Patents
Literature
78 results about "Bit pairing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
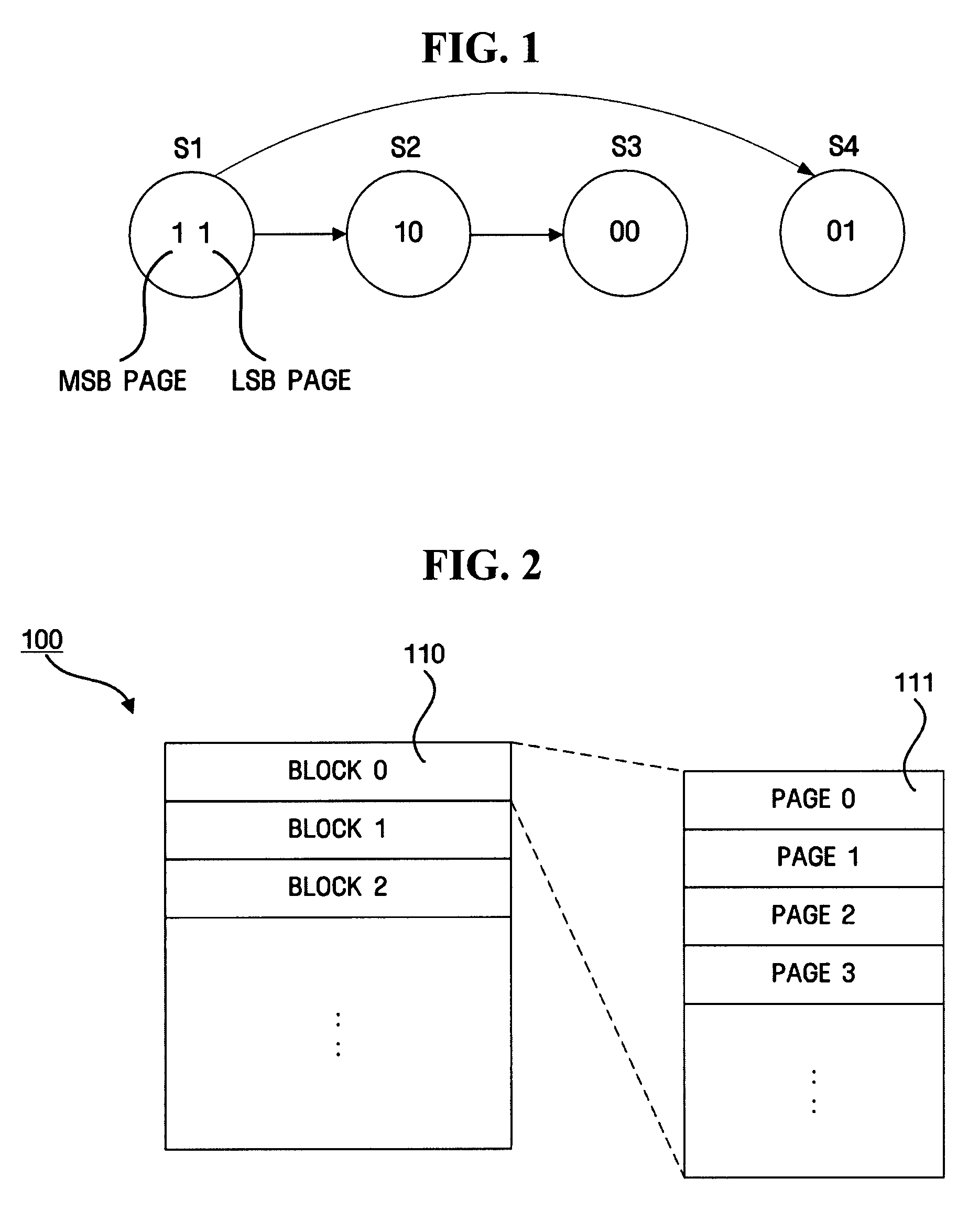
In telecommunication, bit pairing is the practice of establishing, within a code set, a number of subsets that have an identical bit representation except for the state of a specified bit. Note: An example of bit pairing occurs in the International Alphabet No. 5 and the American Standard Code for Information Interchange (ASCII), where the upper case letters are related to their respective lower case letters by the state of bit six.
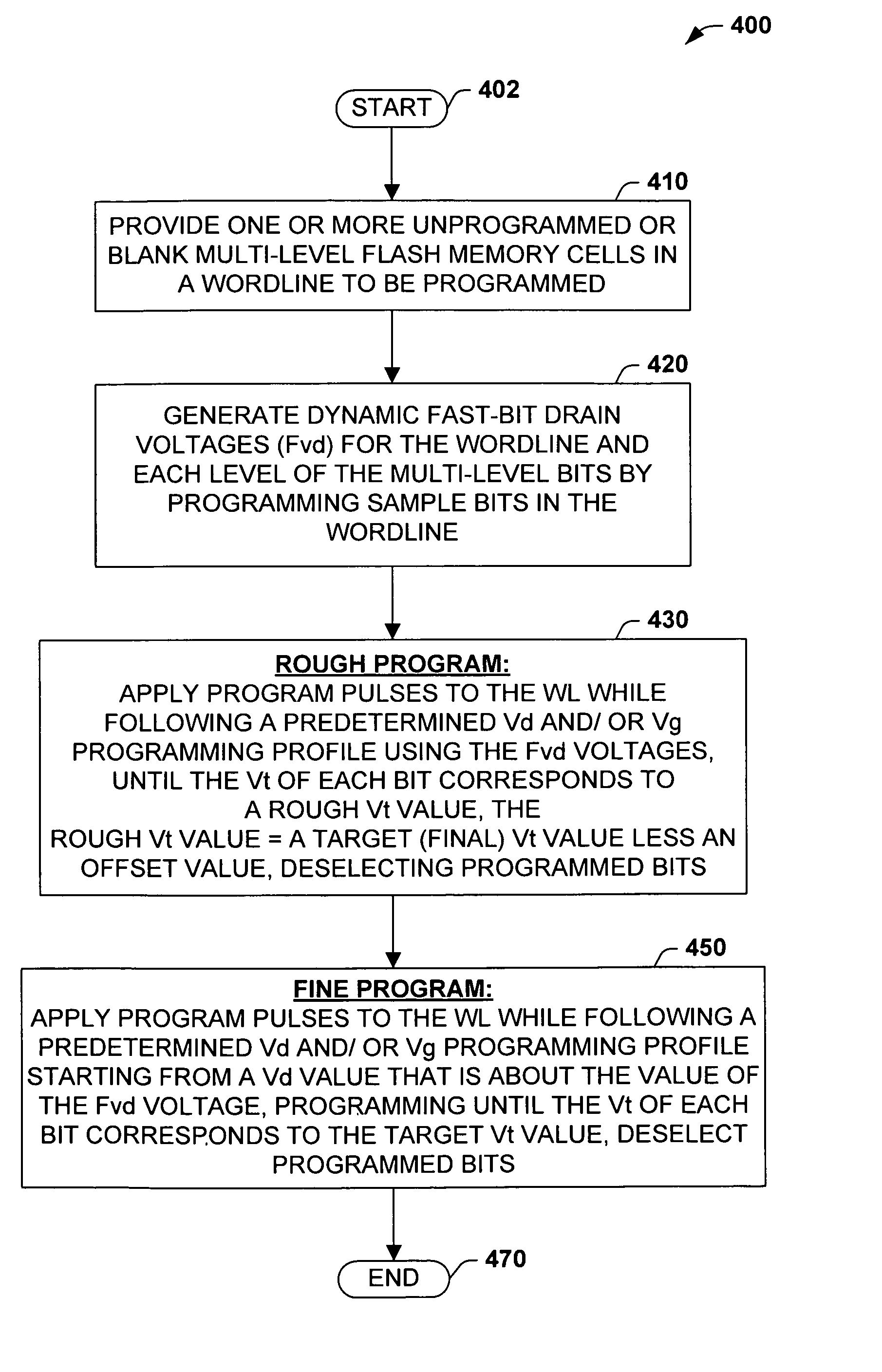
Multi-level ONO flash program algorithm for threshold width control
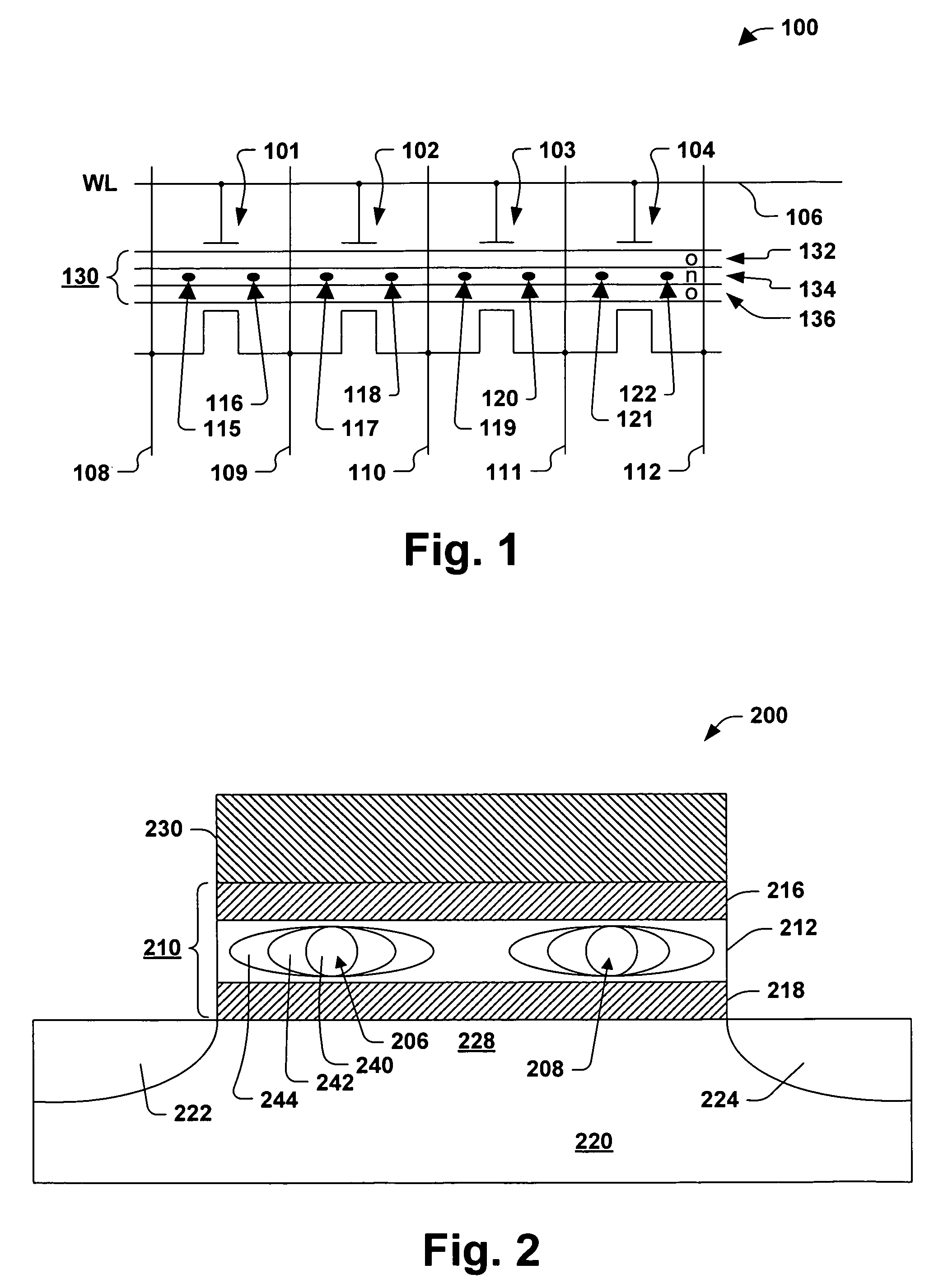
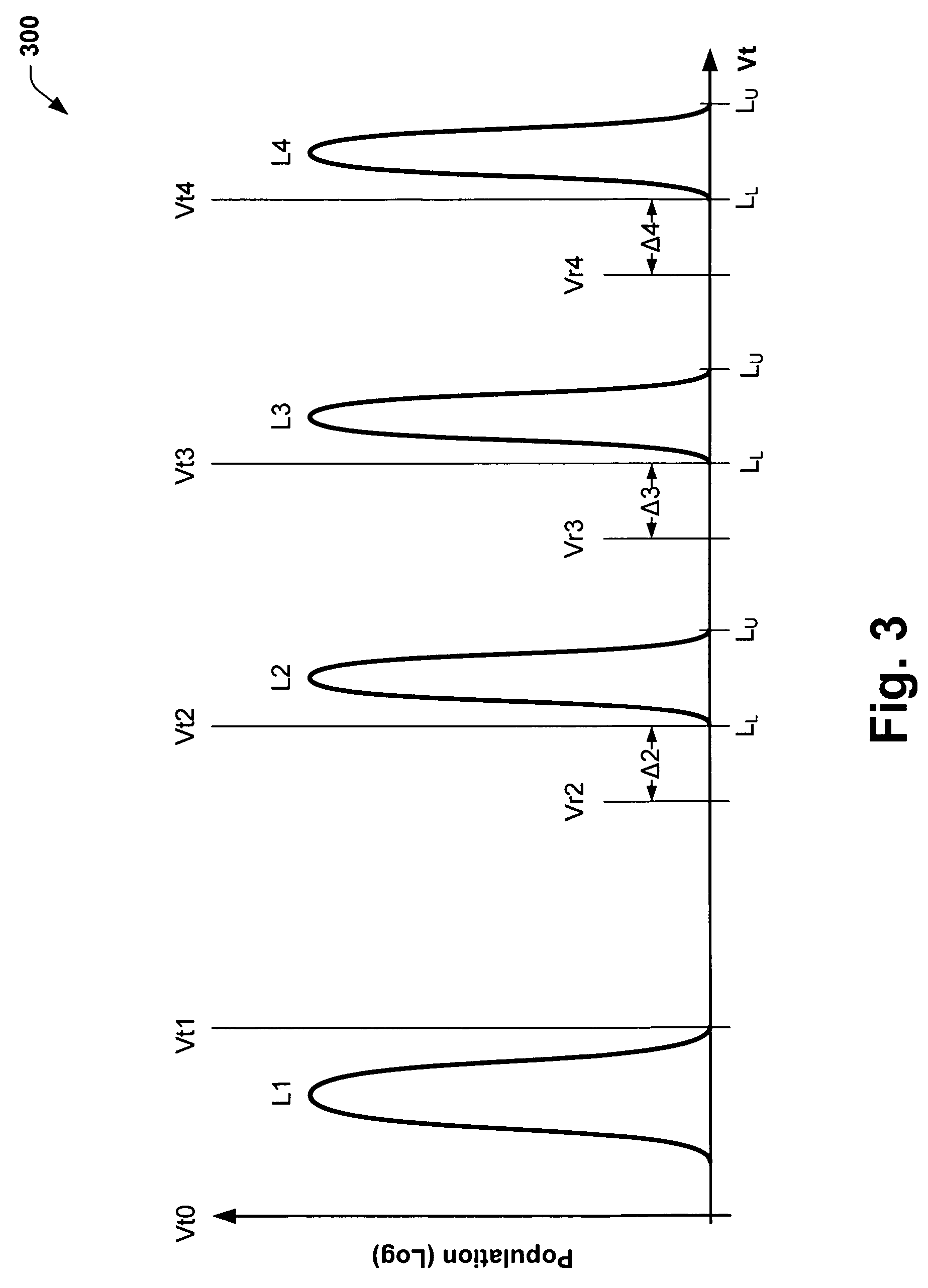
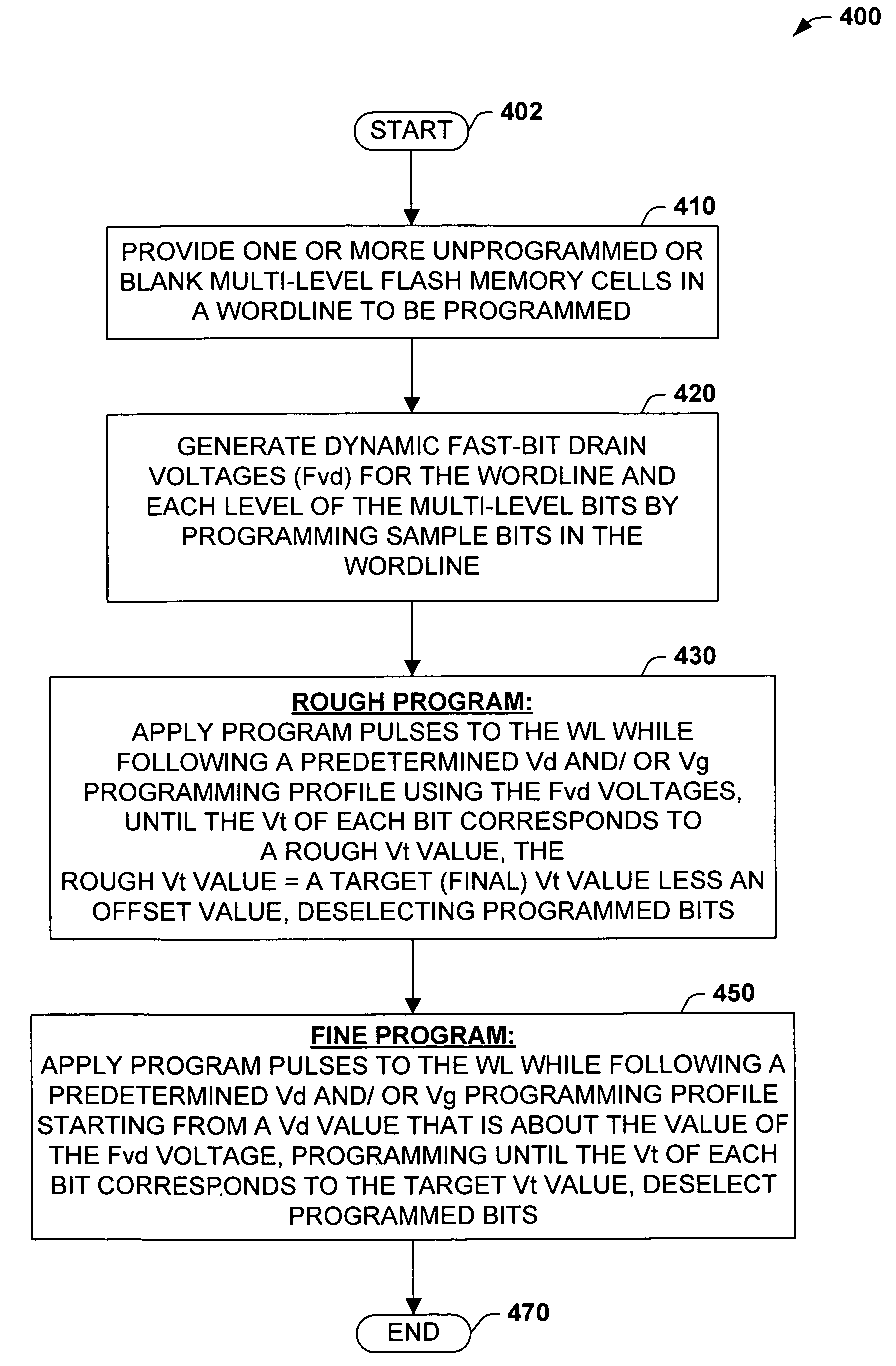
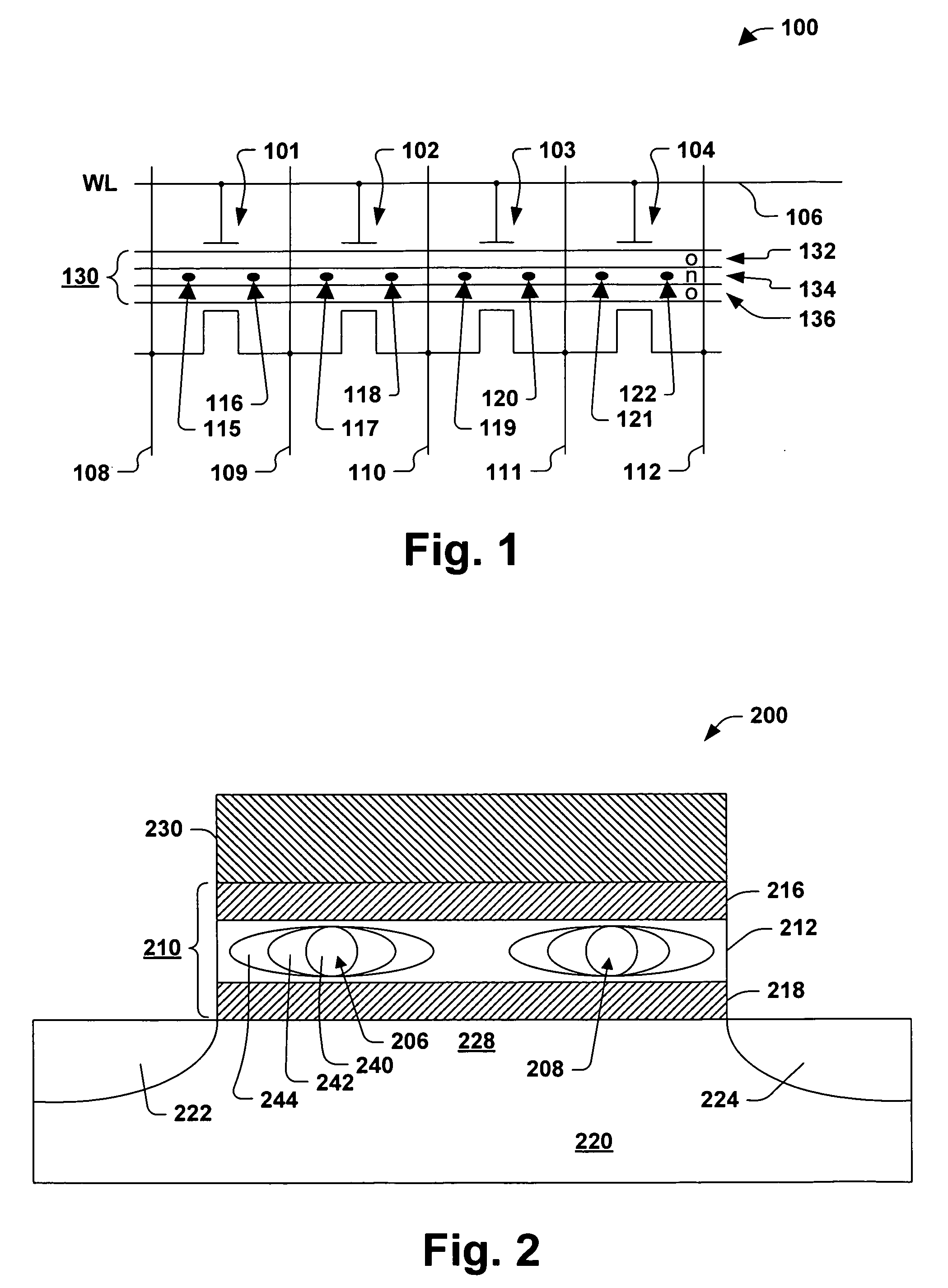
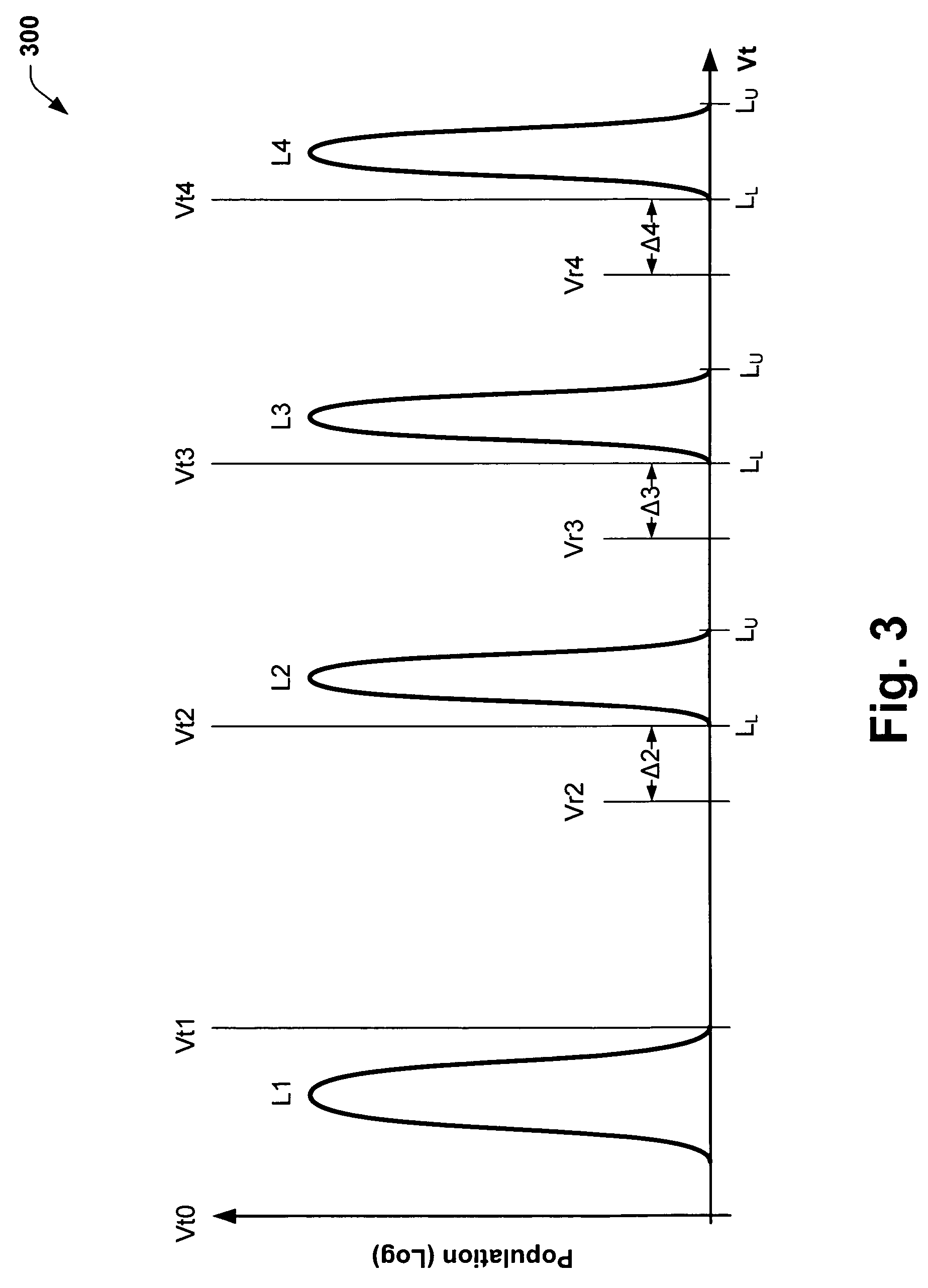
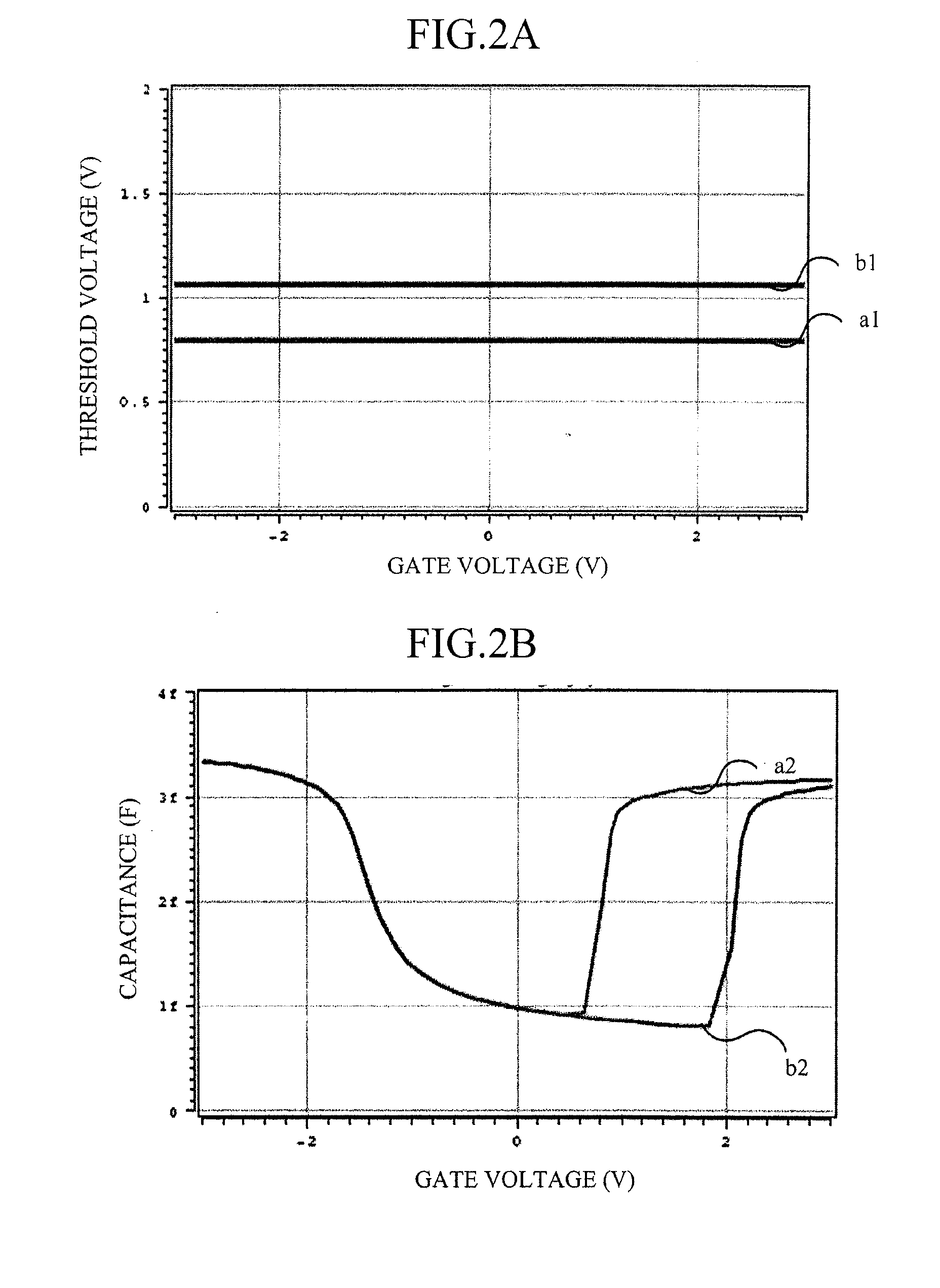
Methods of programming a wordline of multi-level flash memory cells (MLB) having three or more data levels per bit corresponding to three or more threshold voltages are provided. The present invention employs an interactive program algorithm that programs the bits of the wordline of memory cells in two programming phases, comprising a rough programming phase and a fine programming phase to achieve highly compact Vt distributions. In one example, cell bit-pairs that are to be programmed to the same program pattern are selected along a wordline. Groups of sample bits are chosen for each wordline to represent each possible program level. The sample bits are then programmed to determine a corresponding drain voltage at which each sample group is first programmed. This fast-bit drain voltage (Fvd) for each program level essentially provides a wordline specific program characterization of the Vt required for the remaining bits of that wordline. In the rough programming phase, the bits of core cells are then programmed from a starting point that is relative to (e.g., slightly less than or equal to) the fast-bit Vd and according to a predetermined Vd and Vg profile of programming pulses. The bits of the complementary bit-pairs are alternately programmed in this way until the Vt of the bits attains a rough Vt level, which is offset lower than the final target threshold voltage level. Then in the second fine programming phase, the bits of the MLB cells of the wordline are further programmed with another predetermined Vd and Vg profile of programming pulses until the final target threshold voltage is achieved. The Vd and Vg profiles of programming pulses may further be tailored to accommodate the various bit-pair program pattern combinations possible. In this way, the bits of each wordline are fine-tune programmed to a data state to achieve a more precise Vt distribution, while compensating for the effects of complementary bit disturb.
Owner:LONGITUDE FLASH MEMORY SOLUTIONS LTD
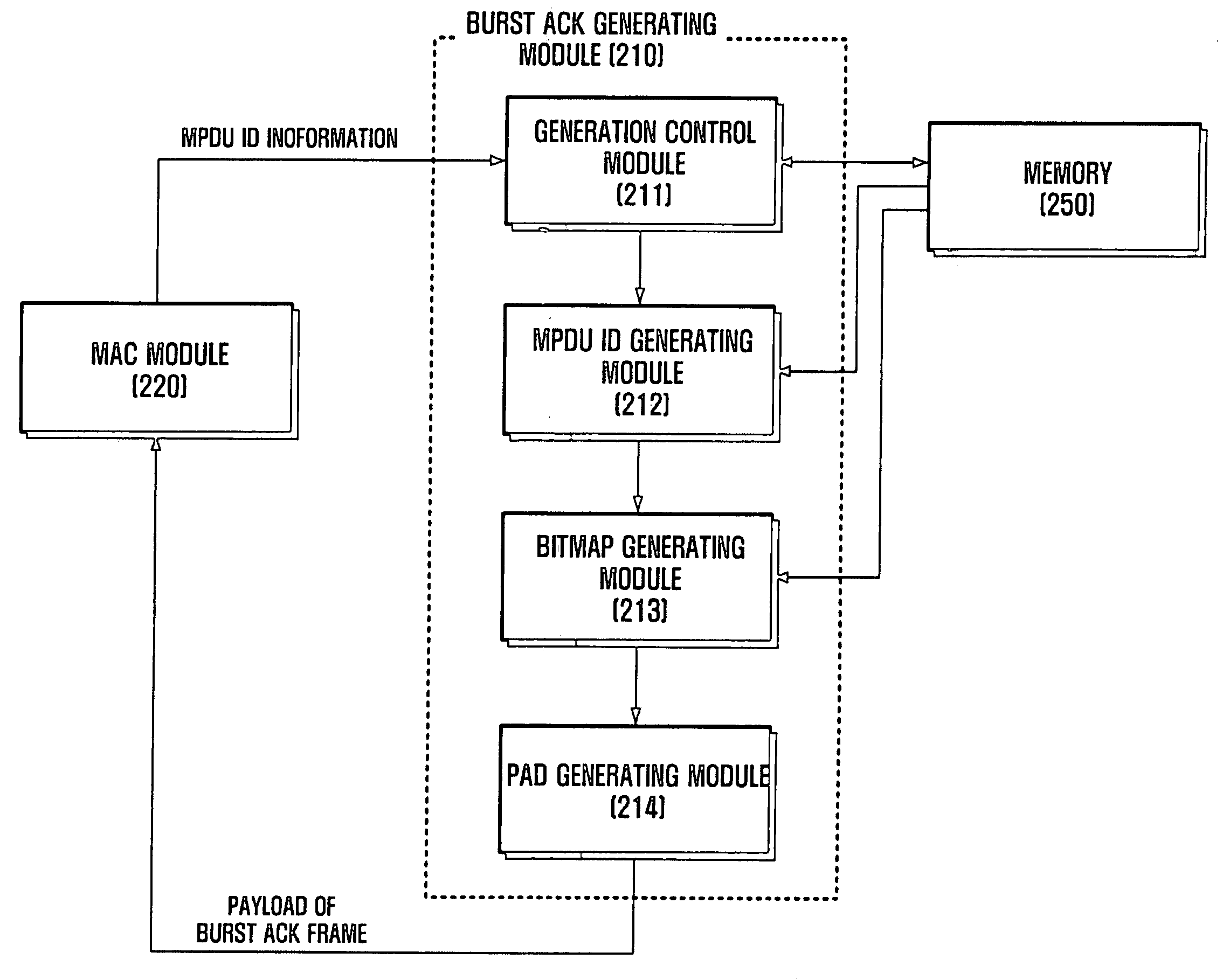
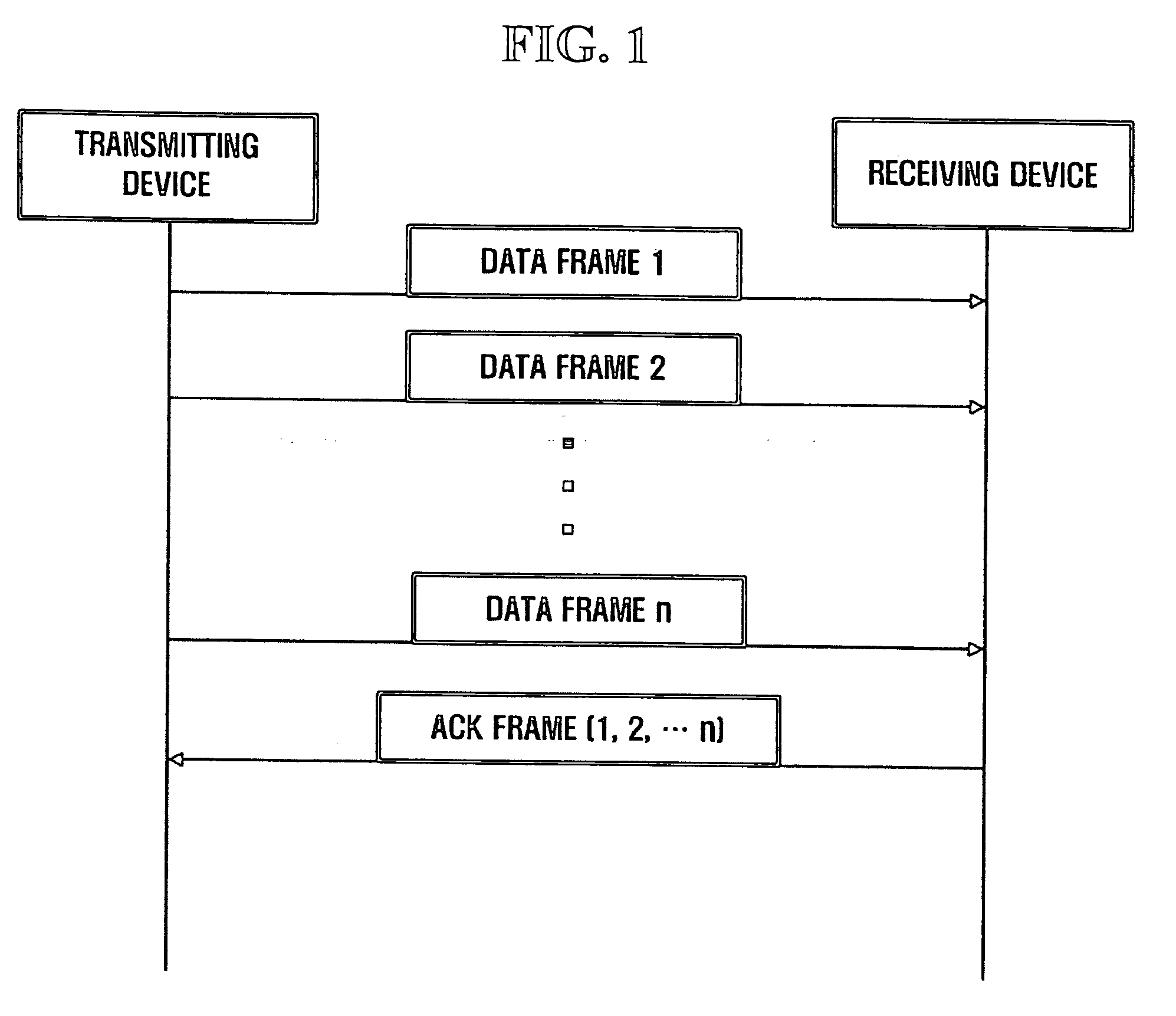
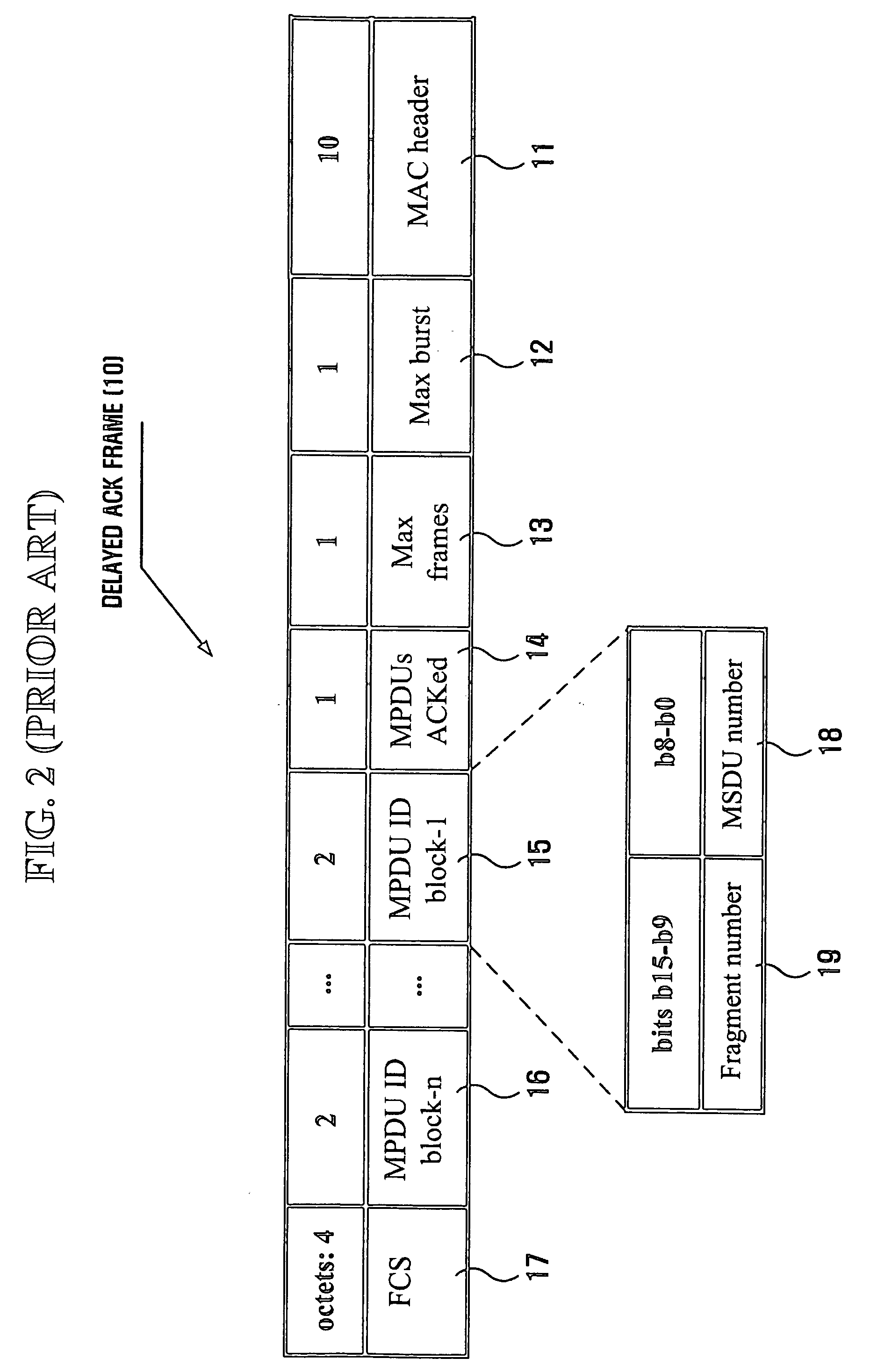
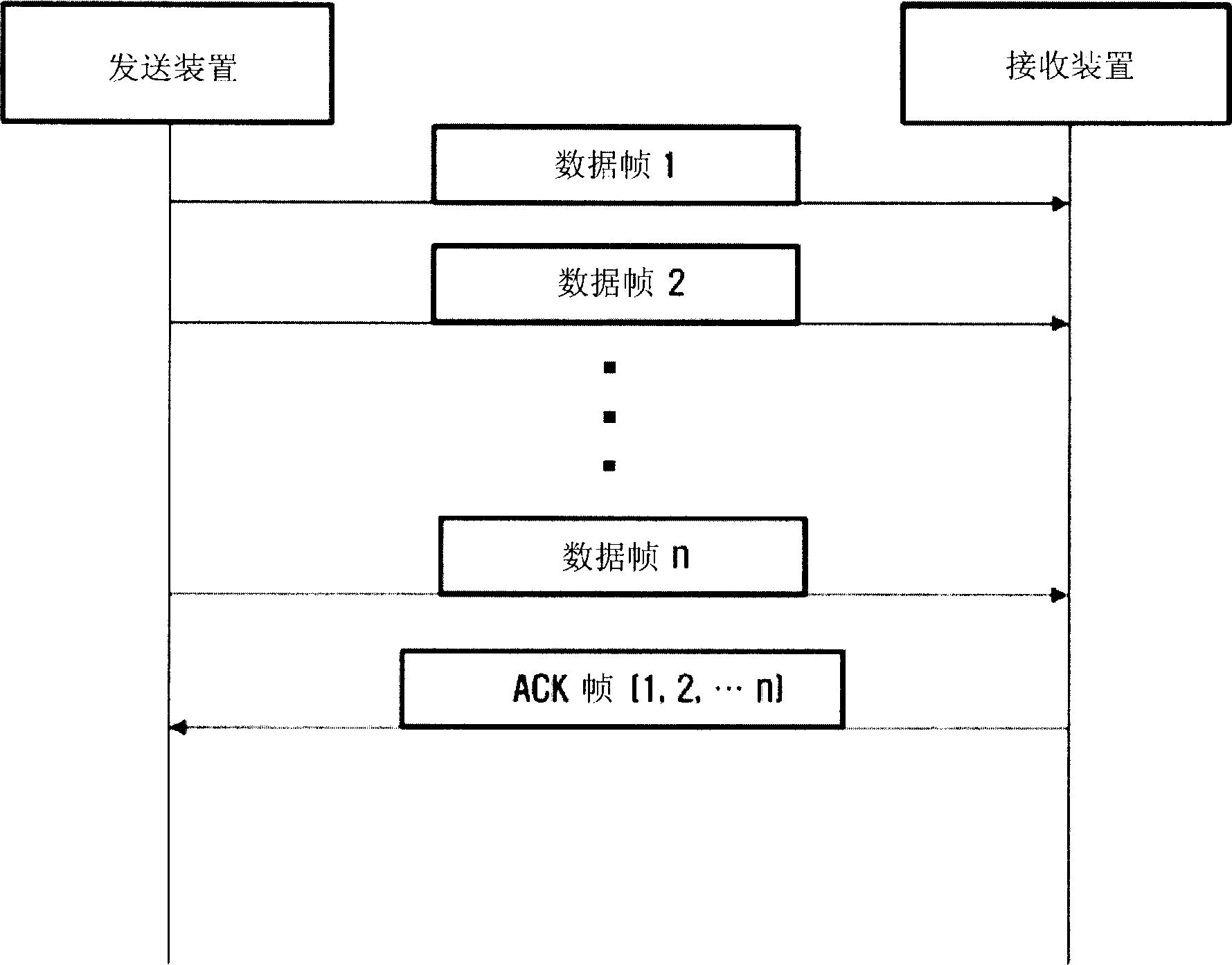
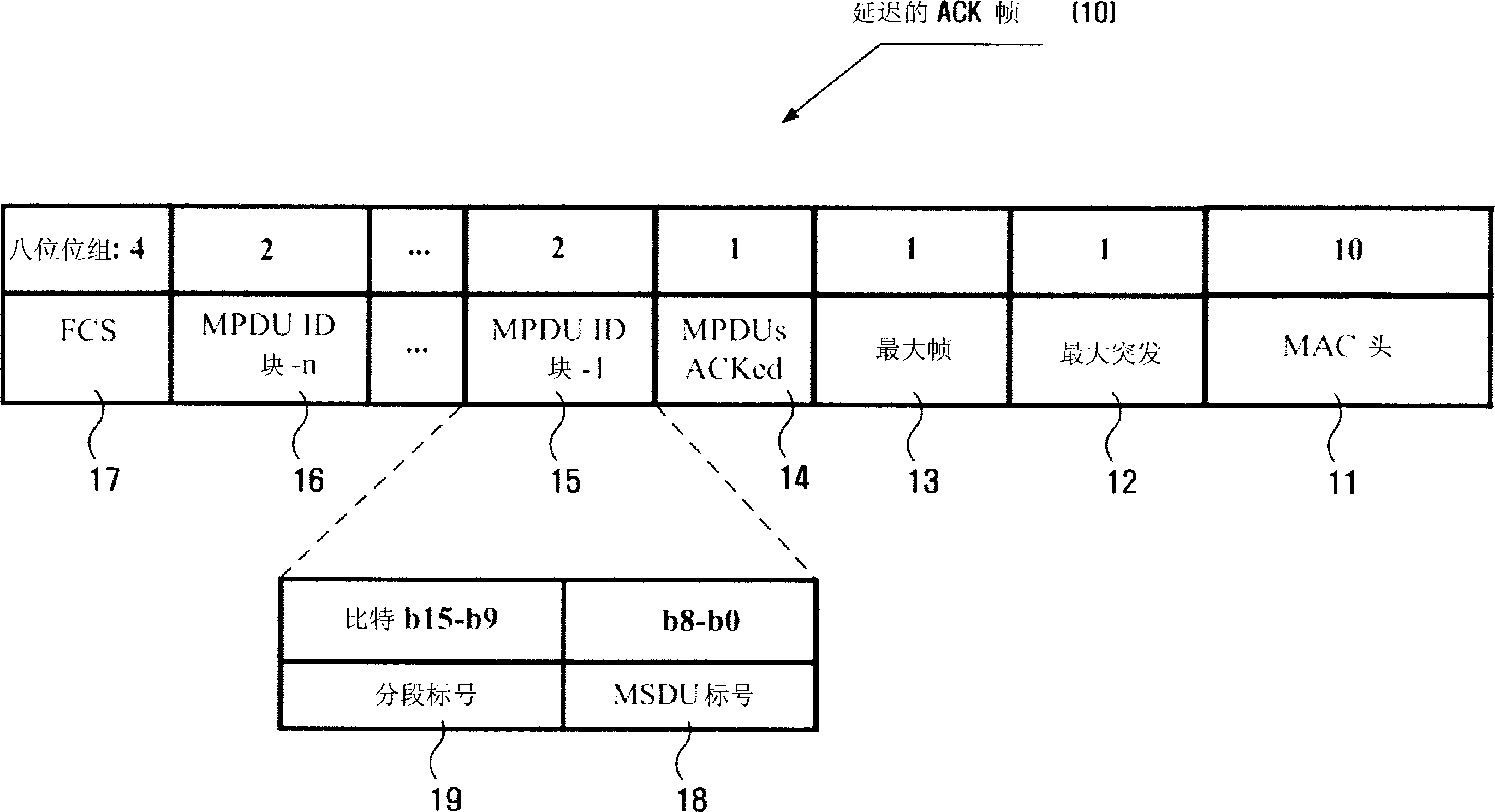
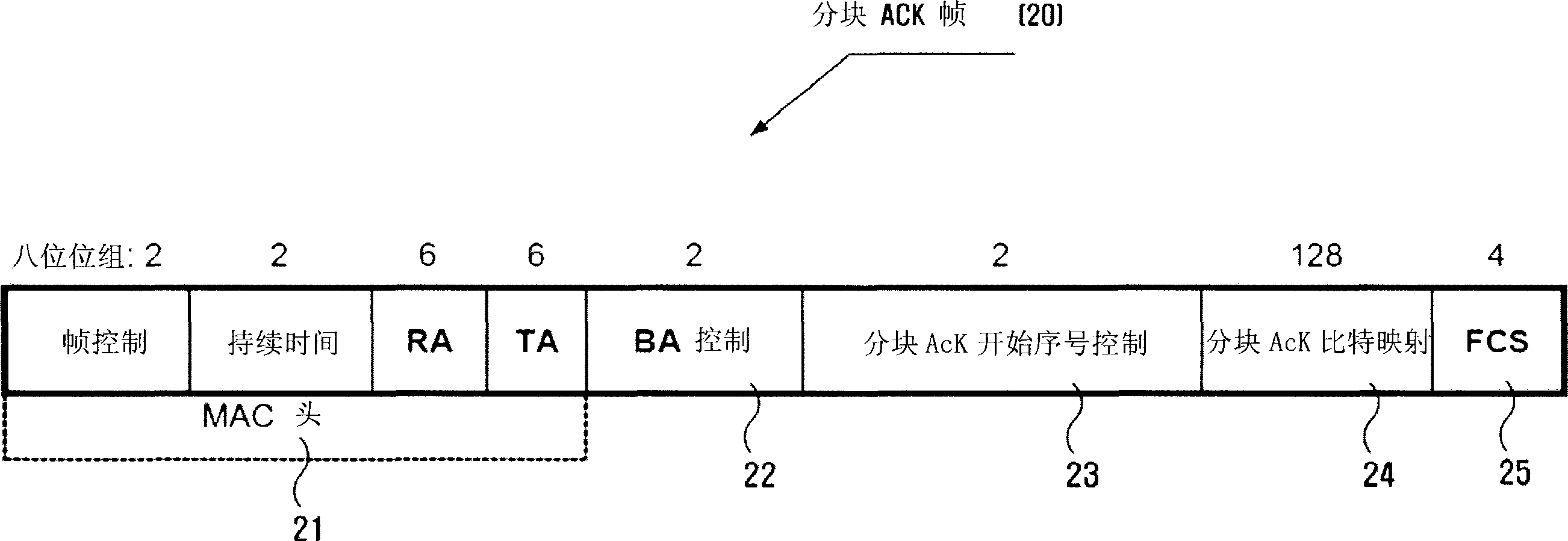
Method and apparatus for transmitting ACK frame
InactiveUS20060034317A1Reduce overheadError preventionData switching by path configurationComputer hardwareBit pairing
An efficient burst ACK method and apparatus in wireless communication environment are provided. An ACK frame transmission method whereby plural frames are received from a transmitting device and receipt of the frames is acknowledged with a single ACK frame includes receiving frames from the transmitting device and storing identification information of the received frames; generating a first field by recording a set of bit pairs to each of the received frames, with the use of the stored identification information; generating an ACK frame including the generated first field; and transmitting the generated ACK frame to the transmitting device, wherein a bit pair includes: a first bit to acknowledge whether any concerned frame is properly received; and a second bit to distinguish whether the first bit is to acknowledge receipt of the concerned frame from whether it is to acknowledge receipt of all the fragments following the concerned frame.
Owner:DEXCOM +1
Quad bit using hot-hole erase for CBD control
ActiveUS7113431B1Easy to controlImprove distribution of cellRead-only memoriesDigital storageVoltageBit pairing
The present invention pertains to a technique for erasing bits in a dual bit memory in a manner that maintains complementary bit disturb control of bit-pairs of memory cells wherein each bit of the dual bit memory cell can be programmed to multiple levels. One exemplary method comprises providing a word of memory cells after an initial erasure and programming of the bits of the word to one or more of the higher program levels. A disturb level is determined for each of the bit-pairs of the word. A combined disturb level is then computed that is representative of the individual disturb levels. A pattern of drain voltages is then applied to the word for a number of program passes until a target pattern is stored in the word of memory cells based on the combined disturb level and the unprogrammed bit of the bit-pairs is erased to a single program level. In this manner the present invention compensates for the disturbance level that exists between the complementary bit-pairs of the word, improves the Vt distribution at the program level of the erased state and thereby improves the accuracy of subsequent higher level programming operations and mitigates false or erroneous reads of the states of such program levels.
Owner:INFINEON TECH LLC
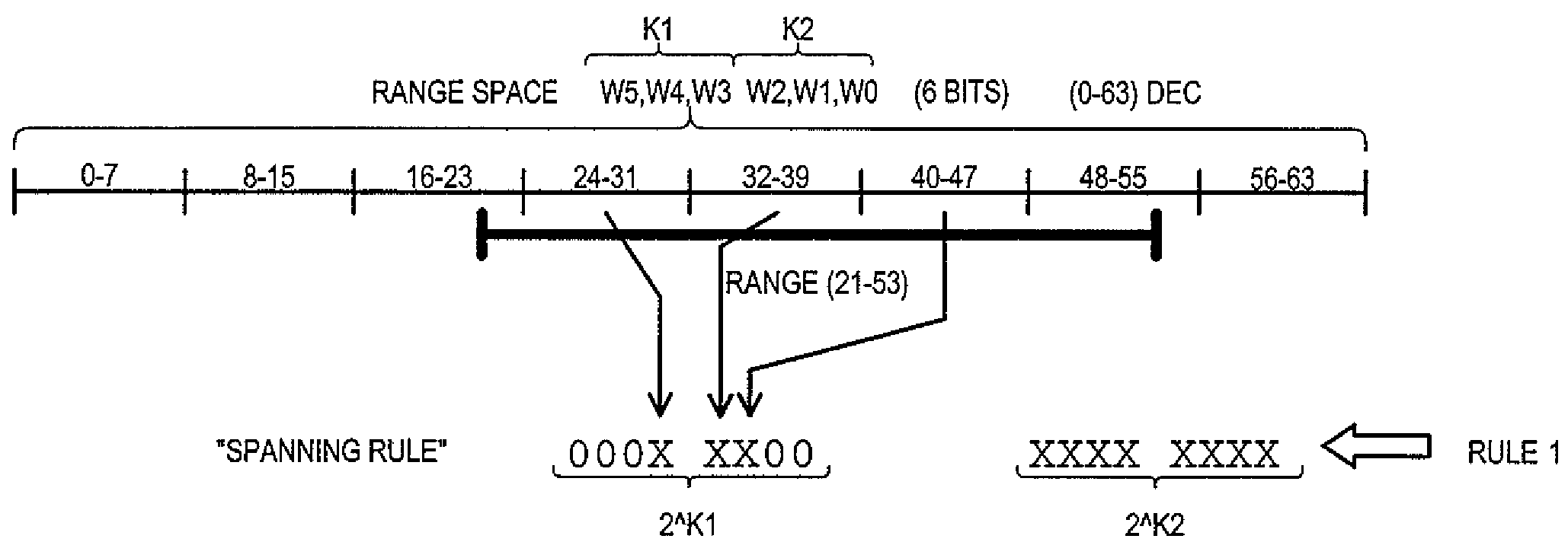
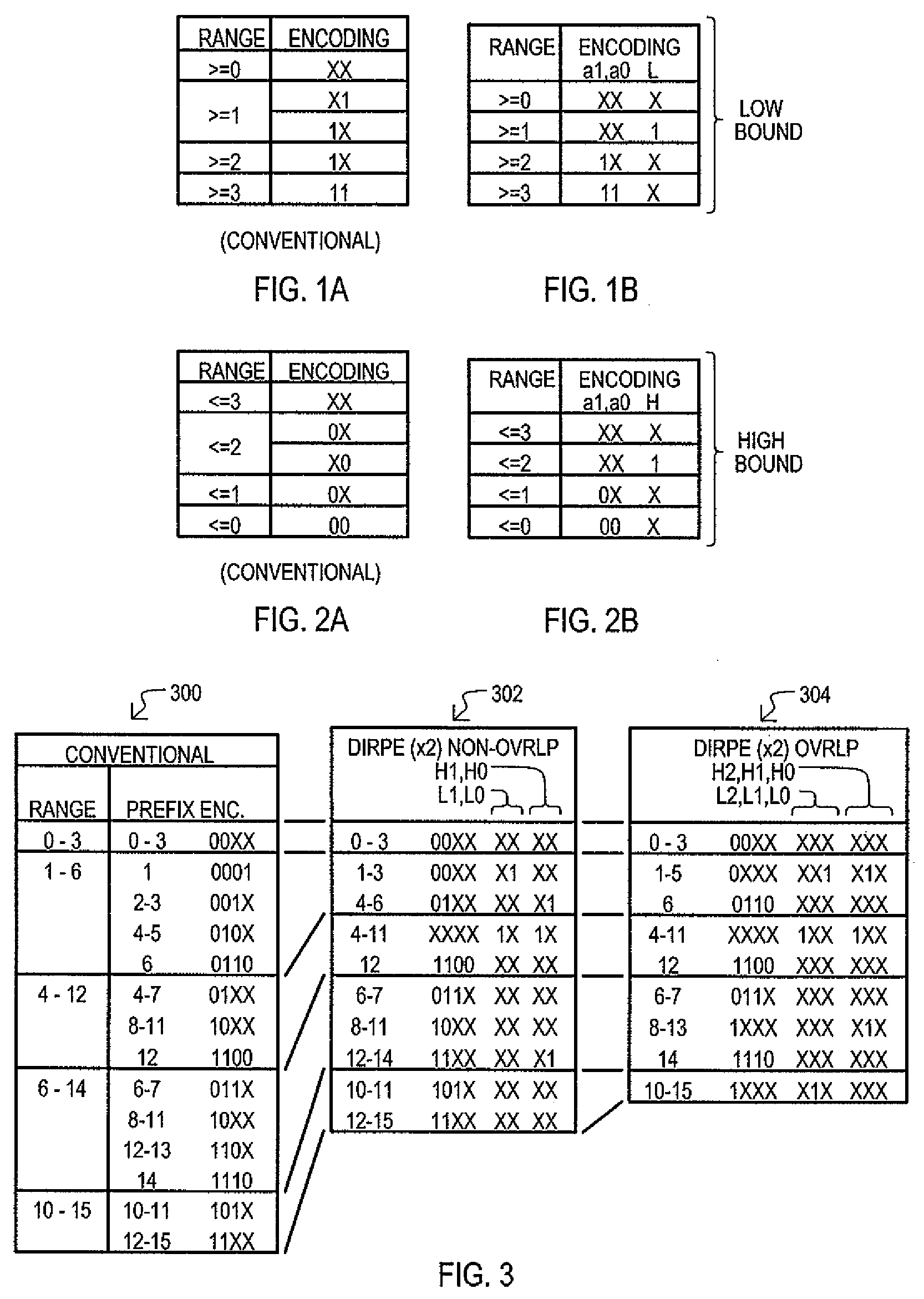
Range code compression method and apparatus for ternary content addressable memory (CAM) devices
InactiveUS7711893B1Reduce in quantityIncrease in sizeDigital storageMemory systemsPartial representationOne-hot
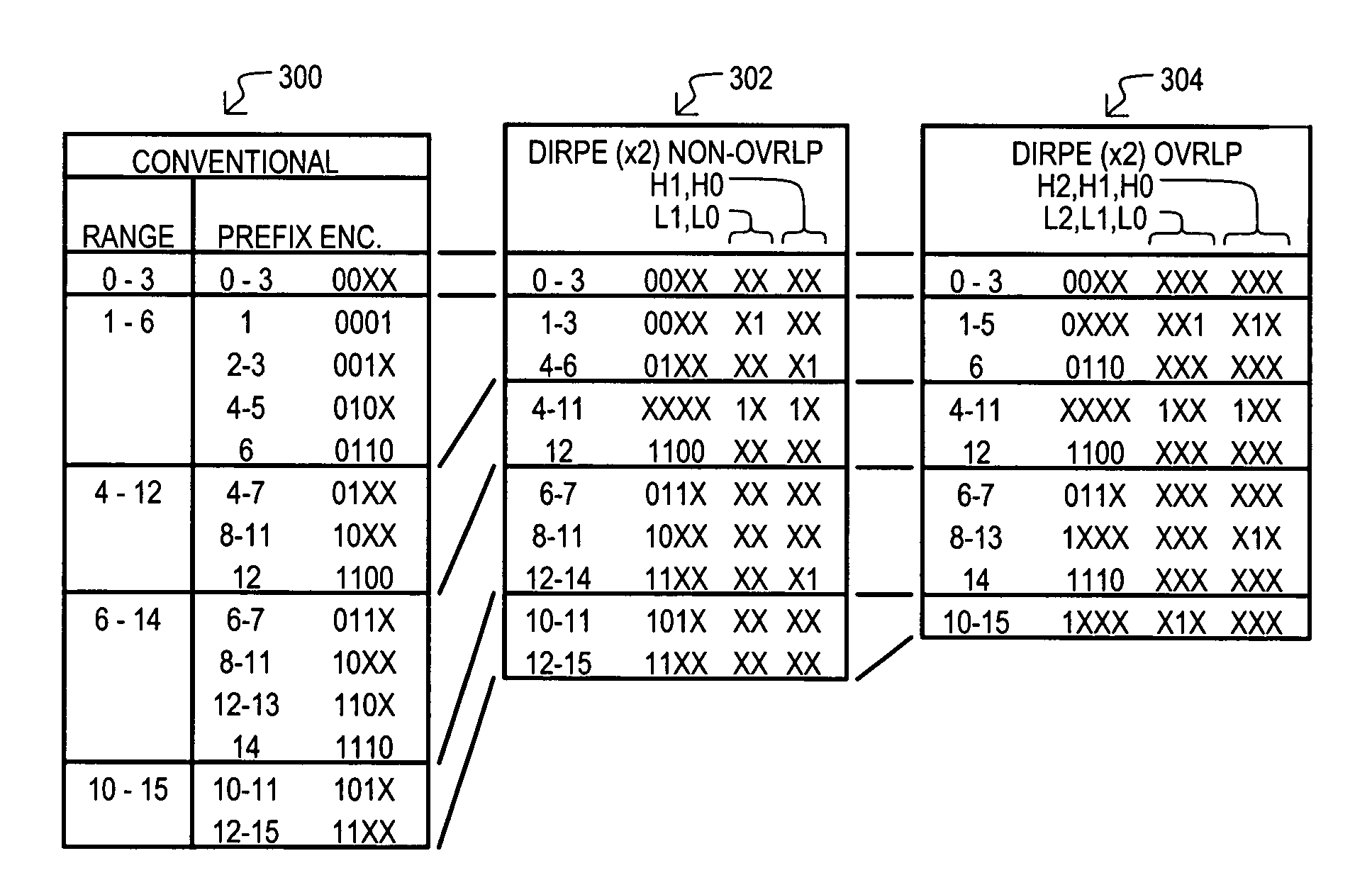
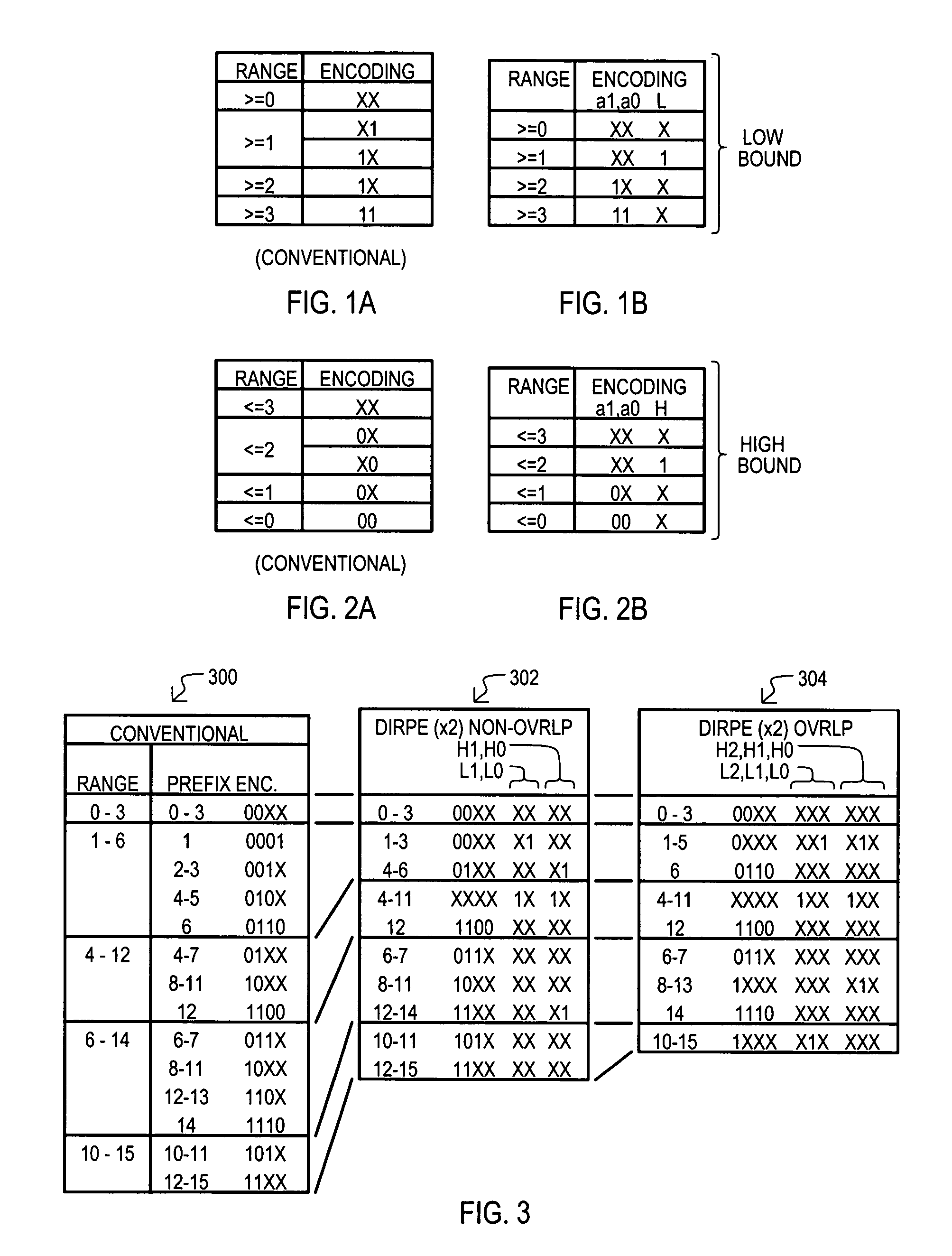
A content addressable memory (CAM) device, method, and method of generating entries for range matching are disclosed. A CAM device (800) according to one embodiment can include a pre-encoder (806) that encodes range bit values W into additional bits E. Additional bits E can indicate compression of range rules according to particular bit pairs. A CAM array (802) can include entries that store compressed range code values (RANGE) with corresponding additional bit values (ENC). Alternate embodiments can include pre-encoders that encode portions of range values (K1 to Ki) in a “one-hot” fashion. Corresponding CAM entries can include encoded value having sections that each represent increasingly finer divisions of a range space.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
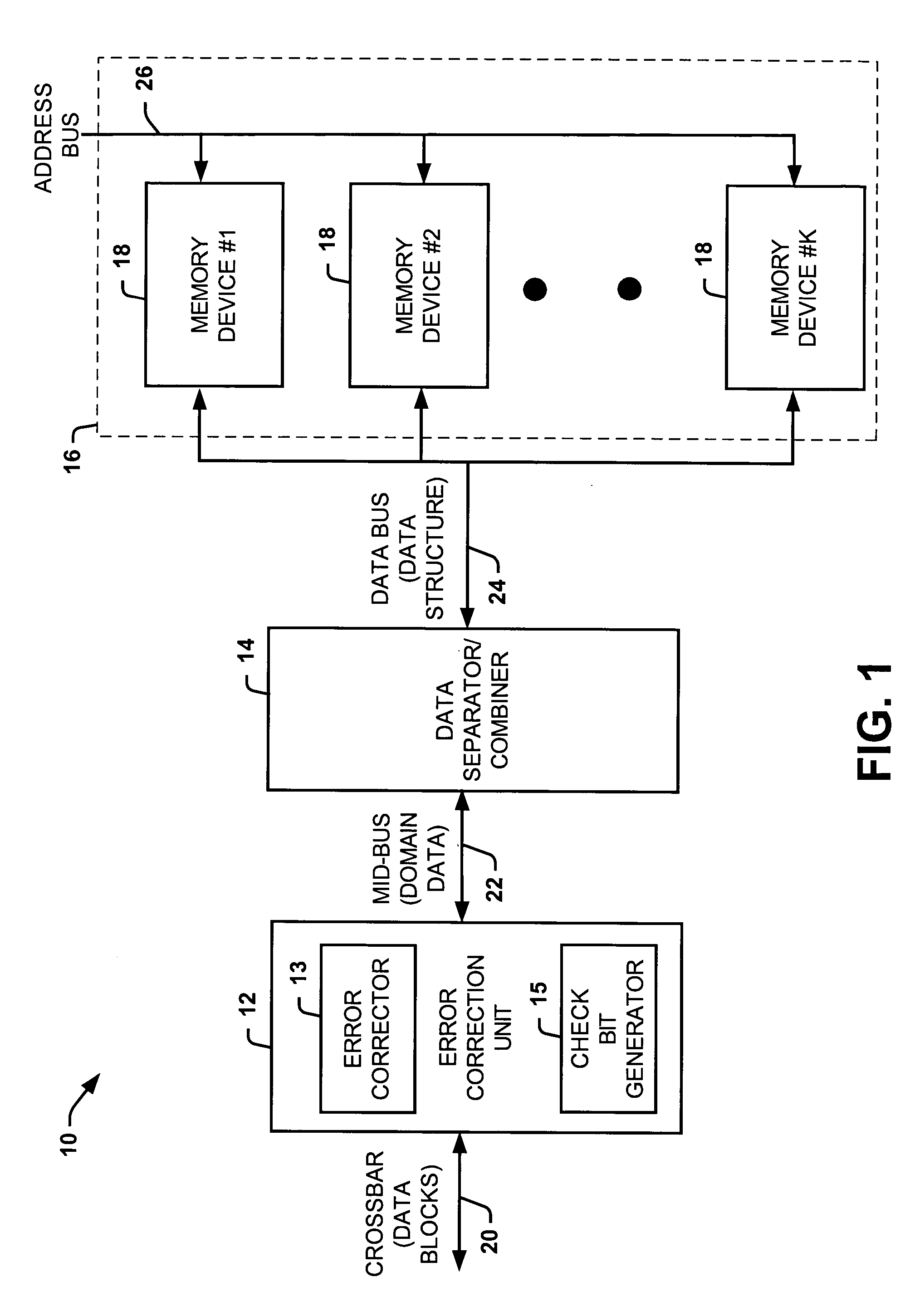
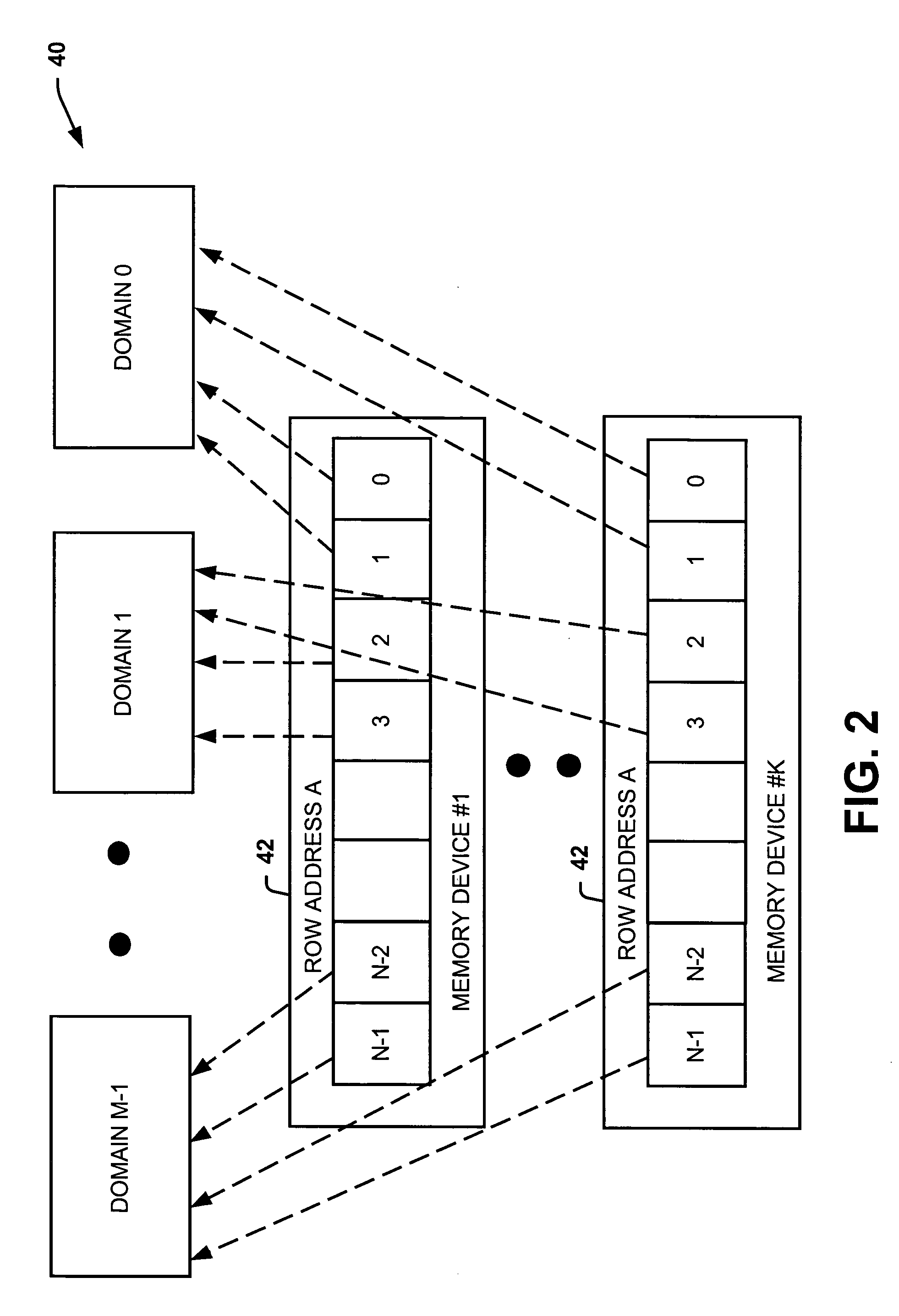
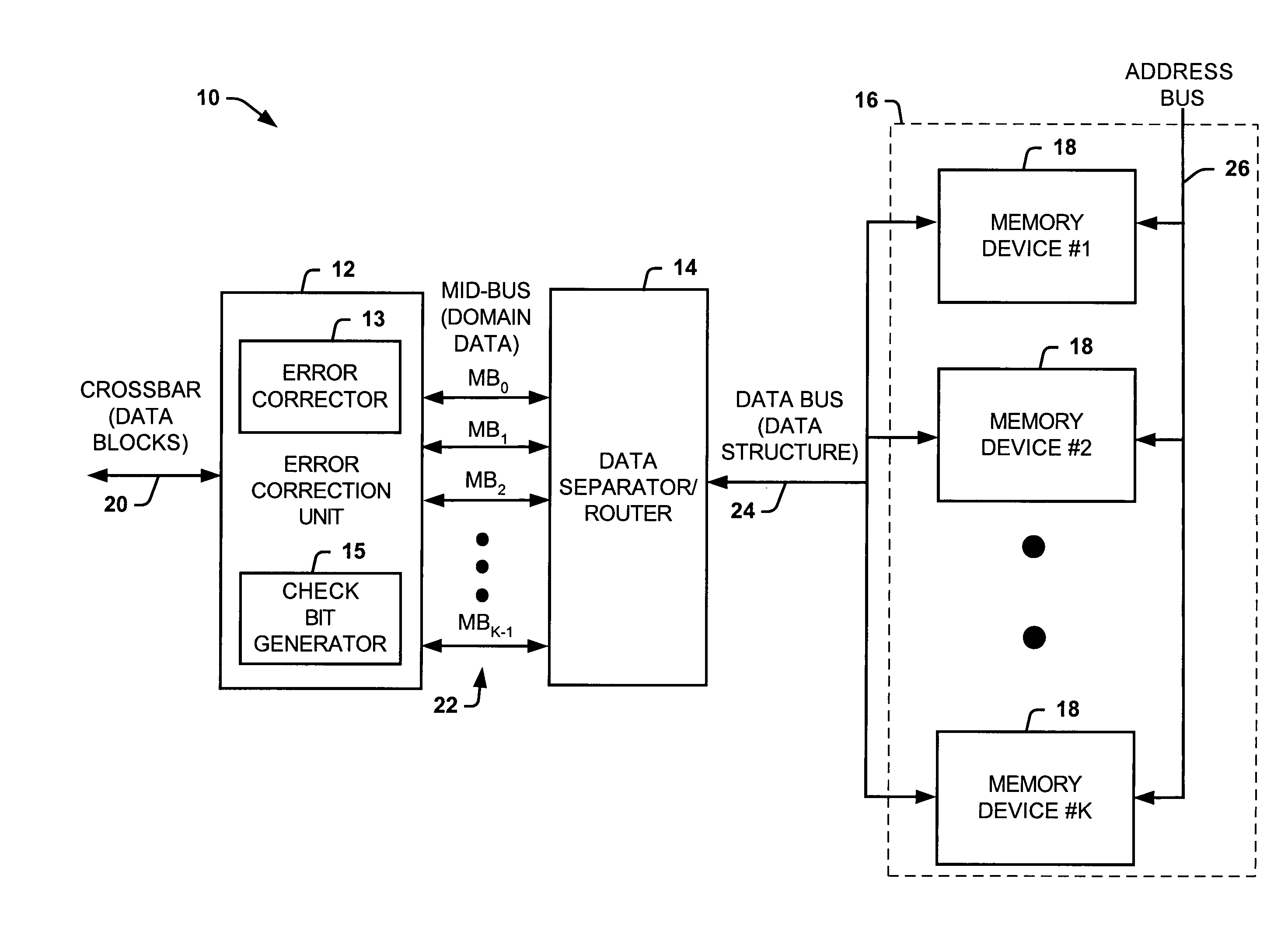
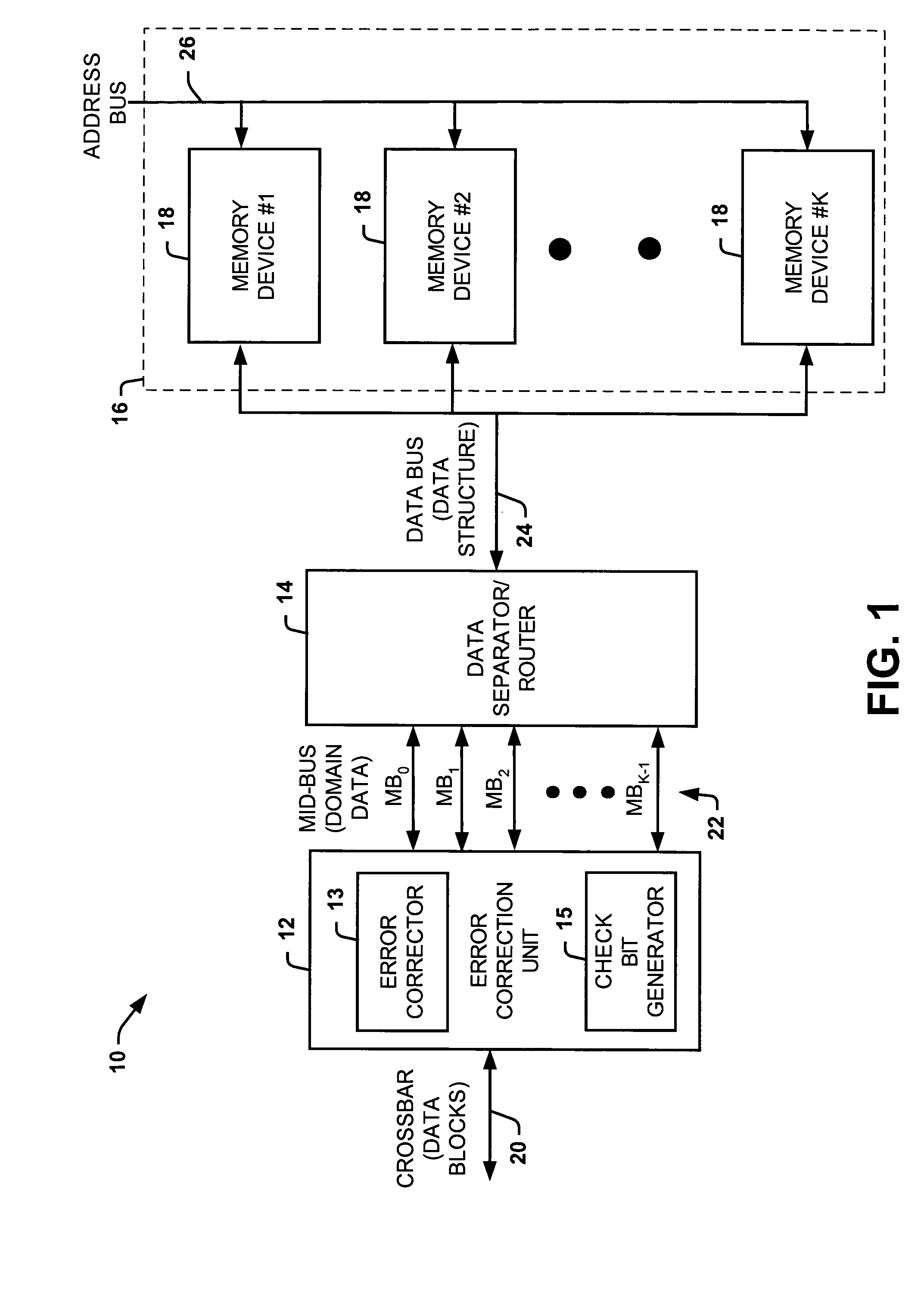
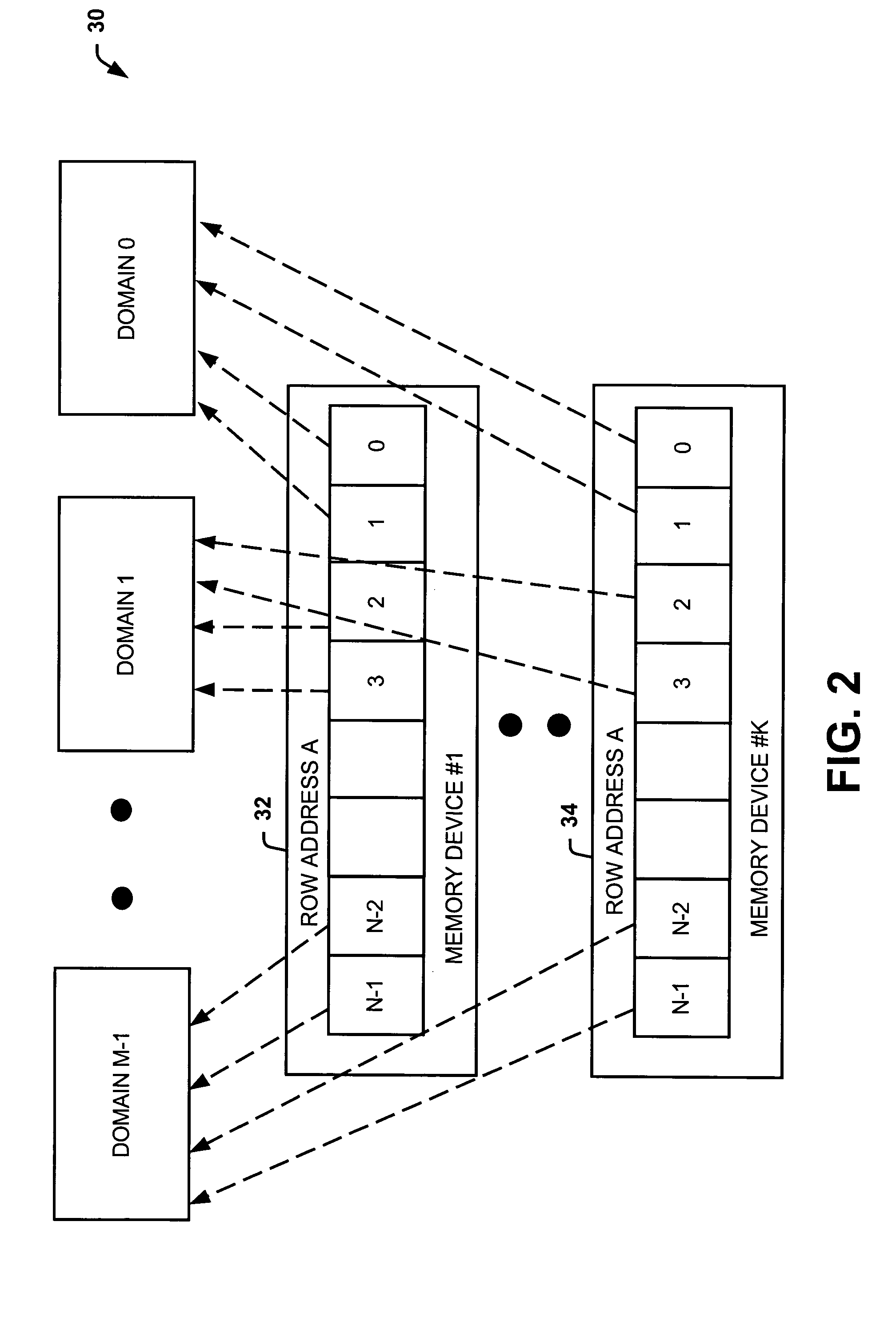
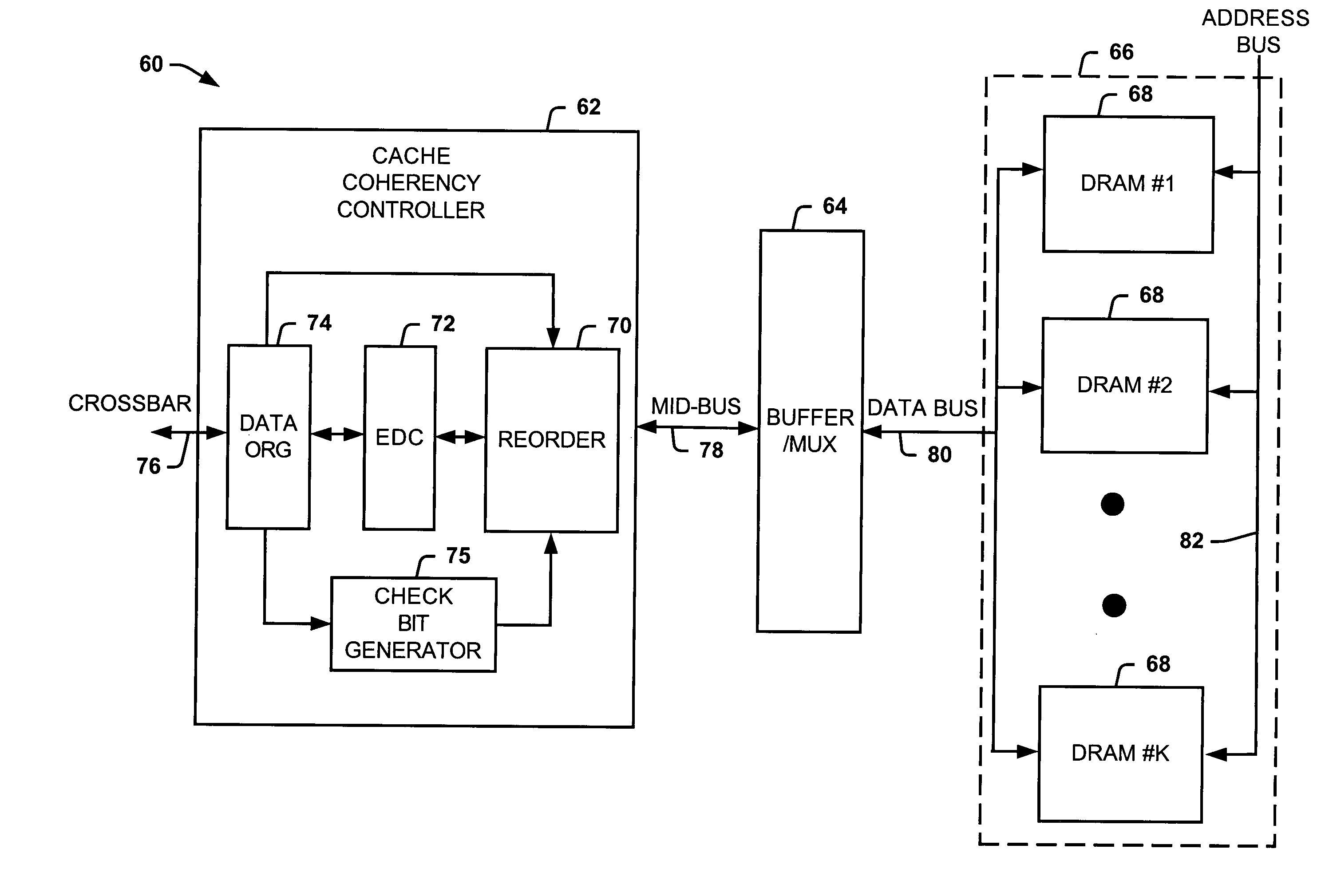
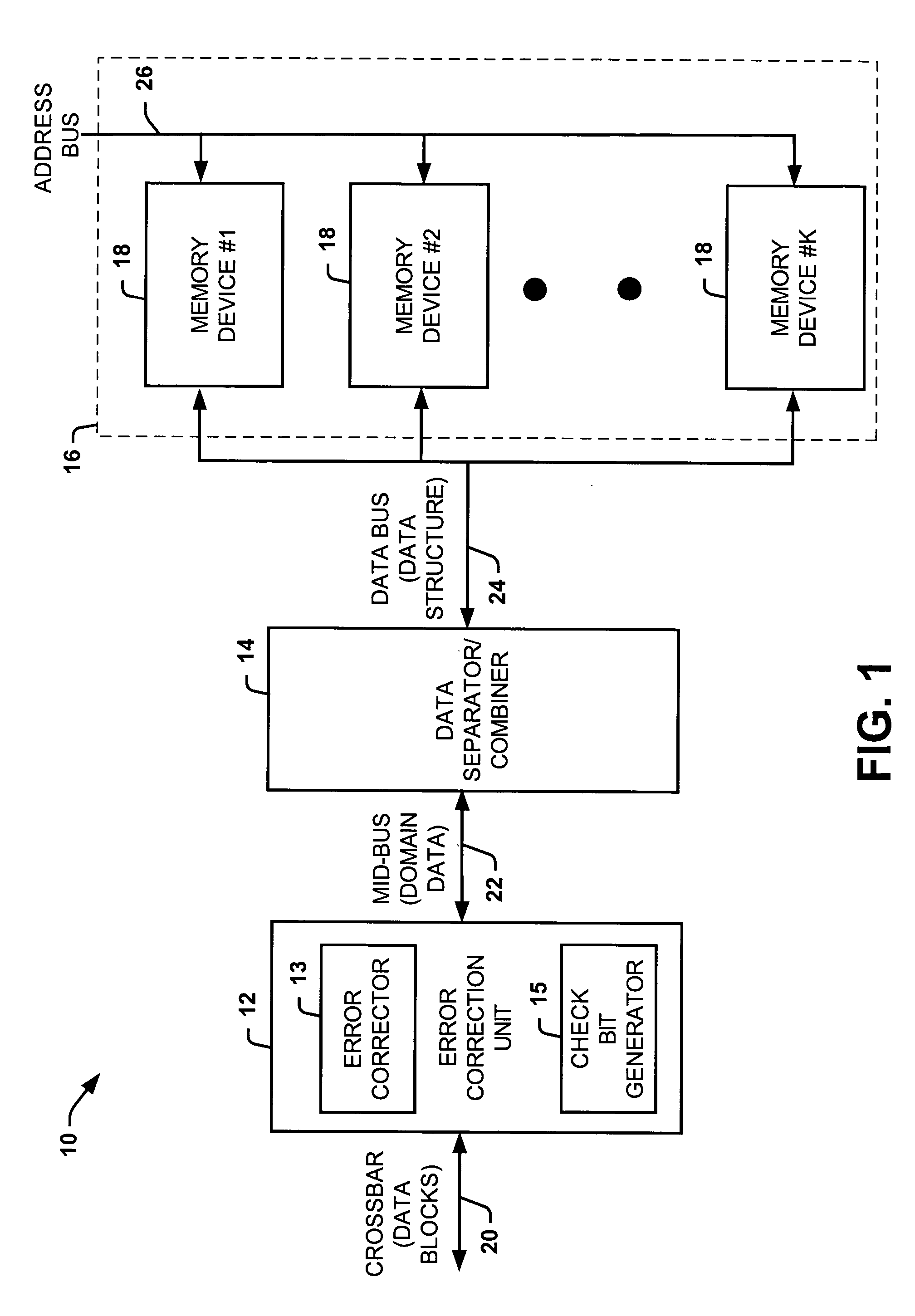
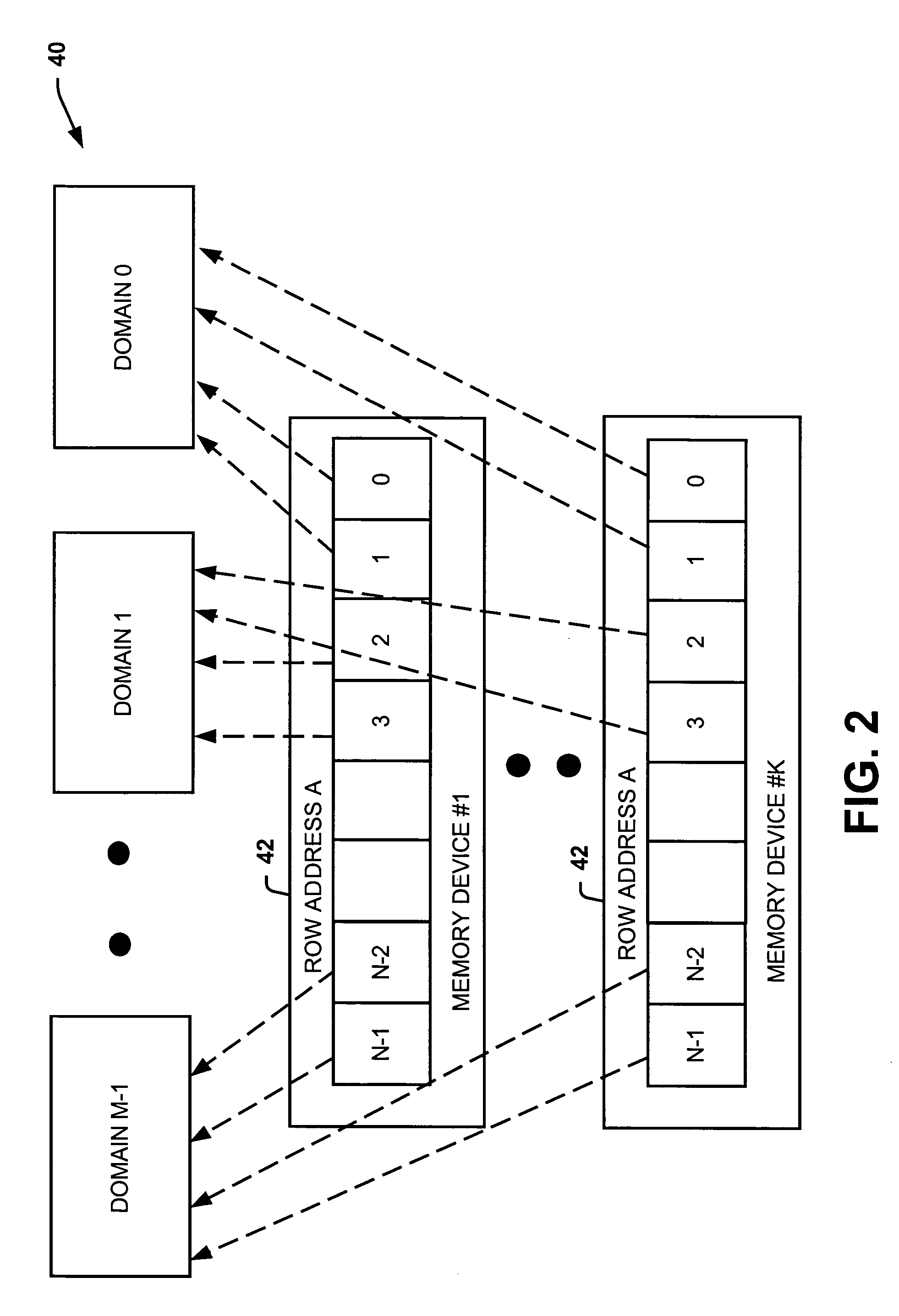
Systems and methods of partitioning data to facilitate error correction
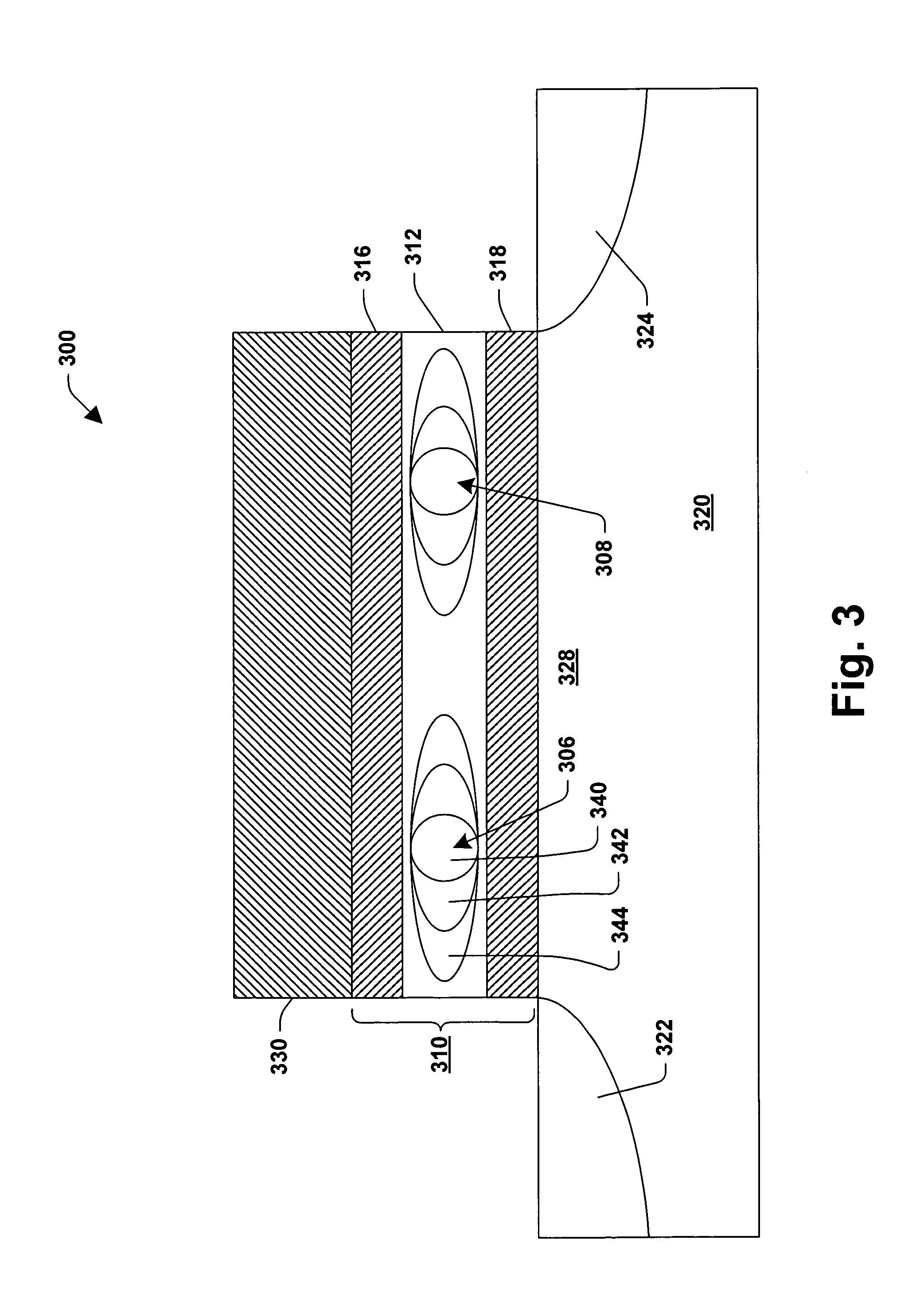
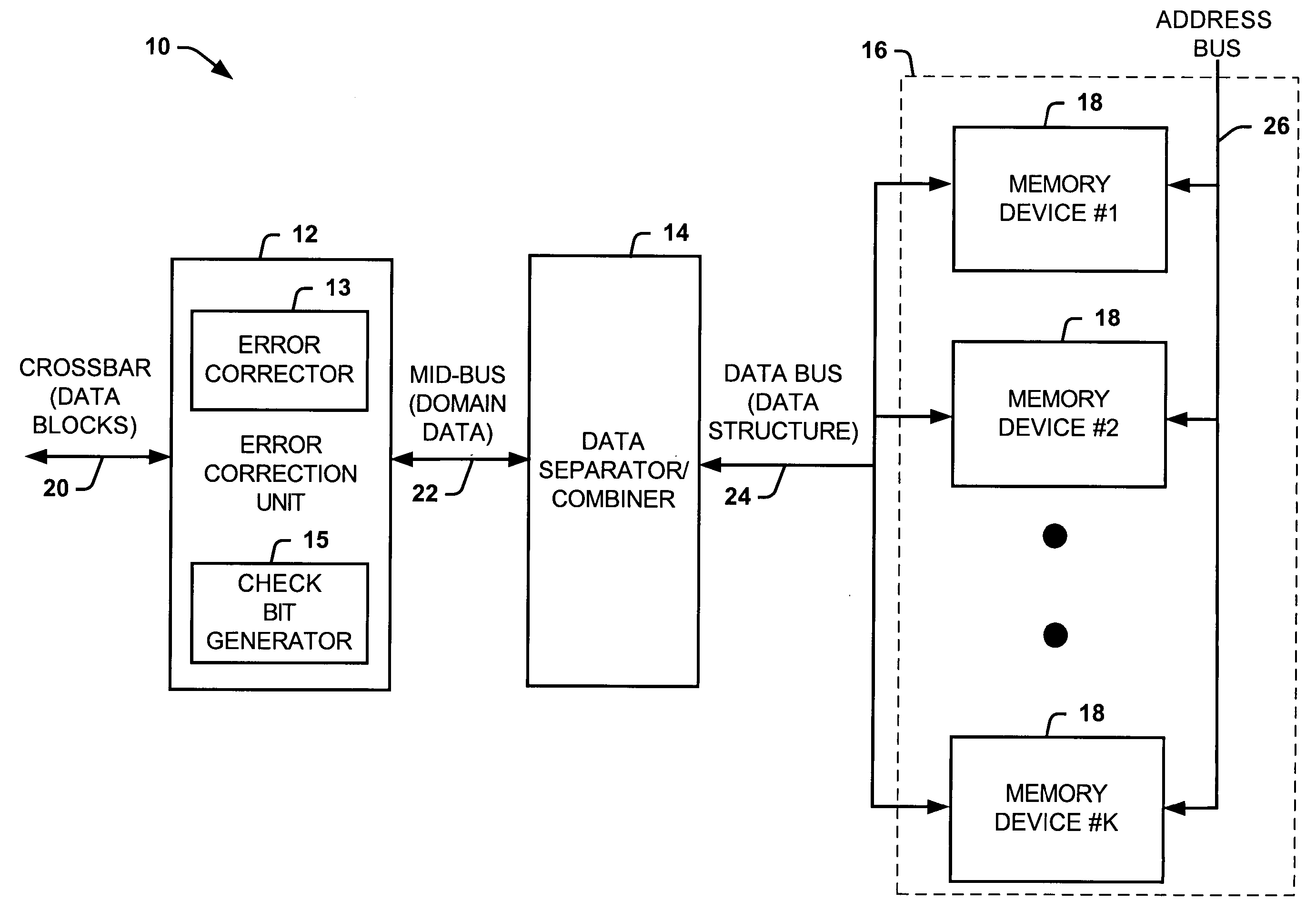
ActiveUS20050028057A1Well formedStatic storageRedundant data error correctionComputer hardwareBit pairing
Systems and methods are provided for detecting and correcting bit errors in data structures. A data block and / or data structure is partitioned into adjacent bit pair domains, such that a single adjacent bit pair from each memory device is assigned to a given adjacent bit pair domain. The bits in the adjacent bit pair domain are processed by an error correction unit sequentially or in parallel, and then recombined to be written into memory or transmitted to a requestor.
Owner:VALTRUS INNOVATIONS LTD +1
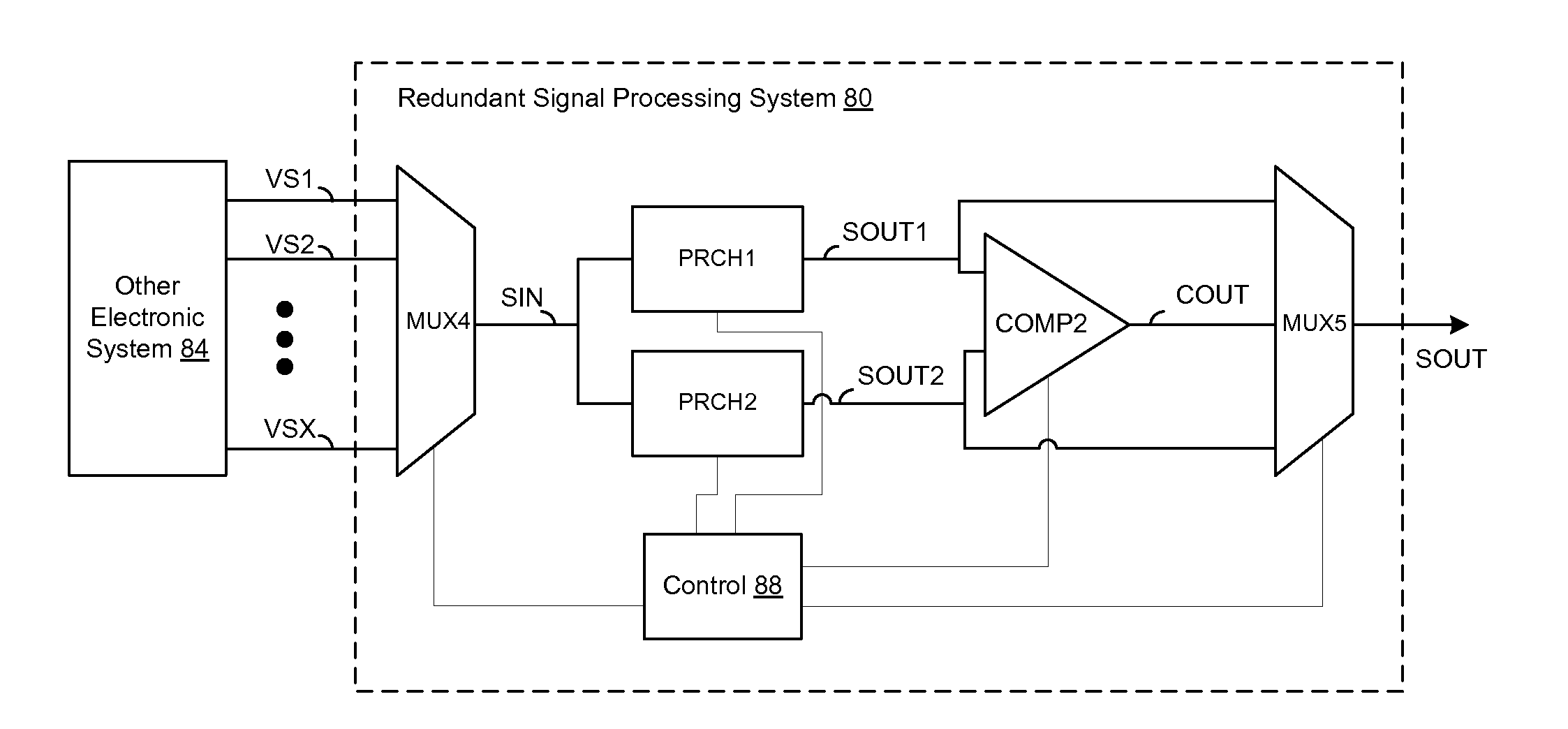
Test circuits and methods for redundant electronic systems
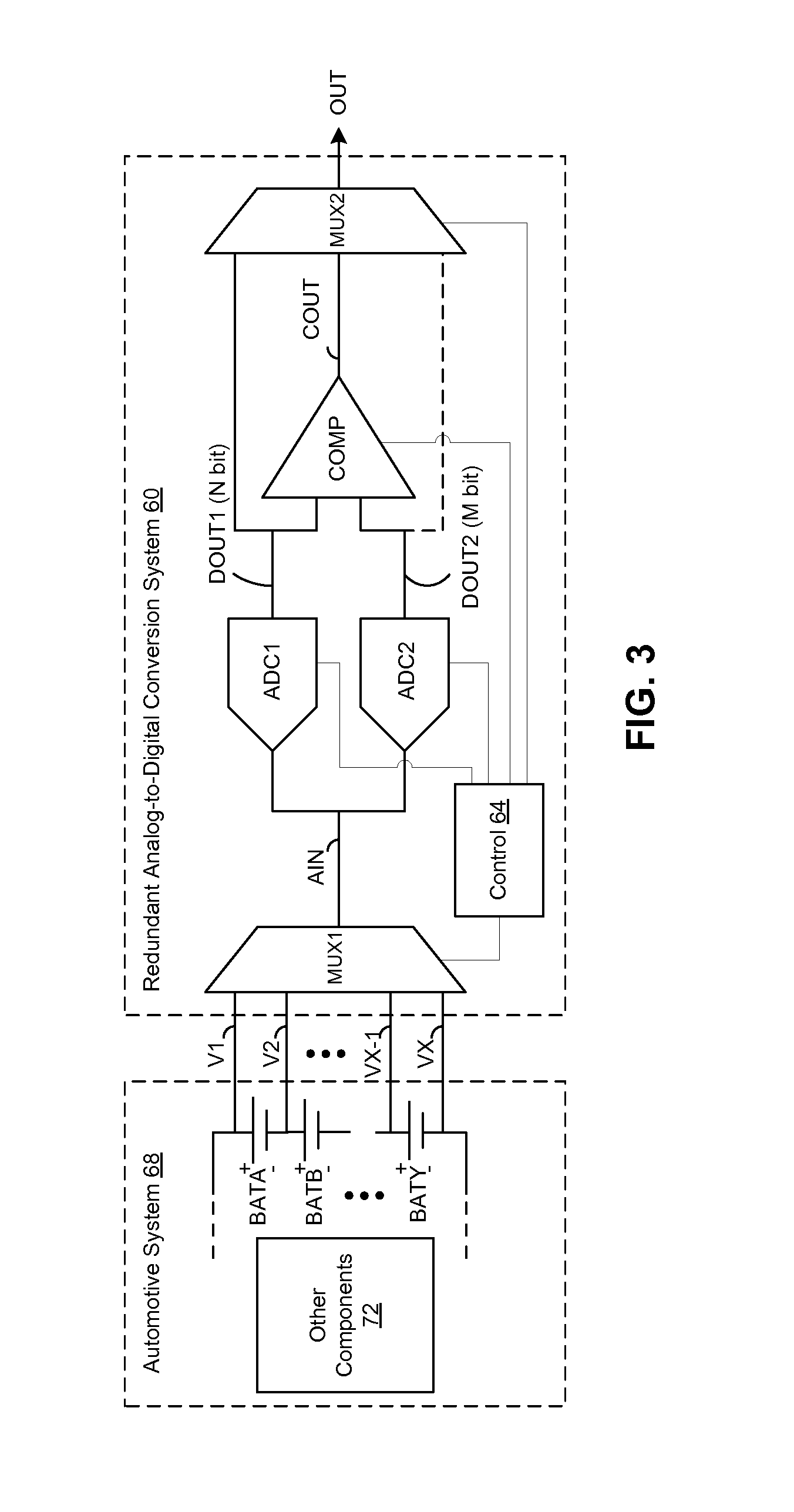
ActiveUS20120206282A1Electric signal transmission systemsSafety arrangmentsMultiplexingElectronic systems
A redundant analog-to-digital conversion system can include at least one input multiplexer, first and second redundant analog-to-digital converters, a comparison circuit and an output multiplexer. The at least one input multiplexer can receive a plurality of analog input signals and output at lest one multiplexed analog input signal. The first and second redundant analog-to-digital converters can convert the at least one multiplexed analog input signal to respectively generate first and second digital output signals, the first digital output having a greater digital resolution than the second digital output. The comparison circuit can produce a comparison output signal as a function of a comparison of a plurality of most significant corresponding bit pairs of the first and second digital output signals. The output multiplexer can produce a multiplexed output including information from the comparison output signal and one of the digital output signals.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
Systems and methods of routing data to facilitate error correction
ActiveUS20050028056A1Well formedEasy to correctStatic storageRedundant data error correctionDatapathBit pairing
Systems and methods are provided for detecting and correcting bit errors in data structures. A data block and / or data structure is partitioned into adjacent bit pair domains, such that a single adjacent bit pair from each memory device is assigned to a given adjacent bit pair domain. The adjacent bit pair domain data is transmitted over a bus having a plurality of data paths, such that data bits associated with a given memory device are transmitted over a same data path.
Owner:VALTRUS INNOVATIONS LTD +1
Multi-level ONO flash program algorithm for threshold width control
ActiveUS20060152974A1Easy to controlNarrow distributionRead-only memoriesDigital storageBit pairingComputer science
Methods of programming a wordline of multi-level flash memory cells (MLB) having three or more data levels per bit corresponding to three or more threshold voltages are provided. The present invention employs an interactive program algorithm that programs the bits of the wordline of memory cells in two programming phases, comprising a rough programming phase and a fine programming phase to achieve highly compact Vt distributions. In one example, cell bit-pairs that are to be programmed to the same program pattern are selected along a wordline. Groups of sample bits are chosen for each wordline to represent each possible program level. The sample bits are then programmed to determine a corresponding drain voltage at which each sample group is first programmed. This fast-bit drain voltage (Fvd) for each program level essentially provides a wordline specific program characterization of the Vt required for the remaining bits of that wordline. In the rough programming phase, the bits of core cells are then programmed from a starting point that is relative to (e.g., slightly less than or equal to) the fast-bit Vd and according to a predetermined Vd and Vg profile of programming pulses. The bits of the complementary bit-pairs are alternately programmed in this way until the Vt of the bits attains a rough. Vt level, which is offset lower than the final target threshold voltage level. Then in the second fine programming phase, the bits of the MLB cells of the wordline are further programmed with another predetermined Vd and Vg profile of programming pulses until the final target threshold voltage is achieved. The Vd and Vg profiles of programming pulses may further be tailored to accommodate the various bit-pair program pattern combinations possible. In this way, the bits of each wordline are fine-tune programmed to a data state to achieve a more precise Vt distribution, while compensating for the effects of complementary bit disturb.
Owner:LONGITUDE FLASH MEMORY SOLUTIONS LTD
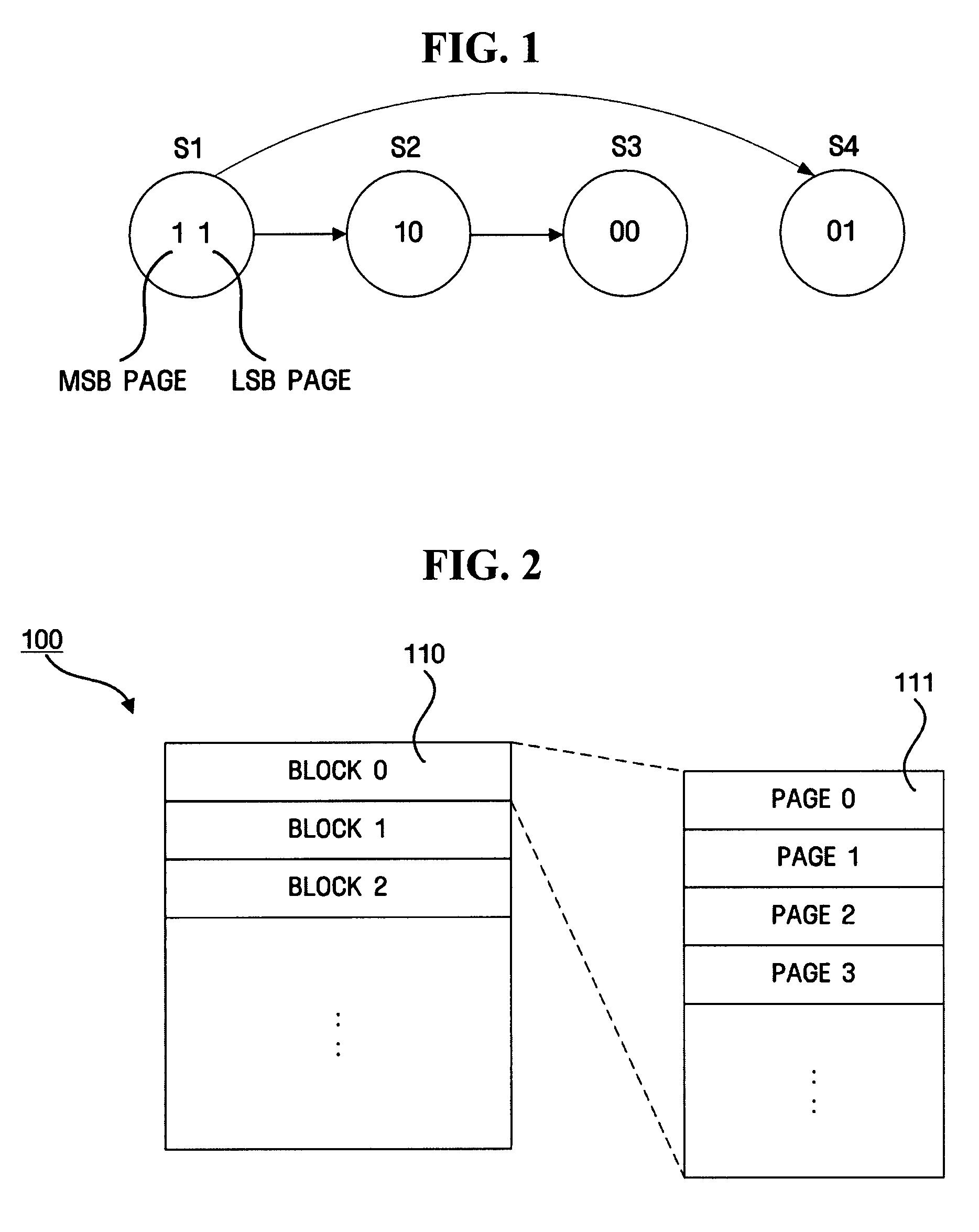
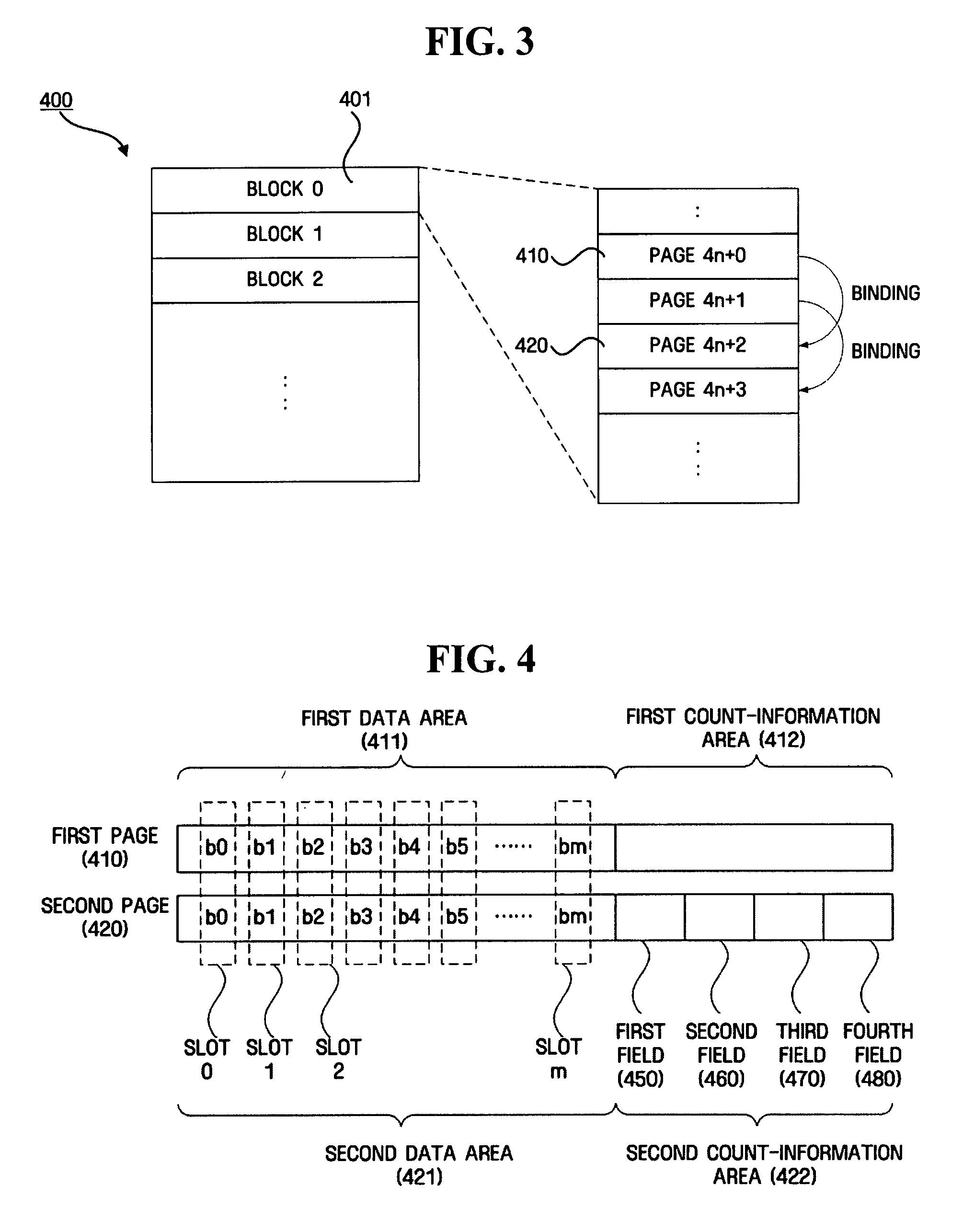
Nonvolatile memory, apparatus and method for determining data validity of the same
ActiveUS20070297265A1Guaranteed correct validityRead-only memoriesDigital storageBit pairingComputer science
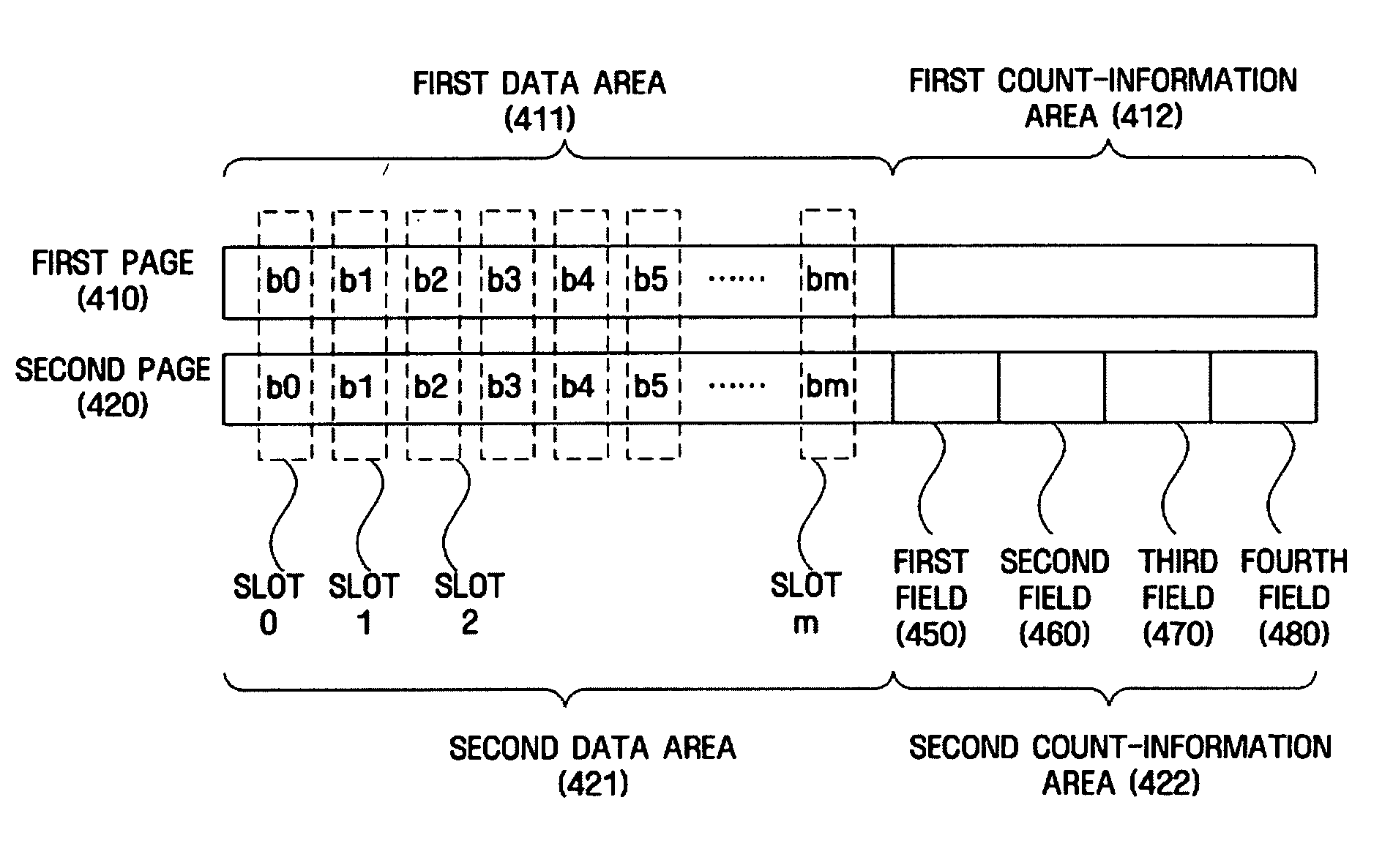
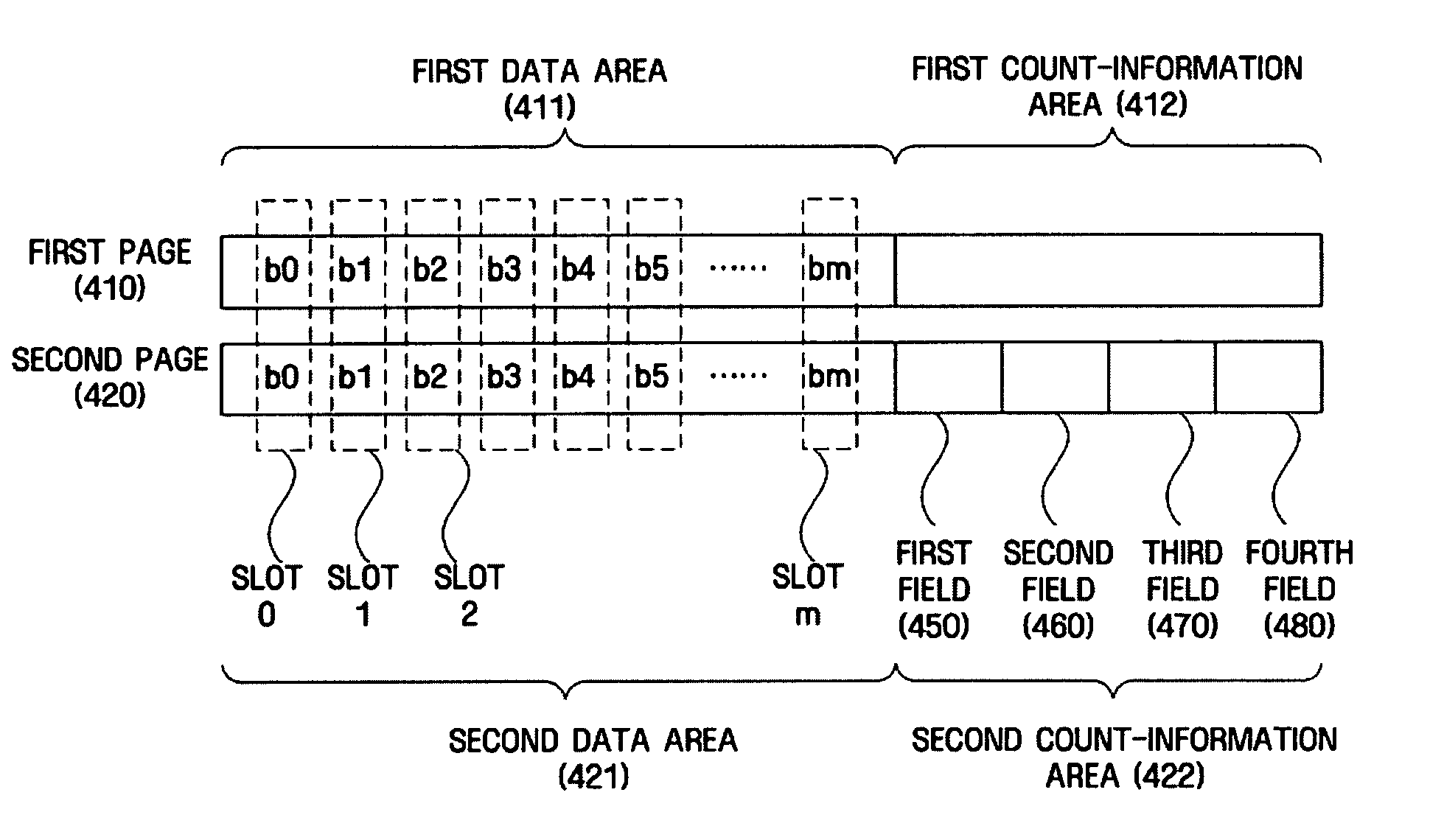
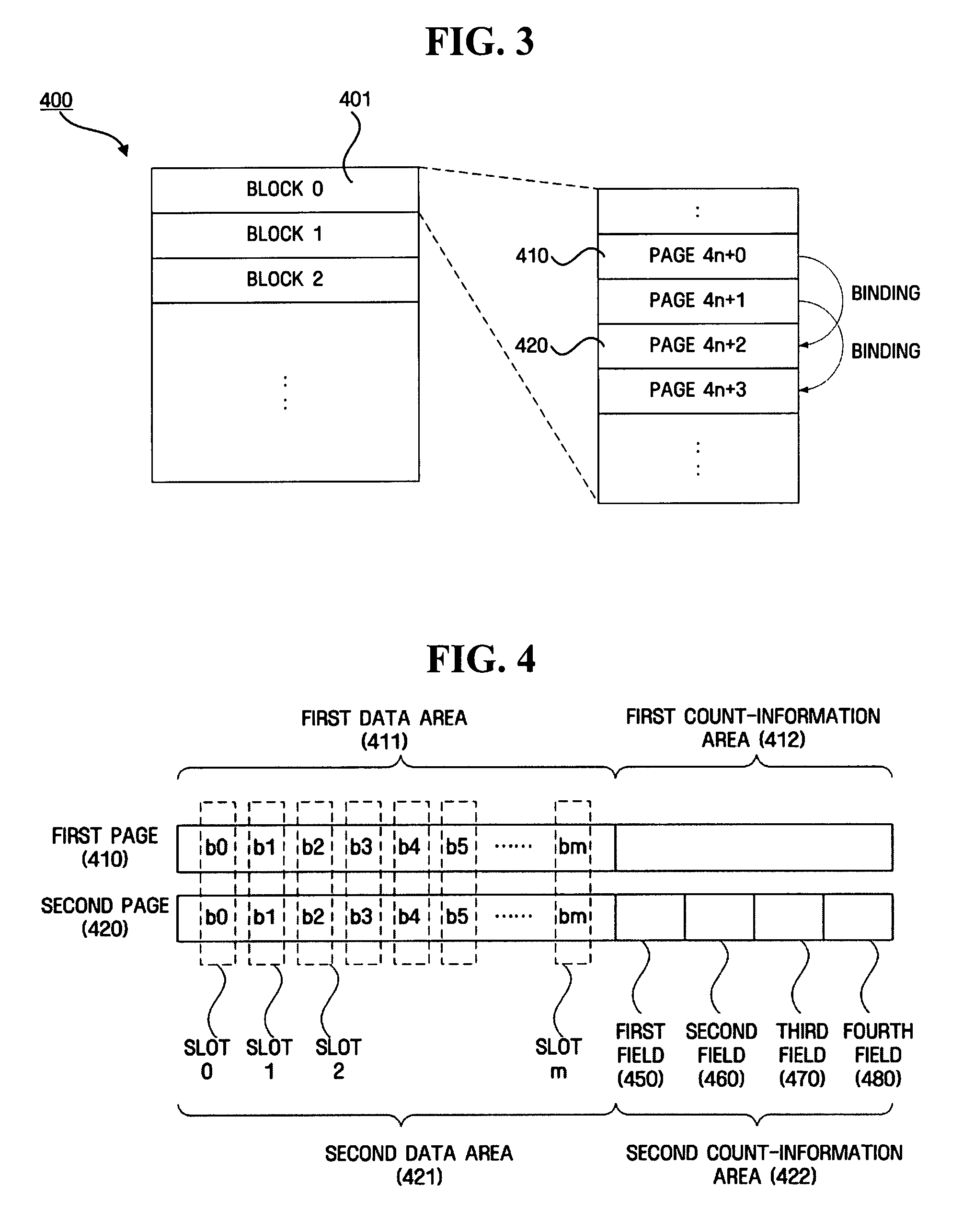
A nonvolatile memory including a memory cell that stores data in a plurality of pages included in a block according to a voltage applied to a memory cell is provided. The nonvolatile memory includes a block that includes a first page including first data that stores data recorded by a user, and a second page including second data area that stores data recorded by a user, wherein the second page records count-information on states represented by a bit pair in the same position of the first data area and the second data area.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method and apparatus for transmitting ACK frame
An efficient burst ACK method and apparatus in wireless communication environment are provided. An ACK frame transmission method whereby plural frames are received from a transmitting device and receipt of the frames is acknowledged with a single ACK frame includes receiving frames from the transmitting device and storing identification information of the received frames; generating a first field by recording a set of bit pairs to each of the received frames, with the use of the stored identification information; generating an ACK frame including the generated first field; and transmitting the generated ACK frame to the transmitting device, wherein a bit pair includes: a first bit to acknowledge whether any concerned frame is properly received; and a second bit to distinguish whether the first bit is to acknowledge receipt of the concerned frame from whether it is to acknowledge receipt of all the fragments following the concerned frame.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
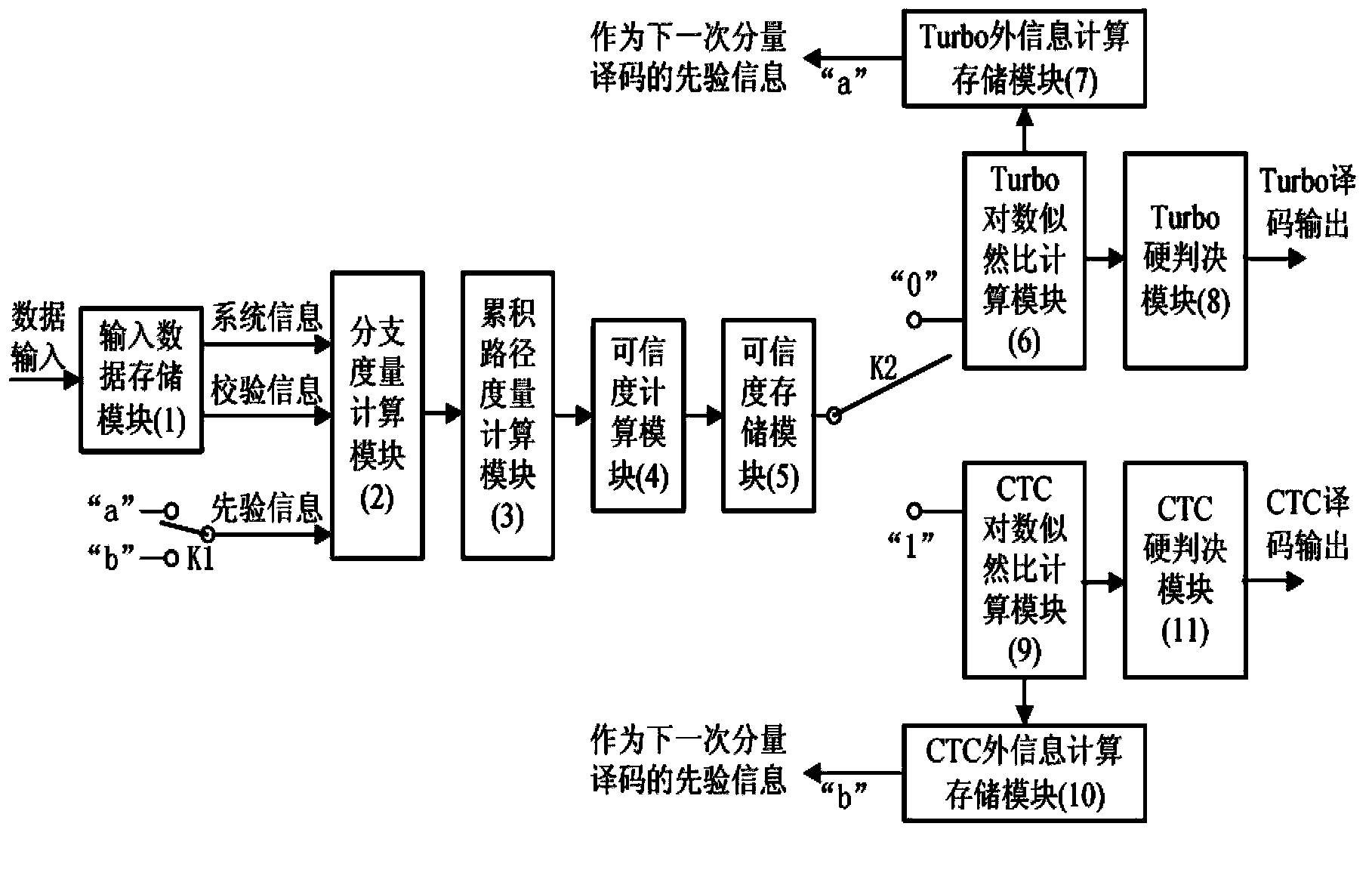
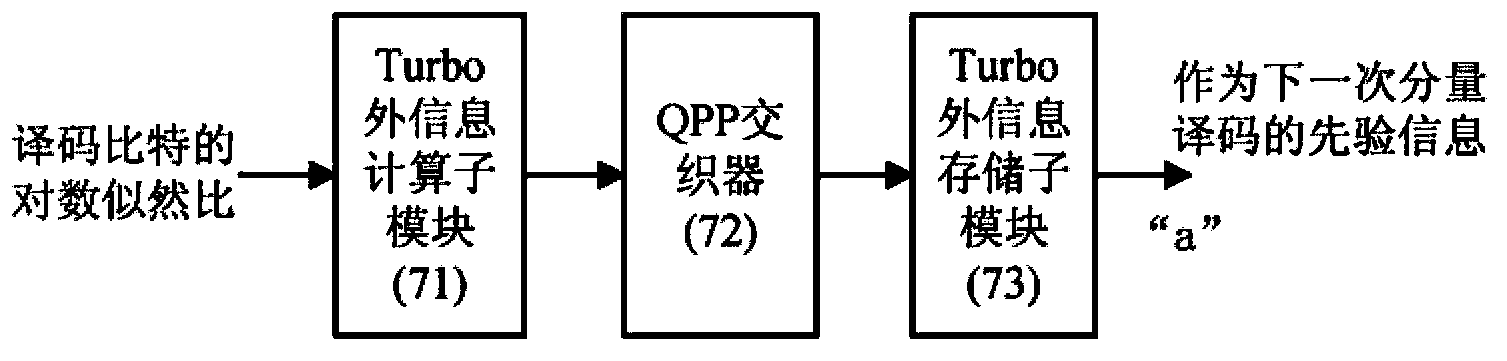
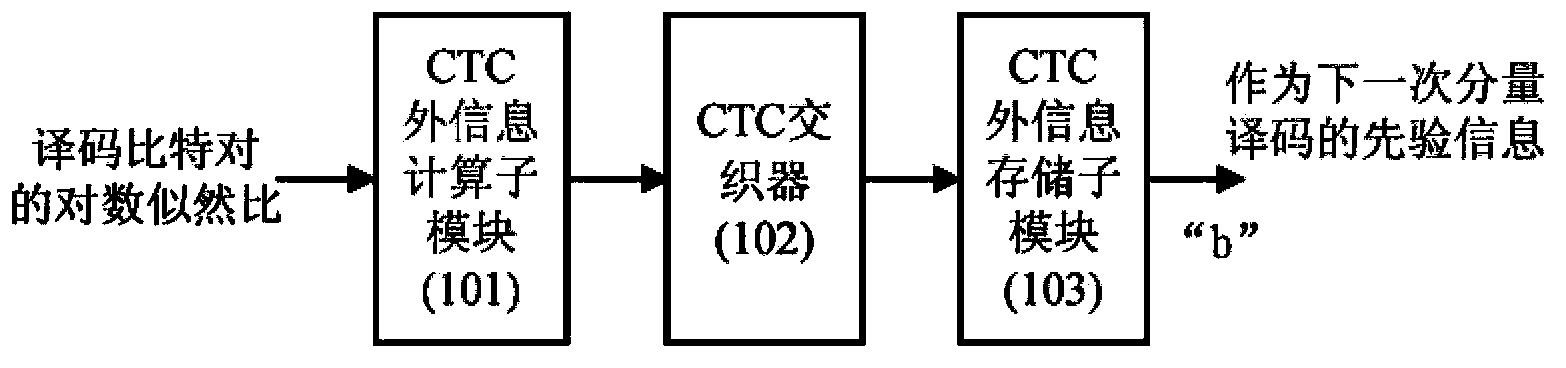
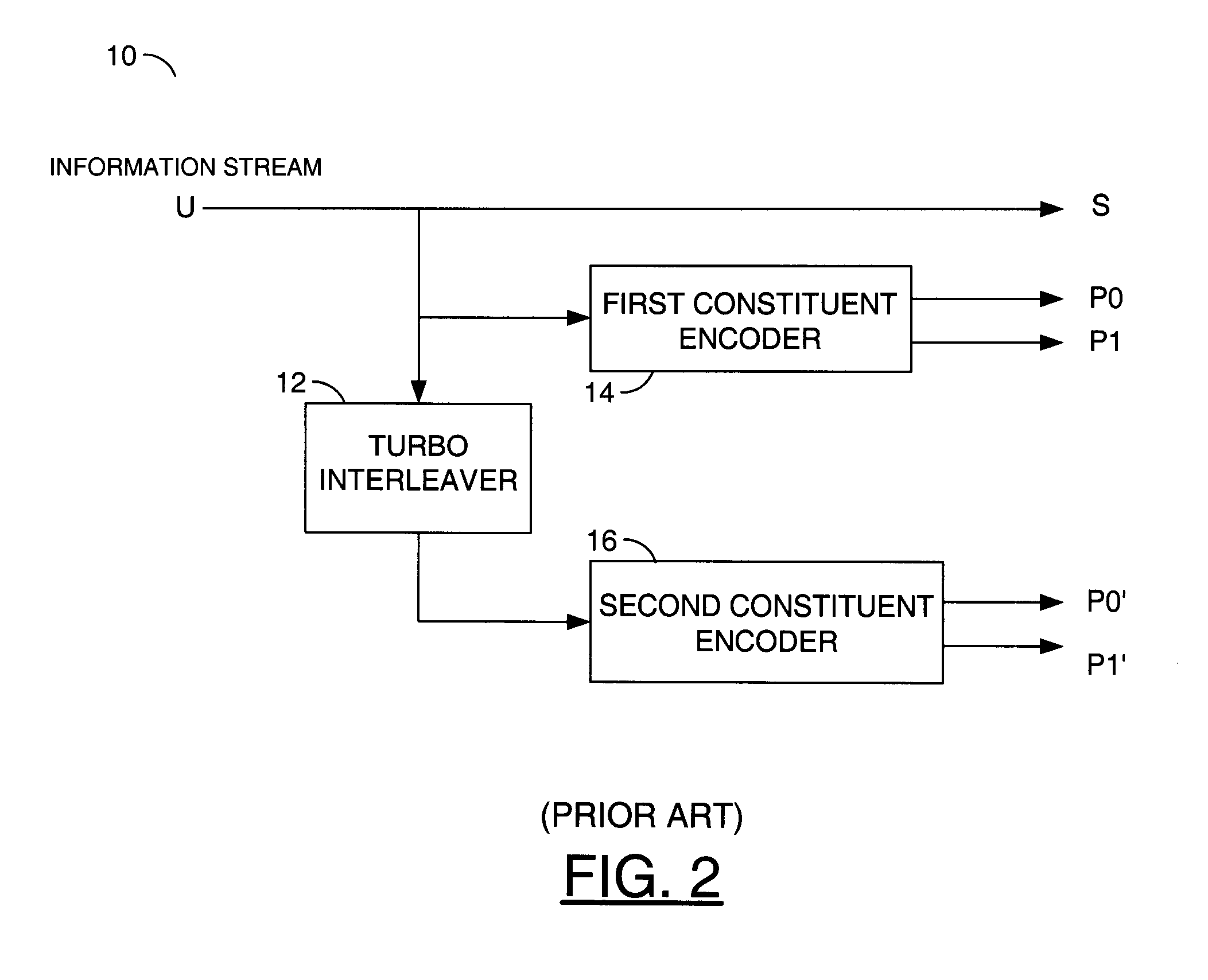
General high-performance Radix-4SOVA decoder and decoding method
InactiveCN103354483AAvoid disadvantagesImprove decoding performanceError preventionComputer architectureSecondary component
The invention discloses a general high-performance Radix-4SOVA decoder and a decoding method. In the prior art, in the Radix-4SOVA decoder, only a binary system Turbo code based on bit interleaving is supported. By using the decoder and the method of the invention, the above problem is mainly solved. The method has the following steps of receiving channel information and storing; reading the channel information of a first component code, carrying out first component decoding which means that a branch metric, a cumulative path metric, credibility, a log-likelihood ratio and extrinsic information are successively calculated, interleaving the extrinsic information and storing; reading the channel information of a second component code and completing secondary component decoding; determining whether a maximum iteration is reached; if the maximum iteration is not reached, starting next iteration decoding; otherwise, carrying out hard decision on the log-likelihood ratio so as to obtain an estimation value of a decoding bit and finishing the decoding. According to the invention, a credibility updating method based on a bit pair is used; the general and configurable high performance decoding of a binary system Turbo code and a duobinary system convolution Turbo code can be realized; the method can be used in a general and configurable Turbo decoder in a LTE and WiMAX system.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
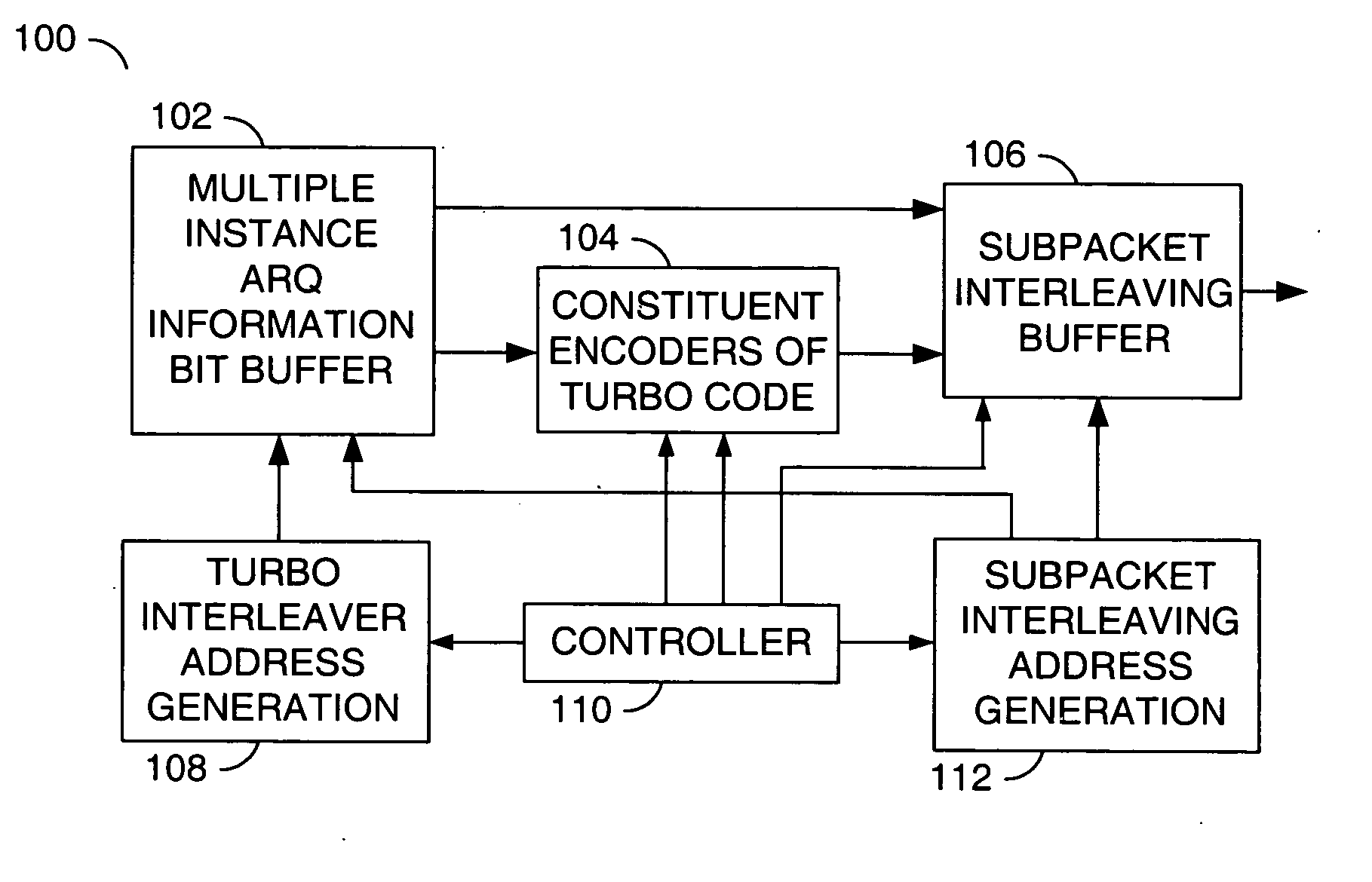
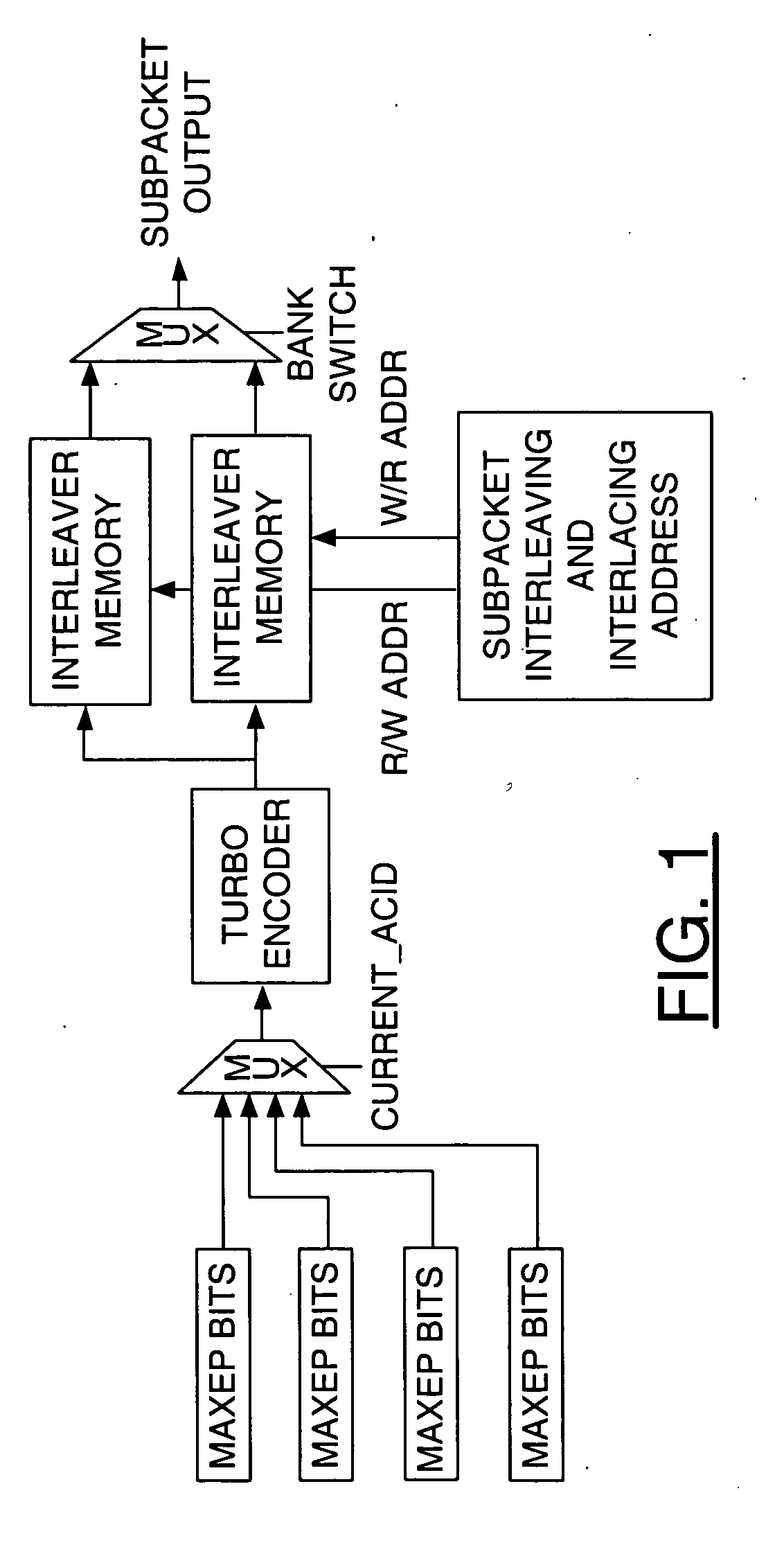
Memory efficient streamlined transmitter with a multiple instance hybrid ARQ
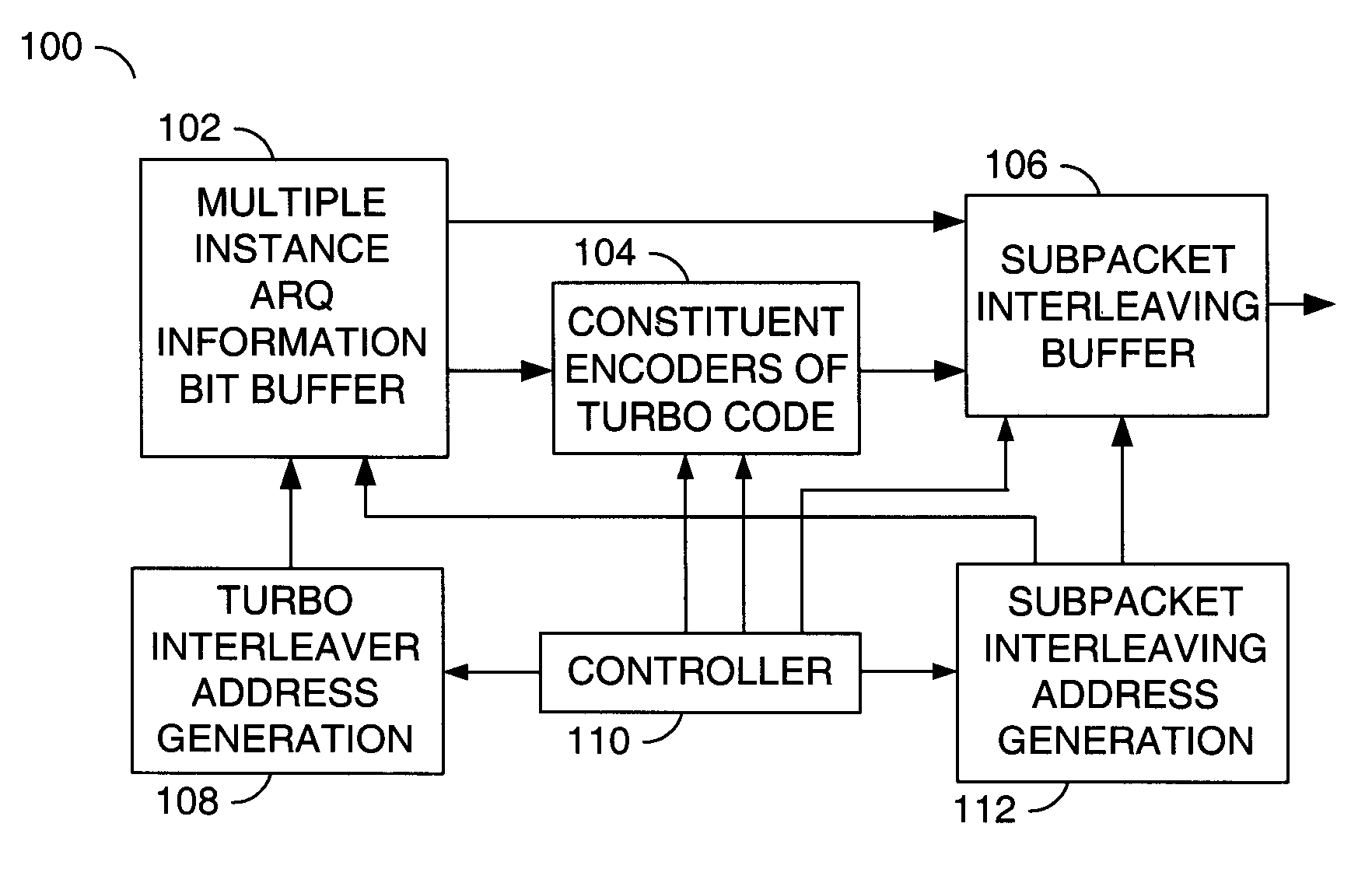
ActiveUS20060206777A1Memory efficientError prevention/detection by using return channelData representation error detection/correctionMultiplexerBit pairing
An apparatus comprising a first circuit, a second circuit and a third circuit. The first circuit may be configured to generate an output signal in response to a first intermediate signal and a second intermediate signal. The second intermediate signal comprises a series of bit pairs. The second circuit comprises a first and a second encoder and may be configured to generate the second intermediate signal in response to a third intermediate signal. The third circuit may be configured to generate the first intermediate signal and the third intermediate signal in response to a first address signal and a second address signal. The third circuit comprises a first multiplexer and a second multiplexer.
Owner:APPLE INC
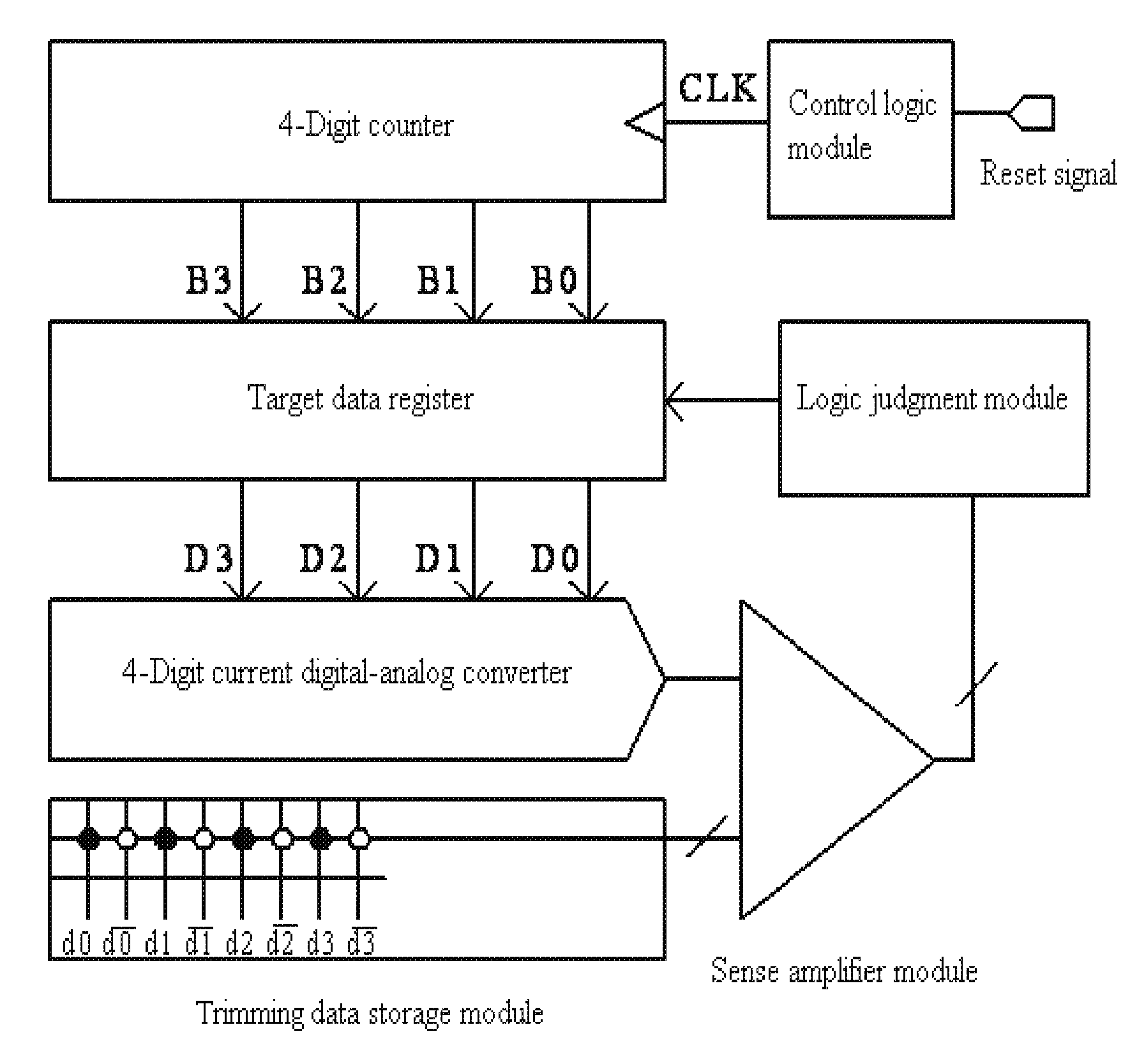
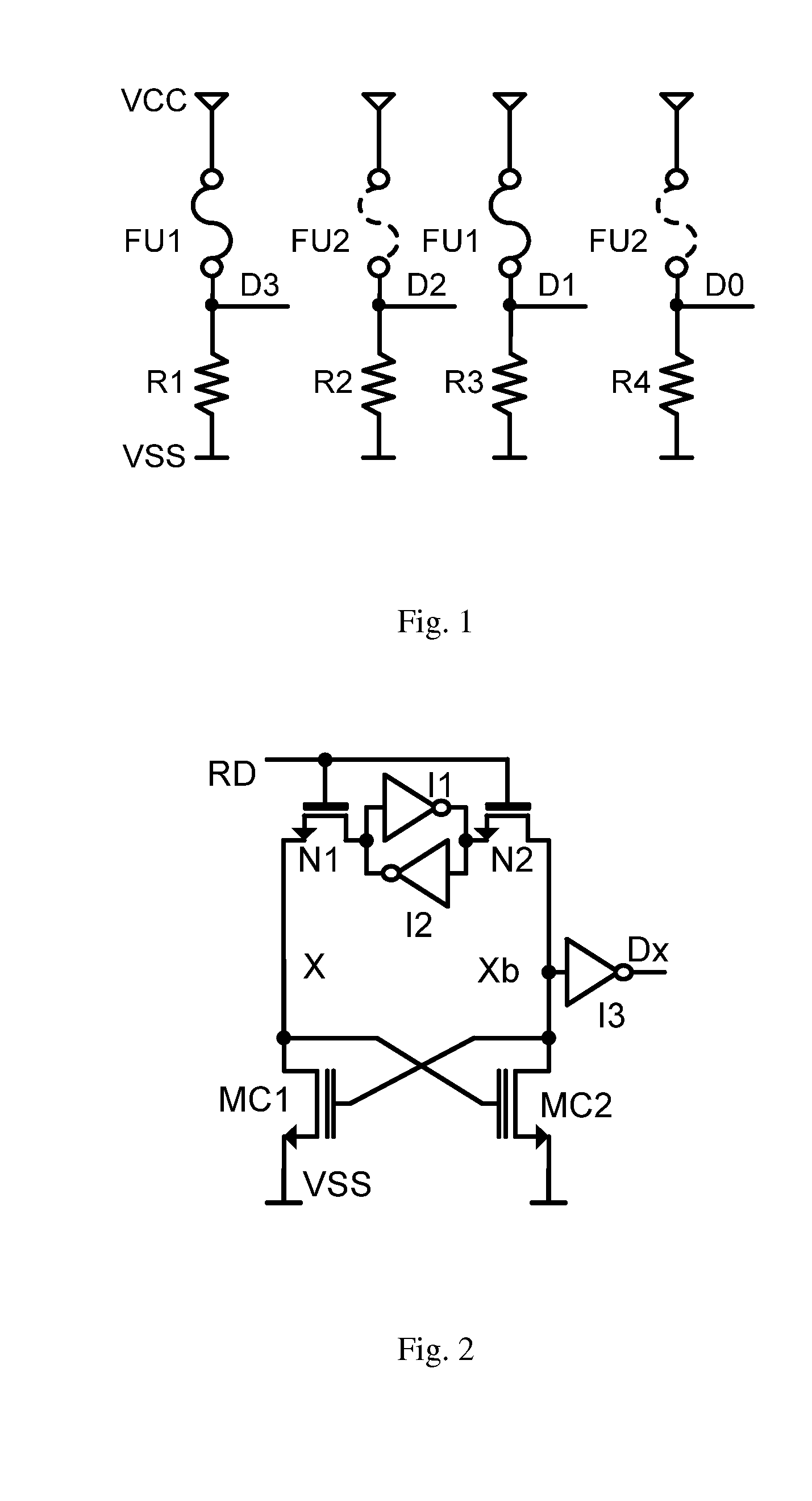
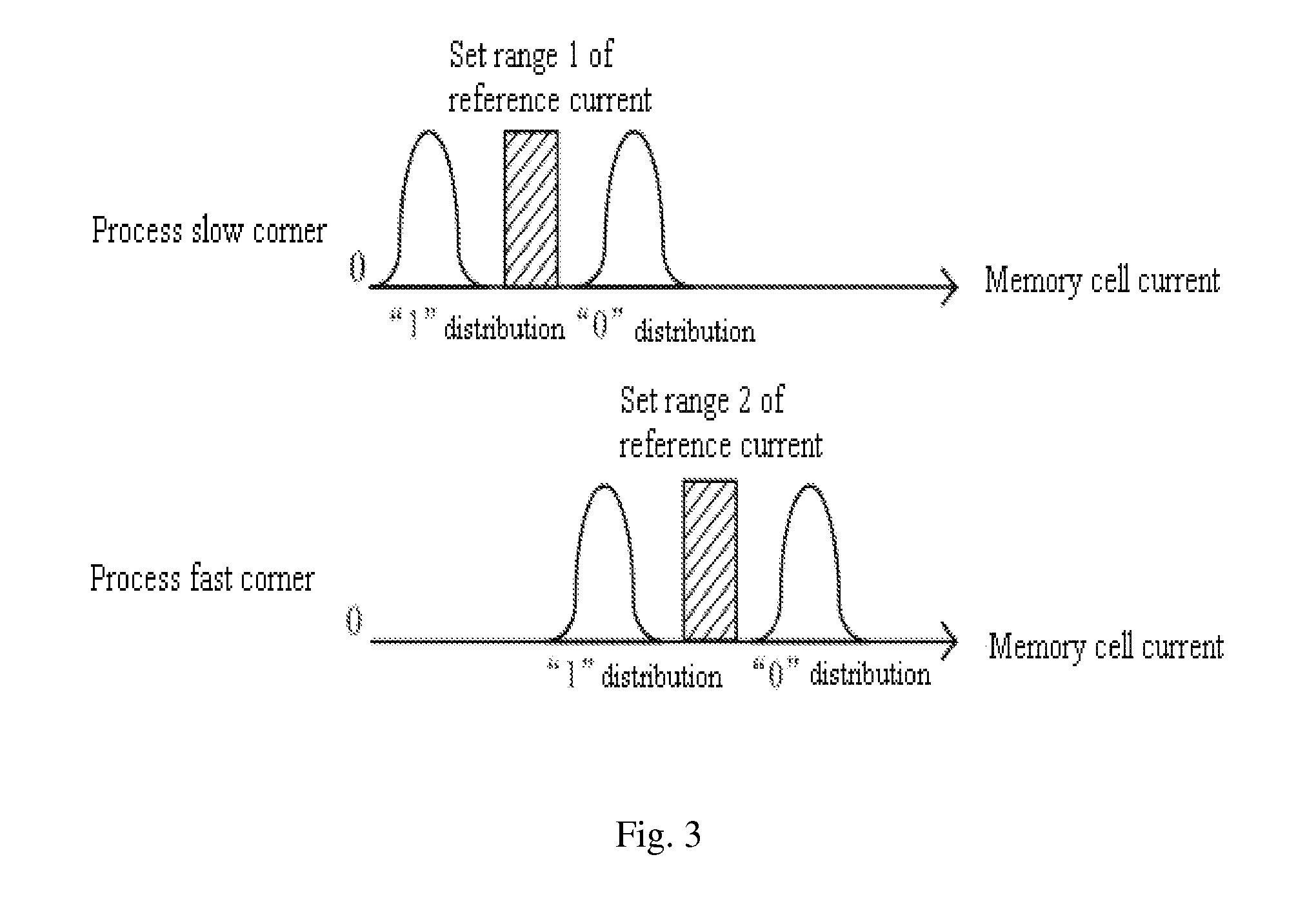
Selfcalibration method and circuit of nonvolatile memory and nonvolatile memory circuit
ActiveUS20100014363A1Increasing area costIncreasing circuit areaRead-only memoriesDigital storageAudio power amplifierReference current
The present invention discloses a selfcalibration method of a reading circuit of a nonvolatile memory, by which trimming data having recorded a reference current are stored in a bit-pair form into the memory and regulate a sense amplifier, and a value of the reference current is obtained according to the trimming data when “0” and “1” in the outputted trimming data have the same quantities. The present invention further discloses a selfcalibration circuit of the nonvolatile memory, which includes a trimming data storage module, a sense amplifier module, a logic judgment module, and a scanning module. The present invention furthermore discloses a nonvolatile memory circuit, which includes a memory cell array and the selfcalibration circuit of the reading circuit of the nonvolatile memory. The present invention, not requiring an additional fuse or differential unit, can solve a deadlock problem securely and reliably without increasing circuit area and test cost, and be widely applied to OTP, MTP and EEPROM of various processes or various nonvolatile memories such as Flash EEPROM, MRAM, and FeRAM, improving reliability of the memory effectively.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUAHONG GRACE SEMICON MFG CORP
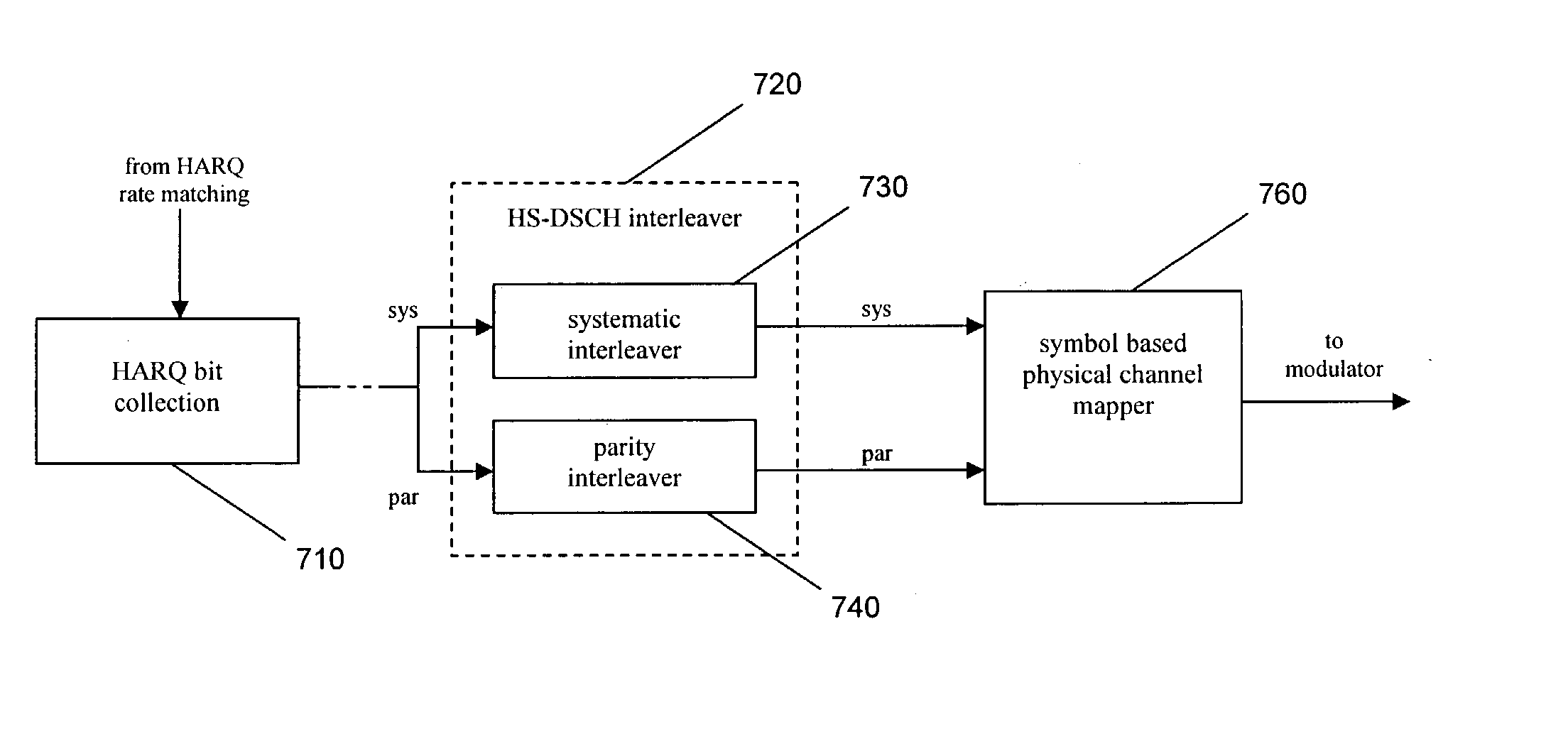
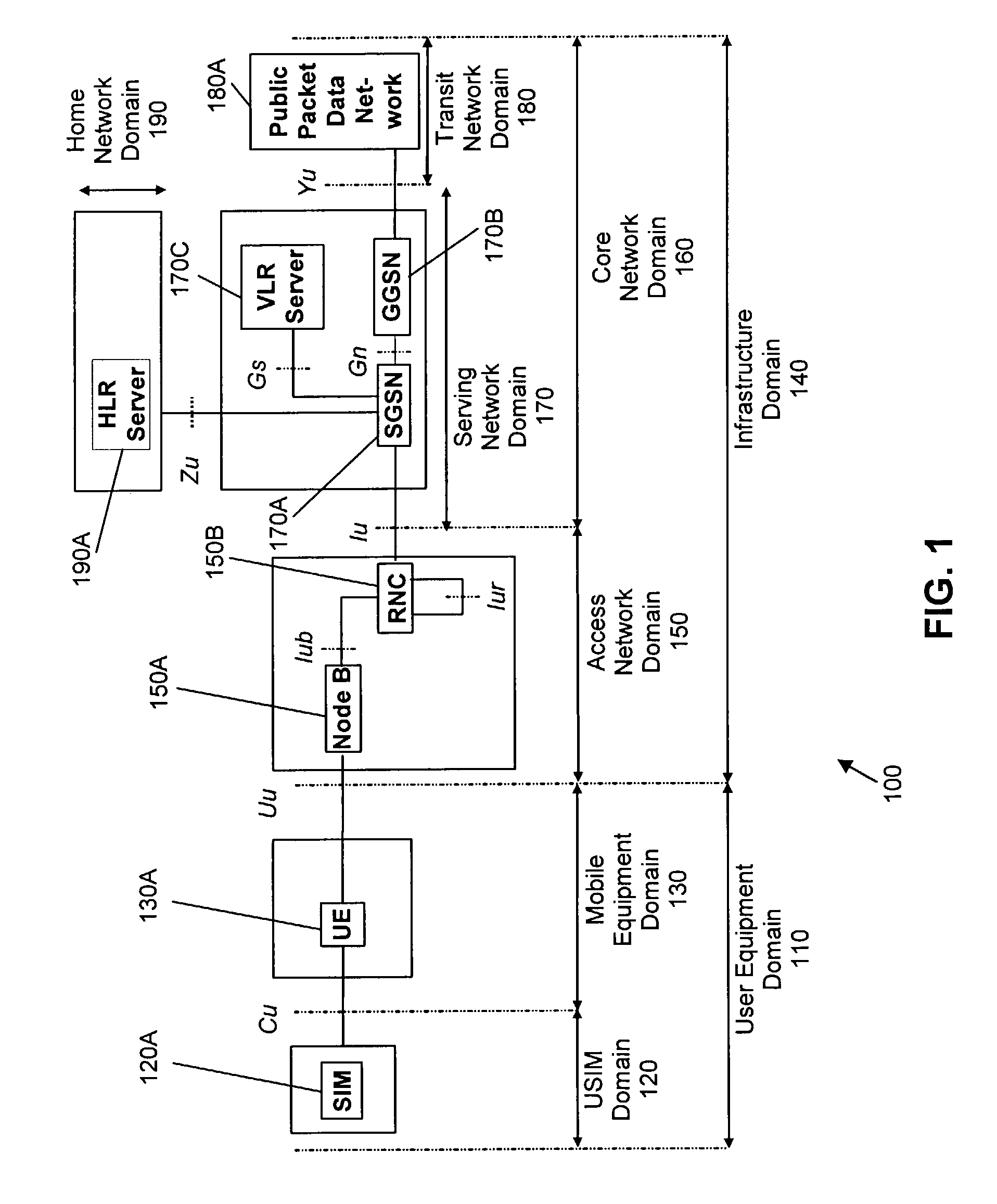
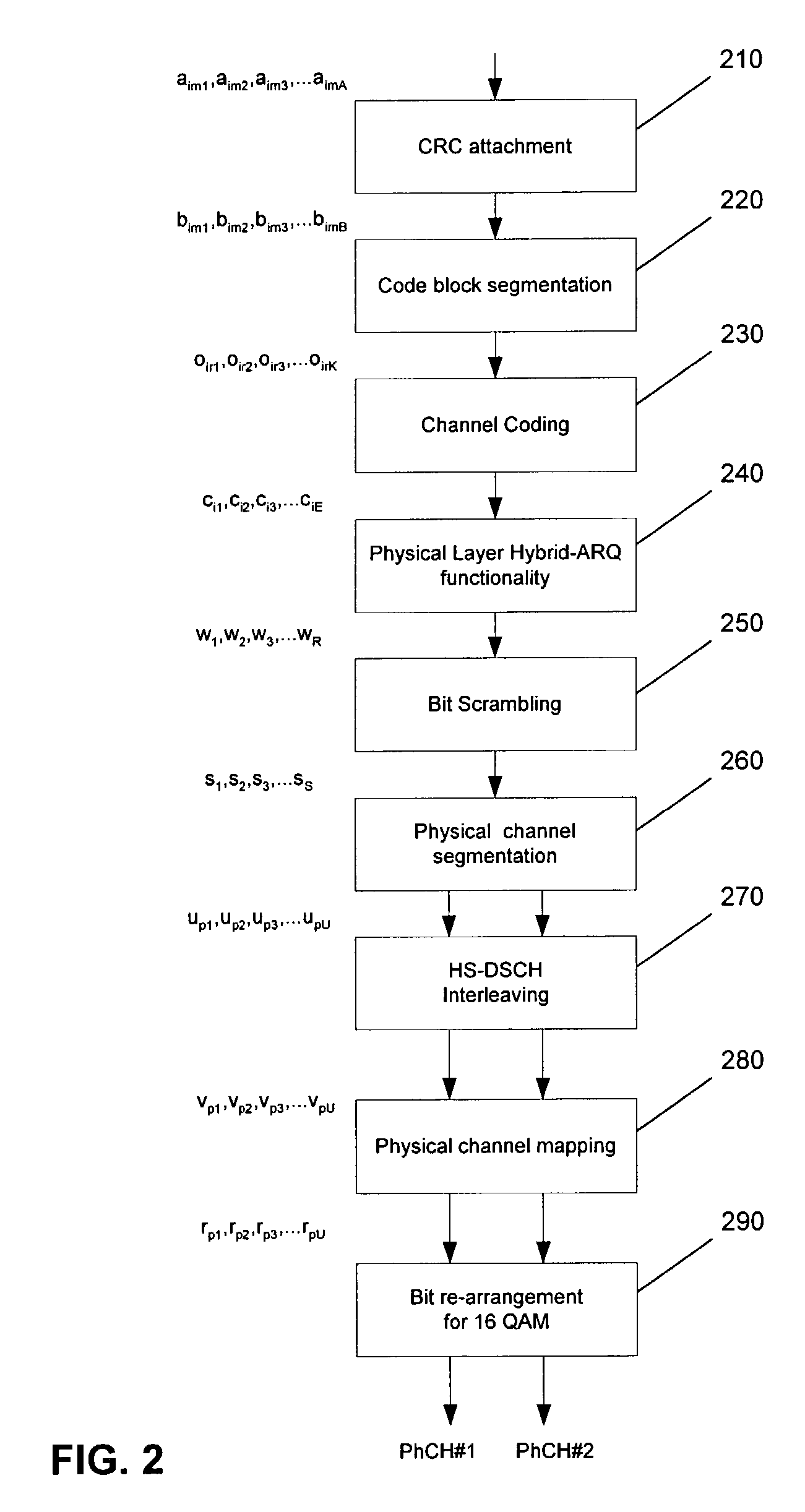
Arrangement and method for channel mapping in a wireless communication system
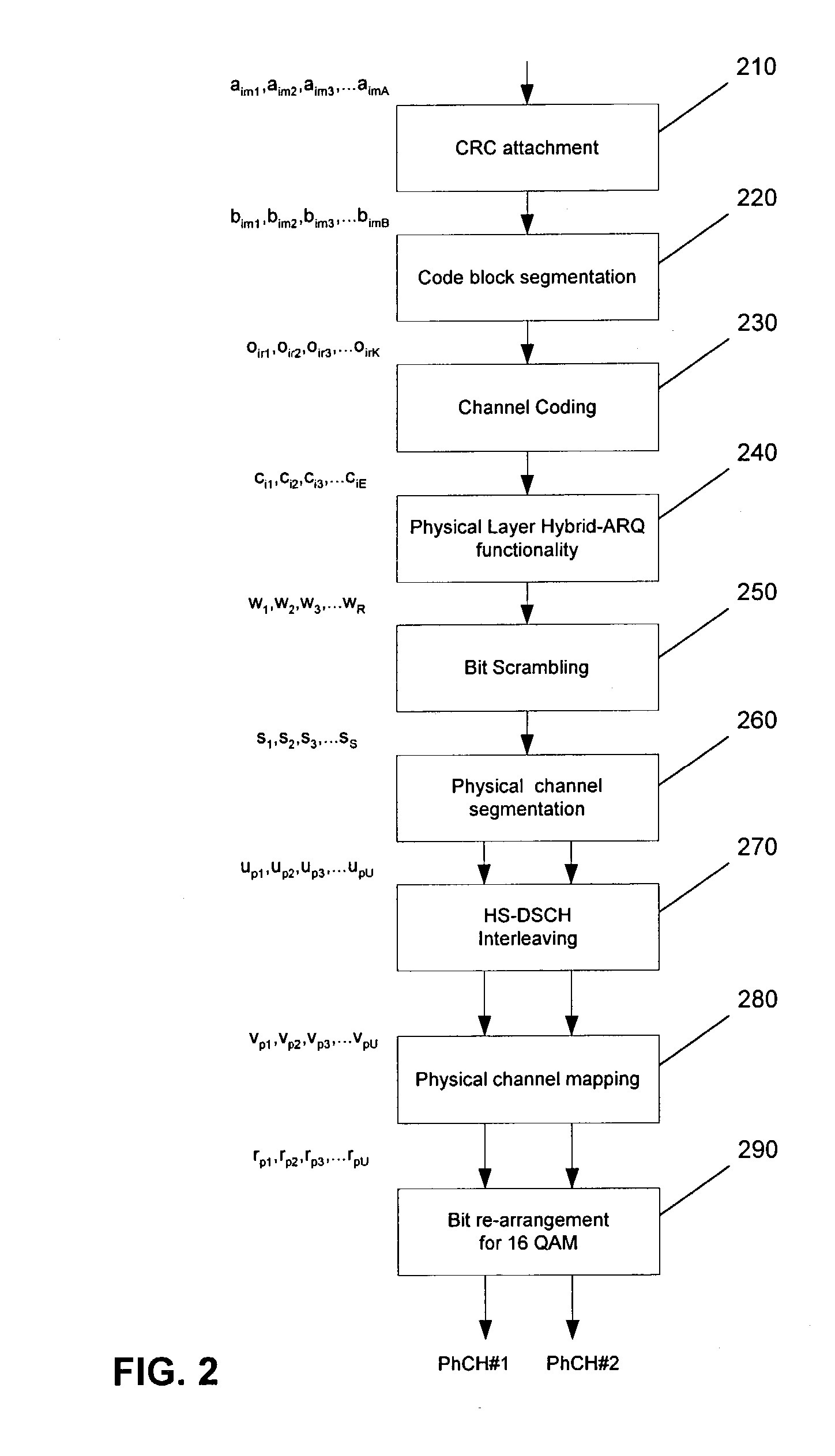
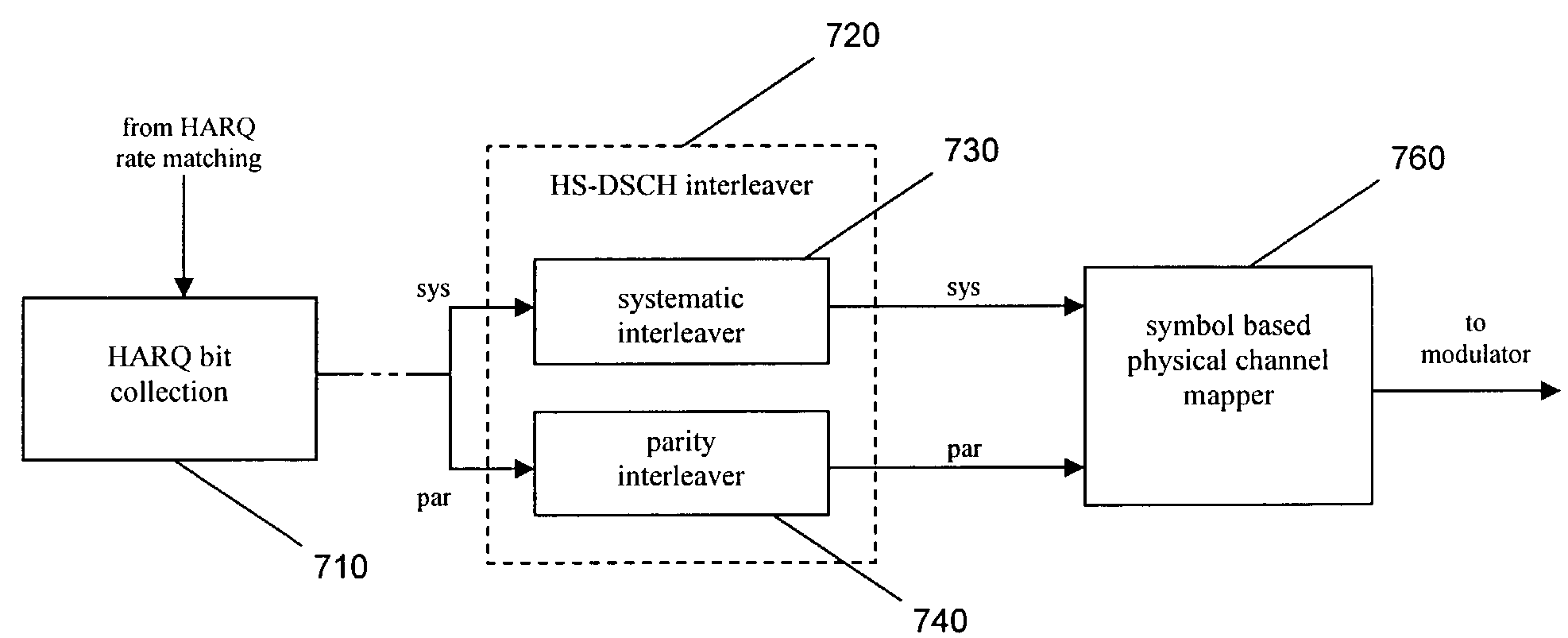
ActiveUS20040071172A1Precise positioningError prevention/detection by using return channelNetwork traffic/resource managementCommunications systemBit pairing
An arrangement and method for channel mapping in a UTRA TDD HSDPA wireless communication system by applying interleaving functions in first (530) and second (540) interleaving means to a bit sequence to produce symbols for mapping to physical channels, the first and second interleaving means being arranged to map symbols from respectively systematic and parity bits in a predetermined scheme, e.g., mapping symbols in a forward direction when a channel has an even index number, and in a reverse direction when a channel has an odd index number. The symbols may comprise bit-pairs, each of a systematic bit and parity bit. Systematic bits are preferably mapped to high reliability bit positions in TDD HSDPA, achieving a performance gain of between 0.2 dB and 0.5 dB. The forwards / reverse mapping allows a degree of interleaving that improves system performance in fading channels or channels disturbed by short time period noise or interference.
Owner:SISVEL INT
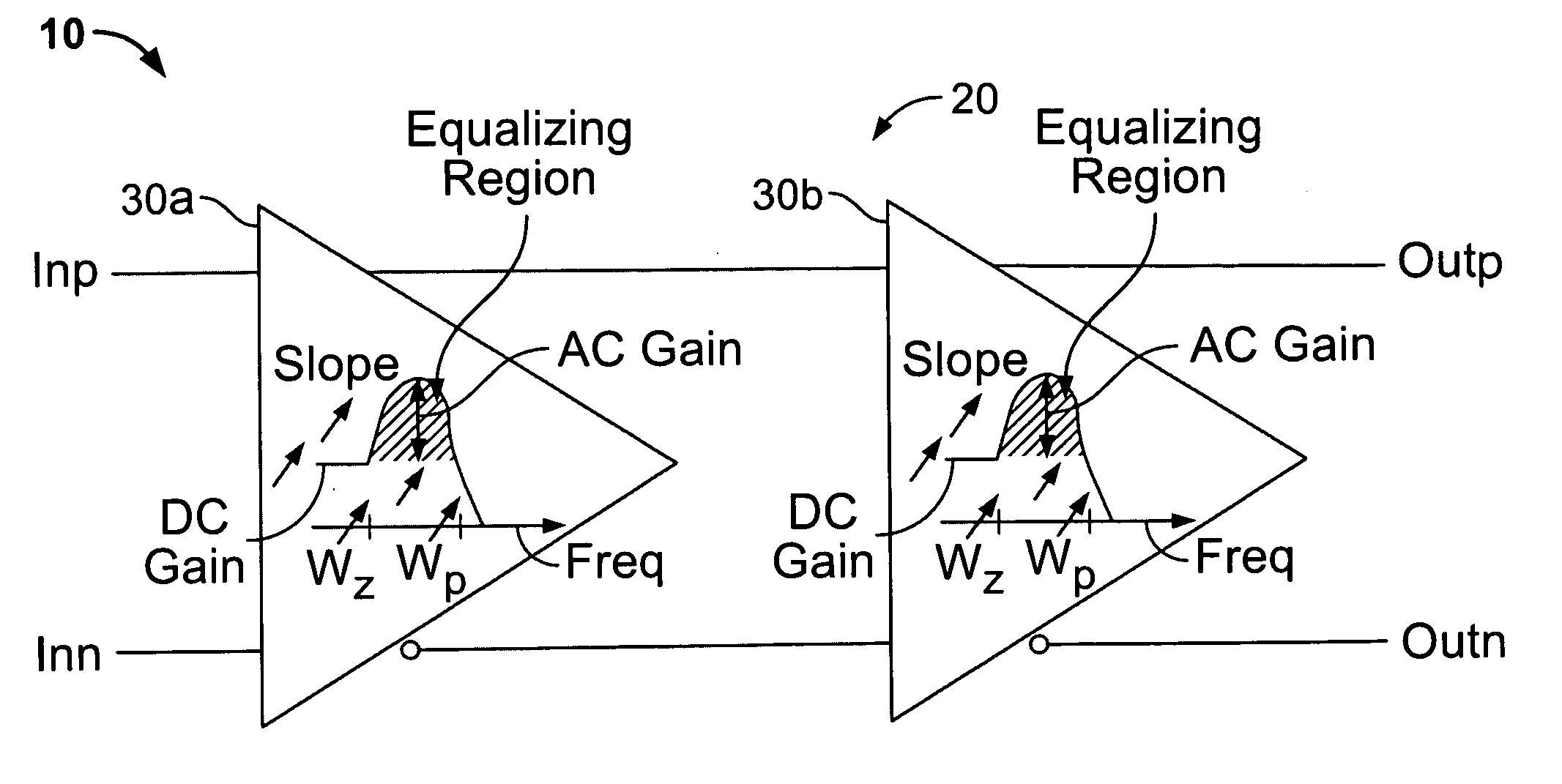
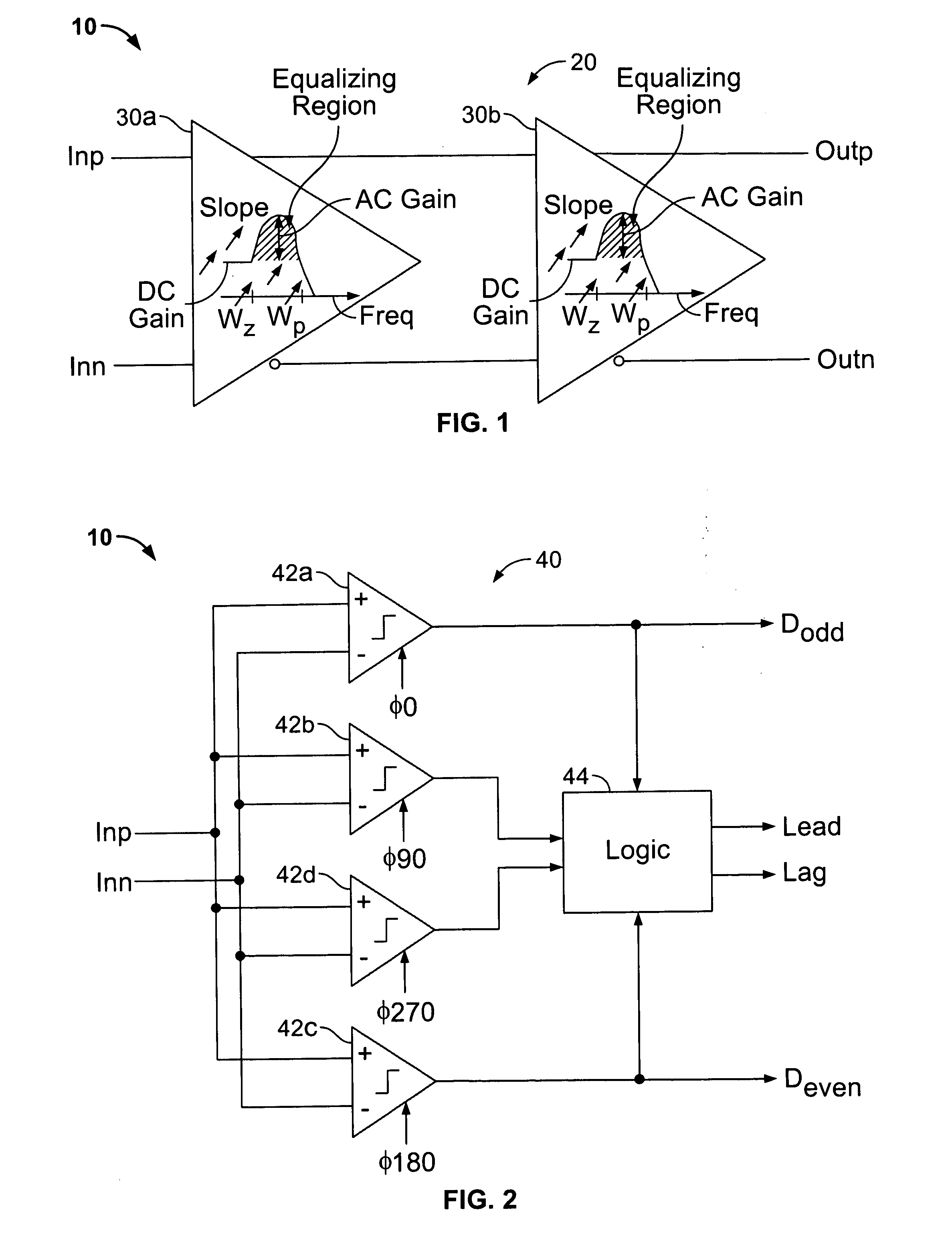
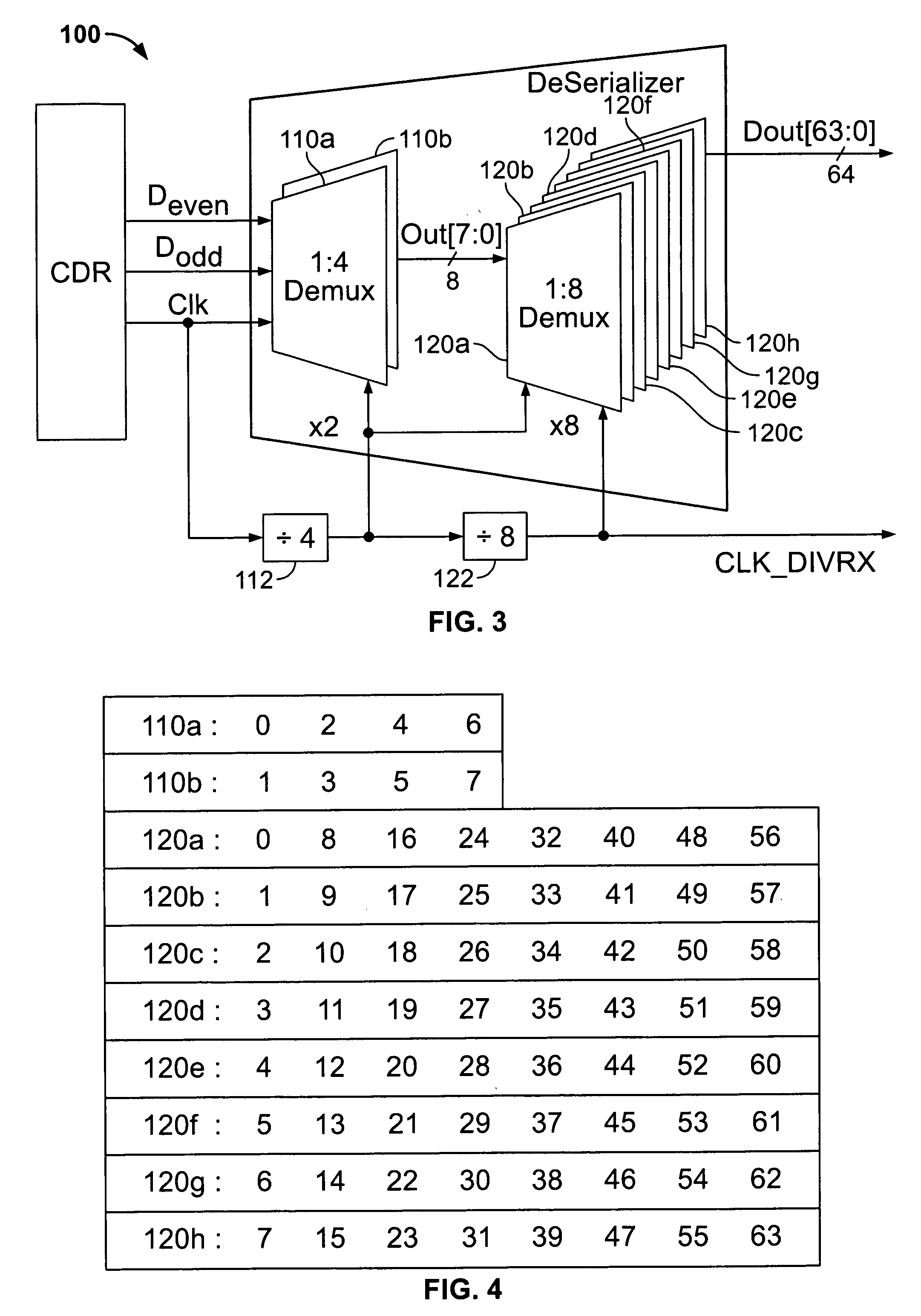
High-speed serial data signal receiver circuitry
Circuitry for receiving a high-speed serial data signal (e.g., having a bit rate in the range of about 10 Gpbs and higher) includes a two-stage, continuous-time, linear equalizer having only two serially connected stages. Phase detector circuitry may be provided for receiving the serial output of the equalizer and for converting successive pairs of bits in that output to successive parallel-form bit pairs. Further demultiplexing circuitry may be provided to demultiplex successive groups of the parallel-form bit pairs to final groups of parallel bits, which can be quite large in terms of number of bits (e.g., 64 parallel bits). Another aspect of the invention relates to multiplexer circuitry for efficiently going in the opposite direction from such relatively large groups of parallel data bits to a high-speed serial data output signal.
Owner:ALTERA CORP
Nonvolatile memory, apparatus and method for determining data validity of the same
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Arrangement and method for channel mapping in a wireless communication system
ActiveUS7710926B2Error prevention/detection by using return channelCode conversionCommunications systemBit pairing
An arrangement and method for channel mapping in a UTRA TDD HSDPA wireless communication system by applying interleaving functions in first (530) and second (540) interleaving means to a bit sequence to produce symbols for mapping to physical channels, the first and second interleaving means being arranged to map symbols from respectively systematic and parity bits in a predetermined scheme, e.g., mapping symbols in a forward direction when a channel has an even index number, and in a reverse direction when a channel has an odd index number. The symbols may comprise bit-pairs, each of a systematic bit and parity bit.Systematic bits are preferably mapped to high reliability bit positions in TDD HSDPA, achieving a performance gain of between 0.2 dB and 0.5 dB. The forwards / reverse mapping allows a degree of interleaving that improves system performance in fading channels or channels disturbed by short time period noise or interference.
Owner:SISVEL INT
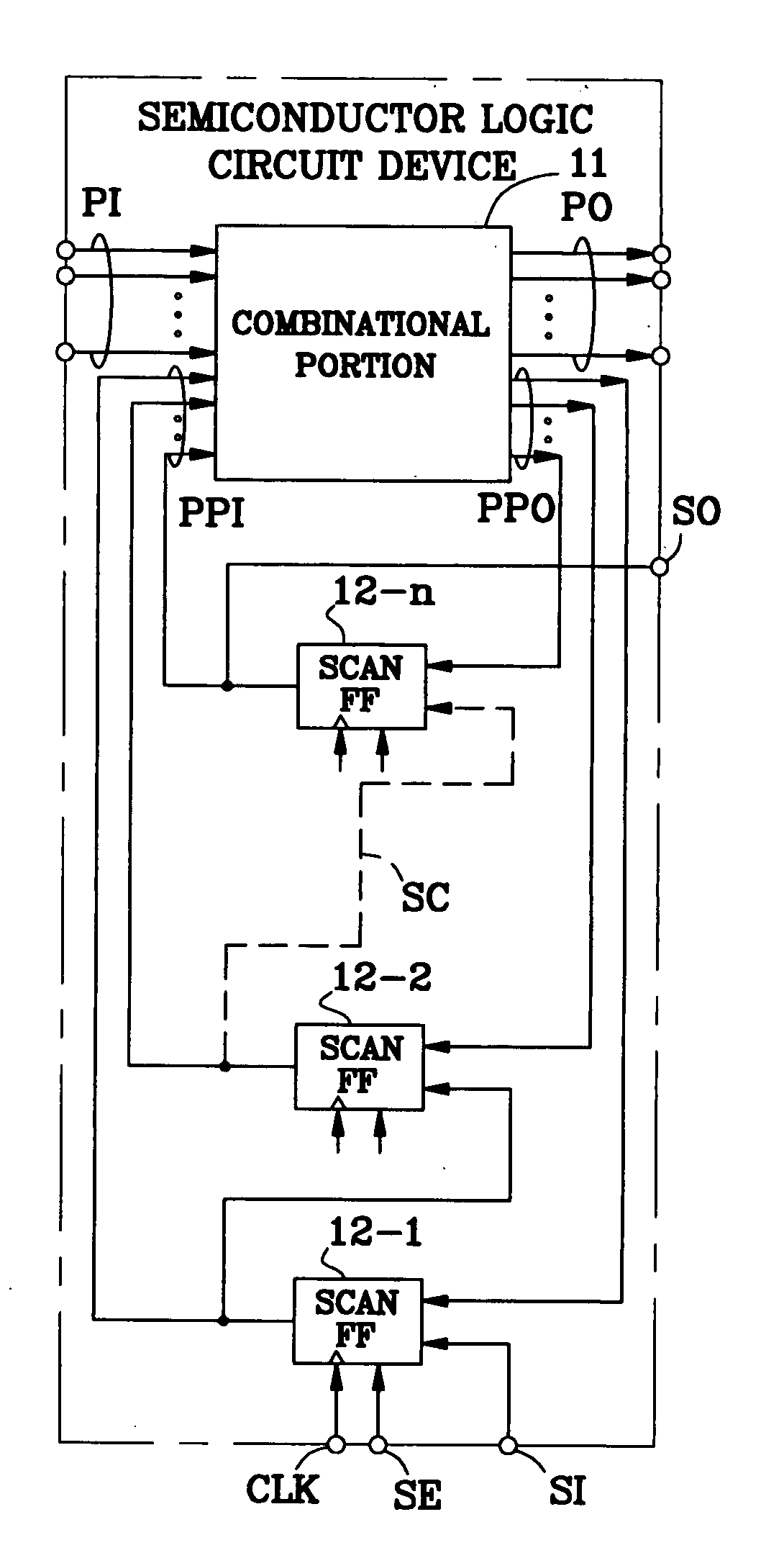
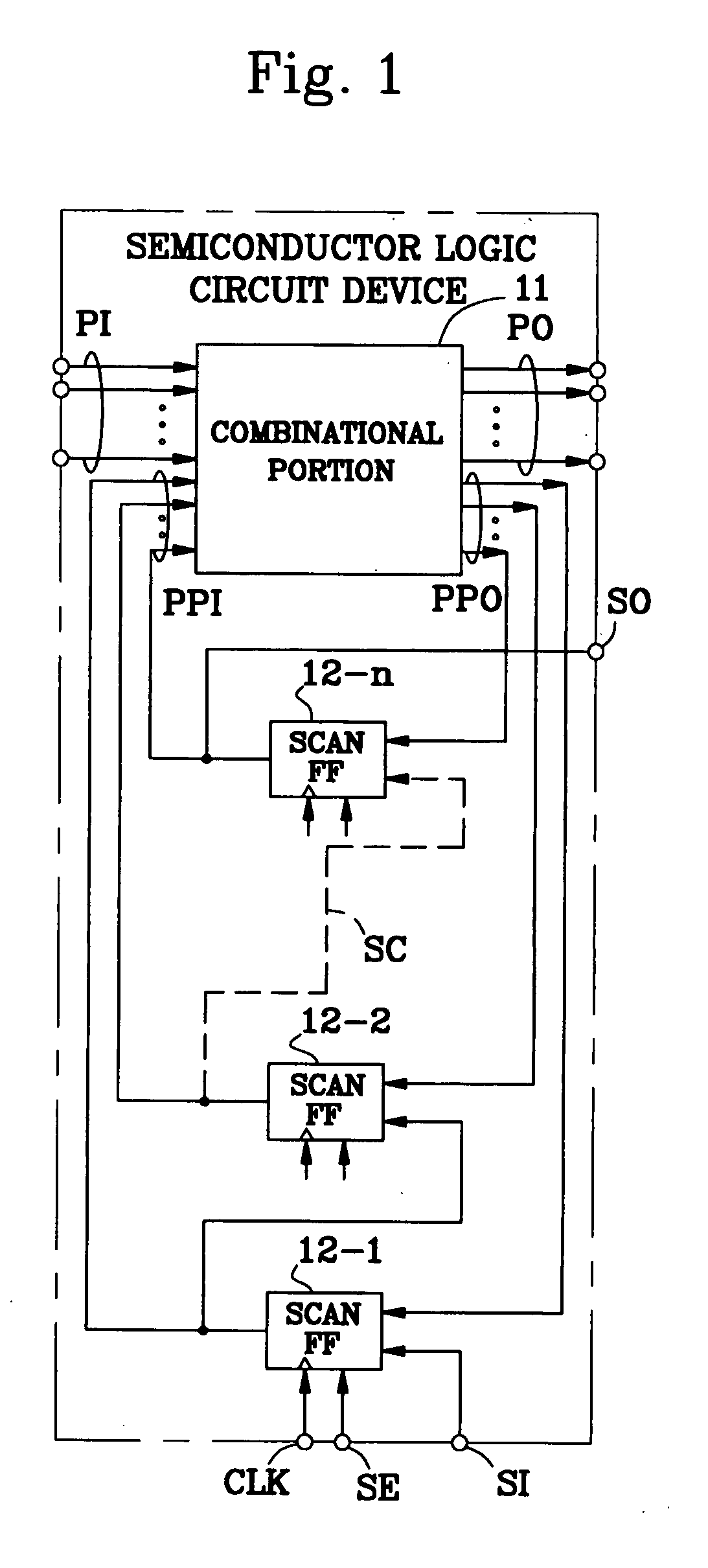
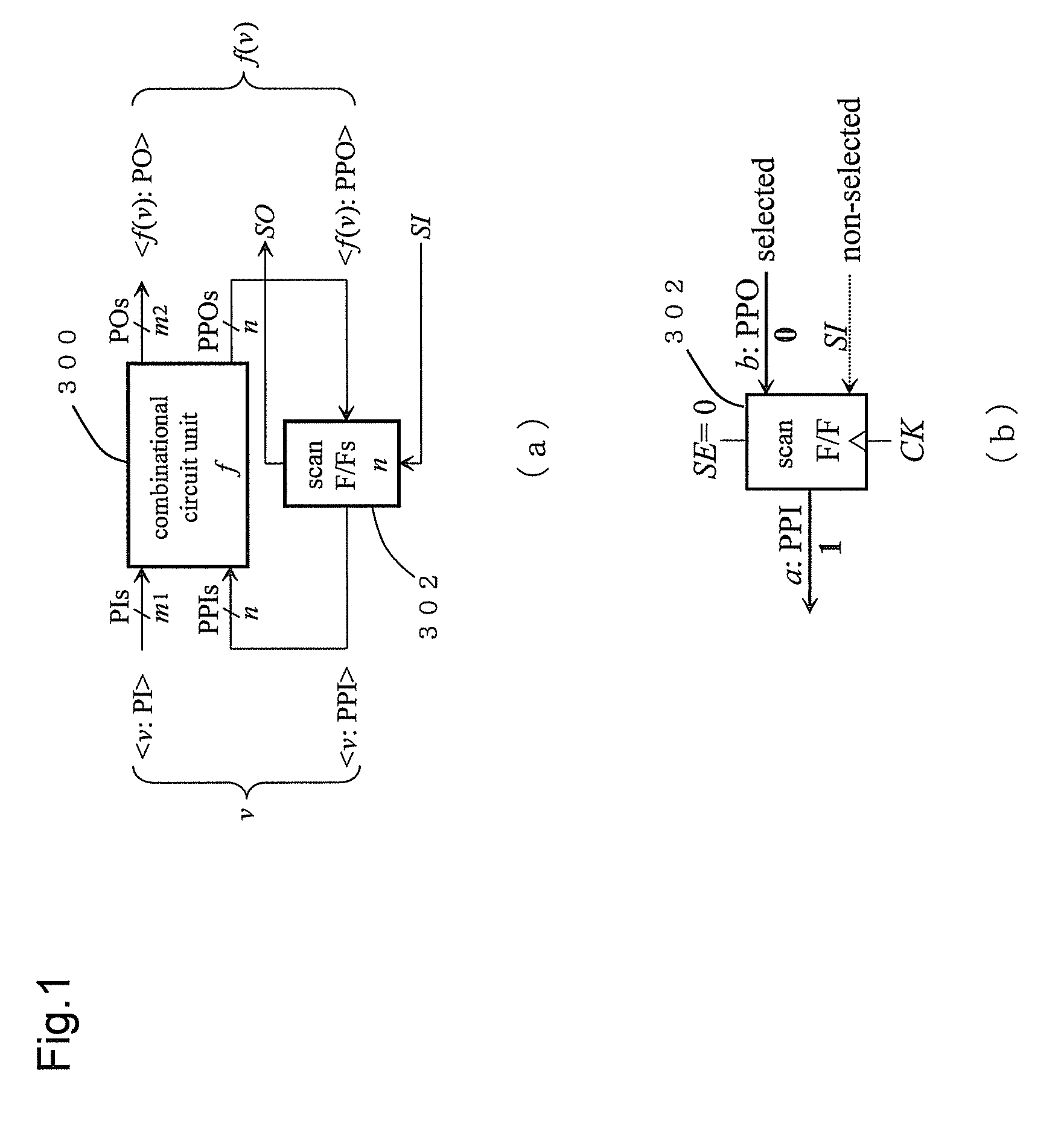
Test Method and Test Program of Semiconductor Logic Circuit Device
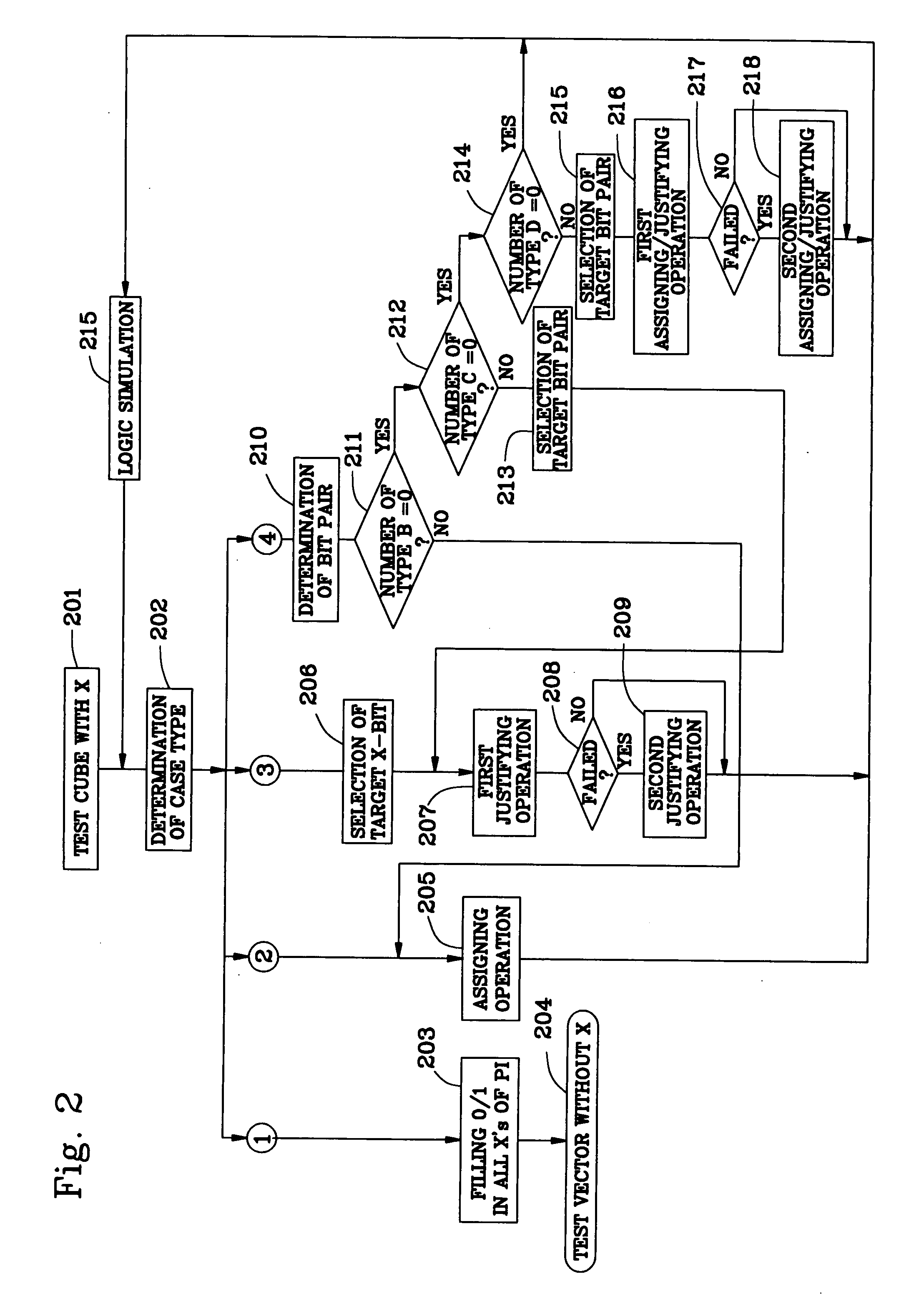
InactiveUS20090083593A1Avoiding erroneous testReduce power consumptionElectronic circuit testingLogical operation testingEngineeringBit pairing
The number of output switching scan flip-flops in a capture operation is decreased, which decreases the capture power consumption, so that the reduction of the power supply voltage can be decreased to decrease generation of an erroneous test. For this purpose, 0 or 1 is filled in unspecified bits within a test cube to decrease the output switching scan flip-flops, to convert the test cube into a test vector with no unspecified bit X. In a combinational portion 11, when there is one or more unspecified bits X in pseudo external input lines PPI and there is no unspecified bit X in pseudo external output lines PPO, an assigning operation is carried out so that the same logic values as bits of the pseudo external output lines PPO corresponding to all the unspecified bits X are assigned thereto (step 205). In the combinational portion 11, when there is one or more unspecified bits X in the pseudo external output lines PPO and there is no unspecified bit X in the pseudo external input lines PPI, first and second justifying operations are carried out, i.e., one unspecified bit X of the pseudo external output lines PPO is selected as a target unspecified bit X, and a necessary logic value is determined for an unspecified bit X of the test cube so that the same logic value as a bit of the pseudo external input lines PPI corresponding to that unspecified bit X or its opposite logic value may appear at that unspecified bit X (steps 207 and 209). In the combinational portion, when there are one more unspecified bits not only in the pseudo external input lines PPI but also the pseudo external output lines PPO, an assigning operation, a justifying operation or first and second assigning / justifying operations are performed upon a focused bit pair “ppi” and “ppo” (steps 210 to 218).
Owner:WEN XIAOQUING +1
Ultra-fast adder
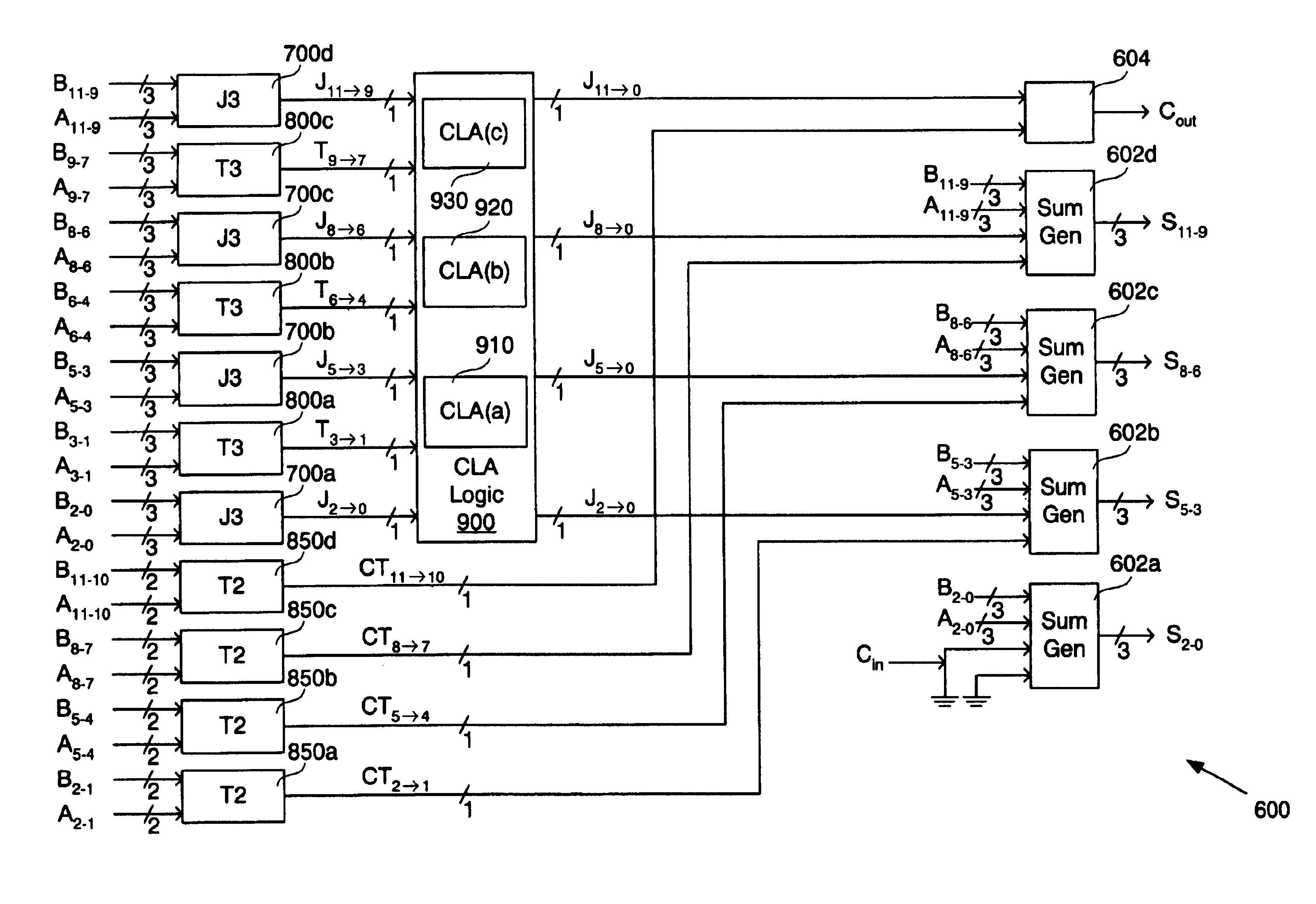
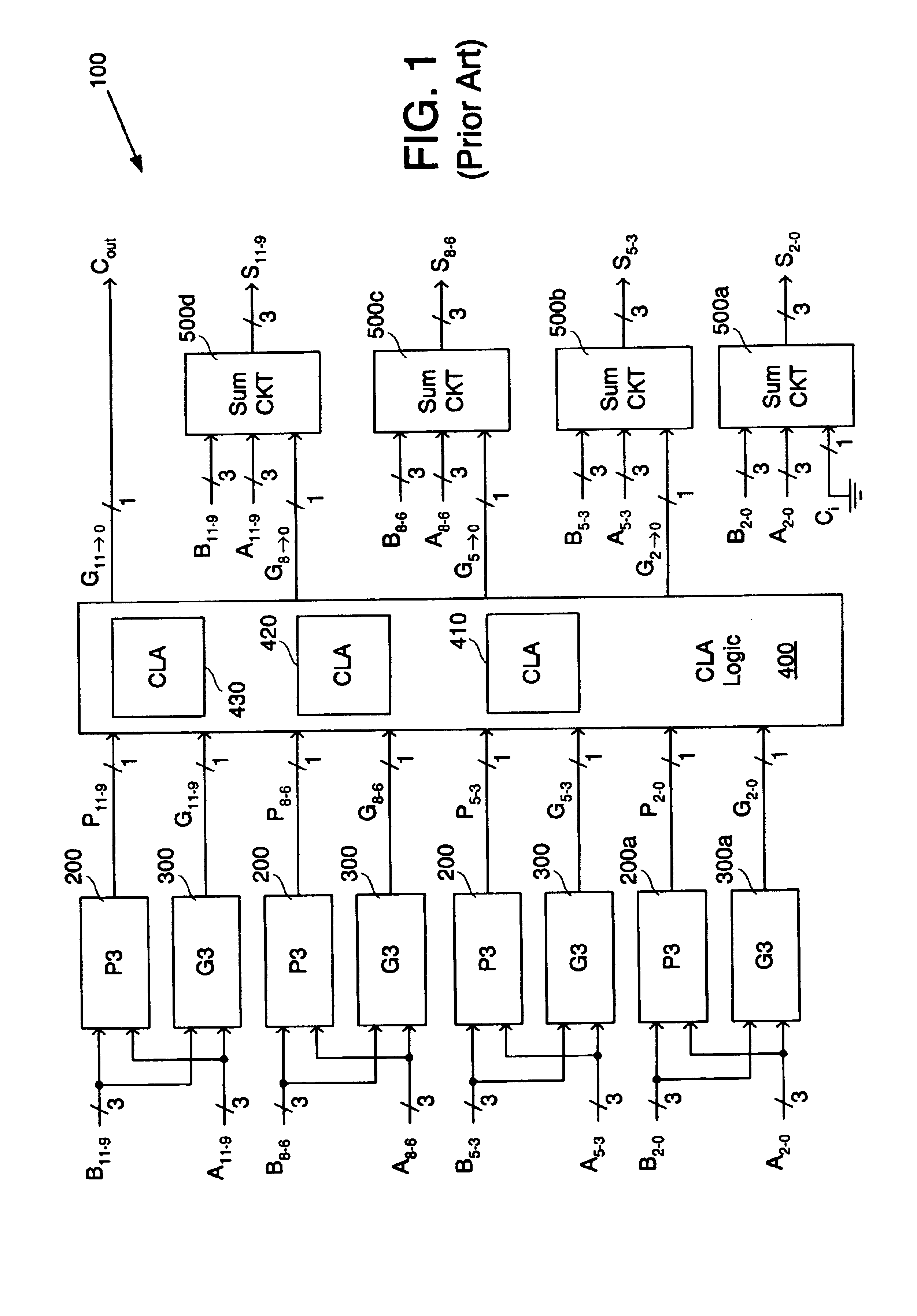
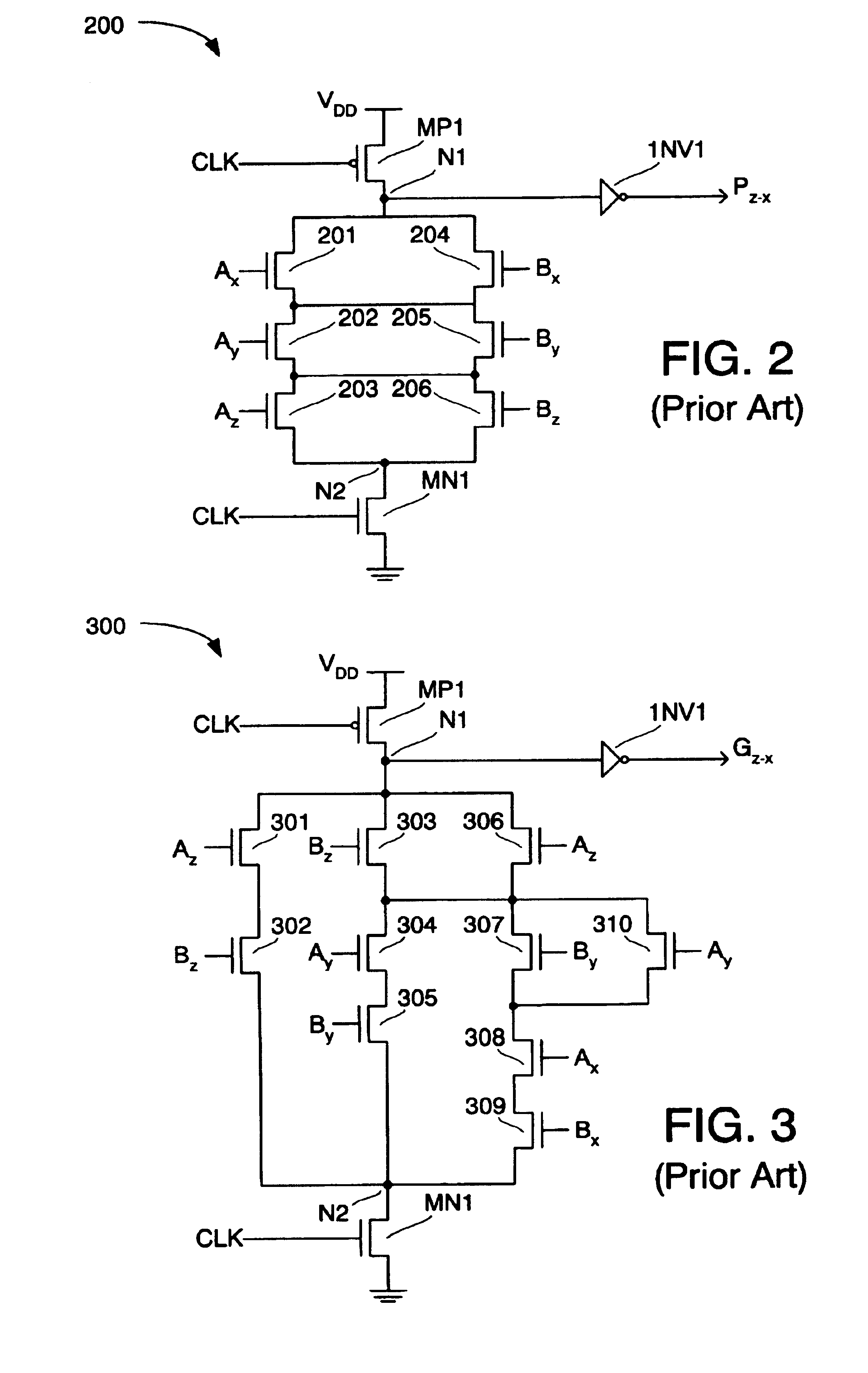
InactiveUS6957245B2Increase speedReduce stack heightComputation using non-contact making devicesUltra fastBit pairing
A carry look-ahead adder capable of adding or subtracting two input signals includes first stage logic having a plurality of carry-create and carry-transmit logic circuits each coupled to receive one or more bits of each input signal. Each carry-create circuit generates a novel carry-create signal in response to corresponding first bit-pairings of the input signals, and each carry-transmit circuit generates a novel carry-transmit signal in response to corresponding second bit-pairings of the input signals. The carry-create and carry-transmit signals are combined in carry look-ahead logic to generate accumulated carry-create signals, which are then used to select final sum bits.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
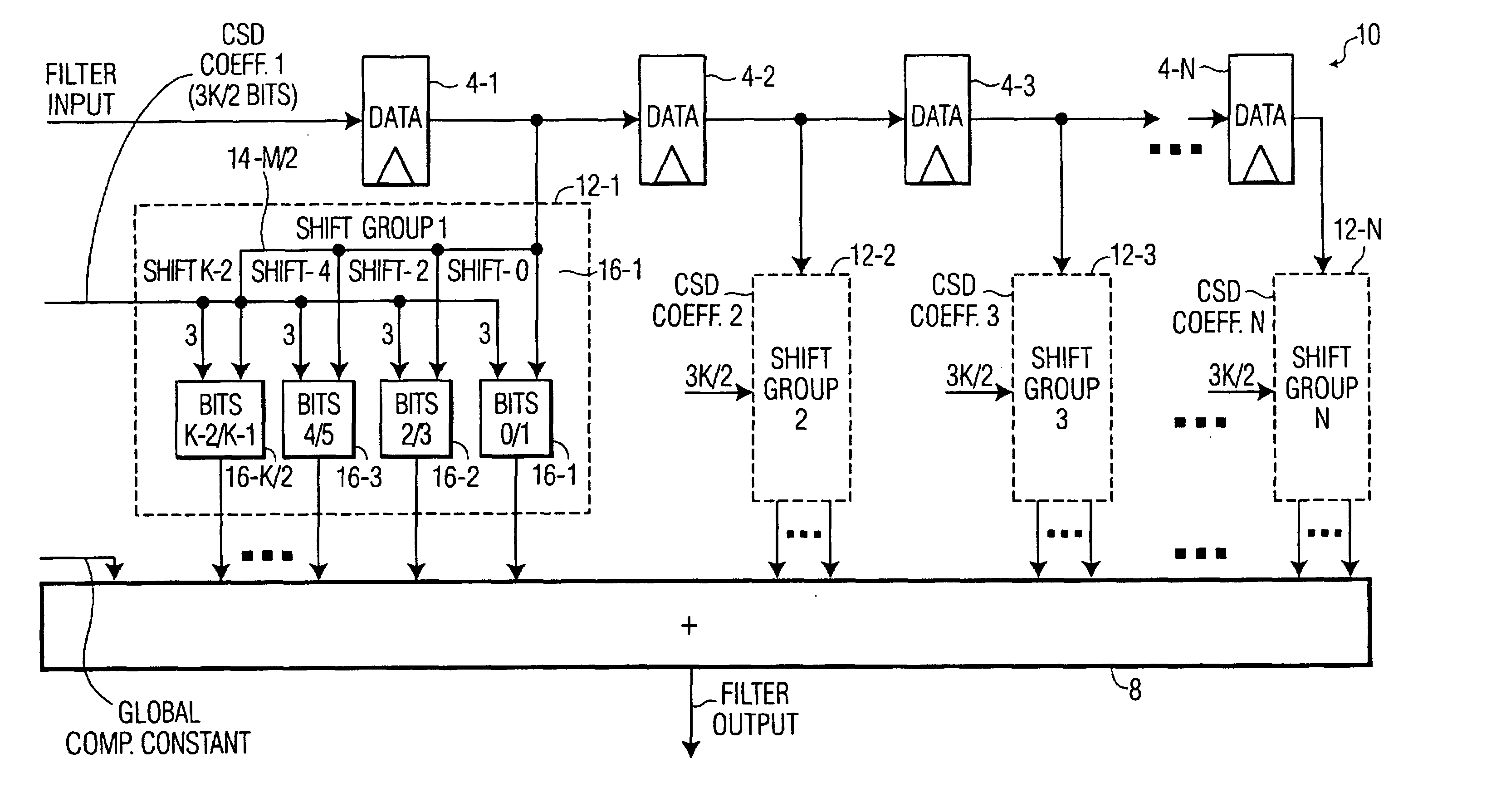
Reconfigurable FIR filter using CSD coefficient representation
InactiveUS7164712B2Multiple-port networksDigital technique networkParallel computingCanonical signed digit
The present invention is directed to a reconfigurable finite impulse response (FIR) filter that processes data tap values with canonical sign digit (CSD) coefficients. The FIR filter according to the present invention includes a shift group associated with at least one of the data tap values and at least one of the CSD coefficients. Each shift group includes a plurality of parallel paths. Each parallel path shifts the data tap value according to a bit pair of the coefficient to produce a weighted product. An adder is also included that combines the weighted products from each of the shift groups.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
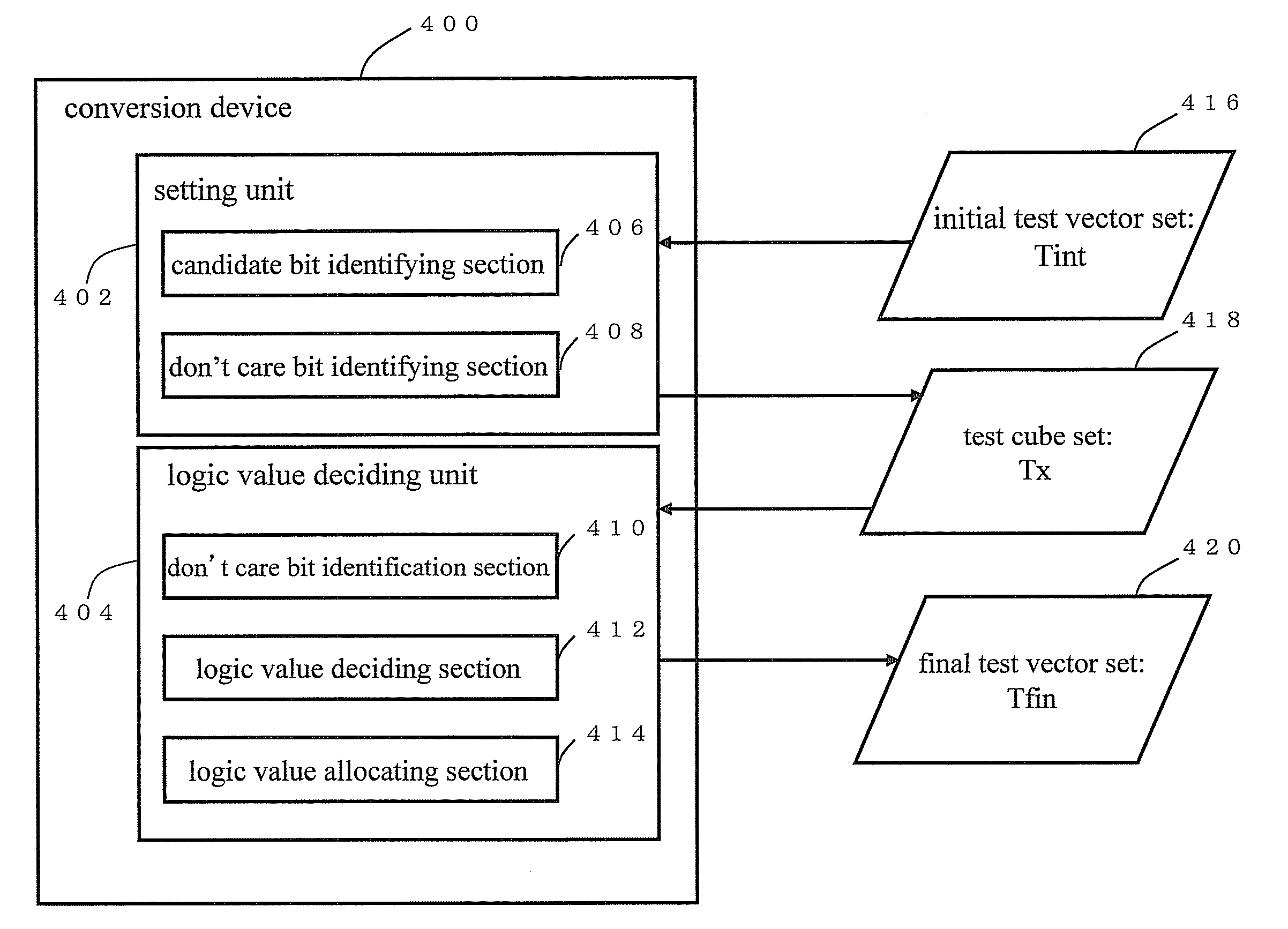
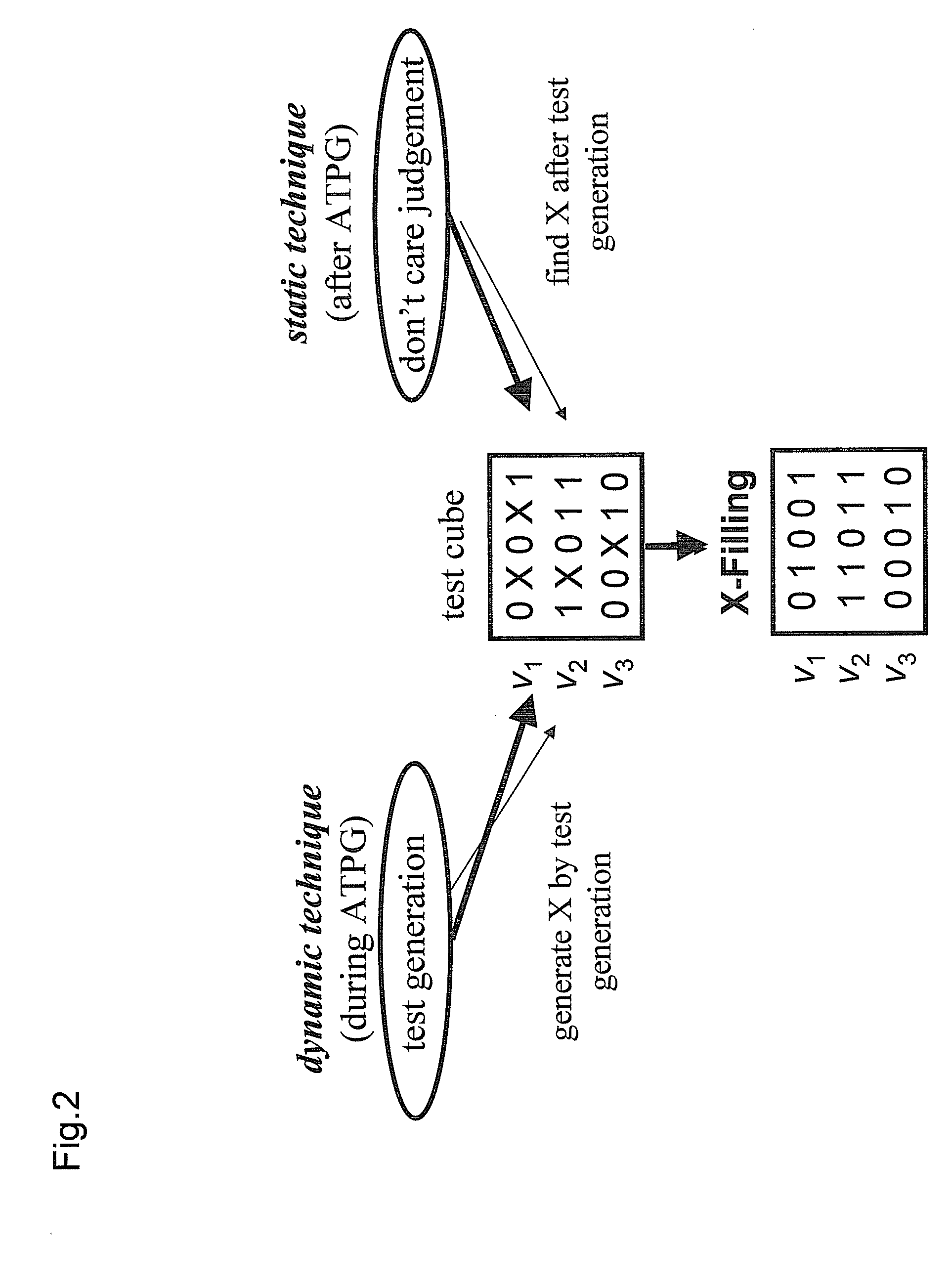
Conversion device, conversion method, program, and recording medium
InactiveUS20080235543A1Control power consumptionFalse testElectronic circuit testingLogical operation testingBit pairingTest vector
Provided are a conversion device and others for converting a test vector set so as to reduce a logic value difference generated before and after scan capture in outputs of scan cells included in a full scan sequential circuit. A conversion device 400 converts a test vector set corresponding to the full scan sequential circuit. The conversion device 400 comprises a setting unit 402 for setting a candidate bit which can be a don't care bit and a fixed bit which cannot be the don't care bit according to predetermined constraint conditions based on an input-output relationship in the logic circuit in order to identify the don't care bit identifiable as don't care from each test vector of the test vector set, and a logic value deciding unit 404 for deciding a logic value for the don't care bit in view of a relationship in a plurality of bit pairs in relation to a test cube including the don't care bit identified by the setting unit 402.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP +2
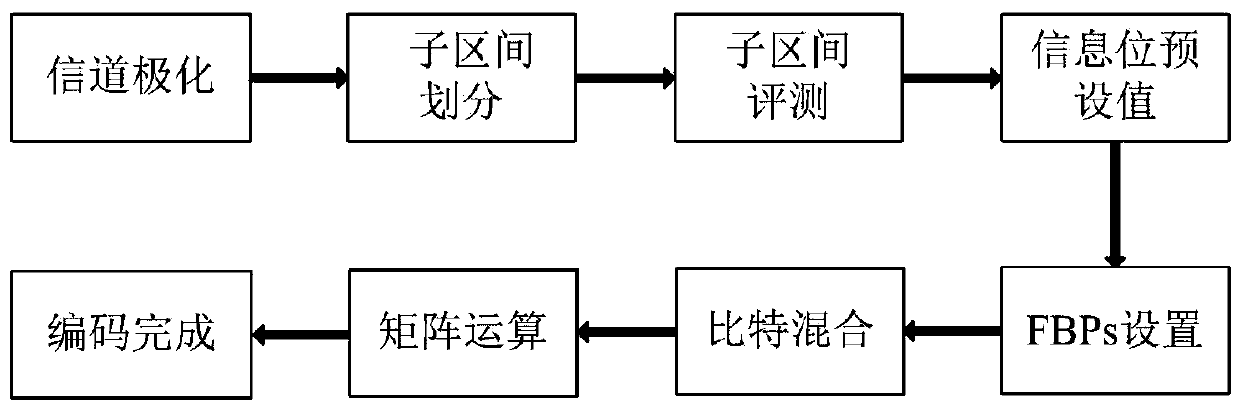
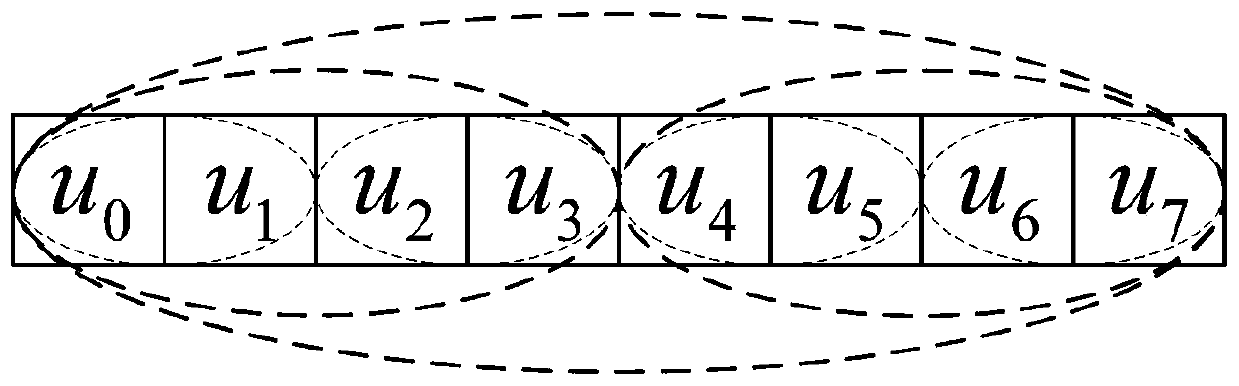
Polar code encoding method and polar code serial offset decoding method and circuit based on frozen bit pairs
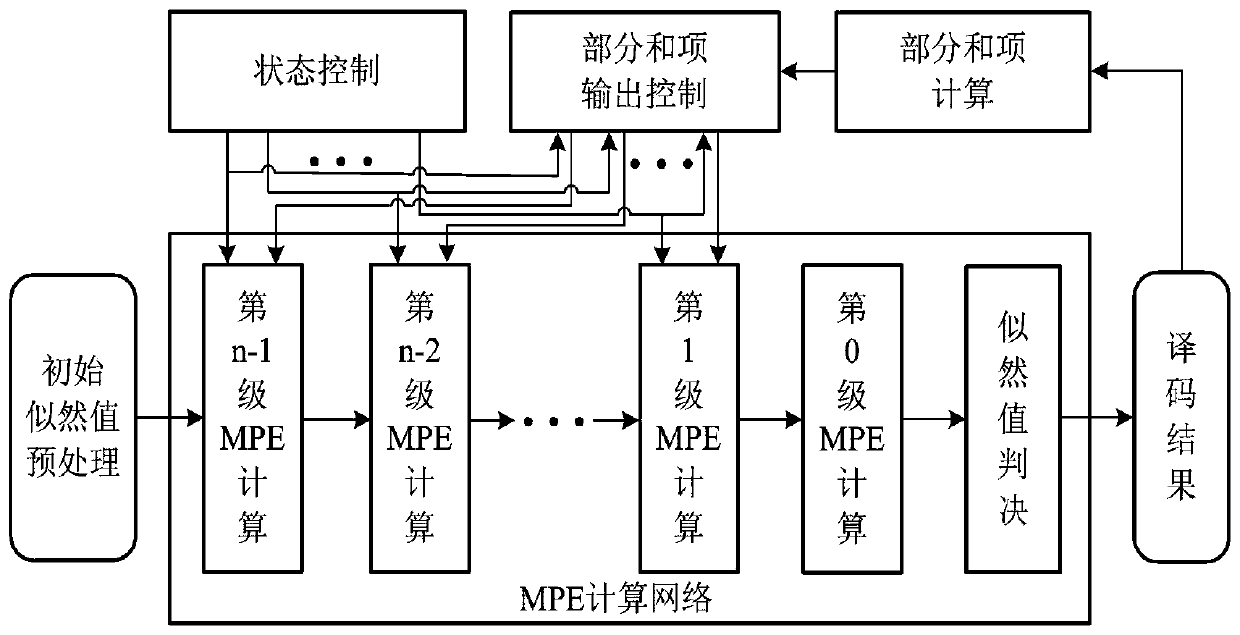
ActiveCN110022188AImprove decoding speedStrong and flexible configuration capabilityError preventionError correction/detection using linear codesDecoding methodsBit pairing
The invention discloses a polar code encoding method based on frozen bit pairs and a polar code serial offset decoding method and circuit. The whole encoding process can be mainly divided into channelpolarization, sub-interval division, sub-interval evaluation, information bit preset values, frozen bit pair setting, bit mixing and matrix operation. The decoding circuit comprises an initial likelihood value preprocessing module, a control state module, a partial sum item calculation module and an MPE calculation network module. The decoder further reduces the decoding delay, improves the datathroughput rate, reduces the consumption of hardware resources, and improves the overall performance of the decoder.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
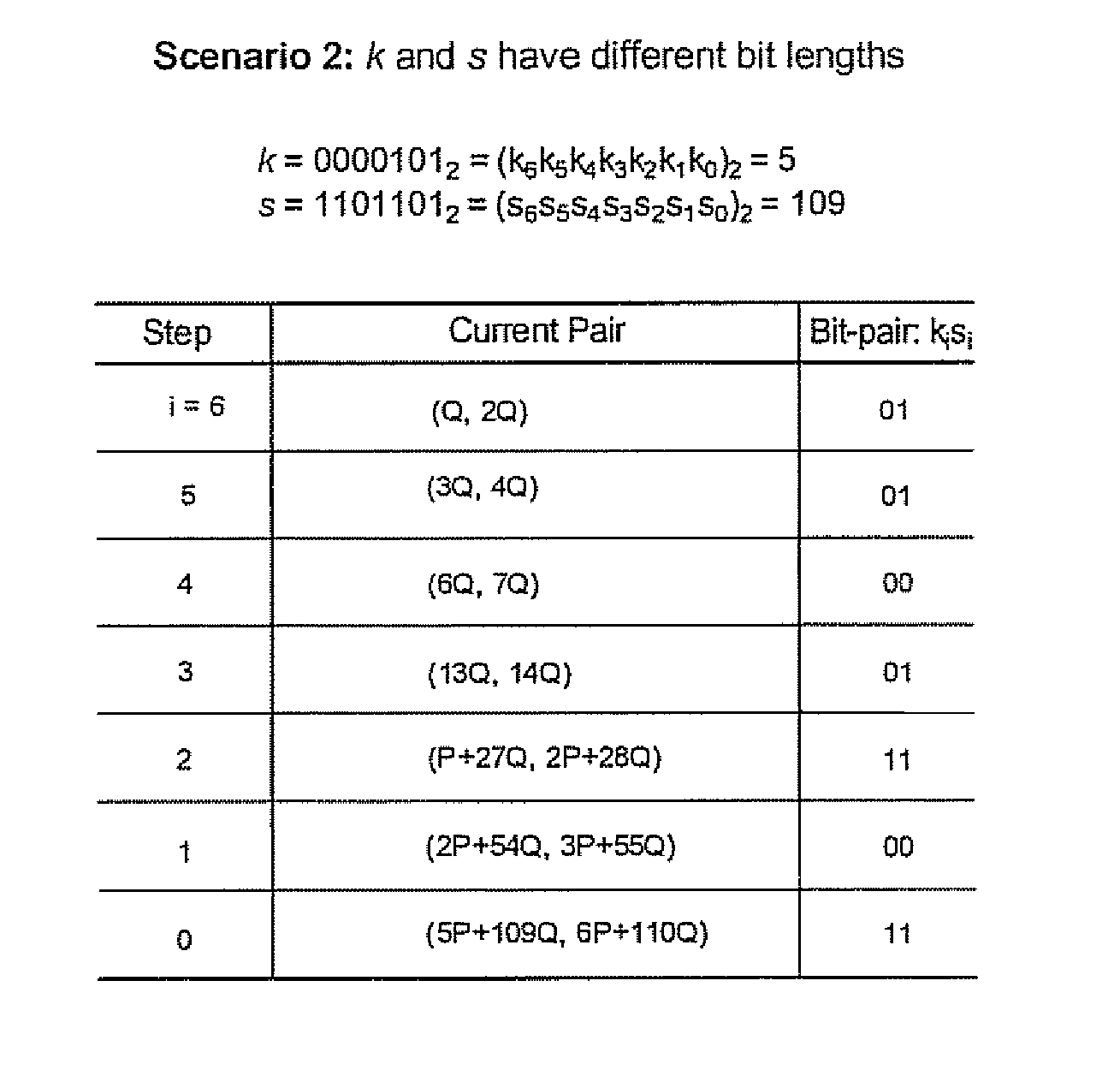
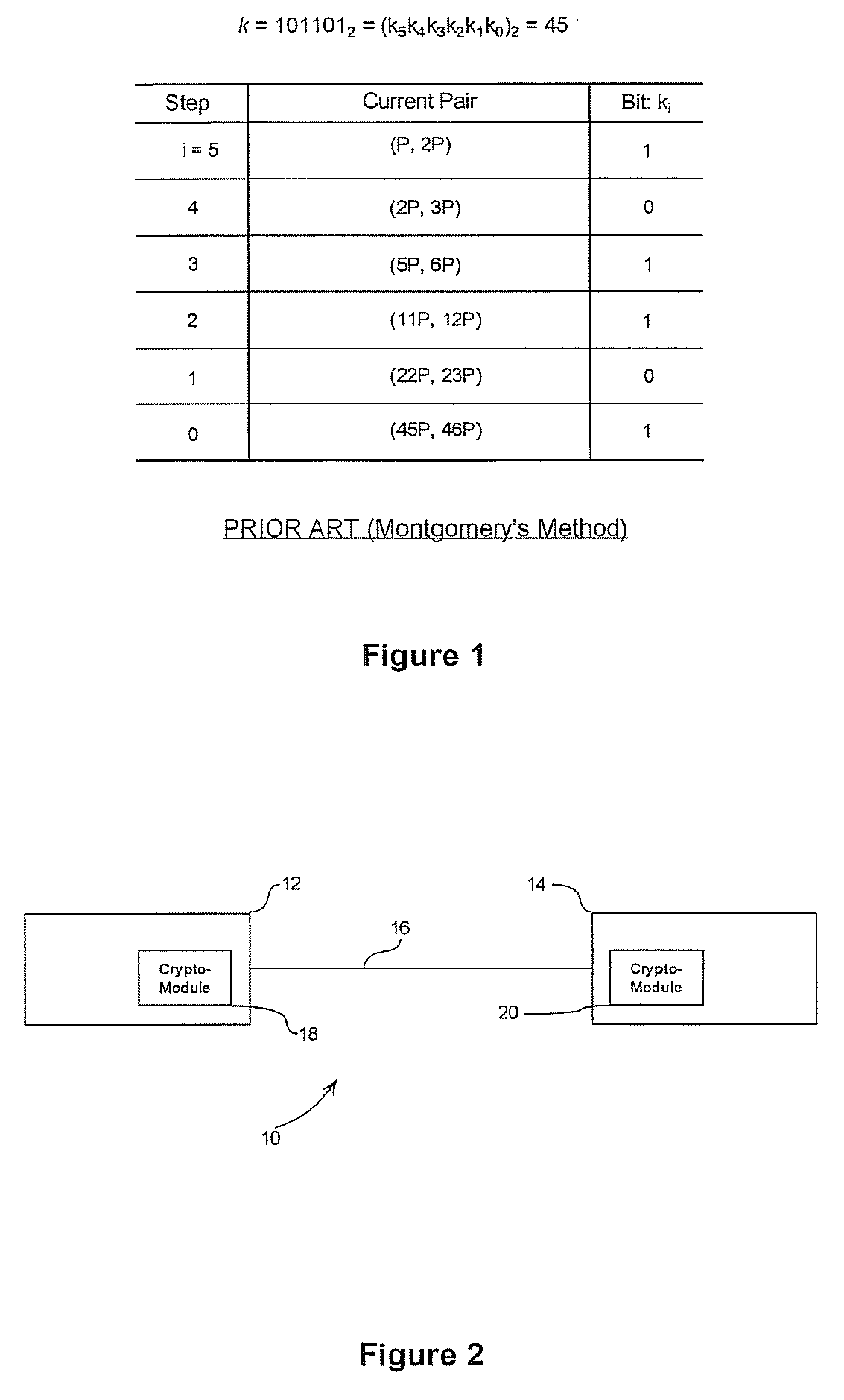
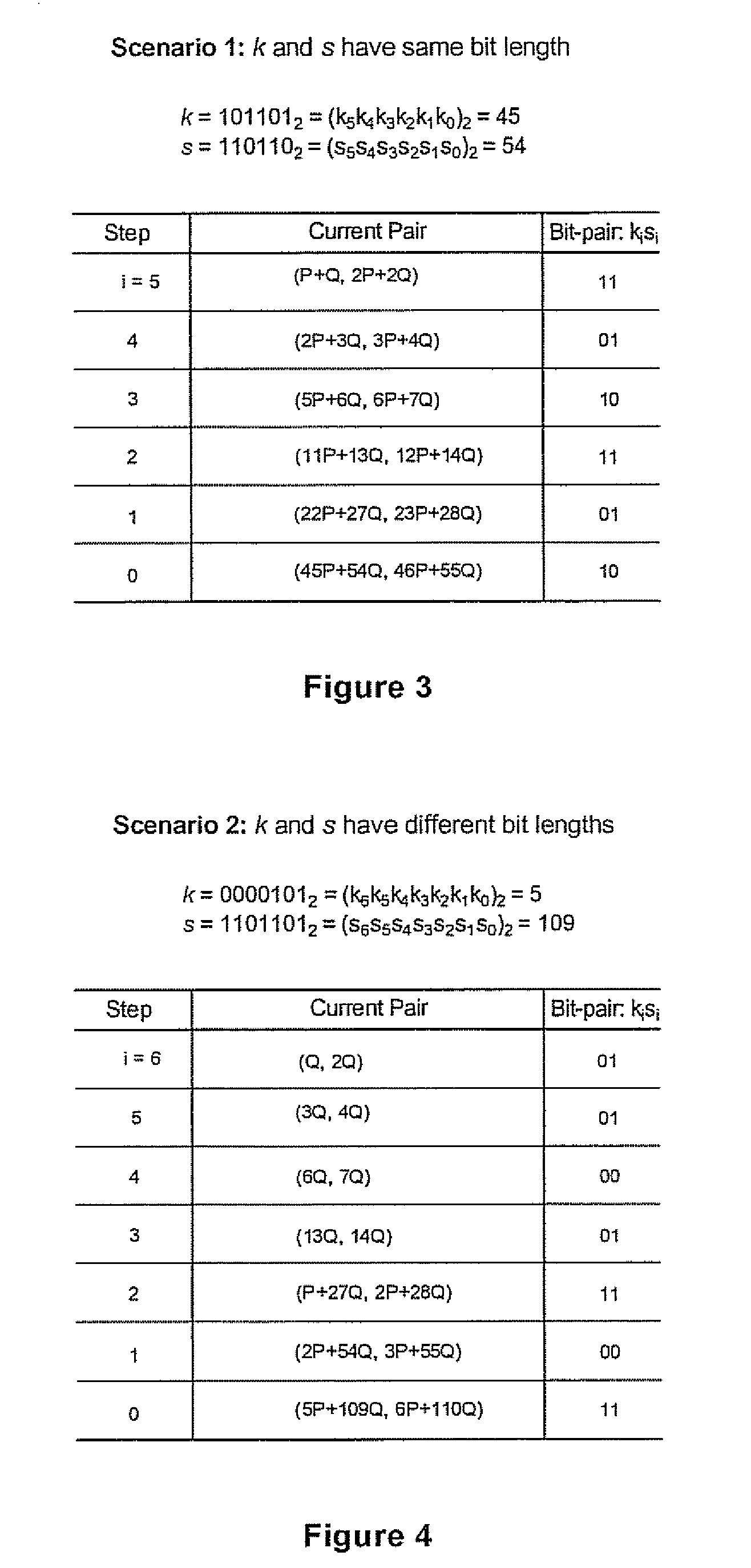
Simultaneous scalar multiplication method
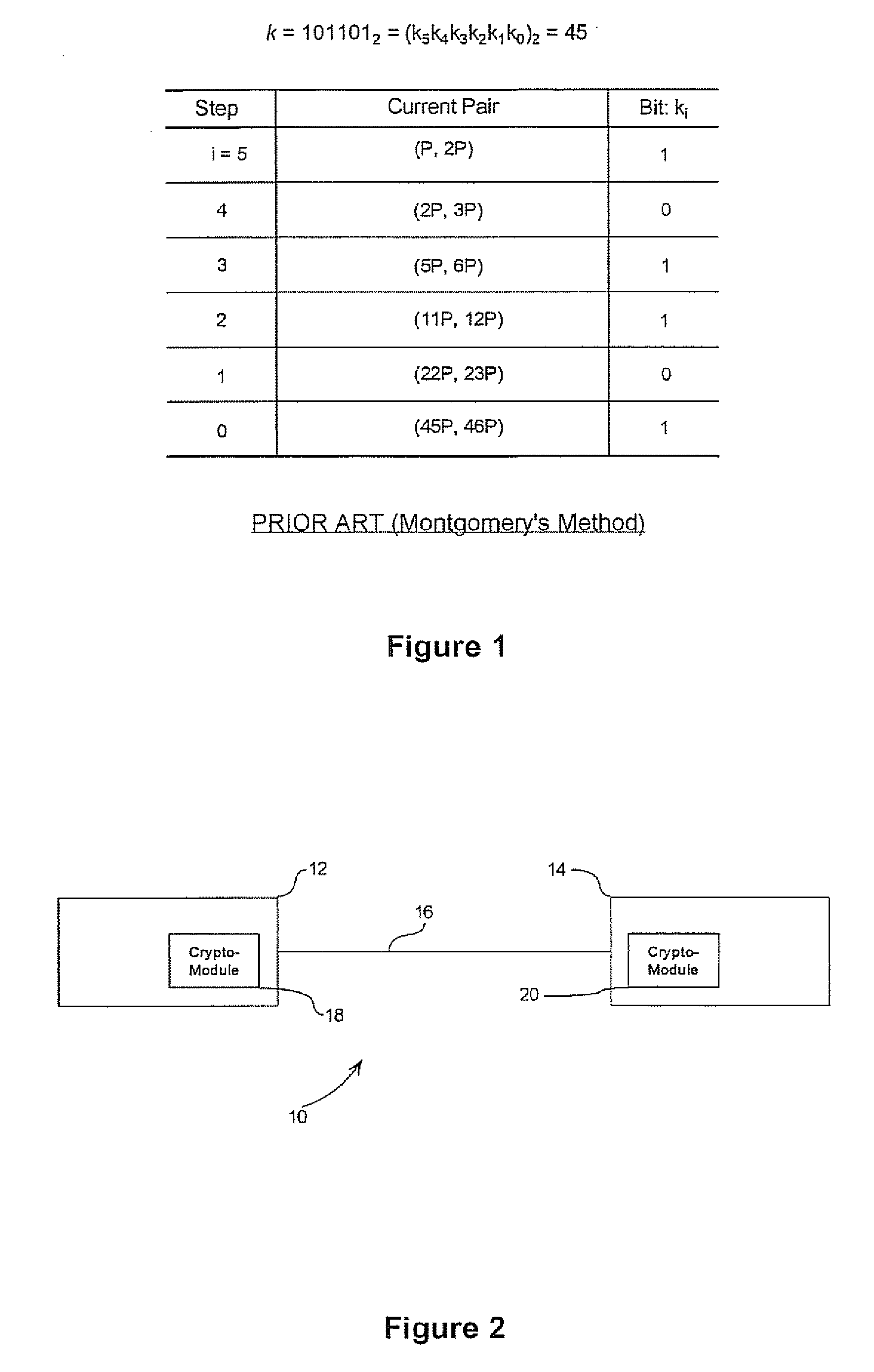
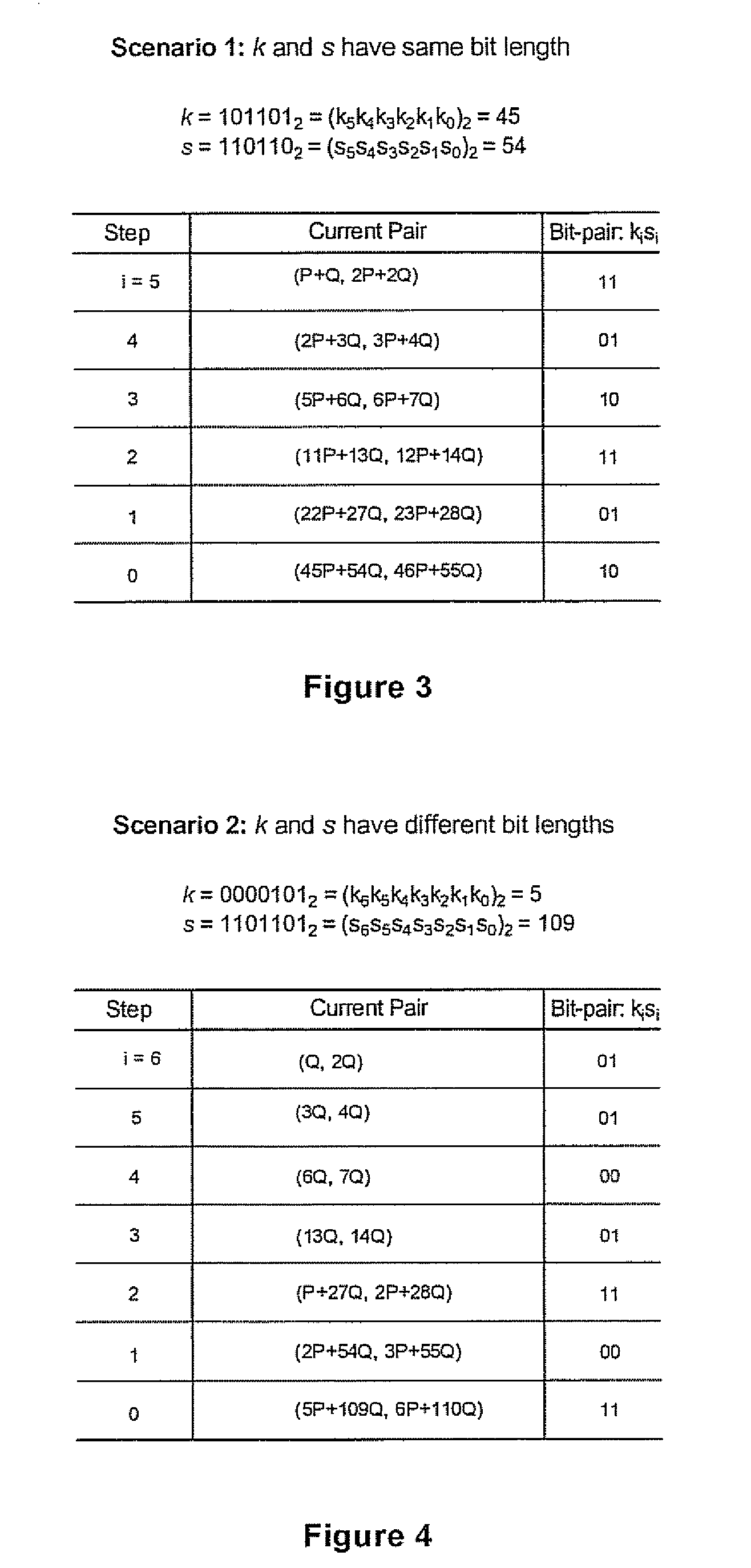
ActiveUS20070098154A1Reduce in quantityKey distribution for secure communicationPublic key for secure communicationAlgorithmSingle pair
In computing point multiples in elliptic curve schemes (e.g. kP and sQ) separately using, for example, Montgomery's method for the purpose of combining kP+sQ several operations are repeated in computing kP and sQ individually, that could be executed at the same time. A simultaneous scalar multiplication method is provided that reduces the overall number of doubling and addition operations thereby providing an efficient method for multiple scalar multiplication. The elements in the pairs for P and Q method are combined into a single pair, and the bits in k and s are evaluated at each step as bit pairs. When the bits in k and s are equal, only one doubling operation and one addition operation are needed to compute the current pair, and when the bits in k and s are not equal, only one doubling operation is needed and two addition operations.
Owner:MALIKIE INNOVATIONS LTD
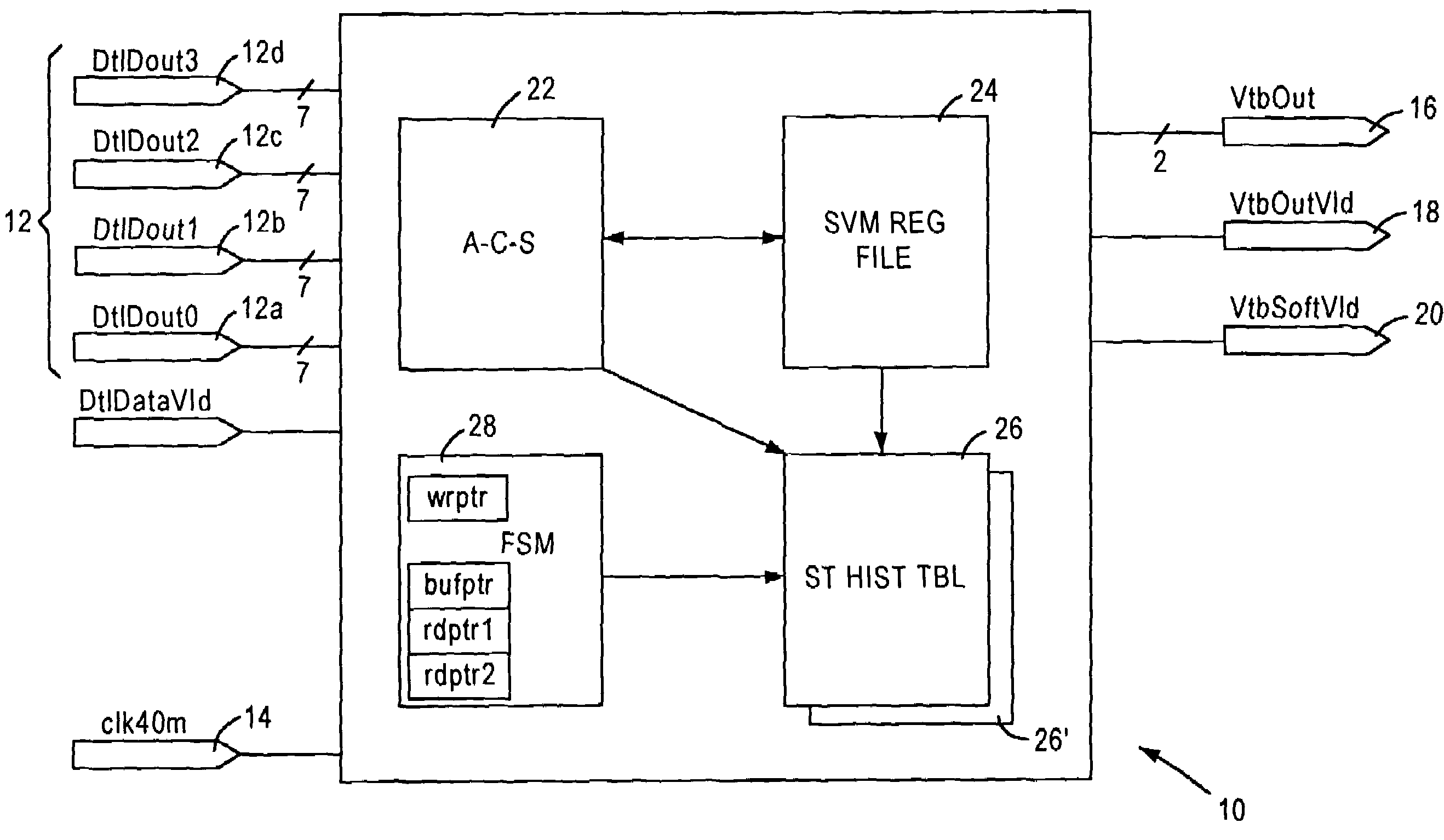
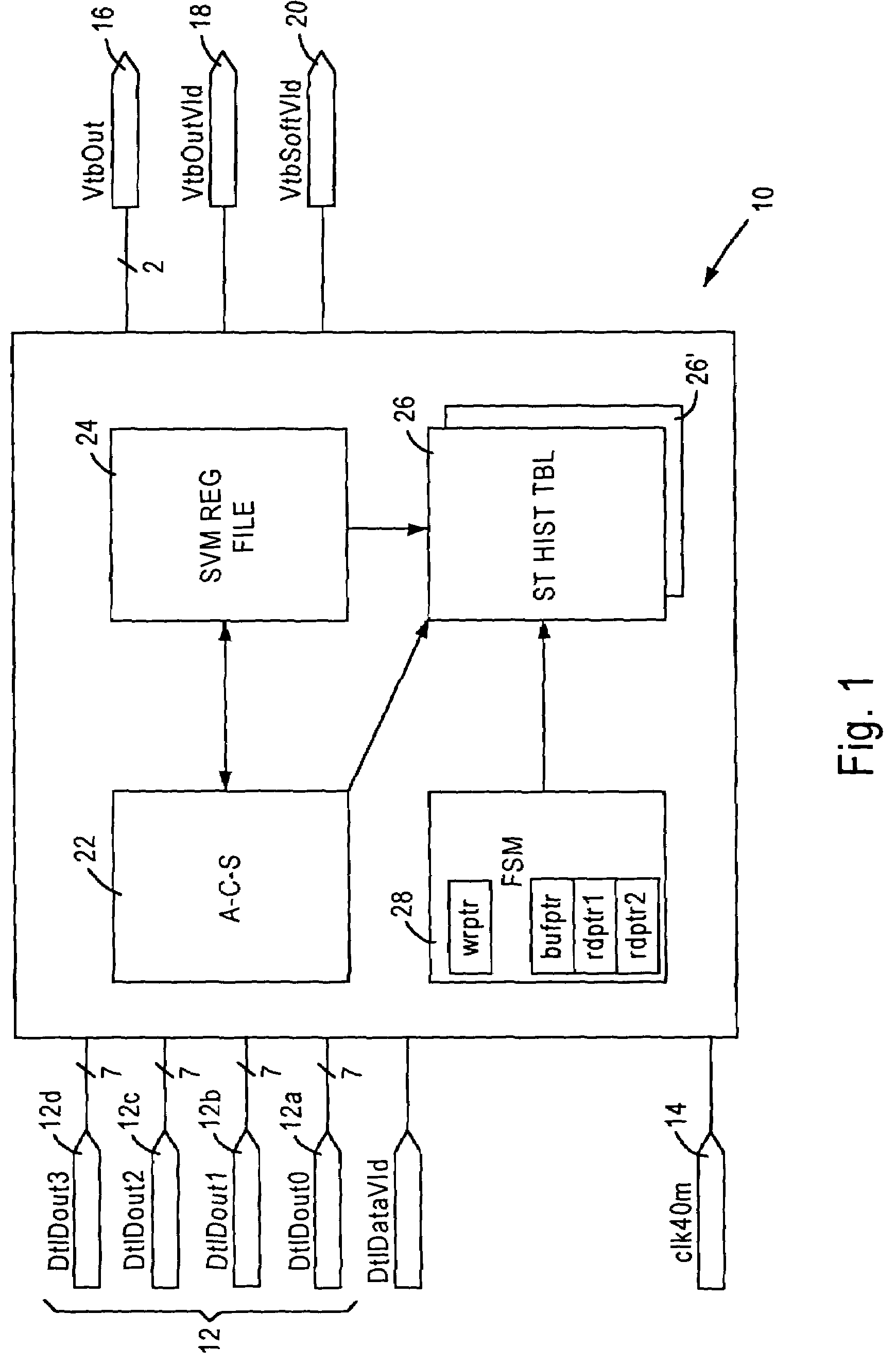
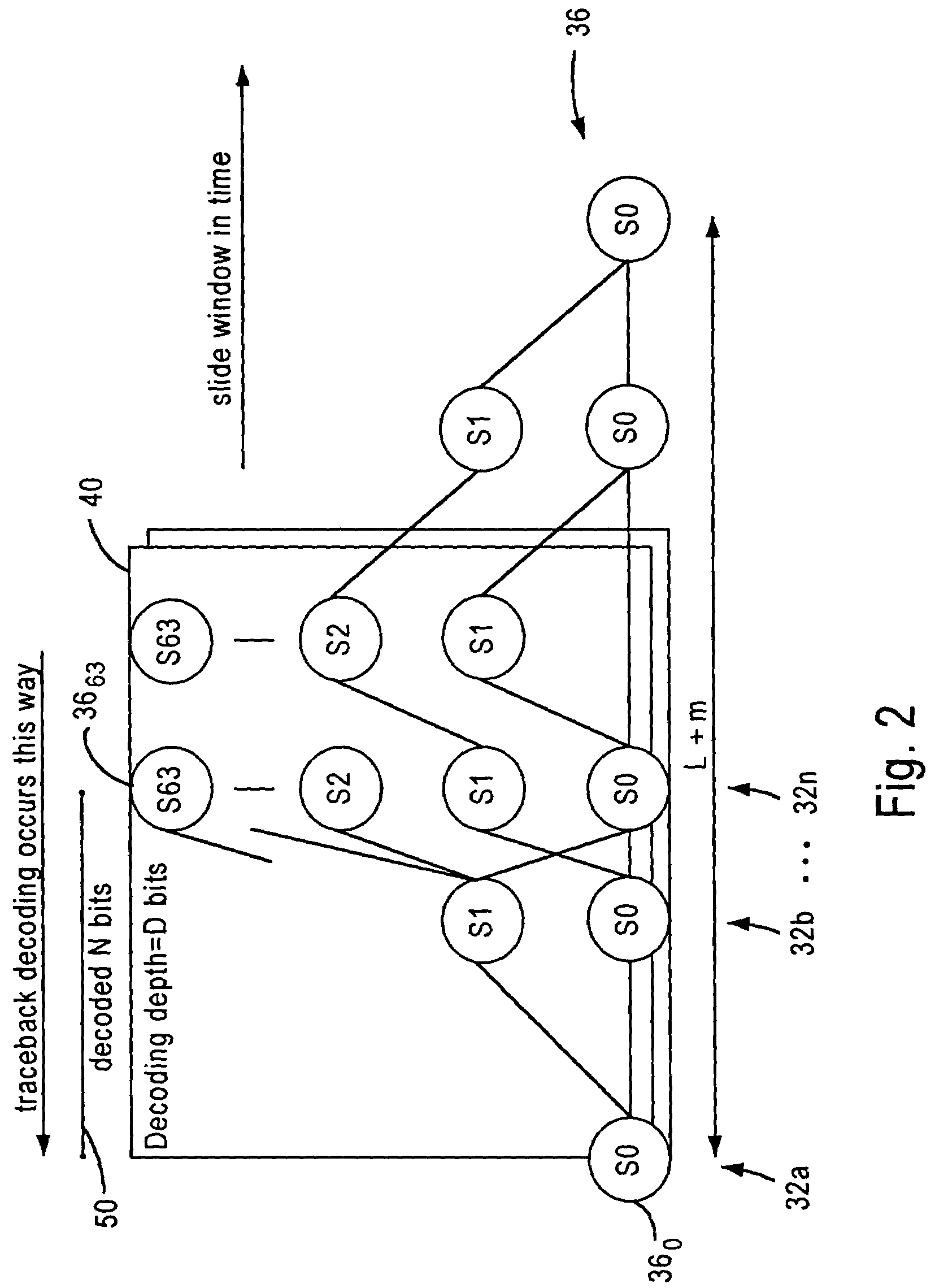
Viterbi decoder utilizing partial backtracing
InactiveUS7248637B2Efficient and economicalReduce in quantityData representation error detection/correctionOther decoding techniquesViterbi decoderBit pairing
A Viterbi decoder is configured for outputting a prescribed plural number of decoded bit pairs upon execution of each backtracing operation based on accessing a second prescribed number of state history table entries from a surviving state history table. The outputting of more bits per backtrace operation lowers the number of memory accesses, and enables the Viterbi decoder to maintain a high throughput of data flow while maintaining an acceptable bit error rate.
Owner:ADVANCED SILICON TECH
Range code compression method and apparatus for ternary content addressable memory (CAM) devices
InactiveUS7904643B1Reduce in quantityIncrease in sizeDigital storageMemory systemsPartial representationOne-hot
A content addressable memory (CAM) device, method, and method of generating entries for range matching are disclosed. A CAM device (800) according to one embodiment can include a pre-encoder (806) that encodes range bit values W into additional bits E. Additional bits E can indicate compression of range rules according to particular bit pairs. A CAM array (802) can include entries that store compressed range code values (RANGE) with corresponding additional bit values (ENC). Alternate embodiments can include pre-encoders that encode portions of range values (K1 to Ki) in a “one-hot” fashion. Corresponding CAM entries can include encoded value having sections that each represent increasingly finer divisions of a range space.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
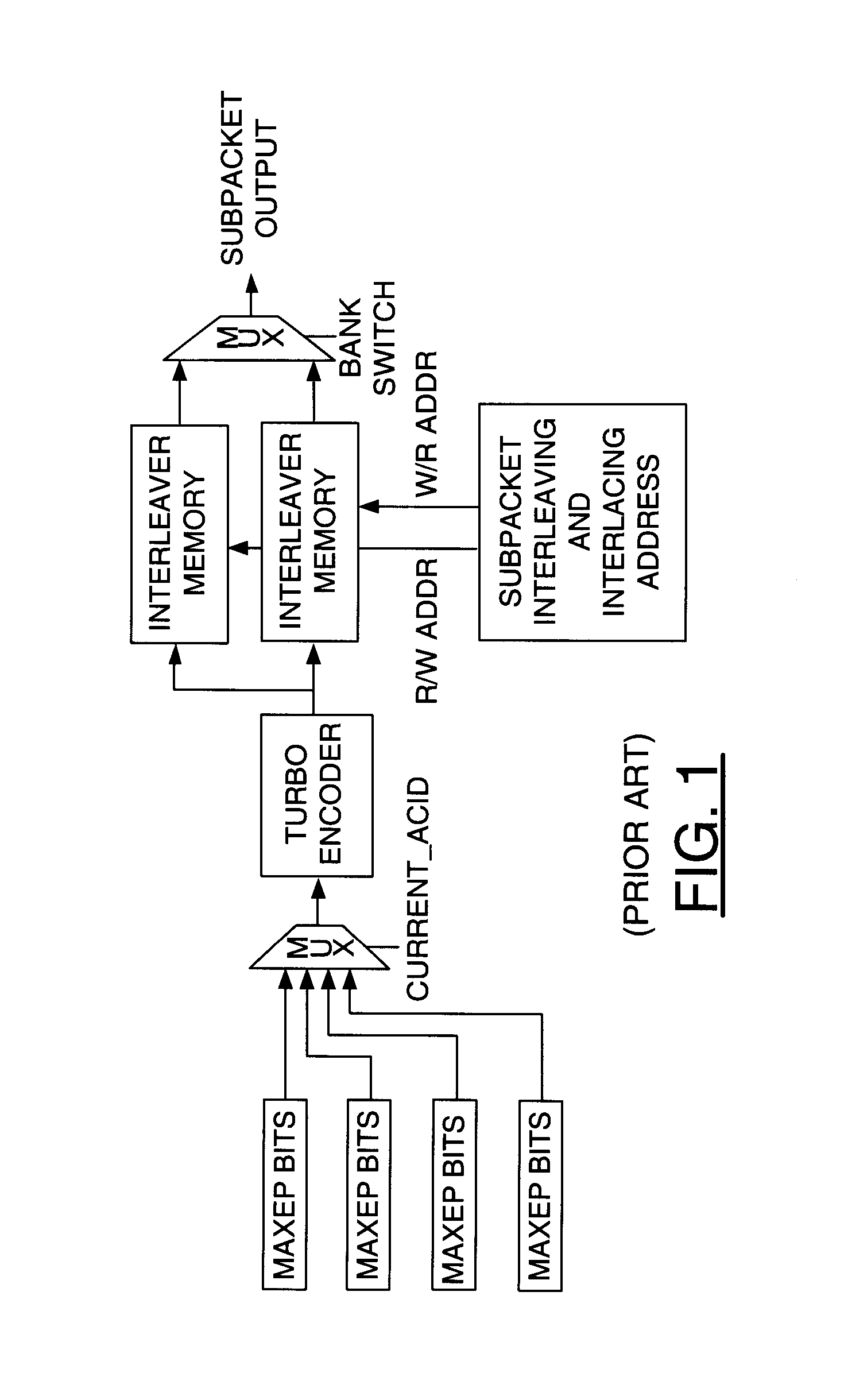
Method to efficiently generate the row and column index for half rate interleaver in GSM
A method and apparatus for interleaving bits in a first sequence is disclosed. An exemplary method comprises storing a set of offset values in at least one table, applying in order each of the set of offset values to identify an adjacent bit pair in the first sequence of the bits for a new interleaved sequence of the bits and incrementing each of the set of offset values until an upper limit is reached to further identify additional adjacent bit pairs in the first sequence of the bits for the new interleaved sequence of the bits. The table is significantly shorter, requiring less memory than that used in a conventional interleaver, particularly a GSM interleaver for half rate speech.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Systems and methods of partitioning data to facilitate error correction
Systems and methods are provided for detecting and correcting bit errors in data structures. A data block and / or data structure is partitioned into adjacent bit pair domains, such that a single adjacent bit pair from each memory device is assigned to a given adjacent bit pair domain. The bits in the adjacent bit pair domain are processed by an error correction unit sequentially or in parallel, and then recombined to be written into memory or transmitted to a requestor.
Owner:VALTRUS INNOVATIONS LTD +1
Simultaneous scalar multiplication method
ActiveUS8045705B2Reduce in quantityReduce the numberKey distribution for secure communicationDigital data processing detailsAlgorithmSingle pair
Owner:MALIKIE INNOVATIONS LTD
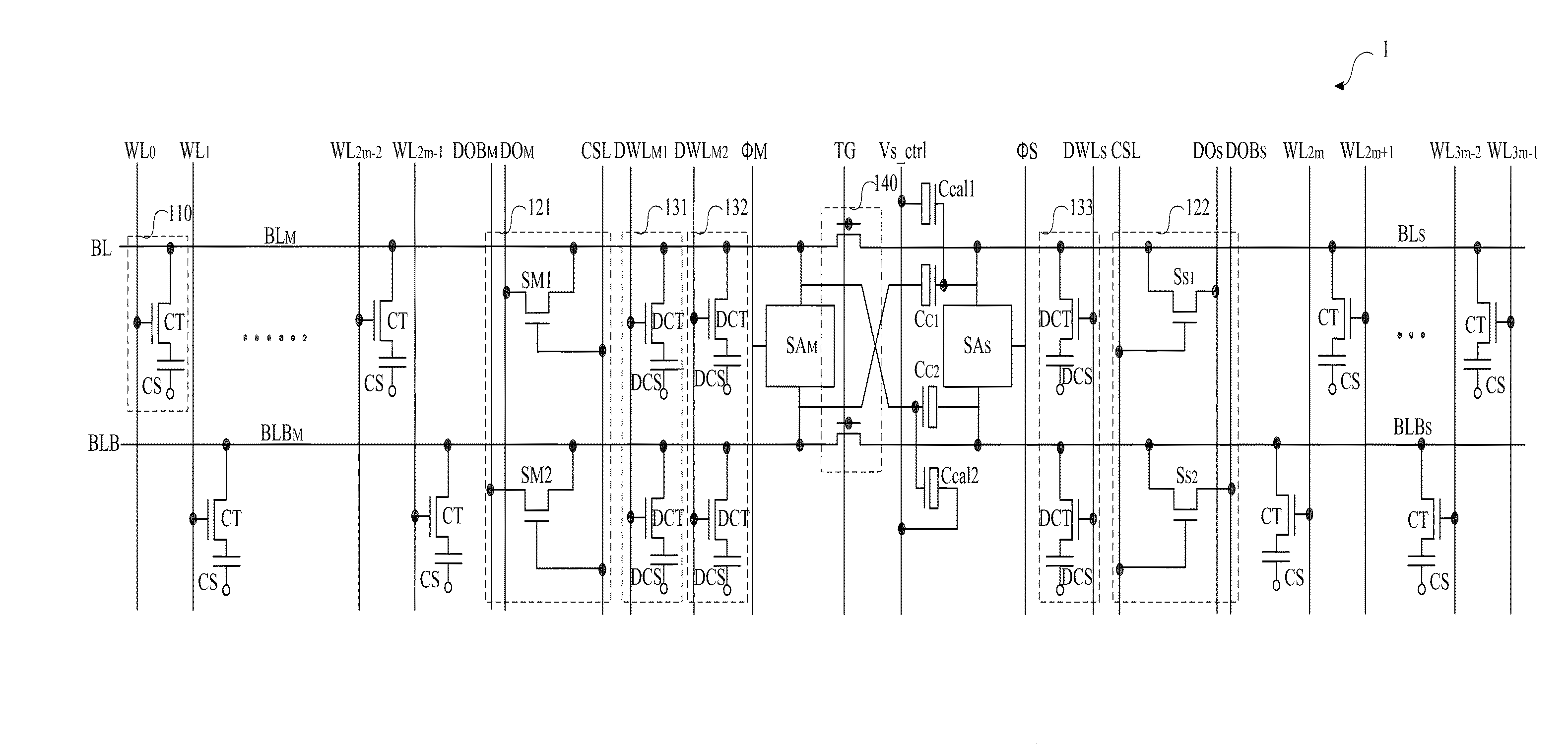
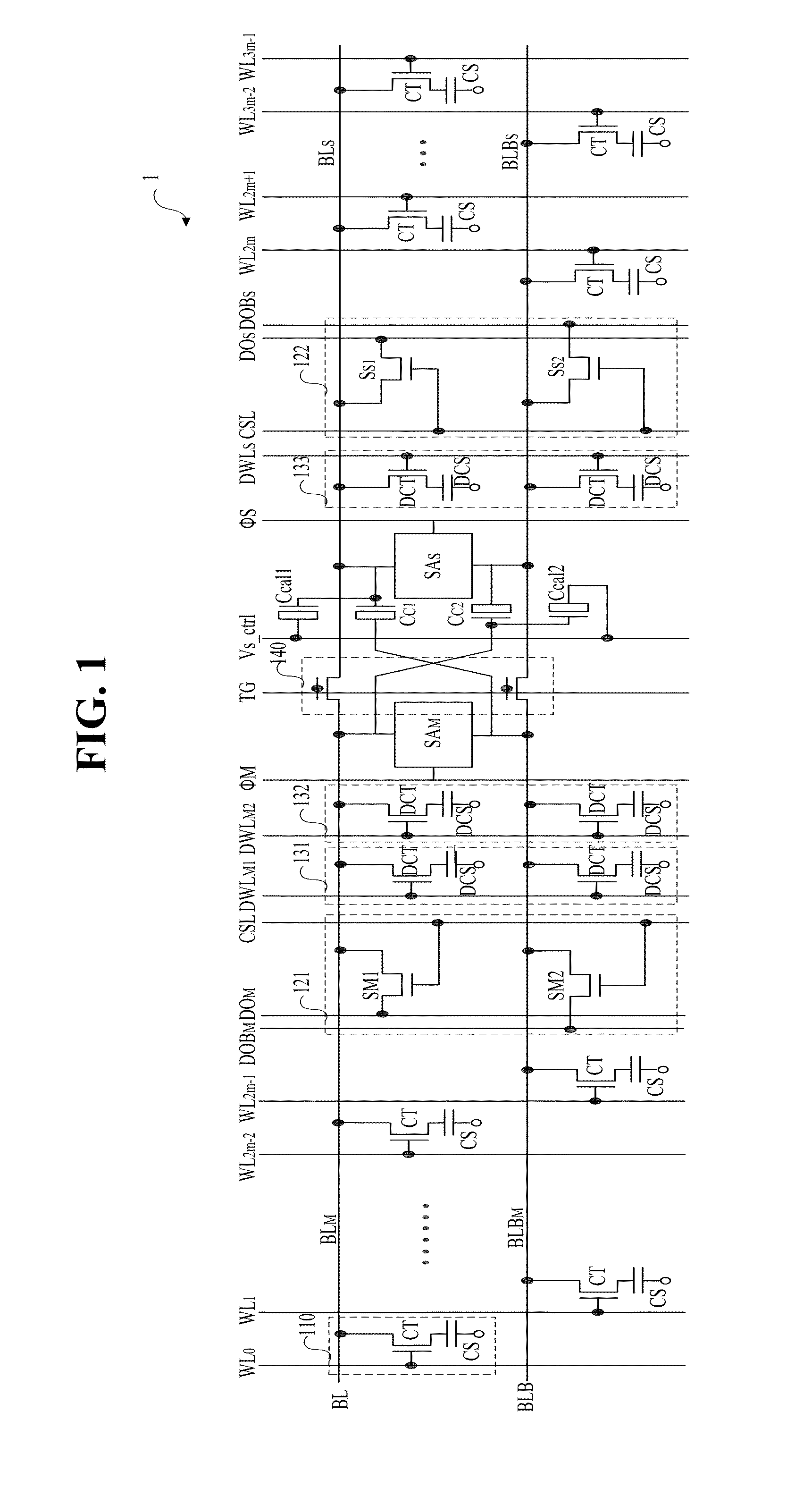
Multi-level dynamic memory device
A multi-level dynamic memory device includes a bit line pair that is divided into a main bit line pair and a sub-bit line pair, first and second sense amplifiers that are connected between the main bit line pair and between the sub-bit line pair, first and second coupling capacitors that are cross-coupled between the main bit pair and the sub-bit pair, respectively; and first and second correction capacitors that are connected in parallel to the first and second coupling capacitors, respectively, and whose capacitance is adjusted by a control voltage signal.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Memory efficient streamlined transmitter with a multiple instance hybrid ARQ
ActiveUS7340669B2Data representation error detection/correctionCode conversionMultiplexerBit pairing
An apparatus comprising a first circuit, a second circuit and a third circuit. The first circuit may be configured to generate an output signal in response to a first intermediate signal and a second intermediate signal. The second intermediate signal comprises a series of bit pairs. The second circuit comprises a first and a second encoder and may be configured to generate the second intermediate signal in response to a third intermediate signal. The third circuit may be configured to generate the first intermediate signal and the third intermediate signal in response to a first address signal and a second address signal. The third circuit comprises a first multiplexer and a second multiplexer.
Owner:APPLE INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com