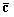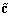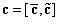Quasi-cyclic low-density parity-check (QC-LDPC) code and correcting and linear coding method thereof
A low-density parity and low-density check technology, which is applied in the field of quasi-cyclic low-density parity check codes and their corrections and linear coding, can solve the problems of difficulty in designing linear complexity coding, and achieve the effect of low coding complexity
Inactive Publication Date: 2011-05-11
PLA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
View PDF2 Cites 18 Cited by
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
[0005]Technical problem: the purpose of this invention is to provide a kind of correction of quasi-cyclic low density parity check code and its linear coding method, to solve the problem of this type of low density parity check The Difficult Design Problem of Linear Complexity Coding
Method used
the structure of the environmentally friendly knitted fabric provided by the present invention; figure 2 Flow chart of the yarn wrapping machine for environmentally friendly knitted fabrics and storage devices; image 3 Is the parameter map of the yarn covering machine
View moreImage
Smart Image Click on the blue labels to locate them in the text.
Smart ImageViewing Examples
Examples
Experimental program
Comparison scheme
Effect test
Embodiment Construction
the structure of the environmentally friendly knitted fabric provided by the present invention; figure 2 Flow chart of the yarn wrapping machine for environmentally friendly knitted fabrics and storage devices; image 3 Is the parameter map of the yarn covering machine
Login to View More PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
The invention relates to a quasi-cyclic low-density parity-check (QC-LDPC) code and a correcting and linear coding method thereof. The variable nodes of the LDPC code, the dimensionality of which is greater than 2, are informational nodes; and the variable nodes the dimensionality of which is 2 form a big end-to-end ring on a bipartite graph. The correcting method comprises the following implementation steps: randomly selecting one edge on the big ring the dimensionality of which is 2, cutting off the edge, and filling 0 in the corresponding position of a low-density check matrix, thereby acquiring a corrected structure of the code. The linear coding method of the corrected code comprises the following implementation steps: firstly, multiplying an input information vector s and a part of the check matrix the load of which is greater than 2 as a vector by a matrix to acquire an intermediate vector u; directly intercepting the corresponding position of the intermediate vector u to acquire a coding vector the variable node dimensionality of which is 1; computing bit by bit from a start bit according to the characteristics of the big ring on the bipartite graph to acquire a coding vector the variable node dimensionality of which is 2; and combining the two coding vectors to finally form a coding vector.
Description
technical field [0001] The invention relates to an encoding method of a low-density parity check code, and belongs to the field of encoding structures and encoding methods of channel error correction encoding. Background technique [0002] Among the encoding methods of Low-Density Parity-Check (LDPC) codes, Richardson wrote in the literature (T.J. Richardson and R.L. Urbane, "Efficient encoding of low-density parity-check codes," IEEE Trans. Inform . Theory, vol.47, no.2, pp. 638-656, Feb. 2001.) proposed a coding method based on the lower triangular check matrix. However, if the check matrix cannot be adjusted into an ideal lower triangular matrix form, the coding complexity is still very high. From the point of view of LDPC codec hardware implementation, unstructured LDPC codes are not conducive to hardware implementation. For this reason, LDPC codes with a quasi-cyclic (Quasi-Cyclic, QC for short) structure have been widely favored by academia and industry. The QC struc...
Claims
the structure of the environmentally friendly knitted fabric provided by the present invention; figure 2 Flow chart of the yarn wrapping machine for environmentally friendly knitted fabrics and storage devices; image 3 Is the parameter map of the yarn covering machine
Login to View More Application Information
Patent Timeline
 Login to View More
Login to View More IPC IPC(8): H03M13/11H03M13/13
Inventor 吴晓富崔龙赵春明尤肖虎
Owner PLA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com