Link damage perception energy efficiency routing method for distinguishing services in elastic optical network
A resilient optical network and differentiated service technology, applied in the field of link damage-aware energy-efficient routing of differentiated services, can solve the problems of affecting the quality of optical path transmission, the degradation of optical signal transmission quality, and the aggravation of physical damage, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0053] The preferred embodiments of the present invention will be described in detail below with reference to the accompanying drawings.
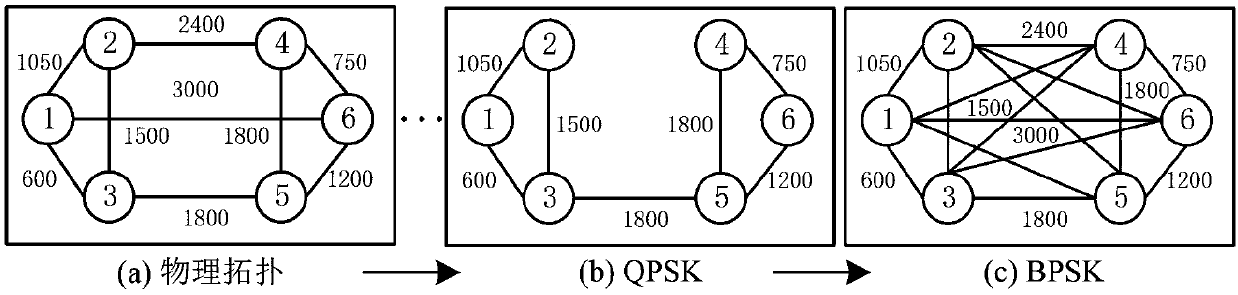
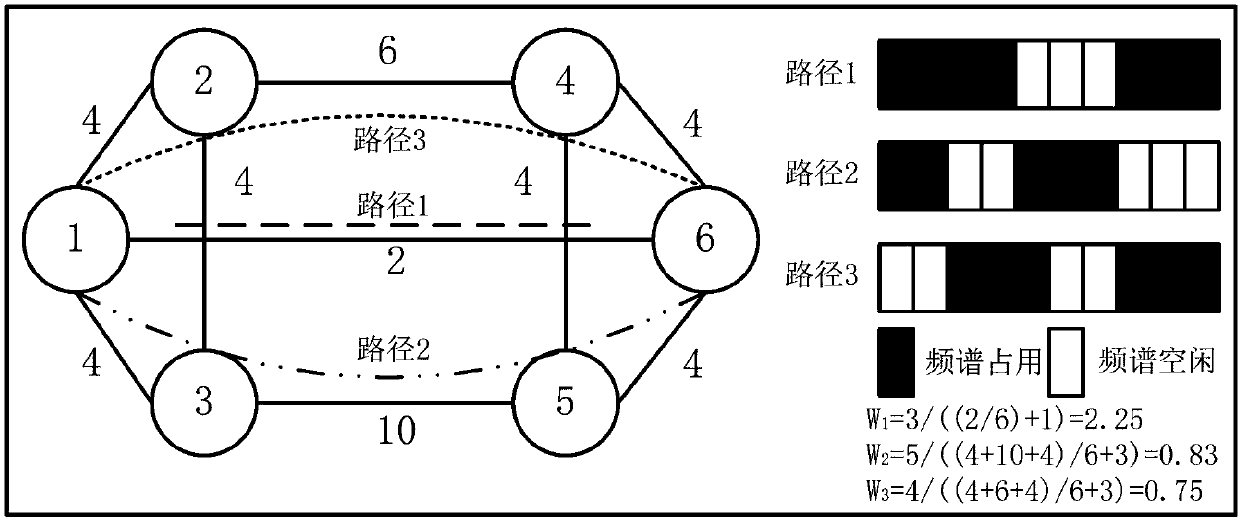
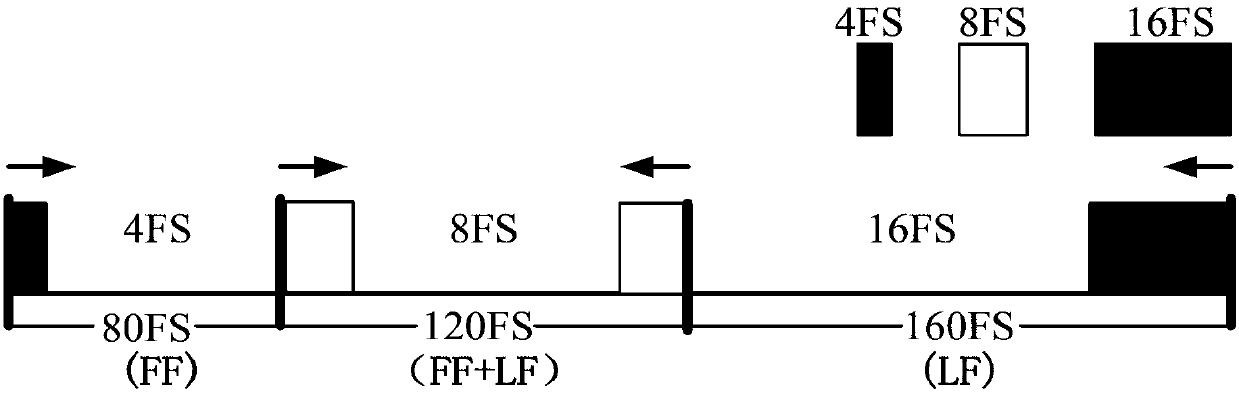
[0054] The present invention provides a link damage-aware energy-efficient routing method for differentiating services in an elastic optical network. When routing a service request, it first constructs a virtual auxiliary map of the modulation mode, starting from the modulation mode with the highest spectral efficiency, and based on the path weight formula: High-quality services are based on the path weight formula that considers link spectrum status and transmission impairments, and calculate K paths with the maximum weight that meet the hop count threshold. At the same time, consider calculating K paths with the lowest energy consumption for low-quality services to reduce network energy consumption. In the spectrum allocation stage, the spectrum resources are partitioned, and the spectrum allocation interval and mode are selected according...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com