Method for removing radioactive cobalt by using graphene loaded nanometer zero-valent iron composite material
A technology of nano-zero-valent iron and composite materials, which is applied in the fields of radioactive purification and nuclear engineering. It can solve the problems of high surface energy, easy agglomeration, and difficult separation, and achieve the effects of easy recovery, mild experimental conditions, and large adsorption capacity.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0017] First prepare graphene oxide (GO), the steps are as follows: add 106mL concentrated sulfuric acid and 1.0g expandable graphite into the reaction vessel, stir in an ice-water bath for 30min; slowly add 5g potassium permanganate, and keep the system temperature not exceeding 15°C After the reaction is completed, withdraw from the ice-water bath, and stir at a constant temperature of 35±1°C for 3 days; then add deionized water three times, add 40mL for the first time, stir at 60±1°C for 60min, add 40mL for the second time, Keep at 90±1°C for 30min, add 40mL of deionized water directly for the third time; finally add 10mL of 30wt% H 2 o 2 , centrifuged at 12000r / min for 30min while hot, discarded the supernatant, centrifuged and washed several times with hydrochloric acid (mass fraction 36-38%) and distilled water at a volume ratio of 1:10, and freeze-dried for later use.
[0018] Then prepare graphene-supported nano zero-valent iron (Fe 0 / GO) composite material, the ste...
Embodiment 2
[0026] Fe 0 The preparation process of the / GO composite material is the same as in Example 1.
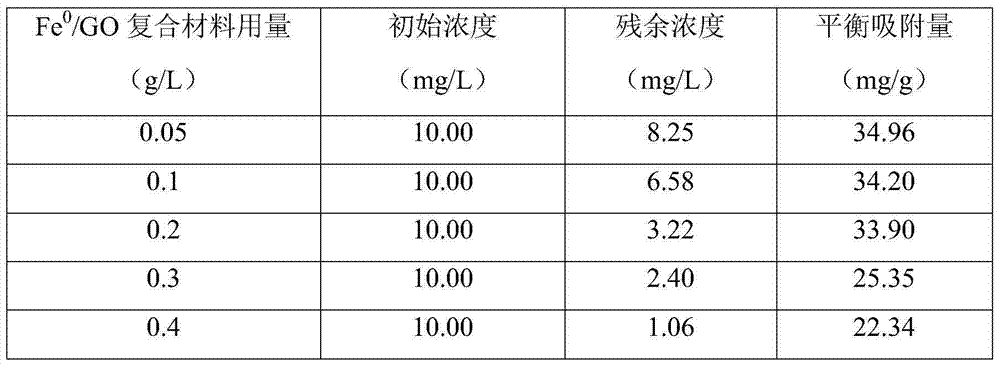
[0027] Will Fe 0 / GO Composite for Adsorption and Removal of Simulated Radionuclide Co 2+ , the steps are as follows: add 15mL of Co to the reactor 2+ Aqueous solution and 0.05g / L Fe 0 / GO composite material, the reactor was sealed and placed in a desktop constant temperature shaking incubator for reaction at a speed of 150 rpm and a temperature of 30 °C. Equilibrium adsorption amount after 7h reaction at different pH (q e ) see Table 2:
[0028] Table 2 Fe at different pH 0 / GO Composite Material Removal of Nuclide Co
[0029] pH
Initial concentration (mg / L)
Residual concentration (mg / L)
Equilibrium adsorption capacity (mg / g)
3
10
5.67
21.67
4
10
3.66
31.69
5
10
2.78
32.82
6
10
2.94
35.32
7
10
2.94
35.32
8
10
3.05
34.74
9
10
2...
Embodiment 3
[0033] Fe 0 The preparation process of the / GO composite material is the same as in Example 1.
[0034] Will Fe 0 / GO Composite for Adsorption and Removal of Simulated Radionuclide Co 2+, the steps are as follows: add 15mL of Co to the reactor 2+ Aqueous solution (pH4) and 0.2g / L Fe 0 / GO composite material, the reactor was sealed and placed in a desktop constant temperature shaking incubator for reaction at a speed of 150 rpm and a temperature of 30 °C. Different Co 2+ Equilibrium adsorption amount after 8h reaction at the initial concentration (q e ) See Table 3:
[0035] Table 3 Different Co 2+ Fe at initial concentration 0 / GO Composite Material Removal of Nuclide Co
[0036] Initial concentration (mg / L)
Residual concentration (mg / L)
Equilibrium adsorption capacity (mg / g)
10.49
3.20
36.45
20.26
10.21
50.25
40.63
28.66
59.85
81.59
69.30
61.45
101.80
88.54
66.31
193.66...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Equilibrium adsorption capacity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com