Patents
Literature
78 results about "Fair distribution" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
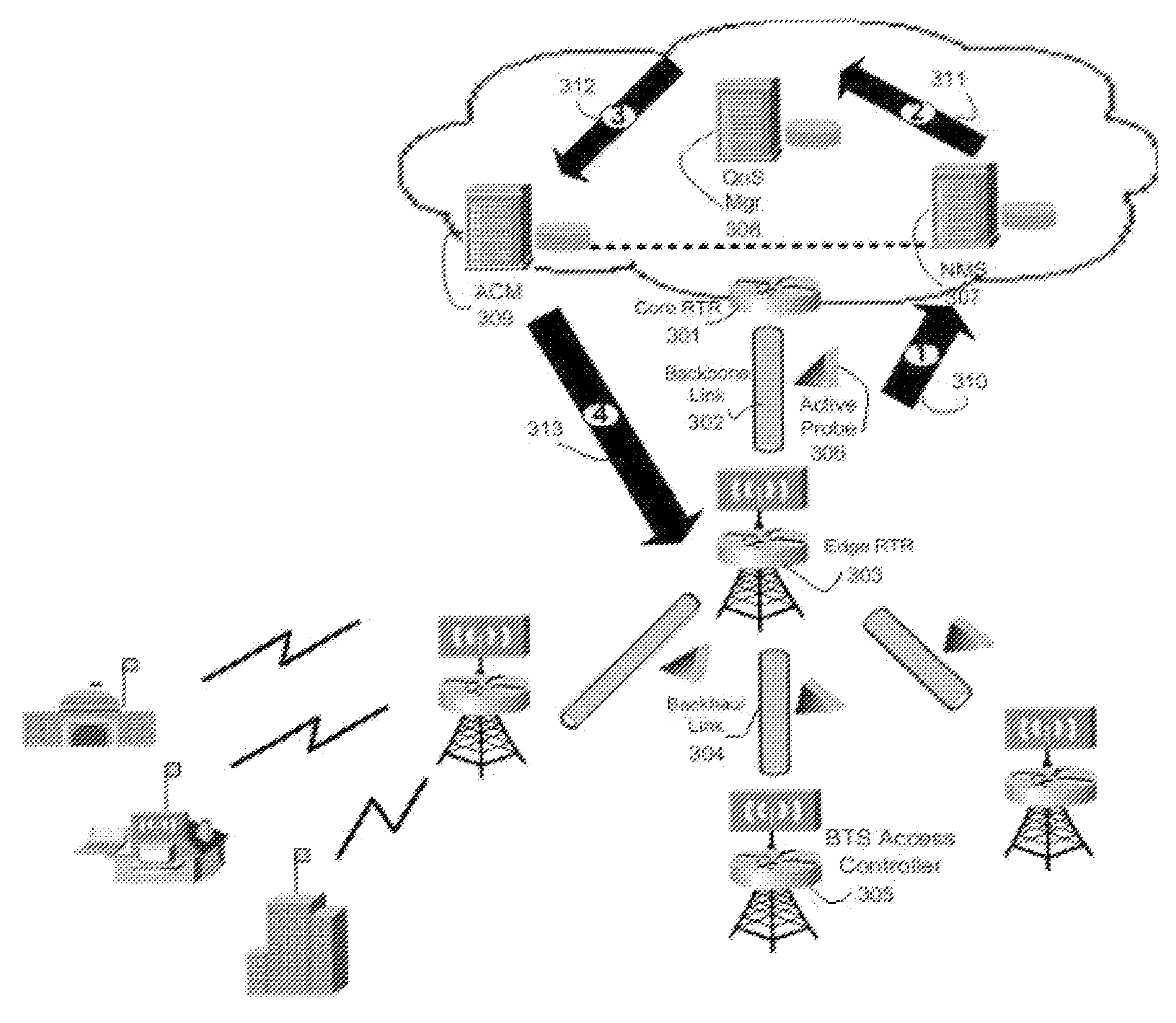
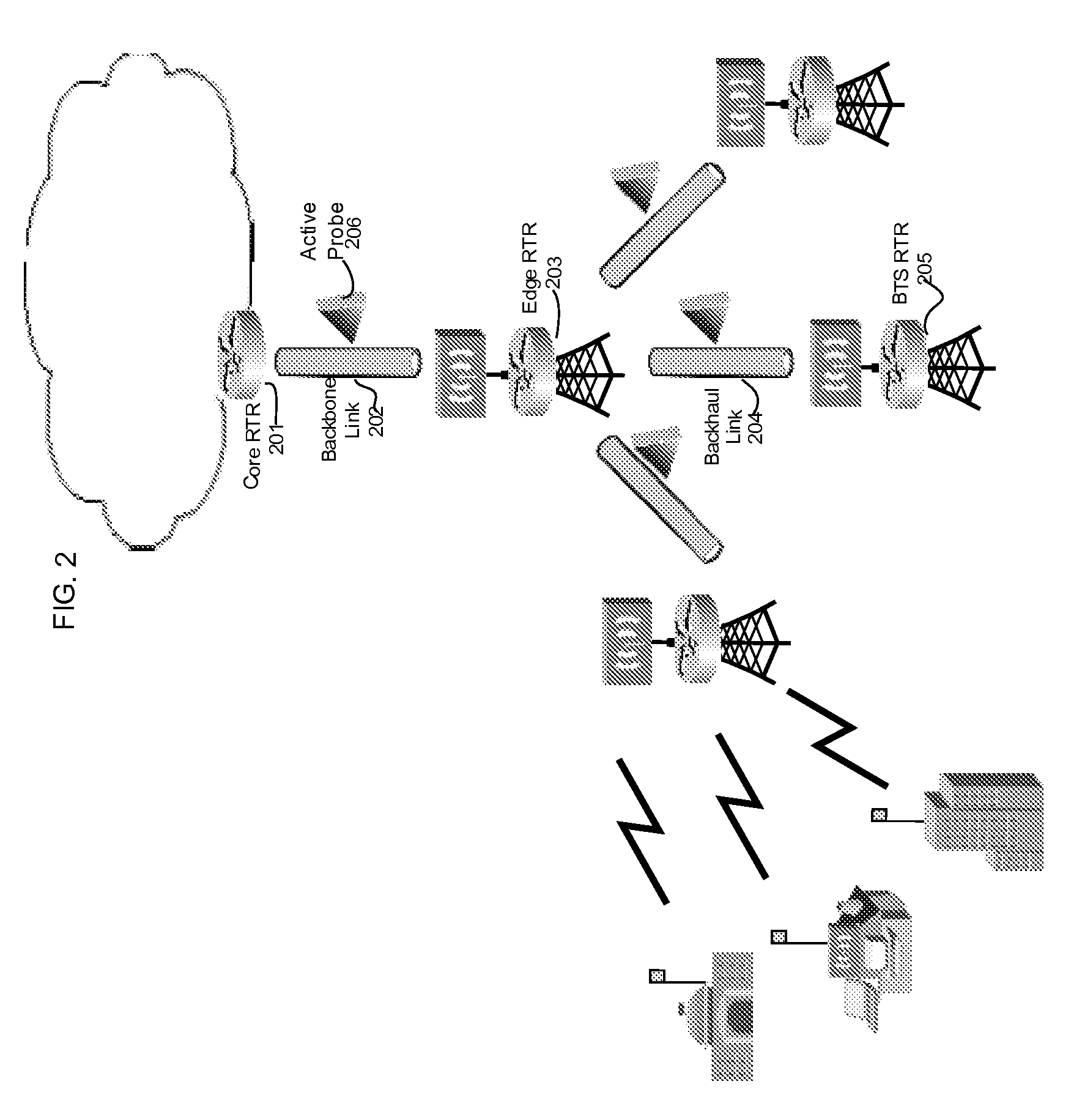
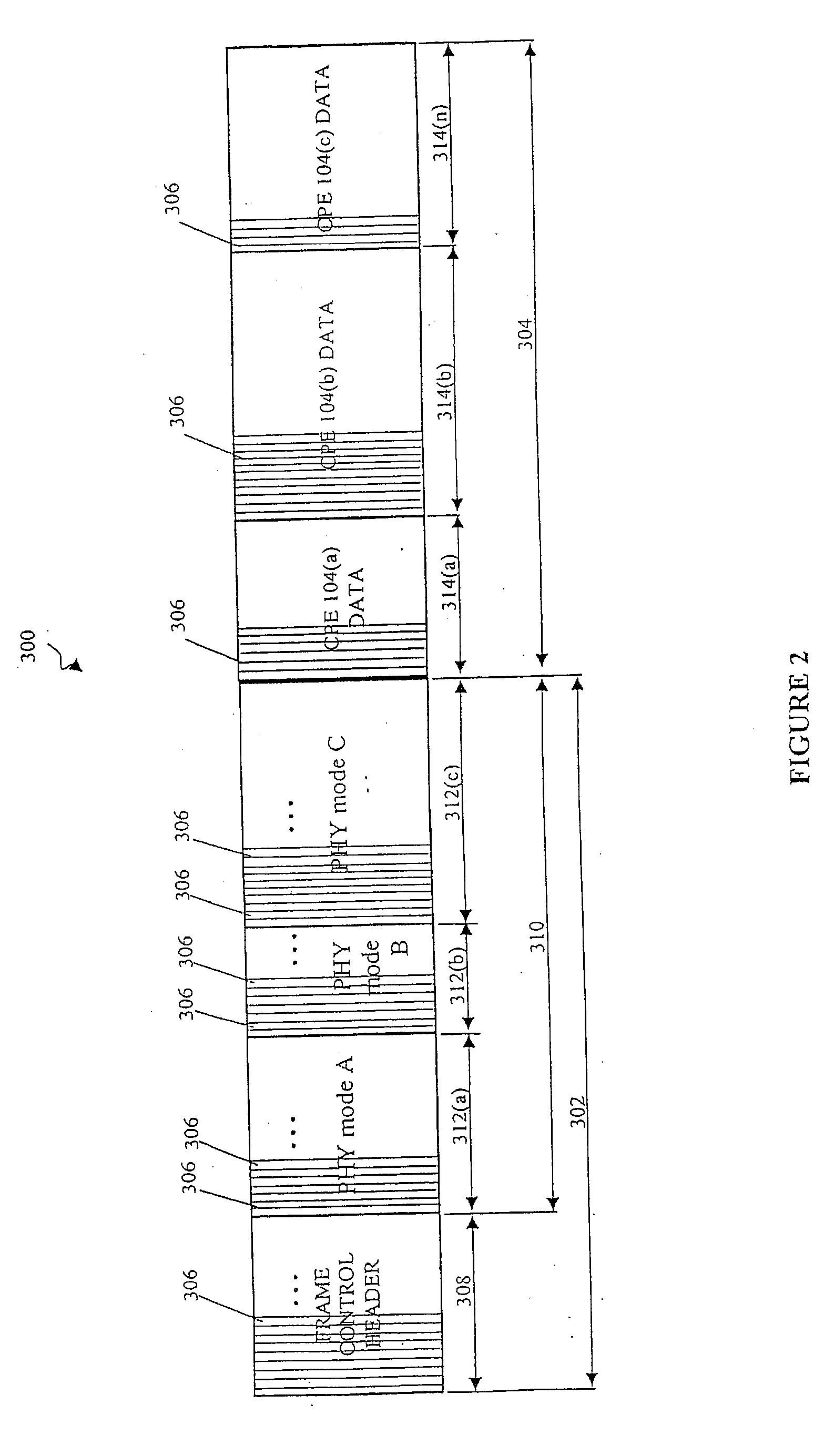
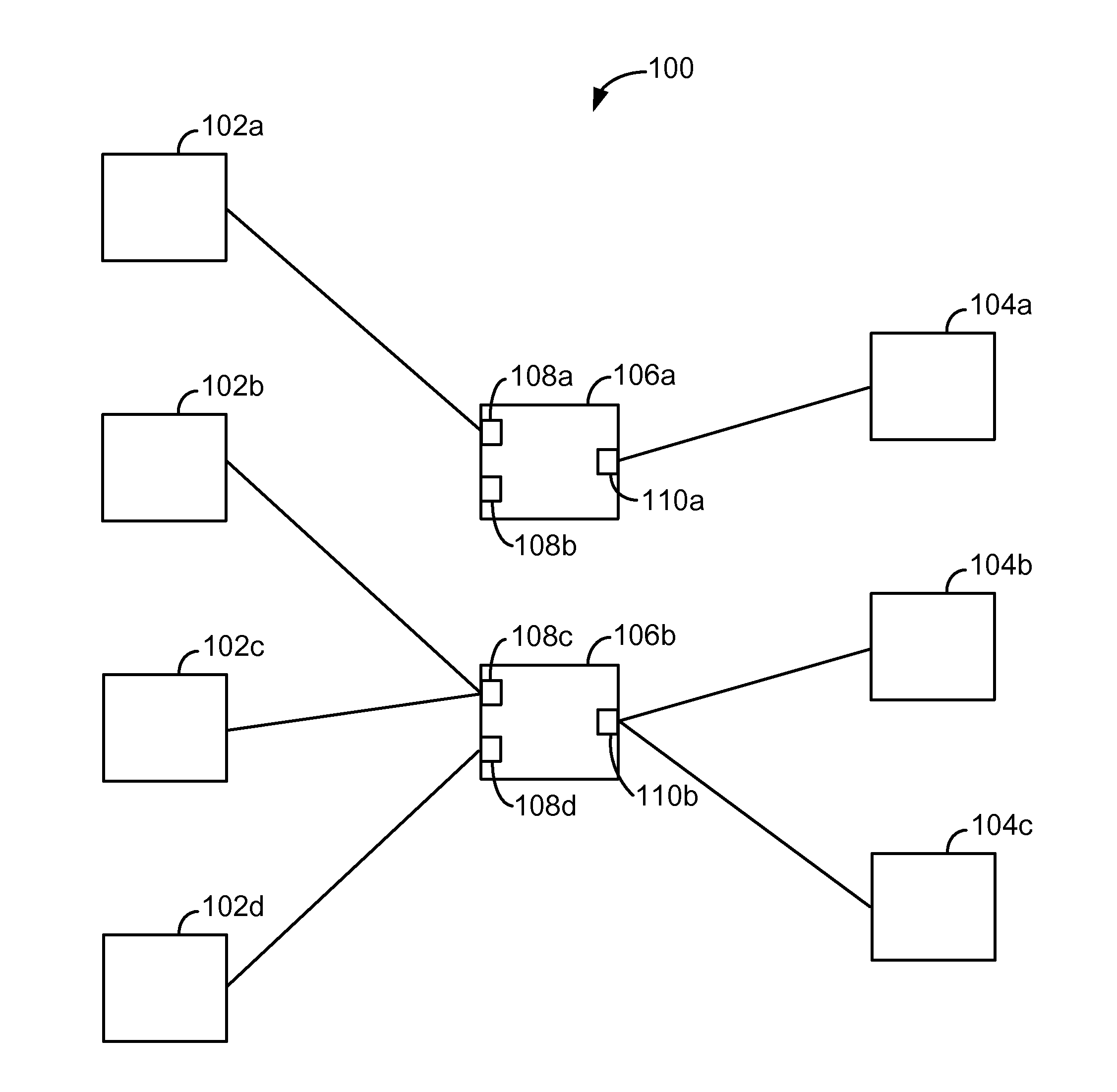
Methods And Systems For Dynamic Bandwidth Management For Quality Of Service In IP Core And Access Networks
InactiveUS20080130495A1Easy to useStringent qualityError preventionTransmission systemsPresent methodKey issues
Proper allocation of network bandwidth is a crucial issue in rendering certain performance guarantees to meet the growing customer demands. Hence, allocation methodologies must explicitly be carried out for these guarantees to be given as efficiently as possible since the shared resources are limited. This invention presents methods and systems for Dynamic Bandwidth Management (DBM) and Quality of Service (QoS) in packet-based networks. DBM is an algorithm that dynamically adjusts the resource allocation in the IP Access Networks based upon measured QoS at the IP Core Network through an implementation of a Feedback Control Mechanism to manage available core transport bandwidth. Such a Feedback Control Mechanism is capable of maintaining a condition of non-congestion, a sufficient and necessary condition to meet end-to-end QoS requirements in a Next Generation Network (NGN). The emphasis is given on the system implementation of QoS policies for the fair distribution of network resources through a scalable architecture comprising key Resource and Admission Control Functional (RACF) entities, namely: a Network Management System (NMS), a QoS Manager, an Access Controller Manager (ACM), the Access Controllers, and the active probes.
Owner:LATITUDE BROADBAND
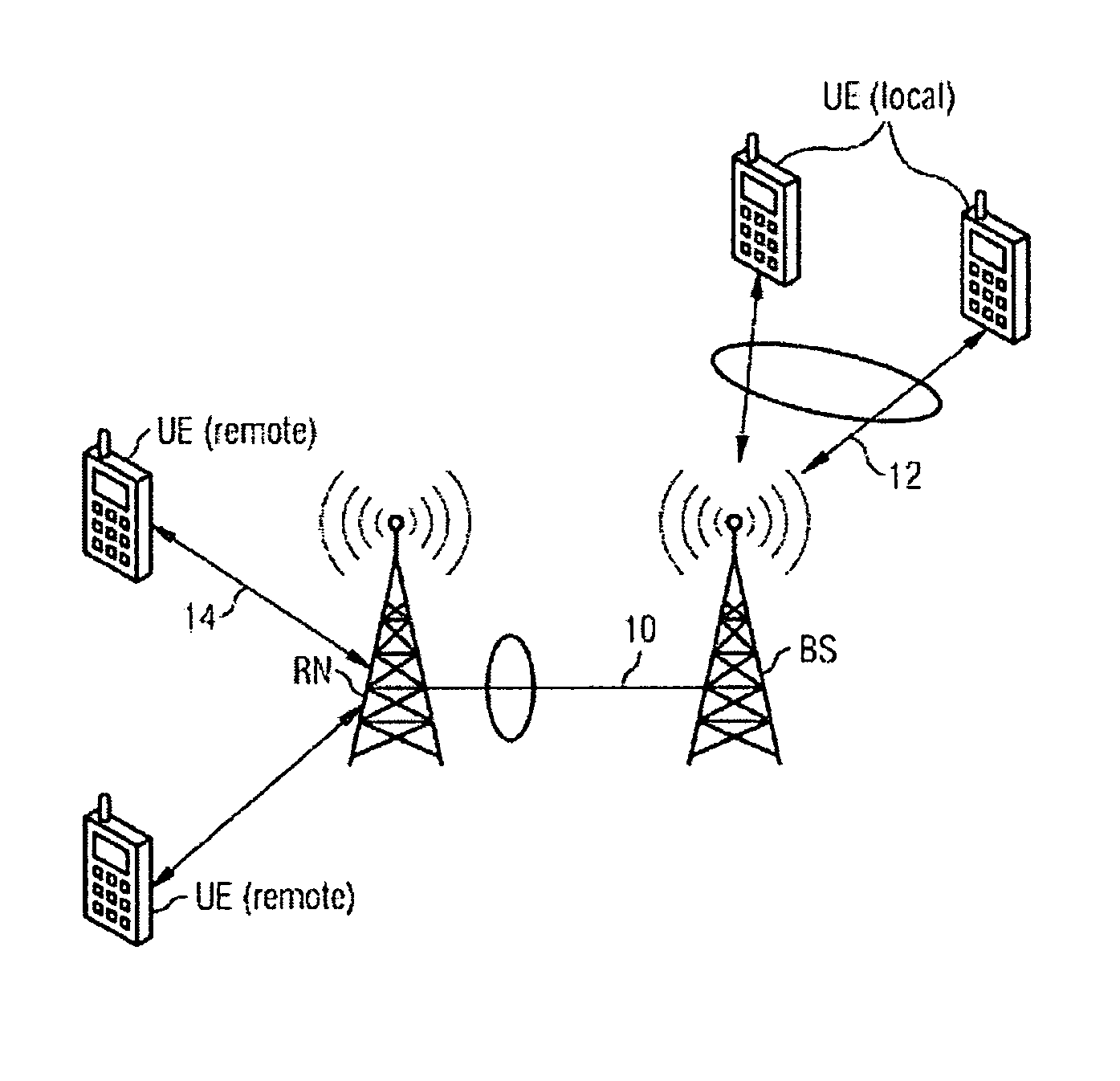
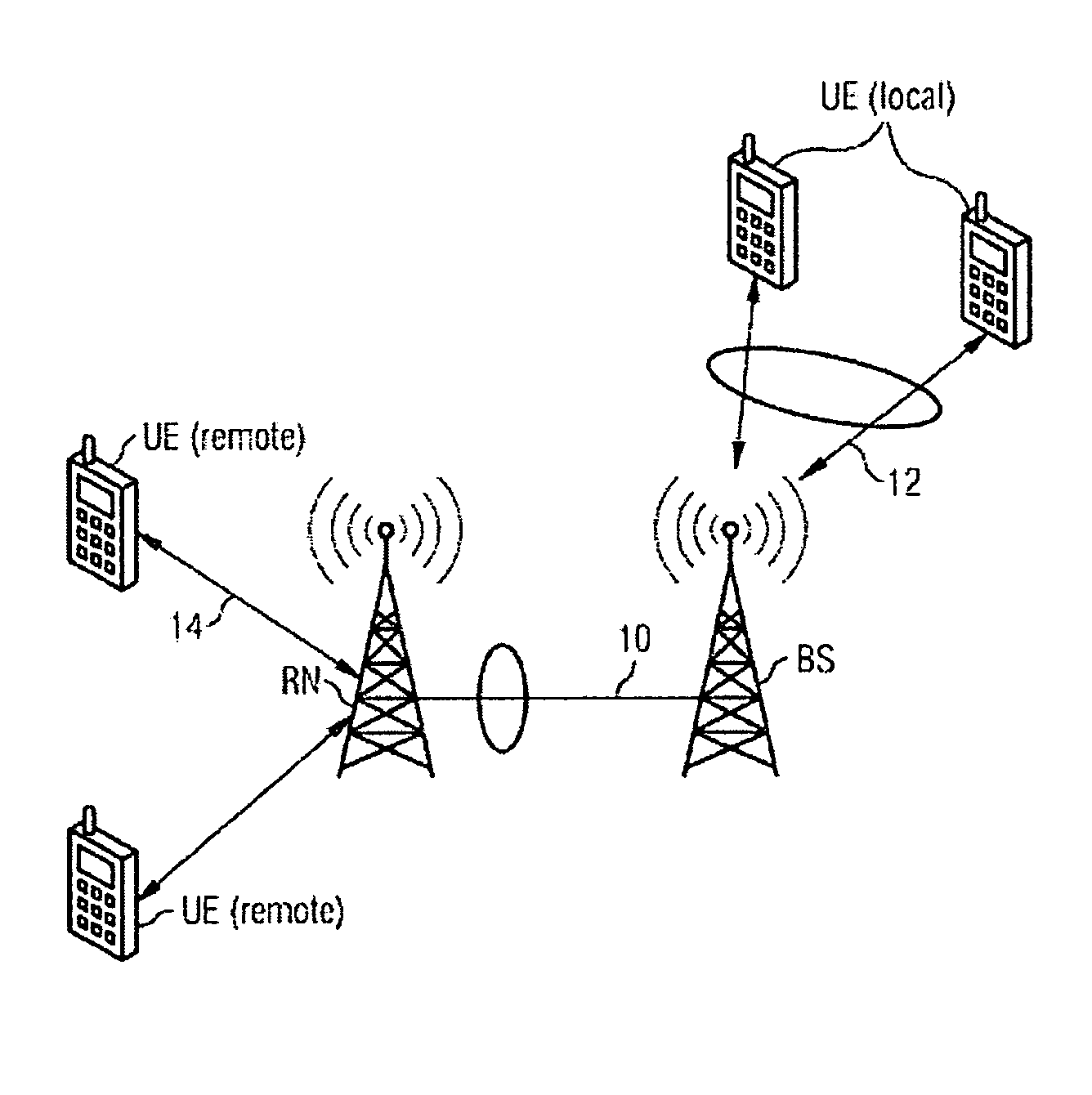
Wireless telecommunication system including a base station, relay node and method for global fair scheduling
ActiveUS8744339B2Fair distributionFrequency-division multiplex detailsNetwork topologiesData streamFair scheduling
The invention relates to a wireless telecommunication system including at least one Base Station (BS) for communicating with at least one multihop Relay Node (RN) using a wireless link of a first type and with at least one local user equipment unit (UE) located within a range of the base station (BS) using at least one wireless link of a second type, wherein the wireless link of the first type is used to transmit a combined data flow encapsulating multiple individual data flows relating to different services and / or remote user equipment (UE) units. In order to enable a global fair scheduling, the base station (BS) is further configured to receive at least one local fairness parameter from the multihop relay node (RN), said local fairness parameter representing a fairness of the distribution of radio resources of the relay node (RN) over the individual data flows in the combined data flow and to execute a global fair scheduling procedure for determining a fair distribution of available radio resources of the base station (BS) over said at least one wireless link of the first type and said at least one wireless link of the second type, wherein the local fairness parameter is used as a parameter in said global fair scheduling procedure.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV +1
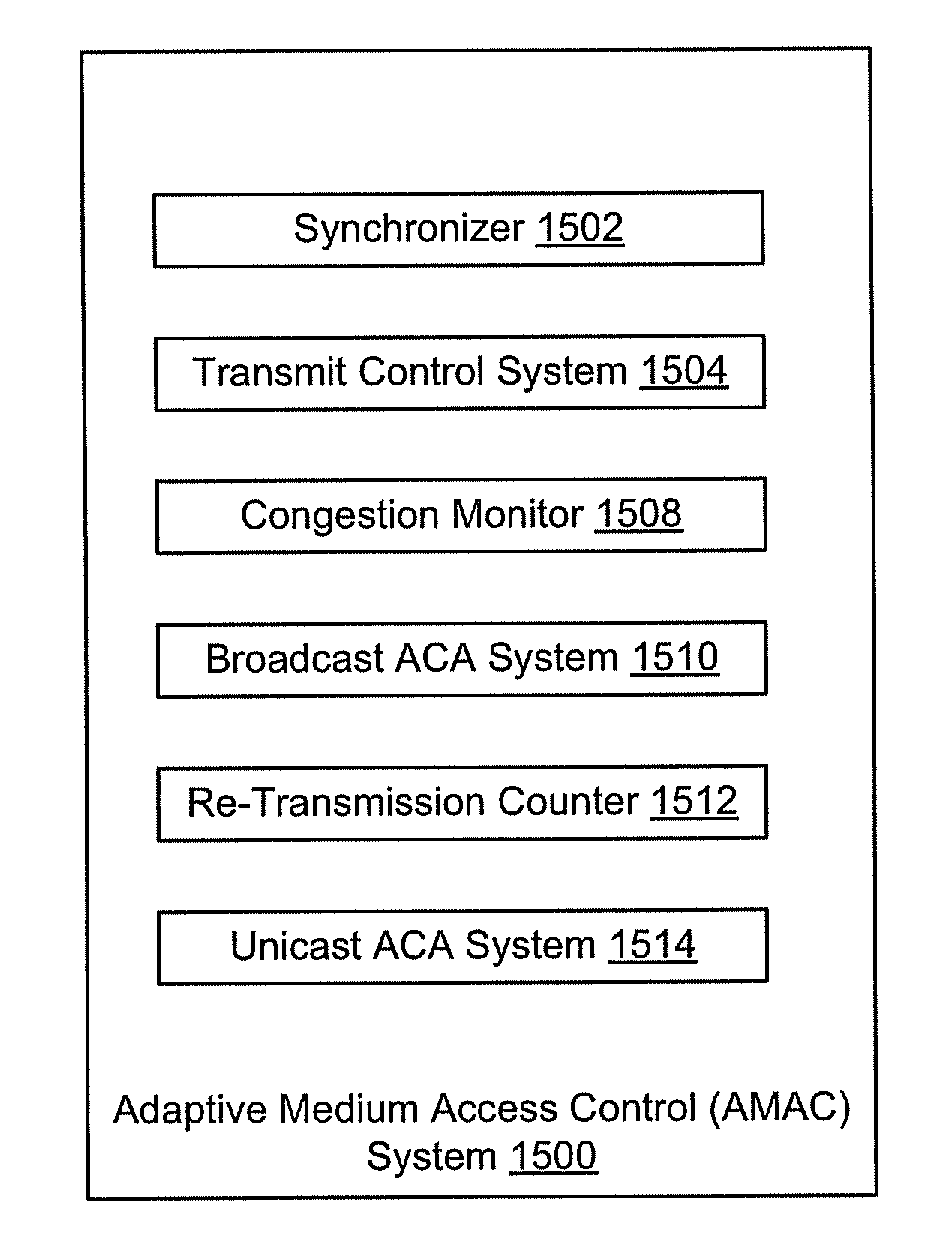
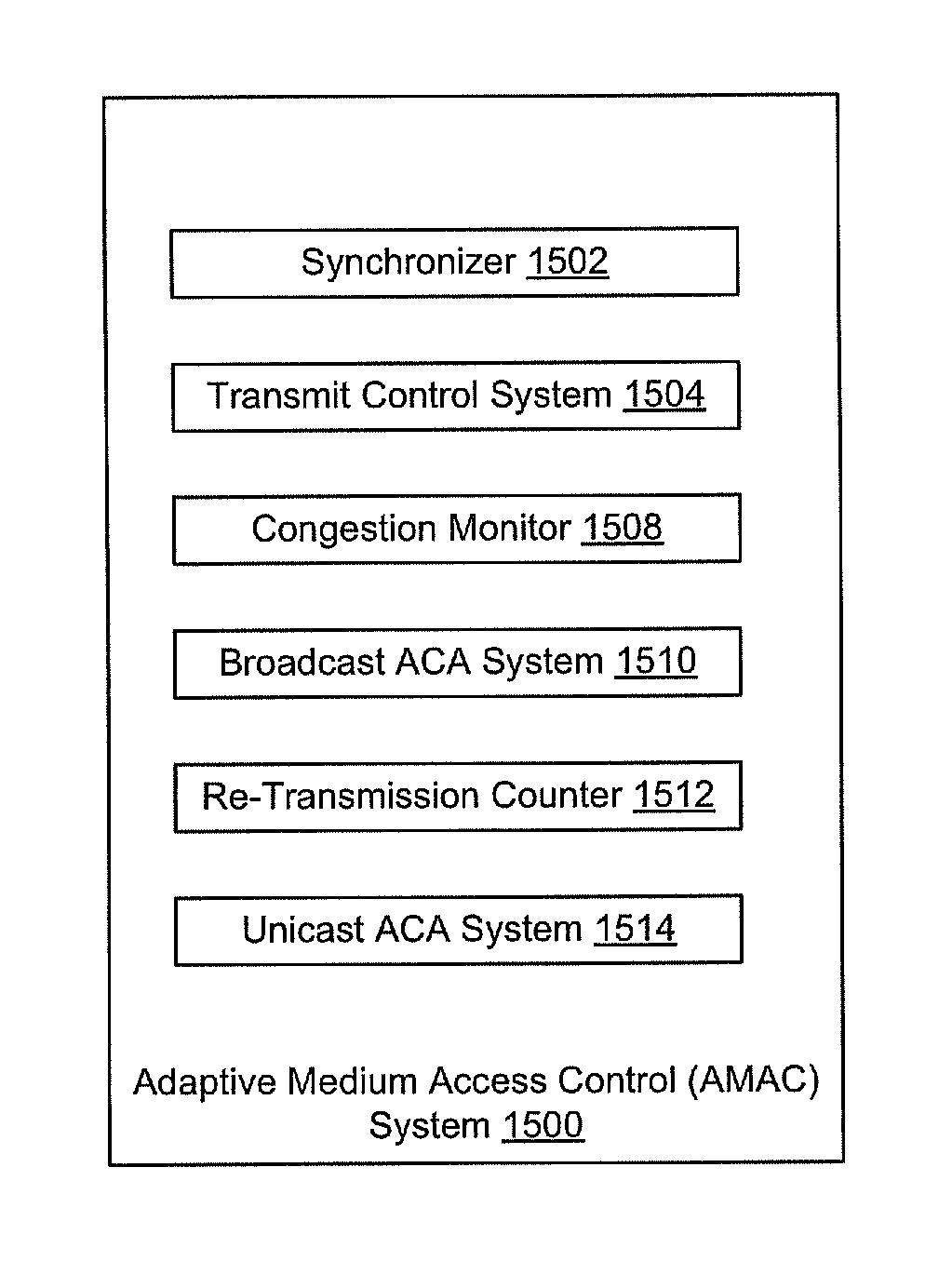
Adaptive Medium Access Control
ActiveUS20120182867A1Controlling the riskError preventionTransmission systemsPerformance enhancementTraffic flow
Bandwidth allocation configuration and fully decentralized adaptive medium access control (AMAC) systems and methods with support for time critical applications, spectrum efficiency, scalability enhancements, and fair allocation of bandwidth among nodes sharing a common channel. The methods fully integrate TDMA and CSMA / CA channel access approaches and incorporate adaptive congestion and collisions avoidance scheme to reduce bandwidth wastage and diminish adverse cross layers interactions. AMAC improves support for multi-media traffic while allowing higher transmission incidents from large number of transmitting devices sharing a common channel, with fair distribution of the available bandwidth, to enable improved multi-level-security connectivity over a common multi-hop wireless network, provide end-to-end performance enhancement for constant bit rate traffic, variable bit rate traffic, and distribute bandwidth fairly amongst competing TCP traffic flows that traverse varying length paths in multi-hop ad-hoc wireless networks.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
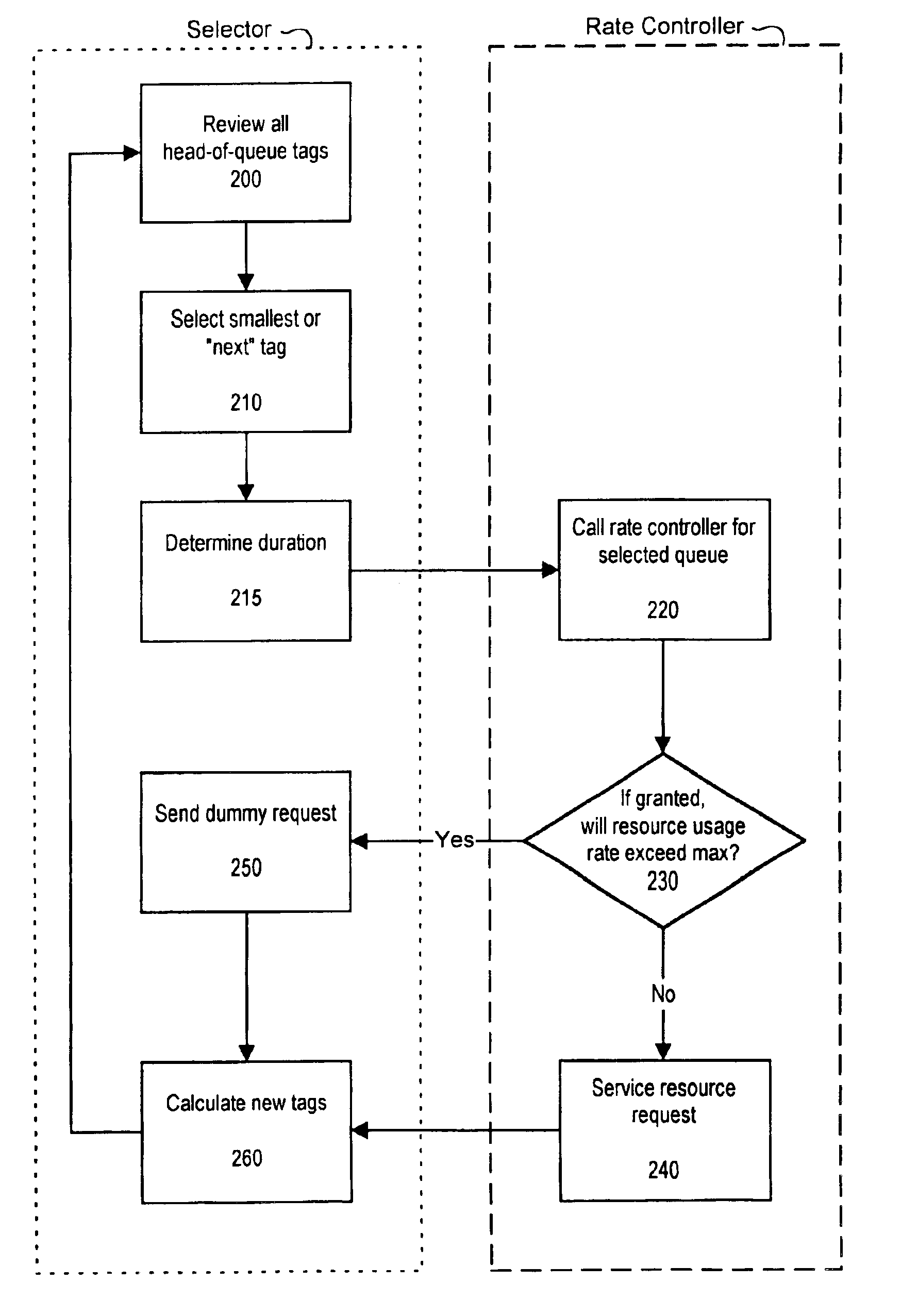
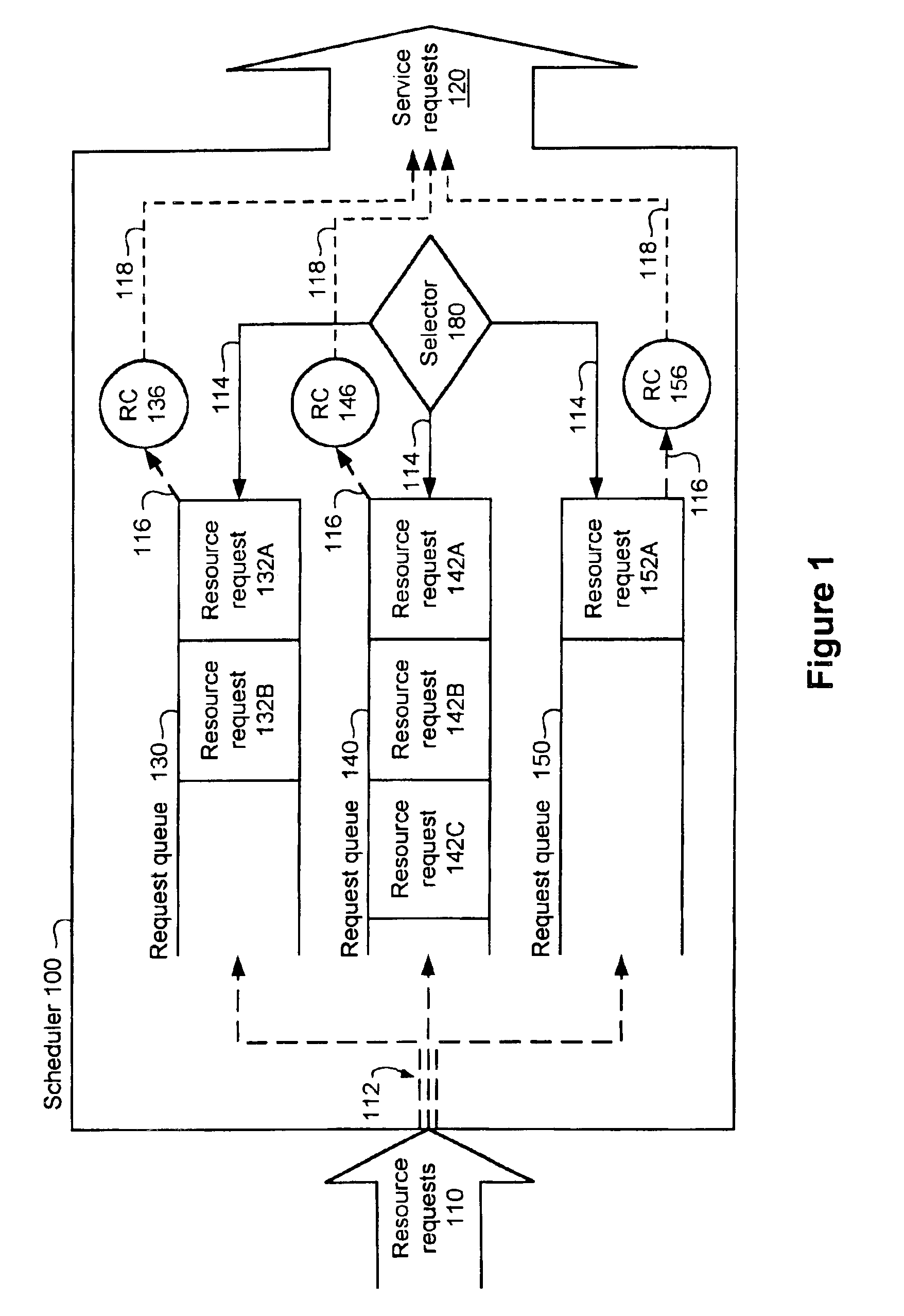
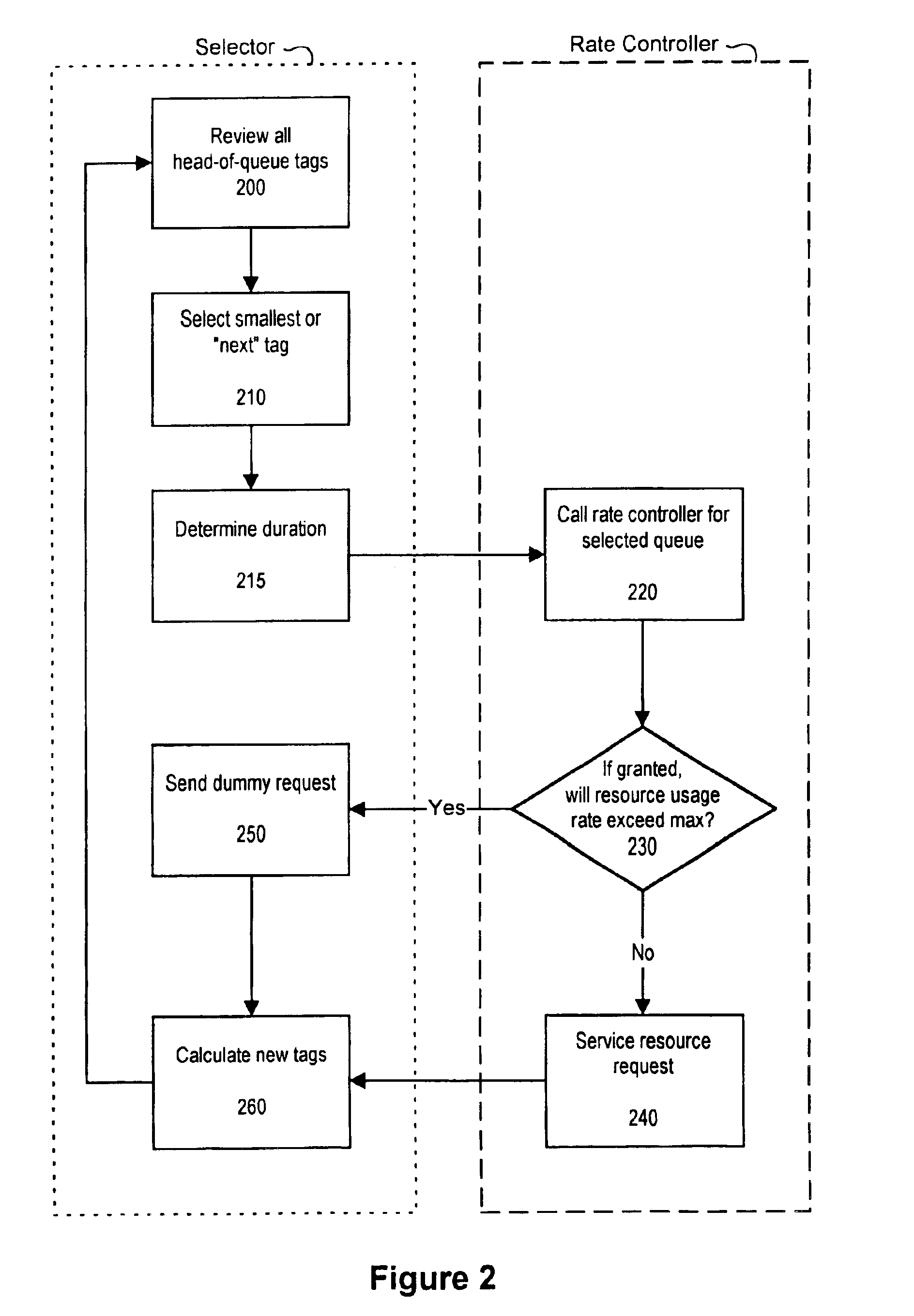
Fairly partitioning resources while limiting the maximum fair share
InactiveUS6909691B1Less memoryImprove scalabilityProgram initiation/switchingError preventionQuality of serviceFair-share scheduling
Resource requests from a plurality of schedulable entities are scheduled while limiting the maximum and minimum quality of service allocated to each schedulable entity. The resource scheduler of the present invention requires less memory maintain state information than existing rate-controlling schedulers, and is thus more easily scalable to large numbers of users. The resource scheduler also schedules resources fairly among competing schedulable entities. A fair-share scheduling algorithm is used by a resource scheduler to select resource requests to service. A rate controller checks to ensure that servicing the selected request will not cause the associated user's maximum quality of service to be exceeded. If the maximum quality of service will not be exceeded, the virtual time used in the scheduling algorithm is incremented, and the request is serviced. If the maximum quality of service will be exceeded, the virtual time is still incremented, but the request is not serviced and remains pending.
Owner:SERVSTOR TECHNOLOGIES LLC
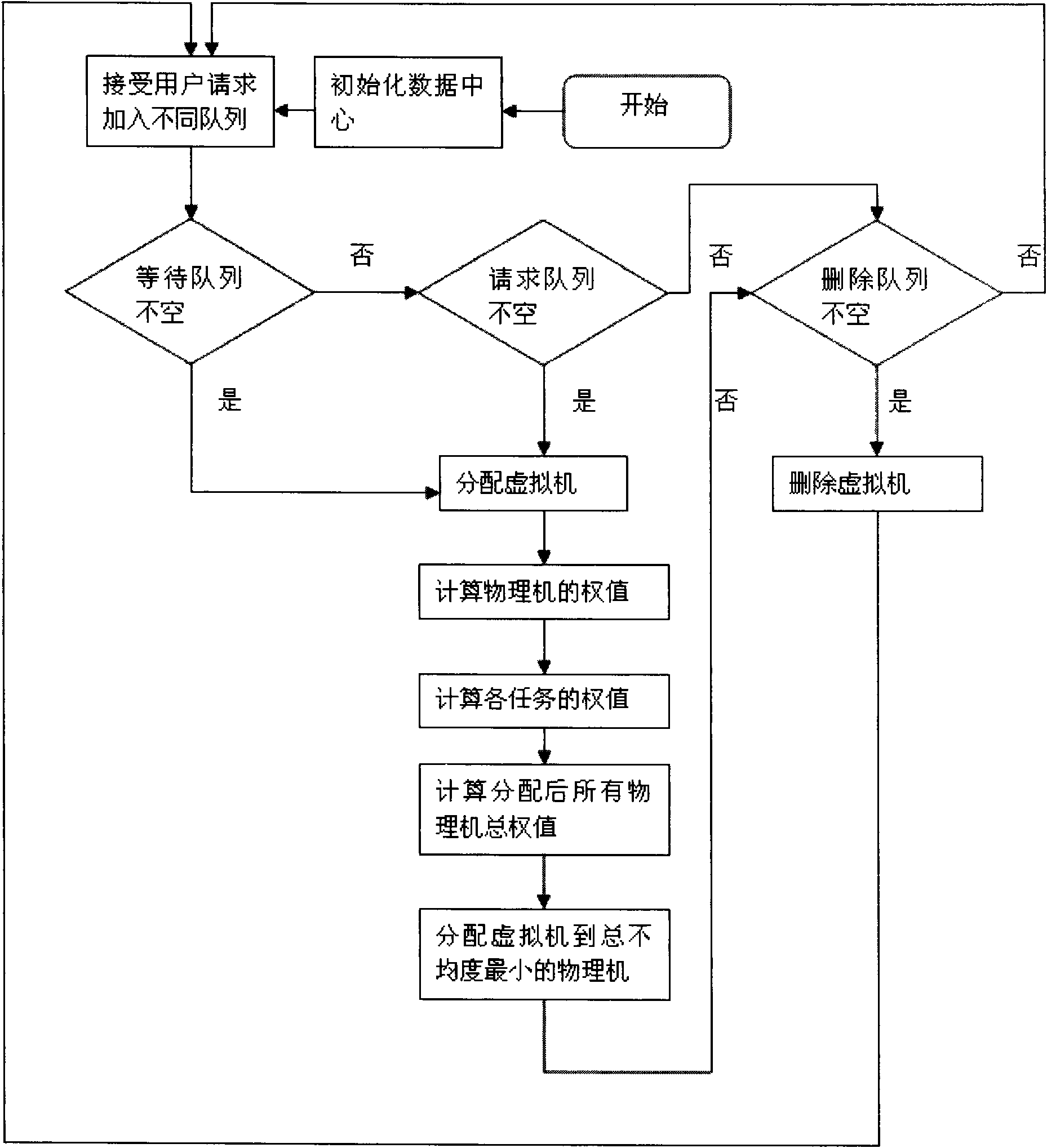
Method and device for realizing data center resource load balance in proportion to comprehensive allocation capability
ActiveCN102185779ATimely determination of load statusSolve load imbalanceData switching networksUser needsData center
The invention relates to a method and a device for realizing data center resource load balance. The method of the technical scheme comprises the following steps of: acquiring the current utilization rates of attributes of each physical machine in a scheduling domain, and determining the physical machine for a currently allocated task according to the principle of fair distribution in proportion to the allocation capability of a server, an actual allocated task weight value and an expected task weight value, wherein the attributes comprise a central processing unit (CPU) load, a memory load and a network load; determining a mean load value of the attributes of the scheduling domain according to the current utilization rates, and calculating a difference between the actual allocated task weight value and expected task weight value of the physical machine according to the mean load value and predicted load values of the attributes of the physical machine; and selecting the physical machine of which the difference between the actual allocated task weight value and the expected task weight value is the smallest for the currently allocated task. The device provided by the invention comprises a selection control module, a calculation processing module and an allocation execution module. By the technical scheme provided by the invention, the problem of physical server load unbalance caused by inconsistency between user need provisions and physical server provisions can be solved.
Owner:田文洪
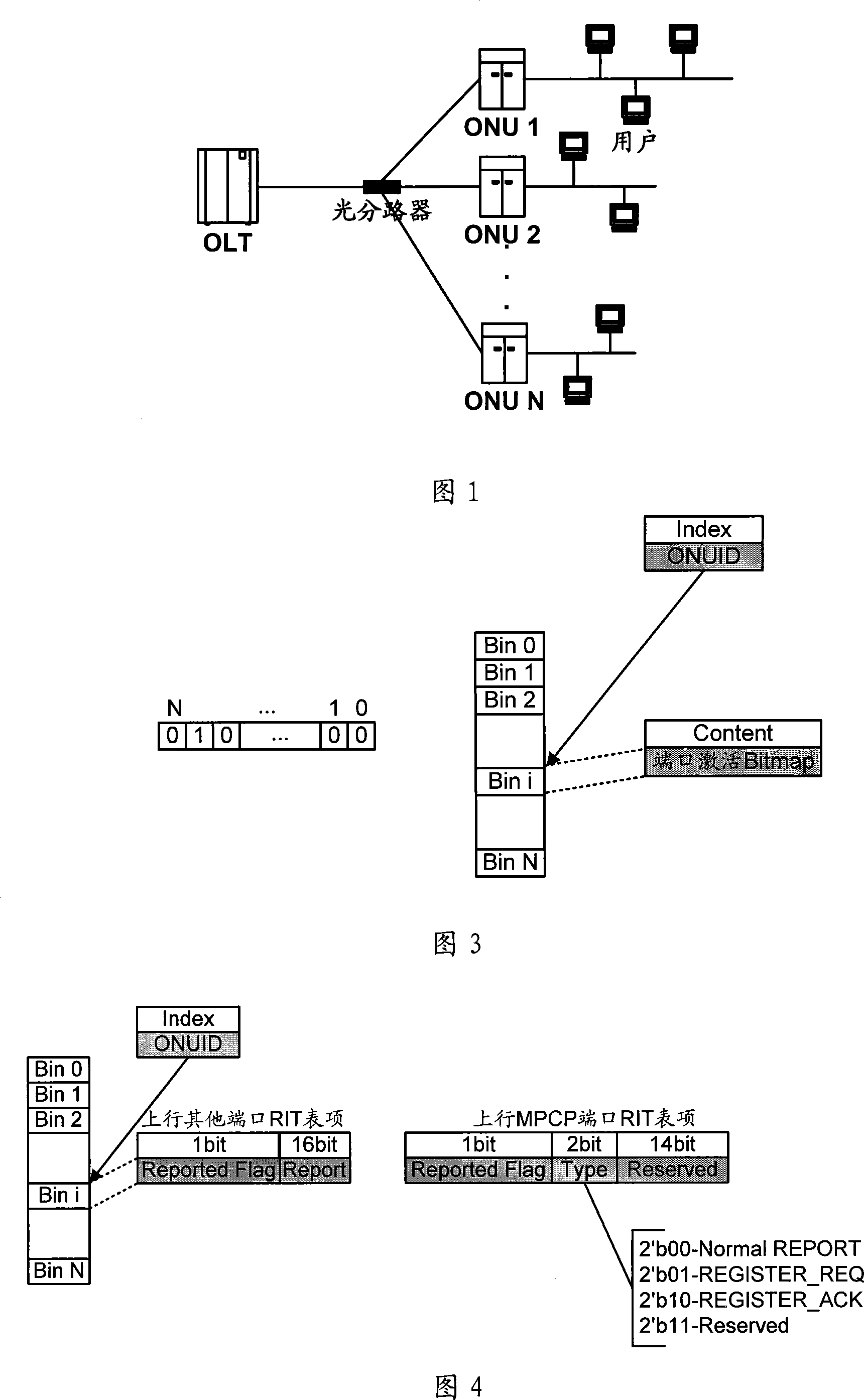
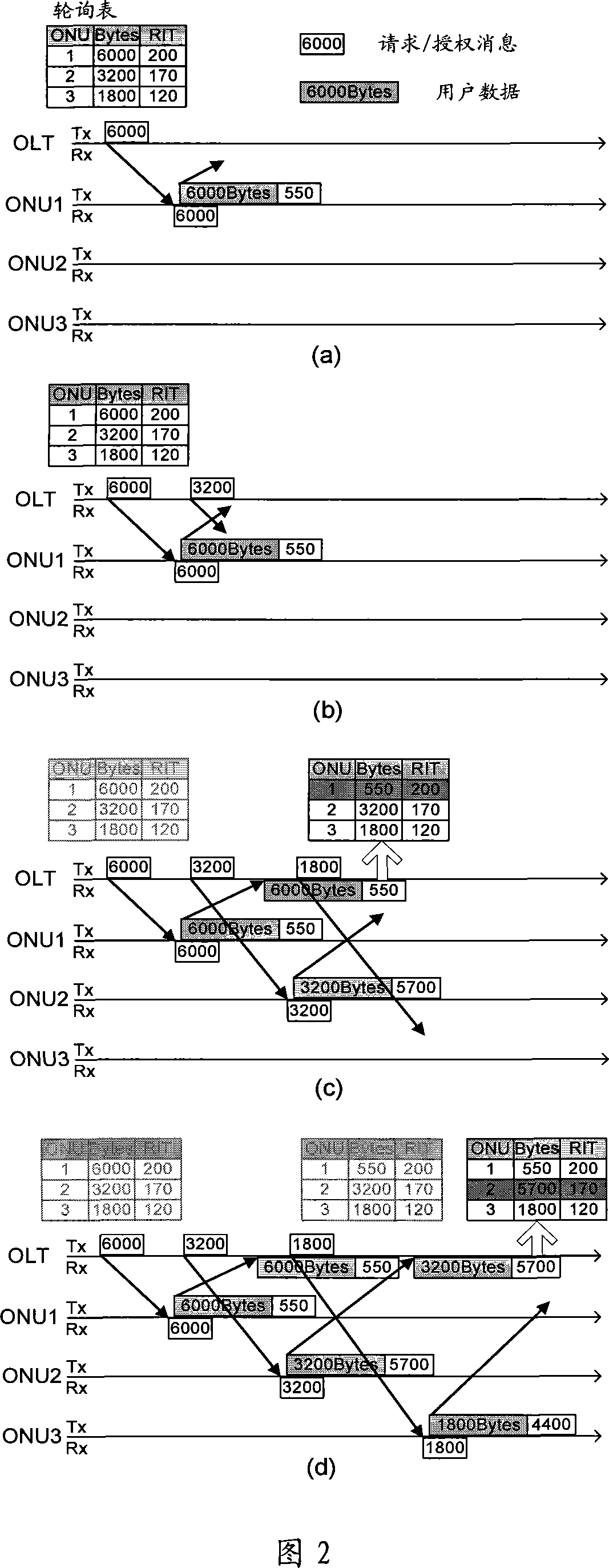
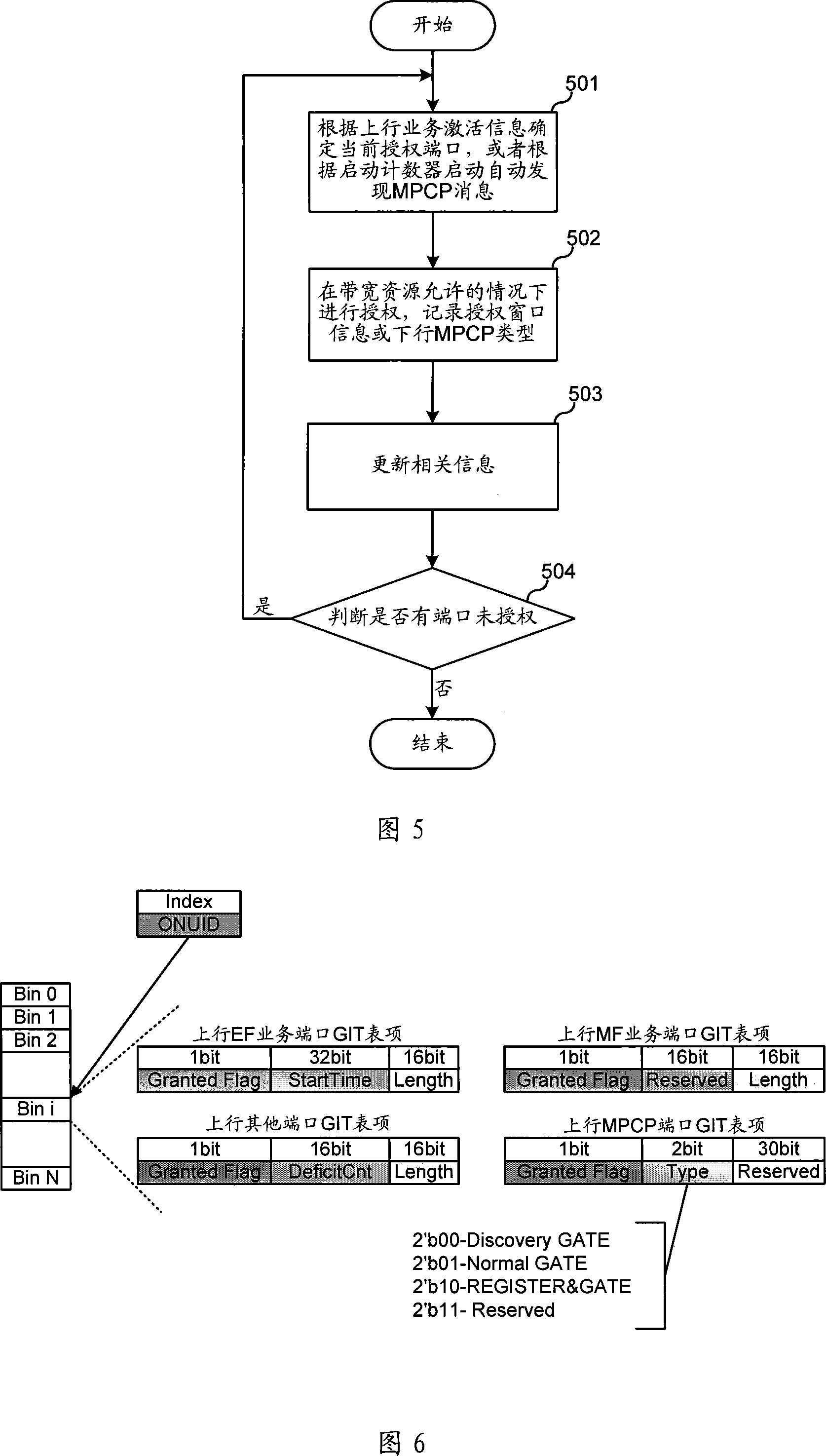
Dynamic bandwidth allocation device and method of passive optical network
ActiveCN101087238AIncrease profitEfficient use ofMultiplex system selection arrangementsStore-and-forward switching systemsService flowOptical communication
The invention relates to optical communication field, discloses a collating device and method for dynamic bandwidth in source-free optical network, and the distribution method for dynamic bandwidth is transparent, which can satisfy the requirement for different service, improve the utilization rate of bandwidth, realize the fair distribution for bandwidth, good haleness, real time, and can distribute bandwidth for different port, and support to release offline bandwidth of ONU. The distributing device for dynamic bandwidth in source-free optical network includes ascending service active fiber network unit bit-mapping register, ascending service active port bit-mapping table, ascending virtual media accessing control sub-layer information table, descending virtual media accessing control sub-layer authorization information table; said distributing device for dynamic bandwidth, consults said fiber network unit active information, port active information and length information of sending data, according to preset priority of different service, process the service flow according to priority according to preset priority, and distributes the dynamic bandwidth for ports.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
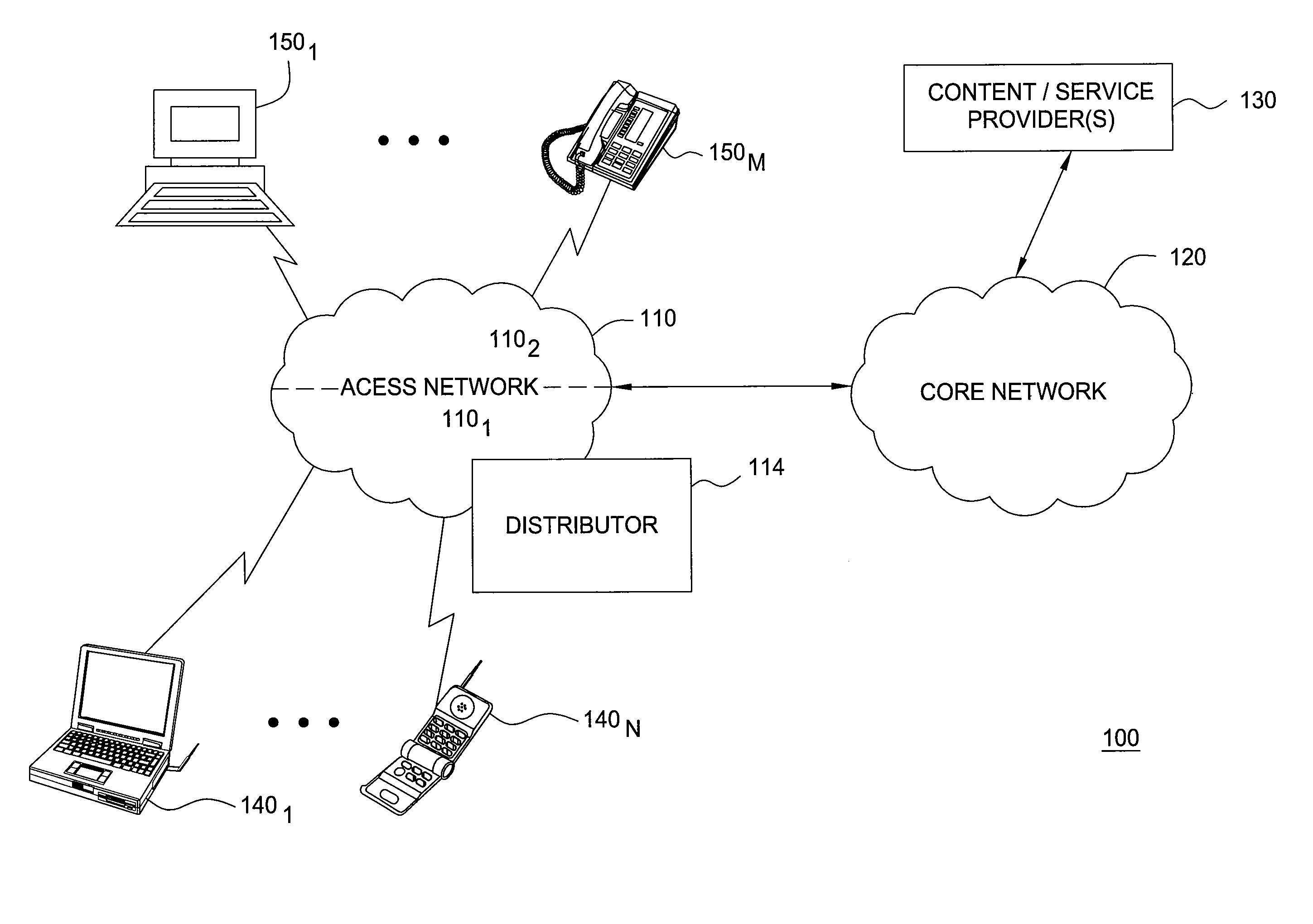
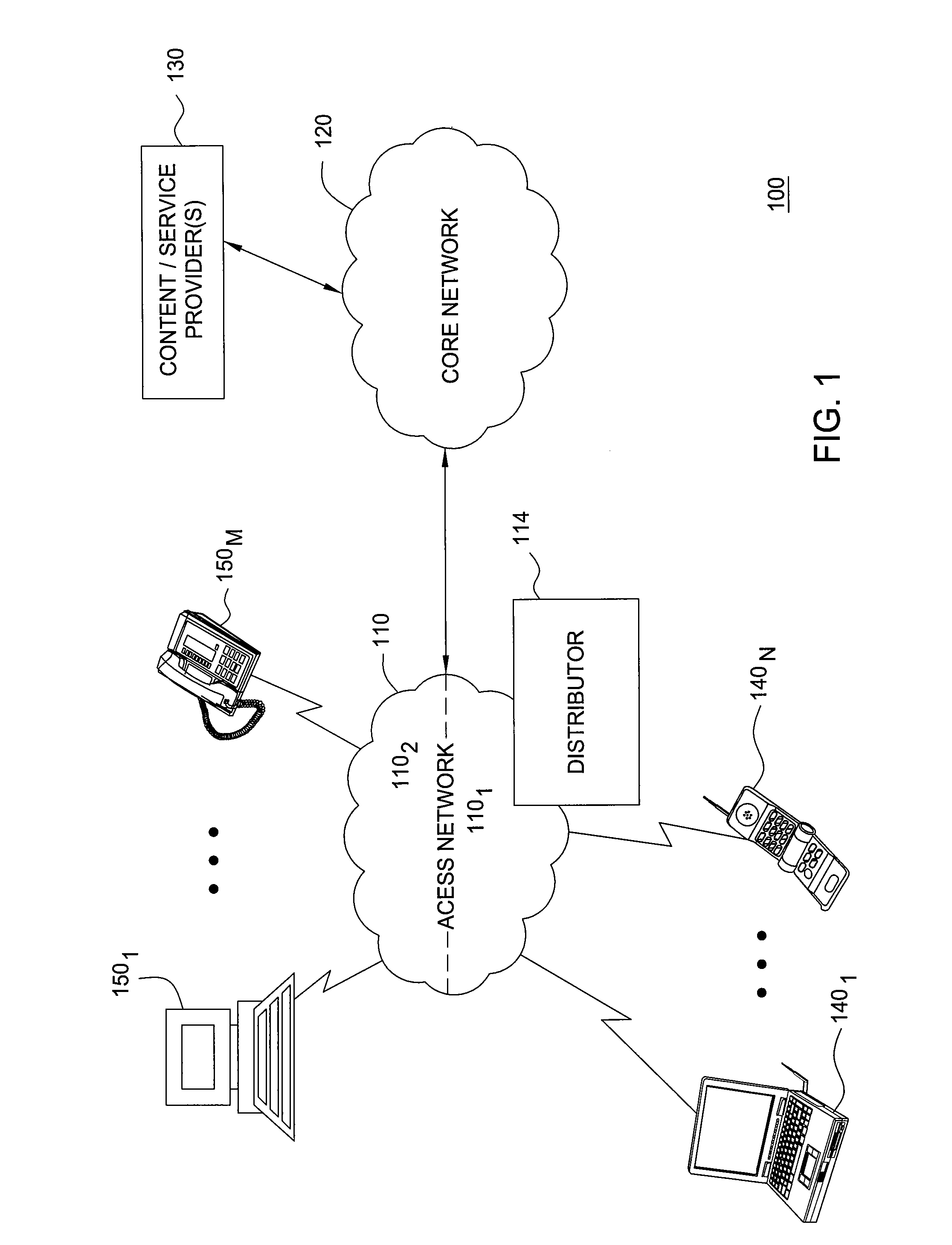
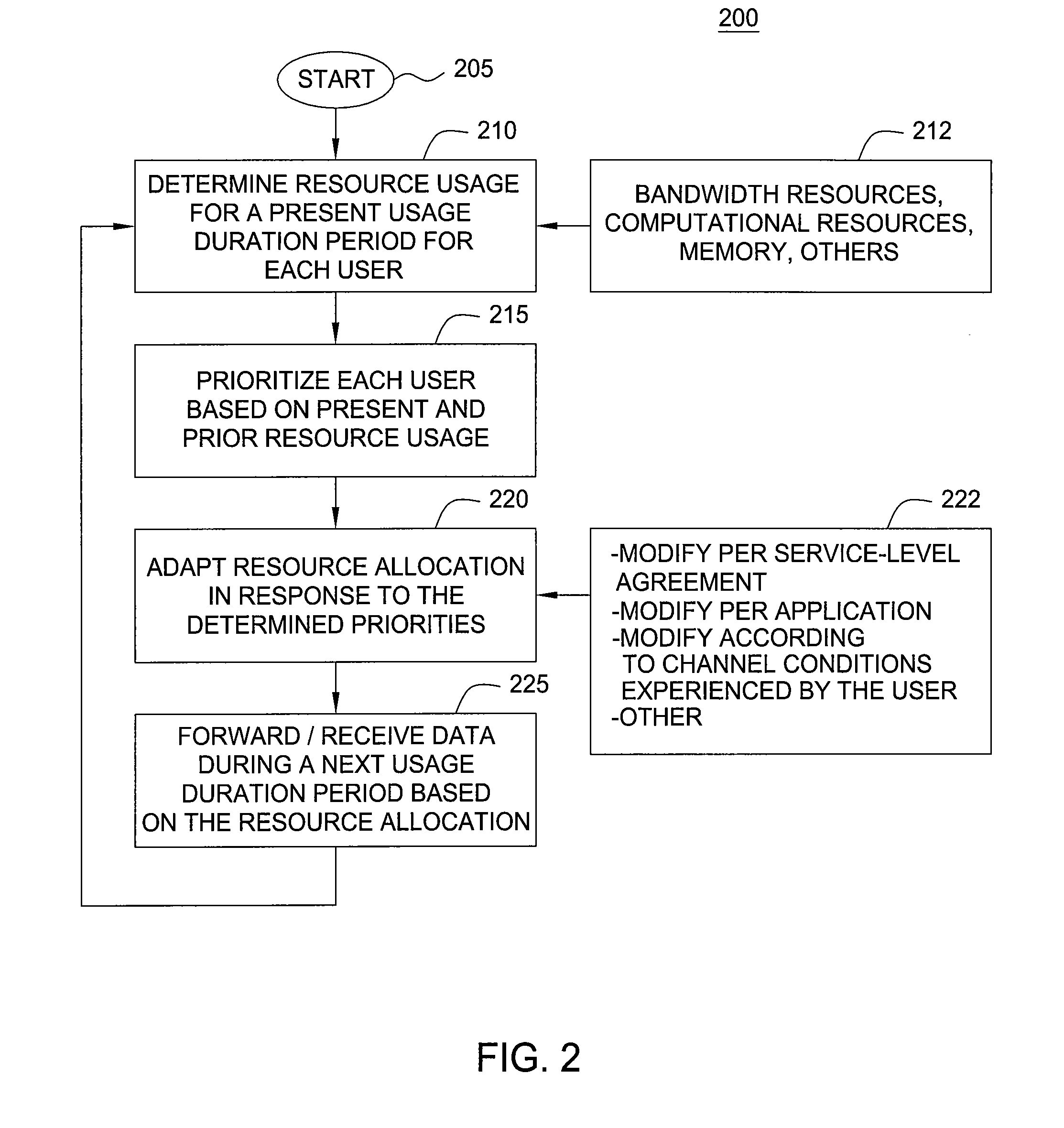
Method and apparatus for managing allocation of resources in a network
InactiveUS20110069666A1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsResource allocationFair distribution
To manage resource allocation between users of a wireless or wireline network, recent resource usage by each user is determined and priorities are assigned accordingly. Then, the network resources are allocated according to the assigned priorities. A respective priority of a user may be inversely proportional to the recent resource usage by that user. To facilitate continuous fair distribution of the network resources, the users may be re-prioritized and resources are re-allocated accordingly. Information about recent resource usages by the users is continuously accumulated, including about users moving from one access point of the network to another. When resource allocation for a particular access point is determined, recent resource usage for a user that has joined the access point from another access point in the network may include prior resource usage by that user at the other access point.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
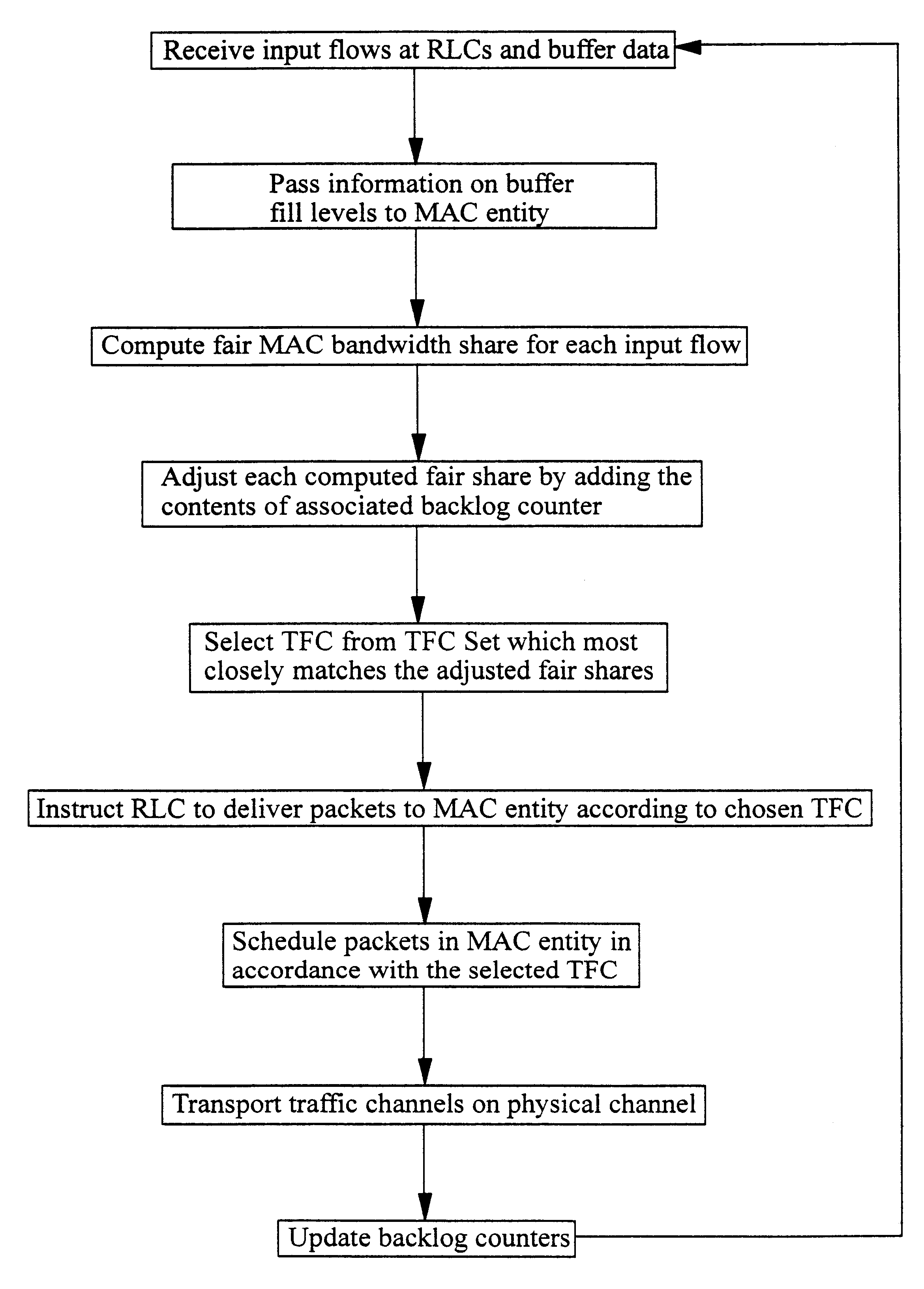
Data transmission in a telecommunications network
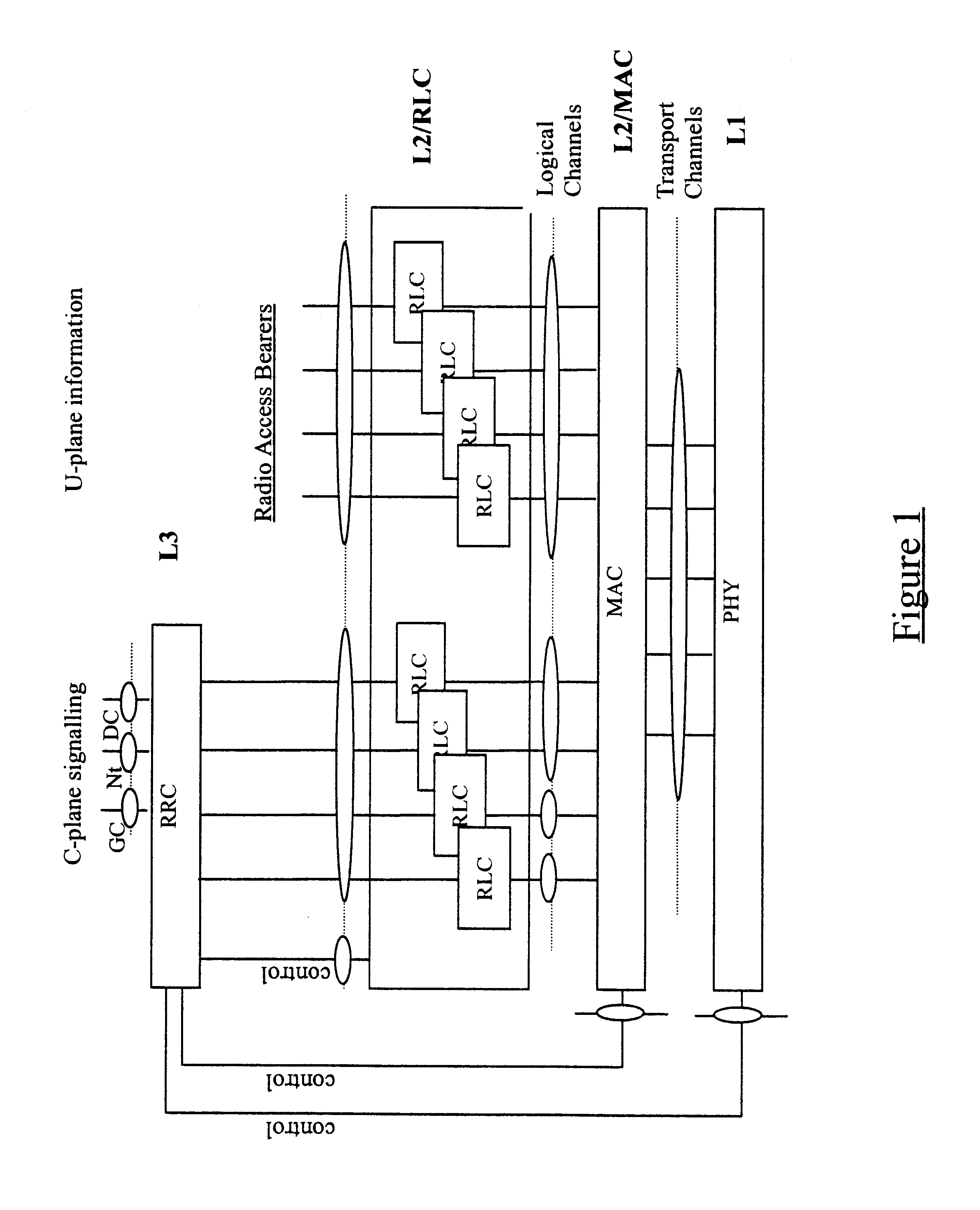
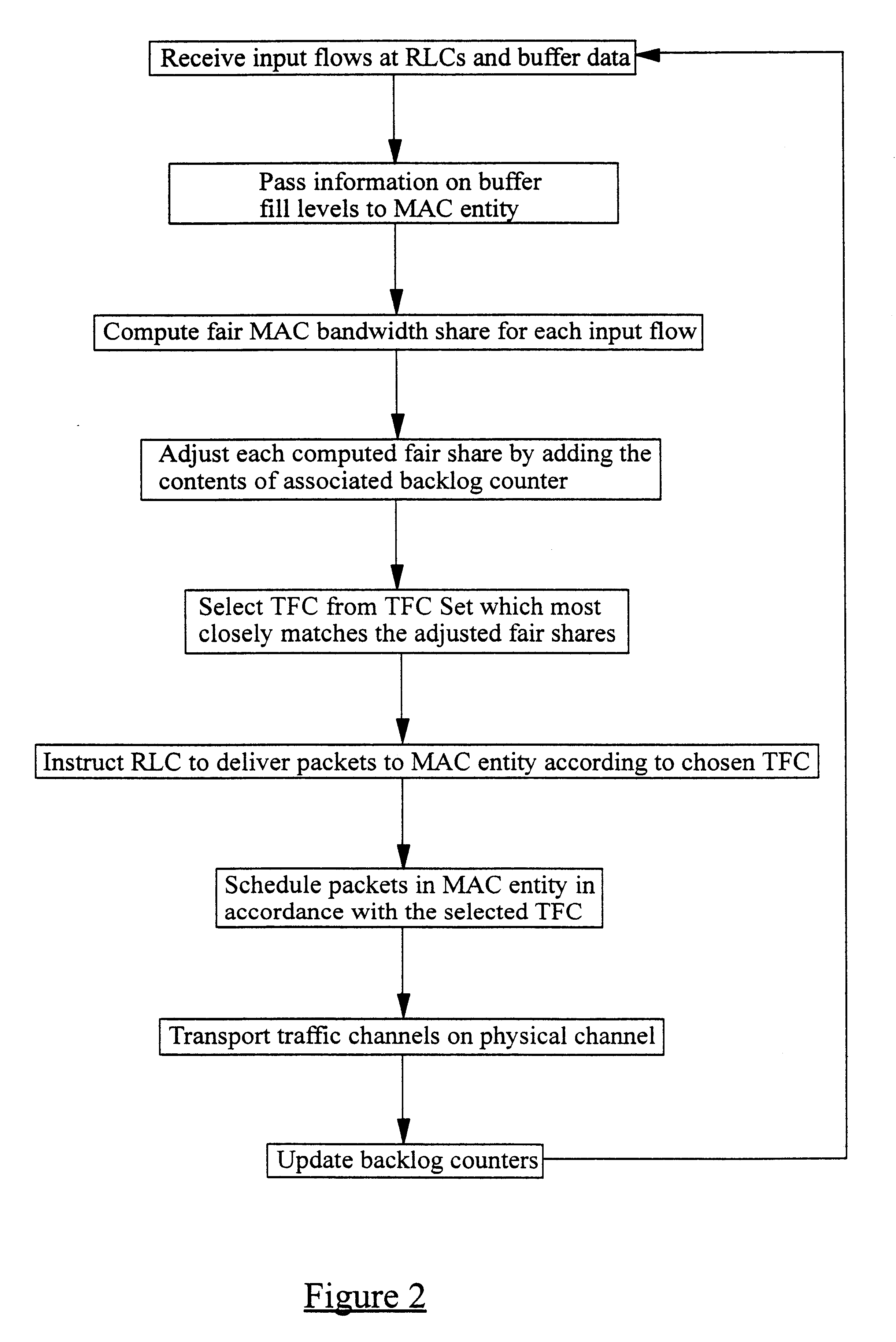
InactiveUS6826193B1Network traffic/resource managementNetwork topologiesData streamTelecommunications network
A method of allocating transmission resources at a Media Access Control (MAC) entity of a node of a Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS). The method comprises, for each frame of an output data flow, computing for each input flow to the MAC entity a fair share of the available output bandwidth of the MAC entity. A Transport Format Combination (TFC) is then identified from a TFC Set (TFCS) on the basis of the bandwidth shares computed for the flows, where the TFC comprises a Transport Format allocated to each input flow. For each input flow, if the allocated TF results in a data transmission rate which is less than the determined fair distribution, the difference is added to a backlog counter for the input flow. The value of the backlog counters is taken into account when selecting a TFC for the subsequent frame of the output data flow.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
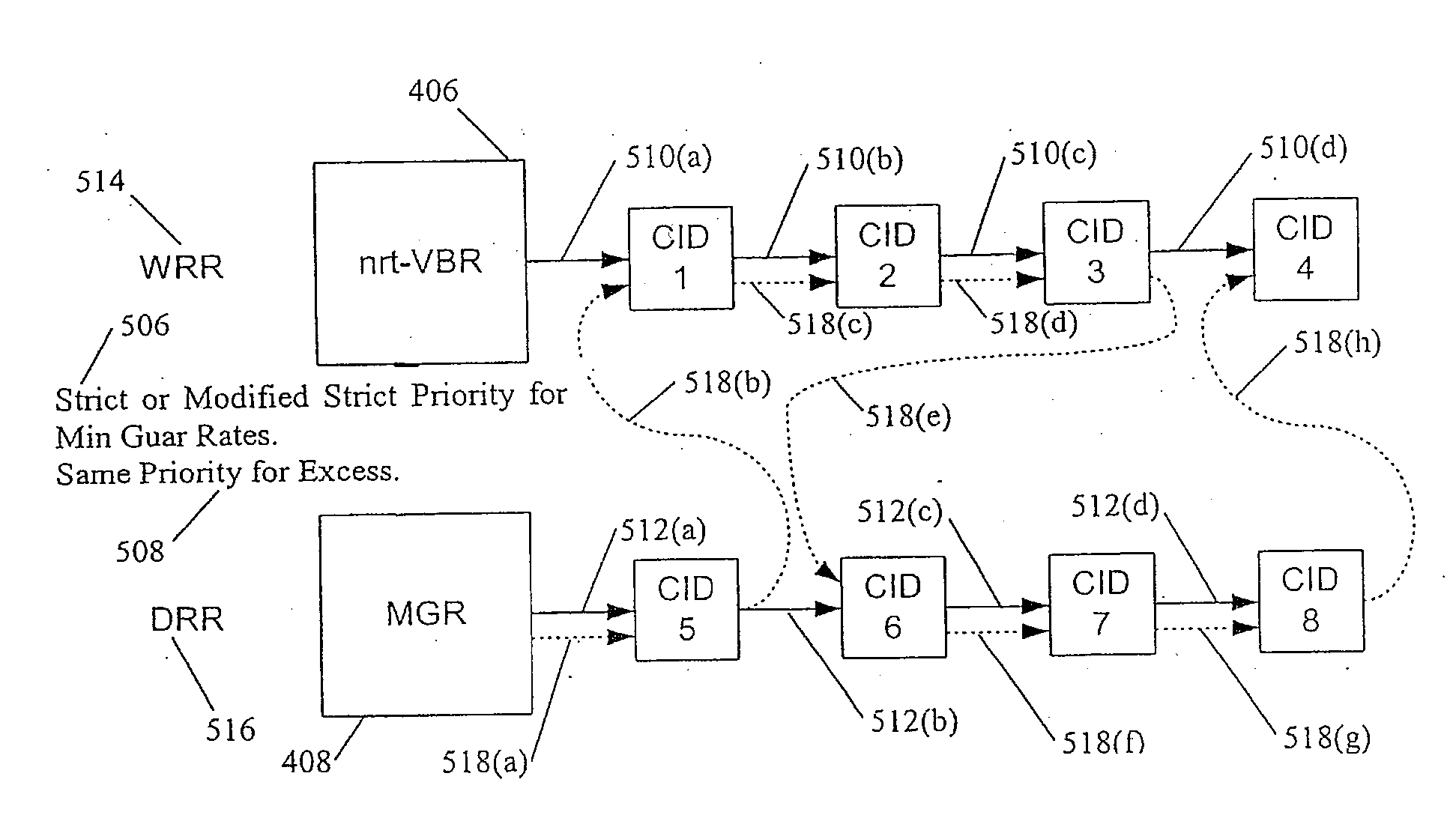
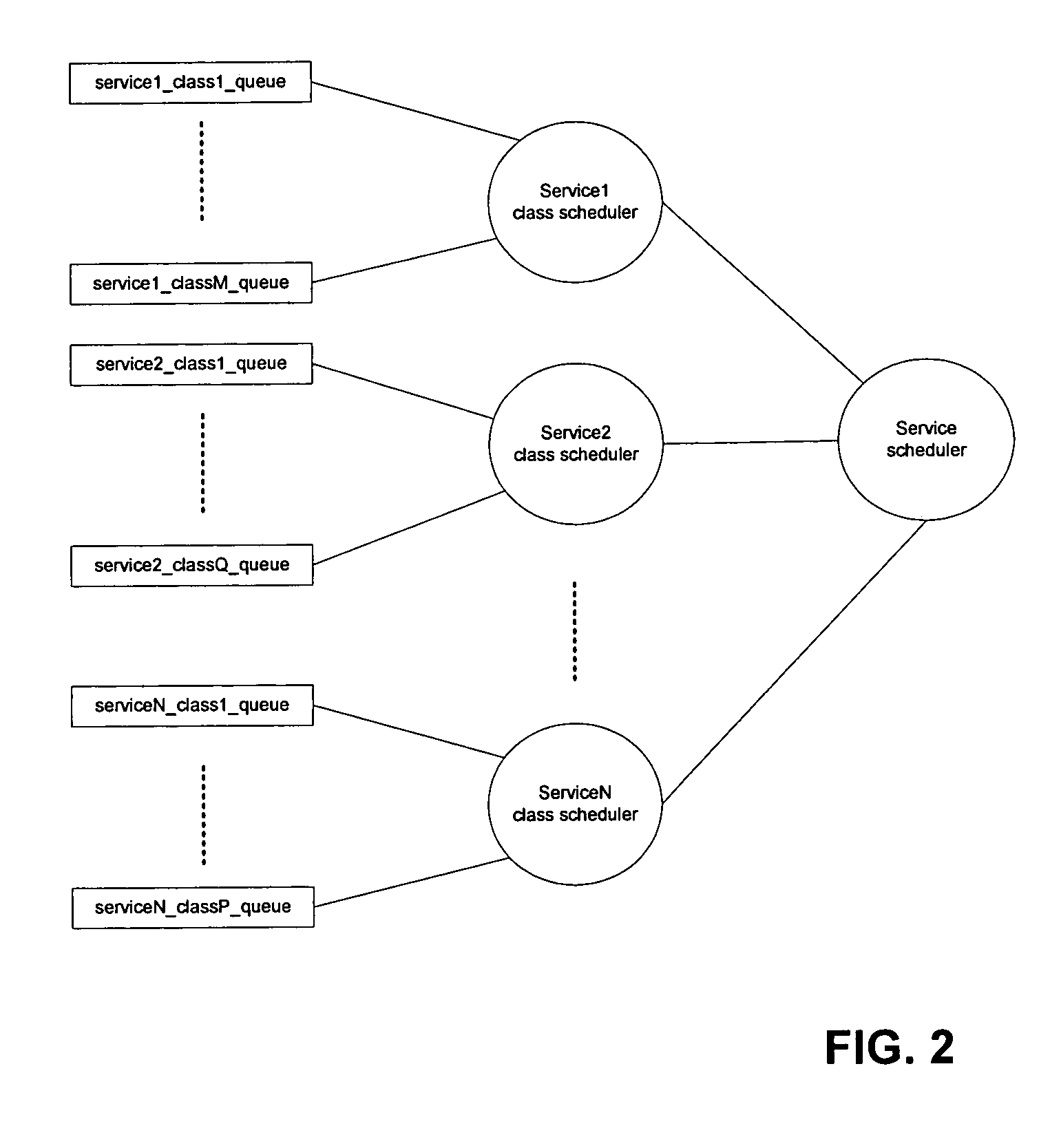
Scheduling Method and System for Communication Systems That Offer Multiple Classes of Service
InactiveUS20070153690A1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsDeficit round robinCommunications system
A method and system for prioritizing connection data that is associated with different classes of service for transmission in a frame based communication system. These classes of service can include CBR, nrt-VBR, MGR, and UBR traffic. One embodiment of the scheduling method and system uses hierarchical round-robin (HRR) with deficit round-robin (DRR). In this embodiment, the scheduling method and system guarantees minimum rates of nrt-VBR and MGR traffic to the connections. The excess bandwidth is then fairly allocated between the existing connections and their classes of service. For example, the excess is allocated for UBR traffic and for the excess demands of the nrt-VBR and MGR connections. In one embodiment, the scheduling method and system allocates the excess bandwidth in a frame to the existing connections using weighted round robin to differentiate between different classes of service. In one embodiment, excess allocation to nrt-VBR and MGR connections is rolled back into the deficit counters for the minimum guaranteed rates of nrt-VBR and MGR connections.
Owner:GAMEHANCEMENT LLC +1
Fair weighted network congestion avoidance
ActiveUS20100027425A1Avoid network congestionError preventionTransmission systemsQuality of serviceTraffic capacity
Systems and methods which provide network congestion avoidance implementing a fairness scheme in which a cost function is used are shown. Transmission cost, for use in network congestion avoidance packet dropping decisions, may be determined from an amount of air time needed to transmit a data packet, a transmission data rate, a size of a packet, an amount of spectral energy or transmit power associated with transmission, etc. A packet dropping probability for a particular packet is preferably determined as a function of the current flow cost and average flow cost to provide fair allocation of network communications resources. Embodiments additionally implement buffer based packet dropping probability calculation in order to provide a robust network congestion avoidance technique. Cost based packet dropping probability calculation and buffer based packet dropping probability calculation implemented according to embodiments are adapted to accommodate quality of service applications.
Owner:FIMAX TECH
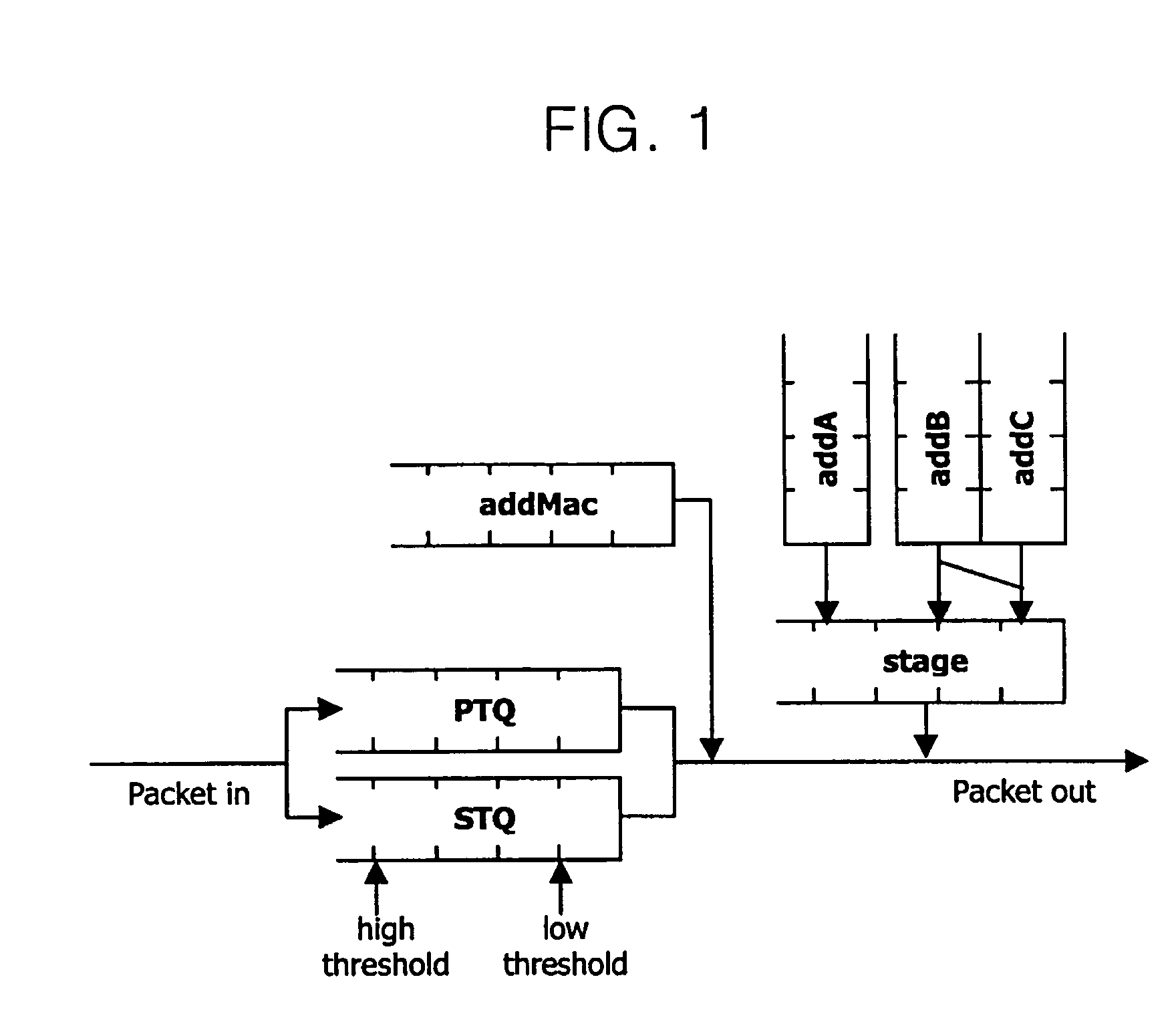
Fair discard system
InactiveUS6717912B1Easy to useEffective distributionError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsClass of serviceMulti dimensional
The present invention is a shared buffer architecture that dynamically allocates buffer size to each of multiple sources depending on buffer pool utilization, estimated per-connection offered load, and the total number of connection established within a given class of service. When the buffer pool is almost empty, each source is allocated a large buffer space, proportional to its estimated offered load. When the buffer pool is more full each source is allocated a reduced buffer space, while maintaining the proportional weighting relationship. The invention keeps track of the amount of input per source and dynamically allocates a proportionate amount of buffer space in the buffer memory for that source. The dynamic allocation is made as a function of the fullness of the memory allocation for all sources. Additionally, thresholds are modulated dynamically as the number of established connections within a given class modulates, providing a predictive aspect to the system, with respect to congestion control. The main objective is to fairly allocate buffer space depending on the amount of traffic and the amount of buffer space taken up by each source. In operation, the memory allocation is readjusted depending on the total number of cells in the buffer memory, the estimated offered load, and the total number of connection established within each class of service, providing a highly dimensional solution to the multi-dimensional problem of congestion management in communication network nodes.
Owner:RIBBON COMM OPERATING CO INC
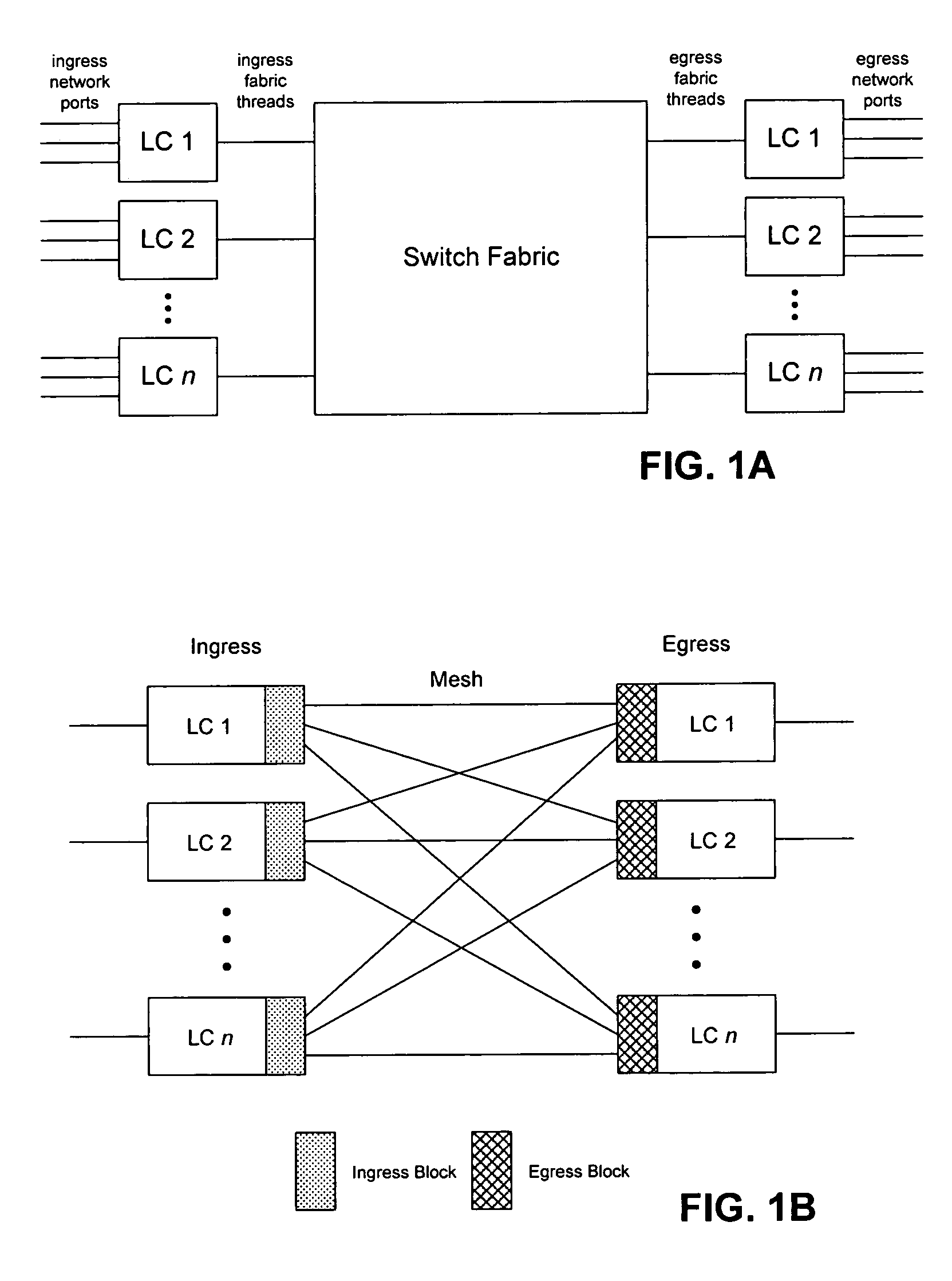
Unified scheduling and queueing architecture for a multiservice switch
ActiveUS7304944B2Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsService level requirementFair scheduling
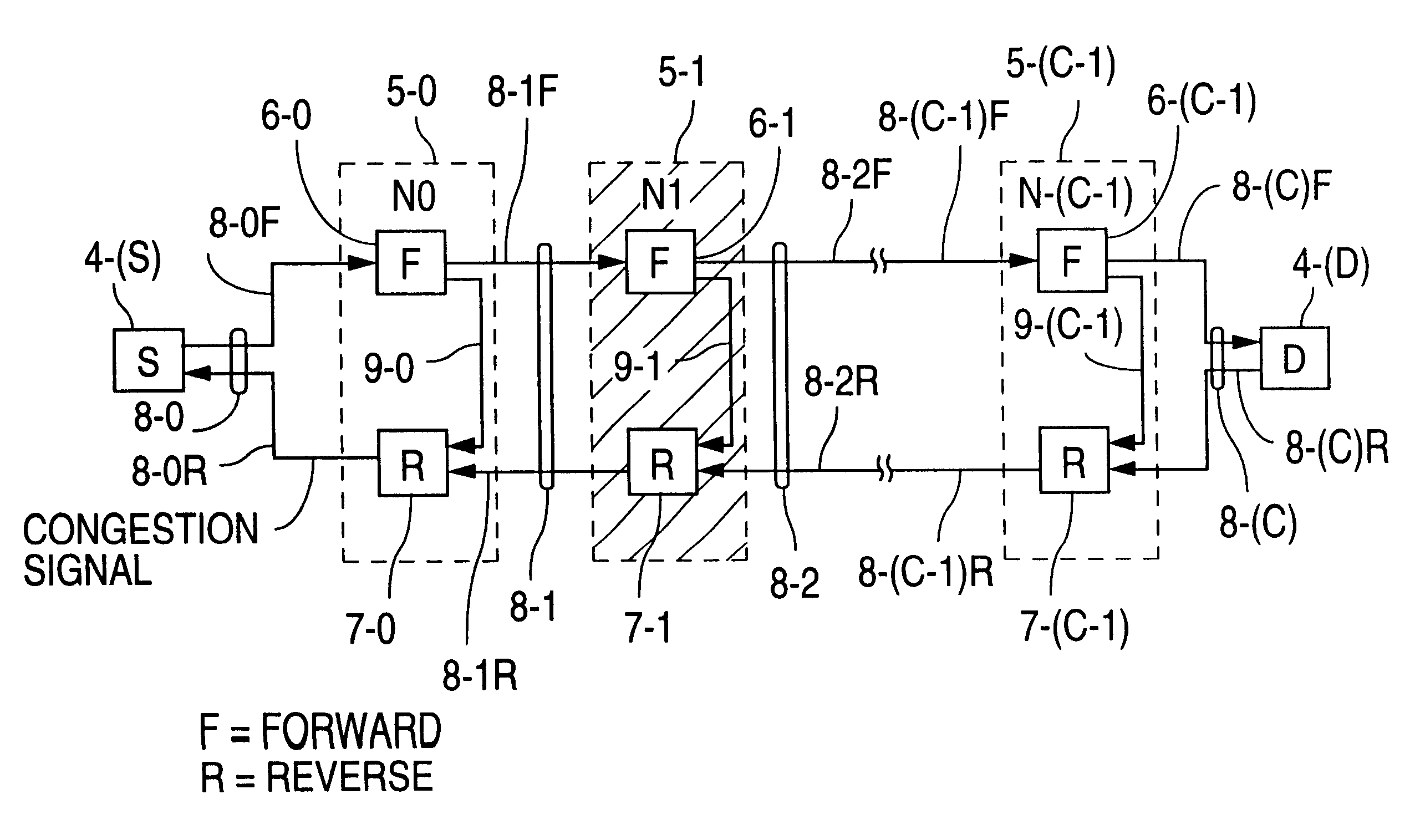
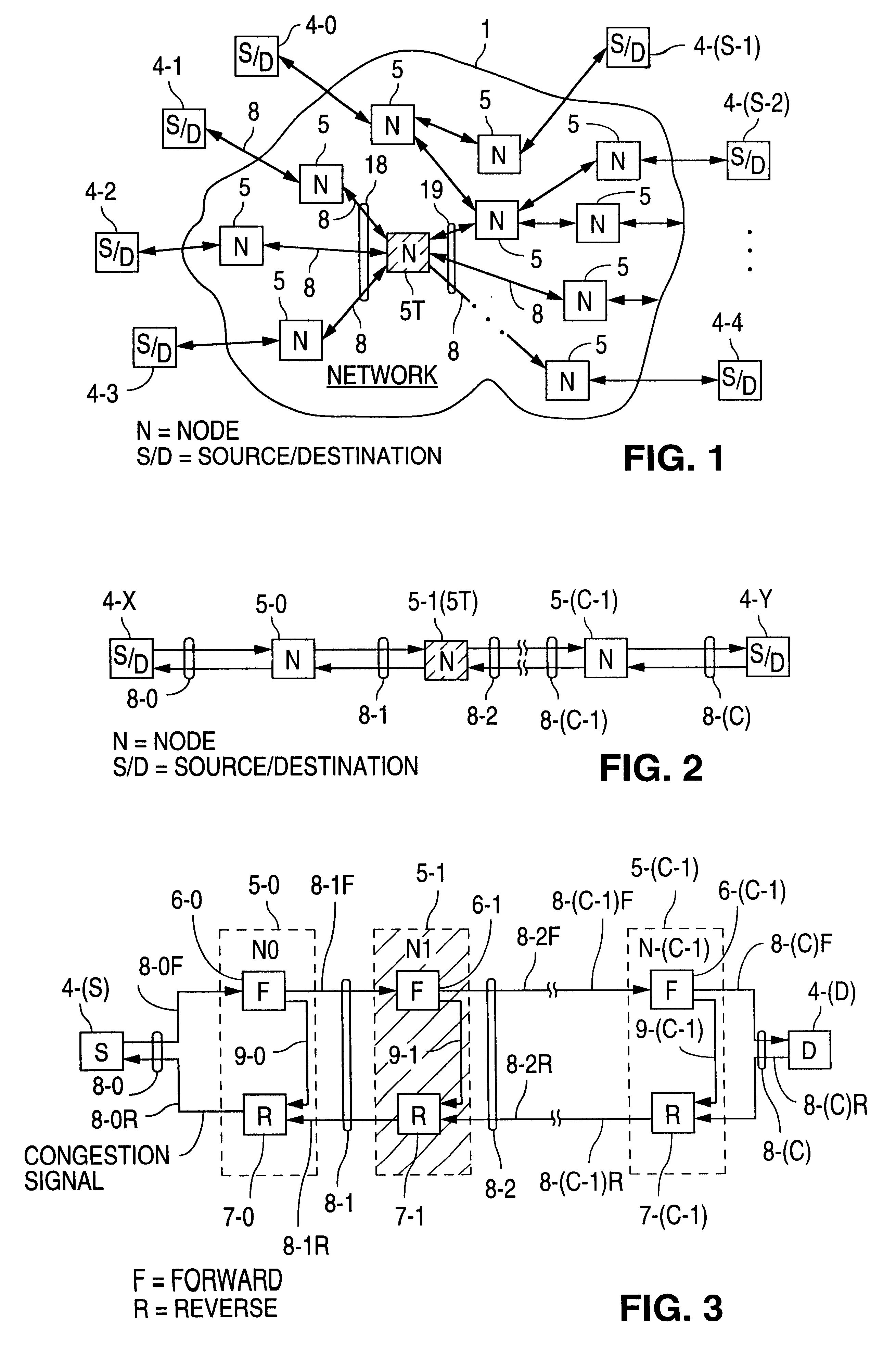
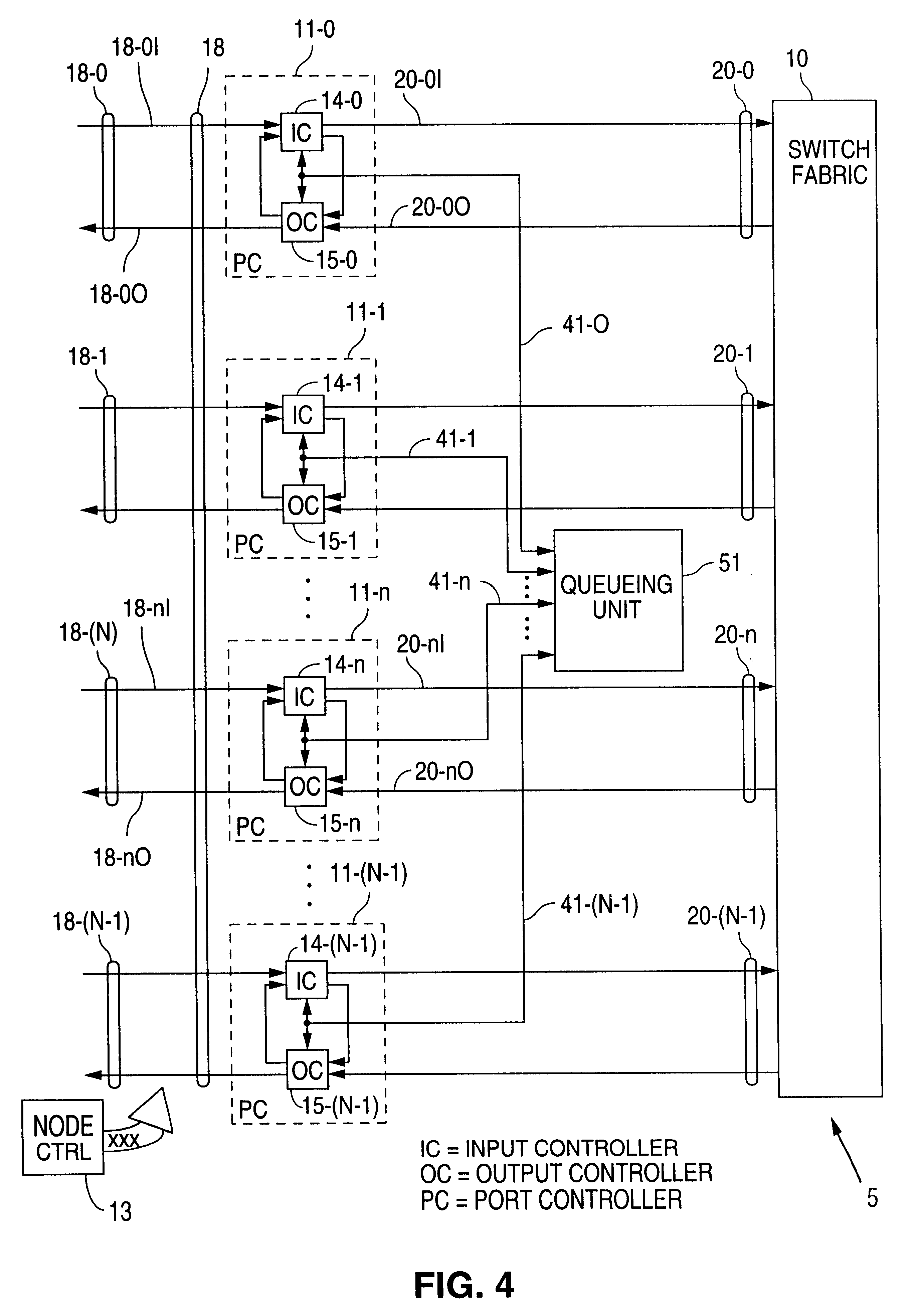
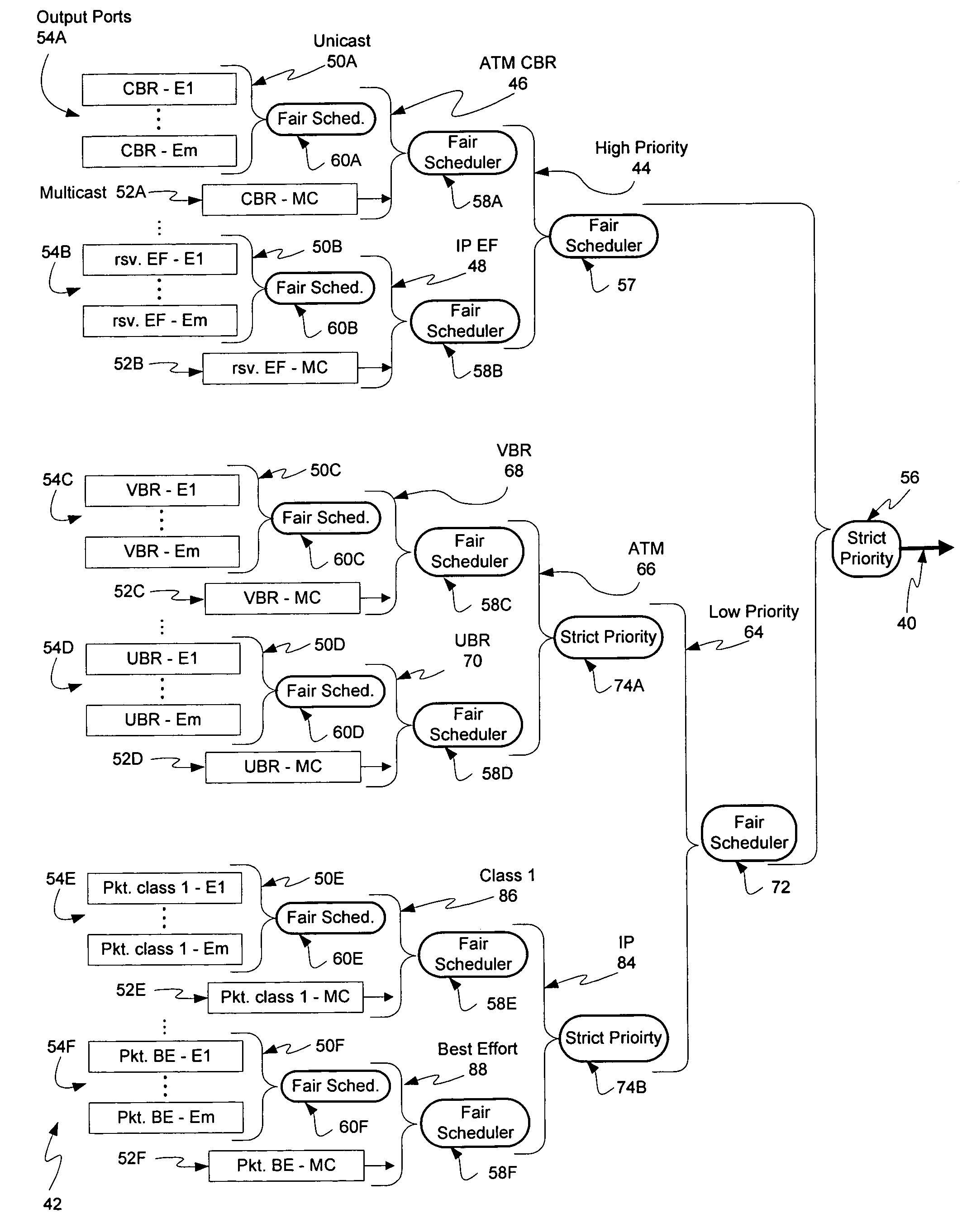
The present invention provides hierarchical structures of queues and schedulers for switches and routers with, preferably fully-connected, mesh fabrics, for efficiently and properly handling the quality or service requirements of multiple network services, such as ATM and IP, in switch or router. The switches of this invention provide, for example, fair allocation of bandwidths to different network services, to different QoS classes within network services, and to different resources within the switch by use of, preferably, weighted, fair scheduling methods. The switches and routers of this invention are particularly directed to multi-protocol, high-throughput communication application, but may have wide applicability in systems generally where data packets are switched or routed.
Owner:RPX CORP +1
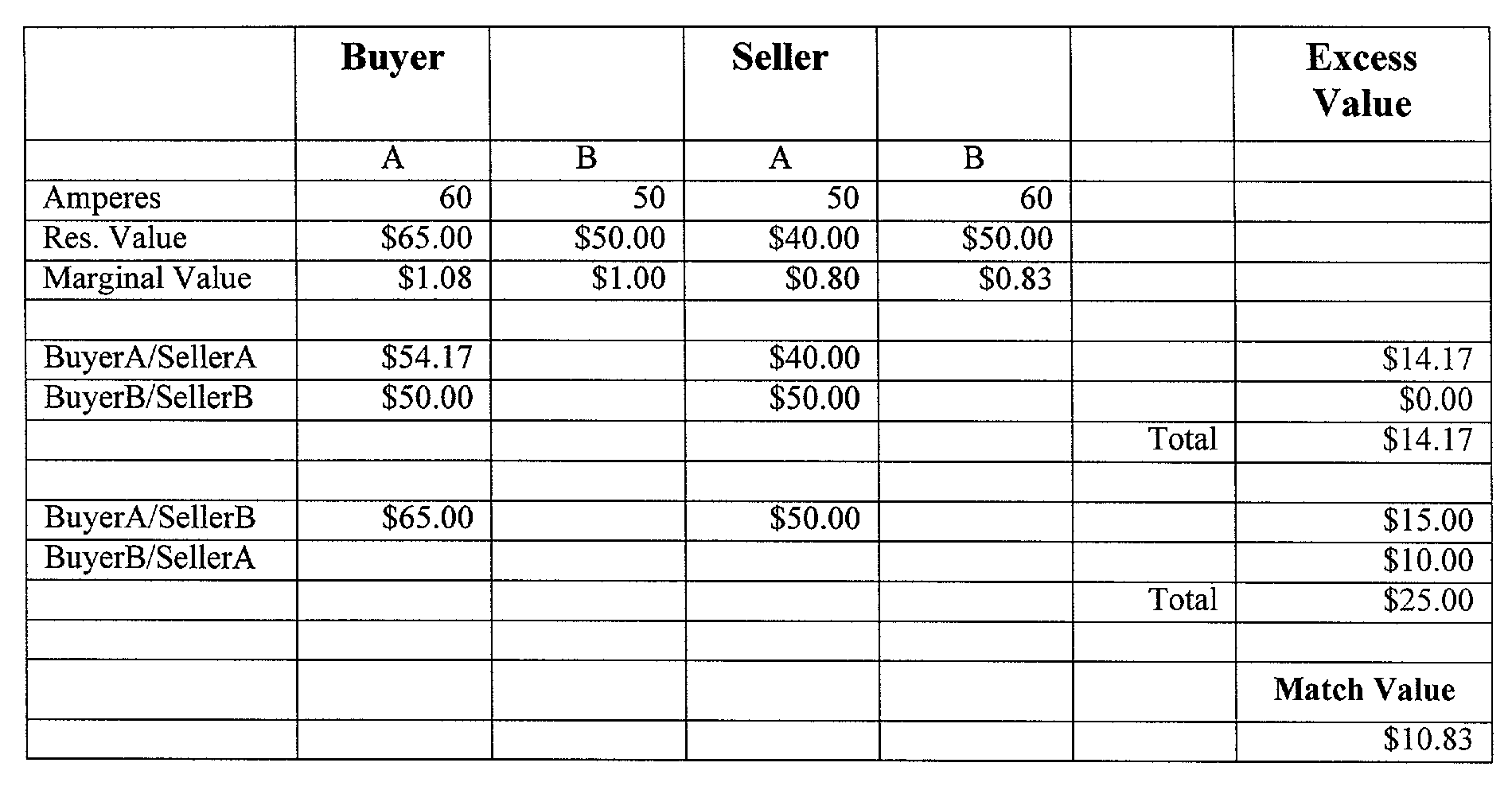
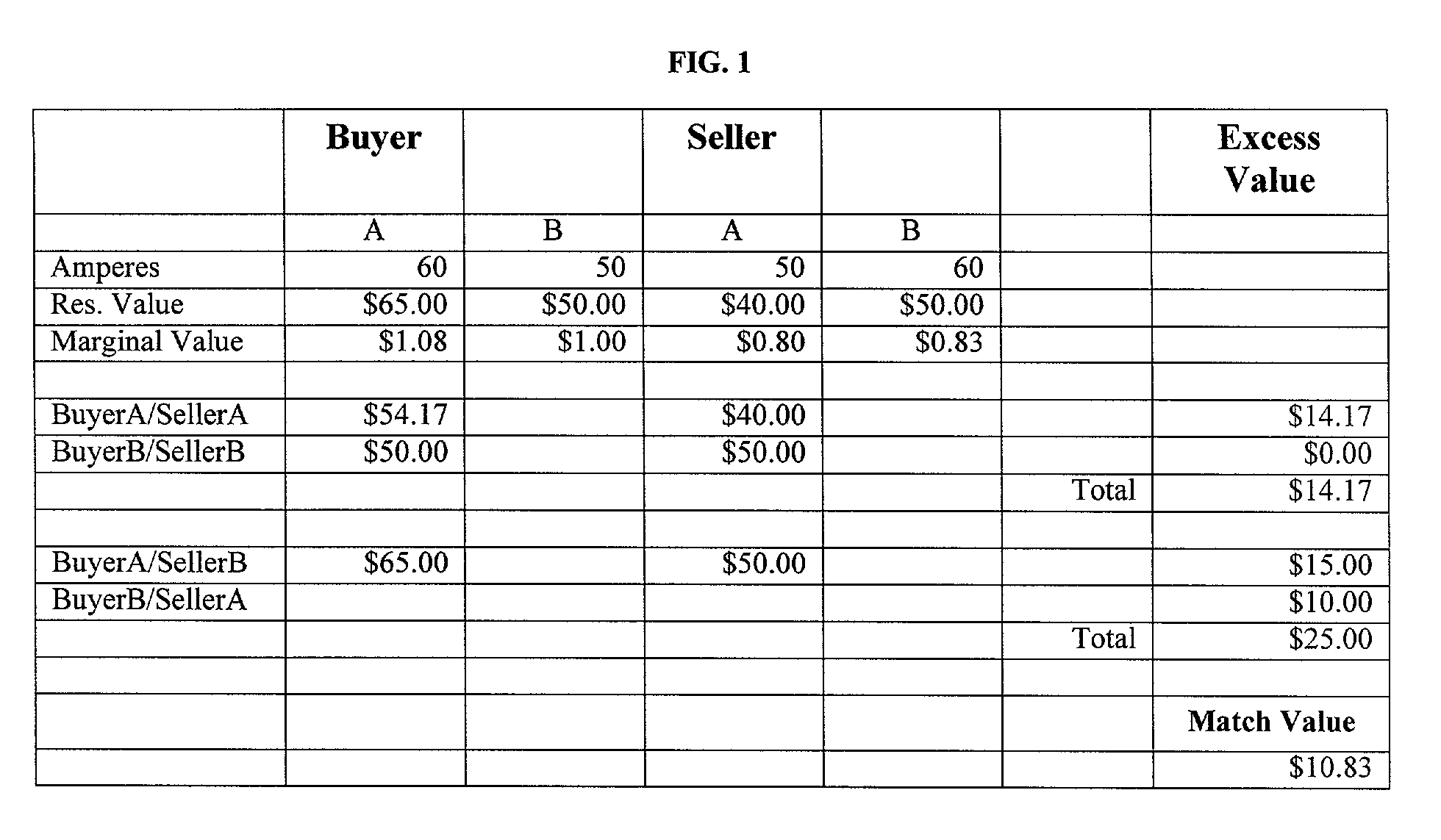
Automated method and system for facilitating market transactions
InactiveUS7512558B1Convenient transactionMarket predictionsFinanceOptimization problemMarket transaction
The present invention relates to a method for finding the best match between buyers (or buyers consortiums) and sellers (or sellers consortiums), by a set of software intermediaries, and for using the information developed in those matches to define monetary and performance commitments between parties, and to create fair distribution of the benefits of the agreement among the respective participants. The system solves three related optimization problems concurrently: the optimal aggregation of individual buyers into buyers consortiums; the optimal aggregation of individual sellers into sellers consortiums, and the optimal match of requirements, posed by the buyers consortium, to offers, posed by the sellers consortium.
Owner:QUANTUM LEAP RES
Dice that recognize the values of their own throws and transmit them to computers, with applications to electronic and casino games
InactiveUS20050215312A1ExperienceSmall modificationLottery apparatusVideo gamesElectricityEngineering
Dice are disclosed that detect their state, i.e., their own value once at rest, using for instance gravity, piezoelectricity, or photoelectric cells that are assigned to all faces to recognize the lower face. Said dice preferably transmit said state to a computer. Said computer may be the same that is used for the game that depends on the throw of the dice, or may be used mostly for display as for some casino games. Electricity is used in the die to let it determine its own state and transmit it. Economical protocols of transmission are used such as Bluetooth. Such dice may securely send alerts whenever deviations from a fair distribution of the outcomes is detected and can monitor small modifications of their balance to maintain their fairness. Part or all of the teaching can be realized as MEMS (micro electro-mechanical systems) or NEMS (nano electromechanical systems) modifications of usual dice.
Owner:TRESSER YUVAL ARIE +1
Smart pause for distributed switch fabric system
Techniques for improving the performance of flow control mechanisms such as Pause are provided. The techniques provide for maintaining a fair distribution of available bandwidth while also allowing for fewer packet drops, and maximizing link utilization, in a distributed system. For example, in one embodiment, techniques are provided for achieving a fair share allocation of an egress port's bandwidth across a plurality of ingress ports contending for the same egress port.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
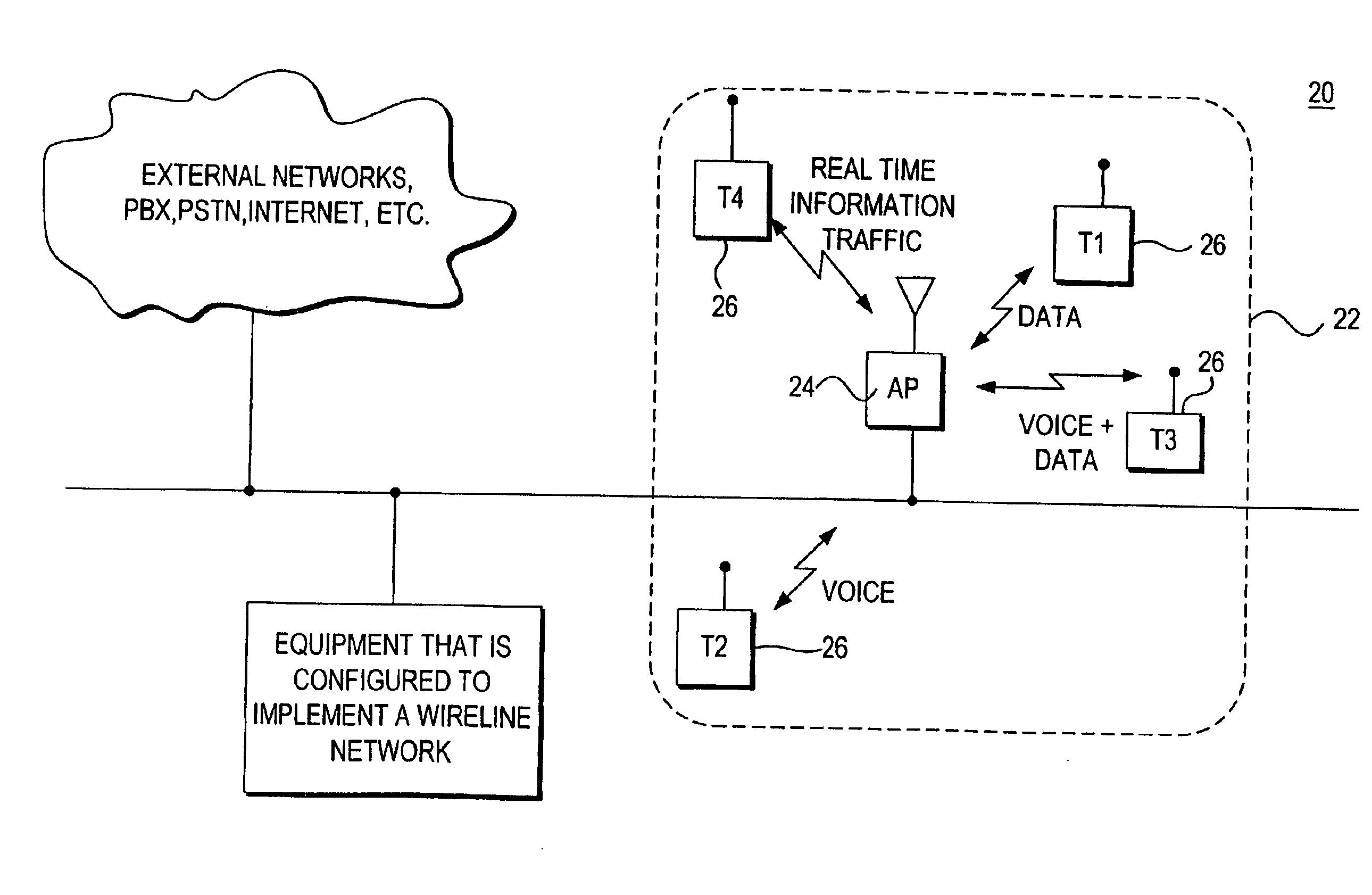
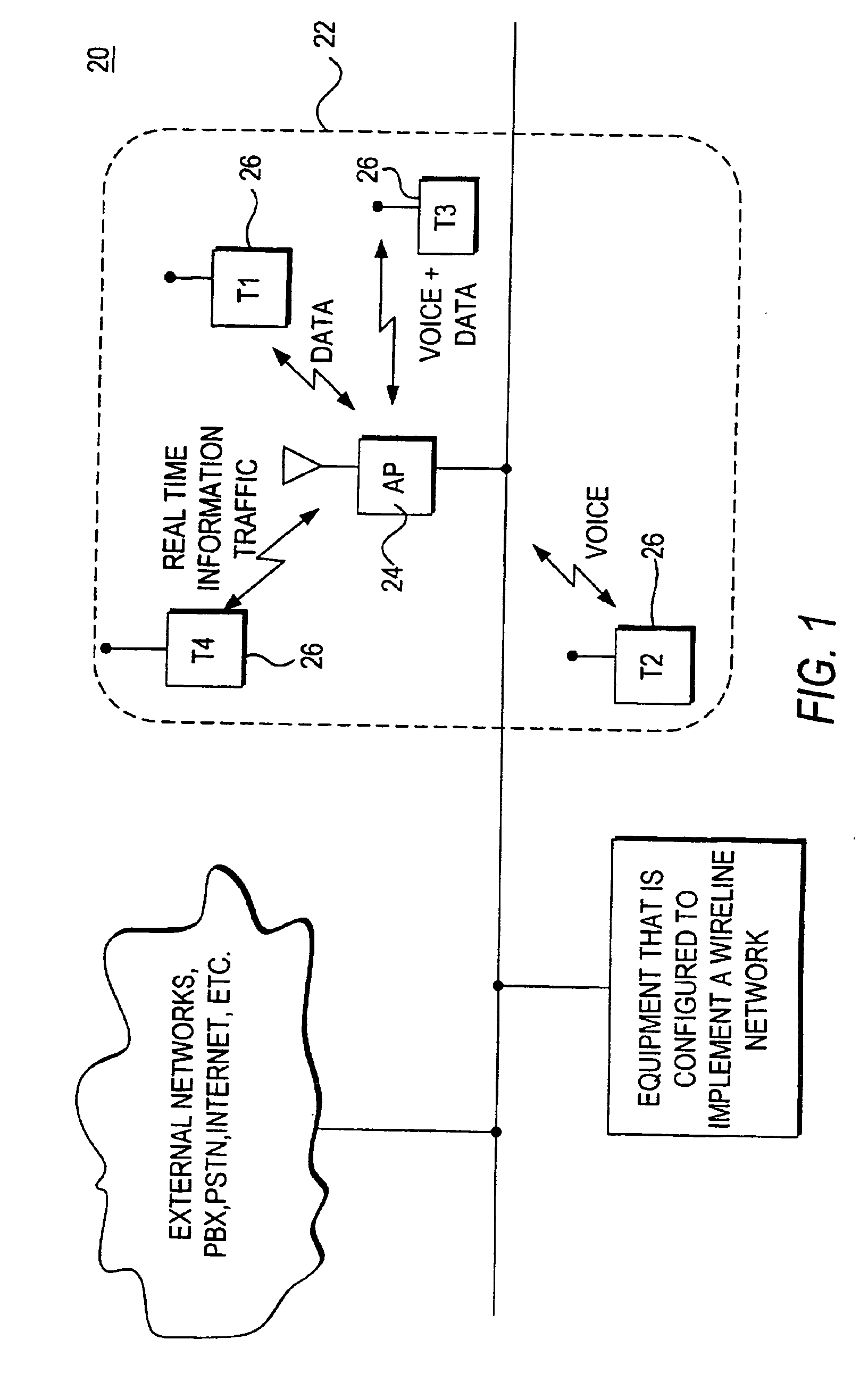
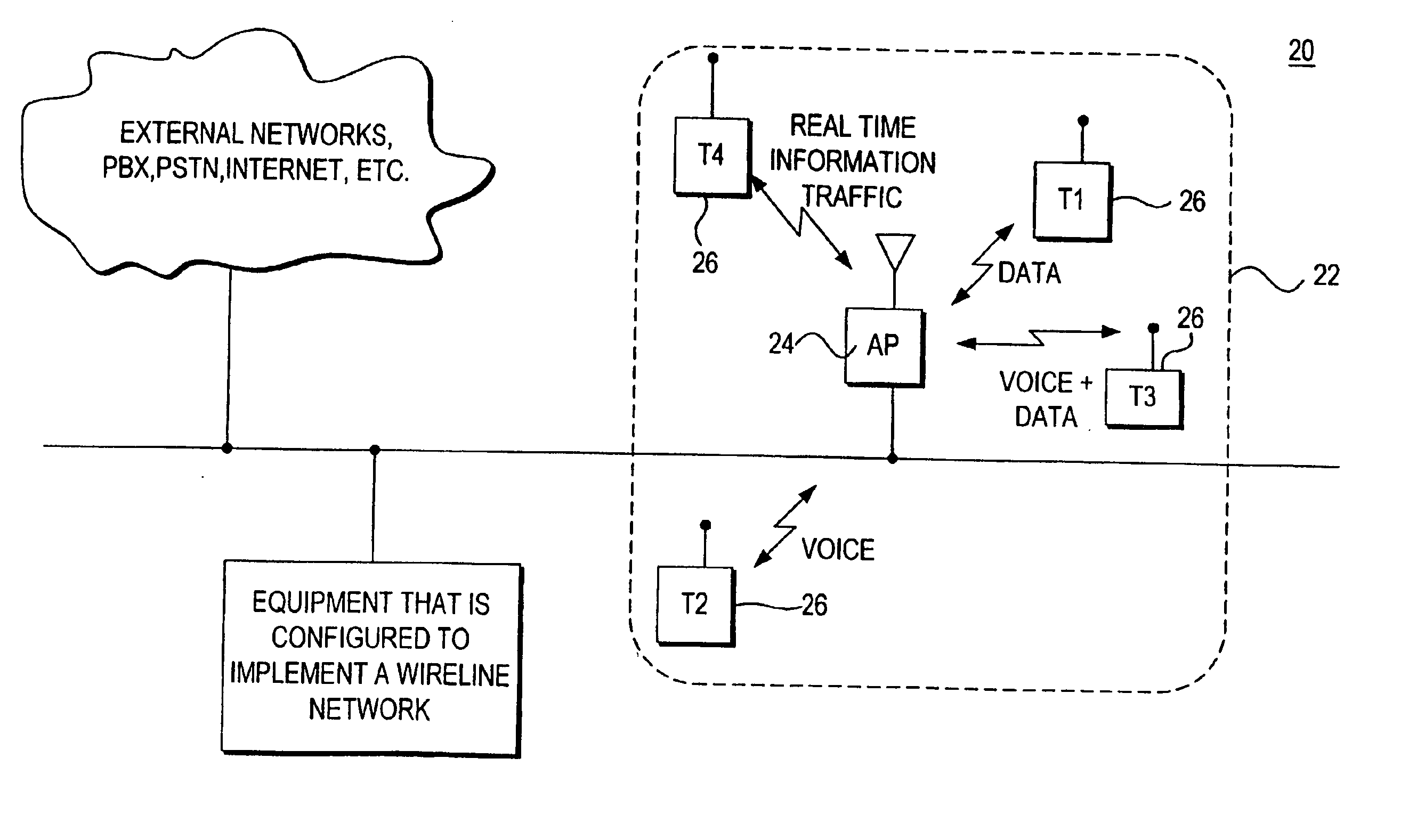
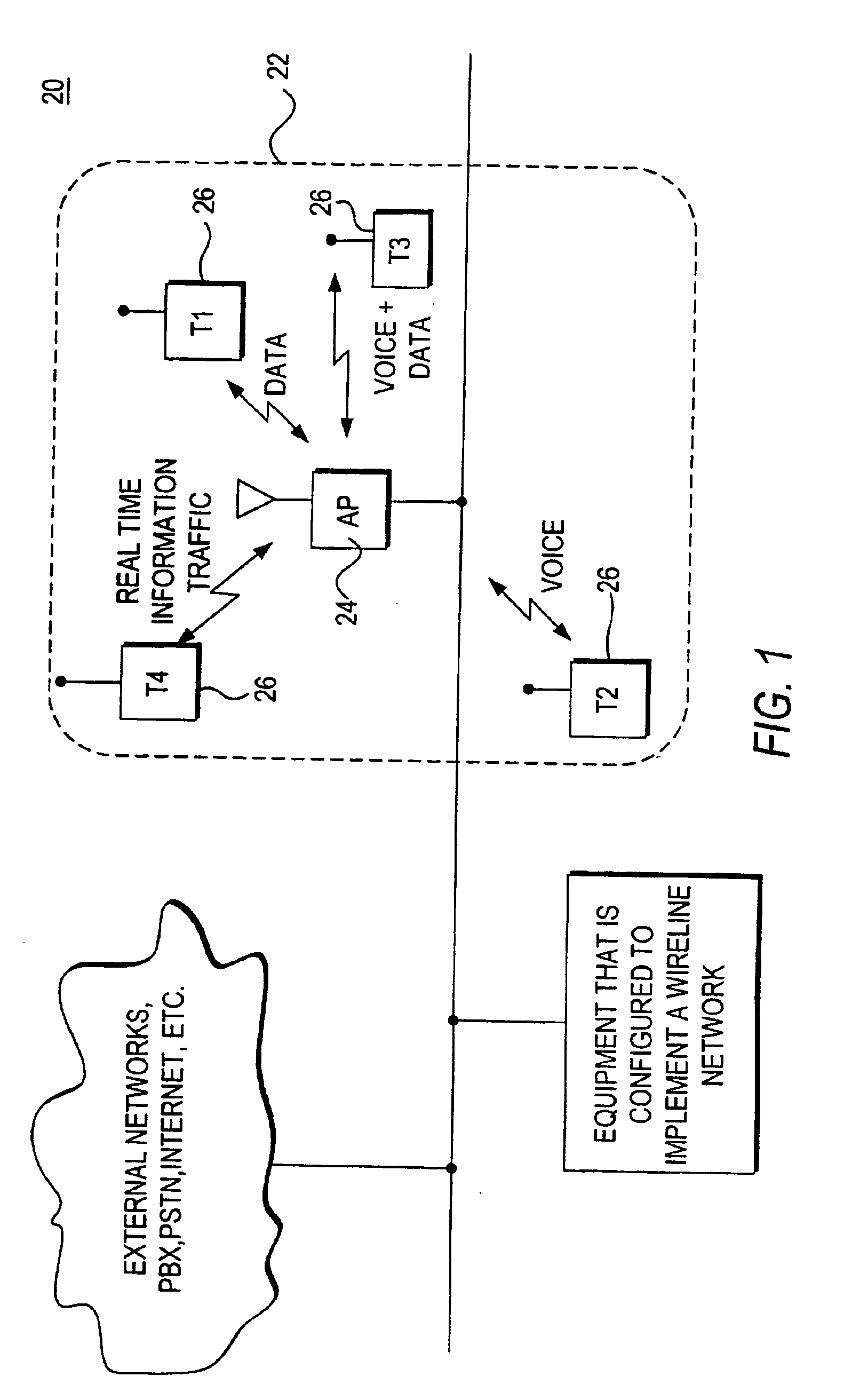
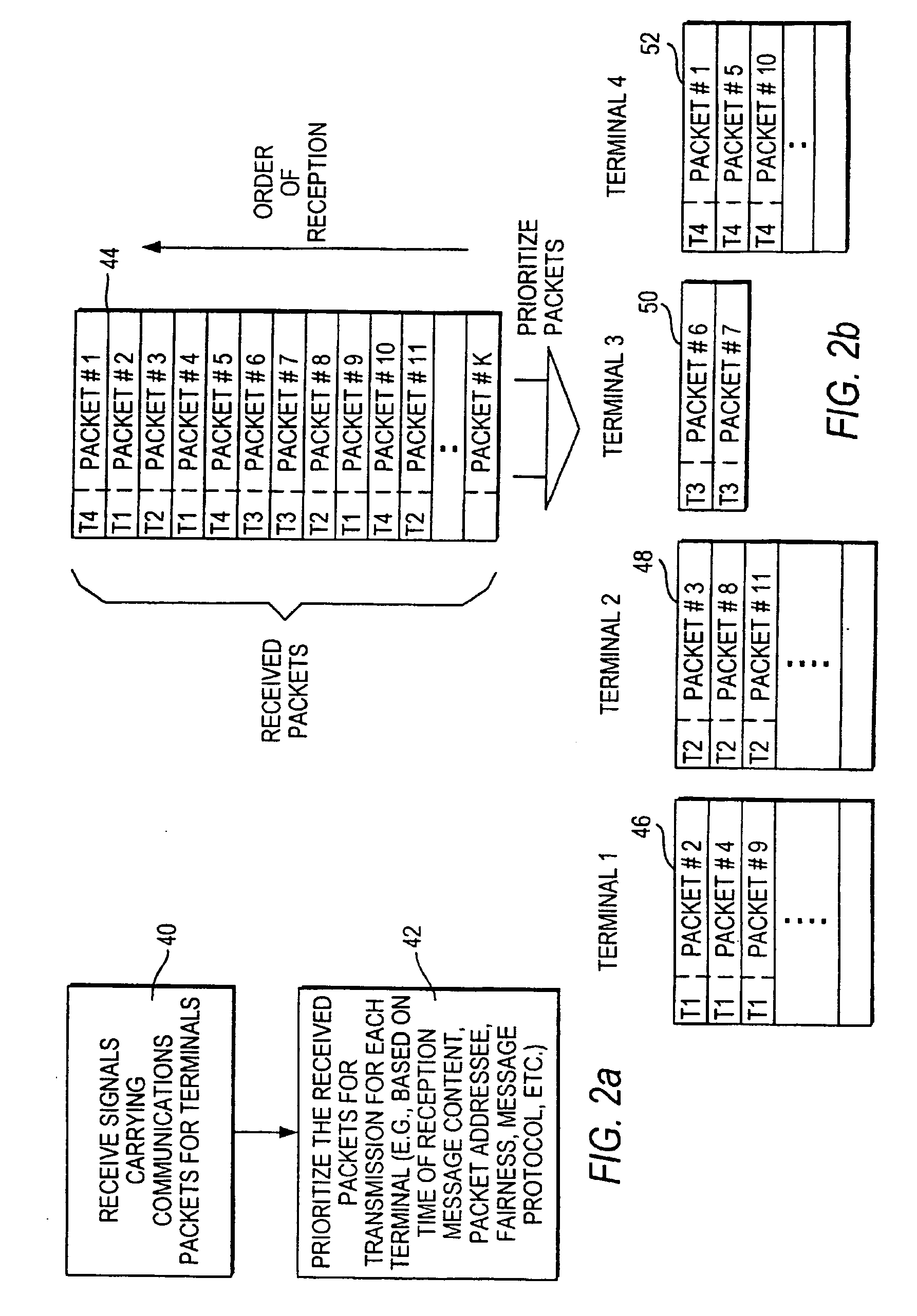
Voice and data wireless communications network and method
InactiveUS20050281235A1Raise priorityNetwork traffic/resource managementNetwork topologiesVoice communicationWireless lan
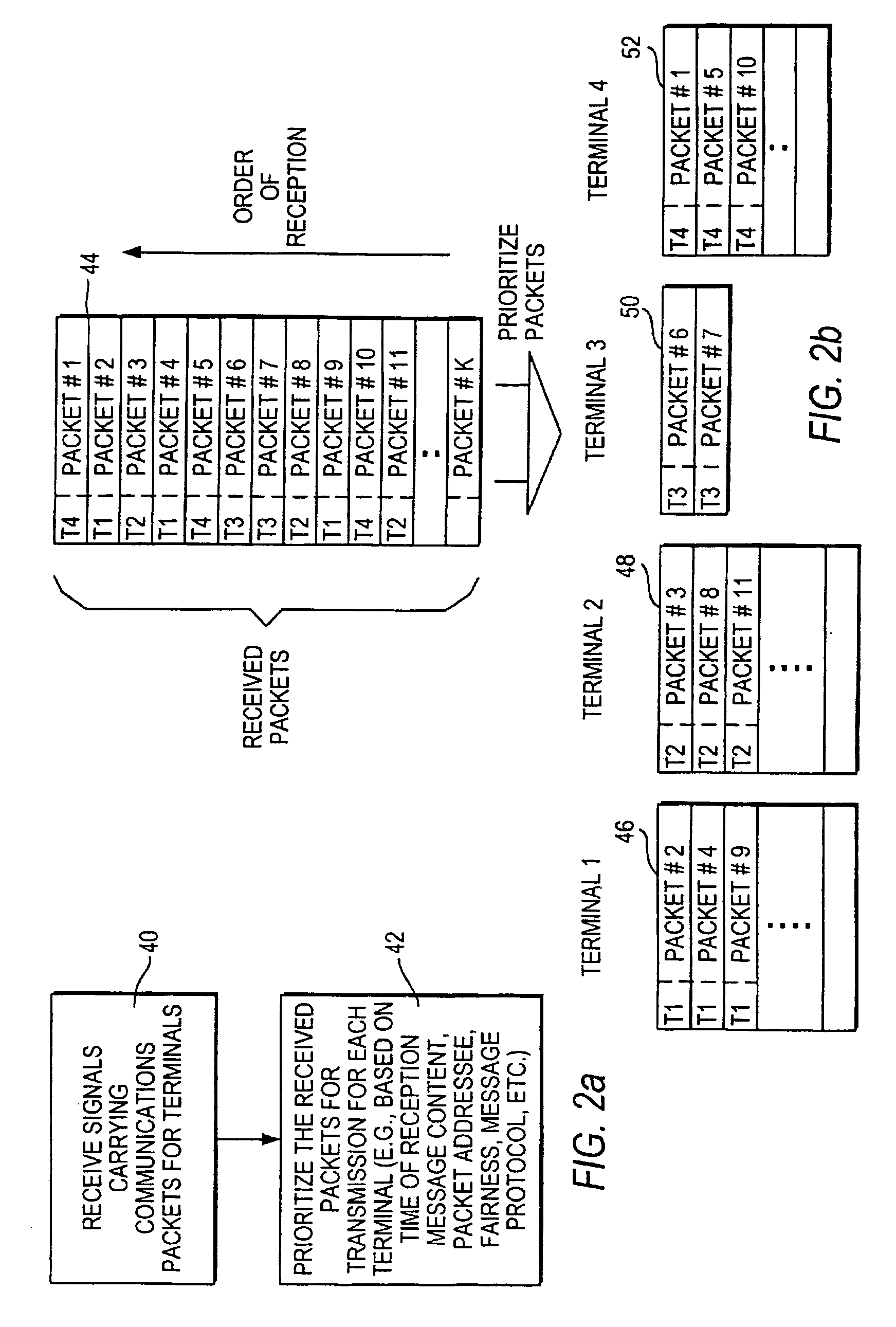
A wireless local area network that carries mixed traffic of voice and data communications may be provided. The wireless local area network may include an access point and a plurality of remote terminals that are associated with the access point. The access point may be operably coupled to a wireline network. The access point may receive voice and other communications packets from the remote terminals and the wireline network. Some of the packets may be for transmission to the remote terminals. The access point manages which packets to transmit and when to transmit packets. The access point may manage traffic to maintain a fair distribution of packets and to give priority to voice communications over other communications.
Owner:EXTREME NETWORKS INC
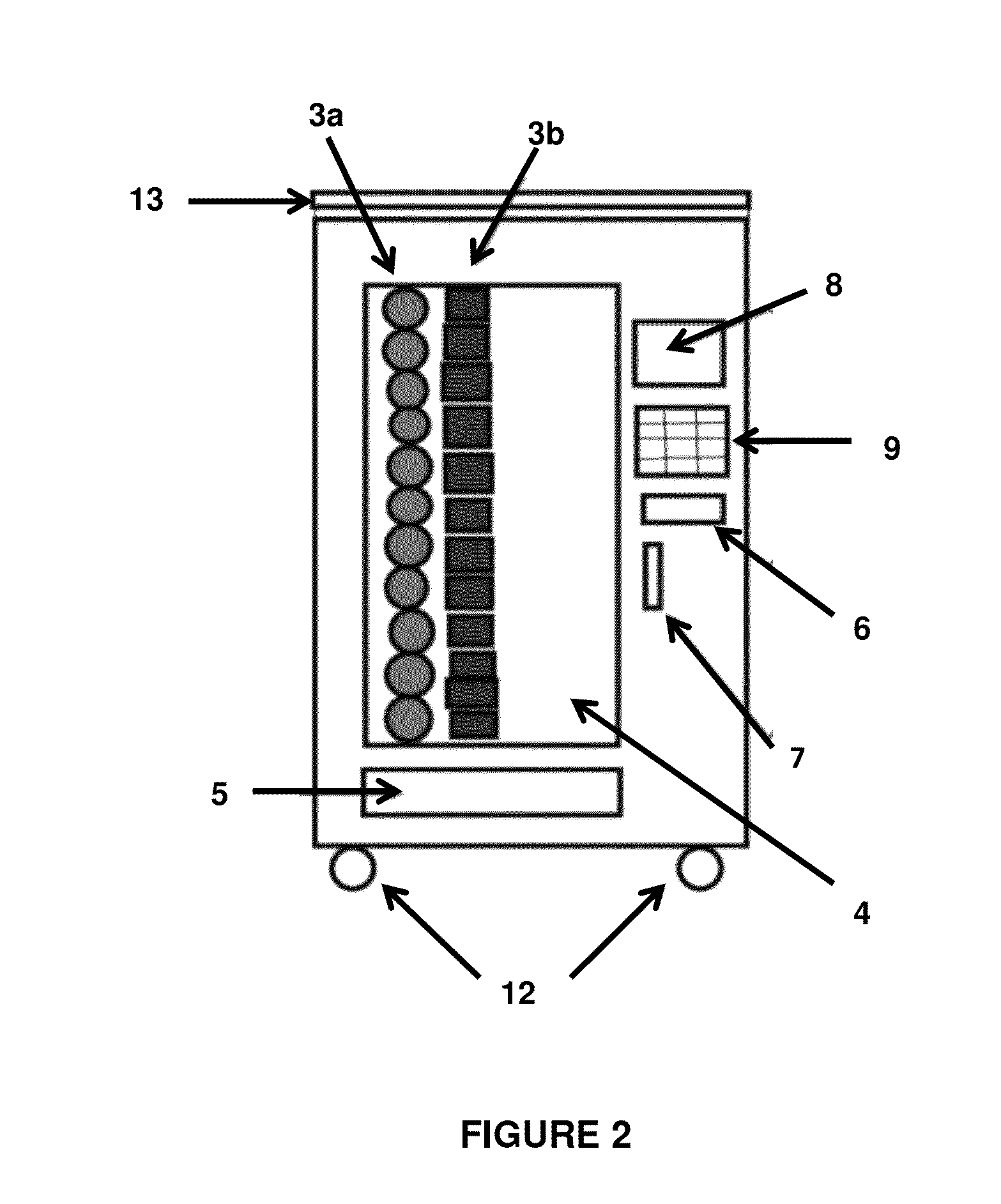
Snack and Food Dispenser for Commercial Aircraft Use
InactiveUS20150057796A1Reduce total usageMeet the requirementsAir-treatment apparatus arrangementsCoin-freed apparatus detailsBetween mealsFood item
Embodiments of the present invention provide snack and food dispensers on passenger transport vehicles, particularly aircraft, that will ensure fair distribution of self-serve snacks provided between meals and / or during flight in an organized, systematic, safe, and sanitary manner as well as allow a more accessible means for buying “Food for Purchase” items with less crew dependence for serving.
Owner:BOODAGHIANS LILLIAN
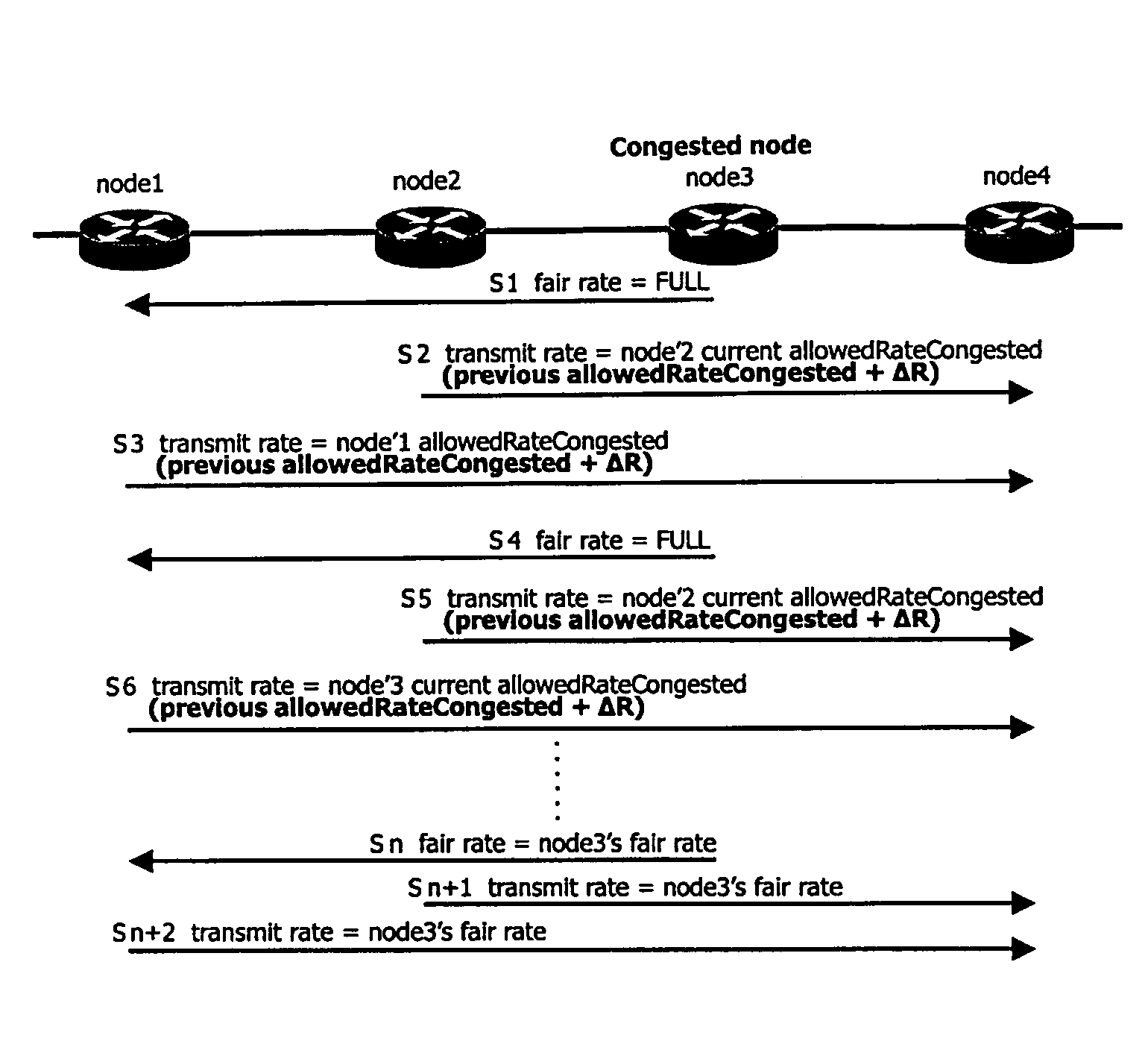
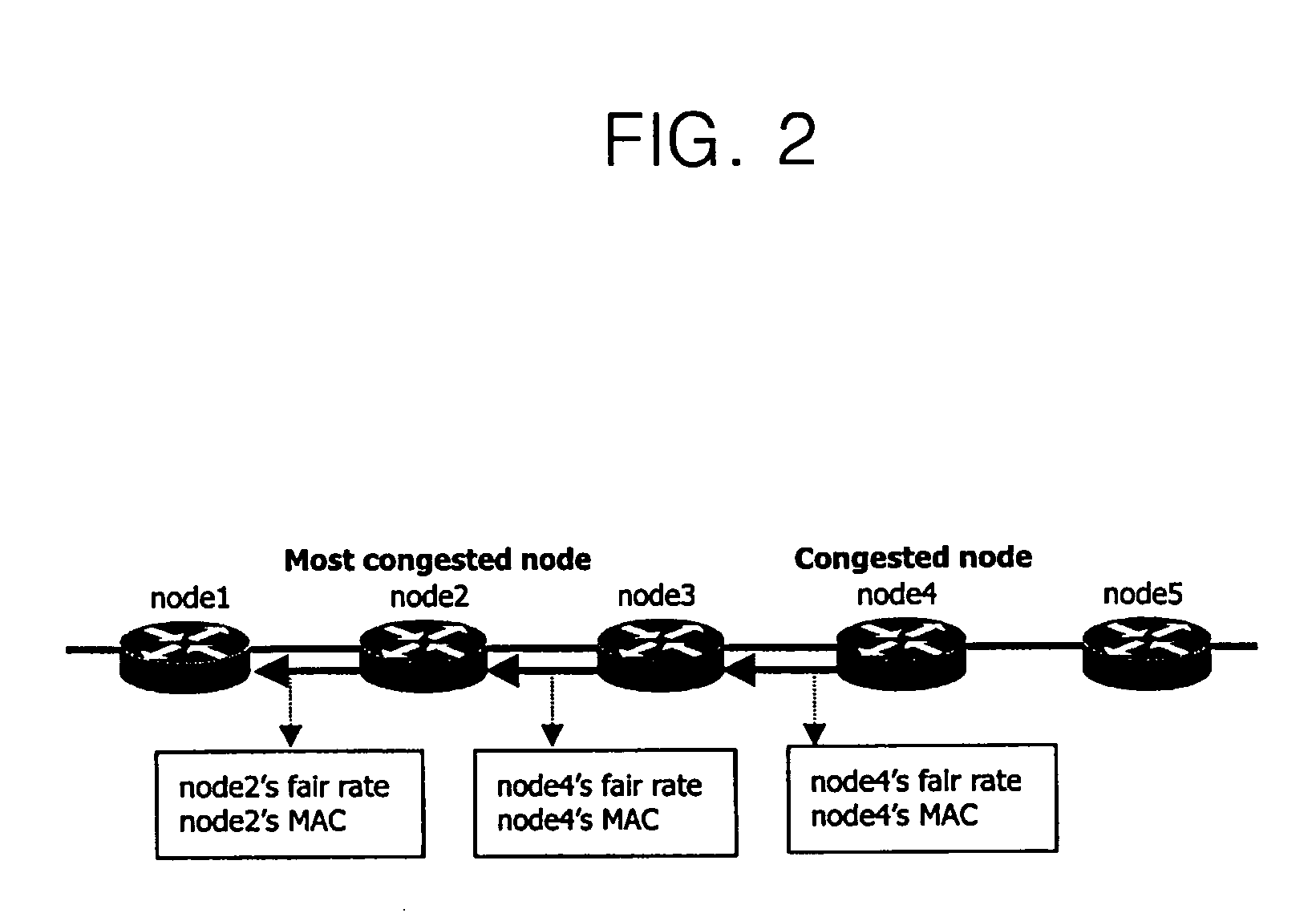
Allocating bandwidth using resilient packet ring (RPR) fairness mechanism
InactiveUS7397813B2Increase usageEvenly distributedLoop networksBus networksResilient Packet RingFair distribution
In allocating bandwidth using a Resilient Packet Ring (RPR) fairness mechanism in a node connected to an RPR network, when congestion occurs, an amount of traffic that the node has transmitted to a ring during one aging interval is stored together with its own identifier in a fairness message as a fairness transmission rate to be advertised to its own upstream nodes. The amount of traffic transmitted from the upstream node during the aging interval is measured and stored. When the congestion has been solved, an available bandwidth is calculated with reference to the fairness transmission rate and the amount of traffic transmitted from the upstream nodes, and the fairness transmission rate is calculated to fairly allocate the available bandwidth to the upstream nodes so that the fairness transmission rate is transmitted to the upstream nodes.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
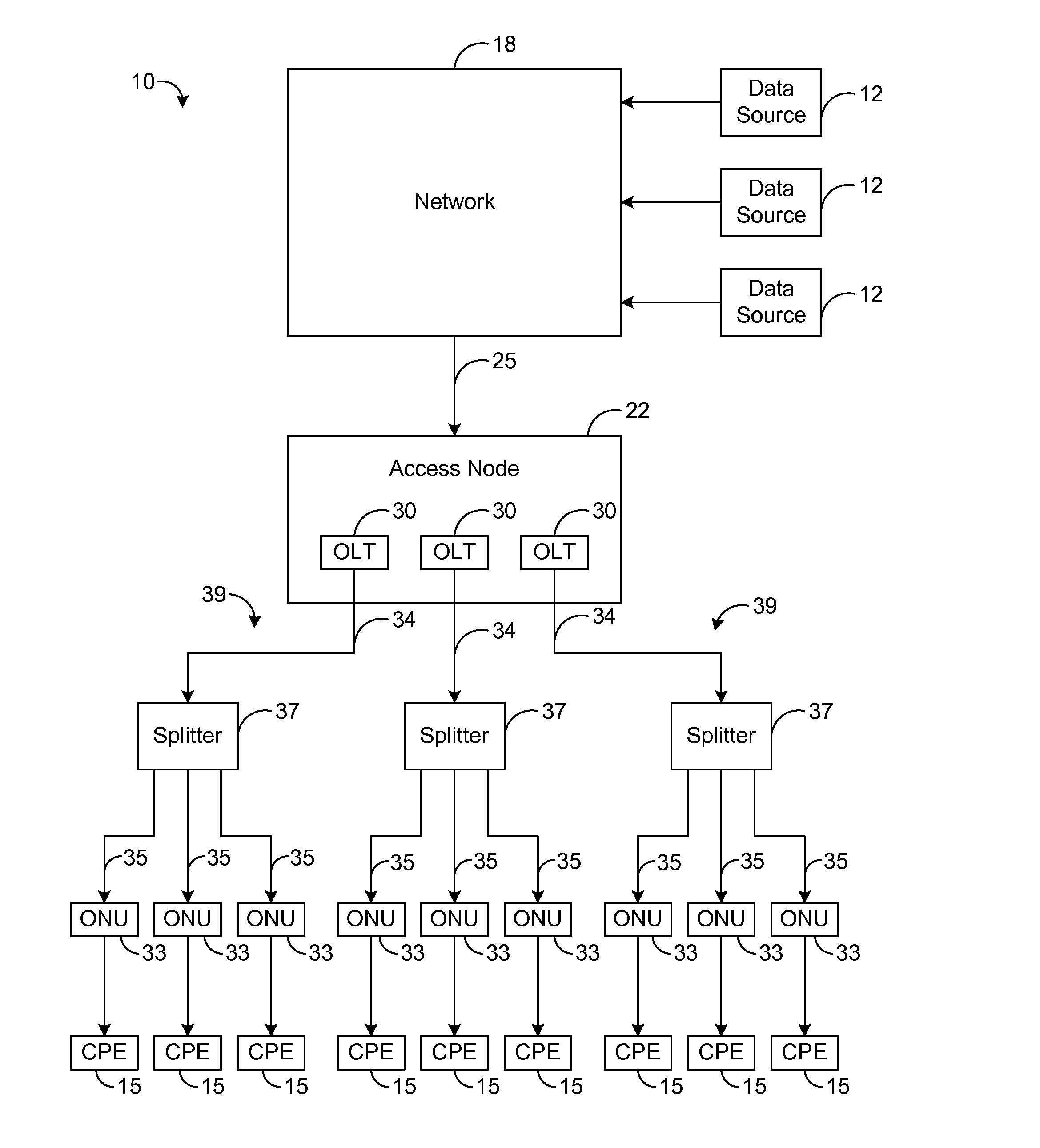
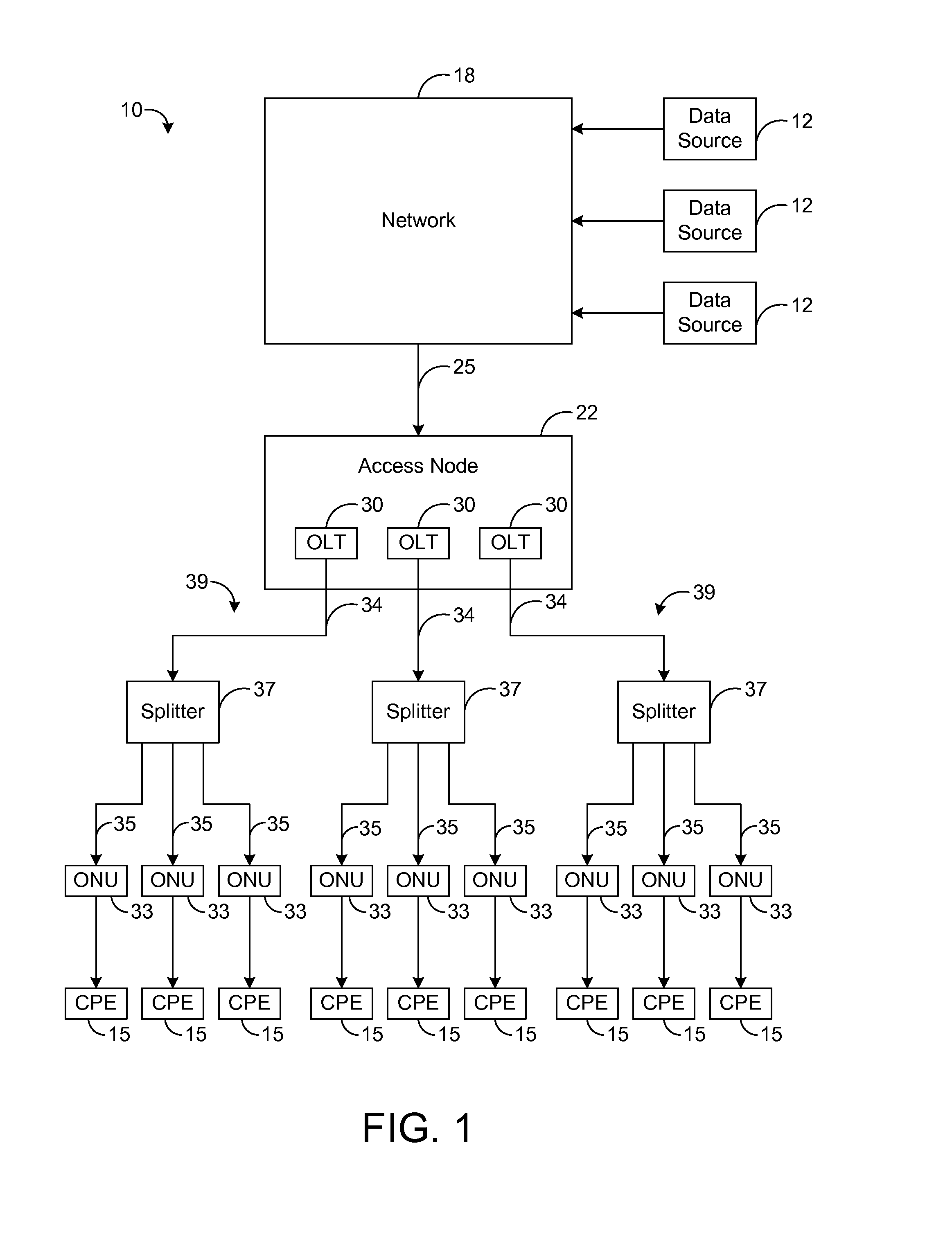
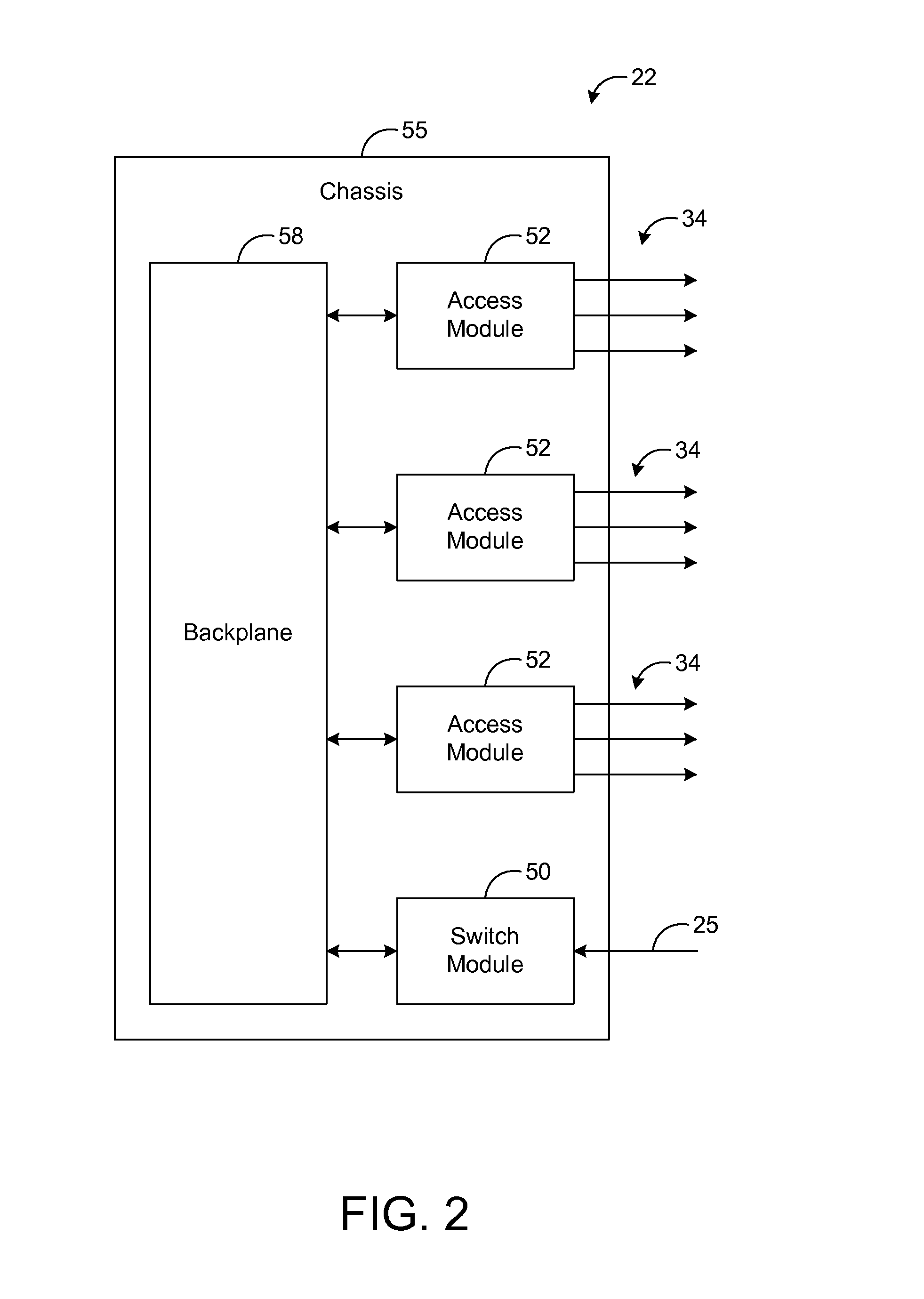
Systems and methods for allocating network bandwidth across access modules
ActiveUS20150350083A1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsDynamic bandwidth allocationCurrent load
A telecommunication system uses a dynamic bandwidth allocation (DBA) algorithm based on current load conditions for controlling transmissions to a plurality of access modules of an access node in order to achieve a fair allocation of network bandwidth at the access node. As an example, access modules at an access node communicate via a control channel with dynamic bandwidth allocation (DBA) logic that receives load information from each of the access modules. Using such load information, the DBA logic dynamically controls the upstream data rates so that a fair allocation of network bandwidth is achieved across all of the access modules. Specifically, the data rates are controlled such that packet flows for services of the same class achieve the same or similar performance (e.g., average data rate) regardless of which access module is receiving each respective packet flow.
Owner:ADTRAN
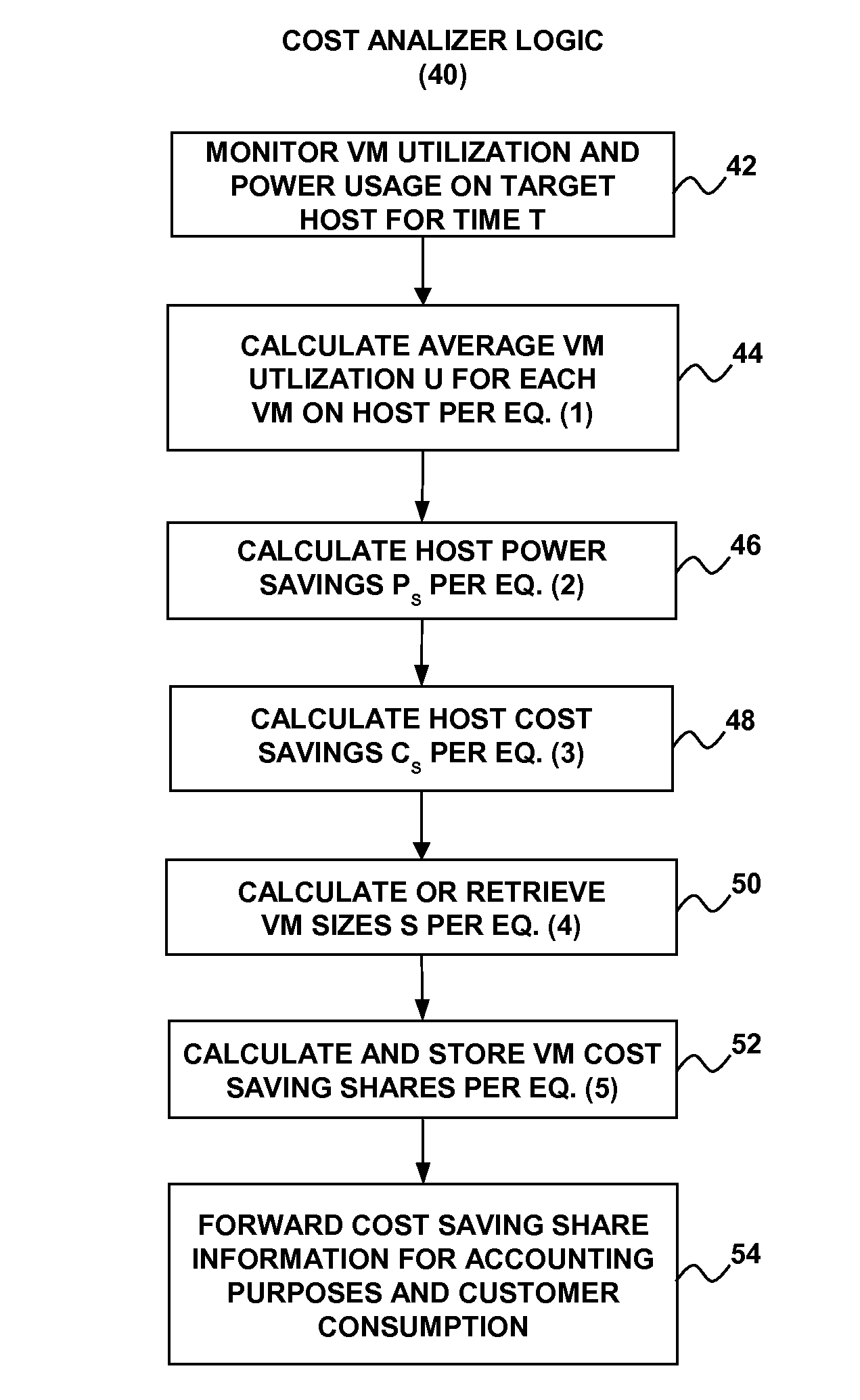
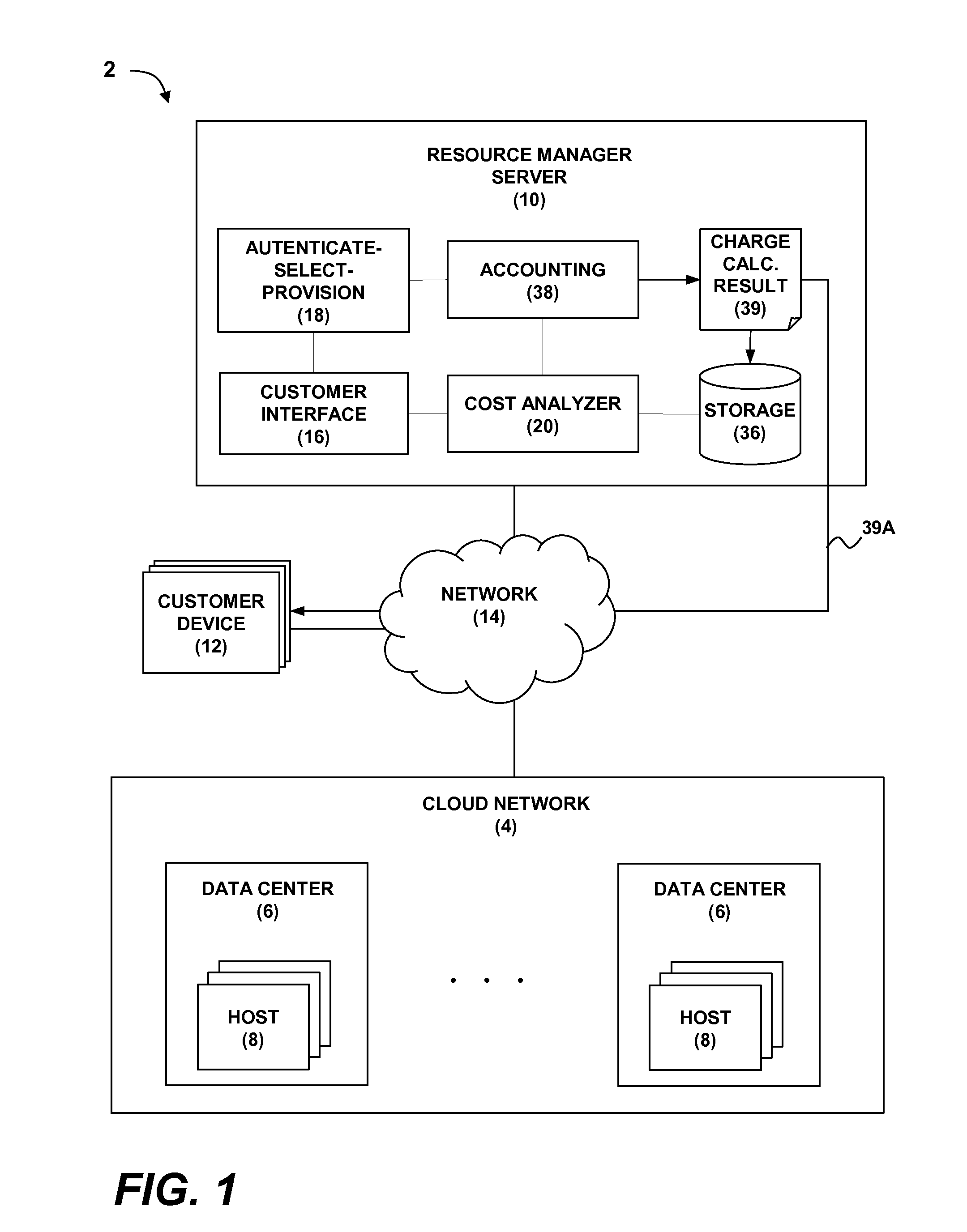
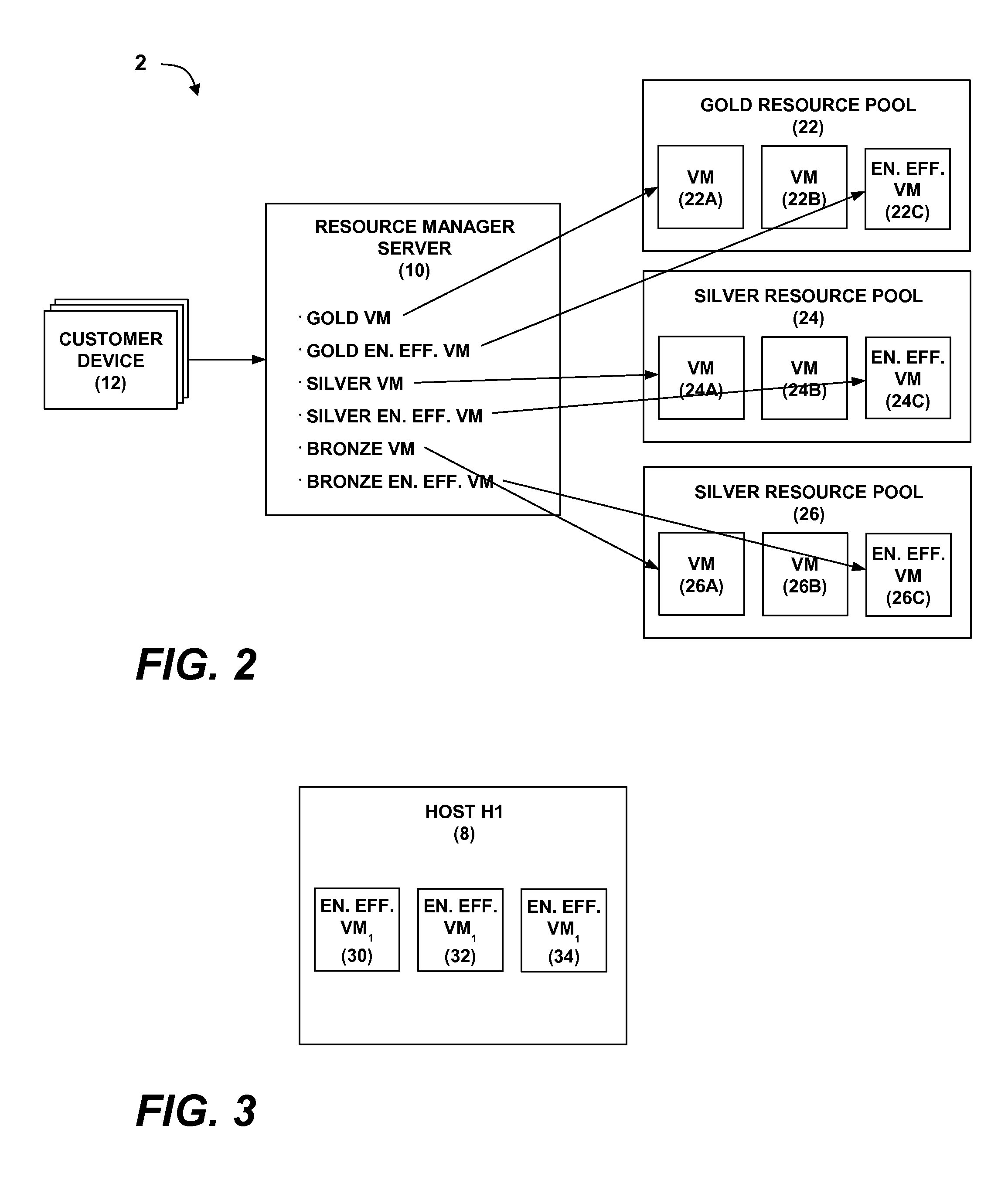
Fair Distribution Of Power Savings Benefit Among Customers In A Computing Cloud
InactiveUS20130339201A1Fair distributionSave powerComplete banking machinesDiscounts/incentivesDistributed powerLarge size
A technique for fairly distributing power savings benefits to virtual machines (VMs) provisioned to customers in a computing cloud. One or more VMs are provisioned on a target cloud host in response to resource requests from one or more customer devices. Host power savings on the target host are monitored. The host power savings are used as a variable component in determining per-customer cloud usage for accounting purposes. The host power savings may be reflected as power related cost savings in a generated cloud usage calculation result that may be distributed proportionately to the VMs based on VM size and utilization. VMs of relatively larger size and lower utilization may receive a higher percentage of the cost savings than VMs of relatively smaller size and higher utilization.
Owner:BANERJEE PRADIPTA K +2
Adaptive medium access control
ActiveUS8675678B2Controlling the riskError preventionTransmission systemsExtensibilityPerformance enhancement
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Method for fair sharing limited resources between multiple customers
InactiveUS20050171786A1Satisfy the demandMeet needsDigital computer detailsResourcesLimited resourcesBusiness enterprise
The invention disclosed comprises a method for encouraging fair sharing of limited material inventory and capacity between multiple customers when creating a production plan. the invention allocates resources among competing demands in a linear programming production planning system by first classifying the demands into fair share sets, wherein all demands within each set have the same priority, calculating the cumulative demand for each resource within each set, and then allocating the resources to the demands in order of fair share set priority. If, during the allocating process, the supply of a given resource cannot satisfy a given cumulative demand of a given set, the given resource is allocated proportionally (e.g., evenly or according to usage proportions) among all demands that contribute to the given cumulative demand within the given set. This is an advanced planning system for optimizing established planning objectives (e.g., customer service, short lead times, low inventory, and prioritized allocation of supply and capacity) to compute a feasible production plan for the enterprise.
Owner:IBM CORP
Voice and data wireless communications network and method
InactiveUS20060002378A1Network traffic/resource managementNetwork topologiesVoice communicationWireless lan
A wireless local area network that carries mixed traffic of voice and data communications may be provided. The wireless local area network may include an access point and a plurality of remote terminals that are associated with the access point. The access point may be operably coupled to a wireline network. The access point may receive voice and other communications packets from the remote terminals and the wireline network. Some of the packets may be for transmission to the remote terminals. The access point manages which packets to transmit and when to transmit packets. The access point may manage traffic to maintain a fair distribution of packets and to give priority to voice communications over other communications.
Owner:SYMBOL TECH INC
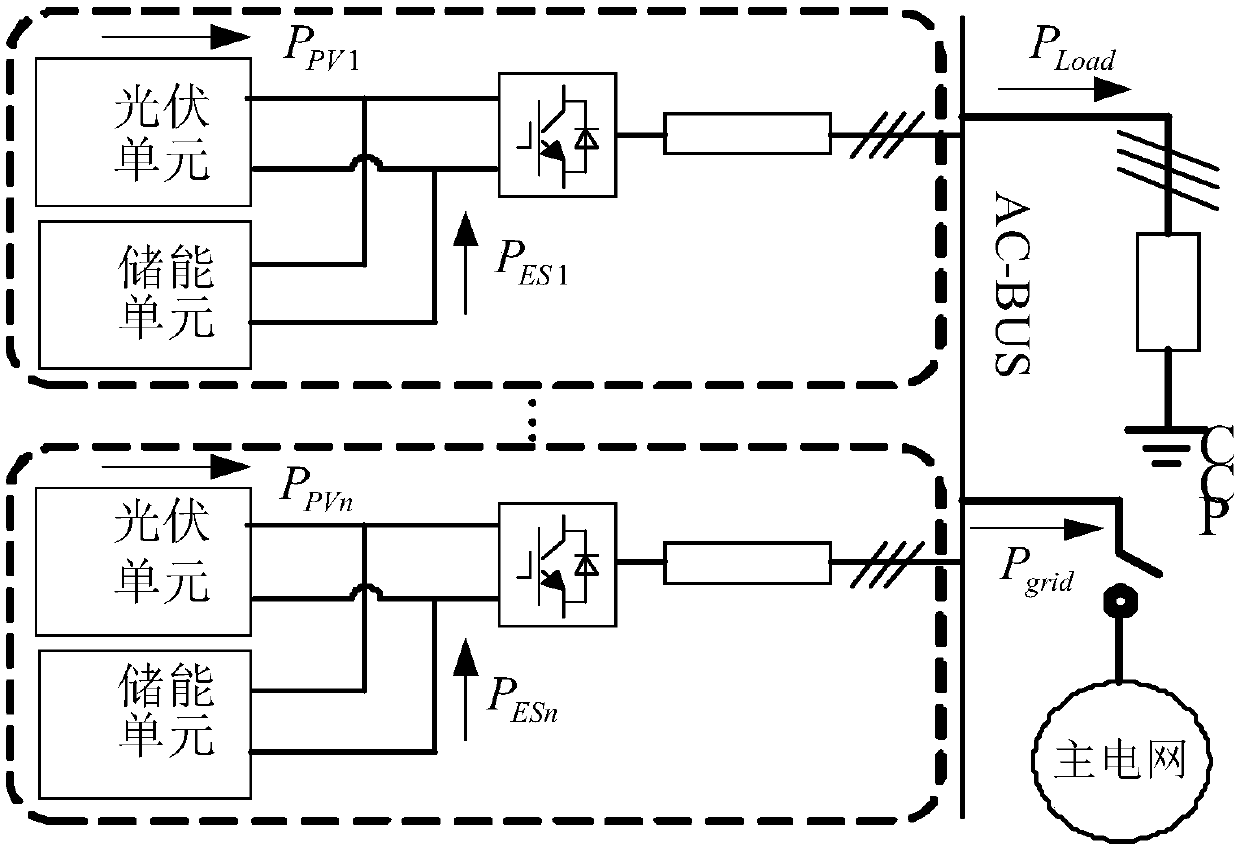
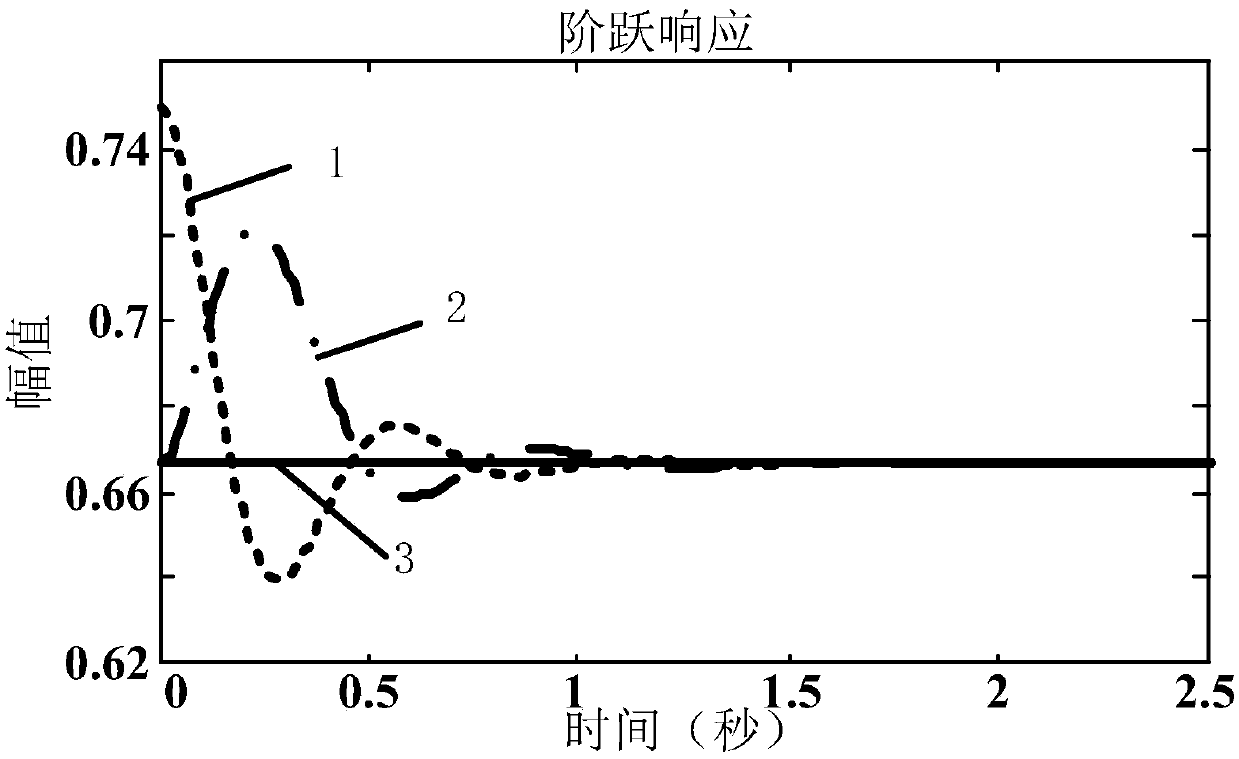
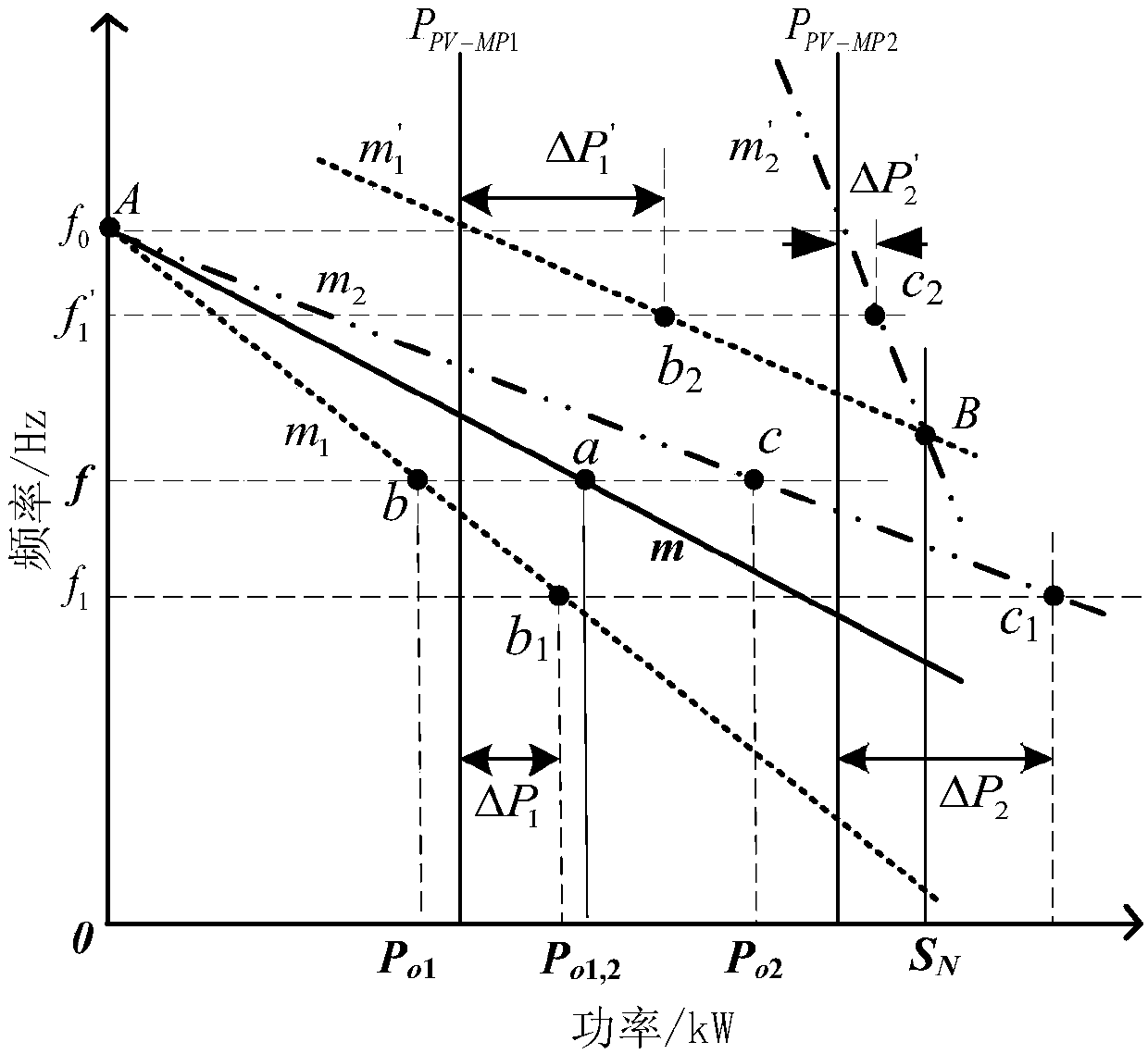
Power distribution and parameter adaptive control method of multi-machine parallel virtual-synchronous generators
ActiveCN107565604AIncrease profitTake advantage ofSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsPhotovoltaic energy generationVirtual synchronous generatorLoad following power plant
The invention discloses a power distribution and parameter adaptive control method of multi-machine parallel virtual-synchronous generators. The method includes: firstly, establishing a small signal model for parallel operation of n virtual-synchronous generators, acquiring a transfer function Gpli between output power and load power of the ith virtual-synchronous generator and then enabling parameters of the virtual-synchronous generators running in parallel to be mutually proportioned to acquire constraint conditions matched with parameters; by the aid of the constraint conditions matched with the parameters, acquiring control parameters of the virtual-synchronous generators of a microgrid system under different running modes. The power distribution and parameter adaptive control methodis applicable to an independent optical storage microgrid system, output power of a direct-current side is fully considered, reasonable and fair distribution of the power on the premise of priority utilization of photovoltaic power is realized, and utilization rate of renewable energy sources of photovoltaic is increased.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
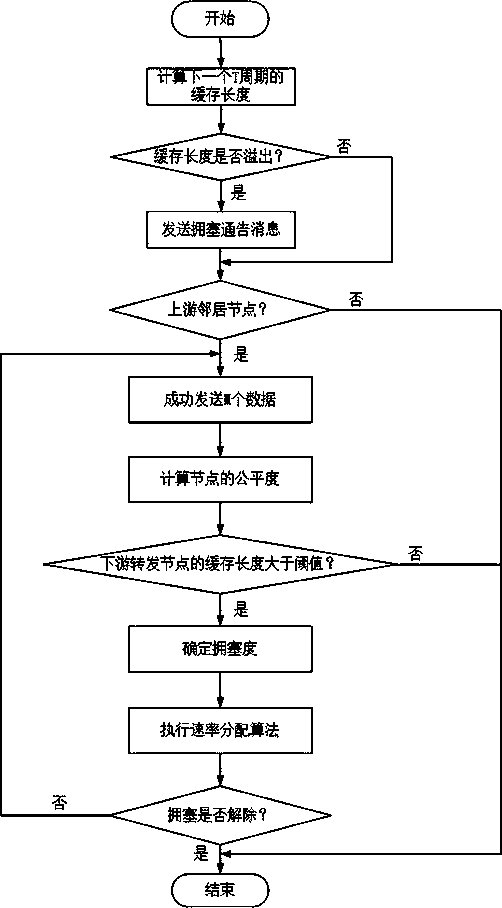
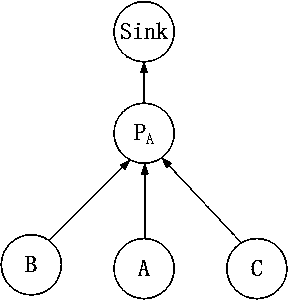
Congestion control method based on node cache length equitable distribution rate
ActiveCN104581821AAvoid false detectionAvoid missing detectionNetwork traffic/resource managementPacket lossAllocation algorithm
The invention discloses a congestion control method based on the node cache length equitable distribution rate. Congestion is detected by estimating the cache length of all nodes at the next moment T. If the cache length exceeds the maximum value of the cache length, congestion announcement information is broadcasted to upstream neighbor nodes to forbid the upstream neighbor nodes to send data, and congestion release is conducted. If the nodes are upstream neighbor nodes, firstly, the cache length of the nodes is estimated according to obtained downstream forward node data; next, congestion is detected according to the cache length of forward nodes; if the forward nodes generate congestion, the node congestion degree, namely the congestion state is graded; finally, a rate allocation algorithm is executed according to the congestion state, and congestion is relieved. If no congestion occurs, no processing is conducted. By means of the congestion control method based on the node cache length equitable distribution rate, fairness of channel using of the nodes is improved, collision can be reduced effectively, the packet loss probability can be reduced effectively, and throughout capacity can be improved effectively.
Owner:XIANGTAN UNIV
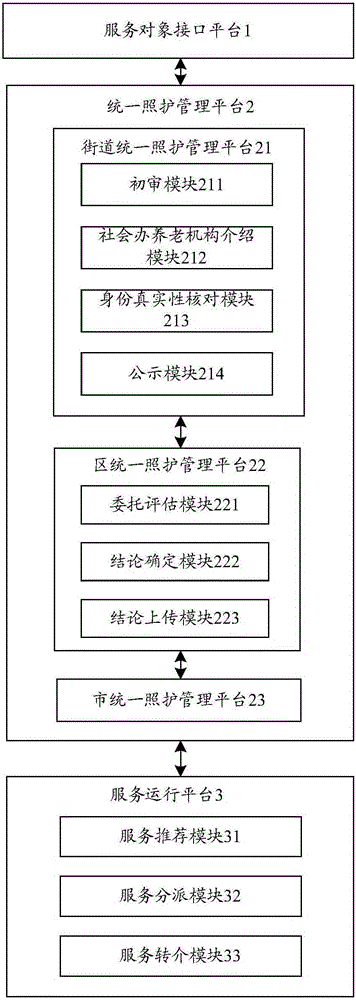
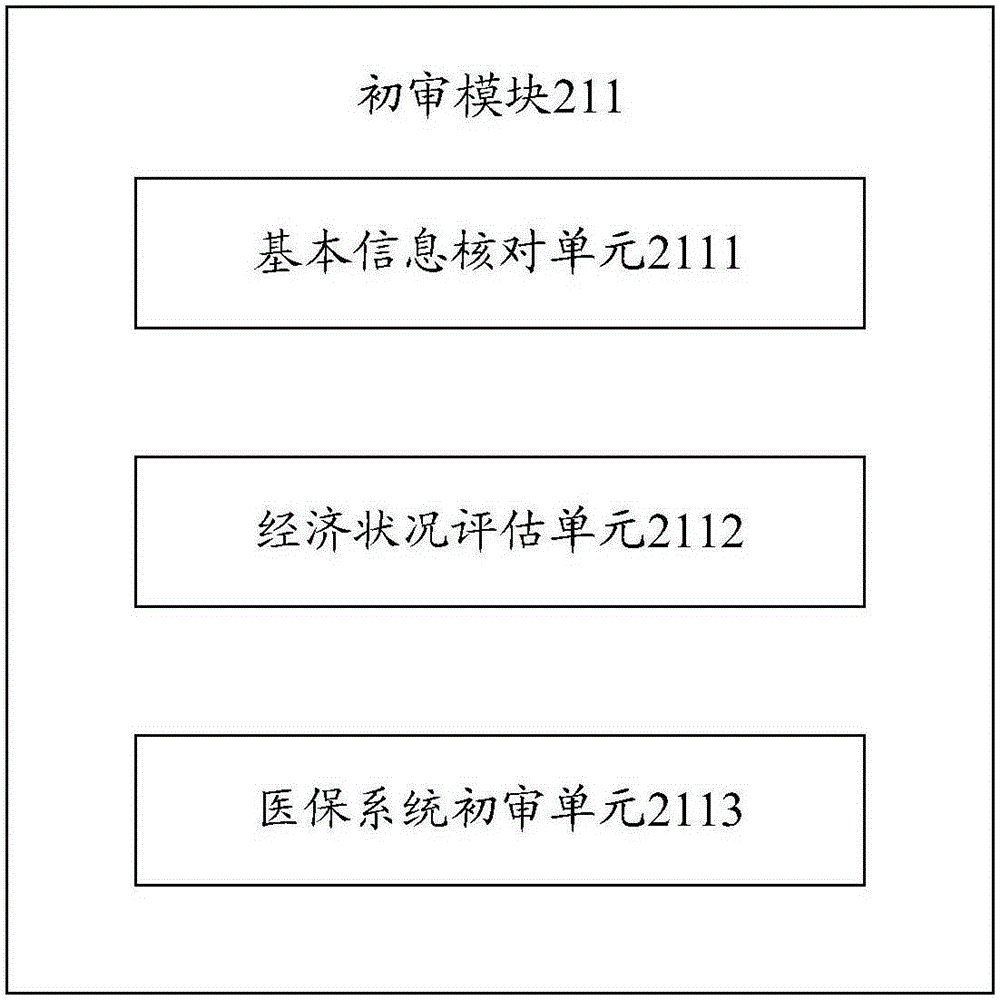
Old person nursing requirement evaluation system
InactiveCN106485629AImprove the policy gradient guarantee systemPerfect supportData processing applicationsOlder peopleLong-term care
The invention discloses an old person nursing requirement evaluation system which realizes reasonable matching between an old person basic nursing requirement and a professional service and promotes fair distribution and effective use of limited old person nursing resources in an area. The old person nursing requirement evaluation system is characterized in that a unified nursing management platform and a service operation platform are built; and old persons access the unified nursing management platform through a service object interface platform. The system of the invention is based on concepts of providing service to the old persons and continuous nursing. The old person nursing requirement evaluation system aims to realize long-term nursing on the old persons and is around the old persons. Furthermore the old person nursing requirement evaluation system continuously perfects a social old person service system.
Owner:上海市徐汇区民政局
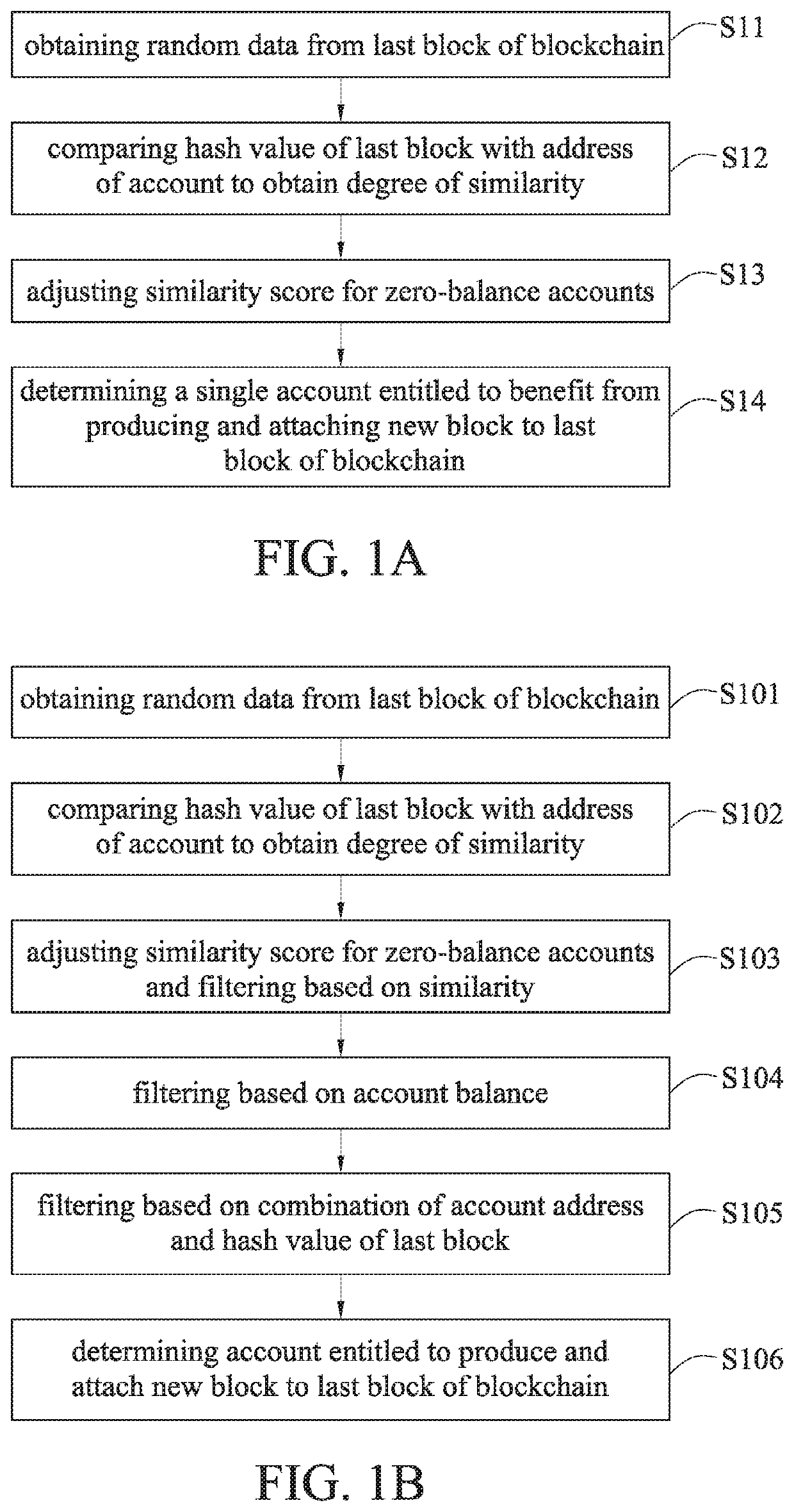
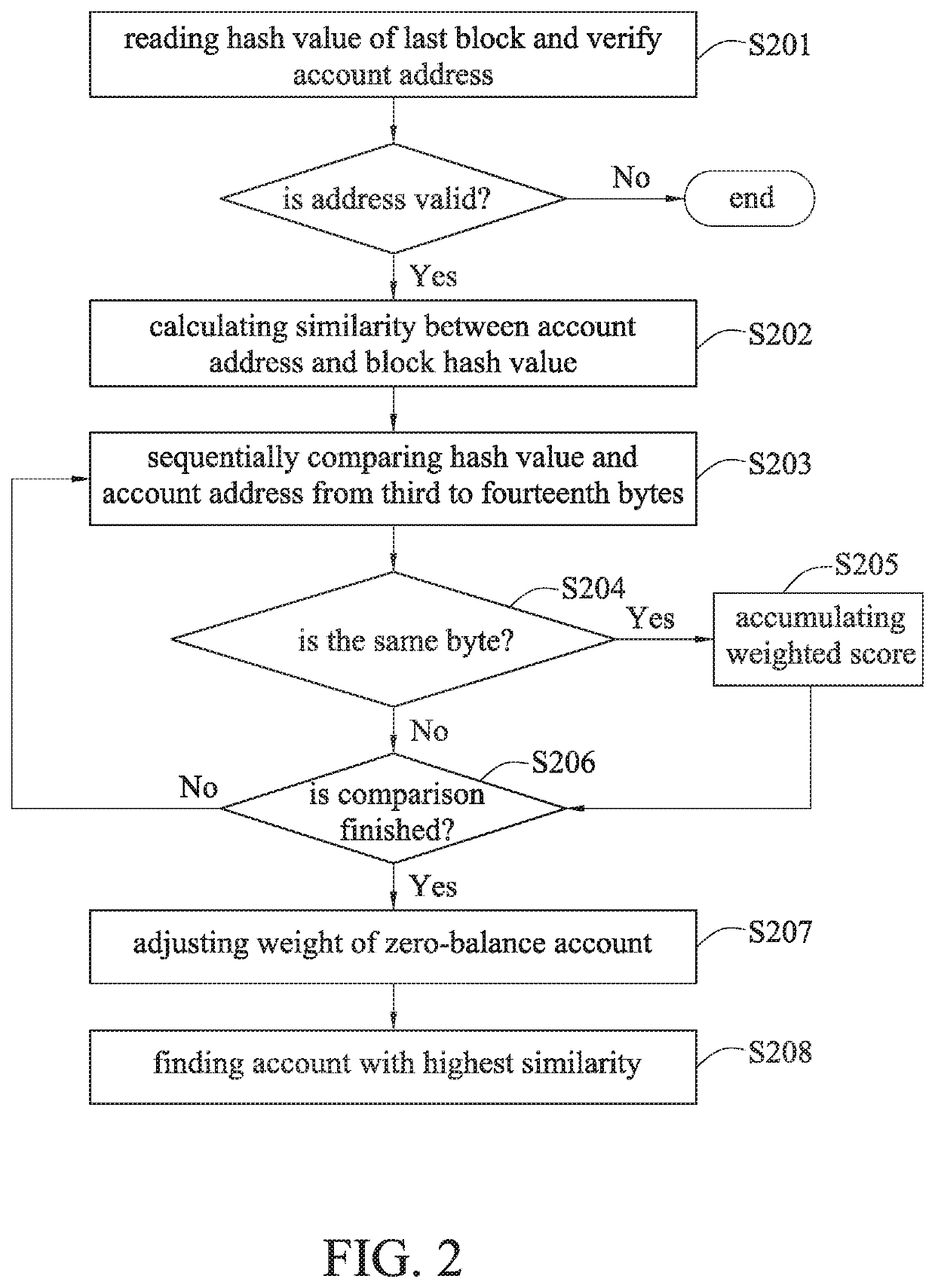
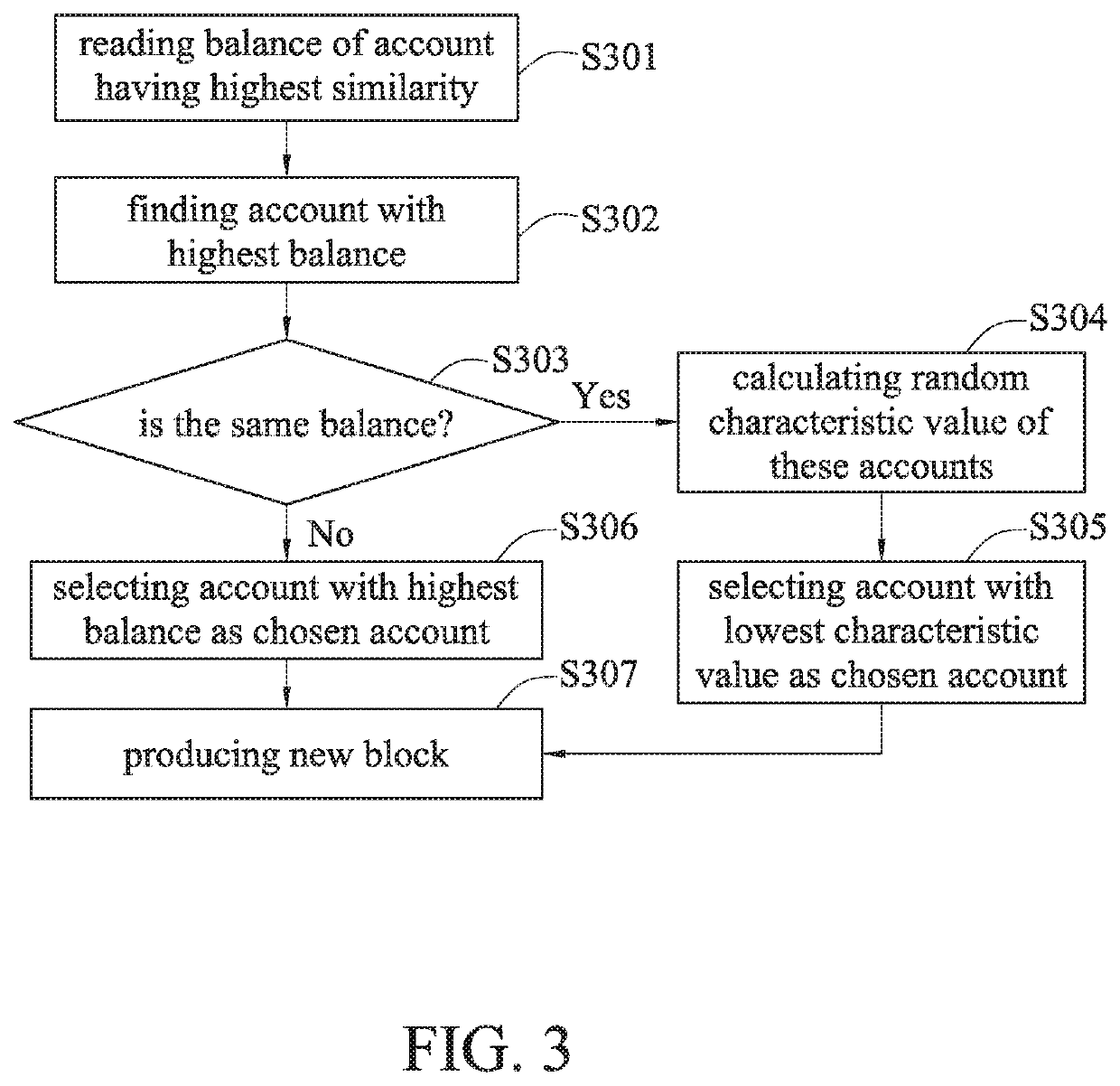
Method for reaching consensus on public distributed ledgers and system using the same
ActiveUS20190379546A1Improve efficiencyFair distributionCryptography processingUser identity/authority verificationDegree of similarityComputer science
A method for reaching consensus on public distributed ledgers and a system using the same are disclosed. The method includes: obtaining a random data of the last block of a blockchain; comparing the random data with an address of an account to obtain a degree of similarity; filtering accounts based on the degree of similarity; performing further filtering based on the account balance; performing ultimate filtering based on a combination of the account address and the random data; and determining an account that is entitled as the beneficiary to produce a new block to be attached to the last block of the blockchain. The present disclosure reaches consensus of generating a new block through multiple levels of filtering, thereby reducing the power consumption caused by large amounts of computations during the ordinary mining process, while significantly improving the efficiency of blockchain transactions and ensuring the fair distribution of mining rights.
Owner:CHUNGHWA TELECOM CO LTD
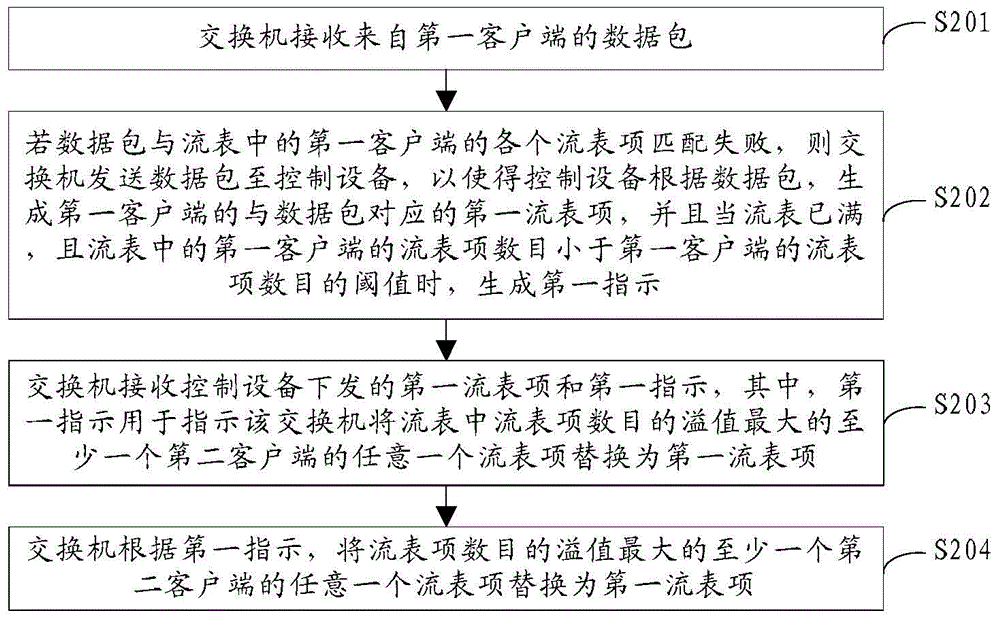
Flow table updating method and device
ActiveCN104869064AMeet needsAchieve fair distributionData switching networksNetwork packetComputer science
The embodiment of the invention provides a flow table updating method and device and relates to the communication field. According to the invention, a flow table can be updated under a full state, so that the requirement of a client to flow table resources is satisfied, and fair distribution of the flow table resources is realized. The method comprises the steps of: according to the information of a first client end and network establishing information, determining a threshold, corresponding to the information of the first client end and the network establishing information, of a flow table item number of the first client end; obtaining a data packet reported by a switch; generating a first flow table item, corresponding to the data packet, of the first client end; if the flow table is full and the flow table item number of the first client end in the flow table is smaller than the threshold of the flow table item number of the first client end, generating a first instruction; and issuing the first flow table item and the first instruction to the switch so as to enable the switch to replace any flow table item of at least one second client end maximum in flow table item number overflow with the first flow table item according to the first instruction.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
System and method for node band width equitable distribution on elastic grouping ring
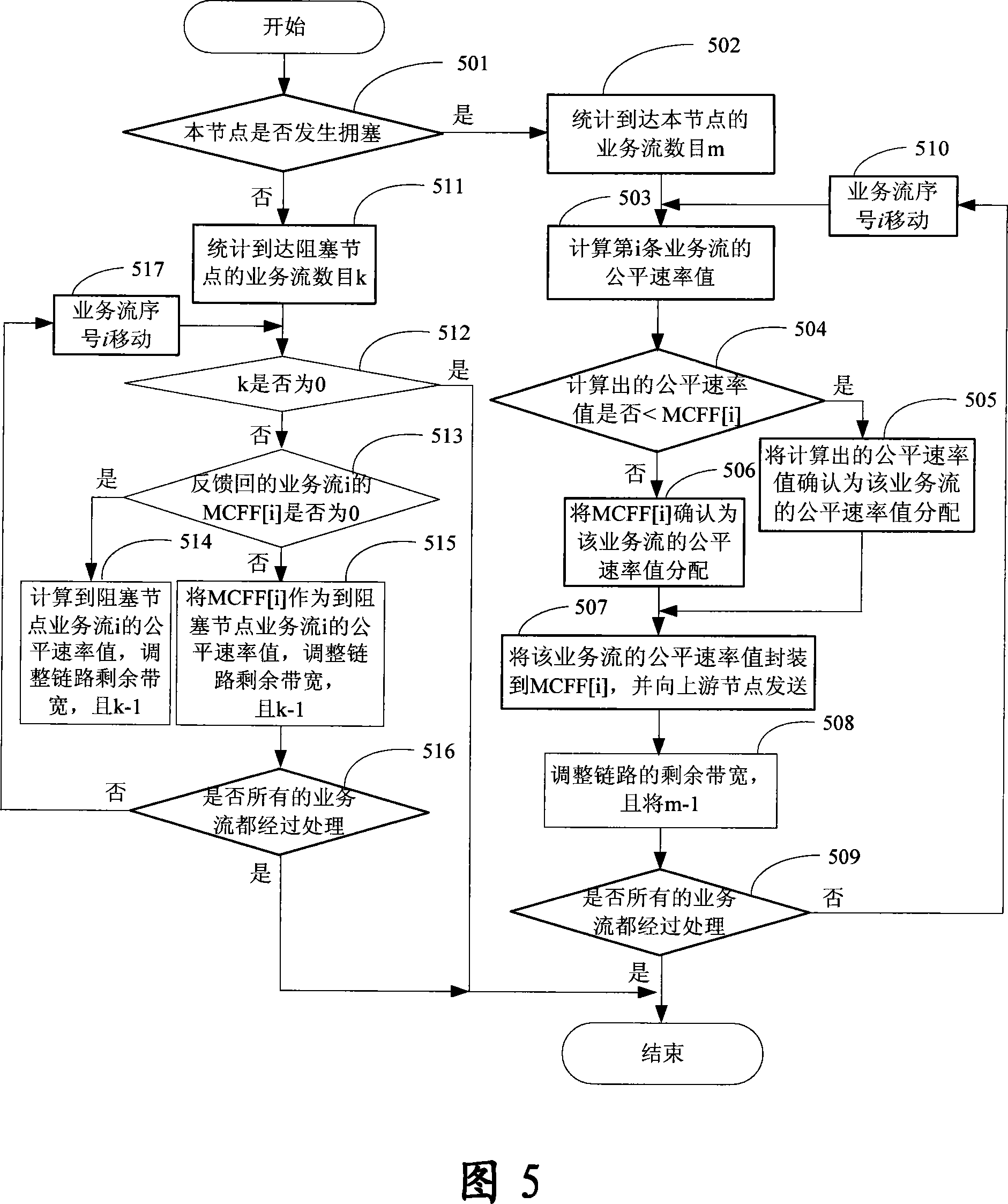
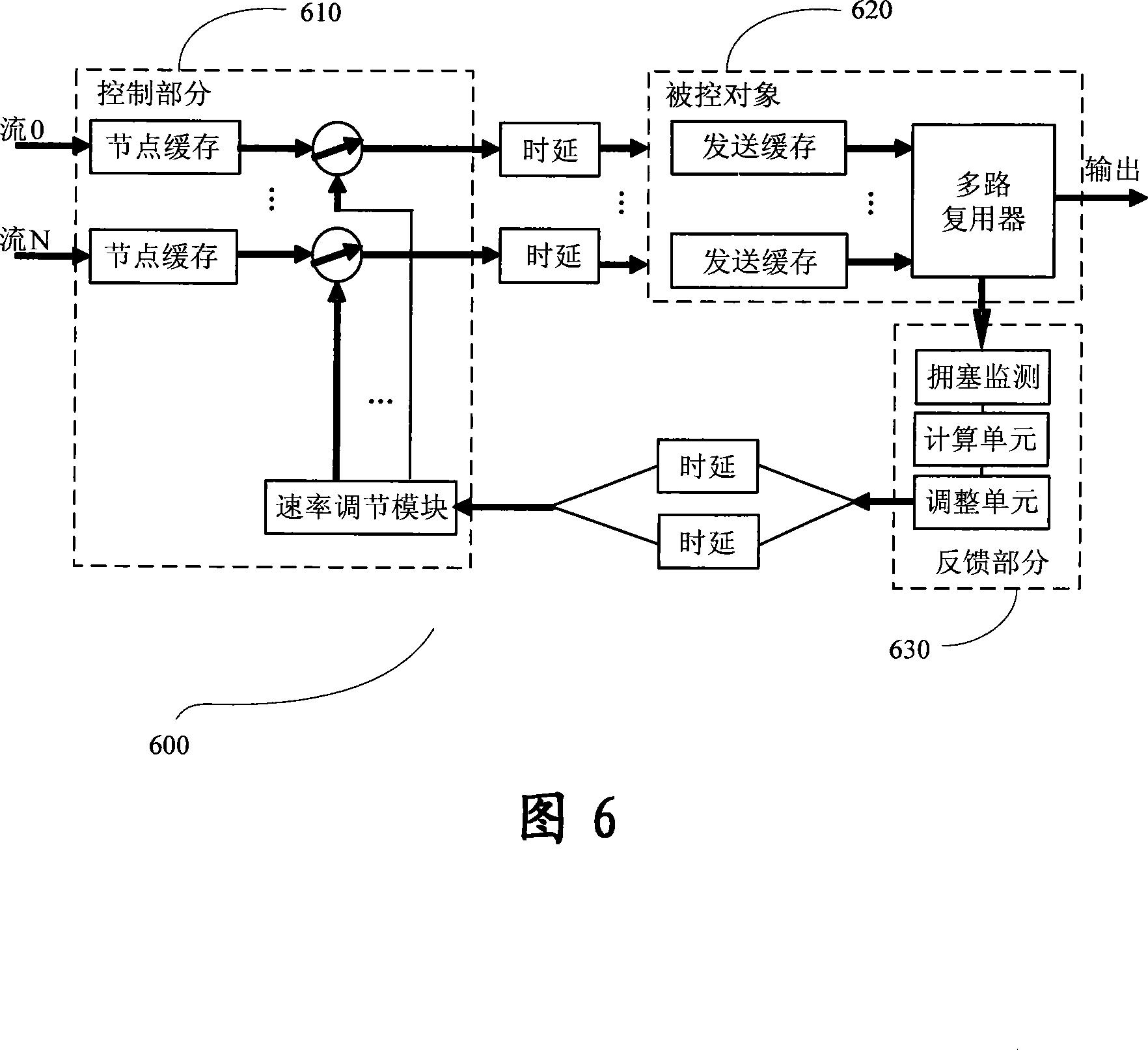
InactiveCN101227369ARealize dynamic fair allocationMaximize UtilizationLoop networksResilient Packet RingComputer science
The invention relates to a method for achieving the purpose of fairly allocating the band width of the upper node of an elastic packet ring, which comprises the following steps: calculating the elastic packet ring EPR to reach the total number k of business flow of blocking node, assuring each fair speed value of each business flow which gets to the blocking node in turn according to the k, and allocating band width for each business stream from current residual band width of the system according to fair speed value which is assured, utilizing the blocking node to seal the fair speed value of the business flow which is assured in a multiple blocking points fair frame MCFF to send to the upper node. The invention improves the capability of a system to resist external disturbance, lowers sensitivity of a system to the internal parameter variation, achieves a goal of dynamically and fairly allocating band width, leads all the nodes to fairly occupy band width according to weight value of local node, and meanwhile, leads the utilization ration of band width to be maximized.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Token-based Internet traffic control method
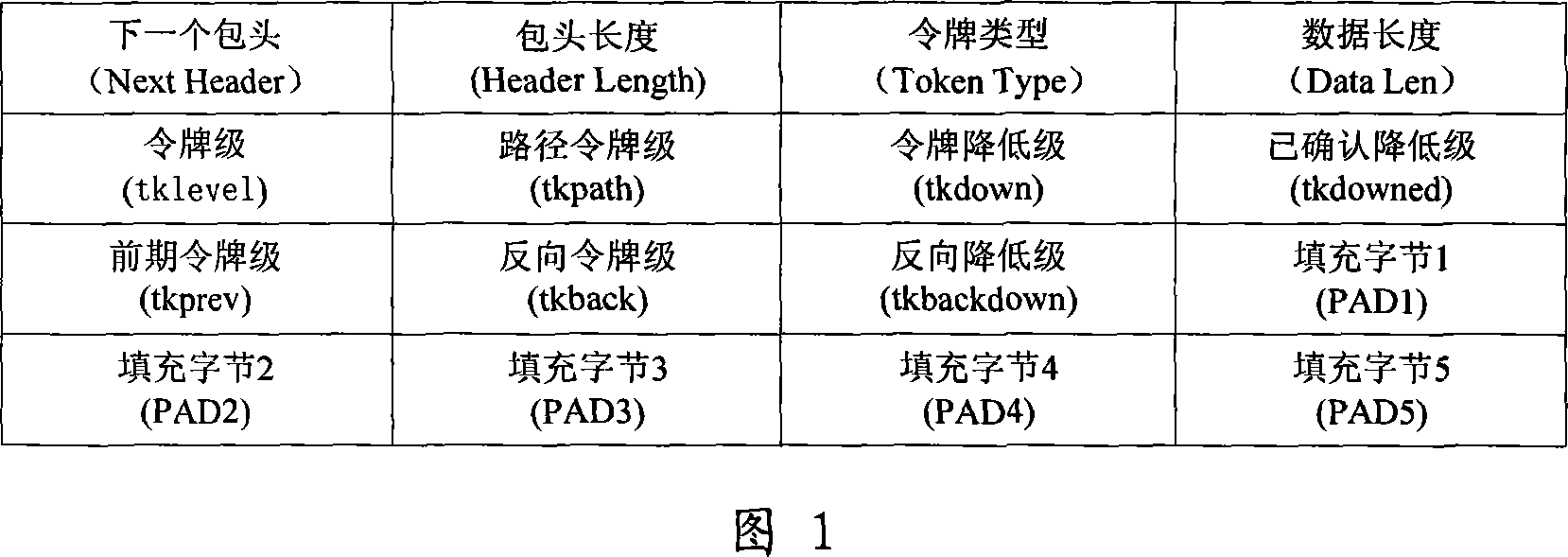
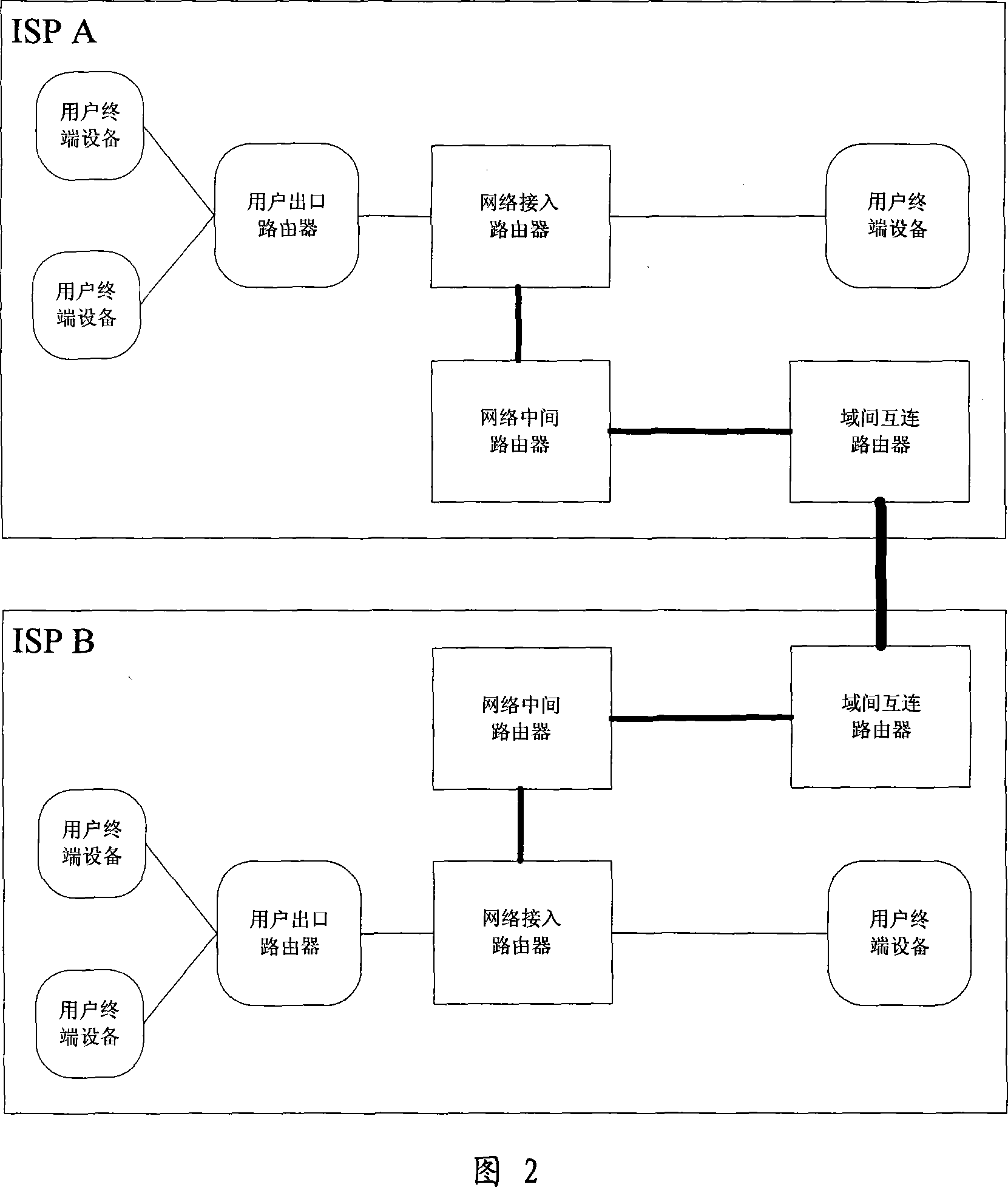
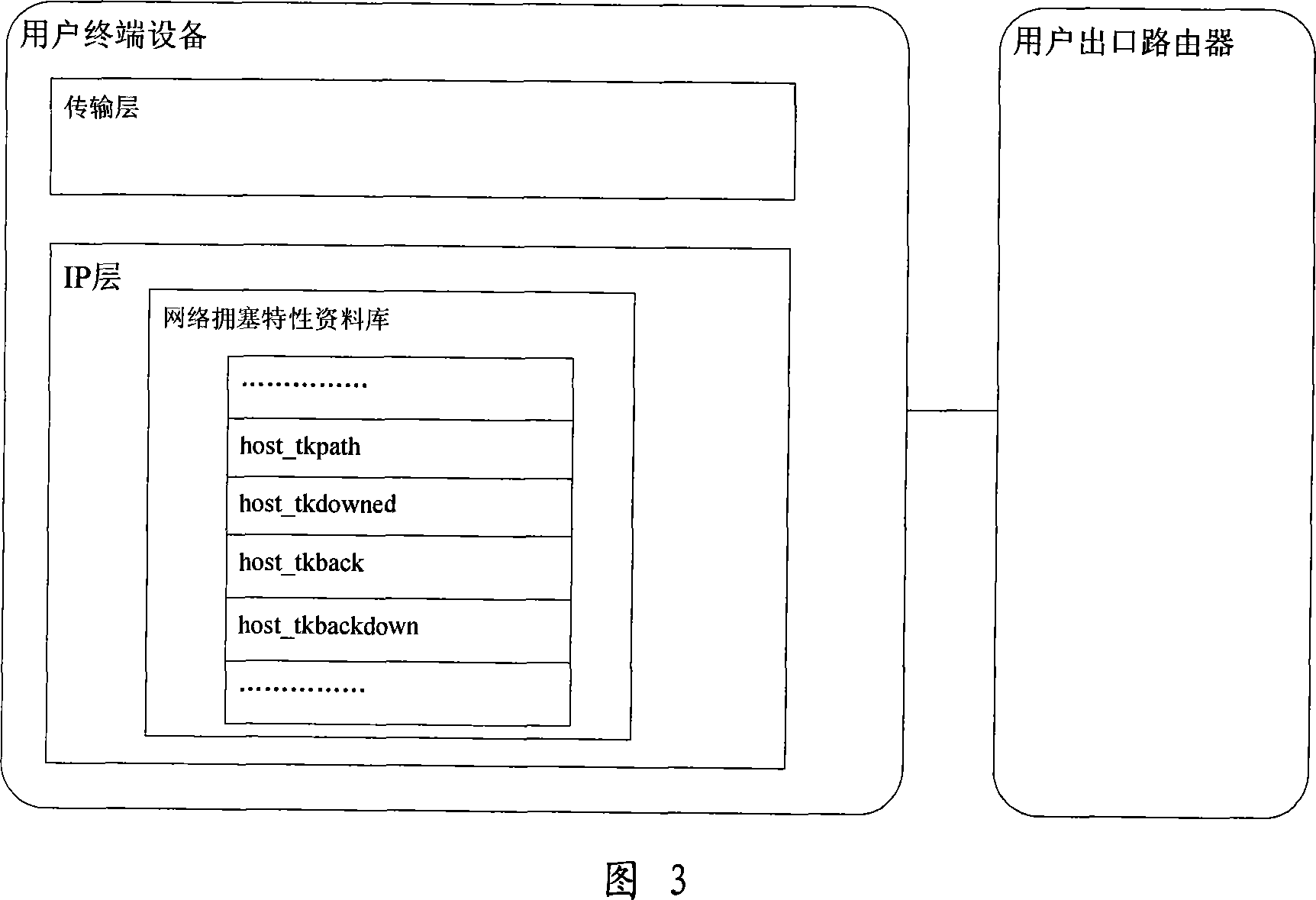
InactiveCN101035078ARealize the access control functionReduce oscillationData switching networksPacket lossExchange network
This invention discloses a Token flow control method based on open Internet, involving packet switching network flow control technology. The methods include: user terminal equipment installed in accordance with network congestion data packets to be sent at the token; The end-user network access control into the network router the token rate; Intermediate routers in the network on the output interface controller Congestion has a physical, physical congestion controller bandwidth resources under the Congestion Adaptive extent to adjust physical congestion index, calculated in accordance with the fair probability of packet loss, random discarded token physical congestion level is less than the index data packets; Domain router interconnection between the output interface not only with physical congestion controller also has a virtual Congestion controller, controller under virtual Congestion token resources to adjust the degree virtual adaptive congestion index, lowering all output data packets token level.
Owner:INST OF SOFTWARE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com