Patents
Literature
105results about "Variable resistance carrier recording" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
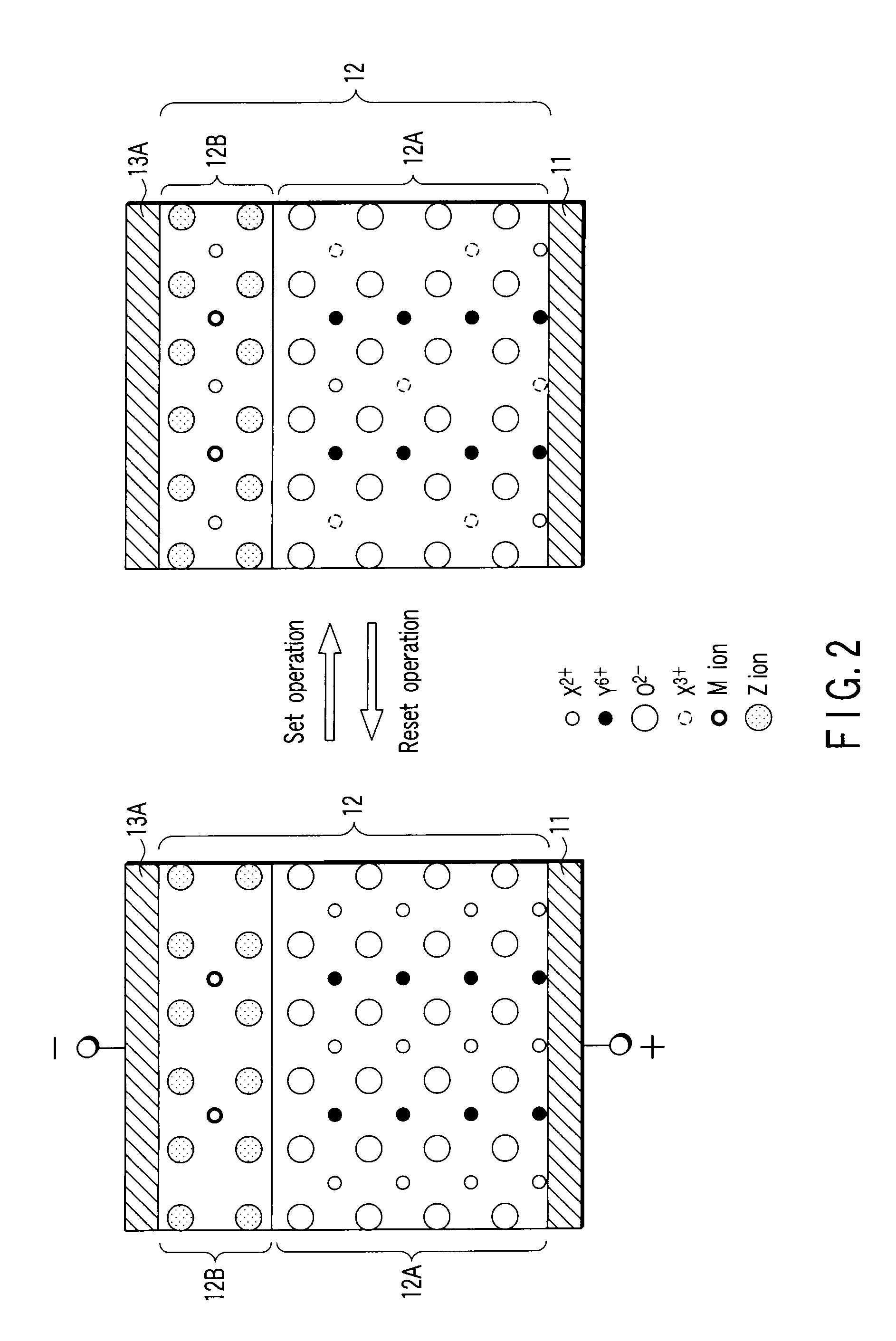
Non-volatile memory with phase-change recording layer
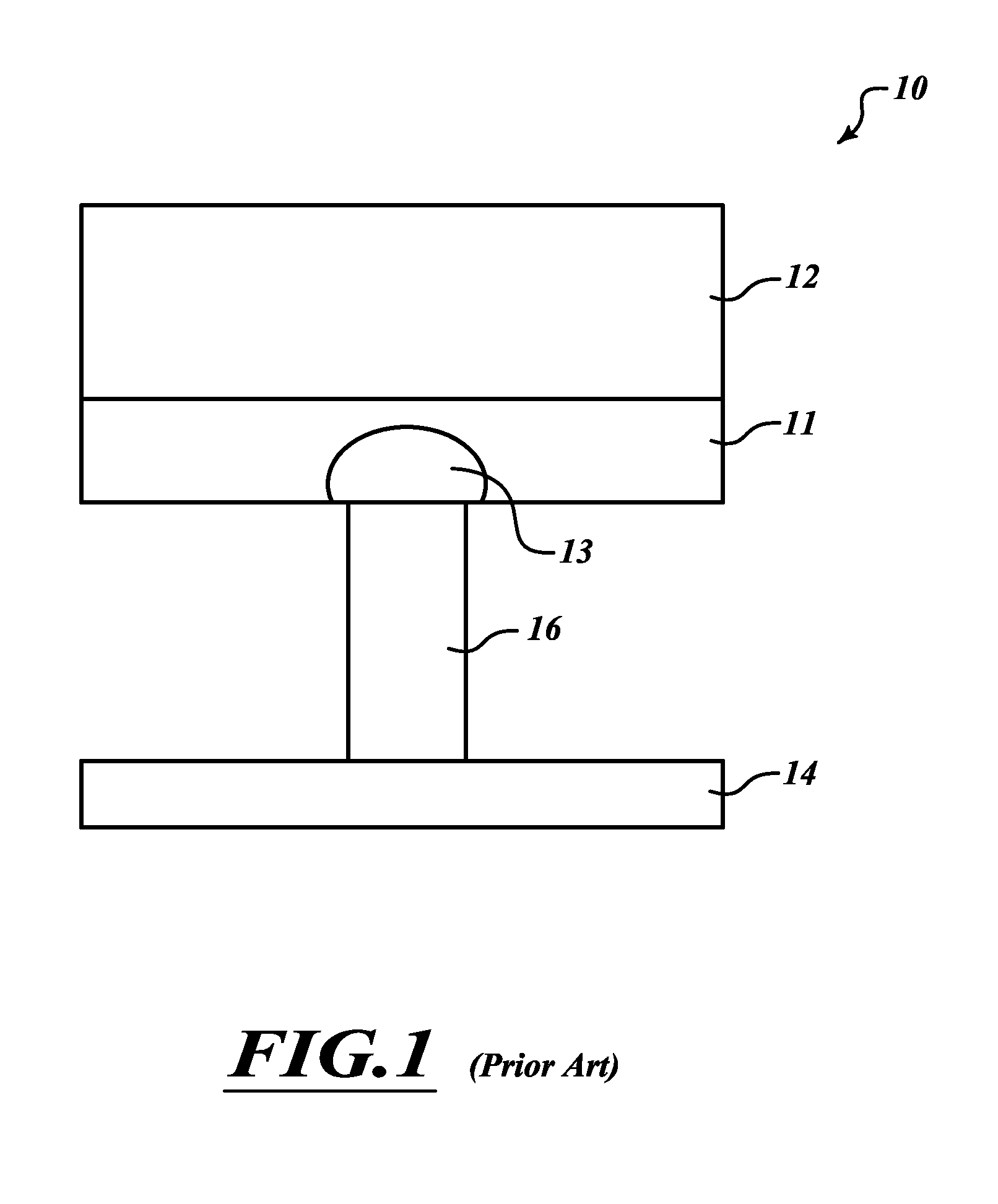
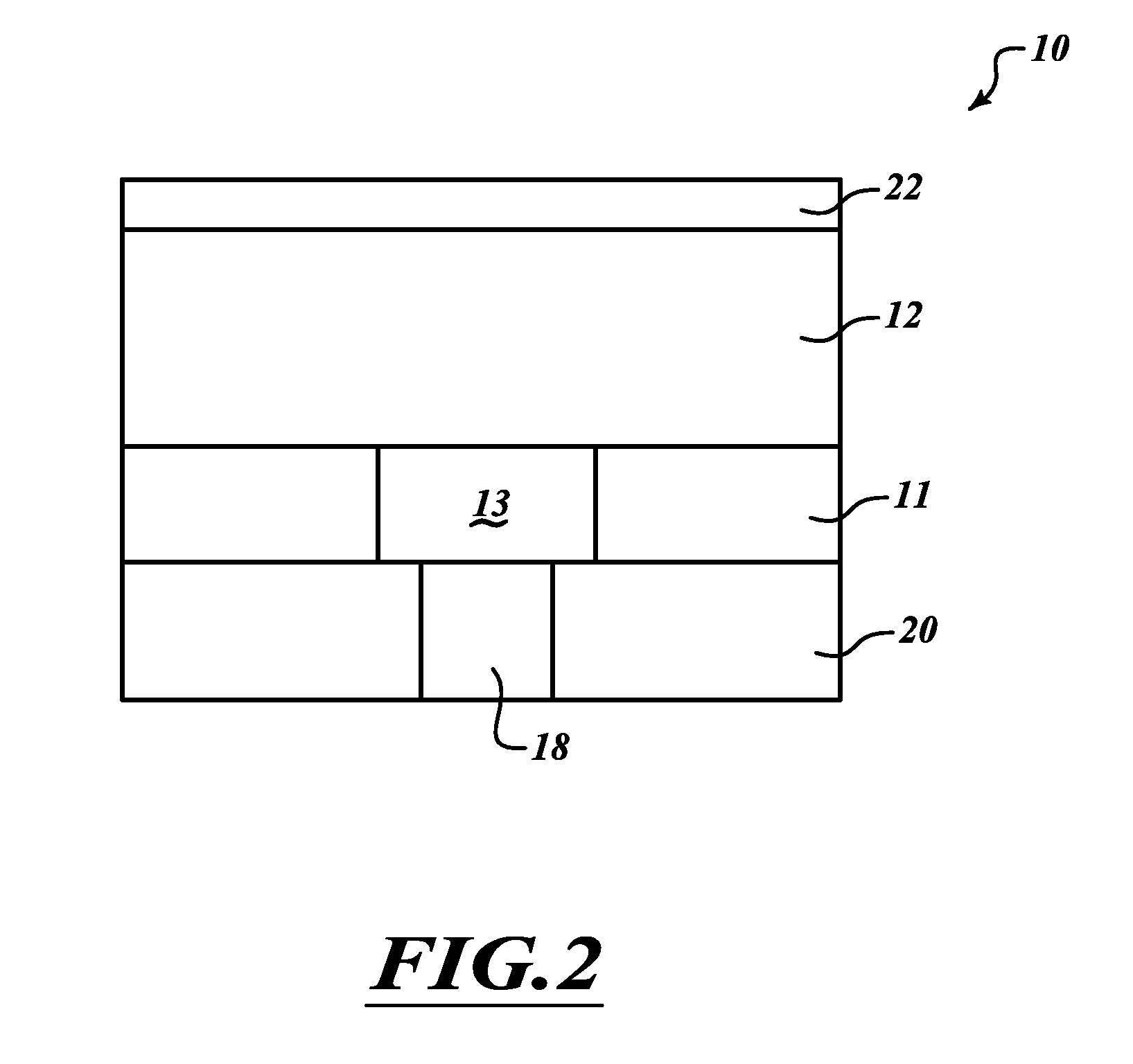
InactiveUS6900517B2Increase possible numberReduce power consumptionTransistorVariable resistance carrier recordingElectrical impulseEngineering
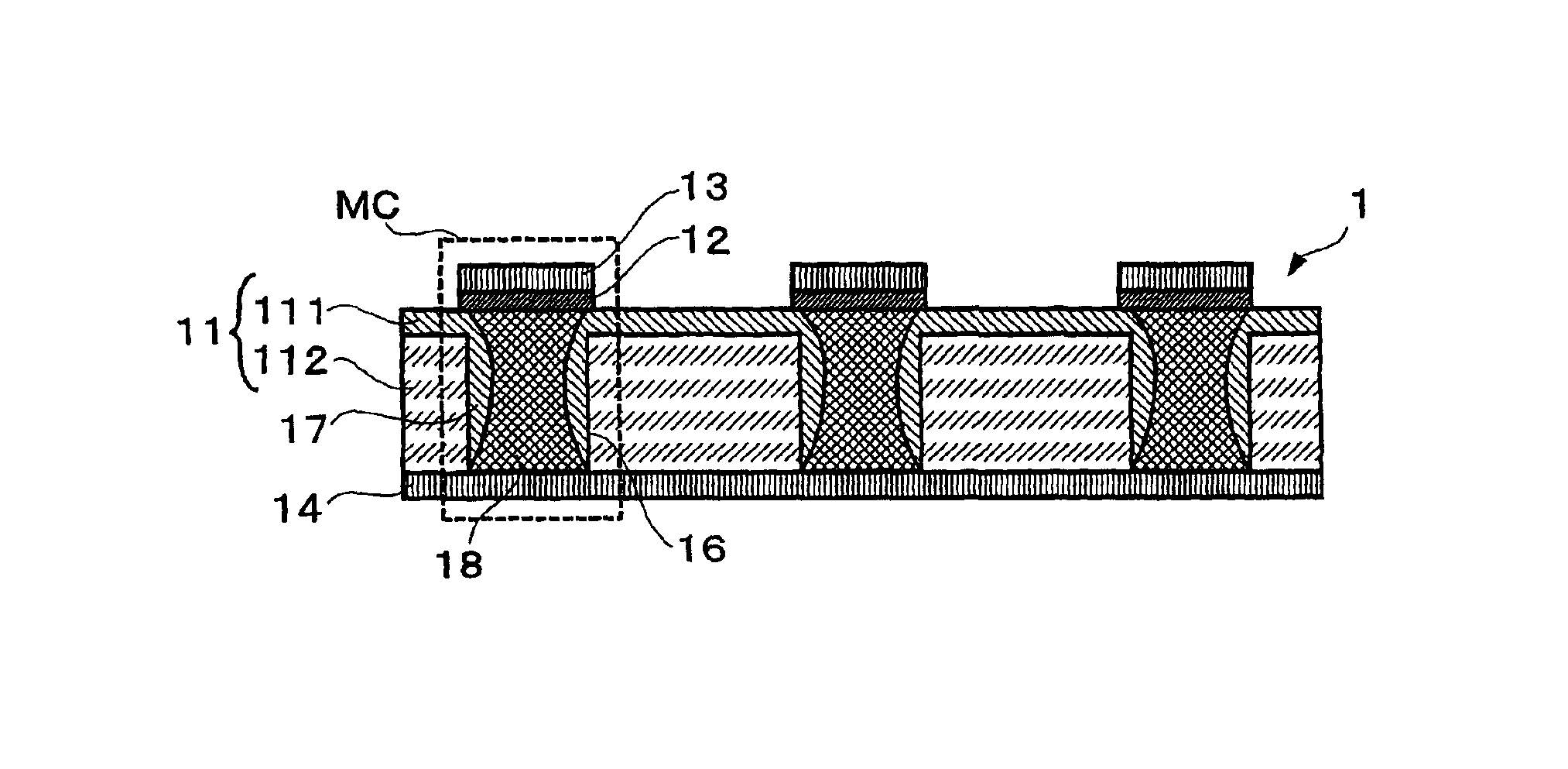
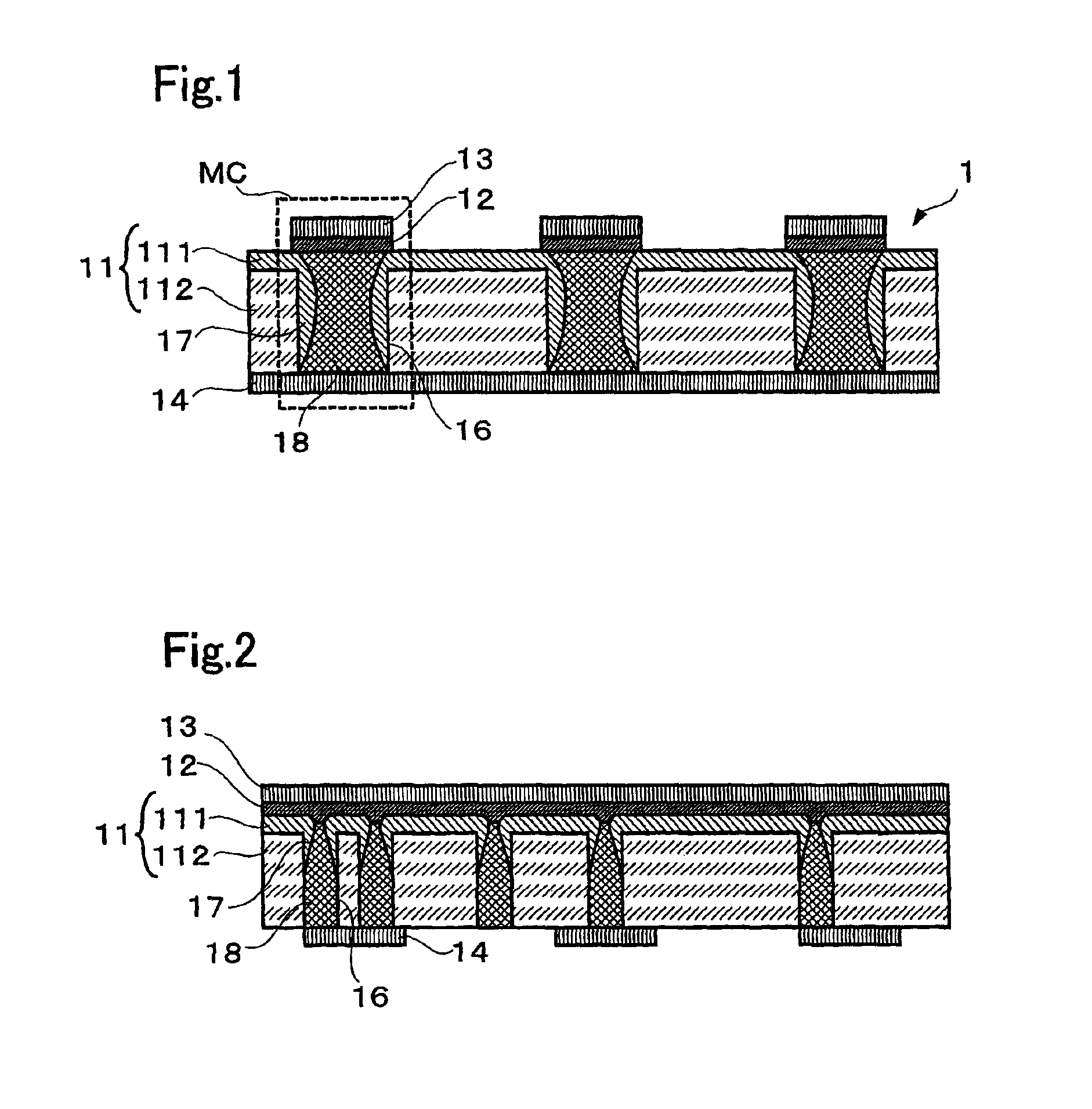
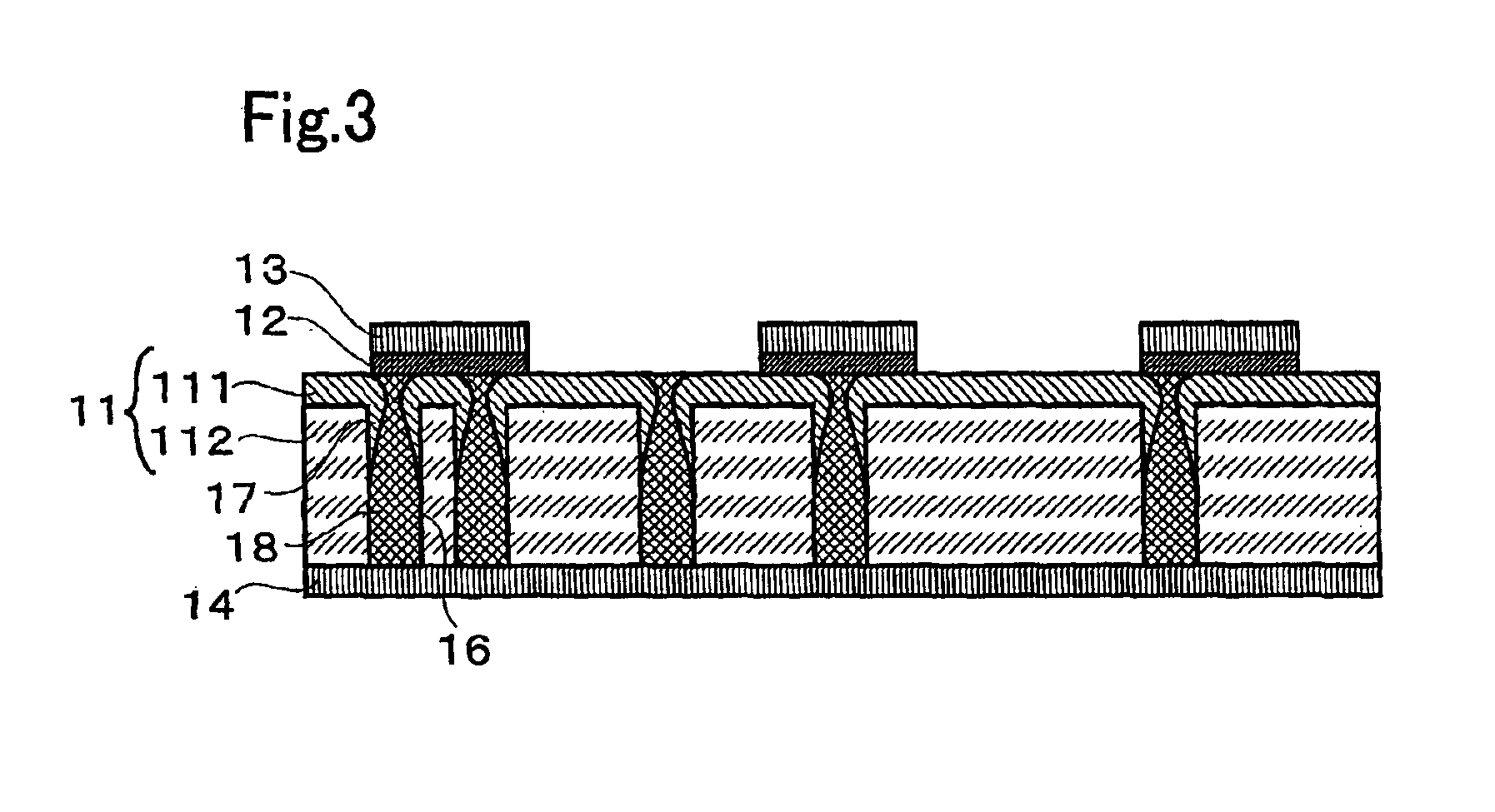
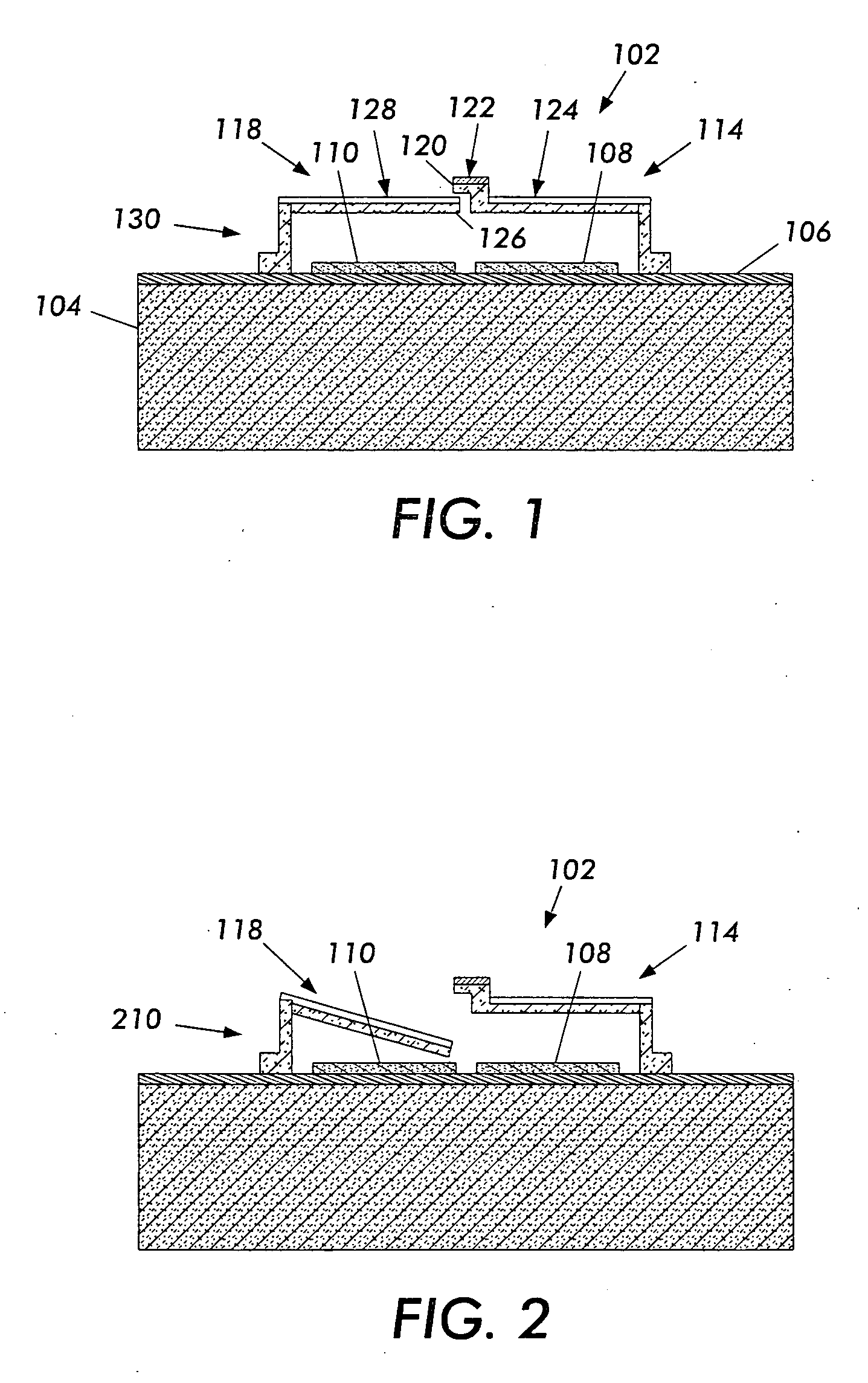
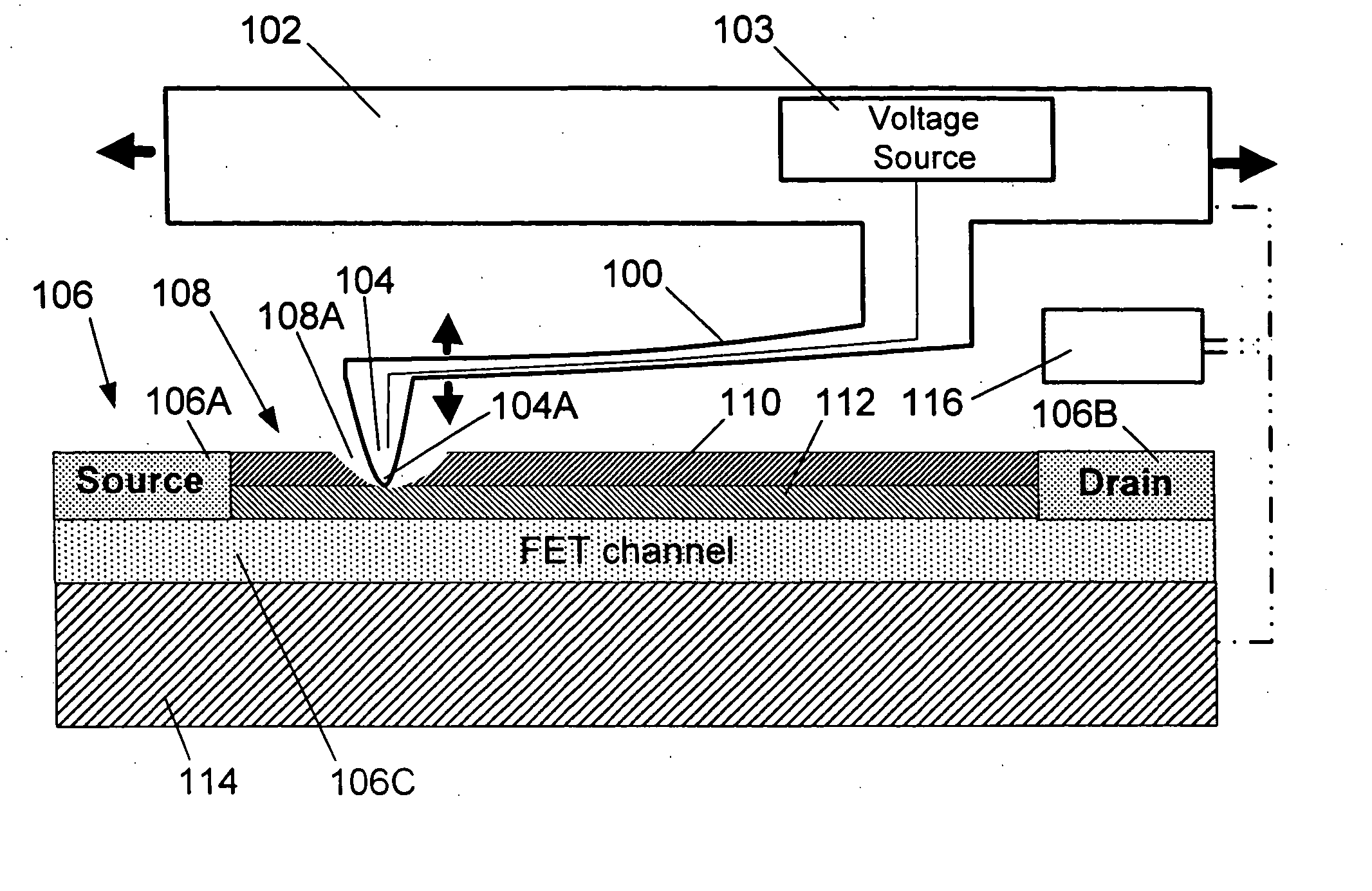
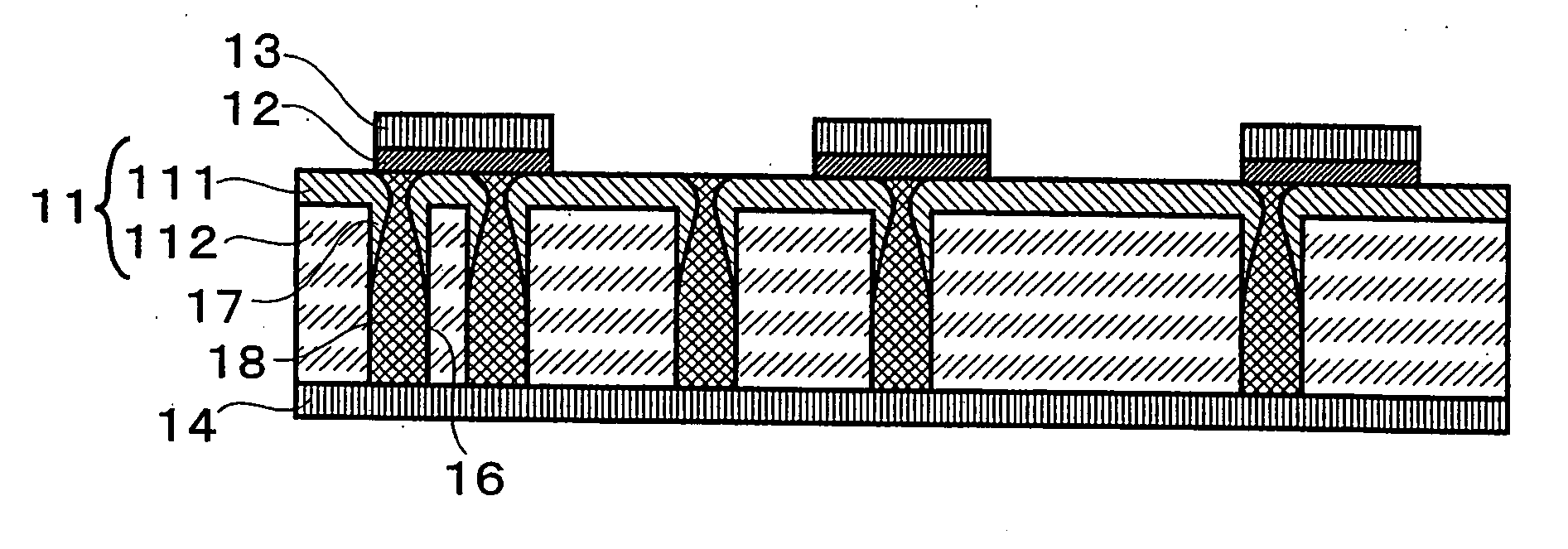
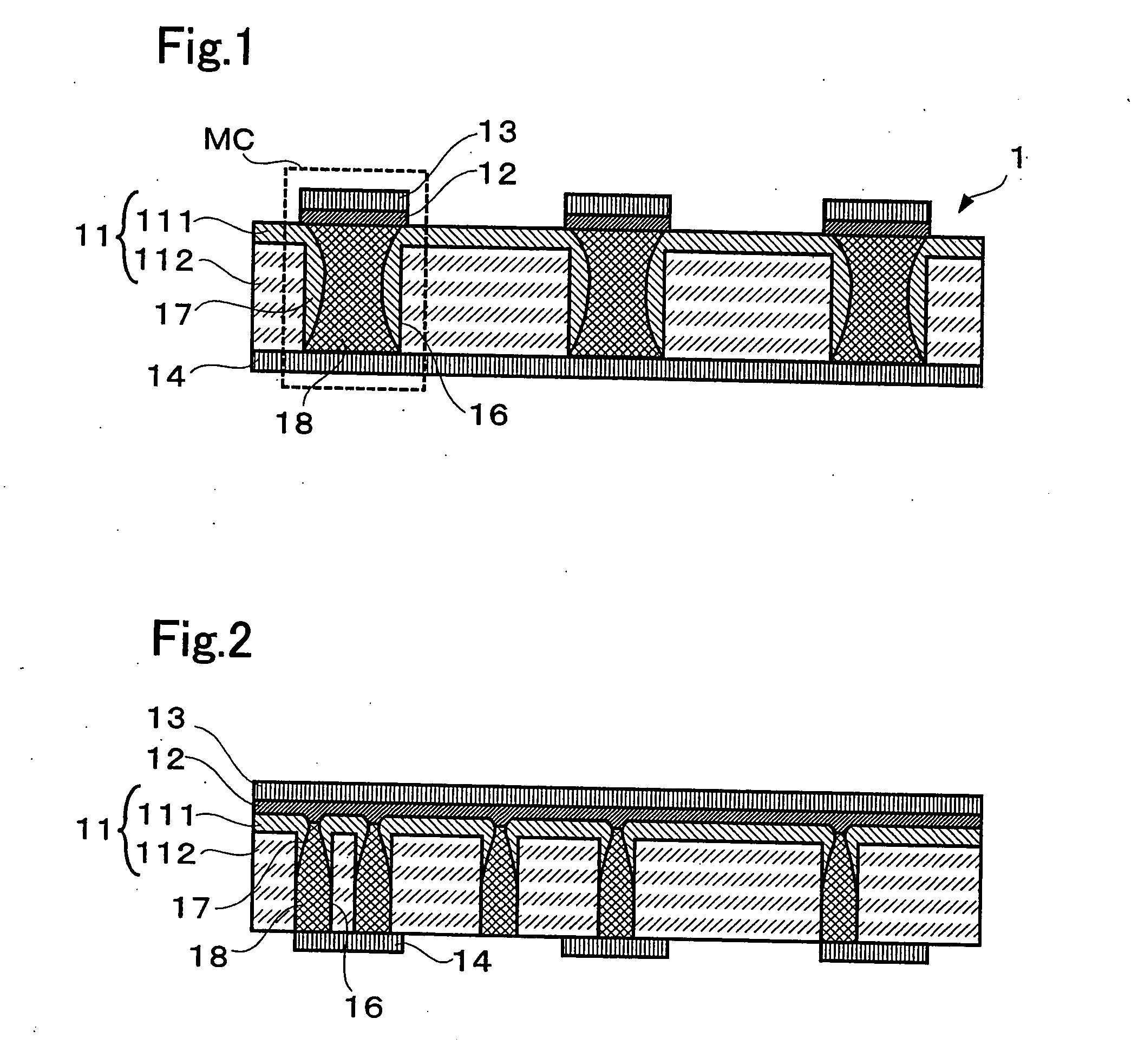
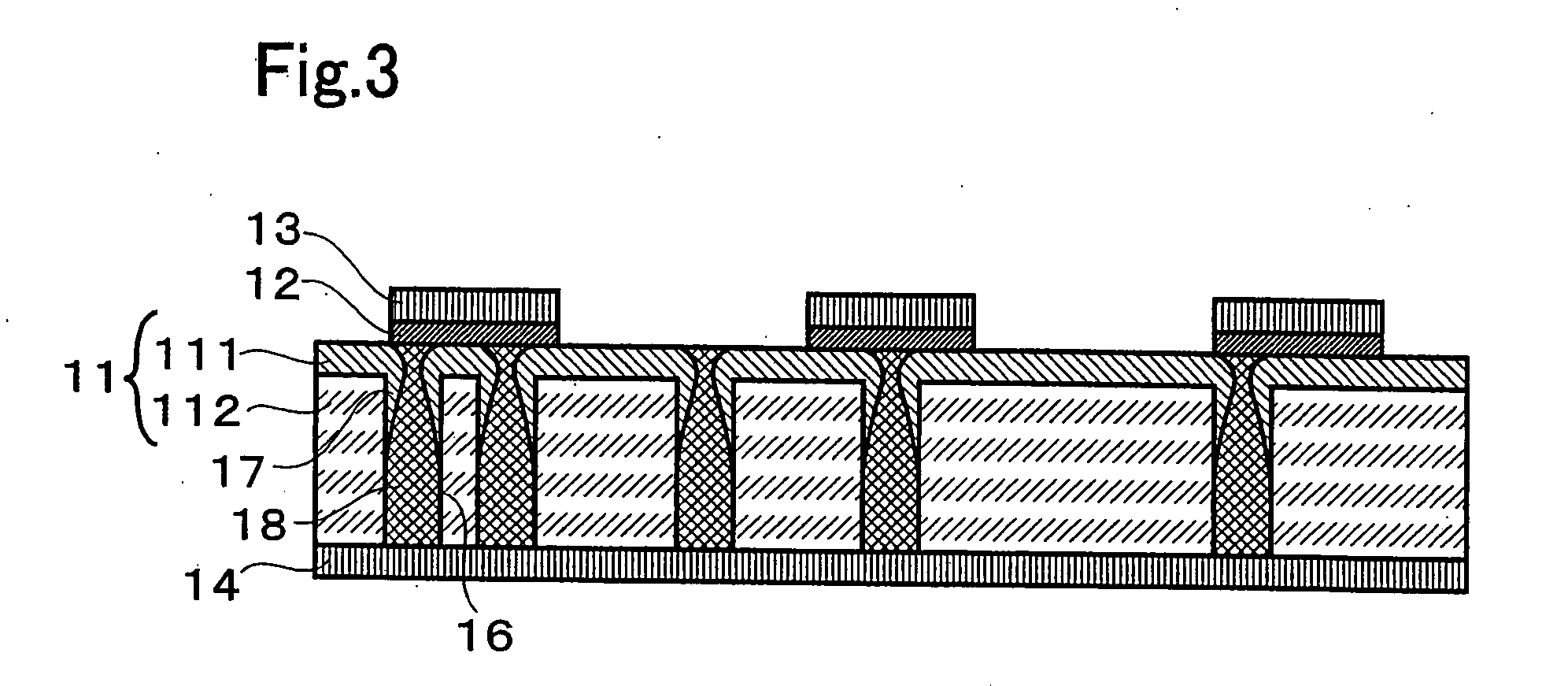
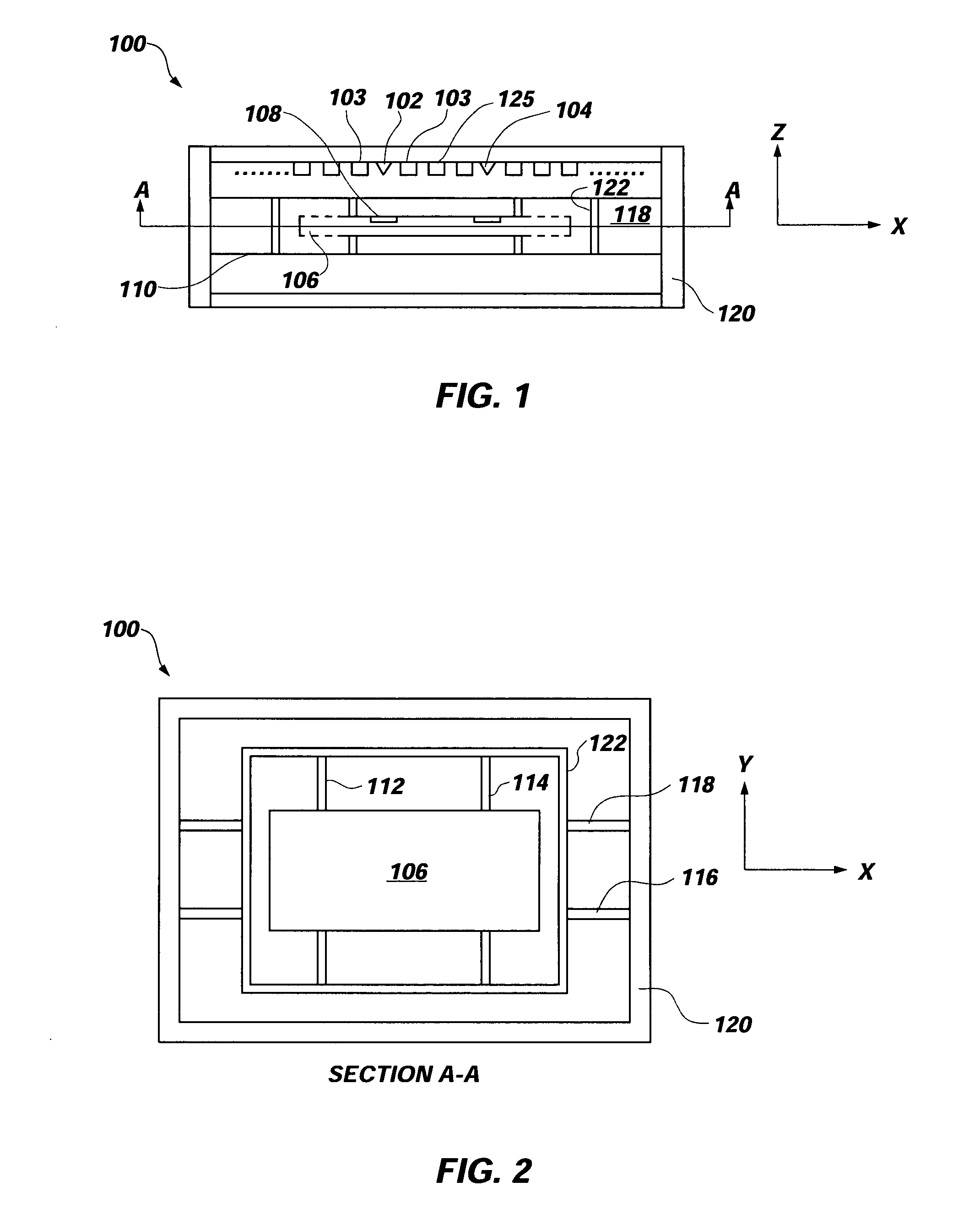
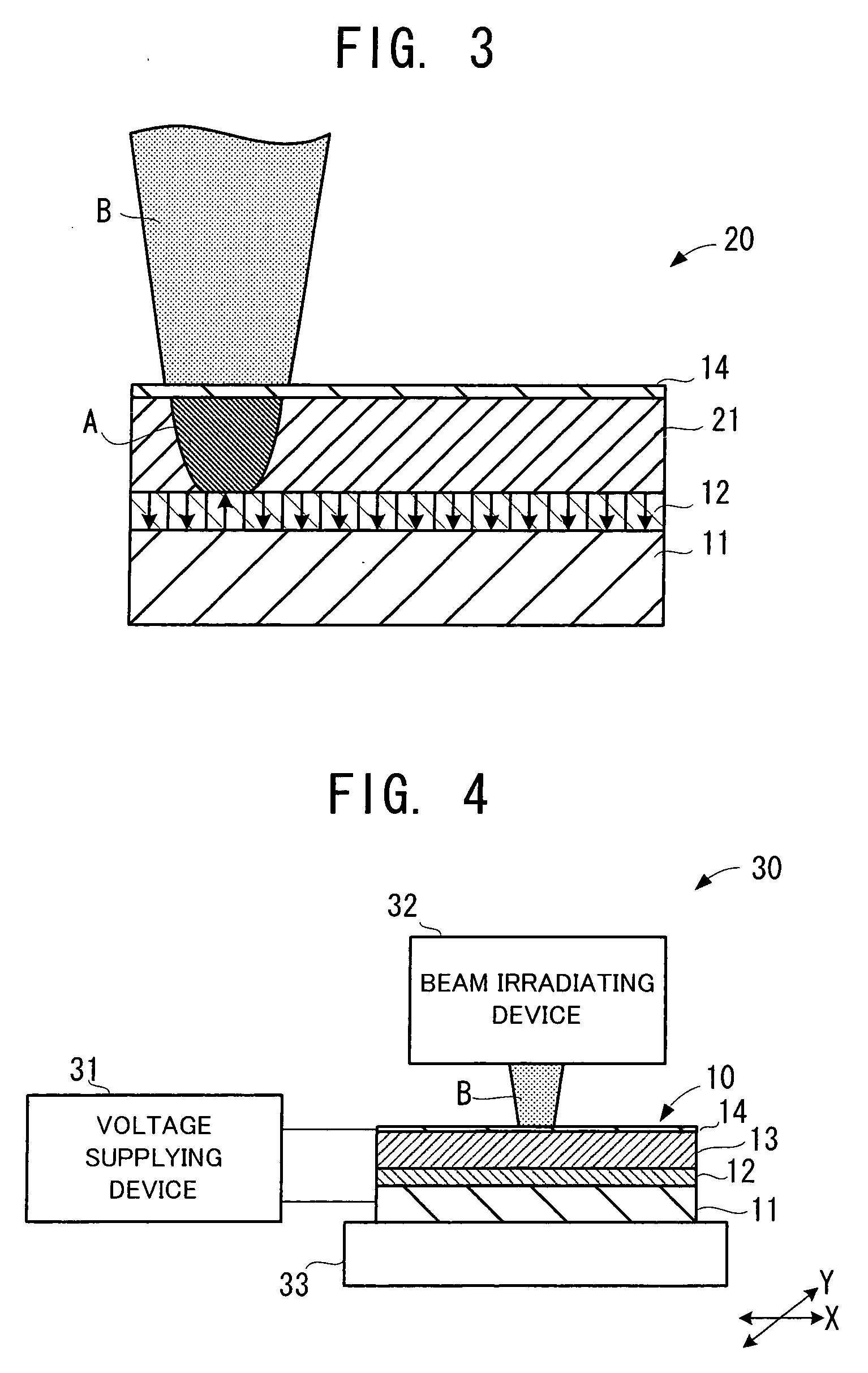
A non-volatile memory, which comprises an insulating substrate (11) that has a first electrode (18) that extends through the substrate from the front surface to the rear surface thereof; a second electrode (13) that is formed on one side of the insulating substrate (11); and a recording layer (12) that is clamped between the first electrode (18) and the second electrode (13) and whose resistance value varies when an electric pulse is applied across the first electrode (18) and the second electrode (13); wherein the insulating substrate (11) has a layered structure composed of an organic dielectric thin film (112) and an inorganic dielectric layer (111) that is thinner than the organic dielectric thin film (112); with the recording layer (12) being formed on the side on which the inorganic dielectric layer is formed. Use of this non-volatile memory increases the possible number of data writing cycles while saving power.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Phase change memory devices, method for encoding, and methods for storing data
ActiveUS9093141B2Electrical apparatusVariable resistance carrier recordingThermal energyPhase-change memory
Phase change memory cells including a phase change media can be encoded using a source of energy that is not integral with the memory cell. External sources of energy include thermal heads, such as those used in direct thermal printing or thermal transfer printing and sources of electromagnetic radiation, such as lasers. Such types of phase change memory devices can be associated with substrates that include thermochromic materials or are suitable for thermal transfer printing so that the memory cells can be encoded and print media applied to the substrate using the same source of thermal energy.
Owner:INTERMEC IP CORP
Data read/ write device
ActiveUS20070133358A1Variable resistance carrier recordingNanoinformaticsComputer hardwareShortest distance
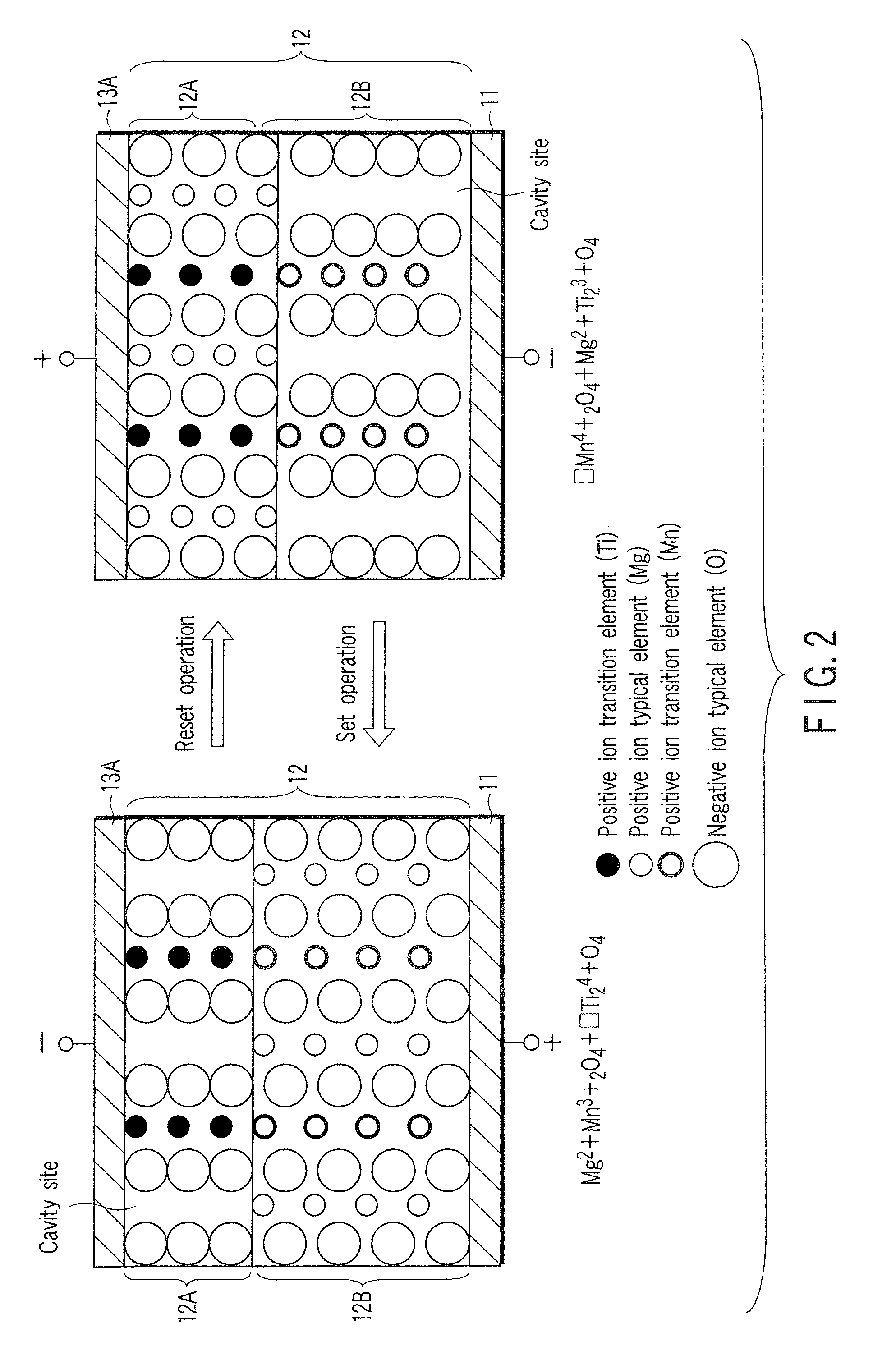
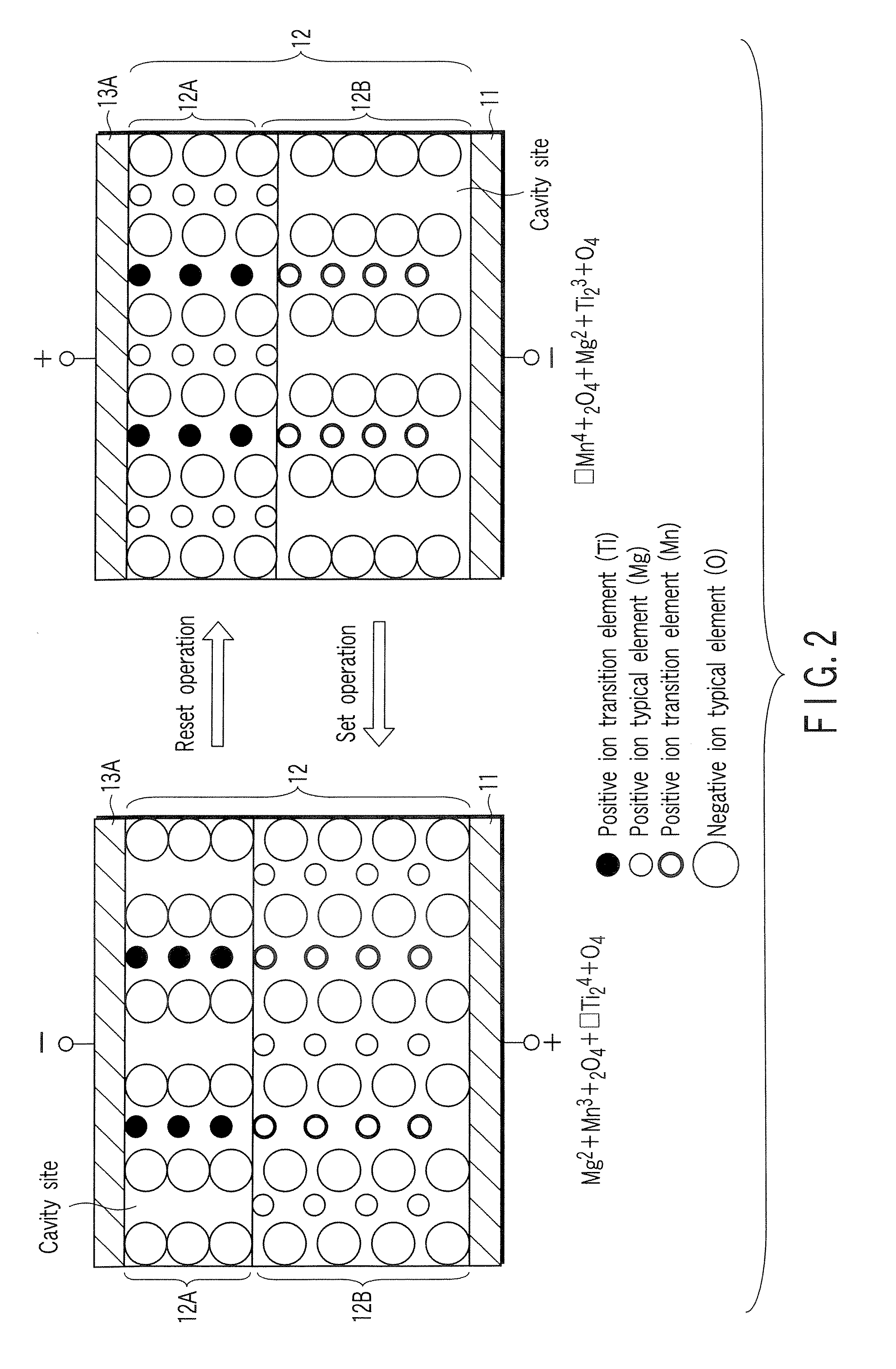
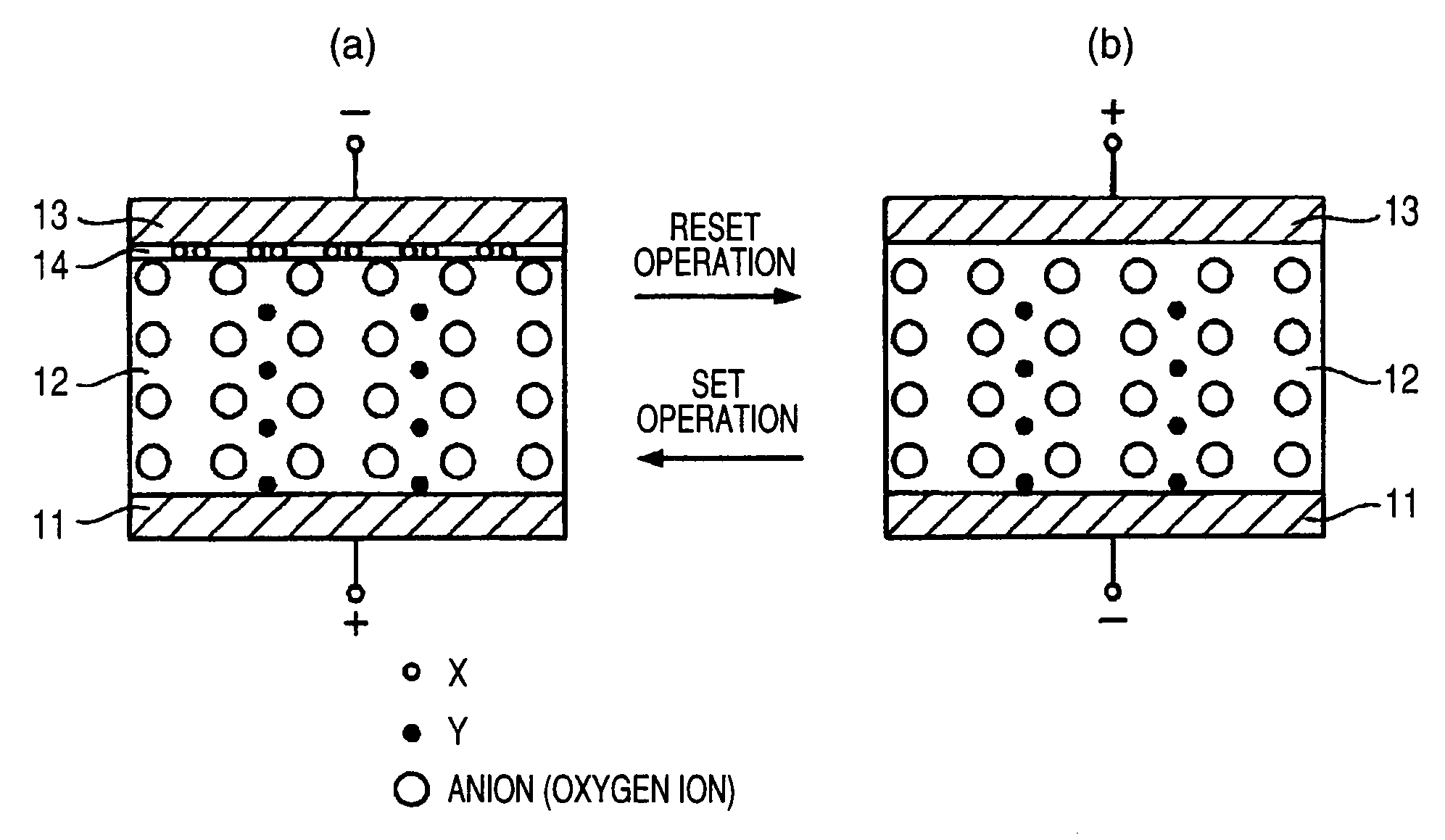
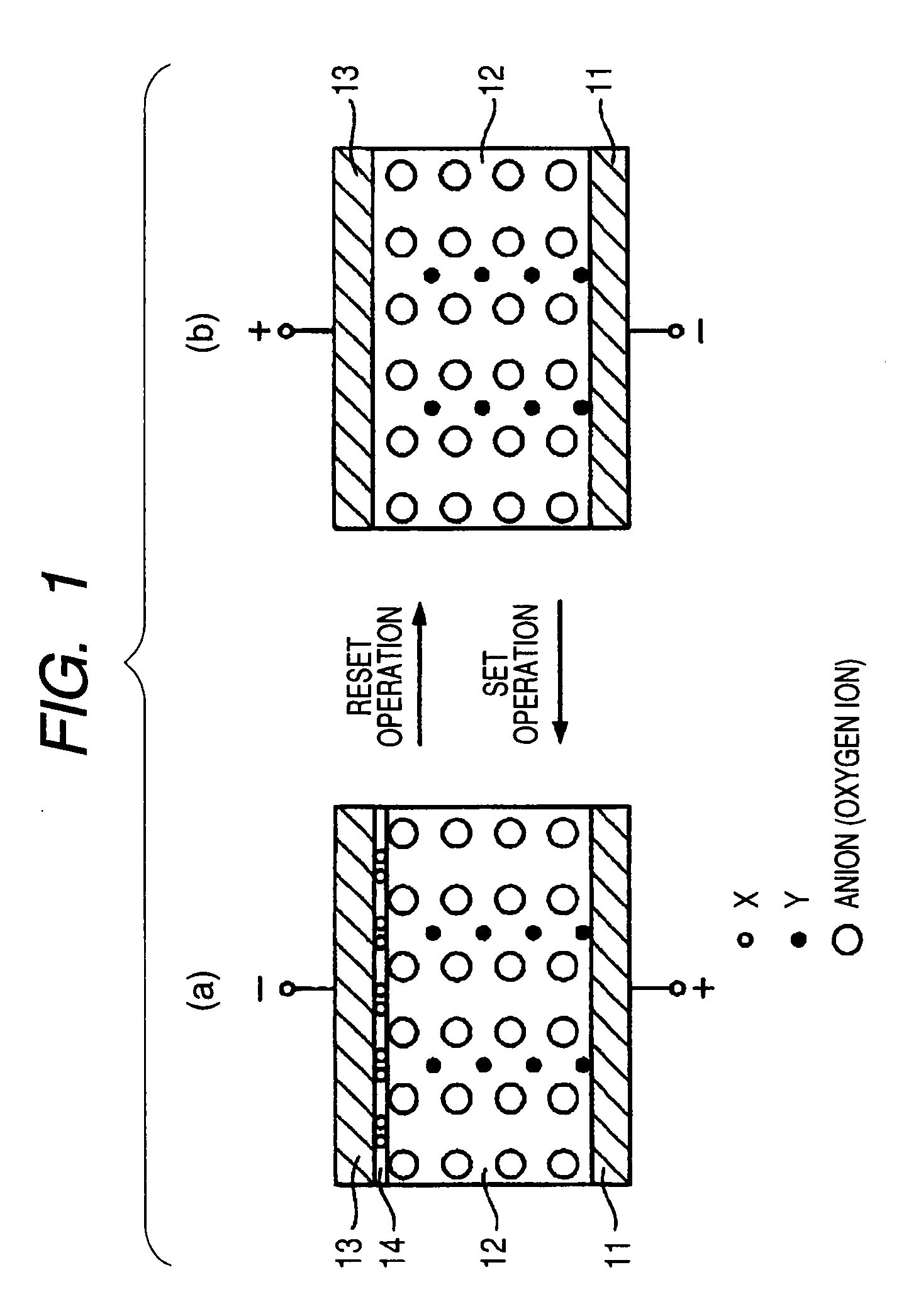
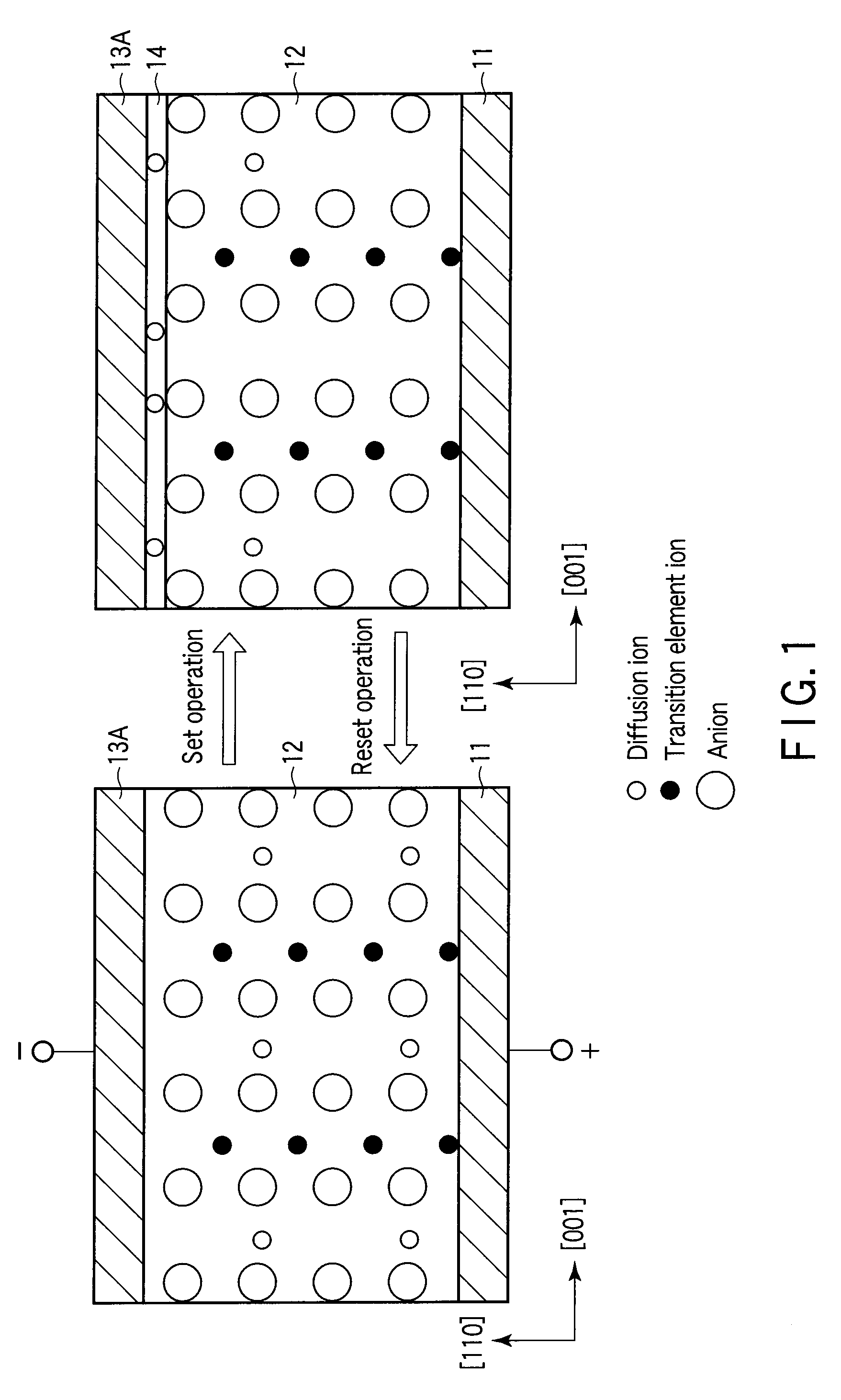
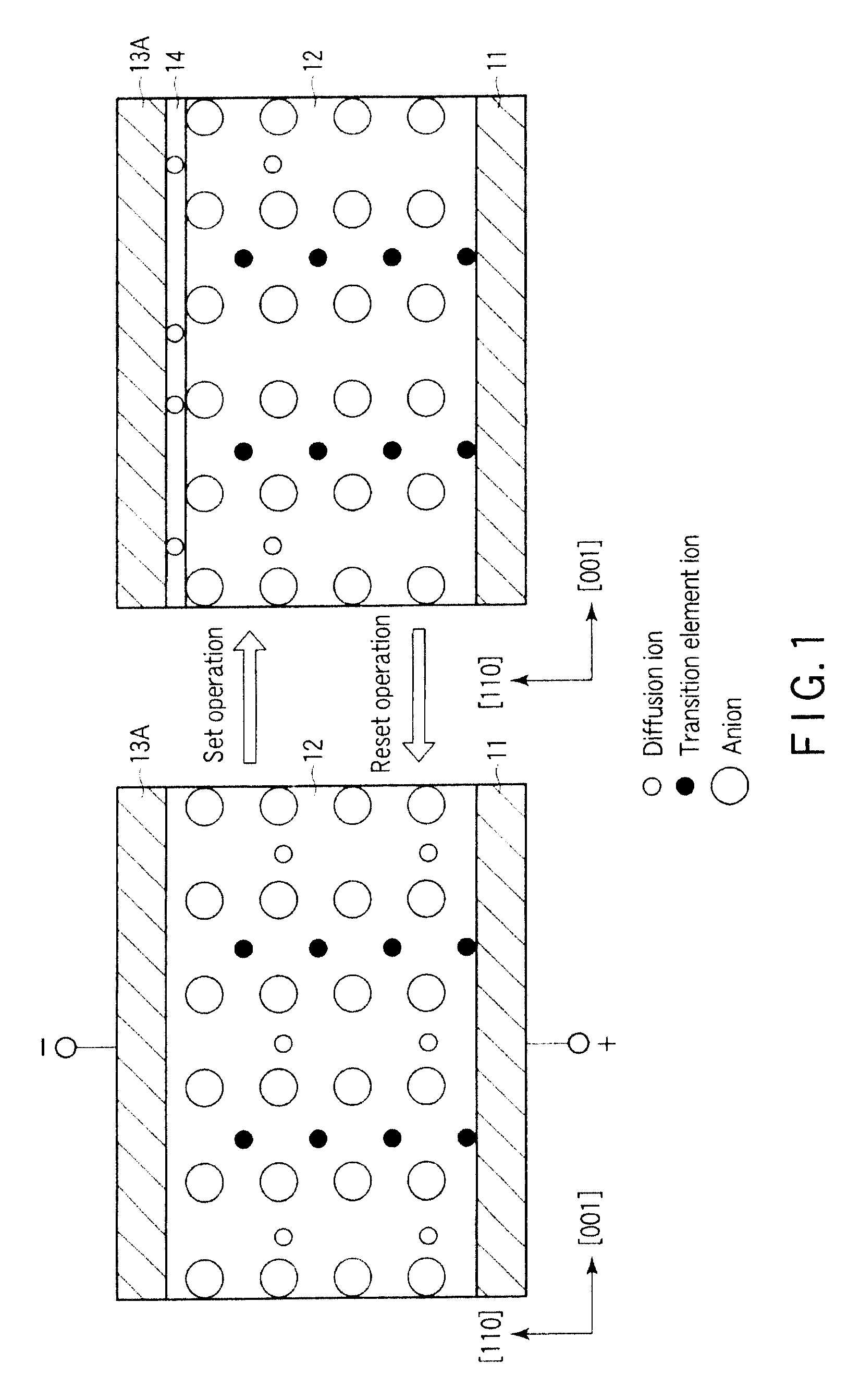
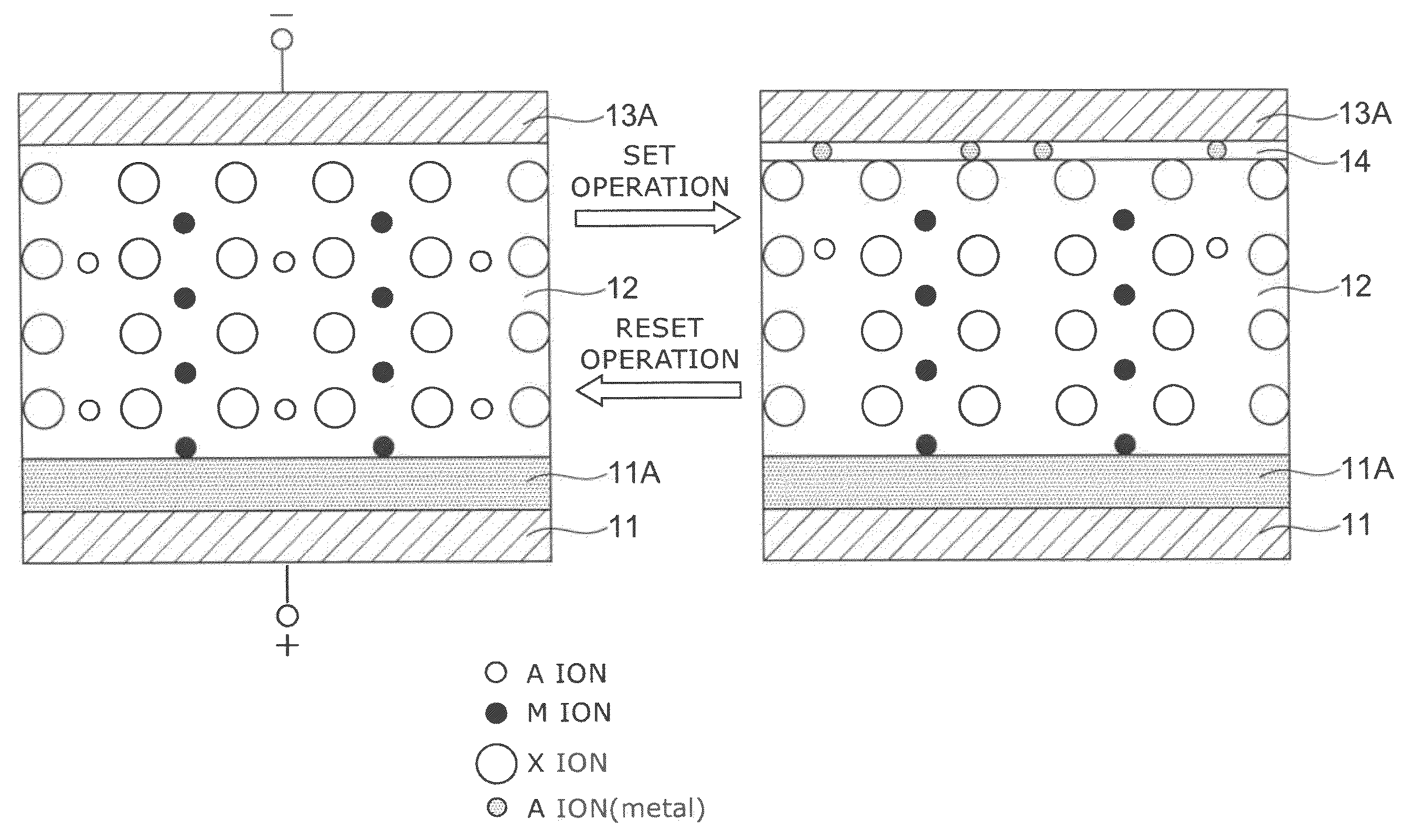
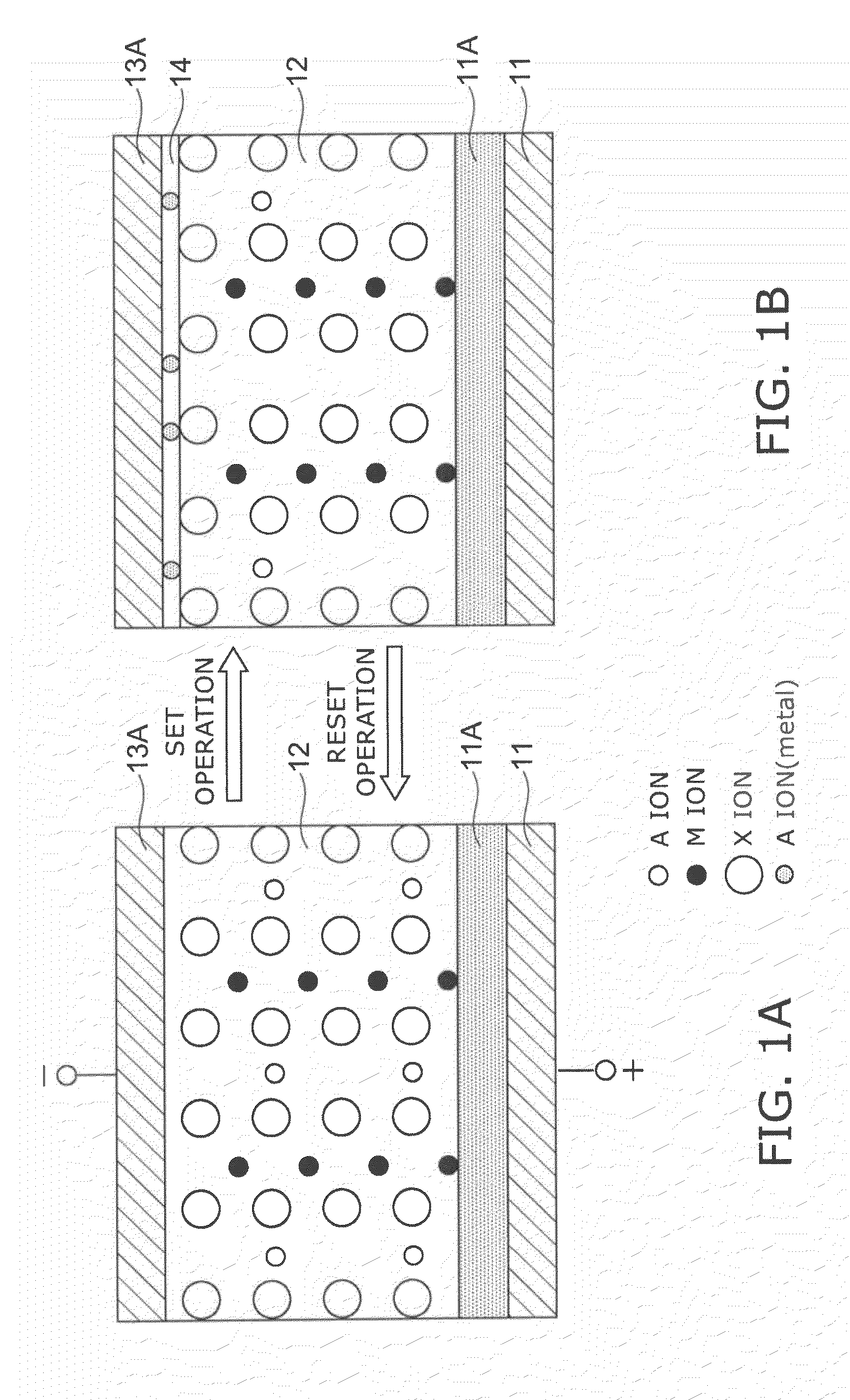
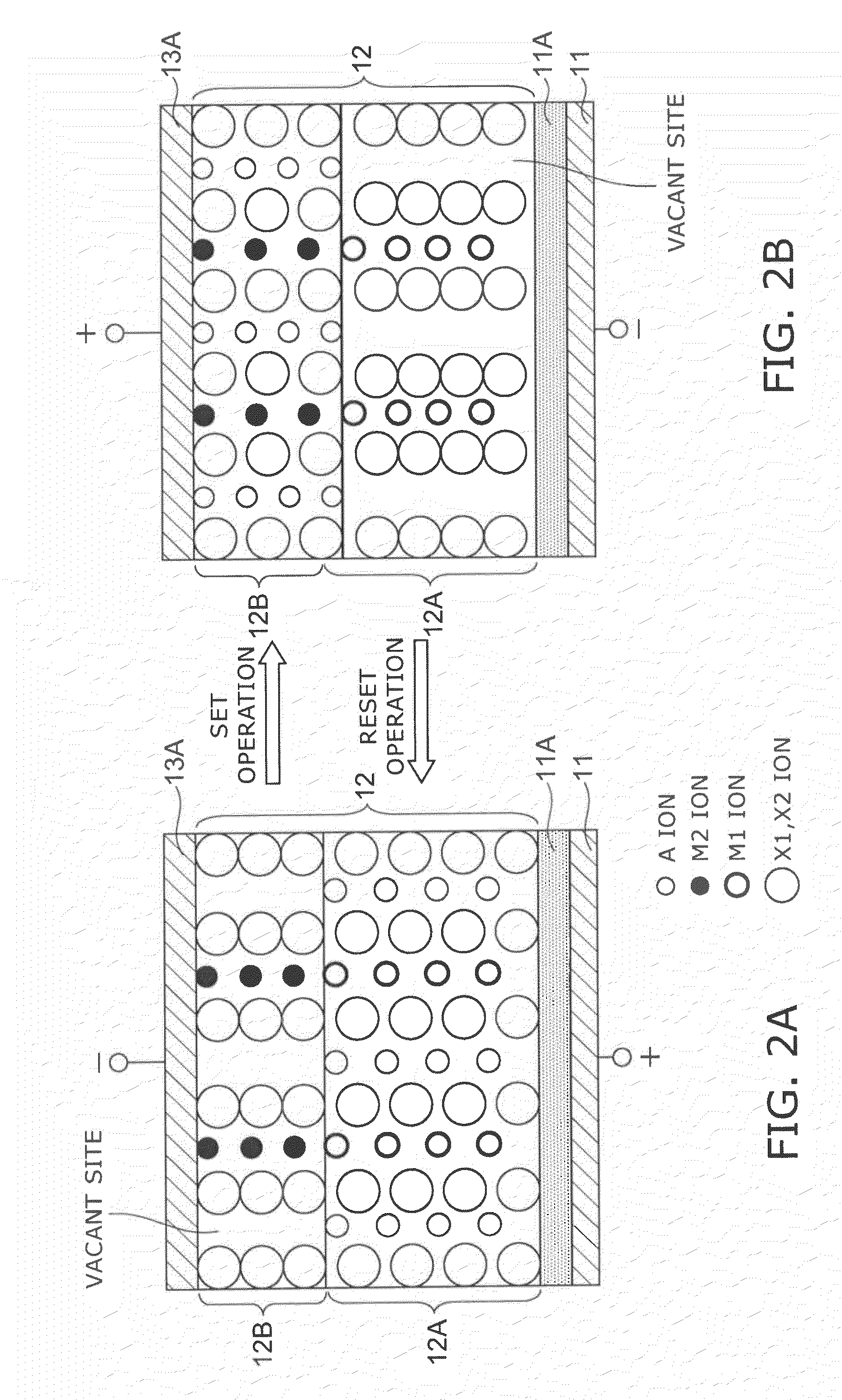
A data read / write device according to an example of the present invention includes a recording layer, and means for applying a voltage to the recording layer, generating a resistance change in the recording layer, and recording data. The recording layer is composed of a composite compound having at least two types of cation elements, at least one type of the cation element is a transition element having a “d” orbit in which electrons have been incompletely filled, and the shortest distance between the adjacent cation elements is 0.32 nm or less.
Owner:KIOXIA CORP
Information recording medium and method for manufacturing the same
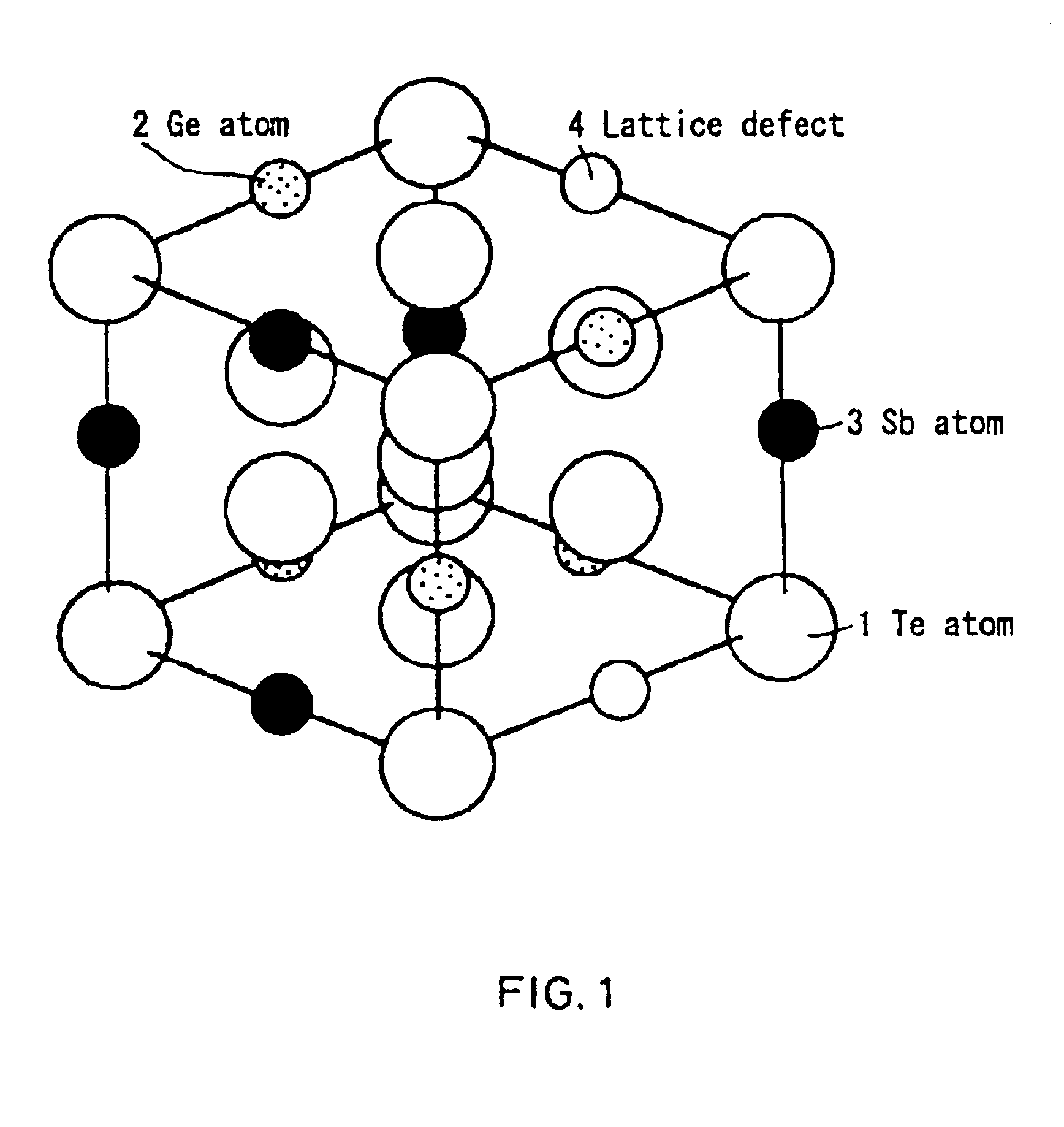
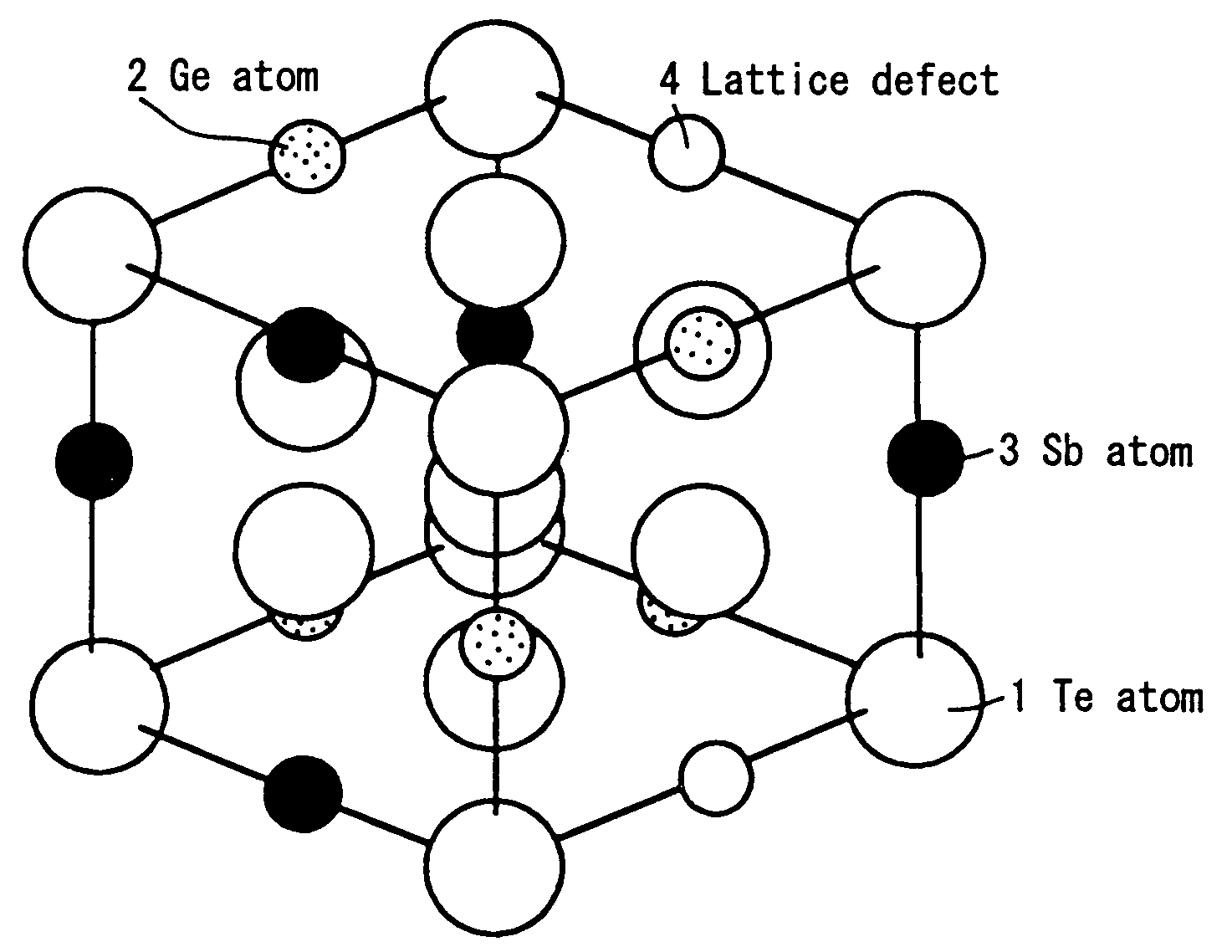
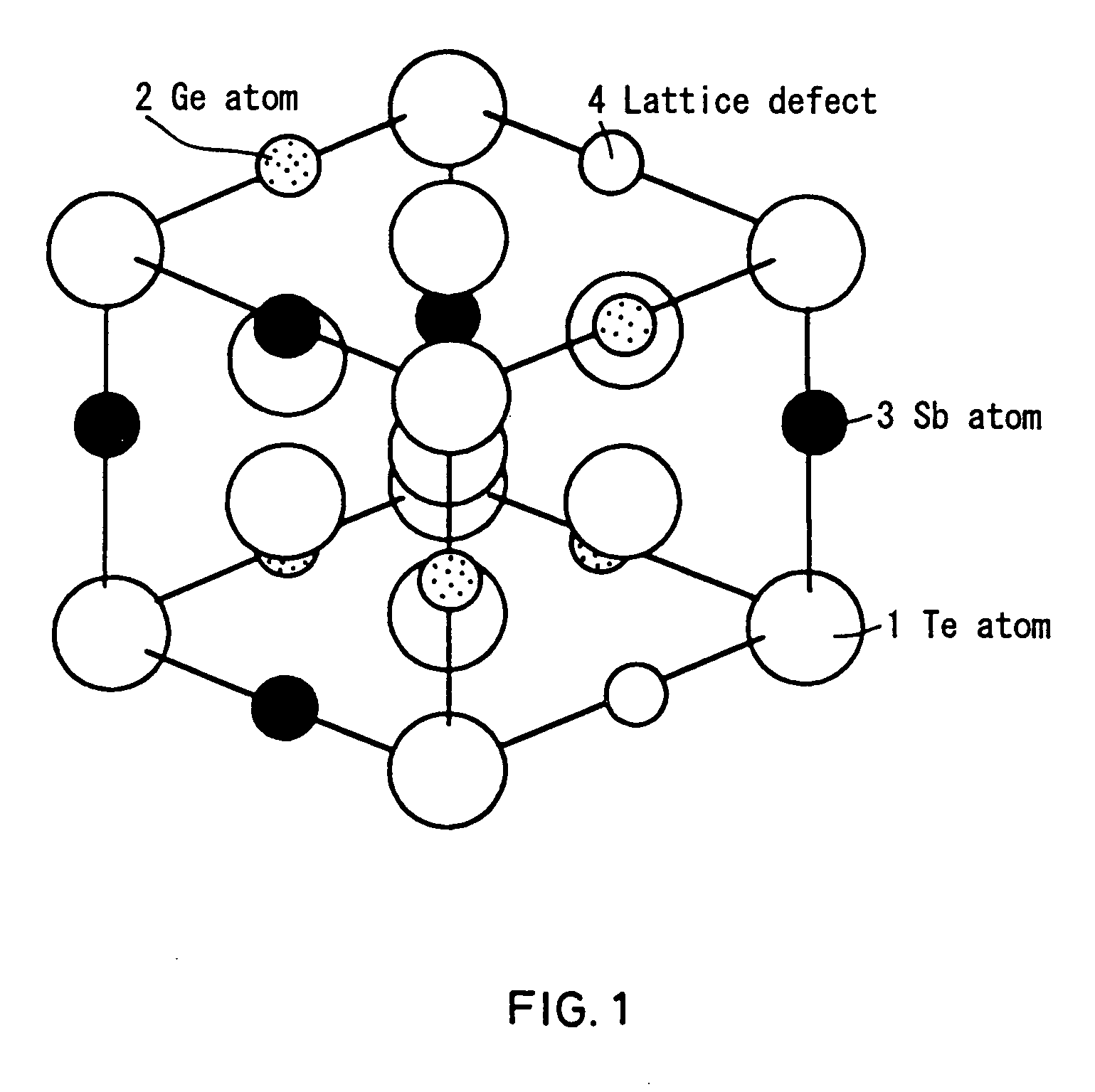
InactiveUS6858277B1Increased repetitionLess influenceRecording by optical meansLayered productsElectricityLattice defects
An information recording medium having such a recording material layer on a substrate where reversible phase change between electrically or optically detectable states can be caused by electric energy or electromagnetic energy. The recording material forming the recording layer is either a material having a crystal structure including lattice defects in one phase of the reversible phase change or a material having a complex phase composed of a crystal portion including a lattice defect in one phase of the reversible phase change and an amorphous portion. Both portions contain a common element. A part of the lattice defects are filled with an element other than the element constituting the crystal structure. The recording medium having a recording thin film exhibits little variation of the recording and reproduction characteristics even after repetition of recording and reproduction, excellent weatherability, strong resistance against composition variation, and easily controllable characteristics.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Magnetic recording apparatus and magnetic recording method
ActiveUS6982845B2High sensitivityMerit on industry is greatRecording by magnetic meansVariable resistance carrier recordingMagnetizationElectrical current
A magnetic recording apparatus comprises a magnetic field impression unit, a current supplying unit and a controlling unit t. The magnetic field impression unit impresses a magnetic field to a magnetic recording medium. The current supplying unit supplies a current to the magnetic recording medium. The controlling unit makes the current supplying unit supply the current to the magnetic recording medium while making the magnetic field impression unit impress the magnetic field to at least a unit of a magnetic recording unit of the magnetic recording medium. Thus, a information is recorded magnetically by making a direction of a magnetization of the magnetic recording unit of the magnetic recording medium in a predetermined direction.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Solid electrolyte probe storage device, system including the device, and methods of forming and using same
InactiveUS20060291364A1Easy and inexpensive to manufactureKeep energy smallVariable resistance carrier recordingNanoinformaticsElectrical conductorElectrical battery
A probe storage system, including programmable cells suitable for storing information, and methods of forming and programming the cells are disclosed. The programmable cells generally include an ion conductor, a plurality of electrodes, and a protective layer between the ion conductor and at least one of the electrodes, wherein one of the electrodes may be in the form of a probe. Electrical properties of the cells may be altered by applying energy to the structure, and thus information may be stored using the system.
Owner:AXON TECH
Optical recording using a waveguide structure and a phase change medium
InactiveUS7596072B2Optical flying-type headsVariable resistance carrier recordingPhase changeElectromagnetic radiation
An apparatus comprises a slider having an air bearing surface, a first waveguide for directing electromagnetic radiation to a focal point adjacent to the air bearing surface, a storage medium position adjacent to the air bearing surface, a detector for detecting electromagnetic radiation reflected from the storage medium, and a structure positioned adjacent to the focal point for collecting the reflected electromagnetic radiation and for transmitted the reflected electromagnetic radiation toward the detector.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
Information recording/reproducing device
InactiveUS20080239797A1Reduce power consumptionImprove thermal stabilityVariable resistance carrier recordingNanoinformaticsPhase changeThermal stability
There is proposed a nonvolatile information recording / reproducing device with low power consumption and high thermal stability. The information recording / reproducing device according to an aspect of the present invention includes a recording layer, and mechanism for recording information by generating a phase change in the recording layer while applying a voltage to the recording layer. The recording layer is comprised one of a Wolframite structure and a Scheelite structure.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Optical recording using a waveguide structure and a phase change medium
InactiveUS20060133230A1Optical flying-type headsVariable resistance carrier recordingElectromagnetic radiationOptical recording
An apparatus comprises a slider having an air bearing surface, a first waveguide for directing electromagnetic radiation to a focal point adjacent to the air bearing surface, a storage medium position adjacent to the air bearing surface, a detector for detecting electromagnetic radiation reflected from the storage medium, and a structure positioned adjacent to the focal point for collecting the reflected electromagnetic radiation and for transmitted the reflected electromagnetic radiation toward the detector.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
Electromechanical memory cell with torsional movement
InactiveUS20070002604A1Variable resistance carrier recordingVariable capacitance carrier recordingElectricityThermal force
A memory cell uses a pair of cantilevers to store a bit of information. Changing the relative position of the cantilevers determines whether they are electrically conducting or not. The on and off state of this mechanical latch is switched by using, for example, electrostatic, electromagnetic or thermal forces applied sequentially on the two cantilevers to change their relative position. The amount of power required to change the state of the cell is reduced by supporting at least one of the cantilevers with at least one lateral projection that is placed in torsion during cantilever displacement. After a bit of data is written, the cantilevers are locked by mechanical forces inherent in the cantilevers and will not change state unless a sequential electrical writing signal is applied. The sequential nature of the required writing signal makes inadvertent, radiation or noise related data corruption unlikely.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Data read/write device
ActiveUS7733684B2Variable resistance carrier recordingNanoinformaticsComputer hardwareShortest distance
Owner:KIOXIA CORP
Movable micro-electromechanical device
InactiveUS6882019B2Permit some movementPrevent movementCarriage/perambulator accessoriesAcceleration measurement using interia forcesOut of plane motionEngineering
A movable system, such as a computer storage device, having a frame, a mover configured to move relative to the frame, and a mechanical suspension operatively coupled between the frame and mover. The mechanical suspension is configured to permit planar movement of the mover while substantially preventing out-of-plane movement, and includes a first flexure configured to flex in response to movement of the mover in a first direction relative to the frame, and a second flexure configured to flex in response to relative movement occurring in a second direction.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Memory array having a layer with electrical conductivity anisotropy
InactiveUS7026676B2TransistorVariable resistance carrier recordingComputational physicsContact region
A memory array includes a memory layer that has hysteretic domains with domain axes extending between first and second memory layer surfaces. A conductive layer on the first memory layer surface has anisotropically increased electrical conductivity in a thickness direction. A movable conductive probe has a contact area on the conductive layer and moves to access a selected hysteretic domain.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
Electromechanical memory cell with torsional movement
InactiveUS7349236B2Variable resistance carrier recordingVariable capacitance carrier recordingElectricityThermal force
A memory cell uses a pair of cantilevers to store a bit of information. Changing the relative position of the cantilevers determines whether they are electrically conducting or not. The on and off state of this mechanical latch is switched by using, for example, electrostatic, electromagnetic or thermal forces applied sequentially on the two cantilevers to change their relative position. The amount of power required to change the state of the cell is reduced by supporting at least one of the cantilevers with at least one lateral projection that is placed in torsion during cantilever displacement. After a bit of data is written, the cantilevers are locked by mechanical forces inherent in the cantilevers and will not change state unless a sequential electrical writing signal is applied. The sequential nature of the required writing signal makes inadvertent, radiation or noise related data corruption unlikely.
Owner:XEROX CORP
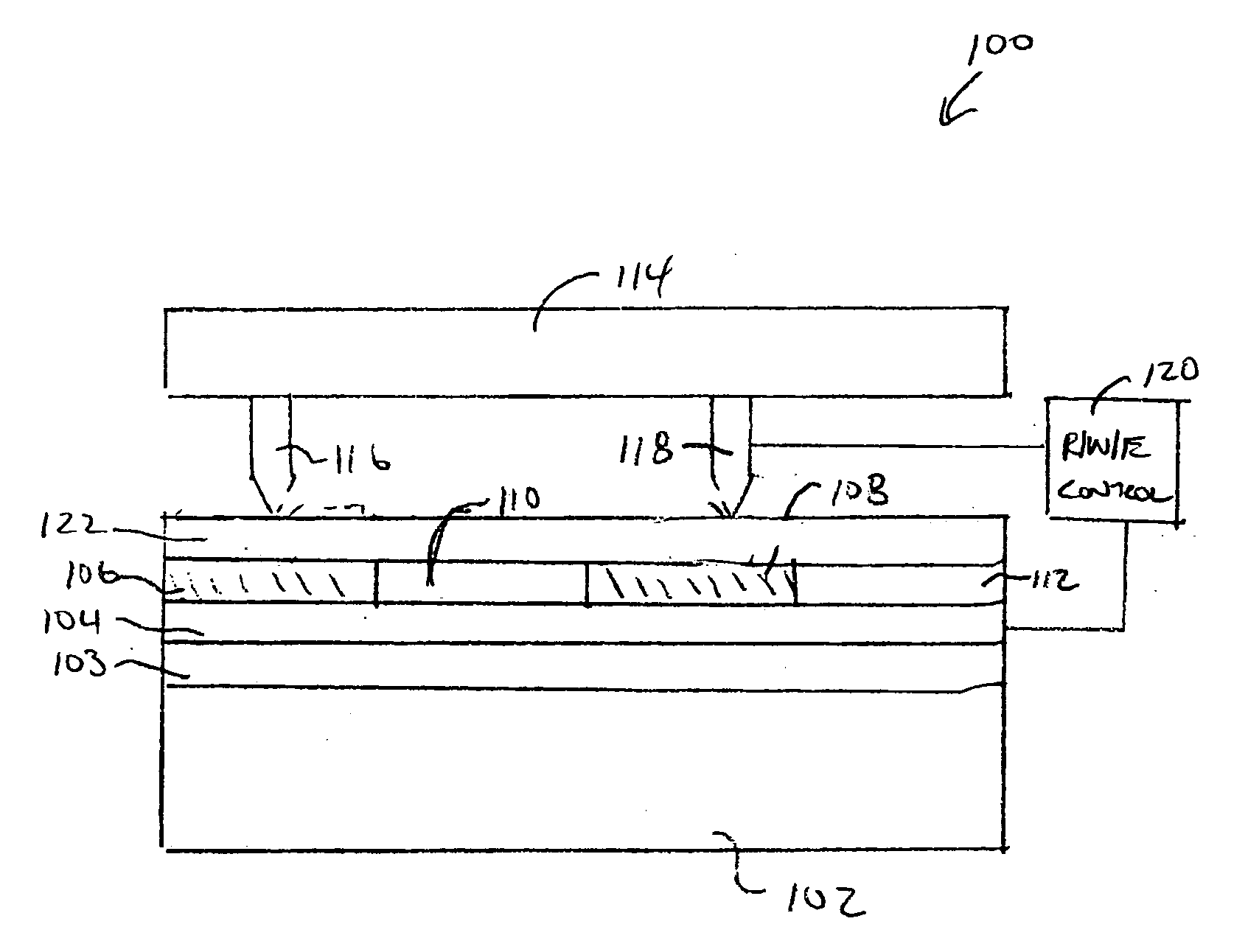
Data storage device and a method of reading data in a data storage device
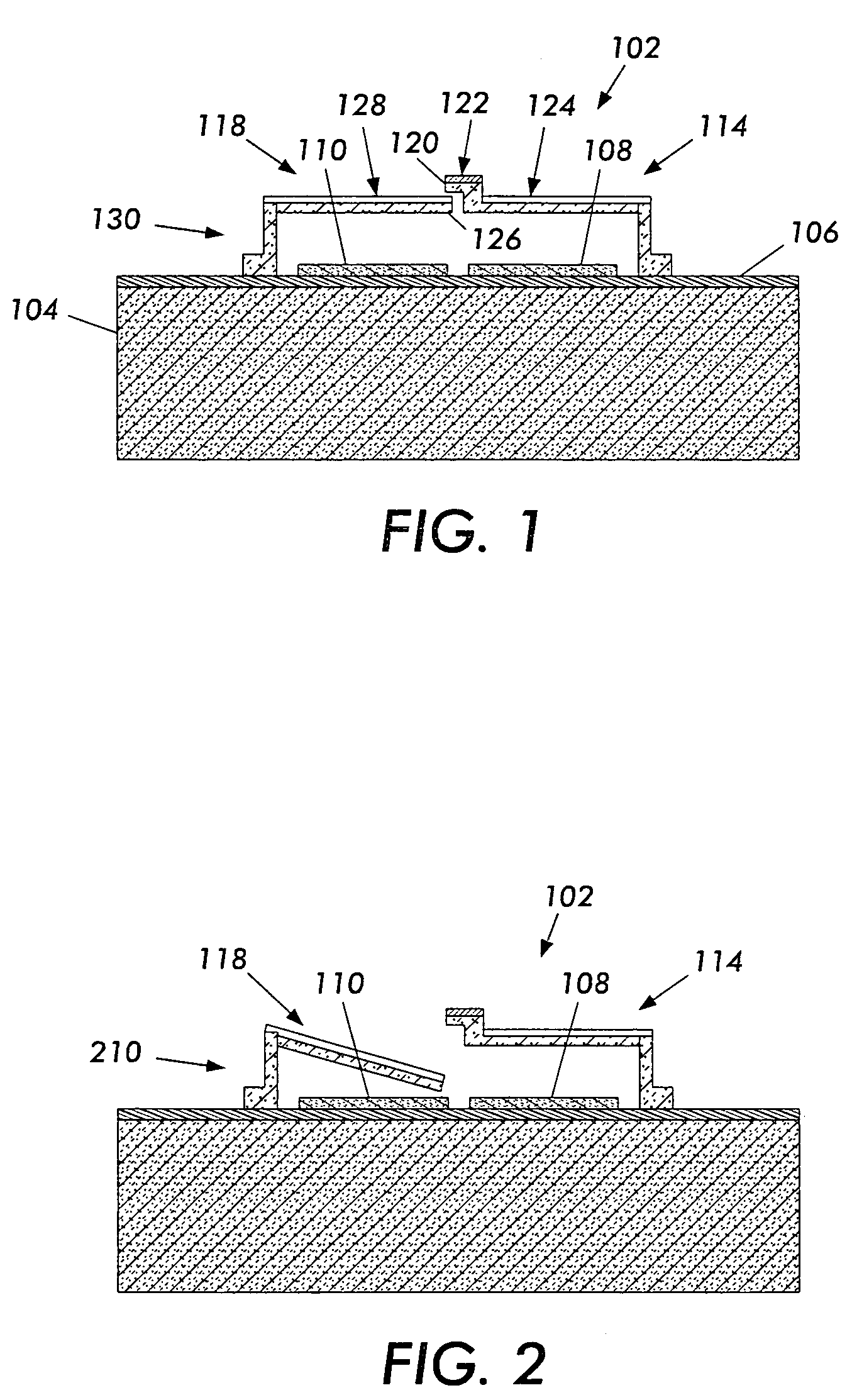
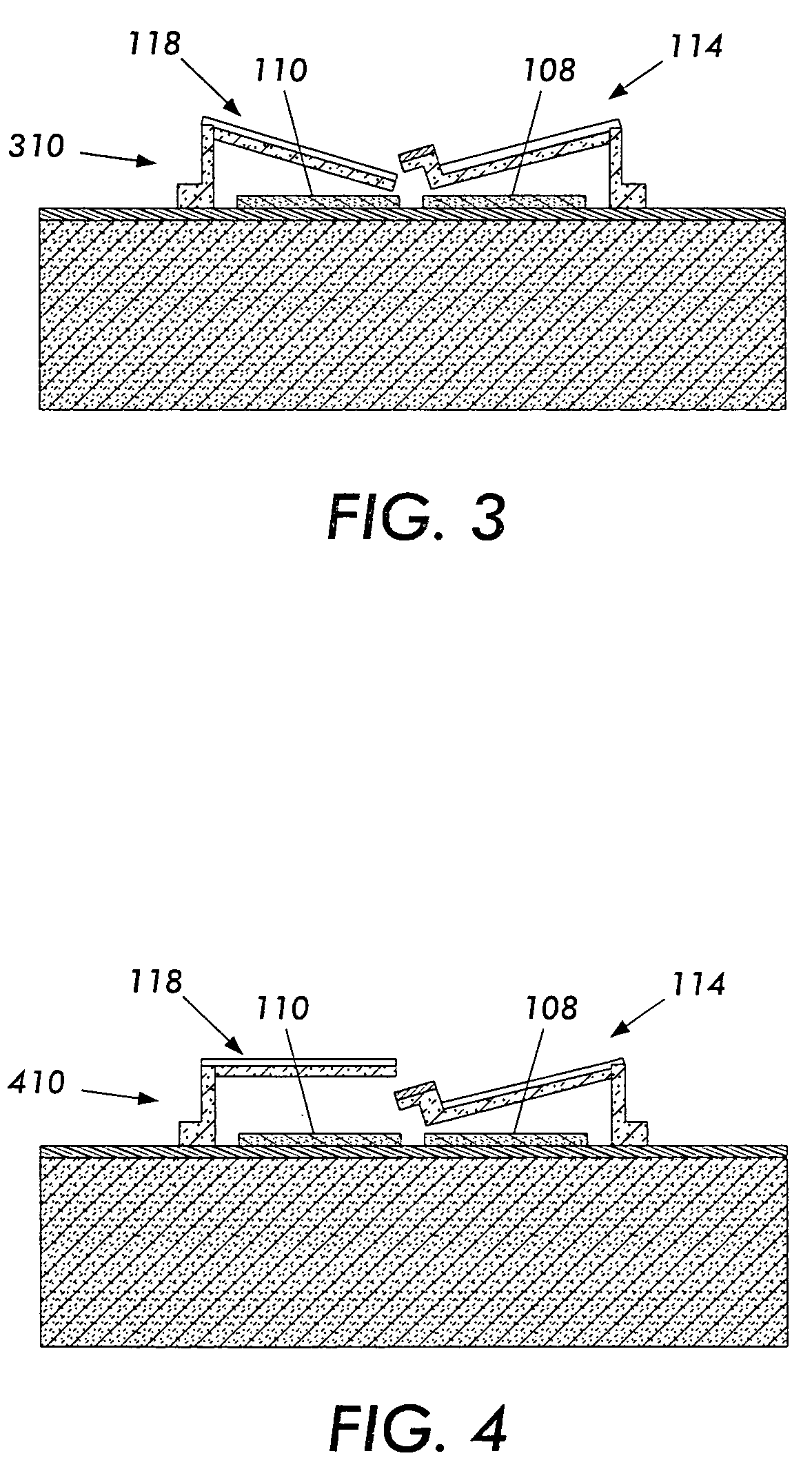
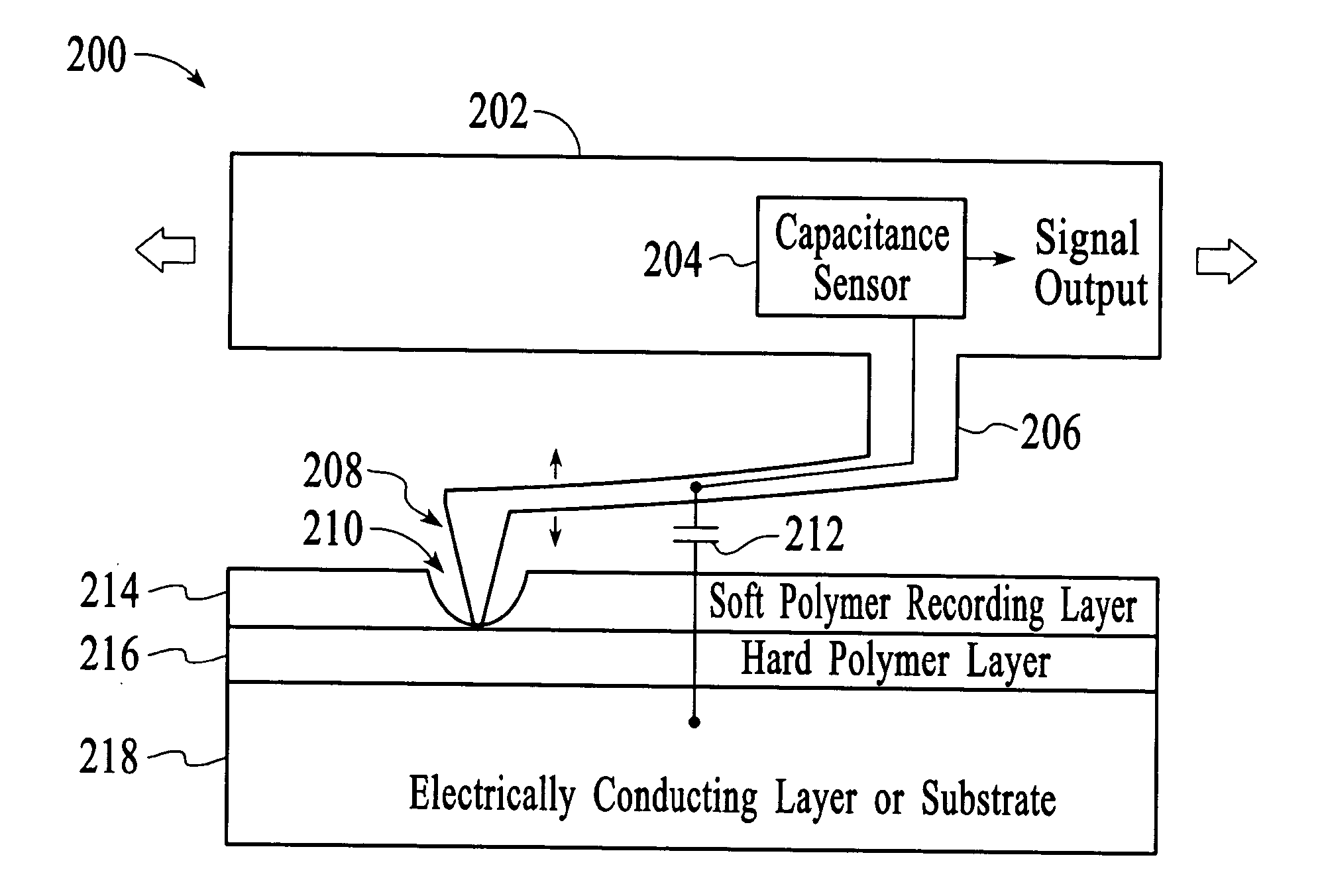
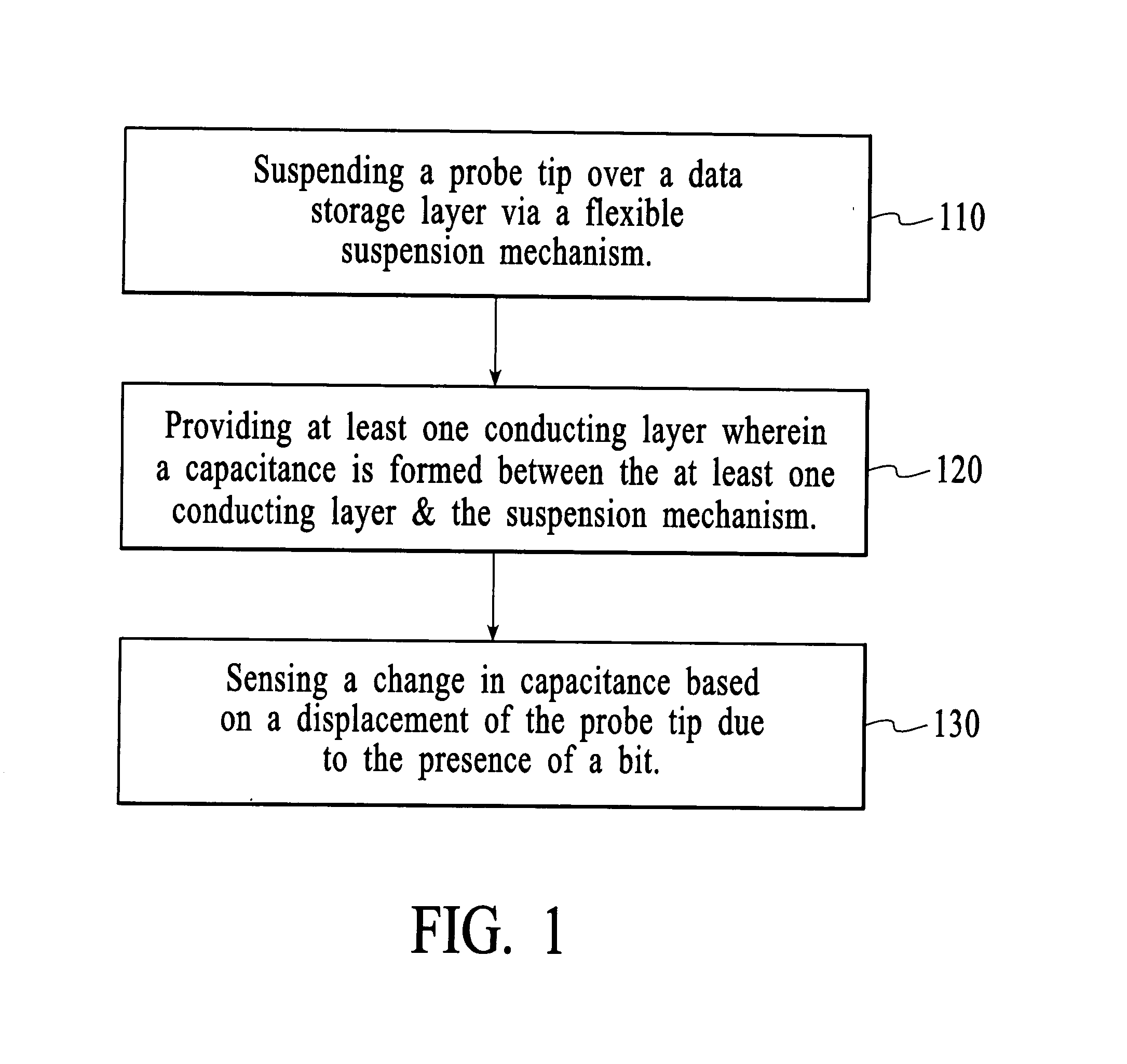
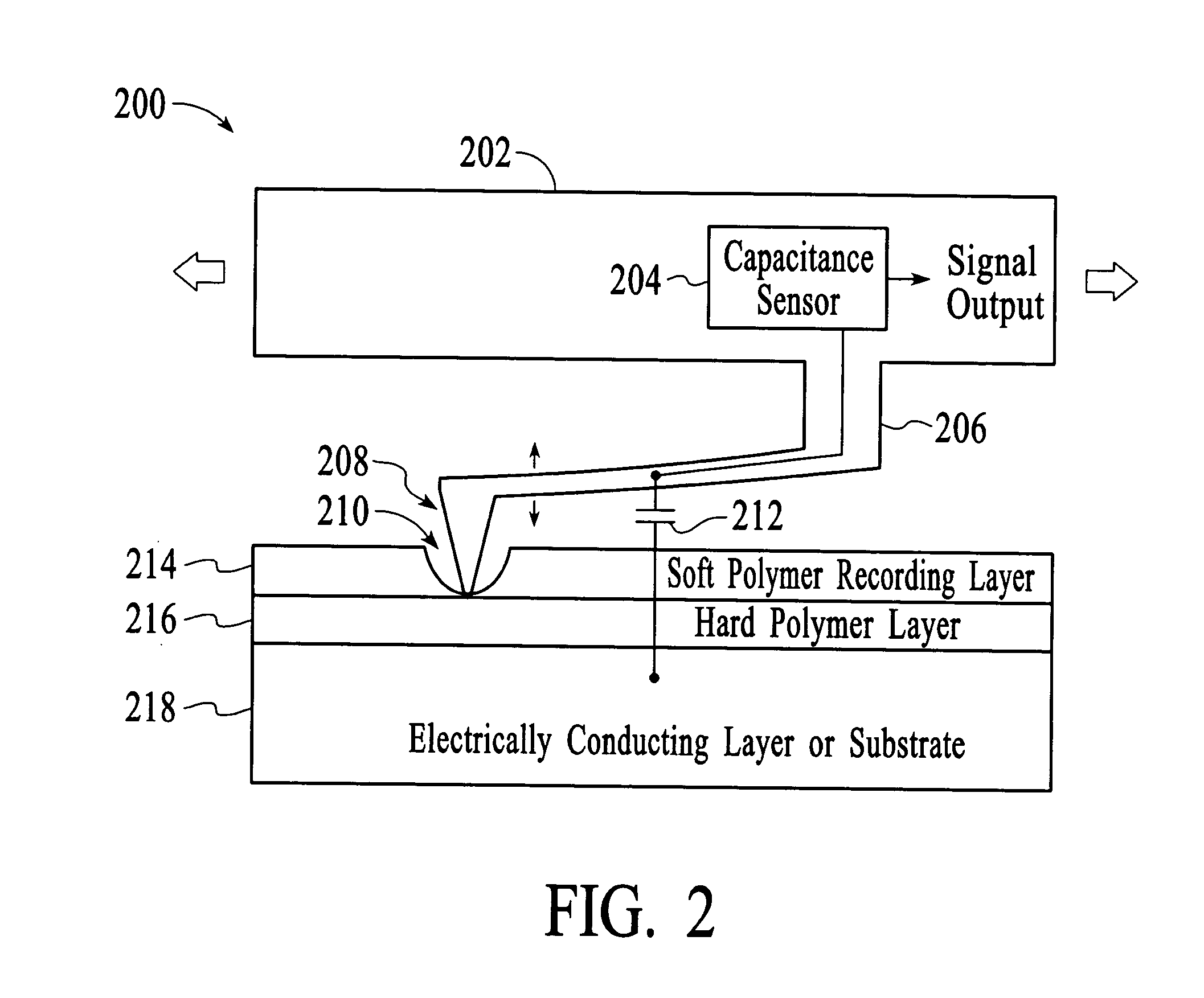
InactiveUS20050055170A1Variable resistance carrier recordingResistance/reactance/impedenceCapacitanceOperating system
The present invention includes a data storage device and a method of reading data in a data storage device. Accordingly, a first aspect of the present invention is a data storage device. The data storage device includes a probe tip mounted on a suspension mechanism, a data storage layer, at least one conducting layer wherein a capacitance is formed between the suspension mechanism and the at least one conducting layer and a sensor for sensing a change in the capacitance based on a displacement of the probe tip due to the presence of a bit.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
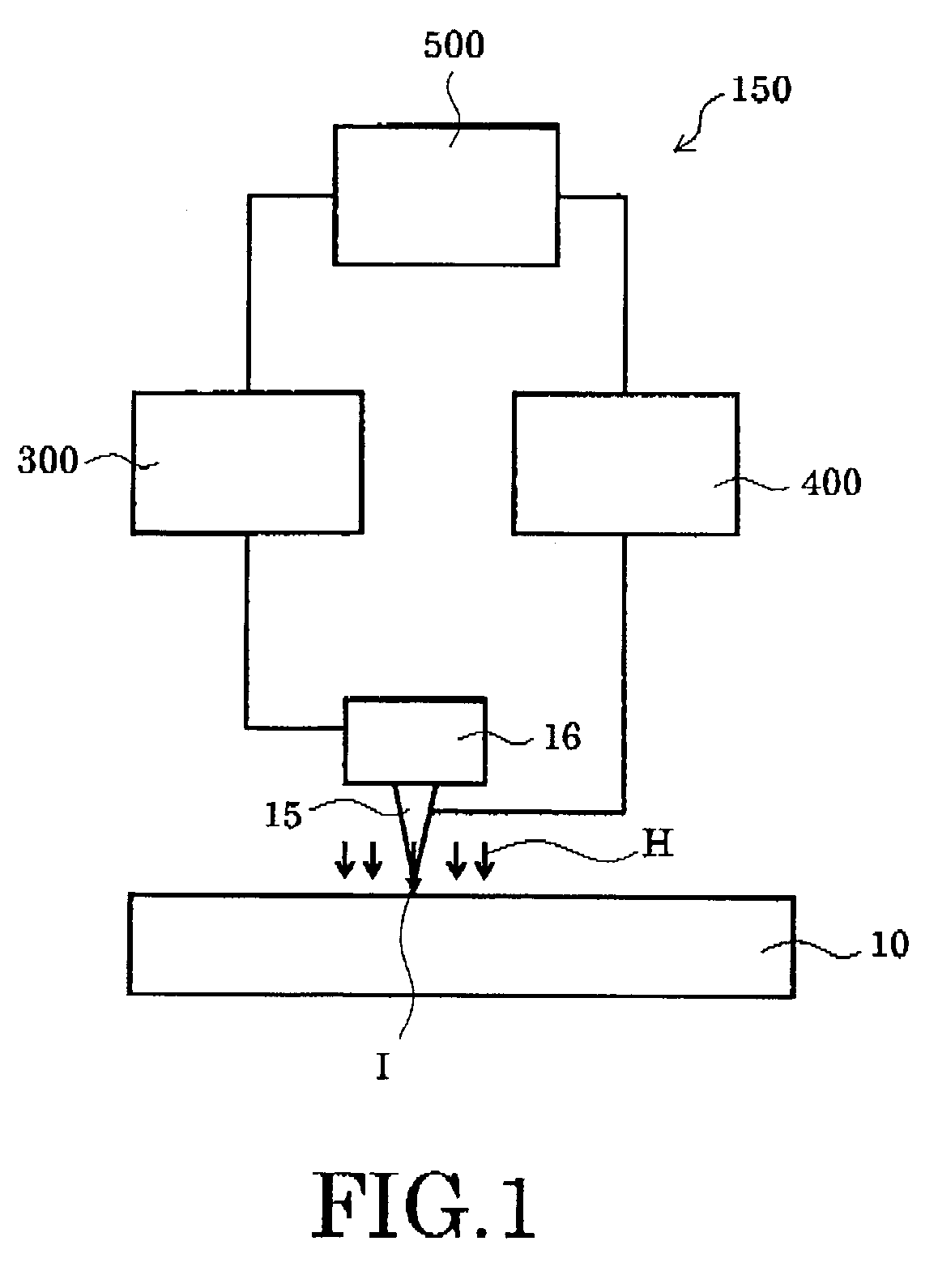
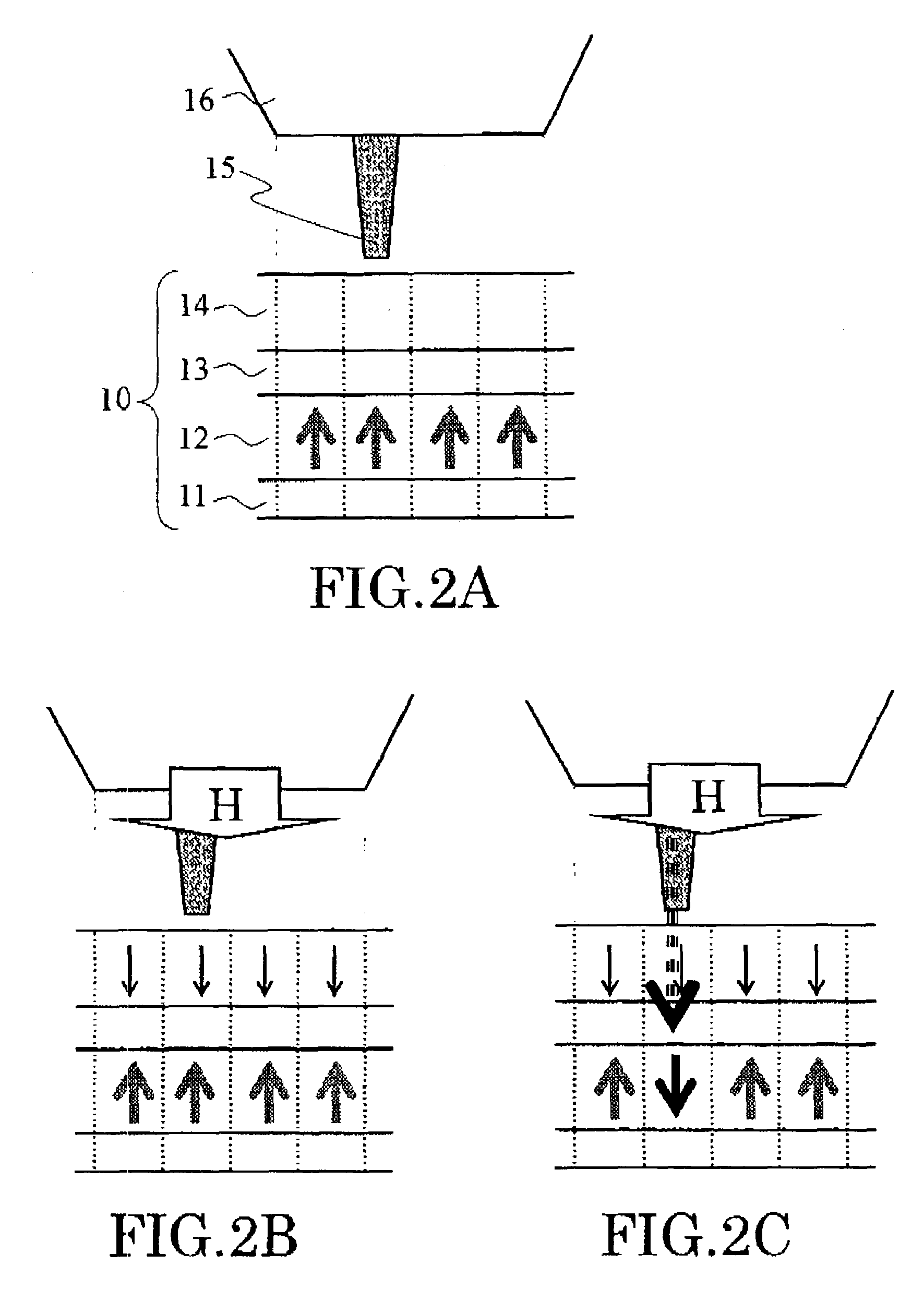
Information recording and reproducing apparatus
InactiveUS20080239932A1Variable resistance carrier recordingMechanical record carriersRecording layerPhase change
A nonvolatile information recording and reproducing device exhibits low power consumption and high thermal stability. The information recording and reproducing apparatus according to an aspect of the present invention includes a recording layer and a unit for recording information by applying a voltage to the recording layer to generate a resistance change to be caused due to a phase change in the recording layer. The recording layer includes a material having a ramsdelite structure.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Data readout arrangement
InactiveUS20050147017A1Variable resistance carrier recordingNanoinformaticsElectric fieldSemiconductor components
A readout arrangement has a base which has a flexible member supporting a probe on a free end thereof so that the probe is movable with respect to the base; a medium in which a superficial data indicative topographical feature can be formed, the superficial data indicative topographical feature being configured to be contacted by the probe, the medium and the base being arranged to be movable relative to one another; and a semiconductor element disposed with one of the base and medium, the semiconductor element being configured to be responsive to an electric field generated in response to interaction between the probe and the superficial data indicative topographical feature.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Information recording/reproducing device
InactiveUS20100142091A1Improve recording densityReduce power consumptionVariable resistance carrier recordingNanoinformaticsChemical compoundData recording
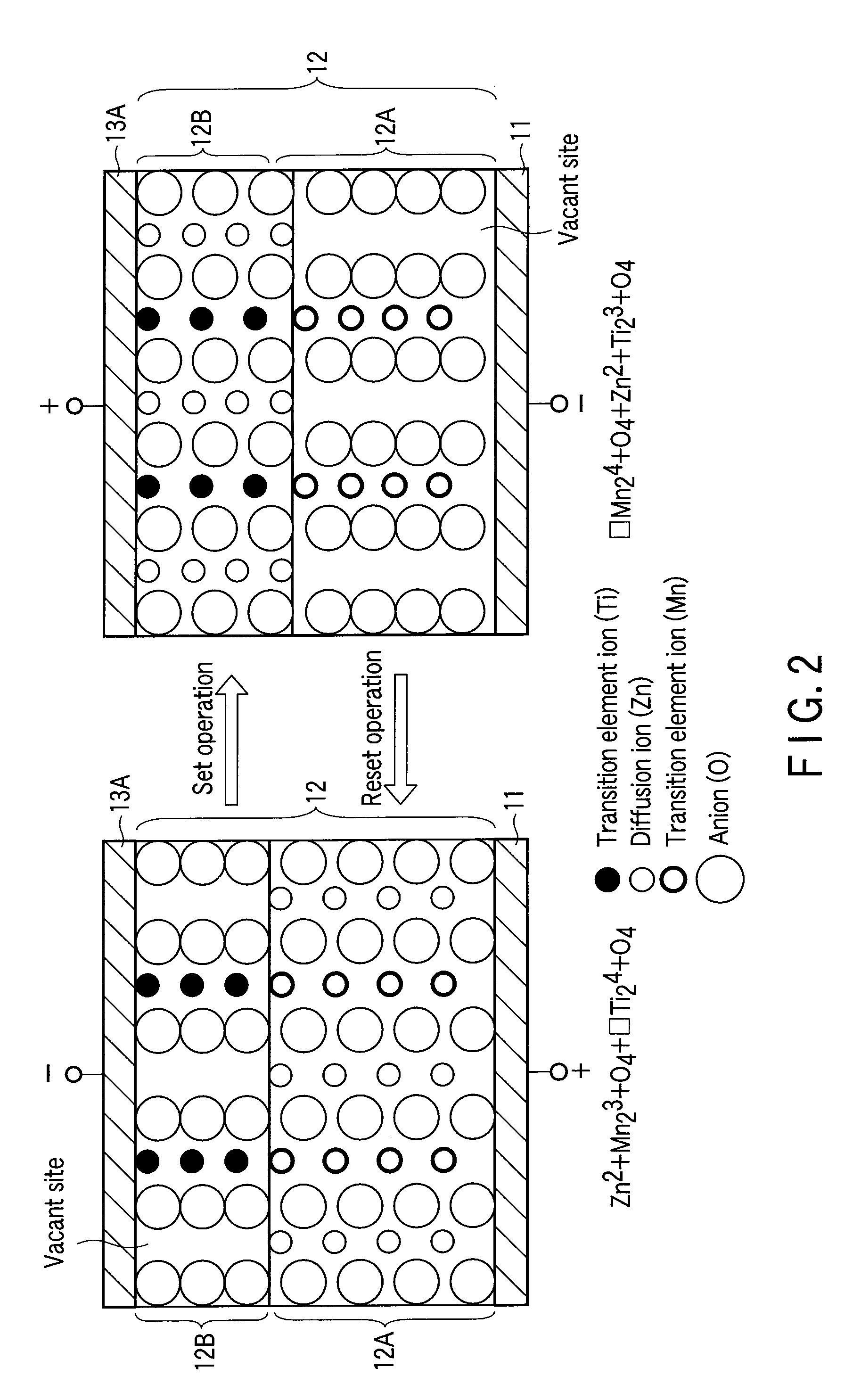
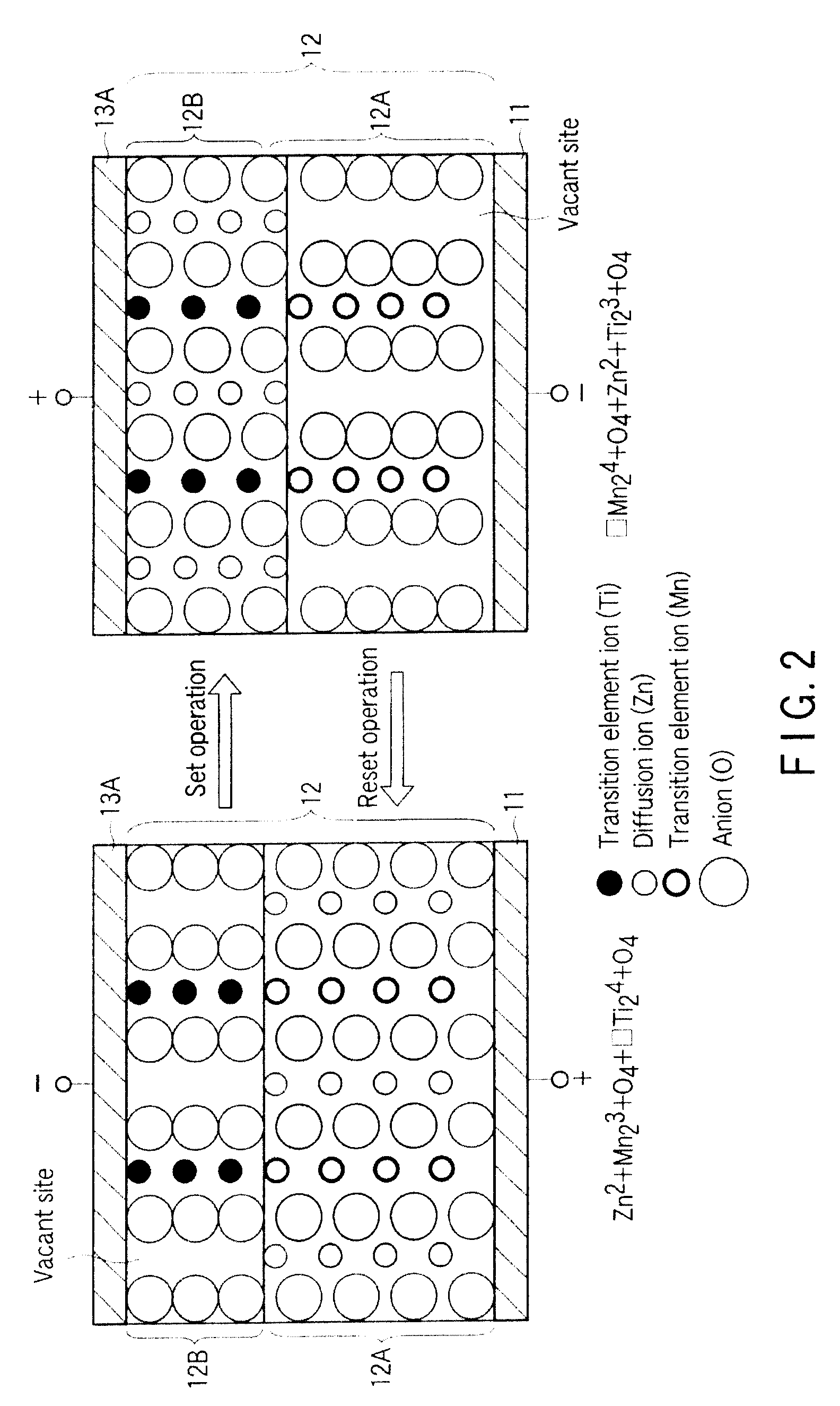
An information recording / reproducing device includes a recording layer, and a recording circuit which records data to the recording layer by generating a phase change in the recording layer. The recording layer includes a first chemical compound having a spinel structure. The recording layer is AxMyX4 (0.1≦x≦2.2, 1.0≦y≦2.0), where A includes one selected from a group of Zn, Cd and Hg, M includes one selected from a group of Cr, Mo, W, Mn and Re, and X includes O.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Data storage device
InactiveUS20050156271A1Driving/moving recording headsVariable resistance carrier recordingEngineeringElectrolyte
The present invention pertains to a data storage device. The data storage device includes a storage medium having an electrode and an electrolyte layer positioned on the electrode. The data storage device also includes at least one probe configured to contact the electrolyte layer. In addition, the storage medium includes a voltage supply device configured to supply voltage through the at least one probe and the electrode to thereby create a circuit between the at least one probe and the electrode. The level of voltage supplied through the at least one probe allows at least one of writing, reading, and erasing operations on the one or more memory cells of the storage medium.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Electrical memory component and a method of construction thereof
InactiveUS7239544B2Variable resistance carrier recordingNanoinformaticsElectricityElectrical connection
An electrical memory component is provided, comprising read / write probes and a chalcogenide storage media. Each read / write probe is adapted for selective electrical connection to a memory portion of the chalcogenide storage media and for performing read and write operations upon the memory portion. The chalcogenide storage media has a second plurality of memory portions, and is movably mounted relative to the first plurality of read / write probes for selective electrical connection of the read / write probes to a subset of the memory portions.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Information recording/reproducing device
InactiveUS20100127235A1Improve recording densityReduce power consumptionVariable resistance carrier recordingNanoinformaticsChemical compoundPhase change
An information recording / reproducing device includes a recording layer, and a recording circuit which records data to the recording layer by generating a phase change in the recording layer. The recording layer includes a first chemical compound having a spinel structure. The recording layer is AxMyX4 (0.1≦x≦2.2, 1.0≦y≦2.0), where A includes one selected from a group of Zn, Cd and Hg, M includes one selected from a group of Ti, Zr, Hf, V, Nb and Ta, and X includes O.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Non-volatile memory and the fabrication method thereof
InactiveUS20050121659A1Increase possible numberReduce power consumptionTransistorVariable resistance carrier recordingElectric forceEngineering
A non-volatile memory, which comprises an insulating substrate (11) that has a first electrode (18) that extends through the substrate from the front surface to the rear surface thereof; a second electrode (13) that is formed on one side of the insulating substrate (11); and a recording layer (12) that is clamped between the first electrode (18) and the second electrode (13) and whose resistance value varies when an electric pulse is applied across the first electrode (18) and the second electrode (13); wherein the insulating substrate (11) has a layered structure composed of an organic dielectric thin film (112) and an inorganic dielectric layer (111) that is thinner than the organic dielectric thin film (112); with the recording layer (12) being formed on the side on which the inorganic dielectric layer is formed. Use of this non-volatile memory increases the possible number of data writing cycles while saving power.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
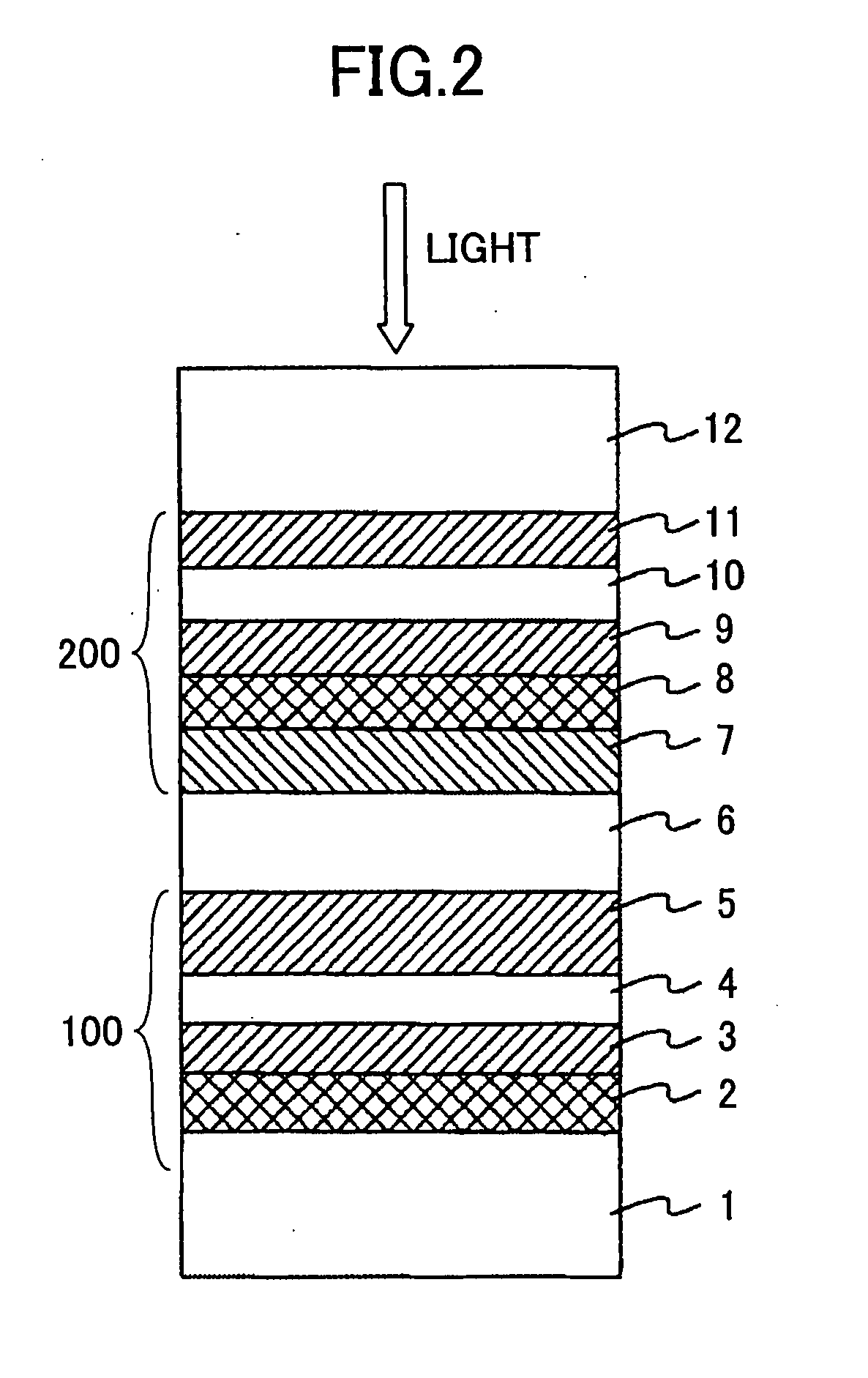
Phase-Change Type Optical Recording Medium and Reproduction Method and Apparatus for Such a Recording Medium
ActiveUS20070237062A1Easy to performPromote reproductionCombination recordingDisposition/mounting of recording headsLower limitAlloy
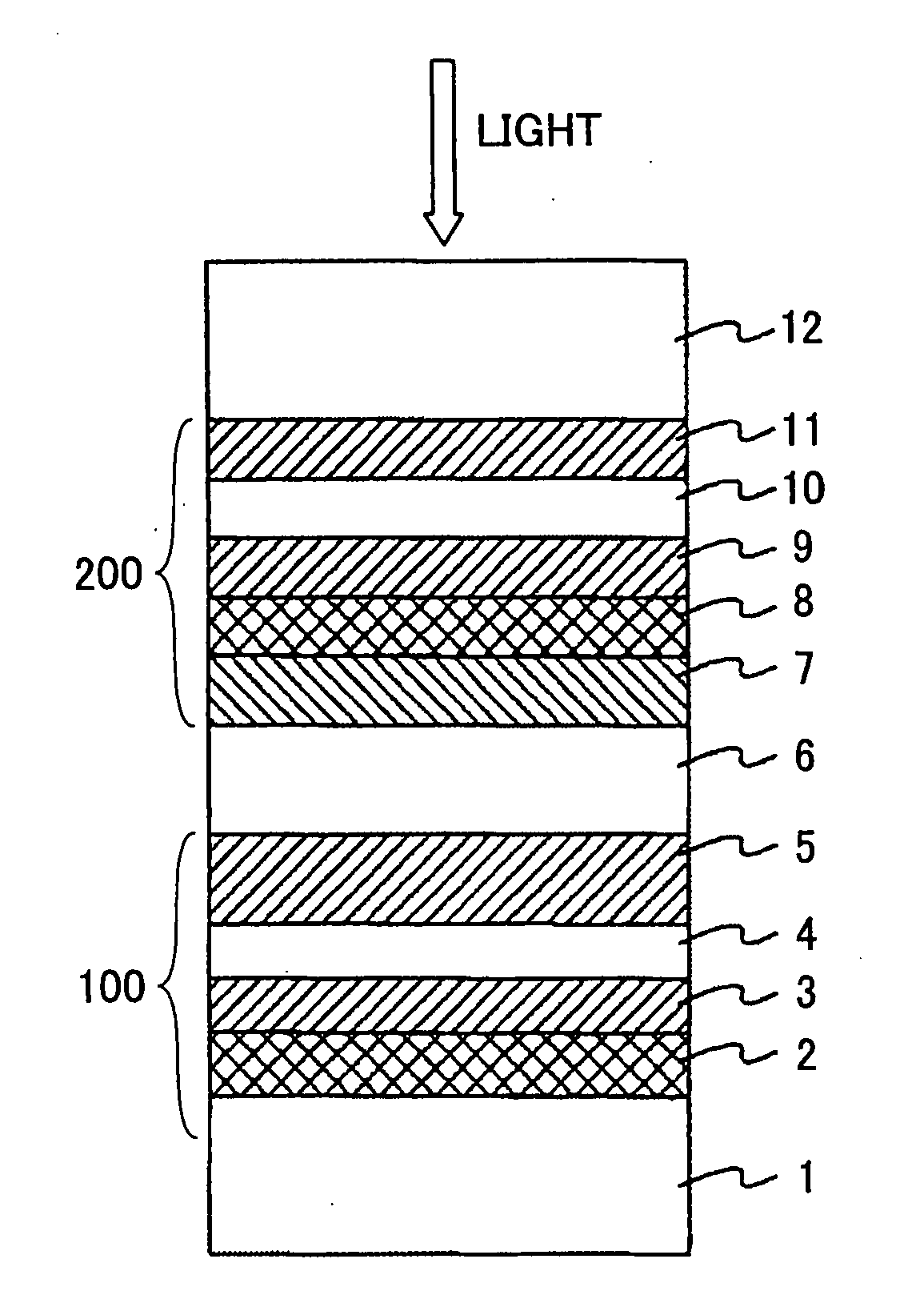
A dual-layer structure phase-change type optical recording medium includes a substrate (1), a reflective layer (2), a first protective layer (3), a first recording layer (4), a second protective layer (5), a resin intermediate layer (6), a third protective layer (7), a heat release layer (8) made of Cu or a Cu alloy, a fourth protective layer (9), a second recording layer (10), a fifth protective layer (11) and a cover substrate (12). A product of a reflectance of a high-reflection part and a modulation after recording is a value equal to or higher than a lower limit value for reproduction.
Owner:RICOH KK
Memory array having a layer with electrical conductivity anisotropy
InactiveUS20050285169A1Improve conductivityTransistorVariable resistance carrier recordingComputational physicsContact region
A memory array includes a memory layer that has hysteretic domains with domain axes extending between first and second memory layer surfaces. A conductive layer on the first memory layer surface has anisotropically increased electrical conductivity in a thickness direction. A movable conductive probe has a contact area on the conductive layer and moves to access a selected hysteretic domain.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
Information recording medium and method for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20050058941A1Increased repetitionLess influenceRecording by optical meansRead-only memoriesLattice defectsCrystal structure
An information recording medium having such a recording material layer on a substrate where reversible phase change between electrically or optically detectable states can be caused by electric energy or electromagnetic energy. The recording material forming the recording layer is either a material having a crystal structure including lattice defects in one phase of the reversible phase change or a material having a complex phase composed of a crystal portion including a lattice defect in one phase of the reversible phase change and an amorphous portion. Both portions contain a common element. A part of the lattice defects are filled with an element other than the element constituting the crystal structure. The recording medium having a recording thin film exhibits little variation of the recording and reproduction characteristics even after repetition of recording and reproduction, excellent weatherability, strong resistance against composition variation, and easily controllable characteristics.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Ultra-high density storage device using phase change diode memory cells and methods of fabrication thereof
InactiveUS20050048733A1Ultra-high densityElectron beam carrier recordingVariable resistance carrier recordingIndiumLight beam
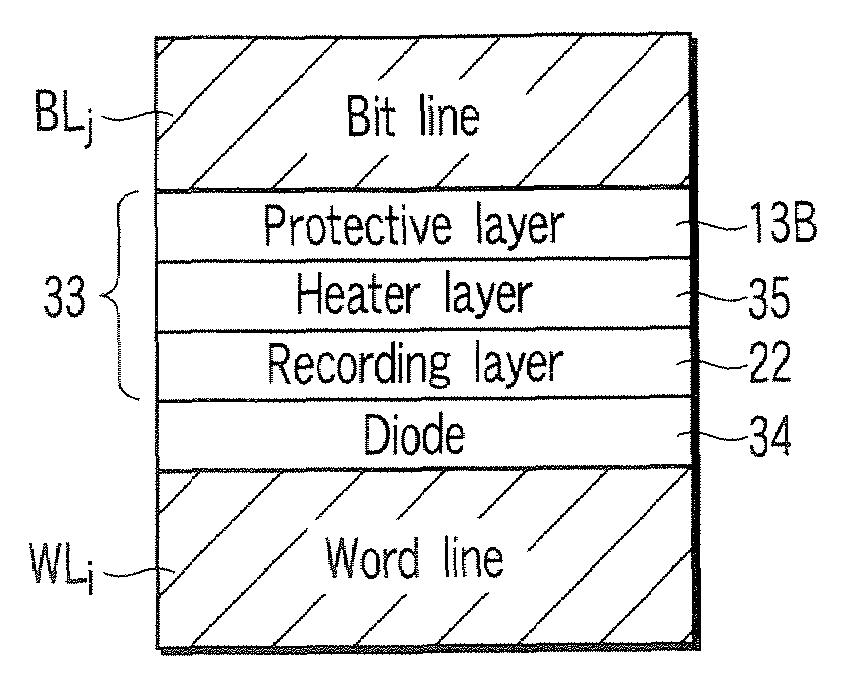
An ultra-high density data storage device using phase-change diode memory cells, and having a plurality of emitters for directing beams of directed energy, a layer for forming multiple data storage cells and a layered diode structure for detecting a memory or data state of the storage cells, wherein the device comprises a phase-change data storage layer capable of changing states in response to the beams from the emitters, and a second layer forming one layer in the layered diode structure, the second layer comprising a material containing copper, indium and selenium. A method of forming a diode structure for a phase-change data storage array, having multiple thin film layers adapted to form a plurality of data storage cell diodes, comprises depositing a first diode layer of CuInSe material on a substrate and depositing a second diode layer of phase-change material on the first diode layer.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Information recording/reproducing device
InactiveUS20100008209A1Variable resistance carrier recordingNanoinformaticsChemical compoundData recording
An information recording / reproducing device according to an aspect of the present invention includes a recording layer, and a recording circuit which records data to the recording layer by generating a phase change in the recording layer. The recording layer includes a first chemical compound having one of a Wolframite structure and a Scheelite structure.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Storage device having a resistance measurement system
ActiveUS7085151B2Electron beam carrier recordingVariable resistance carrier recordingInformation layerOperating system
A storage device and a storage system employing the storage device. In one embodiment, the storage device comprises an electron emitter and a storage medium comprising an information layer having at least a first state and a second state for storing information. The storage device comprises a resistance measurement system coupled to the storage medium for reading the information stored at the information layer by measuring resistance to determine a state of a storage area on the information layer.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Information recording and reproducing apparatus
InactiveUS7995382B2Variable resistance carrier recordingNanoinformaticsShortest distanceRecording layer
An information recording and reproducing apparatus, includes: a recording layer including a first layer including a first compound, the first compound being a conjugated compound including at least two types of cation elements, at least one selected from the cation elements being a transition element having a d orbit incompletely filled by electrons, a shortest distance between adjacent cation elements being not more than 0.32 nm; a voltage application unit that applies a voltage to the recording layer, produces a phase change in the recording layer, and records information; an electrode layer that applies a voltage to the recording layer; and an orientation control layer provided between the recording layer and the electrode layer to control an orientation of the recording layer.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
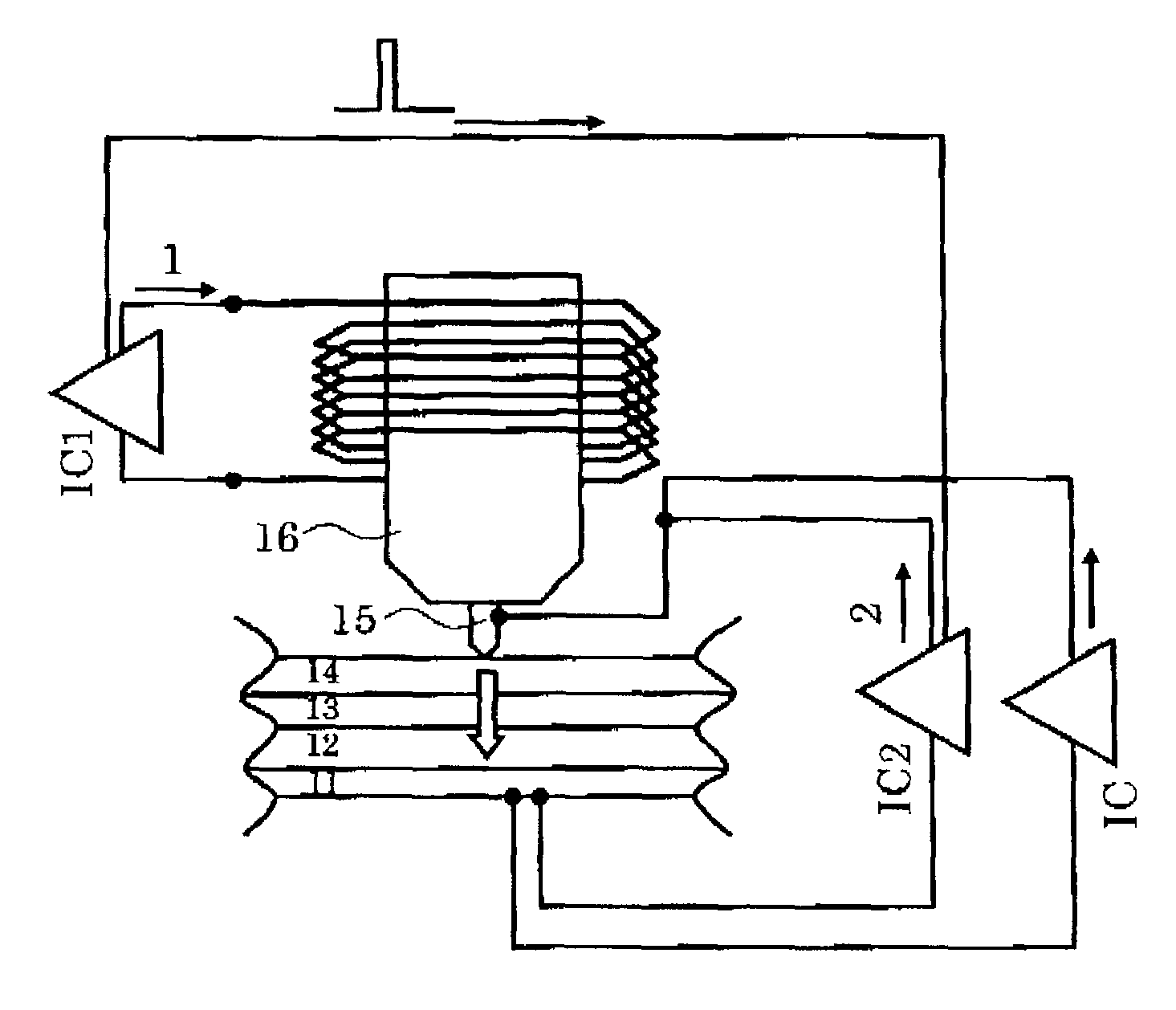
Recording medium using ferroelectric substance, recording apparatus and reproducing apparatus
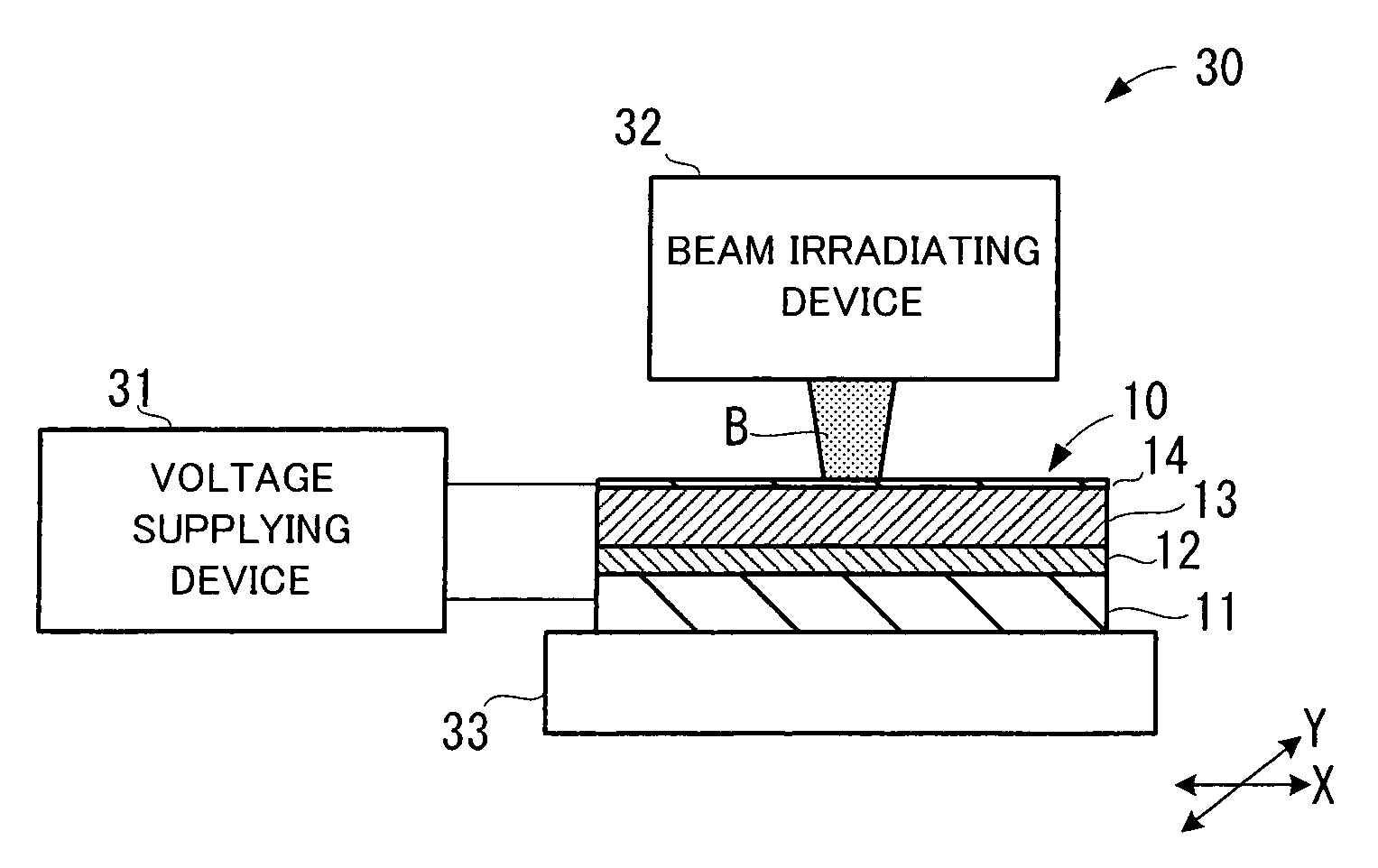
InactiveUS20050163021A1Increased durabilitySpeed up scanElectron beam carrier recordingVariable resistance carrier recordingEngineeringVoltage
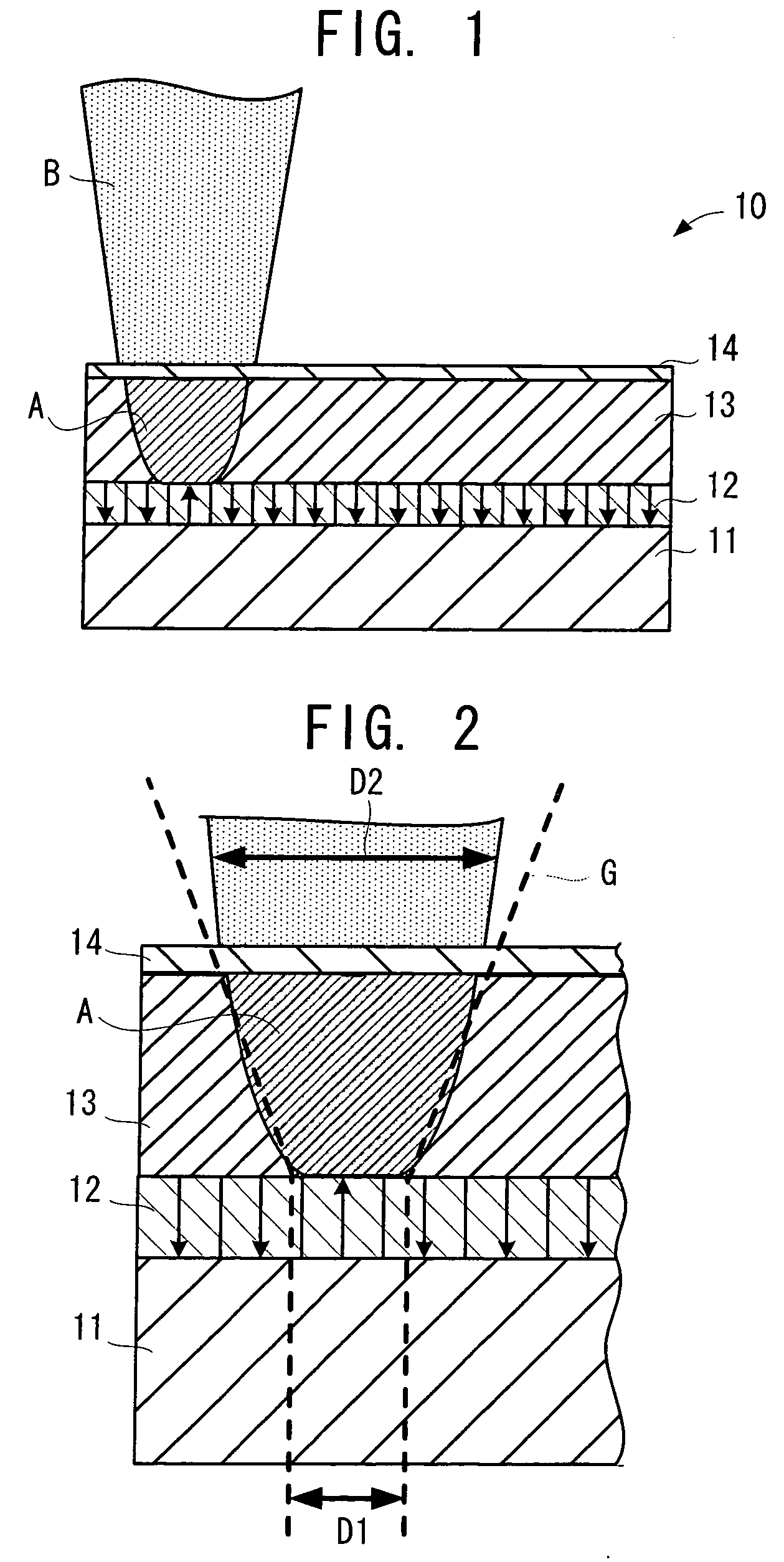
A recording medium (10) is formed by laminating a conductive layer (11), a ferroelectric layer (12), a control layer (13), and a conductive layer (14), in order. Moreover, the control layer (13) is formed from a material that has an insulation property in a normal state but becomes conductive by irradiation of an energy beam. Then, the insulation property and conductivity of the control layer (13) is changed by presence or absence, or strength or weakness of the irradiation of the energy beam (B). When the control layer (13) exhibits the conductivity, a voltage supplied between the conductive layers (11, 14) is applied to the ferroelectric layer (12). When the control layer (13) exhibits the insulation property, the application of the voltage is cut off. The application and cut-off of the voltage to the ferroelectric layer (12) realize recording of information into the ferroelectric layer (12).
Owner:PIONEER CORP
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com