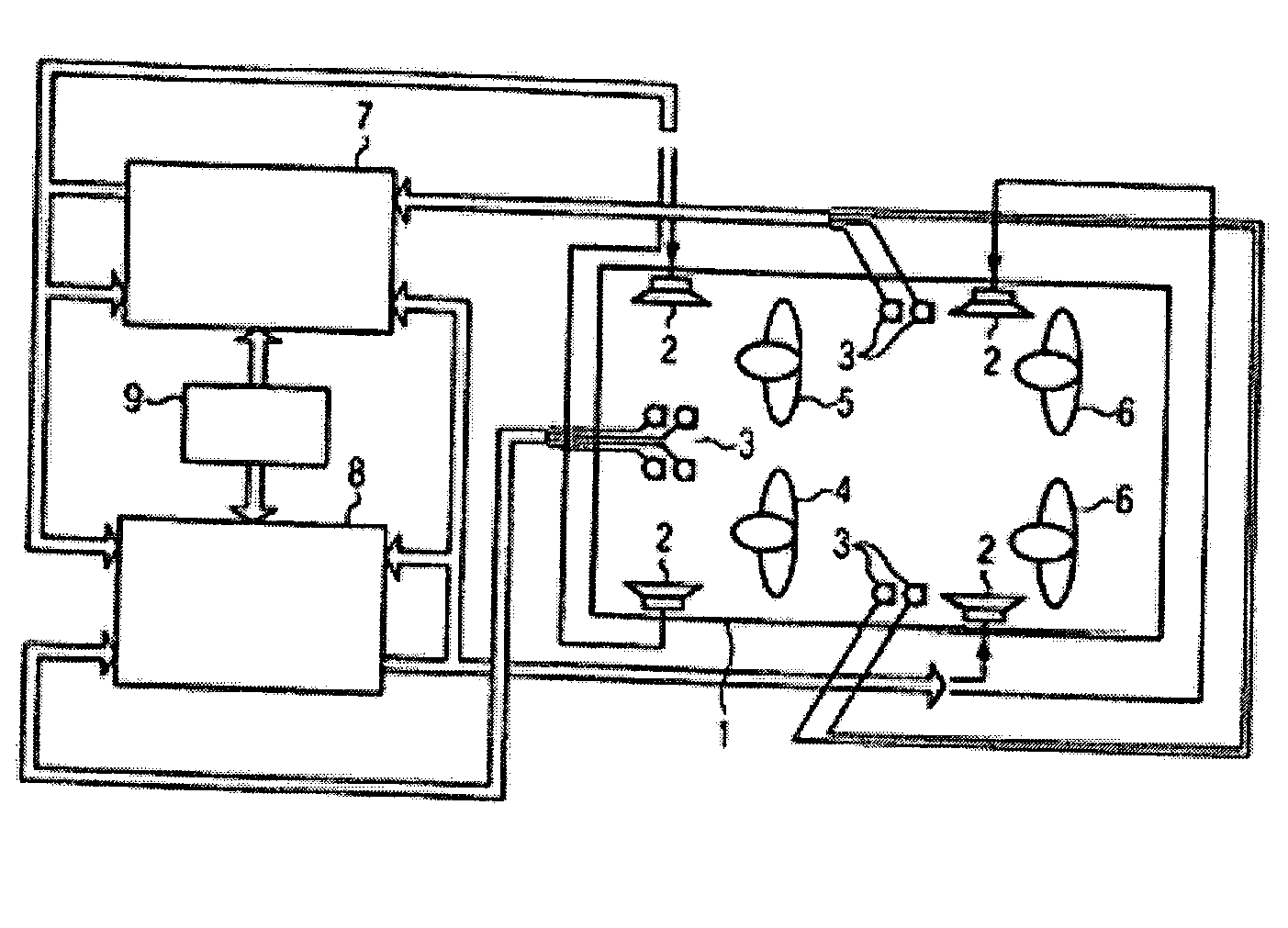
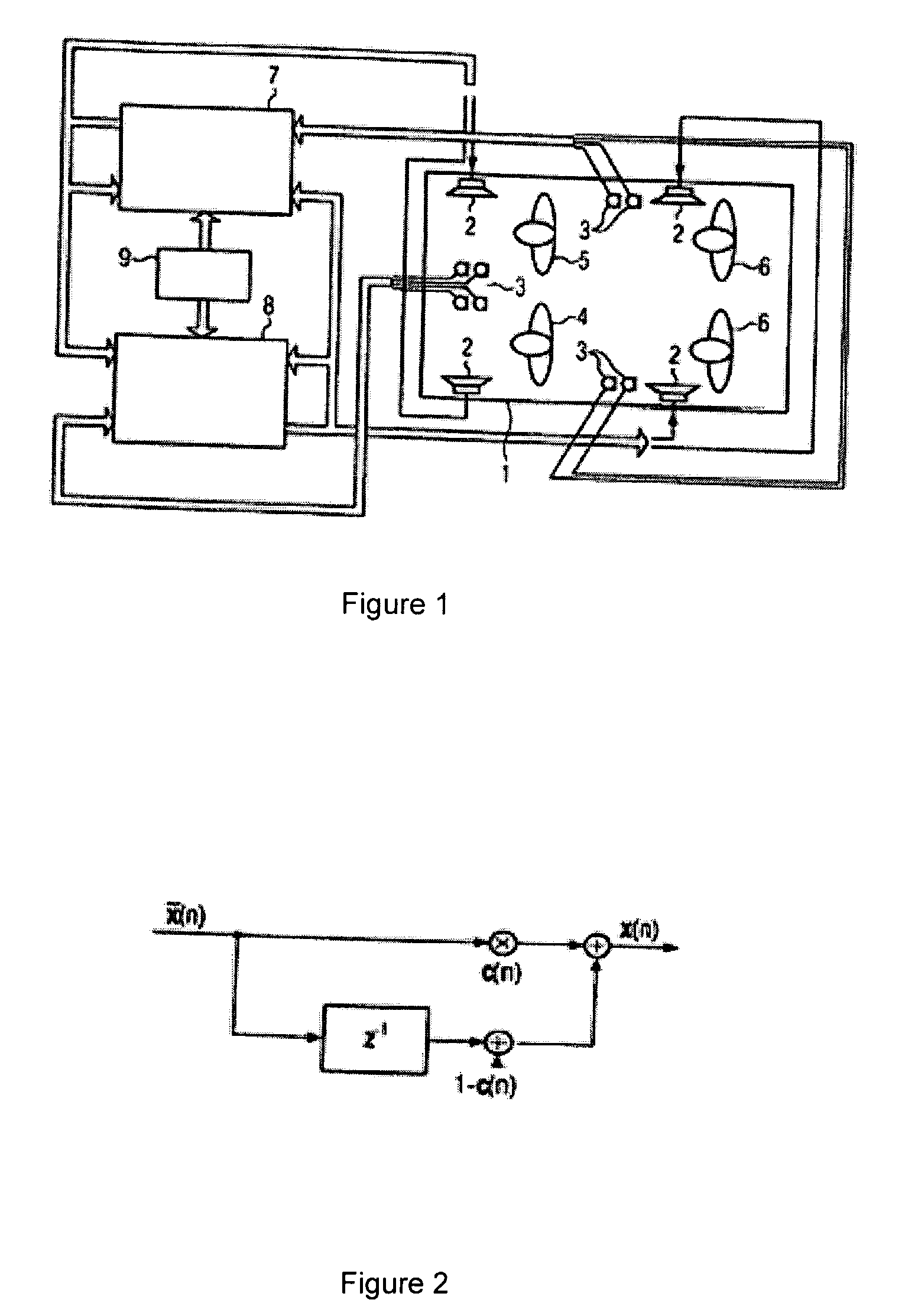
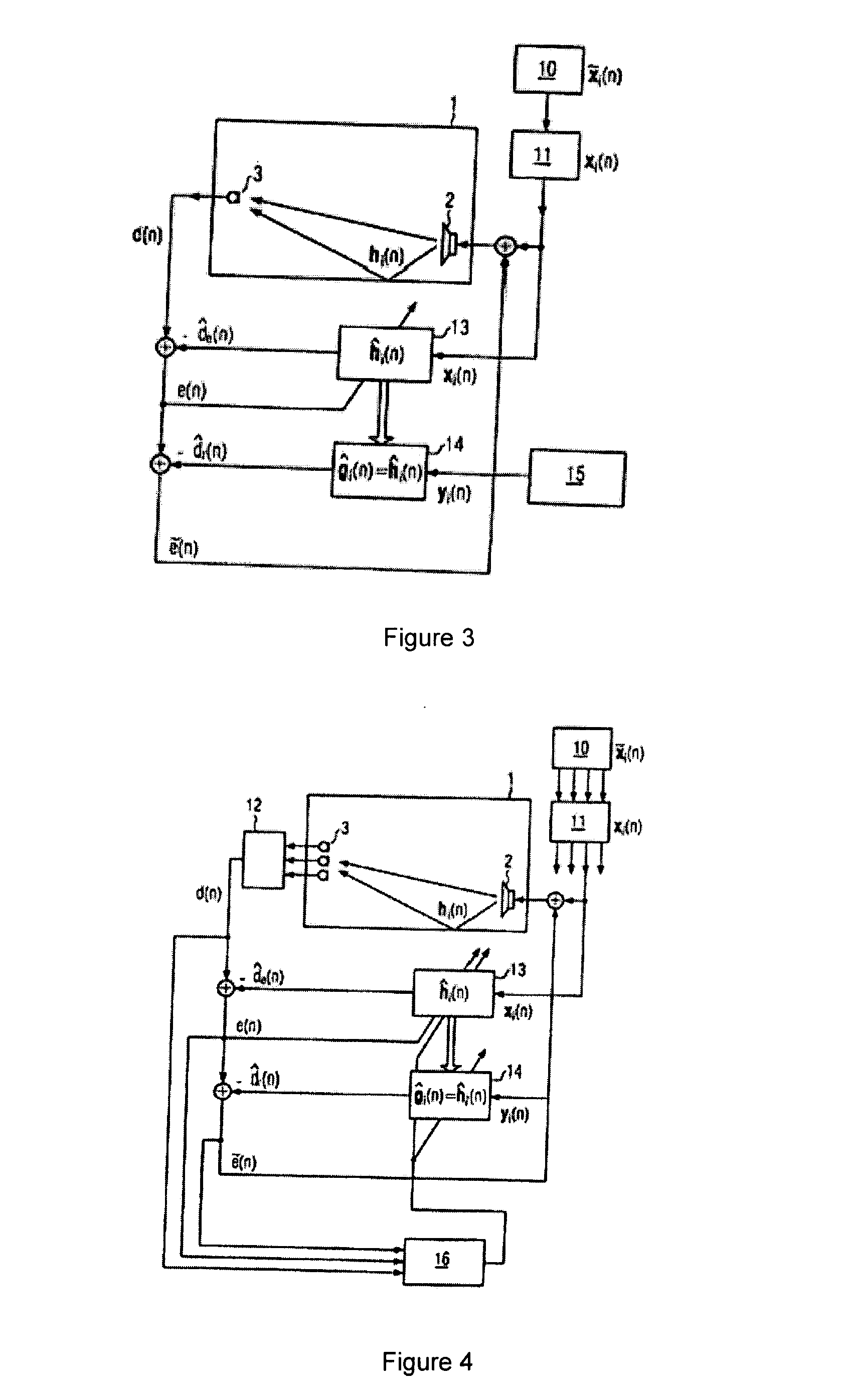
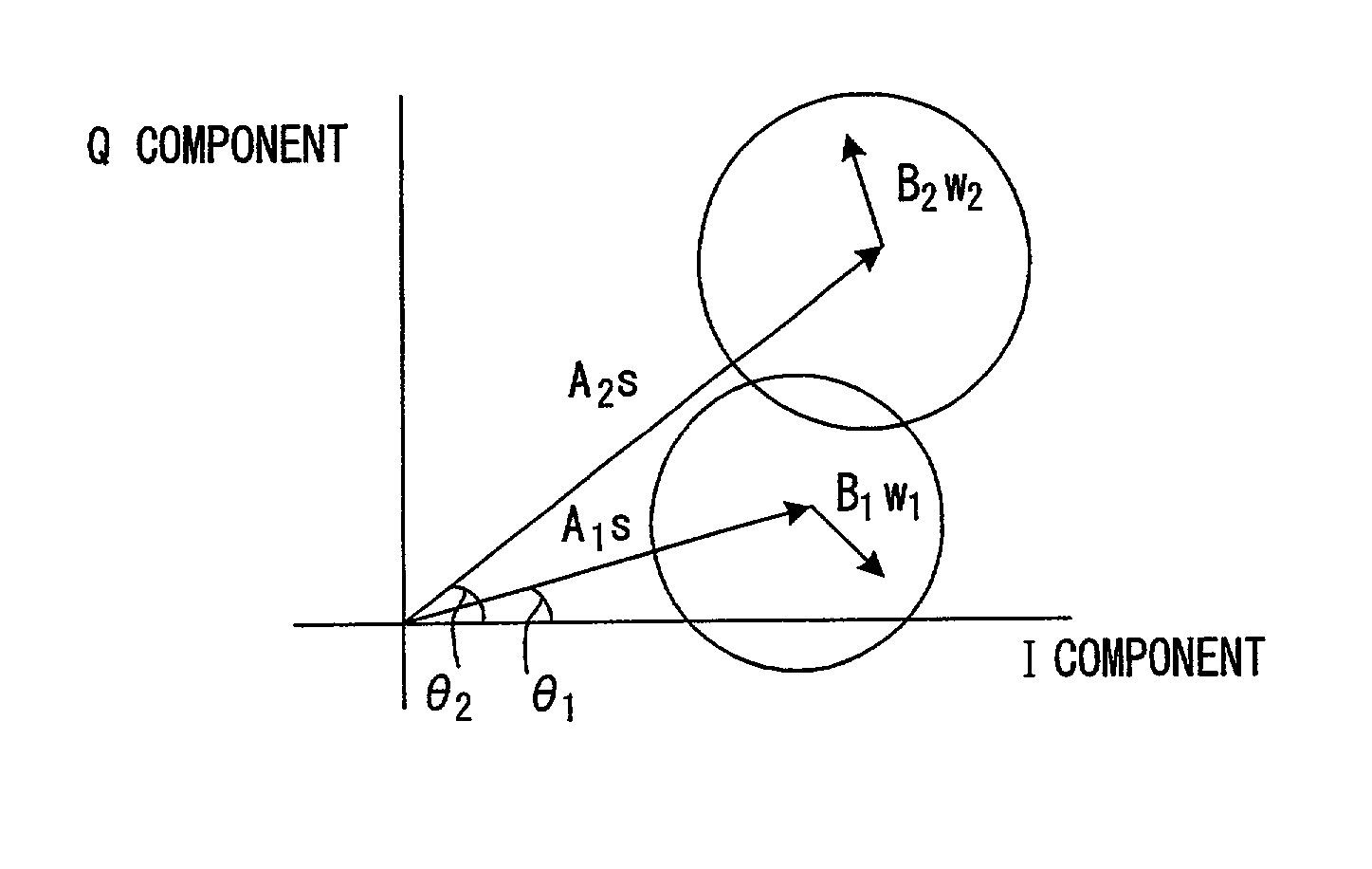
Patents
Literature
172 results about "Noise correlation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
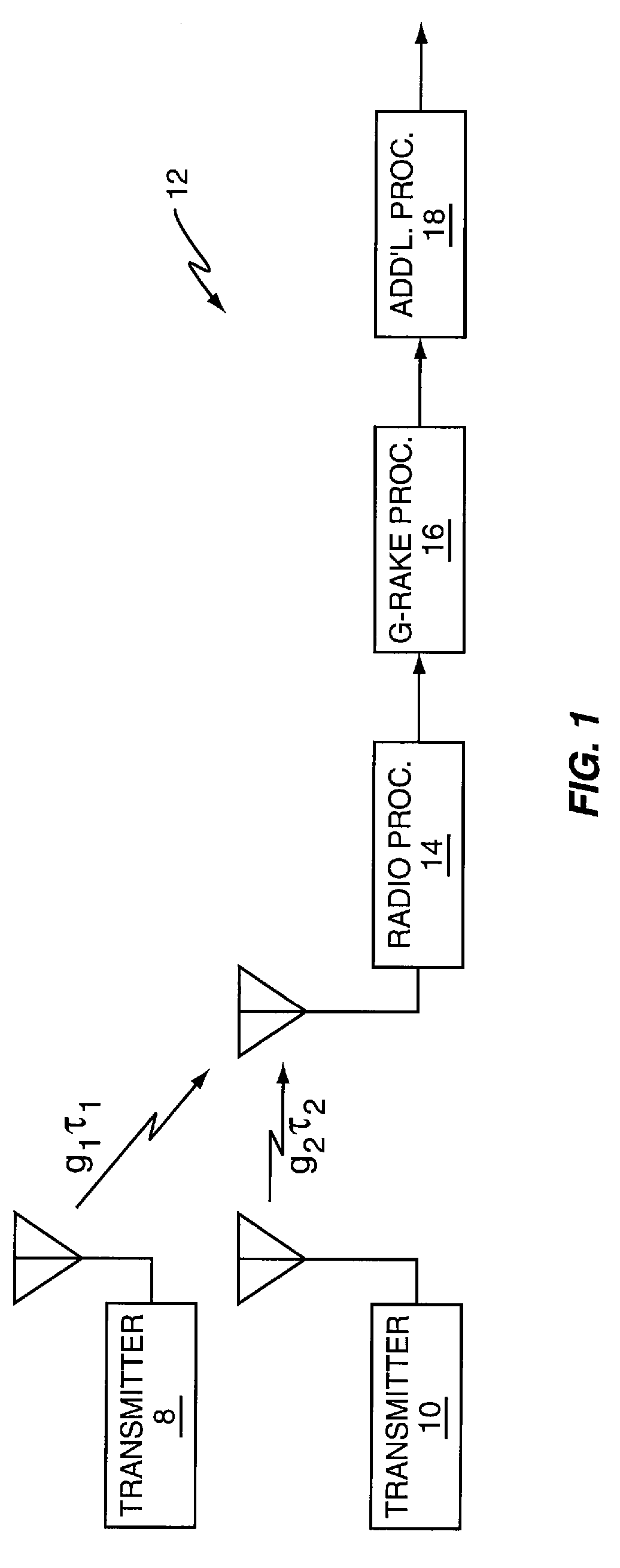
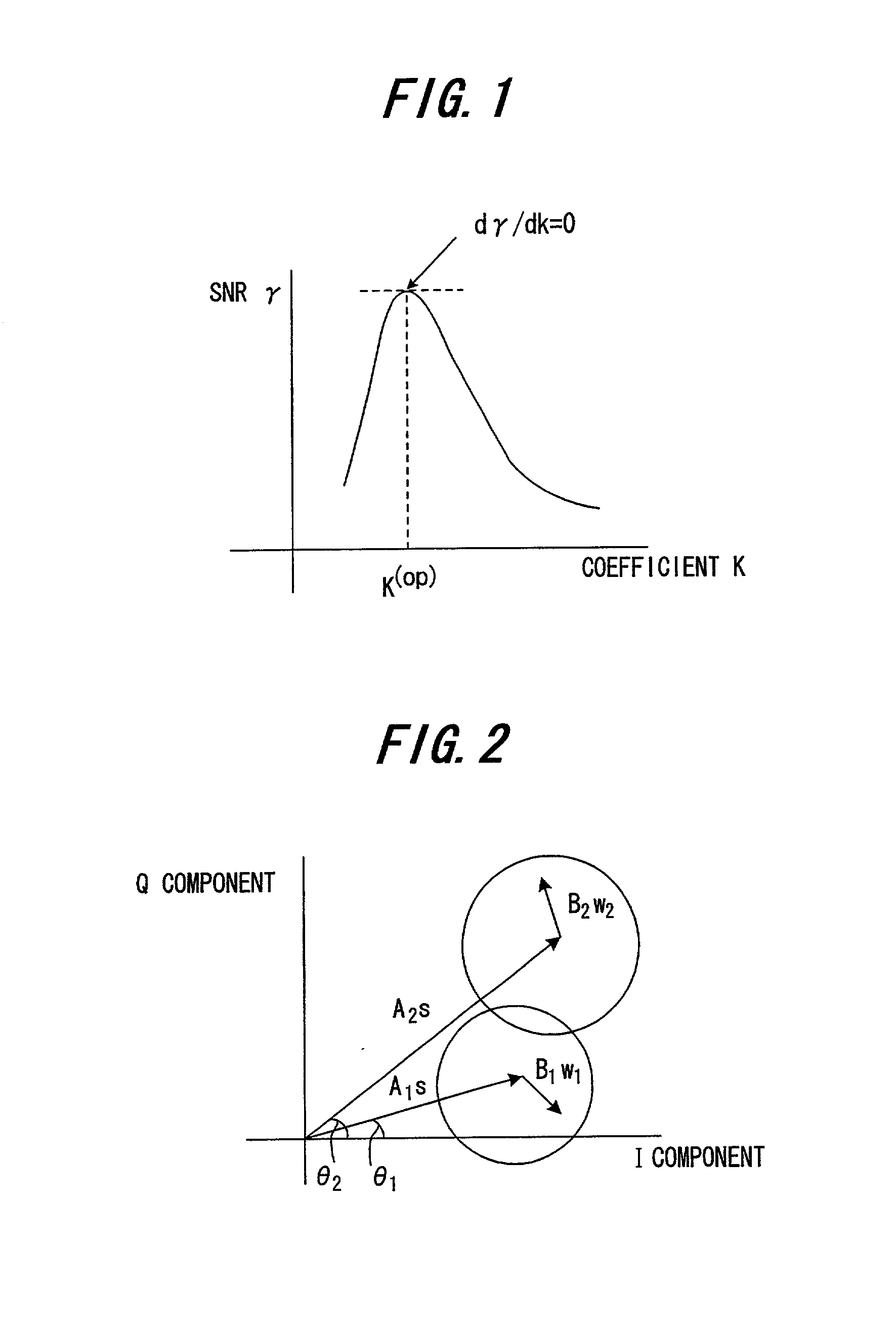
Method and device for multi-user channel estimation
InactiveUS6765969B1Modulated-carrier systemsChannel estimationComputation complexityWeight coefficient
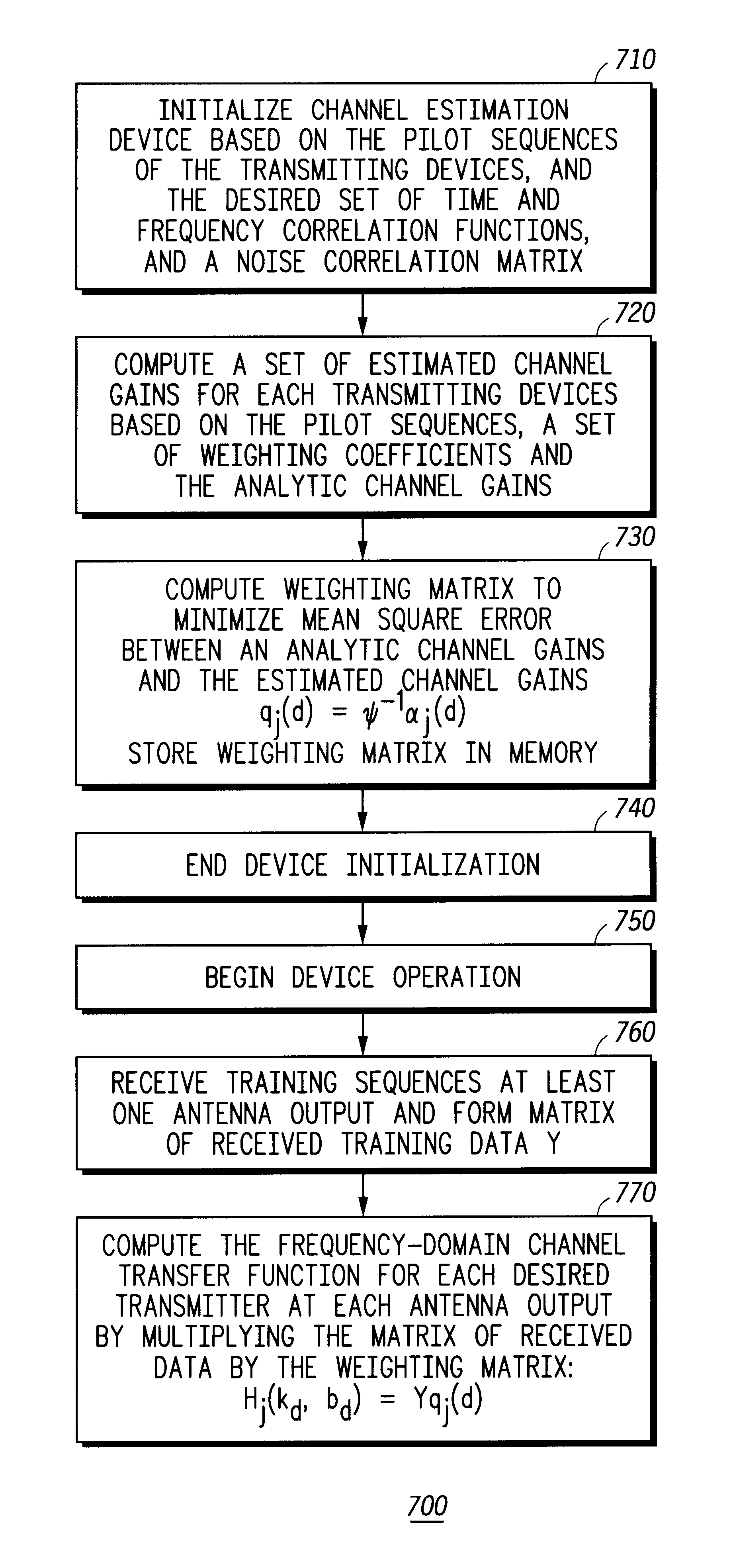
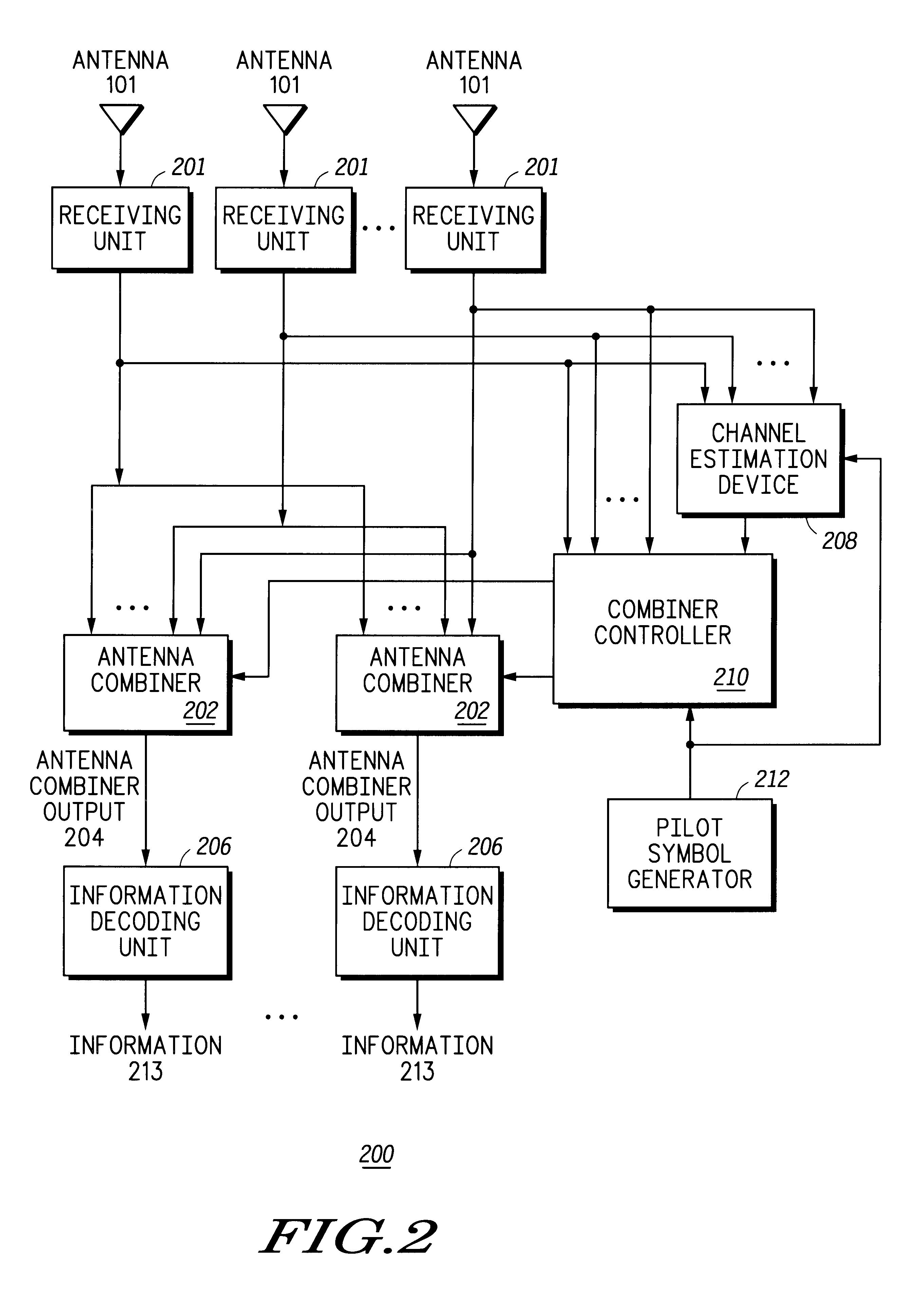
The invention computes frequency-domain channel gains by compiling a set of estimated channel gains as a function of pilot sequences, a set of analytical channel gains variables, and a set of weighting coefficients variables. A plurality of weighting coefficients are computed as a function of time and frequency correlation functions, a noise correlation matrix, and pilot sequences. A weighting matrix is computed from the weighting coefficients. After receiving a training sequence from at least one transmitter, a received data matrix is computed from the training sequence. The weighting matrix and the received data matrix are used to compute the frequency-domain channel gains. The invention also provides a method for reducing the computational complexity of estimating the time and frequency response of at least one desired signal received by at least one antenna. Also, the time and frequency response of at least one desired signal received by at least one antenna can be both interpolated and predicted with the present invention.
Owner:MOTOROLA SOLUTIONS INC
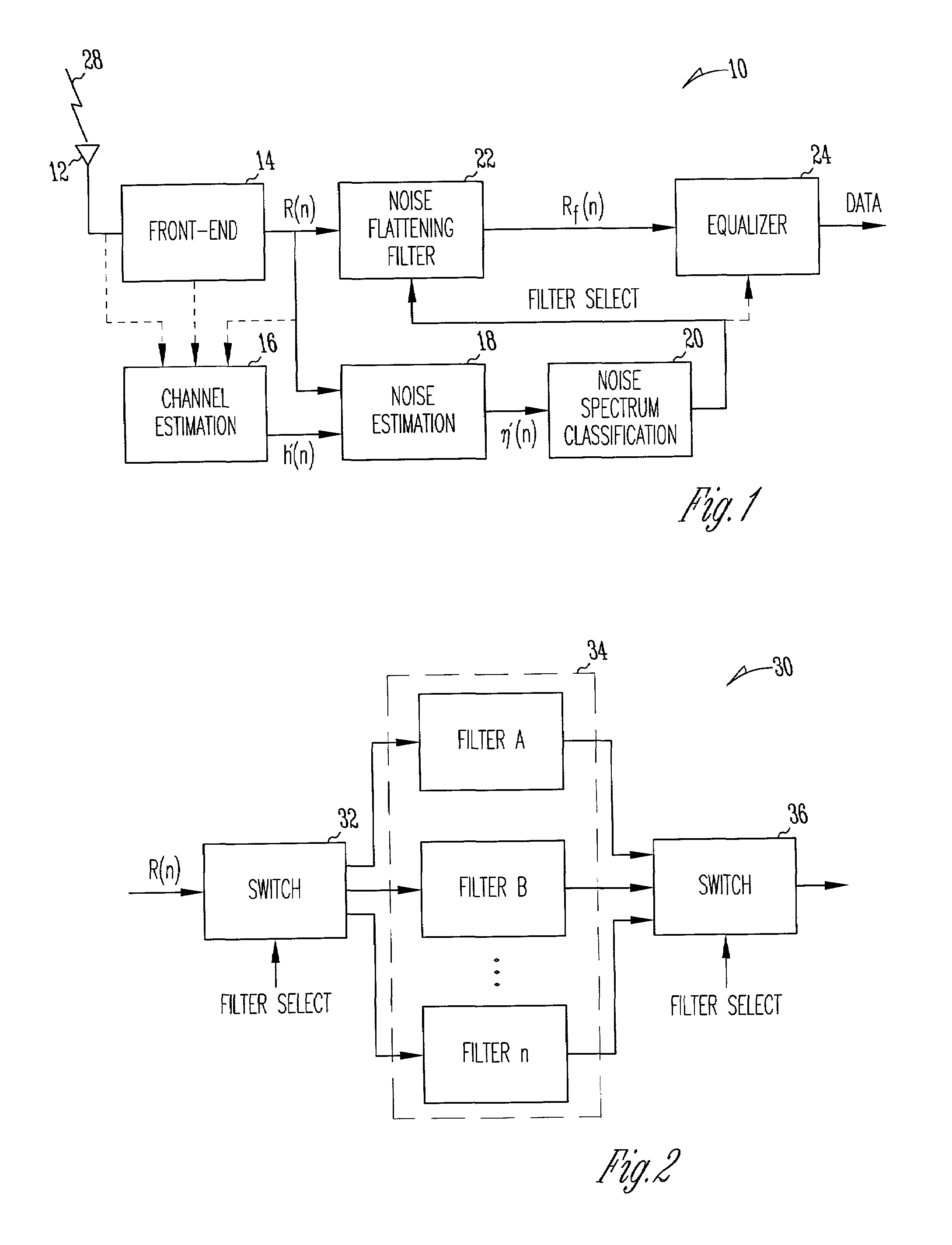
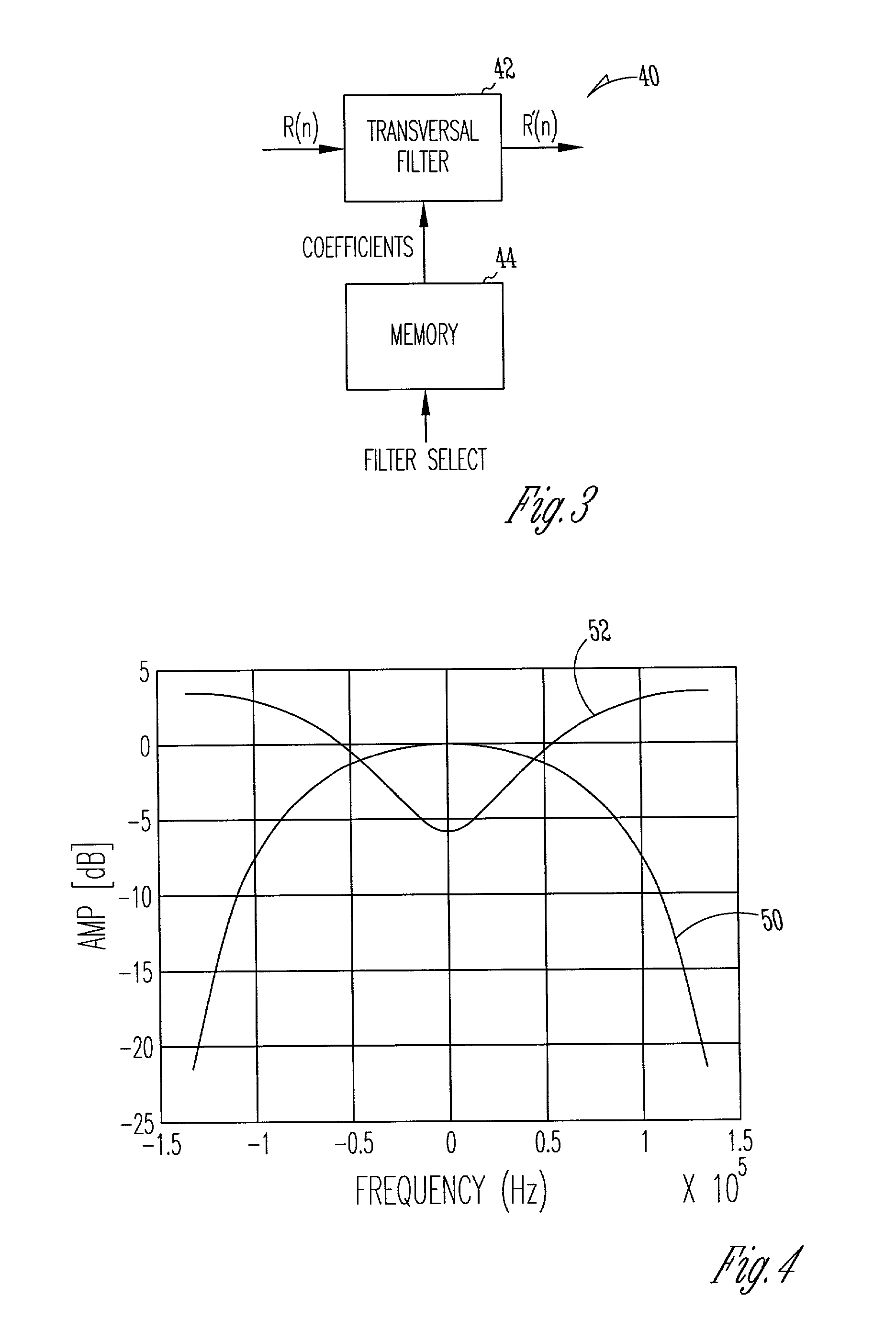
Noise dependent filter
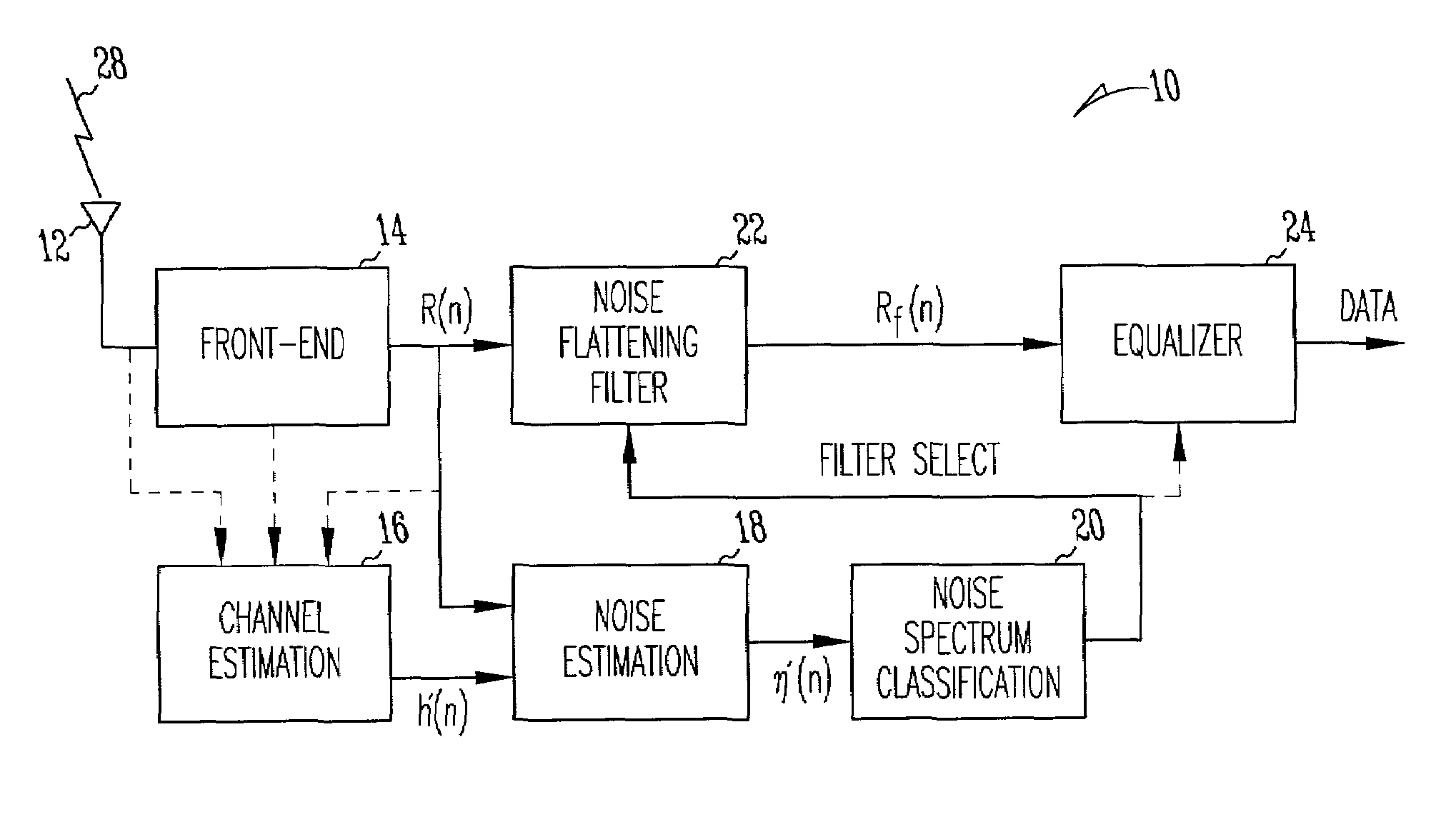
A communication device includes a noise flattening filter having a filter response that dynamically adjusts based on the current noise spectrum in a wireless channel. The noise spectrum of the wireless channel is estimated and used to determine a noise classification for the channel. A noise flattening filter response is then selected based upon the noise classification for use in filtering signals received from the channel. The filtered signals are then delivered to an equalizer for further processing.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Autocalibrating parallel imaging reconstruction method from arbitrary k-space sampling with reduced noise
ActiveUS20120092009A1Measurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionParallel imagingReconstruction method
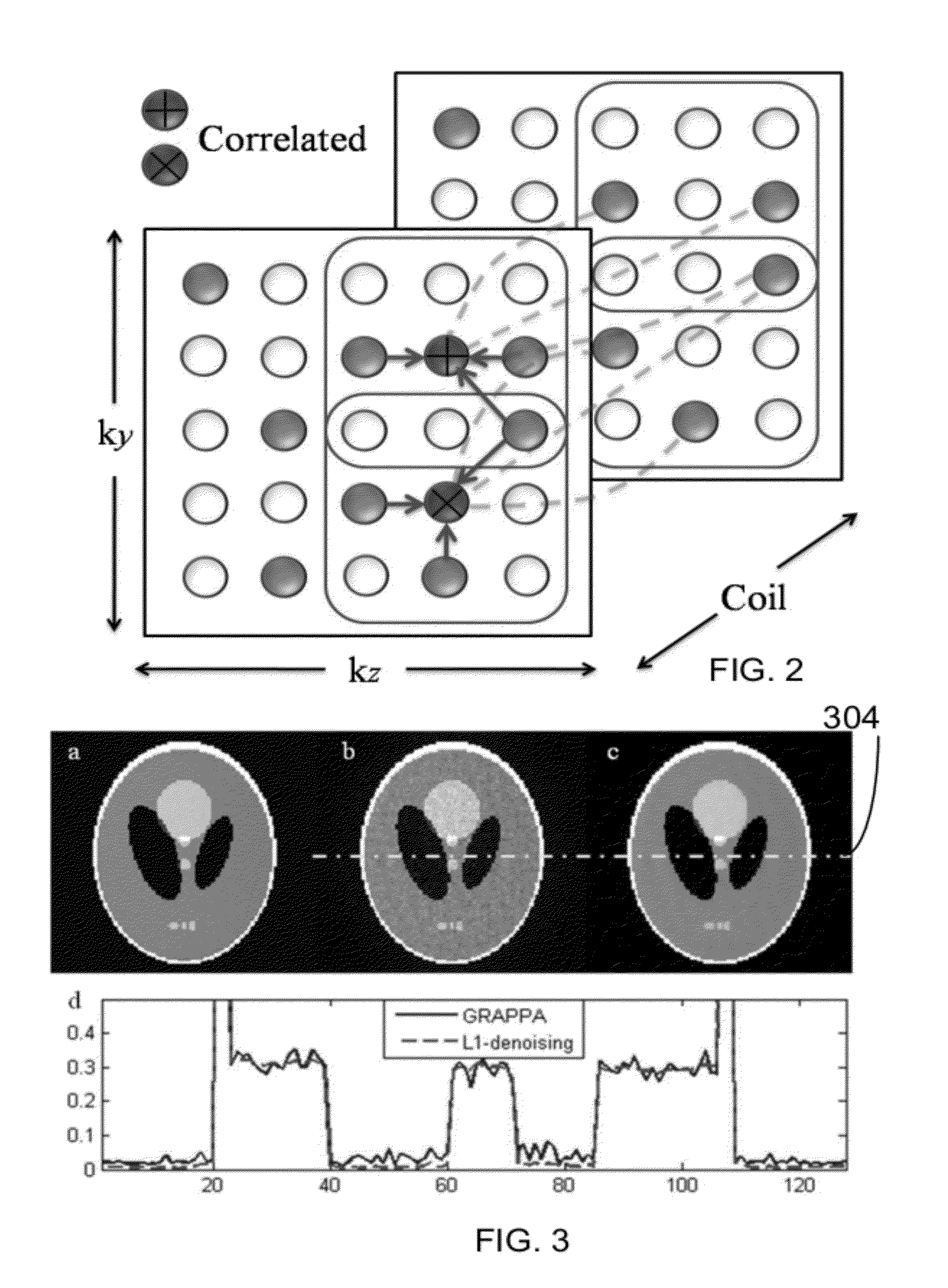
A computer implemented method for magnetic resonance imaging is provided. A 3D Fourier Transform acquisition is performed with two phase encode directions, wherein phase code locations are chosen so that a total number of phase encodes is less than a Nyquist rate, and closest distances between phase encode locations takes on a multiplicity of values. Readout signals are received through a multi-channel array of a plurality of receivers. An autocalibrating parallel imaging interpolation is performed and a noise correlation is generated. The noise correlation is used to weight a data consistency term of a compressed sensing iterative reconstruction. An image is created from the autocalibration parallel imaging using the weighted data consistency term. The image is displayed.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Method and apparatus for noise tomography
The subject invention pertains to an imaging technique and apparatus which can utilize an array of RF probes to measure the non-resonant thermal noise which is produced within a sample, such as a body, and produce a non-resonant thermal noise correlation. The detected noise correlation is a function of the spatial overlap of the electromagnetic fields of the probes and the spatial distribution of the conductivity of the sample. The subject technique, which can be referred to as Noise Tomography (NT), can generate a three-dimensional map of the conductivity of the sample. Since the subject invention utilizes detection of the thermal noise generated within the body, the subject method can be non-invasive and can be implemented without requiring external power, chemicals, or radionuclides to be introduced into the body. The subject imaging method can be used as a stand along technique or can be used in conjunction with other imaging techniques.
Owner:INVIVO CORP
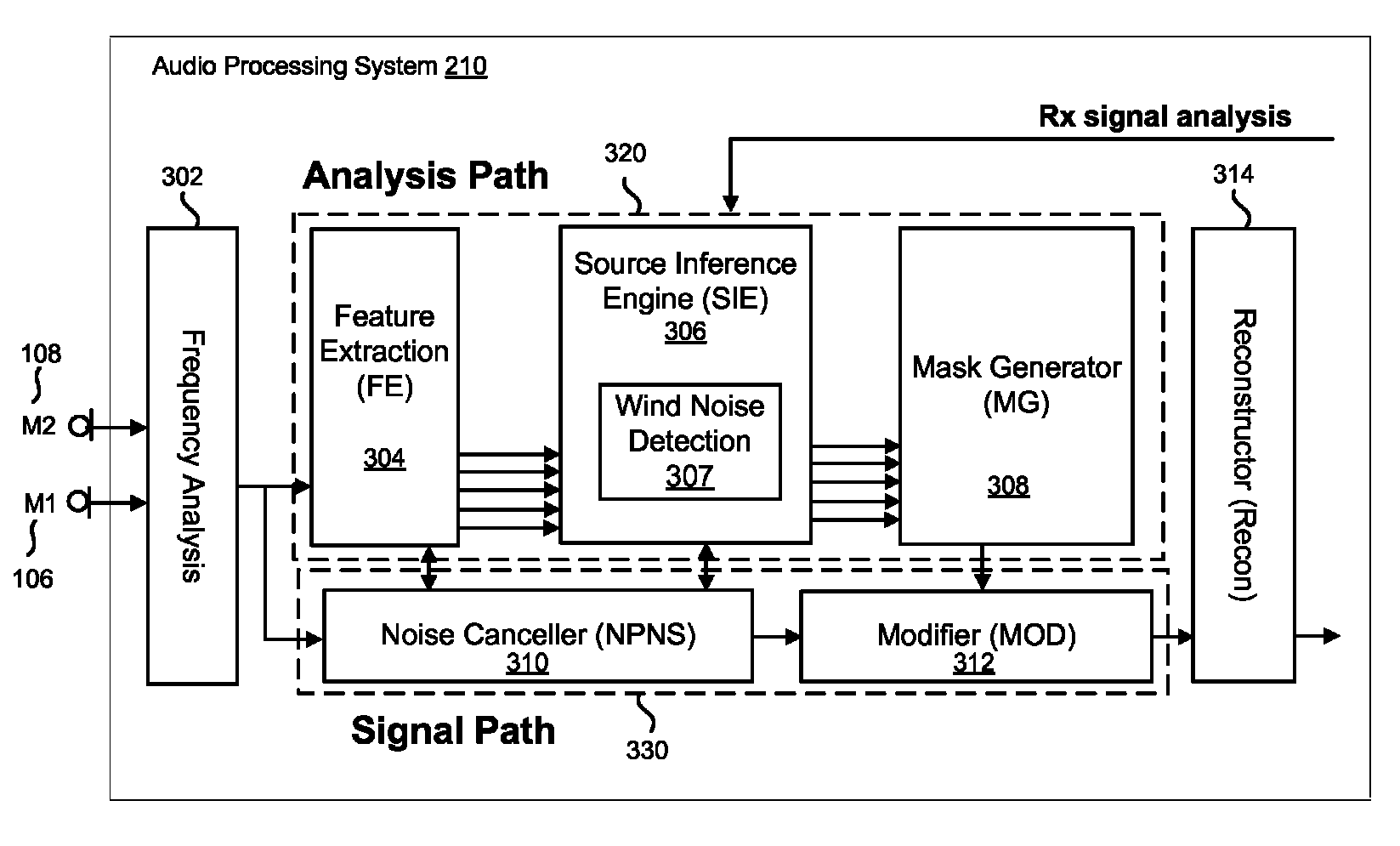
Wind noise detection and suppression
ActiveUS8781137B1Detects and remove wind noiseSuppress wind noiseMicrophonesSignal processingSignal classificationEngineering
Wind noise is detected in and removed from an acoustic signal. Features may be extracted from the acoustic signal. The extracted features may be processed to classify the signal as including wind noise or not. The wind noise may be removed before or during processing of the acoustic signal. The wind noise may be suppressed by estimating a wind noise model, deriving a modification, and applying the modification to the acoustic signal. In audio devices with multiple microphones, the channel exhibiting wind noise (i.e., acoustic signal frame associated with the wind noise) may be discarded for the frame in which wind noise is detected.
Owner:KNOWLES ELECTRONICS INC
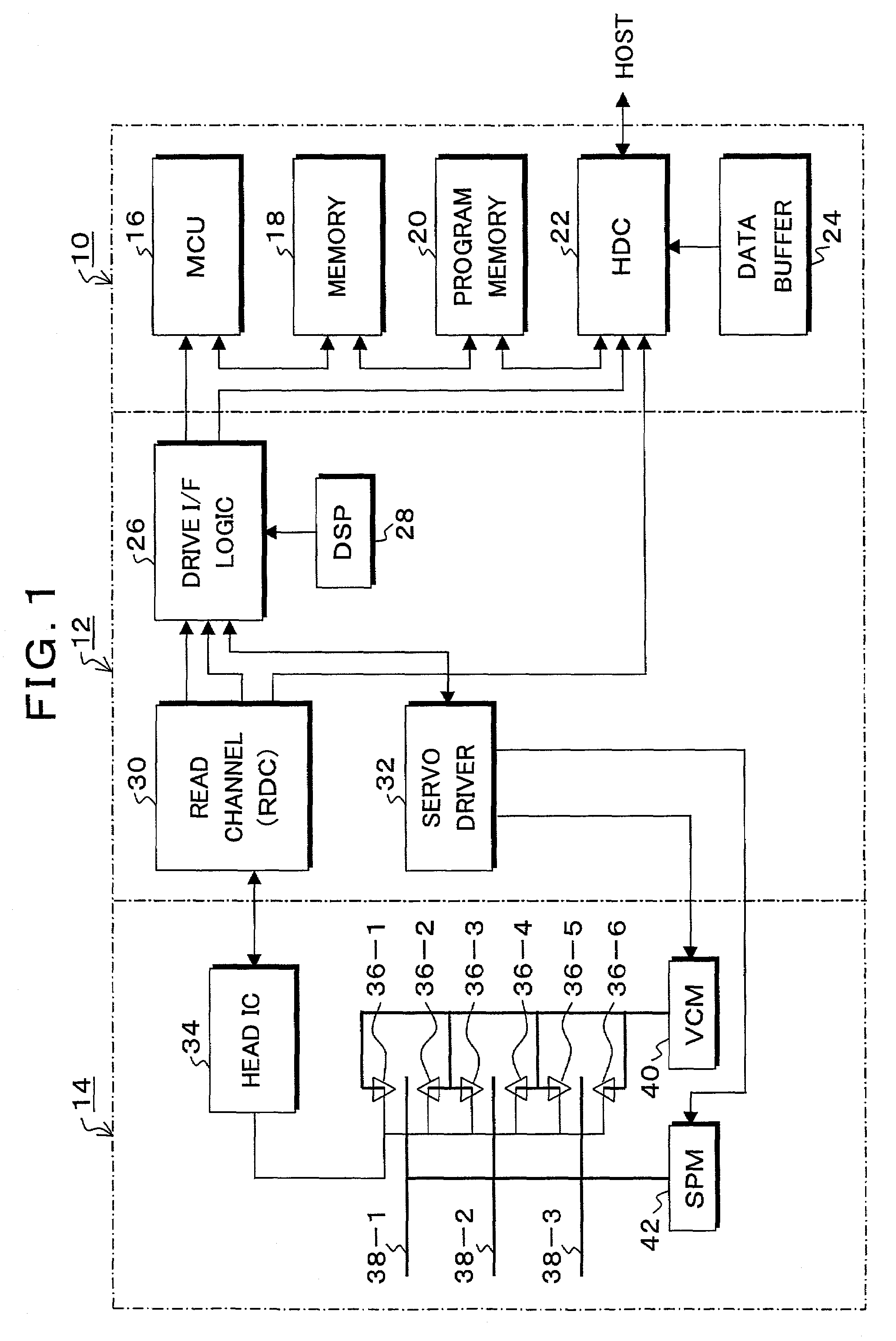
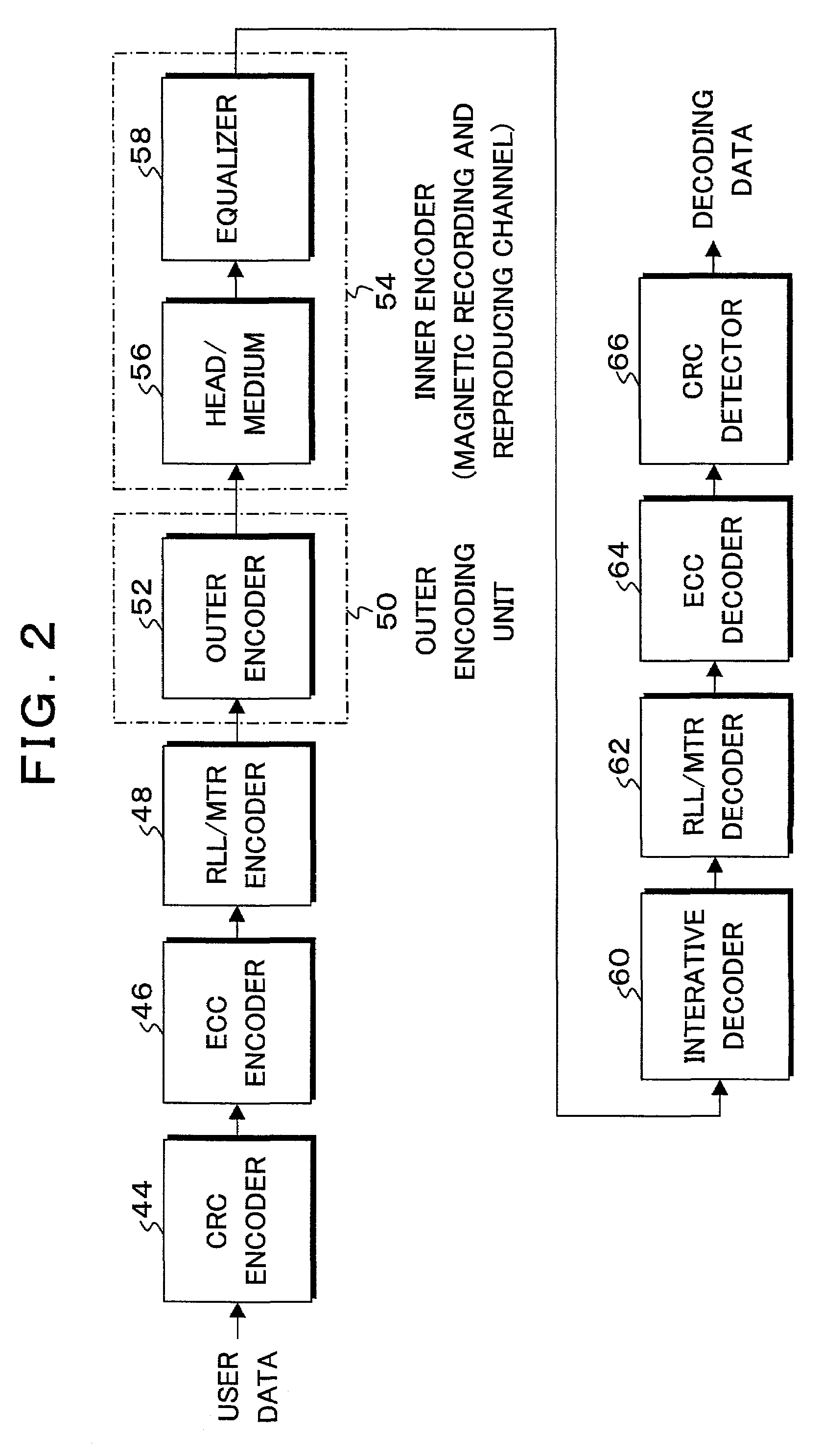
Information recording and reproducing apparatus and method and signal decoding circuit having improved noise processing characteristics
InactiveUS7031090B2Effective applicationImprove decoding performanceModification of read/write signalsOther decoding techniquesMaximum a posteriori estimationComputer science
In a Maximum A posteriori Probability decoding (MAP decoding), a correlation and a deviation of noises for past and future states which depend on input signal patterns in past N bits and future Q bits are calculated by training by a noise correlation arithmetic operating unit 84 and they are stored. Upon reproduction, in a white noise arithmetic operating unit 91, white noise values for the past and future states in which colored noises are converted into white noises are obtained by using the stored correlation and deviation of the noises. In an input signal arithmetic operating unit 92, an input signal (channel information) Λc(yk|Smk) of the MAP decoding is calculated from the white noise values and the deviation for the past and future states. A likelihood in the MAP decoding is obtained from the input signal.
Owner:TOSHIBA STORAGE DEVICE CORP
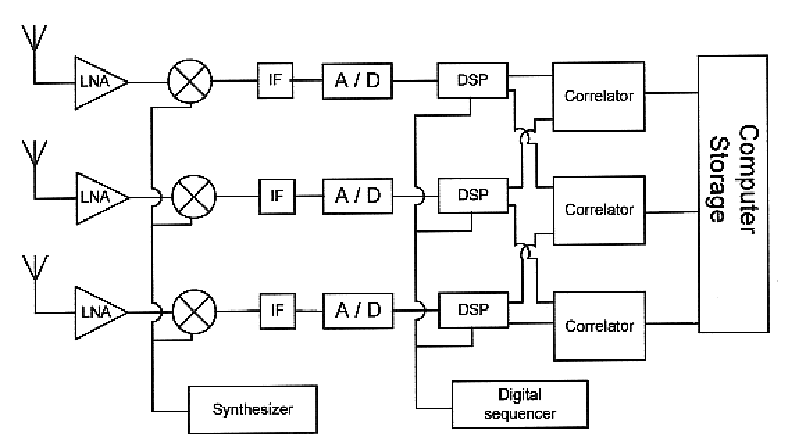
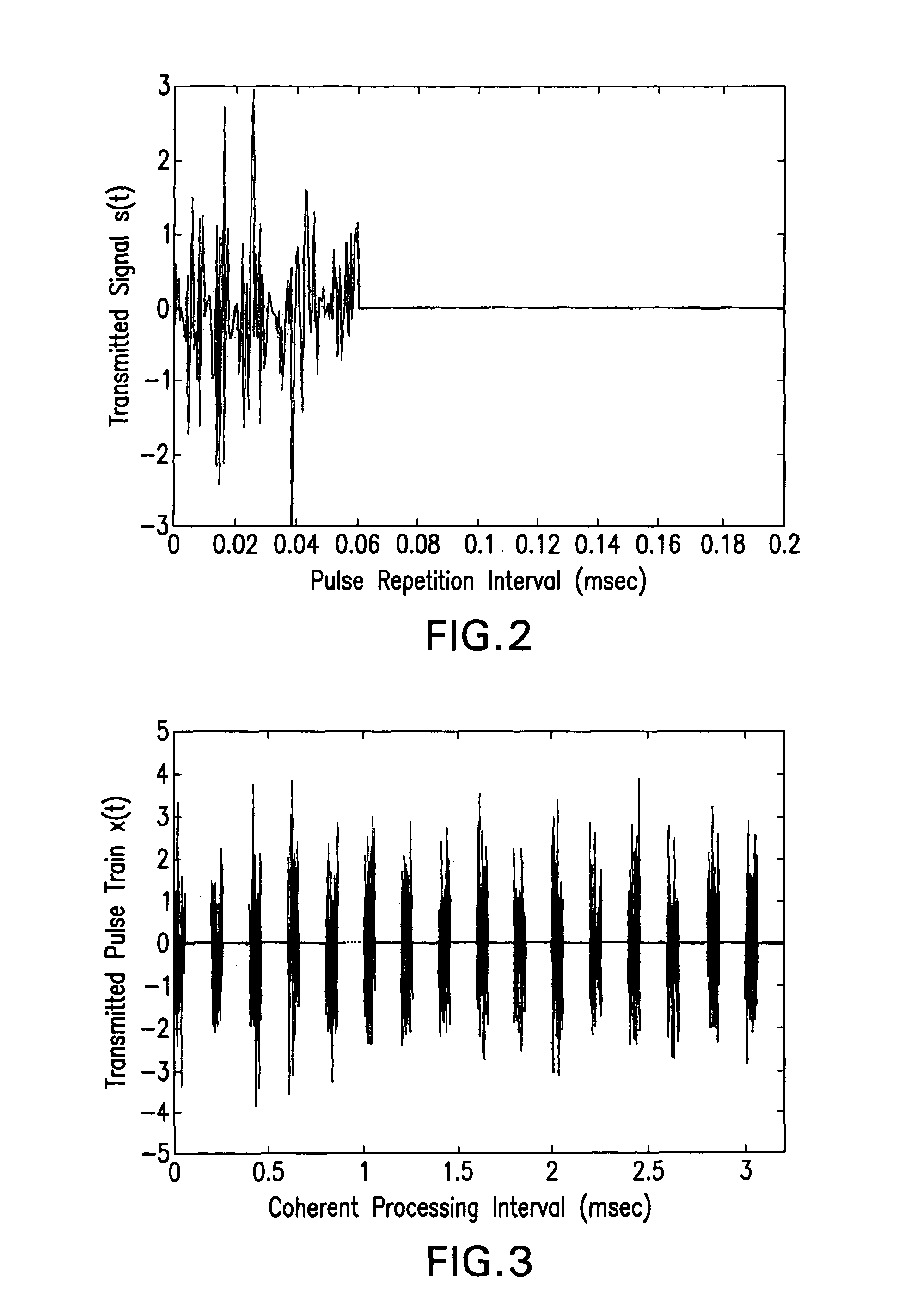
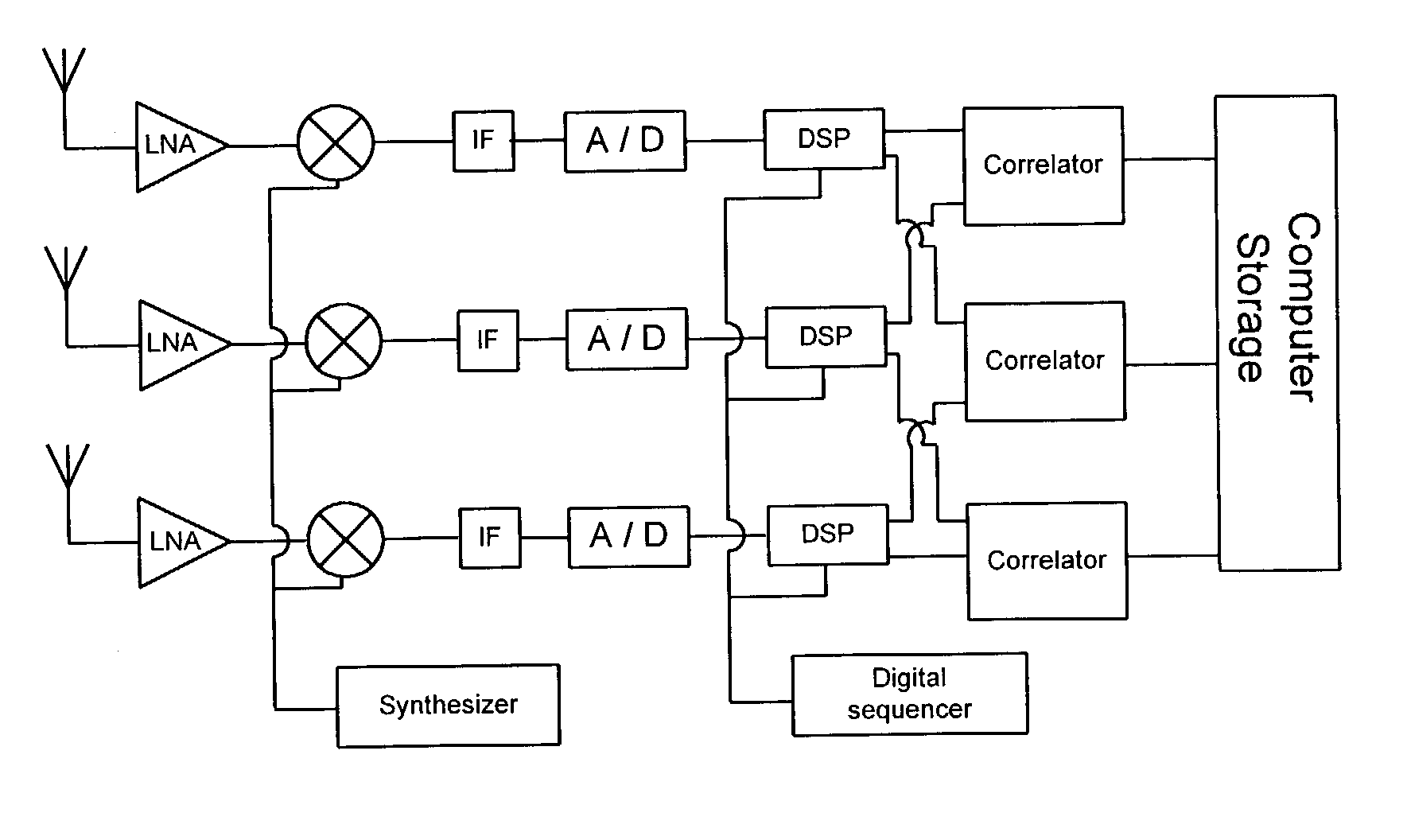
Noise correlation radar devices and methods for detecting targets with noise correlation radar
InactiveUS8035551B1Instantaneous band widthIncrease the carrier frequencyRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRadar systemsFrequency modulation
A pulsed compression noise correlation radar uses noise modulation and pulse compression technology to scramble recognizable transmit signal characteristics and reduce transmit energy. The pulsed noise correlation radar advantageously uses pulse compression technology, a pulsed linear frequency modulated noise correlation mixer, and a new and innovative noise fused waveform to automatically correlate the pulsed linear frequency modulated (LFM) noise waveform with the received signal. The pulsed noise correlation radar apparatus and system now make it possible to effectively reduce transmitting power, preserve high band widths through oversampling in the receiver, and achieve multi-channel array frequency diversity. A secure pulsed compression noise correlation radar system and methods for undetected target detection with pulsed noise correlation radar and a pulsed LFM fused noise waveform are also provided.
Owner:ARMY US SEC THE
Method and apparatus for noise tomography
The subject invention pertains to an imaging technique and apparatus which can utilize an array of RF probes to measure the non-resonant thermal noise which is produced within a sample, such as a body, and produce a non-resonant thermal noise correlation. The detected noise correlation is a function of the spatial overlap of the electromagnetic fields of the probes and the spatial distribution of the conductivity of the sample. The subject technique, which can be referred to as Noise Tomography (NT), can generate a three-dimensional map of the conductivity of the sample. Since the subject invention utilizes detection of the thermal noise generated within the body, the subject method can be non-invasive and can be implemented without requiring external power, chemicals, or radionuclides to be introduced into the body. The subject imaging method can be used as a stand along technique or can be used in conjunction with other imaging techniques.
Owner:INVIVO CORP
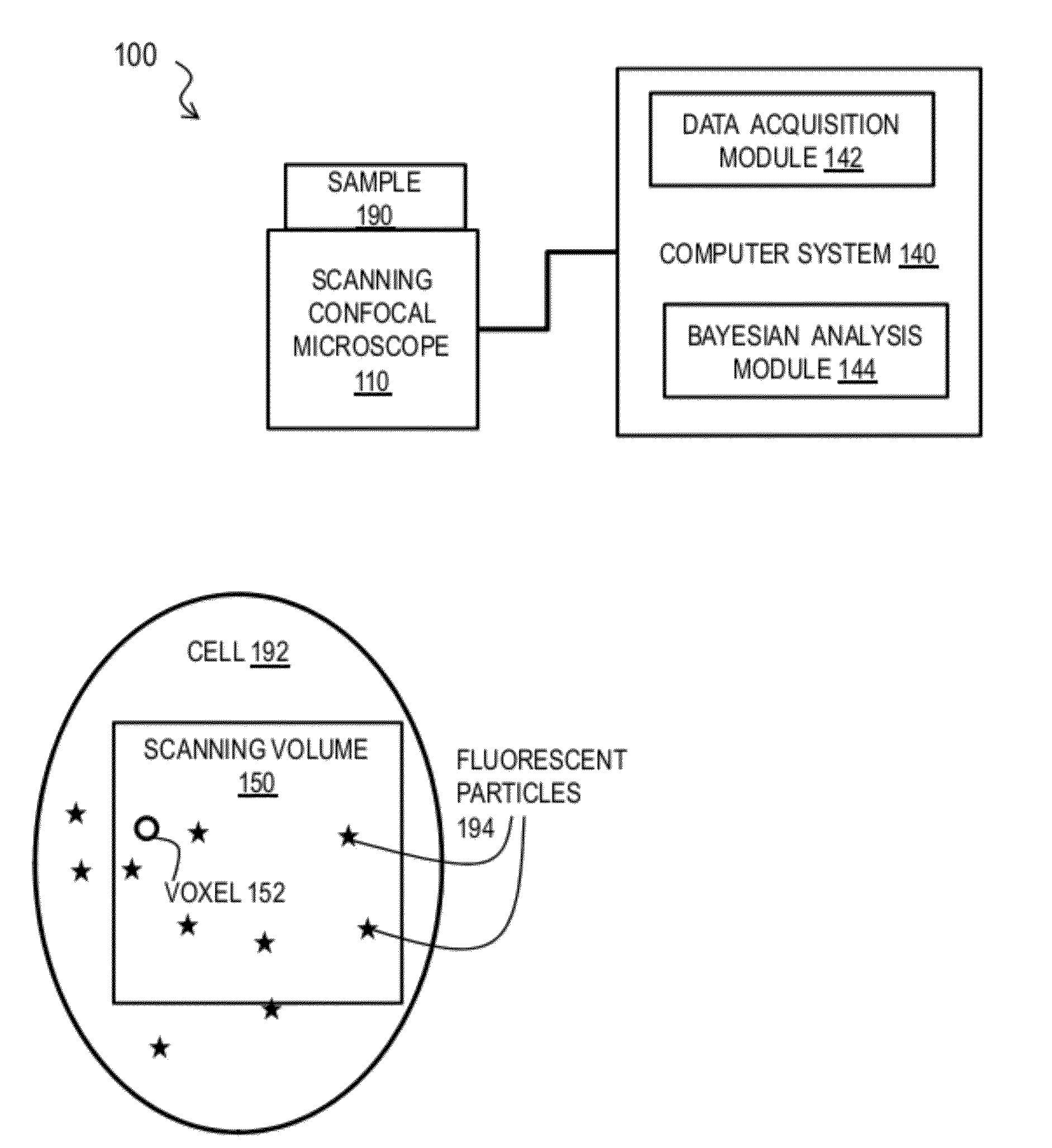
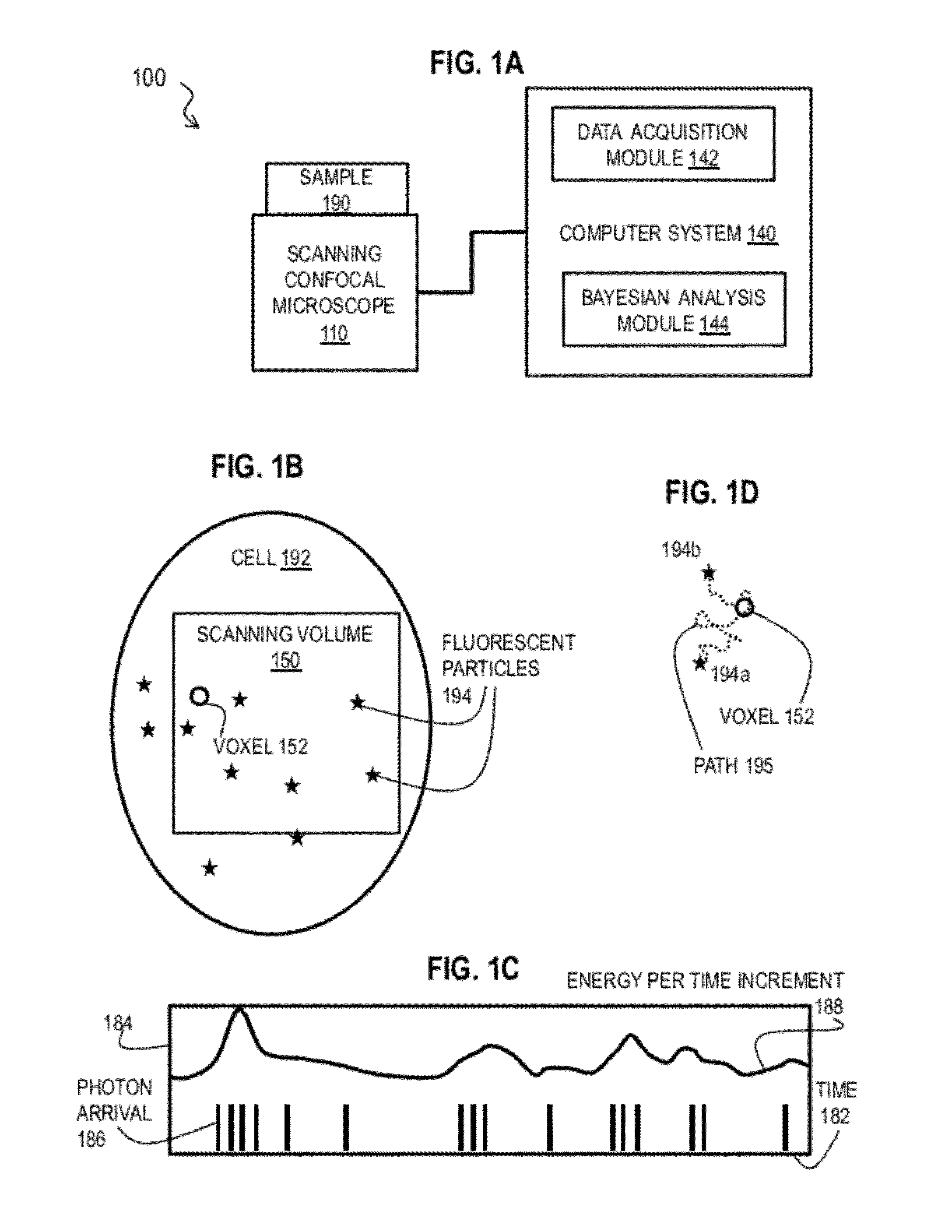
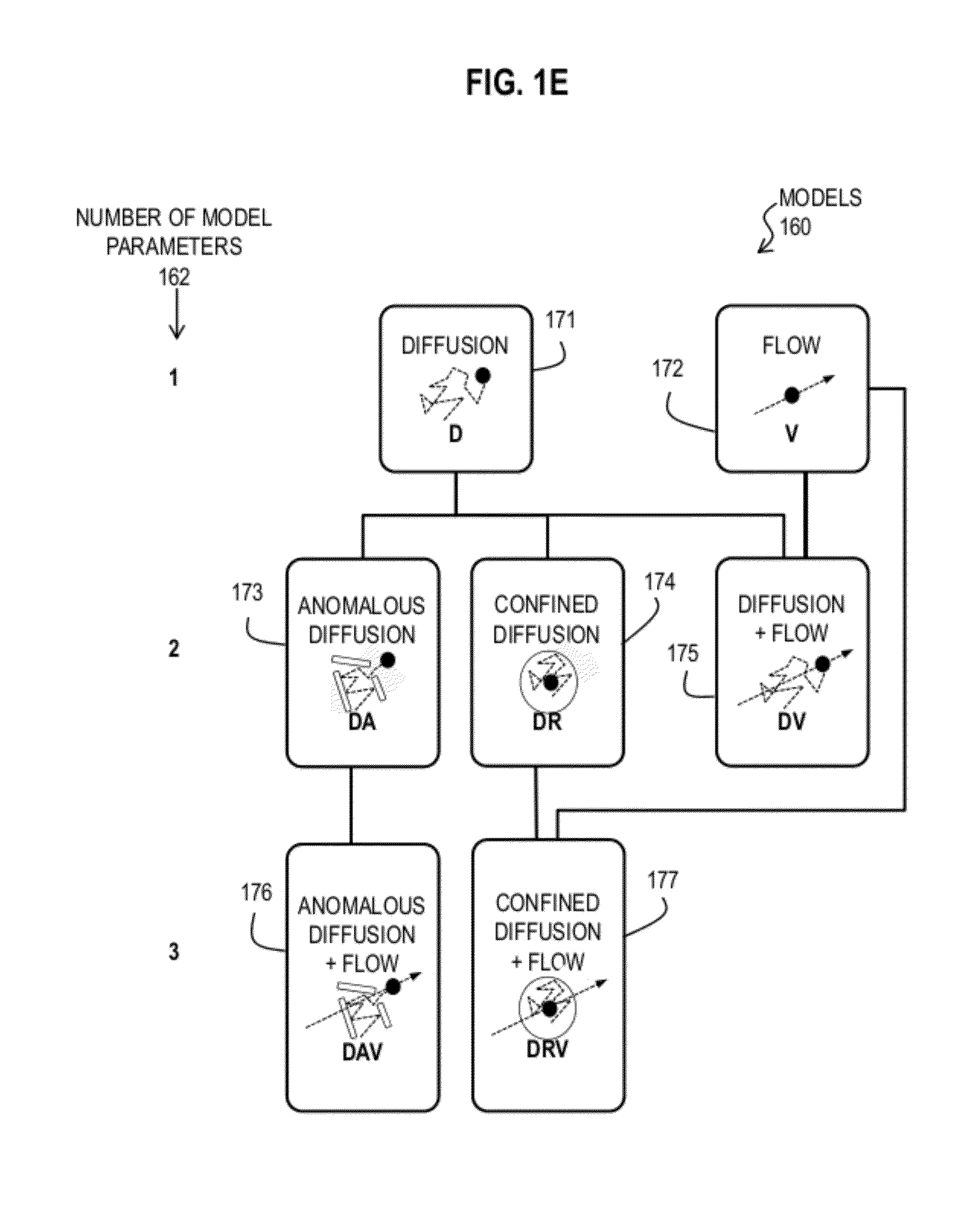
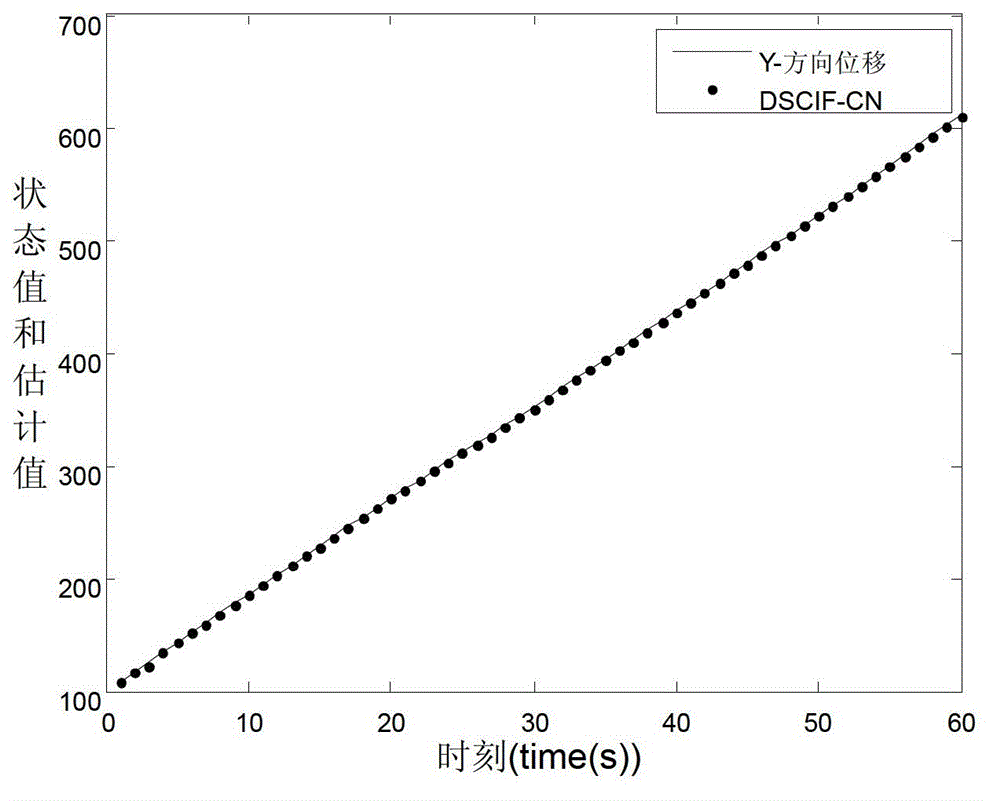
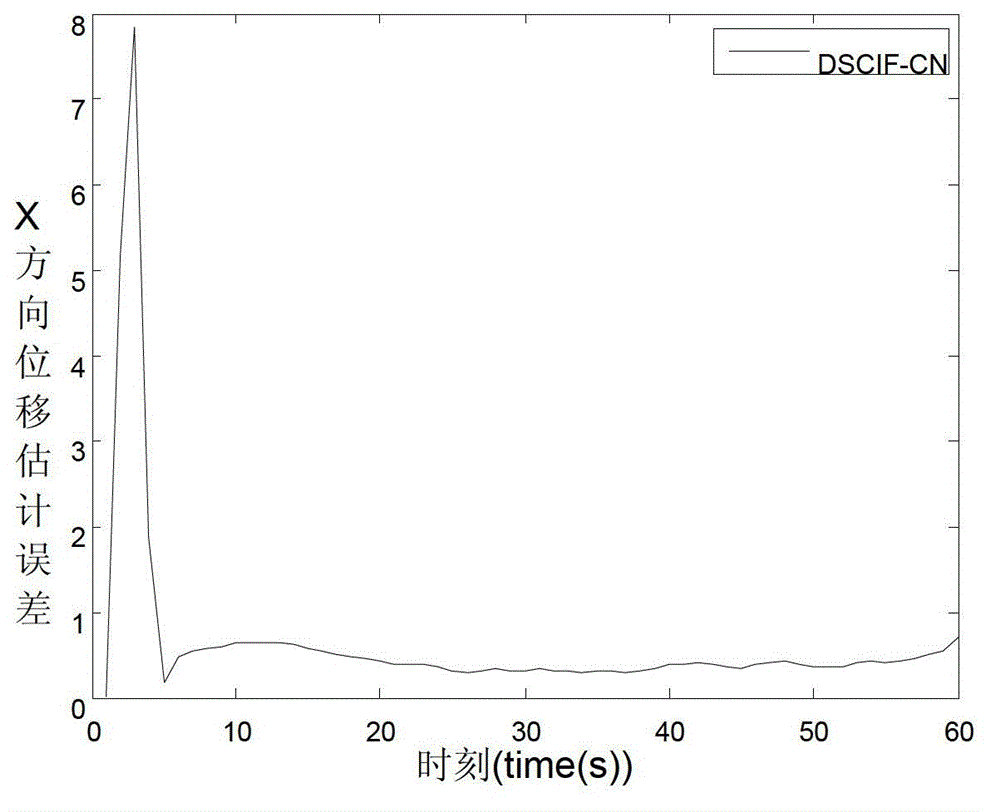
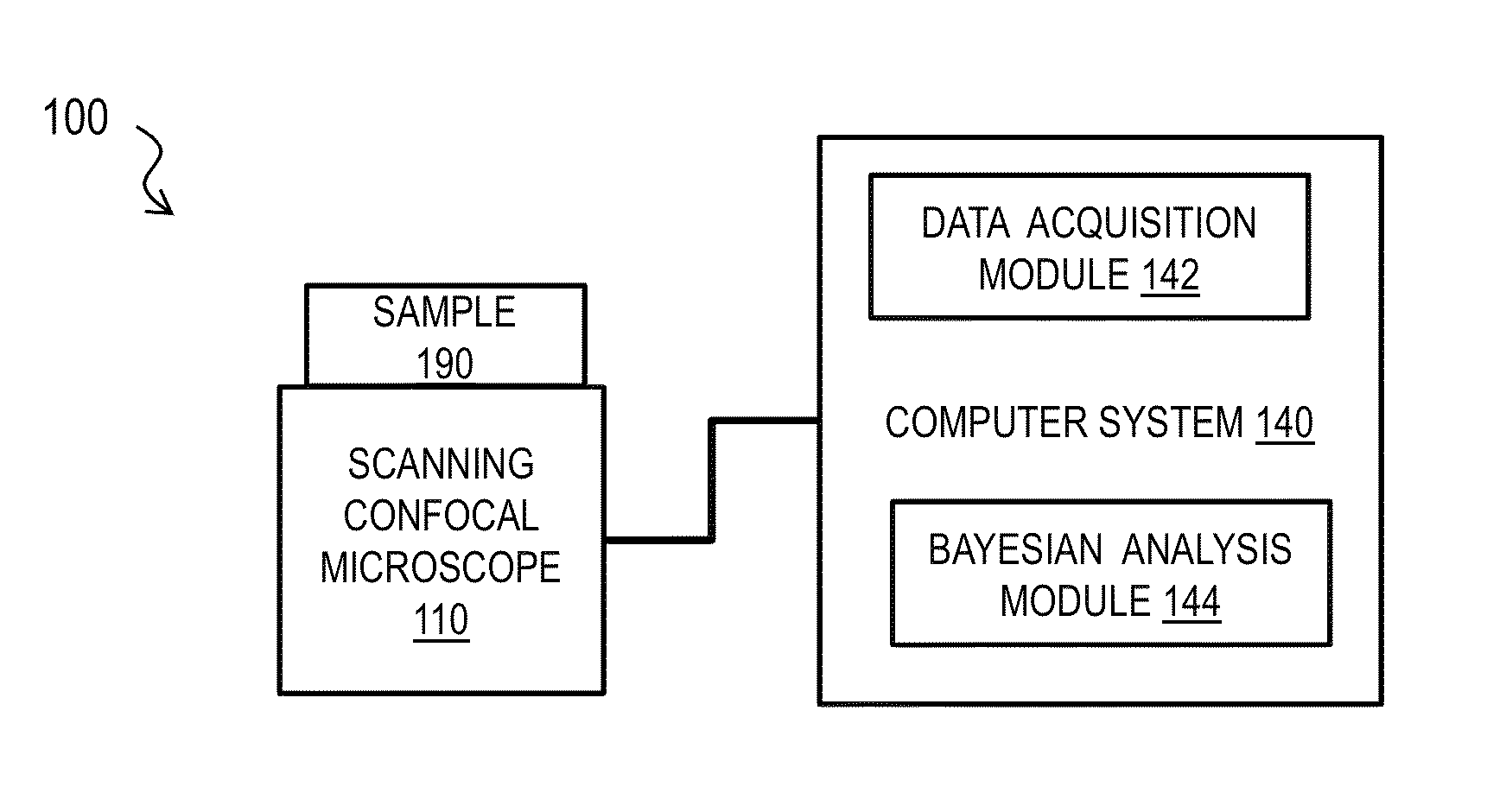
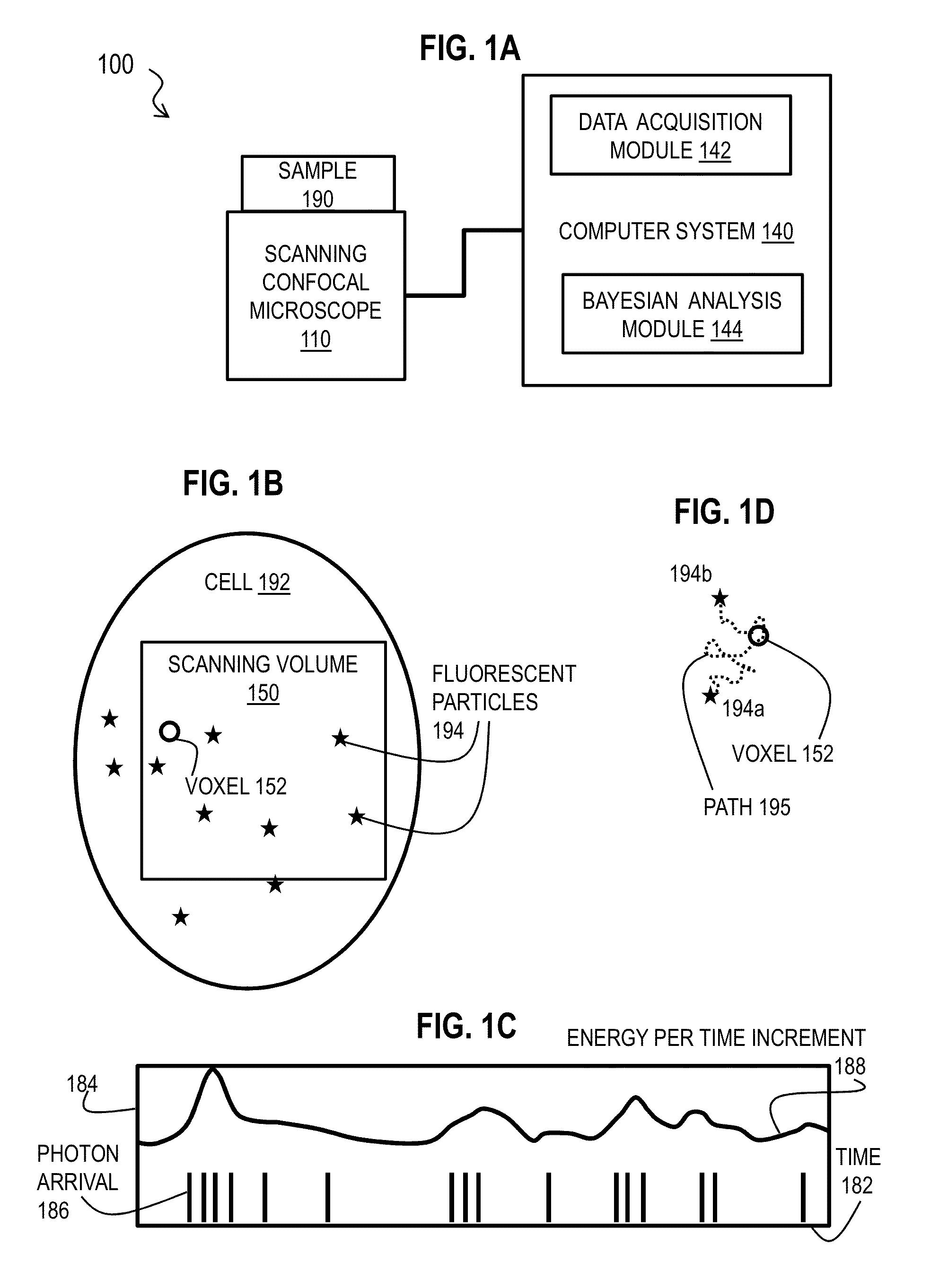
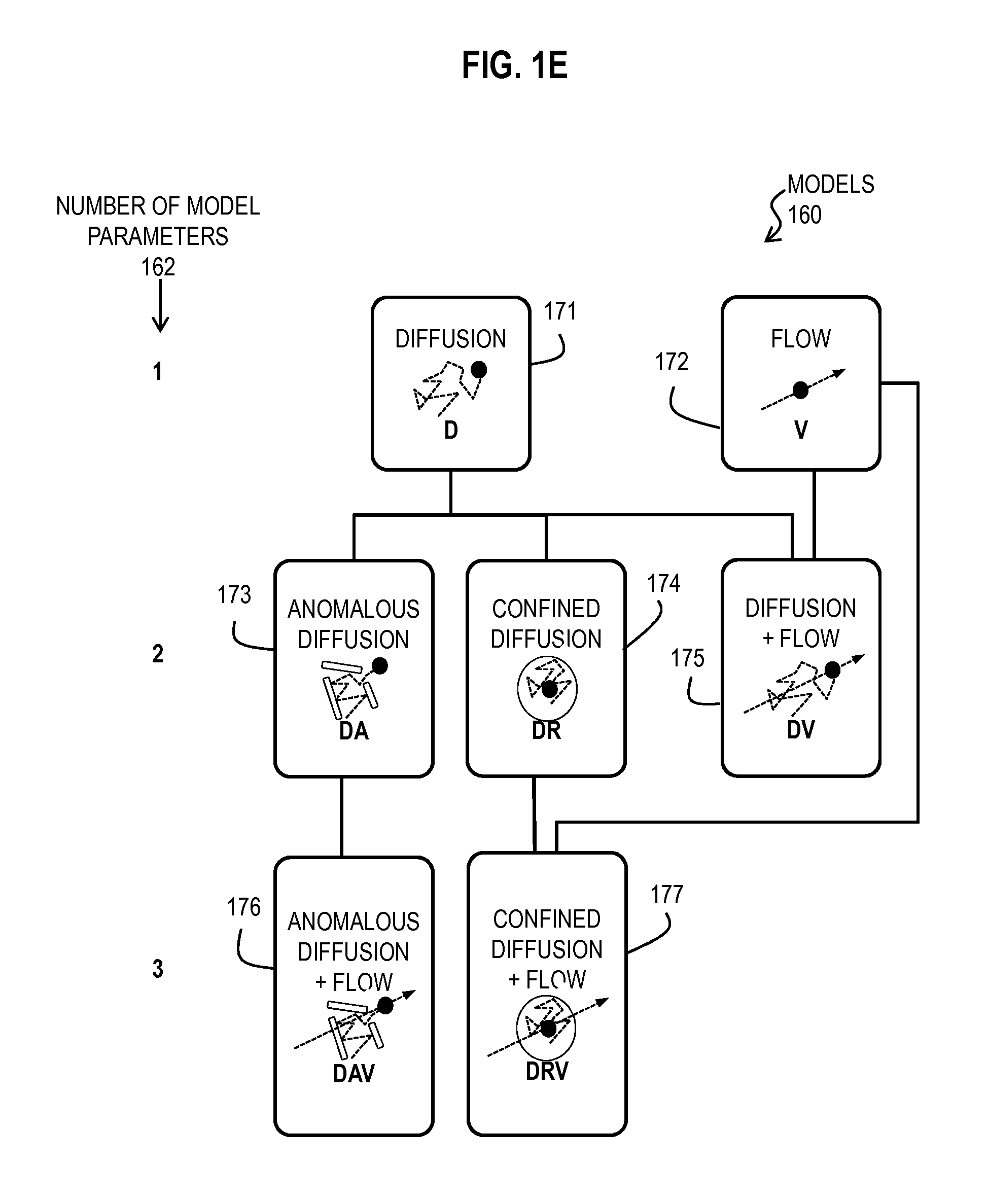
Bayesian Inference of Particle Motion and Dynamics from Single Particle Tracking and Fluorescence Correlation Spectroscopy
Techniques for inferring particle dynamics from certain data include determining multiple models for motion of particles in a biological sample. Each model includes a corresponding set of one or more parameters. Measured data is obtained based on measurements at one or more voxels of an imaging system sensitive to motion of particles in the biological sample; and, determining noise correlation of the measured data. Based at least in part on the noise correlation, a marginal likelihood is determined of the measured data given each model of the multiple models. A relative probability for each model is determined based on the marginal likelihood. Based at least in part on the relative probability for each model, a value is determined for at least one parameter of the set of one or more parameters corresponding to a selected model of the multiple models.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
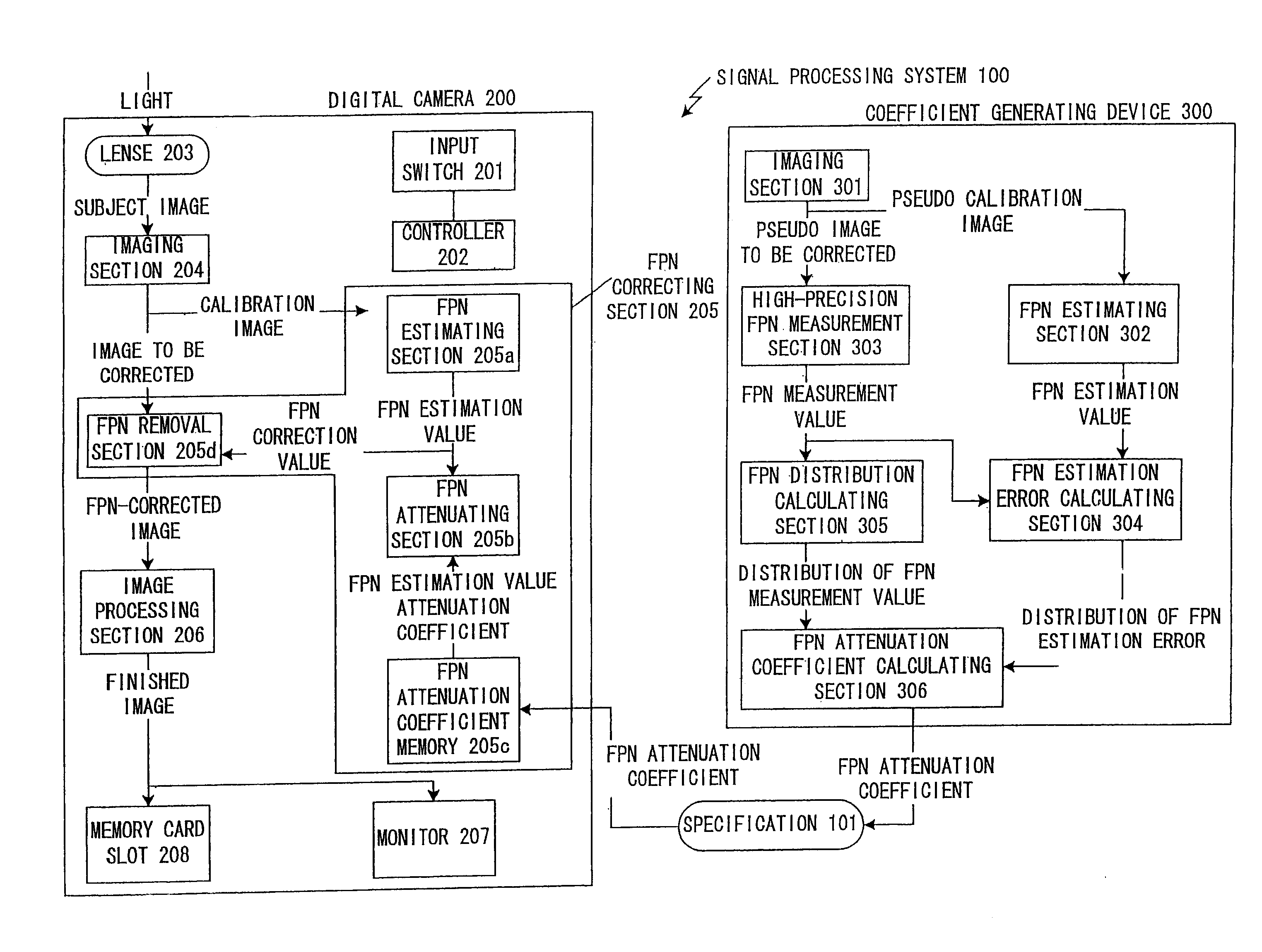
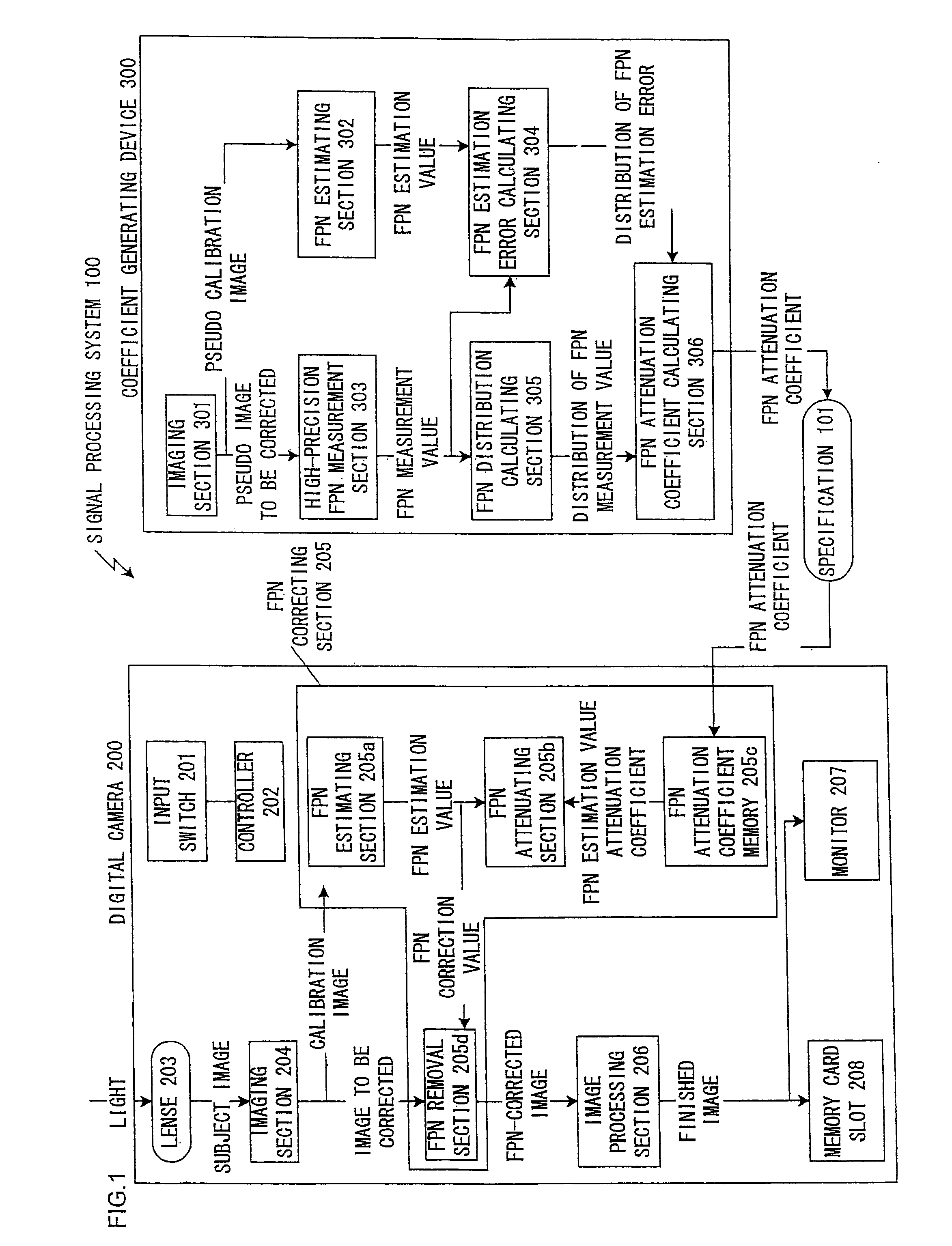
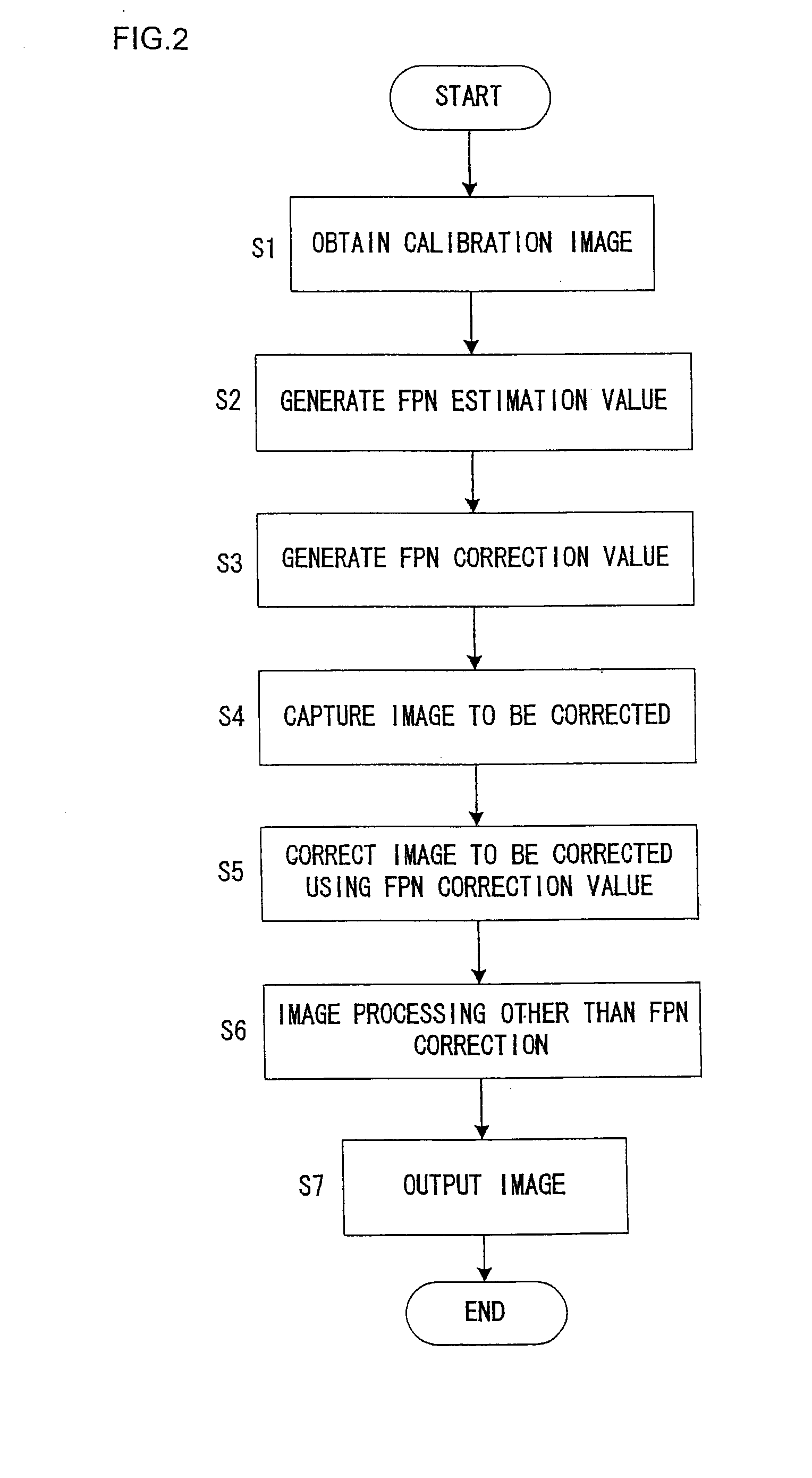
Signal processing method, signal processing system, coefficient generating device, and digital camera
An estimated noise shape estimated to be included in the signal to be corrected is calculated based on a calibration signal including a noise correlating with the noise of the signal to be corrected so as to correct a noise of a signal to be corrected. A correction value of a noise shape is generated by attenuating an amplitude of the estimated noise shape, and the noise of the signal to be corrected is corrected by using the correction value of the noise shape thus generated.
Owner:NIKON CORP
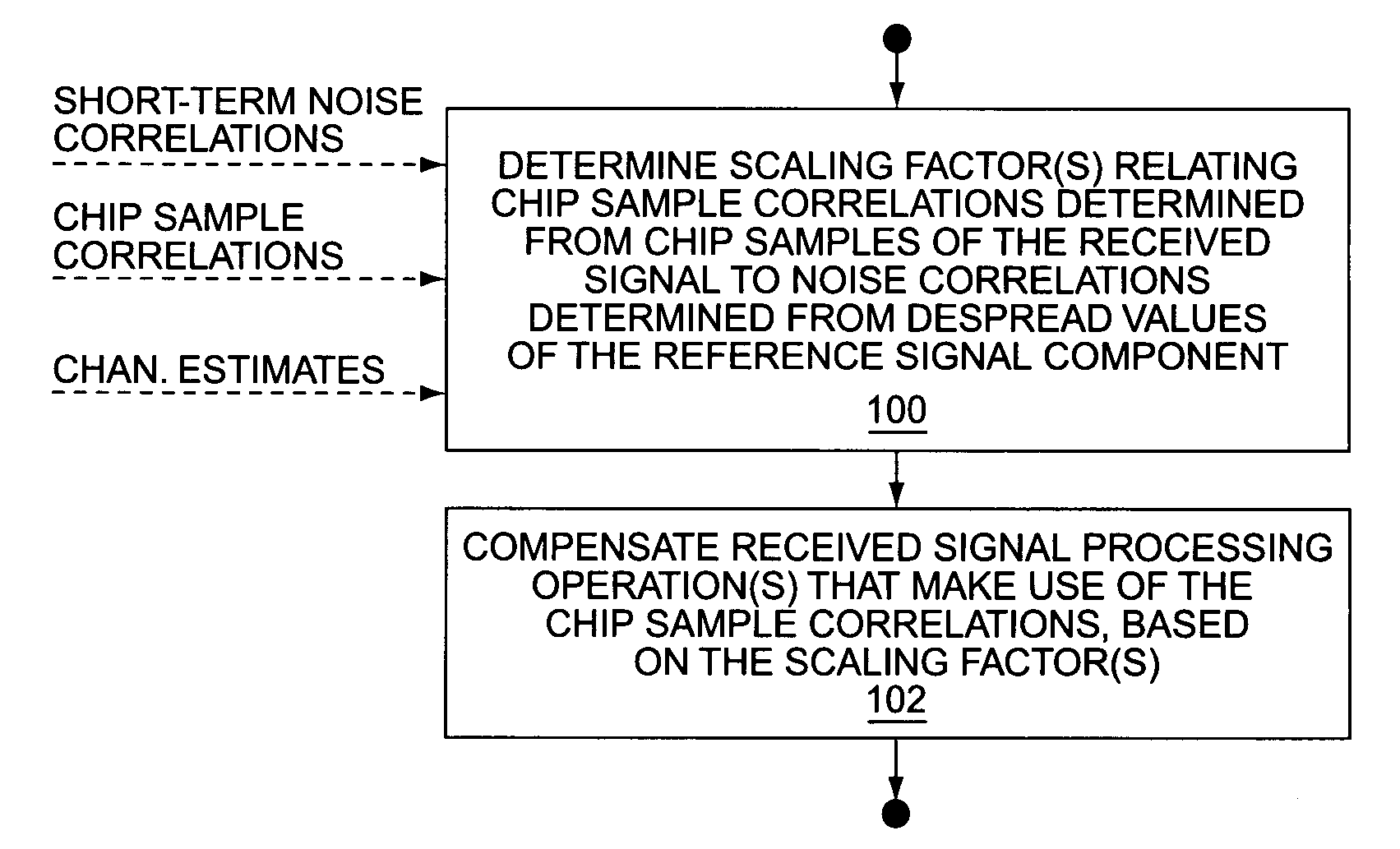
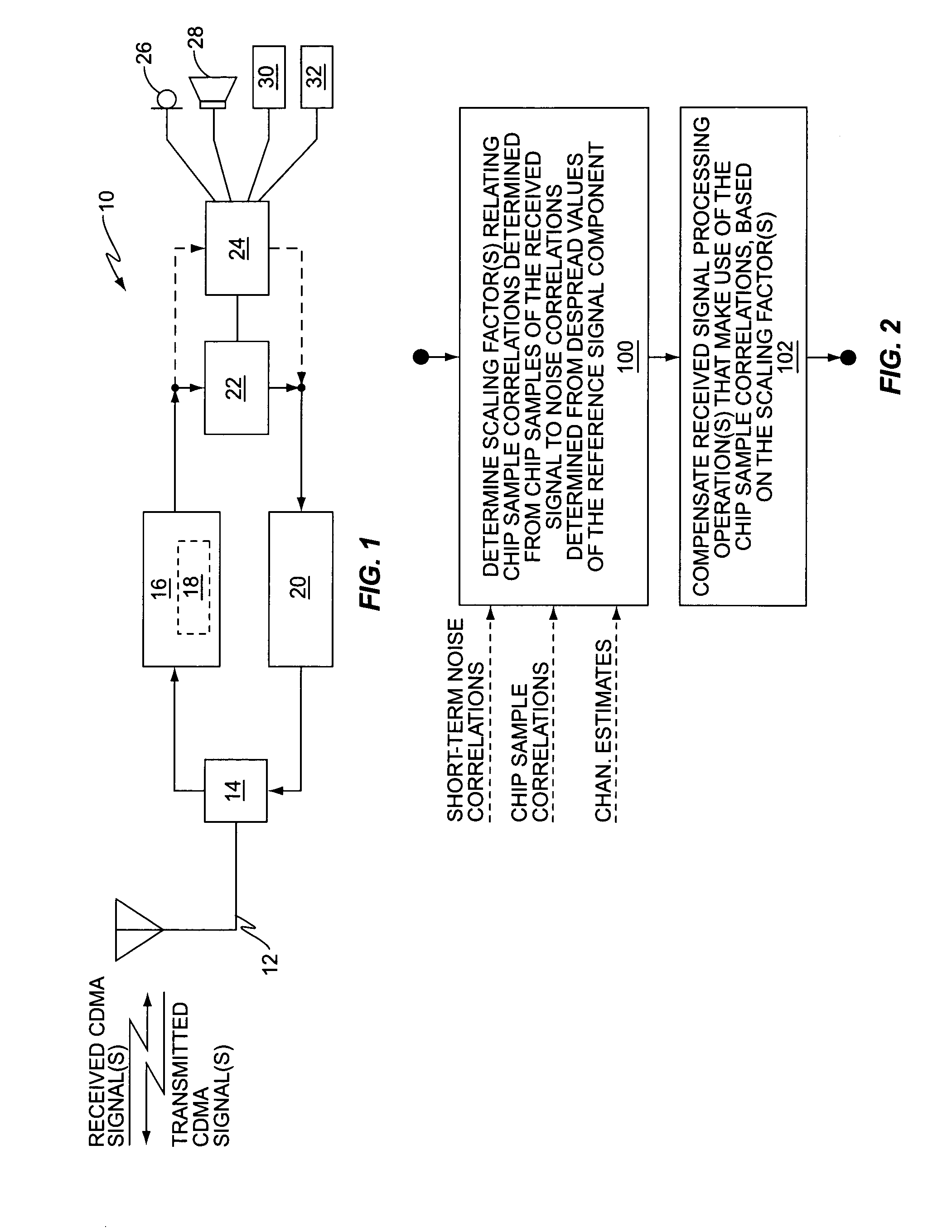
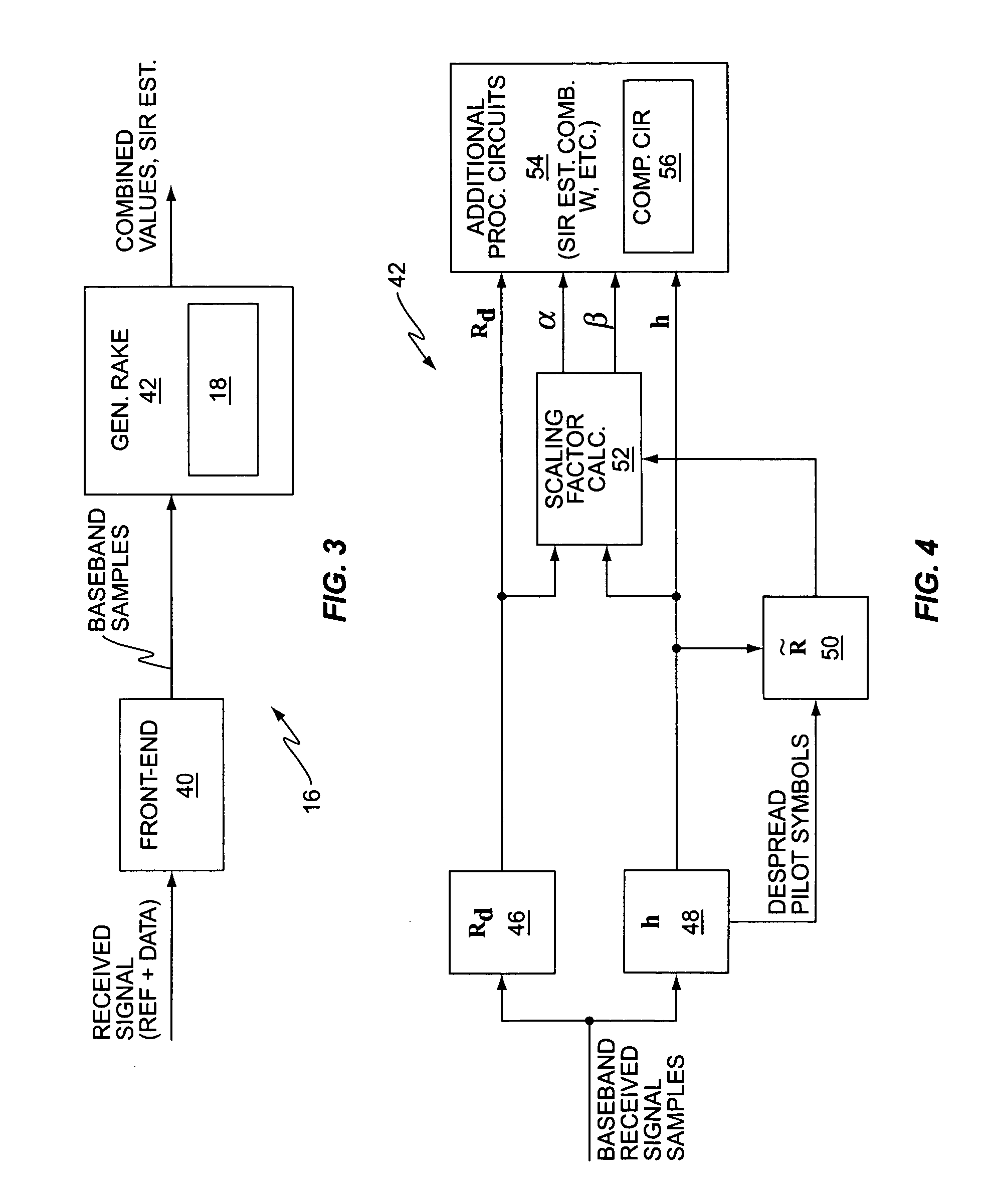
Method and apparatus for using chip sample correlations in one or more received signal processing operations
A wireless communication receiver obtains improved performance under certain fast fading conditions by basing one or more received signal processing operations on pre-despreading chip sample correlations rather than on post-despreading noise correlations, but preserves soft scaling information by determining one or more scaling factors that relate the chip sample correlations to the noise correlations. By way of non-limiting examples, a Generalized RAKE receiver circuit may base combining weight generation on chip sample correlations rather than on post-despreading pilot symbol noise correlations, but scale the combining weights as a function of the one or more scaling factors, or, equivalently, scale the combined values generated from the combining weights. Similar scaling may be performed with respect to chip equalization filter combining weights in a chip equalization receiver circuit. Further, Signal-to-Interference Ratio (SIR) estimation may be improved in terms of fast fading responsiveness by using chip sample correlations, while preserving the proper scaling.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
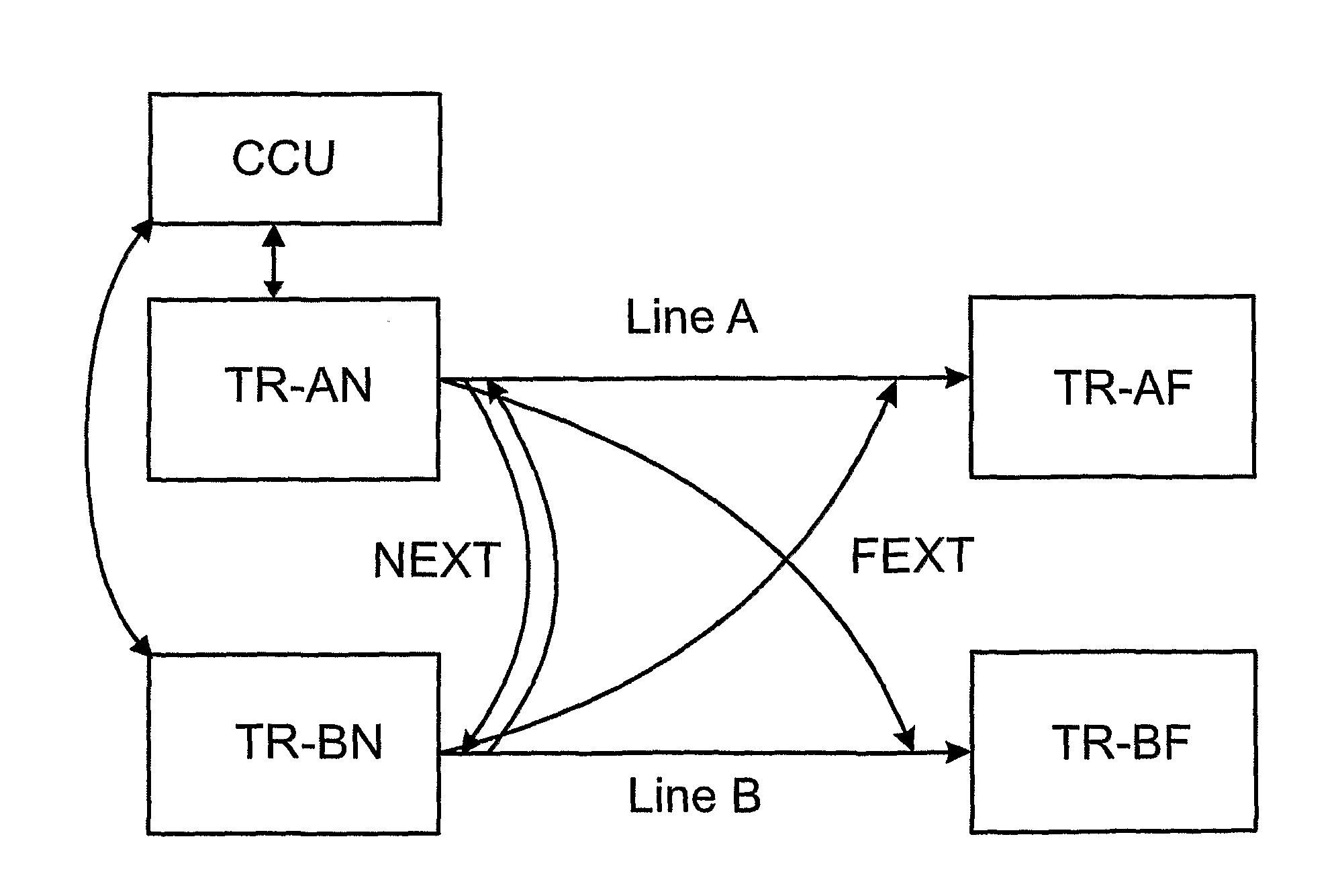
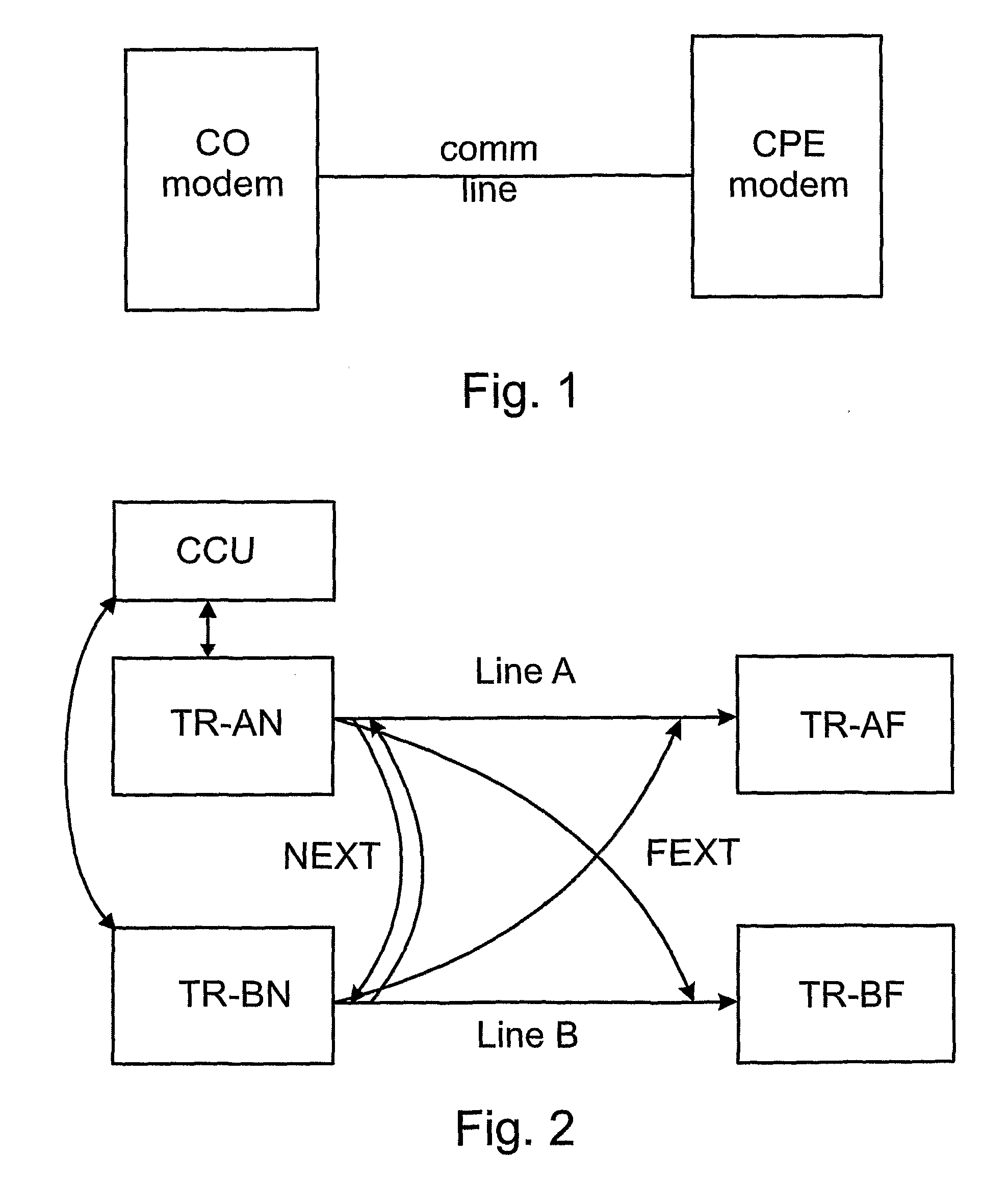
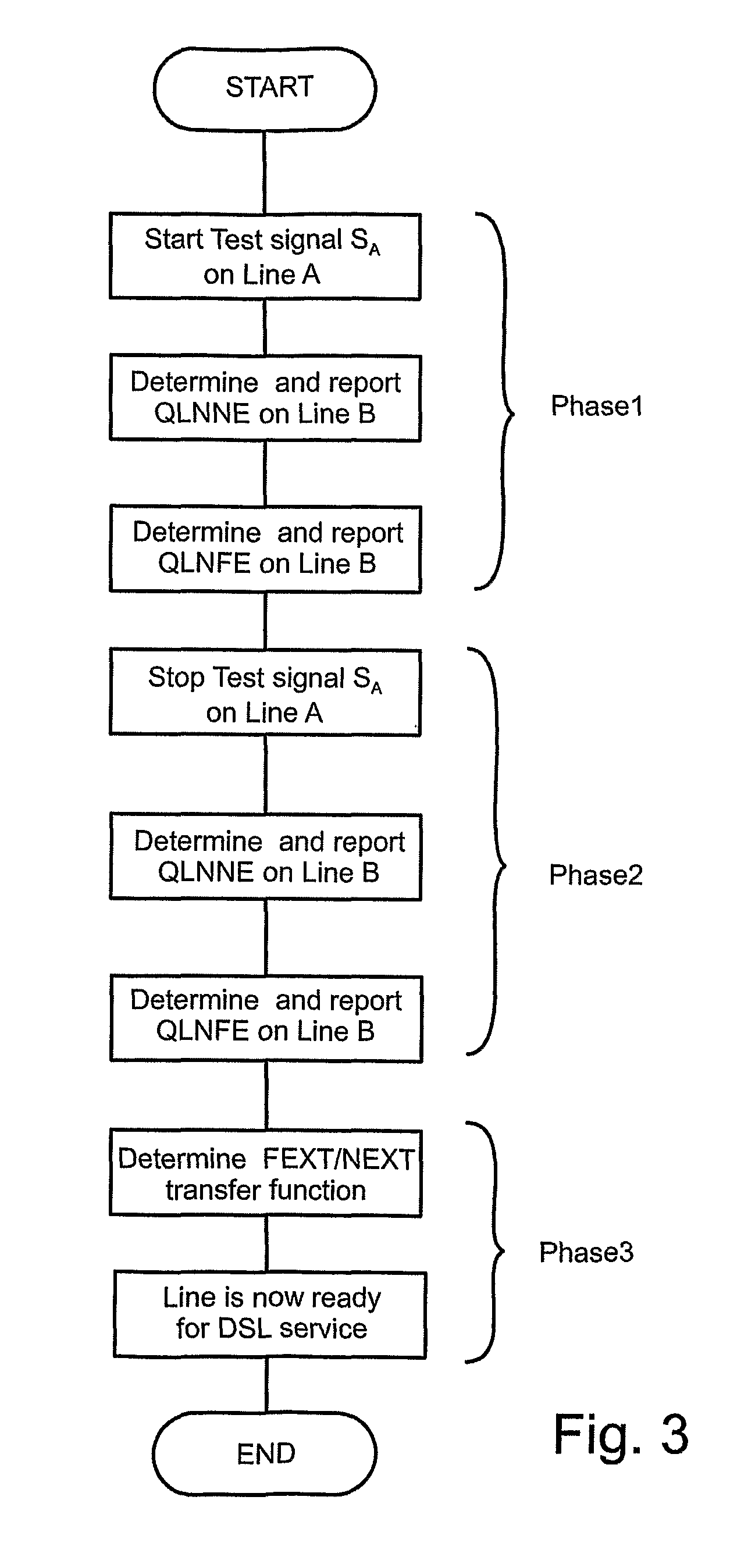
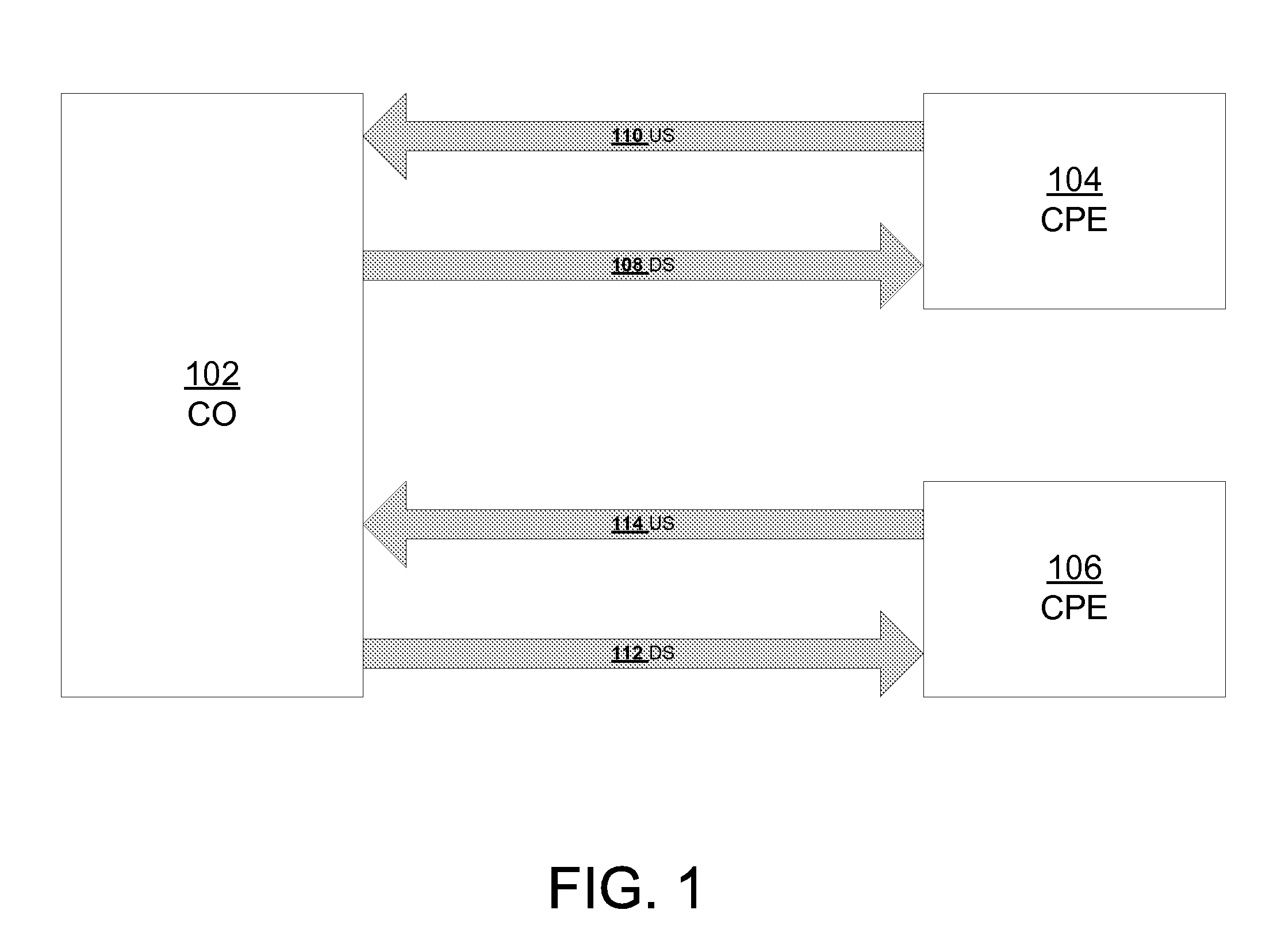
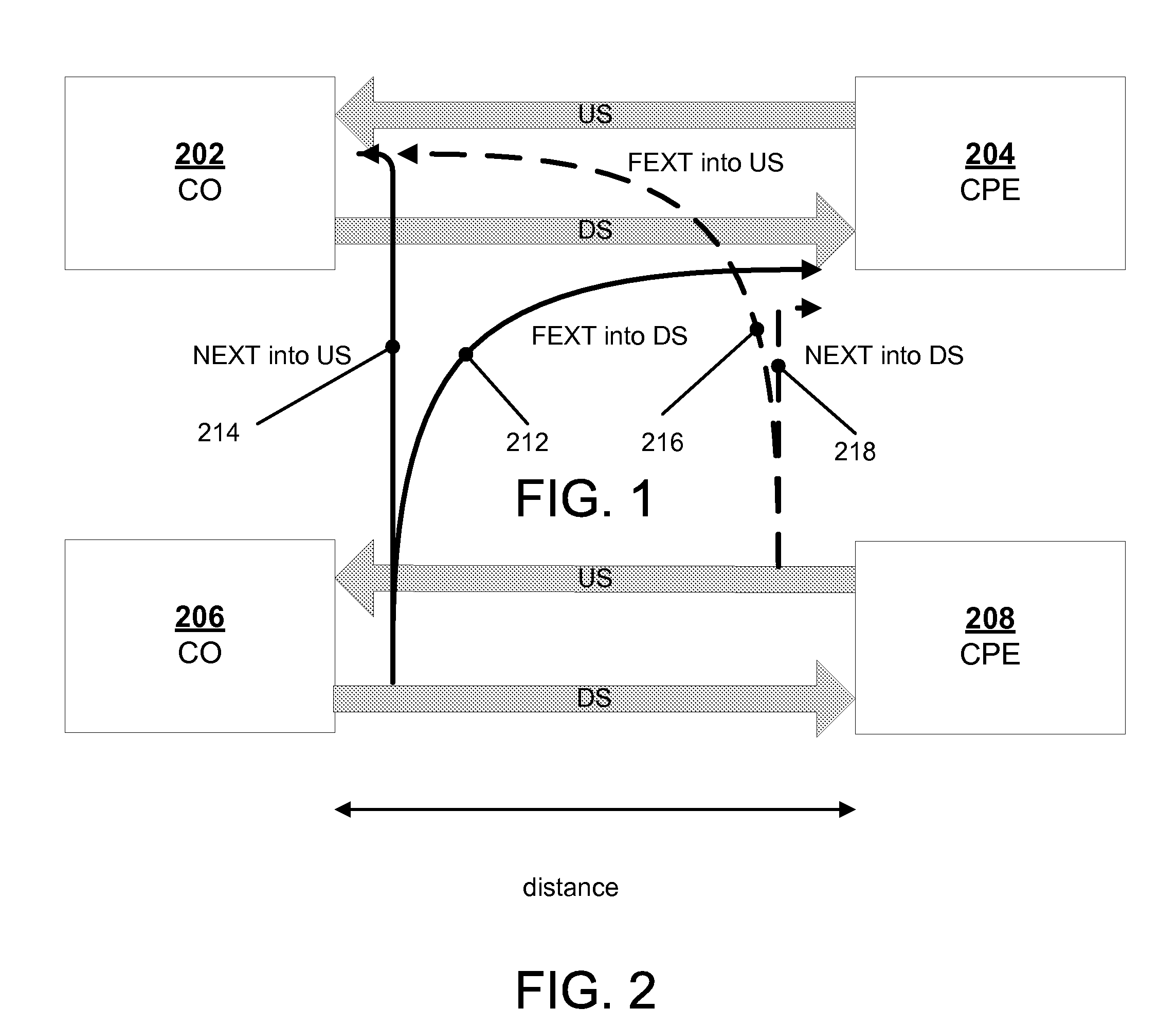
Method for Determining Automatically a Fext/Next Transfer-Function
ActiveUS20100208785A1Eliminate needError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsDigital subscriber lineProximal point
A method of automatically determining a far-end crosstalk (FEXT) and near-end crosstalk (NEXT) transfer function in communication lines such as Digital Subscriber Lines (DSL). In a first phase, an input test signal with a known power density spectrum (PSD) covering a frequency range of interest is transmitted at the near end of line A while a received signal or noise-related quantity or PSD is measured at both the near end and far end of line B. In a second phase, transmission of the test signal is stopped, and a received signal or noise-related quantity or PSD is again measured at both ends of line B. In a third phase, the FEXT / NEXT transfer function is determined based on the measurements of the first and second phases.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
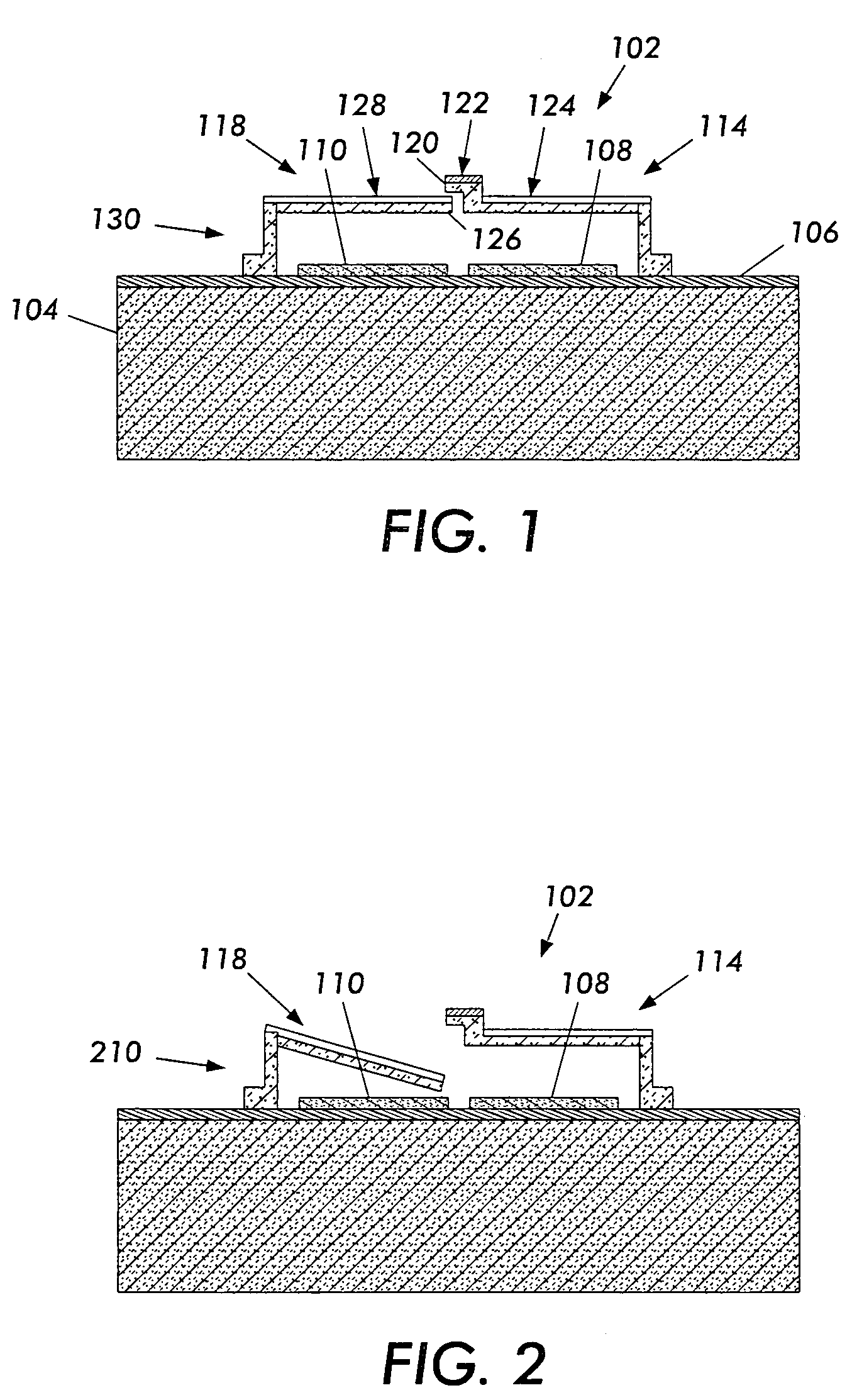
Electromechanical memory cell with torsional movement
InactiveUS20070002604A1Variable resistance carrier recordingVariable capacitance carrier recordingElectricityThermal force
A memory cell uses a pair of cantilevers to store a bit of information. Changing the relative position of the cantilevers determines whether they are electrically conducting or not. The on and off state of this mechanical latch is switched by using, for example, electrostatic, electromagnetic or thermal forces applied sequentially on the two cantilevers to change their relative position. The amount of power required to change the state of the cell is reduced by supporting at least one of the cantilevers with at least one lateral projection that is placed in torsion during cantilever displacement. After a bit of data is written, the cantilevers are locked by mechanical forces inherent in the cantilevers and will not change state unless a sequential electrical writing signal is applied. The sequential nature of the required writing signal makes inadvertent, radiation or noise related data corruption unlikely.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Electromechanical memory cell with torsional movement
InactiveUS7349236B2Variable resistance carrier recordingVariable capacitance carrier recordingElectricityThermal force
A memory cell uses a pair of cantilevers to store a bit of information. Changing the relative position of the cantilevers determines whether they are electrically conducting or not. The on and off state of this mechanical latch is switched by using, for example, electrostatic, electromagnetic or thermal forces applied sequentially on the two cantilevers to change their relative position. The amount of power required to change the state of the cell is reduced by supporting at least one of the cantilevers with at least one lateral projection that is placed in torsion during cantilever displacement. After a bit of data is written, the cantilevers are locked by mechanical forces inherent in the cantilevers and will not change state unless a sequential electrical writing signal is applied. The sequential nature of the required writing signal makes inadvertent, radiation or noise related data corruption unlikely.
Owner:XEROX CORP
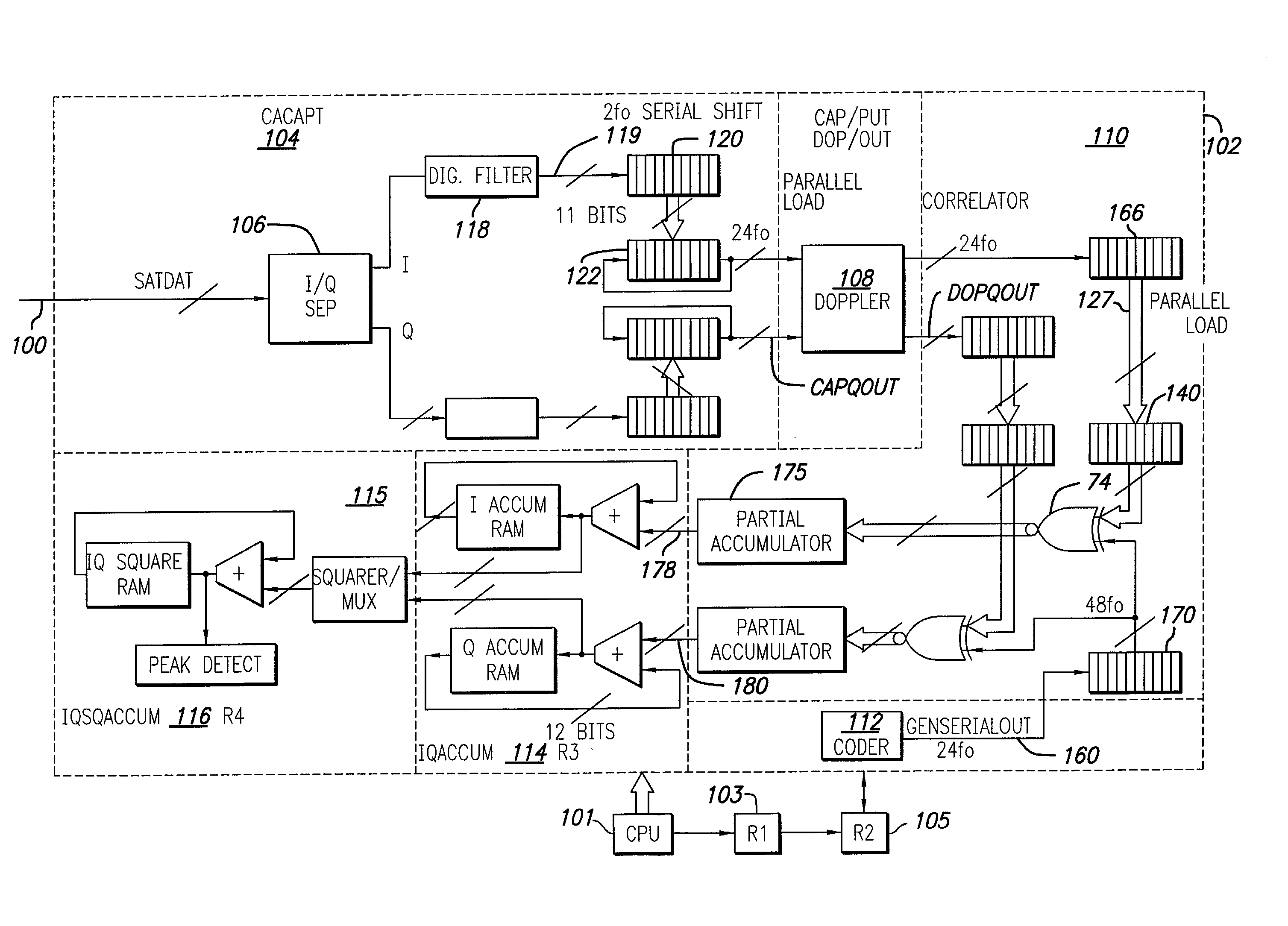
Pseudo-noise correlator for GPS spread-spectrum receiver
InactiveUS20020146065A1Instruments for road network navigationPosition fixationTime delaysMultipath interference
A terrestrial C / A code GPS receiver system digitally samples, filters and stores a segment of 11 half chips of the received composite as a binary number and multiplexes this number for parallel correlation with each of a series of multibit code replicas for the satellites to be tracked. Each of the time delay specific correlation products are accumulated in a cell of a memory matrix so that at least twenty two delays for each satellite may be evaluated each code period providing fast reacquisition, even within a city intersection, as well as correction of multipath tracking and multipath interference. All cells of the memory matrix may be used for an acquisition of a single satellite in about 4 ms. Two satellite tracking, in addition to altitude hold, uses cross track hold alternating with clock hold to update the cross track estimate. Single satellite tracking uses cross track and clock hold together. Navigation data is updated with detected changes in motion including turns.
Owner:CSR TECH INC
Method and system for linear processing of an input using Gaussian Belief Propagation
ActiveUS20100074342A1Polarisation/directional diversityLine-faulsts/interference reductionBelief propagationIterative method
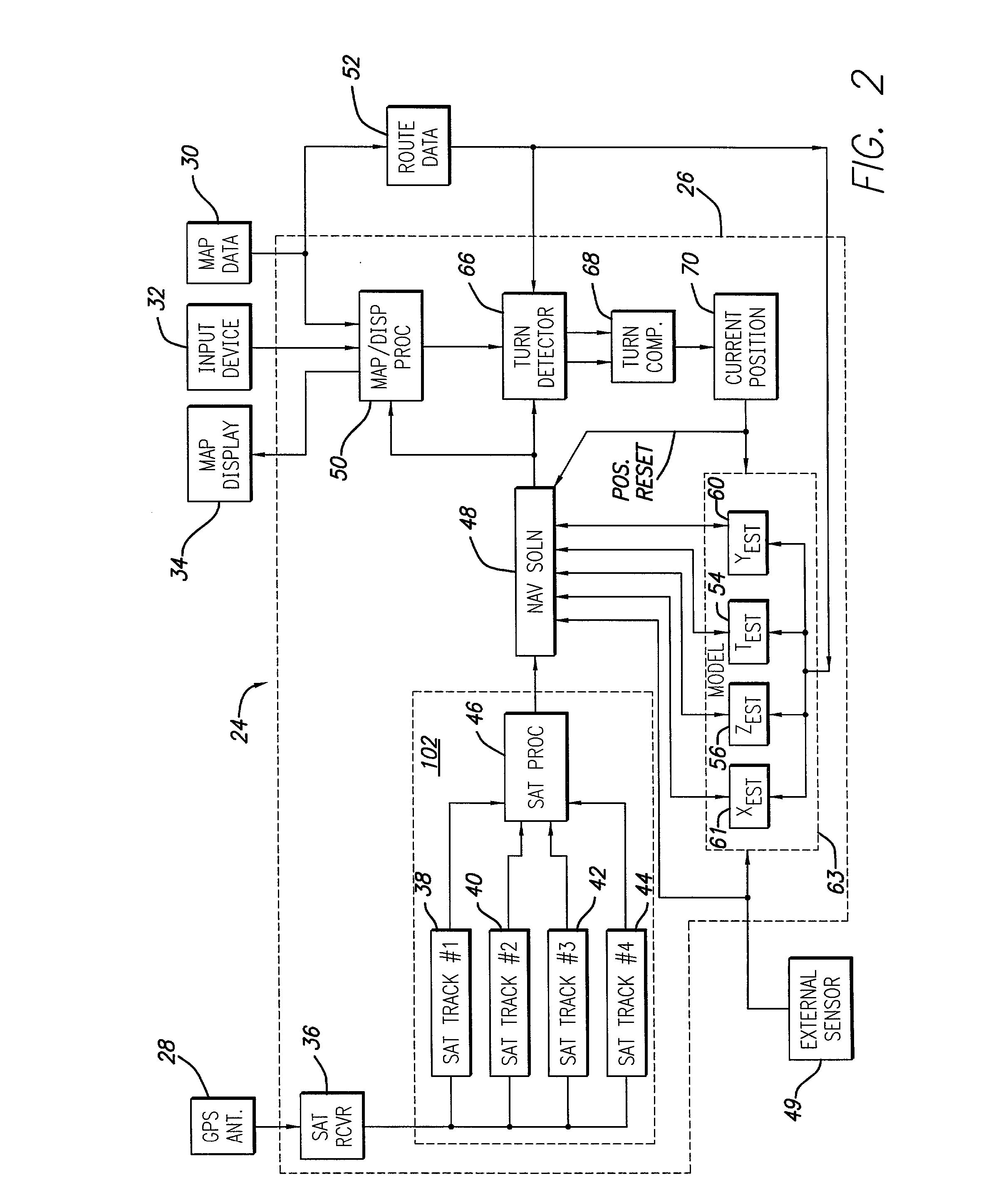
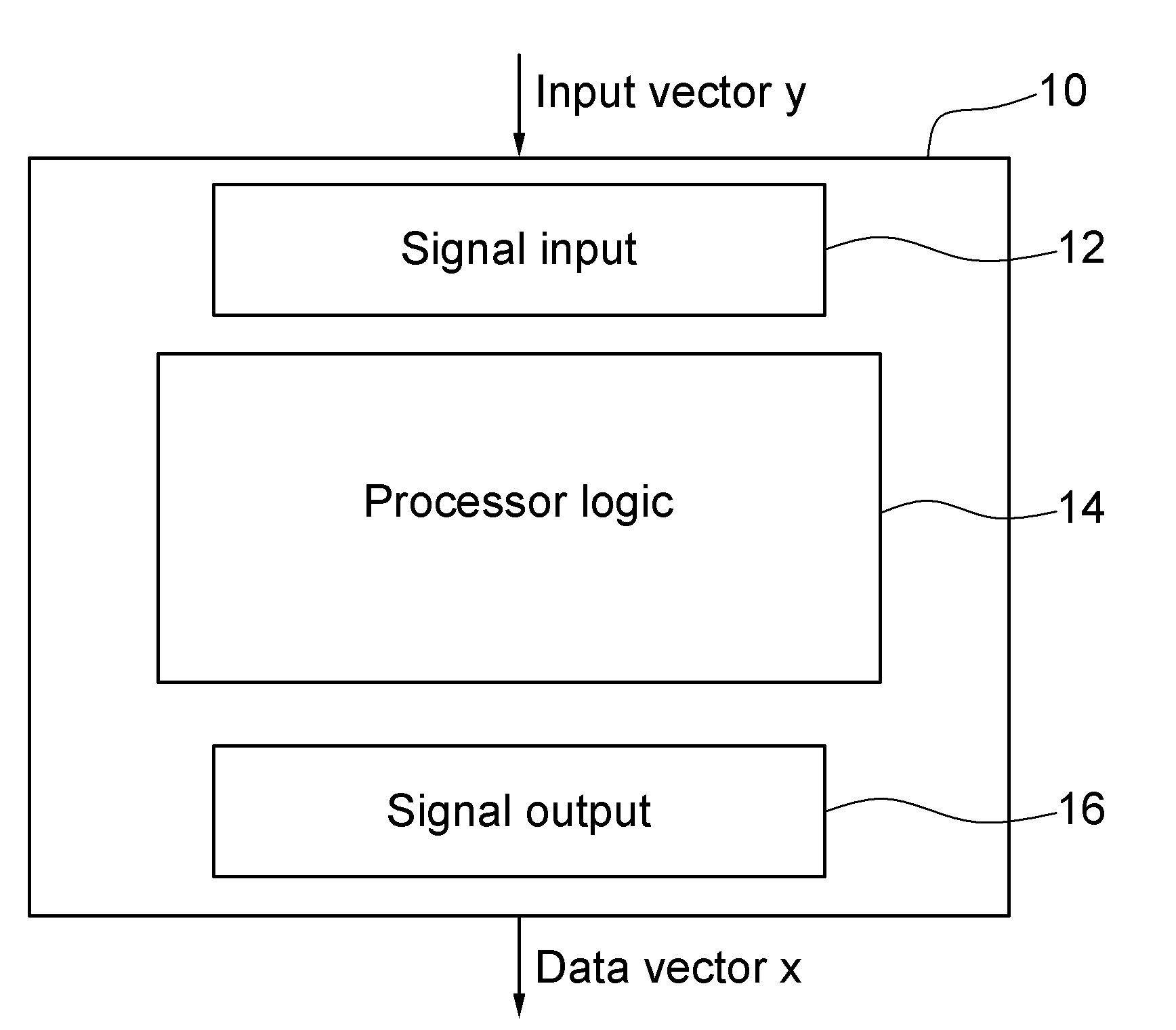
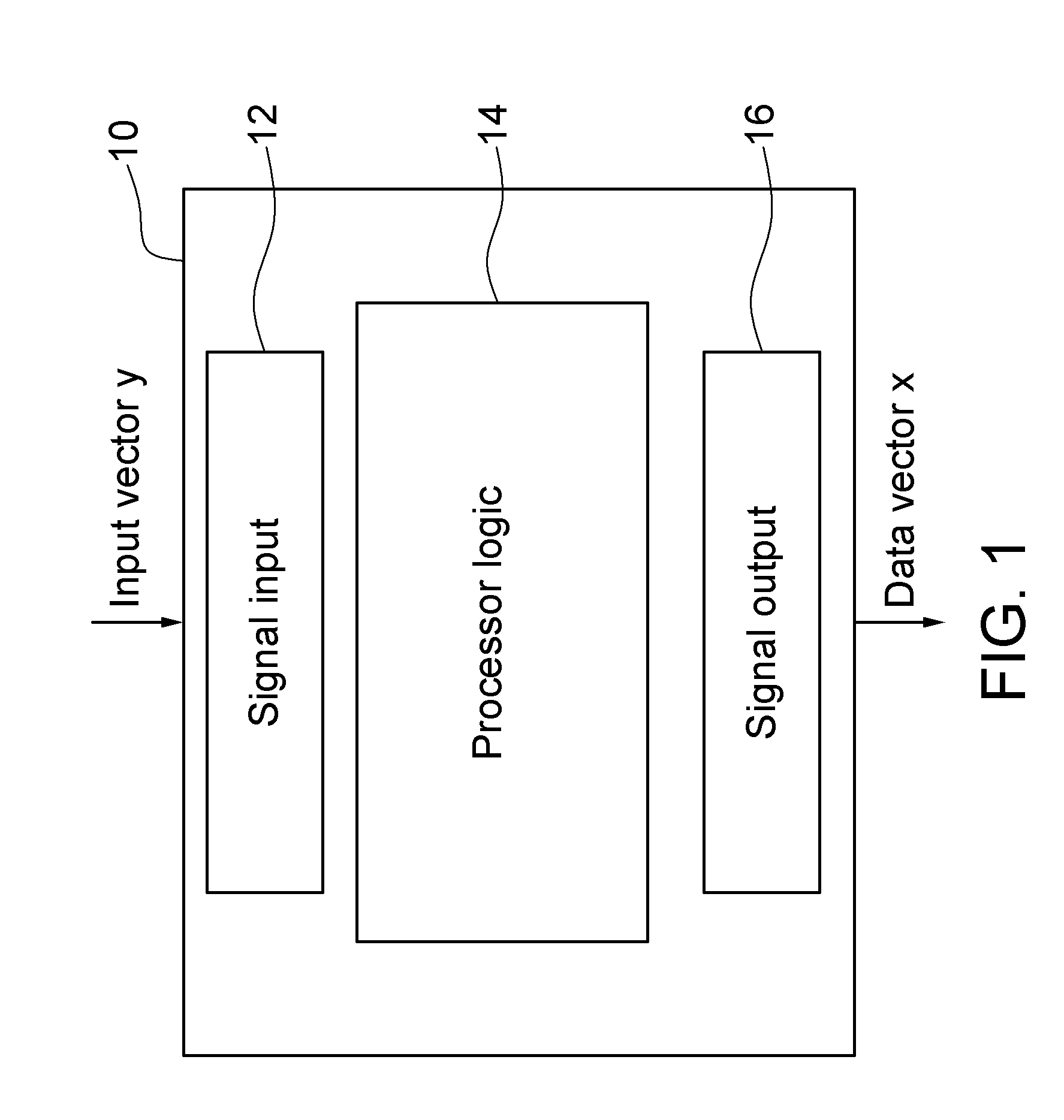
Methods and systems for processing an input. An input vector y is received that represents a noisy observation of Ax, where A is a data matrix and x is a data vector of unknown variables. Data vector x is recovered from the received input vector y via an iterative method. The recovering comprises determining an inference of a vector of marginal means over a graph G, where the graph G is of a joint Gaussian probability density function p(x) associated with noise in the received input vector y.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
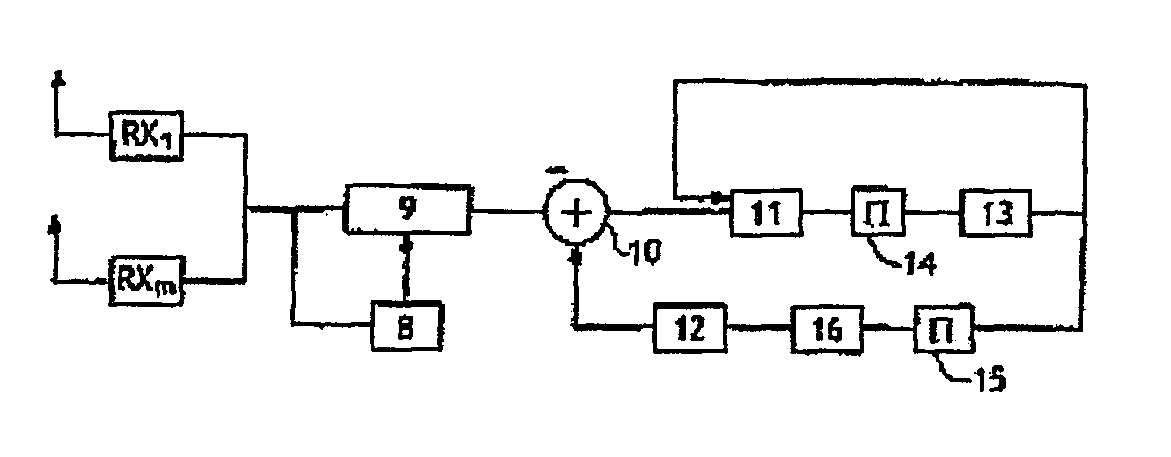
Iterative decoding and equalizing method for high speed communications on multiple antenna channels during transmission and reception
ActiveUS7760828B2Less complexImprove performanceMultiple-port networksDelay line applicationsMean squareChannel decoder
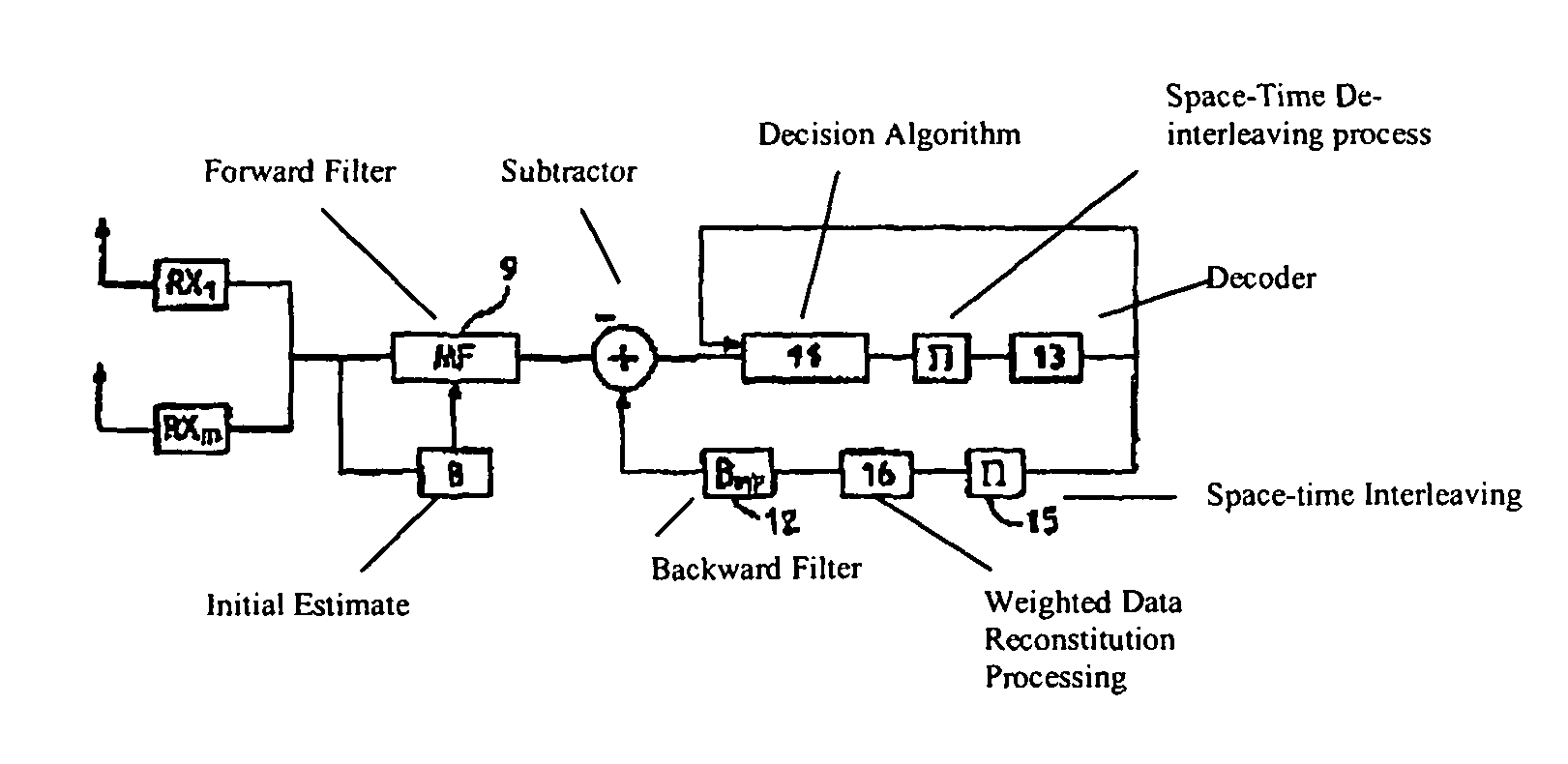
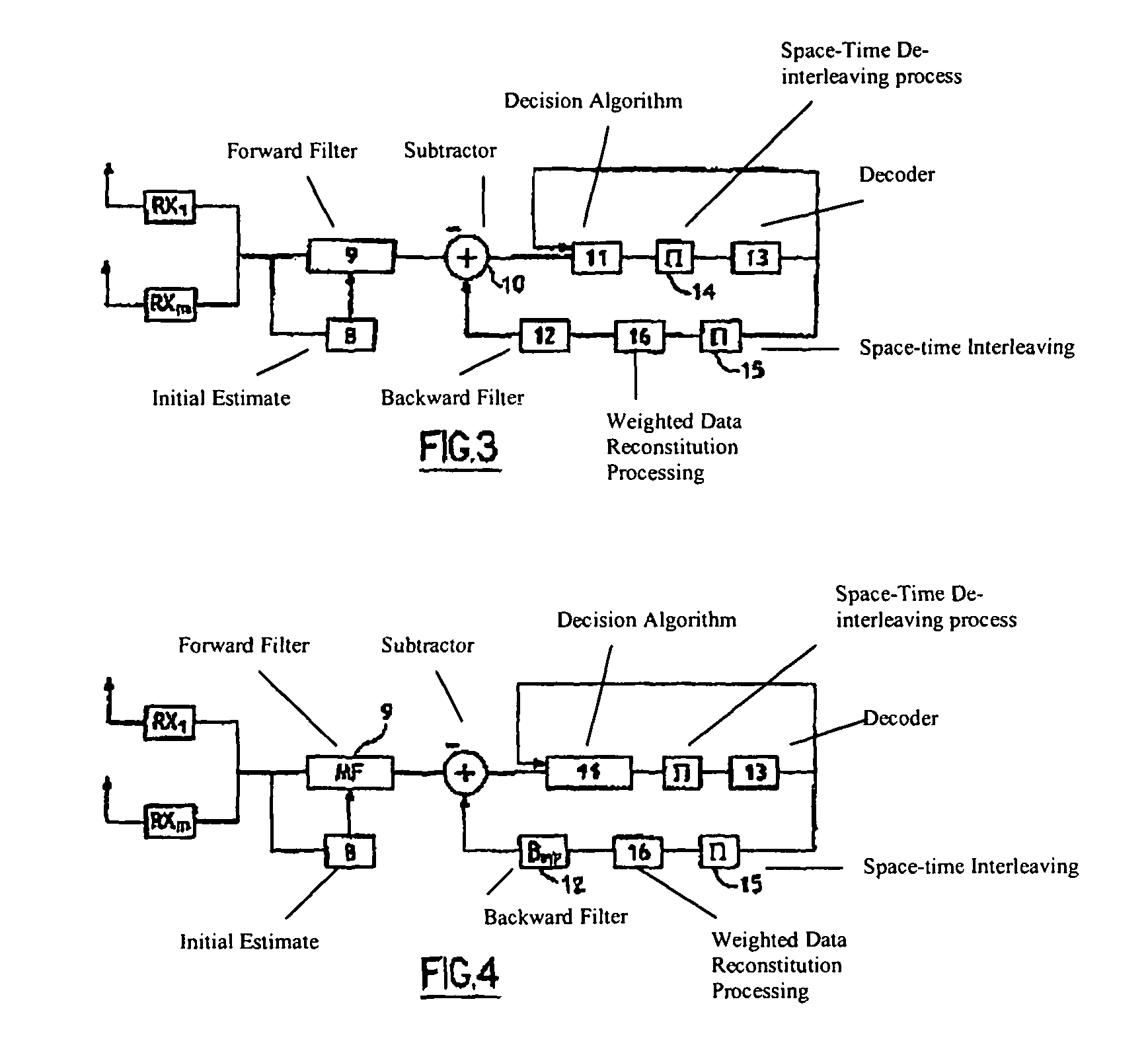
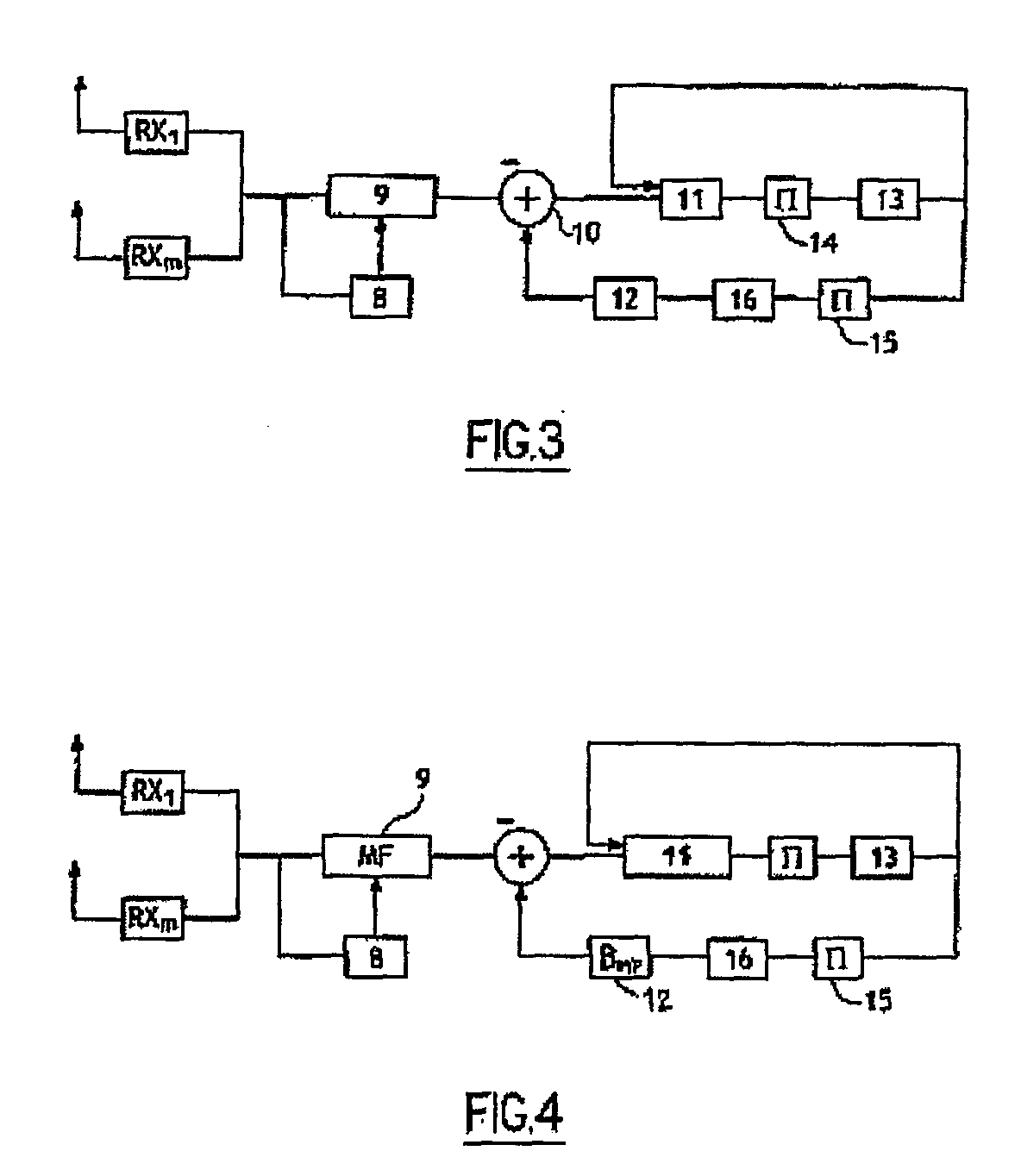
An iterative decoding and equalizing device for high bit rate communication over frequency-selective channels with multiple transmit and receive antennas, said device including a decision feedback equalizer adapted to receive data from different receive antennas and including a forward filter (9) and a recursive backward filter (12) fed with calculated weighted reconstituted data from the output of a decoder (13) fed by decision means (11) and means for subtracting the output of said backward filter (12) from the output data of the forward filter (9) whereby the subtracted data is fed to the input of the decision means (11) with the output of the decoder (13) and the decision means (11) produce a statistic which is forwarded to a channel decoder with weighted inputs and outputs and said decision means (11) take into account the space noise correlation at the output of the subtraction means (10) and the decision means (11) and the decoder (13) are separated by space-time interleaving at bit level, which device is characterized in that the forward filter (9) and the backward filter (12) are iteratively adapted to minimize the mean square error at the output of the subtractor (10).
Owner:FRANCE TELECOM SA
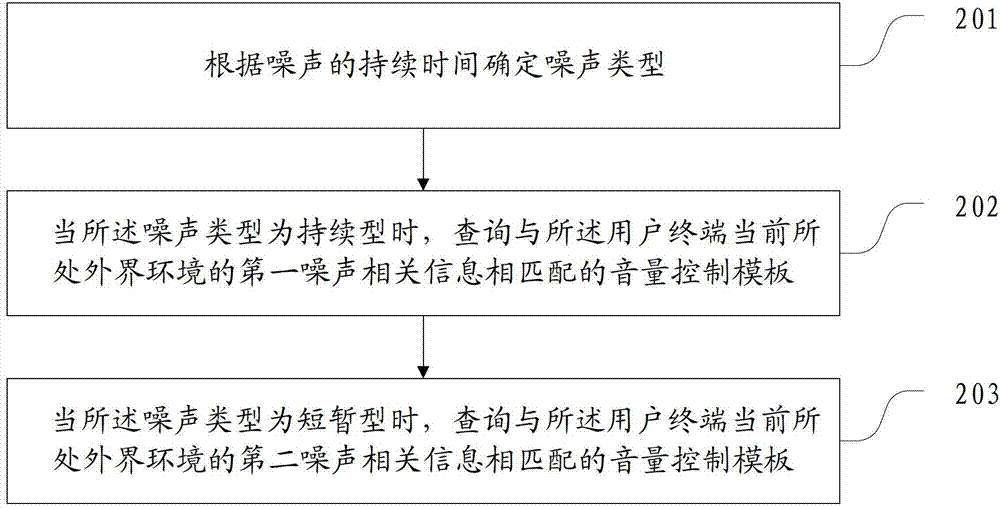
Volume control method and terminal thereof
ActiveCN103595849AReduce interferenceSubstation speech amplifiersControl engineeringComputers technology
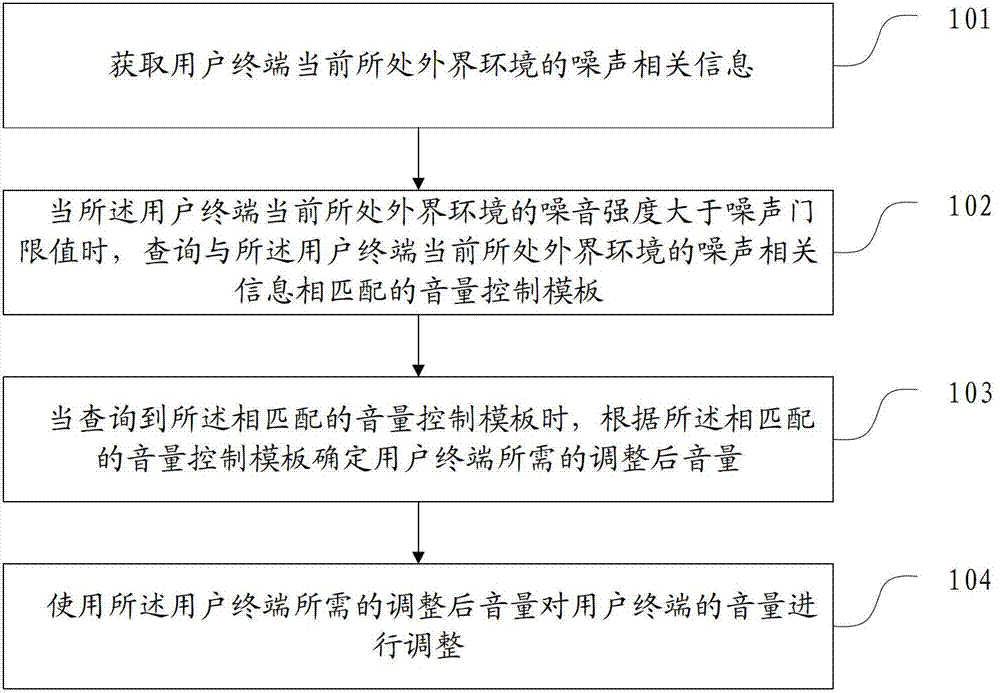
Embodiments of the invention provide a volume control method and a terminal thereof and relate to the computer technology field. By using the method and the terminal, the volume can be adaptively adjusted according to changes of an external environment. The method comprises the following steps of acquiring noise correlation information of the external environment where a user terminal is currently located; when a noise intensity of the external environment where the user terminal is currently located is greater than a noise threshold, inquiring a volume control template which is matched with the noise correlation information of the external environment where the user terminal is currently located; when the matched volume control template is inquired, determining the volume after adjustment needed by the user terminal according to the matched volume control template; using the volume after adjustment needed by the user terminal to adjust the volume of the user terminal. The method and the terminal in the embodiments of the invention are applied in a volume control process of the user terminal.
Owner:TENCENT TECH (SHENZHEN) CO LTD
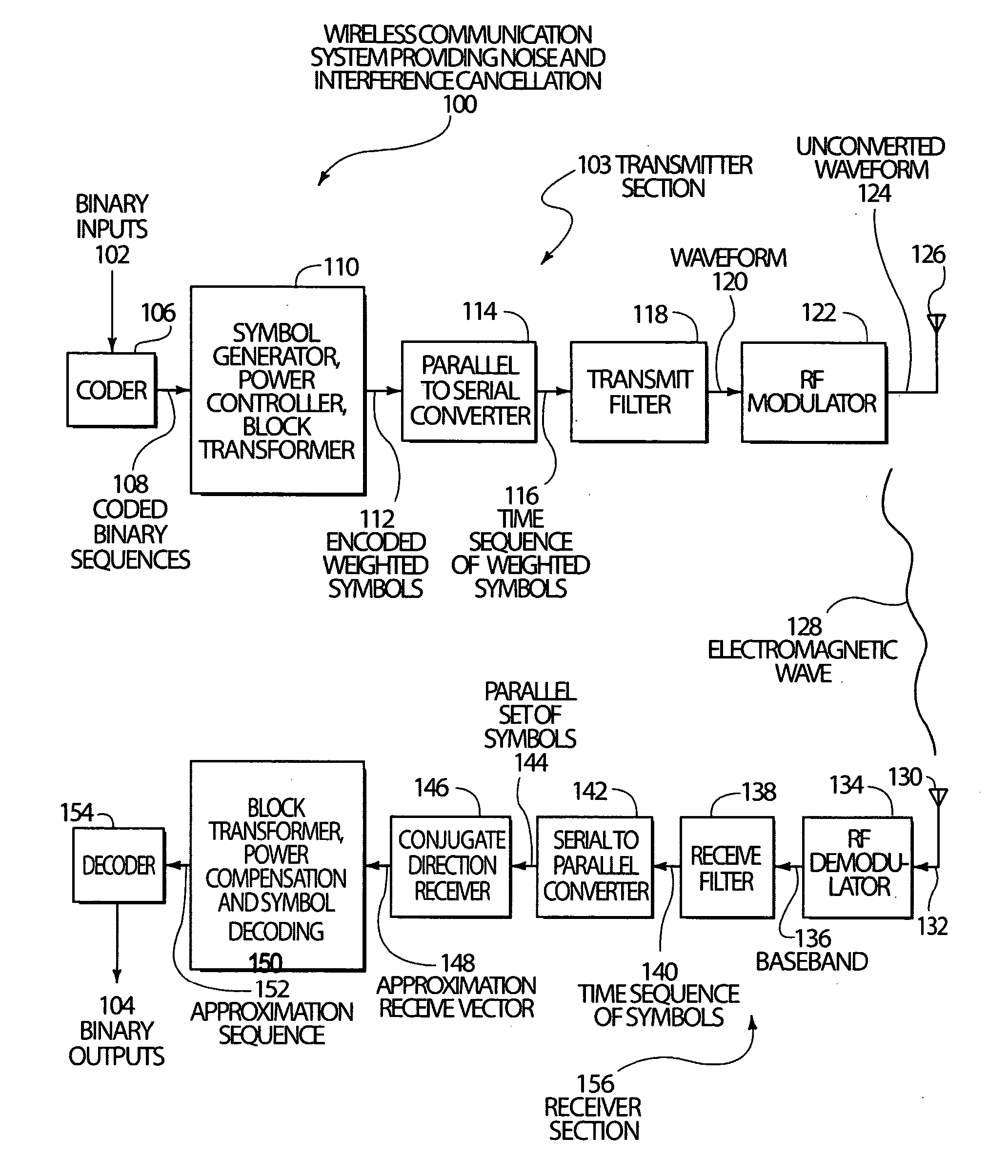
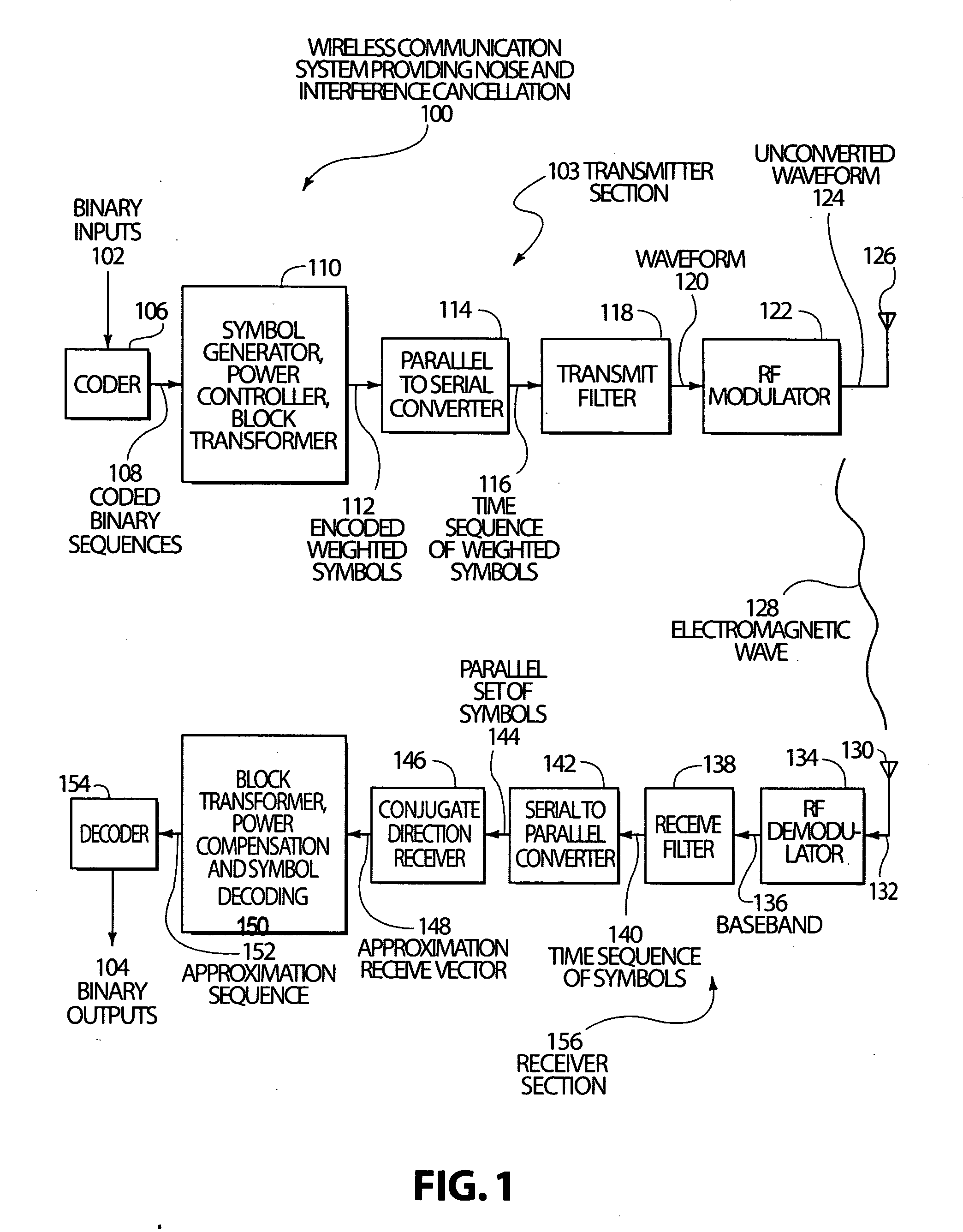
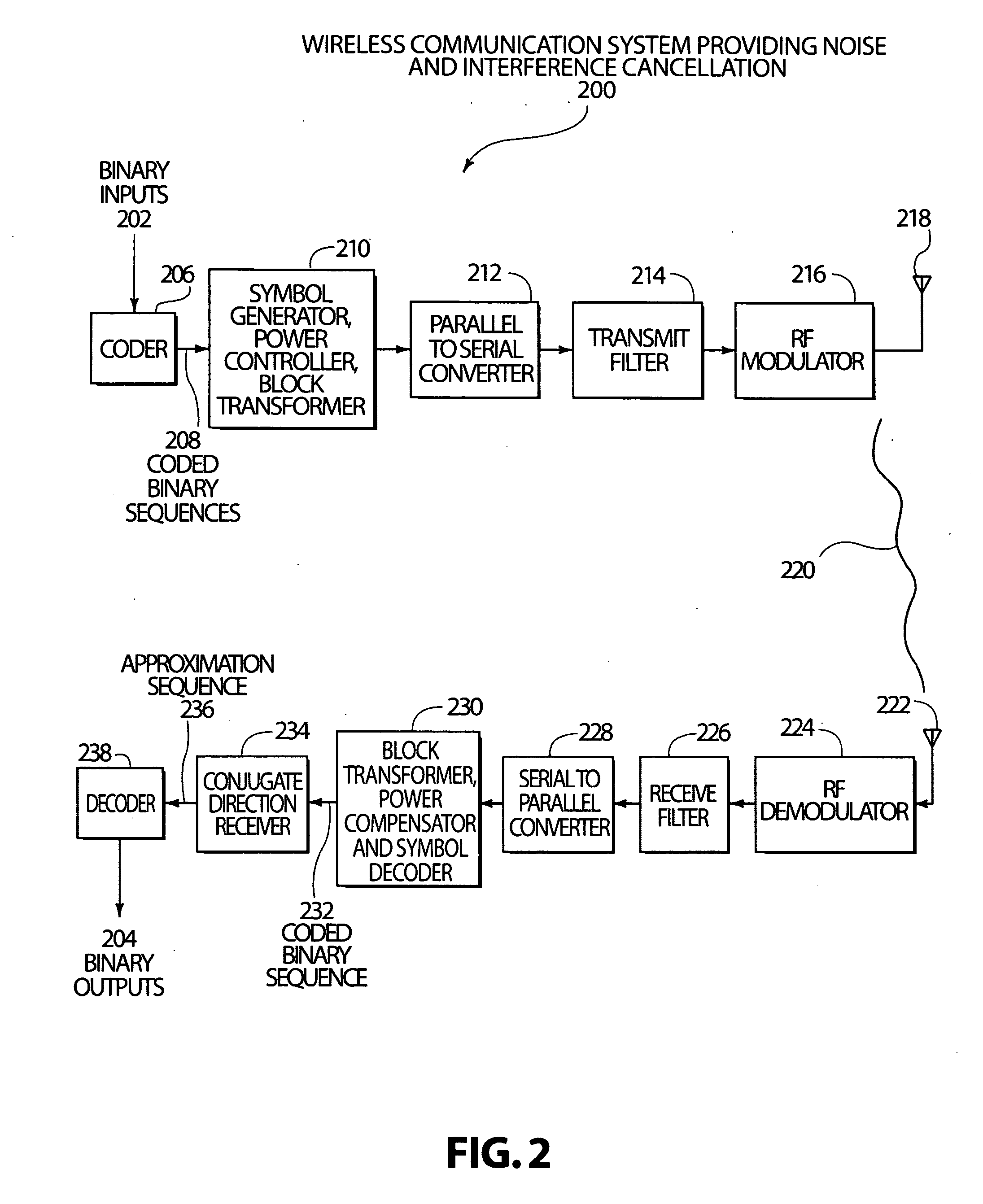
Code, signal and conjugate direction design for rapidly-adaptive communication receivers and electromagnetic, acoustic and nuclear array processors
A system and method are disclosed that substantially reduce the complexity of receivers in digitally modulated wireless communication systems such as systems that use CDMA and similar multi-access coding. Transmitted signals are designed to use orthogonal or non-orthogonal codes with specific amplitudes that reduce the number of distinct eigenvalues in a code correlation matrix or in a code-plus-interference-plus-noise correlation matrix, so that a few steps of a conjugate direction calculation will compute a reduced rank Wiener filter that can be used to provide approximate de-correlation type receivers in a substantially reduced number of steps when compared to inverse correlation matrix calculations, or when compared to conjugate direction computations run on correlation matrices with un-shaped eigenvalues. These techniques can also be applied to active or passive imaging systems such as sonar, ultrasound and radar imaging systems and phased array systems that use beam forming. Cancellation of interference and noise can also be accomplished by exploiting eigenvalue shape or by designing the codes and amplitudes of the transmitted signal and using the reduced rank Wiener filter to filter interference and noise from the receive signal. The techniques enable the use of code design and power control for the control of system complexity and bandwidth.
Owner:NEW JERSEY INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
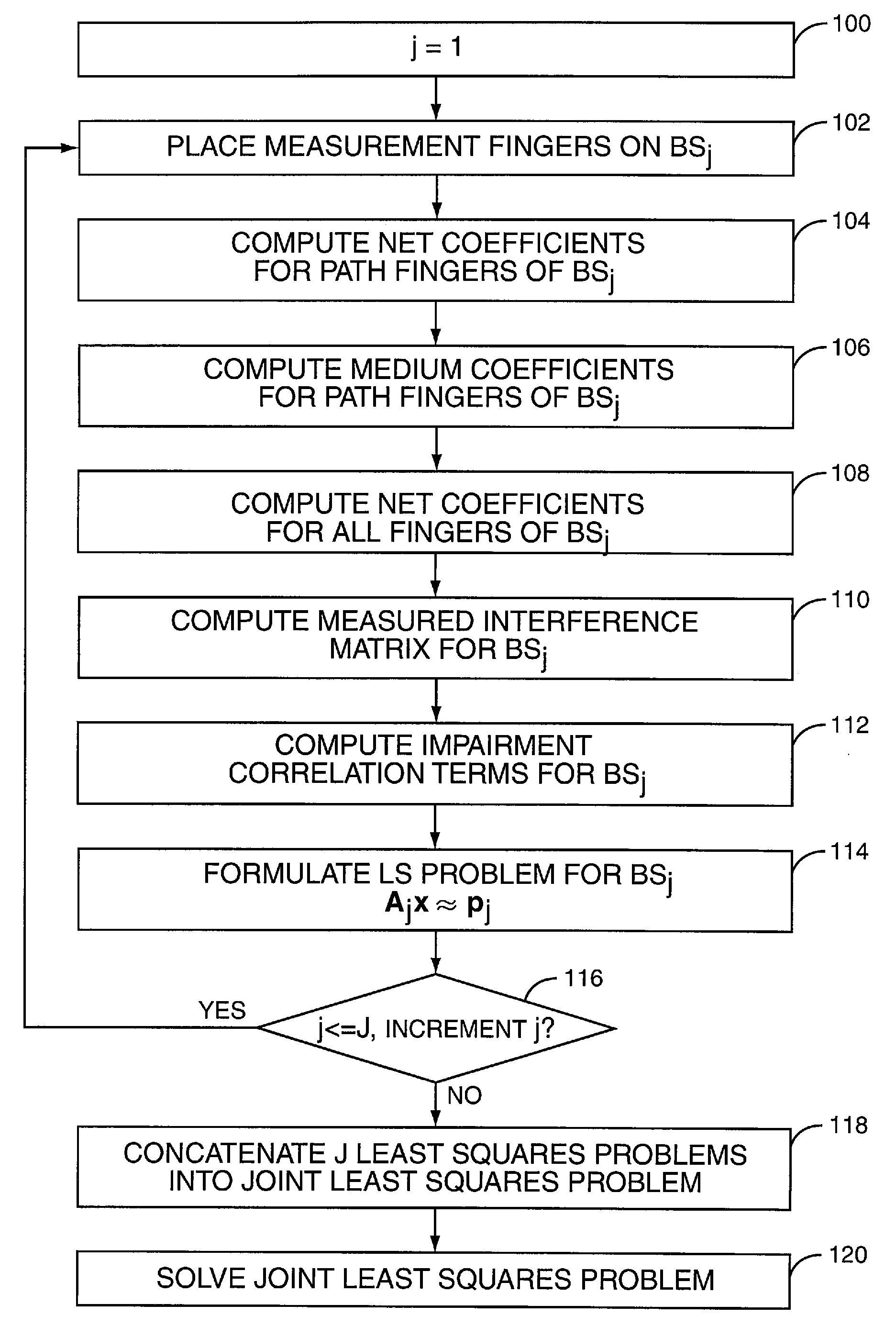
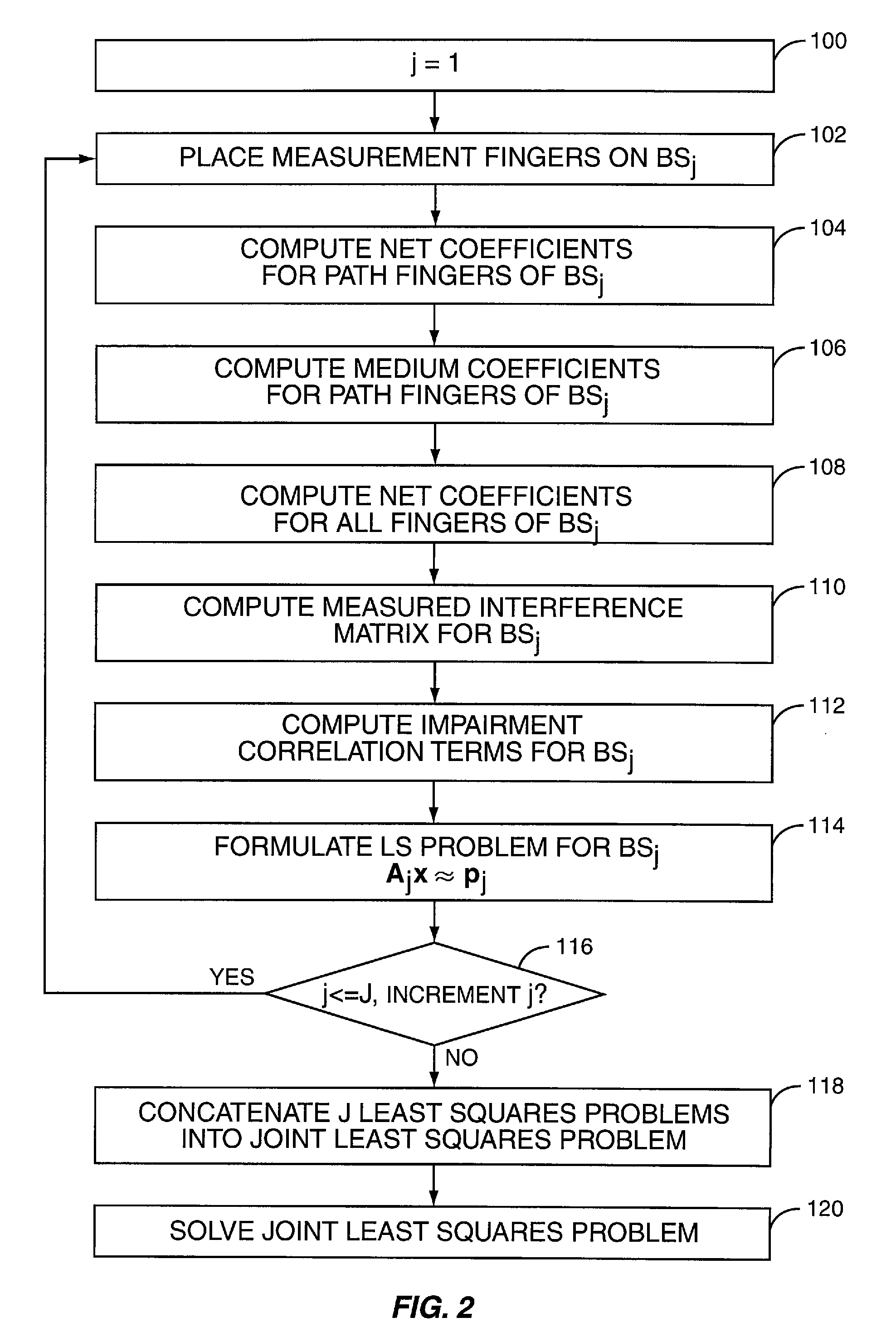
Method and Apparatus for Extended Least Squares Estimation for Generalized Rake Receiver Parameters Using Multiple Base Stations
Exemplary combining weight generation is based on estimating received signal impairment correlations using a weighted summation of interference impairment terms, such as an interference correlation matrix associated with a transmitting base station, and a noise impairment term, such as a noise correlation matrix, the impairment terms scaled by fitting parameters. The estimate is updated based on adapting the fitting parameters responsive to measured signal impairment correlations. The interference matrices are calculated from channel estimates and delay information, and knowledge of the receive filter pulse shape. Instantaneous values of the fitting parameters are determined by fitting the impairment correlation terms to impairment correlations measured at successive time instants and the fitting parameters are adapted at each time instant by updating the fitting parameters based on the instantaneous values.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Nonlinear system target tracking method based on distributed volume information filtering
InactiveCN103065037AReduce dimensionalityResolve dependenciesSpecial data processing applicationsPattern recognitionCurse of dimensionality
The invention belongs to the field of target tracking and mainly relates to a target tracking nonlinear system target tracking method based on distributed volume information filtering. The existing volume Kalman nonlinear system target tracking method is achieved on the premise that premise noise and measurement noise are not relevant and each measurement noise is not relevant, so that using scope of the volume Kalman nonlinear system target tracking method is greatly limited. The target tracking nonlinear system target tracking method deduces noise related expanding Kalman information filtering, volume Kalman information filtering is embedded in a time updating process and a measurement updating process, a noise relevant problem is solved, and practical applicability of the method is greatly strengthened. In addition, the method is based on decentralization, a theory of matrix diagonalization is used, dimensionality of a matrix is reduced to great extent, and dimensionality curses caused by high dimensions are avoided.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
Bayesian inference of particle motion and dynamics from single particle tracking and fluorescence correlation spectroscopy
Techniques for inferring particle dynamics from certain data include determining multiple models for motion of particles in a biological sample. Each model includes a corresponding set of one or more parameters. Measured data is obtained based on measurements at one or more voxels of an imaging system sensitive to motion of particles in the biological sample; and, determining noise correlation of the measured data. Based at least in part on the noise correlation, a marginal likelihood is determined of the measured data given each model of the multiple models. A relative probability for each model is determined based on the marginal likelihood. Based at least in part on the relative probability for each model, a value is determined for at least one parameter of the set of one or more parameters corresponding to a selected model of the multiple models.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
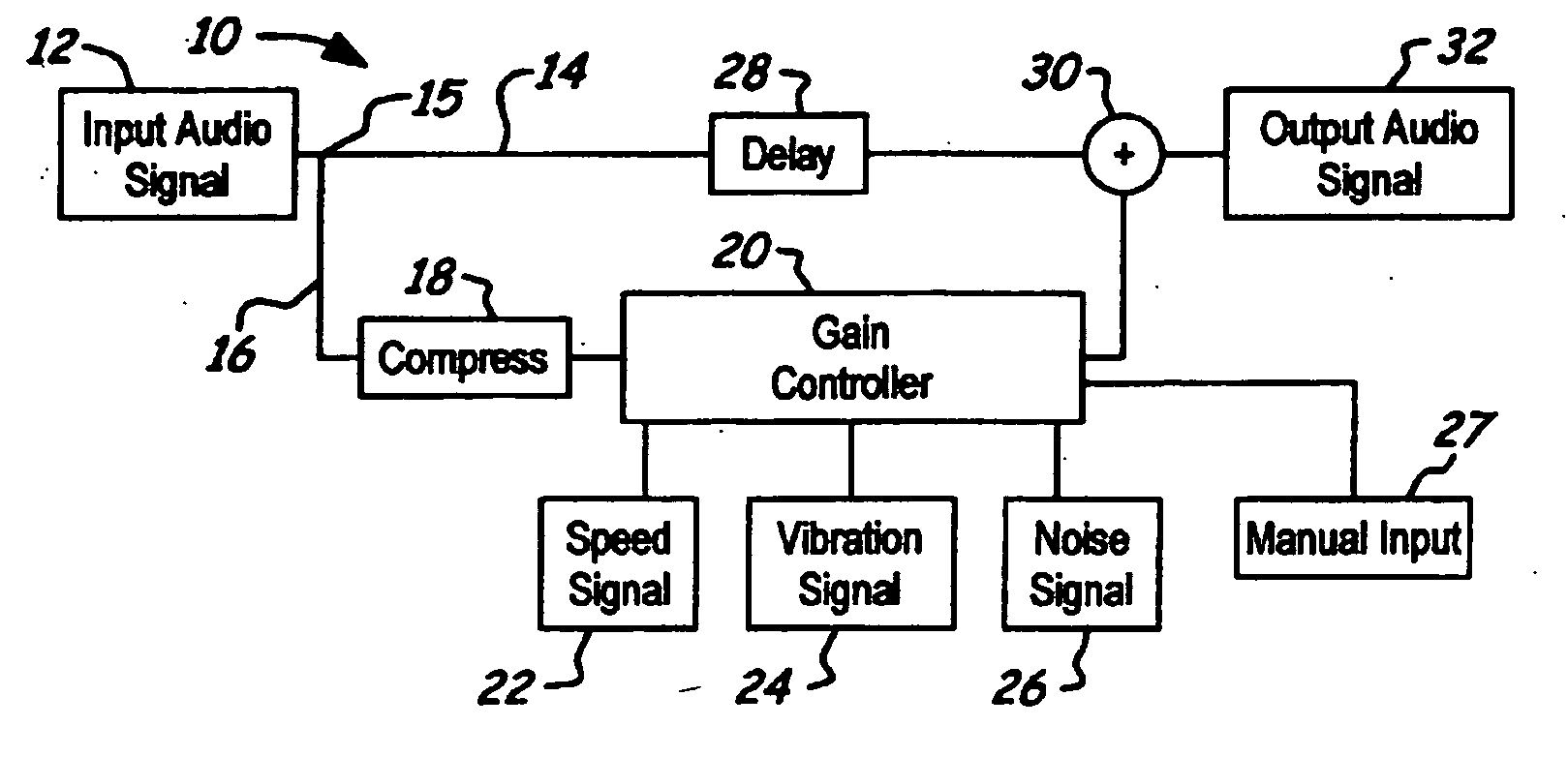
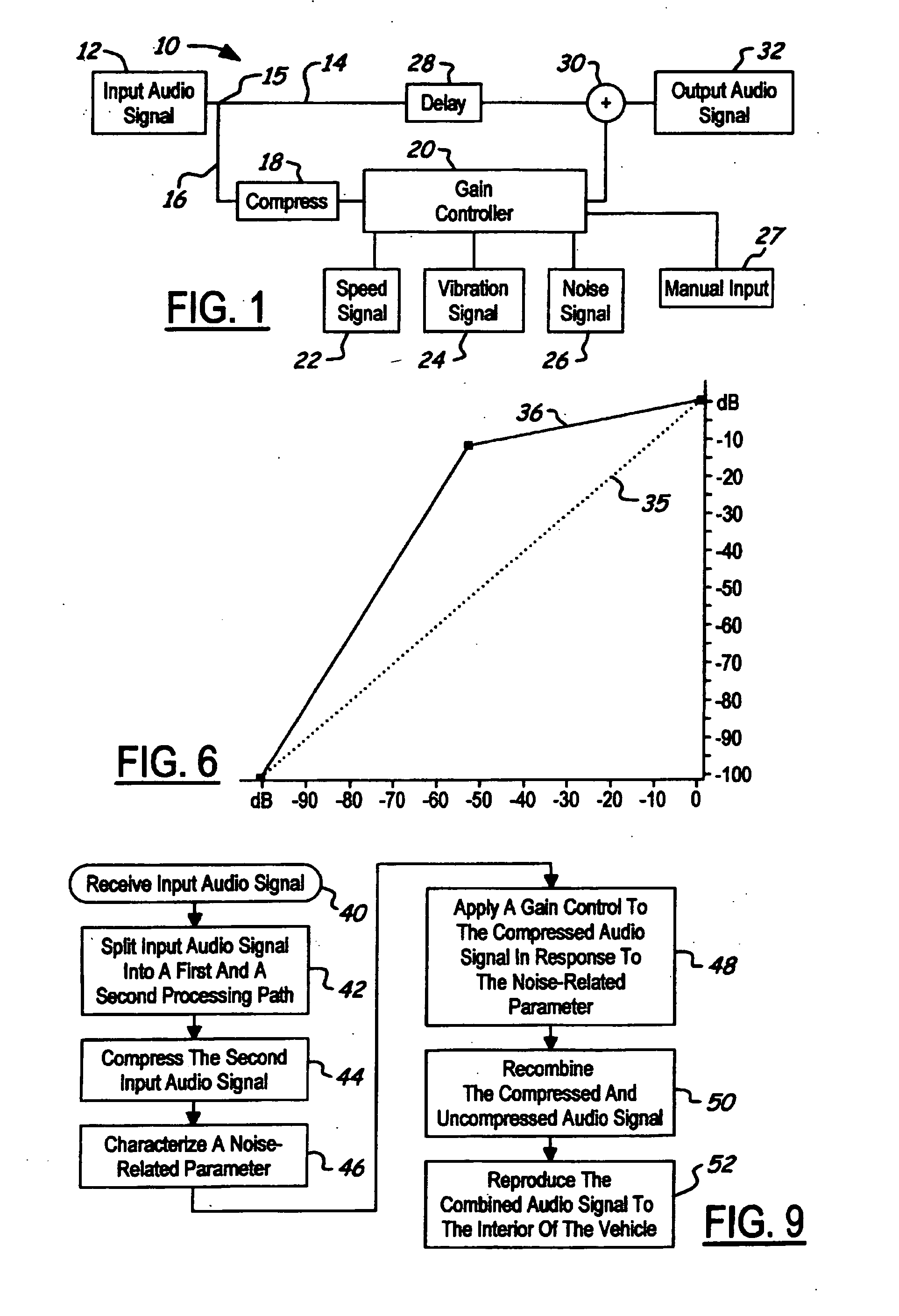
NVH dependent parallel compression processing for automotive audio systems
InactiveUS20050135635A1Combination control in untuned amplifierVolume compression/expansionParallel compressionCar audio system
A method is provided for controlling a dynamic range of audio reproduction in an interior of a vehicle. An input audio signal is received by an audio processor. The input audio signal is split into a first and a second processing path. The input audio signal of the second processing path is compressed. A noise-related parameter of the vehicle is characterized. A gain control is applied to the compressed audio signal of the second processing path in response to the noise-related parameter. The compressed and uncompressed audio signals are synchronously recombined. The combined audio signal is reproduced to the interior of the vehicle.
Owner:LEAR CORP
Dereverberation and feedback compensation system
ActiveUS20070110254A1Reduce echoEnhanced noise correlation signalInterconnection arrangementsEar treatmentSpeech soundComputer science
A dereverberation and feedback compensation system reduces the echo received by a first audio device while reducing the speech feedback received from a second audio device. A decorrelation logic decorrelates audio signals from the first audio device. A first processor generates a noise compensation signal based on the decorrelated audio signals and system determined filter coefficients. The second processor generates an enhanced noise correlation signal based on speech signals of a second audio device and the filter coefficients used by the first processor.
Owner:APPLE INC
Mobile communications receiving apparatus and method
InactiveUS20030045313A1SNR can be maximizedSpatial transmit diversityWireless commuication servicesEngineeringExecution control
In a mobile communication receiving apparatus in which signals received on a plurality of receiving paths (branches) are combined by a combiner, correlation between noise signals contained in the signals received on respective ones of the branches is detected by a noise correlation calculating unit, and control is exercised so as to maximize signal-to-noise power ratio of the combined signal based upon the correlation calculated in the noise correlation calculating unit. Signal-to-noise power ratio can be maximized even if noise components contained in respective ones of the branch signals are mutually correlated.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
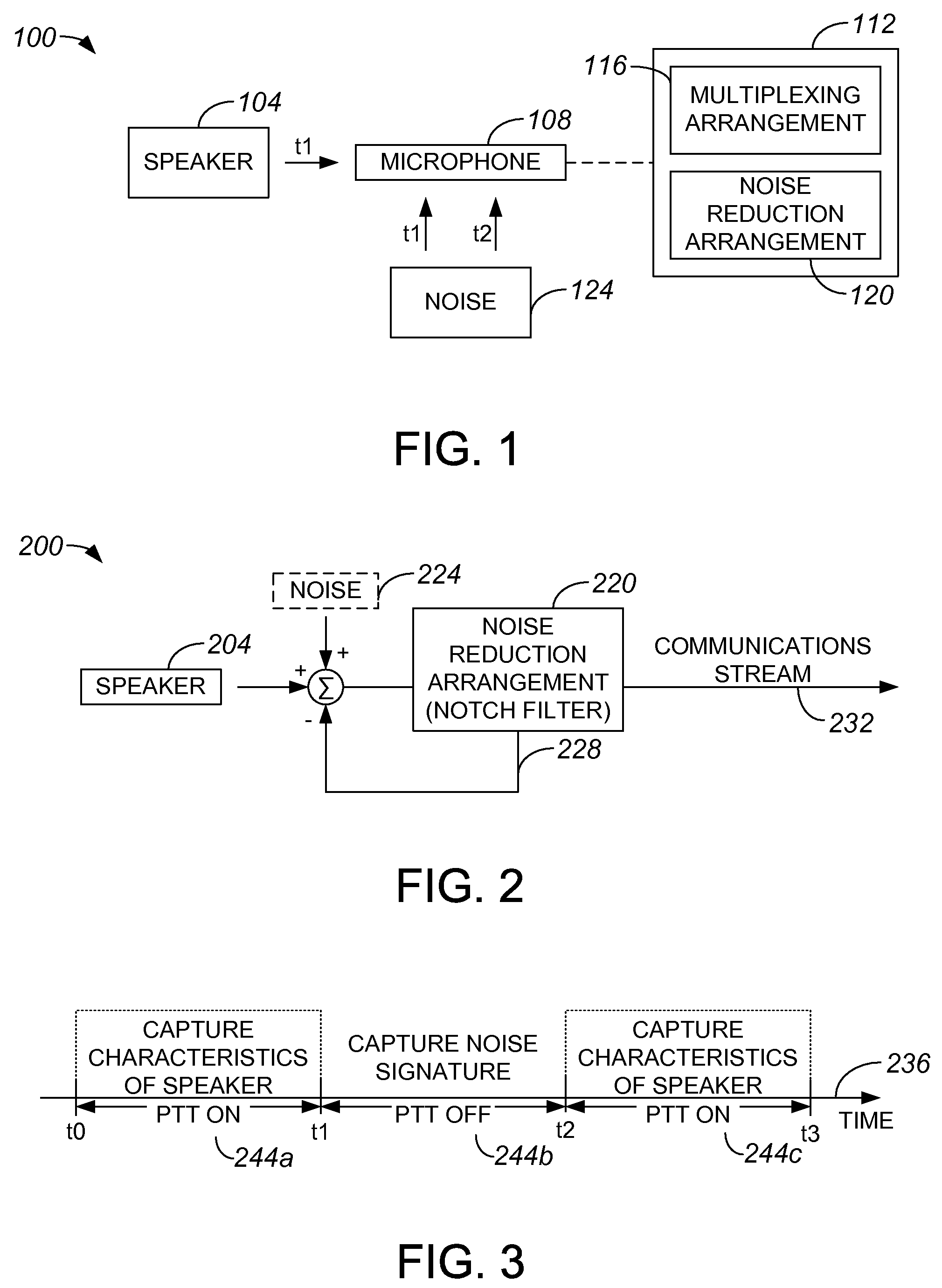
Push-to-talk system with enhanced noise reduction
Methods and apparatus for reducing the effect of surrounding noise in a push-to-talk (PTT) system are disclosed. In one embodiment, a method includes obtaining a first media stream using a microphone when a PTT functionality of a PTT communications system is in a first state, and identifying a first set of characteristics associated with noise in the first media stream. The method also includes obtaining a second media stream using the microphone that includes the noise and a first sound when the PTT functionality is in a second state. A second set of characteristics associated with the first sound in the second media stream is identified, and parameters associated with a filtering arrangement are determined using the first and second sets of characteristics. Finally, the method includes applying the filtering arrangement to the second media stream to filter out the noise such that a communications stream is created.
Owner:STA GRP LLC
Capacity information filtering-based pure direction tracking method of noise-related system
InactiveCN102999696AResolve dependenciesEasy to trackSpecial data processing applicationsProcess noiseEngineering
The invention relates to a capacity information filtering-based pure direction tracking method of a noise-related system, which belongs to the field of target tracking. The conventional capacity kalman non-linear system target tracking method is implemented on hypothetic premise that process noise is not related to measurement noise, so that the use range of the method is greatly limited. According to the method, on premise that expanded kalman information filtering related to the noise is deducted, capacity kalman information filtering is embedded into two processes of time updating and measurement updating. The problem of noise relevance is solved, and therefore the practicability of the method provided by the invention is greatly improved.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
Crosstalk Recognition in Presence of Radio Frequency Interference
InactiveUS20080267392A1Remove background noiseInterconnection arrangementsSubstations coupling interface circuitsProximal pointNoise level
Crosstalk interference induced by the adjacent pairs is one of the major performance limiting factors of DSL systems. As there is a rapid increase in the deployment of DSL services worldwide, the need to provide information about noise related parameters to the operators and the service providers is of utmost importance. Satisfying such a need enables operators to anticipate the line capacity and understand the noise level characteristics of the loop environment. Specifically, crosstalk and more particularly upstream near end crosstalk (NEXT) in the presence of narrowband interference can be classified to isolate the particular service type causing the upstream NEXT. The identification of the service type of the upstream NEXT would enable operators to address the disturber.
Owner:IKANOS COMMUNICATIONS
Iterative decoding and equalingzing method for hgih speed communications on multiple antenna channels during transmission and reception
ActiveUS20060251164A1Control performanceLess complexMultiple-port networksDelay line applicationsMean squareChannel decoder
An iterative decoding and equalizing device for high bit rate communication over frequency-selective channels with multiple transmit and receive antennas, said device including a decision feedback equalizer adapted to receive data from different receive antennas and including a forward filter (9) and a recursive backward filter (12) fed with calculated weighted reconstituted data from the output of a decoder (13) fed by decision means (11) and means for subtracting the output of said backward filter (12) from the output data of the forward filter (9) whereby the subtracted data is fed to the input of the decision means (11) with the output of the decoder (13) and the decision means (11) produce a statistic which is forwarded to a channel decoder with weighted inputs and outputs and said decision means (11) take into account the space noise correlation at the output of the subtraction means (10) and the decision means (11) and the decoder (13) are separated by space-time interleaving at bit level, which device is characterized in that the forward filter (9) and the backward filter (12) are iteratively adapted to minimize the mean square error at the output of the subtractor (10).
Owner:FRANCE TELECOM SA
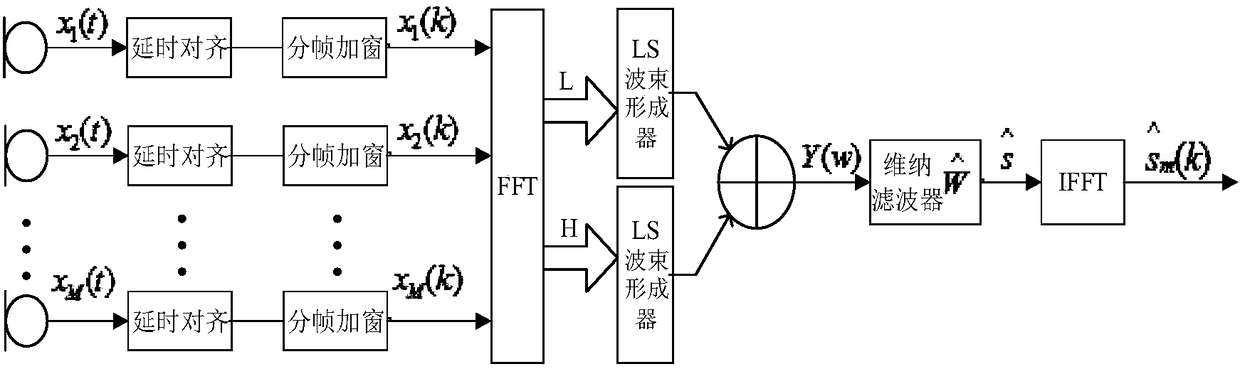
LS beam-forming reverberation suppression method based on Wiener post-filter
The invention provides a least squares beam-forming reverberation suppression method with Wiener post-filtering. According to the method, a voice signal after reverberation is divided into a direct arrival part and a reverberation part to obtain Wiener post-filter gain estimation; because of the high noise correlation of the low-frequency part of the voice signal, frequency division is carried outby using a least squares beam forming algorithm; and then an optimal weight value is calculated. The method has the following advantages: the signal after reverberation is divided into the direct arrival part and the reverberation part to obtain the improved Wiener post-filter gain estimation, the voice signal after reverberation is divided into a high-frequency component and a low-frequency component because of the high noise correlation of the low-frequency part of the voice signal, and then optimal weight values of the high-frequency component and the low-frequency component are calculatedby using the least squares beam forming algorithm, so that the reverberation suppression accuracy and voice quality are improved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF INFORMATION SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com