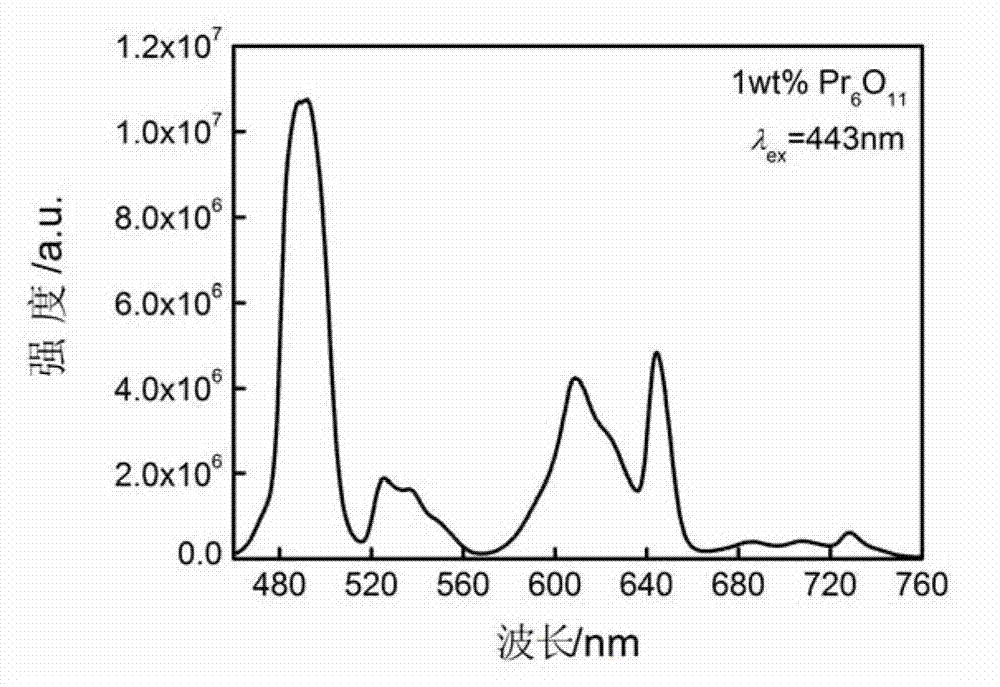
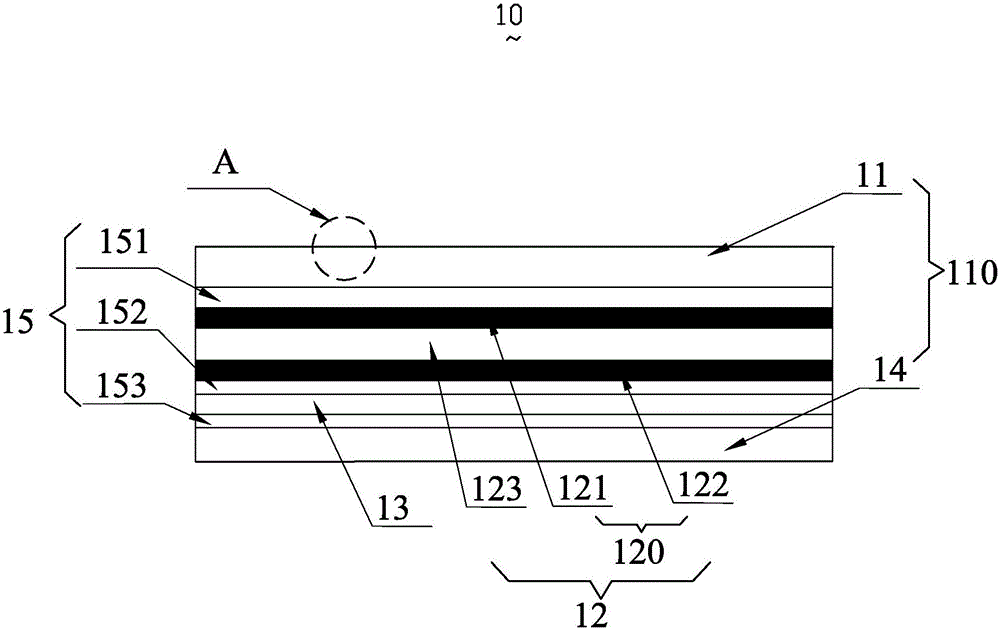
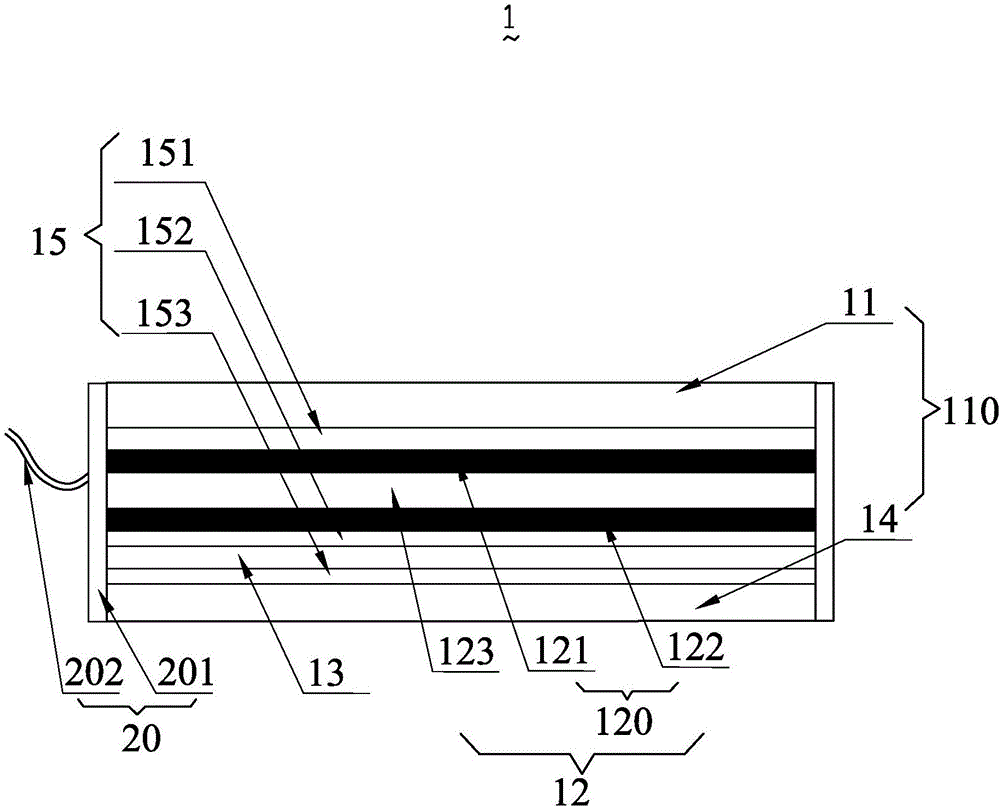
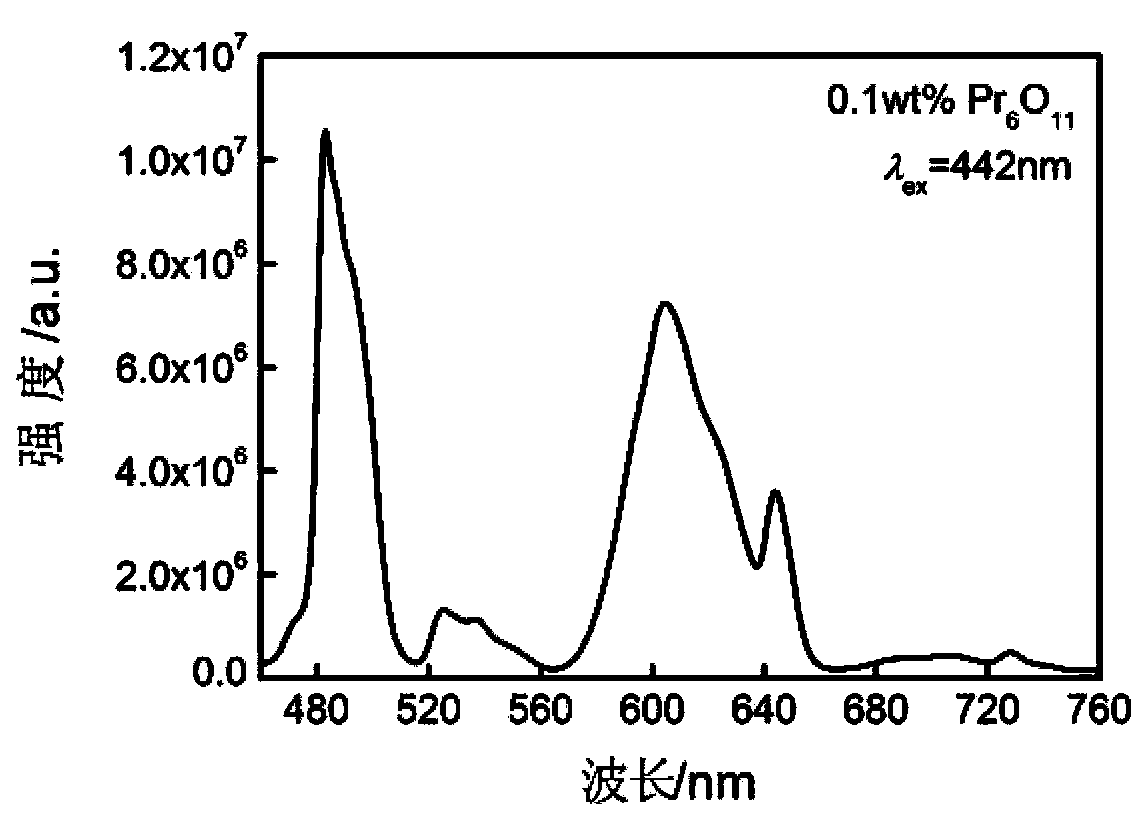
Patents
Literature
36 results about "Glass waveguide" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Scintillating substance and scintillating wave-guide element
InactiveUS6278832B1Improve light outputShorten the timePolycrystalline material growthOptical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingFiberAdditive ingredient
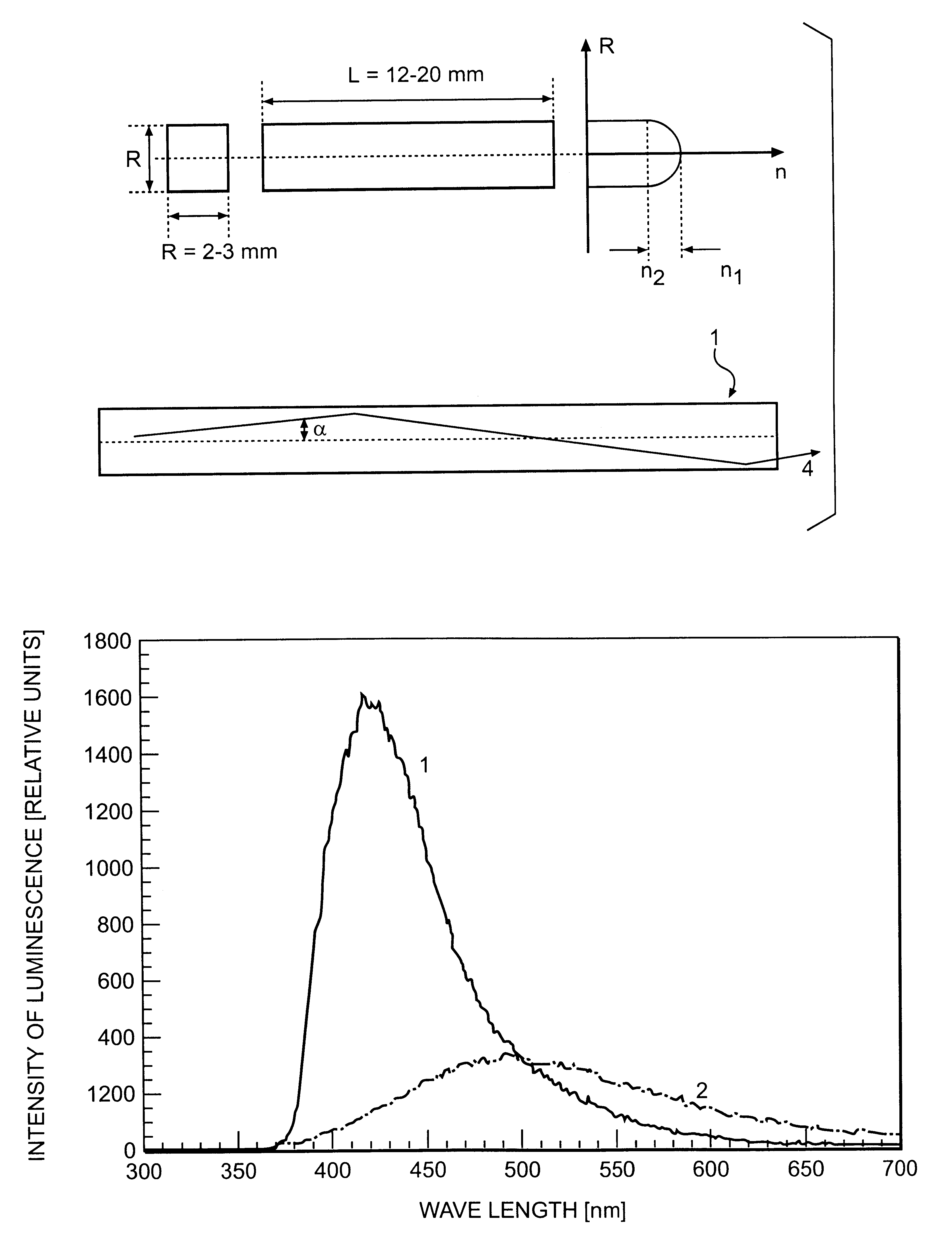
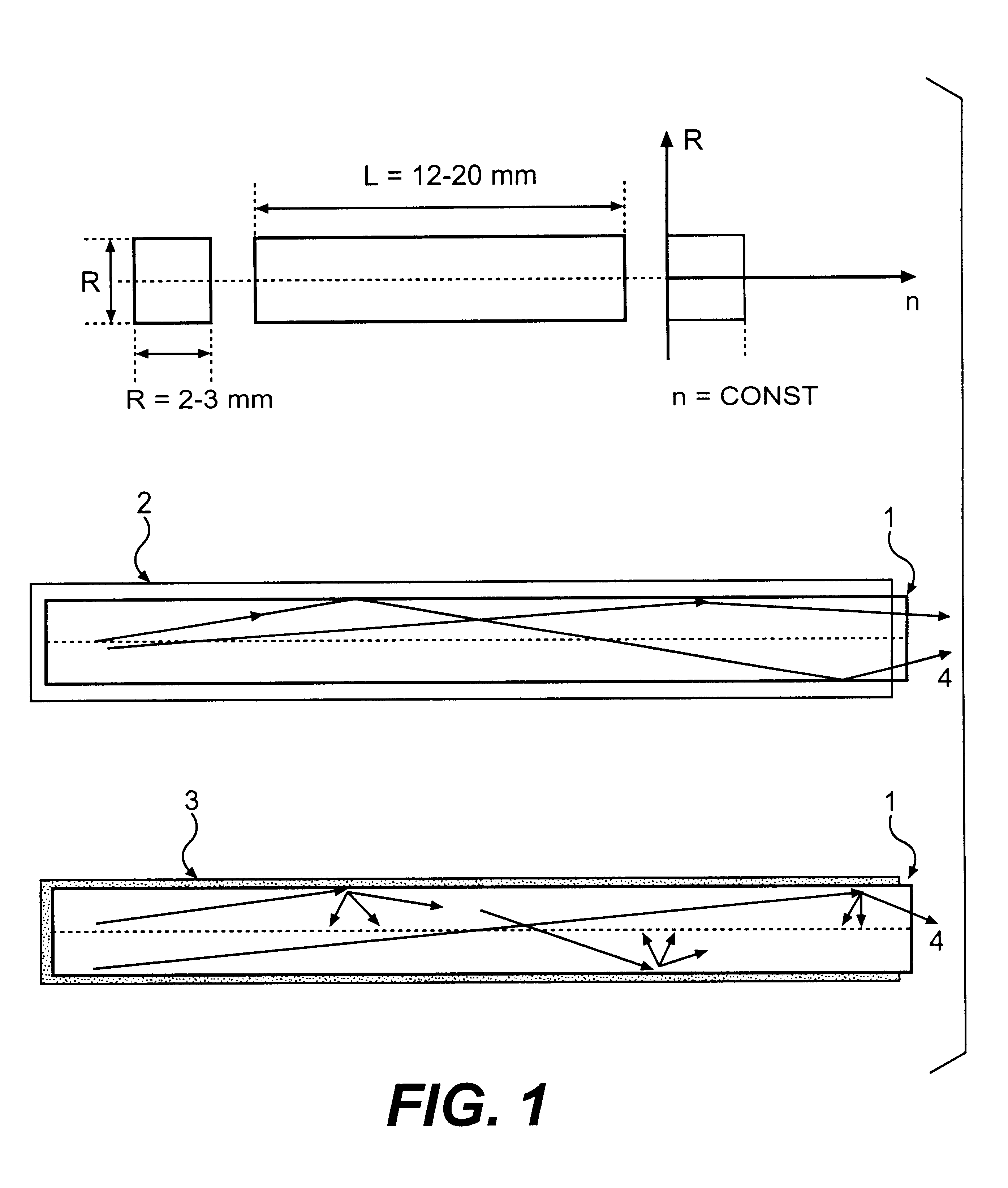
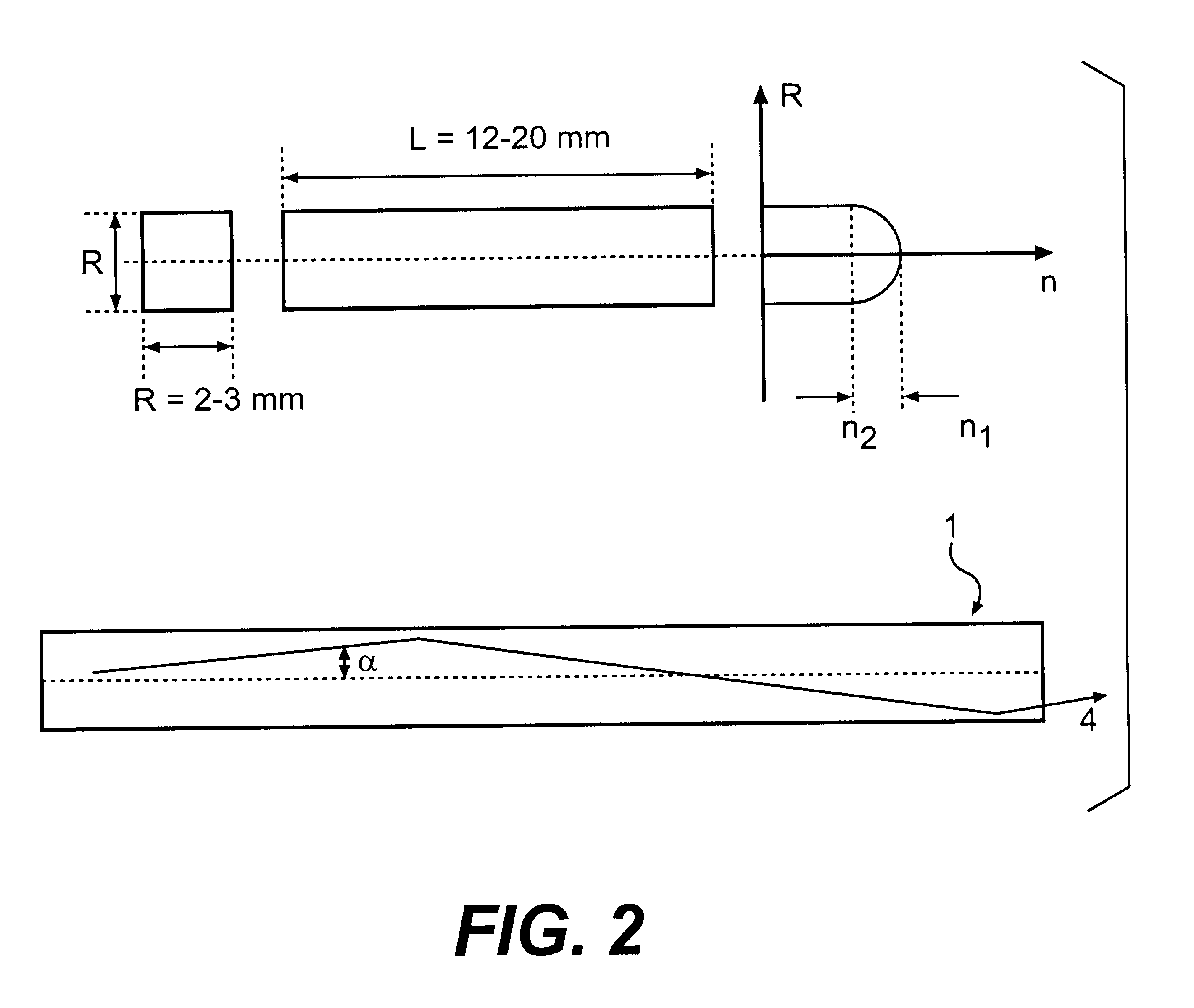
The invention is related to nuclear physics, medicine and oil industry, namely to the measurement of x-ray, gamma and alpha radiation; control for trans uranium nuclides in the habitat of a man; non destructive control for the structure of heavy bodies; three dimensional positron-electron computer tomography, etc.The essence of the invention is in additional ingredients in a chemical composition of a scintillating material based on crystals of oxyorthosilicates, including cerium Ce and crystallized in a structural type Lu2SiO5.The result of the invention is the increase of the light output of the luminescence, decrease of the time of luminescence of the ions Ce3+, increase of the reproducibility of grown crystals properties, decrease of the cost of the source melting stock for growing scintillator crystals, containing a large amount of Lu2O3, the raise of the effectiveness of the introduction of SCintillating crystal luminescent radiation into a glass waveguide fibre, prevention of cracking of crystals during the production of elements, creation of waveguide properties in scintillating elements, exclusion of expensive mechanical polishing of their lateral surface.
Owner:SOUTHBOURNE INVESTMENTS
Microstructuring optical wave guide devices with femtosecond optical pulses
InactiveUS20040071420A1Optical fibre with multilayer core/claddingCoupling light guidesRefractive indexLaser light
The present invention is directed to the creation of zones of permanently altered refractive index characteristics in glass waveguiding devices, including optical fibers and optical waveguides pre-existed in a glass substrate. Such zones in which the refractive index has been permanently altered are created in glass using a very high intensity laser beam which is produced by focusing the light output from an ultrafast pulsed laser at a predetermined target region in the glass. The preferred laser is a Ti:Sapphire amplified, frequency-doubled Erbium-doped fiber laser system, providing light pulses of approximately 100 femtosecond duration, each with an energy of between about 1 nanojoule and 1 millijoule, and preferably at a pulse repetition rate of between 500 Hz and 1 GHz. The repetition rate is chosen to deliver pulses faster than the thermal diffusion time over the dimensions of the volume element being modified. This latter process is to accumulate heat to the point of liquefying the material in order to increase material compliance to the femtosecond writing process and increase the subsequent thermal barrier to relaxation of the written structural element and thereby increase the lifetime of the device or structural function. One or more zones of permanently altered refractive index characteristics can be formed in a waveguiding device, such as an optical fiber by utilizing a focused, pulsed, laser light source which generates a focal region having an intensity greater than the threshold for inducing permanent refractive index changes in the device. The focal region is aligned with the device and relative movement between the focal region and the device has the effect of sweeping the focal region across the device in a predetermined path. The result is a zone within the device in which the refractive index characteristics of the device have been permanently altered so as to control amplitude, phase, spatial propagation or polarization states of light within the material.
Owner:OZ OPTICS
System and Method for Permanently Writing a Diffraction Grating in a Low Phonon Energy Glass Medium
A system and method for permanently writing diffraction gratings in low phonon energy glass waveguides are shown. Ultrashort light pulses are generated and made to form two beams synchronously superimposed in the waveguide, therefore forming an interference pattern corresponding to the desired grating. The light pulses are focussed so that the light intensity in the waveguide exceeds a filamentation threshold. The exposure of the waveguide to these light pulses is controlled temporally and spatially in order to limit detrimental thermal effects induced by the high-intensity pulses in the glass medium of the waveguide.
Owner:UNIV LAVAL
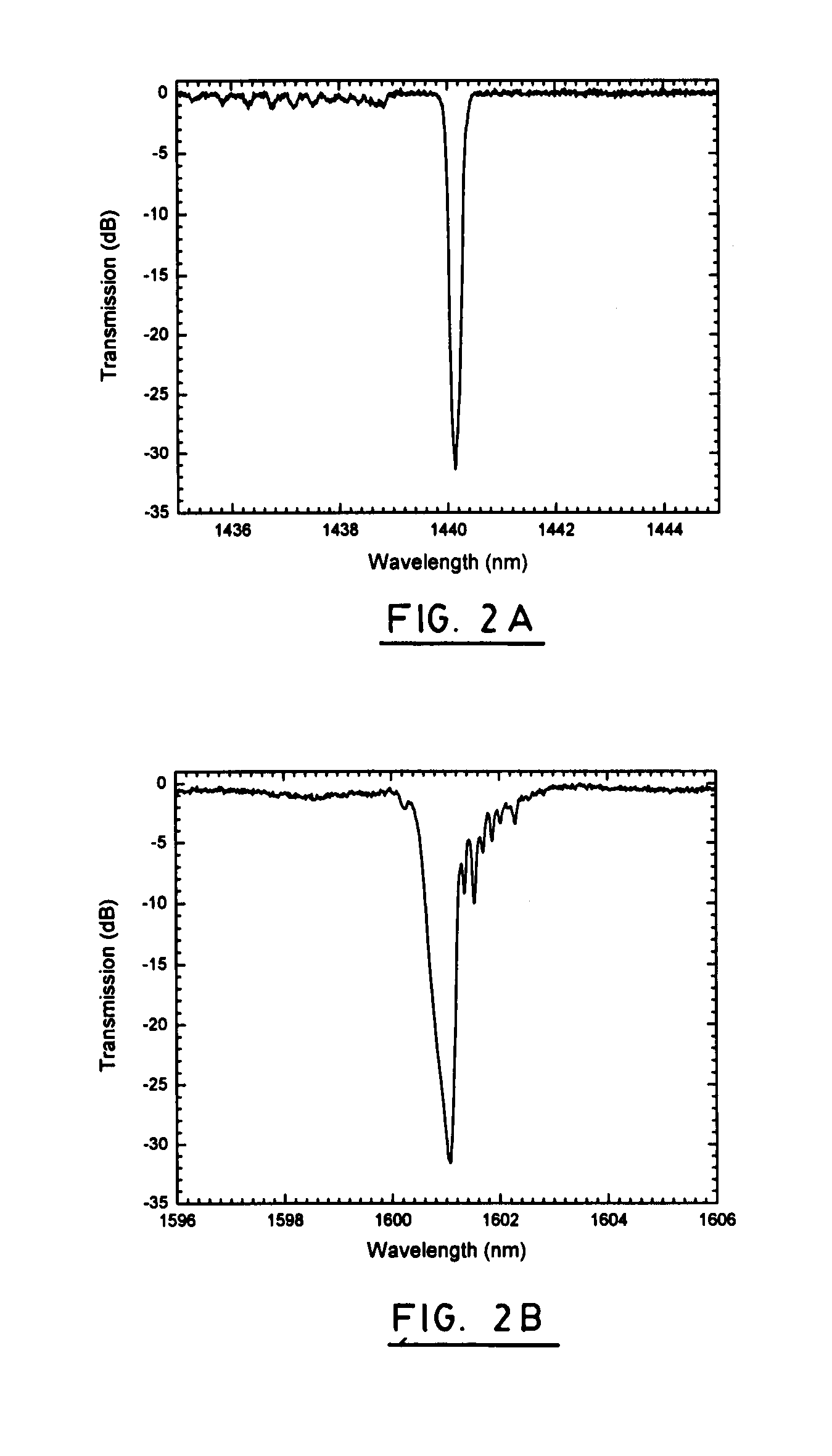
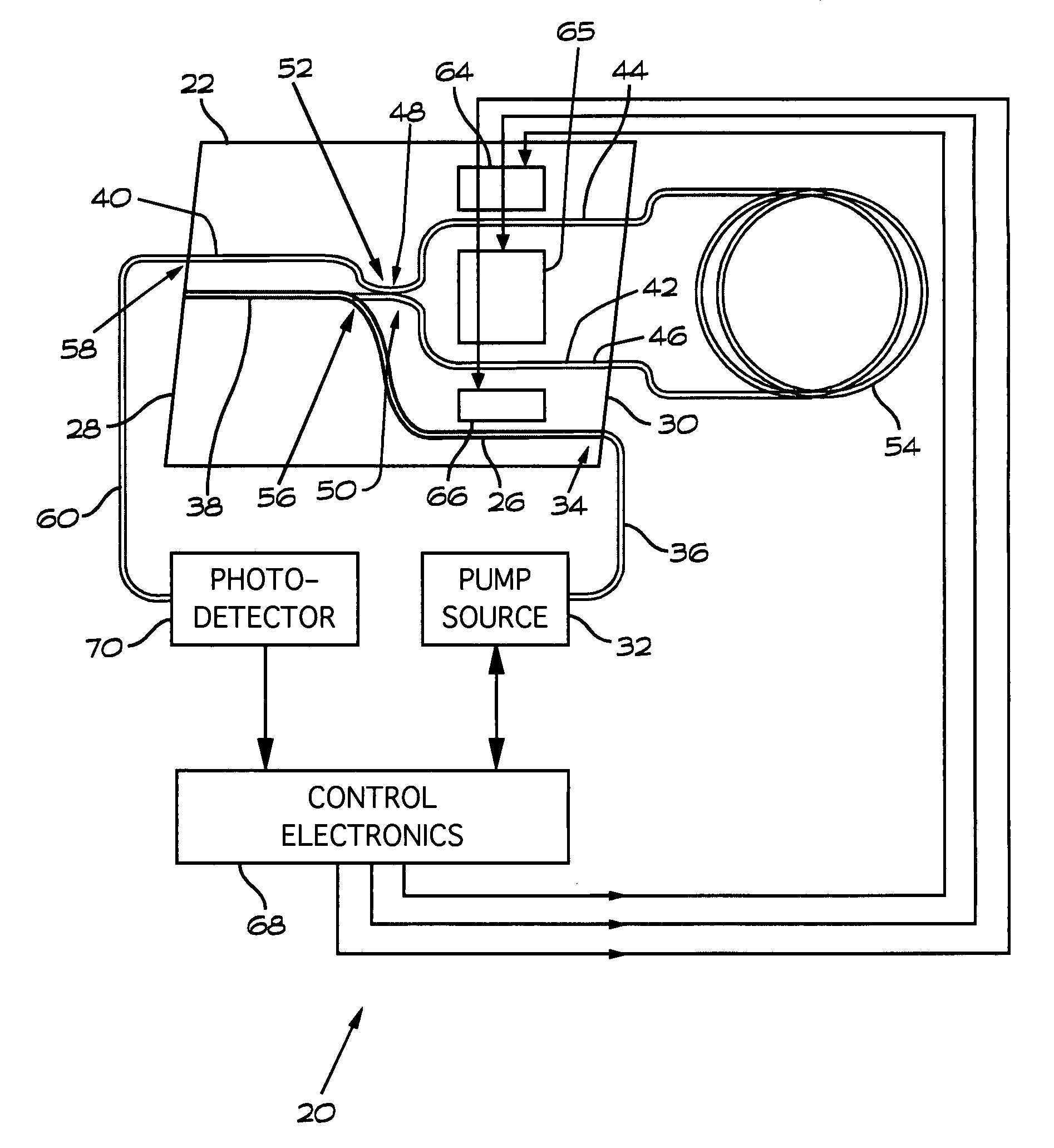
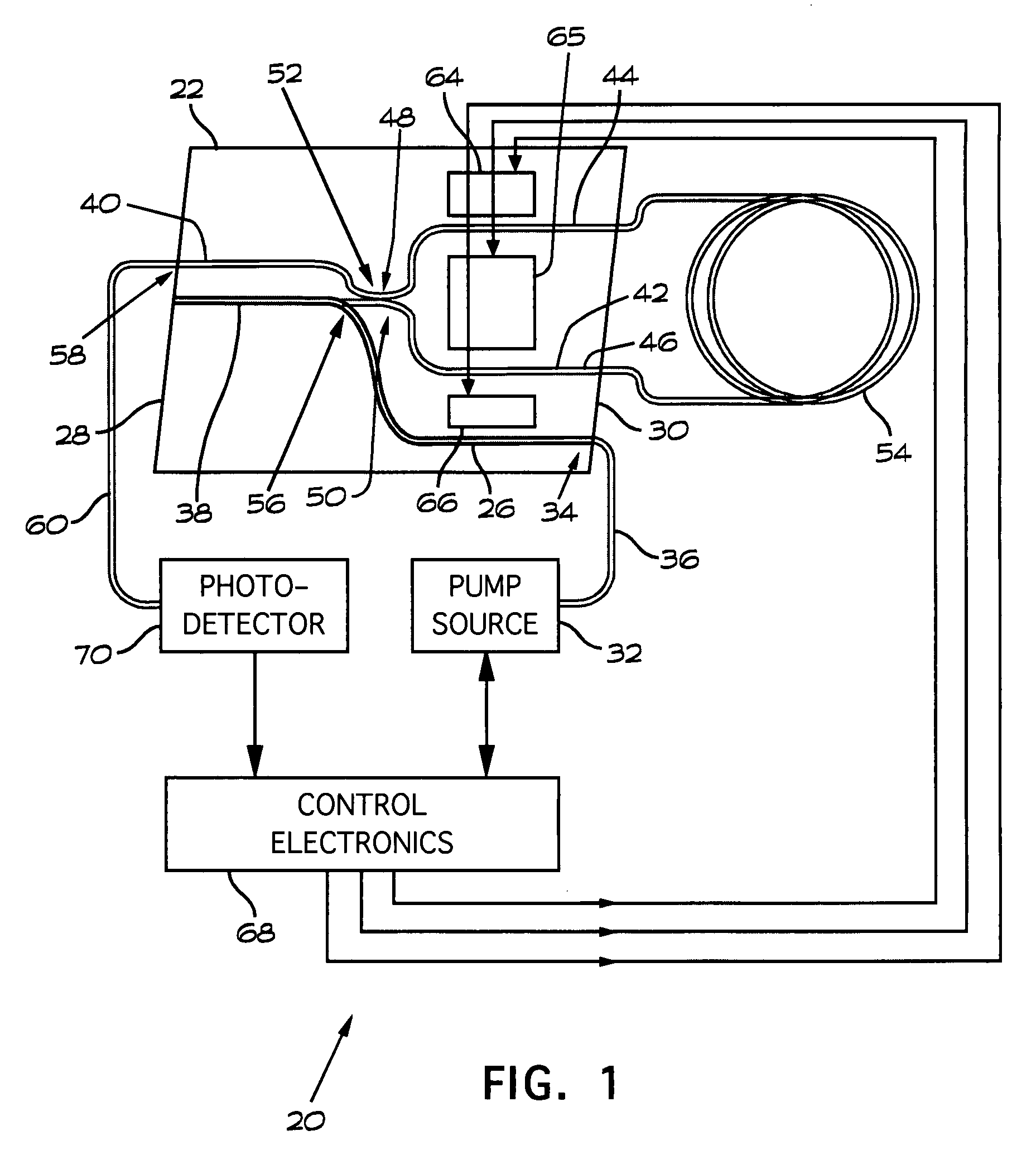
Fiber optic gyroscope with integrated light source
InactiveUS20080291459A1Short manufacturing timeAvoid excessive errorSagnac effect gyrometersSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsFiberRare earth
An integrated module for a fiber optic gyroscope system includes a fiber optic sensing coil arranged to sense rotations about a sensing axis via the Sagnac effect comprises a substrate, an optical waveguide formed on the substrate, a light source comprising a doped waveguide formed on the substrate. The light source and the optical waveguide are arranged to produce counterpropagating light waves in the fiber optic sensing coil. The light source may be formed as a rare earth doped polymer waveguide or as a rare earth doped glass waveguide.
Owner:LITTON SYST INC
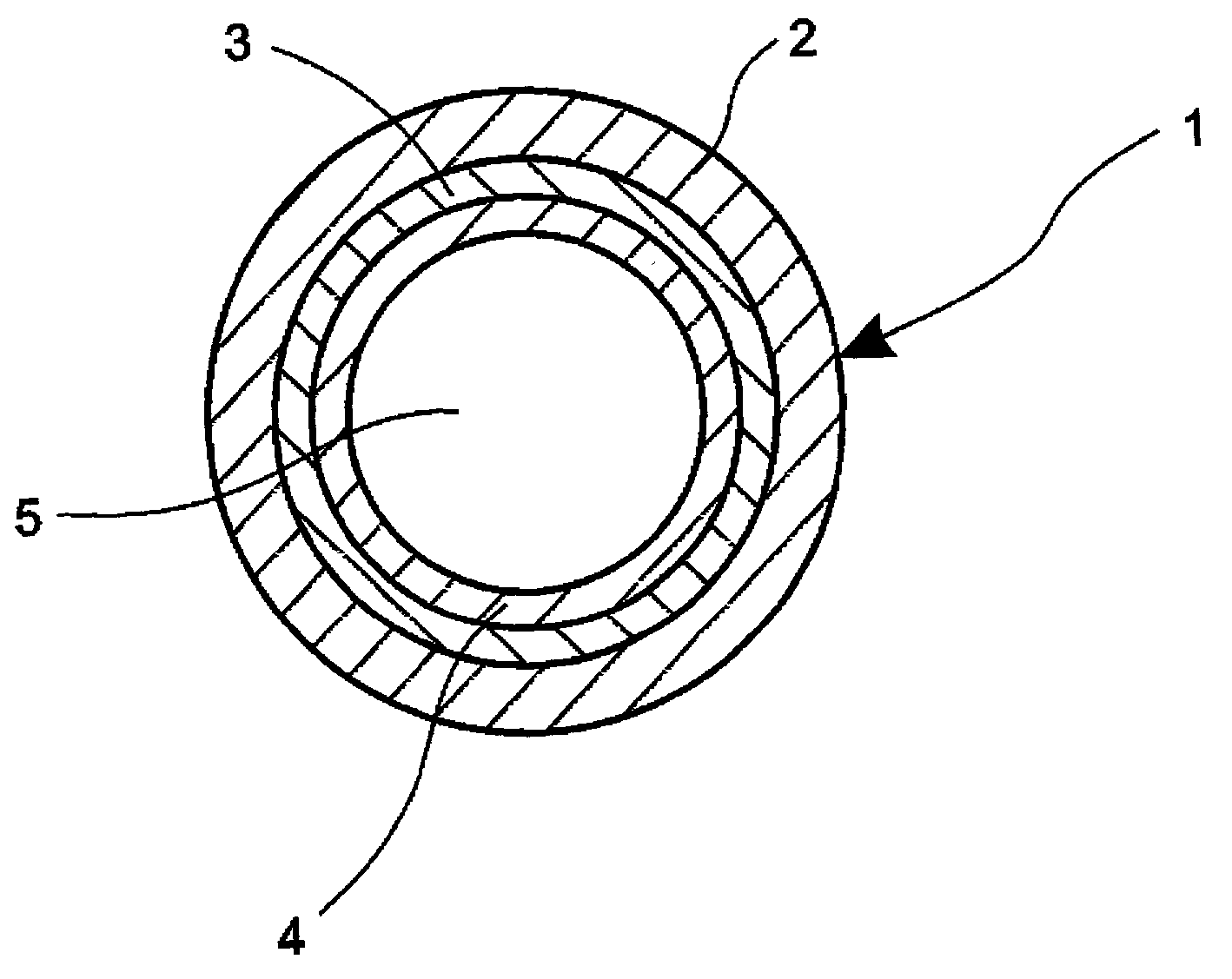
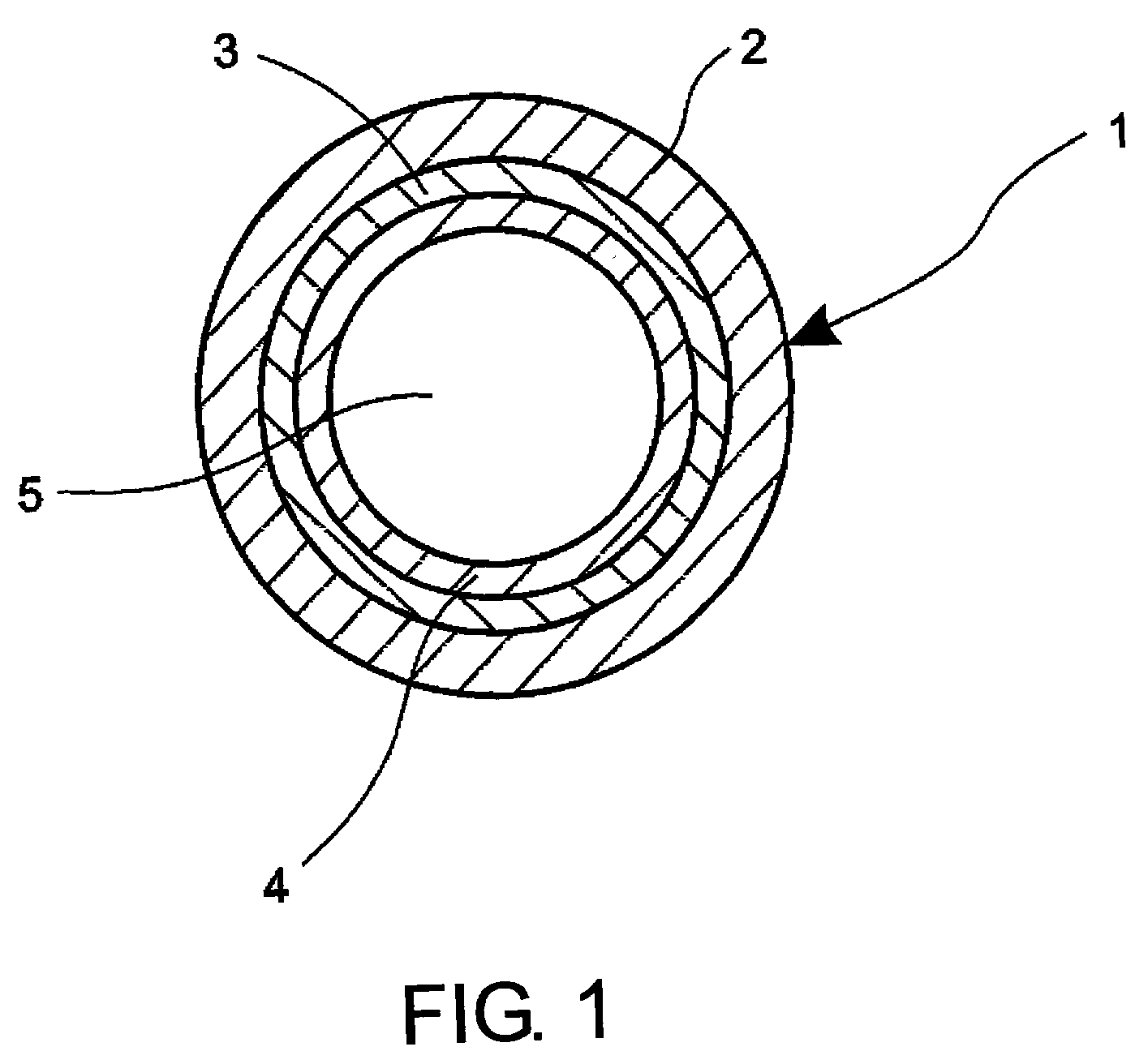
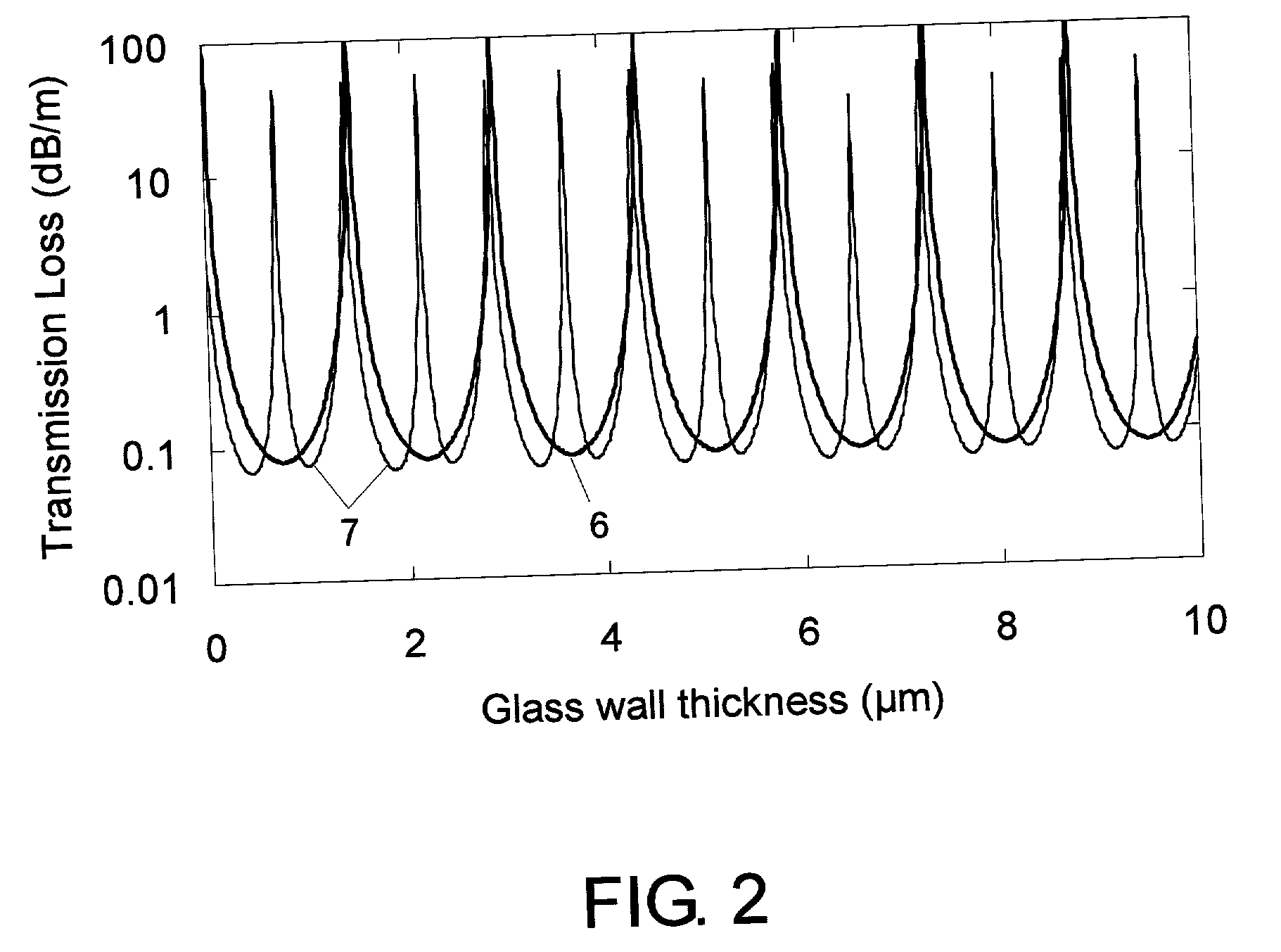
Method for making hollow glass optical waveguide
A method for making optical hollow-glass waveguide. The present invention comprises a glass drawing and following metal coating processes. The waveguide produced by this method provides low transmission loss at target wavelengths in ultraviolet, visible, and infrared regions when the wall thickness of the glass tube is well controlled so as to fit to the designed parameter.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Method for preparing glass waveguide by single-side molten salt electric field assistant ion exchange
InactiveCN1844963AGuaranteed to continueAvoid destructionOptical waveguide light guideIon exchangeMolten salt
The invention discloses a method for producing buried glass optical waveguide by single-side fused salt electric field auxiliary ion exchange technique. Wherein, first processing the ion exchange on the glass basic plate with mask in the fused salt with high polarized ion, to attain the ion exchange area on the glass surface; preparing a baffle layer on the surface of glass basic plate and far away from the core of optical waveguide, to stop ion passing said glass basic plate in the following ion exchange process, while the passed ion will reduce the cathode and destroy the metallic film electrode; at last, the anode uses the fused salt without high polarized ion, and the cathode uses metallic film, and using single-side fused salt electric field auxiliary ion exchange technique to prepare optical waveguide. The invention can effectively restrain the hurt of cathode metallic film in the process of electric field auxiliary ion exchange, to improve the property of glass optical waveguide.
Owner:ZHEJIANG NANFANG COMM GROUP +1
Microporous glass waveguides doped with selected materials
The present invention concerns waveguides made from porous glass which have been doped with certain selected materials which exhibit optical properties. In the context of the invention, the selected materials are optical materials which exhibit optical activity or a Faraday effect, such as an electro-optic material, and more specifically a polymer. Devices made according to the present invention can be used as phase modulators.
Owner:INSTITUT NATIONAL D'OPTIQUE
Optical waveguide, corresponding coupling arrangement, apparatus and method
An optical waveguide includes a glass waveguide body and a waveguide core through which optical radiation propagates. The waveguide core includes: a body portion extending within the waveguide body, a coupling portion extending at the surface of the waveguide body, and an S-bent intermediate portion coupling the body portion and the coupling portion. An optical coupling arrangement (e.g., for coupling one or more optical fibers to a silicon photonics device) includes one such optical waveguide and a second optical waveguide including a respective waveguide body and one or more waveguide members. The second optical waveguide is coupled with the first optical waveguide with the waveguide member(s) facing the coupling portion of the first optical waveguide.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
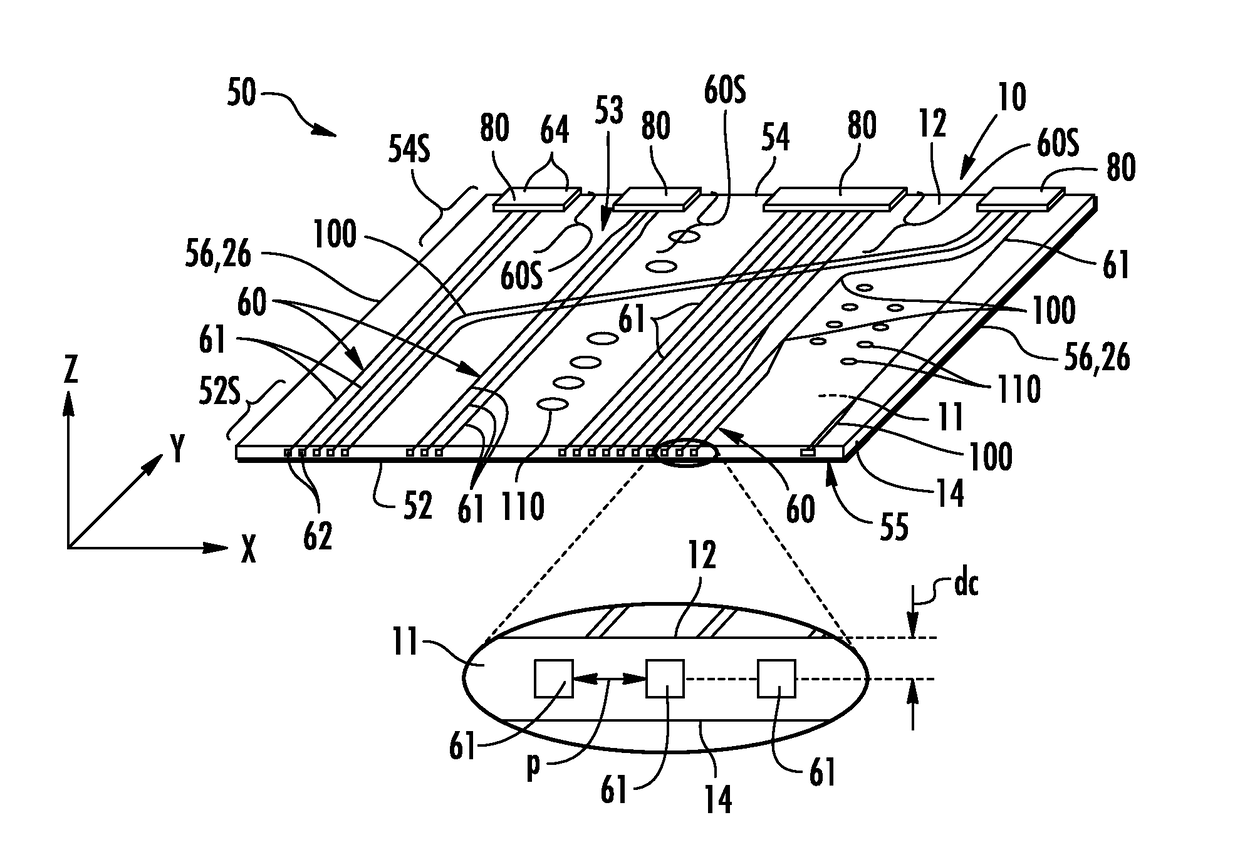
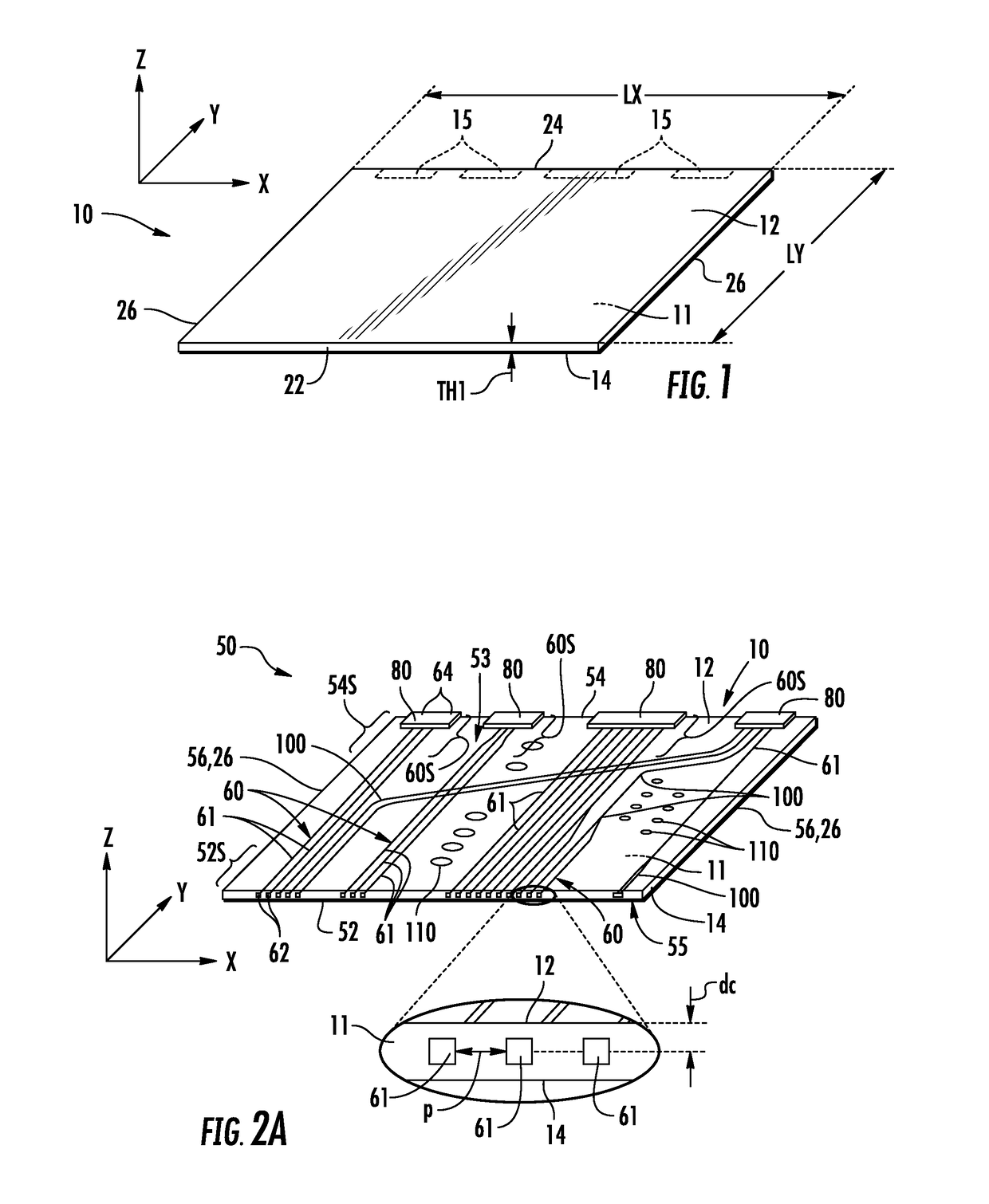
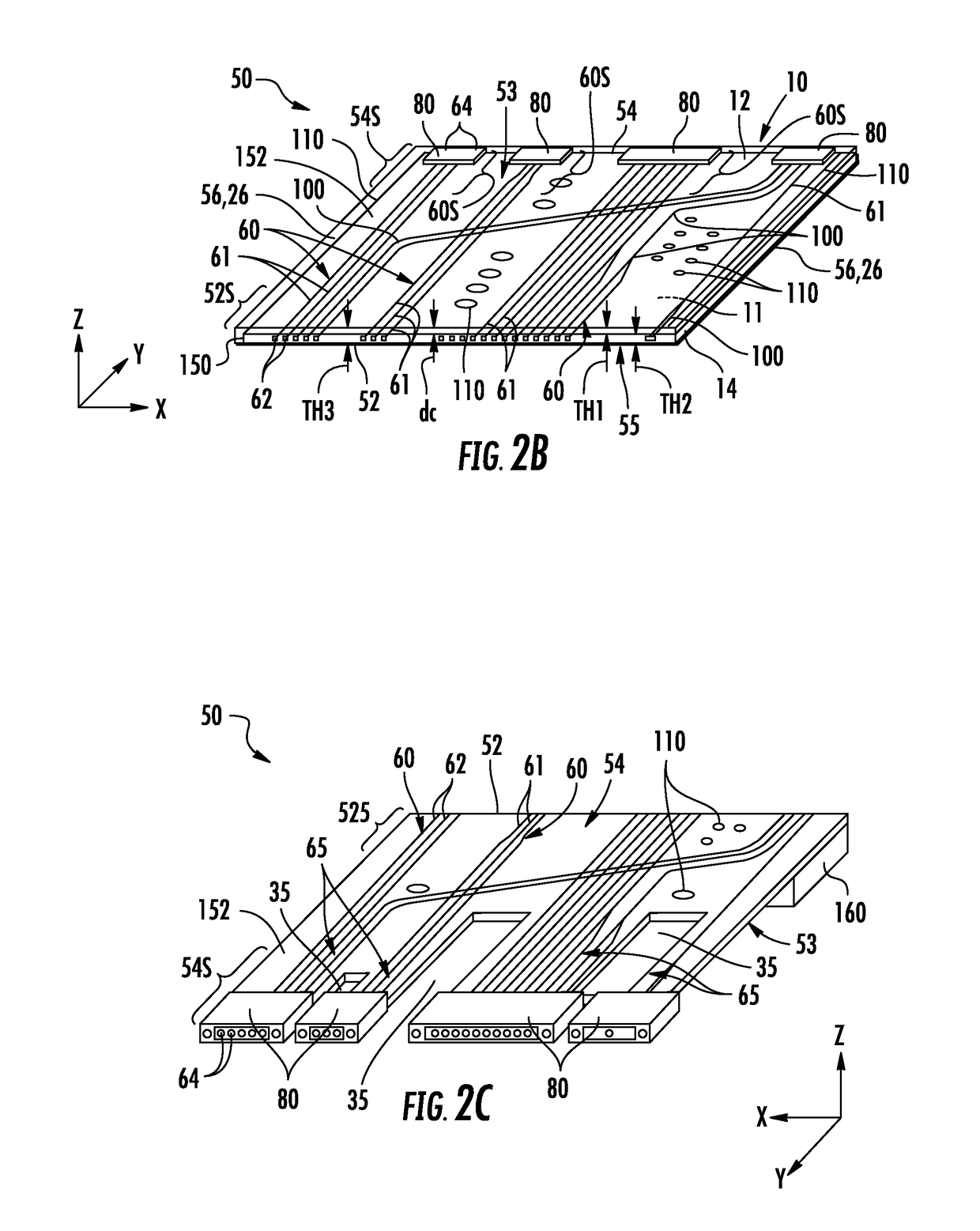
GLASS WAVEGUIDE ASSEMBLIES FOR OE-PCBs AND METHODS OF FORMING OE-PCBs
ActiveUS20180217326A1Avoid the needSimplify OE-PCB fabrication processCircuit optical detailsPrinted circuit aspectsEngineeringPhotonic integrated circuit
The glass waveguide assembly includes a substrate with glass optical waveguides formed in the body of the glass substrate without adding or removing any glass from the substrate body. The glass optical waveguides run generally from a front-end section to a back-end section. A protective coating is formed over at least a portion of the top surface of the glass substrate where the glass optical waveguides reside. Optical connectors are formed at or adjacent the back end at corresponding connector regions. Each connector includes an end portion of at least one of the glass optical waveguides. In some configurations, the glass waveguide assembly includes a bend section that facilitates forming an optical interconnection in a photonic system between an optical-electrical printed circuit board and photonic integrated circuit.
Owner:CORNING OPTICAL COMM LLC
Method for preparing glass waveguide by ion mask
InactiveCN1844964AImprove performanceEasy to implementOptical waveguide light guideSelective leachingIon exchange
The invention discloses a method for producing glass optical waveguide with ion mask. Wherein, first using K+ ion exchange technique to form a K+ disperse area on the glass basic plate, as the mask of following ion exchange; then using mask inversion technique to form a film on the K+ ion disperse area, to baffle the dispersion of high-refractive ion that though the K+ disperse area in the following ion exchange process; at least, using fused salt with high-polarized ion to exchange ion, and attain high-refractive ion disperse area with improved shape on the glass basic plate. The invention can avoid film preparation and selective erosion technique; and since the film can completely stop the dispersion of high-polarized ion through the ion mask, the invention can attain better bar optical waveguide.
Owner:ZHEJIANG NANFANG COMM GROUP +1
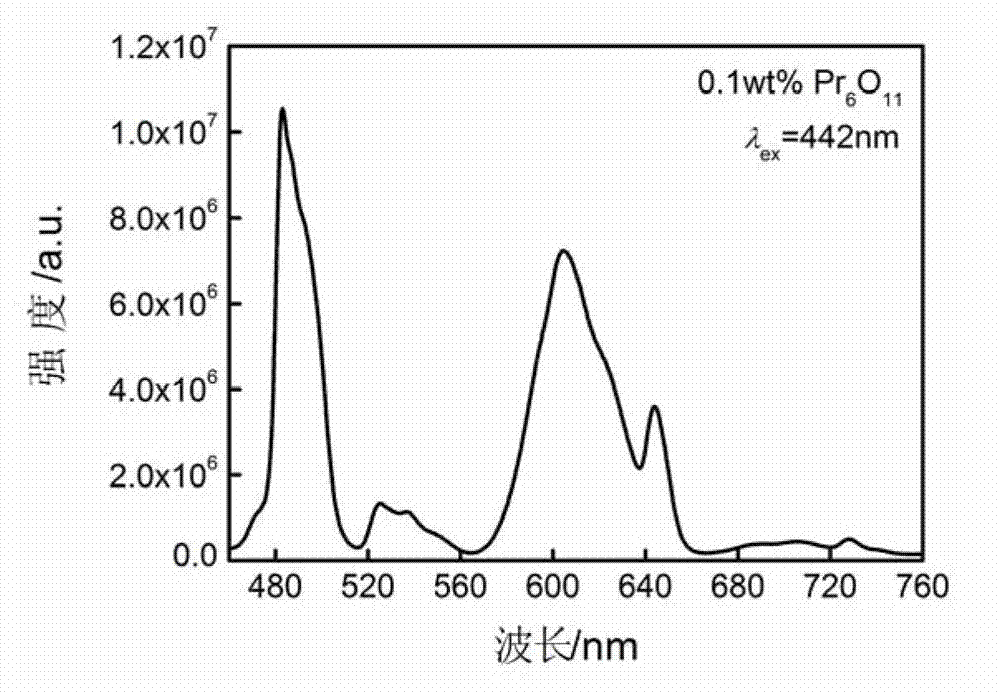
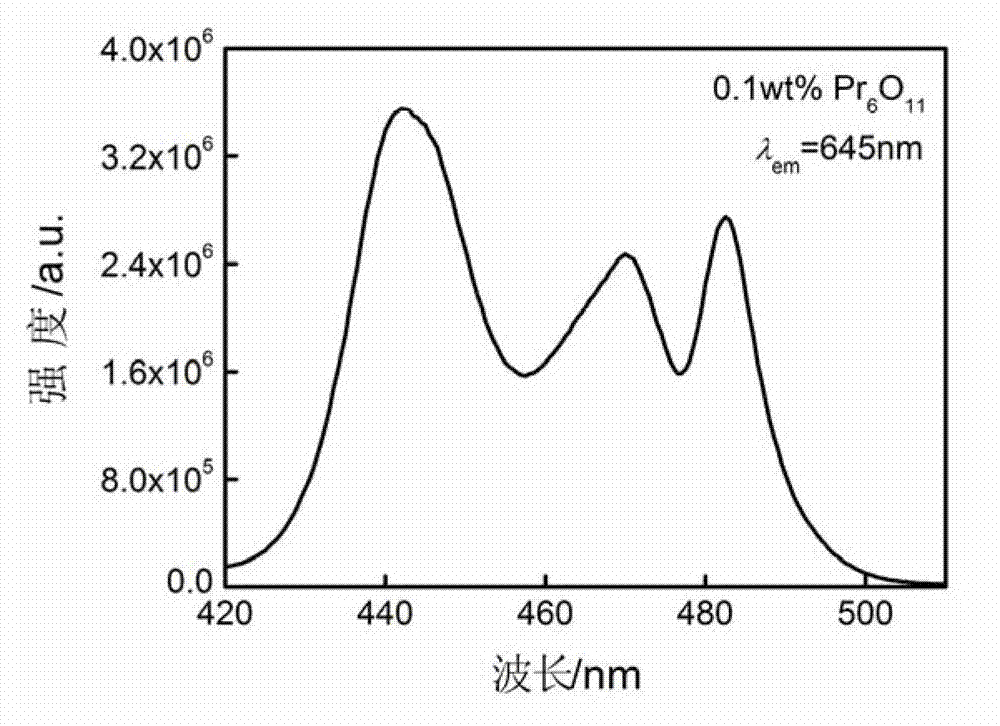
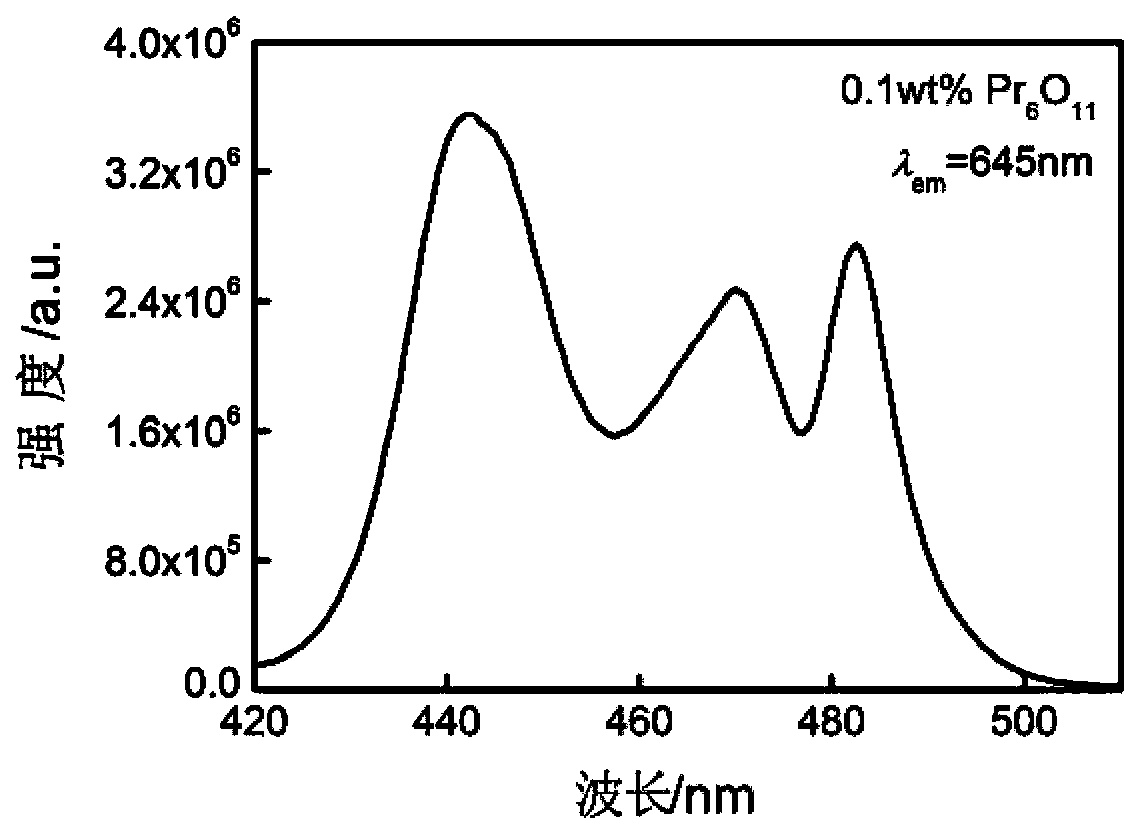
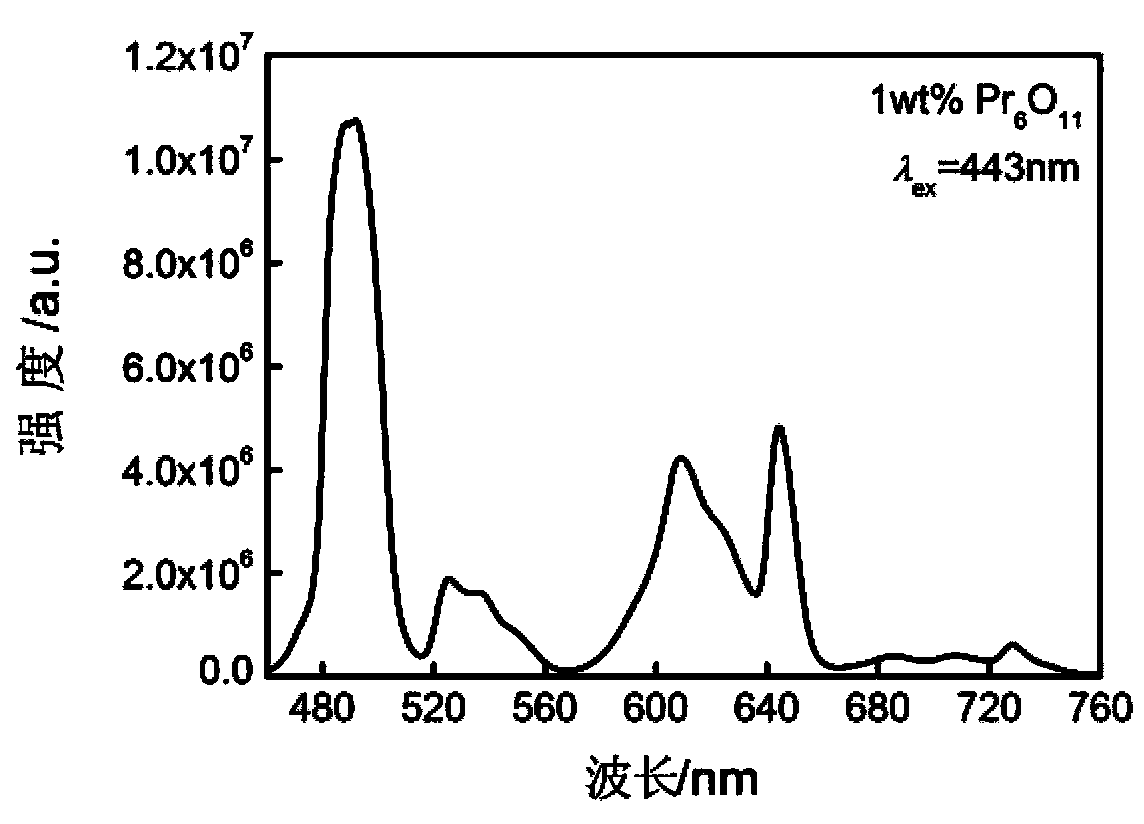
Method for preparing praseodymium-doped ion exchange aluminate and germanate glass waveguide
InactiveCN102809779AImprove solubilityEfficient launchGlass tempering apparatusOptical light guidesHigh energyFluorescence
The invention discloses a method for preparing a praseodymium-doped ion exchange aluminate and germanate glass waveguide. The method includes melting praseodymium-doped aluminate and germanate glass at first, processing the melted praseodymium-doped aluminate and germanate glass into a glass substrate, evaporating an aluminum coating on the glass substrate, and opening an ion exchange window with the width ranging from 8 micrometers to 50 micrometers on the surface of the glass substrate by micro-machining technique and a wet chemical corrosion method; and soaking the glass substrate in potassium nitrate melted salt or mixed molten salt of silver nitrate and potassium nitrate to exchange ions, washing the melted salt and the aluminum coating which are remained on the surface of the glass substrate, and then polishing the washed glass substrate to obtain the praseodymium-doped ion exchange aluminate and germanate glass waveguide. The method solves the problem that effective radiative transition of rare earth ions cannot be realized due to high energy of phonons of an oxide glass waveguide, and spontaneous radiation fluorescence is continuously amplified by praseodymium ions in a visible light wavelength range for the first time. The method has a good application prospect in fields of minimally-invasive photodynamic cancer therapy, laser, communication, lighting and the like.
Owner:DALIAN POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY
Fluorescence waveguide light condensation module, solar power generation device and application thereof
ActiveCN106229371AAvoid exposureExtended service lifePhotovoltaic energy generationSemiconductor devicesFluorescencePhotoelectric conversion
The invention relates to the field of solar power generation and particularly relates to a fluorescence waveguide light condensation module, a solar power generation device and application thereof. The fluorescence waveguide light condensation module comprises two opposite glass waveguide layers, a fluorescencelight condensationwaveguide layer and a reflection layer, wherein the fluorescencelight condensationwaveguide layer and the reflection layer are successively arranged between the two glass waveguide layers; the light condensationwaveguide layer comprises two fluorescence layers and an optically thinner medium layer arranged between the two fluorescence layers; the optical density of the optically thinner medium layer is smaller than that of the fluorescence layers. The invention also provides the solar power generation device and the application thereof. The solar power generation device with high sunlight utilization rate is produced by connecting the fluorescence waveguide light condensation module with a photoelectric conversion element; the solar power generation device can be used as building glass. The fluorescence waveguide light condensation module and the solar power generation device have the advantages of simple structure, simple preparation process, low production cost and high sunlight utilization rate.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Double-depth imaging method based on polarized light sensitive grating AR glasses waveguide
ActiveCN110133801ARealize Optical ImagingNo electronic control deviceOptical light guidesGratingDepth imaging
The invention relates to a double-depth imaging method based on polarized light sensitive grating AR glasses waveguide. A first image source emits light, and the light is changed into P light througha polarization device to enter a first coupling grating; after being refracted by the first coupling grating, the light is totally reflected on a first waveguide substrate, and finally the light is introduced into the coupling grating; the light is led out by the coupling grating and then is changed into S light through a second half-wave plate, and the light is emitted through the output gratingwithout influence, so that optical imaging of one depth is formed in a human eye; a second image source emits light, and the light is changed into S light through the polarization device and enters asecond coupling grating; the light does not change when passing through the first coupling grating, and the light is refracted by the second coupling grating and is totally reflected on a second waveguide substrate, and finally the light is guided into the output grating, and the light is guided out by the output grating and then forms optical image of another depth in the human eye. The method has the advantages of simplicity, convenience, stability, high response speed and the like.
Owner:LIGHTIN INC
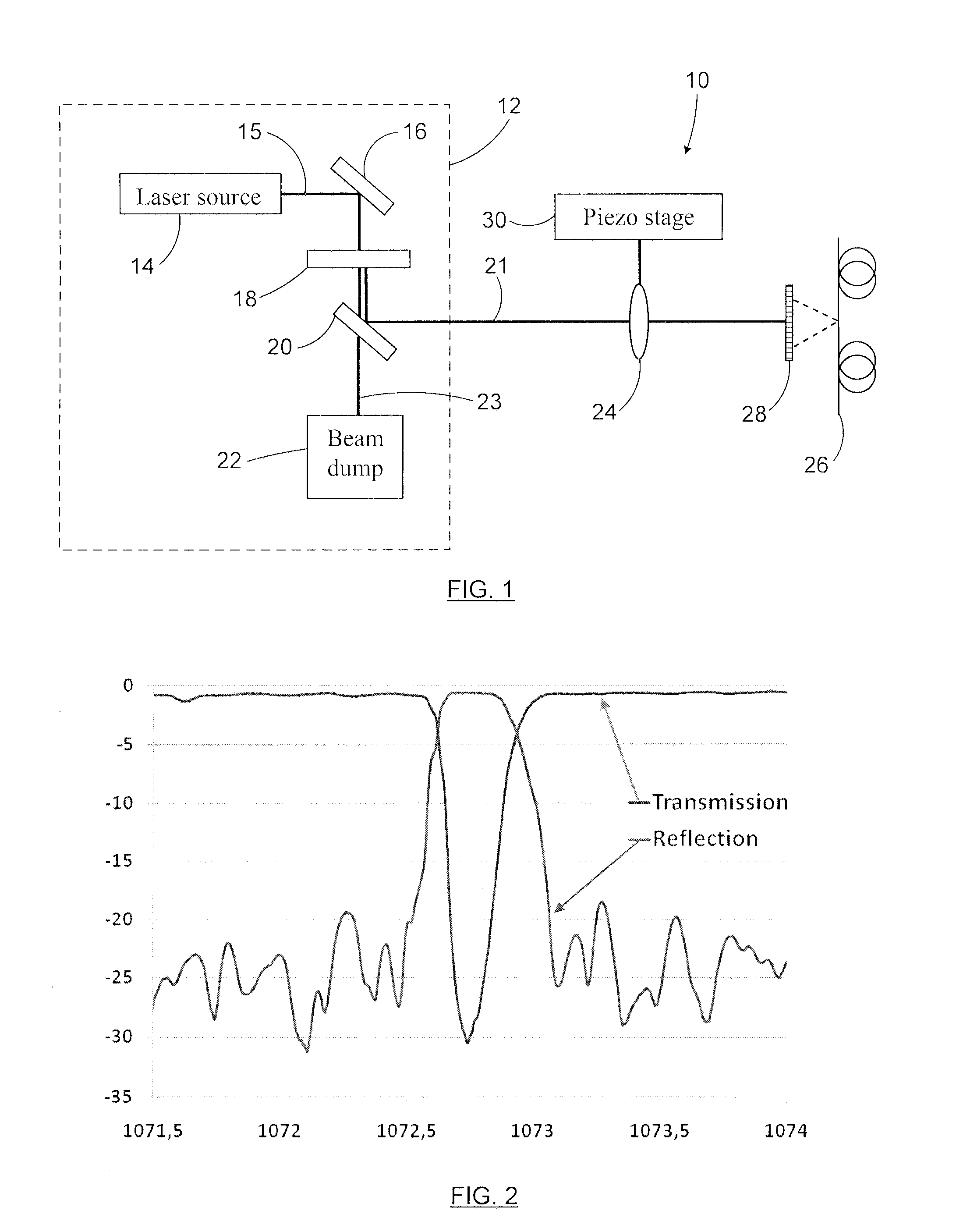
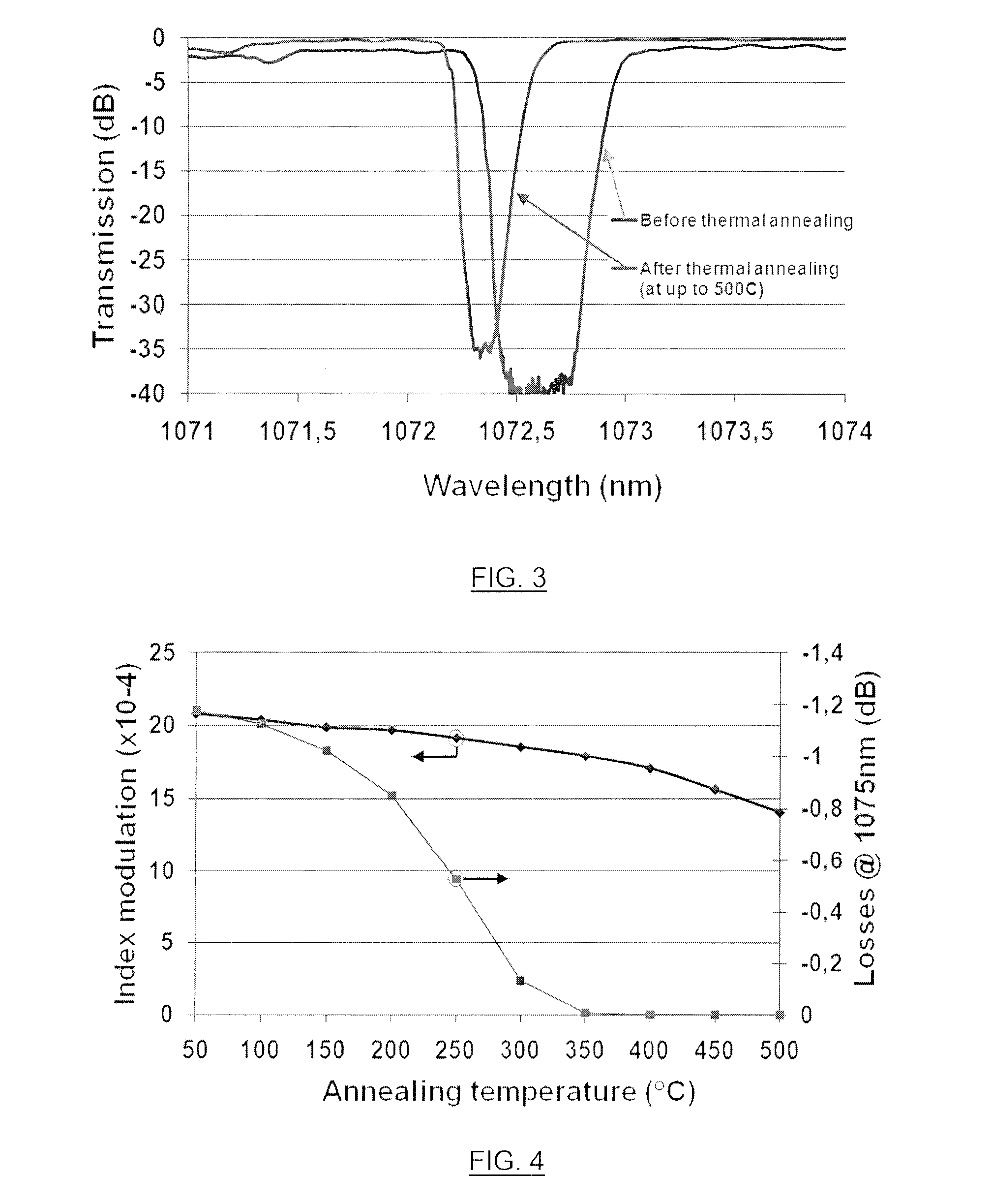
Method For Writing High Power Resistant Bragg Gratings Using Short Wavelength Ultrafast Pulses
ActiveUS20120128301A1Eliminate photodarkening effectEliminate the effects ofCoupling light guidesBragg resonanceGrating
A method for writing a Bragg grating in a rare-earth doped glass optical waveguide is provided. Ultrafast optical pulses are generated, preferably in the femtosecond range and having a writing wavelength in the range of 300 nm to 700 nm and an intensity sufficient to induce a change of refractive index in the rare-earth doped glass waveguide through densification. The optical pulses are diffracted using a phase mask, to generate an interference pattern having a pitch providing a fundamental Bragg resonance corresponding to the target wavelength to be reflected by the grating. The interference pattern is impinged on a region of the rare-earth doped glass waveguide, which is heated to a temperature above a threshold of about 350° C., for a predetermined heating period. Advantageously, the heating step allows the elimination of photodarkening effects which would otherwise be present in the waveguiding properties of the waveguide.
Owner:UNIV LAVAL
Microporous glass waveguides doped with selected materials
The present invention concerns waveguides made from porous glass which have been doped with certain selected materials which exhibit optical properties. In the context of the invention, the selected materials are optical materials which exhibit optical activity or a Faraday effect, such as an electro-optic material, and more specifically a polymer. Devices made according to the present invention can be used as phase modulators.
Owner:INSTITUT NATIONAL D'OPTIQUE
Optical fiber composite light spot laser beam combiner and manufacturing method thereof
PendingCN110640308AImprove reliabilityLow costLaser beam welding apparatusLaser processingLight spot
The invention discloses an optical fiber composite light spot laser beam combiner. The optical fiber composite light spot laser beam combiner comprises a hollow tubular glass waveguide formed throughtapering, multiple outer ring input optical fibers evenly distributed and welded to the section of the tube wall of the tubular glass waveguide, multiple central input optical fibers arranged on the center of the tubular glass waveguide in a beam combining manner, and a large-mold-field optical transmission optical fiber located on the tube wall tapering end of the tubular glass waveguide and welded and condensed. The tube wall of the tubular glass waveguide, the input laser on the center position of the waveguide and the output laser of the large-mold-field optical transmission optical fiberare effectively coupled to form the composite light spots. The combiner has the advantages that the same laser device can modulate the light spot quality and the light spot form, and can be applied todifferent laser machining applications, and the efficiency of the same laser in the different applications at the same time can be improved.
Owner:NANJING FIBER FOTON TECH CORP LTD
Method for writing high power resistant bragg gratings using short wavelength ultrafast pulses
ActiveUS8515224B2Eliminate photodarkening effectEliminate the effects ofCoupling light guidesBragg resonanceElectrical resistance and conductance
A method for writing a Bragg grating in a rare-earth doped glass optical waveguide is provided. Ultrafast optical pulses are generated, preferably in the femtosecond range and having a writing wavelength in the range of 300 nm to 700 nm and an intensity sufficient to induce a change of refractive index in the rare-earth doped glass waveguide through densification. The optical pulses are diffracted using a phase mask, to generate an interference pattern having a pitch providing a fundamental Bragg resonance corresponding to the target wavelength to be reflected by the grating. The interference pattern is impinged on a region of the rare-earth doped glass waveguide, which is heated to a temperature above a threshold of about 350° C., for a predetermined heating period. Advantageously, the heating step allows the elimination of photodarkening effects which would otherwise be present in the waveguiding properties of the waveguide.
Owner:UNIV LAVAL
Erbium-doped wedge-shaped waveguide amplifier capable of achieving high efficiency, large energy and small size
InactiveCN111769427AImprove absorption efficiencyIncrease absorption lengthOptical resonator shape and constructionActive medium shape and constructionWaveguide amplifierHigh energy
The invention discloses an erbium-doped wedge-shaped waveguide amplifier capable of realizing high efficiency, large energy and small volume. A wedge-shaped double-cladding erbium glass waveguide structure is used, pump light is fully absorbed after passing through a gain medium for multiple times, and the absorption length and the absorption uniformity of the gain medium are increased, so that the heat effect is improved, and the pump absorption efficiency is effectively improved. A gain medium wraps the four sides of a material which absorbs 1.5 microns and does not absorb pump light, so that a self-excited oscillation loop is cut off, the influence of ASE is improved, the energy storage efficiency is improved, and the output laser energy is improved. The novel waveguide structure is small in size and compact in structure. The inner cladding and the outer cladding play a role of heat sink for the erbium glass, so that the gain medium can better dissipate heat, the temperature gradient of the center and the side surface of the gain medium is effectively improved, the heat effect is reduced, and high-energy output is realized. The amplifier gain medium is prepared by adopting a bonding technology, so that the whole structure of the amplifier is simpler and more compact, and integration and structural miniaturization are easy to realize.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
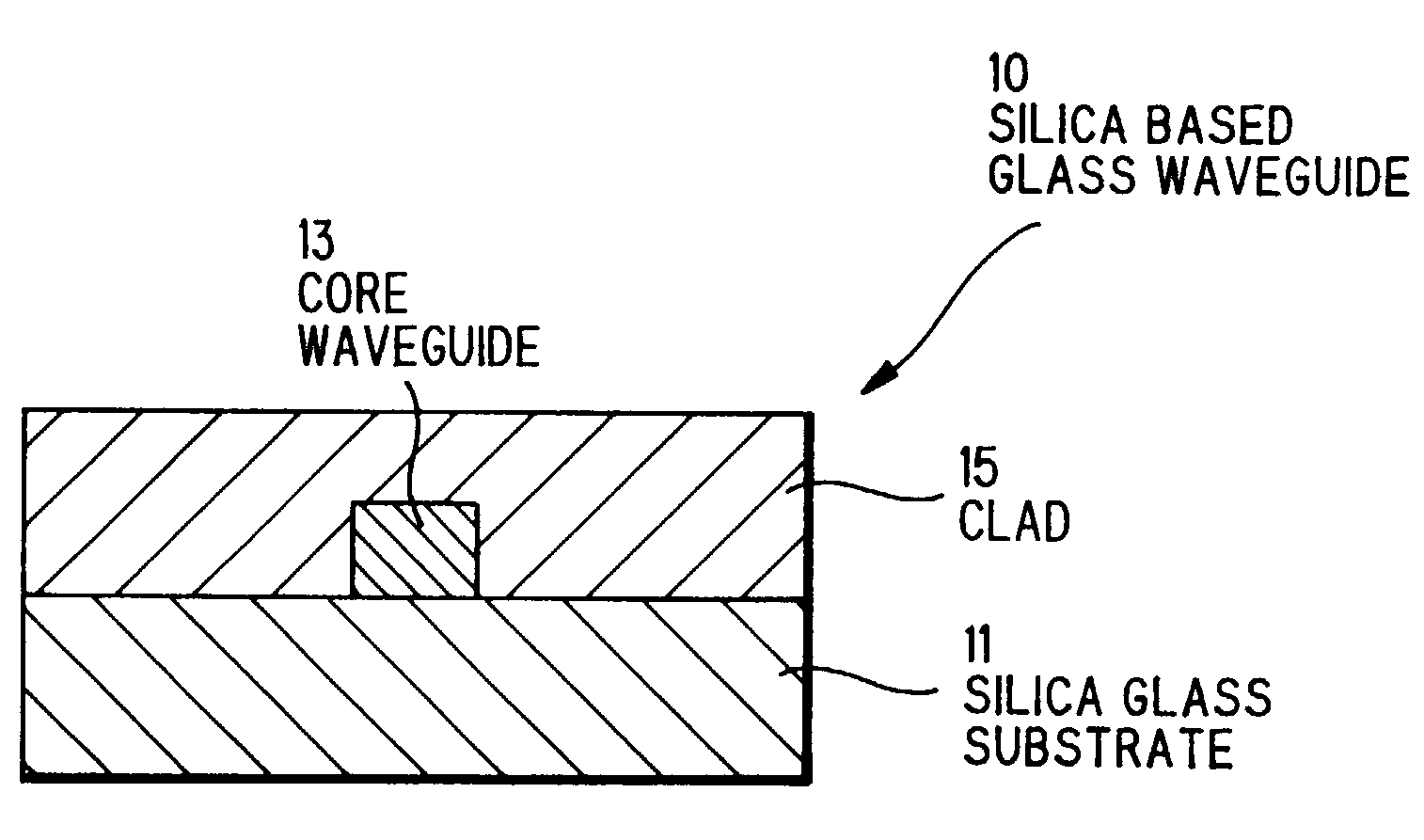
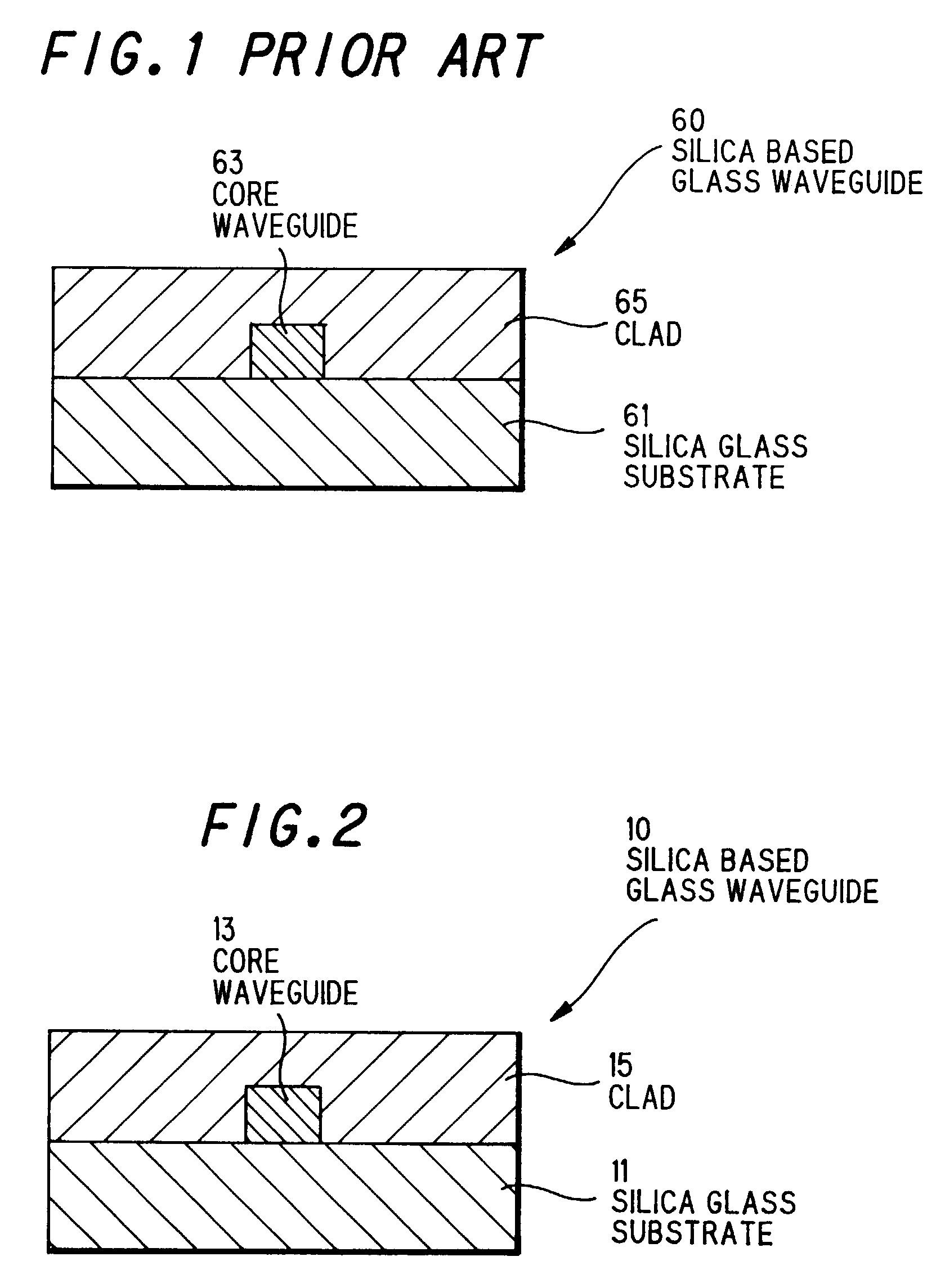
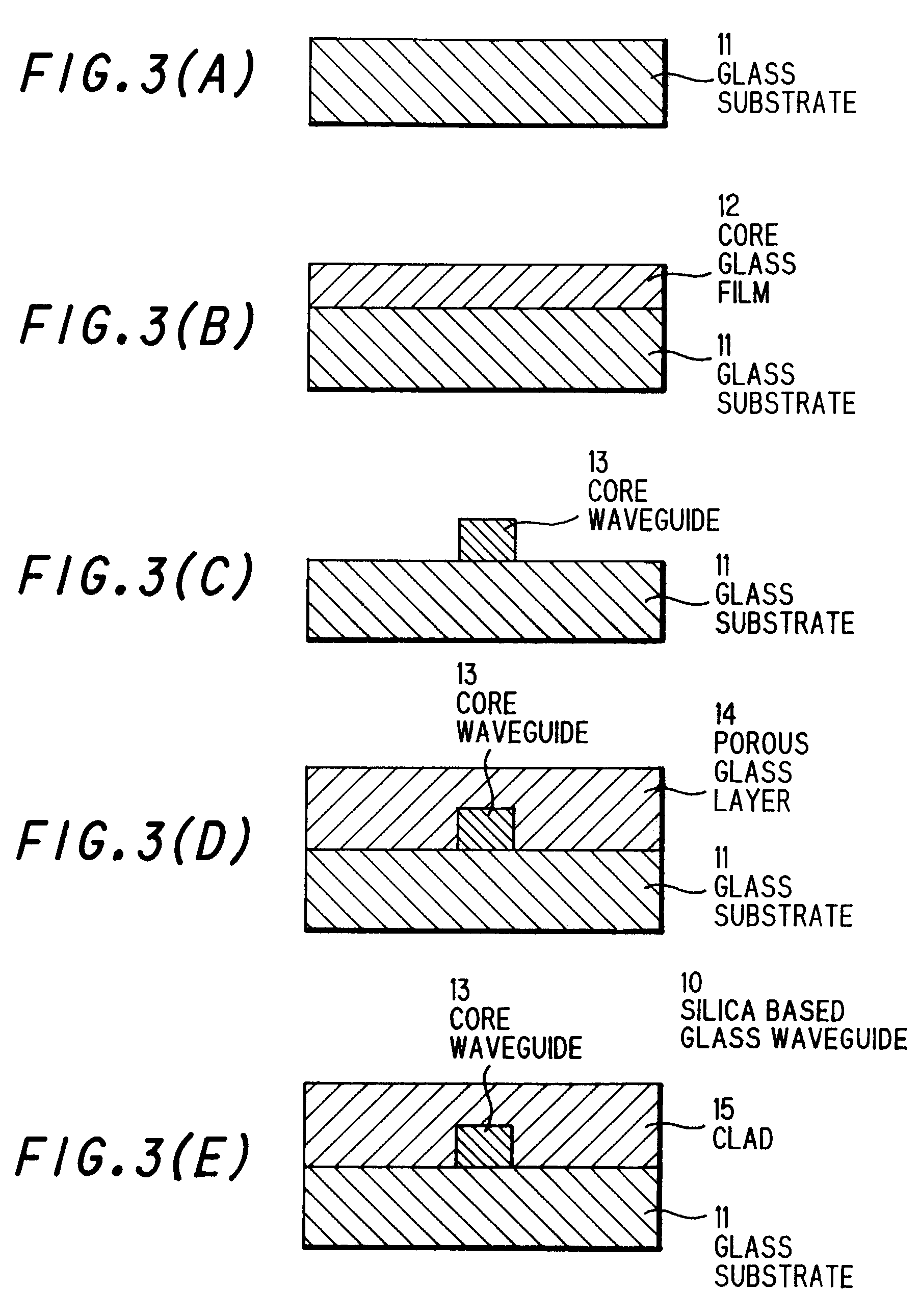
Silica based glass waveguide and optical module using the same
InactiveUS7415183B2Excellent optical propertiesReduce lossesOptical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingGlass waveguideWaveguide
A silica based glass waveguide having almost the same optical characteristics as designed value and an optical module using a silica based glass waveguide having excellent optical characteristics and reduced connecting loss are provided. A silica based glass waveguide is comprising a core waveguide and a clad, a core waveguide is formed rectangular in cross section and of SiO2—TiO2 group glass on a synthetic silica glass substrate, and a clad is formed of SiO2—B2O3—P2O5 group glass or etc. on a synthetic silica glass substrate and a core waveguide. A synthetic silica glass substrate is formed of pure SiO2 and having birefringence quantity less than 10 nm / cm.
Owner:HITACHI METALS LTD
Optical fiber coating for short data network
ActiveUS20140376867A1Improve fatigue resistanceImprove thermal stabilityGlass optical fibreCoatingsMeth-Engineering
A hybrid cladding for optical fibers used in short data networks. The hybrid cladding surrounds a glass waveguide fiber and is surrounded by a primary coating. The hybrid cladding has low adhesion to the primary coating. The low adhesion permits stripping of the primary coating from the hybrid cladding without damaging the hybrid cladding and without leaving residue of the primary coating on the surface of the hybrid cladding. The hybrid cladding may be formed by curing a composition that includes a monomer with a radiation-curable functional group, a slip component, and a photoinitiator. The radiation-curable functional group may be a (meth)acrylate group. The slip component may contain silicon or silicone and may further contain a radiation-curable functional group. Silicone di(meth)acrylate is an illustrative slip component.
Owner:CORNING INC
Optical fiber coating for short data network
ActiveUS9322986B2Improve fatigue resistanceImprove thermal stabilityGlass optical fibreCoatingsFiberMeth-
A hybrid cladding for optical fibers used in short data networks. The hybrid cladding surrounds a glass waveguide fiber and is surrounded by a primary coating. The hybrid cladding has low adhesion to the primary coating. The low adhesion permits stripping of the primary coating from the hybrid cladding without damaging the hybrid cladding and without leaving residue of the primary coating on the surface of the hybrid cladding. The hybrid cladding may be formed by curing a composition that includes a monomer with a radiation-curable functional group, a slip component, and a photoinitiator. The radiation-curable functional group may be a (meth)acrylate group. The slip component may contain silicon or silicone and may further contain a radiation-curable functional group. Silicone di(meth)acrylate is an illustrative slip component.
Owner:CORNING INC
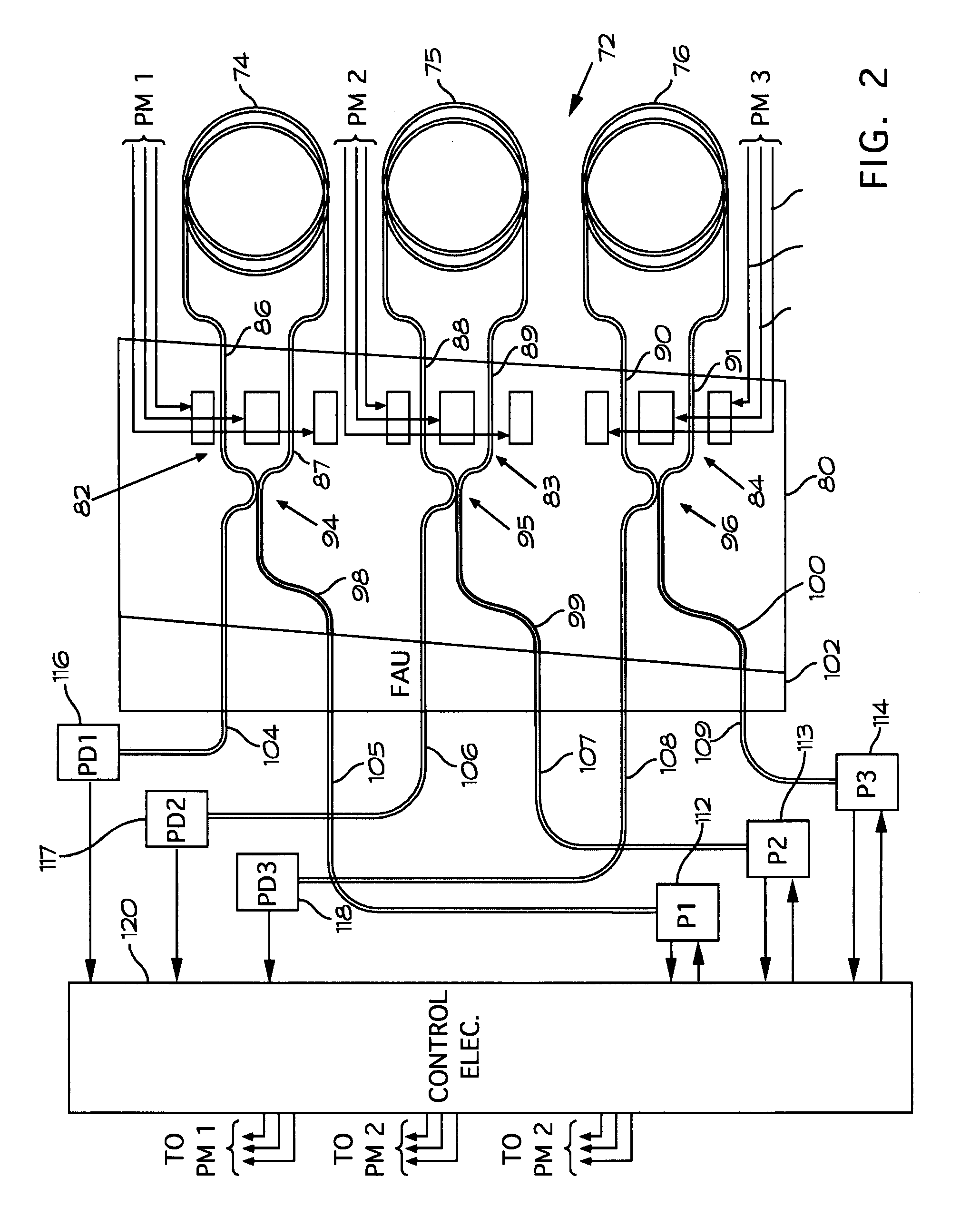
Integrated optical network chip used for triaxial interference type optical fibre gyro
InactiveCN101571391AReduce volumeImprove consistencySagnac effect gyrometersCoupling light guidesMiniaturizationEngineering
The invention discloses an integrated optical network chip used for a triaxial interference type optical fibre gyro, comprising a buried low-loss glass waveguide, a 3*3 coupler, a first integrated 2*2 coupler, a second integrated 2*2 coupler and a third integrated 2*2 coupler; the third integrated 2*2 coupler is integrated on the buried low-loss glass waveguide; and three exit ends of the 3*3 coupler is respectively connected with an incident end of the first integrated 2*2 coupler, an incident end of the second integrated 2*2 coupler and an incident end of the third integrated 2*2 coupler. Compared with the traditional triaxial interference type optical fibre gyro system using four independent couplers, the integrated optical network chip greatly reduces the volume of the triaxial interference type optical fibre gyro system and is beneficial to miniaturization and engineering of the triaxial interference type optical fibre gyro.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for preparing glass waveguide by ion mask
InactiveCN100392446CImprove performanceEasy to implementOptical waveguide light guideSelective leachingRefractive index
The invention discloses a method for producing glass optical waveguide with ion mask. Wherein, first using K+ ion exchange technique to form a K+ disperse area on the glass basic plate, as the mask of following ion exchange; then using mask inversion technique to form a film on the K+ ion disperse area, to baffle the dispersion of high-refractive ion that though the K+ disperse area in the following ion exchange process; at least, using fused salt with high-polarized ion to exchange ion, and attain high-refractive ion disperse area with improved shape on the glass basic plate. The invention can avoid film preparation and selective erosion technique; and since the film can completely stop the dispersion of high-polarized ion through the ion mask, the invention can attain better bar optical waveguide.
Owner:ZHEJIANG NANFANG COMM GROUP +1
Active glass waveguide coupling microannular resonant cavity and active controller thereof
InactiveCN1645173AOvercome defectsImprove performanceCoupling light guidesFibre transmissionResonant cavityRare earth
A micro-ring resonant cavity of glass active waveguide couple is prepared by interlinking passive straight waveguide module with active ring waveguide module. The dynamic control device of it is featured as connecting a pumping laser to an input port of wavelength division complexer, using another port as signal light input port and connecting output end of the waveguide division complexer to straight waveguide.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for preparing praseodymium-doped ion exchange aluminate and germanate glass waveguide
InactiveCN102809779BImprove solubilityEfficient launchGlass tempering apparatusOptical light guidesFluorescenceHigh energy
The invention discloses a method for preparing a praseodymium-doped ion exchange aluminate and germanate glass waveguide. The method includes melting praseodymium-doped aluminate and germanate glass at first, processing the melted praseodymium-doped aluminate and germanate glass into a glass substrate, evaporating an aluminum coating on the glass substrate, and opening an ion exchange window with the width ranging from 8 micrometers to 50 micrometers on the surface of the glass substrate by micro-machining technique and a wet chemical corrosion method; and soaking the glass substrate in potassium nitrate melted salt or mixed molten salt of silver nitrate and potassium nitrate to exchange ions, washing the melted salt and the aluminum coating which are remained on the surface of the glass substrate, and then polishing the washed glass substrate to obtain the praseodymium-doped ion exchange aluminate and germanate glass waveguide. The method solves the problem that effective radiative transition of rare earth ions cannot be realized due to high energy of phonons of an oxide glass waveguide, and spontaneous radiation fluorescence is continuously amplified by praseodymium ions in a visible light wavelength range for the first time. The method has a good application prospect in fields of minimally-invasive photodynamic cancer therapy, laser, communication, lighting and the like.
Owner:DALIAN POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY
Chalcogenide glass waveguides for refractive non-mechanical beam steerer
ActiveUS10690992B2Reduce absorption lossReduce absorptionNon-linear opticsLiquid crystallineChalcogenide glass
A method for making a chalcogenide glass waveguide in a liquid crystal-based non-mechanical beam steering device that permits steering in the mid-wave infrared. The waveguide core, the subcladding, or both comprise a chalcogenide glass. A mask is used to produce a tapered subcladding. Also disclosed is the related non-mechanical beam steering device that includes a chalcogenide waveguide.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
Glass waveguide light amplifier
InactiveCN1417632AHigh cost performanceHighly integratedElectromagnetic transmissionNon-linear opticsFiberCommunications system
The glass waveguide light amplifier includes two passive light waveguides, each of which consists of glass substrate and greater refraction index area on the surface or inside the substrate; and one active light waveguide, which consists of substrate with at least one kind of infiltrated phosphate or silicate of La family element and greater refraction index area on the surface or inside the substrate. Two passive light waveguides are set on two sides of the active light waveguide and the greater refraction index areas in the light waveguides are connected together. The glass waveguide light amplifier of the present invention has high performance / cost ratio, high integration level, small size and great gain in unit length, and may be used in high-capacity fiber communication system.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Waveguide formation method and SF6 gas passive sensor comprising waveguide
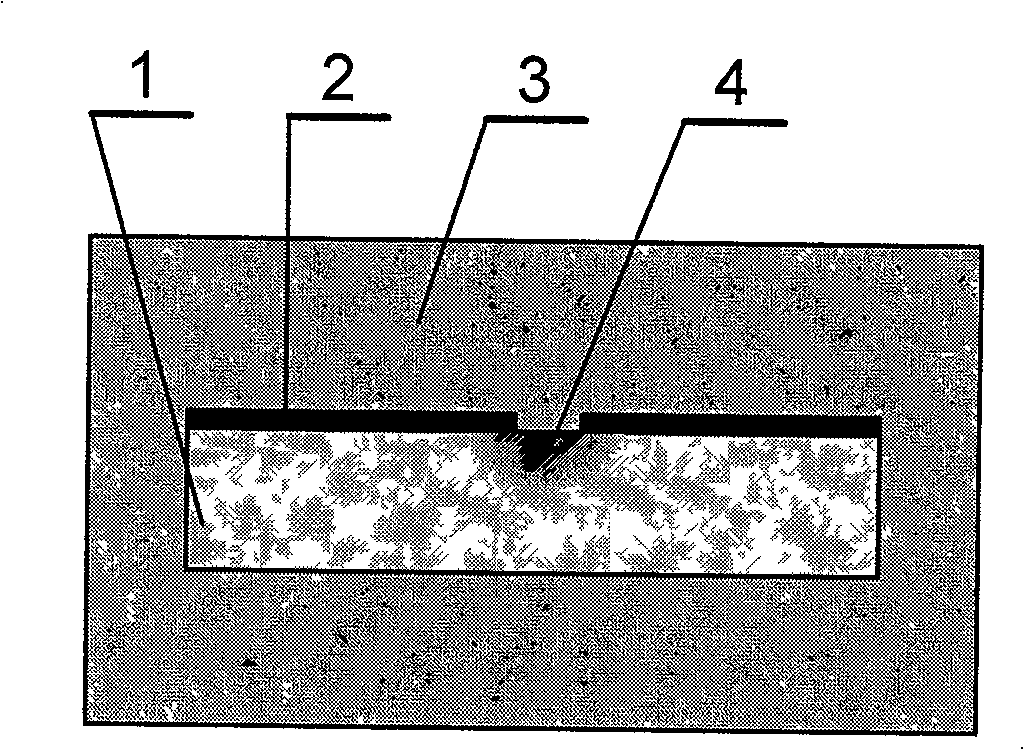
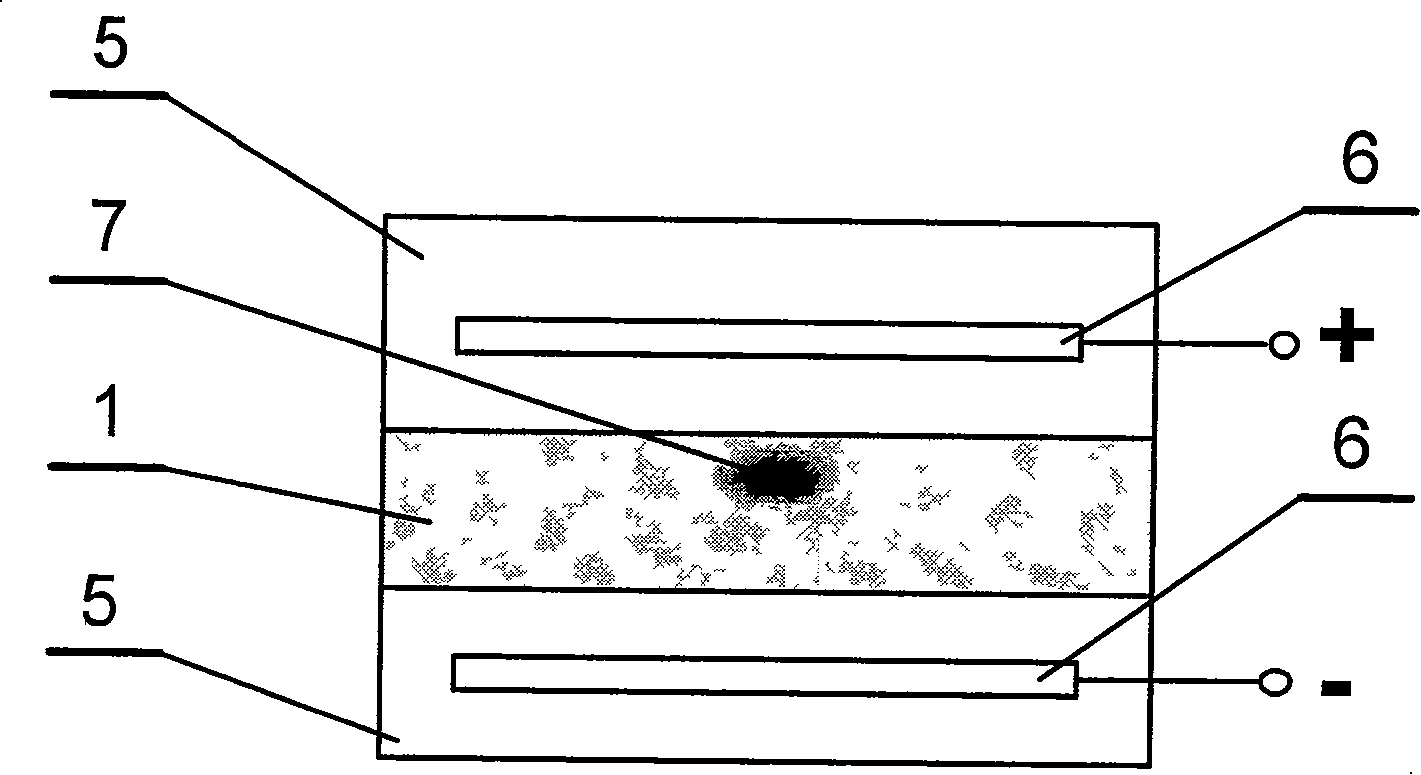
ActiveCN110501781AHigh sensitivityReduce volumeColor/spectral properties measurementsOptical waveguide light guideInsulation layerGas phase
The invention discloses a waveguide formation method and an SF6 gas passive sensor comprising the waveguide. The waveguide formation method comprises the following steps: growing an insulation layer on a silicon substrate; spin coating photoresist on the surface of the insulation layer; photoetching the photoresist and forming a waveguide structure; carrying out vapor deposition of glass in the waveguide structure to form a glass waveguide layer; removing the photoresist that is not photoetched and the glass outside the waveguide structure through the stripping technology to form a waveguide main body; spin coating a polymer on the waveguide main body; photoetching the polymer and carrying out curing to form cavity pillars; and processing the tops of the cavity pillars through the bondingtechnology to form cavities, wherein the multiple cavities are connected to form a waveguide. The waveguide formation method and the SF6 gas passive sensor comprising the waveguide, through passive design, increase product life, improve sensor sensitivity and have a real-time online monitoring function.
Owner:BEIJING SMARTCHIP MICROELECTRONICS TECH COMPANY +3
Method for preparing glass waveguide by single-side molten salt electric field assistant ion exchange
InactiveCN100412583CGuaranteed to continueAvoid destructionOptical waveguide light guideIon exchangeMolten salt
The invention discloses a method for producing buried glass optical waveguide by single-side fused salt electric field auxiliary ion exchange technique. Wherein, first processing the ion exchange on the glass basic plate with mask in the fused salt with high polarized ion, to attain the ion exchange area on the glass surface; preparing a baffle layer on the surface of glass basic plate and far away from the core of optical waveguide, to stop ion passing said glass basic plate in the following ion exchange process, while the passed ion will reduce the cathode and destroy the metallic film electrode; at last, the anode uses the fused salt without high polarized ion, and the cathode uses metallic film, and using single-side fused salt electric field auxiliary ion exchange technique to prepare optical waveguide. The invention can effectively restrain the hurt of cathode metallic film in the process of electric field auxiliary ion exchange, to improve the property of glass optical waveguide.
Owner:ZHEJIANG NANFANG COMM GROUP +1
A multi-depth imaging method for polarization-sensitive AR glasses waveguide
The invention relates to a multi-depth imaging method for polarization-sensitive AR glasses waveguide. The light emitted by the image source becomes linearly polarized light through the polarizing device and enters the corresponding in-coupling grating of the waveguide substrate. The light is refracted by the in-coupling grating, totally reflected on the waveguide substrate, and finally introduced into the out-coupling grating area; no electric field is applied to the liquid crystal layer In the case of control, the linearly polarized light is refracted through the outcoupling grating, and then exported through the liquid crystal layer and the output grating, thereby forming a deep optical image in the human eye; The grating is refracted, and then the polarization rotation occurs through the liquid crystal layer, and then the output grating is refracted to form an optical imaging different from the original linearly polarized light, so as to realize the optical imaging control of two depths. The invention has the advantages of simplicity, convenience, stability, fast response speed and the like.
Owner:LIGHTIN INC
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com