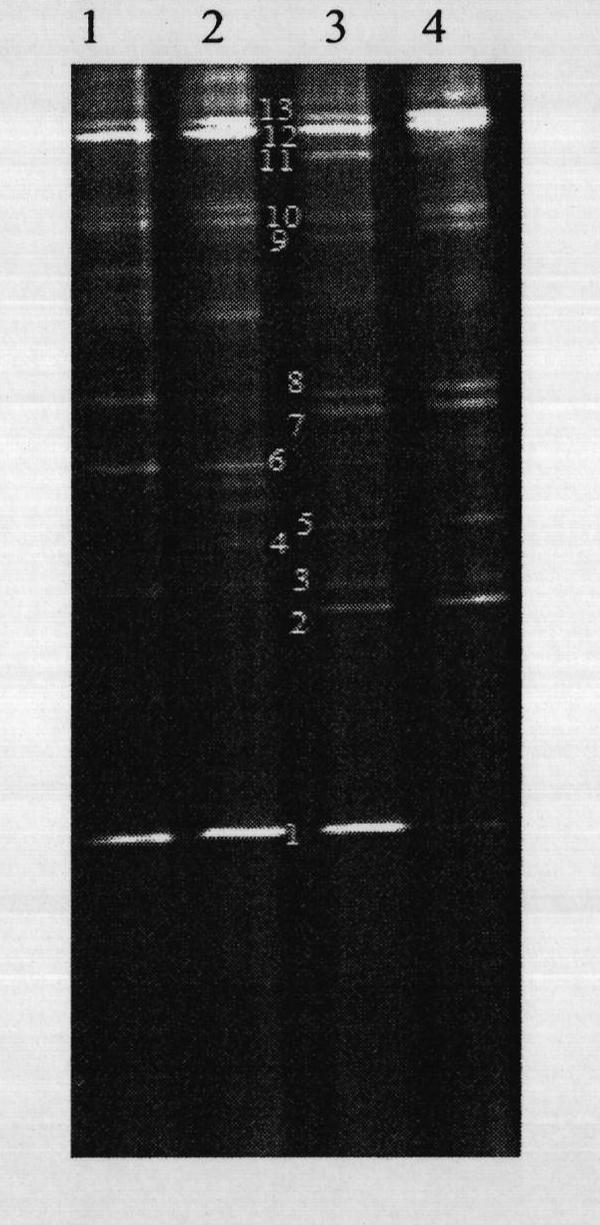
Method for studying structural diversity of daqu bacterial community
A technology of community structure and diversity, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, determination/inspection of microorganisms, etc., can solve the problem of inseparability of microorganisms, which is difficult to directly study, and achieve the effect of avoiding a large number of losses.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0009] For better understanding of the present invention, below in conjunction with example further elaborates the present invention.
[0010] a) Daqu samples selected for analysis (different batches and different types of Luzhou-flavor liquor Daqu from the same origin);
[0011] b) Weighing 1 g of Daqu sample, adding the extract to extract the genomic DNA in the sample;
[0012] c) Select the primer pair F338gc and the R518 primer pair specific to the 16S rRNA gene V3 region of most bacteria and archaea, and add a GC hairpin structure at the 5' end of the forward primer of the primer pair. The sequence of the primer pair is : F338gc: (5′- CGC CCGCCGCGCGCGGCGGGCGGGGCGGGGGCACGGGGGG ACTCCTACGGAGGCAGCAG-3', the underlined part is the hairpin structure), R518: (5'-ATTACCGCGGCTGCTGG-3');
[0013] d) Use the genomic DNA extracted in step b) as a template, and use the primer pair in step c) as primers for PCR amplification. The PCR reaction system is: 50 μL of the PCR reaction sy...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com