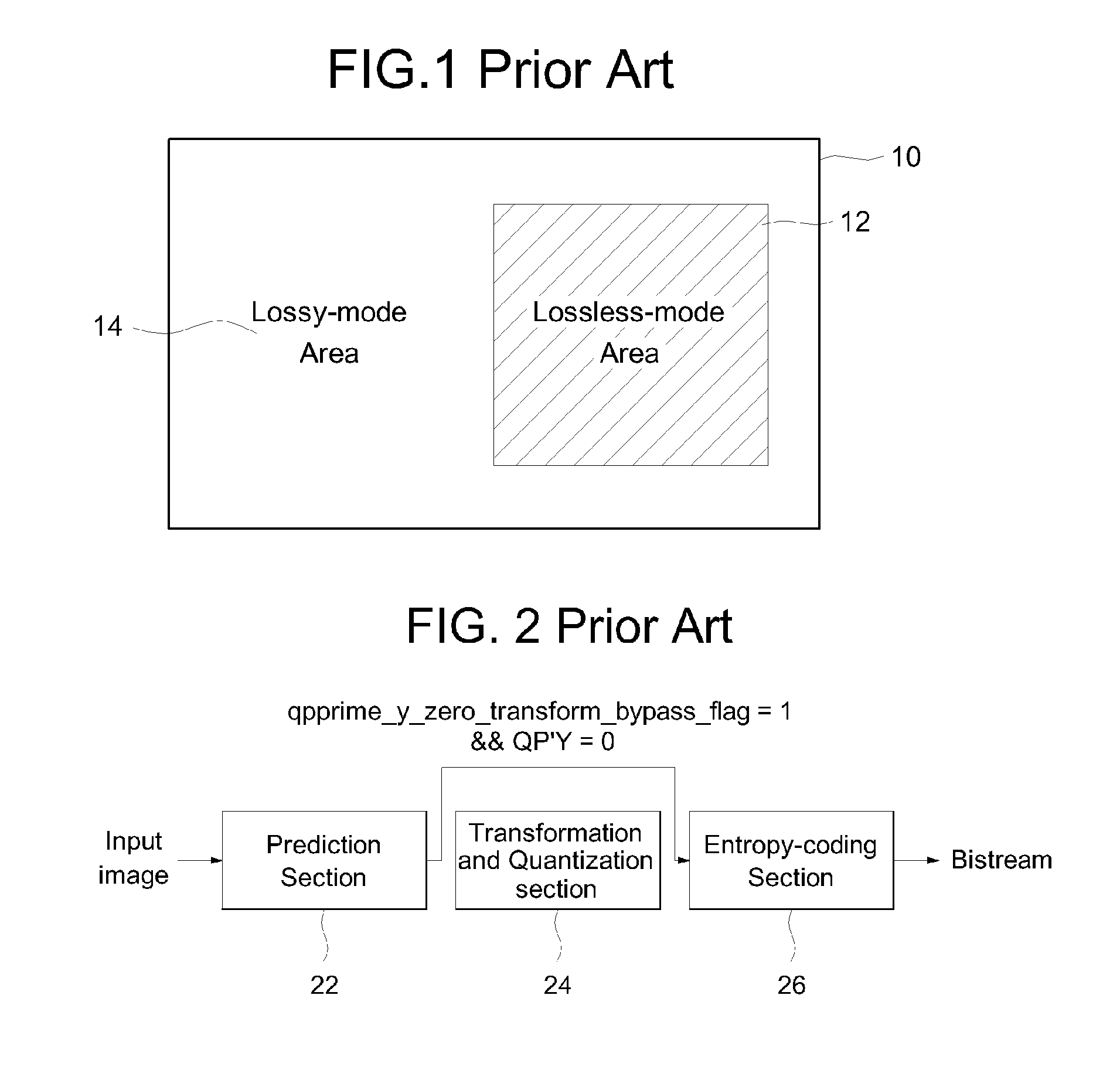
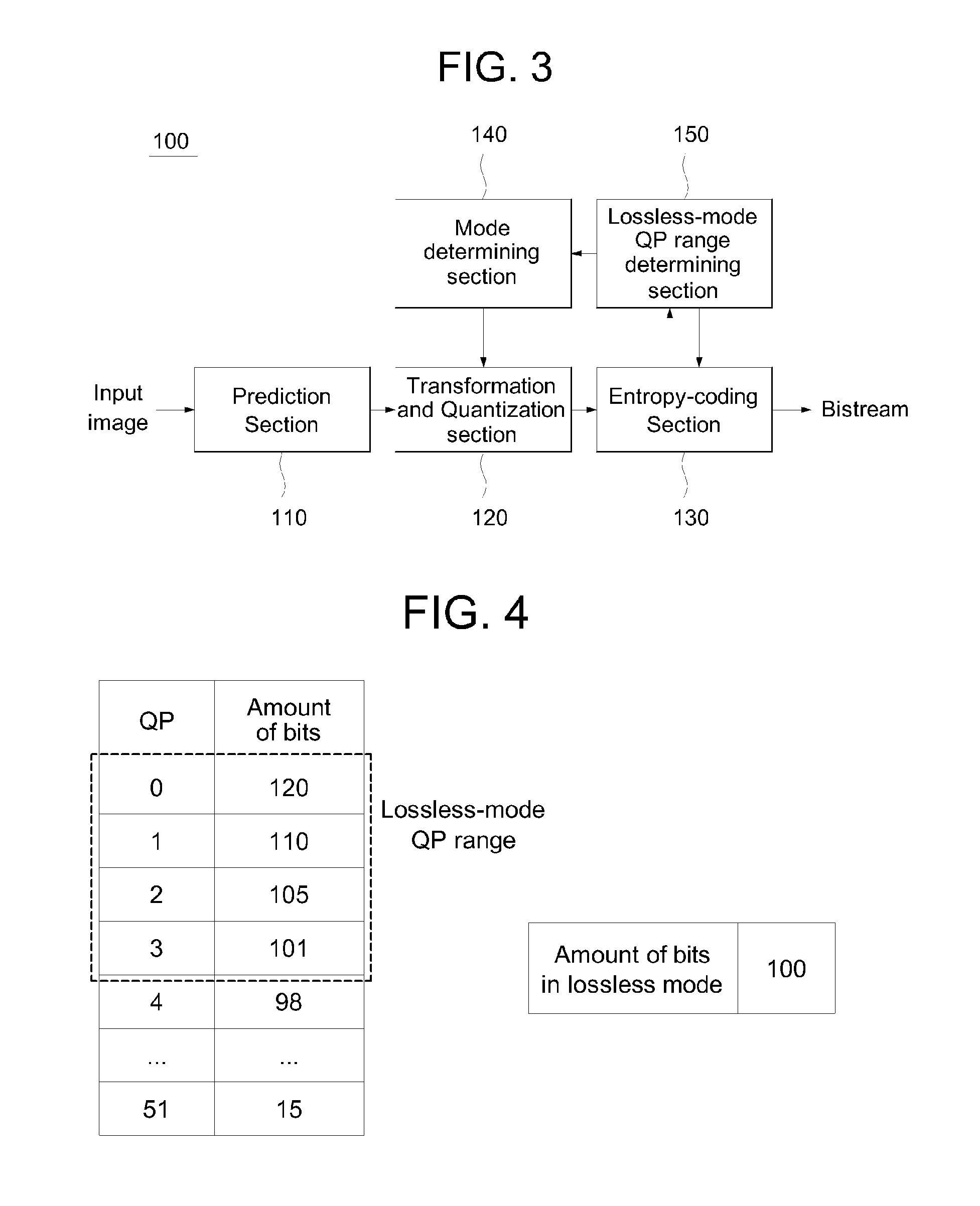
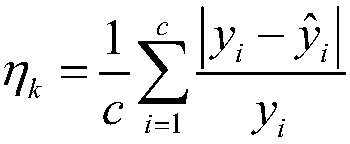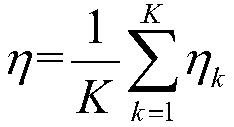Patents
Literature
195 results about "Spatial prediction" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
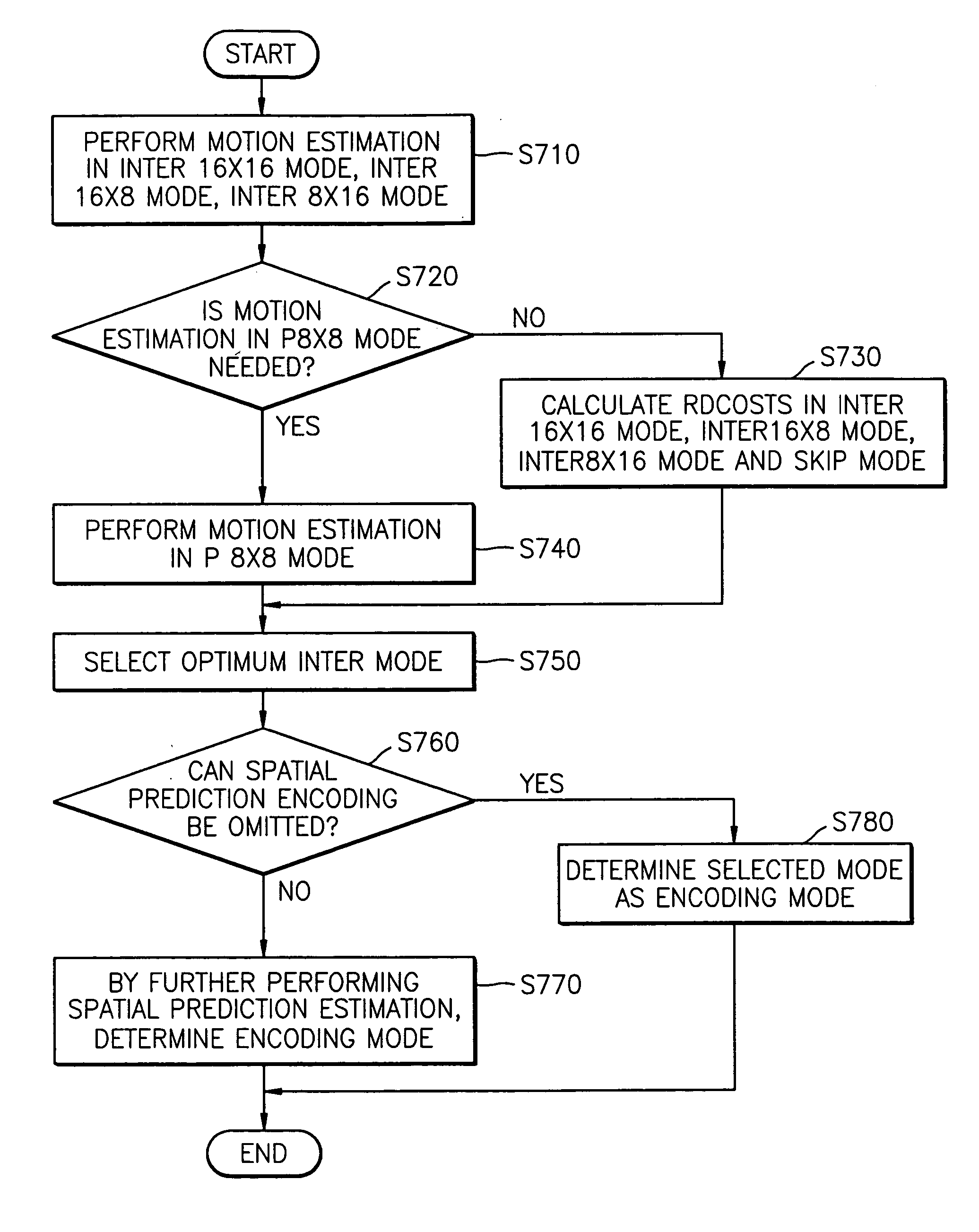
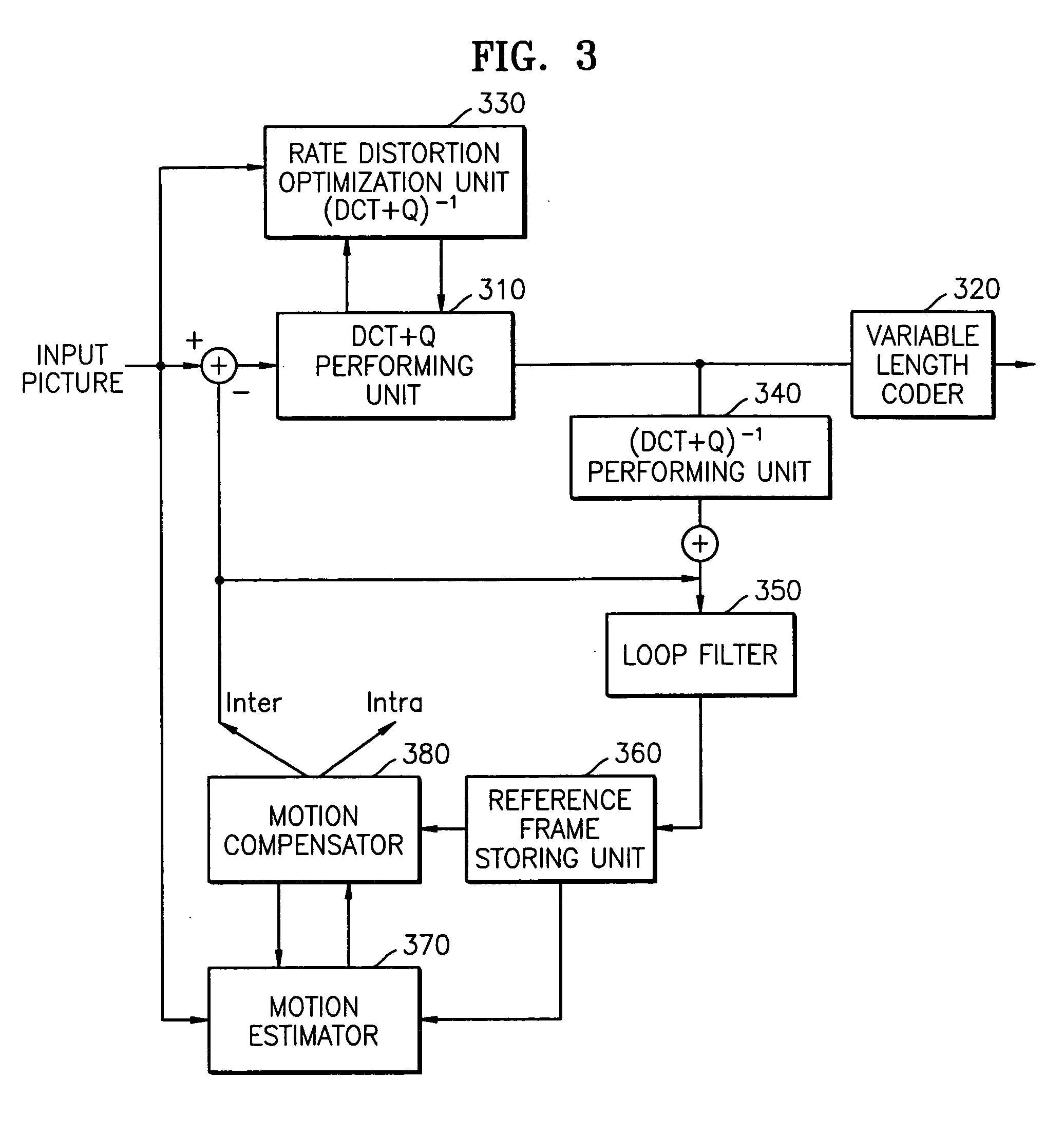
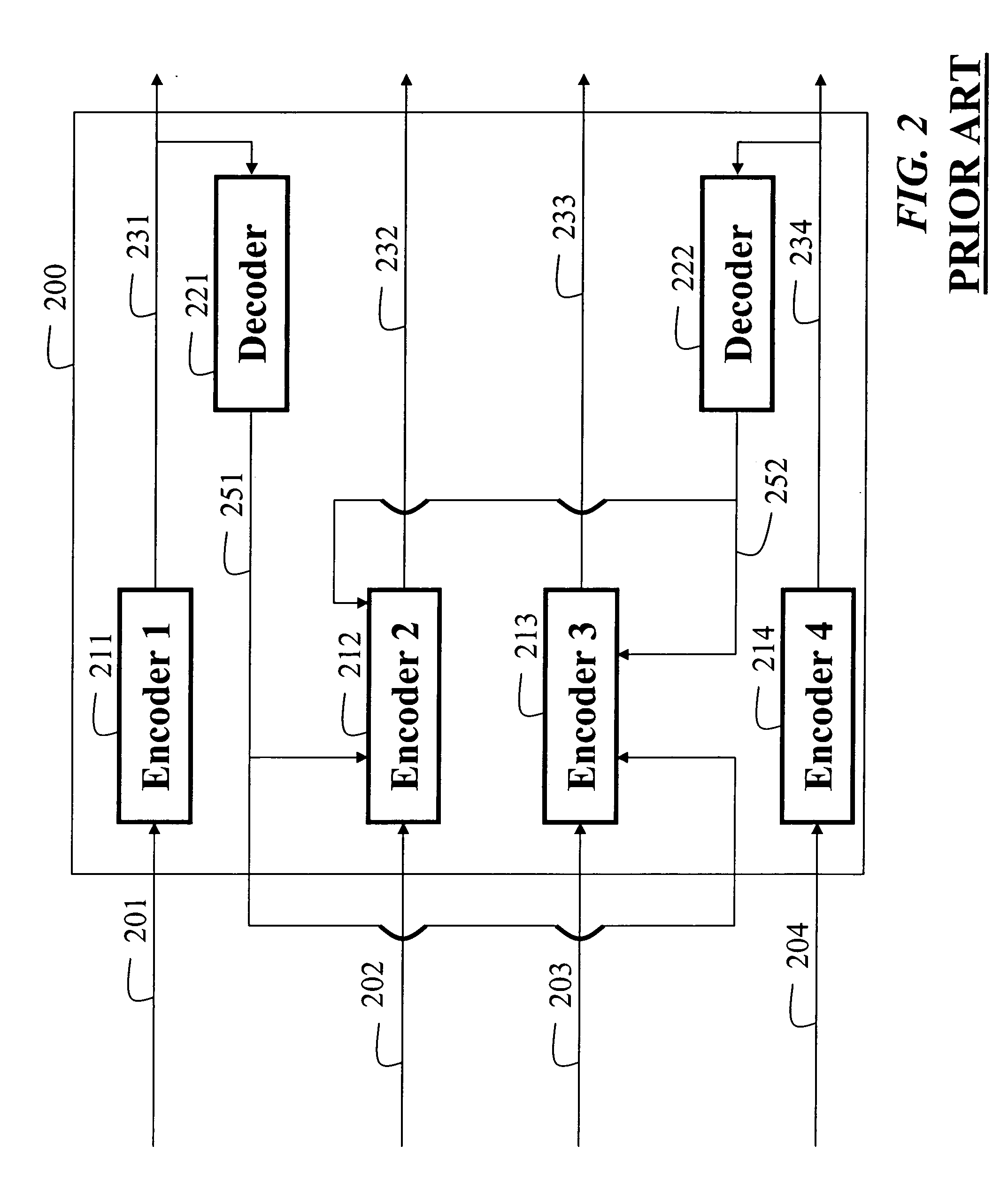
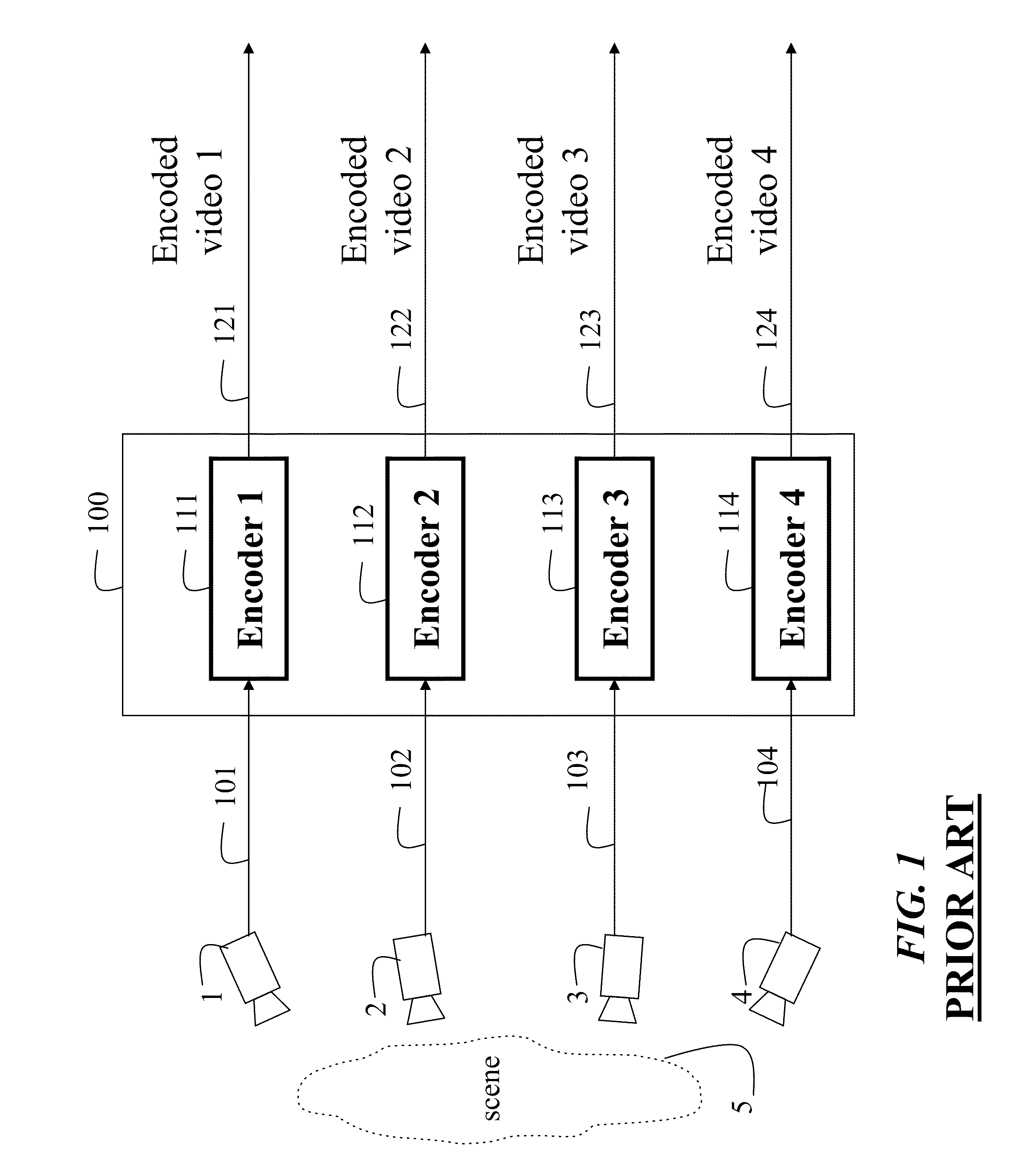
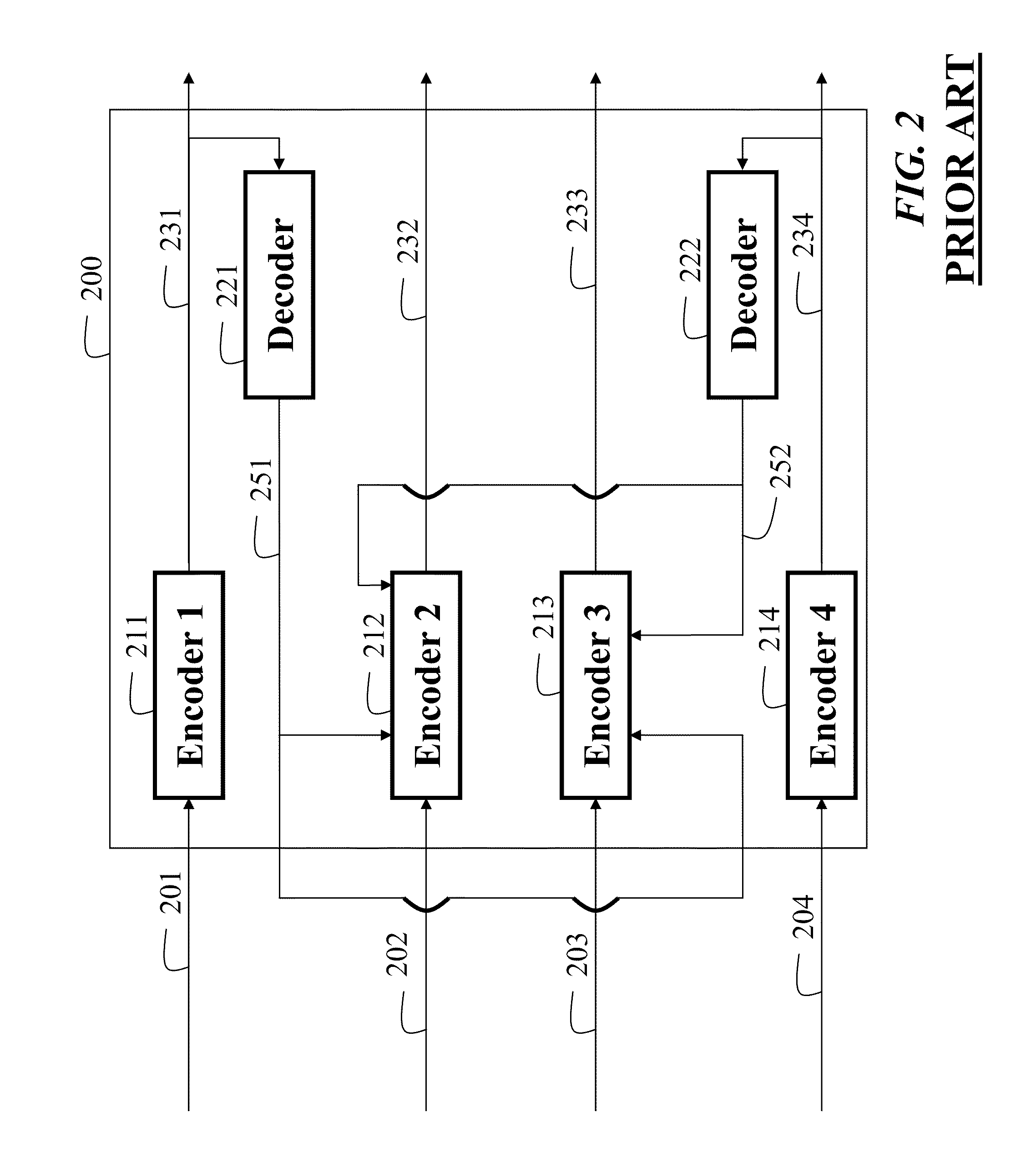
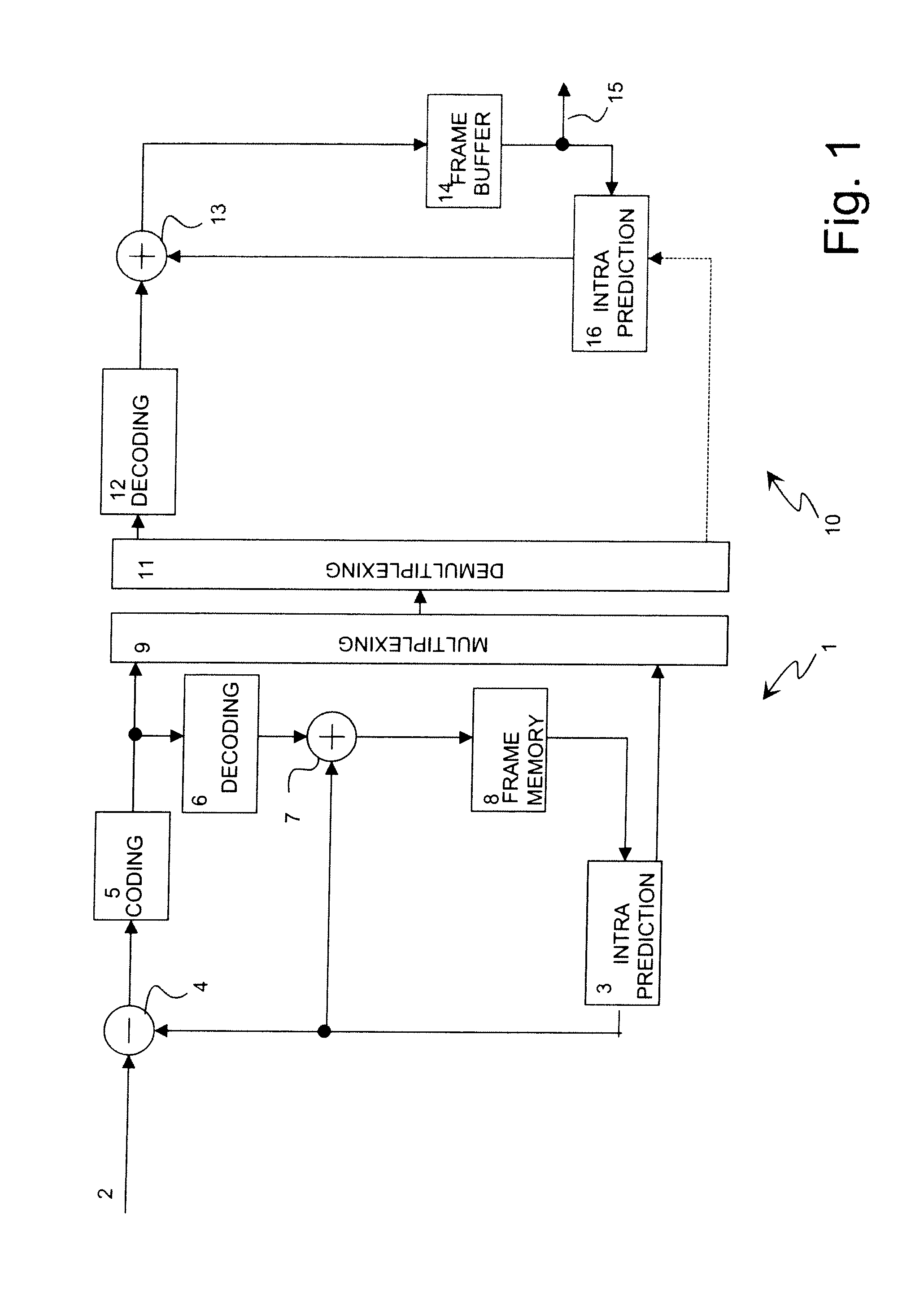
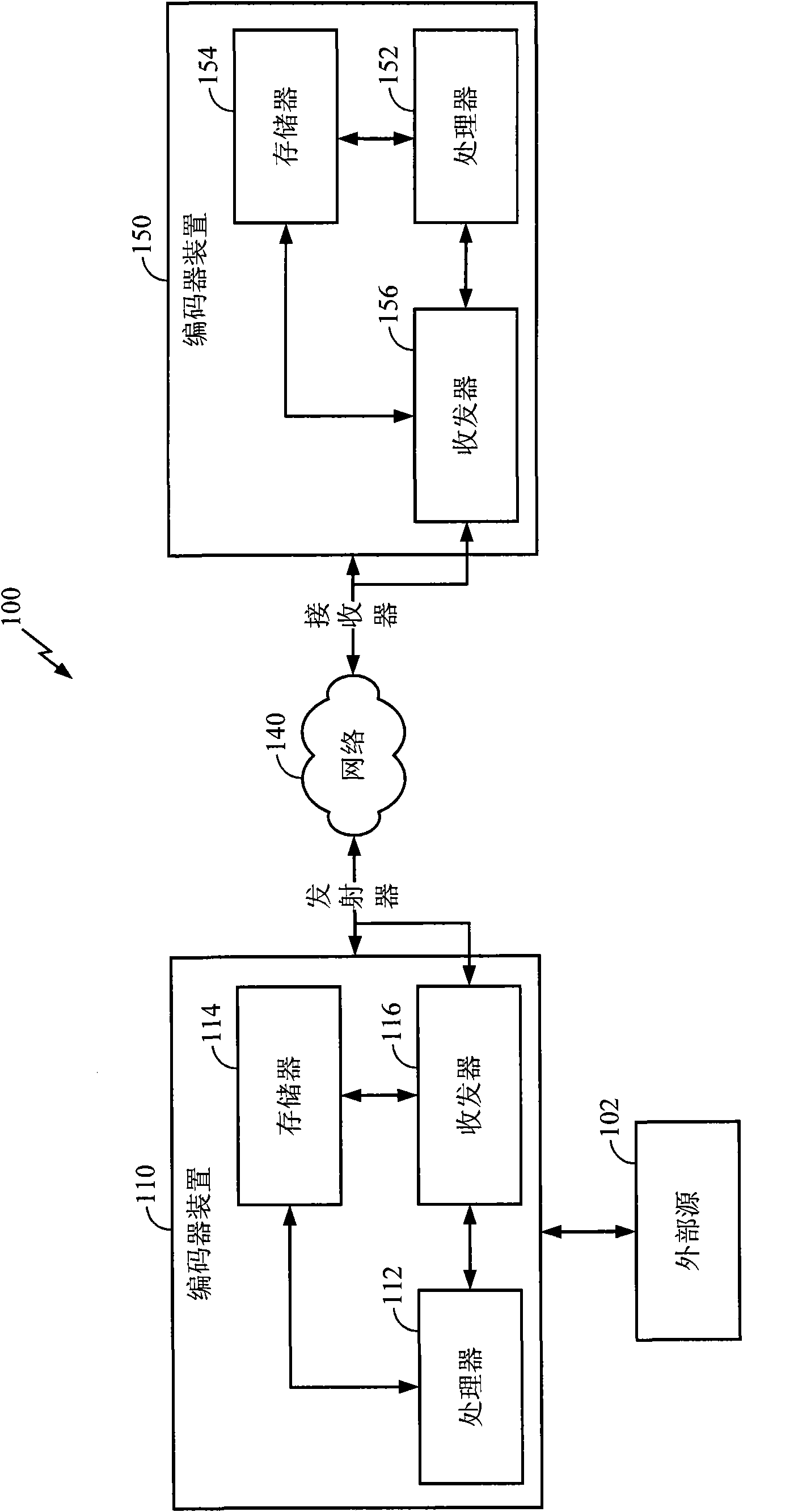
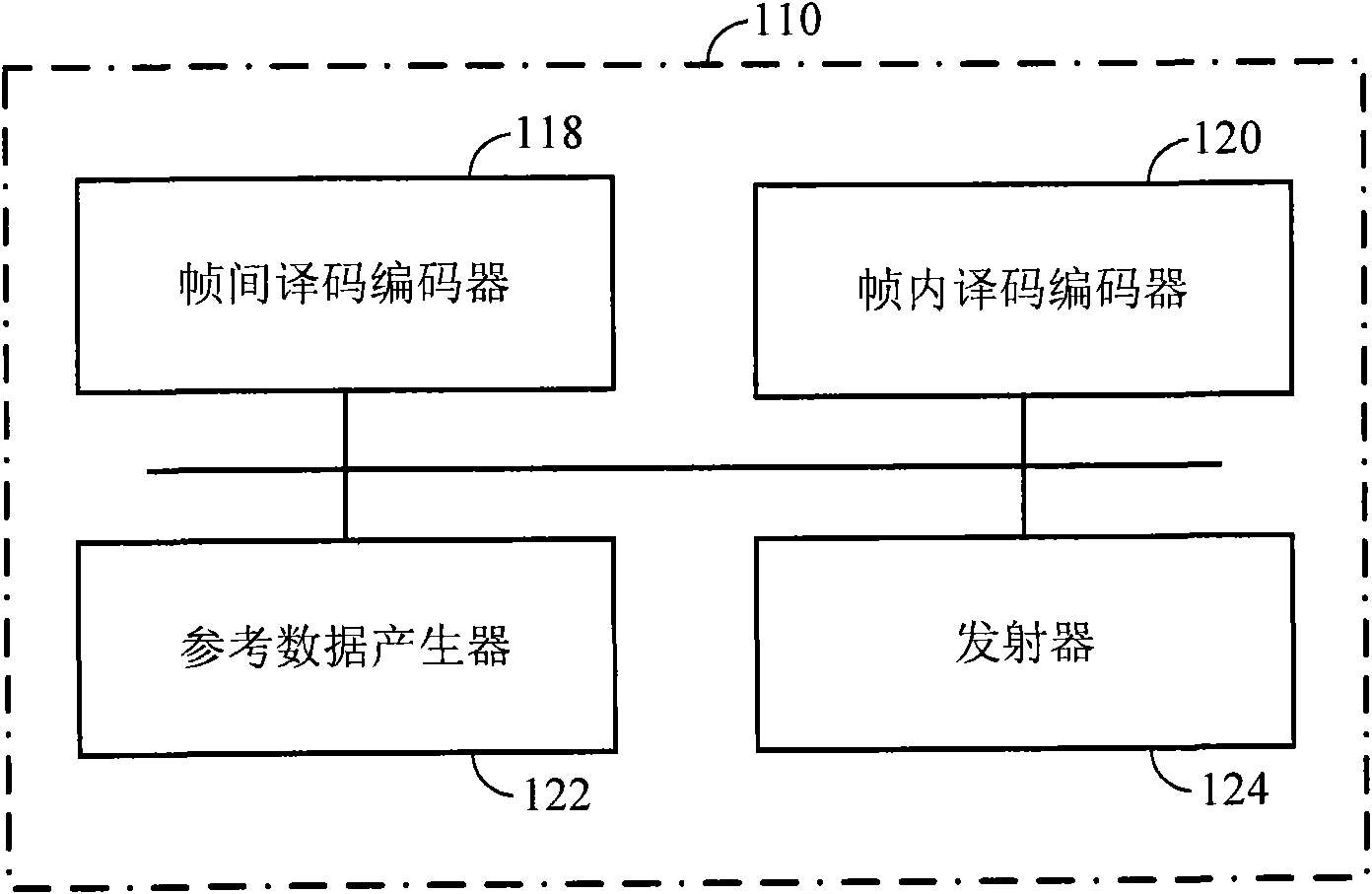
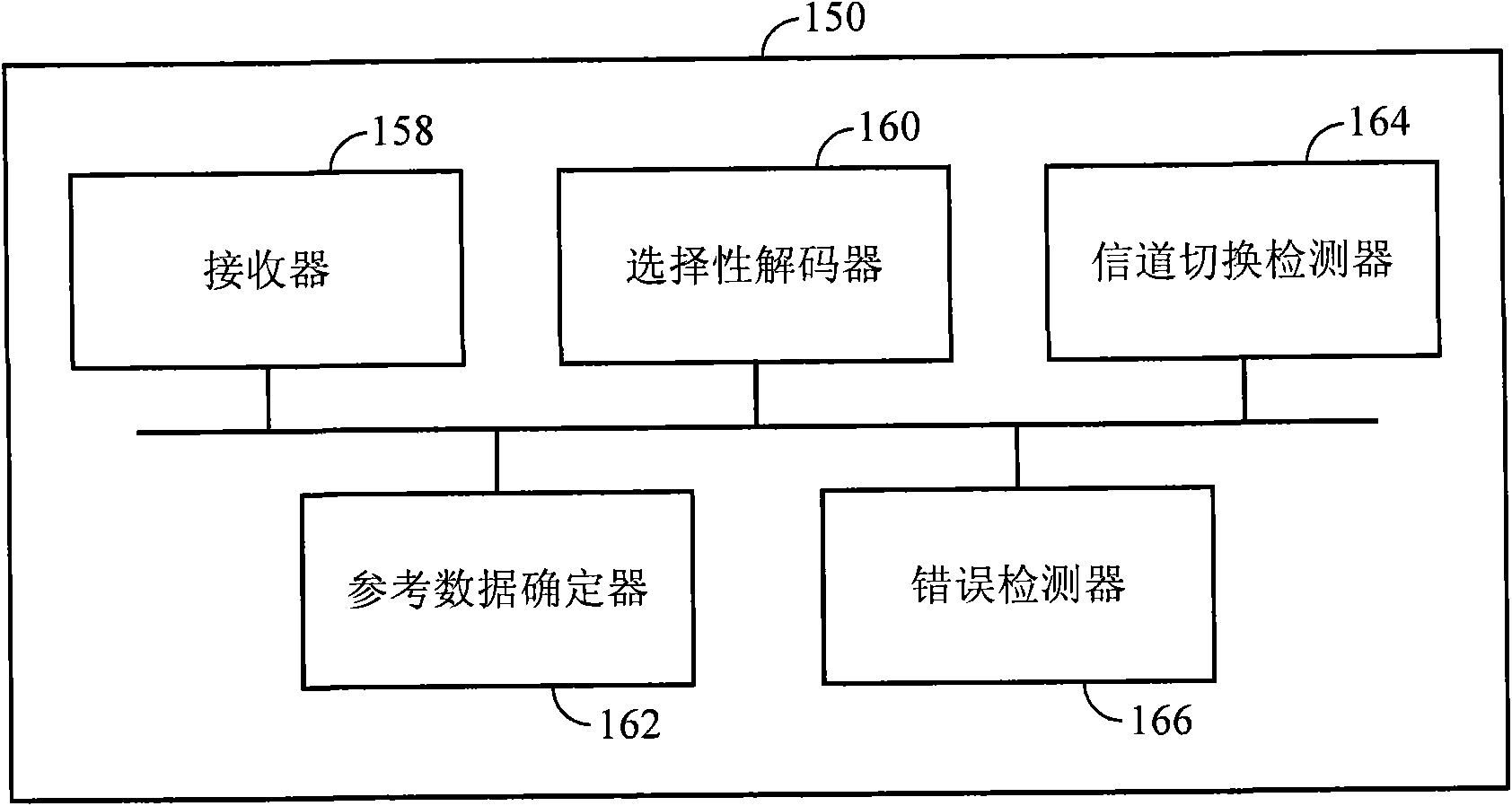
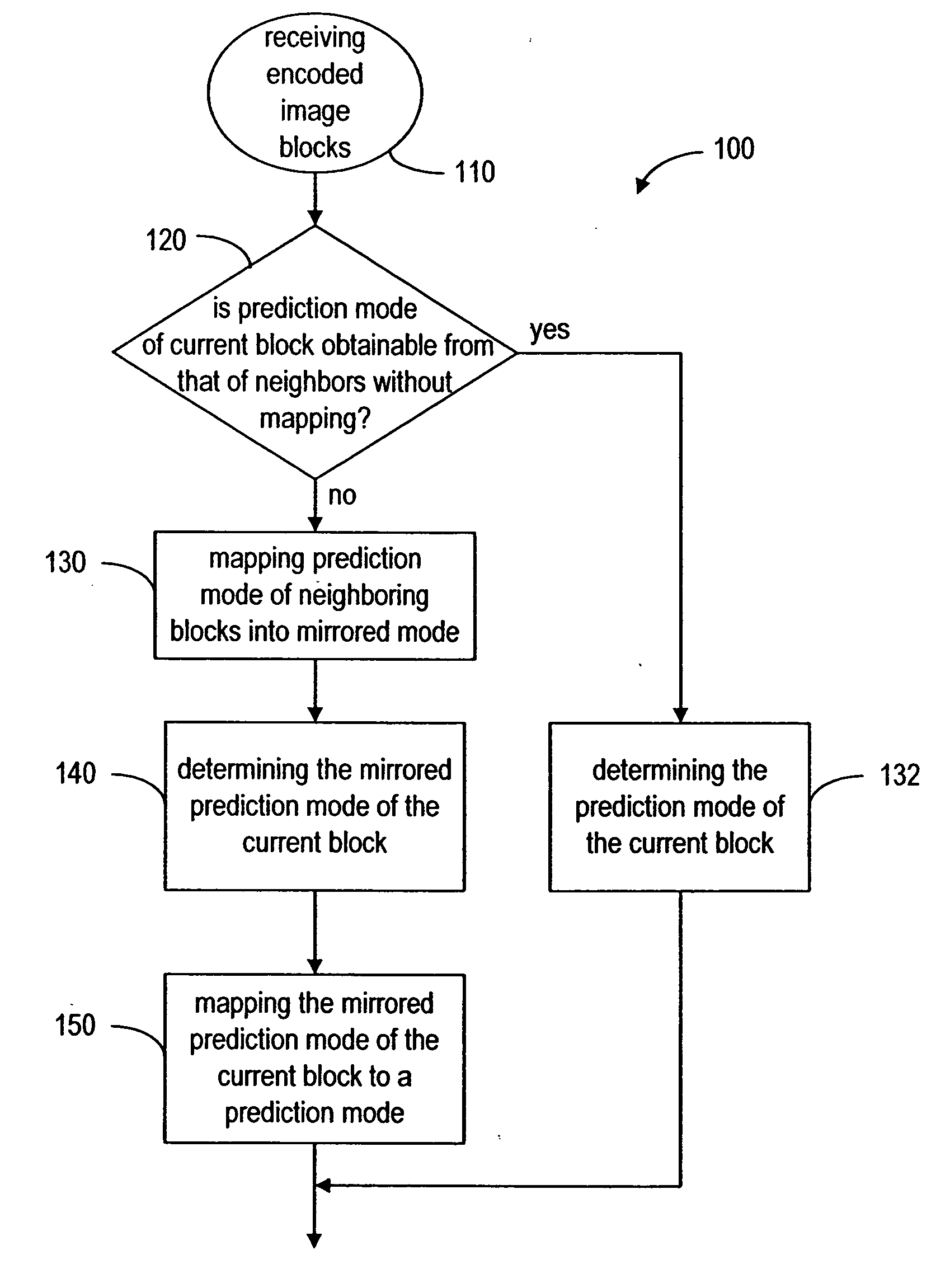
Method of encoding mode determination, method of motion estimation and encoding apparatus
InactiveUS20050135484A1Efficiently omittedQuick fixTelevision system detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesSpatial predictionRate distortion
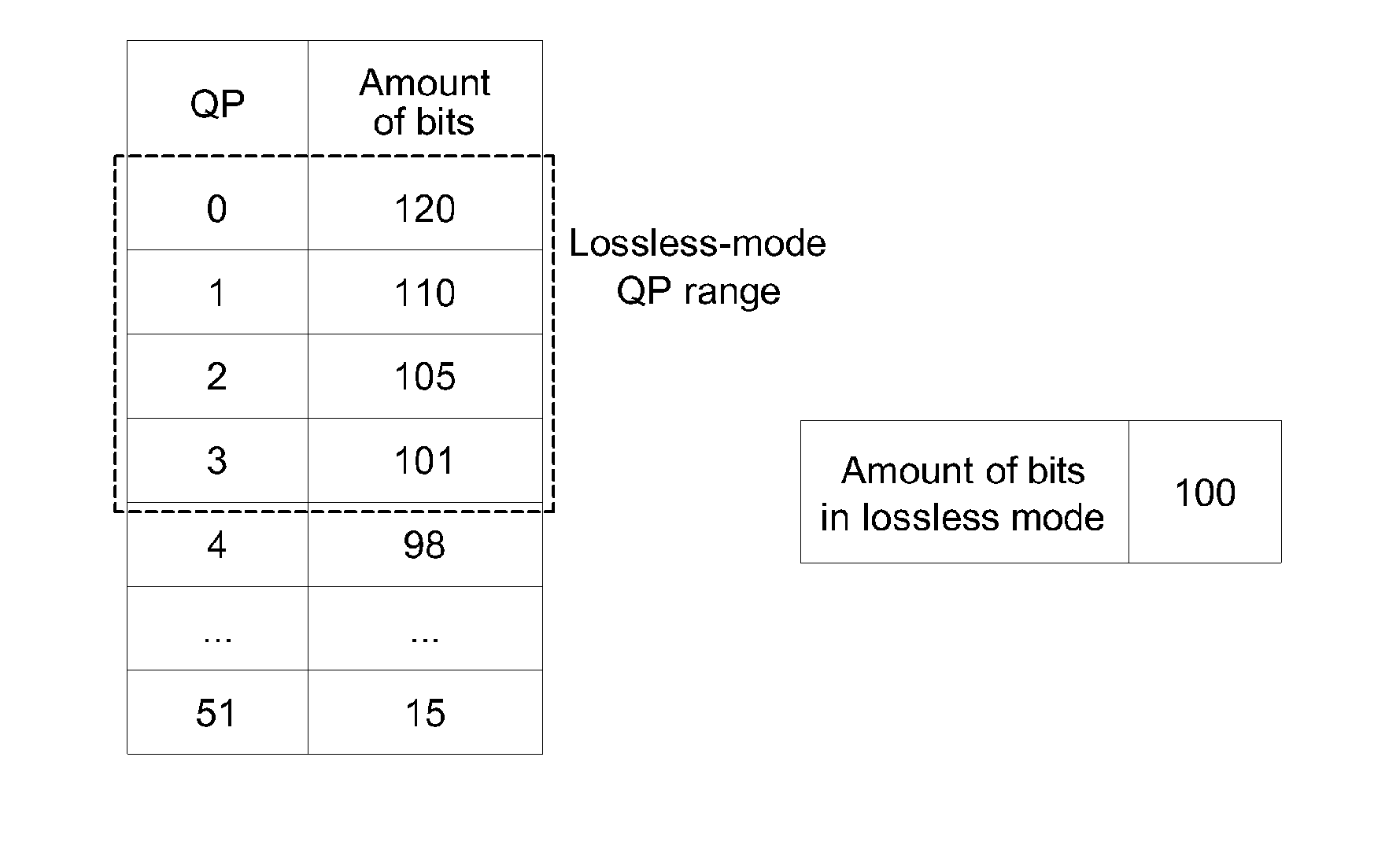
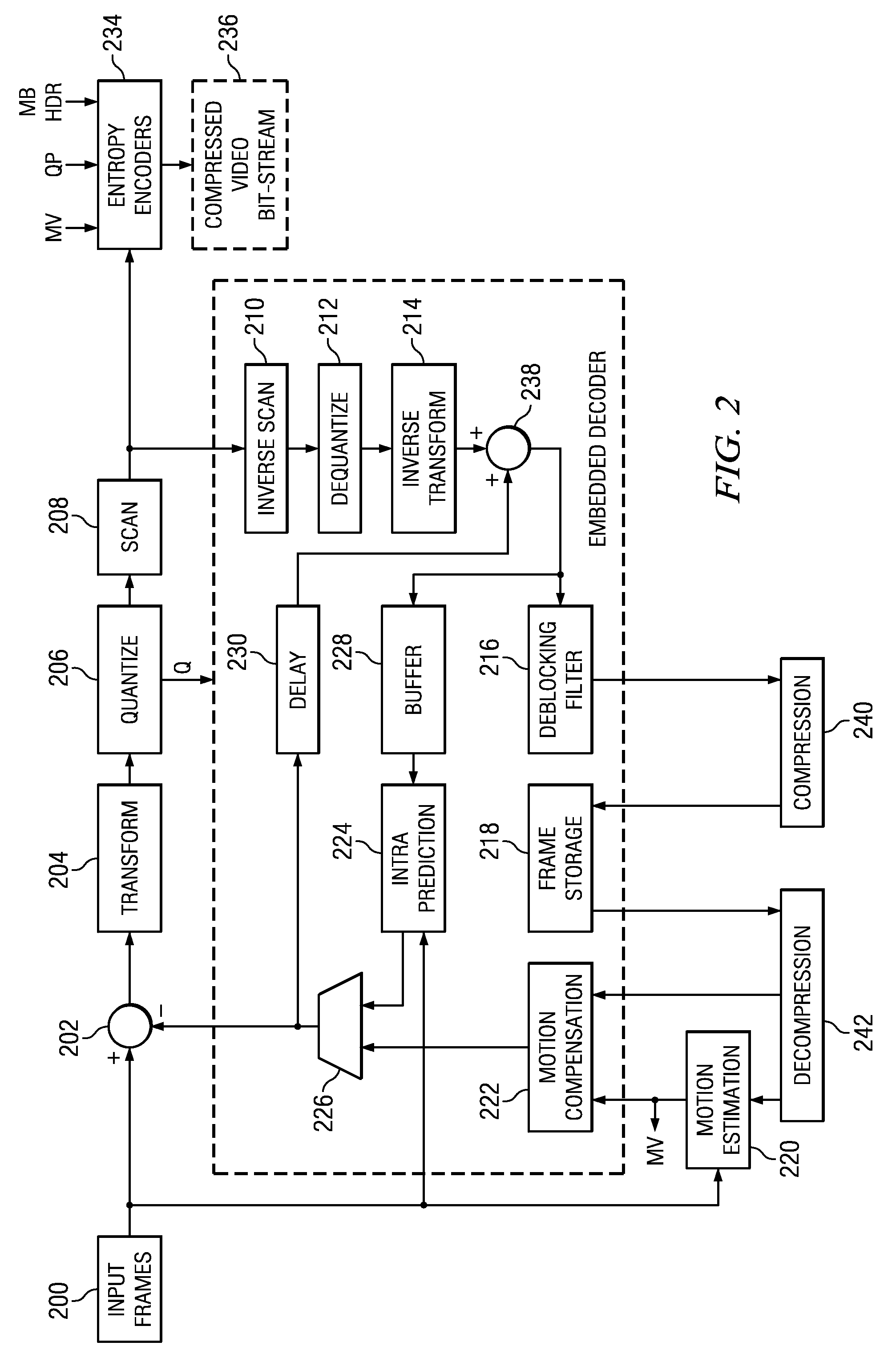
Motion estimation of a macro block in inter16×16, inter16×8, and inter8×16 modes is performed and a determination of whether to further perform motion estimation in a P8×8 mode is made. Motion estimation in P8×8 mode is either omitted or performed and one mode is determined according to a rate distortion cost of the respective modes. Spatial prediction encoding may then be performed or omitted based on comparing the rate distortion cost of the one mode with a predetermined value. Accordingly, by selectively omitting variable block motion estimation and spatial prediction encoding which are the most complicated operations in an H.264 encoder, determining an encoding mode is rapidly performed such that encoding speed increases.
Owner:DAEYANG FOUND SEJONG UNIV +1
Method and system for randomly accessing multiview videos with known prediction dependency
ActiveUS20070121722A1Reduce in quantityTelevision system detailsColor television with pulse code modulationSpatial predictionComputer graphics (images)
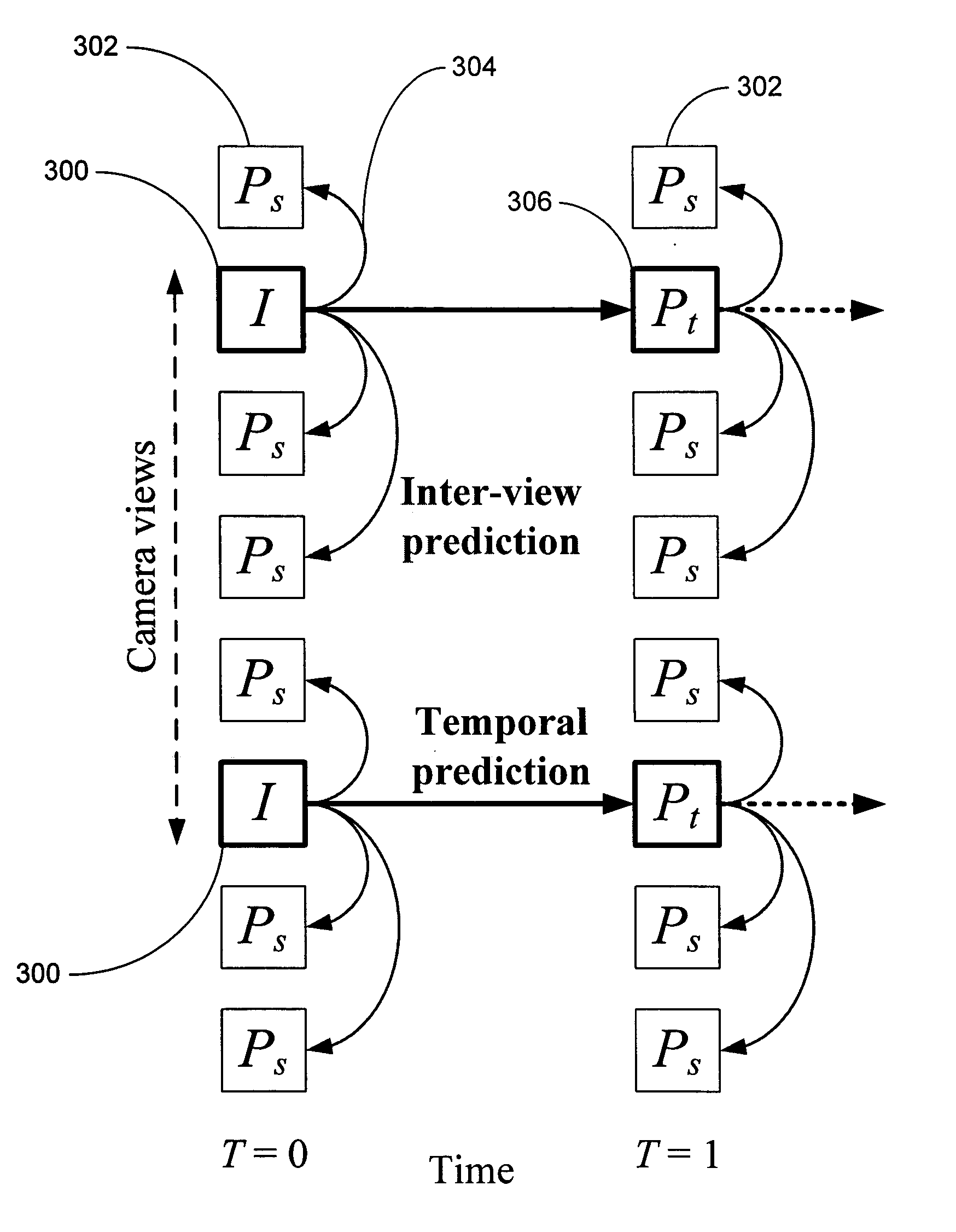
A method randomly accesses multiview videos. Multiview videos are acquired of a scene with corresponding cameras arranged at poses, such that there is view overlap between any pair of cameras. V-frames are generated from the multiview videos. The V-frames are encoded using only spatial prediction. Then, the V-frames are inserted periodically in an encoded bit stream to provide random temporal access to the multiview videos. Additional view dependency information enables the decoding of a reduced number of frames prior to accessing randomly a target frame for a specified view and time, and decoding the target frame.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
Method and system for randomly accessing multiview videos with known prediction dependency
ActiveUS7903737B2Reduce in quantityTelevision system detailsColor television with pulse code modulationSpatial predictionComputer vision
A method randomly accesses multiview videos. Multiview videos are acquired of a scene with corresponding cameras arranged at poses, such that there is view overlap between any pair of cameras. V-frames are generated from the multiview videos. The V-frames are encoded using only spatial prediction. Then, the V-frames are inserted periodically in an encoded bit stream to provide random temporal access to the multiview videos. Additional view dependency information enables the decoding of a reduced number of frames prior to accessing randomly a target frame for a specified view and time, and decoding the target frame.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
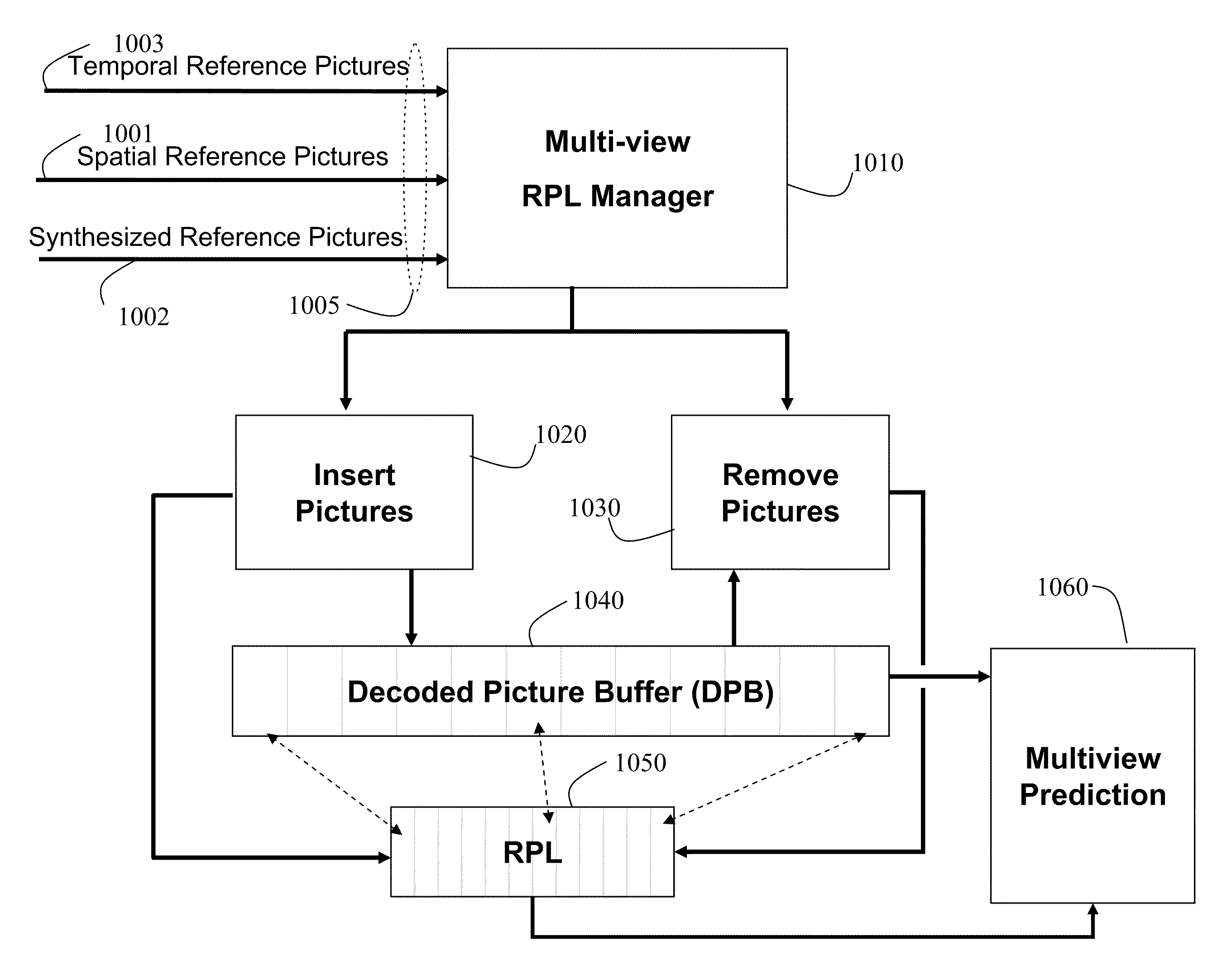
Method and System for Decoding Multiview Videos with Prediction Dependencies
ActiveUS20100322311A1Reduce in quantityTelevision system detailsColor television with pulse code modulationSpatial predictionComputer vision
Multiview videos are acquired of a scene with corresponding cameras arranged at poses, such that there is view overlap between any pair of cameras. V-frames are generated from the multiview videos. The V-frames are encoded using only spatial prediction. Then, the V-frames are inserted periodically in an encoded bit stream to provide random temporal access to the multiview videos. Additional view dependency information enables the decoding of a reduced number of frames prior to accessing randomly a target frame for a specified view and time, and decoding the target frame. The method also decodes multiview videos by maintaining a reference picture list for a current frame of a plurality of multiview videos, and predicting each current frame of the plurality of multiview videos according to reference pictures indexed by the associated reference picture list.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
Method for randomly accessing multiview videos
InactiveUS20060146141A1Television system detailsColor television detailsSpatial predictionComputer vision
A method randomly accesses multiview videos. Multiview videos are acquired of a scene with corresponding cameras arranged at poses, such that there is view overlap between any pair of cameras. V-frames are generated from the multiview videos. The V-frames are encoded using only spatial prediction. Then, the V-frames are inserted periodically in an encoded bitstream to provide random temporal access to the multiview videos.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
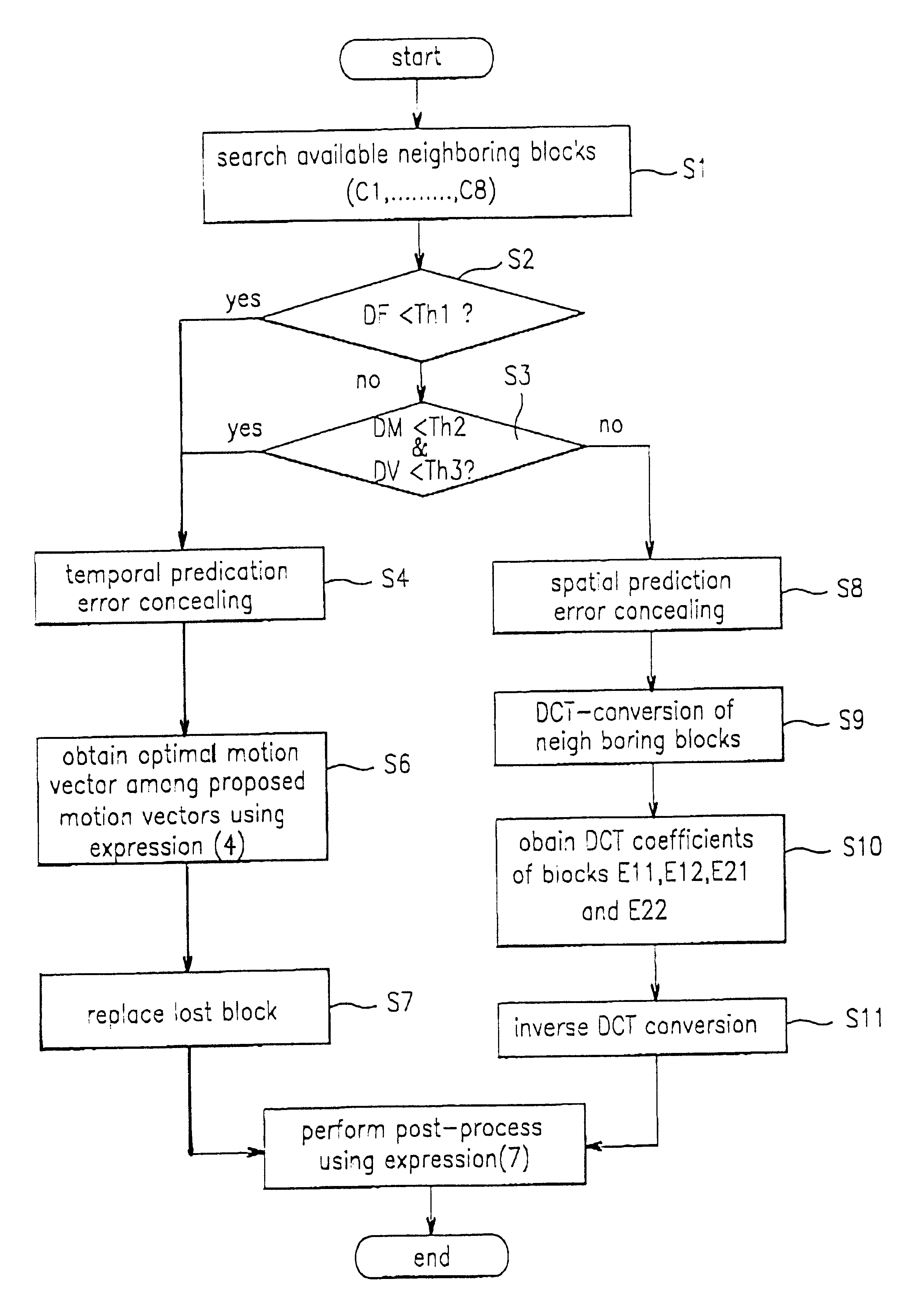
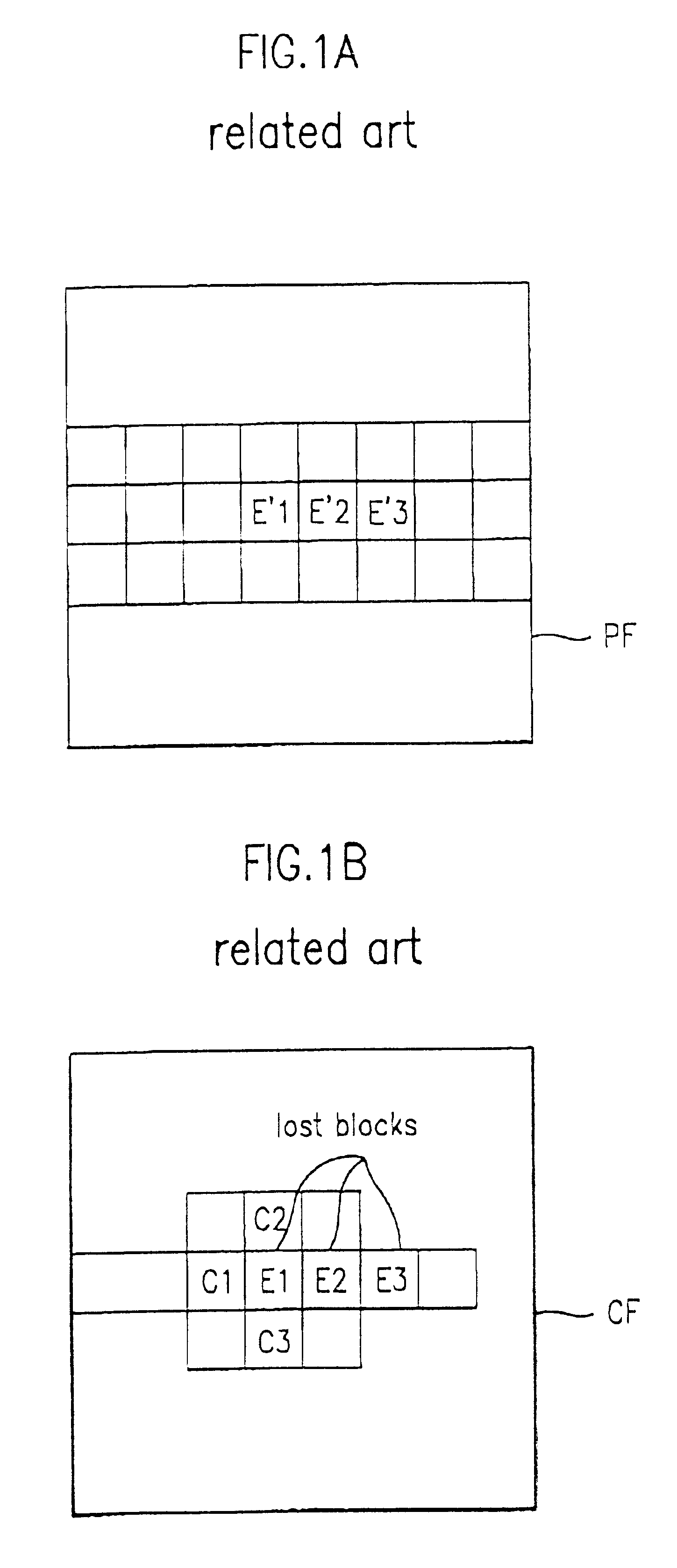
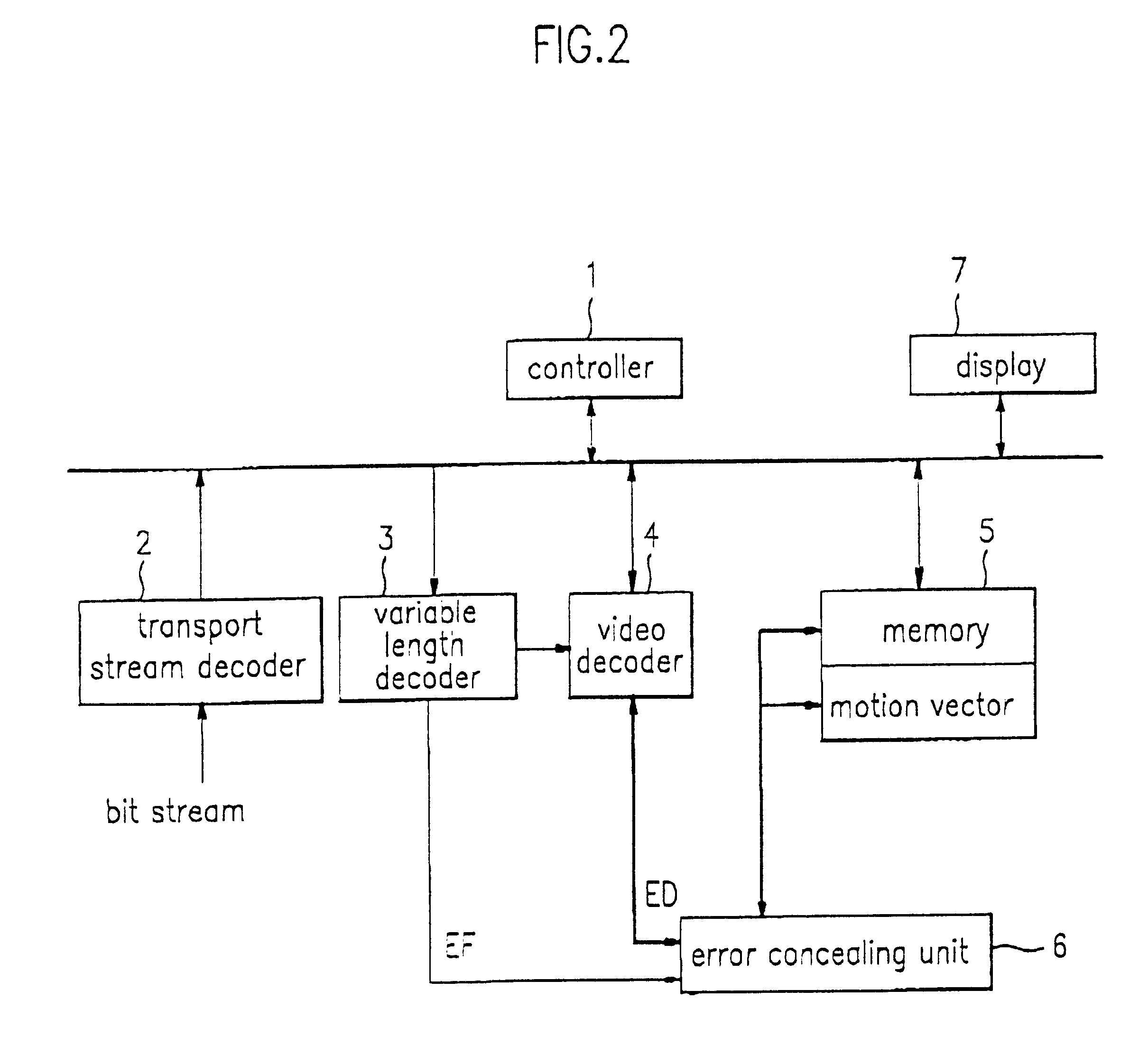
Method for concealing error
InactiveUS6636565B1Color television with pulse code modulationPulse modulation television signal transmissionPattern recognitionSpatial prediction
A moving picture compression / decompression system utilizes a method for concealing errors in a received picture. A macro block, lost due to an error, is compensated using either a temporal or spatial prediction method, depending upon the type of frame and the characteristics of the picture. Thus, the displayed picture quality can be significantly improved.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Method for randomly accessing multiview videos
InactiveUS7710462B2Television system detailsColor television detailsSpatial predictionComputer vision
A method randomly accesses multiview videos. Multiview videos are acquired of a scene with corresponding cameras arranged at poses, such that there is view overlap between any pair of cameras. V-frames are generated from the multiview videos. The V-frames are encoded using only spatial prediction. Then, the V-frames are inserted periodically in an encoded bitstream to provide random temporal access to the multiview videos.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
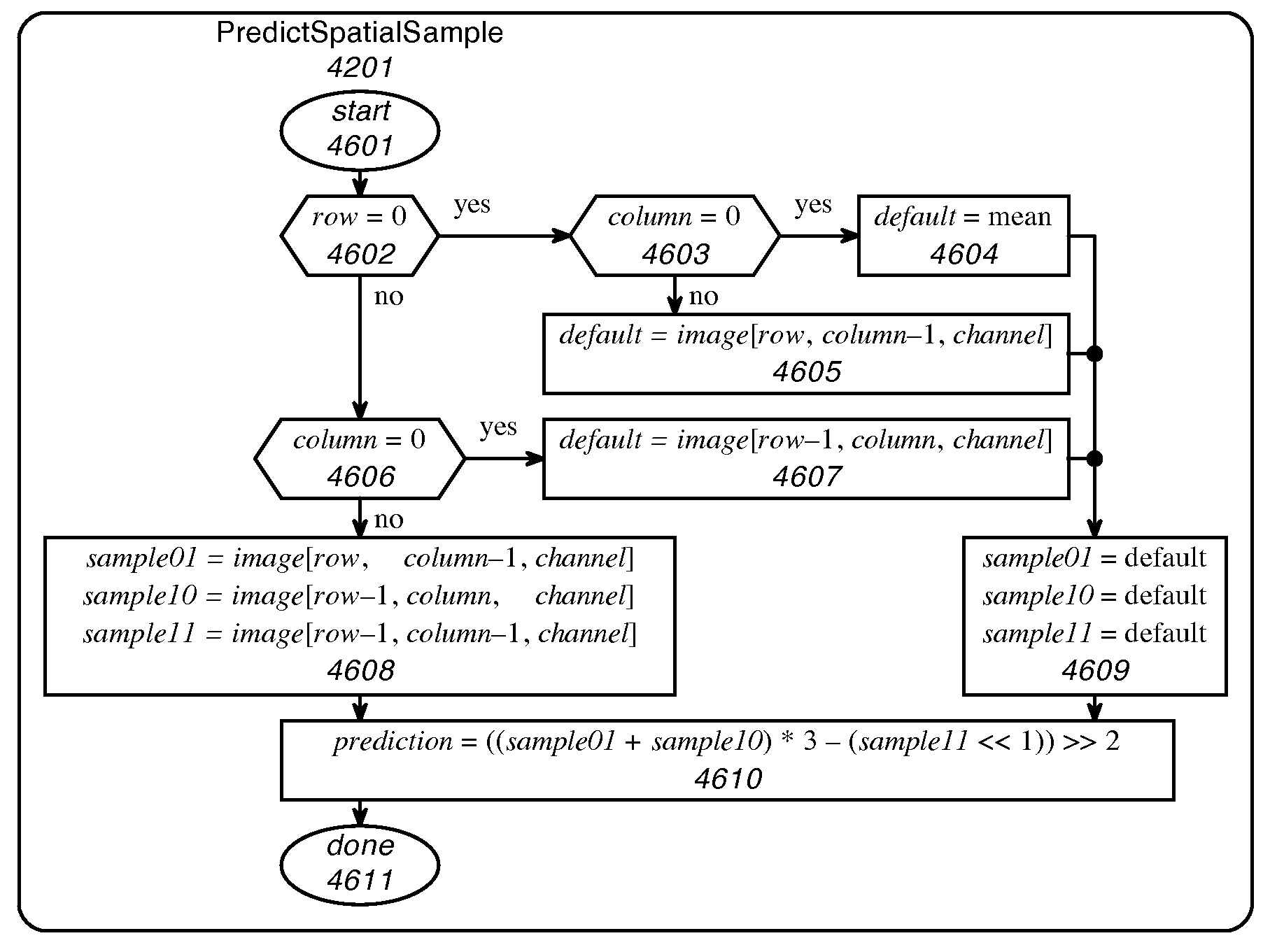
Pixel adaptive intra smoothing
ActiveUS20120140821A1Efficient intra predictionColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionSpatial predictionDigital image
The present invention relates to spatial prediction of pixels of a block, the block being a block of a digital image. In particular, for a block pixel at least one reference pixel(s) is selected and out of the selected reference pixel(s), the block pixel is predicted. In particular, the prediction of the block pixel is performed depending on the distance of this pixel to the reference pixel(s) from which it is to be predicted.
Owner:SUN PATENT TRUST
Video decoder for decoding macroblock adaptive field/frame coded video data with spatial prediction
ActiveUS7480335B2Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionSpatial predictionComputer vision
Described herein is a video decoder for decoding macroblock adaptive field / frame coded video data with spatial prediction. In one embodiment, there is presented a spatial predictor for processing a macroblock pair. The spatial predictor comprises a first buffer, a second buffer, a third buffer, and arithmetic logic. The first buffer stores pixels from a first portion of the picture, the first portion neighboring the portion. The second buffer stores pixels from a second portion of the picture, the second portion neighboring the portion. The third buffer stores one or more pixels from a third portion of the picture, the third portion neighboring the portion. The arithmetic logic processes the portion from at least one of the pixels from the first buffer, at least one of the pixels from the second buffer, and at least one of the pixels from the third buffer.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
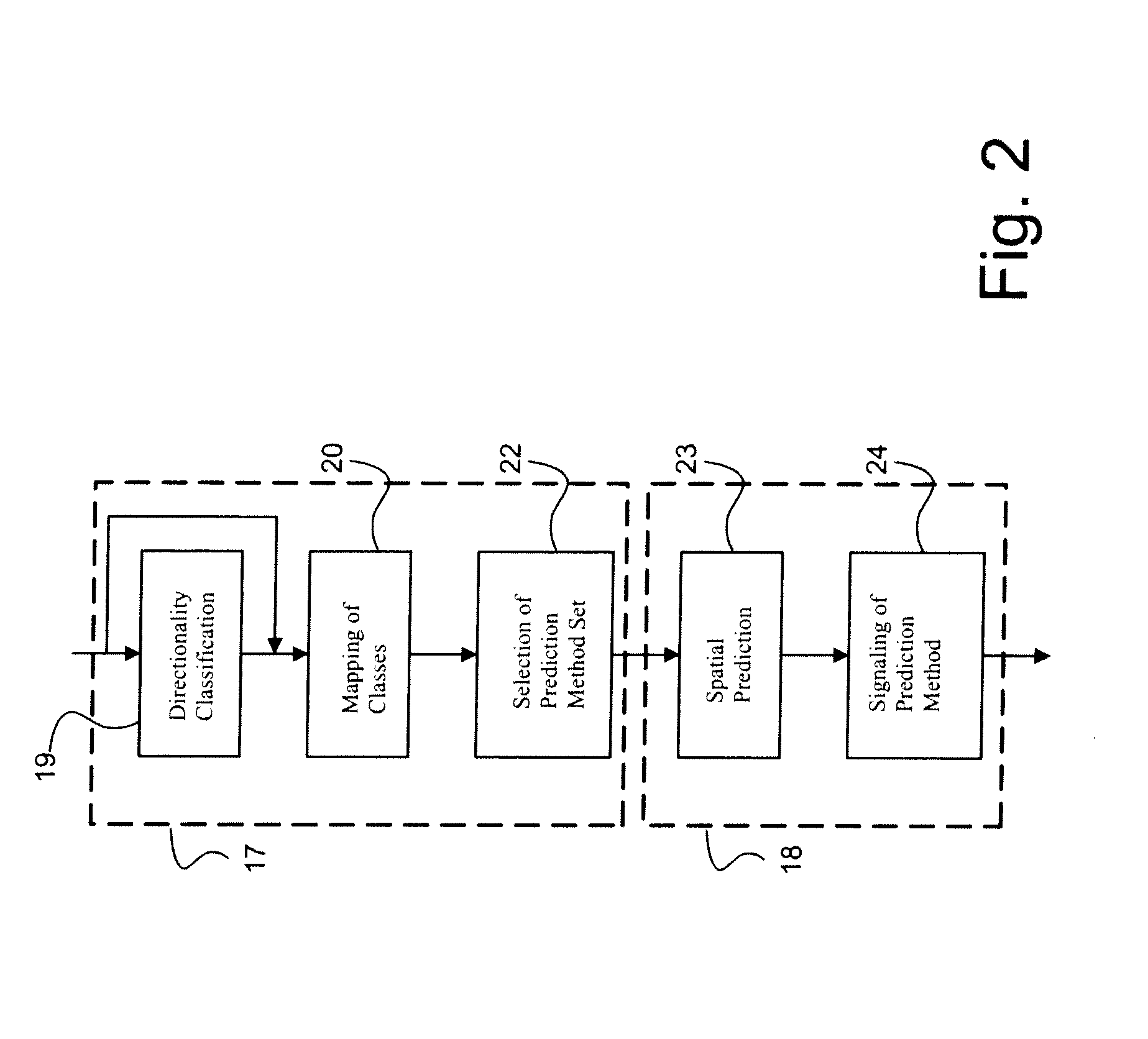
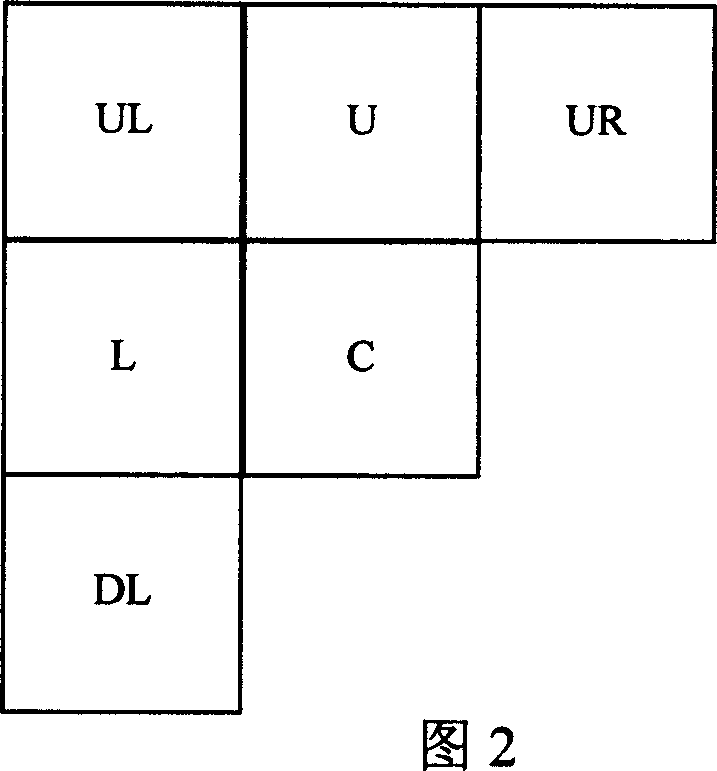
Method for Encoding Images, and an Image Coder
InactiveUS20080247657A1Reduce the amount of informationCode conversionCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionSpatial prediction
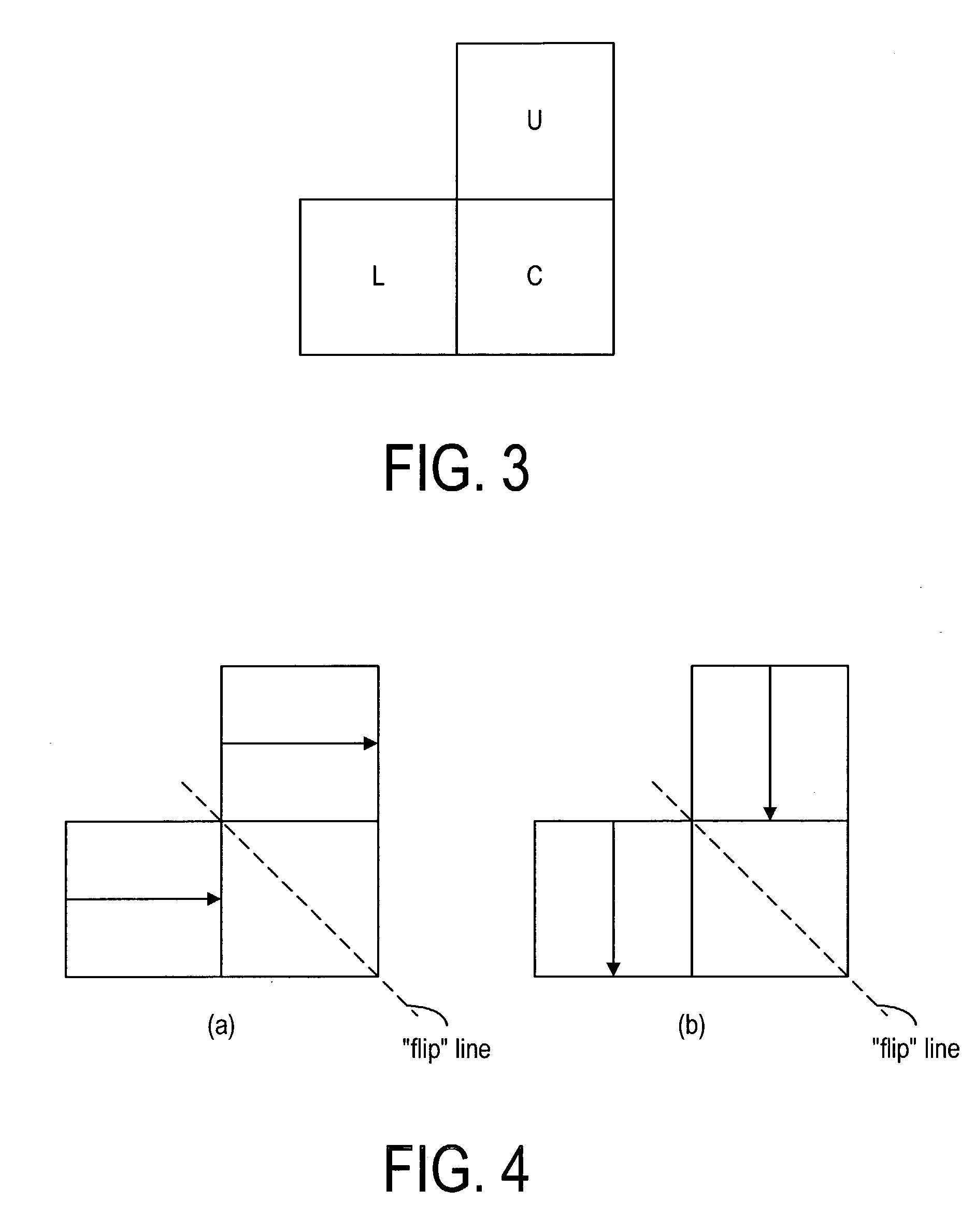
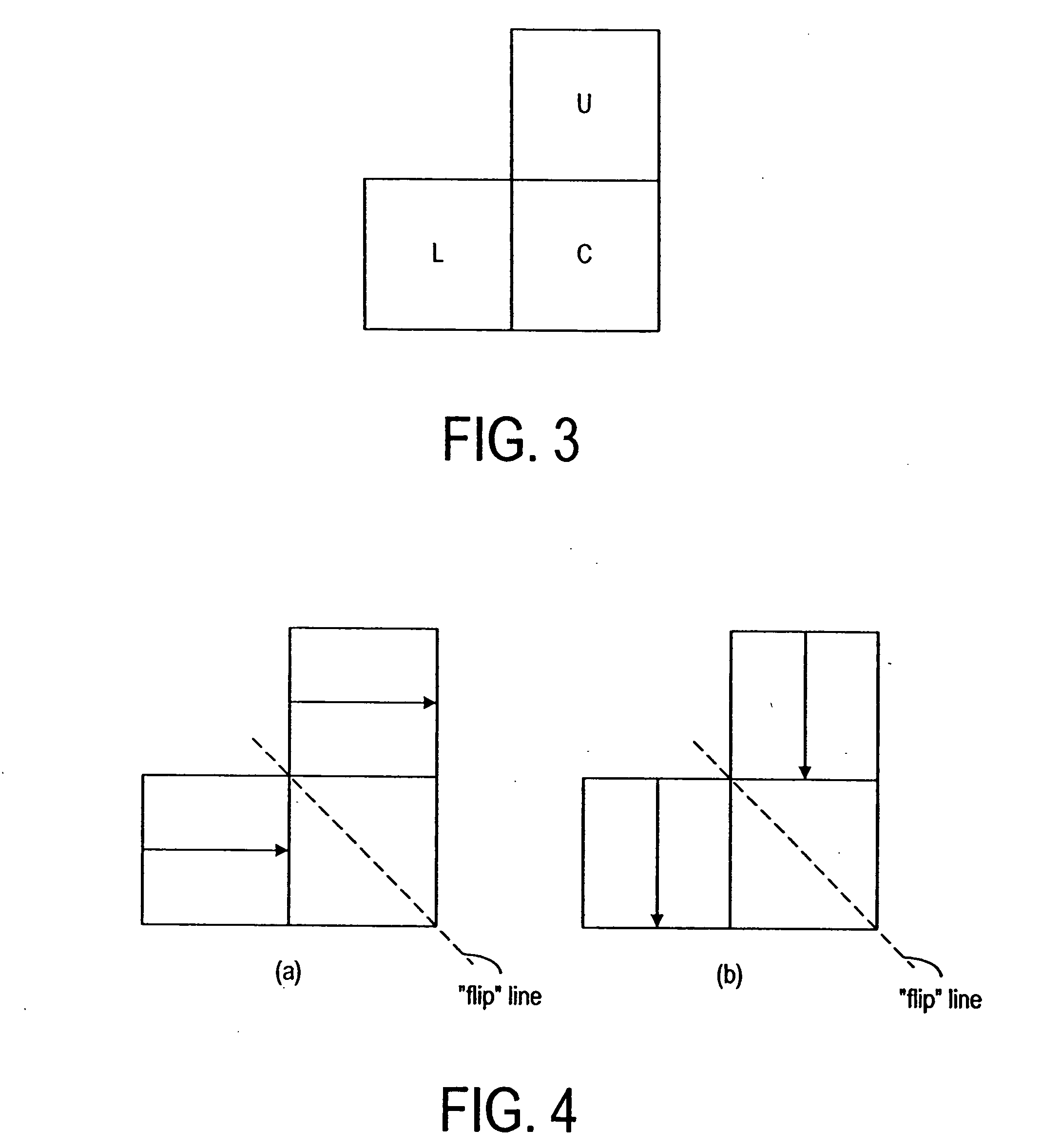
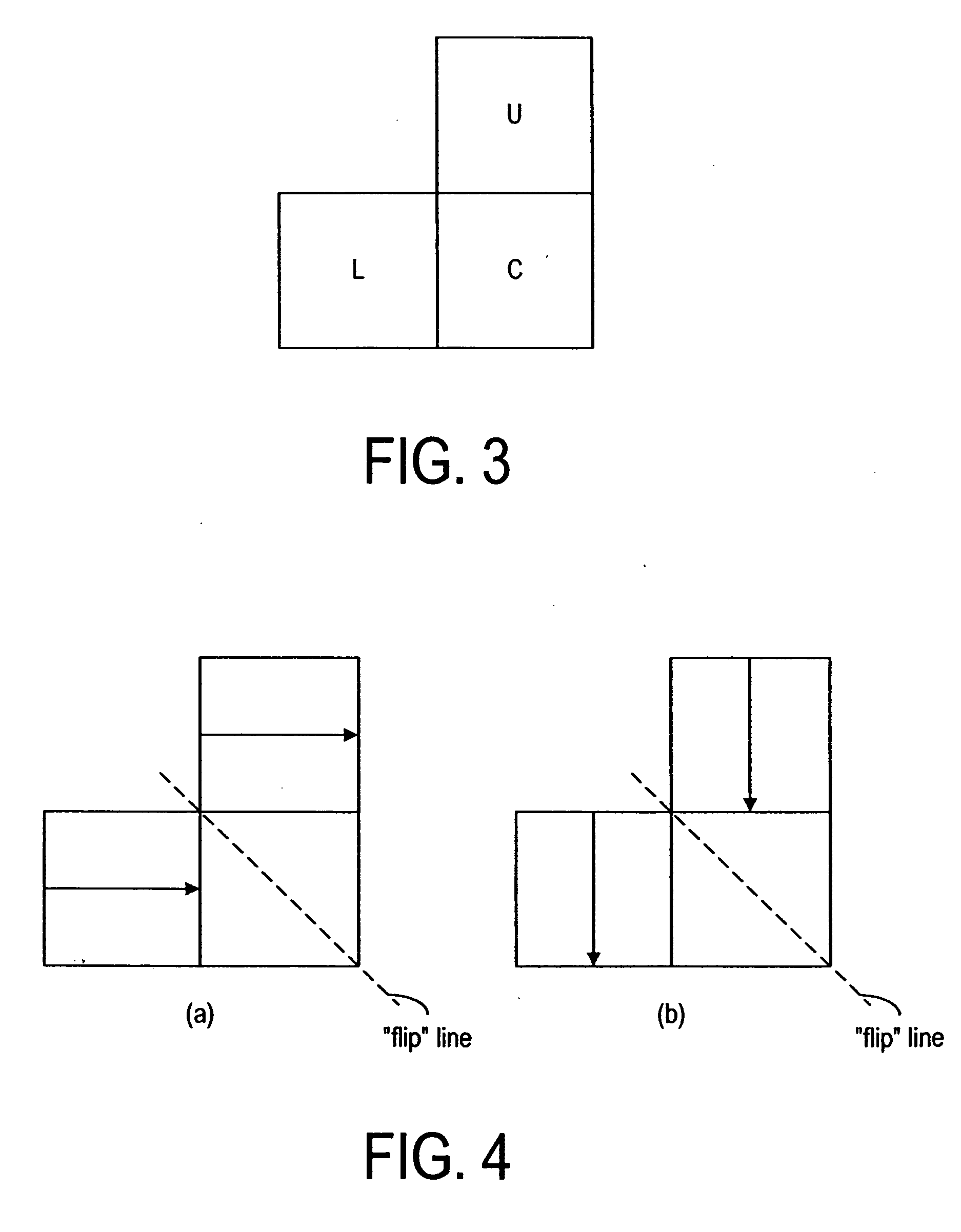
The invention relates to a method for encoding a digital image, in which method the digital image is divided into blocks (C, L, U, UL, UR). In the method a spatial prediction for a block (C) is performed to reduce the amount of information to be transmitted, wherein at least one prediction method (P1-P13) is defined. In the method a classification is determined for at least one neighbouring block (L, U) of said block (C) to be predicted according to the contents of the neighbouring block (L, U), and a prediction method (P1-P13) is selected for the current block (C) on the basis of at least one classification.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
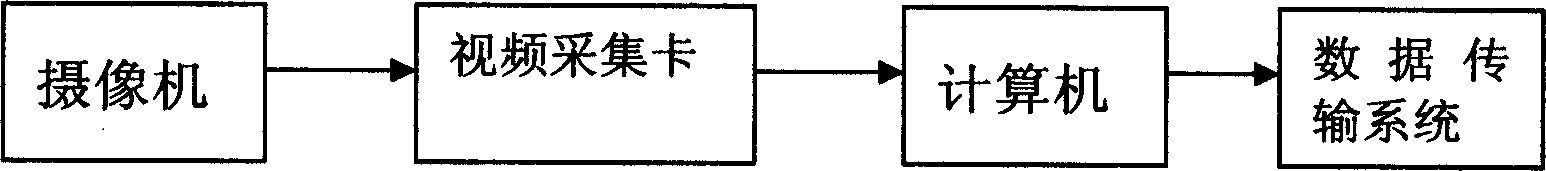
Inframe prediction method used for video frequency coding
InactiveCN1535027AImprove encoding qualityNo degradation in encoding performanceTelevision systemsDigital video signal modificationDigital videoComputation complexity
An in-frame predication method for video encode in order to improve video encode quality is disclosed. The original video stream taken by camera is used as input, which is input to computer by video acquisition card, and then processed by computer and the JVT video encode technique. An operation rule for calculating the DC predication mode by use of the samples of the decoded pixel in adjacent blocks is defined. Multiple predication modes can be recombined and sorted.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Spatial prediction based intra coding
A method and device for coding a digital image using intra-mode block prediction, wherein a list of prediction modes for each combination of prediction modes of the neighboring blocks is obtained. The modes assigned to each combination of prediction modes may be divided into two groups. The first group includes n (where n is smaller than the overall number of available modes) most probable prediction modes and the second group includes the remaining modes. The modes in the first group are ordered according to their probability. This order may be specified as a list of modes ordered from most probable to the least probable mode. The modes belonging to the second group may be ordered in some predetermined manner, which may be specified depending on the information already available to the decoder.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
Encoding method, decoding method and apparatus thereof
InactiveUS20110150072A1Reduce digitsEffective compression ratioColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionSpatial predictionVideo encoding
Owner:MTEKVISION CO LTD
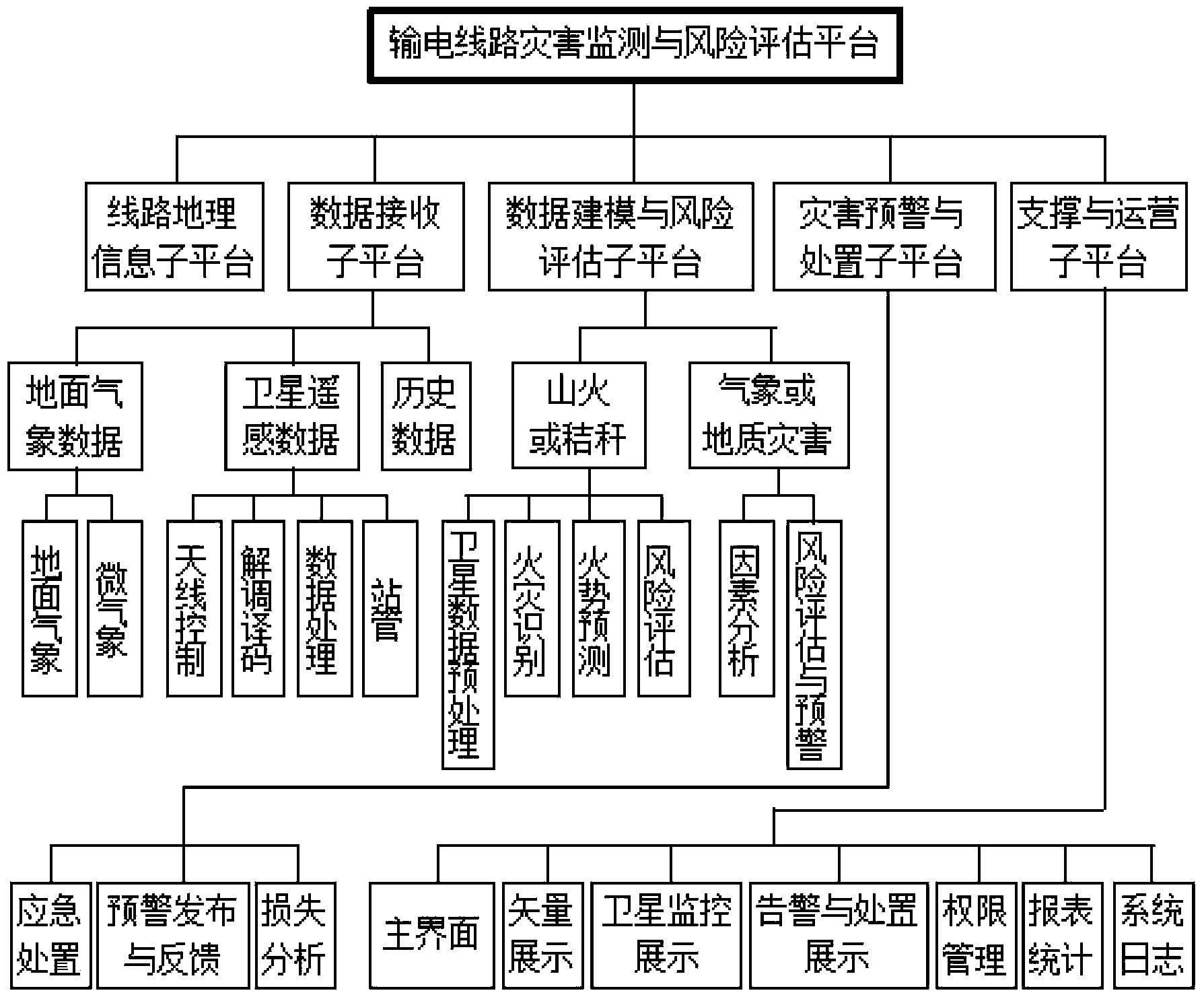
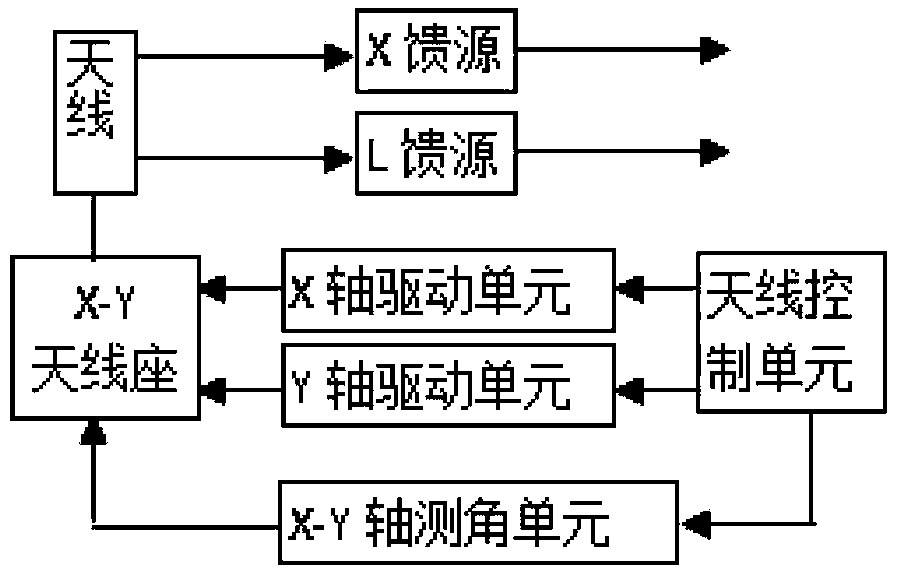
Power transmission line disaster monitoring and risk assessment platform based on satellite and weather information
ActiveCN103455708AImprove the immunityReduce workloadSpecial data processing applicationsICT adaptationMoving averageData modeling
The invention provides a power transmission line disaster monitoring and risk assessment platform based on satellite and weather information in order to effectively warn disasters. The platform comprises a power transmission line geographic information sub-platform, a satellite remote sensing data receiving sub-platform, a data modeling and risk assessment sub-platform, a disaster warning and treatment sub-platform, and a support and operation sub-platform. The data modeling and risk assessment sub-platform comprises a fire development trend prediction submodule; the submodule predicts time sequence of fire data by a time prediction method, auto-regressive integrated moving average, captures cross-fire hidden spatial correlation by a spatial prediction method through dynamic regression neural network, simulates stochastic disturbance by a Markov chain model, and acquires space-time integrated and disturbance-removing prediction results by means of statistical regression.
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER RES INST OF STATE GRID ANHUI ELECTRIC POWER
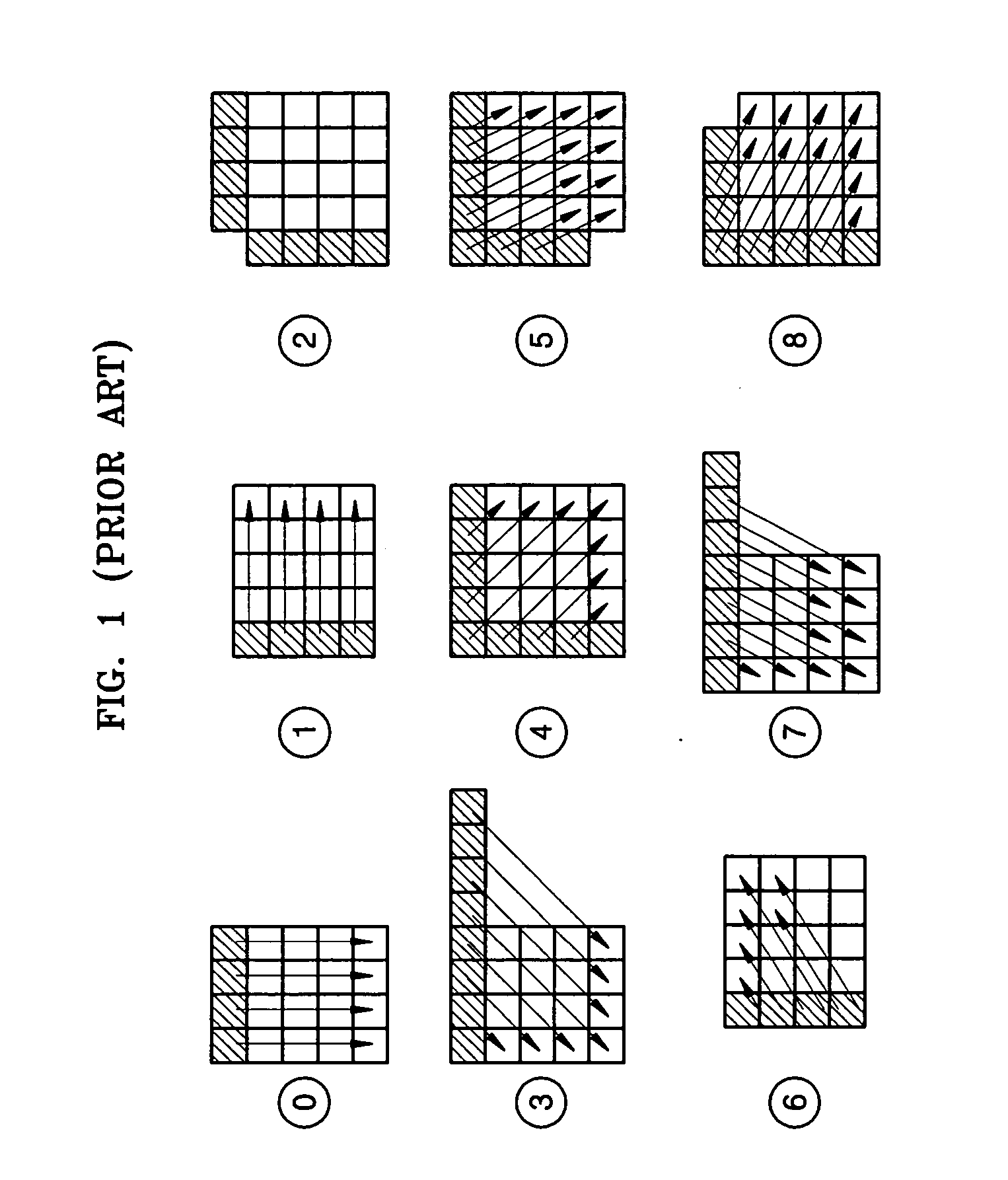
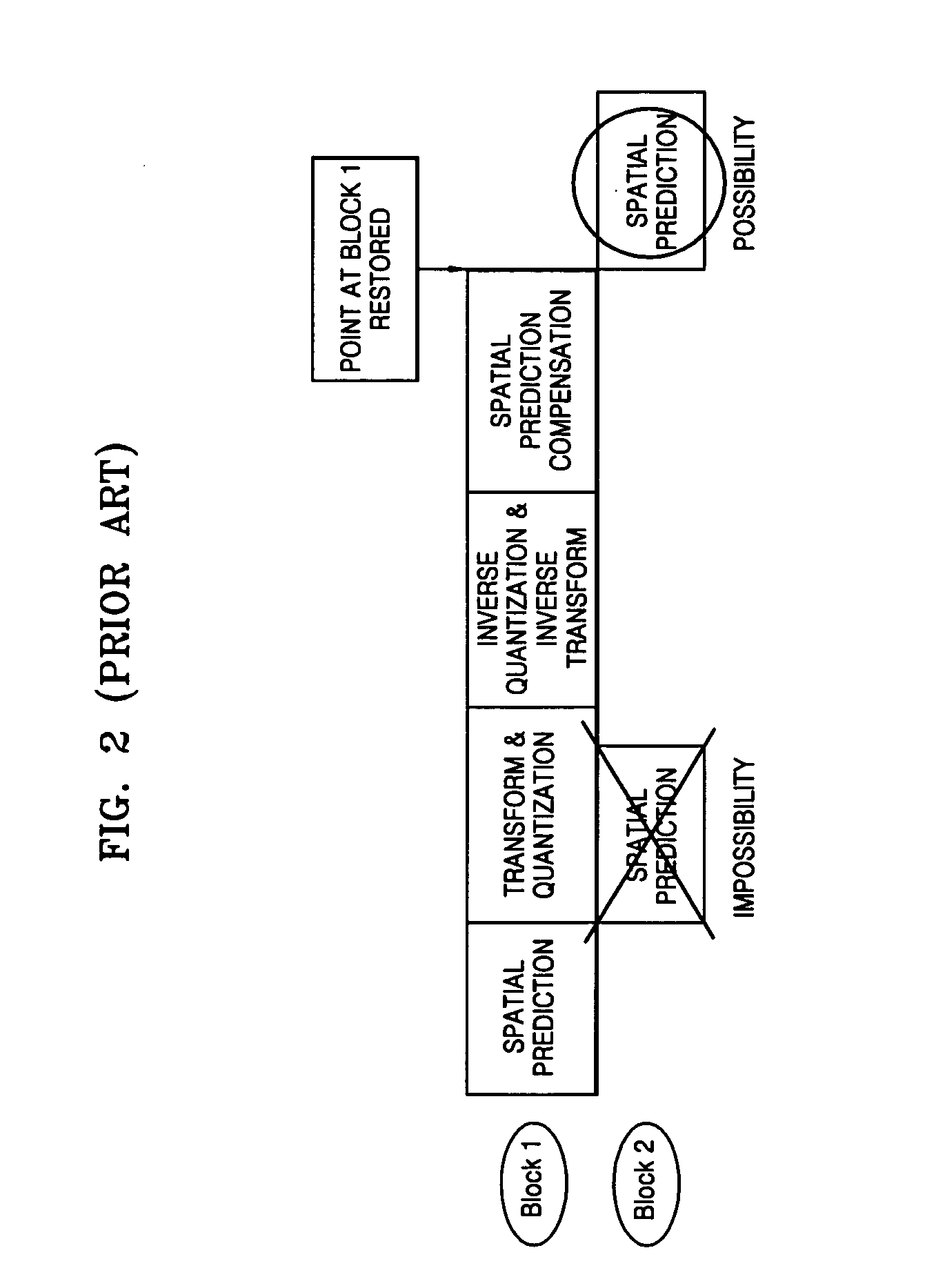
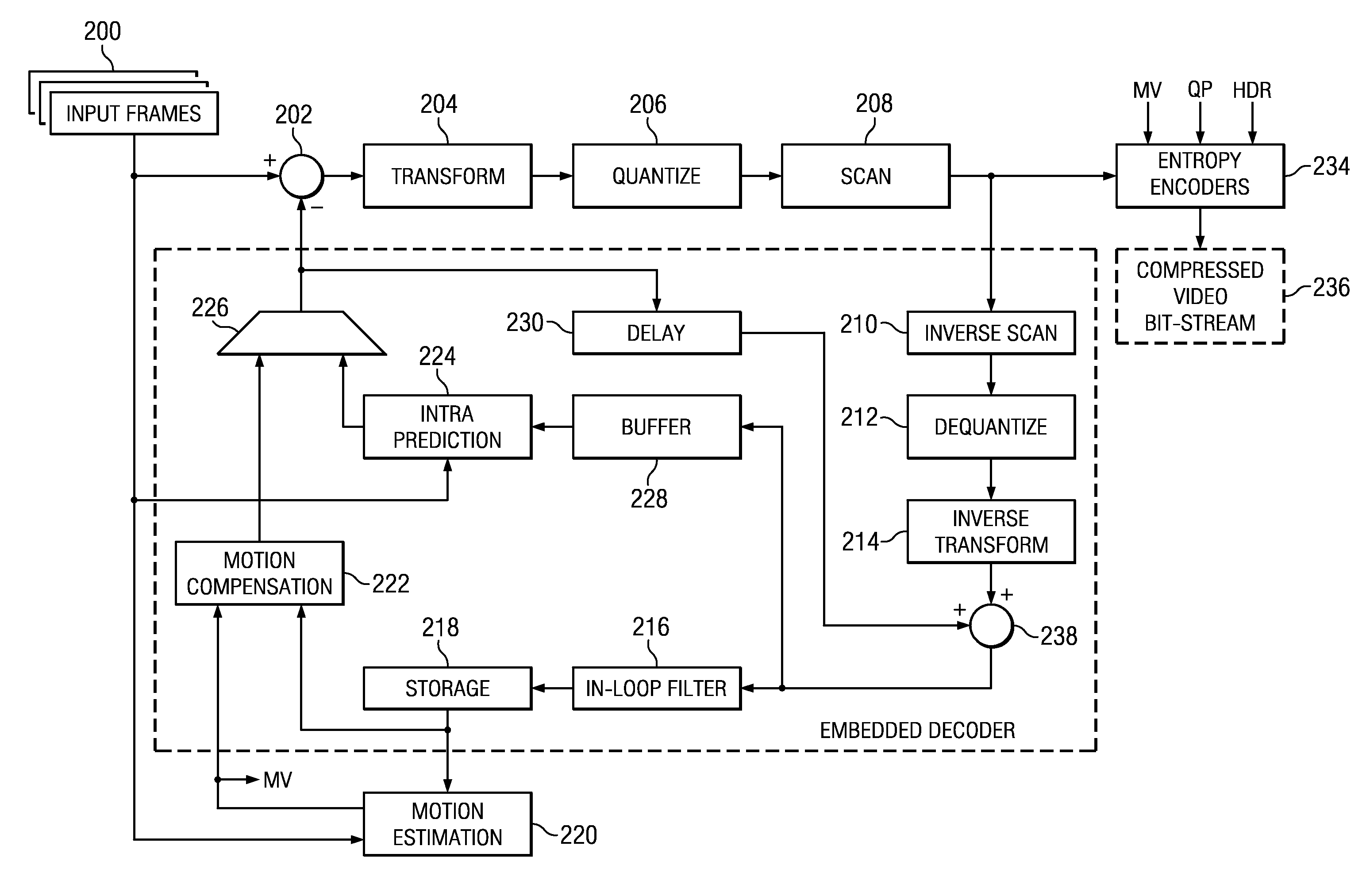
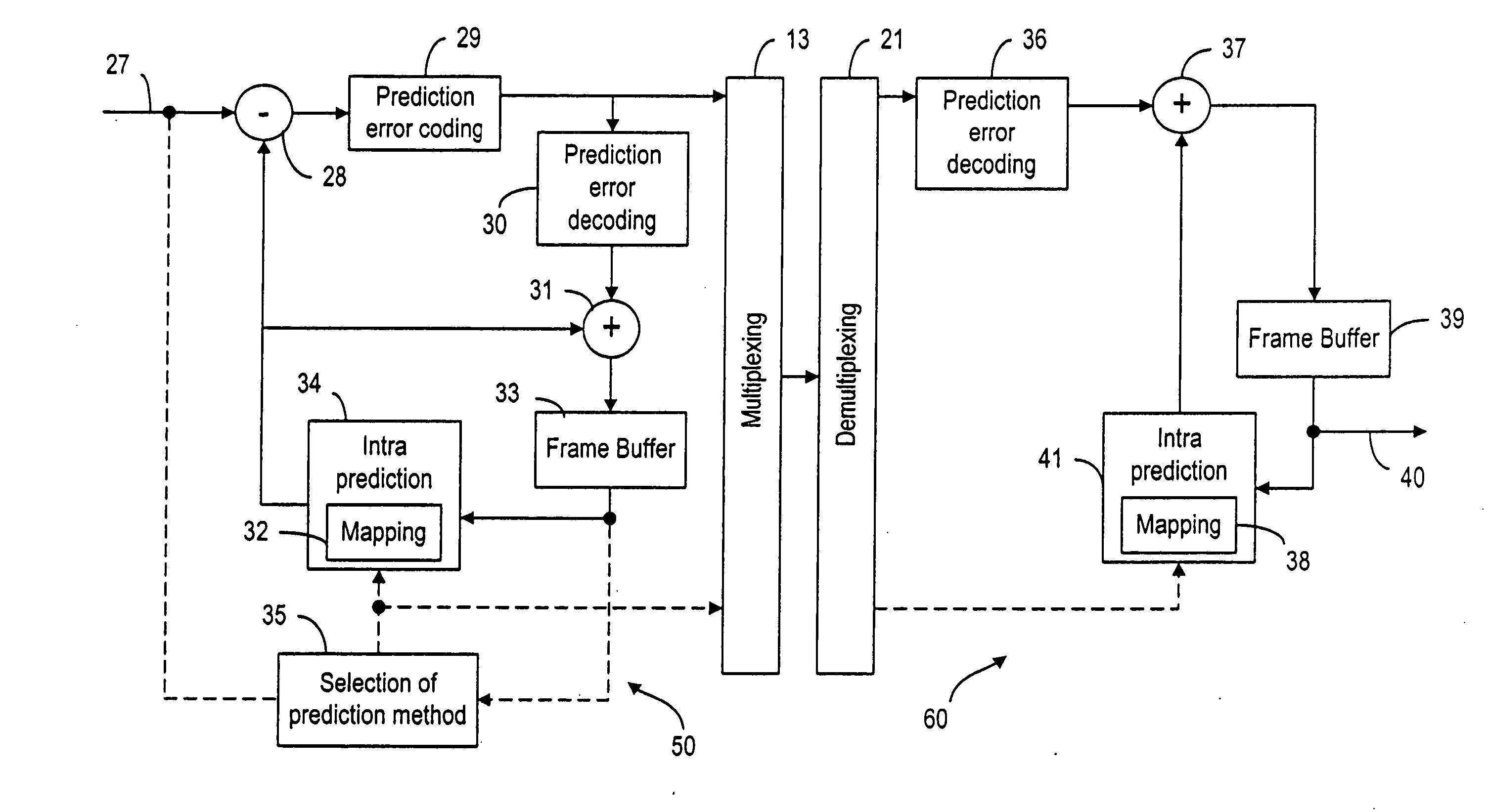
Encoding and/or decoding system, medium, and method with spatial prediction and spatial prediction compensation of image data
ActiveUS20070253483A1Prevent error propagationColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionSpatial predictionAlgorithm
An encoding and / or decoding system, medium, and method with spatial prediction and spatial prediction compensation. The system may include a spatial prediction unit that spatially predicts pixel values of a current block of an image using neighboring blocks in a row immediately above the current block among neighboring blocks that are spatially adjacent to the current block. The spatial prediction unit performs spatial prediction using replaced pixel values of neighboring blocks in a row immediately above the current block every predetermined row unit, with the pixel values of neighboring blocks in a row immediately above the current block every predetermined row unit being replaced with a predetermined reference value.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
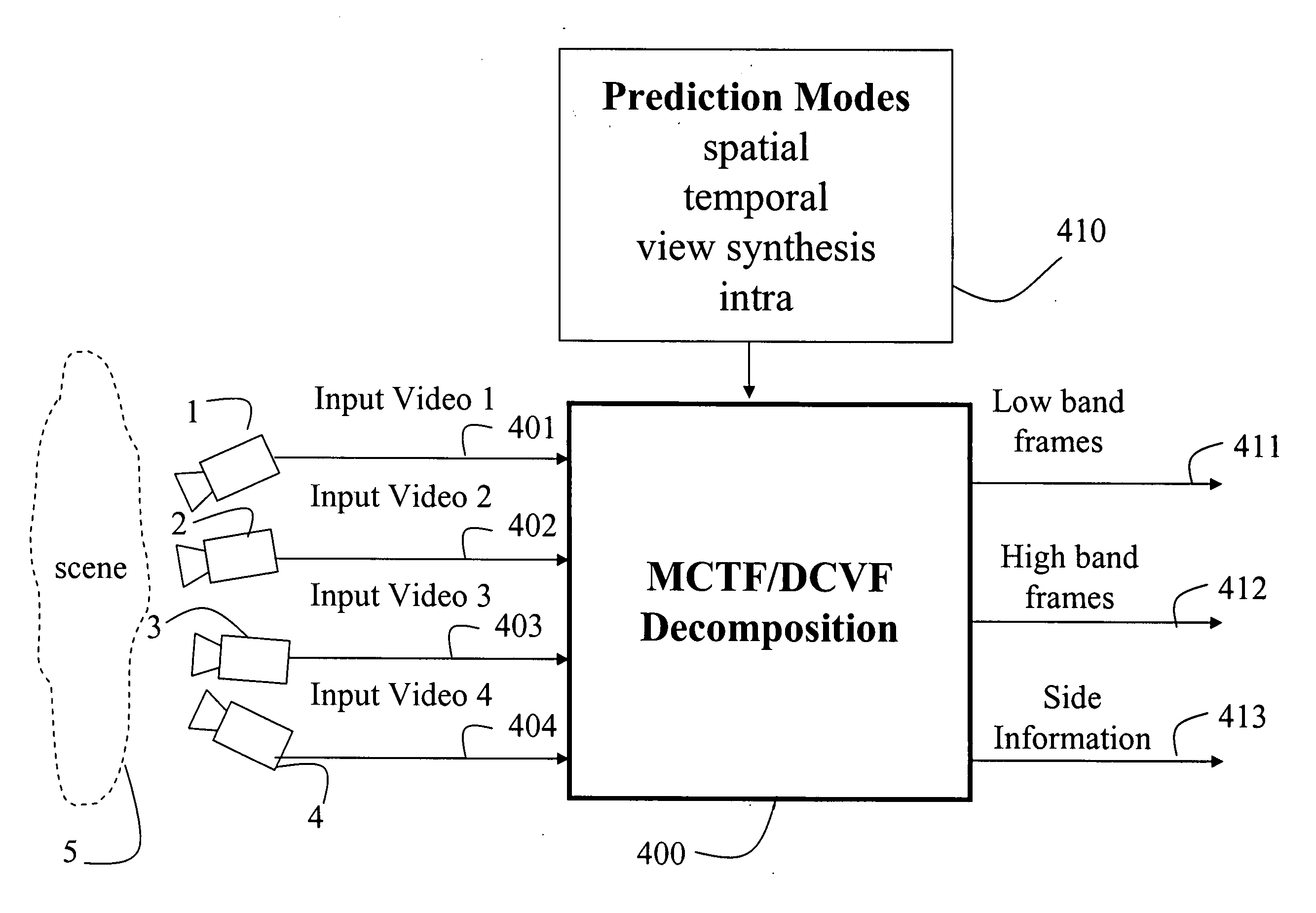
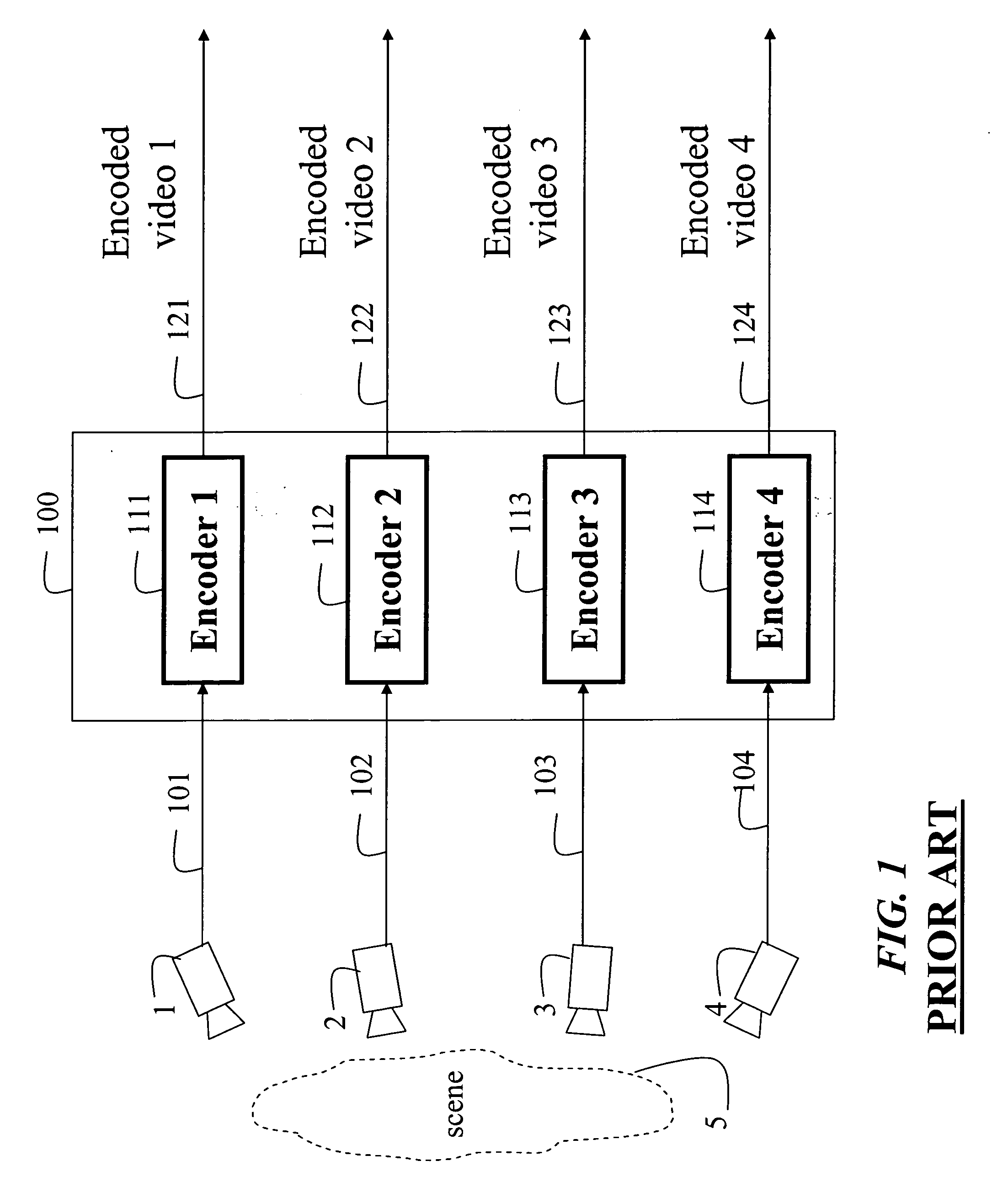
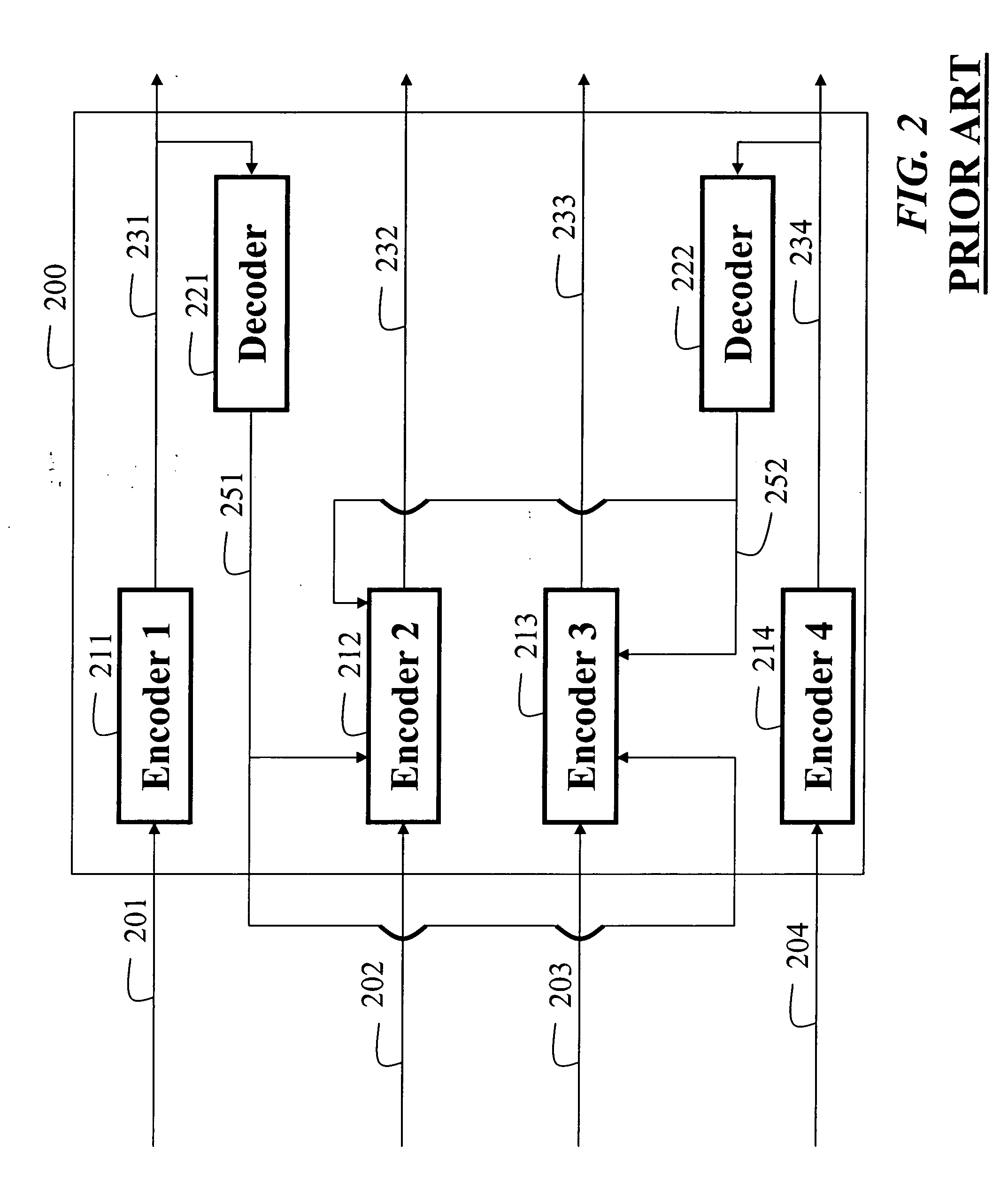
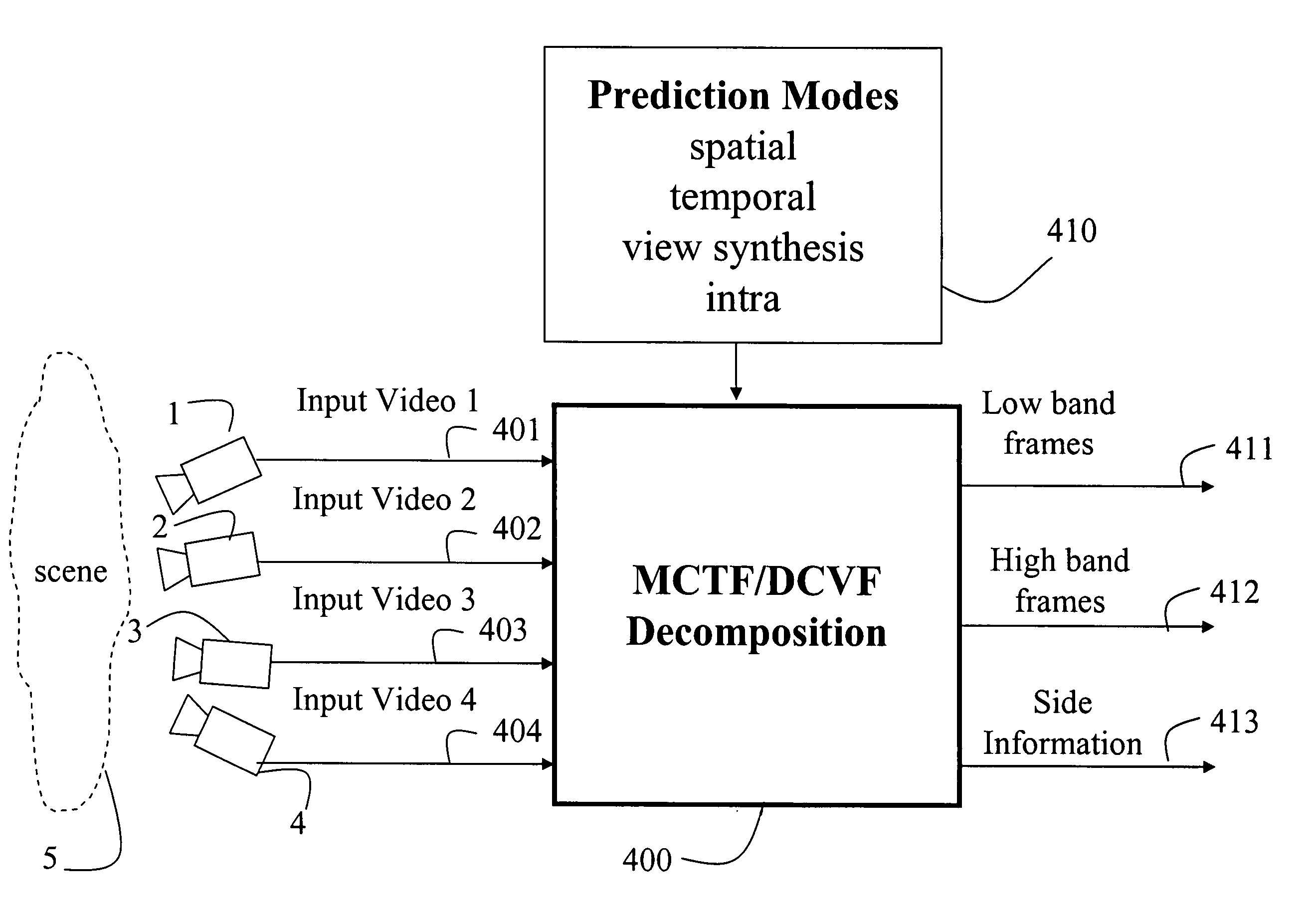
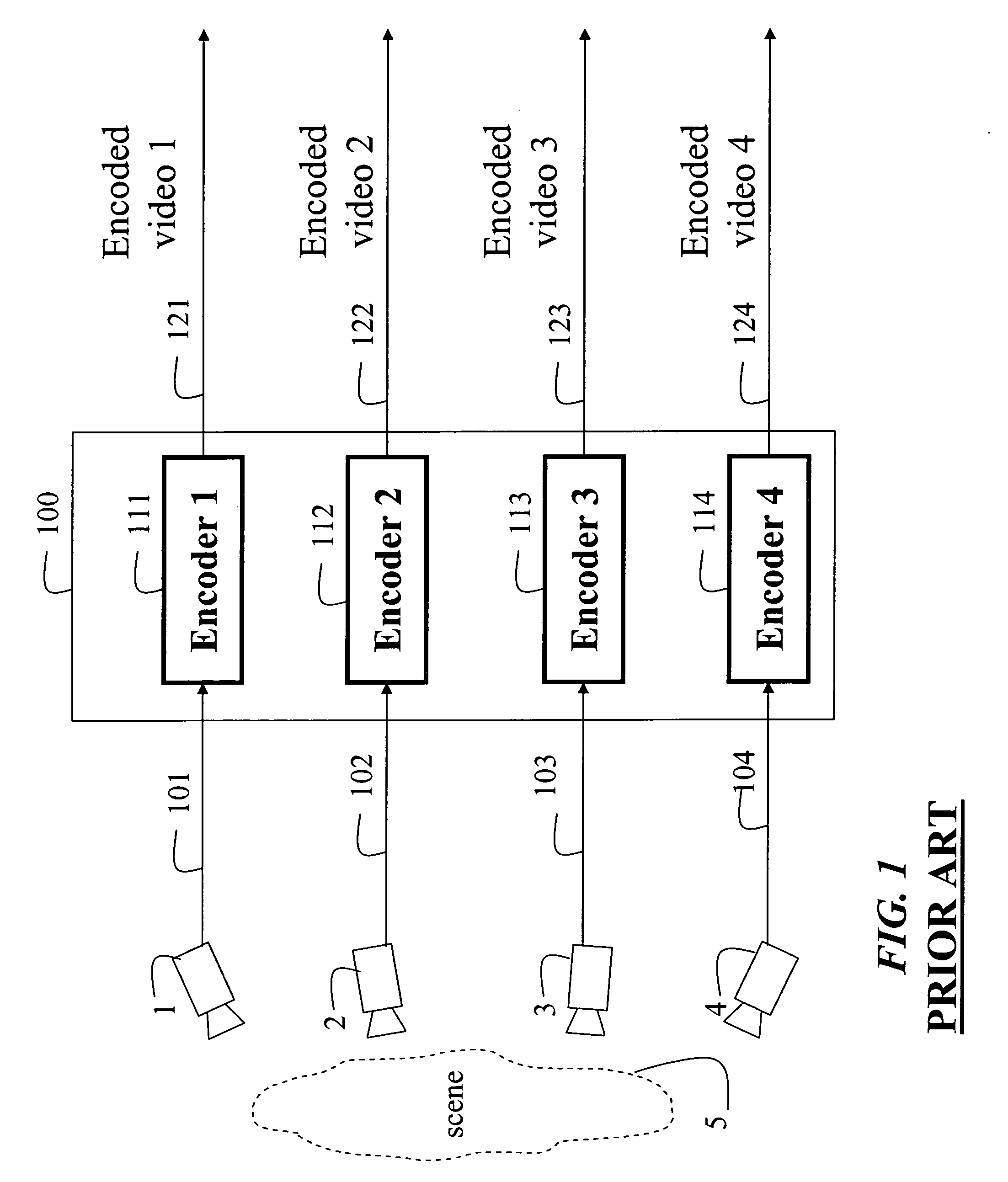
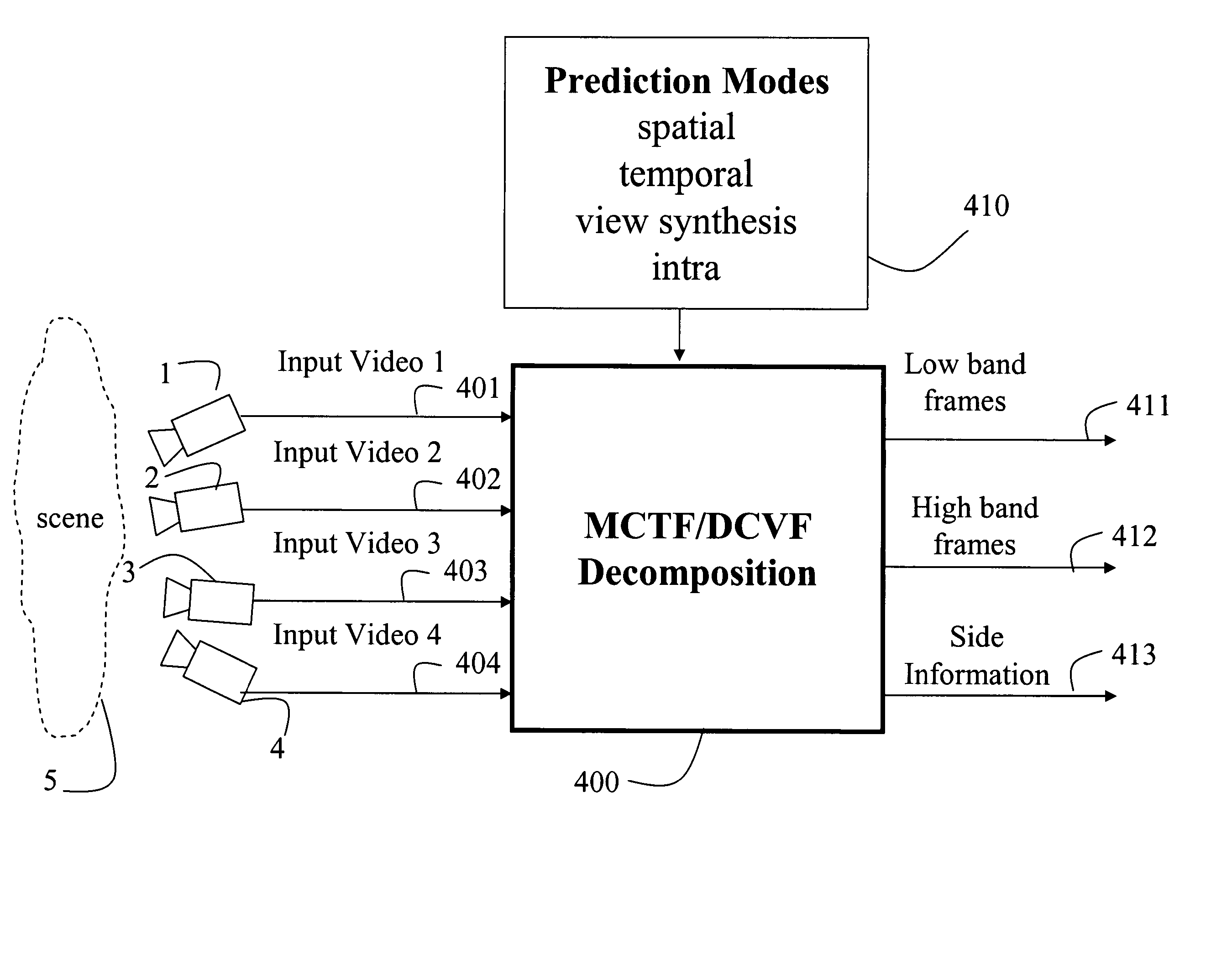
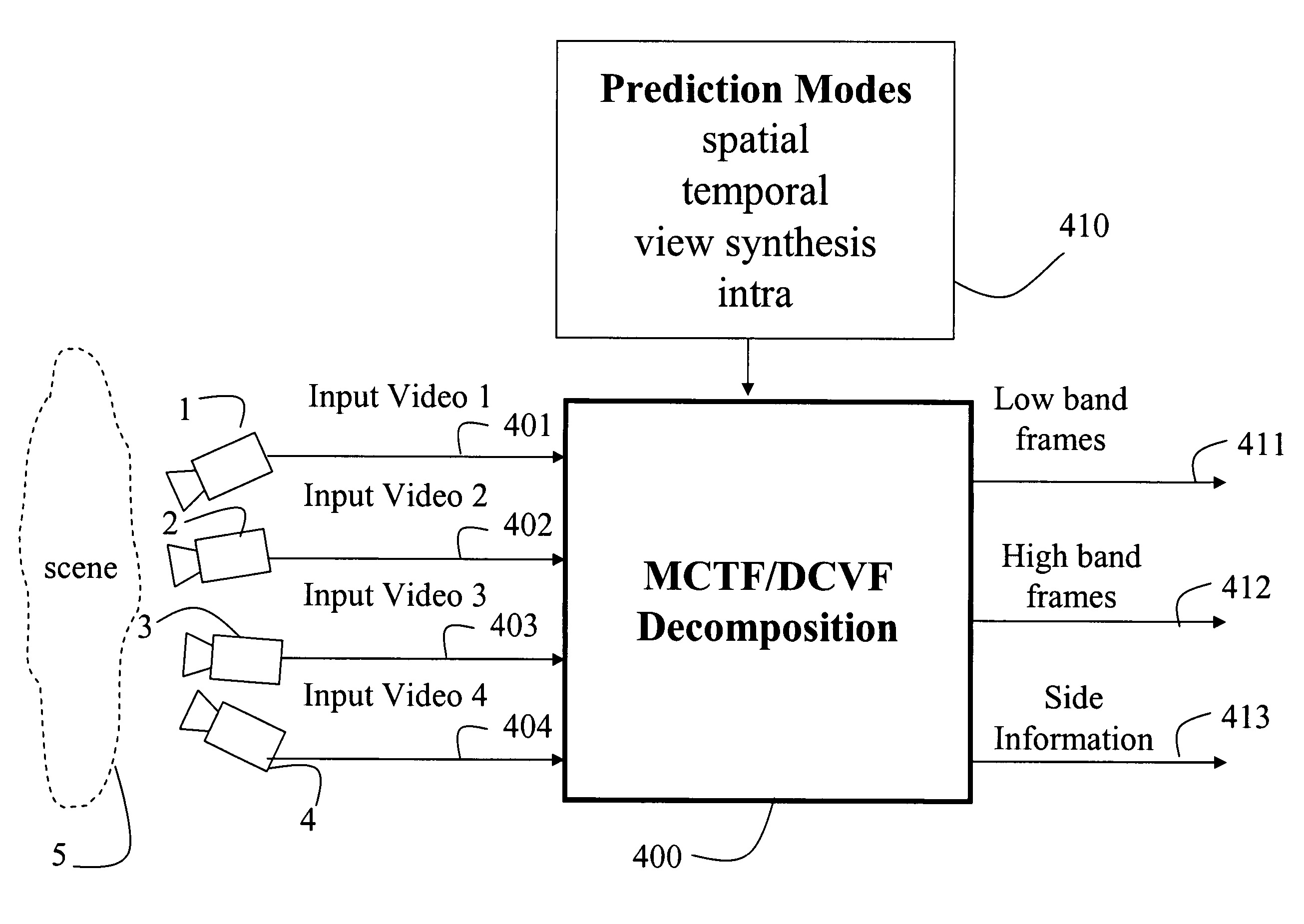
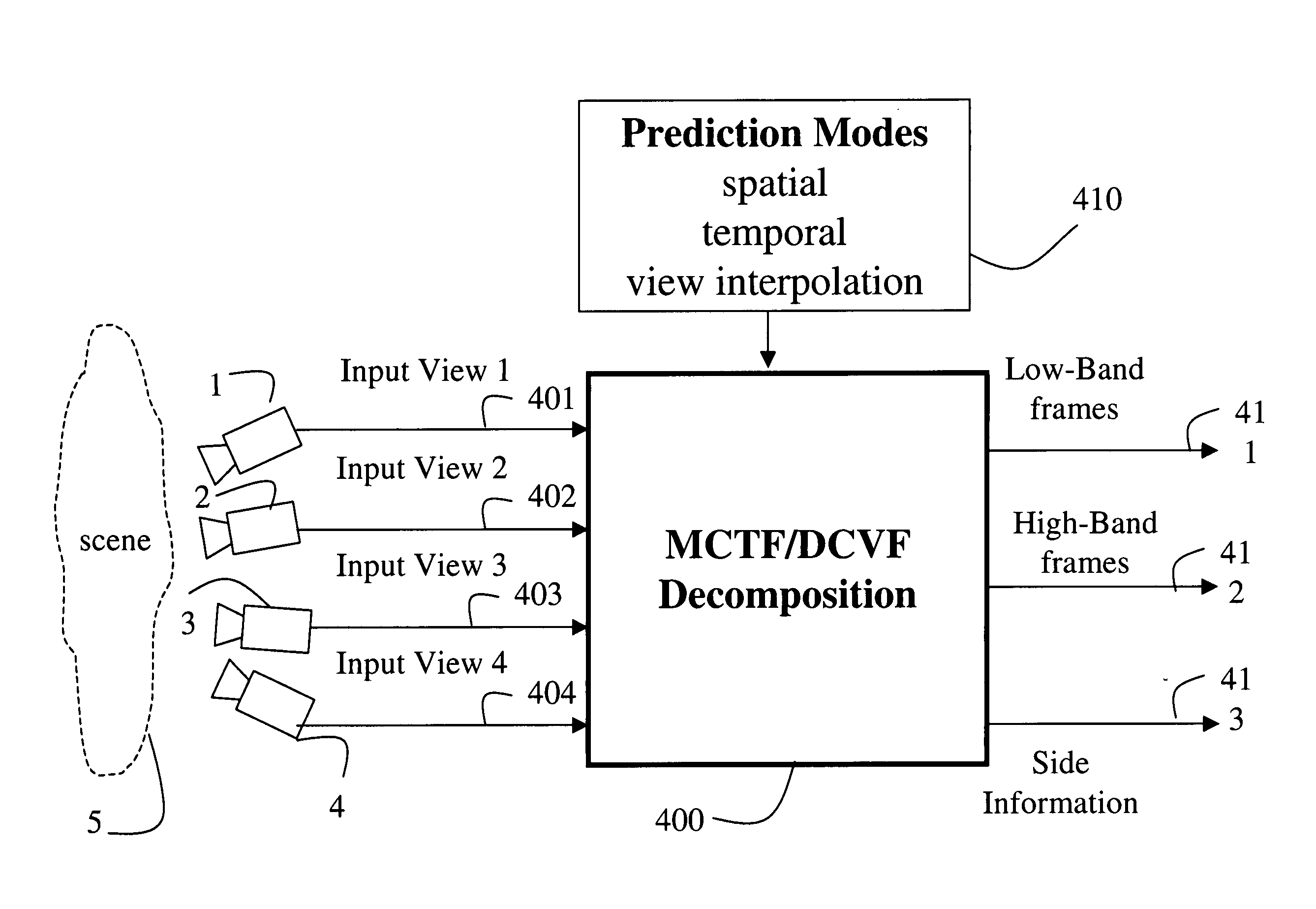
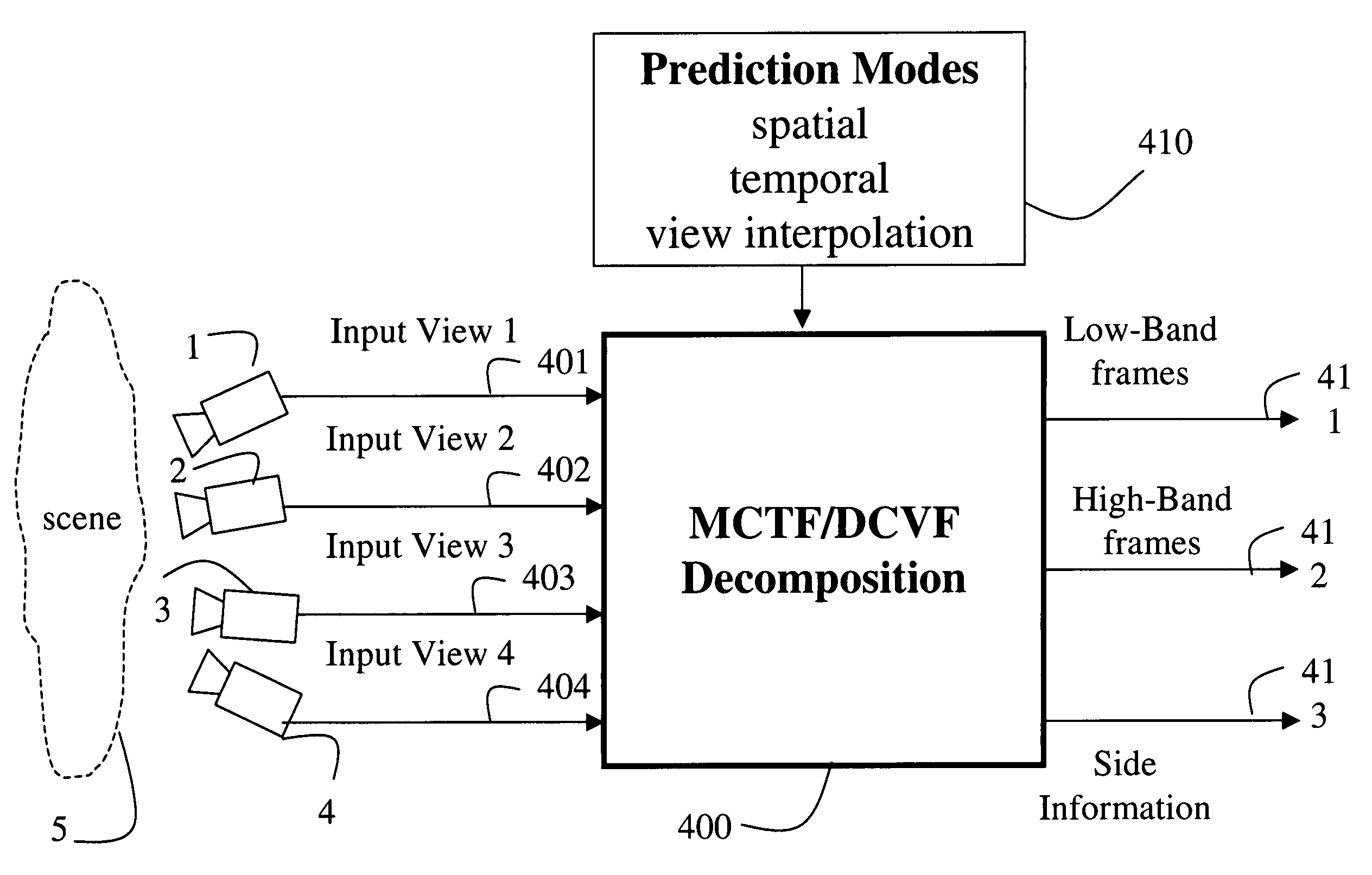
Multiview video decomposition and encoding
InactiveUS20060132610A1Television system detailsPicture signal generatorsSpatial predictionSide information
A method decomposes multiview video acquired of a scene by multiple cameras. Each multiview video includes a sequence of frames, and each camera provides a different view of the scene. A prediction mode is selected from a temporal prediction mode, a spatial prediction mode, and a view interpolation prediction mode. The multiview videos are then decomposed into low band frames, high band frames, and side information according to the selected prediction mode.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
Apparatus and method for spatially predicting image data, apparatus and method for encoding image data, apparatus and method for compensating for spatial prediction of image data, and apparatus and method for decoding image data
InactiveUS20060126727A1Picture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPicture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanningSpatial predictionComputer vision
An apparatus and method for spatially predicting image data, an apparatus and method for encoding image data, an apparatus and method for compensating for spatial prediction of image data, and an apparatus and method for decoding image data. The spatial prediction apparatus of image data includes: a spatial prediction unit performing a spatial prediction of pixel values of a current block using pixel values of blocks adjacent to an upper row of the current block. A pipeline process is possible when the spatial prediction is performed, thereby performing real time encoding and decoding.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Line-Based Compression for Digital Image Data
ActiveUS20110080947A1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionPattern recognitionSpatial prediction
A method of compressing digital image data is provided that includes selecting an entropy code for encoding a line of pixels in the digital image data, wherein the entropy code is selected from a plurality of variable length entropy codes, using spatial prediction to compute a pixel predictor and a pixel residual for a pixel in the line of pixels, and selectively encoding the pixel residual using one of the entropy code or run mode encoding.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
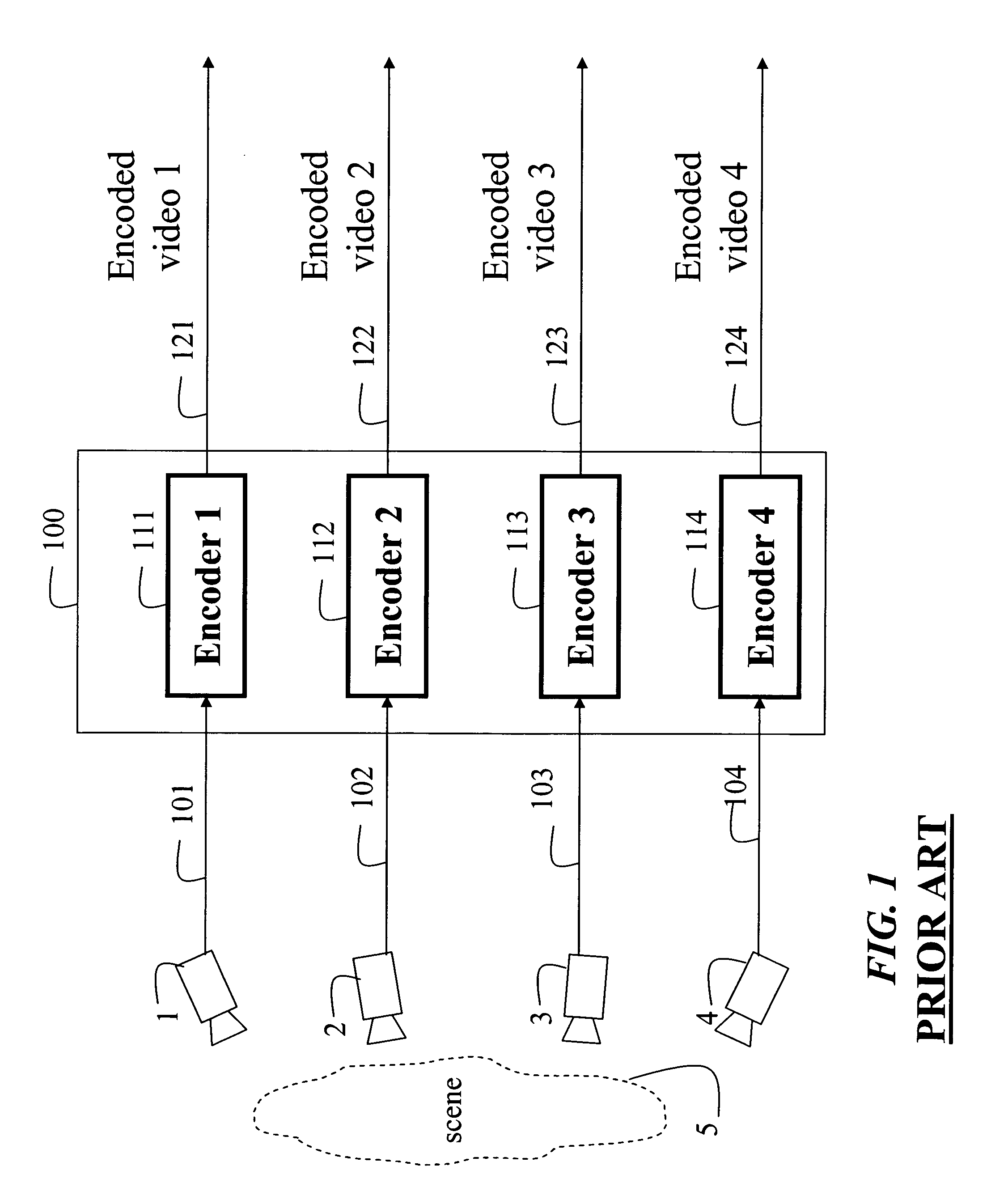
System and process for compressing and decompressing multiple, layered, video streams employing spatial and temporal encoding
InactiveUS20060029134A1Easy to explainTelevision system detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesSpatial predictionViewpoints
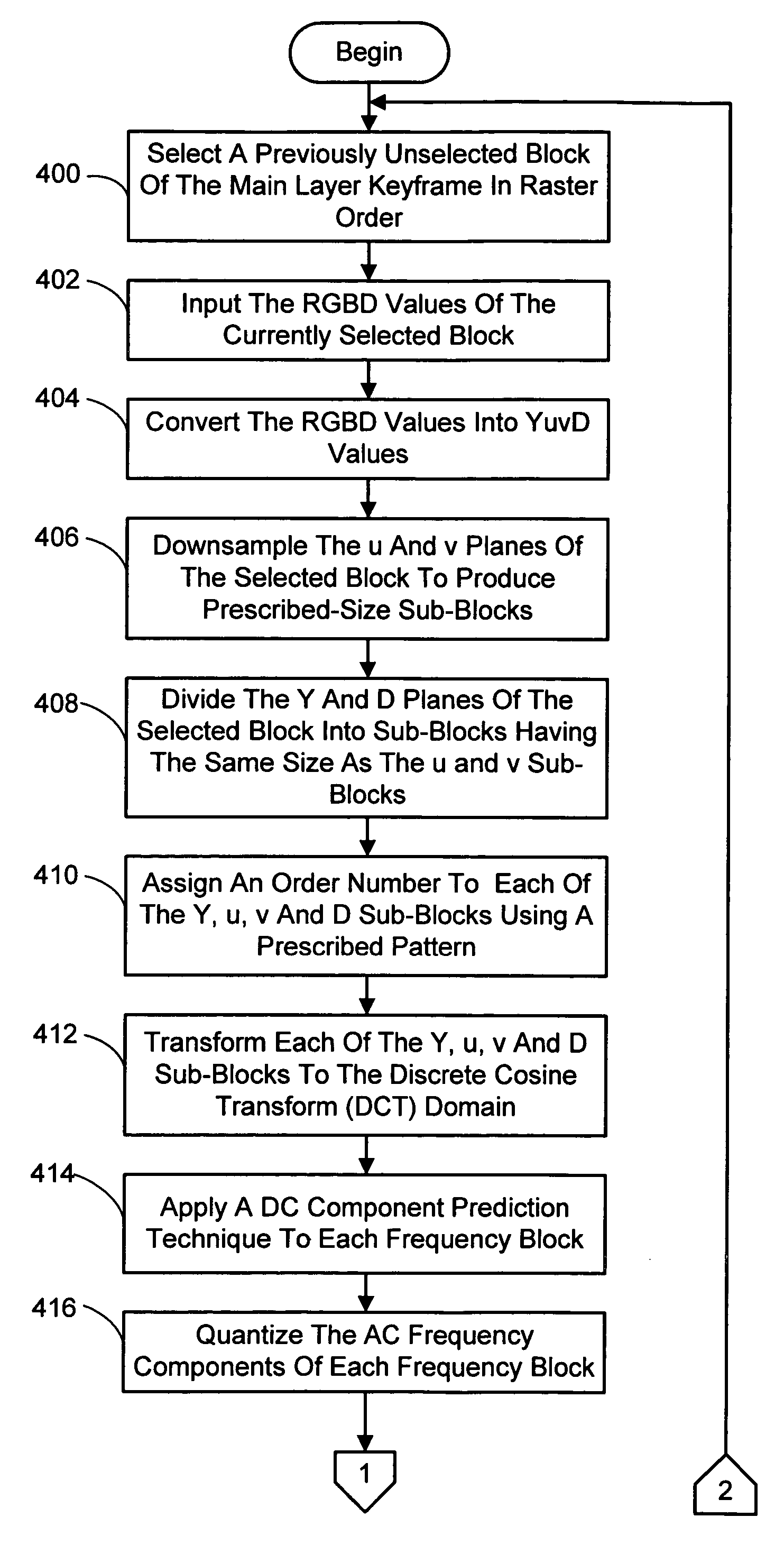
A system and process for compressing and decompressing multiple video streams depicting substantially the same dynamic scene from different viewpoints. Each frame in each contemporaneous set of video frames of the multiple streams is represented by at least a two layers—a main layer and a boundary layer. Compression of the main layers involves first designating one or more of these layers in each set of contemporaneous frames as keyframes. For each set of contemporaneous frames in time sequence order, the main layer of each keyframe is compressed using an inter-frame compression technique. In addition, the main layer of each non-keyframe within the frame set under consideration is compressed using a spatial prediction compression technique. Finally, the boundary layers of each frame in the current frame set are each compressed using an intra-frame compression technique. Decompression is generally the reverse of the compression process.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
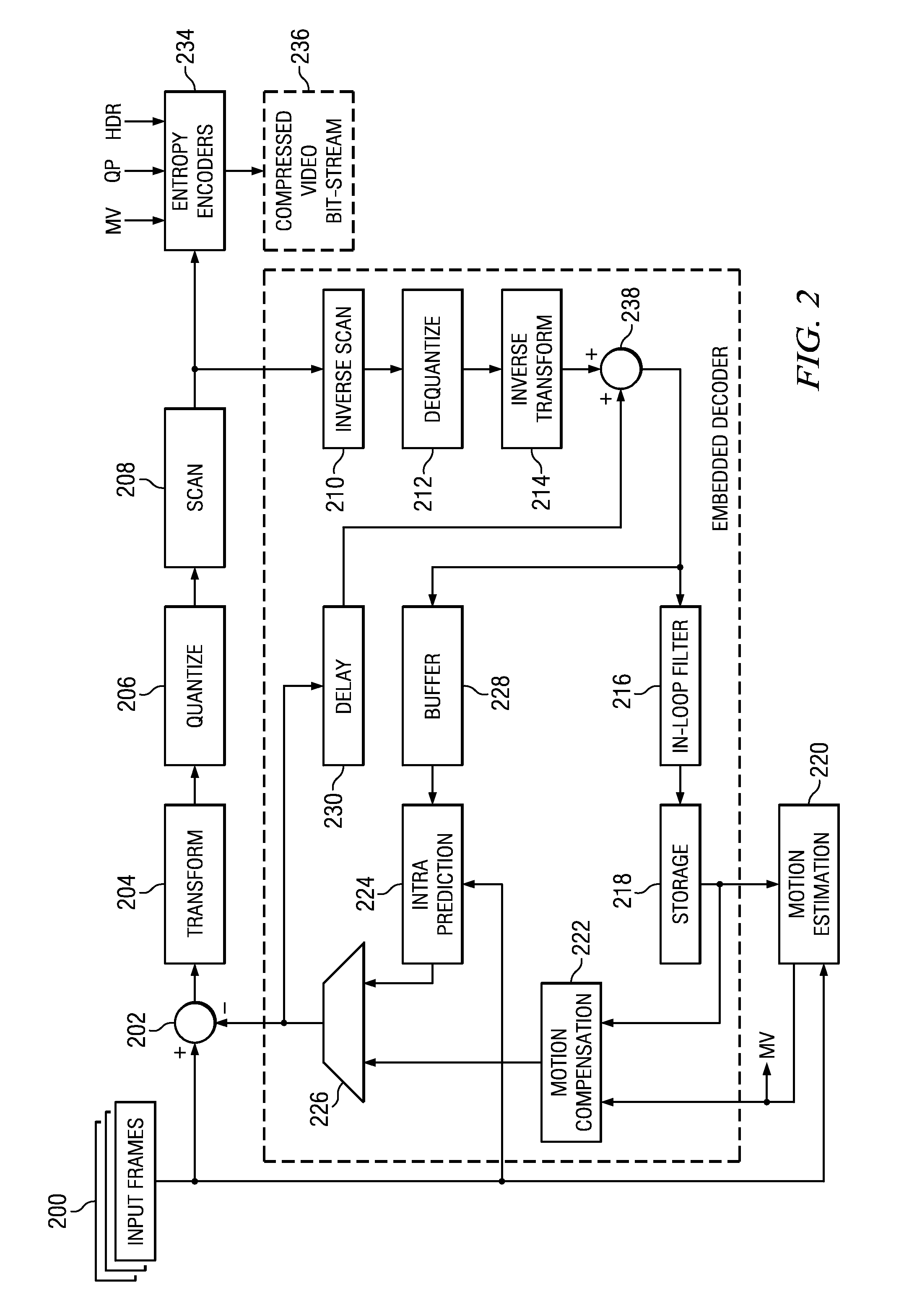
Method and System for Intracoding in Video Encoding
ActiveUS20110170594A1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionCoding blockDigital video
A method of intra-coding blocks of pixels in a digital video sequence is provided that includes selecting a block transform of a plurality of block transforms according to a spatial prediction mode used in generating a block of pixel residual values from a block of pixels, wherein the block transform is based on a single directional transform matrix predetermined for the spatial prediction mode and is a same size as the block of pixel values, applying the block transform to the block of pixel residual values to generate transform coefficients of the residual pixel values, and entropy coding the generated transform coefficients.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Method and apparatus for faster-than-real-time lossless compression and decompression of images
InactiveUS7693339B2Minimized on demandSame amount of timeCharacter and pattern recognitionDigital video signal modificationFrequency spectrumSpatial prediction
Image compression wherein a spatial prediction filter combines two adjacent samples and a corner sample in the proportion 3:3:−2, or wherein chunked decode tables are used to decode embedded prefix codes more than one bit at a time. A spectral prediction filter might be used in conjunction with the spatial prediction filter. Chunked decode tables might be used in combination with simple prediction filters.
Owner:WITTENSTEIN ANDREAS
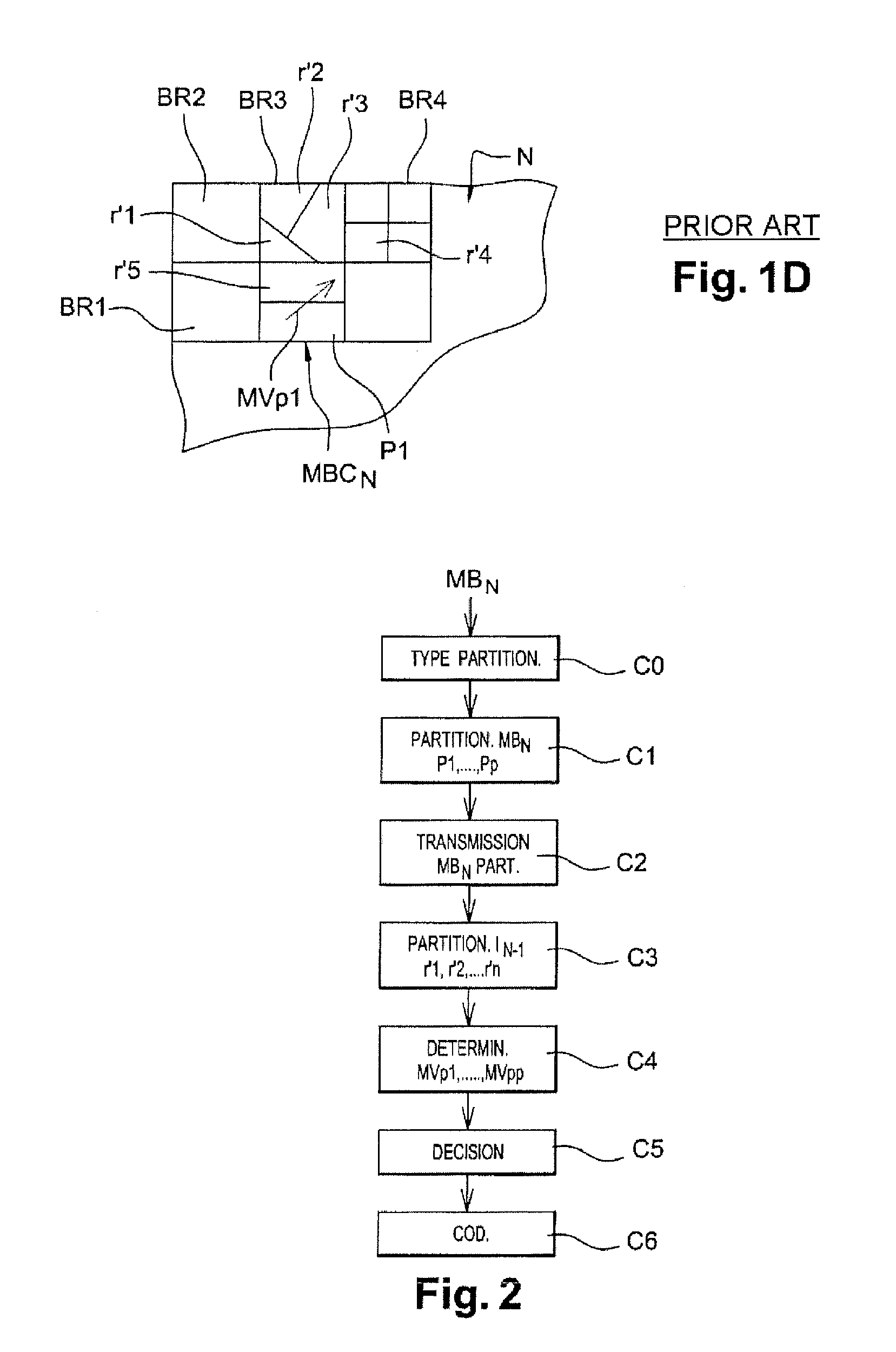
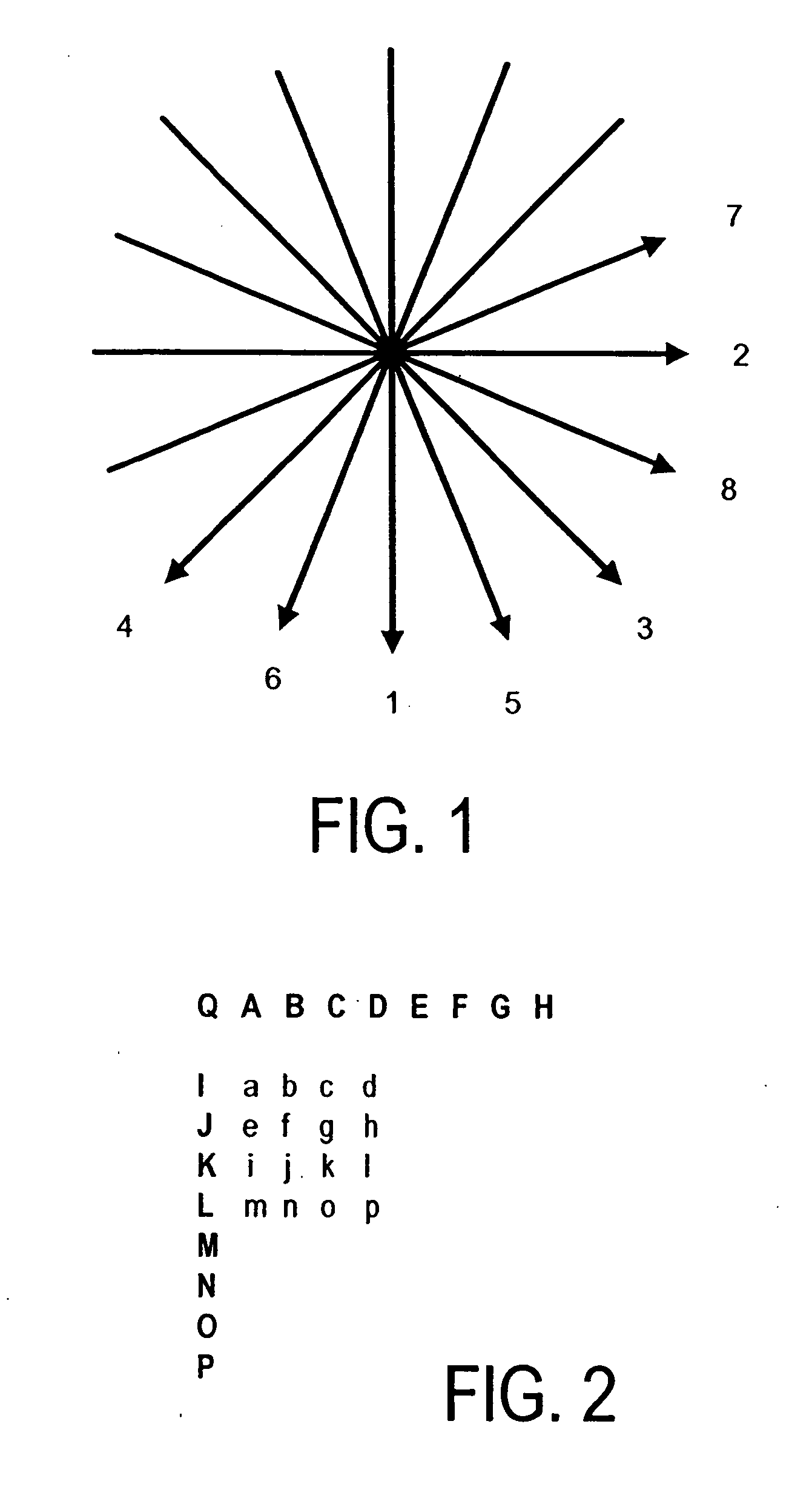
Prediction of a movement vector of a current image partition having a different geometric shape or size from that of at least one adjacent reference image partition and encoding and decoding using one such prediction
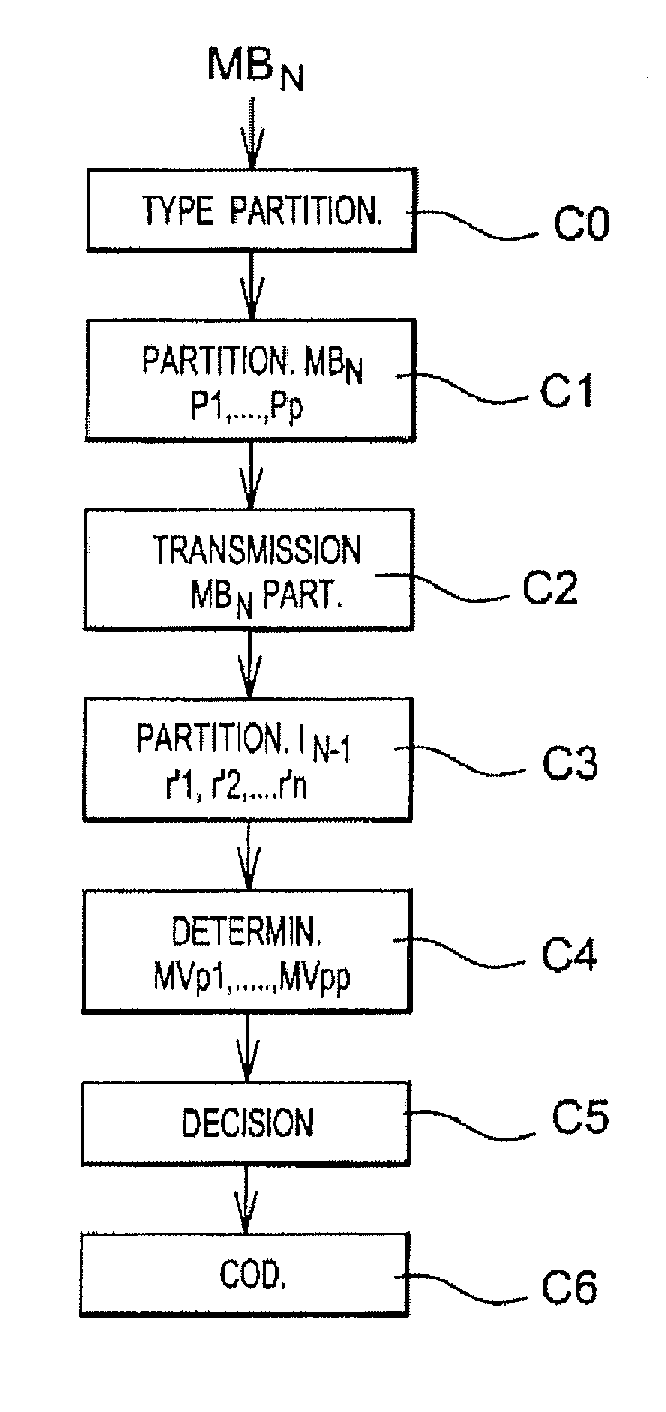
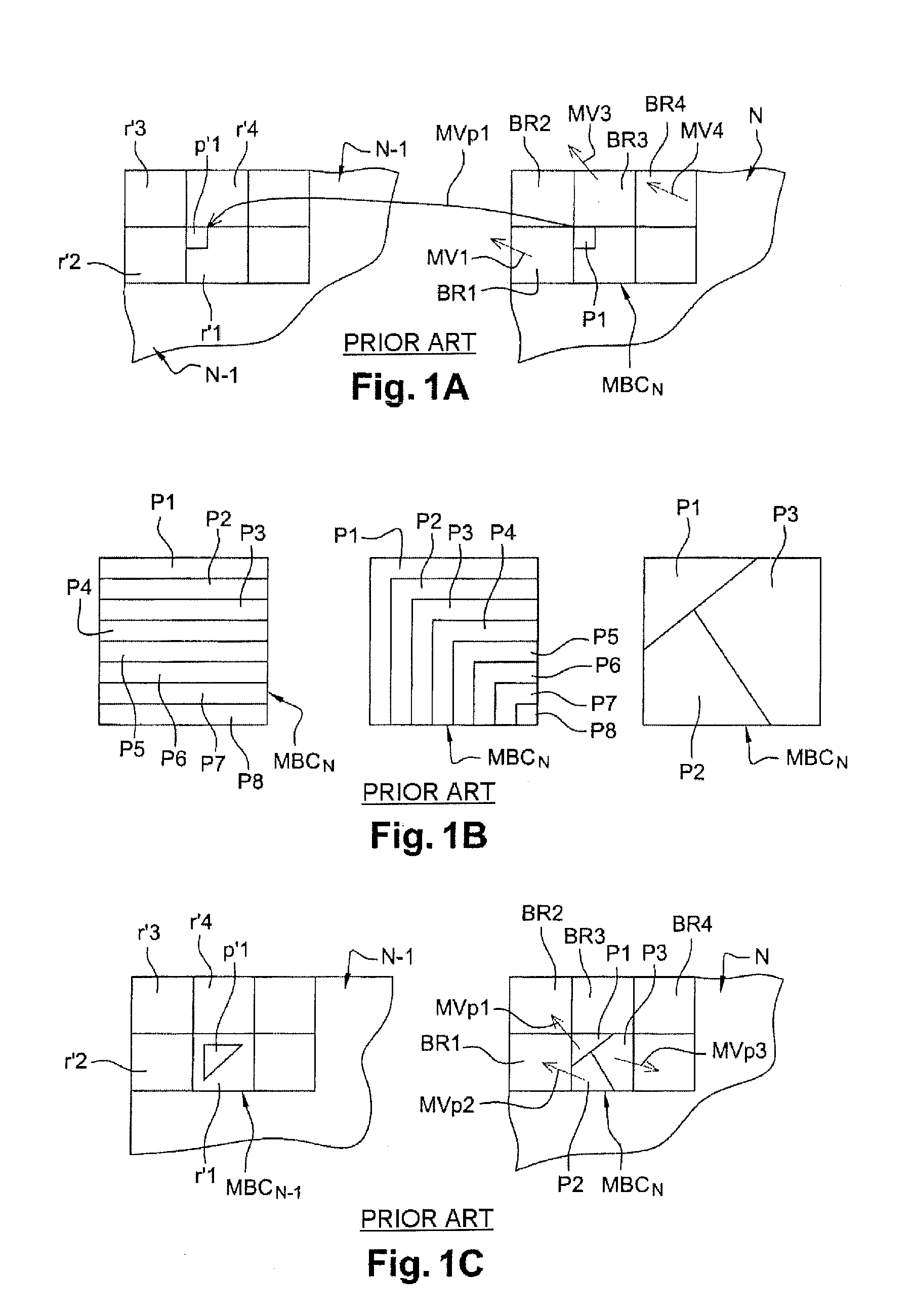
ActiveUS20120106647A1Choose accuratelyHigh precisionColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionSpatial predictionMotion vector
The invention relates to a method for predicting a movement vector (MVp1) of a partition (P1) of a current image (IN) from a plurality of n reference movement vectors associated respectively with n reference partitions that have been previously encoded and decoded. For a spatial prediction of one such vector, when the geometric shape of the current partition is different from that of k adjacent reference partitions (pr1, pr2, . . . prk), with k≦n, the movement vector of the current image partition is determined from a function of at least one reference movement vector belonging to a set of k reference movement vectors associated respectively with k adjacent reference partitions.
Owner:FRANCE TELECOM SA
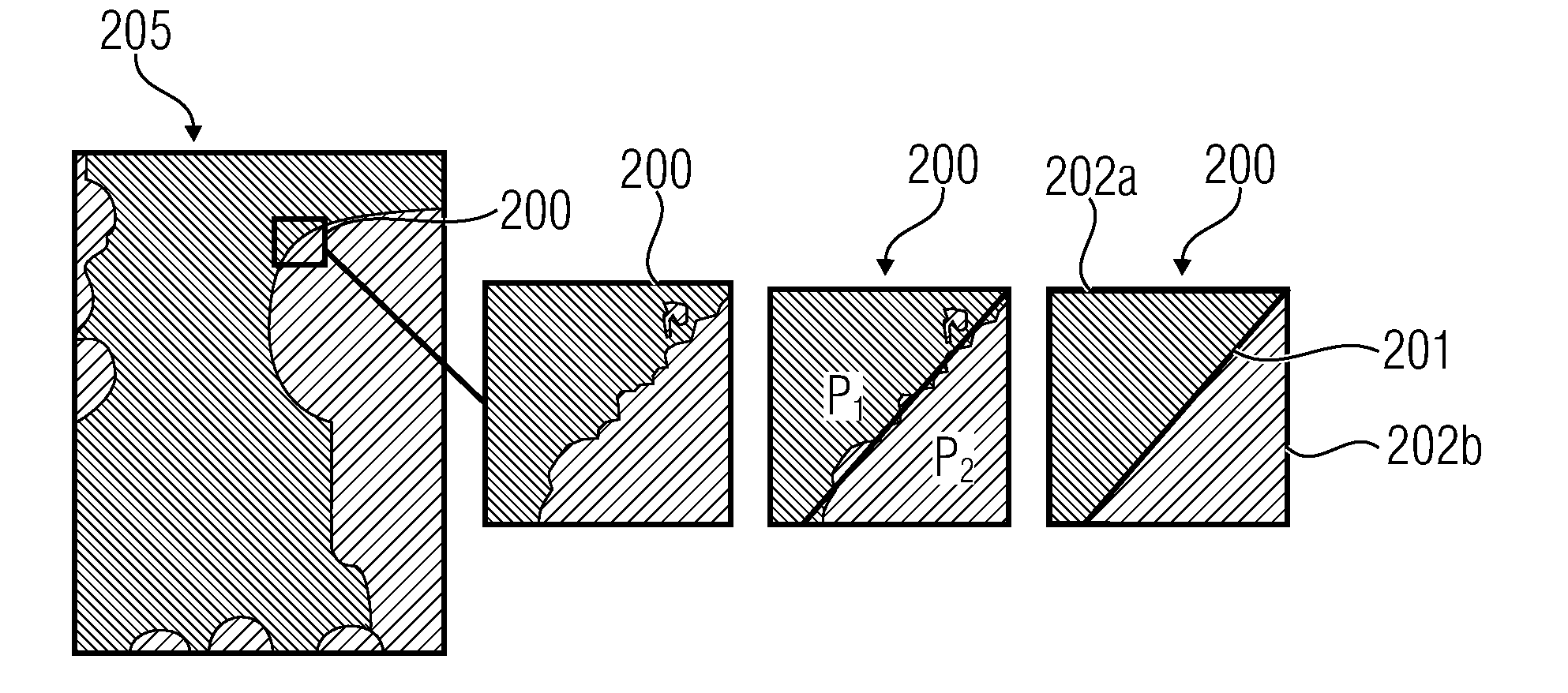
Effective wedgelet partition coding using spatial prediction
ActiveUS20140341290A1Reduce probabilityColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionSpatial predictionSide information
In accordance with a first aspect, the intra prediction direction of a neighboring, intra-predicted block is used in order to predict the extension direction of the wedgelet separation line of a current block, thereby reducing the side information rate necessitated in order to convey the partitioning information. In accordance with a second aspect, the idea is that previously reconstructed samples, i.e. reconstructed values of blocks preceding the current block in accordance with the coding / decoding order allow for at least a prediction of a correct placement of a starting point of the wedgelet separation line, namely by placing the starting point of the wedgelet separation line at a position of a maximum change between consecutive ones of a sequence of reconstructed values of samples of a line of samples extending adjacent to the current block along a circumference thereof. Both aspects may be used individually or in combination.
Owner:GE VIDEO COMPRESSION LLC
Systems and methods for efficient spatial intra predictabilty determination (or assessment)
InactiveCN101622877ATelevision systemsDigital video signal modificationSpatial predictionTheoretical computer science
Techniques for efficient determination of a macroblock's spatial predictability quality with respect to the H.264 specification are provided. A device comprises a processor operable to estimate a first subset of spatial prediction modes based on a first pixel subset of a current subblock of an intra-frame. The processor is also operable to estimate a second subset of spatial prediction modes based on a second pixel subset of the current subblock. The first subset of prediction modes is different from the second subset of prediction modes.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
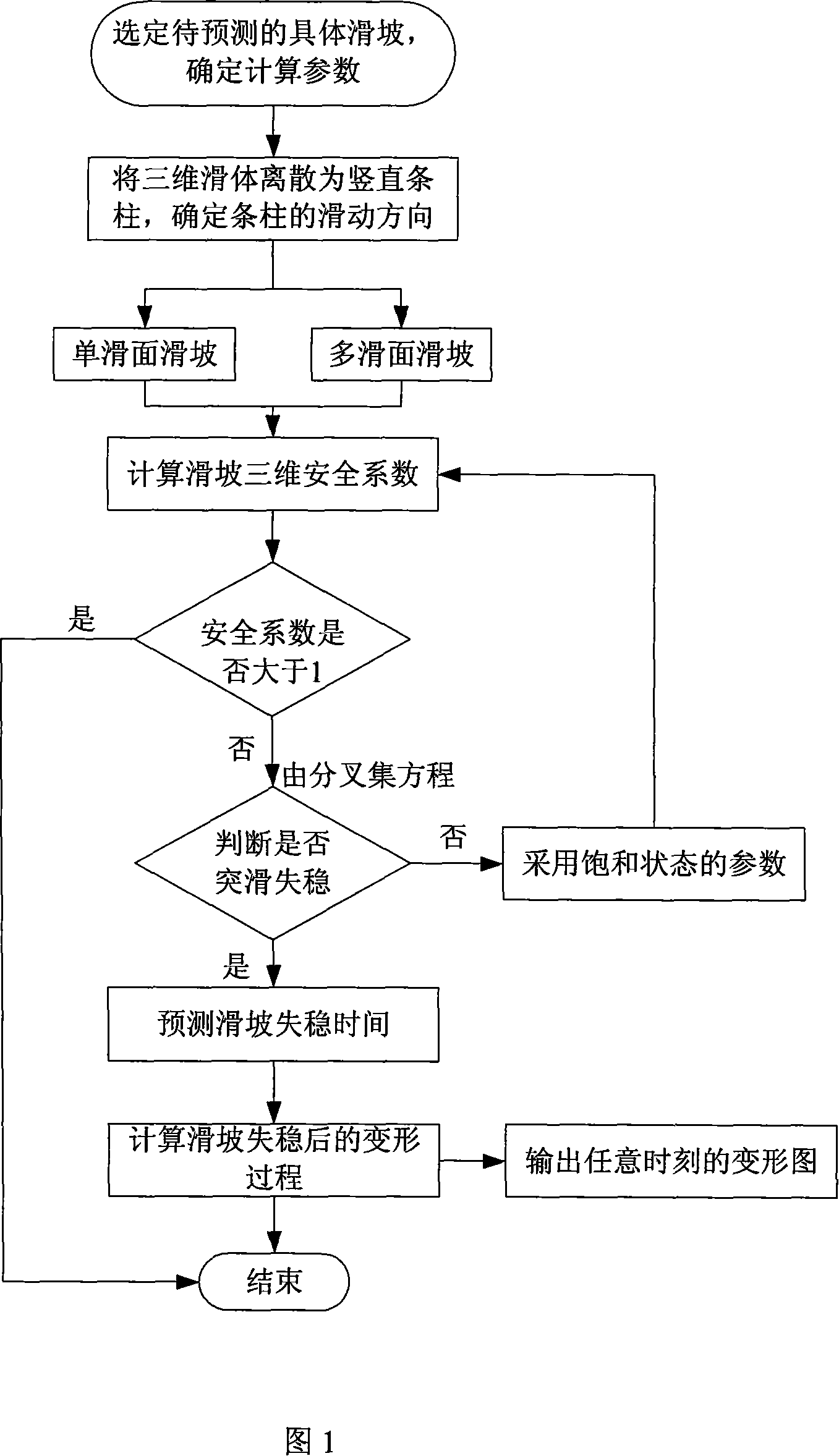
Intelligent method of temporal-spatial prediction in disaster-changing of landslide
The invention relates to an intelligent method for carrying out space-time prediction of the landslide catastrophe process. The invention is carried out via a computer, comprising the following steps of: 1) choosing a detained landslide to be predicted, confirming calculation parameters; 2) establishing a geometric model of the landslide intelligent prediction; 3) intelligently predicting the 3D stability of the landslide; 4) intelligently predicting the unstable state of the landslide; 5) intelligently predicting the activity intensity of the landslide as follows: computing the landslide deformation process in the unstable state, outputting deformation maps in real time until the end of the landslide. Compared with the prior art, the invention reduces the workload, improves the precision, simplifies the judging method of space-time predicting of the landslide catastrophe process with much convenience and reliability, and improves the maneuverability of the space-time predicting of the landslide catastrophe process. Therefore the invention is the simple, intuitionistic, economical and high-efficient space-time prediction of the landslide catastrophe process.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Spatial prediction based intra coding
InactiveUS20080013629A1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionSpatial predictionDigital image
A method and device for coding a digital image using intra-mode block prediction, wherein a list of prediction modes for each combination of prediction modes of the neighboring blocks is obtained. The modes assigned to each combination of prediction modes may be divided into two groups. The first group includes n (where n is smaller than the overall number of available modes) most probable prediction modes and the second group includes the remaining modes. The modes in the first group are ordered according to their probability. This order may be specified as a list of modes ordered from most probable to the least probable mode. The modes belonging to the second group may be ordered in some predetermined manner, which may be specified depending on the information already available to the decoder.
Owner:KARCZEWICZ MARTA
Spatial prediction based intra-coding
InactiveUS20060188165A1Reduce decreaseCharacter and pattern recognitionImage codingSpatial predictionDigital image
Owner:KARCZEWICZ MARTA
Small-scale air quality index prediction method and system for city
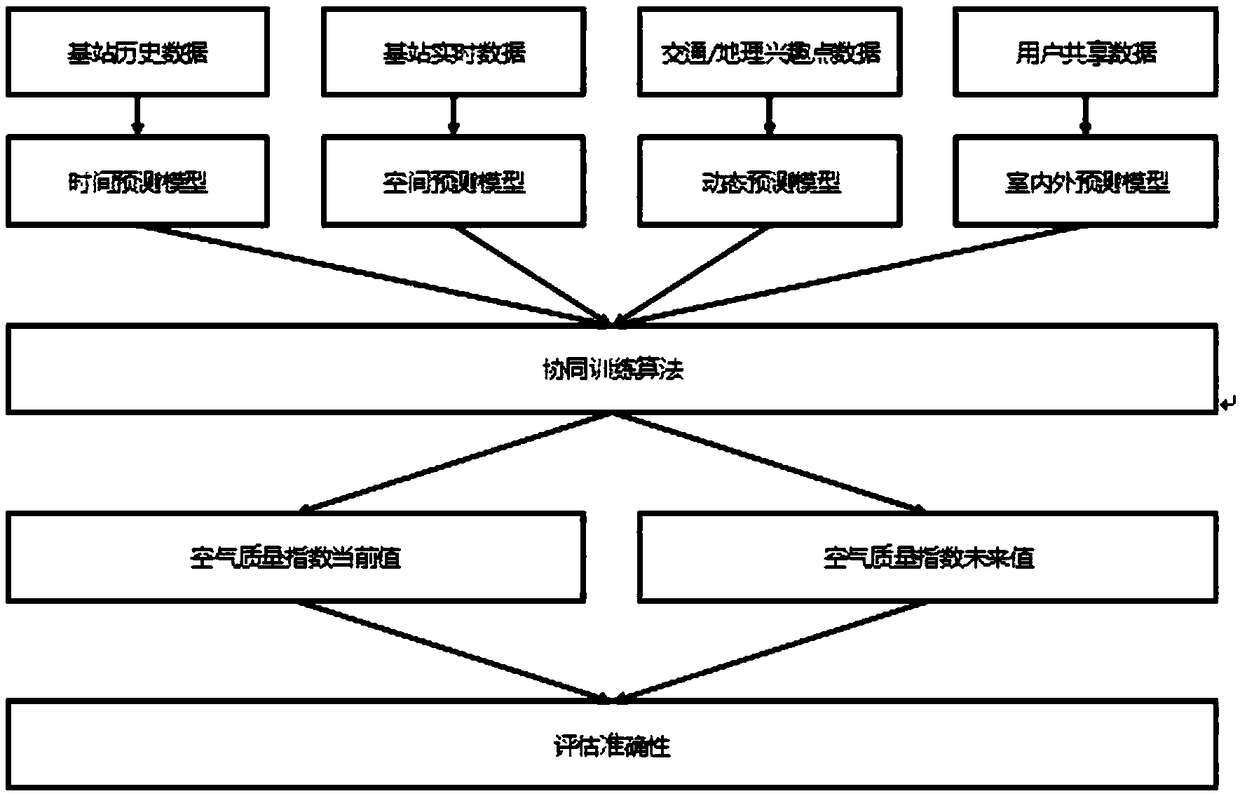
InactiveCN108701274AAchieving Air Quality PredictionImprove accuracyForecastingInformaticsEngineeringOutdoor air quality
The invention discloses a small-scale air quality index prediction method and system for a city, which firstly divides a city area into a plurality of to-be-predicted locations in a grid form; and then acquires historical data related to each model, and based on historical data: establishing corresponding correspondences The current time prediction and the time prediction model predicted at each moment in the future time, establish a spatial prediction model for air quality prediction at the specified coordinates, and establish a dynamic prediction model that characterizes the relationship between traffic data and geographic interest point data and air quality index, an indoor and outdoor prediction model that characterizes the relationship between the indoor air quality index and the outdoor air quality index; when performing the prediction, the established time prediction model, the spatial prediction model, and the dynamic prediction are performed for any real-time moments to be predicted. The model and the indoor and outdoor prediction models are cooperatively trained to fuse the prediction results of all the models, that is, the predicted values of the air quality index at each moment in the respective current and future time periods of each to-be-predicted location.
Owner:BEIJING QUALITY TECH CO LTD
System and process for compressing and decompressing multiple, layered, video streams of a scene captured from different viewpoints forming a grid using spatial and temporal encoding
ActiveUS20060031915A1Easy to explainTelevision system detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesSpatial predictionViewpoints
A system and process for compressing and decompressing multiple video streams depicting substantially the same dynamic scene from different viewpoints that from a grid of viewpoints. Each frame in each contemporaneous set of video frames of the multiple streams is represented by at least a two layers—a main layer and a boundary layer. Compression of the main layers involves first designating one or more of these layers in each set of contemporaneous frames as keyframes. For each set of contemporaneous frames in time sequence order, the main layer of each keyframe is compressed using an inter-frame compression technique. In addition, the main layer of each non-keyframe within the frame set under consideration is compressed using a spatial prediction compression technique. Finally, the boundary layers of each frame in the current frame set are each compressed using an intra-frame compression technique. Decompression is generally the reverse of the compression process.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Multiview video decomposition and encoding
InactiveUS7468745B2Television system detailsPicture signal generatorsSpatial predictionSide information
A method decomposes multiview video acquired of a scene by multiple cameras. Each multiview video includes a sequence of frames, and each camera provides a different view of the scene. A prediction mode is selected from a temporal prediction mode, a spatial prediction mode, and a view interpolation prediction mode. The multiview videos are then decomposed into low band frames, high band frames, and side information according to the selected prediction mode.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com