Method and apparatus for testing digital multiplier
A technique of multiplication and factoring, used in the field of inspection of digital multipliers and devices, to achieve the effect of improving efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
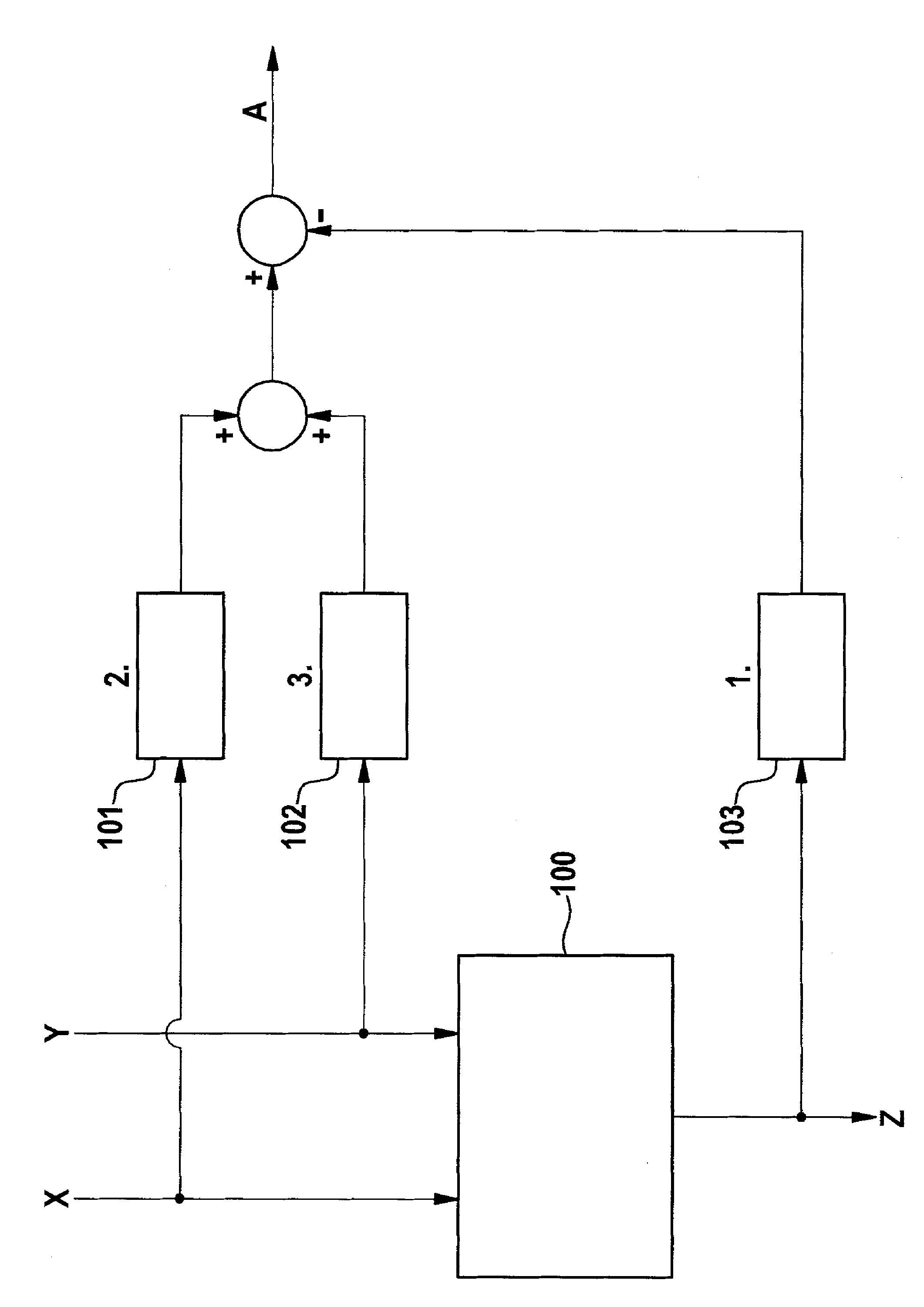
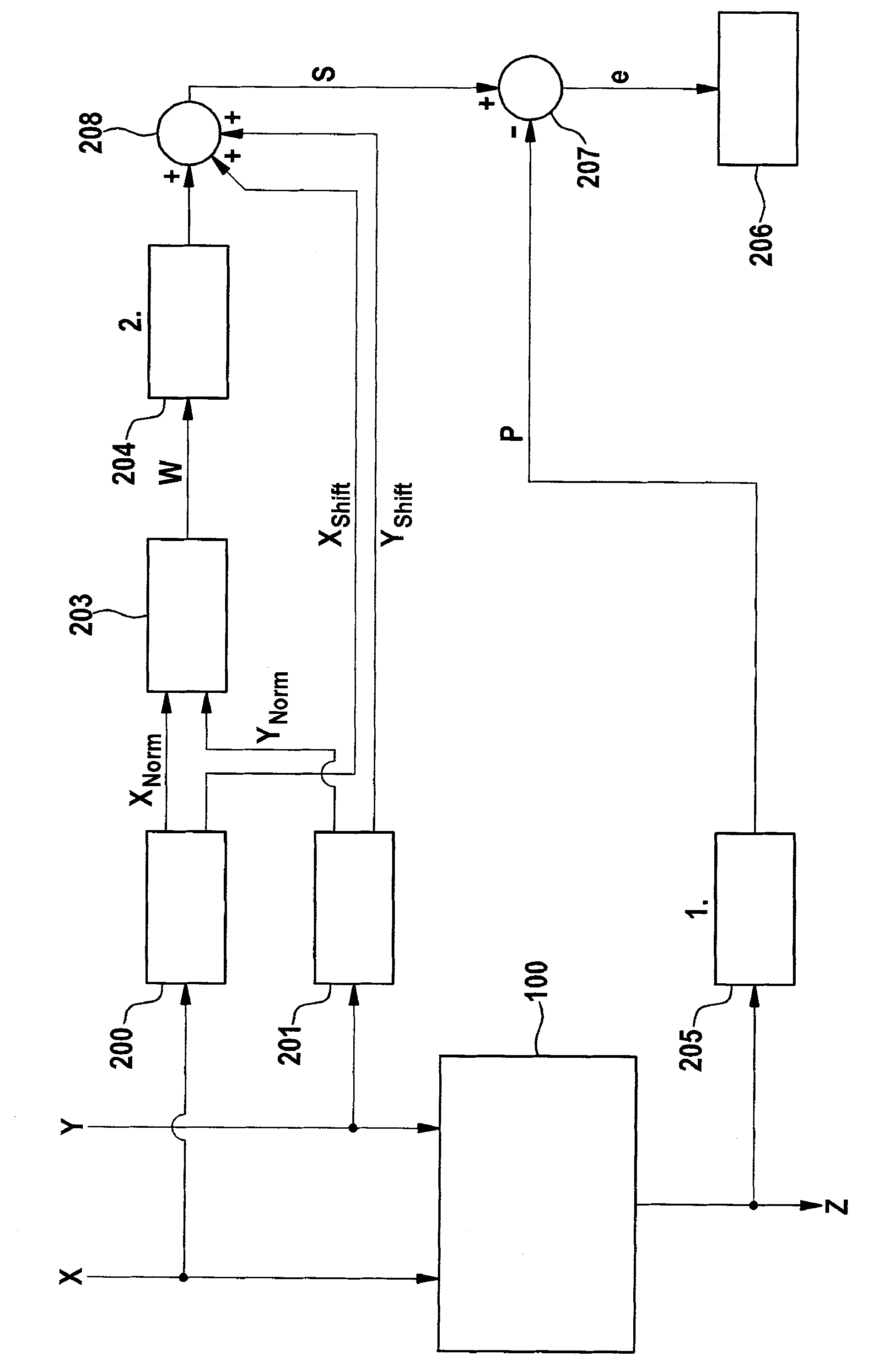
[0041] exist figure 1 The setup for applying equation (1) to the test is shown in . A first multiplication unit 100 , a first logarithmic means 103 , a second logarithmic means 101 and a third logarithmic means 102 are shown. The first factor X is delivered to the second logarithmic device 101 and the first input of the first multiplication unit 100, and the second factor Y is delivered to the third logarithmic device 102 and the second input of the first multiplication unit 100 end. The first multiplication unit presents at its output the product Z=X·Y of the values applied to its two inputs. This product Z is fed to a first logarithm taker 103 .
[0042] The outputs of the second logarithm means 101 and the third logarithm means 102 are added, the output of the first logarithm means 103 is subtracted from these outputs and the output signal A is thus obtained.
[0043]In the error-free case and if the logarithm can be calculated approximately exactly, the output signal...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com