Patents
Literature
676 results about "Relay lens" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
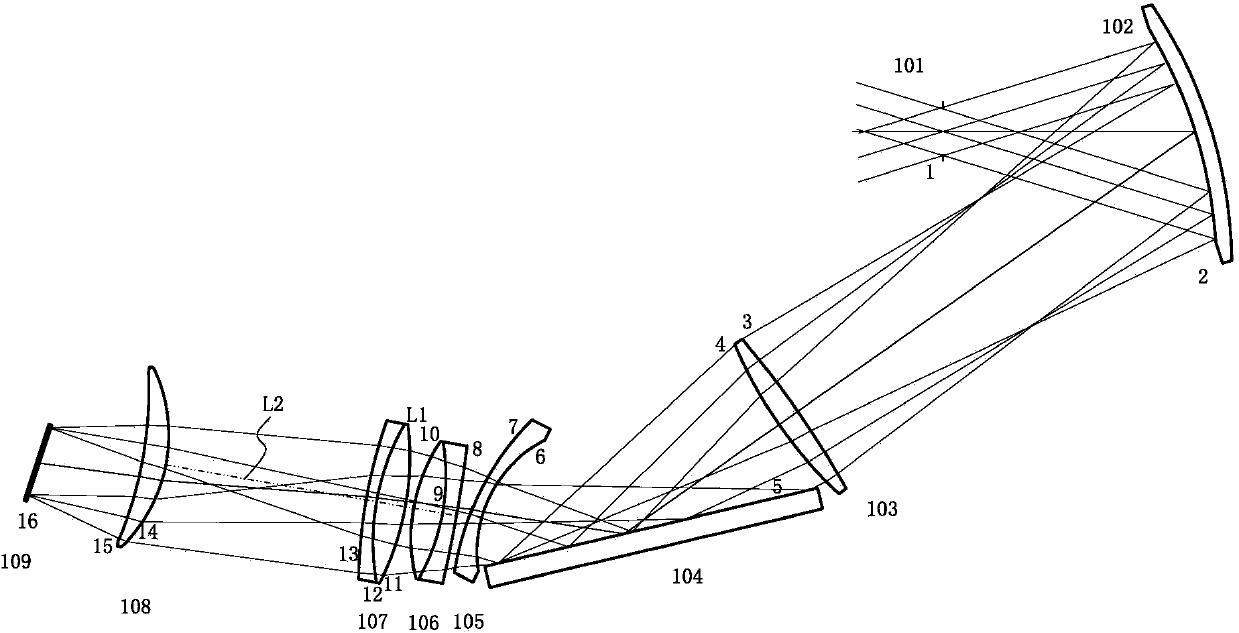
In optics, a relay lens is a lens or lens group that inverts an image and extends the optical tube. Relay lenses are found in refracting telescopes, endoscopes and periscopes for the purpose of extending the length of the system, and before eyepieces for the purpose of inverting an image. They may be made of one or more conventional lenses or achromatic doublets, or a long cylindrical gradient-index of refraction lens (a GRIN lens).
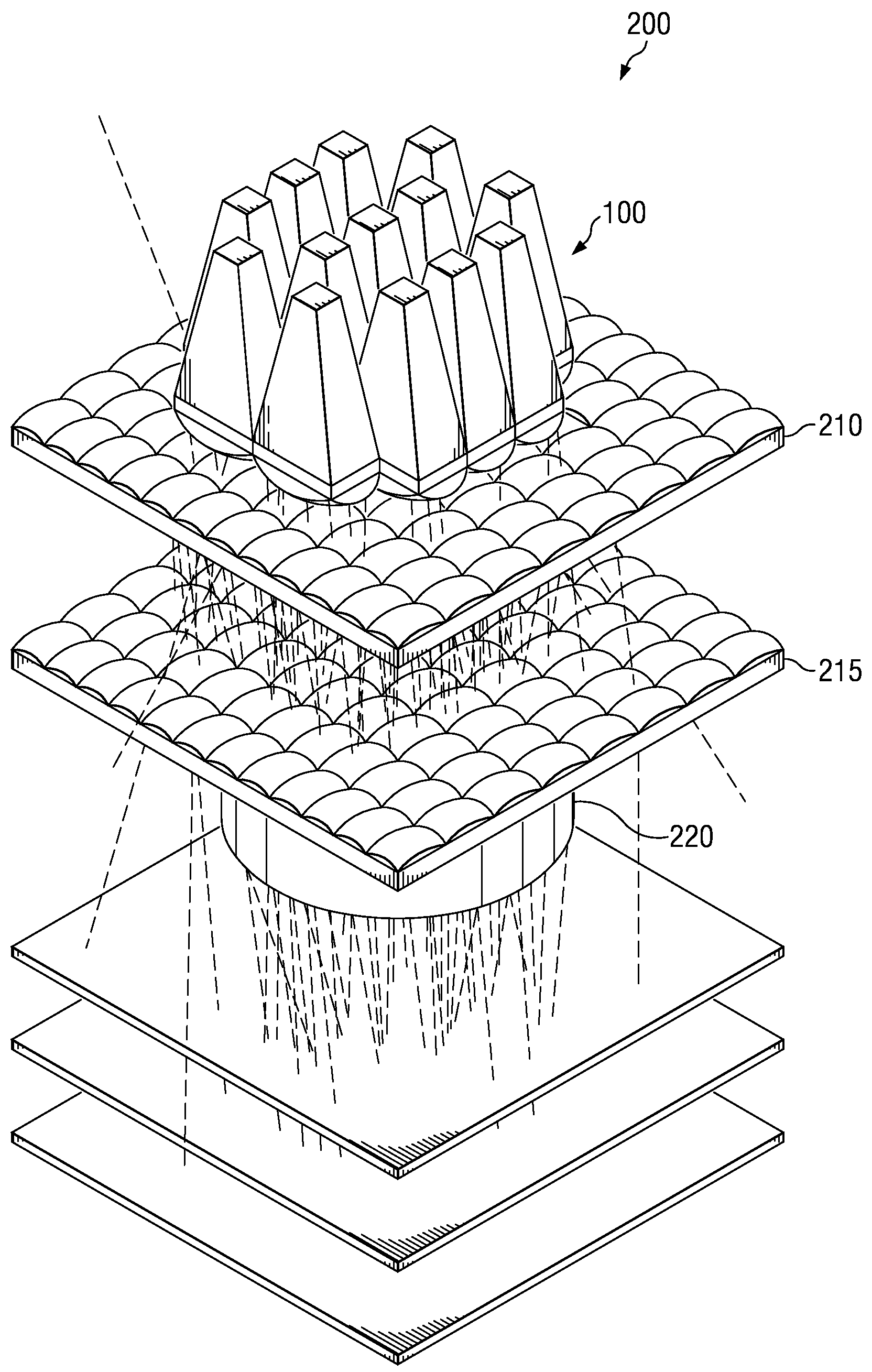
Method of combining dispersed light sources for projection display
ActiveUS7537347B2Technical advantageGood for arrayingShow cabinetsImpedence networksHigh definition tvHigh-definition television
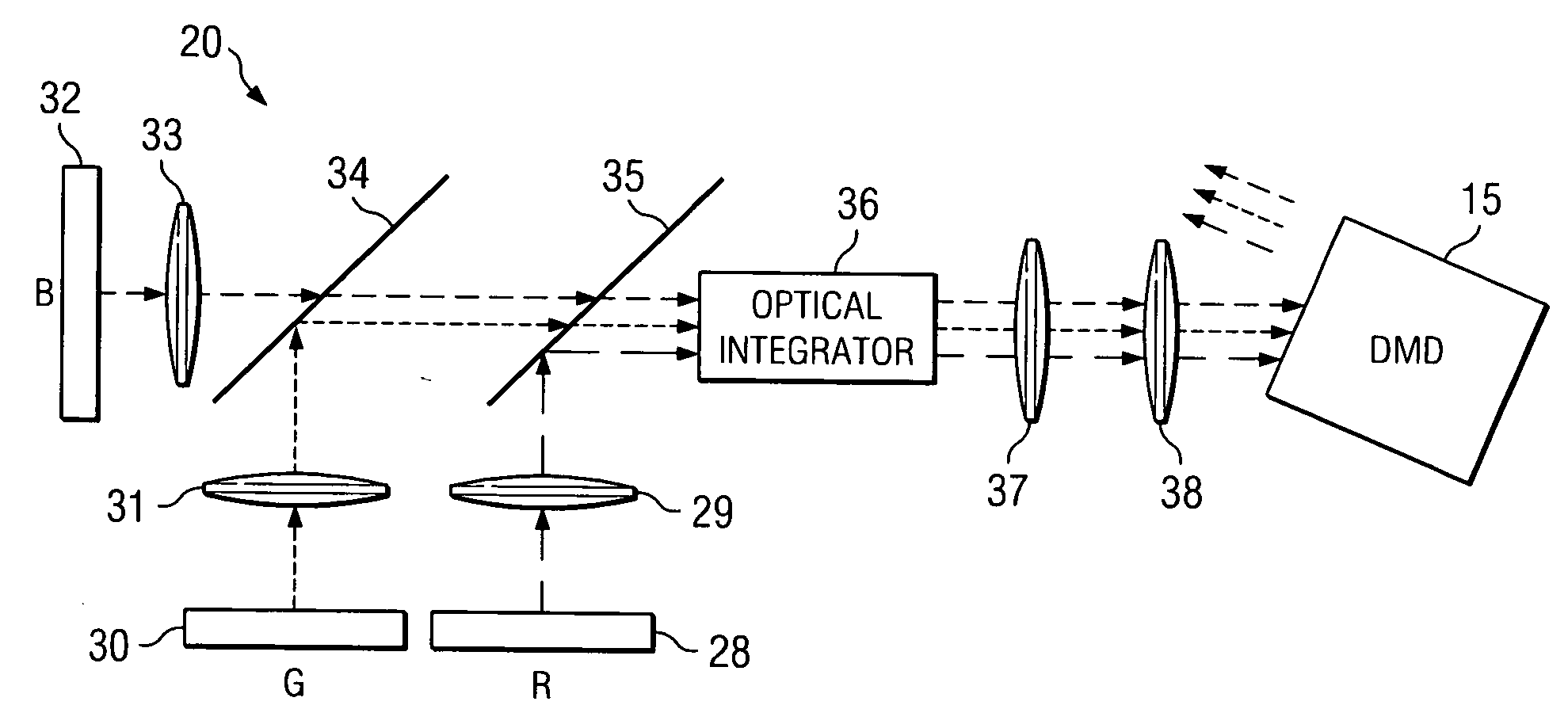
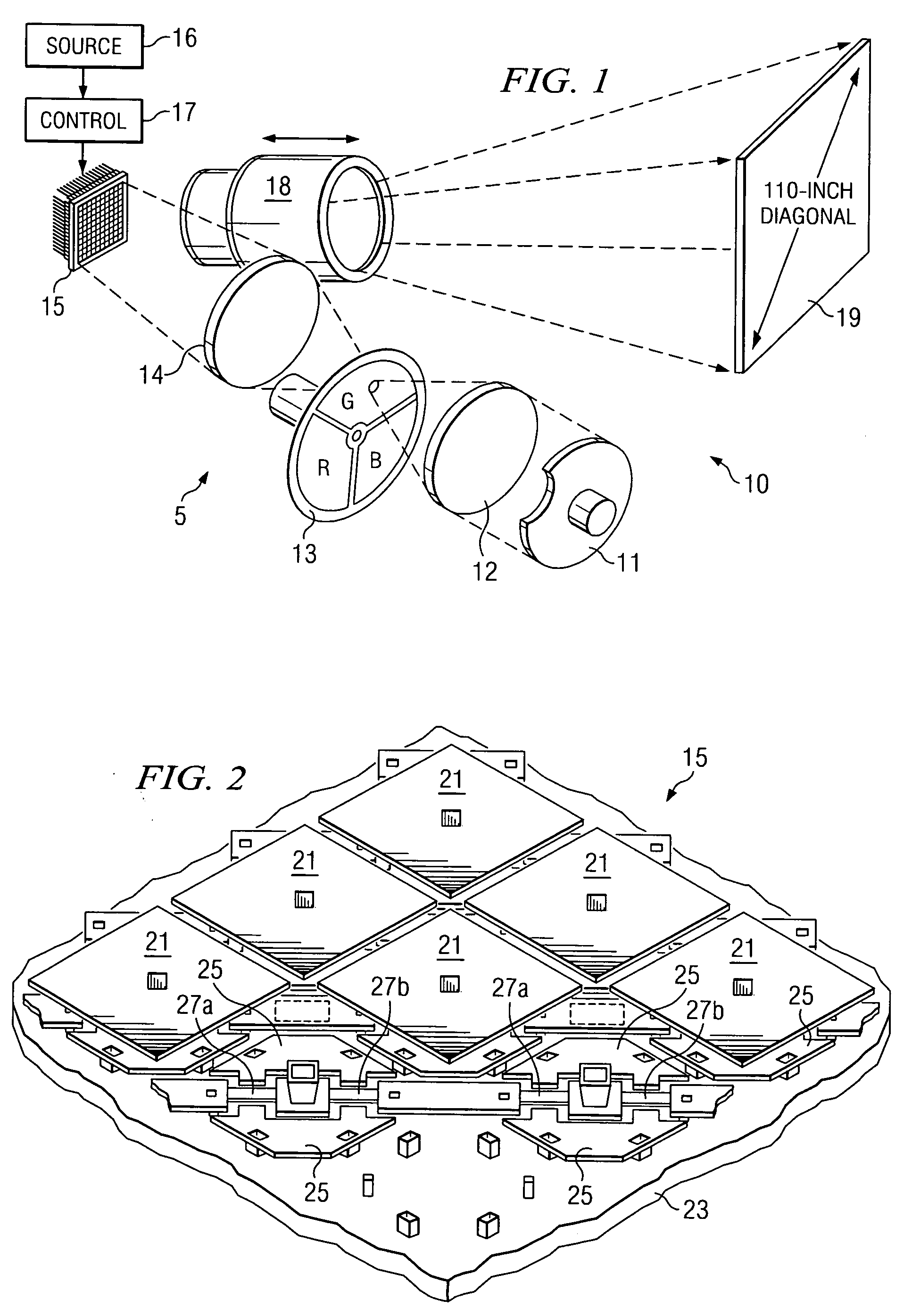
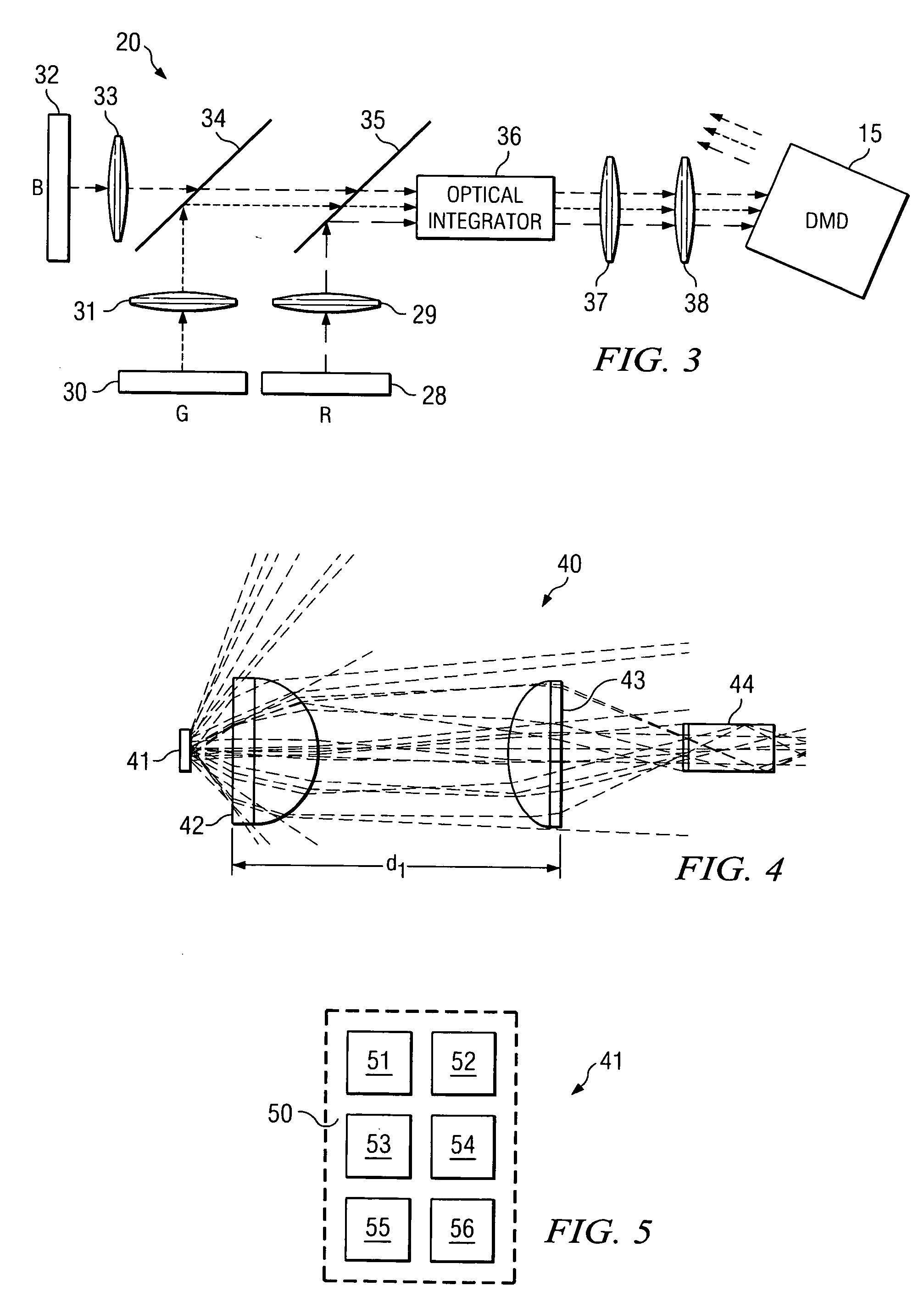
A method and system for combining light emitted by dispersed light sources for use in a projection display or similar system. A plurality of elongated and tapered light integrators are placed side by side forming an array, each having at their small input end a light source, such as an LED. Light collimated by each light integrator is further collimated by a convex lens disposed immediately at the output end of the light integrator. From the convex lenses, the light falls upon an array integrator, preferably a fly-eye type integrator, and passes through it to a second array integrator. Light emerging from the second array integrator is then passed through one or more relay lenses and falls upon a light modulator, such as a digital mircomirror device (DMD). The modulated light beam then passes through a projection lens and onto a visual image display screen. The display screen may, for example, be the screen of a high definition television (HDTV).
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Image display unit and projection optical system
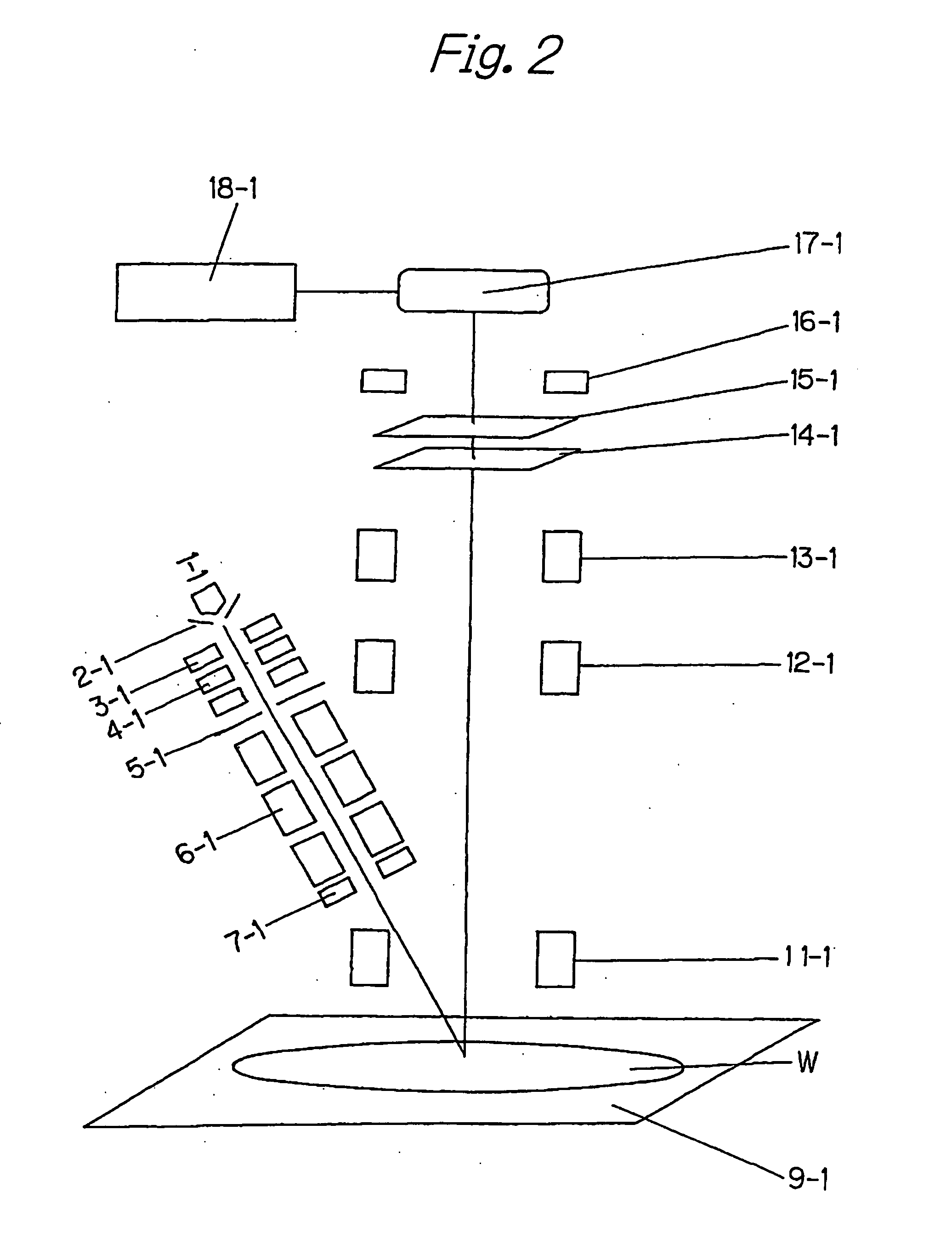
InactiveUS20060072215A1Telecentricity is deterioratedCathode-ray tube indicatorsTelescopesIntermediate imageEyepiece
An intermediate image of an image from the LCD module 142 is deflected by reflection mirrors M1 and M2 via zoom automatic focus control system (g) and then is formed on diffusion glass 131 via relay lens (b) and reflection mirrors M3 and M4. The LCD image is projected on the retina of eyeballs via eyepiece lens 132 by the light flux diffused at an order of ±20 degrees by diffusion glass 131. One side of the eyepiece lens 132 close to the crystal balls 2 has an aspherical shape of a Conic surface and a Conic coefficient of the Conic surface is −1 and less. Thereby the optical system that has a viewing angle of 60 degrees and over and has a small aberration can be obtained.
Owner:NISHI KENJI
Superwide-angle lens optical system, and imaging unit and display unit comprising the same
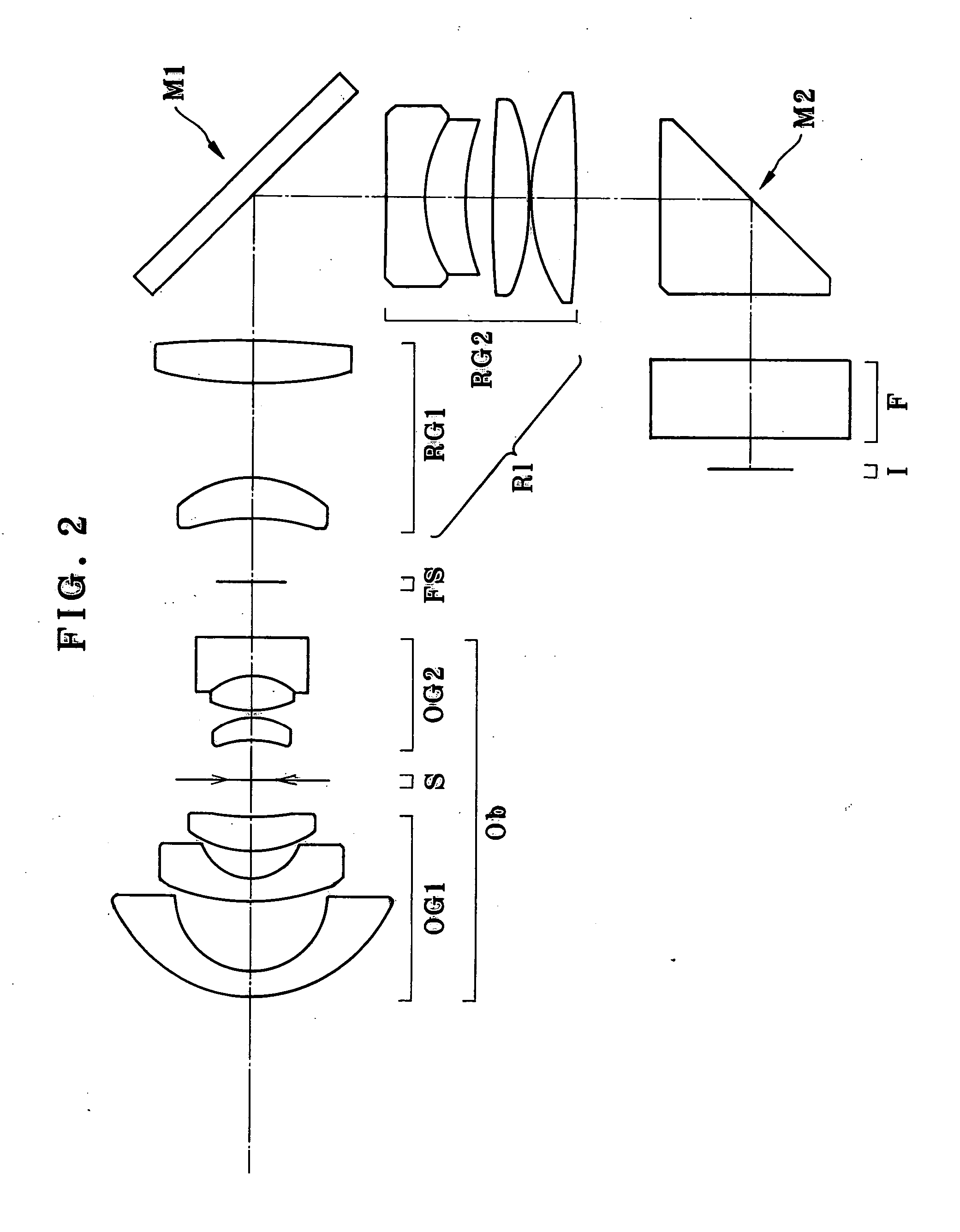
InactiveUS20050088762A1The implementation process is simpleShort back focusTelescopesSteroscopic systemsOphthalmologyMicroscope objective
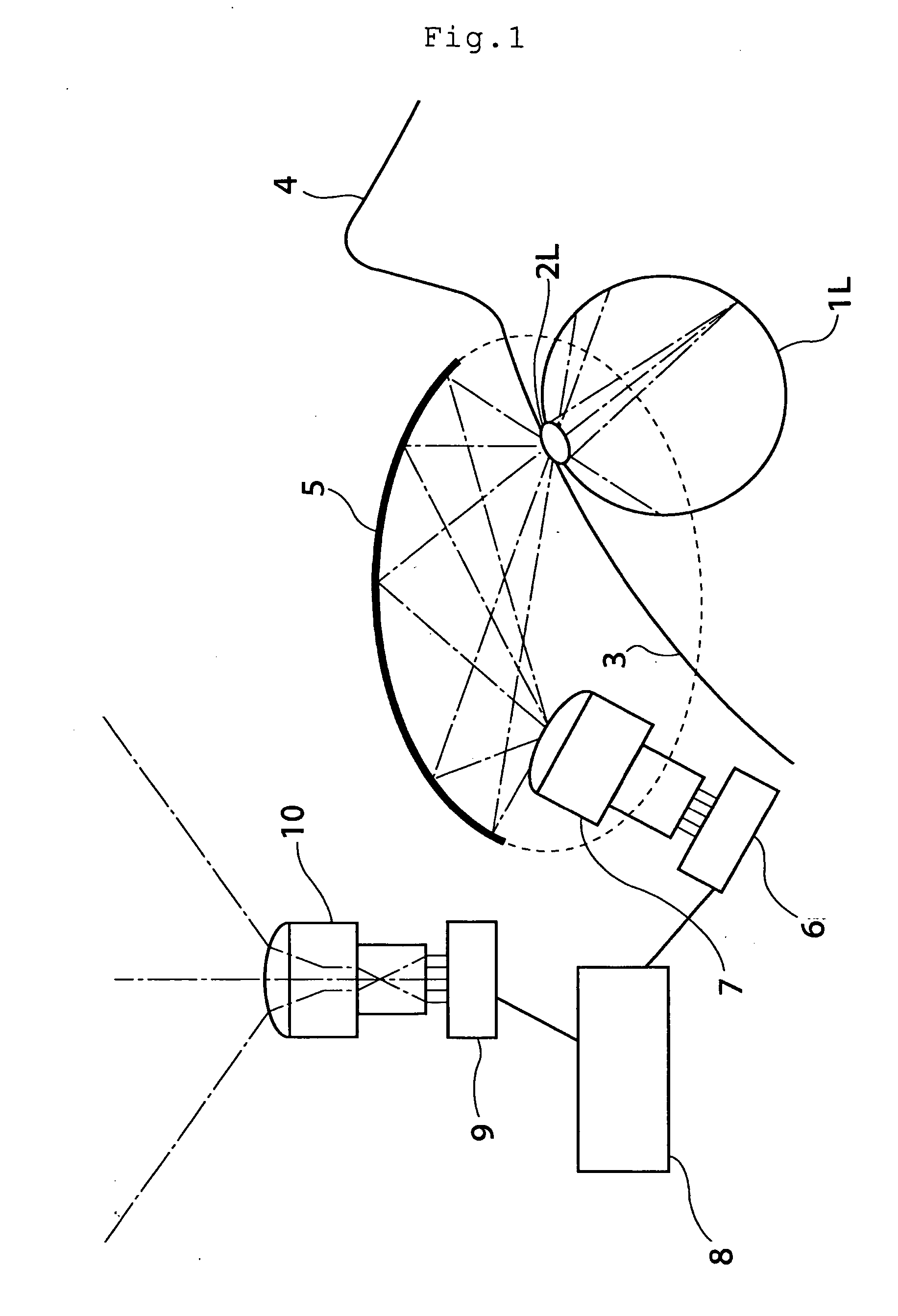
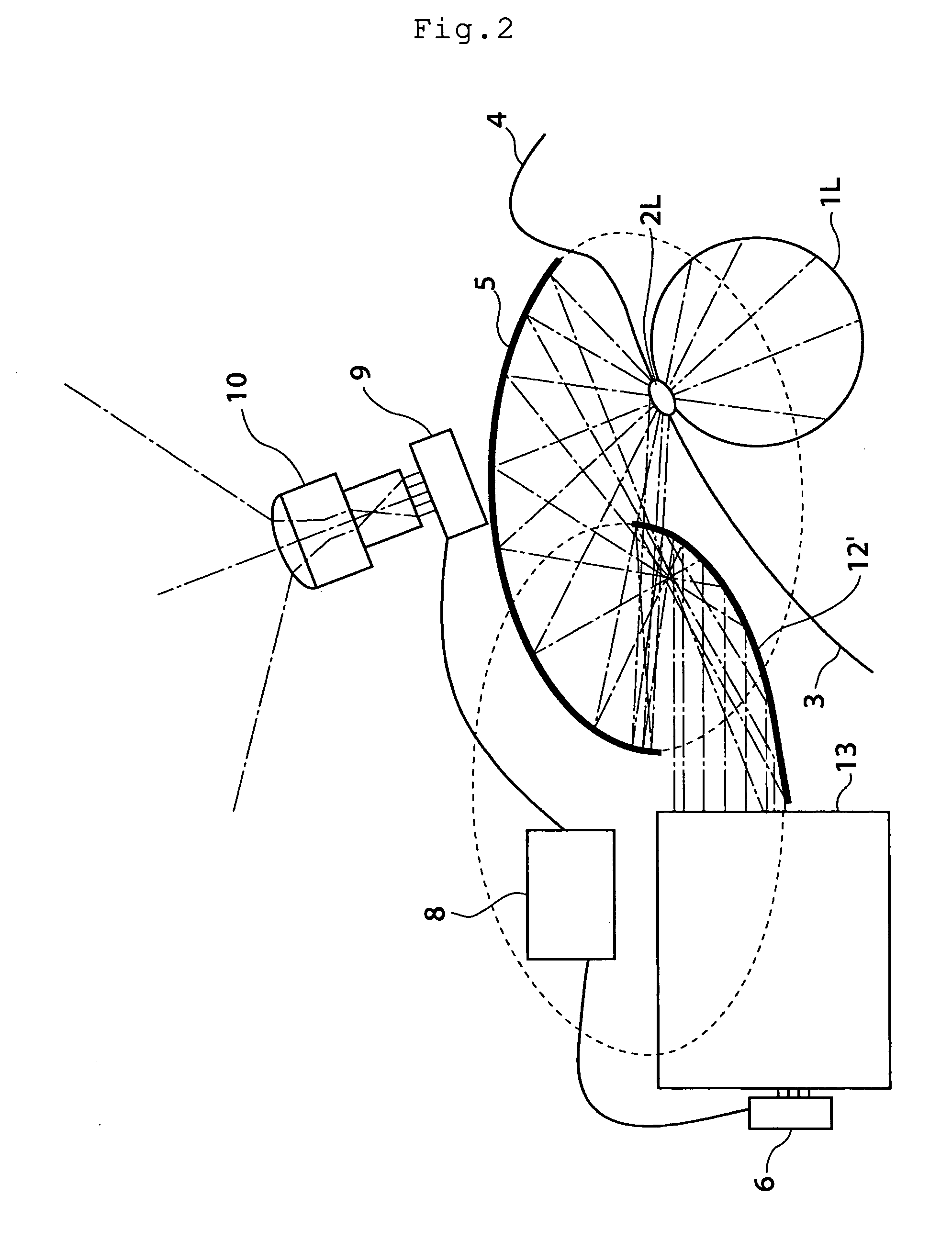
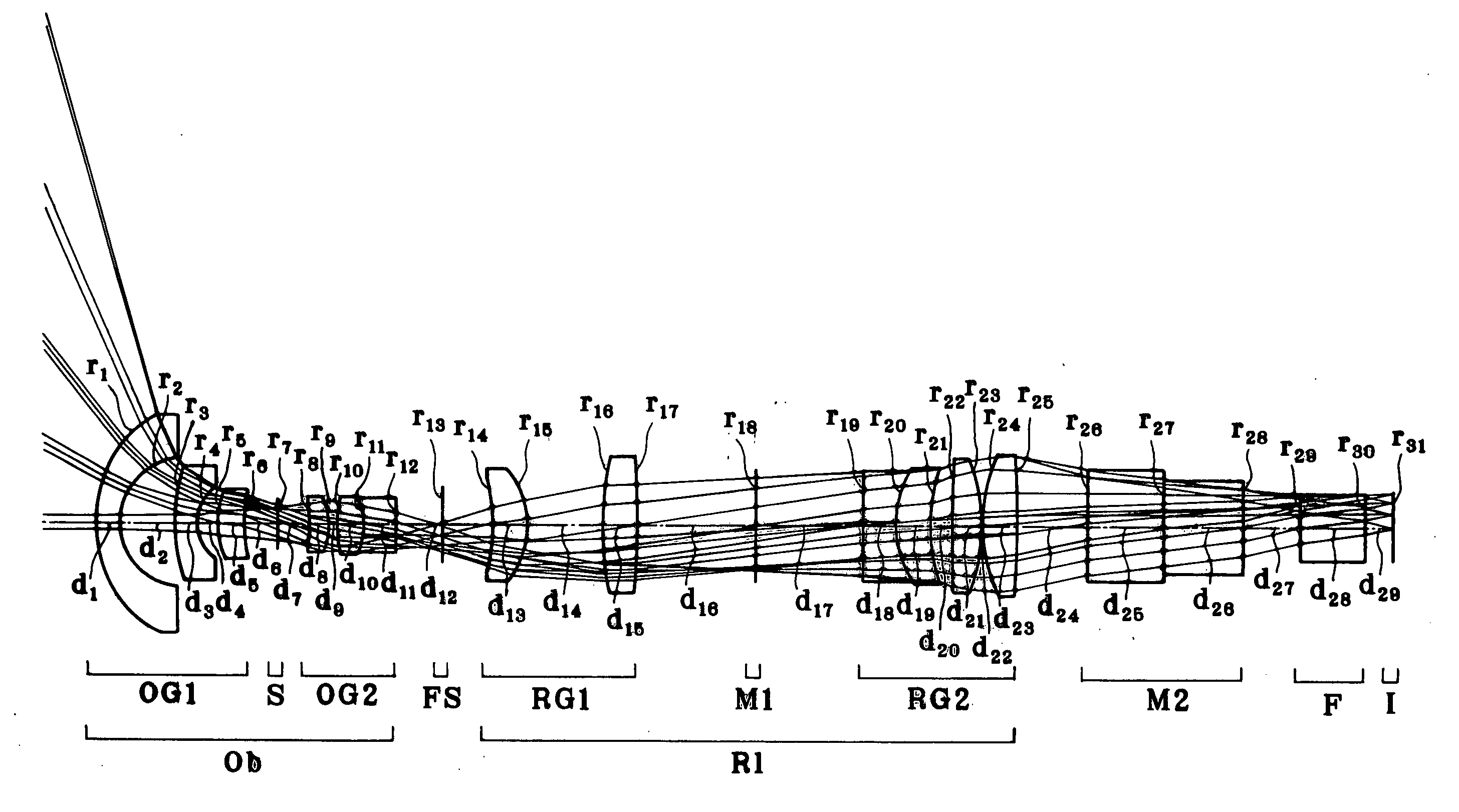
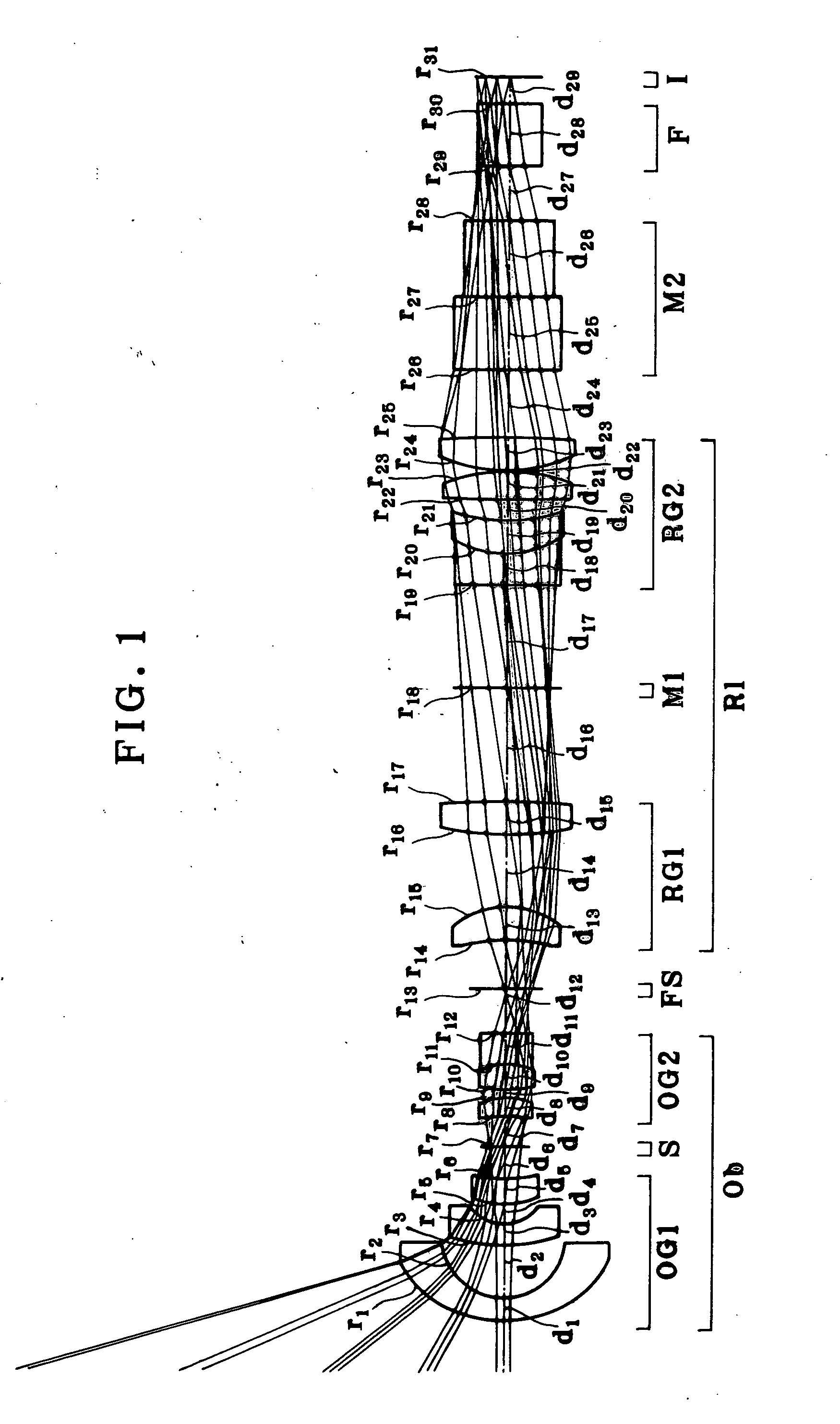
The invention relates to a superwide-angle lens optical system having a long back-focus lens arrangement and comprising a relay lens group. The optical system is constructed of, in order from an object side thereof, an objective lens group Ob having positive refracting power, a primary image-formation plane formed by the objective lens group Ob and a relay lens group R1 having positive refracting power. A field stop FS is positioned at or near the primary image-formation plane, and condition (1-1) is satisfied. h / fo>1.8 (1-1) Here fo is the focal length of the objective lens group Ob, and h is the diameter of an image circle on the primary image-formation plane.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
Projection apparatus using telecentric optics
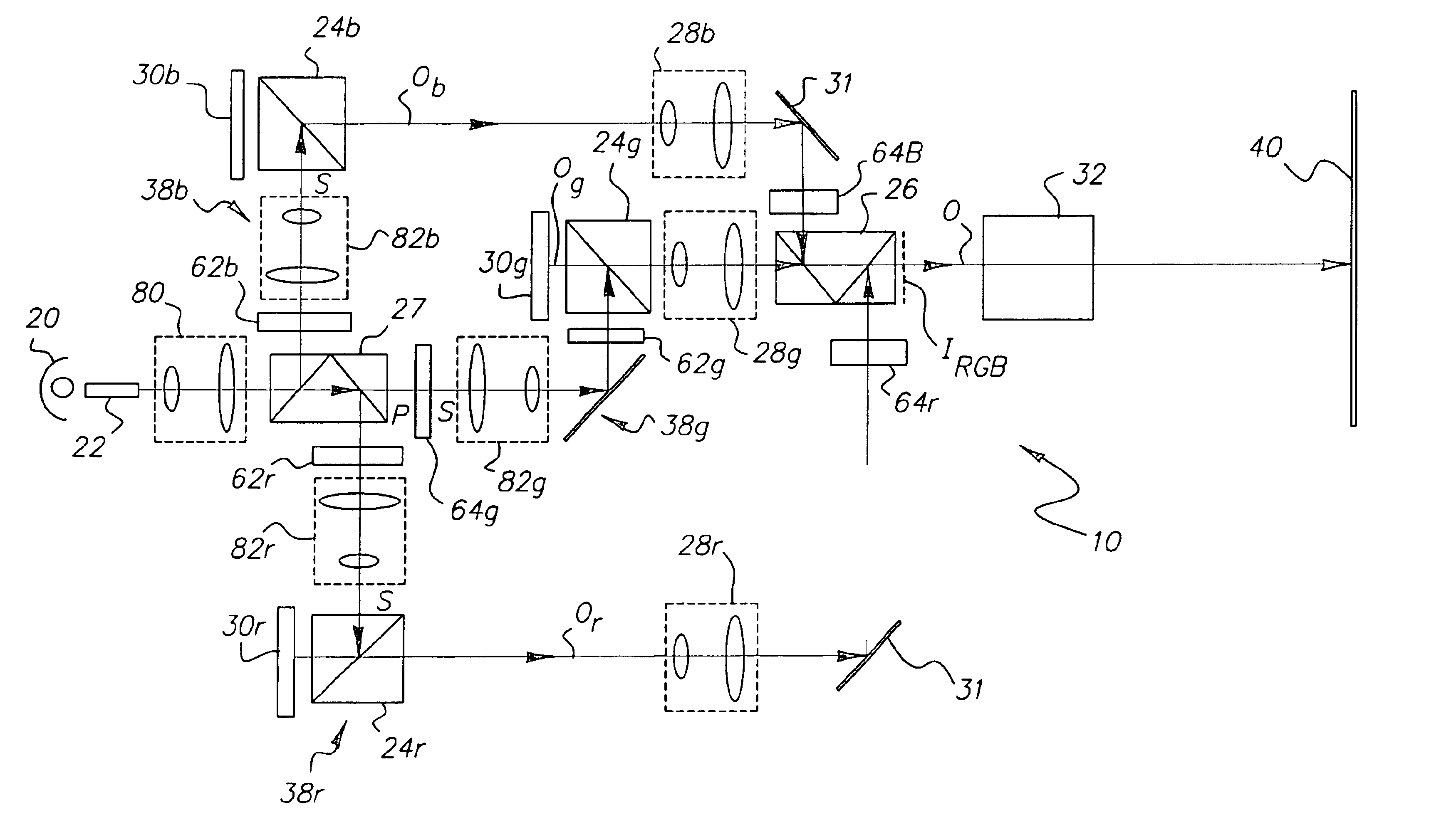
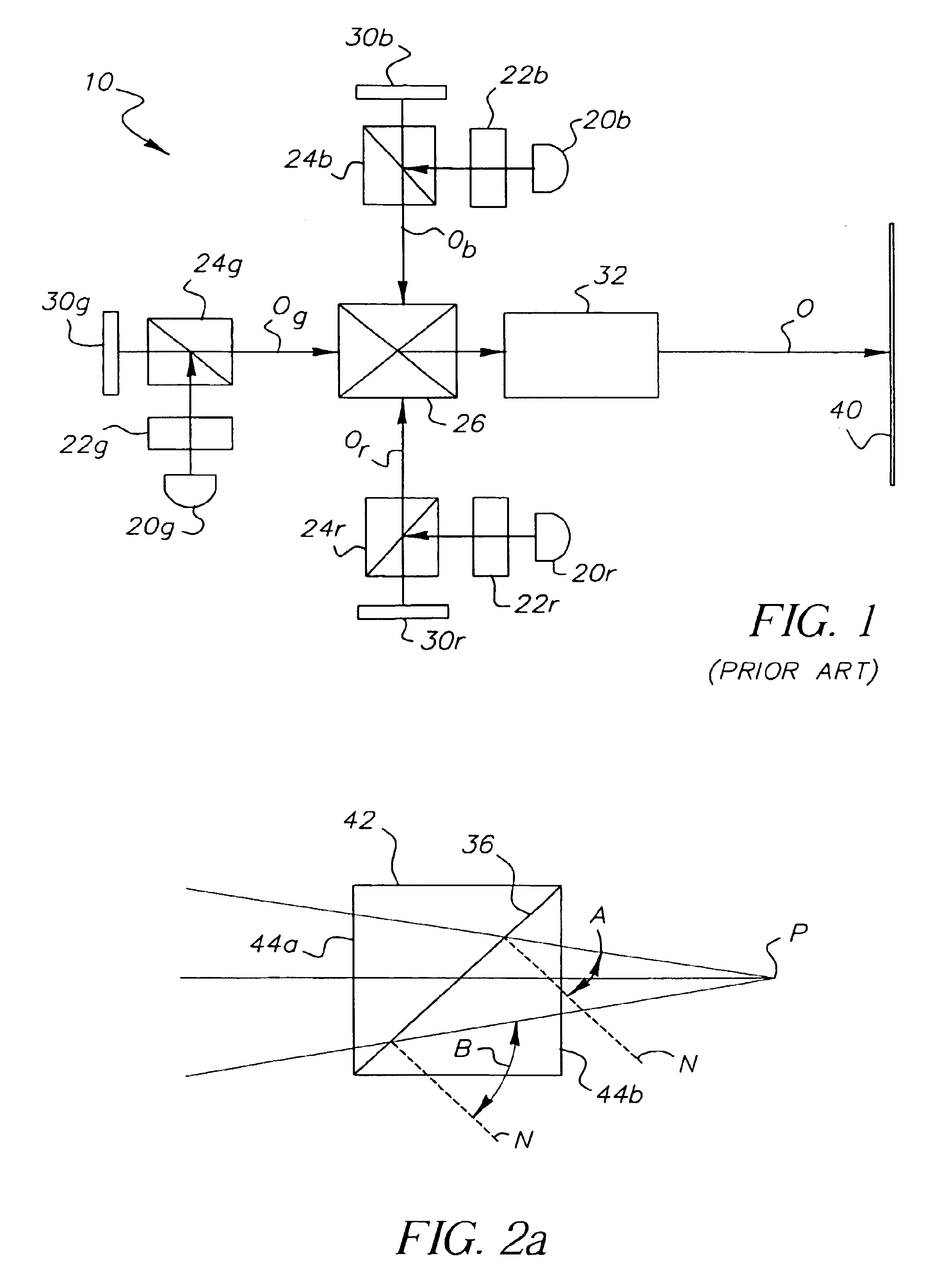
InactiveUS6758565B1Less-expensive dichroic coatingEasy to changeTelevision system detailsProjectorsSpatial light modulatorOphthalmology
A digital projection apparatus (10) for projection of a multicolor image uniformizes polychromatic light from a light source (20) and provides magnification to the uniformized illumination beam using a base condenser relay (80), providing a reduced numerical aperture for conditioning at a dichroic separator (27). For each monochromatic component color provided from the dichroic separator (27), a reducing relay (82) then demagnifies the illumination beam to provide source illumination to a spatial light modulator (30) at an increased numerical aperture. The modulated beam from the spatial light modulator (30) is then magnified by a magnifying relay lens assembly (28) and directed, at a lower numerical aperture, to a dichroic combiner (26) and to a projection lens (32). As a result, the projection lens (32) has reduced working distance, color shading across the field is minimized, and brightness is optimized.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
Stereoendoscope wherein images having passed through plural incident pupils are transmitted by common relay optical systems
InactiveUS6976956B2Reduce the number of partsVariationEndoscopesEye treatmentLight guideImage formation
The illuminating light transmitted by the light guide inserted through the elongate inserted section is projected out of the distal end surface of the inserted section. The illuminated objects pass through the respective pupils of the two objective lens systems arranged in parallel within the distal end section of the inserted section and their images are formed on the focal surface. The respective images are transmitted to the rear side by one common relay lens system. The transmitted final images are formed respectively on the image taking surfaces of the image taking devices. The respective images photoelectrically converted by the respective image taking devices are processed to be signals, are displayed in the monitor and are stereo-inspected through shutter spectacles.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
Free-form surface goggles-based see-through helmet mounted display device
InactiveCN101915992AEasy to correctMeet the efficacy characteristicsHelmetsHelmet coversExit pupilFree form
The invention discloses a free-form surface goggles-based see-through helmet mounted display device. A pair of free-form surface goggles is arranged in front of a helmet body, wherein micro-display imaging devices and relay lens assemblies are arranged in front of the helmet body and on the two sides of the upper part of the free-form surface goggles respectively; the two relay lens assemblies are arranged at an inclination angle of 42 degrees; each relay lens assembly comprises a first relay lens, a second relay lens, a third relay lens, a fourth relay lens, a fifth relay lens and a sixth relay lens; and the first relay lens, the second relay lens, the third relay lens, the fourth relay lens, the fifth relay lens and the sixth relay lens are arranged in turn. In the device, a tire tread-shaped free-form surface is used for imaging, so the device can realize a large off-axis angle of 33 degrees, correct the aberration well and obviously improve the imaging quality and has a simple structure; the device is suitable to be arranged on a human head and conforms to the characteristic of man-machine efficacy; and by using the design of a short-focus large angle of view, the device has an exit pupil of between 12 and 15mm and an angle of view of between 40 and 50 degrees.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV +1
Confocal wafer inspection method and apparatus using fly lens arrangement
InactiveUS6867406B1Severe signal variationThe process is fast and efficientMaterial analysis by optical meansMicroscopesLight energyTransmitter
A semiconductor wafer inspection system and method is provided which uses a multiple element arrangement, such as an offset fly lens array. The preferred embodiment uses a laser to transmit light energy toward a beam expander, which expands the light energy to create an illumination field. An offset fly lens array converts light energy from the illumination field into an offset pattern of illumination spots. A lensing arrangement, including a first lens, a transmitter / reflector, an objective, and a Mag tube imparts light energy onto the specimen and passes the light energy toward a pinhole mask. The pinhole mask is mechanically aligned with the offset fly lens array. Light energy passing through each pinhole in the pinhole mask is directed toward a relay lens, which guides light energy onto a sensor. The offset fly lens array corresponds to the pinhole mask. The offset pattern of the offset fly lens array is chosen such that spots produced can be recombined into a continuous image, and the system utilizes a time delay and integration charge coupled device for rapid sensing along with an autofocus system that measures and cancels topological features of the specimen.
Owner:KLA CORP
Image display unit and projection optical system
InactiveUS7068444B2Telecentricity is deterioratedCathode-ray tube indicatorsTelescopesEyepieceIntermediate image
An intermediate image of an image from the LCD module 142 is deflected by reflection mirrors M1 and M2 via zoom automatic focus control system (g) and then is formed on diffusion glass 131 via relay lens (b) and reflection mirrors M3 and M4. The LCD image is projected on the retina of eyeballs via eyepiece lens 132 by the light flux diffused at an order of ±20 degrees by diffusion glass 131. One side of the eyepiece lens 132 close to the crystal balls 2 has an aspherical shape of a Conic surface and a Conic coefficient of the Conic surface is −1 and less. Thereby the optical system that has a viewing angle of 60 degrees and over and has a small aberration can be obtained.
Owner:NISHI KENJI
Autoclavable endoscope
InactiveUS6955644B2Reduced susceptibility to damageReduce sensitivitySurgeryEndoscopesEyepieceThermal expansion
A rigid endoscope includes an outer housing subassembly that supports an optics subassembly. The outer body subassembly includes concentric tubes with optical fiber for providing object illumination. The optics subassembly includes a tubular sheath sealed at both ends. A compression spring is positioned between a proximal most relay lens element and a distal most eyepiece element. The spring exerts a distally acting force on the elements of an optical objective and relay lens system. It also produces a proximally directed force on optical elements in the eyepiece. This minimizes differential thermal expansion stresses during autoclaving operations.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
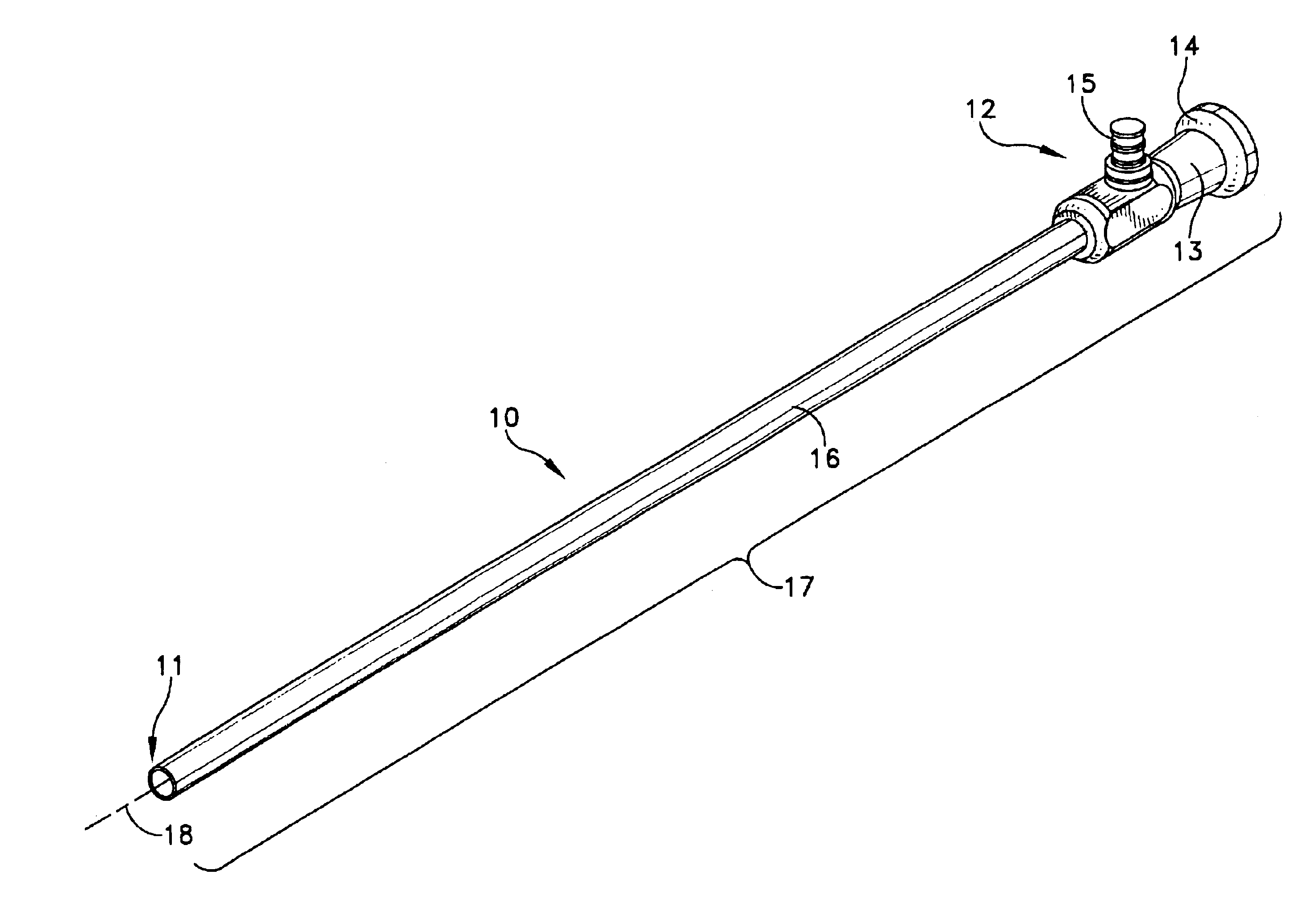
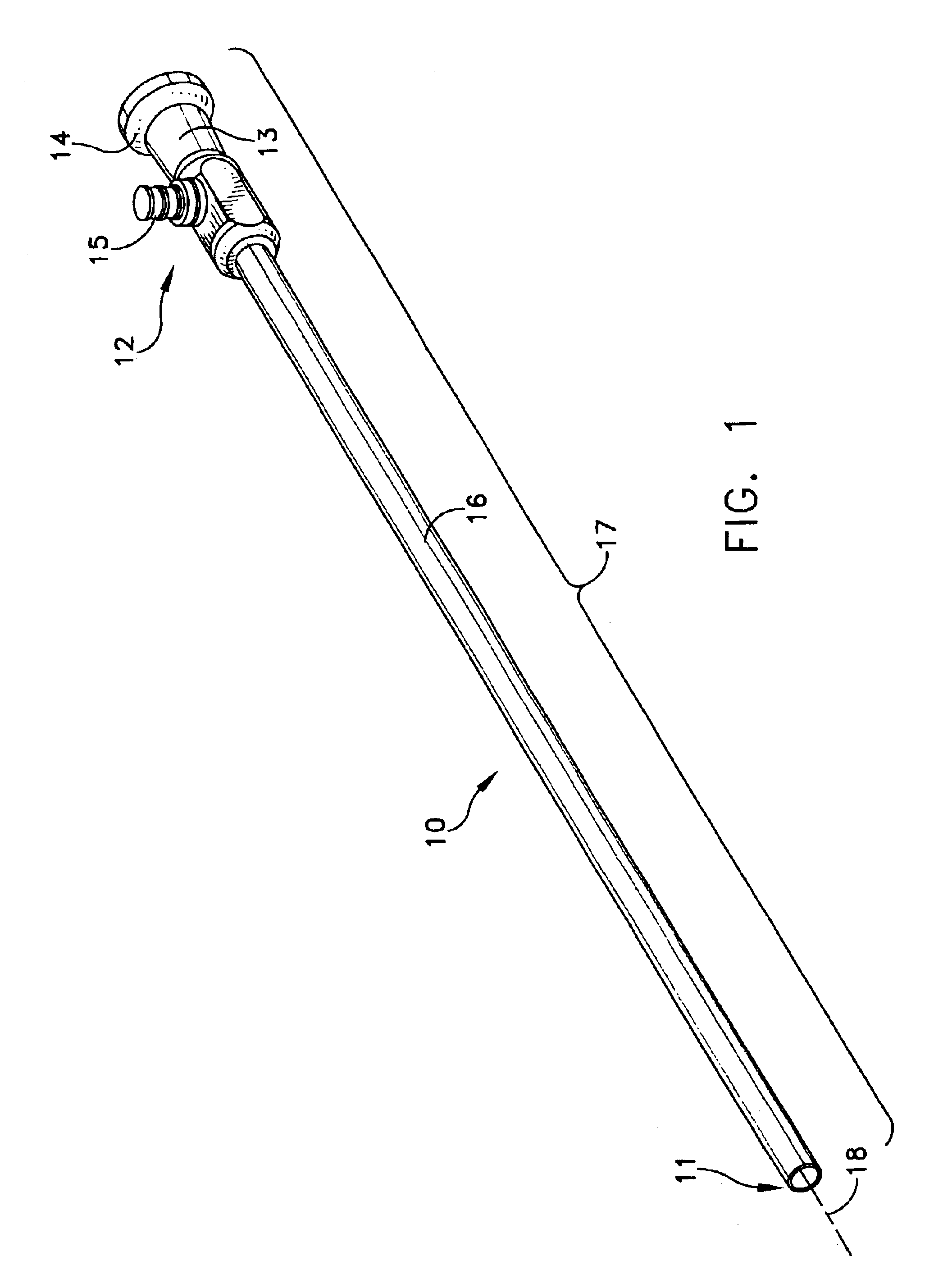
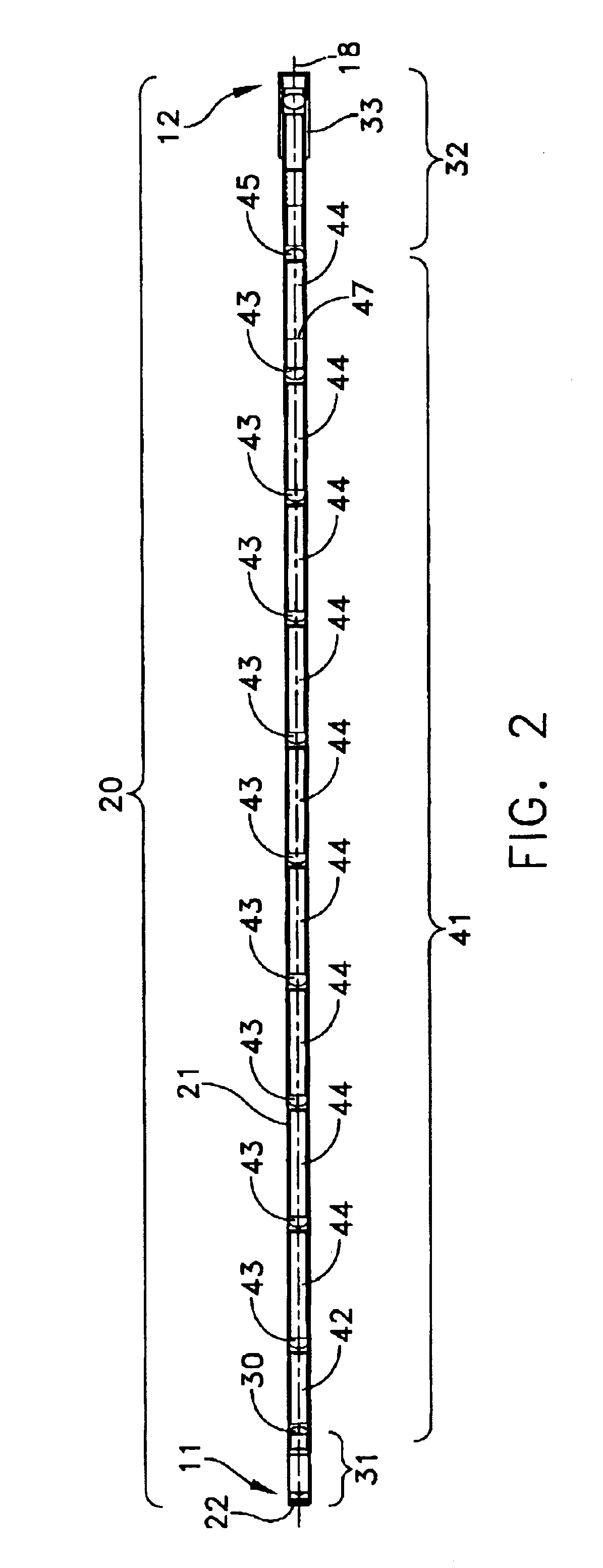
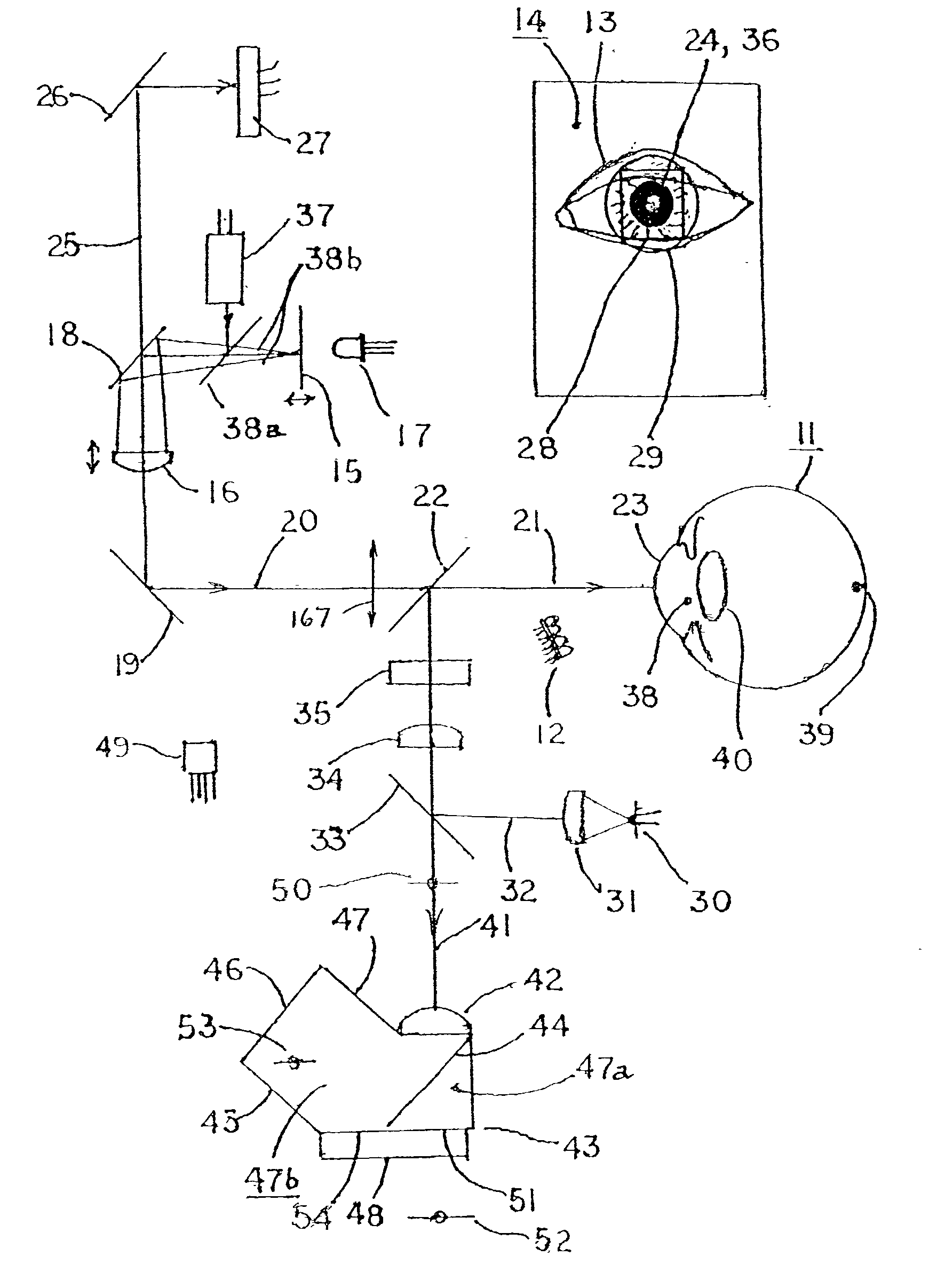
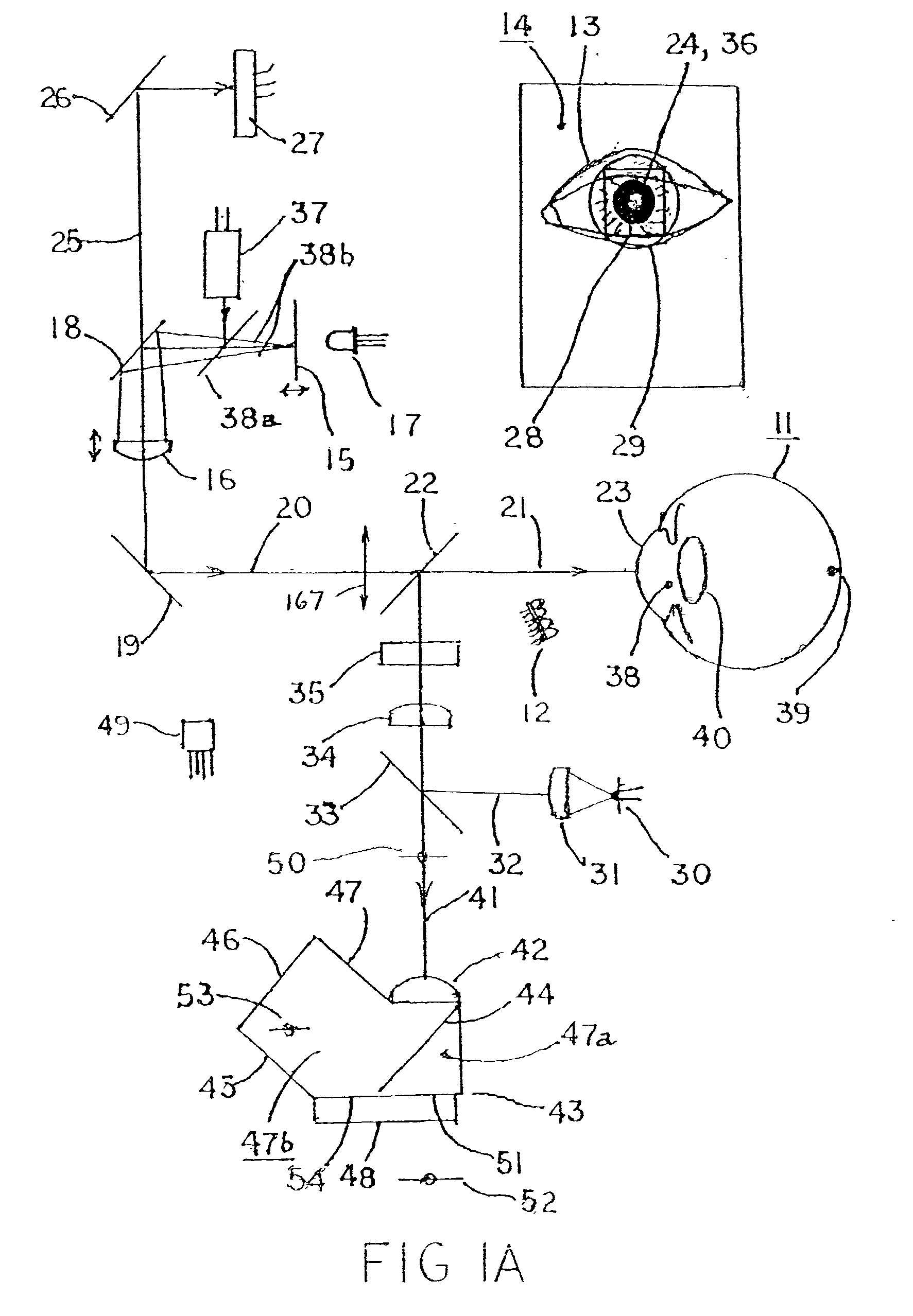
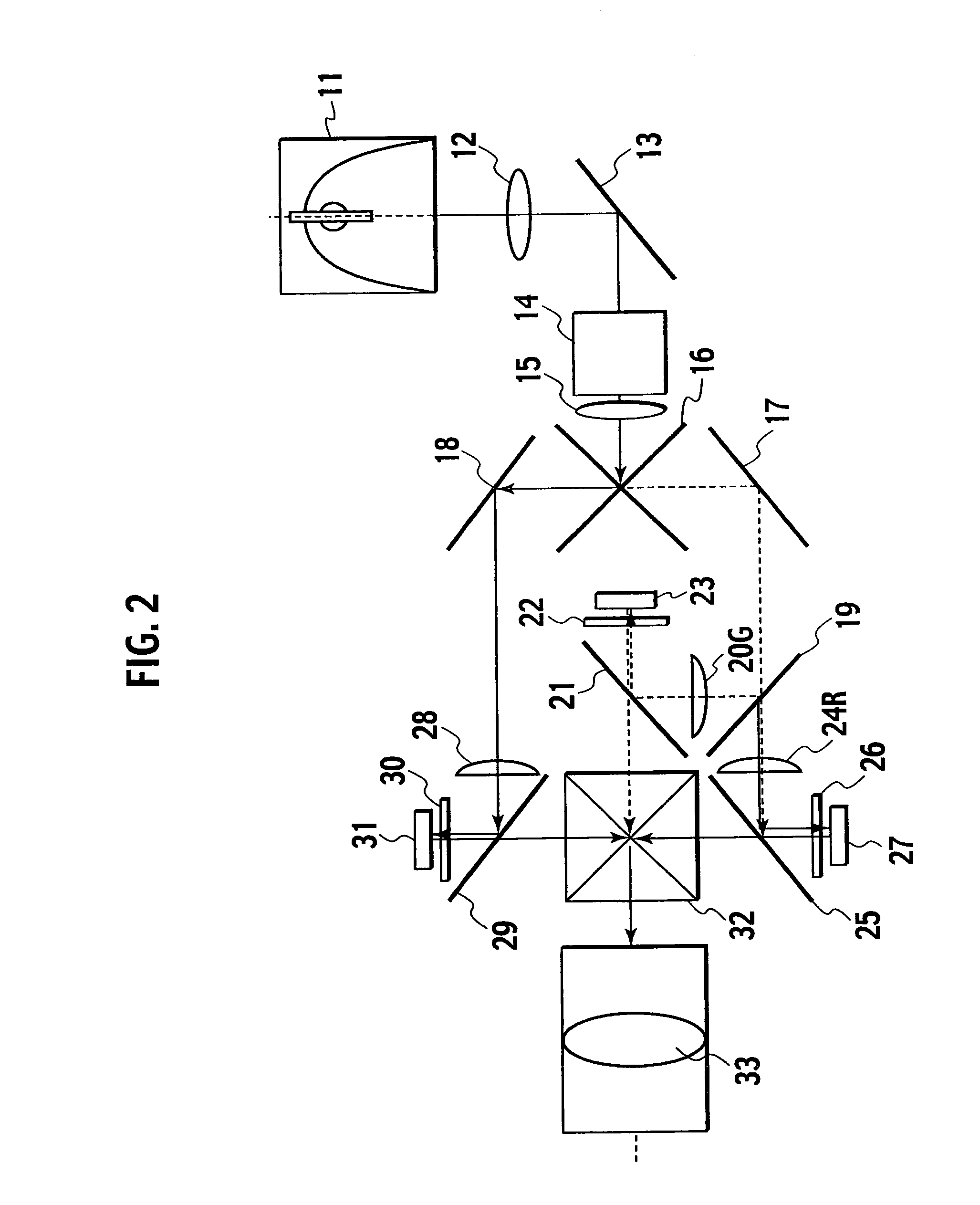
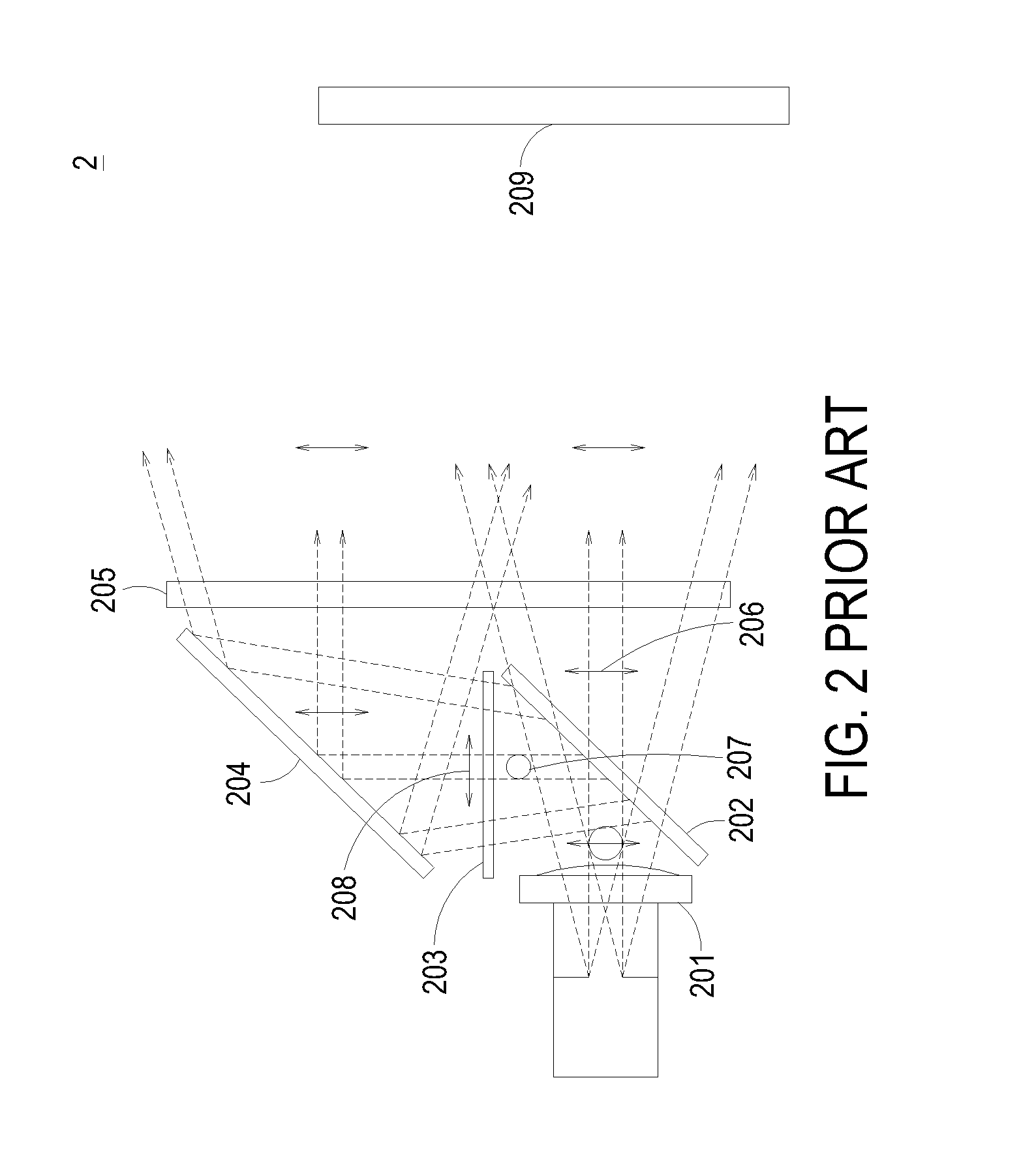
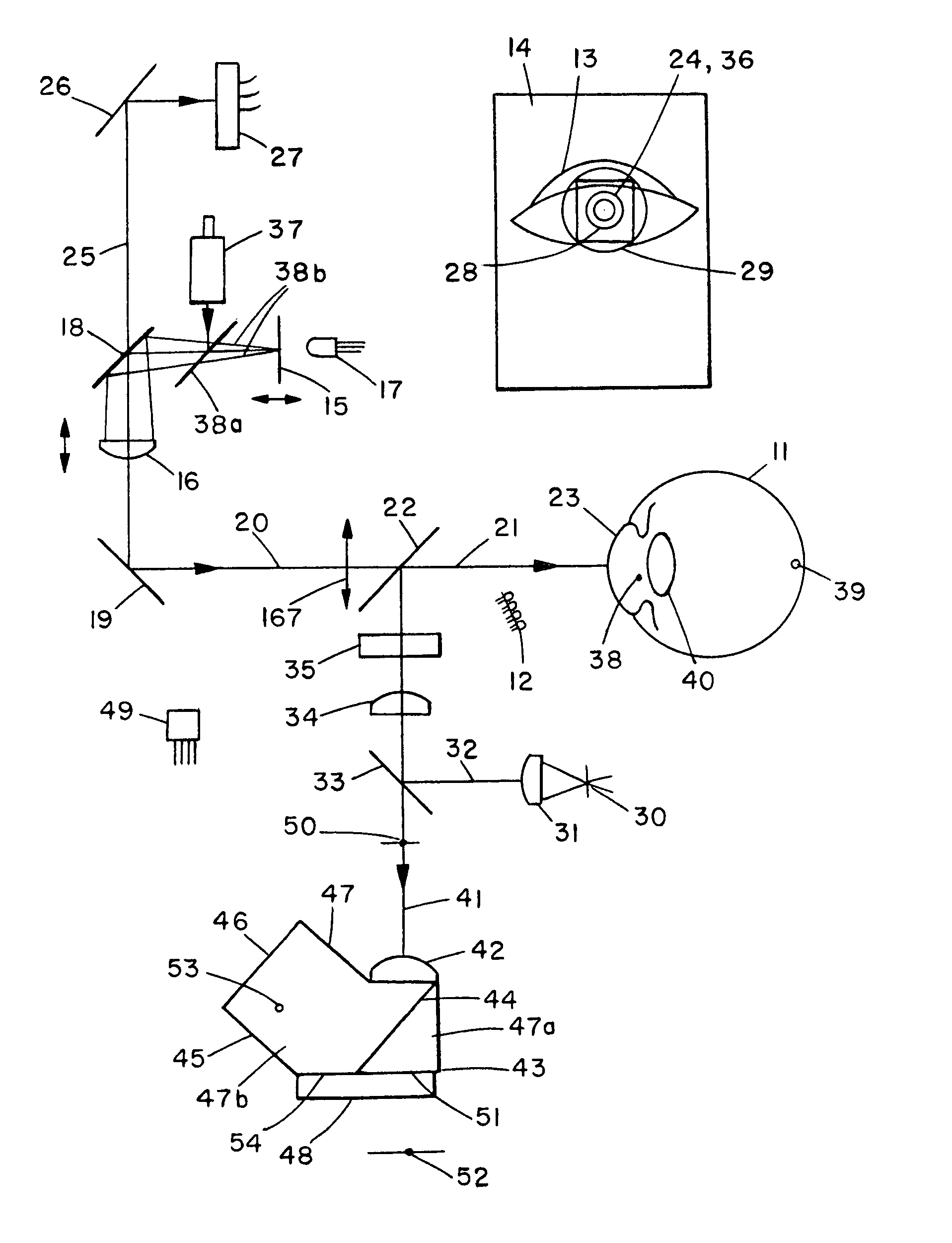
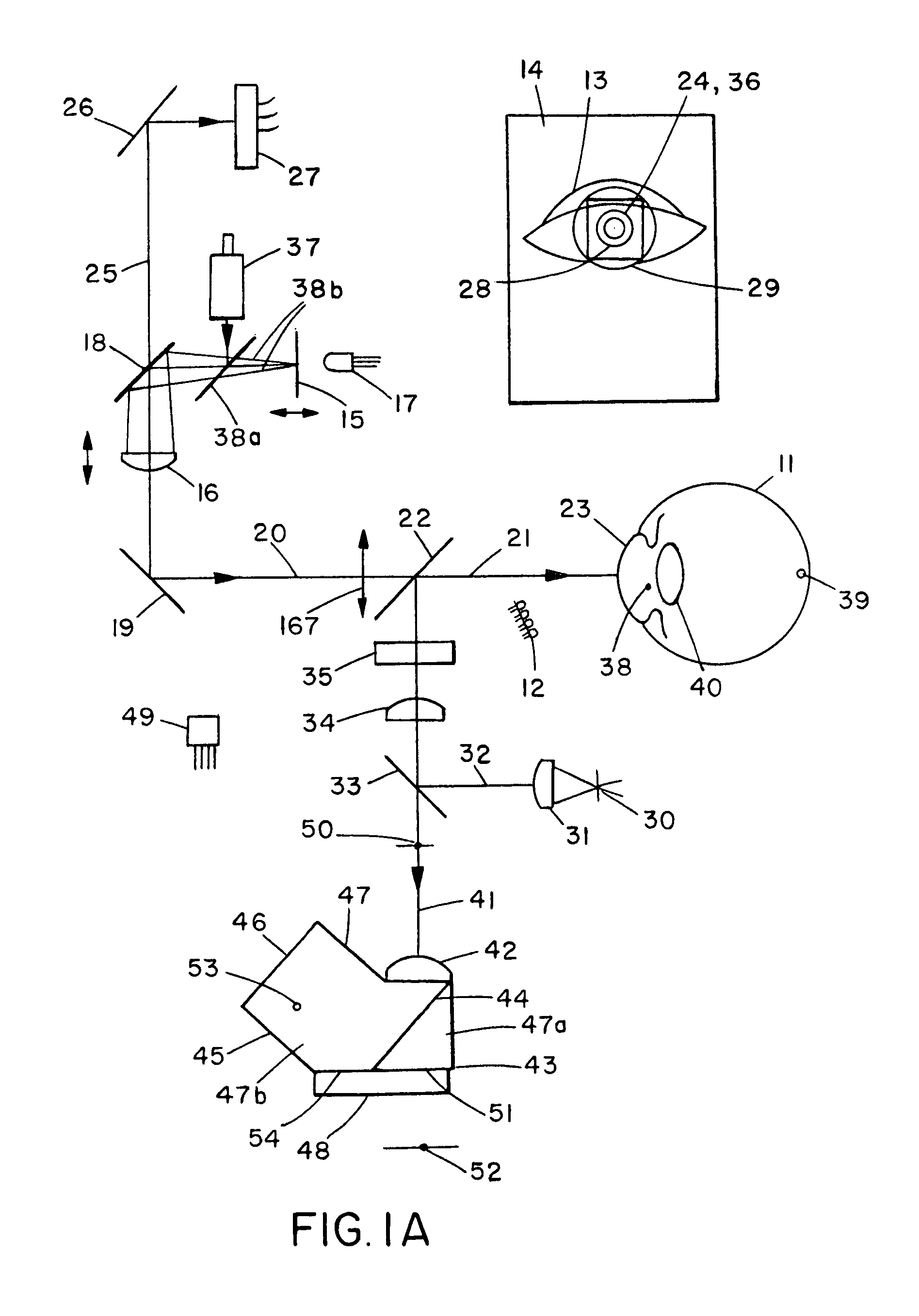
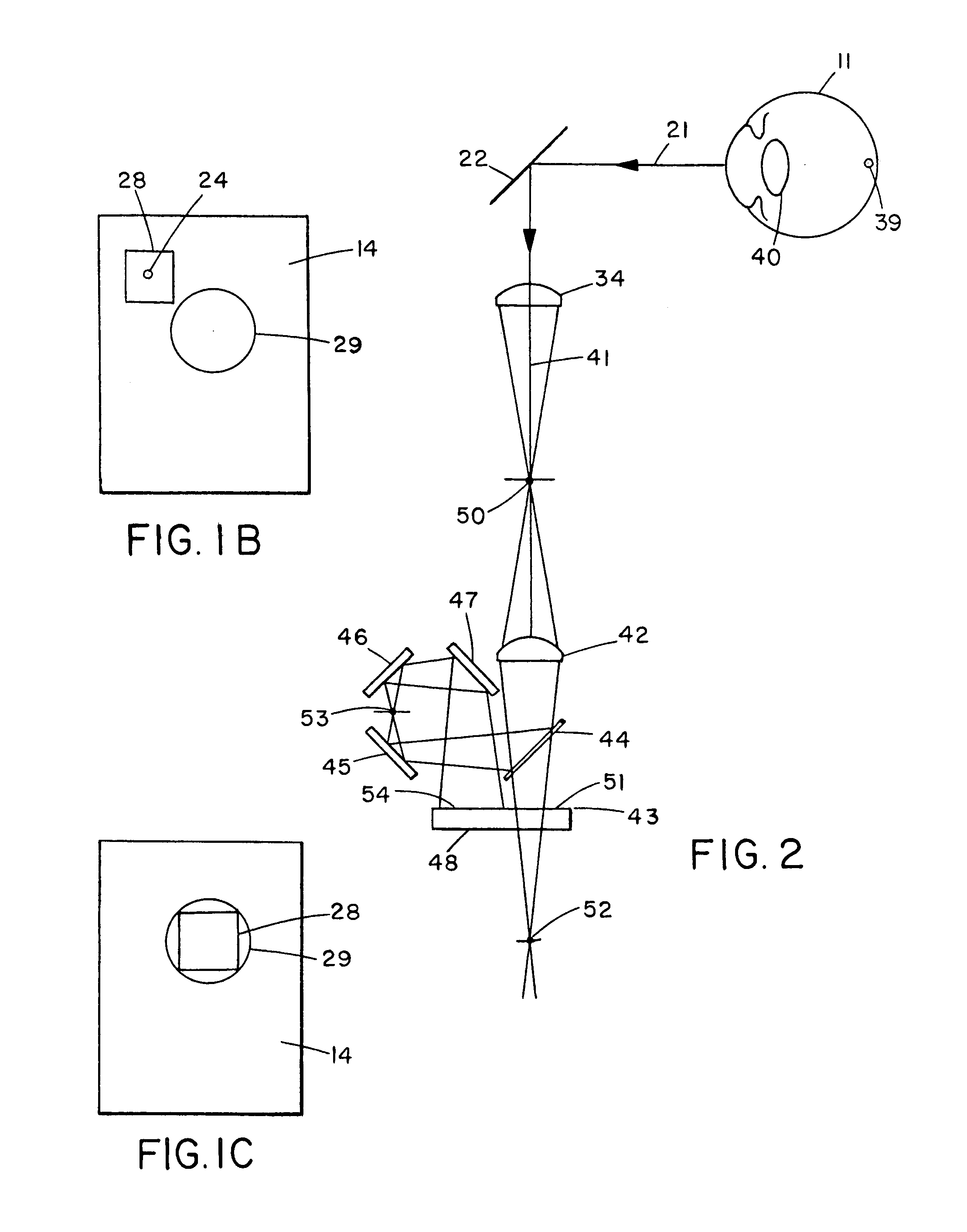
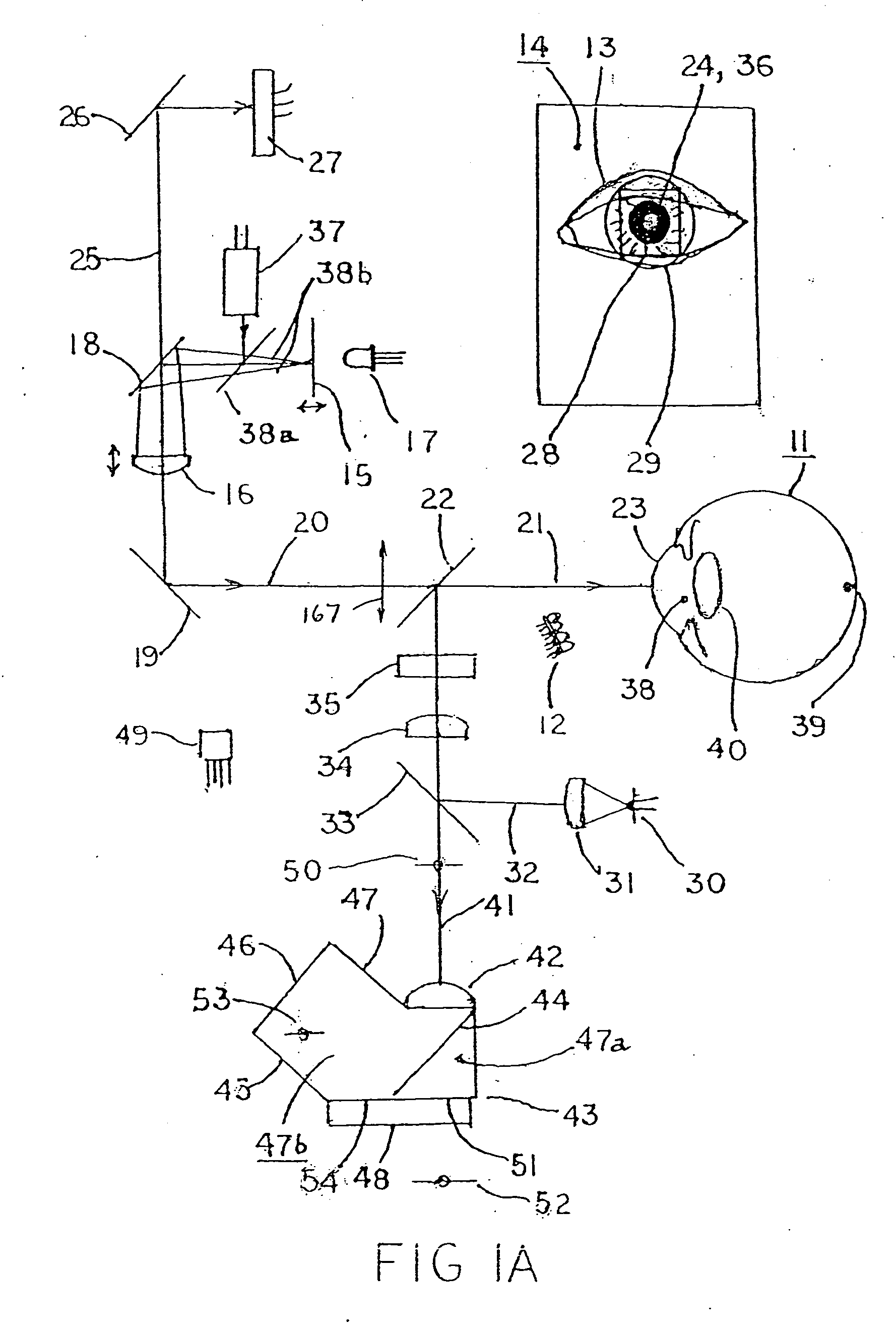
Complete autorefractor system in an ultra-compact package
An autorefractor system in an ultra-compact package is described for rapidly and objectively measuring the refractive state of the eye. The autorefractor detector system, in conjunction with a secondary light source, uses one photodetector such as a charge coupled device ("CCD") or one photodiode, to intercept a light beam at two distances from a secondary retinal light source created by one relay lens, one pupil emitter conjugate lens and one pupil detector conjugate lens. The signals produced by the photodetector are used to determine the full spherocylindrical refraction of the eye. A novel illumination and imaging system provides multiple capabilities to image the eye, control accommodation, and acquire and maintain optical alignment, while obtaining other measurements of the eye.
Owner:DAPHNE INSTR
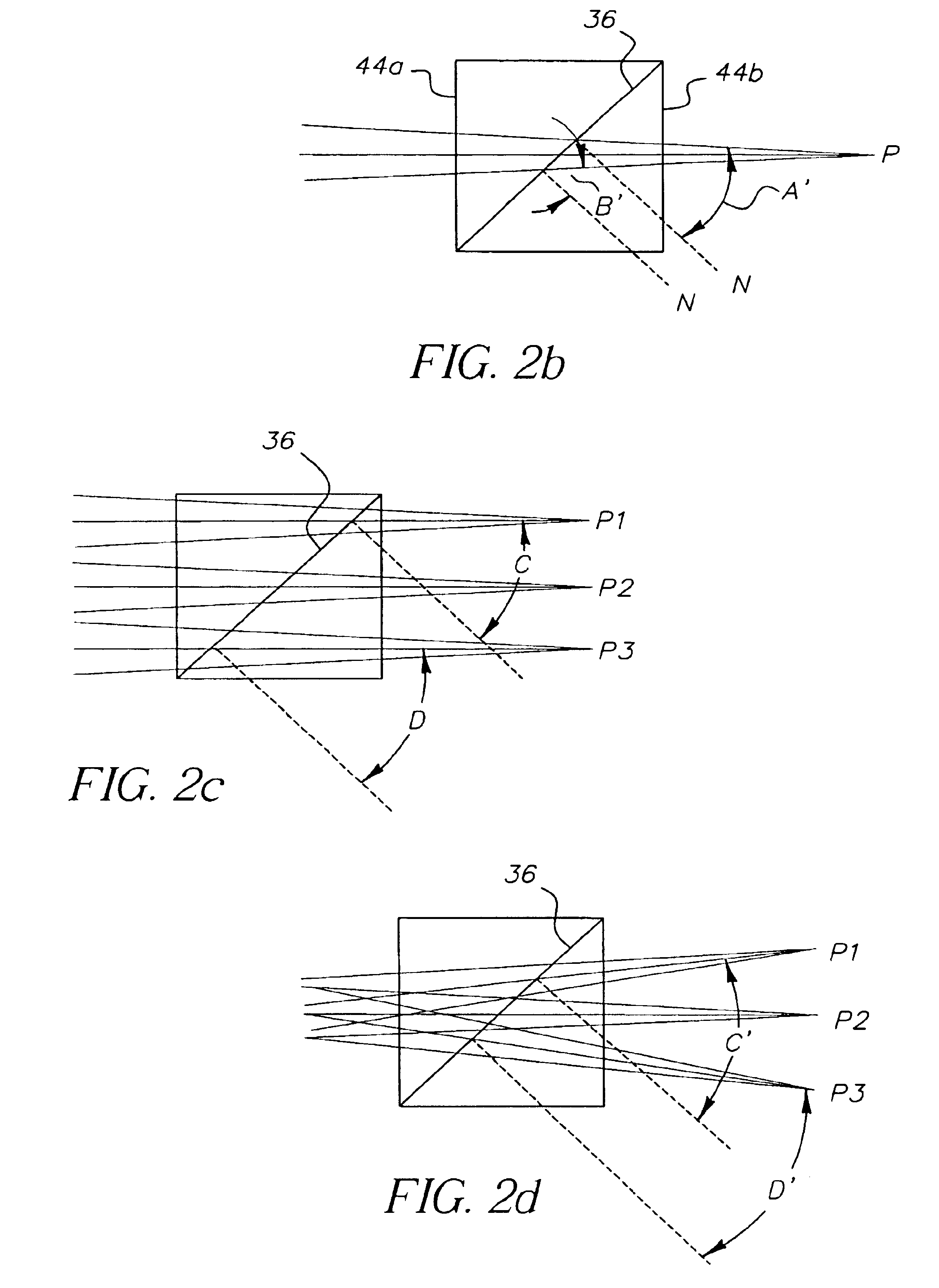
Optical system and projection display device
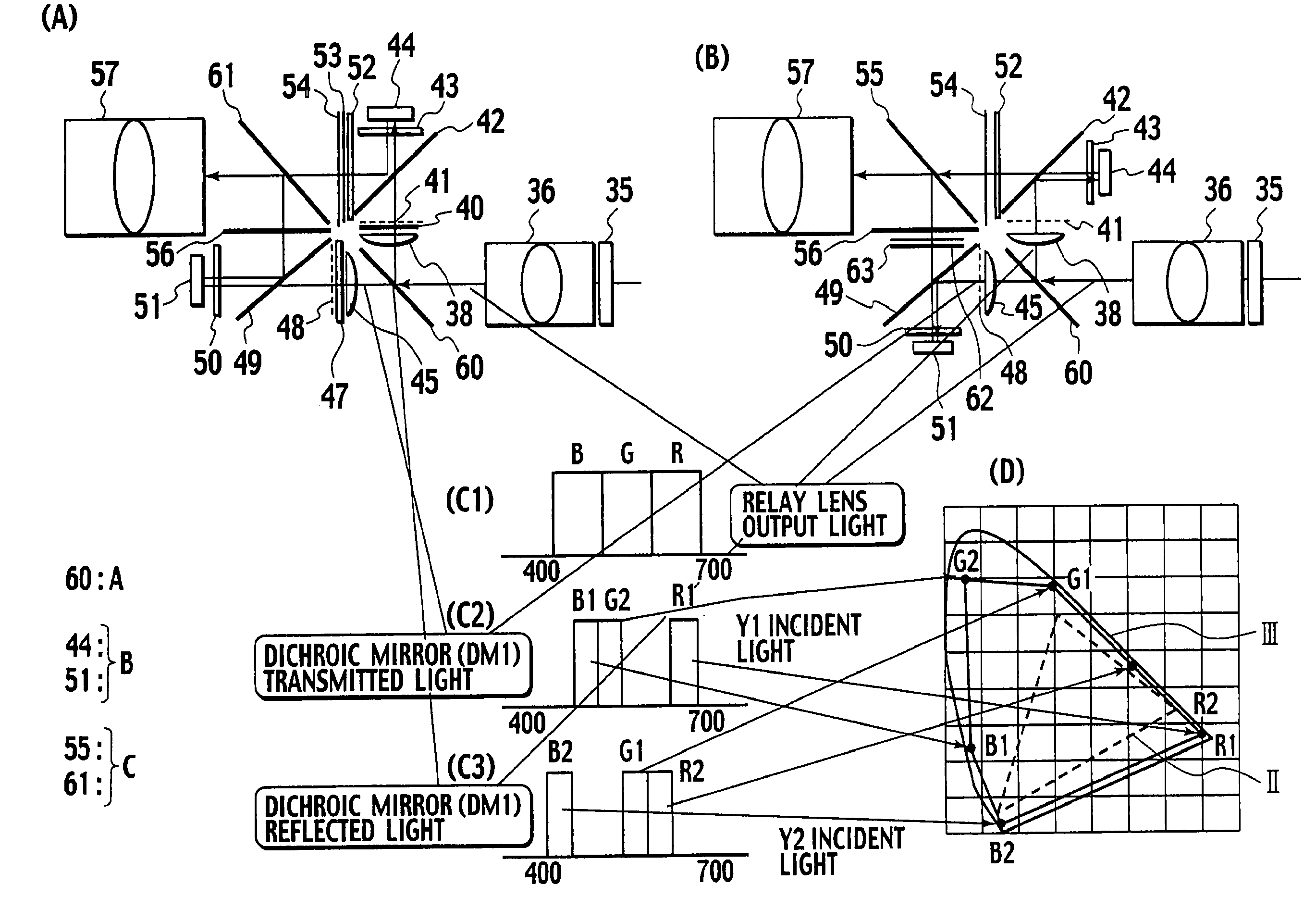
ActiveUS7686455B2Reduce manufacturing costHigh-contrast imageTelevision system detailsProjectorsWire gridSpectral filtering
Light in primary colors RGB modulated in a first modulation optical system is transmitted through a relay lens (36) and further divided into a P-polarized light and an S-polarized light by a PS separation wire grid (37). The S-polarized light is transmitted through a wavelength spectral filter (39) to select red / green / blue light components R1, G1, B1 of 615, 515, 450 nm in wavelength, which are then modulated by a Y1 device (44). The P-polarized light is transmitted through a wavelength spectral filter (46) to select red / green / blue light components R2, G2, B2 of 650, 550, 475 nm in wavelength, which are then modulated by a Y2 device (51). The 3 -primary color lights modulated by the Y1 / Y2 devices (44), (51) are combined with each other at a PS composite wire grid (55) to project a synthetic light on a screen.
Owner:JVC KENWOOD CORP +1
Stereoscopic displays with addressable focus cues
Owner:THE ARIZONA BOARD OF REGENTS ON BEHALF OF THE UNIV OF ARIZONA
Stage lighting methods and apparatus
ActiveUS20060007686A1Image be preventLighting applicationsMechanical apparatusLight equipmentStage lighting
Spot illumination apparatus and methods are described. According to one implementation a spot luminaire includes a light source for emitting a beam of light and a projection lens configured to project the beam of light towards a distant target. A first field stop, through which the beam of light passes, is positioned between the light source and the projection lens. A filter apparatus is positioned proximate the first field stop and is adapted for selectively moving at least one variable density filter across the beam of light. A relay lens group is positioned between the first field stop and the projection lens. The relay lens group is configured to prevent the at least one variable density filter from being imaged by the projection lens. Methods for providing stage lighting are also described.
Owner:WHITEROCK DESIGN
Method of combining dispersed light sources for projection display
ActiveUS20070121085A1Good for arrayingTechnical advantageShow cabinetsImpedence networksHigh definition tvHigh-definition television
A method and system for combining light emitted by dispersed light sources for use in a projection display or similar system. A plurality of elongated and tapered light integrators are placed side by side forming an array, each having at their small input end a light source, such as an LED. Light collimated by each light integrator is further collimated by a convex lens disposed immediately at the output end of the light integrator. From the convex lenses, the light falls upon an array integrator, preferably a fly-eye type integrator, and passes through it to a second array integrator. Light emerging from the second array integrator is then passed through one or more relay lenses and falls upon a light modulator, such as a digital mircomirror device (DMD). The modulated light beam then passes through a projection lens and onto a visual image display screen. The display screen may, for example, be the screen of a high definition television (HDTV).
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Polarization conversion system and stereoscopic projection system employing same
InactiveUS20120057134A1Improve image qualityProjectorsPolarising elementsIntermediate imageLight beam
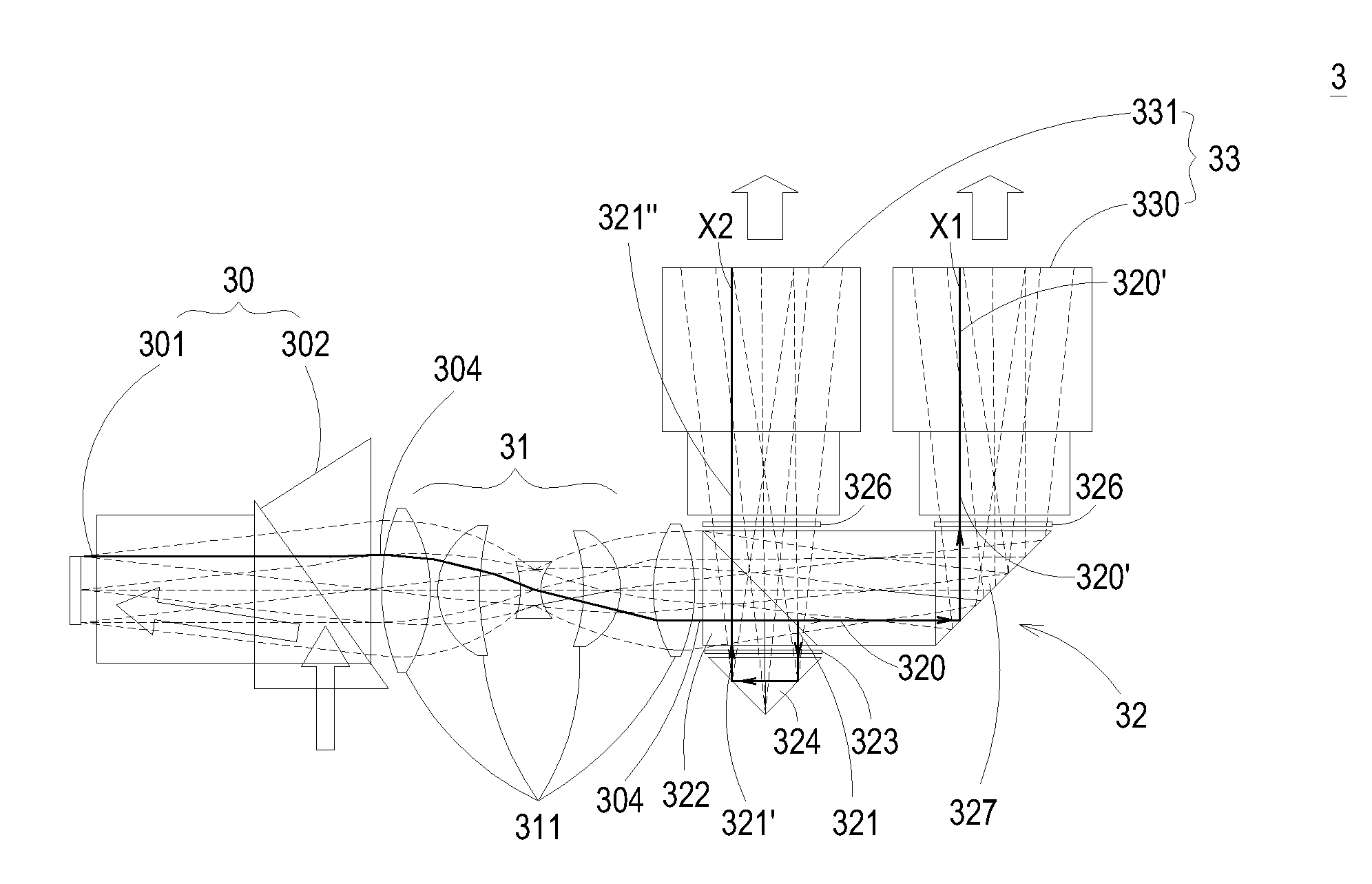
A stereoscopic projection system includes an optical engine, a relay lens group, a polarization conversion system and two identical projection lenses. The optical engine is used for outputting a non-polarized image light. The non-polarized image light is imaged into the polarization conversion system through the relay lens group to produce an intermediate image. The polarization conversion system includes a polarization beam splitter, a polarization rotating element and a polarization switch. The polarization beam splitter is used for splitting the non-polarized image light into a first-state first polarized beam and a second-state second polarized beam, which have the same total optical length. By the polarization switch, the first output polarized beam and the second output polarized beam are alternately switched between the first state and the second state. The projection lenses are located in the first optical path and the second optical path for projecting the intermediate image.
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS INC
Complete autorefractor system in an ultra-compact package
InactiveUS7001020B2Easy to useRapidly and objectively measureRefractometersSkiascopesPhotodetectorPupil
An autorefractor system in an ultra-compact package is described for rapidly and objectively measuring the refractive state of the eye. The autorefractor detector system, in conjunction with a secondary light source, uses one photodetector such as a charge coupled device (“CCD”) or one photodiode, to intercept a light beam at two distances from a secondary retinal light source created by one relay lens, one pupil emitter conjugate lens and one pupil detector conjugate lens. The signals produced by the photodetector are used to determine the full spherocylindrical refraction of the eye. A novel illumination and imaging system provides multiple capabilities to image the eye, control accommodation, and acquire and maintain optical alignment, while obtaining other measurements of the eye.
Owner:DAPHNE INSTR
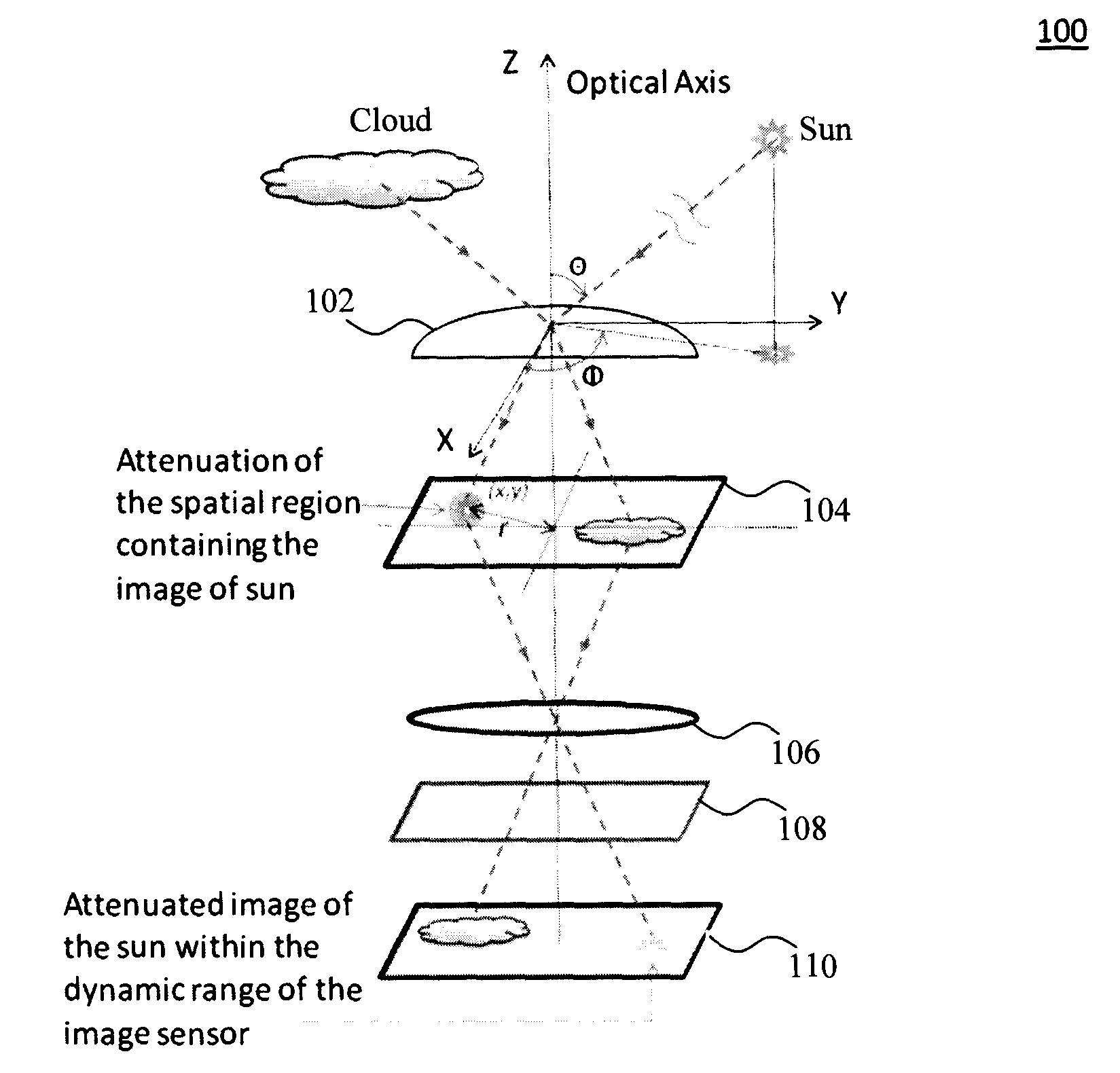
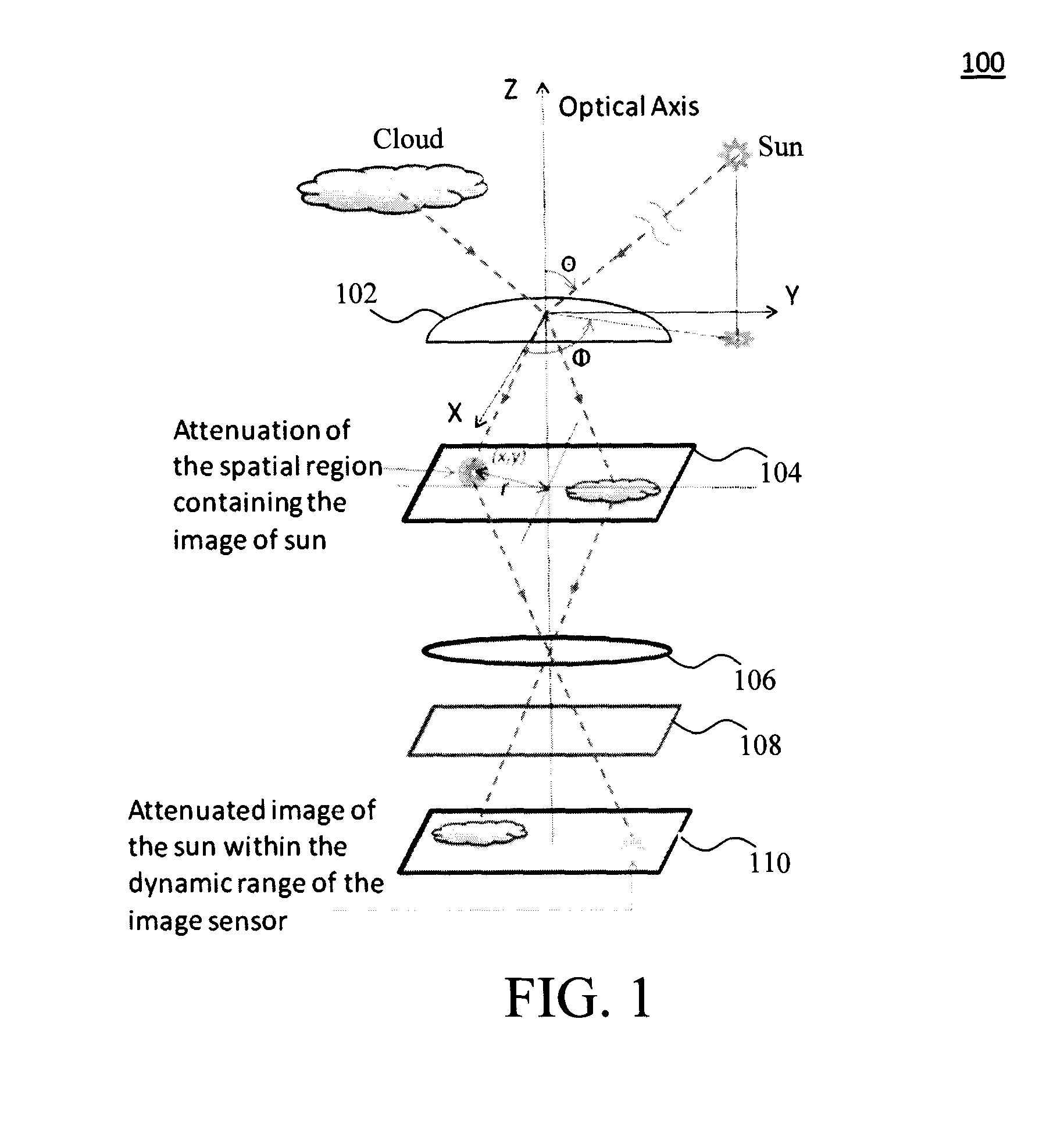
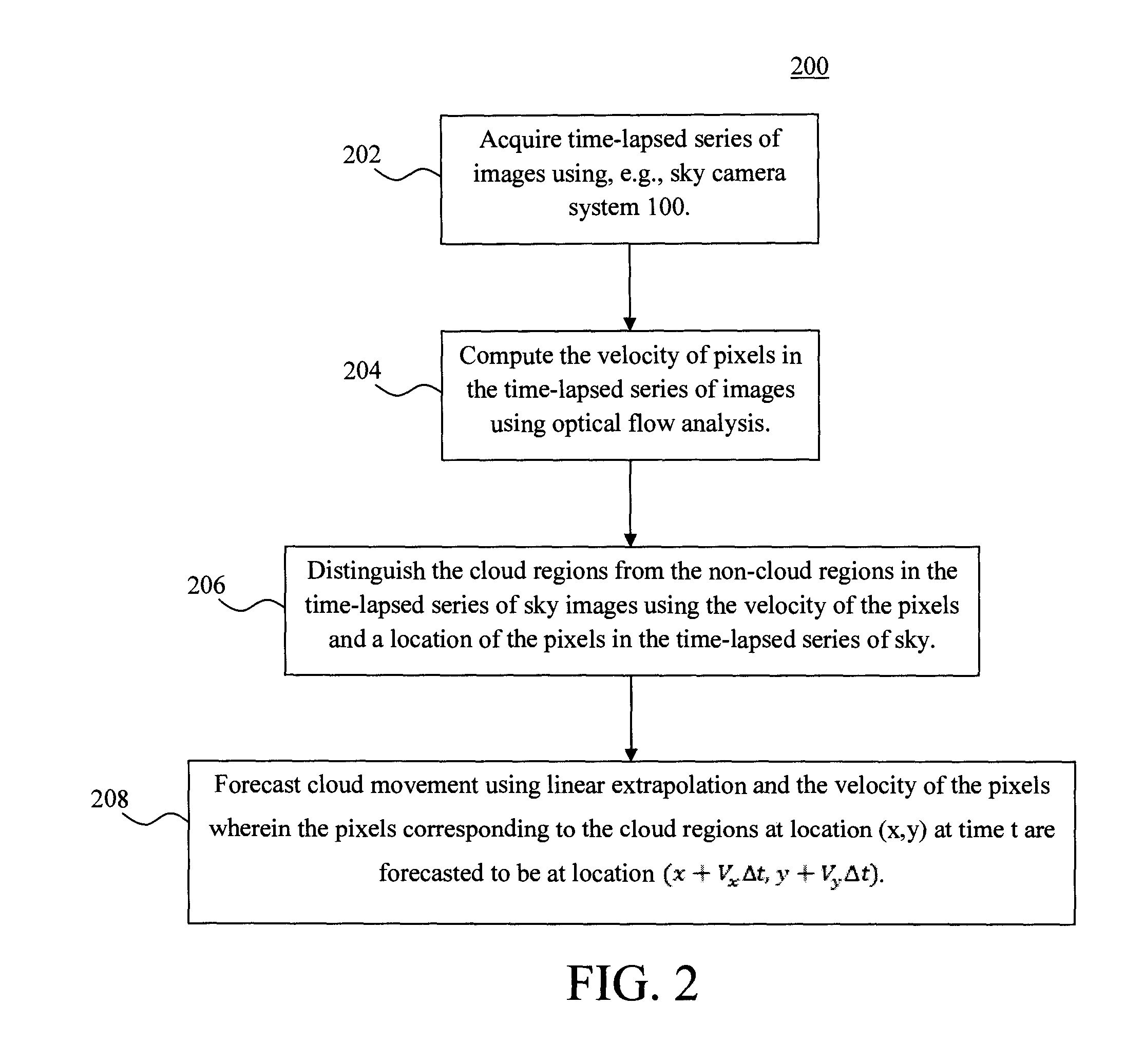
Multifunctional Sky Camera System for Total Sky Imaging and Spectral Radiance Measurement
InactiveUS20140320607A1Sunshine duration recordersImage enhancementSpatial light modulatorOptical flow
A multifunctional sky camera system and techniques for the use thereof for total sky imaging and spectral irradiance / radiance measurement are provided. In one aspect, a sky camera system is provided. The sky camera system includes an objective lens having a field of view of greater than about 170 degrees; a spatial light modulator at an image plane of the objective lens, wherein the spatial light modulator is configured to attenuate light from objects in images captured by the objective lens; a semiconductor image sensor; and one or more relay lens configured to project the images from the spatial light modulator to the semiconductor image sensor. Techniques for use of the one or more of the sky camera systems for optical flow based cloud tracking and three-dimensional cloud analysis are also provided.
Owner:IBM CORP
Camera module test platform
The invention discloses a camera module test platform which comprises a base, a first bracket, a close shot target, a stain test board, a relay lens and a second bracket, wherein the base is provided with a sliding shaft parallel to the surface of the base; the first bracket is arranged in a sliding manner along the axial direction of the sliding shaft; the close shot target, the stain test board and the relay lens are arranged on the first bracket; the second bracket is arranged on the base, and a long shot target is arranged on the second bracket; and the distance between the long shot target and the surface of the base is greater than the distance between the relay lens and the surface of the base. In a process of testing a camera module by use of the camera module test platform, the long shot focusing test, close shot focusing test and stain and vignetting test on the camera module can be finished simply by horizontally switching the close shot target, the stain test board and the relay lens. The camera module test environment has good consistency, and the reliability of the camera module test result is improved.
Owner:TRULY OPTO ELECTRONICS
Electron beam apparatus
ActiveUS20050253066A1Increase brightnessExtended service lifeMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationElectric discharge tubesImaging processingHigh flux
An electron beam apparatus is provided for evaluating a sample at a high throughput and a high S / N ratio. As an electron beam emitted from an electron gun is irradiated to a sample placed on an X-Y-θ stage through an electrostatic lens, an objective lens and the like, secondary electrons or reflected electrons are emitted from the sample. The primary electron beam is incident at an incident angle set at approximately 35° or more by controlling a deflector. Electrons emitted from the sample is guided in the vertical direction, and focused on a detector. The detector is made up of an MCP, a fluorescent plate, a relay lens, and a TDI (or CCD). An electric signal from the TDI is supplied to a personal computer for image processing to generate a two-dimensional image of the sample.
Owner:EBARA CORP
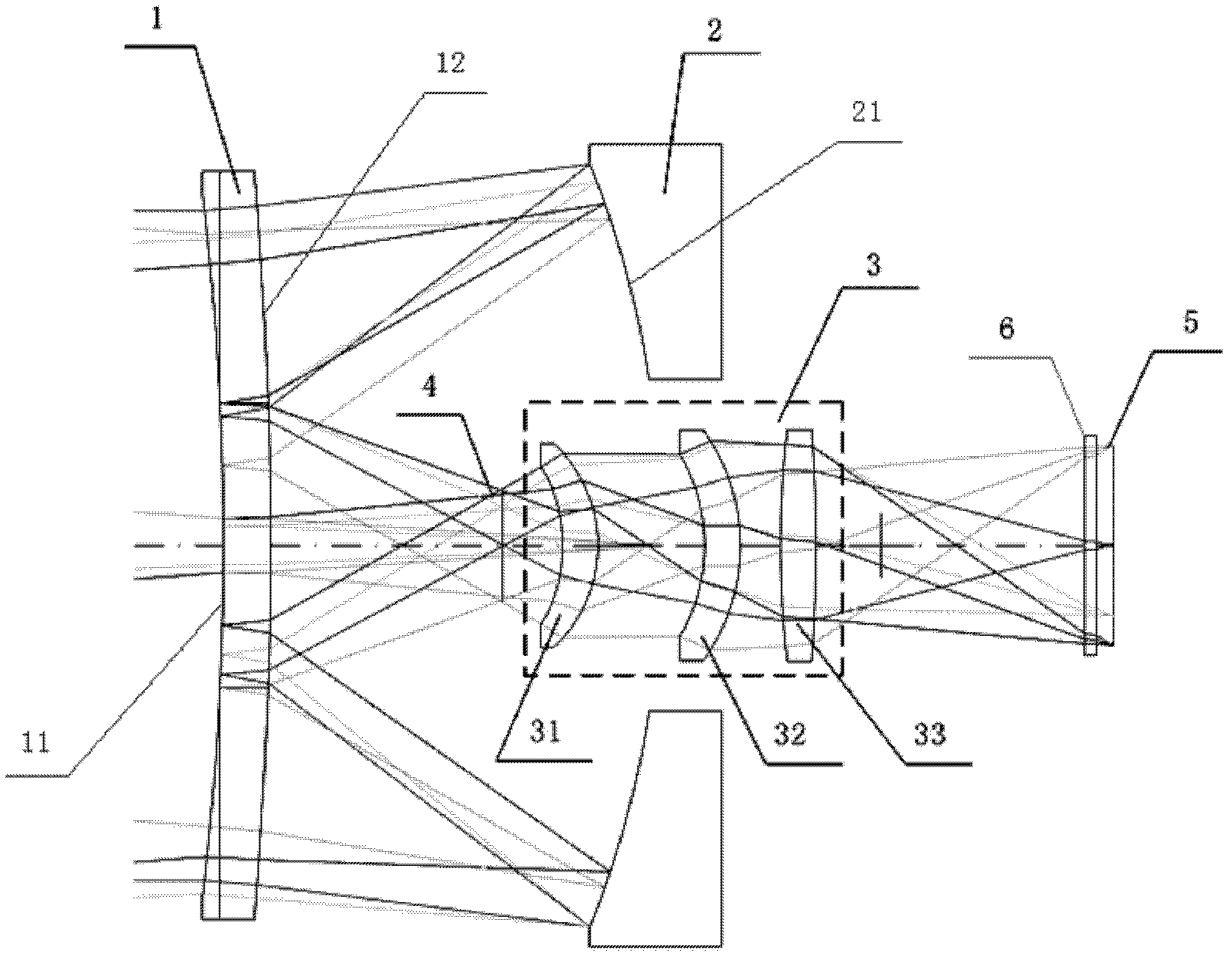
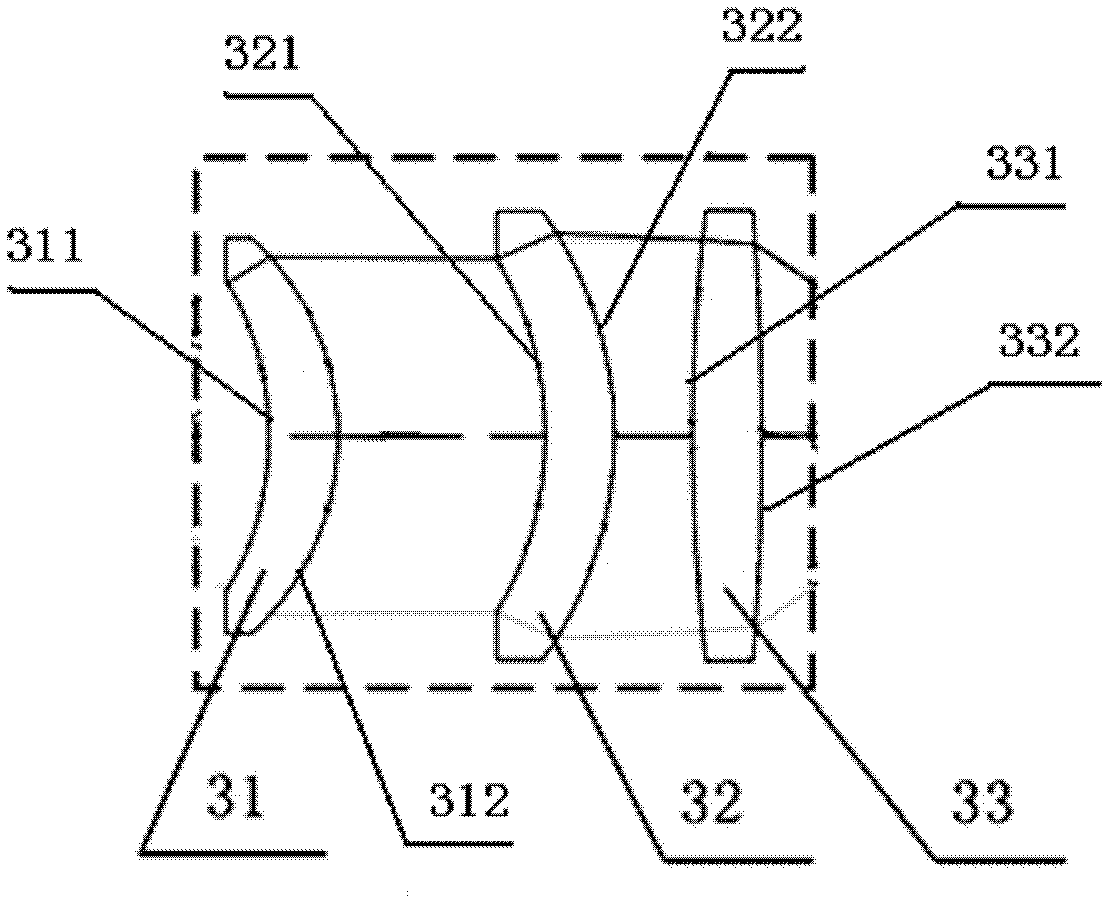
Projection optical system improving light utilization rate and projection brightness
The invention belongs to the field of design projection equipment optical systems, particularly relates to a projection optical system improving a light utilization rate and projection brightness, andaims to solve the problem of low light utilization rate and complex system structure which exist in the prior art. Polarized light P emitted by a laser source passes through a convergent mirror and is transmitted by a polarized beam splitter prism, polarized light P transmitted by the polarized beam splitter prism passes through a color wheel, an integral square rod and a relay lens group in sequence and is incident to a DMD, emergent light in a projection direction of the DMD is emergent through a project lens, emergent light in a non-projection direction of the DMD passes through a reflex lens group to obtain polarized light S, and polarized light S reflected by the polarized beam splitter prism and the polarized light P transmitted by the polarized beam splitter prism are coaxially incident to the color wheel; and the reflex lens group includes a total reflector A, a relay lens group B, a total reflector B and a 1 / 2 wave plate; and the emergent light in the non-projection directionof the DMD is sequentially reflected by the total reflector A and refracted by the relay lens group B and 1 / 2 wave plate to obtain polarized light S.
Owner:BEIJING GUOWANG OPTICAL TECH CO LTD
Optical display device and projection-type display device
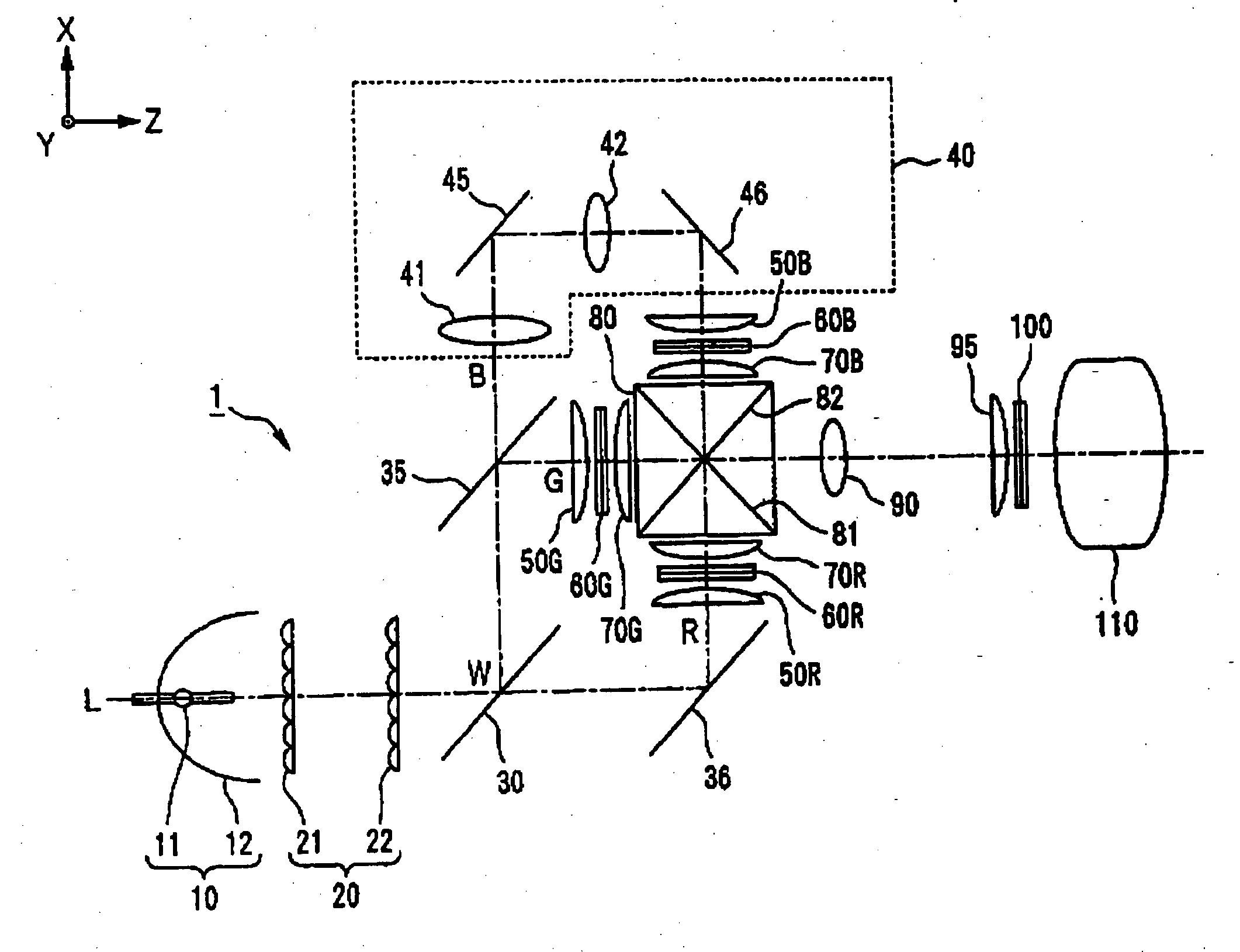
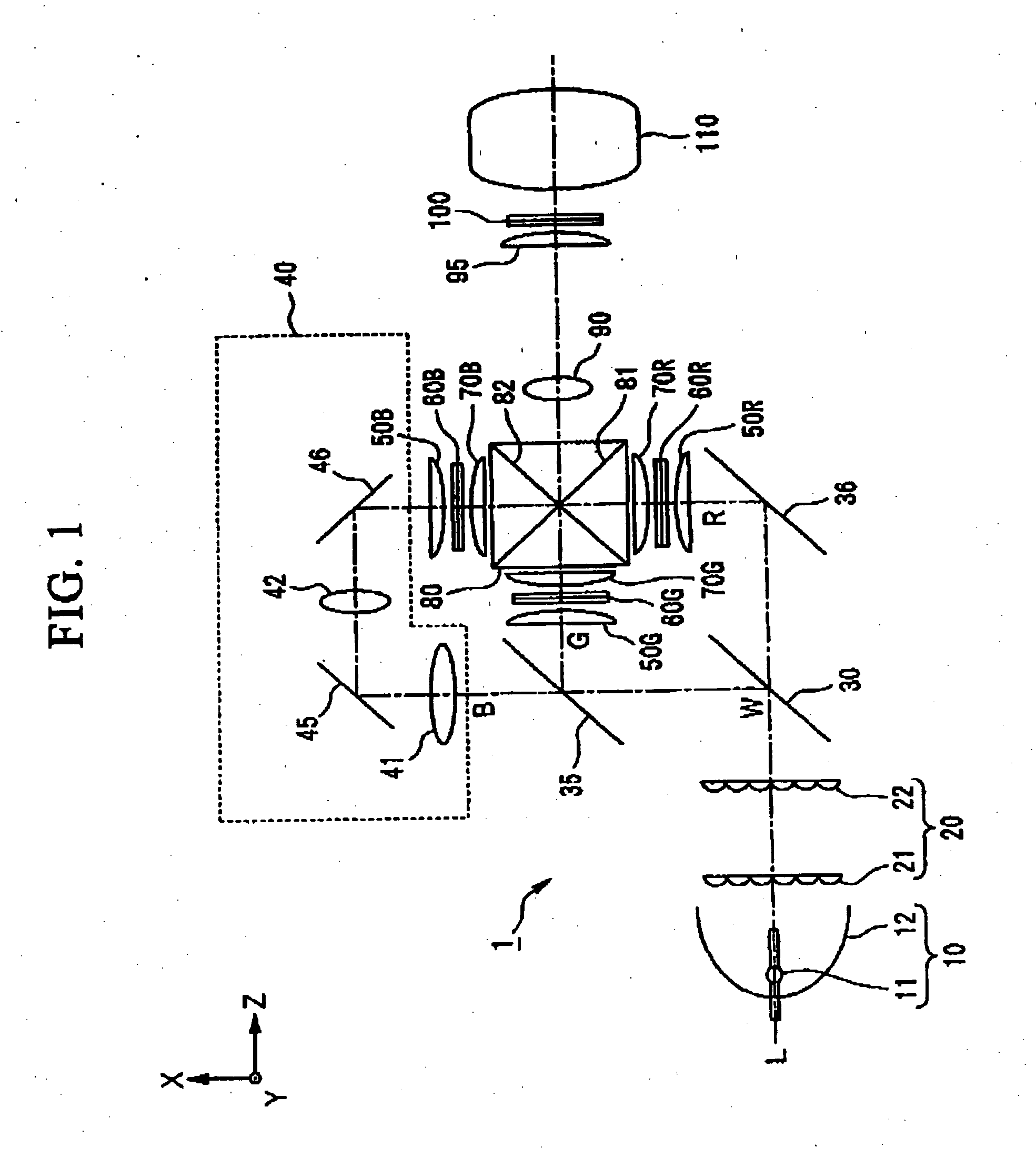
InactiveUS20050174495A1Improve accuracyHigh numberTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsIntegratorDichroic prism
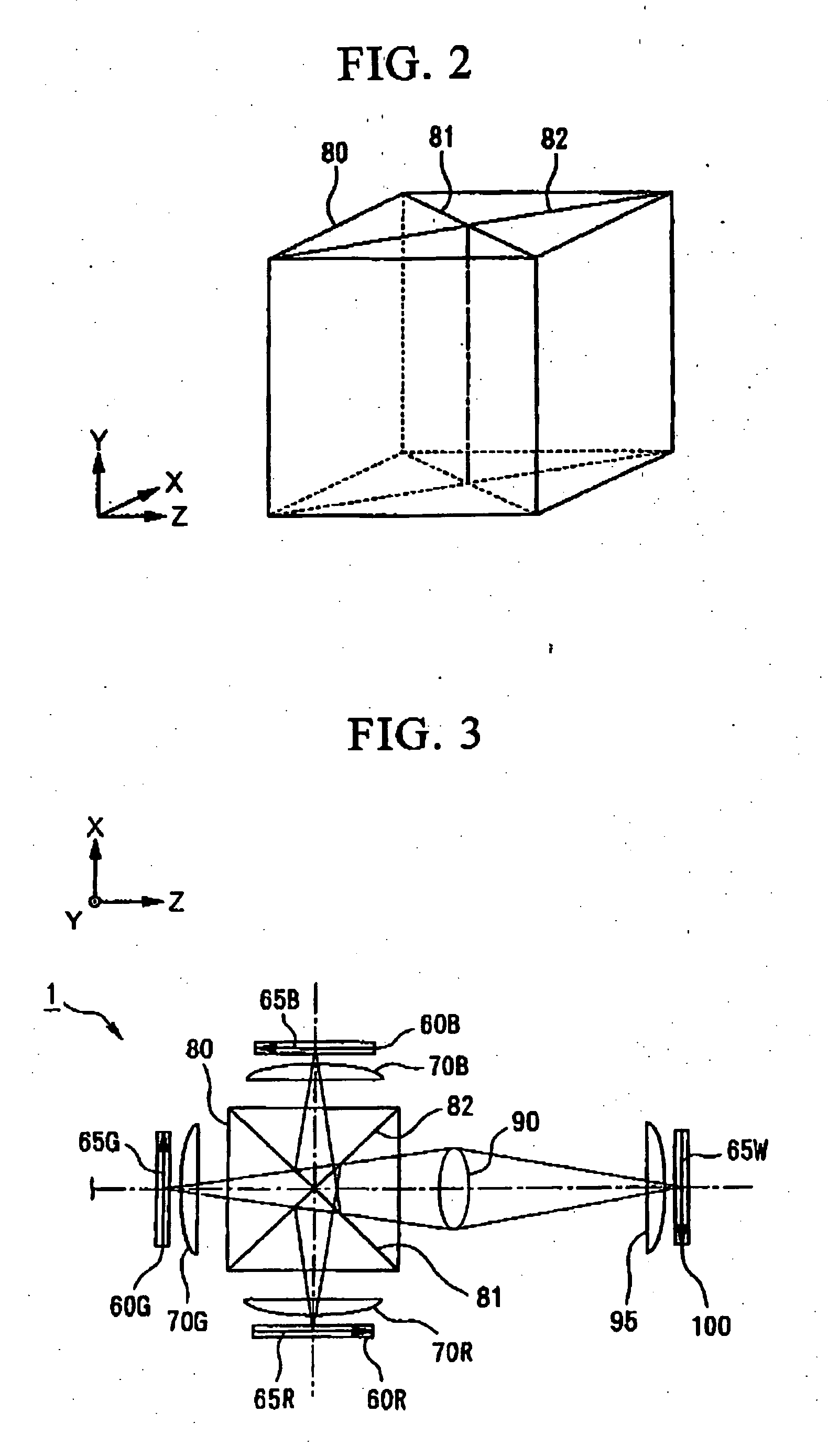
A projection-type display device 1 including a light source 10, an optical integrator 20, dichroic mirrors 30 and 35, a reflecting mirror 36, a relay optical system 40, parallelizing lenses 50B, 50G and 50R, liquid crystal light valves 60B, 60G and 60R, incident side lenses 70B, 70G and 70R, a light-synthesizing cross dichroic prism 80, a relay lens 90, an emergent side lens 95, a liquid crystal light valve 100 and a projection lens 110, and liquid crystal light valve 100 is provided in the rear stage of liquid crystal light valves 60B, 60G and 60R.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Compact catadioptric long-wave infrared athermal imaging optical system
InactiveCN102520506AAchieve long focal length imagingCompact structureOptical elementsMangin mirrorLight beam
The invention relates to a compact catadioptric long-wave infrared athermal imaging optical system, which comprises a secondary lens, a primary reflective lens and a relay lens. The secondary lens is a catadioptric optical component with negative focal power and comprises an annular light transmission part and a central Mangin mirror; a light beam from an object is transmitted into the primary reflective lens through the annular light transmission part of the secondary lens and is then transmitted into the Mangin mirror of the secondary lens after reflection by the primary reflective lens, and catadioptric focusing is carried out by the Mangin mirror so that the target is imaged on a first image plane; the target on the first image plane is then transferred by the relay lens and focuses again on a second image plane; and the second image plane is overlapped with the focal plane of an image receiver. Image of long focal length can be realized, and the system has a compact structure and a large view field and can be applied in the optical imaging field of aviation and aerospace.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Image-displaying apparatus
InactiveUS20060044795A1Reduce uneven illuminanceBrighter illuminationColor television detailsMountingsPrismLight-emitting diode
An image-displaying apparatus comprising a light-emitting diode, a relay lens, a secondary light source-forming prism arranged between the light-emitting lens and the relay lens, and a light valve, said secondary light source-forming prism having opposed first and second opposed rectangular planes and at least four polygonal planes, said first and second rectangular planes being positioned on sides of the light-emitting diode and the light valve, respectively, and an area of the first rectangular plane being greater than that of the second rectangular plane, wherein a light emitted from the light-emitting diode is illuminated upon the light valve through the relay lens and the secondary light source-forming prism.
Owner:RICOH KK
Complete autorefractor system in an ultra-compact package
InactiveUS20050110951A1Easy to useRapidly and objectively measureDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsPhotovoltaic detectorsPhotodetector
An autorefractor system in an ultra-compact package is described for rapidly and objectively measuring the refractive state of the eye. The autorefractor detector system, in conjunction with a secondary light source, uses one photodetector such as a charge coupled device (“CCD”) or one photodiode, to intercept a light beam at two distances from a secondary retinal light source created by one relay lens, one pupil emitter conjugate lens and one pupil detector conjugate lens, as well as a field lens. The signals produced by the photodetector are used to determine the full spherocylindrical refraction of the eye. A novel illumination and imaging system provides multiple capabilities to image the eye, control accommodation, and acquire and maintain optical alignment, while obtaining other measurements of the eye.
Owner:DAPHNE INSTR
Diopter-adjustable optical system for helmet display
ActiveCN103995355AReduce complexitySimple structureMountingsMagnifying glassesFar-sightednessDisplay device
The invention provides a diopter-adjustable optical system for a helmet display. The diopter-adjustable optical system comprises a glasses-shaped lens and a relay lens set. The glasses-shaped lens is arranged before the human eyes, and the relay lens set is arranged between a micro-display and the inner surface of the glasses-shaped lens. Image light rays sent by the micro-display of the helmet display are transmitted to the inner surface of the glasses-shaped lens by the relay lens set, and then the glasses-shaped lens is used for reflecting the light rays to the human eyes. The relay lens set is used for imaging an image of the micro-display to the position between the glasses-shaped lens and the relay lens set, and the glasses-shaped lens is used for magnifying the real image into a virtual image before the human eyes. The distance between the virtual image and the human eyes is changed according to the vision level of a user through zooming of the relay lens set, and therefore people with the normal eyes, the myopic eyes and the hypermetropic eyes can clearly see the image of the micro-display. Imaging and zooming of the relay lens set can be achieved by adopting six lenses, the complex degree of the relay lens set is reduced, and the structure is simplified.
Owner:BEIJING NEDPLUSAR DISPLAY TECH CO LTD
Light emitting diode projector
ActiveUS20120099308A1Simple materialImprove stabilityNon-electric lightingPoint-like light sourceLight-emitting diodeSolid angle
The invention relates to a light emitting diode (LED) light source comprising an LED die, or a closely packed die array or matrix of die arrays, substantially and efficiently coupled to non-imaging collection optics. The non-imaging collection optics operate to provide a homogenized LED output having a near field whose intensity is highly uniform and a reduced far field extent substantially preserving the étendue (area, solid angle, index squared product) of the LED output. The near field, in turn, is imaged by a downstream relay lens to an illumination plane a specific distance away.
Owner:BRUKILACCHIO THOMAS J
Structured light lighting optical system
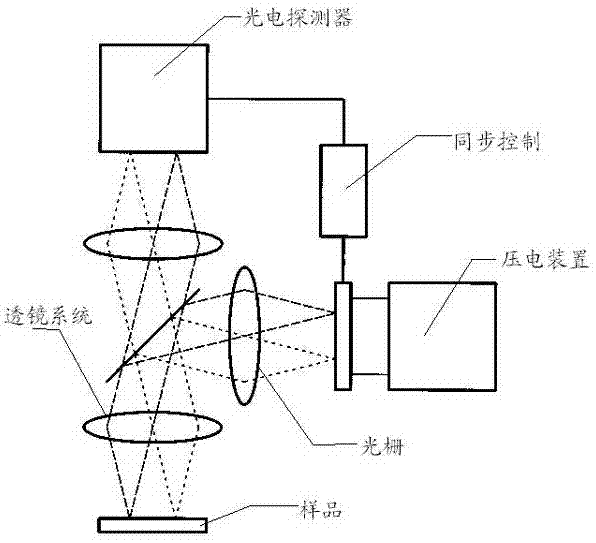
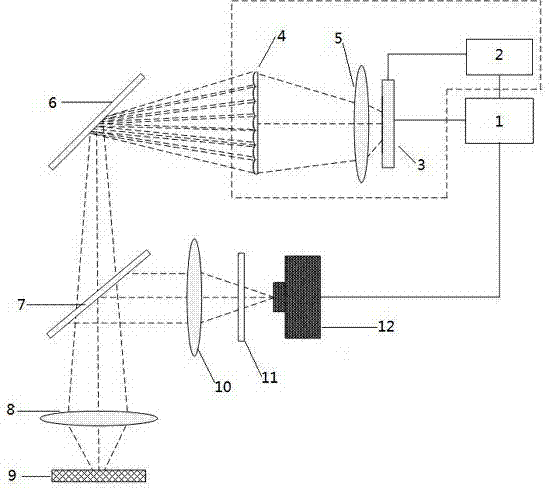
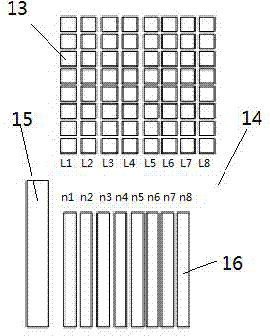
ActiveCN103792654ASuitable for real-time 3D imaging researchReduce volumeMicroscopesSpatial light modulatorGrating
The invention discloses a structured light lighting optical system. The structured light lighting optical system comprises a computer, a synchronous control system, an ultra-high brightness LED excitation light source, a relay lens set, a fly-eye lens array, a middle image plane, a dichroscope, a projection objective, an objective table, a tube mirror, a spike filter and a photoelectric detector. A multi-chip structure of the ultra-high brightness LED excitation light source is controlled by the adoption of the computer to obtain initial strip light, the number of strips is multiplied through the relay lens set and the fly-eye lens array, and the light is imaged on the lighting objective table through the projection objective according to a certain magnification to form structured light lighting. Structured light lighting is achieved by adopting the mode of electrical control over LED chips, the disadvantages, of being high in cost, large in size and low in strip phase shifting speed, caused by the adoption of an optical grating and a spatial light modulator are abandoned, and the structured light lighting optical system can be applied to a rapid real-time three-dimensional imaging research on living body biological cells.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF BIOMEDICAL ENG & TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
High-resolution optical field microimaging system and method based on sub-pixel translation
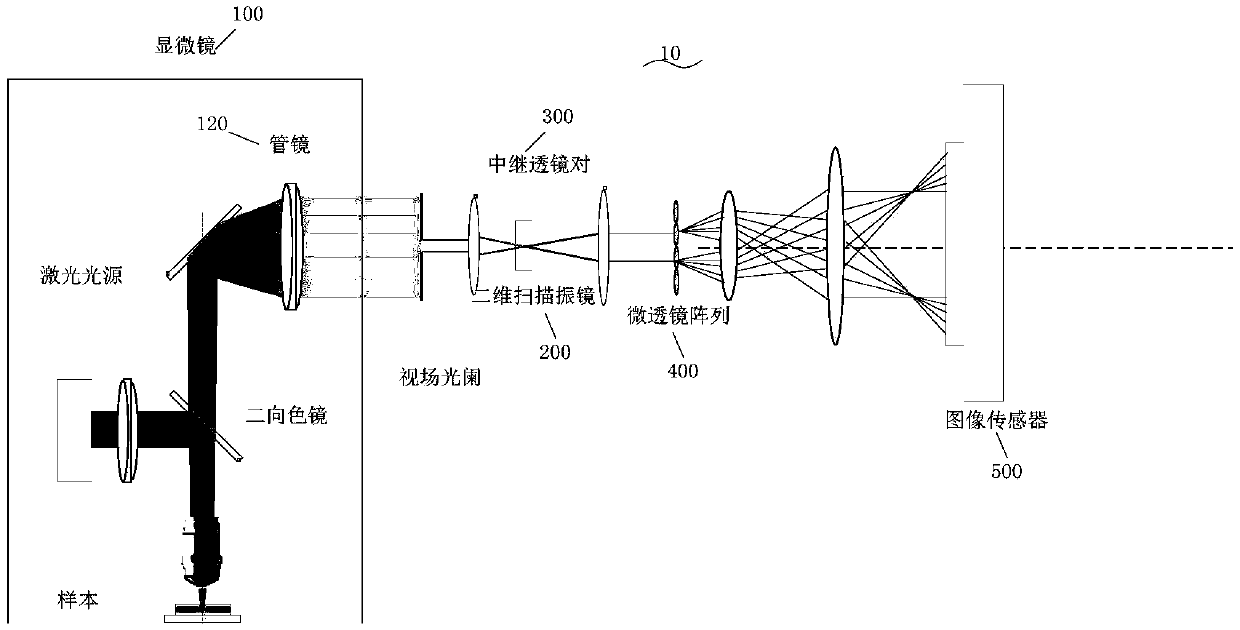
InactiveCN109541791AImprove spatial resolutionQuick observationMicroscopesSteroscopic systemsLight beamGalvanometer
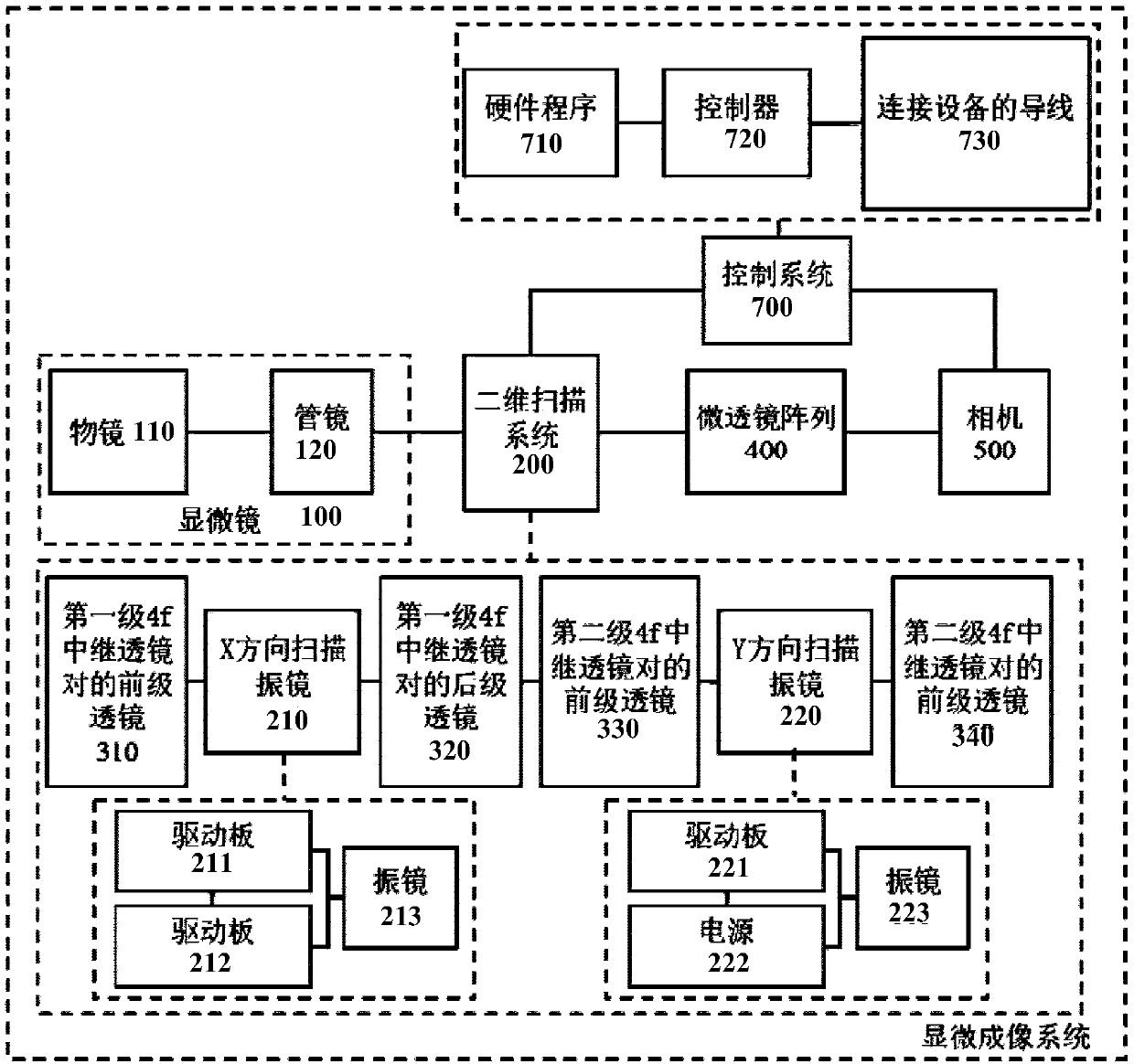
The invention discloses a high-resolution optical field microimaging system and method based on sub-pixel translation. The system comprises a microscope, a two-dimensional scanning galvanometer, a relay lens pair, a microlens array, an image sensor and a reconstruction module; the microscope is used for simplifying a target sample and imaging on a first image plane of the microscope; the two-dimensional scanning galvanometer is used for rotating an optical path angle in a frequency domain plane, and translating a first image plane in the sub-pixel; the relay lens pair is used for amplifying orshrinking the first image plane; the microlens array is used for modulating the beam with the preset angle to a target space location on a rear focal plane of the microlens array and obtaining multiple modulation images; the image sensor is used for recording multiple modulation images; and a reconstruction module for acquiring multiple modulation images recorded by the image sensor, and reconstructing a three-dimensional structure of the target sample through multiple modulation images. The system has the advantages of being simple in structure, low in cost, fast, and suitable for the livingcell observation.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Optical scanning device and image forming apparatus
An optical scanning device includes a light source, a deflector, and an image-forming optical system. The deflector includes a deflecting surface for deflecting light beams in a main scanning direction. The image-forming optical system includes two relay lenses having a positive power in the main scanning direction. The relay lenses cause main light beams of light beams emitted from the light source to cross near the deflecting surface in the main scanning direction.
Owner:RICOH KK
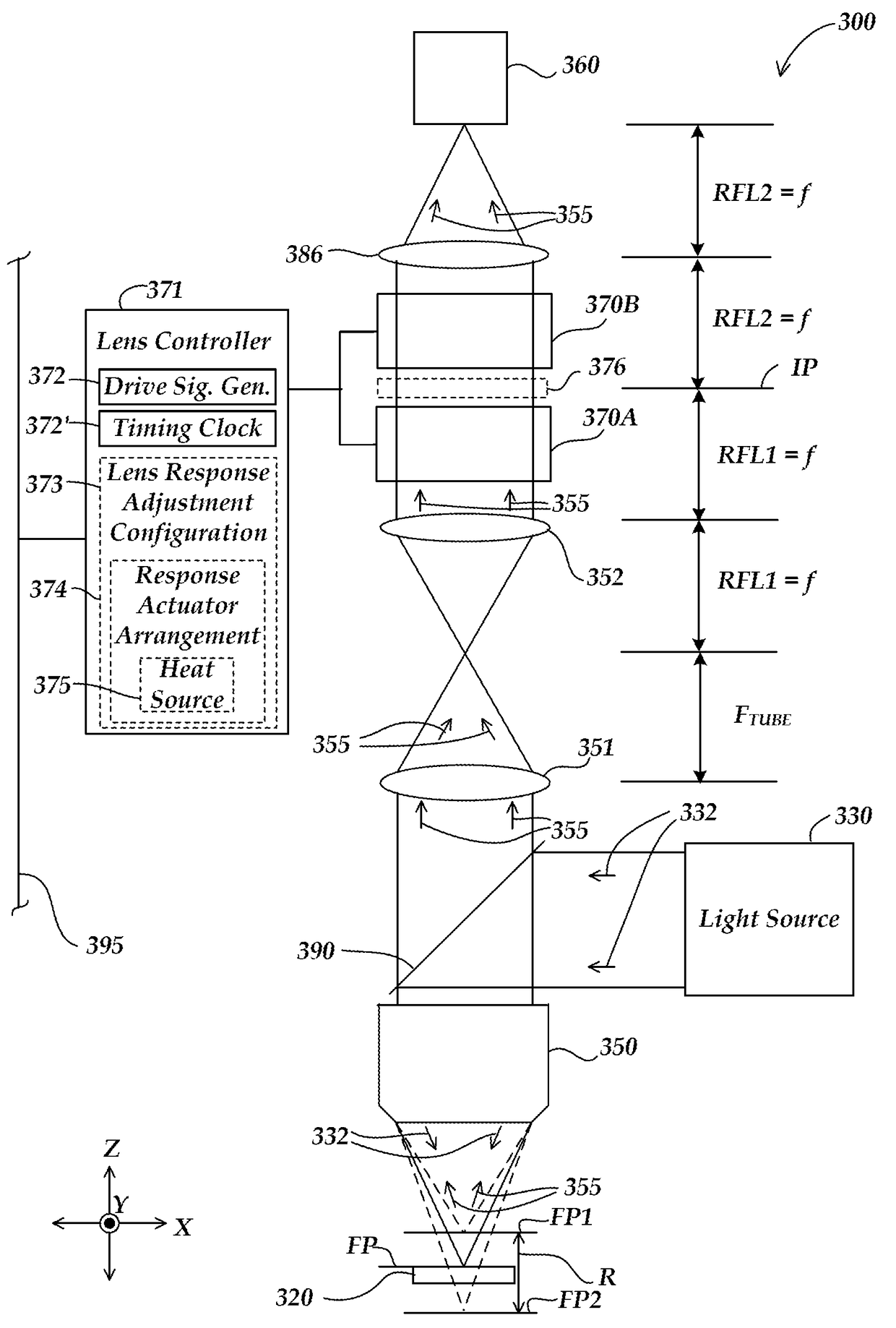
Variable focal length imaging system
A variable focal length (VFL) imaging system comprises a camera system, a first high speed variable focal length (VFL) lens, a second high speed variable focal length (VFL) lens, a first relay lens comprising a first relay focal length, a second relay lens comprising a second relay focal length, and a lens controller. The first relay lens and the second relay lens are spaced relative to one another along an optical axis of the VFL imaging system by a distance which is equal to a sum of the first relay focal length and the second relay focal length. The first high speed VFL lens and the second high speed VFL lens are spaced relative to one another along the optical axis on opposite sides of an intermediate plane which is located at a distance equal to the first relay focal length from the first relay lens. The lens controller is configured to provide synchronized periodic modulation of the optical power of the first high speed VFL lens and the optical power of the second high speed VFL lens.
Owner:MITUTOYO CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com