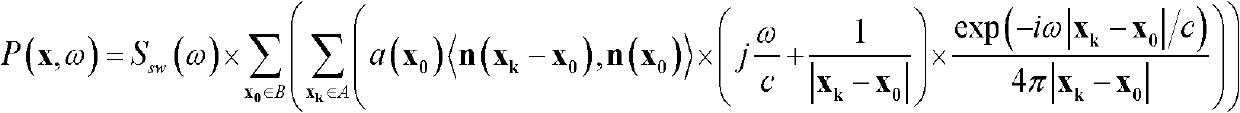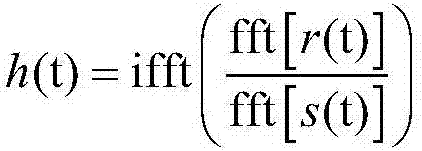Patents
Literature
44 results about "Room acoustics" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Room acoustics describes how sound behaves in an enclosed space.
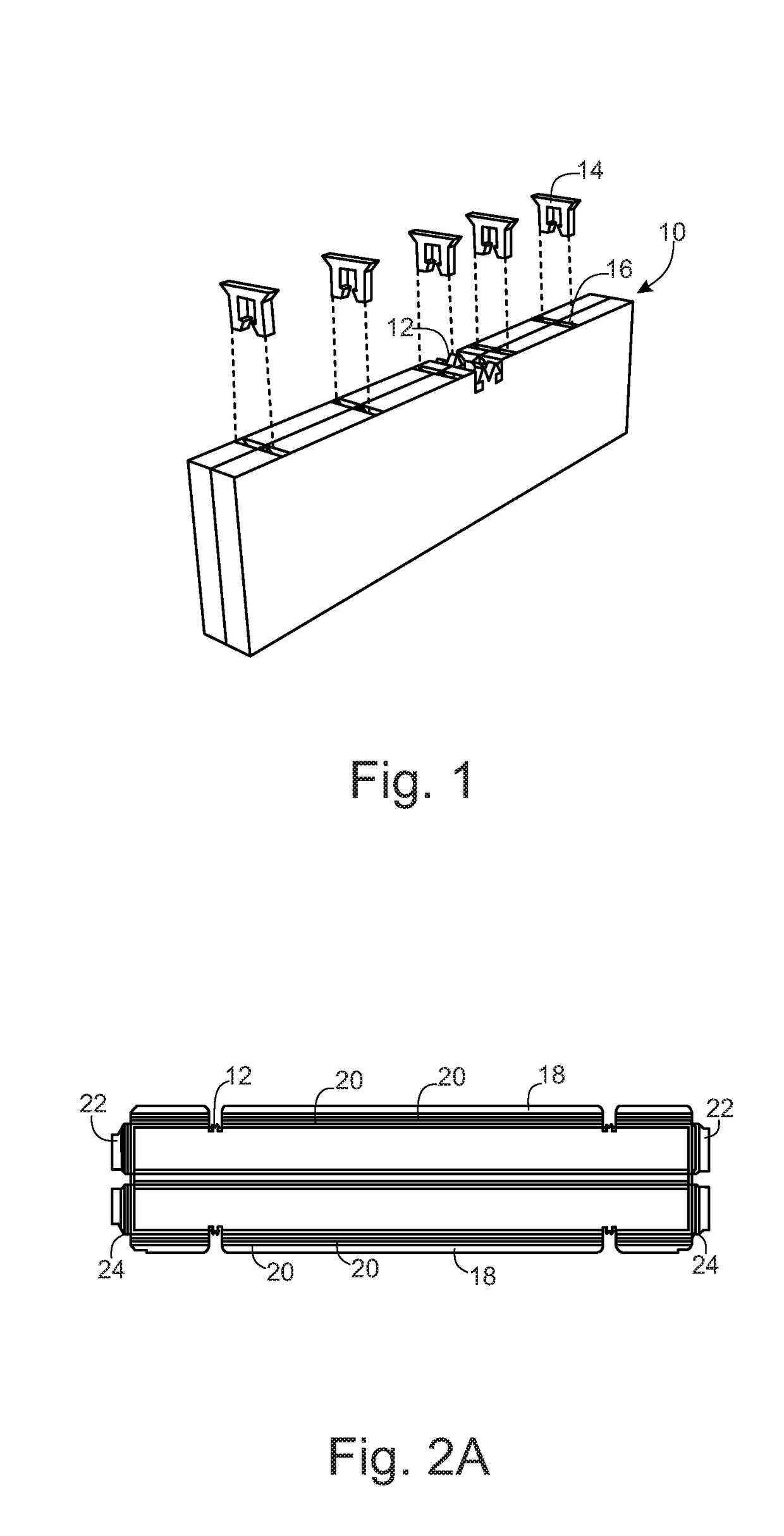
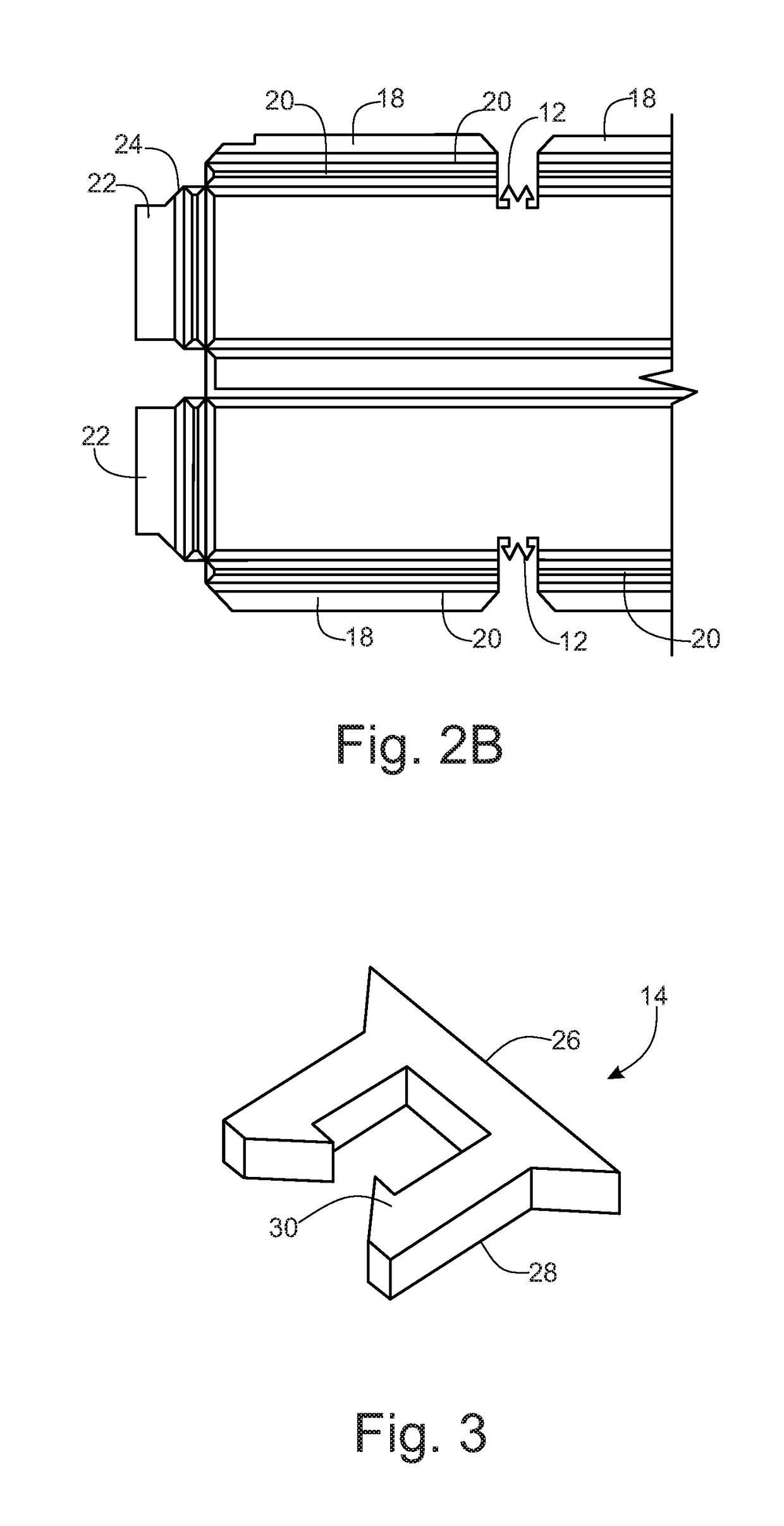
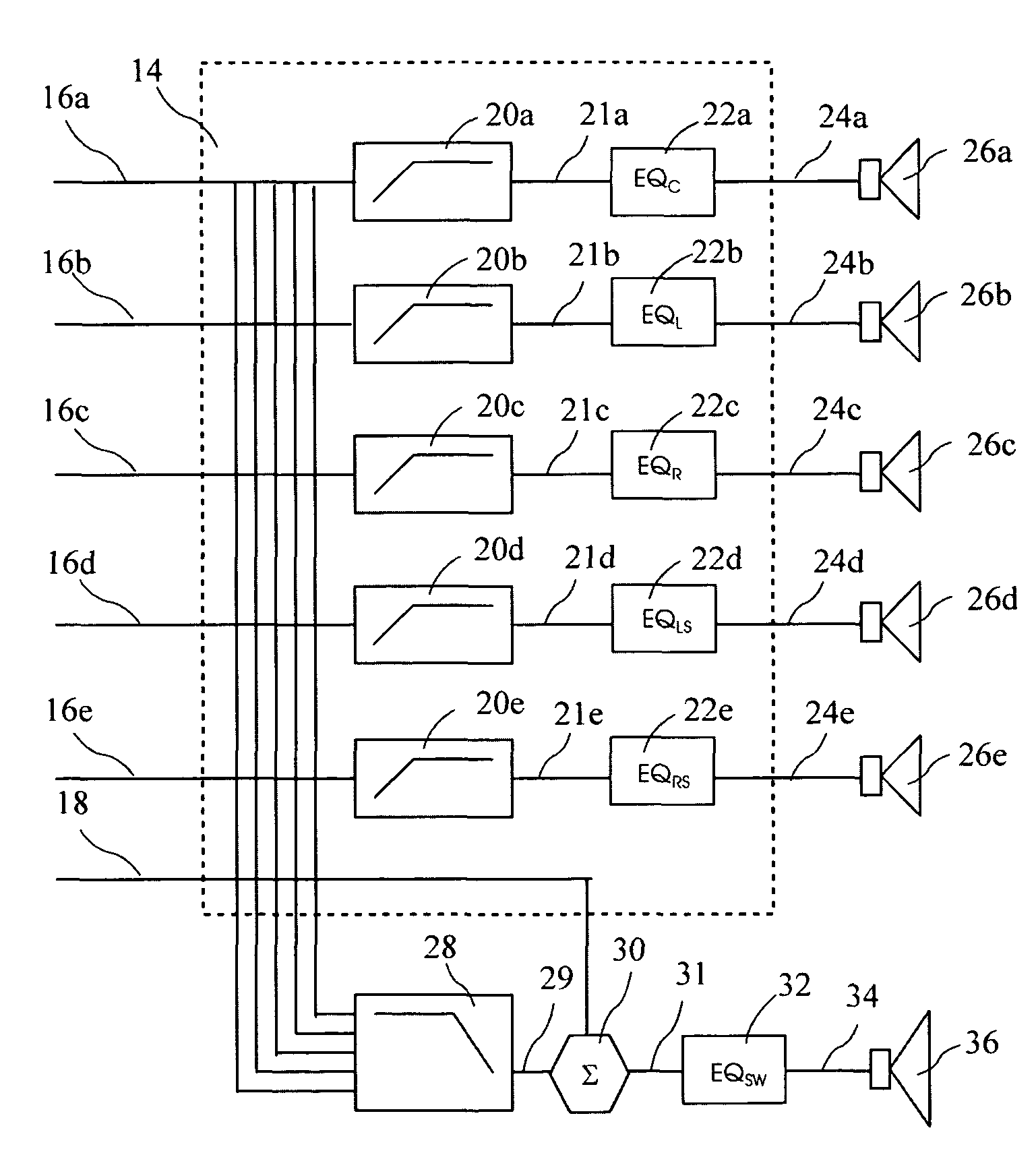
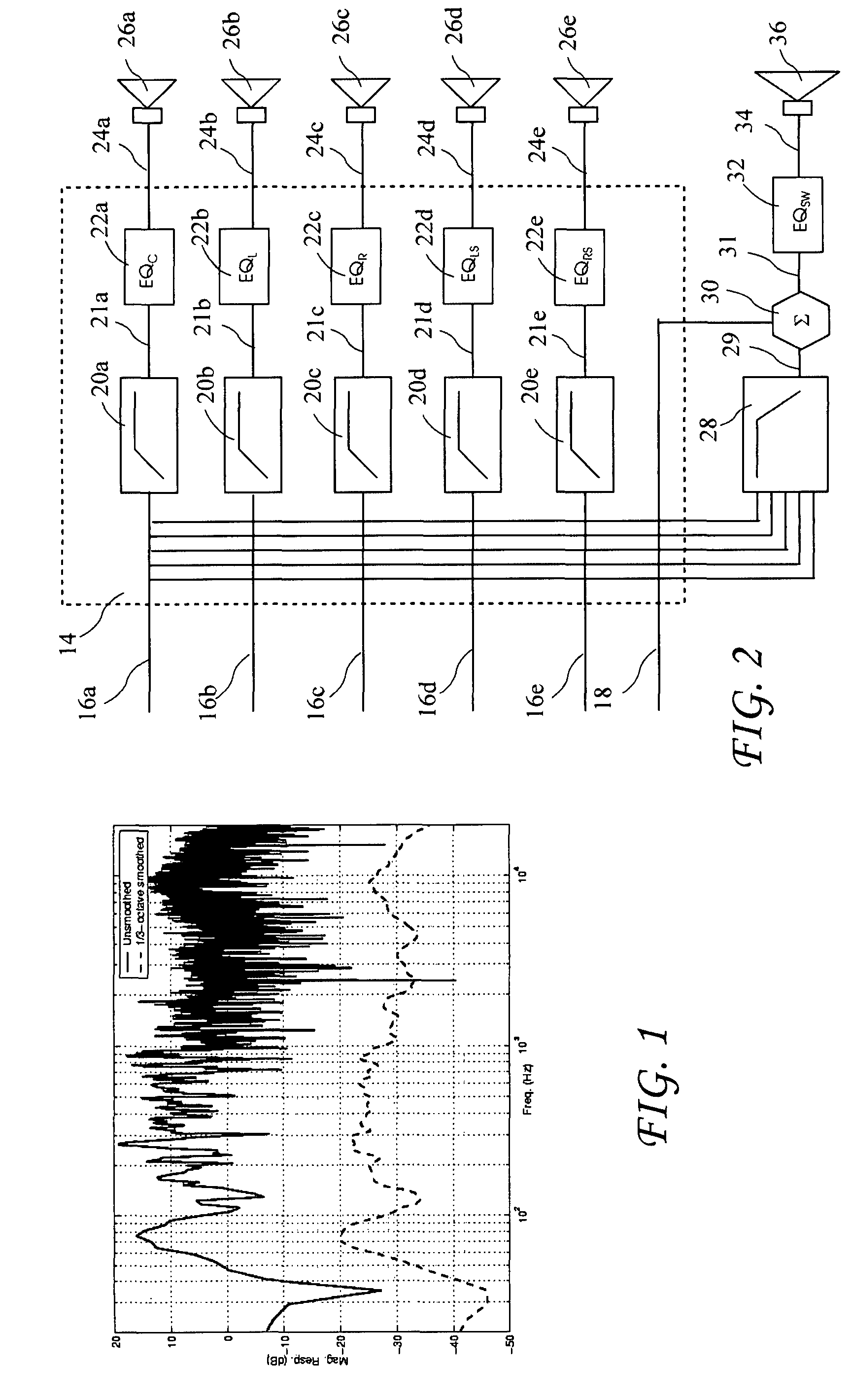
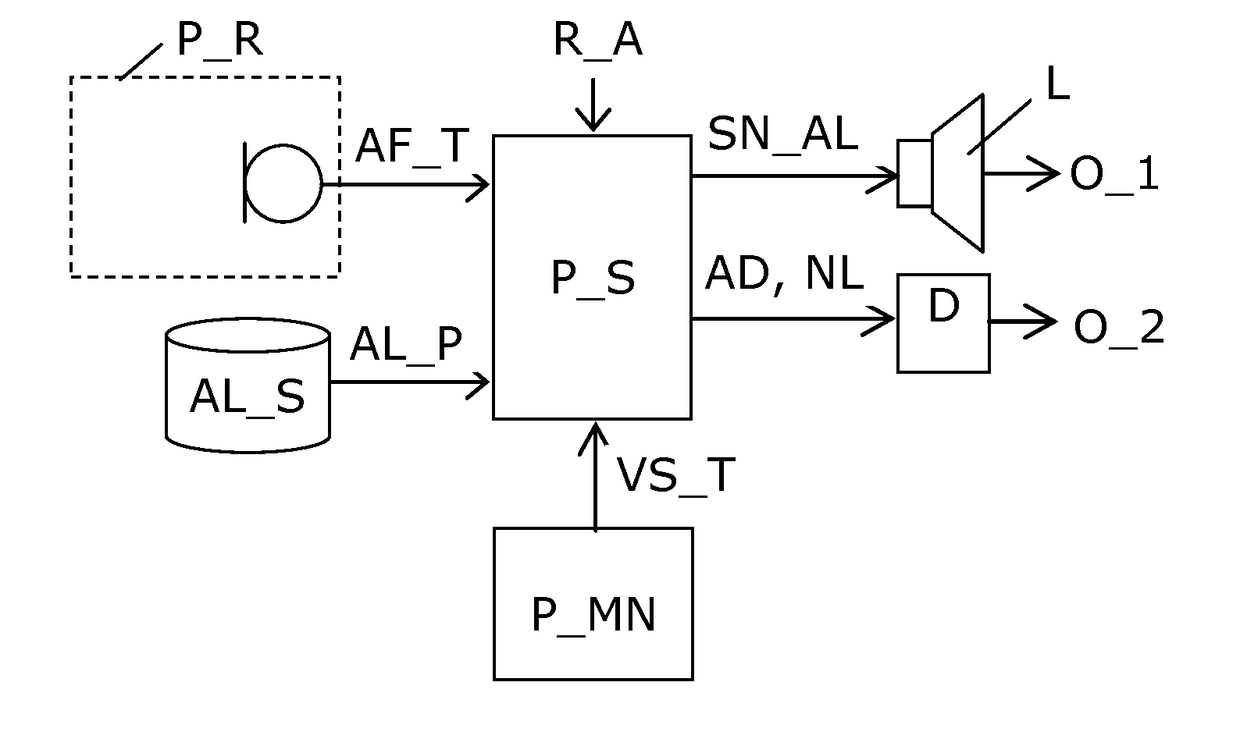
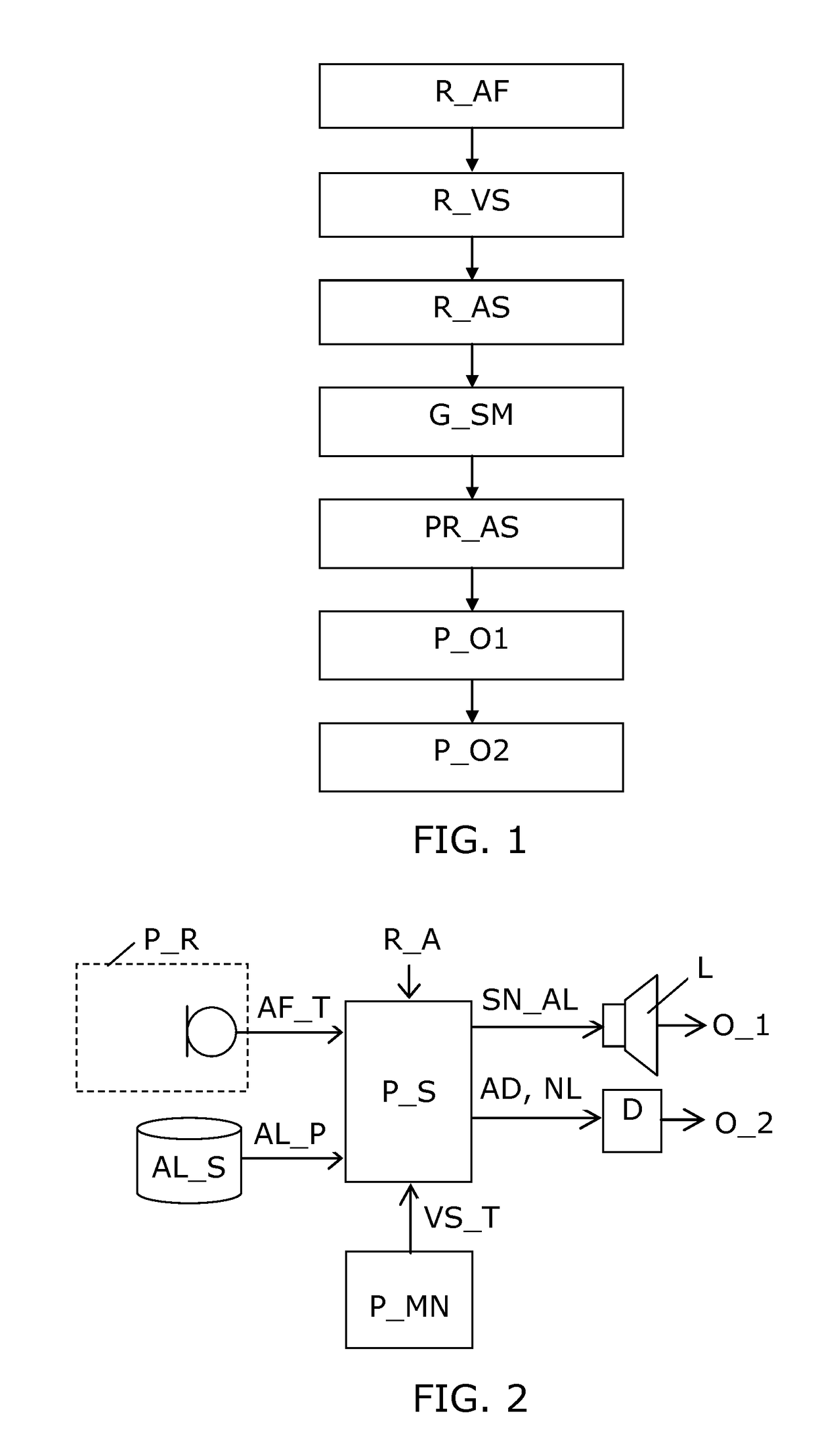
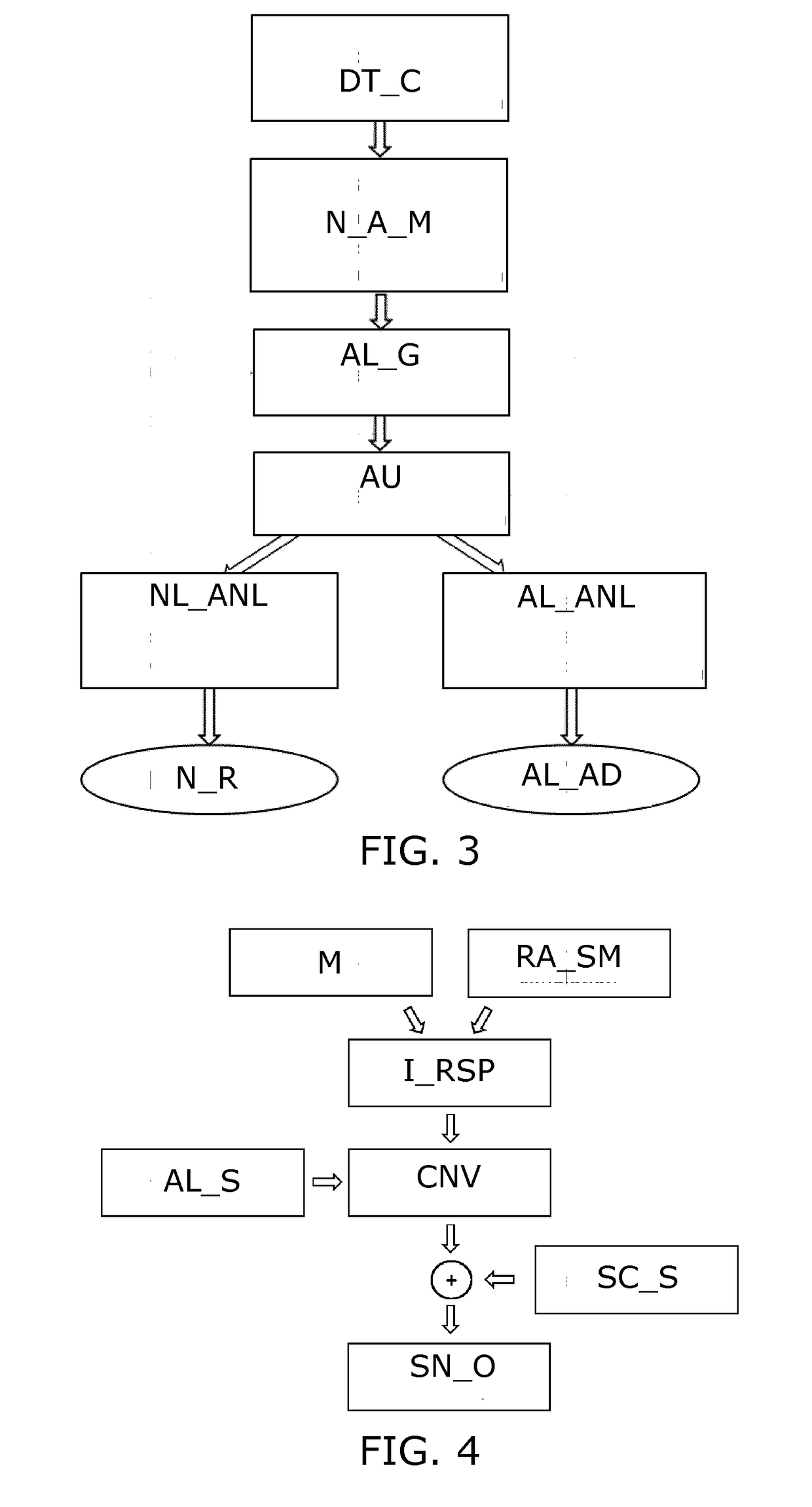
Listener specific audio reproduction system
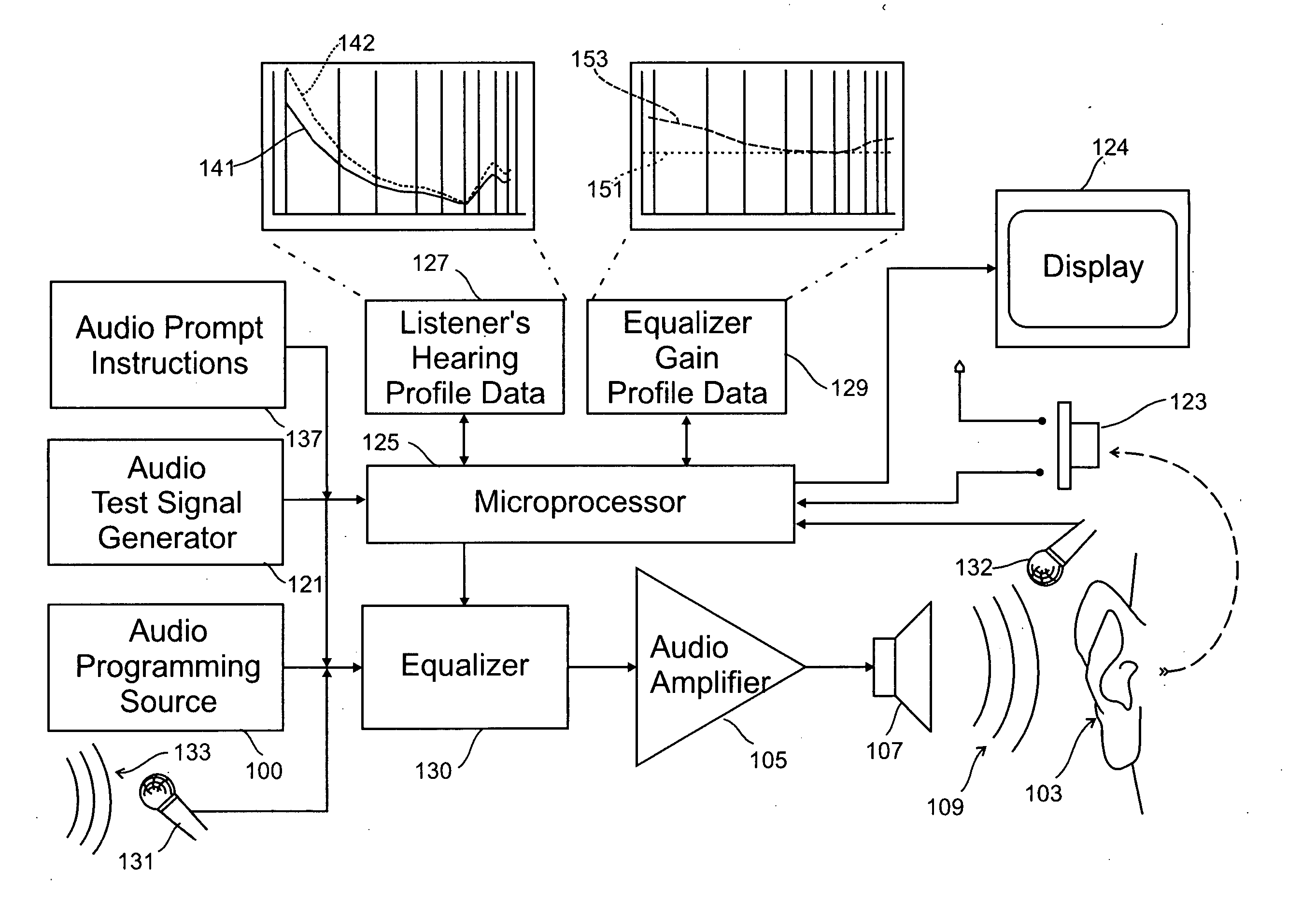
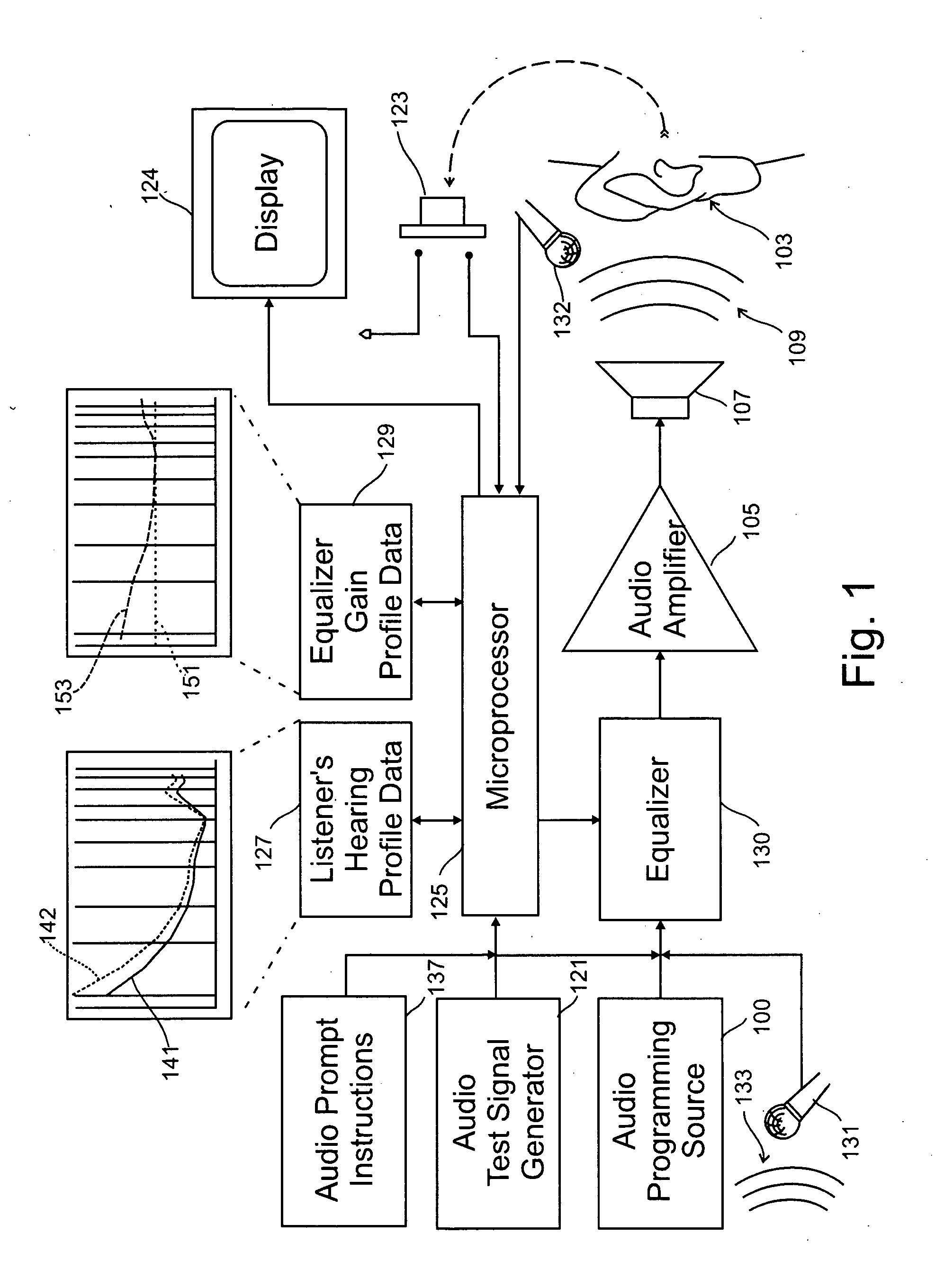
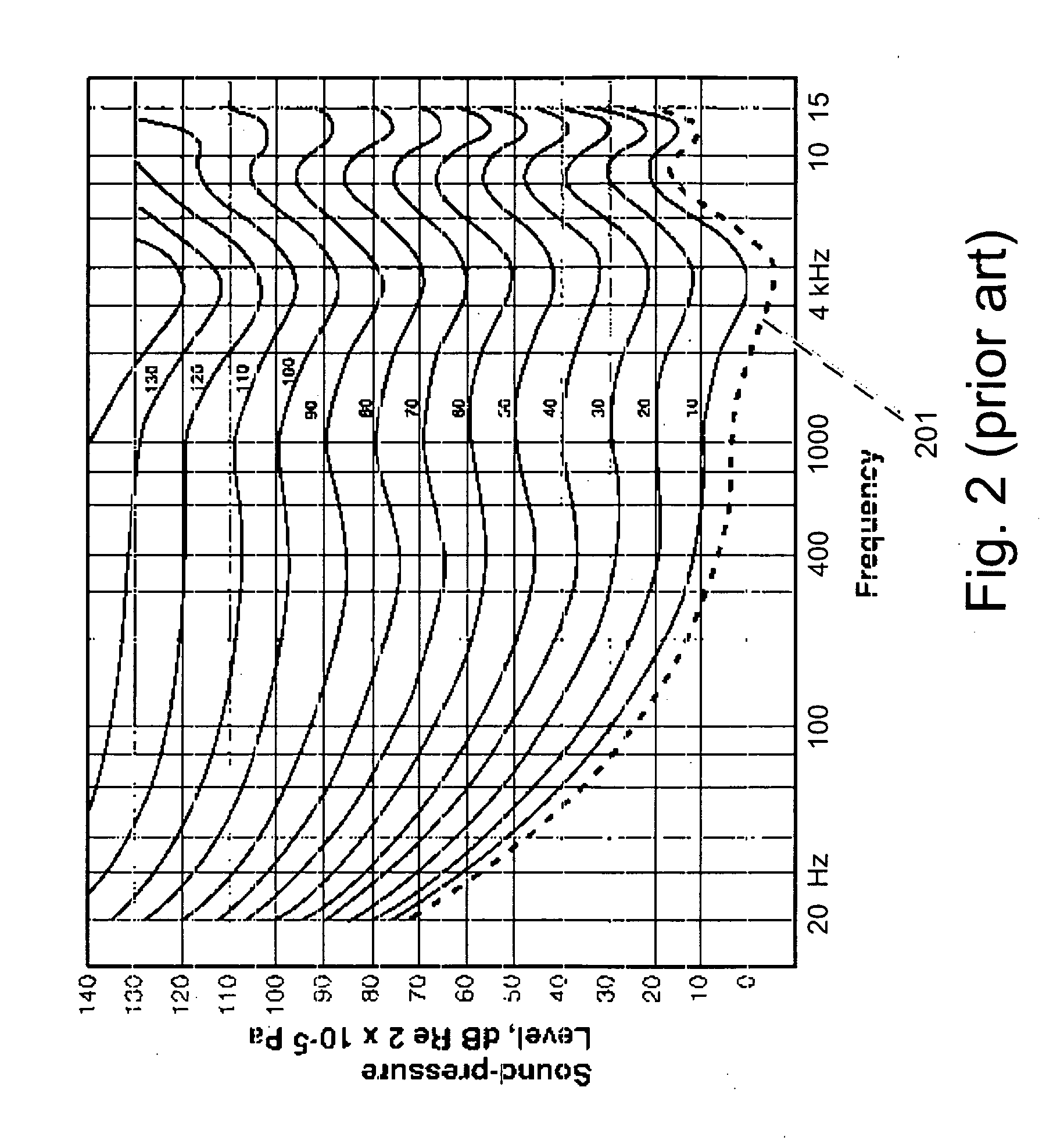
ActiveUS20050094822A1Quality improvementImprove sound qualityStereophonic circuit arrangementsHearing impaired stereophonic signal reproductionRoom acousticsEngineering
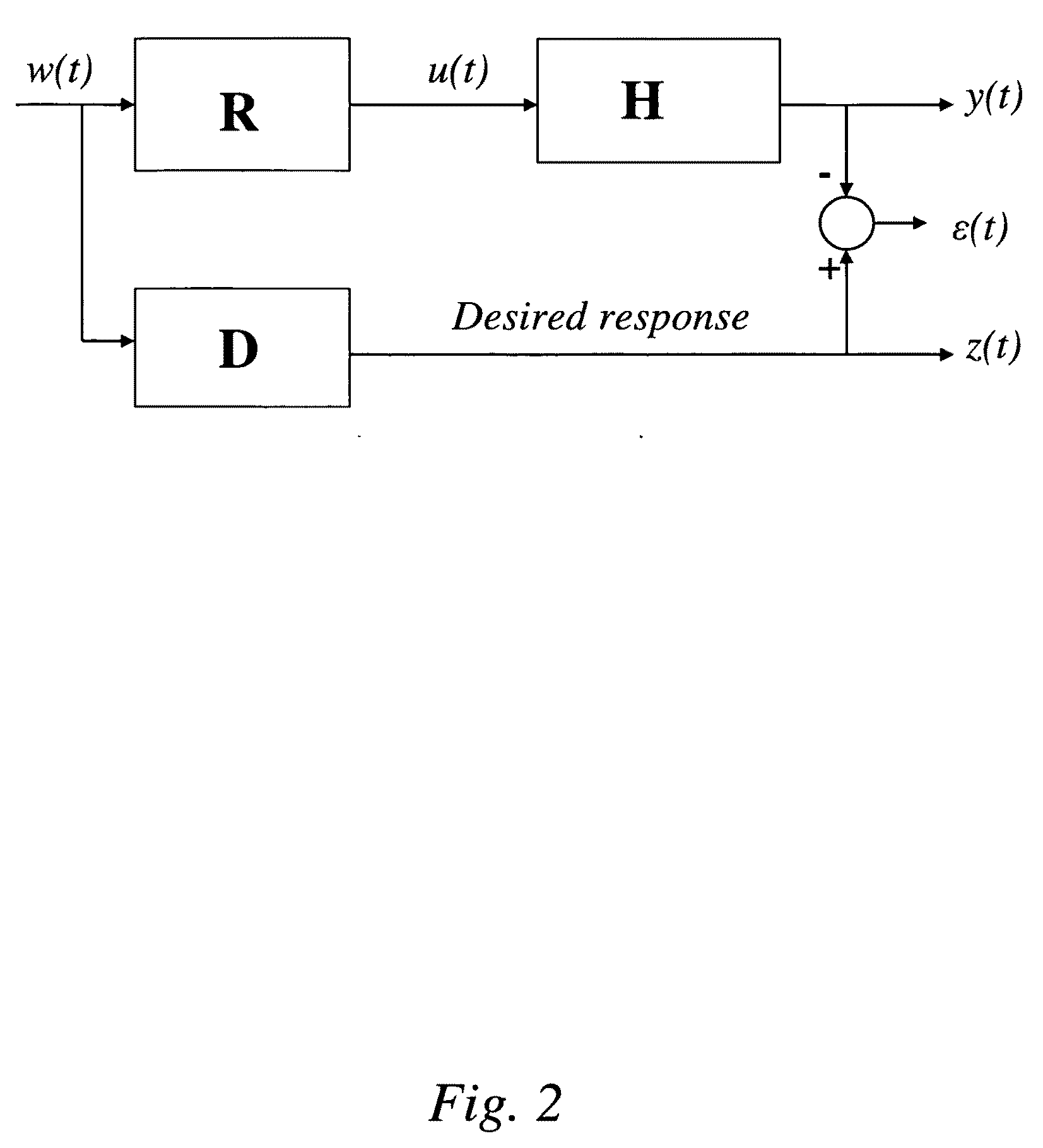
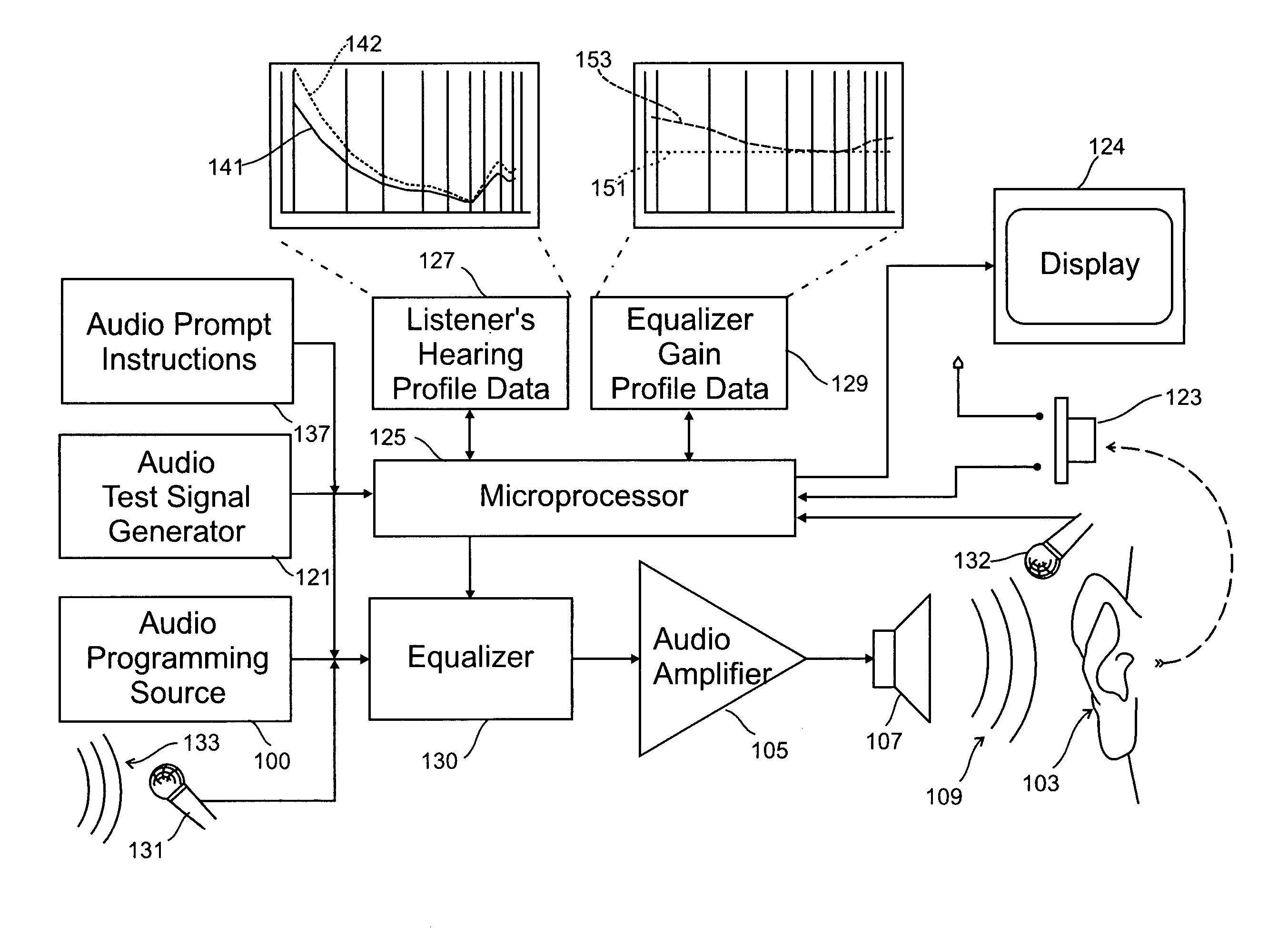
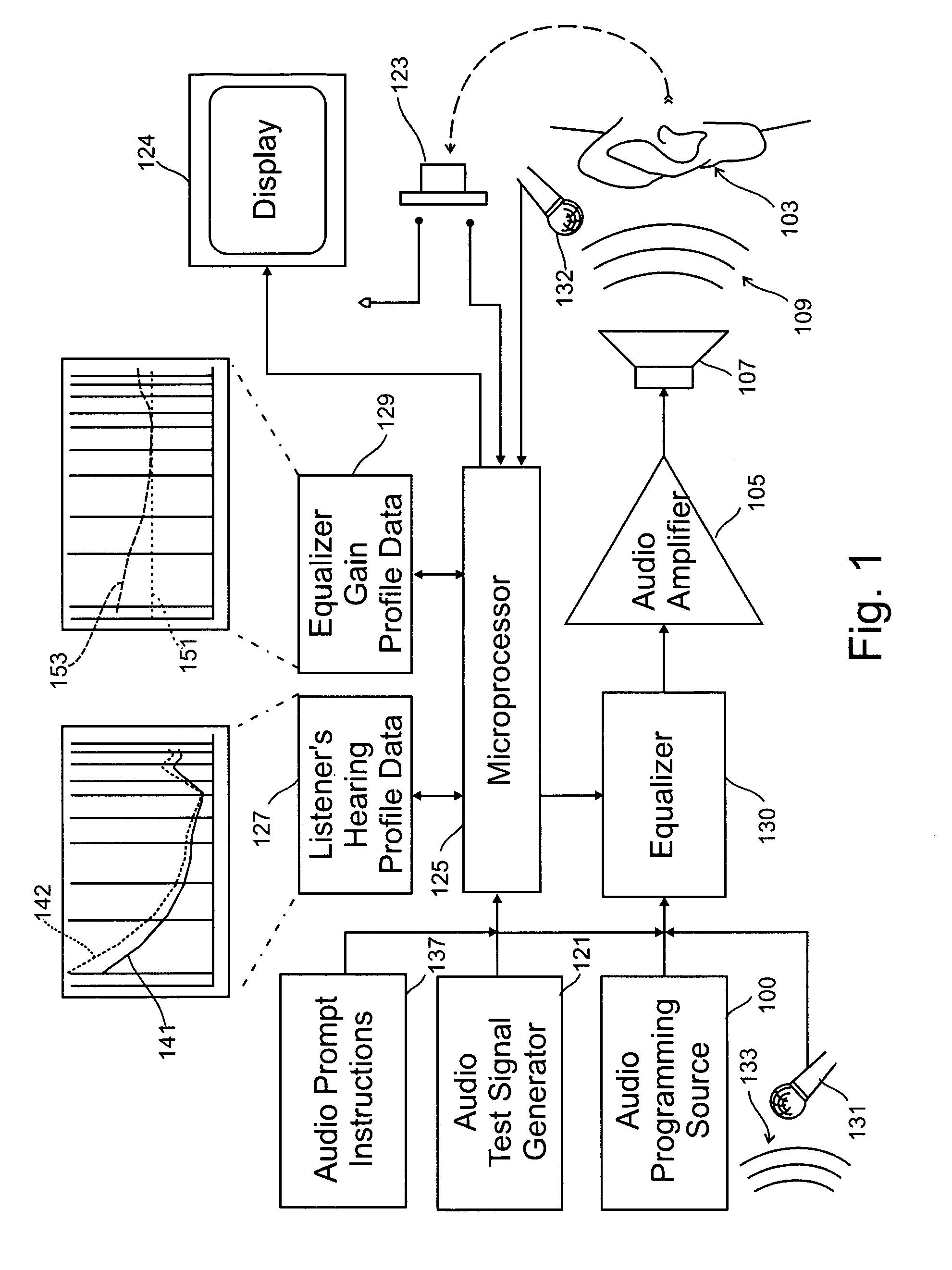
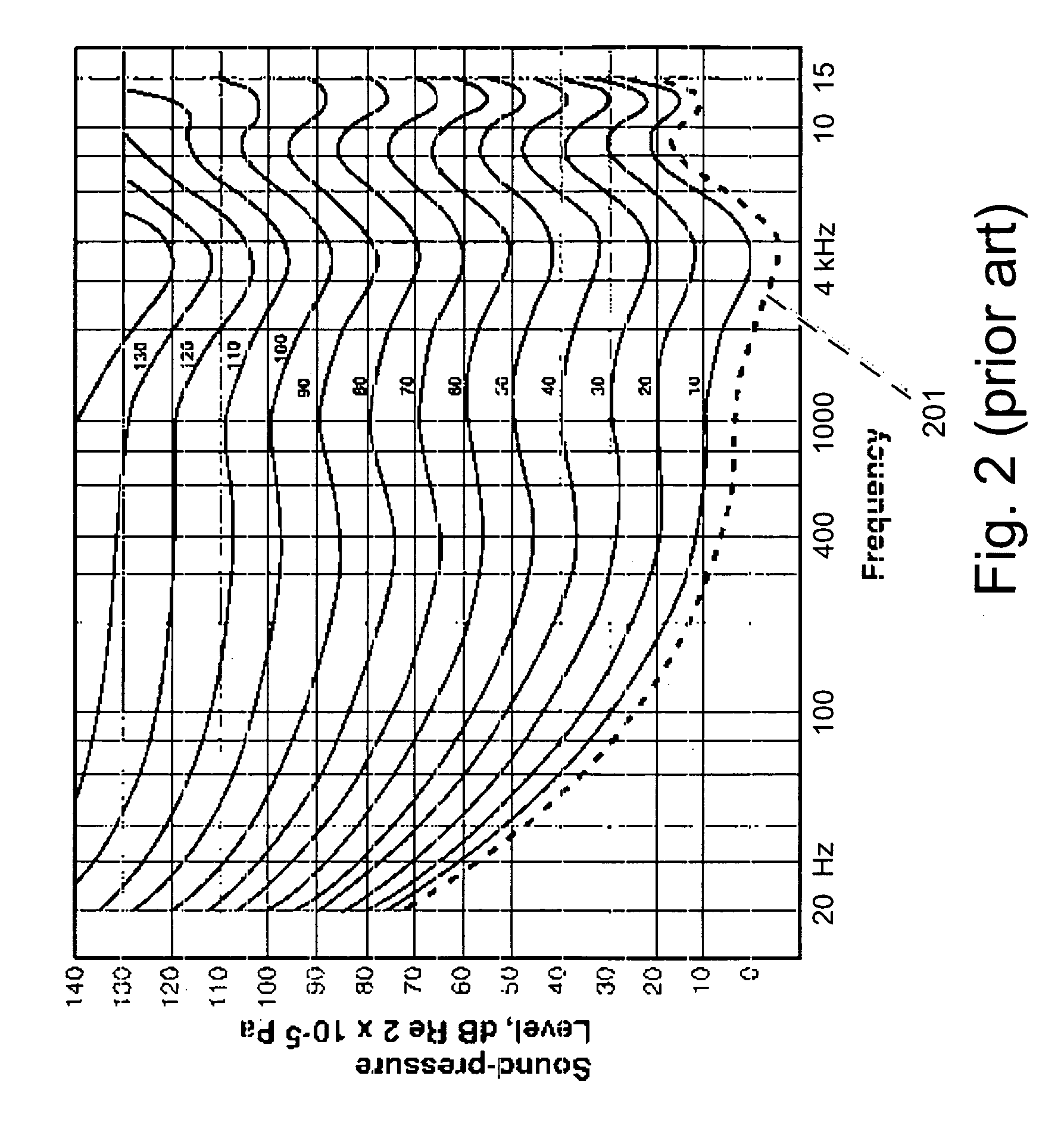
A system for use with an audio reproduction system that corrects for distortion caused by the system as well as any hearing impairment suffered a listener. Test signals are introduced into the input of the system to produce test sounds that are perceptible by the listener. Using a pushbutton, the listener indicates when a test signal of progressively increasing volume reaches an audible level. The resulting measured values of the listener's threshold of hearing at different frequencies is compared with comparable data for a normal listener to generate correction values that are used to program an equalizer which compensates for not only the listener's hearing impairments but also any distortion produced by system components or room acoustics.
Owner:DTS
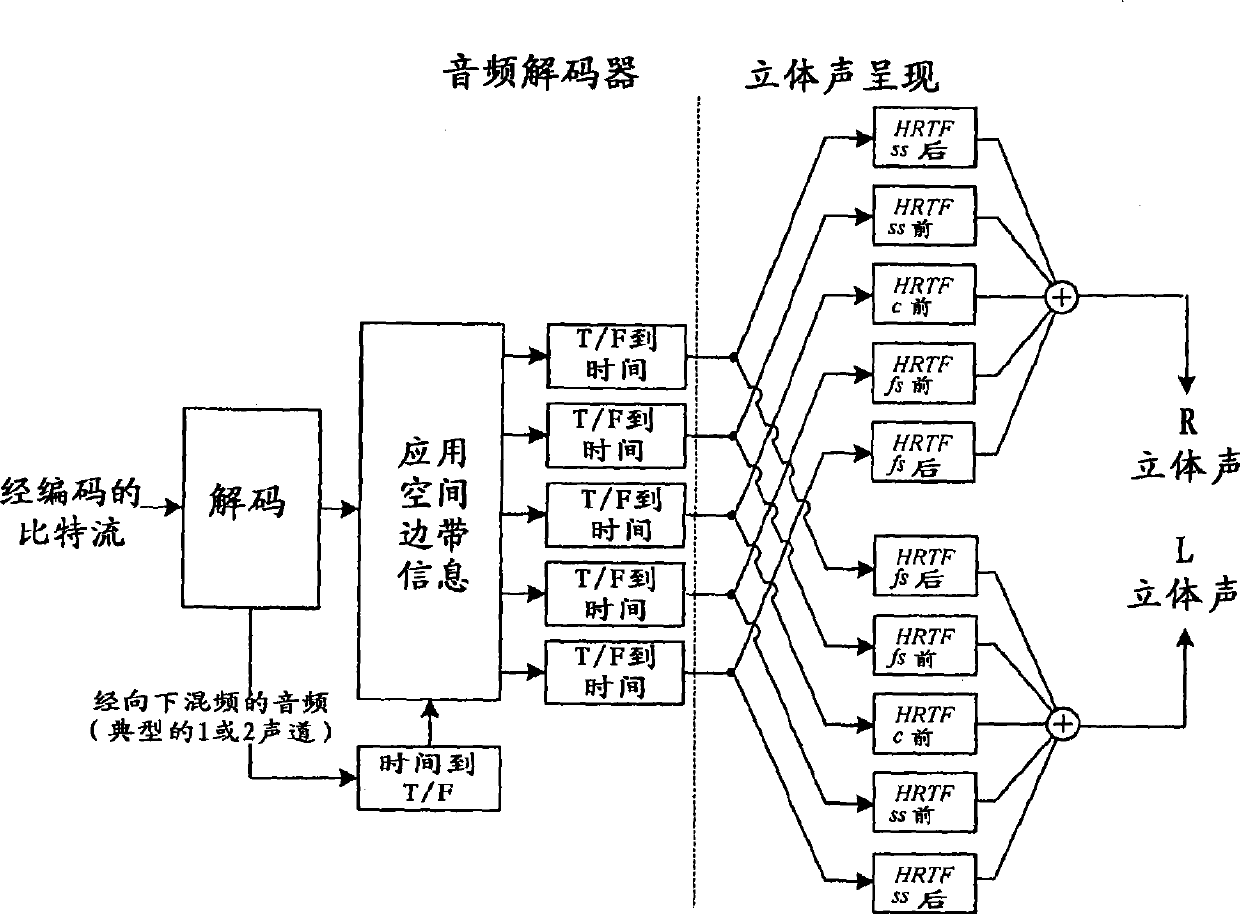
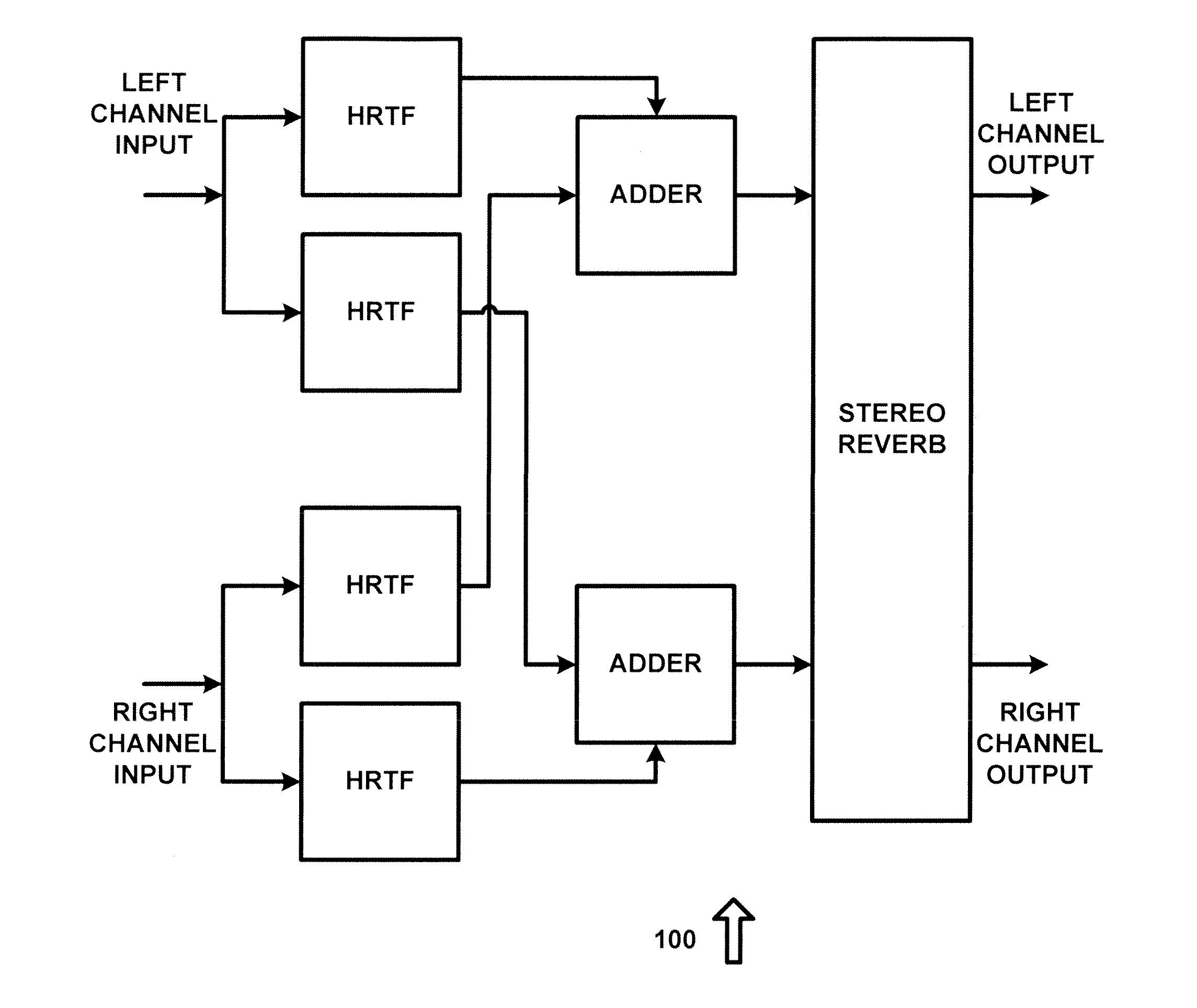
Binaural rendering using subband filters
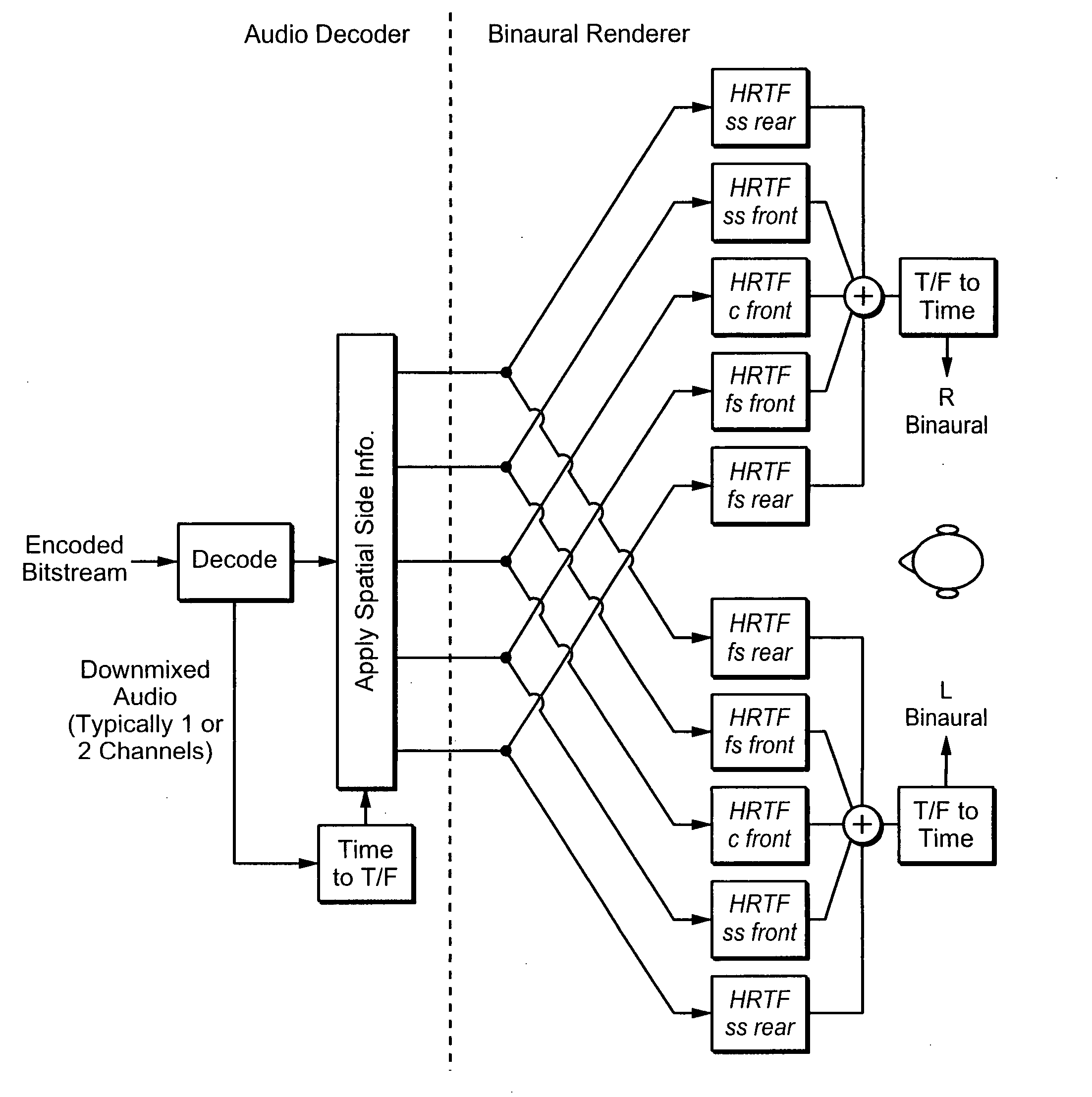
InactiveUS20080025519A1Efficient implementationComputational complexity is reducedSpeech analysisStereophonic systemsPhase correctionFrequency spectrum
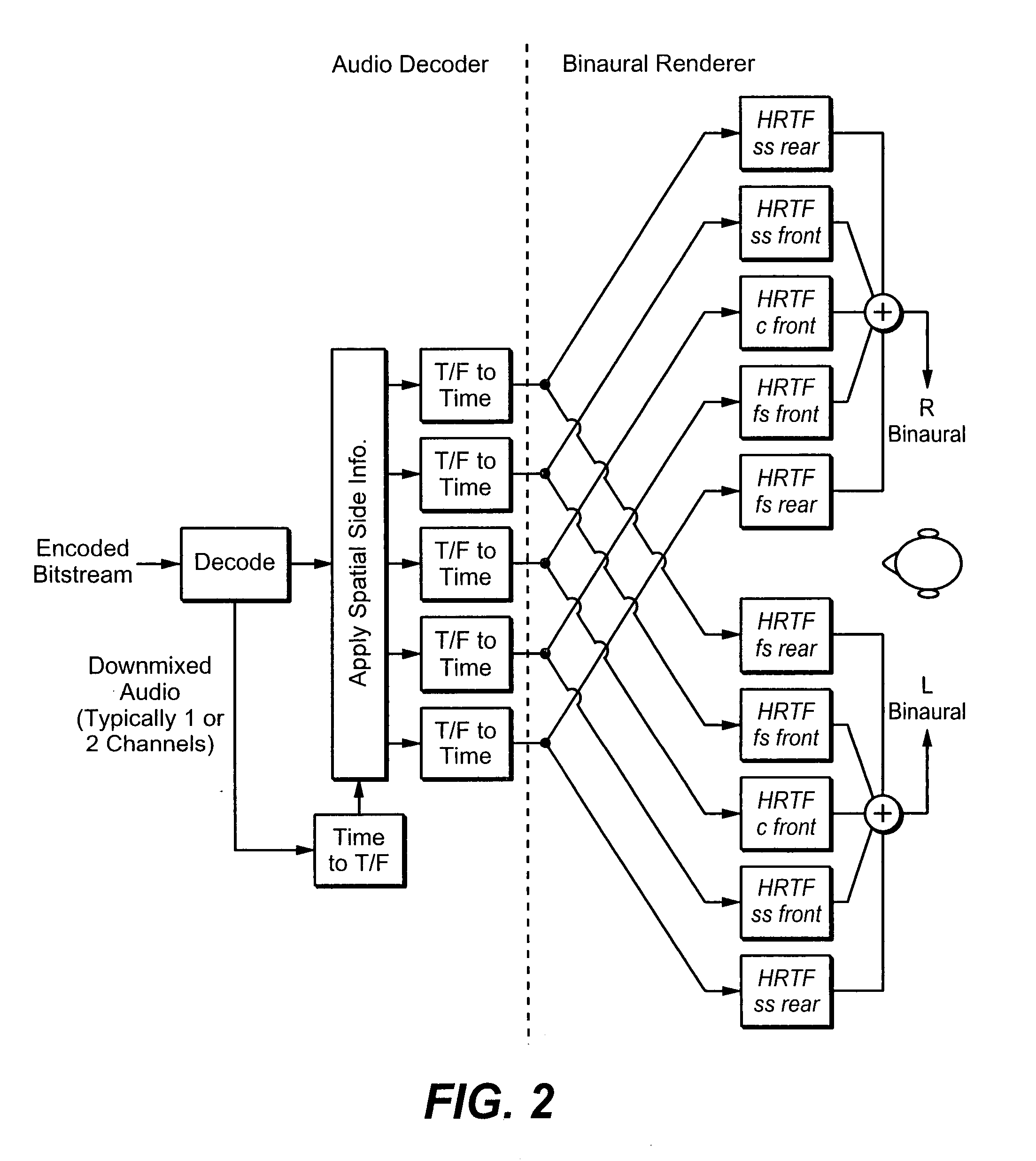
Transfer functions like Head Related Transfer Functions (HRTF) needed for binaural rendering are implemented efficiently by a subband-domain filter structure. In one implementation, amplitude, fractional-sample delay and phase-correction filters are arranged in cascade with one another and applied to subband signals that represent spectral content of an audio signal in frequency subbands. Other filter structures are also disclosed. These filter structures may be used advantageously in a variety of signal processing applications. A few examples of audio applications include signal bandwidth compression, loudness equalization, room acoustics correction and assisted listening for individuals with hearing impairments.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
Sound field control in multiple listening regions
ActiveUS20100305725A1Improve performanceStereophonic systemsSpecial data processing applicationsFinite impulse responseMulti input
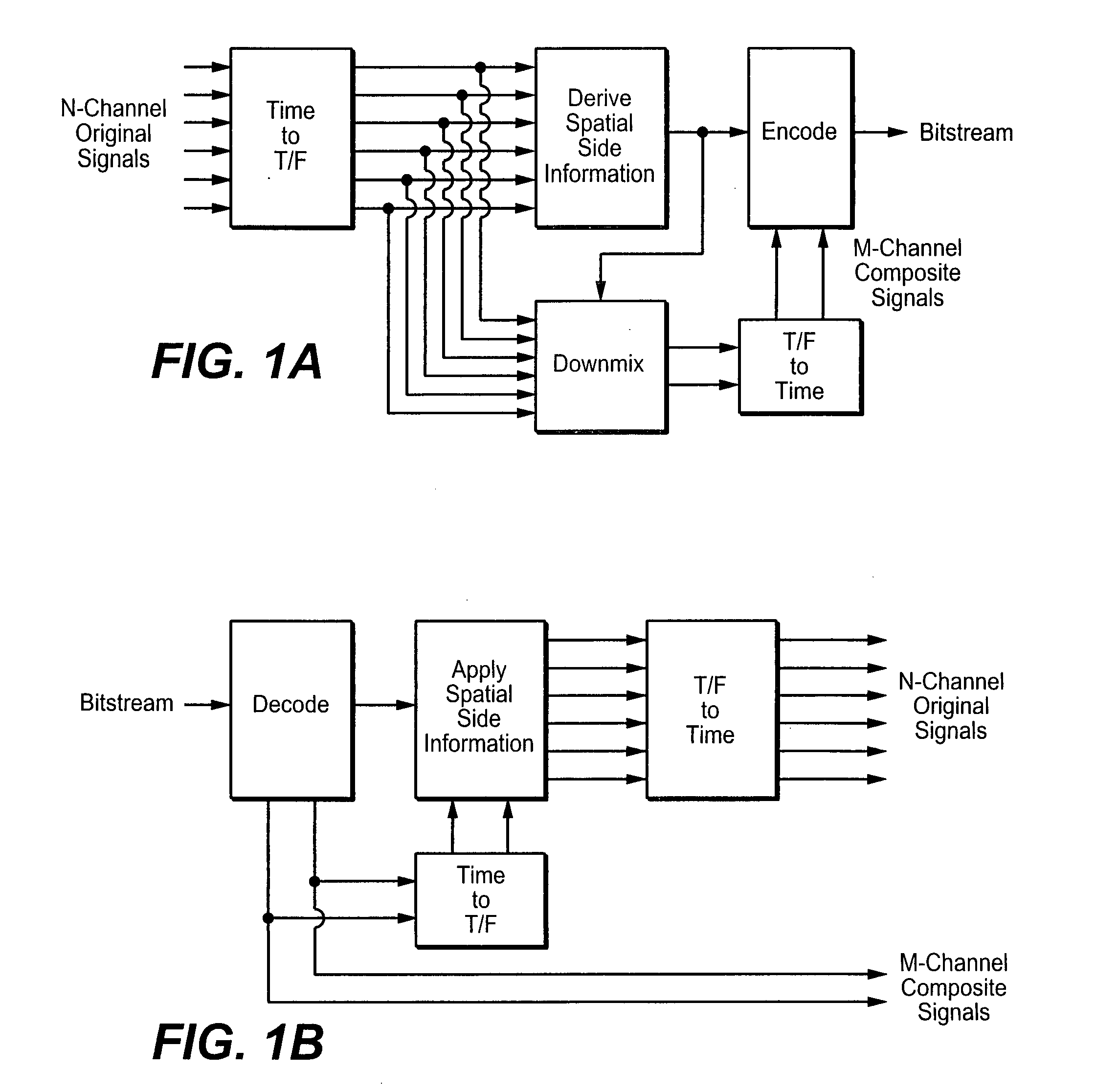
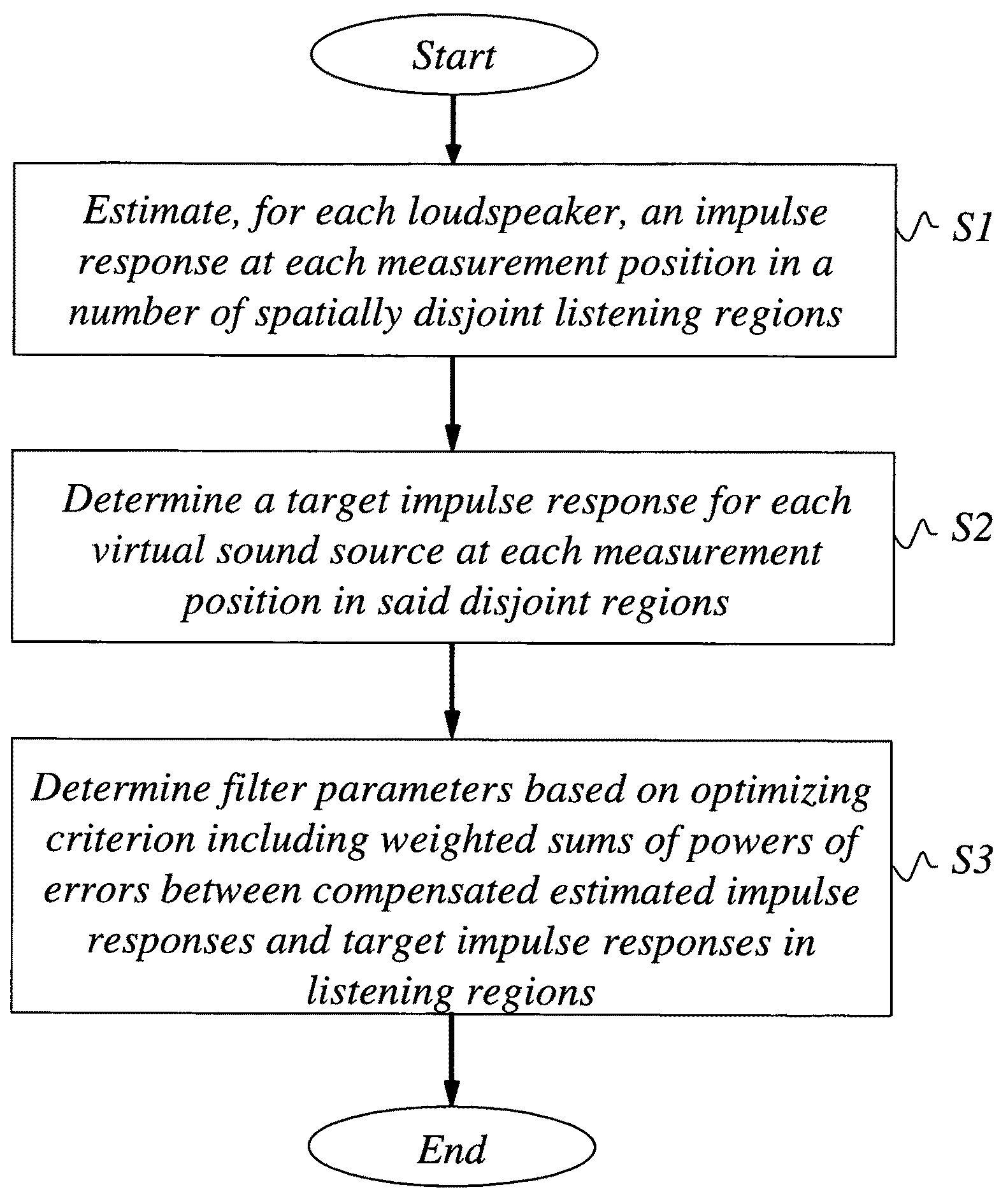
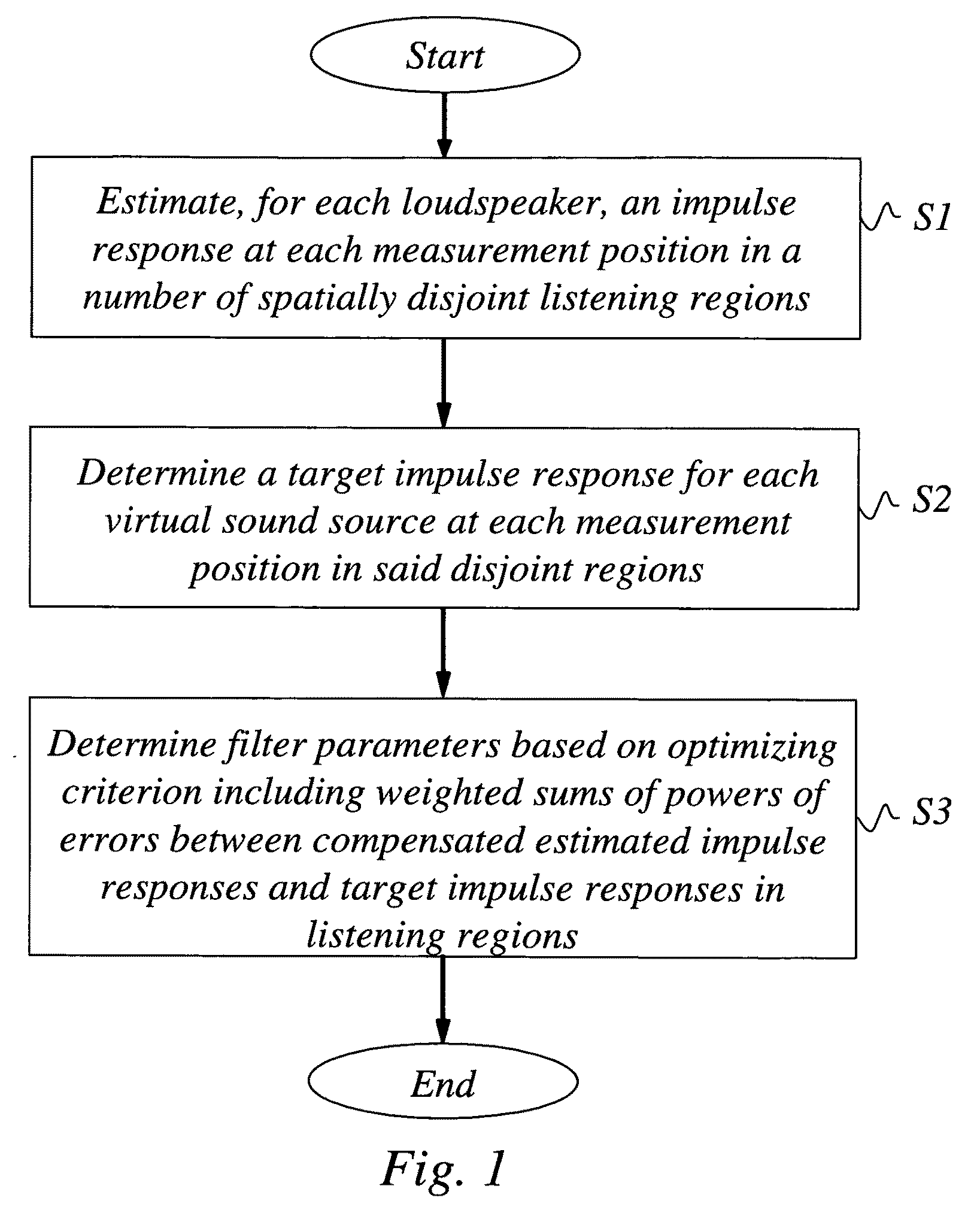
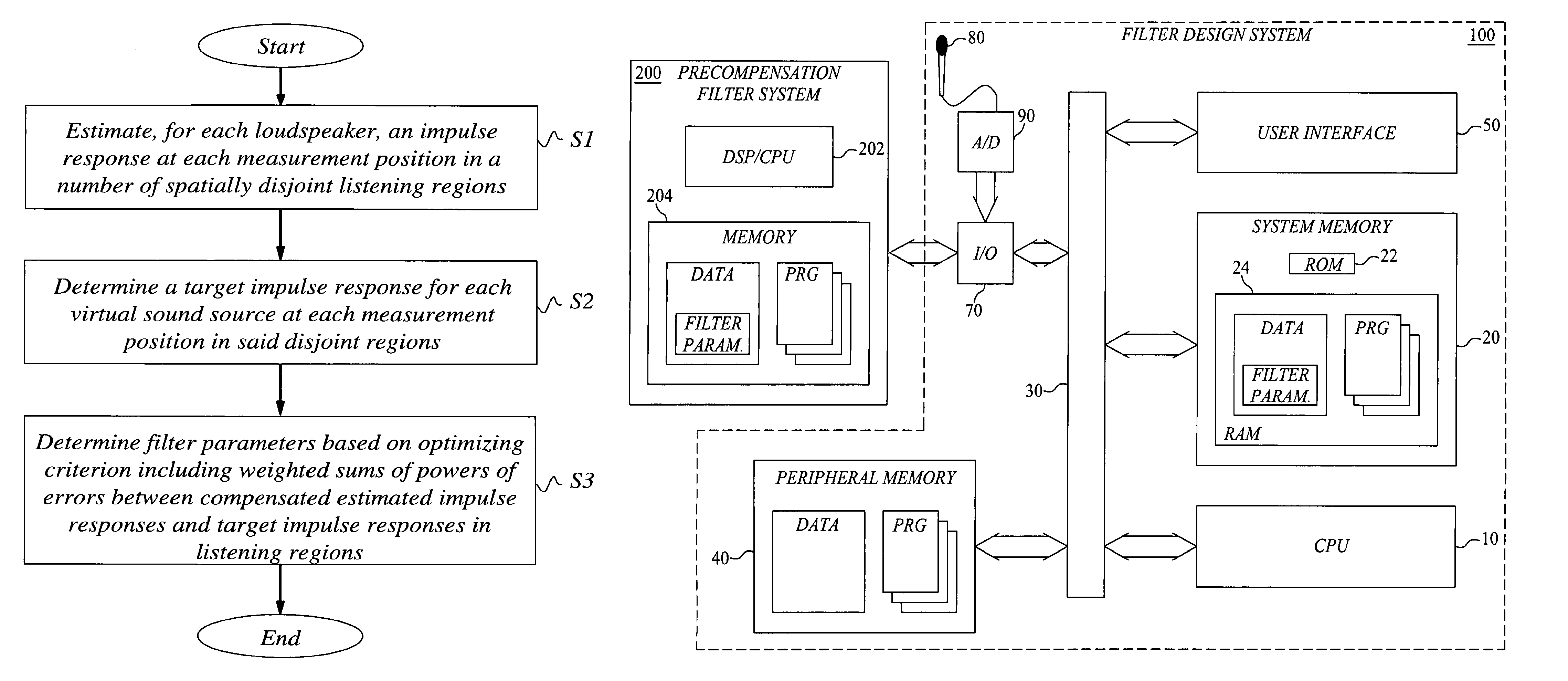
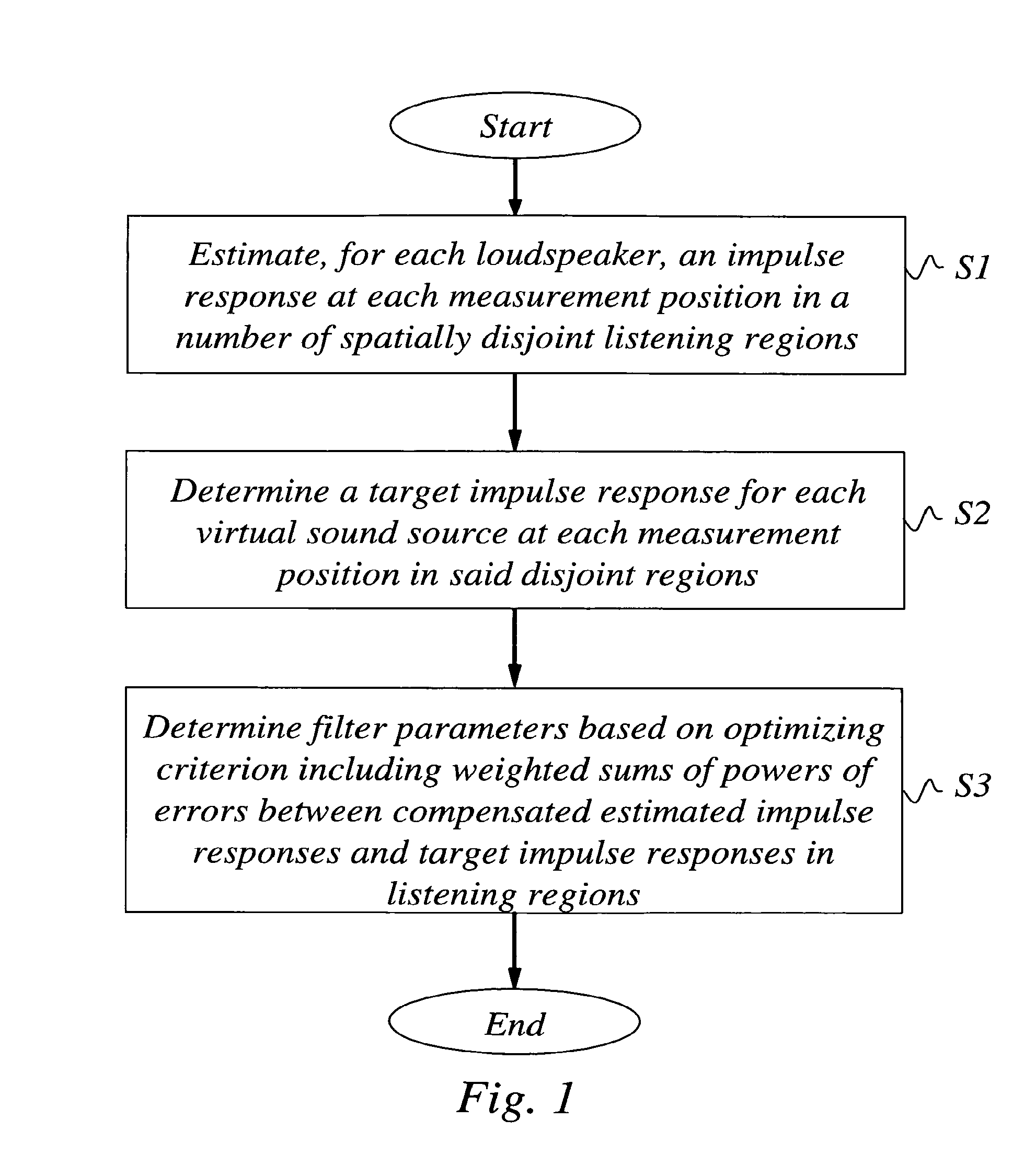
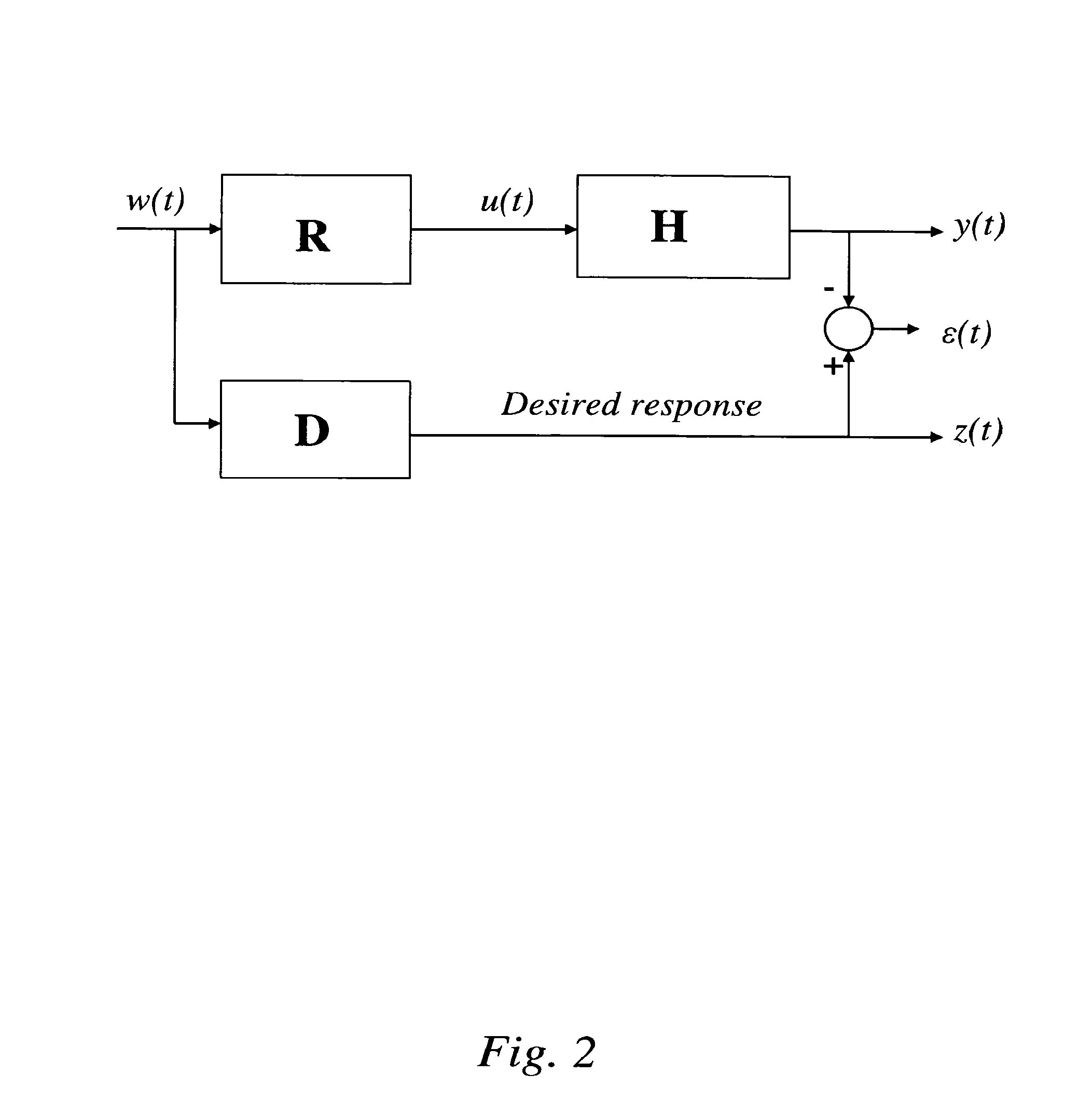
A scheme to design an audio precompensation controller for a multichannel audio system, with a prescribed number N of loudspeakers in prescribed positions so that listeners positioned in any of P>1 spatially extended listening regions should be given the illusion of being in another acoustic environment that has L sound sources located at prescribed positions in a prescribed room acoustics. The method provides a unified joint solution to the problems of equalizer design, crossover design, delay and level calibration, sum-response optimization and up-mixing. A multi-input multi-output audio precompensation controller is designed for an associated sound generating system including a limited number of loudspeaker inputs for emulating a number of virtual sound sources. Method includes: estimating, for each loudspeaker input signals, an impulse response at each of a set of measurement positions that cover the P listening regions; specifying a target impulse response (target stages) for each virtual sound source at each measurement position; and determining adjustable filter parameters of the audio precompensation controller so that a criterion function is optimized.
Owner:DIRAC RES
Listener specific audio reproduction system
ActiveUS7564979B2Quality improvementImprove sound qualityStereophonic circuit arrangementsHearing impaired stereophonic signal reproductionRoom acousticsEngineering
A system for use with an audio reproduction system that corrects for distortion caused by the system as well as any hearing impairment suffered a listener. Test signals are introduced into the input of the system to produce test sounds that are perceptible by the listener. Using a pushbutton, the listener indicates when a test signal of progressively increasing volume reaches an audible level. The resulting measured values of the listener's threshold of hearing at different frequencies is compared with comparable data for a normal listener to generate correction values that are used to program an equalizer which compensates for not only the listener's hearing impairments but also any distortion produced by system components or room acoustics.
Owner:DTS
Method and device for modelling room acoustic based on measured geometrical data
InactiveUS20160109284A1Convenient verificationEasily be real-time updatedReverberation timeFrequency/directions obtaining arrangementsAcoustic transmissionRough surface
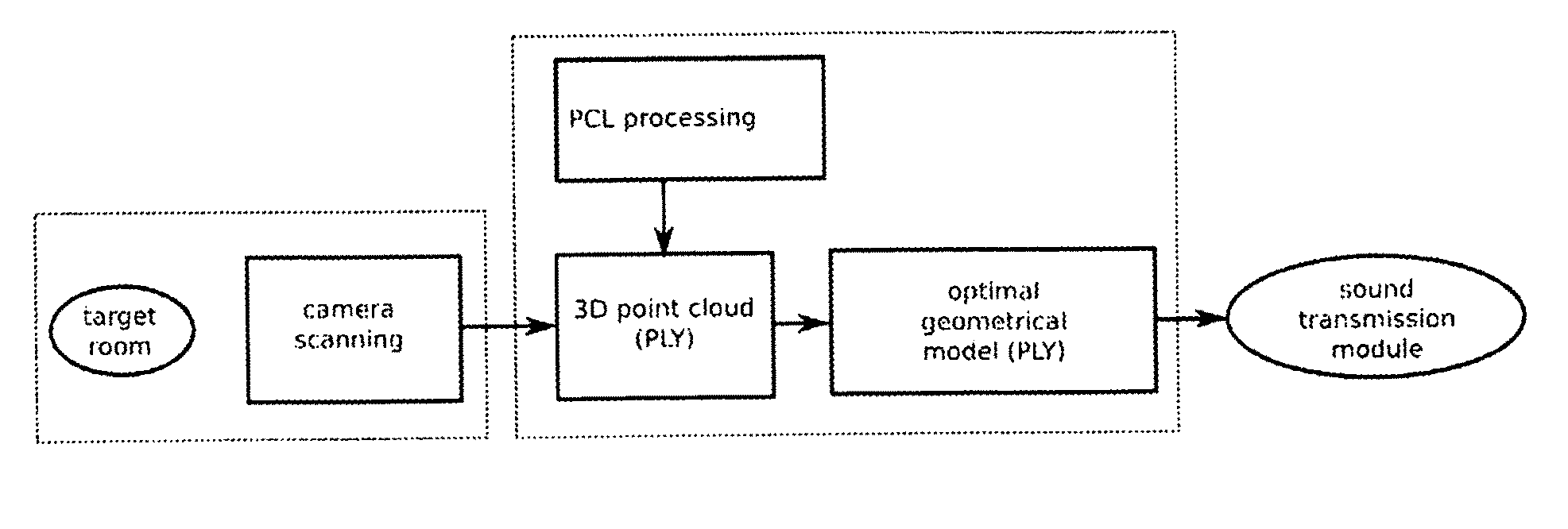
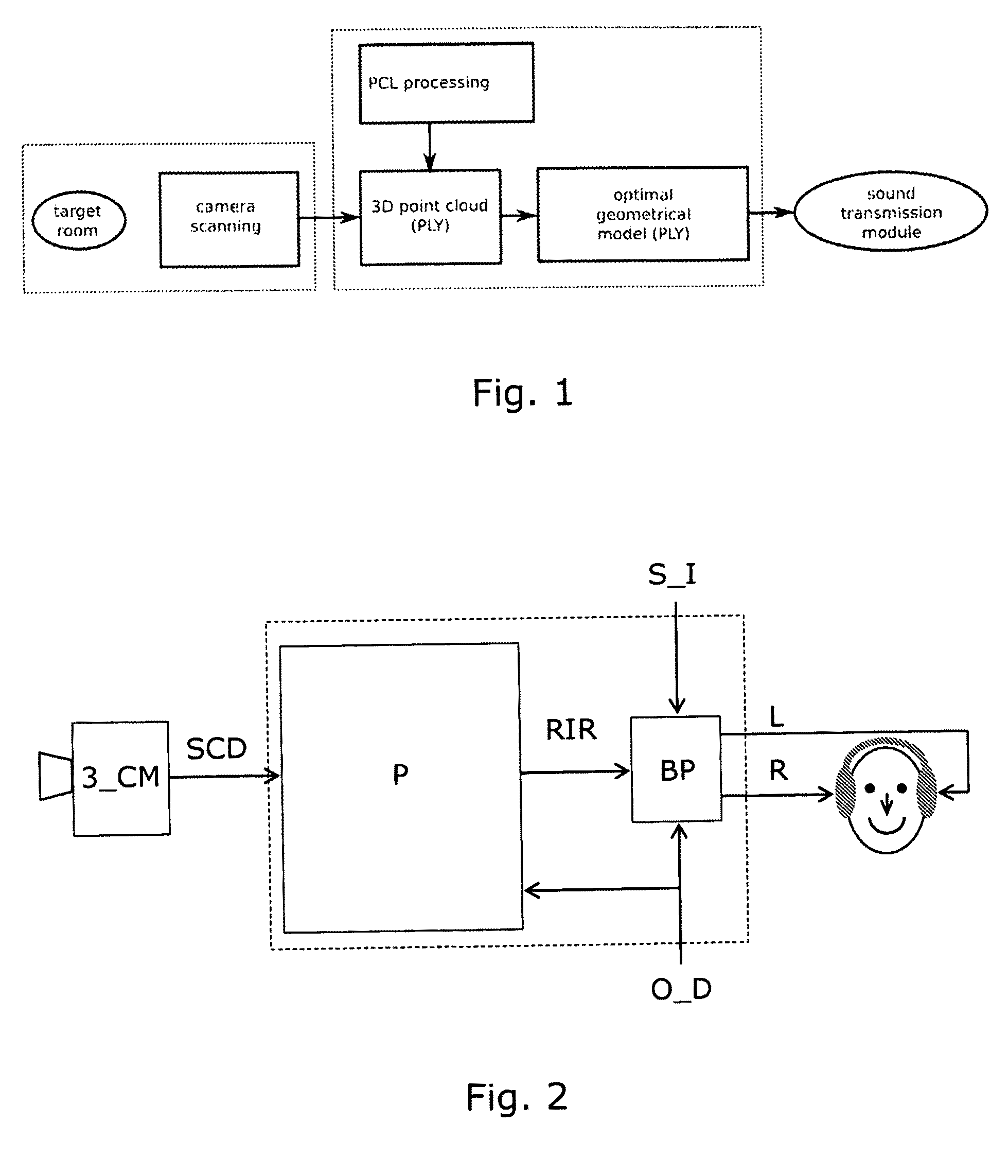
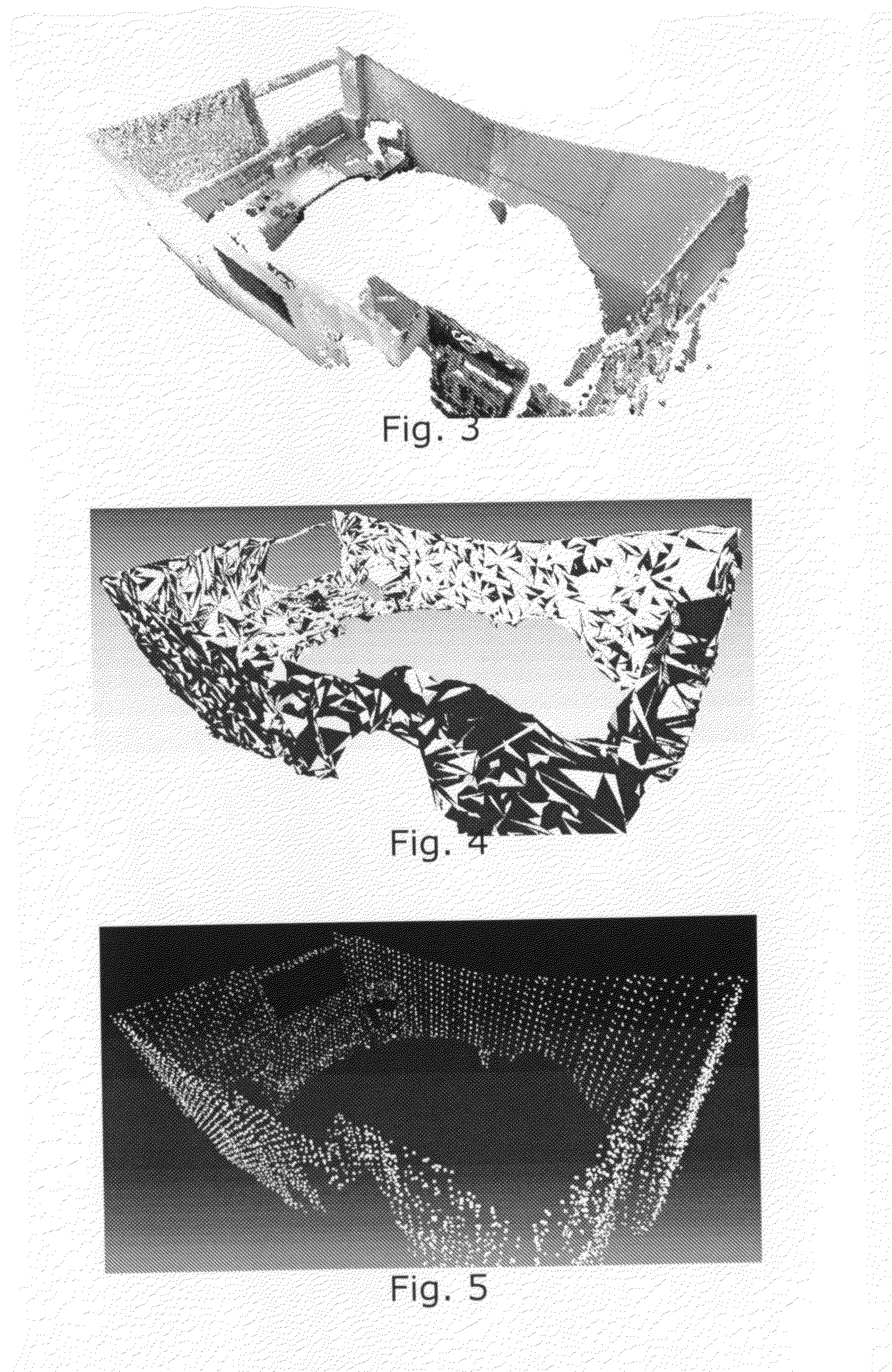
The invention provides a method for generating an output indicative of acoustical sound transmission in a room. By using e.g. a point cloud representation of an acoustic environment, it is possible to calculate its acoustics from the interior information obtained from the depth camera. This approach is suitable e.g. for run-time applications since it is not based on an audible excitation that can disturb running audio. Also, the point-cloud model can be updated in real time according to the scene changes detected by depth-camera. This allows efficient acoustical simulation of dynamic, interactive environments. Although only geometrical information of a room is provided, high amount of surface details leaves possibility for implementation of material recognition algorithms that involve semantic mapping. This can provide information of reflective properties of surfaces or objects at a point level. Also, a high amount of details allows a good approximation of complex geometries, e.g. porous materials, and rough surfaces, thus a more natural simulation of wave phenomena like diffraction and scattering is possible.
Owner:AALBORG UNIV
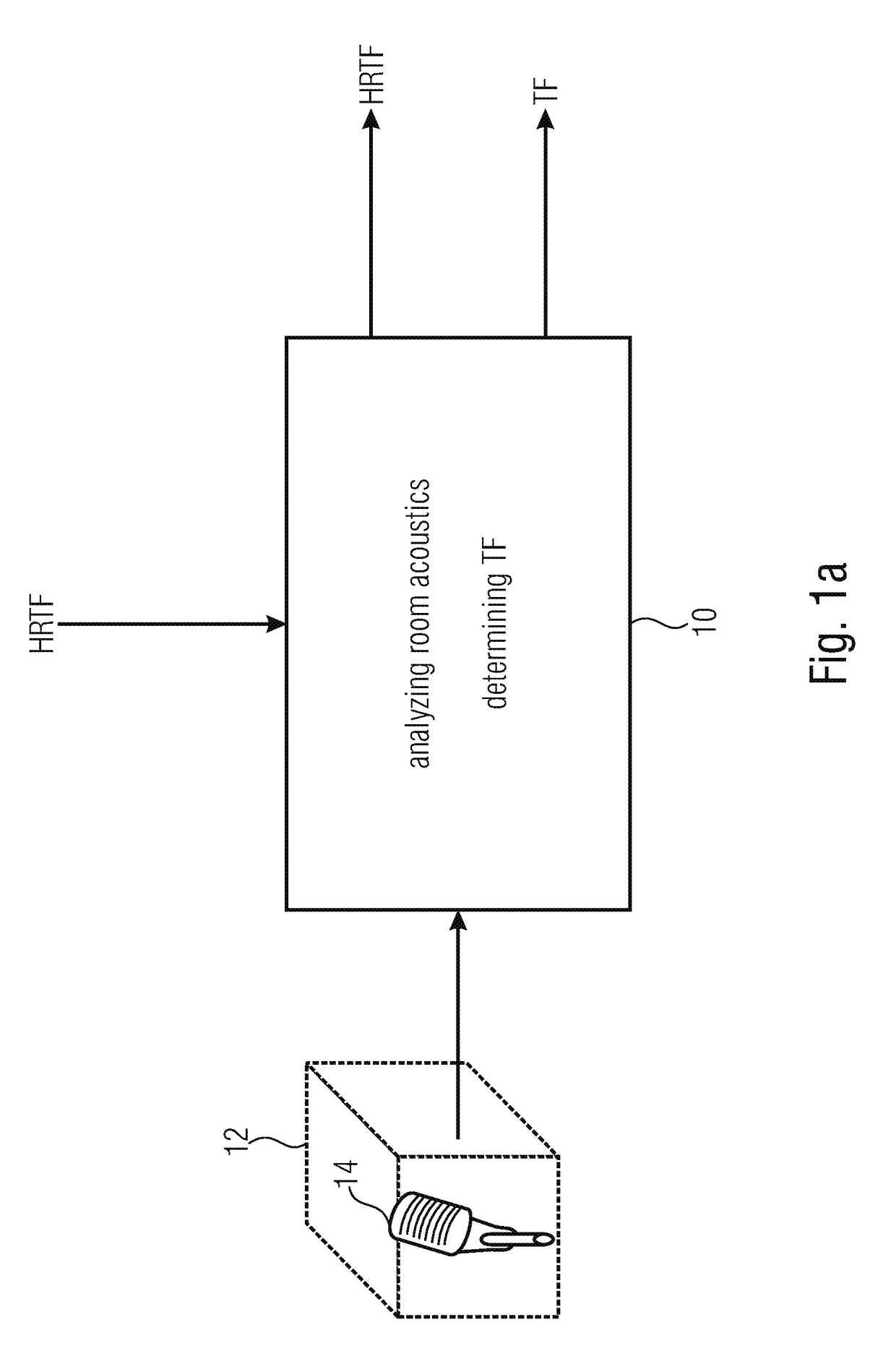
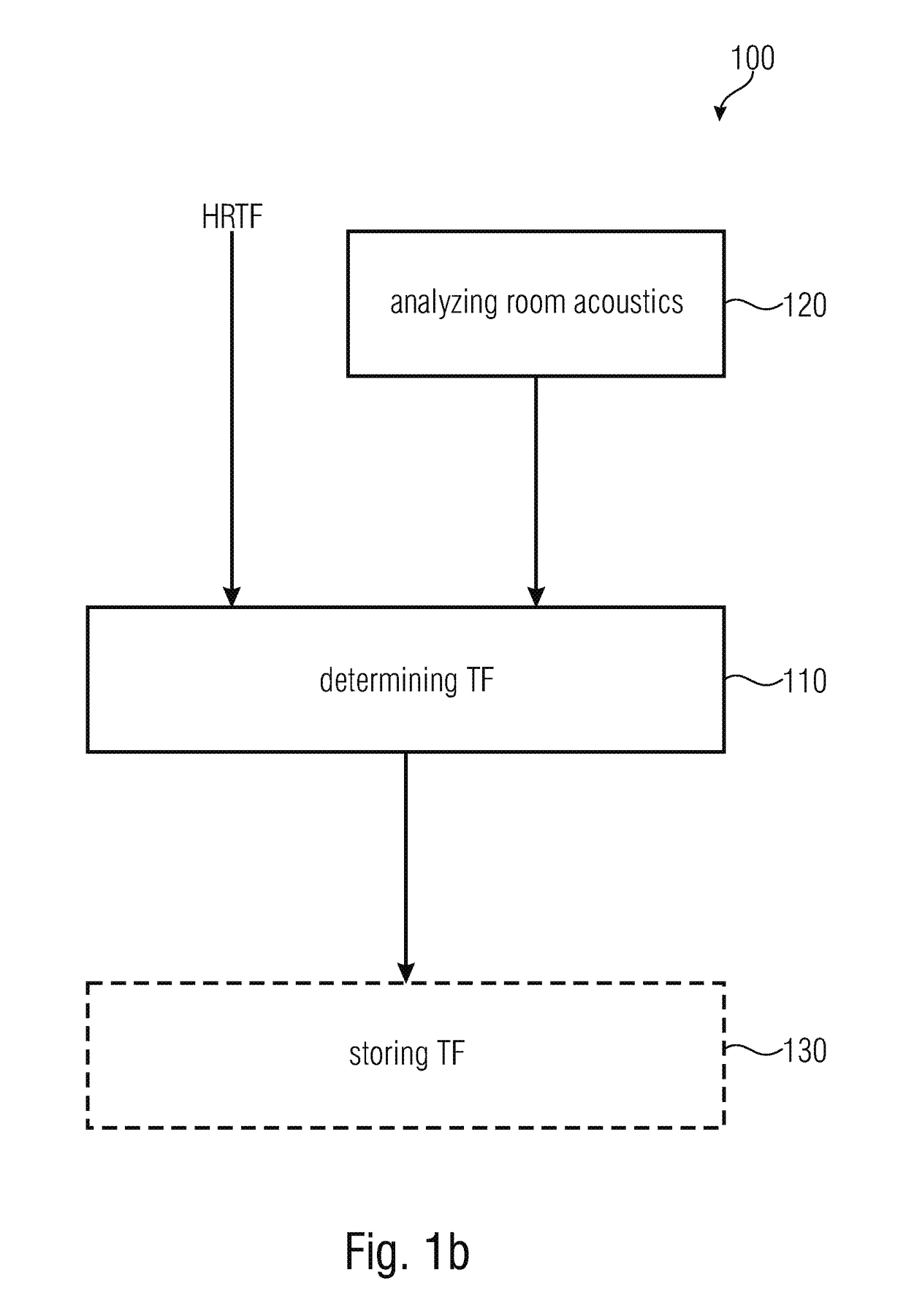
Determining and using room-optimized transfer functions
ActiveUS20170078820A1Reduce disagreementSignal processingStereophonic systemsRoom acousticsTransducer
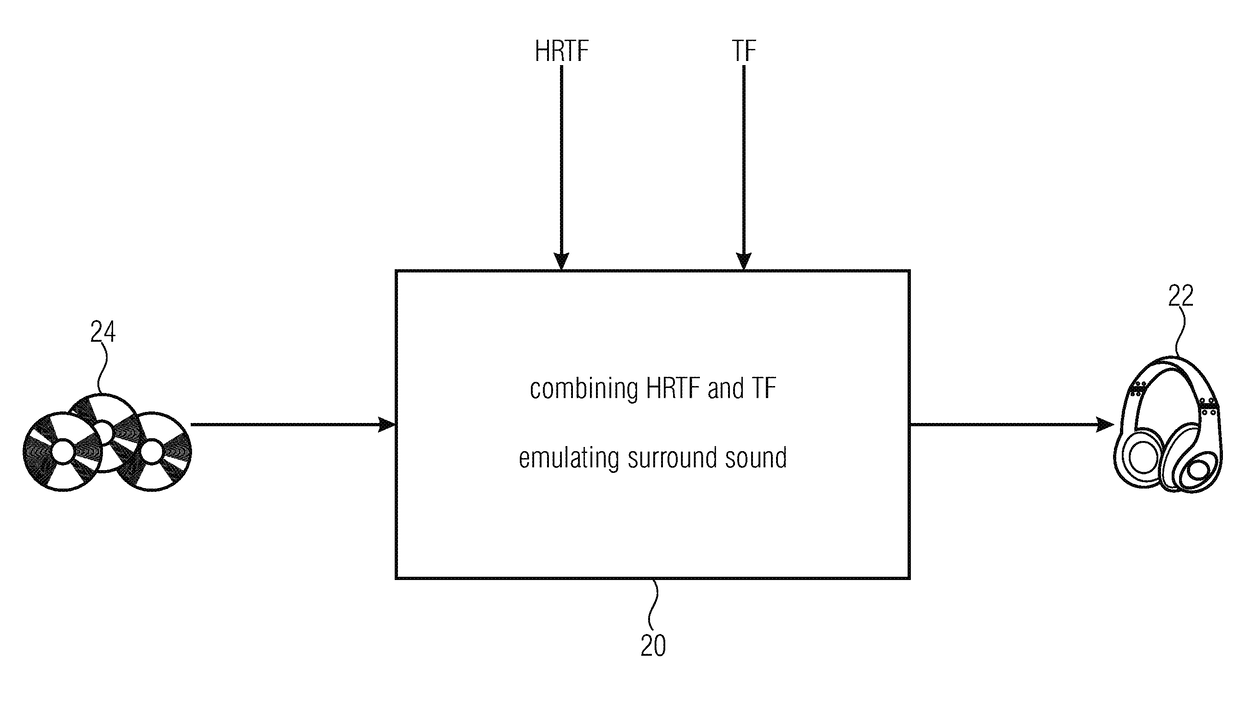
A device for determining room-optimized transfer functions for a listening room serving for room-optimized post-processing of audio signals in spatial production, is configured to analyze room acoustics of the listening room and to determine, based on the analysis of the room acoustics, the room-optimized transfer functions for the listening room where the spatial reproduction by means of a binaural close-range sound transducer is to take place. The spatial reproduction of the audio signals by means of the binaural close-range sound transducer may then be emulated using known head-related transfer functions und using the room-optimized transfer functions, wherein a room to be synthesized may be emulated based on the head-related transfer functions, and wherein the listening room may be emulated based on the room-optimized transfer functions.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV +1
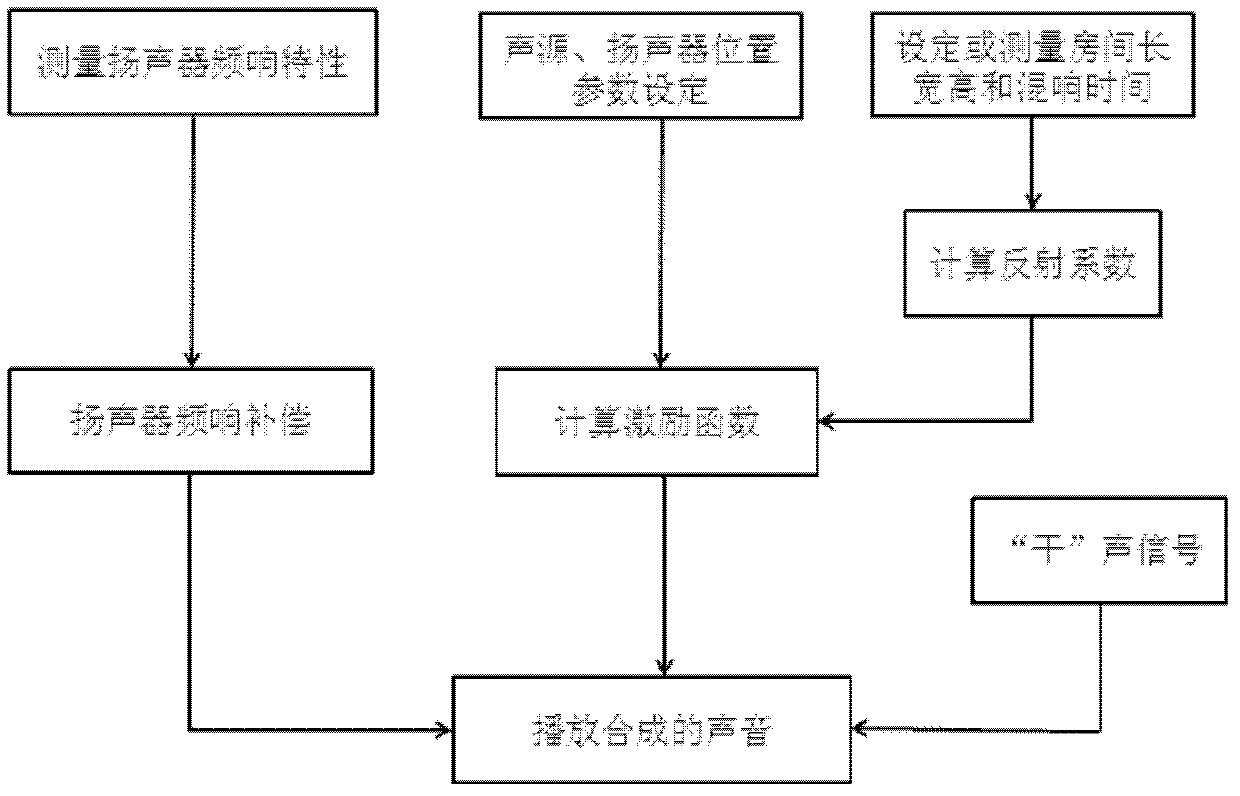
Distance sense synthetic method in three-dimensional sound field synthesis
ActiveCN102790931AImprove realismEnhanced 3D RealismFrequency/directions obtaining arrangementsTransducer circuitsSound sourcesRoom acoustics
The invention relates to a distance sense synthetic method in three-dimensional sound field synthesis. The method comprises firstly setting reverberation time of a room to be synthesized and the length, the width and the height of the room; or using acoustic pressure levels to measure reverberation time of a room to be replayed and the length, the width and the height of the room; secondly measuring frequency response of a loudspeaker, obtaining a reflection coefficient beta i according to a formula; and finally obtaining corresponding excitation functions of each loudspeaker according to setting position coordinates of each loudspeaker and each sound source. In the formula, P (chi, omega) is sound pressure synthesized in a bounded area V, and Ssw(omega) is a source signal frequency domain expression. Therefore, relation between room acoustics and traditional WFS technology is built, and the excitation function is finally used to enable a three-dimensional sound field to have direction sense and the distance sense.
Owner:INST OF ACOUSTICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Sound field control in multiple listening regions
ActiveUS8213637B2Improve performanceSpecial data processing applicationsStereophonic systemsMulti inputFinite impulse response
Owner:DIRAC RES
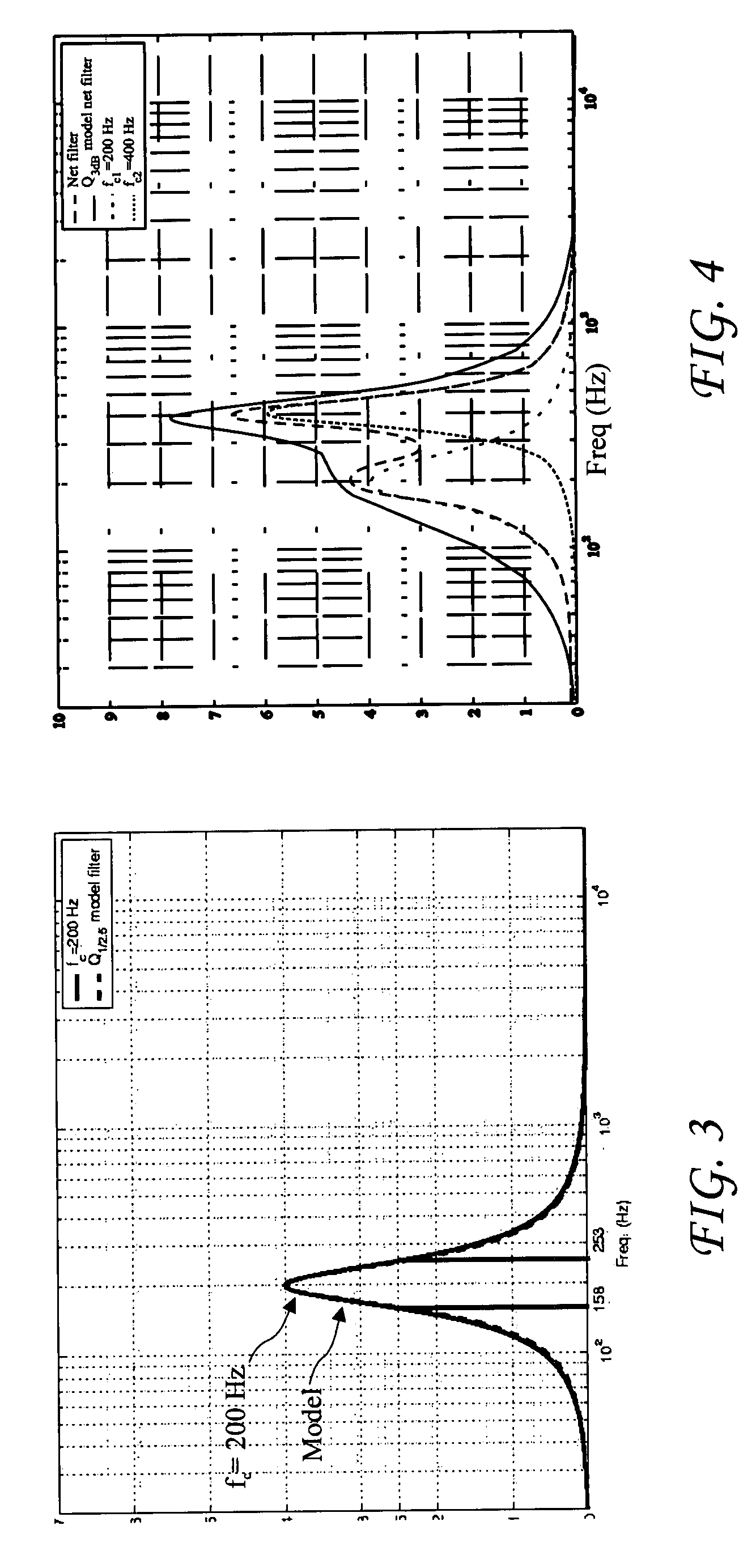
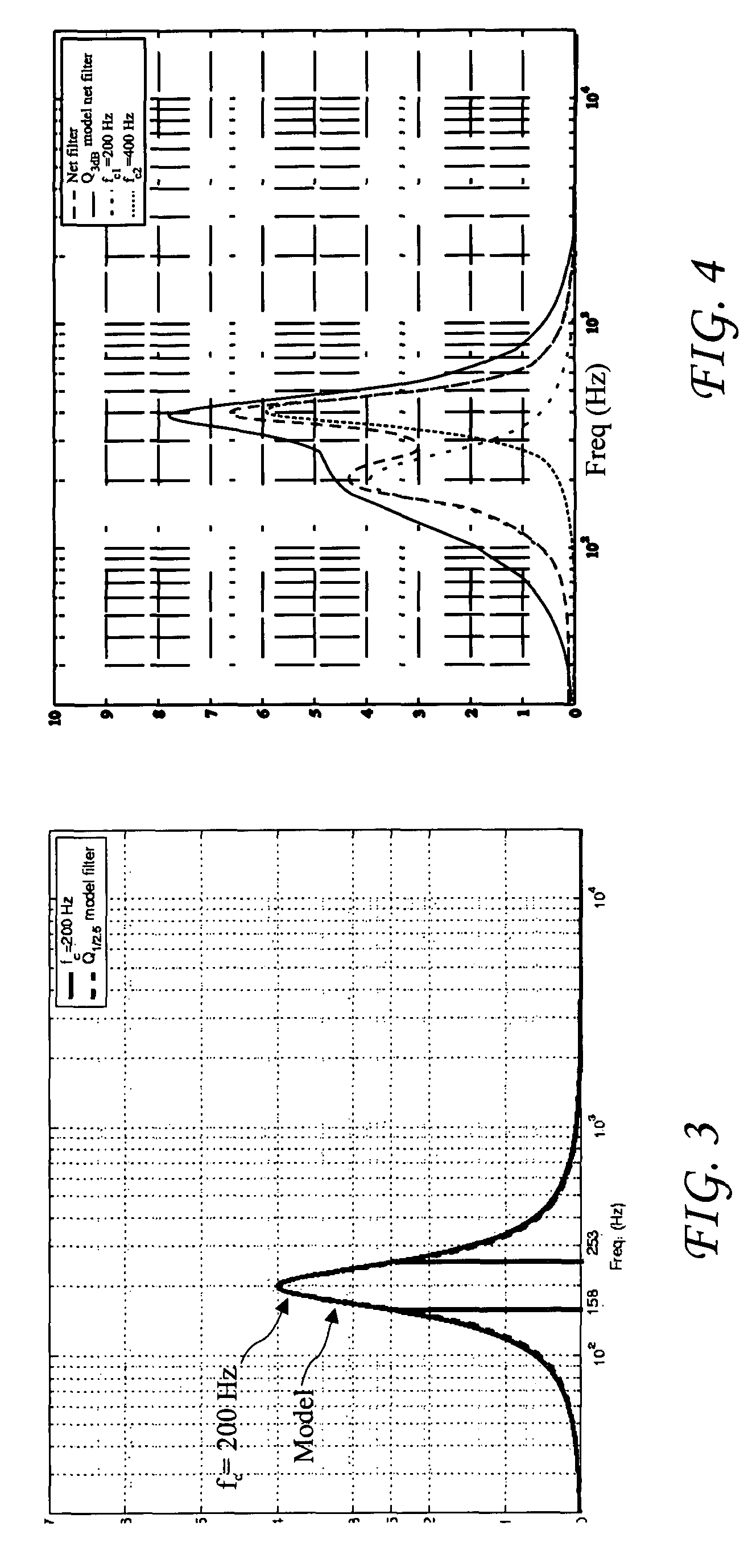
Room acoustic response modeling and equalization with linear predictive coding and parametric filters
A method for determining coefficients of a family of cascaded second order Infinite Impulse Response (IIR) parametric filters used for equalizing a room response. The method includes determining parameters of each IIR parametric filter from poles or roots of a reasonably high-order Linear Predictive Coding (LPC) model. The LPC model is able to accurately model the low-frequency room response modes providing better equalization of loudspeaker and room acoustics, particularly at the low frequencies. Advantages of the method include fast and efficient computation of the LPC model using a Levinson-Durbin recursion to solve the normal equations that arise from the least squares formulation. Due to possible band interactions between the cascaded IIR parametric filters, the method further includes optimizing the Q value of each filter to better equalize the room response.
Owner:AUDYSSEY LABORATORIES
Architectural sound enhancement with pre-filtered masking sound
InactiveUS7548854B2High precisionLess annoyingPublic address systemsVacuum gauge using compression chambersRoom acousticsDistribution system
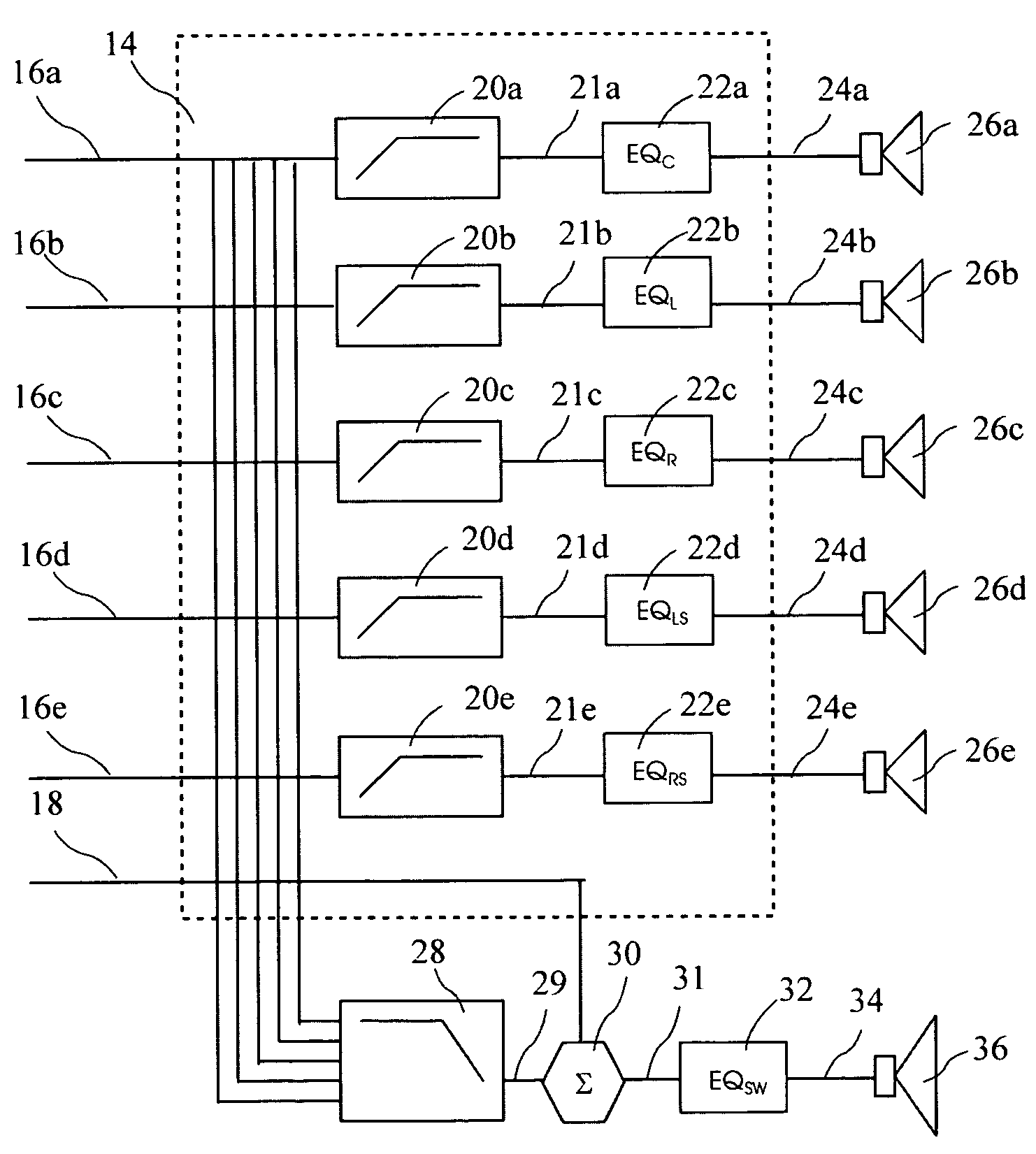
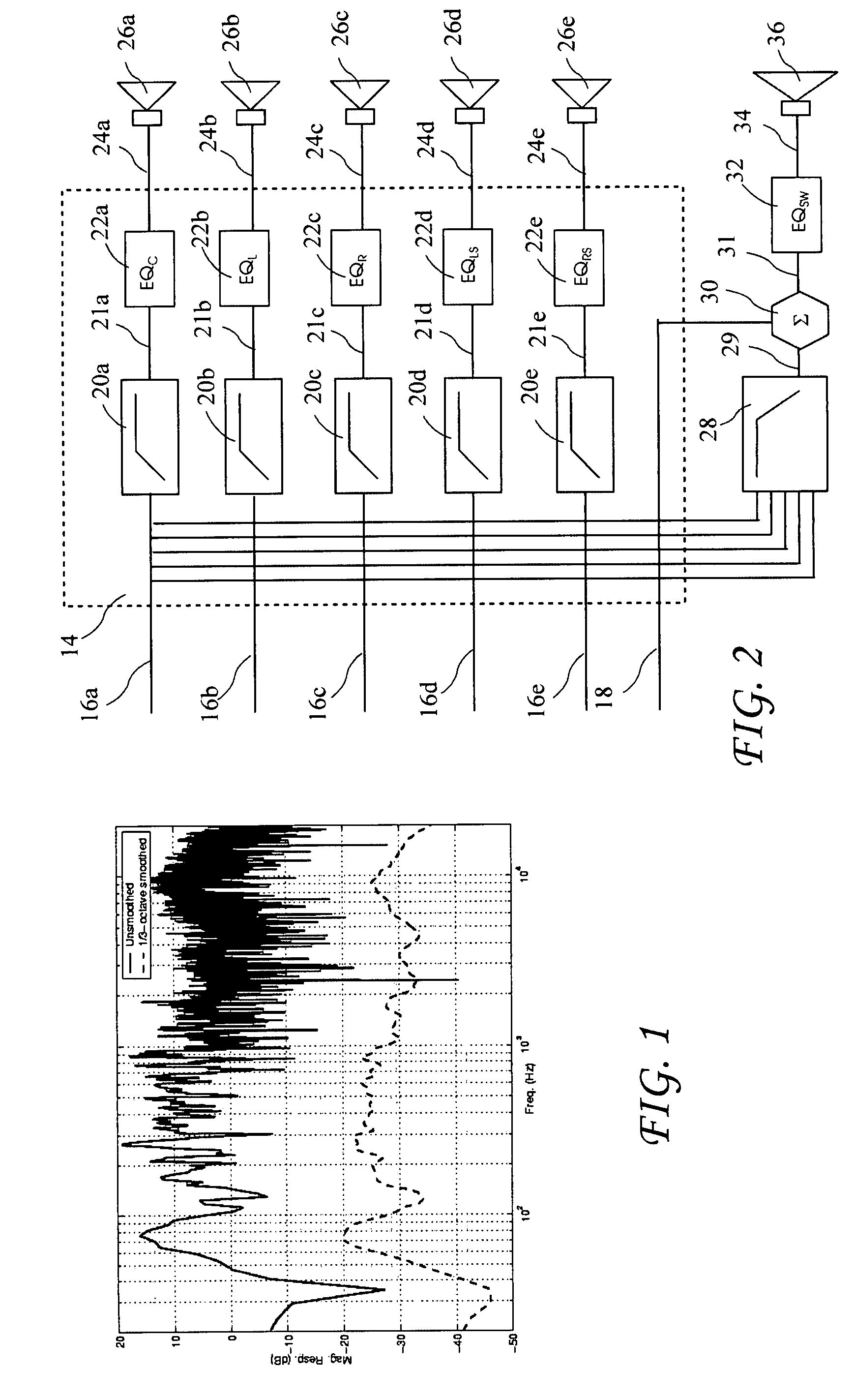
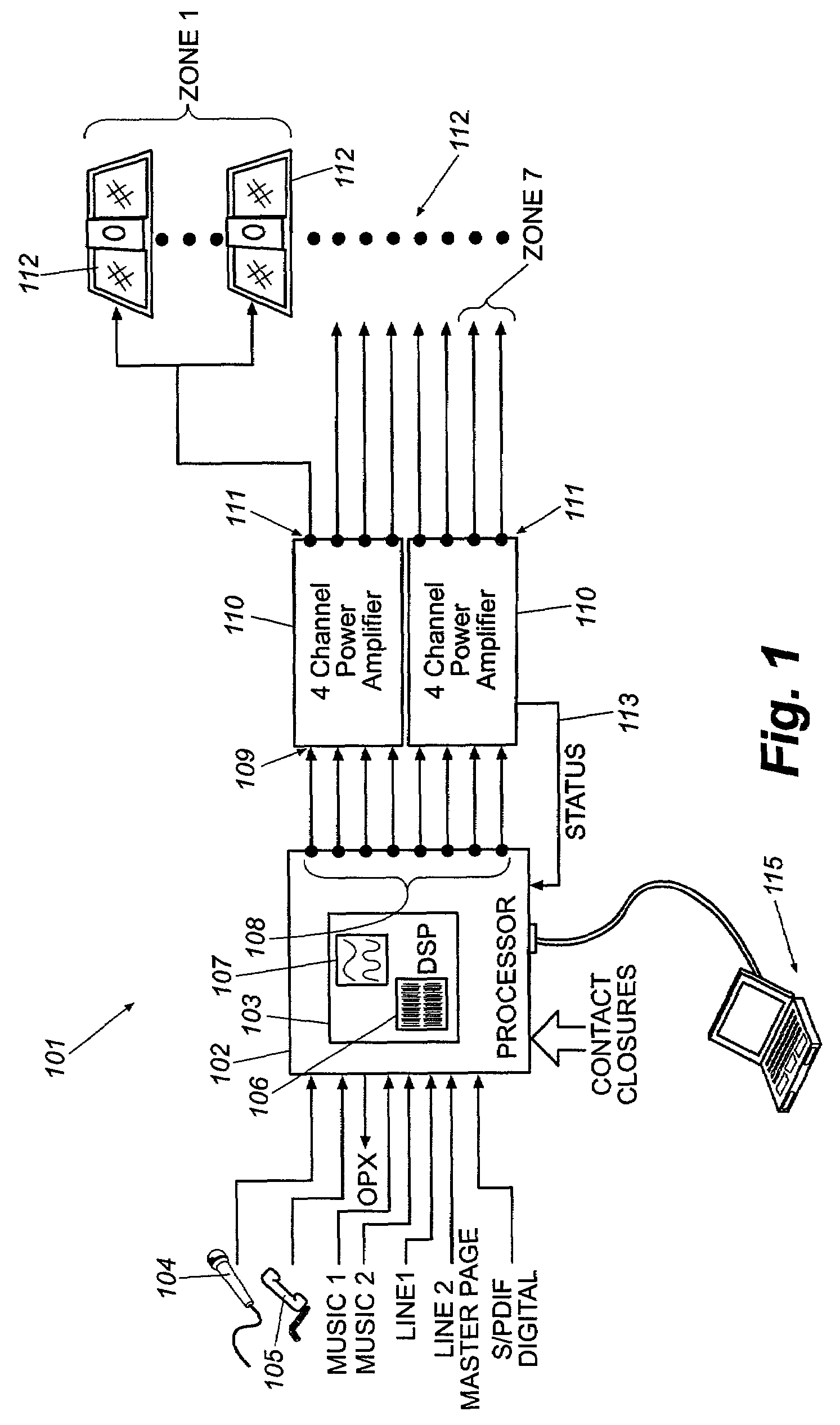
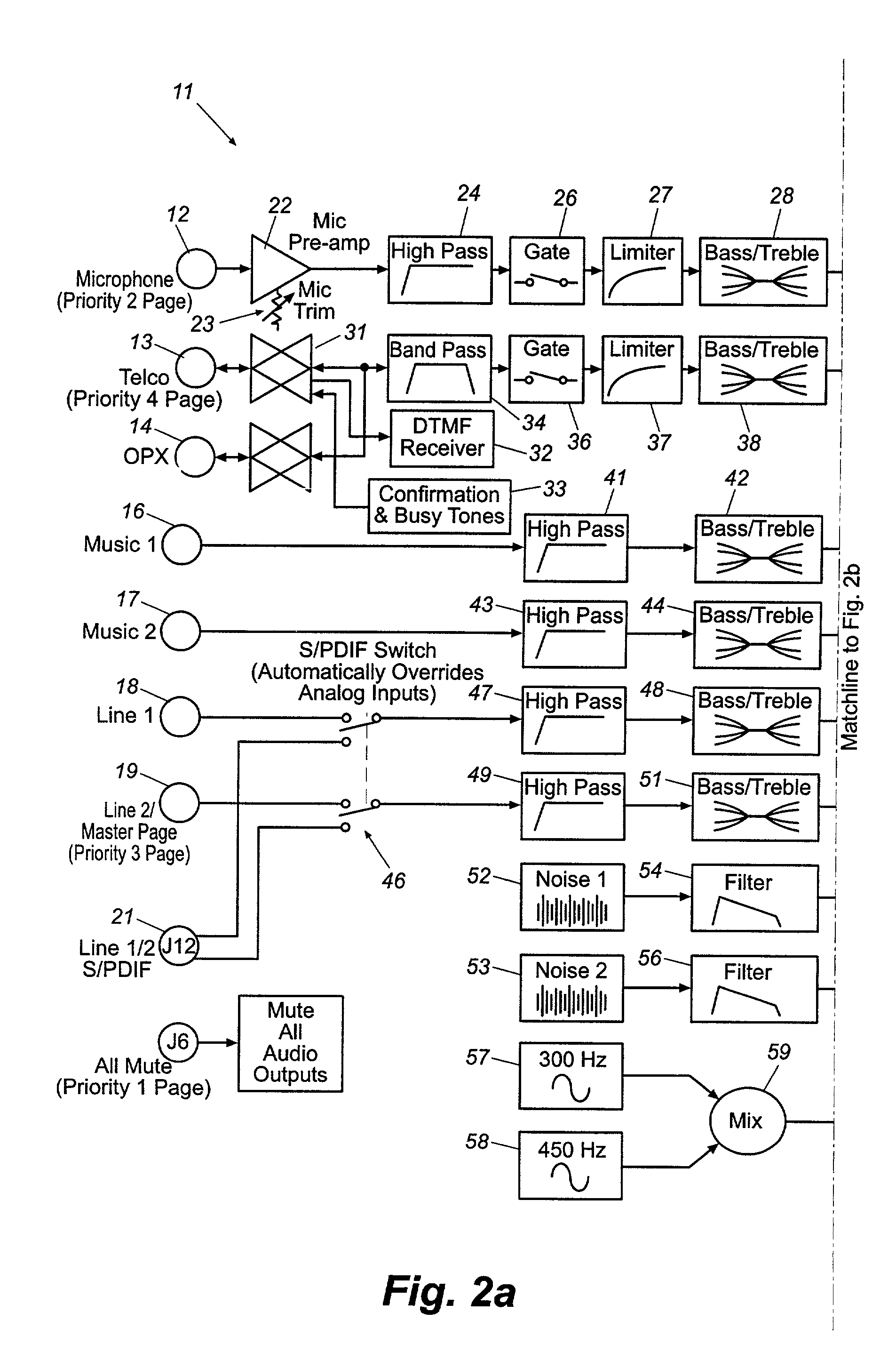
A unique, fully integrated, fully programmable, and highly flexible sound distribution system and methodology for providing masking sound, background music, and paging capabilities in up to eight zones of a building or space is provided. The methodology embodied in the system includes internal masking sounds that are uniquely pre-filtered to provide efficient and effective masking of distracting sounds within selectable zones of the space with a minimum masking sound dB sound level and with a pleasant sounding and non-annoying masking sound. The system also incorporates the capacity to be controlled from a remote or local telephone to adjust the volume level in any zone serviced by the system by issuing appropriate DTMF codes from the telephone's keypad. Unique bi-tone diagnostic functions are provided for assuring that the entire system is correctly wired and installed and for troubleshooting operational anomalies. ⅓ octave equalization is provided to compensate for known frequency response characteristics of the flat panel radiators of the system and to compensate for varying room acoustics to provide a low special variation of sound among the various zones of the space. The result is a high quality high fidelity sound that is consistent from zone to zone.
Owner:AWI LICENSING
Ceiling baffle apparatus and ceiling baffle system for a dynamic acoustic ceiling and methods thereof
Owner:TURF DESIGN INC
Binaural rendering using subband filters
InactiveCN101401455AEliminate redundant filteringReduce computational complexitySpeech analysisStereophonic systemsPhase correctionRoom acoustics
Transfer functions like Head Related Transfer Functions (HRTF) needed for binaural rendering are implemented efficiently by a subband-domain filter structure. In one implementation, amplitude, fractional-sample delay and phase-correction filters are arranged in cascade with one another and applied to subband signals that represent spectral content of an audio signal in frequency subbands. Other filter structures are also disclosed. These filter structures may be used advantageously in a variety of signal processing applications. A few examples of audio applications include signal bandwidth compression, loudness equalization, room acoustics correction and assisted listening for individuals with hearing impairments.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
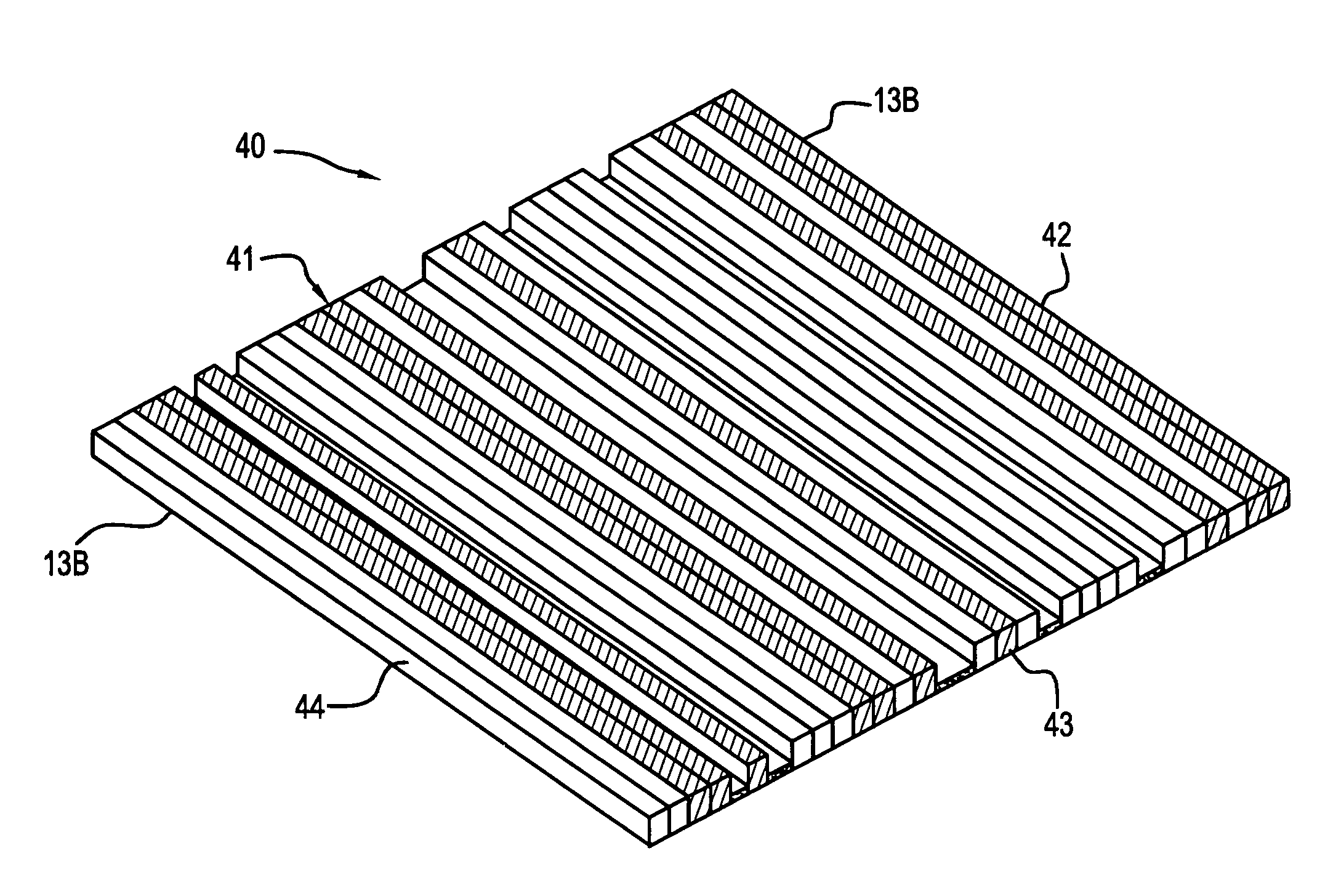
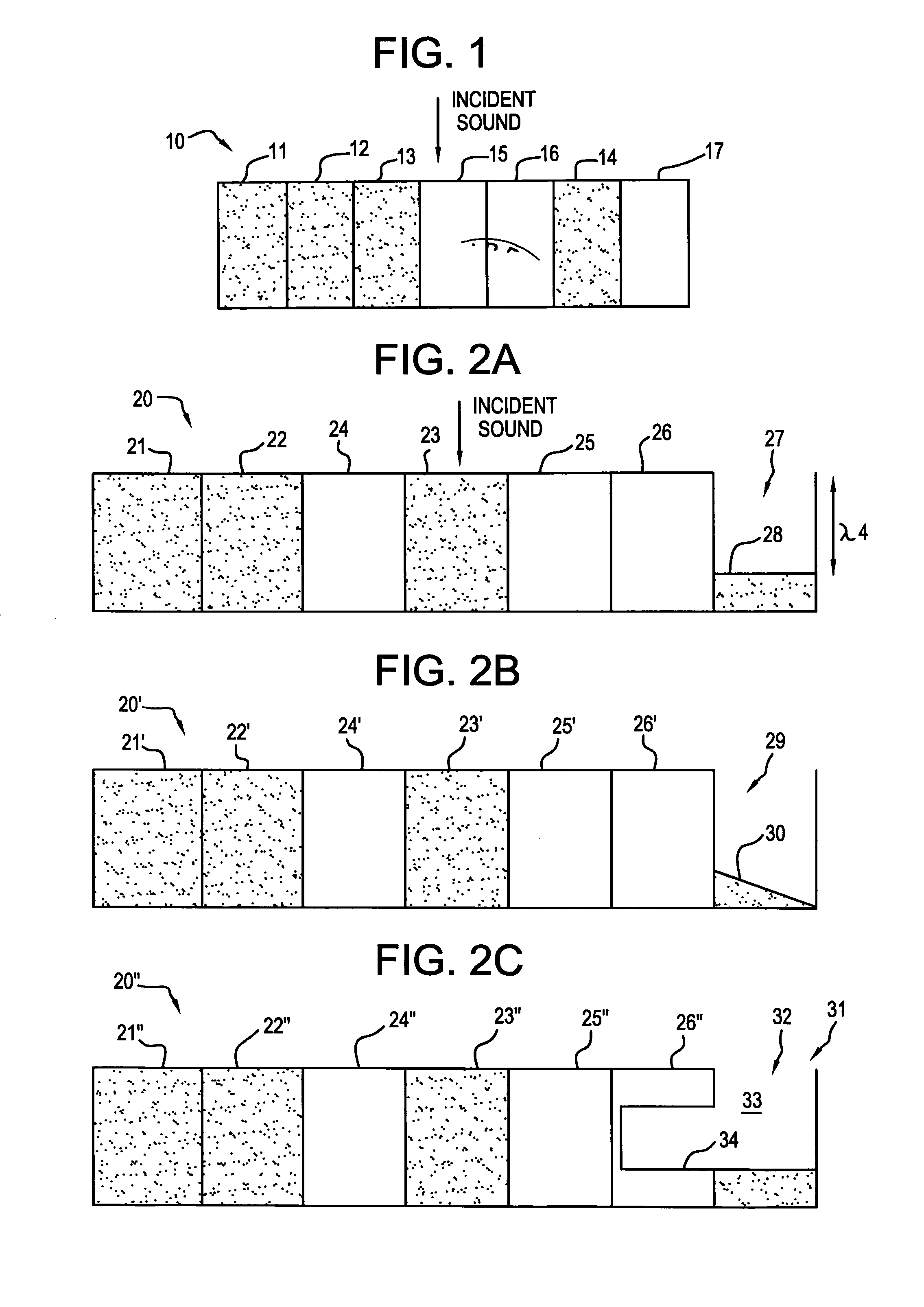
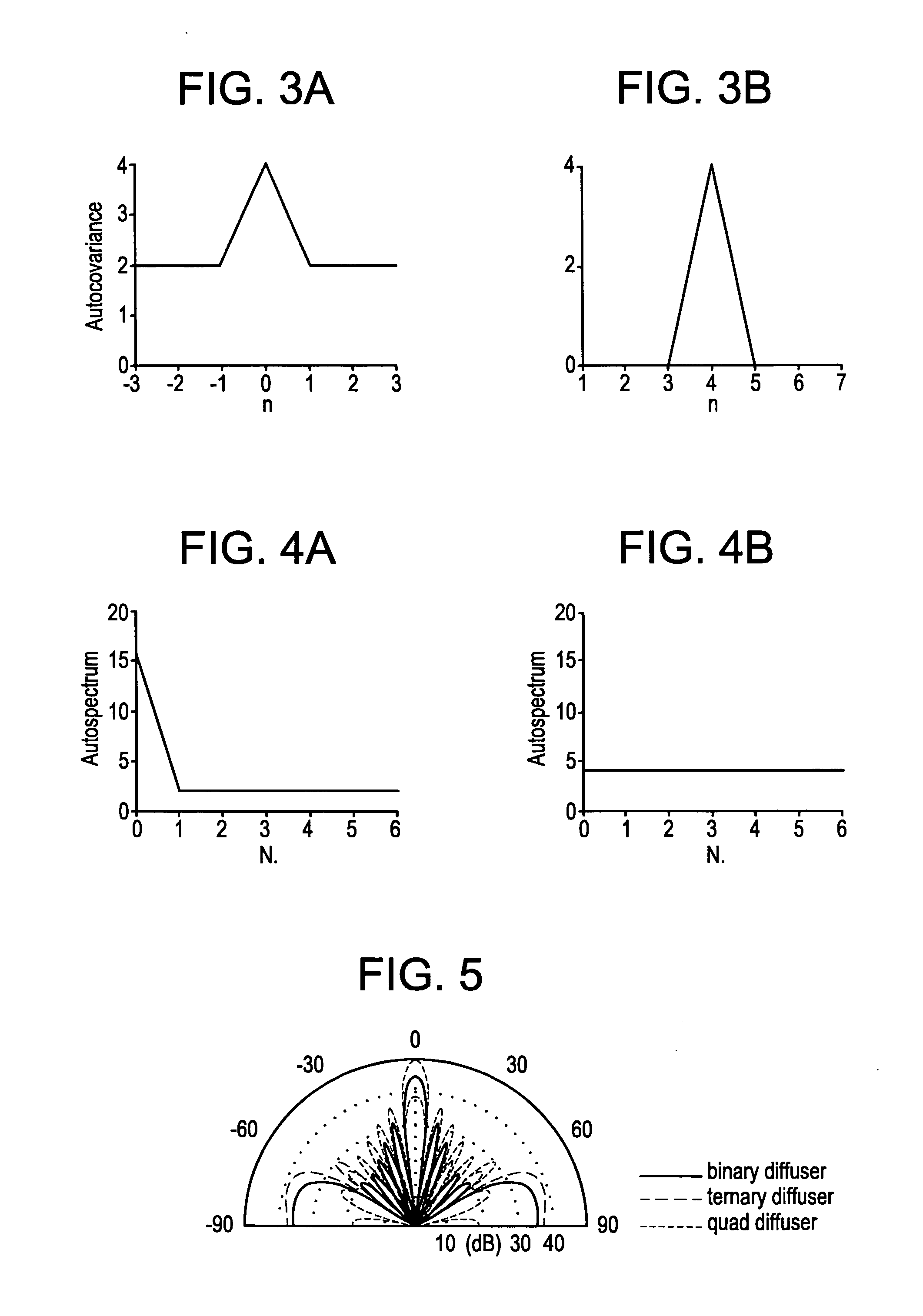
Hybrid amplitude-phase grating diffusers
InactiveUS20070034448A1Spread evenlyIncrease the lengthSound proofingSound producing devicesReflection coefficientOut of phase
A room acoustic diffuser exploits interference, by reflecting waves out-of-phase with the specular energy, making it possible to diminish specular energy. This is achieved by using a diffuser based on a ternary sequence, which nominally has reflection coefficients of 0, −1 and +1. A method for obtaining the design sequence for Quaternary diffusers is also disclosed. Also, design methods for forming the sequences into arrays, and forming hemispherical diffusers are explained.
Owner:DANTONIO PETER
Apparatus and system for dynamic acoustic locking ceiling system and methods thereof
ActiveUS20180127975A1Reduce unwanted noiseReduce room acousticCeilingsSound proofingLocking mechanismEngineering
A dynamic acoustic locking ceiling baffle and a dynamic acoustic locking ceiling system, that includes a single piece of material folded into acoustic locking ceiling baffles, using locking pieces and locking mechanisms, to quickly and easily install the acoustic locking ceiling baffle onto construction ceiling hangers to provide an aesthetically pleasing image, along with a reduction in unwanted noise or room acoustics.
Owner:TURF DESIGN INC
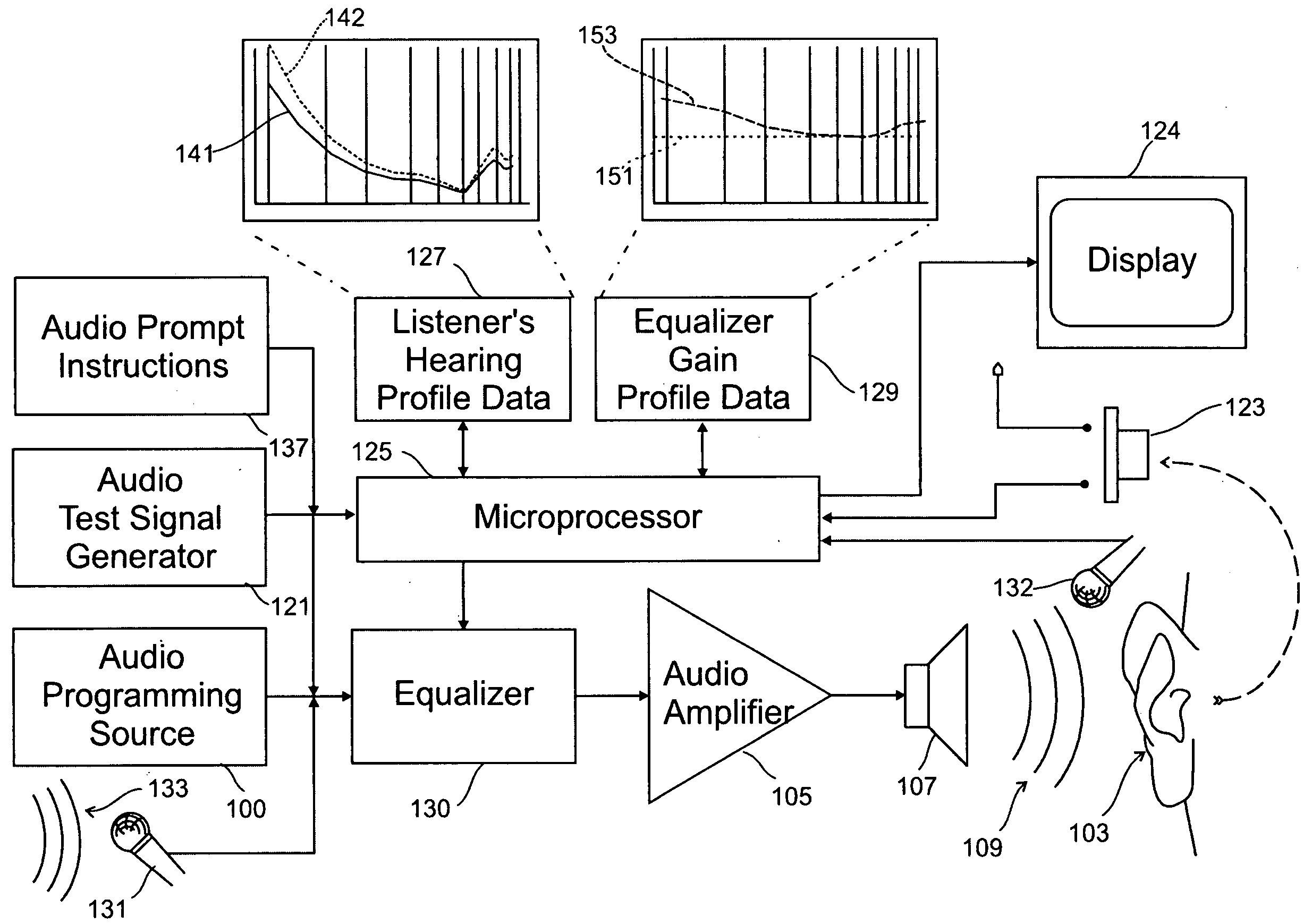
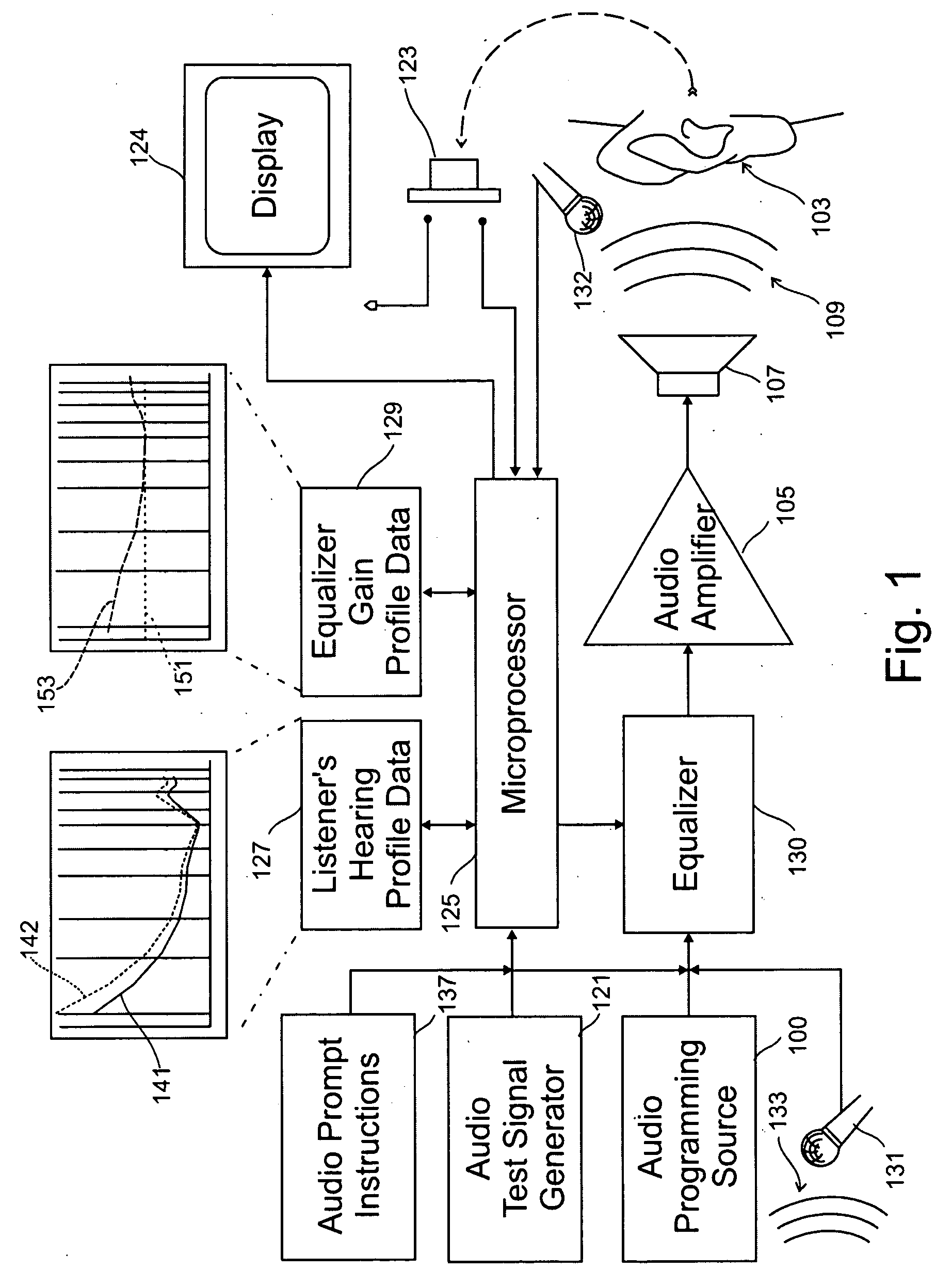
Listener Specific Audio Reproduction System
InactiveUS20090279707A1Quality improvementImprove sound qualityStereophonic circuit arrangementsHearing impaired stereophonic signal reproductionRoom acousticsHearing perception
A system for use with an audio reproduction system that corrects for distortion caused by the system as well as any hearing impairment suffered a listener. Test signals are introduced into the input of the system to produce test sounds that are perceptible by the listener. Using a pushbutton, the listener indicates when a test signal of progressively increasing volume reaches an audible level. The resulting measured values of the listener's threshold of hearing at different frequencies is compared with comparable data for a normal listener to generate correction values that are used to program an equalizer which compensates for not only the listener's hearing impairments but also any distortion produced by system components or room acoustics.
Owner:SWARTZ ROBERT
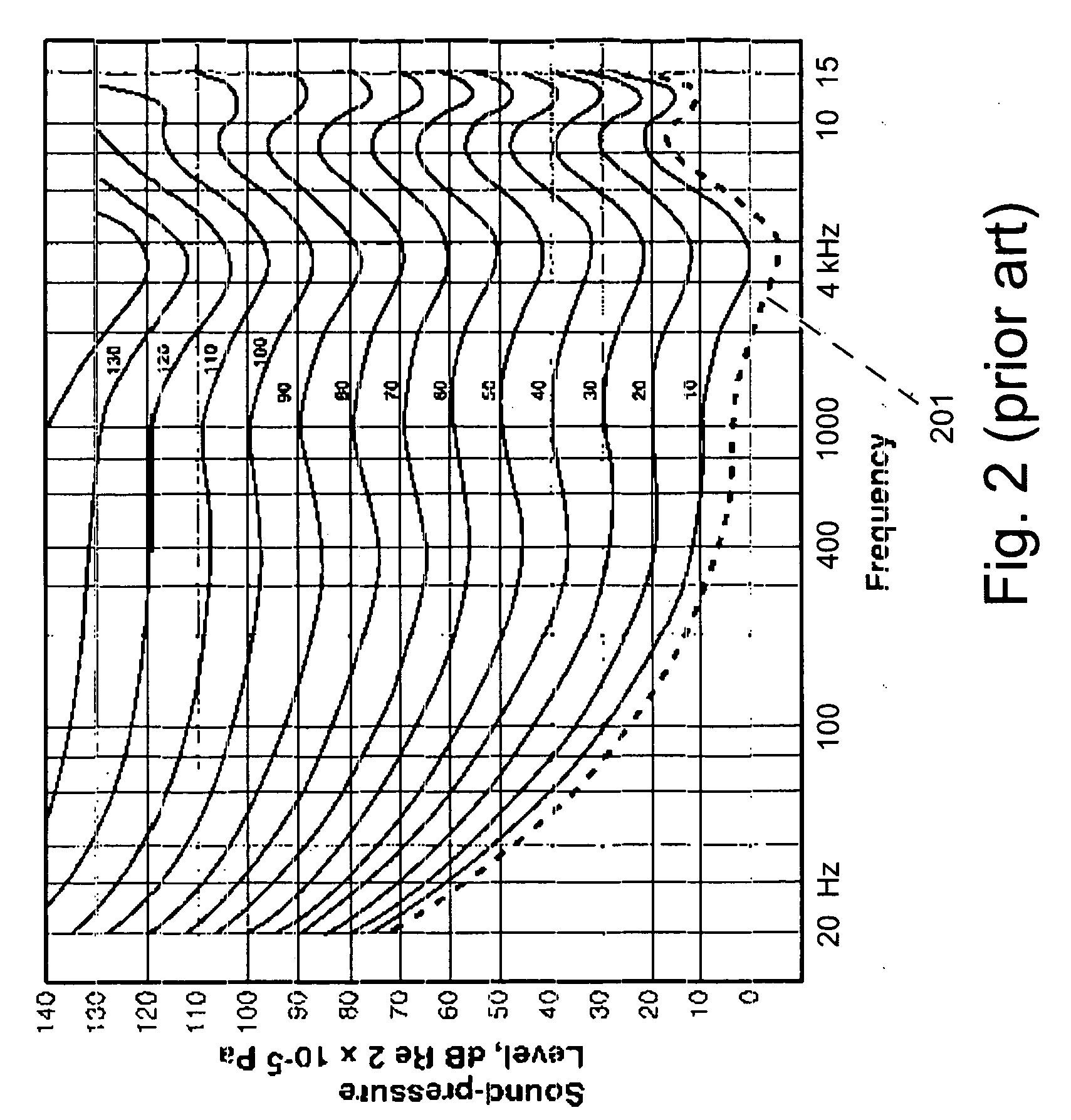
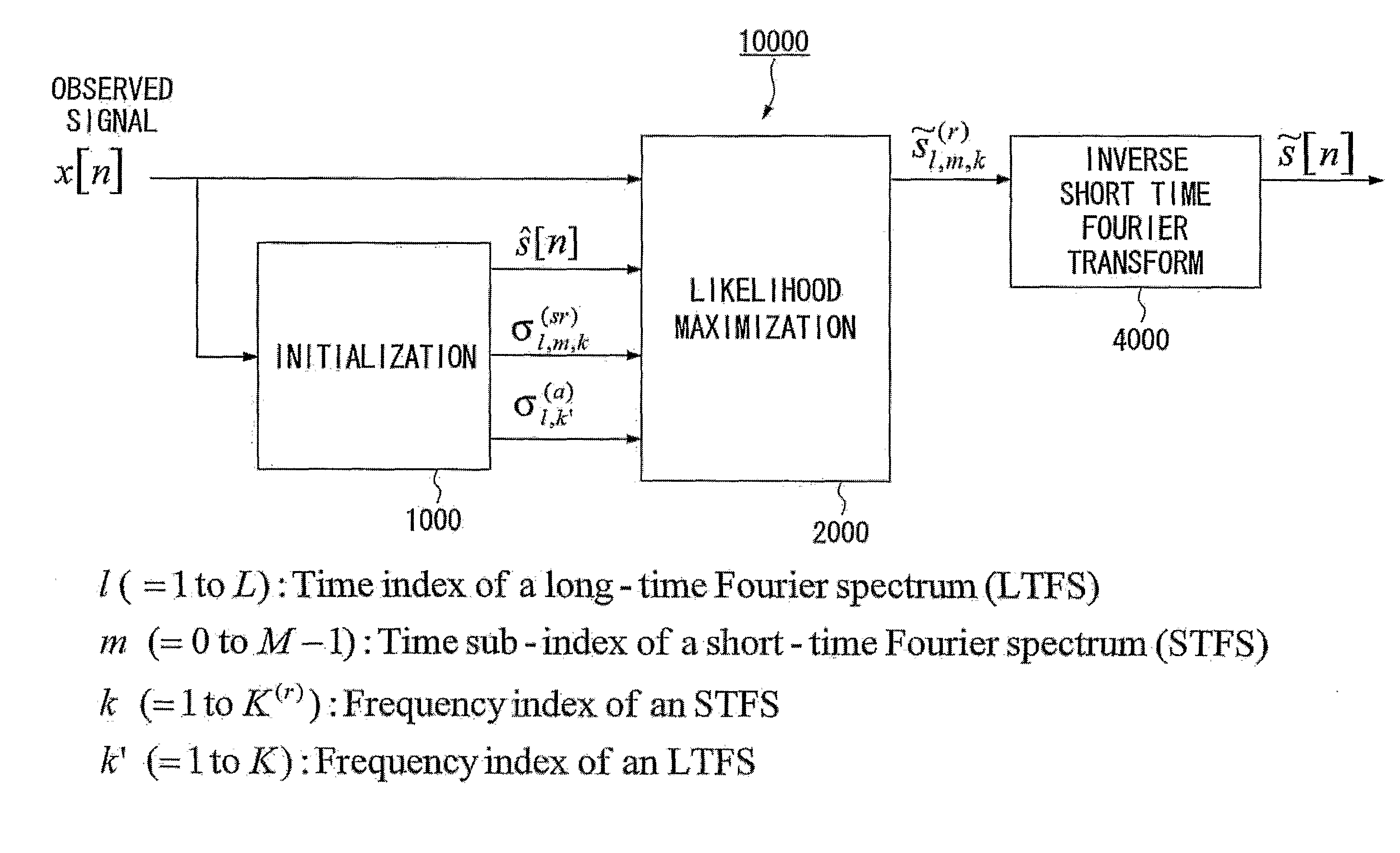
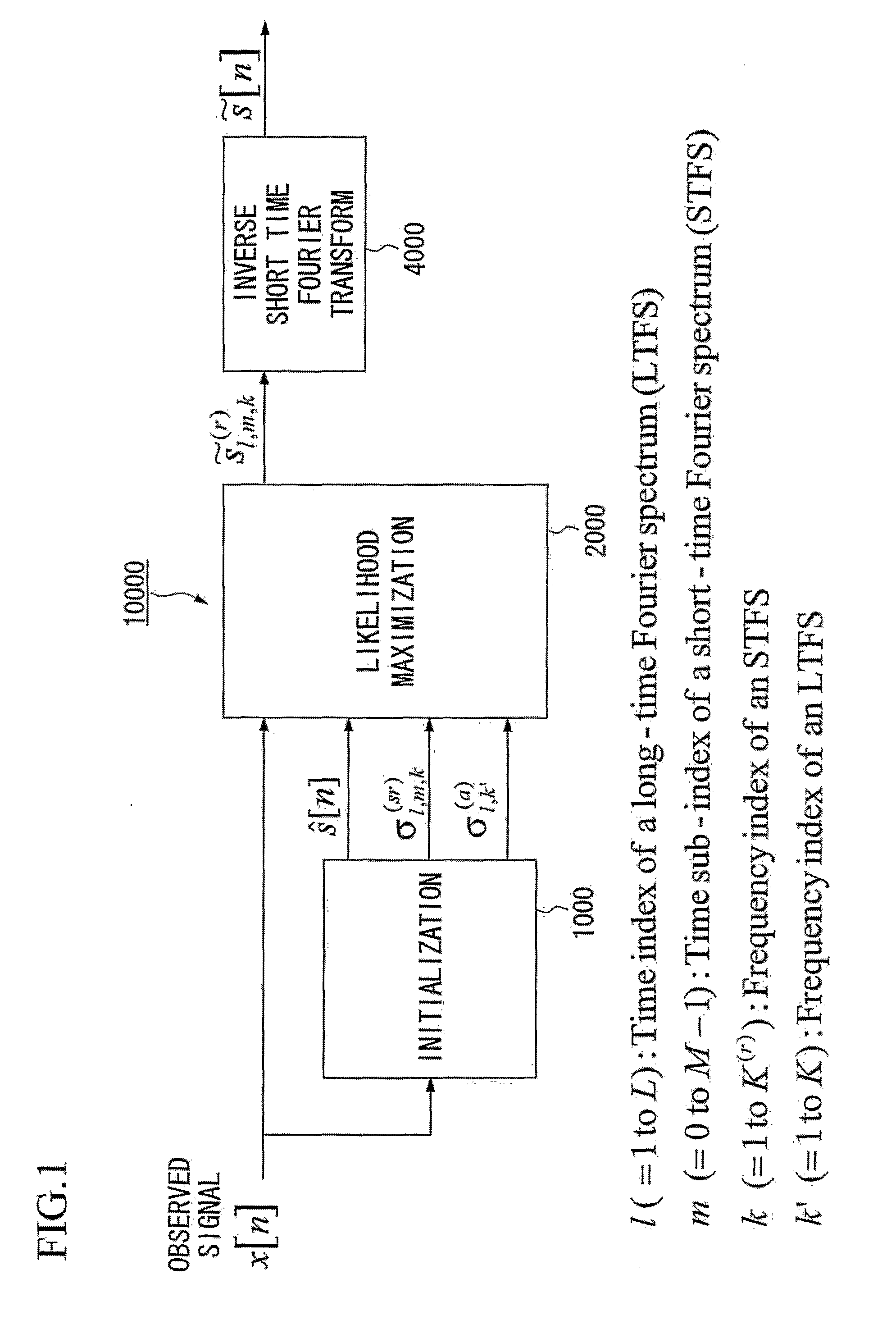
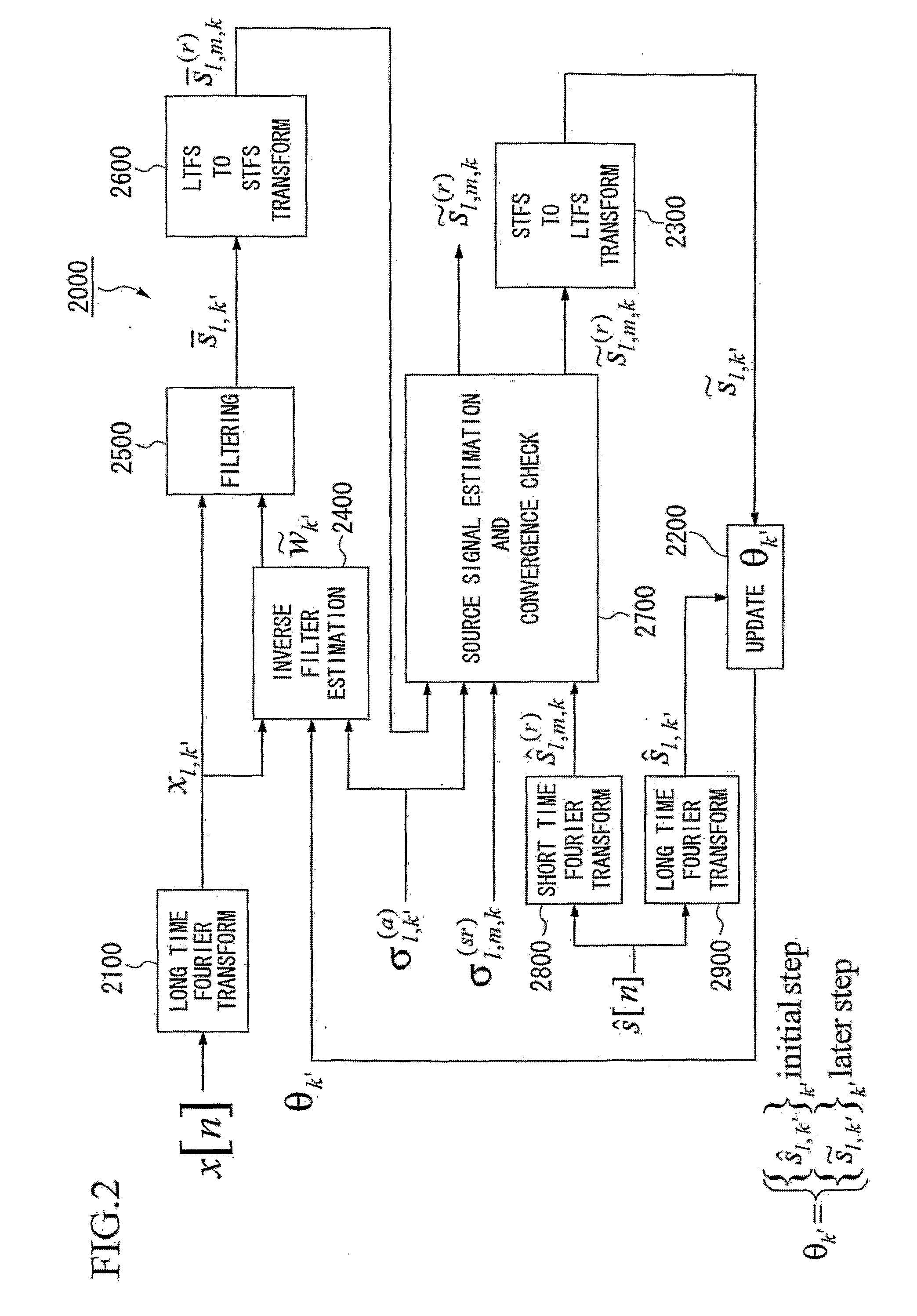
Method and Apparatus for Speech Dereverberation Based On Probabilistic Models Of Source And Room Acoustics
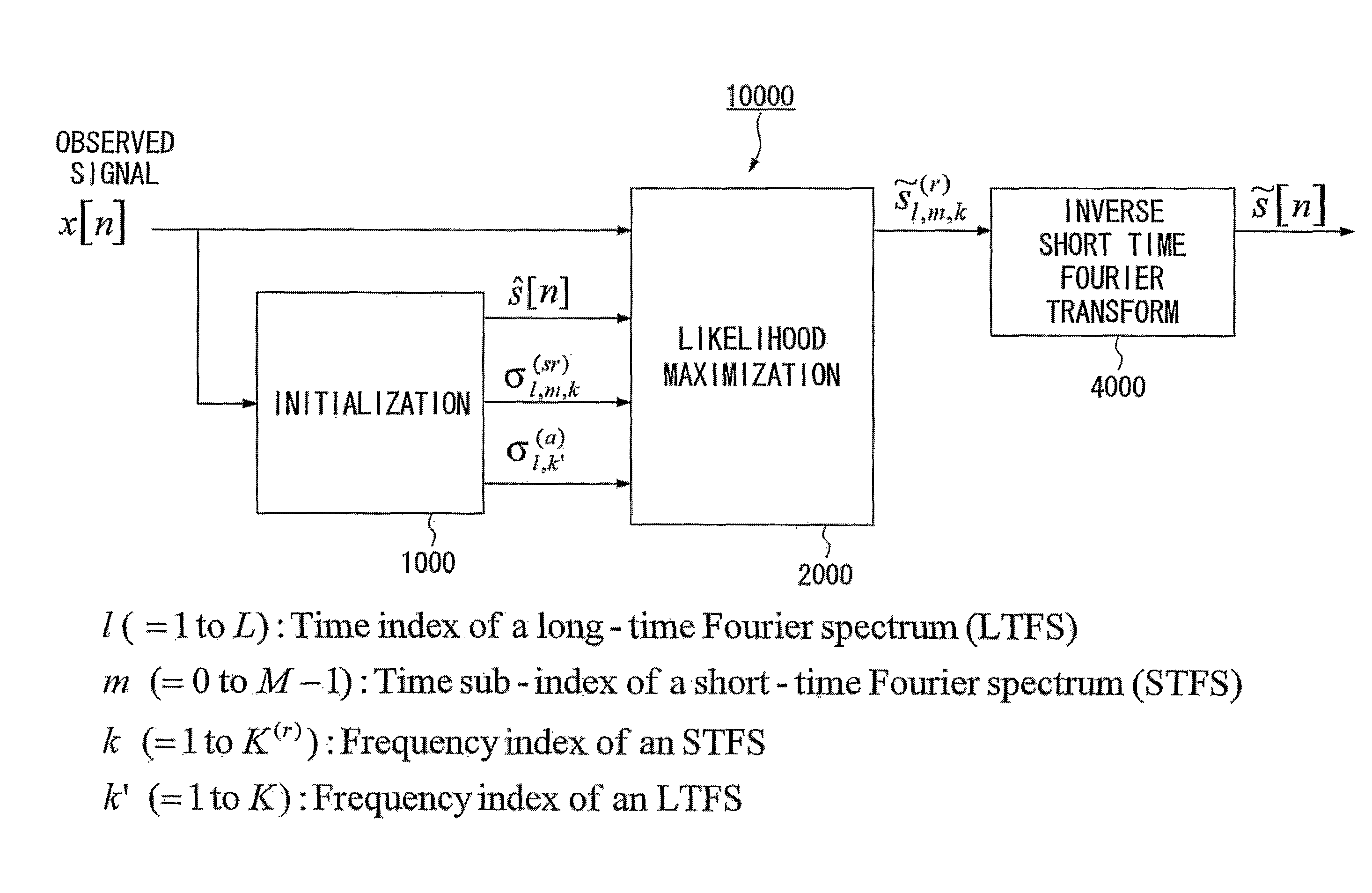
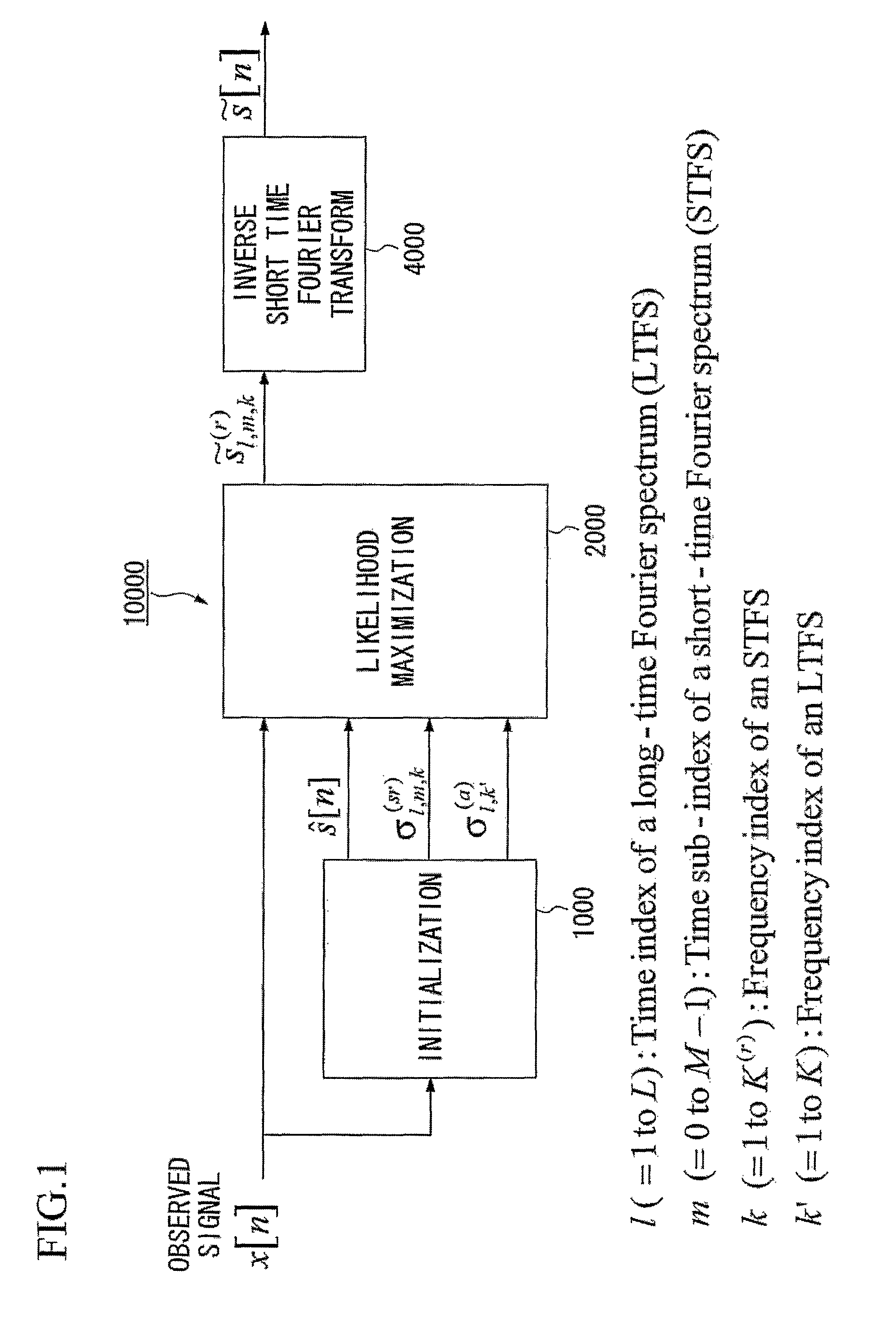
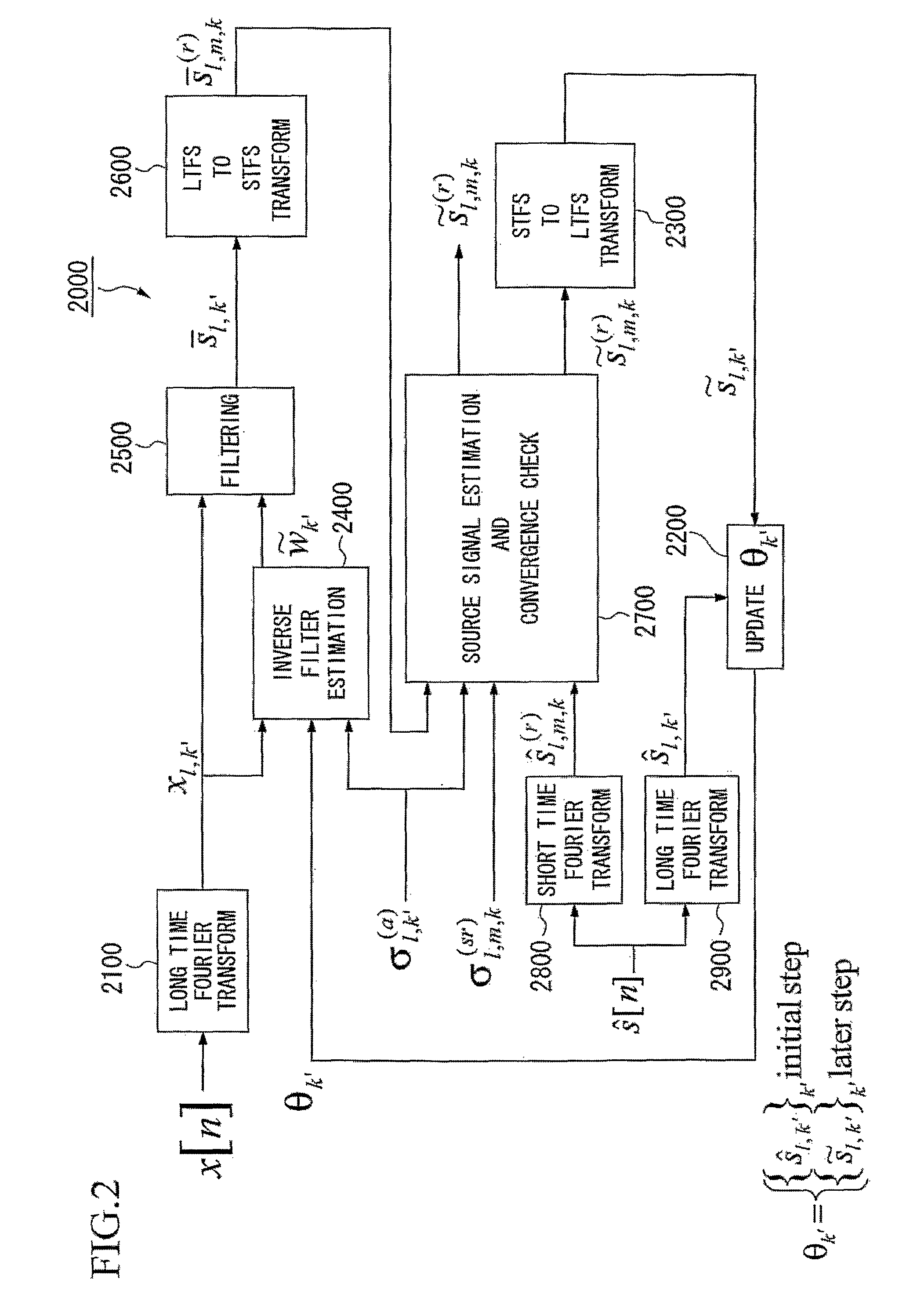
Speech dereverberation is achieved by accepting an observed signal for initialization (1000) and performing likelihood maximization (2000) which includes Fourier Transforms (4000).
Owner:NIPPON TELEGRAPH & TELEPHONE CORP +1
Method and apparatus for speech dereverberation based on probabilistic models of source and room acoustics
Speech dereverberation is achieved by accepting an observed signal for initialization (1000) and performing likelihood maximization (2000) which includes Fourier Transforms (4000).
Owner:NIPPON TELEGRAPH & TELEPHONE CORP +1
Acoustic paint
ActiveUS20170130059A1Excellent characteristicsImprove clarityPowdery paintsSound producing devicesElectricityRoom acoustics
An acoustic paint to be applied to the walls of a room in which a source of audible sound is located to improve the acoustic characteristics of the room and correspondingly improve the clarity (e.g., the warmth, richness and detail) of the sound that is generated by the source and detected by the ear of a listener located within the room. The acoustic paint includes a paint foundation into which is mixed a powdered piezoelectric material or a powdered non-piezoelectric crystalline material having a resonant frequency so that the powdered material will react to the sound generated within the room and thereby control the room acoustics depending upon the type of material and the resonant frequency thereof. An optional catalyst, such as an electrically conductive powdered graphite or powdered graphene, is mixed into the paint foundation. The mixture is stirred and then applied to the walls of the room by means of a brush, a roller, or the like.
Owner:UEF LABS LLC
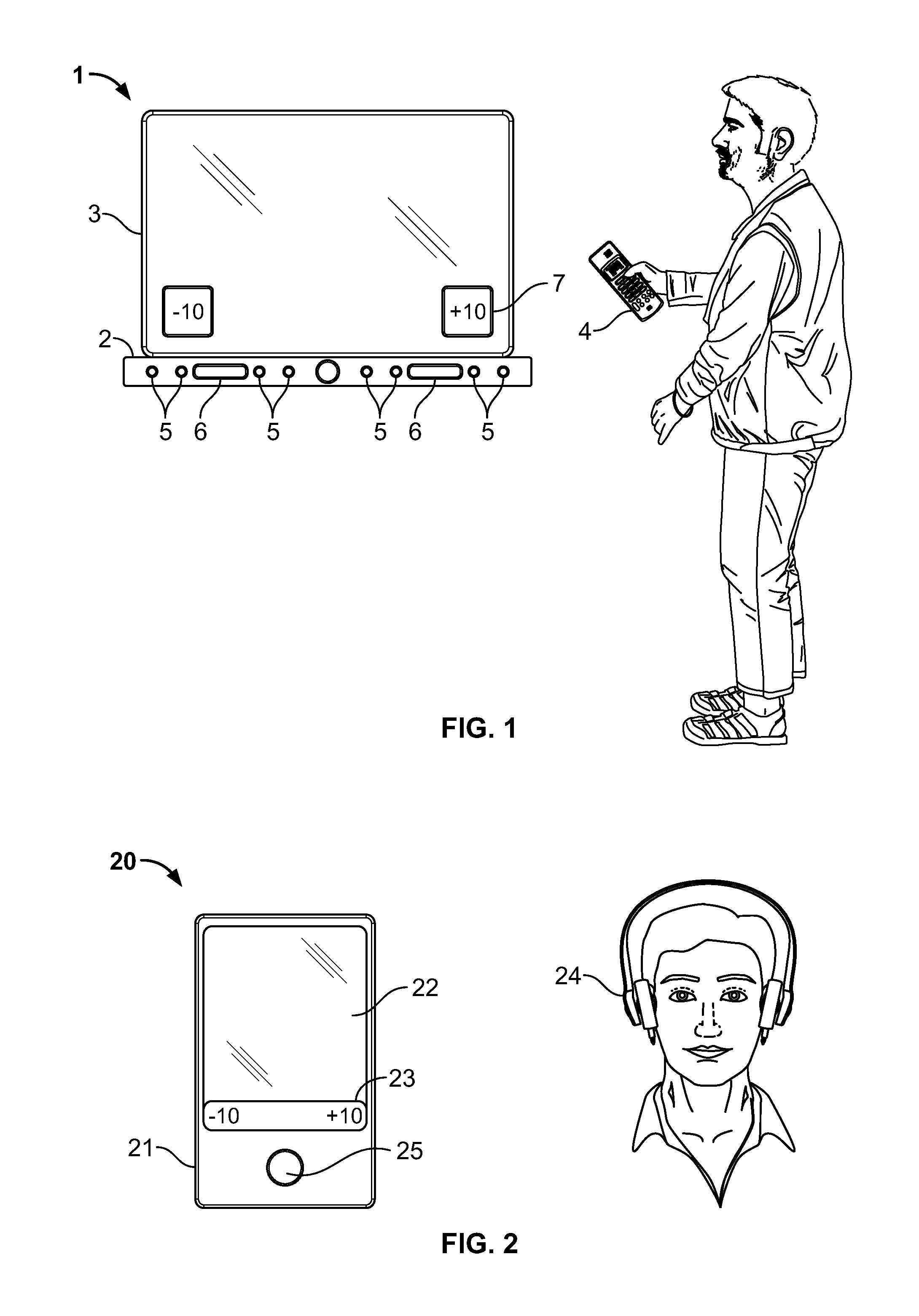
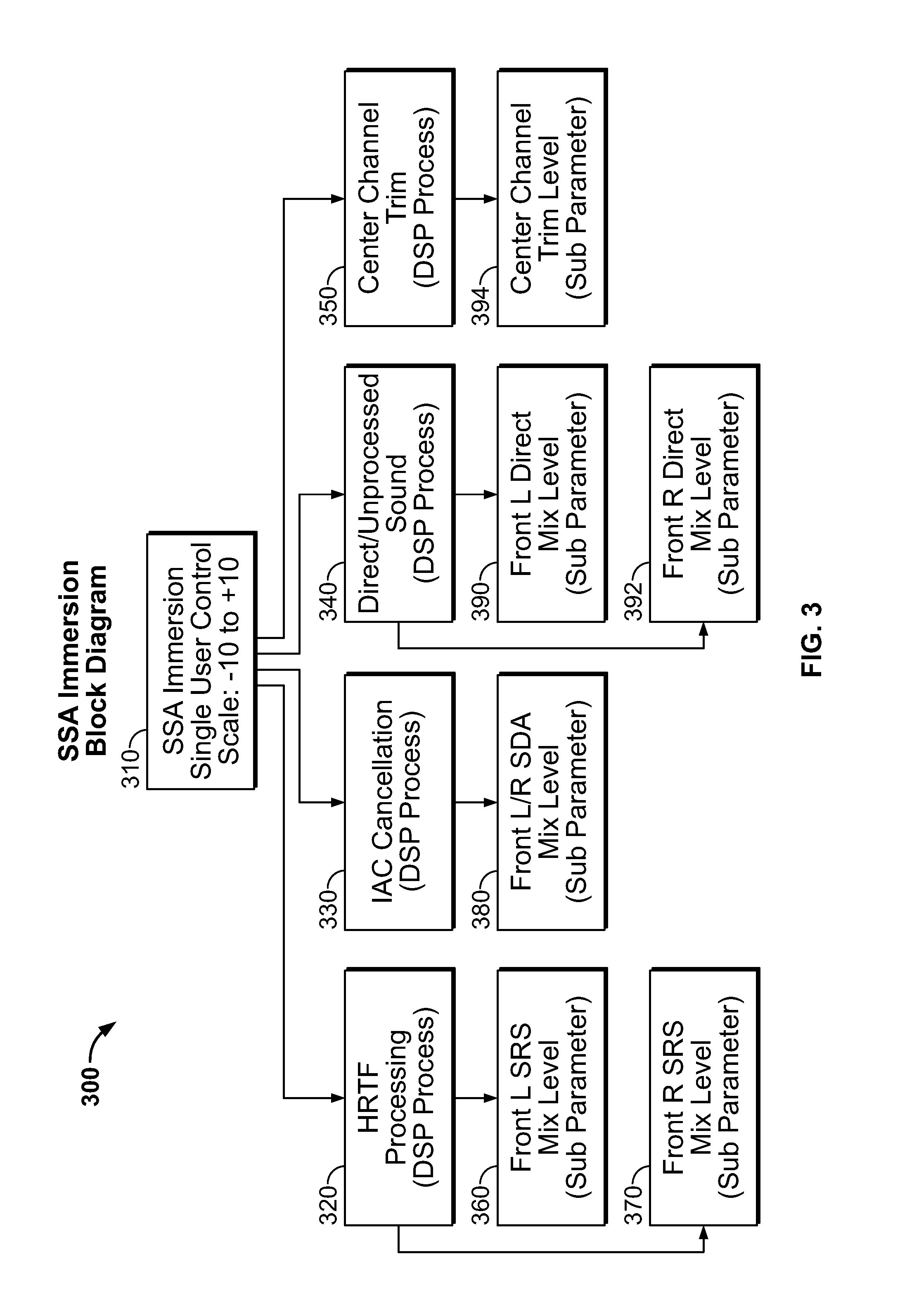
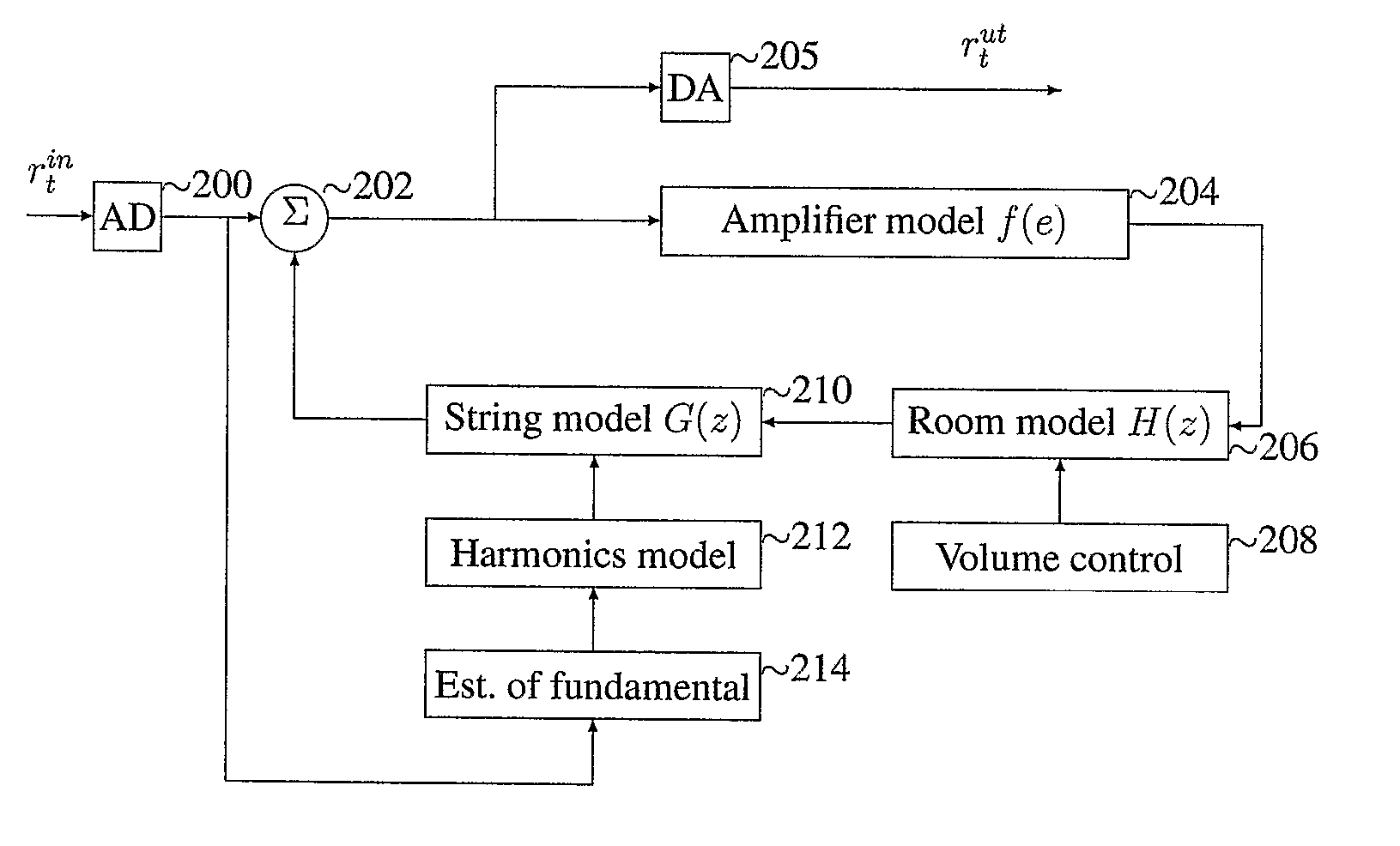
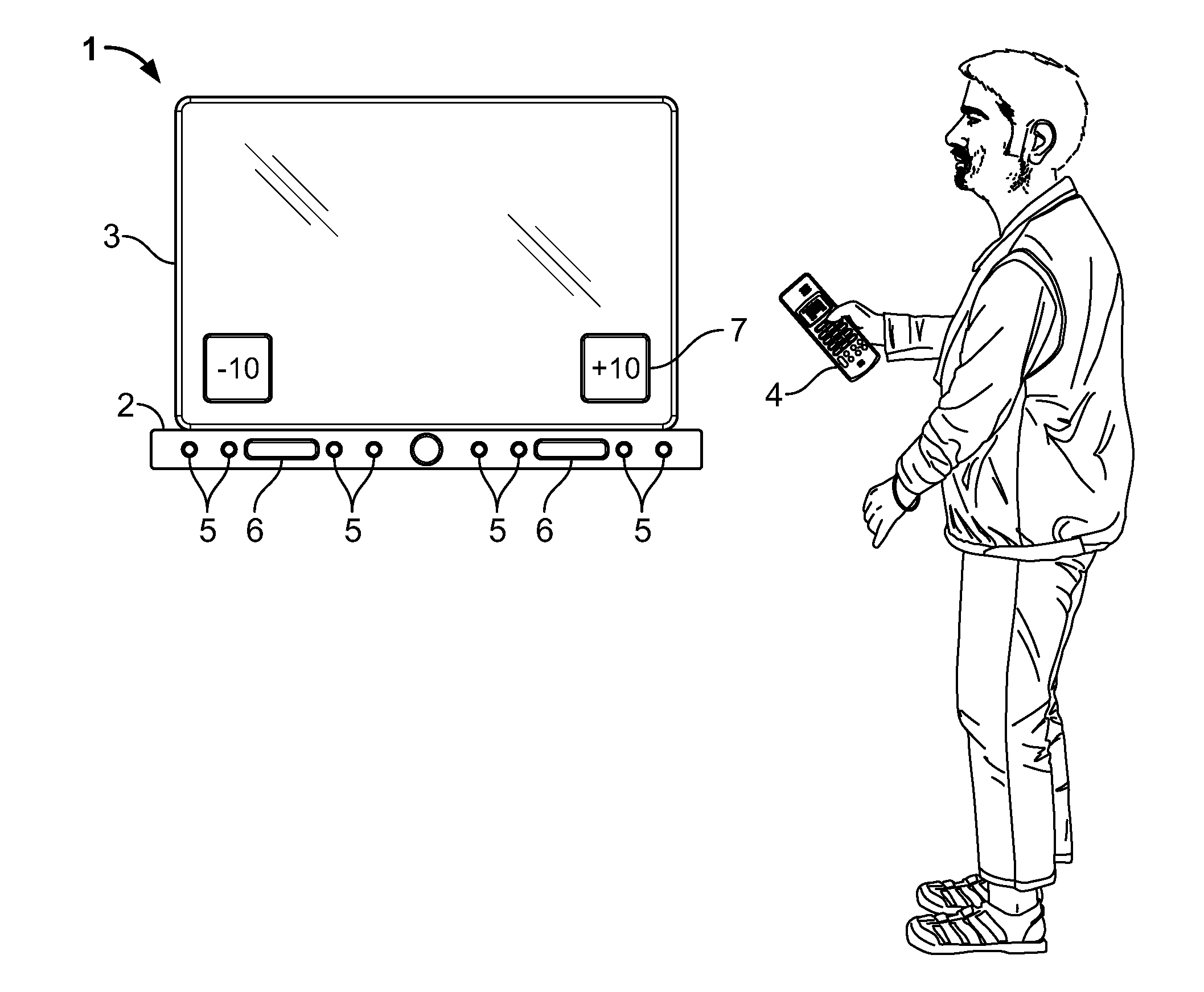
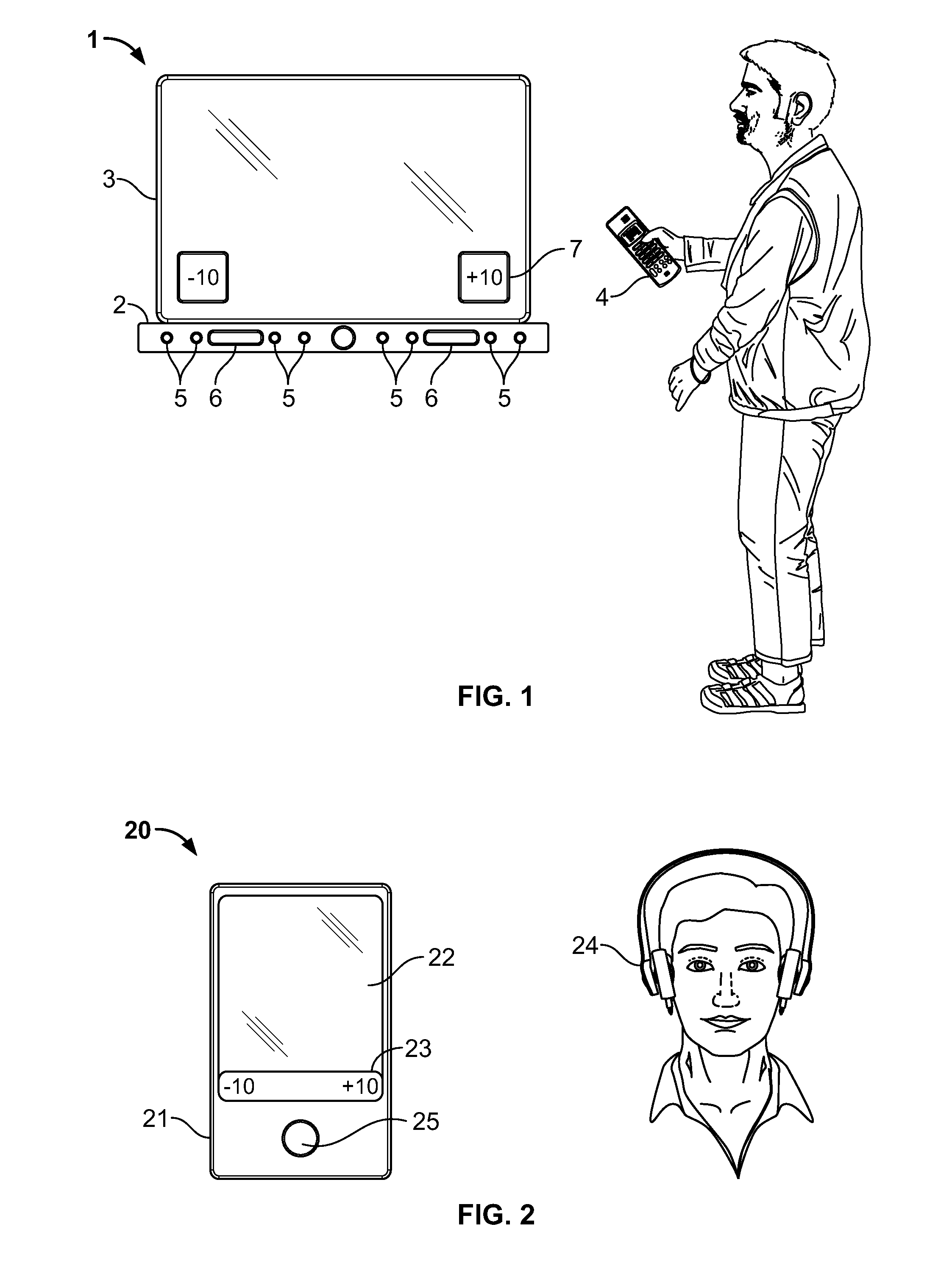
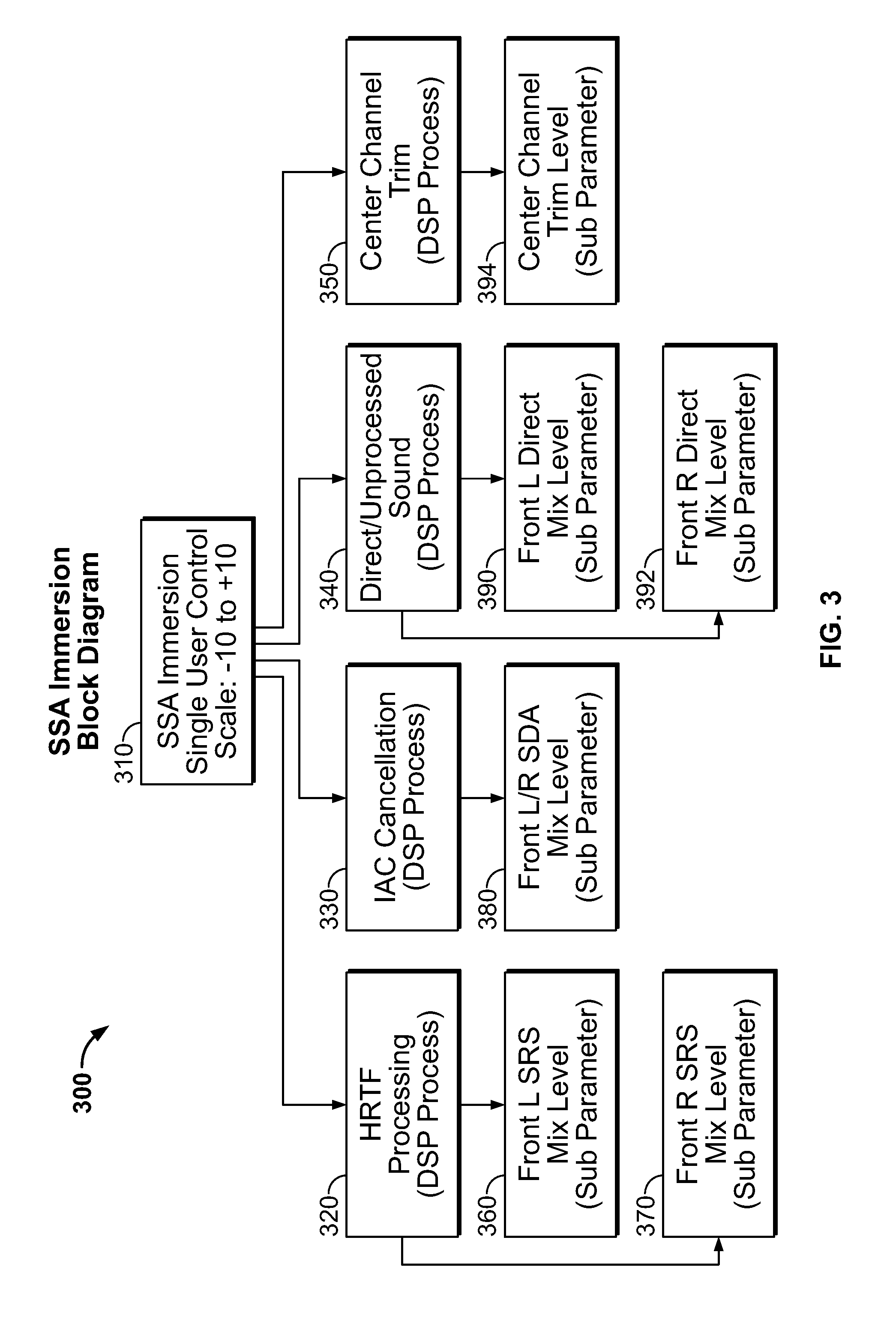
Acoustic surround immersion control system and method
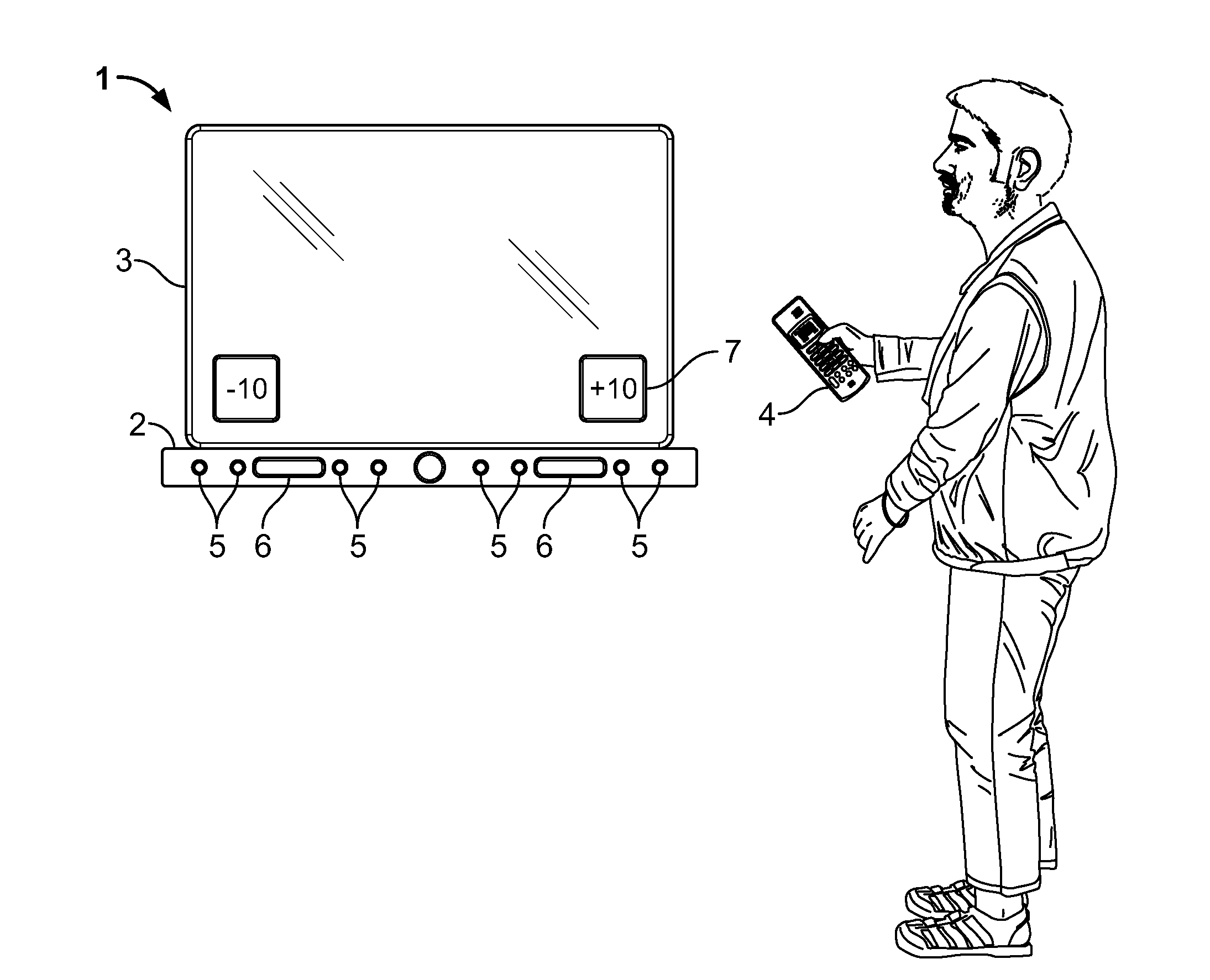
ActiveUS20150341738A1Realistic reproduction of spatial acoustic experience of the listenerMaximum sound stage immersionTransducers for sound channels pluralityStereophonic circuit arrangementsControl systemRoom acoustics
A method and speaker system that provides a single, user adjustable tool for controlling how and which spatialization parameters are used in a single speaker multi-driver system to enhance the sound stage. The tool creates the desired amount of audio surround effect to enhance the sound stage experience or effects in multiple sound recording mode, such as music or movies. The tool is represented in a scale that runs from ‘−10’ (less immersive) to ‘+10’ (more immersive) is set to taste by the listener and will vary with room acoustics and placement.
Owner:POLK AUDIO LLC
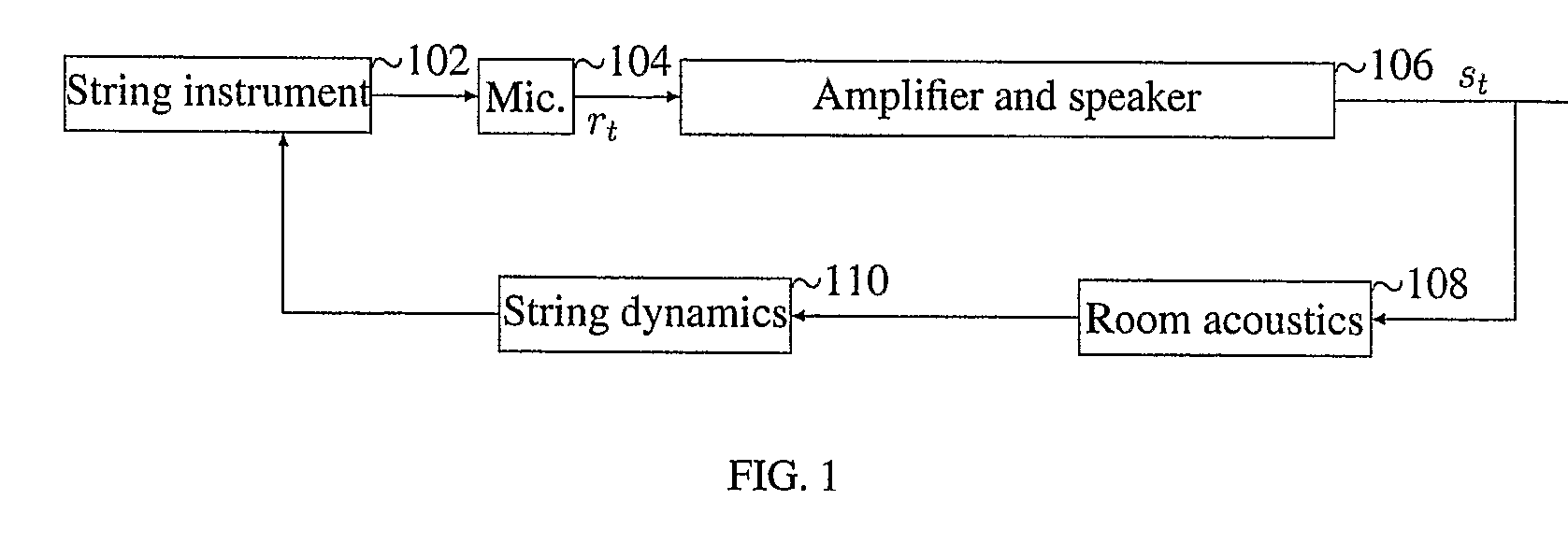
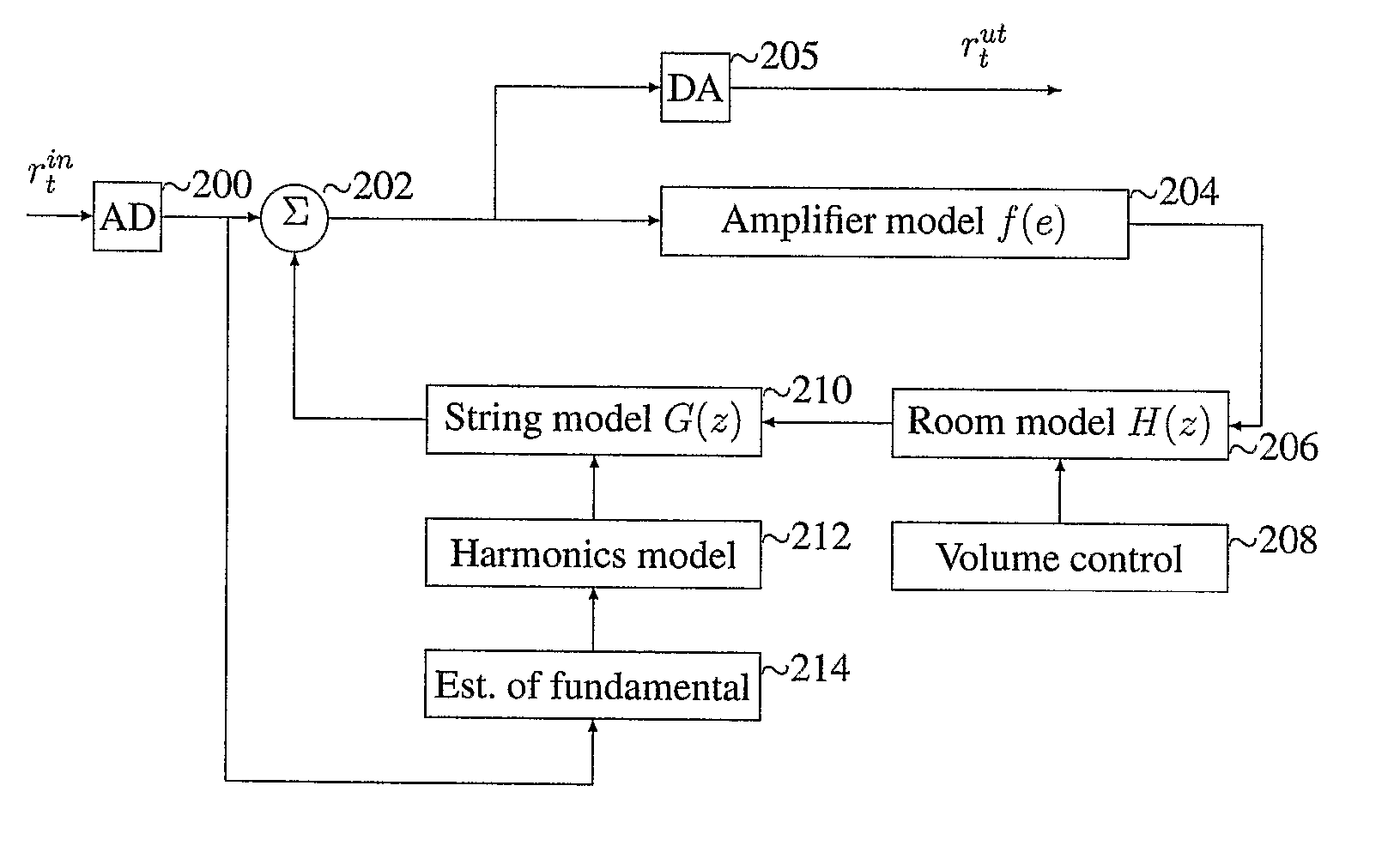
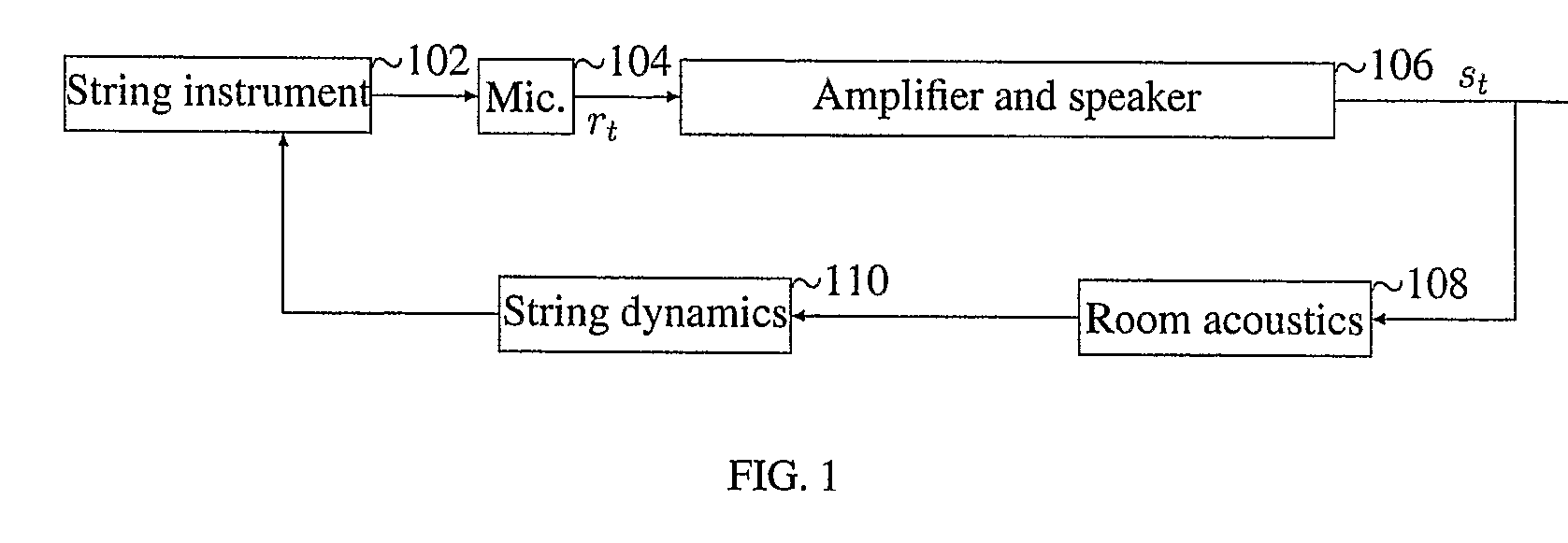
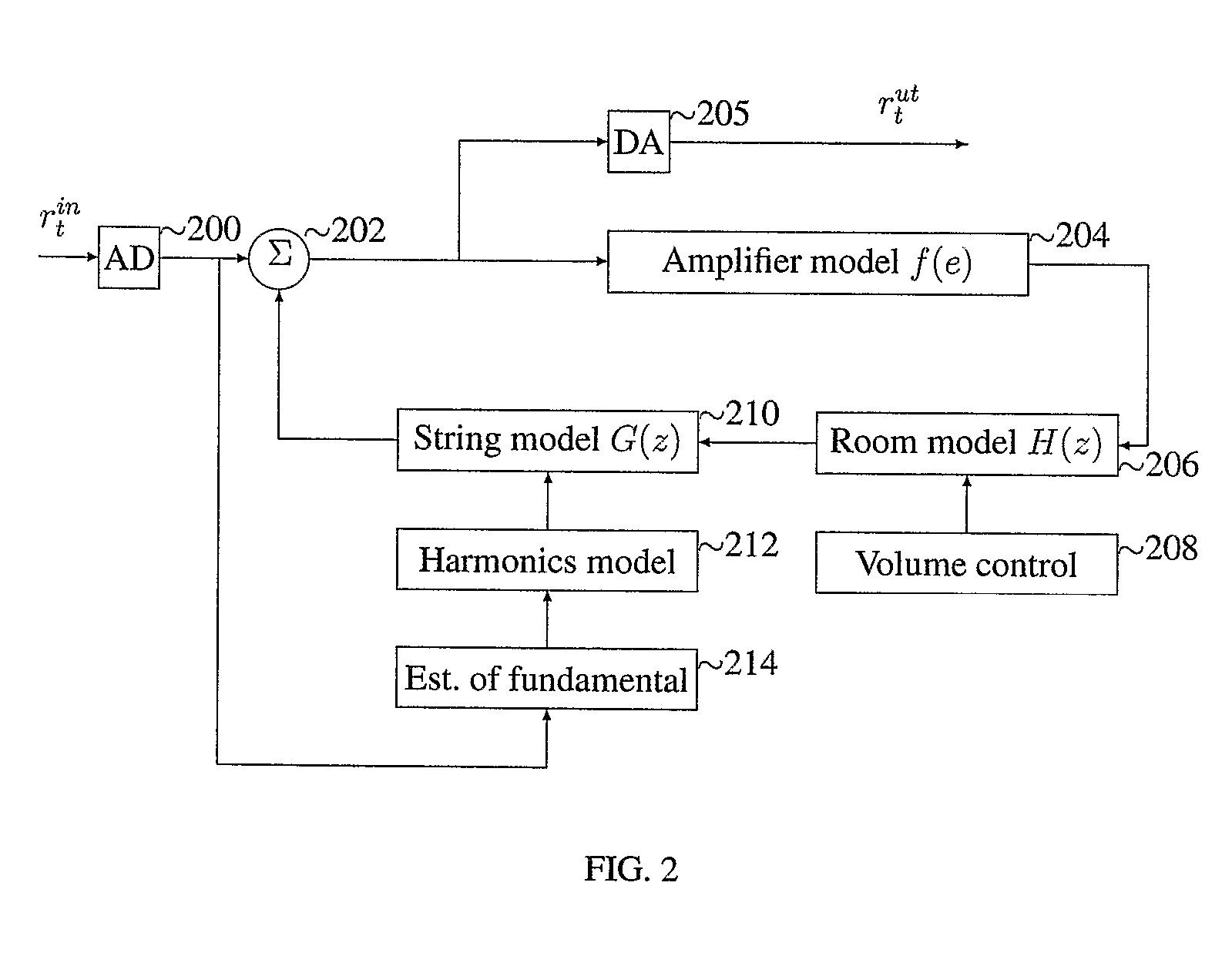
System And Method For Simulation Of Acoustic Feedback
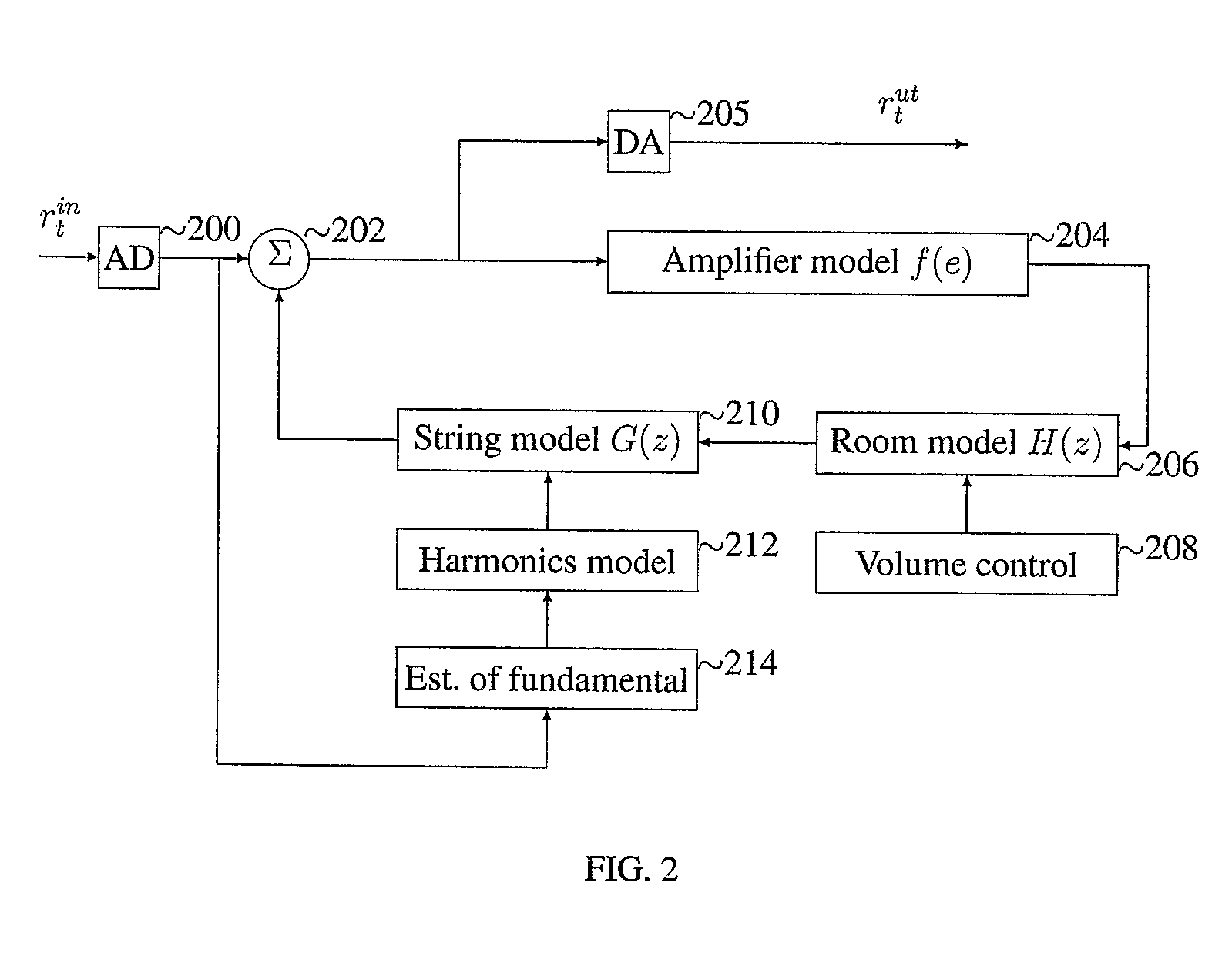
InactiveUS20080091393A1Oscillation stabilityElectrophonic musical instrumentsAnalogue computers for heat flowFeedback effectAudio power amplifier
The invention describes an apparatus for software or hardware emulation of acoustic feedback effects. The invention comprises an analog to digital interface (200) for the input, whose output is summed (202) with a feedback of this digital signal passing through an amplifier model (204), a room acoustics model (206) and a string model (210). The summed signal (202) is converted from digital to analog (205) and can then be connected to a standard amplifier. The room acoustic model comprises a volume control (208) where the degree of feedback is controlled, while the string model contains a model (212) of which harmonics to feed back, and finally an algorithm (214) that decides which fundamental frequencies that the incoming digital signal contains.
Owner:SOFTUBE AB
Ceiling baffle apparatus and ceiling baffle system for a dynamic acoustic ceiling and methods thereof
ActiveUS20180127976A1Reduce unwanted noiseReduce room acousticCeilingsSound proofingRoom acousticsAcoustic insulation
A dynamic acoustic ceiling baffle and a dynamic acoustic ceiling baffle system, that includes multiple shaped baffles that can be quickly and easily installed onto construction ceiling hangers without the need for additional tools, to provide an aesthetically pleasing image, such as an undulating image, along with a reduction in unwanted noise or room acoustics.
Owner:TURF DESIGN INC
Sound diffuser inspired by cymatics phenomenon
InactiveUS9058799B2Improve sound qualityDecent sound performanceSound proofingSound producing devicesInterior spaceAcoustic energy
Sound diffusers are important components in enhancing the quality of room acoustics. The present disclosure relates to a sound diffuser obtained by using properties of the cymatics phenomena. Cymatics is the study of sound and vibration made visible, typically on the surface of a plate, diaphragm or membrane. Two examples of diffusers are designed by the cymatic shapes and modeled by using a quadratic quadratic residue sequence. It is found that this type of acoustic diffusers can be used to maintain the acoustic energy in a room and at the same time can treat unwanted echoes and reflections by scattering sound waves in many directions. The design allows for creating different interior space designs by changing the arrangement of the diffuser panels, and this leads to different applications for the diffusers.
Owner:IMAM ABDULRAHRNAN BIN FAISAL UNIVERSITY
Sound diffuser inspired by cymatics phenomenon
InactiveUS20140339015A1Improvement of indoor sound qualityDecent sound performanceSound proofingSound producing devicesInterior spaceRoom acoustics
Sound diffusers are important components in enhancing the quality of room acoustics. The present disclosure relates to a sound diffuser obtained by using properties of the cymatics phenomena. Cymatics is the study of sound and vibration made visible, typically on the surface of a plate, diaphragm or membrane. Two examples of diffusers are designed by the cymatic shapes and modeled by using a quadratic quadratic residue sequence. It is found that this type of acoustic diffusers can be used to maintain the acoustic energy in a room and at the same time can treat unwanted echoes and reflections by scattering sound waves in many directions. The design allows for creating different interior space designs by changing the arrangement of the diffuser panels, and this leads to different applications for the diffusers.
Owner:IMAM ABDULRAHRNAN BIN FAISAL UNIVERSITY
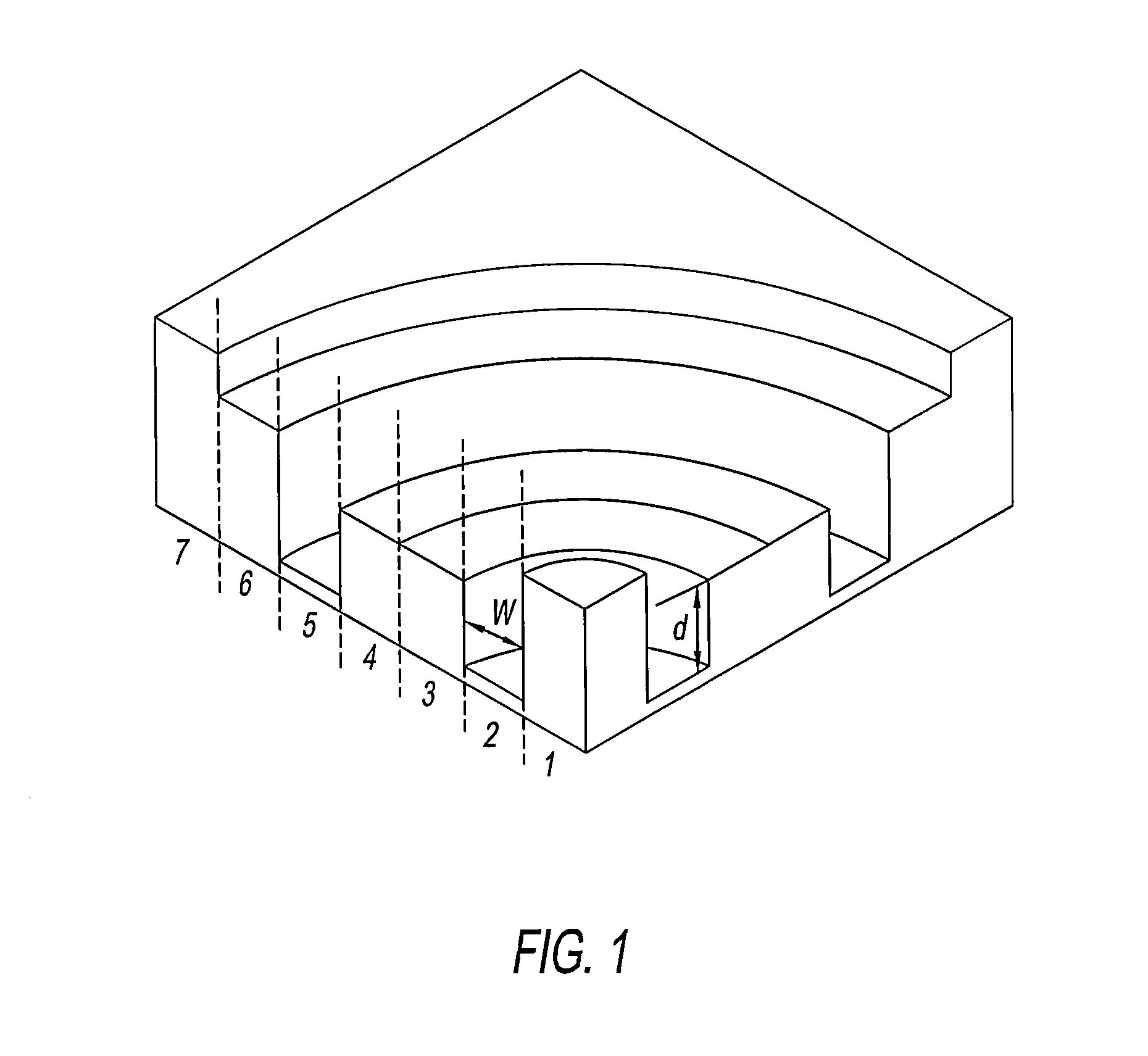
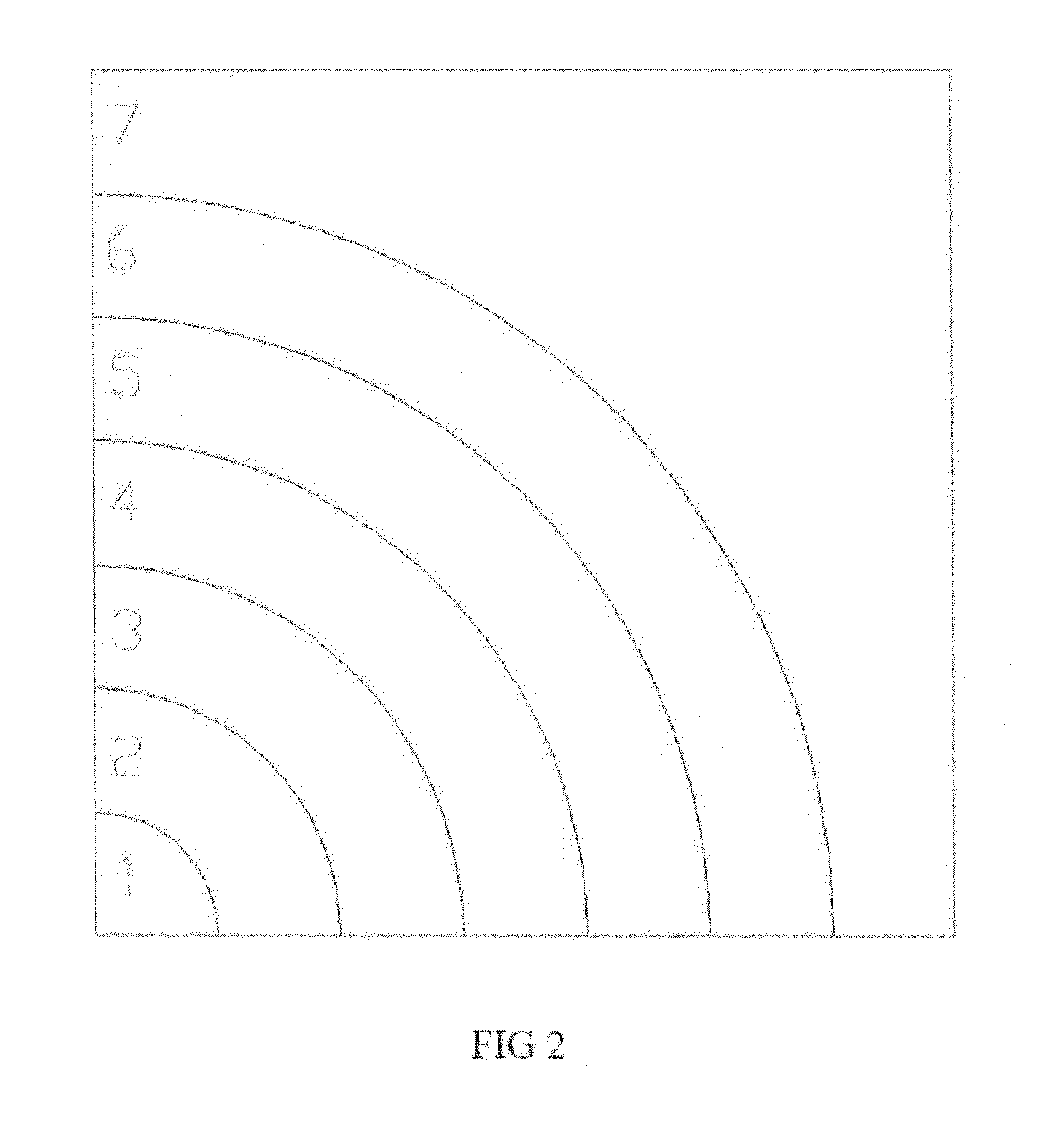
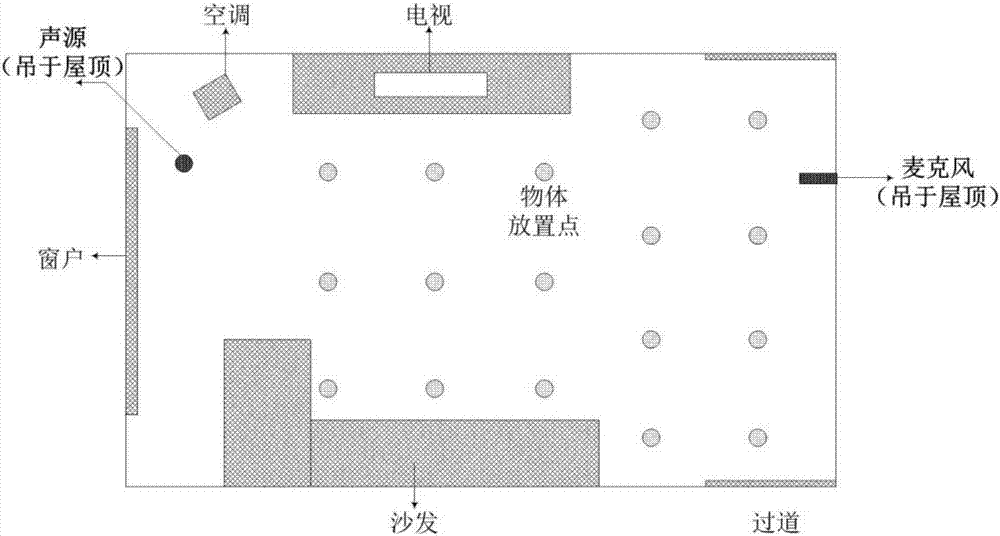
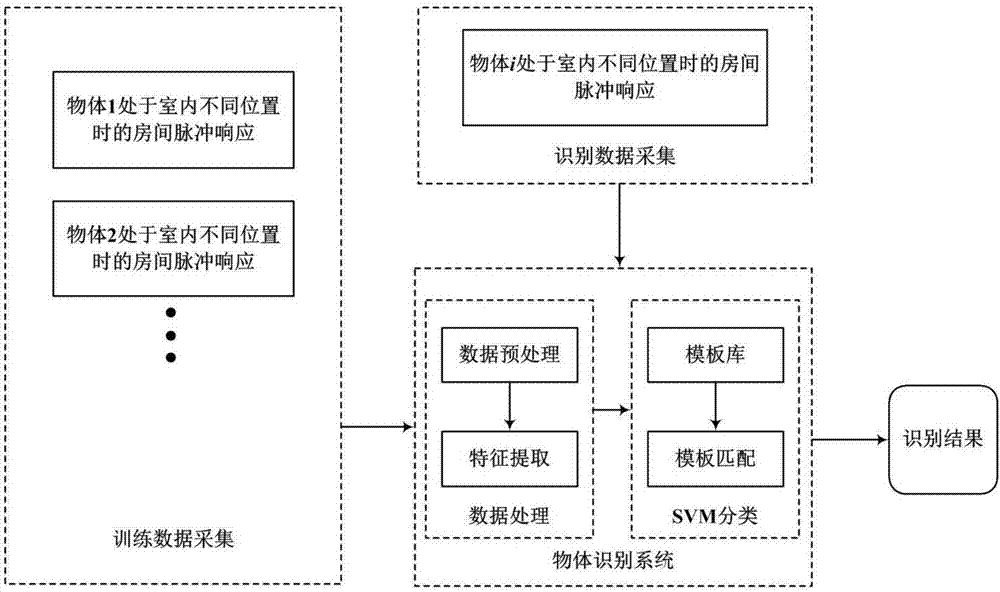
Object identification method based on room acoustics channel disturbance analysis
ActiveCN107202559ANon-visual identificationReduce utilizationUsing subsonic/sonic/ultrasonic vibration meansProcessing detected response signalFeature extractionRoom acoustics
The present invention provides an object identification method based on room acoustics channel disturbance analysis. The method is completed through two phases. The first phase is the establishing of a sample database, and the second phase is a realistic identification phase. In the room application environment scene, different types of objects for identification in future are selected, acoustics channels are measured when the objects are located at different positions in a room, the measurement signals are subjected to feature extraction to summarize the features of different objects, and a result is taken as a sample feature library; and in the realistic identification process, the acoustics channel is measured again when there is a certain object, and a measurement result is subjected to feature extraction according to the feature extraction method and is subjected to cooperation processing with data in the sample database so as to finally identify the objects in the room. The object identification method based on the room acoustics channel disturbance analysis has the advantages of non-visual identification and adoption of few hardware devices compared to widely applied video identification and WIFI identification. The object identification method based on the room acoustics channel disturbance analysis fully utilizes the acoustics information of the room channels, is simple to calculate, and high in location efficiency.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Room acoustic response modeling and equalization with linear predictive coding and parametric filters
A method for determining coefficients of a family of cascaded second order Infinite Impulse Response (IIR) parametric filters used for equalizing a room response. The method includes determining parameters of each IIR parametric filter from poles or roots of a reasonably high-order Linear Predictive Coding (LPC) model. The LPC model is able to accurately model the low-frequency room response modes providing better equalization of loudspeaker and room acoustics, particularly at the low frequencies. Advantages of the method include fast and efficient computation of the LPC model using a Levinson-Durbin recursion to solve the normal equations that arise from the least squares formulation. Due to possible band interactions between the cascaded IIR parametric filters, the method further includes optimizing the Q value of each filter to better equalize the room response.
Owner:AUDYSSEY LABORATORIES
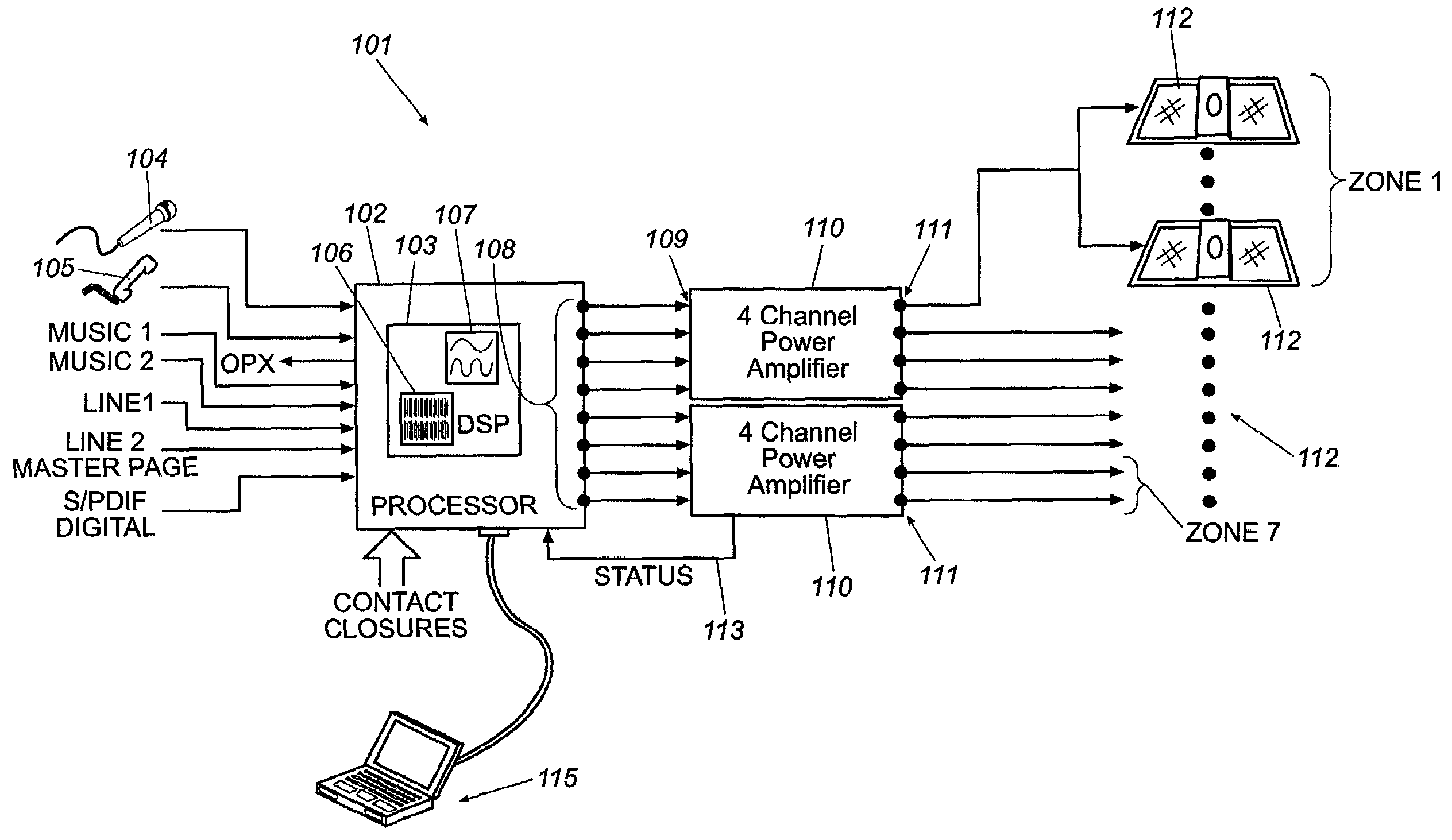
Method and device for effective audible alarm settings
A method for assisting a user in selecting audible alarm settings of a patient monitoring system for monitoring a patient is provided. A synthesis model is generated in response to 1) data indicative of audio features derived from audio recorded in the patient room, and 2) data indicative of vital signs recorded from the patient monitoring system. Sets of audio parameters indicative of respective plurality of audible alarm settings are then processed according to the synthesis model so as to generate respective outputs, e.g. indicative of audibility of the plurality of alarm sounds according to the audible alarm settings synthesized to be played in or outside the patient room. These outputs can then be presented to a user, so as to allow the user to evaluate e.g. alarm audibility and noise level impact of the plurality of audible alarm settings, and e.g. adjust the settings accordingly, such as alarm thresholds etc. The synthesis model may comprise an auralization module, so as to generate synthesized audio outputs to the user. The synthesis model may take into account actual room acoustics in or outside the patient room, so as to allow a precise calculation and / or audio synthesis of an alarm sound to be played in the environment. Alternatively, or additionally, the systhesis model can generate objective and / or subjective metrics that allows the user to find a suitable balance between alarm audibility and impact on noise level.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
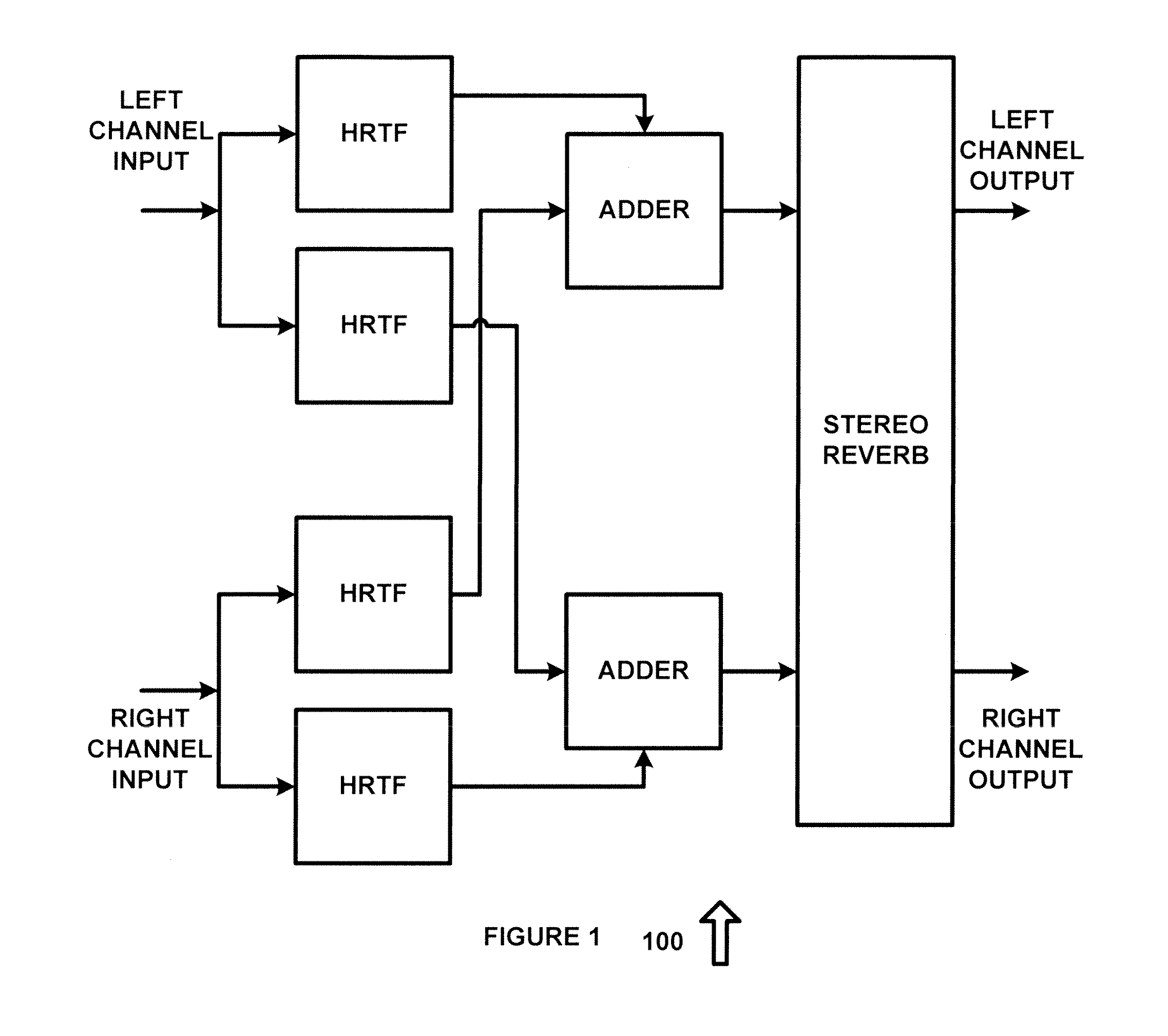
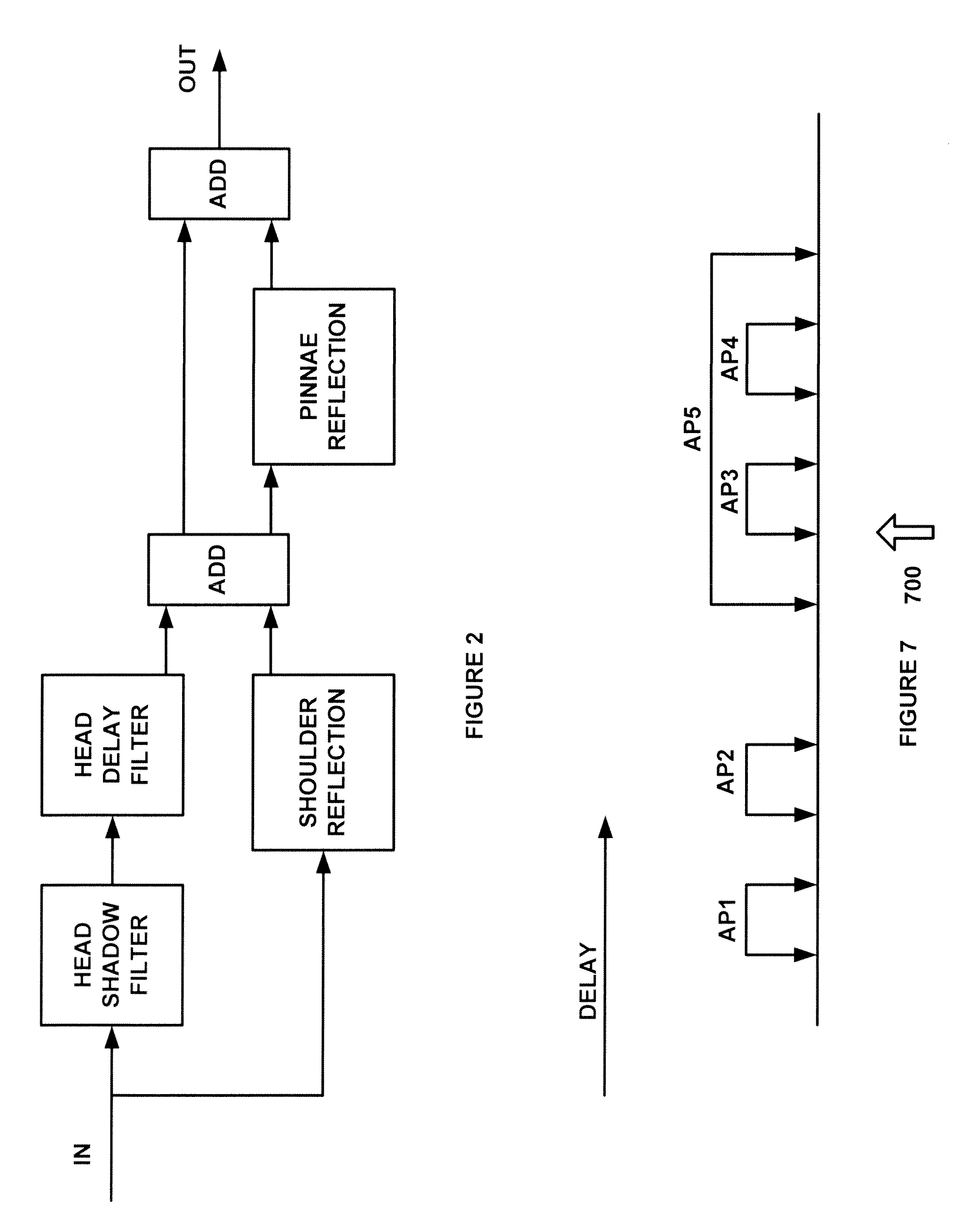
Speaker and room virtualization using headphones
ActiveUS20130216073A1Headphones for stereophonic communicationGain controlVirtualizationRoom acoustics
A system for audio processing comprising a room reflection emulation system for emulating sound reflections in a room. A room acoustics emulation system for emulating acoustic properties of the room. A head, shoulder and ear emulation system for emulation sound reflections near the head.
Owner:SYNAPTICS INC
Acoustic surround immersion control system and method
ActiveUS9226091B2Realistic reproduction of spatial acoustic experience of the listenerMaximum sound stage immersionTransducers for sound channels pluralityStereophonic circuit arrangementsControl systemRoom acoustics
Owner:POLK AUDIO LLC
Acoustic paint
ActiveUS9732234B2Excellent characteristicsImprove clarityCovering/liningsInksElectricityRoom acoustics
An acoustic paint to be applied to the walls of a room in which a source of audible sound is located to improve the acoustic characteristics of the room and correspondingly improve the clarity (e.g., the warmth, richness and detail) of the sound that is generated by the source and detected by the ear of a listener located within the room. The acoustic paint includes a paint foundation into which is mixed a powdered piezoelectric material or a powdered non-piezoelectric crystalline material having a resonant frequency so that the powdered material will react to the sound generated within the room and thereby control the room acoustics depending upon the type of material and the resonant frequency thereof. An optional catalyst, such as an electrically conductive powdered graphite or powdered graphene, is mixed into the paint foundation. The mixture is stirred and then applied to the walls of the room by means of a brush, a roller, or the like.
Owner:UEF LABS LLC
System and method for simulation of acoustic feedback
InactiveUS7572972B2Electrophonic musical instrumentsAnalogue computers for heat flowFeedback effectAudio power amplifier
The invention describes an apparatus for software or hardware emulation of acoustic feedback effects. The invention comprises an analog to digital interface (200) for the input, whose output is summed (202) with a feedback of this digital signal passing through an amplifier model (204), a room acoustics model (206) and a string model (210). The summed signal (202) is converted from digital to analog (205) and can then be connected to a standard amplifier. The room acoustic model comprises a volume control (208) where the degree of feedback is controlled, while the string model contains a model (212) of which harmonics to feed back, and finally an algorithm (214) that decides which fundamental frequencies that the incoming digital signal contains.
Owner:SOFTUBE AB
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com