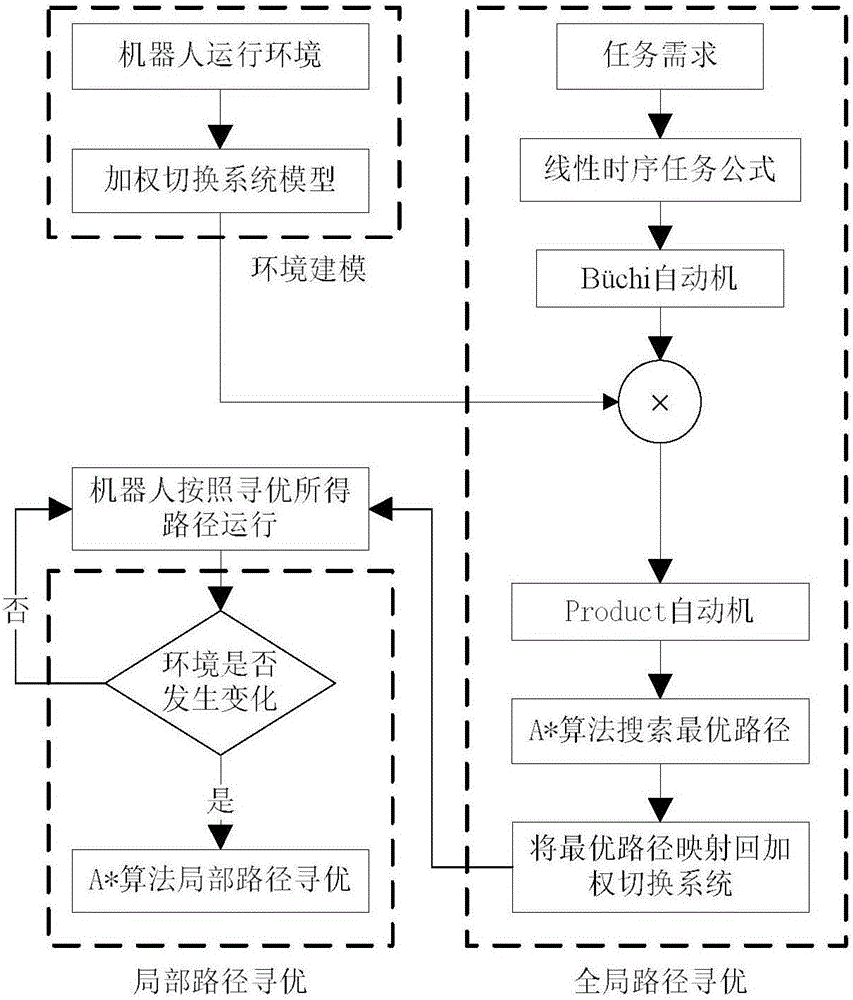
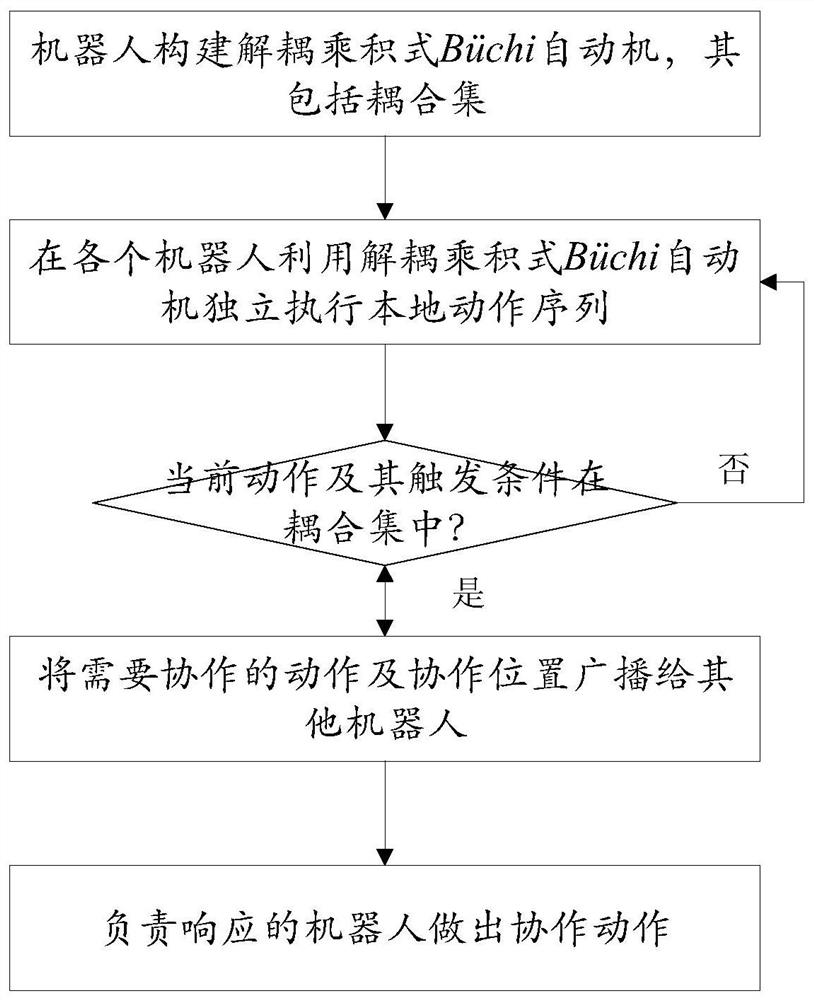
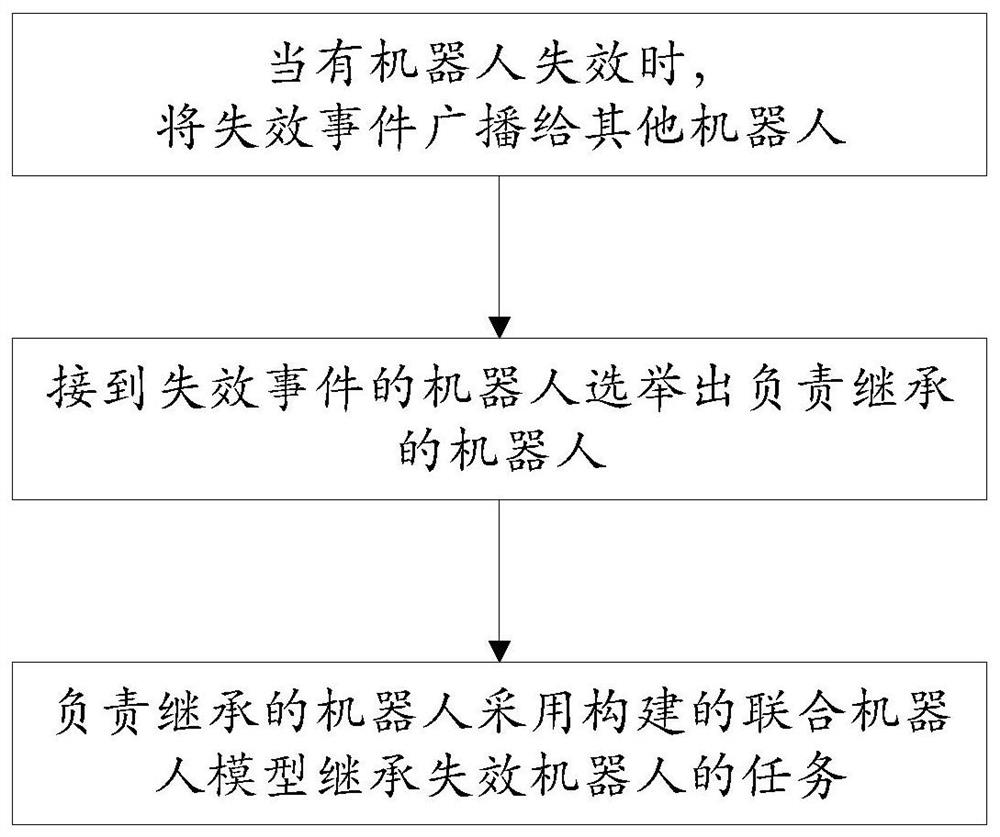
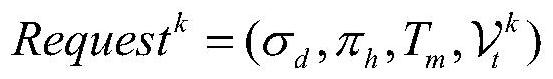Patents
Literature
42 results about "Linear temporal logic" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In logic, linear temporal logic or linear-time temporal logic (LTL) is a modal temporal logic with modalities referring to time. In LTL, one can encode formulae about the future of paths, e.g., a condition will eventually be true, a condition will be true until another fact becomes true, etc. It is a fragment of the more complex CTL*, which additionally allows branching time and quantifiers. Subsequently LTL is sometimes called propositional temporal logic, abbreviated PTL. Linear temporal logic (LTL) is a fragment of first-order logic.
Single mobile robot optimal itineration control method based on target tracking control strategy
ActiveCN104834309AEasy searchHigh precisionPosition/course control in two dimensionsDecompositionClosed loop
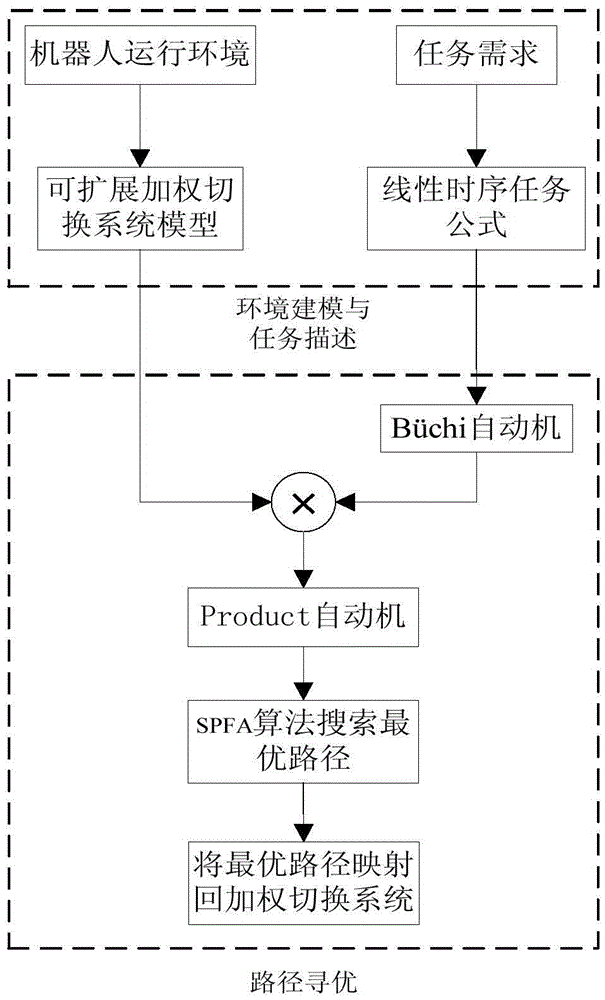
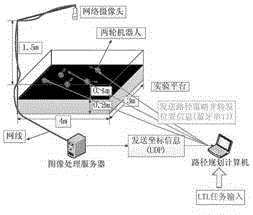
Provided is a single mobile robot optimal itineration control method based on a target tracking control strategy. The method comprises seven steps of map construction, task description, topology construction, optimal path searching, task decomposition, target tracking control, and pose information feedback. The method comprises: firstly, based on a linear temporal logic theory, combining a constructed weighting switching system and a linear temporal logic task formula, establishing task feasible network topology; then, using an optimal path searching method based on a Dijkstra algorithm to search an optimal path, and storing discrete coordinate points in environment corresponding to the optimal path in cache, and sending the discrete coordinate points to a target tracking controller in order; then, using a target tracking control method to give a controlled quantity to control a robot to move to a target point according to distance between the robot and the target point and deviation of angles; and finally, in an operation process of the robot, using a global camera to acquire present position coordinate and orientation information of the robot in real time, and feeding back to the target tracking controller, so as to realize closed-loop control.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Storage robot path program method based on linear temporal logic theory
ActiveCN105467997AGuaranteed optimalityComplete efficientlyPosition/course control in two dimensionsVehiclesShortest Path Faster AlgorithmLinear temporal logic
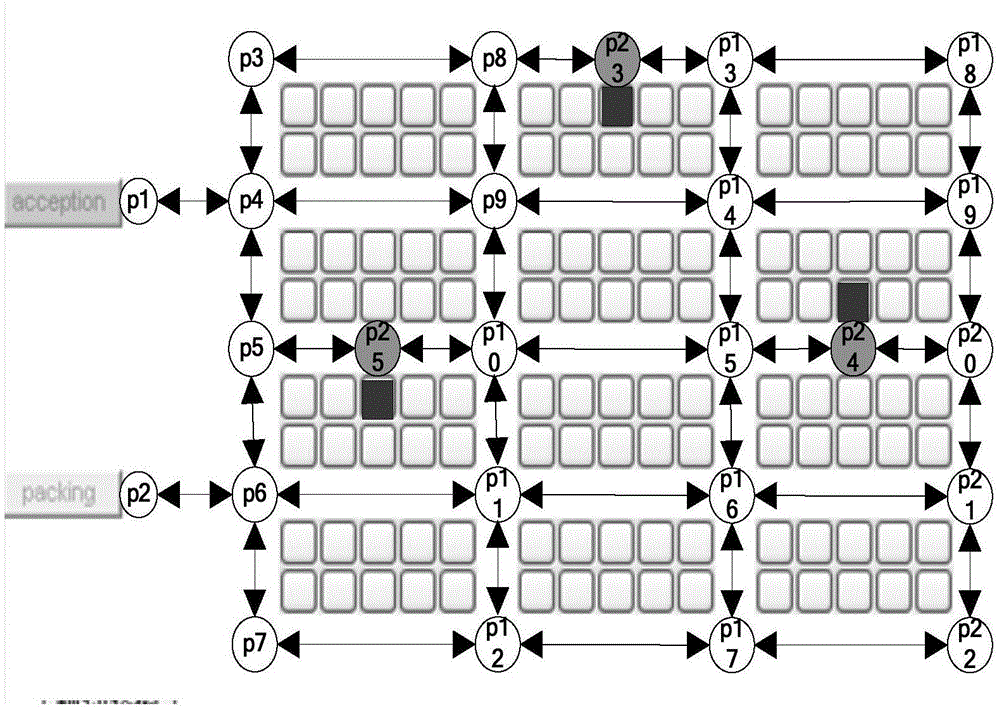
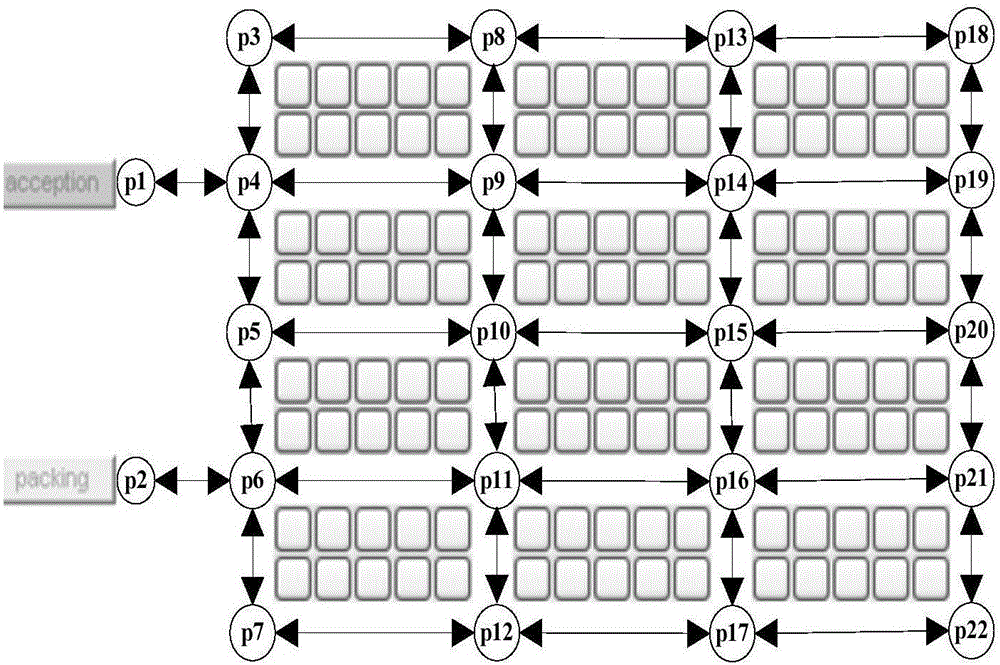
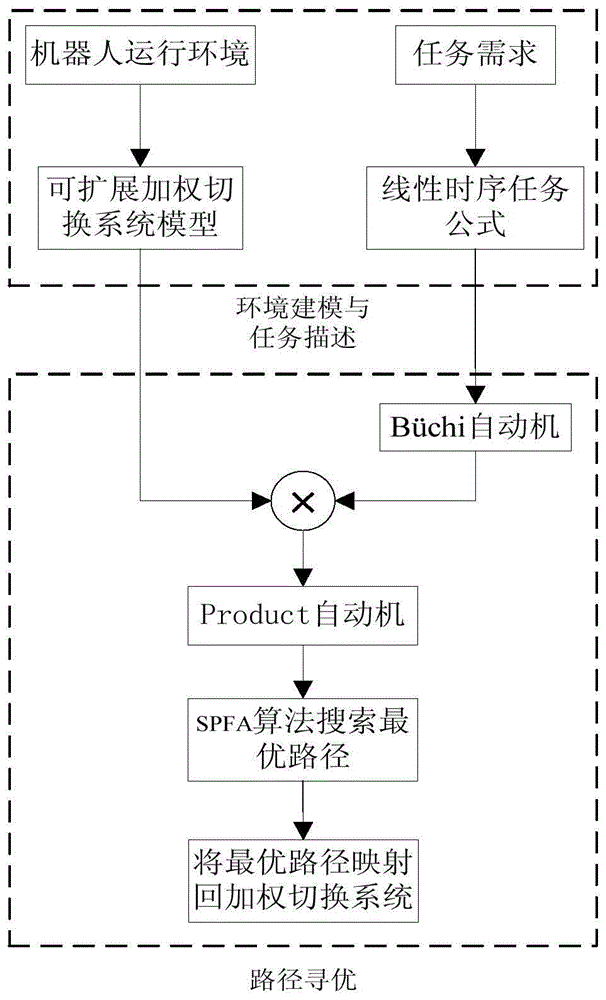
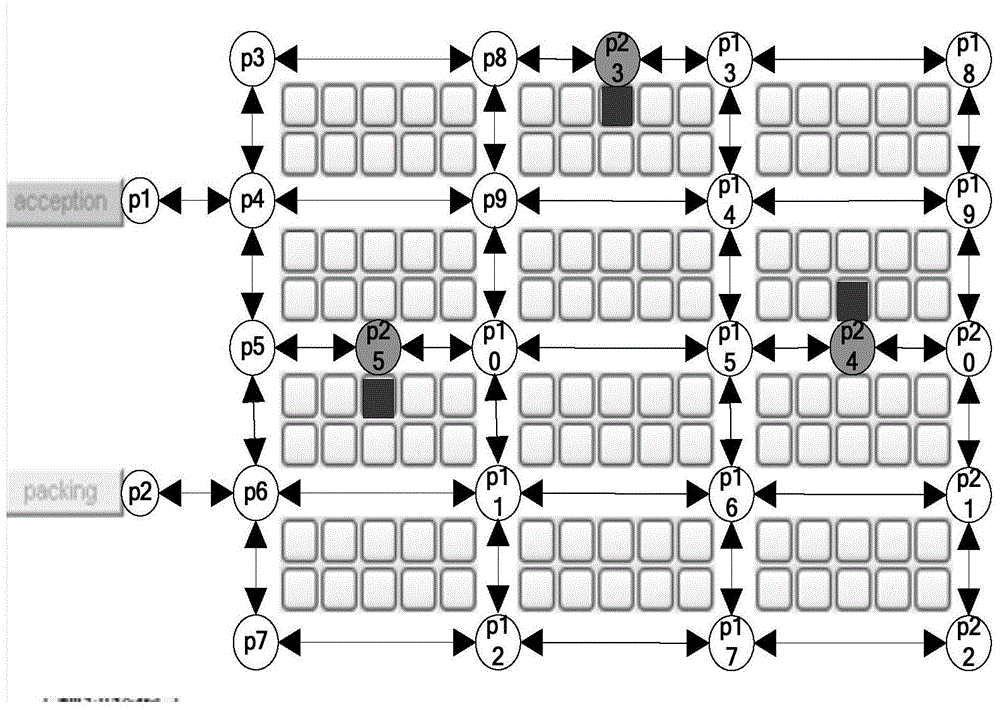
A storage robot path program method based on linear temporal logic theory comprises the steps of modeling a storage environment into a weight switching system based on assignment nodes; describing complex assignment tasks of the storage system by using the linear temporal logic language (LTL); then, switching the task formula into a Buchi automatic machine through an LTL2BA tool kit; conducting cartesian product to the extensible weight switching system and the Buchi automatic machine to form a task feasible network topology; employing SPFA(Shortest Path Faster Algorithm) on the topology to search an optimal path, wherein the task feasible network topology includes storage environment information and package-taking task information, guaranteeing that the searched obtained path is the optimal path and isn't influenced by the order of the selected assignment node; mapping the obtained optimal path from the task feasible network topology to the corresponding optimal path in the storage environment, and sending the optimal path to a storage robot by radio communication through a PC to finish the packaging-taking and assignment task.
Owner:FOSHAN KINGPENG ROBOT TECH CO LTD
Optimal itineration control method satisfying complex requirement
InactiveCN104834308AImprove efficiencyEfficient integrationPosition/course control in two dimensionsSimulationLinear temporal logic
Provided is a robot optimal itineration control method satisfying complex requirements. The method comprises six steps of establishing a weighting switching system, establishing a task chart of a Buchi automata, establishing task feasible network topology of a Product automata, searching an optimal path, performing fuzzy logic control, and feeding back pose information. The method comprises: firstly, based on linear temporal logic, combining with robot operation environment information, programming the optimal path satisfying task requirements; and then, by using a fuzzy control strategy, combining with present position coordinate and orientation information of the robot fed back in real time, according to angular deviation [alpha] and distance deviation d between a present mobile robot and a target point, giving controlled quantities of speed vl and vr of a left wheel and a right wheel of the robot, so as to realize optimal path tracking control. The method can plan the optimal path which conforms to robot operation environment and satisfies complex itineration task requirements, and the method can effectively control the robot to realize optimal path tracking, so as to complete appointed tasks.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
LTL-A*-A*optimal path planning method applicable to dynamic environment
ActiveCN106500697AEfficient executionImprove search efficiencyNavigational calculation instrumentsAdaptive controlLocal optimumPlanning approach
The invention discloses an LTL-A*-A*optimal path planning method applicable to dynamic environment. The advantage of meeting complex mission requirements in actual application of linear temporal logic (LTL) and the advantage of being high in search efficiency of the A*algorithm are combined, and the method mainly includes LTL-A*global path optimization and local path optimization based on the A*algorithm. First, the optimal path meeting the task requirement in the environment is partially searched out through LTL-A*global path optimization; then, a robot tracks the global optimal path obtained through searching and detects environment information; finally, when local environment changes, a part segment in the global optimal path cannot continue allowing passage, the local optimal path is searched for by adopting the A*algorithm, the segment not allowing passage is bypassed, and operation continues along the global optimal path to complete an appointed task.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Method, system, and computer-accessible medium for inferring and/or determining causation in time course data with temporal logic
ActiveUS20110167031A1Facilitate richer causal relationshipFacilitate causal relationshipFuzzy logic based systemsKnowledge representationTime courseLinear temporal logic
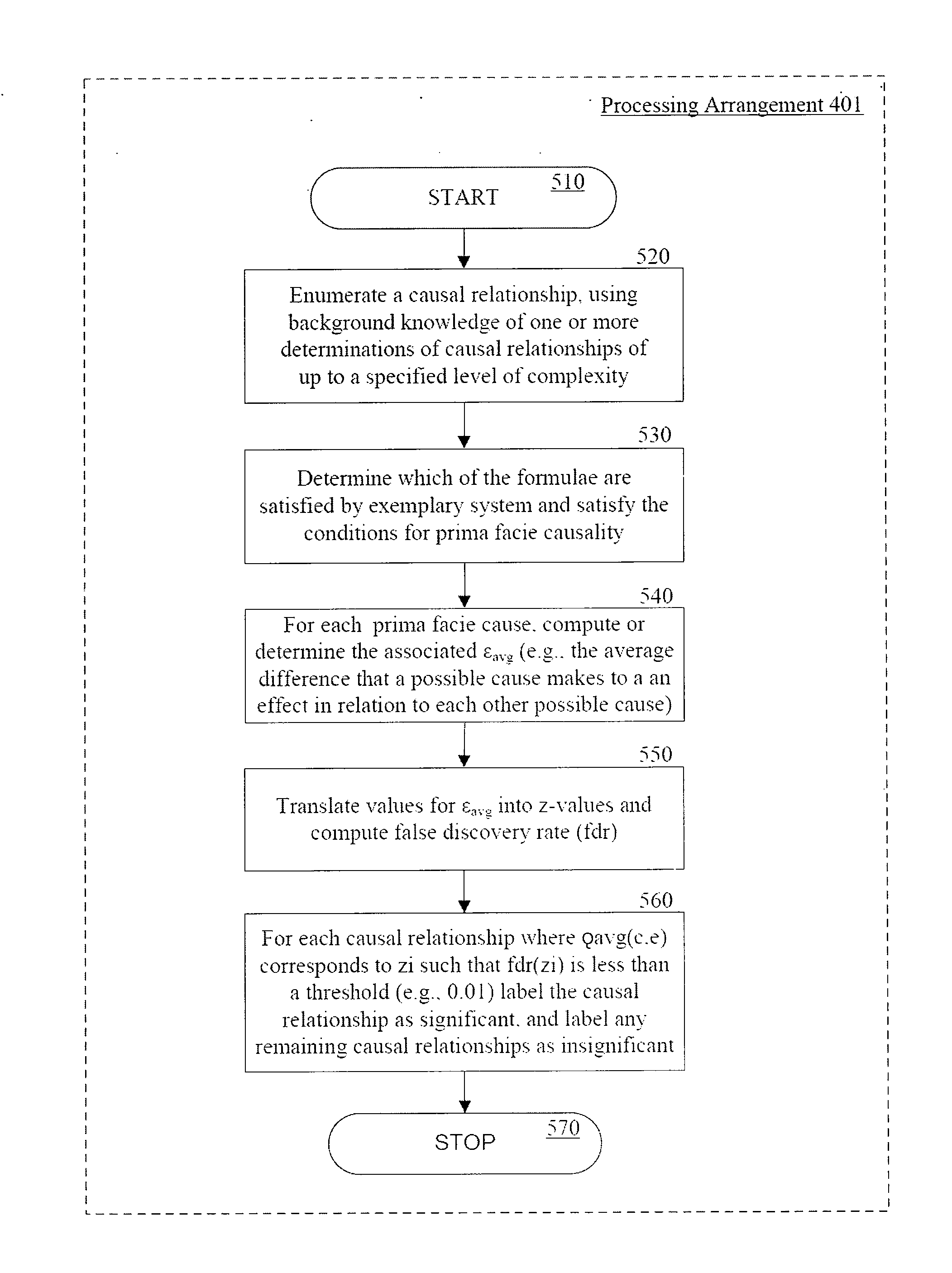
Time-course data with an underlying causal structure may appear in a variety of domains, including, e.g., neural spike trains, stock price movements, and gene expression levels. Provided and described herein are methods, procedures, systems, and computer-accessible medium for inferring and / or determining causation in time course data based on temporal logic and algorithms for model checking. For example, according to one exemplary embodiment, the exemplary method can include receiving data associated with particular causal relationships, for each causal relationship, determining average characteristics associated with cause and effects of the causal relationships, and identifying the causal relationships that meet predetermined requirement(s) as a function of the average characteristics so as to generate a causal relationship. The exemplary characteristics associated with cause and effects of the causal relationships can include an associated average difference that a cause can make to an effect in relation to each other cause of that effect.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
Efficient source of infeasibility identification in timed automata traces
ActiveUS8645310B2Chaos modelsNon-linear system modelsLinear temporal logicTheoretical computer science
A method for verifying the performance of a real-time system modeled as a timed automaton. An abstract model of the system is checked against an initial Linear Temporal Logic specification. If a path to an undesirable state is found, the counterexample is validated or invalidated using negative cycle detection. If a negative cycle is detected, optimization is undertaken to identify a minimal infeasible fragment in the negative cycle. The specification is then refined to eliminate usage of the minimal infeasible fragment, and the abstract model is then checked against the refined specification.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Hybrid nanotube/CMOS dynamically reconfigurable architecture and an integrated design optimization method and system therefor
InactiveUS8117436B2EfficiencyLong latencySolid-state devicesDigital computer detailsLinear temporal logicEngineering
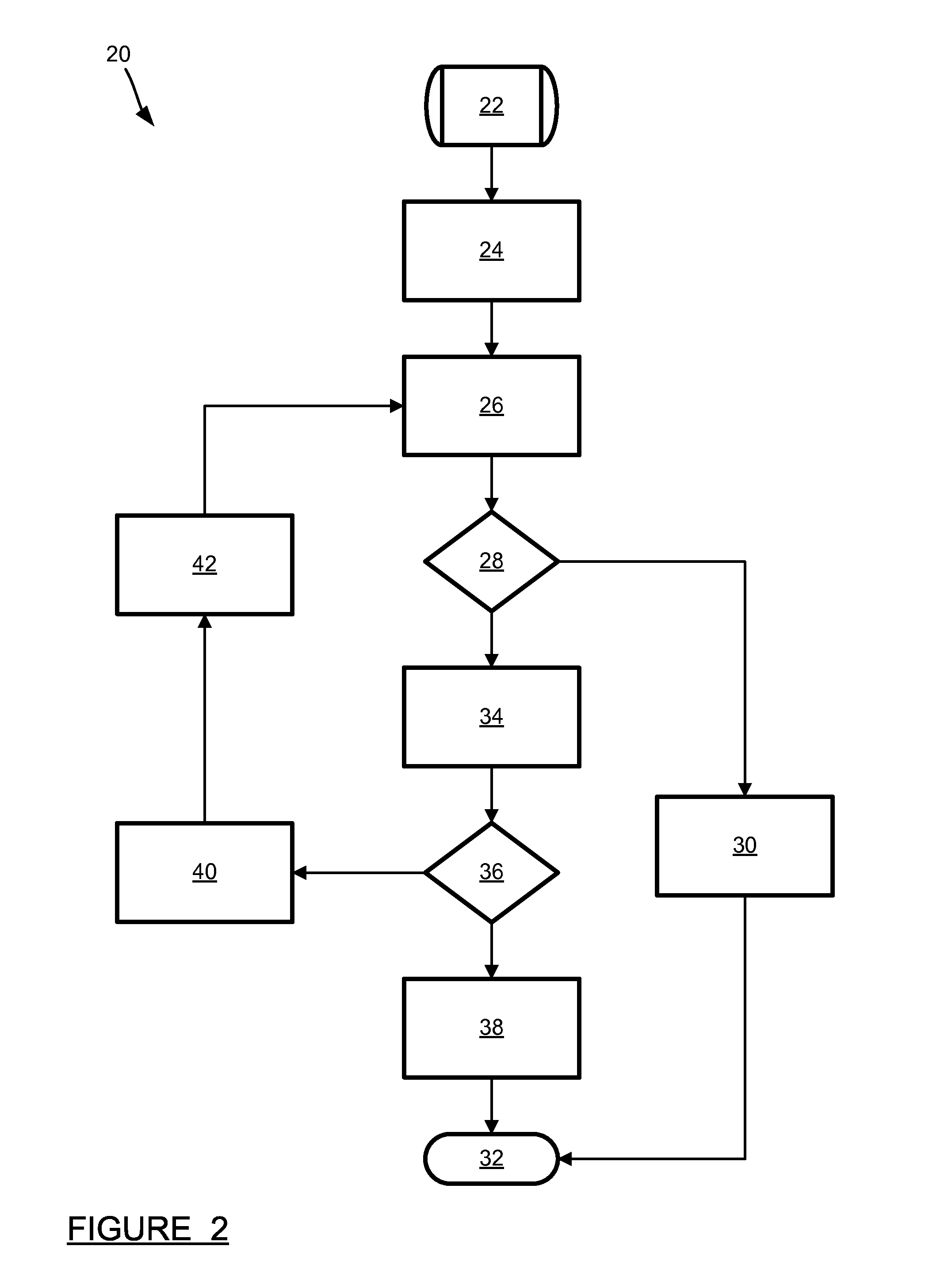
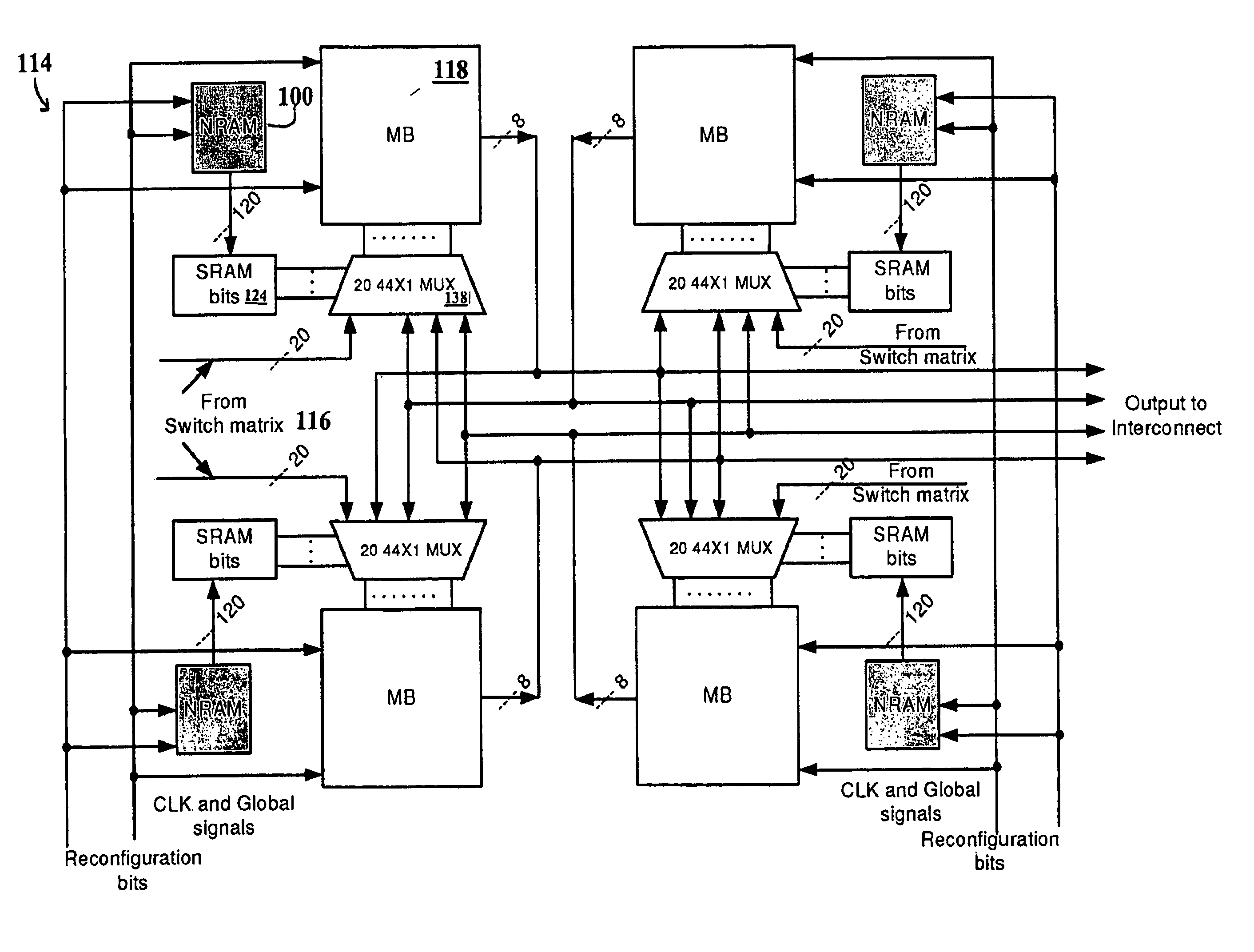
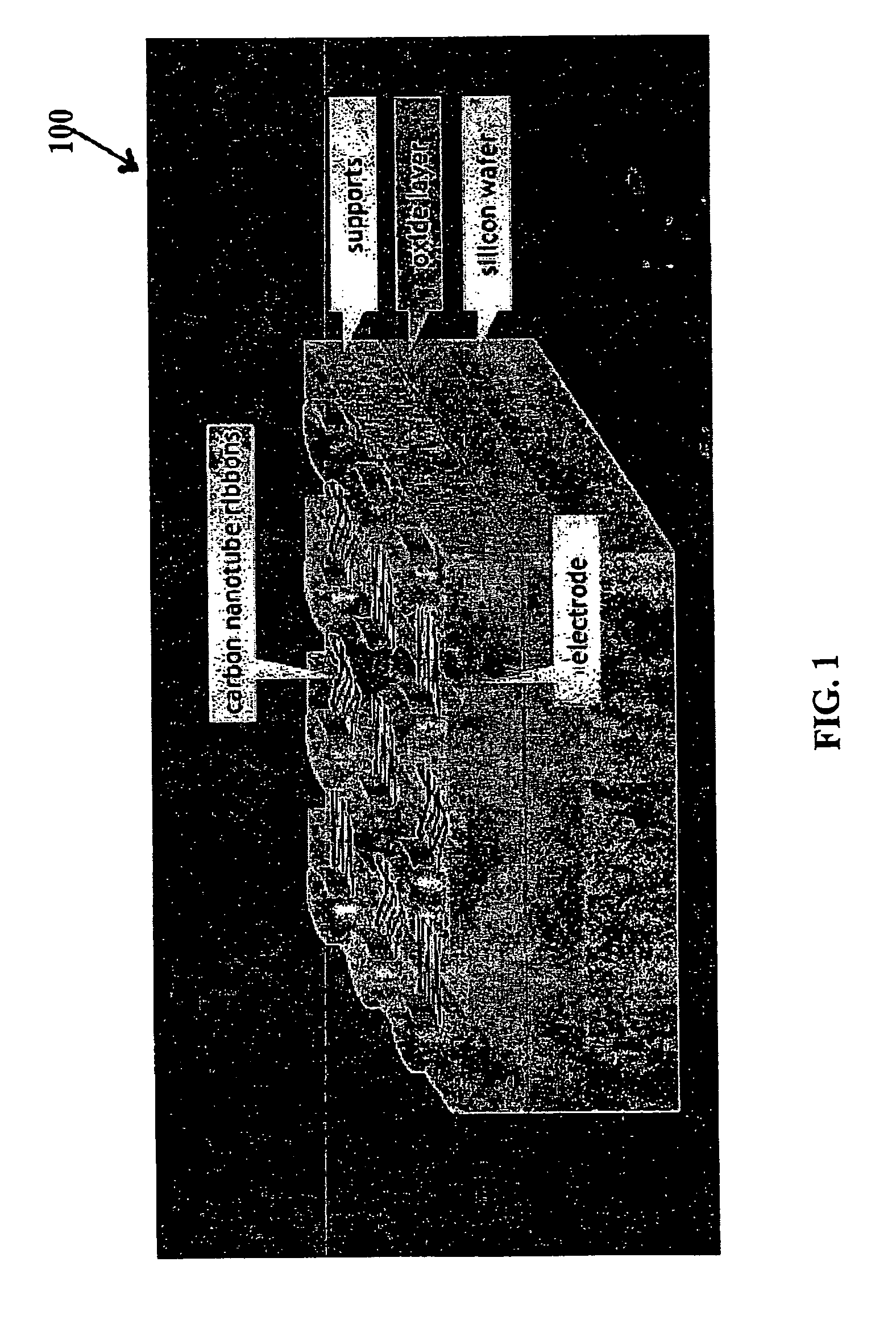
A hybrid nanotube, high-performance, dynamically reconfigurable architecture, NATURE, is provided, and a design optimization flow method and system, NanoMap. A run-time reconfigurable architecture is provided by associating a non-volatile universal memory to each logic element to enable cycle-by-cycle reconfiguration and logic folding, while remaining CMOS compatible. Through logic folding, significant logic density improvement and flexibility in performing area-delay tradeoffs are possible. NanoMap incorporates temporal logic folding during the logic mapping, temporal clustering and placement steps. NanoMap provides for automatic selection of a best folding level, and uses force-direct scheduling to balance resources across folding stages. Mapping can thereby target various optimization objectives and user constraints. A high-density, high-speed carbon nanotube RAM can be implemented as the universal memory, allowing on-chip multi-context configuration storage, enabling fine-grain temporal logic folding, and providing a significant increase in relative logic density.
Owner:QUEENS UNIV OF KINGSTON +1
Method for removing memory thrashing through efficient LTL ((Linear Temporal Logic) model detection of large-scale system
InactiveCN106371765AReduce complexityIncrease the number of operationsInput/output to record carriersLinear temporal logicTheoretical computer science
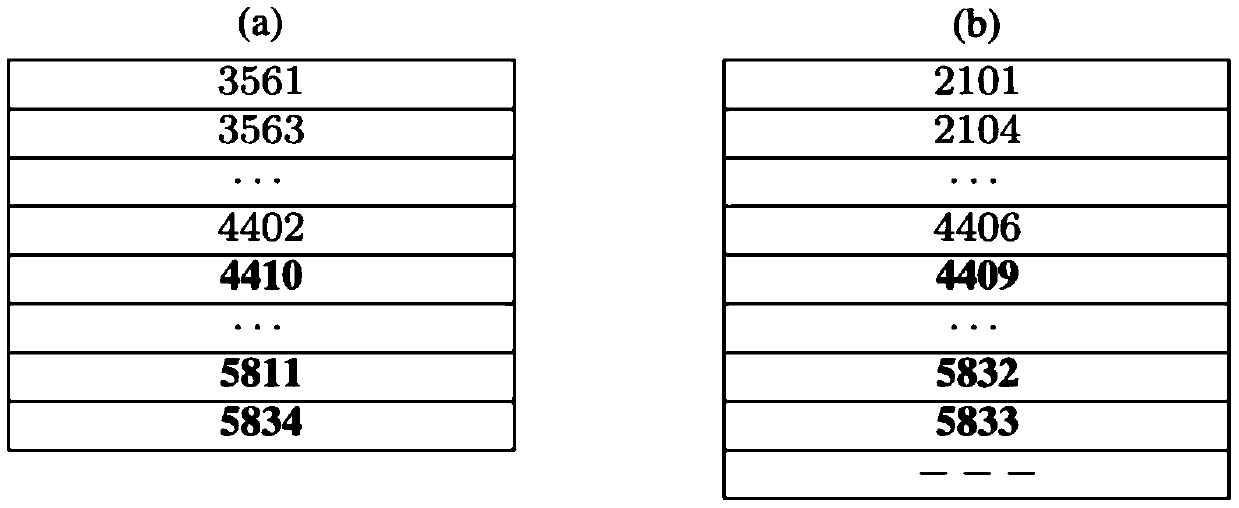
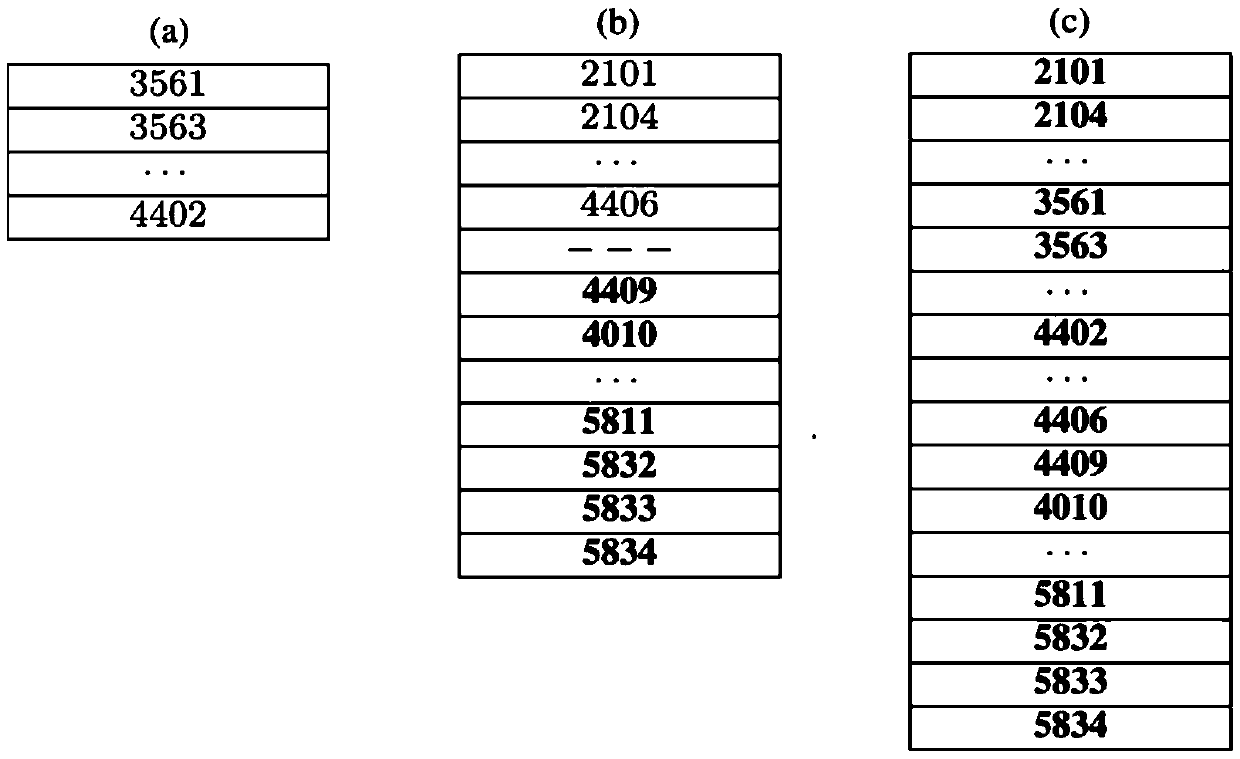
The invention discloses a method for removing memory thrashing through the efficient LTL ((Linear Temporal Logic) model detection of a large-scale system. A LHS (Linear Hash Storage) algorithm is adopted to mainly aim at quickly finding a Hash value stored in a Hash table in a disk; no matter whether the classification of the Hash table in the memory is empty or not, the Hash table can be stored in an external memory and is processed by a new technology after being stored in the external memory, and the complexity of I / O is a linear size which is the same with the Hash table; and a CDD (Cached Duplicate Detection) technology permits a duplicate in the memory to be detected through effective access, duplicate detection complexity can be lowered through the LHS and the CDD, the plan of DPM (Dynamic Path Management) enables two nested depth-first stacks to dynamically share a memory cell, and the memory thrashing problem can be solved through the effective management of the stack and the state, wherein the memory thrashing means that the frequent movement of the state in the memory may obviously increase I / O operation frequencies so as to lower the efficiency of the algorithm.
Owner:CHENGDU KEHONGDA TECH
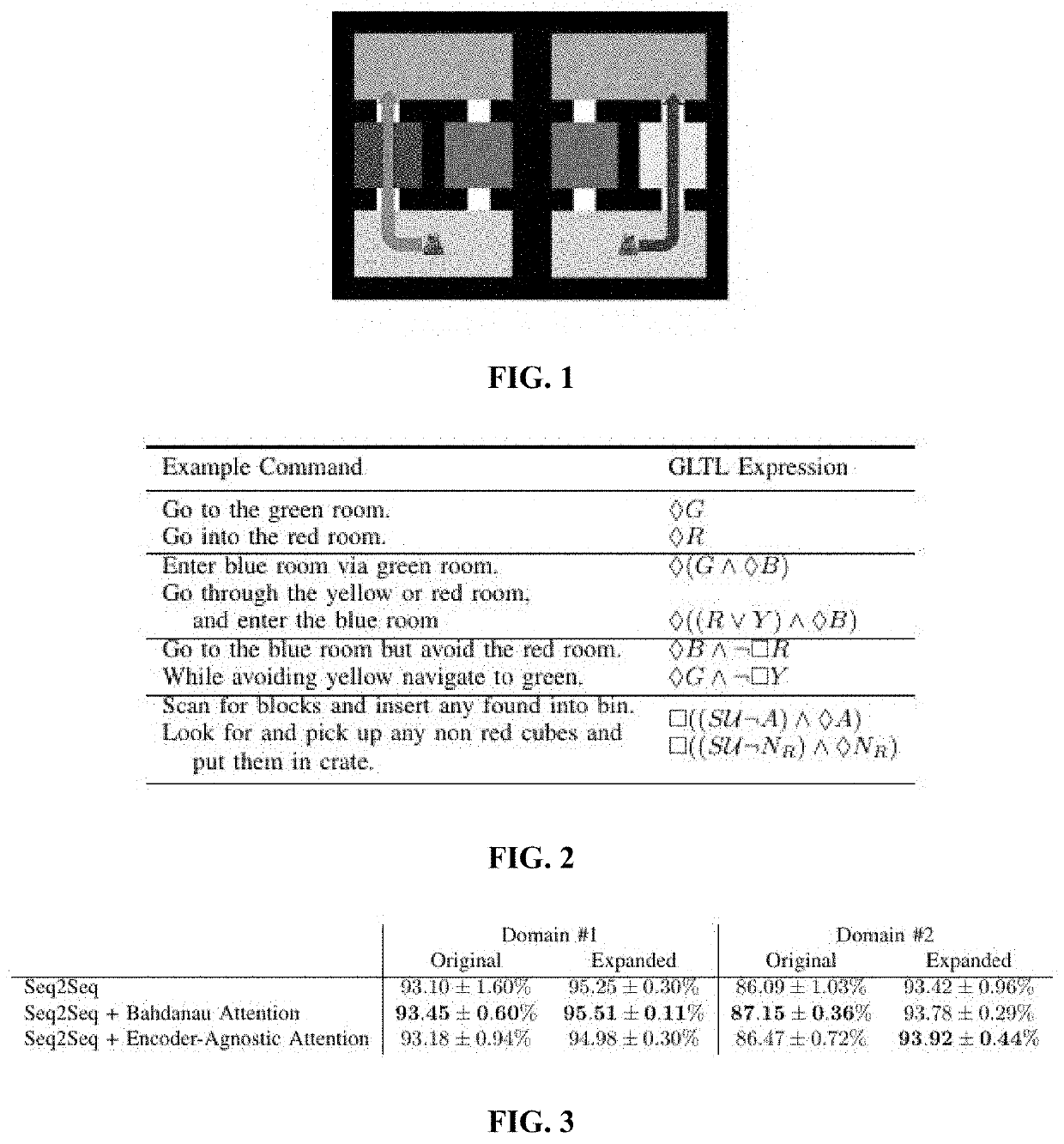
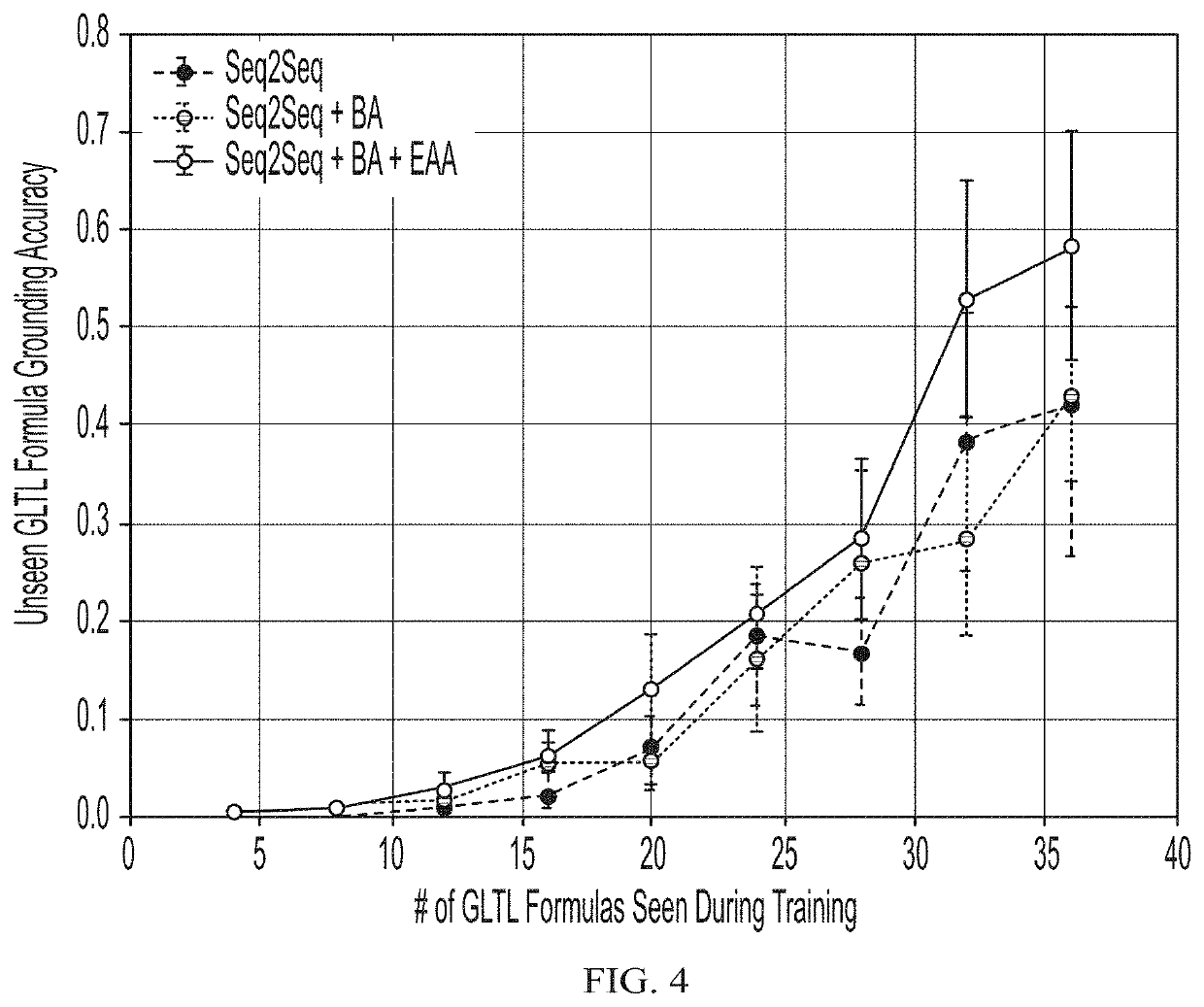
Sequence-to-Sequence Language Grounding of Non-Markovian Task Specifications
ActiveUS20200023514A1Well formedProgramme controlNatural language translationSequence learningAlgorithm
A method includes enabling a robot to learn a mapping between English language commands and Linear Temporal Logic (LTL) expressions, wherein neural sequence-to-sequence learning models are employed to infer a LTL sequence corresponding to a given natural language command.
Owner:BROWN UNIVERSITY
Inter-procedural dataflow analysis of parameterized concurrent software
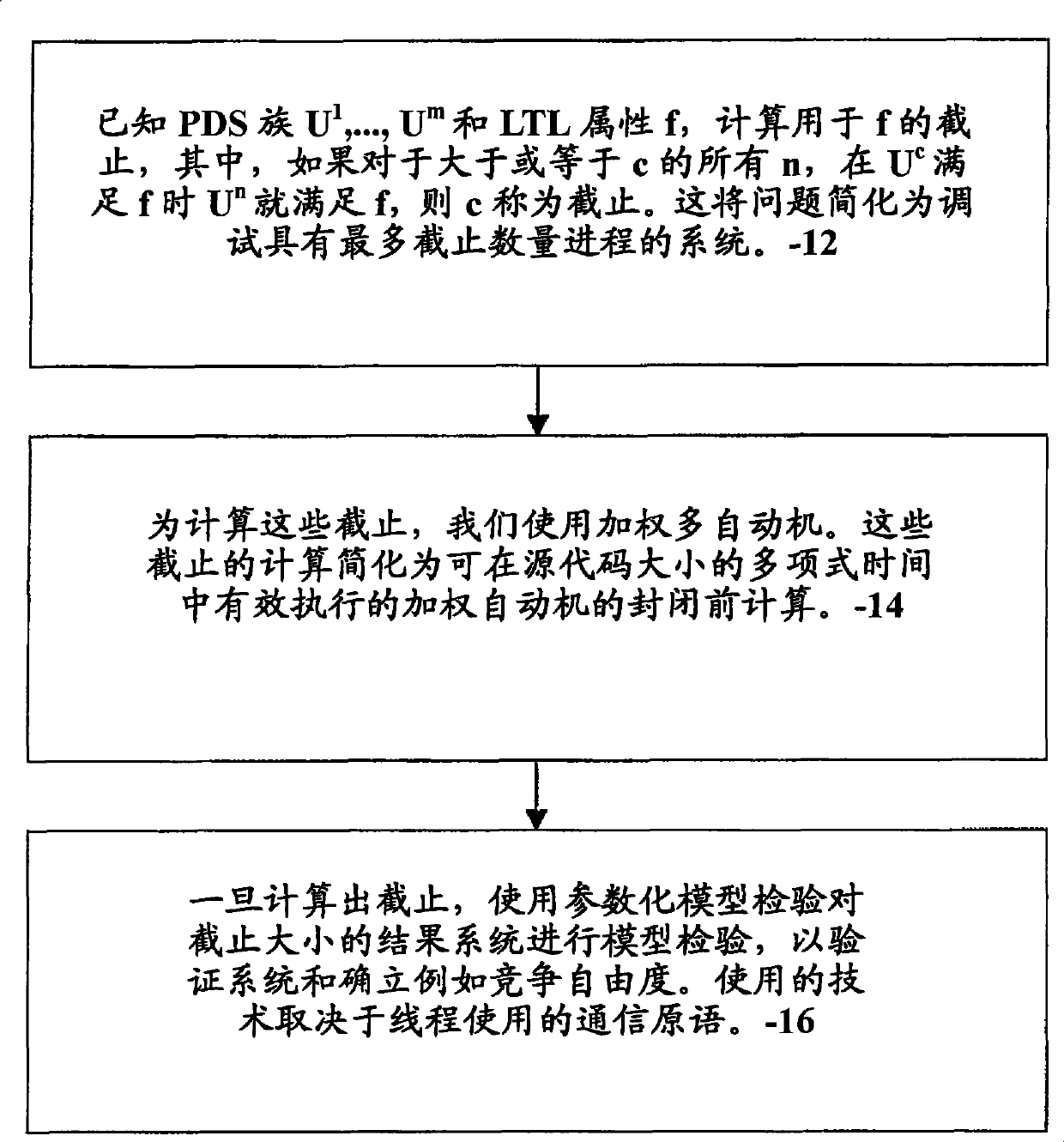
InactiveCN101438234AProgram control using stored programsDesign optimisation/simulationComputerized systemLinear temporal logic
A system and method for computing dataflow in concurrent programs of a computer system, includes, given a family of threads (U1,..., If) and a Linear Temporal Logic (LTL) property, f, for a concurrent program, computing (12) a cutoff for the LTL property, f, where c is called the cutoff if for all n greater than or equal to c, Un satisfies f if Uc satisfies f. The cutoff is computed using (14) weighted multi-automata for internal transitions of the threads. Model checking (16) a cutoff number of processes is performed to verify race freedom in the concurrent program.
Owner:NEC CORP
CPS rare event probability prediction method based on statistical model inspection
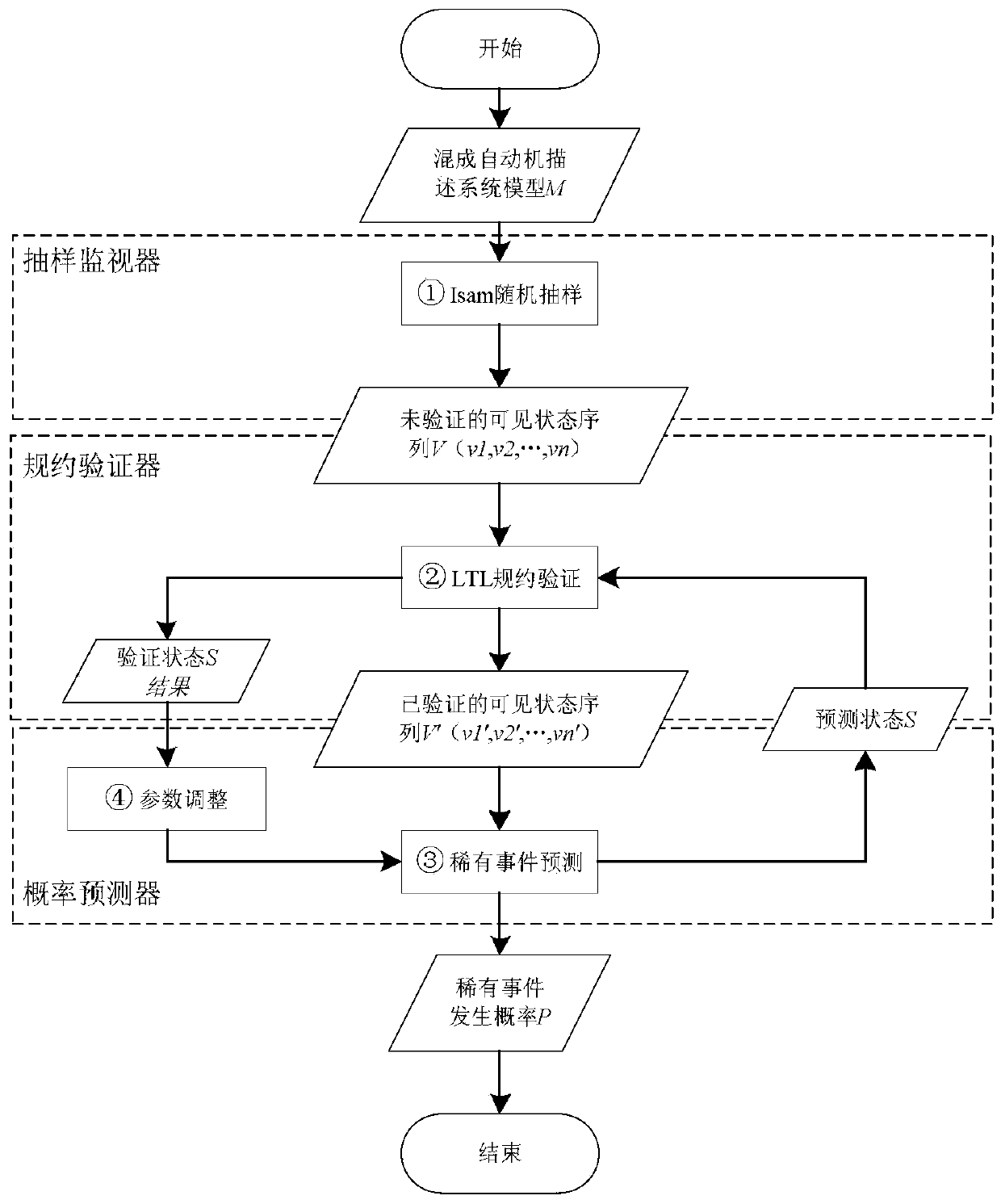
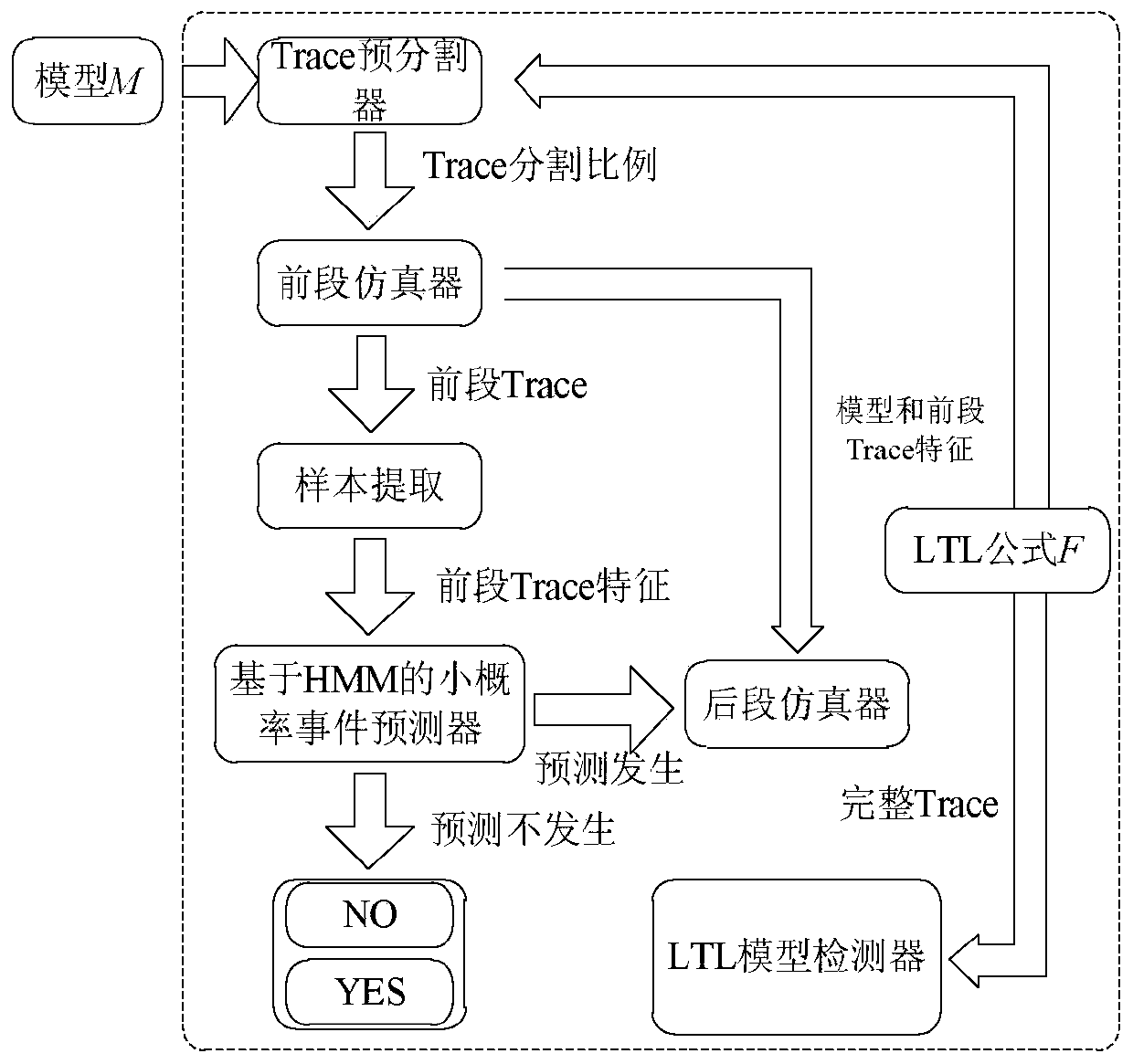
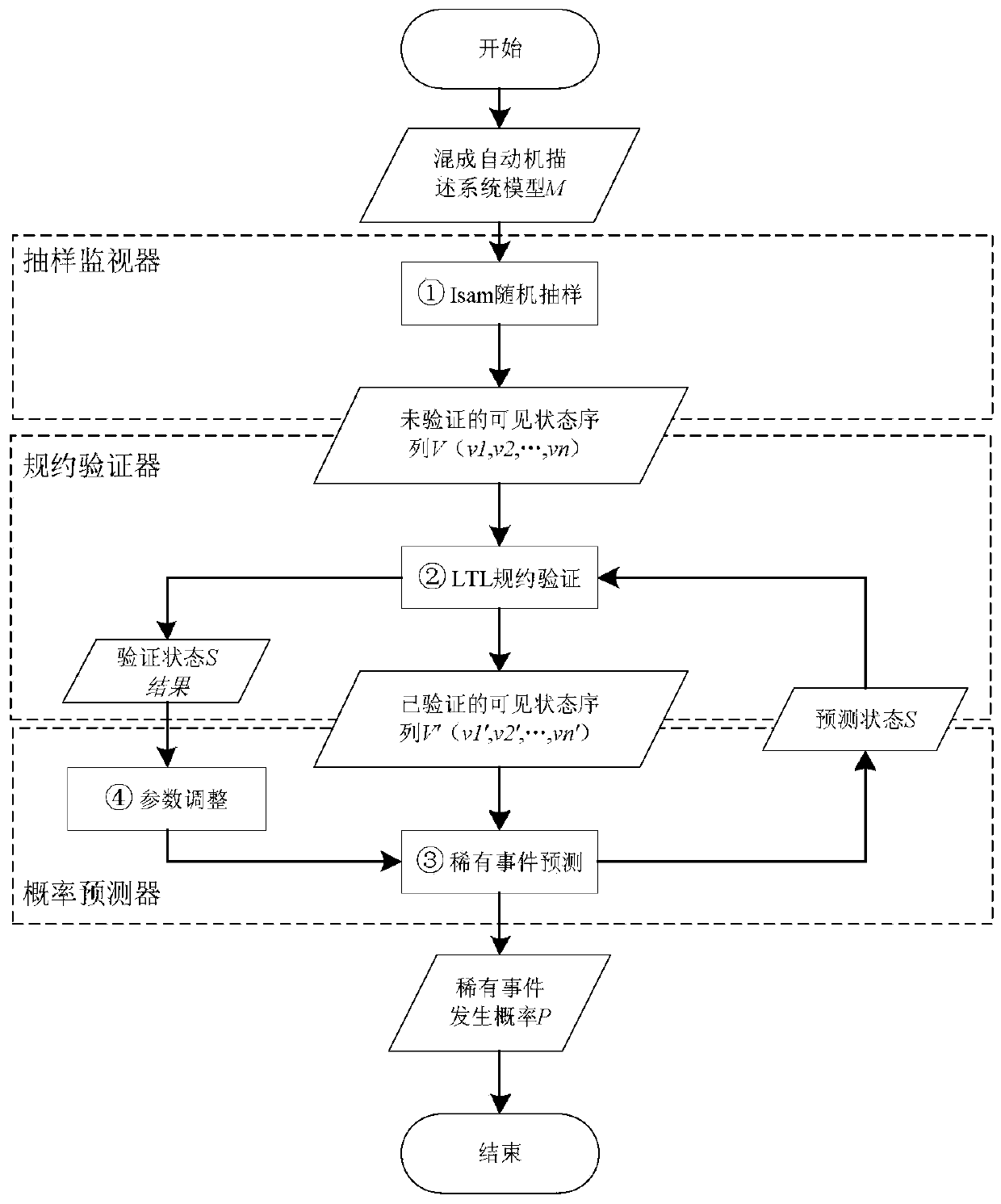
PendingCN109961172AIncrease probabilityChange the law of probability of evolutionForecastingComplex mathematical operationsLinear temporal logicHybrid automaton
The invention discloses a CPS rare event probability prediction method based on statistical model inspection. The system is based on a statistical model inspection method and is composed of a samplingmonitor, a protocol verifier and a probability predictor. The method comprises the specific implementation steps that a sampling monitor adopts an importance random sampling algorithm to randomly sample and generate a CPS system state feature sequence described based on a hybrid automaton; a protocol verifier based on linear temporal logic can generate a system visible characteristic state sequence and a verification result corresponding to protocol satisfaction, and the verifier can take the verification result as a training sample set of a probability predictor based on an HMM implicit Markov model; on the basis of sufficient sample set learning, the probability predictor calculates the probability that the subsequent state of the system is a rare event state, and outputs the result, inaddition, the method also has the function of correcting the prediction capability of the predictor by using the probability prediction result.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
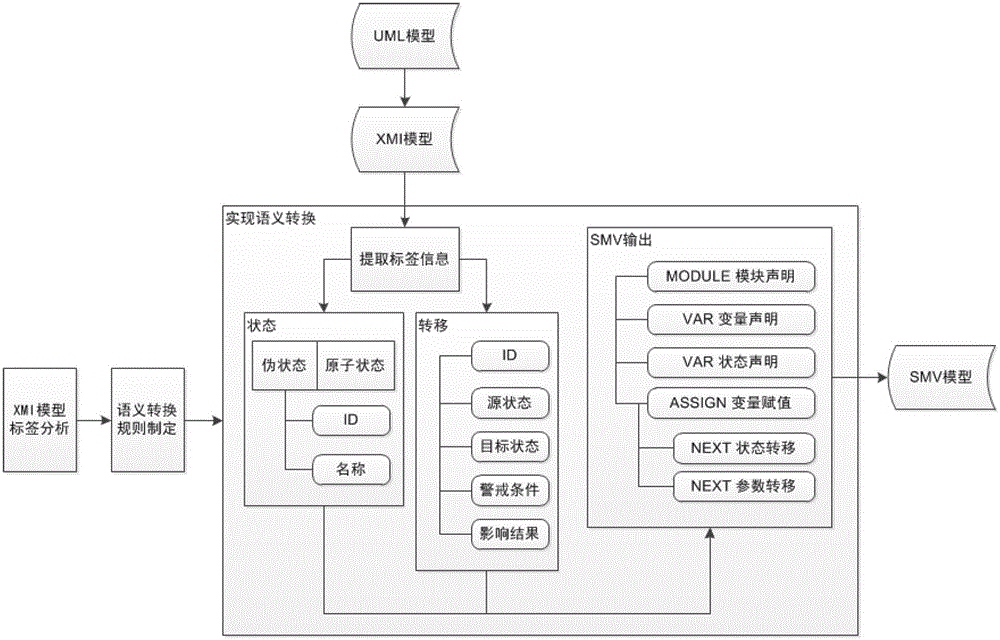
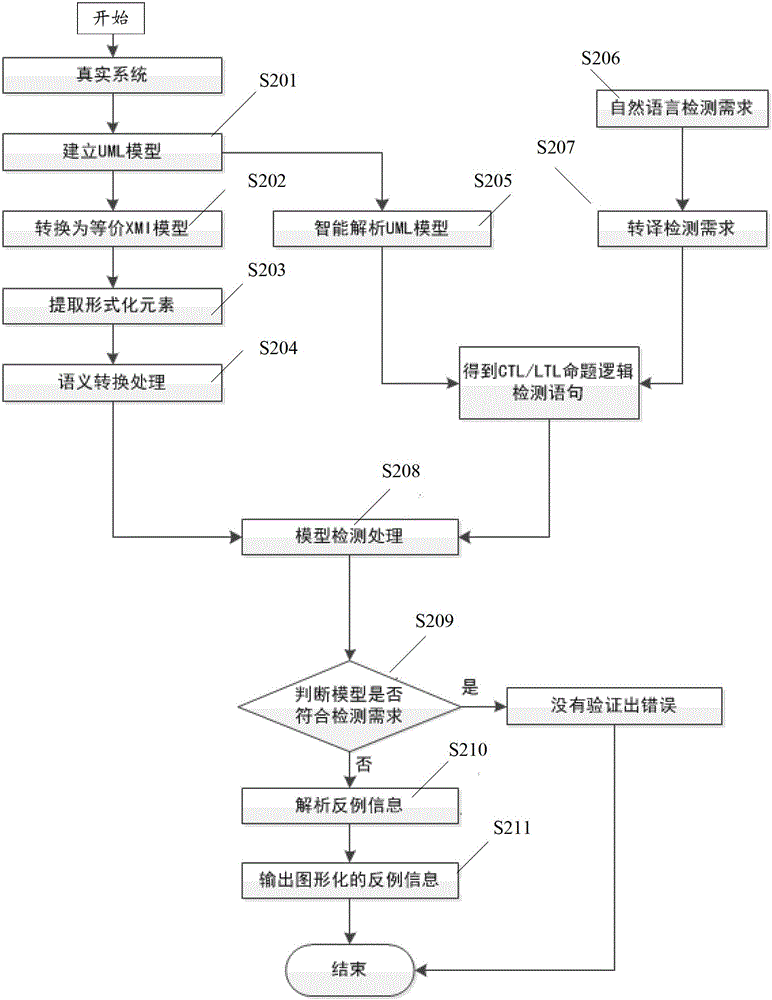
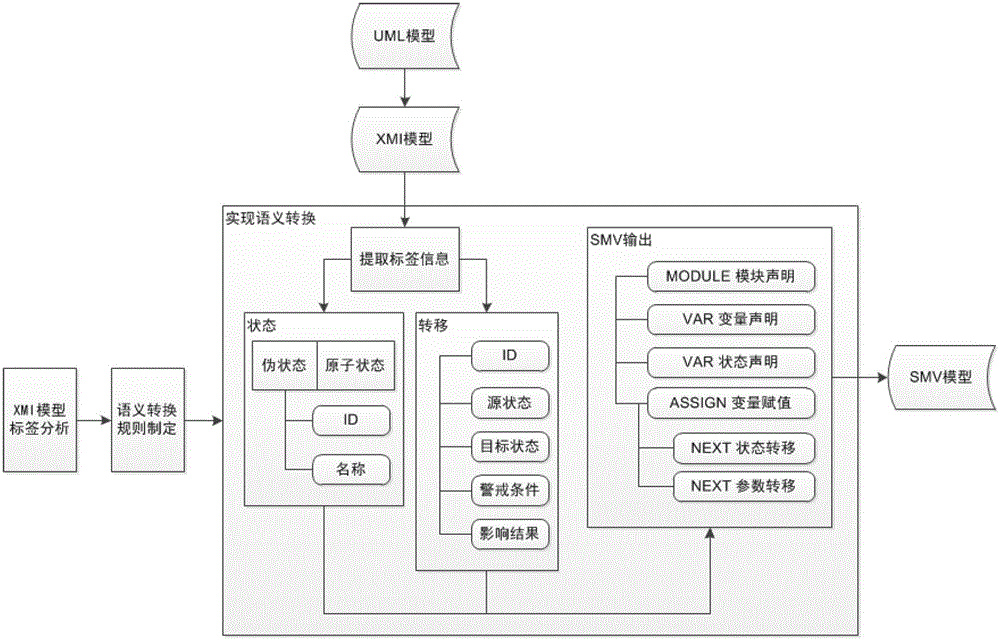
Formalized detection method of intelligent UML (Unified Modeling Language) model and device
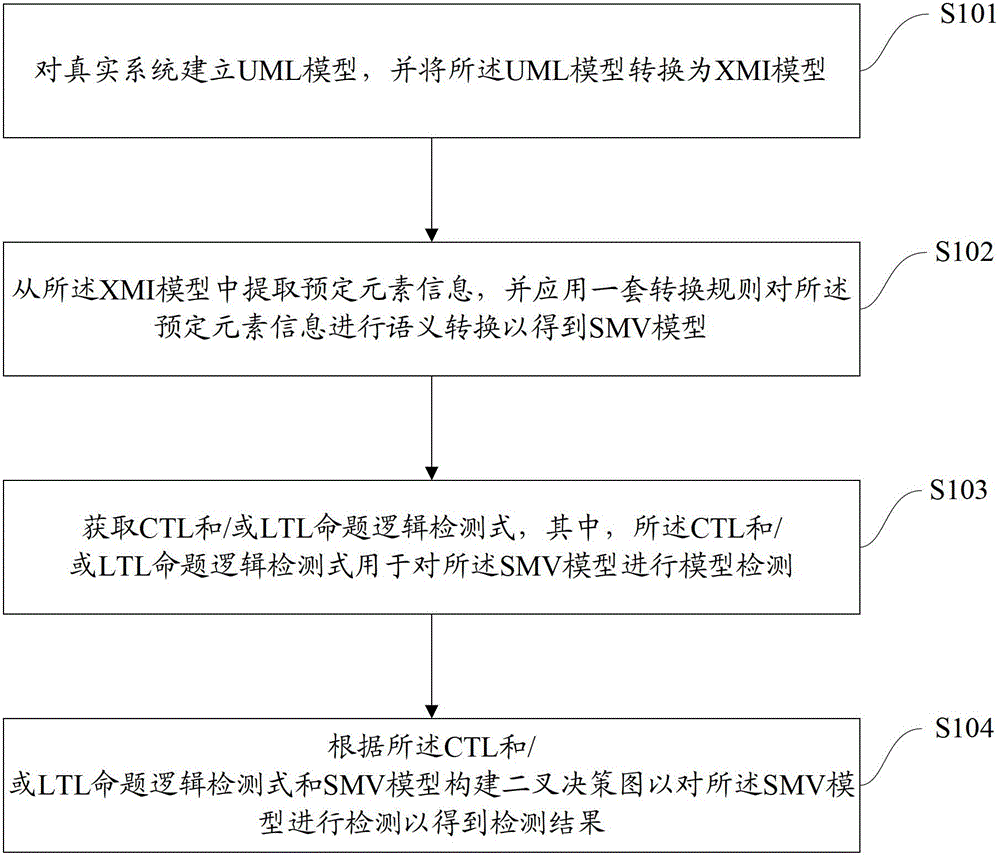
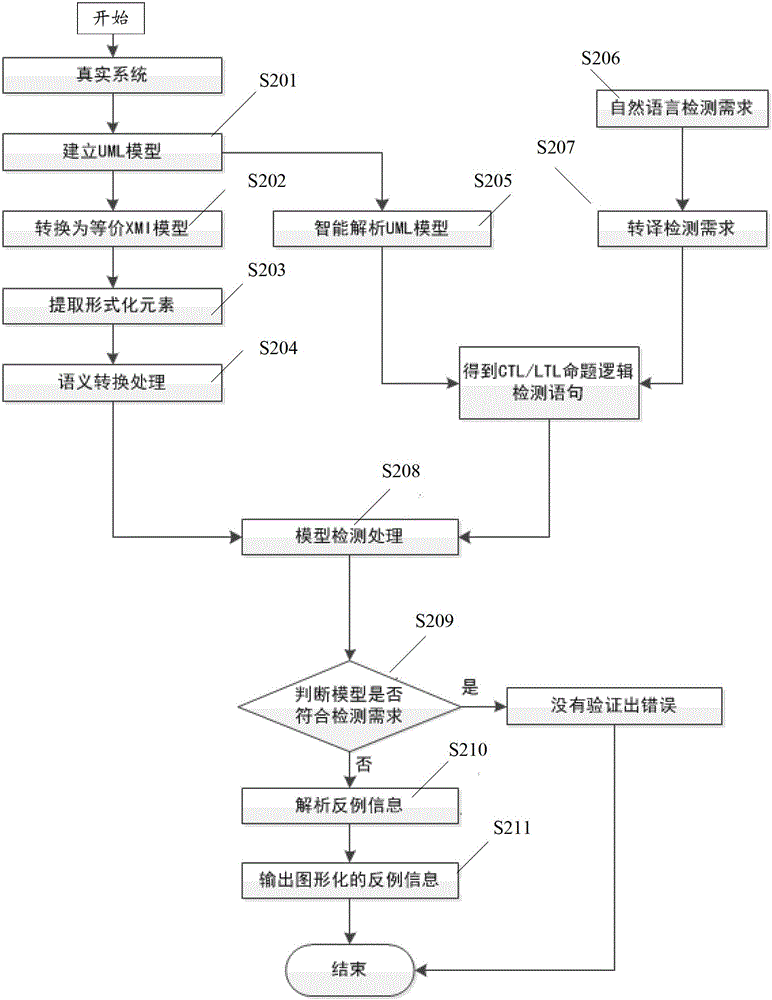
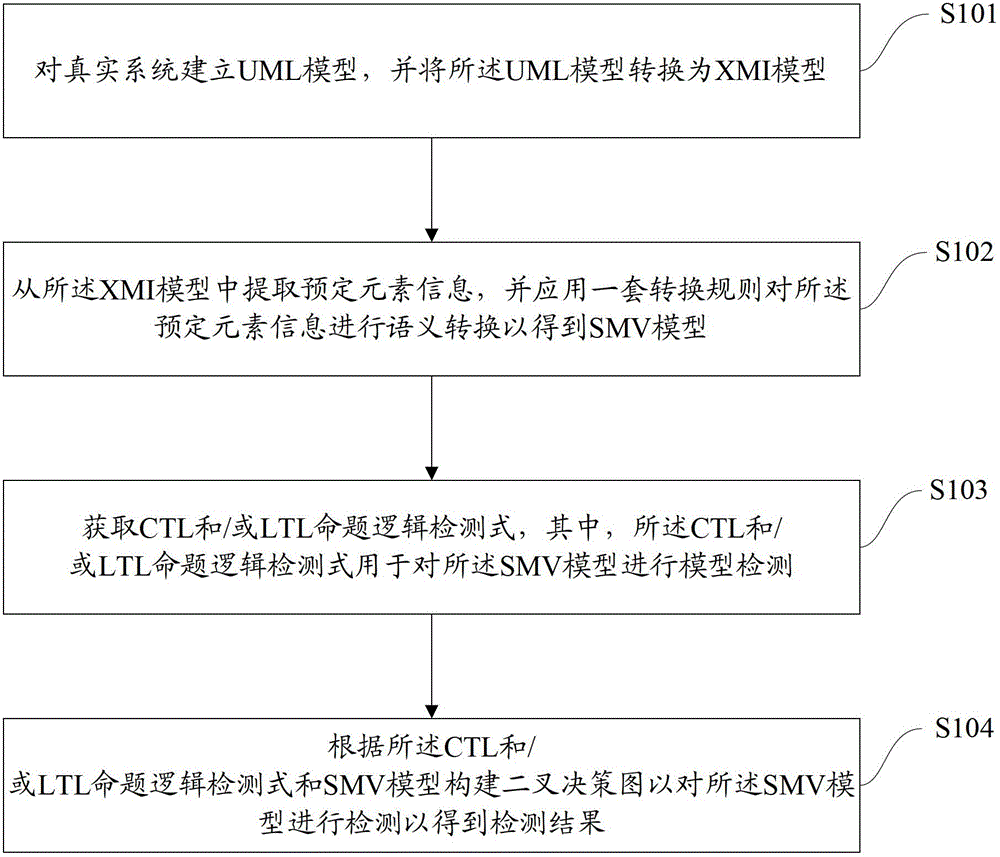
ActiveCN102722441AImprove user experienceGood application effectSoftware testing/debuggingSoftware development processBinary decision diagram
The invention provides a formalized detection method of an intelligent UML (Unified Modeling Language) model and a device. The method comprises the steps of: establishing an UML model for a true system and converting the UML model into an XMI (Extensible Markup Language) model; extracting predetermined element information from the XMI model and converting the predetermined element information semantically to obtain an SMV (Symbolic Modeling Verification) model by applying a set of conversion rule; acquiring an CTL (Complementary Transistor Logic) and / or an LTL (Linear Temporal Logic) propositional logic detection formula, wherein the CTL and / or LTL propositional logic detection formula are / is used for detecting the SMV model; and constructing a binary decision diagram according to the CTL and / or LTL propositional logic detection formula and the SMV model to detect the SMV model so as to obtain a detection result. According to the embodiment disclosed by the invention, the formalized detection method has the advantages of high detection accuracy and wide application, and can comprehensively detect the UML model which has higher demand on safety in a software development process.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
General parallel mining method for linear temporal logic specifications
InactiveCN106886417AEfficient acquisitionReverse engineeringSpecific program execution arrangementsParallel miningTheoretical computer science
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV +1
Optimal strategy solution of mobile robot in dynamic environment
ActiveCN109409592ASatisfy mission requirementsExecute tasks efficientlyForecastingGuidelineLinear temporal logic
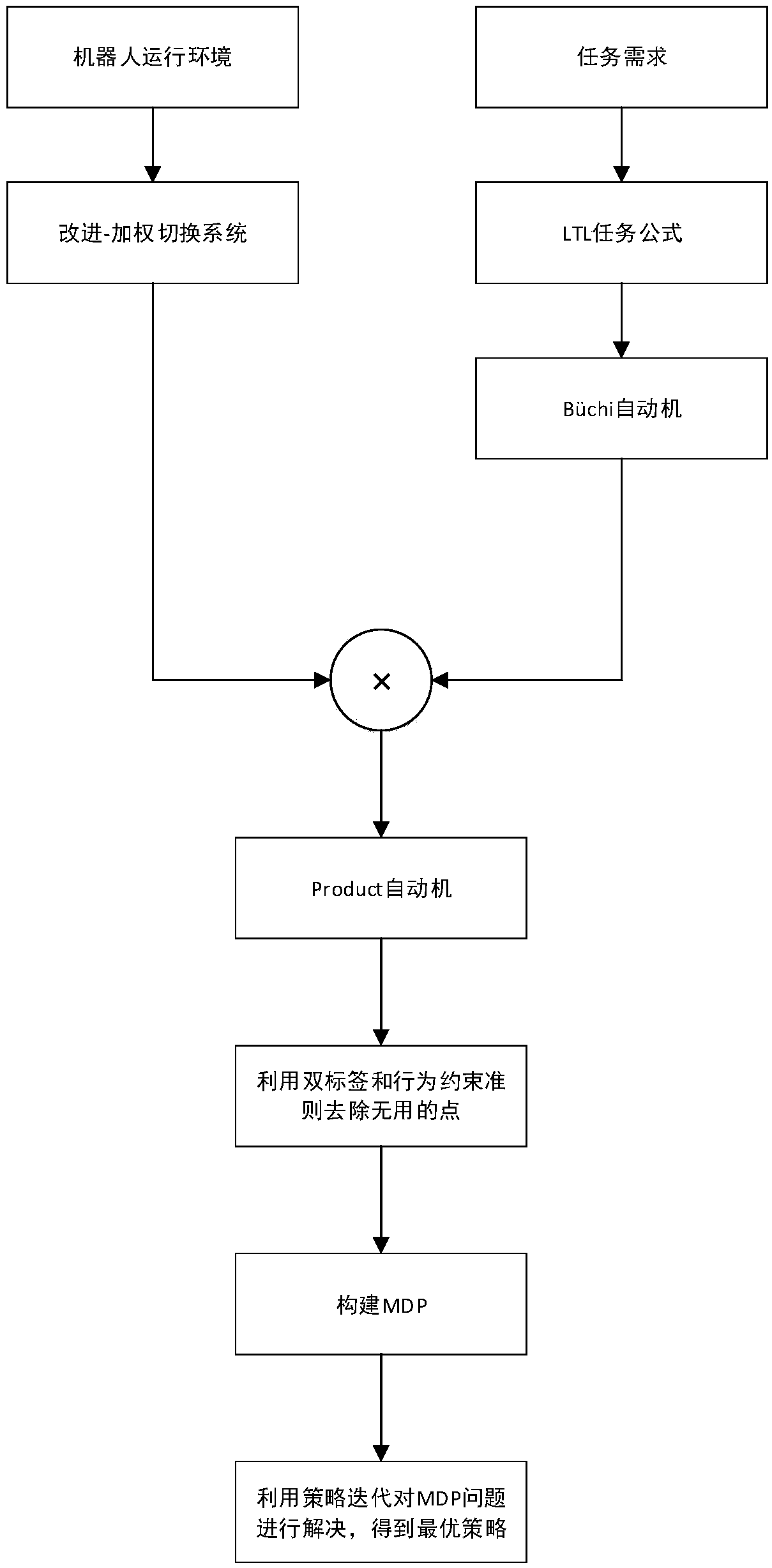
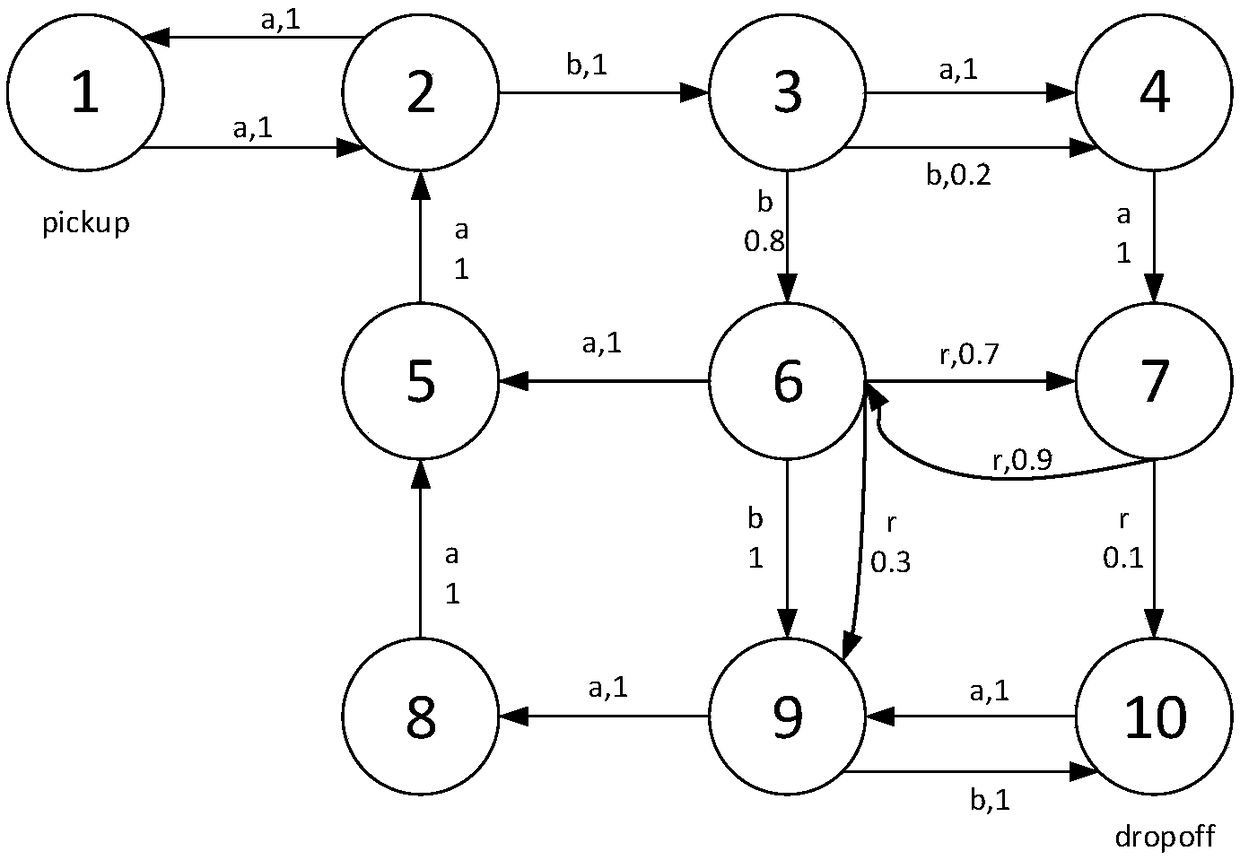
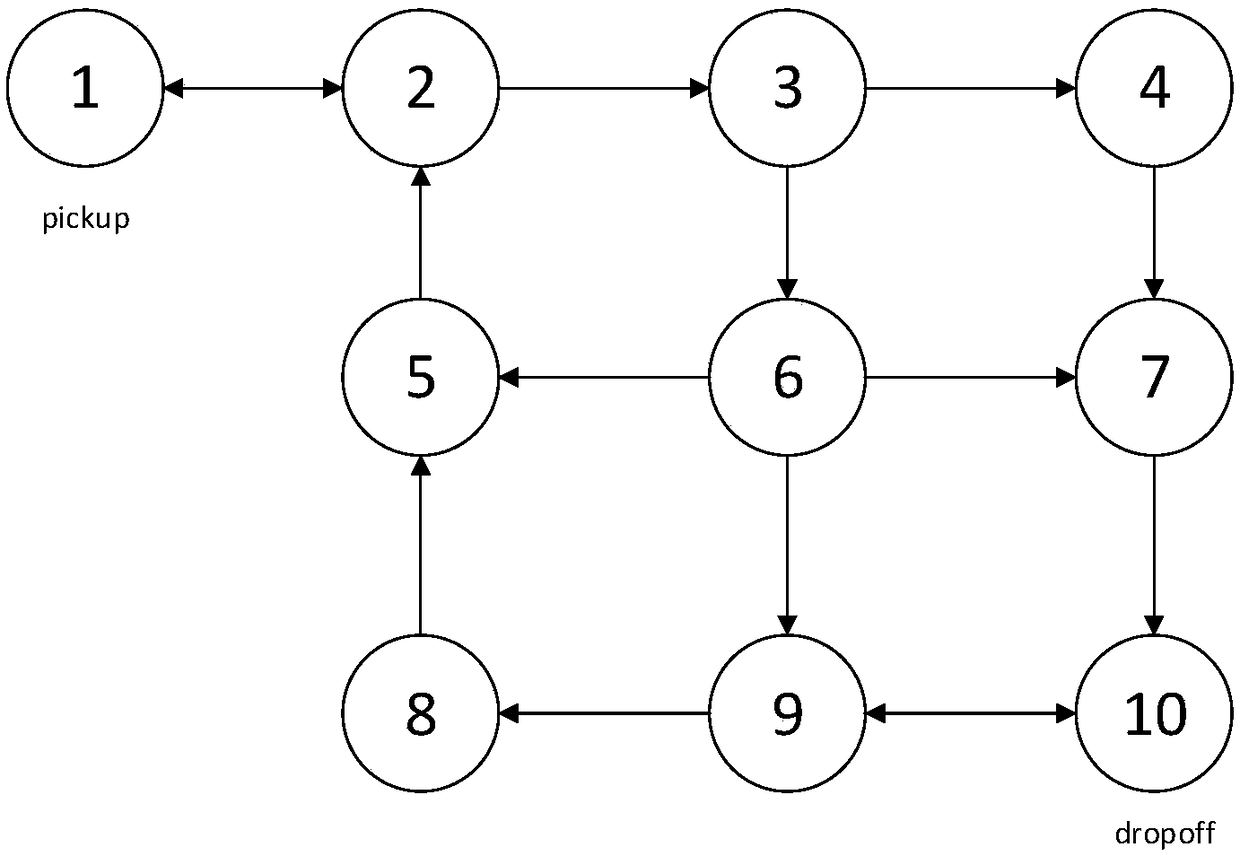
The optimal strategy solution of mobile robot in dynamic environment includes the following steps: Firstly, according to the running environment of the robot, the improvement is constructed. Weightedswitching system, according to the task requirements, the task requirements are expressed mathematically by linear temporal logic (LTL), and the LTL task formulas are transformed into B u chi automataby LTL2BA toolkit. Then Cartesian product is used to get Product automata, which contains task requirement and environment information. The useless points on the feasible network topology graph are removed, and the availability of state points is further judged according to the double-label and behavior constraint criterion, thus the number of state points is simplified. The remaining points areconstructed as MDP model, and the optimal strategy is obtained by policy iteration. The invention not only solves the situation that there is no DRA, but also reduces the number of available points, reduces the complexity of the constructed MDP, and can obtain the optimal strategy more quickly.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
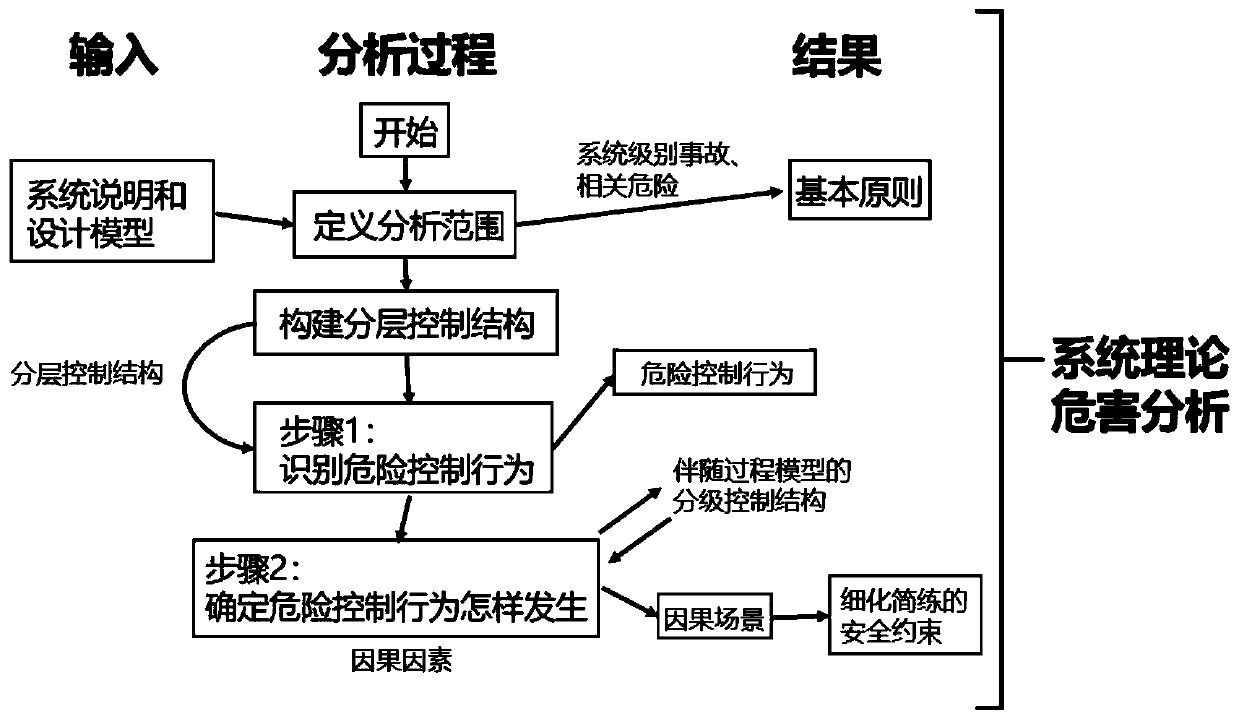
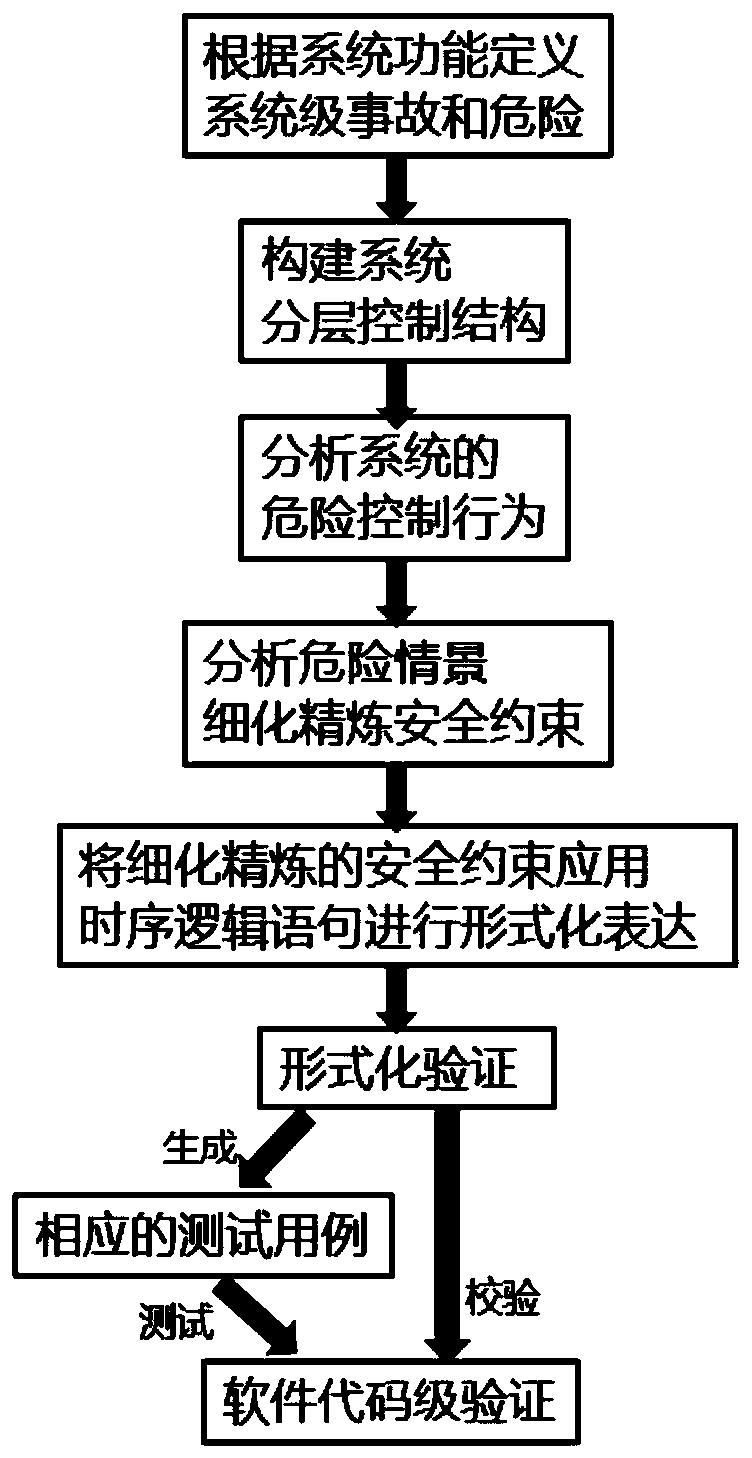
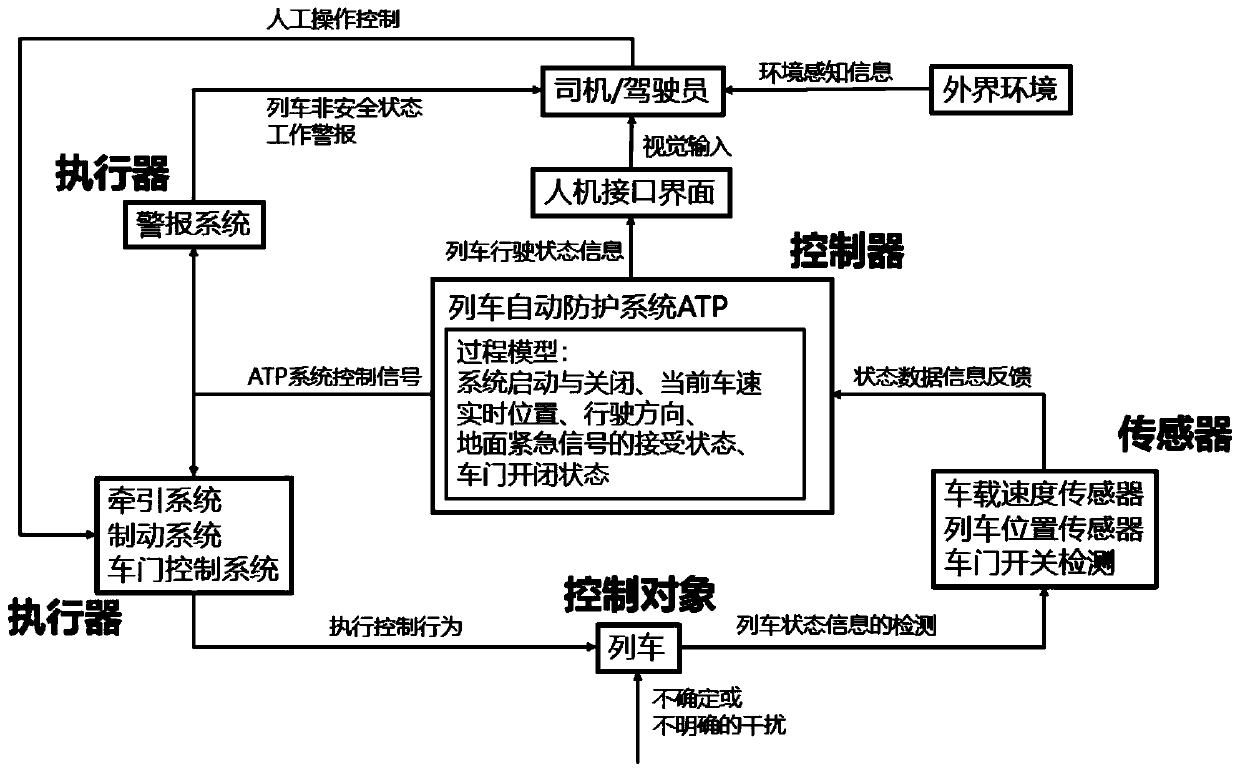
Train automatic protective system safety analysis method based on system theory hazard analysis
ActiveCN110843859AComprehensive failure analysis coverageHigh analytical efficiencyGeometric CADRailway traffic control systemsControl engineeringLinear temporal logic
Owner:CRRC QISHUYAN CO LTD
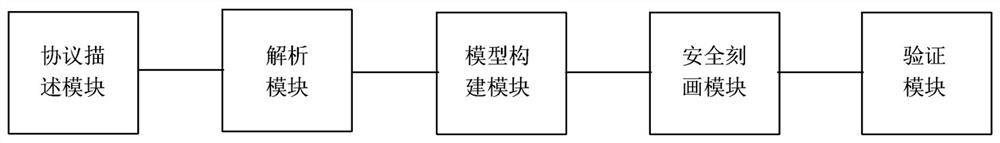
Verification method and system for security protocol formalization
The invention relates to a verification method and system for security protocol formalization, and relates to the technical field of network security, and the method comprises the steps: describing a to-be-verified security protocol, and obtaining a security protocol specification; analyzing the security protocol specification to obtain a protocol configuration object; constructing a protocol model according to the protocol configuration object; constructing an attacker model based on the protocol model, and optimizing the attacker model; describing the security attribute of the security protocol according to the linear temporal logic; and constructing a communication environment based on the optimized attacker model, verifying whether the protocol model meets the security attribute or not through a model detector SPIN in the communication environment, and if not, outputting an attack path by the model detector SPIN. According to the method, modeling can be carried out on different types of security protocols, universality is achieved, the security of the security protocols can be automatically verified, and automation is achieved.
Owner:EAST CHINA JIAOTONG UNIVERSITY
Path Planning Method for Warehousing Robot Based on Linear Sequential Logic Theory
ActiveCN105467997BGuaranteed optimalityComplete efficientlyPosition/course control in two dimensionsVehiclesShortest Path Faster AlgorithmSimulation
The warehousing robot path planning method based on linear temporal logic theory includes: modeling the warehousing environment as a weighted switching system that is scalable based on dispatch nodes; using linear temporal logic language (LTL) to describe the complex dispatch tasks of the warehousing system; then, The task formula is converted into a Büchi automaton through the LTL2BA toolkit; the Cartesian product of the scalable weighted switching system and the Büchi automaton is used to form a feasible network topology for the task; the SPFA (Shortest Path Faster Algorithm) algorithm is used on this topology to search for the optimal path , the task feasibility network topology includes warehousing environment information and pickup task information. The path obtained by searching can be guaranteed to be the optimal path and is not affected by the selected order of dispatching single nodes; map the optimal path obtained on the task feasibility network topology back to the warehousing environment The corresponding optimal path is sent to the warehousing robot through wireless communication through the PC to complete the task of picking up and dispatching orders.
Owner:FOSHAN KINGPENG ROBOT TECH CO LTD
Temporal logic-based microcontroller runtime verification method
InactiveCN106933714AReal-time verificationGet the possibility output spaceFunctional testingMicrocontrollerRuntime verification
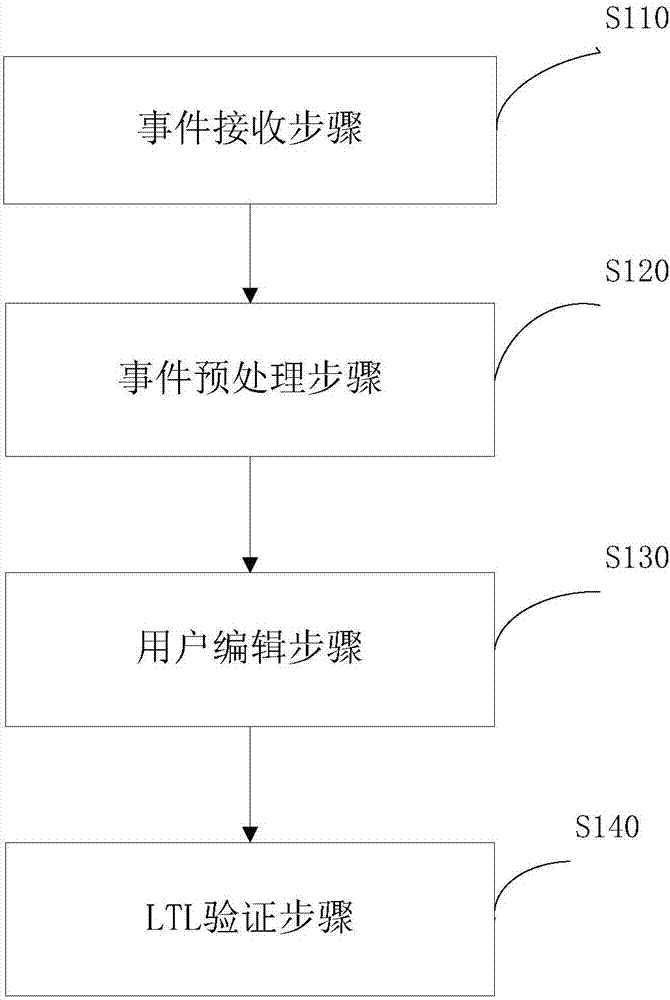
The invention discloses a temporal logic-based microcontroller runtime verification method. The method comprises an event reception step, an event pre-processing step, a user edition step and an LTL verification step, wherein the event reception step indicates receiving an event sequence sent by a microcontroller; the event preprocessing step indicates pre-processing events received in the event reception step, converting the events into independent atomic propositions, establishing one-to-one mapping between variable identifiers and the atomic propositions, and outputting an event sequence character string; the user edition step indicates providing an edition interface for a user so that the user can edit the atomic propositions and an LTL formula; and the LTL verification step indicates verifying whether the execution carried out on the event sequence character string by the microcontroller satisfies the LTL formula input by the user or not. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the real-time verification of microcontrollers can be realized, the possible output spaces of the microcontrollers can be obtained, and certain illegal events can be artificially authenticated.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV +1
A Bounded Runtime Verification Method for Linear Temporal Logic Properties with Past Tense
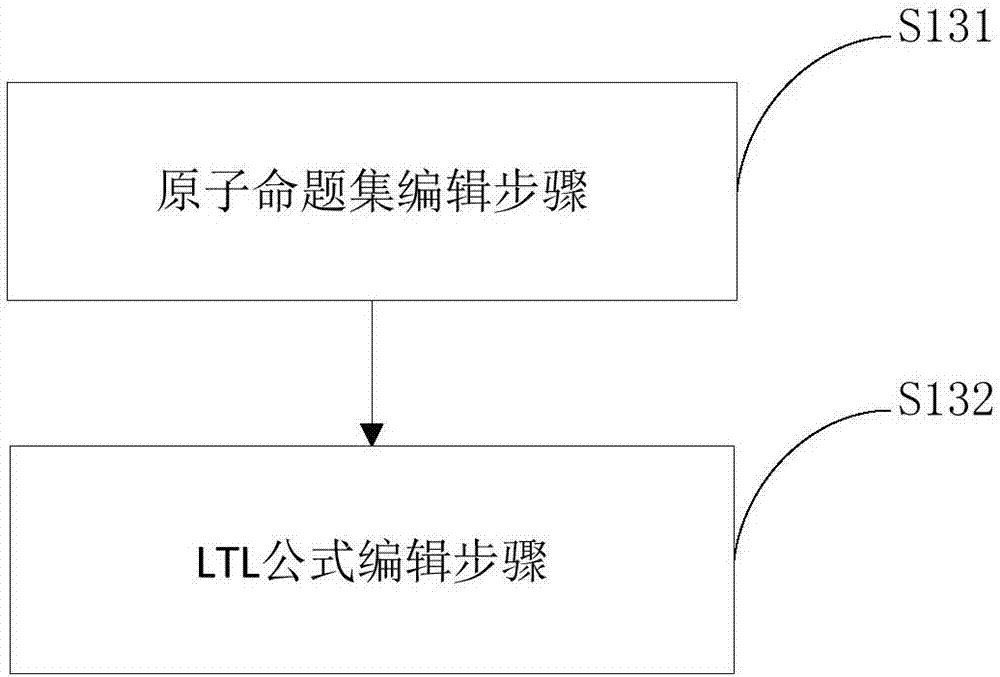
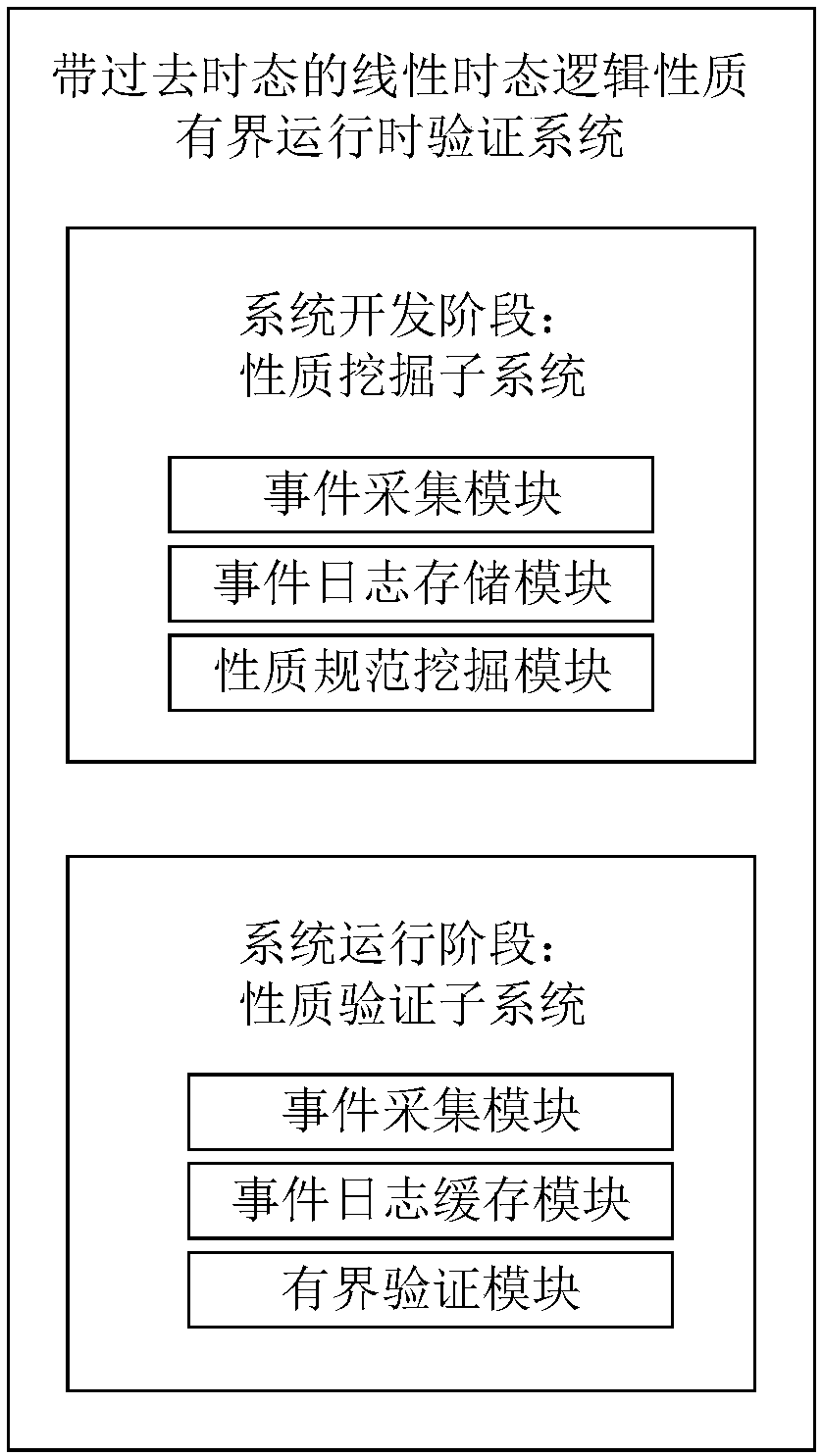
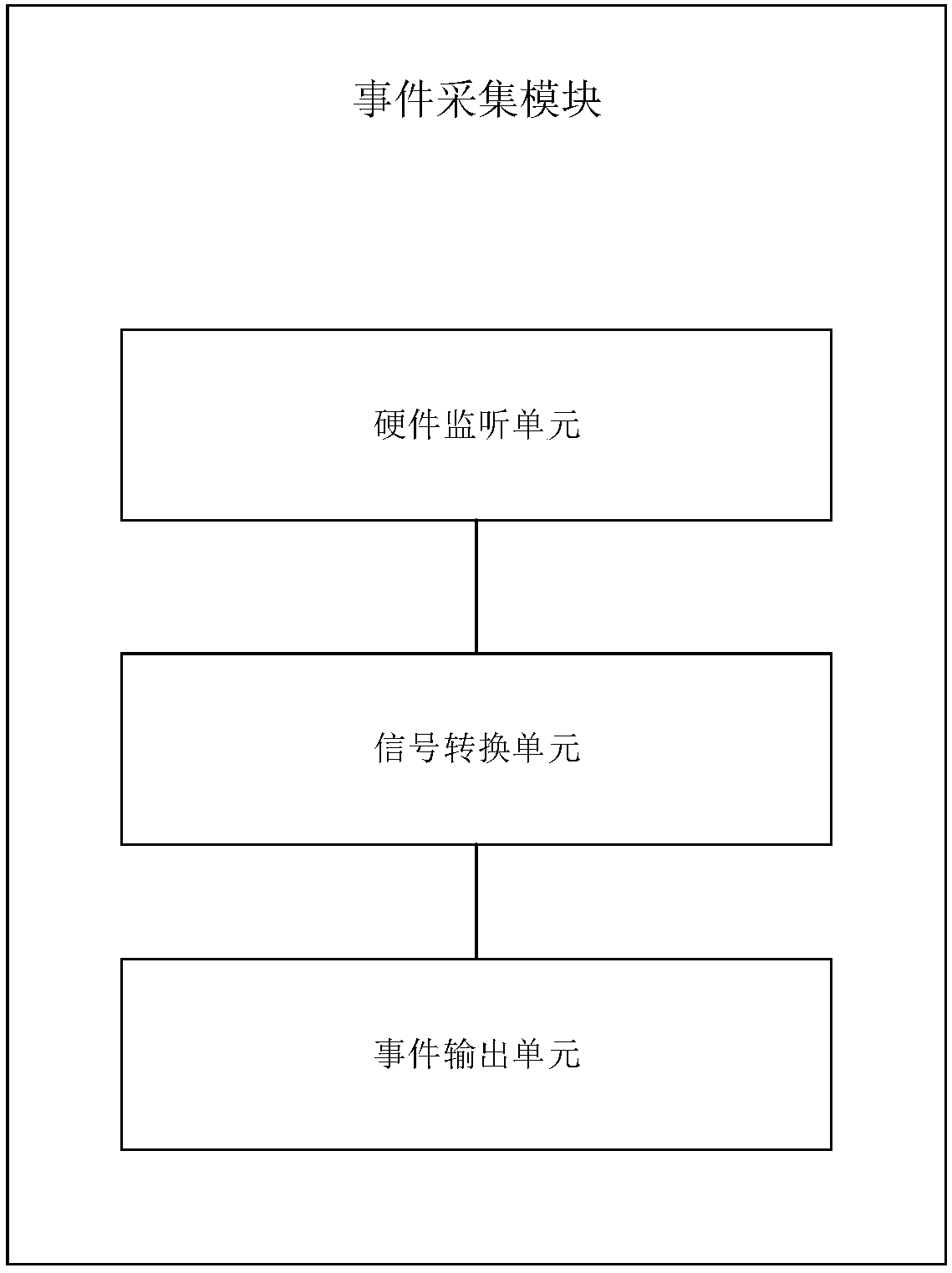
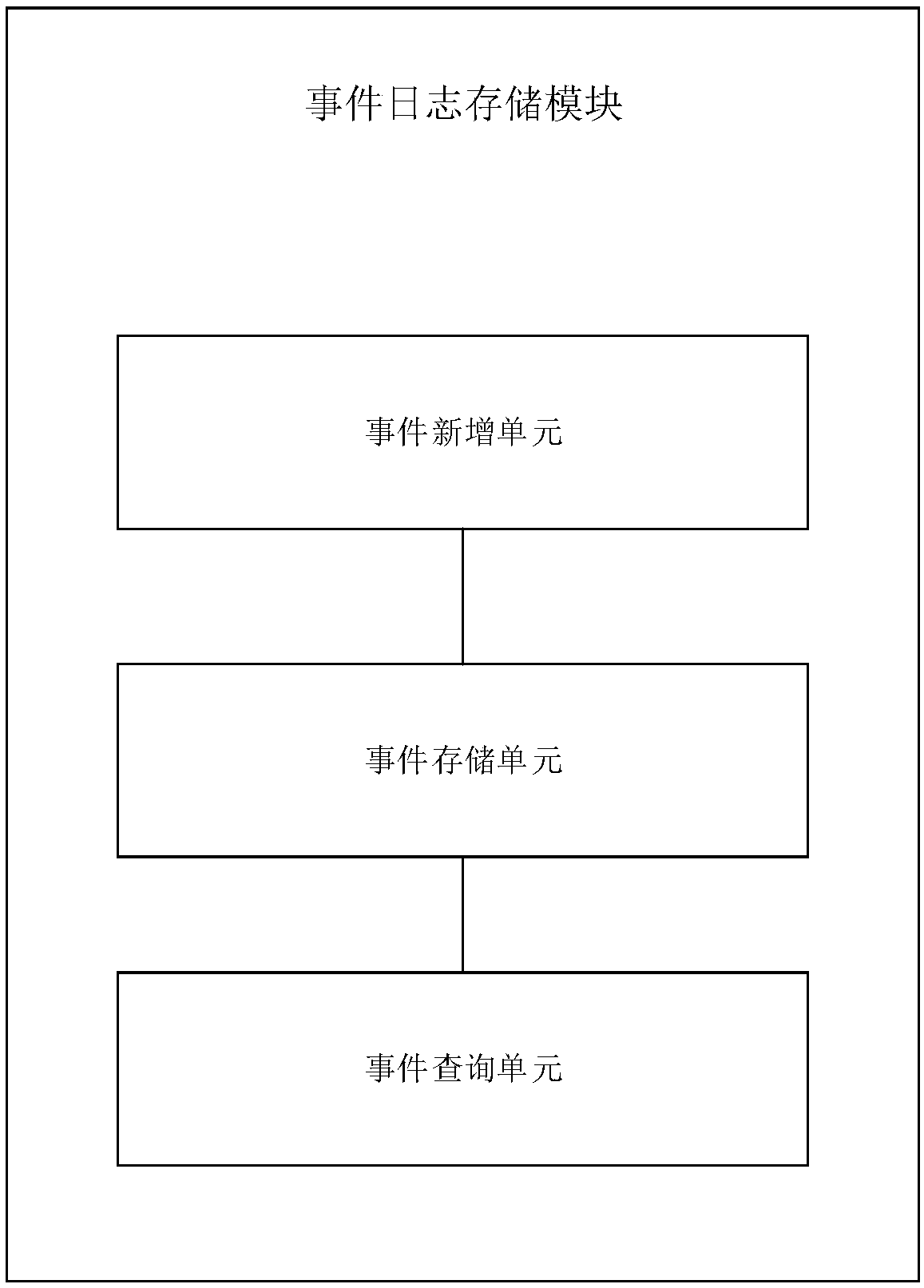
ActiveCN107229568BAutomatic verificationHigh degree of automationSoftware testing/debuggingSoftware metricsSystems designComputer architecture
The invention discloses a bounded runtime verification method of linear temporal logical properties with past tenses. The method comprises the steps that simulation system run is performed by using testing data through a property subsystem at a system development stage so as to obtain event information in actual run of the system and store the information in event logs, all the linear temporal logical properties with past tenses in the system run process are automatically obtained from the event logs and are stored in screenable property standard sets; system events are monitored at a system run stage through a property verification subsystem, and tense property checking and verification are conducted on the system by using the screened property standard sets. The verification standards at a design stage can be applied to a runtime verification stage, a non-system design and development persons can conveniently solve the problems which cannot be solved without special system design and development persons themselves, and meanwhile verification procedure redevelopment is also avoided.
Owner:上海丰蕾信息科技有限公司
Robot multi-task motion implementation method based on sequential logic, medium and equipment
PendingCN114489055AReduce computational complexityQuick planningComplex mathematical operationsPosition/course control in two dimensionsComputation complexityRound complexity
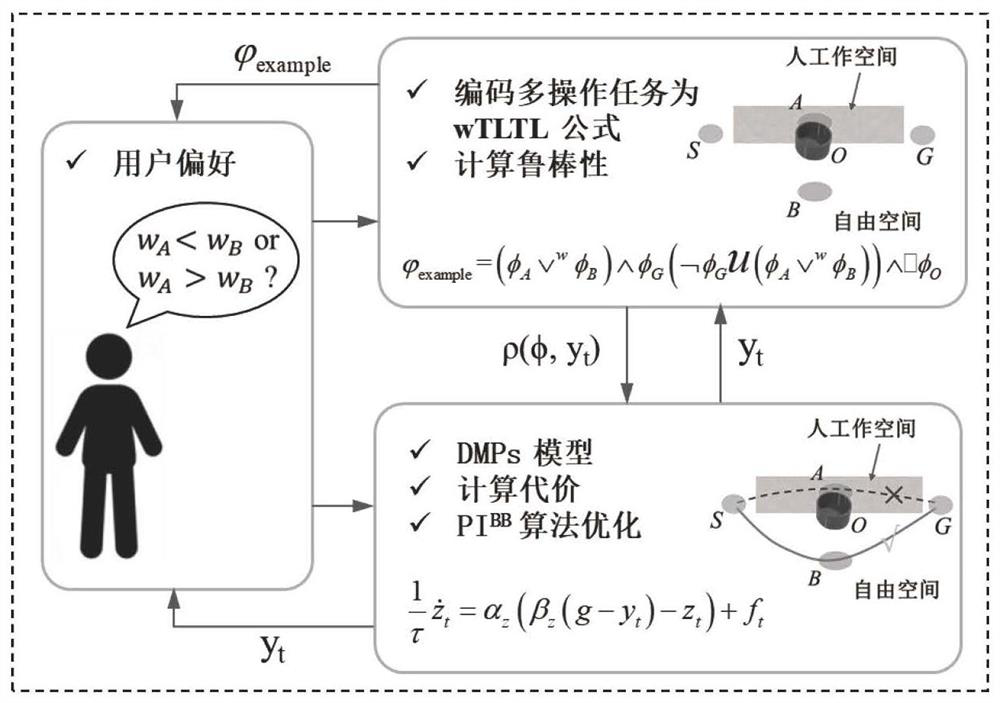
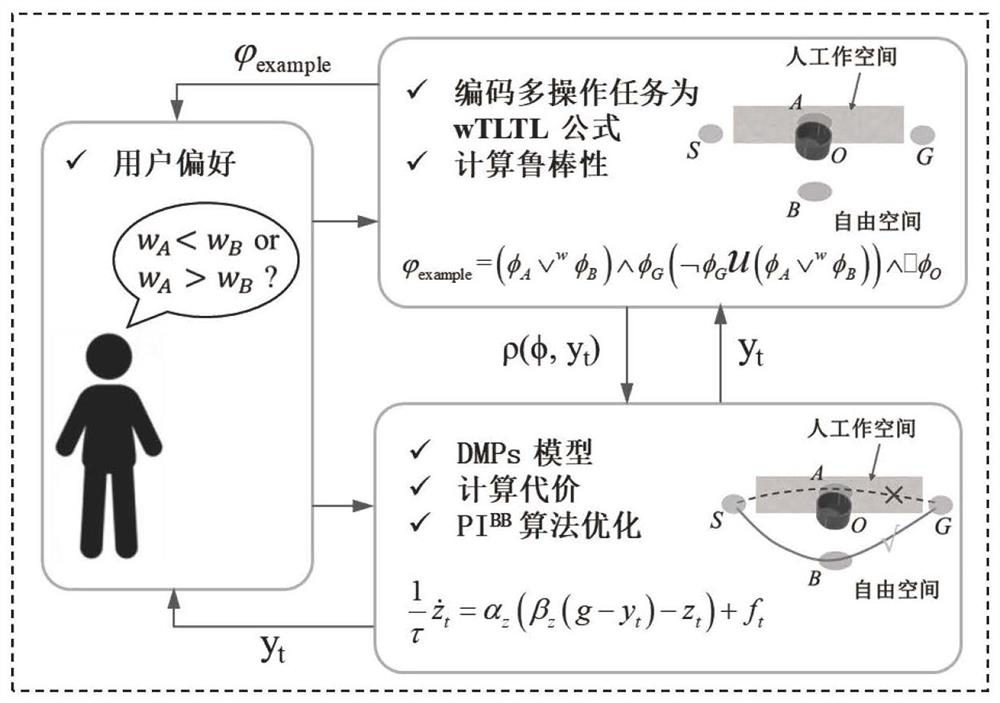
According to the robot multi-task motion implementation method based on the sequential logic, the medium and the equipment, the traditional TLTL is expanded to the wTLTL (Weighted Trunked Linear Temporal Logic, hereinafter referred to as wTLTL) according to the method, and the DMPs and the wTLTL are combined, so that complex operation tasks with user preferences are achieved. The DMPs are used for approximating a track with user preference, the shape of the track is determined by parameters of the DMPs, and optimization is carried out through a black box optimization strategy (hereinafter referred to as PIBB) based on a weighted average covariance matrix. The wTLTL provides an interpretable task specification, a cost function with user preference can be designed according to quantitative semantics, an improved PIBB algorithm is utilized, then the optimal shape parameter of the DMPs is recognized, and then the motion trail of a complex operation task is achieved. The user preferences are embodied by adjusting weights in the wTLTL. Compared with a traditional multi-task operation motion planning method, the method has the advantages that the motion trails of the complex operation tasks with user preferences can be quickly planned, the calculation complexity is low, and the planning efficiency is high.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
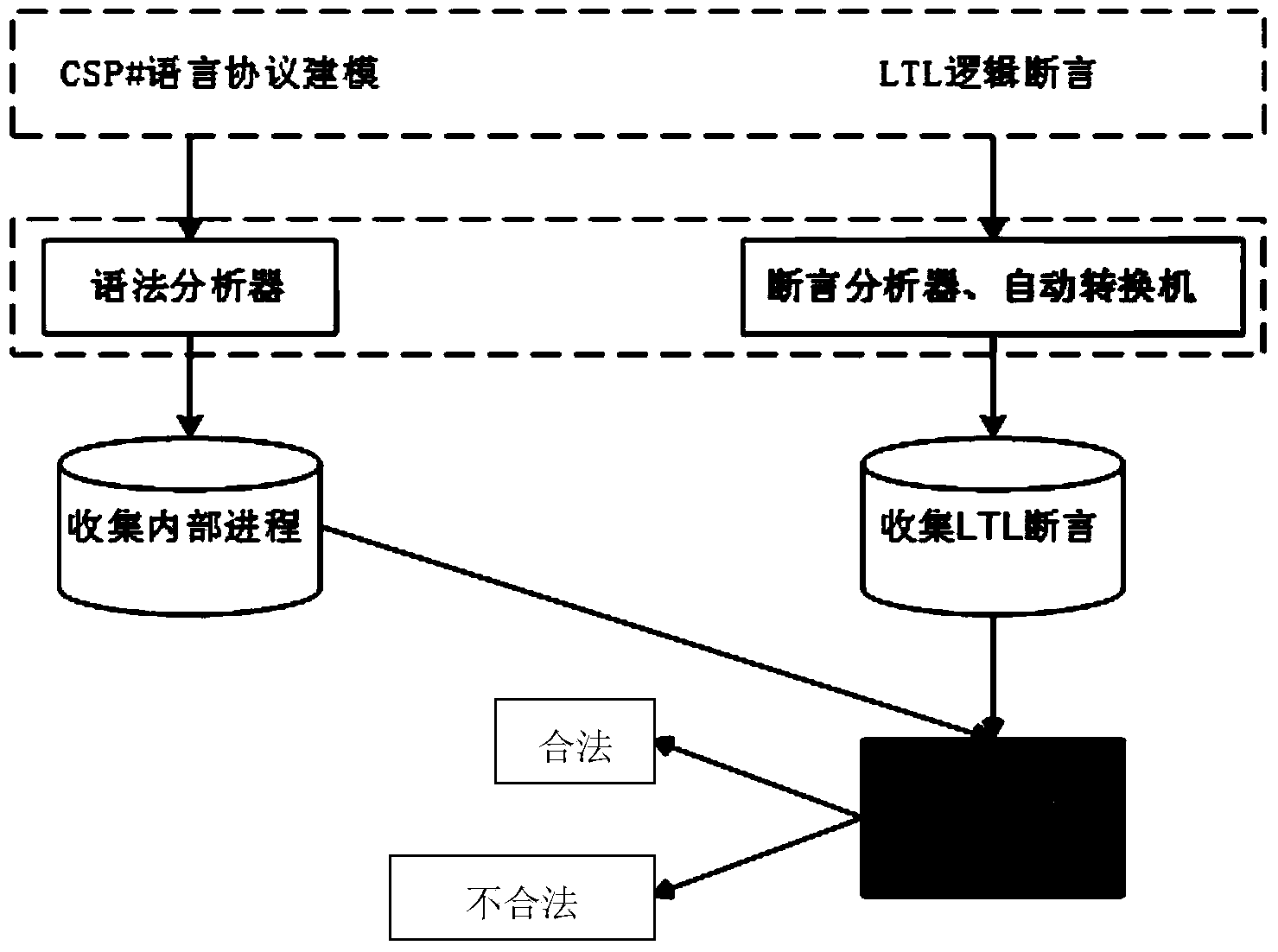
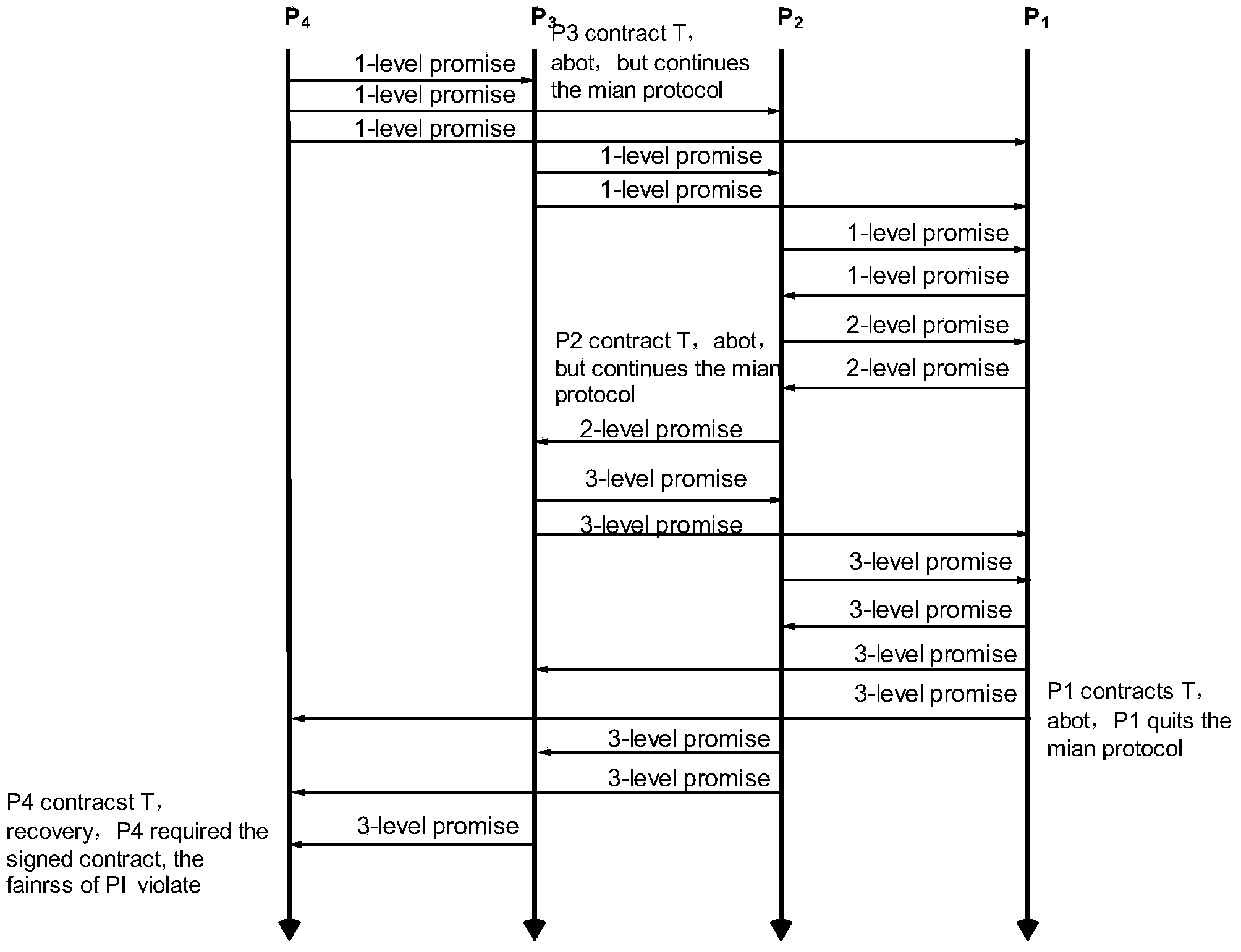
Multi-party contract signing protocol fairness verification method based on CSP# and LTL
The invention discloses a multi-party contract signing protocol fairness verification method based on the CSP# and LTL. The method includes the following steps that first, a multi-party contract signing protocol is modeled with the CSP# language; second, the fairness of the protocol is described in a formalized mode through the linear temporal logic (LTL), and the formal description includes state reduction and protocol fairness description; third, model check on a PAT platform is achieved, and fairness verification and a visual attack path are given out. With the method, the fairness can be automatically verified just by inputting a CSP# model of the protocol and the LTL fairness description on the basis of the protocol rules, operation is easy to perform, and the nature of the protocol can be verified practically. A state reduction rule is given for the state space explosion problem, state branch reduction is well completed, and meanwhile, the time and space complexity is reduced. The automatic tracking attack path is given so that the protocol can be improved and competed.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
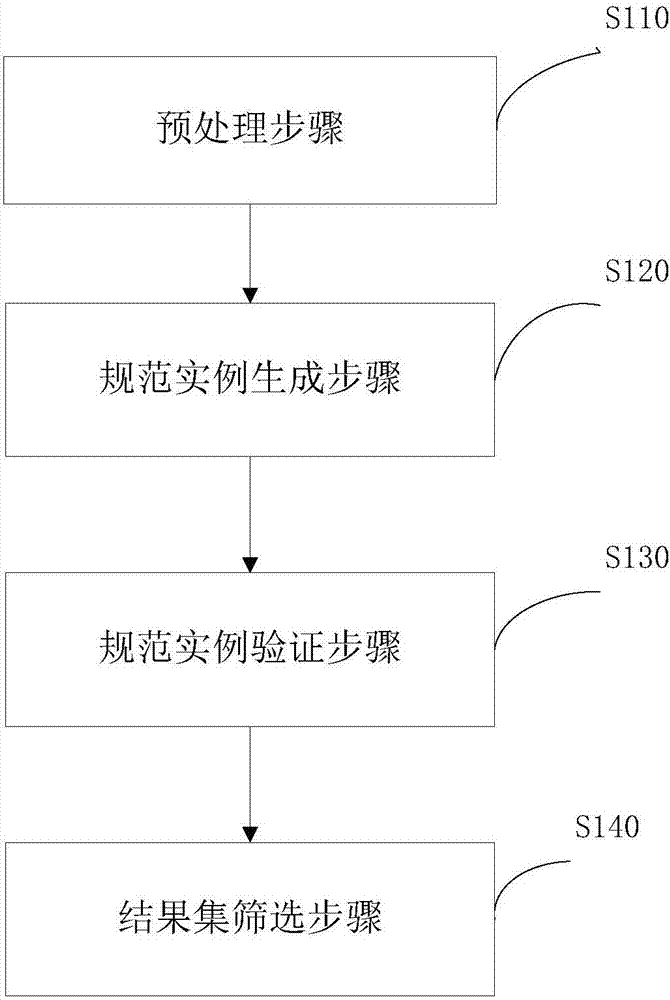
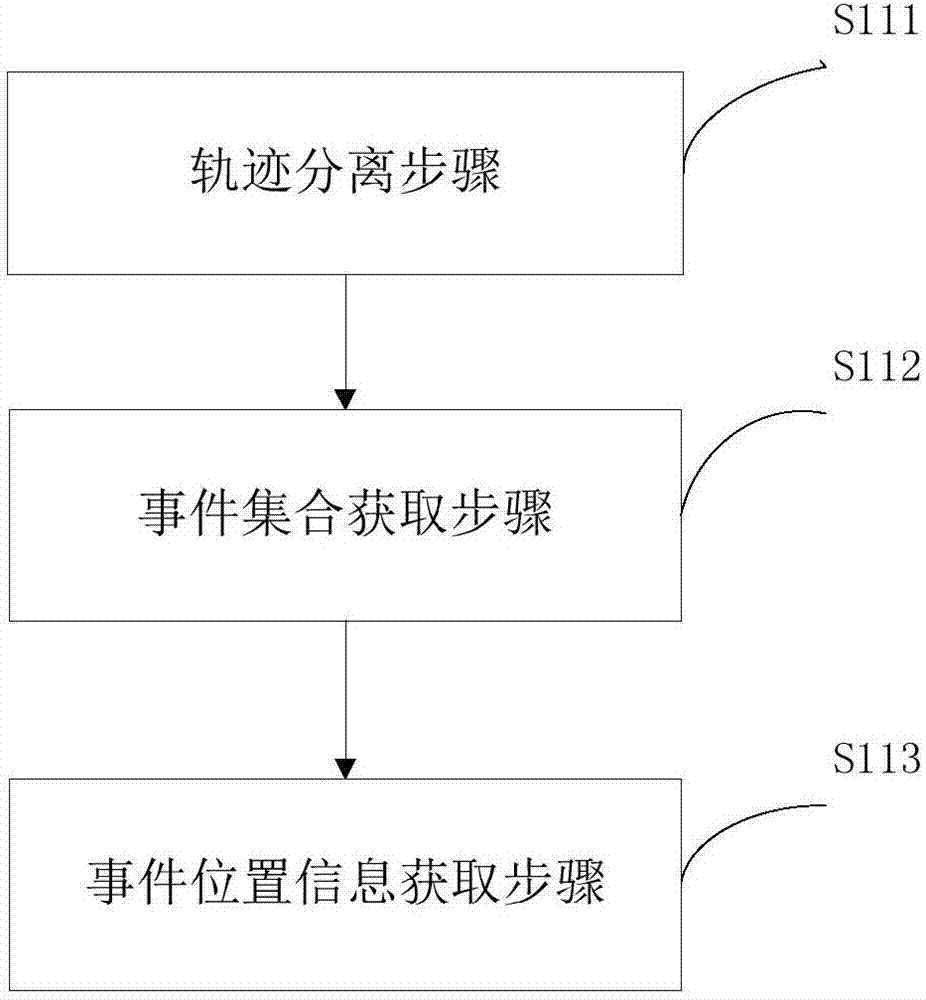
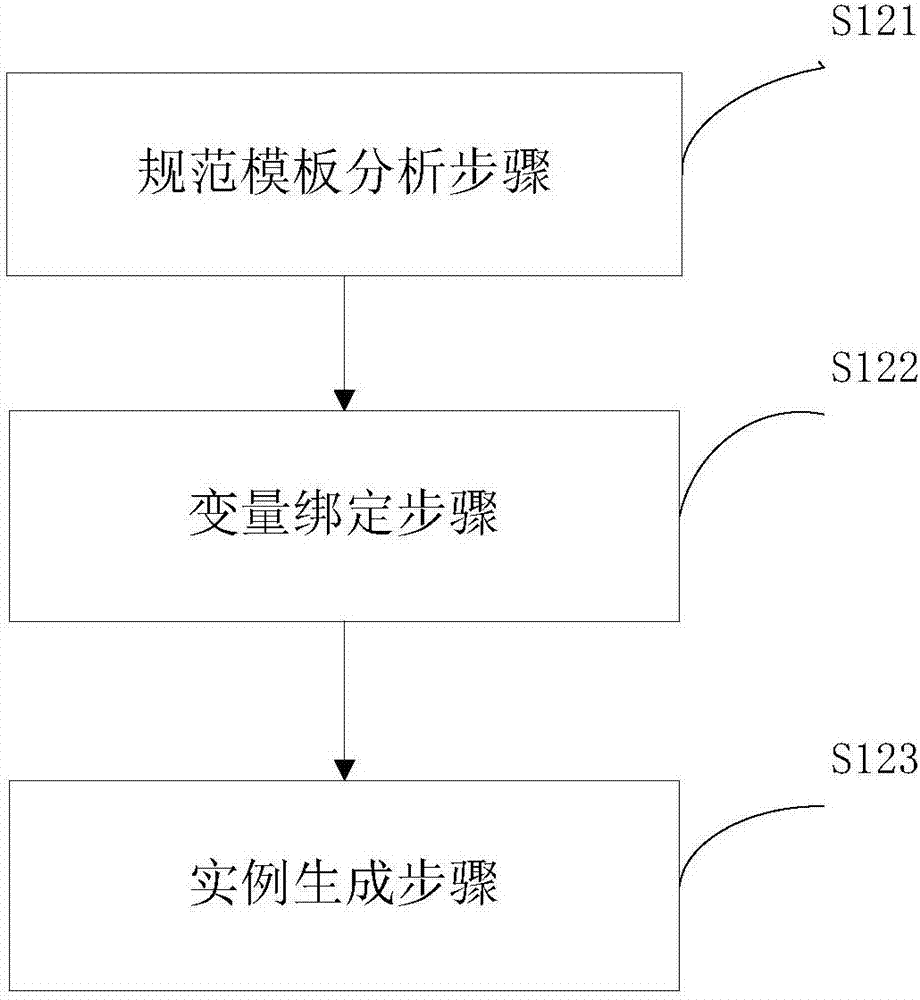
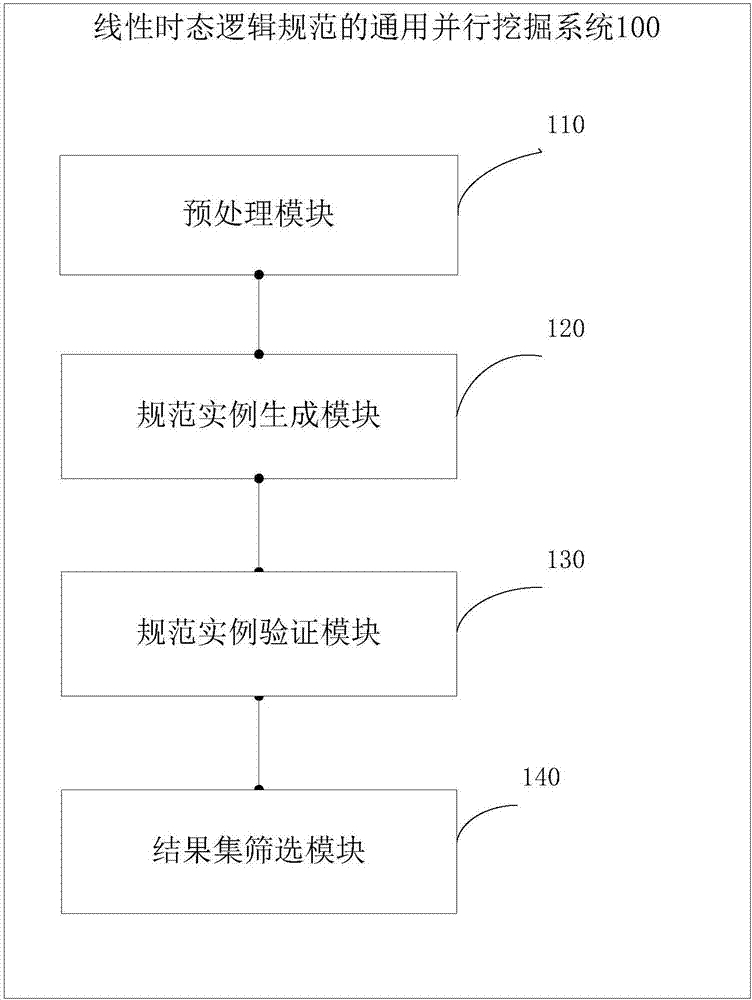
Universal parallel mining system for linear temporal logic specifications
InactiveCN106970791AEfficient acquisitionVersion controlSoftware metricsParallel miningLinear temporal logic
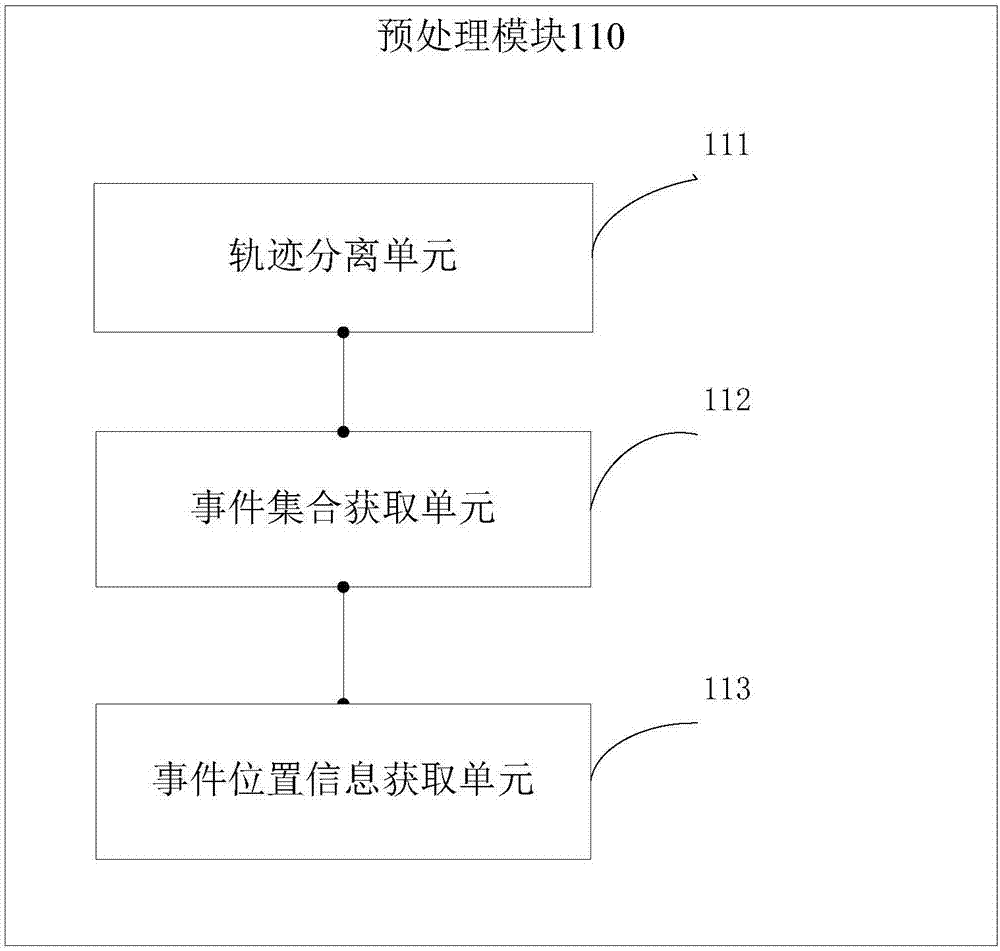
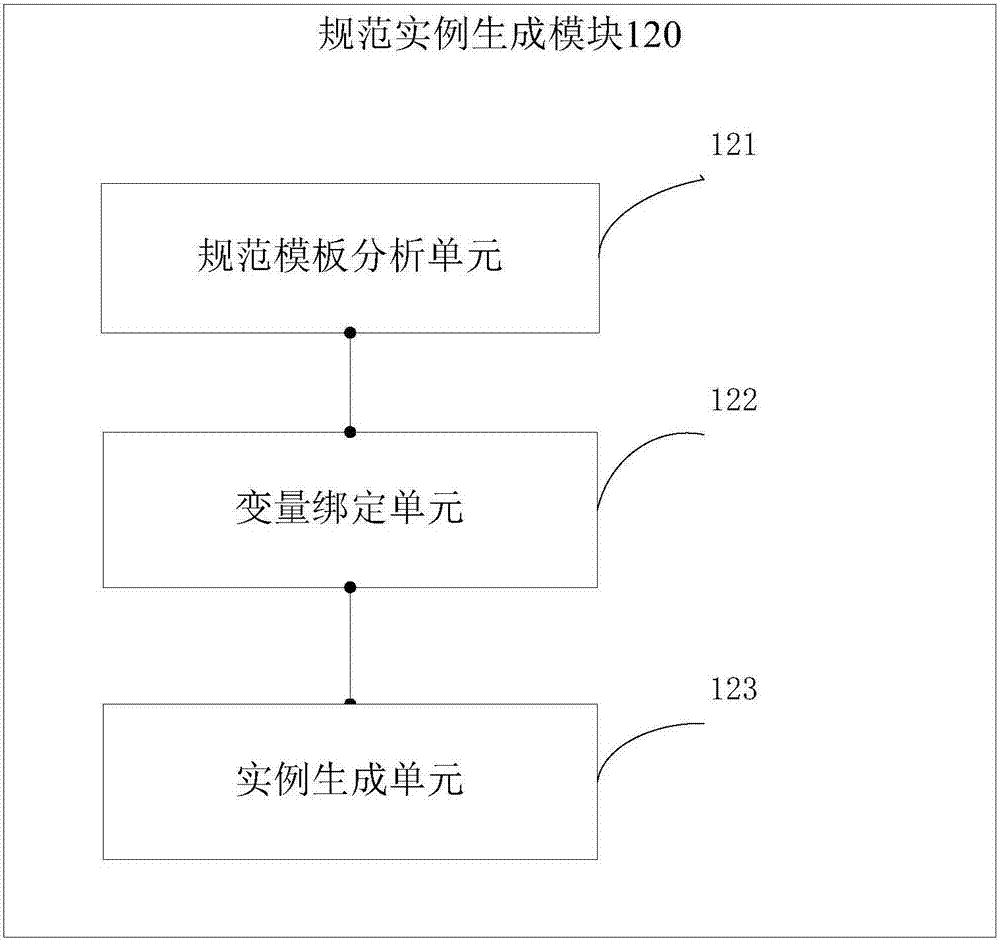
The invention discloses a universal parallel mining system for linear temporal logic specifications. The system comprises a preprocessing module, a specification instance generation module, a specification instance verification module and a result screening module, wherein the preprocessing module performs segmentation processing on a log file, obtains an event set occurring in a log and collects occurrence position information of events in the log; the specification instance generation module generates specific linear temporal logic specification instances in combination with the event set in the log by utilizing an input specification template; the specification instance verification module is in charge of calculating support degrees and confidence degrees of the specification instances in the log by utilizing the preprocessed event position information; and the result screening module is in charge of screening a mined result set to remove the specification instances with the support degrees and the confidence degrees not meeting the mining requirements. According to the mining system, a multithread technology is fully utilized to perform parallel computing, so that any type of the linear temporal logic specification can be efficiently mined.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV +1
A distributed multi-agent task cooperation method based on linear temporal logic
ActiveCN111340348BReduce time complexityImprove COPResourcesLinear temporal logicCollaborative intelligence
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Computer-assisted design of mechatronic systems to comply with textual system description
PendingCN109791575ADesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsSystems designAlgorithm
A method for computer-assisted system design of dynamic systems is described herein. In accordance with one embodiment the method comprises: providing a textual system description; converting, using acomputer, the textual system description into a linear temporal logic LTL formula; converting, using a computer, the LTL formula into a first automaton; providing, using a computer, a second automaton representing the system dynamics; and generating, using a computer, a testing automaton by combining the first and the second automaton.
Owner:科特罗尔有限责任公司
An Efficient Large-Scale System LTL Model Checking Method for De-memory Jittering
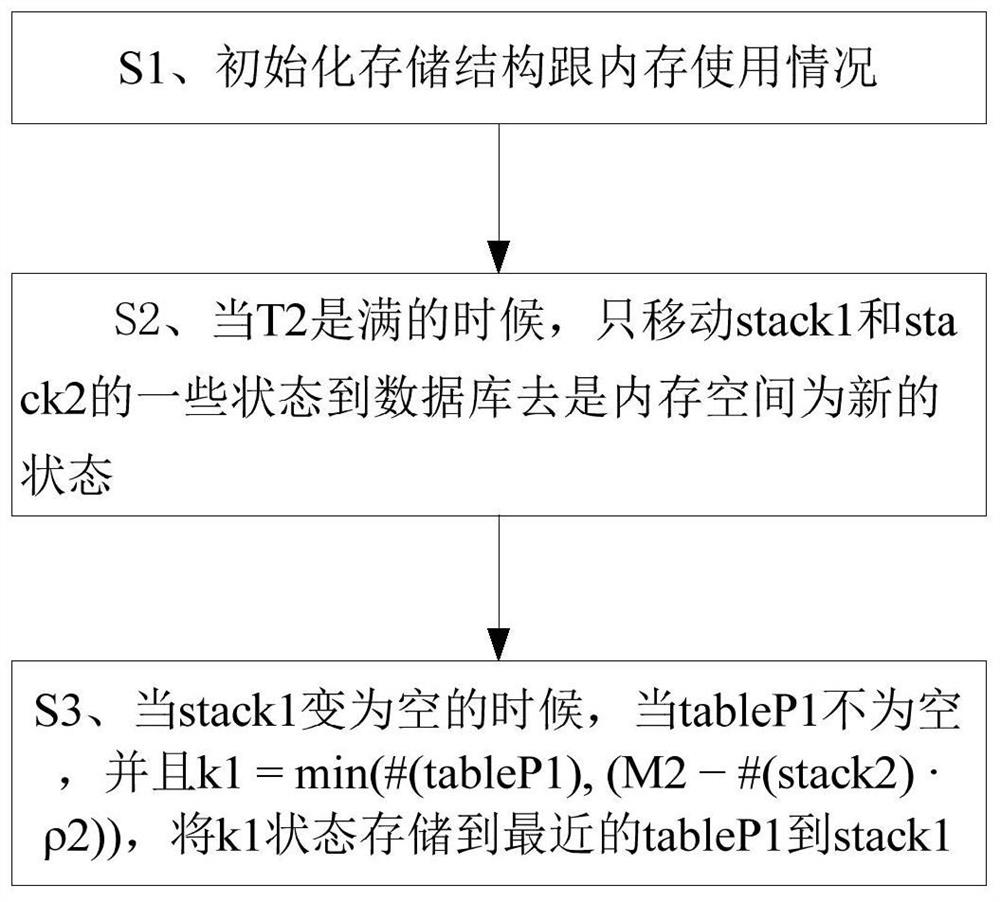
InactiveCN106371765BReduce complexityIncrease the number of operationsInput/output to record carriersThrashingMemory cell
The invention discloses a method for removing memory thrashing through the efficient LTL ((Linear Temporal Logic) model detection of a large-scale system. A LHS (Linear Hash Storage) algorithm is adopted to mainly aim at quickly finding a Hash value stored in a Hash table in a disk; no matter whether the classification of the Hash table in the memory is empty or not, the Hash table can be stored in an external memory and is processed by a new technology after being stored in the external memory, and the complexity of I / O is a linear size which is the same with the Hash table; and a CDD (Cached Duplicate Detection) technology permits a duplicate in the memory to be detected through effective access, duplicate detection complexity can be lowered through the LHS and the CDD, the plan of DPM (Dynamic Path Management) enables two nested depth-first stacks to dynamically share a memory cell, and the memory thrashing problem can be solved through the effective management of the stack and the state, wherein the memory thrashing means that the frequent movement of the state in the memory may obviously increase I / O operation frequencies so as to lower the efficiency of the algorithm.
Owner:CHENGDU KEHONGDA TECH
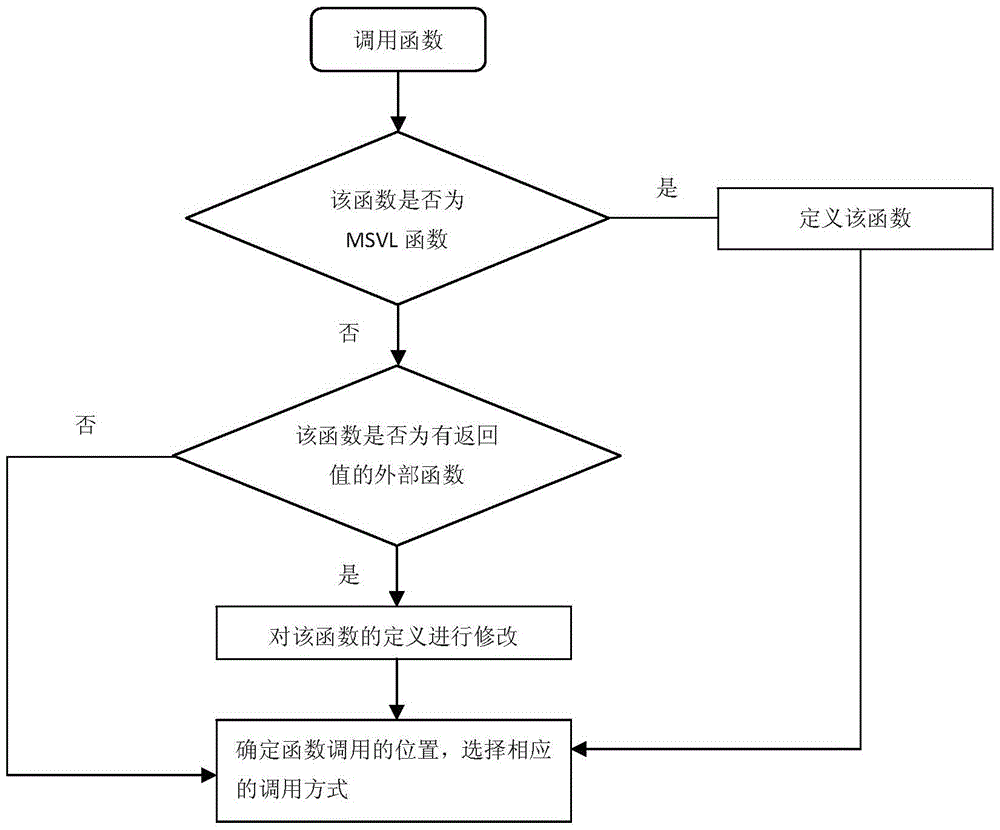
A function calling method based on temporal logic language msvl
ActiveCN104281480BReduce difficultyEasy to integrateProgram controlMemory systemsFunctional methodsLinear temporal logic
The invention discloses a function call method based on a temporal logic language MSVL (modeling, simulation and verification language). The method includes: firstly, judging whether a called function is an MSVL function, an external function with a return value or an external function without a return value in type, and defining the called function or modifying the definition thereof according to different function types; secondly, judging the position of the called function, and calling the function via different modes according to different function call positions and the corresponding called function type. By the method, the called function is explained with different modes in the same program; the function compiled with the C language and the Java language can be called in the MSVL program, integration of various different programming language programs is facilitated, difficulty in program development is lowered effectively, and code reuse rate is increased.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
An Efficient LTL Model Checking Method for Large-Scale Systems
InactiveCN106293544BReduce complexityIncrease the number of operationsInput/output to record carriersAlgorithmLinear temporal logic
The invention discloses a high-efficient LTL (Linear Temporal Logic) model detection method of large scale system. The LTL model detection method is characterized in that by adopting an LHS (Linear Hash Storage) algorithm, hash values stored in hash tables in a hard disc can be quickly found, and the hash tables can be stored in an outer memory by a new technique no matter whether the classification of the hash tables in an inner memory is empty or not, and the complexity of I / O (input / output) is the linearity size of the hash tables; by adopting a CDD (Cache Copy Detection) technique, a copy in the inner memory can be detected by effective accessing; by adopting HLS and CDD, the complexity of copy detection can be decreased; by adopting a DPM (dynamic path management) plan, the two embedded deep priority stacks can dynamically share an inner memory unit, and the jittering of the inner memory is solved by the effective stacking and state management, wherein the jittering of the inner memory refers to the frequent movement of the state in the inner memory, which may cause obvious increasing of I / O operation times, thereby reducing the algorithm efficiency.
Owner:CHENGDU KEHONGDA TECH
Formal detection method and device of intelligent uml model
ActiveCN102722441BImprove user experienceGood application effectSoftware testing/debuggingSoftware development processPattern recognition
The invention provides a formalized detection method of an intelligent UML (Unified Modeling Language) model and a device. The method comprises the steps of: establishing an UML model for a true system and converting the UML model into an XMI (Extensible Markup Language) model; extracting predetermined element information from the XMI model and converting the predetermined element information semantically to obtain an SMV (Symbolic Modeling Verification) model by applying a set of conversion rule; acquiring an CTL (Complementary Transistor Logic) and / or an LTL (Linear Temporal Logic) propositional logic detection formula, wherein the CTL and / or LTL propositional logic detection formula are / is used for detecting the SMV model; and constructing a binary decision diagram according to the CTL and / or LTL propositional logic detection formula and the SMV model to detect the SMV model so as to obtain a detection result. According to the embodiment disclosed by the invention, the formalized detection method has the advantages of high detection accuracy and wide application, and can comprehensively detect the UML model which has higher demand on safety in a software development process.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
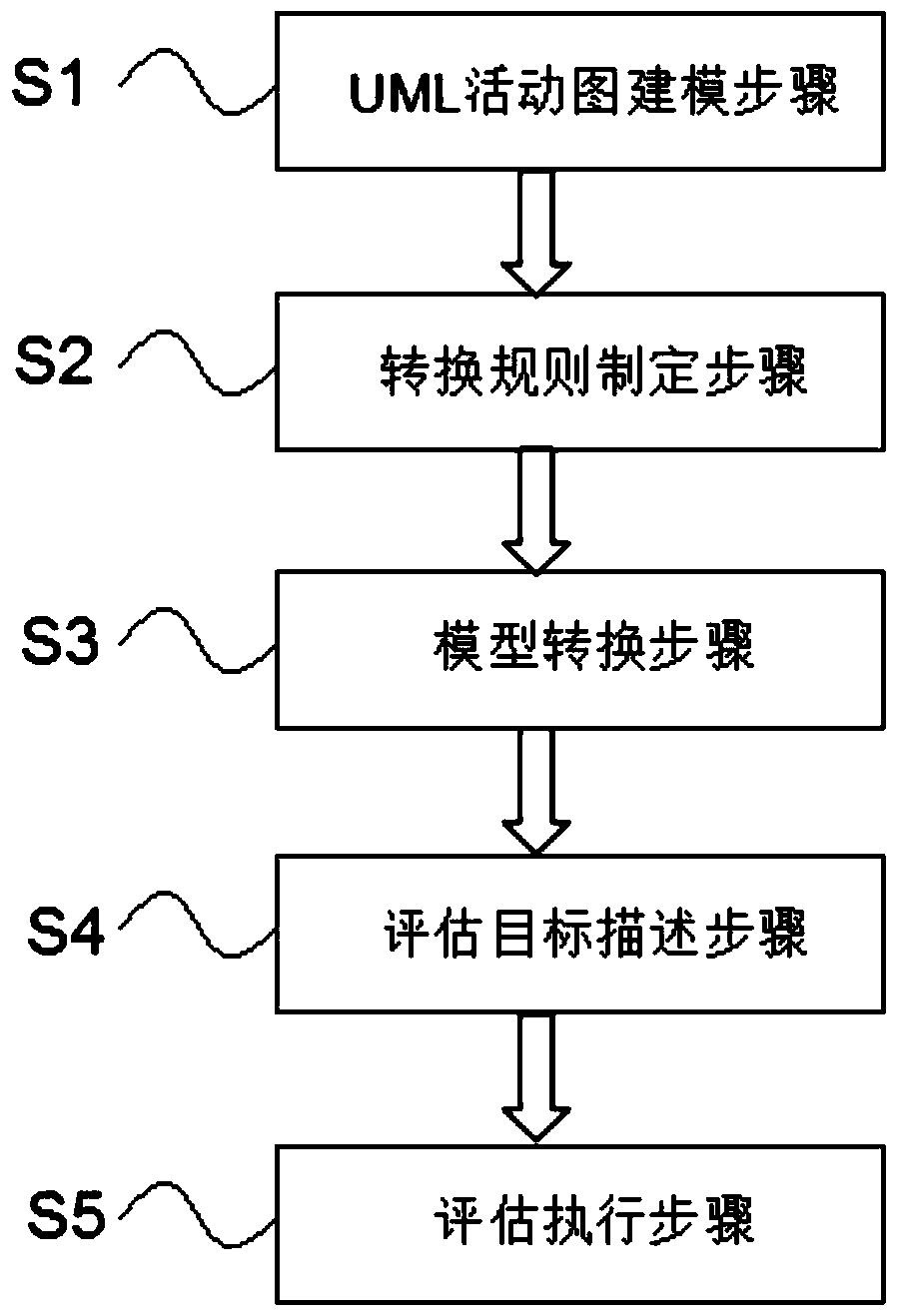
A uml activity diagram evaluation method based on statistical model testing
ActiveCN104572101BImprove the evaluation effectExtended assessment contentSpecific program execution arrangementsTime informationStatistical model checking
The invention discloses a method for evaluating a UML activity diagram based on statistical model inspection, comprising: a UML activity diagram modeling step: modeling the engineering system according to the engineering system logic to generate a corresponding UML activity diagram model; a conversion rule formulation step: Establish conversion rules between UML activity diagram model and time automaton model; model transformation step: map UML activity diagram model to time automaton model, and introduce single task execution time interval and distribution information into time automaton model; evaluate Goal description step: describe the coverage criterion with linear temporal logic, and the coverage criterion includes more than one evaluation goal; evaluation execution step: use the statistical model checking method to verify the coverage rate of the time automata model meeting the coverage criterion, so as to obtain the evaluation result. The invention supplements the time modeling ability in the model description ability, can strengthen the evaluation ability for UML activity diagrams, expand the evaluation content, and improve the evaluation quality.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
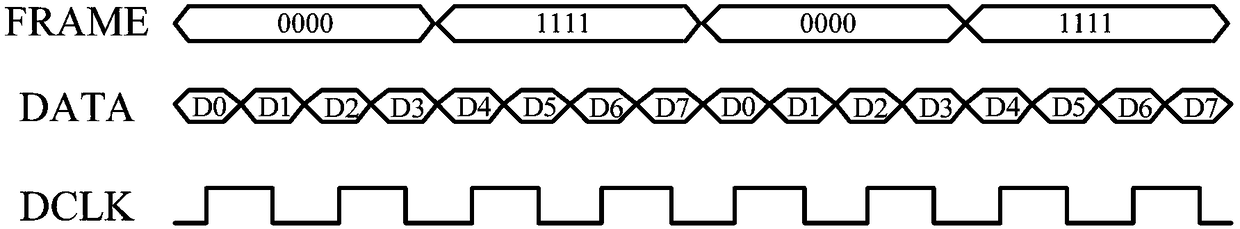
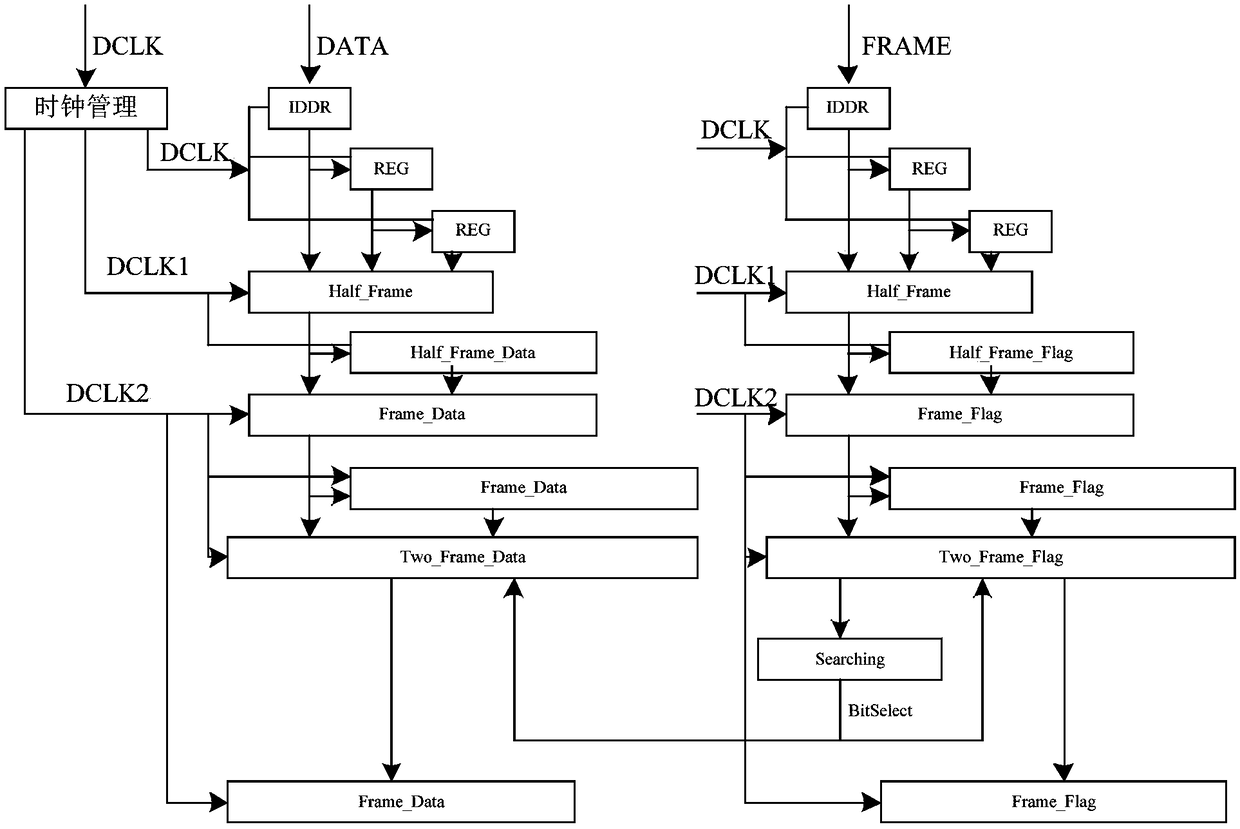
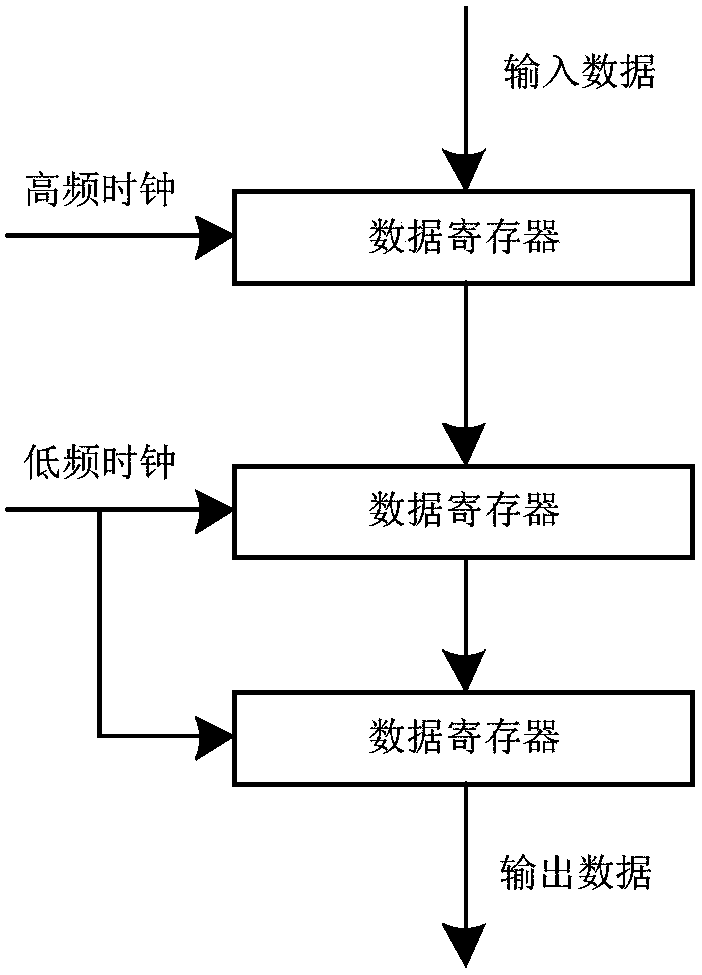
A real-time deserialization processing method of cmos image sensor data signal
ActiveCN106060432BImprove real-time performanceGuaranteed relative phaseTelevision system detailsColor television detailsData streamPhase difference
The invention discloses a real-time deserialization processing method of a CMOS image sensor data signal. The invention proposes a new real-time processing method of CMOS image sensor data signal, which replaces the circular search and search of the state machine of the traditional scheme, and realizes the real-time decoding processing of the high-speed serial source synchronous signal. The real-time processing method of the CMOS image sensor data signal is based on a linear time logic circuit, and uses the bit clock DCLK output by the CMOS image sensor to perform double-edge latching on the serial data stream with a double data rate to ensure the relative phase of the latch clock and the data signal ; Use the bit clock DCLK to generate half-frame clock DCLK1 and frame clock DCLK2 with the same phase, which ensures that the phase difference between different frequency clock domains is small, which is conducive to the stable transmission of signals across clock domains; using two consecutive latching techniques, Realize the effective data transmission from the high-frequency clock domain to the lower-frequency clock domain, so as to finally realize the high real-time performance of sensor data processing.
Owner:NORTHWEST INST OF NUCLEAR TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com