Method for tracking and positioning mobile node of wireless sensor network
A wireless sensor and mobile node technology, applied in radio wave measurement systems, instruments, services based on location information, etc., can solve the problems of hardware size and power consumption that cannot be used for sensor nodes, low power, and low cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
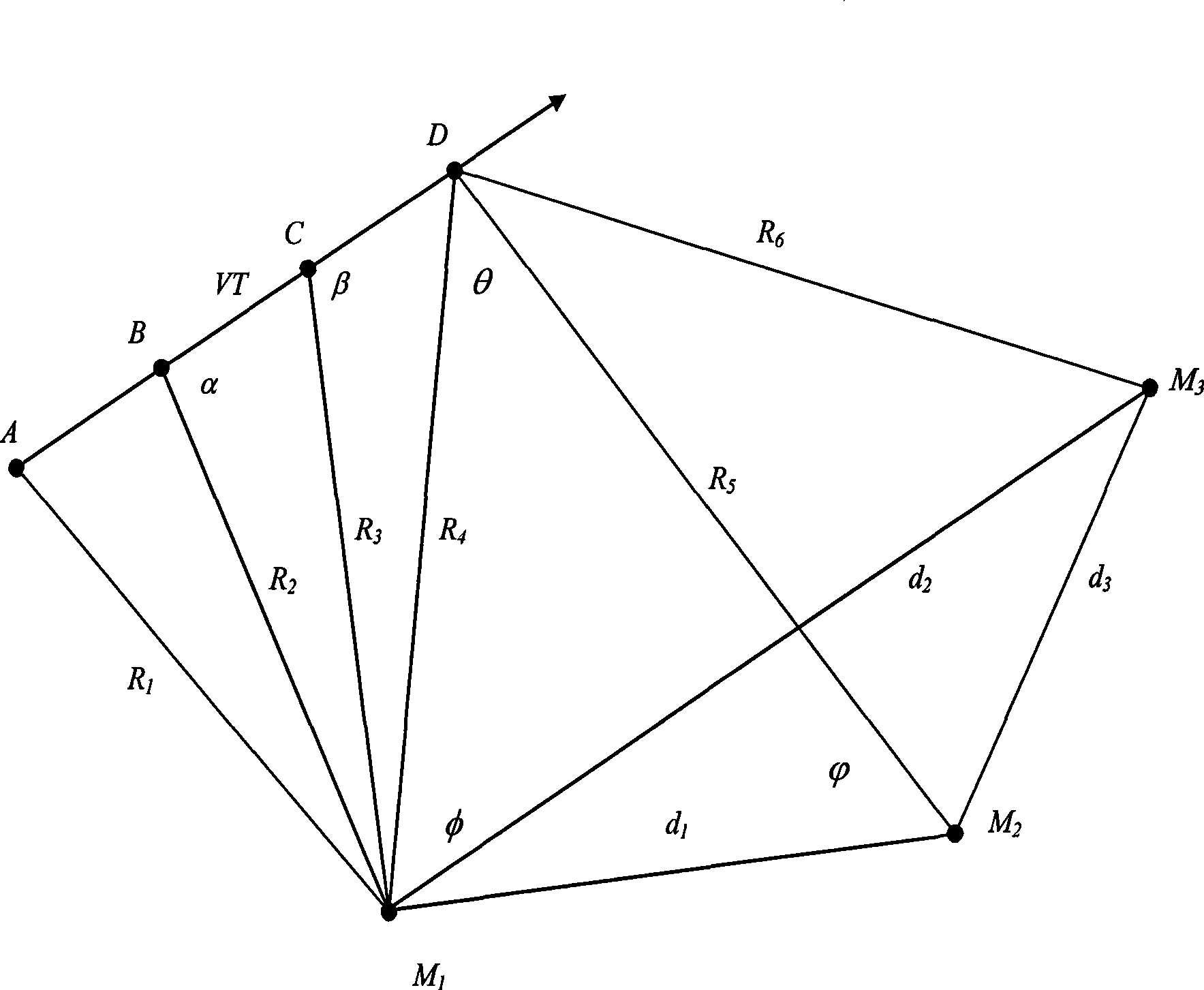
[0053] A method for tracking and locating mobile nodes in a wireless sensor network, figure 1 The geometry relation of tracking and measuring mobile node S by three anchor nodes Mi using low repetition frequency beacon, self-time difference measurement technology and beacon forwarding mode is given. Figure 2 shows the workflow of the system.
[0054] A low-repetition-frequency beacon is a pulse signal that is repeatedly transmitted at a fixed period, and the periodic interval of transmission is relatively long. Using the relative time difference measurement technology, the process of positioning and calculating the mobile node with the low-repetition-frequency beacon transmission function in the two-dimensional (2D) area will be simpler than the positioning of the stationary node, such as only measuring the mobile node and the anchor. The relative distance between nodes and the movement speed of mobile nodes only need to use one anchor node.
[0055] The wireless sensor netw...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com