Patents
Literature
290 results about "Dichroic prism" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
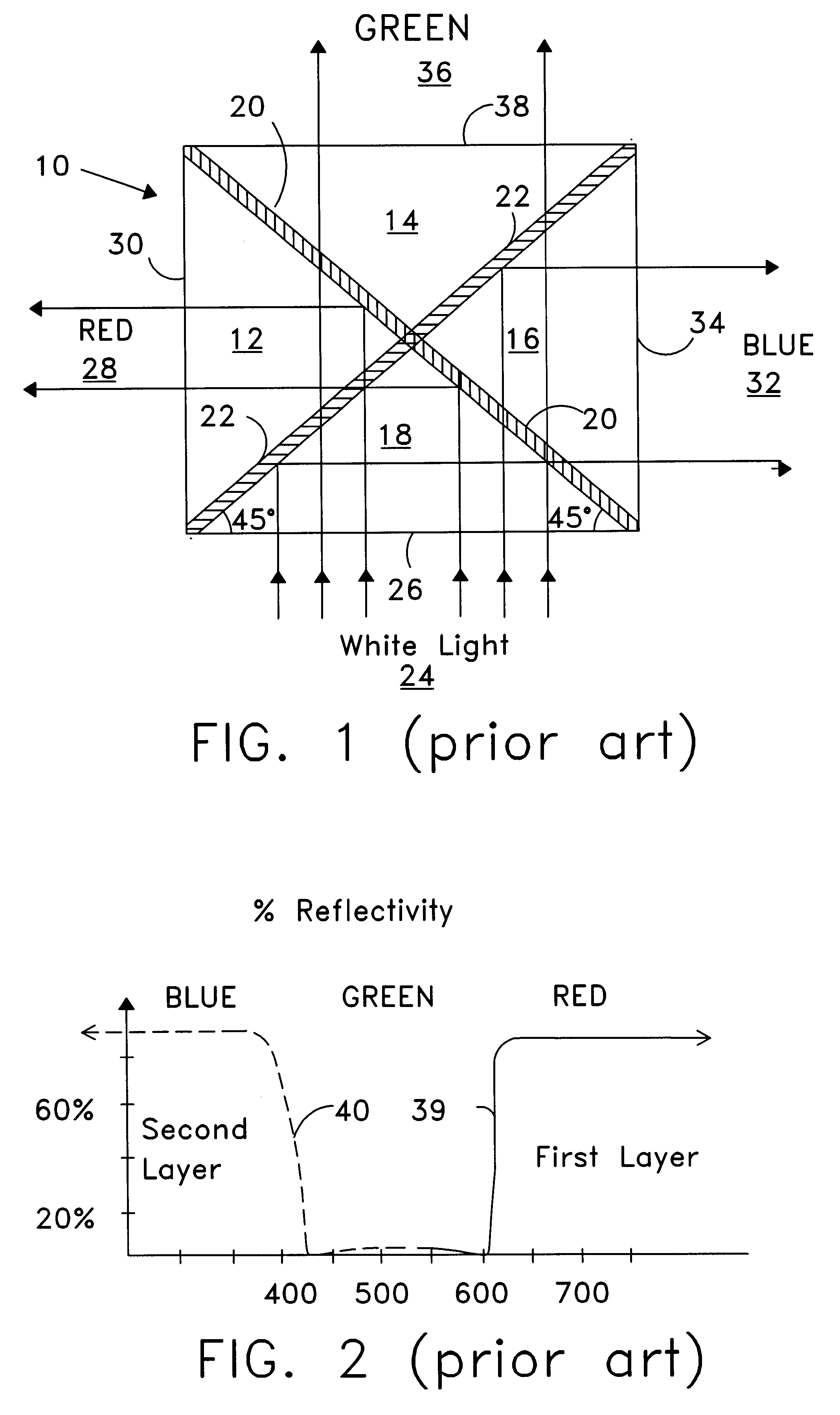
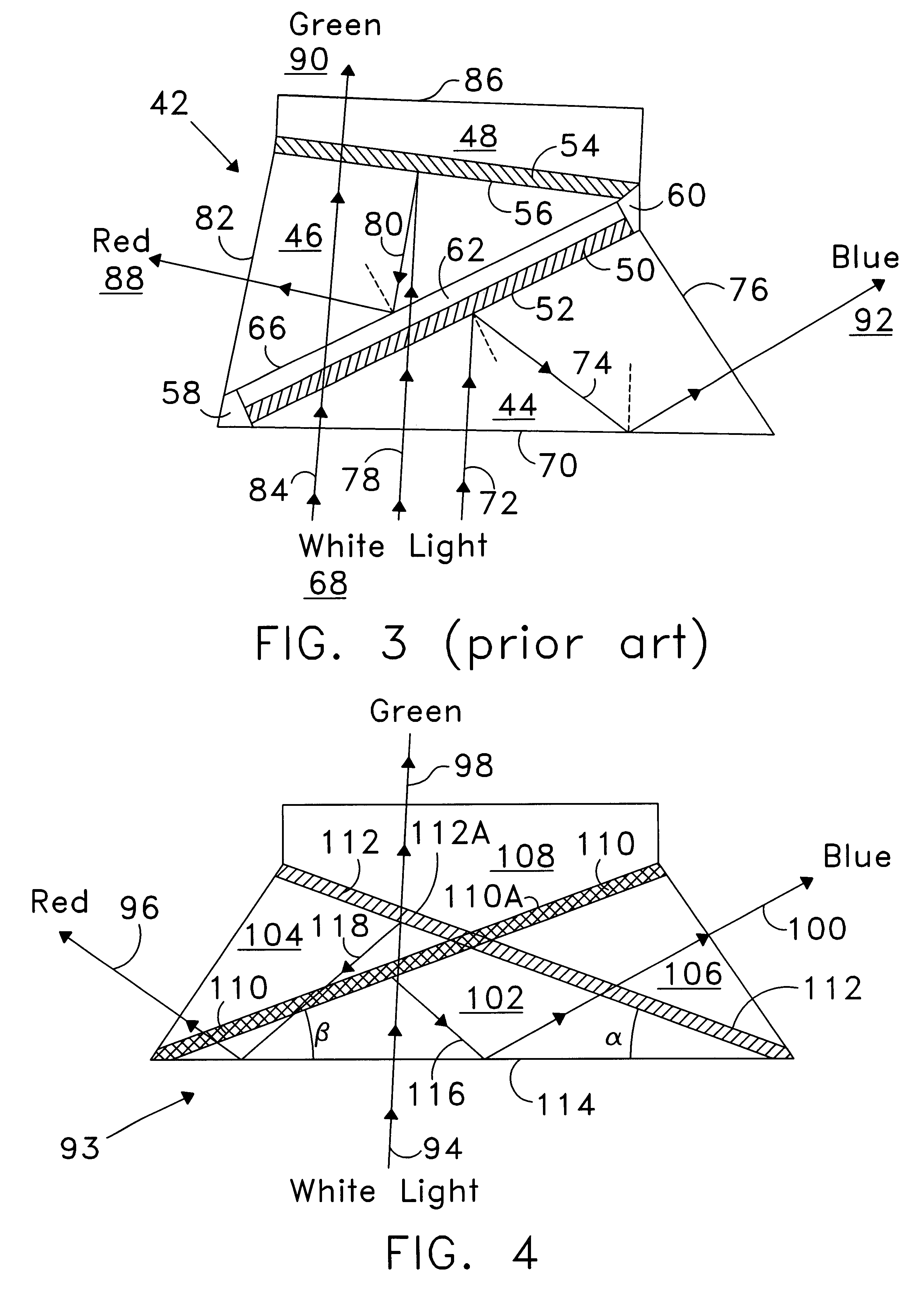
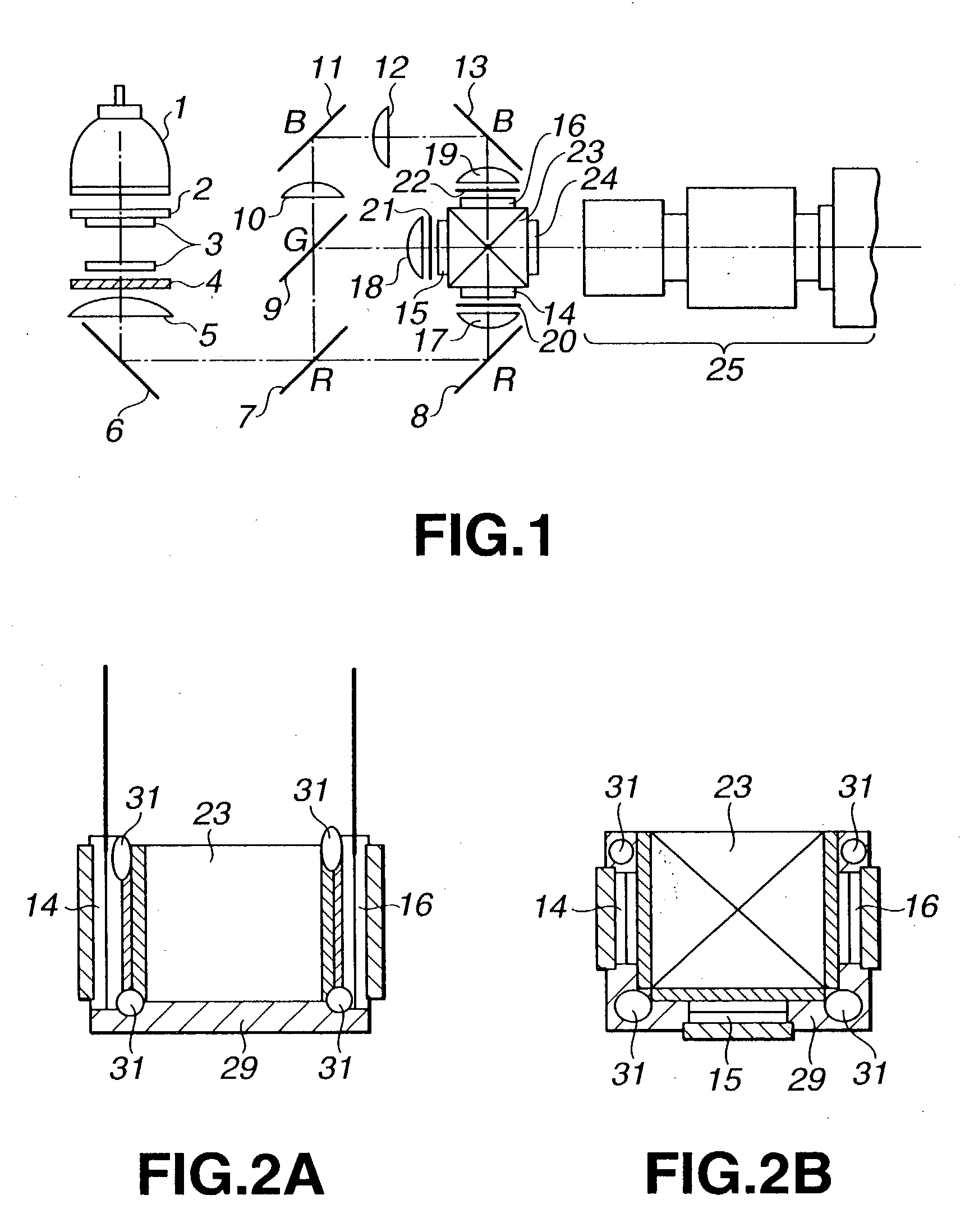
A dichroic prism is a prism that splits light into two beams of differing wavelength (colour). A trichroic prism assembly combines two dichroic prisms to split an image into 3 colours, typically as red, green and blue of the RGB colour model. They are usually constructed of one or more glass prisms with dichroic optical coatings that selectively reflect or transmit light depending on the light's wavelength. That is, certain surfaces within the prism act as dichroic filters. These are used as beam splitters in many optical instruments. (See: Dichroism, for the etymology of the term.)
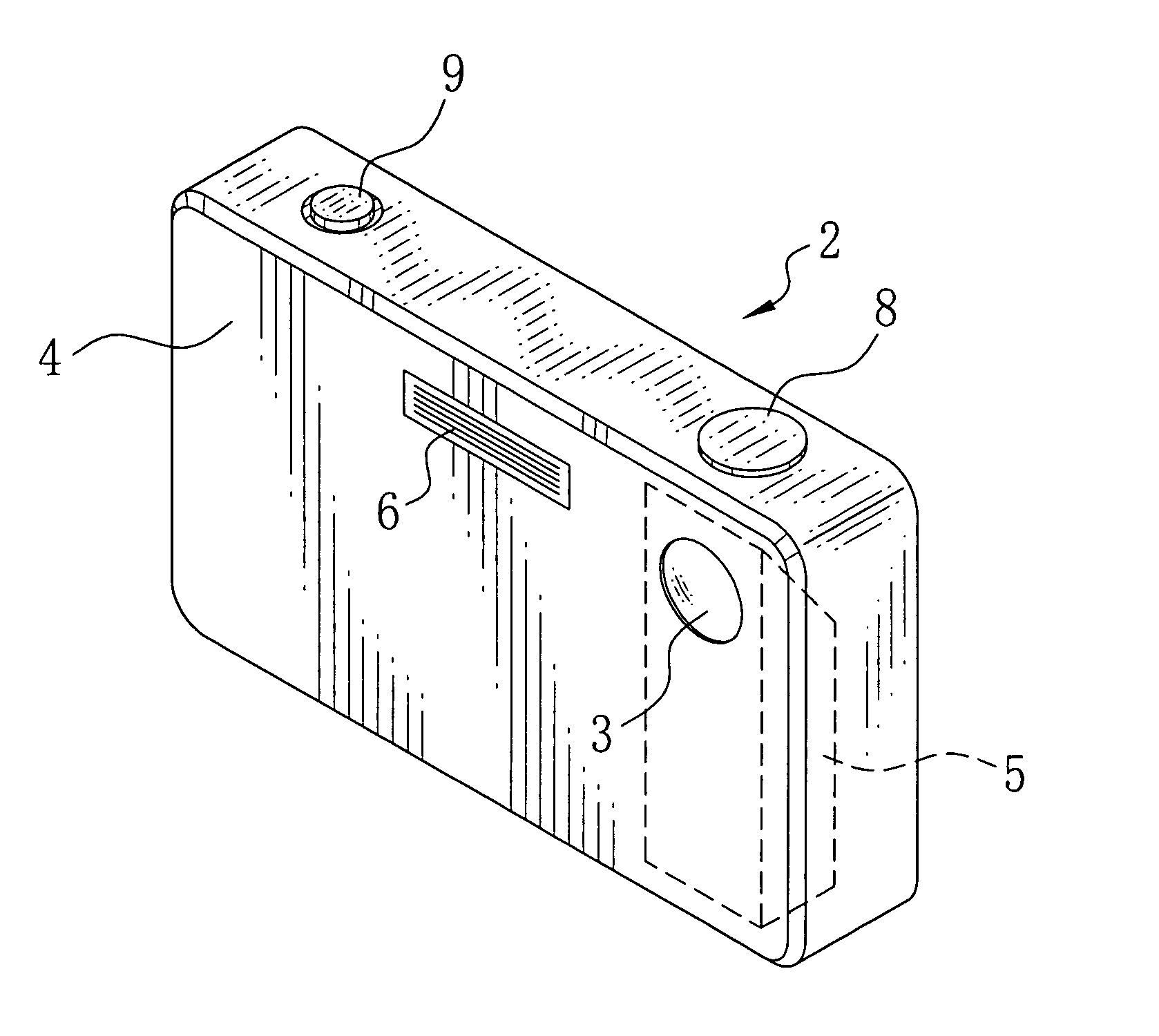
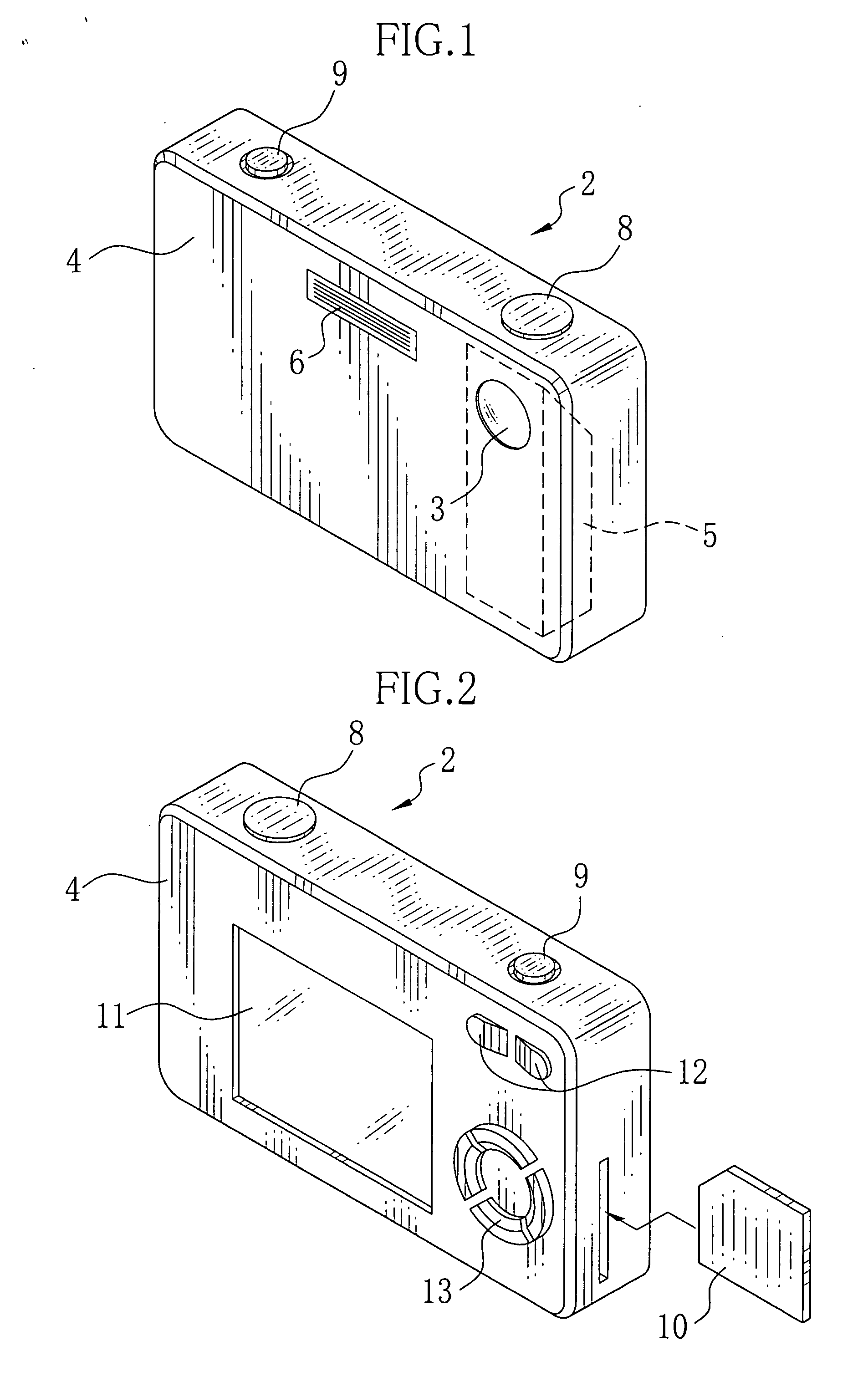
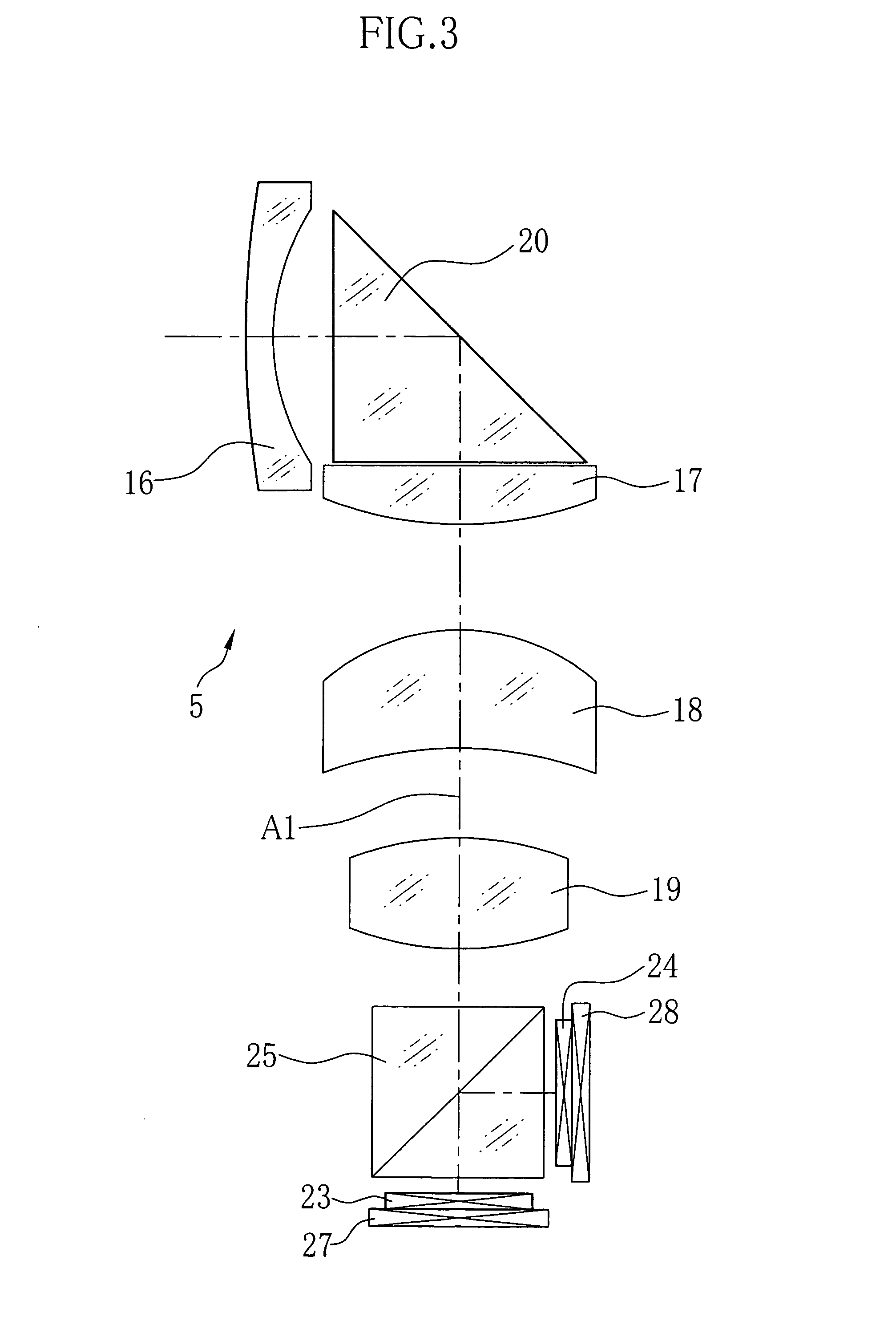
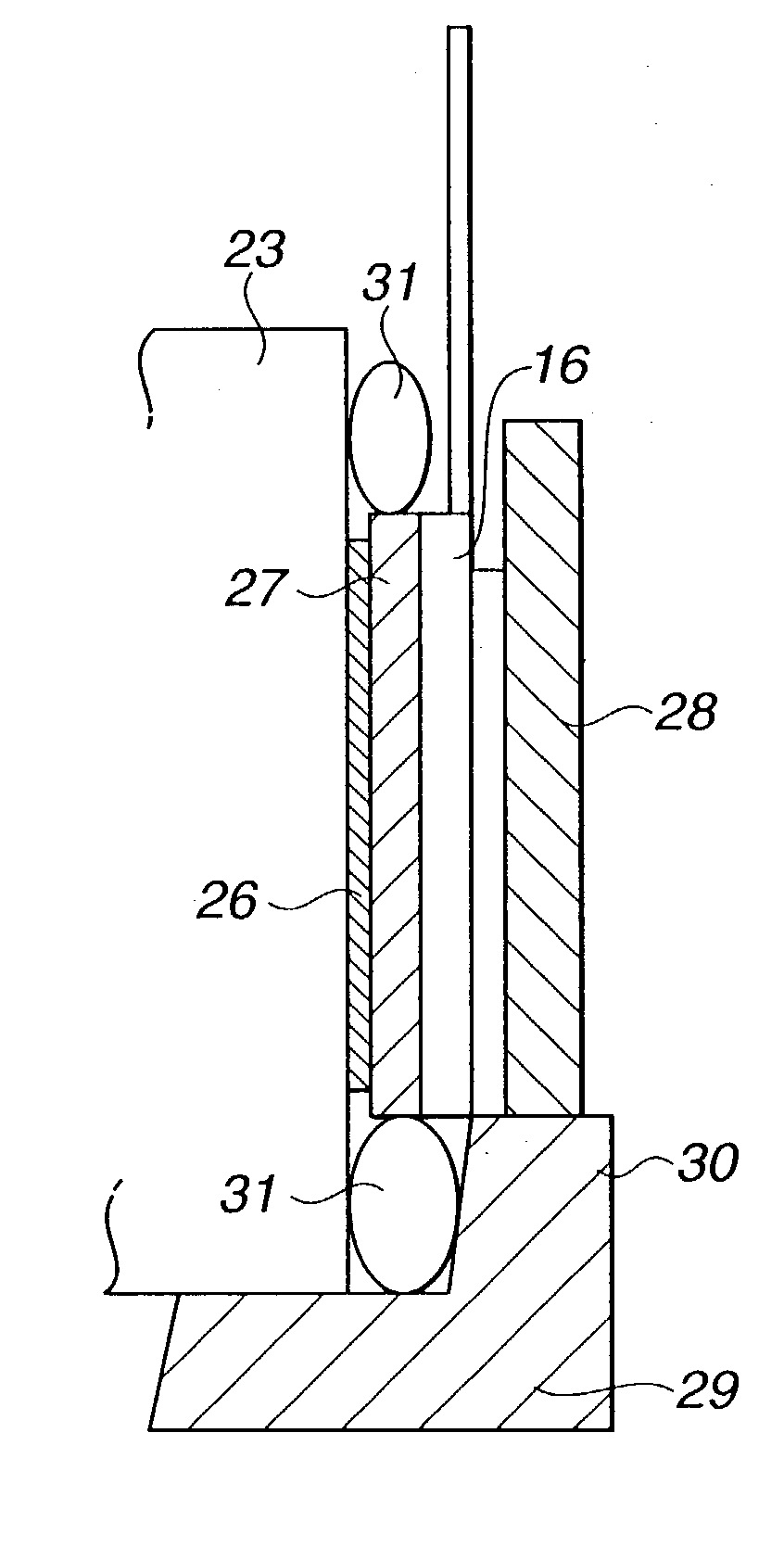
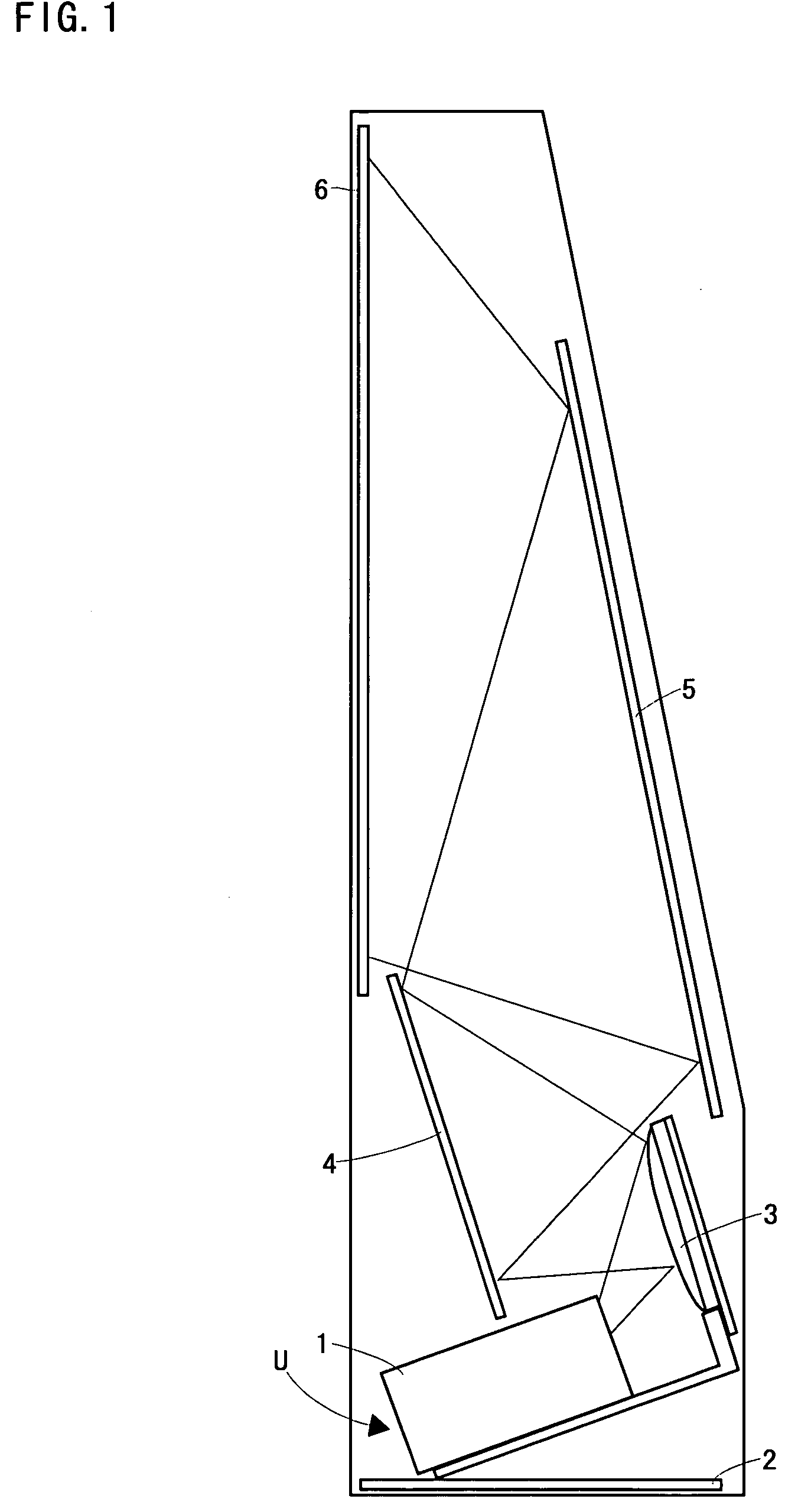
2-dimensional image display device, illumination light source and exposure illumination device
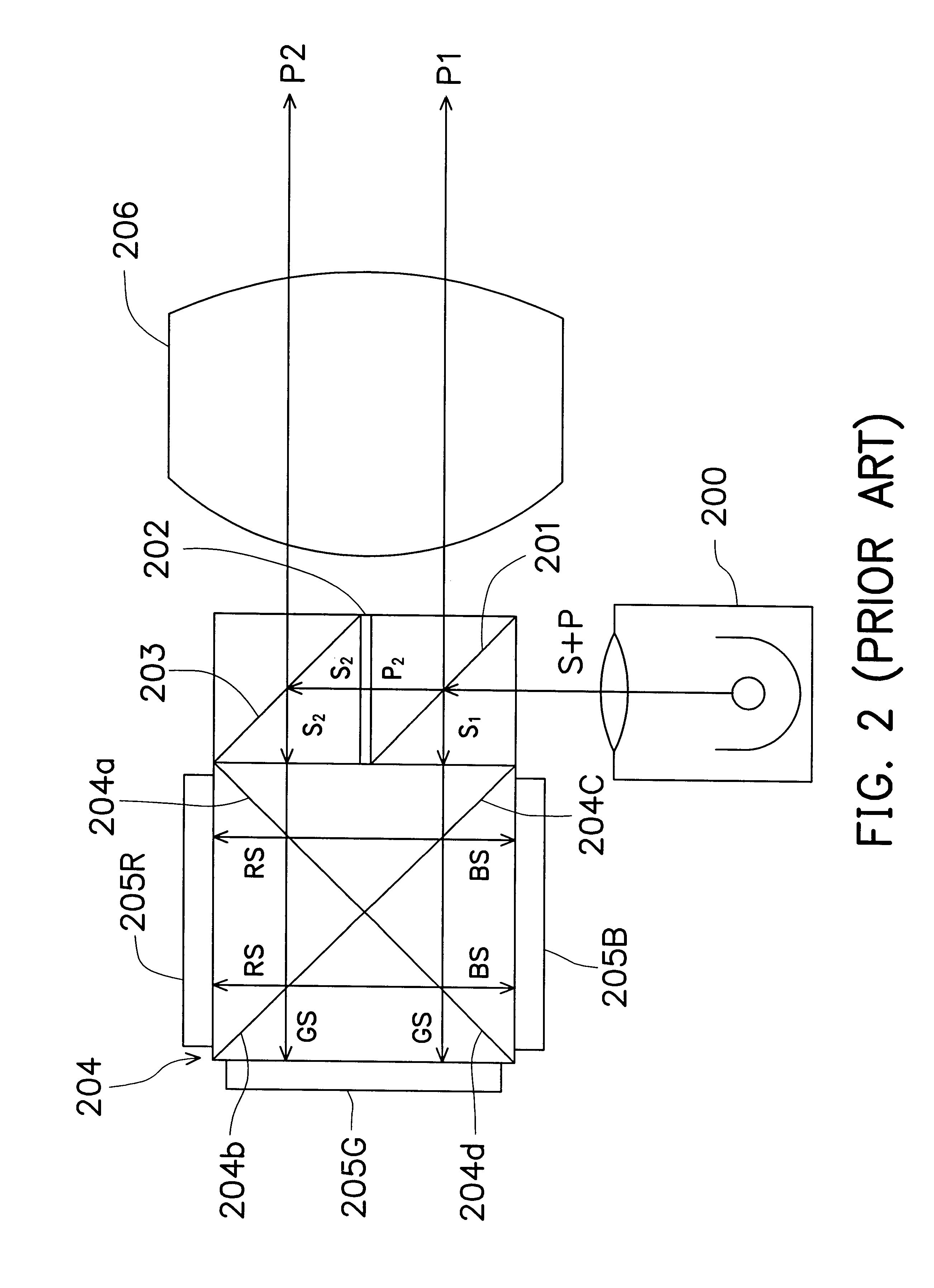
ActiveUS20100020291A1Suppress speckle noiseUniform lightProjectorsColor photographyColor imageDichroic prism
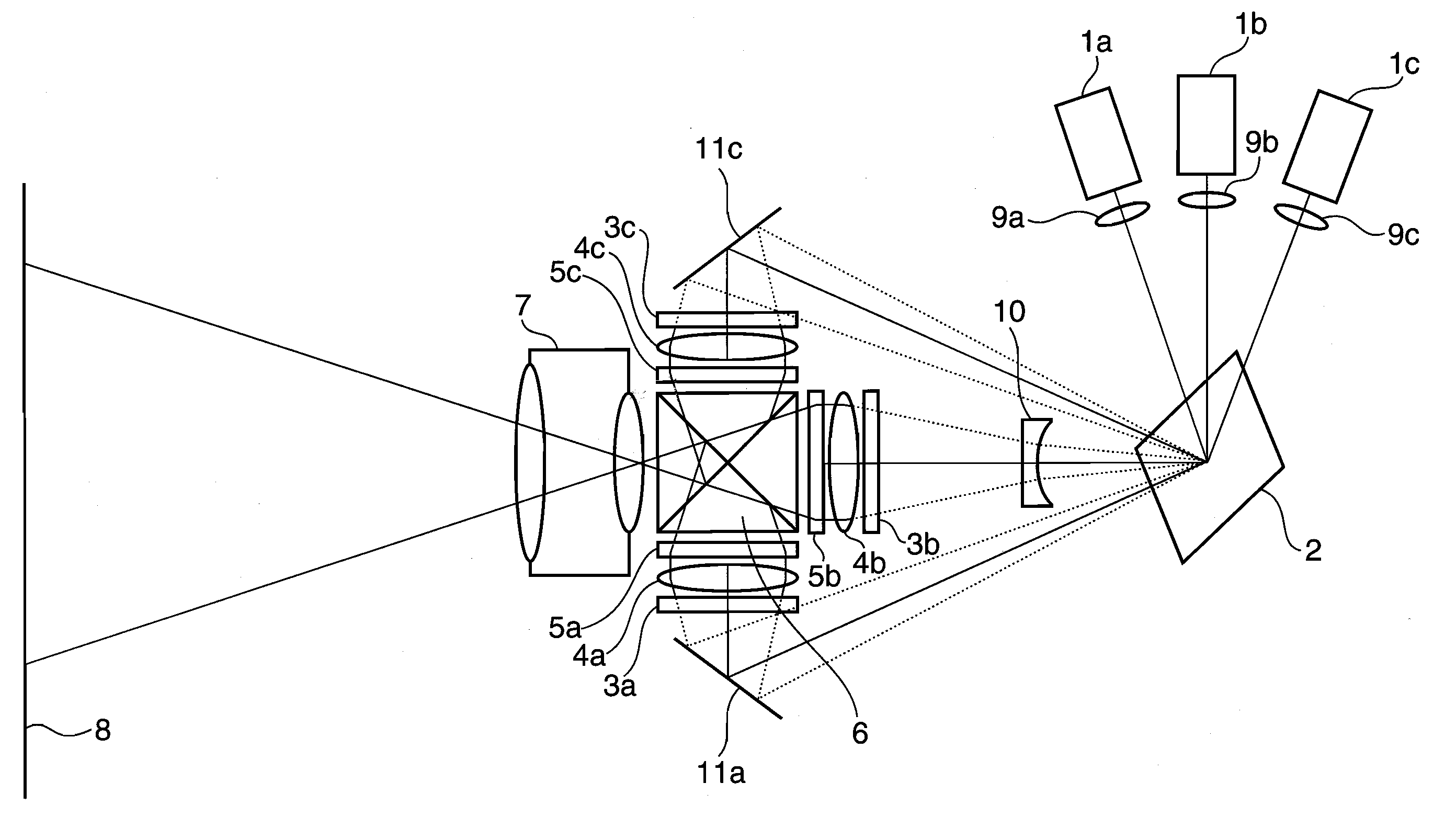
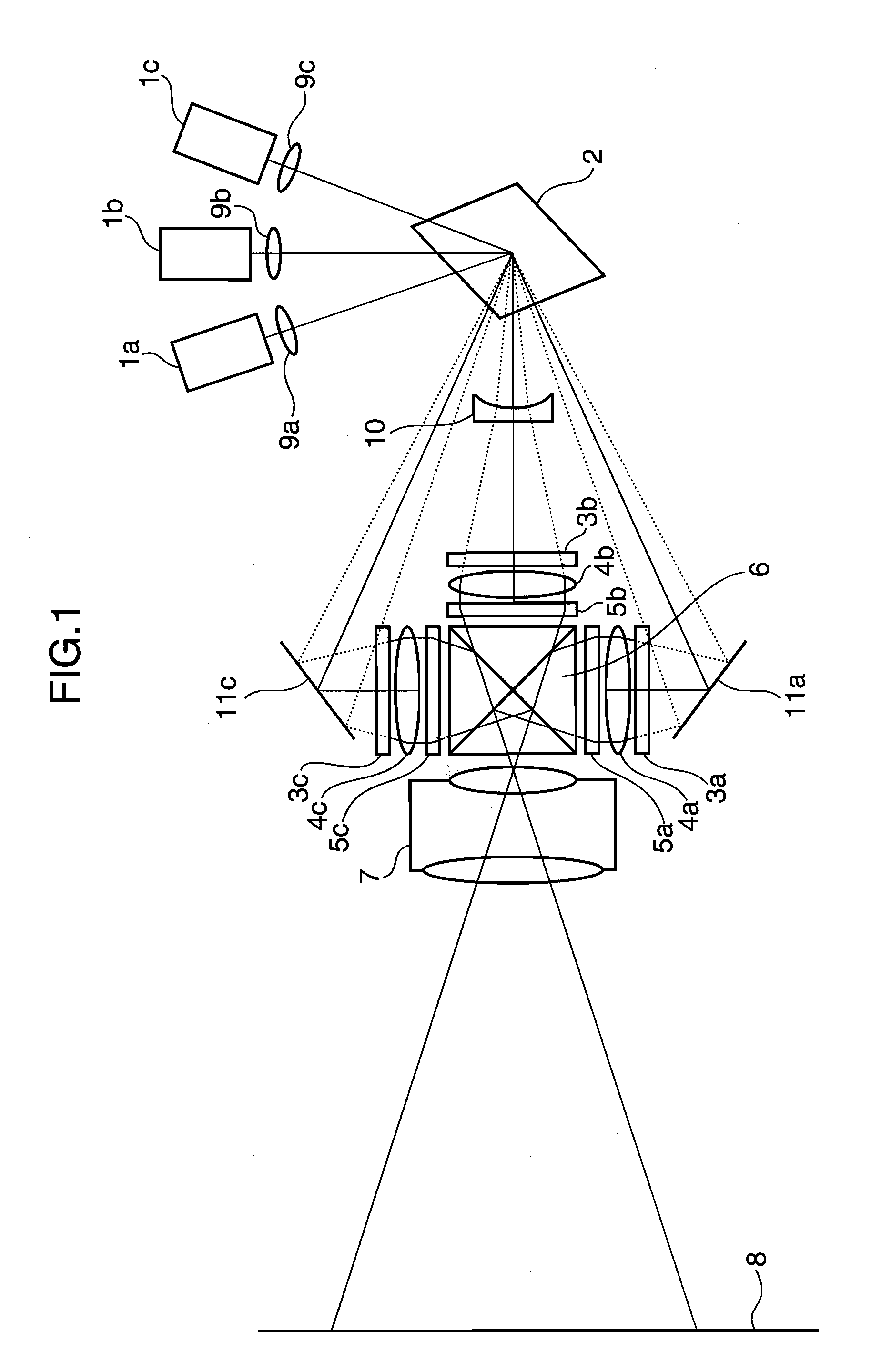
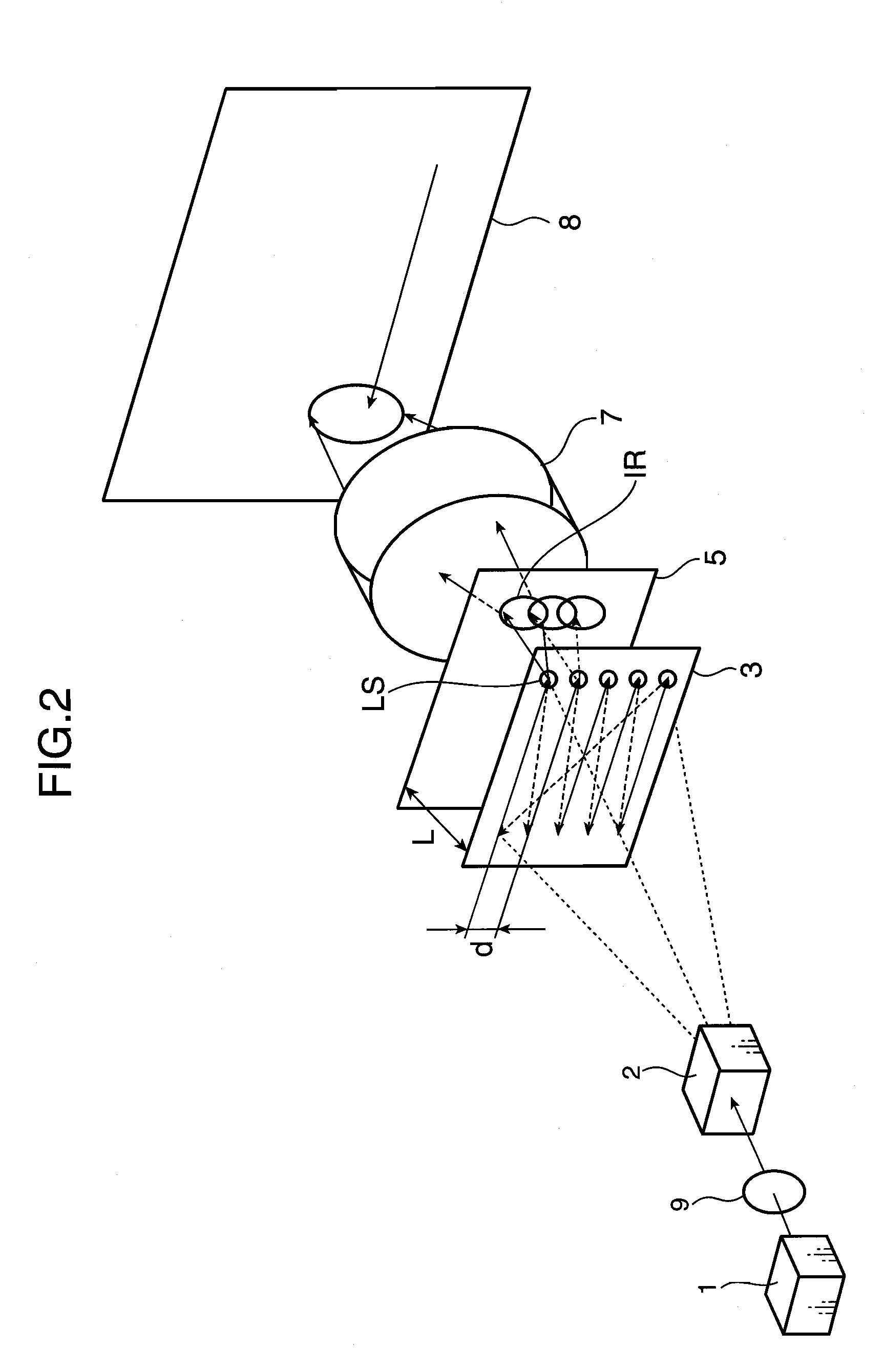
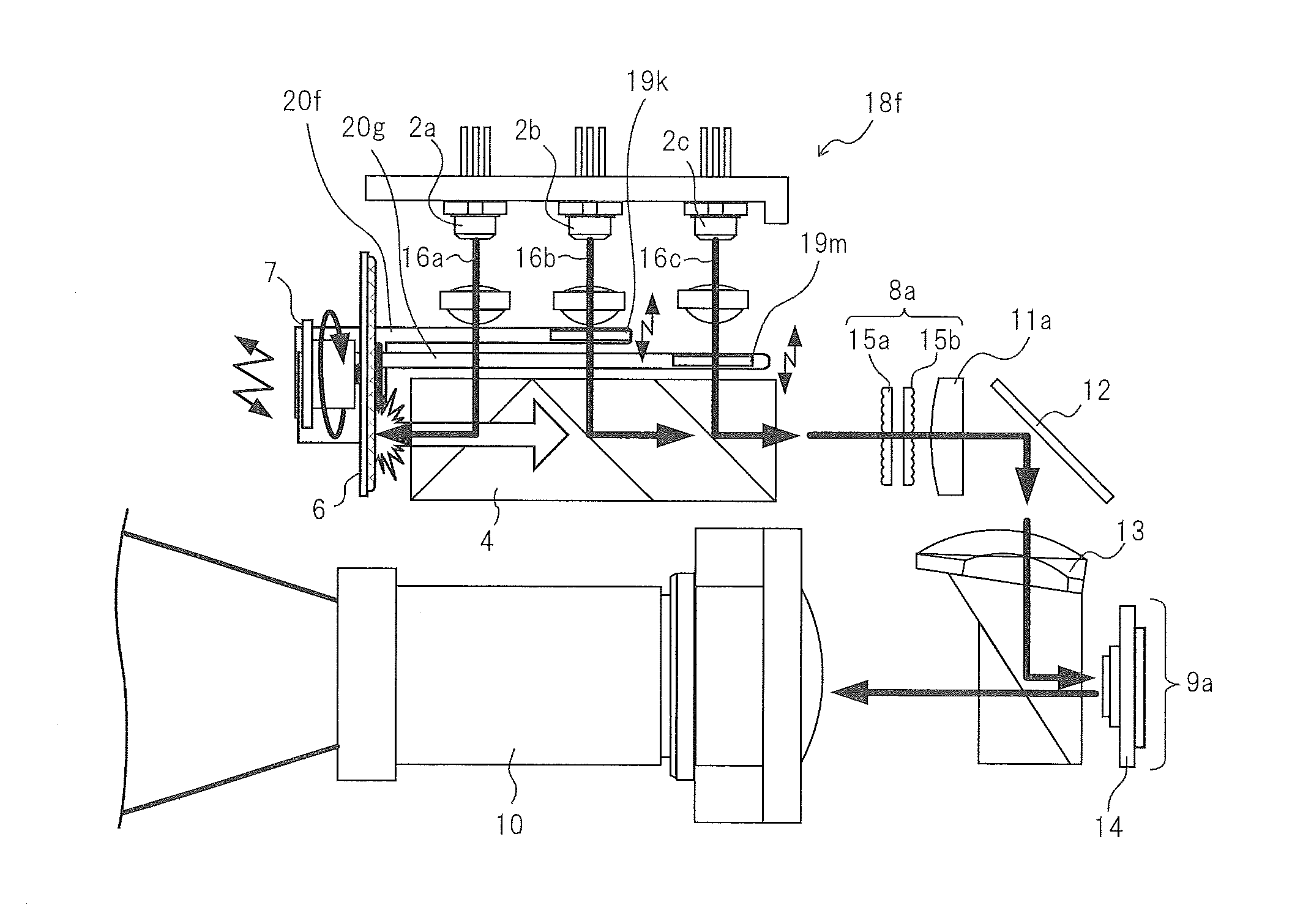
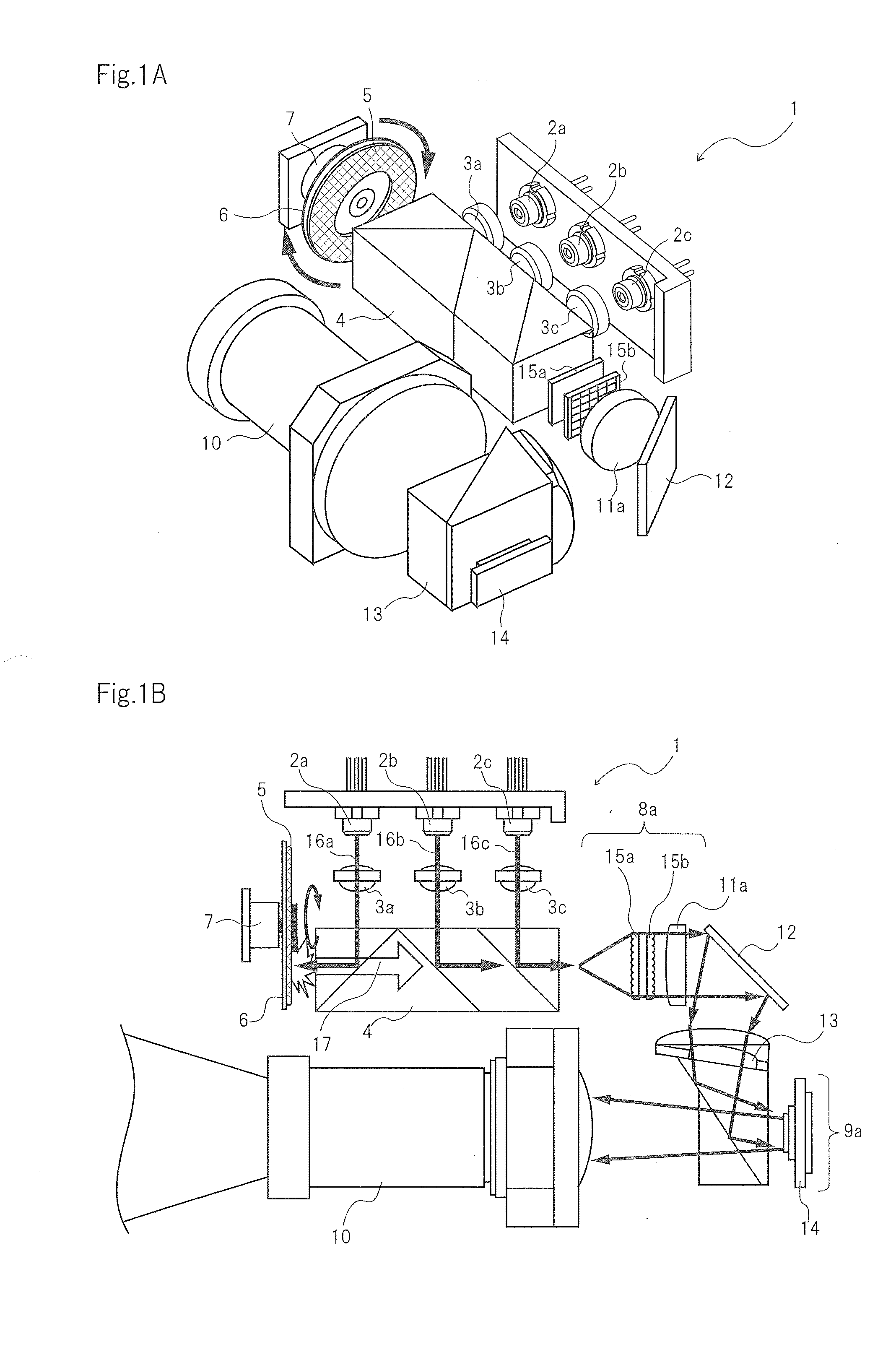
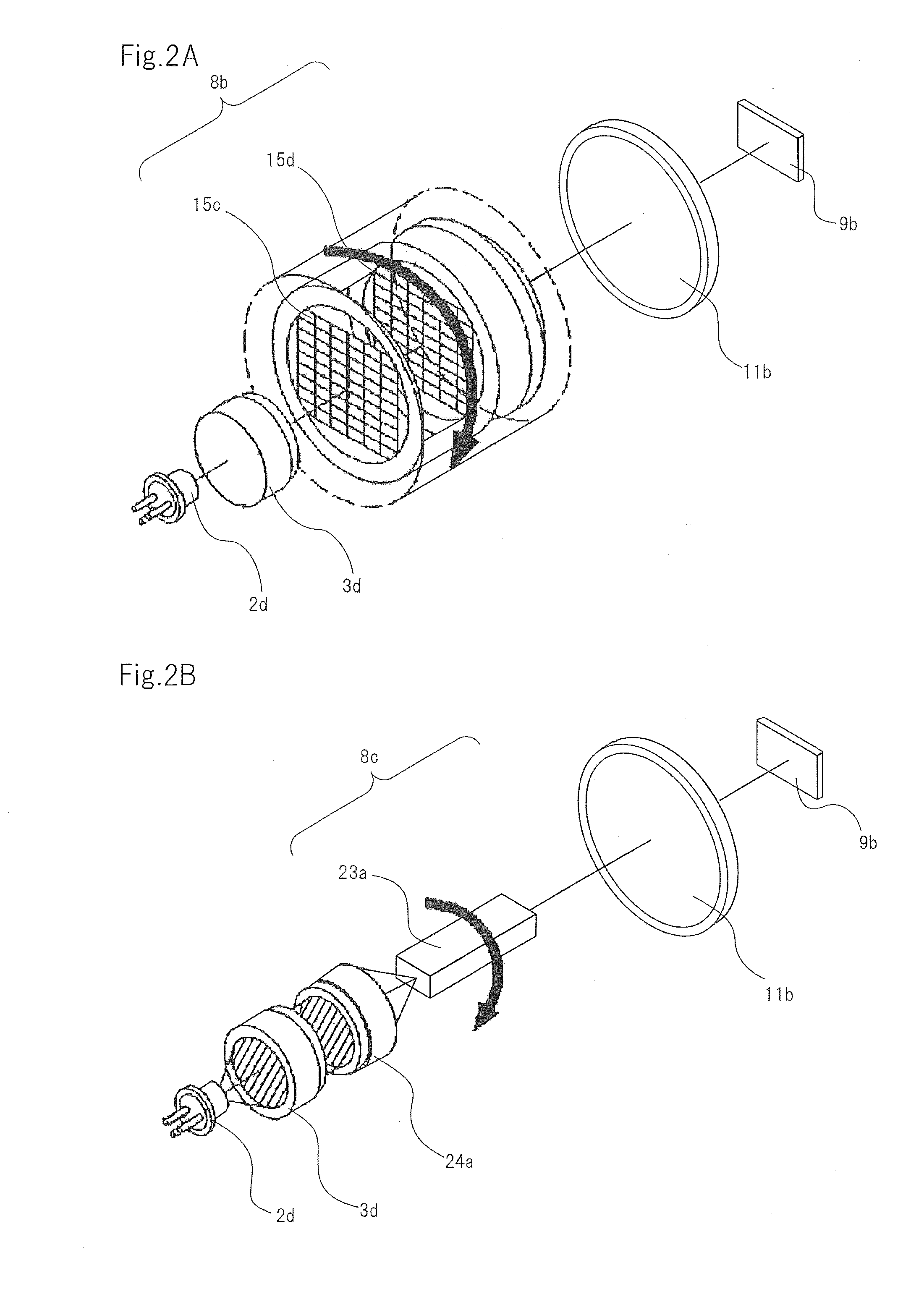
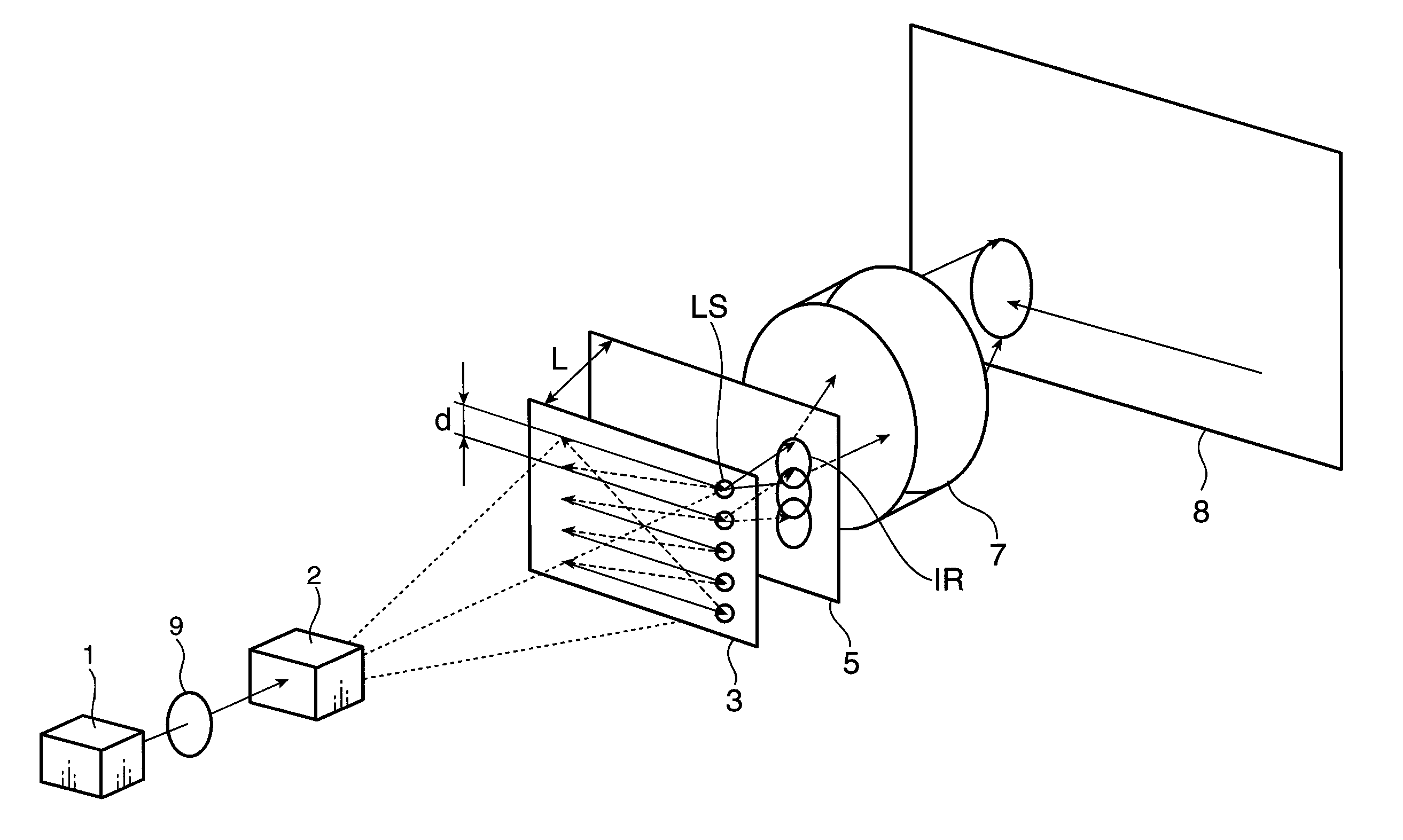
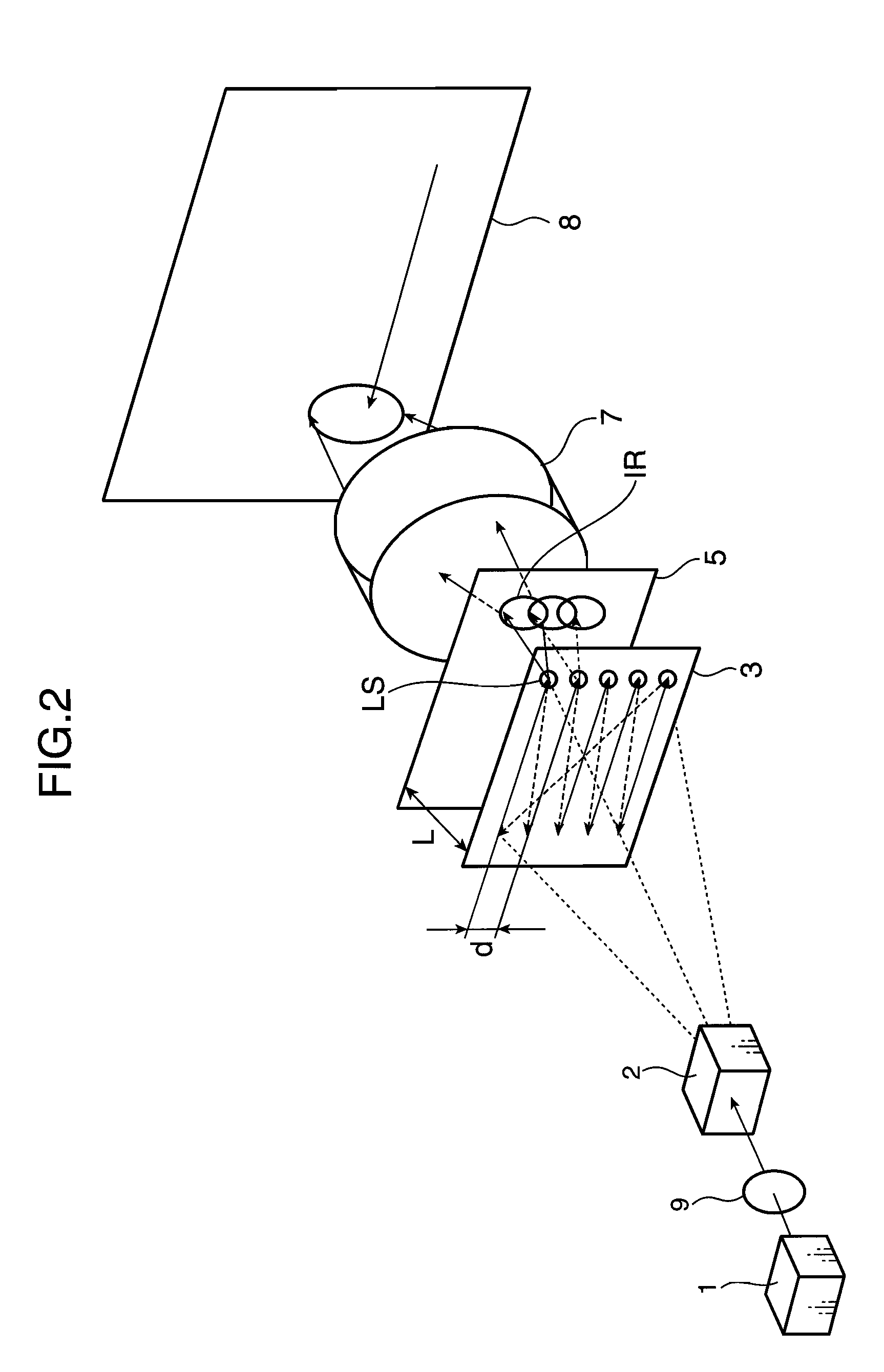
A 2-dimensional beam scan unit (2) reflects emission beams from a red laser light source (1a), a green laser light source (1b) and a blue laser light source (1c) and scans in a 2-dimensional direction. Diffusion plates (3a, 3b, 3c) diffuse the respective light beams scanned in the 2-dimensional direction to introduce them to corresponding spatial light modulation elements (5a, 5b, 5c). The respective spatial light modulation elements (5a, 5b, 5c) modulate the respective lights in accordance with video signals of the respective colors. A dichroic prism (6) multiplexes the lights of the three colors after the modulation and introduces the multiplexed lights to a projection lens (7) so that a color image is displayed on a screen (8). Since the 2-dimensional light emitted from the beam scan unit is diffused to illuminate the spatial light modulation element, it is possible to change the optical axis of the beam emerging from the light diffusion member for irradiating the spatial light modulation element moment by moment, thereby effectively suppressing speckle noise.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Light source device including a planar light source having a single, substantially continuous light emission area and display device incorporating the light source device
InactiveUS6882379B1Display deviceImprove efficiencyStatic indicating devicesNon-linear opticsContinuous lightLiquid-crystal display
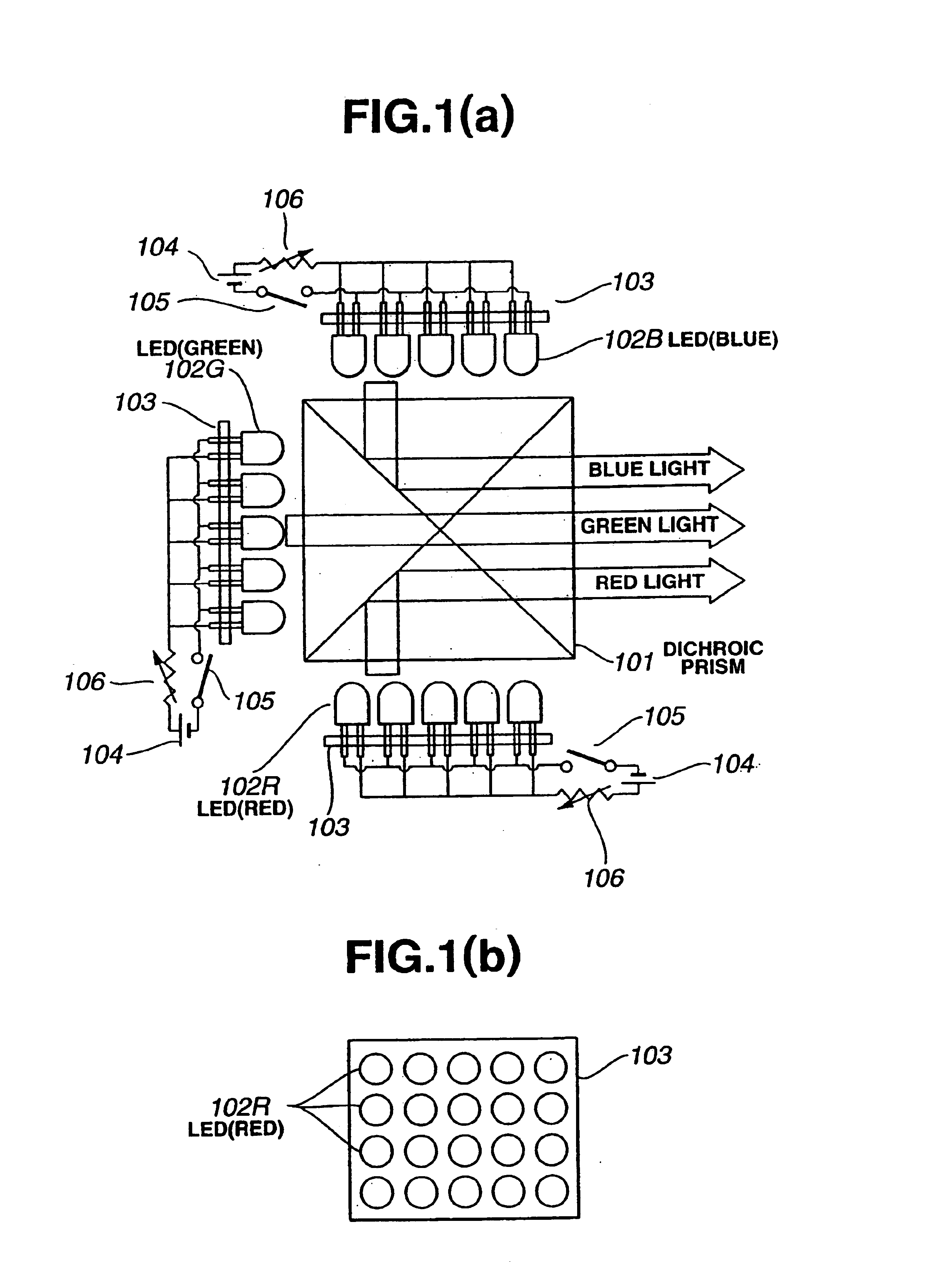
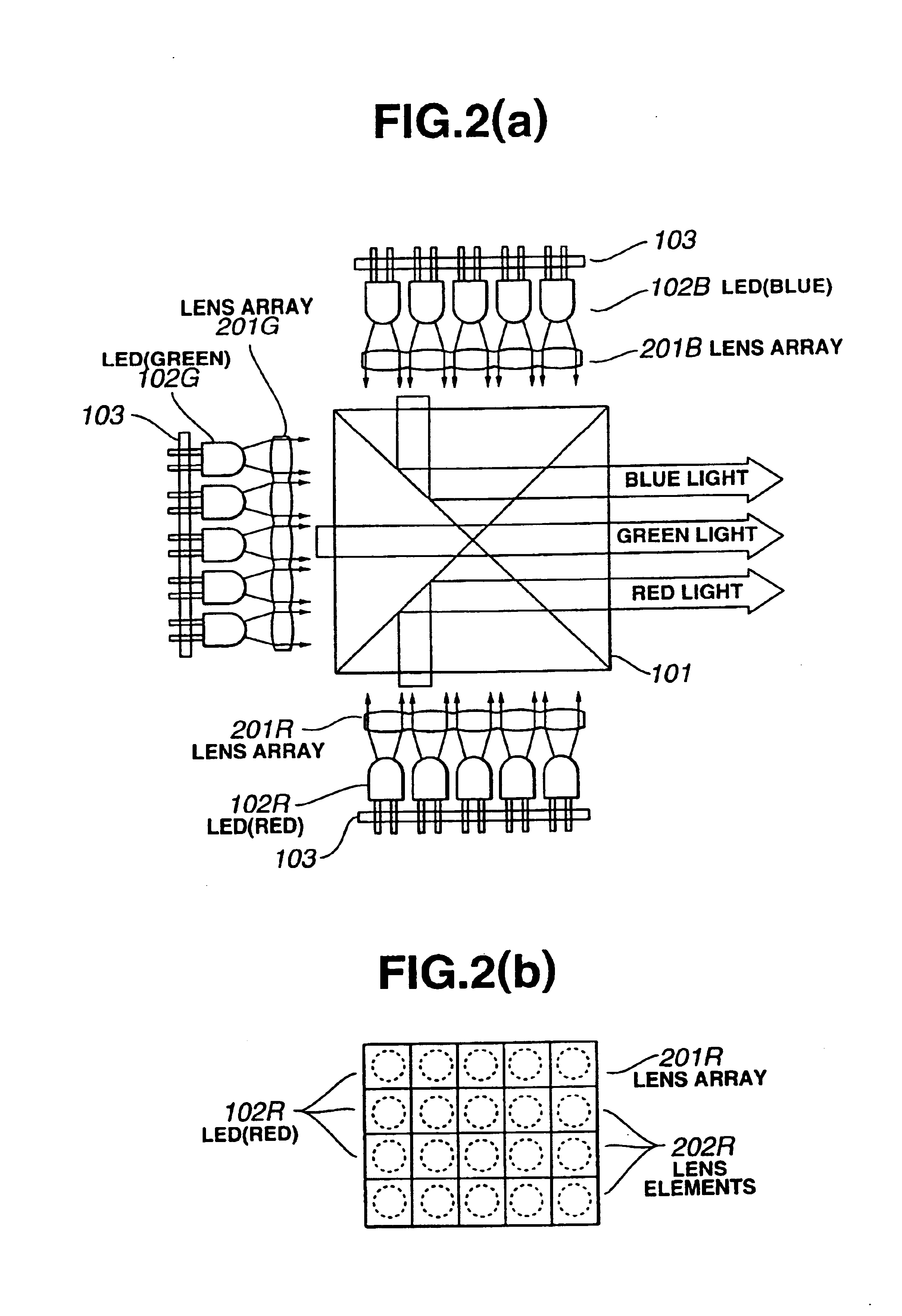
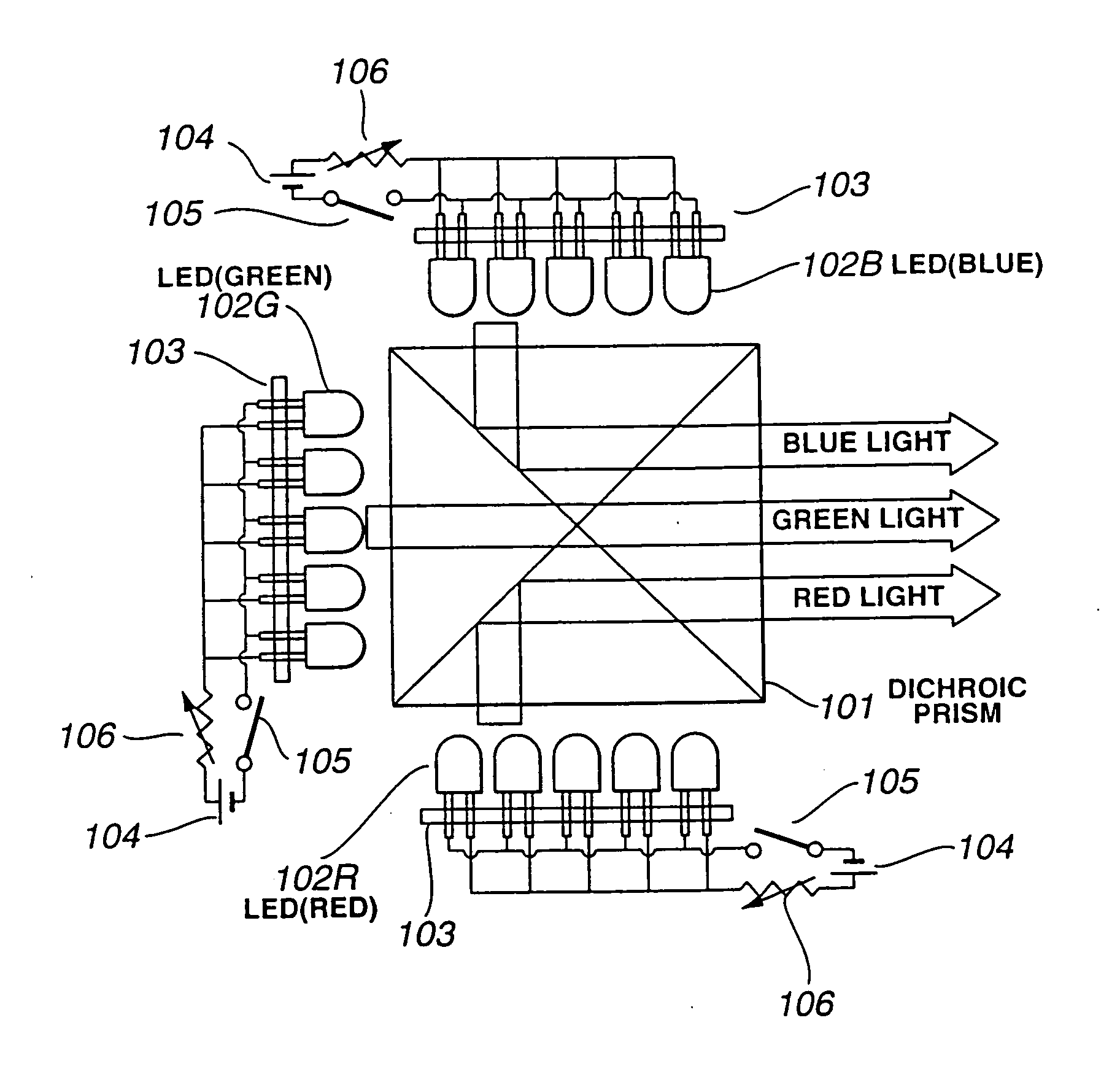
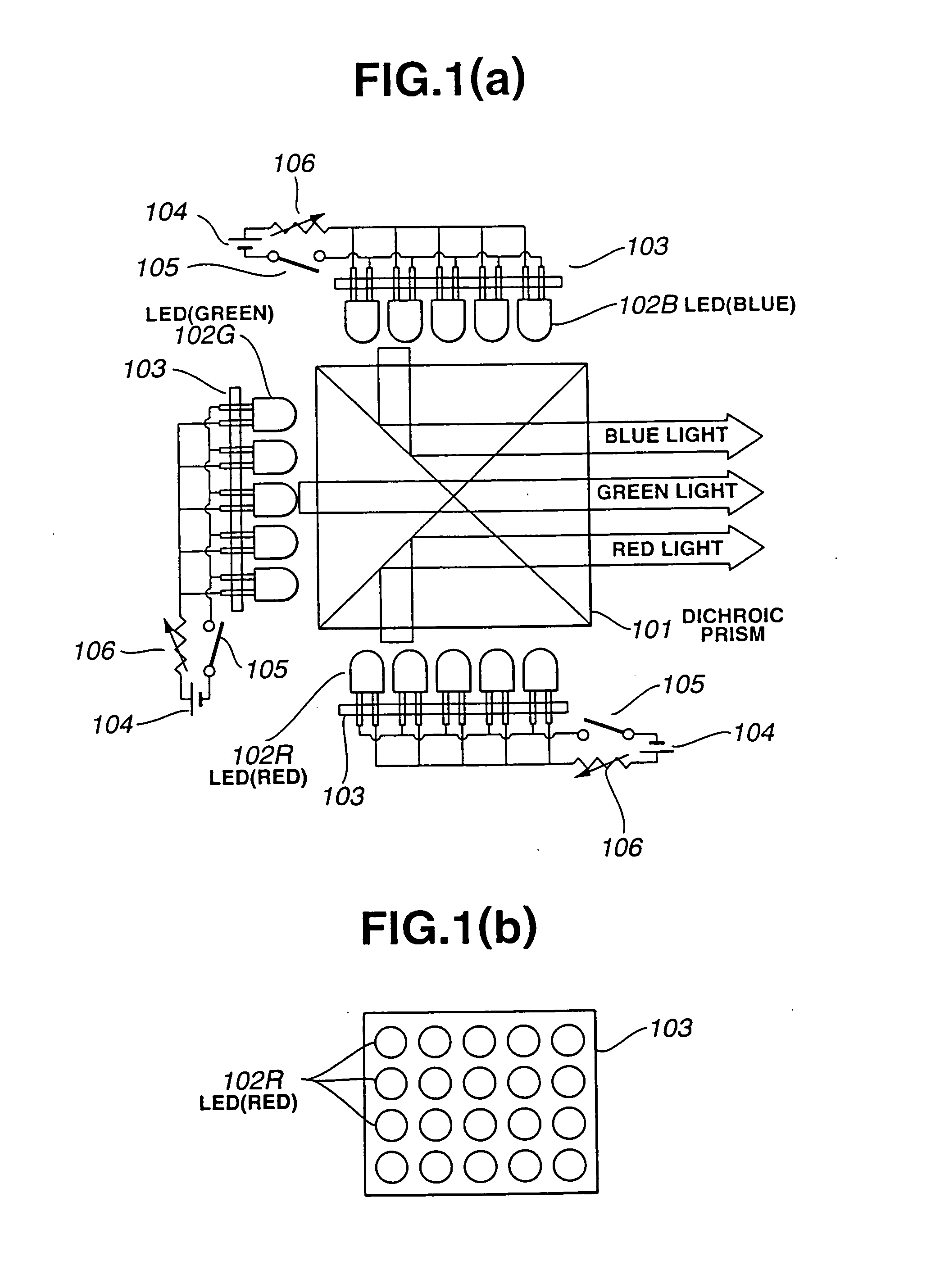
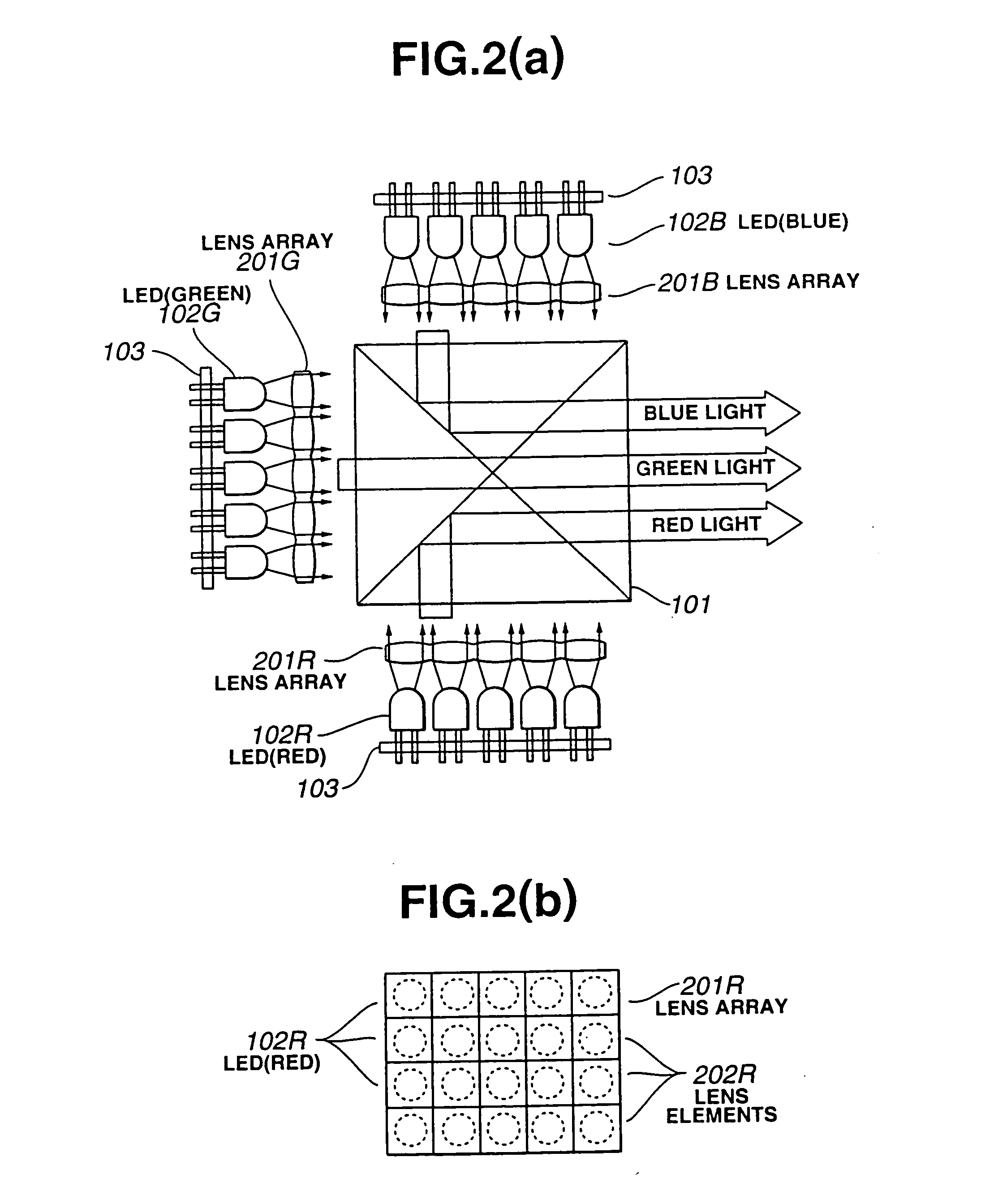
A red light source comprising an array of LEDs 102R that emit light of a red color, a green light source comprising an array of LEDs 102G that emit light of a green color, and a blue light source comprising an array of LEDs 102B that emit light of a blue color are deployed about the periphery of a dichroic prism 101. A liquid crystal display element is illuminated by a light source device configured such that the light from the respective light sources is synthesized into white light by the dichroic prism, and projection type liquid crystal display devices and the like are configured.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Light source device including a planar light source having a single, substantially continuous light emission area and display device incorporating the light source device
InactiveUS20050146652A1Display deviceImprove efficiencyStatic indicating devicesProjectorsContinuous lightLiquid-crystal display
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Visible and infrared light photographing lens system
ActiveUS7417682B2Increase in sizeEasily photographTelevision system detailsColor television detailsCamera lensDichroic prism
The present invention provides a visible and infrared light photographing lens system. A color separating prism or the like divides an object light entering a photographing lens and then passing through a focus lens, into an object light in a visible light region and an object light in an infrared light region. A visible light image pickup element and an infrared light image pickup element are used to pick up images of the respective object lights. Further, a compensation lens can be used to adjust a position where an image of the object light in the infrared light region is formed. Consequently, visible light photographing and infrared light photographing can be simultaneously carried out by focusing on an object at the same distance.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Light source device and projection-type display device
ActiveUS20140125956A1Effective vibrationReduce speckle noiseLighting heating/cooling arrangementsProjectorsDiffusionDichroic prism
A light source device includes: a laser light source; a circular substrate which has fluorescent body that emits light by using light from the laser light source as excitation light; a wheel motor which rotates circular substrate; a dichroic prism which transmits the light from fluorescent body while reflecting the light from the laser light source; a diffusion plate which diffuses the light from the laser light source; and a plate spring which interconnects diffusion plate and wheel motor.
Owner:SHARP NEC DISPLAY SOLUTIONS LTD
Lighting system and back-light device using this lighting system
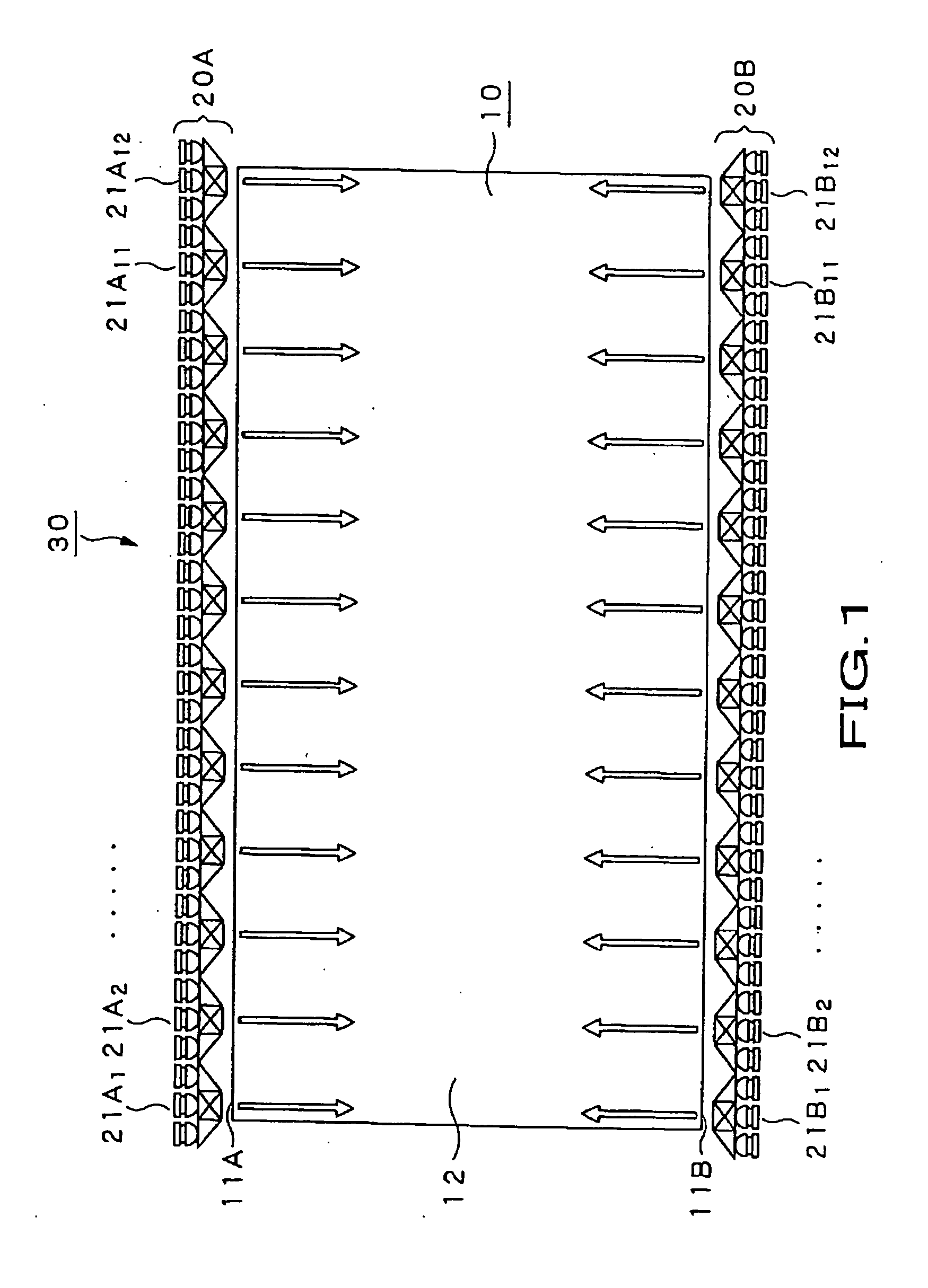
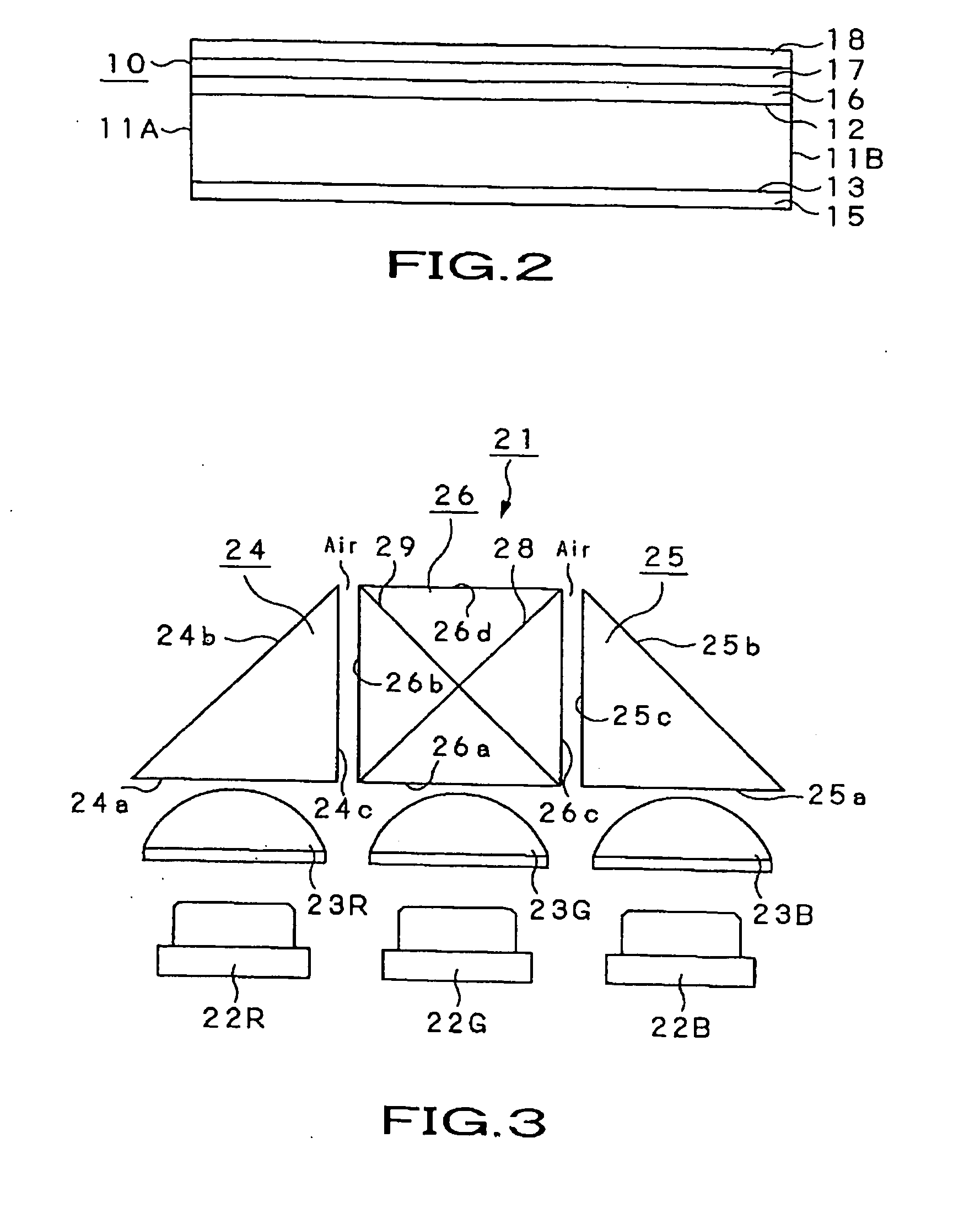
InactiveUS20070064417A1Inhibition lossImprove utilization efficiencyMechanical apparatusPoint-like light sourceOptical propertyDichroic prism
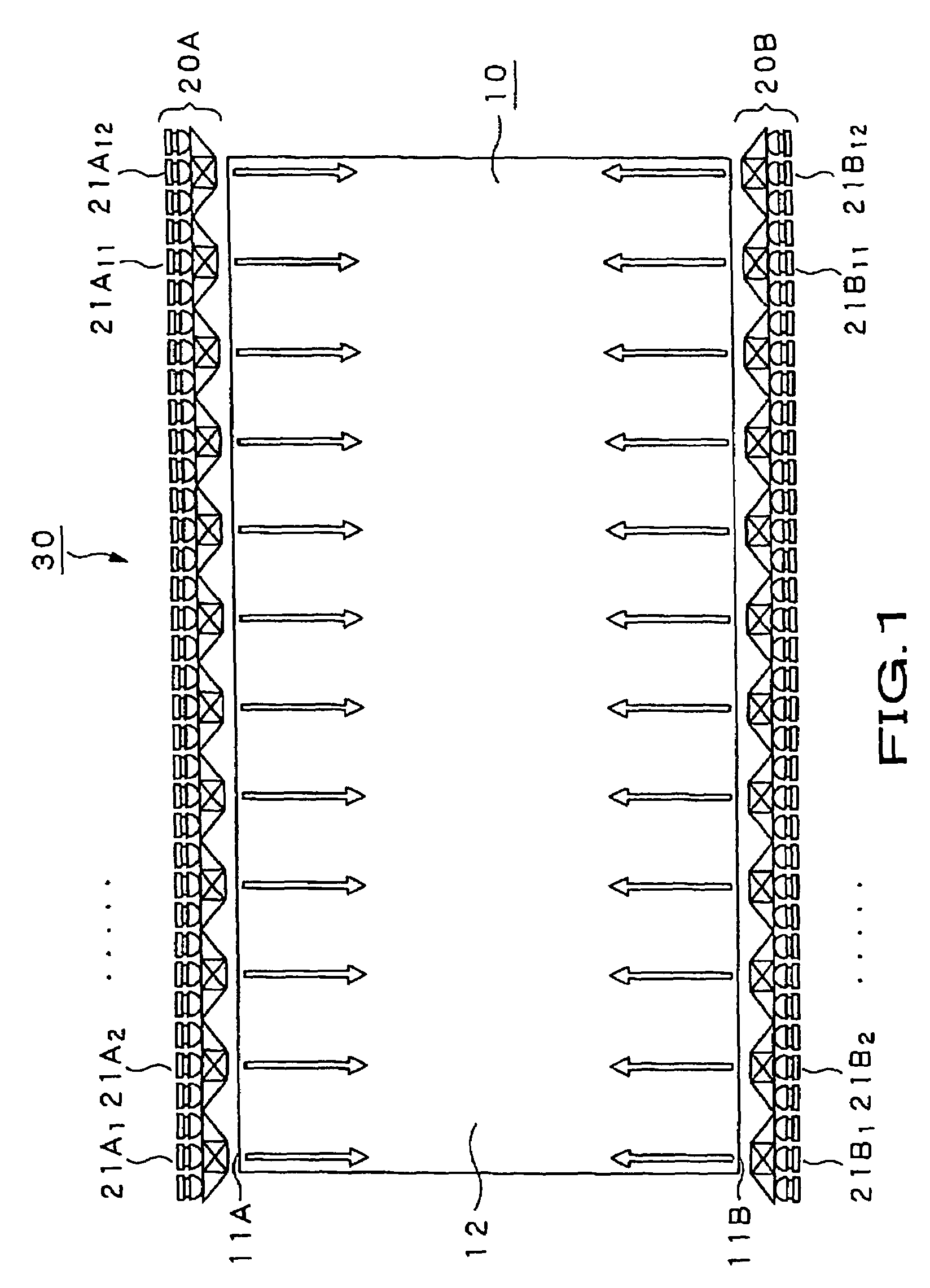
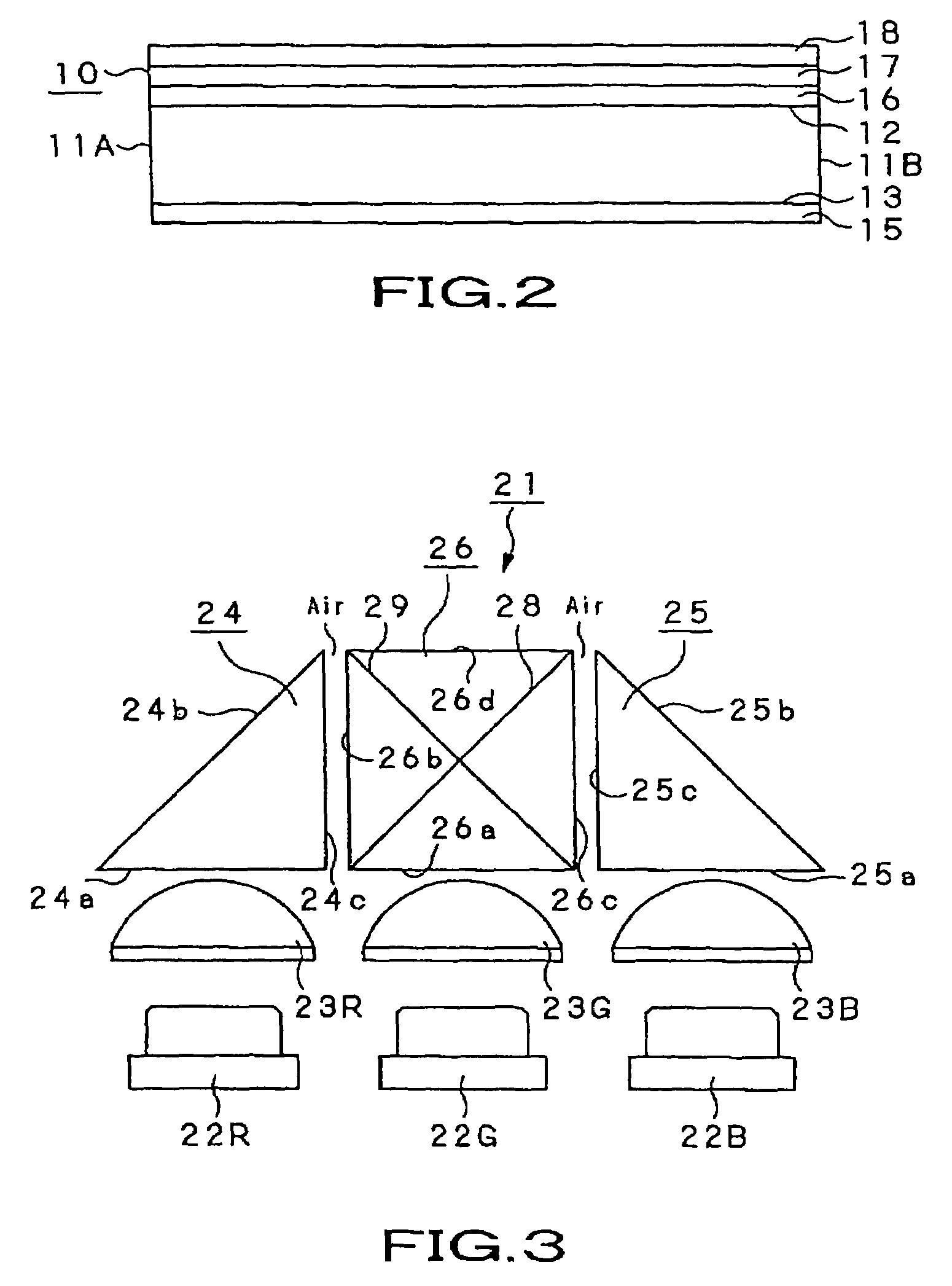
Disclosed is an illuminating device which, as a light source for a backlight device, mixes the colors of light rays of three prime colors radiated by light emitting diodes to emit white light. The illuminating device includes a first light source (22R) radiating light rays of the first prime color, a second light source (22G) radiating light rays of the second prime color, a third light source (22B) radiating light rays of the third prime color, optical units (23R), (23G) and (23B) which refract divergent light rays contained in the light rays of the first prime color, emitted by the first light source (22R), the light rays of the second prime color, emitted by the second light source (22G) and in the light rays of the third prime color, emitted by the third light source (22B), to form collimated light rays, and triangular prisms (24) and (25) or a dichroic prism (26) mixing the light rays of the first, second and third prime colors, emitted by these optical units, by selective transmission and reflection, based on optical properties of the light rays of the respective prime colors.
Owner:SONY CORP
Liquid crystal display system and light projection system
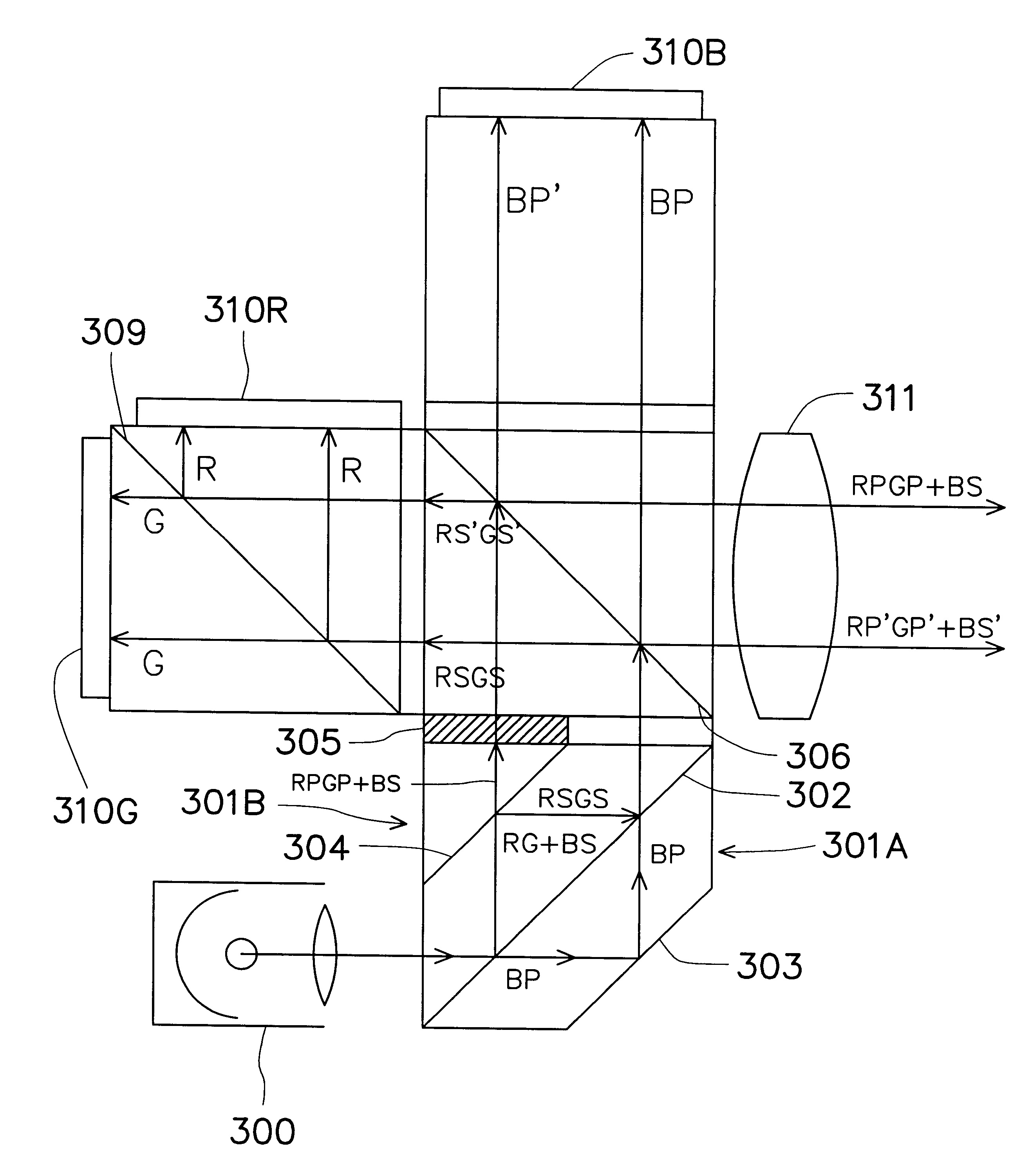
A projection system used in a liquid crystal display (LCD) system is provided. The projection system has a light source, a polarization set which further includes a double dove prism, a vertical prism and a half-wave plate, a polarization beam splitter (PBS), a dichroic prism, and a projection lens. The light source emits a white light, which enters the polarization set and is split into a P-state polarized blue light and a mixed light. The mixed light includes an S-state polarized red light and an S-state polarized green light. The PBS allows the P-state polarized blue light to transmit and enter onto a blue light LCD panel, and deflects the mixed light by 90°. The dichroic prism splits the S-state polarized red light and the S-state polarized green light of the mixed light, which respectively enter a red light LCD panel and a green light LCD panel. The projection lens collects light from the red, green, blue LCD panels and project the lights onto a screen.
Owner:TRANSPACIFIC IP II
Projector having a light shielding member
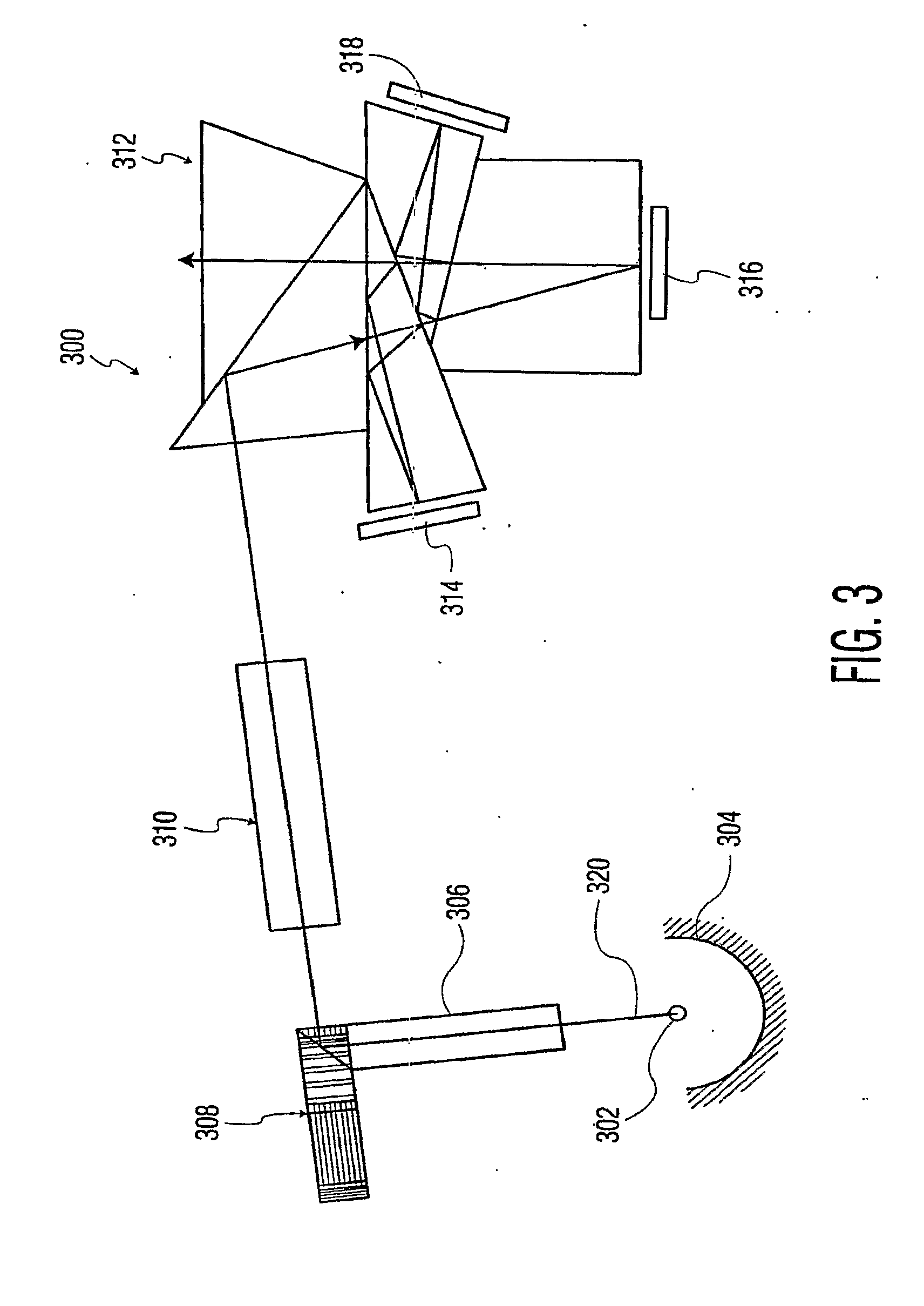
InactiveUS6488380B1Quality improvementSmall sizeTelevision system detailsProjectorsDichroic prismLuminous flux
To provide a projector in which the quality of projected images does not deteriorate when the size of the projector is reduced. A light shielding member for shielding leakage light from gaps between each liquid crystal panel, and a crossed dichroic prism toward a projection lens side is provided. The leakage light from the gaps between each liquid crystal panel and the crossed dichroic prism can be shielded, and only the luminous flux emitted by the crossed dichroic prism can be applied to the projection lens, whereby the quality of projected images does not deteriorate when the device is reduced in size.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Optical device and projector having the optical device
InactiveUS6844993B2Improve cooling effectIncrease illuminationTelevision system detailsProjectorsDichroic prismPrism
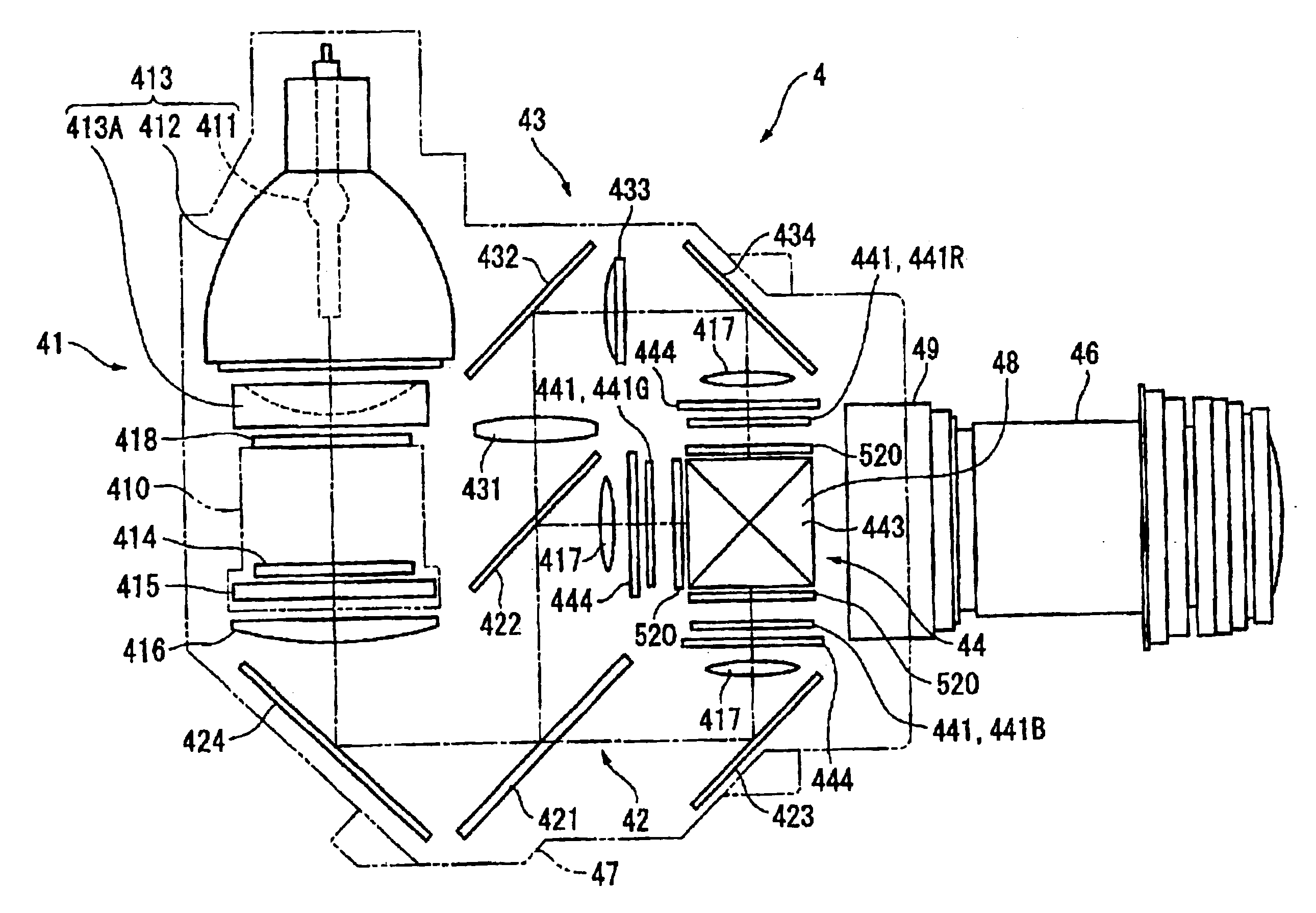
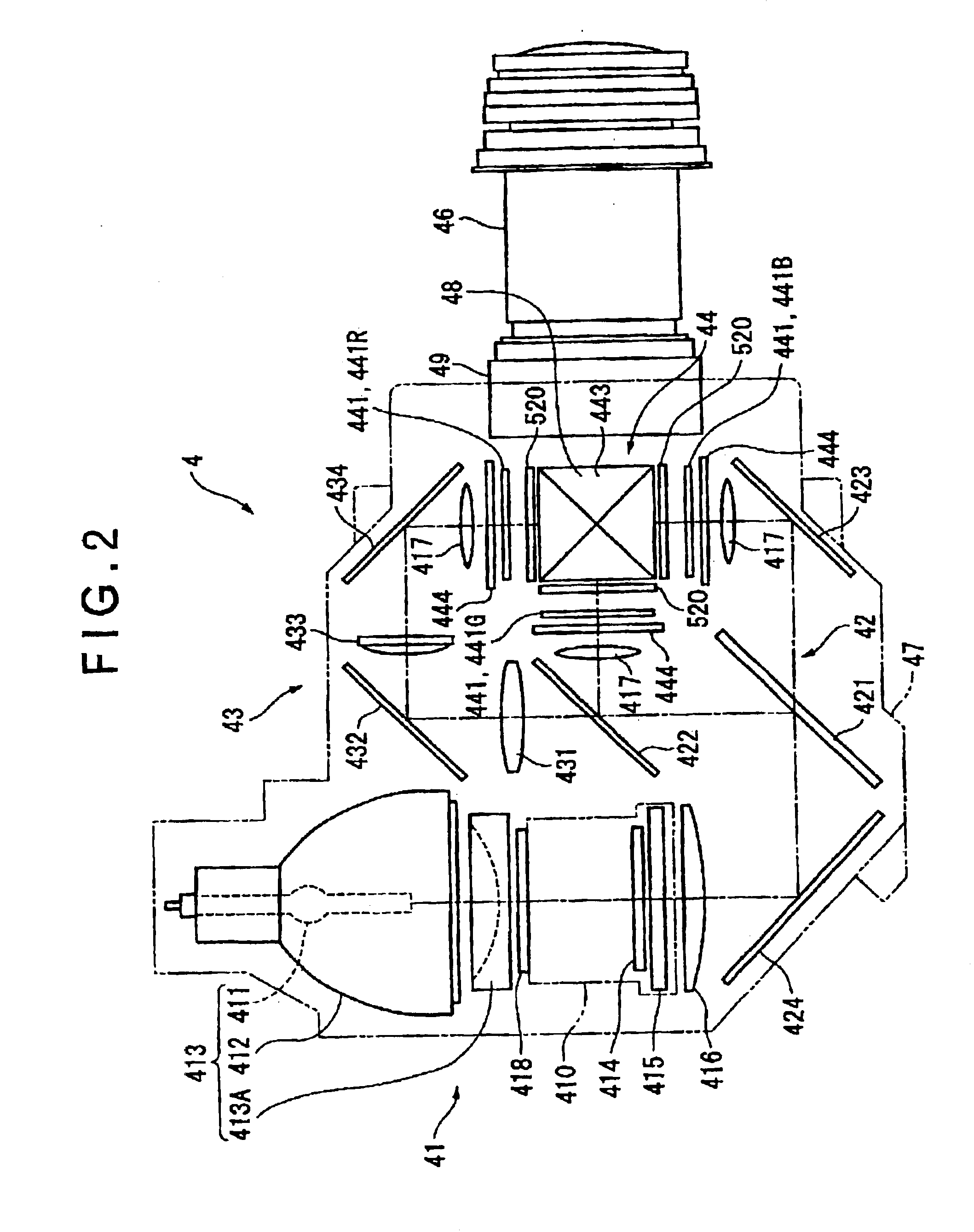
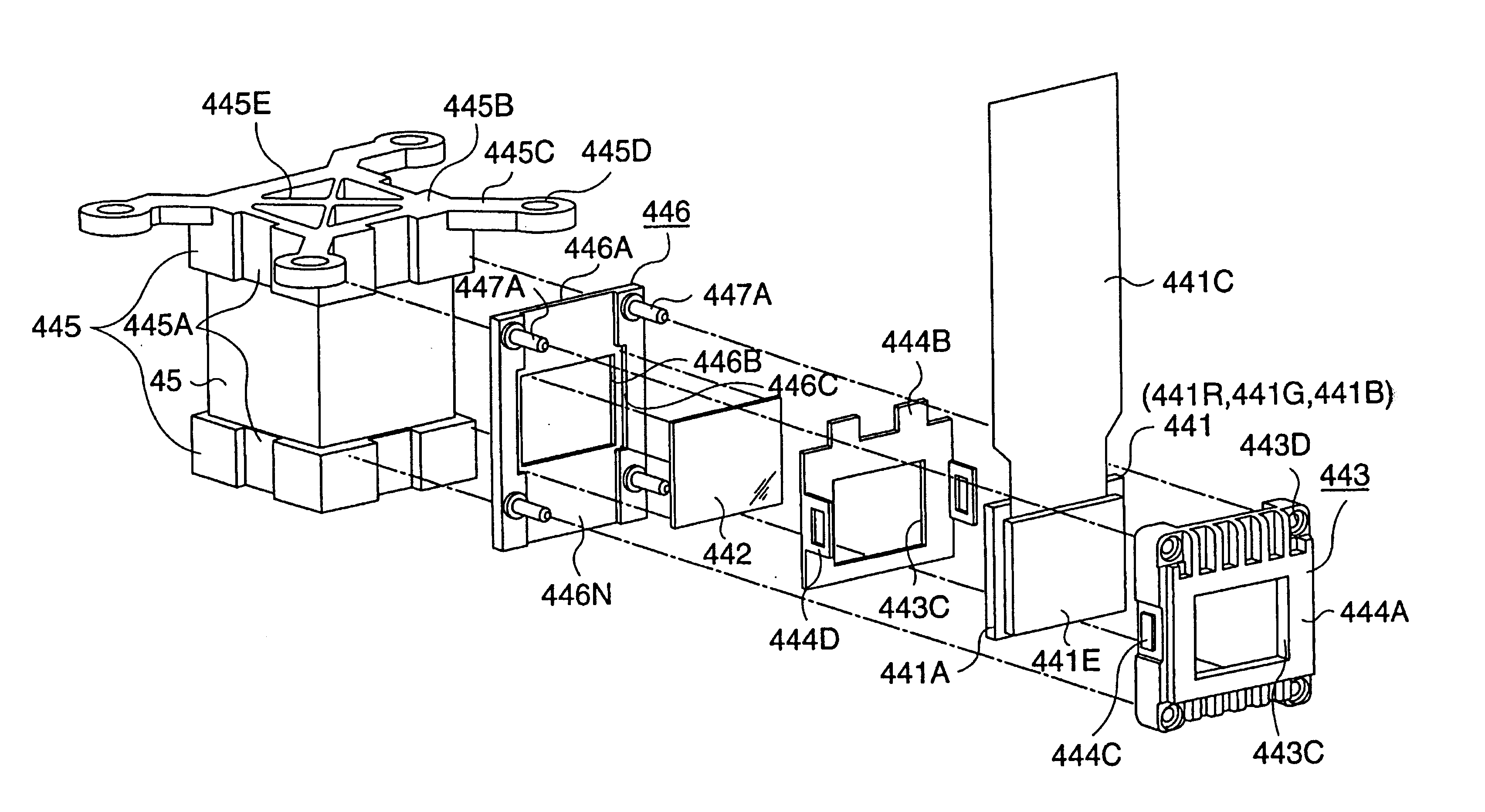
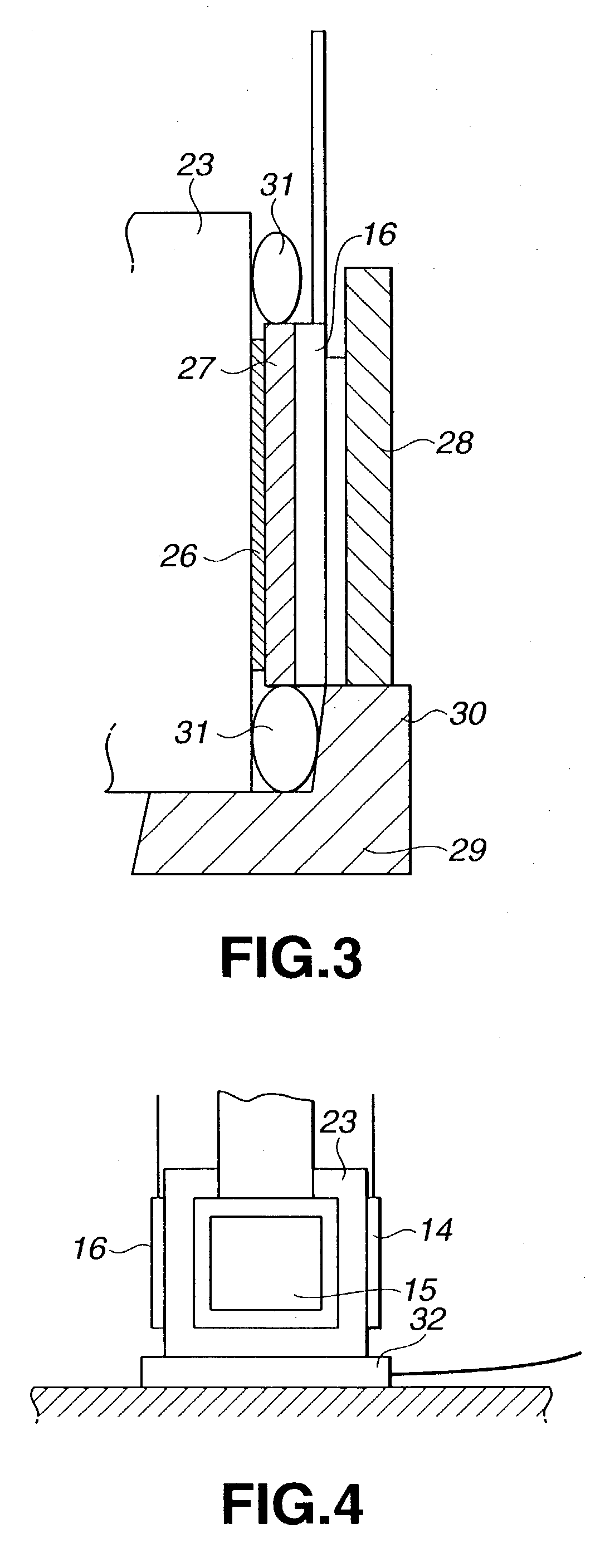
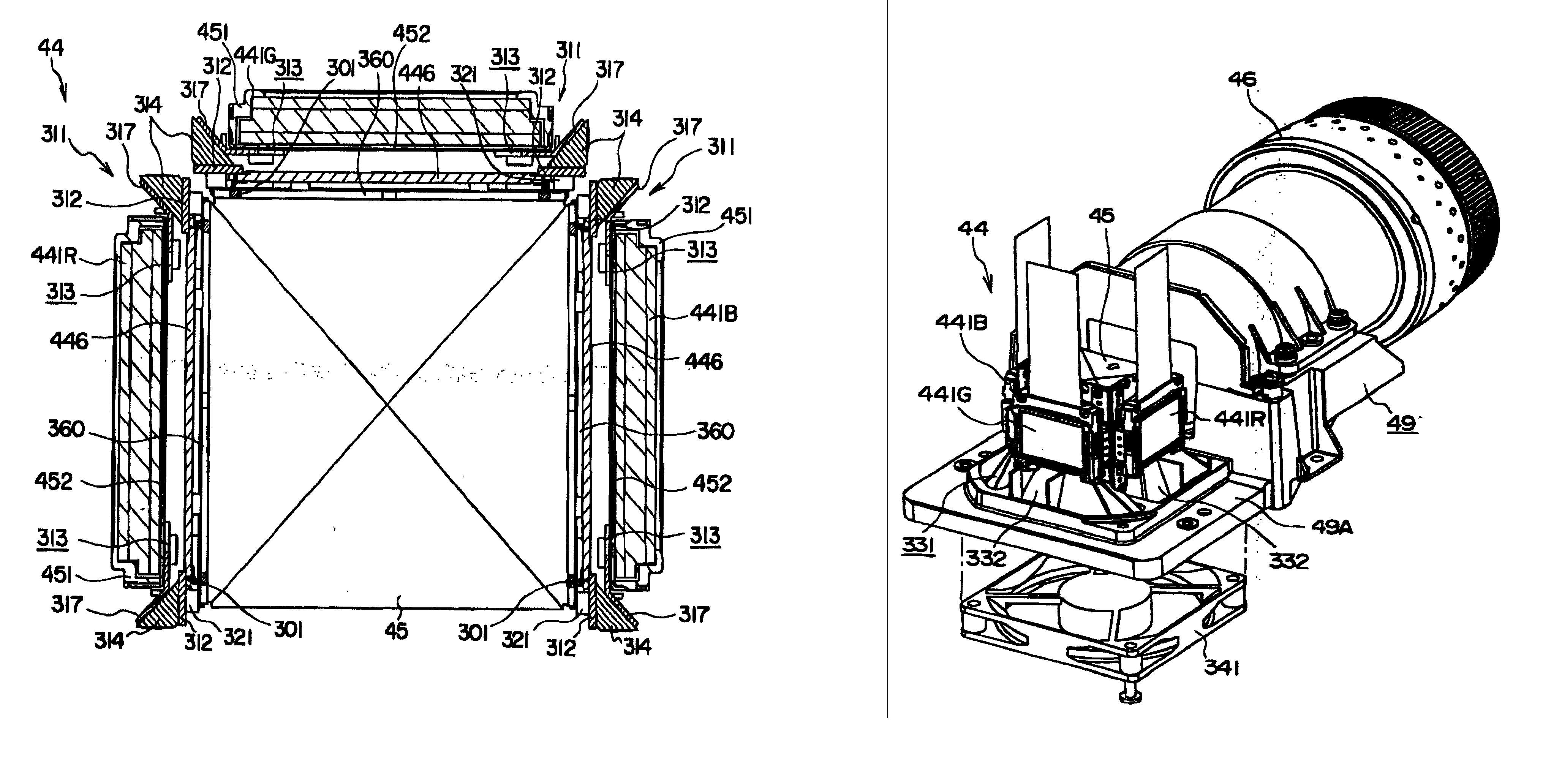
An optical device has: a metal cooling device (500) disposed between a liquid crystal panel (441) and a light-incident side of a cross dichroic prism (443) and having a holding surface for holding polarization plates (521, 522) attached with a polarization films (521A and 522A) in a mutually spaced manner, the cooling device cooling the polarization films; a base (445) provided on the upper and lower sides of the cross dichroic prism (443) and having a cooling device attachment surface (449A) for the cooling device (500) to be attached; and a fixing member (600) provided on a light-incident side of the cross dichroic prism for locating and fixing the liquid crystal panel (441) on the light-incident side, the fixing member (600) being formed with a attachment surface (631) on which a pin (730) for mounting the liquid crystal panel (441) is formed.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Optical device and projector
InactiveUS20050001985A1Low production costGood cooling functionProjectorsPicture reproducers using projection devicesOptical propertyDichroic prism
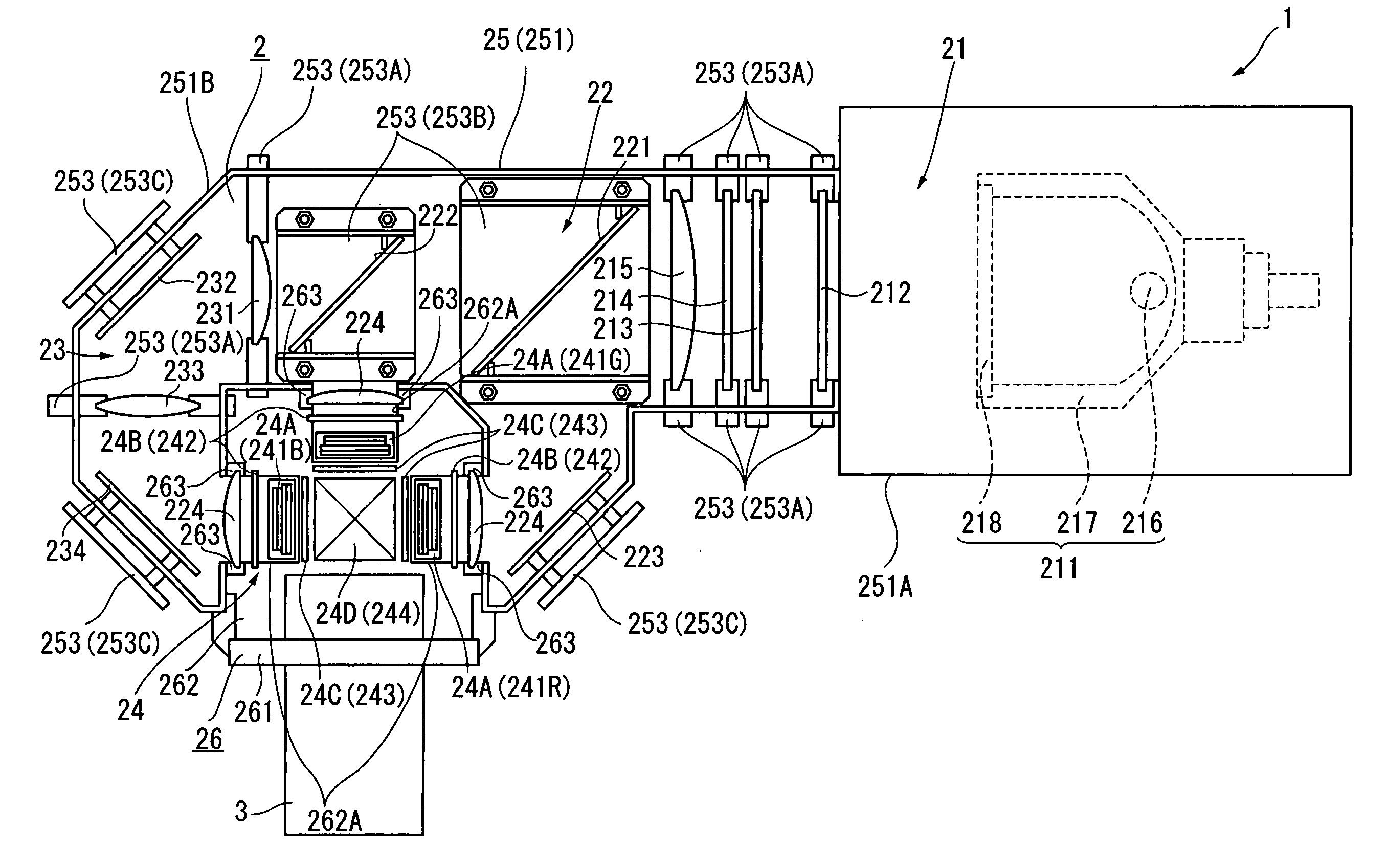
An optical device (24) includes: three optical modulators (24A) for modulating respective color lights in accordance with image information; a cross dichroic prism (244) for combining the respective color lights modulated by the optical modulators (24A); a base (247) made of heat-conductive material and fixed to upper and lower faces of the cross dichroic prism (244); an irradiation-side polarization plate (243) having polarization films (243A2 and 243B2) as optical conversion films for converting an optical property of a light beam irradiated by the optical modulators (24A) and substrates (243A1 and 243B1) made of heat-conductive material and provided with the polarization films (243A2 and 243B2) attached thereto; and an irradiation-side retaining plate (246) made of heat-conductive material for supporting and fixing the irradiation-side polarization plate (243). The irradiation-side retaining plate (246) is fixed to a lateral face of the base (247).
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
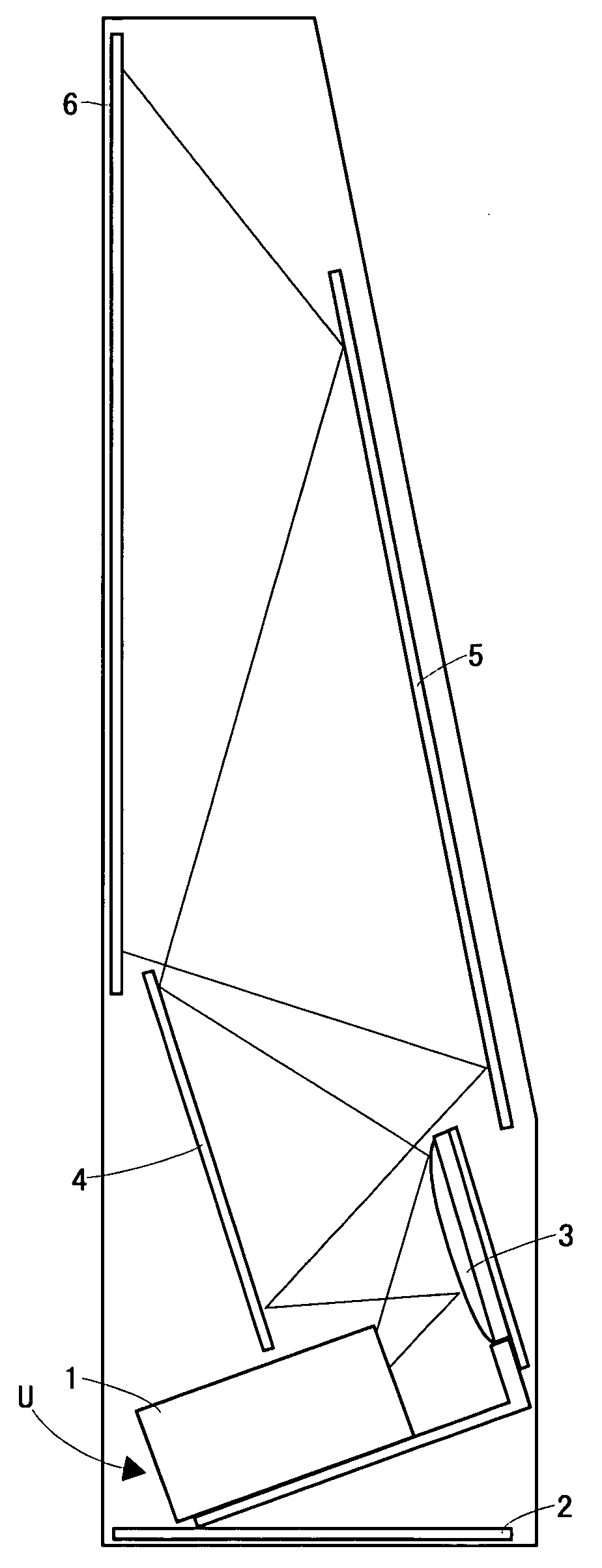
Projection-type display apparatus
InactiveUS6120152AQuality improvementAvoid noiseTelevision system detailsProjectorsLuminous intensityDichroic prism
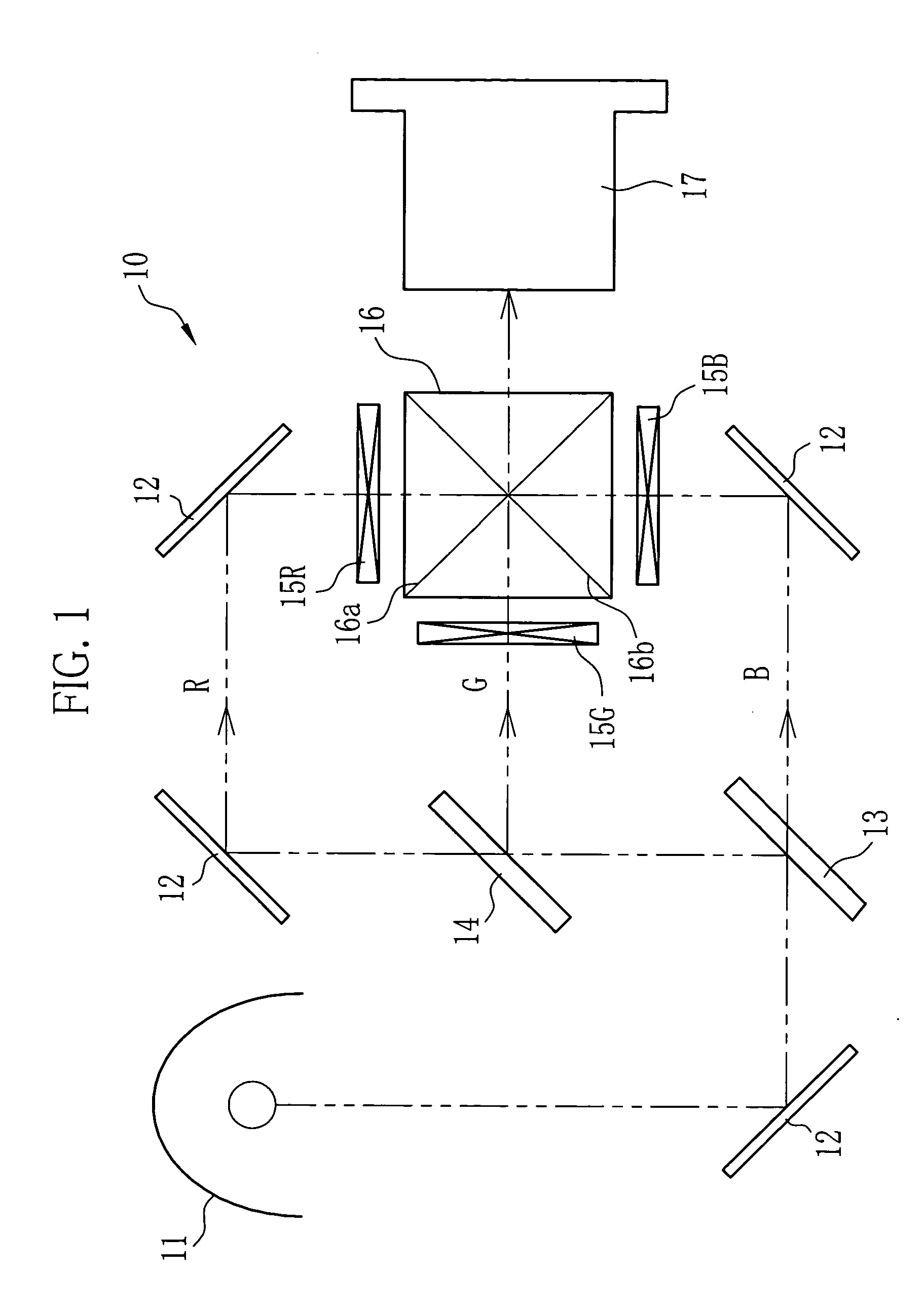
A projection-type display apparatus includes a light source, a uniform illumination optical system, a color separating system for separating a white light beam emitted from the uniform illumination optical system into three color beams, three liquid crystal panels for respectively modulating each of the separated color beams, a light guide system located on an optical path of the color beam having the longest optical path among the separated color beams, a dichroic prism for synthesizing the beams modulated through the liquid crystal panels, and a projection lens for projecting the synthesized and modulated beam onto a screen. The uniform illumination optical system is provided with a uniform illumination optical device for converting the white light beam emitted from the light source into a uniform beam. Since the dichroic prism, which is an optical element that is rotationally symmetrical about the chief axis of a projection optical system, is employed as a color synthesizing system, and the uniform illumination optical device for restricting unevenness in color and luminous intensity is incorporated in the system, it is possible to realize a display apparatus which causes little unevenness in color and luminous intensity and which has a high illumination efficiency.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Optical display device and projection-type display device
InactiveUS20050174495A1Improve accuracyHigh numberTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsIntegratorDichroic prism
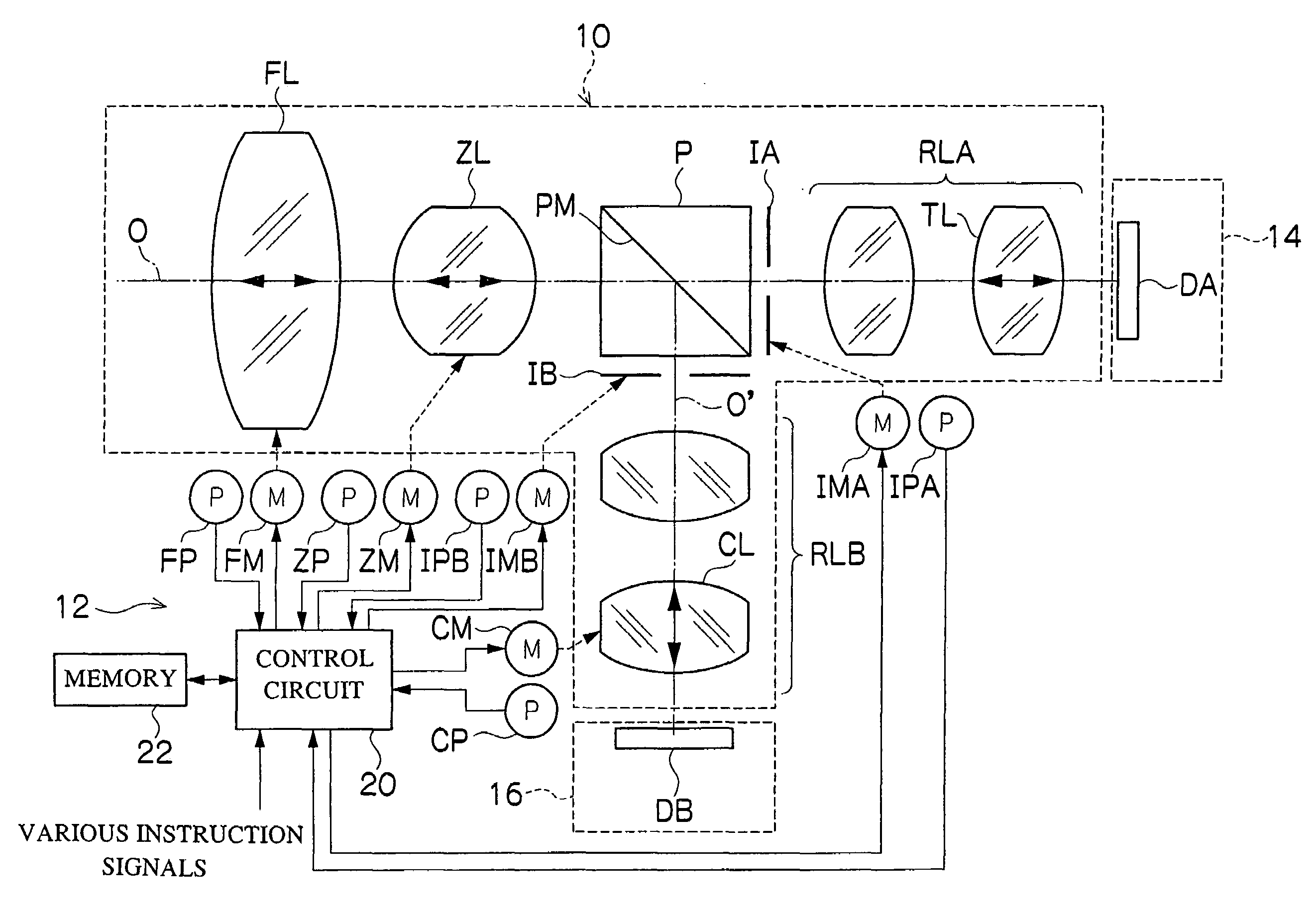
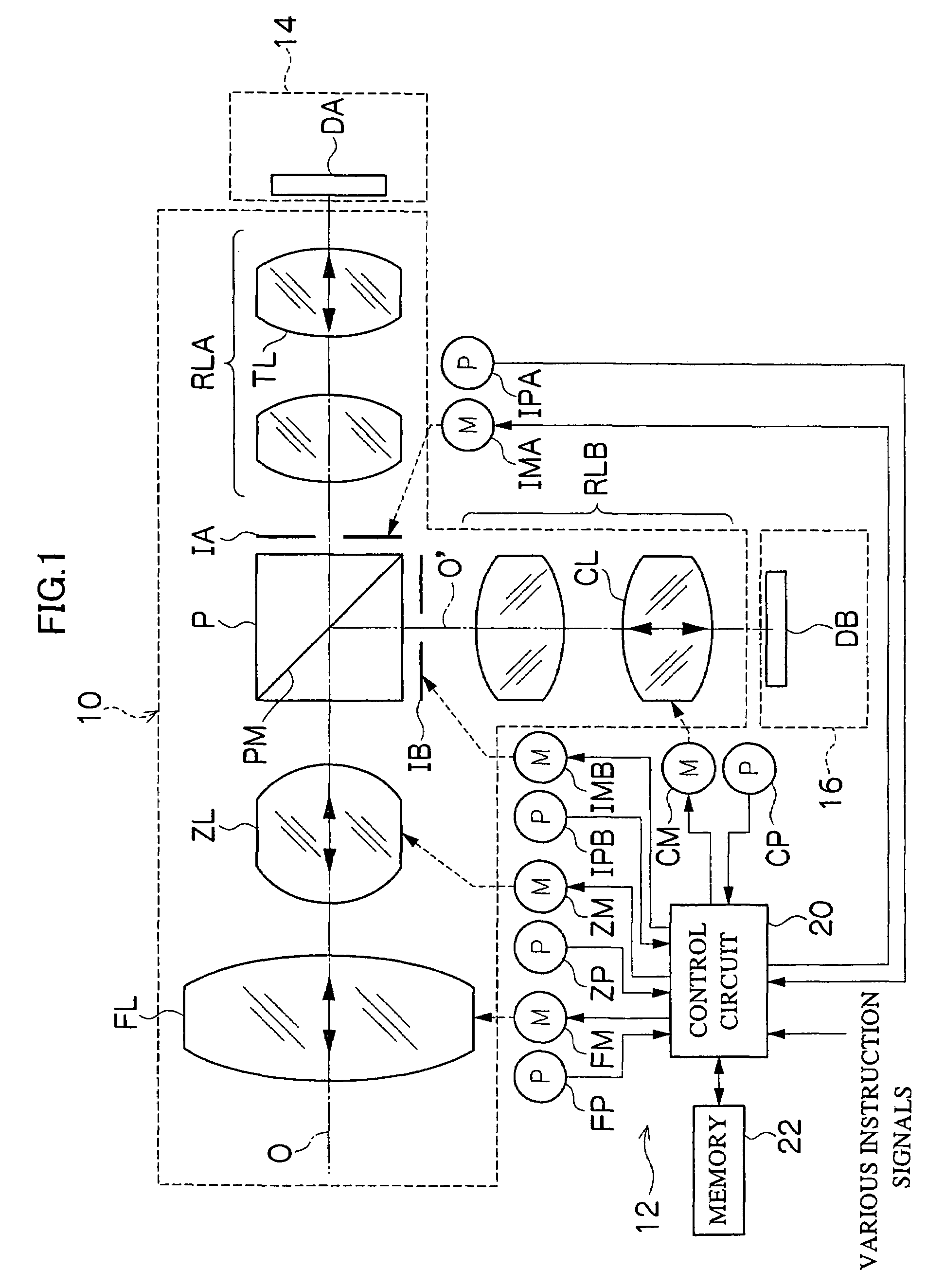
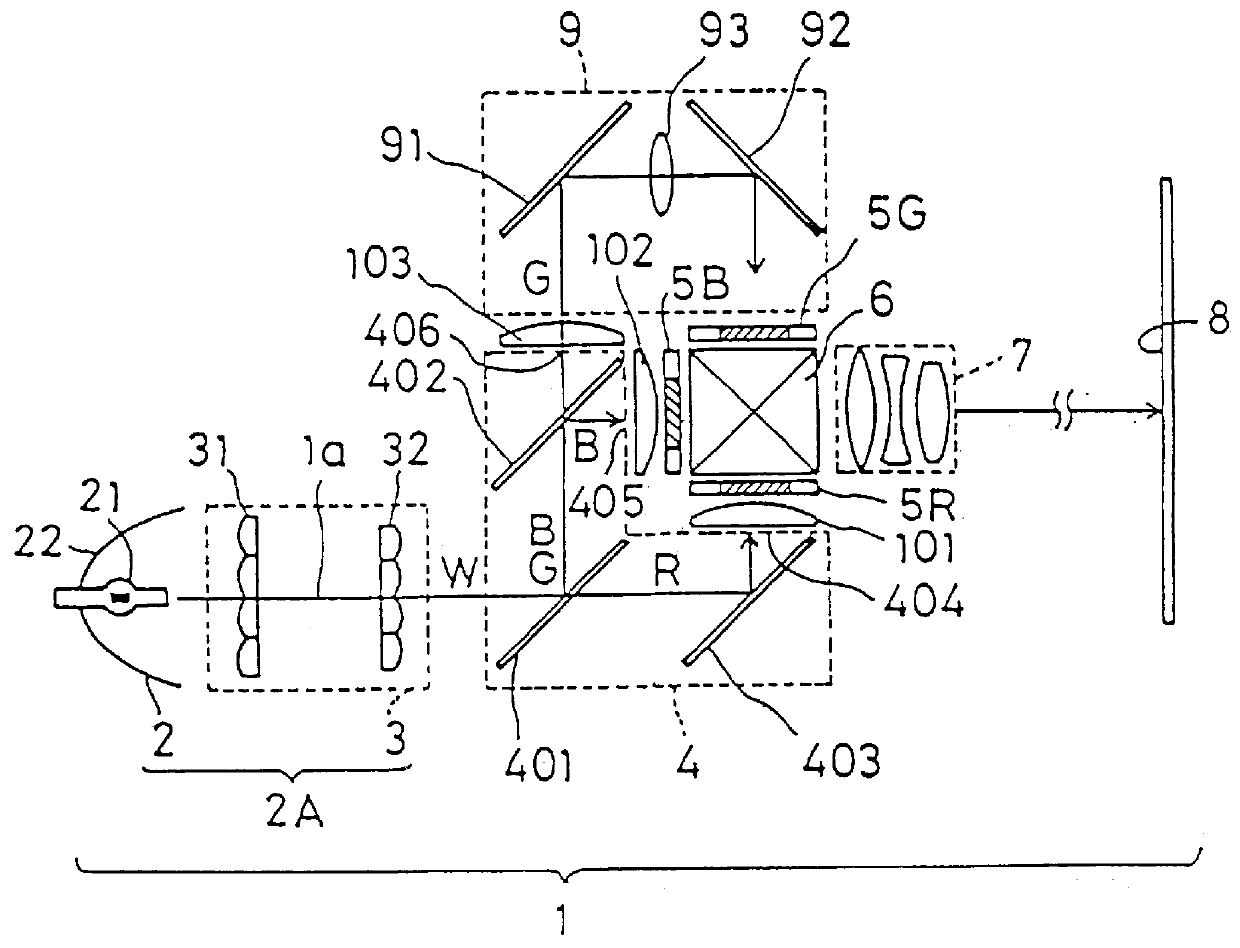
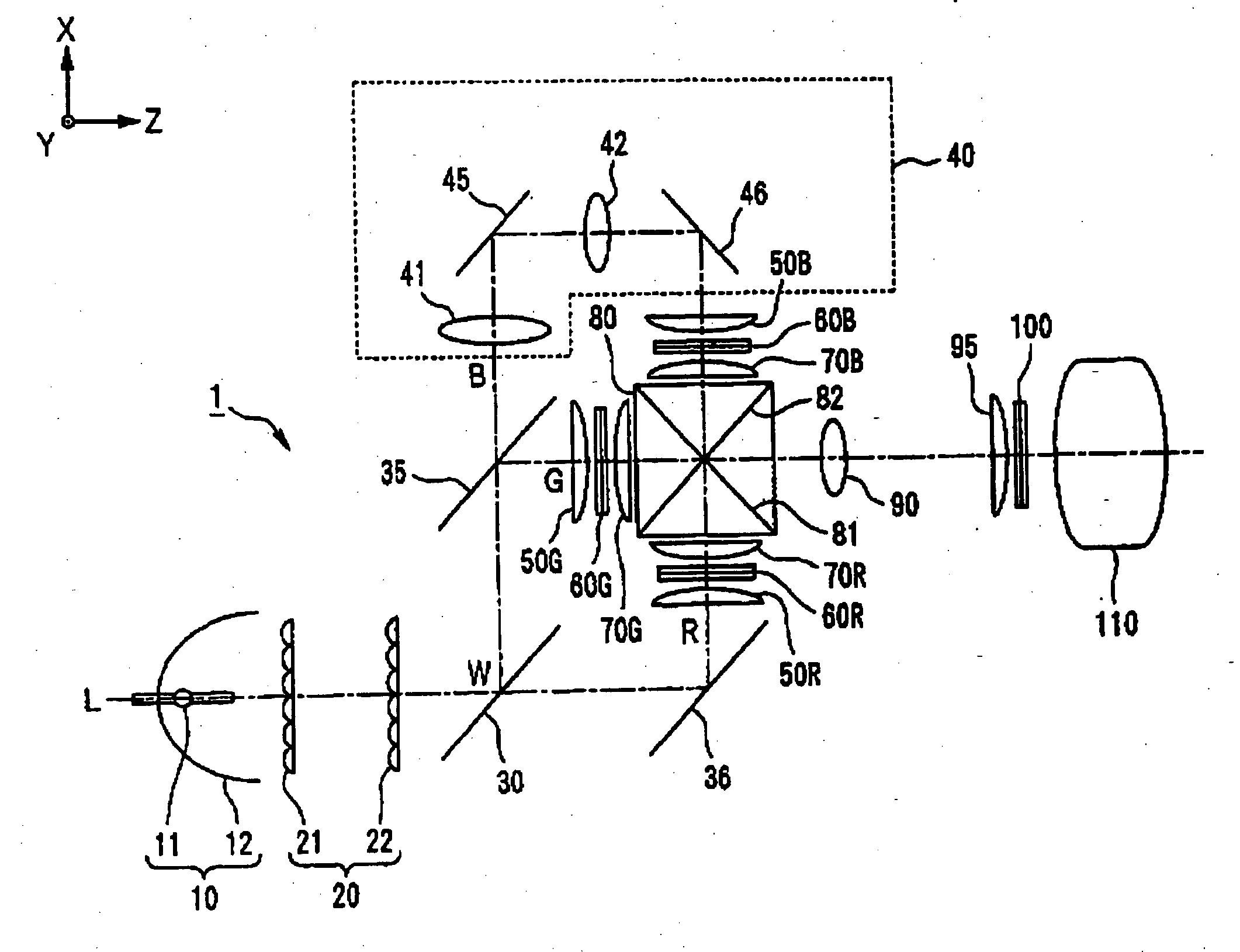
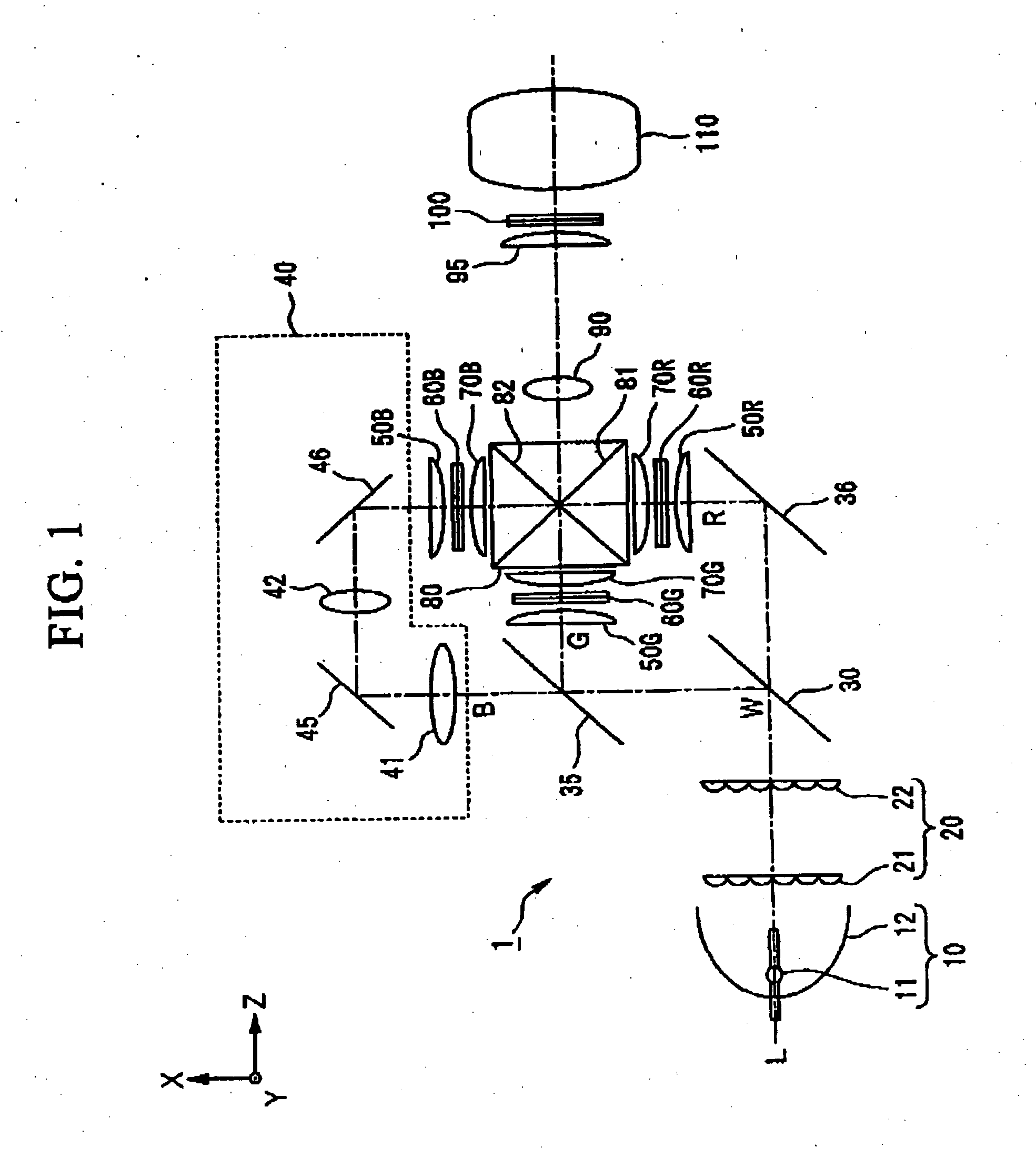
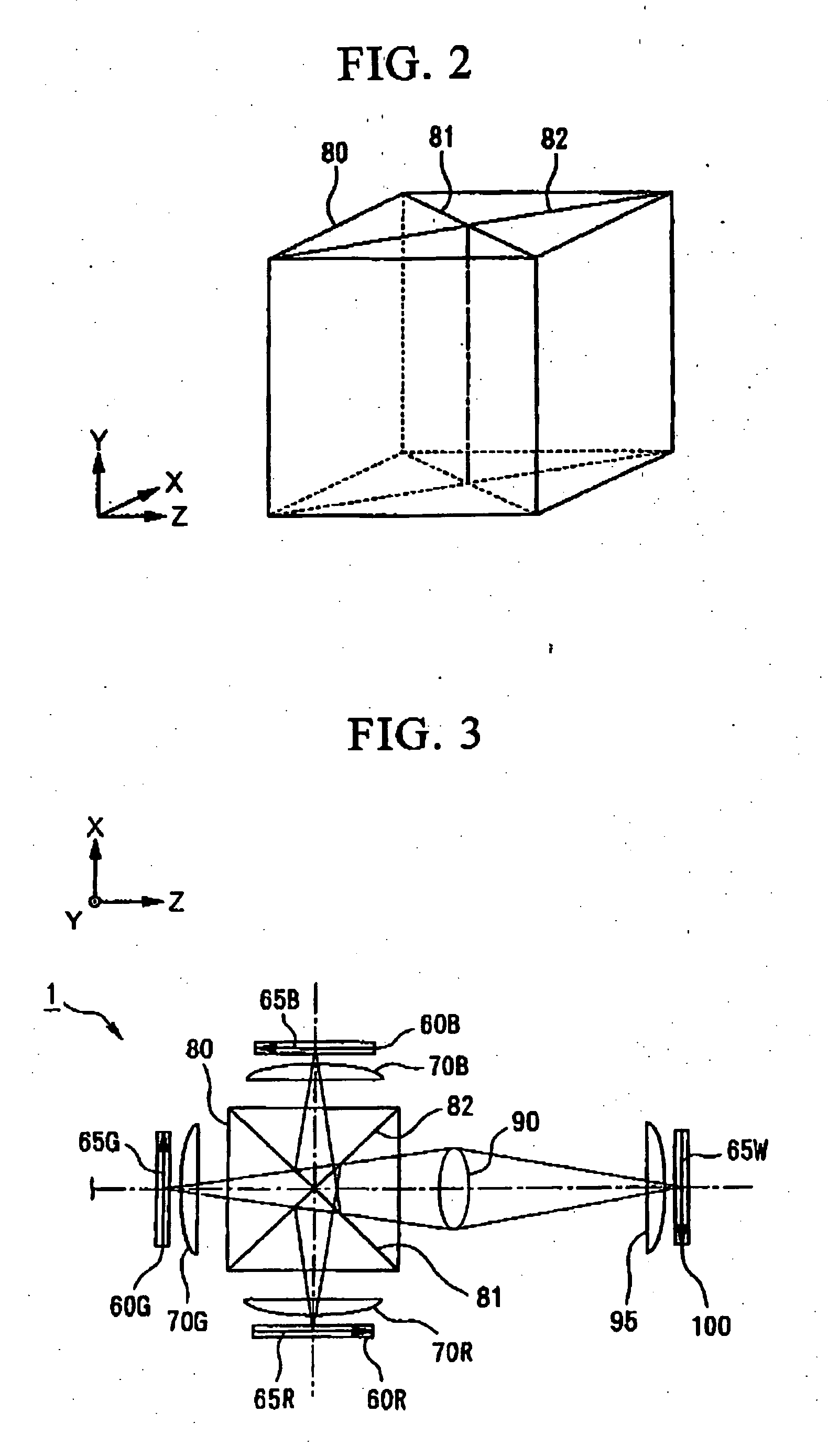
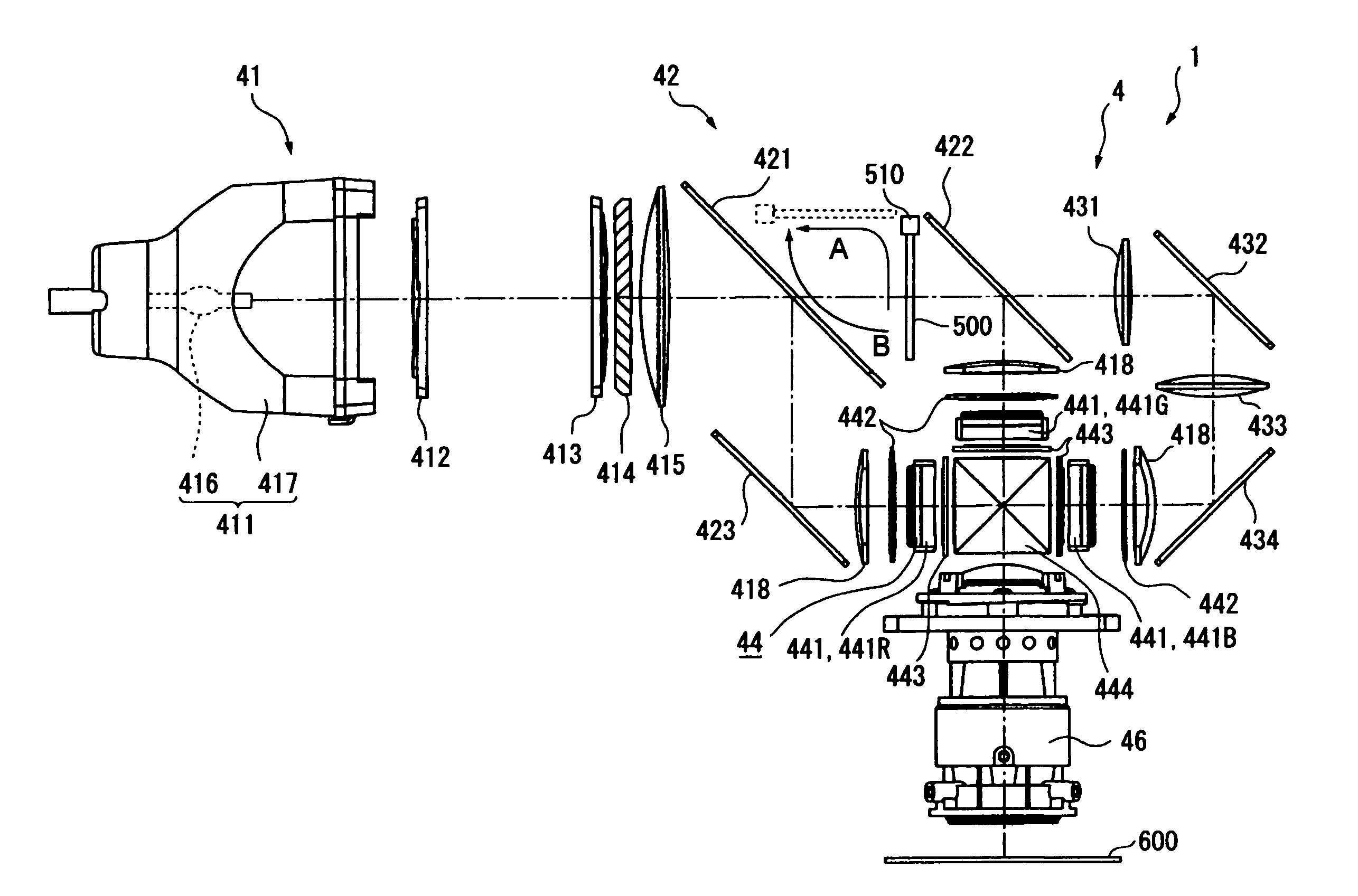
A projection-type display device 1 including a light source 10, an optical integrator 20, dichroic mirrors 30 and 35, a reflecting mirror 36, a relay optical system 40, parallelizing lenses 50B, 50G and 50R, liquid crystal light valves 60B, 60G and 60R, incident side lenses 70B, 70G and 70R, a light-synthesizing cross dichroic prism 80, a relay lens 90, an emergent side lens 95, a liquid crystal light valve 100 and a projection lens 110, and liquid crystal light valve 100 is provided in the rear stage of liquid crystal light valves 60B, 60G and 60R.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Optical device and projector
InactiveUS6854848B2Improve cooling effectSmall sizeTelevision system detailsProjectorsDichroic prismEngineering
The invention provides a structure to attach a liquid crystal panel to a prism, which enables further enhancements in cooling capabilities. The structure includes a storing member fixed on a base and holding a holding frame, where a liquid crystal panel is held. Erected pieces to form a space to receive the holding frame are formed protruding on both left and right sides at the light incident side. Protrusions to form an air path with a cross-dichroic prism are formed on both left and right sides on the light emitting side. The liquid crystal panel is attached to the cross-dichroic prism through a holding member having an opening at a portion corresponding to the panel face of the liquid crystal panel.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Illuminating device and backlight device employing the illuminating device
InactiveUS7344291B2Thin display thicknessImprove efficiencyMechanical apparatusPoint-like light sourceOptical propertyDichroic prism
Disclosed is an illuminating device which, as a light source for a backlight device, mixes the colors of light rays of three prime colors radiated by light emitting diodes to emit white light. The illuminating device includes a first light source (22R) radiating light rays of the first prime color, a second light source (22G) radiating light rays of the second prime color, a third light source (22B) radiating light rays of the third prime color, optical units (23R), (23G) and (23B) which refract divergent light rays contained in the light rays of the first prime color, emitted by the first light source (22R), the light rays of the second prime color, emitted by the second light source (22G) and in the light rays of the third prime color, emitted by the third light source (22B), to form collimated light rays, and triangular prisms (24) and (25) or a dichroic prism (26) mixing the light rays of the first, second and third prime colors, emitted by these optical units, by selective transmission and reflection, based on optical properties of the light rays of the respective prime colors.
Owner:SONY CORP
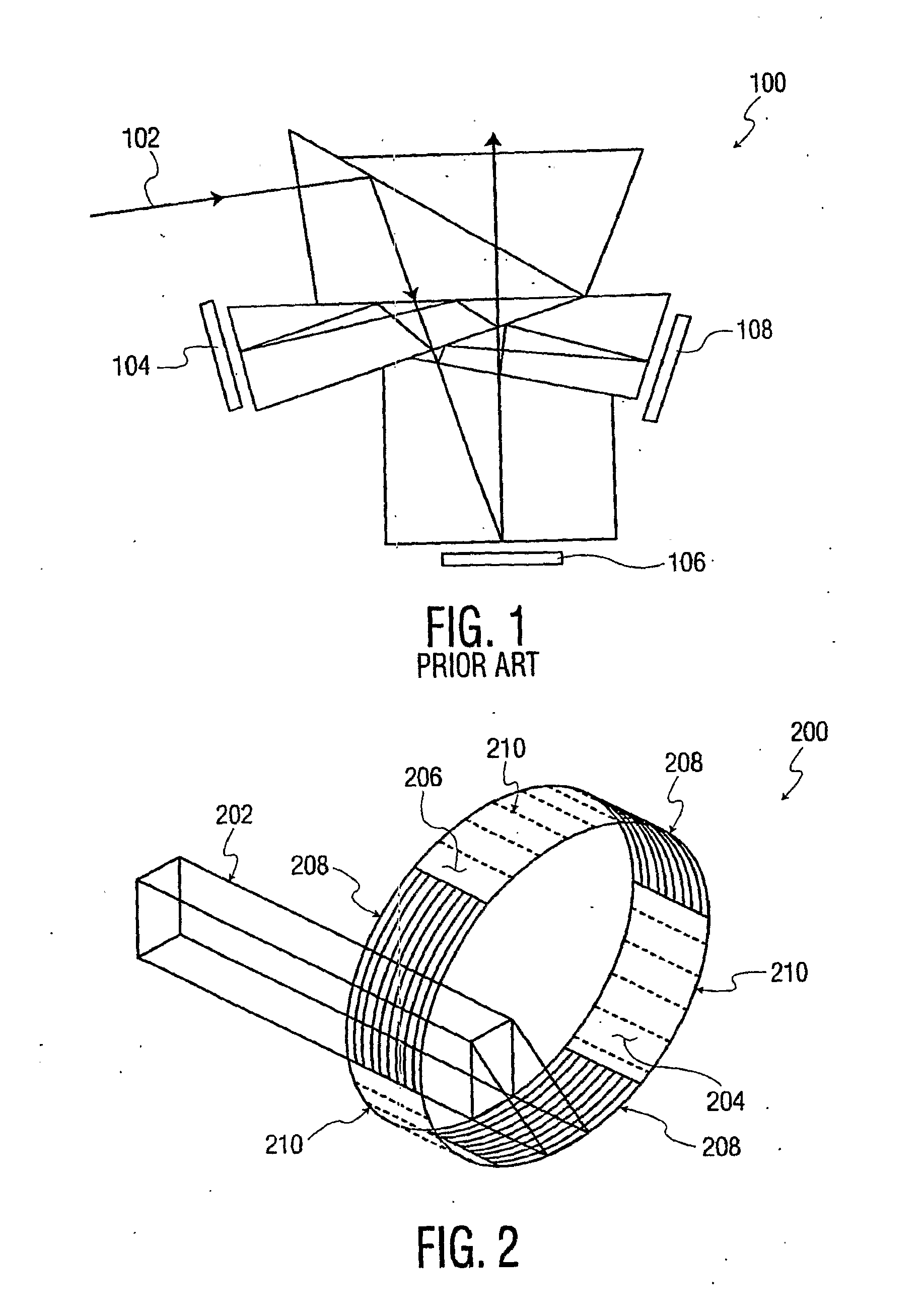
Producing colored light beams from white light
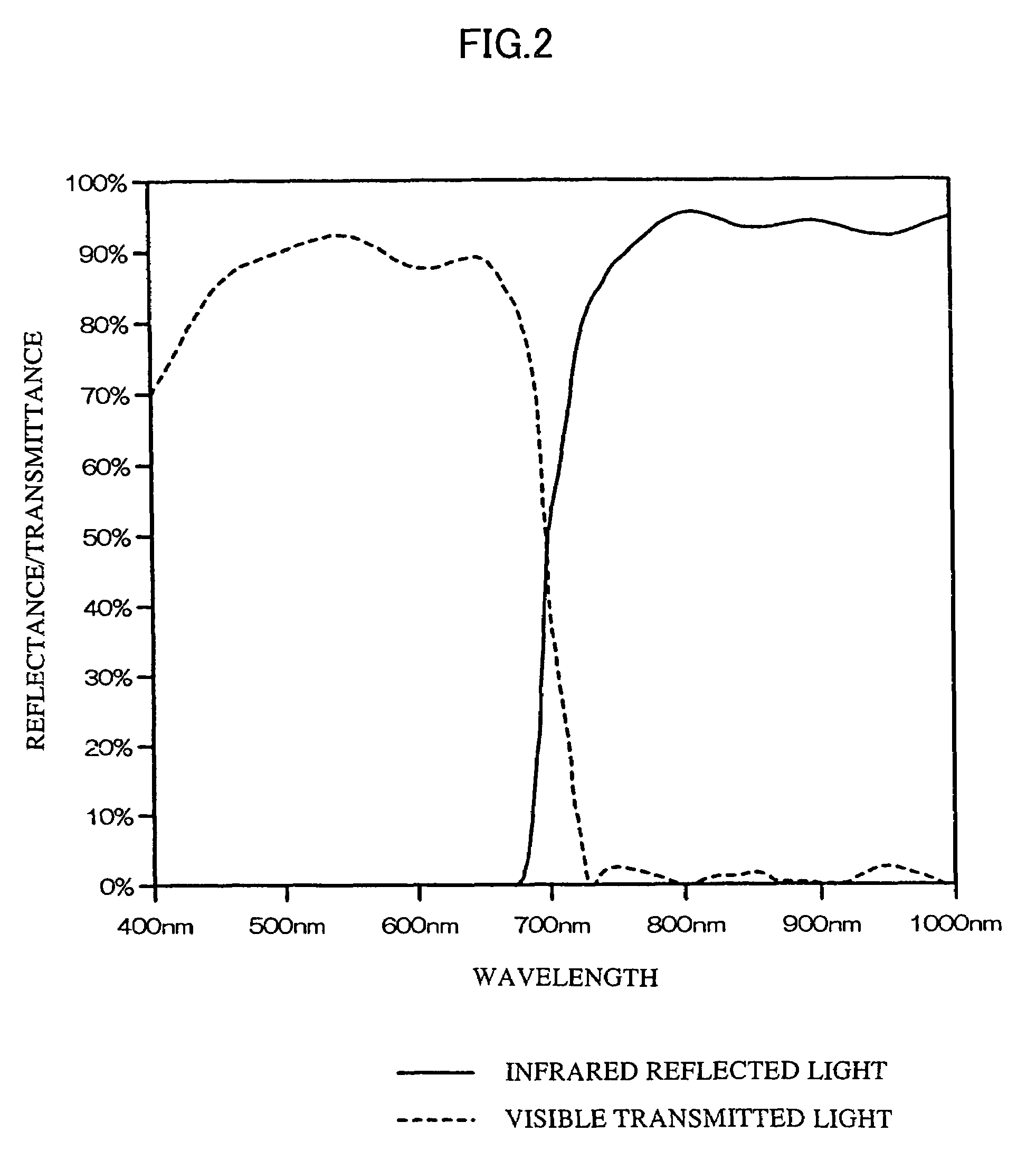
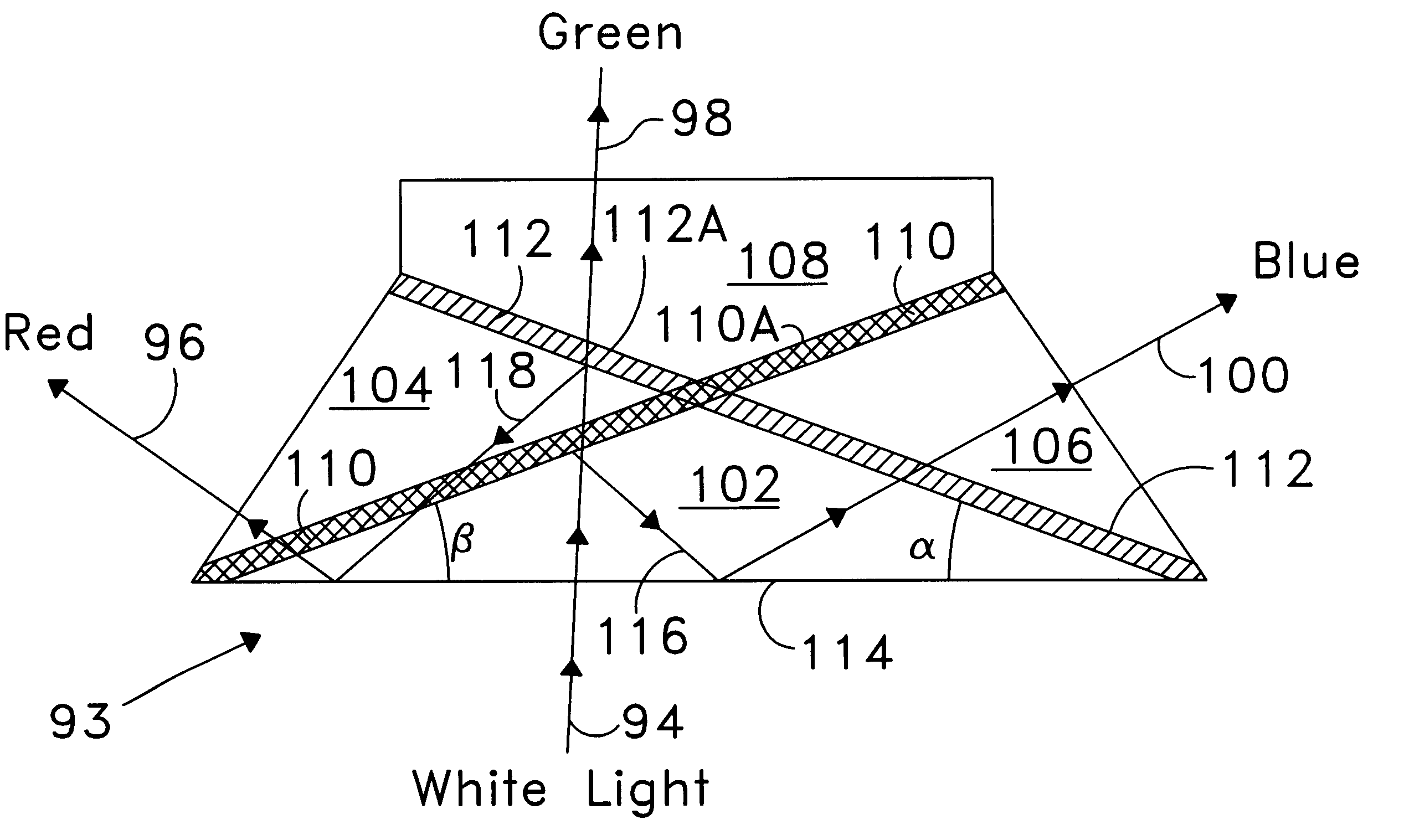
A color-separating prism includes first, second, and third component prisms that form first and second adjacent pairs of faces and include nonadjacent faces. The third component prism has a front surface or face. The color-separating prism includes a first reflective layer disposed in part between the first adjacent pair of faces and in part on one nonadjacent face and a second reflective layer disposed in part between the second adjacent pair of faces and in part on another nonadjacent face. The first and second reflective layers are inclined to reflect portions of light incident on the front surface back toward the front surface for total internal reflection. The color-separating may be used to produce narrow-spectral light from broader spectral light. A first portion of a light beam substantially in a first wavelength range is reflected from the first reflective layer back toward the front face of the prism. A second portion of the light beam substantially in a second wavelength range is reflected from the second reflective layer back toward the front face of the prism. The first and second portions are totally internally reflected from the front face. The color-separating prism can be used in display systems.
Owner:DUKE UNIV
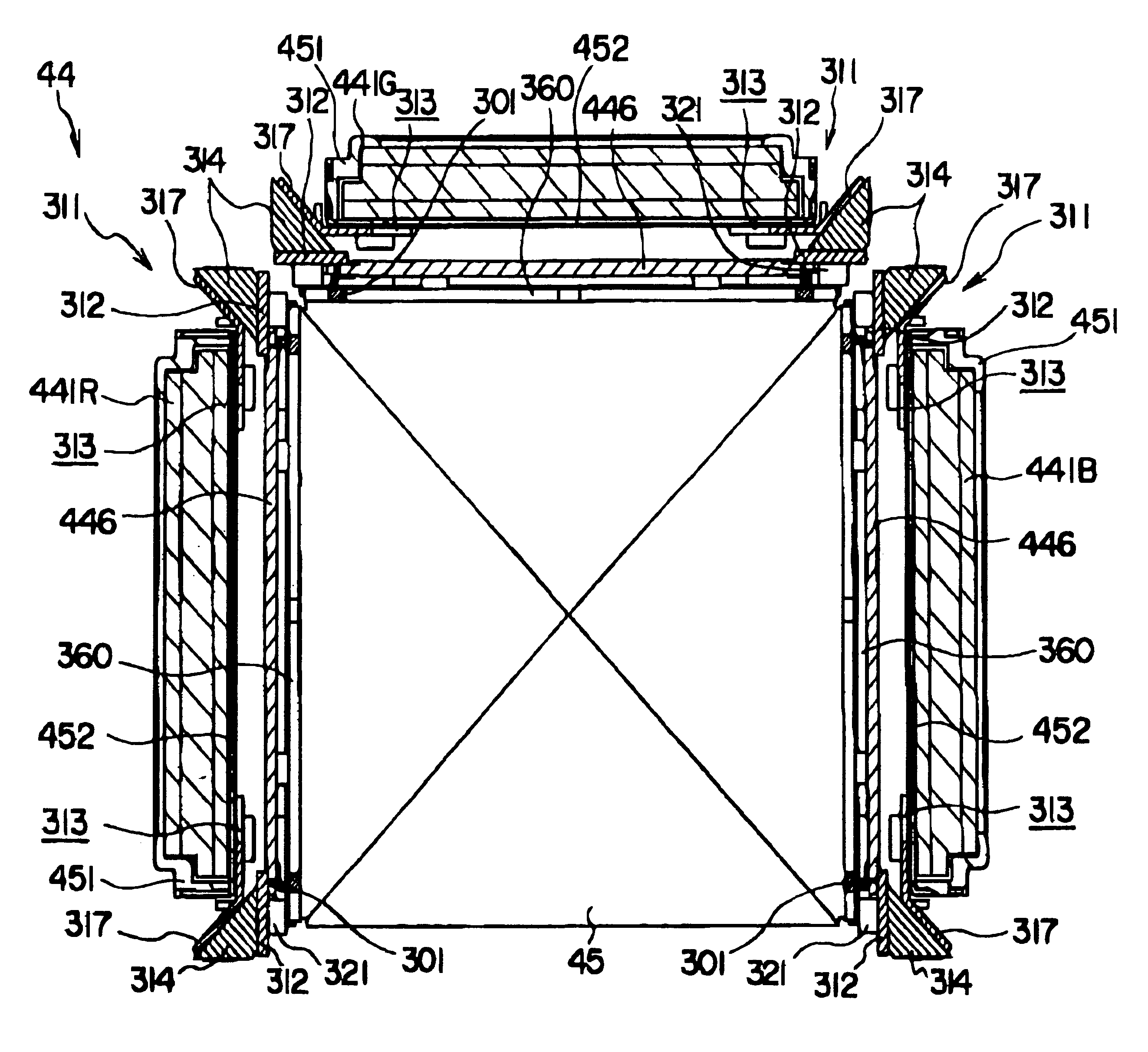
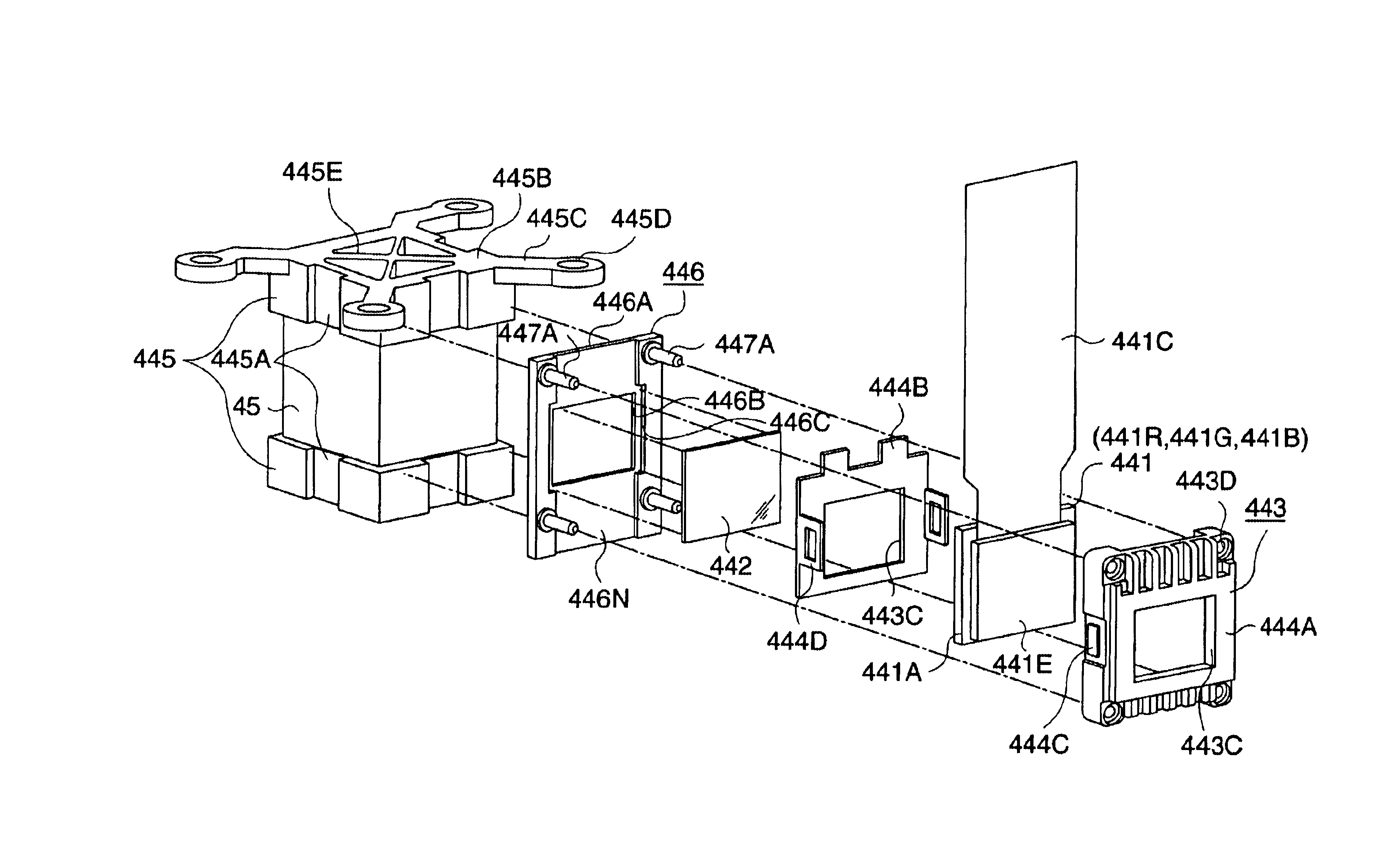
Cooling mechanism of optical modulator, optical modulator attachment unit and projector
InactiveUS6639743B2Improve cooling effectWell formedStatic indicating devicesProjectorsDichroic prismPolarizer
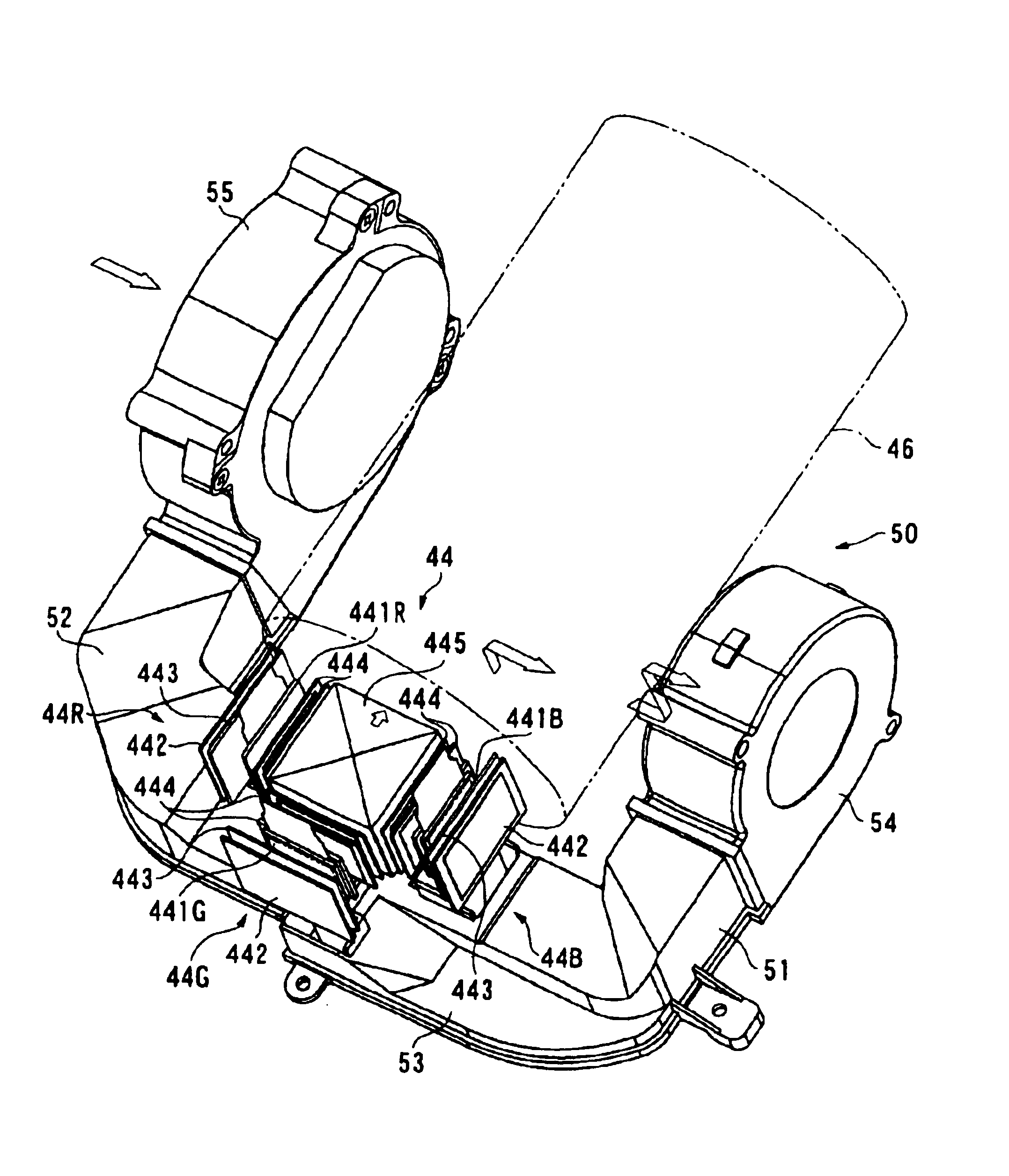
A support member (311) for supporting liquid crystal panels (441R, 441G, 441B) is disposed parallel to a cooling air flow channel formed between a light-incident end of a cross dichroic prism (45) and the respective liquid crystal panels and is constructed by a pair of components for supporting a neighborhood of the ends of the respective liquid crystal panels, so that the gap between the light-incident end of the cross dichroic prism and the respective liquid crystal panels facing the cooling air flow channel can be enlarged, thereby flowing cooling air sufficient for cooling a polarizer (446) and the respective liquid crystal panels in a direction of the cooling air flow channel for efficiently cooling them.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Imaging apparatus
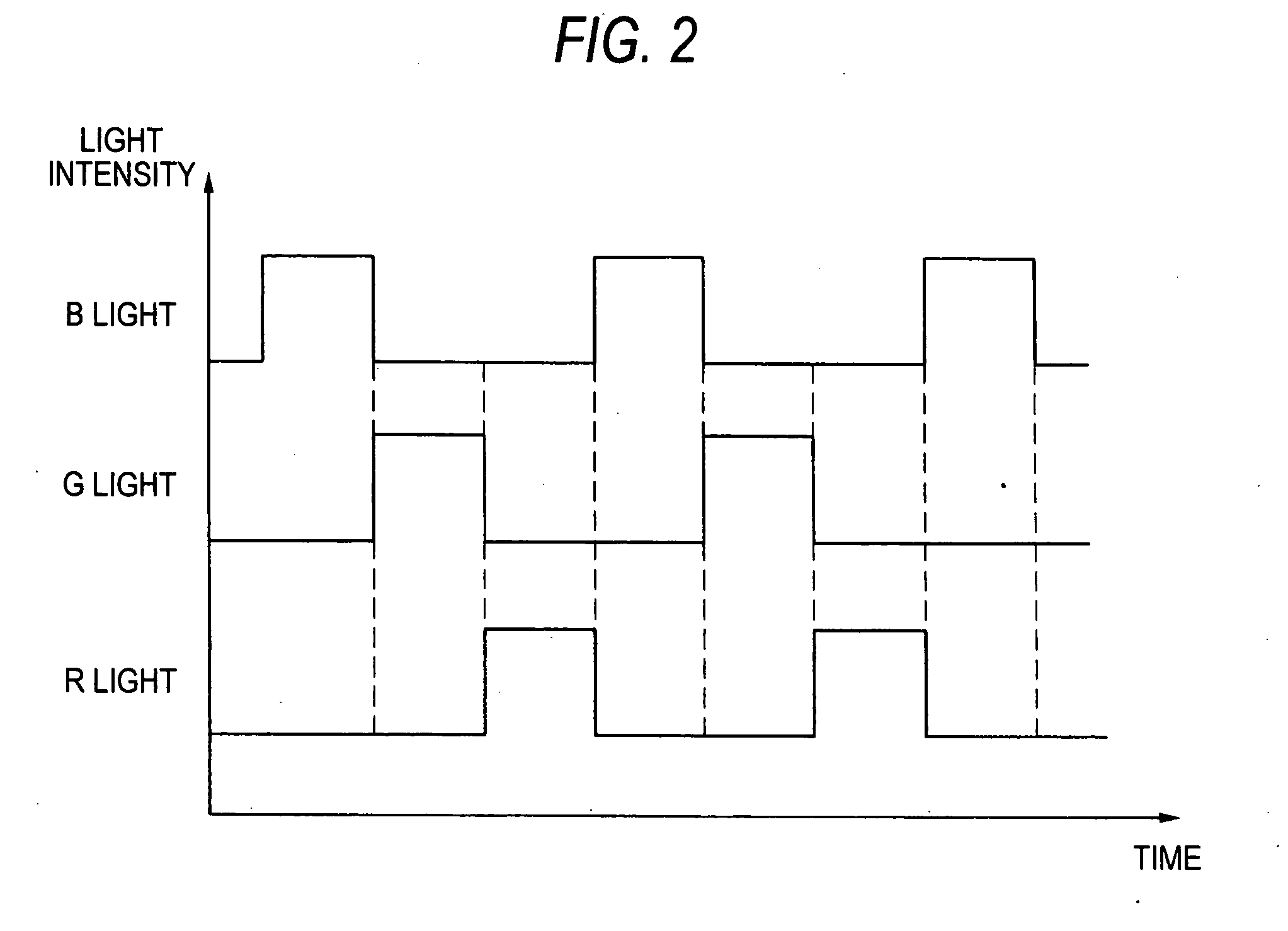
InactiveUS20060177208A1Low costSmall sizeTelevision system detailsCamera body detailsOptical axisDichroic prism
A lens unit is provided with two CCD image sensors and a color-separation prism for separating subject light into green light (G light), and a mixture of red light (R light) and blue light (B light). The color-separation prism allows the G light to enter into one of the CCD image sensors, and the mixture of the R and B light to enter into the other CCD image sensor. Sensor moving mechanisms drive the CCD image sensors individually in a plane perpendicular to an optical axis when camera shake is detected, thereby preventing the image from blurring.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP +1
Liquid crystal display device and liquid crystal projector device
InactiveUS20030147036A1Solve the real problemAvoid reliabilityTelevision system detailsStatic indicating devicesDichroic prismEngineering
The present invention is a liquid crystal projector device using a liquid crystal panel. The device mounts a liquid crystal panel (16) on a light incident plane of a polyhedral dichroic prism (23) in a bonded state so as to integrate the panel with the prism, and comprises a heat sink (29) and a heat pipe (31) which forcedly cools the integrated structure statically. The liquid crystal projector device comprising the structure describe above cools the liquid crystal panel efficiently without bringing any trouble caused by fan noise or raise of dust.
Owner:SONY CORP
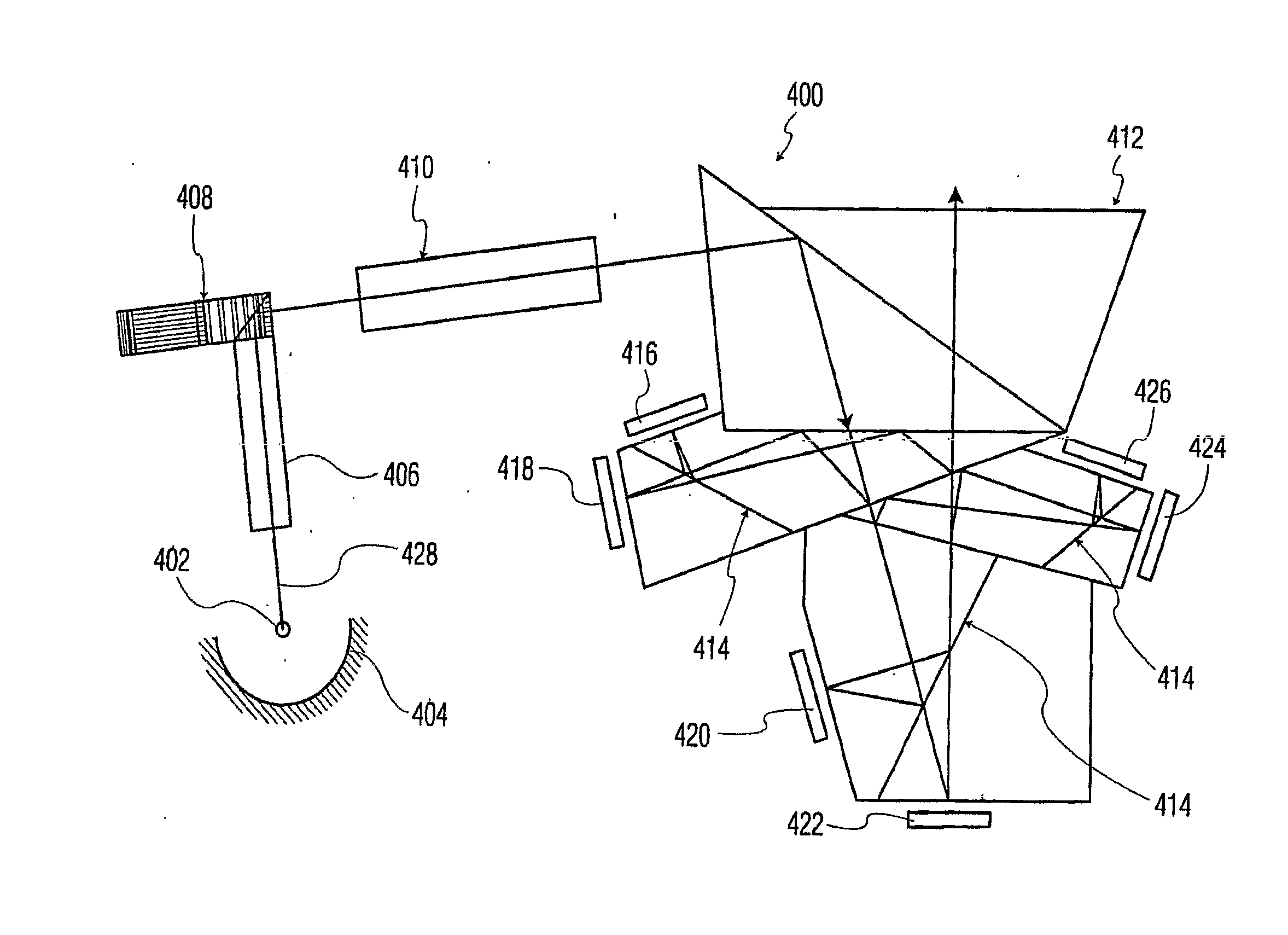
Wide color gamut projector
A wide color gamut projector having a plurality of dichroic prisms configured to split a light beam into six primary color components and direct each of the six primary color components to separate digital micromirror devices is disclosed. The projector further comprises a translucent rotatable drum having different polarization sections, wherein the light beam is capable of being passed orthogonally through a wall of the drum.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL CE PATENT HLDG
Projector
InactiveUS20050162621A1Shorten the timePrecise positioningPrismsProjectorsLiquid-crystal displayDichroic prism
In a base plate, projections for being inserted into openings in a lower bracket, and for supporting a bottom surface of a cross-dichroic prism, are provided. The lower bracket and the cross-dichroic prism are fixed to the base plate by adhesive agent filled into a clearance between the lower bracket and the bottom surface of the cross-dichroic prism supported on the projections. Holes are provided on a liquid-crystal panel, and holding arms provided on an upper bracket and the lower bracket are inserted into the holes. Then the adhesive agent is applied into the holes to fix the liquid-crystal display to the upper and lower brackets.
Owner:FUJI PHOTO OPTICAL CO LTD
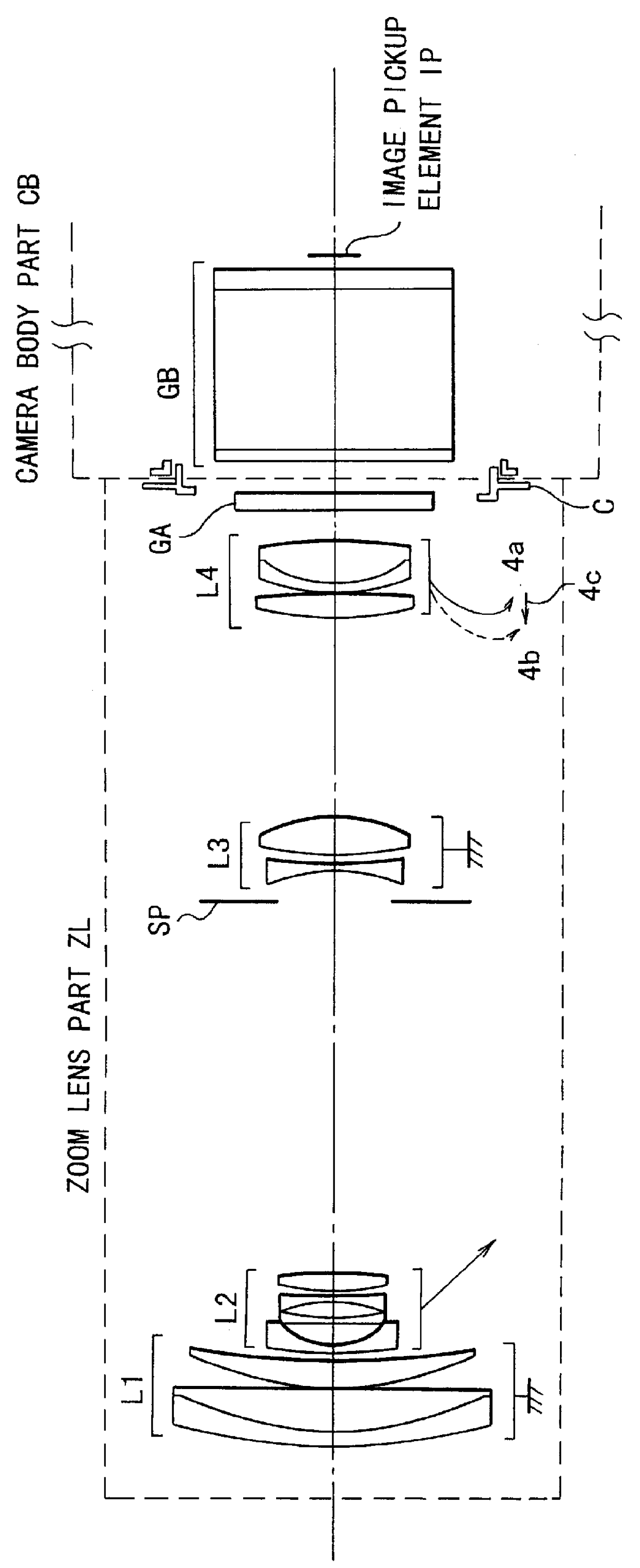
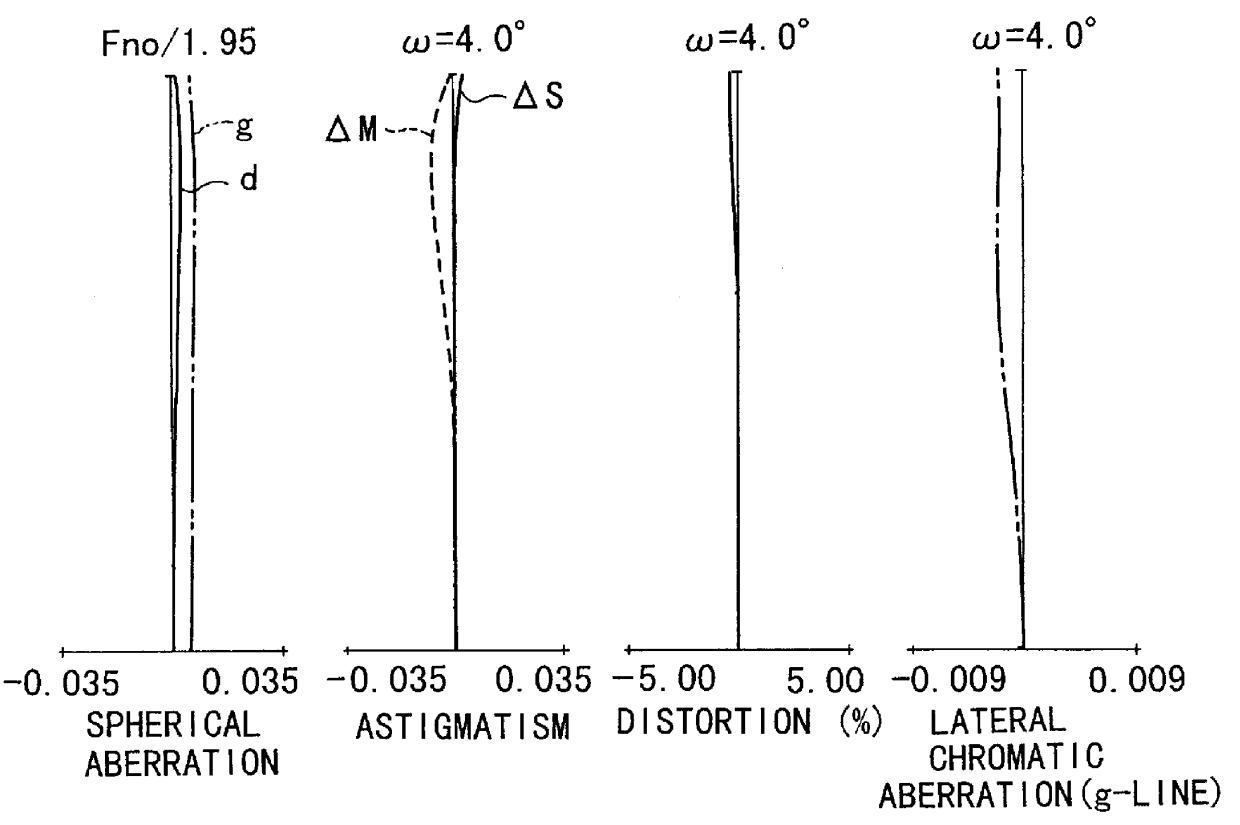
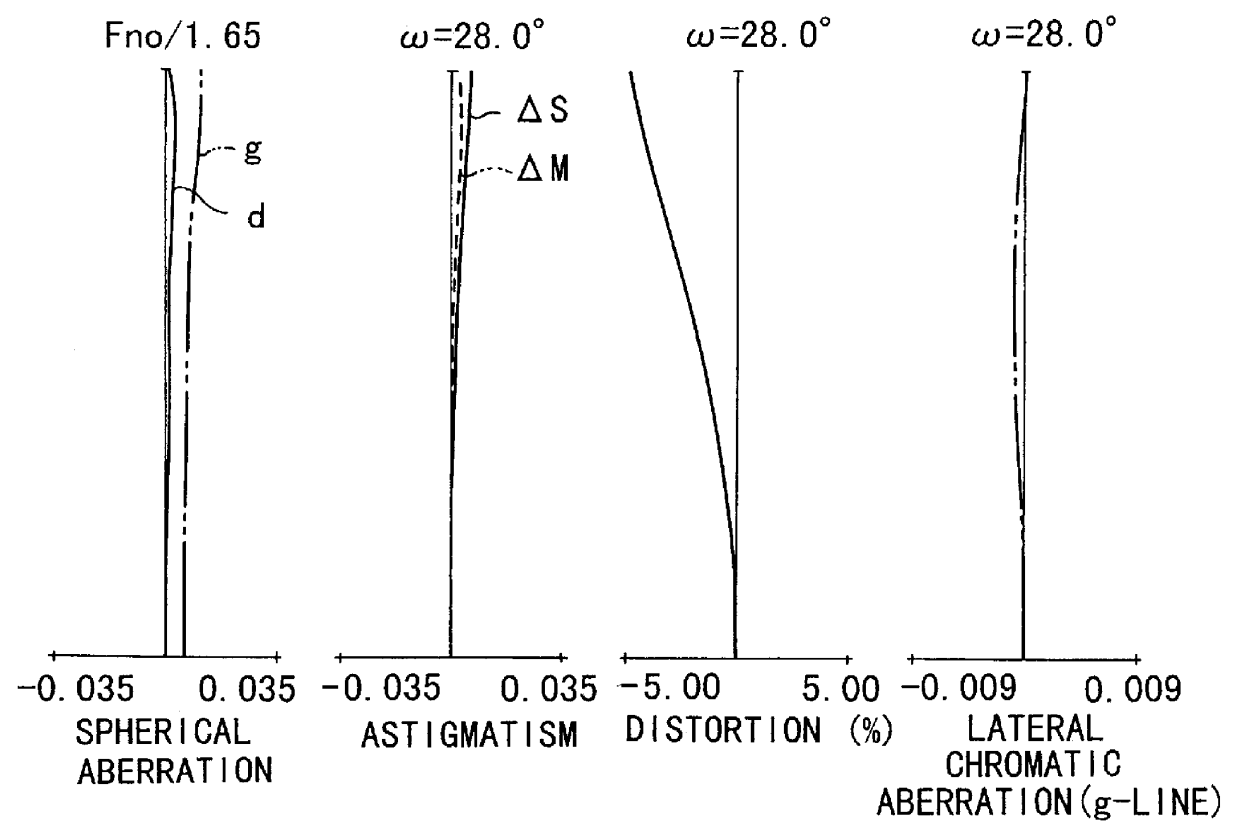
Zoom lens of rear focus type and image pickup apparatus
A zoom lens of the rear focus type having an increased range with the back focal length long enough to accommodate a color separation prism, includes, in order from an object side to an image side, a first lens unit of positive refractive power, a second lens unit of negative refractive power, a third lens unit of positive refractive power and a fourth lens unit of positive refractive power, the second and the fourth lens units moving axially to effect zooming and the fourth lens unit moving axially to effect focusing, wherein the second lens unit is constructed with a negative first lens, a negative second lens, a negative third lens and a positive fourth lens.
Owner:CANON KK
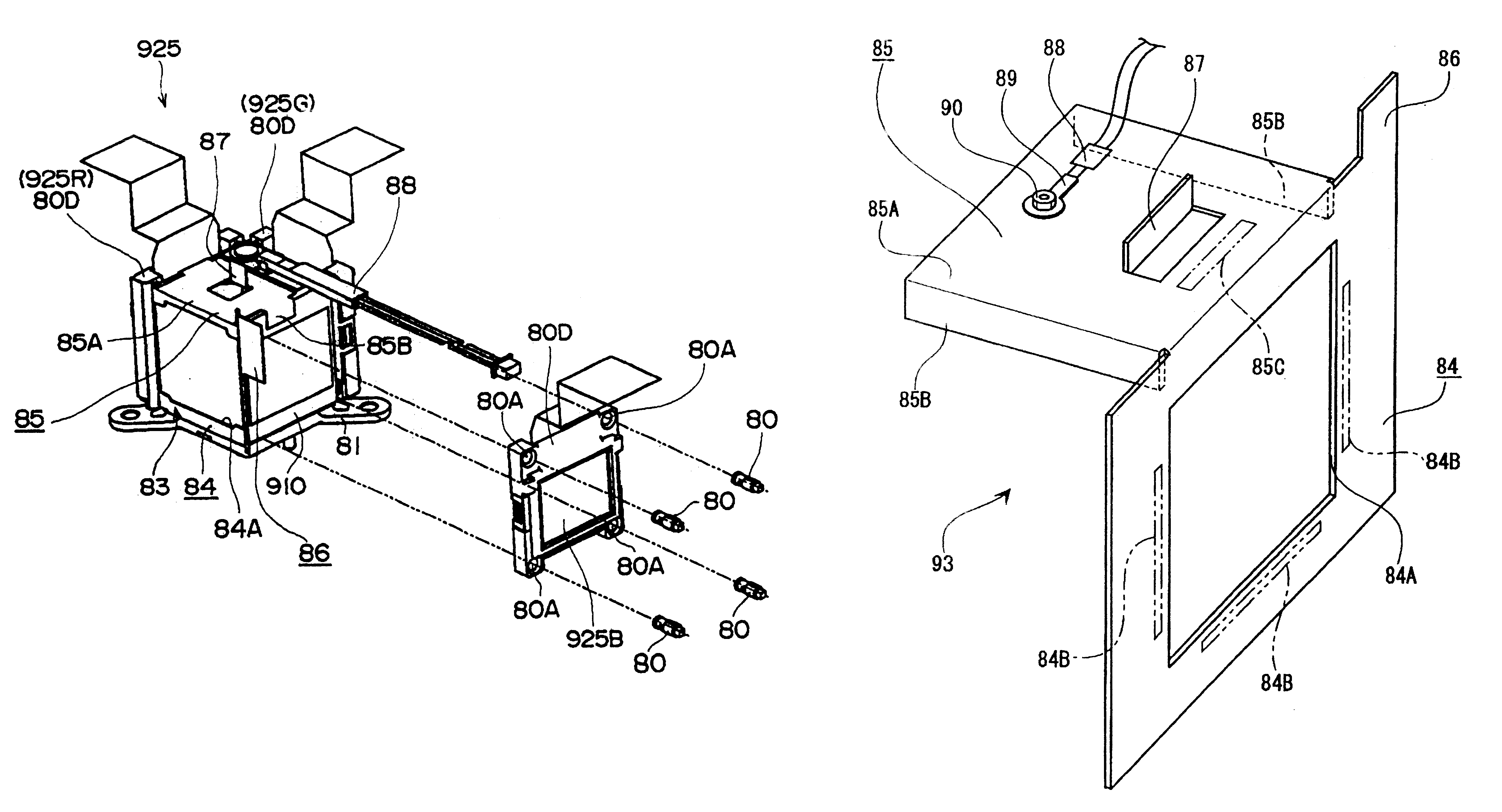
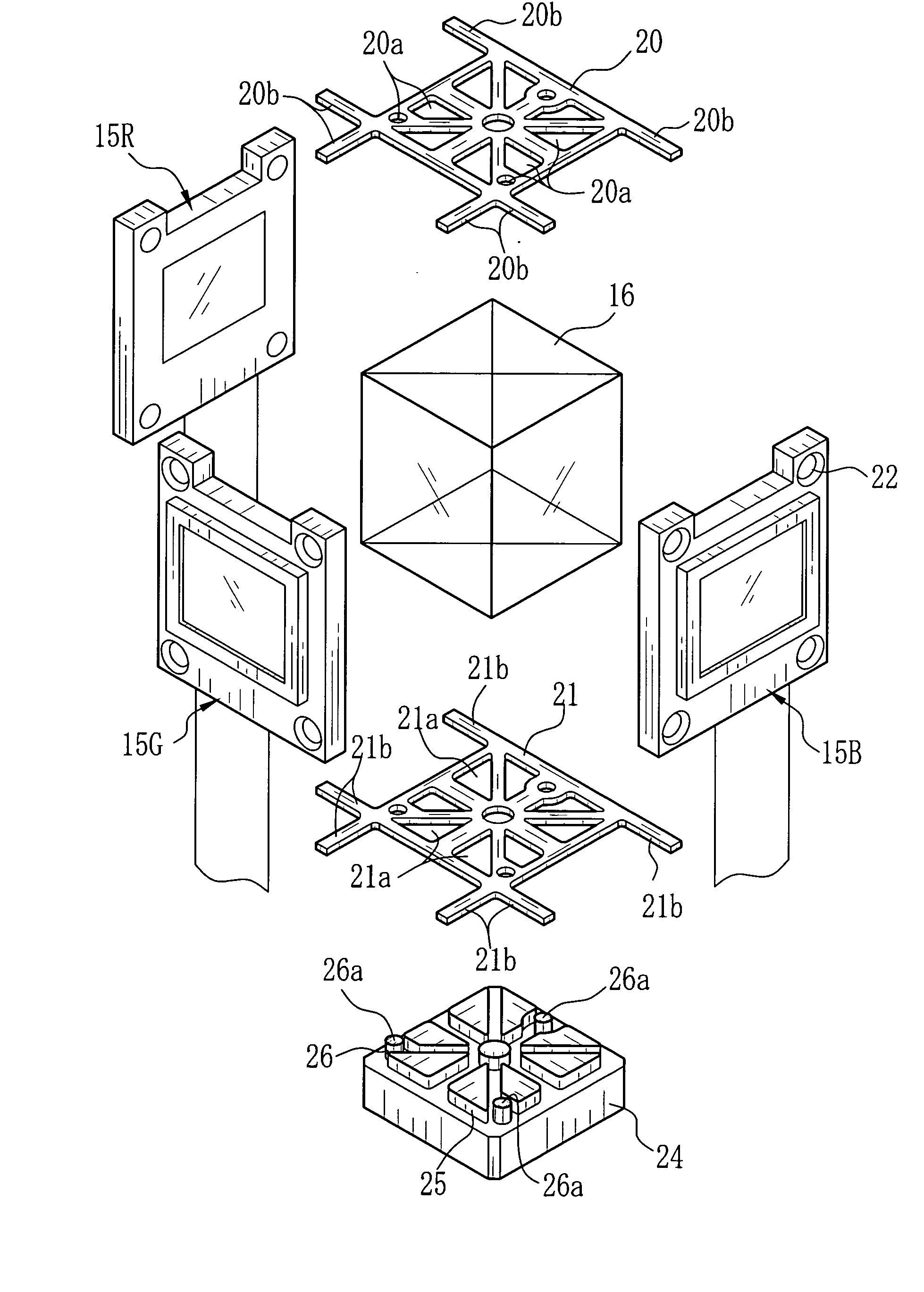
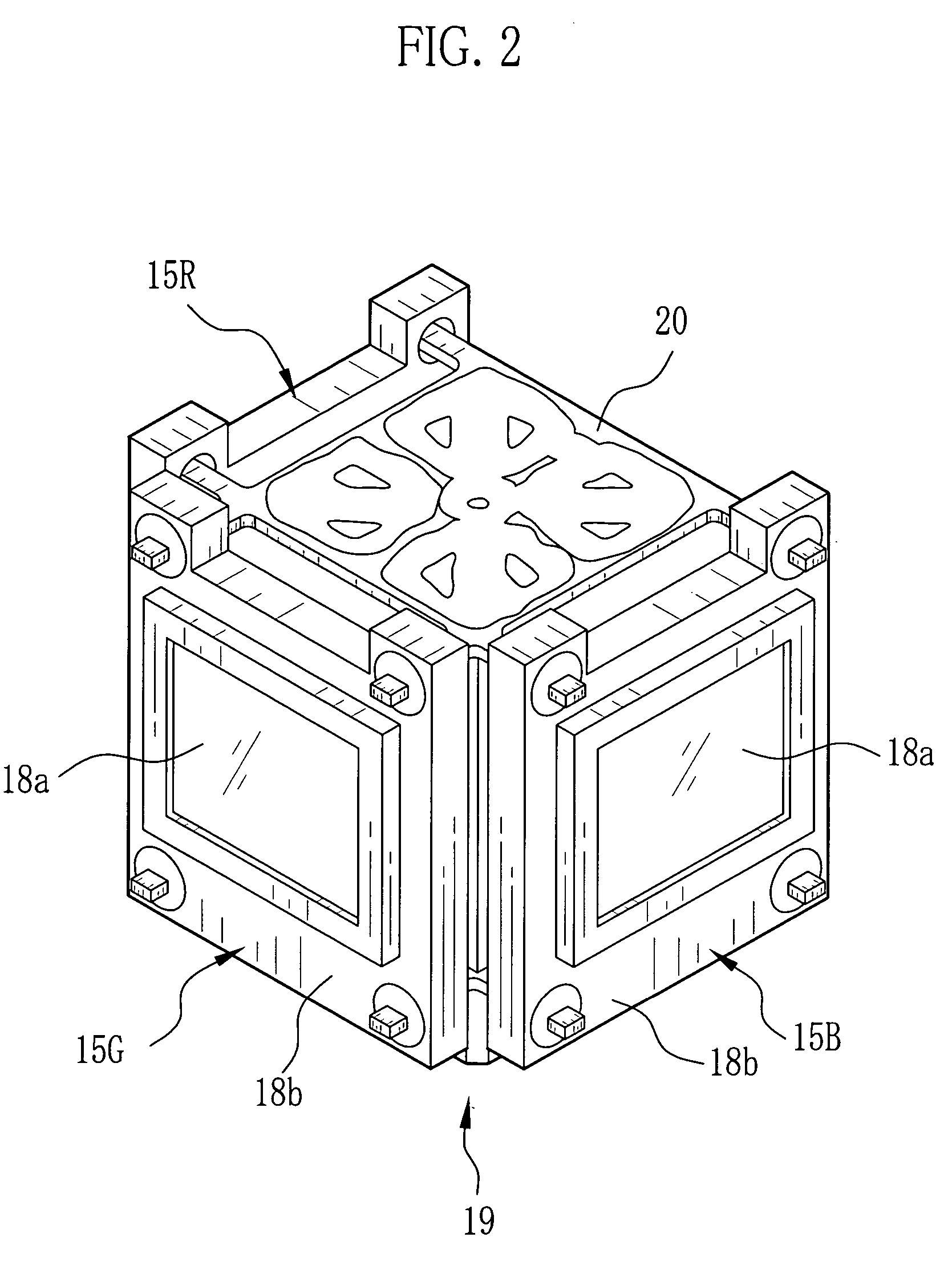
Optical device, method for manufacturing optical device, and projector
InactiveUS6935745B1Simple structureReduce manufacturing stepsTelevision system detailsProjectorsDichroic prismImaging quality
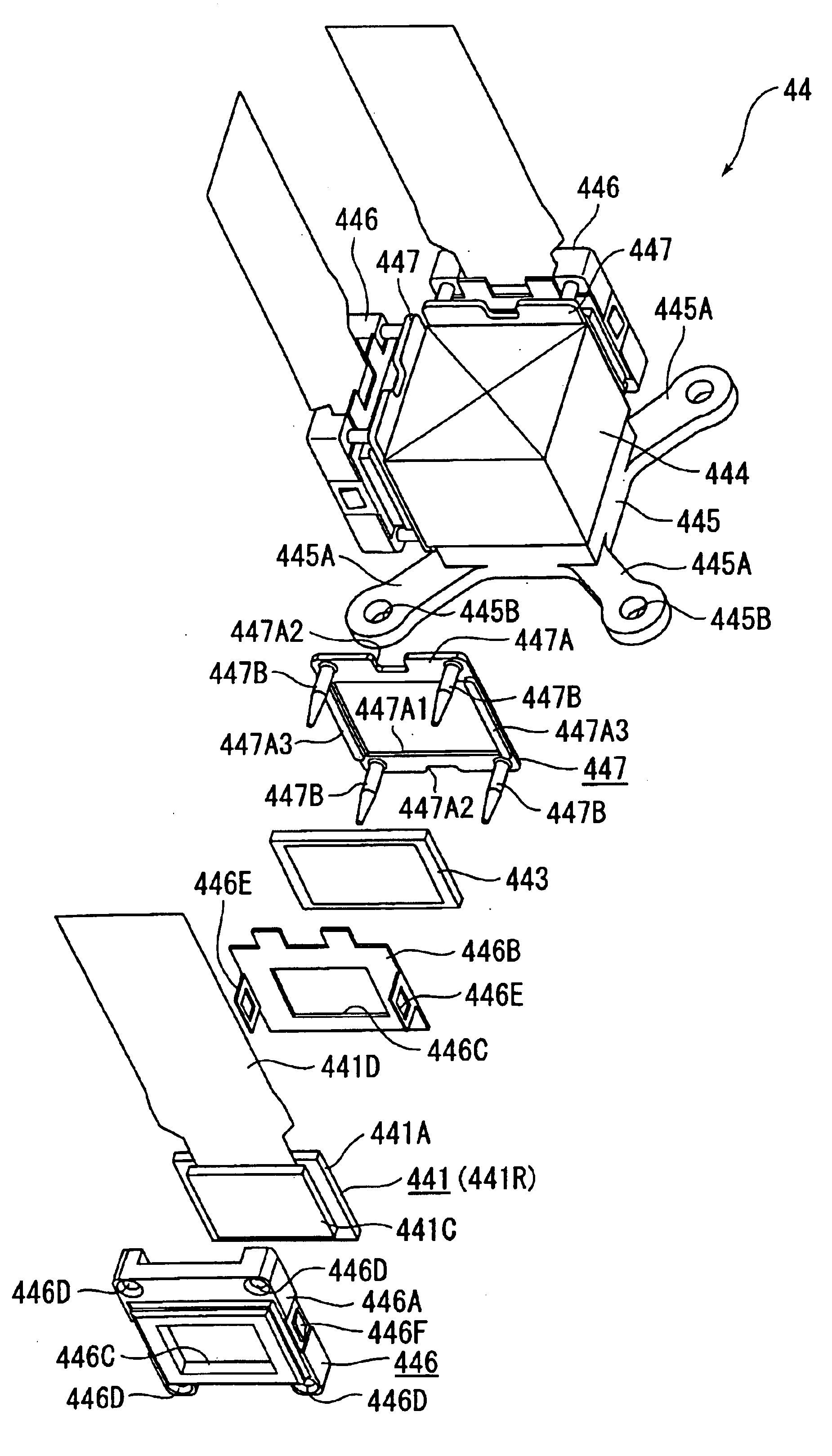
The present invention provides an optical device that achieves reduction in size, reduction in manufacturing costs, improved image quality, and so forth, by simplification and the like of a panel in prisms (POP) structure wherein light-modulating devices and a color synthesizing optical element are integrally formed. A POP structure is configured wherein pins integrally formed with a holding member are inserted through holes formed in the four corners of holding frames storing the liquid crystal panelsso as to fix the holding frames and holding members by adhesion. End faces of holding members opposite to the pins are fixed by adhesion to the side faces of bases fixed on the upper and lower faces of a cross-dichroic prism.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Light source device and projector
InactiveUS20070127240A1Improve utilization efficiencyBroad emissionColor photographyColor television detailsDichroic prismRefractive lens
An R-light optical system 14, a G-light optical system 15, and a B-light optical system 16 are disposed correspondingly to an R-light LED chip 11, a G-light LED chip 12, and a B-light LED chip 13, which emit an red light (R light), a green light (G light), and a blue light (B light), respectively. The R-light optical system 14, the G-light optical system 15, and the B-light optical system 16 are formed by combining a reflecting plate, a refractive lens, and a diffraction grating appropriately. The R-light optical system 14, the G-light optical system 15, and the B-light optical system 16 distribute all of the R light, the G light, and the B light, which are diffused widely, toward a cross dichroic prism 17.
Owner:FUJI PHOTO OPTICAL CO LTD
Projector
InactiveUS6986582B2Reduce noiseImprove cooling efficiencyTelevision system detailsProjectorsDichroic prismMiniaturization
An aspect of the invention provides a duct capable of cooling optical modulation systems with high efficiency while realizing miniaturization and reduction of the mounted number of cooling fans. The duct can be used for a projector including plural optical modulation systems, a dichroic prism, and a projection lens, and the respective optical modulation systems include liquid crystal panels, entrance side polarization plates, viewing angle correction plates, and exit side polarization plates. The duct can have plural air guide paths through which cooling air passes, a discharge opening, entrance side discharge openings, and exit side discharge openings formed in these air guide paths. With the optical modulation systems as targets of independent cooling, the entrance side discharge openings and the exit side discharge openings with respect to the targets of independent cooling are formed in different air guide paths.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Cooling mechanism of optical modulator, optical modulator attachment unit and projector
InactiveUS20020036819A1Improve cooling effectWell formedStatic indicating devicesProjectorsDichroic prismPolarizer
A support member (311) for supporting liquid crystal panels (441R, 441G, 441B) is disposed parallel to a cooling air flow channel formed between a light-incident end of a cross dichroic prism (45) and the respective liquid crystal panels and is constructed by a pair of components for supporting a neighborhood of the ends of the respective liquid crystal panels, so that the gap between the light-incident end of the cross dichroic prism and the respective liquid crystal panels facing the cooling air flow channel can be enlarged, thereby flowing cooling air sufficient for cooling a polarizer (446) and the respective liquid crystal panels in a direction of the cooling air flow channel for efficiently cooling them.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Projector
ActiveUS20040246448A1Reduce and prevent contrastProjectorsPicture reproducers using projection devicesDichroic prismOptical axis
A projector includes a light source, a color separating optical system, liquid crystal panels, a cross dichroic prism, and a projection lens, in which an optical filter is disposed to reflect a predetermined spectral component in the light flux between a dichroic mirror and a dichroic mirror where an angle by which the light flux expands falls within 20° with respect to an illumination optical axis L of the light flux on an optical path from the light source device to a light flux-emitting surface of the projecting lens. Thus, carrying out spectrum correction can reduce or prevent the contrast degradation of the projected image. Furthermore, it allows the difference of an incident angle to the light flux-incident surface of the light flux to be smaller, thereby reducing color unevenness.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
2-dimensional image display device or illumination device for obtaining uniform illumination and suppressing speckle noise
InactiveUS8016428B2Suppress speckle noiseUniform lightProjectorsColor photographyColor imageDichroic prism
A 2-dimensional beam scan unit reflects emission beams from a red laser light source, a green laser light source and a blue laser light source and scans in a 2-dimensional direction. Diffusion plates diffuse the respective light beams scanned in the 2-dimensional direction to introduce them to corresponding spatial light modulation elements. The respective spatial light modulation elements modulate the respective lights in accordance with video signals of the respective colors. A dichroic prism multiplexes the lights of the three colors after the modulation and introduces the multiplexed lights to a projection lens so that a color image is displayed on a screen. Since the 2-dimensional light emitted from the beam scan unit is diffused to illuminate the spatial light modulation element, it is possible to change the optical axis of the beam emerging from the light diffusion member for irradiating the spatial light modulation element moment by moment, thereby effectively suppressing speckle noise.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Optical device and projector
ActiveUS6866389B2ObtainedProjected image is blockedProjectorsNon-linear opticsDichroic prismImage formation
An optical device (44) has a holding frame (446) that holds a liquid crystal panel (441) as an optical modulator and has an opening (446C) at a part corresponding to an image formation area of the liquid crystal panel (441), and a panel fixing plate (447) disposed between the holding frame (446) and a cross dichroic prism (444). The panel fixing plate (447) is made of a component having a thermal expansion coefficient lying midway between the thermal expansion coefficients of the holding frame (446) and the cross dichroic prism (444). The liquid crystal panel (441) is fixed on a side of the cross dichroic prism (444) through the holding frame (446) and the panel fixing plate (447). Accordingly, a thermal stress generated on the boundaries between the panel fixing plate (447), and the holding frame (446) and the cross dichroic prism (444) are reduced, thereby preventing the position shift of the liquid crystal panel (441).
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Rear projection display
InactiveUS20060139577A1Easily broughtImprove performanceBuilt-on/built-in screen projectorsColor television detailsLiquid-crystal displayLed array
A rear projection display, not requiring a dichroic prism, and capable of rendering a generation system of each image light in color independent of the other generation systems so as to optimally construct and improve easiness of assembly of, and so on, each generation system, is provided. Each unit for projecting image-light is formed of an LED array, a rod integrator, a liquid crystal display panel, and a projection lens. A projection optical axis of the projection lens of each unit for projecting image-light is parallel each other. A unit for projecting image light in red is provided with an LED array for emitting light of a wavelength band in red, a unit for projecting image light in green is provided with an LED array for emitting light of a wavelength band in green, and a unit for projecting image light in blue is provided with an LED array for emitting light of a wavelength band in blue. Each image light in color obtained as a result of passing through the liquid crystal display panel is projected by the projection lens, and displayed on a screen. As a result, each image light in color is superposed on the screen, and an image in full color is displayed.
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
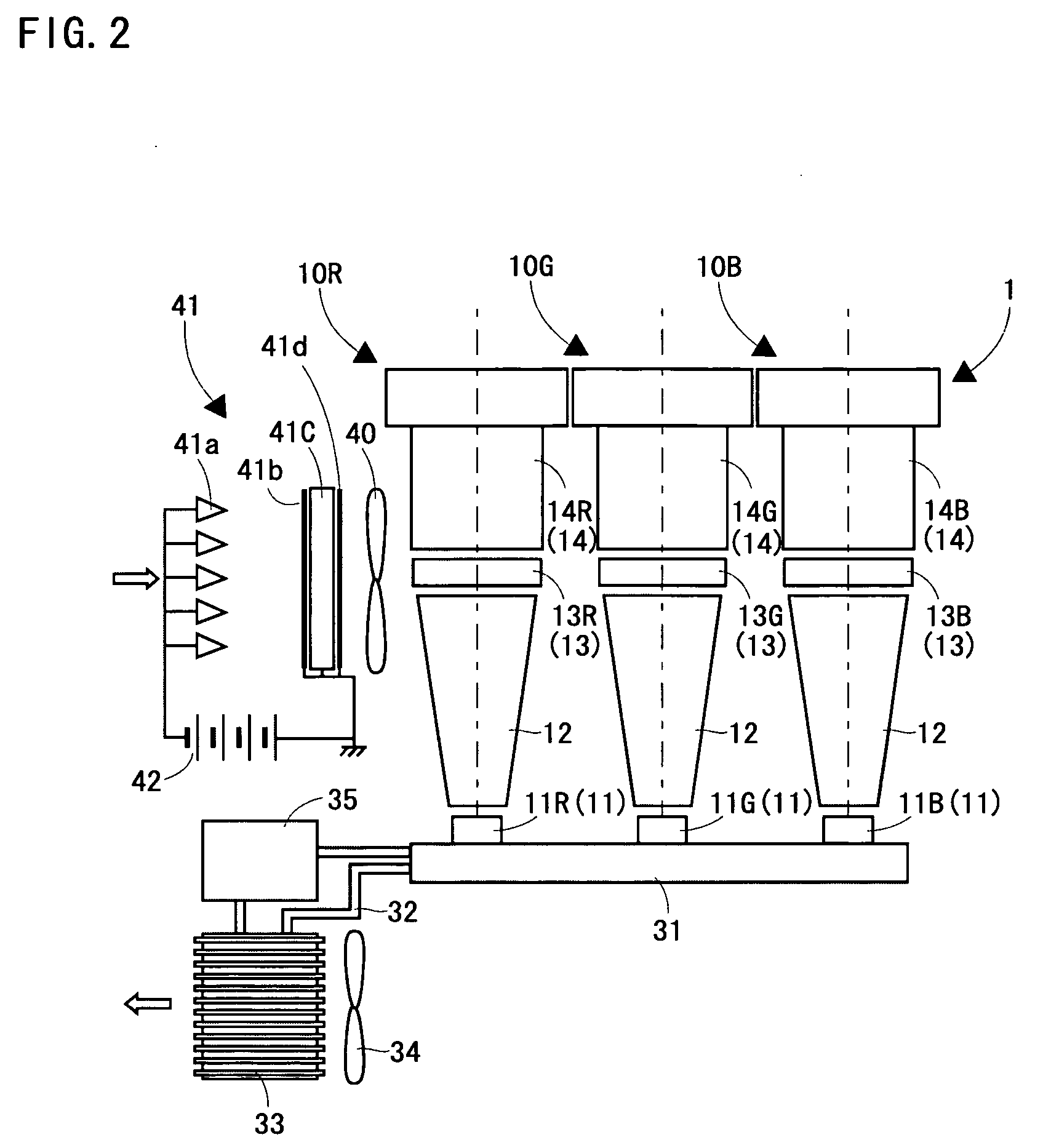
Optical arrangement for non-inverting illumination system
ActiveUS20050185143A1Reduce chanceAvoiding orTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsColor imageDichroic prism
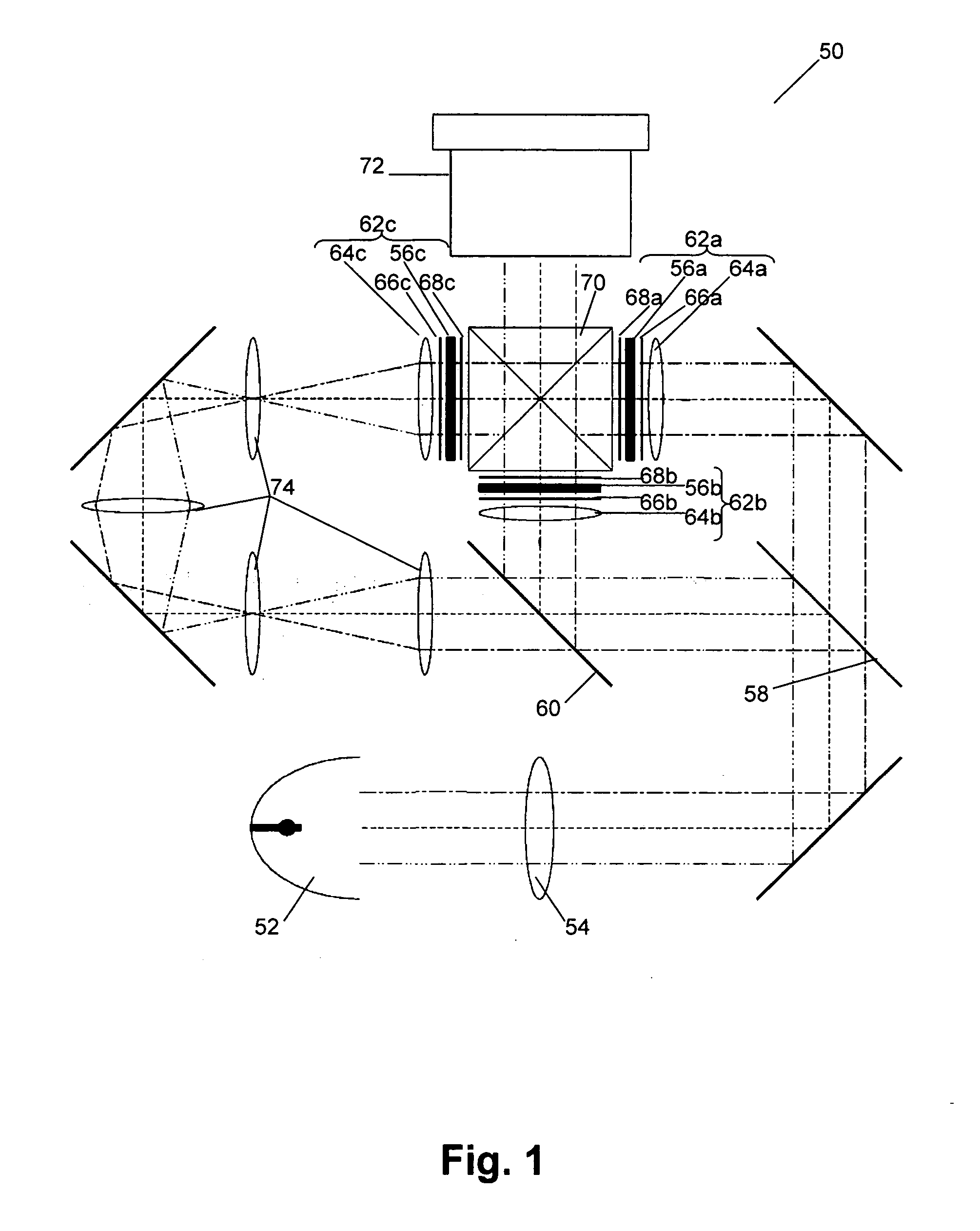
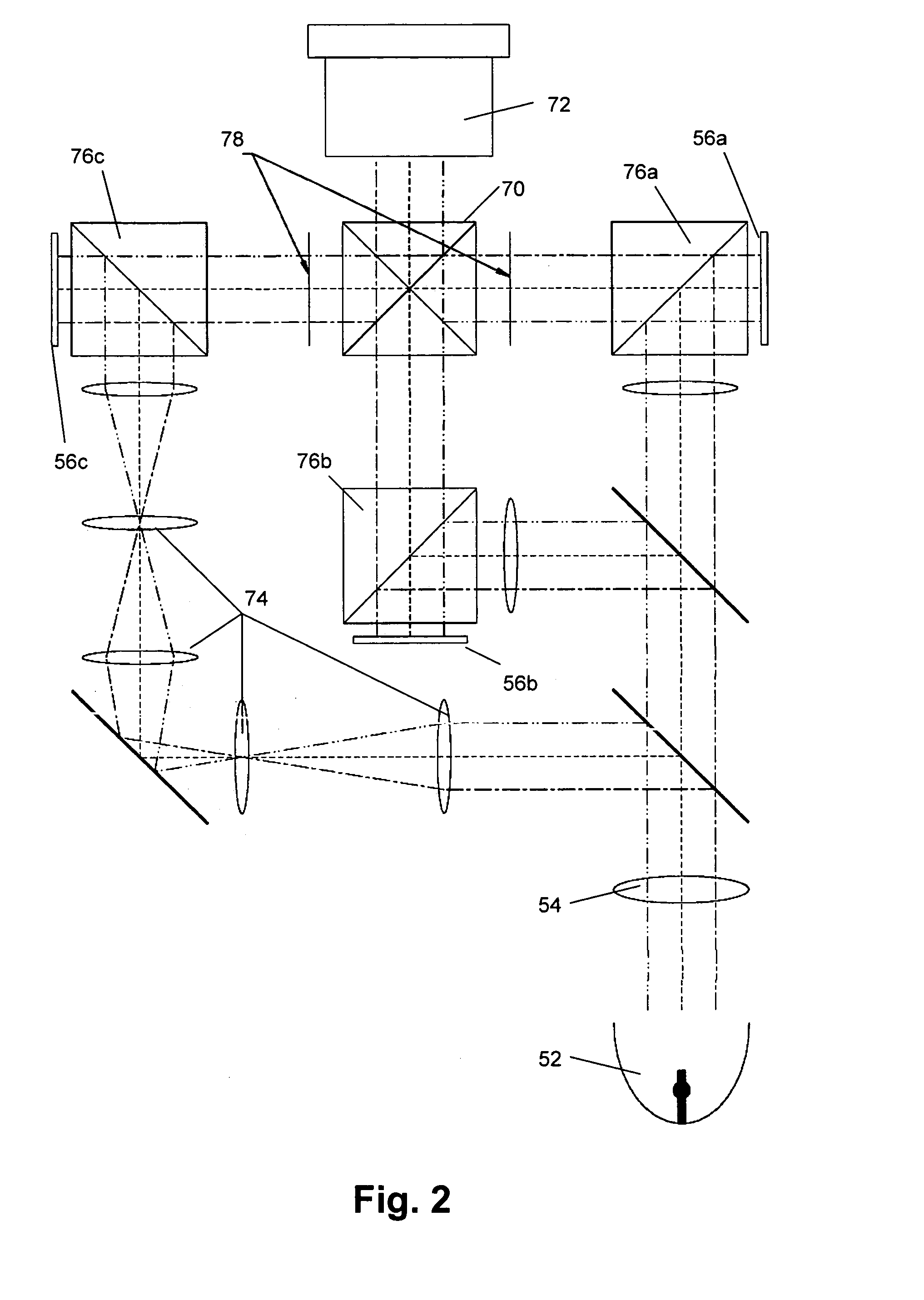
An optical design is described to be used in a color projection system. The system comprises a white light source (52), a light splitting means to split the white beam into color subbeams, optical components to direct each color subbeam on a light modulating means (56) and a dichroic prism (70). The light splitting means and the optical components are arranged such that each of the images of the color subbeams imaged on the light modulating means (56) has equal size and orientation, i.e. such that the magnification of the color subimage on the light modulating means (56) is equal. This is obtained by providing equal light paths for each color subbeam or by providing optical components such that either all different color images on the screen are inverted or none of the different color images are inverted.
Owner:BARCO NV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com