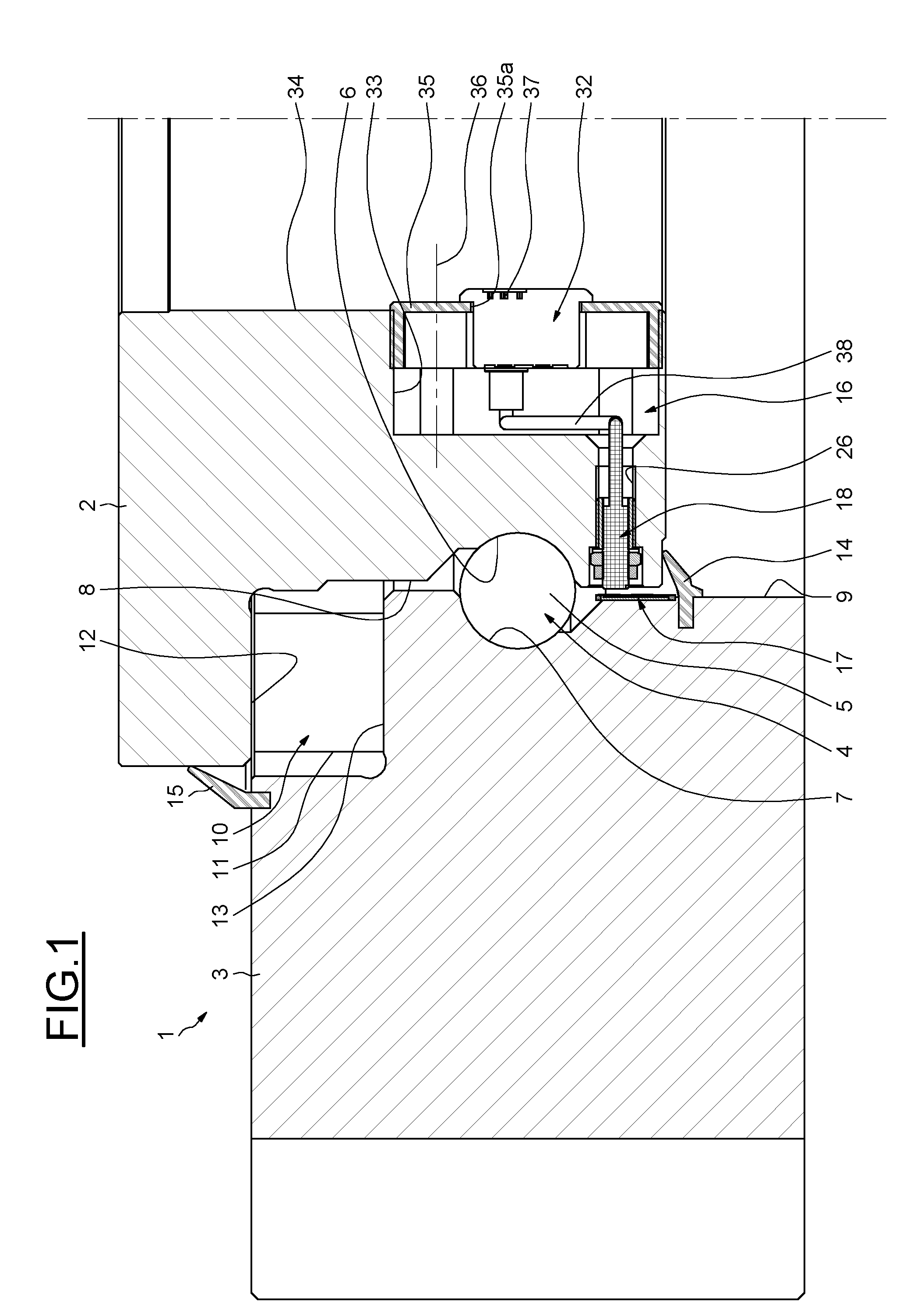
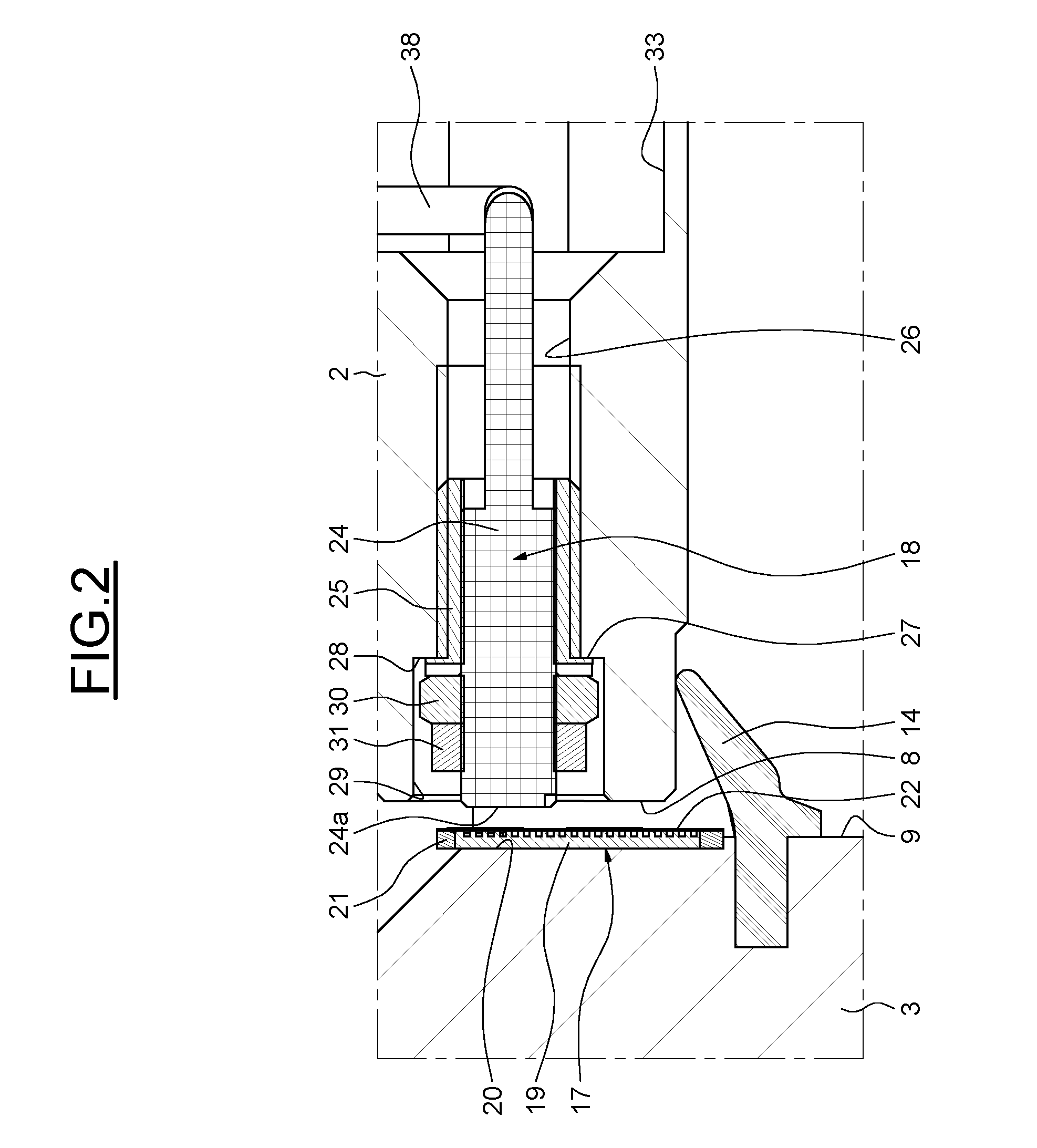
Patents
Literature
240 results about "Linear encoder" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A linear encoder is a sensor, transducer or readhead paired with a scale that encodes position. The sensor reads the scale in order to convert the encoded position into an analog or digital signal, which can then be decoded into position by a digital readout (DRO) or motion controller.
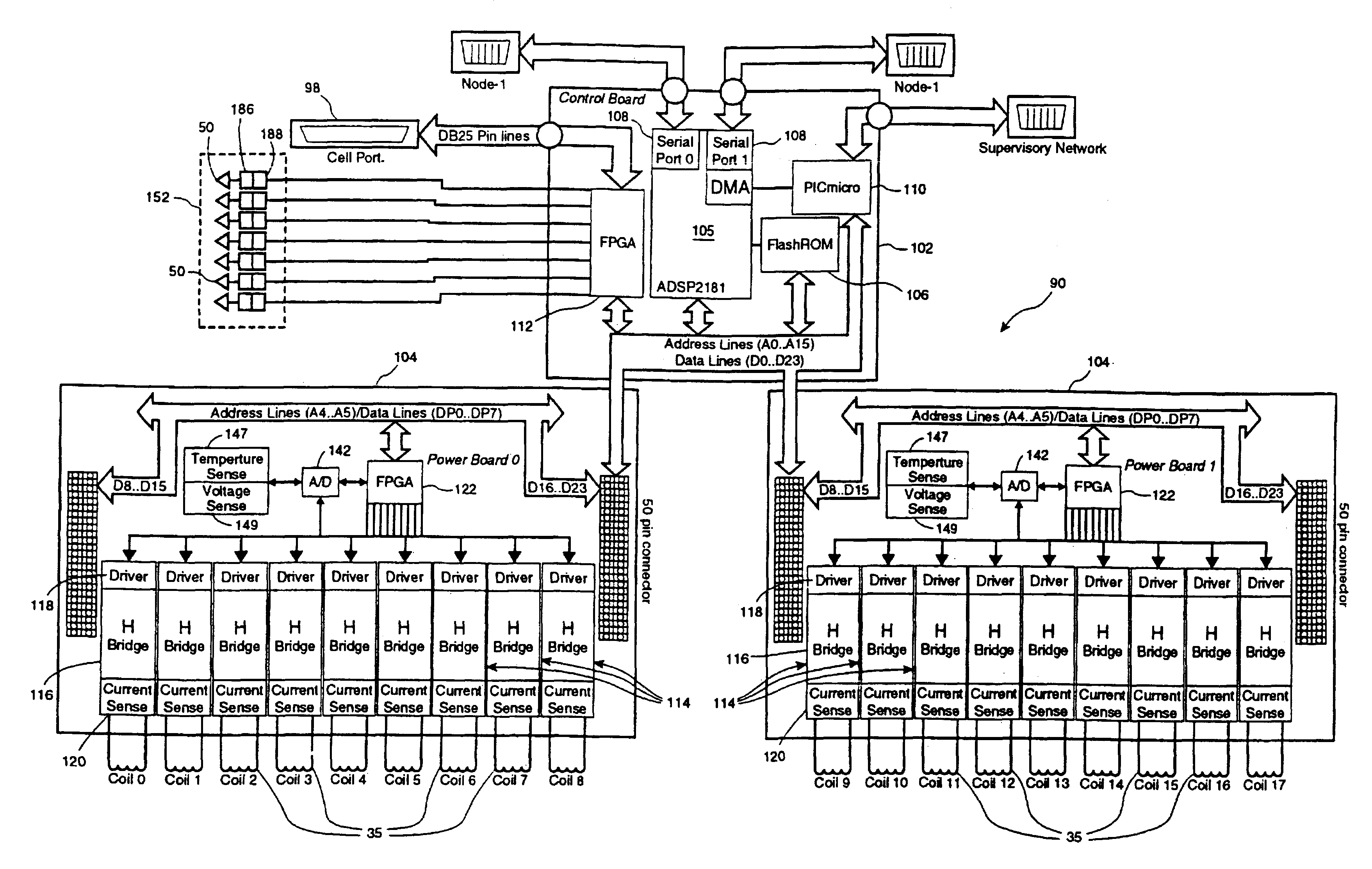
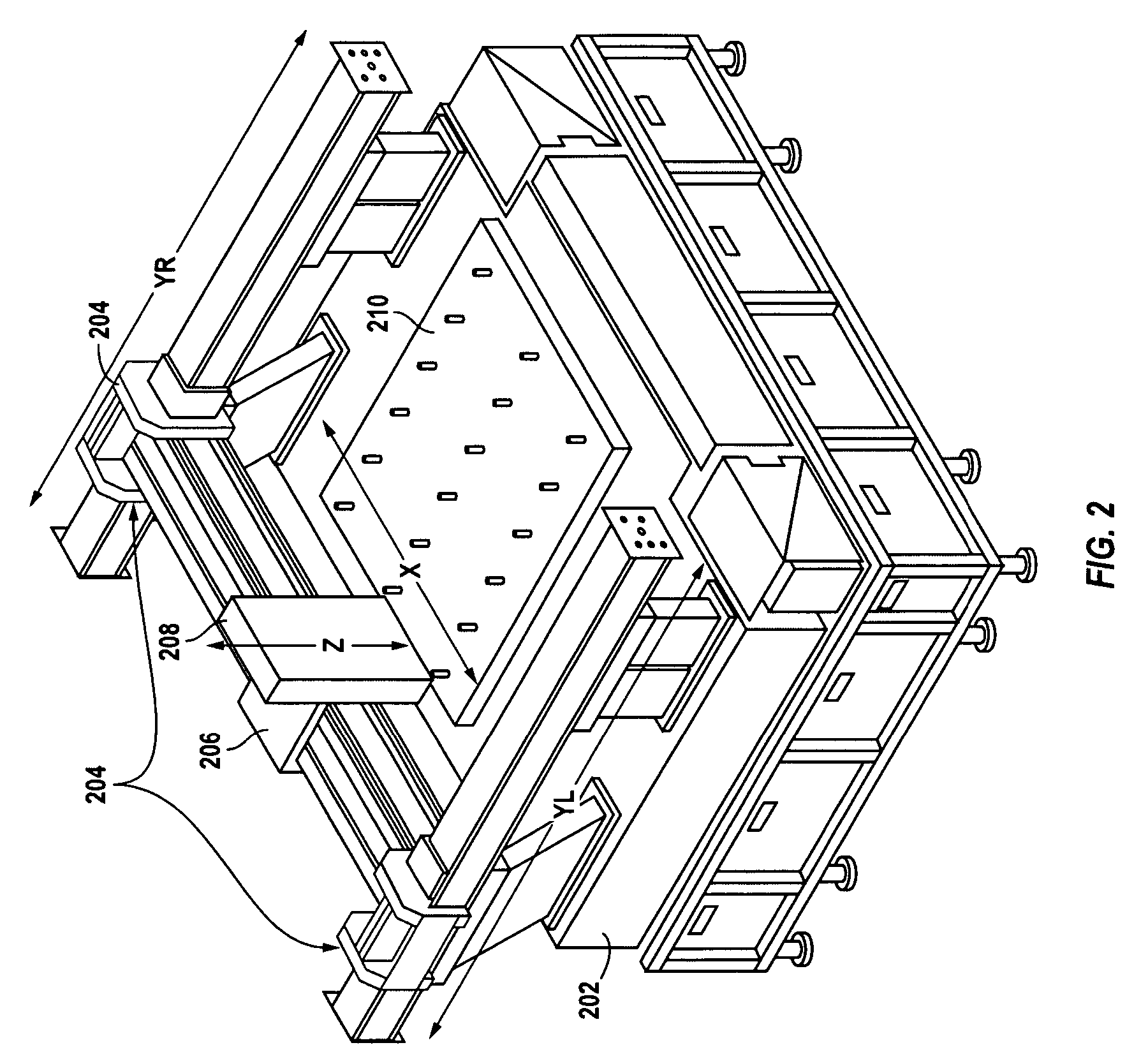
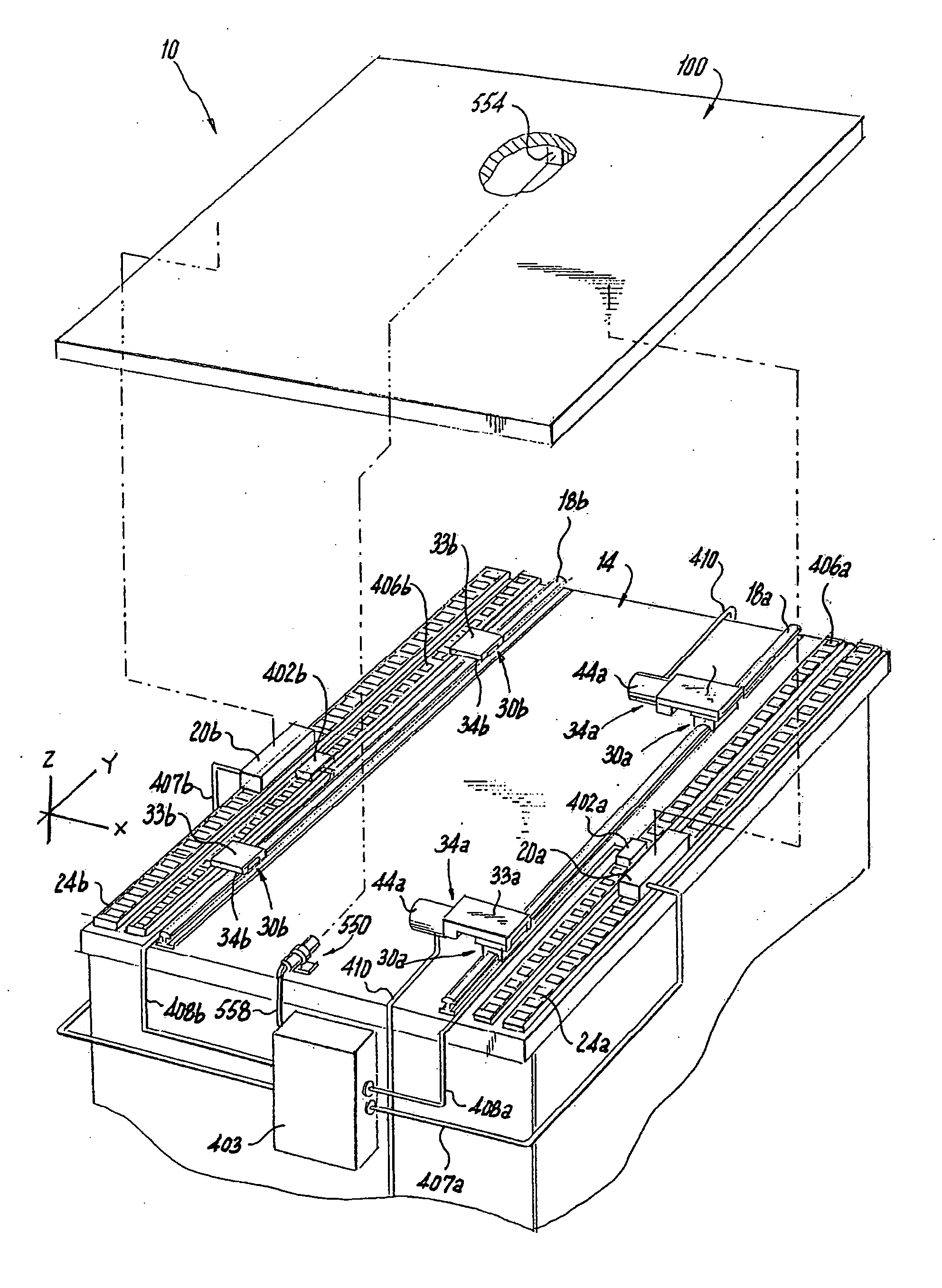
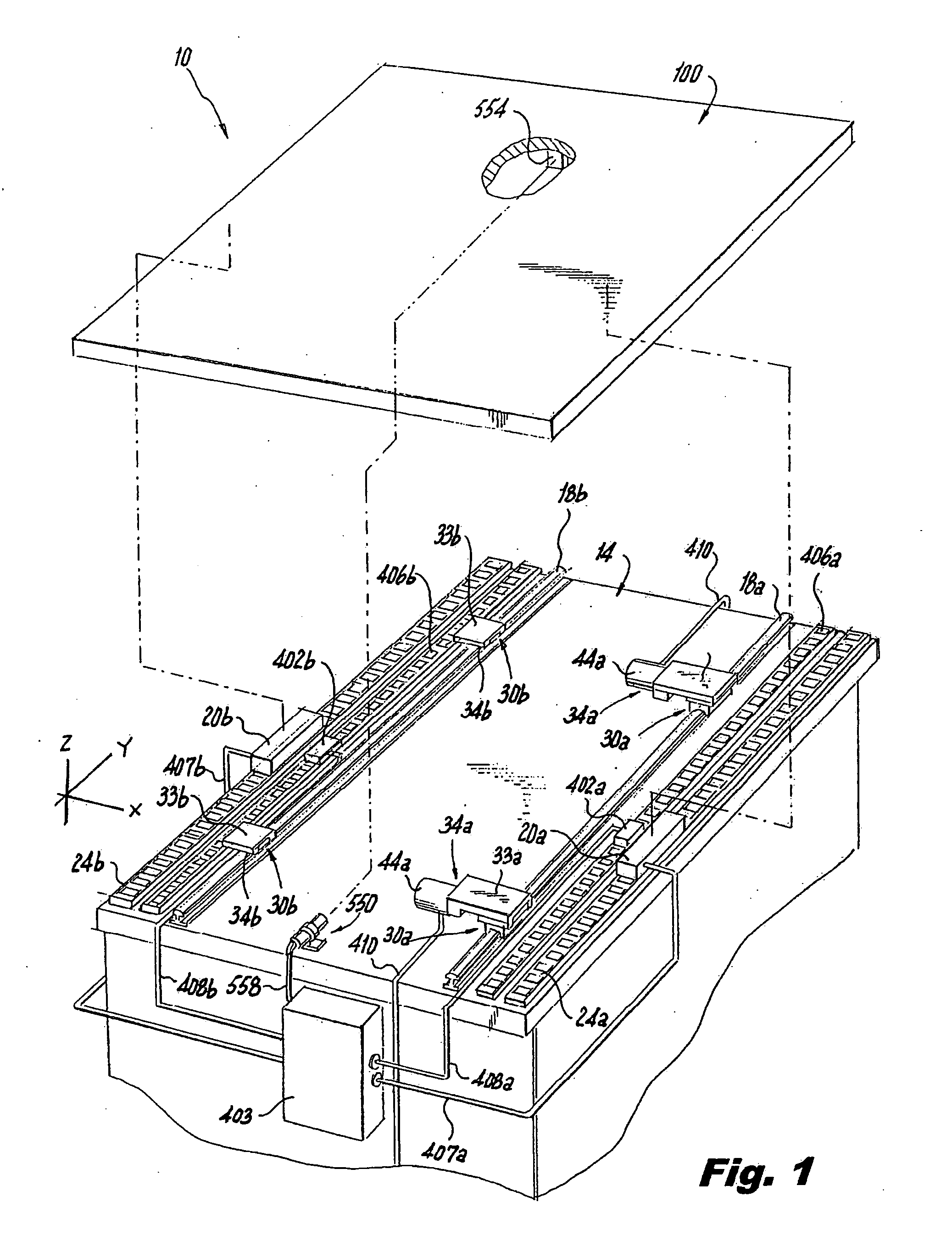
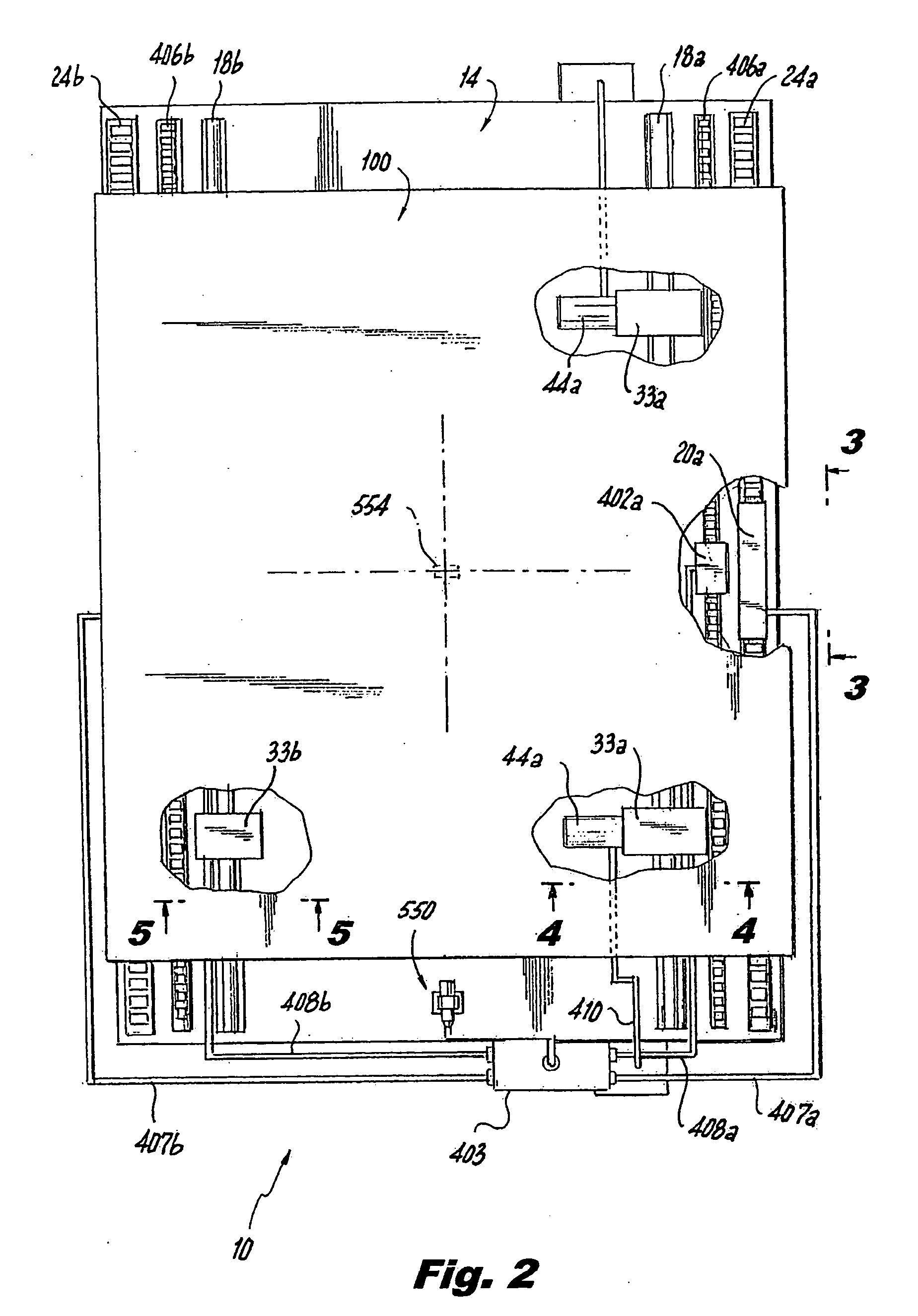
Modular conveyor system having multiple moving elements under independent control
InactiveUSRE39747E1Unrestricted mobility along the trackLighten the taskDC motor speed/torque controlRailway vehiclesTelecommunications linkModularity
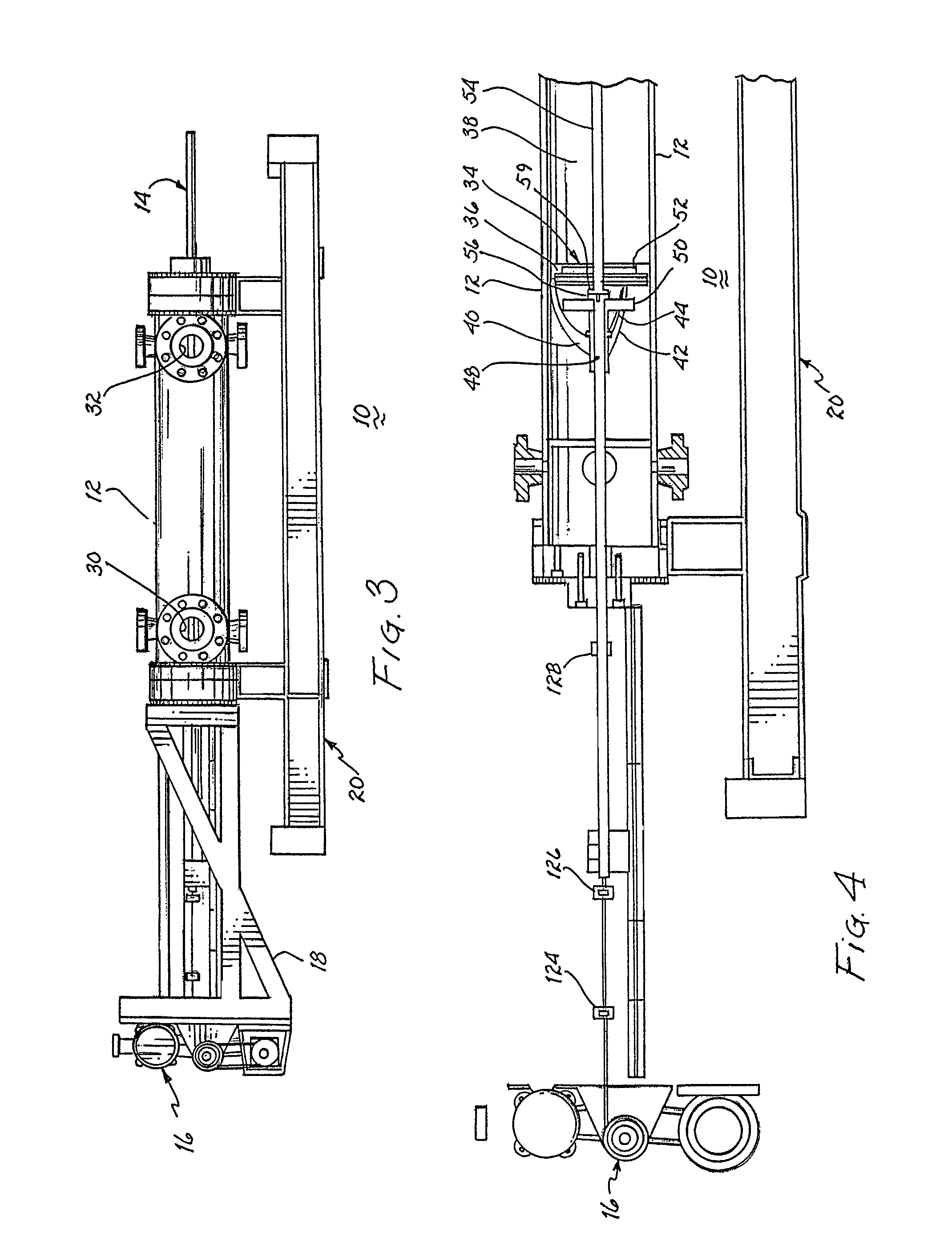
The modular conveyor system comprises N interconnected track sections, forming a continuous track, wherein each track section features a plurality of individually controlled coils stretching along the length thereof. Plural pallets, each having thrust producing magnets, travel independently alone the track. The track also comprises multiple linear encoder readers spaced at fixed positions therealong, and each pallet includes a linear encoder strip having a length R greater than the spacing E between the readers. Track section controllers associate the encoder strips with only one reader at any time in order to resolve the position of the pallets based on the fixed position of the readers and the relative positions of the strips in relation thereto. The section controllers also regulate and commutate the coils of the corresponding track sections in order to independently control each pallet. Communication links interface adjacent section controllers situated in adjacent track sections. The electromagnetic structure and distributed control architecture of the conveyor system enable it to independently control multiple practical pallets yet be constructed out of modular track sections, with little practical restriction on the length of the conveyor system or the number of pallets controlled thereby.
Owner:ATS AUTOMATION TOOLING SYSTEMS
Head and disk tester with a thermal drift-compensated closed-loop positioning system
InactiveUS6023145APrecise positioningEliminates temperature driftTrack finding/aligningTemperatue controlElectricityPiezoelectric actuators
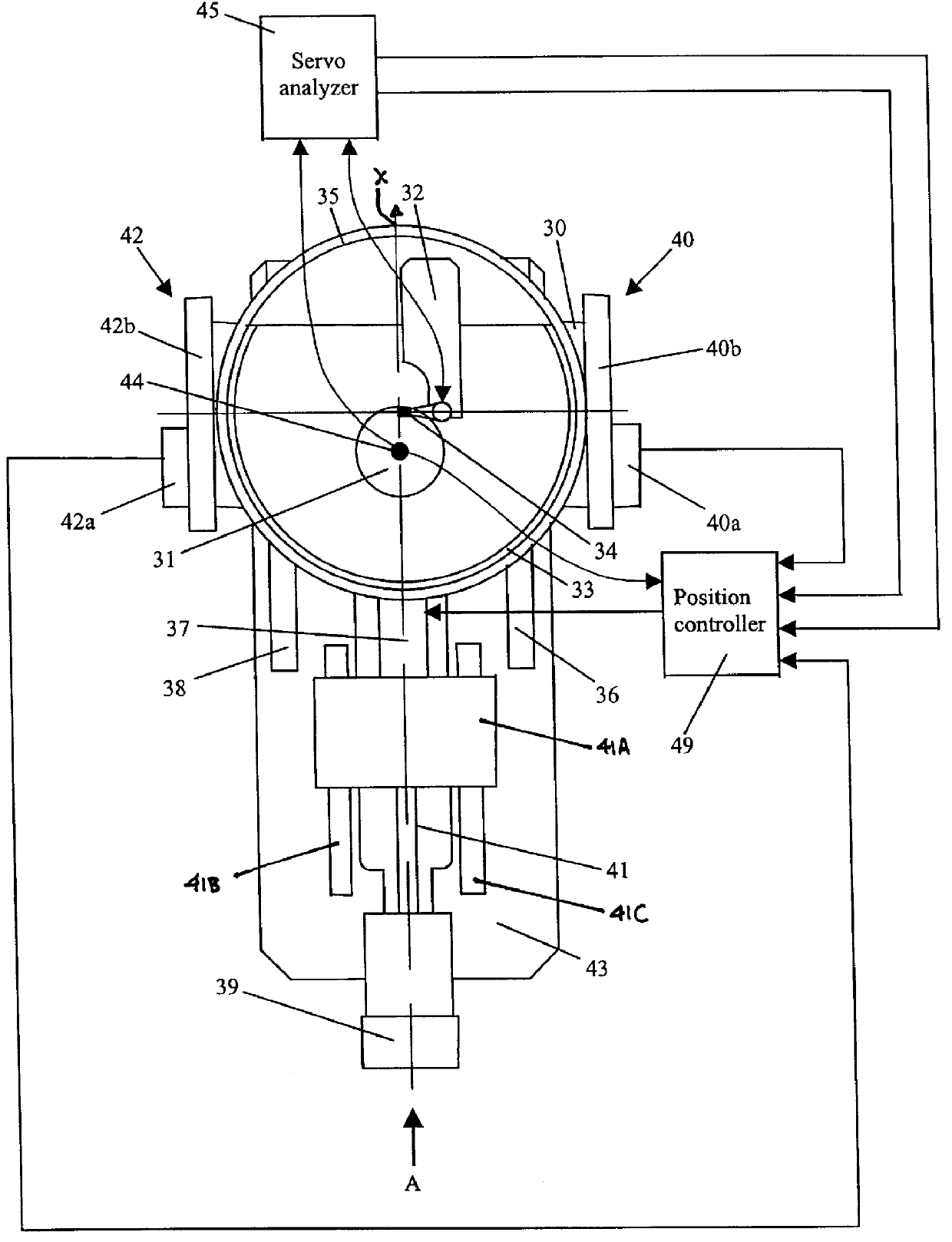
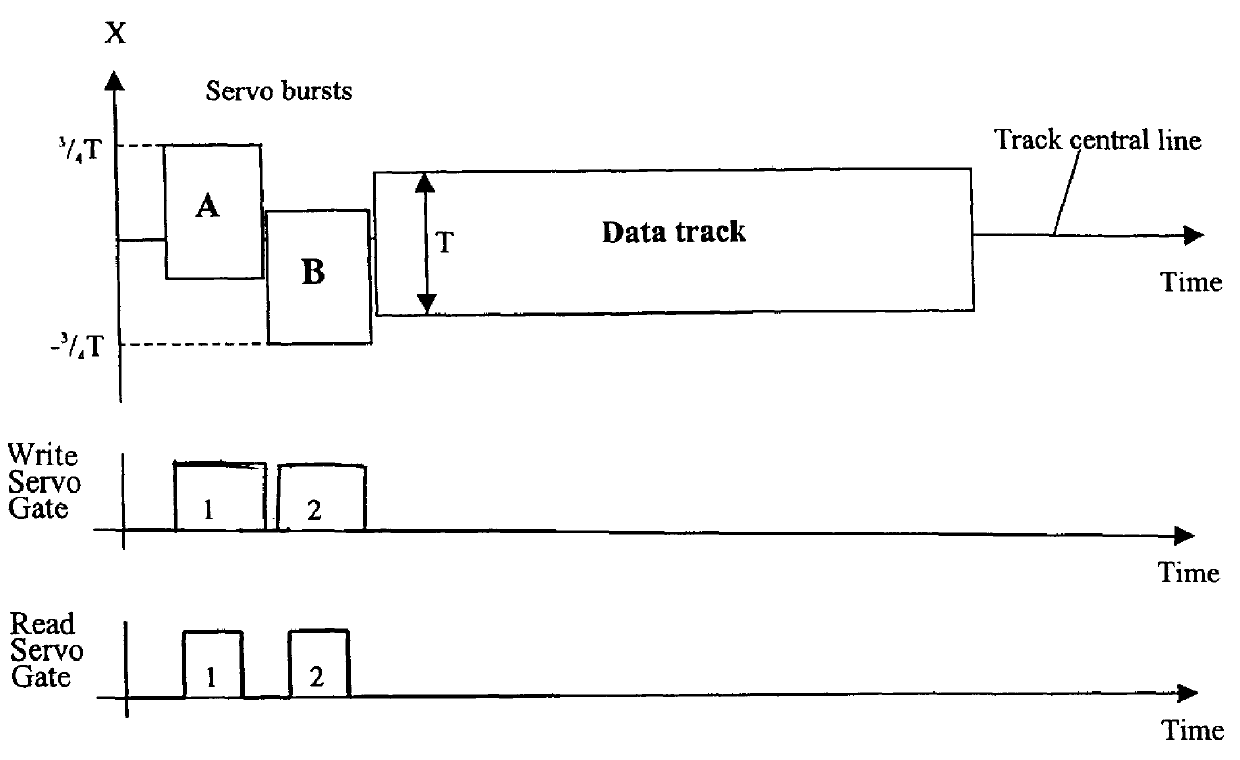
The head / disk tester of the invention has a housing 43 that houses spindle 44 that rotatingly supports a magnetic disk 31. The housing supports a moveable carriage 30 that, in turn, supports a magnetic head 32. Positioning means 39 and 41 are used to move the carriage and the magnetic head across the magnetic disk. These positioning means include stepper motors that realize coarse positioning of the magnetic head, and a piezo actuator 37 that is used for fine positioning. Linear encoders 40 and 42 located at both sides of the carriage provide feedback information to a closed-loop positioning system that controls the piezo actuator. A set of special signals ("servo bursts") pre-written at a given track of the magnetic disk is used as an additional source of feedback information for the same closed-loop positioning system. This positioning system includes a servo analyzer 45 that reads and processes servo burst signals from the magnetic disk, and a position controller 49 that controls the piezo actuator. The controller contains two control loops: a proportional-integral-derivative (PID) loop and an additional servo burst loop. During any movement of the magnetic head to a prescribed command position, the servo burst feedback is turned off, and feedback from linear encoders is used by the PID loop to move the head. When the magnetic head reaches the prescribed command position, servo burst loop is turned on; it changes the command position of the PID loop in a way to keep the ratio of pre-written burst signals constant. As a result, the position of the magnetic head with respect to the data track remains the same for as long as necessary, even in unstable temperature conditions.
Owner:GUZIK TECHN ENTERPRISES
Induction-type position measuring apparatus
InactiveUS20010020846A1High precision measurementElectric/magnetic position measurementsUsing electrical meansClosed loopElectrical polarity
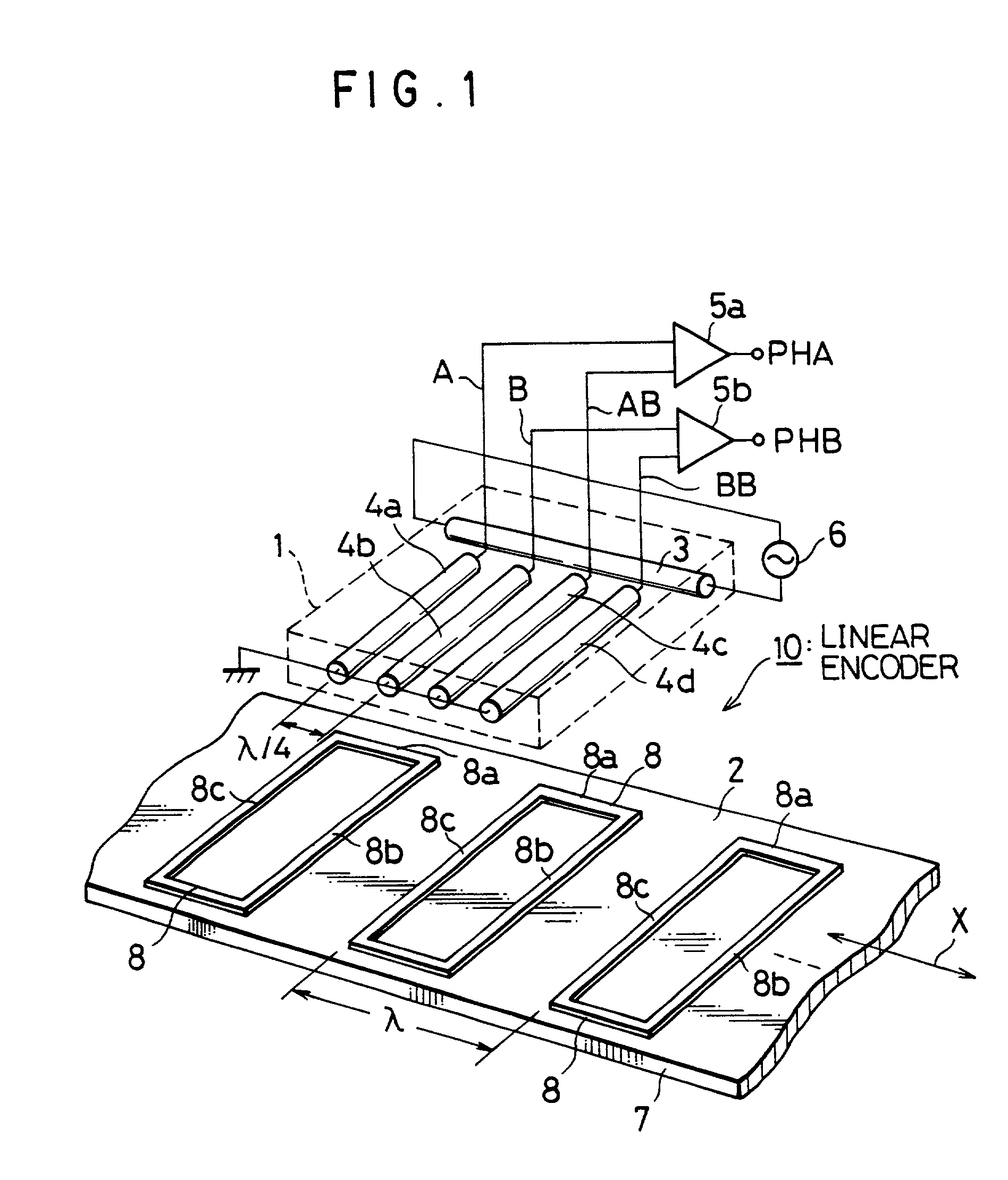
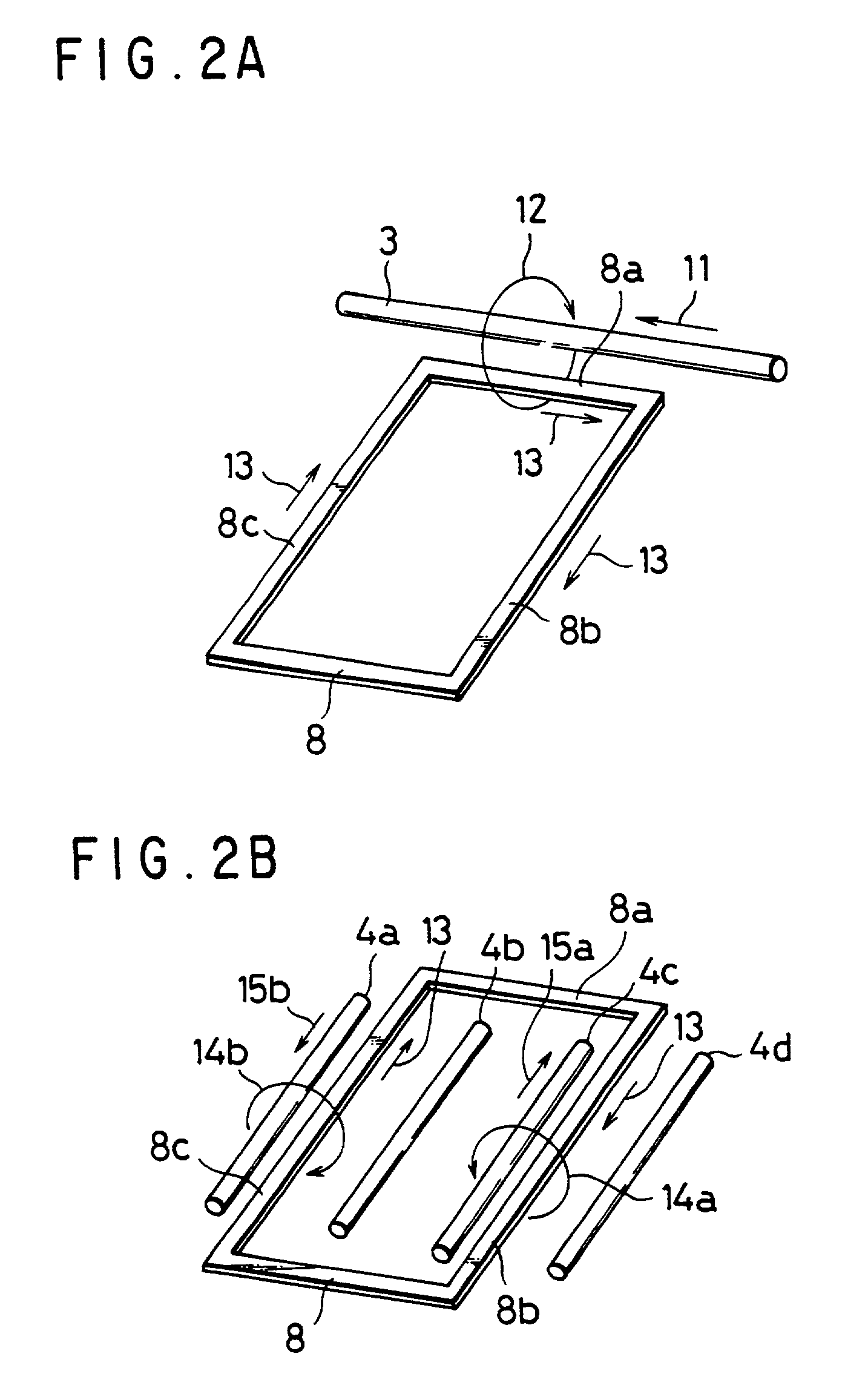
An inductive linear encoder (10) has a position sensor (1) and scale (2) which are movably disposed relative to each other. The sensor (1) is with a drive wire (3) to which an alternating current is supplied, and one set of detection wires (4a-4d) at right angles to the drive wire (3) in the same plane. The scale (2) is configured including an elongate substrate (7) having its surface on which a series combination of conductive closed loop patterns (8) are periodically arranged at equal intervals. These conductive closed loop (8) are linearly laid out on the substrate (7) in the relative movement direction. Each loop (8) consists essentially of a reception conductor segment (8a) and signal transmit conductor segments (8b, 8c) integral with the former (8a). The receive conductor segment (8a) is responsible for generation of an induced current due to a first variable magnetic field creatable from the drive coil (3). The transmit conductor segments (8b, 8c) are to create second variable magnetic fields that are opposite in polarity to each other and are perpendicular to the first magnetic field. Creation of such second magnetic fields results in flow of an induced current in the detector wire (4) of sensor (1), which in turn acts as a position detection output current.
Owner:MITUTOYO CORP
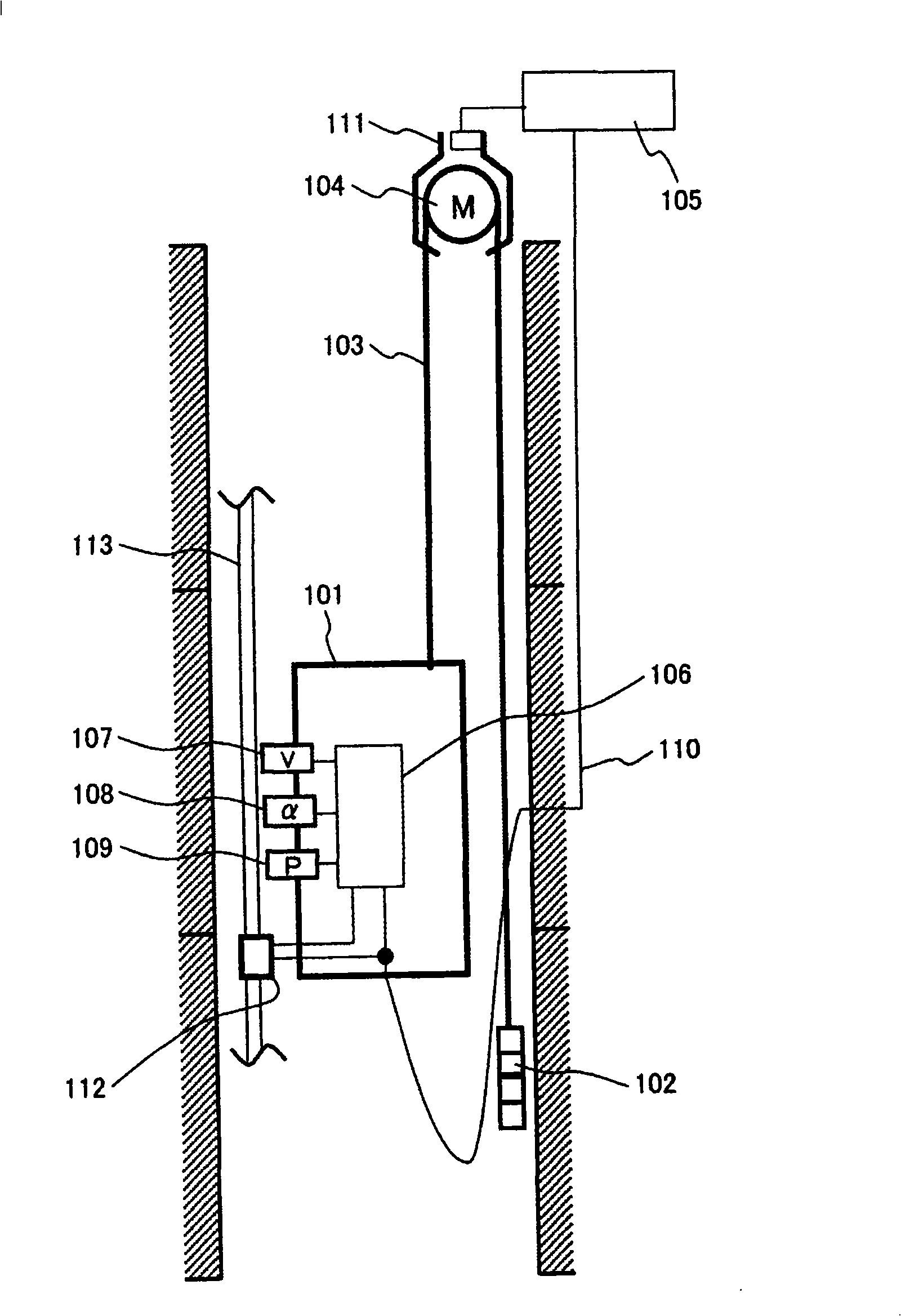
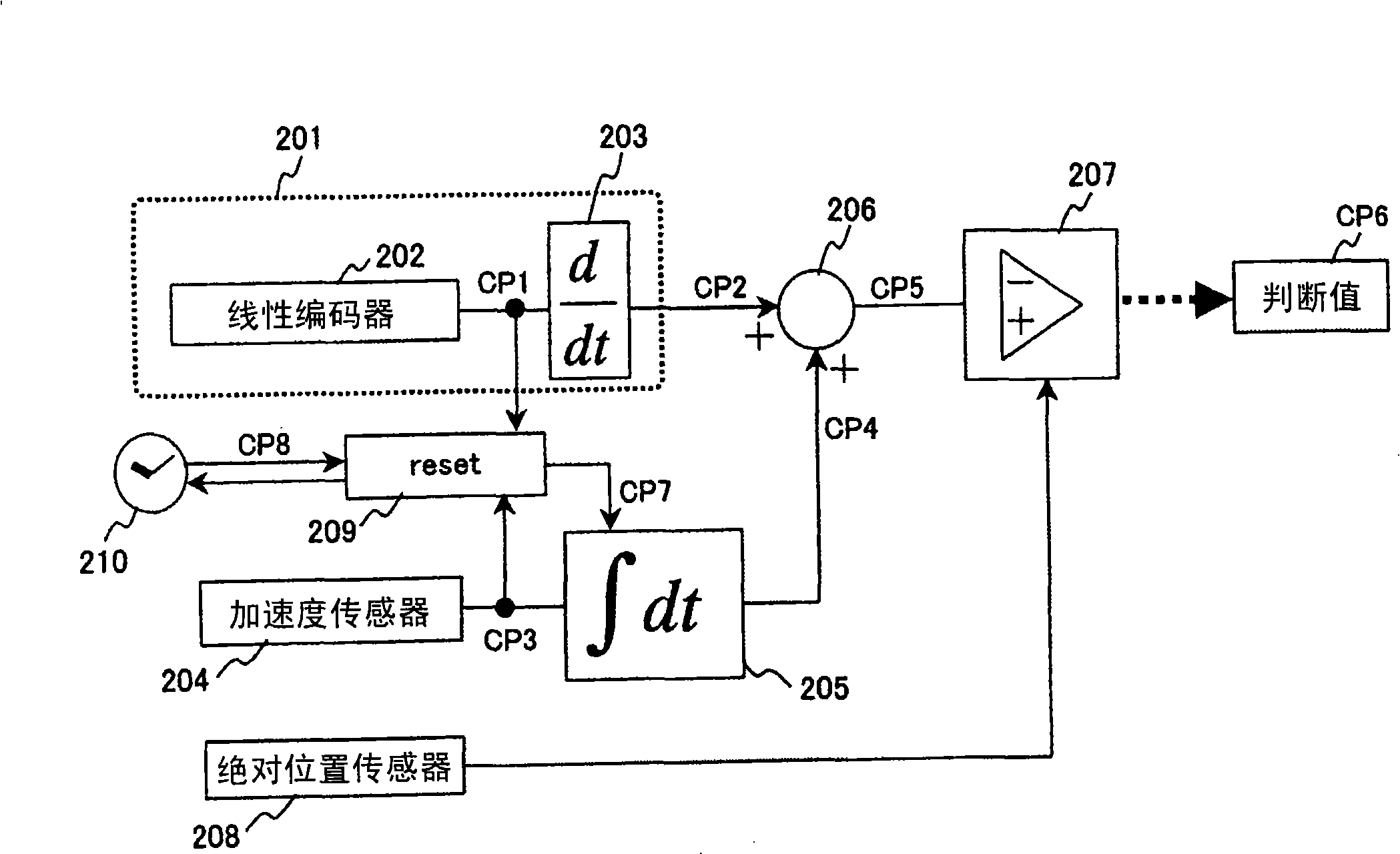
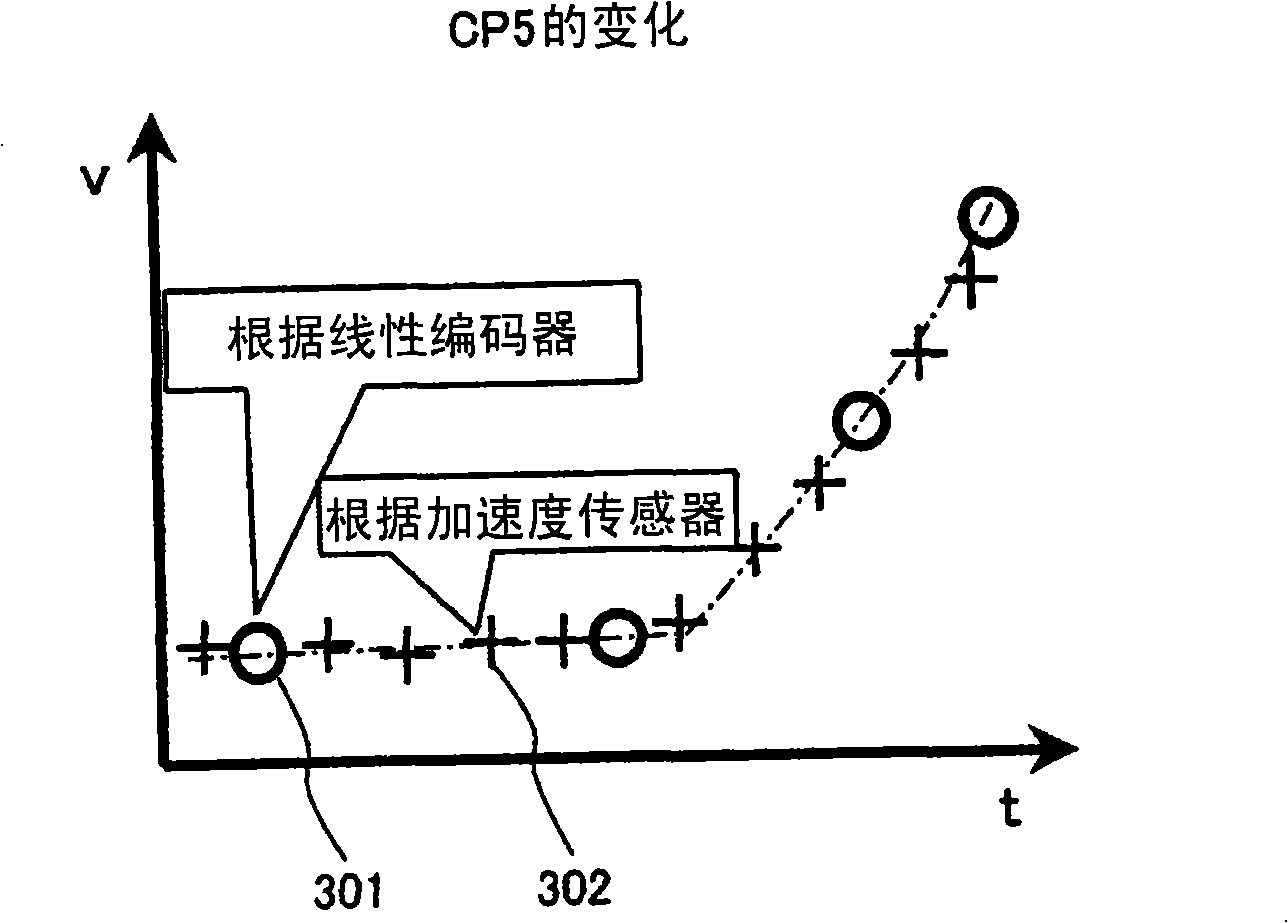
Speed detection method and apparatus of moving body
The invention provides a speed detecting method of a moving body and a device thereof. In the lift using terminal floor reduction device, the device is able to obtain the necessary overspeed detecting response time near the terminal floor by the speed detector equipped in the lift car without using the linear coder having high position resolving capability. The position differential value from the linear coder and the acceleration integral quantity from the acceleration sensor are combined into speed value to carry out the overspeed judgment. The acceleration integral quantity is reset and differed at pulse edge of the linear coder. The necessary response time detecting the overspeed near the terminal floor is improved, and the speed needed by the terminal floor reduction device is accurately processed.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
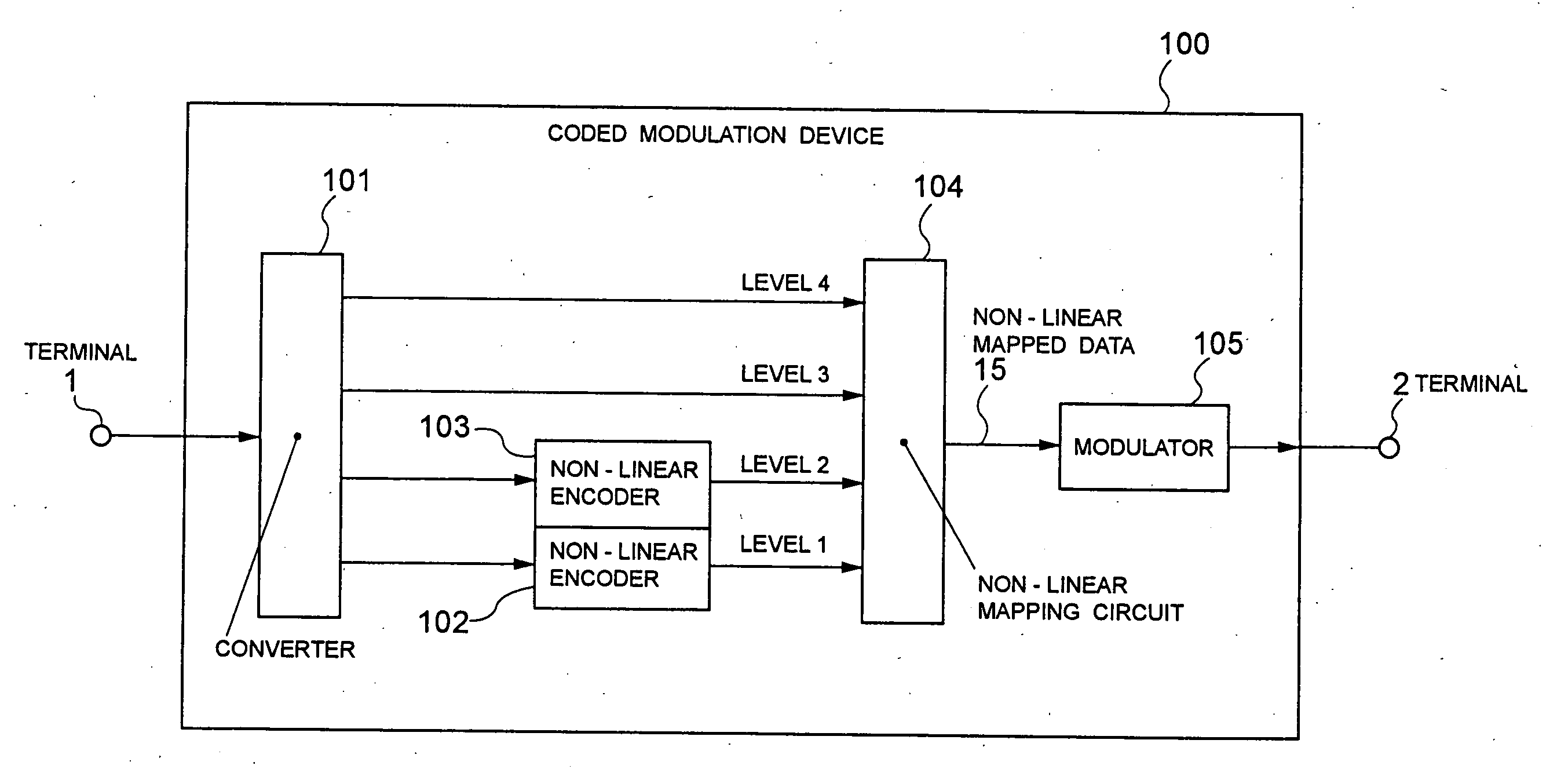
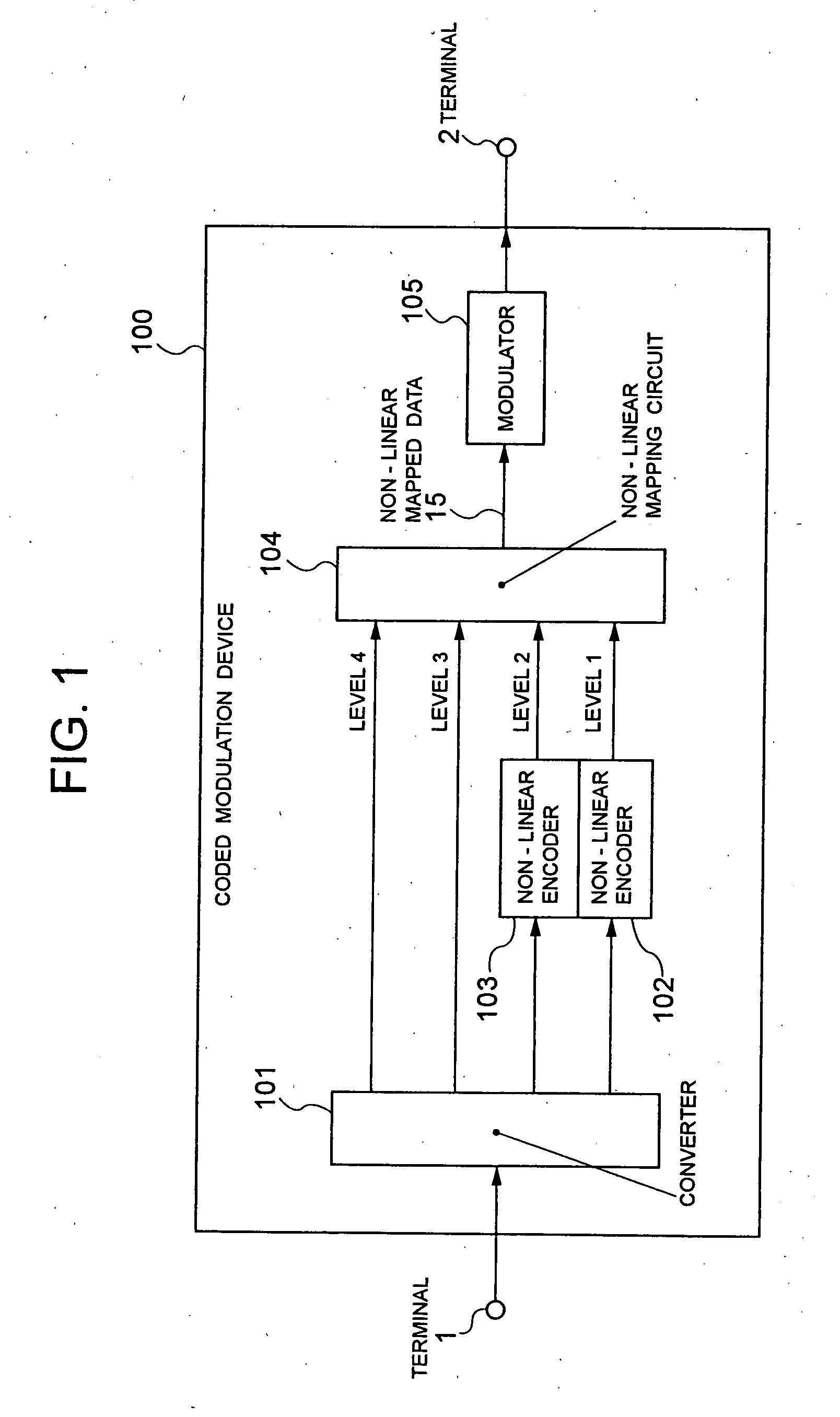
Coded modulation device and method
InactiveUS20050207507A1Higher coding gainError correction/detection using trellis codingPhase-modulated carrier systemsLinear codingCarrier signal
The present invention realizes a high coding gain employing a non-linear coding and a non-linear mapping. A converter converts one row of data that is inputted from a terminal into plural rows of data. The non-linear encoders non-linearly encode-lower level two rows of data in plural rows of converted data, and outputs them as data of level 1 and level 2 to a non-linear mapping circuit. The non-linear mapping circuit maps the data non-linearly encoded by the non-linear encoders and the uncoded data so that each codeword distance may be optimal. A modulator modulates a carrier wave with two-dimensional data that are mapped by the non-linear mapping circuit.
Owner:NEC CORP
Wide range and high precision free curved surface measuring method
The wide range and high precision free curved surface measuring method includes setting the curved surface on one platform capable of shifting precisely in both X and Y directions, integrating laser displacement sensor and grating displacement sensor and linear coder, installing the laser displacement sensor onto one servo mechanism capable of moving in Z direction, obtaining the Z coordinates of the curved surface with the laser displacement sensor and grating displacement sensor and linear coder, and obtaining the X and Y coordinates with the precisely shifting platform. The present invention fuses several sensors, has the features of high efficiency, wide range and high precision in free curved surface measurement, and will find its wide application in manufacture technology.
Owner:NANTONG GUOSHENG INTELLIGENCE TECH GRP CO LTD
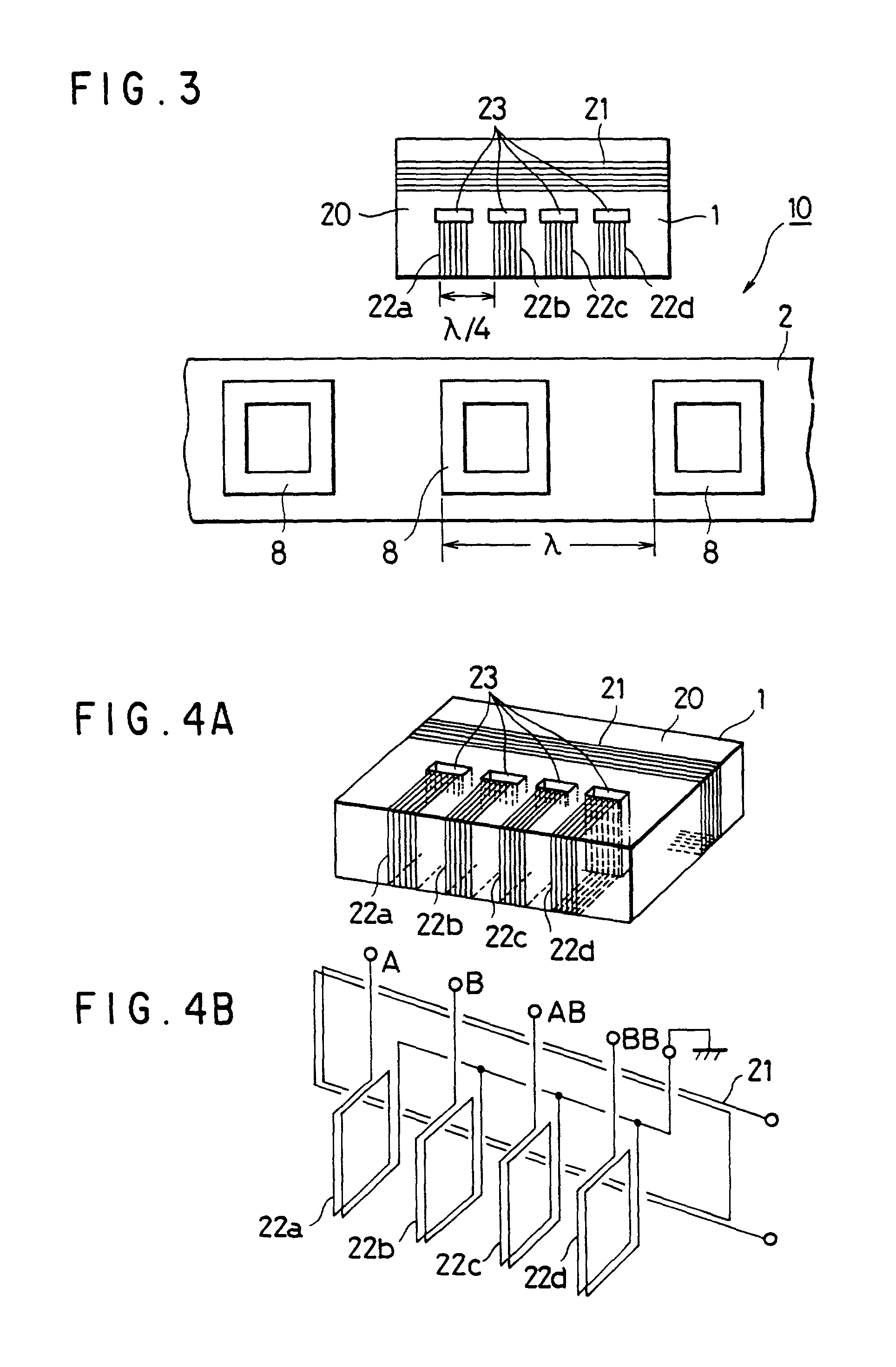
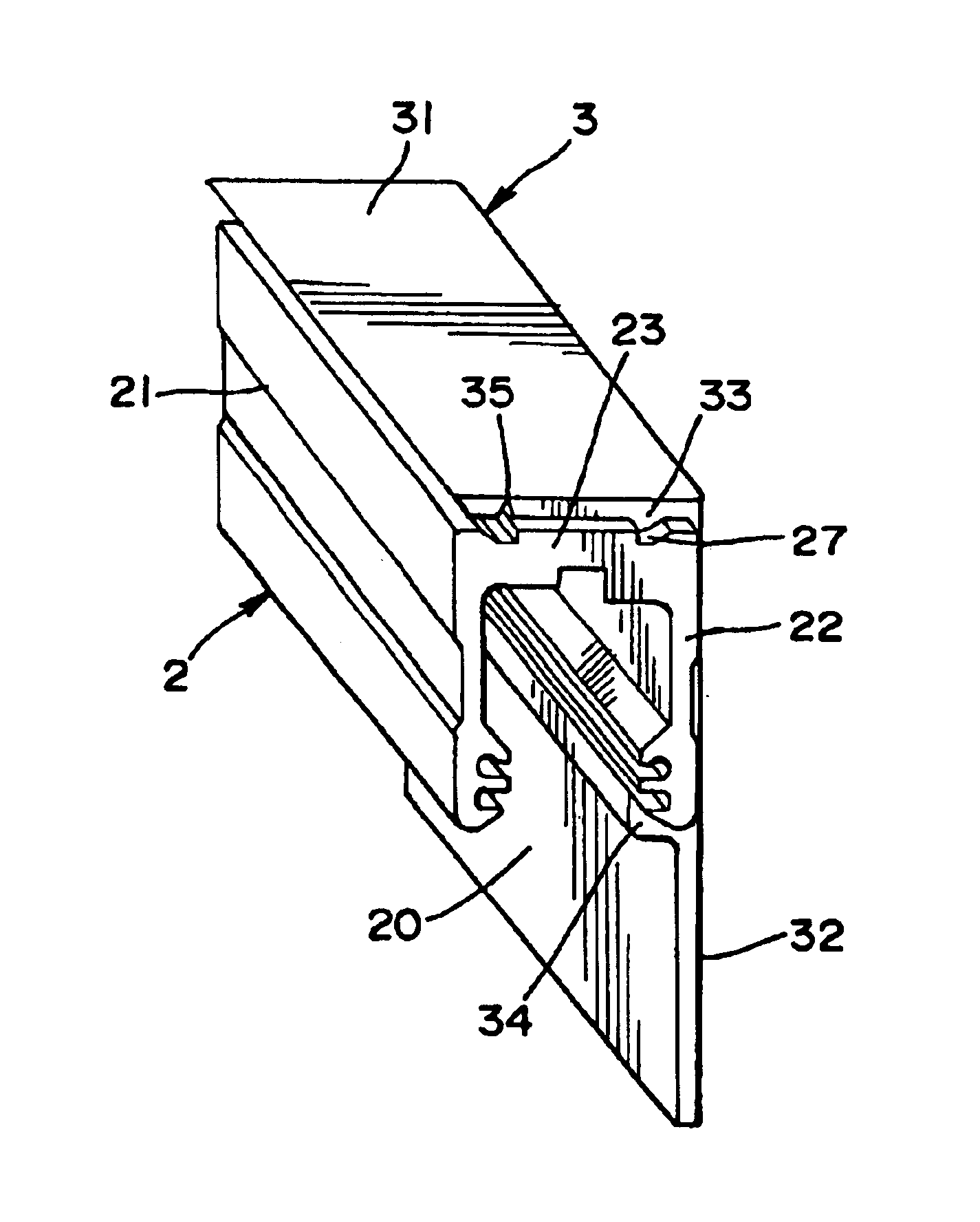
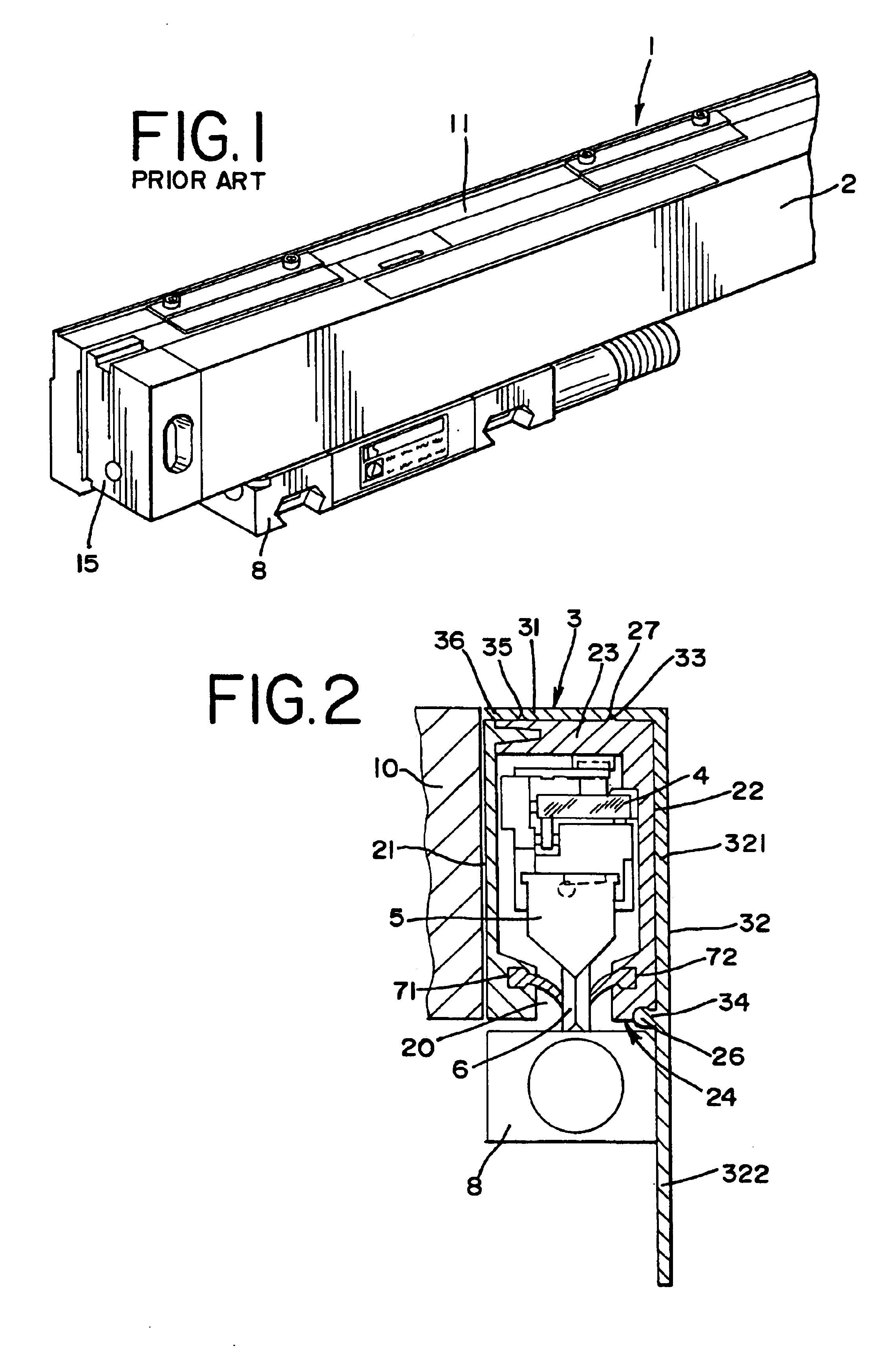
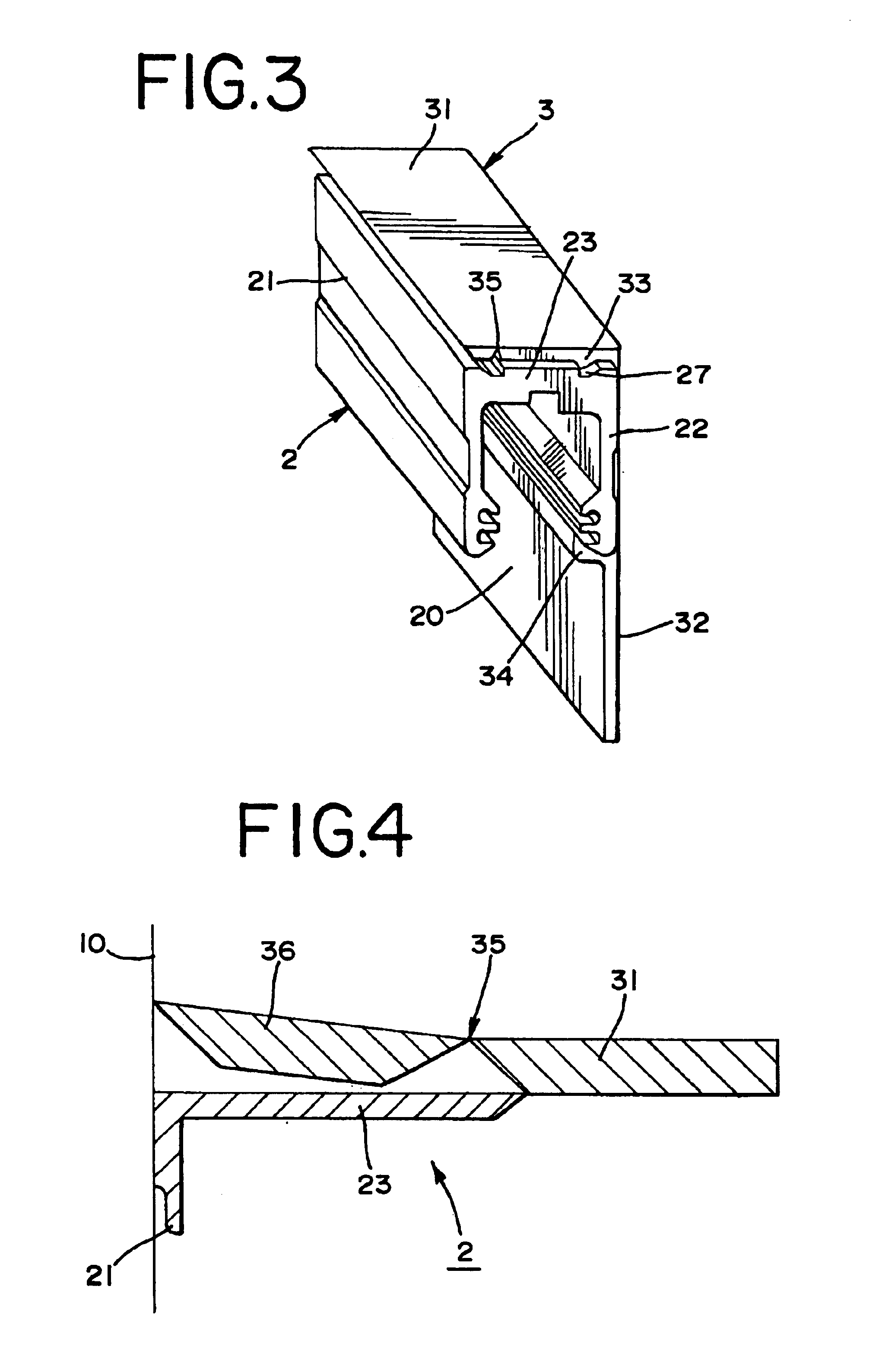
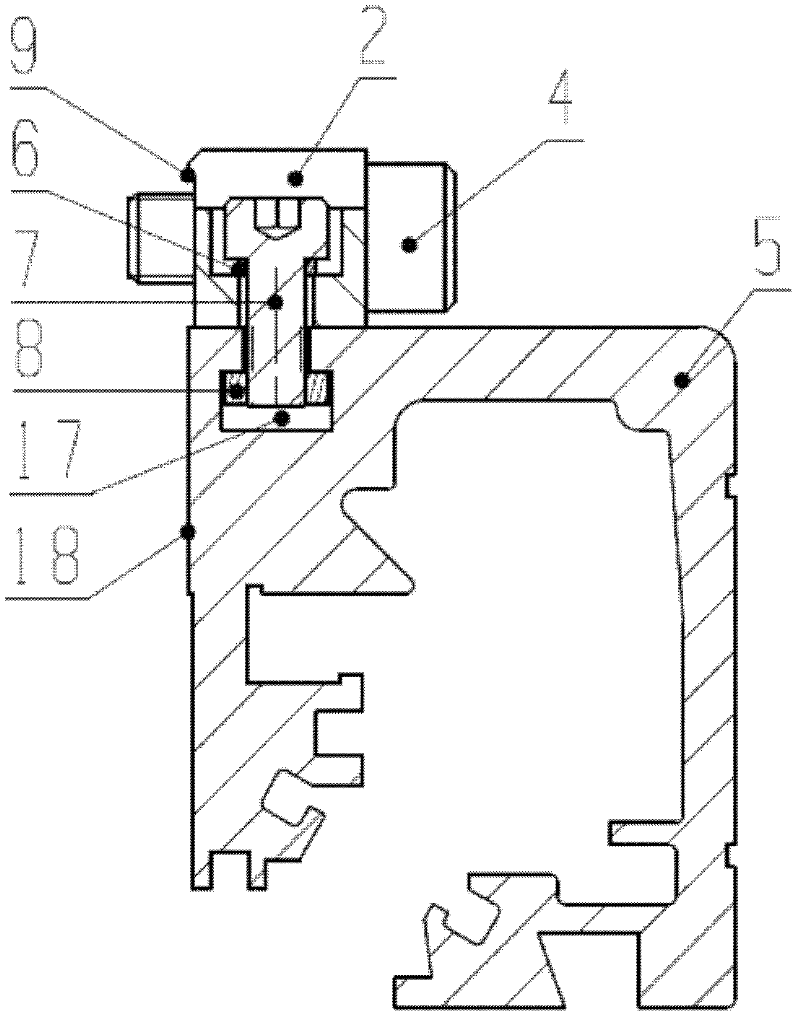
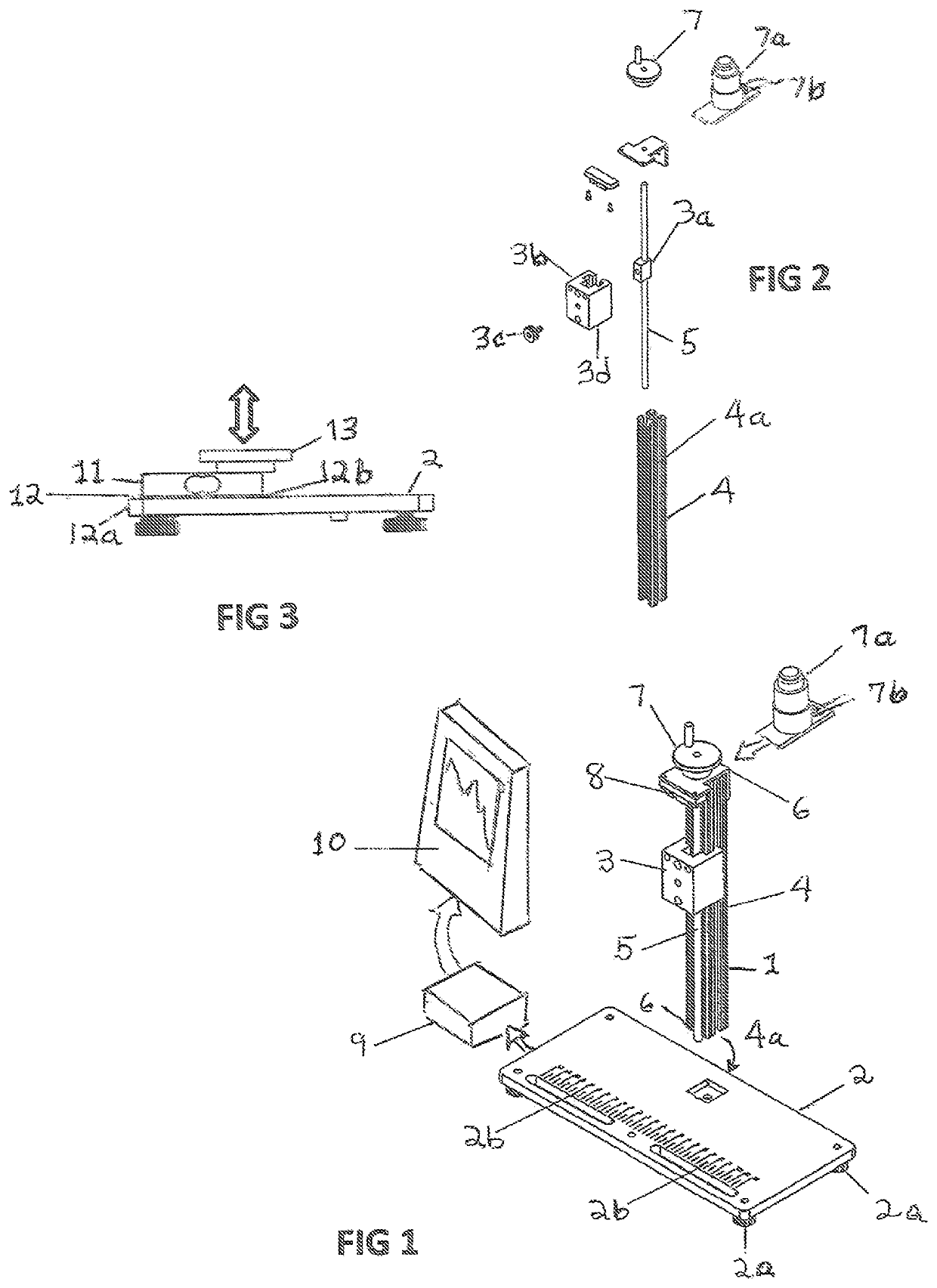
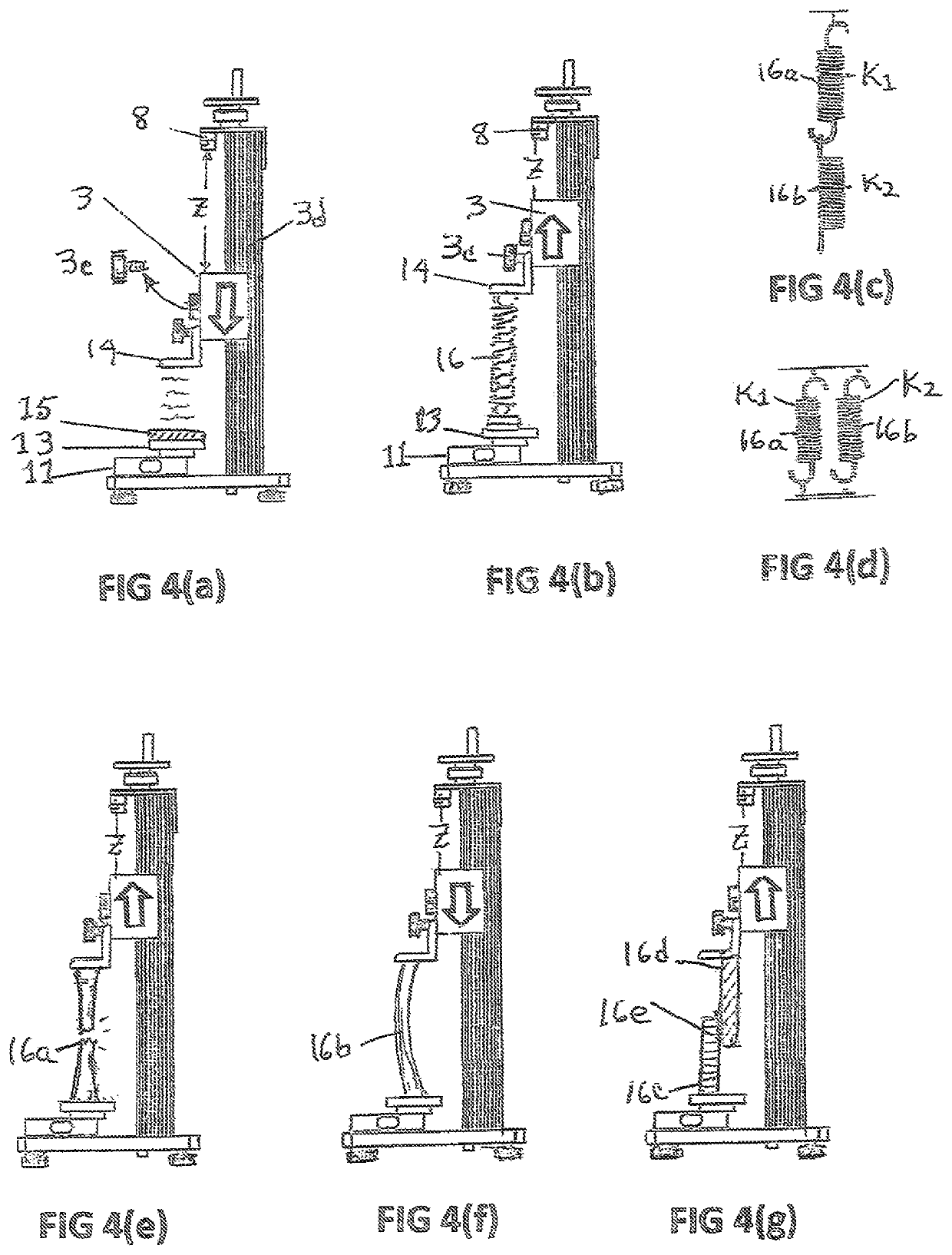
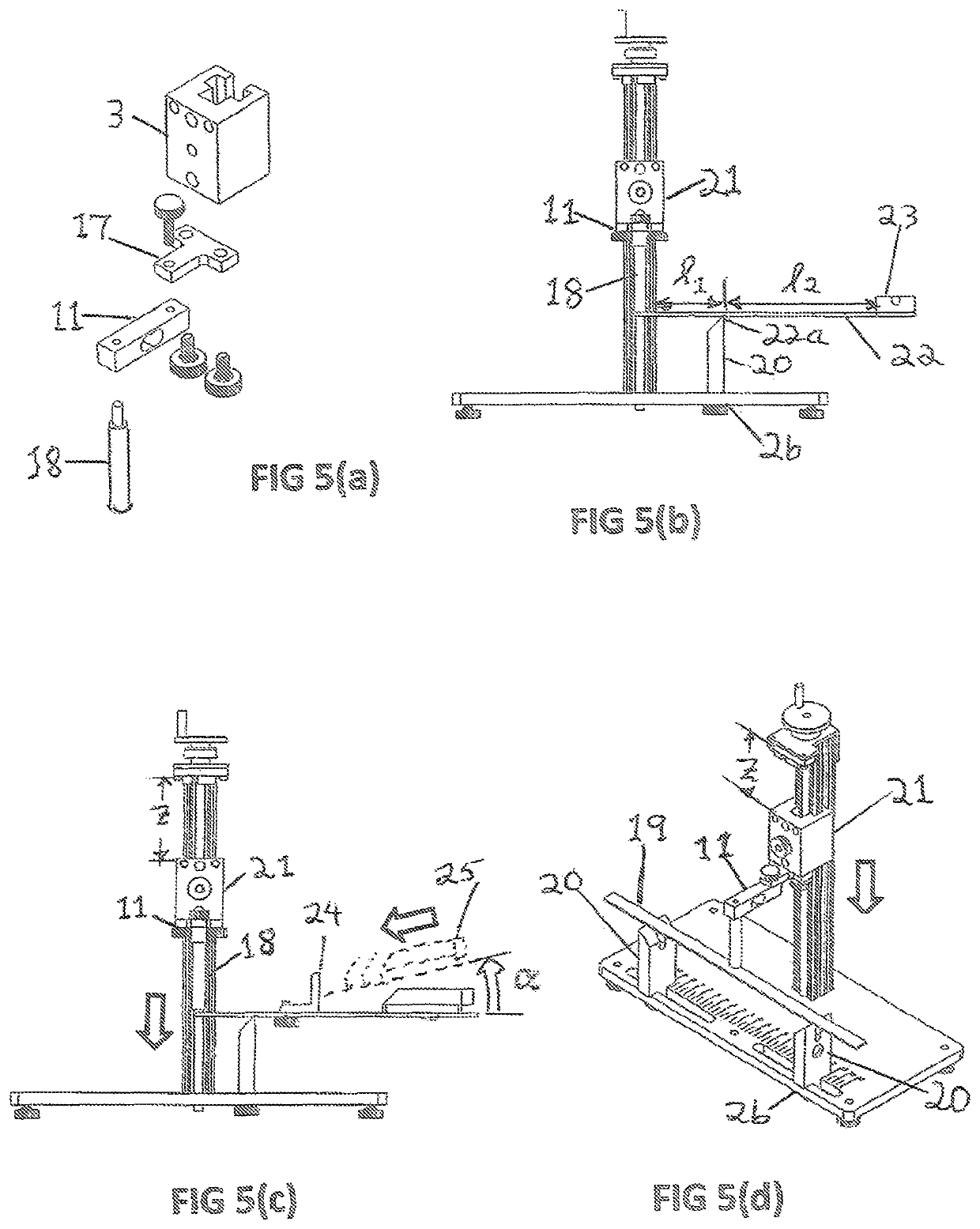
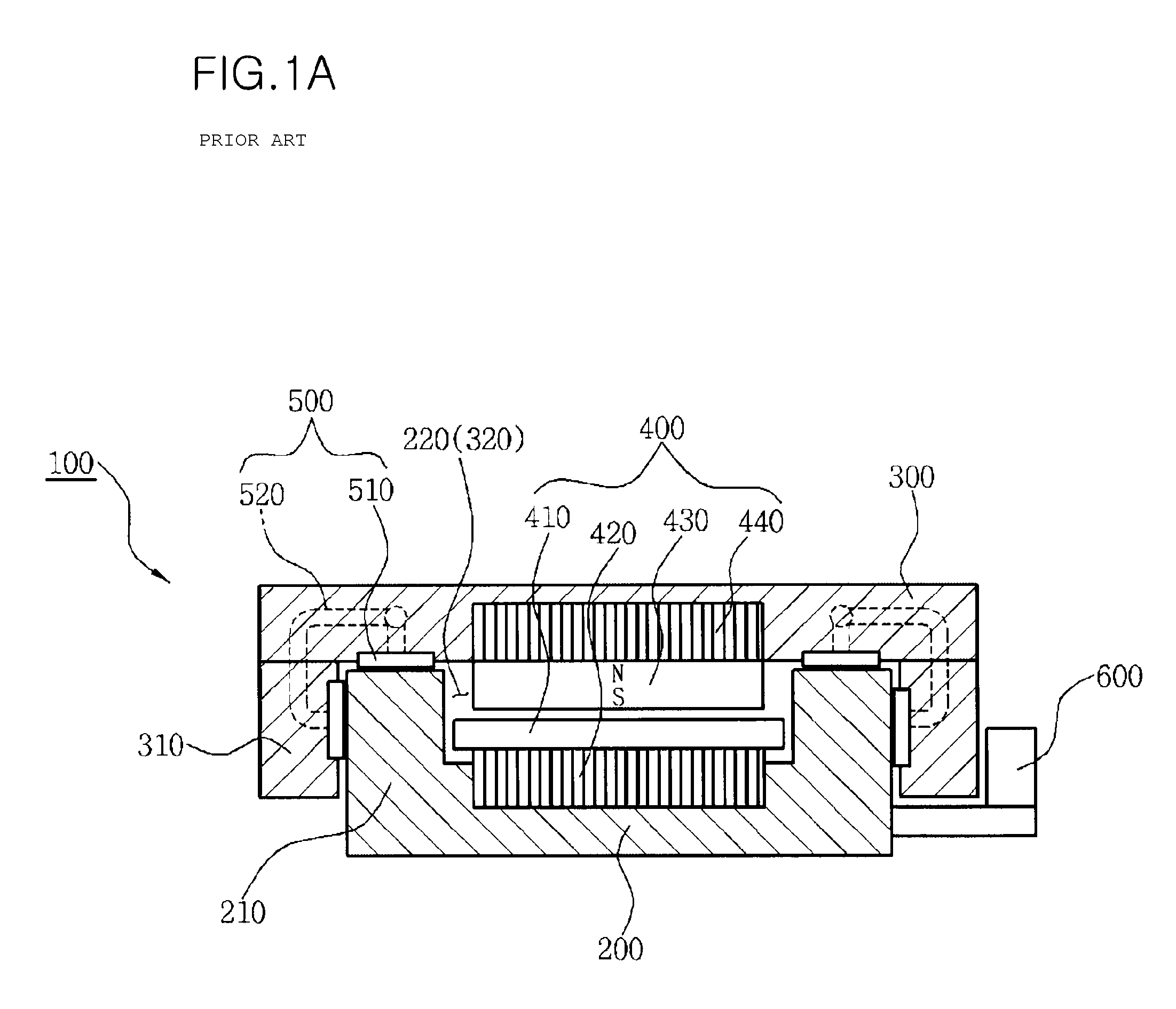
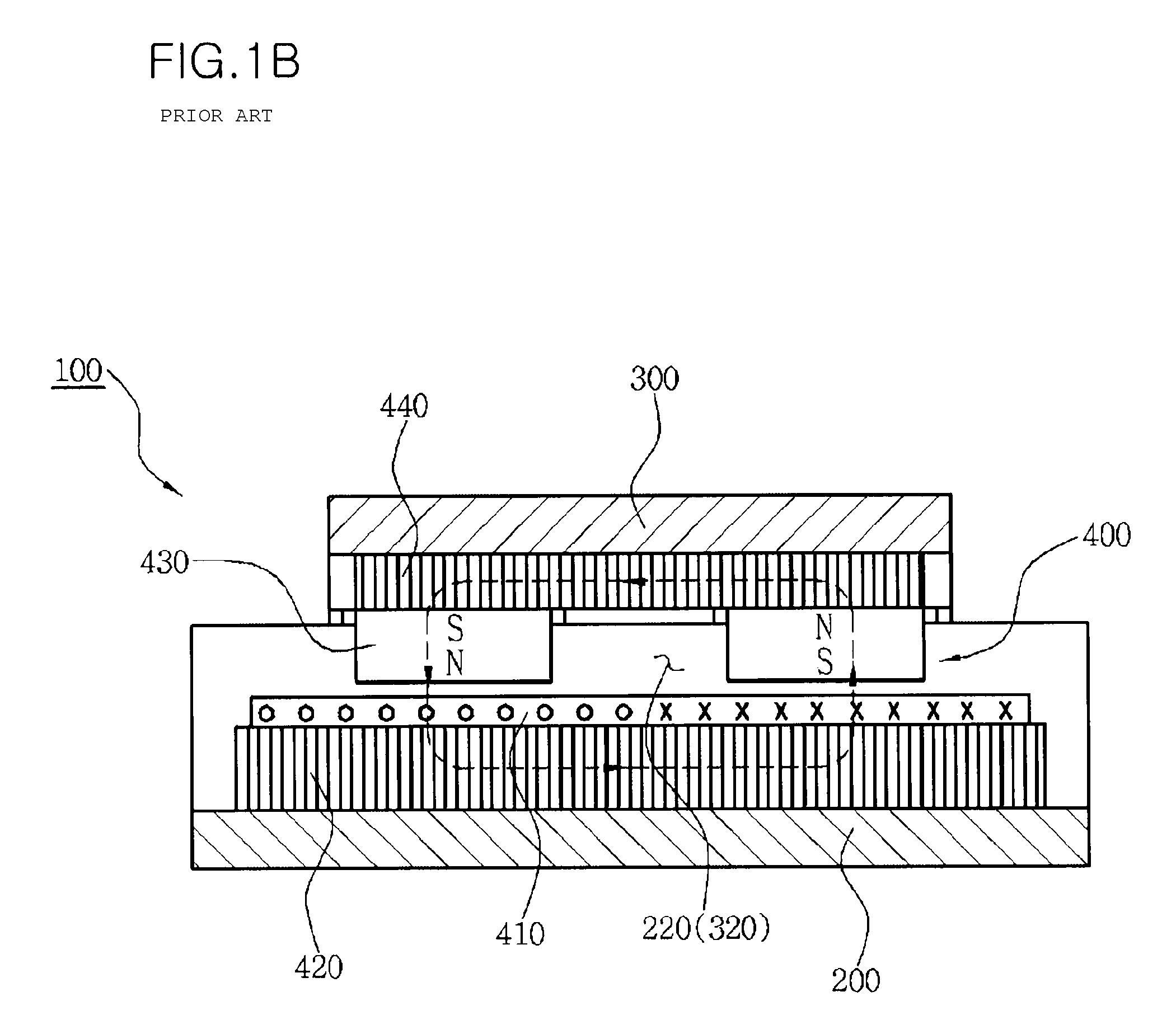
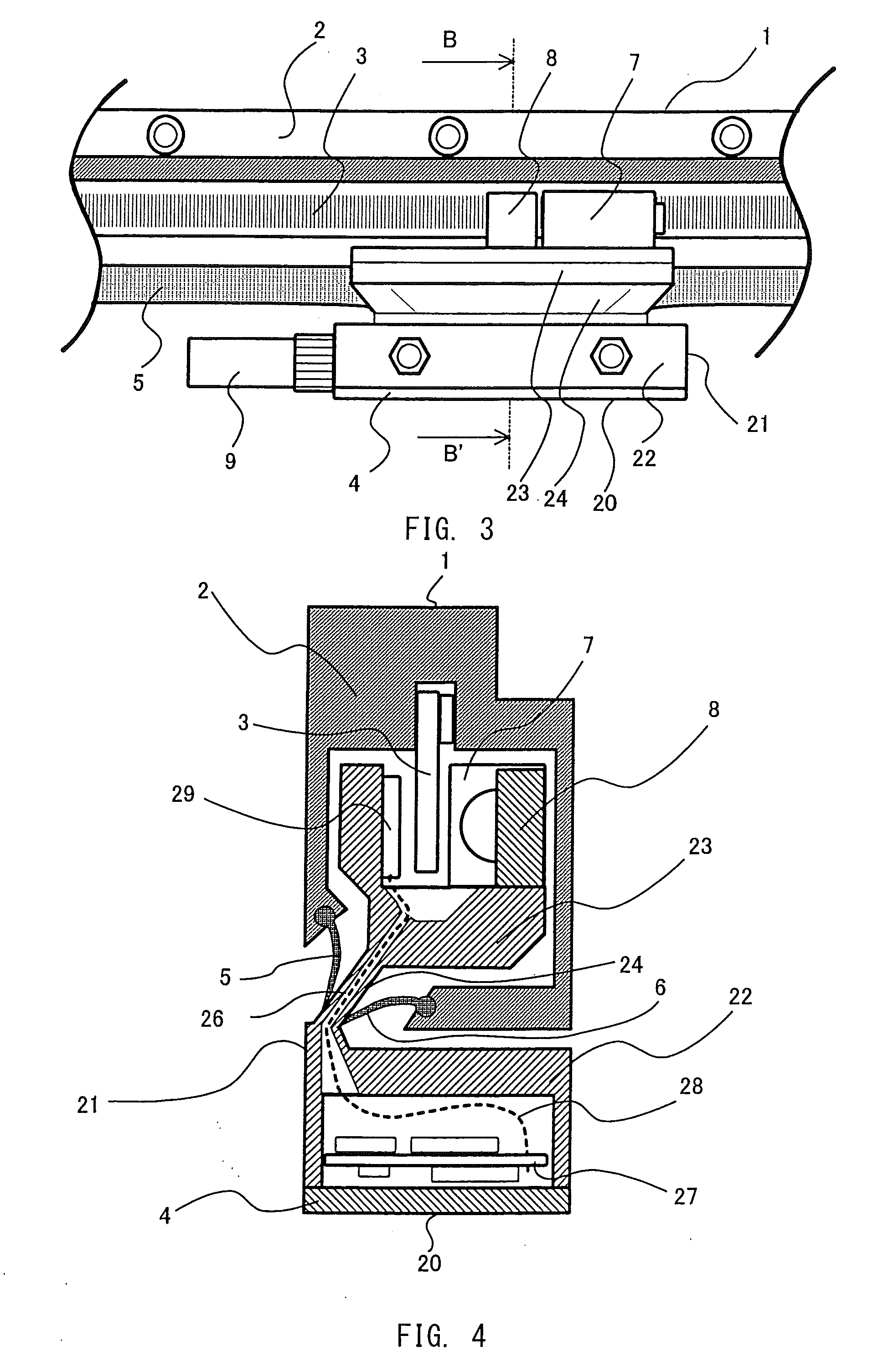
Cover for a sealed linear encoder and a sealed linear encoder
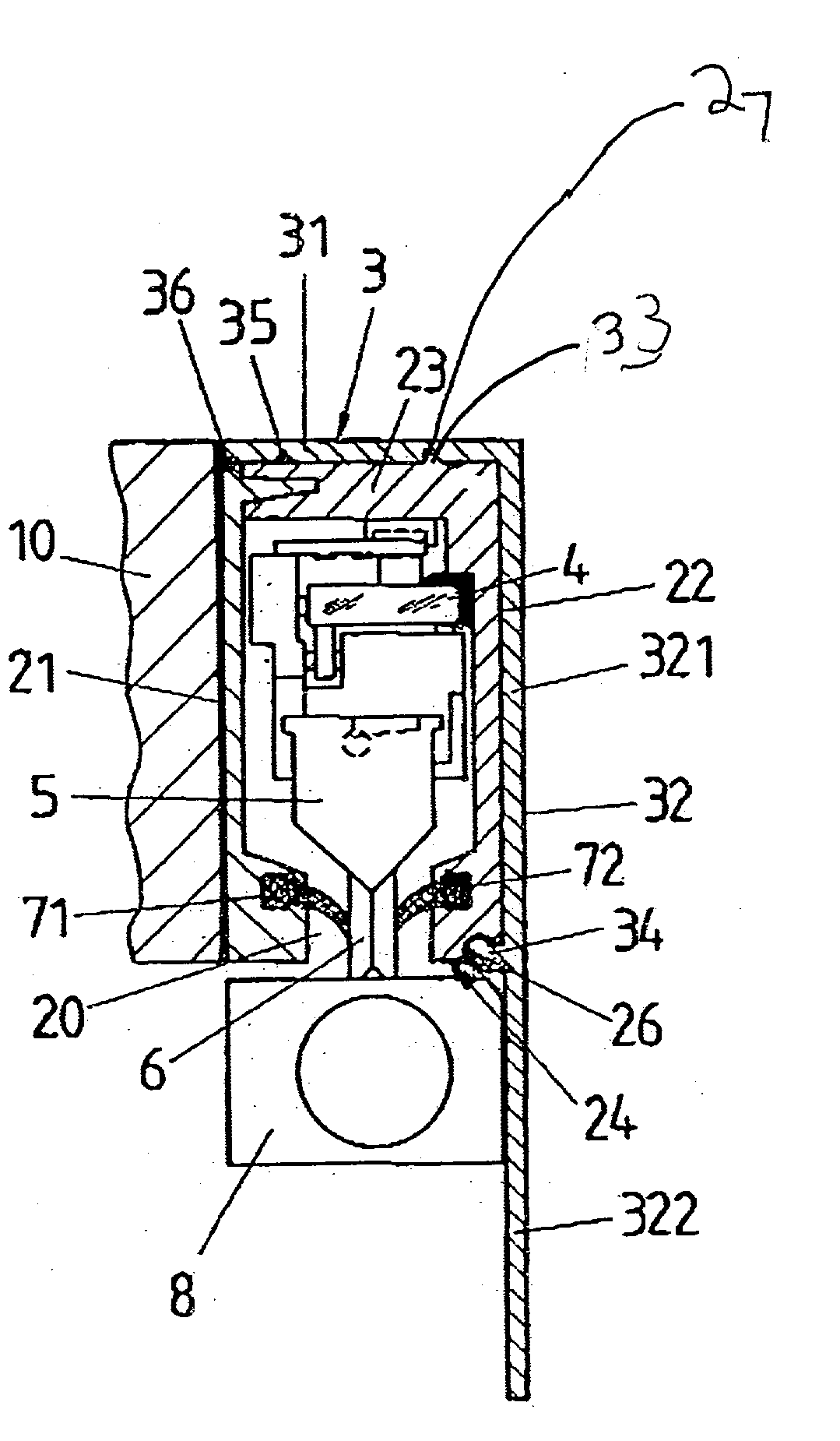
InactiveUS6739067B2Simple to manufacture and to mountEffective protectionWalking sticksUsing mechanical meansScale unitLinear encoder
A sealed linear encoder for determining the relative position of a first object and a second object. The sealed linear encoder includes a scale unit arranged in a hollow body that is mounted to a mounting structure associated with the first object and includes a slot which extends in a direction of measurement. A scanning unit for scanning the scale unit and a carrier connected to the second object, wherein the carrier extends through the slot. Sealing lips arranged at the hollow body and abutting the carrier so as to seal the carrier and a cover form-fitted to the hollow body for covering at least the slot.
Owner:HEIDENHAIN CORP +1
Real-time catheter intervention information measuring device in cardiovascular interventional operation
InactiveCN103239791ARealize information monitoringImprove surgical safetyCatheterDiagnostic recording/measuringGratingAngular degrees
The invention discloses a real-time catheter intervention information measuring device in a cardiovascular interventional operation. The information measuring device comprises a six-dimensional force sensor, a linear encoder and an angle photoelectric encoder. In the operation, a catheter penetrates through the six-dimensional force sensor, and is connected to a force bearing end of the six-dimensional force sensor in a clamping manner through a clamping device; when an operator clamps the catheter to contact with a vessel wall through a clamping shaft, the resistance and the resistance moment between the catheter and the vessel wall can be measured in real time through the six-dimensional force sensor; when the operator operates the catheter to rotate axially through the clamping shaft, the rotary angle can be measured through the angle photoelectric encoder; and when the operator operates the catheter to move forwards or backwards through the clamping shaft, the number of grating pulse is counted by a reading head to measure the displacement in real time. By the information measuring device, information monitoring during the operation can be realized, safety of the operation can be improved, and quantitative data are provided for evaluating a virtual operation training system.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Tracking auto focus system
InactiveUS7301133B2Eliminate timeFocusBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsOptically investigating flaws/contaminationAudio power amplifierLinear encoder
A tracking auto-focus system maintains a microscope pointed at a TFT array continuously in focus so as to eliminate the auto-focusing time that would otherwise be required. The tracking auto-focus system includes, in part, a microscope Z actuator, an auto-focus sensor, an analog-to-digital converter (ADC), a signal conditioner, a digital proportional integrating and differentiating (PID) controller, and a digital-to-analog converter. The actuator adjusts the distance between the microscope's objective lens and the target and includes, in part, an amplifier, a linear motor, and a linear encoder which provides positional feedback. The auto-focus sensor together with the ADC and signal conditioner continuously monitor and detect the distance between the microscope's objective lens and the target and supply the measured distance to the amplifier. The PID controller together with the DAC stabilizes the distance separating the microscope's objective lens and the target to maintain the best focus.
Owner:PHOTON DYNAMICS
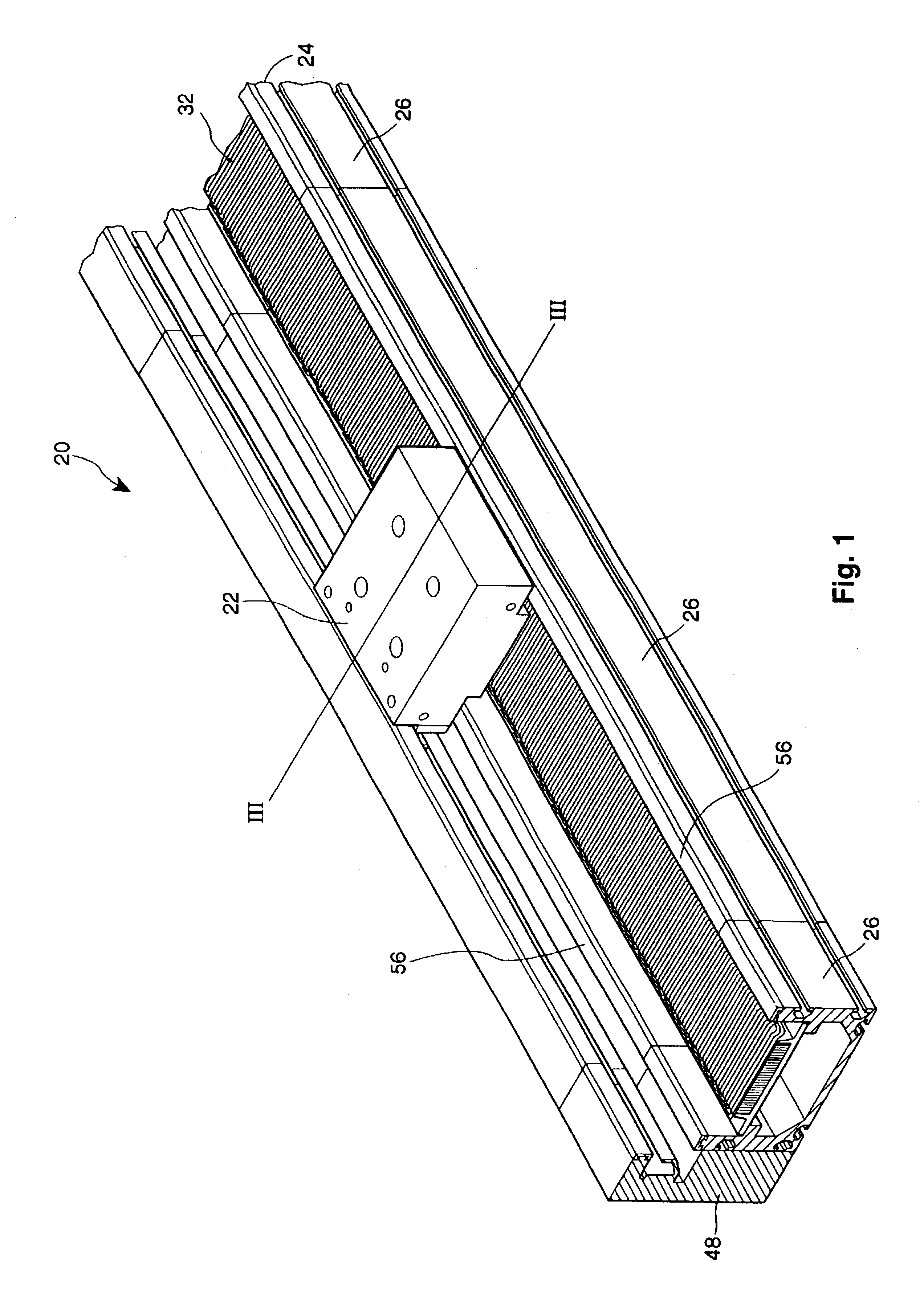
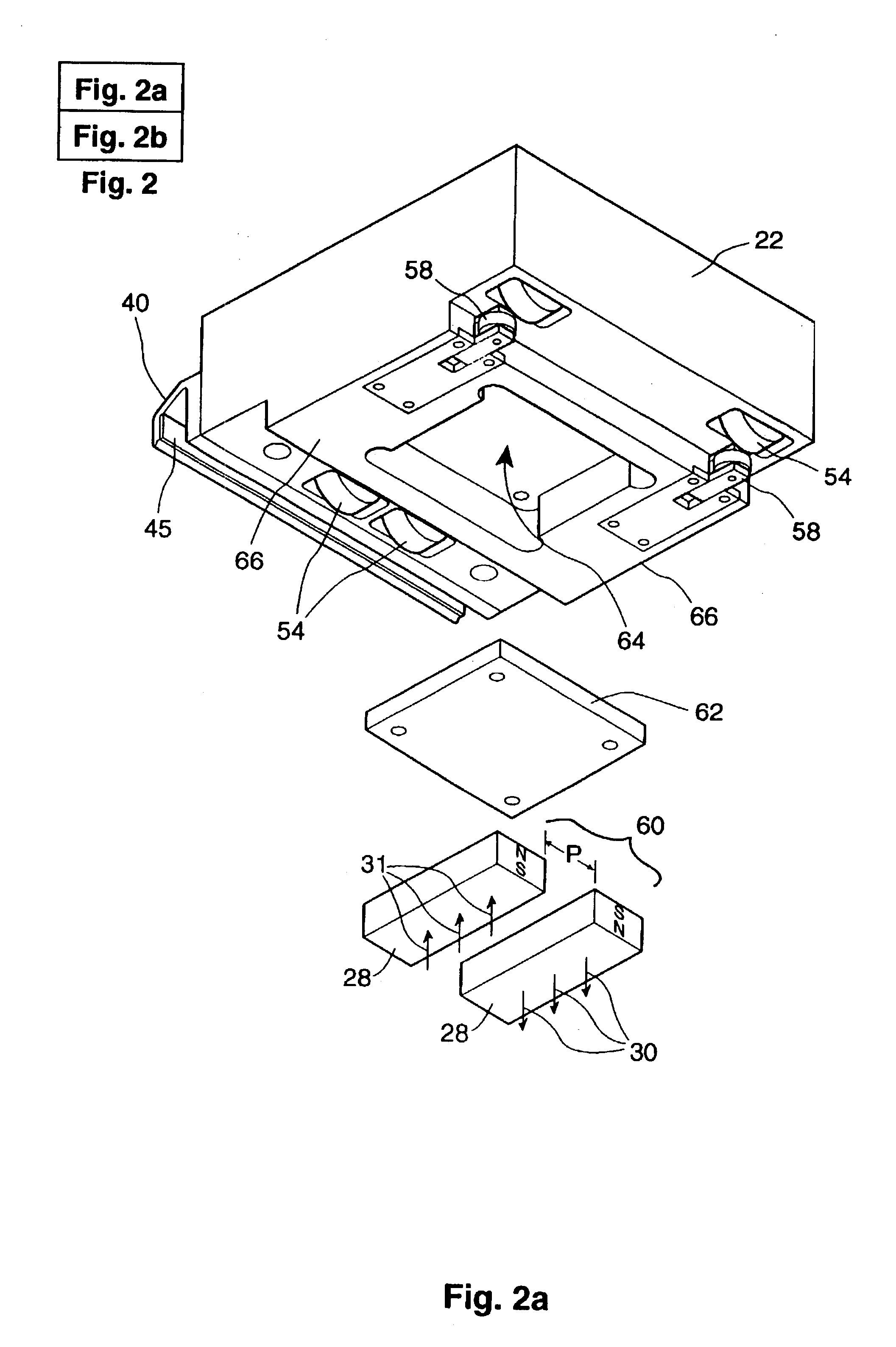
Linear motor
InactiveUS6441515B1Easy to manageAccurate detectionStructural associationPropulsion systemsEngineeringLinear encoder
A linear motor includes a frame linearly extending in a longitudinal direction and having a channel-shaped cross section. The frame has sidewalls and a bottom wall that define a channel. A core is disposed on each of the side walls of the frame. An armature-side block is disposed in the channel of the frame. The armature-side block has a plurality of armatures, each of the armatures having two end surfaces at positions opposing to the cores provided on the side walls of the frame. One linear guide is disposed between the frame and the armature-side block. The linear guide has a rail fixed to the bottom wall of the frame and a slide block fixed to the armature-side block, such that one of the frame and the armature-side block is linearly movable relative to the other. A linear encoder having a linear scale and a sensor spaced a distance from the linear scale are disposed within the channel of the frame.
Owner:SANKYO SEIKI MFG CO LTD
Method of Setting the Origin of a Linear Motor
InactiveUS20080265826A1Motor/generator/converter stoppersDC motor speed/torque controlLinear motorMagnetic characteristic
A movable member is moved in a preset direction in a linear motor. A characteristic-change position-detecting unit detects a position where the magnetic characteristic of the magnets has abruptly changed. The position detected is used as an origin-setting reference position. A reference position for the absolute position of the magnetic linear encoder is set based on the reference position.
Owner:WAKO GIKEN
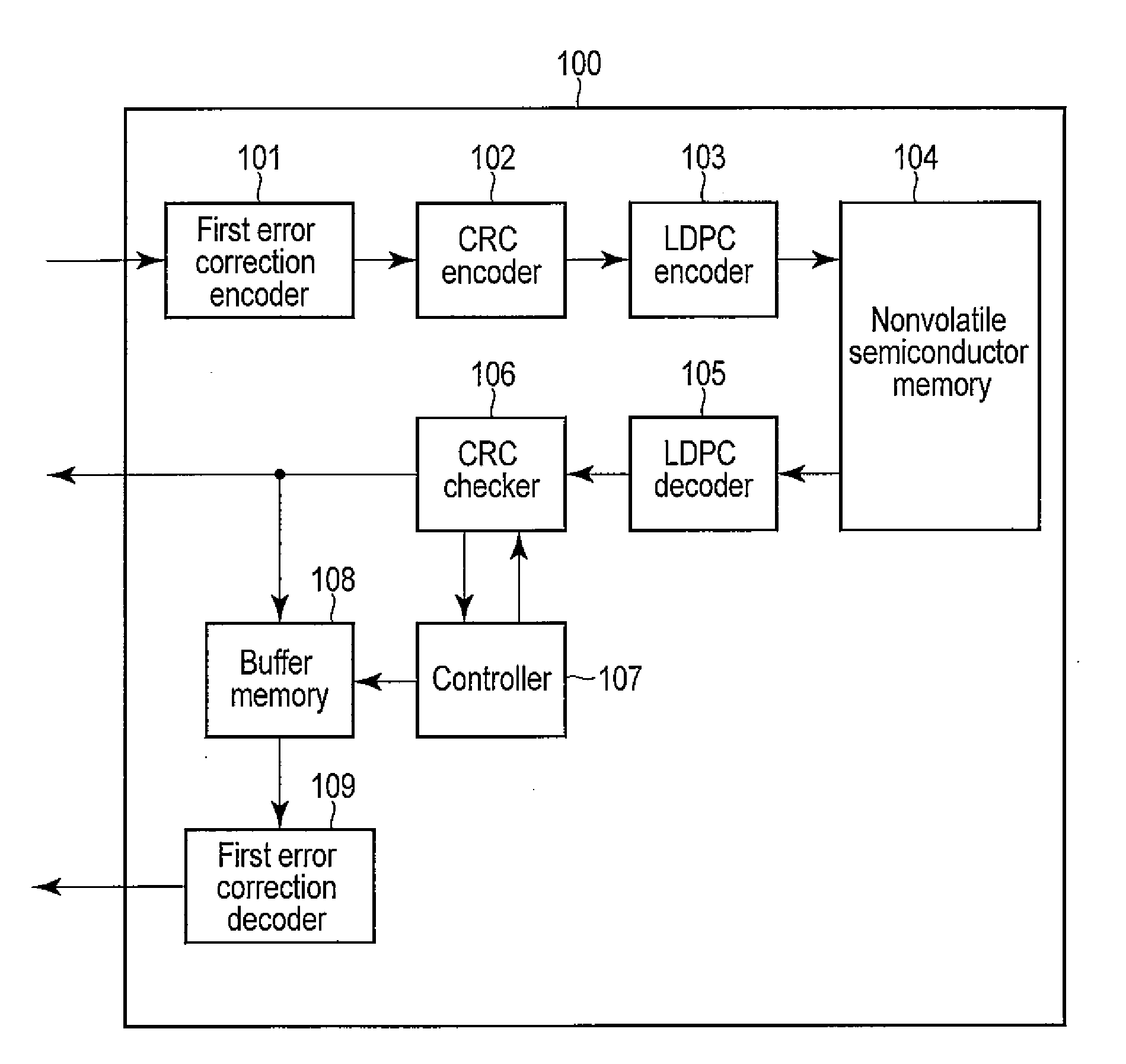
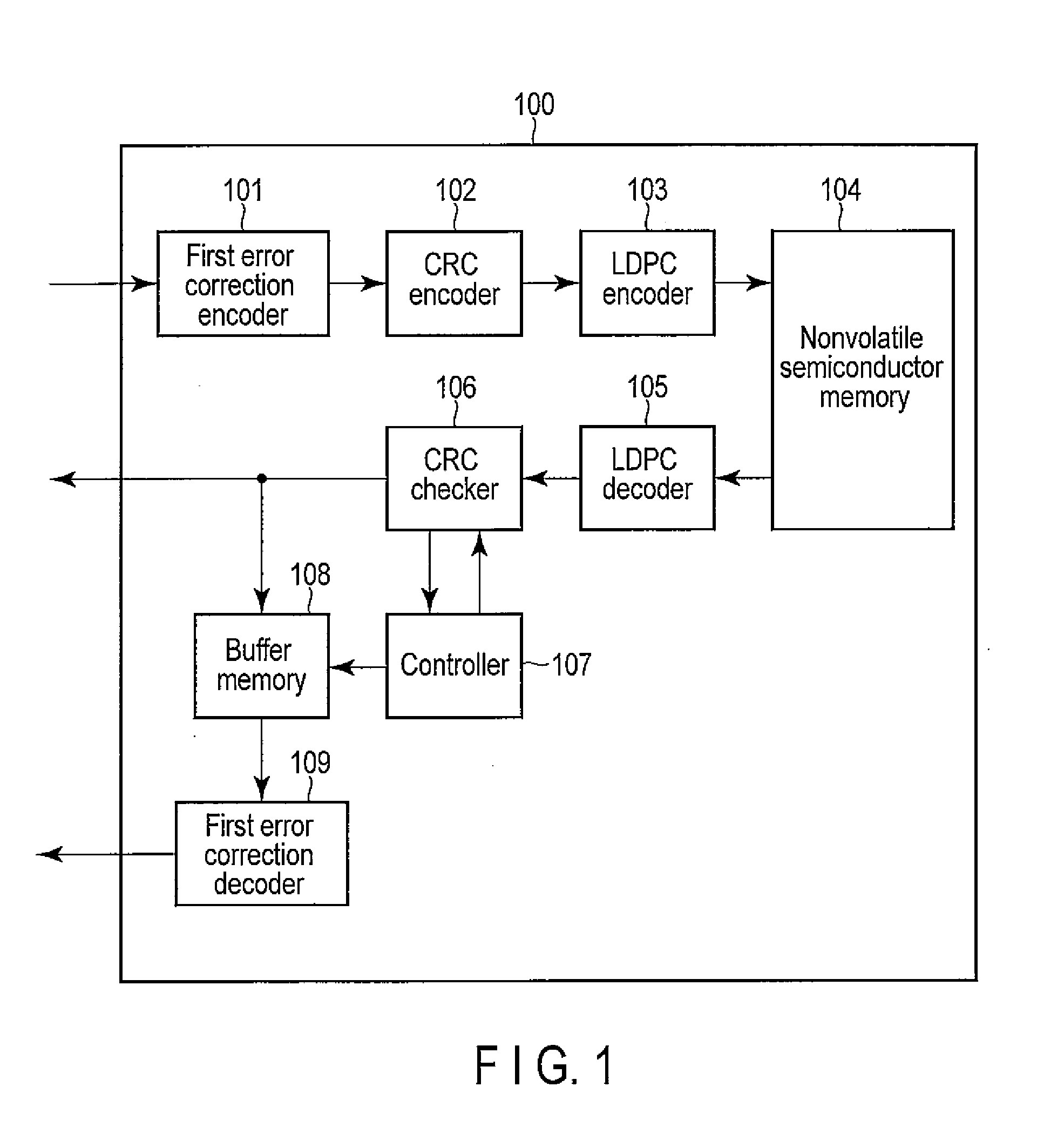
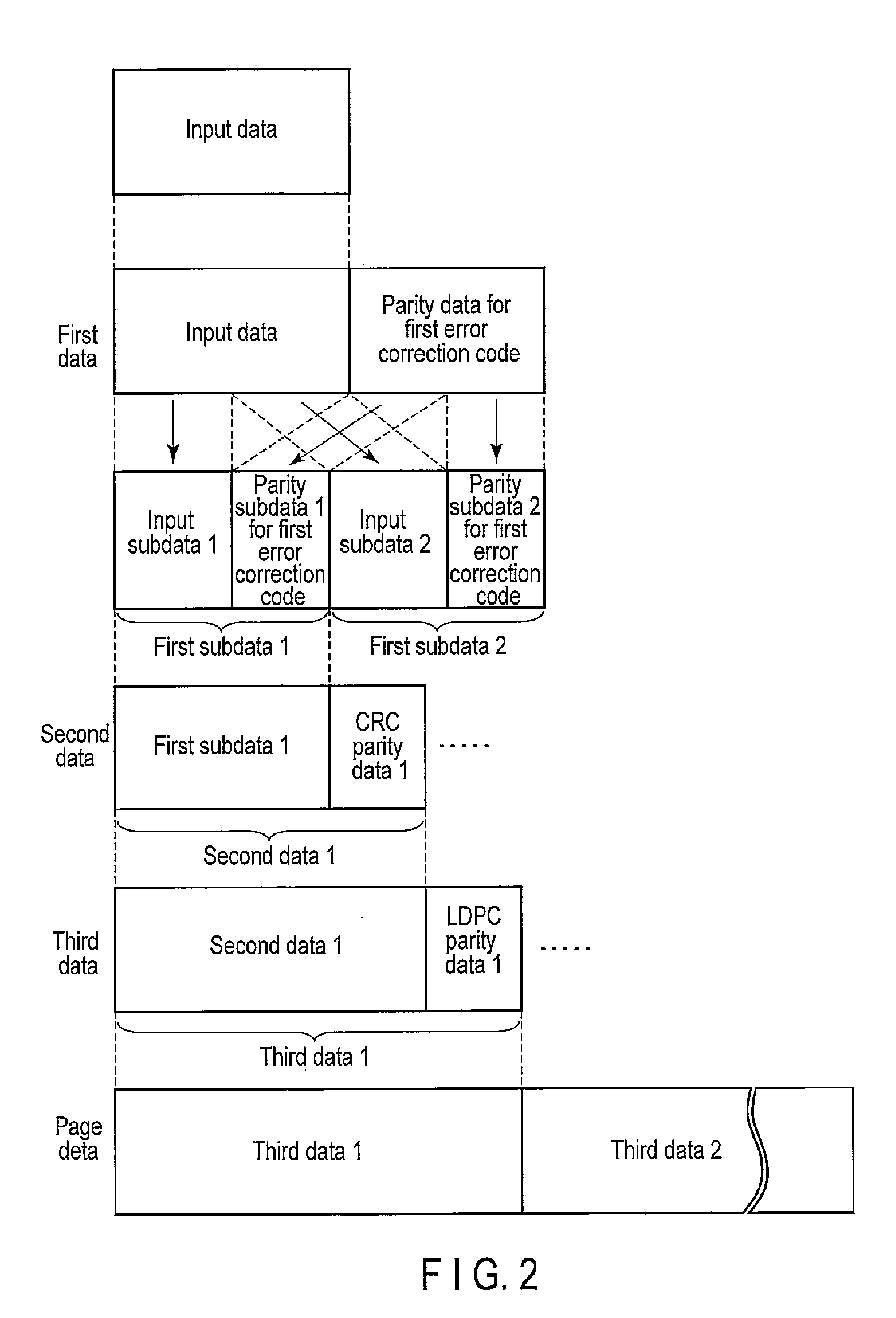
Error correction encoding apparatus, error correction decoding apparatus, nonvolatile semiconductor memory system, and parity check matrix generation method
ActiveUS20130055050A1Code conversionChecking code calculationsLinear codingTheoretical computer science
According to one embodiment, an error correction encoding apparatus includes a linear encoder and a low-density parity check (LDPC) encoder. The linear encoder supports a linear coding scheme enabling a parity check to be carried out by a division using a generating polynomial and applies the generating polynomial to input data to obtain linear coded data. The LDPC encoder applies a generator matrix corresponding to a parity check matrix for an LDPC code to the linear coded data to obtain output data. The parity check matrix satisfies Expression (1) shown in the specification.
Owner:KIOXIA CORP
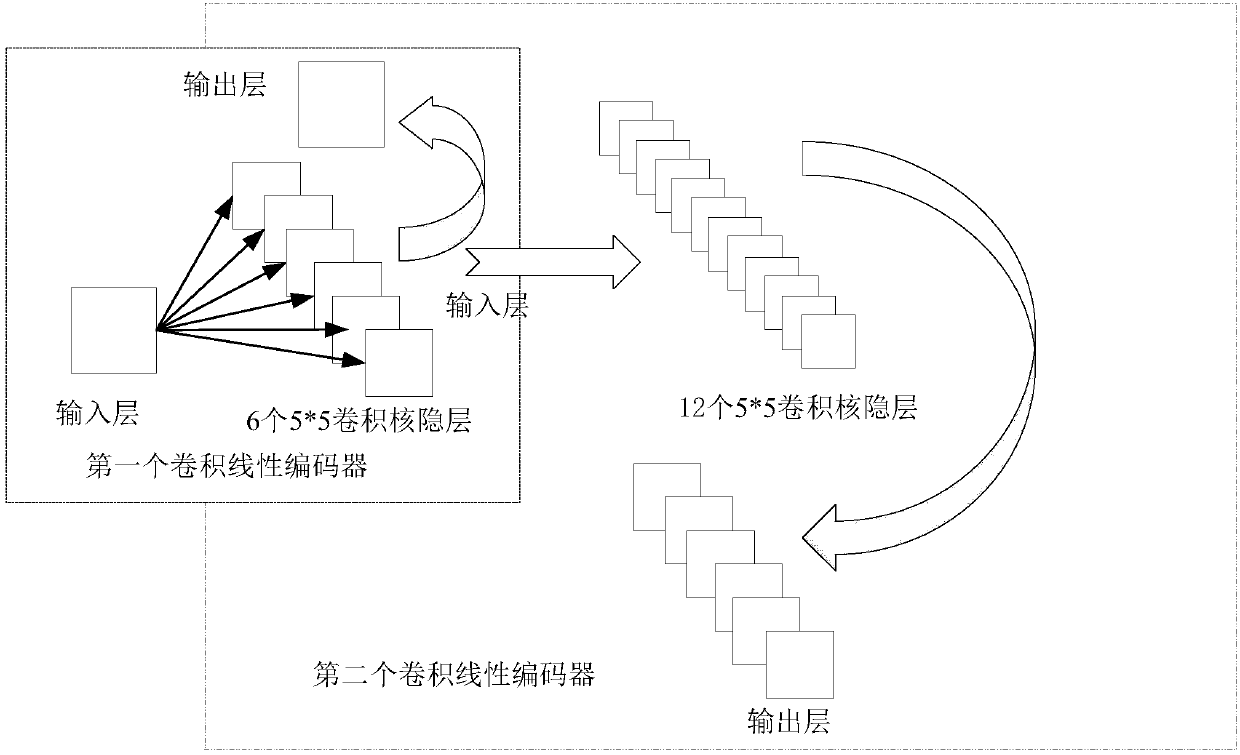
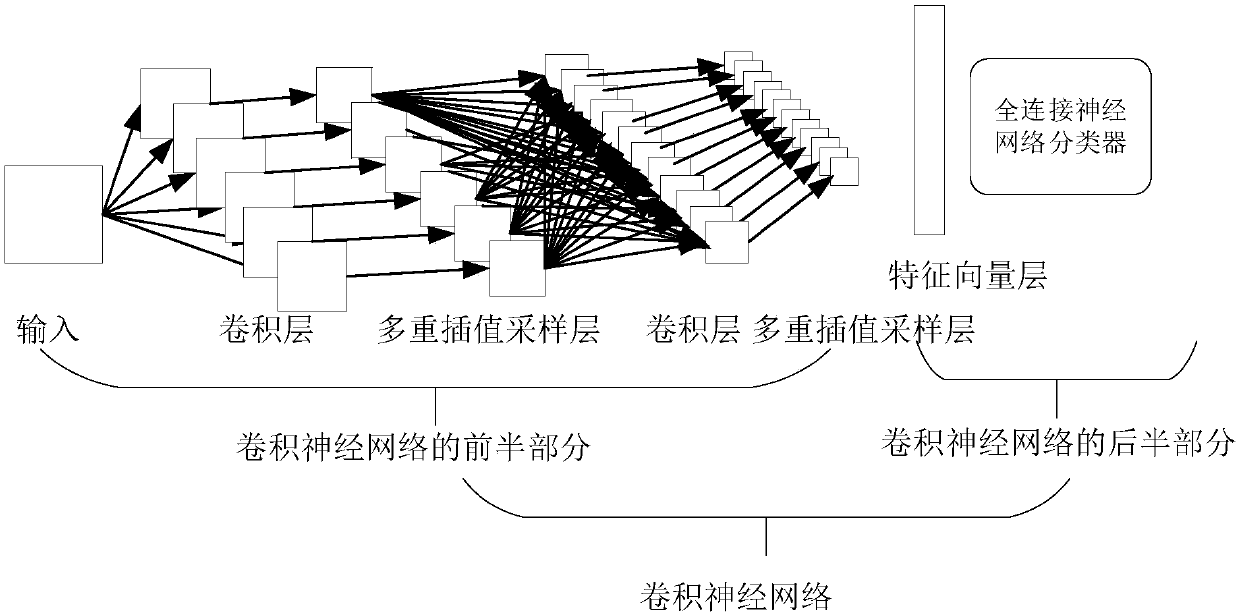
Method for optimizing convolutional neural network based on linear decoder and interpolation sampling
ActiveCN107609638AFast convergenceHigh precisionGeometric image transformationCharacter and pattern recognitionAcquired characteristicForward propagation
The invention belongs to the field of image recognition, and particularly relates to a method for optimizing a convolutional neural network based on a linear decoder and interpolation sampling. The constructed convolutional neural network comprises an input layer, a convolution layer, a pooling layer, a full-connection network layer and an output layer. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, training with a convolution linear encoder to obtain a weight value, and taking the weight value as an initial value of the convolution neural network, then performing multi-interpolation sampling and pooling on the characteristic pattern obtained by the convolution layer, and through the forward propagation and reverse adjustment, finally obtaining the local gradient of each neuron in eachlayer and the weight value of the convolution kernel of each convolution layer. Through the comparison with an existing method, the experiment result shows that when the convolutional neural networkconstructed by the method is used for classifying images, the convolutional neural network has the advantages of being higher in convergence speed and higher in accuracy.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV OF TECH
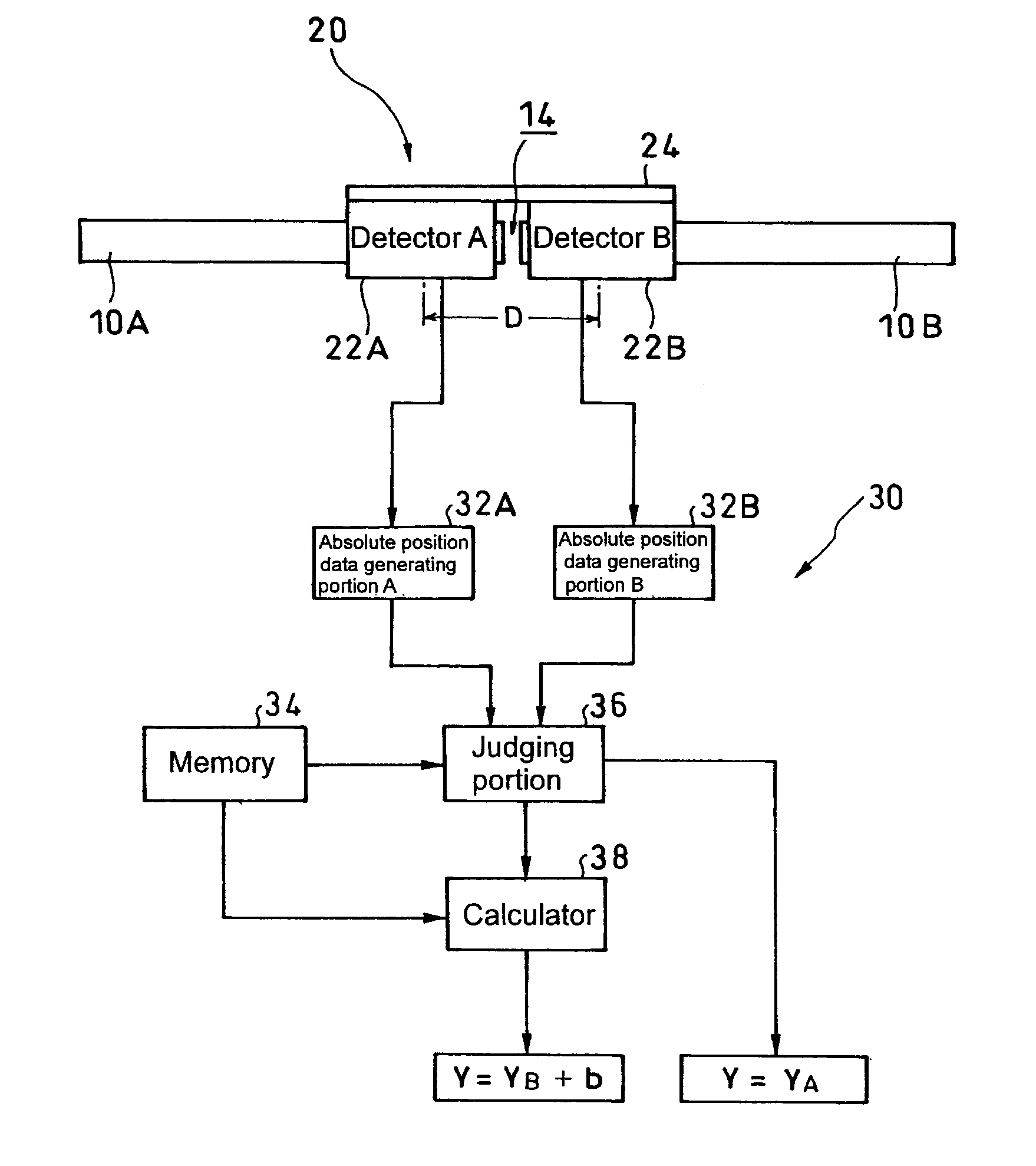
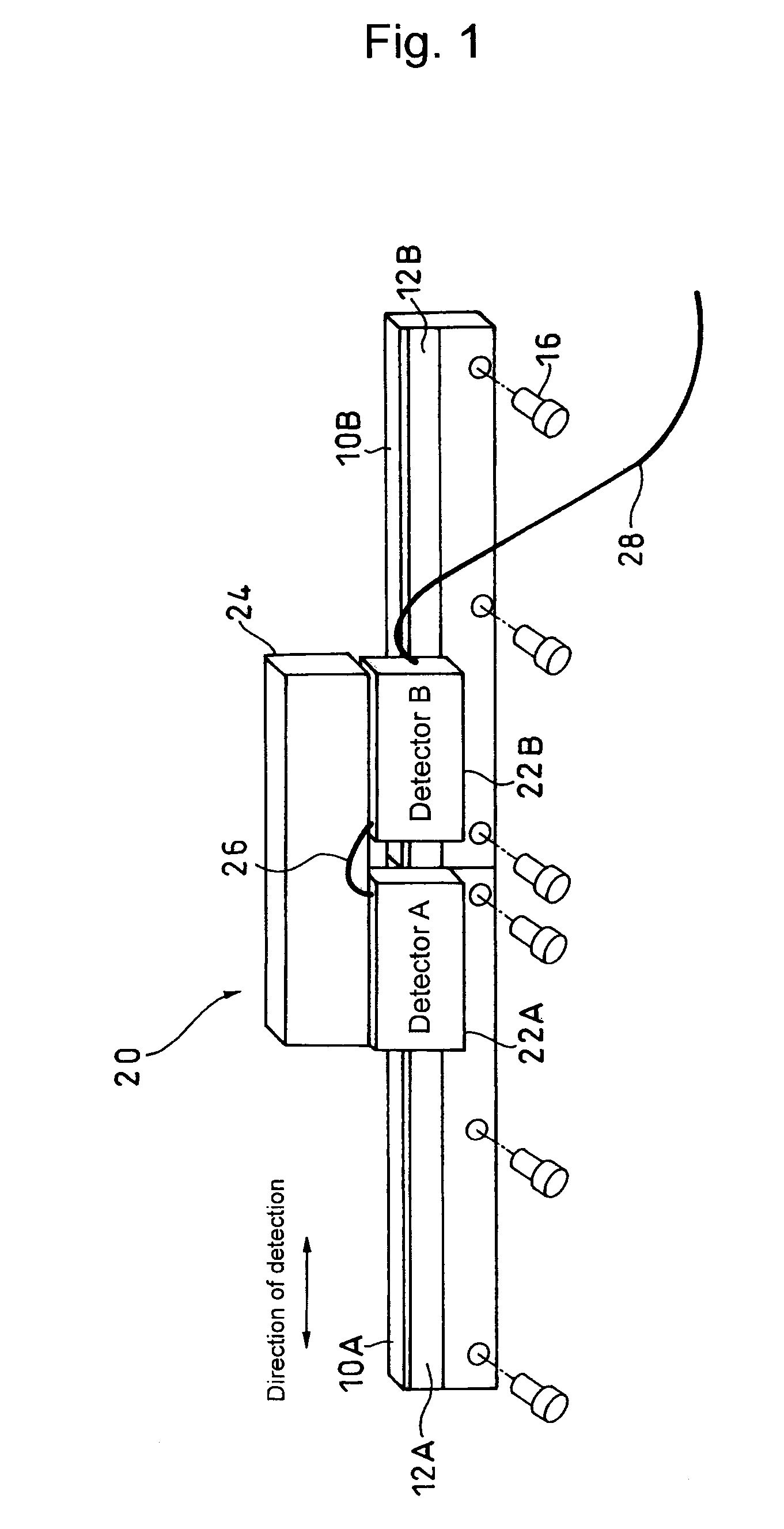
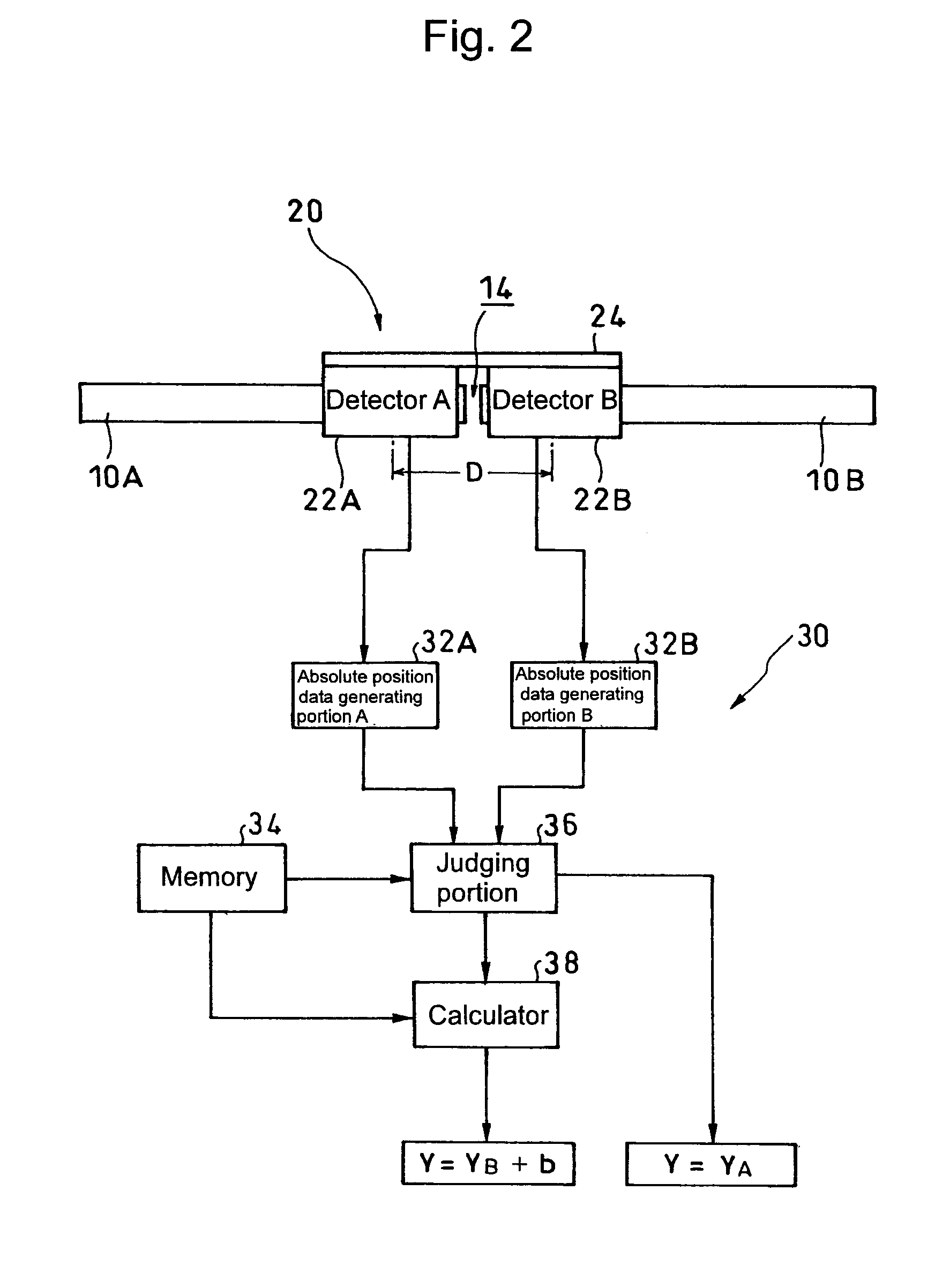
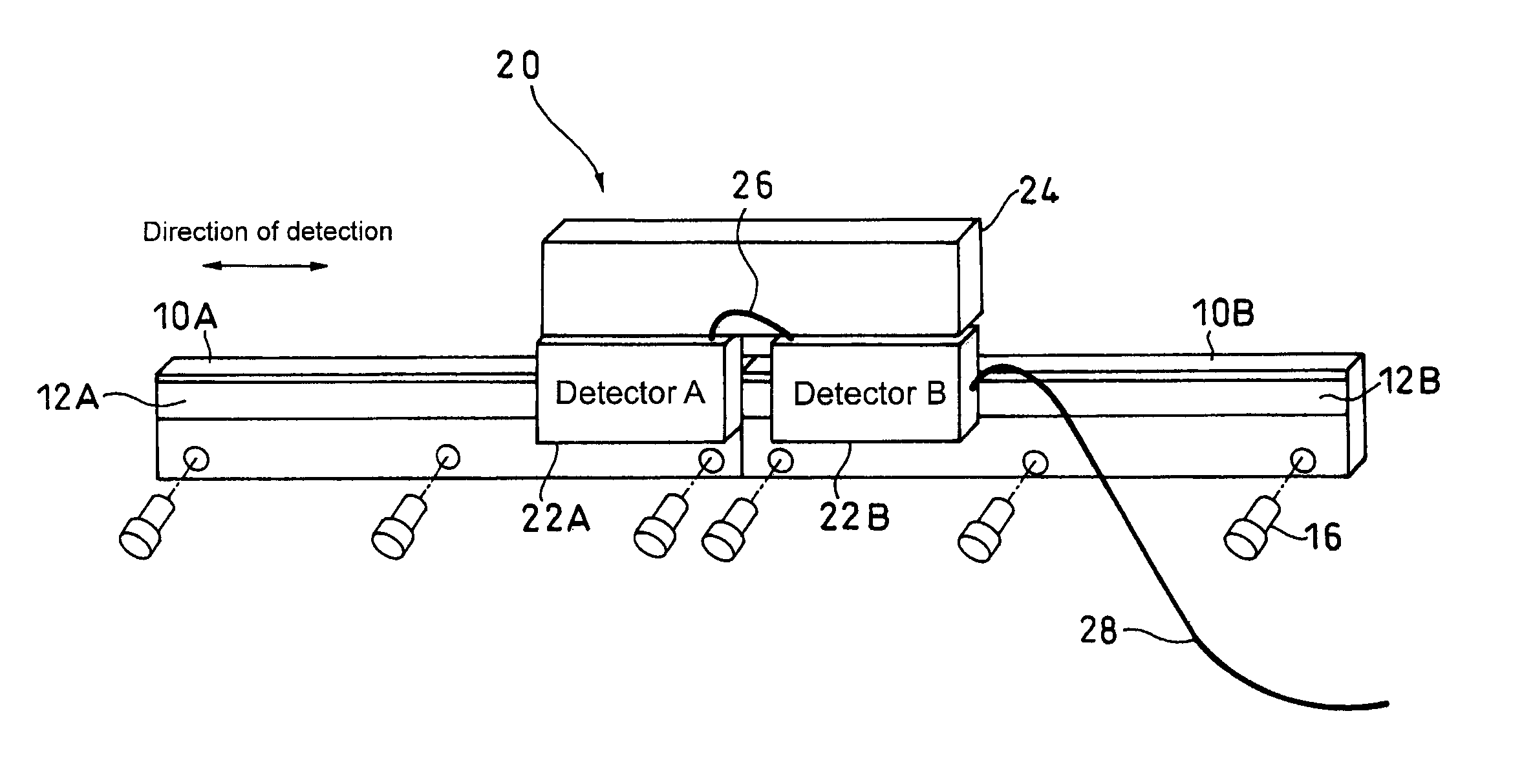
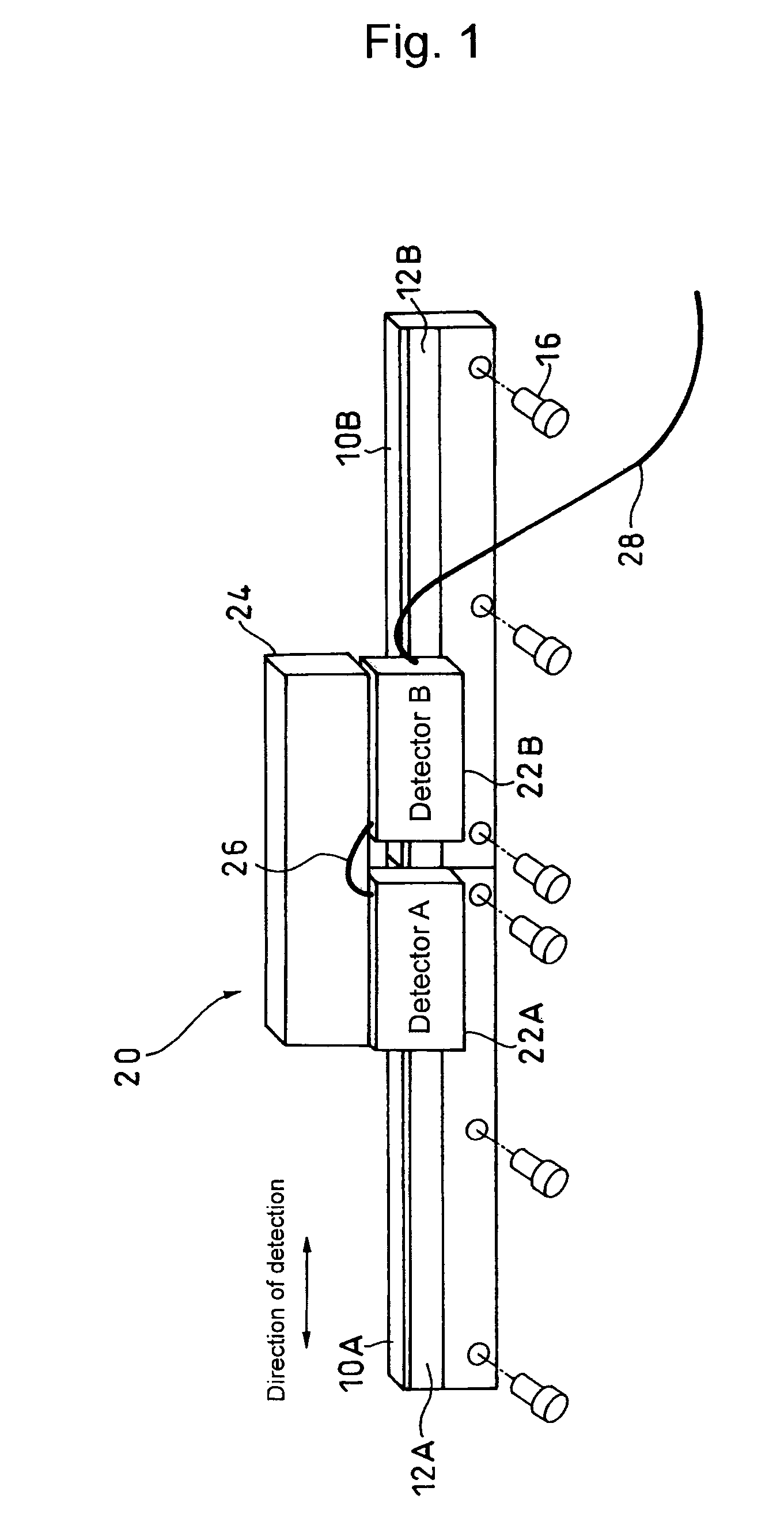
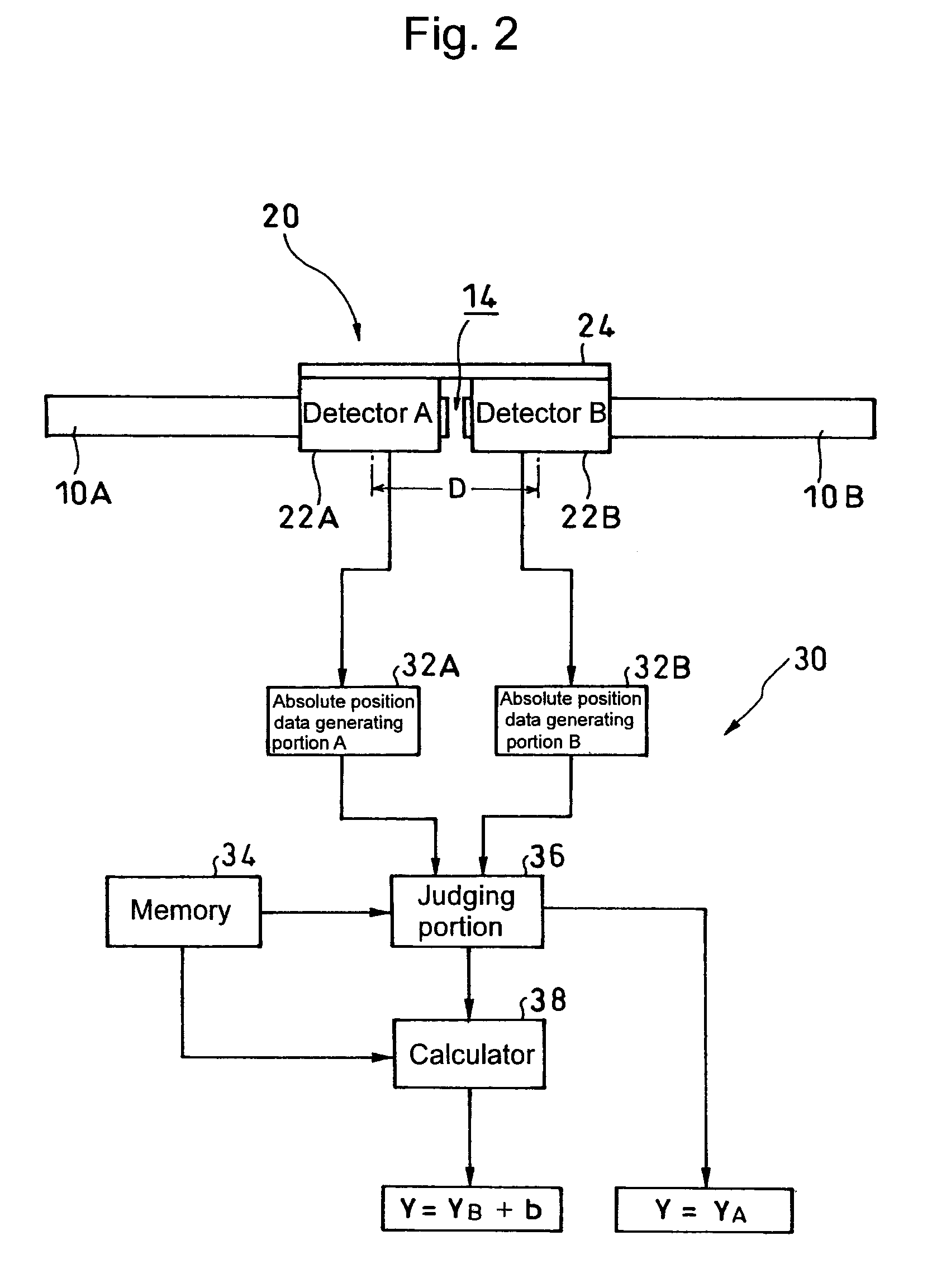
Absolute linear encoder
ActiveUS20070069117A1Easy to transportGood adhesionElectric signal transmission systemsMaterial analysis by optical meansAbsolute calibrationLinear encoder
An absolute linear encoder includes a plurality of absolute scales aligned in the detection direction with absolute calibrations, a plurality of detectors for detecting the calibrations on the absolute scales, absolute position data generating portions of each scale for generating absolute position data of each detector, and a calculator for outputting an absolute position over the whole length of connected whole absolute scales adding the absolute position data of each detector and the distance between the detectors. The detectors are fixed at such intervals as to simultaneously detect the calibrations of the two absolute scales adjoining in a scale connecting section. Thus, the long absolute linear encoder which is easy to use is realized at low costs.
Owner:MITUTOYO CORP
Absolute linear encoder
ActiveUS7432497B2Easy to transportGood adhesionAngles/taper measurementsElectric signal transmission systemsAbsolute calibrationLinear encoder
Owner:MITUTOYO CORP
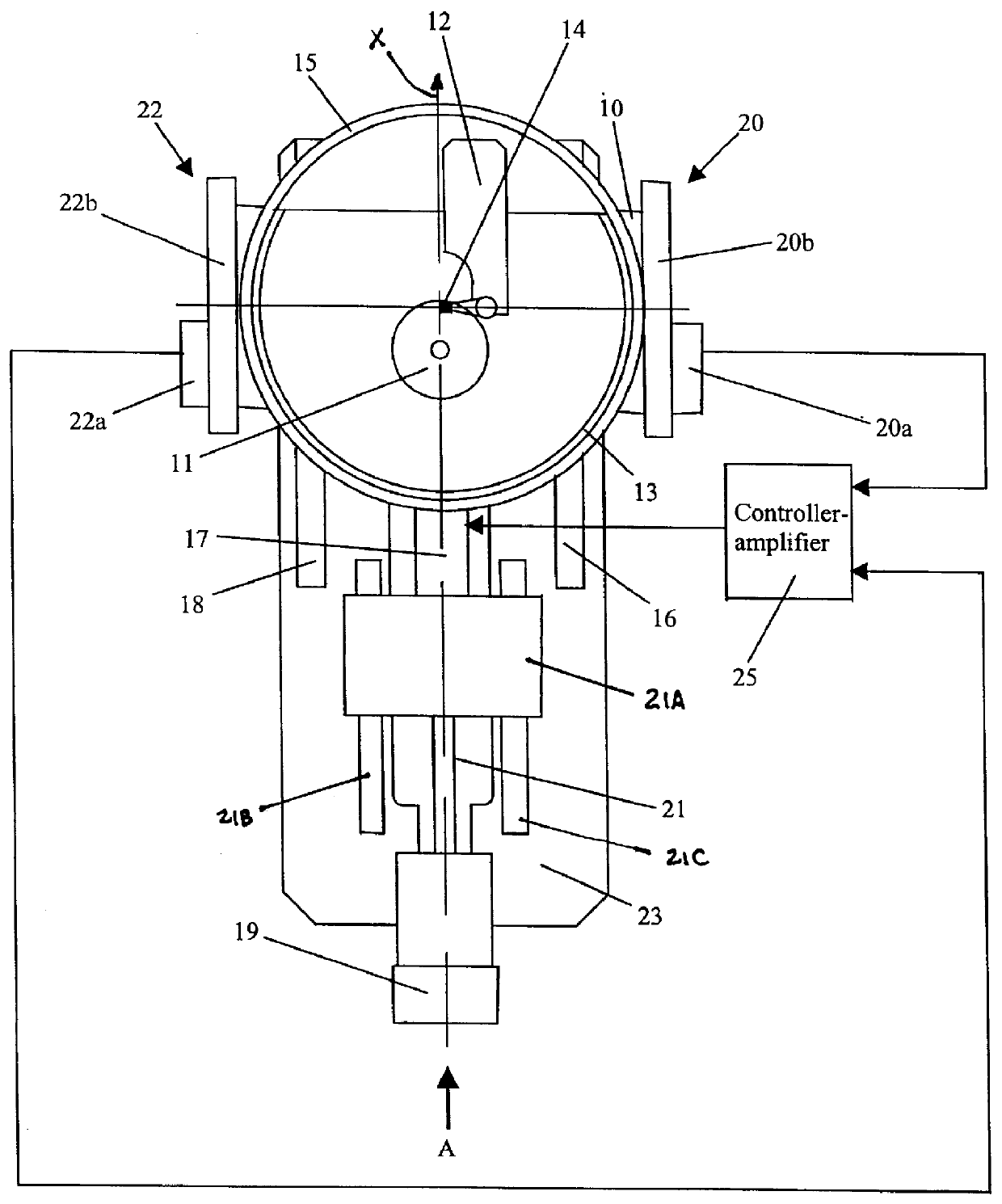
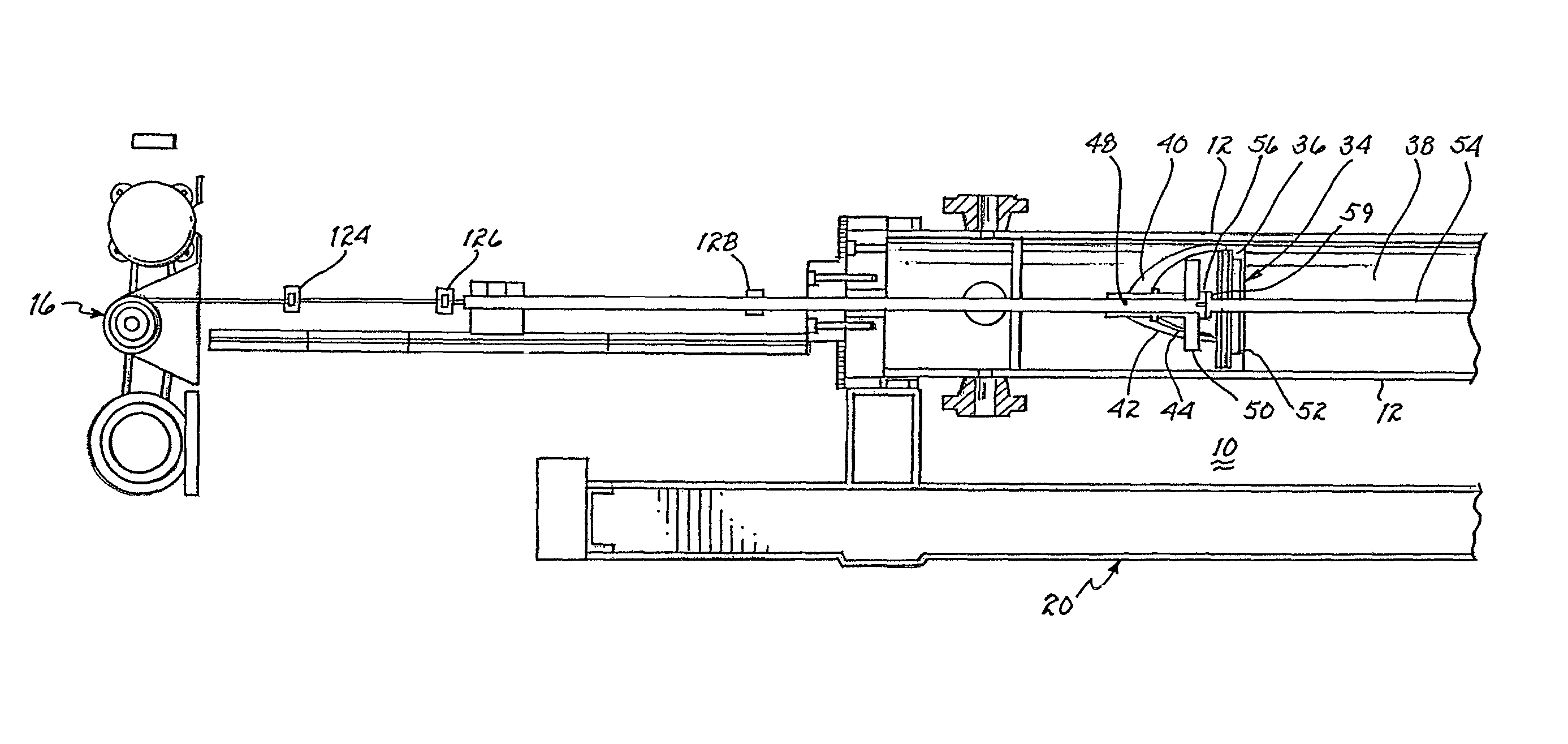
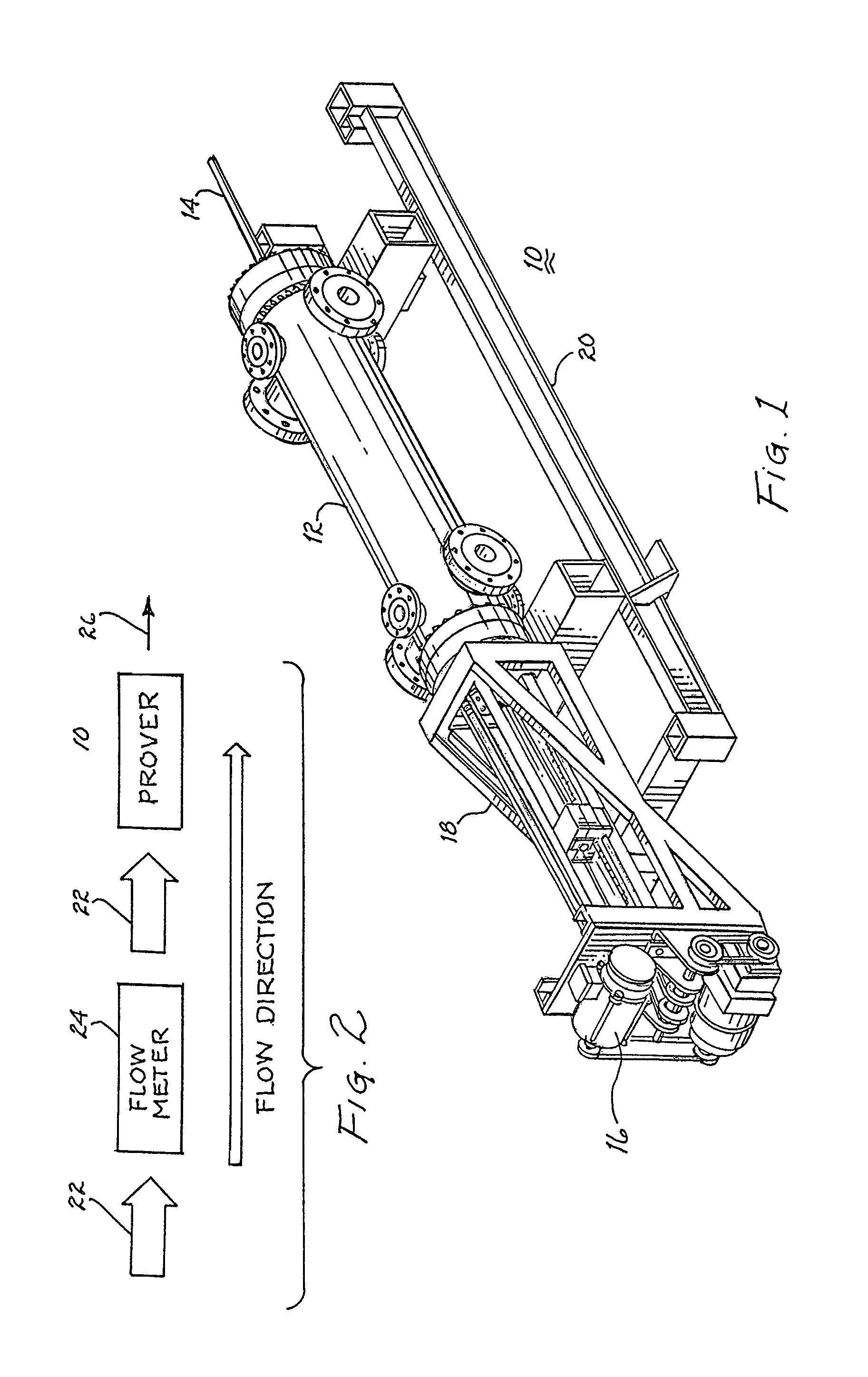
Prover self testing and validation apparatus
A prover includes a piston supporting rod extending longitudinally through a cylinder, which cylinder receives and discharges a fluid to measure the volume and flow rate of the fluid by translation of the piston from the fluid receiving end to the fluid discharging end. Motive means includes at least one element for drawing the rod and piston toward the fluid receiving end of the cylinder. Travel of the piston in the direction from the fluid receiving end to the fluid discharging end of the cylinder is sensed at discrete locations to provide an indication of the quantity of fluid therebetween and the related flow rate. Each of a plurality of switches, linear encoder or laser detector provides position sensing signals reflective of the volume and rate of fluid flowing in the cylinder. These signals, representative of this volume and flow rate, are compared with preset parameters to determine the degree of equivalence. Thereby, self testing and validation occurs.
Owner:FLOW MANAGEMENT DEVICES
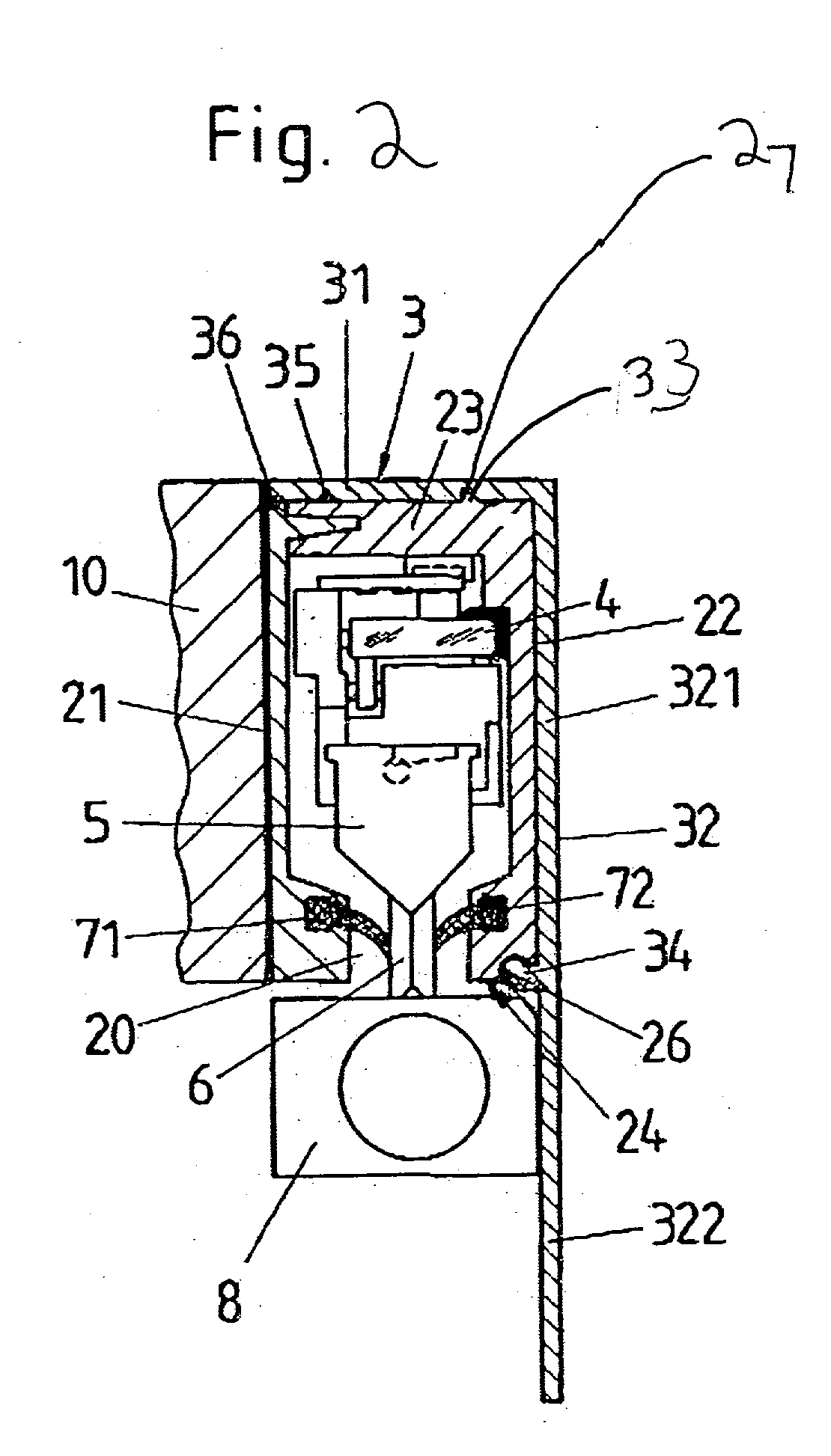
Cover for a sealed linear encoder and a sealed linear encoder
InactiveUS20030200671A1Simple to manufacture and to mountEffective protectionWalking sticksUsing mechanical meansScale unitEngineering
A sealed linear encoder for determining the relative position of a first object and a second object. The sealed linear encoder includes a scale unit arranged in a hollow body that is mounted to a mounting structure associated with the first object and includes a slot which extends in a direction of measurement. A scanning unit for scanning the scale unit and a carrier connected to the second object, wherein the carrier extends through the slot. Sealing lips arranged at the hollow body and abutting the carrier so as to seal the carrier and a cover form-fitted to the hollow body for covering at least the slot.
Owner:HEIDENHAIN CORP +1
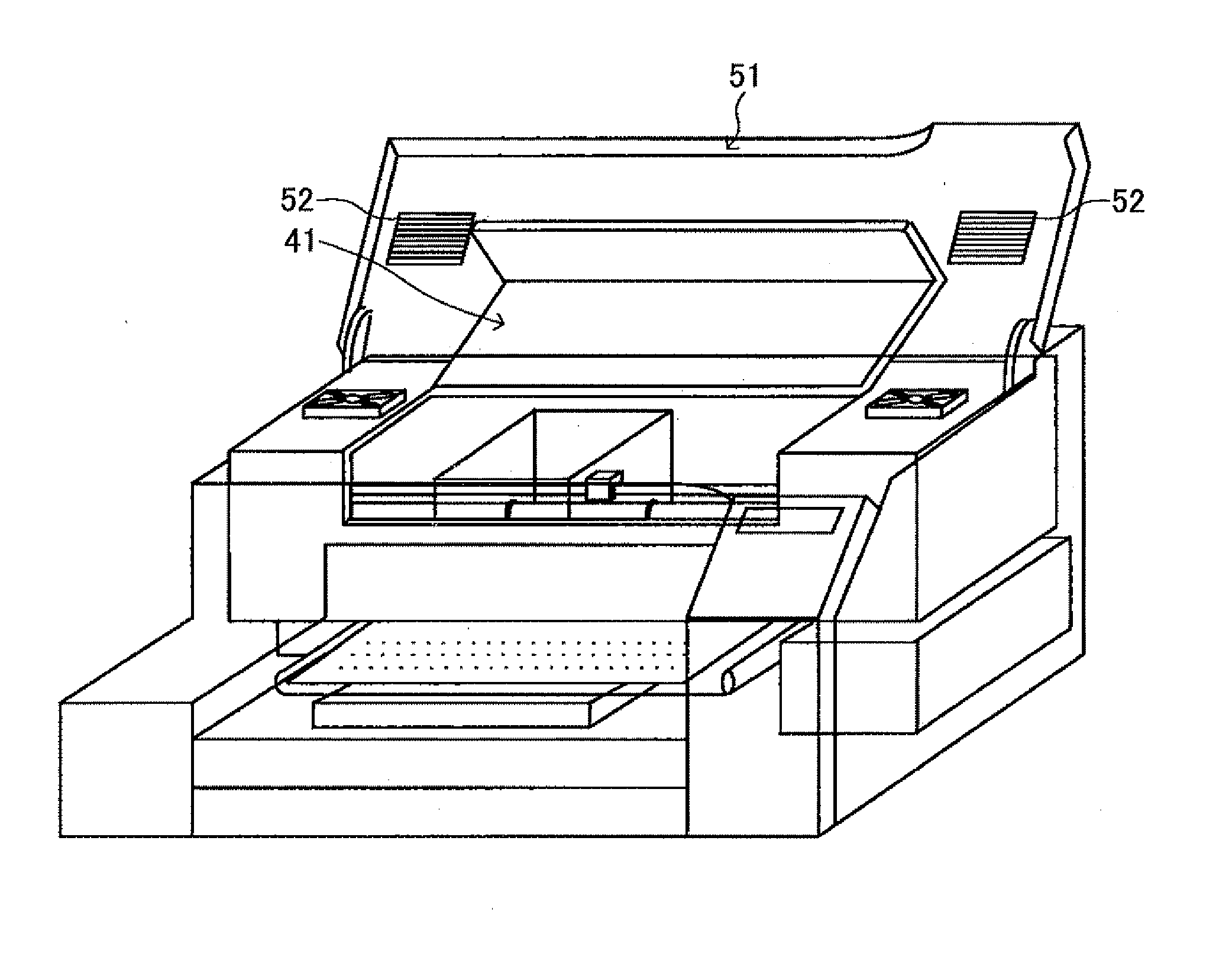
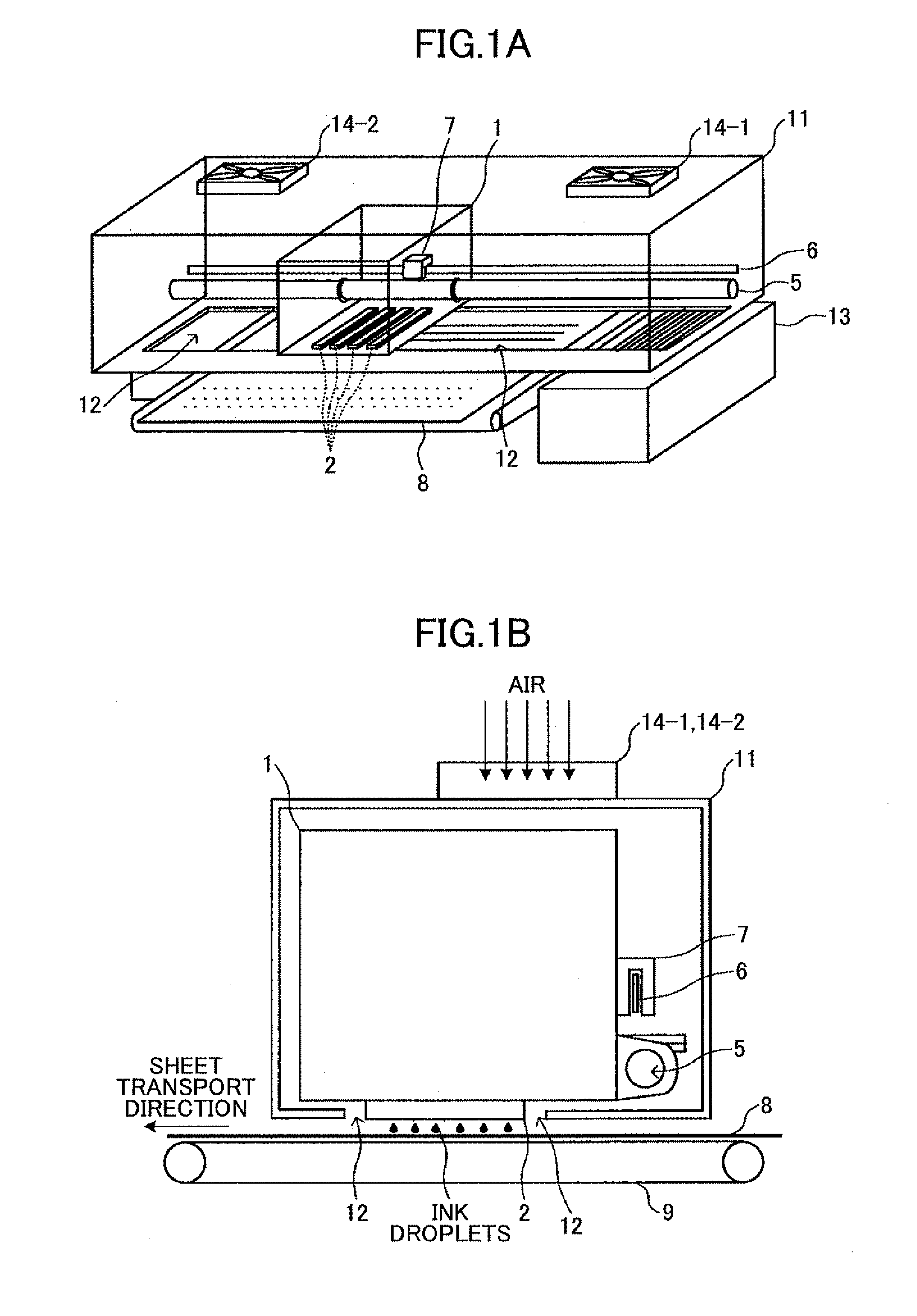
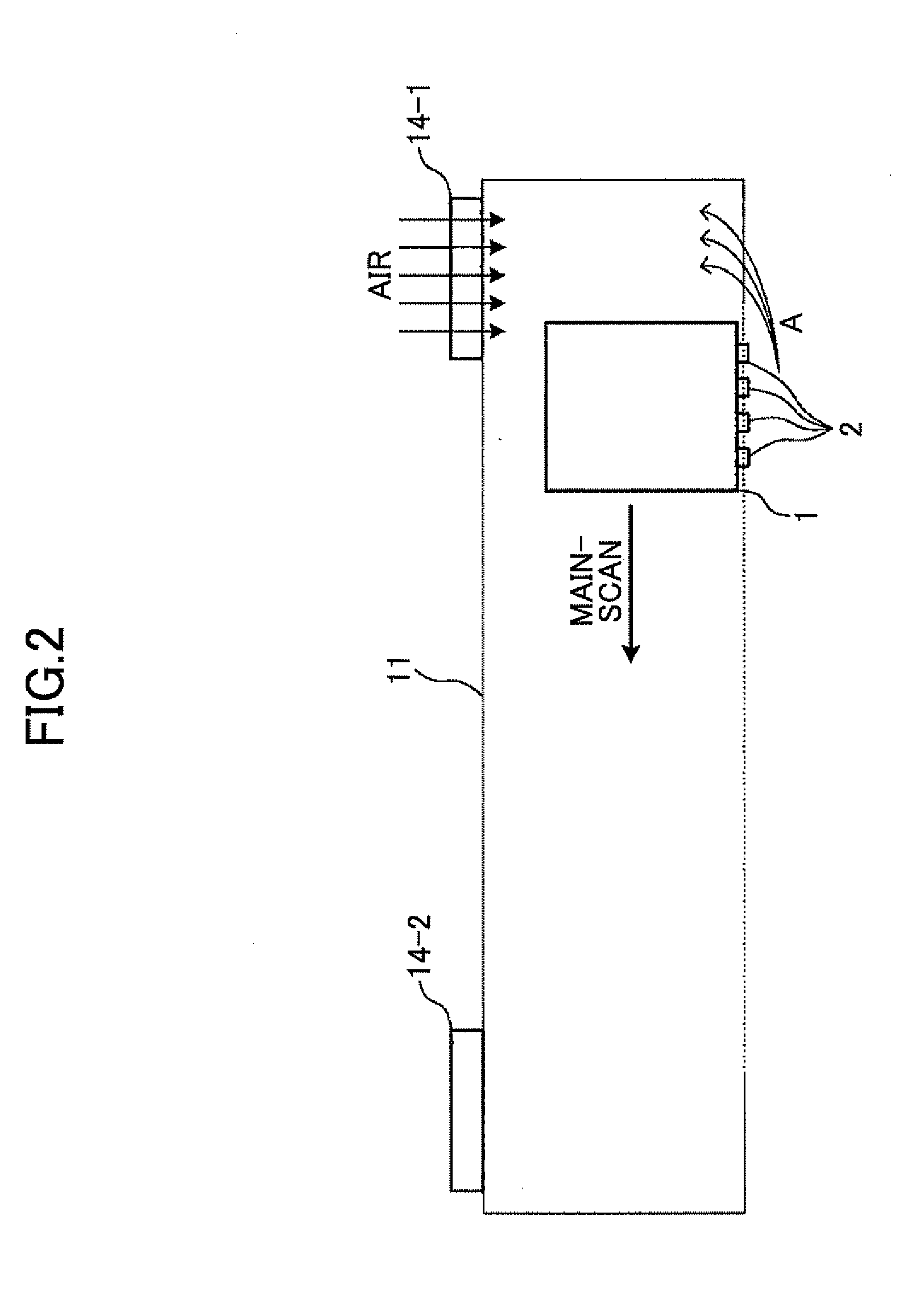
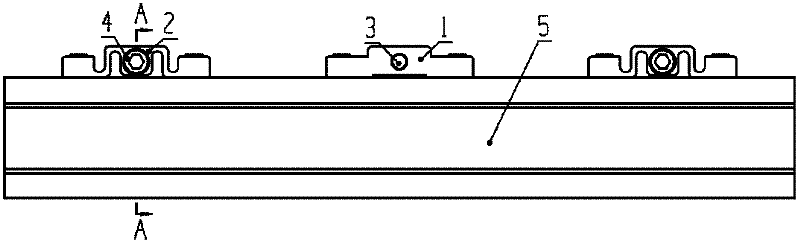
Image forming apparatus having ink-mist blocking mechanisms
An image forming apparatus includes a printing head having an ink nozzle configured to discharge ink droplets onto a recording medium in order to form an image on the recording medium in a recording operation; a carriage on which the printing head is mounted and being moved in a main-scan direction during the recording operation; a linear encoder sheet having a counter for detecting a position of the carriage; an encoder sensor mounted on the carriage and detecting the position of the carriage by optically reading the counter of the linear encoder sheet; an carriage unit enclosure in which at least the carriage, the linear encoder sheet, and the encoder sensor are disposed; and an internal pressure adjusting unit adjusting an internal pressure of the carriage unit enclosure to be other than a negative pressure.
Owner:RICOH KK
Fastening device for casing of linear encoder
InactiveCN102538676AControl deformationGuaranteed measurement accuracyUsing optical meansEngineeringLinear encoder
A fastening device for a casing of a linear encoder belongs to the technical field of optics and is used for firmly fastening the casing to a part to be detected, and for effectively controlling deformation of the linear encoder upon temperature effect to be within a small range so that the linear coder has certain repeatable temperature property. The fastening for the casing of the linear encoder comprises a rigid casing support and a plurality of flexible casing supports, wherein the rigid casing support is fixed in the middle of the casing, and the flexible casing supports are fixed at equal intervals on the casing and disposed on two sides of the rigid casing support in bilateral symmetry. The rigid casing support is provided with a pin hole in the middle, each flexible casing support is provided with a through hole in the middle, and each flexible casing support is provided with grooves which are reserved on two sides of the through hole in bilateral symmetry. By the aid of the designed structure of the rigid casing support and the flexible casing supports, the deformation of the linear encoder upon temperature effect is controlled well, and the certain repeatable temperature property of the linear encoder is realized.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
System and method for lossy source-channel coding at the application layer
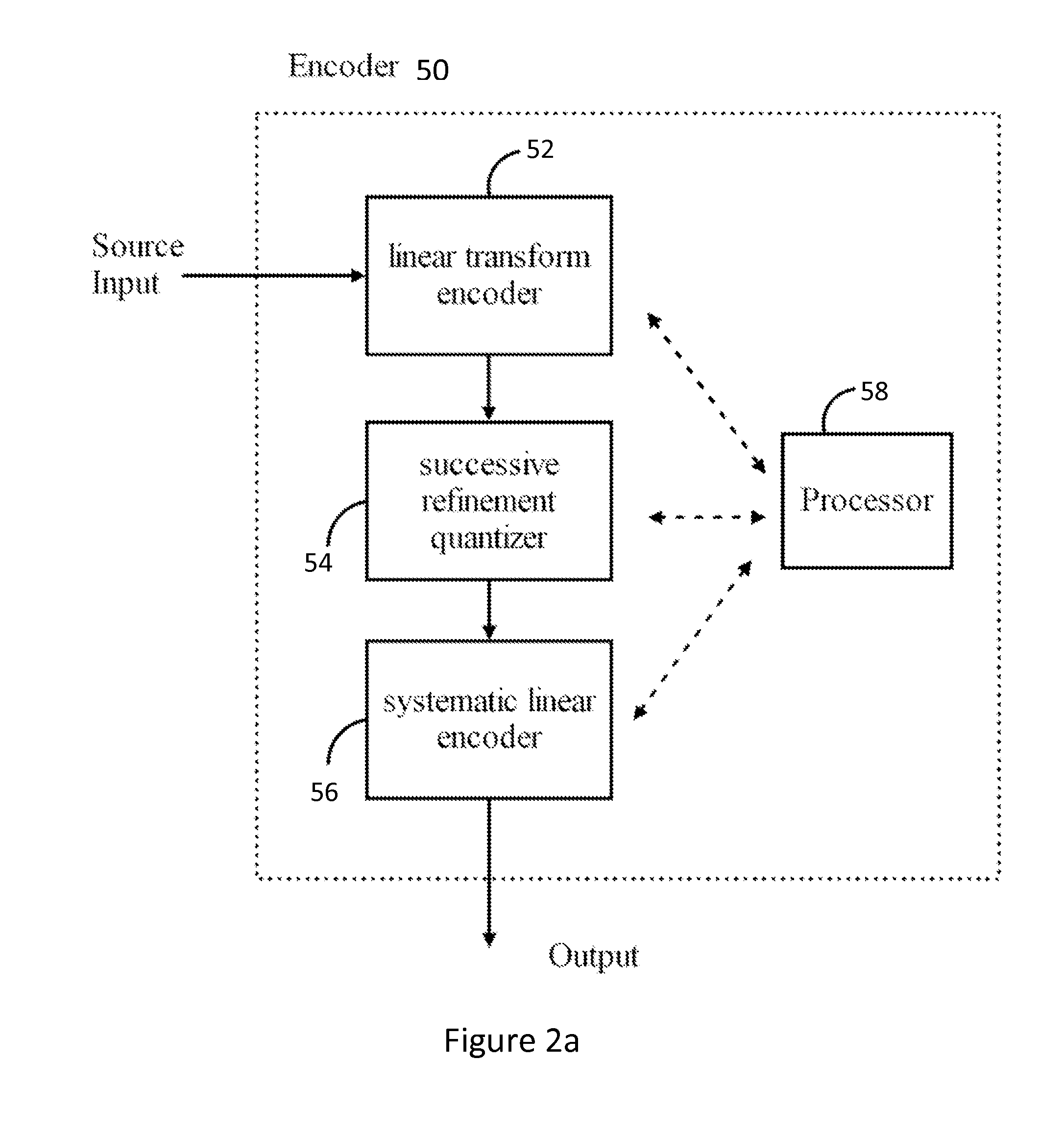
ActiveUS20120039385A1Reduce resolutionBig gapColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionChannel decoderDiscrete cosine transform
A source channel encoder, source channel decoder and methods for implementing such devices are disclosed herein. The source channel encoder includes a linear transform encoder configured to generate a plurality of source components. A successive refinement quantizer is configured to generate a plurality of bit planes based on the source components. A systematic linear encoder configured to map the bit planes into channel-encoded symbols. The linear transform encoder may be configured to apply a Discrete Cosine Transform (DCT) or a Discrete Wavelet Transform (DWT). The linear transform encoder may be configured for differential encoding.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA +1
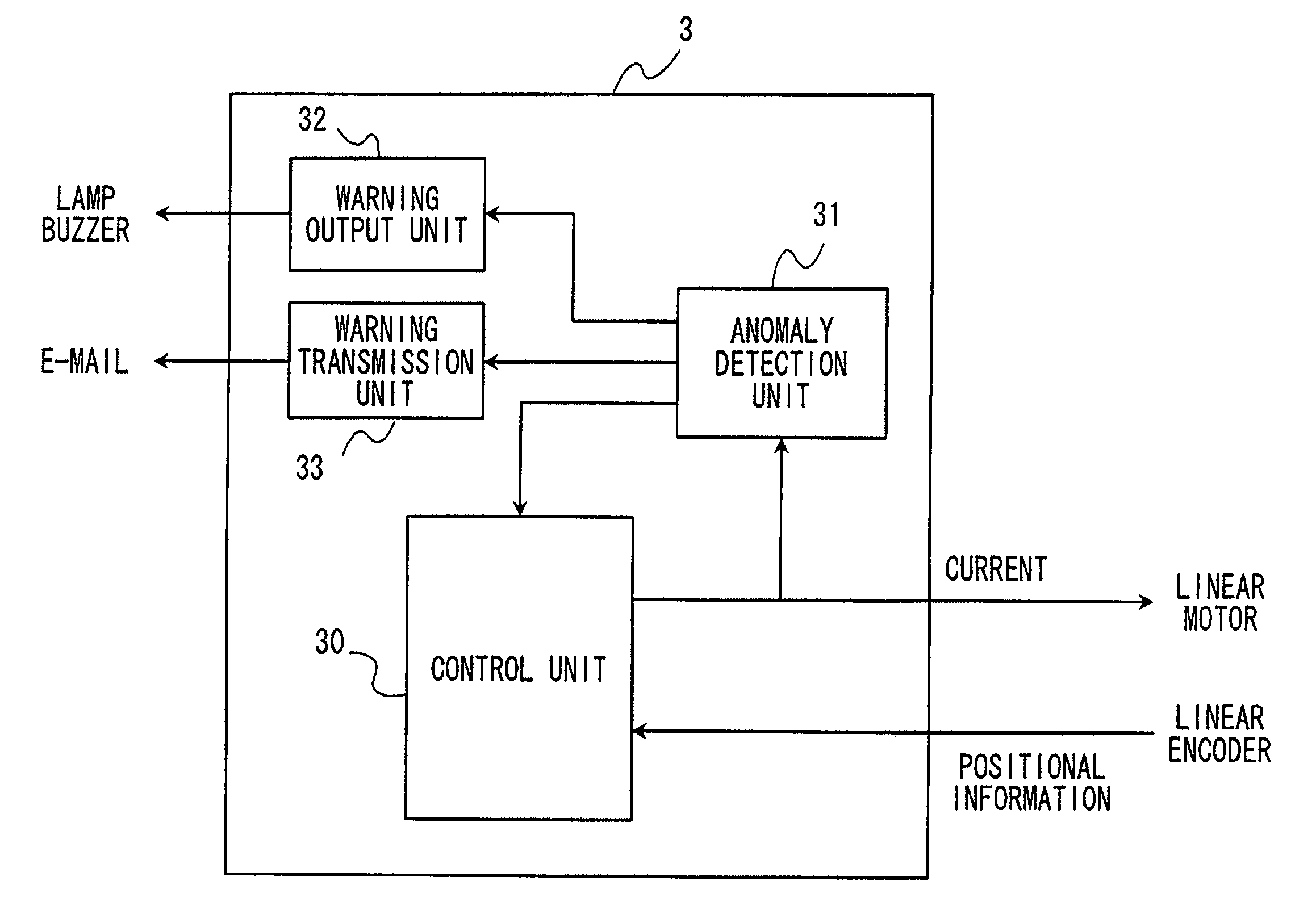
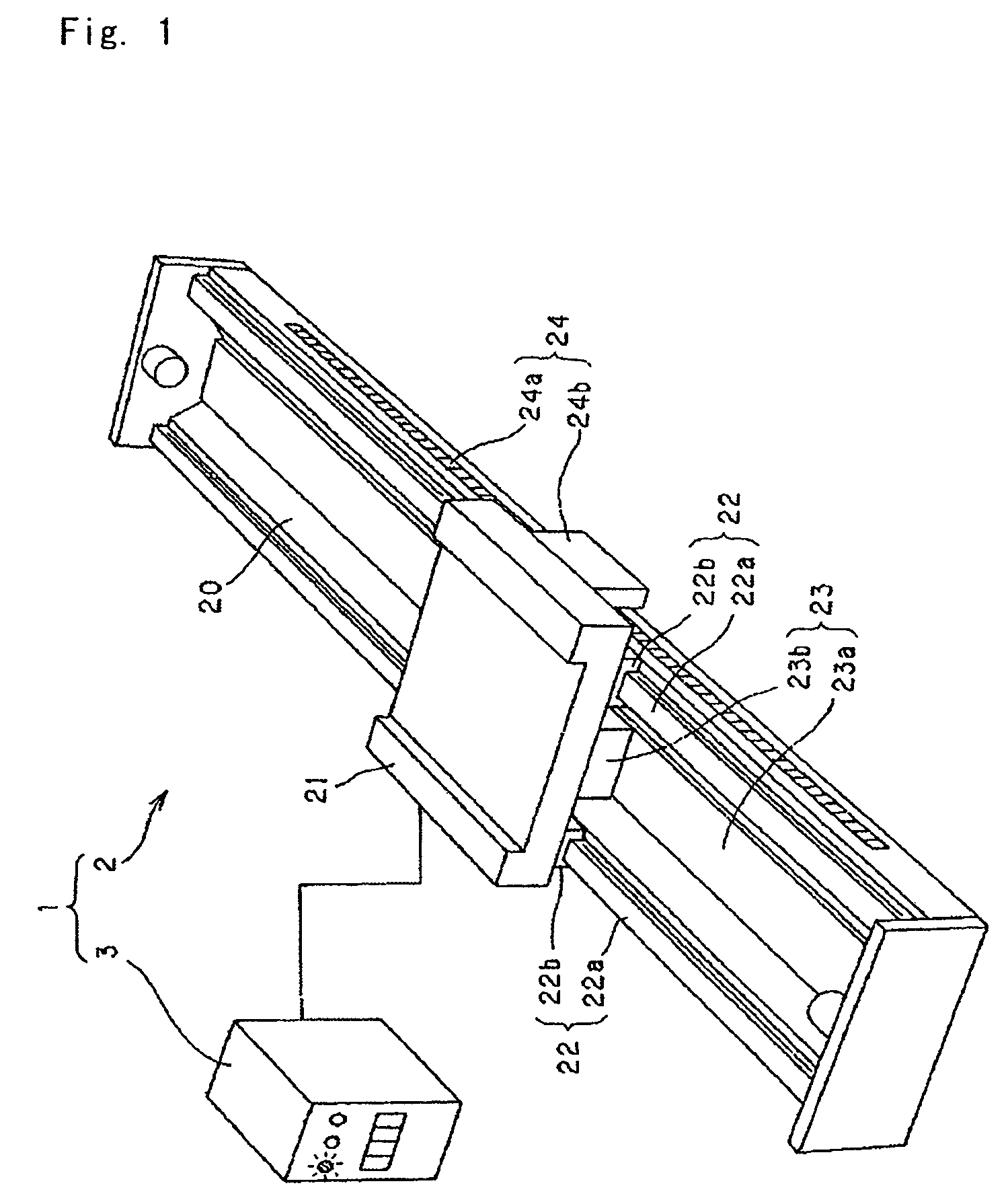
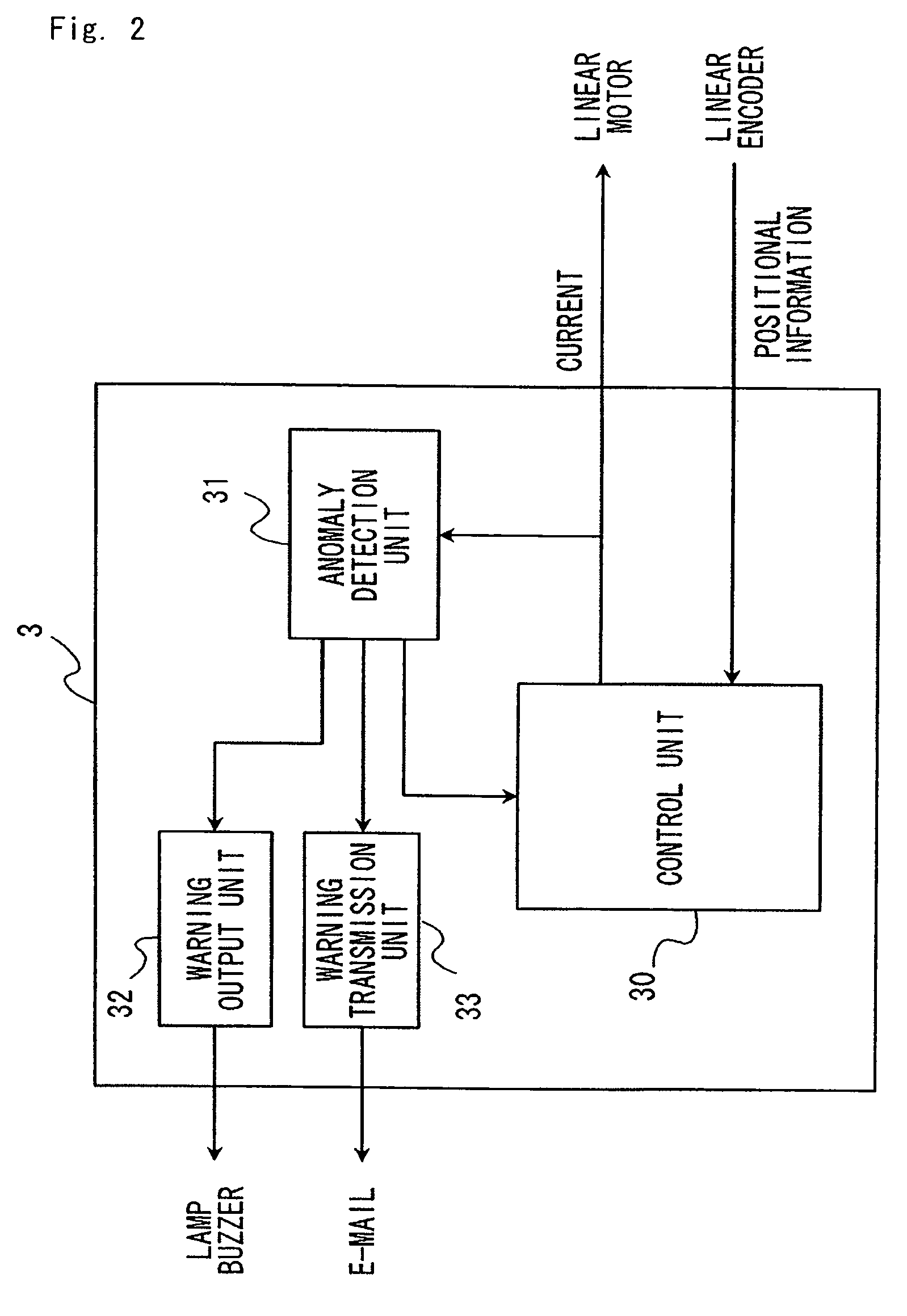
Anomaly detection method and motor control device
ActiveUS7439693B2Prevent breakage and failureImprove performanceSynchronous motors startersAC motor controlLinear motionMotor drive
Owner:THK CO LTD
Reconfigurable learning aid for performing multiple science experiments
ActiveUS10565899B1Easy to carryEasy to storeEducational modelsElectrical appliancesEngineeringLinear encoder
This invention is an apparatus consisting of components that can be assembled and reassembled in various configurations allowing students to perform multiple physics and engineering experiments, with sensors and electronics integrated into the apparatus that allowing extraction of data via integrated data links, while computing and displaying results graphically in near real time. The principal component of the system is a linear drive system with a movable carriage, the position of which is measureable by various rotary and linear encoders. Load cells are able to measure forces of compression and tension. Temperature and Pressure sensors are able to measure gas pressure and the thermal conductivity of materials. The various components of this flexible educational tool can be disassembled and stored in a portable “toolkit”, the size of a small briefcase.
Owner:MENTIS SCI
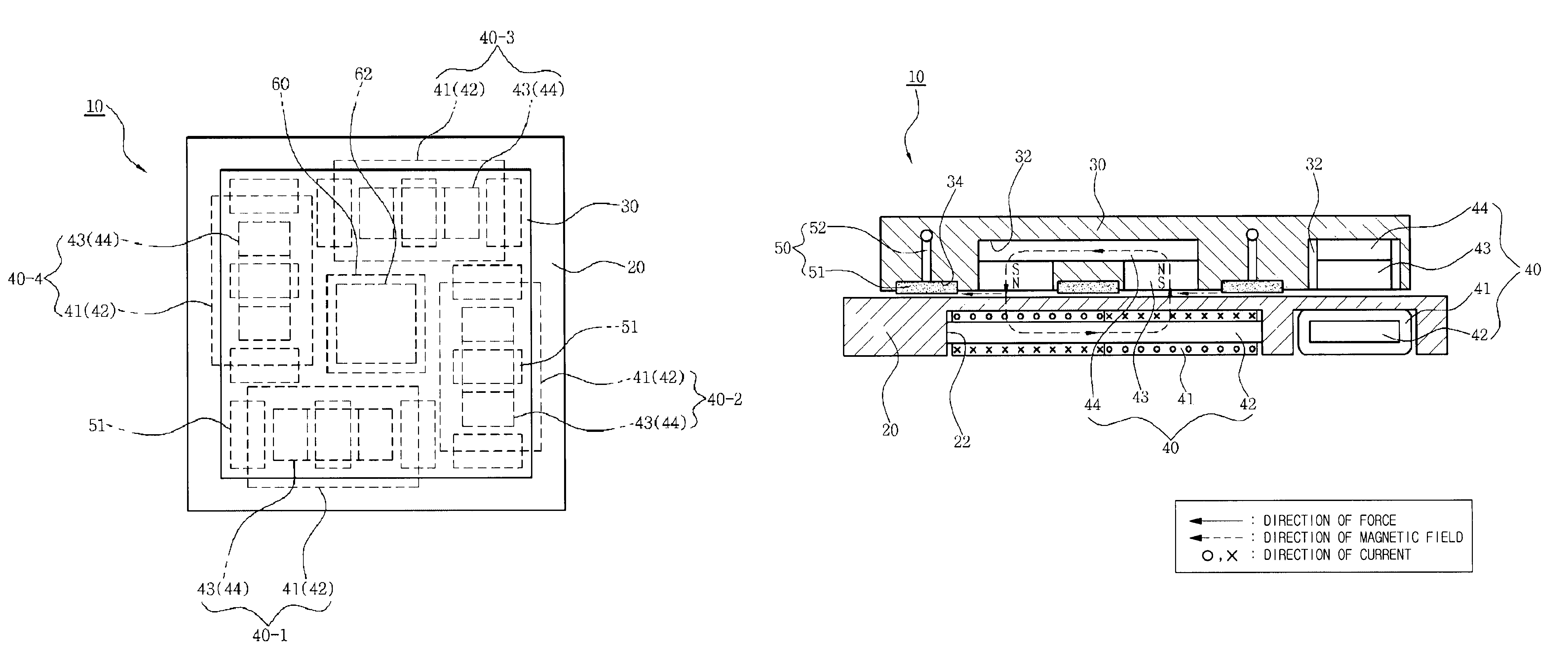
Planar stage moving apparatus for machine
A planar stage moving apparatus for a machine includes: first to fourth linear motors for applying, between a base, i.e. a fixed body and a table, i.e. a movable body, a movement force to the table, each linear motor including a stator core on which a coil is wound and which is fixed to the base and a mover core to which a permanent magnet is attached and which is fixed to the table; an air bearing unit provided between the base and the table to move the table under the influence of magnet fields when currents are applied to the coils of the linear motors; and a linear encoder installed on one side of the table to measure movement of the table.
Owner:KOREA INST OF MACHINERY & MATERIALS
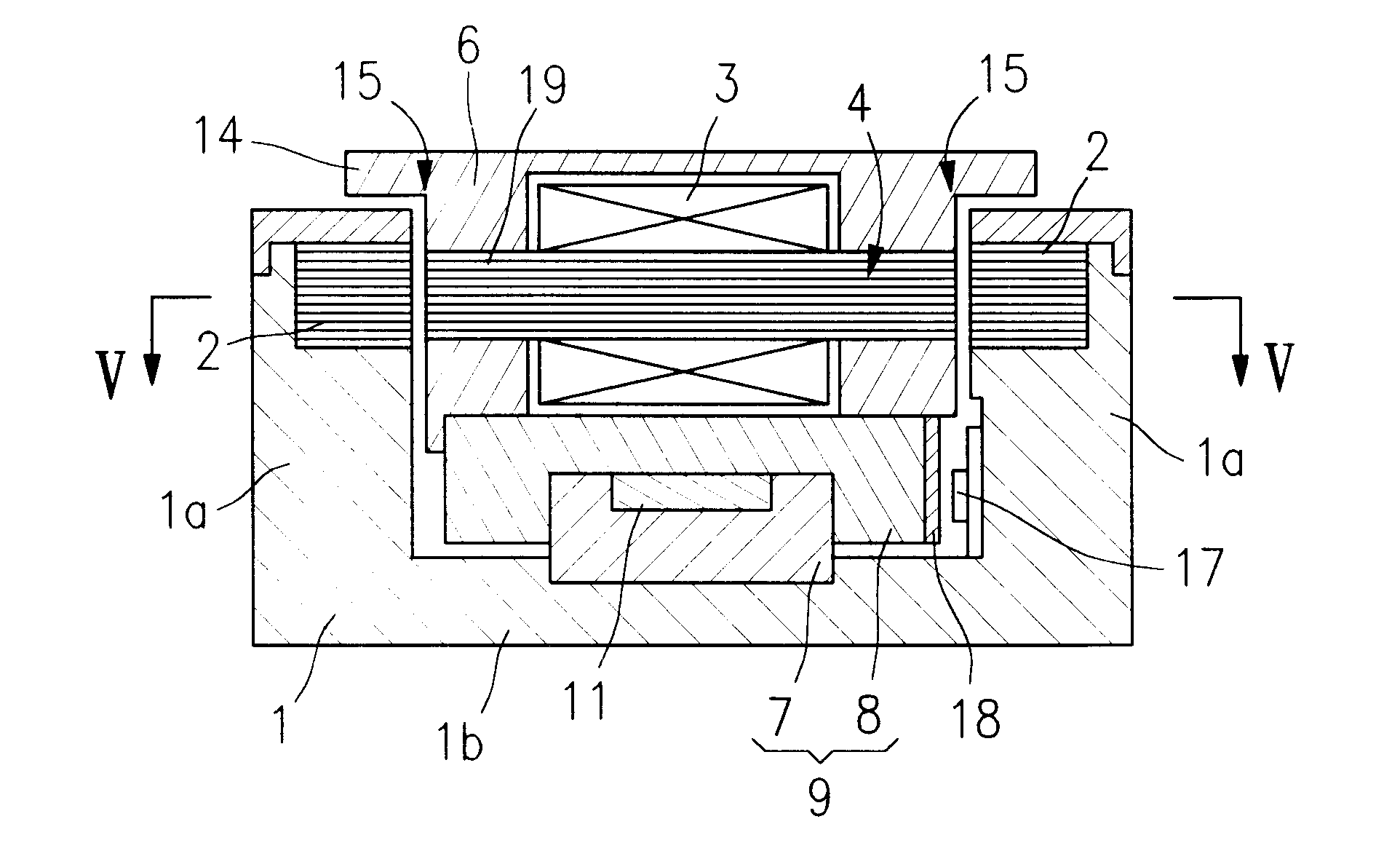
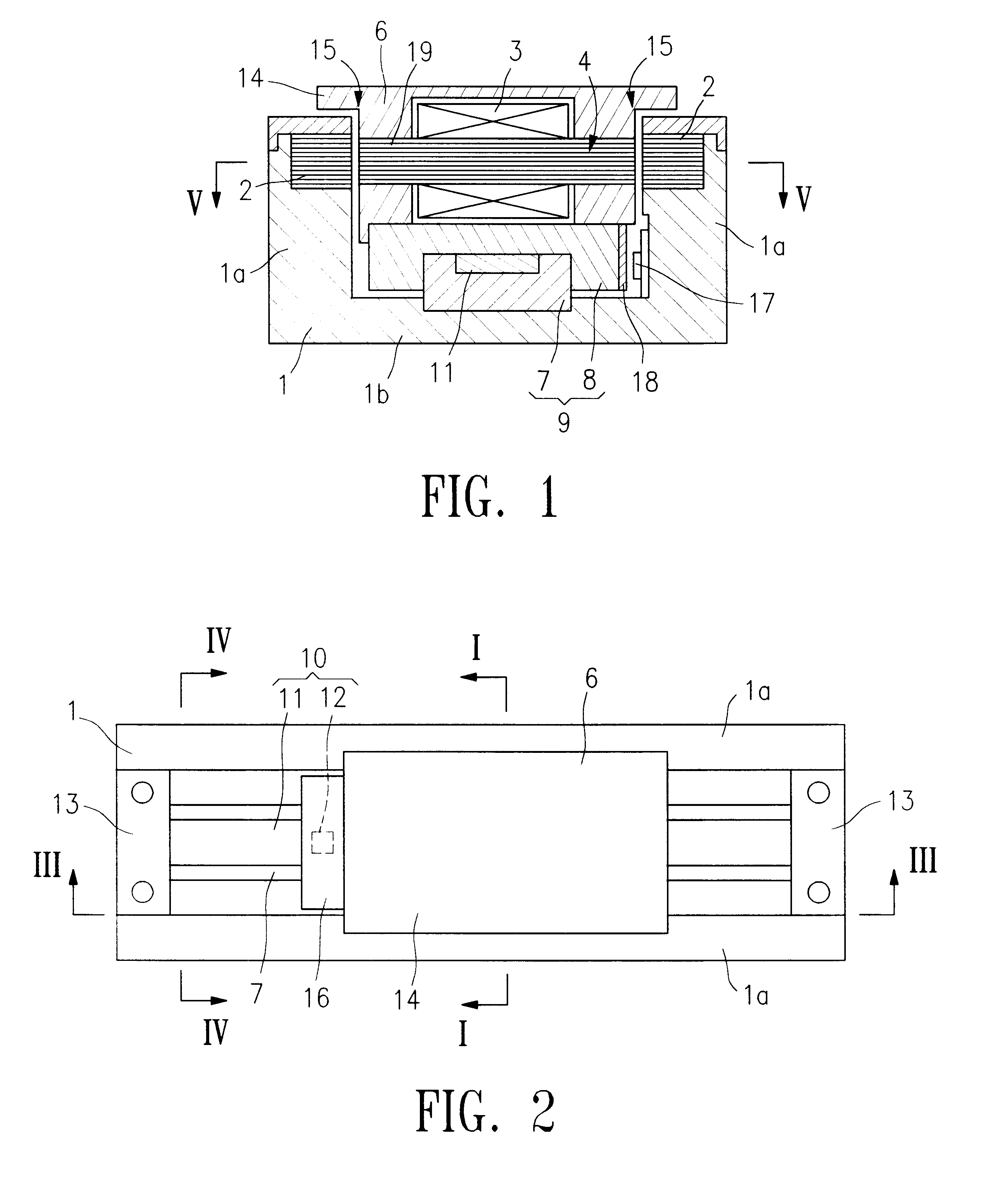
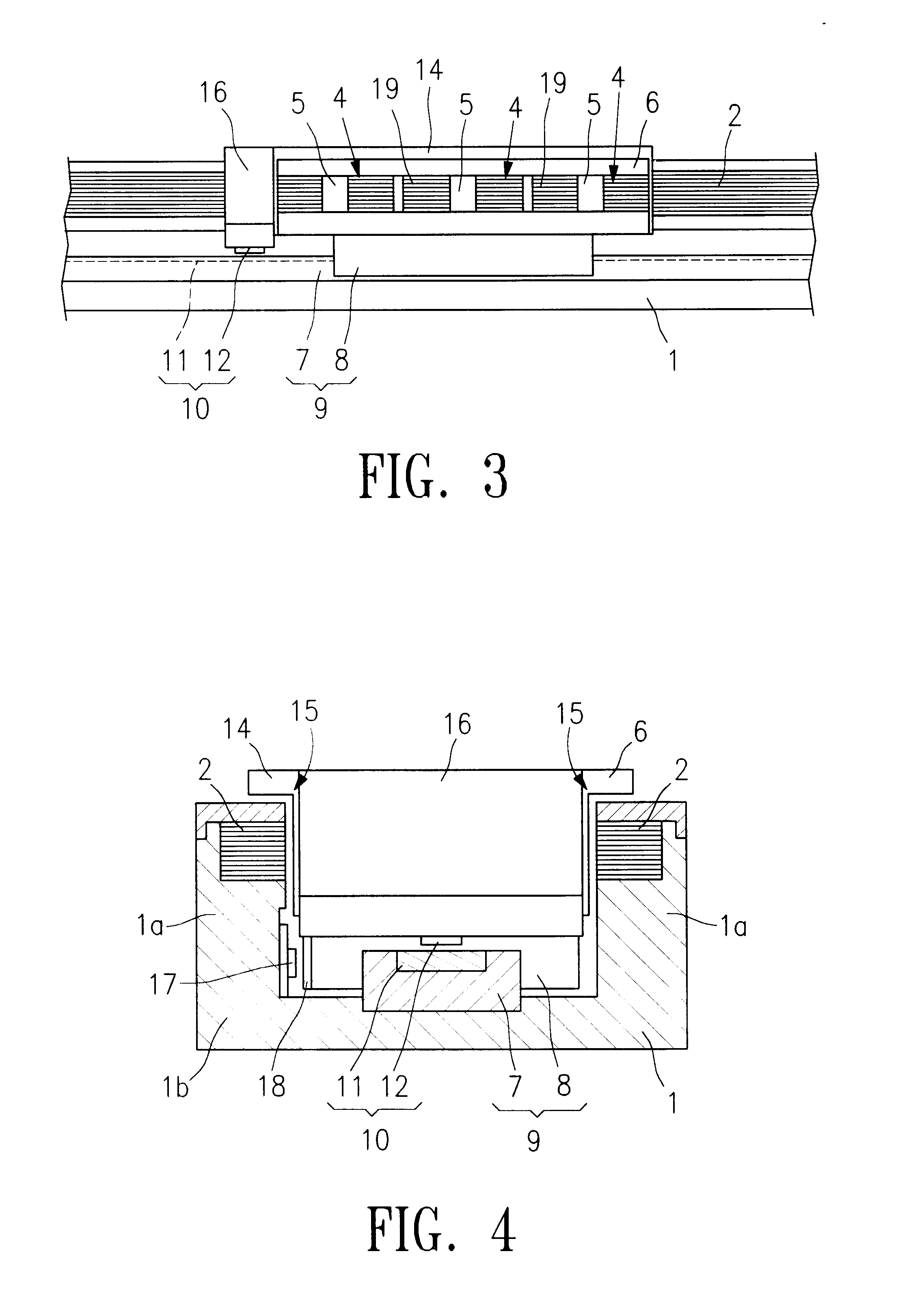
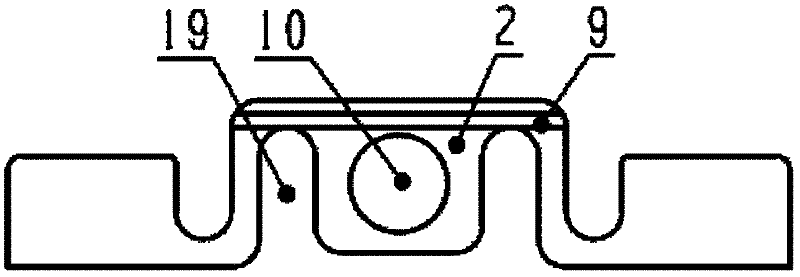
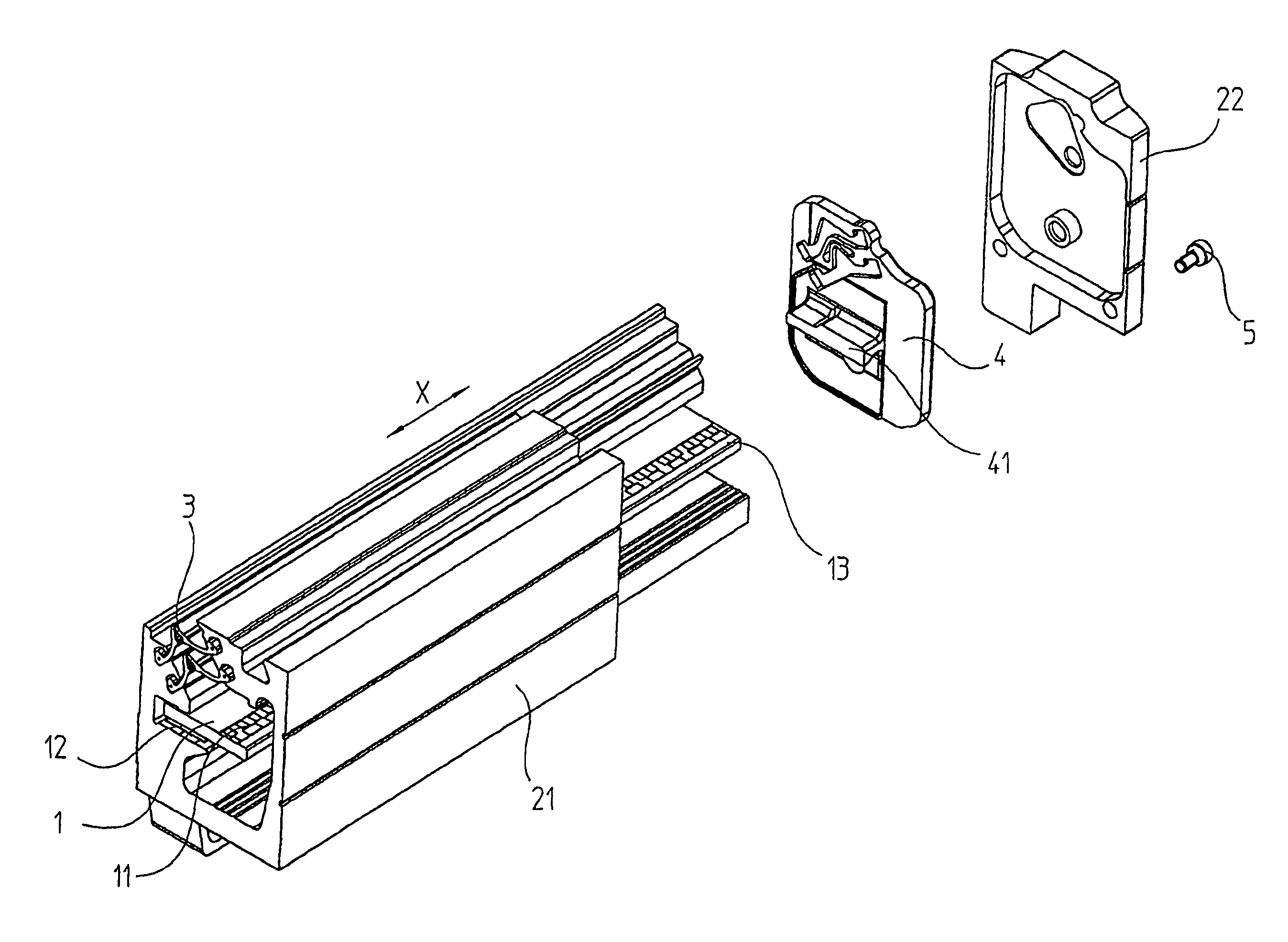
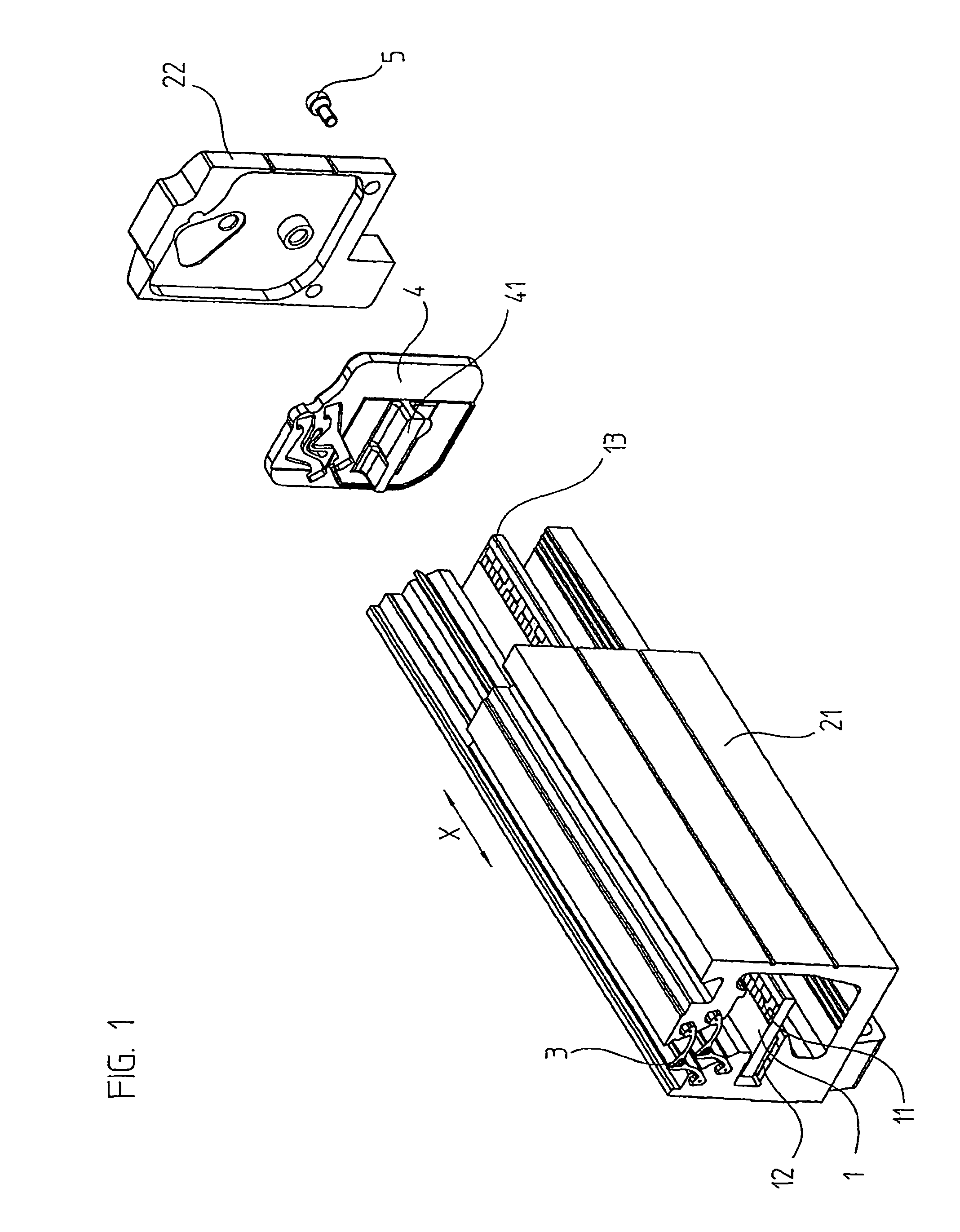
Linear encoder
ActiveUS8234792B2Easy to assembleSimple structureWalking sticksUsing electrical meansElectrical connectionEngineering
A linear encoder that includes a housing having: an elongated hollow profile section including a first face end and a second face end; a cap disposed on the first face end; and a seal which is disposed in sealing fashion between the hollow profile section and the cap, wherein the seal includes an electrically conductive connecting element. The linear encoder further includes a scale made of electrically nonconductive material, wherein the scale is disposed inside the housing and the scale includes a measuring graduation that is scannable by a scanning unit, which is movable in a measurement direction relative to the housing. The linear encoder includes a shunt made of electrically conductive material, wherein the shunt is mounted on the scale and extends in the measurement direction and wherein the electrically conductive connecting element is configured so as to establish an electrical connection between the shunt and at least one of the hollow profile section and the cap.
Owner:DR JOHANNES HEIDENHAIN GMBH
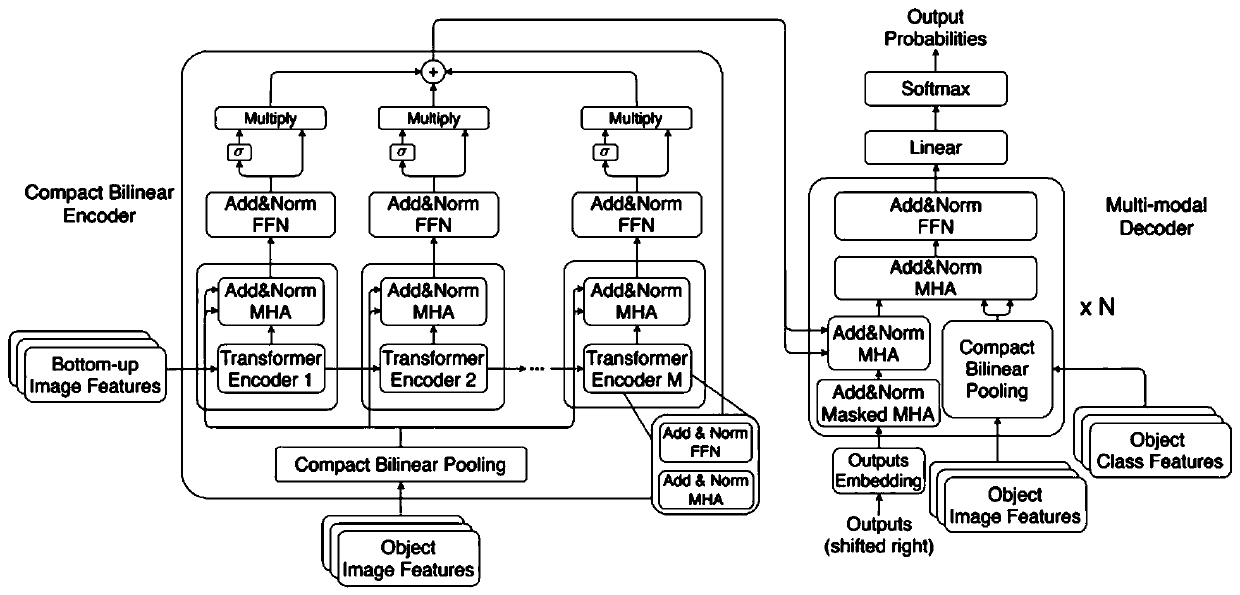
Image description method
ActiveCN111523534AEvaluate performanceSemantic analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionComputer graphics (images)Image description
The invention discloses an image description method, which is characterized in that a bilinear encoder and a multi-mode decoder are adopted to improve image description with fine-grained region objectfeatures. In the encoder, bilinear pooling is used for encoding fine-grained region image features, a simple encoder of a transformer is used for encoding region-of-interest features of an image, andall the encoded features are fused with a gate structure to serve as overall encoding features of the image. In the decoder, multi-modal features are extracted from the fine-grained region image features and category features and fused with the overall encoding features, and semantic information is decoded to generate a description. Compared with the prior art, the image description method provides a new solution for image description and application of the image description, and is simple, convenient and high in efficiency.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
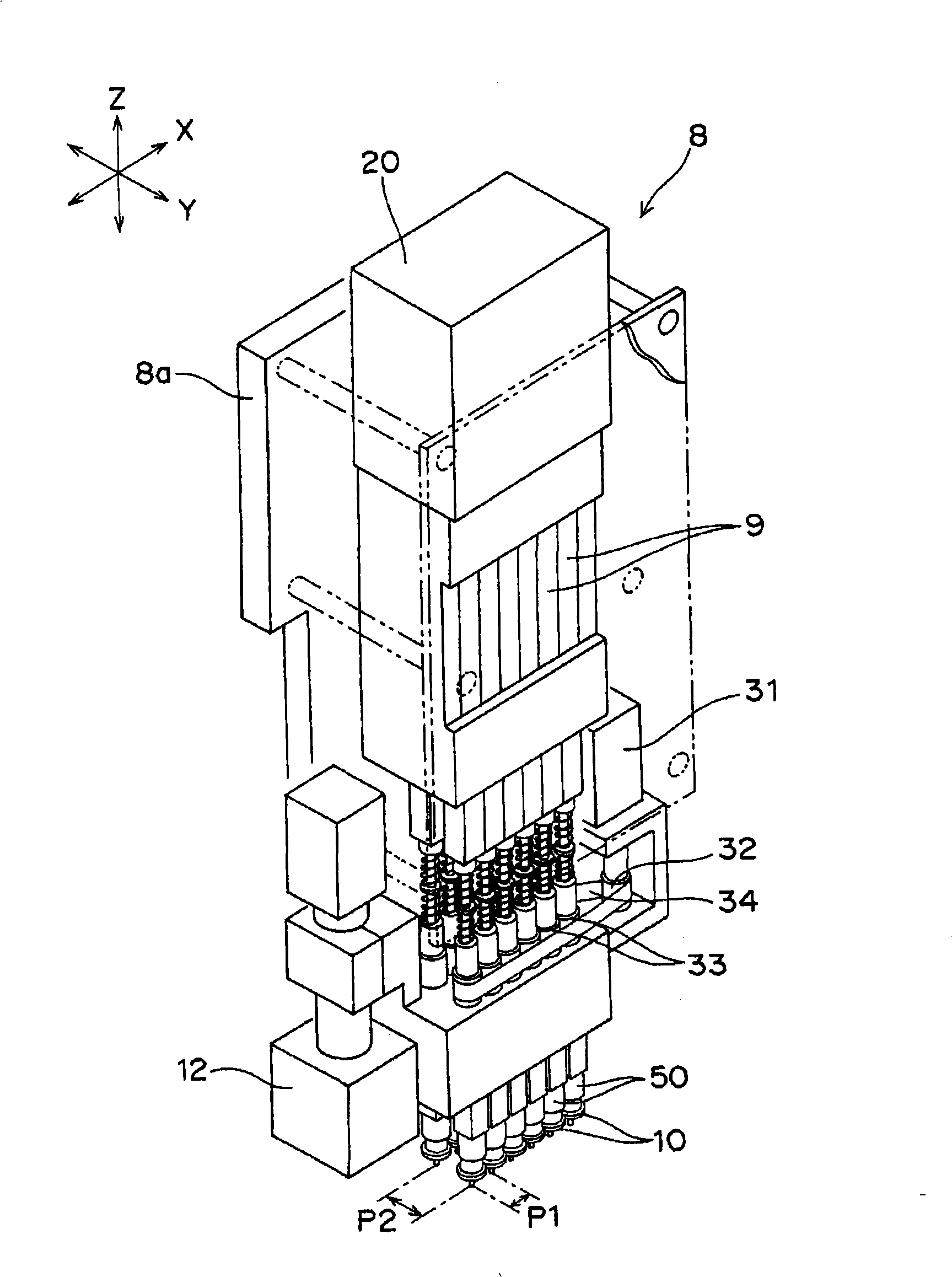
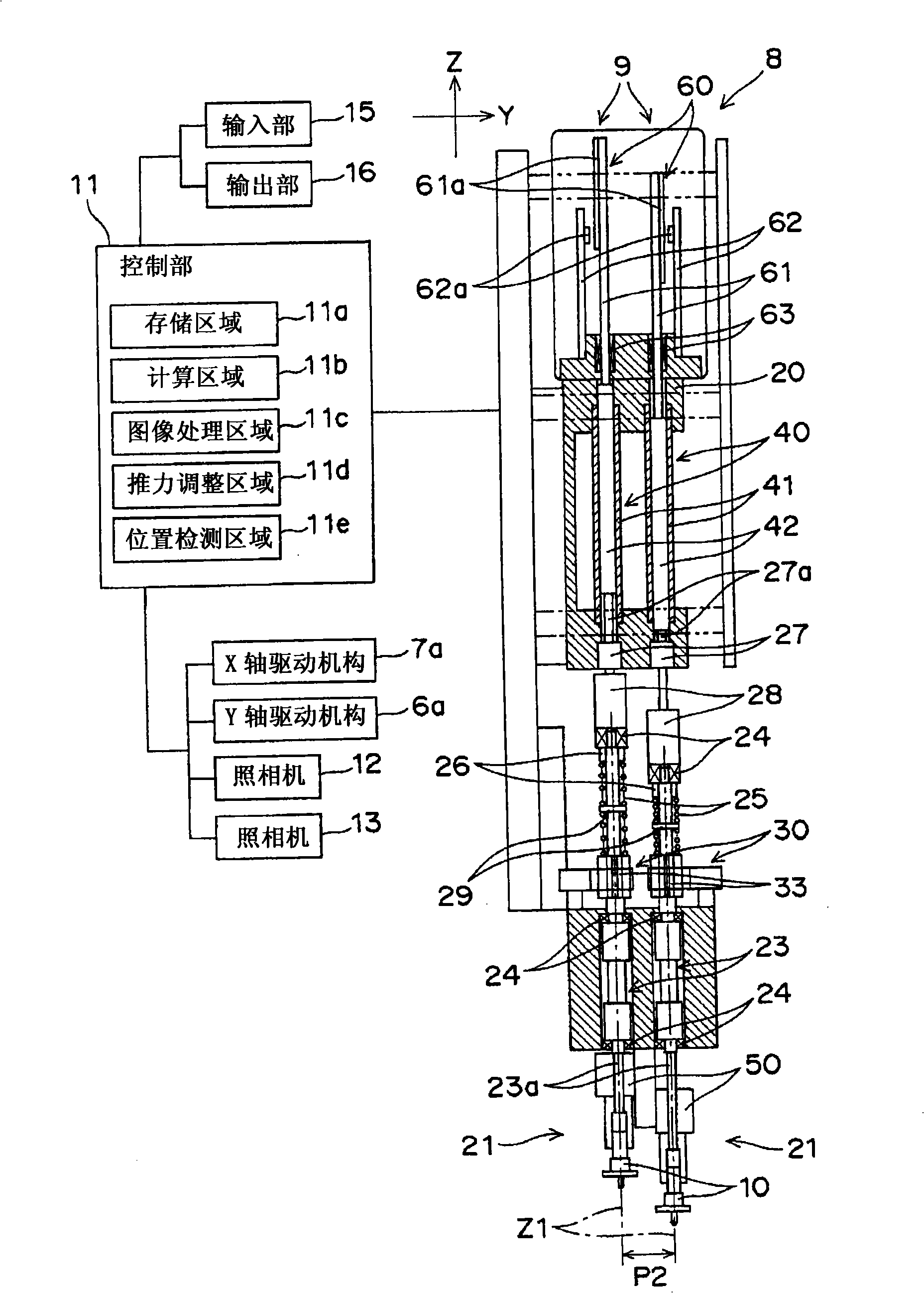
Nozzle mechanism, mounting head, and electronic component mounting equipment
In electronic component mounting equipment, a nozzle mechanism is constituted by disposing a shaft type linear motor vertically above a nozzle unit and disposing a linear encoder vertically above the shaft type linear motor so that it has a slim shape. Consequently, occupied area of each nozzle mechanism can be reduced in the XY direction (horizontal direction), a pitch between adjoining nozzles can be made smaller, and a smaller mounting pitch in electronic components on a miniaturized, high-integration substrate can be dealt with.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Linear encoder
ActiveUS20160011017A1Shorten the lengthEasy millingWalking sticksConverting sensor outputScale unitEngineering
To provide a linear encoder including a scale unit and a slider that slides along the scale unit, wherein the slider includes a slider enclosure including a slider holding unit, a detection head holding unit mounted inside a scale enclosure of the scale unit, and a pillar extending between the outside and inside of the scale enclosure to connect these two holding units, and a part of the pillar closer to the detection head holding unit and a part of the detection head holding unit closer to the pillar are bored by a thickness larger than a thickness of the pillar.
Owner:OKUMA CORP
Error corrected positioning stage
A movable positioning apparatus for positioning a work piece, which includes a base having linear motors attached thereto for supporting and moving a stage or work piece in a longitudinal direction relative to the base. The apparatus includes two linear encoders to measure rotation error by calculating the difference in measured positions. An alignment laser measures straightness errors. Two slides control yaw by moving in opposite directions, and the slides control straightness by moving in the same direction.
Owner:CHITAYAT ANWAR K
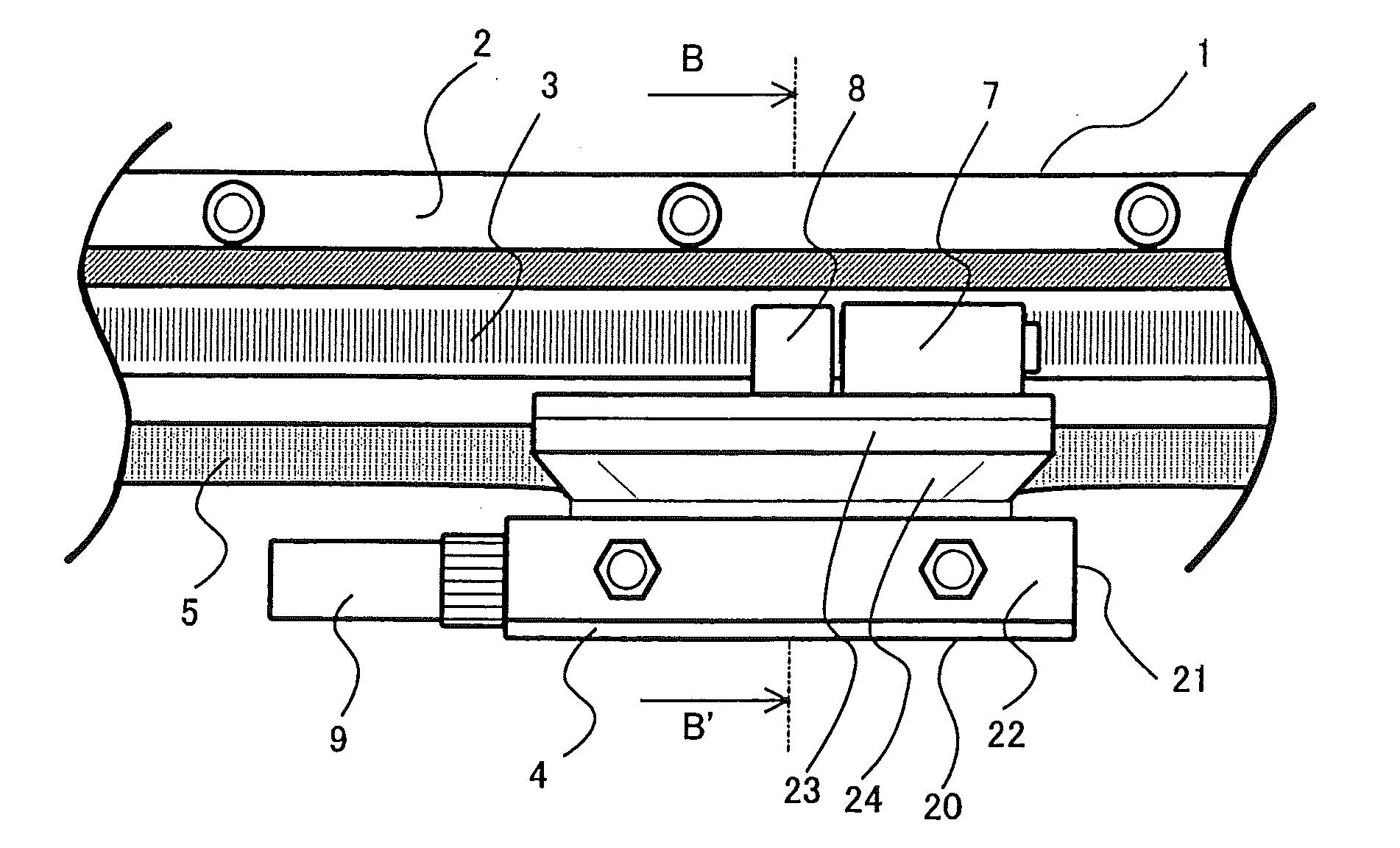
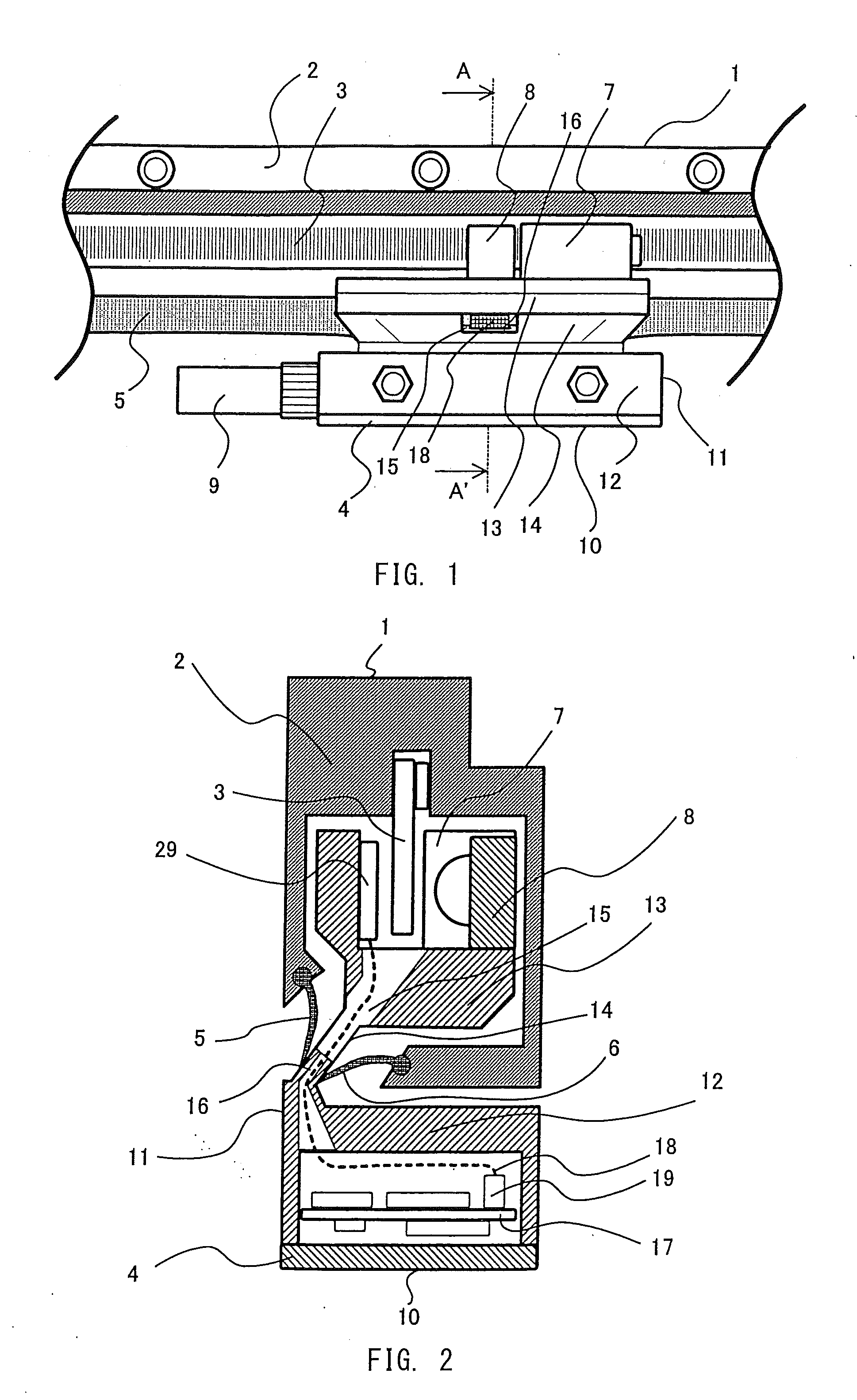
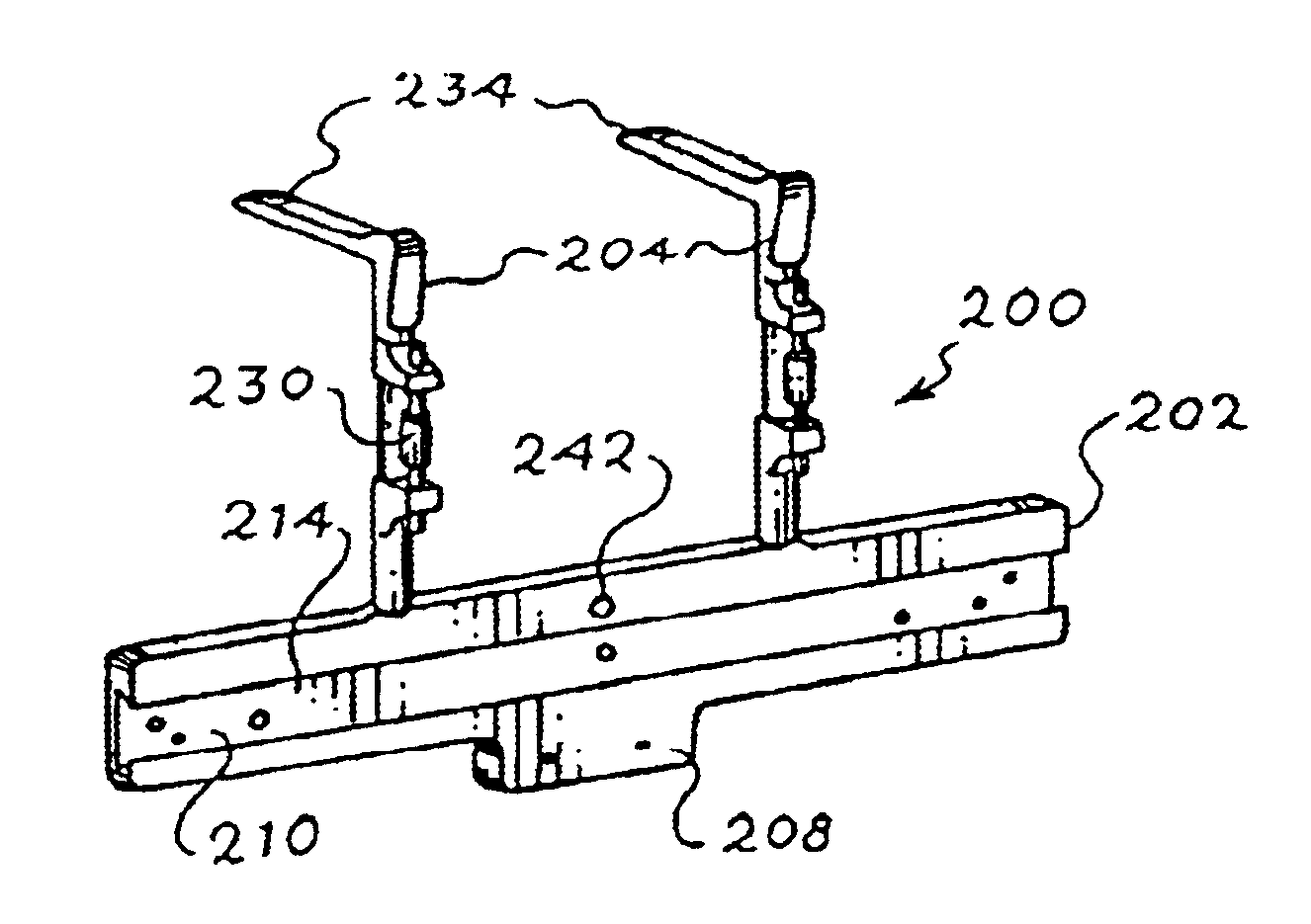
Mounting tool for linear encoders
InactiveUS6820348B2Walking sticksMeasurement/indication equipmentsLinear encoderMechanical engineering
Owner:HEIDENHAIN CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com