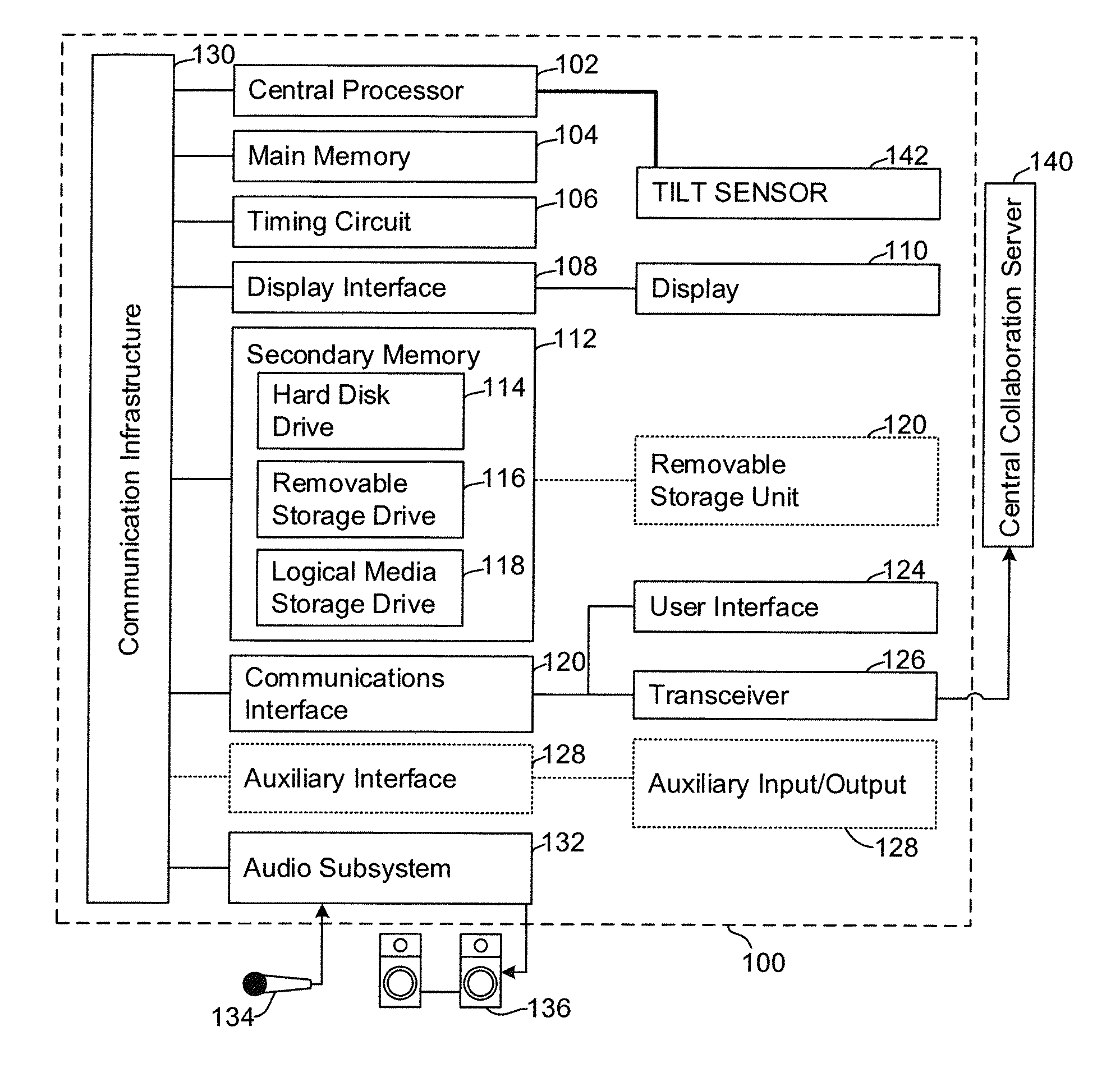
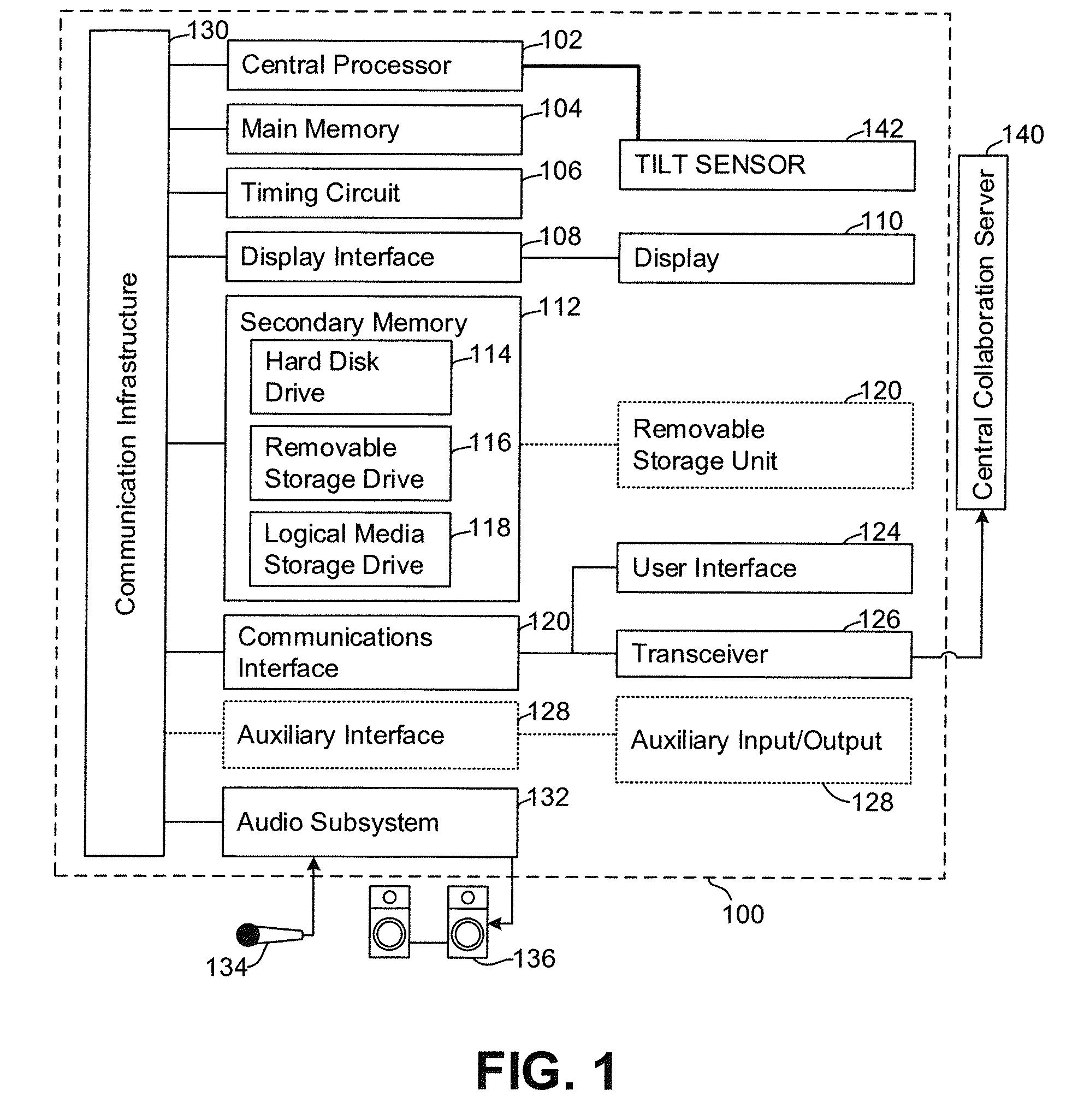
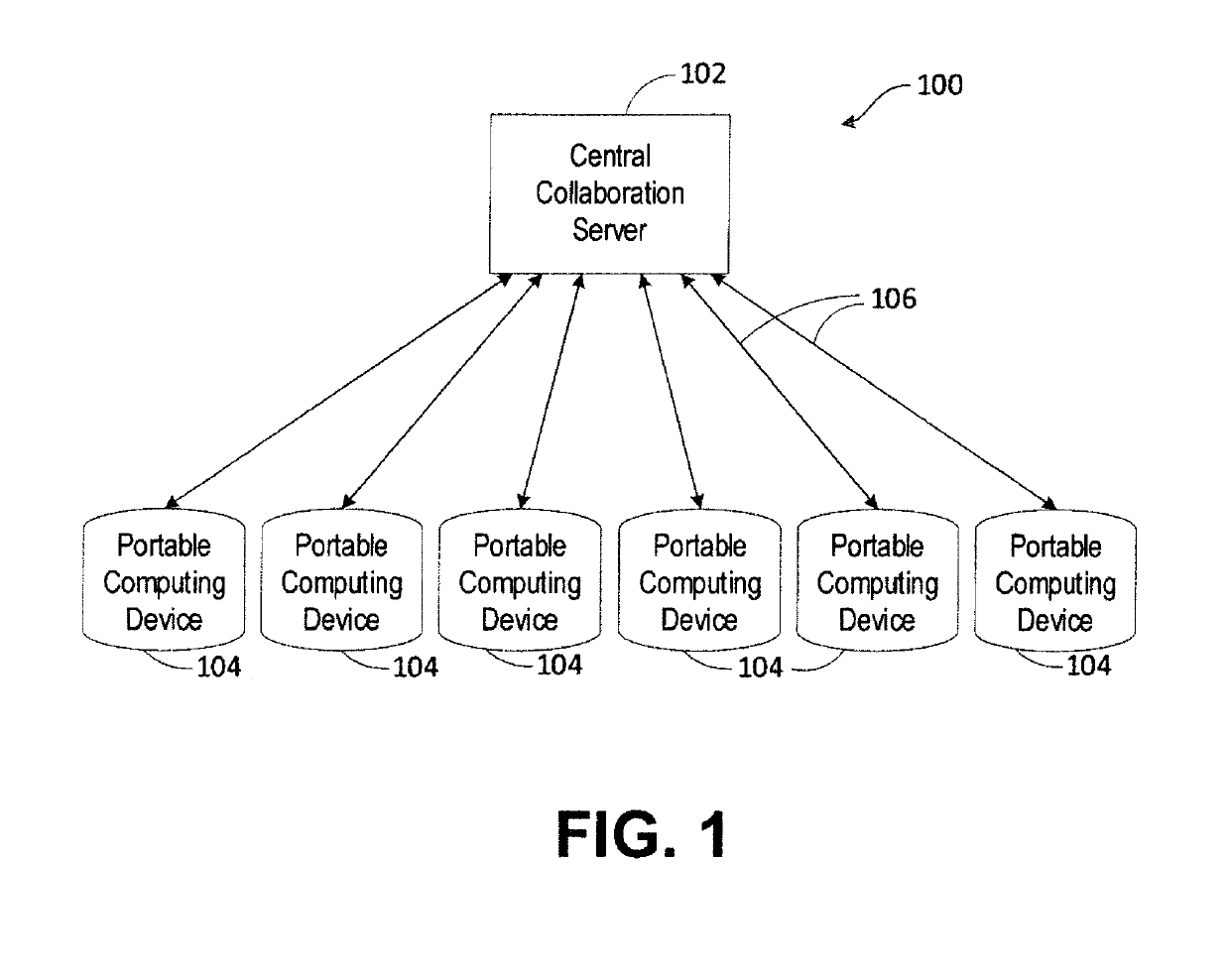
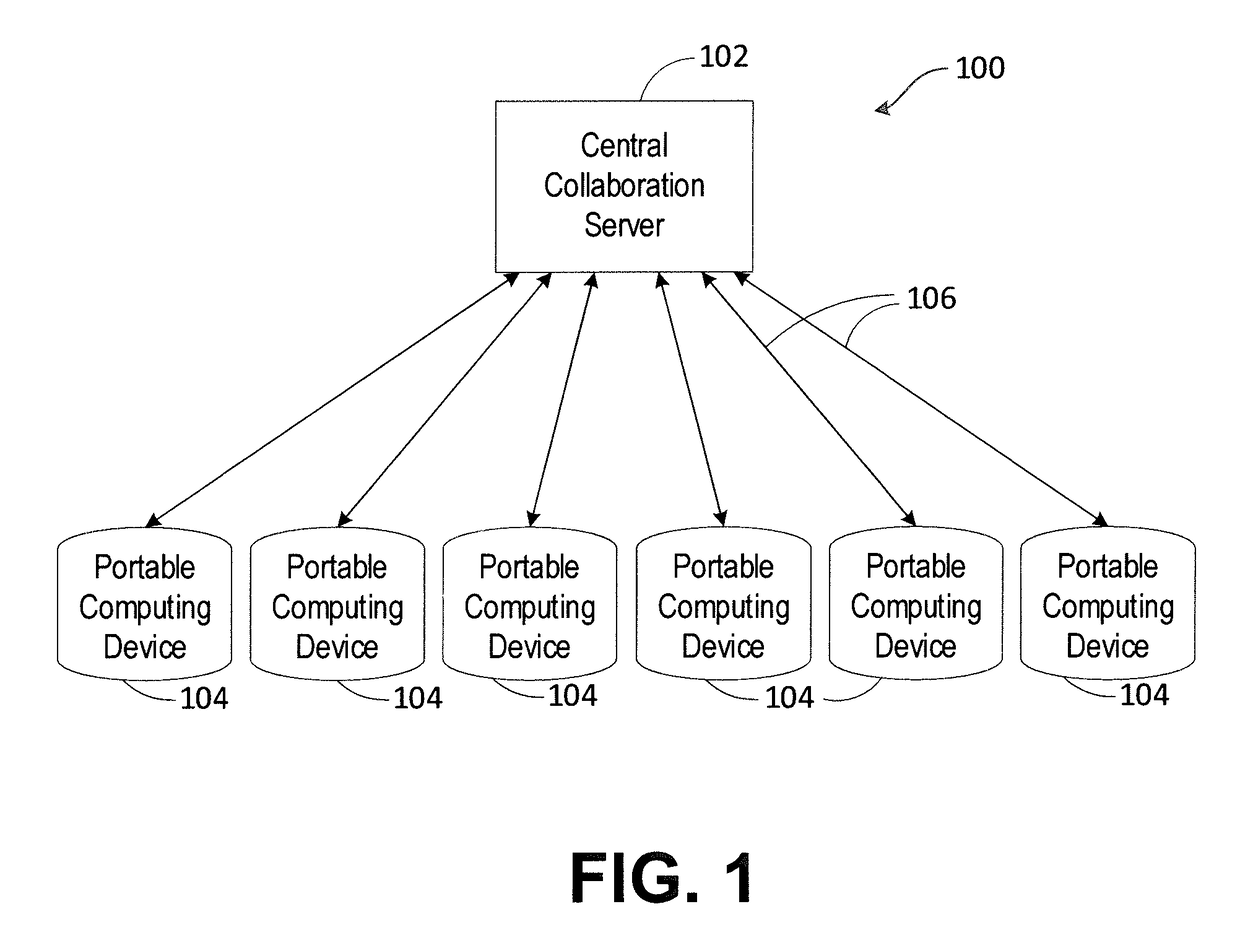
Dynamic systems for optimization of real-time collaborative intelligence
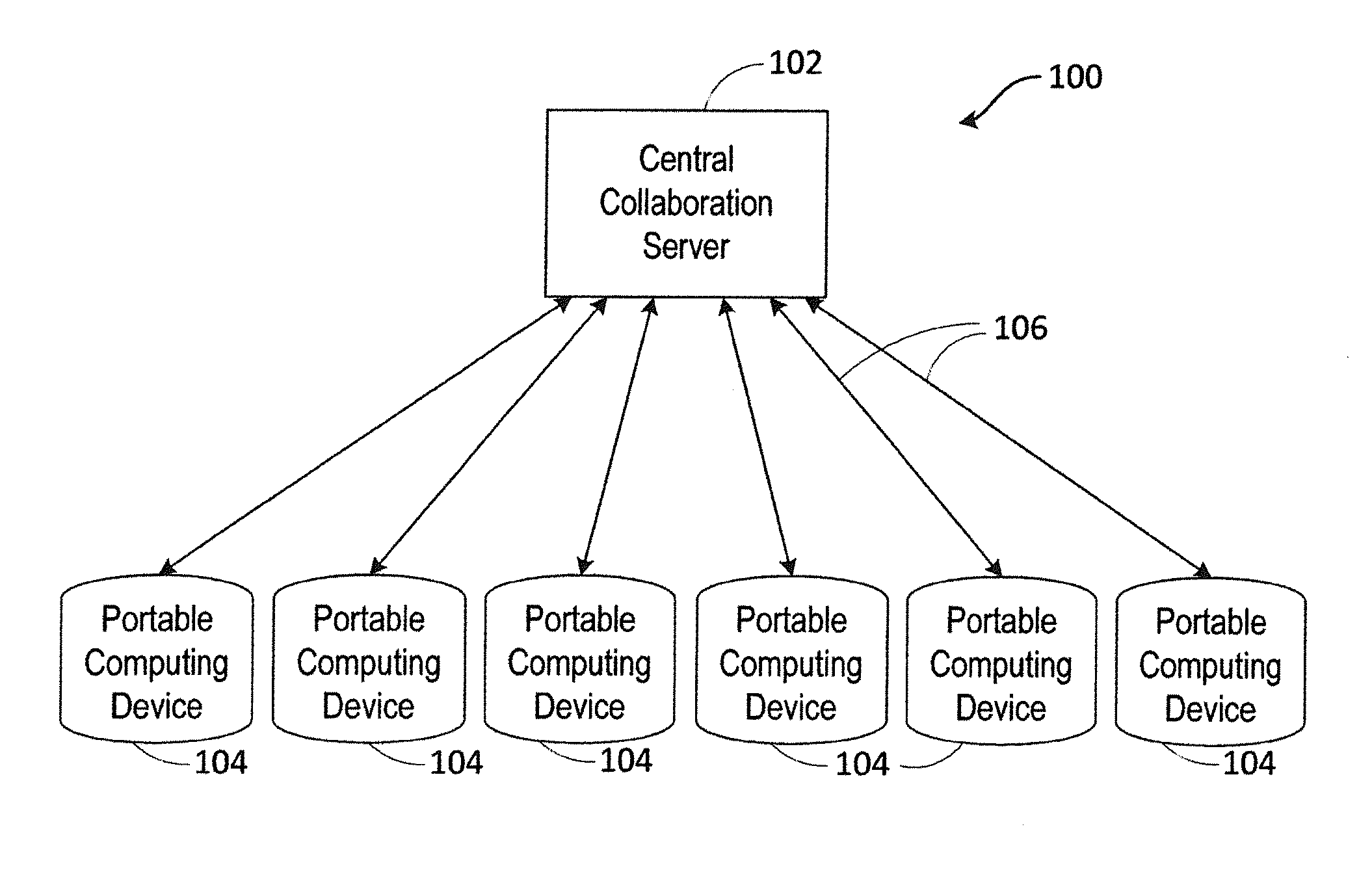
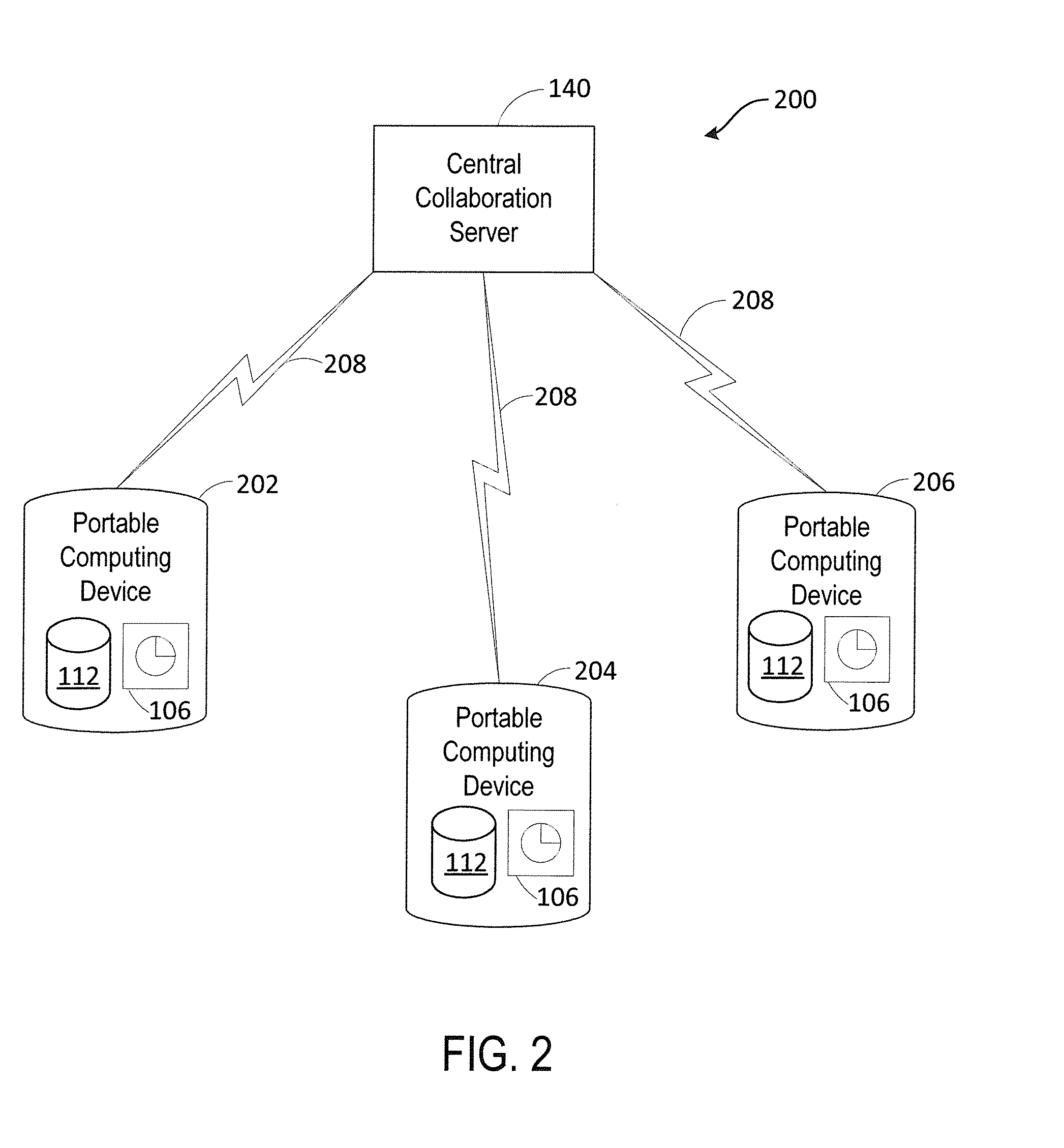
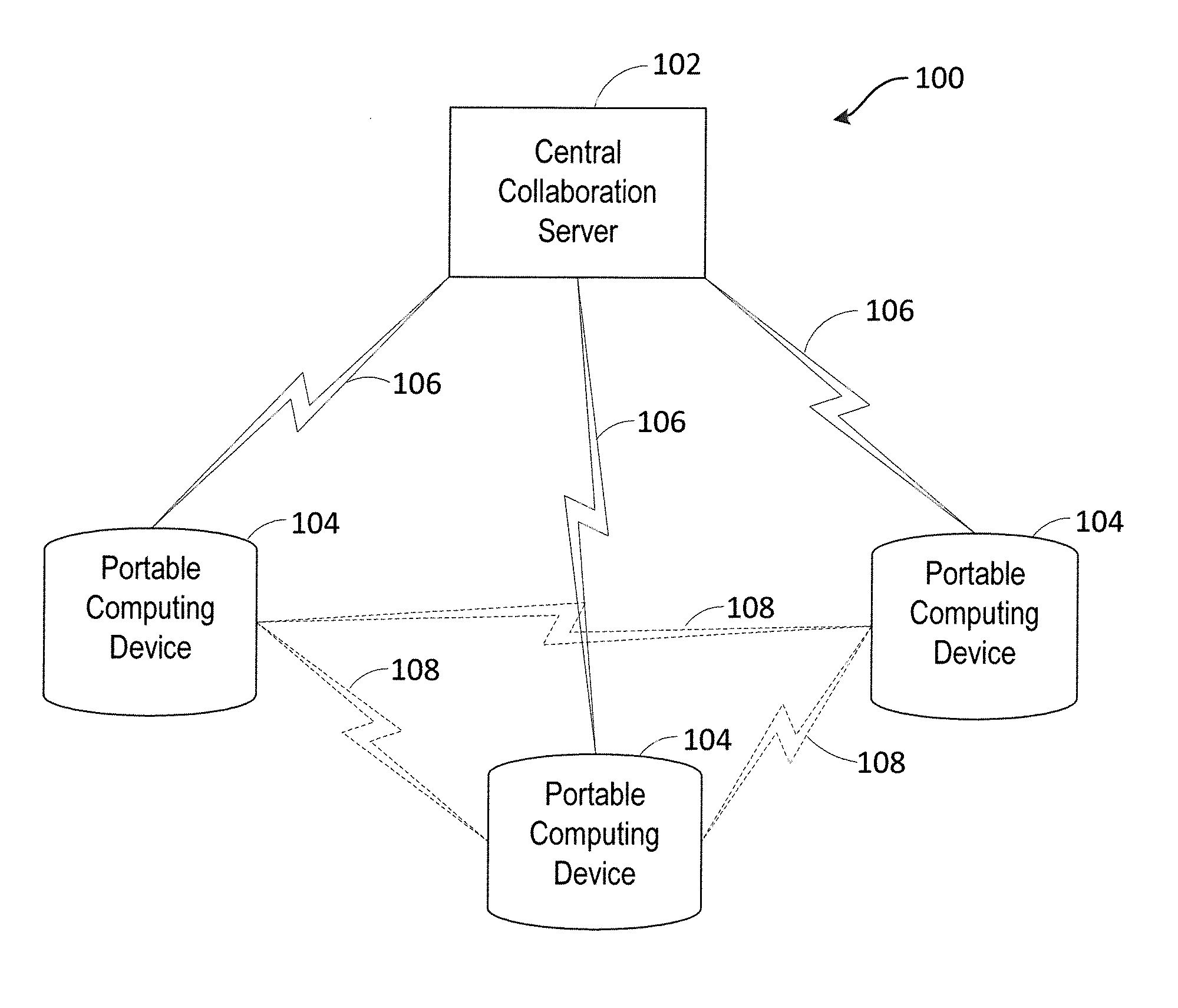
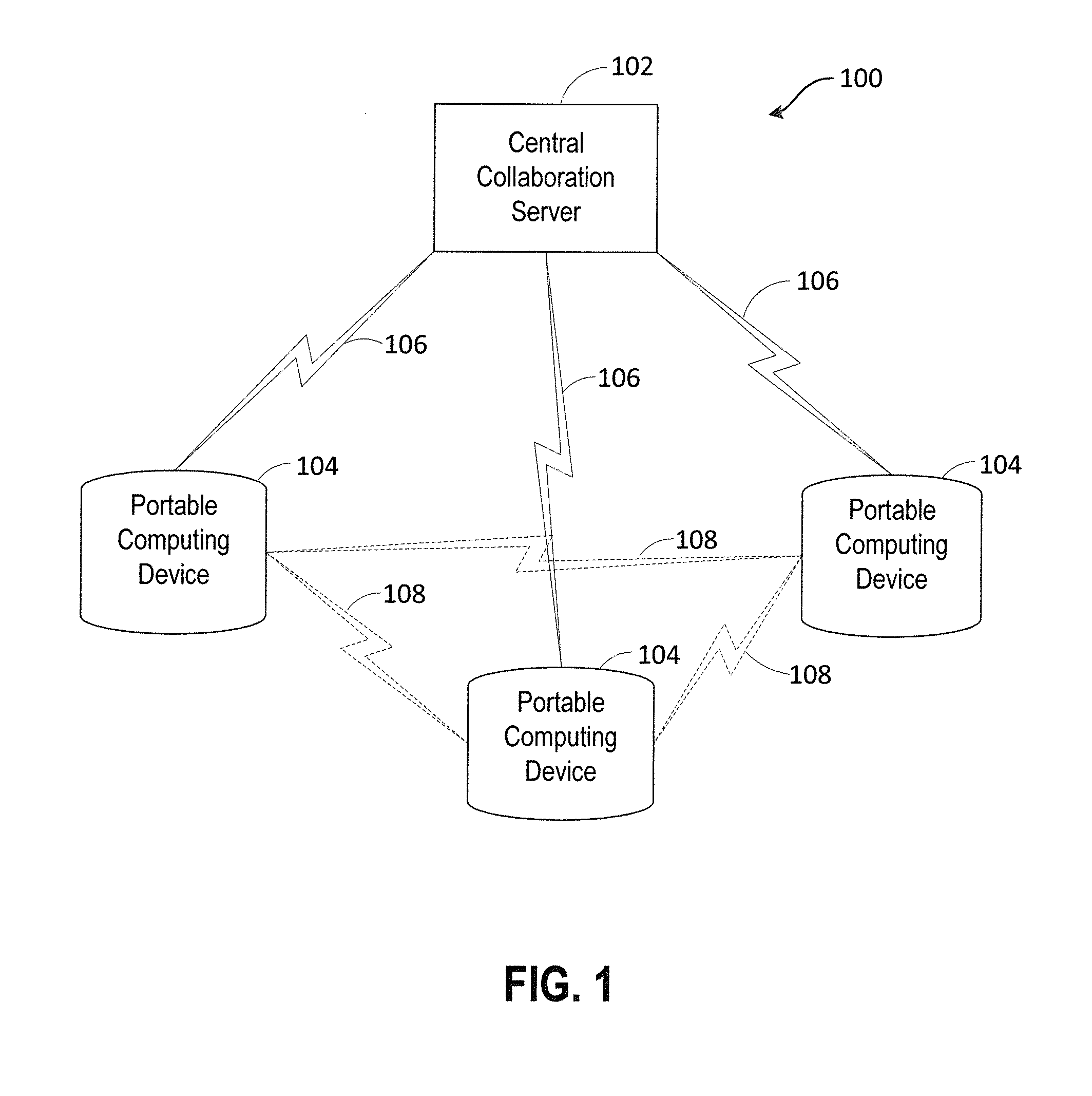
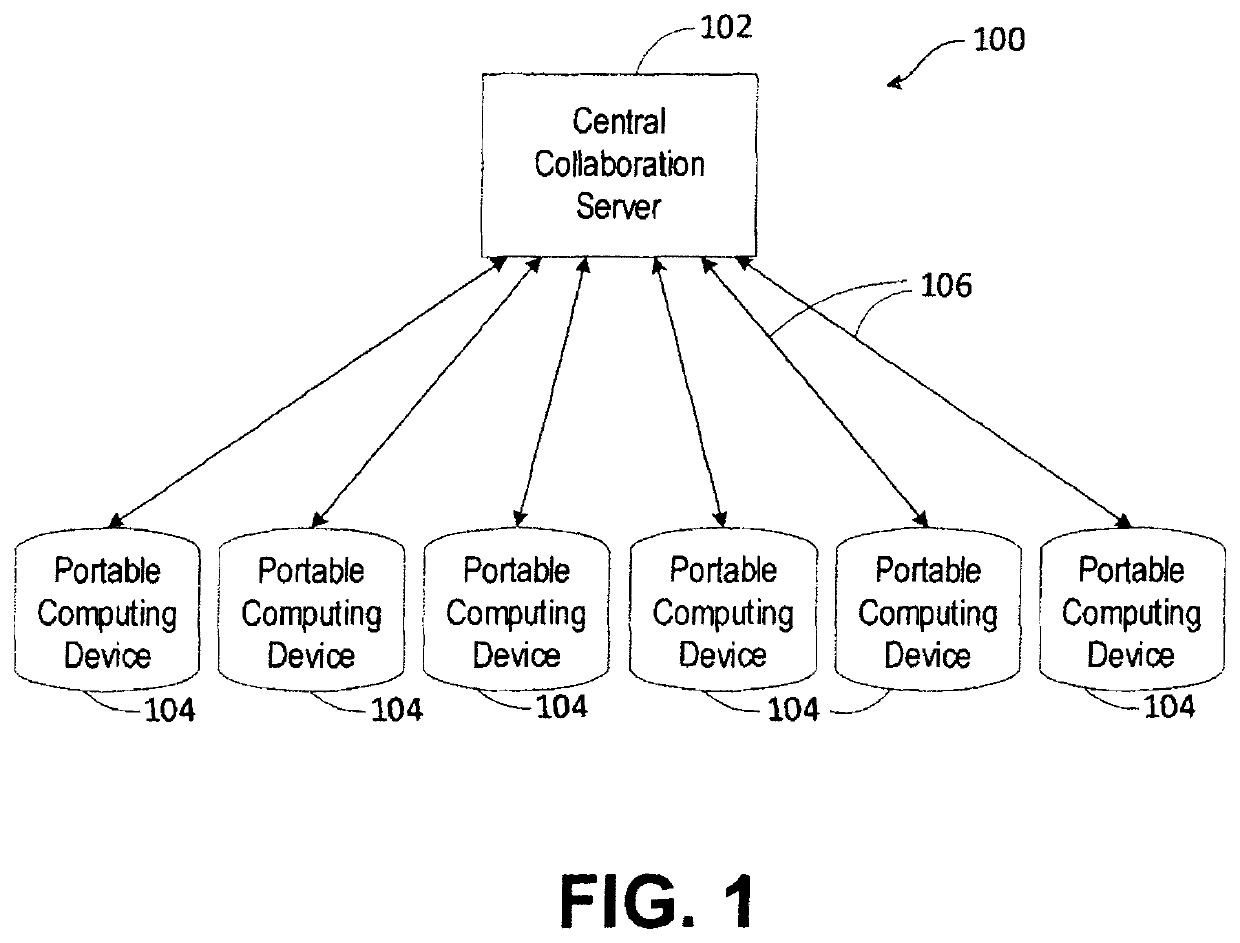
Systems and methods for real-time collaborative computing and collective intelligence are disclosed. A collaborative application runs on a collaborative server connected to a plurality of computing devices. Collaborative sessions are run wherein a group of independent users, networked over the internet, collaboratively answer questions in real-time, thereby harnessing their collective intelligence. Systems and methods for determining a group intent vector from a plurality of user intent vectors in response to user input, the group intent vector including a bias restoring vector to correct positional bias resulting from a target layout.
Owner:UNANIMOUS A I
Multi-phase multi-group selection methods for real-time collaborative intelligence systems
ActiveUS20160048274A1TransmissionInput/output processes for data processingUser inputCollaborative intelligence
Systems and methods for real-time collaborative computing and collective intelligence are disclosed. A collaborative application runs on a collaborative server connected to a plurality of computing devices. Collaborative sessions are run wherein a group of independent users, networked over the internet, collaboratively answer questions in real-time, thereby harnessing their collective intelligence. Systems and methods for selection among a set of user-input suggestions. The group is divided into subgroups, each subgroup selecting one suggestion from a subgroup of suggestions. The process is repeated with the remaining selected suggestions until one final target is selected, by the entire group, from the remaining suggestions.
Owner:UNANIMOUS A I
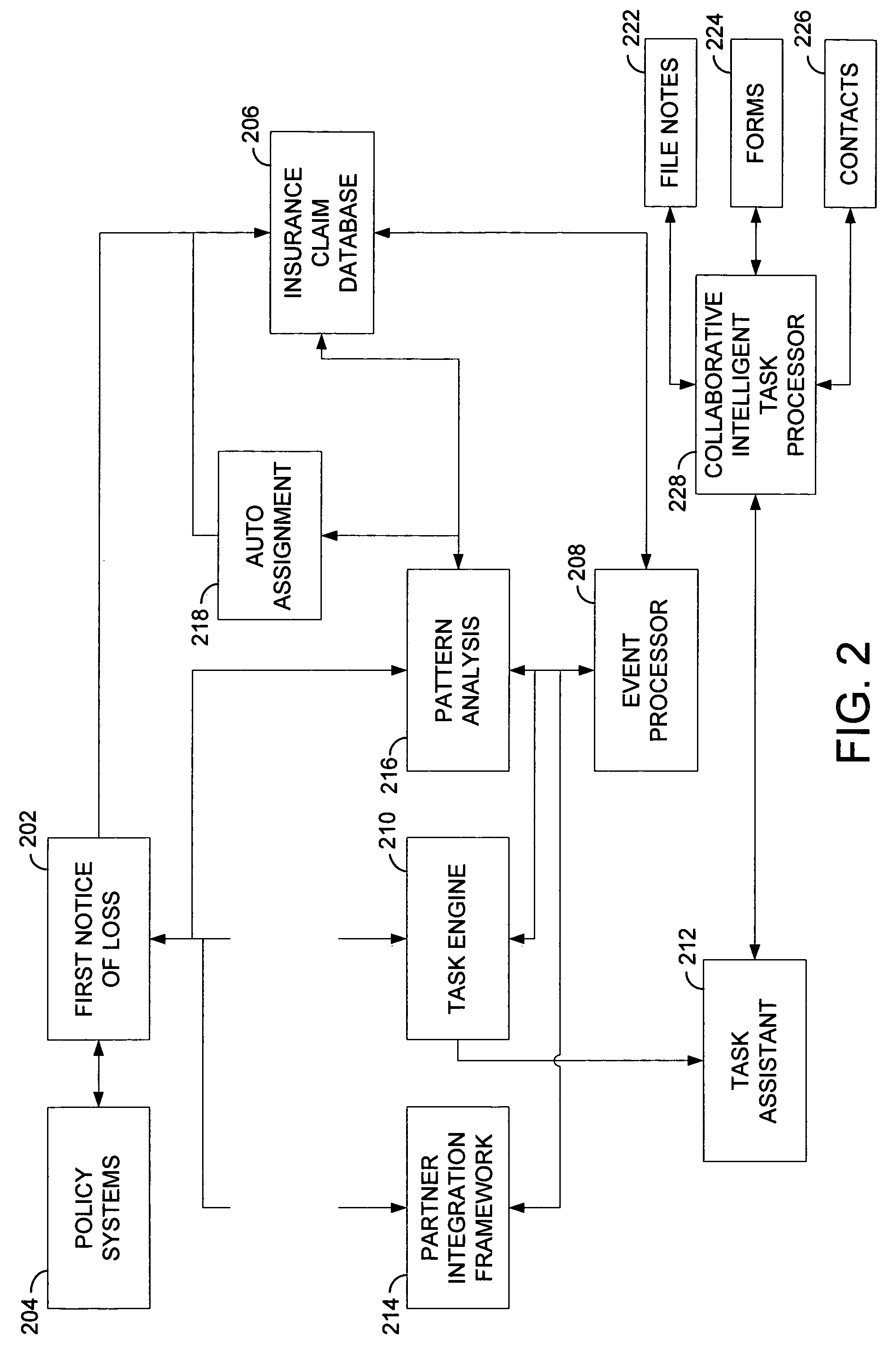
Collaborative intelligent task processor for insurance claims
ActiveUS7933786B2Improve the level ofThe result is accurateFinanceResourcesProgram planningAction plan
An insurance claim processing system may include an insurance claim database, an event processor component, a task engine component and a collaborative intelligent task processor. The insurance claim database may be configured to store and provide access to data in a data record that is related to an insurance claim. The event processor component may be executable with a computer to iteratively monitor the data in the data record and identify events. The task engine component may be executable with a computer in response to one of the identified events to generate tasks indicative of information that needs to be acquired based on the contents of the data record. The collaborative intelligent task processor may be executable with a computer to analyze a task generated by the task engine component and select an action plan that is responsive to the task. The action plan may include a first procedure that enables the collaborative intelligent task processor to acquire information related to the insurance claim, and a second procedure that enables the collaborative intelligent task processor to process the information to yield a result responsive to the task.
Owner:DUCK CREEK TECH LTD
Iterative suggestion modes for real-time collaborative intelligence systems
InactiveUS20160154570A1TransmissionInput/output processes for data processingUser inputCollaborative intelligence
Systems and methods for real-time collaborative computing and collective intelligence are disclosed. A collaborative application runs on a collaborative server connected to a plurality of computing devices. Collaborative sessions are run wherein a group of independent users, networked over the internet, collaboratively answer questions in real-time, thereby harnessing their collective intelligence. Systems and methods for iterative selection among a set of user-input suggestions.
Owner:UNANIMOUS A I
Methods and systems for enabling a credit economy in a real-time collaborative intelligence
Systems and methods are for enabling a group of individuals, each using an individual computing device, to collaboratively answer questions or otherwise express a collaborative will / intent in real-time. The collaboration system comprises a plurality of computing devices, each of the devices being used by an individual user, each of the computing devices enabling its user to contribute to the emerging real-time group-wise intent. A collaboration server is disclosed that communicates remotely to the plurality of individual computing devices. Herein, a variety of inventive methods are disclosed for implementing a credit economy for the collaboration system. A credit amount is associated with each user. Credits are awarded to one or more users for certain events, such as successful completion of a collaborative session. Credits are decremented to one or more users for other events, such as for asking a question to be answered by the group.
Owner:UNANIMOUS A I
Apparatus and method for creating probability-based radio map for cooperative intelligent robots
InactiveUS20140195049A1Computer controlSimulator controlTelecommunicationsCollaborative intelligence
An apparatus for creating a radio map includes a radio signal acquiring unit that acquires information on radio signals between one or more cooperative intelligent robots, a radio environment modeling unit that estimates radio strength for each cell configuring the radio map from the information on radio signals acquired by the radio signal acquiring unit, and a radio map creating unit that classifies a communication region of each cell and models the radio map according to the radio strength for each cell estimated by the radio environment modeling unit.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
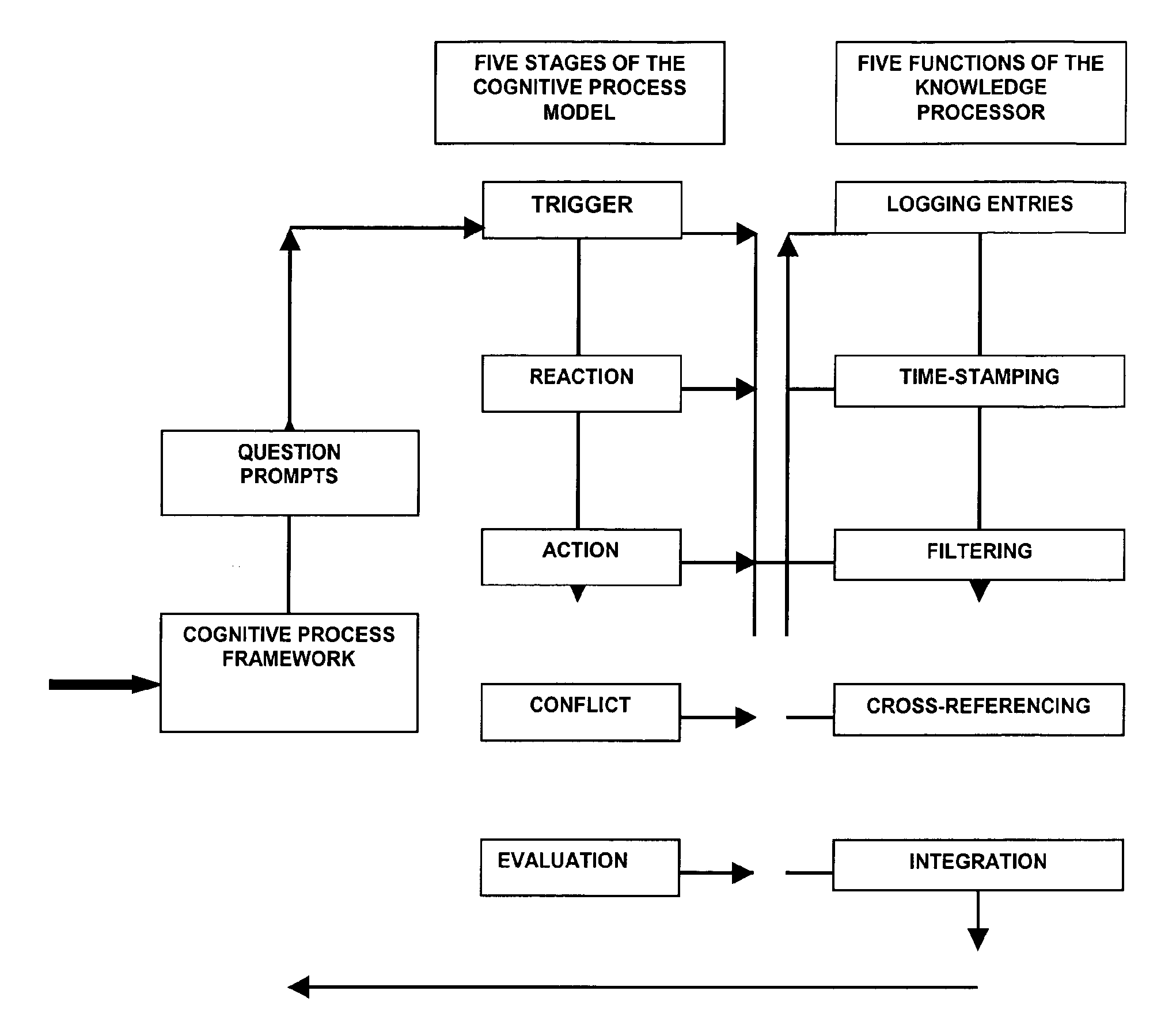
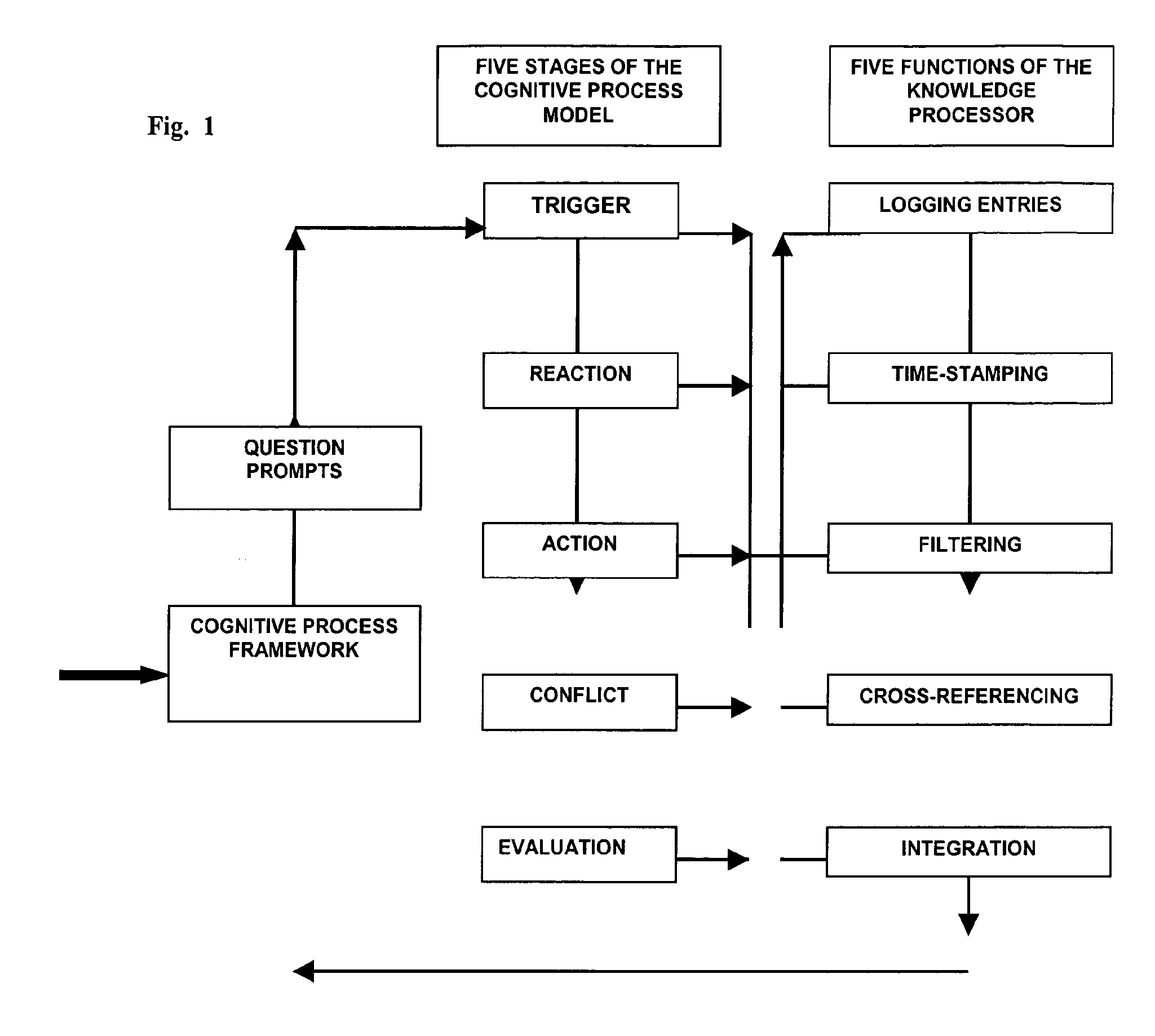
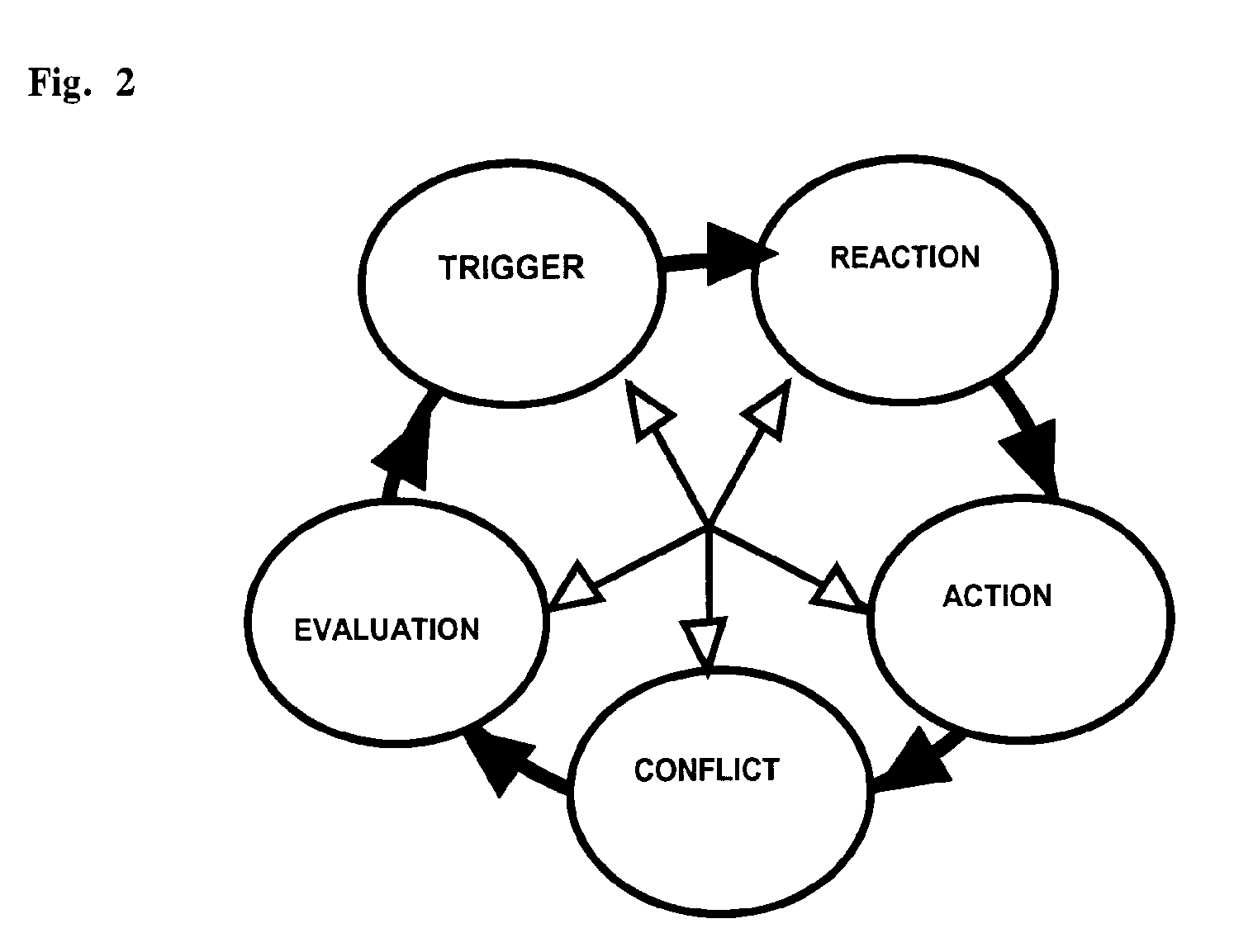
Natural language knowledge processor using trace or other cognitive process models
InactiveUS7853551B1Chaos modelsNon-linear system modelsCollaborative intelligenceOrganizational framework
A computer implemented method for process data management displays a set of natural language questions and provides an organizational framework for passively and actively collecting natural language information so users can coordinate problem-solving and project development. It addresses the application domain of collaborative group process and / or collaborative intelligence among humans and / or intelligent agents. In one embodiment, the method collects responses to the trigger questions; displays natural language reaction questions relating to collection of reactions to the triggers and receiving responses to the reaction questions; receives inputs of action steps to address the problem based on the triggers and reactions; guides the user to identify conflicts based on the triggers, reactions, and actions steps; generates a navigable map based on the triggers, reactions, actions steps, and conflicts for use to support and track the problem-solving process; and displays prompts for evaluating the problem based on the map.
Owner:GILL SUSAN P ZANN
Intuitive interfaces for real-time collaborative intelligence
Systems and methods for user interfaces for use on a computing device of a real-time collaborative computing system. A collaborative application runs on the computing device and displays information and data regarding the collaboration system and also receives user input via the user interface. The display interface arrangement may vary based on a type of collaborative session. Graphical user interfaces include a user interface based on a magnetic force model.
Owner:UNANIMOUS A I
Dynamic systems for optimization of real-time collaborative intelligence
Owner:UNANIMOUS A I
Methods and systems for real-time closed-loop collaborative intelligence
Owner:UNANIMOUS A I
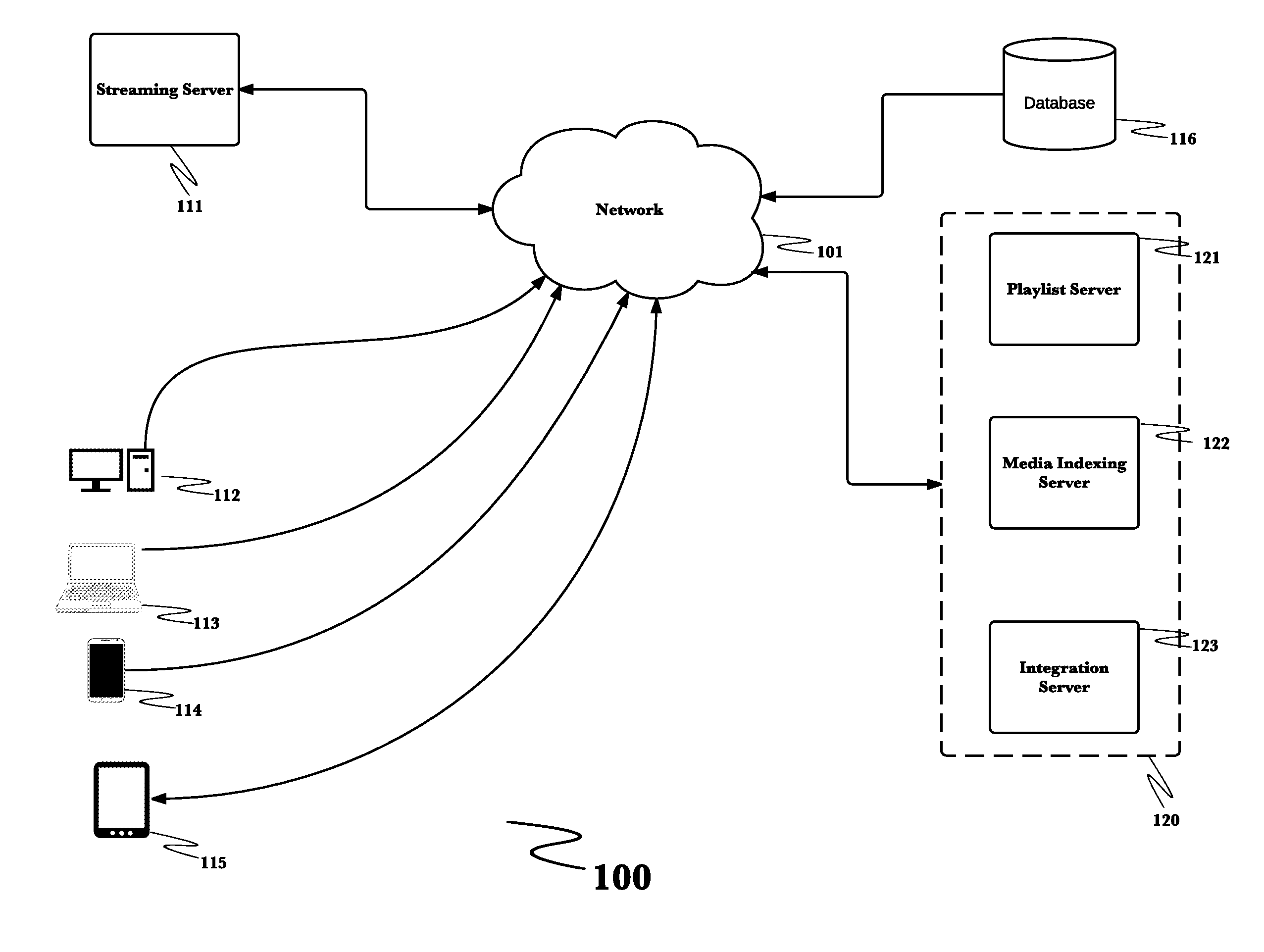
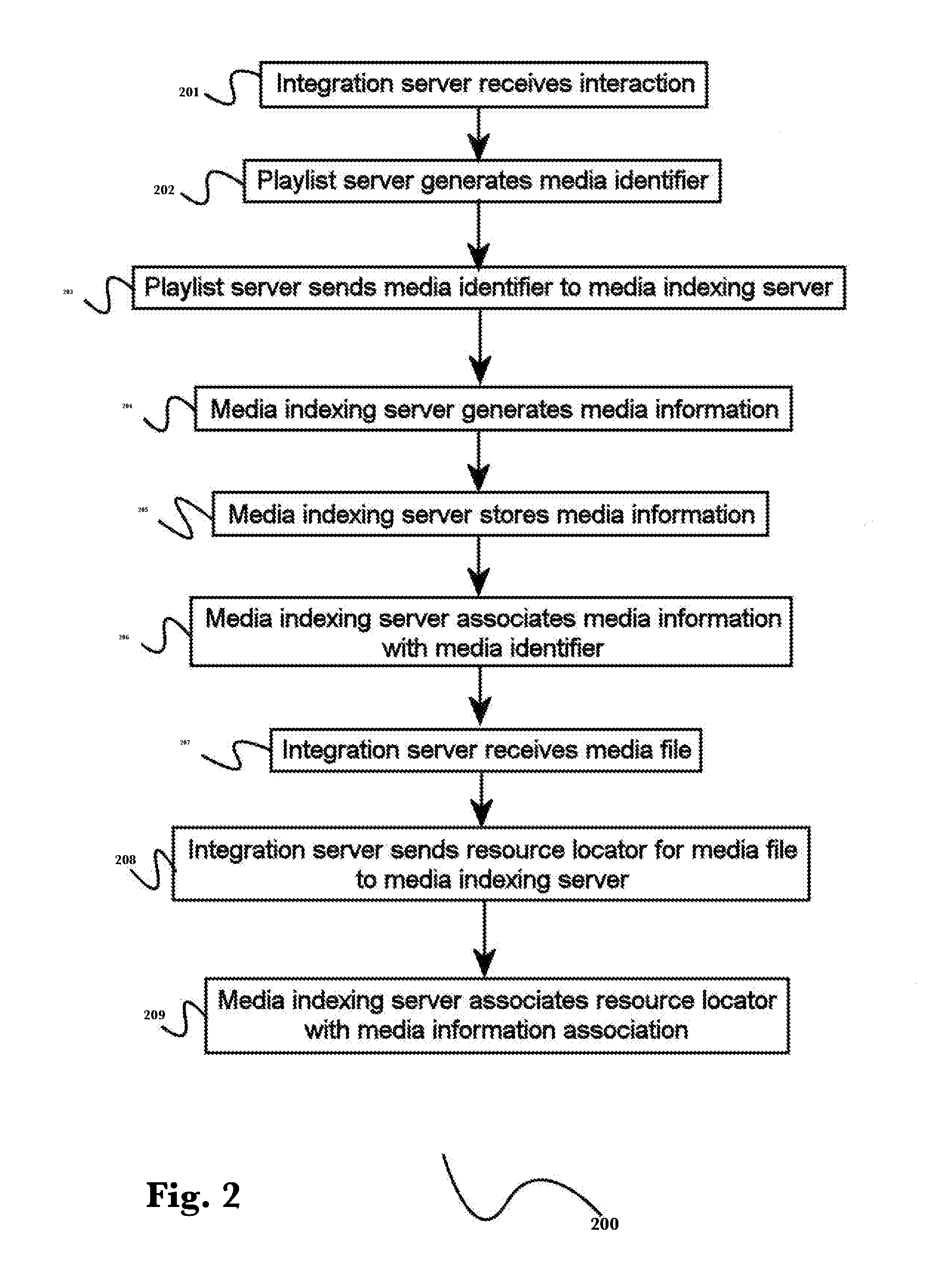
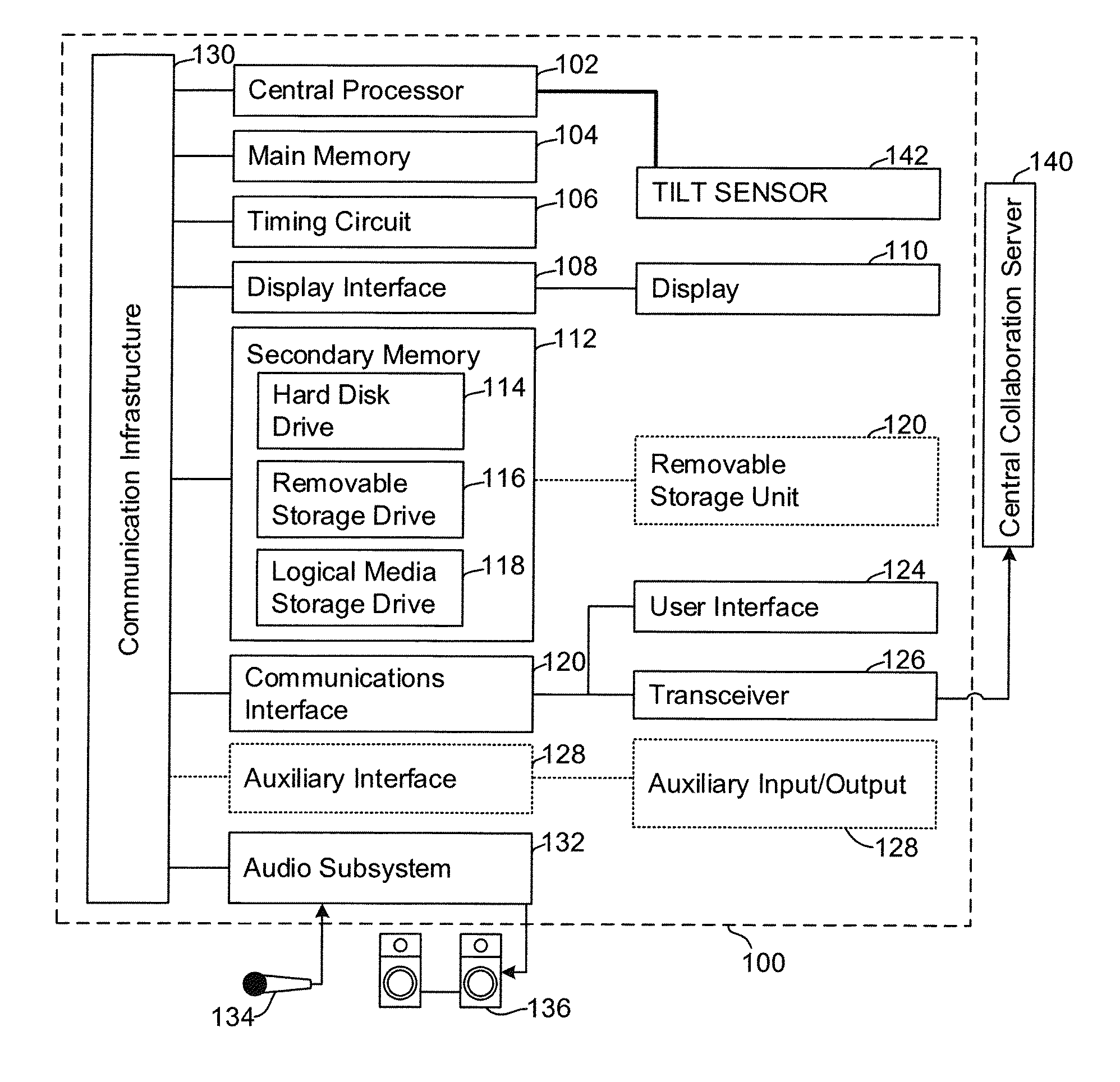
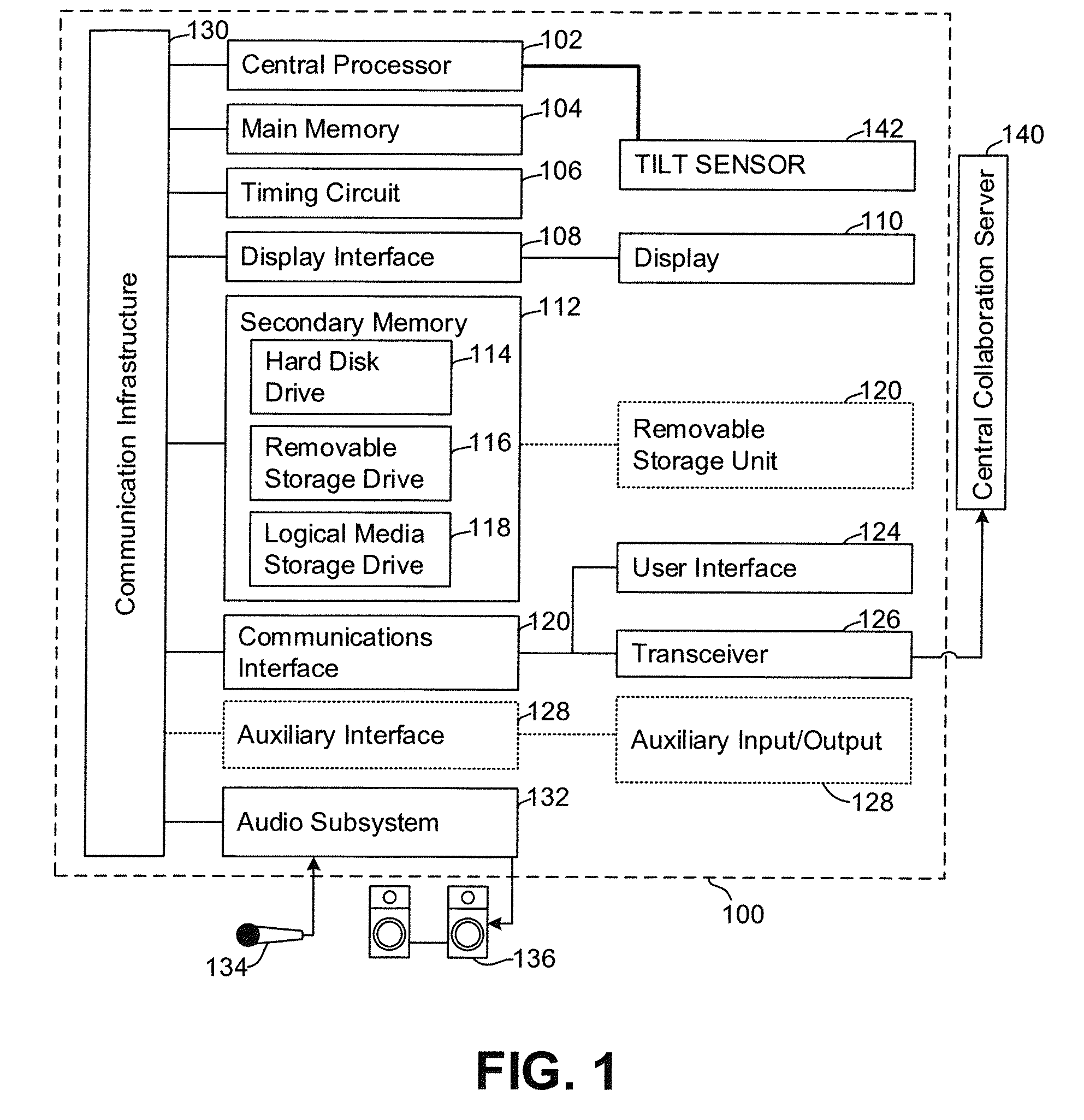
Collaborative intelligent media playlists
InactiveUS20160328396A1Many stepsMultimedia data indexingTransmissionCollaborative intelligenceSoftware
A system for providing collaborative intelligent media playlists, comprising a playlist server that stores and operates an ordered list of media identifiers, a media indexing server that stores media identifiers and media resource locators, and an integration server that operates software-based interfaces for communication with electronic devices via a network, and a method for providing collaborative intelligent media playlists.
Owner:ROKU INCORPORATED
Methods and systems for real-time closed-loop collaborative intelligence
Systems and methods are for enabling a group of individuals, each using an individual computing device, to collaboratively answer questions or otherwise express a collaborative will / intent in real-time. The collaboration system comprises a plurality of computing devices, each of the devices being used by an individual user, each of the computing devices enabling its user to contribute to the emerging real-time group-wise intent. A collaboration server is disclosed that communicates remotely to the plurality of individual computing devices. Herein, a variety of inventive methods are disclosed for interfacing users in a real-time synchronized group-wise experience, and for deriving a convergent group intent from the collective user input.
Owner:UNANIMOUS A I
Multi-group methods and systems for real-time multi-tier collaborative intelligence
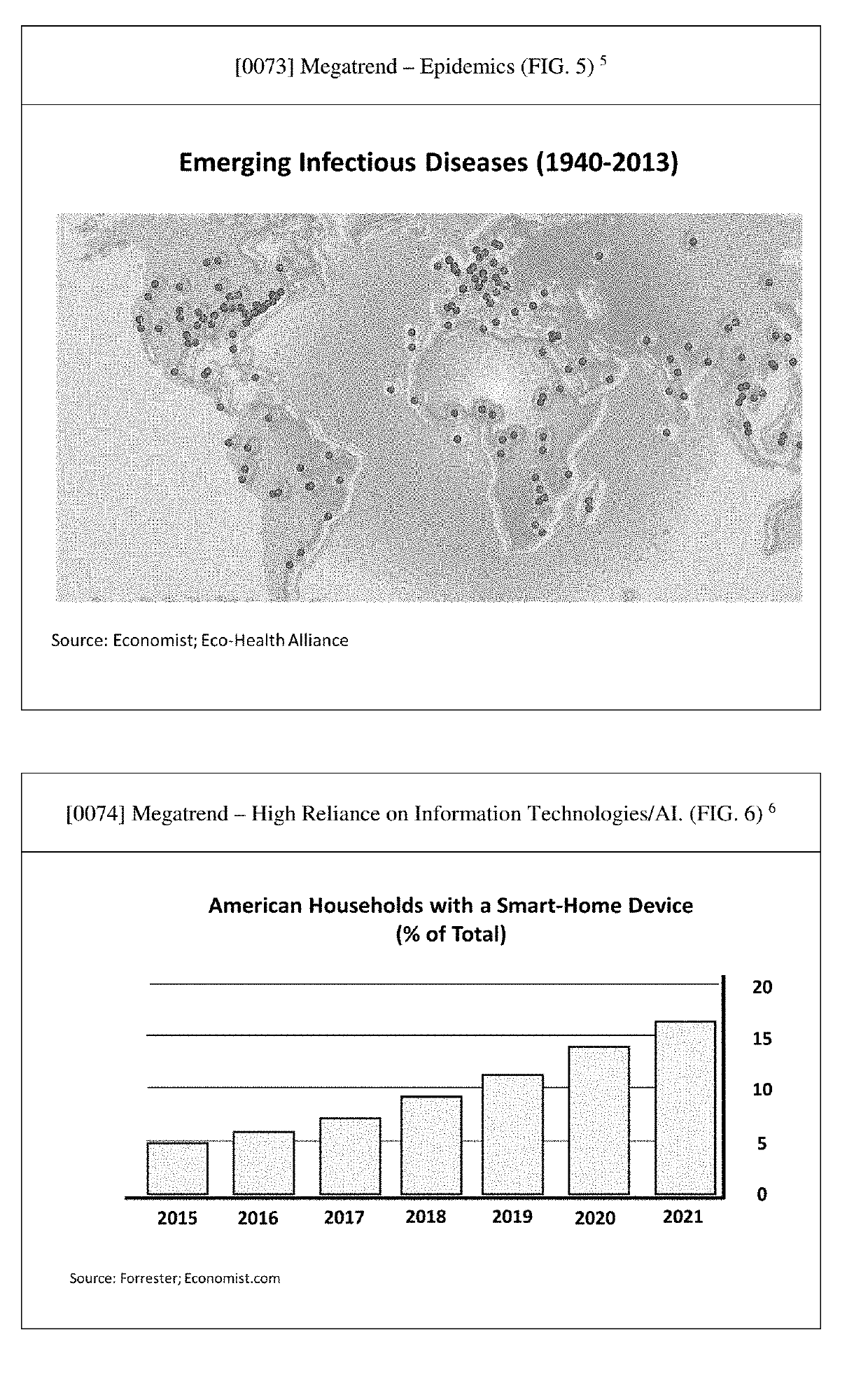
InactiveUS20160277457A9TransmissionInput/output processes for data processingCollaborative intelligenceGroup method
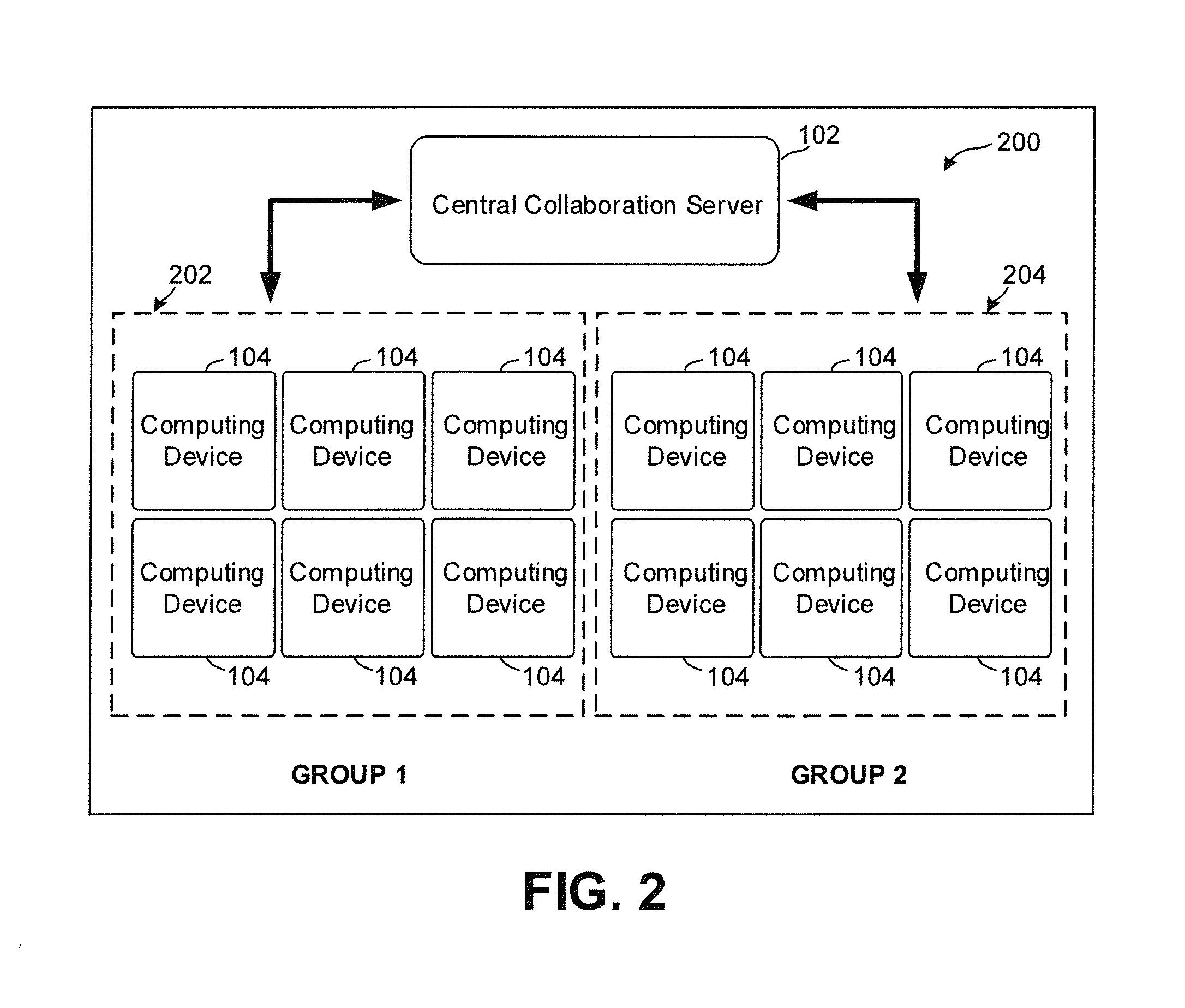
Systems and methods for deriving a real-time closed-loop collaborative intelligence from a plurality of users of a plurality of computing devices, the computing devices in communication with a central server. In some embodiments, a multi-level collaborative system divides the portable device users into groups, with one group providing feedback to another group. In other embodiments, a multi-tier system is used to designate multiple host devices in lieu of the central server. In some embodiments, the central server is used with a plurality of the multi-tier systems. Input methods for collaborative target selection and rating of group collaborative responses are also disclosed.
Owner:UNANIMOUS A I
Systems and methods for assessment and optimization of real-time collaborative intelligence systems
Systems and methods for real-time collaborative computing and collective intelligence are disclosed. A collaborative application runs on a collaborative server connected to a plurality of computing devices. Collaborative sessions are run wherein a group of independent users, networked over the internet, collaboratively answer questions in real-time, thereby harnessing their collective intelligence. A user performance value is determined for each of a plurality of independent users in the group based on each user's participation as compared to other users in the collaborative group. A group cohesiveness score is determined that quantifies the group's overall collaborative effectiveness. In some embodiments, the group cohesiveness score and user performance values are used to adjust weighting factors that affect the relative impact of each of the plurality of users in the collaborative group. In some embodiments, adjusting the weighting factors is performed with the objective of increasing the effectiveness of the resulting collective intelligence.
Owner:UNANIMOUS A I
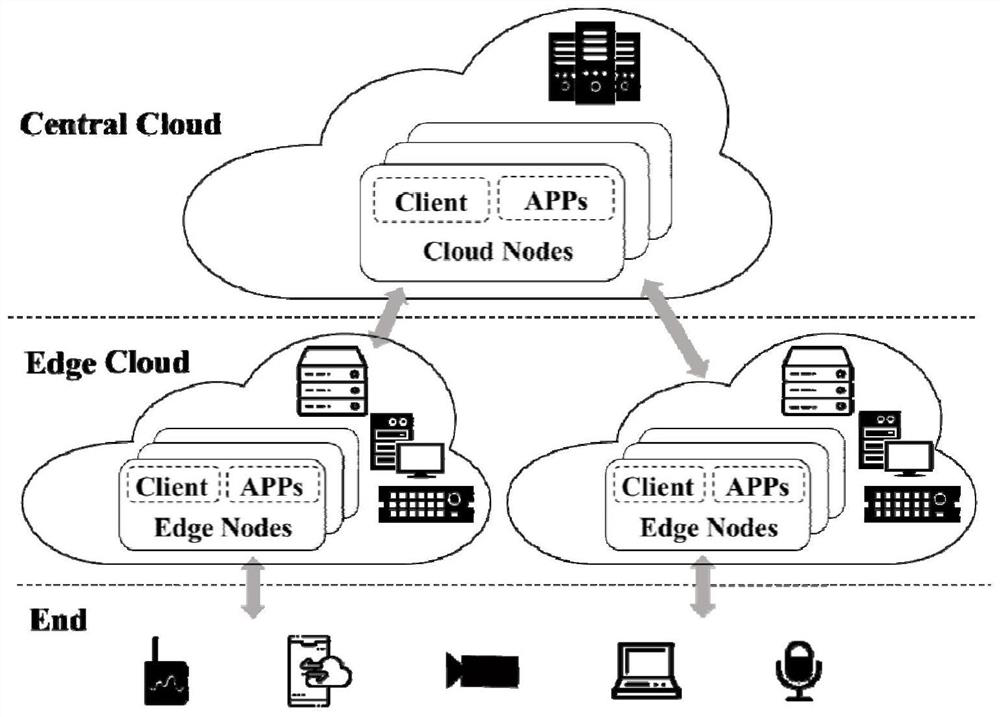
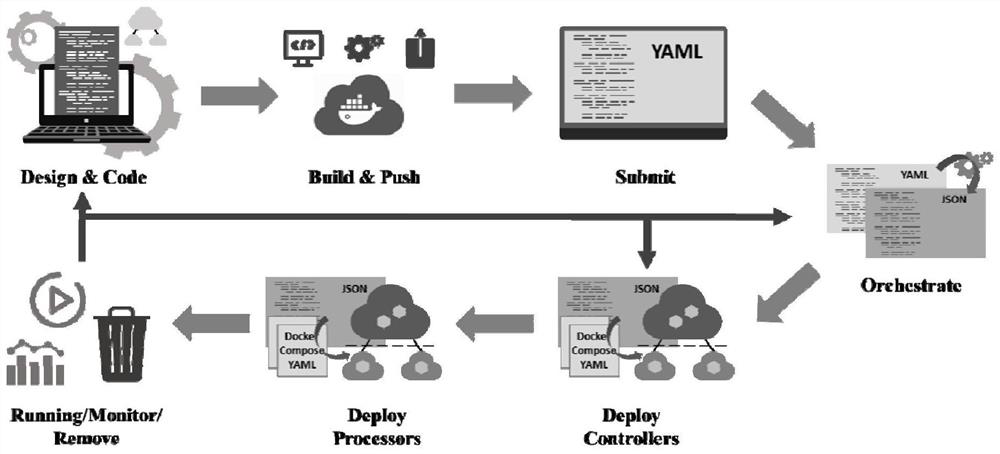
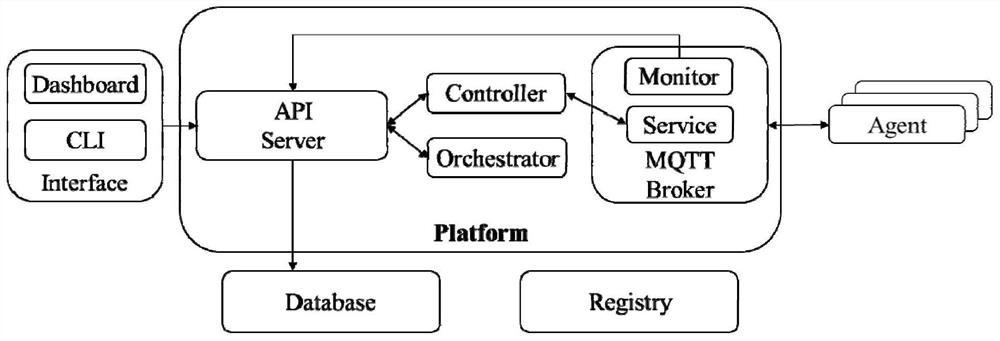
Platform management system and method for realizing side-cloud collaborative intelligent instant service
ActiveCN112272234AResource allocationDatabase management systemsSoftware engineeringCollaborative intelligence
The invention discloses a platform management system and method for realizing side-cloud collaborative intelligent instant service. The system is characterized in that the system comprises an interface service module, a controller, an orchestrator, MQTT message middleware, a node agent, a mirror image warehouse, a database, and a user interface; wherein the user interface, the database, the controller and the orchestrator are connected to the interface service module, the controller is further connected with MQTT message middleware, the MQTT message middleware is connected with the node agent,and the MQTT message middleware is connected with the interface service module. The platform management system for realizing side-cloud collaborative intelligent instant service provides an application description mode suitable for a universal side-cloud collaborative intelligent application, and further provides a platform management system for realizing side-cloud collaborative intelligence asa service through a data processing logic and a deployment scheme which contain the information and completely represent a complex cross-side-cloud artificial intelligence application in the description mode; a convenient interface is provided through the platform assembly to support efficient control of infrastructure and application life cycles.
Owner:杭州卷积云科技有限公司
Analyzing information technology systems using collaborative intelligence data anonimity
An information technology (IT) system of interest is analyzed using collaborative, community-based sharing of expert knowledge, analysis and advice through user-submitted analysis rules and / or user-submitted report templates. Users may submit rules that have been found to be useful in analyzing or managing IT systems. A rule may analyze a particular item of configuration data or performance data according to a predetermined criterion. Other users may apply these rules to their own systems' data and, thereby, utilize the collective expertise of the people who submitted the rules. Performance and configuration data from IT systems or components of the systems in various enterprises is collected and then sanitized by removing or masking identifying information before storing the sanitized data in a data warehouse. An IT manager may compare data from his / her IT system to historical data from the system or to data from IT systems having similar workloads, configurations, problems or according to other matching criteria, without obtaining confidential information about the comparison systems. Such comparisons may use the user-submitted rules. Reports are generated from these analyses and comparisons according to predefined and / or user-submitted report templates and report component templates for items such as text blocks, tables, graphs, charts and block diagrams.
Owner:TIMMINS SOFTWARE CORP
Multi-phase multi-group selection methods for real-time collaborative intelligence systems
ActiveUS10551999B2TransmissionInput/output processes for data processingUser inputCollaborative intelligence
Systems and methods for real-time collaborative computing and collective intelligence are disclosed. A collaborative application runs on a collaborative server connected to a plurality of computing devices. Collaborative sessions are run wherein a group of independent users, networked over the internet, collaboratively answer questions in real-time, thereby harnessing their collective intelligence. Systems and methods for selection among a set of user-input suggestions. The group is divided into subgroups, each subgroup selecting one suggestion from a subgroup of suggestions. The process is repeated with the remaining selected suggestions until one final target is selected, by the entire group, from the remaining suggestions.
Owner:UNANIMOUS A I
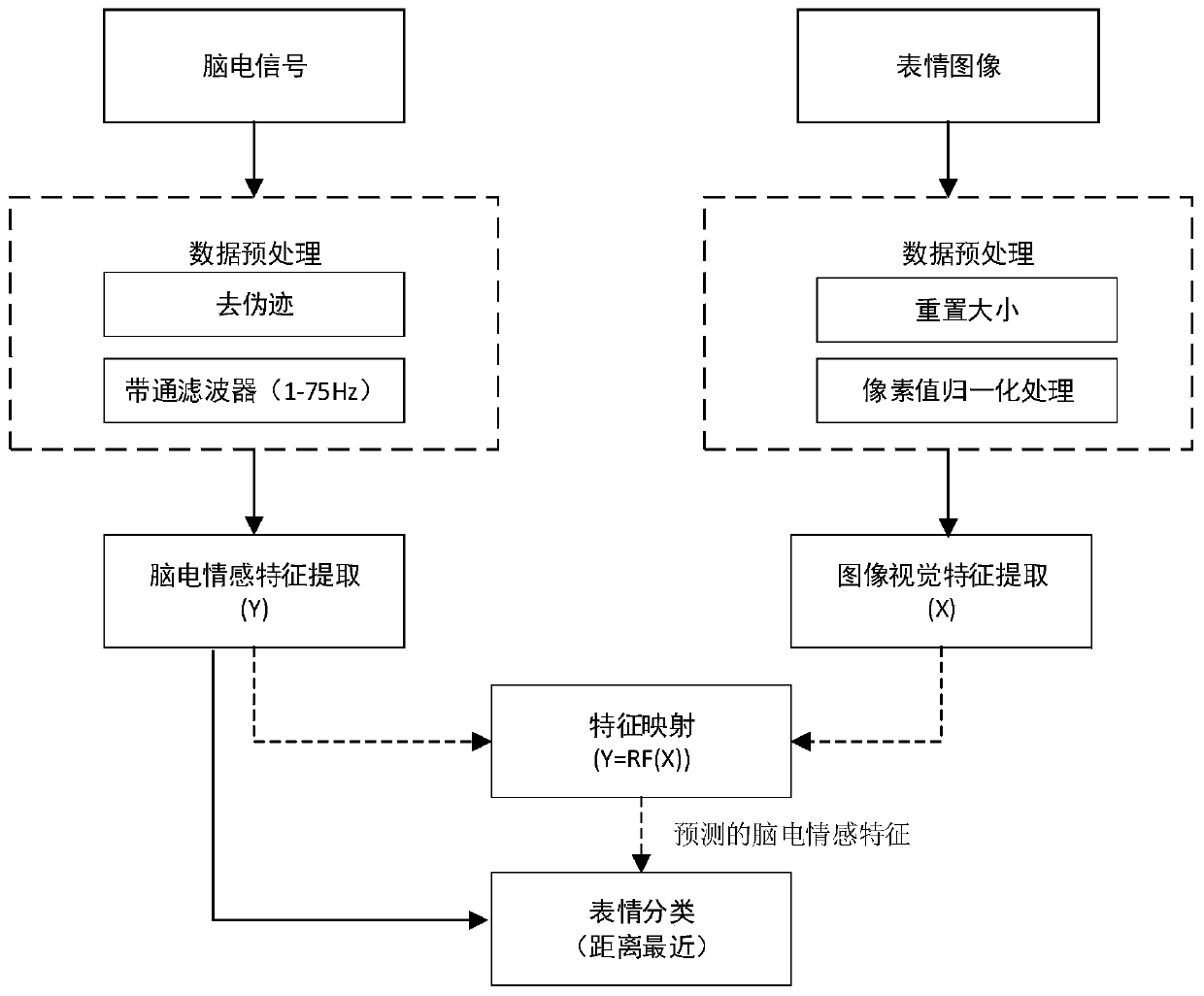
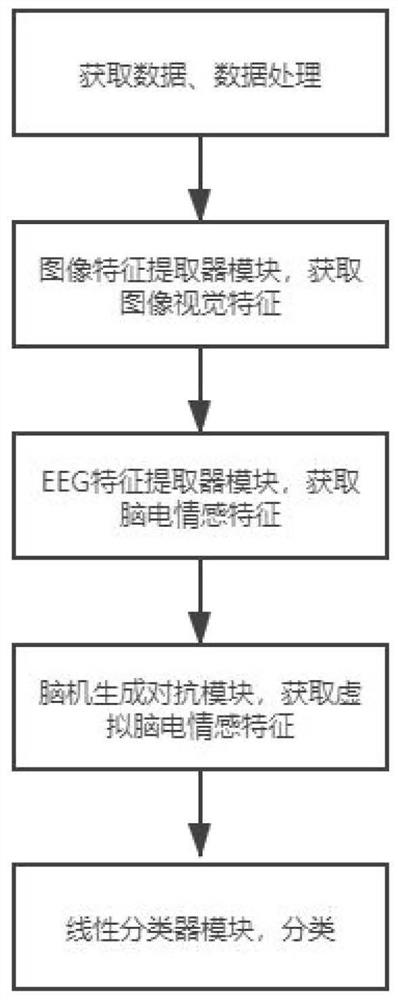
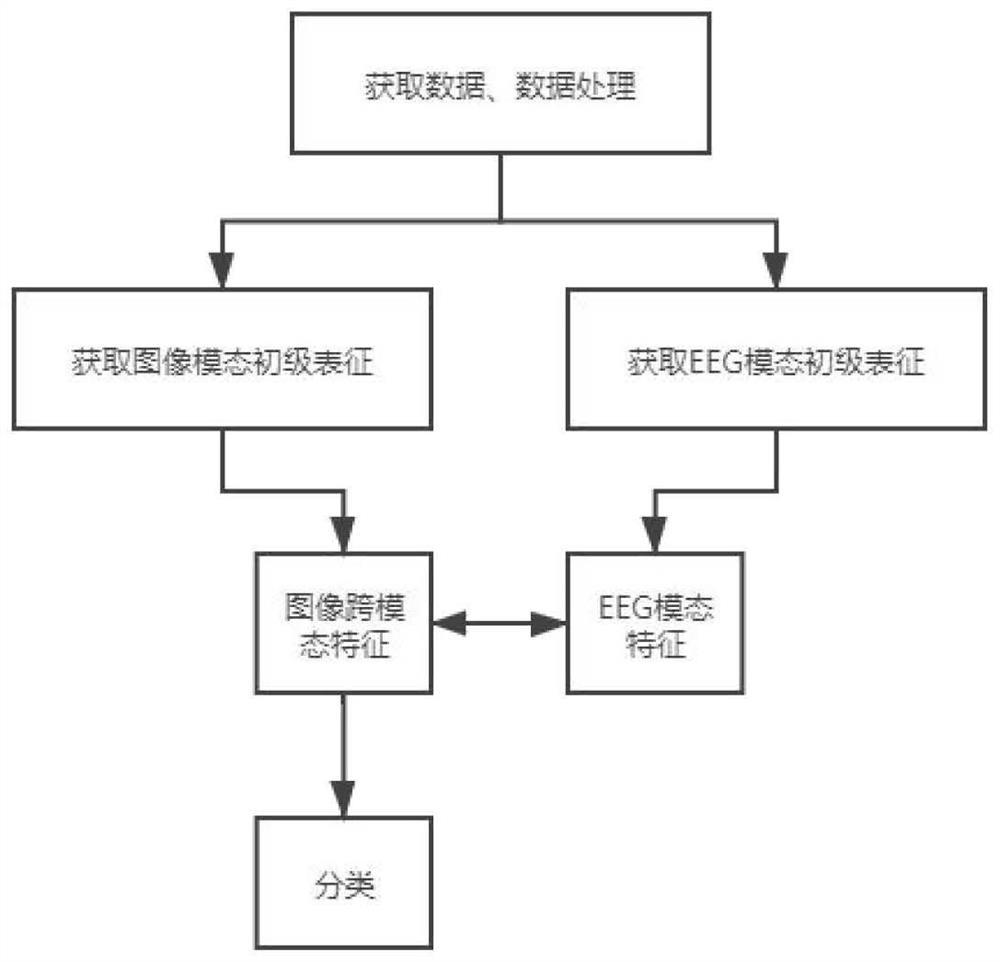
Expression recognition method based on brain-computer collaborative intelligence
ActiveCN110135244AAvoid fit problemsAvoid the modeling processMultiple biometrics useAcquiring/recognising facial featuresData acquisitionCollaborative intelligence
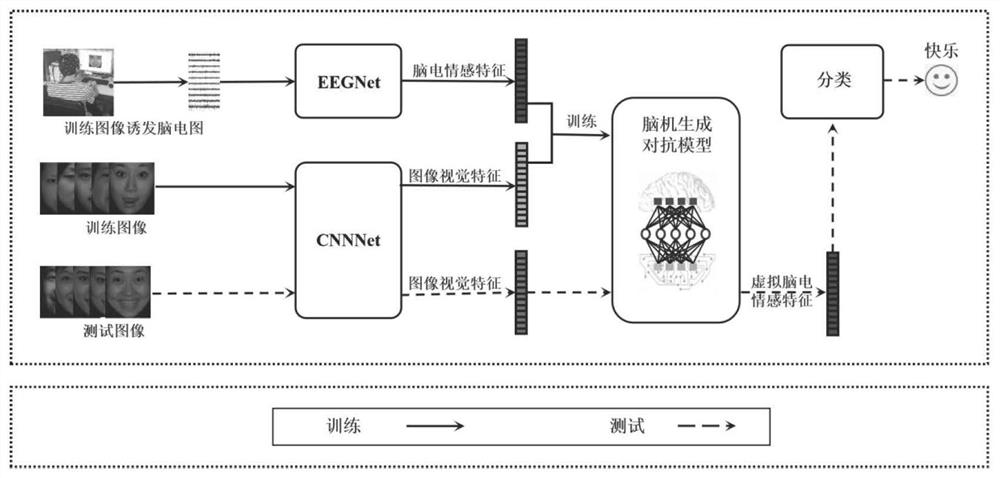
The invention relates to an expression recognition method based on brain-computer collaborative intelligence. The method mainly adopts a two-layer convolutional neural network to extract image visualfeatures of human face expressions, adopts a plurality of gating circulation units to extract electroencephalogram emotion features induced when the expressions are watched, establishes a mapping relation between the two features through a random forest regression model, and finally adopts K-neighbor classifier to carry out expression classification on the predicted electroencephalogram emotion features obtained by the regression model. The method comprises the steps of data acquisition, data preprocessing, image visual feature extraction, electroencephalogram emotion feature extraction, feature mapping and expression classification. Expression classification results show that a good classification result is obtained by adopting the predicted electroencephalogram emotion features. Comparedwith a traditional image vision method, the expression recognition method based on brain-computer collaborative intelligence is a promising emotion calculation method.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
Emotion recognition method based on brain-computer generative adversarial
ActiveCN113974627AEasy to collectImprove accuracySensorsPsychotechnic devicesMedicineCollaborative intelligence
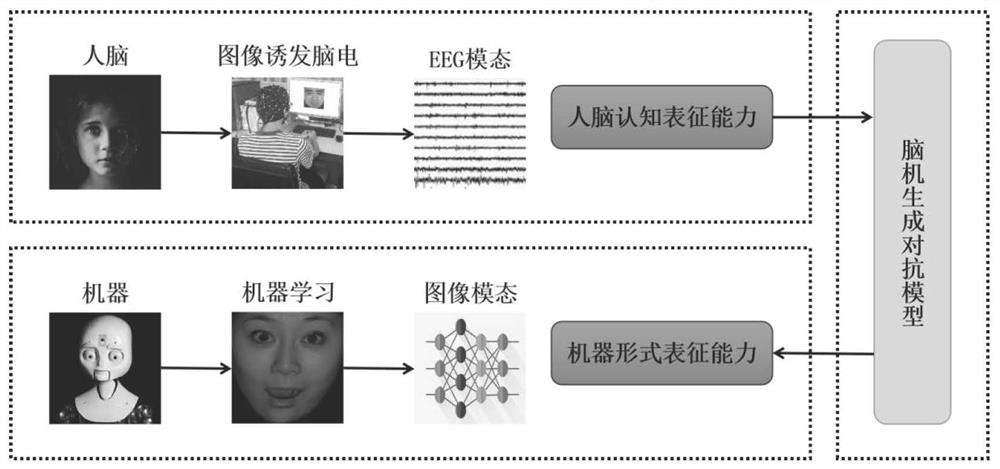
The invention discloses an emotion recognition method based on brain-computer generative adversarial. For an emotion recognition task, cognitive representation with emotions is obtained after the human brain processes information, while a machine only learns representation in an image form. If a generation relation between the cognitive representation with emotions and the representation in an image form can be established, a machine can be guided to learn through the human brain and endowed with the emotion cognitive ability of the human brain. In order to give information perceived by a human brain to a machine, a generation model from image visual features to electroencephalogram emotion features needs to be established, so that generation from formal representation to cognitive representation is realized. According to the method, the relation between electroencephalogram emotion features and image visual features is explored, the relation between formal representation and cognitive representation is established, and brain-computer collaborative intelligence is achieved. In order to reduce the difference between cognitive representation and formal representation and enable the formal representation to infinitely approach the cognitive representation, the invention designs an emotion recognition method based on brain-computer generative adversarial.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
Global digital framework integrated to develop economically competitive municipalities
InactiveUS20190228490A1Improve thinking processesSpeed up the processPayment architectureOffice automationDigital videoCollaborative intelligence
A global digital framework integrated by methods, systems, processes, and new thinking technologies focused on the development of secure, sustainable, collaborative, intelligent, resilient, and economically competitive municipalities. The frameworks intends to provide high quality knowledge, multimedia information, and municipal / city strategies in sectors such as education, security, energy, water, health, information technologies (IT), transportation, construction, food, environment, waste, and fmance; through the use of virtual reality technologies, algorithms, personal computer technology, big-data technologies, smart-phone technology, GPS technology, artificial intelligence systems, digital videos, behavioral change technologies, augmented reality systems, and digital advisory systems among other technologies.
Owner:PRIETO MARQUEZ RICARDO ALEJANDRO +2
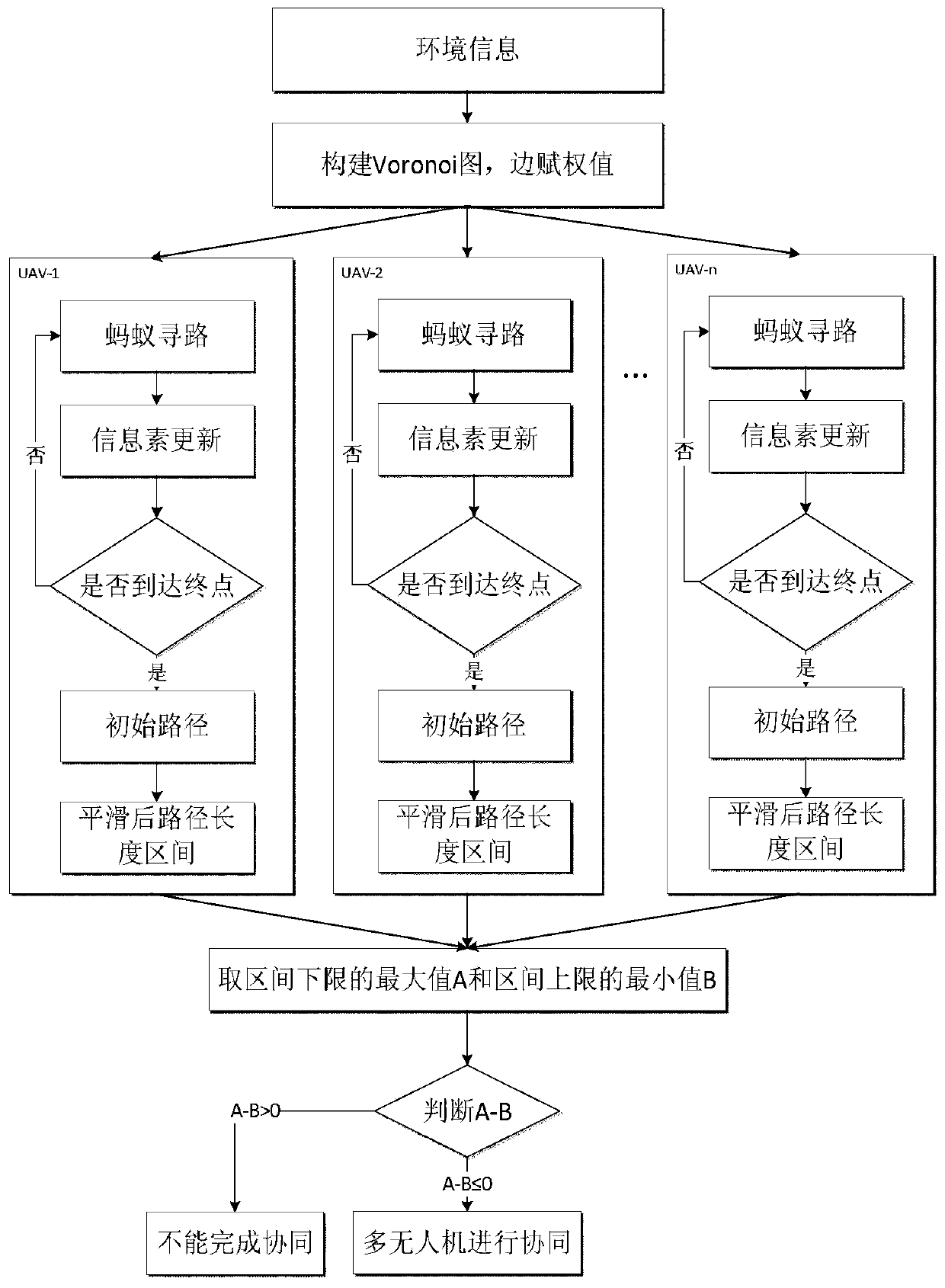
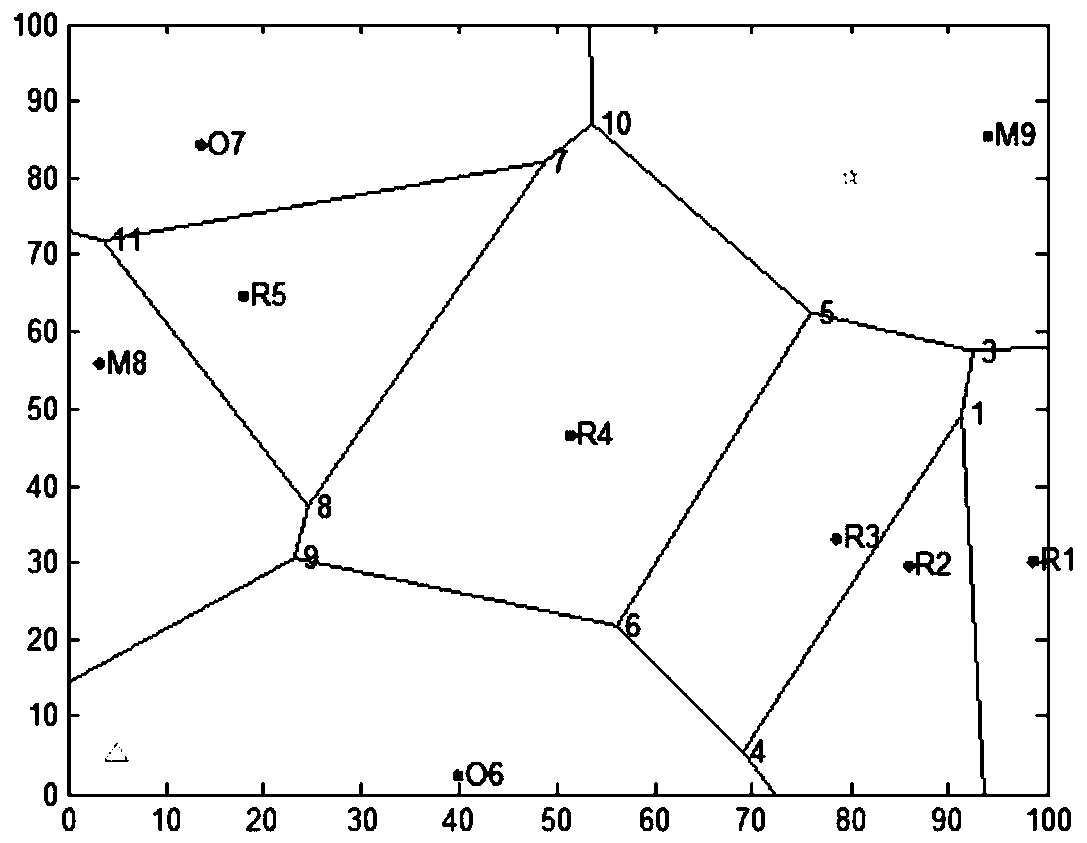
A multi-UAV collaborative path planning method based on ant colony algorithm
ActiveCN106705970BEnsure flight safetyImprove the detection rateNavigational calculation instrumentsUncrewed vehicleCollaborative intelligence
Owner:CHINESE AERONAUTICAL RADIO ELECTRONICS RES INST
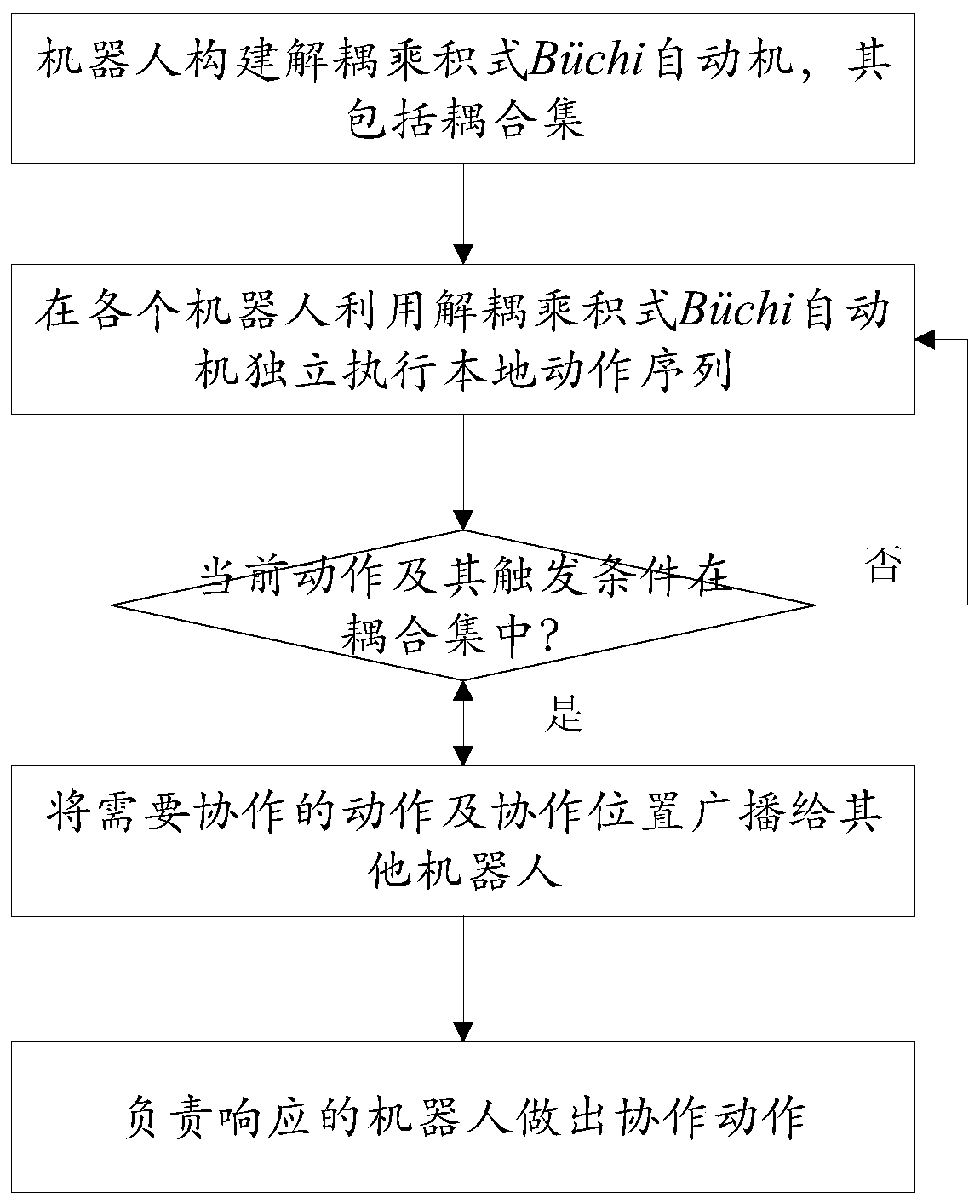
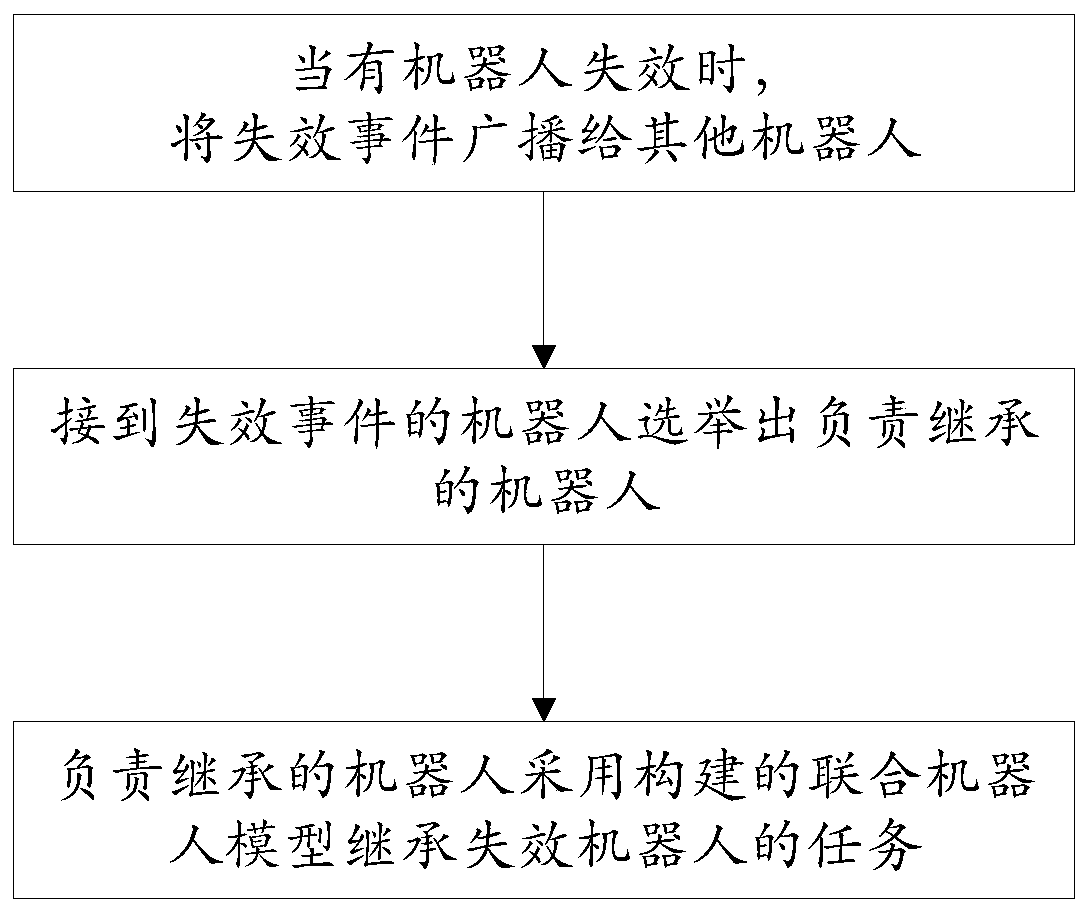
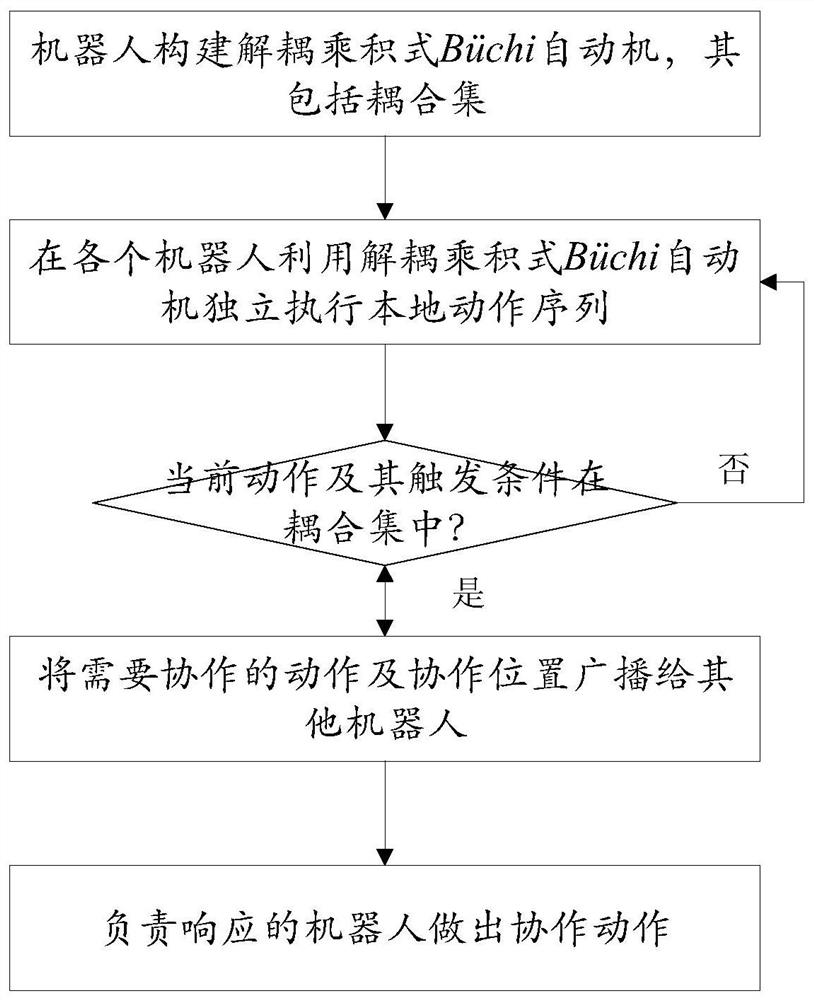
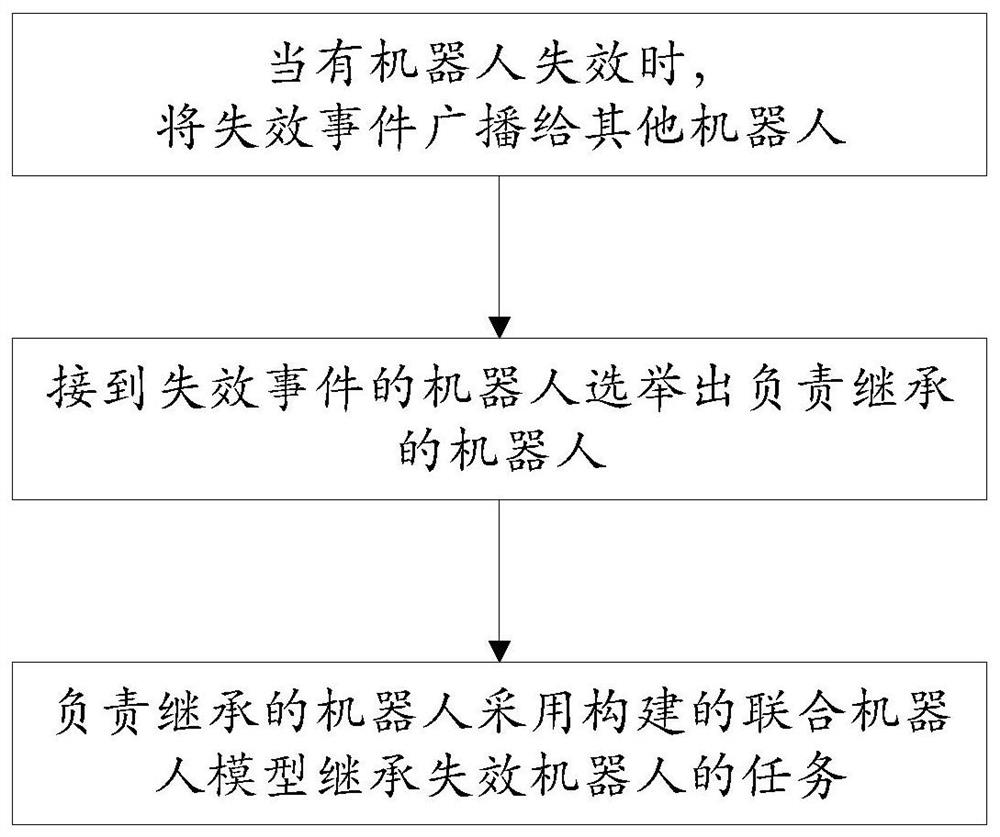
Distributed multi-agent task cooperation method based on linear sequential logic
The invention discloses a distributed multi-agent task cooperation method based on linear sequential logic, and solves the problem of multi-agent task decoupling. Each intelligent agent constructs a decoupling product Buchi automatic machine of the intelligent agent by detecting a coupling edge, and constructs an action sequence of the intelligent agent through the decoupling product Buchi automatic machine; the endpoints of the coupling edges correspond to actions needing cooperation; when each intelligent agent independently executes an action sequence of the intelligent agent by utilizing the decoupling product Buchi automaton, whether a currently executed action and a corresponding triggering condition are in the coupling set or not is judged, and if so, it is determined that the currently executed action is an action needing cooperation, and the cooperative intelligent agent is asked to cooperatively make an action; and when the agent fails, the task that the agent responsible forinheritance inherits the failed agent is elected.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
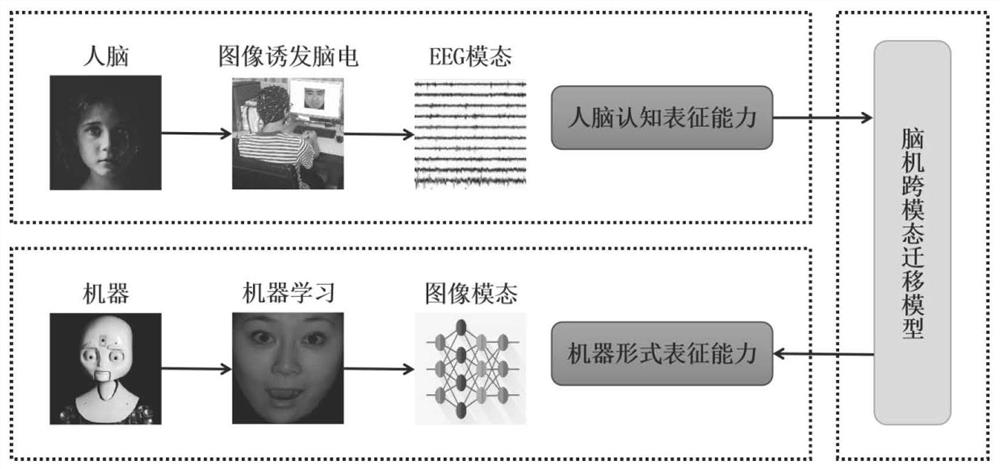
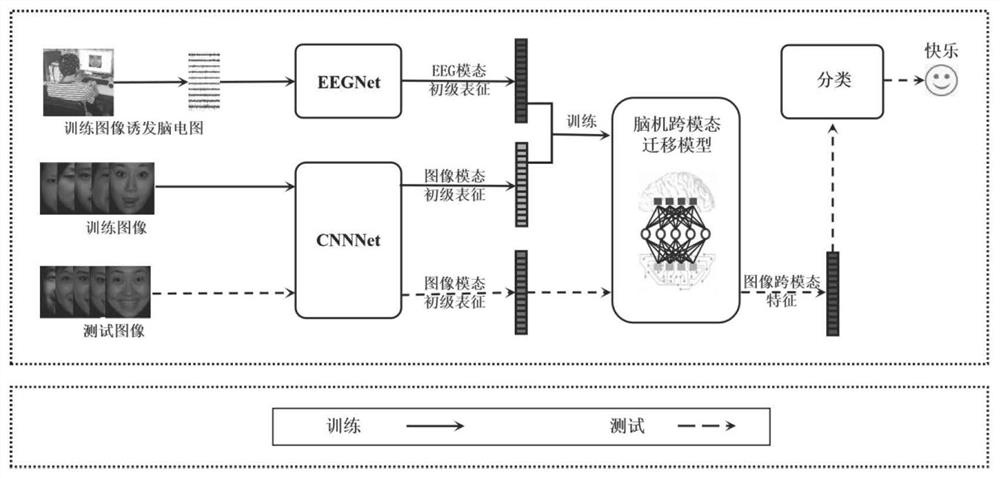
Emotion recognition method based on brain-computer cross-modal migration
PendingCN113974625AImprove accuracyImprove stabilityCharacter and pattern recognitionSensorsCollaborative intelligenceEmotion identification
The invention discloses an emotion recognition method based on brain-computer cross-modal migration. For an emotion recognition task, cognitive representation with emotions is obtained after a human brain processes information, what is obtained by machine learning is only the formal representation of an image, and if a migration relation between the cognitive representation and the formal representation can be established, machine learning is guided through the human brain, and the machine is endowed with the emotion cognitive ability of the human brain; in order to give information perceived by the human brain to the machine, a cross-modal migration model of an image mode and an electroencephalogram mode needs to be established, so that the migration relation between the formal representation and cognitive representation is obtained. According to the method, the migration relation between the electroencephalogram mode and the image mode is explored, the relation between formal representation and cognitive representation is established, and brain-computer collaborative intelligence is achieved. In order to reduce the difference between the cognitive representation and formal representation and enable the formal representation to infinitely approach the cognitive representation, the invention designs the emotion recognition method based the brain-computer cross-modal migration.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
A distributed multi-agent task cooperation method based on linear temporal logic
ActiveCN111340348BReduce time complexityImprove COPResourcesLinear temporal logicCollaborative intelligence
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com