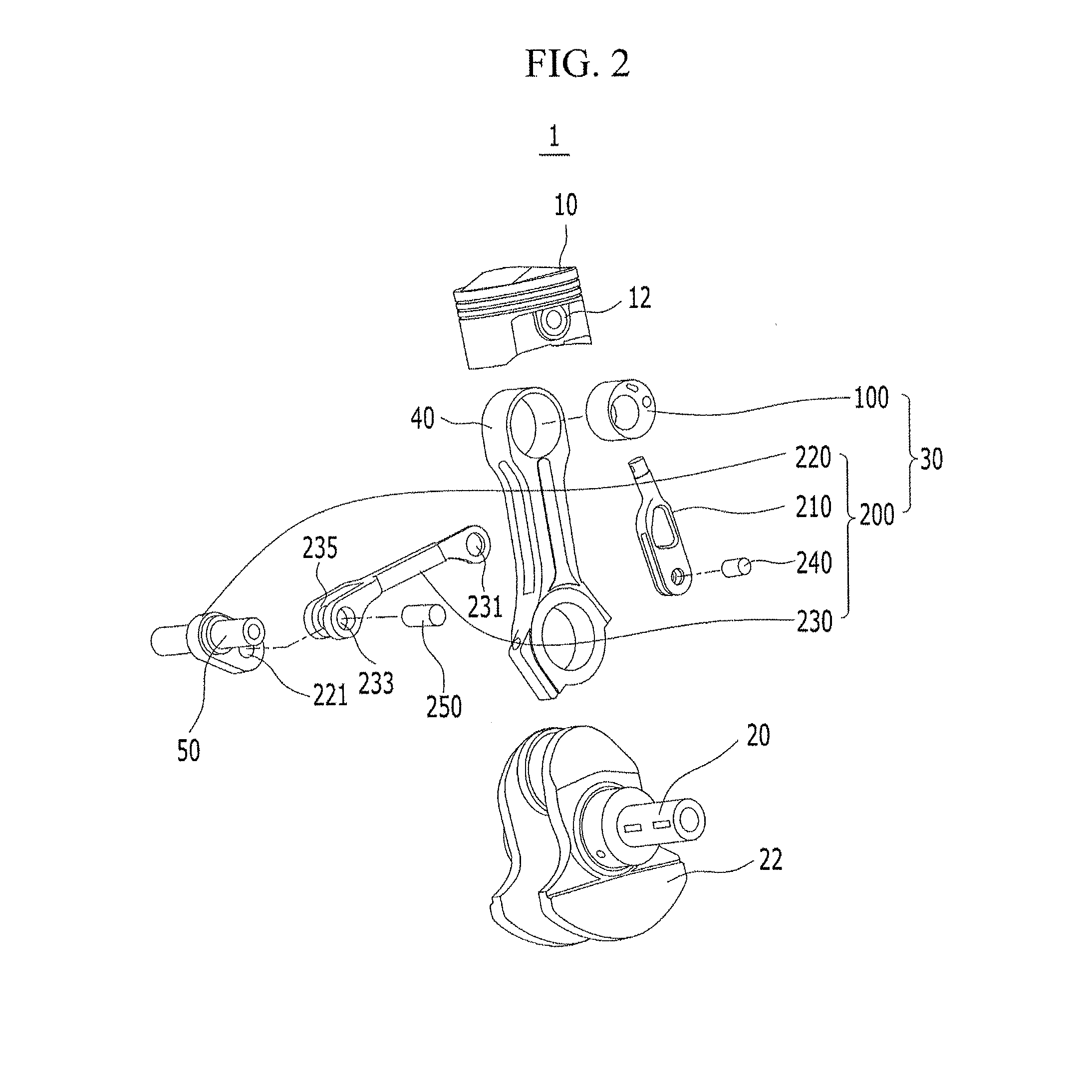
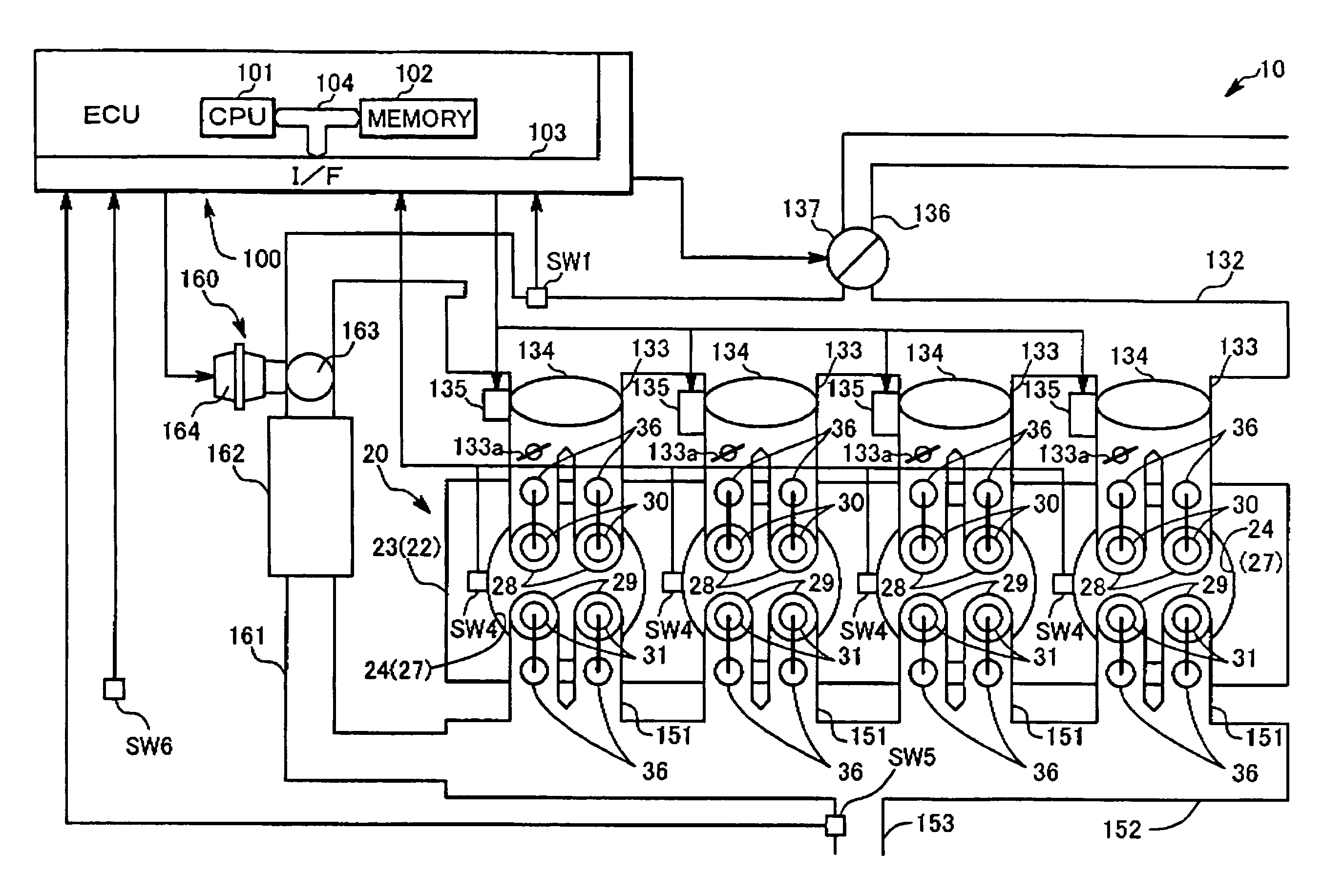
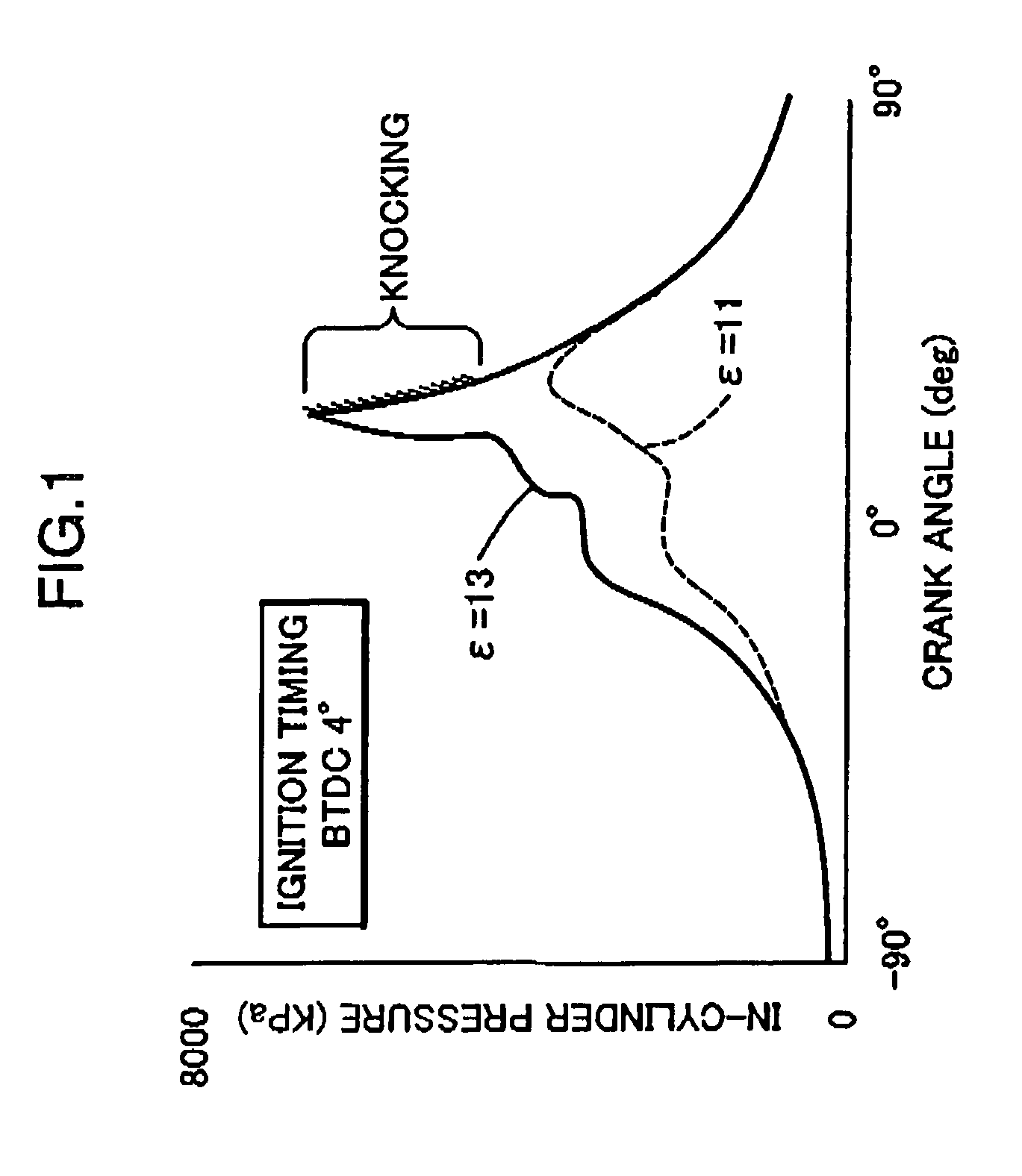
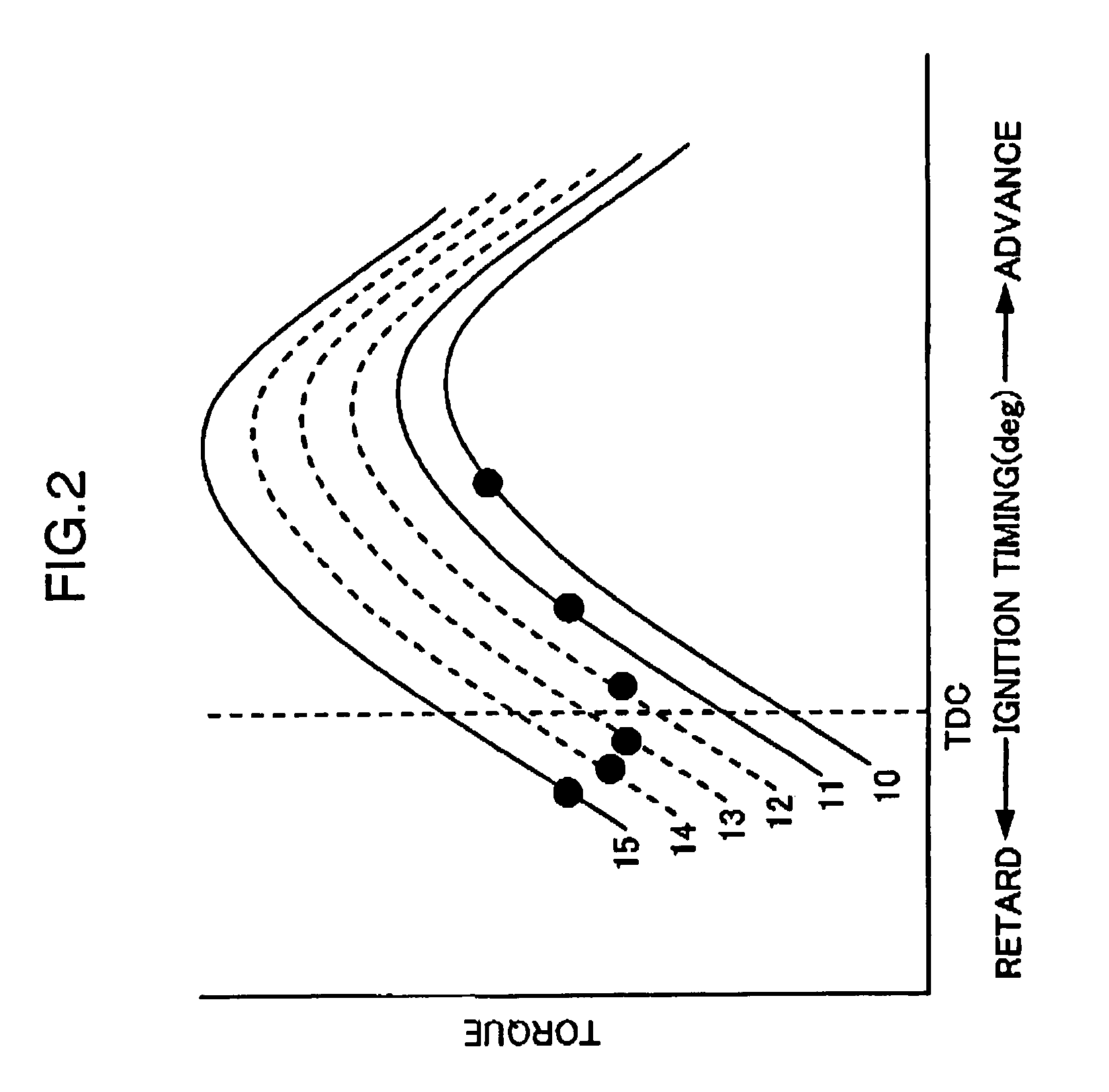
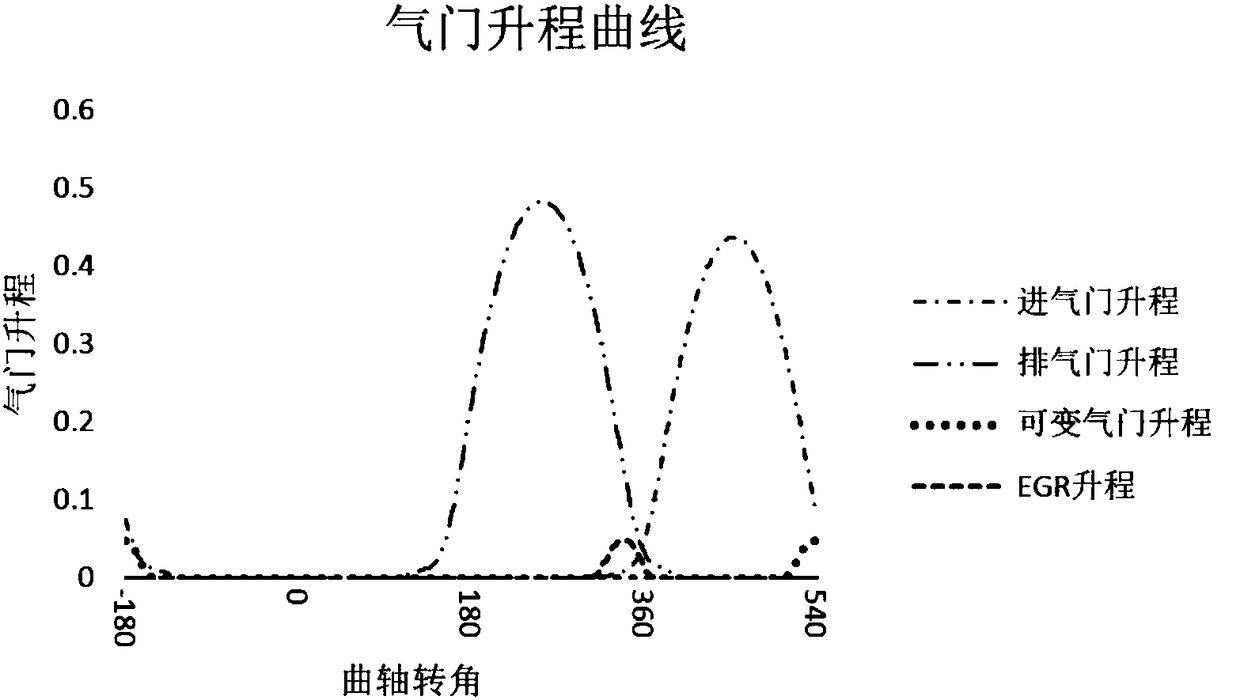
Patents
Literature
37results about How to "Effective compression ratio" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
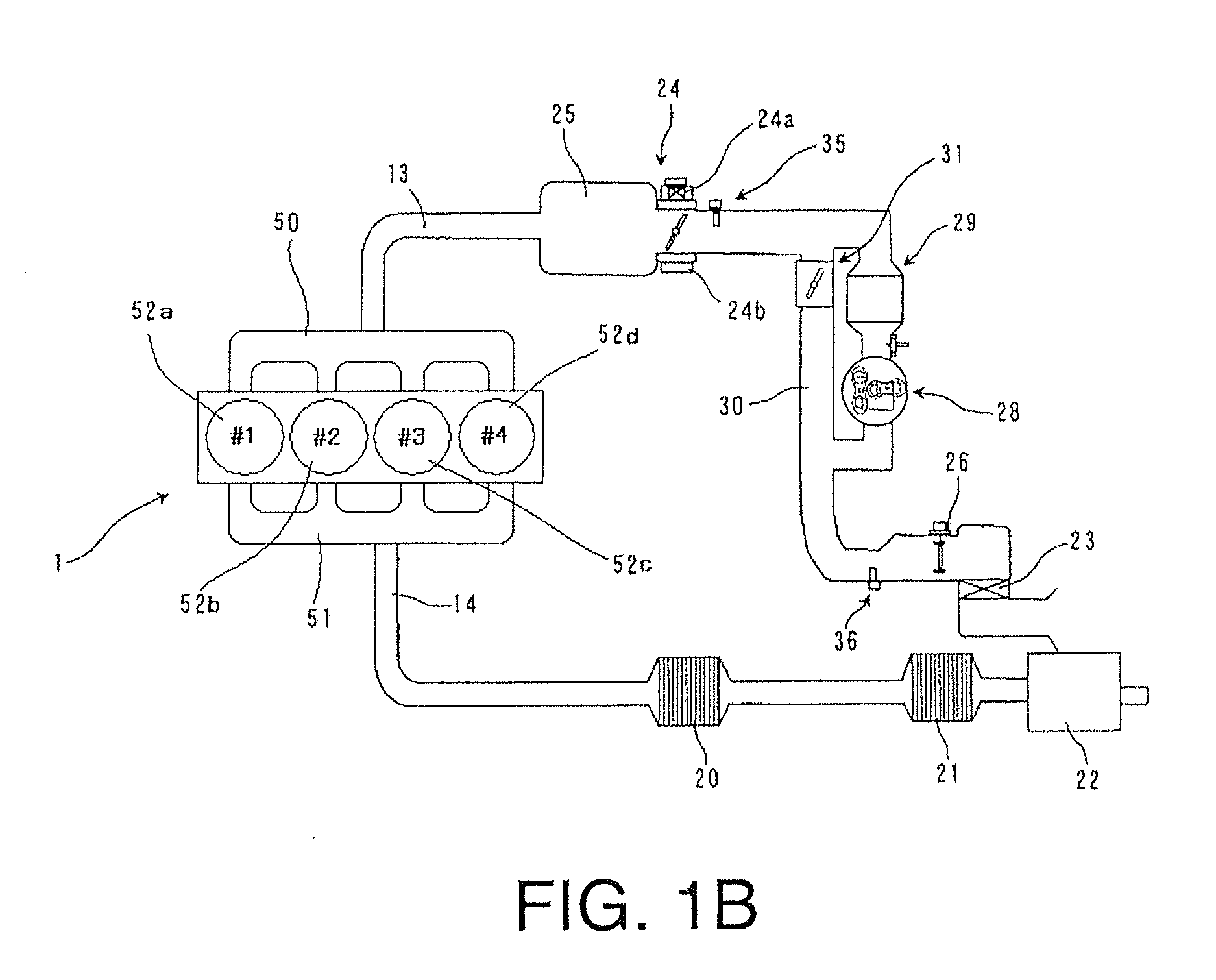
Spark-ignition gasoline engine
ActiveUS20090159045A1Quantity minimizationReduce consumptionElectrical controlAutomatic controlLow speedExhaust valve
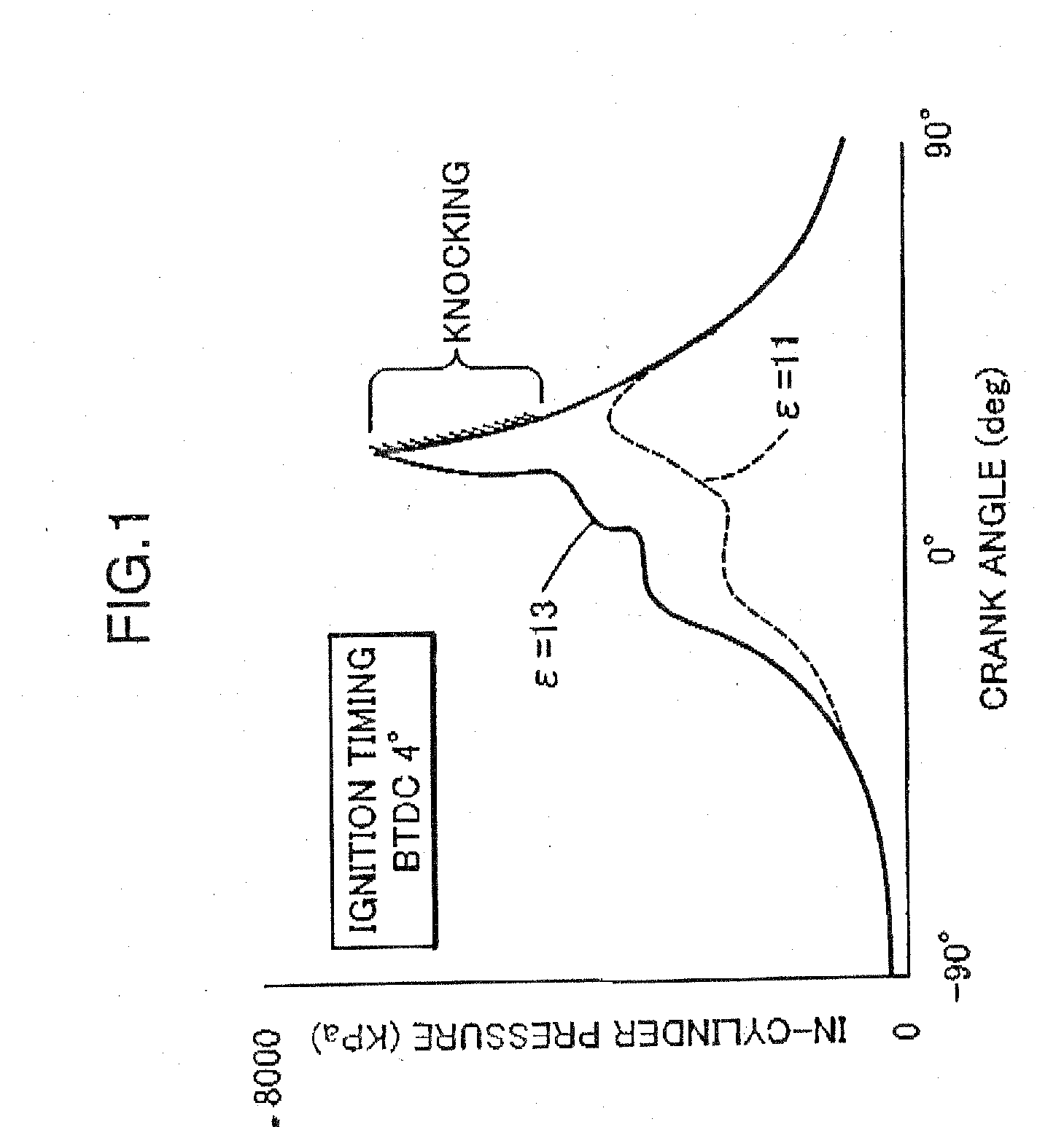
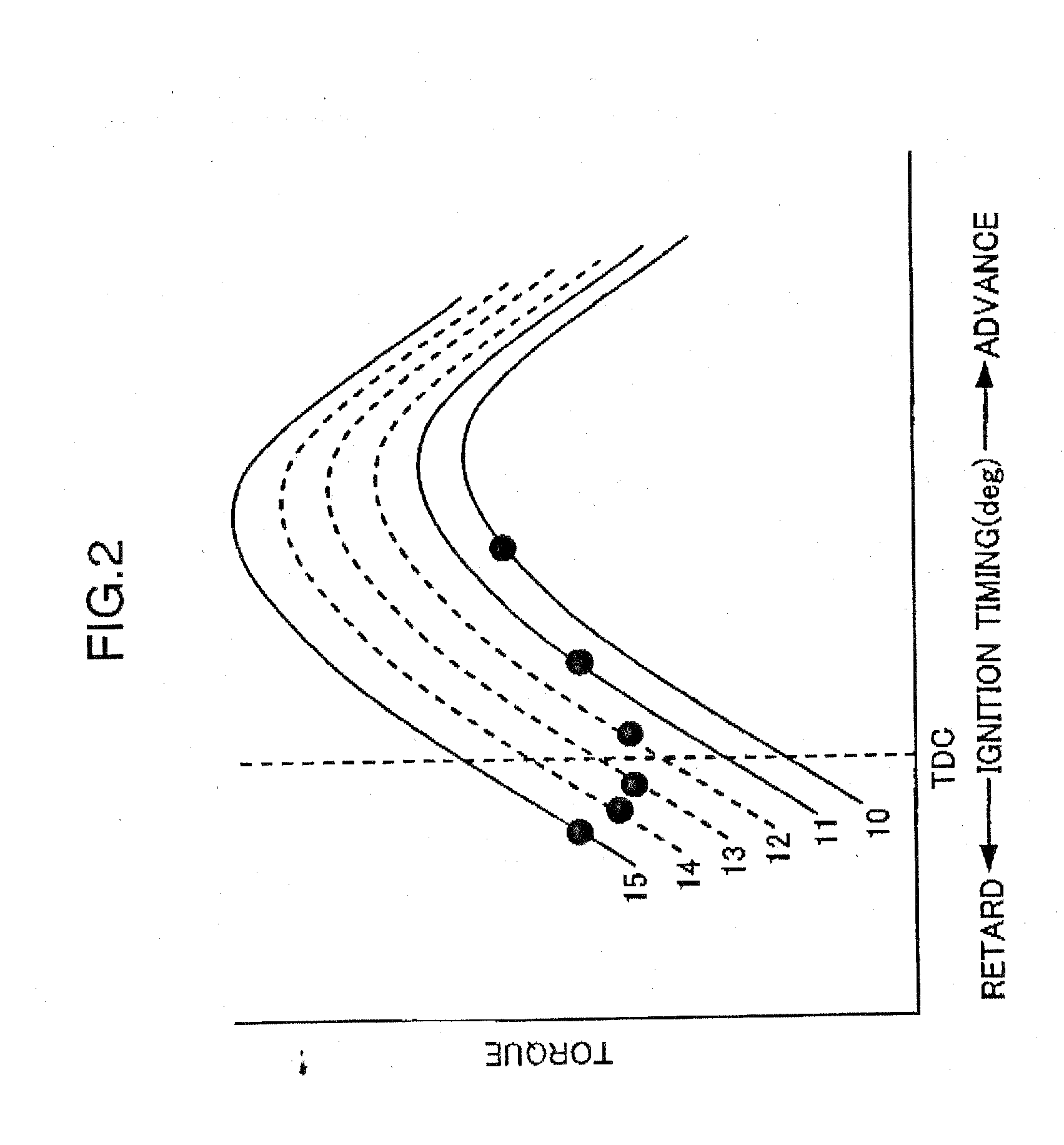
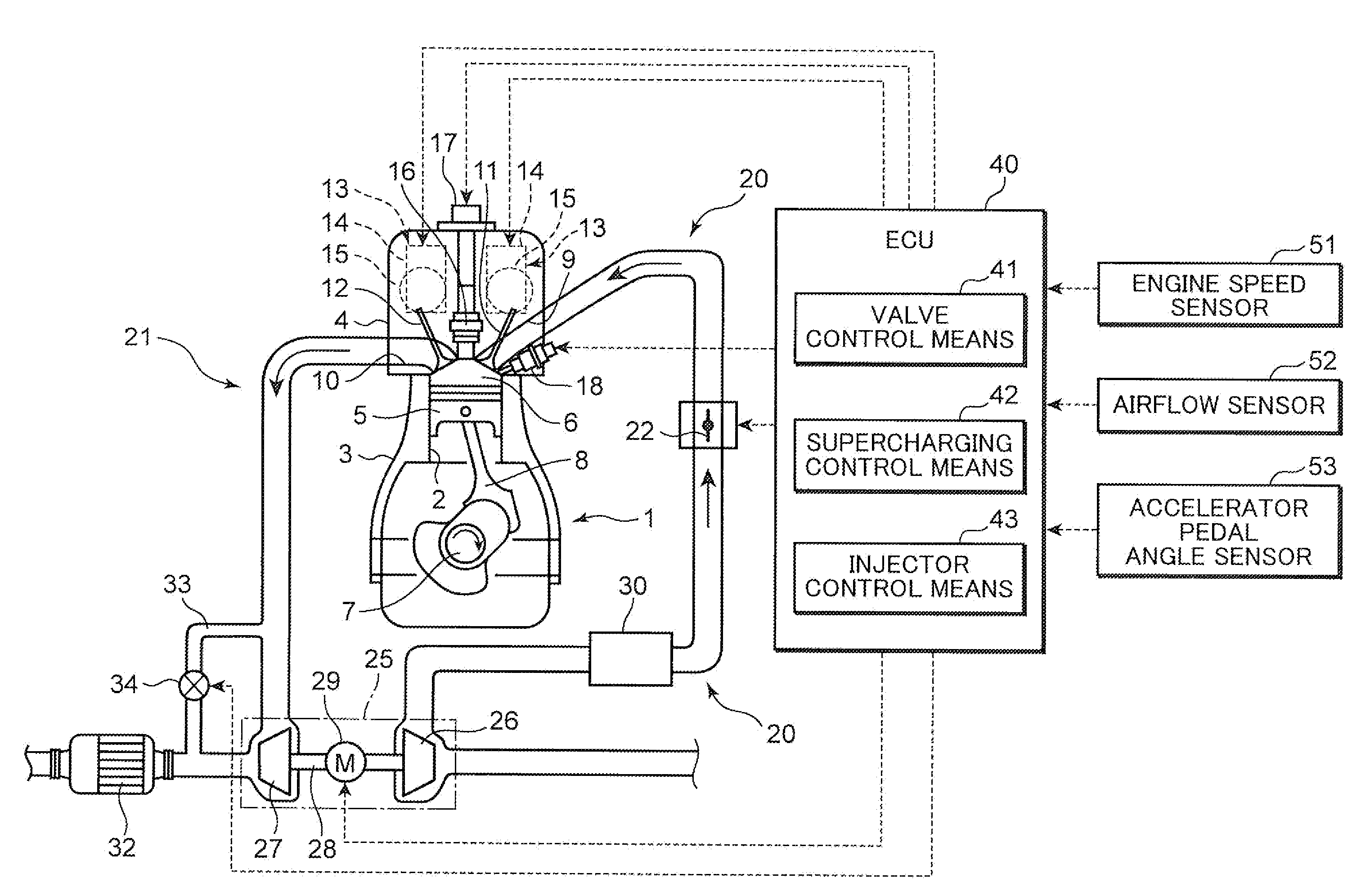
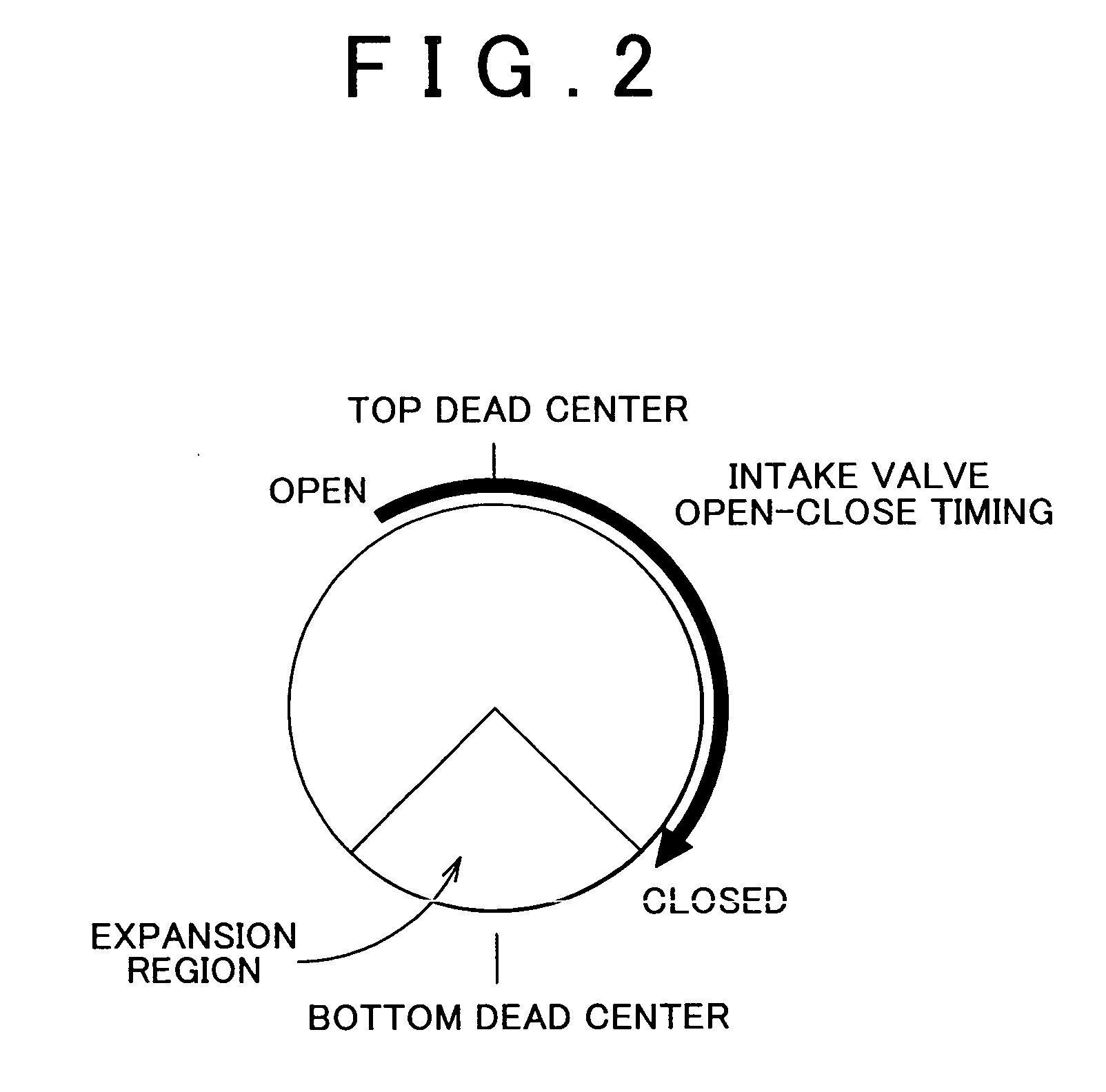
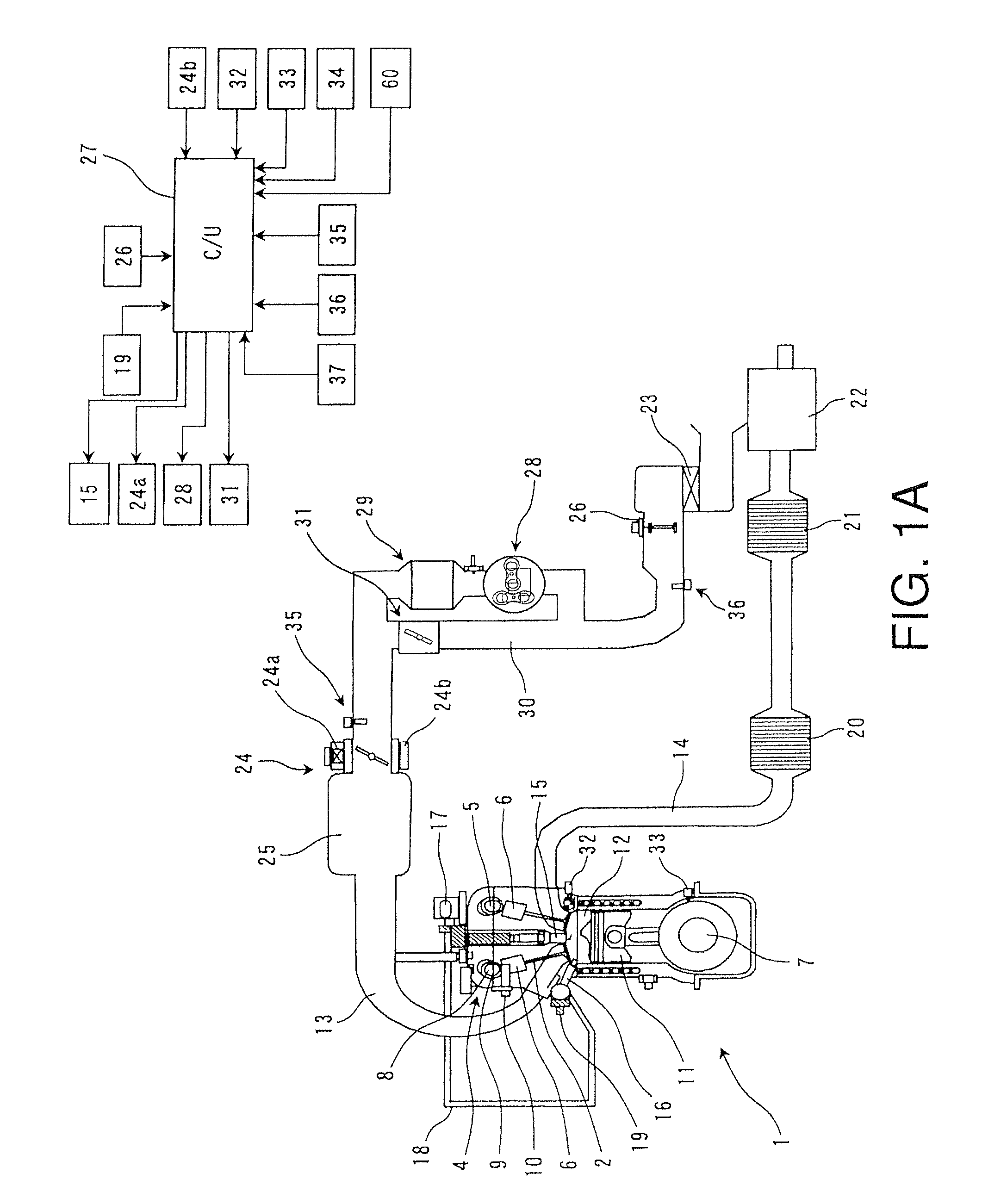
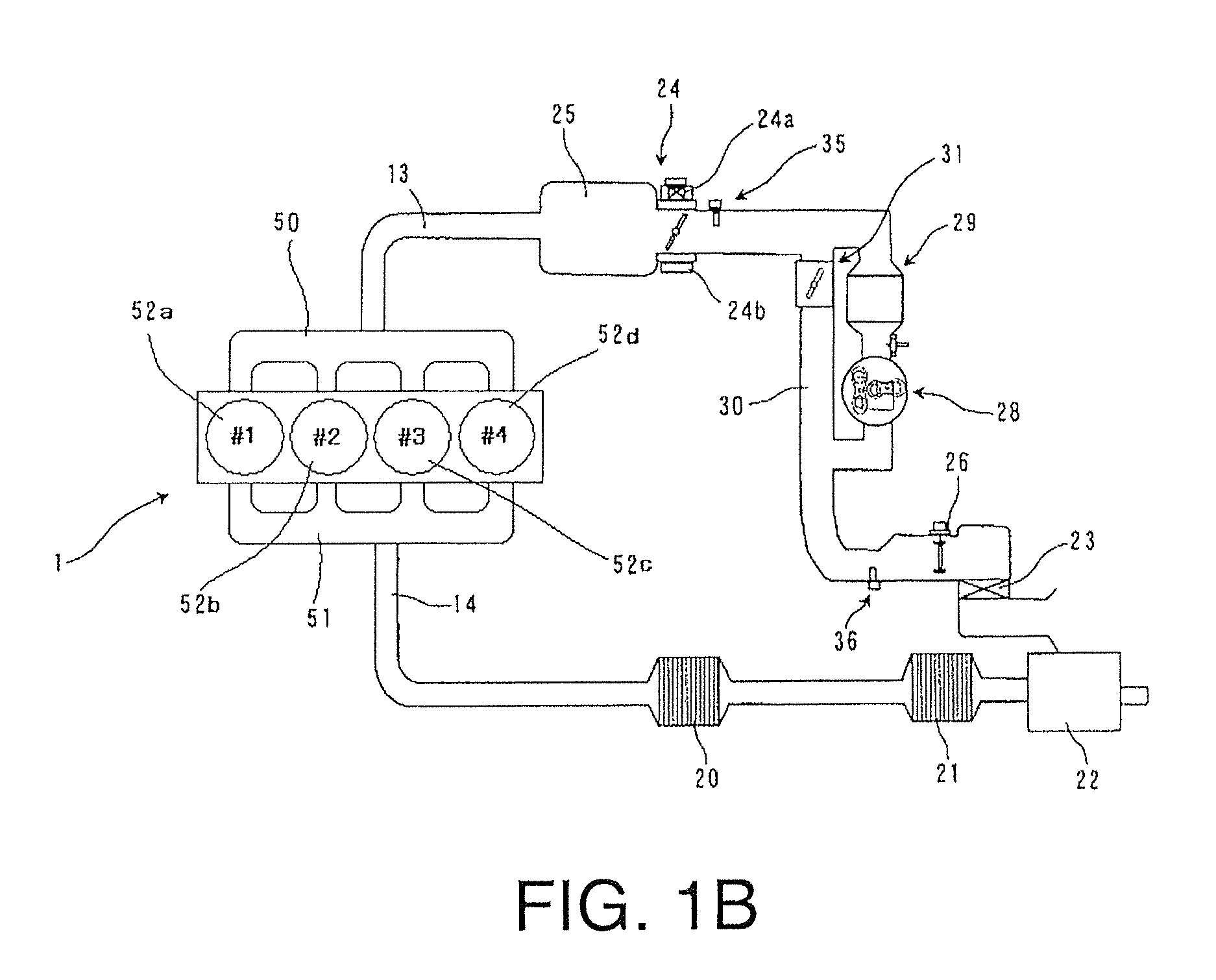
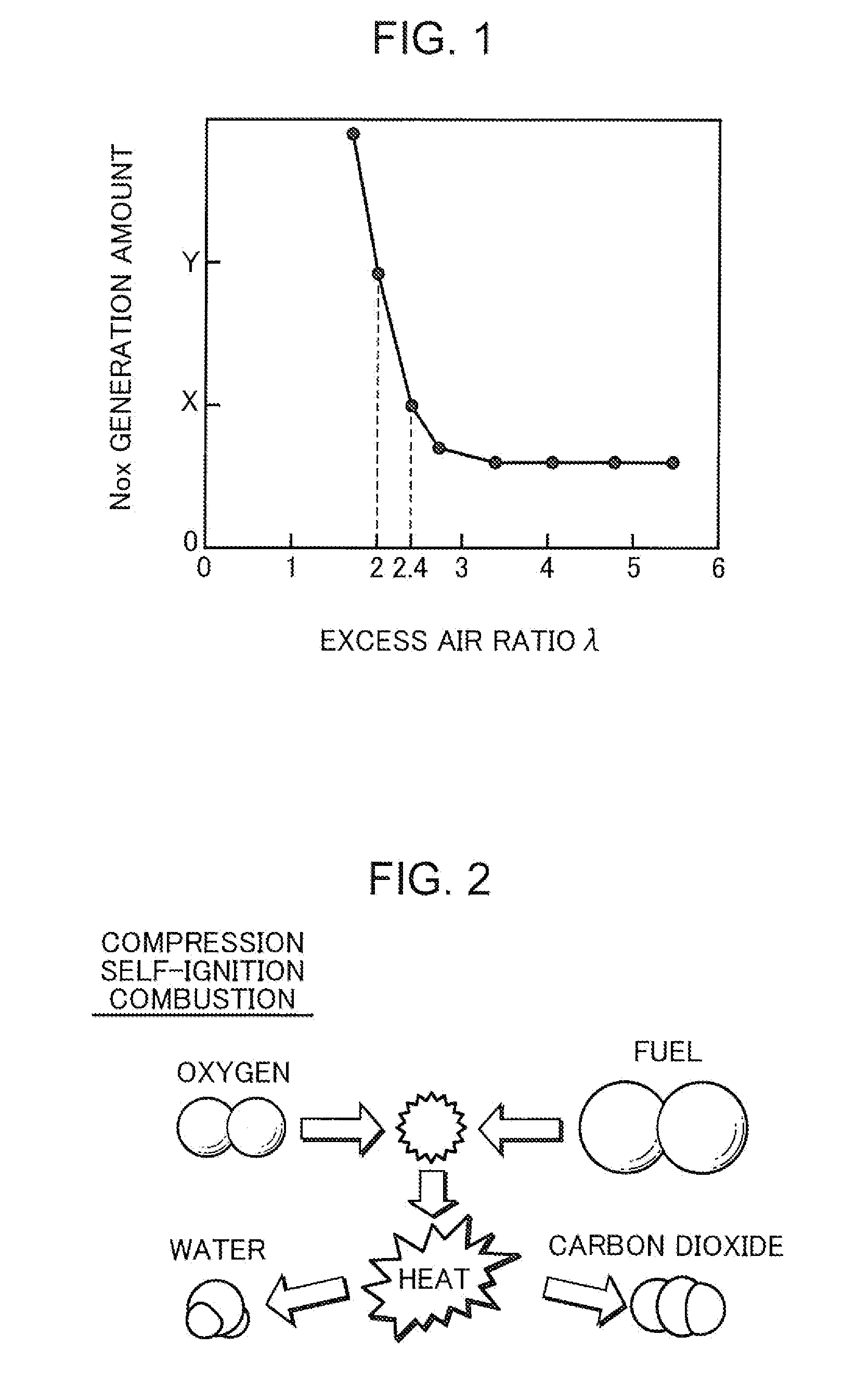
A spark-ignition gasoline engine having at least a spark plug, the engine including an engine body having a geometrical compression ratio set at 14 or more, and an intake valve and an exhaust valve provided, respectively, in intake and exhaust ports connected to each of a plurality of cylinders of the engine body. The intake and exhaust valves are adapted to open and close corresponding respective ones of the intake and exhaust ports. The engine further includes an operation-state detector adapted to detect an operation state of the engine body and a control system adapted, based on detection of the operation-state detector, to perform at least an adjustment control of an ignition timing of the spark plug, the control system being operable, when an engine operation zone is a high-load operation zone including a wide open throttle region within at least a low speed range, to retard the ignition timing to a point within a predetermined stroke range just after a top dead center of a compression stroke.
Owner:MAZDA MOTOR CORP
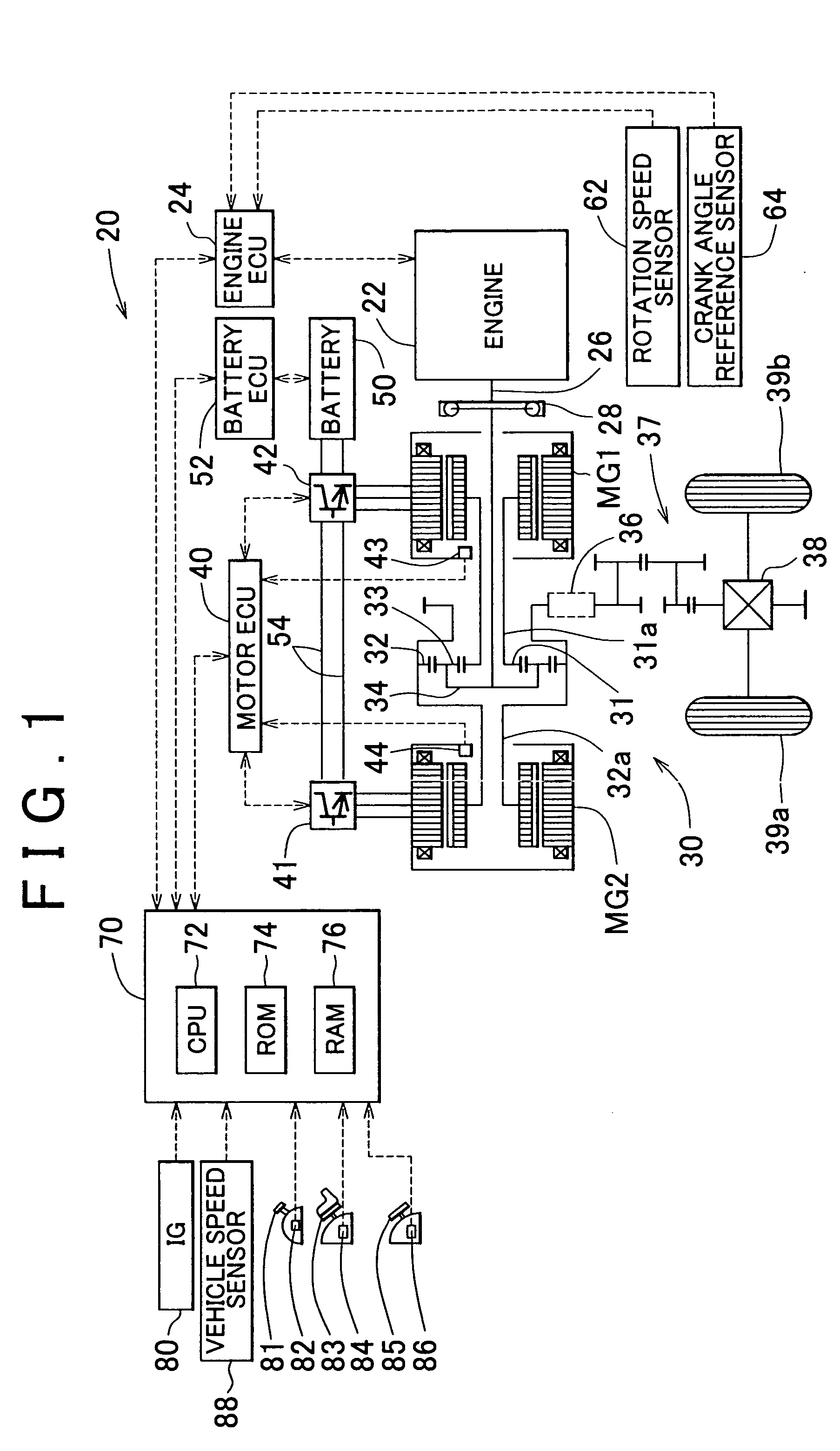
Drive apparatus, control method thereof, and motor vehicle equipped with the apparatus and the method
ActiveUS20050066933A1High expansion rateEffective compression ratioHybrid vehiclesValve arrangementsOutput deviceControl theory
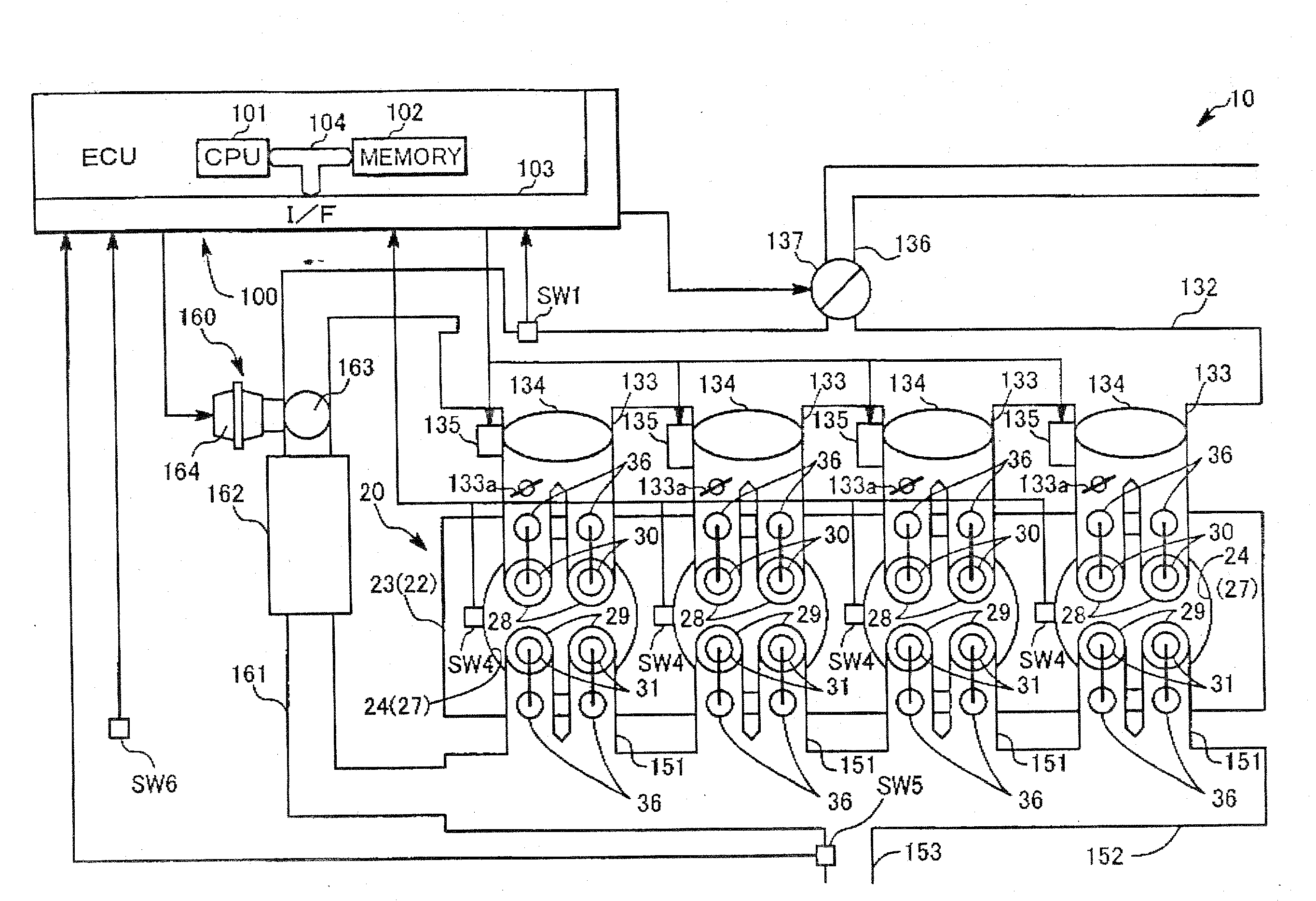
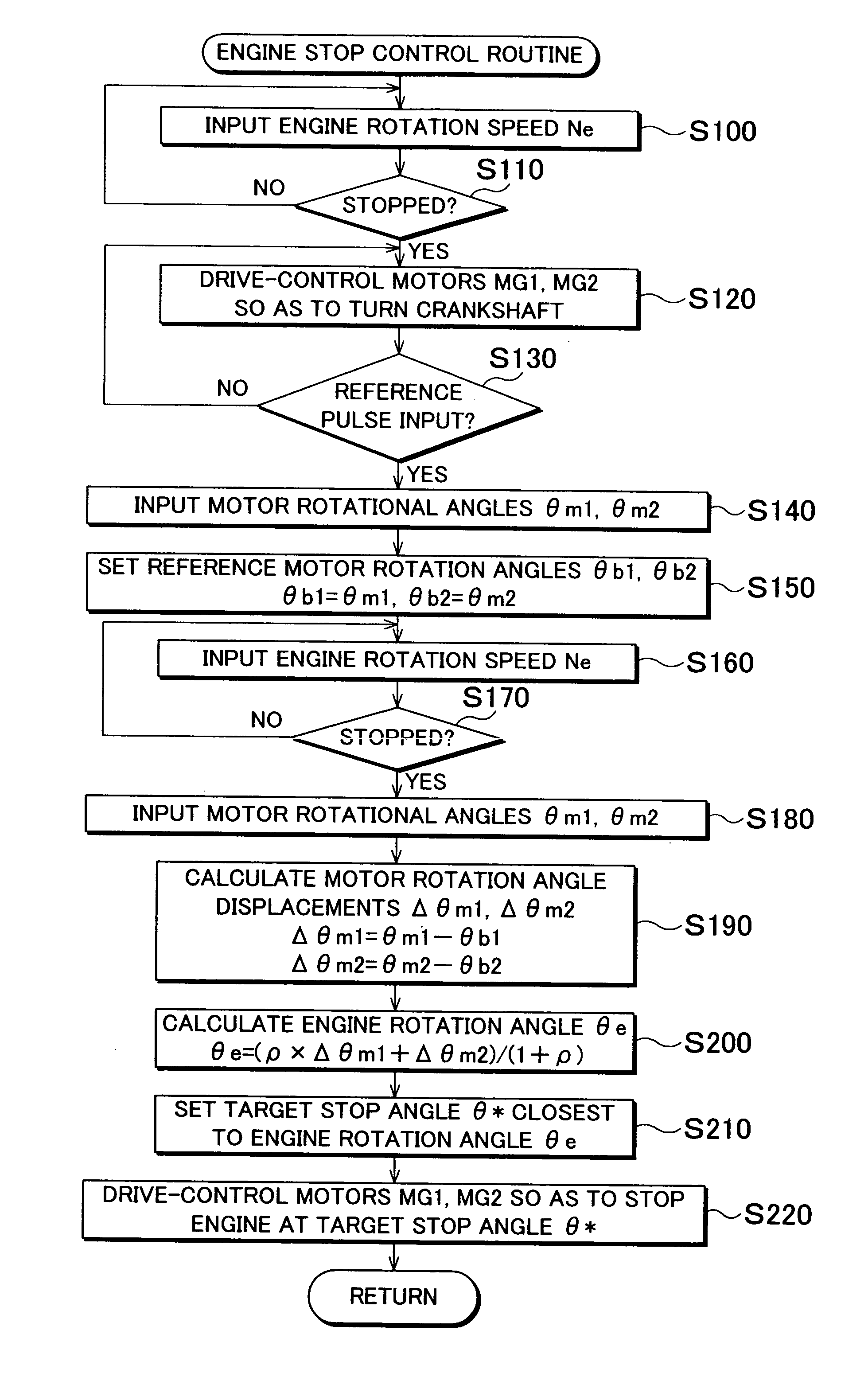
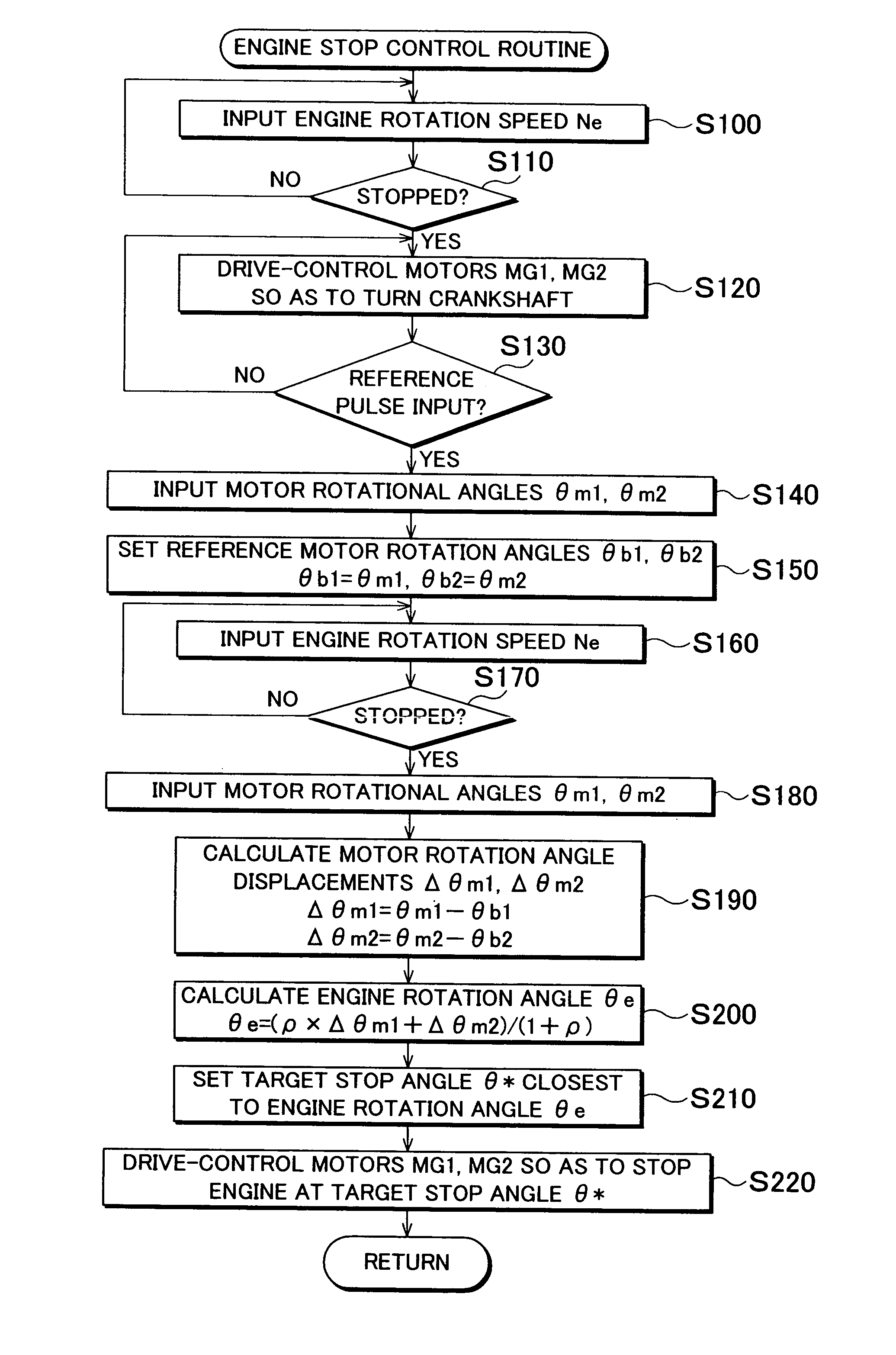
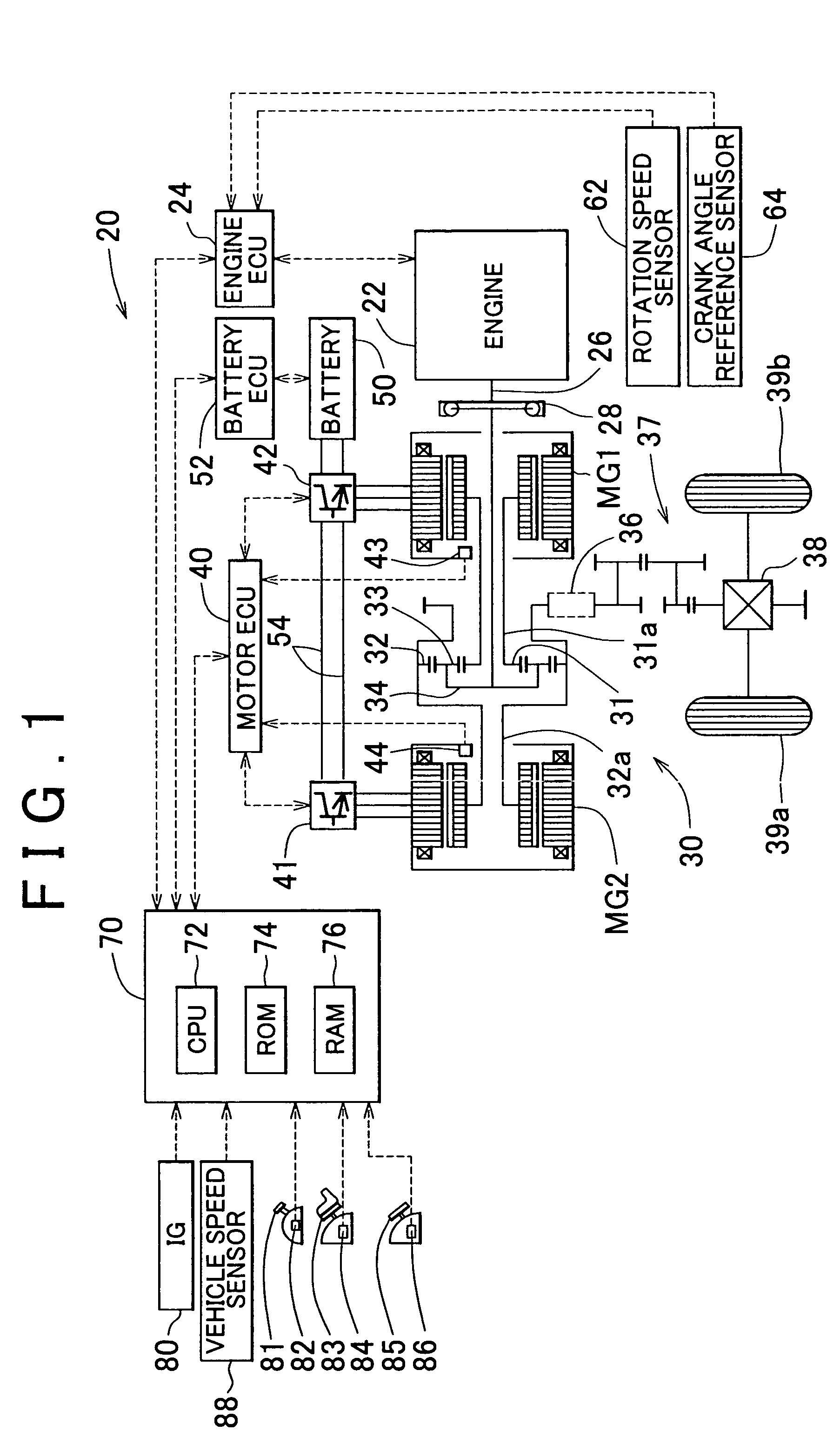
Provided herein are a drive apparatus that includes an internal combustion engine capable of operating with a high expansion ratio by reducing an effective compression ratio through advancement of an intake valve closing timing, and a control method of the drive apparatus, and a motor vehicle equipped with the apparatus and method. The drive apparatus further includes a torque output device capable of outputting a torque to an output shaft of the internal combustion engine. Upon a command to stop operation of the internal combustion engine, the apparatus controls the driving of the torque output device so that the internal combustion engine stops at a target stop position which is set outside a region that leads to an increased compression ration in an initial compression stroke when the internal combustion engine is next stated.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Control apparatus for internal combustion engine
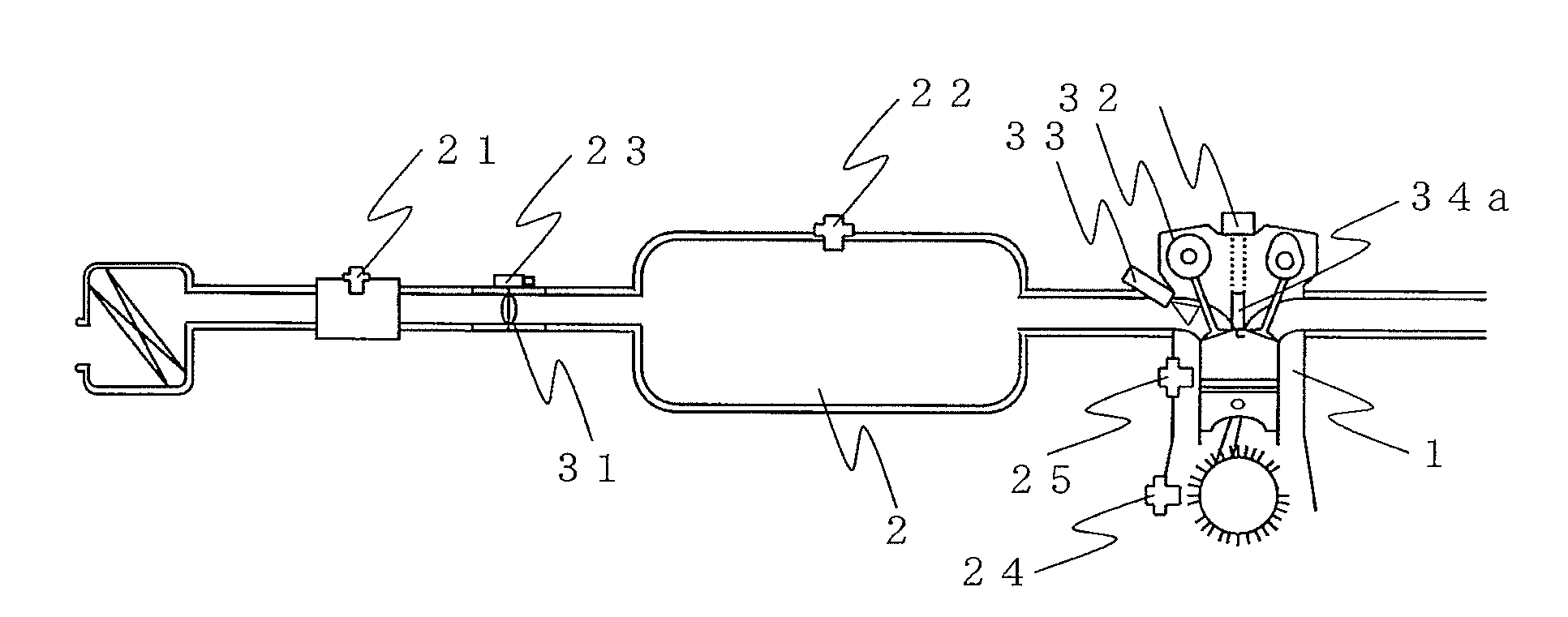
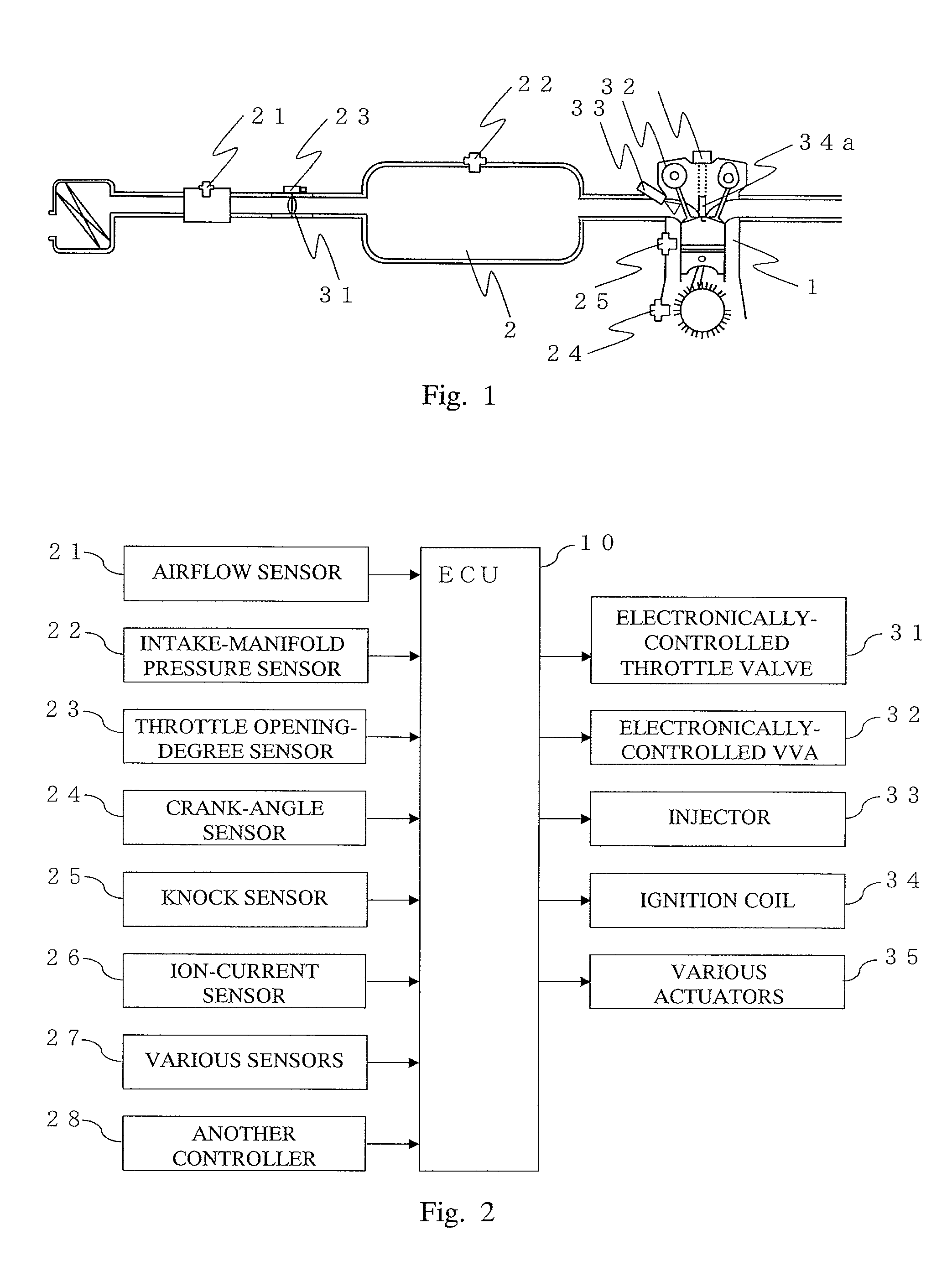
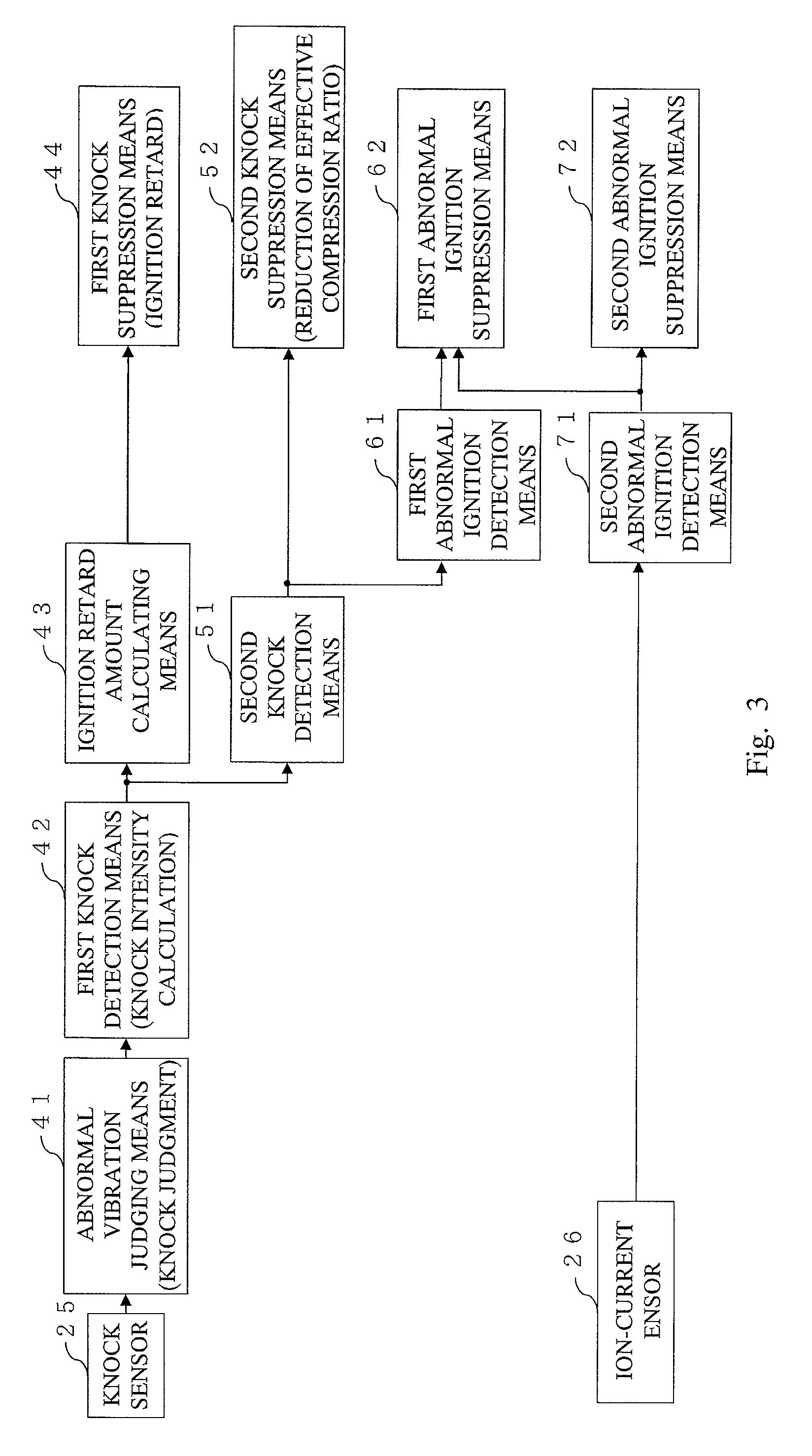
ActiveUS20110093186A1Shorten the durationReduce fluctuationAnalogue computers for vehiclesElectrical controlIgnition timingCompression ratio
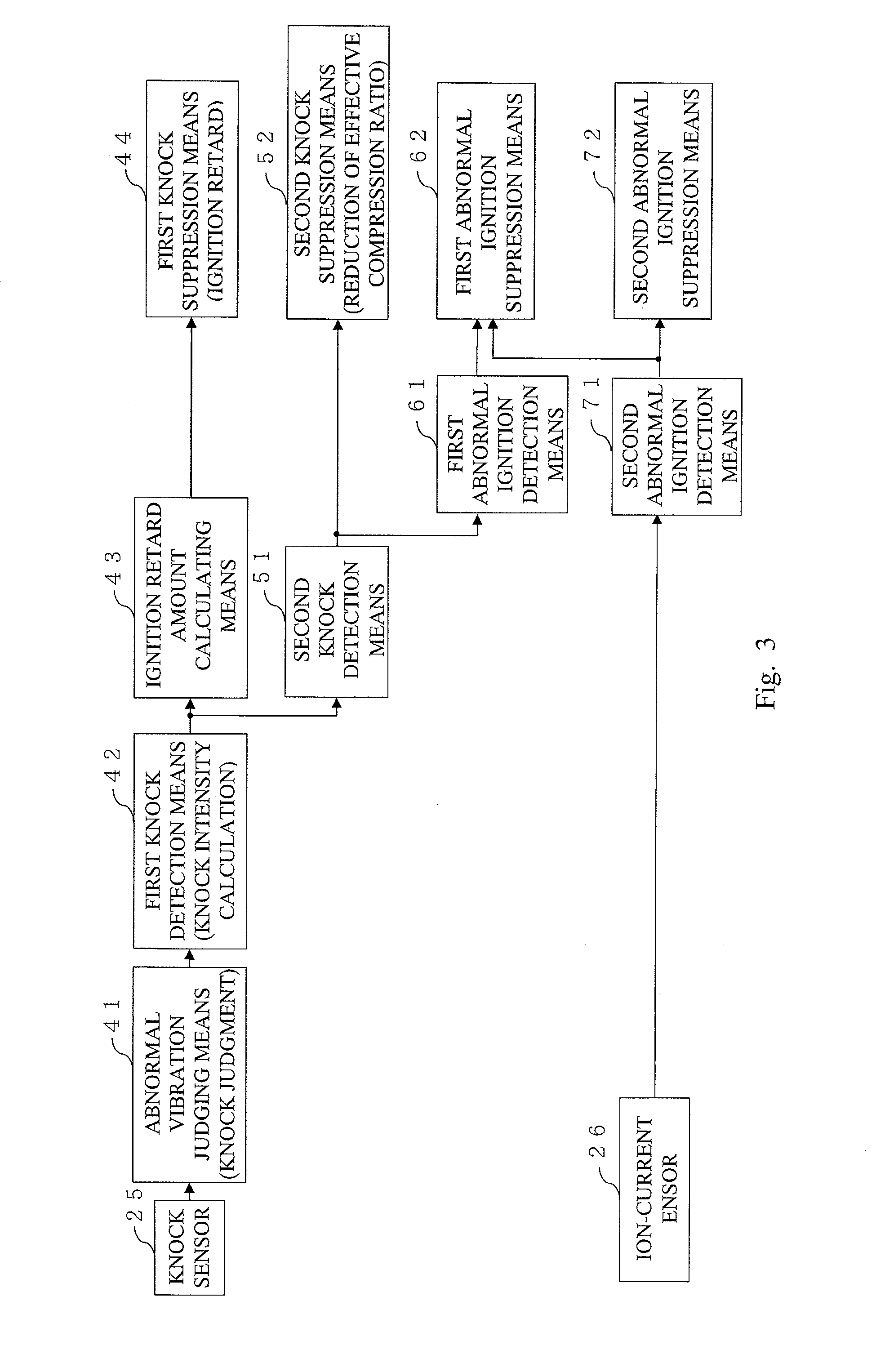
Control apparatus for an internal combustion engine including: a second knock detection unit for detecting occurrence of a second knock due to an effective compression ratio when ignition timing is on a retard side of a predetermined value in the case where a first knock is detected; a second knock suppression unit for suppressing the second knock when the second knock is detected; a first abnormal ignition detection means for detecting occurrence of first abnormal ignition due to the pre-ignition or the post-ignition when a knock intensity of the second knock is equal to or larger than a predetermined value; and a first abnormal ignition suppression unit for suppressing the first abnormal ignition by performing fuel control for the internal combustion engine when the first abnormal ignition is detected.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP +1
Method and apparatus for controlling supercharged engine
ActiveUS20110180047A1Increase compression ratioReduce amount of airElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesAutomotive engineeringForced induction
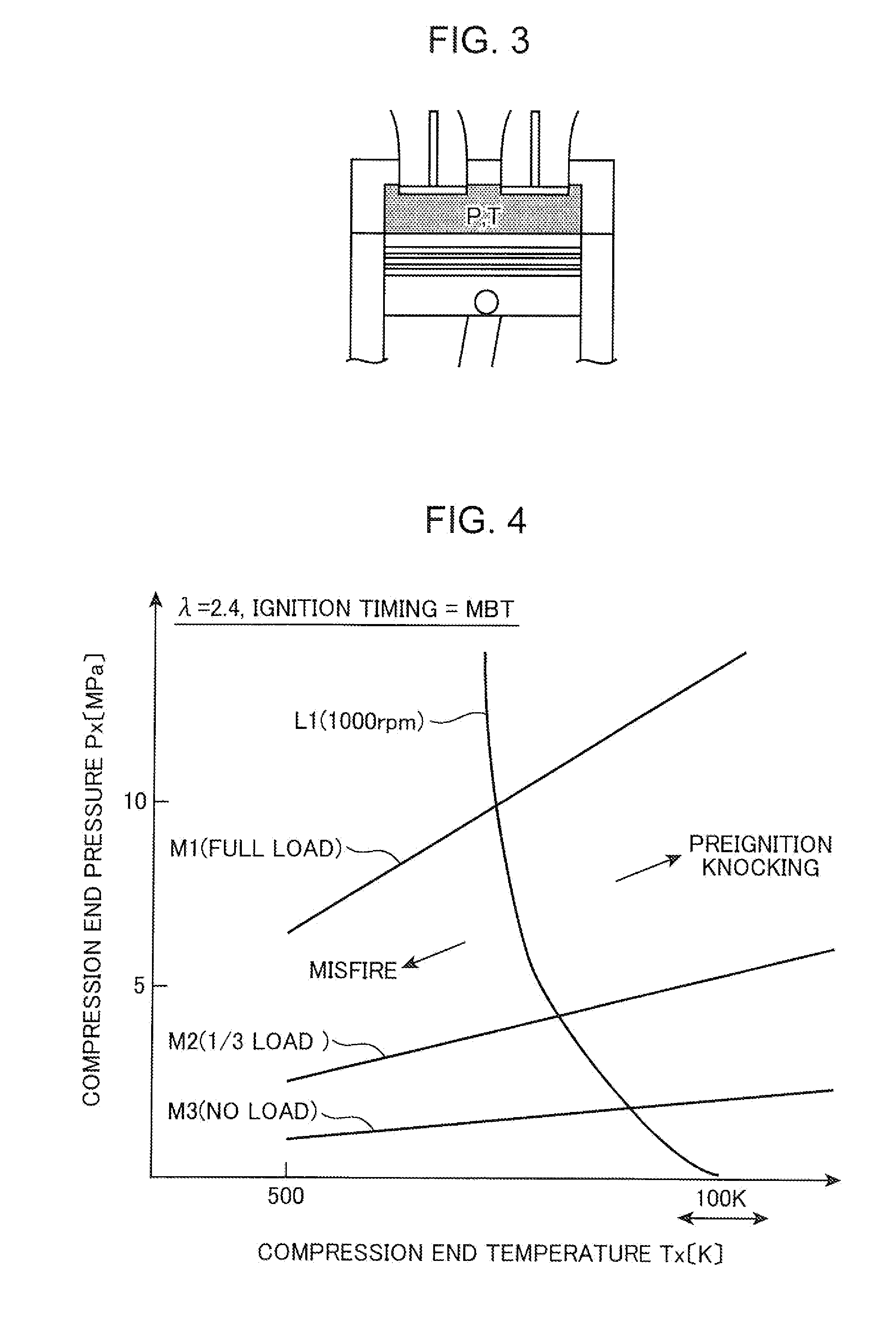
A supercharged engine has a geometric compression ratio ser to 16 or more and is designed to perform a compression self-ignition combustion under an air-fuel ratio leaner than a stoichiometric air-fuel ratio at least in a low engine speed range. On a lower engine load side than a given engine load within an engine operating region at which the compression self-ignition combustion is performed, a fresh air amount is reduced and an effective compression ratio (ε′) is increased, as compared with a higher engine load side than the given engine load within the engine operating region, and, on the higher engine load side than the given engine load, a supercharging pressure based on a supercharger (25) is increased to increase the fresh air amount, and the effective compression ratio (ε′) is reduced, as compared with the lower engine load side than the given engine load. This makes it possible to perform the compression self-ignition combustion under a lean air-fuel ratio in a wider engine load range to effectively enhance engine thermal efficiency, while eliminating a need for an operation of forcedly raising / lowering a temperature of fresh air.
Owner:MAZDA MOTOR
Control apparatus for internal combustion engine
ActiveUS8316824B2Shorten the durationReduce fluctuationAnalogue computers for vehiclesElectrical controlIgnition timingUltimate tensile strength
Control apparatus for an internal combustion engine including: a second knock detection unit for detecting occurrence of a second knock due to an effective compression ratio when ignition timing is on a retard side of a predetermined value in the case where a first knock is detected; a second knock suppression unit for suppressing the second knock when the second knock is detected; a first abnormal ignition detection means for detecting occurrence of first abnormal ignition due to the pre-ignition or the post-ignition when a knock intensity of the second knock is equal to or larger than a predetermined value; and a first abnormal ignition suppression unit for suppressing the first abnormal ignition by performing fuel control for the internal combustion engine when the first abnormal ignition is detected.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP +1
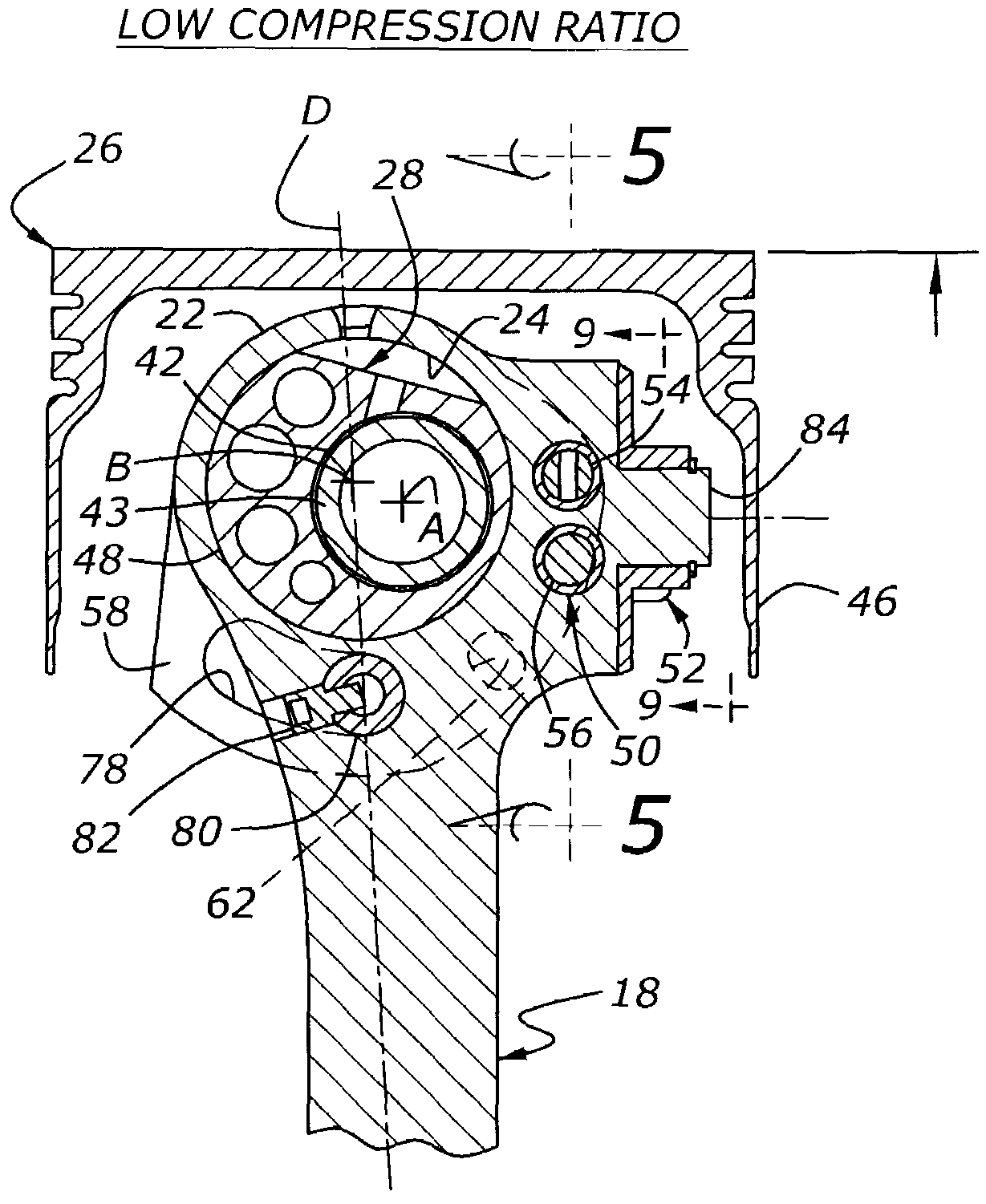
Variable compression ratio engine with dedicated bumper
InactiveUS7533638B1Effective compression ratioEngine controllersMachines/enginesFlangeVariable compression ratio
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
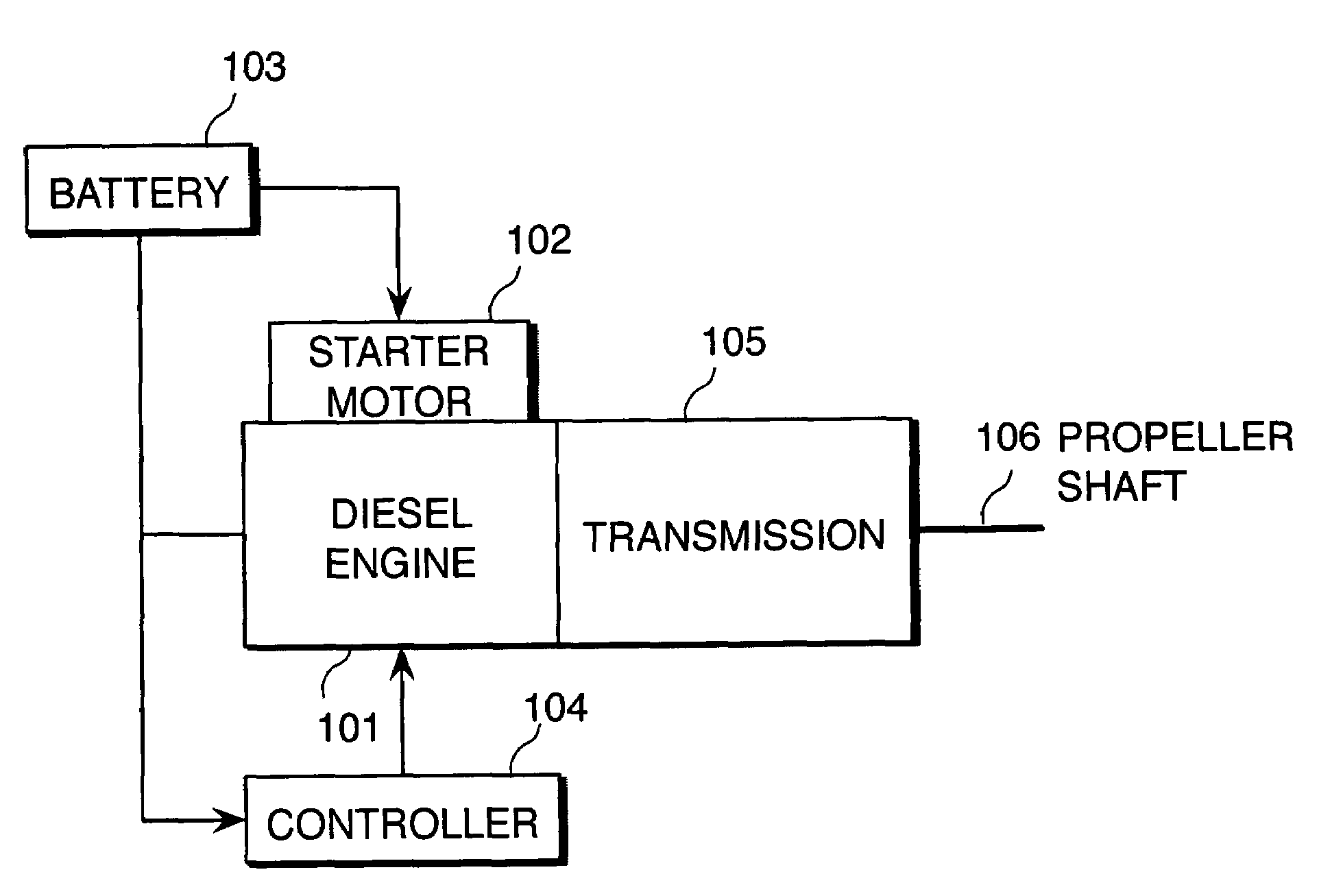
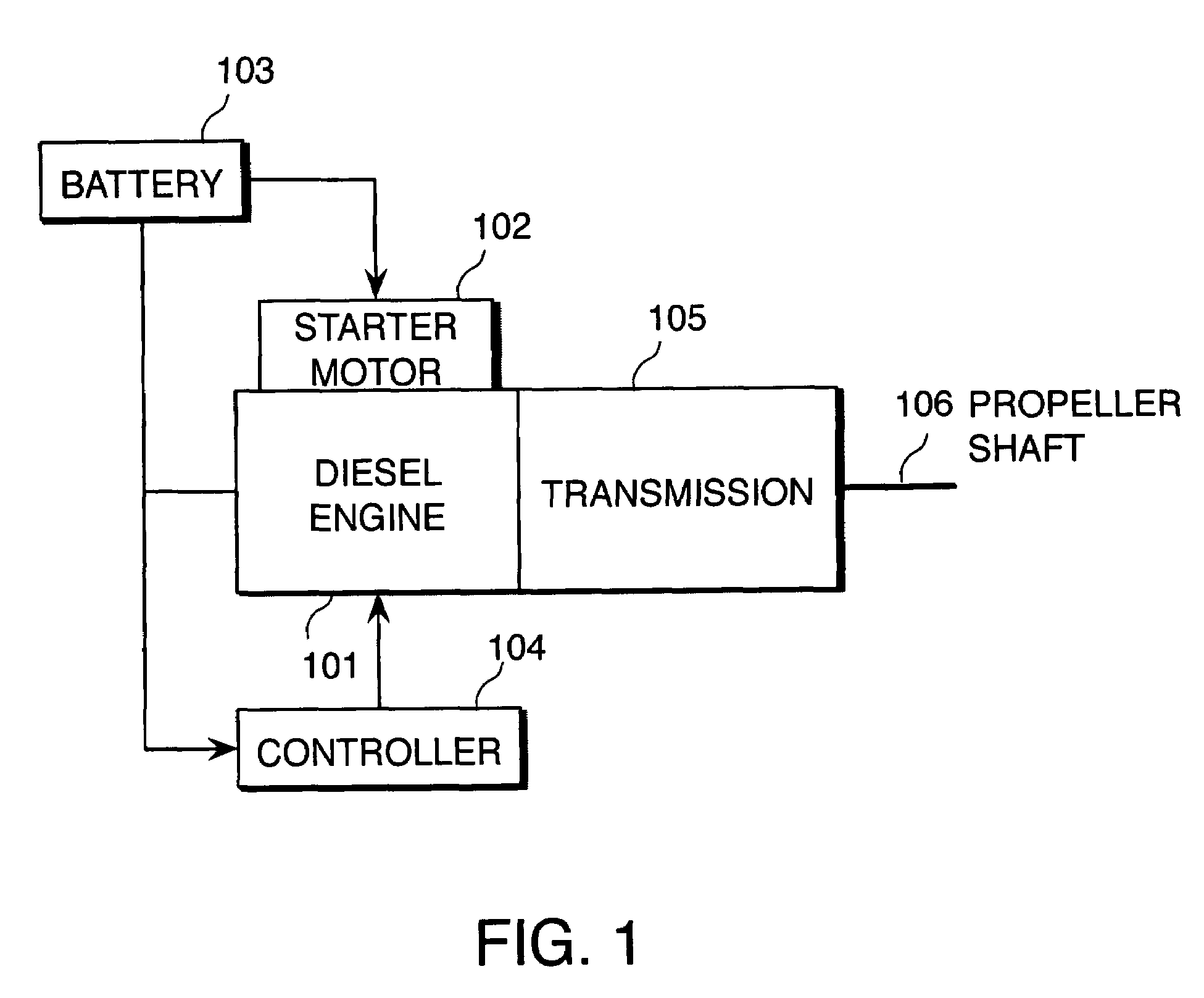
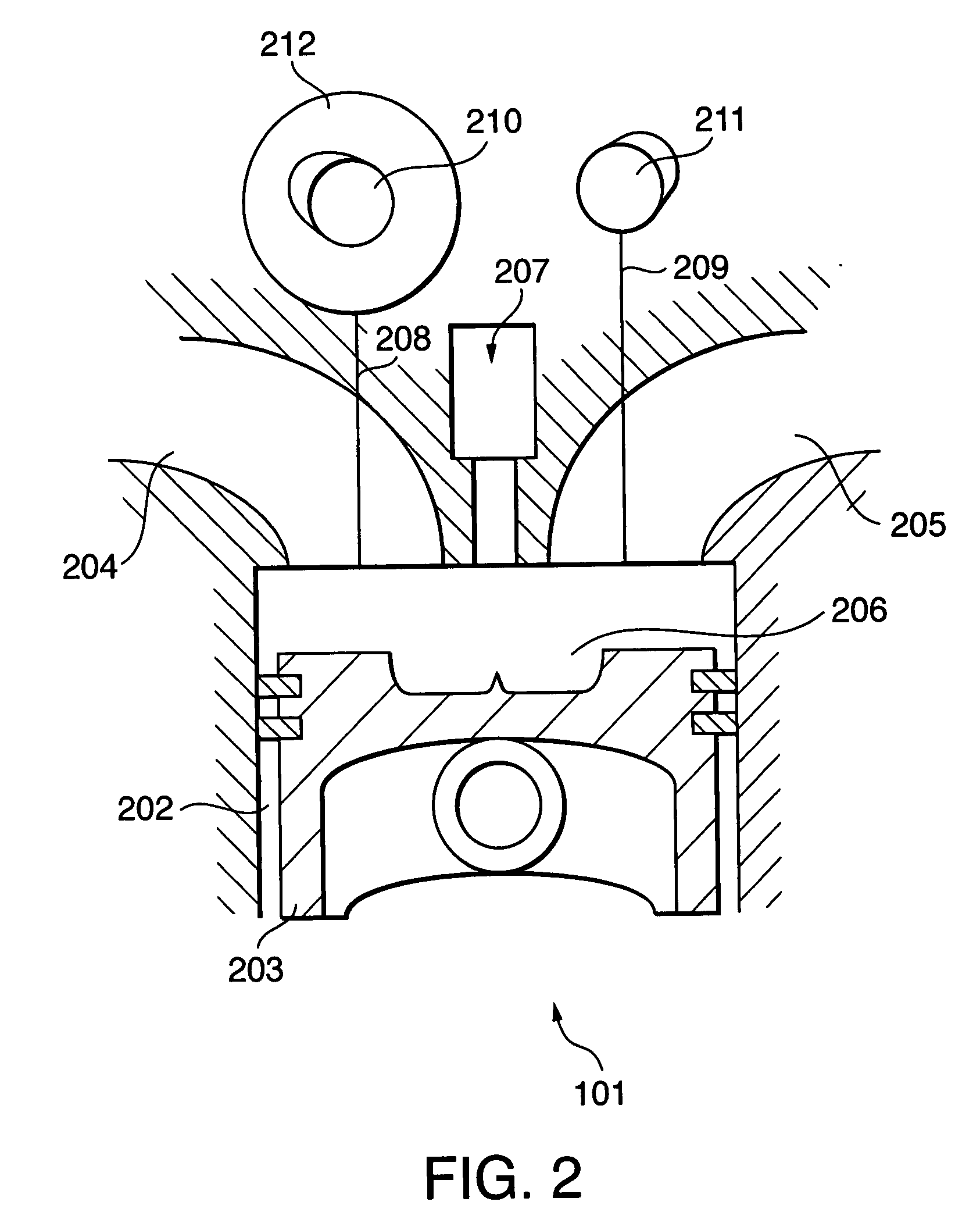
Start-up control for internal combustion engine
InactiveUS20070234990A1Effective compression ratioDefect occurrenceHybrid vehiclesValve arrangementsCombustionResonance
An internal combustion engine (101, 601, 901) alters an effective compression ratio from an effective compression ratio for a start-up operation to a larger effective compression ratio for a normal operation when an engine rotation speed (NE) increases beyond a resonance rotation speed region during cranking. A controller (104, 610, 910) determines whether or not the engine (101, 601, 901) has reached a combustion possible state on the basis of the engine rotation speed (NE) during cranking and an operating parameter (PA, TA, TW, P_Rail, V_Ang) other than the engine rotation speed (NE) (S1102, S1202, S1204). When the determination is negative, the controller (104, 610, 910) inhibits fuel supply to the engine (101, 601, 901) by a fuel supply device (207), even when the engine rotation speed has increased beyond the resonance rotation speed region (S406). In so doing, a combustion defect such as a misfire is prevented.
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD
Pre-ignition estimation/control device for an internal combustion engine
ActiveUS20120089315A1Control changesEffective compression ratioAnalogue computers for vehiclesElectrical controlPhase controlEngineering
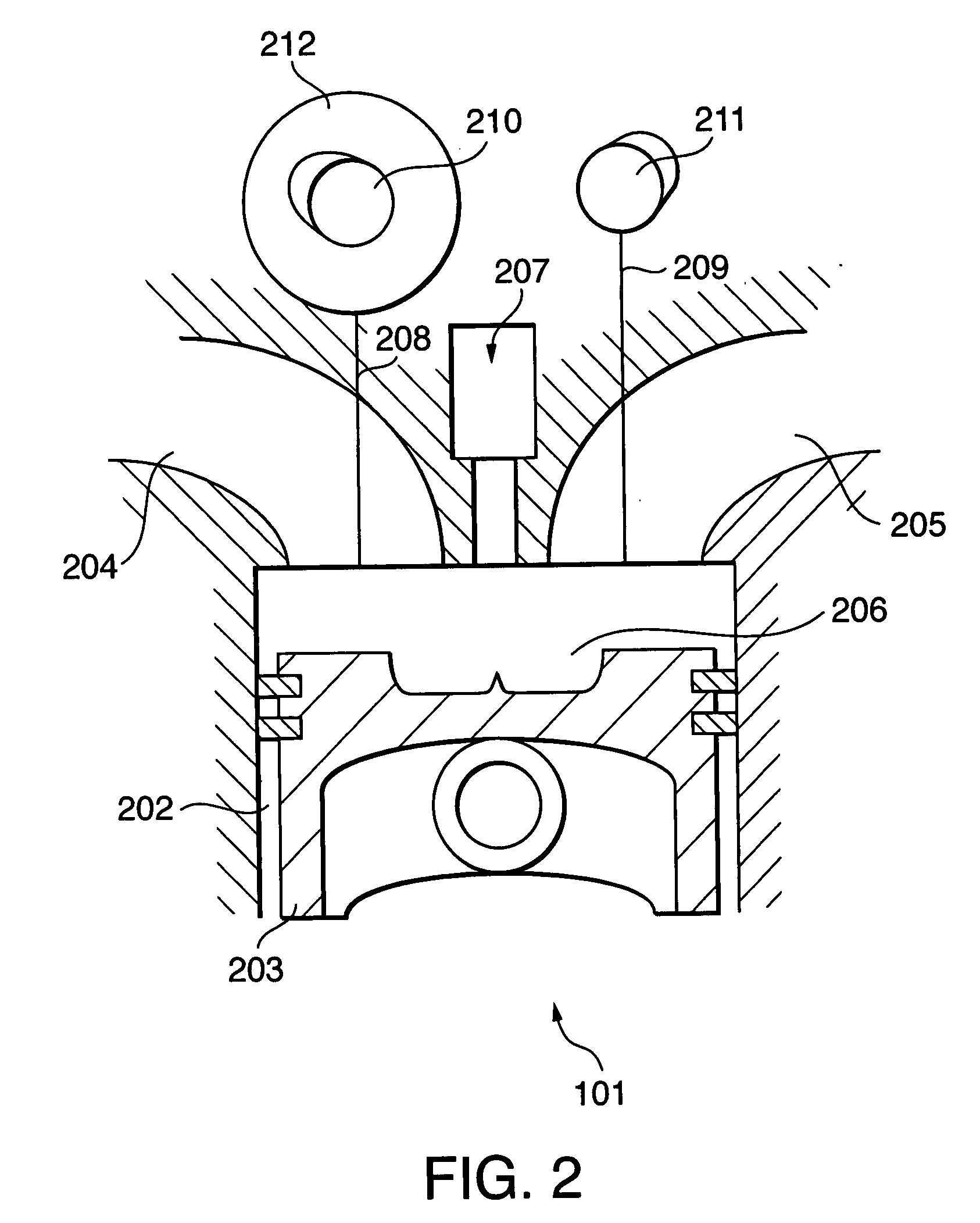
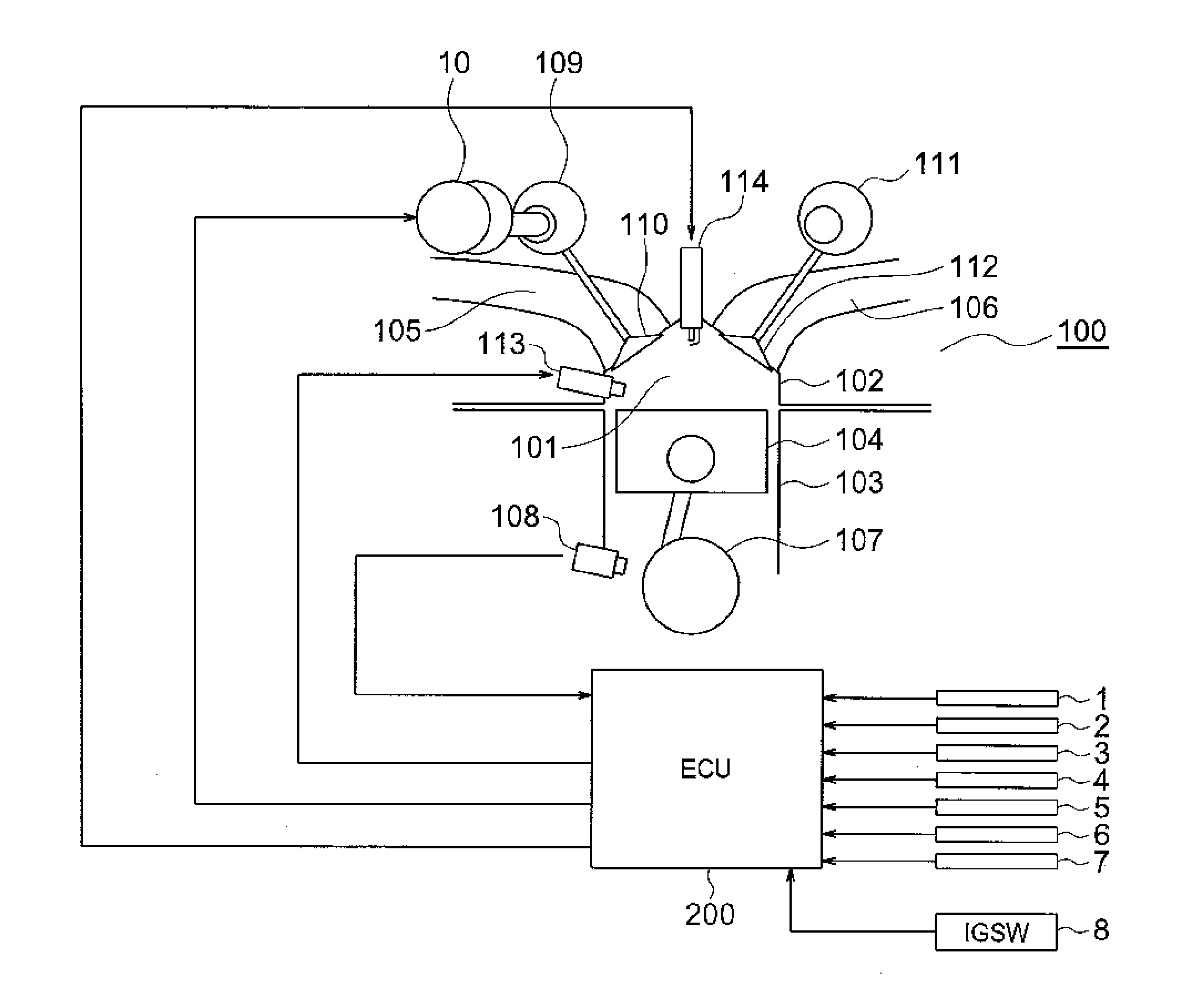
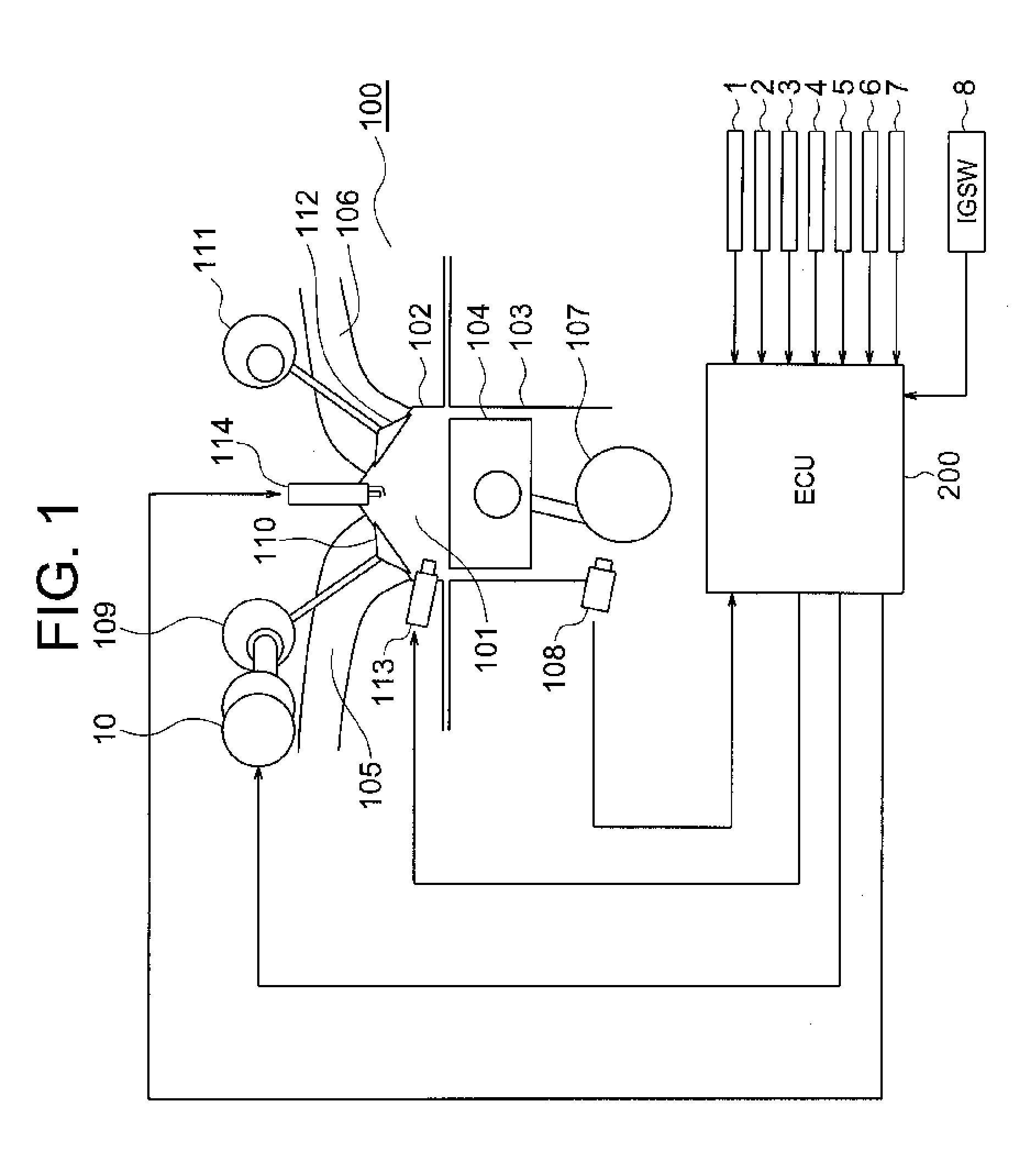
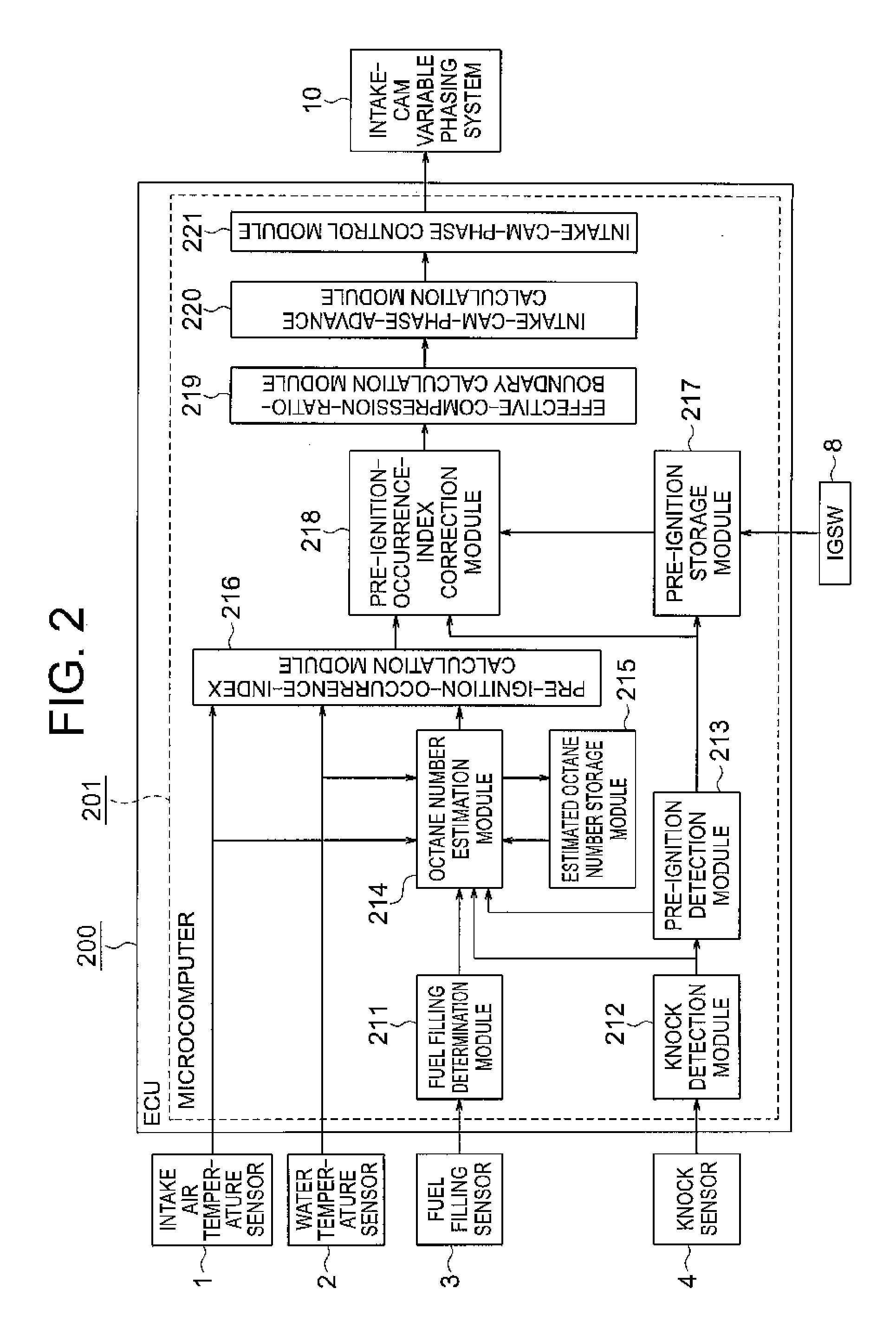
A pre-ignition estimation / control device includes: an octane number estimation module for estimating an octane number of a fuel based on detection signals received from an intake air temperature sensor, a water temperature sensor, etc; a pre-ignition-occurrence-index calculation module for calculating a pre-ignition occurrence index based on the estimated octane number and the like; a pre-ignition-occurrence-index correction module for correcting the pre-ignition occurrence index so as to cause the pre-ignition more likely to occur; an effective-compression-ratio-boundary calculation module for calculating a boundary of an effective compression ratio based on the pre-ignition occurrence index; an intake-cam-phase-advance calculation module for calculating a phase advance of an intake cam based on the boundary of the effective compression ratio and the like; and an intake-cam-phase control module for controlling an intake-cam variable phasing system based on the phase advance of the intake cam, to thereby restrict a change in phase advance.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Auto-ignition internal combustion engine with partial deactivation and method for the operation of an internal combustion engine of said type
ActiveUS20130276755A1Increase loadReduce specific fuel consumptionElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesDependent mannerCompression ratio
Methods and systems are provided for optimizing the operation of a multi-cylinder auto-ignition internal combustion engine. By configuring the cylinders in multiple groups based on compression ratios, and operating the cylinders in a load-dependent manner, fuel consumption may be optimized.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Variable compression ratio engine with isolated actuator
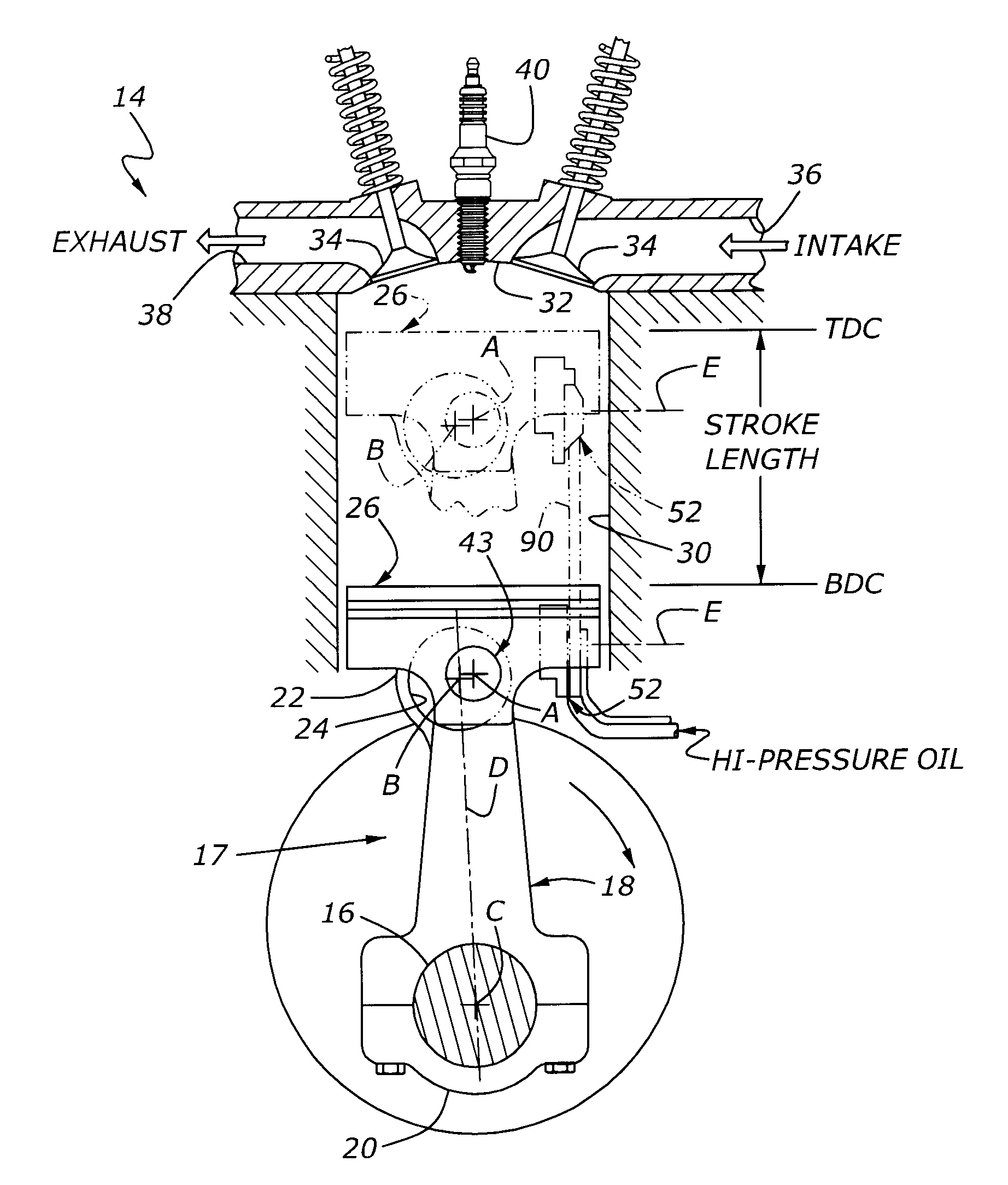
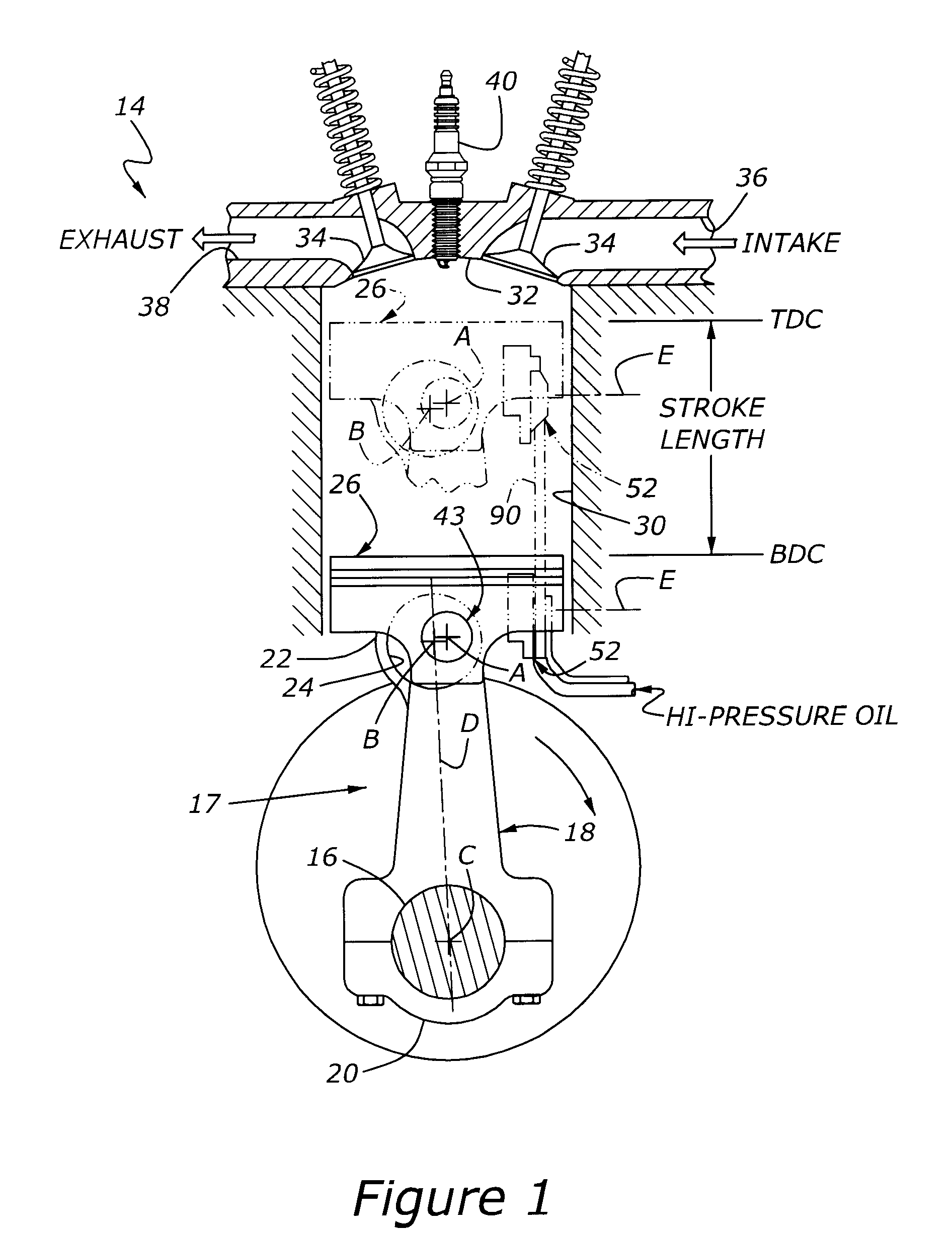
InactiveUS7685974B2Prevents unintended spatial displacementEffective compression ratioEngine controllersMachines/enginesEngineeringActuator
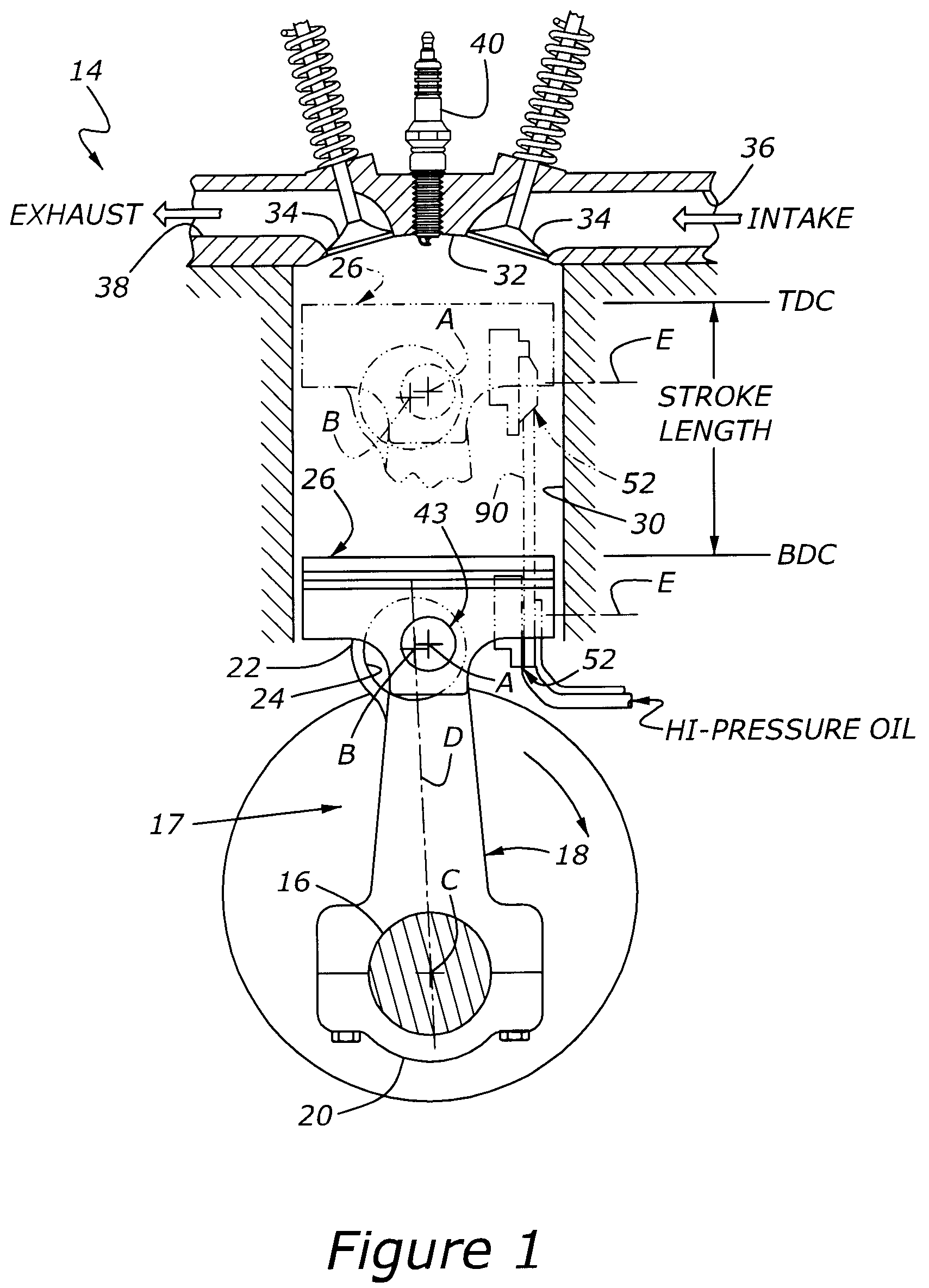
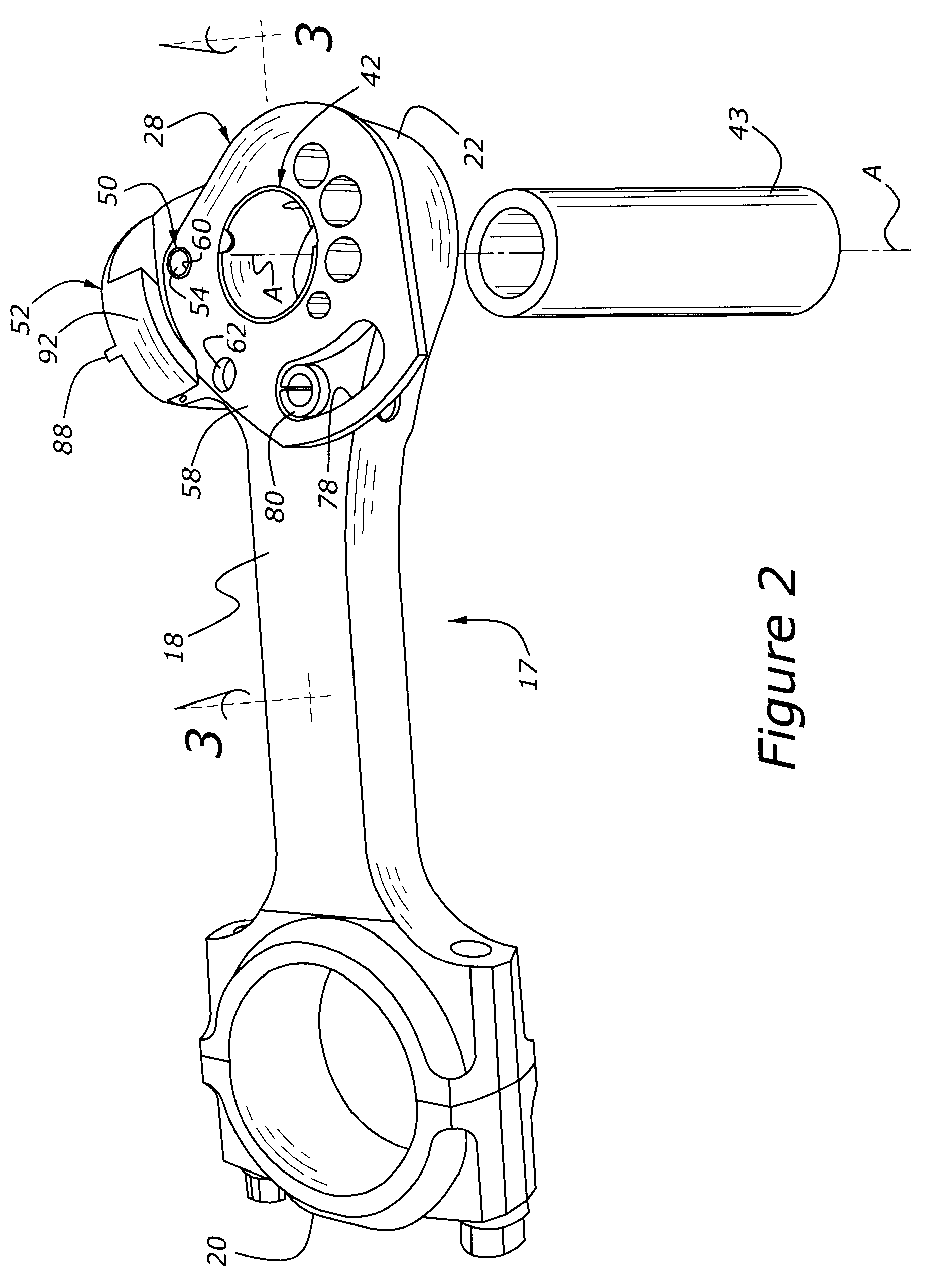
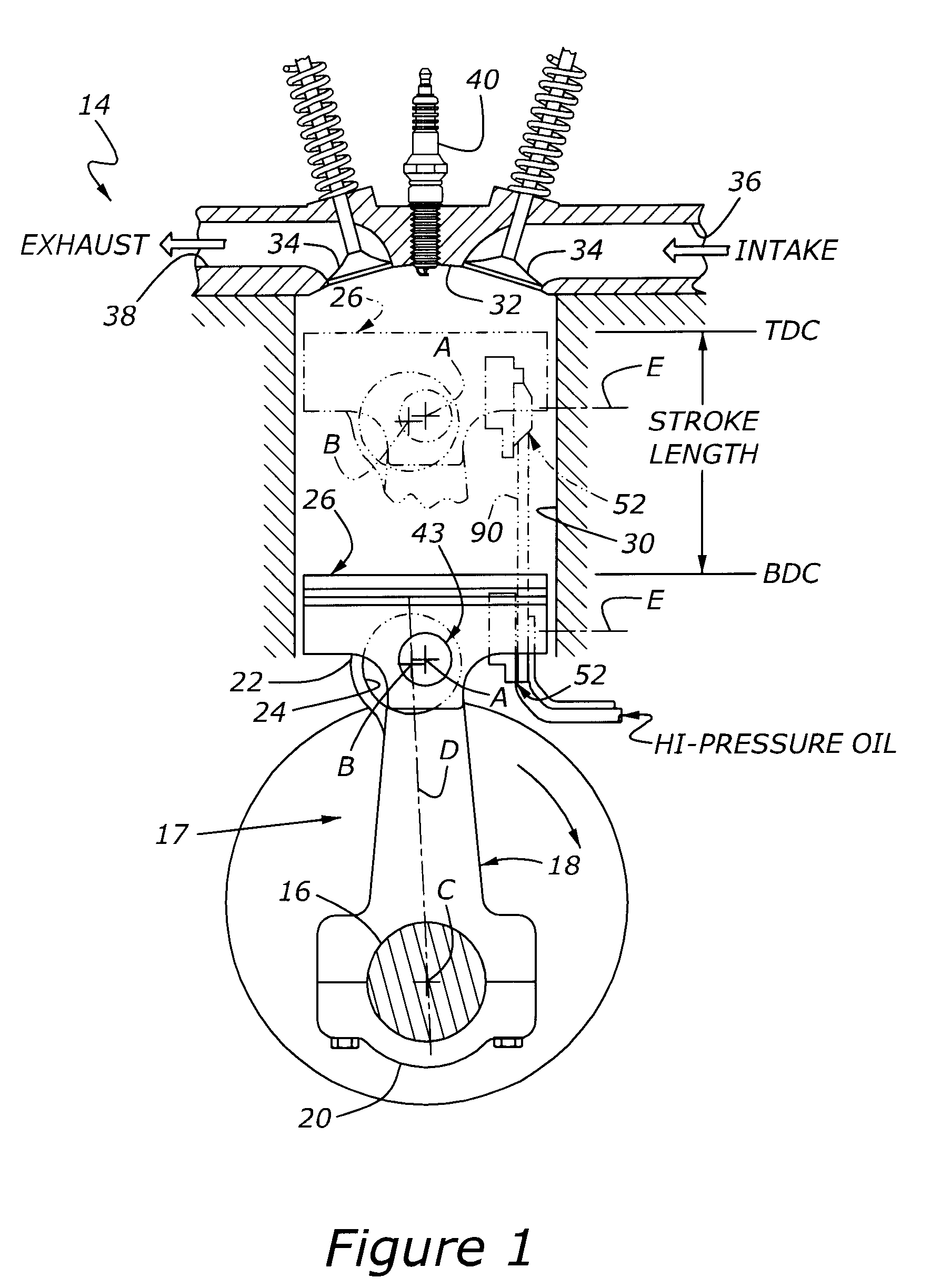
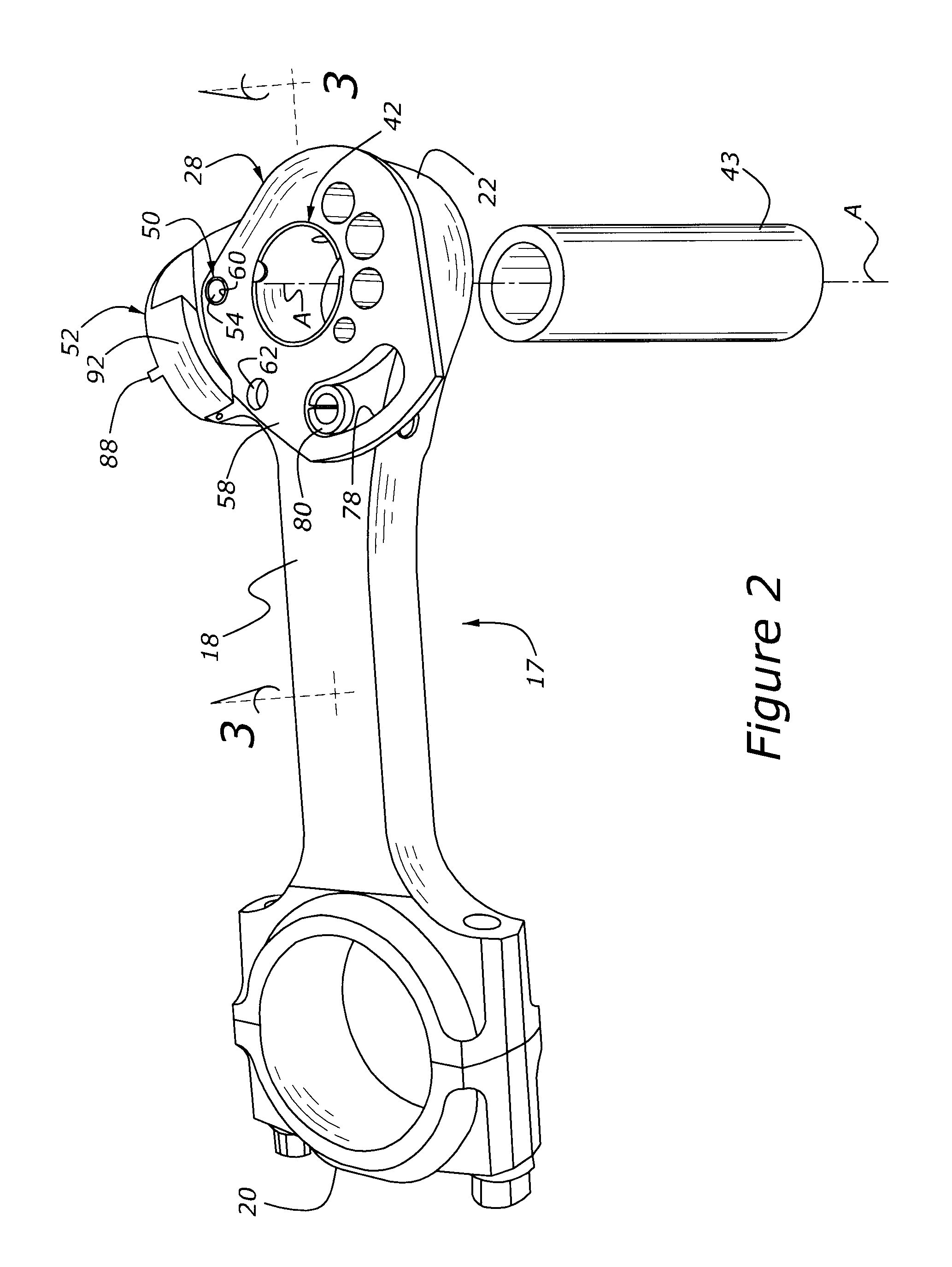
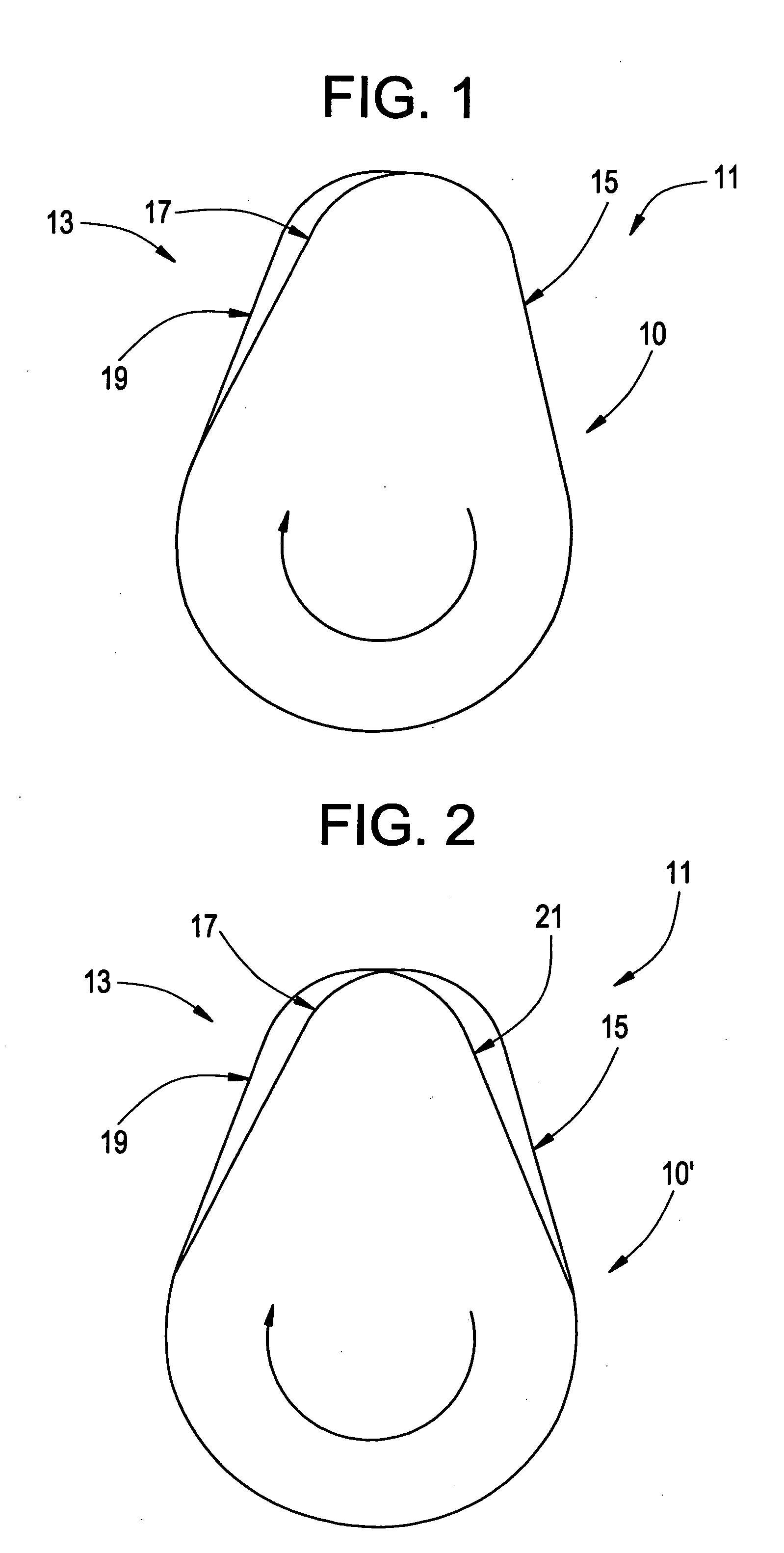
A variable compression ratio piston (26) and connecting rod (18) assembly for an internal combustion engine (14) includes an eccentric bushing (28) that carries a piston pin bushing (42) and contains a journaled portion (48) held in the rod bore (24) of the connecting rod (18). The eccentric bushing (28) can be selectively rotated between either of two angle adjusted positions to effect a change in the height of the piston (26) relative to the connecting rod (18), and thus change the compression ratio of the assembly. A latch (50) mechanism is actuated by oil jets (90, 91) external to the connecting rod (18). The latch (50) includes bolts (54, 56) with tapered tips that seat in oblong holes (60, 62) in a flange plate (58) to reduce destructive lash. A resilient stop post (80) bears the brunt of stresses associated with stopping the flange plate (58) during switching events to protect the latching bolts (54, 56).
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Variable compression ratio apparatus
ActiveUS20140014071A1Effective compression ratioSimple structureEngine controllersMachines/enginesCombustionEngineering
A variable compression ratio apparatus mounted on an engine configured to receive combustion force of a mixer from a piston to rotate a crankshaft, and configured to change a compression ratio of the mixer may include an eccentric bearing assembly connected with the piston through a piston pin, and including an eccentric ring including an eccentric hole through which the piston pin passes so that the piston pin may be rotatably installed while being eccentric to the eccentric ring, and an eccentric link connected to the eccentric ring to transfer rotation force thereof to the eccentric ring, a connecting rod including one end provided with a mounting hole into which the eccentric ring may be rotatably inserted, a central portion provided with an operation hole, wherein the eccentric link may be movable through the operation hole, and the other end rotatably connected to the crankshaft while being eccentric to the crankshaft, and a control shaft connected to the eccentric link and configured to rotate the eccentric bearing assembly.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOTOR CO LTD
Spark-ignition gasoline engine
ActiveUS7484498B2Quantity minimizationReduce consumptionValve arrangementsElectrical controlLow speedTop dead center
Owner:MAZDA MOTOR CORP
Drive apparatus, control method thereof, and motor vehicle equipped with the apparatus and the method
ActiveUS7114484B2High expansion rateEffective compression ratioHybrid vehiclesValve arrangementsMobile vehicleExternal combustion engine
Provided herein are a drive apparatus that includes an internal combustion engine capable of operating with a high expansion ratio by reducing an effective compression ratio through advancement of an intake valve closing timing, and a control method of the drive apparatus, and a motor vehicle equipped with the apparatus and method. The drive apparatus further includes a torque output device capable of outputting a torque to an output shaft of the internal combustion engine. Upon a command to stop operation of the internal combustion engine, the apparatus controls the driving of the torque output device so that the internal combustion engine stops at a target stop position which is set outside a region that leads to an increased compression ration in an initial compression stroke when the internal combustion engine is next stated.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
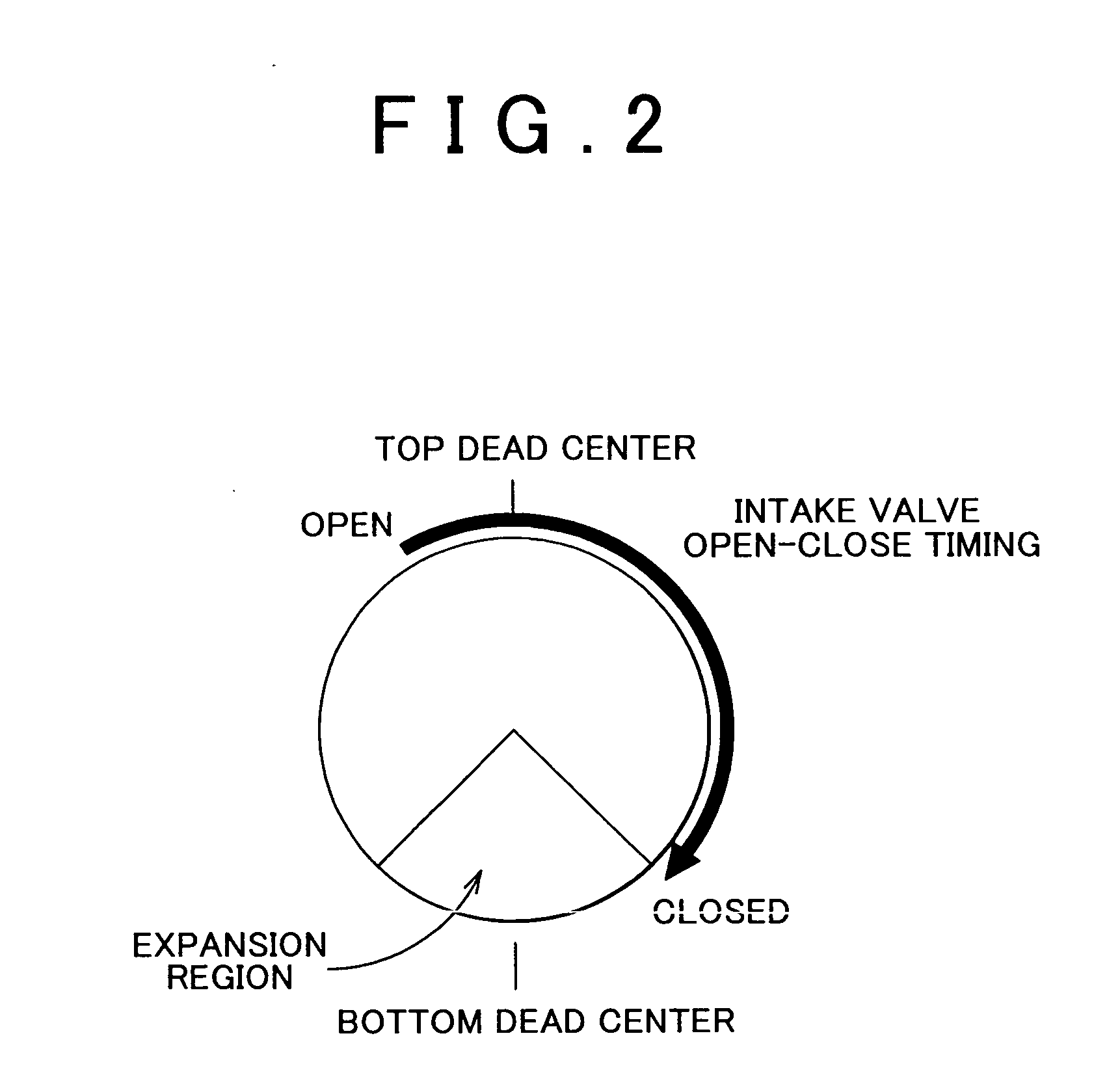
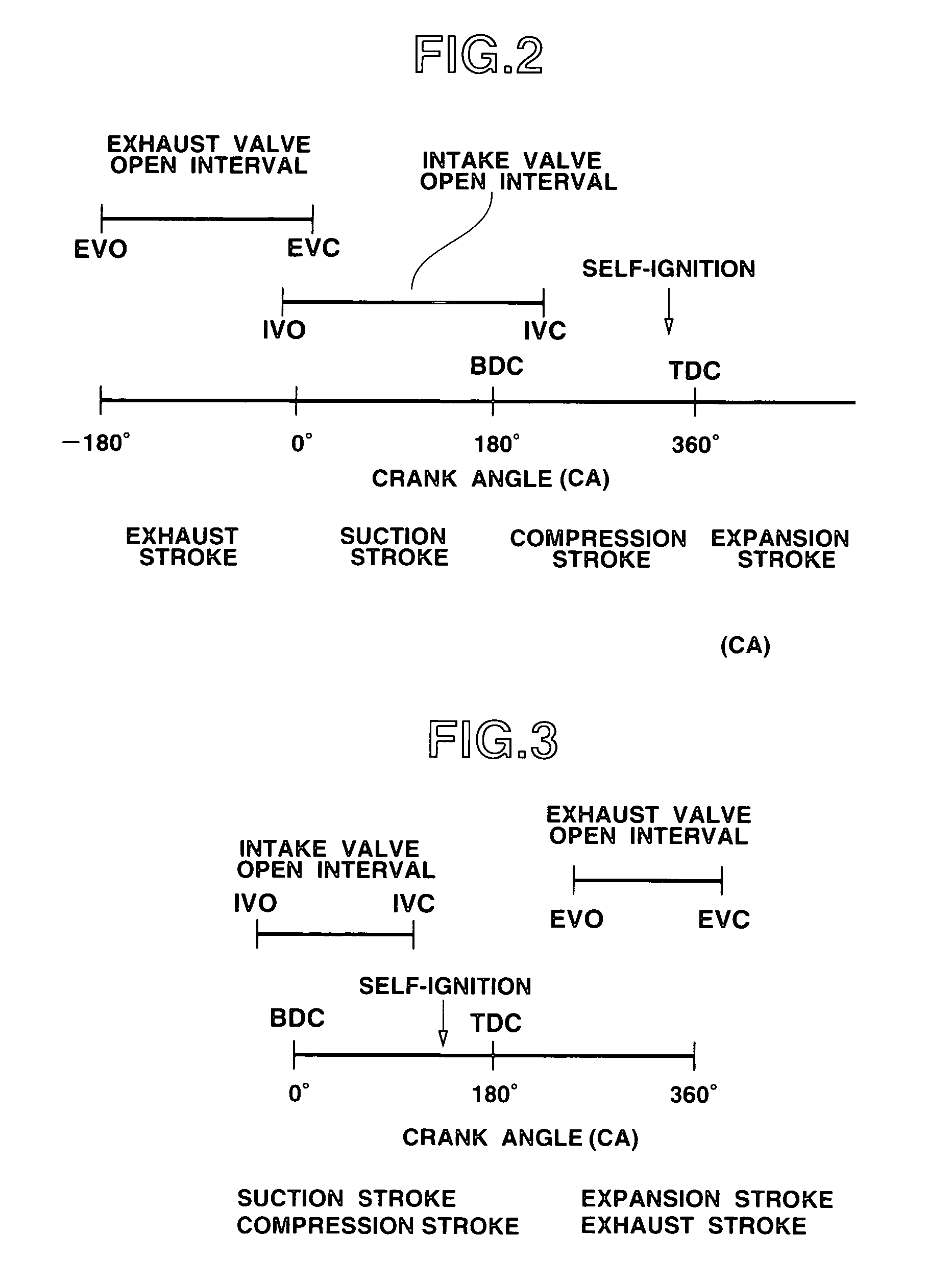
Diesel engine with dual-lobed intake cam for compression ratio control
ActiveUS7036483B2Reduce compressionShorten effective compression strokeValve arrangementsMachines/enginesInlet valveEngineering
Dual-lobed cams mounted on the intake camshaft of a diesel engine selectively retard timing of the intake valve closure. The purpose of retarding timing of the intake valves is to retard valve closing sufficiently to shorten the effective compression strokes of the pistons and thus reduce the effective compression ratio. This occurs when the intake valves remain open past piston bottom dead center for a desired period into the normal compression stroke phase of engine operation. This reduces compression pressures so that combustion temperatures are reduced and exhaust emissions, primarily NOx, may be thus limited under conditions of warmed-up engine operation. Dual-lobed cams may also be employed to retard timing of the intake valve opening to throttle admitted air during cold running conditions to effect higher in-cylinder charge temperatures to reduce hydrocarbon and white smoke emissions due to poor ignition and incomplete combustion.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
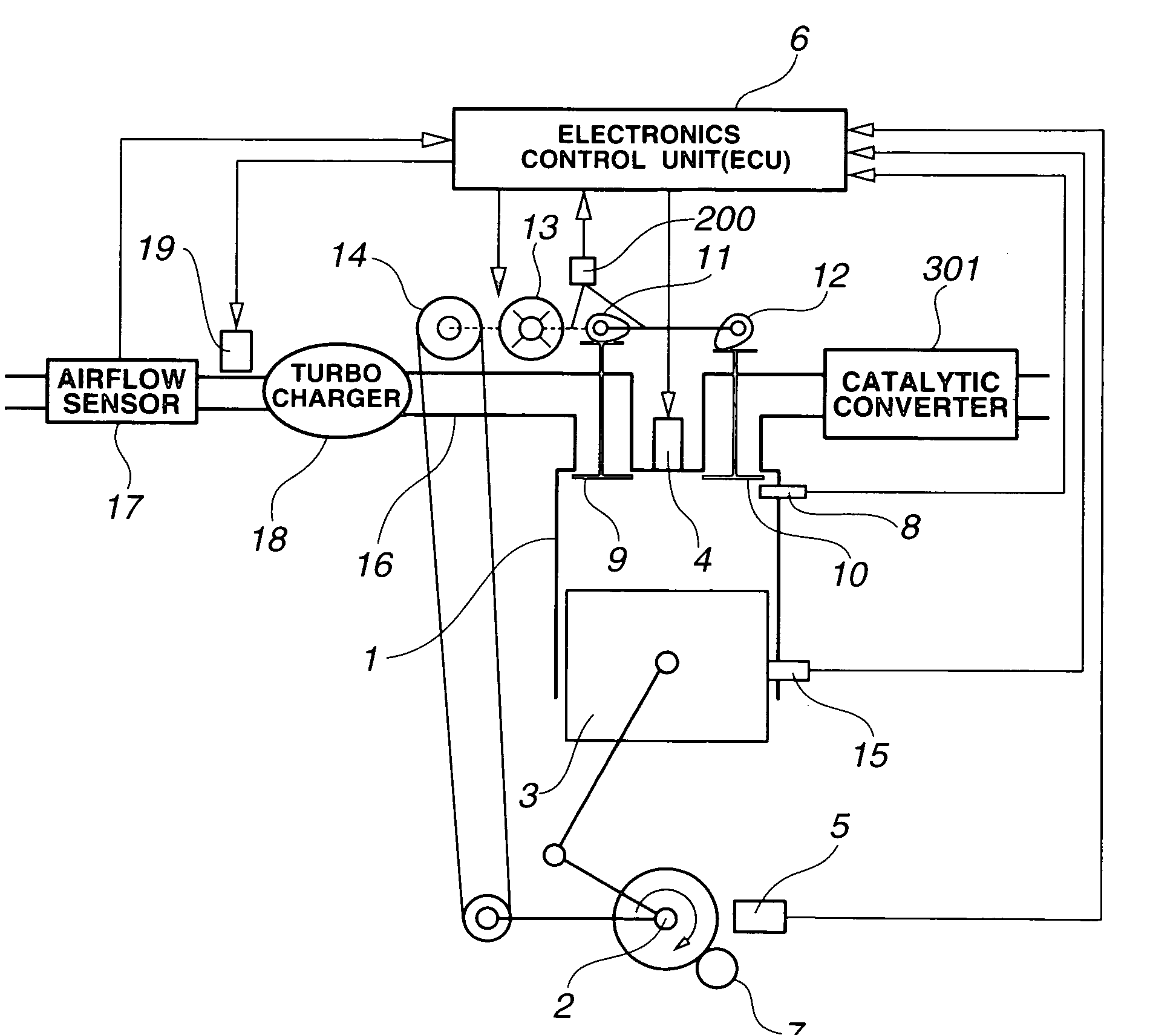
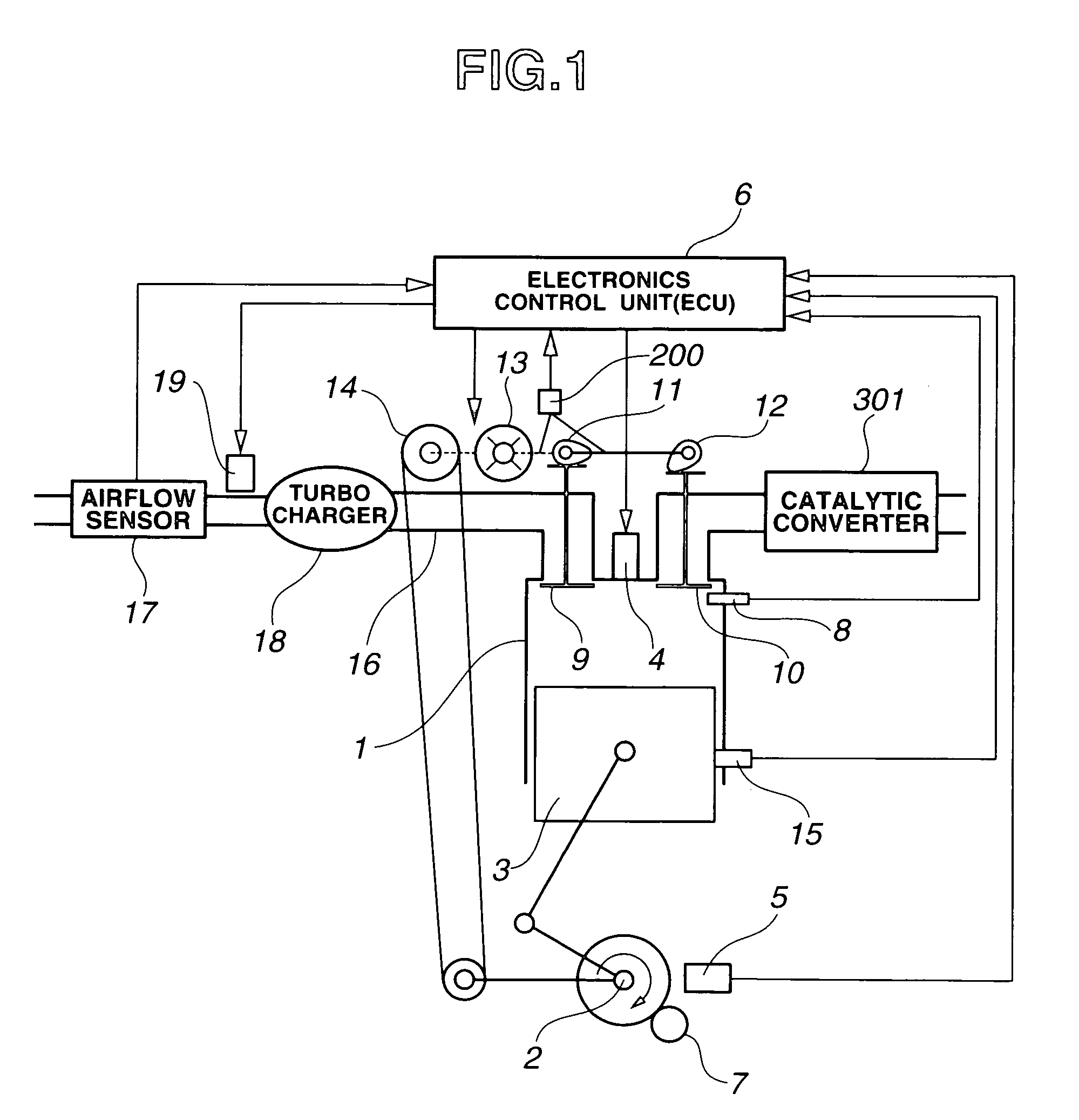
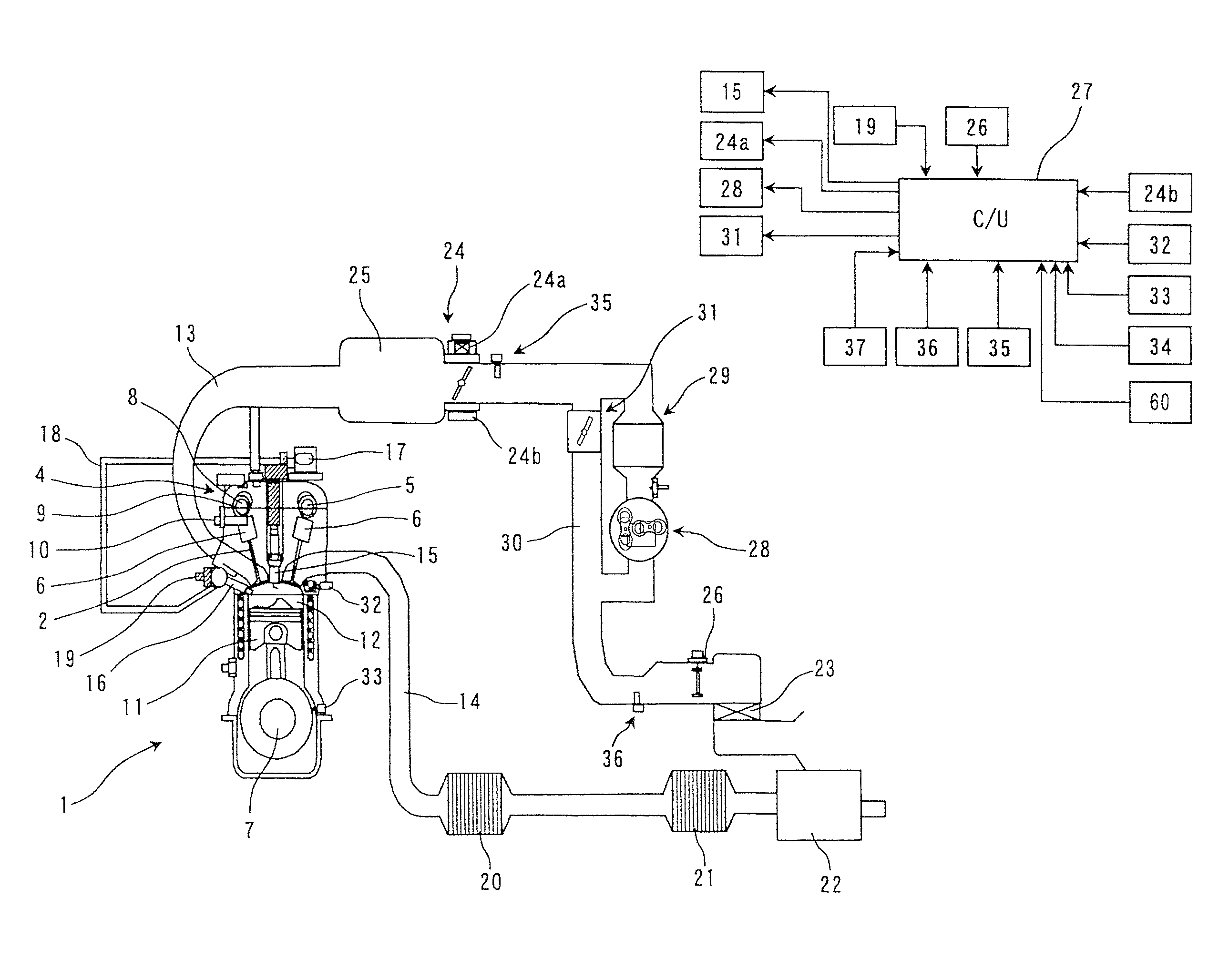
Apparatus for engine control
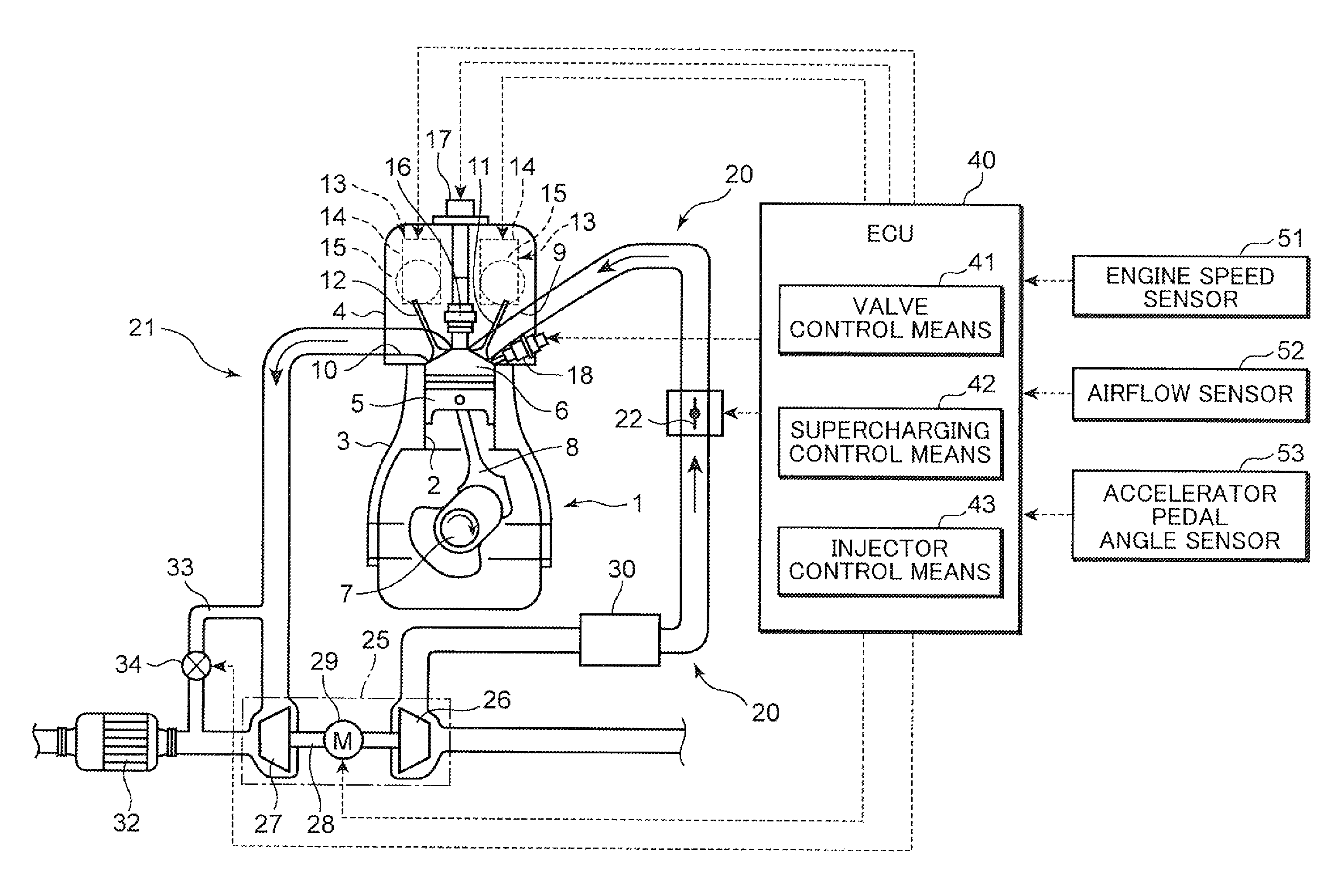
InactiveUS20110139119A1Effective compression ratioValve arrangementsElectrical controlEngineeringIgnition timing
An engine control apparatus is provided with an engine, an ignition device, a valve timing changing mechanism, an intake valve close timing detecting device, a supercharger and a controller. The engine achieves a Miller cycle by the valve timing changing mechanism setting an intake valve close timing to occur after a bottom dead center timing. The controller controls an ignition timing of the ignition device, the open timing of the intake valve and the close timing of the intake valve. The controller retards the ignition timing during supercharging and when a detected value of the intake valve close timing is earlier than a target value of the intake valve close timing by at least a prescribed value in comparison with a situation in which the detected value matches the target value of the intake valve close timing.
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD
Variably operated valve system for compression ignition engine
InactiveUS7478614B2Effective compression ratioImprove reliabilityValve drivesOutput powerInlet valveEngineering
In a variably operated valve system for a compression ignition engine, an adjustment mechanism is controlled by means of a control section to detach an intake valve closure timing from a bottom dead center in accordance with an engine driving condition, and an engine start securing section guarantees an engine start even at least one of cases during a failure in the control section, during a stop of the engine, and during a start of the engine.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Start-up control for internal combustion engine
InactiveUS7412954B2Effective compression ratioDefect occurrenceHybrid vehiclesValve arrangementsCombustionResonance
An internal combustion engine (101, 601, 901) alters an effective compression ratio from an effective compression ratio for a start-up operation to a larger effective compression ratio for a normal operation when an engine rotation speed (NE) increases beyond a resonance rotation speed region during cranking. A controller (104, 610, 910) determines whether or not the engine (101, 601, 901) has reached a combustion possible state on the basis of the engine rotation speed (NE) during cranking and an operating parameter (PA, TA, TW, P_Rail, V_Ang) other than the engine rotation speed (NE) (S1102, S1202, S1204). When the determination is negative, the controller (104, 610, 910) inhibits fuel supply to the engine (101, 601, 901) by a fuel supply device (207), even when the engine rotation speed has increased beyond the resonance rotation speed region (S406). In so doing, a combustion defect such as a misfire is prevented.
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD
Apparatus for engine control
InactiveUS8186330B2Effective compression ratioValve arrangementsElectrical controlInlet valveEngineering
An engine control apparatus is provided with an engine, an ignition device, a valve timing changing mechanism, an intake valve close timing detecting device, a supercharger and a controller. The engine achieves a Miller cycle by the valve timing changing mechanism setting an intake valve close timing to occur after a bottom dead center timing. The controller controls an ignition timing of the ignition device, the open timing of the intake valve and the close timing of the intake valve. The controller retards the ignition timing during supercharging and when a detected value of the intake valve close timing is earlier than a target value of the intake valve close timing by at least a prescribed value in comparison with a situation in which the detected value matches the target value of the intake valve close timing.
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD
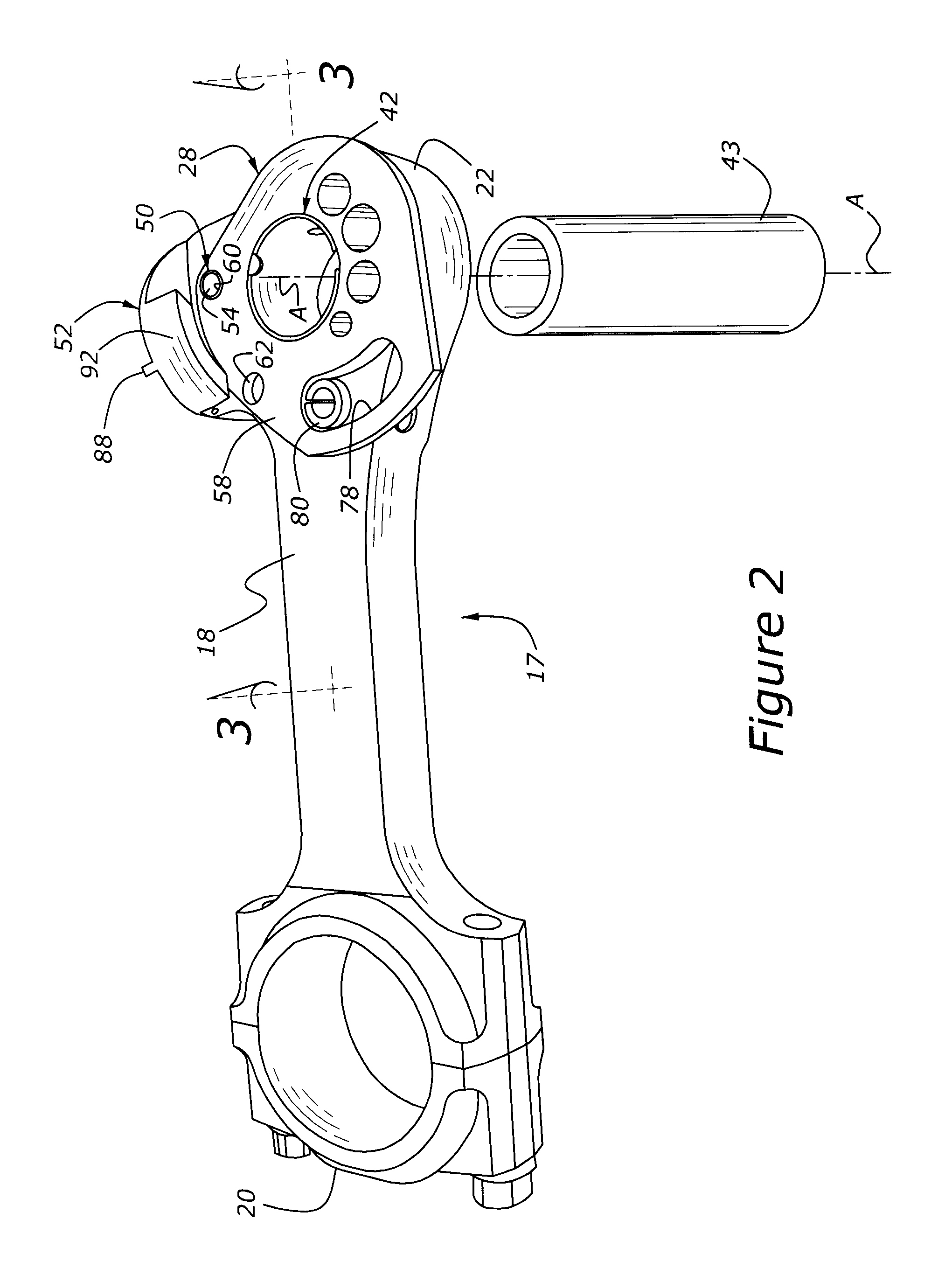
Variable compression ratio engine with dedicated bumper
InactiveUS20090107466A1Effective compression ratioEffectively altering compression ratioEngine controllersMachines/enginesVariable compression ratioFlange
A variable compression ratio piston (26) and connecting rod (18) assembly for an internal combustion engine (14) includes an eccentric bushing (28) that carries a piston pin bushing (42) and contains a journaled portion (48) held in the rod bore (24) of the connecting rod (18). The eccentric bushing (28) can be selectively rotated between either of two angle adjusted positions to effect a change in the height of the piston (26) relative to the connecting rod (18), and thus change the compression ratio of the assembly. A latch (50) mechanism is actuated by oil jets (90, 91) external to the connecting rod (18). The latch (50) includes bolts (54, 56) with tapered tips that seat in oblong holes (60, 62) in a flange plate (58) to reduce destructive lash. A resilient stop post (80) bears the brunt of stresses associated with stopping the flange plate (58) during switching events to protect the latching bolts (54, 56).
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
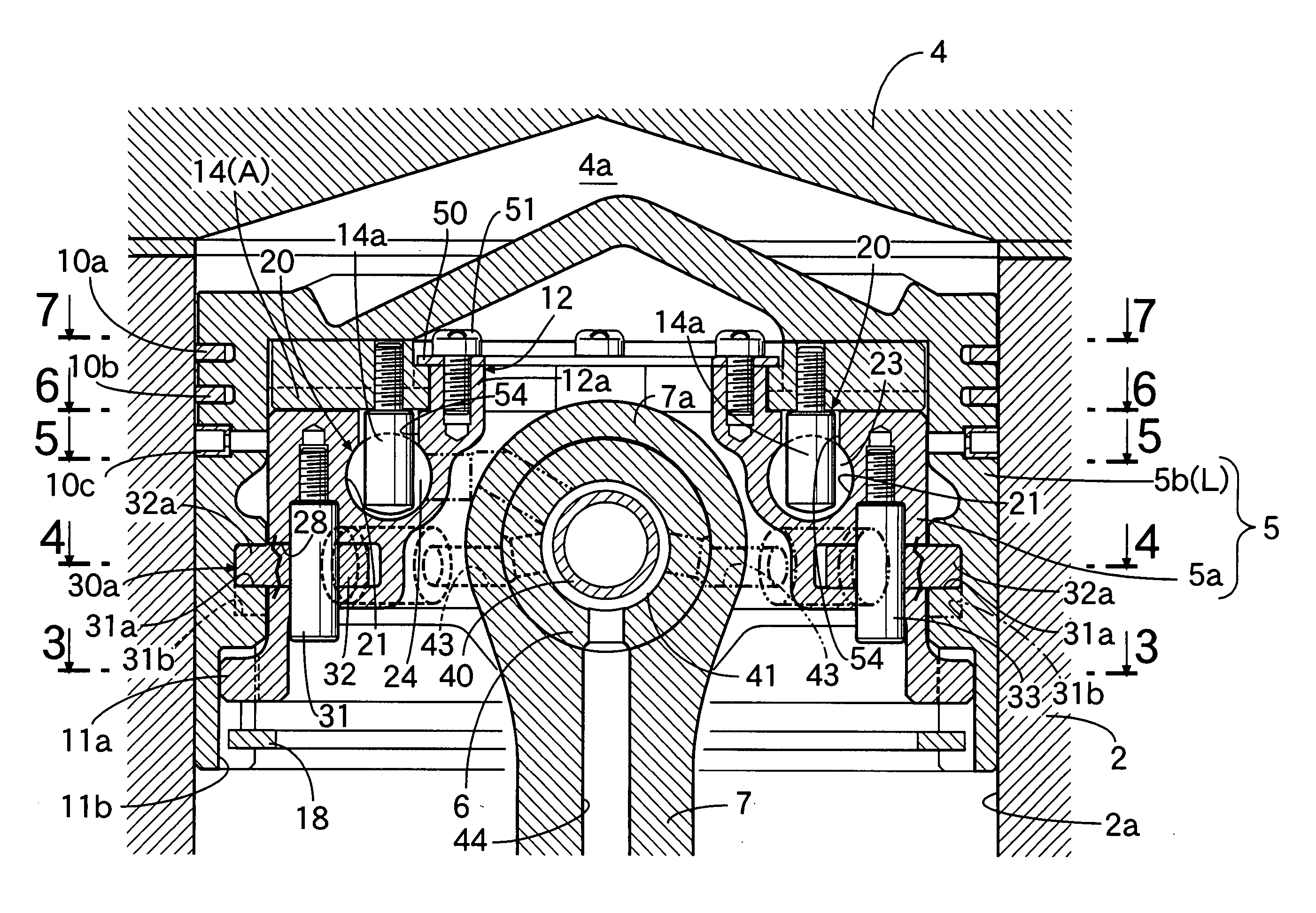
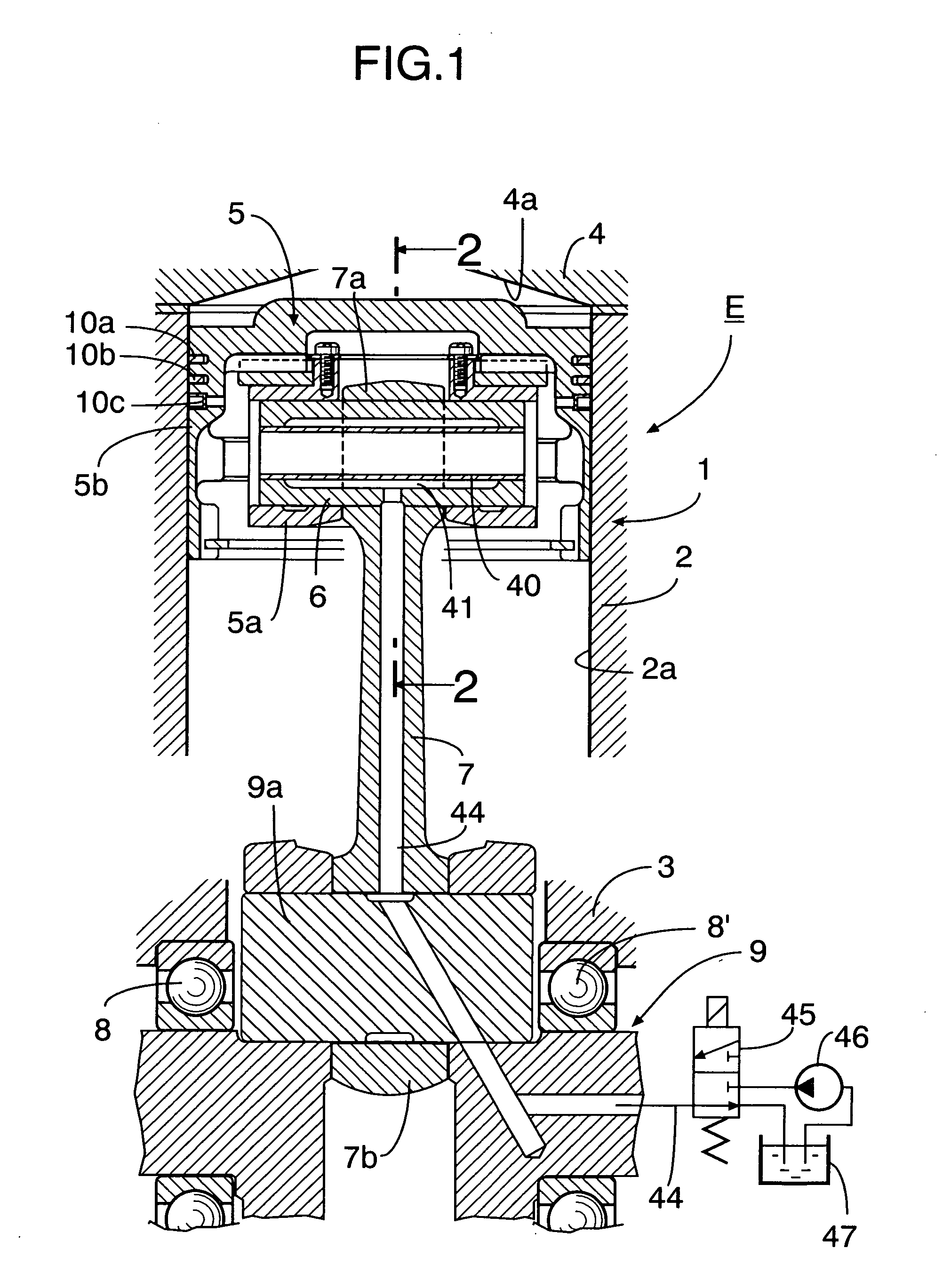
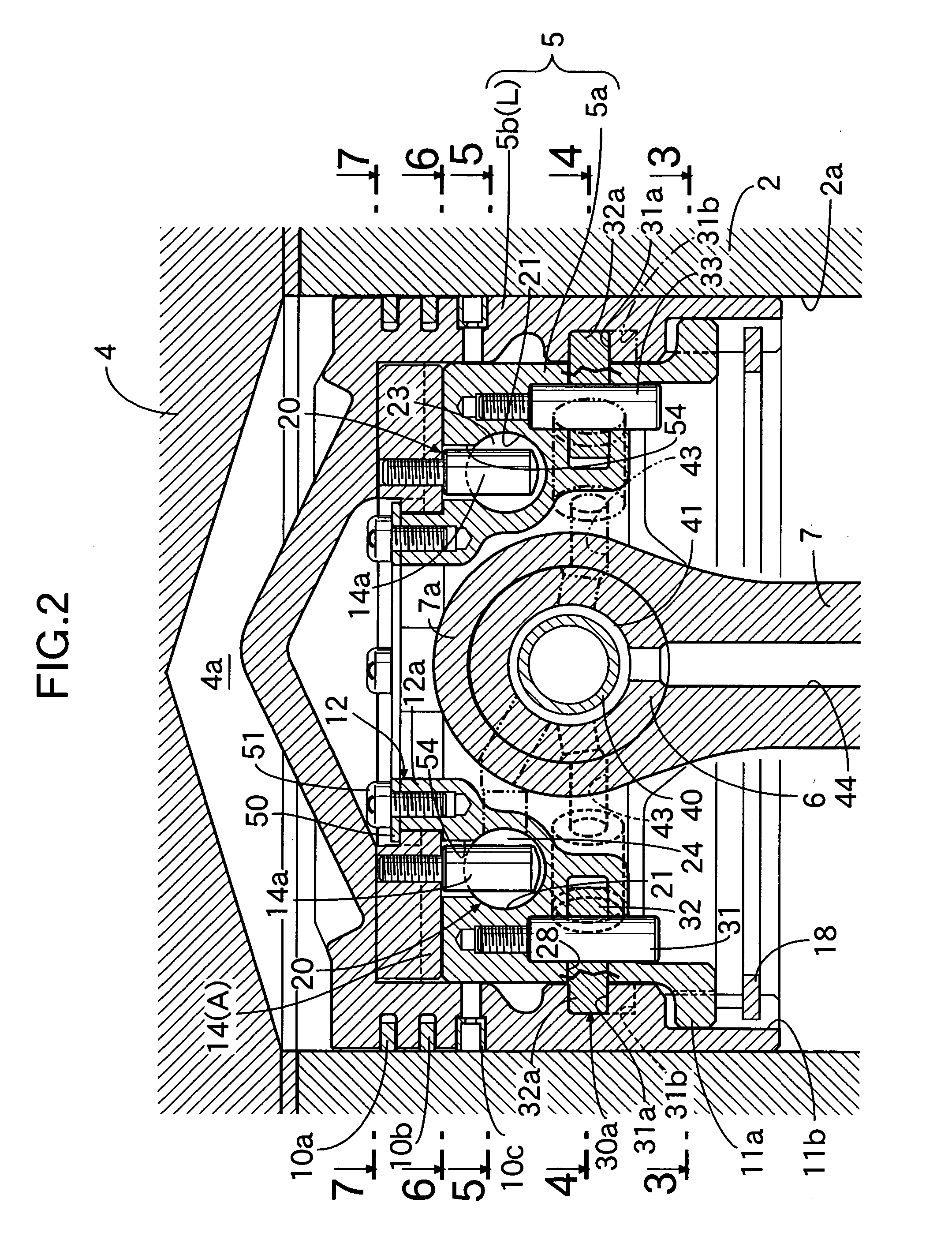
Compression ratio variable device of internal combustion engine
InactiveUS20060090715A1Simple arrangementReduce the compression ratioEngine controllersMachines/enginesVariable compression ratioActuator
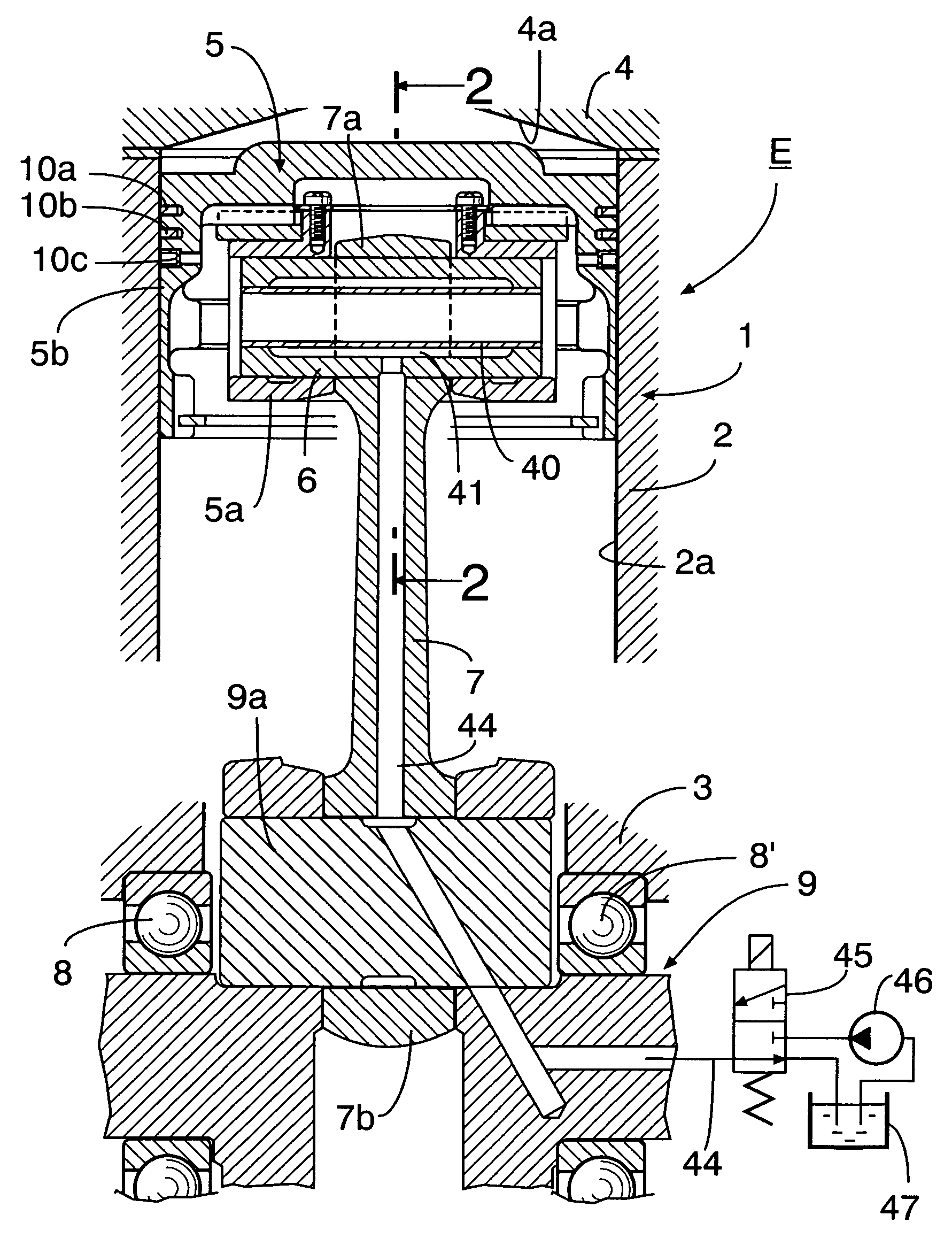
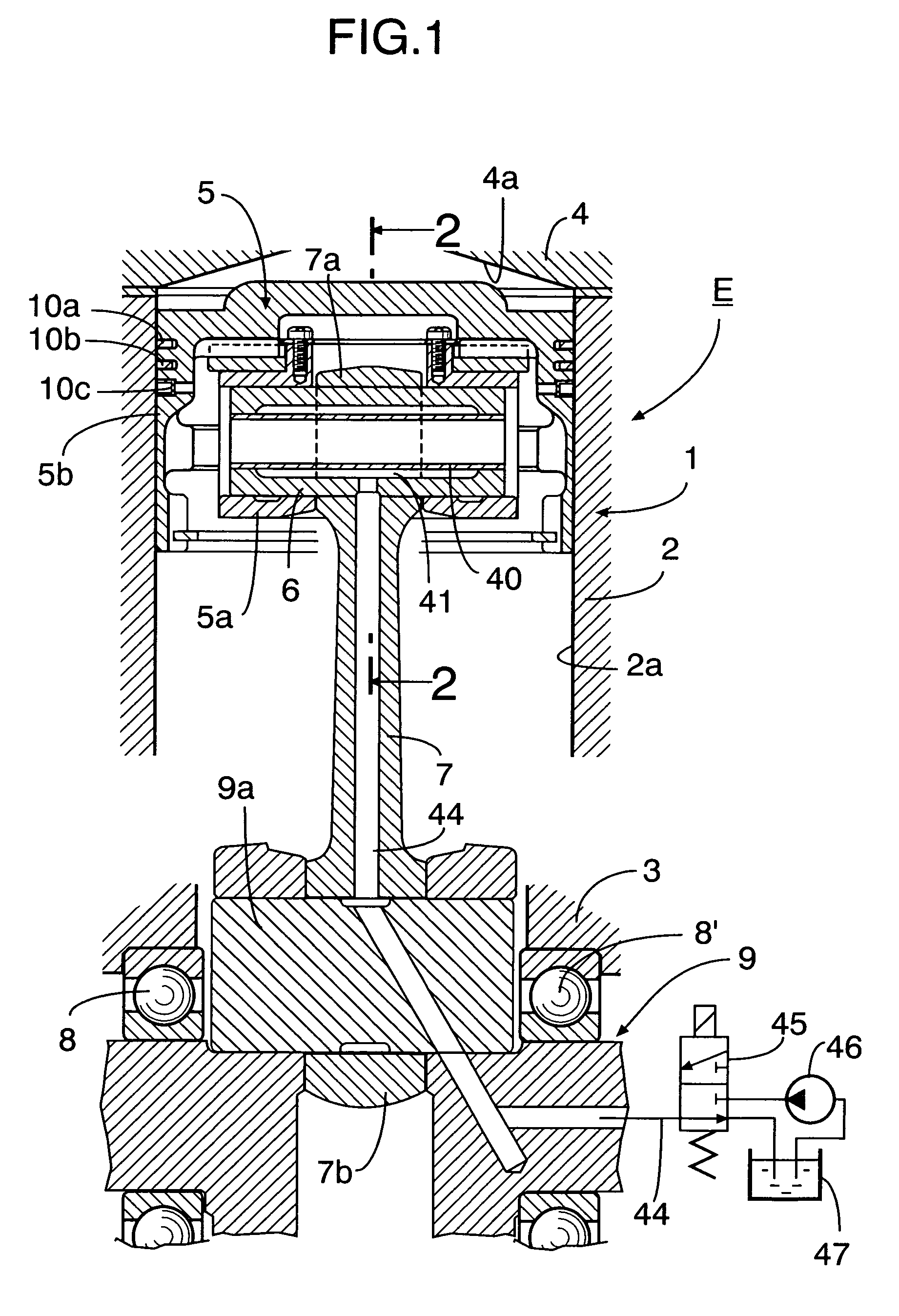
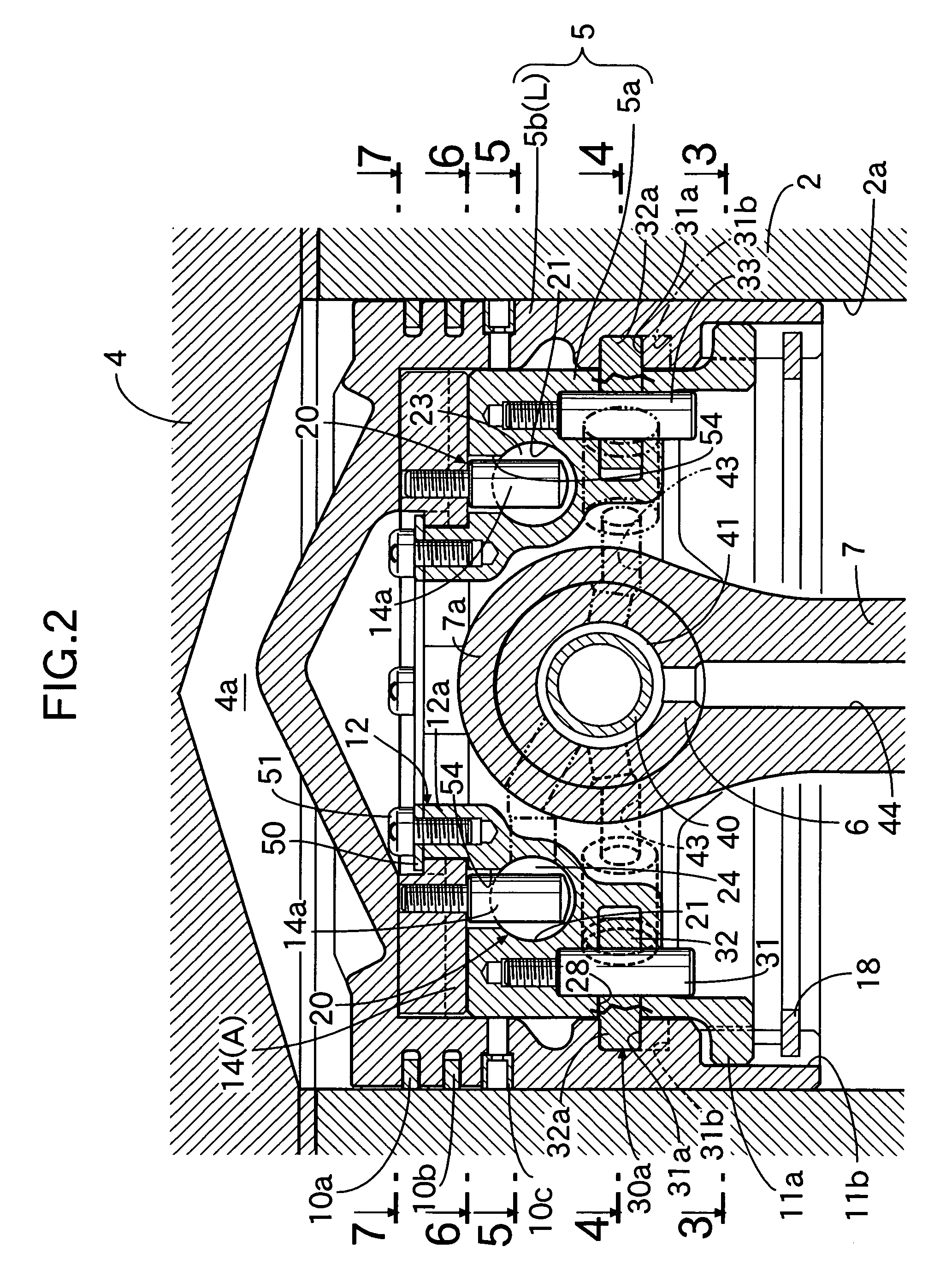
An internal combustion engine variable compression ratio system is provided that includes a piston inner (5a), a piston outer (5b) that is fitted around the outer periphery of the piston inner (5a) so that it can slide only in the axial direction and is capable of moving between a low compression ratio position (L) and a high compression ratio position (H), a raising member (14) that can pivot around axes of the piston inner and outer (5a, 5b) between a non-raised position (A) and a raised position (B), and an actuator (20) connected to the member (14) and pivoting it to the non-raised position (A) or the raised position (B), in which piston outer high compression ratio position latching means (30b) is disposed between the piston inner (5a) and the piston outer (5b) and operates, when the piston outer (5b) has reached the high compression ratio position (H), so as to prevent relative axial movement of the piston inner (5a) and the piston outer (5b). It is thereby possible to provide a variable compression ratio system that enables the piston outer to be moved to the low compression ratio position and the high compression ratio position simply and reliably without rotating the piston outer.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Compression ratio variable device of internal combustion engine
InactiveUS7353785B2Reduce the compression ratioIncrease the compression ratioEngine controllersMachines/enginesEngineeringActuator
An internal combustion engine variable compression ratio system is provided that includes a piston inner (5a), a piston outer (5b) that is fitted around the outer periphery of the piston inner (5a) so that it can slide only in the axial direction and is capable of moving between a low compression ratio position (L) and a high compression ratio position (H), a raising member (14) that can pivot around axes of the piston inner and outer (5a, 5b) between a non-raised position (A) and a raised position (B), and an actuator (20) connected to the member (14) and pivoting it to the non-raised position (A) or the raised position (B), in which piston outer high compression ratio position latching means (30b) is disposed between the piston inner (5a) and the piston outer (5b) and operates, when the piston outer (5b) has reached the high compression ratio position (H), so as to prevent relative axial movement of the piston inner (5a) and the piston outer (5b). It is thereby possible to provide a variable compression ratio system that enables the piston outer to be moved to the low compression ratio position and the high compression ratio position simply and reliably without rotating the piston outer.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Method and apparatus for controlling supercharged engine
ActiveUS8459021B2Wide load rangeImprove thermal efficiencyElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesAir volumeEngineering
A supercharged engine has a geometric compression ratio ser to 16 or more and is designed to perform a compression self-ignition combustion under an air-fuel ratio leaner than a stoichiometric air-fuel ratio at least in a low engine speed range. On a lower engine load side than a given engine load within an engine operating region at which the compression self-ignition combustion is performed, a fresh air amount is reduced and an effective compression ratio (ε′) is increased, as compared with a higher engine load side than the given engine load within the engine operating region, and, on the higher engine load side than the given engine load, a supercharging pressure based on a supercharger (25) is increased to increase the fresh air amount, and the effective compression ratio (ε′) is reduced, as compared with the lower engine load side than the given engine load. This makes it possible to perform the compression self-ignition combustion under a lean air-fuel ratio in a wider engine load range to effectively enhance engine thermal efficiency, while eliminating a need for an operation of forcedly raising / lowering a temperature of fresh air.
Owner:MAZDA MOTOR CORP
Diesel engine with dual-lobed intake cam for compression ratio control
ActiveUS20050132982A1Reduce compressionShorten effective compression strokeValve arrangementsCombustion enginesHydrocotyle bowlesioidesSmoke Emission
Dual-lobed cams mounted on the intake camshaft of a diesel engine selectively retard timing of the intake valve closure. The purpose of retarding timing of the intake valves is to retard valve closing sufficiently to shorten the effective compression strokes of the pistons and thus reduce the effective compression ratio. This occurs when the intake valves remain open past piston bottom dead center for a desired period into the normal compression stroke phase of engine operation. This reduces compression pressures so that combustion temperatures are reduced and exhaust emissions, primarily NOx, may be thus limited under conditions of warmed-up engine operation. Dual-lobed cams may also be employed to retard timing of the intake valve opening to throttle admitted air during cold running conditions to effect higher in-cylinder charge temperatures to reduce hydrocarbon and white smoke emissions due to poor ignition and incomplete combustion.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Gas intensifier with lubrication
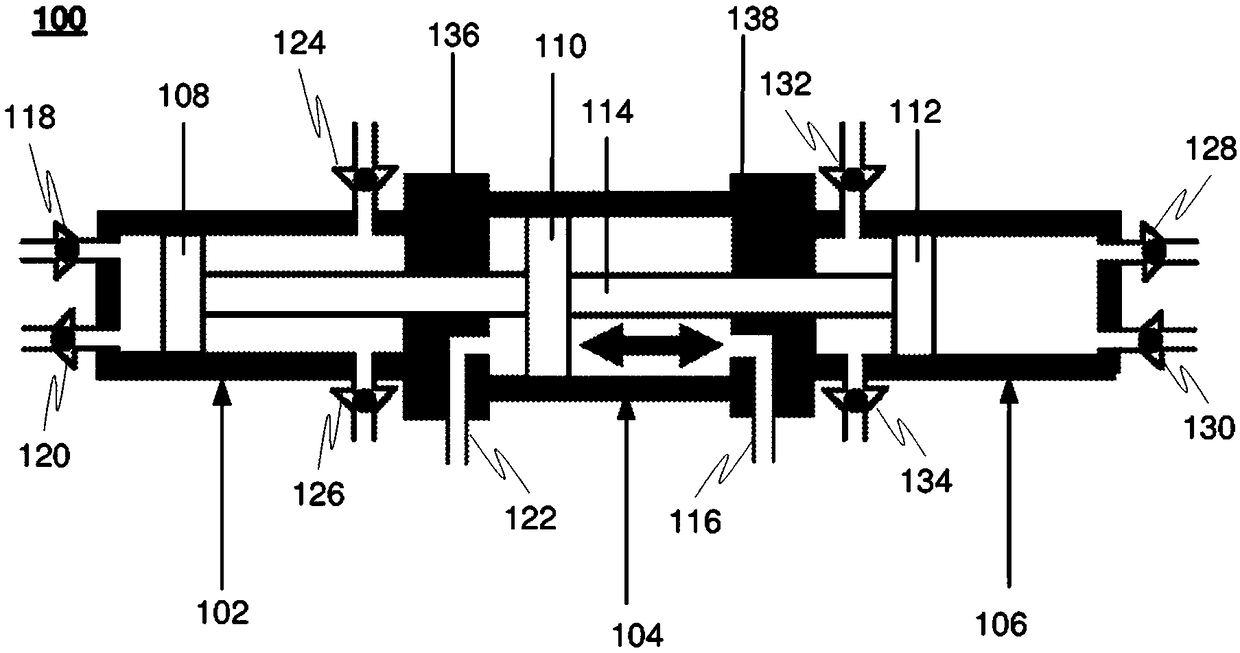
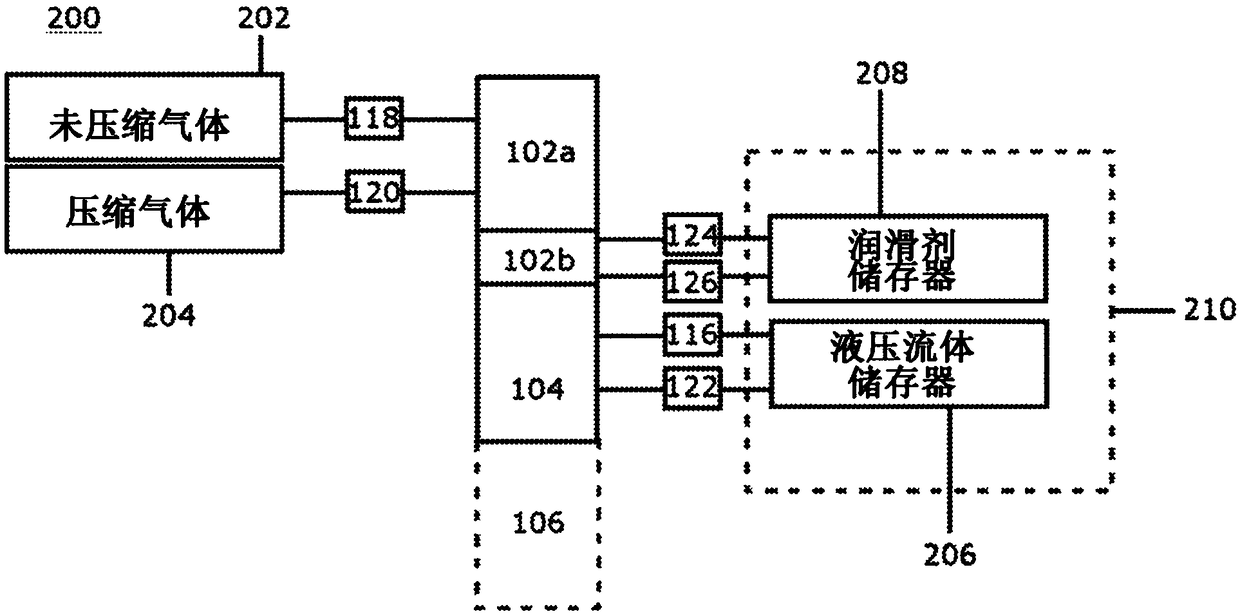
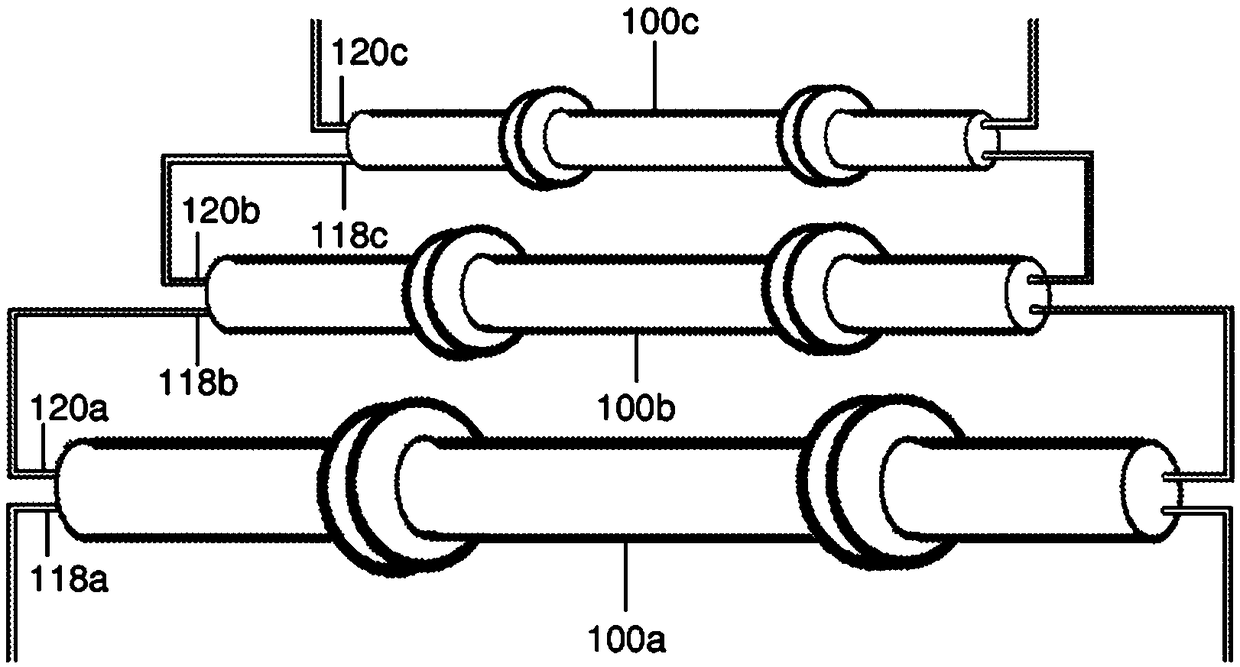
InactiveCN109154311AEasy to transportExtend your lifePositive displacement pump componentsFluid-pressure convertersCouplingEngineering
A hydraulically driven intensifier (100) for increasing pressure of gas comprising a piston-driven (108) compression chamber (102) for gas, operatively connected to an adjacent hydraulic chamber (104), with lubricant coupling (124, 126) in the compression chamber (102) of the intensifier to circulate the lubricating fluid for cooling and lubricating the piston (108). A multistage compression system for gas, comprising the aforementioned intensifier (100), preferably several thereof operatively connected in series.
Owner:METENER OY
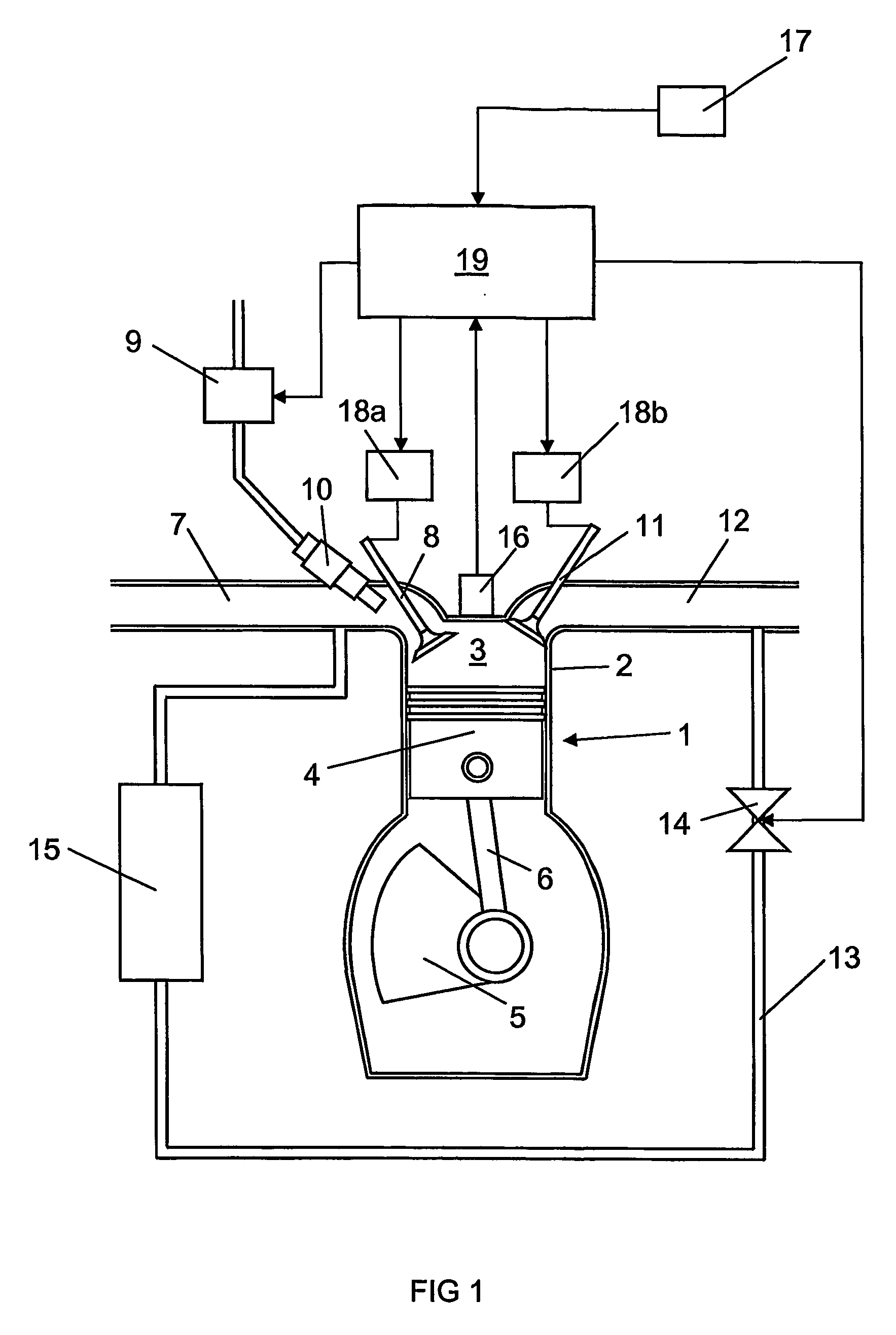
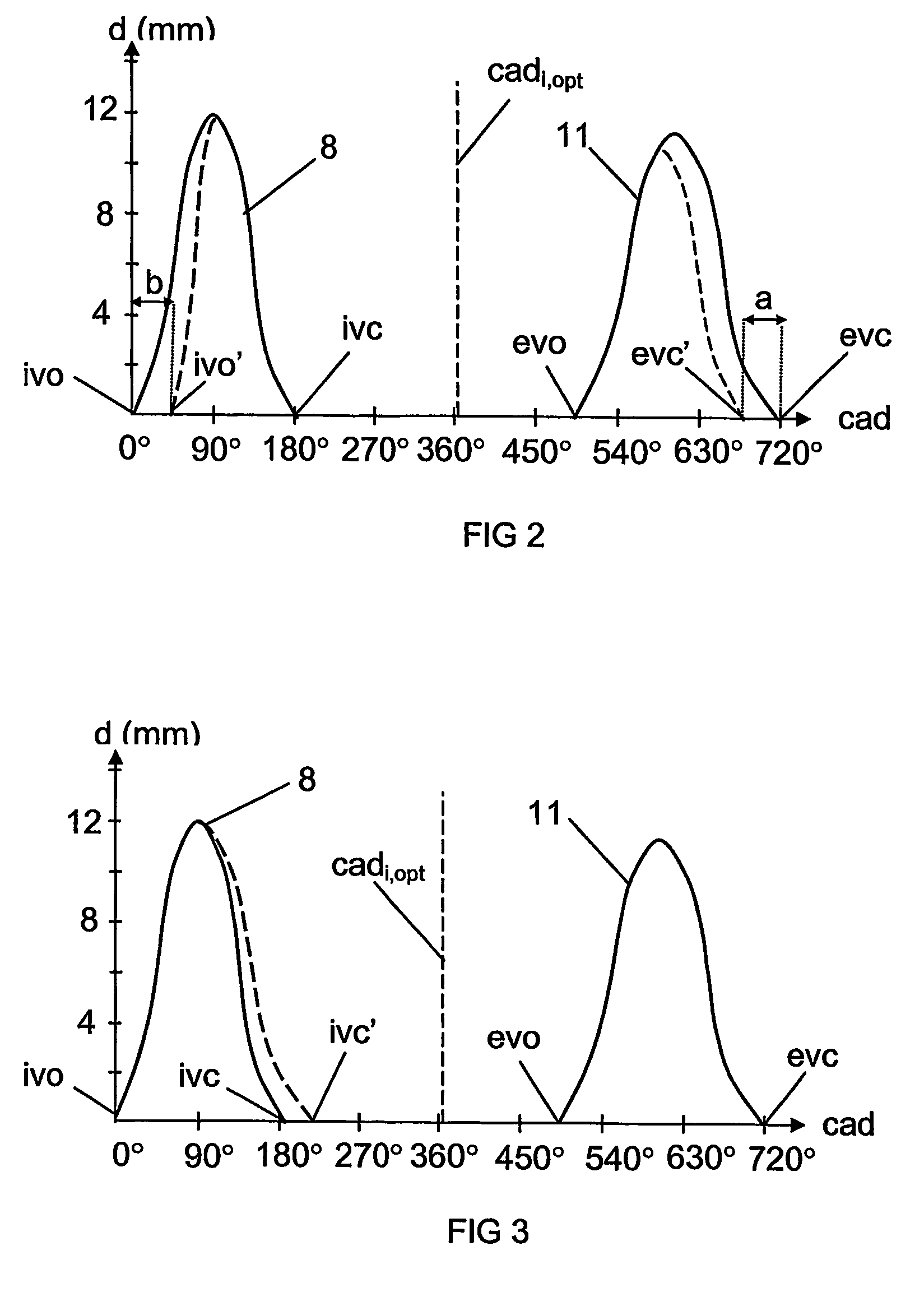
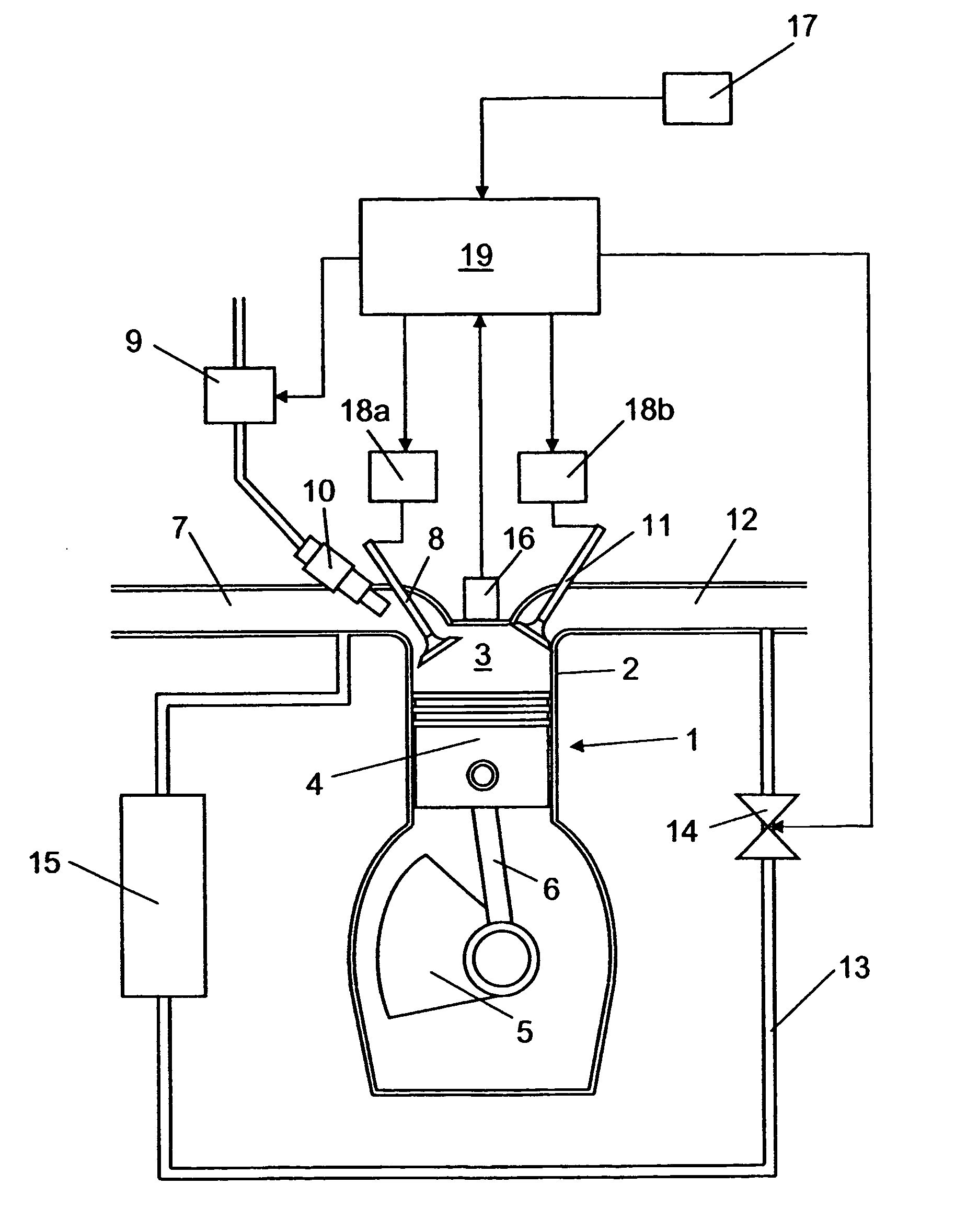
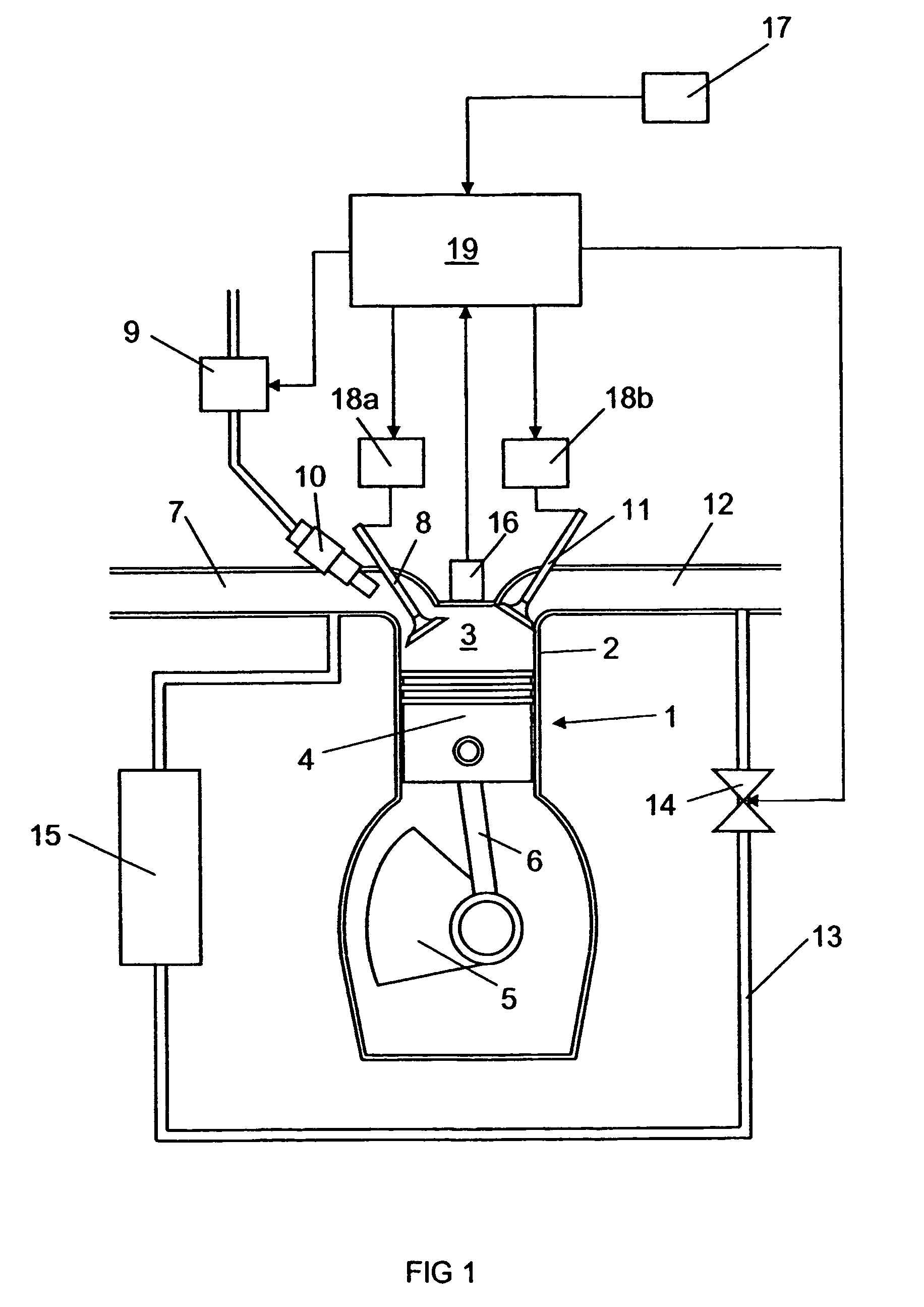
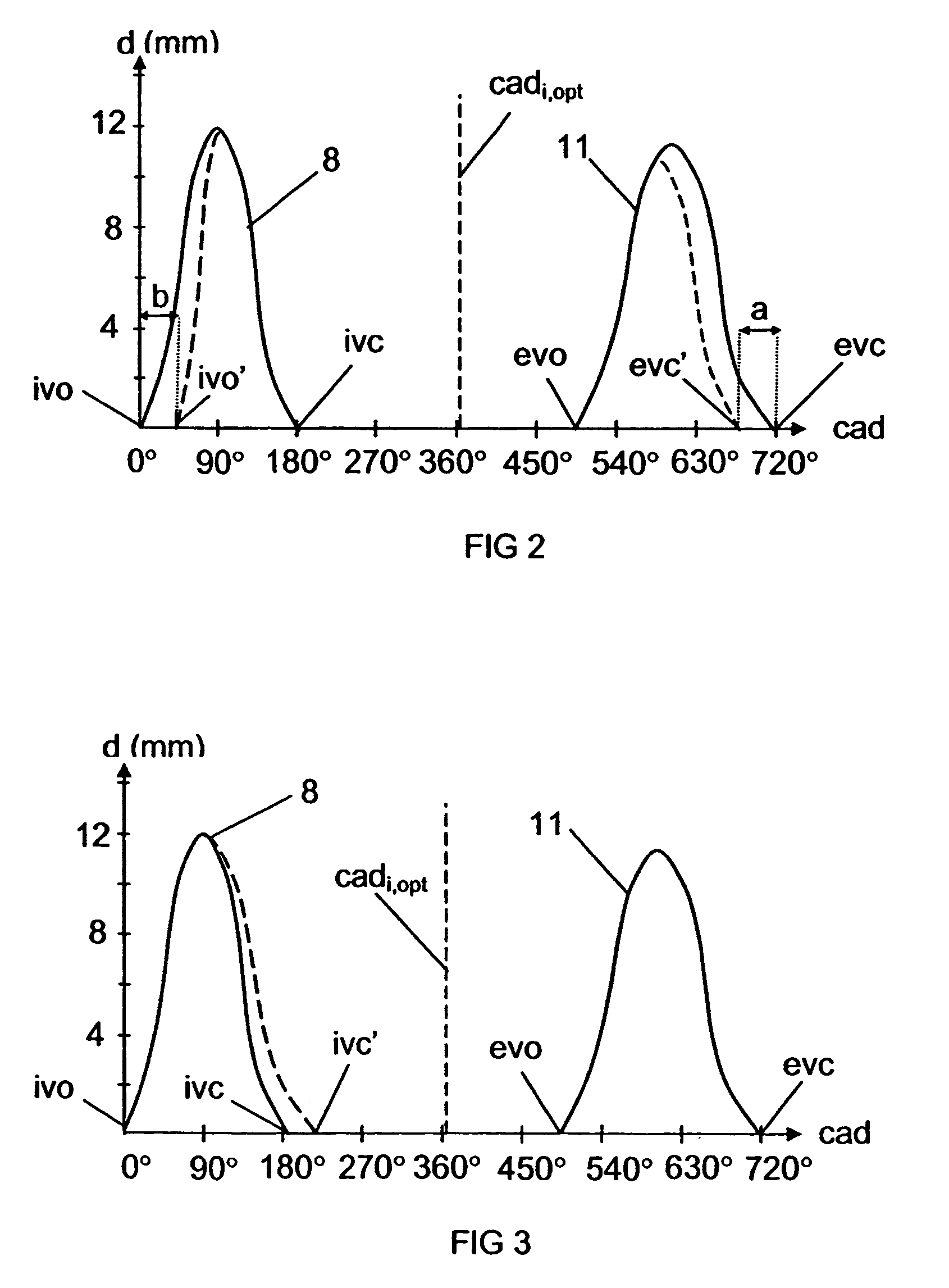
Arrangement and method for controlling a combustion engine
InactiveUS20060225673A1Large loading rangeEffective controlValve arrangementsElectrical controlCombustion chamberCrankshaft
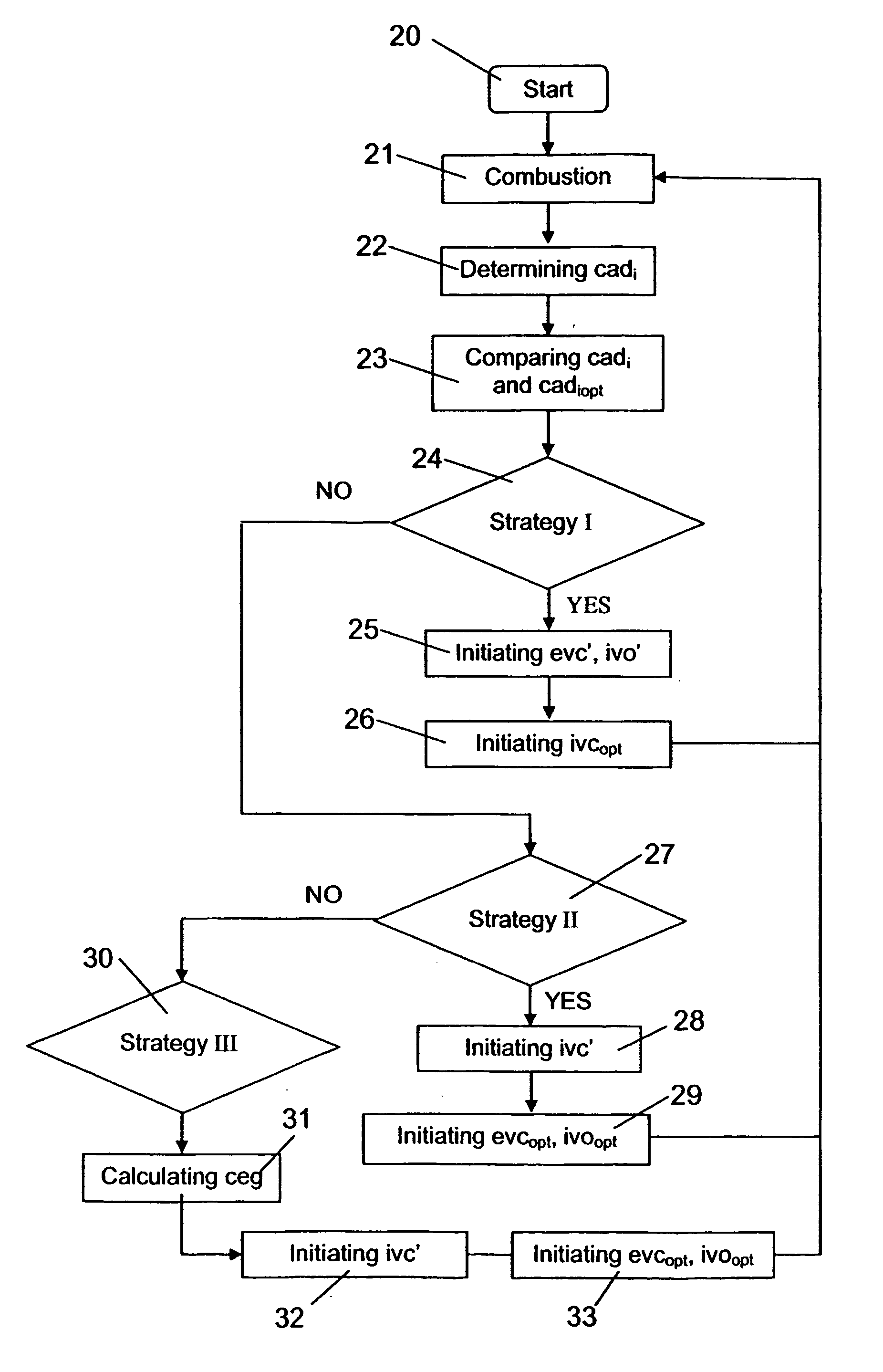
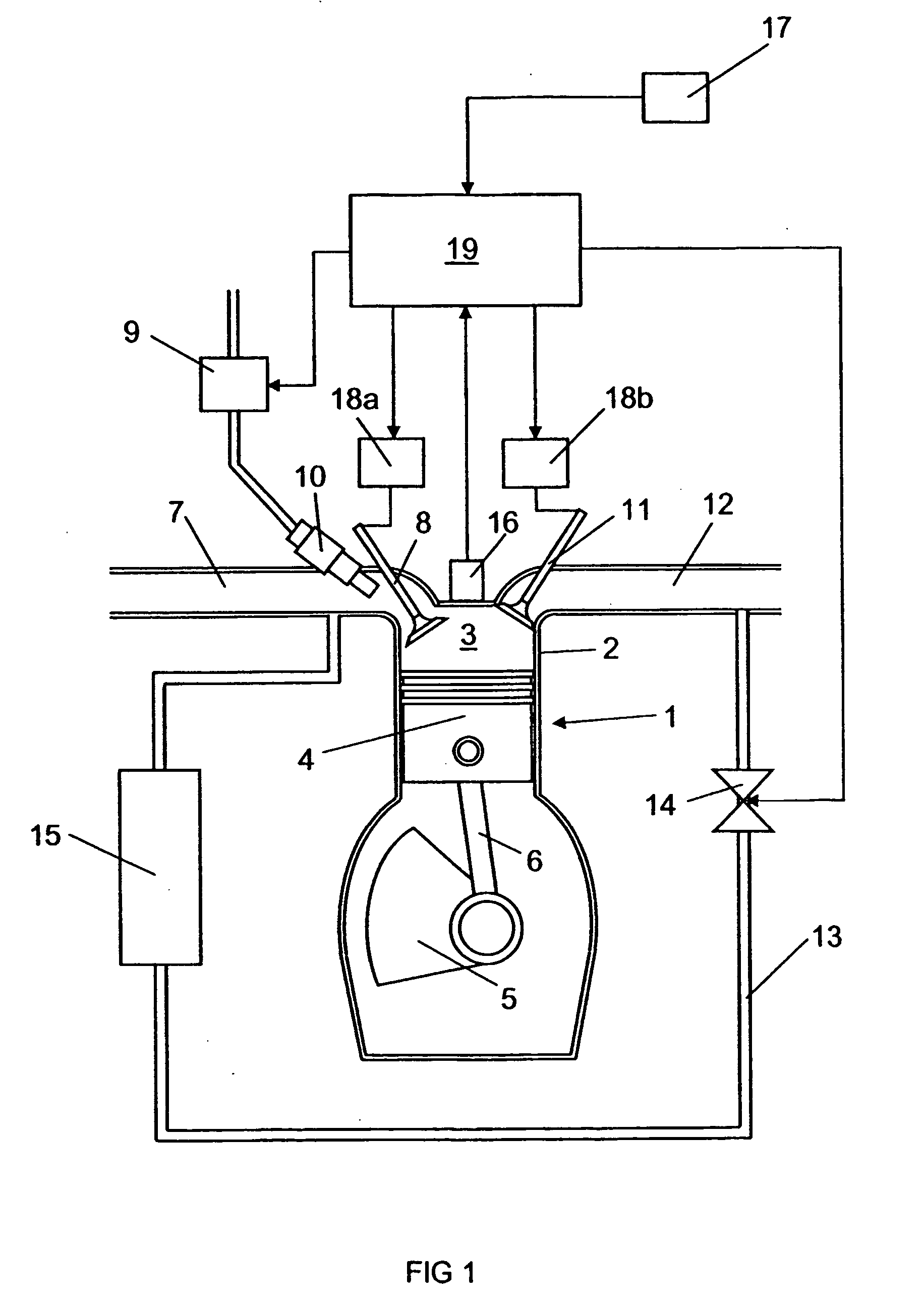
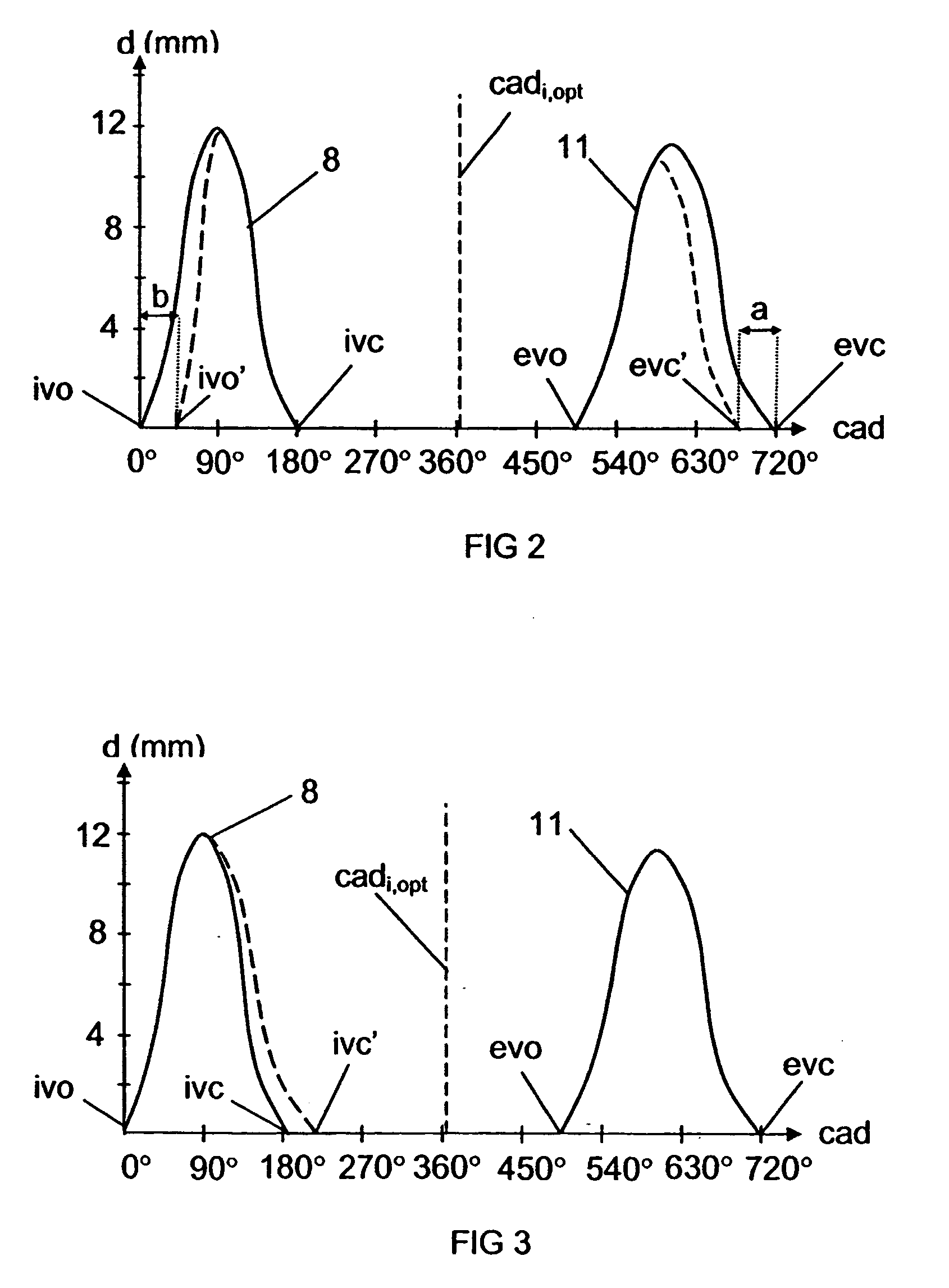
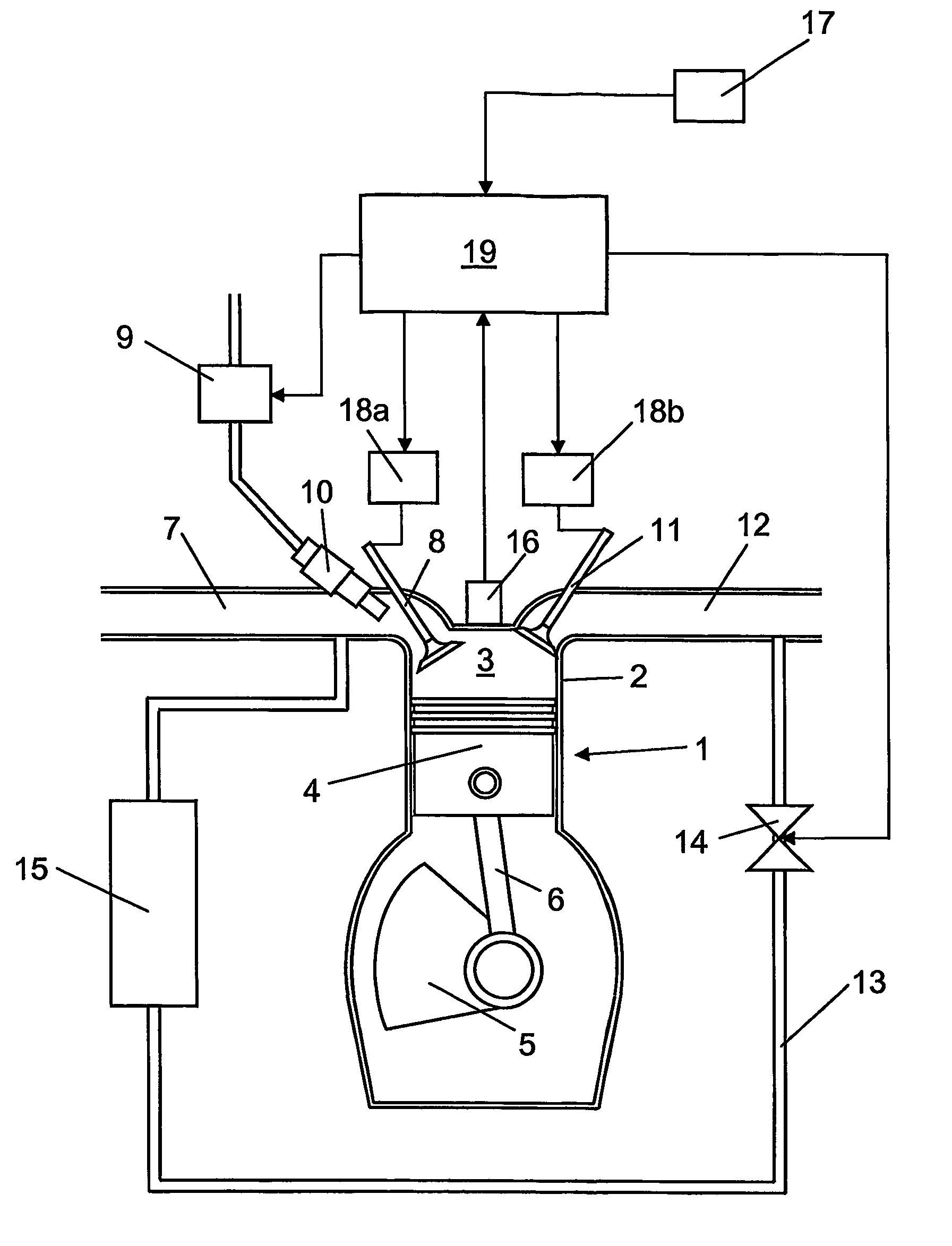
An arrangement and a method for controlling a combustion engine, e.g. of the type called HCCI engine. A control unit for controlling the self-ignition of the fuel mixture towards an optimum crankshaft angel (cadiopt) within a load range (Ltot). The load range (Ltot) can be divided into at least two subranges (LI, LII) and the control unit is adapted to controlling the self-ignition of the fuel mixture towards an optimum crankshaft angle (cadiopt) within a first subrange (LI) by means of a strategy (I) which entails a variable amount of hot exhaust gases being supplied to or retained in the combustion chamber, and within a second subrange (LII) by means of another strategy (II) which entails the effective compression ratio (c) in the cylinder being varied.
Owner:SCANIA CV AB
Arrangement and method for controlling a combustion engine
InactiveUS20060225704A1Large loading rangeEffective controlValve arrangementsElectrical controlCombustion chamberEngineering
An arrangement and a method for controlling a combustion engine, e.g. of the type called HCCI engine. A control unit is operable for controlling the self-ignition of the fuel mixture towards an optimum crankshaft angle (cadiopt) within a load range (Ltot). The load range (Ltot) can be divided into at least two subranges (LII, LIII). The control unit is operable to controlling the self-ignition of the fuel mixture towards an optimum crankshaft angle (cadiopt) within one of the subranges (LII) by a strategy (II) which entails the effective compression ratio (c) in the cylinder being varied, and within the second subrange (LIII) by another strategy (III) which entails a variable amount of cooled exhaust gases (ceg) being led to the combustion chamber also enabling in the second subrange (LIII) to control the self-ignition of the fuel mixture towards an optimum crankshaft angle (cadiopt) by variation of the effective compression ratio (c) in the cylinder without it falling below a lowest acceptable value {circle around (c)}min).
Owner:SCANIA CV AB
Arrangement and method for controlling a combustion engine
InactiveUS7261085B2Large loading rangeEffective controlValve arrangementsElectrical controlCombustion chamberCrankshaft
An arrangement and a method for controlling a combustion engine, e.g. of the type called HCCI engine. A control unit for controlling the self-ignition of the fuel mixture towards an optimum crankshaft angel (cadiopt) within a load range (Ltot). The load range (Ltot) can be divided into at least two subranges (LI, LII) and the control unit is adapted to controlling the self-ignition of the fuel mixture towards an optimum crankshaft angle (cadiopt) within a first subrange (LI) by means of a strategy (I) which entails a variable amount of hot exhaust gases being supplied to or retained in the combustion chamber, and within a second subrange (LII) by means of another strategy (II) which entails the effective compression ratio (c) in the cylinder being varied.
Owner:SCANIA CV AB
Method for operating an internal combustion engine and internal combustion engine
ActiveUS9506410B2Reduce consumptionGreat massElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesExternal combustion engineInlet valve
A method for operating an internal combustion engine includes a fuel supply device for at least one first and one second fuel, wherein the internal combustion engine has at least one cylinder which includes at least one intake valve and into which air, in particular fresh air, can be supplied via an intake pipe. In a first operating mode of the internal combustion engine, the first fuel is introduced only into the intake pipe, and in a second operating mode, the second fuel is exclusively introduced directly into the cylinder, and in the second operating mode an intake valve opening time period is adjusted to be shorter than in the first operating mode.
Owner:AUDI AG
Variable compression ratio system of internal combustion engine, and internal combustion engine
PendingCN108194207AReduce the effective compression ratioImprove thermal efficiencyMechanical controlValve arrangementsDetonationInlet channel
The invention discloses a variable compression ratio system of an internal combustion engine, and the internal combustion engine, and relates to the field of internal combustion engine auxiliary systems. The variable compression ratio system comprises an auxiliary connecting pipe, an auxiliary gas channel and a variable auxiliary gas valve; the auxiliary gas channel is formed in a gas cylinder cover connected with a gas cylinder and is connected with a gas inlet branch pipe through the auxiliary connecting pipe, the variable auxiliary gas valve is assembled in the auxiliary gas channel, and the maximum lift and the longest duration of the variable auxiliary gas valve correspond to 0.3-0.5 times of the maximum lift and the longest duration of a gas inlet valve; the variable auxiliary gas valve is driven by the variable gas valve system, and the variable gas valve system is connected with an ECU. Under the high-load steady working condition, the ECU can output a command to the variable gas valve of the variable gas valve system for timing controlling the variable auxiliary gas valve to be opened at the initial stage of compression; a specific proportion of mixture gas is stored between the auxiliary gas channel and a gas inlet channel for the next work cycle, and the effective compression ratio of the internal combustion engine is reduced; and the internal combustion engine comprises the variable compression ratio system of the internal combustion engine, and detonation of the internal combustion engine under the high-load steady working condition is prevented.
Owner:CHANGAN UNIV
Method for compressing digital values of image, audio and/or video files
InactiveCN103262424ASimple compression methodFunctionalCode conversionImage codingPropagation of uncertaintyComputer graphics (images)
Owner:简·克劳德·科林
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com