Patents
Literature
265 results about "Code reuse" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Code reuse, also called software reuse, is the use of existing software, or software knowledge, to build new software, following the reusability principles.
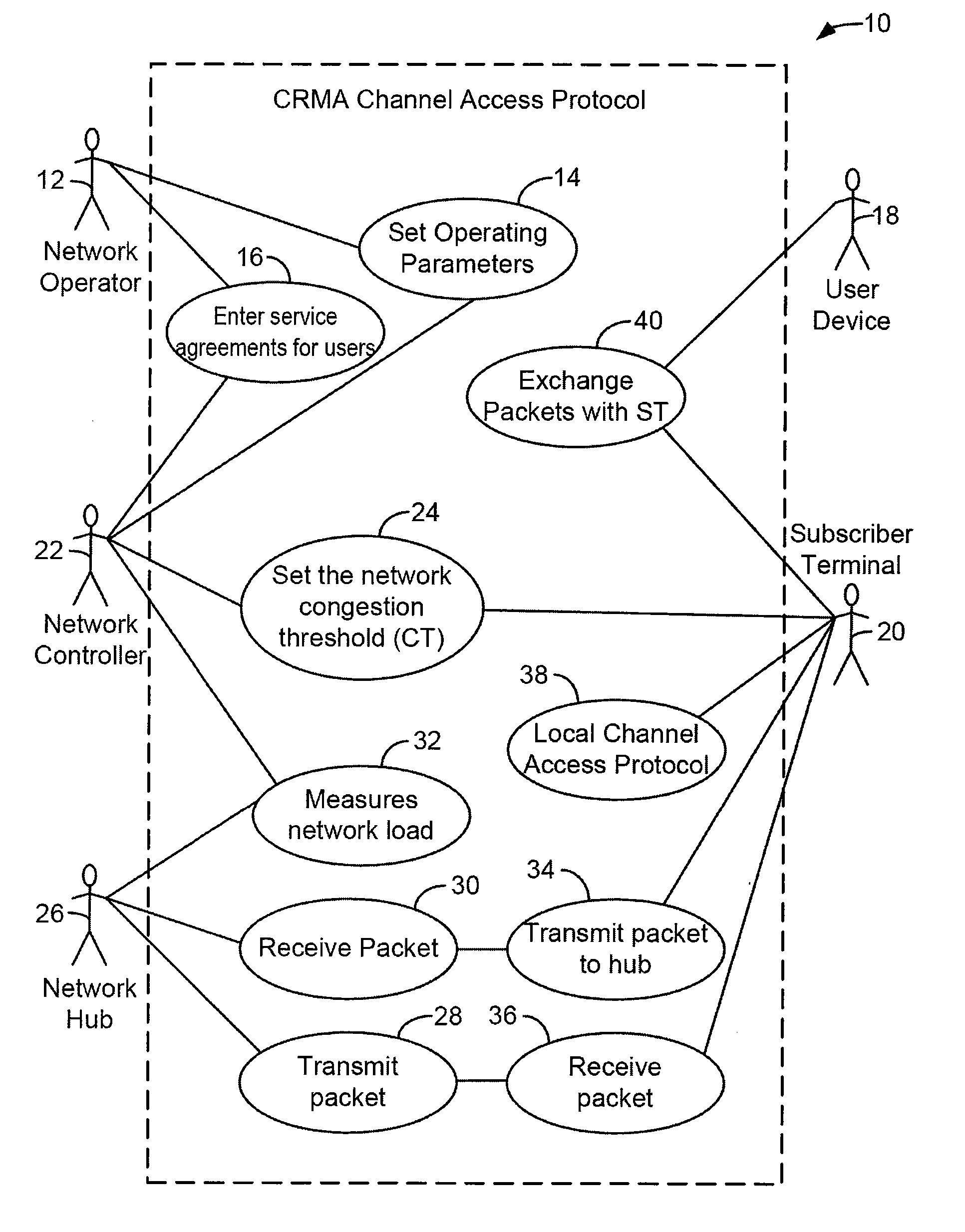
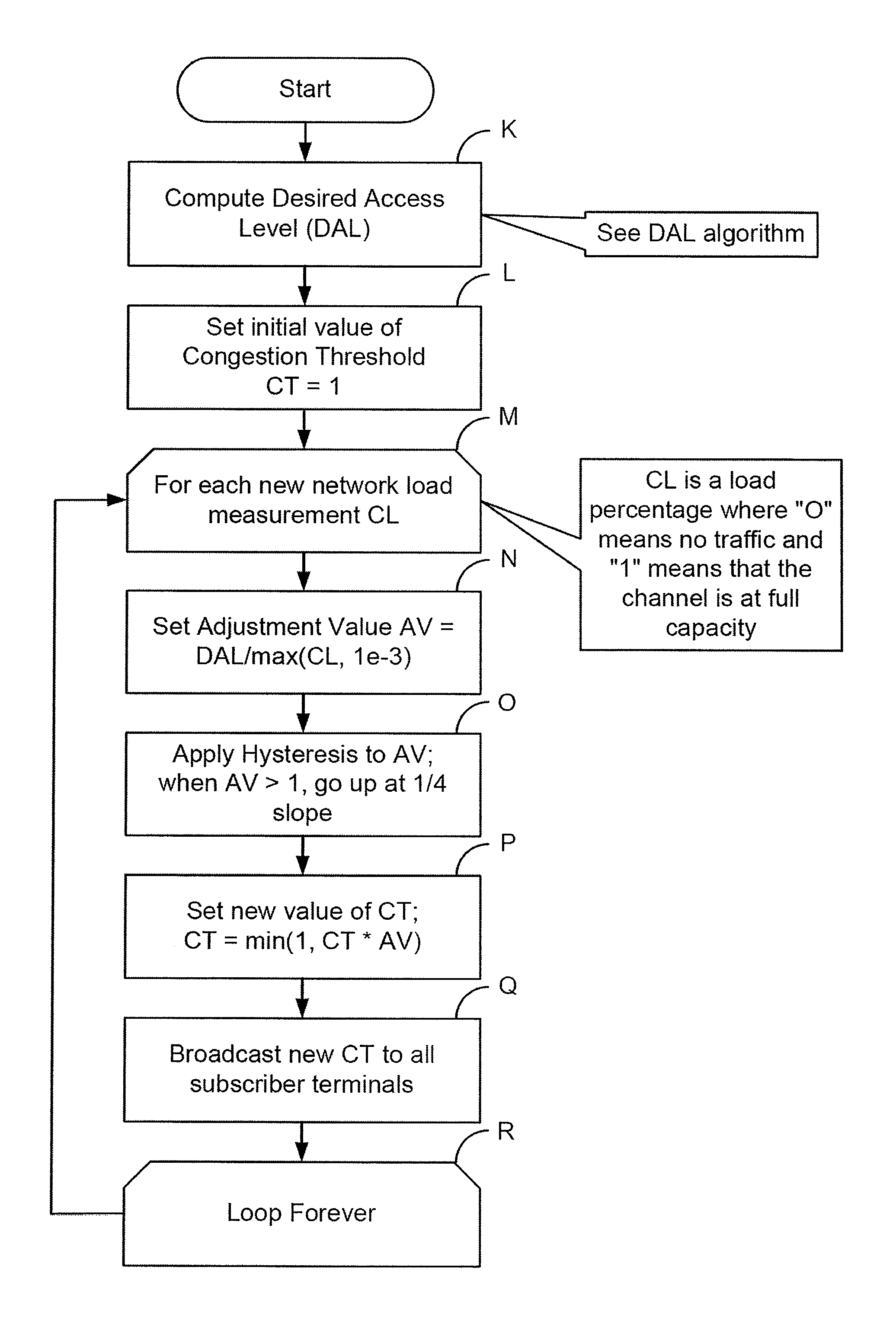
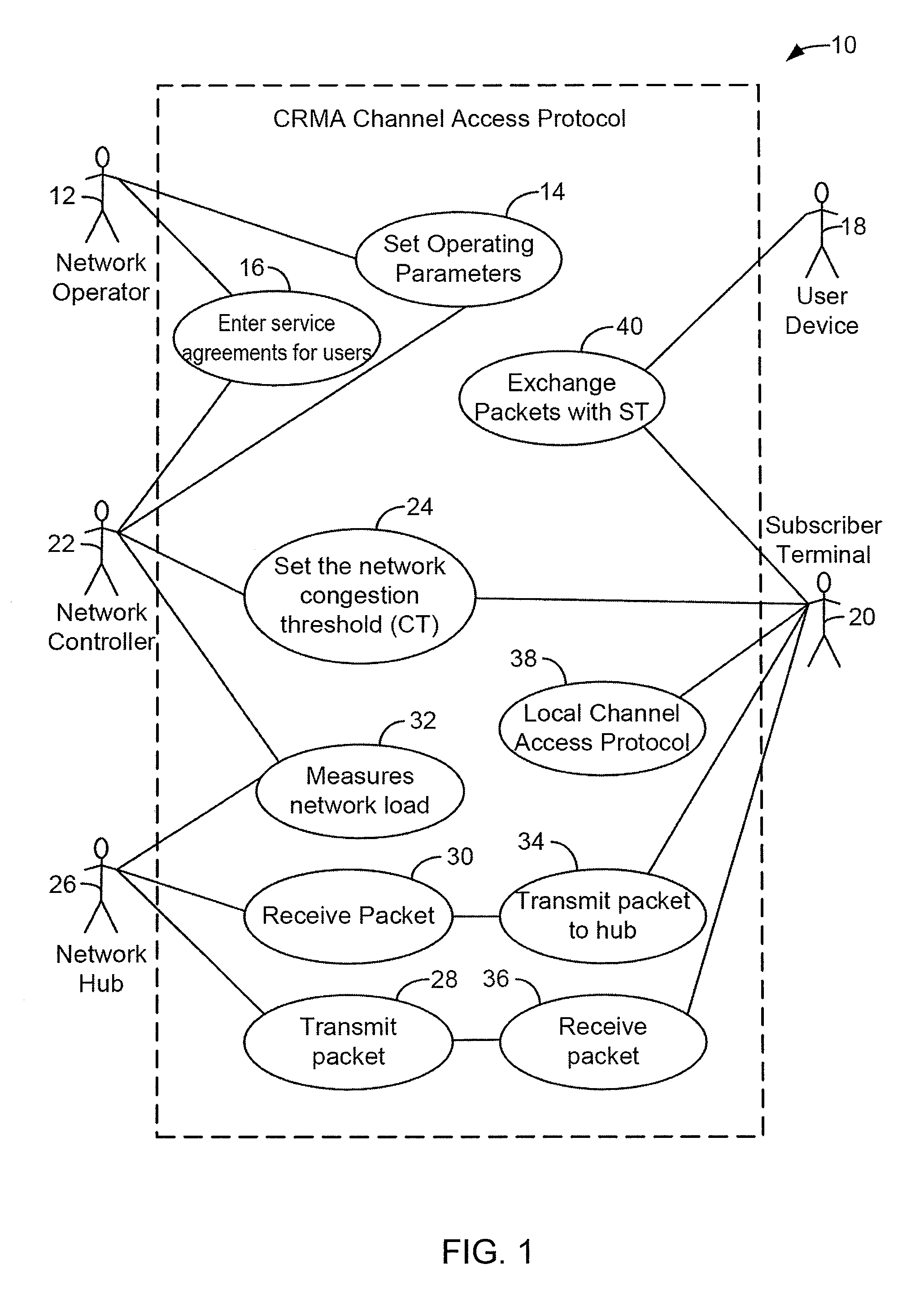
Method For Channel Congestion Management
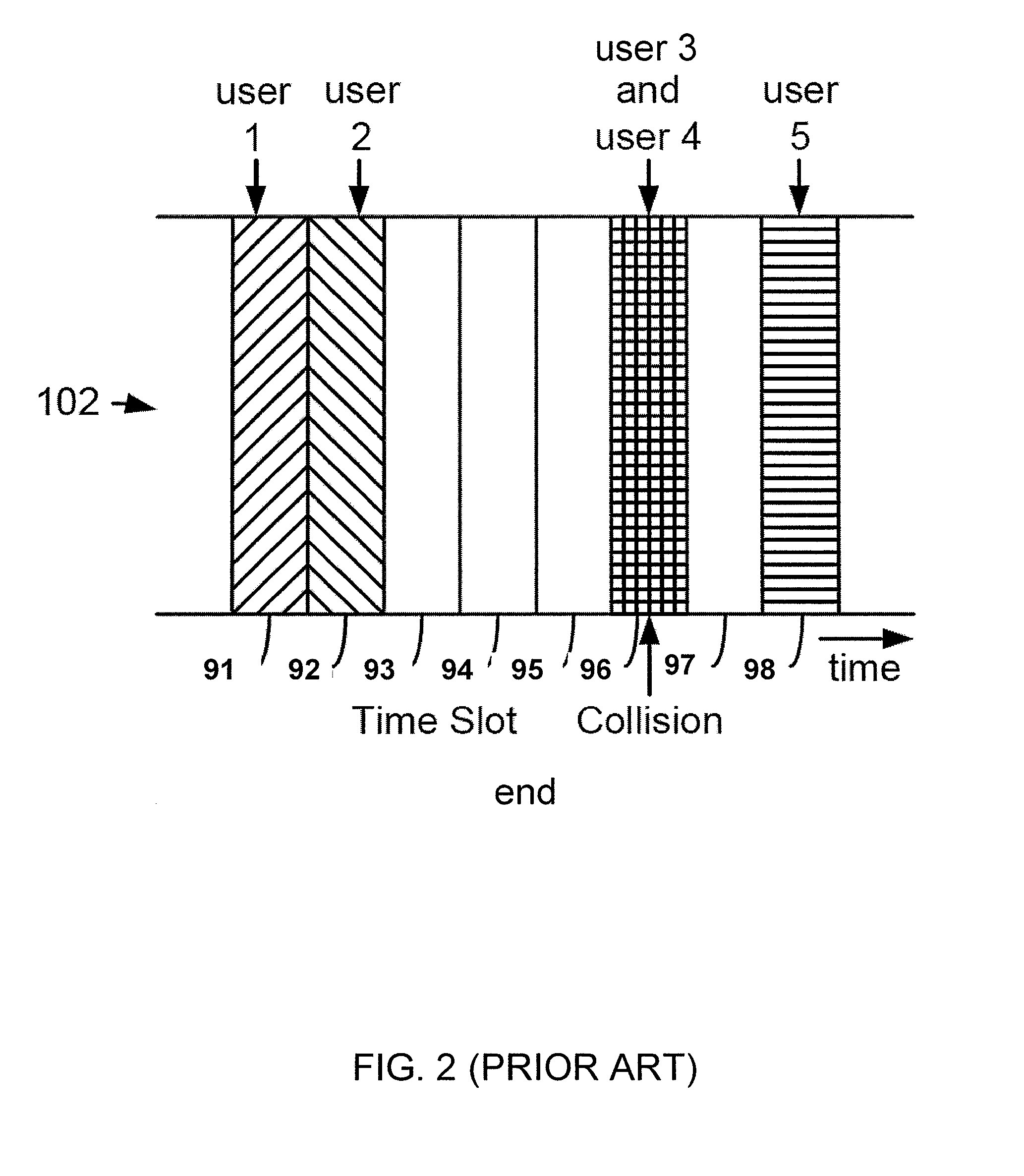
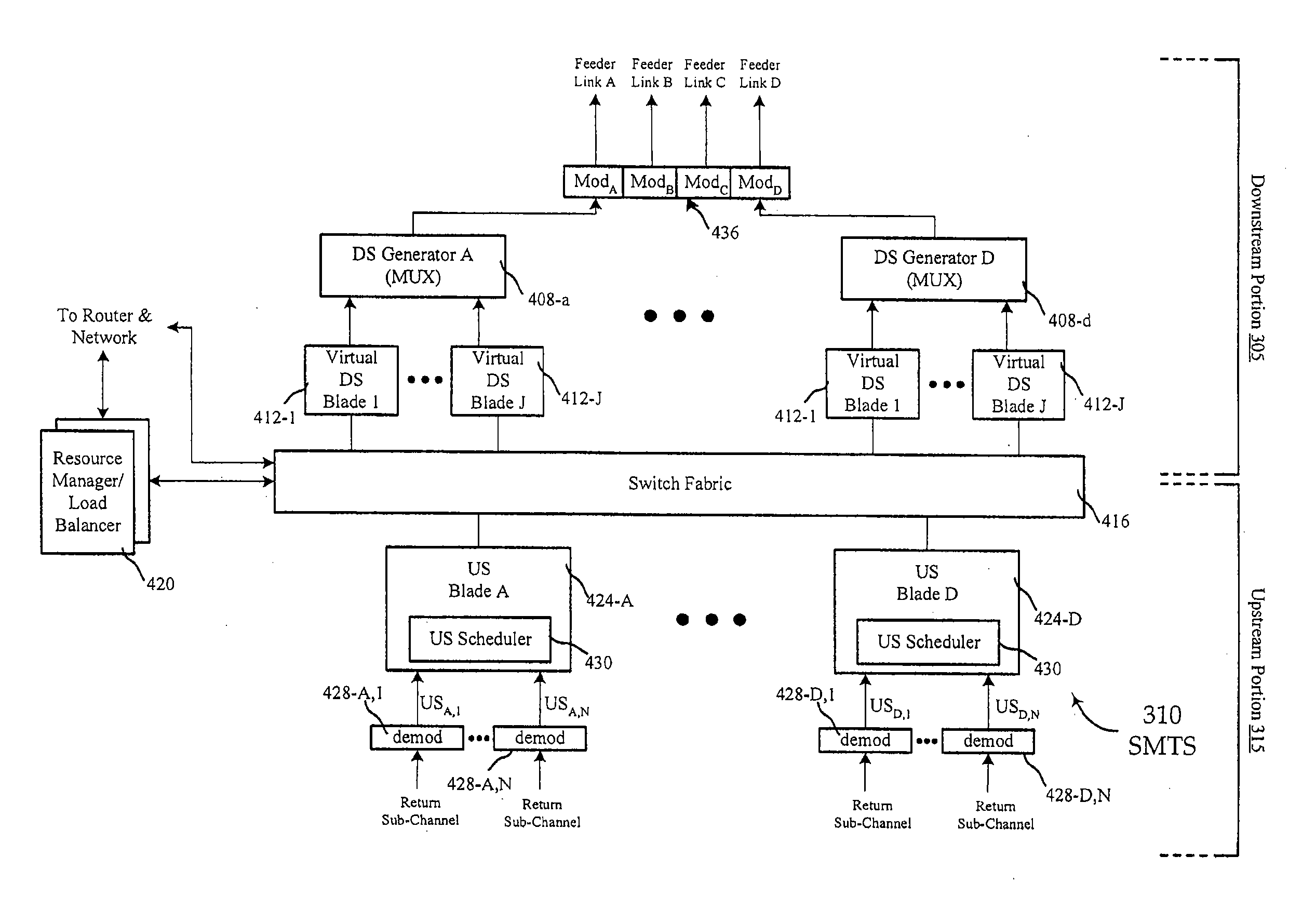
ActiveUS20070110098A1Useful operationReduce cloggingTime-division multiplexMultiple digital computer combinationsNumber generatorData traffic
A method for managing data traffic in a multi-user multiple-simultaneous-access (MUMSA) environment, for example in a code reuse multiple access (CRMA) environment or other physical environment having true random access with more than one transmission present at the same time, the method including estimating channel load for multiple users, then using the estimate of channel load to calculate a congestion threshold on an ongoing basis, at each terminal performing an experiment using that congestion threshold value and a random number generator to determine if a packet is eligible to be transmitted, transferring downstream virtual channel traffic and redistributing user terminals to affiliate with the proper downstream virtual channel.
Owner:VIASAT INC
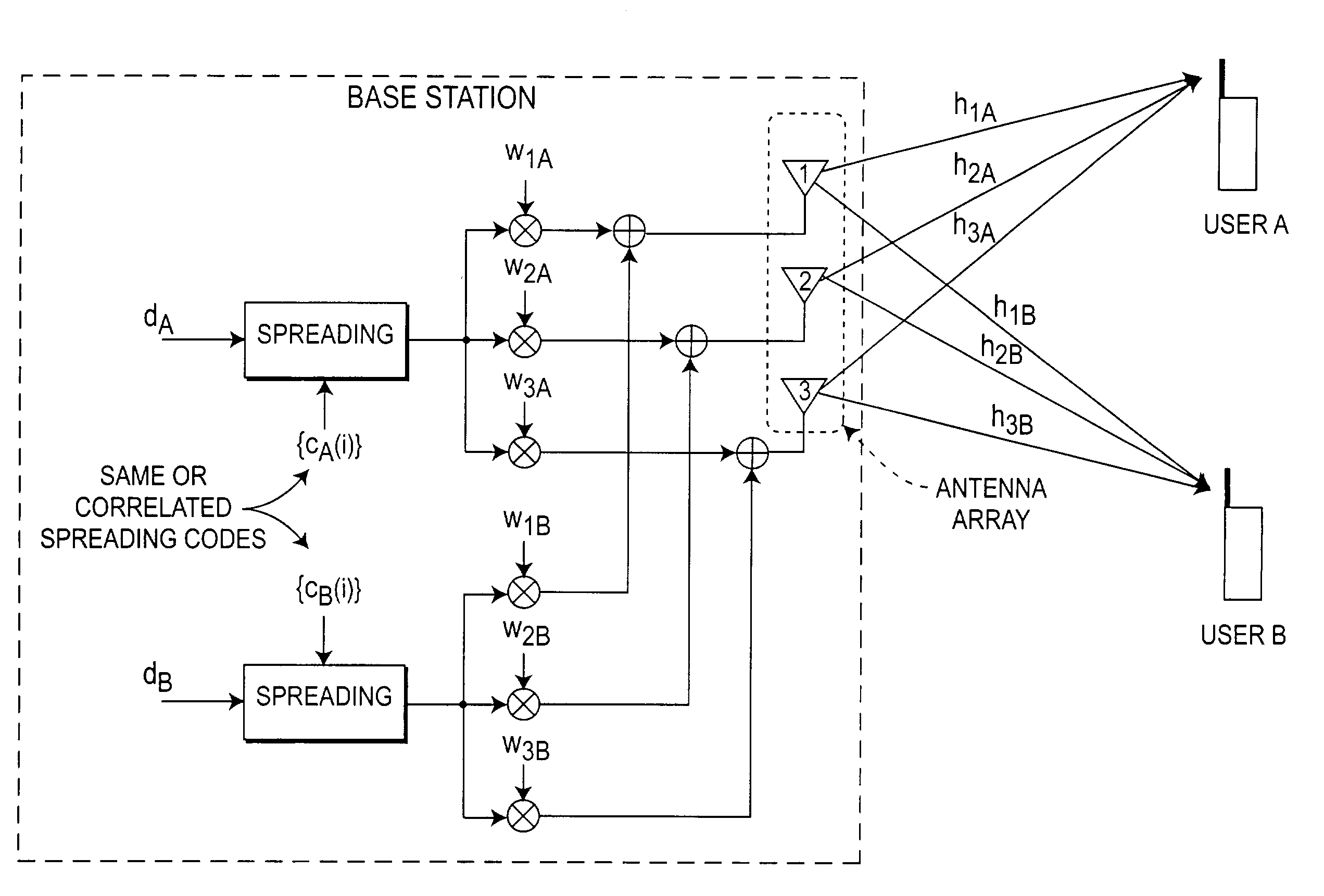
Method and system for code reuse and capacity enhancement using null steering
InactiveUS7218684B2Increase capacityMaintain propertiesSpatial transmit diversityAntenna arraysData capacityEngineering
The number of users and data capacity of wireless systems are increased by employing apparatus and method for increasing the number of spreading codes available in the system by providing a mechanism to reuse the already allocated spreading code or use the codes that may correlate to those already being used within the same sector / cell. This, in return, provides capacity improvement proportional to the number of added base station (BS) antennas for each cell. An antenna null steering technique for code allocation maintains the cross correlation properties of the codes only for the desired user and to obtain a gain in capacity improvement.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL TECH CORP
Method for channel congestion management
ActiveUS7650379B2Reduce cloggingReduce channel congestionError preventionTransmission systemsNumber generatorData traffic
A method for managing data traffic in a multi-user multiple-simultaneous-access (MUMSA) environment, for example in a code reuse multiple access (CRMA) environment or other physical environment having true random access with more than one transmission present at the same time, the method including estimating channel load for multiple users, then using the estimate of channel load to calculate a congestion threshold on an ongoing basis, at each terminal performing an experiment using that congestion threshold value and a random number generator to determine if a packet is eligible to be transmitted, transferring downstream virtual channel traffic and redistributing user terminals to affiliate with the proper downstream virtual channel.
Owner:VIASAT INC
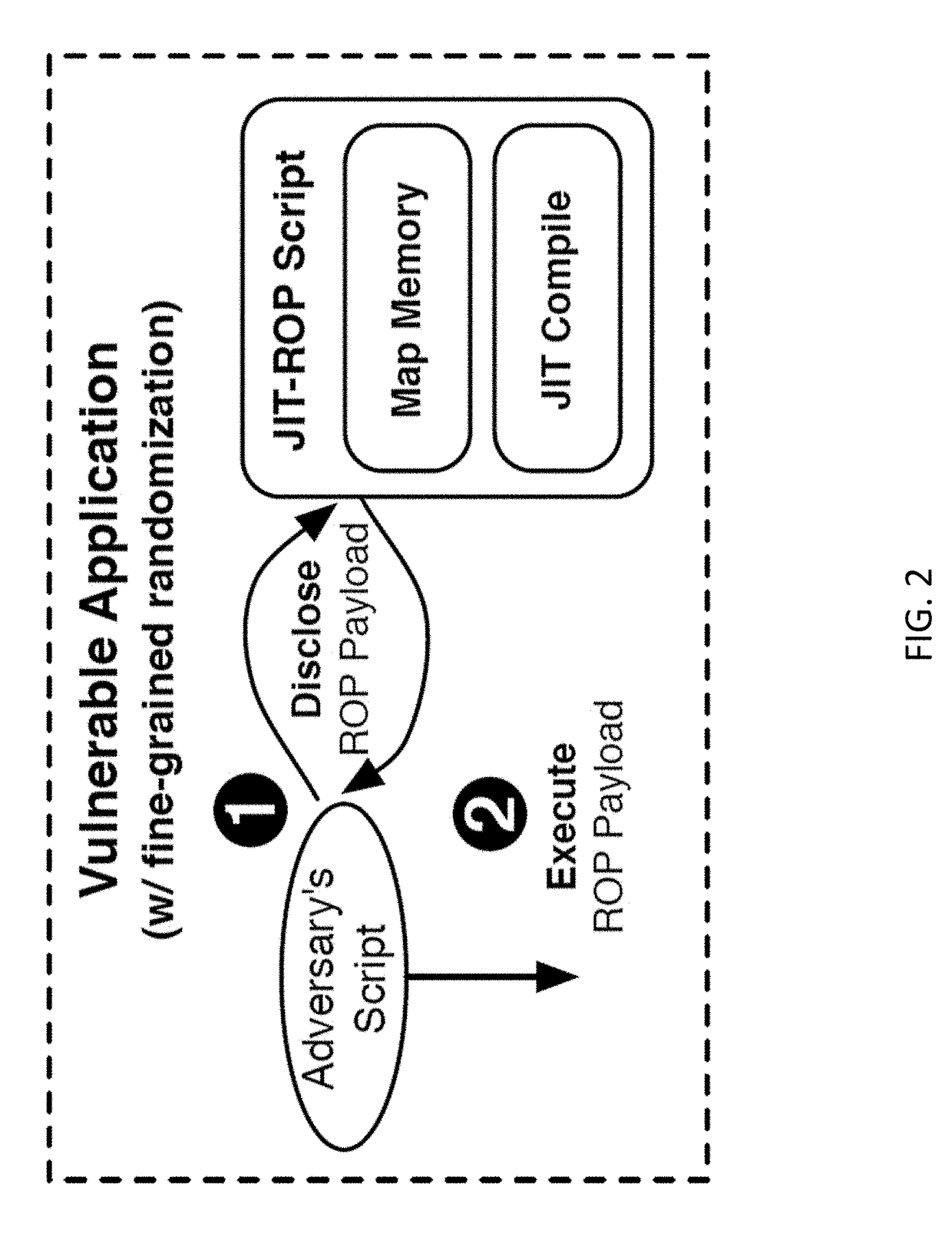
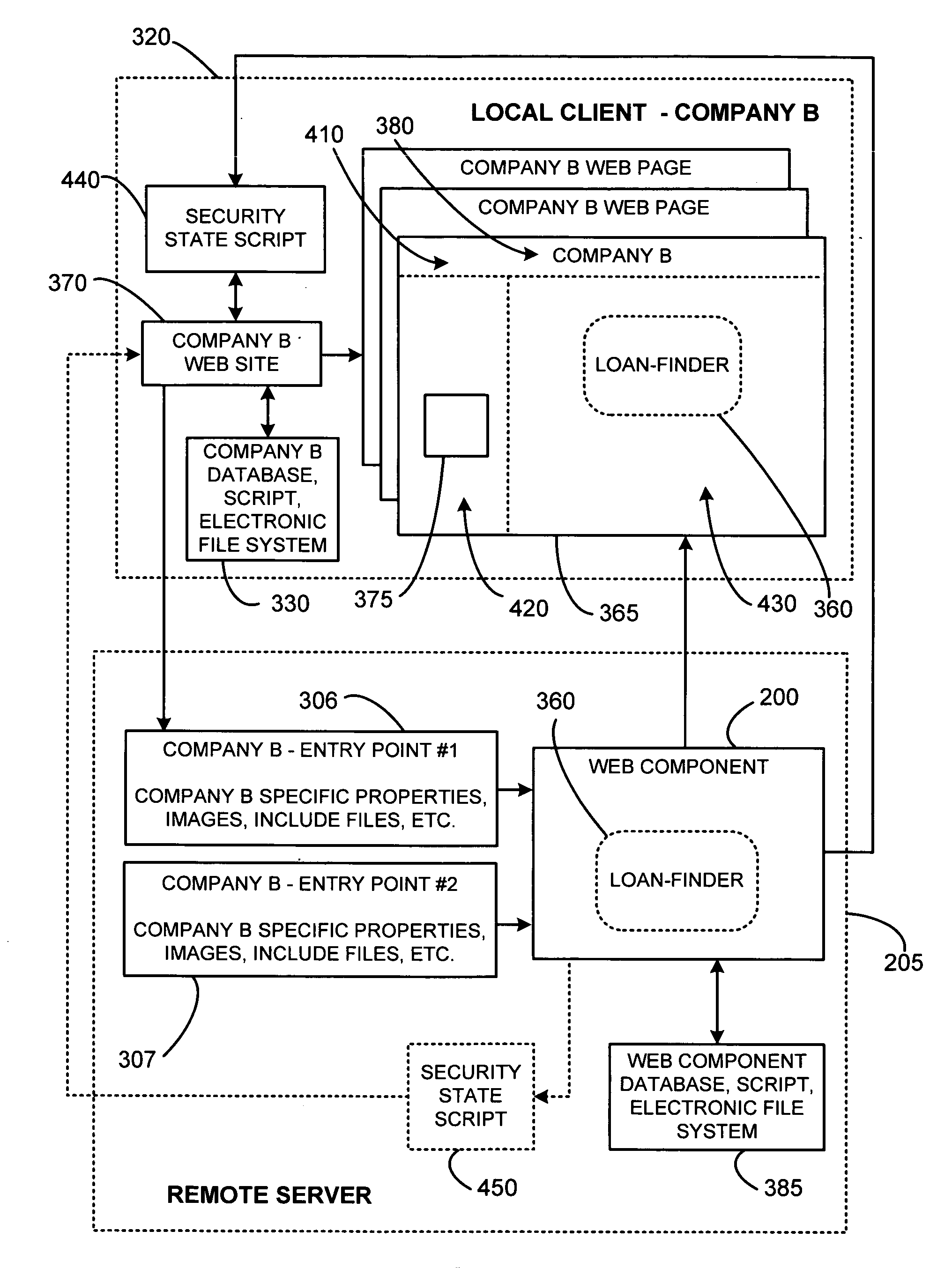
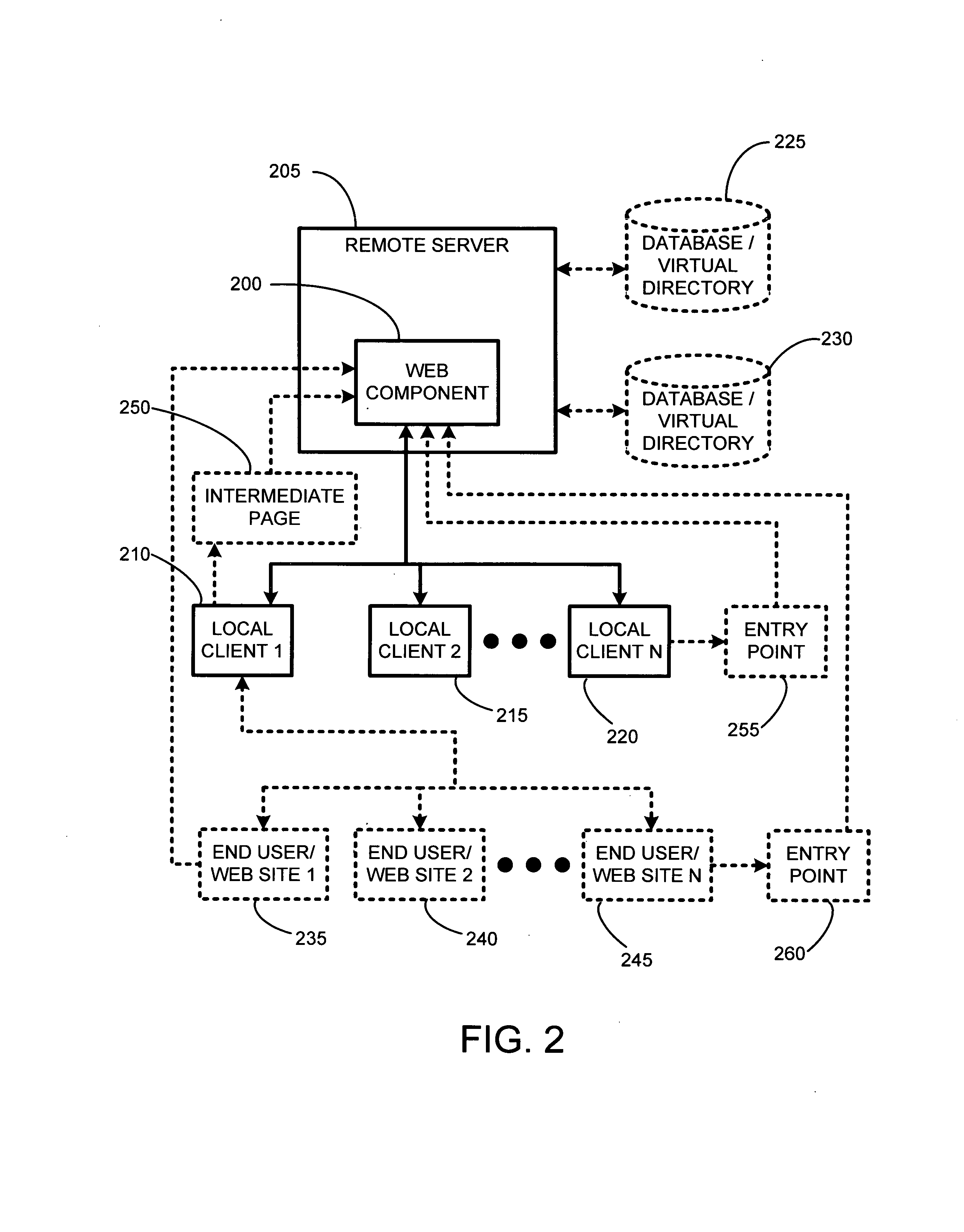
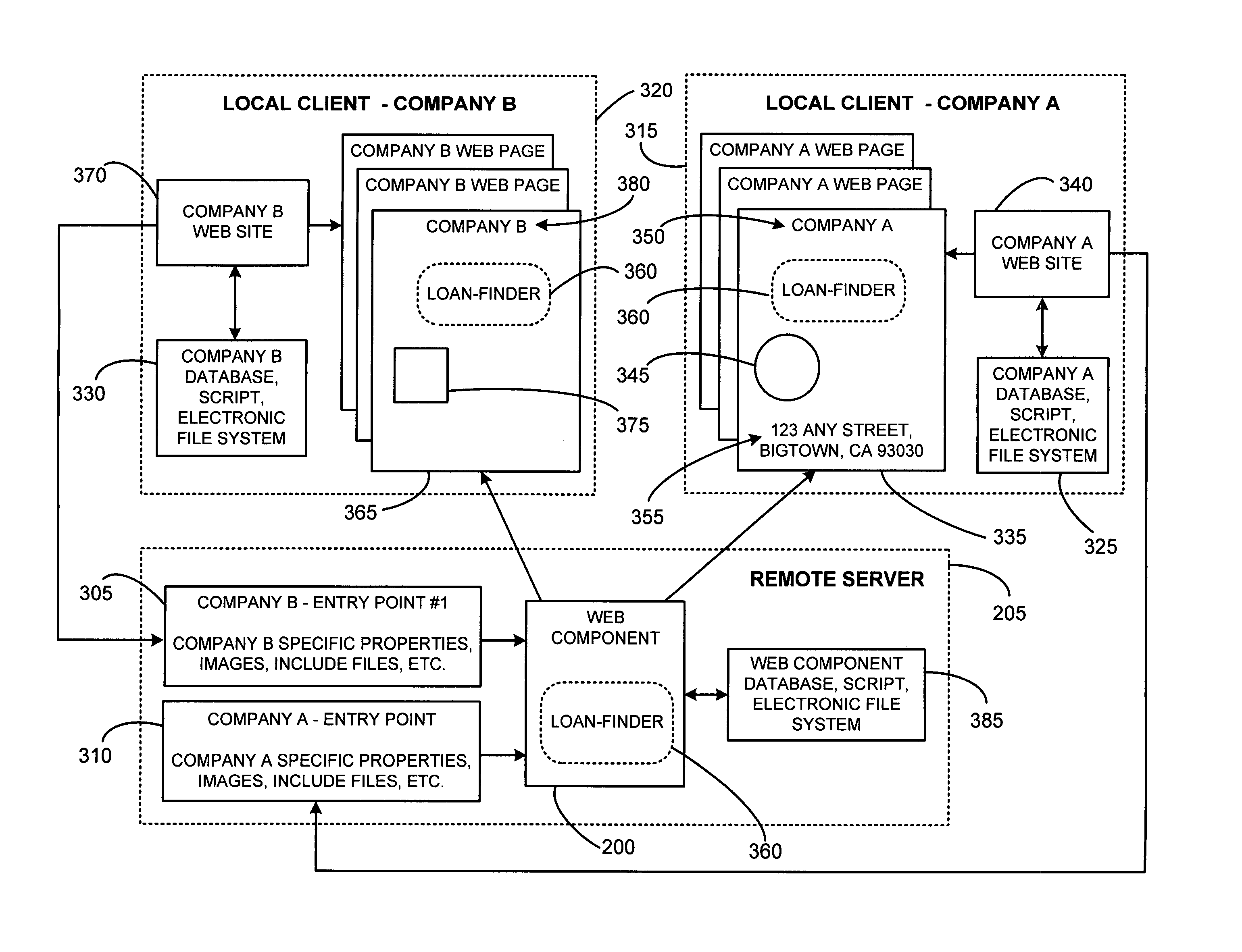
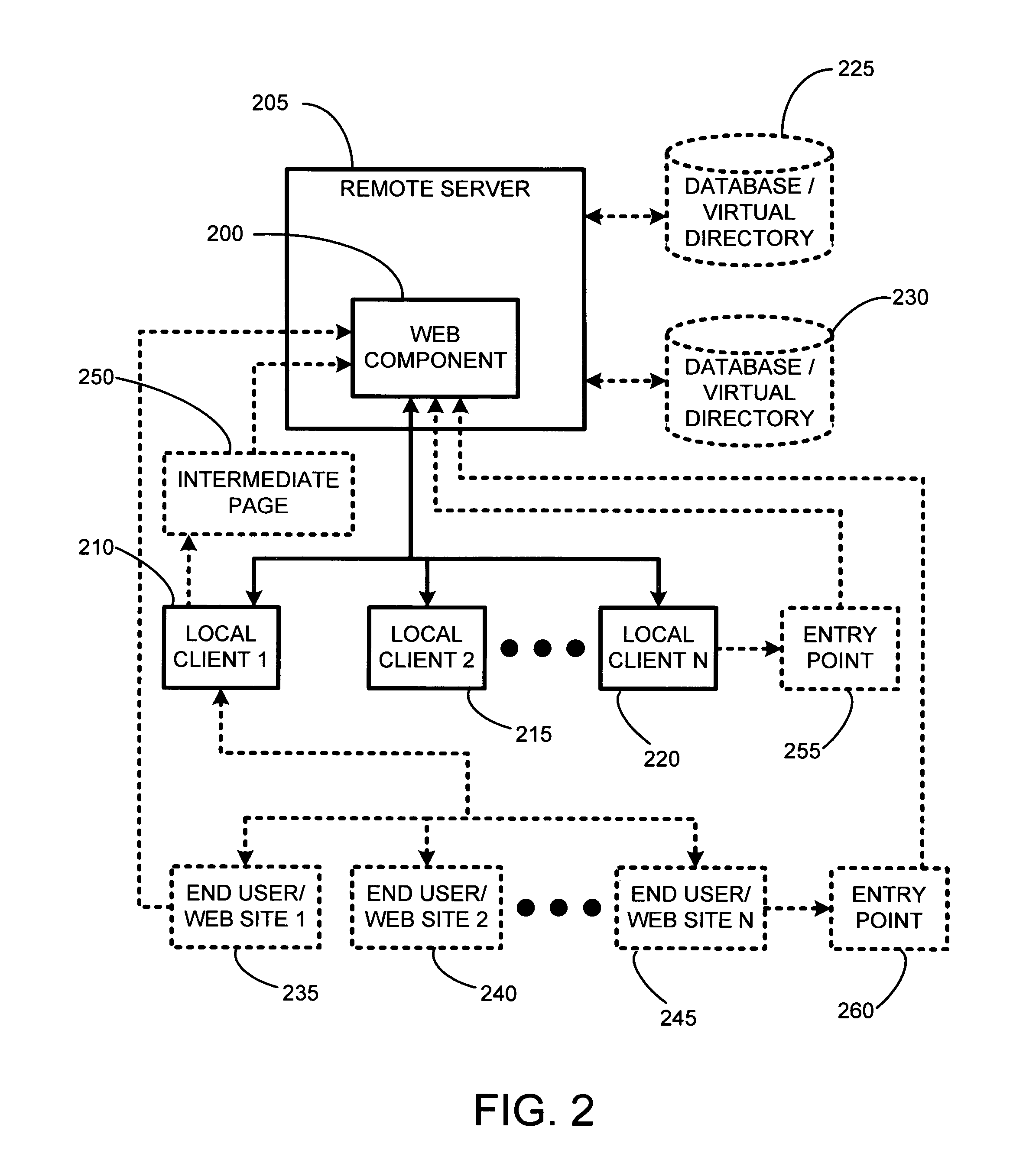
System and method for using dynamic web components to remotely control the security state of web pages
ActiveUS7000107B2Reduce test costsFaster time-to-marketDigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationAutomatic controlWeb browser
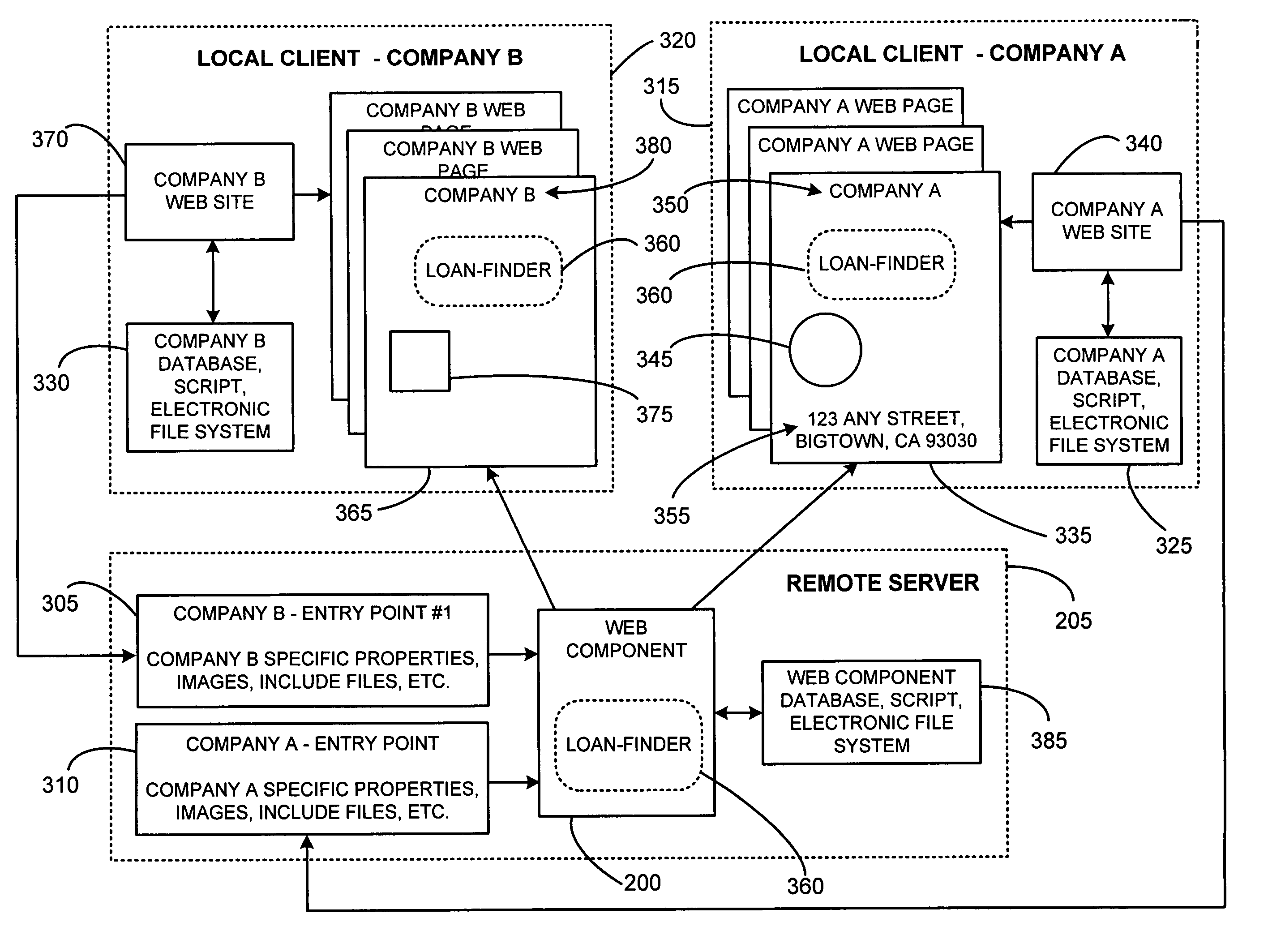
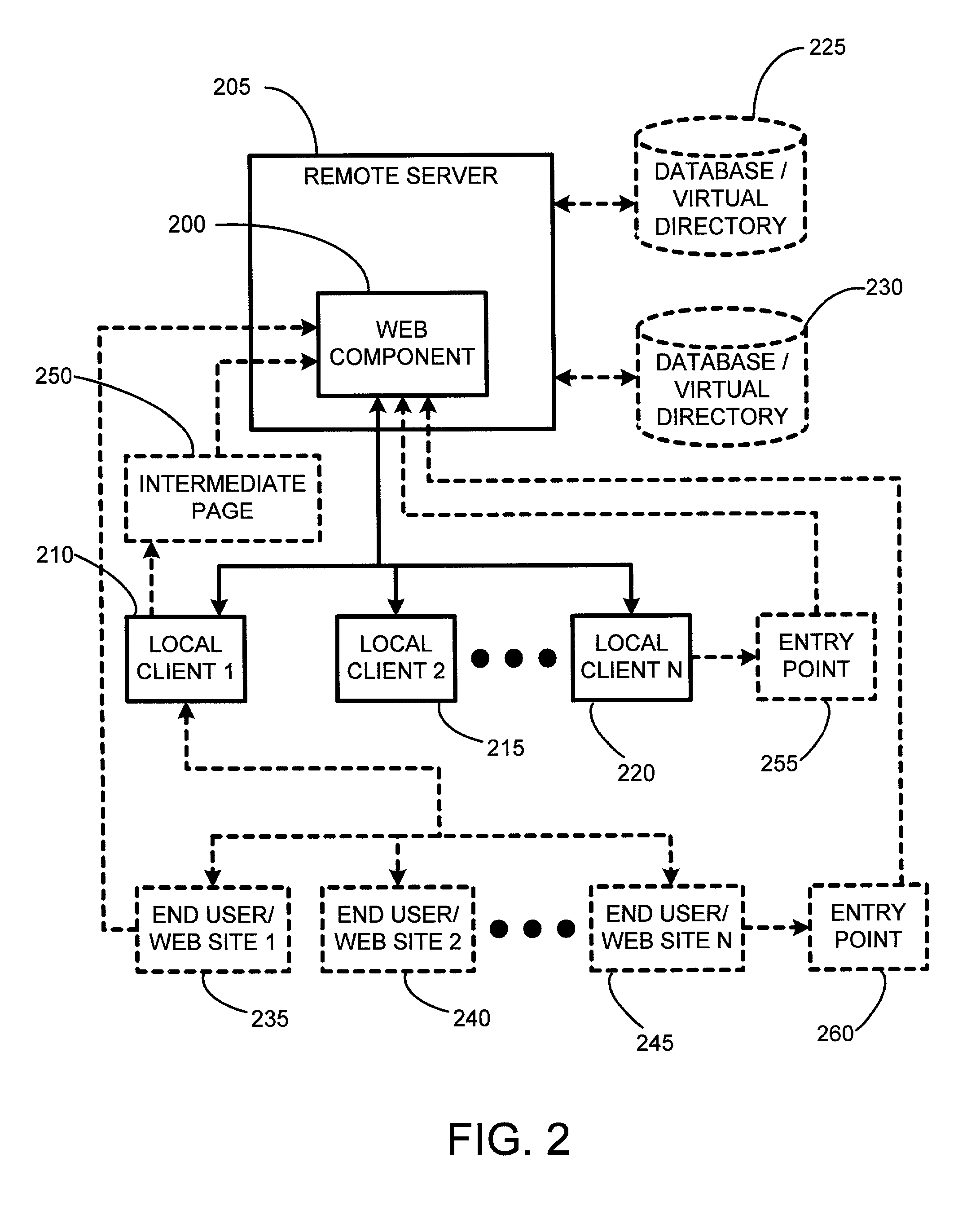
The present invention involves a new system and process for automatically controlling whether a displayed web page and associated frames displayed within a window of a web browser are secure or non-secure. For example, whether the displayed web page and associated frames are provided via a secure socket layer (SSL), i.e. a web page from an HTTPS address (secure), or simply via an HTTP address (non-secure), respectively. Specifically, the present invention uses a dynamic “Web Component” to remotely control web page security states. Further, the Web Component according to the present invention uses the same script and HTML for all implementations or instantiations of the Web Component, regardless of which, or how many, unique local clients make use of the Web Component. This code reuse is accomplished by using entry web pages, or “entry points,” as described in further detail below, to set the value of function properties or parameters of the Web Component for dynamically and controlling the security state of a web page having at least two frames. The script and / or HTML source code of the Web Component pages does not change based on each new implementation or instantiation. Consequently, little setup work is required for each implementation, and only a basic verification test pass is needed for each unique automatically customized Internet web page.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
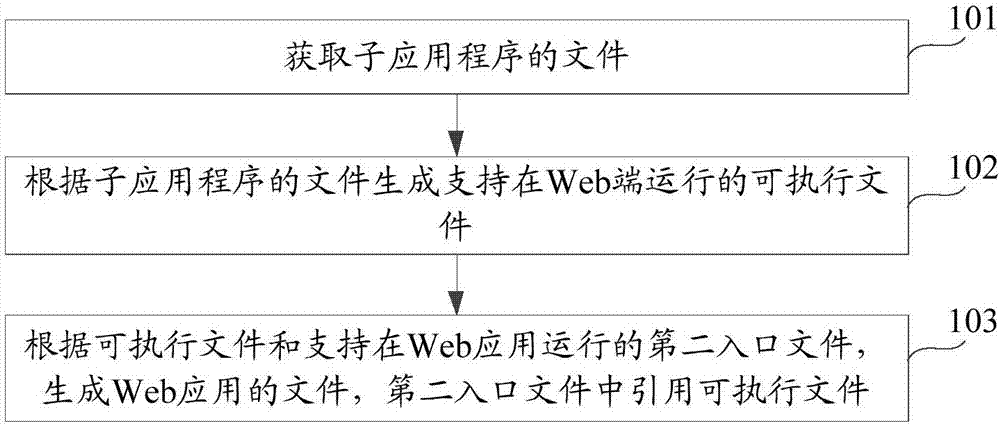
Application converting method and device and equipment
ActiveCN107239318AImprove reuse rateSave labor costSoftware engineeringProgram controlWeb applicationTime cost
The invention provides an application converting method and device and equipment. The method comprises the steps that a file of an application subprogram is obtained, wherein the application subprogram is an application program running depending on a master application program; according the file of the application subprogram, an executable file supporting running at a Web terminal is generated; according to the executable file and the second entry file supporting running at the Web terminal, a Web application file is generated, and the executable file is quoted in the second entry file. In the application converting method and device and the equipment, the technical scheme that the file of the application subprogram is converted into the file of the Web application is provided, so that the Web application with the functions identical to that of the application subprogram does not need to be developed separately, so that the labor and time cost required for developing the Web application is saved, the development efficiency is improved, the Web application and the application subprogram which are identical in function share the same set of basic source codes, and the code reuse rate is improved.
Owner:TENCENT TECH (SHENZHEN) CO LTD
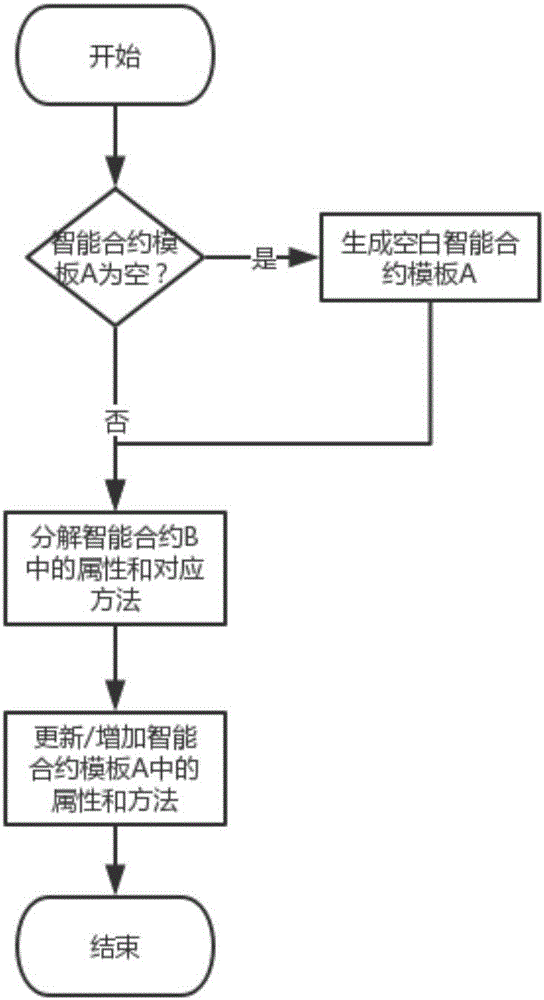
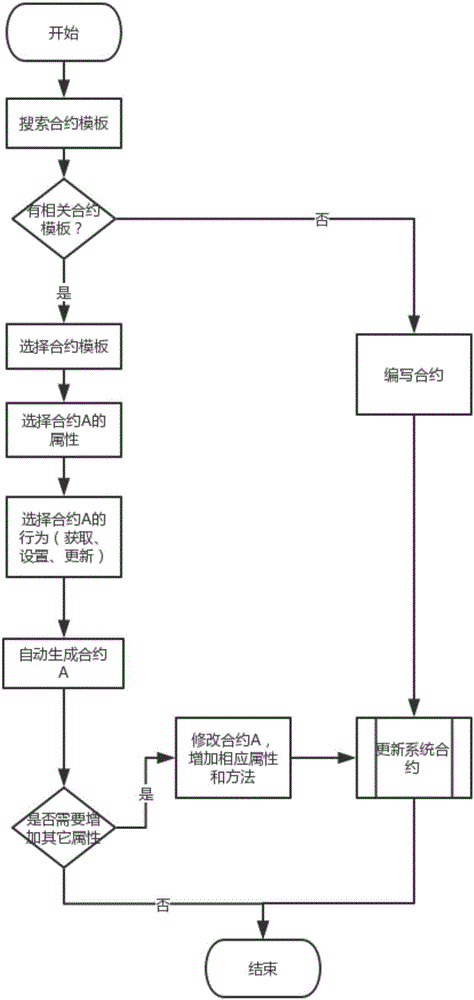
Method for automatically generating intelligent contract
ActiveCN106681739ASave material costsSave time and costSoftware designOffice automationMaterial resourcesSmart contract
The invention discloses a method for automatically generating an intelligent contract. Intelligent contracts used in the same industry or similar industries are similar, and some fixed features exist in the intelligent contracts; according to the code reuse thought, these fixed features are extracted to compile a data structure and corresponding code fragments, and these code fragments are saved in a code database. According to the method for automatically generating the intelligent contract, an intelligent contract template is utilized to greatly save manpower and material resources and time cost, and the method can be applied to all intelligent contracts having similarities, such as a transaction history contract, a stock contract and a property contract.
Owner:HANGZHOU YUNXIANG NETWORK TECH
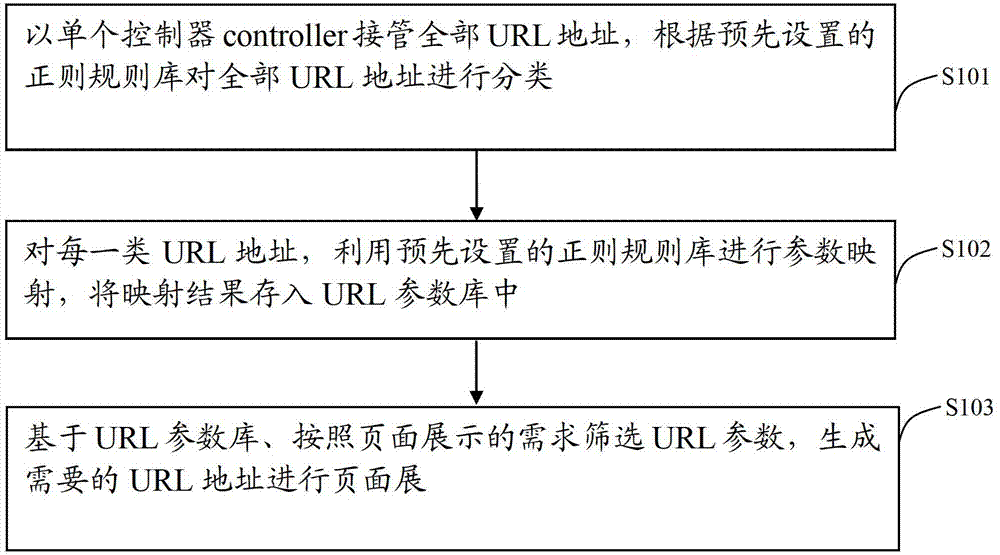
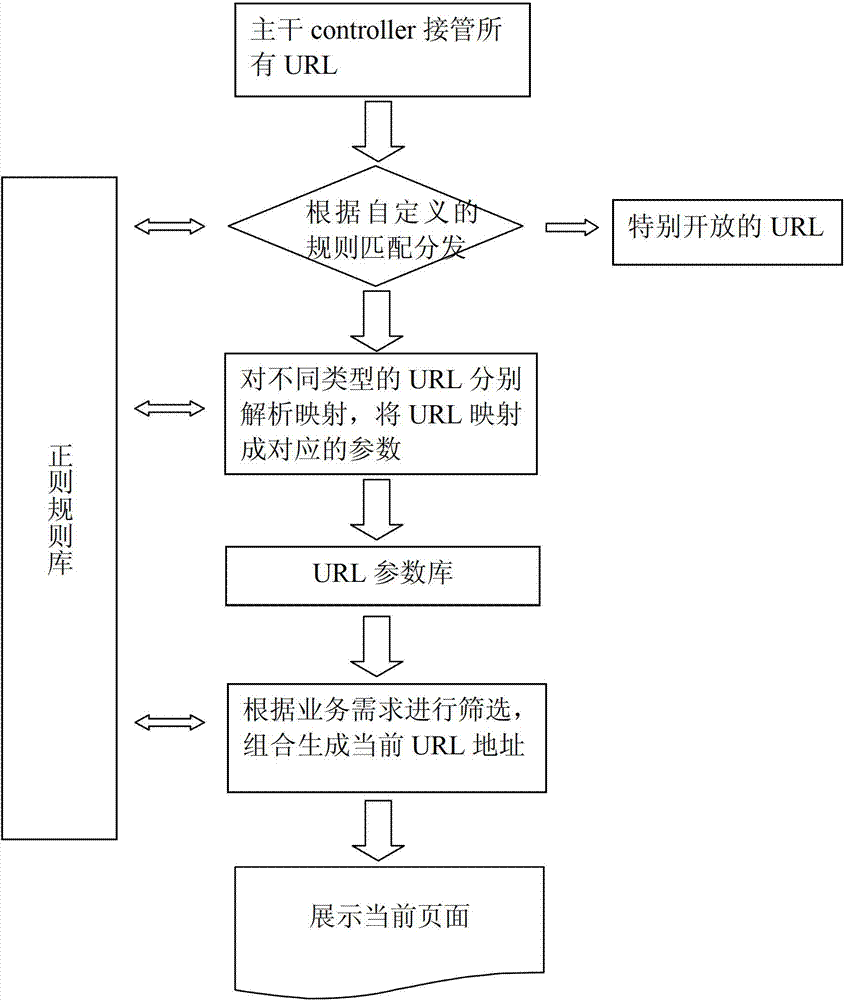
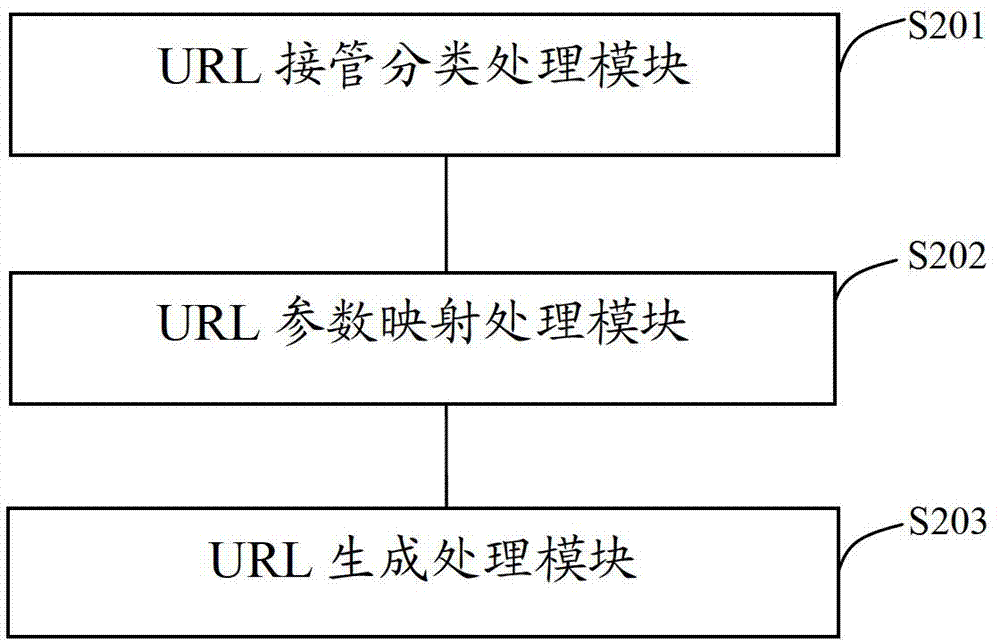
Dynamic matching method and dynamic matching device of uniform resource locator (URL)
ActiveCN102902780ASimplify complexityImprove good performanceSpecial data processing applicationsUniform resource locatorMatching methods
The invention discloses a dynamic matching method and a dynamic matching device of a uniform resource locator (URL). The method includes utilizing a single controller to take over all URL addresses, classifying all URL addressed according to a preset regular rube base, utilizing the regular rule base to conduct parameter mapping on the URL addresses in each class, storing the mapping result into a URL parameter base and screening the URL parameter according to page display requirements based on the URL parameter base to generate required URL addresses to conduct page display. The method and the device reduce the number of the controller in the system, simplify code complexity, conduct screening and combination on conditions that the parameter corresponds to according to business requirements when a new URL is generated, retain required condition, remove needless conditions, conduct automatic arrangement and splicing according to regular rule definition sequence in combination, dynamically generate a unique URL address, improve code reuse rate and page display flexibility and reduce maintenance cost.
Owner:WUBA
Code reuse method applied to test system
ActiveCN104156314AEasy to packImprove work efficiencySoftware testing/debuggingSpecific program execution arrangementsOperation modeRegular expression
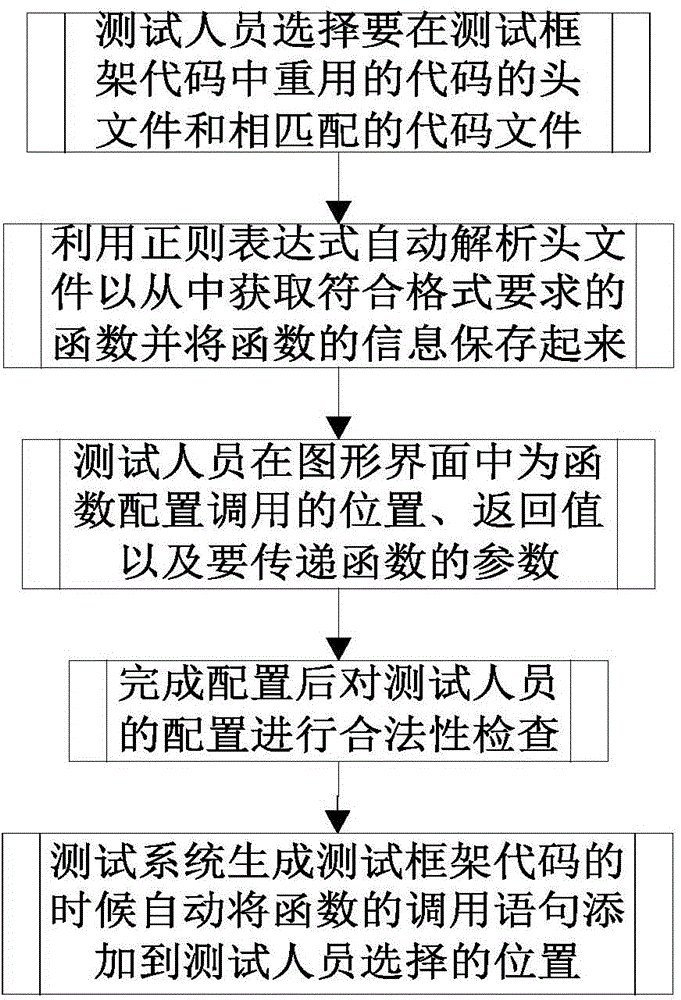
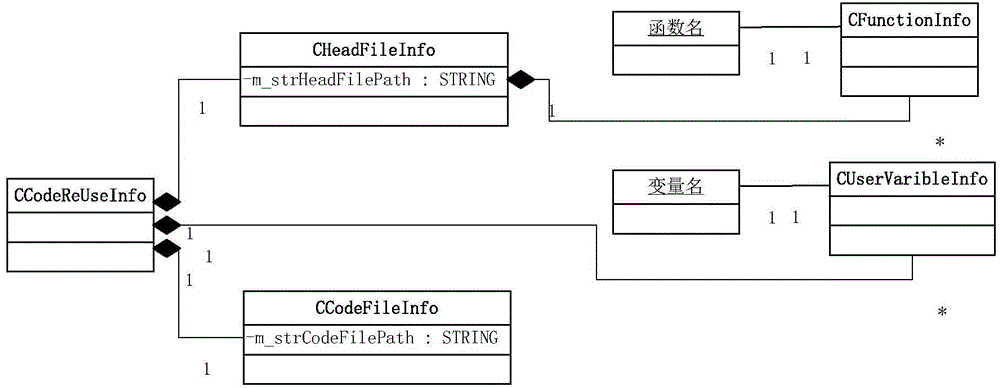
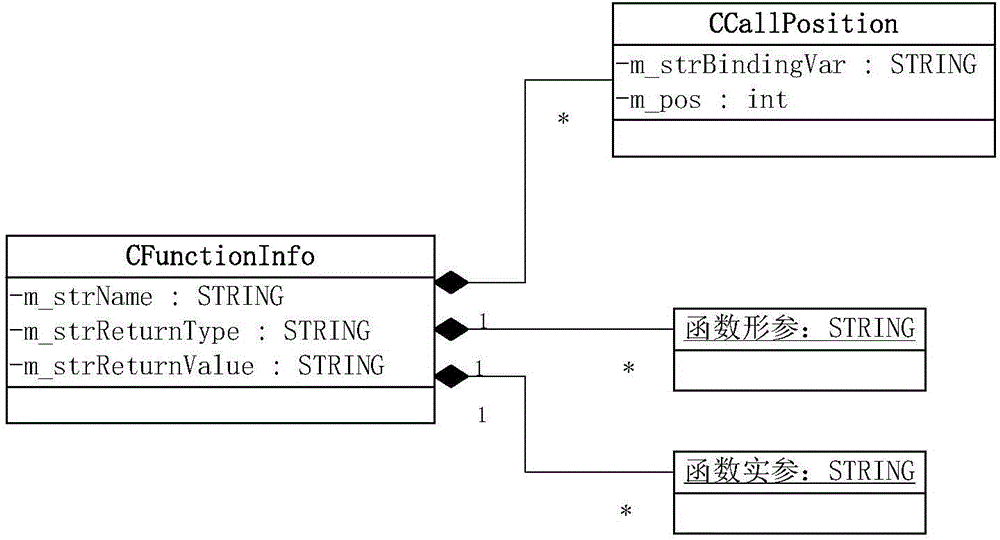
The invention discloses a code reuse method applied to a test system. The method comprises the steps that a header file and a code file matched with the header file of a reused code among test framework codes are selected; the header file is analyzed automatically through a regular expression, and a function meeting format requirements is obtained from the header file; analyzed information is displayed in a graphical interface, and a call position, a return value and parameters to be transmitted to the function are configured for the function in the graphical interface; after configuration is completed, validity check is automatically conducted on the configuration; a call statement of the function is automatically added to the selected position, statements contained in the header file are added to corresponding positions, and the header file, the code file and other generated code files are jointly compiled to generate an executable program. According to the code reuse method, the call statement of the function is generated automatically according to test demands and added to the required position; the codes can be analyzed automatically, and information related to the function can be obtained, so testing personnel can complete configuration of code reuse conveniently in a graphical interface operation mode.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
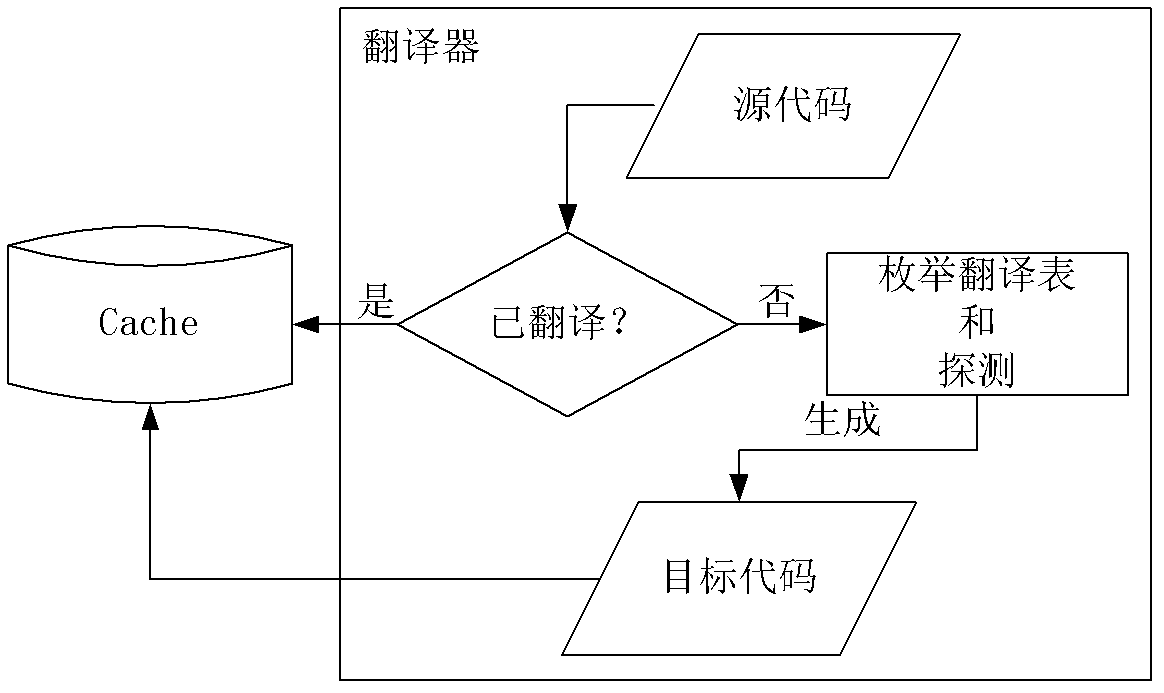
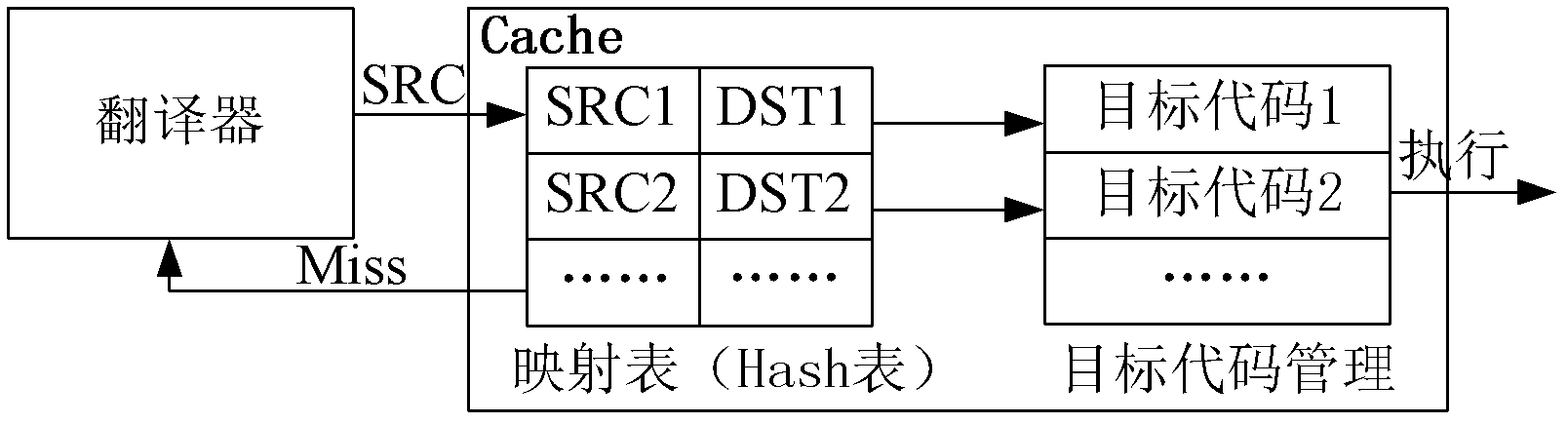
Code reuse attack detection system based on dynamic binary translation framework
InactiveCN102662830AGuaranteed operating efficiencyImprove executionSoftware testing/debuggingPlatform integrity maintainanceControl flowComputer module
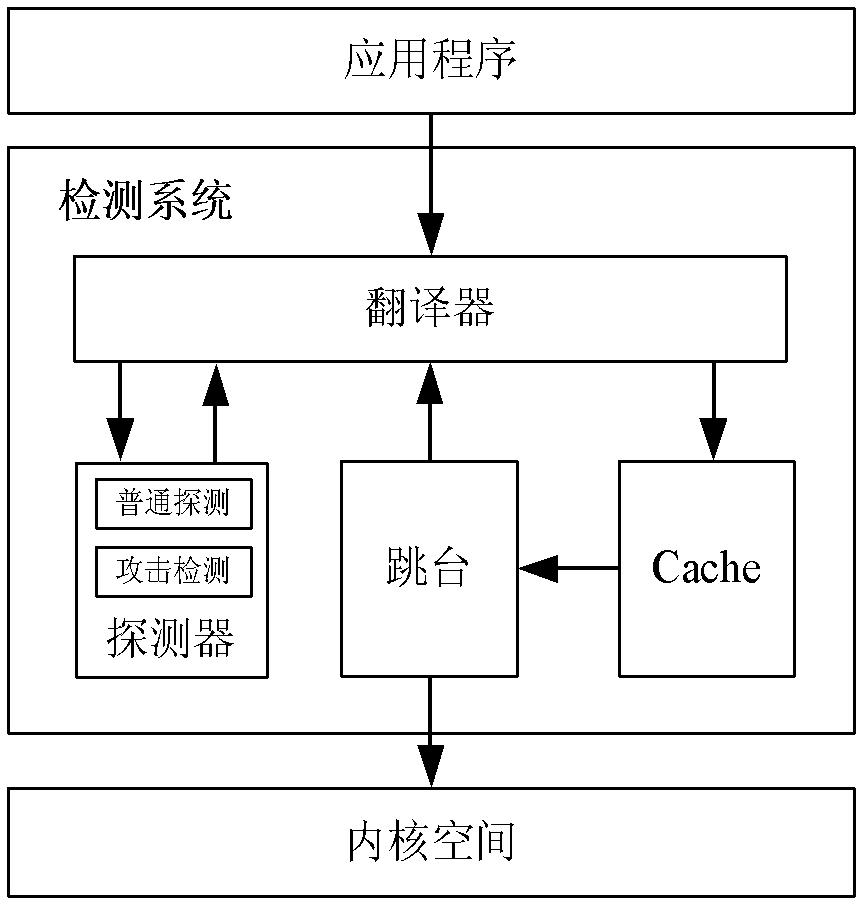
The invention belongs to the field of computer security, and discloses a code reuse attack detection system based on a dynamic binary translation framework. The detection system comprises a translator, a detector, a cache and transition platforms. The translator is used for decoding binary data of a program item by item by using basic blocks as unit. The detector is used for processing commands after decoding, normal operation is guaranteed on the basis of conventional detection, and behaviors of the commands are acquired and detected by centering on attack detection. Mapping relation between sources and translation addresses of the basic blocks are established by the cache, and target codes of the basic blocks, which are generated by translation, are cached. Control flows of the program are managed through the transition platforms, program translation and ordered execution are guaranteed, and a detection and optimization mechanism is provided for commands of the same type. The system can be used for processing non-open source programs, and guaranteeing safe execution of the programs.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Methods, systems, and computer readable media for preventing code reuse attacks
ActiveUS20170213039A1Avoid attackMemory architecture accessing/allocationUnauthorized memory use protectionComputer hardwareCode reuse
Methods, systems, and computer readable media for preventing code reuse attacks are disclosed. According to one method, the method includes executing, on a processor, code in a memory page related to an application, wherein the memory page is protected. The method also includes detecting a read request associated with the code. The method further includes after detecting the read request, modifying, without using a hypervisor, at least one memory permission associated with the memory page such that the code is no longer executable after the code is read.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK +1
Using dynamic web components to remotely control the security state of web pages
InactiveUS20060123230A1Easy to customizeAutomatically generating the web pageDigital data processing detailsAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsWeb browserEntry point
The invention automatically controls whether displayed web pages and associated frames displayed within a web browser are secure or non-secure. A dynamic “Web Component” remotely controls web page security states. The Web Component uses the same script and HTML for all implementations or instantiations of the Web Component, regardless of how many unique clients make use of the Web Component. This code reuse is accomplished using entry web pages, or “entry points,” to set the value of function properties or parameters of the Web Component for dynamically and controlling the security state of a web page having at least two frames. The script and / or HTML source code of the Web Component pages does not change based on each new implementation or instantiation. Consequently, little setup work is required for each implementation, and only a basic verification test pass is needed for each unique automatically customized Internet web page.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Using dynamic web components to remotely control the security state of web pages
InactiveUS7340604B2Easy to customizeAutomatically generating the web pageDigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationAutomatic controlWeb browser
The invention automatically controls whether displayed web pages and associated frames displayed within a web browser are secure or non-secure. A dynamic “Web Component” remotely controls web page security states. The Web Component uses the same script and HTML for all implementations or instantiations of the Web Component, regardless of how many unique clients make use of the Web Component. This code reuse is accomplished using entry web pages, or “entry points,” to set the value of function properties or parameters of the Web Component for dynamically and controlling the security state of a web page having at least two frames. The script and / or HTML source code of the Web Component pages does not change based on each new implementation or instantiation. Consequently, little setup work is required for each implementation, and only a basic verification test pass is needed for each unique automatically customized Internet web page.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
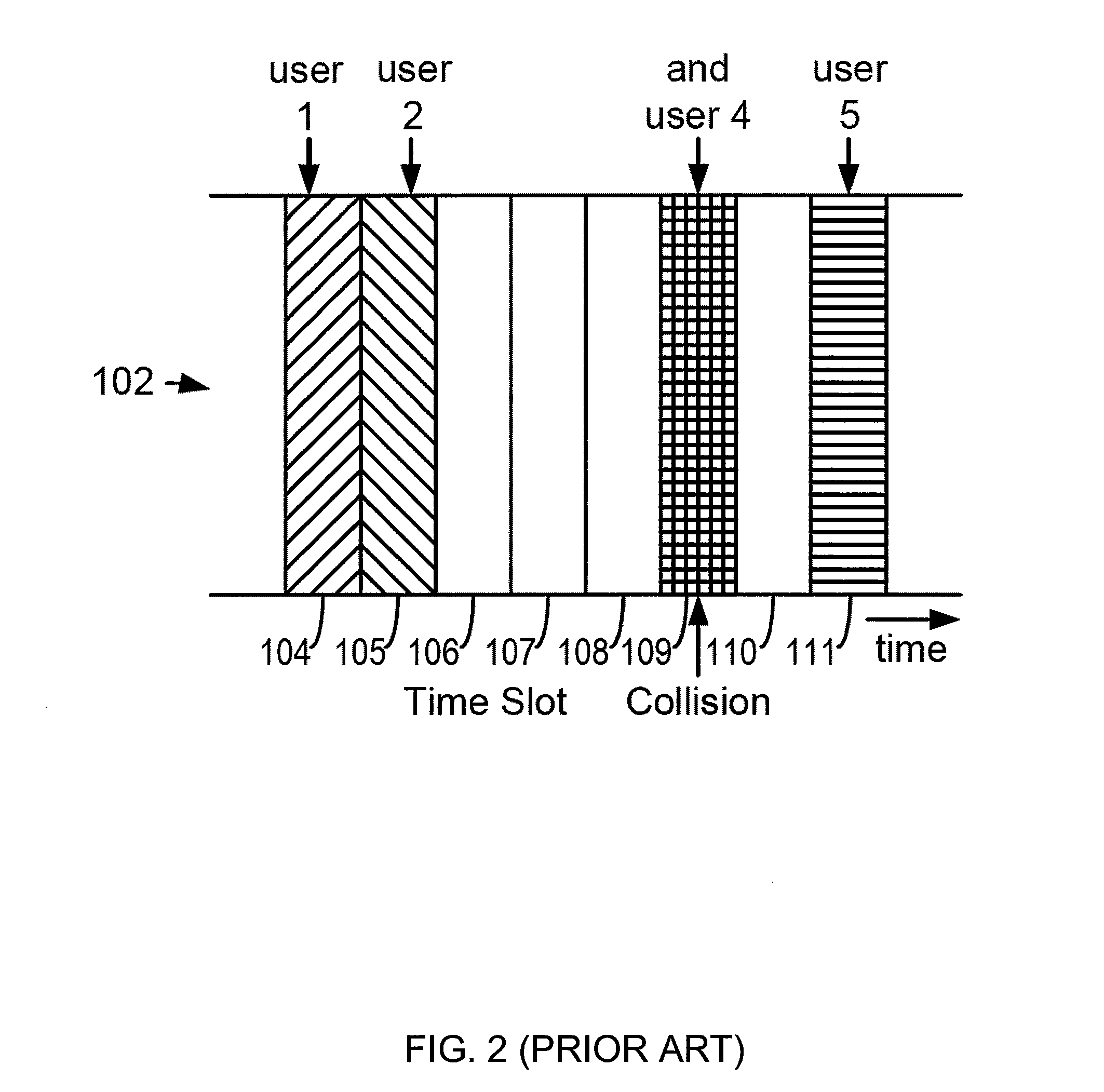
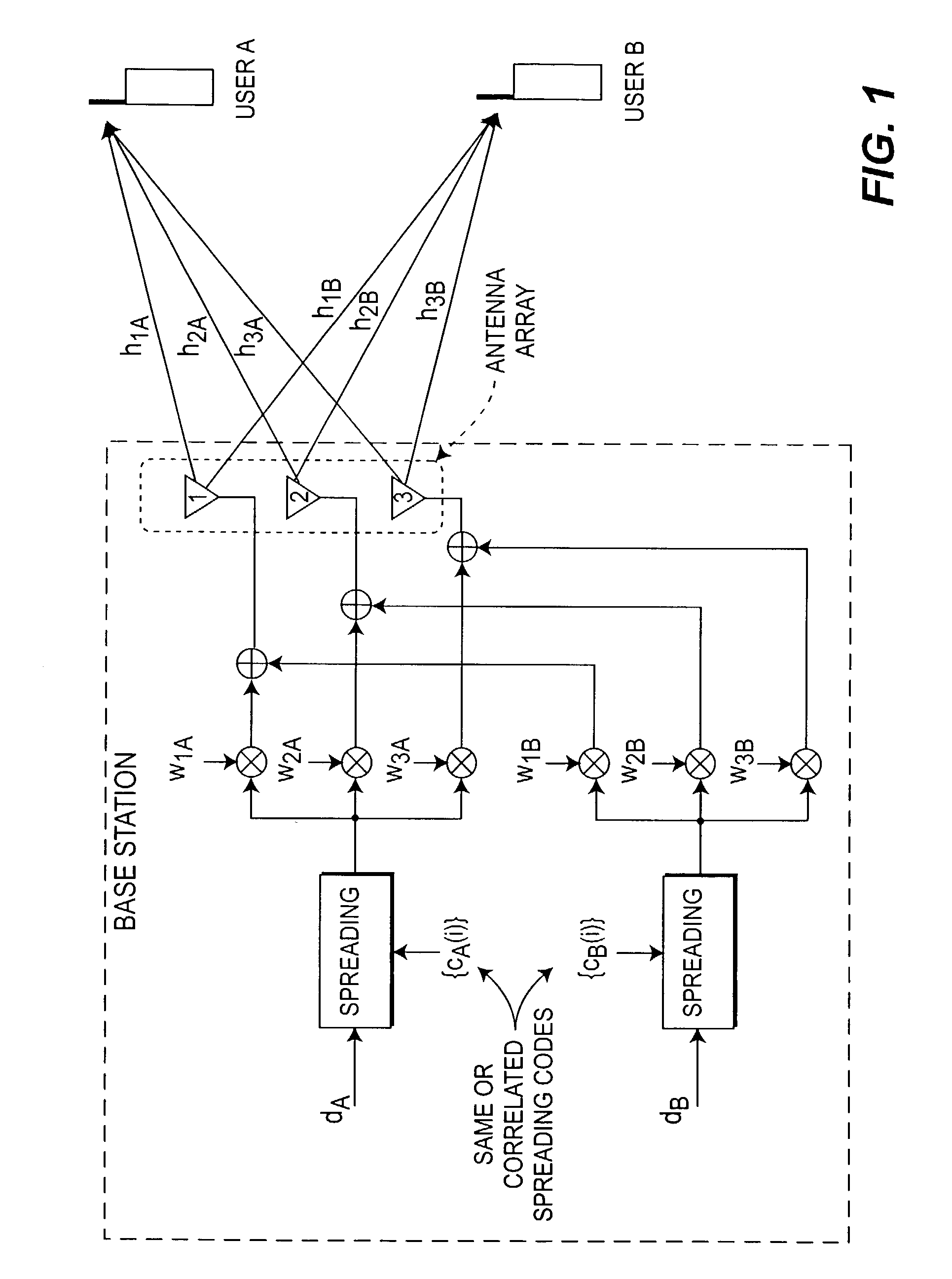
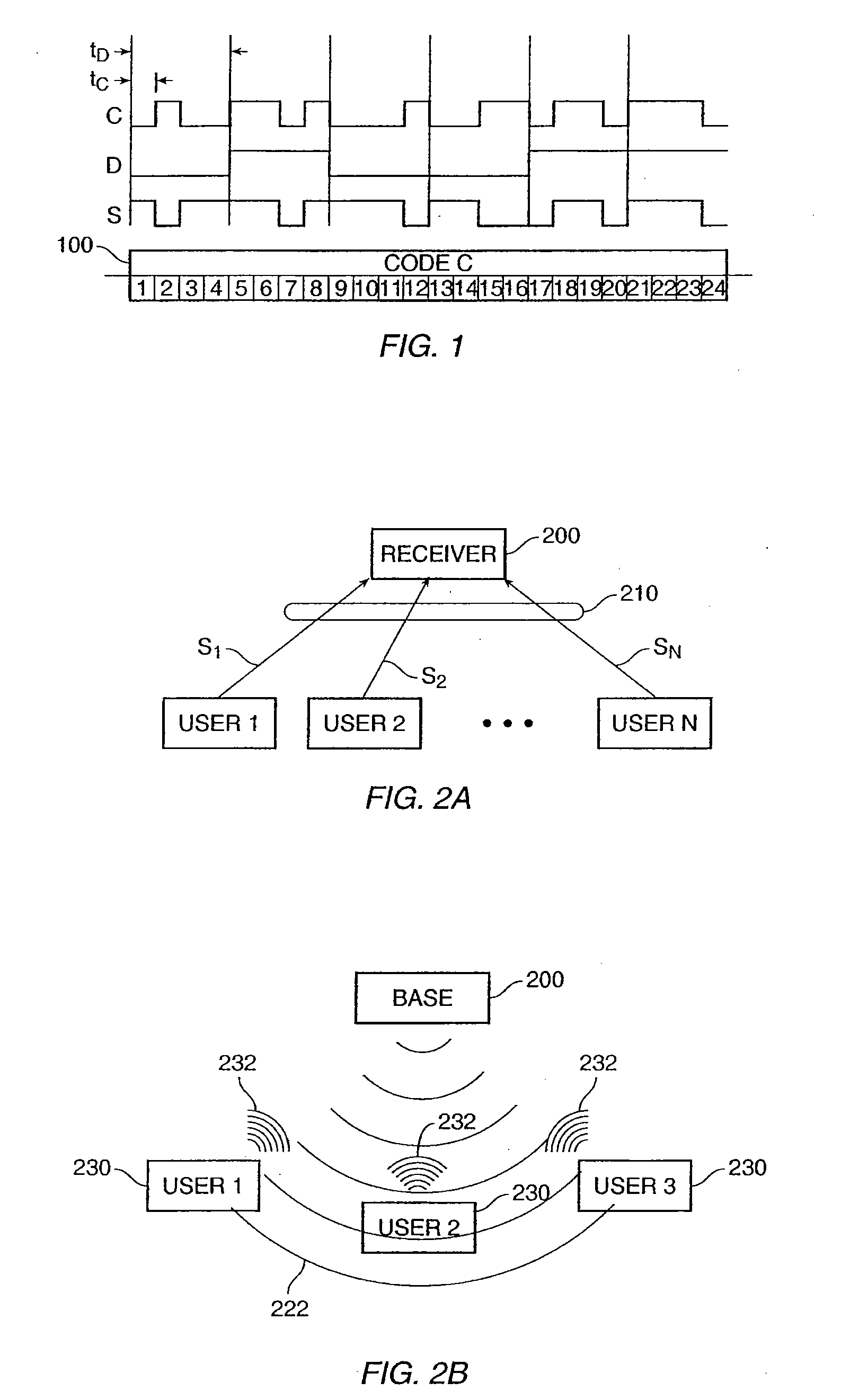
Method and apparatus for multiple access over a communication channel
InactiveUS7065125B1Improve performanceEfficiently receiving signalSynchronisation signal speed/phase controlRadio transmission for post communicationDirect-sequence spread spectrumMulti access
This invention is a multiple access communication technique by which a multitude of transmitters communicate with receivers using direct sequence spread spectrum signaling. The direct sequence codes are reused by a large number of simultaneous transmitters, so the system is named Code Reuse Multiple Access (“CRMA”). This reuse method requires only a small number of codes relative to the number of simultaneous transmitters, and can use as few as one code for all the users. The direct sequence codes are not required to have special properties such as maximal length. The lengths of the spreading codes employed are not necessarily related to the bit or symbol interval. CRMA can be implemented on a Paired Carrier Multiple Access (“PCMA”) system with or without a novel receiver structure which is also described.
Owner:VIASAT INC
Software set-value profiling and code reuse
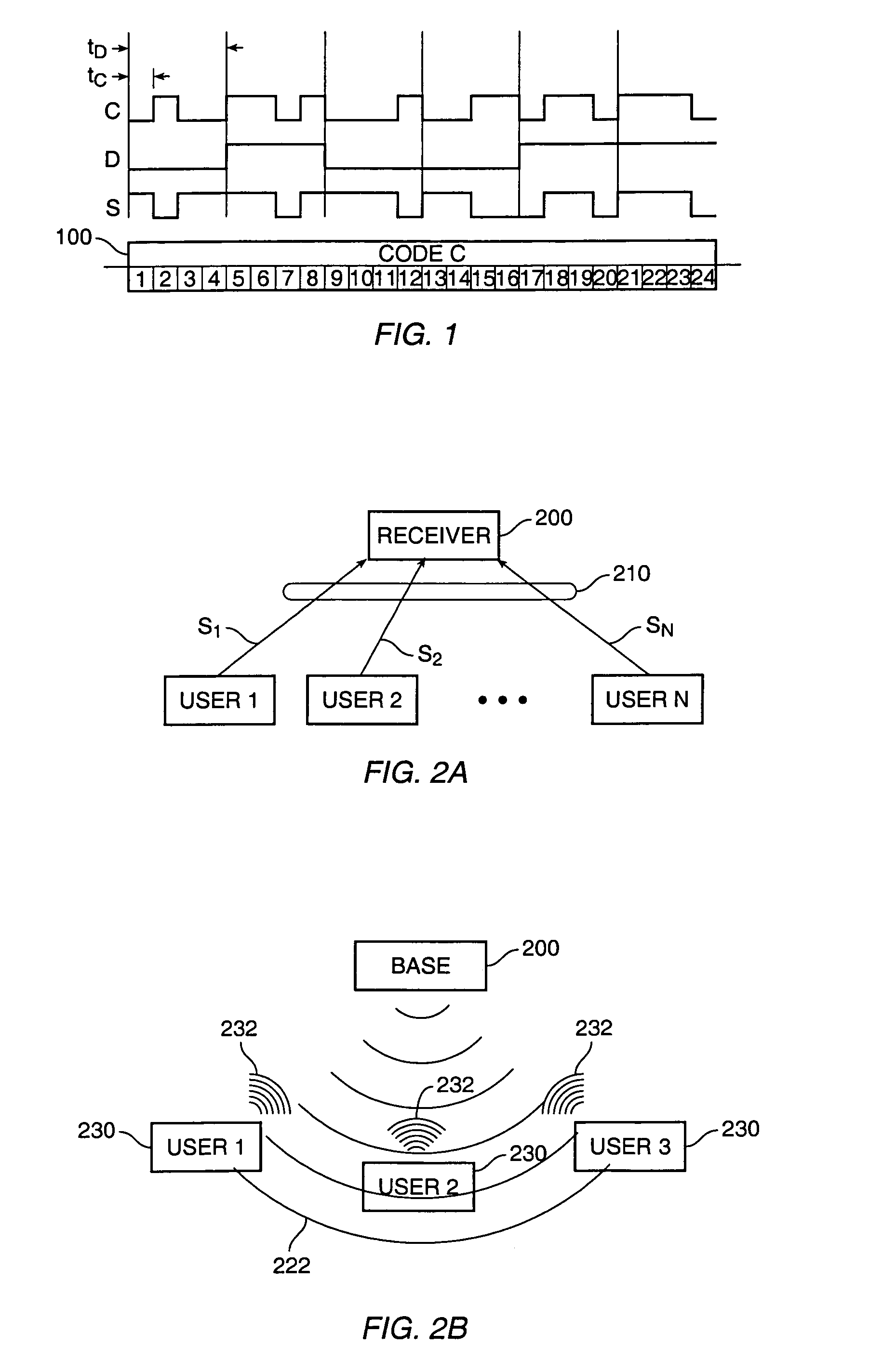
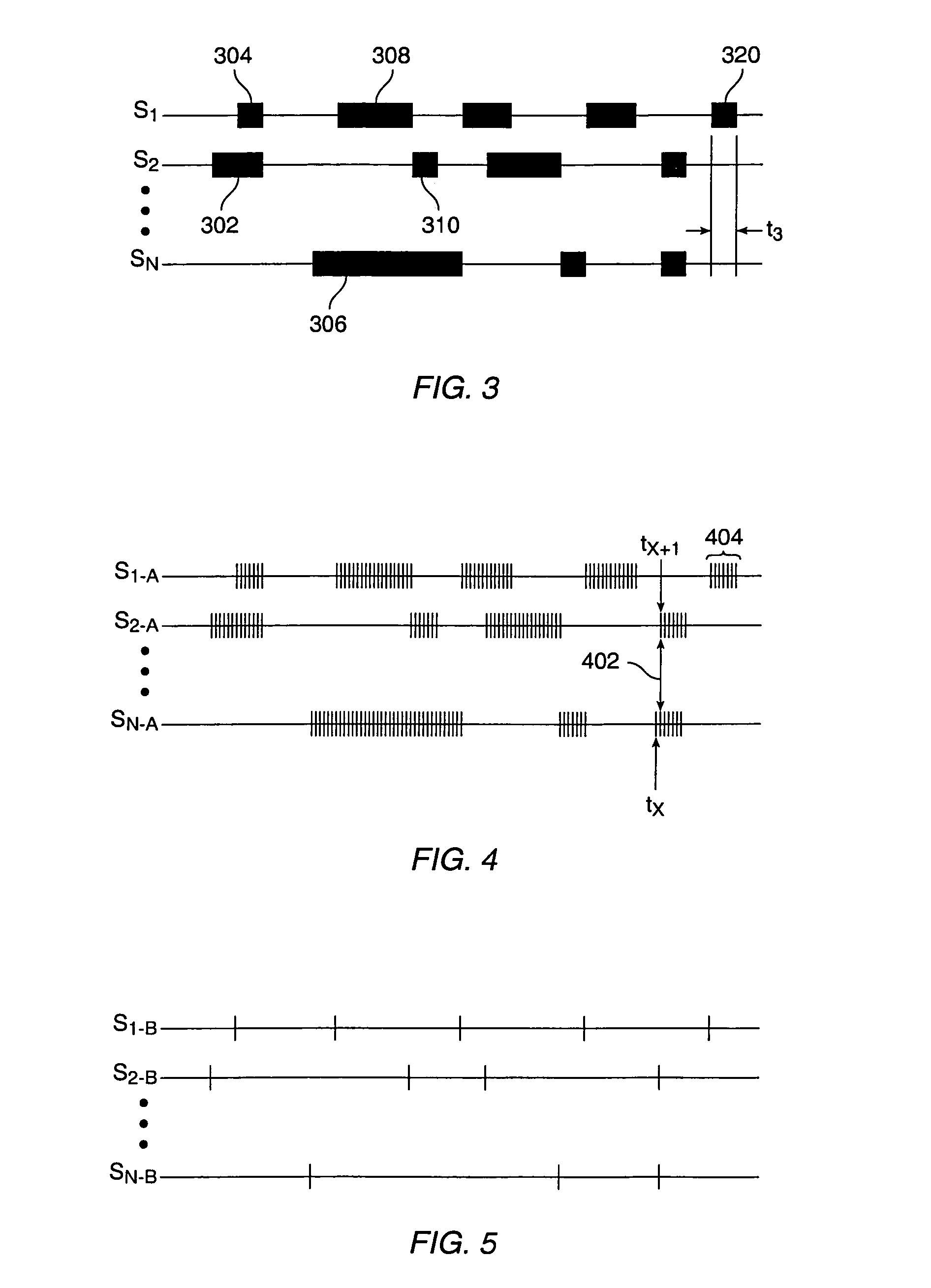
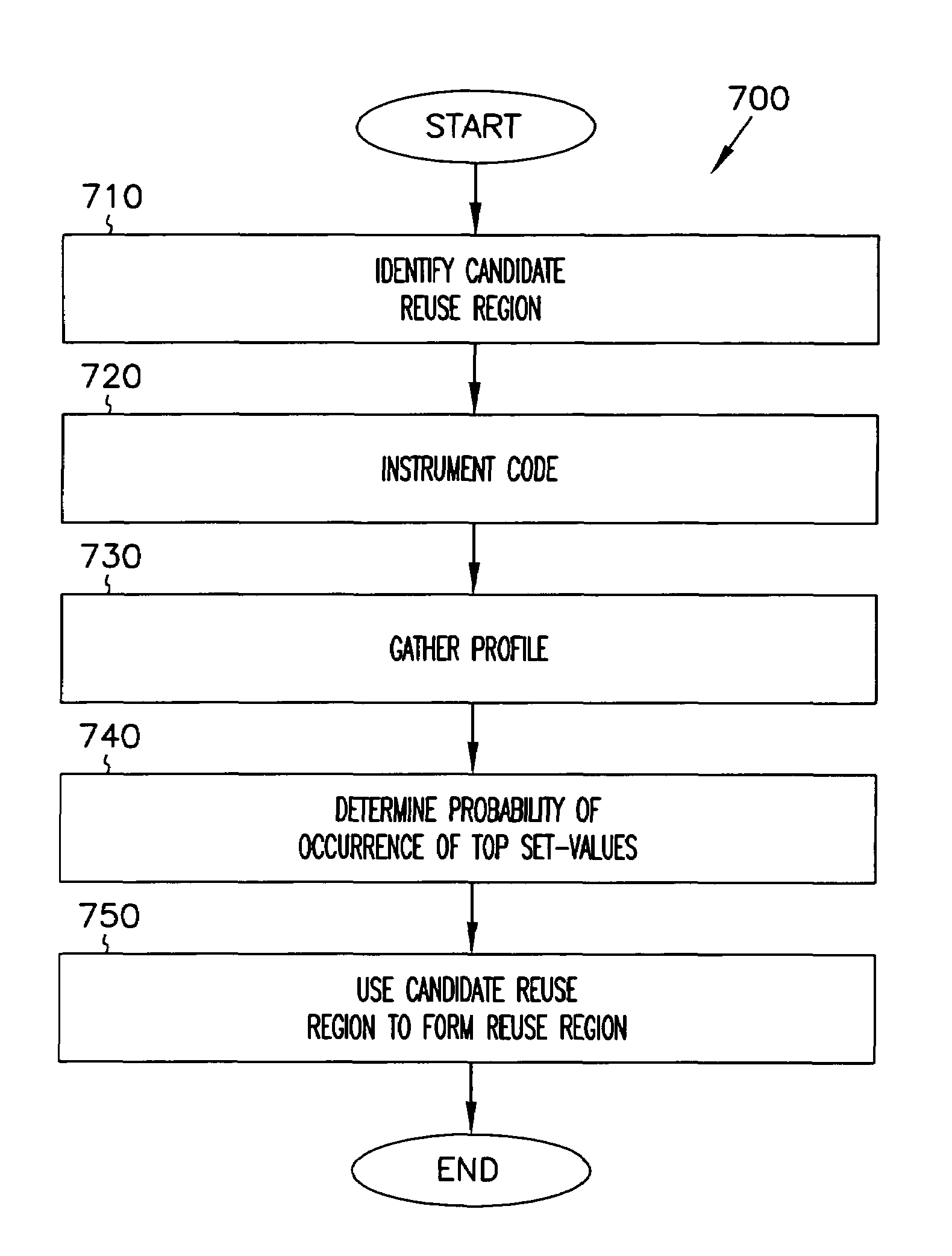
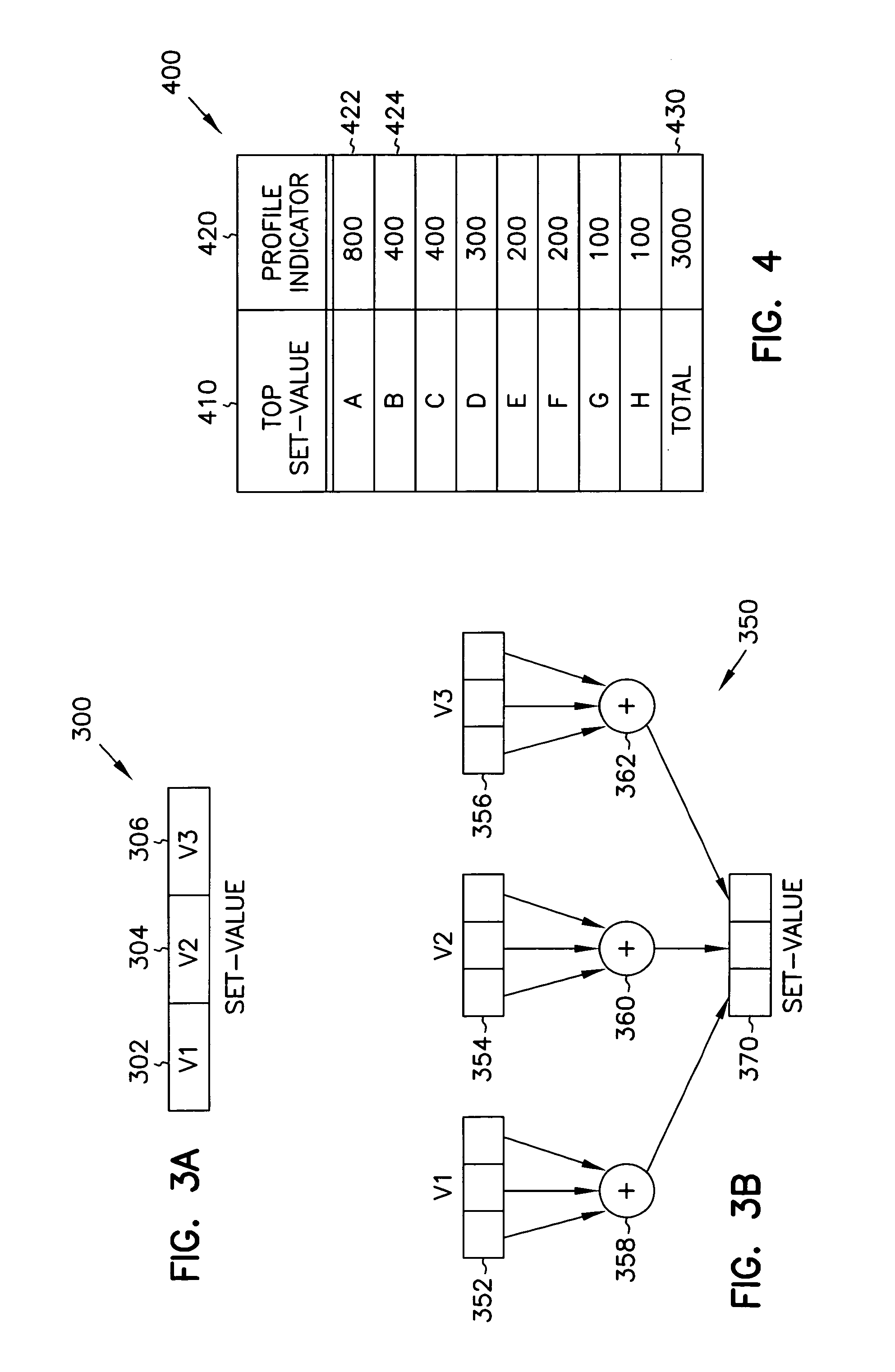
InactiveUS7100155B1Software engineeringSpecific program execution arrangementsCode reuseLoad instruction
Owner:INTEL CORP
Code Reuse Multiple Access For Satellite Return Link
InactiveUS20070127553A1Improve performanceEfficient processingOrthogonal multiplexTransmissionDirect-sequence spread spectrumComputer science
This invention is a multiple access communication technique by which a multitude of transmitters communicate with receivers using direct sequence spread spectrum signaling. The direct sequence codes are reused by a large number of simultaneous transmitters, so the system is named Code Reuse Multiple Access (“CRMA”). This reuse method requires only a small number of codes relative to the number of simultaneous transmitters, and can use as few as one code for all the users. The direct sequence codes are not required to have special properties such as maximal length. The lengths of the spreading codes employed are not necessarily related to the bit or symbol interval. CRMA can be implemented on a Paired Carrier Multiple Access (“PCMA”) system with or without a novel receiver structure which is also described. In an environment having virtual channels, a clock is derived from the received signal in the uplink by sampling the signal to detect symbol edges.
Owner:VIASAT INC
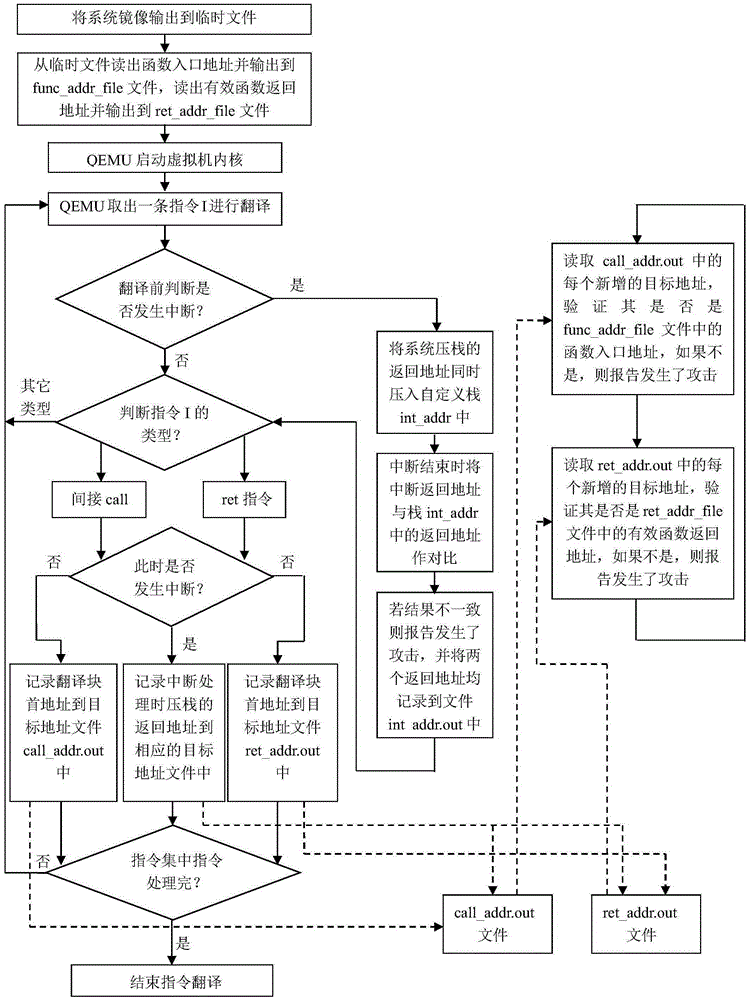
Kernel-level code reuse type attack detection method based on QEMU
ActiveCN105260659AProtection securityLow costPlatform integrity maintainanceControl flowOperational system
The invention discloses a kernel-level code reuse type attack detection method based on QEMU. The method mainly solves the problem of relying on hardware or need of modifying kernel source code in the prior art. According to the method, a function module of a QEMU virtual machine manager is expanded; each instruction which operates on the function module and in an operating system kernel is traversed and detected; jumping instructions relevant to the control flow process are recognized from the instructions, wherein the jumping instructions include ret and indirect call instructions; the jumping target addresses of the instructions are recorded; then, the target addresses are compared with legal target addresses in the system normal execution flow process for detecting whether a system is normally executed or not; and meanwhile, the interruption return addresses pushed into a stack during the interruption occurrence and the return addresses used during interruption actual return are subjected to comparison verification, so that whether attack occurs or not is judged. The kernel-level code reuse type attack detection method has the advantages that by aiming at the characteristic that the system original execution flow process needs to be changed for the code reuse type attack, the attack can be effectively discovered by monitoring the kernel execution flow process change instructions (and positions), and the kernel-level code reuse type attack detection method can be used for protecting the security of an operating system.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
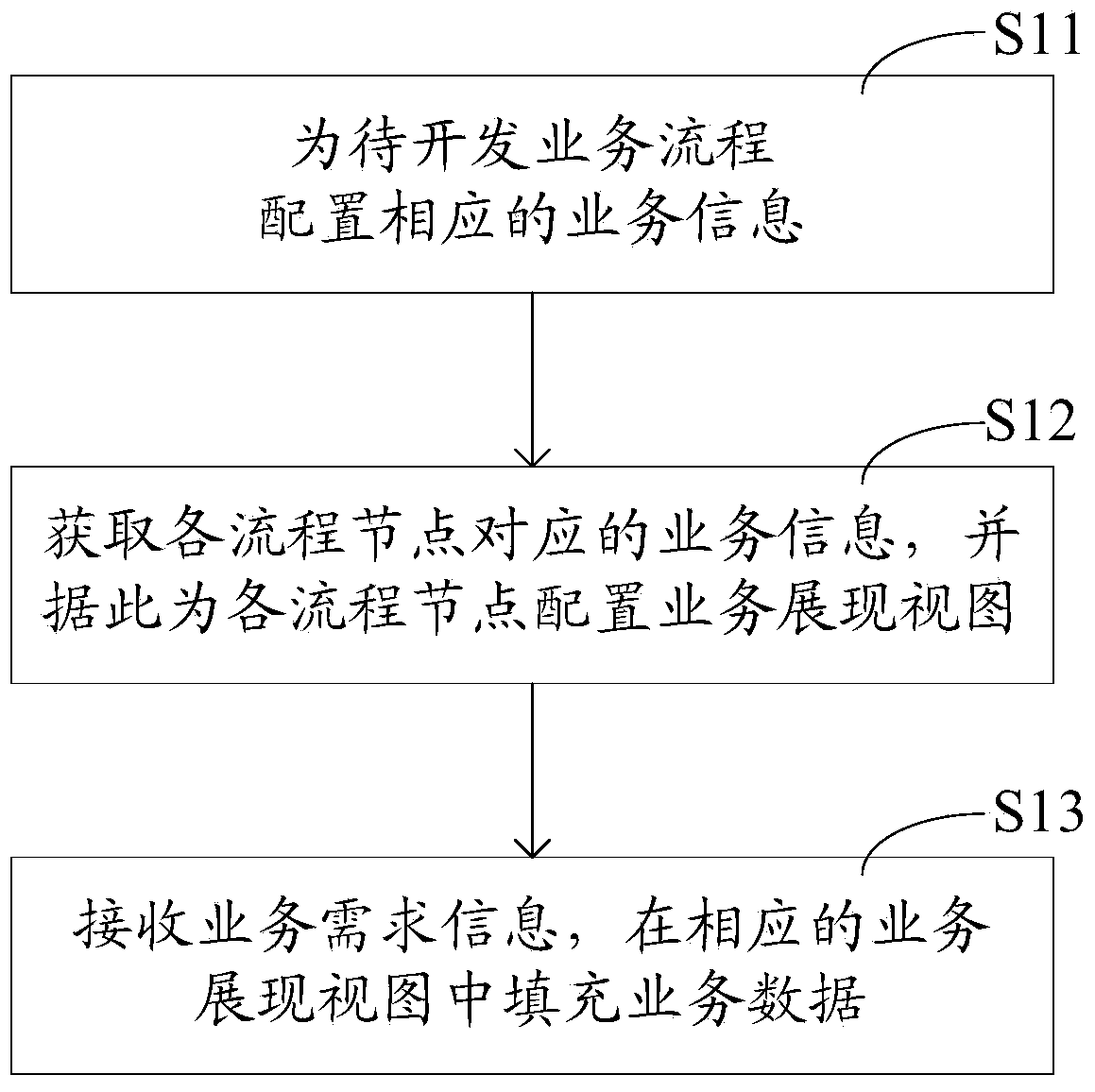
Method, device and processor for developing business processes
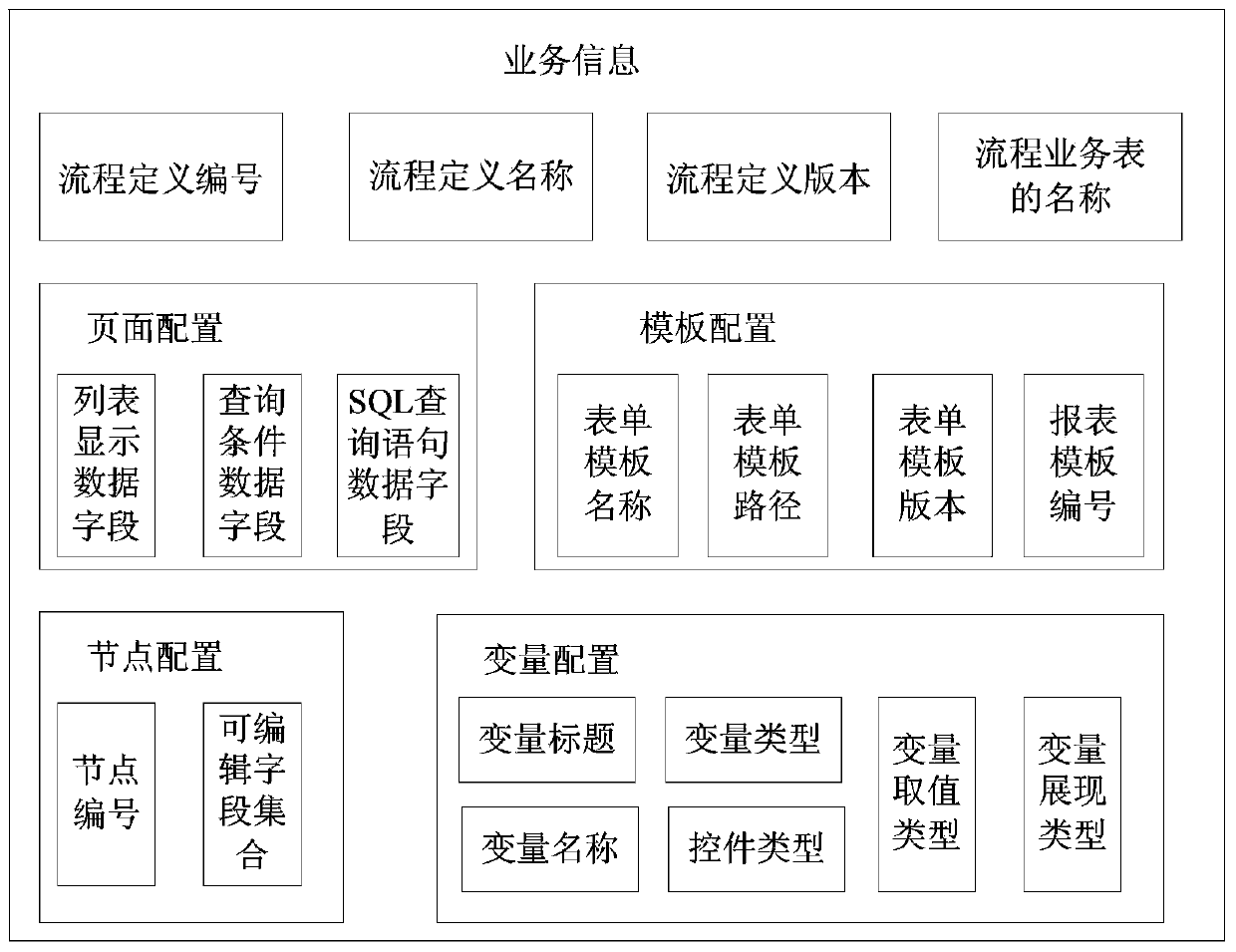
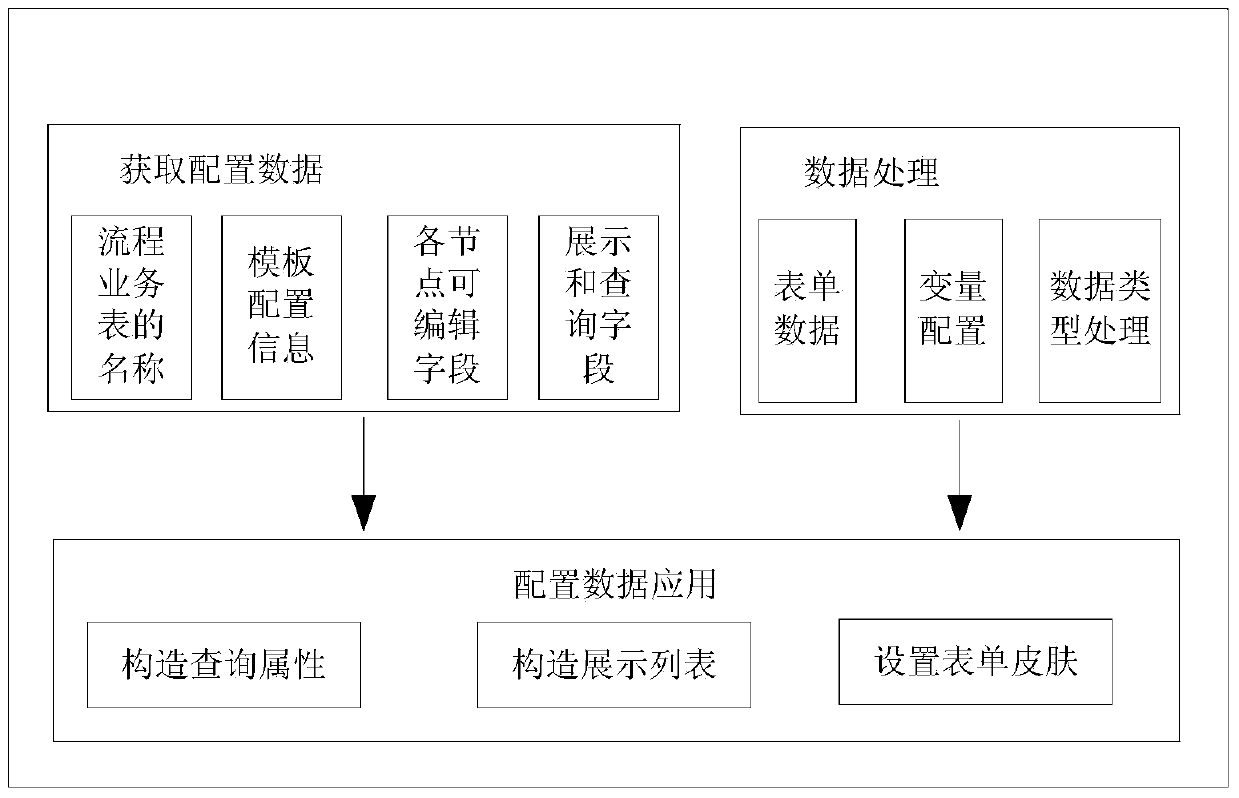
InactiveCN103617047ARealize developmentSolve redundancyResourcesSpecific program execution arrangementsProcess configurationLogisim
The invention relates to the technical field of computers and discloses a method, device and processor for developing business processes. The logic that business process developing is converted into attribute configuration from code writing is adopted, so that the developing process of the business processes are converted into the configuration performed on the business process. According to the method for developing the business process, firstly, the business processes to be developed are configured with corresponding business process information, then the business process information is obtained and includes configuration information corresponding to all nodes, corresponding business presentation views are configured, then business requirement information is received for filling, and complete business presentation views are obtained. Due to the fact that according to the method for developing the business processes, the configuration means is adopted for configuring the corresponding business information for the business processes to be developed according to the similarities of the business processes, needed business can be developed according to business information and the received business requirement information, and then the problems that in the prior art, when the business processes are developed, code redundancy and a low code reuse rate exist are solved.
Owner:BEIJING CHINA POWER INFORMATION TECH +1
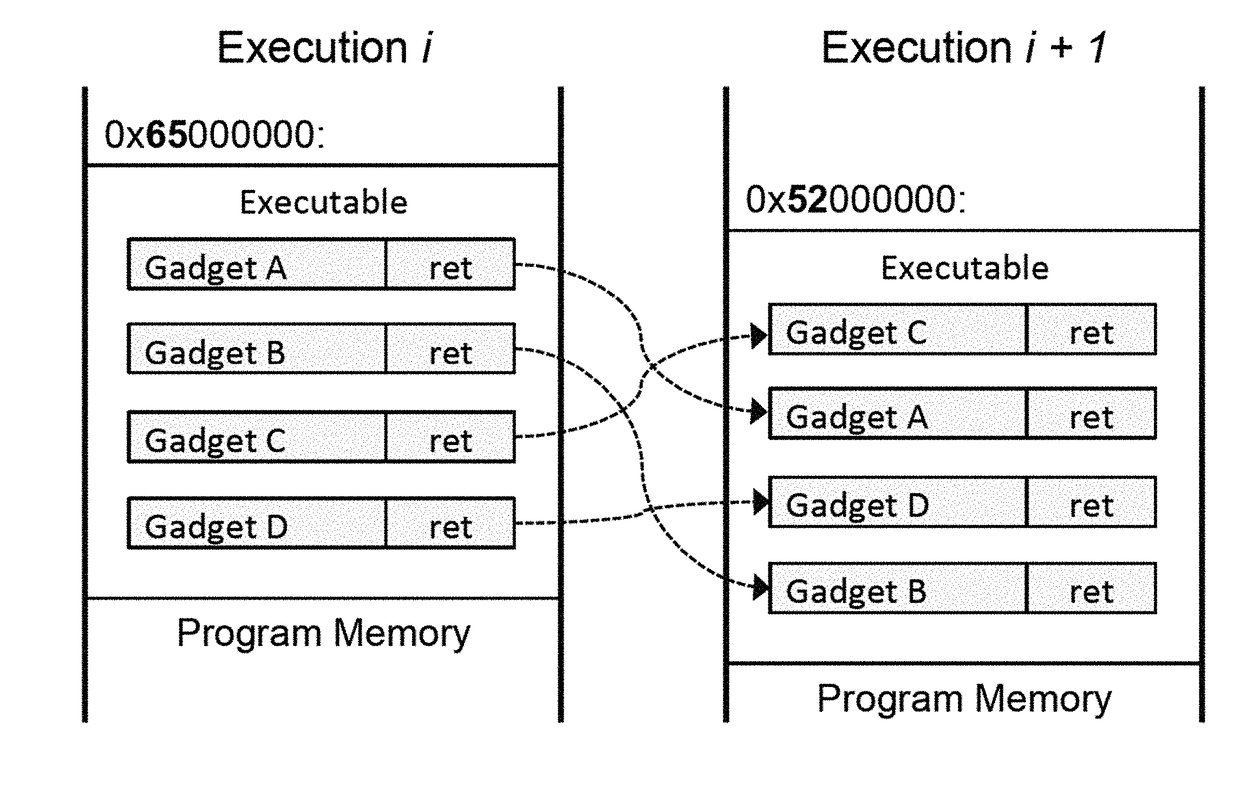
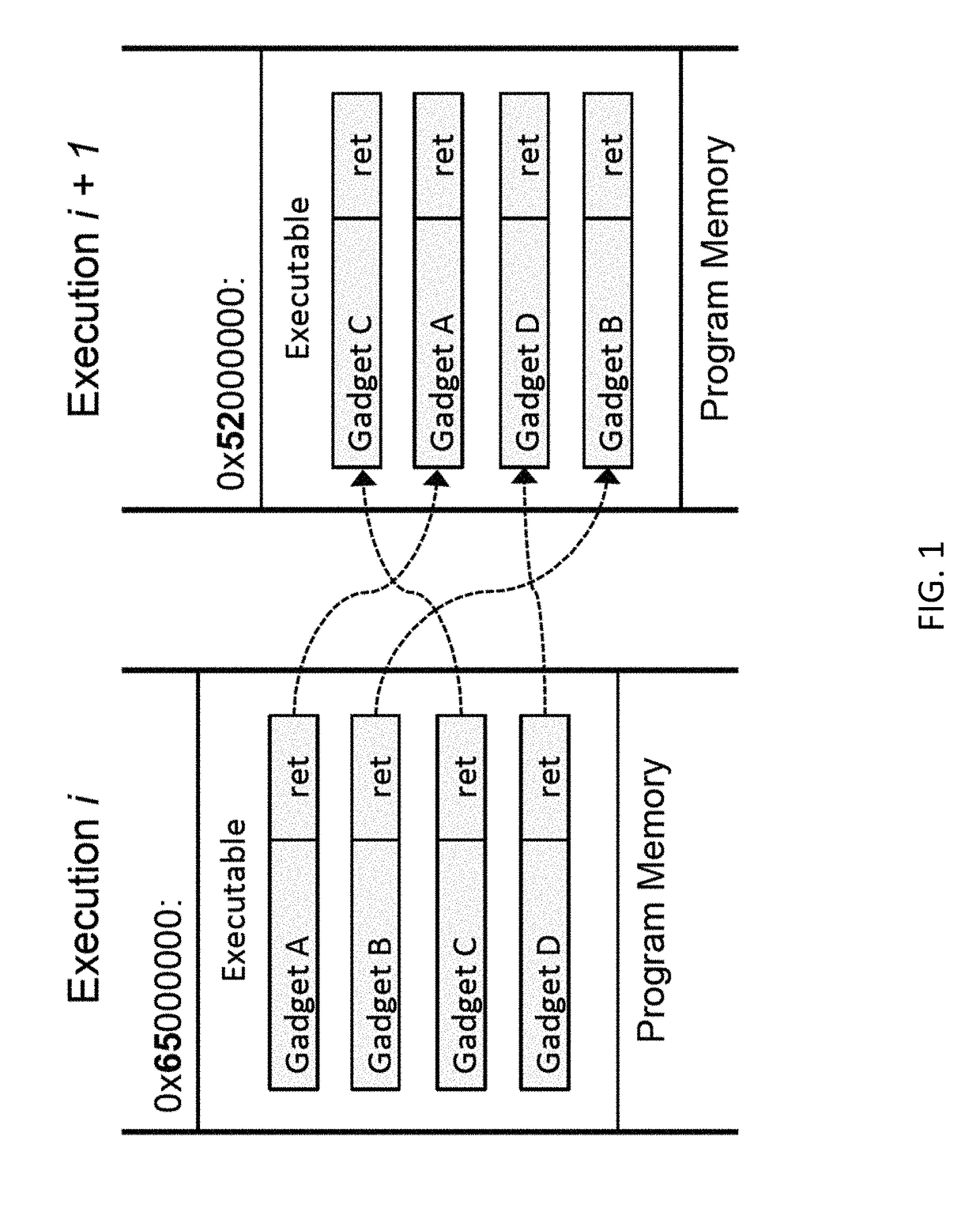
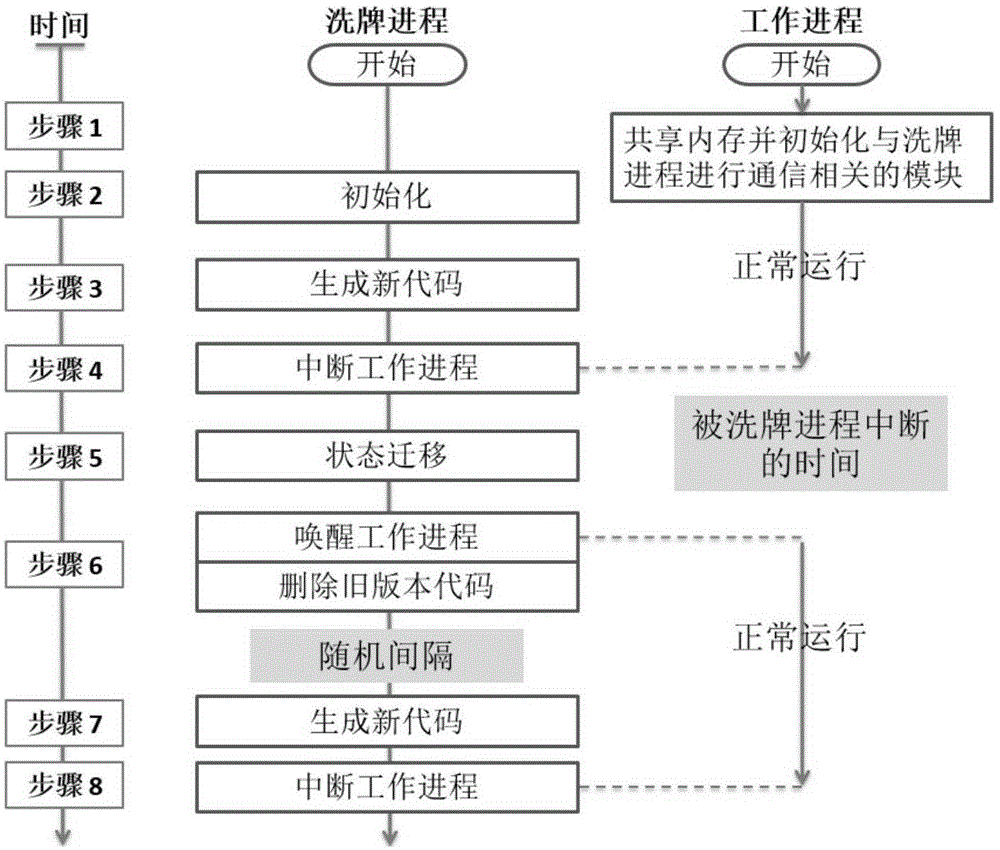
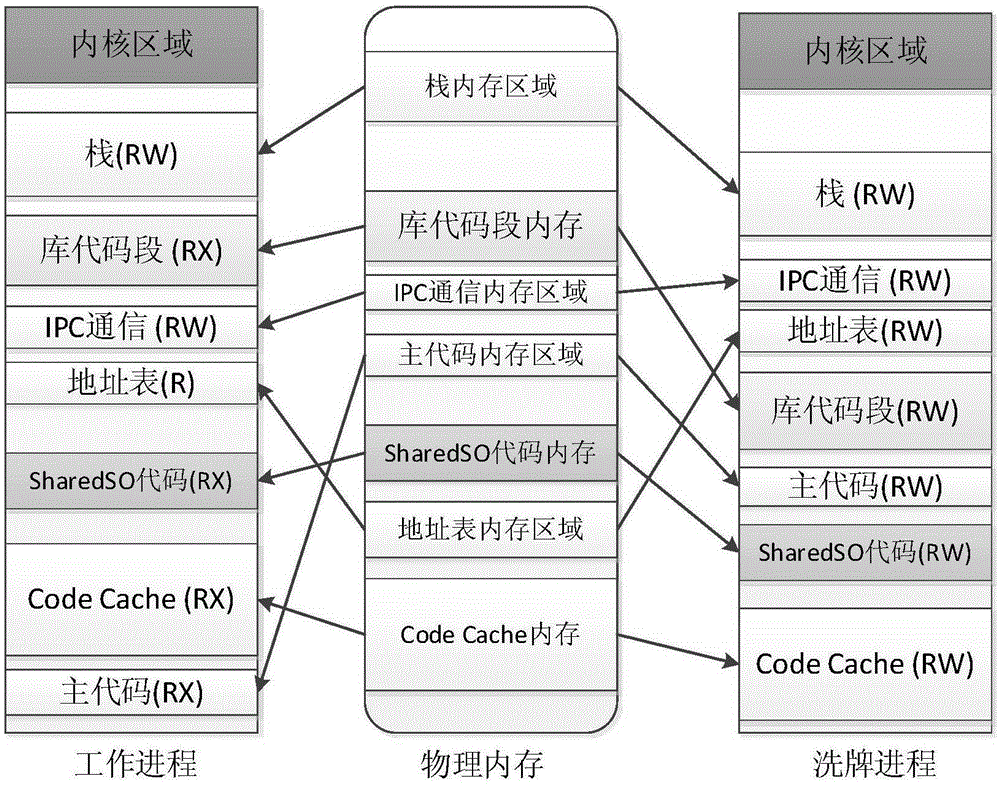
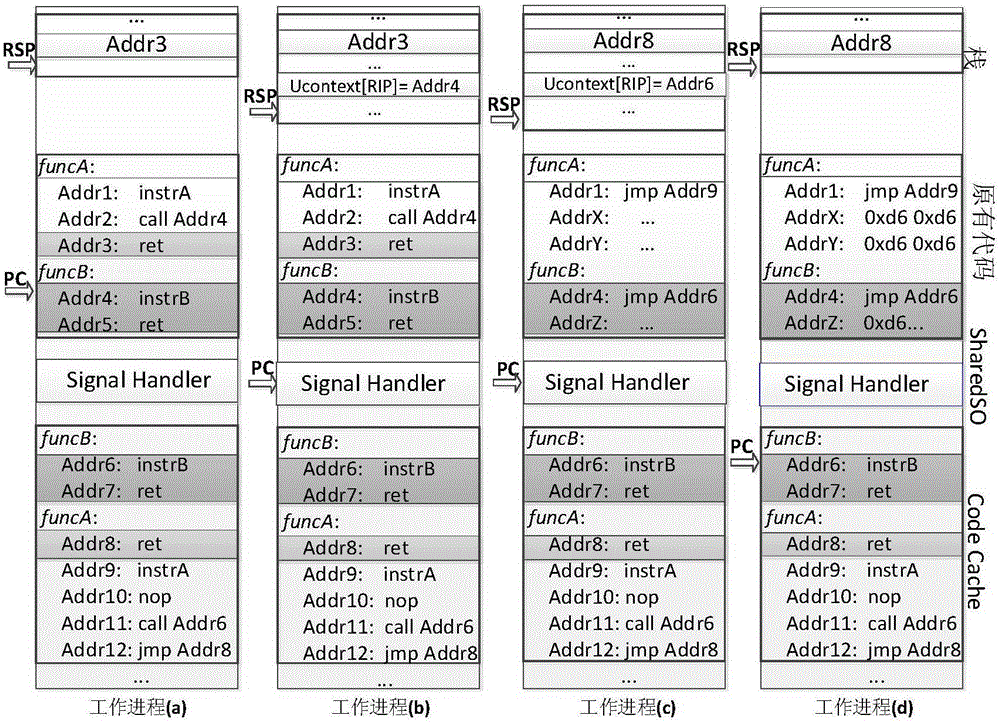
Code reuse attack-resisting work progress randomization method and system
The invention discloses a code reuse attack-resisting work progress randomization method and system. The method comprises the following steps: 1, presetting a new progress, sharing memory space of the work progress to the new progress, initiating the new progress, disassembling all the code segments in the new progress and recording intermediate representation, recognizing function information in the code segments, and analyzing execution streams in the function information and dividing basic blocks; 2, randomizing the code segments according to the intermediate representation so as to generate new code segments, sending a signal interrupt instruction to the work progress by the new progress, carrying out state transition operation by the new progress when the new progress confirms that the work progress is interrupted and the work progress stores corresponding information, and deleting the code segments when the new progress confirms that the work progress starts to execute the new code segments after the state transition operation is finished; and 3, circularly executing the steps 1 to 2.
Owner:INST OF COMPUTING TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Format conversion method and device of special interface tool
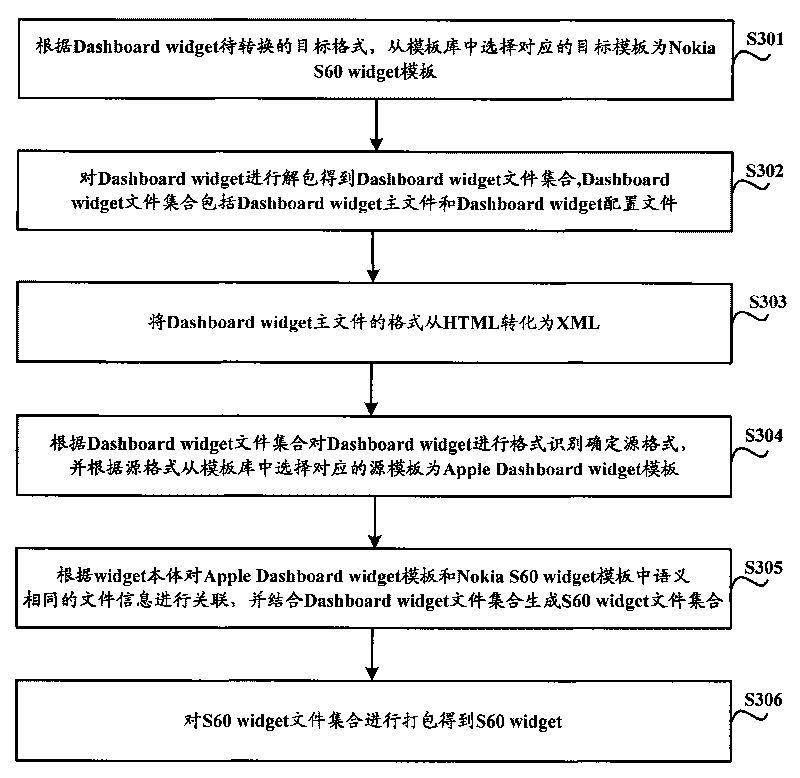
ActiveCN101763255AReduce development costsImprove development efficiencySpecial data processing applicationsSpecific program execution arrangementsTemplate basedDatabase
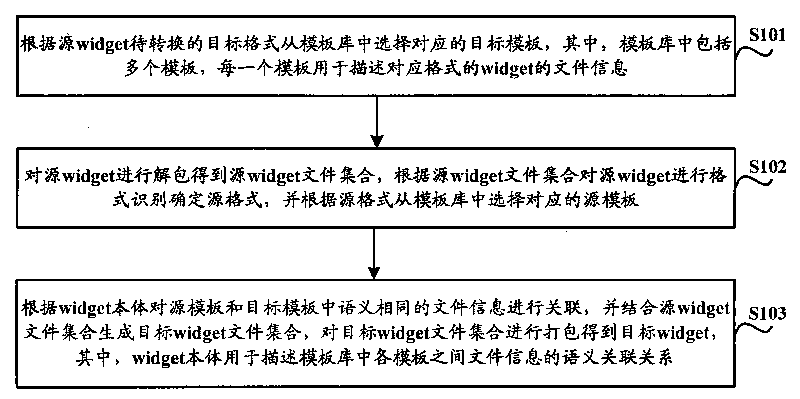
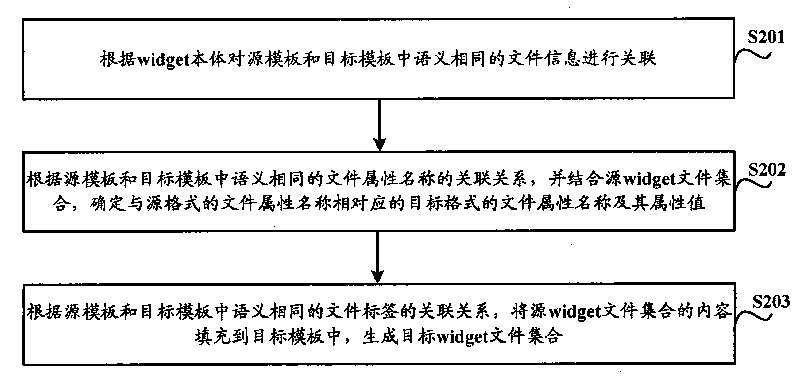
The invention discloses format conversion method and device of a special interface tool, which are used for realizing the conversion of widget among arbitrary formats. The widget format conversion method comprises the following steps of: selecting a corresponding target template from a template base according to a target format to be converted of a source widget, wherein each template in the template base is used for describing file information of a widget in a corresponding format; unpacking the source widget to obtain a source widget file set; carrying out format recognition according to the source widget file set to determine a source format, and selecting a corresponding source template from the template base according to the source format; carrying out correlation on the file information with the same semanteme in the source template and the target template according to a widget body, and generating a target widget file set on the basis of the source widget file set; and packing the target widget file set to obtain a target widget, wherein the widget body is used for describing the semanteme correlation of the file information among each template in the template base. The invention reduces the development cost of the widget and improves the development efficiency of the widget and code reuse ratio.
Owner:CHINA MOBILE COMM GRP CO LTD
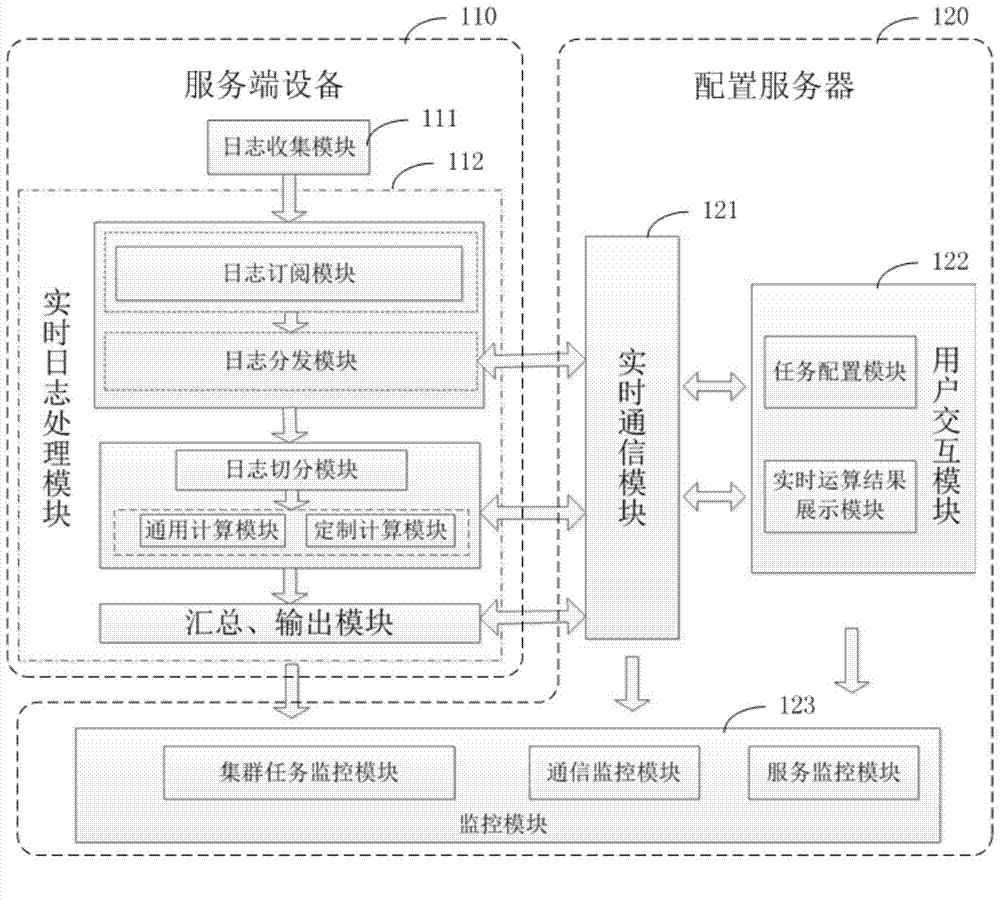
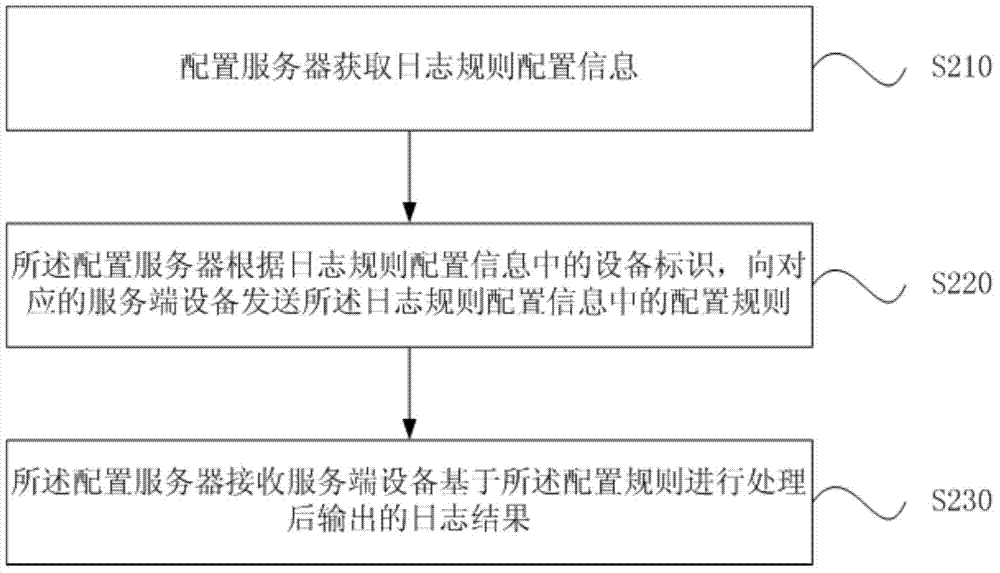
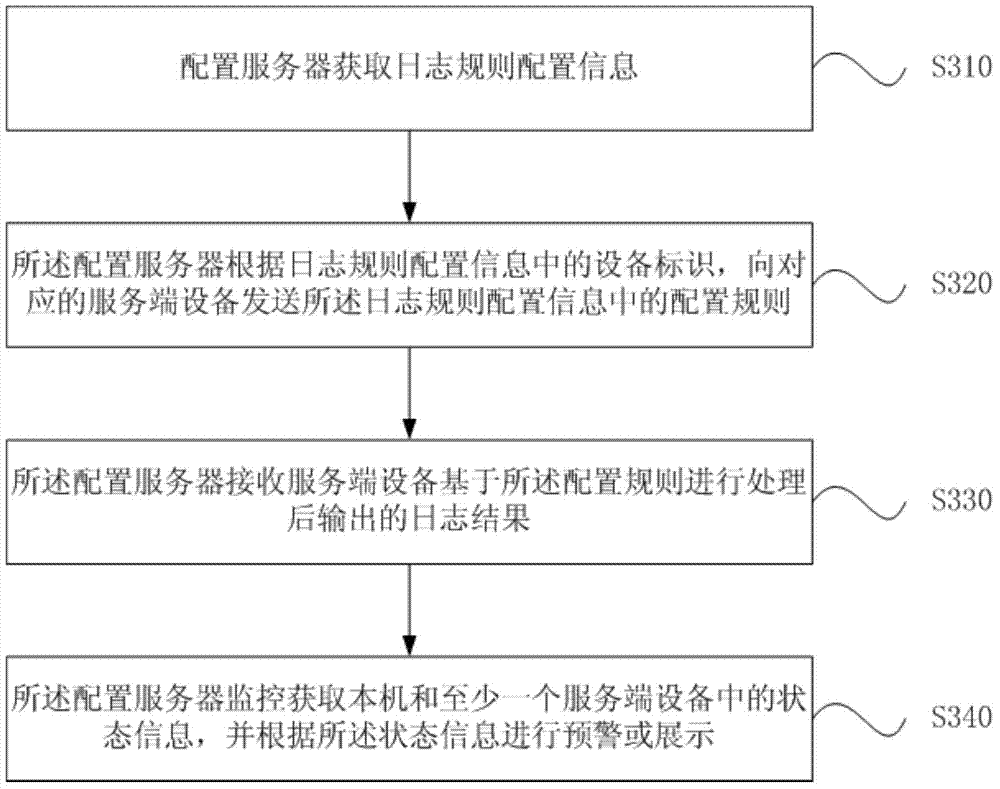
Log processing and configuration method, configuration server, service end device and system
ActiveCN103929329AImprove reuseReduce development costsData switching networksOperating systemCode reuse
The invention discloses a log processing and a configuration method, a configuration server, a service end device and system. The log processing method includes the steps that the service end device acquires the configuration rule provided by the configuration server; the service end device changes log processing parameters in a native machine according to the configuration rule; the service end device processes the collected logs based on the changed log processing parameters to acquire the log result; the service end device outputs the log result. By means of the log processing and the configuration method, the configuration server, the service end device and system, the code reuse rate is improved, and cost of redevelopment is reduced.
Owner:深圳太乐文化科技有限公司
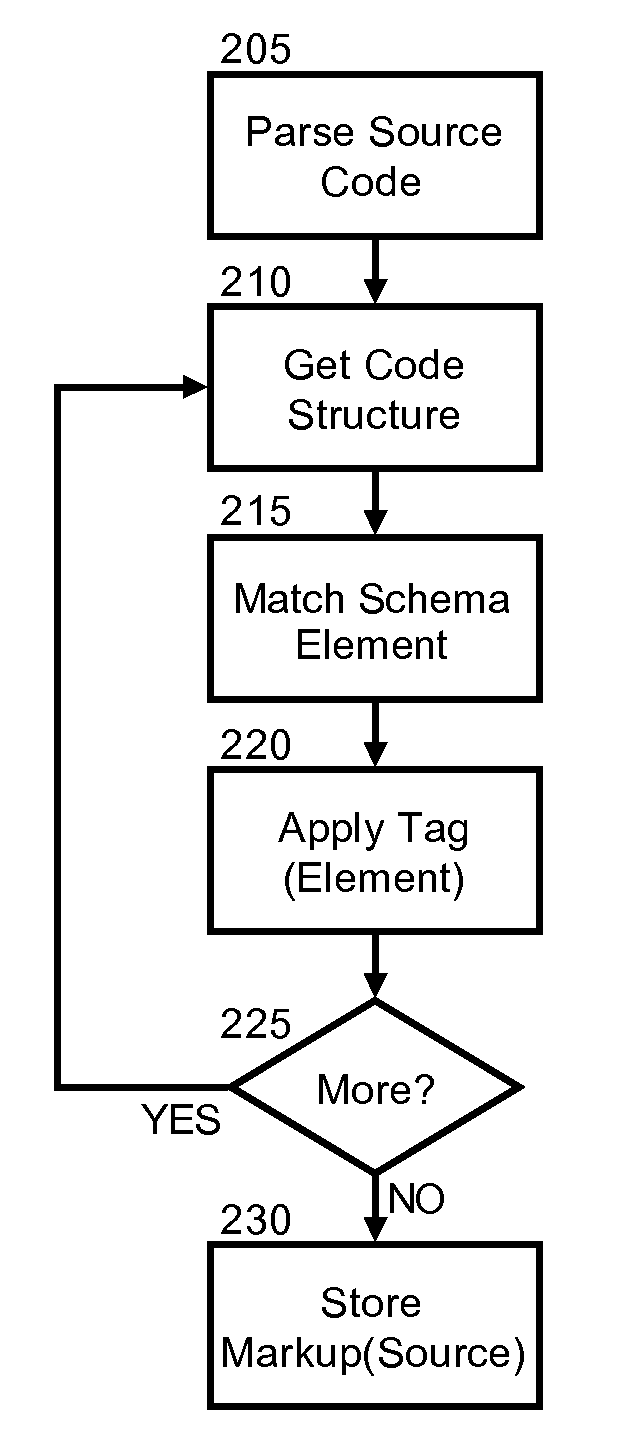
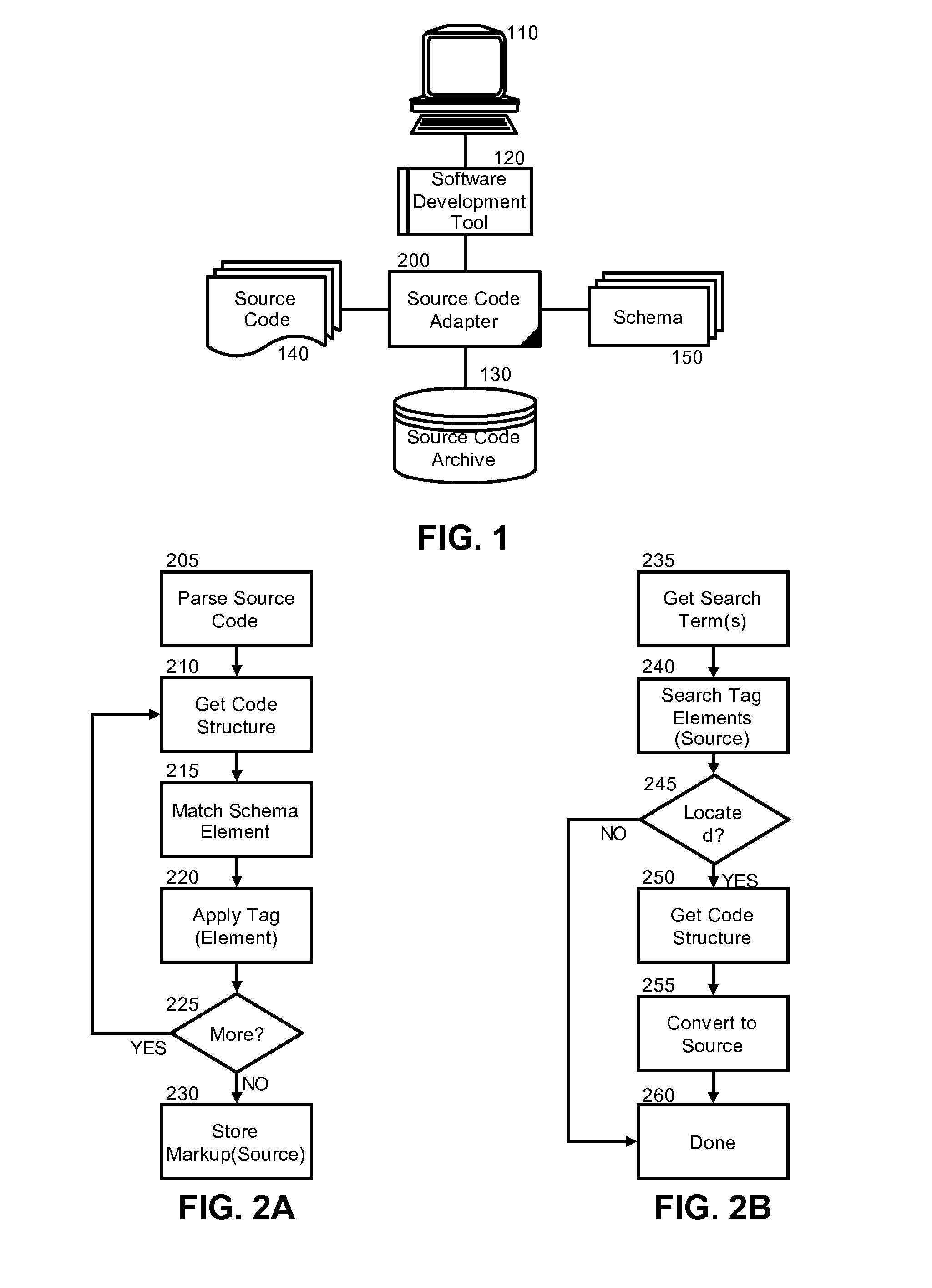
Source code analysis archival adapter for structured data mining
Embodiments of the present invention address deficiencies of the art in respect to code reuse management and provide a method, system and computer program product for source code archival adapter for structured data mining In one embodiment of the invention, a method for adapting archived source code for structured data mining for source code reuse can be provided. The method can include parsing source code to identify individual classification elements within the source code, generating a markup language formatted set of code constructs corresponding to the classification elements, and storing the markup language formatted set of code constructs in a source code archives
Owner:IBM CORP
Parameter verification method and device and network management server
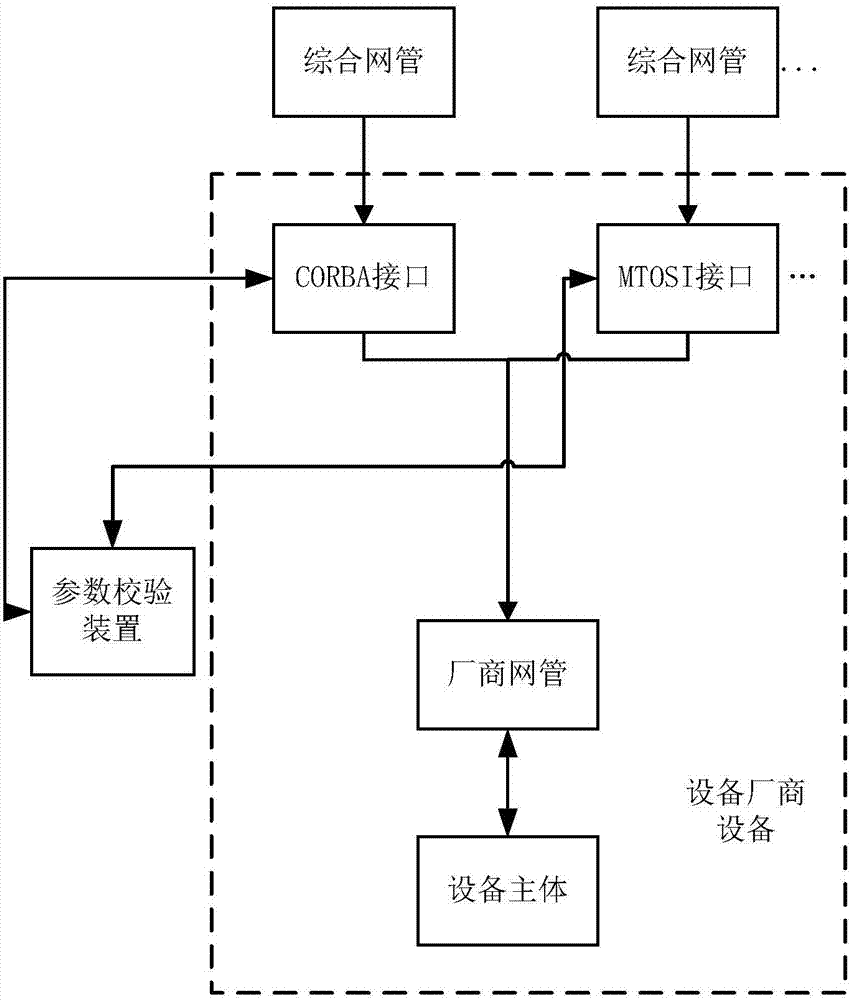
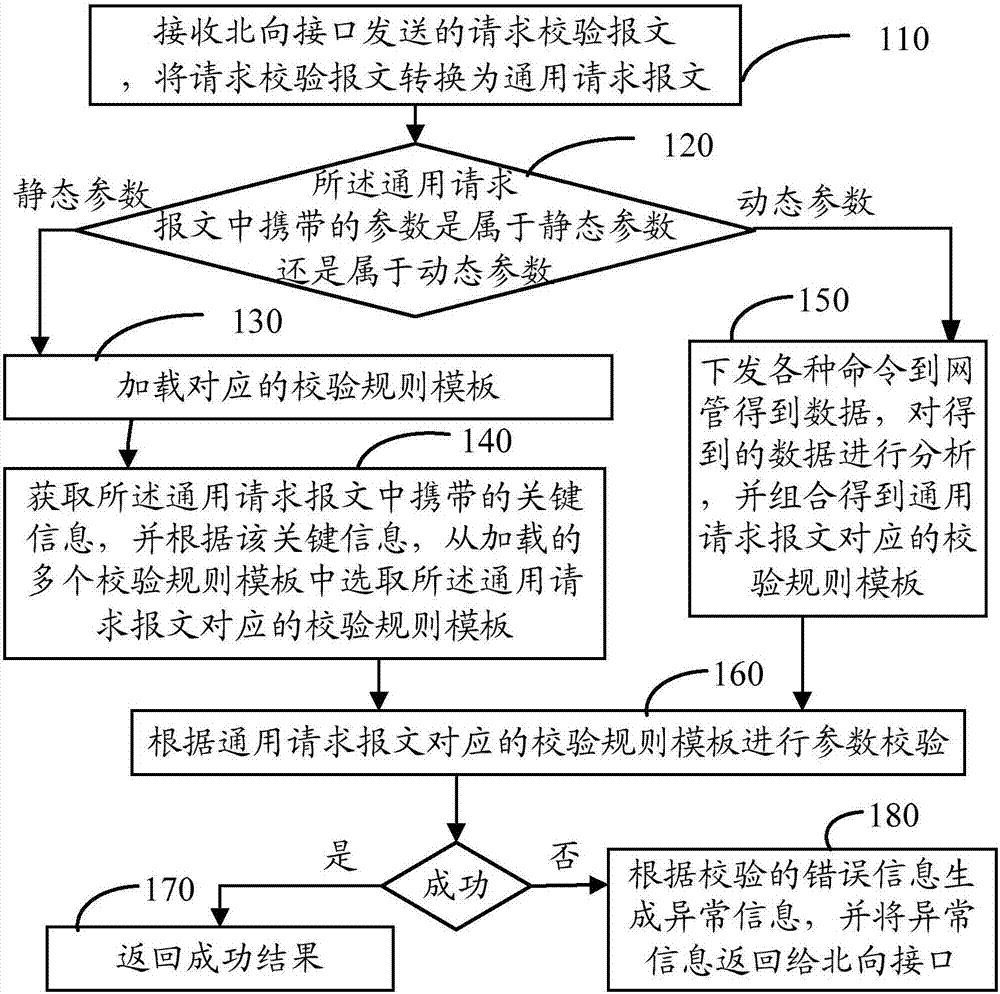
InactiveCN107579836AReduce maintenance costsImprove development efficiencyData switching networksNetwork managementData combination
The invention discloses a parameter verification method and device and a network management server. The method comprises the steps of distinguishing whether the parameters carried in a universal request message belong to static parameters or dynamic parameters; when the parameters are static parameters, selecting a verification rule template corresponding to the general request message from a plurality of preset verification rule templates; when the parameters are dynamic parameters, obtaining the verification rule template corresponding to the universal request message according to the data combination obtained by the network management. According to the scheme, a parameter verification scheme is provided, and the code reuse rate is high. When the parameter verification scheme is appliedto different equipment, a corresponding verification rule template can be selected from a plurality of preset verification rule templates, or a corresponding verification rule template is obtained through dynamic combination, and parameter verification is completed according to the verification rule template, so that the development of the northbound interface is easy to add. The difference of various equipment is shielded, and the maintenance cost of codes is reduced.
Owner:ZTE CORP
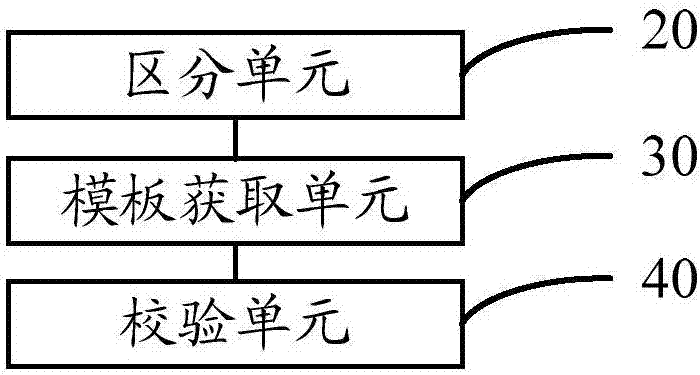
QT-based user interface control generating method and device
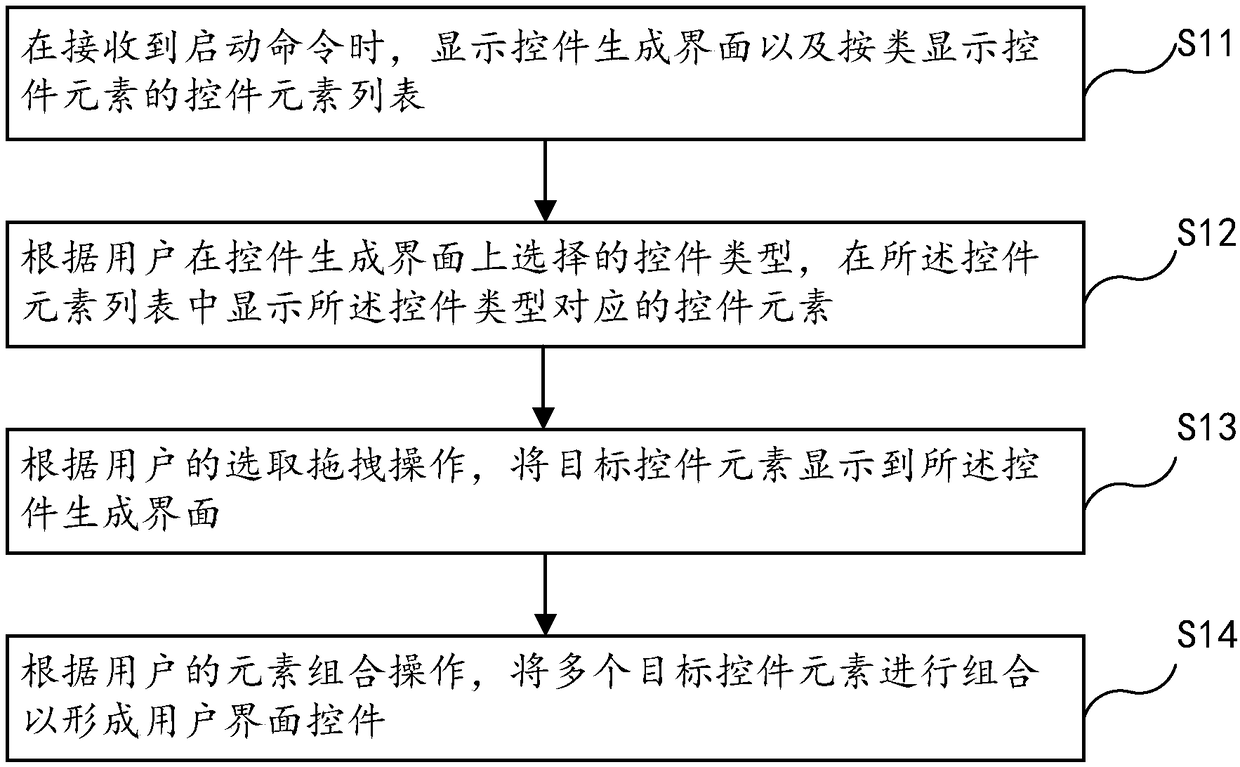
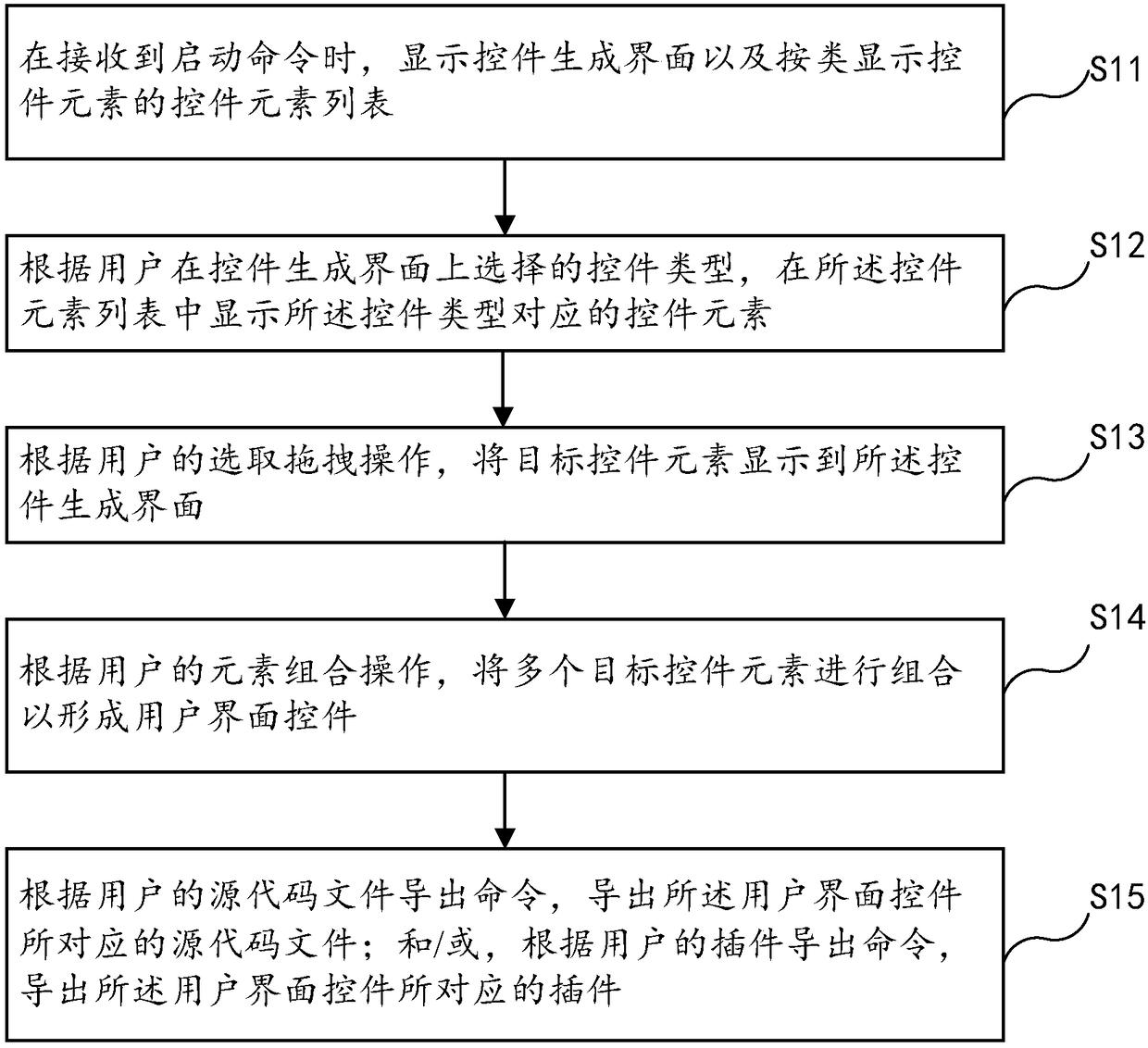
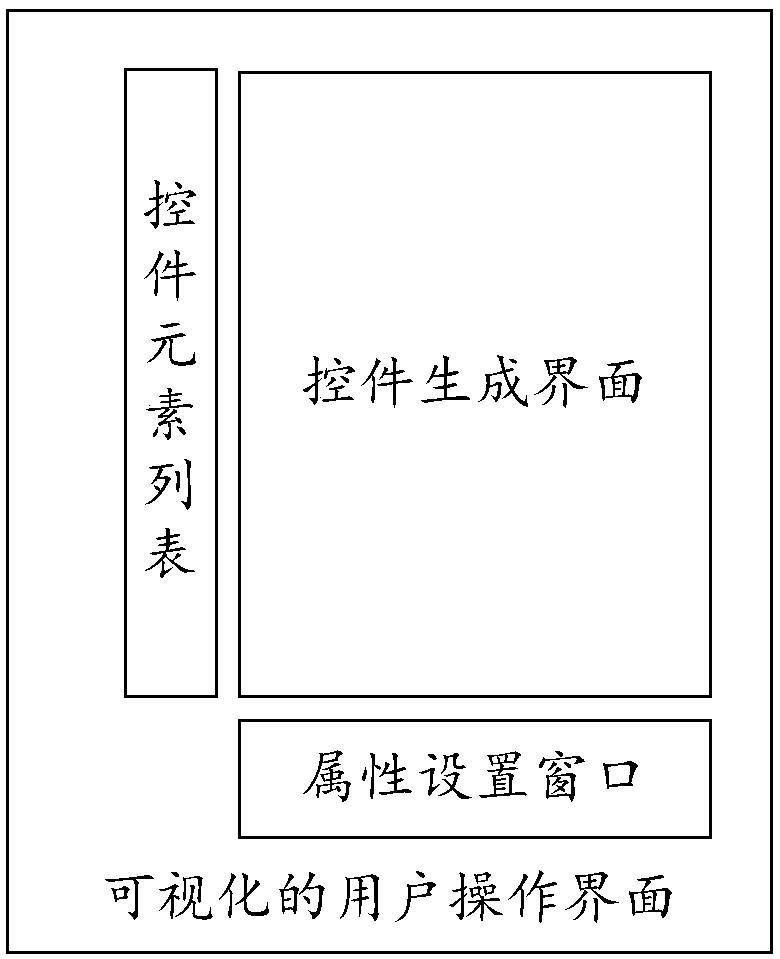
ActiveCN108228287AImprove development efficiencyImprove reuse rateSoftware engineeringExecution for user interfacesSource codeHuman–computer interaction
The invention provides a QT-based user interface control generating method and device. The method comprises the steps of displaying a control generation interface when a starting instruction is received, and displaying a control element list of control elements according to the types; according to the control type selected by a user on the control generation interface, displaying the control element list corresponding to the control type in the control element list; according to a dragging operation selected by the control elements of the user, displaying target control elements on the controlgeneration interface; according to the user's control element combination operation, combining the multiple selected target control elements to form a user interface control. The method has the advantages that operation is easy, the process is visualized, and the code reuse rate is high, corresponding source codes and plug-ins are automatically generated while the user interface control type is generated, cross-platform usage and compatibility of QT are achieved, and therefore the developing efficiency of the user interface control can be improved.
Owner:LOONGSON TECH CORP
Intelligent parameter checking device
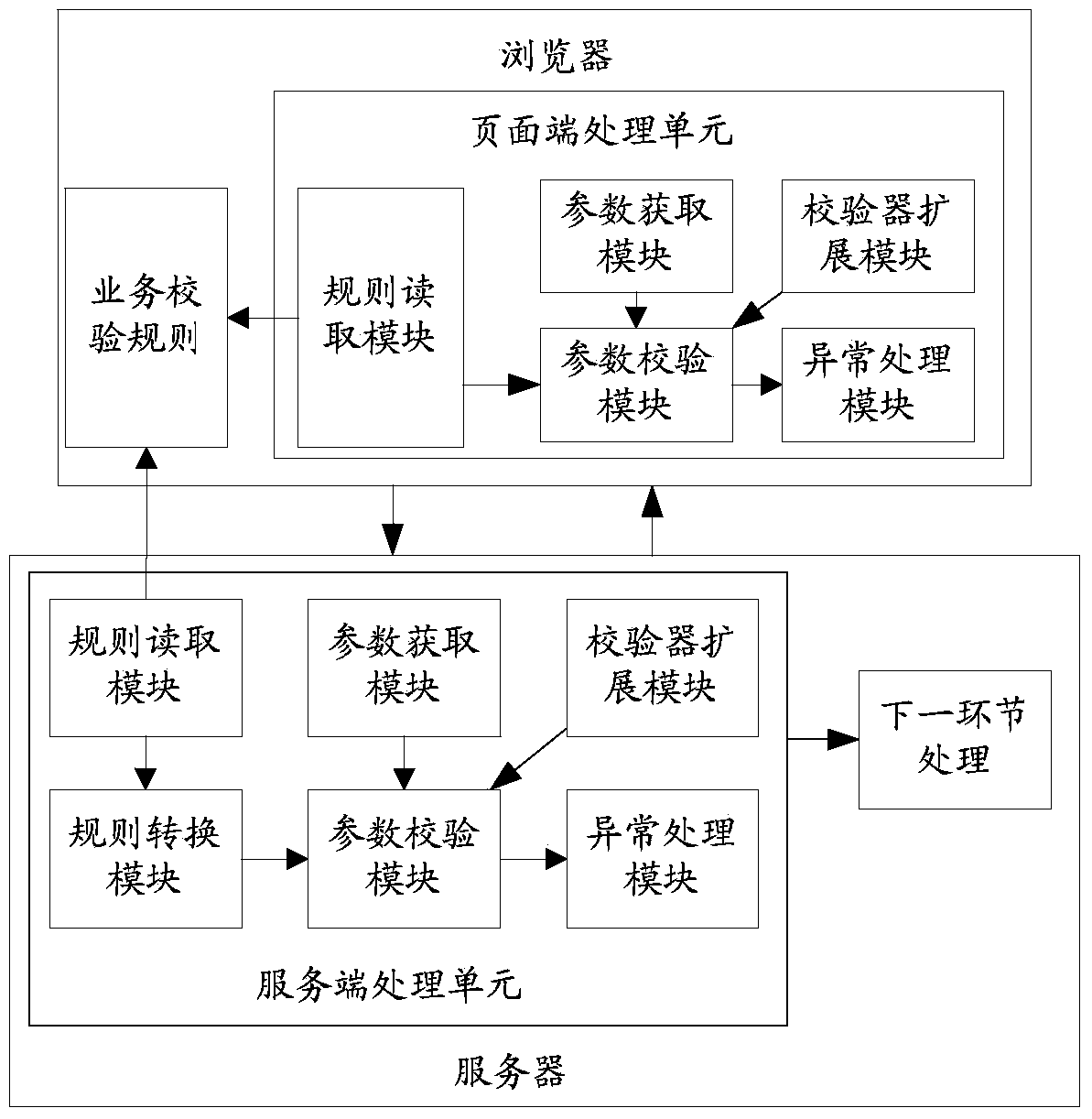
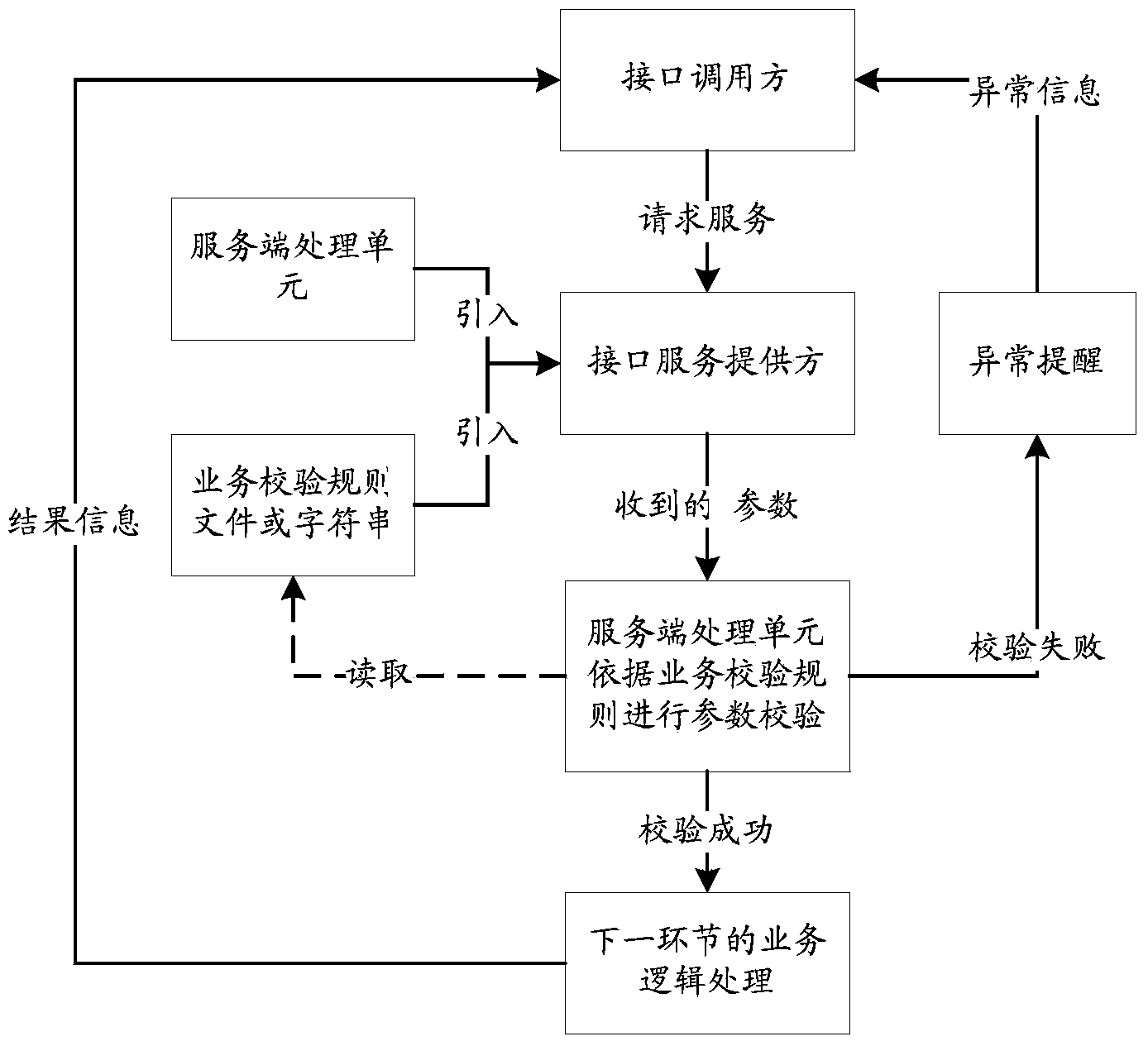
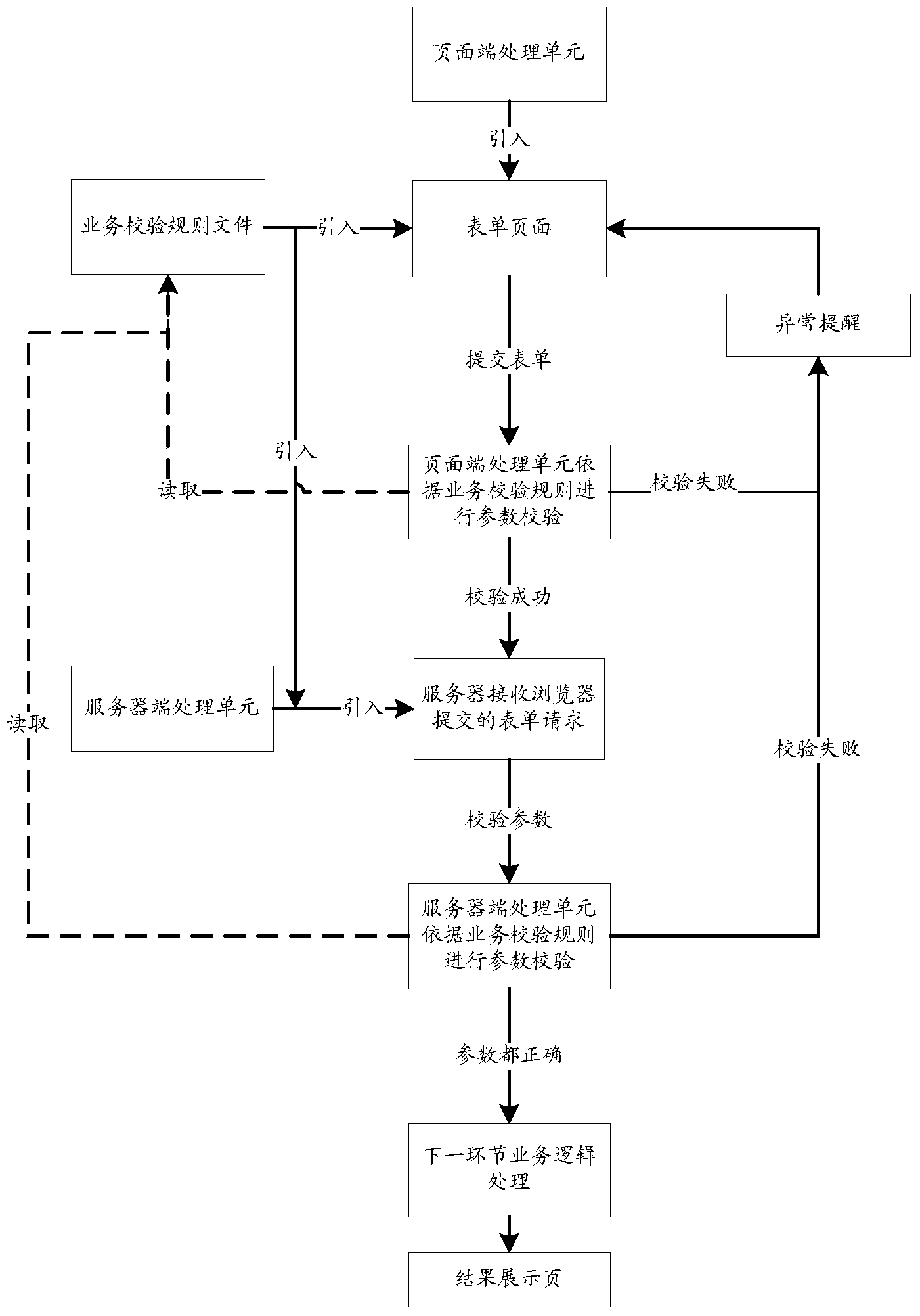
InactiveCN104360937AImprove reuseFlexible formSoftware testing/debuggingPerceptionException handling
The invention provides an intelligent parameter checking device which comprises a page processing unit and / or a server processing unit, wherein the page processing unit comprises a rule reading module, a parameter acquisition module, a checker expansion module, a parameter checking module and an exception handling module, and the server processing unit comprises a rule reading module, a parameter acquisition module, a checker expansion module, a parameter checking module, an exception handling module and a rule conversion module. The device has the following advantages: 1, high code reuse rate, 2, wide application scope, 3, flexible checking rule representation form, 4, easiness in use and expansion, 5, improvement of user experience and perception, 6, improvement of development efficiency, and 7, lowered maintenance cost.
Owner:中电福富信息科技有限公司
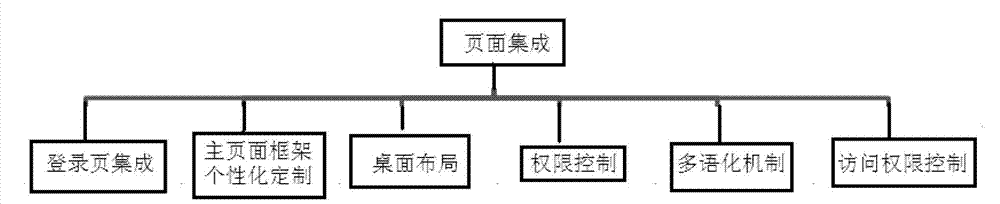
Page for achieving Web page reuse based on extension point
InactiveCN102902725AEasy to implementReduce complexitySpecial data processing applicationsReusabilityWeb page
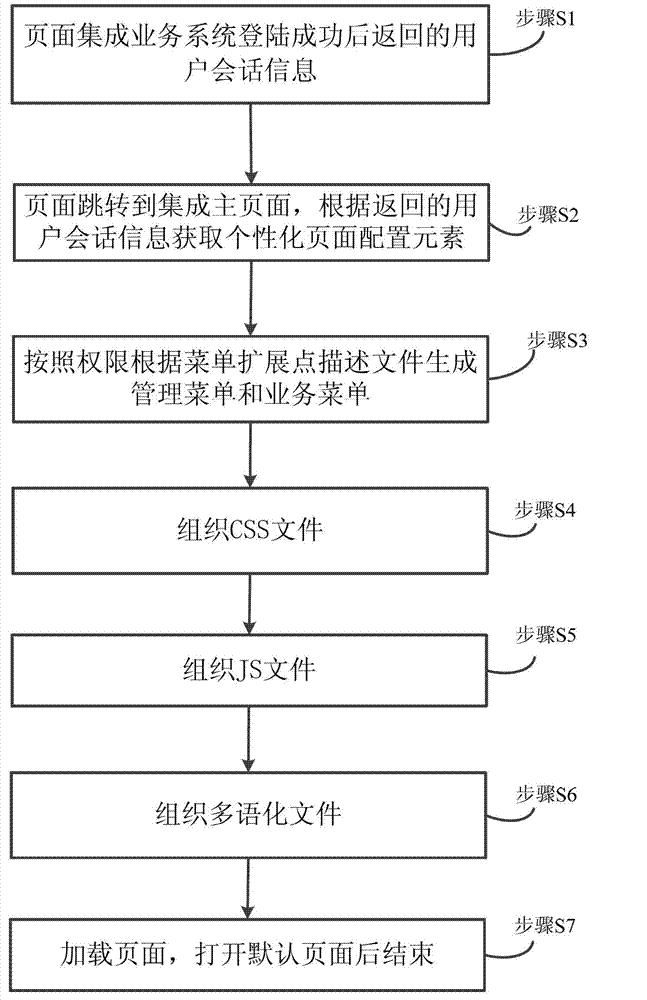
The invention provides a page for achieving Web page reuse based on an extension point. The page comprises a basic page frame and at least two subsystems, wherein the subsystems takes a page integration frame as the dependence and introduces the frame into the basic page frame, therefore the subsystems are enabled to be subjected to integration with other subsystems in an extension point mode in the page integration frame, and functional integration of a plurality of different subsystems is achieved for the page; and the subsystems store administration menus, business menus, cascading style sheet (CSS) files and JavaScript (JS) files in the extension point form. According to the page, reusability of Web pages is achieved in a page frame mode which replaces the code reuse.
Owner:DAWNING INFORMATION IND BEIJING
A method and system for code generation
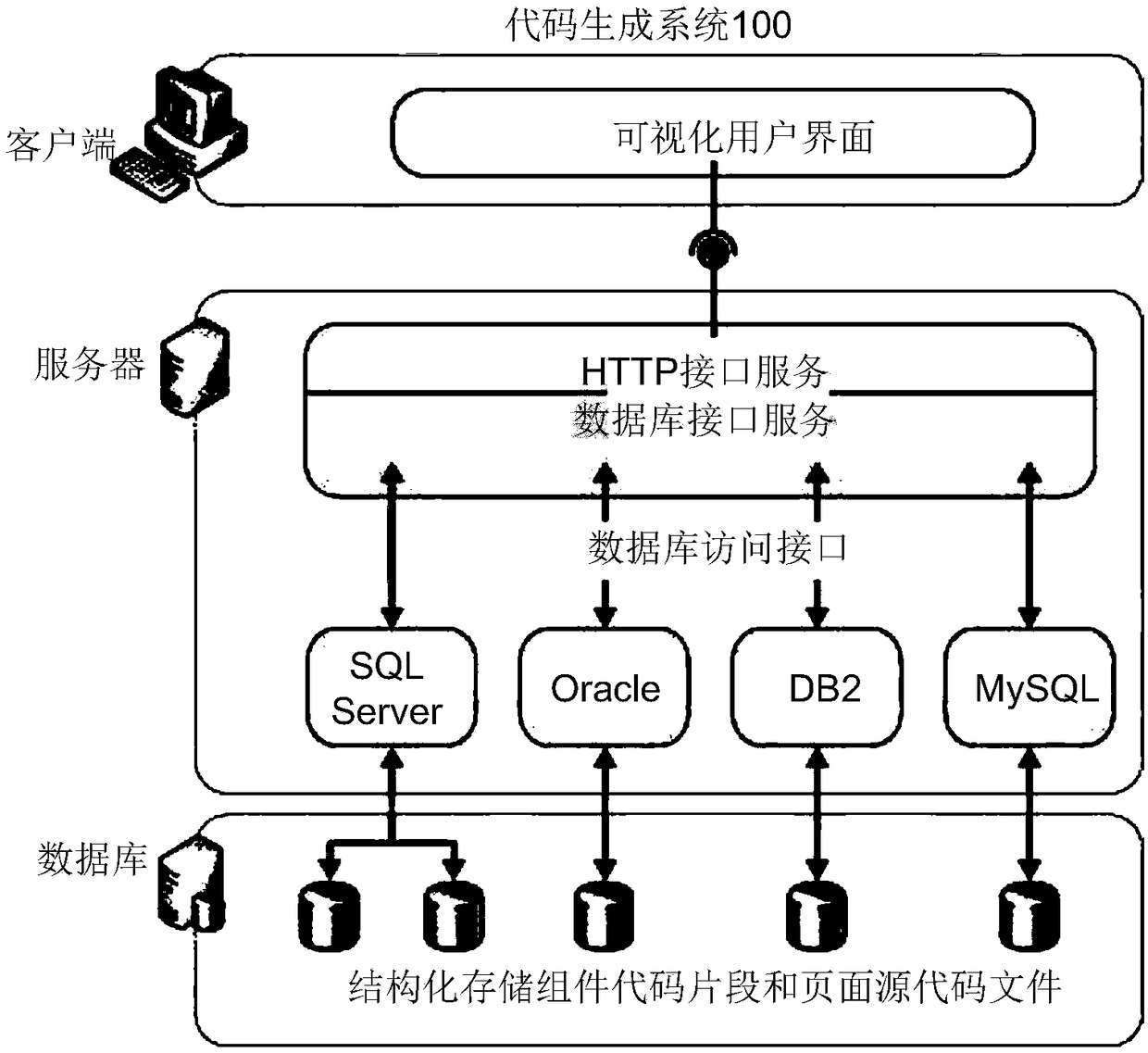
The invention discloses a code generation method, which is suitable for execution in a server. The method comprises the following steps: sending a user interface configuration file to a client for presenting a visual user interface at the client. Receiving operation information on a visualized user interface presented by a user on a client, the operation information including component informationto be manipulated, page information and layout information of the component on the page; Sending an access request to the database in order to obtain a code snippet corresponding to the component anda page source code file; And integrating the corresponding code snippets of the components into the corresponding positions in the page source code file based on the layout information of the components on the page. This scheme can automatically integrate the structured code snippets, solve the flexibility of code reuse, and improve the efficiency of front-end development.
Owner:BEIJING TENGYUN TIANXIA SCI & TECH CO LTD
Method for generating routing protocol component in software development of reconfigurable router
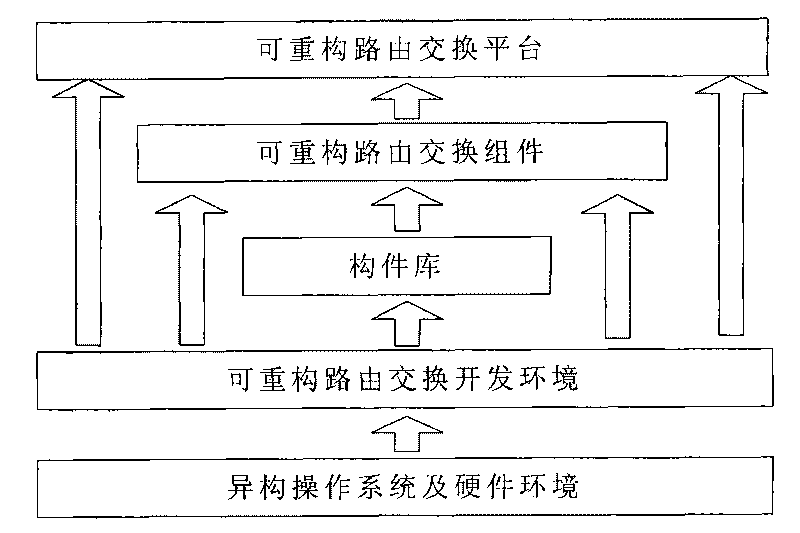
InactiveCN101719921AImprove reuseShort cycleData switching networksSpecific program execution arrangementsSoftware development processCoupling
The invention relates to a method for generating a BGP routing protocol component in software development of a reconfigurable router, which belongs to the research field of reconfigurable networks and is characterized in that the method comprises the steps of describing functional interfaces of the component, behavior, environment and basic static information, selecting meta components required for the component from a meta component library, generating the component, and then testing the functions of the interfaces of the component, the functions of the component and the performances of the component. The method has the advantages of little encoding workload, low coupling degree, good integration and high code reuse degree.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Real-time data calculation method, device and equipment and computer readable storage medium
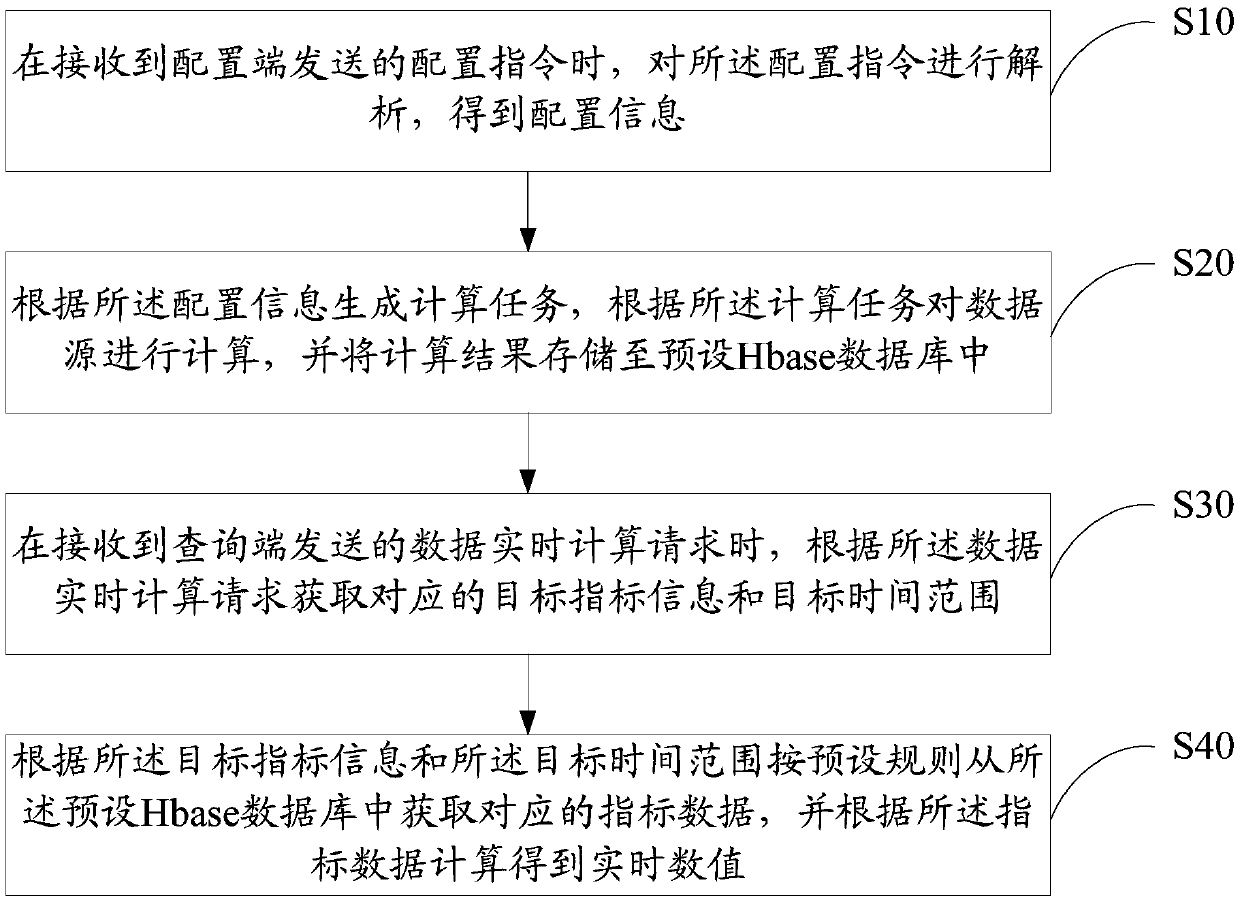
PendingCN109597842AImprove reuse rateReduced development effortDatabase management systemsSpecial data processing applicationsTime rangeReal-time data
The invention discloses a real-time data calculation method. The real-time data calculation method comprises the following steps: when a configuration instruction sent by a configuration end is received, analyzing the configuration instruction to obtain configuration information; generating calculation task is generated according to the configuration information, calculating a data source according to the calculation task, and storing a calculation result in a preset Hbase database; When a data real-time calculation request sent by a query end is received, obtaining corresponding target indexinformation and a target time range according to the data real-time calculation request; According to the target index information and the target time range, obtaining corresponding index data from the preset Hbase database according to a preset rule, and obtaining a real-time value through calculation according to the index data. The invention further discloses a data real-time calculation deviceand equipment and a computer readable storage medium. According to the invention, the development cost can be reduced, and the code reuse rate is improved.
Owner:WEBANK (CHINA)
Interface logic control method based on 3D (three-dimensional) model
ActiveCN103019725AReduce development difficultyImprove reuseSpecific program execution arrangementsState variationCoupling
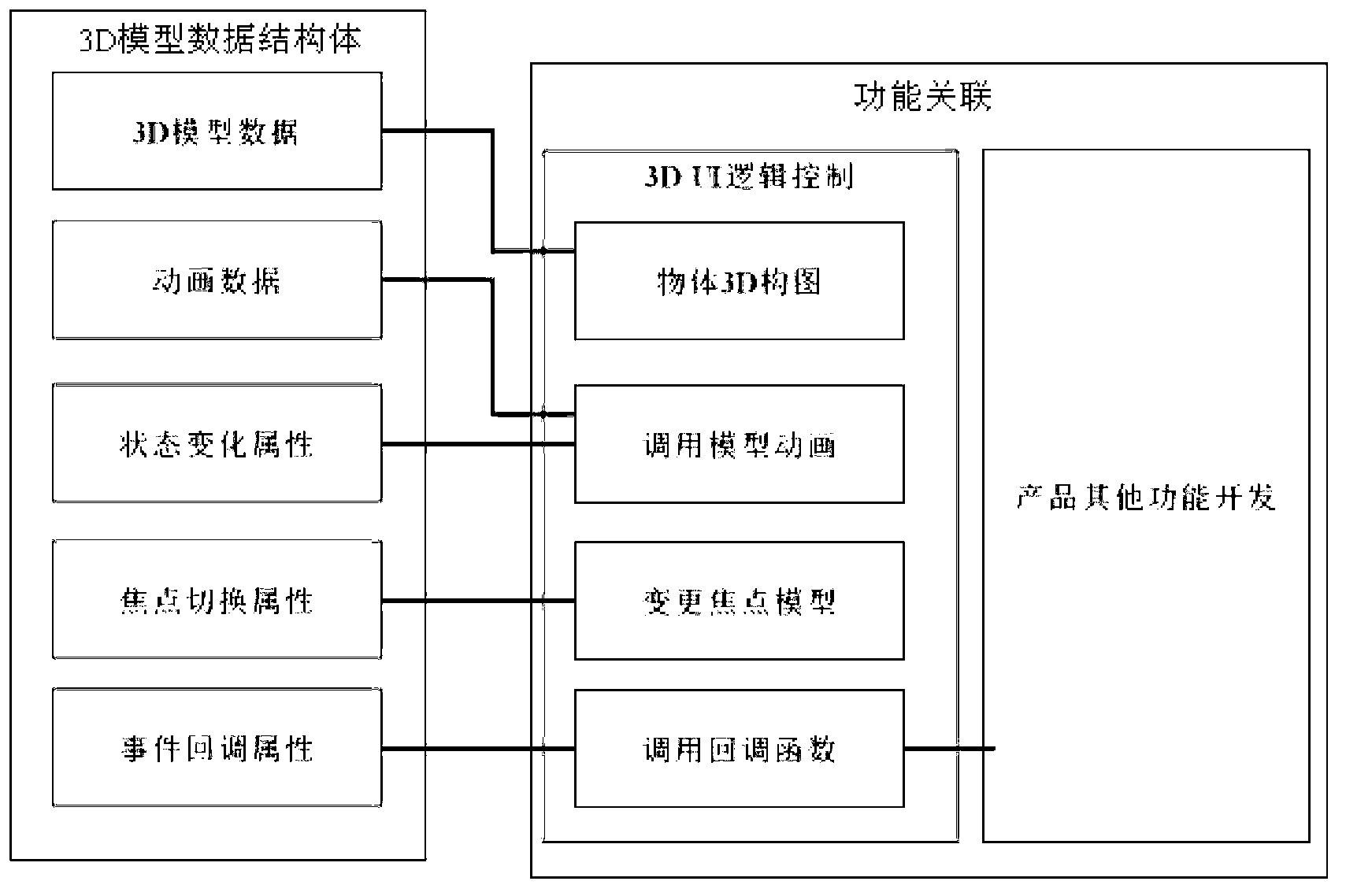
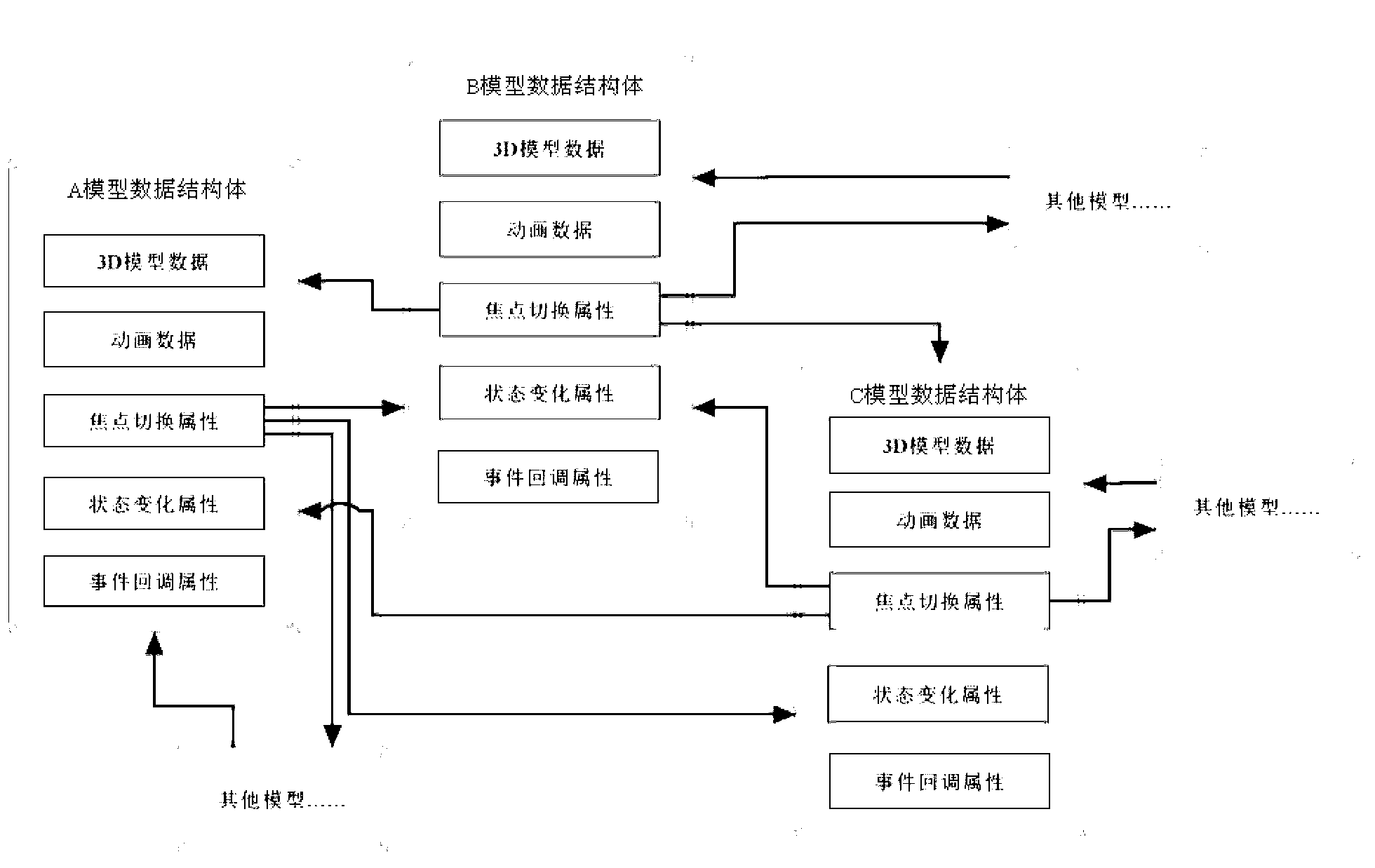
The invention relates to an interface logic control method based on a 3D (three-dimensional) model. The interface logic control method based on the 3D model comprises the following steps of: a) loading a 3D model, and storing the information of the 3D model into a data structural body; b) storing animation data in the data structural body as one data block in the data structural body; and c) setting a focal point switchover attribute, a state change attribute and a event call-back attribute in the data structural body, wherein the focal point switchover attribute is used for setting a next focal point model after the focal point is changed, the state change attribute is used for invoking a corresponding animation in the data block to be played, and the event call-back attribute is used for calling the corresponding call-back attribute. With the method disclosed by the invention, the 3D model is packaged and subjected to attribute setting, so that the attributes and corresponding events are correlative instead of directly coupling the interface with functions, the interface development and the function development are mutually independent, thus the 3D interface development difficulty is lowered, the code reuse ratio is improved, deep coupling between the interface and the corresponding functions is removed, and the development efficiency is improved.
Owner:SICHUAN CHANGHONG ELECTRIC CO LTD
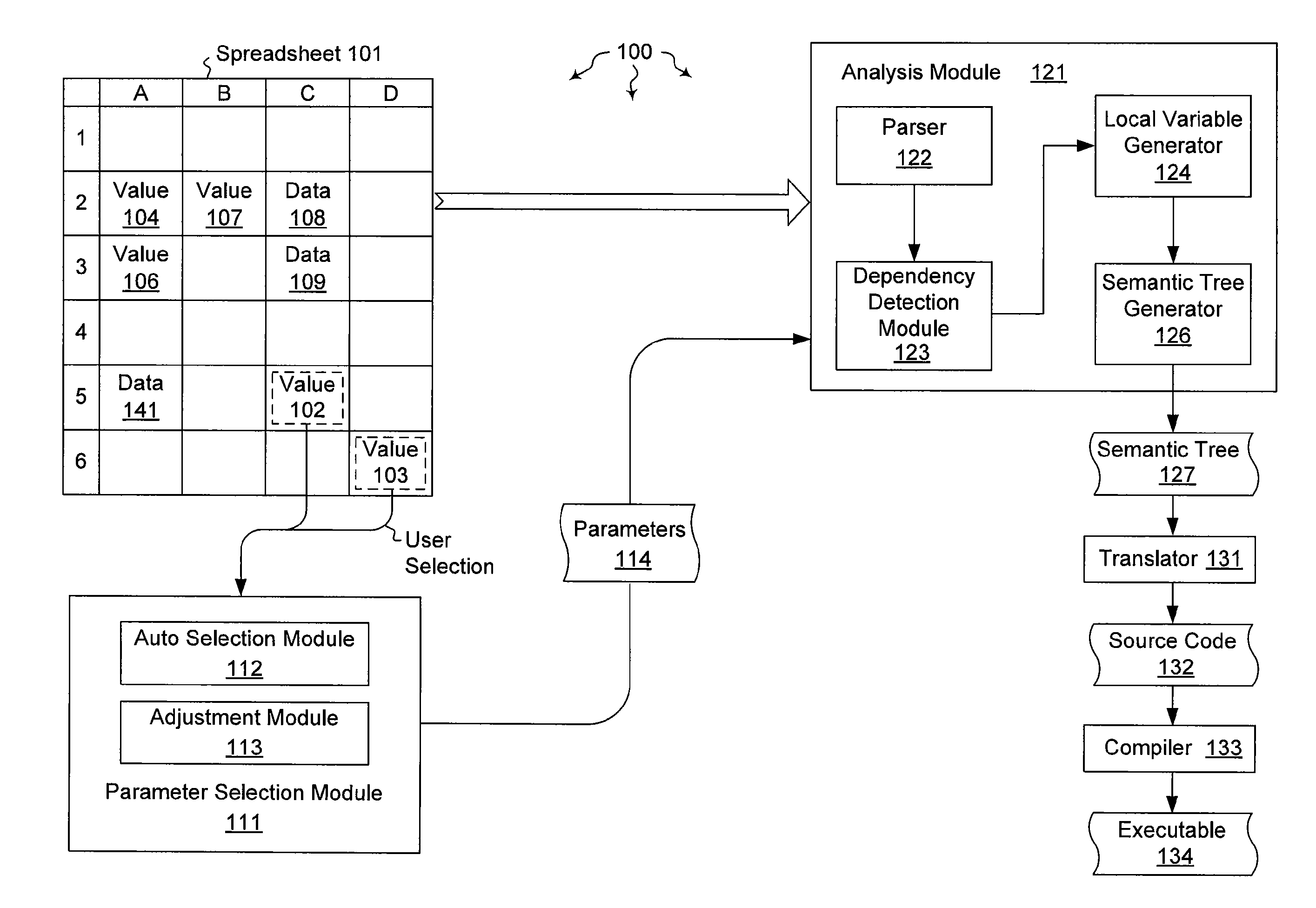
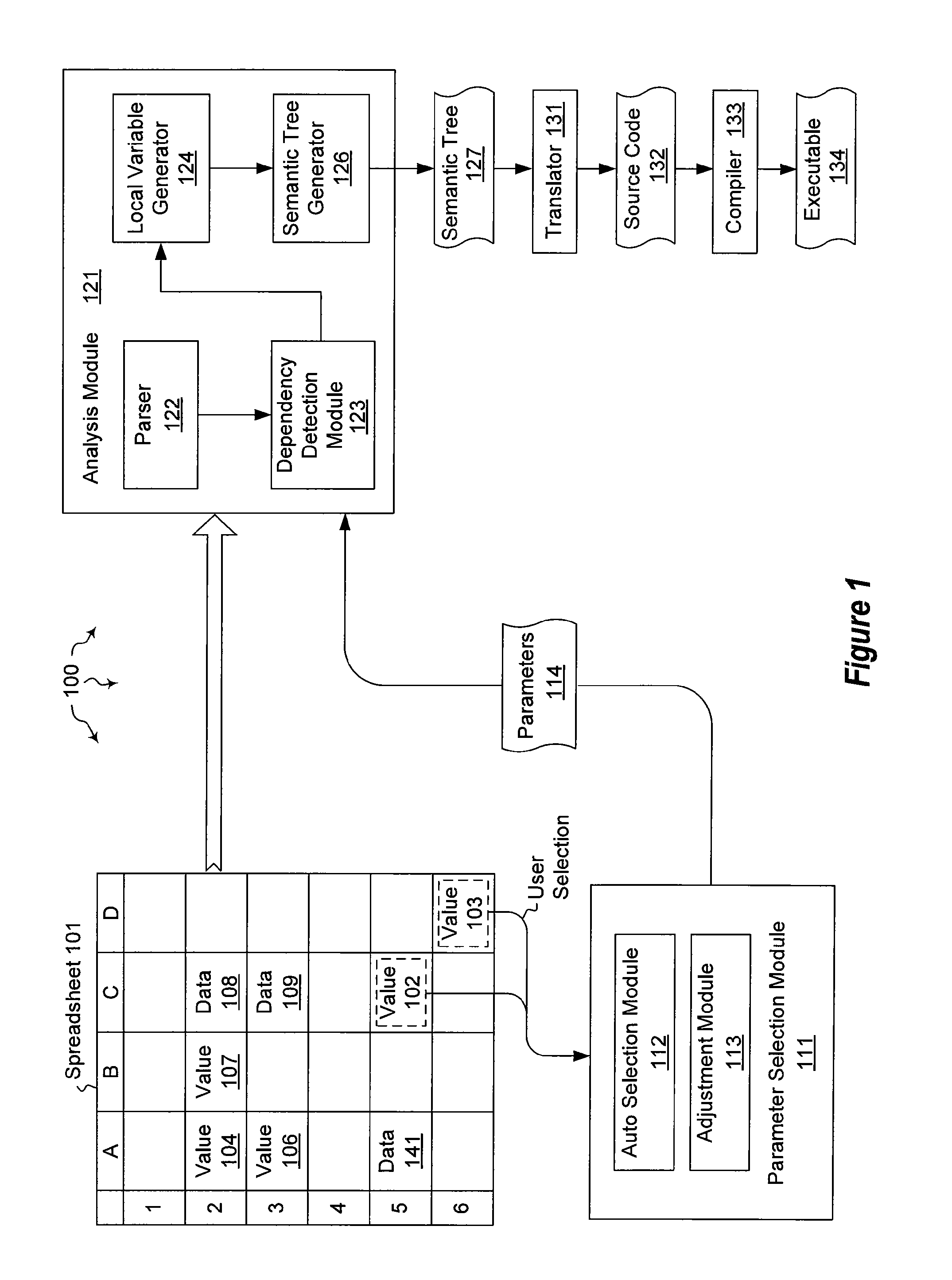
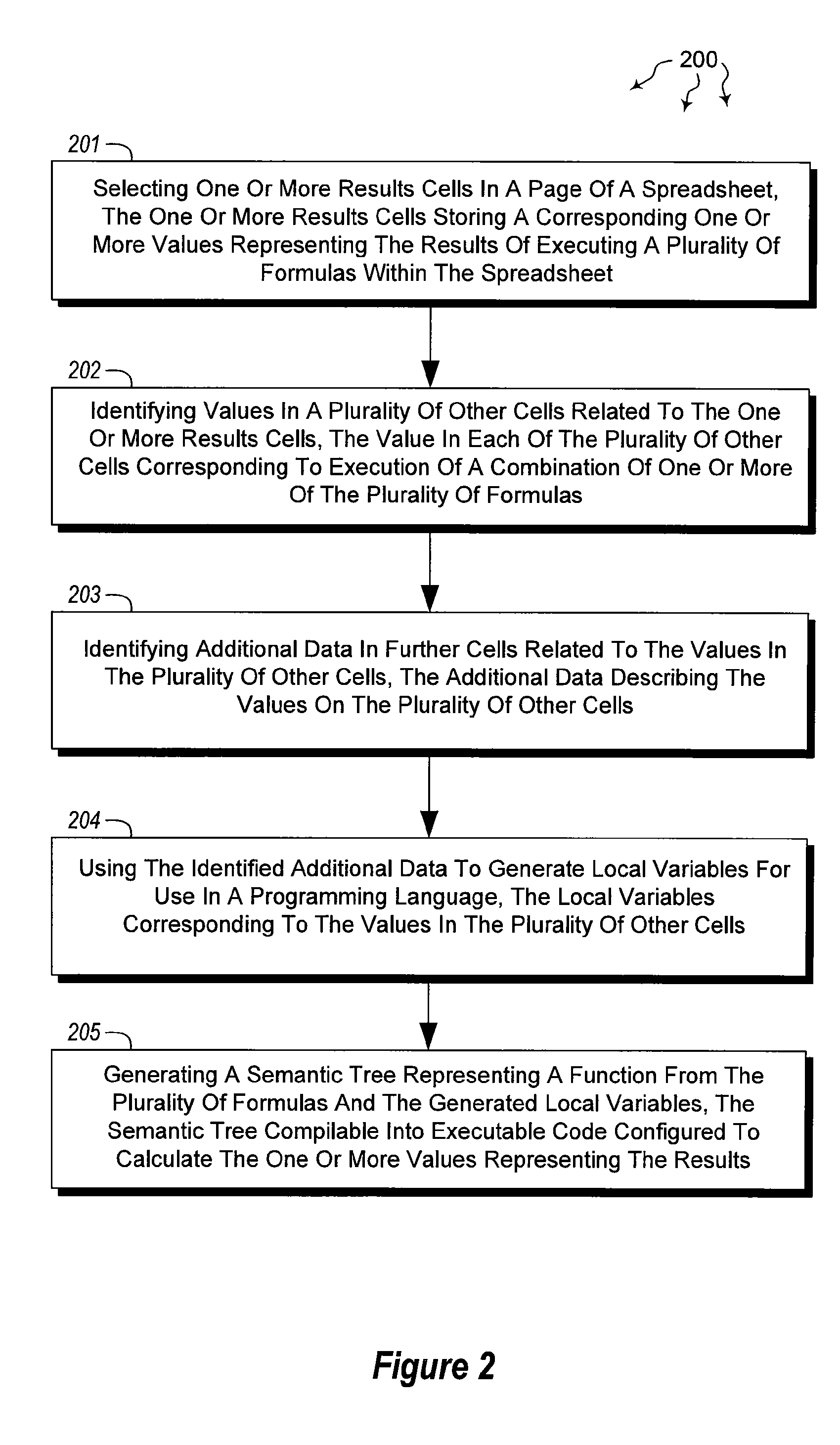
Creating text functions from a spreadsheet
The present invention extends to methods, systems, and computer program products for creating text functions form a spreadsheet. Embodiments of the invention extract functions from spreadsheets and represent the functions in textual form. Representation in textual form promotes code reuse, clarify, expressive power, and better performance. Text can be rendered in virtually any programming language, such as, for example, C#, C++, Visual Basic (“VB”), etc. In some embodiments, programming language extensibility to support spreadsheet compatible data types and functions is utilized.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com