Code reuse attack-resisting work progress randomization method and system
A work process and code reuse technology, applied in code generation, application software security and protection fields, can solve problems such as high overhead, no way to achieve asynchronous, legacy code cannot be well protected, etc., to achieve low overhead Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
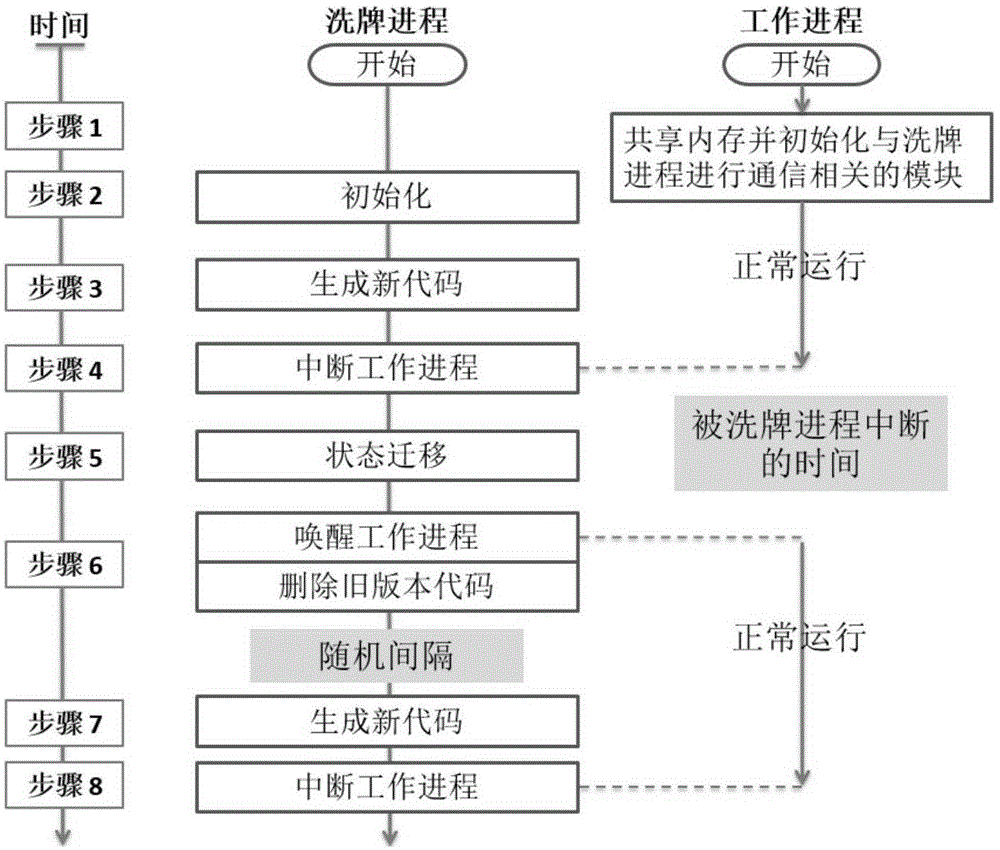
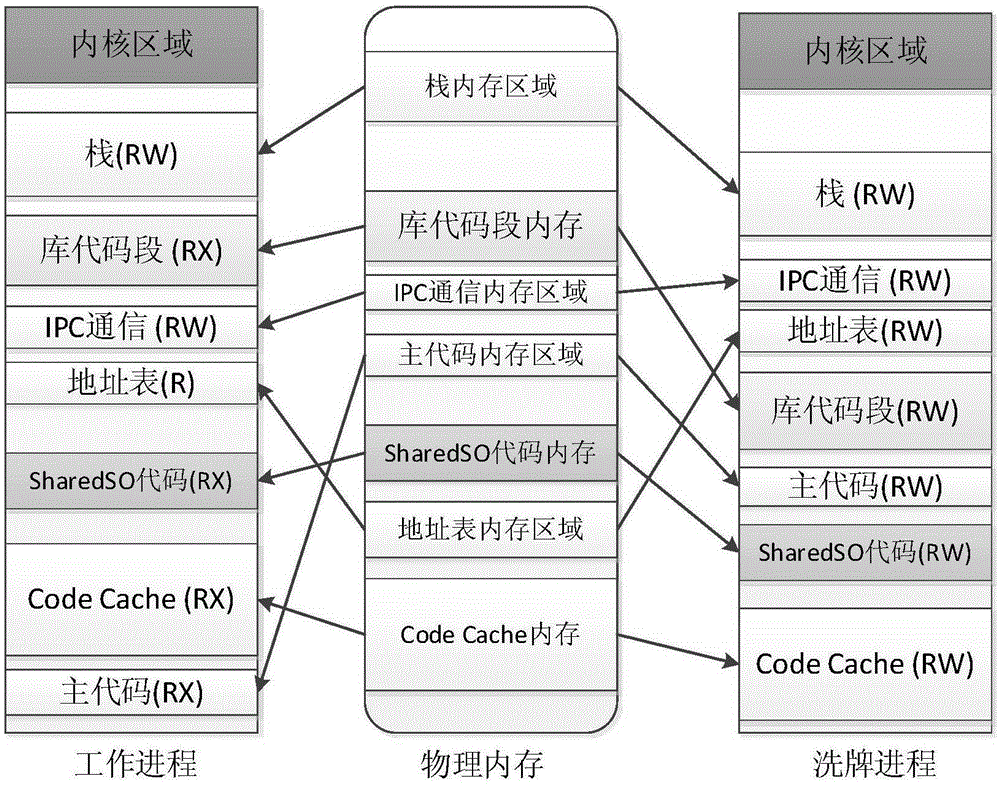
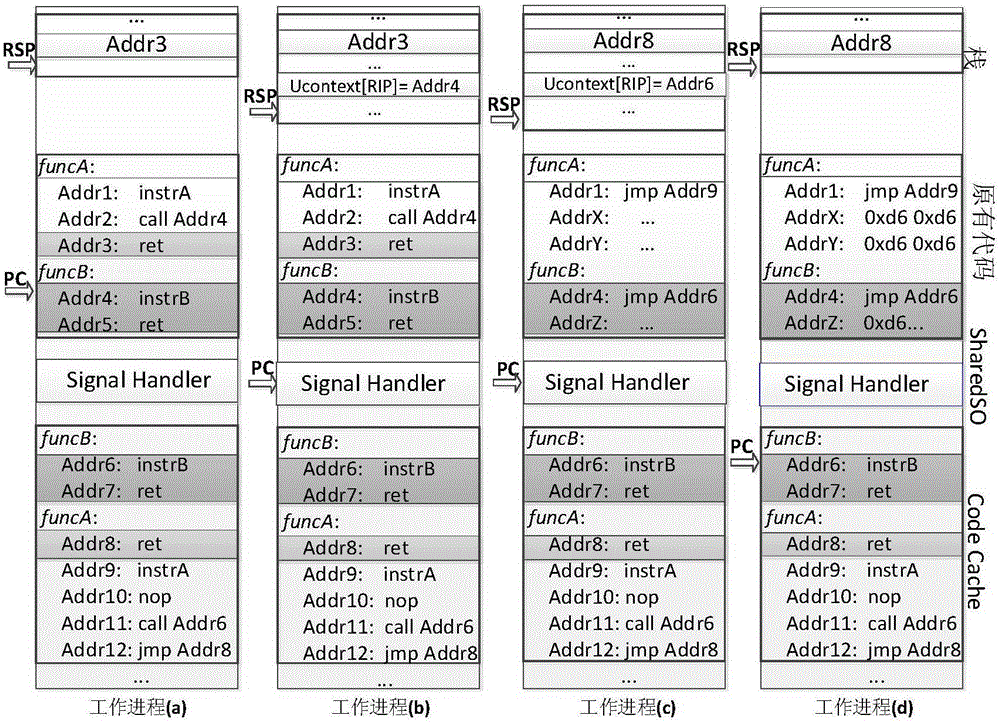
[0036] Due to the design of the current hardware CPU, it is impossible to make the code page executable but not readable. The existing three methods to prevent the code page from being readable all need to modify the kernel or use new hardware. Modifying the kernel is the most users' choice. Unacceptable, because adding code to the kernel also has security problems and the problem is more serious. The biggest limitation of using new hardware is whether all CPUs have the support of this hardware, so the existing ones prevent attackers from using memory leak vulnerabilities to read The method of code is very difficult to deploy, but there are many problems in the method of tolerating attackers to read the code: the diversification of execution flow also has very serious performance problems and will also destroy the DEP mechanism; the existing method of continuous randomization only supports kernel randomization And the need to rewrite the kernel also destroys the DEP mechanism. ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com