Patents
Literature
376results about How to "Increase the working distance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
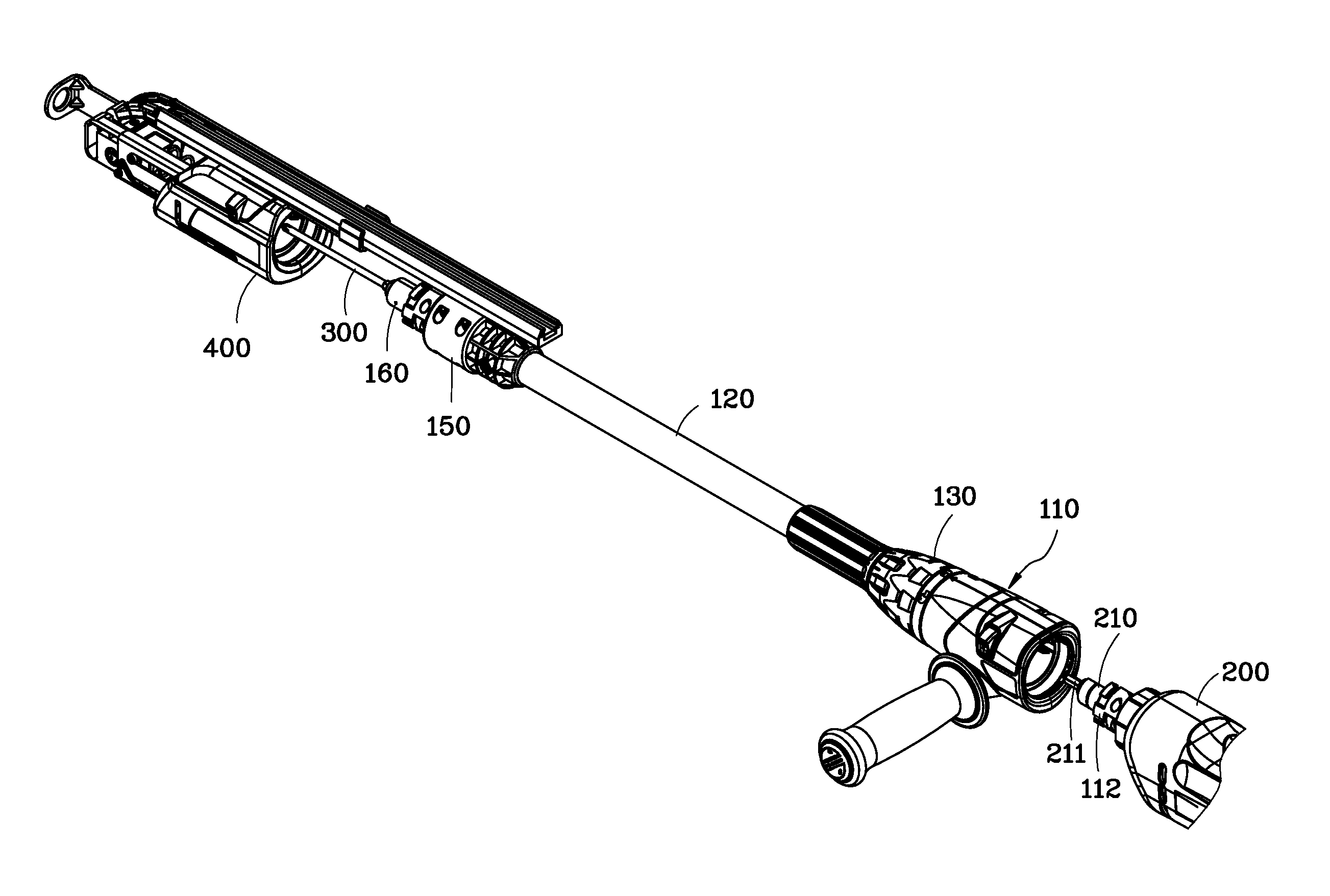
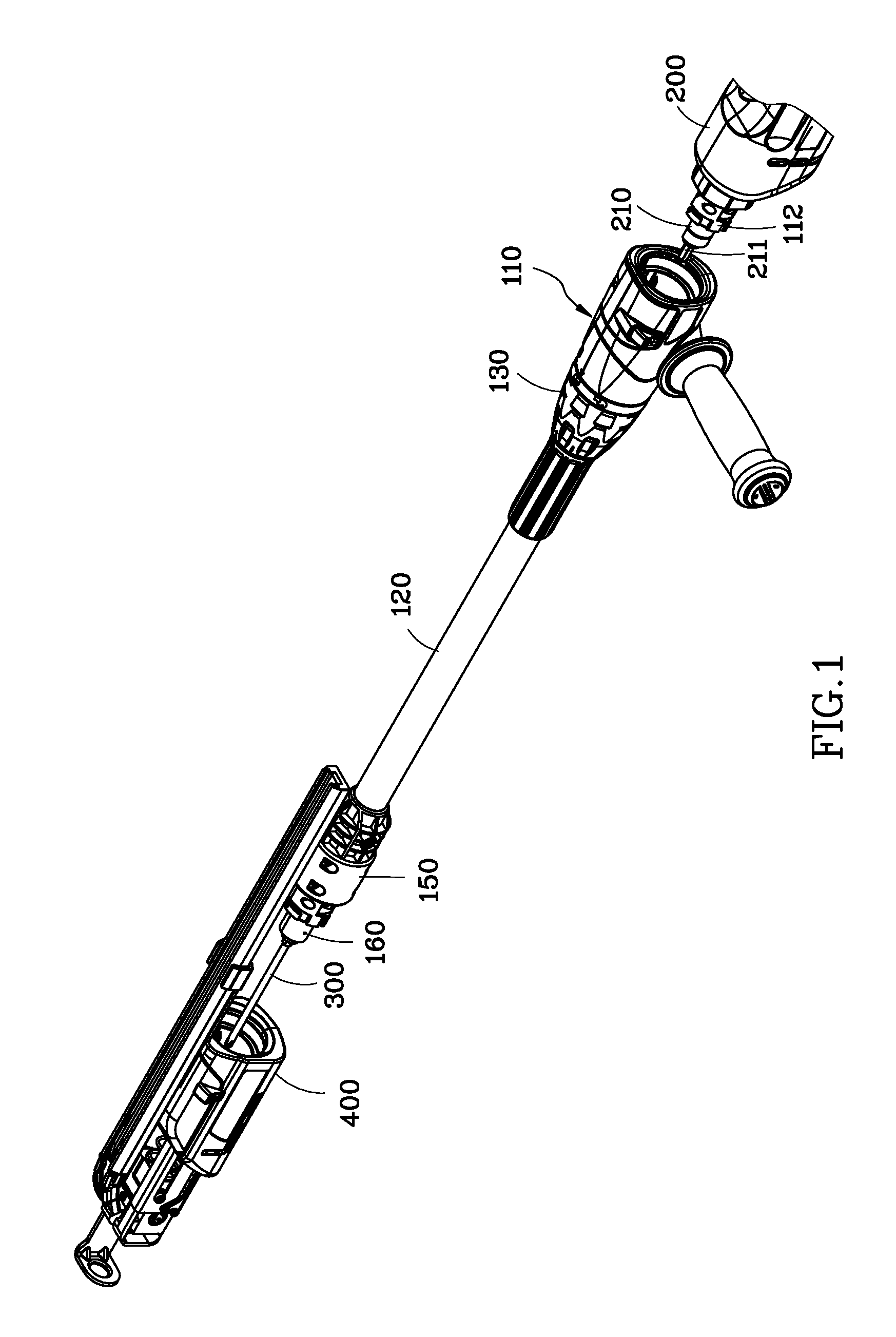
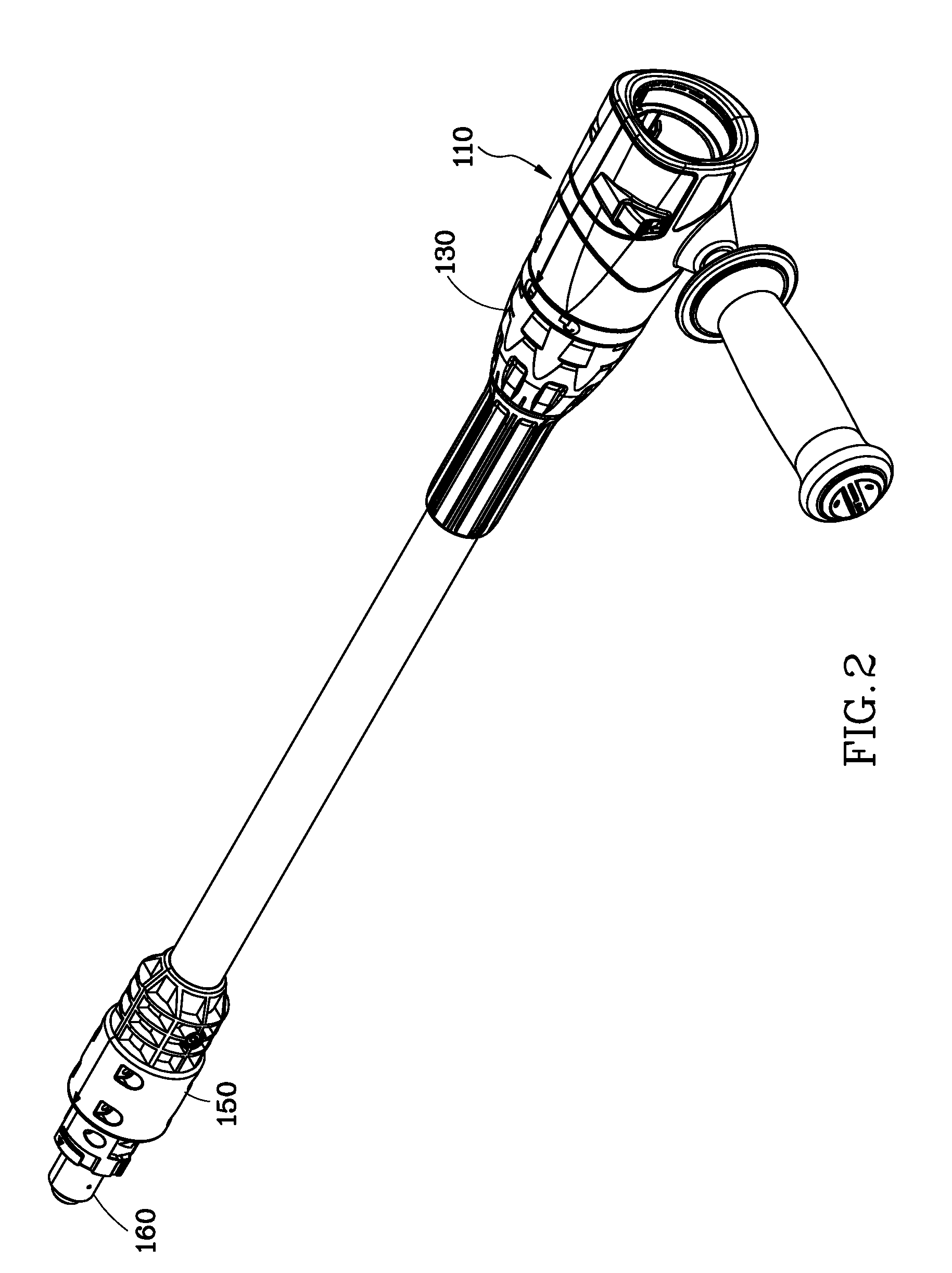
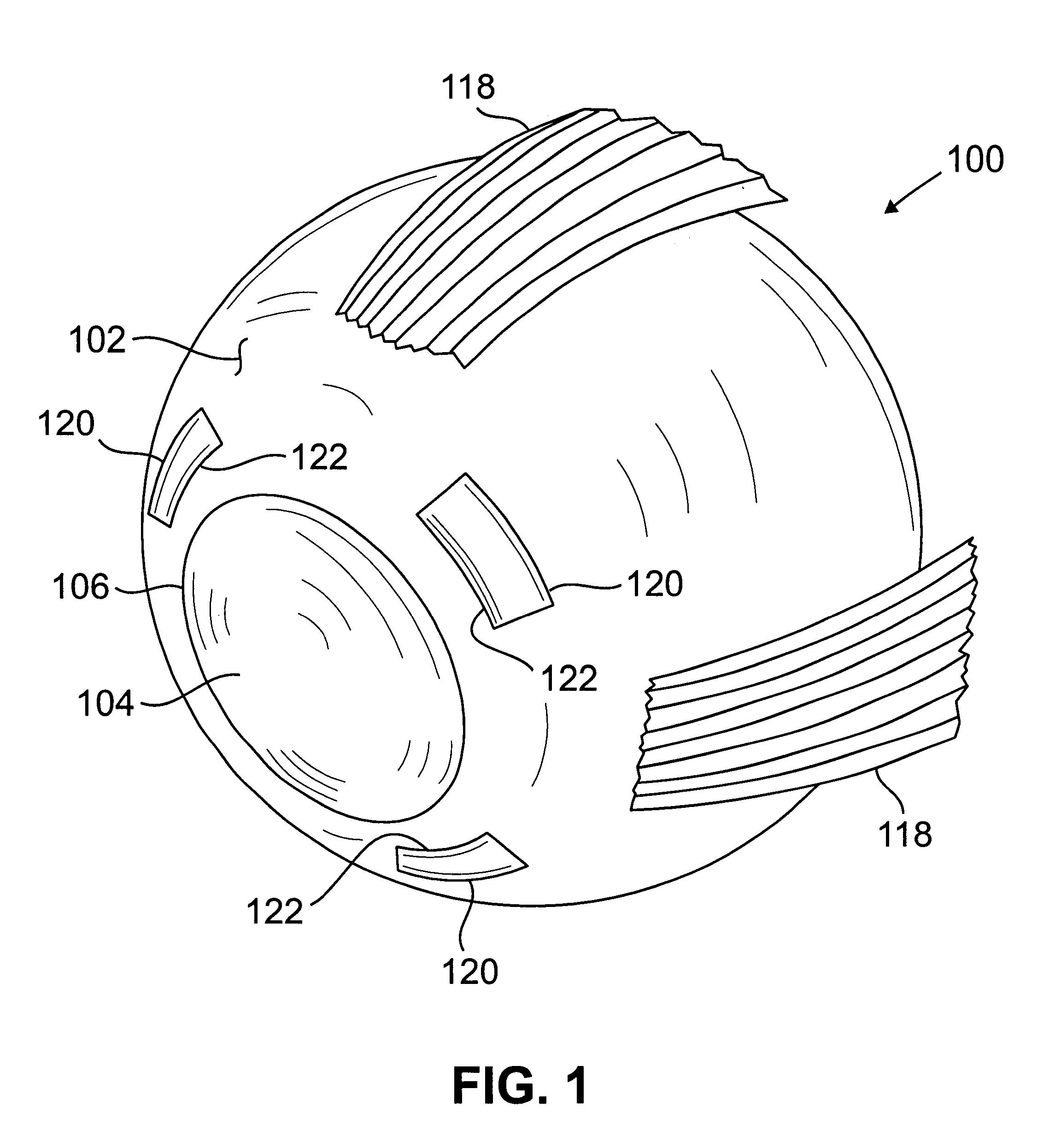
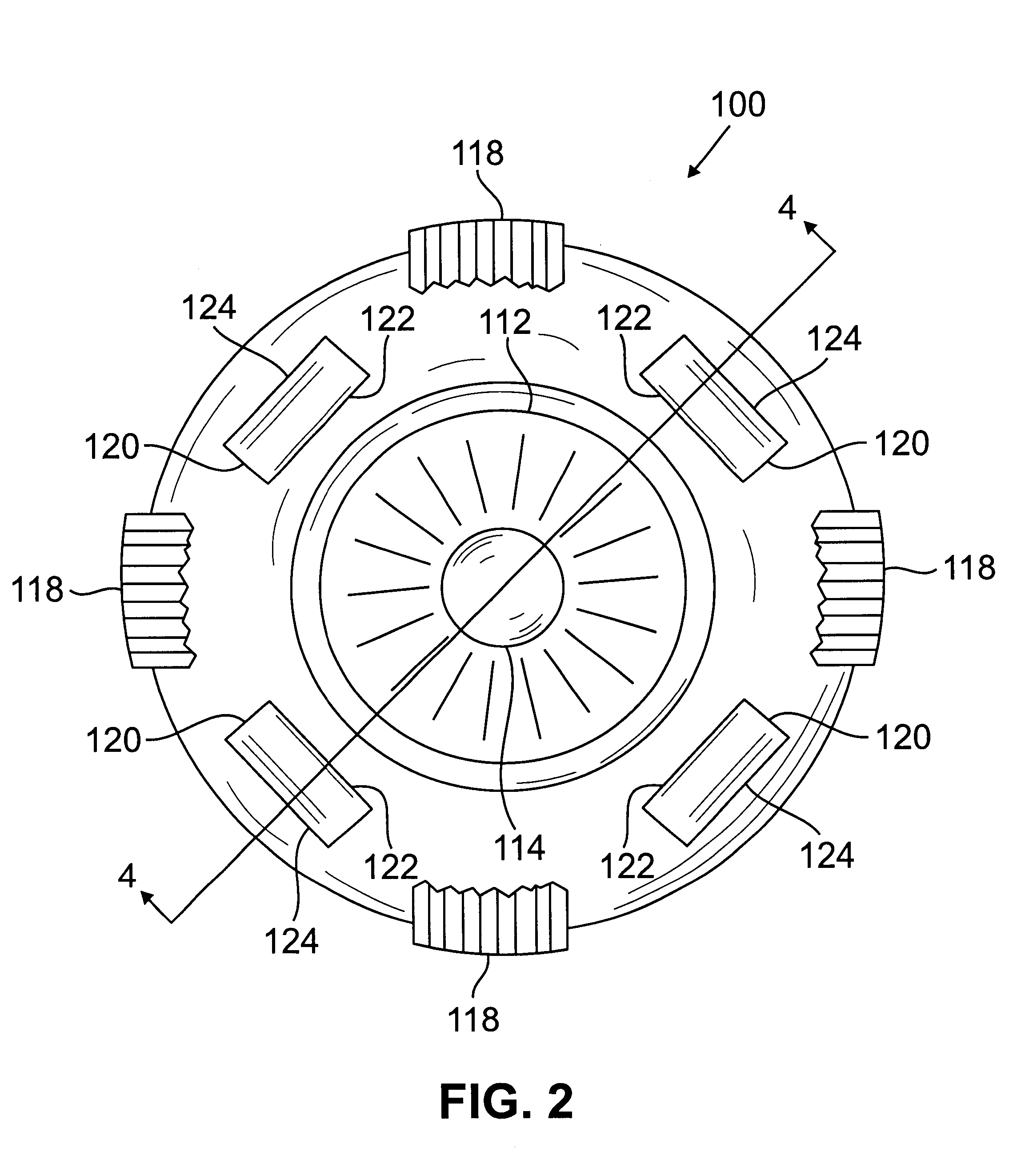
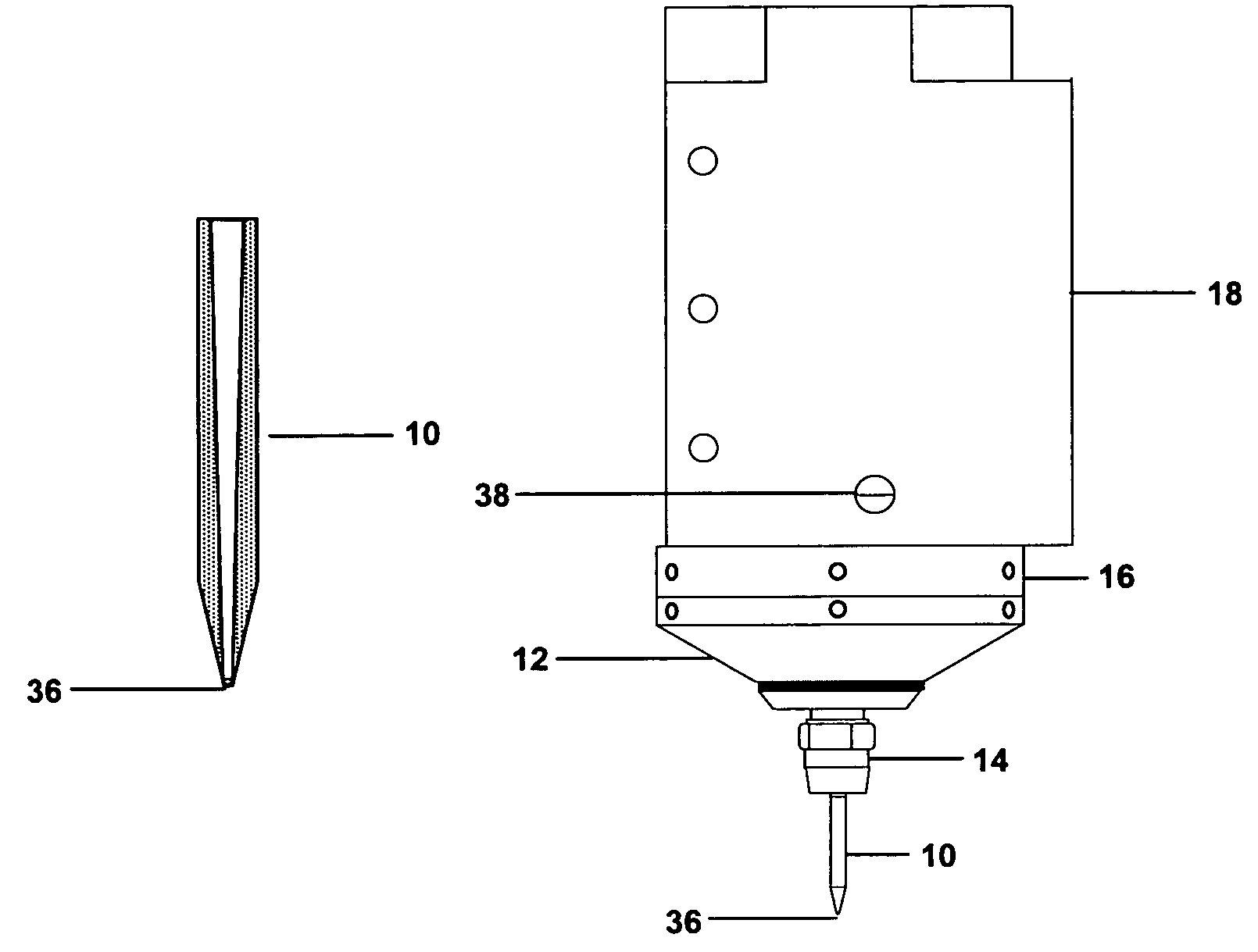
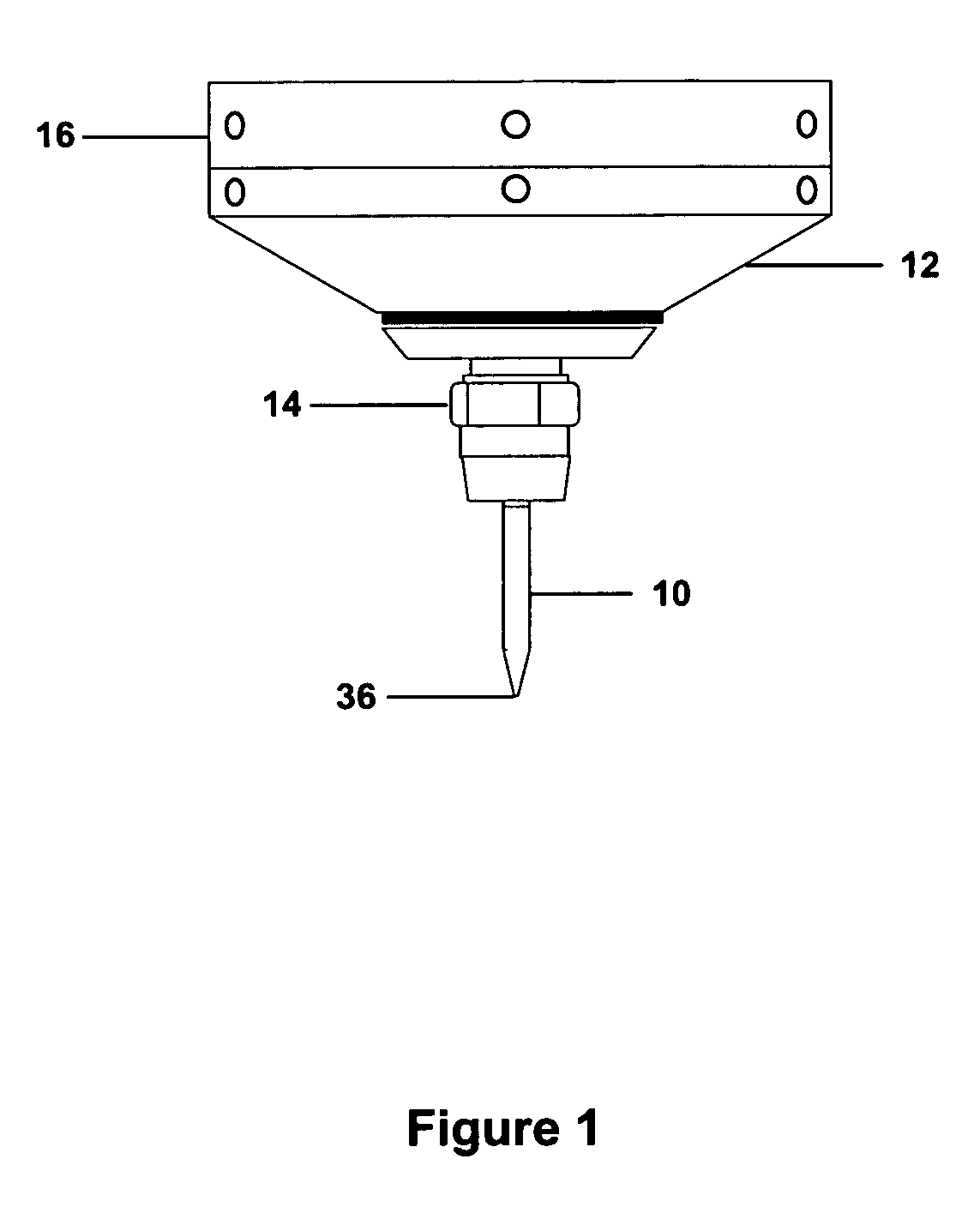
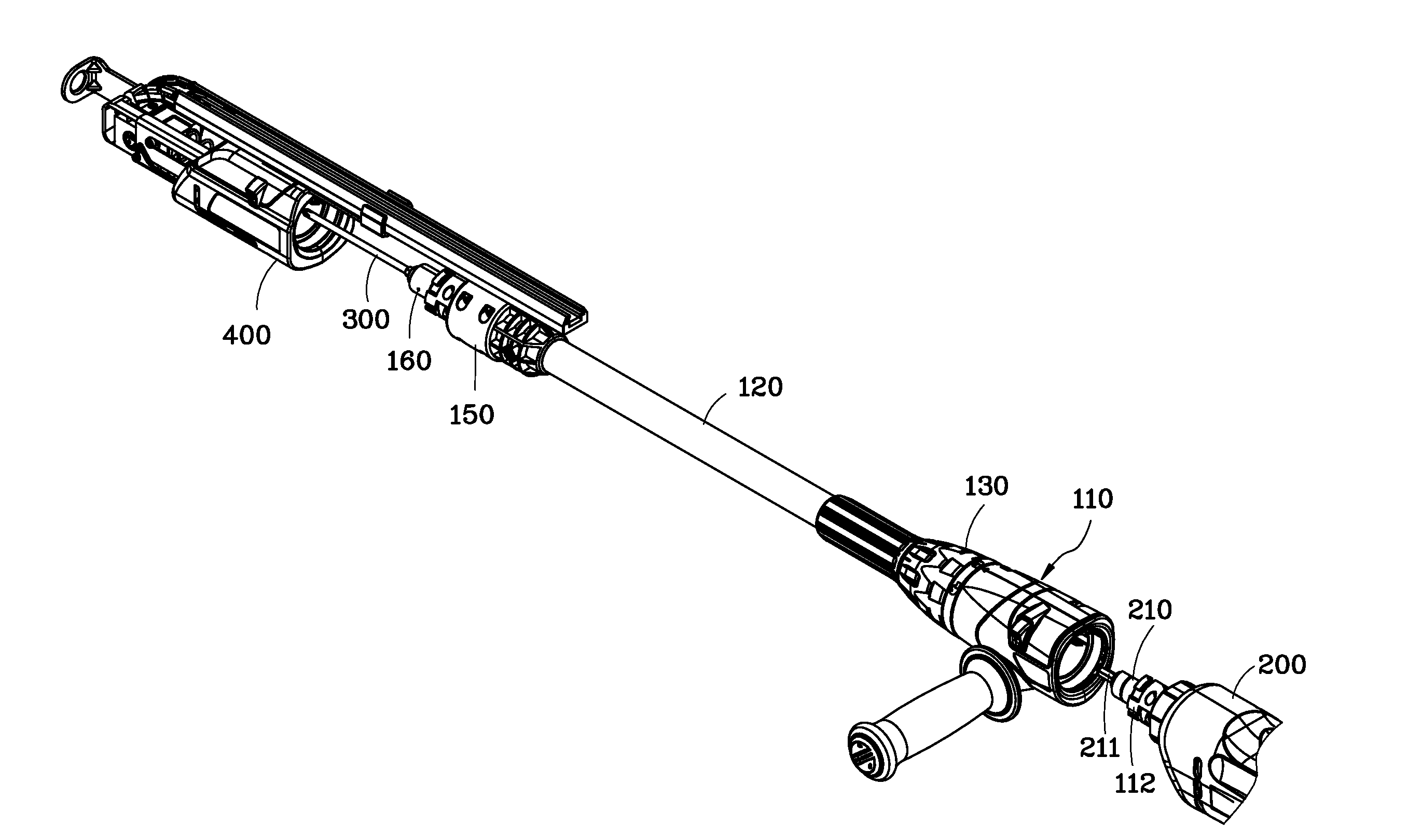
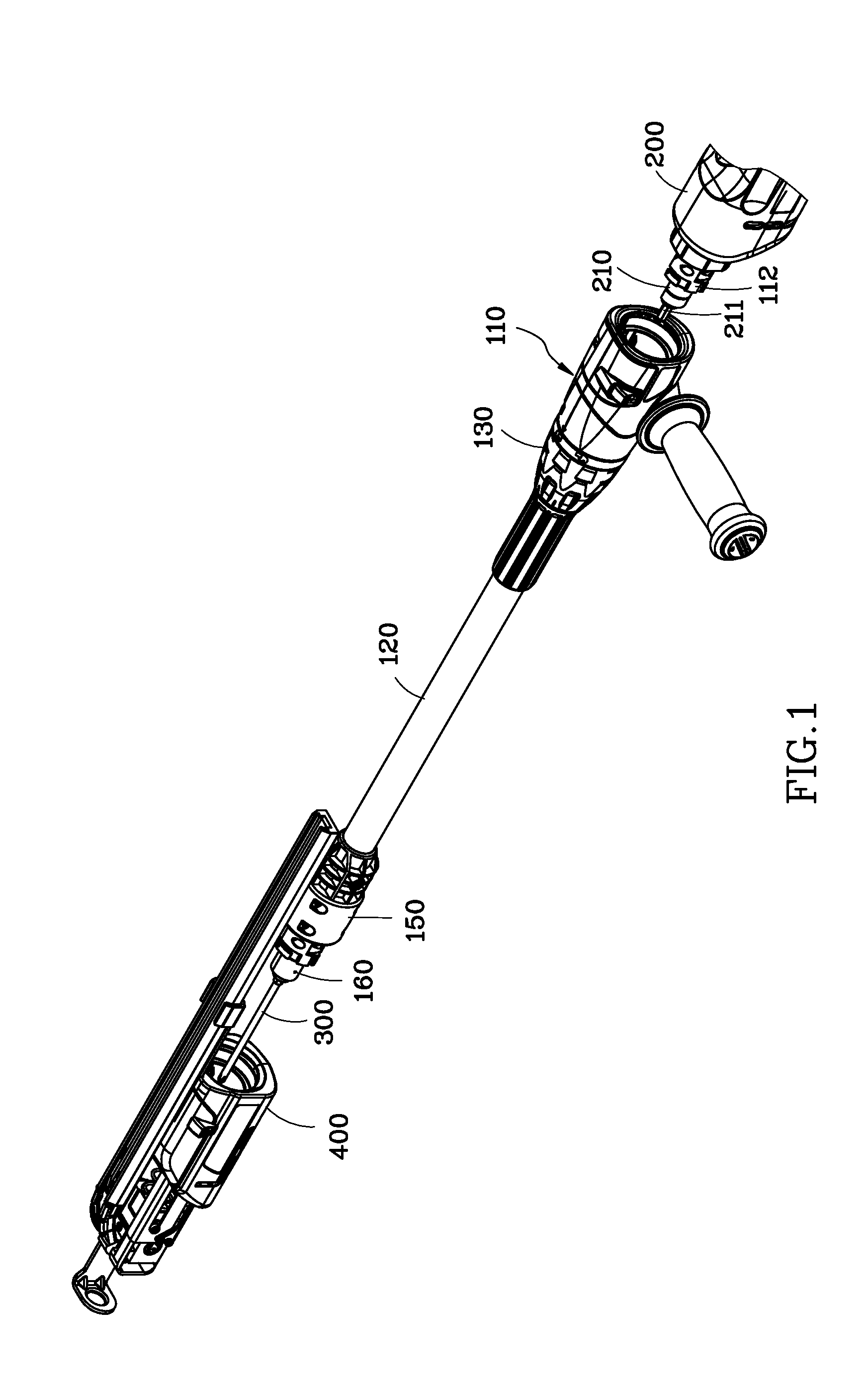
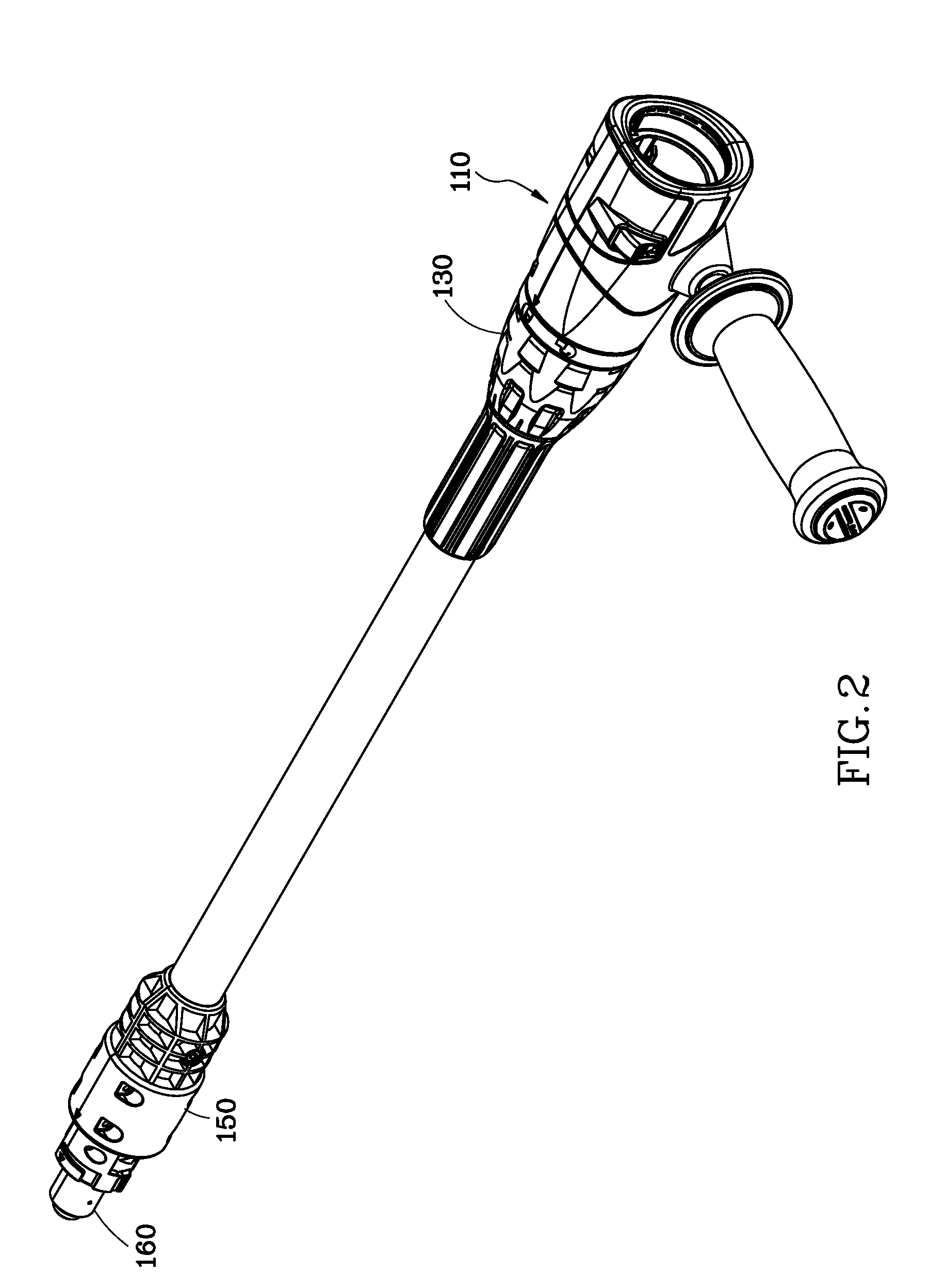
Transmission extension adapter for power hand tool
InactiveUS8220367B2Increase the working distanceEasy to useSleeve/socket jointsSpannersDrive shaftEngineering
A transmission extension adapter for connection between a work head and the chuck of a power hand tool includes a cylindrical cap shell coupled to the power hand tool around the chuck and having radial through holes and a positioning member in each radial through hole. An axle sleeve is rotatably coupled to the cylindrical cap shell and has locating holes on the periphery thereof. A transmission axle is inserted through the axle sleeve and has a rear end connected to the chuck and a front end connected with a supplementary chuck for holding the work head. A front cap assembly is affixed to the front end of the axle sleeve to hold an automatic feeder for allowing rotation of the automatic feeder with the axle sleeve. A multi-angle positioning device is adapted for holding down the positioning members in the locating holes to lock the axle sleeve.
Owner:MOBILETRON ELECTRONICS
Scleral prosthesis for treatment of presbyopia and other eye disorders
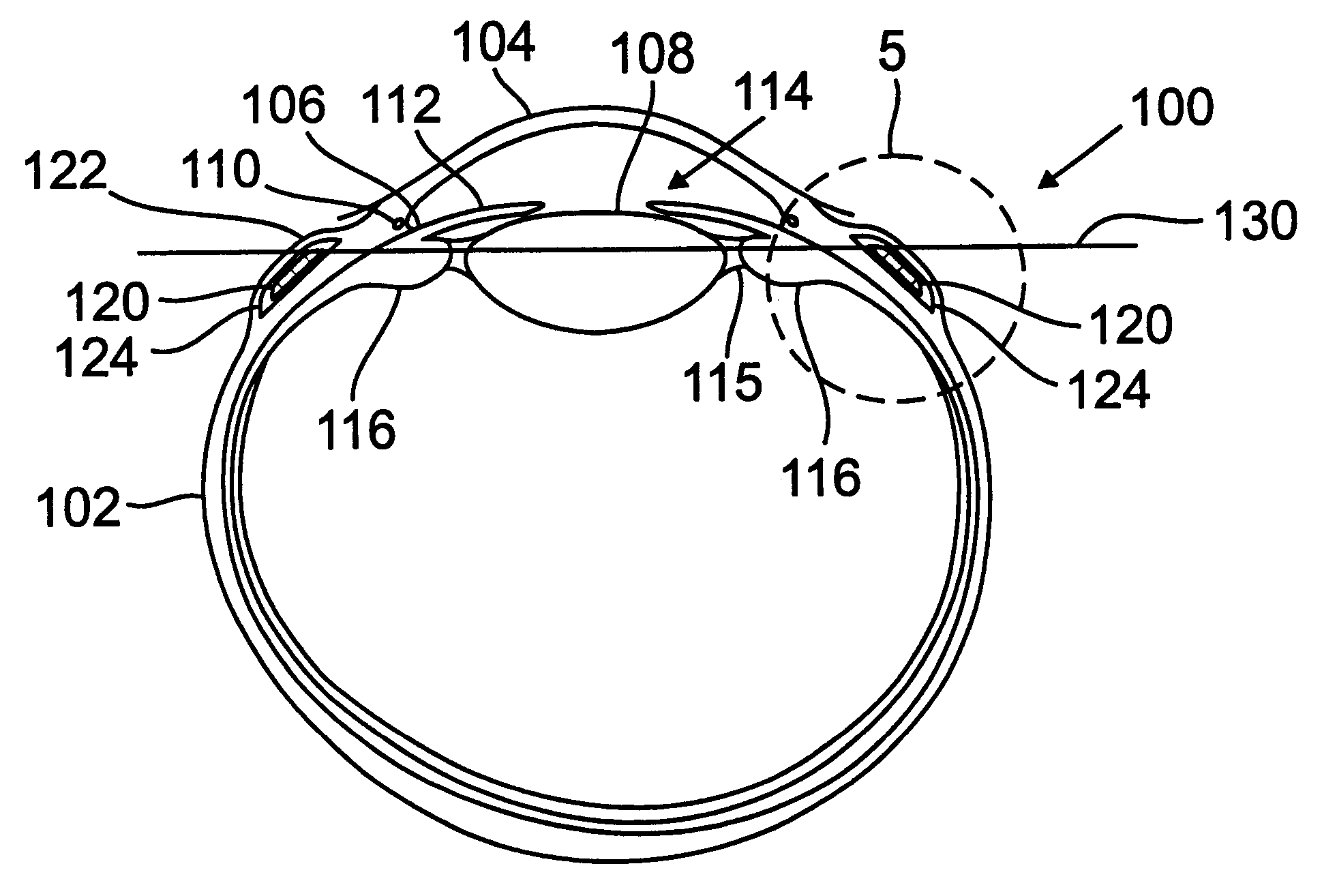
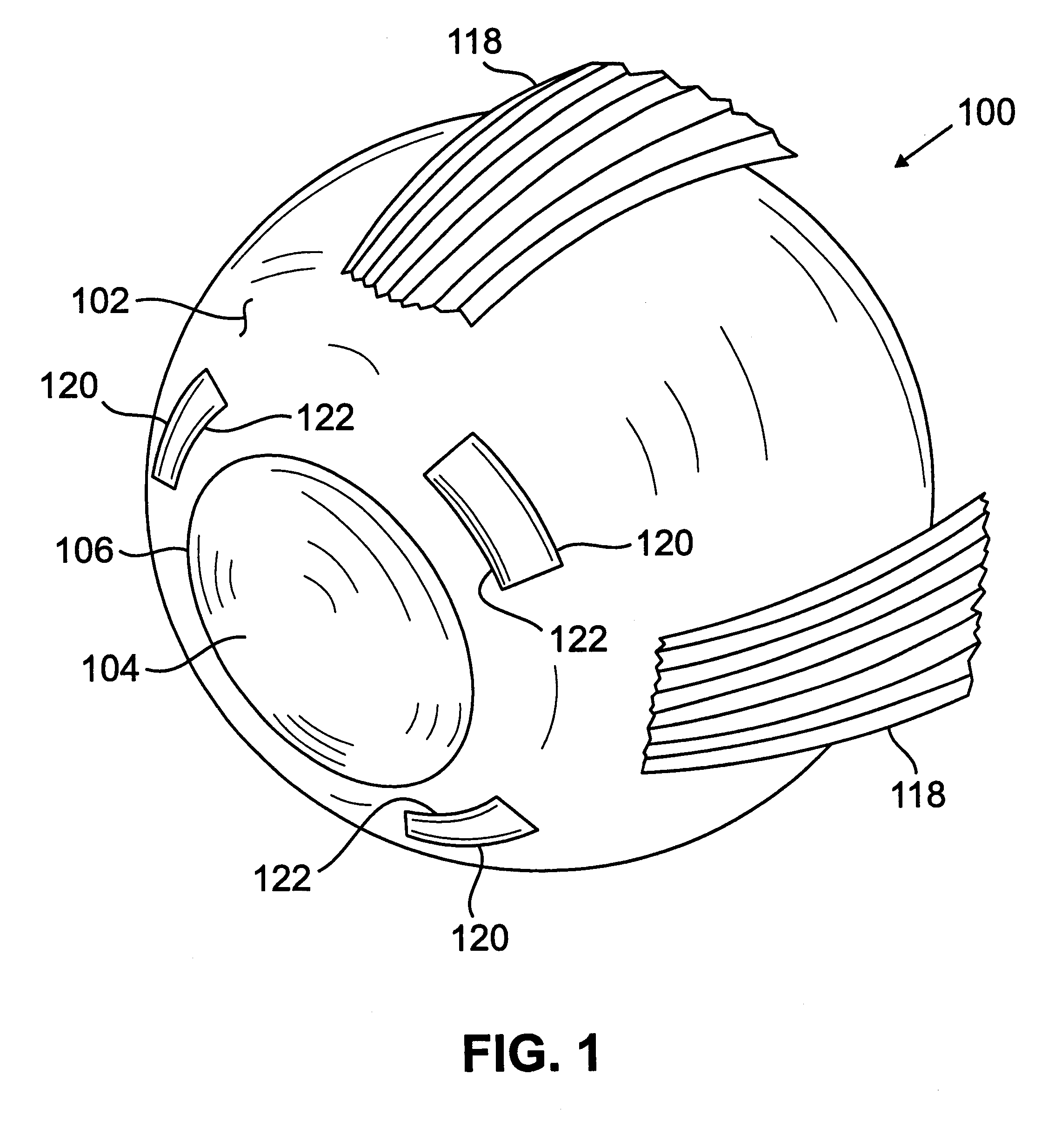
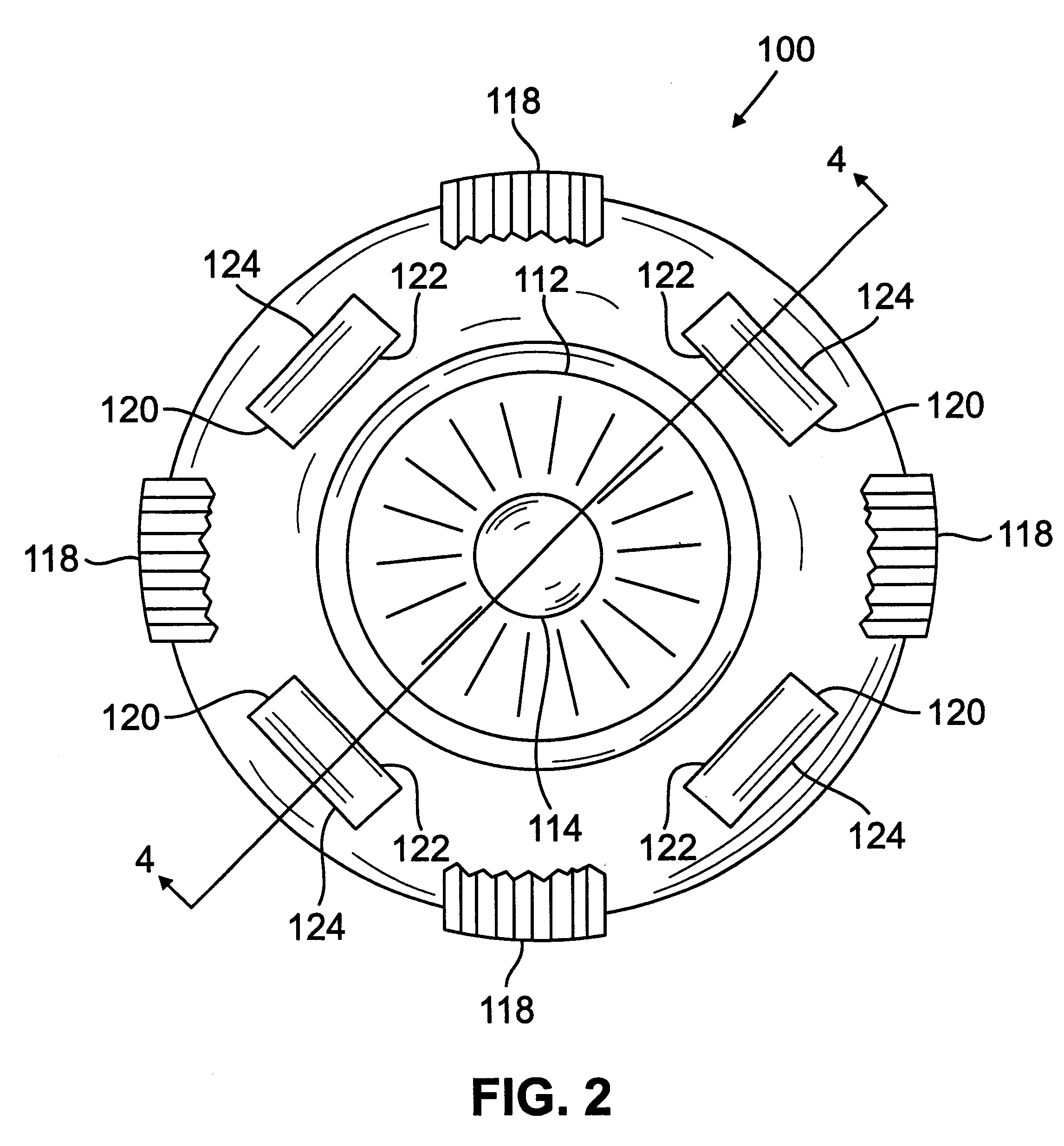
InactiveUS6280468B1Increase the effective working distanceIncrease the working distanceLaser surgeryEye implantsDiseaseOpen angle glaucoma
Presbyopia is treated by implanting within a plurality of elongated pockets formed in the tissue of the sclera of the eye transverse to a meridian of the eye, a prosthesis having an elongated body having a first surface and a second surface opposite the first surface to contact the base and flap of the scleral pocket. The first and second surfaces are spaced apart a distance so that the implanted prosthesis exerts an outward force on the flap of the scleral pocket which results in an outward traction on at least the anterior margin of the scleral pocket. The combined effect of the implanted prostheses is to exert a radially outward traction on the sclera in the region overlying the ciliary body which expands the sclera in the affected region together with the underlying ciliary body. The expansion of the ciliary body restores the effective working distance of the ciliary muscle in the presbyopic eye and thereby increases the amplitude of accommodation. Hyperopia, primary open angle glaucoma and / or ocular hypertension can be treated by increasing the effective working distance of the ciliary muscle according to the invention. A preferred embodiment of the scleral prosthesis has a major surface adapted to contact the base or flap of the pocket and an opposite surface or ridge spaced from the major surface.
Owner:REFOCUS GROUP
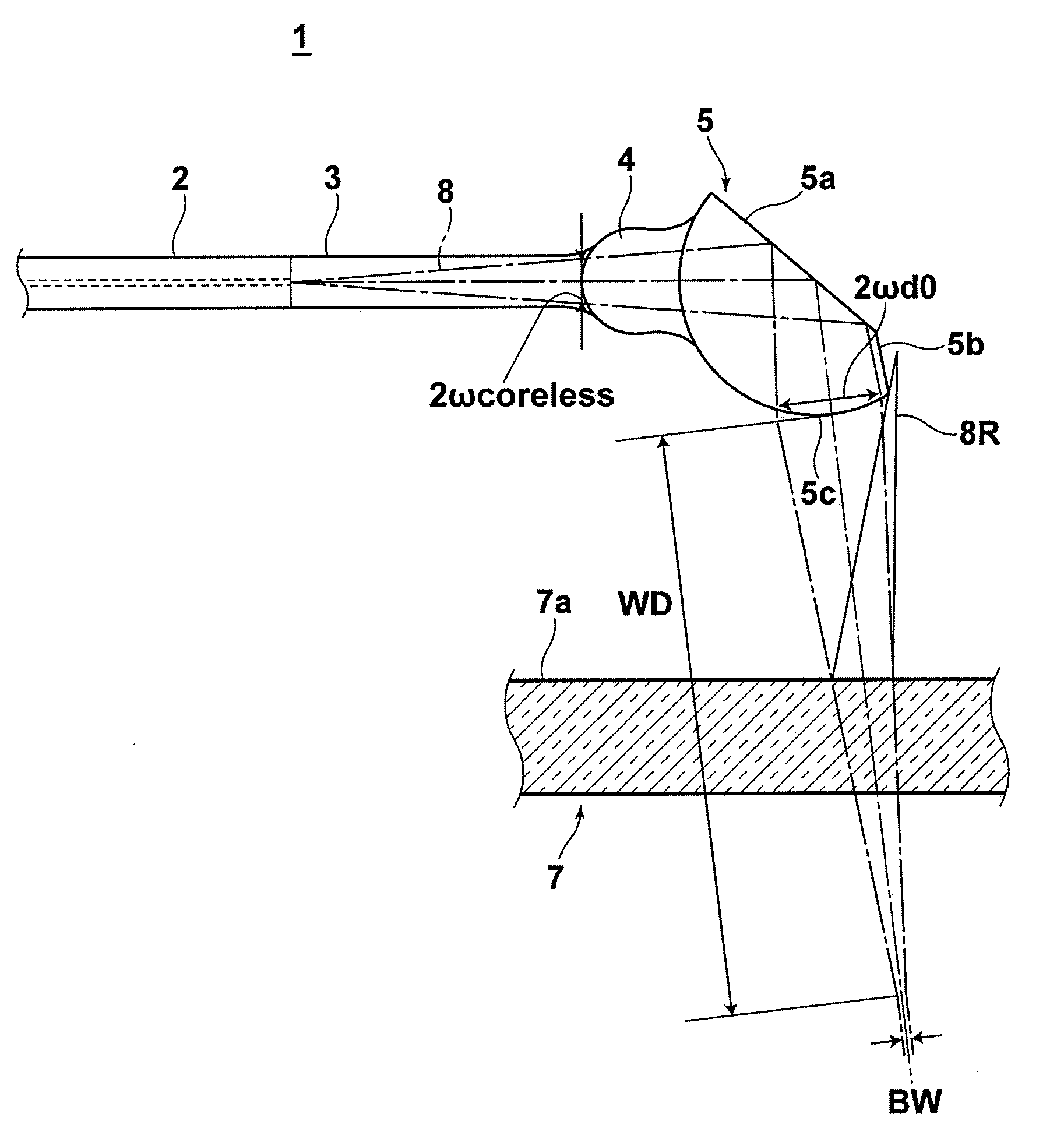
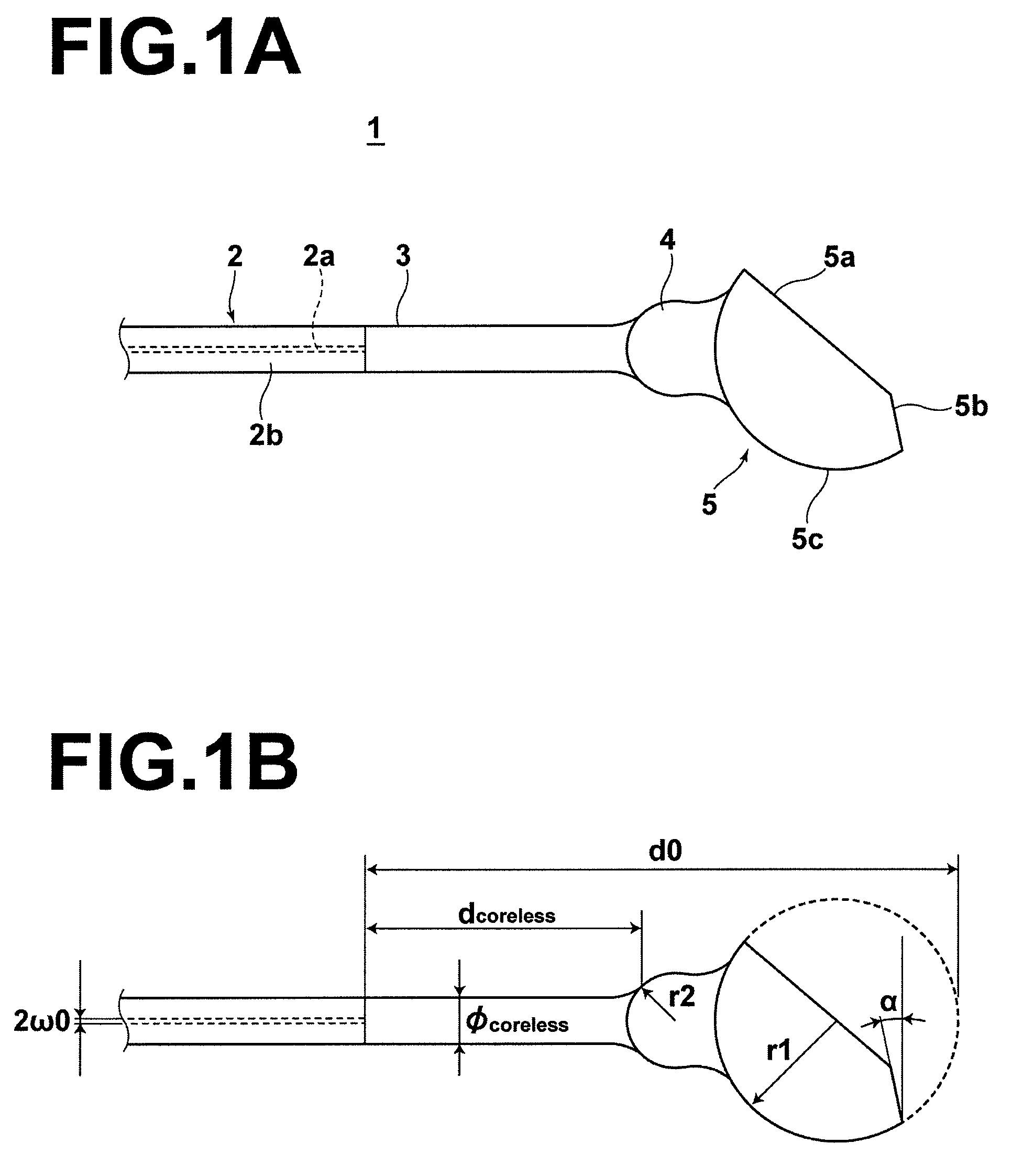
OCT probe for eliminating ghost images
InactiveUS7805034B2Reduce the overall diameterIncrease the working distanceMaterial analysis by optical meansCatheterPhoto irradiationMedicine
An OCT probe has a sheath to be inserted into a subject; and an optical system within the sheath, for changing the direction of light which propagates from a light source through an optical fiber to irradiate the light onto the subject through a transparent portion of the sheath, and for reflecting the light beam, which is reflected by the subject, to guide the light into the optical fiber. A light output surface, for causing the light to be output from the reflecting surface in a direction obliquely inclined with respect to the inner surface of the sheath, and a reflected light sheath entrance preventing portion, for preventing light reflected by the inner surface of the sheath from entering the optical fiber, are provided in the optical system. The reflected light sheath entrance preventing portion may be formed by providing a cut planar surface portion on the lens.
Owner:NAMIKI PRECISION JEWEL CO LTD
Corneal treatment system and method
InactiveUS20120083772A1Big distanceEasy accessUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsBiocideOxygenRadiation pattern
A system for bilateral or monocular photochemical cross-linking of corneal collagen employs selectable light in a selected wavelength band as the excitation source and riboflavin as the photosensitizer. The system has an illumination source which may have multi-spectral capability, light guides for delivery of light to the optical head for projection onto the corneal surface, selectable radiation patterns to accommodate individual corneal architecture, and red light phototherapy to limit apoptosis and accelerate healing time. Aiming beams provide alignment of the optical head to the patient cornea. A microprocessor-controlled rotary solenoid mechanical shutter provides discontinuous illumination for tissue reoxygenation, and devices and methods may be included for the in situ determination of oxygen utilization and the riboflavin content of the cornea.
Owner:CXL OPHTHALMICS
Scleral prosthesis for treatment of presbyopia and other eye disorders
InactiveUS6299640B1Increase the effective working distanceIncrease the working distanceLaser surgeryEye implantsDiseaseOpen angle glaucoma
Presbyopia is treated by implanting within a plurality of elongated pockets formed in the tissue of the sclera of the eye transverse to a meridian of the eye, a prosthesis having an elongated base member having an inward surface adapted to be placed against the inward wall of the pocket and having a ridge on the inward surface of the base extending along at least a major portion of the major dimension of the base. The combined effect of the implanted prostheses is to exert a radially outward traction on the sclera in the region overlying the ciliary body which expands the sclera in the affected region together with the underlying ciliary body. The expansion of the ciliary body restores the effective working distance of the ciliary muscle in the presbyopic eye and thereby increases the amplitude of accommodation. Hyperopia, primary open angle glaucoma and / or ocular hypertension can be treated by increasing the effective working distance of the ciliary muscle according to the invention.
Owner:REFOCUS GROUP
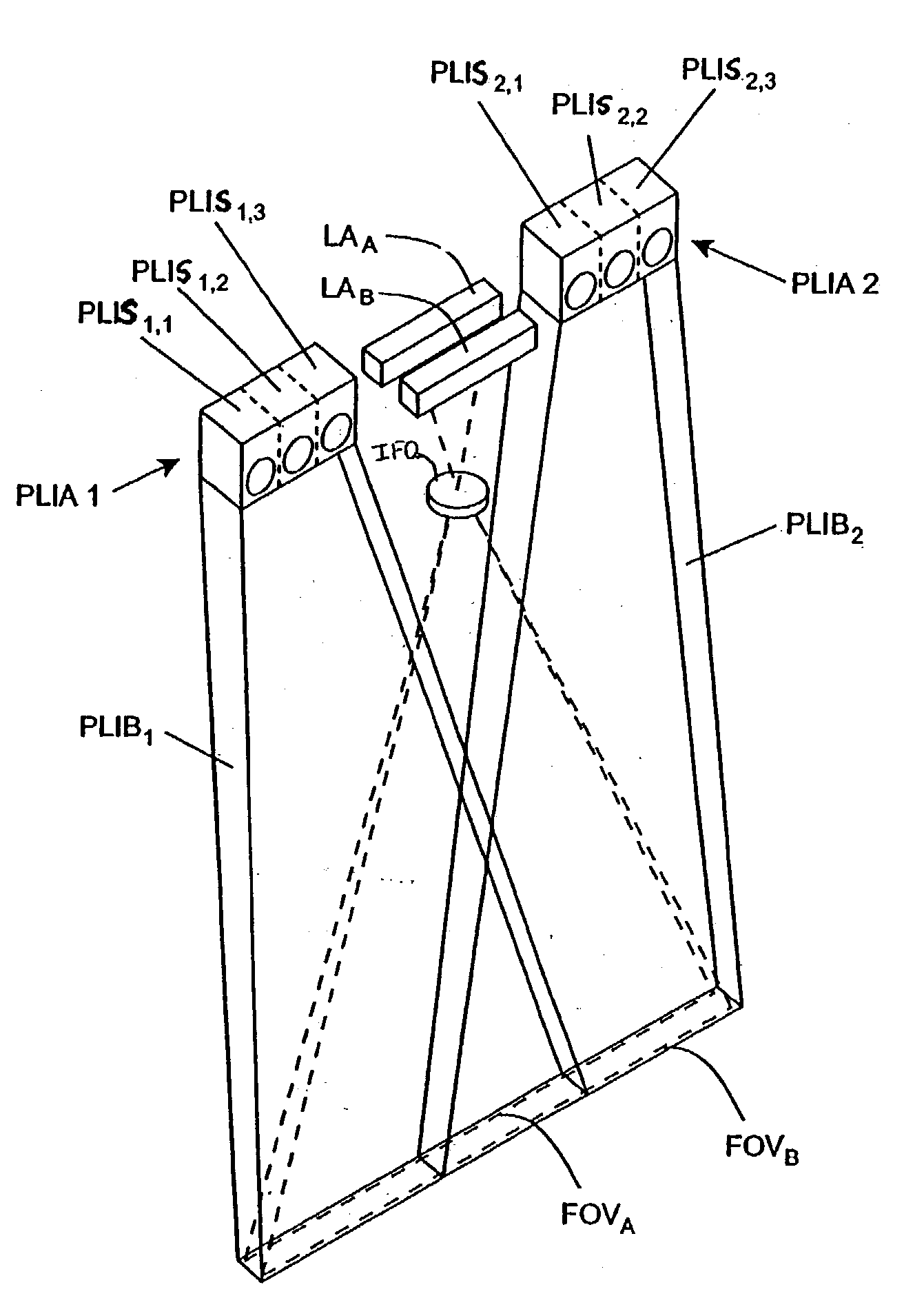
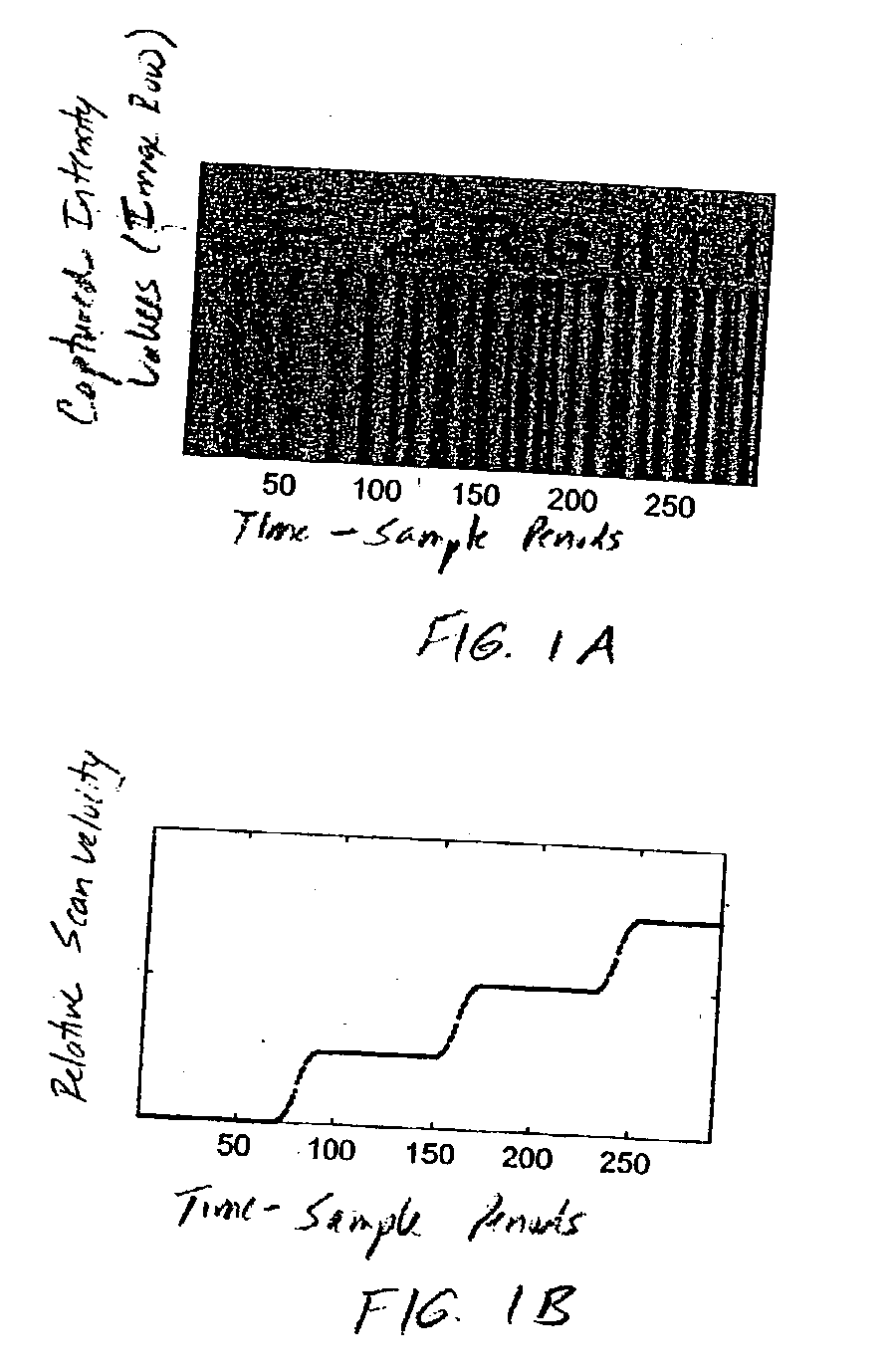
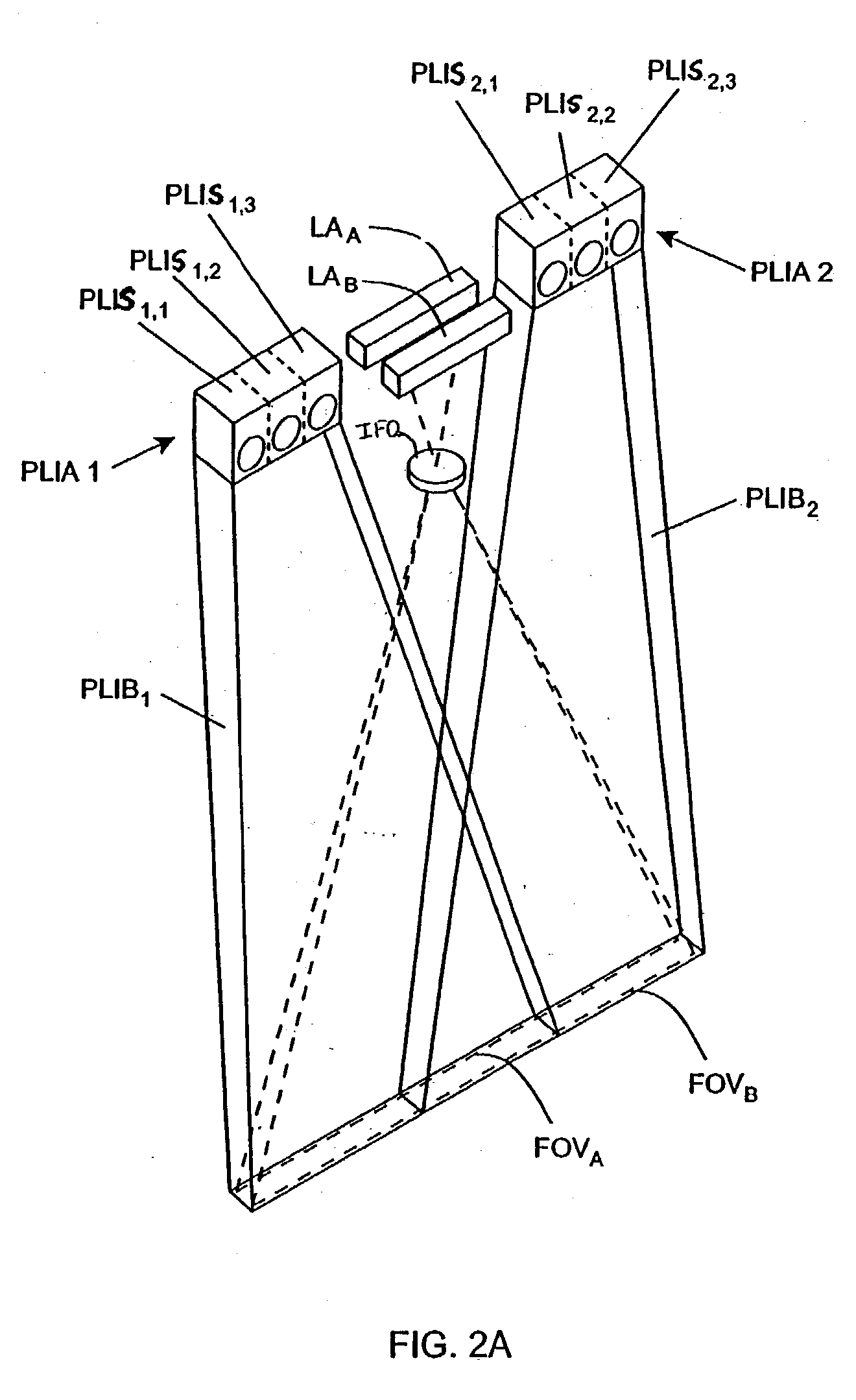
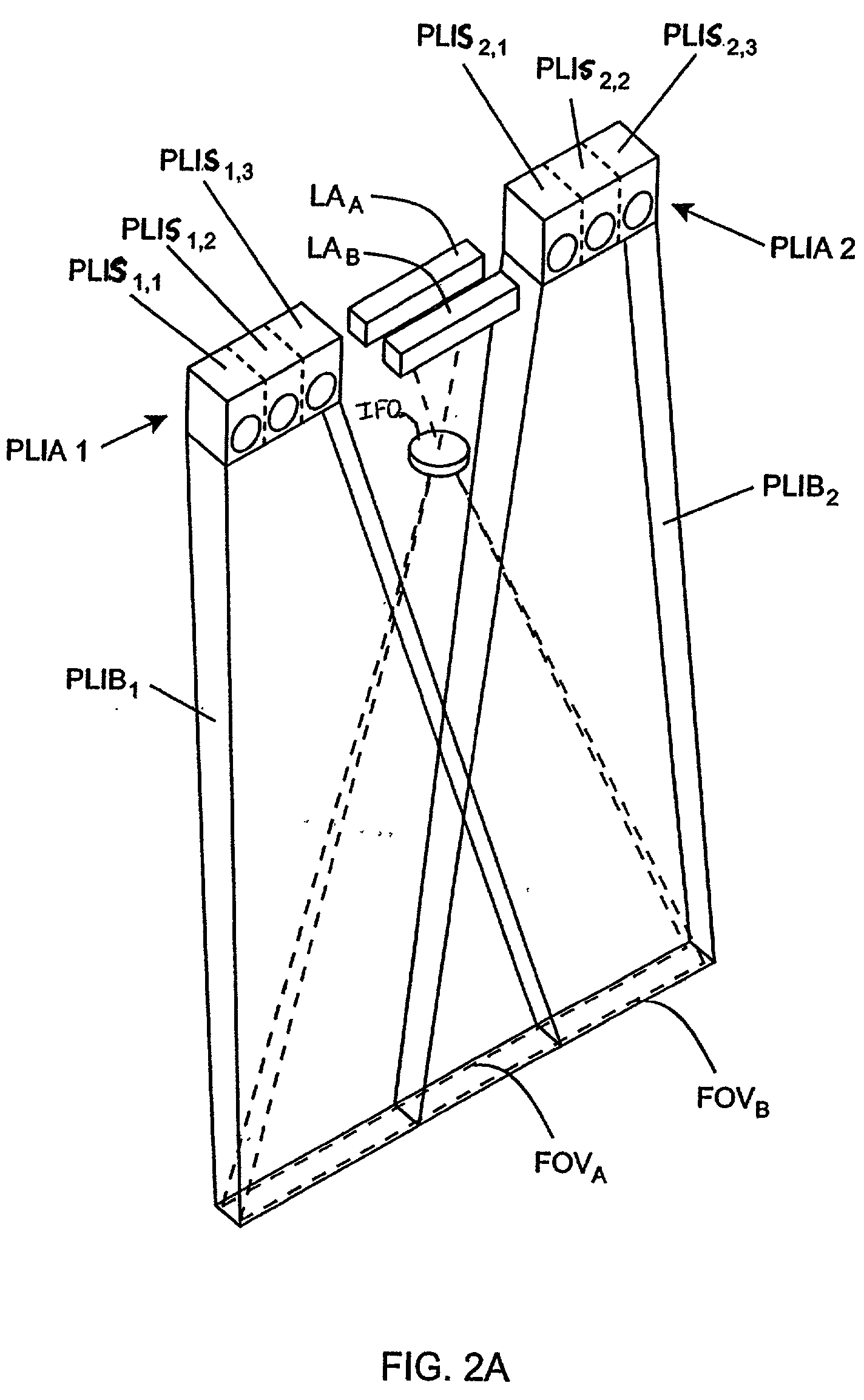
Handheld imaging device employing planar light illumination and linear imaging with image-based velocity detection and aspect ratio compensation
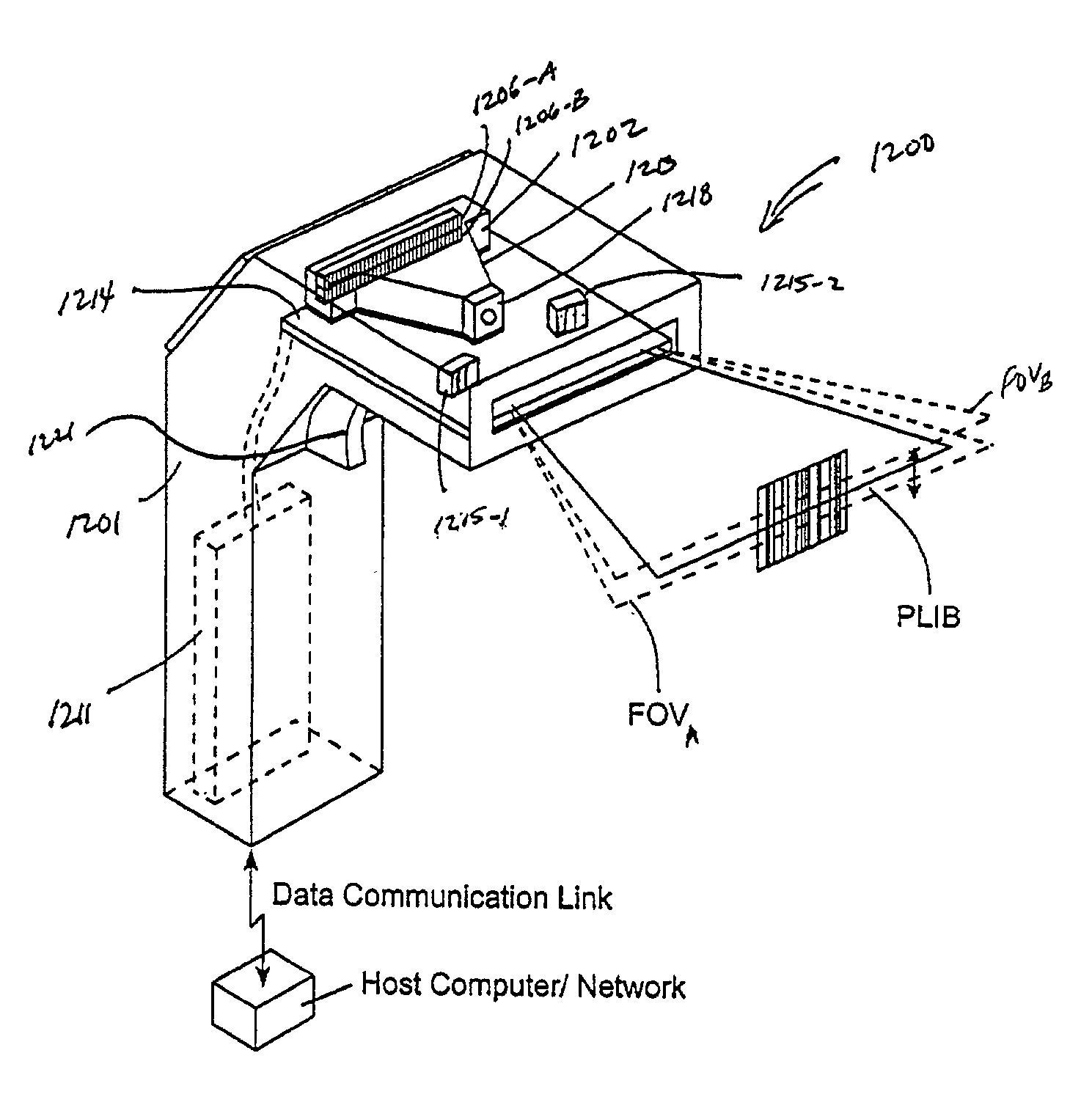
InactiveUS20030098352A1Low costReduce speckle noiseSensing by electromagnetic radiationCamera controlHand movements
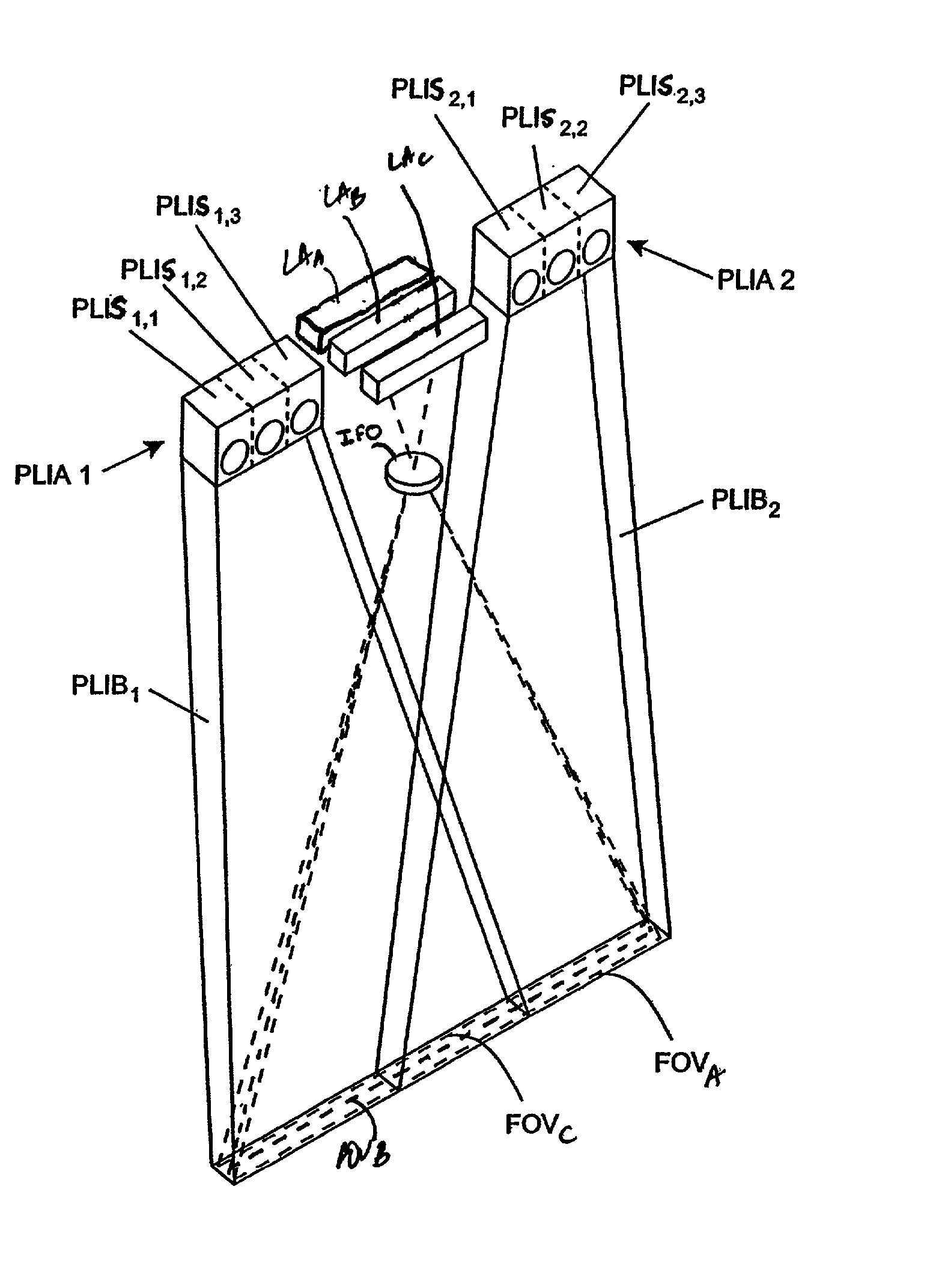
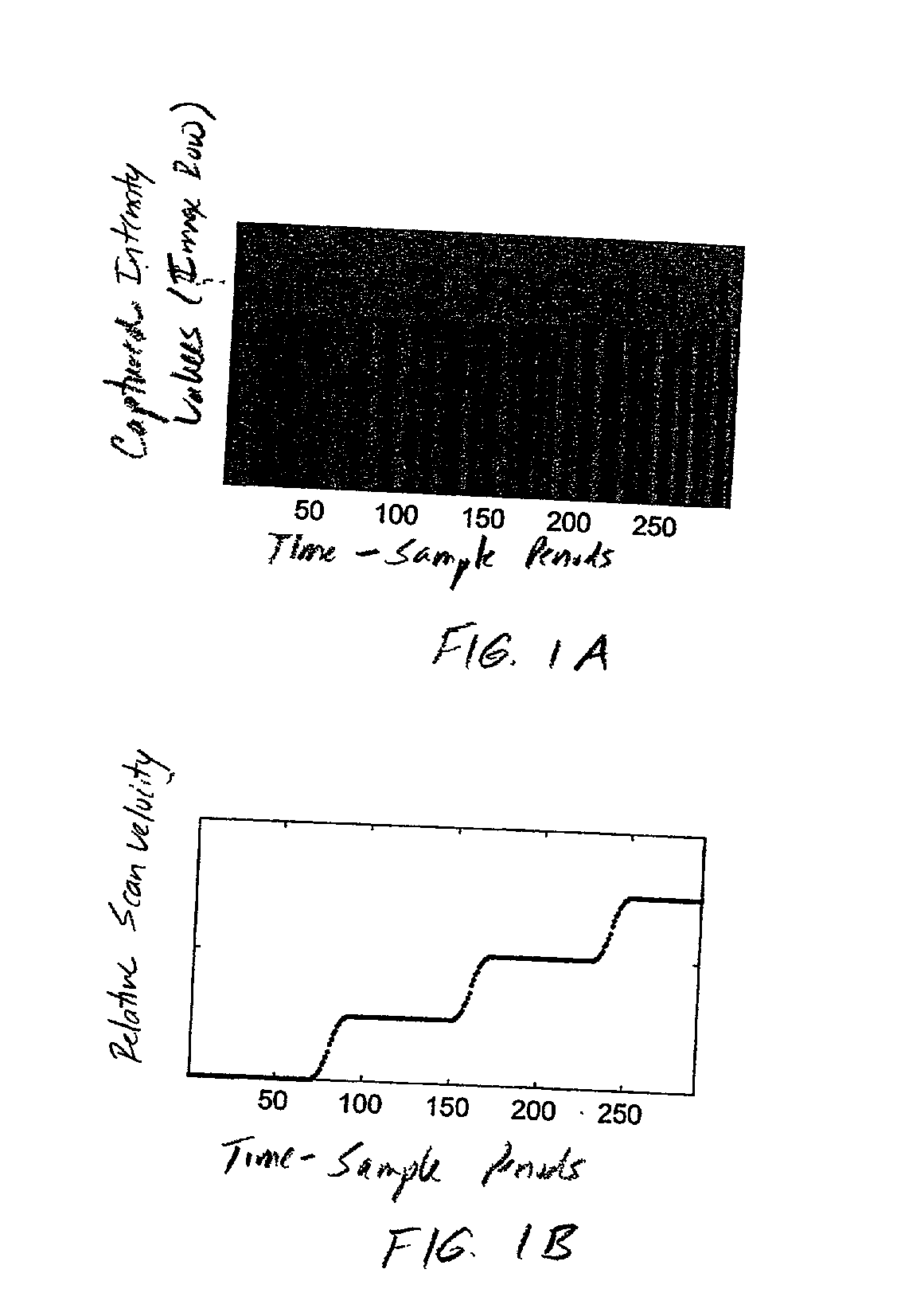
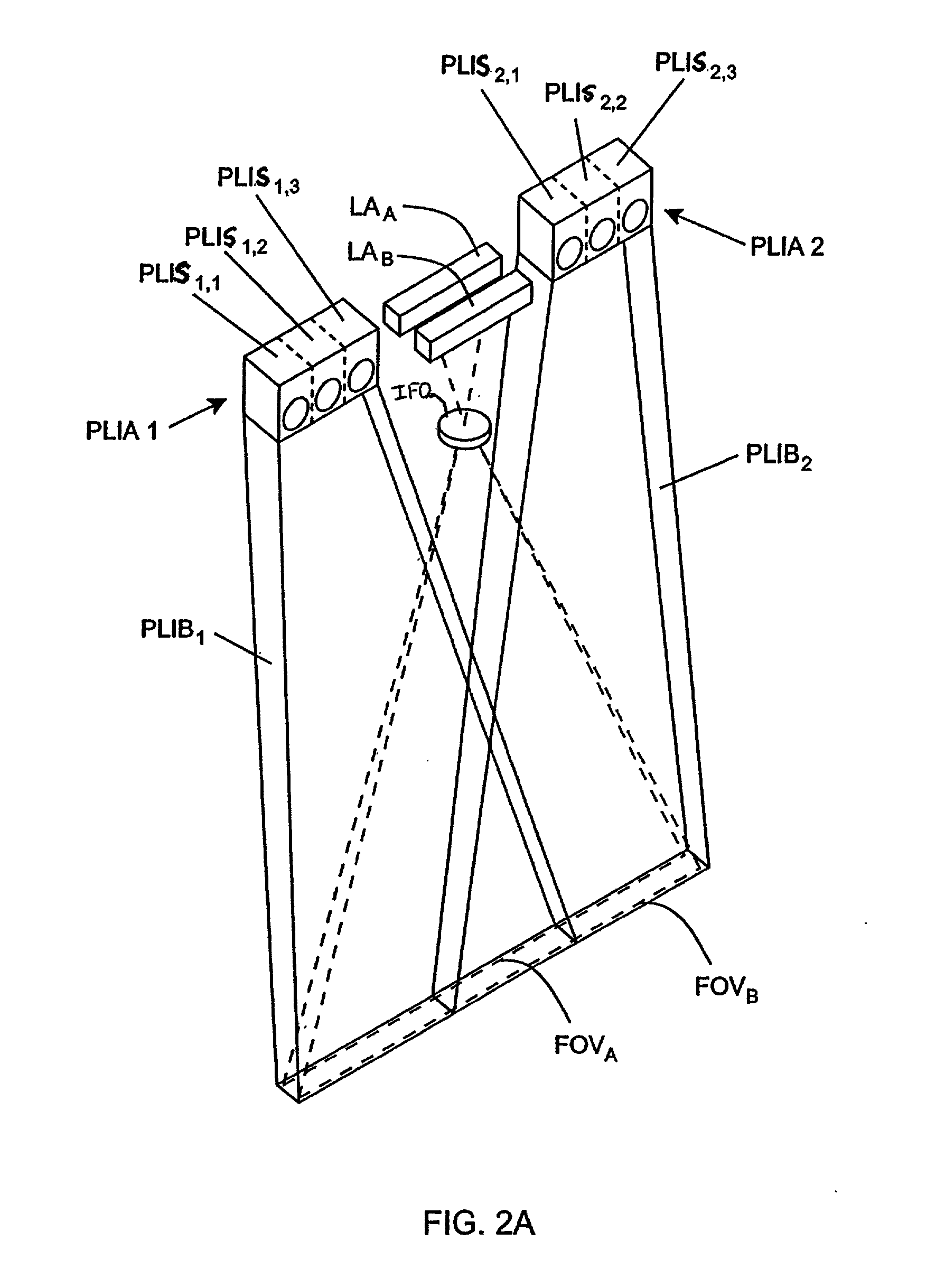
A hand-held imaging device includes a plurality of linear imaging arrays, image formation optics, at least one illumination module and image processing circuitry that are embodied within a hand-holdable housing that is moved by hand movement past a target object to capture images of the target object. The plurality of linear imaging arrays and image formation optics provide field of views corresponding to the plurality of linear image arrays. The at least one illumination module produces planar light illumination that substantially overlaps the field of views corresponding to the plurality of linear imaging arrays. The image processing circuitry performs image-based velocity estimation operations, which analyzes pixel data values of a plurality of composite 2D images each derived from sequential image capture operations of a corresponding one linear imaging array to derive velocity data that represents an estimated velocity of the imaging device with respect to target object. The image processing circuitry produces a first image of portions of the target object, the first image having substantially constant aspect ratio, utilizing image transformation operations (or camera control operations) that are based upon the velocity data, to thereby compensate for aspect ratio distortions that would otherwise result from variations in velocity of the imaging device with respect to the target object(s). In addition, the image processing circuitry preferably carries out image-based horizontal jitter estimation and compensation operations, which estimate the horizontal jitter of the imaging device relative to the target object over the image capture operations from which the first image is derived, and transform the first image utilizing shift operations that are based upon such estimated horizontal jitter to produce a second image of portions of the target object which compensates for horizontal jitter distortion that would otherwise result therefrom. The first image, second image (or image derived from sharpening the first or second images) is preferably subject to image-based bar code detection operations and / or OCR operations carried out by the image processing circuitry, or output for display to a display device.
Owner:METROLOGIC INSTR
Millimeter-wave time-division linear frequency modulation multiple-target detection colliding-proof radar for car
InactiveCN101354438AIncrease the working distanceImprove signal-to-noise ratioRadio wave reradiation/reflectionLow noiseAcousto-optics
The invention relates to the technical field of radio fix radars, in particular to a millimetre wave time-division linear frequency modulation multi-object detection automobile anti-collision radar. The radar of the invention adopts full phase parameter receiving / emitting benchmark signal and time-division and time-sequence asynchronous control to receive / emit a dual-purpose quasi-light integrated medium lens antenna array, and scans the objects possible to be collided on the warning road surfaces by DSP according to lane scanning wave beam; the road situation photographing combined with the vehicle speed and GPS data MCU to control time-division n-passage modulation frequency and waveform millimetre wave linear locking phase frequency modulation; emission is carried out sequentially by R / T2, a circulator, a wave beam switch and the antenna array; echo passes through the antenna array, the wave beam switch, the circulator, the R / T1, low noise high amplifier, subharmonic mixing, middle amplifier and a time-dividing circuit and multi-object signal corresponding matching filter wave and is processed and controlled by MCU at DSP; when a plurality of road barriers are encountered, the orientation, distance and relative speed are determined by DSP restriction virtual warning; three-dimensional images are displayed by a CRT; the closer the distance of the object is, the higher the resolution is; the object which is closest to the vehicle is recognised; sound and light alarm are carried out when the distance is less than safety distance; when the distance is near to the dangerous distance, the vehicle can intelligently avoid the barrier or reduce the speed or brake; the radar of the invention can make a choice according to the control reference road situation, the vehicle speed and the GPS data, thus obviously improving the driving safety of the vehicle.
Owner:阮树成
Annular aerosol jet deposition using an extended nozzle
InactiveUS20060008590A1Increase the working distanceRapid varianceSpray nozzlesFire rescueEngineeringBiological materials
Method and apparatus for improved maskless deposition of electronic and biological materials using an extended nozzle. The process is capable of direct deposition of features with linewidths varying from a few microns to a fraction of a millimeter, and can be used to deposit features on targets with damage thresholds near 100° C. or less. Deposition and subsequent processing may be performed under ambient conditions and produce linewidths as low as 1 micron, with sub-micron edge definition. The extended nozzle reduces particle overspray and has a large working distance; that is, the orifice to target distance may be several millimeters or more, enabling direct write onto non-planar surfaces. The nozzle allows for deposition of features with linewidths that are approximately as small as one-twentieth the size of the nozzle orifice diameter, and is preferably interchangeable, enabling rapid variance of deposited linewidth.
Owner:OPTOMEC DESIGN CO
Annular aerosol jet deposition using an extended nozzle
InactiveUS7938079B2Increase the working distanceRapid varianceSpray nozzlesFire rescueSpray nozzleEngineering
Method and apparatus for improved maskless deposition of electronic and biological materials using an extended nozzle. The process is capable of direct deposition of features with linewidths varying from a few microns to a fraction of a millimeter, and can be used to deposit features on targets with damage thresholds near 100° C. or less. Deposition and subsequent processing may be performed under ambient conditions and produce linewidths as low as 1 micron, with sub-micron edge definition. The extended nozzle reduces particle overspray and has a large working distance; that is, the orifice to target distance may be several millimeters or more, enabling direct write onto non-planar surfaces. The nozzle allows for deposition of features with linewidths that are approximately as small as one-twentieth the size of the nozzle orifice diameter, and is preferably interchangeable, enabling rapid variance of deposited linewidth.
Owner:OPTOMEC DESIGN CO
Planar light illumination and linear imaging (PLILIM) device with image-based velocity detection and aspect ratio compensation
InactiveUS20030156303A1Low costReduce speckle noiseCharacter and pattern recognitionPictoral communicationCamera controlDisplay device
An imaging device comprising a plurality of linear imaging arrays and image formation optics that provide field of views corresponding to the plurality of linear image arrays. At least one illumination module produces planar light illumination that substantially overlaps the field of views corresponding to the plurality of linear imaging arrays. Image processing circuitry performs image-based velocity estimation operations, which analyzes pixel data values of a plurality of composite 2-D images each derived from sequential image capture operations of a corresponding one linear imaging array to derive velocity data that represents an estimated velocity of the imaging device with respect to at least one target object disposed in the fields of view. Preferably, the image processing circuitry also produces a first image of portions of the target object(s), the first image having substantially constant aspect ratio, utilizing image transformation operations (or camera control operations) that are based upon the velocity data, to thereby compensate for aspect ratio distortions that would otherwise result from variations in velocity of the imaging device with respect to the target object(s). In addition, the image processing circuitry preferably carries out image-based horizontal jitter estimation and compensation operations, which estimate the horizontal jitter of the imaging device relative to the target object(s) over the image capture operations from which the first image is derived and transform the first image utilizing shift operations that are based upon such estimated horizontal jitter to produce a second image of portions of the target object(s) which compensates for horizontal jitter distortion that would otherwise result therefrom. The first image or second image (or image derived from sharpening the first or second images) is preferably subject to image-based bar code detection operations and / or OCR operations, or output for display to a display device.
Owner:METROLOGIC INSTR
Oct probe
InactiveUS20090190883A1Avoid ghostingAvoid it happening againMaterial analysis by optical meansCatheterLight beamLight source
An OCT probe has a sheath to be inserted into a subject; and an optical system within the sheath, for changing the direction of light which propagates from a light source through an optical fiber to irradiate the light onto the subject through a transparent portion of the sheath, and for reflecting the light beam, which is reflected by the subject, to guide the light into the optical fiber. A light output surface, for causing the light to be output from the reflecting surface in a direction obliquely inclined with respect to the inner surface of the sheath, and a reflected light sheath entrance preventing portion, for preventing light reflected by the inner surface of the sheath from entering the optical fiber, are provided in the optical system. The reflected light sheath entrance preventing portion may be formed by providing a cut planar surface portion on the lens.
Owner:NAMIKI PRECISION JEWEL CO LTD
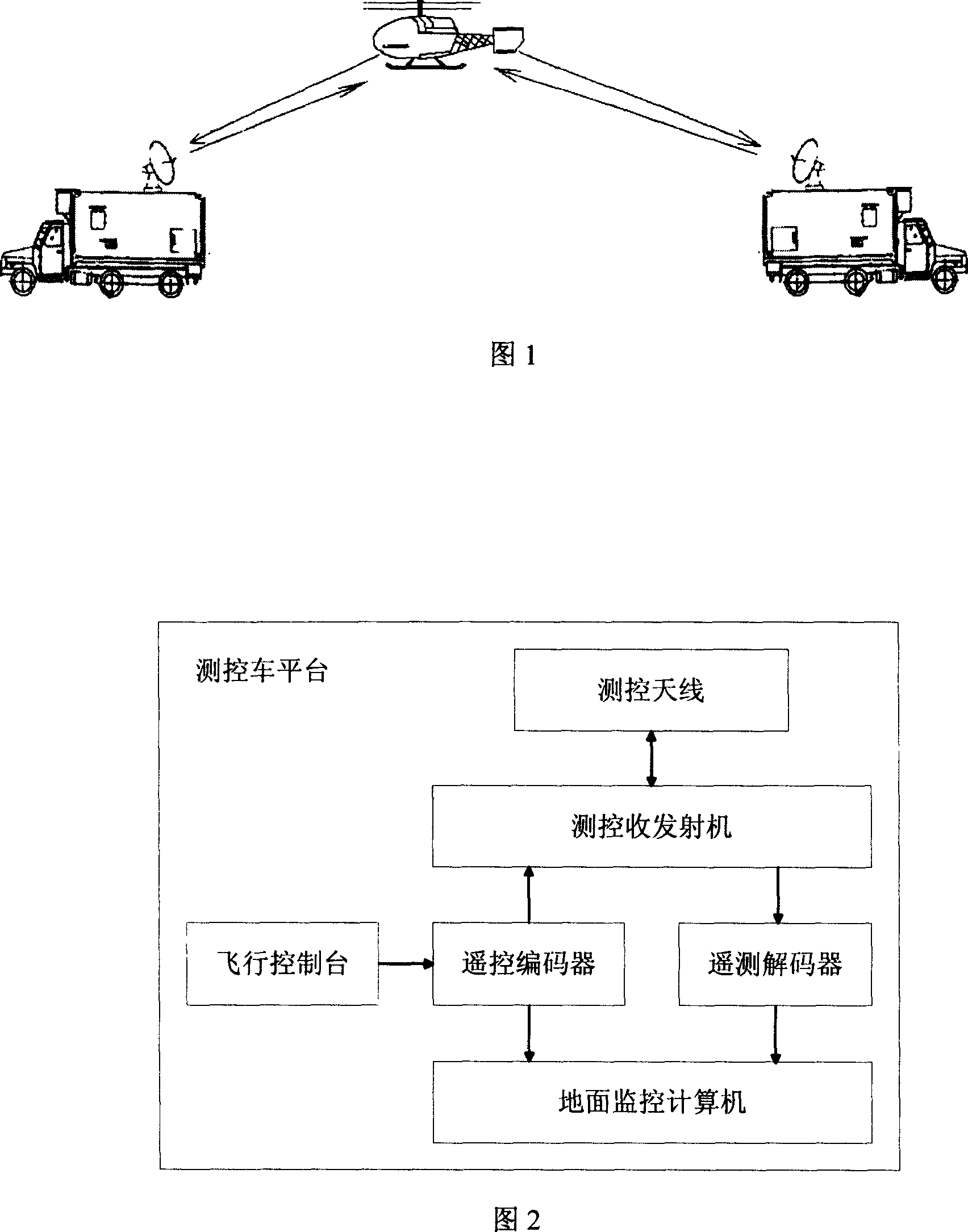
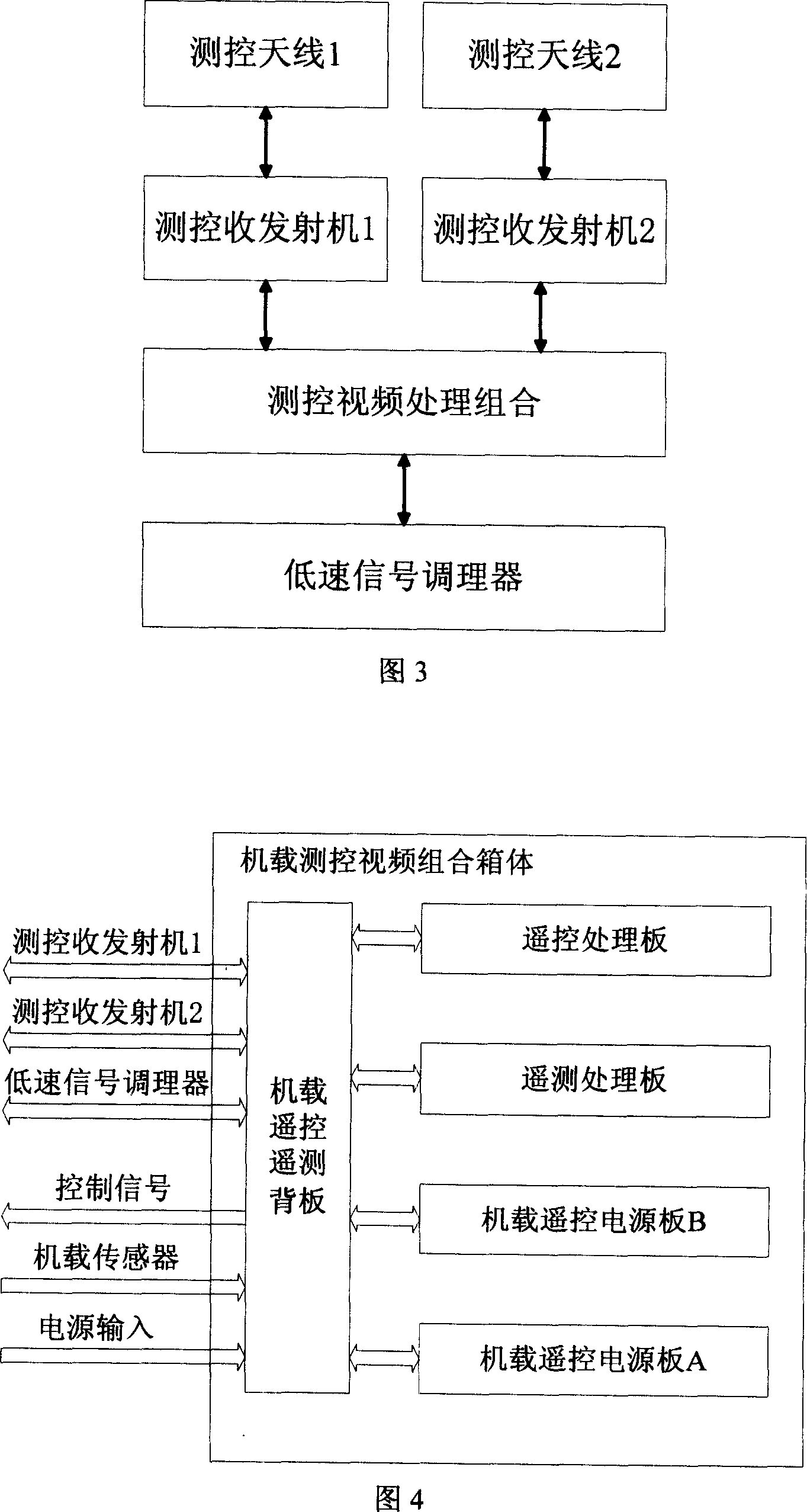
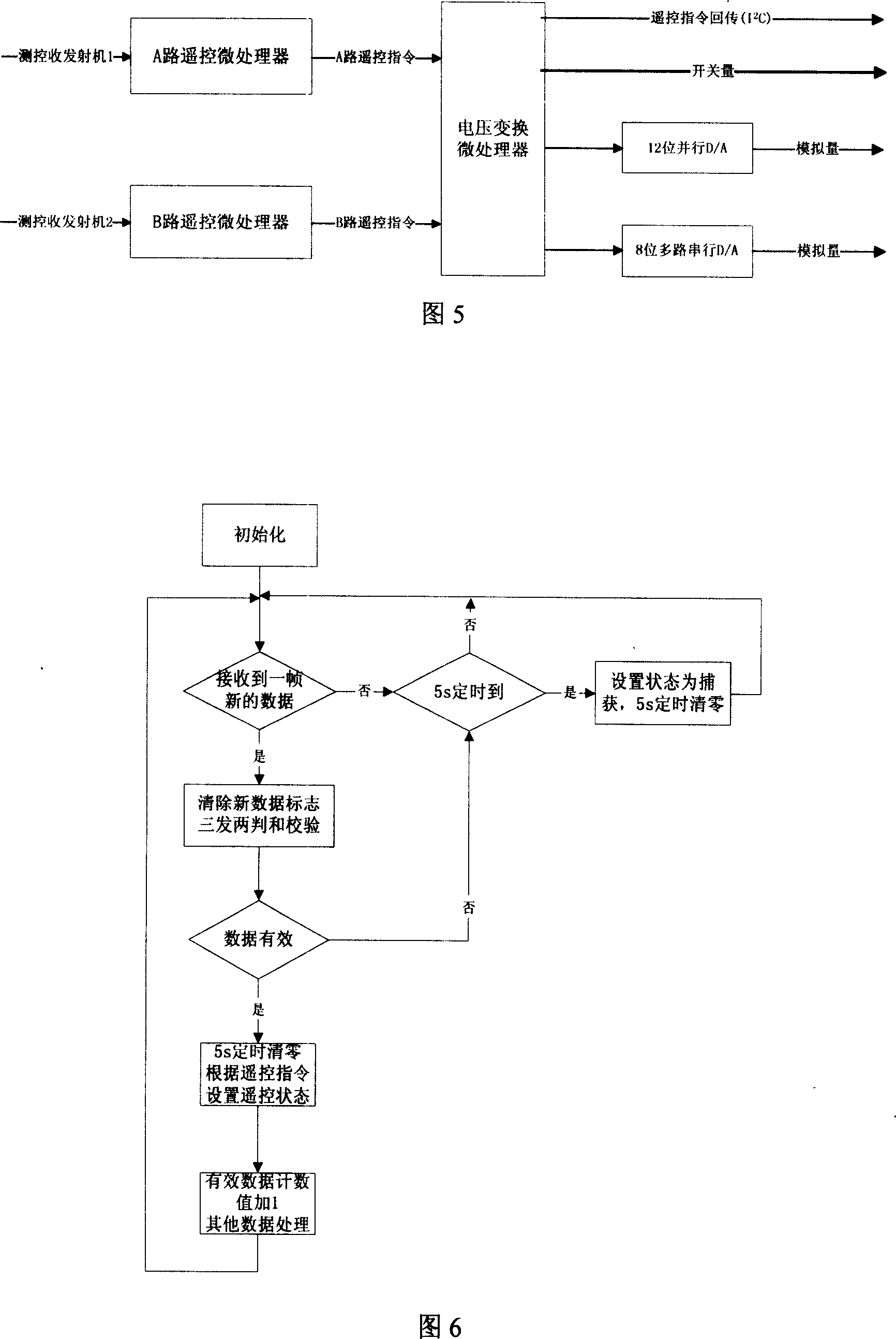
Double measurement and control system in use for coaxial dual rotors of unmanned helicopter
InactiveCN101004607AKnow the effectiveness of the controlsEasy to operate and controlSafety arrangmentsTransmission systemsFly controlTelecommunications link
A dumachine control system of coaxial pilotless heligyro comprises two sets of ground units and one set of heligyro unit. It is featured as forming said ground unit by control machine platform, flying control table , remote control coder, remote detection decoder, ground control computer, control emitter / receiver and control antenna; forming heligyro unit by control antenna, control emitter / receiver, control video processing combination and low speed signal regulator.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Working device setted on one place and engineering machinery using it
InactiveCN1831253AShorten the timeImprove operational skillsMechanical machines/dredgersVehiclesState of artEngineering
The invention is a working device arranged in some place, composed of two or above working devices arranged in some place, back-to-back, side-arranged, opposite, staggered, side-by-side, up and down, rotatable, inclinable, turnable, movable, liftable or in other form. And an engineering machine applying it is composed by arranging it in corresponding position on a corresponding vehicle or chassis or connecting it with the correspond position. And it can compose various engineering machines by various vehicles or chassises, compact, multifunctional, low-cost, high-efficiency and energy-saving, and having strong practicality.
Owner:姚实现
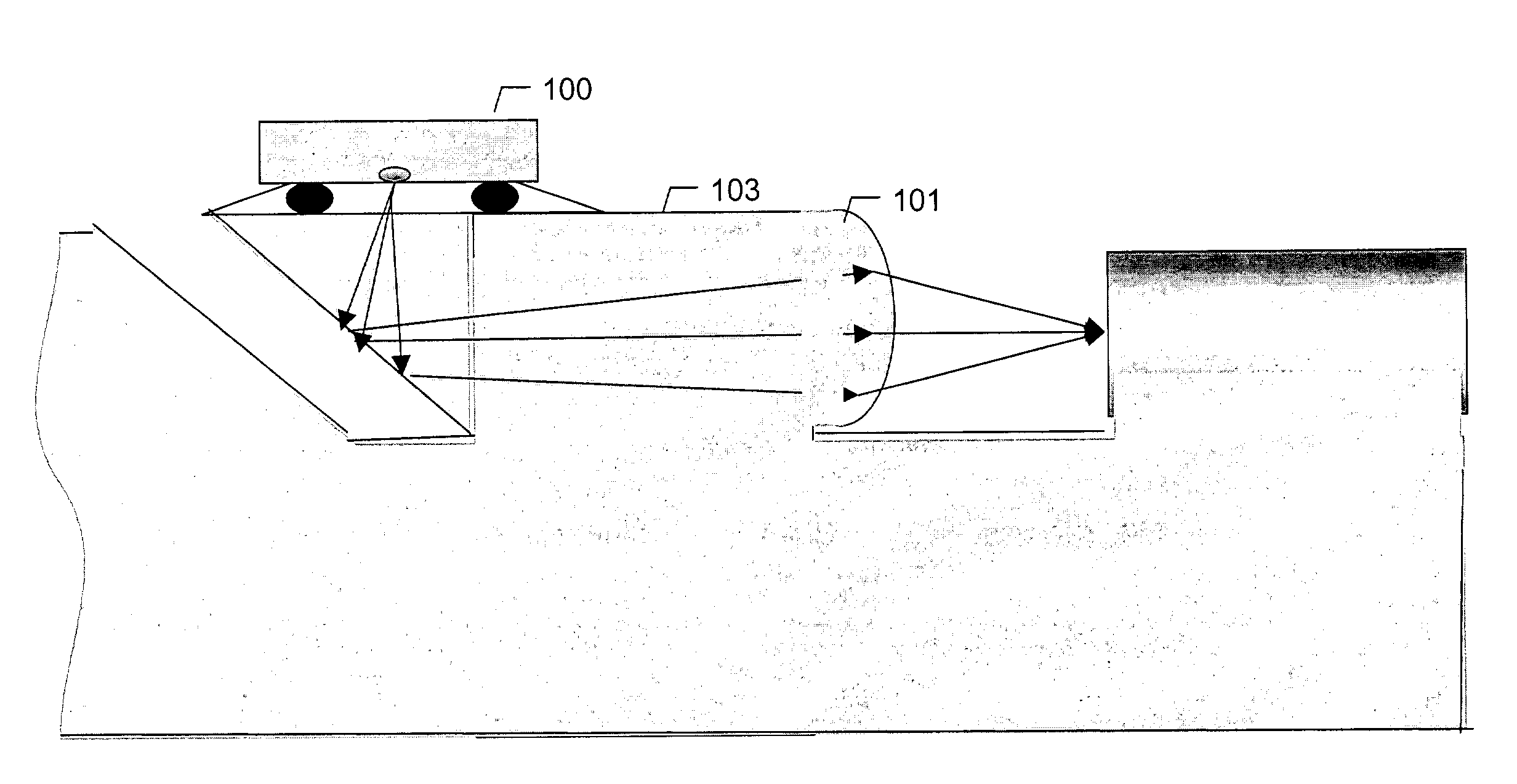
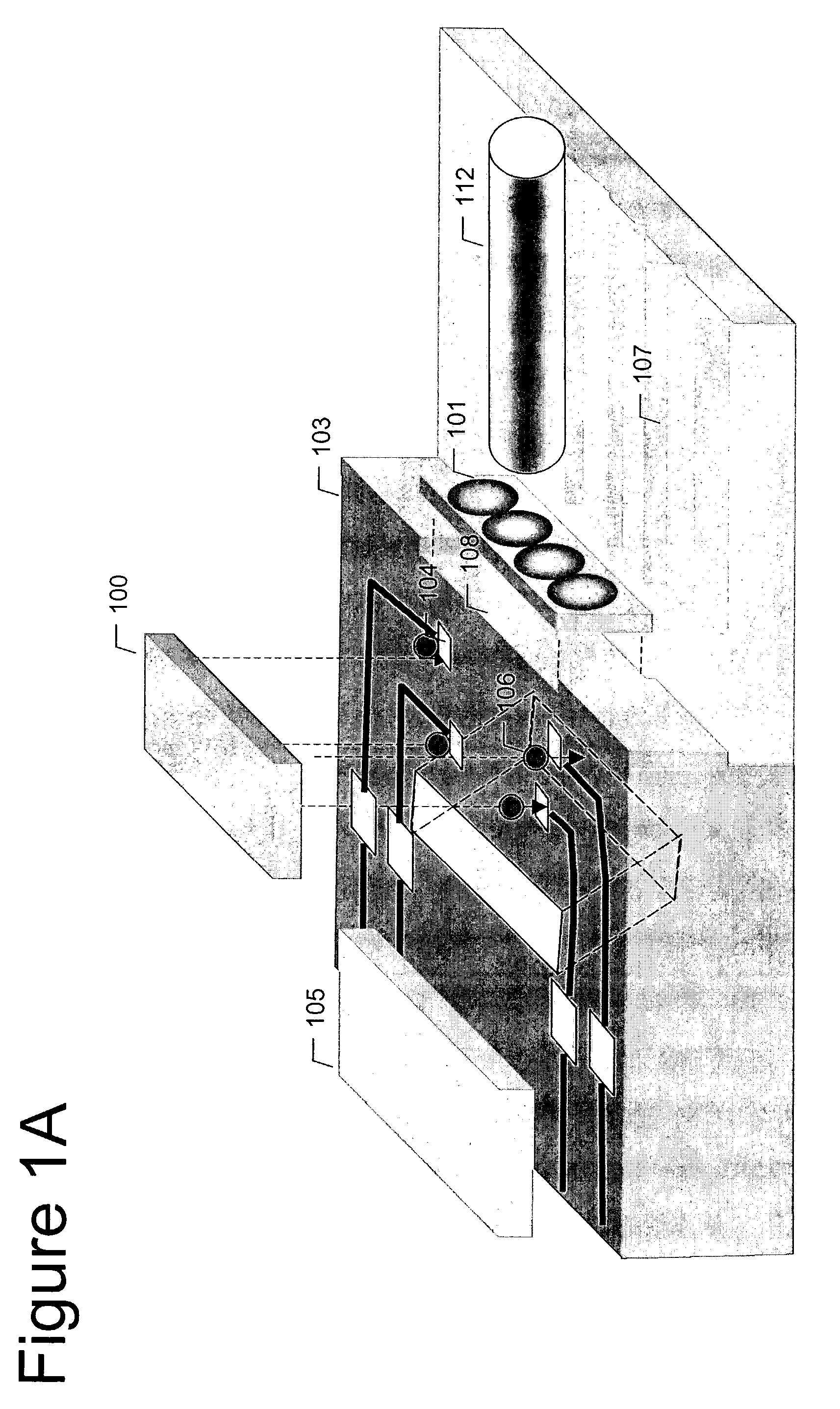
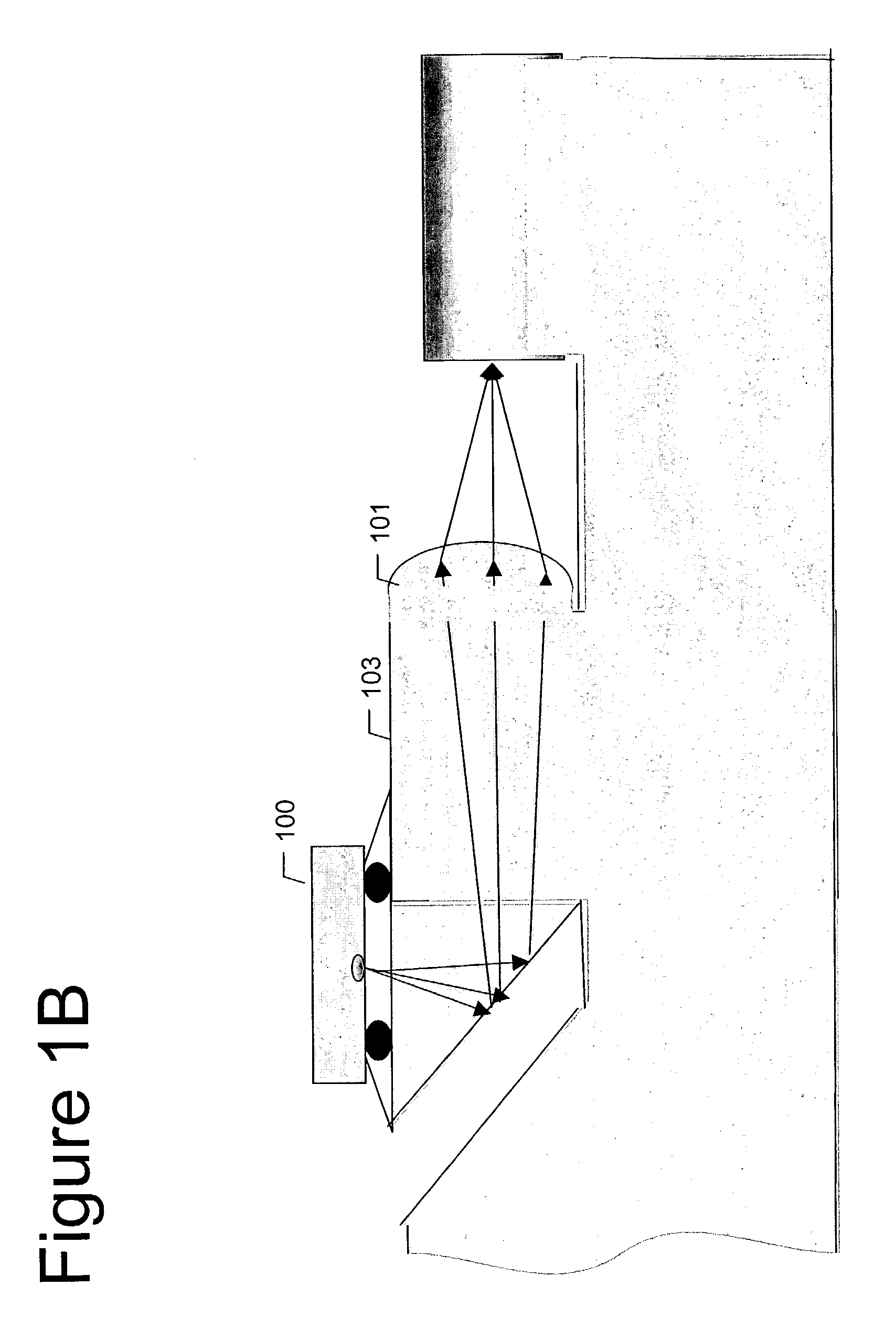
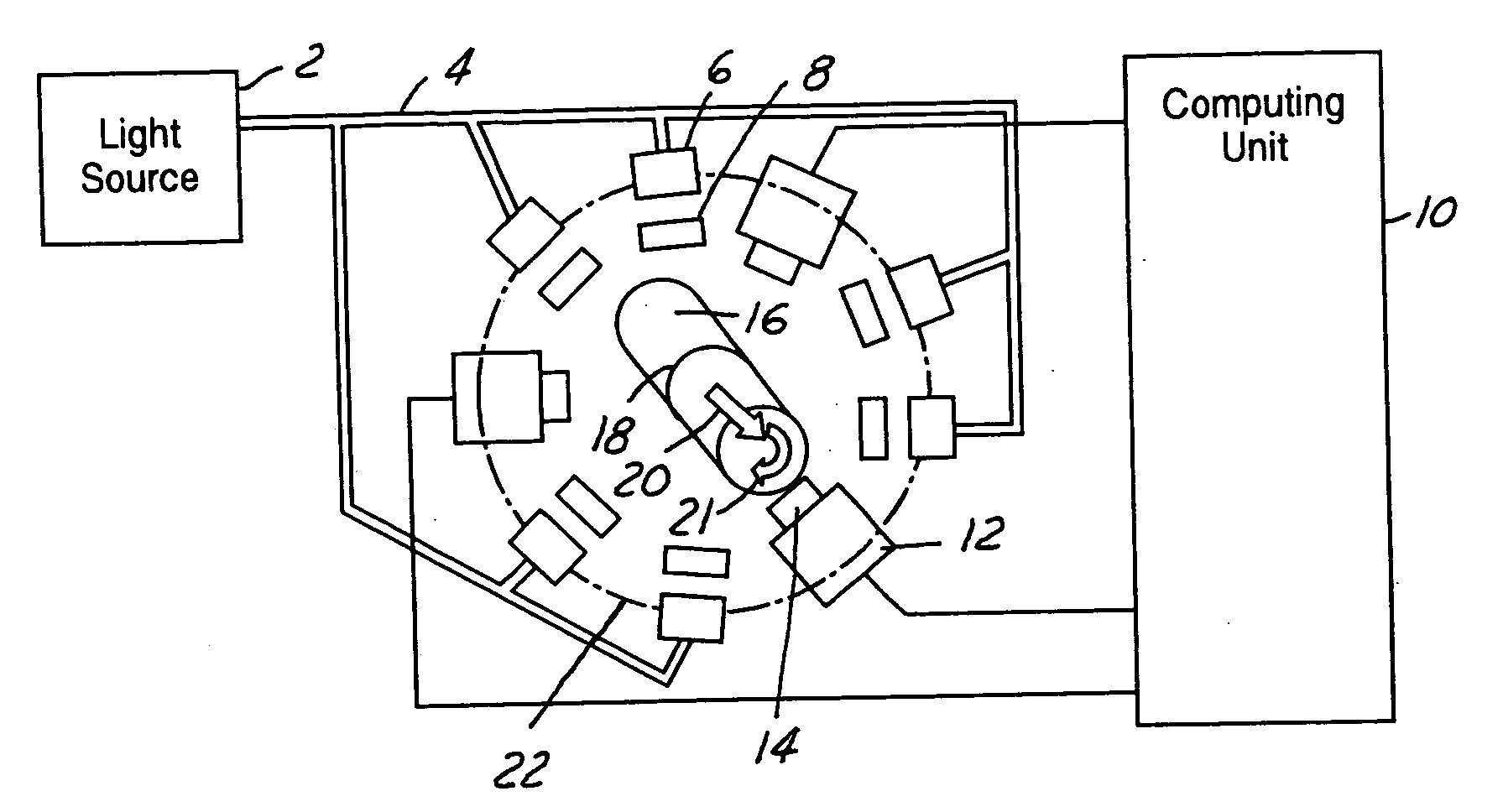
Apparatus and method for detecting surface defects on a workpiece such as a rolled/drawn metal bar
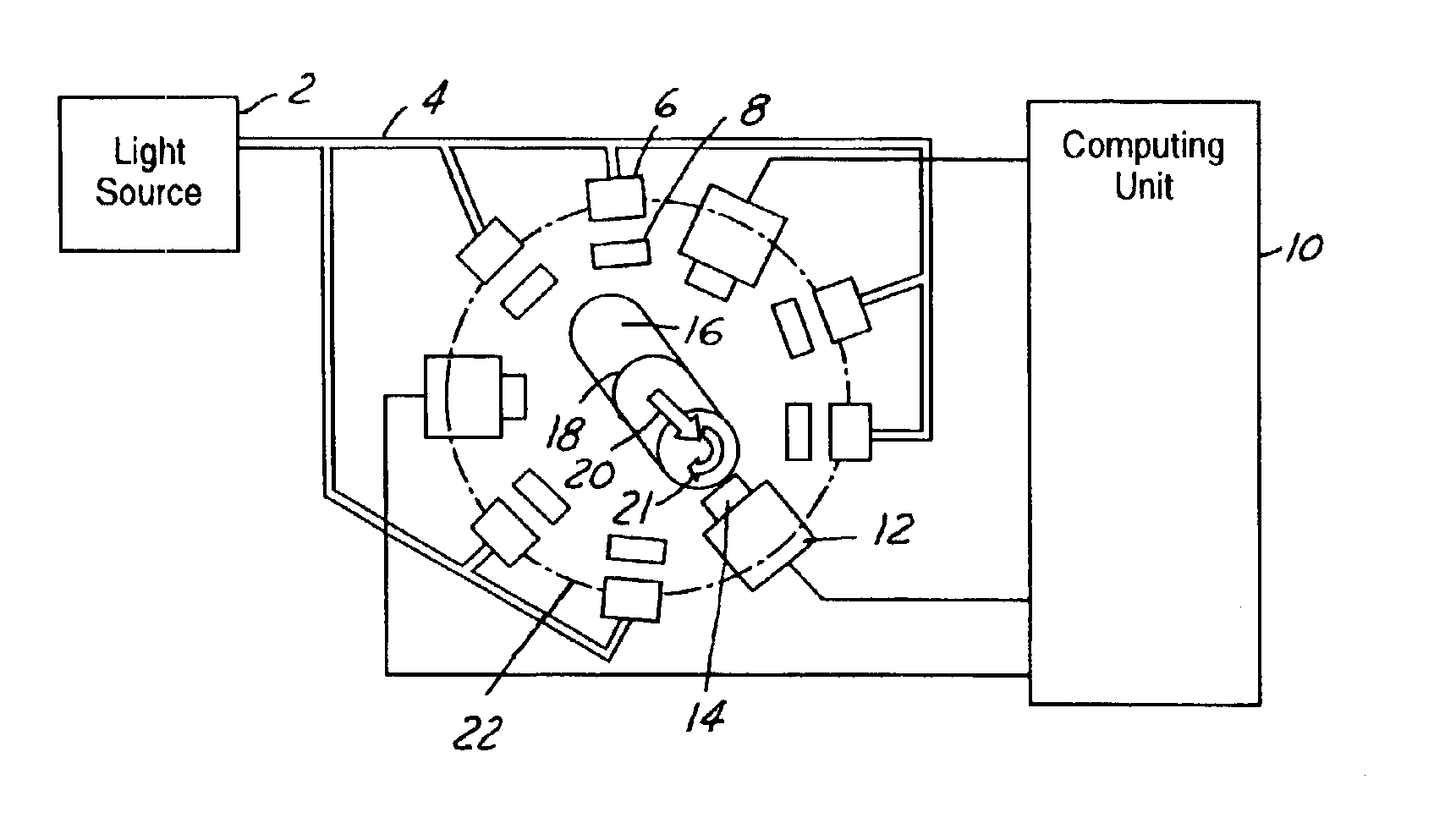
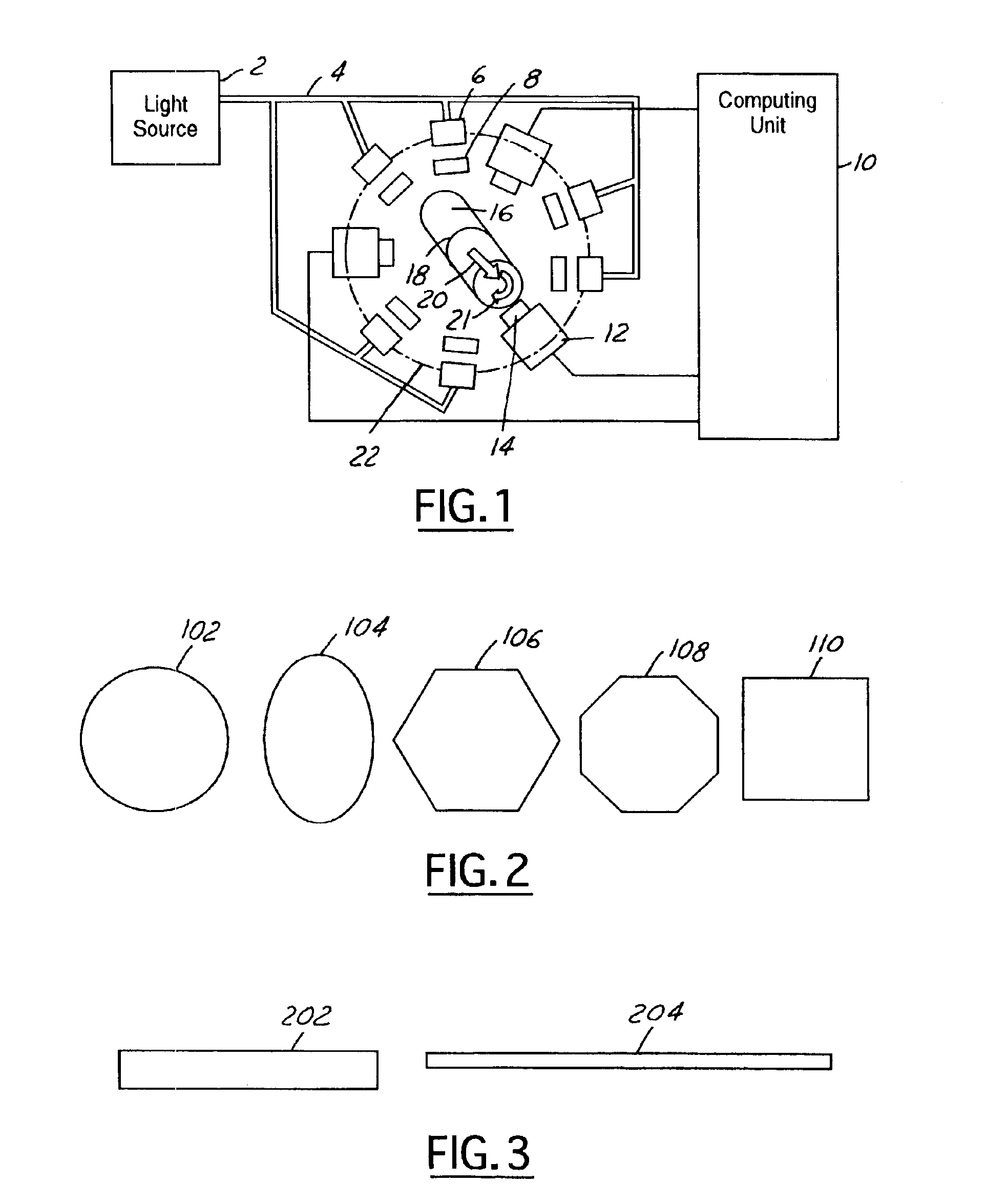
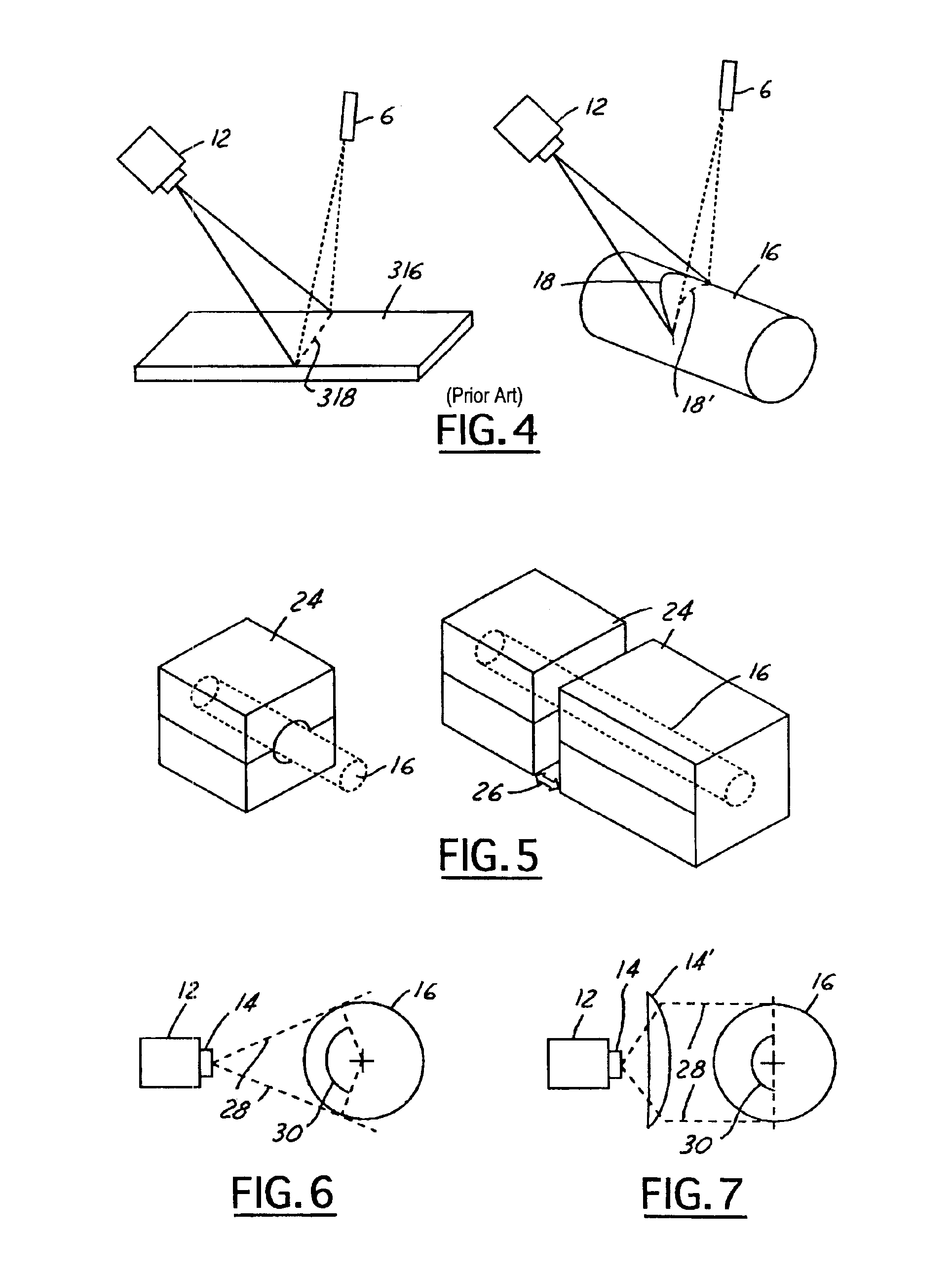
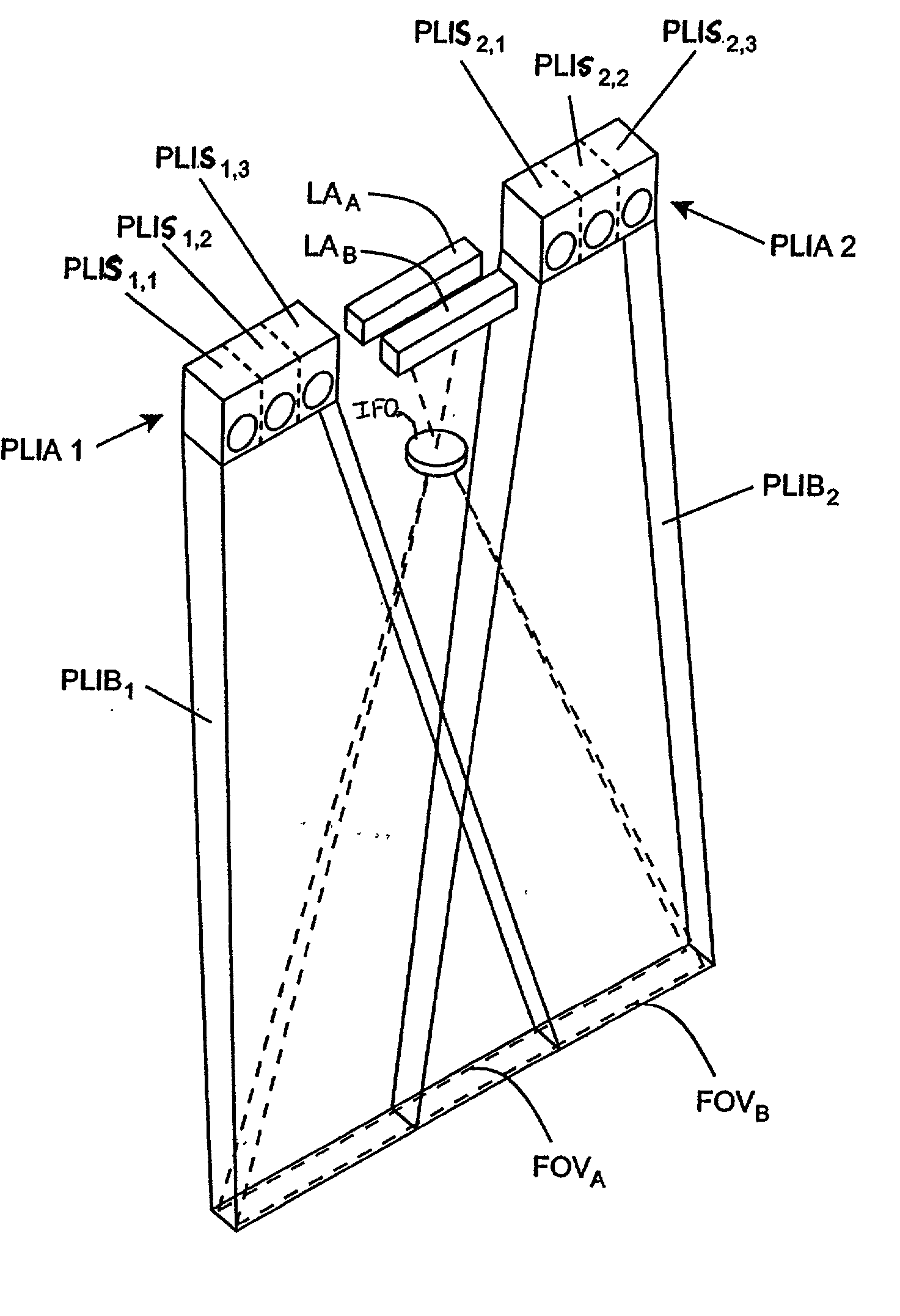
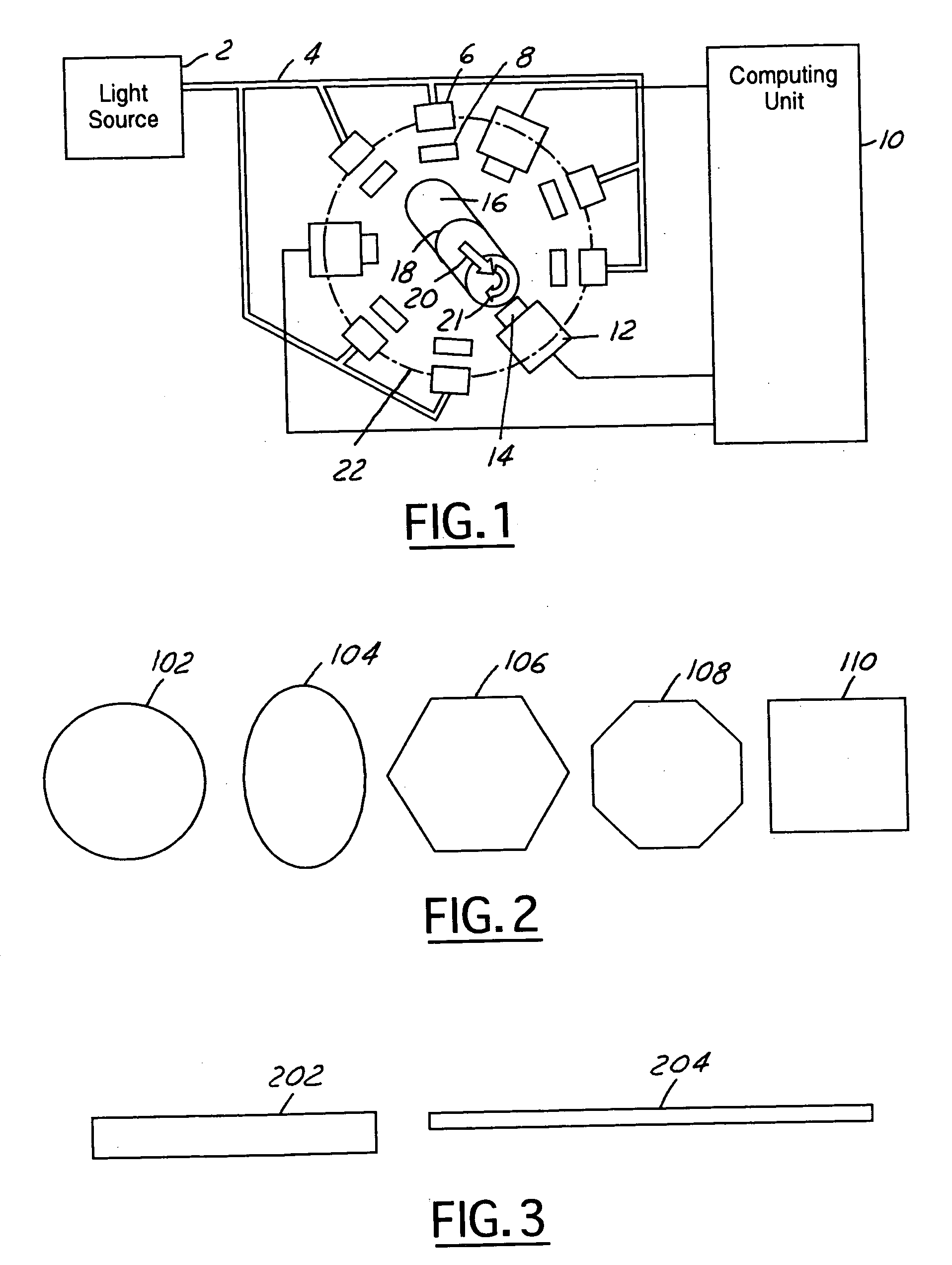
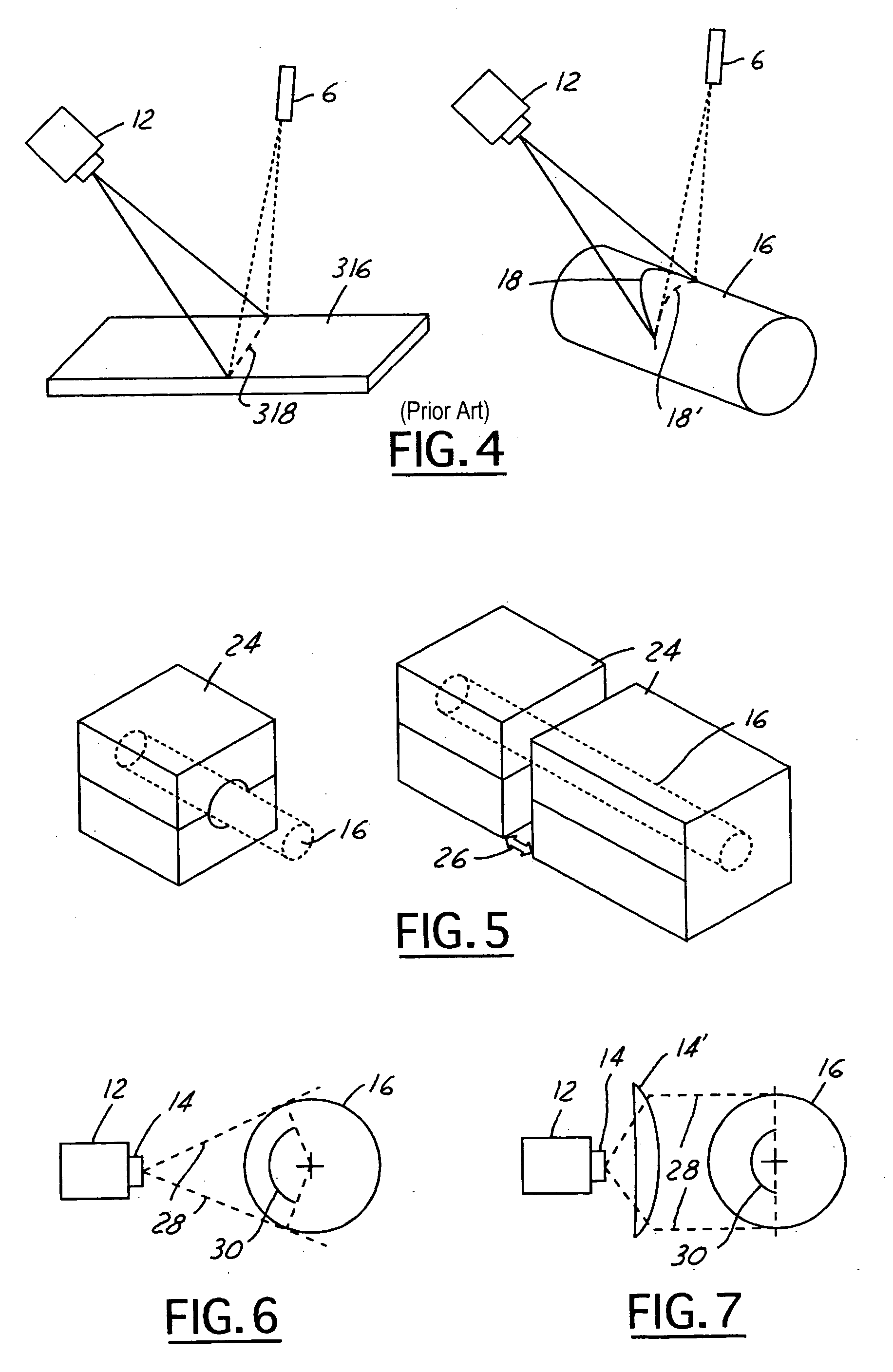
ActiveUS6950546B2Efficiently employedIncrease the working distanceCharacter and pattern recognitionColor synchronisationNon destructiveEngineering
The present invention is directed to solving the problems associated with the detection of surface defects on metal bars as well as the problems associated with applying metal flat inspection systems to metal bars for non-destructive surface defects detection. A specially designed imaging system, which is comprised of a computing unit, line lights and high data rate line scan cameras, is developed for the aforementioned purpose. The target application is the metal bars (1) that have a circumference / cross-section-area ratio equal to or smaller than 4.25 when the cross section area is unity for the given shape, (2) whose cross-sections are round, oval, or in the shape of a polygon, and (3) are manufactured by mechanically cross-section reduction processes. The said metal can be steel, stainless steel, aluminum, copper, bronze, titanium, nickel, and so forth, and / or their alloys. The said metal bars can be at the temperature when they are being manufactured.
Owner:OG TECH INC
Imaging engine employing planar light illumination and linear imaging
InactiveUS20030091244A1Low costReduce speckle noiseCharacter and pattern recognitionRecord carriers used with machinesTime signalImage based
An imaging engine includes a plurality of linear imaging arrays, image formation optics, at least one illumination module and supporting circuitry that are embodied within a modular engine housing. The plurality of linear imaging arrays and image formation optics are mounted on an optical bench (which is integral to the engine housing) and provide field of views corresponding to the plurality of linear image arrays. The at least one illumination module produces planar light illumination that substantially overlaps the field of views corresponding to the plurality of linear imaging arrays. The supporting circuitry includes: timing signal generation circuitry that supplies timing signals to the linear imaging arrays in order to read out the row image data produced by such arrays (such row image data may be read out at a constant line rate or at a variable line rate); illumination control circuitry that supplies current to the illumination sources in the at least one illumination module; analog-to-digital conversion circuitry, which optionally filters row data image signal supplied thereto (to remove unwanted noise components) and converts the row image data supplied thereto into digital form; and data buffering circuitry, for storing the digital row image data generated by the analog-to-digital conversion circuitry and communicating the row image data stored therein over a data communication bus. One linear image array (e.g., linear imaging array C) may have a variable line rate that is controlled by the timing signals supplied thereto such that the image capture operations performed by the one linear imaging array (e.g. linear imaging array C) maintain a substantially constant aspect ratio, to thereby compensate for aspect ratio distortions that result from variations in velocity of engine with respect to target object(s). The variable line rate is based upon velocity estimates derived from processing of the pixel data values of other linear imaging arrays disposed therein. The supporting circuitry may optionally include a line rate adjustment module, preferably realized as part of a programmed controller, that is operably coupled to timing signal generation circuitry and adjusts the variable line rate of the one linear image device (e.g., linear imaging array C); output illumination control module, preferably realized as part of the programmed controller, that is operably coupled to the illumination control circuitry and adjusts the optical power level and / or illumination time period for the illumination that overlaps one or more of the FOVs of the linear imaging arrays of the engine for speckle reduction / constant white levels; and / or imaging processing circuitry, operably coupled to the data buffering circuitry over the data communication bus, that realizes portions of image-based mechanisms / techniques for image velocity estimation, aspect ratio compensation, jitter estimation and compensation, bar code detection, OCR, and image lift.
Owner:METROLOGIC INSTR
Integrated platform for passive optical alignment of semiconductor device with optical fiber
InactiveUS7289701B2Reduced feature requirementsEffective demagnificationCoupling light guidesElectricityVertical-cavity surface-emitting laser
A platform for converting a signal between optical and electrical form and vice versa is provided. The platform includes a dielectric mount, a semiconductor light source and optical fibers. Some of these components are fabricated separately and then brought together in an integrated assembly together with a focusing lens. The platform permits the self-alignment of the optical fibers in a flip-chip vertical cavity surface emitting laser (VCSEL) array module package. The self-alignment of the optical fibers is achieved by the engineering of the geometrical dimensions of the platform. The techniques may be used to form large-scale integrated opto-electronic circuits and switching networks.
Owner:CLOUD LIGHT TECH LTD
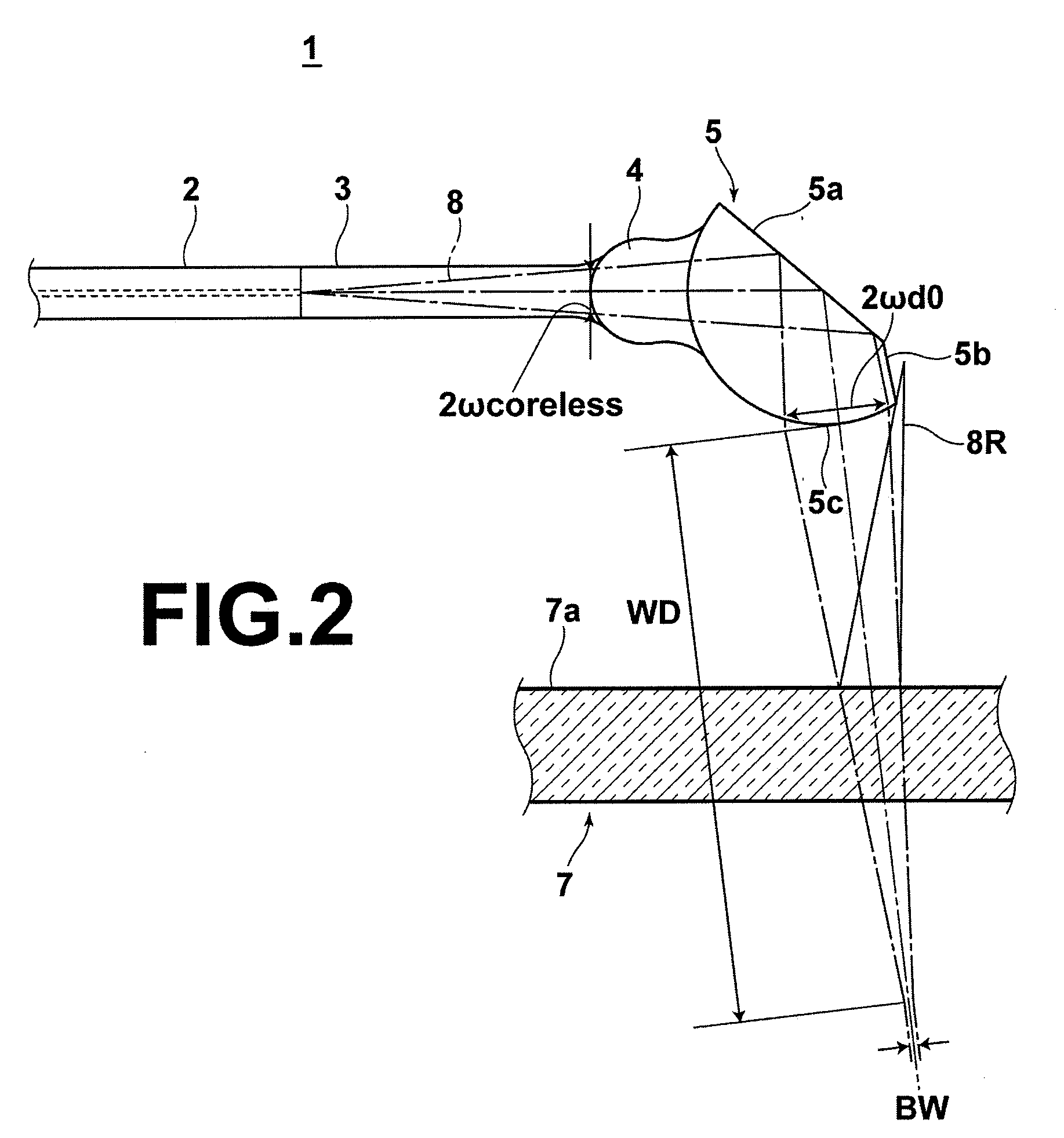
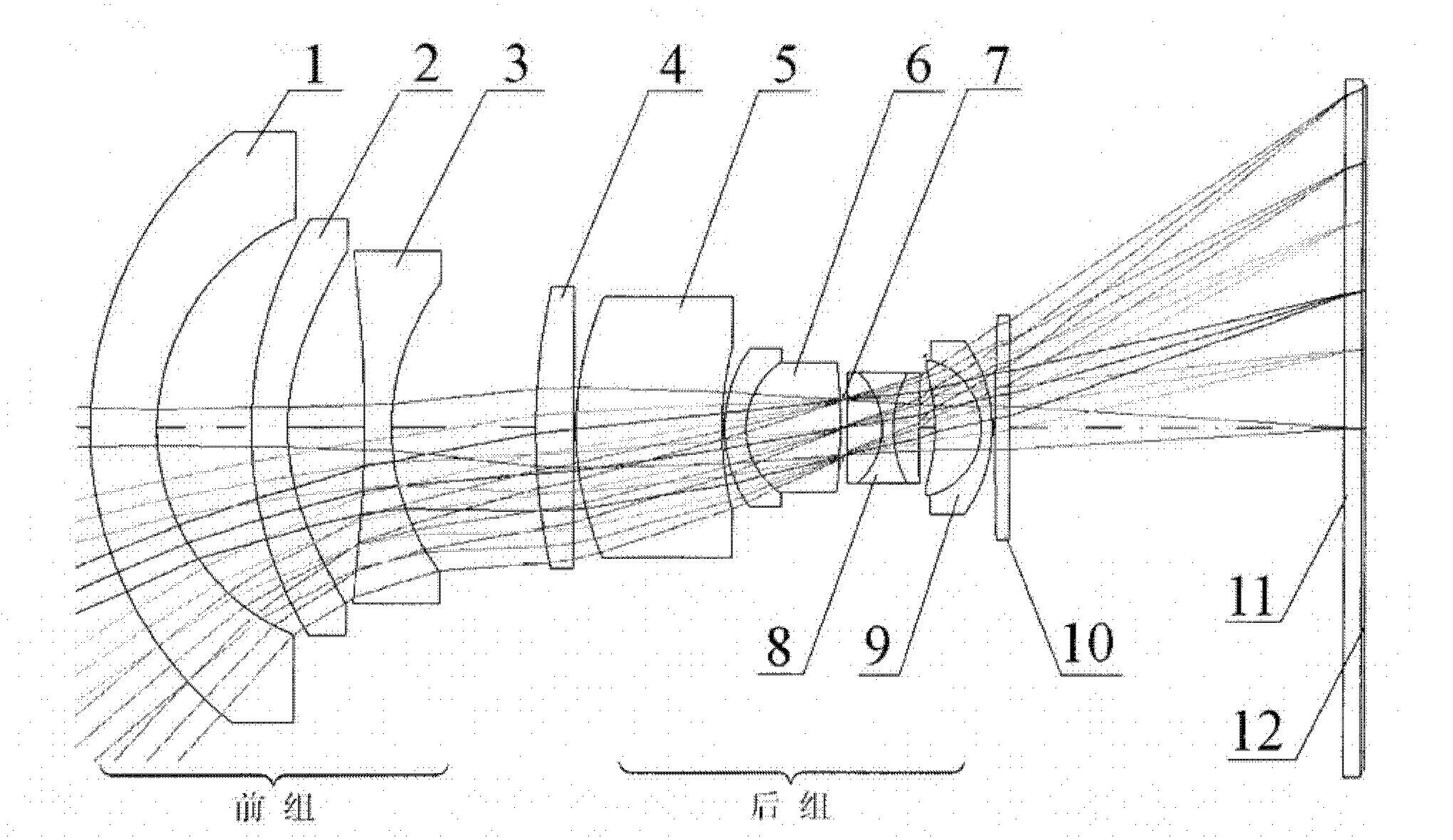
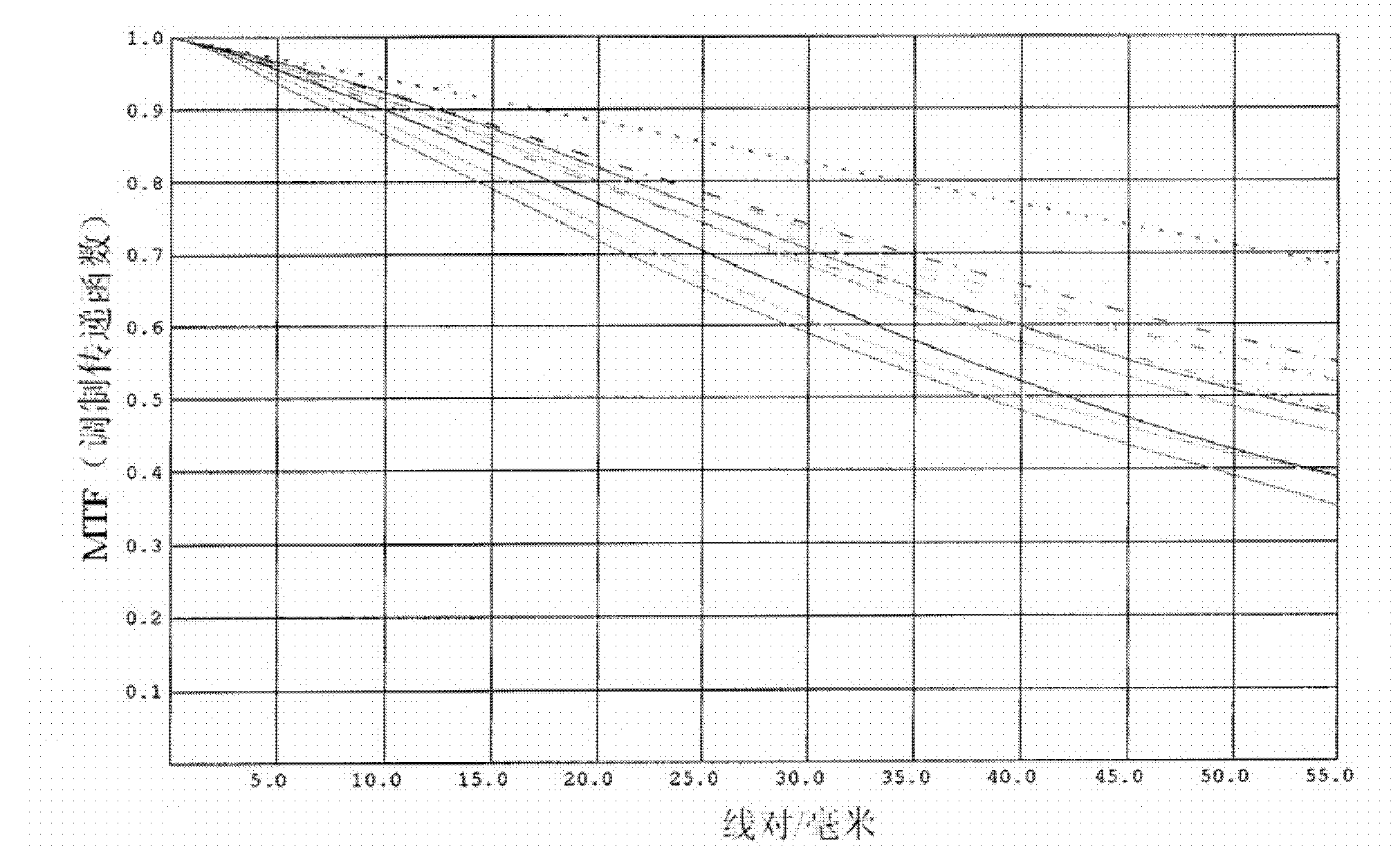
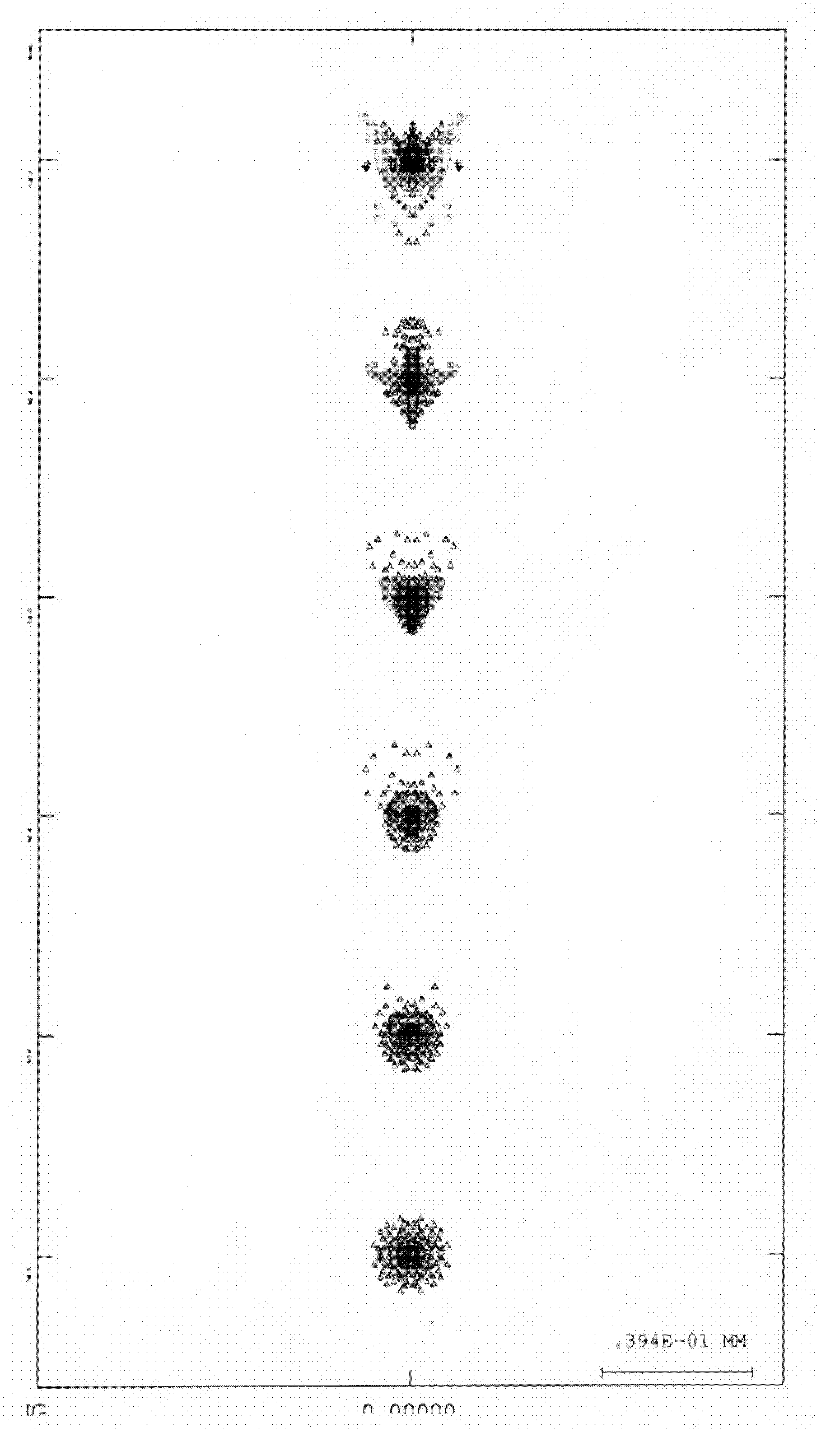
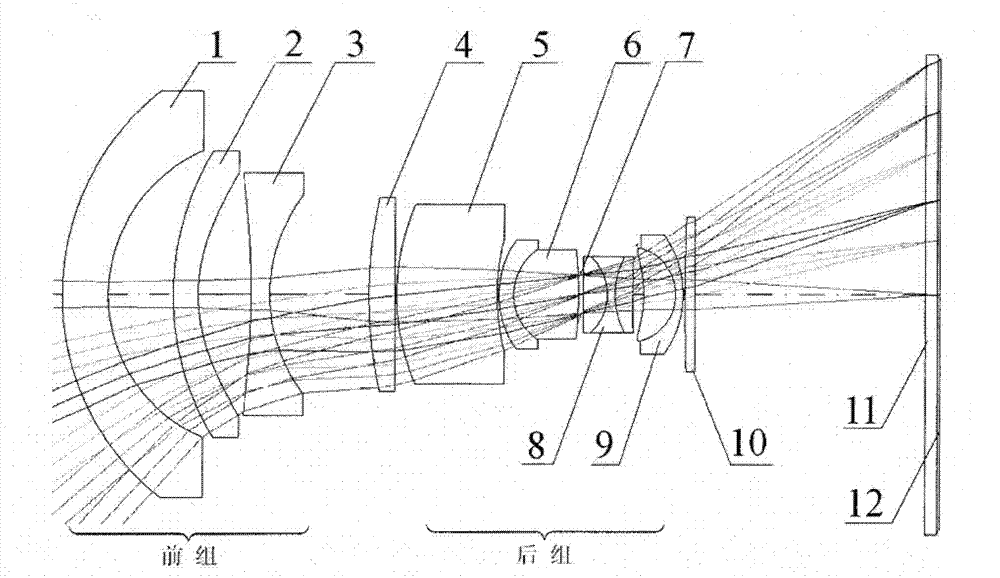
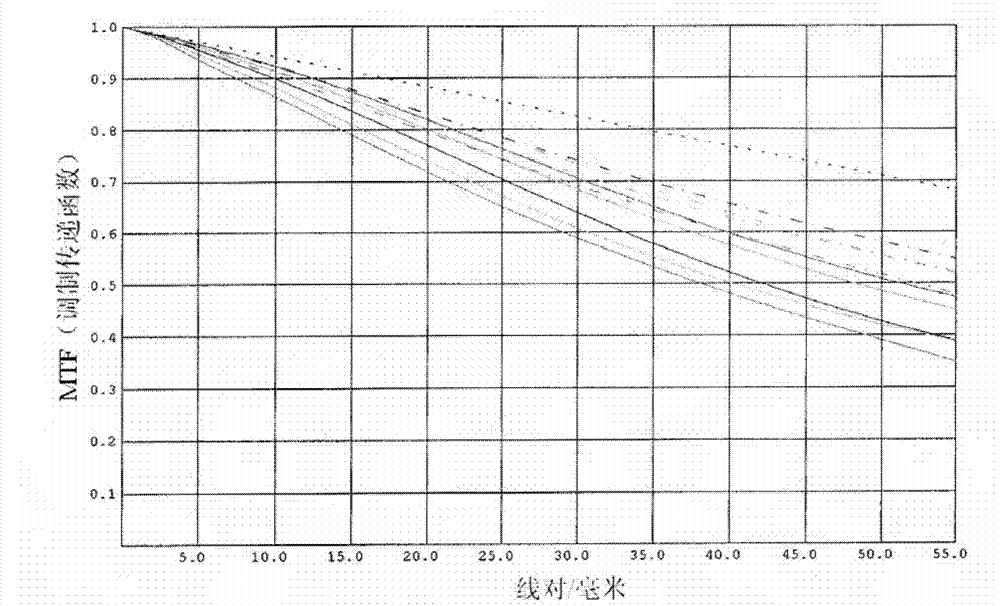
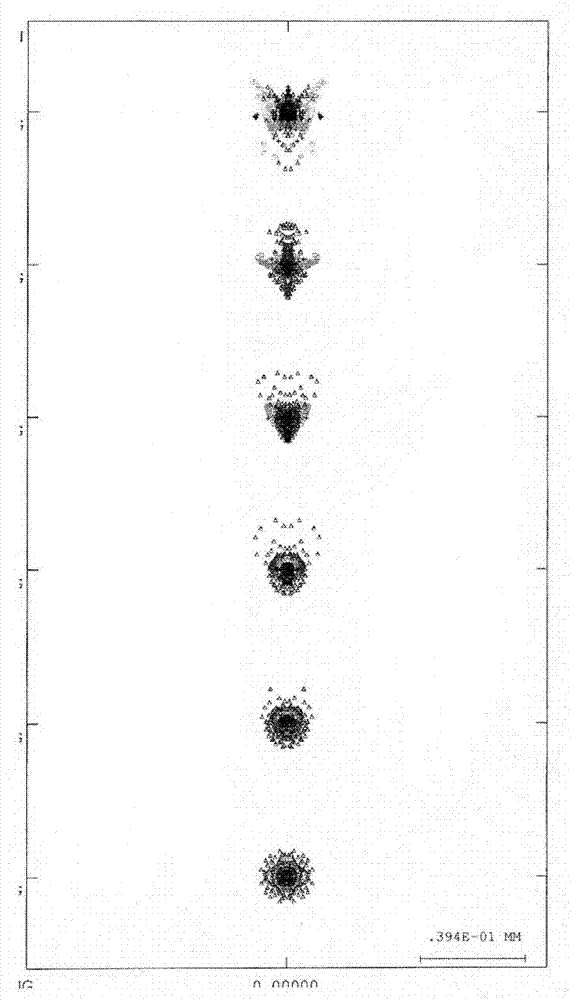
Panchromatic objective lens of aerial camera for realizing wide angle as well as long and rear operating distance
The invention relates to a panchromatic objective lens of an aerial camera realizing wide angle as well as long and rear operating distance. The panchromatic objective lens adopts a reverse long-distance type structure, namely, a separation structure of a negative lens and a positive lens; a negative power lens group is used as a front group; a positive power lens group is used as a rear group; the front group consists of a first lens, a second lens and a third lens that are arranged sequentially; the rear group consists of a fourth lens, a five lens, a first pair of balsaming lens, a diaphragm, a triplet lens, a second pair of balsaming lens and a convex plane lens that are arranged sequentially; and components in each group of the front group and the rear group are sequentially arrangedalong an optical axis. The panchromatic objective lens of the aerial camera simultaneously realizes big field of view, long and rear operating distance, high resolution and low distortion.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Apparatus and method for detecting surface defects on a workpiece such as a rolled/drawn metal bar
InactiveUS20060002605A1Efficiently employedEfficient detectionCharacter and pattern recognitionColor television detailsMetal stripsAlloy
The present invention is directed to solving the problems associated with the detection of surface defects on metal bars as well as the problems associated with applying metal flat inspection systems to metal bars for non-destructive surface defects detection. A specially designed imaging system, which is comprised of a computing unit, line lights and high data rate line scan cameras, is developed for the aforementioned purpose. The target application is the metal bars (1) that have a circumference / cross-section-area ratio equal to or smaller than 4.25 when the cross section area is unity for the given shape, (2) whose cross-sections are round, oval, or in the shape of a polygon, and (3) are manufactured by mechanically cross-section reduction processes. The said metal can be steel, stainless steel, aluminum, copper, bronze, titanium, nickel, and so forth, and / or their alloys. The said metal bars can be at the temperature when they are being manufactured.
Owner:OG TECH INC
Method and system for extracting natural gas hydrate through thermal jet flow
ActiveCN105134152APromote decompositionInhibition of reformationConstructionsFluid removalProcess engineeringSystem structure
The invention provides a method and system for extracting natural gas hydrate through thermal jet flow. The method includes the steps that a combustion reaction device is lowered to a downhole target position of a natural gas hydrate reservoir, oxygen and fuel are injected into the downhole target position, the combustion reaction device is powered on, ignition is performed, combustion products are jet out of the combustion reaction device to form high-speed jet flow, the jet flow and heat generated during combustion act on the natural gas hydrate reservoir so that natural gas hydrate can be decomposed, and decomposed natural gas returns upwards to the ground; the amount of injected fuel is gradually reduced till injection stops, meanwhile part of the natural gas returning upwards to the ground and water are injected and mixed with oxygen for continuous combustion, and natural gas hydrate can be furthermore decomposed. The system at least comprises the combustion reaction device, a continuous oil tube inner tube, a continuous oil tube outer tube, a cable, a production sleeve, a water supply device, a fuel supplying device, an oxygen supplying device, a natural gas storing, collecting and supplying device and a pump set. The method and system for extracting natural gas hydrate through thermal jet flow have the advantages that extracting cost is low, extracting efficiency is high and the system structure is simple.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (BEIJING)
Panchromatic objective lens of aerial camera for realizing wide angle as well as long and rear operating distance
InactiveCN102147519BIncrease the working distanceReduce the image square half angle of view ω′Optical elementsLow distortionOptical axis
The invention relates to a panchromatic objective lens of an aerial camera realizing wide angle as well as long and rear operating distance. The panchromatic objective lens adopts a reverse long-distance type structure, namely, a separation structure of a negative lens and a positive lens; a negative power lens group is used as a front group; a positive power lens group is used as a rear group; the front group consists of a first lens, a second lens and a third lens that are arranged sequentially; the rear group consists of a fourth lens, a five lens, a first pair of balsaming lens, a diaphragm, a triplet lens, a second pair of balsaming lens and a convex plane lens that are arranged sequentially; and components in each group of the front group and the rear group are sequentially arrangedalong an optical axis. The panchromatic objective lens of the aerial camera simultaneously realizes big field of view, long and rear operating distance, high resolution and low distortion.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Space tumbling target de-spinning control method based on permanent magnet eddy current effect
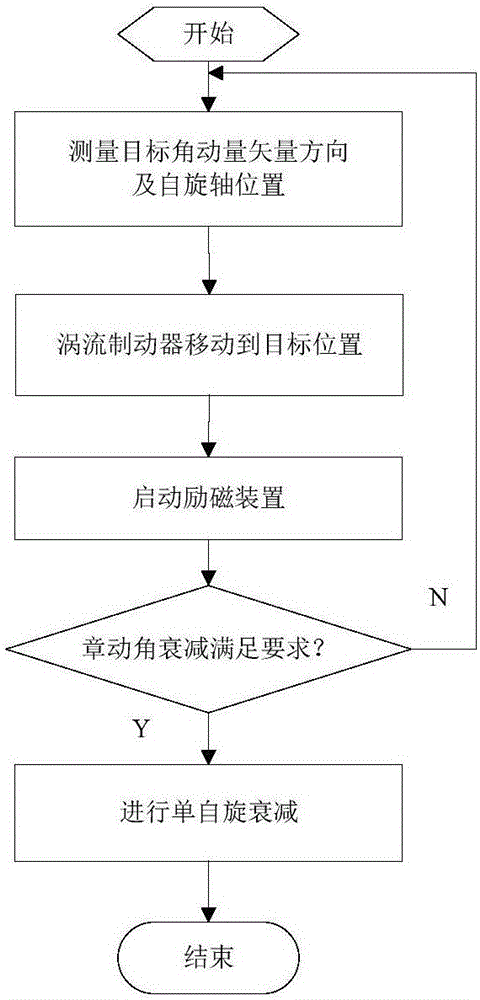
ActiveCN106406329AMeet the attitude adjustment control requirementsIncrease the working distanceCosmonautic vehiclesCosmonautic partsNutationEngineering
Disclosed is a space tumbling target de-spinning control method based on a permanent magnet eddy current effect. The method comprises the following steps: a service spacecraft docks in the working space of a mechanical arm, and is kept at a safety distance from a tumbling non-cooperative target; a visual inspection system carried by the service spacecraft measures the direction of a target angular momentum vector H and the direction of a spin axis position vector Zb, and the mechanical arm drives a permanent magnet eddy current braking device at the end to an initial de-spinning position, and the docking position is 100mm from the surface of the target in the direction of the target angular momentum vector; the permanent magnet eddy current braking device is started, the direction of a vector outputting an external torque T1 is corrected according to the real-time change of attitude angle in the tumbling process of the target until the angle of nutation attenuates completely, and the rotation state of the target is changed to a single spinning motion state; the position of the permanent magnet eddy current braking device is adjusted to the side of the tumbling non-cooperative target, the permanent magnet eddy current braking device is started to output a brake torque T2 until the single spinning motion state attenuates completely; after the target is completely de-spun, an end actuator is replaced with a grasping paw, and the target is captured directly by the mechanical arm.
Owner:黑龙江省工研院资产经营管理有限公司
Transmission extension adapter for power hand tool
InactiveUS20090194954A1Increase the working distanceEasy to useSleeve/socket jointsSpannersDrive shaftPower tool
A transmission extension adapter for connection between a work head and the chuck of a power hand tool includes a cylindrical cap shell coupled to the power hand tool around the chuck and having radial through holes and a positioning member in each radial through hole. An axle sleeve is rotatably coupled to the cylindrical cap shell and has locating holes on the periphery thereof. A transmission axle is inserted through the axle sleeve and has a rear end connected to the chuck and a front end connected with a supplementary chuck for holding the work head. A front cap assembly is affixed to the front end of the axle sleeve to hold an automatic feeder for allowing rotation of the automatic feeder with the axle sleeve. A multi-angle positioning device is adapted for holding down the positioning members in the locating holes to lock the axle sleeve.
Owner:MOBILETRON ELECTRONICS
Method for tracking and positioning mobile node of wireless sensor network
InactiveCN101520502AIncrease the working distanceReduce densityBeacon systemsLocation information based serviceWireless mesh networkWireless sensor networking
The invention relates to a method for tracking and positioning a mobile node of a wireless sensor network, which comprises the following steps: in a measurement positioning period, sending low repeated frequency pulse beacon signals for at least four times at known time intervals by the mobile node approximately keeping uniform speed rectilinear motion, receiving the beacon signals continuously for four times by a main anchoring node, measuring self time difference to acquire three self time difference relation expressions relative to an initial measurement moment, providing two trigonometric function equations from a positioning measurement triangle consisting of a motion locus of the mobile node and a motion radius vector of detection wave by using the cosine theorem, and simultaneously solving the equations so as to determine the relative distance and speed between the mobile node and the anchoring nodes; and further, by adopting the technology of beacon retransmission, retransmitting the beacon signals sent by the mobile node for the last time to the main anchoring node by two auxiliary anchoring nodes so as to achieve asynchronous coordinate positioning of the mobile node. The method can achieve tracking and positioning of a mobile target without time synchronization among the anchoring nodes.
Owner:CHINESE AERONAUTICAL RADIO ELECTRONICS RES INST
Direct type backlight source
InactiveCN102644883AIncrease the working distanceShorten the mixing distanceNon-linear opticsRefractorsReflectivityLight source
The invention discloses a direct type backlight source comprising a light-emitting body, a reflection sheet located below the light-emitting body, a back plate located below the reflection sheet, and a diffusion plate located above the light-emitting body. The direct type backlight source further comprises a semi-transparent semi-reflecting layer arranged between the diffusion plate and the light-emitting body, wherein the reflection rate of the semi-transparent semi-reflecting layer is more than 0 and less than 1. With the adoption of the technical scheme, the thickness of the direct type backlight source is effectively reduced.
Owner:BOE TECH GRP CO LTD +1
Auto-collimation three-dimensional angle measuring device and method based on polarizing beam splitting
ActiveCN109579780ACapable of 3D angle measurementHigh measurement accuracyAngle measurementBeam splitterLight spot
The invention belongs to the technical field of precision measurement and the field of optical engineering, and particularly relates to an auto-collimation three-dimensional angle measuring device andmethod based on polarizing beam splitting. The device is composed of a light source, a polarizer, a beam splitter, a polarizing beam splitter, image sensors, a collimating mirror, a fixed plane mirror and a cooperative target. According to the method, a measuring beam is divided into two mutually perpendicular measuring light by the cooperative target, the measuring light returns after being reflected by the fixed plane mirror and the cooperative target, and corresponding images are separately formed on the image sensors; and the positions of the two images are adopted to calculate a pitch angle, a yaw angle and a roll angle of the cooperative target with respect to an optical axis, so that a capability of detecting a three-dimensional corner of the measured object space. Since the principle of optical lever amplification is adopted to the roll angle and is consistent with the measurement principle of the pitch angle and the yaw angle, therefore, the technical advantages of high precision and large working distance for the three-dimensional angle measurement are achieved, and the advantage that the measurement accuracy is increased under the same working distance or the working distance is increased under the same measurement precision is achieved; two measuring light spots are received by two image sensors, the requirements for the subsequent image processing technique is reduced, and the frequency response of the measuring device is improved; and in addition, the designed cooperative target has the technical advantages of simple structure and low production cost.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Millimeter wave time-division passive frequency modulation multichannel colliding-proof radar for car
InactiveCN101373218AImprove anti-interference abilityImprove crash performanceRadio wave reradiation/reflectionLow noiseFrequency multiplier
The invention relates to the radio-positioning technical field, particularly a millimeter-wave time-division passive frequency modulation multi-channel automotive anti-collision radar, which is realized through the following steps: adopting the full-phase parameters to receive / transmit reference signals; asynchronously controlling the time division and the time sequence; watching the targets which are prone to collision on the w surface in an omni-directional manner through DSP cyclic scanning wave beams by a quasi-optical dielectric lens antenna circular array; controlling the time division SAW multi-channel passive frequency modulation through road condition cameras, an own vehicle speed, a GPS signal MCU; sending to antenna array to transmit through an up-converter, an amplitude limiter, T / R3, a frequency multiplier and a power amplifier, T / R2, an isolator and a wave beam switch; filtering the returning wave in a conjugating and matching manner with the transmitting SAW through the antenna array, the wave beam switch, the isolator, R / T1, the low-noise high amplifier, a down-converter, a medium amplifier, the time-division circuit and the SAW multi-channel signals; processing and controlling DSP and MCU; controlling the false-alarm when encountering a plurality of road barrier targets DSP and confirming the position, the distance and the relative speed; displaying the three-dimensional image on a CRT, wherein the closer the vehicle gets to the target, the higher the resolution power is; identifying the nearest distance to the vehicle; giving an alarm when the distance is smaller than the safety distance; and intelligently avoiding the barriers or reducing or braking if the distance is close to a risk distance, wherein the control is determined based on the actual condition of the road surface environment combined with the own vehicle speed and the GPS data, thereby improving the travelling safety.
Owner:阮树成
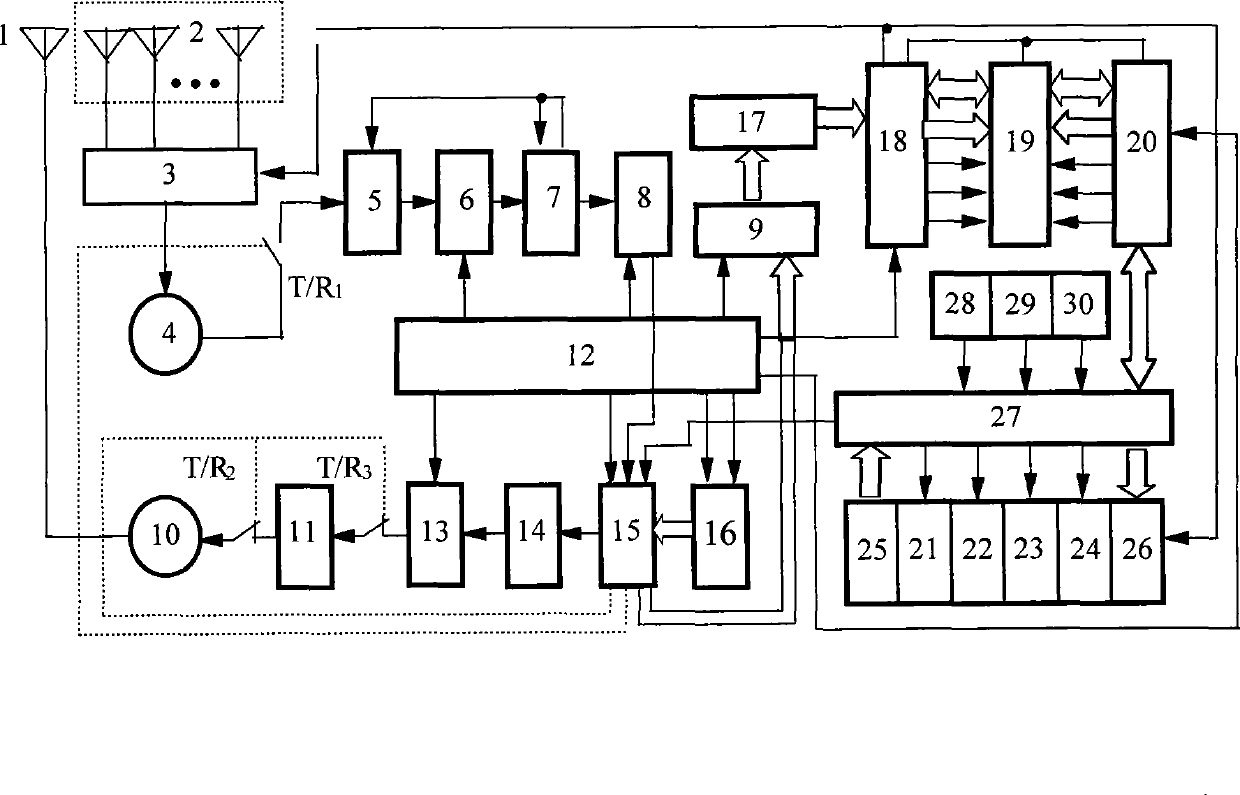
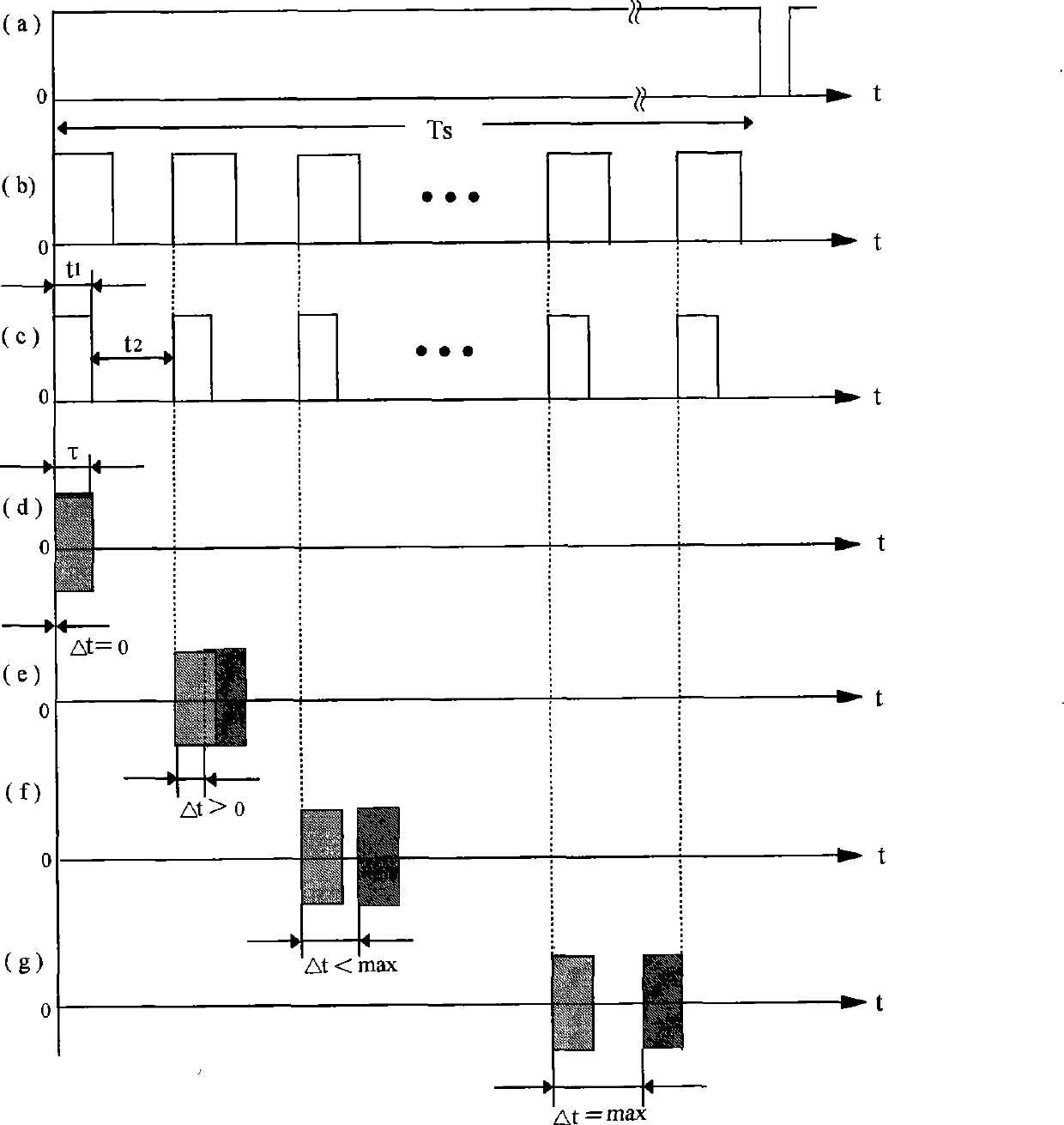
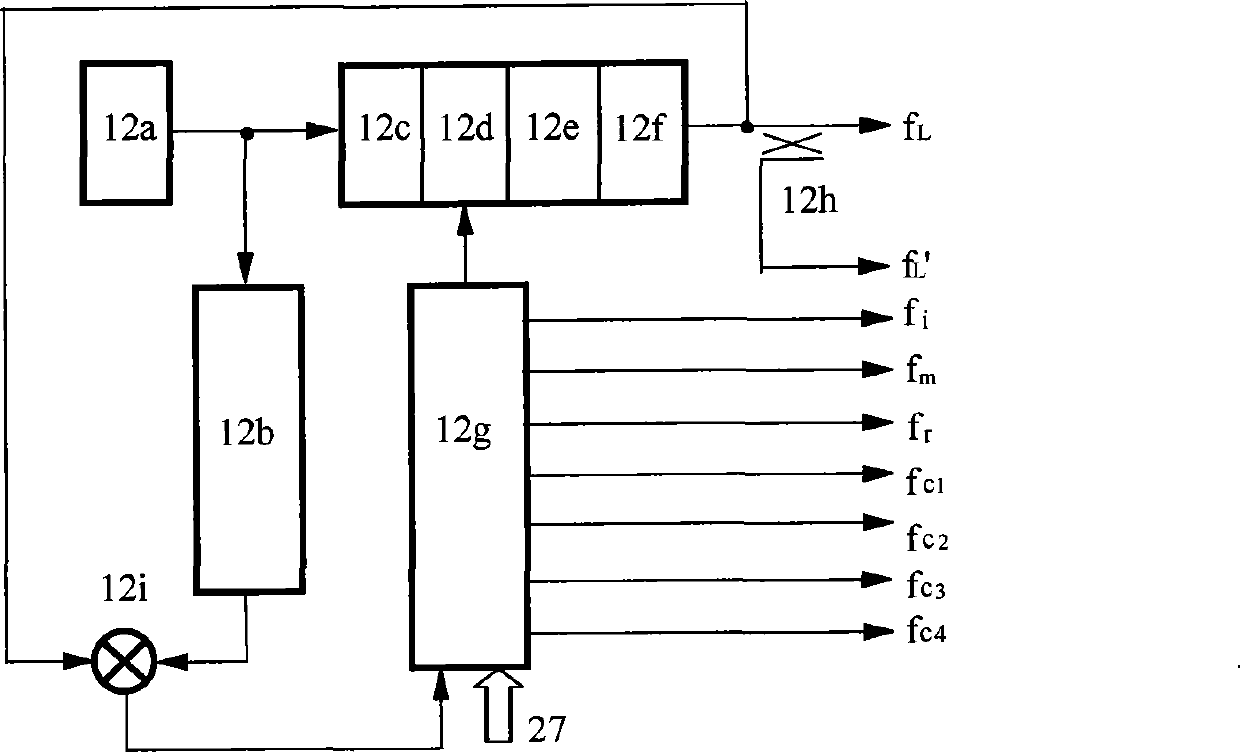
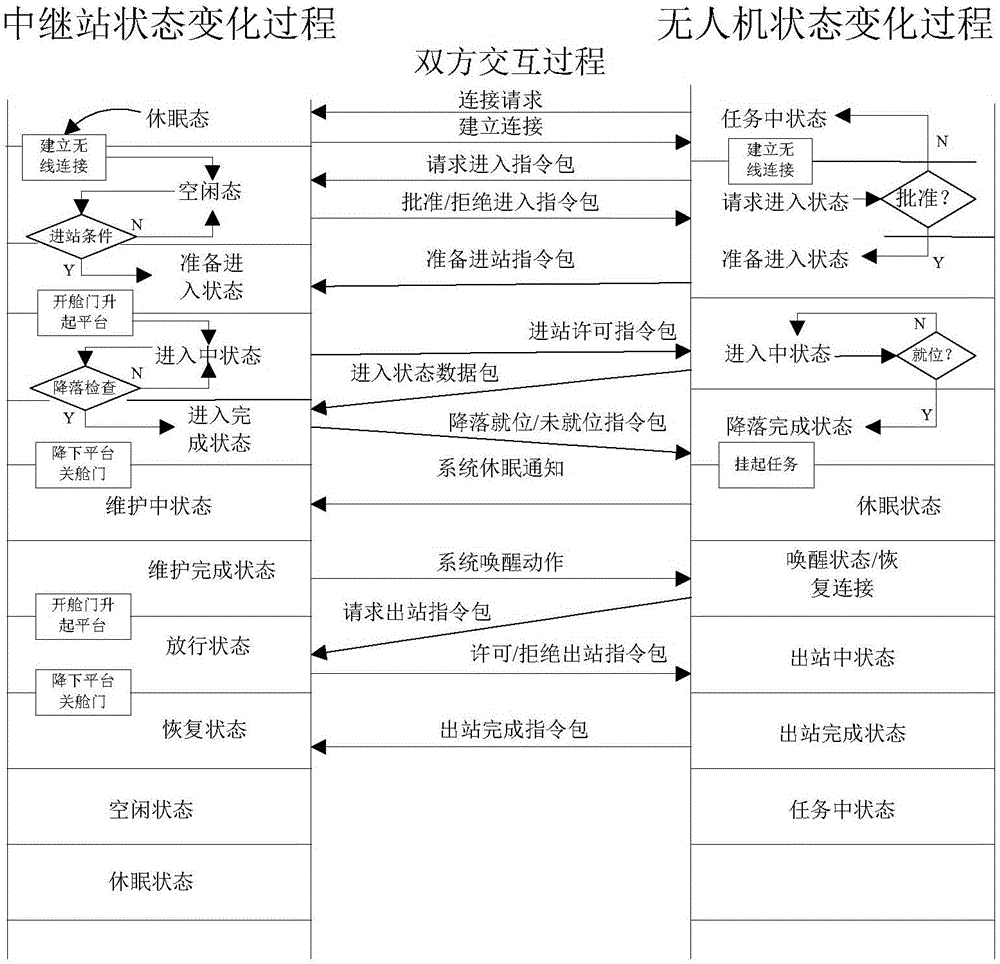
Interaction butt-joint control methods adopted when unmanned aerial vehicles enter or exit from relay service stations
InactiveCN105759831AConvenient communication connectionEasy accessAttitude controlPosition/course control in three dimensionsFindings methodsProcess interaction
The invention discloses interaction butt-joint control methods adopted when unmanned aerial vehicles enter or exit from relay service stations.The interaction butt-joint control methods include the unmanned-aerial-vehicle and relay-service-station mutual finding method, the station-entering-process interaction control method, the task-suspension-recovering control method and the station-exiting-process interaction control method.According to the methods, the communication process between the unmanned aerial vehicles and the relay service stations and state changes and control flow of the unmanned aerial vehicles and the relay service stations during stopping are regulated through the wireless communication technology and a formative data packet protocol; the unmanned aerial vehicles can be like trains and can be stopped and subjected to supplying and continue to execute tasks at the stations in sequence when executing the tasks within a long distance; unmanned aerial vehicles of different manufacturers or relay service stations of different manufactures can carry out the butt-joint relay service on the basis of complying with the standard control protocol and the flow; in this way, the problems that the power of batteries of rotor-wing unmanned aerial vehicles is rapidly consumed, and the use distance and the use time are limited are solved, and a solution is provided for long-distance full-automatic task execution and relay service load relaying of the unmanned aerial vehicles.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV OF TECH
Planar light illumination and imaging device with modulated coherent illumination that reduces speckle noise induced by coherent illumination
InactiveUS20030089779A1Lower costReduce speckle noiseCharacter and pattern recognitionSensing by electromagnetic radiationImage capturePower level
An imaging device including at least one imaging array and image formation optics that provide a field of view corresponding to the imaging array. At least one illumination module (which includes at least one source of coherent illumination) produces planar light illumination that substantially overlaps the field of view corresponding to the imaging array. Illumination control circuitry modulates the power level of illumination produced by the source of coherent illumination during each photo-integration time period of the imaging array to thereby reduce speckle noise in images captured by the imaging array. The illumination control circuitry preferably modulates the power level of illumination by controlling the number and / or duration of time periods corresponding to different power levels of illumination produced by the source of coherent illumination during each photo-integration time period of the imaging array. Moreover, the illumination control circuitry preferably controls number and / or duration of the time periods such that substantially constant energy is produced by the source of coherent illumination over the time periods (thereby enabling the different speckle patterns produced over the timer periods to optimally cancel each other out).
Owner:METROLOGIC INSTR
Passive ultrahigh frequency radio frequency identification label with automatic impedance matching function
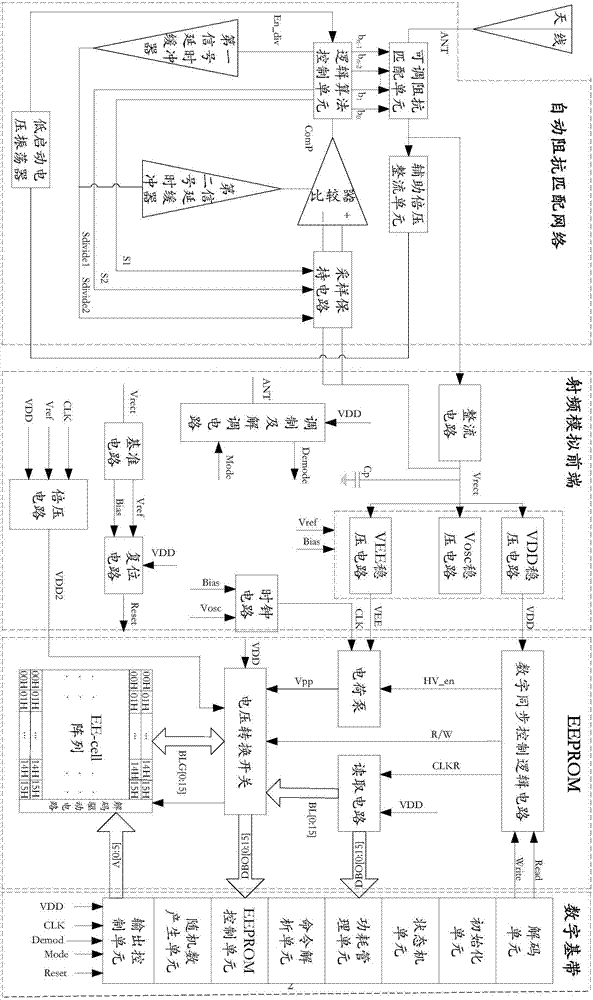
ActiveCN107171697AIncrease the working distanceEnables maximum power harvestingAntenna supports/mountingsNear-field in RFIDImpedance matchingUltrahigh frequency
The invention relates to a passive ultrahigh frequency radio frequency identification label with an automatic impedance matching function. The passive ultrahigh frequency radio frequency identification label with the automatic impedance matching function comprises an automatic impedance matching network and a passive ultrahigh frequency radio frequency identification label; the automatic impedance matching network is used for adjusting an overall impedance of the passive ultrahigh frequency radio frequency identification label by detecting a partial voltage of the passive ultrahigh frequency radio frequency identification label to enable the overall impedance of the passive ultrahigh frequency radio frequency identification label to match with the impedance of an antenna; and the passive ultrahigh frequency radio frequency identification label is used for obtaining the maximum energy from the antenna based on the impedance matching and finishing radio frequency identification of the energy. By performing impedance adjustment at the chip end of the passive ultrahigh frequency radio frequency identification label, the impedance of a label circuit can be adjusted dynamically in a relatively big frequency range when the circuit is in different working states and the working distance changes; the label load impedance and the impedance at the interior of the antenna are matched; the maximum power collection is realized; and the working distance of the label in different working states is accordingly improved.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Multiple parallel confocal system and surface measurement method using the same
ActiveUS20150085289A1Reduce formationIncrease the working distanceScattering properties measurementsMicroscopesMicro lens arraySurface measurement
The present invention relates to a multiple parallel confocal system including: a light source for irradiating light; a relay lens unit through which the light traveling toward a measuring object or the light reflected from the measuring object is passed, the relay lens unit having one or more lens for focusing the light irradiated from the light source; a multiple optical probe having a microlens array on which a plurality of microlenses is arranged, the microlenses into which the focused light through the relay lens unit is incident; and a photo detector for detecting the incident light reflected from the measuring object and passed through the microlenses and the relay lens unit.
Owner:IND ACADEMIC CORP FOUND YONSEI UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com