Patents
Literature
313results about "Microscopic probe carrier recording" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
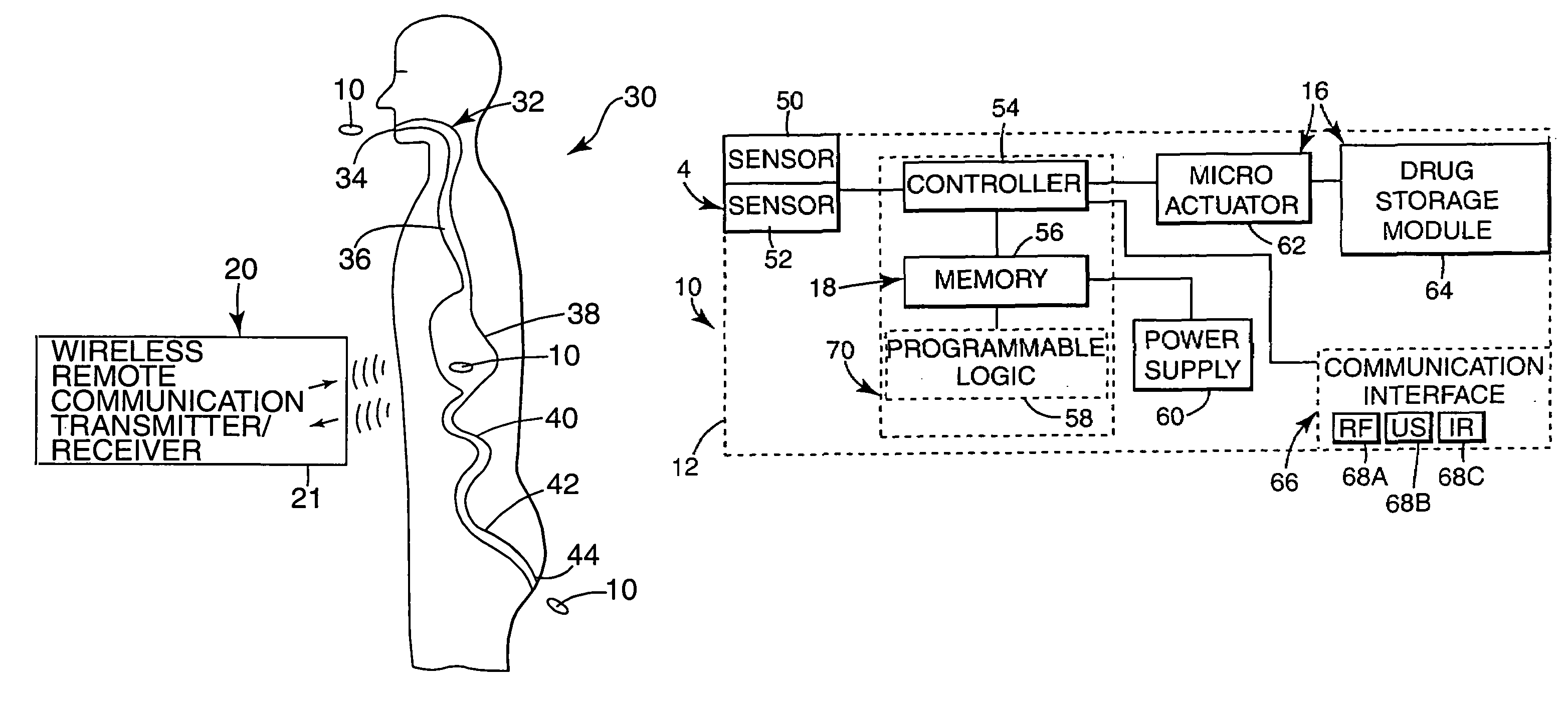
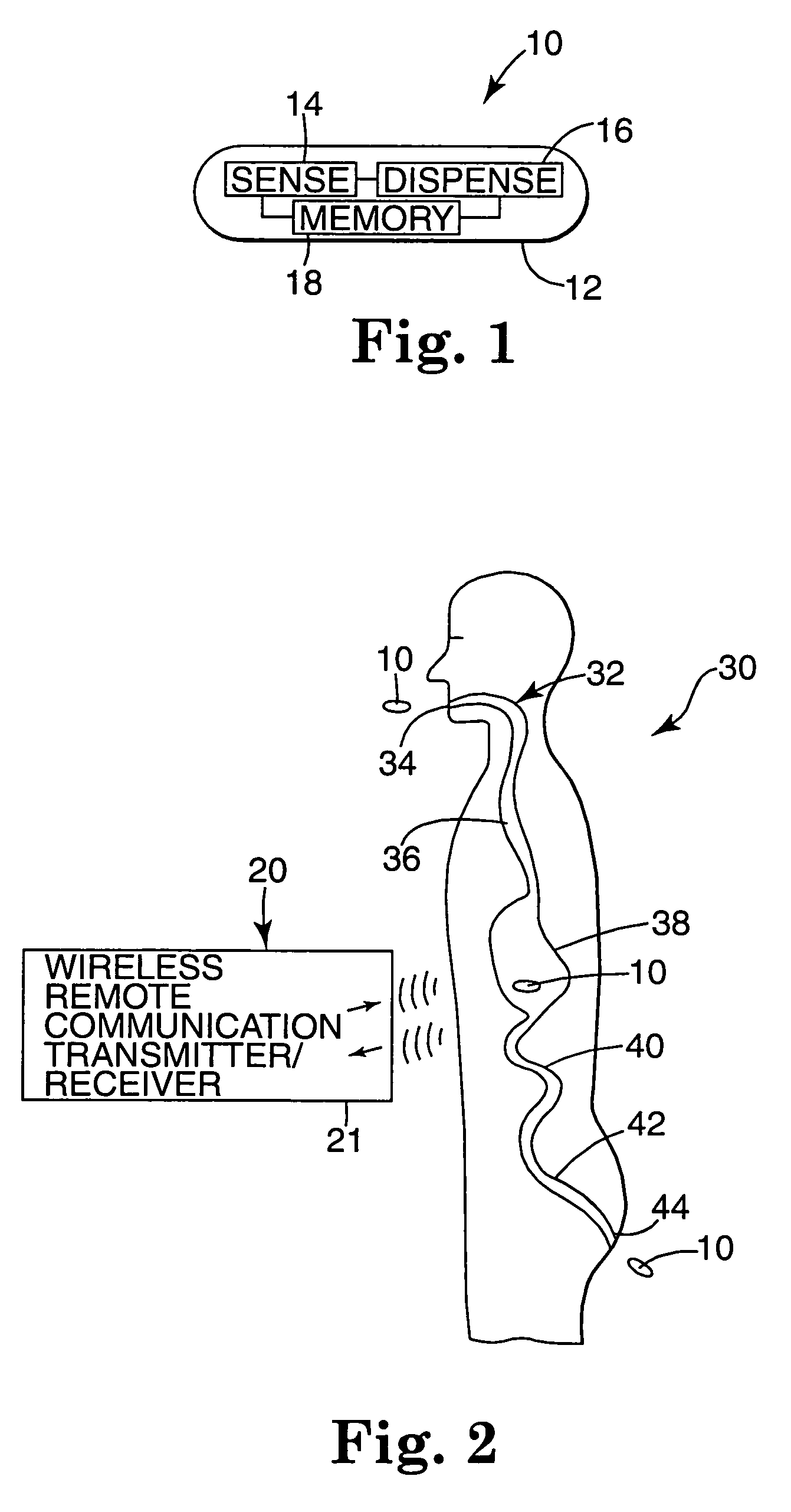
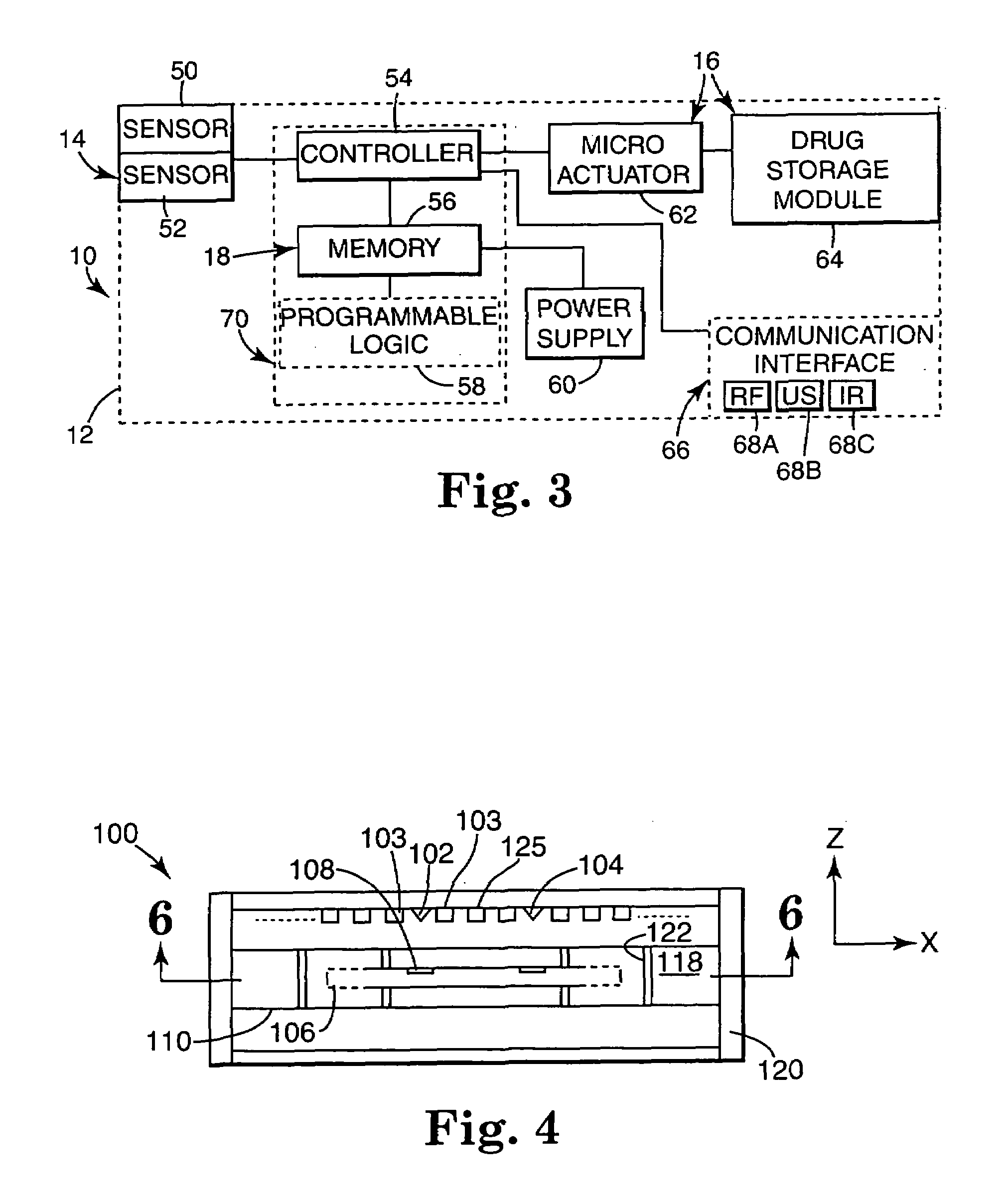
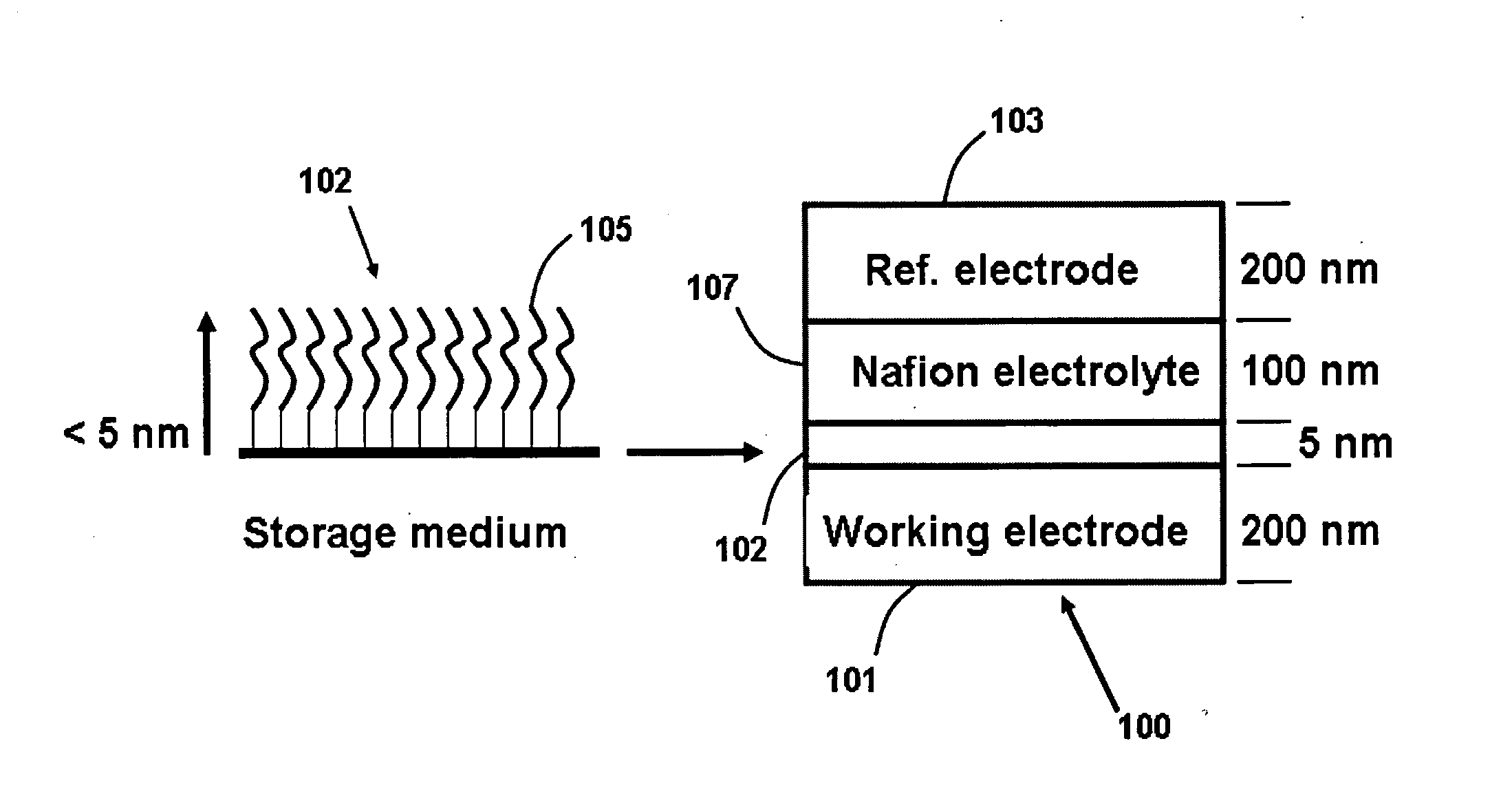
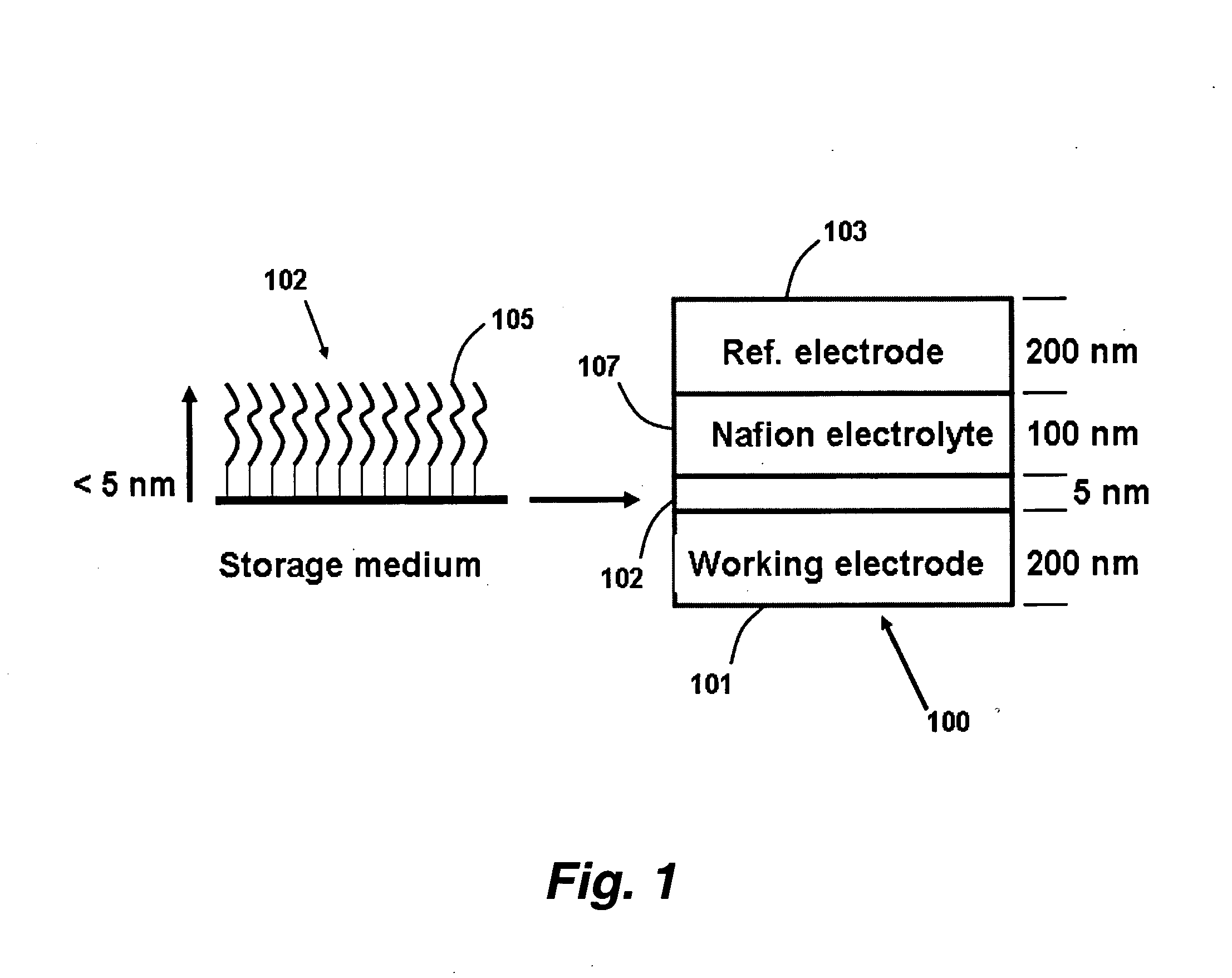
Internal drug dispenser capsule medical device
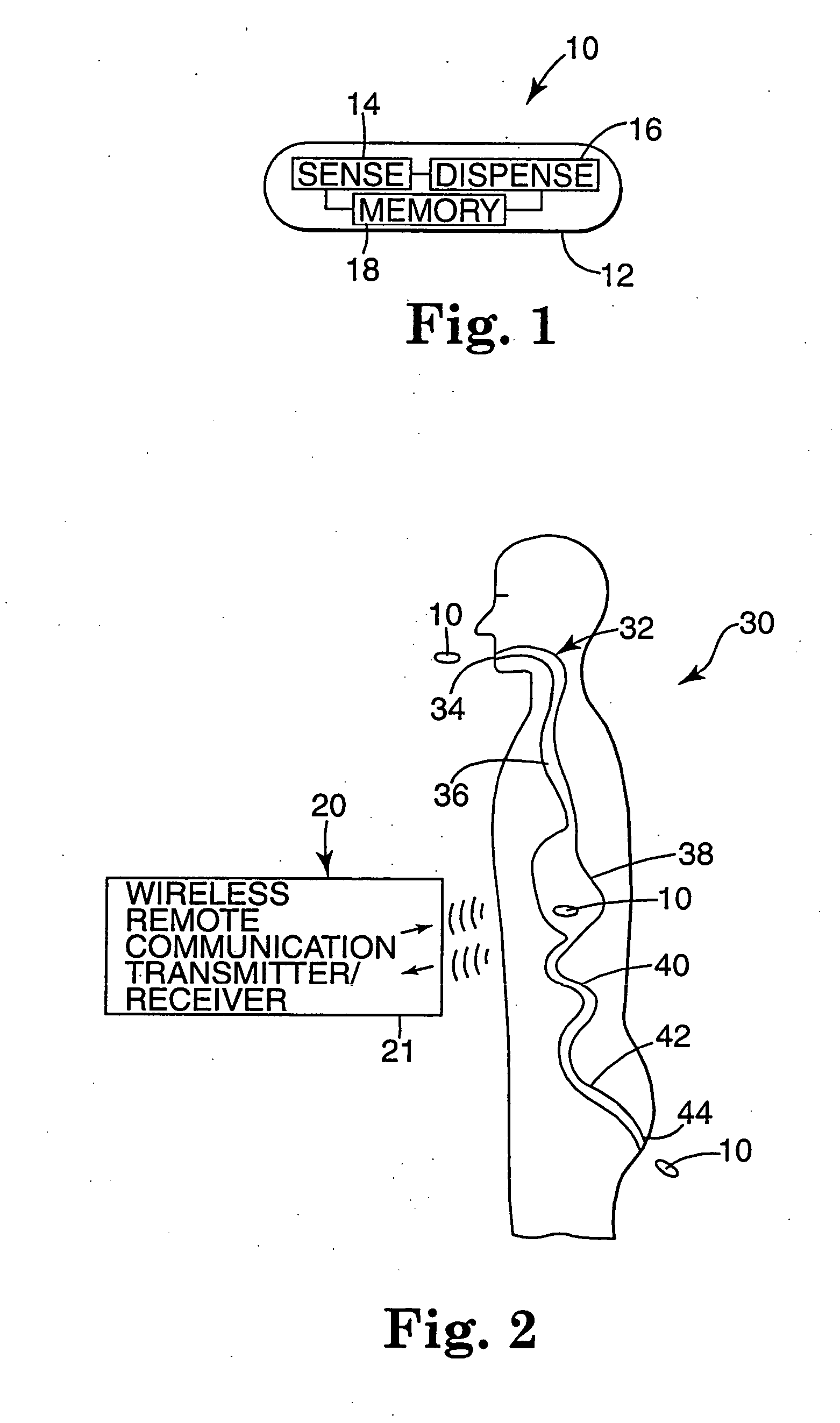
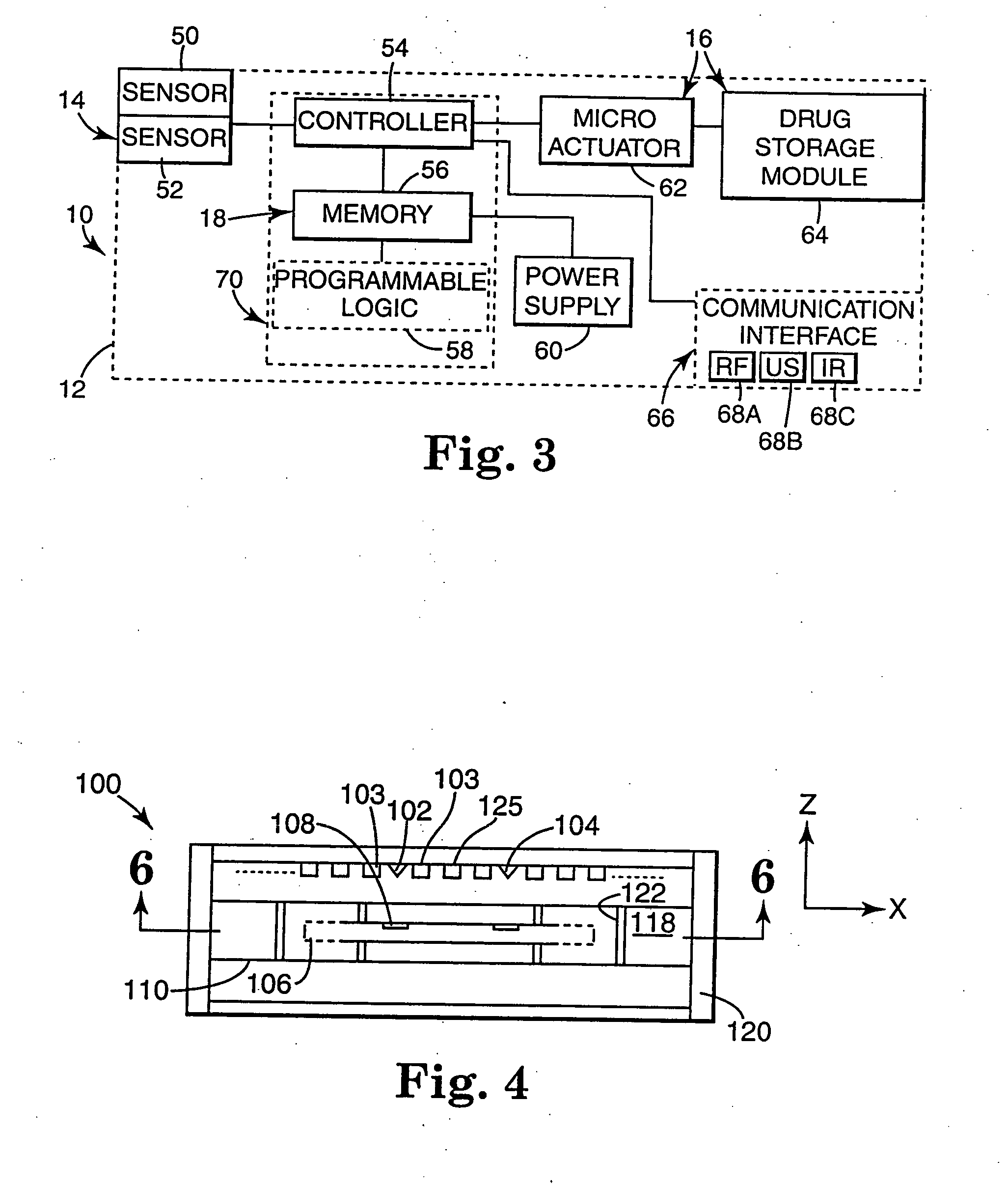
The present invention provides a swallowable internal drug medical device. The device includes a swallowable capsule. A sensing module is disposed in the capsule. A bioactive substance dispenser is disposed in the capsule. A memory and logic component is disposed in the capsule and in communication with the sensing module and the dispenser.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Capping layer for enhanced performance media
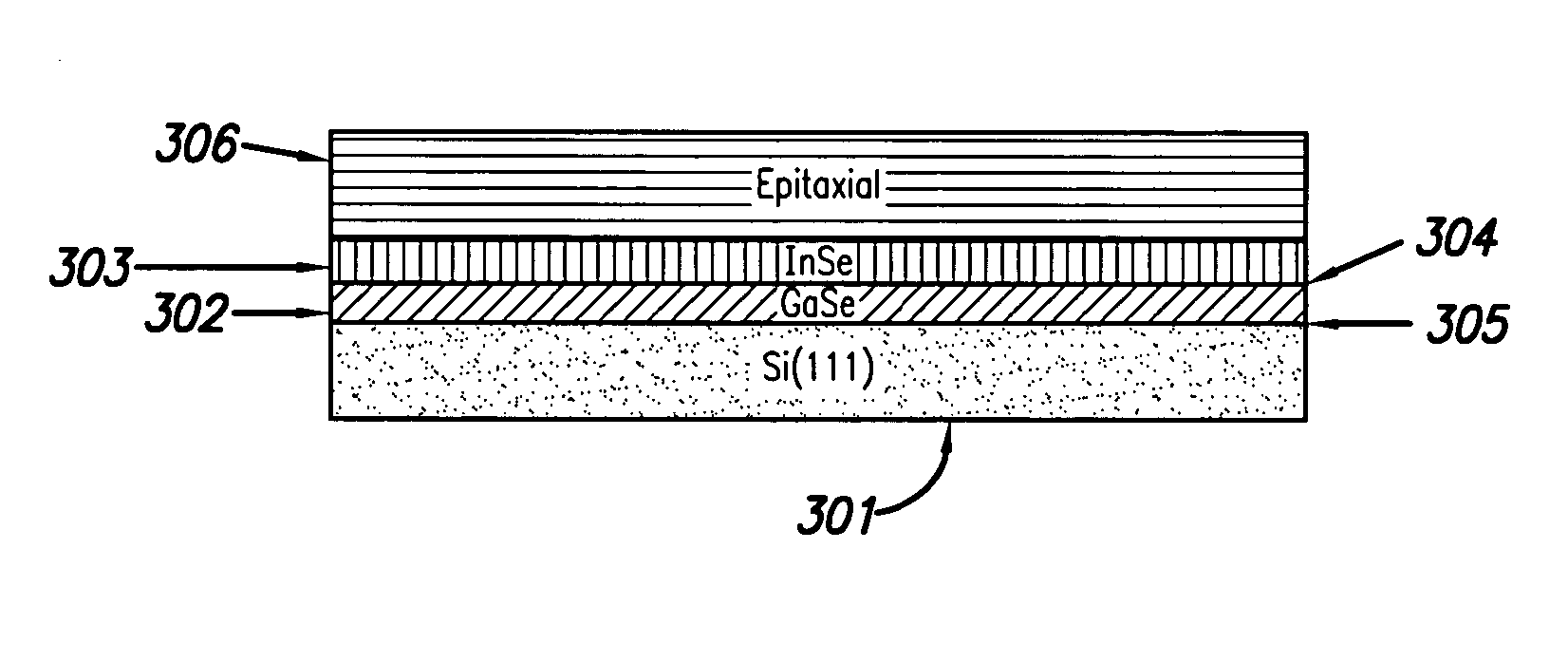
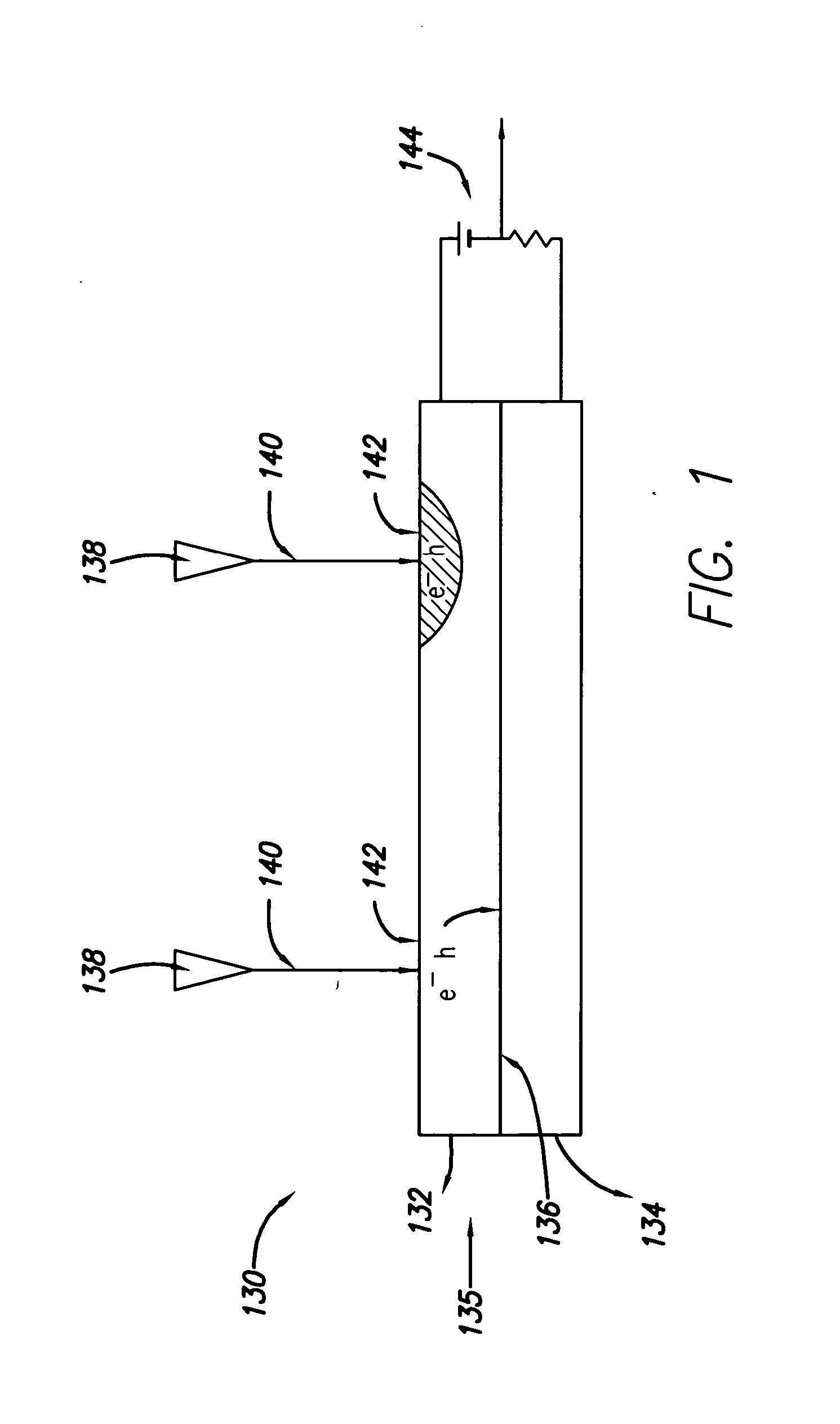
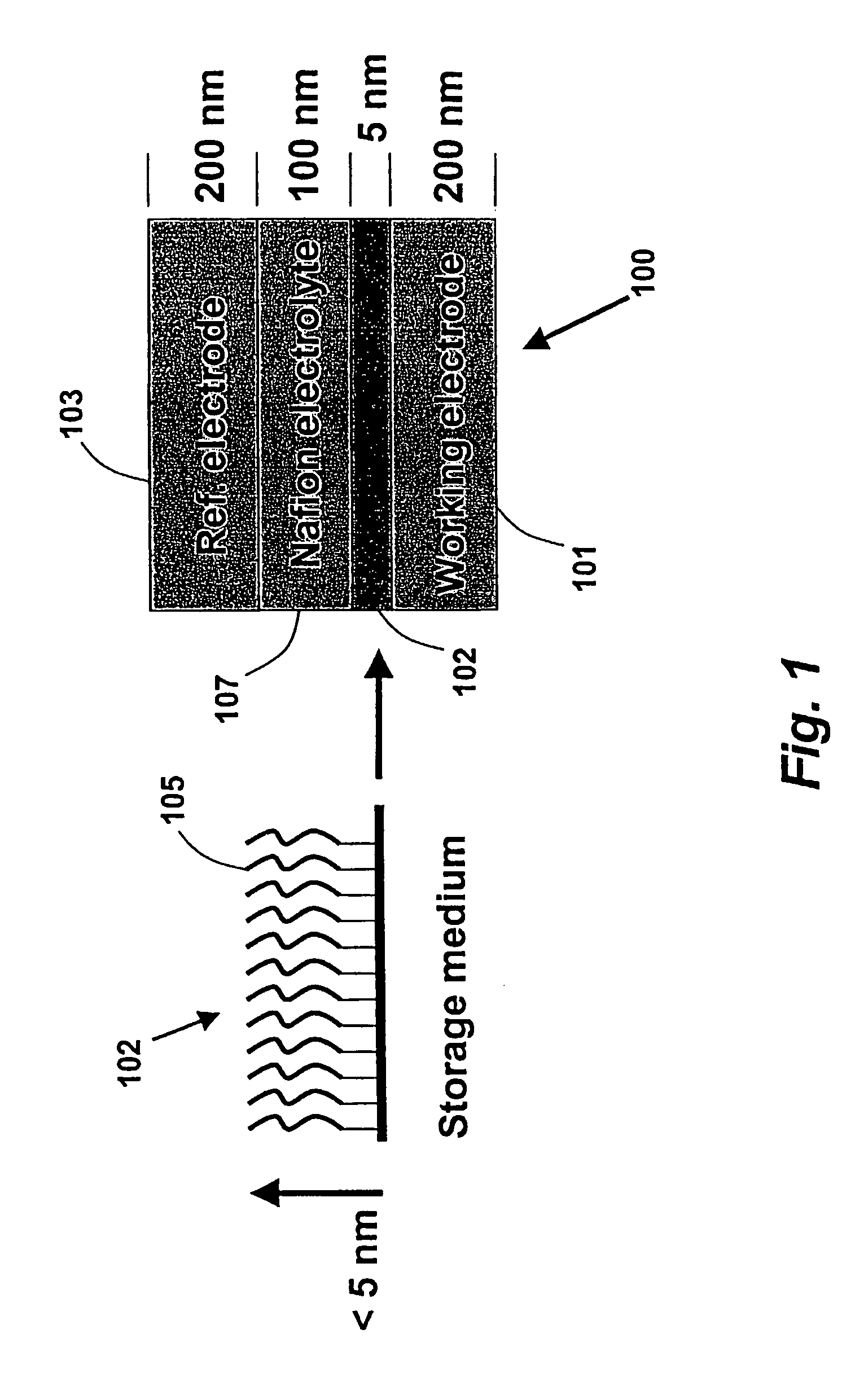
InactiveUS20050074576A1High materialElectrostatic charge injection carrier recordingElectron beam carrier recordingEpitaxial materialConductive materials
A media storage device and method for fabricating said device is provided. The device comprises a data layer capable of storing and erasing data via application of an energy beam, such as a near field optical non diffraction limited beam or electron beam. A separate capping layer is deposited on the data layer. The separate capping layer is relatively transparent to the energy beam and may be formed from various materials, including but not limited to an epitaxial material, a conducting material, and a robust high melting point material, such as Molybdenum.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Internal drug dispenser capsule medical device
The present invention provides a swallowable internal drug medical device. The device includes a swallowable capsule. A sensing module is disposed in the capsule. A bioactive substance dispenser is disposed in the capsule. A memory and logic component is disposed in the capsule and in communication with the sensing module and the dispenser.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Non-volatile memory with phase-change recording layer
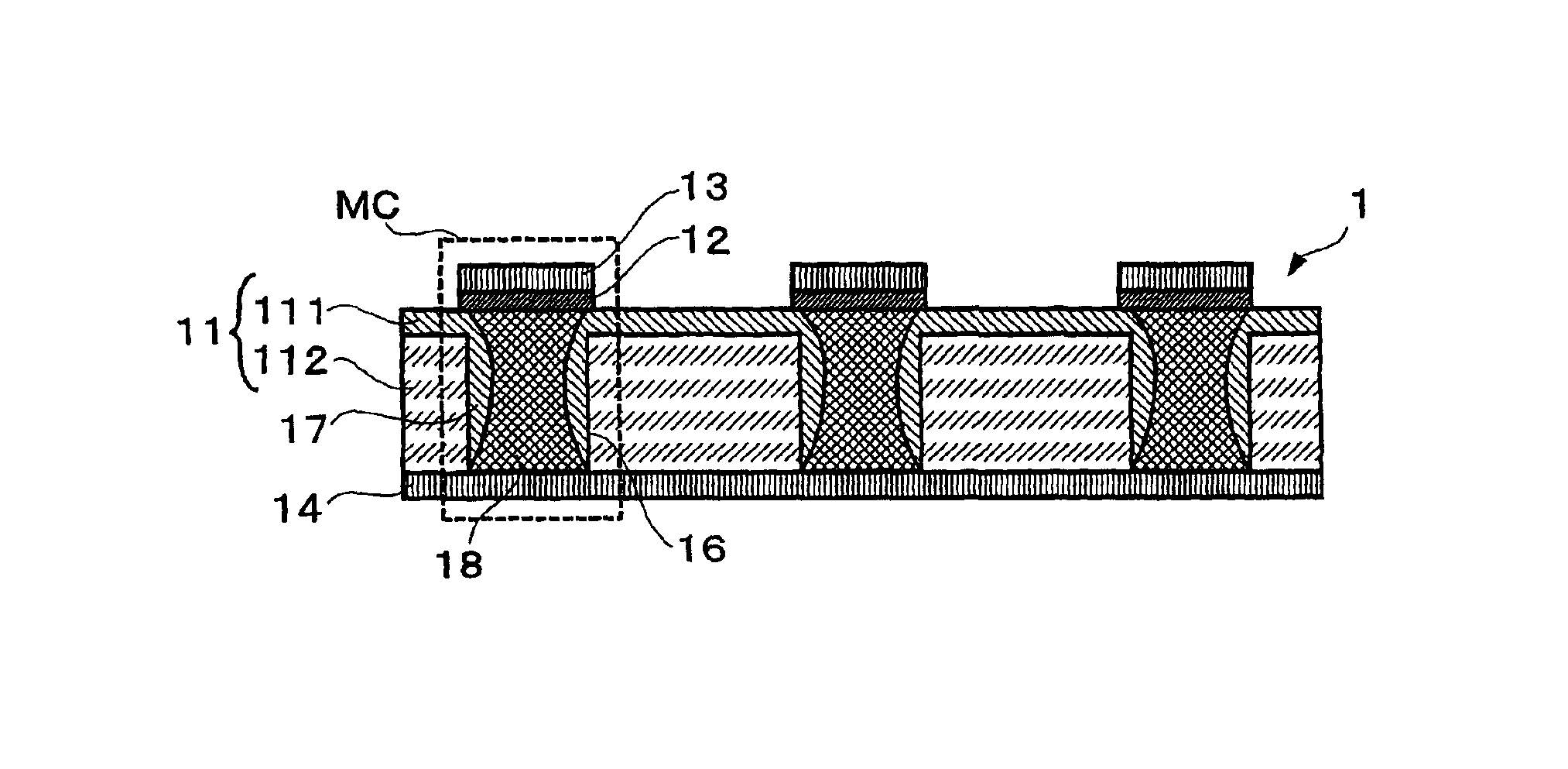
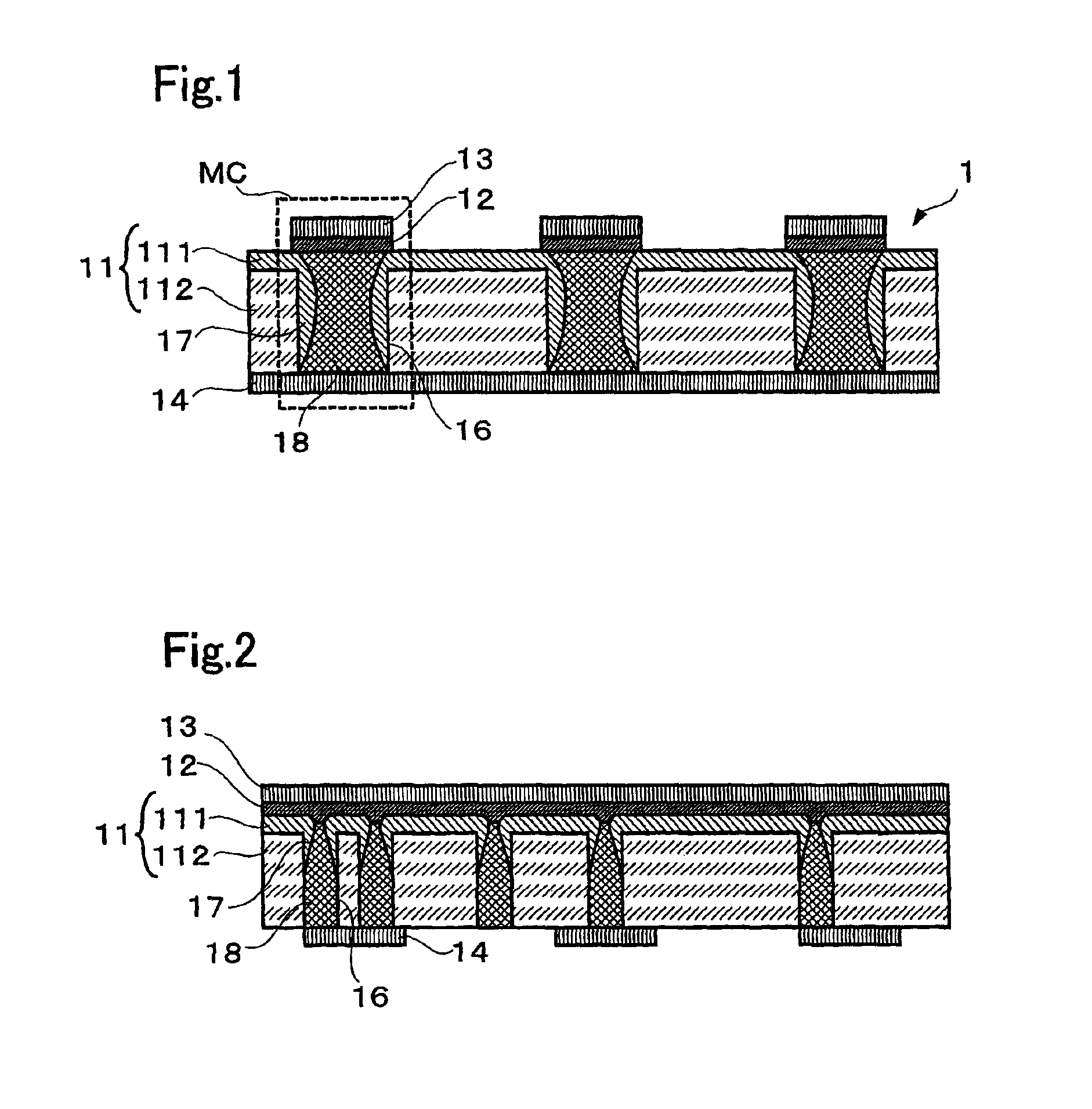
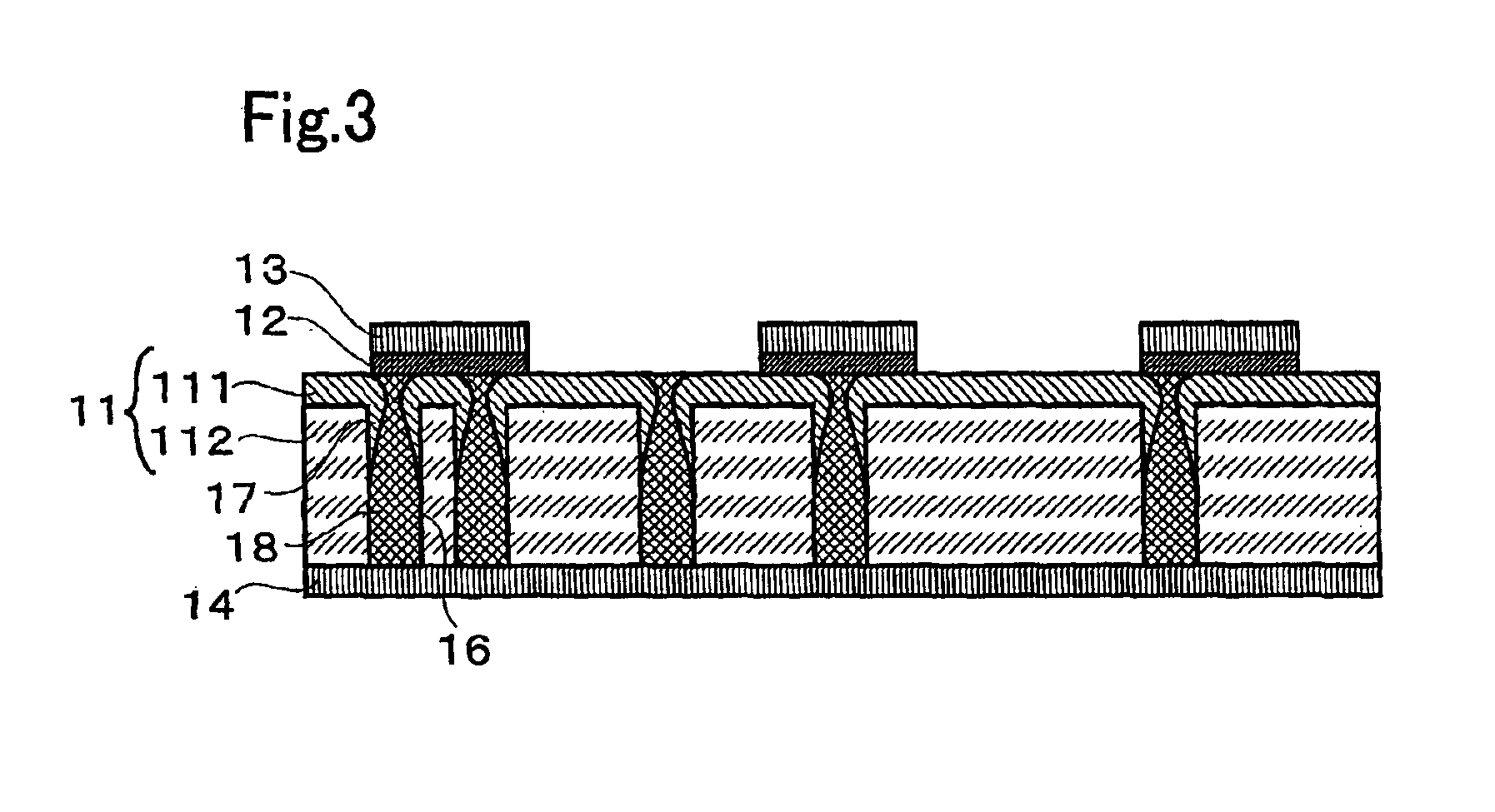
InactiveUS6900517B2Increase possible numberReduce power consumptionTransistorVariable resistance carrier recordingElectrical impulseEngineering
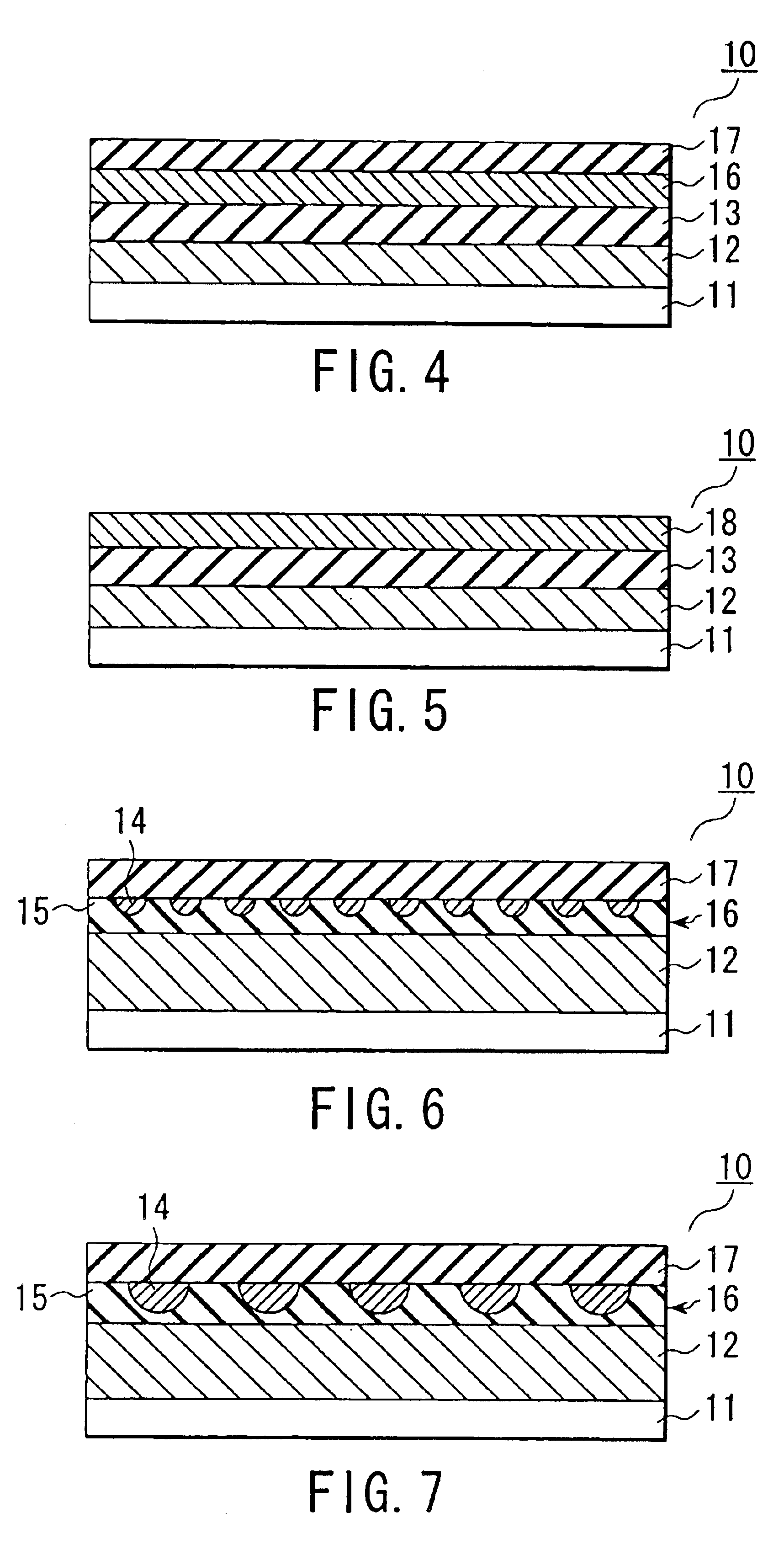
A non-volatile memory, which comprises an insulating substrate (11) that has a first electrode (18) that extends through the substrate from the front surface to the rear surface thereof; a second electrode (13) that is formed on one side of the insulating substrate (11); and a recording layer (12) that is clamped between the first electrode (18) and the second electrode (13) and whose resistance value varies when an electric pulse is applied across the first electrode (18) and the second electrode (13); wherein the insulating substrate (11) has a layered structure composed of an organic dielectric thin film (112) and an inorganic dielectric layer (111) that is thinner than the organic dielectric thin film (112); with the recording layer (12) being formed on the side on which the inorganic dielectric layer is formed. Use of this non-volatile memory increases the possible number of data writing cycles while saving power.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
High density non-volatile memory device
InactiveUS20050041494A1Suitable mechanical propertyPrevent charge leakageNanoinformaticsSolid-state devicesChemical synthesisFault tolerance
This invention provides novel high density memory devices that are electrically addressable permitting effective reading and writing, that provide a high memory density (e.g., 1015 bits / cm3), that provide a high degree of fault tolerance, and that are amenable to efficient chemical synthesis and chip fabrication. The devices are intrinsically latchable, defect tolerant, and support destructive or non-destructive read cycles. In a preferred embodiment, the device comprises a fixed electrode electrically coupled to a storage medium having a multiplicity of different and distinguishable oxidation states wherein data is stored in said oxidation states by the addition or withdrawal of one or more electrons from said storage medium via the electrically coupled electrode.
Owner:NORTH CAROLINA STATE UNIV +1
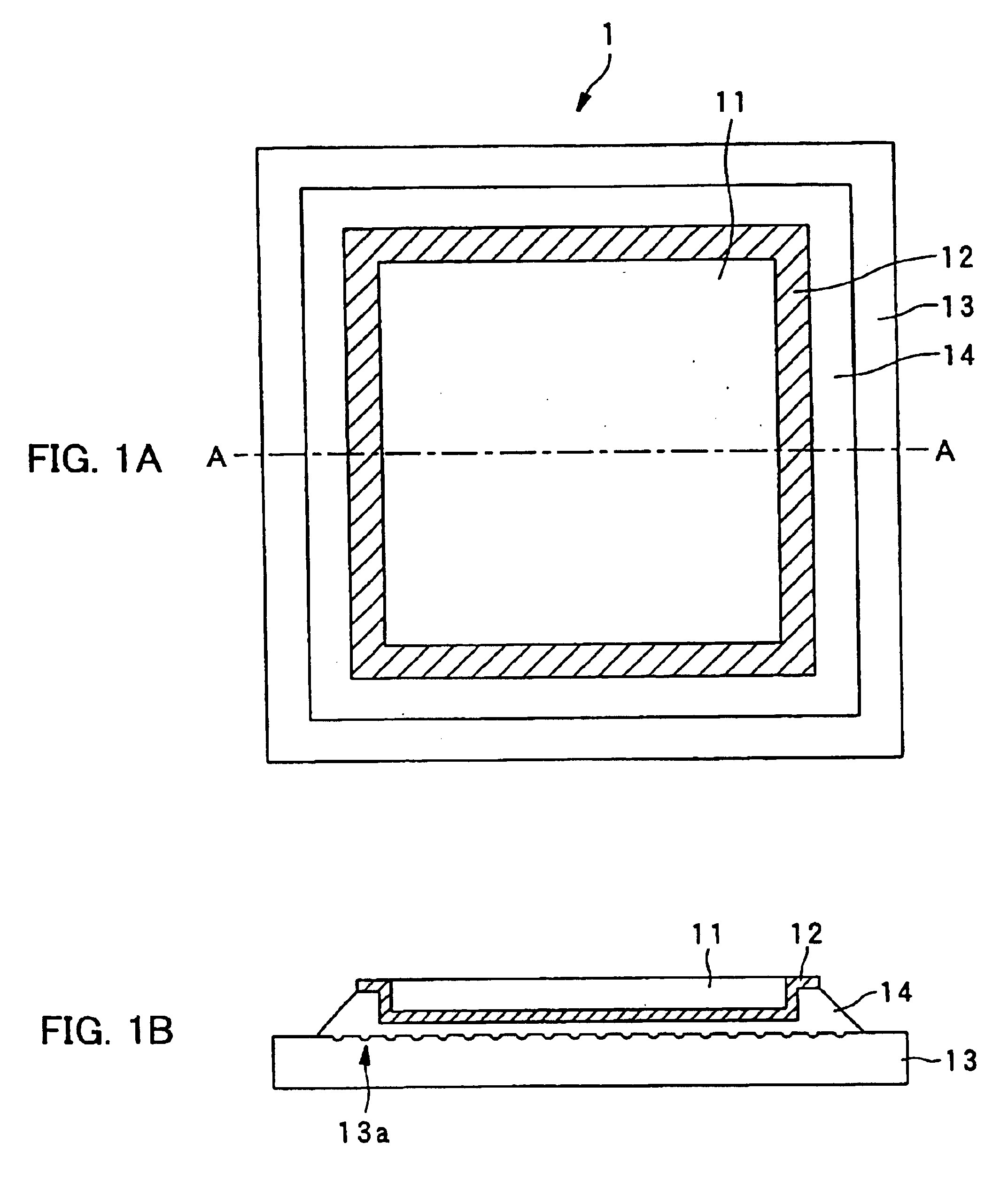
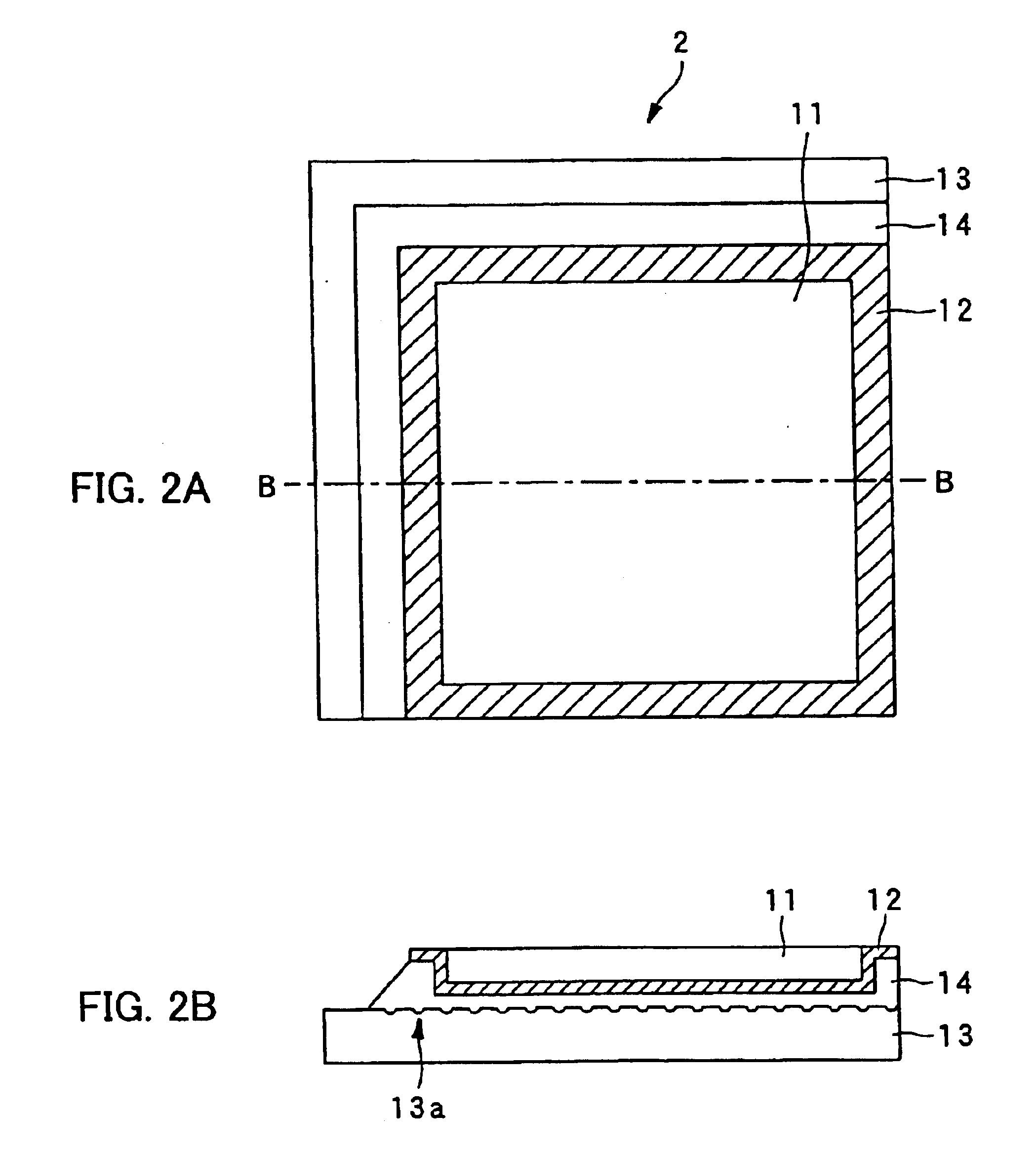
Dielectric recording medium, and method of and apparatus for producing the same
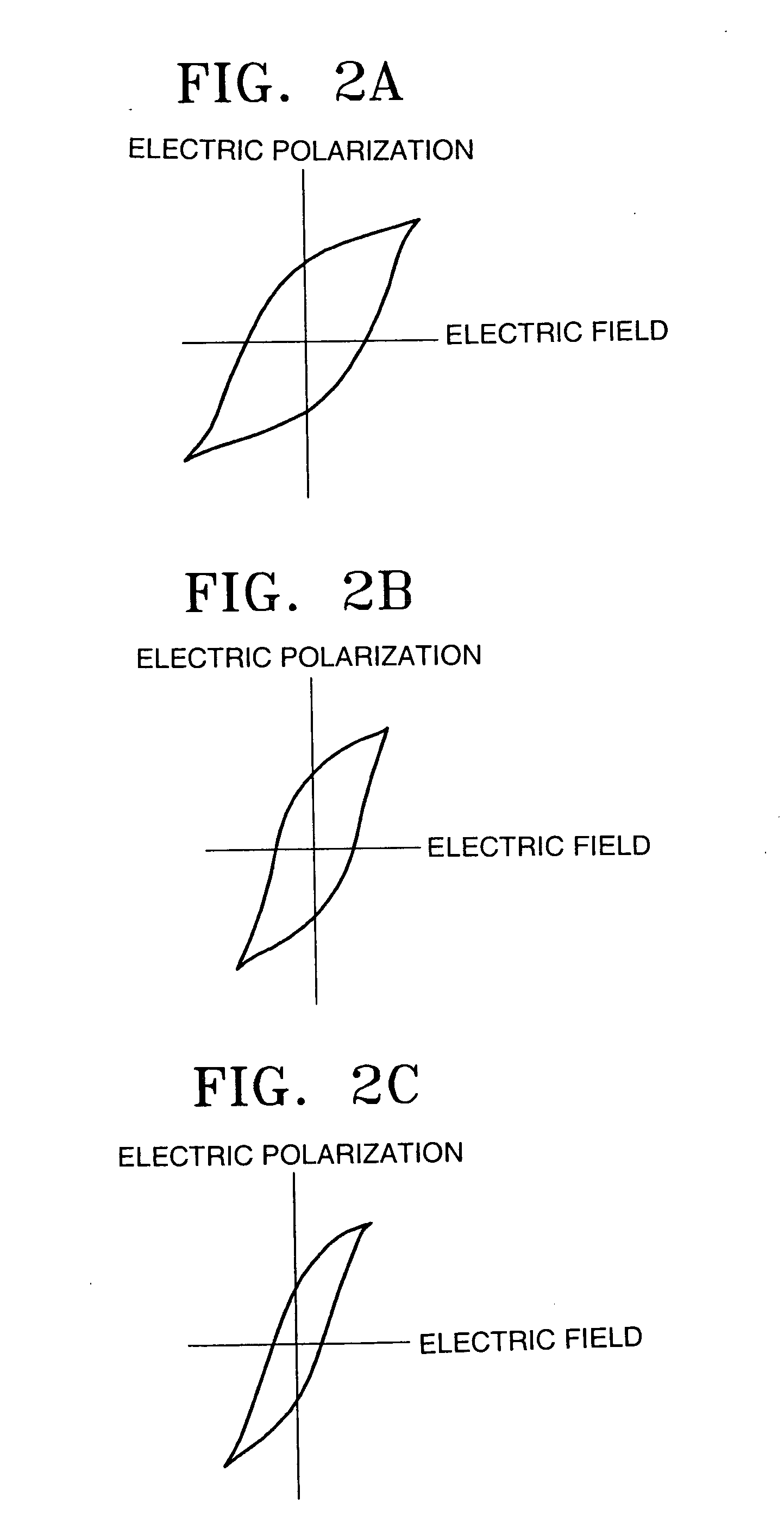
InactiveUS6841220B2Remove electric charge on the recording surface rapidlyImprove abilitiesNanoinformaticsFerroelectric carrier recordingSingle crystalOptoelectronics
The dielectric recording medium is provided with a dielectric material, a conductive thin film, and a substrate. The conductive thin film and the substrate are bonded by a resin adhesive. The dielectric material is constructed of a ferroelectric single crystal having a uniform thickness, and its one surface is used for a recording and / or reproducing surface, on the order of mm on a side and about 5000 Å thick. The conductive thin film, about 1000 to 2000 Å thick, is placed on a surrounding portion and a back surface of the recording and / or reproducing surface of the dielectric material. The substrate is intended to preserve the thin dielectric material and maintain the planarity, and concave portions are formed on the adhesive surface. The concave portions absorb excessive resin adhesive when the dielectric material is bonded onto the substrate, which makes the adhesive surface uniform and flat.
Owner:PIONEER CORP +1
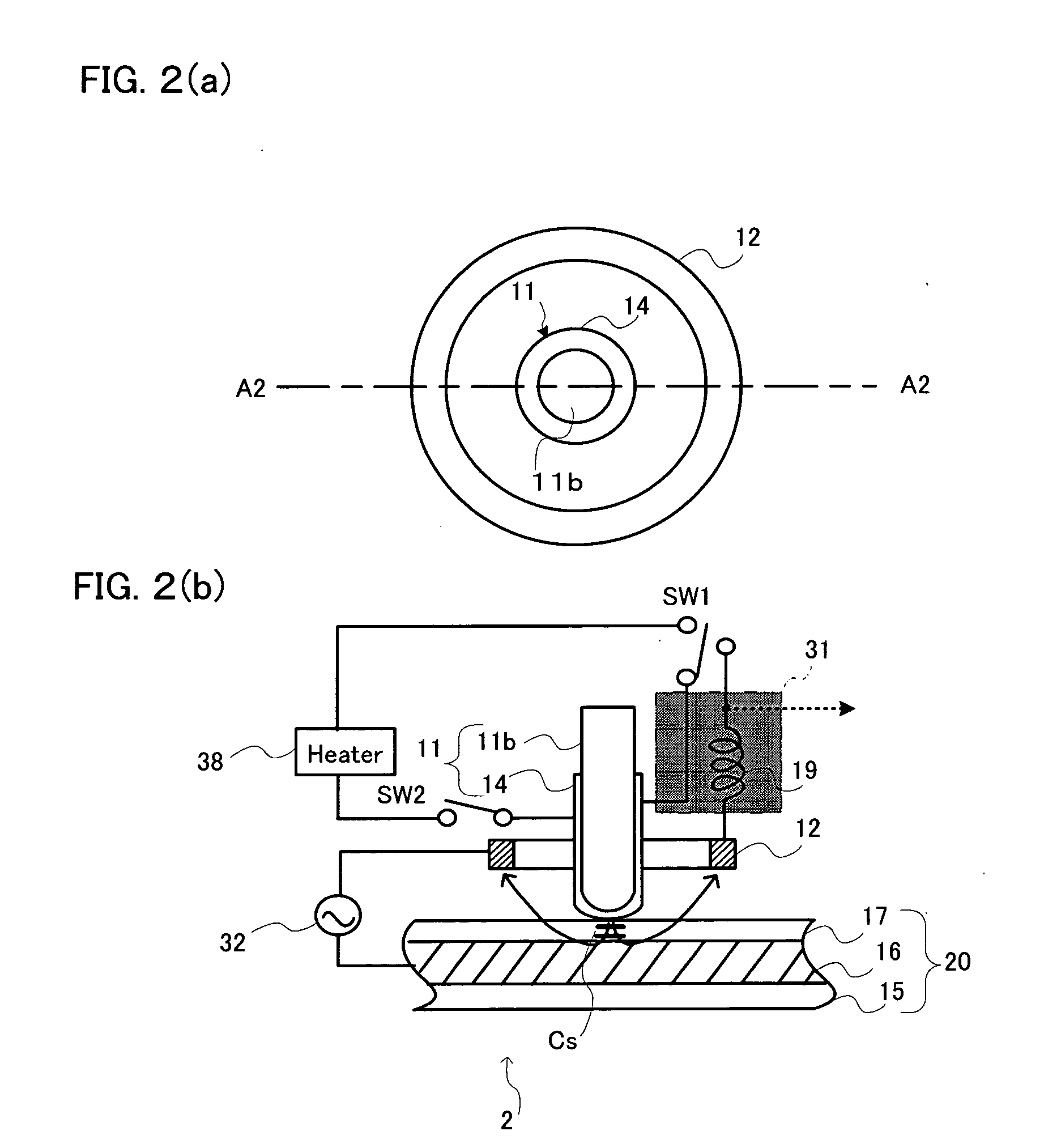
Contact probe storage fet sensor and write heater arrangements
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Information recording/reproducing apparatus and recording medium
InactiveUS20050099895A1Scan accuratelyReliable recordCombination recordingNanoinformaticsDisplacement controlComputer science
The scan range of each probe of a probe array is increased so that two or more recording areas formed on a recording surface of a recording medium can be scanned by using one probe. Moreover, displacement control information is recorded in advance between the recording areas which are mutually adjacent on the recording surface of the recording medium. On the basis of the displacement control information, the displacement of the probes are stabilized at a constant speed, and then the recording areas are scanned.
Owner:PIONEER CORP
Optical near-field generator and recording apparatus using the optical near-field generator
InactiveUS7529158B2Reduce the impactReduce impactNanomagnetismOptical flying-type headsPenetration depth
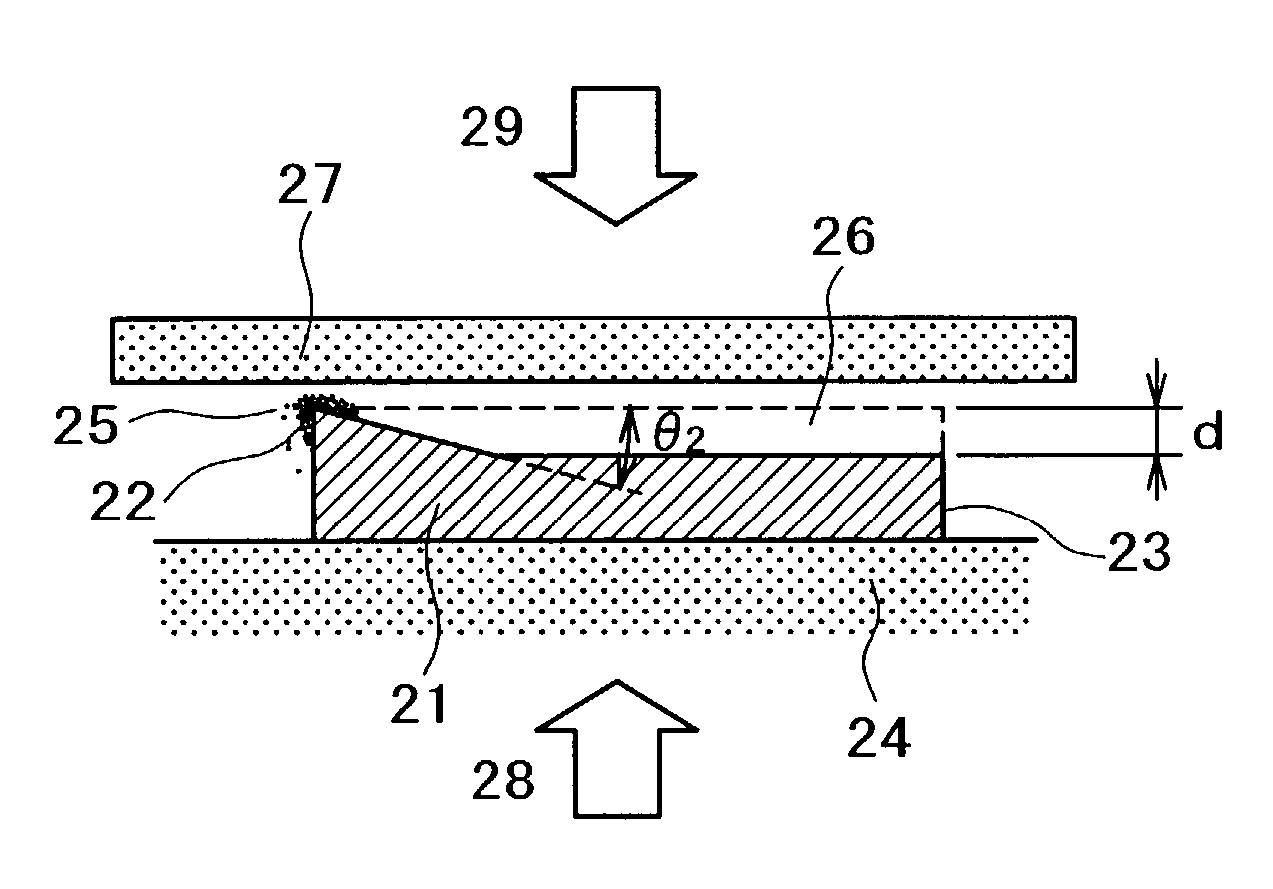
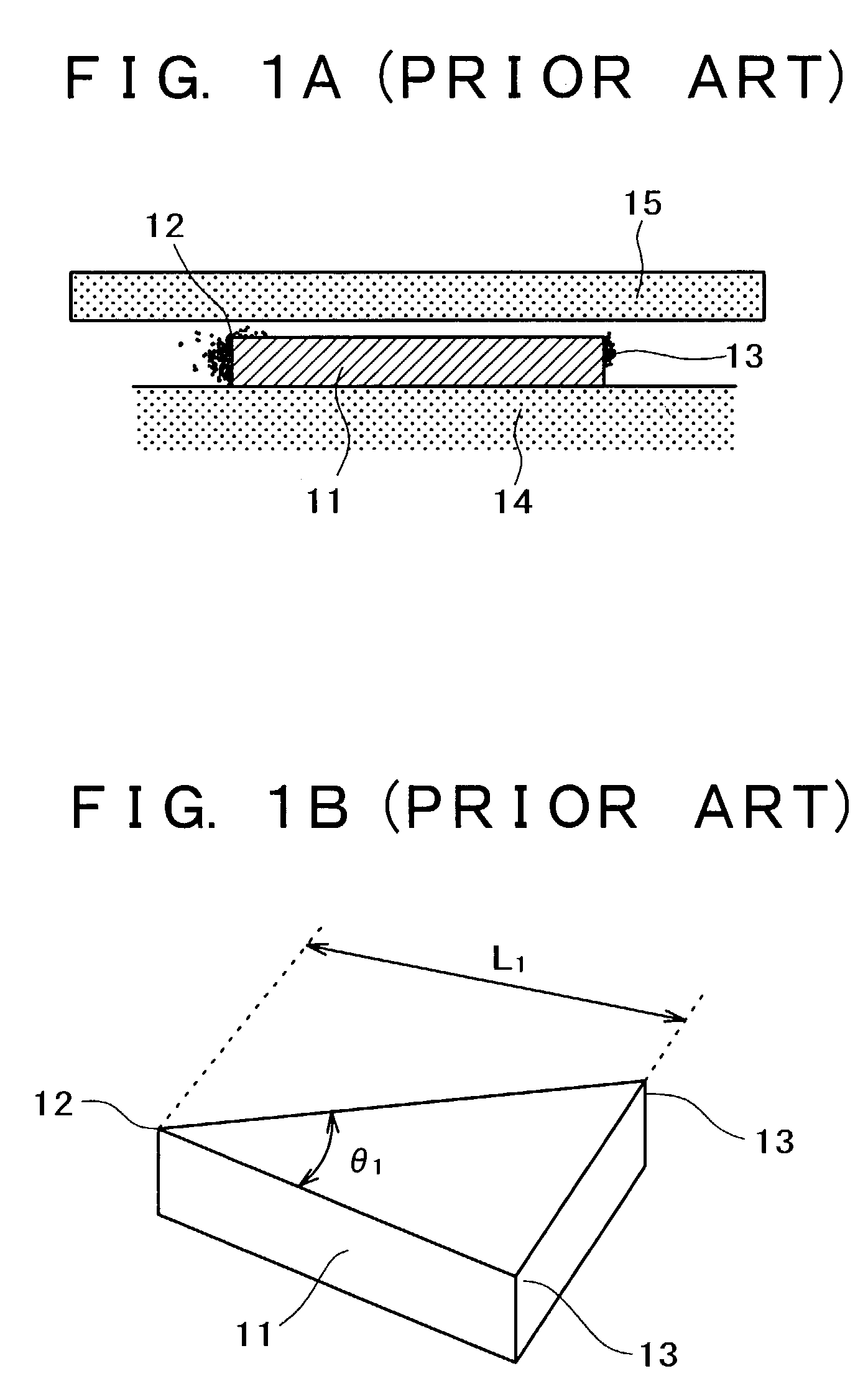
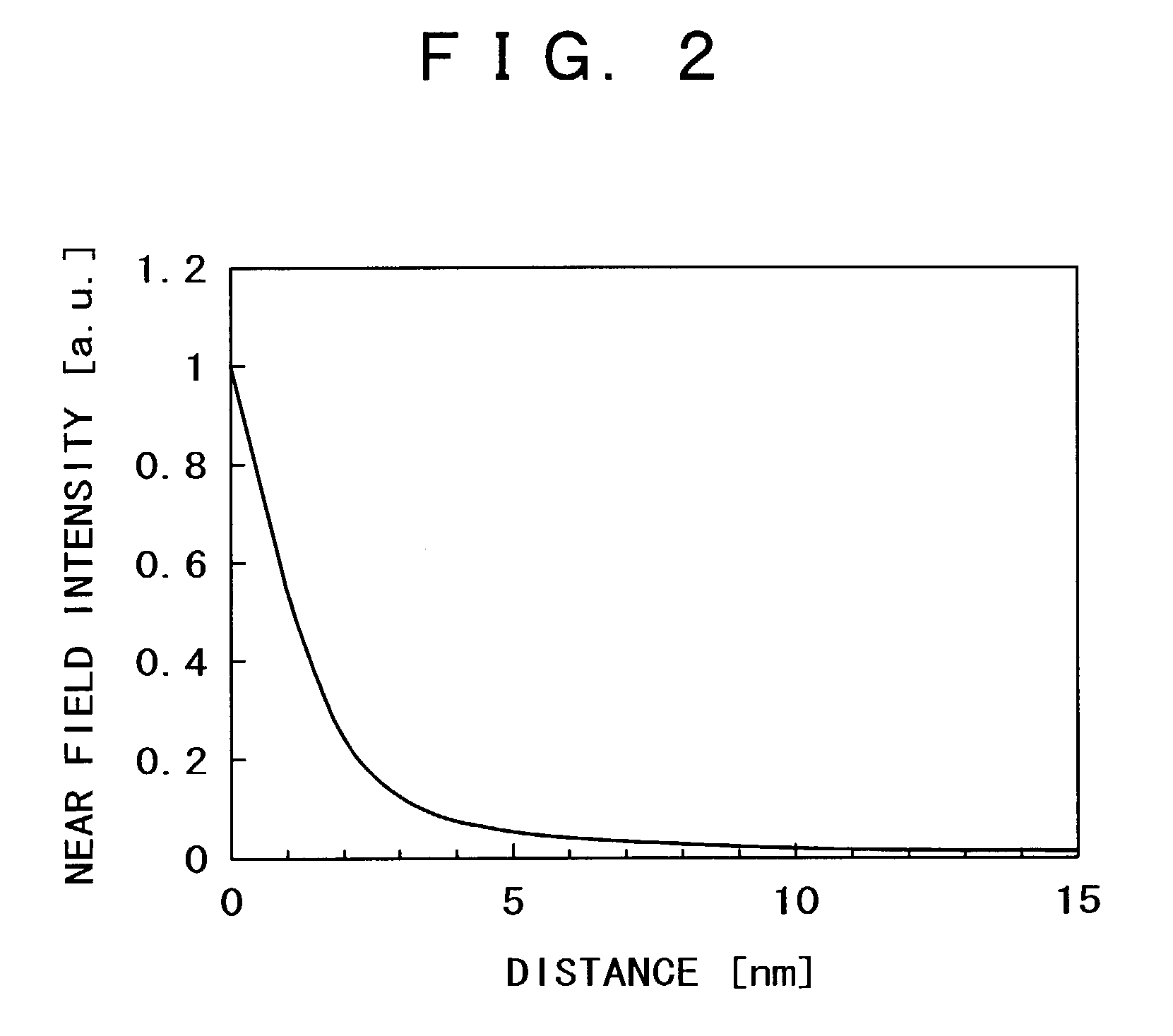
A near-field optical probe and optical near-field generator are provided. A problem of a probe having a scatterer in which optical near-field noises are generated at the parts other than for a point at which an intense optical near-field is generated, is solved. In one example of the probe, a surface of the parts except for a vertex of the scatterer at which the intense optical near-field is generated is etched so that an etching depth becomes not less than a penetration depth of the optical near-field. The probe facilitates control of noises when a sample is observed or recording marks are reproduced.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Devices and methods for storing data
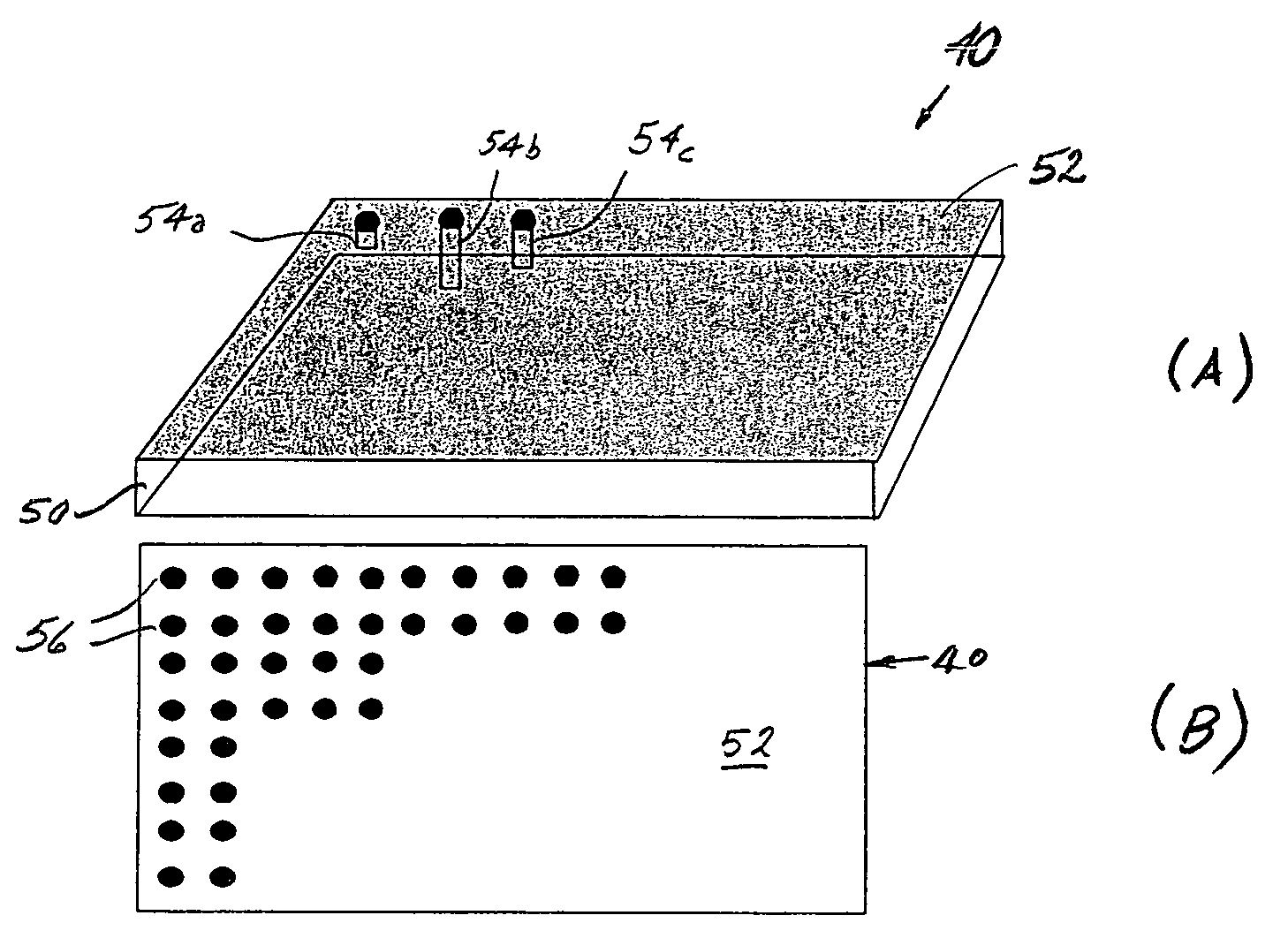
Data-storage devices and methods are disclosed. An exemplary data-storage device includes a medium having at least two dimensions and having a surface. Multiple data-containing loci are arranged on the surface. Each locus has a respective amount of magnetically responsive particles. The respective amounts are different in at least some of the loci. The respective amount at a particular locus corresponds, at least in part, to a respective unit of data contained by the locus. The loci can be substantially two-dimensional or three-dimensional, the latter being configured as respective holes, containing respective amounts of magnetically responsive particles, extending depth-wise into the medium. The loci typically range in size from the micrometer range to the nanometer range. The medium can be any of various configurations such as cards, sheets, films, etc.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT NEVADA SYST OF HIGHER EDUCATION ON BEHALF OF THE UNIV OF NEVADA RENO
Solid electrolyte probe storage device, system including the device, and methods of forming and using same
InactiveUS20060291364A1Easy and inexpensive to manufactureKeep energy smallVariable resistance carrier recordingNanoinformaticsElectrical conductorElectrical battery
A probe storage system, including programmable cells suitable for storing information, and methods of forming and programming the cells are disclosed. The programmable cells generally include an ion conductor, a plurality of electrodes, and a protective layer between the ion conductor and at least one of the electrodes, wherein one of the electrodes may be in the form of a probe. Electrical properties of the cells may be altered by applying energy to the structure, and thus information may be stored using the system.
Owner:AXON TECH
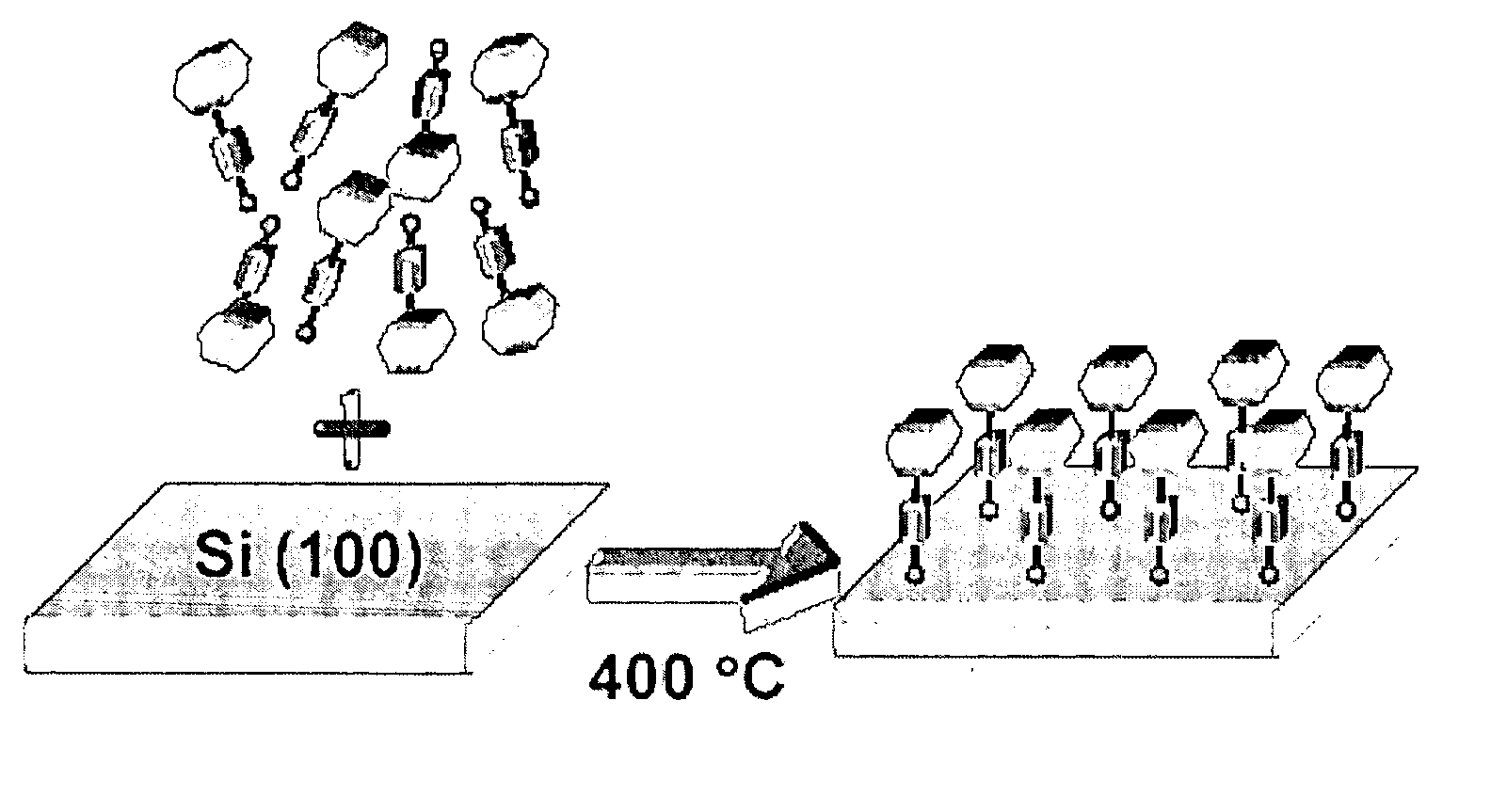
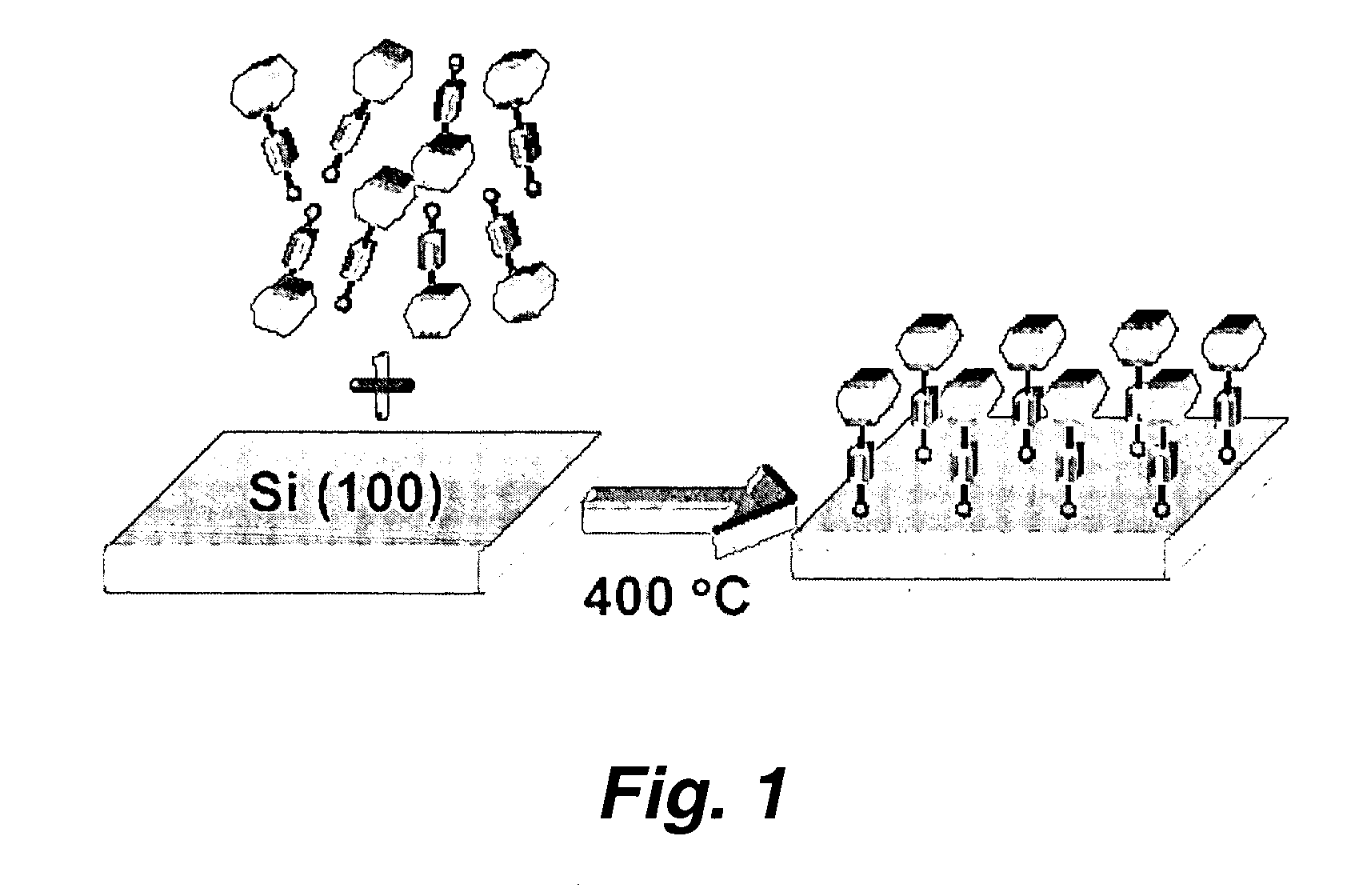
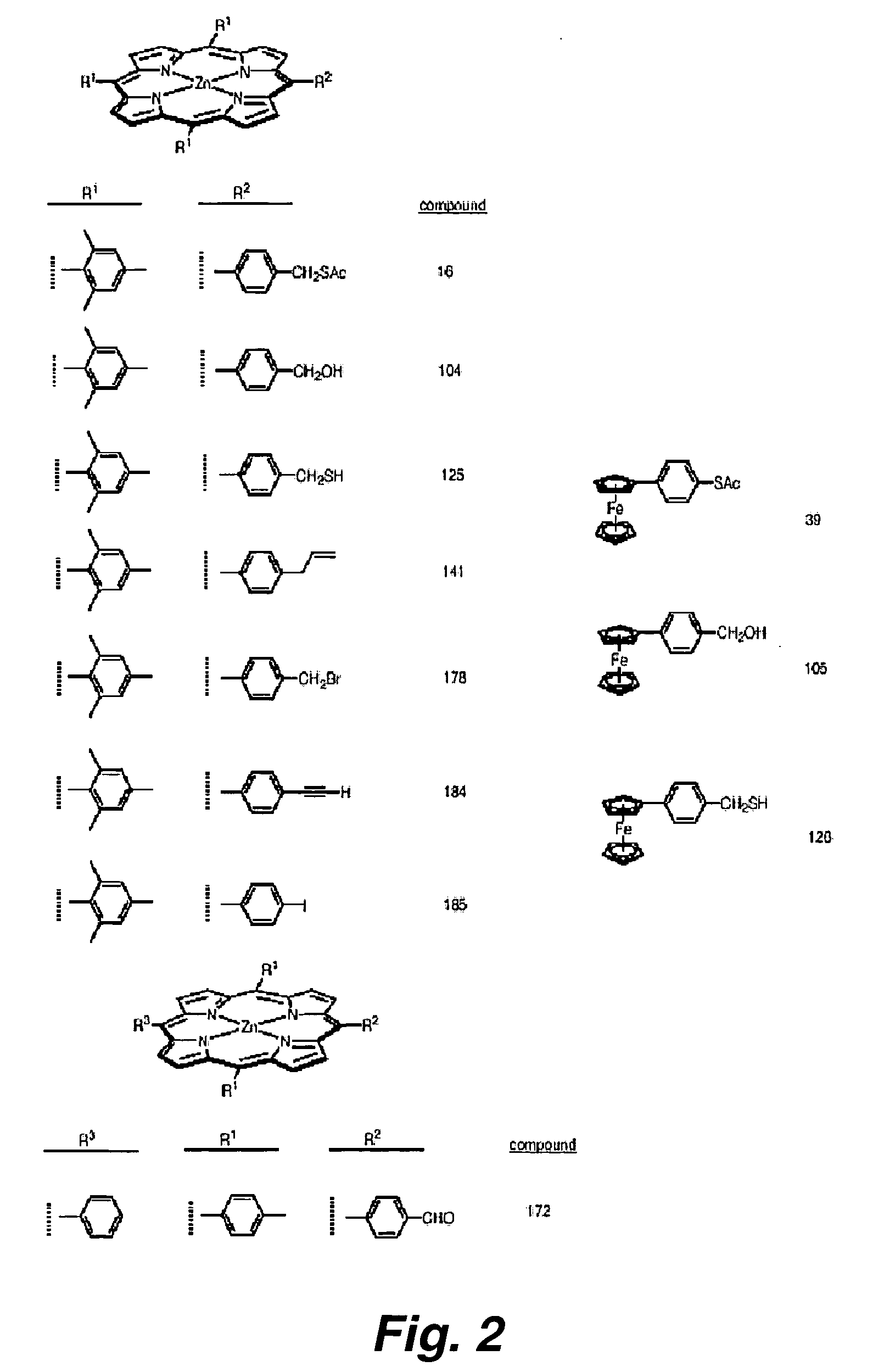
High temperature attachment of organic molecules to substrates
InactiveUS20050048691A1Highly integratedShort timeCell electrodesNanoinformaticsFerroceneMolecular materials
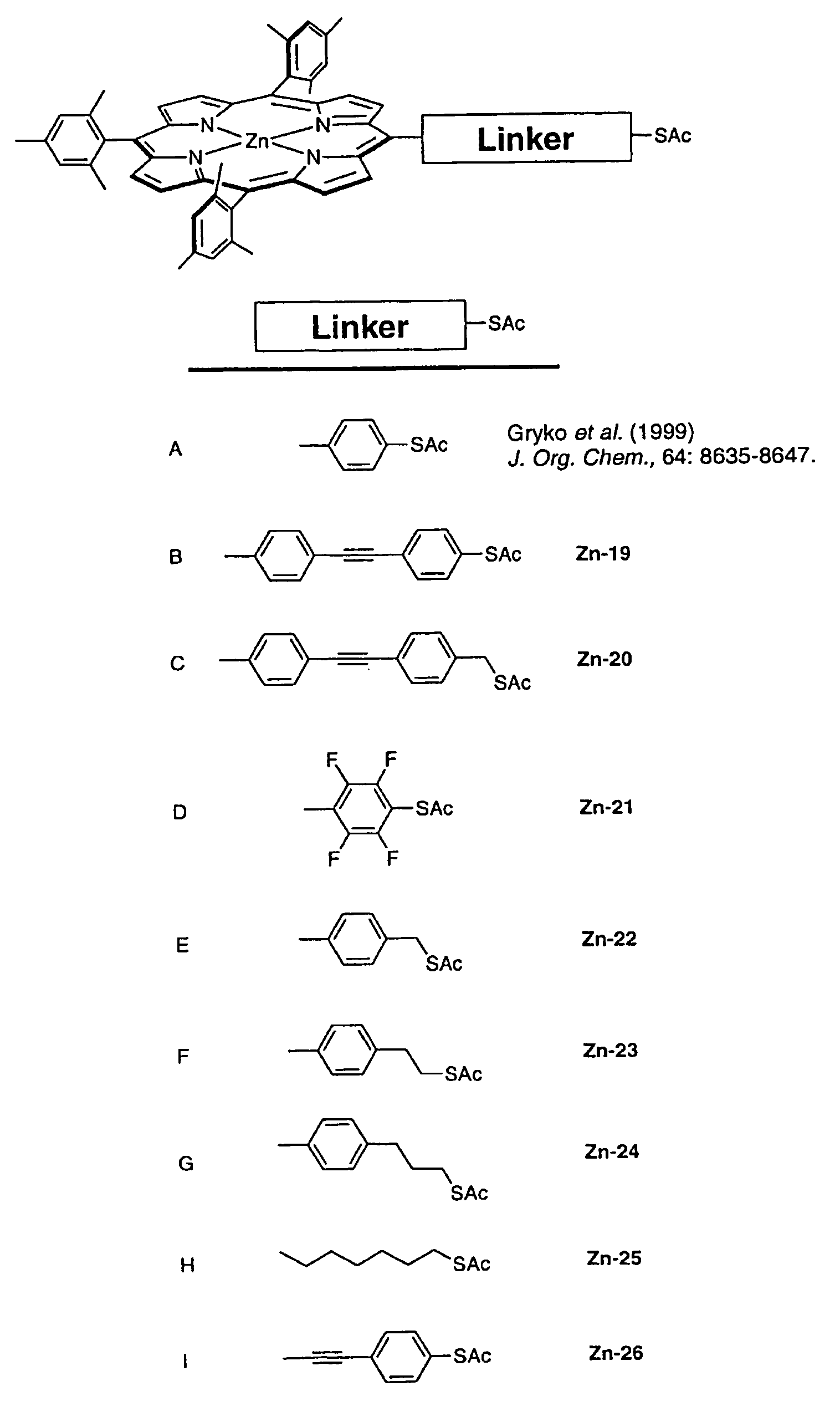
This invention provides a new procedure for attaching molecules to semiconductor surfaces, in particular silicon. The molecules, which include, but are not limited to porphyrins and ferrocenes, have been previously shown to be attractive candidates for molecular-based information storage. The new attachment procedure is simple, can be completed in short times, requires minimal amounts of material, is compatible with diverse molecular functional groups, and in some instances affords unprecedented attachment motifs. These features greatly enhance the integration of the molecular materials into the processing steps that are needed to create hybrid molecular / semiconductor information storage devices.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
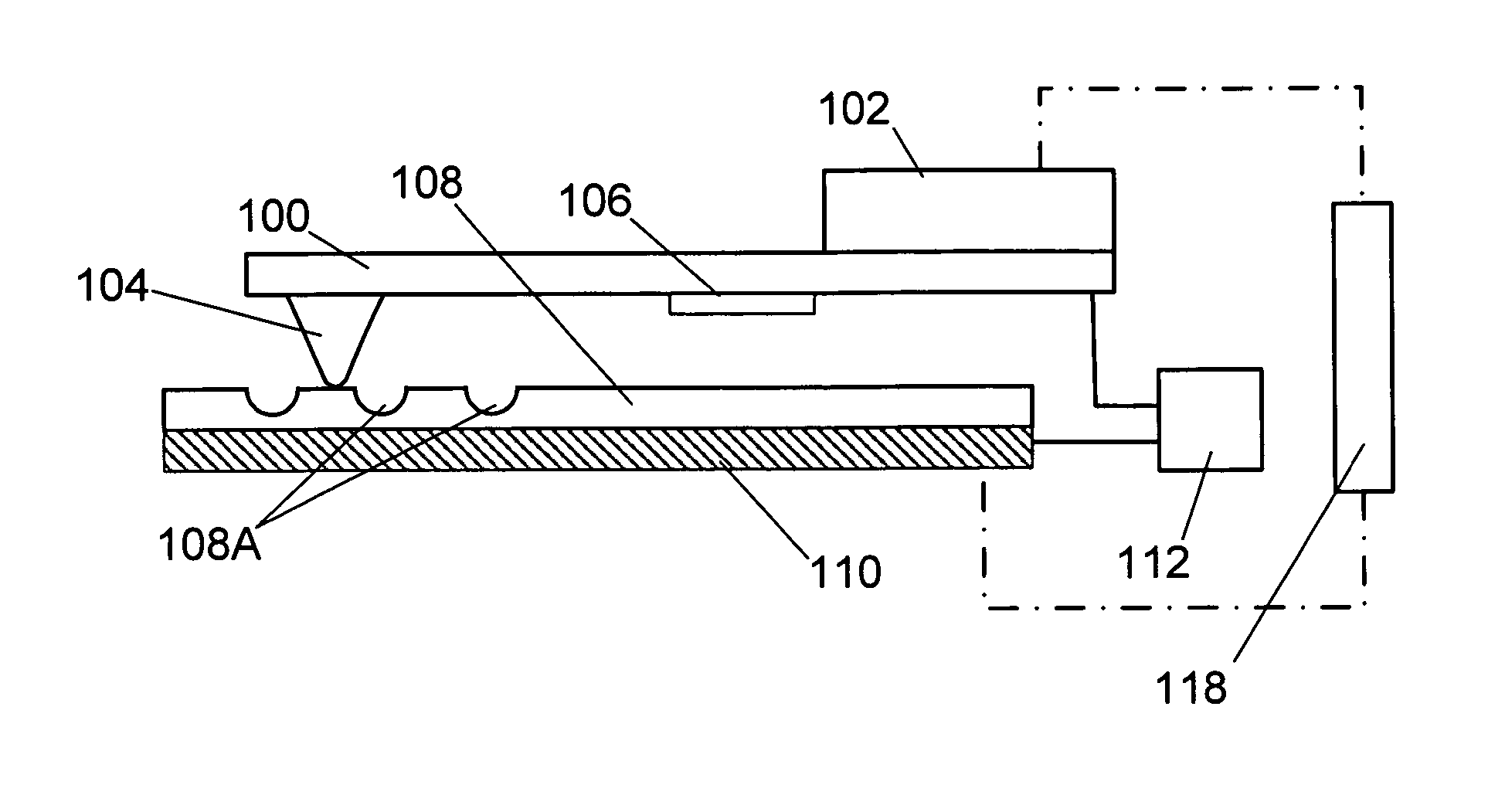
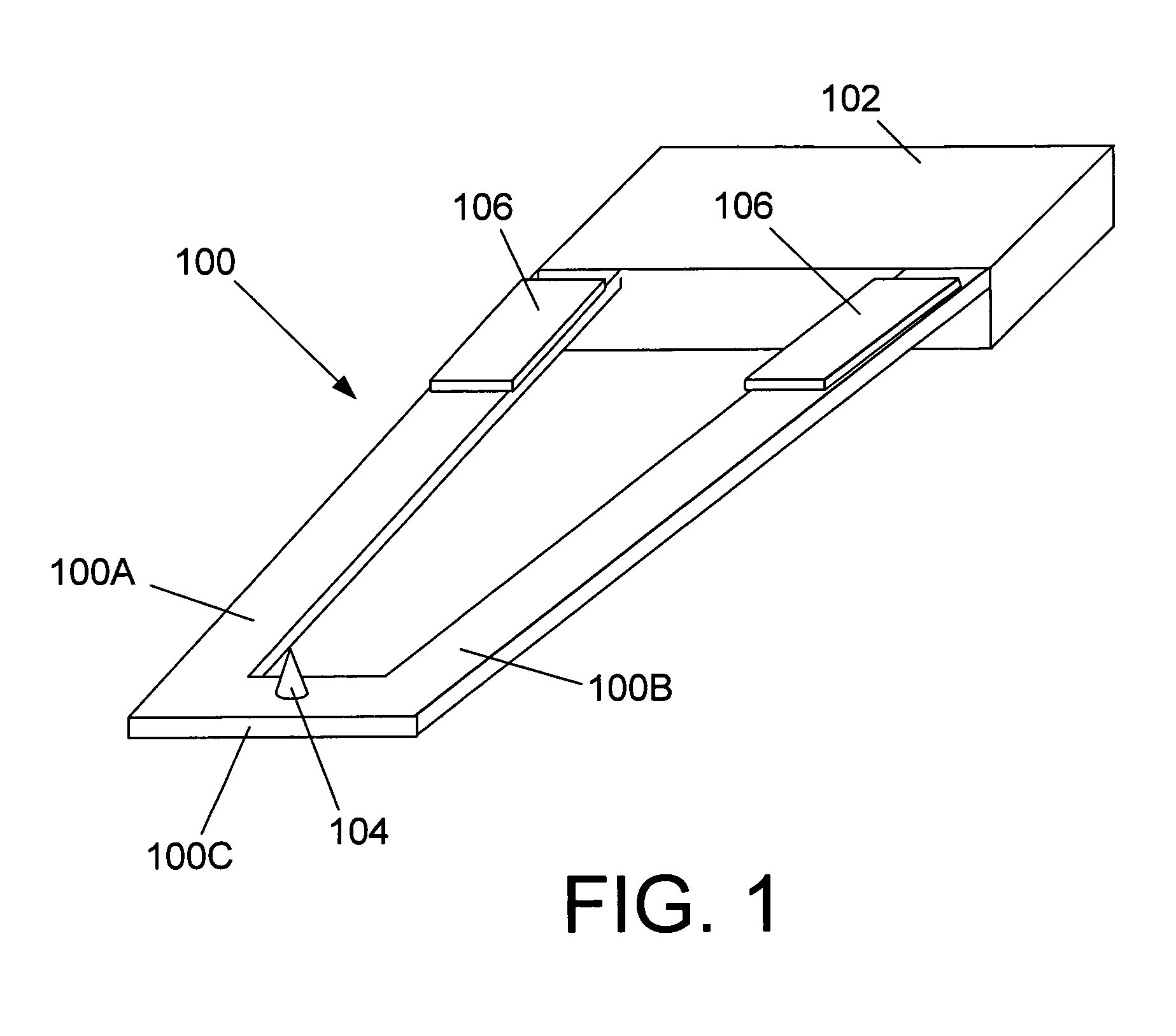
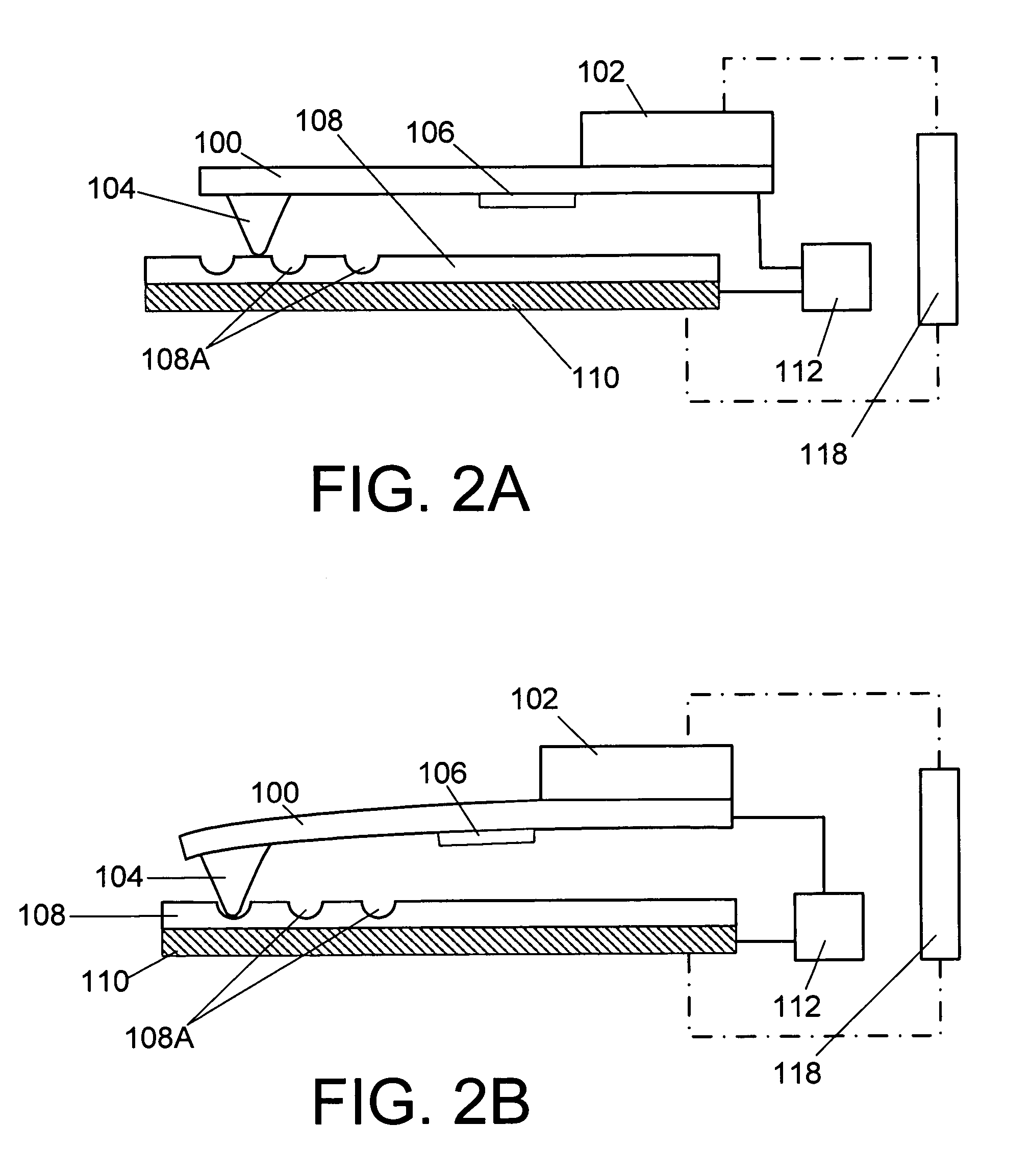
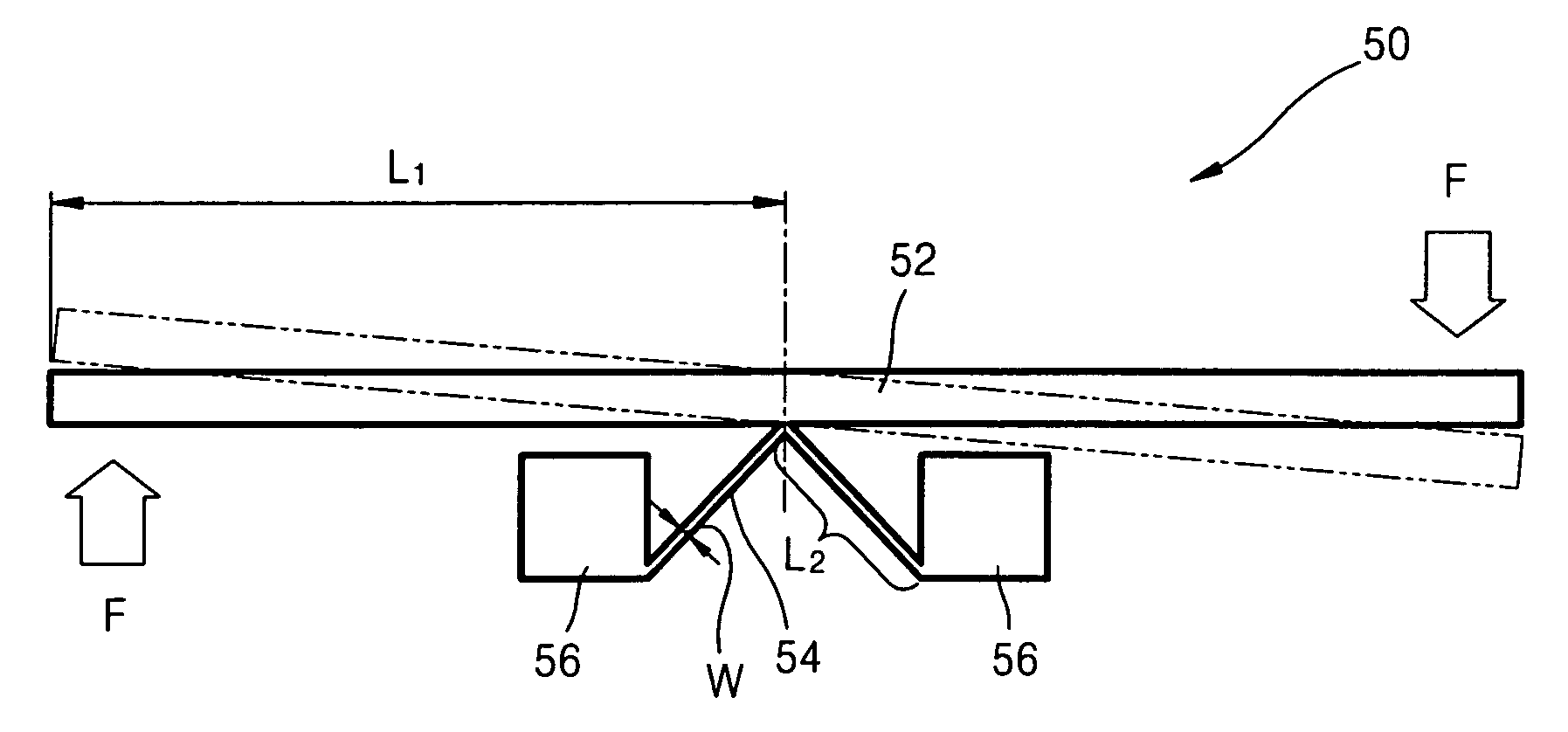
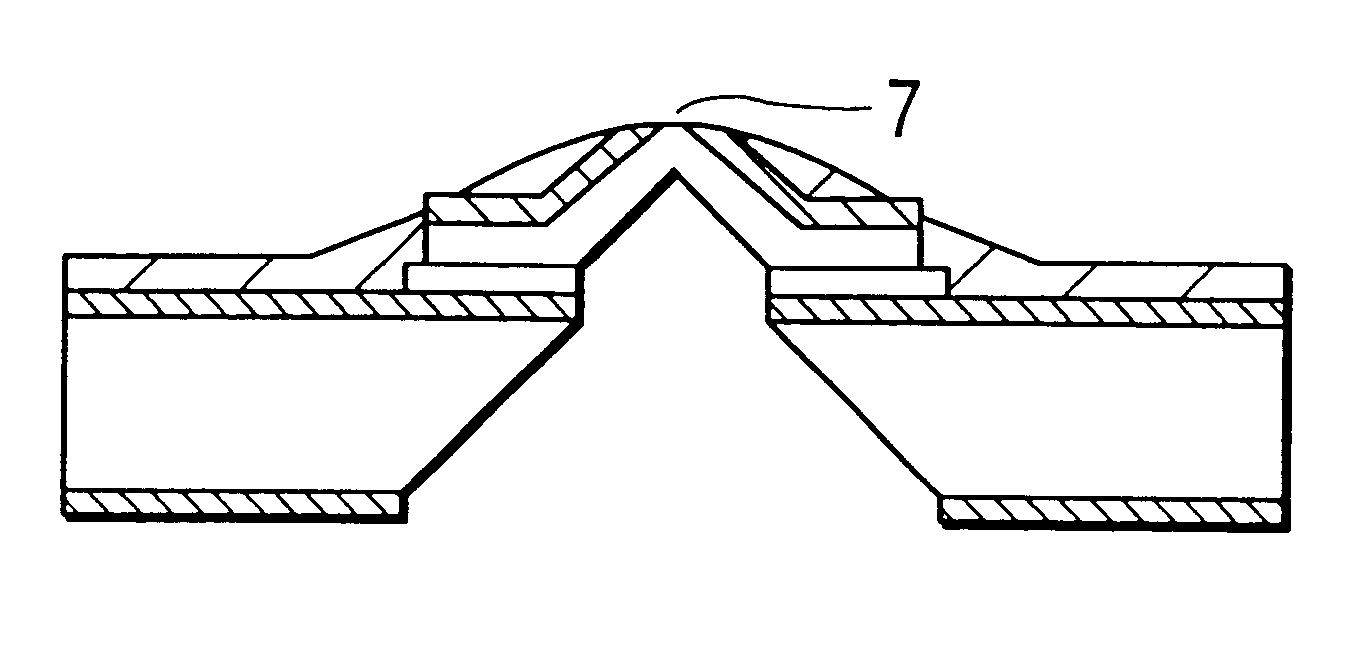
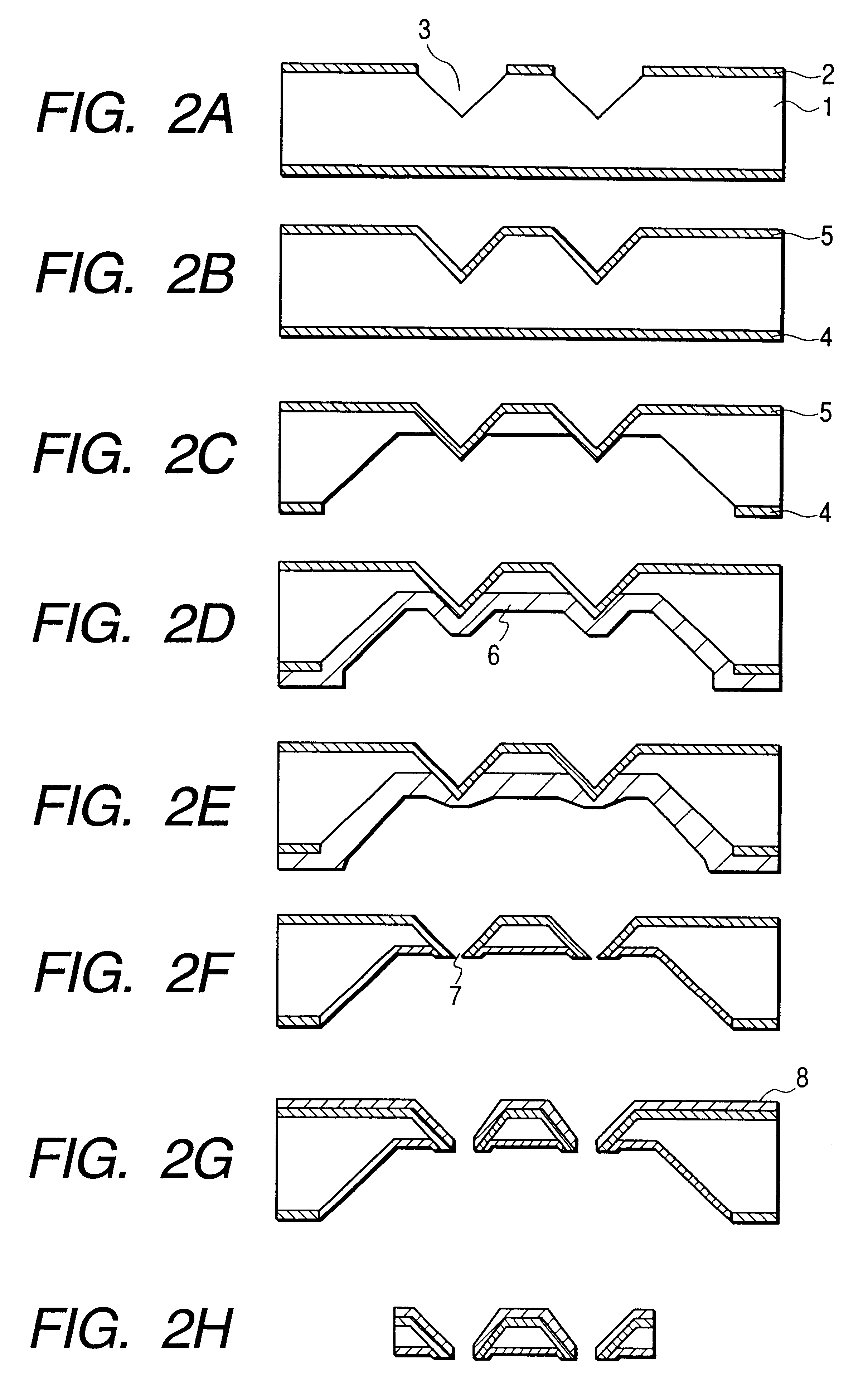
Recording/reproducing head, method of producing the same, and recording apparatus and reproducing apparatus
InactiveUS20050122886A1Easily and efficiently producedRecord data with stabilityElectrostatic charge injection carrier recordingVariable capacitance carrier recordingComputer hardwareHead parts
A recording / reproducing head for performing at least one of a record operation of recording information onto a dielectric recording medium and a reproduction operation of reproducing the information from the dielectric recording medium, the recording / reproducing head provided with: a support member which extends in a longitudinal direction of the recording / reproducing head; and a projection portion which is mounted on the support member such that a tip of the projection portion faces the dielectric recording medium, the projection portion having a ridge-line on the tip, the projection portion being capable of contacting the dielectric recording medium at one point on the ridge-line.
Owner:PIONEER CORP
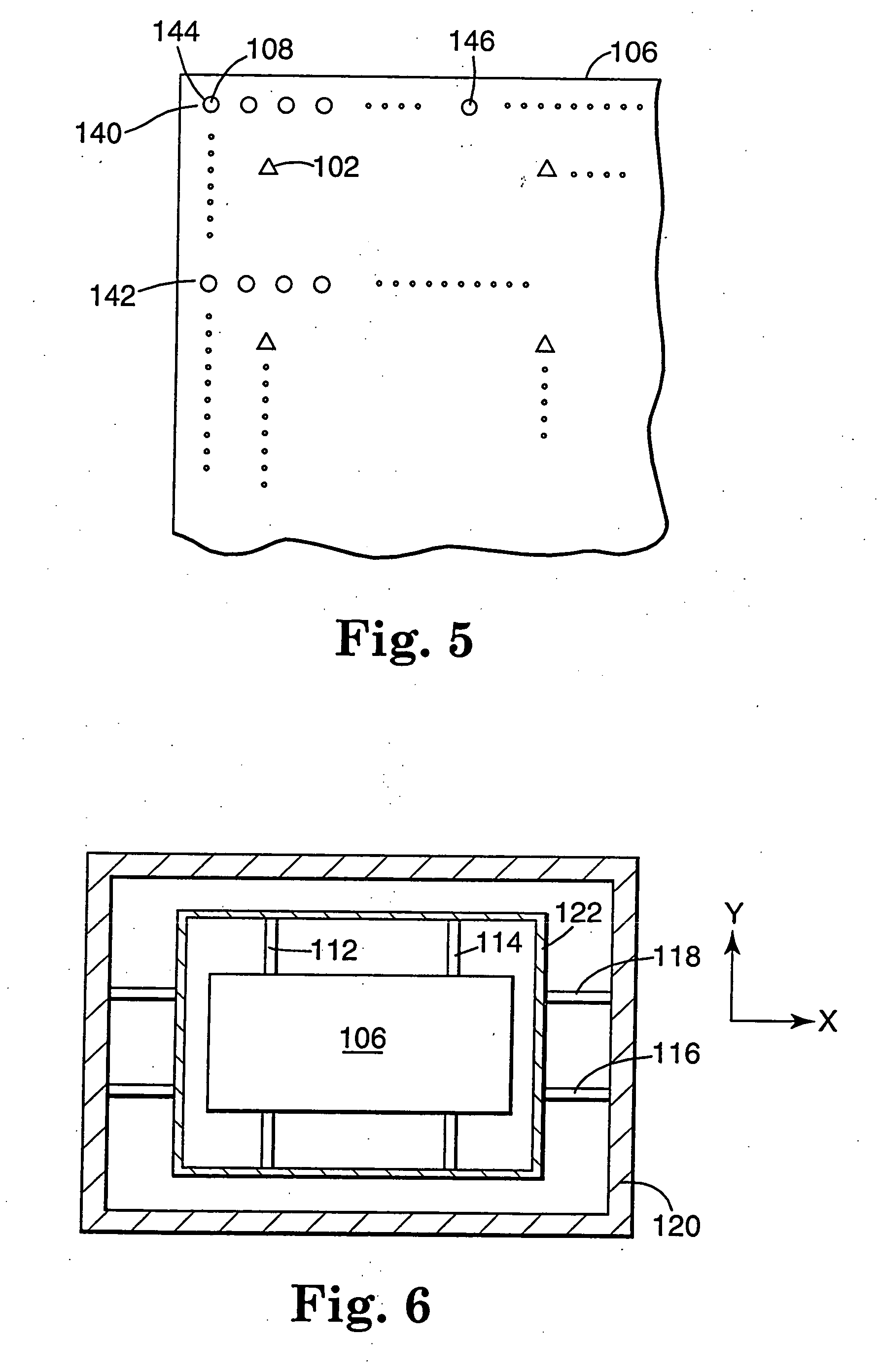
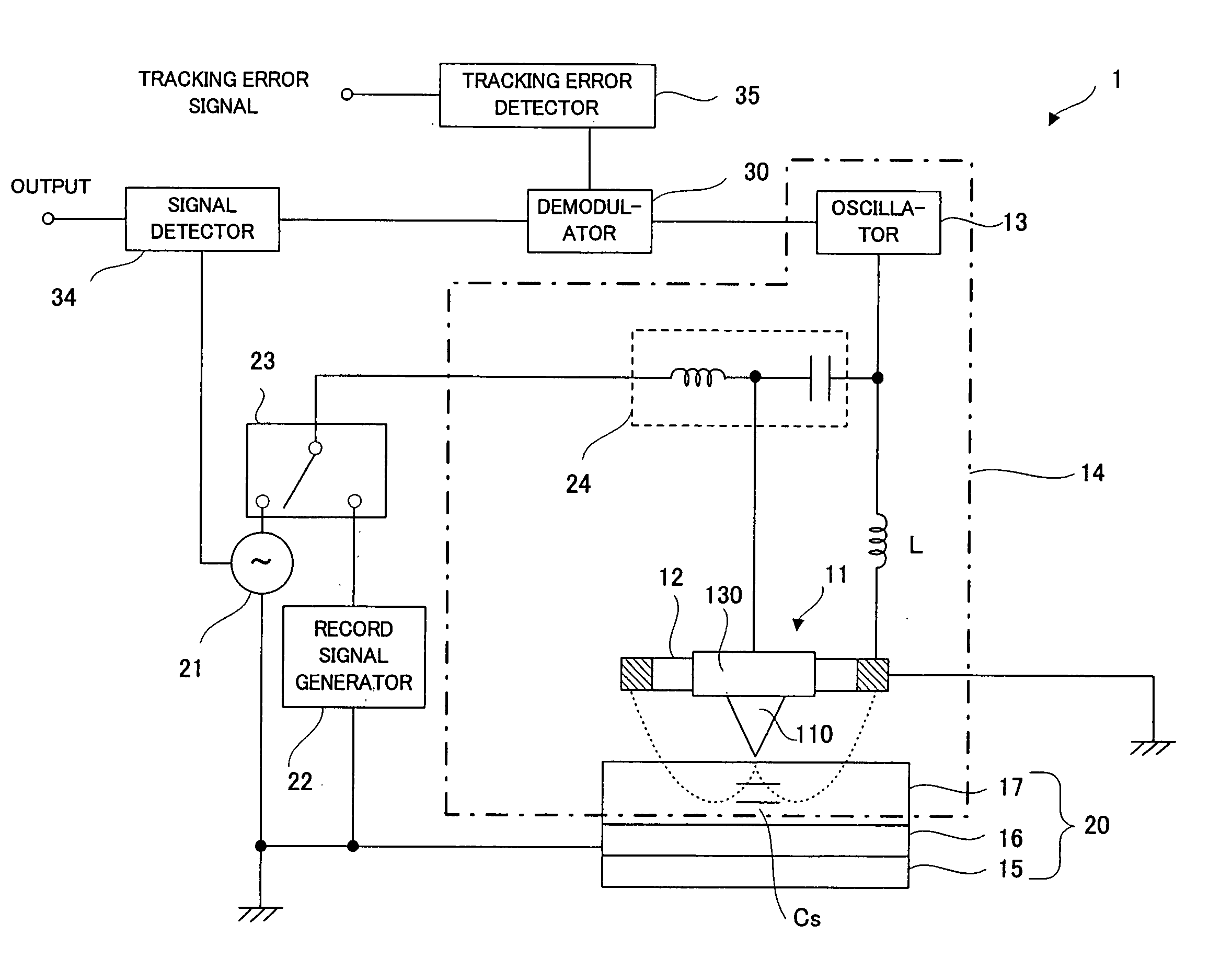
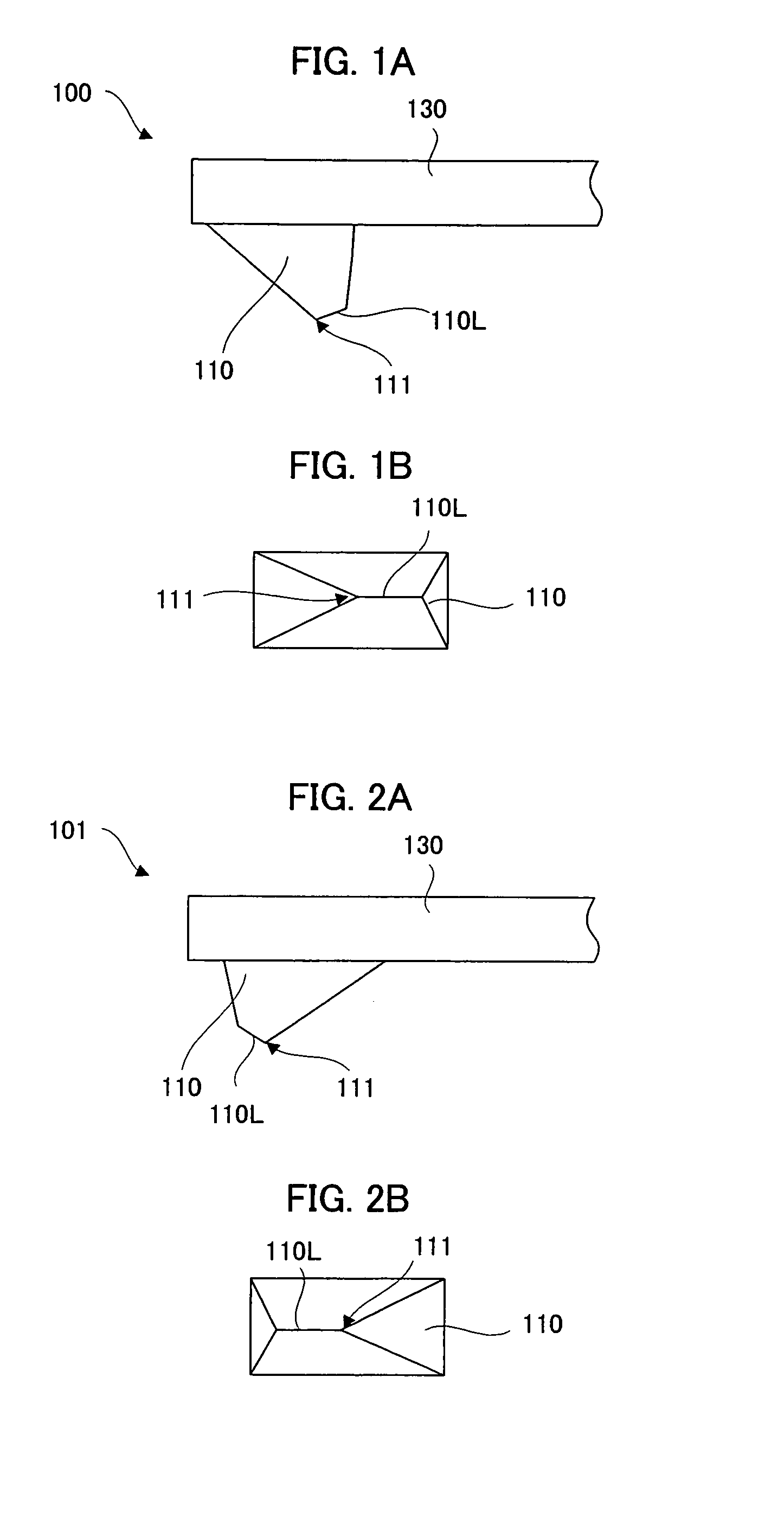
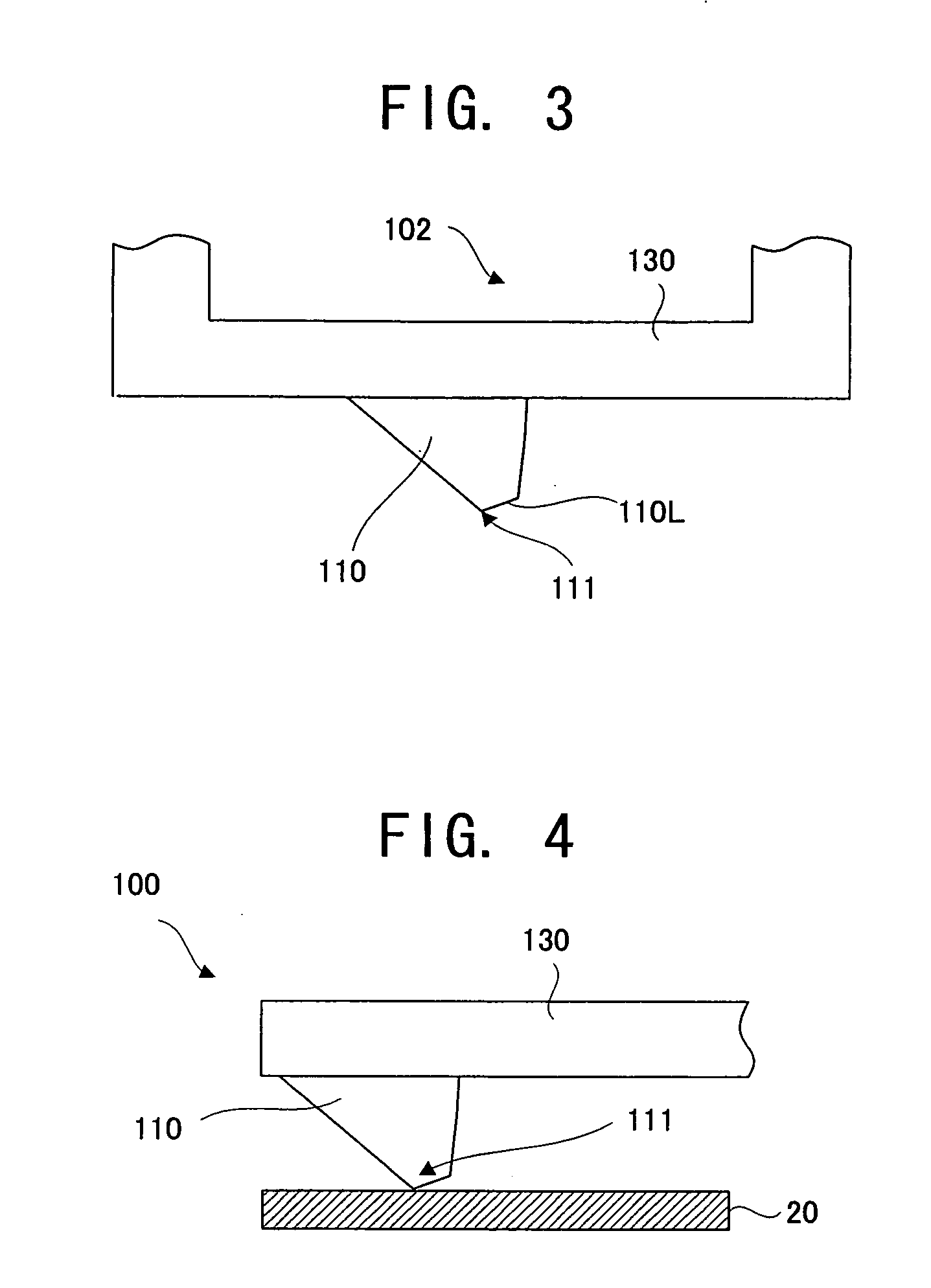
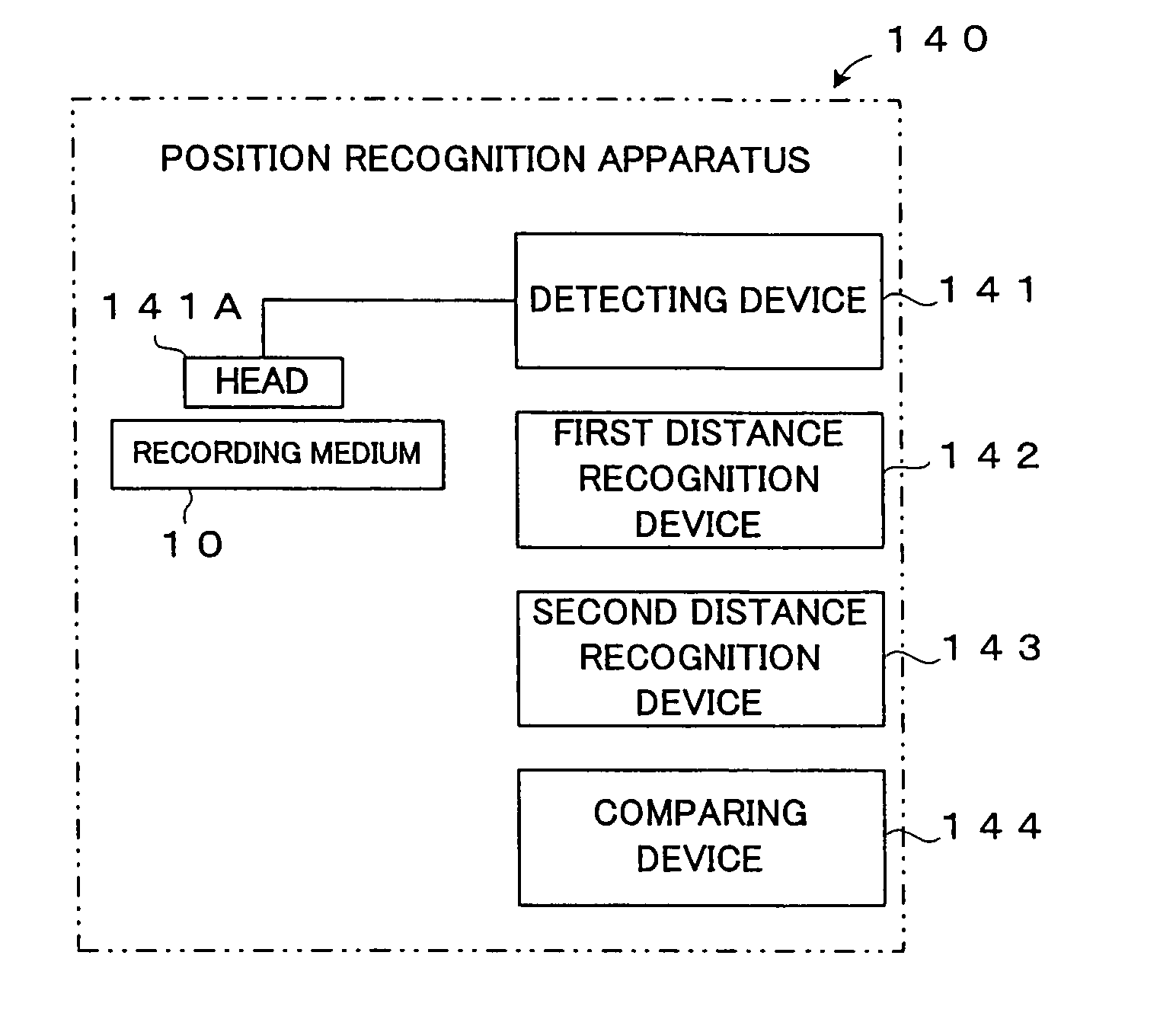
Recording medium having position recognition structure, and position recognition apparatus and method
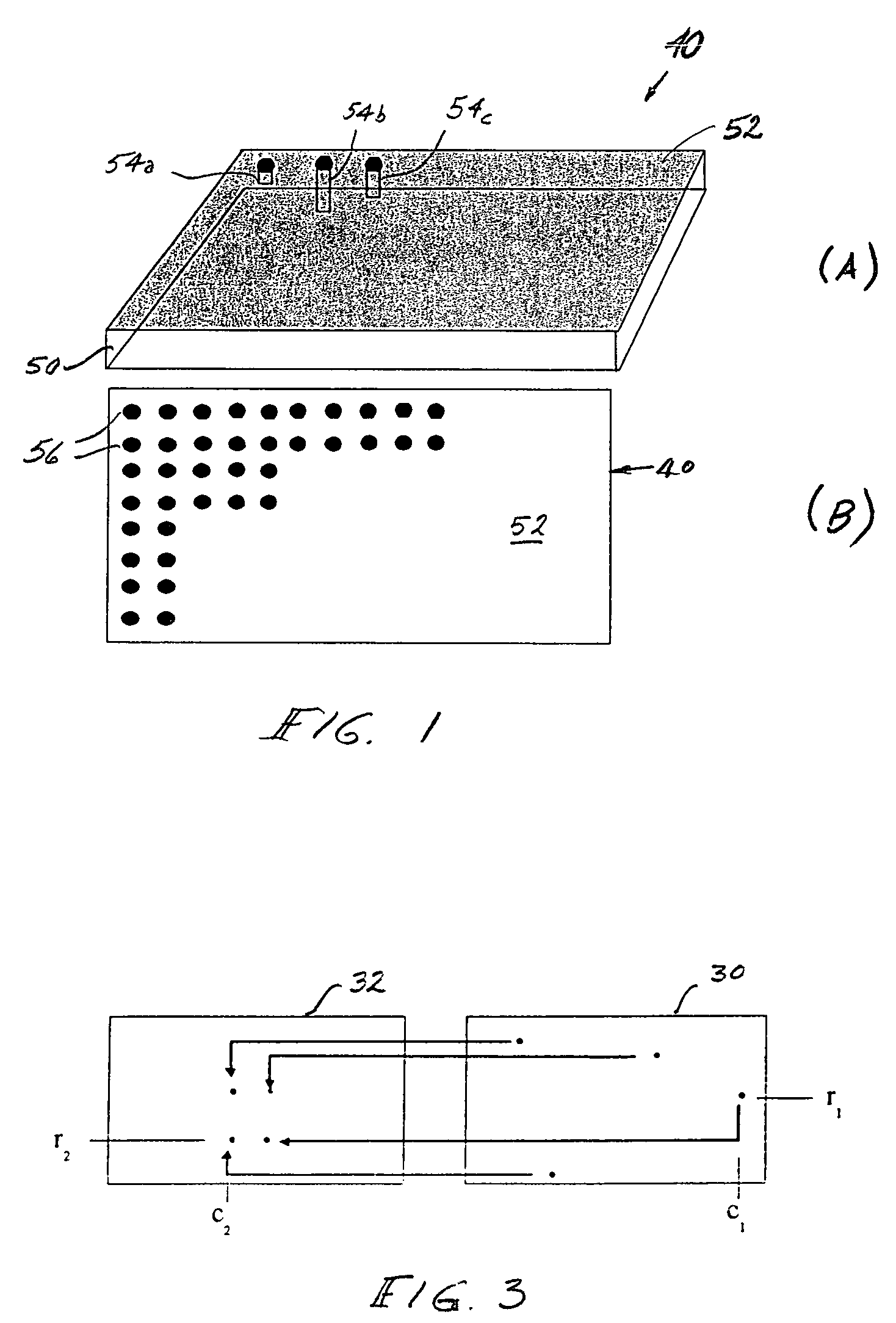
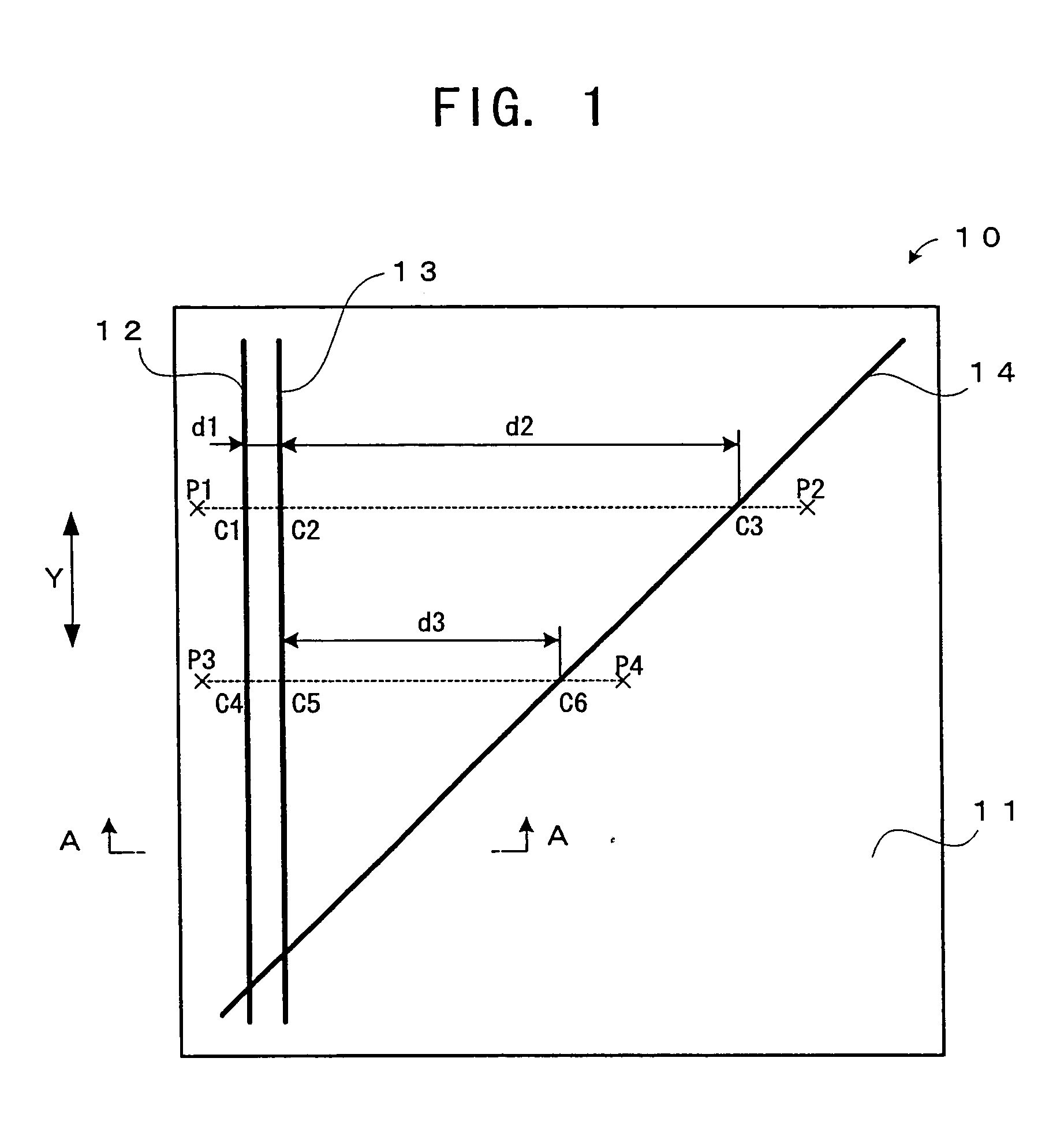
InactiveUS20050047288A1Accurate identificationShorten the length of timeFilamentary/web record carriersNanoinformaticsComputer graphics (images)Scan line
Position information is formed on a recording surface 11 of a recording medium 10. The position information is constructed from first line segments, which are parallel to each other, and a second line segment, which crosses the first line segments. On the basis of a distance between (i) an intersection C1 of one of the first line segment and a scan line and (ii) an intersection C2 of another of the first line segments and the scan line, the intersection C2 and an intersection C3 of the second line segment and the scan line are measured or calculated. By this, a position of a head in a Y direction is recognized.
Owner:PIONEER CORP
Recording medium, recording apparatus and recording method
InactiveUS6850480B1Improve recording densityImprove conductivityElectrostatic charge injection carrier recordingIndividual molecule manipulationCharge injectionEngineering
The present invention provides a recording medium having a plurality of charge accumulating regions each containing a first material capable of accumulating an electric charge and a photoconductive region containing a second material whose conductivity is increased by light absorption, a recording apparatus including such a recording medium, and a method recording information on such a recording medium. In the present invention, information is recorded on the recording medium by irradiating the photoconductive region with light and by injecting an electric charge into the charge accumulating region via that portion of the photoconductive region which is irradiated with light.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
High density memory device
InactiveUS20060209587A1Easy constructionEasy to manufactureMaterial nanotechnologyNanoinformaticsFault toleranceChemical synthesis
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
Apparatus for use in magnetic-field detection and generation devices
InactiveUS6211673B1Improve spatial resolutionWeaken influenceNanomagnetismNanoinformaticsMagnetic storageEngineering
A magnetic-field-detecting and / or generating apparatus comprises a non-ferromagnetic tip with a longitudinal member of ferromagnetic material embedded in the tip. Further, magnetic-shield means is arranged around the tip. At the end of the longitudinal member a magnetic-field device is arranged. The same principle can be applied to read / write heads for use in magnetic-storage devices.
Owner:IBM CORP
High density molecular memory device
InactiveUS7061791B2Suitable mechanical propertyPrevent charge leakageNanoinformaticsSolid-state devicesFault toleranceChemical synthesis
This invention provides novel high density memory devices that are electrically addressable permitting effective reading and writing, that provide a high memory density (e.g., 1015 bits / cm3), that provide a high degree of fault tolerance, and that are amenable to efficient chemical synthesis and chip fabrication. The devices are intrinsically latchable, defect tolerant, and support destructive or non-destructive read cycles. In a preferred embodiment, the device comprises a fixed electrode electrically coupled to a storage medium having a multiplicity of different and distinguishable oxidation states wherein data is stored in said oxidation states by the addition or withdrawal of one or more electrons from said storage medium via the electrically coupled electrode.
Owner:NORTH CAROLINA STATE UNIV +1
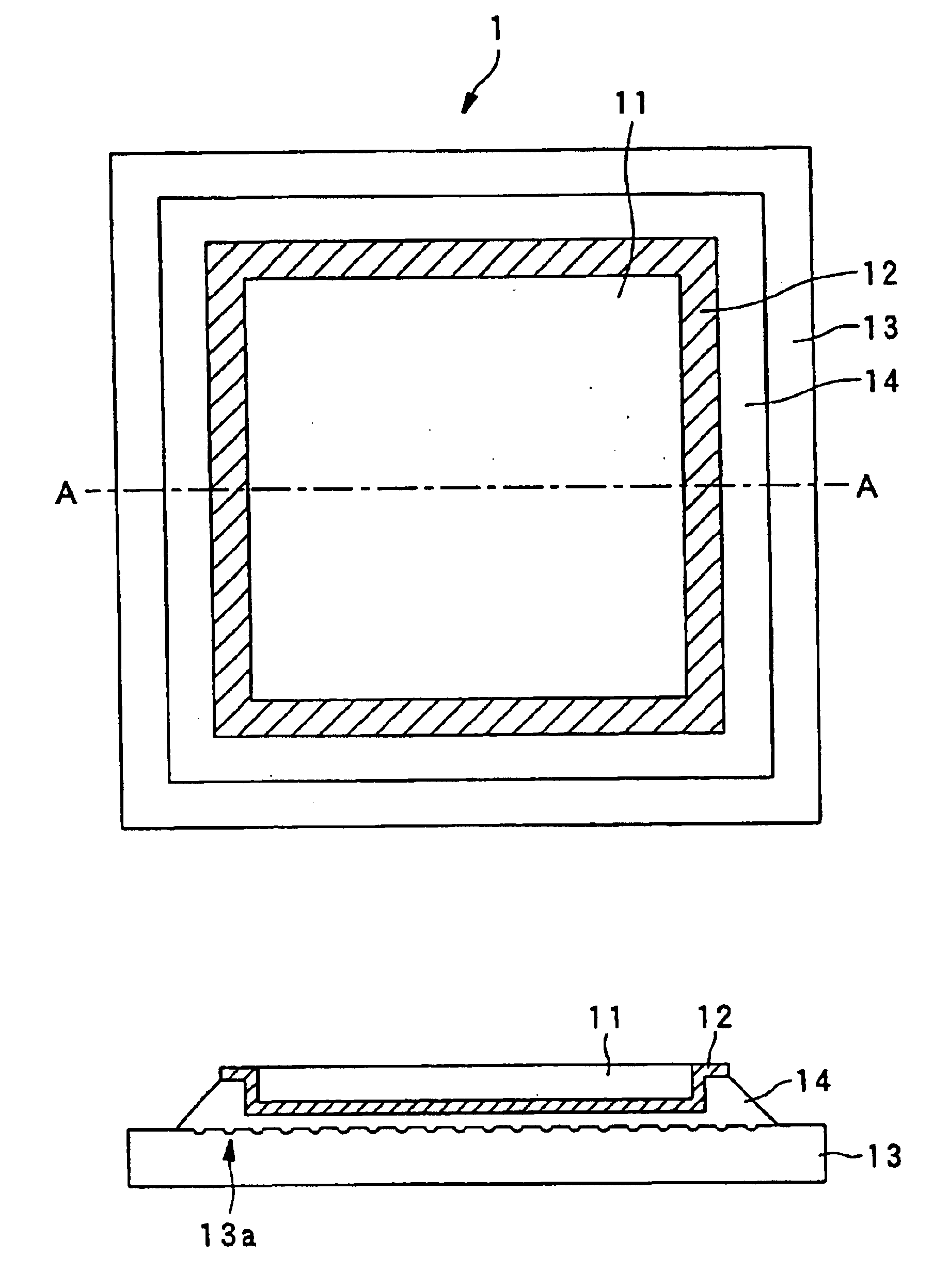
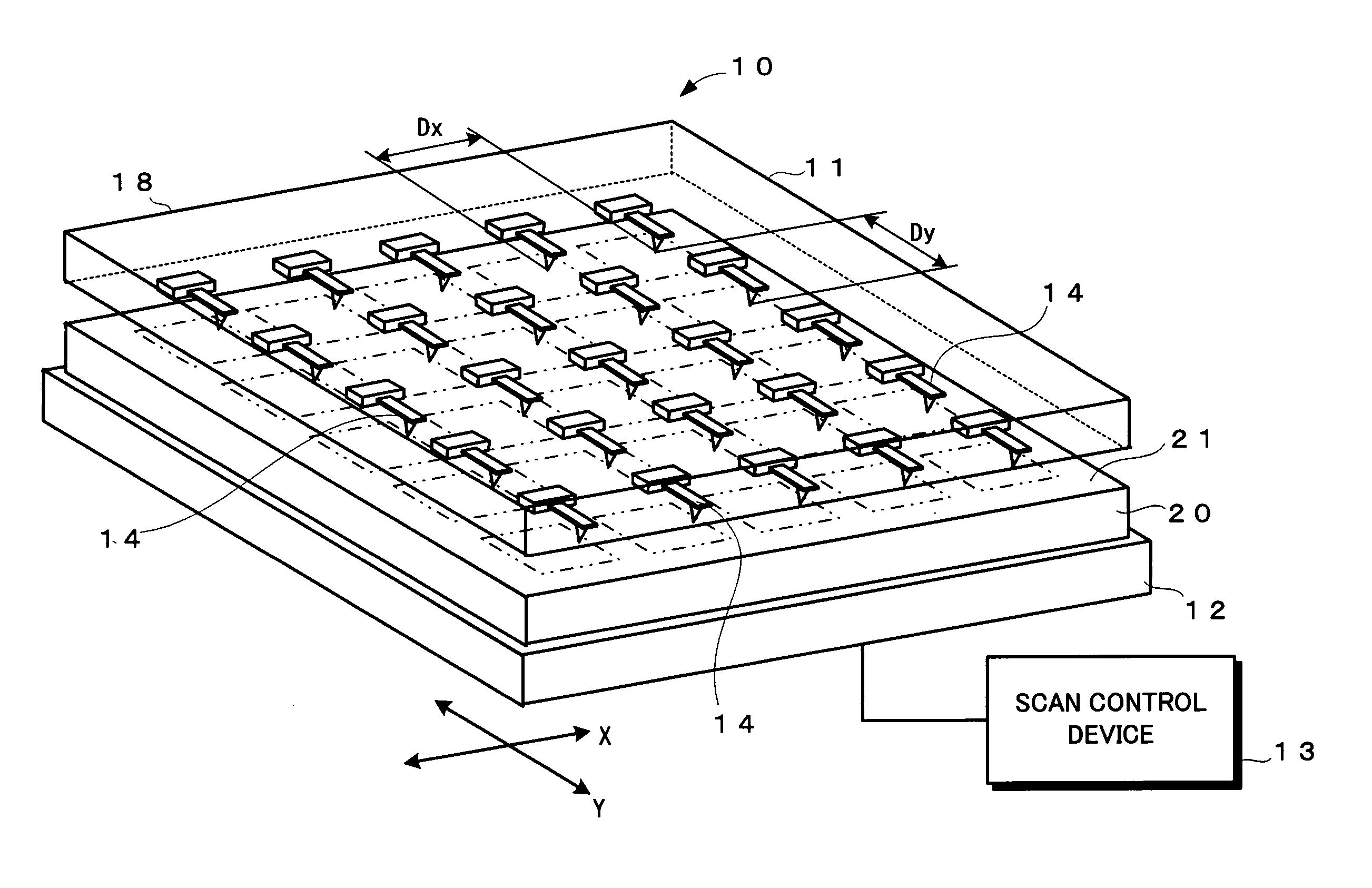
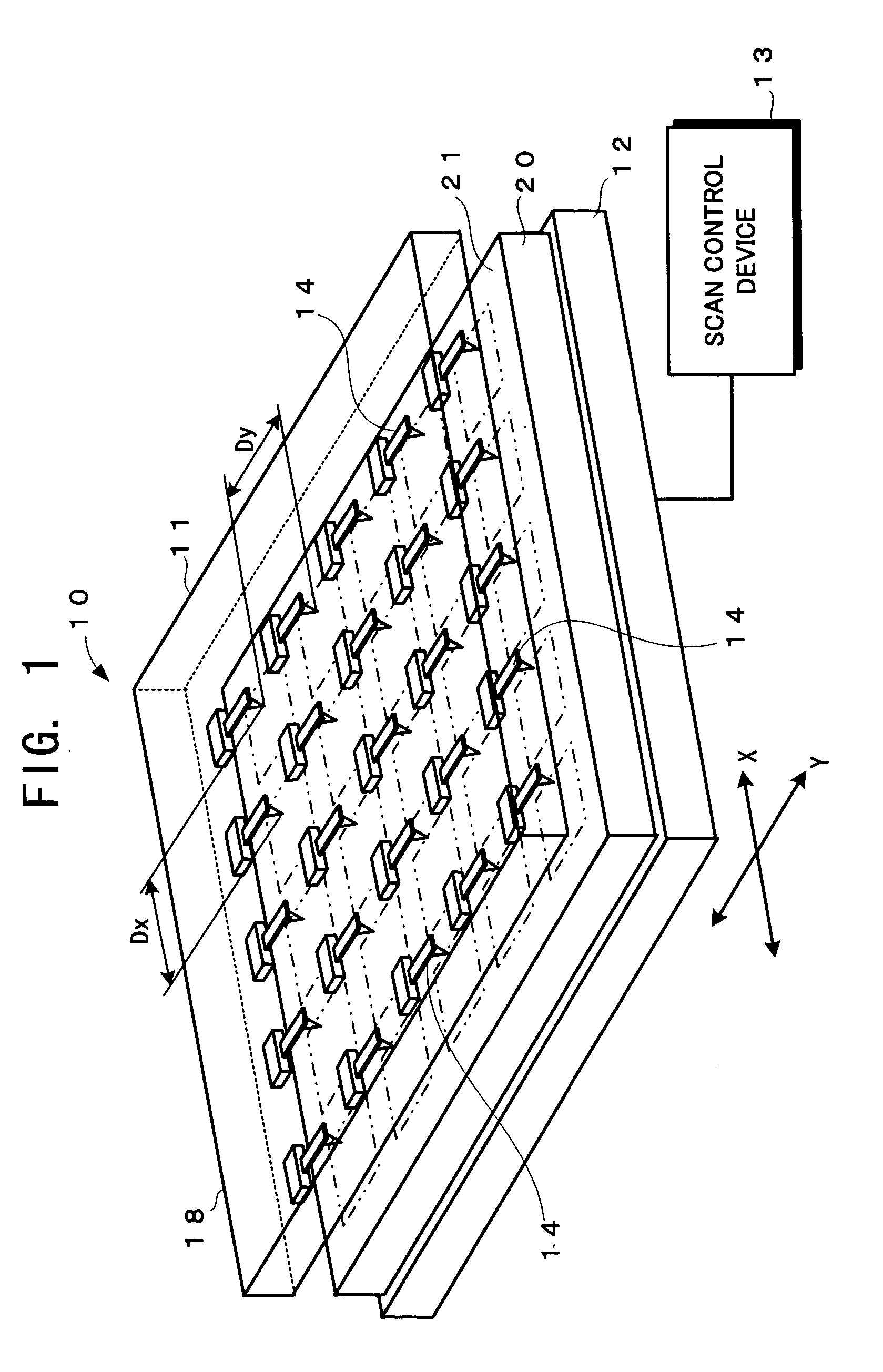
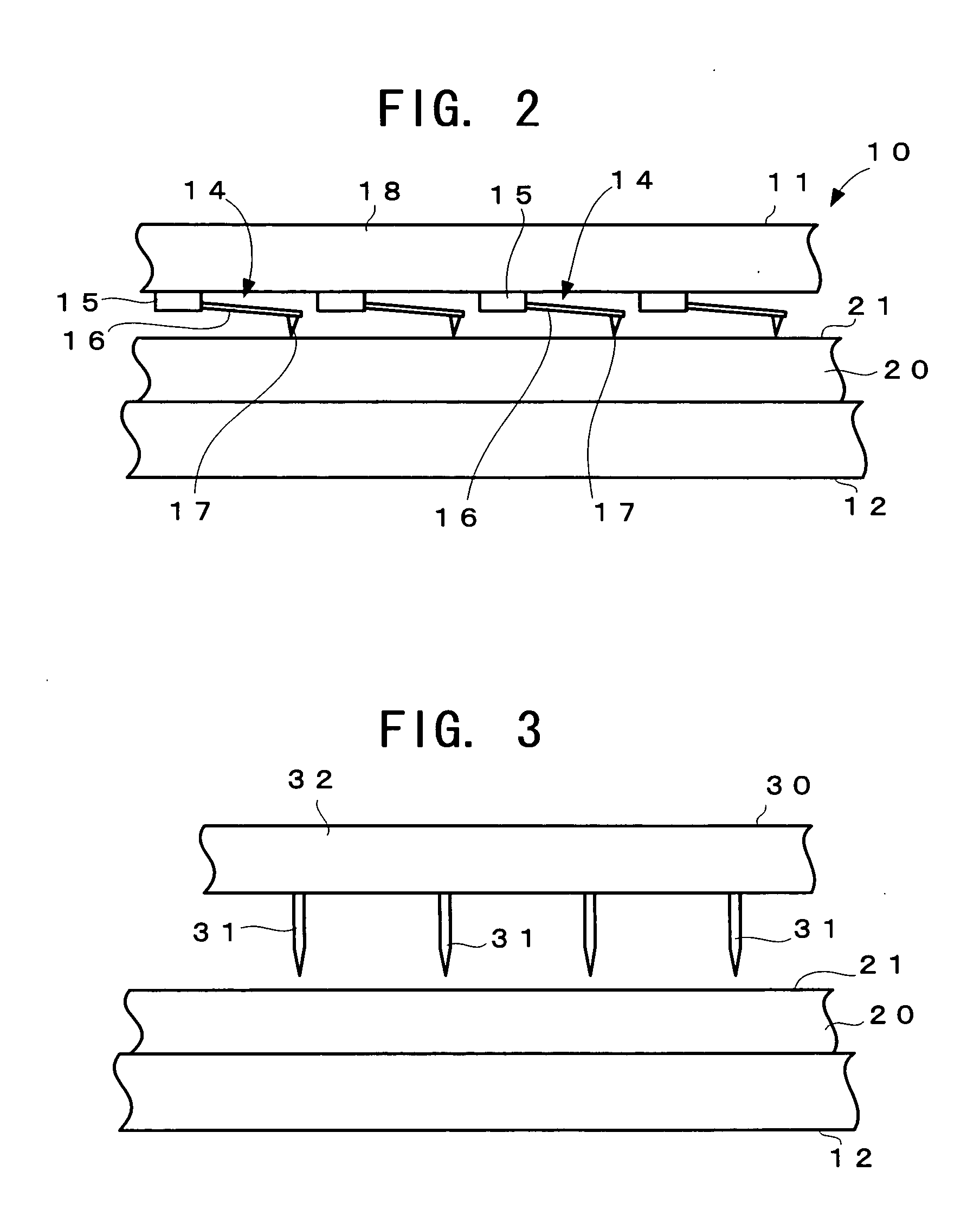
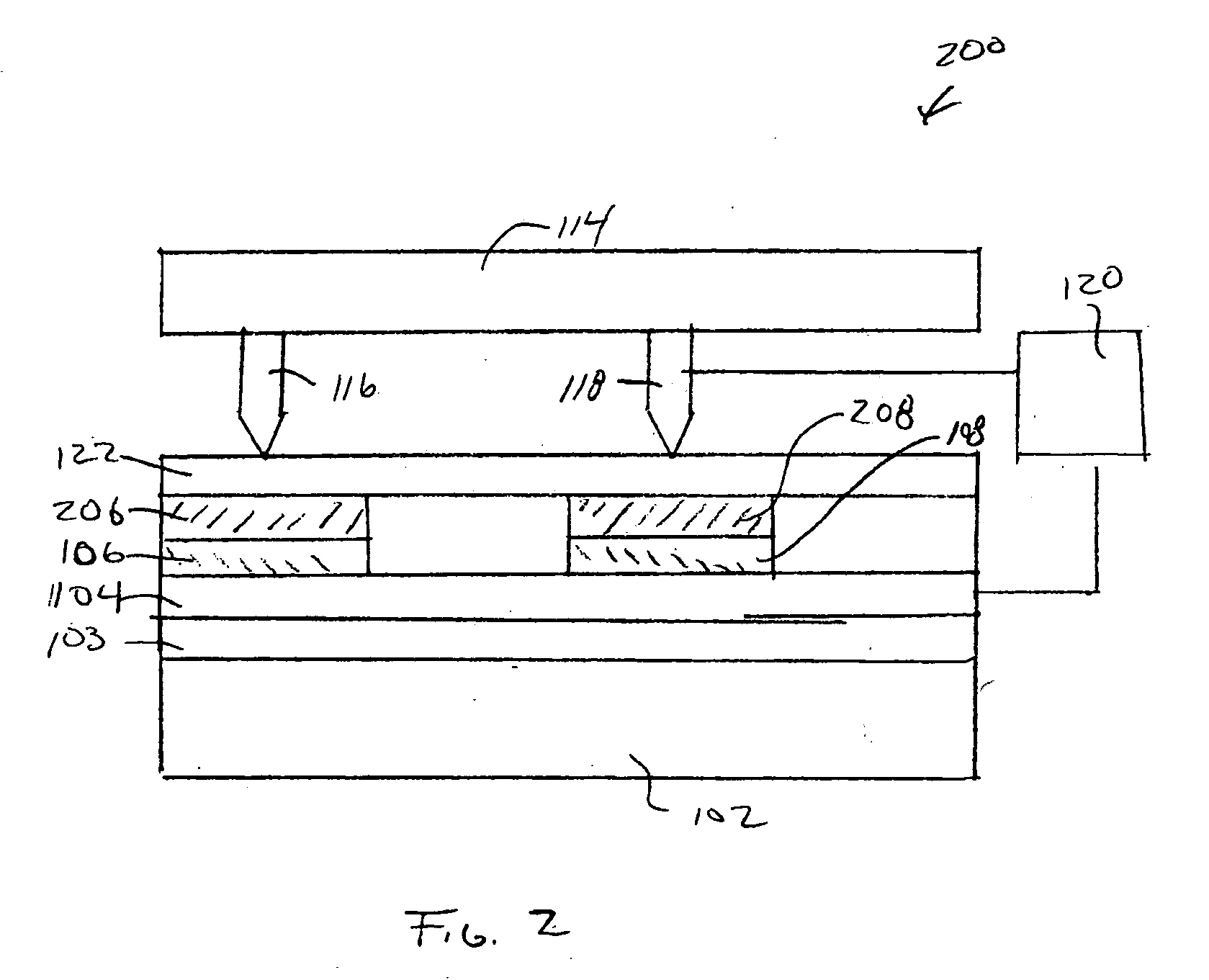
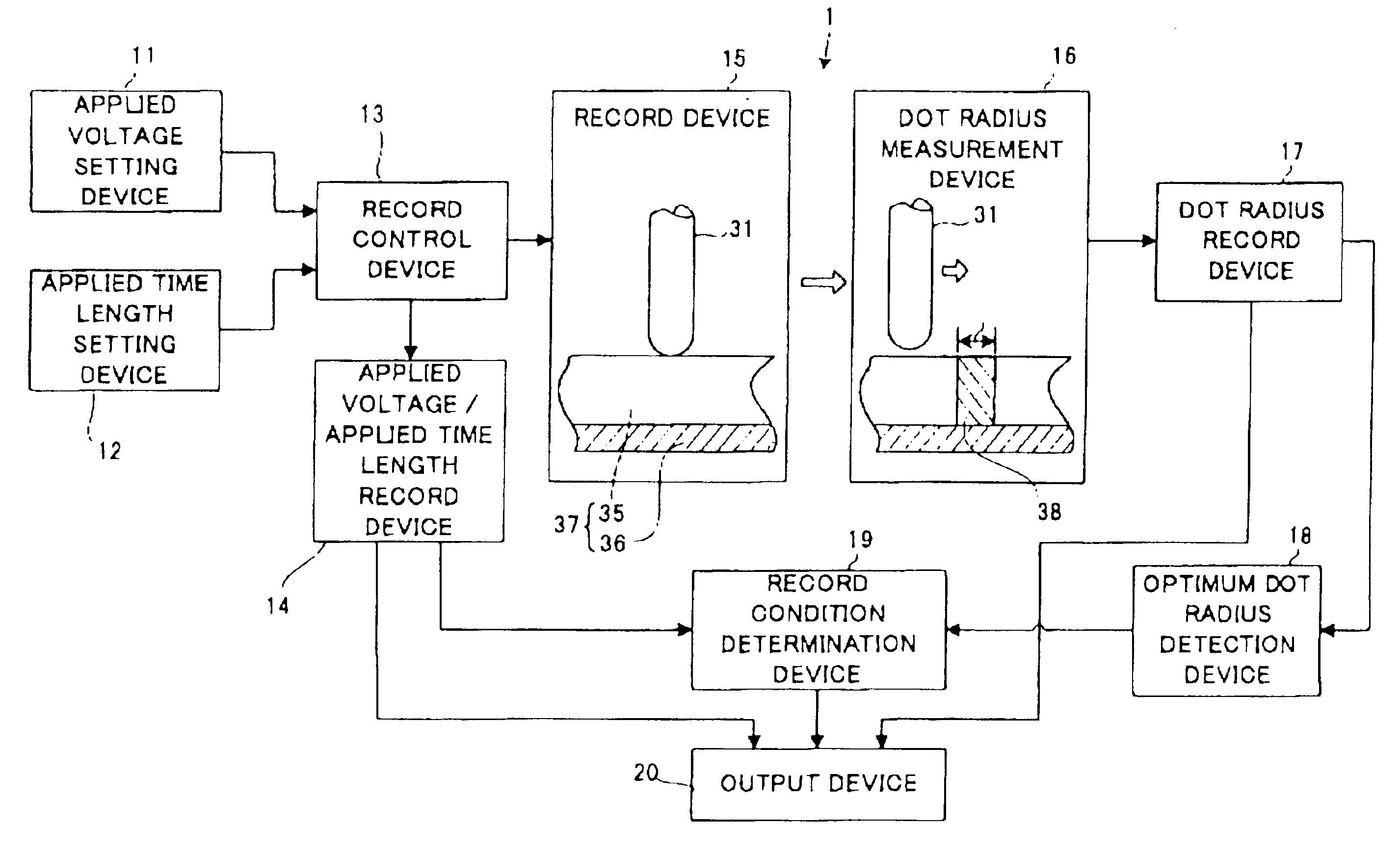
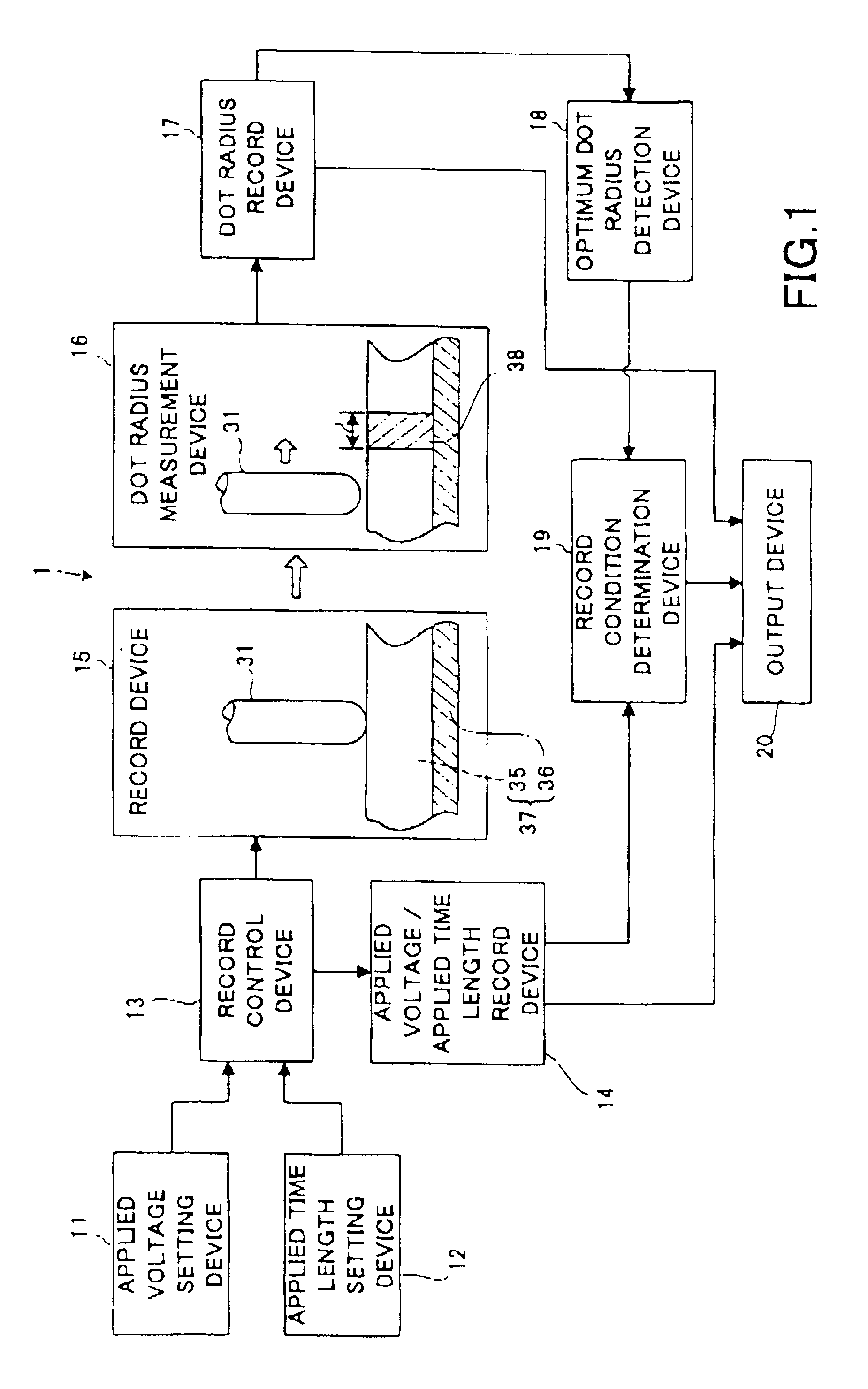
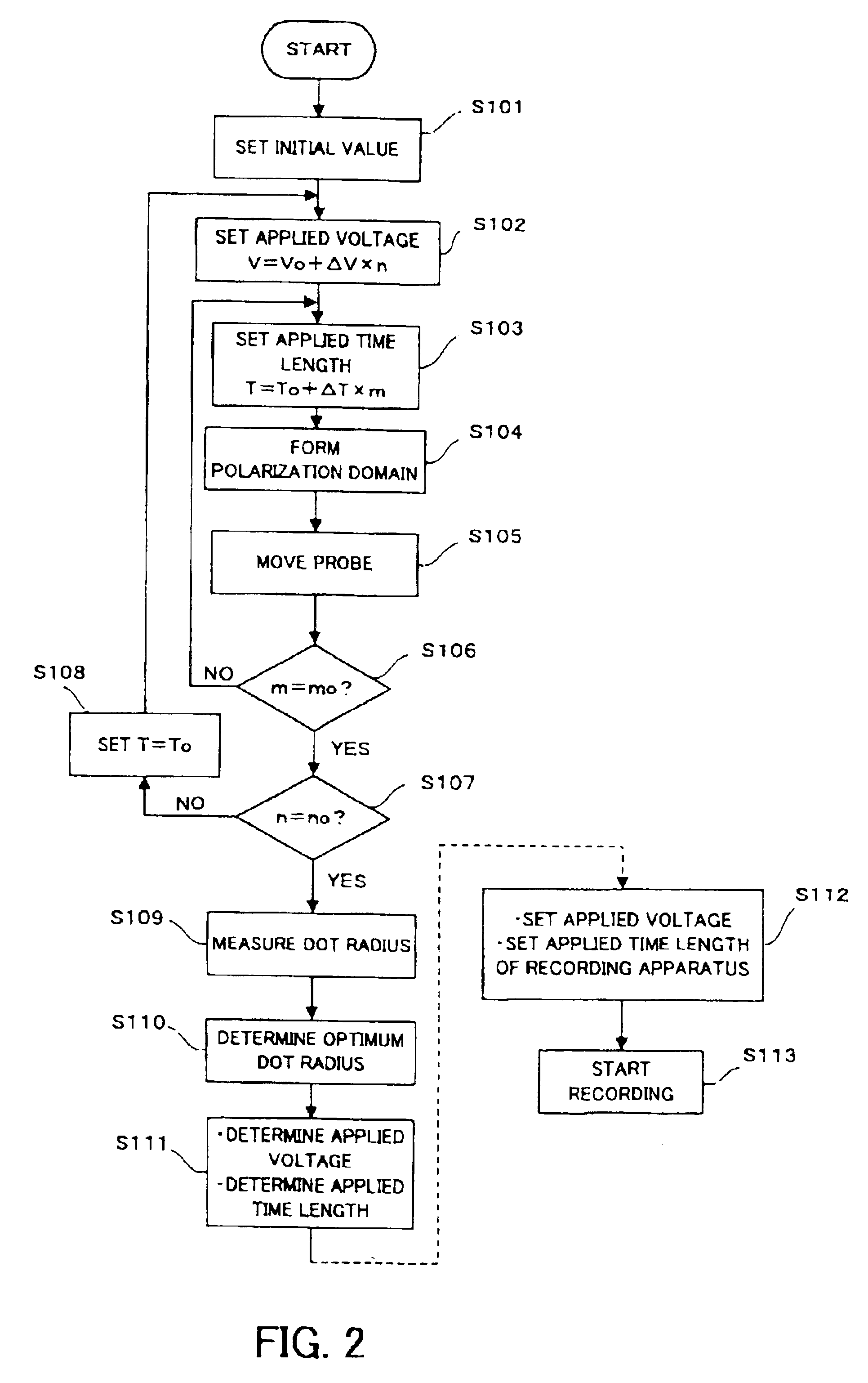
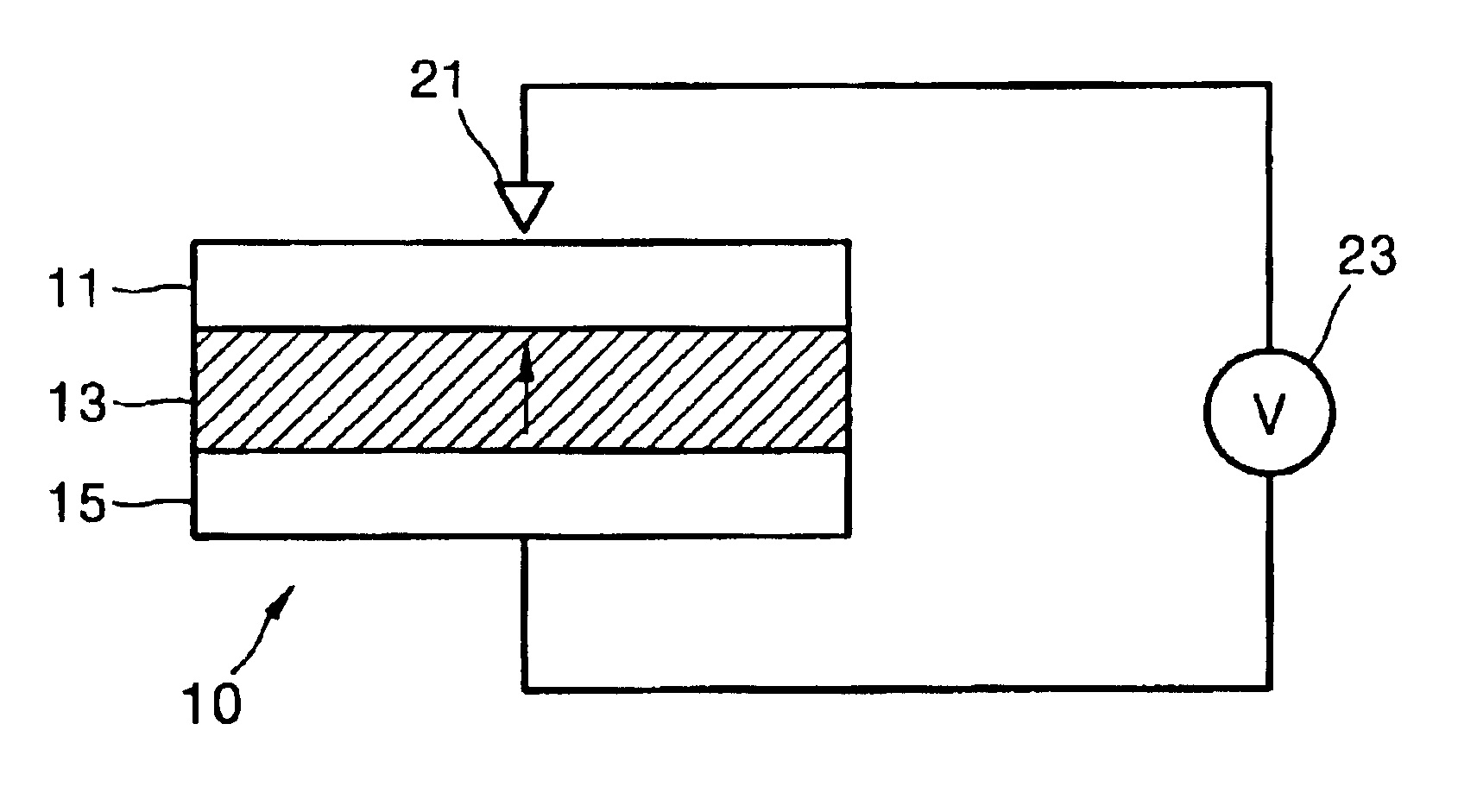
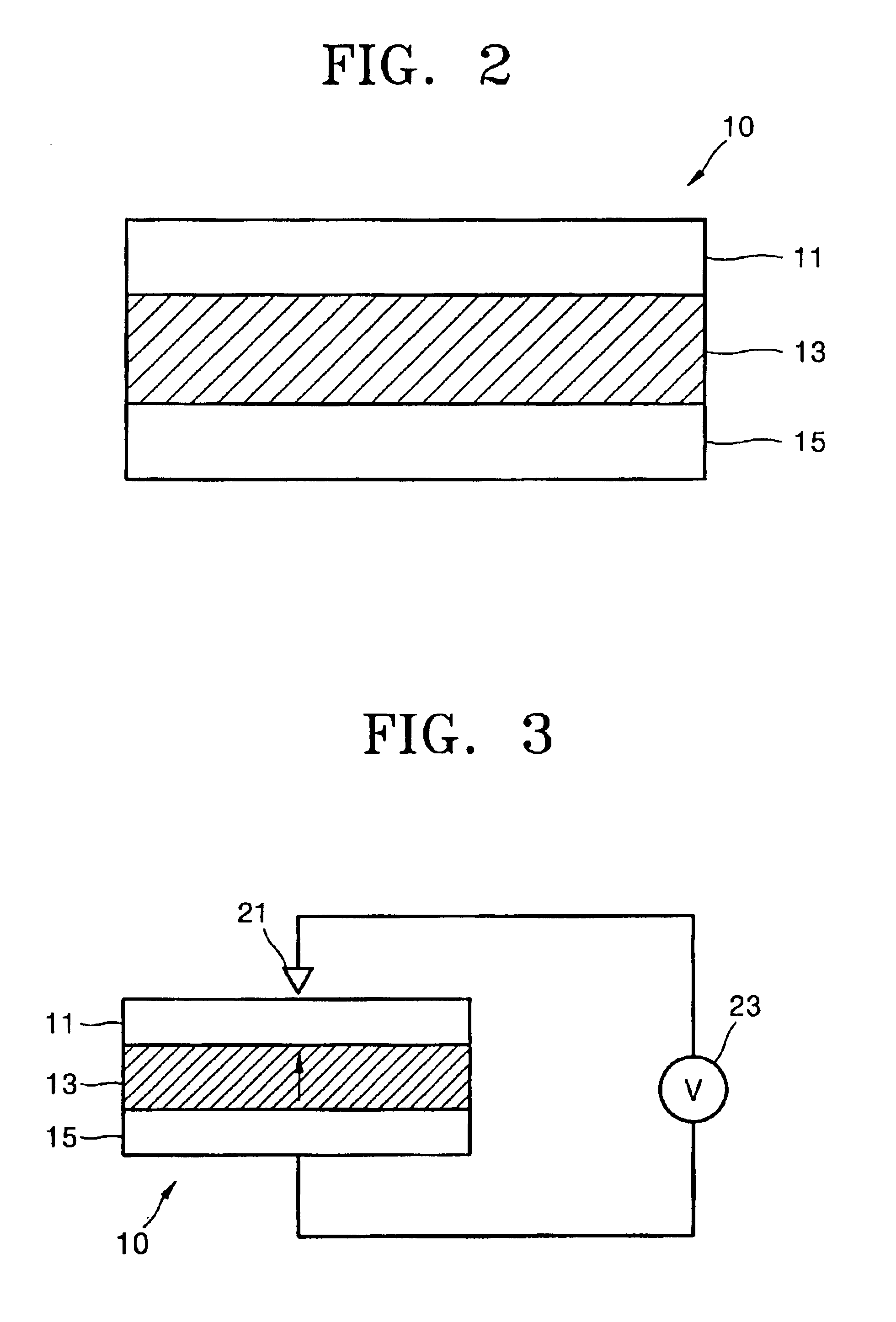
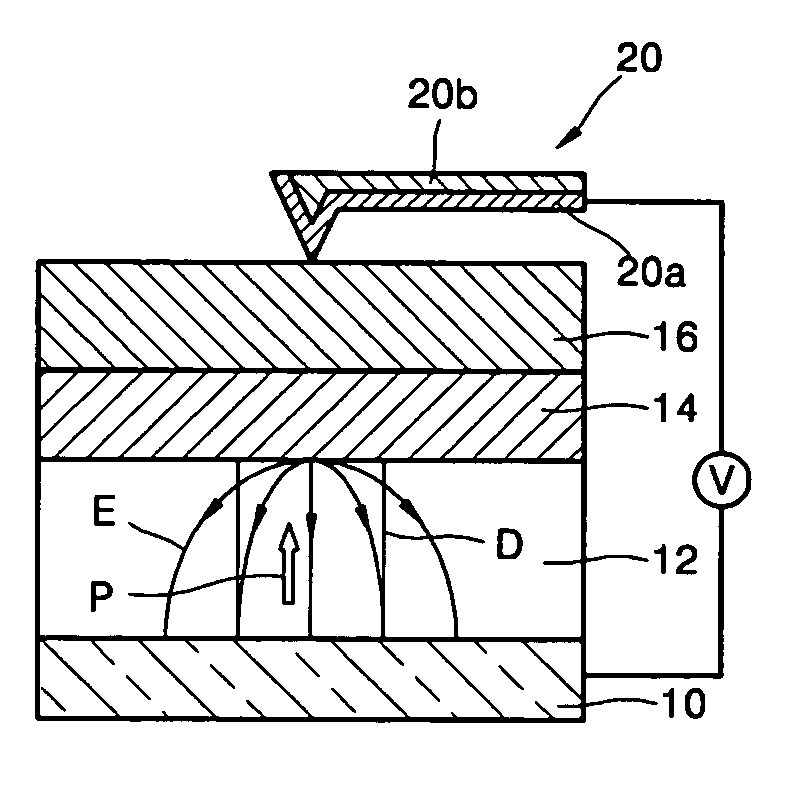
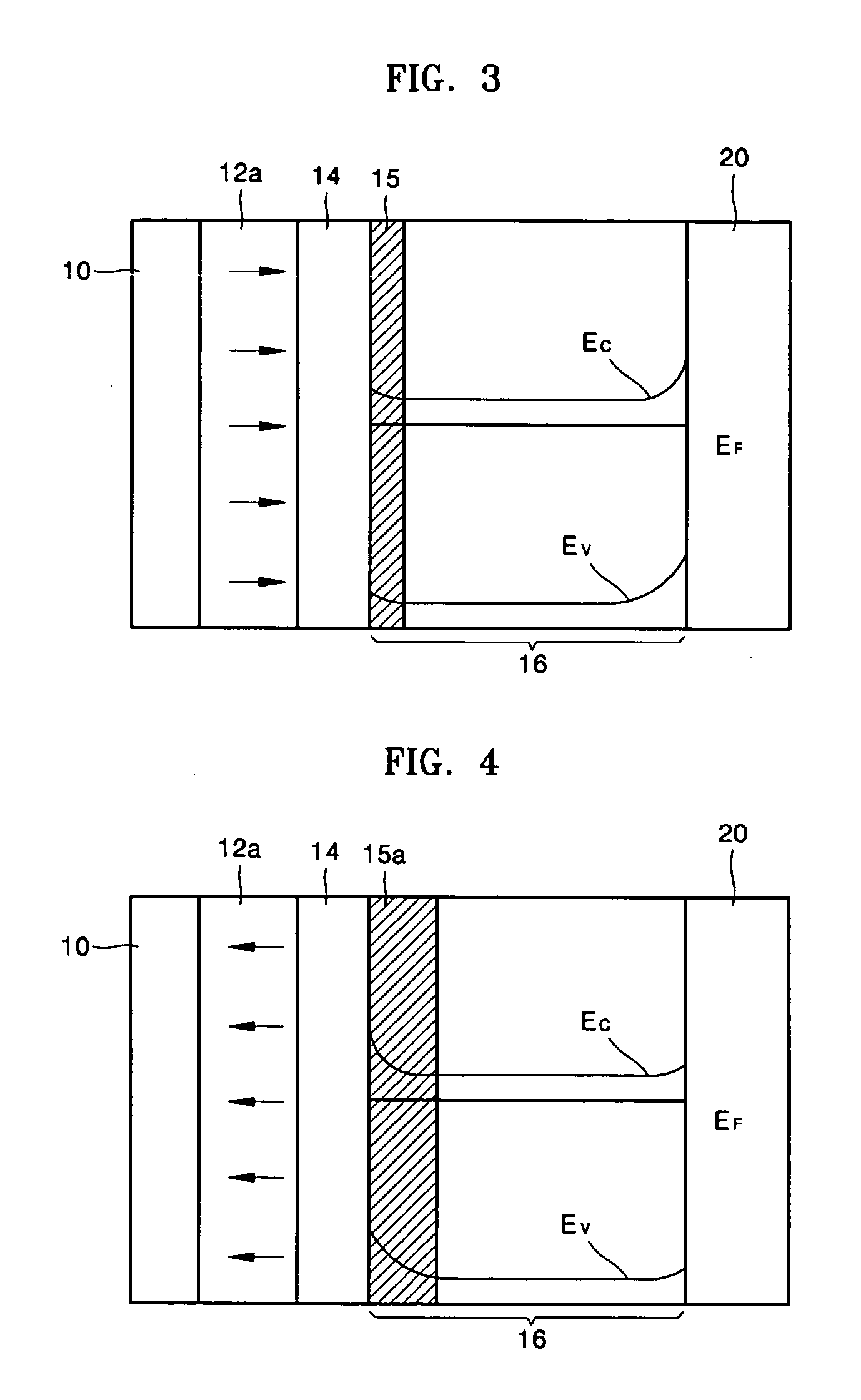
Record condition extraction system and method of dielectric recording medium, and information recording apparatus
InactiveUS6912193B2High-density and stable microdomainHigh-density and stableNanoinformaticsFerroelectric carrier recordingMeasurement deviceOutput device
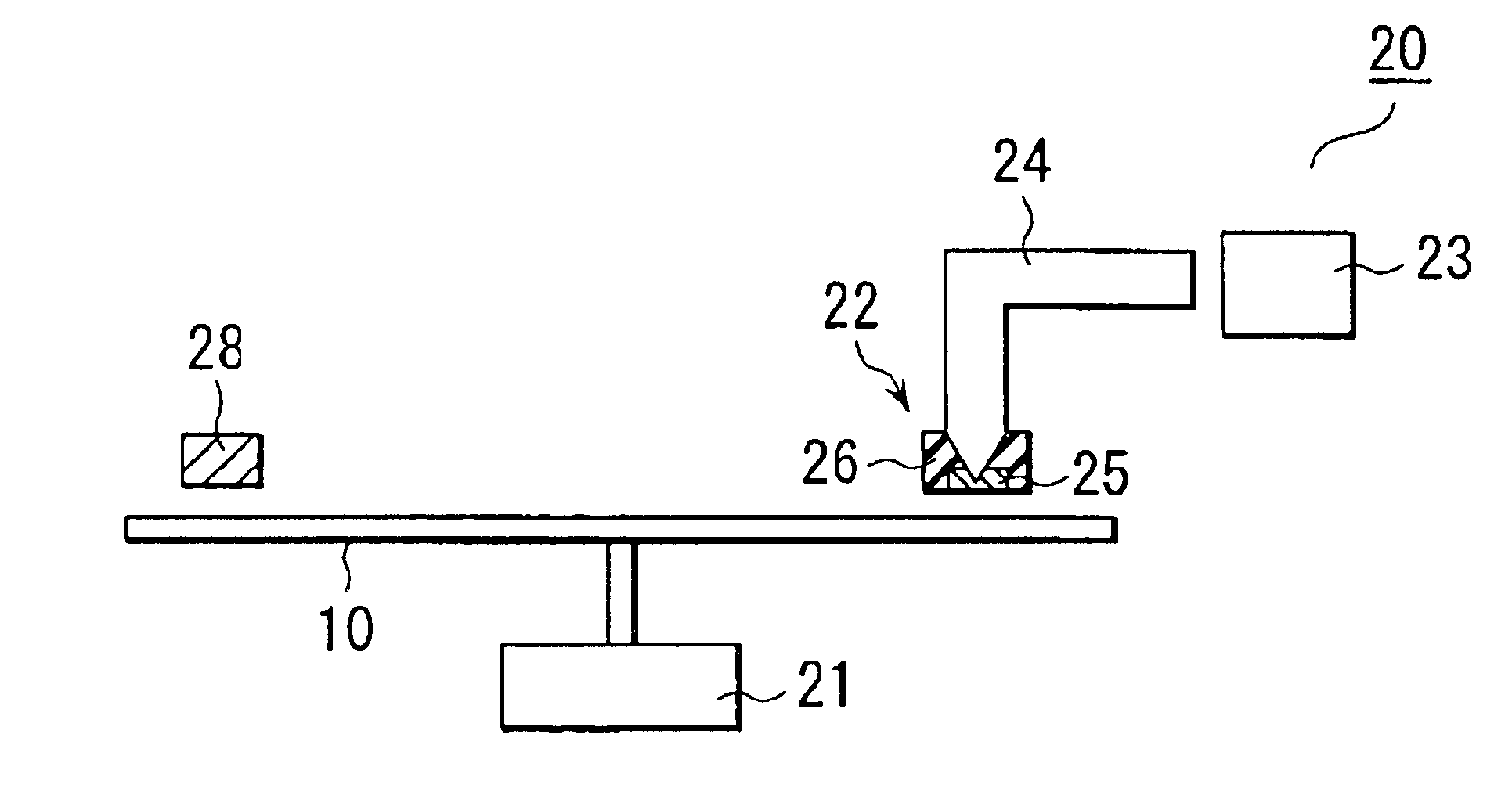
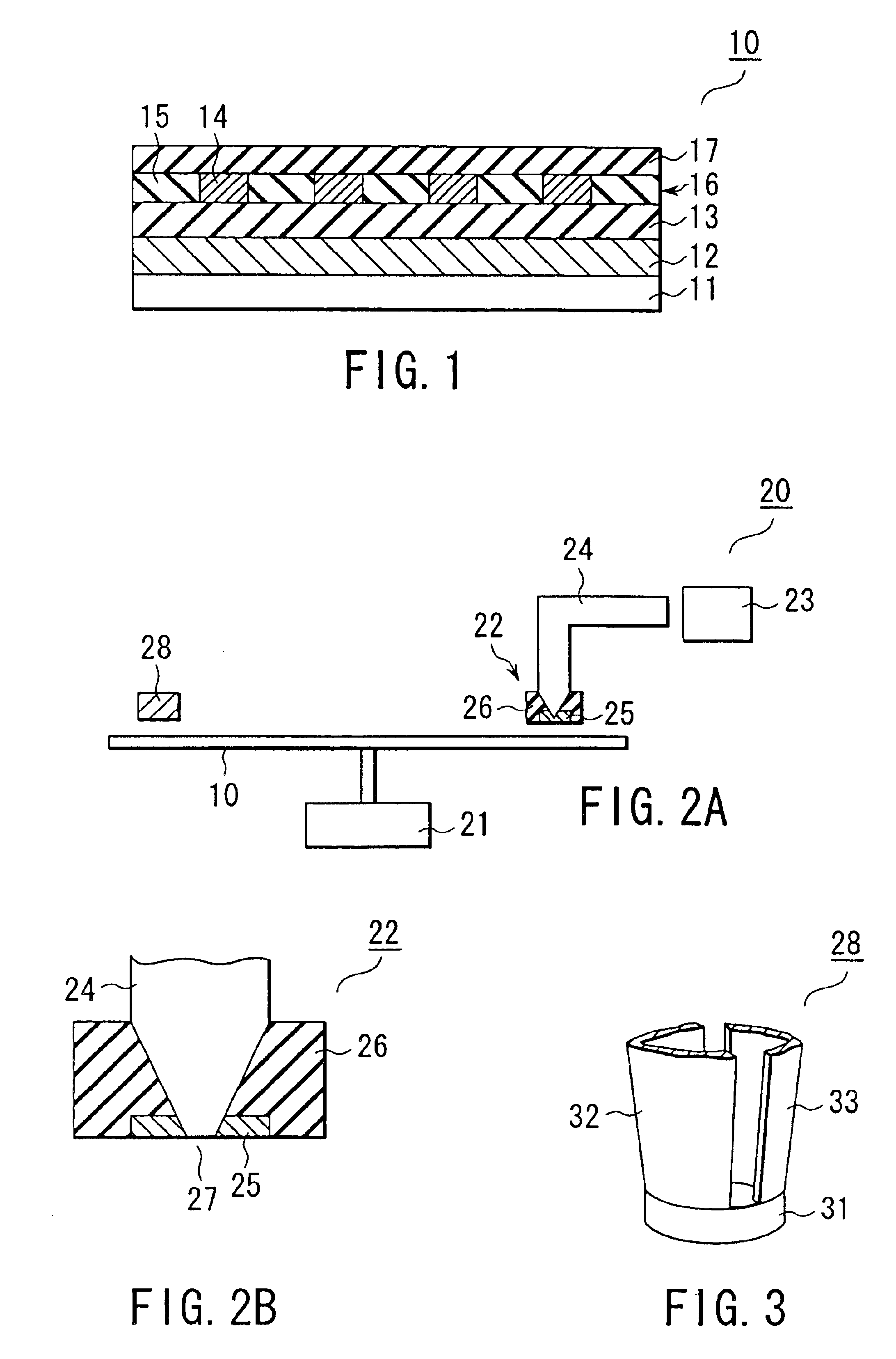
The record condition extraction system (1) of a dielectric recording medium is intended to obtain an applied voltage and an applied time length to be recorded when recording information in the dielectric recording medium. The record condition extraction system (1) is provided with: an applied voltage setting device (11); an applied time length setting device (12); a record control device (13); an applied voltage / applied time length record device (14); a record device (15); a dot radius measurement device (16); a dot radius record device (17); an optimum dot radius detection device (18); a record condition determination device (19); and an output device (20). The applied voltage setting device (11) and the applied time length setting device (12) set a voltage and a time applied to a probe (31) of the record device (15), respectively. The dot radius of a polarization domain 38, which is recorded at the record device (15), is measured at the dot radius measurement device (16), and the optimum polarization domain (38) is obtained at the optimum dot radius detection device (18). The applied voltage and the applied time length which have formed the polarization domain (38) are extracted as an optimum record condition.
Owner:YASUO CHO +1
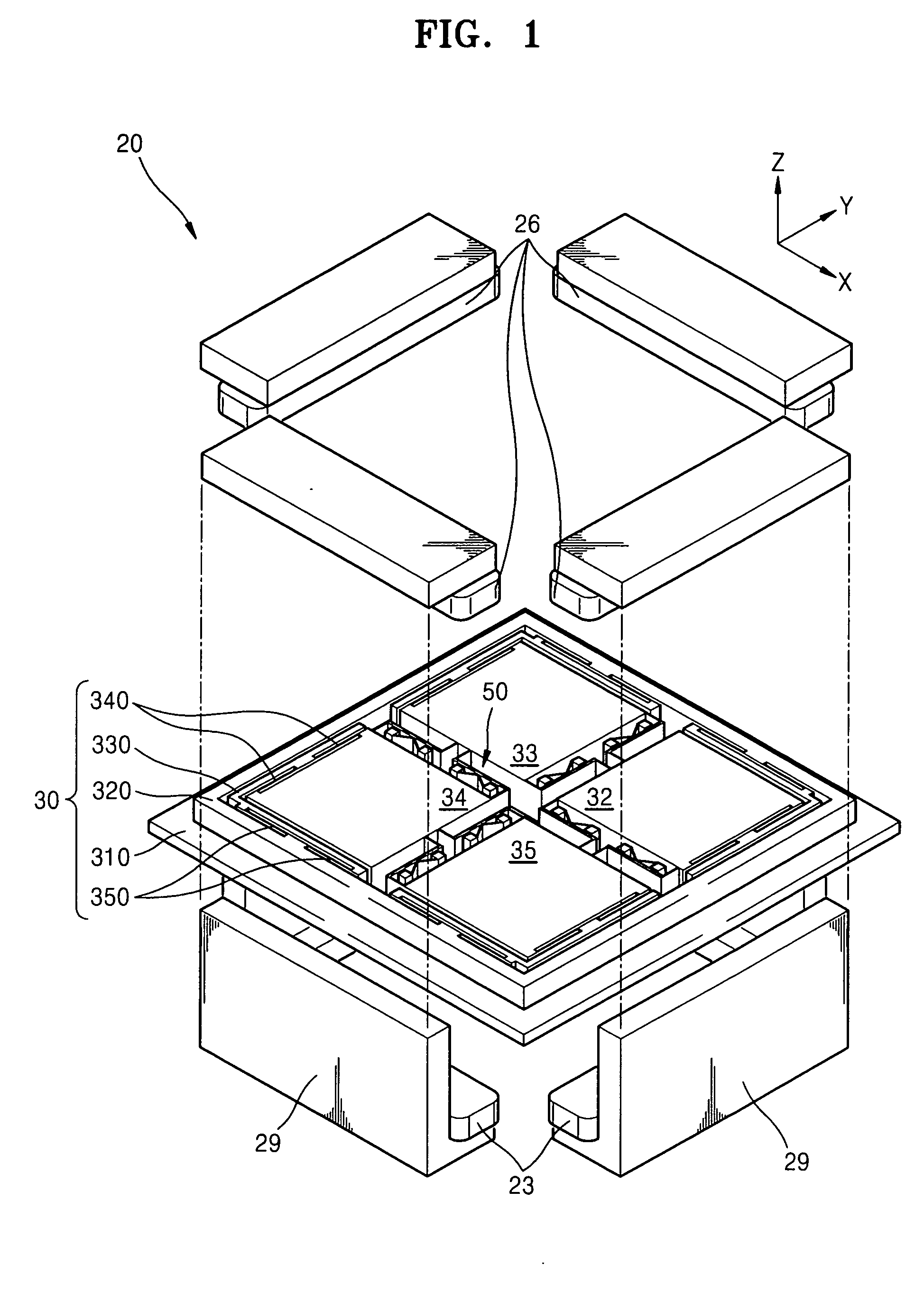
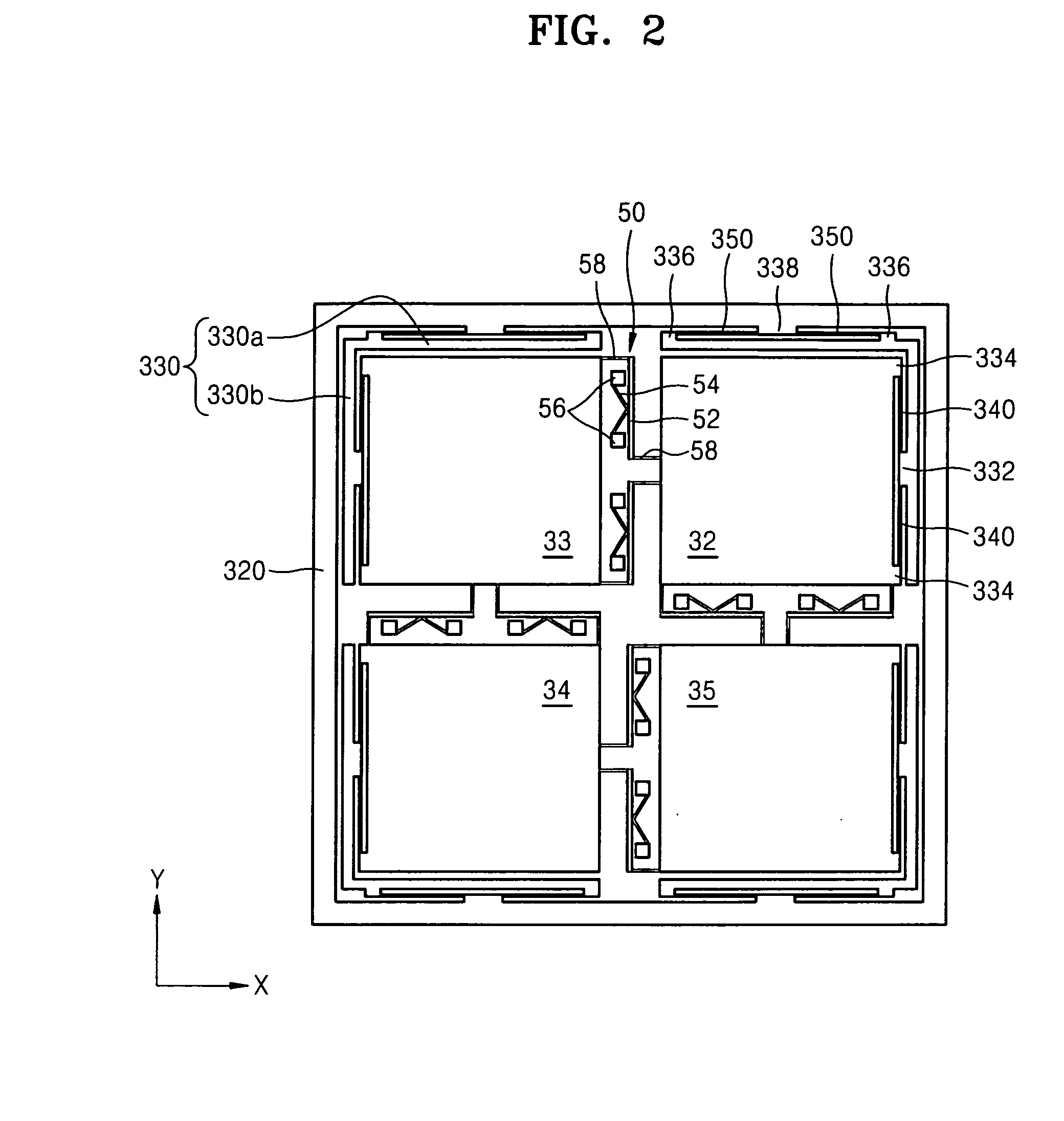
Micro actuator and data storage apparatus employing the same
ActiveUS20070153430A1Improve area efficiencyHigh enduranceDental implantsDisposition/mounting of recording headsMicro actuatorEngineering
A micro actuator having separated stages and a data storage apparatus employing the same are provided. The micro actuator includes: a supporting unit; stages that are elastically supported by the supporting unit, each stage having a mounting surface where a target driven body is mounted thereon, and arranged adjacent to each other; levers which are disposed between the stages, each lever having two ends respectively connected to adjacent stages, and which apply force to the adjacent stages so that when one of the stages is moved, an adjacent stage is moved in an opposite direction to a moving direction of the moved stage; and driving units which respectively provide a driving force to the stages.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
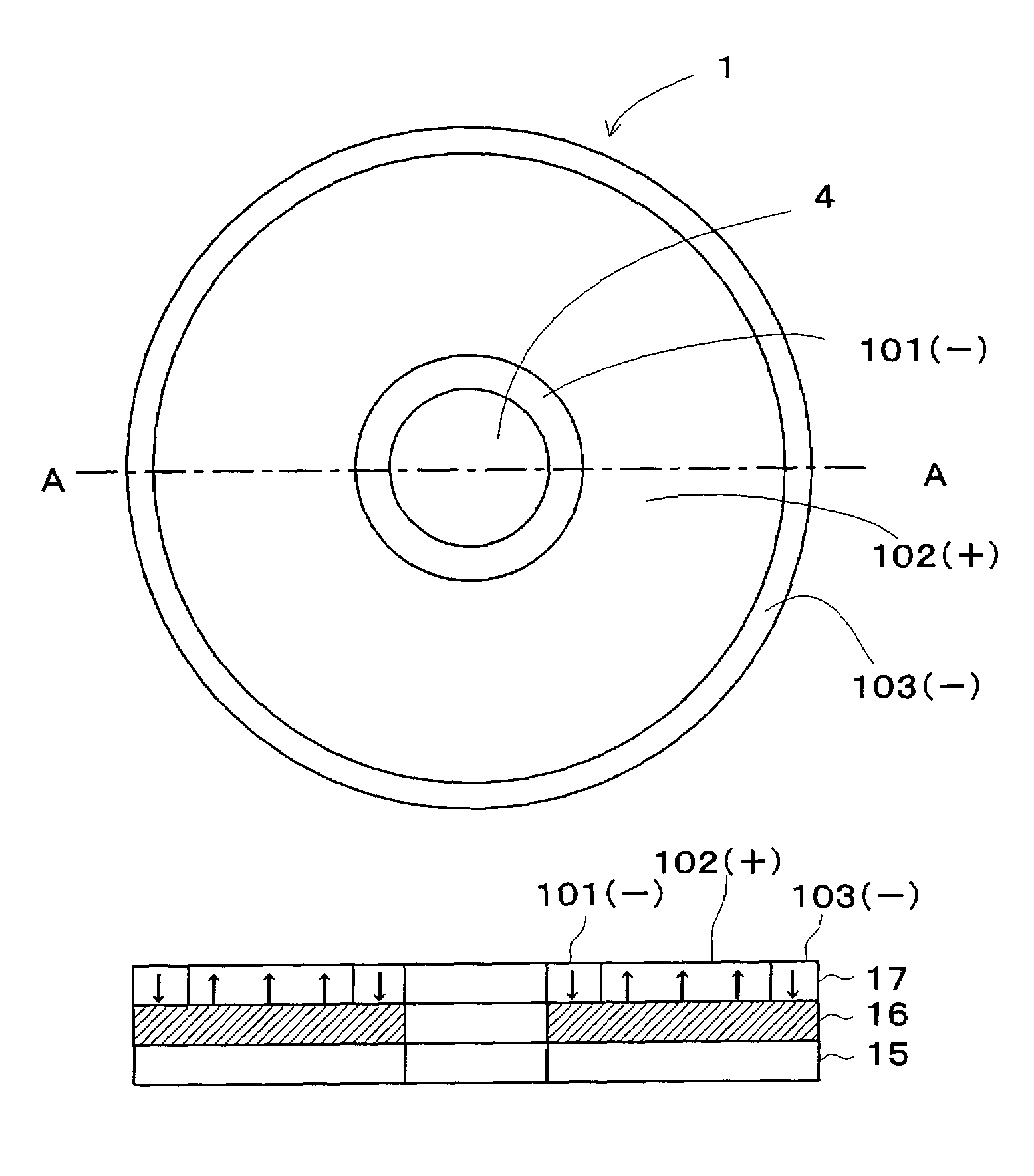
Apparatus for recording information in and/or reproducing information from a ferroelectric recording medium
InactiveUS7149180B2Increase ratingsImprove signal-to-noise ratioVariable capacitance carrier recordingNanoinformaticsPhysicsInternal zone
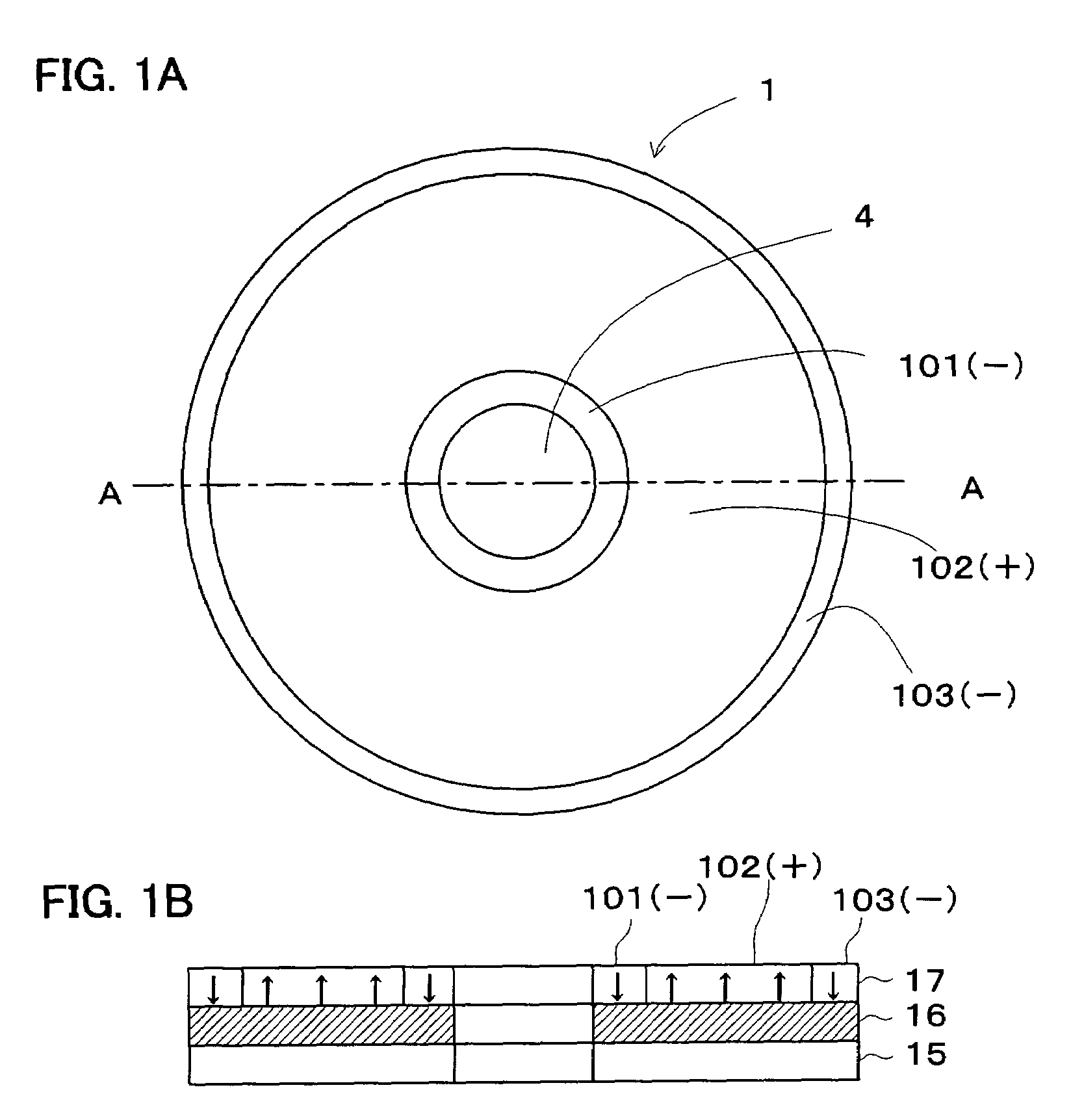
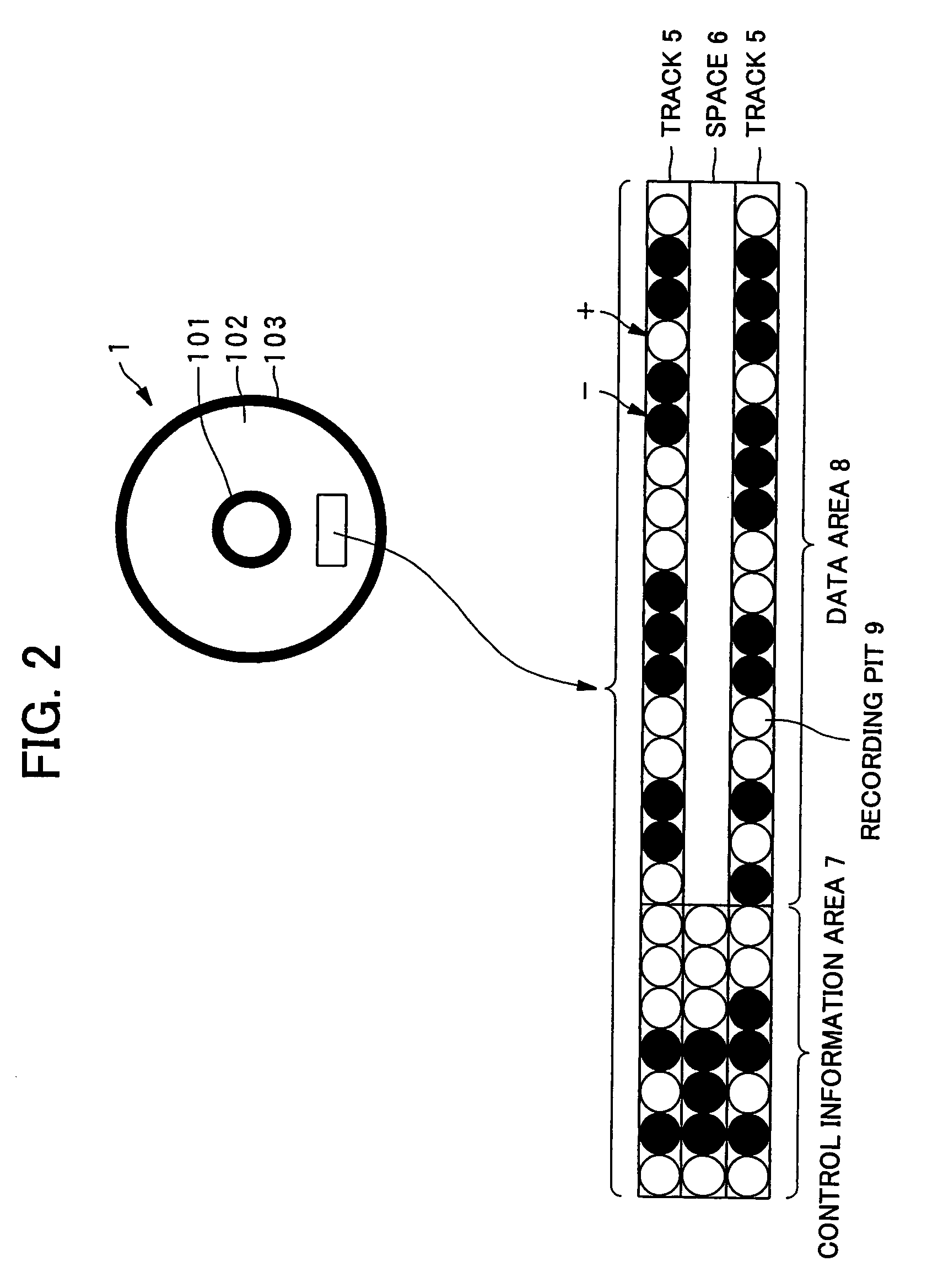
A dielectric recording medium in a disc form is provided with: a center hole; an inner area; a recording area; and an outer area, arranged concentrically from the inside in this order. The inner area, the recording area, and the outer area contain a uniform and flat dielectric material and are polarized with the polarization direction of the recording area opposite to that of the inner area and the outer area in their initial condition. The recording area in which data is recorded has tracks and spaces, each of which is between two of the tracks, and is provided with areas in which control information about the recording / reproducing is recorded, in the track and the space.
Owner:PIONEER CORP +1
Recording/reproduction head and recording/reproduction device
InactiveUS20070014047A1Improve recording densityOvercome obstaclesConstruction of head windingsManufacture head surfaceCapacitanceInsulation layer
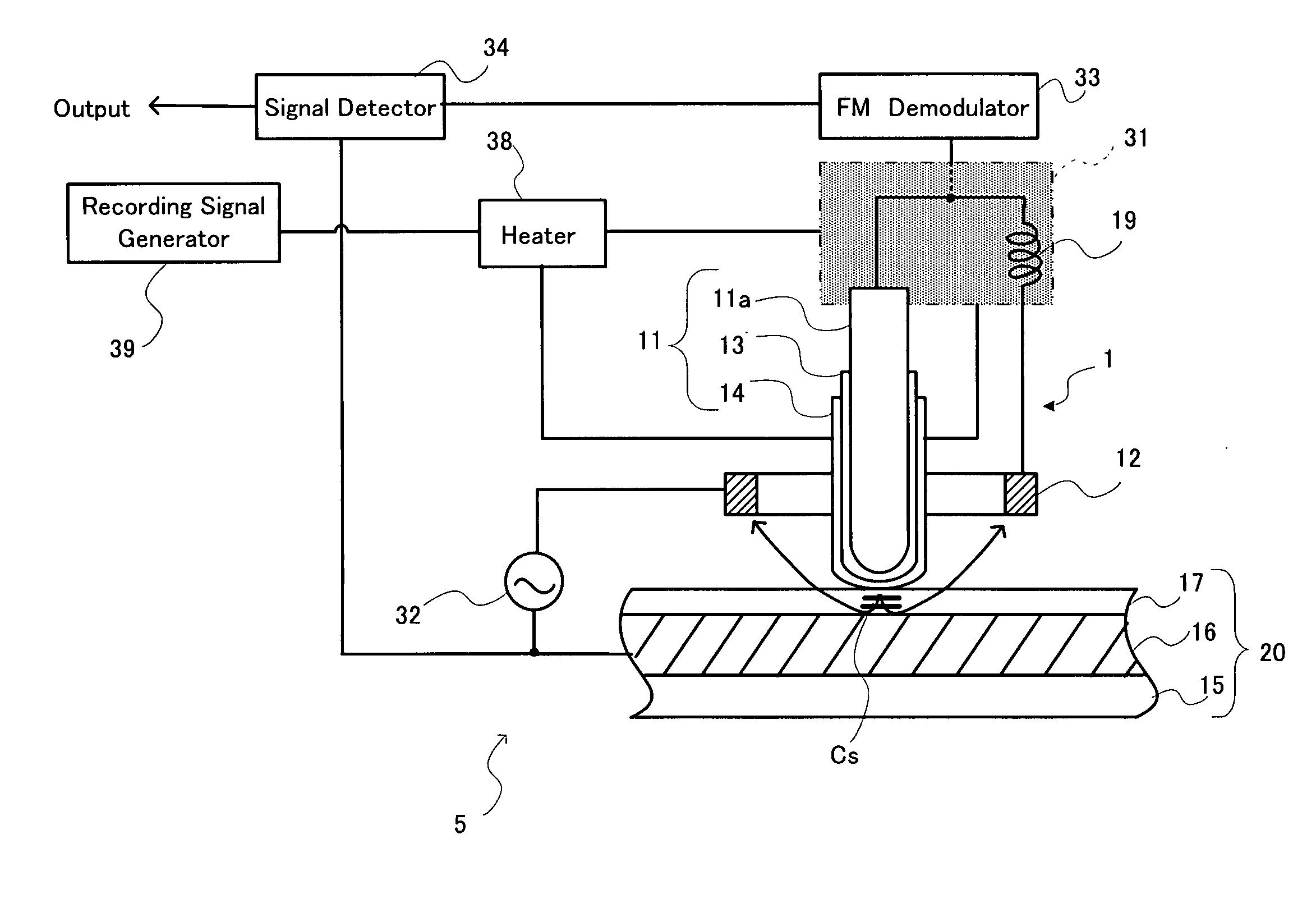
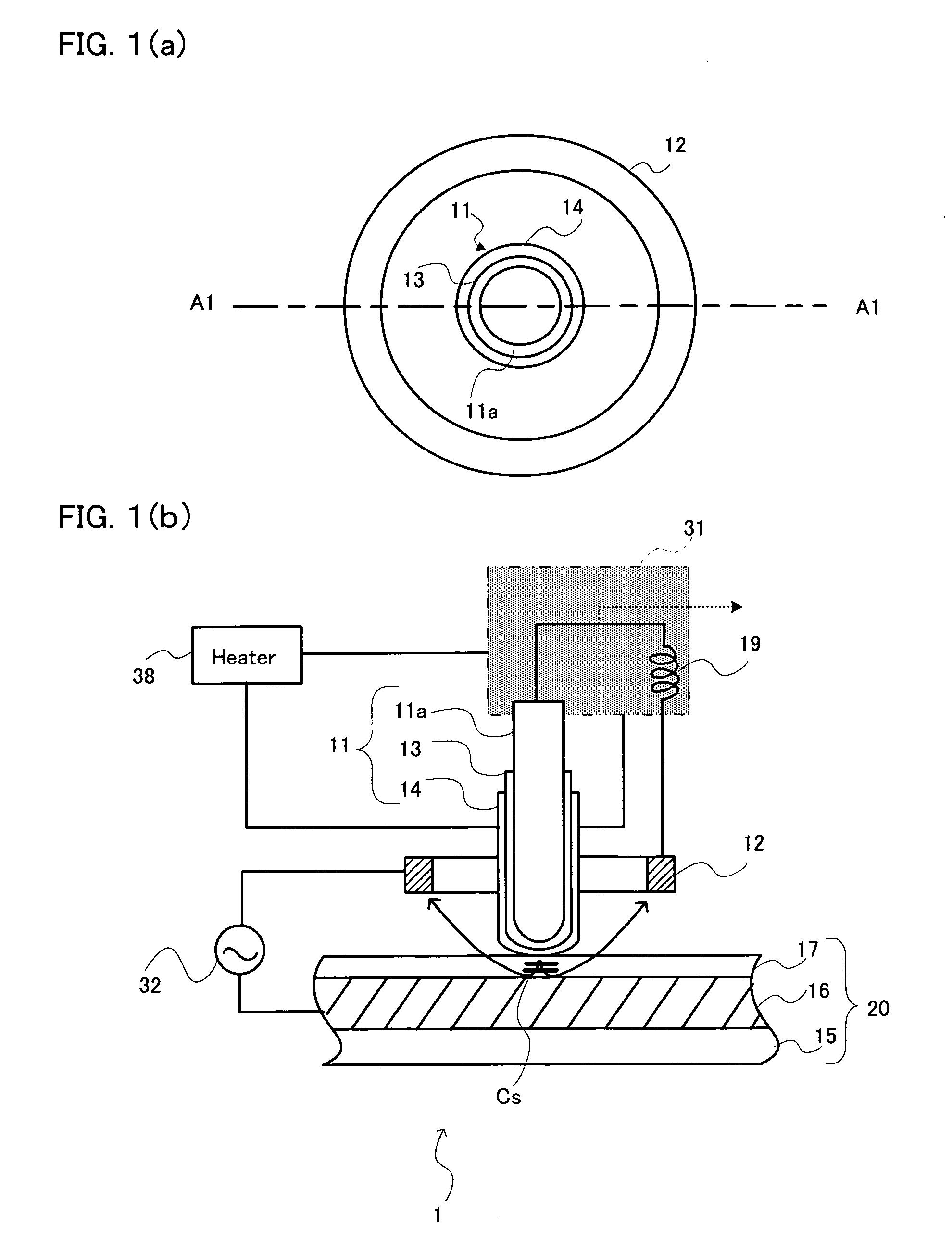
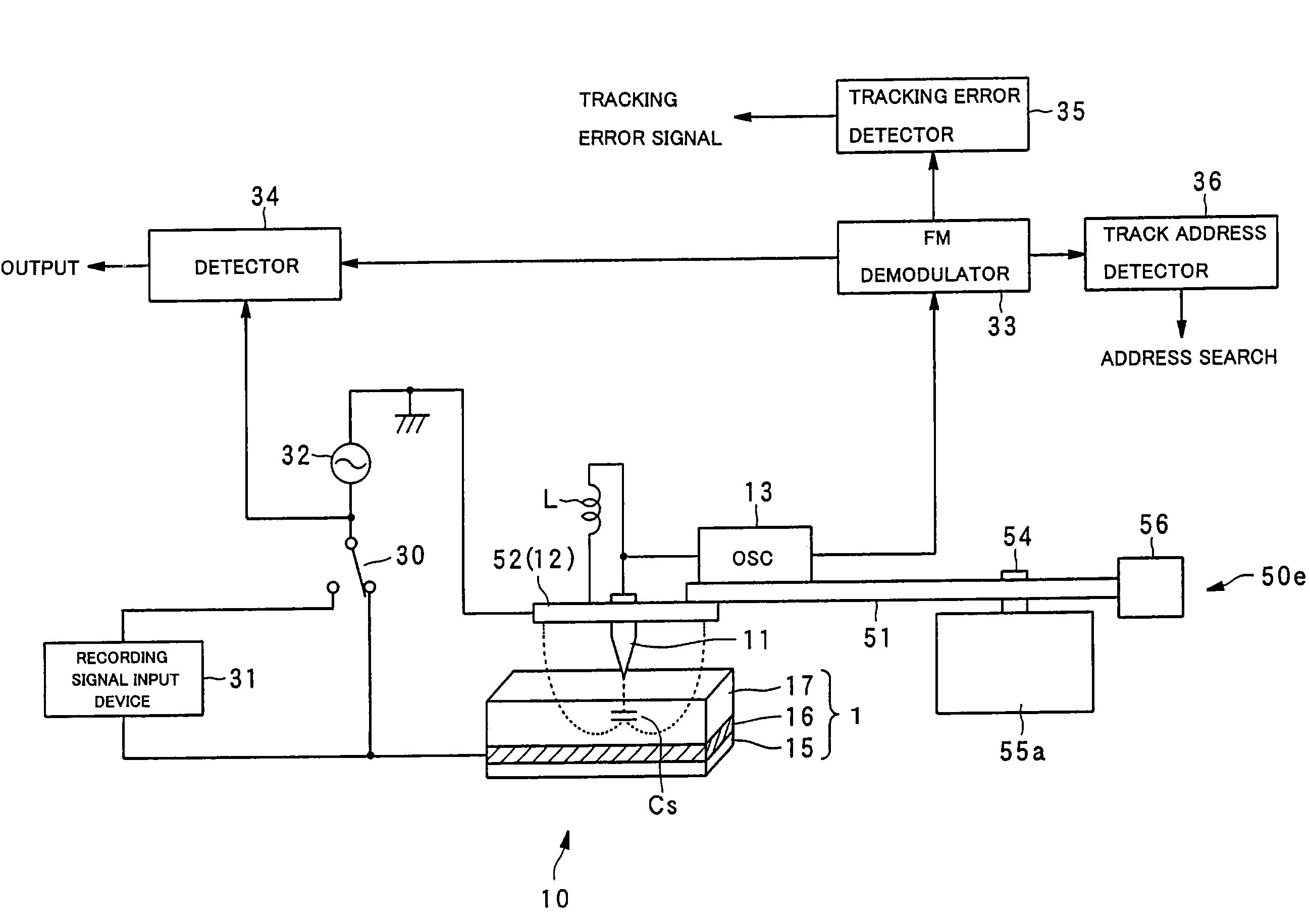
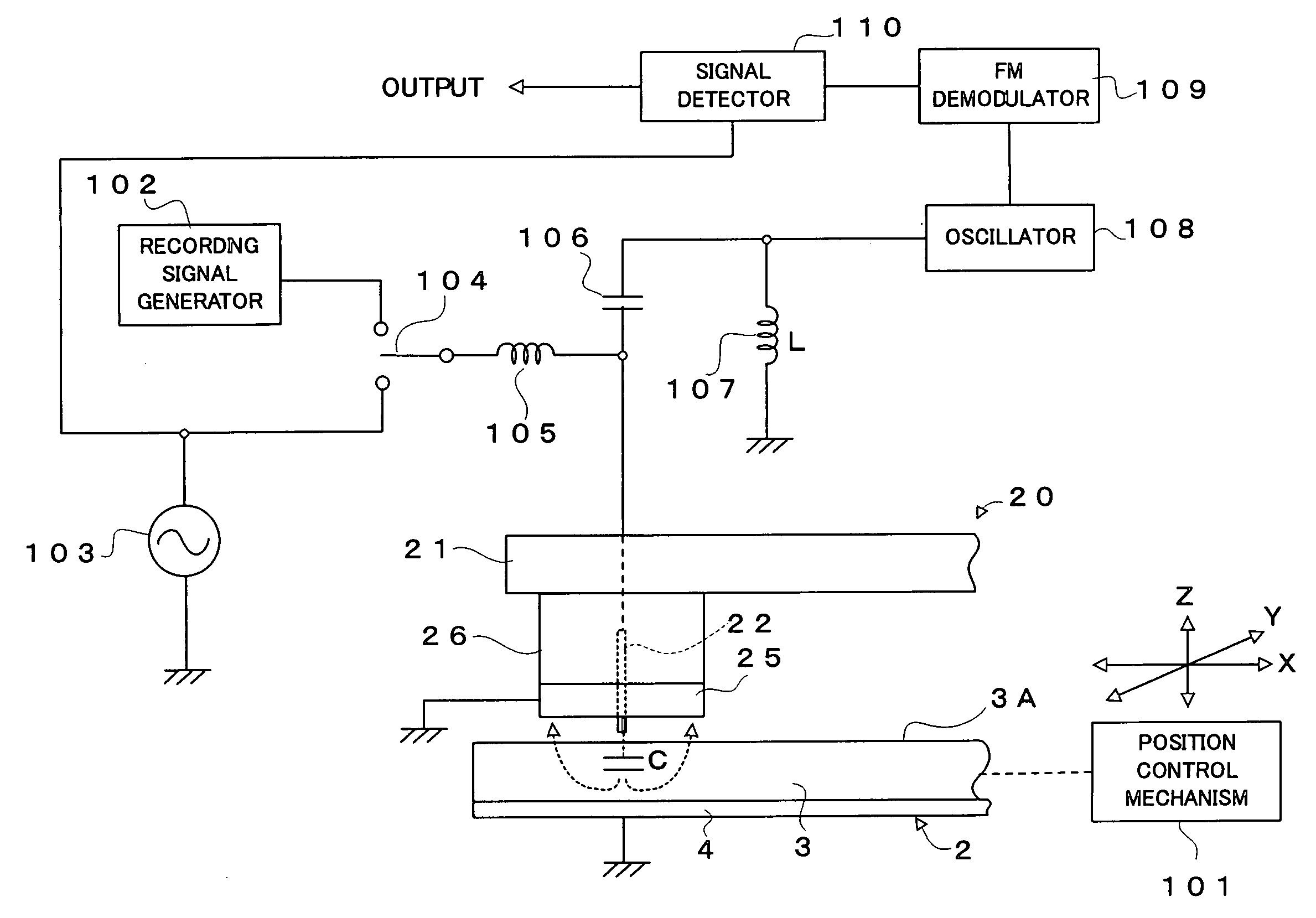
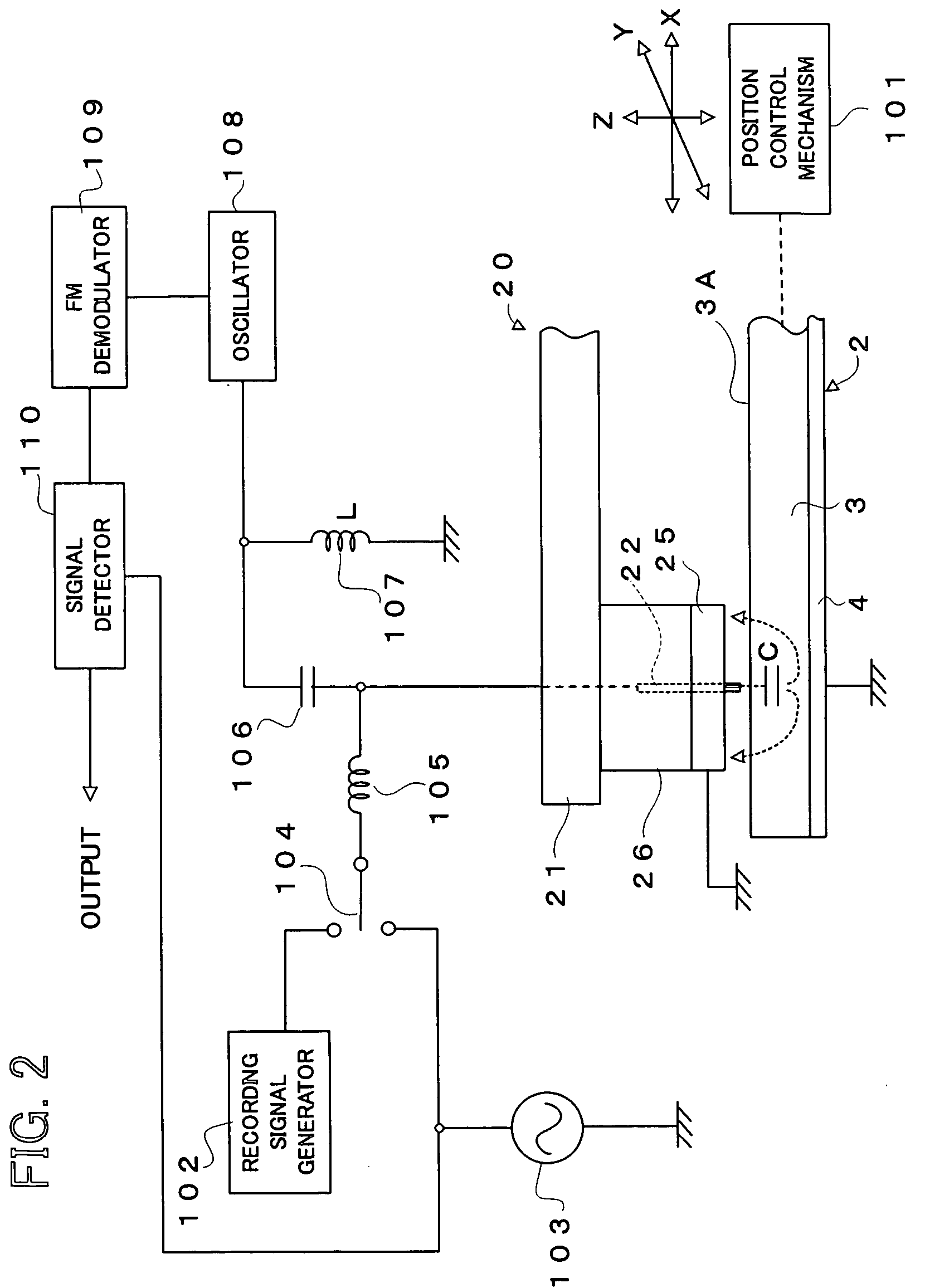
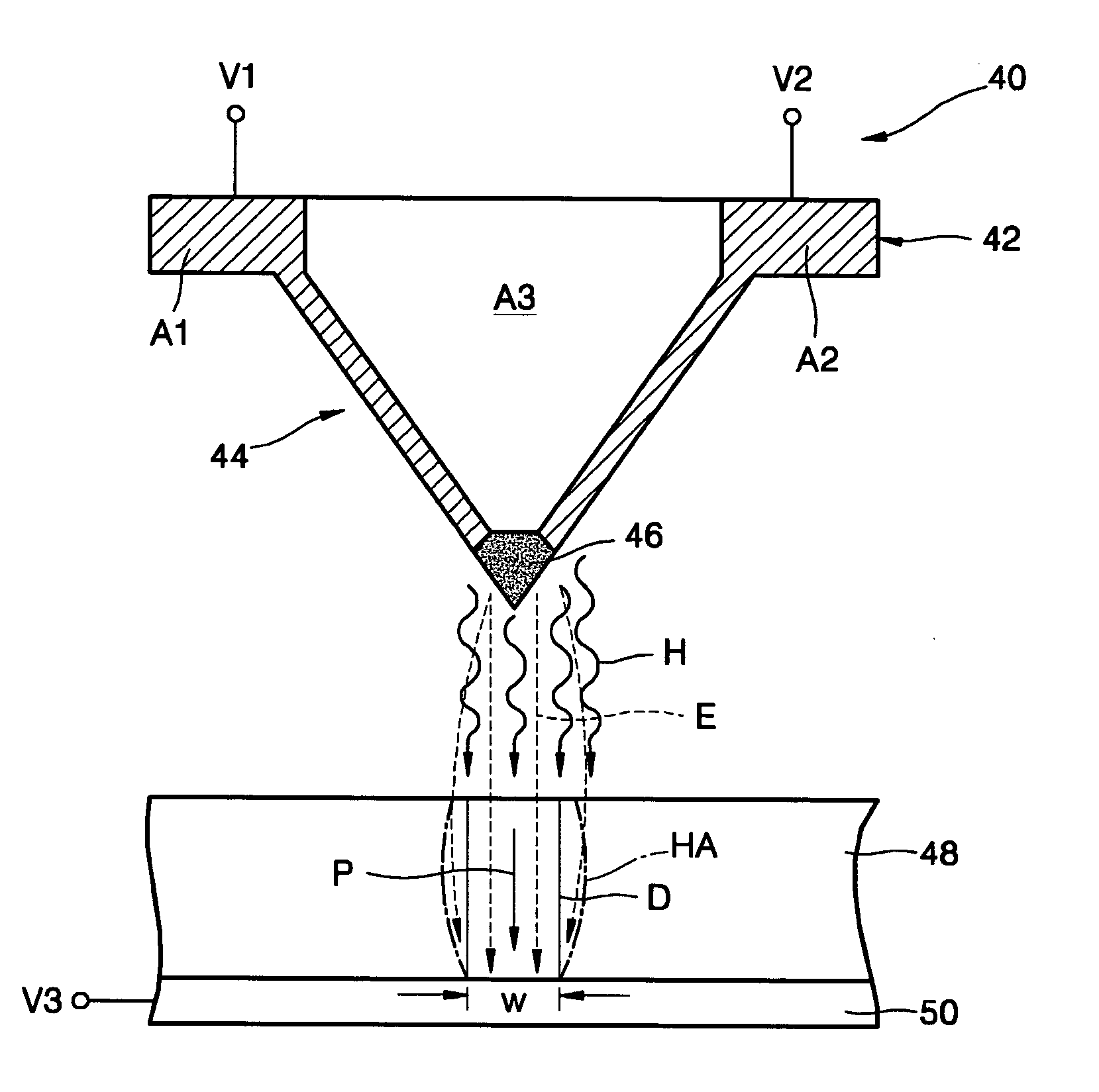
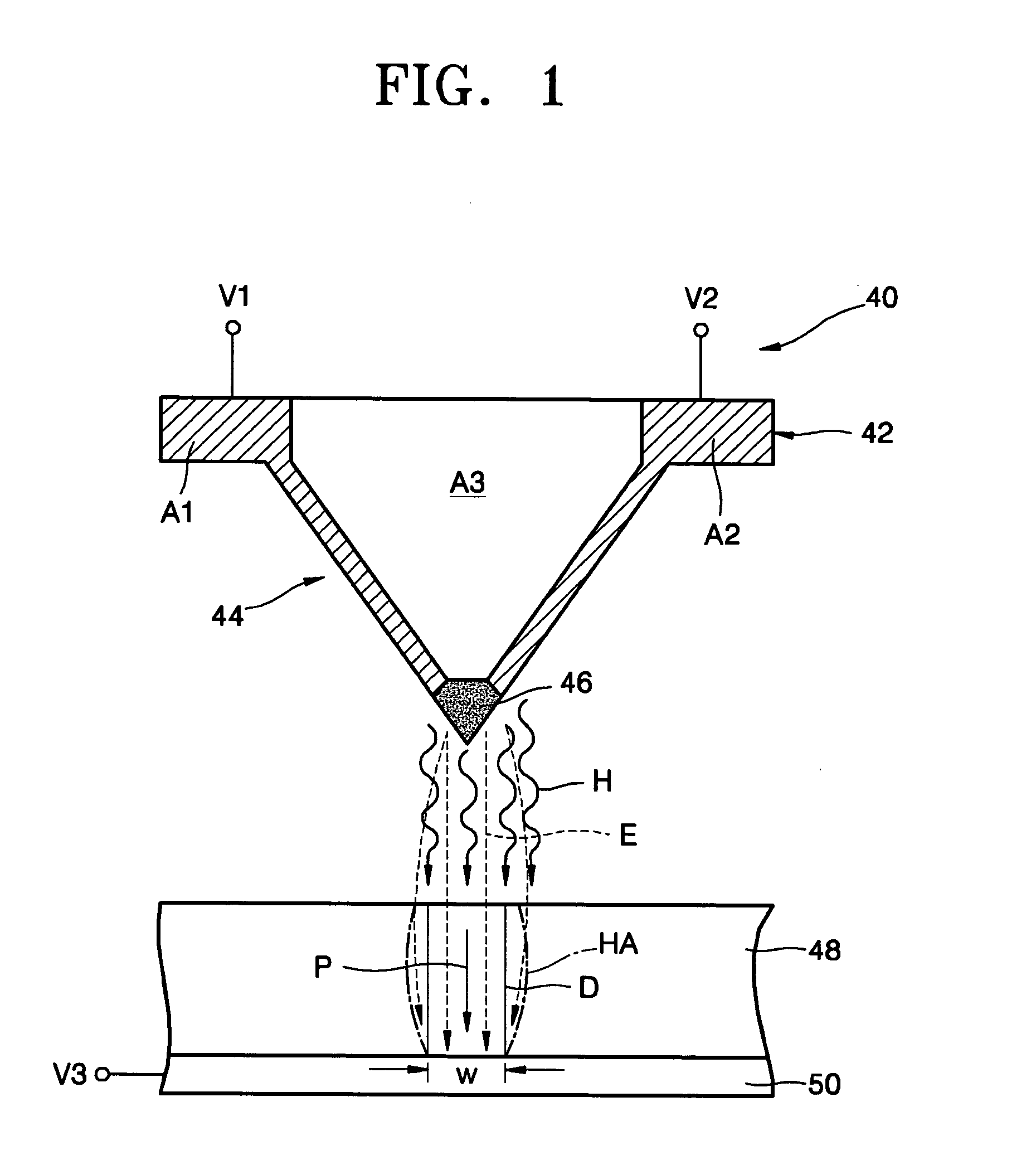
A phase-change recording / reproduction head includes: a probe consisting of a recording / reproduction electrode, an insulation layer arranged on the tip portion of the recording / reproduction electrode, and a resistor arranged on the insulation layer; and a return electrode arranged around the probe. During recording, voltage corresponding to the recording data is applied to the resistor so that the phase change recording medium is changed from a crystalline state to an amorphous state. During reproduction, FM-modulated frequency of an oscillator oscillating according to the capacity corresponding to the dielectric constant of the crystalline state and the amorphous state is demodulated, thereby reproducing data with a high SN ratio.
Owner:CHO YASUO +1
Information storage apparatus using semiconductor probe
InactiveUS6854648B2Increase speedSimple compositionElectrostatic charge injection carrier recordingNanoinformaticsEngineeringP–n junction
An information storage apparatus includes a recording medium and a head. The recording medium has an electrode layer, a ferroelectric film that is stacked on the electrode layer, and a semiconductor layer that is stacked on the ferroelectric film. The head has a semiconductor probe for forming a dielectric polarization on the ferroelectric film to record information and reproducing information from the dielectric polarizations on the ferroelectric film by making a p-n junction with the recording medium. Thus, it is possible to manufacture a small-sized information storage apparatus which is capable of repeatedly recording and reproducing information at a high speed.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Pickup device
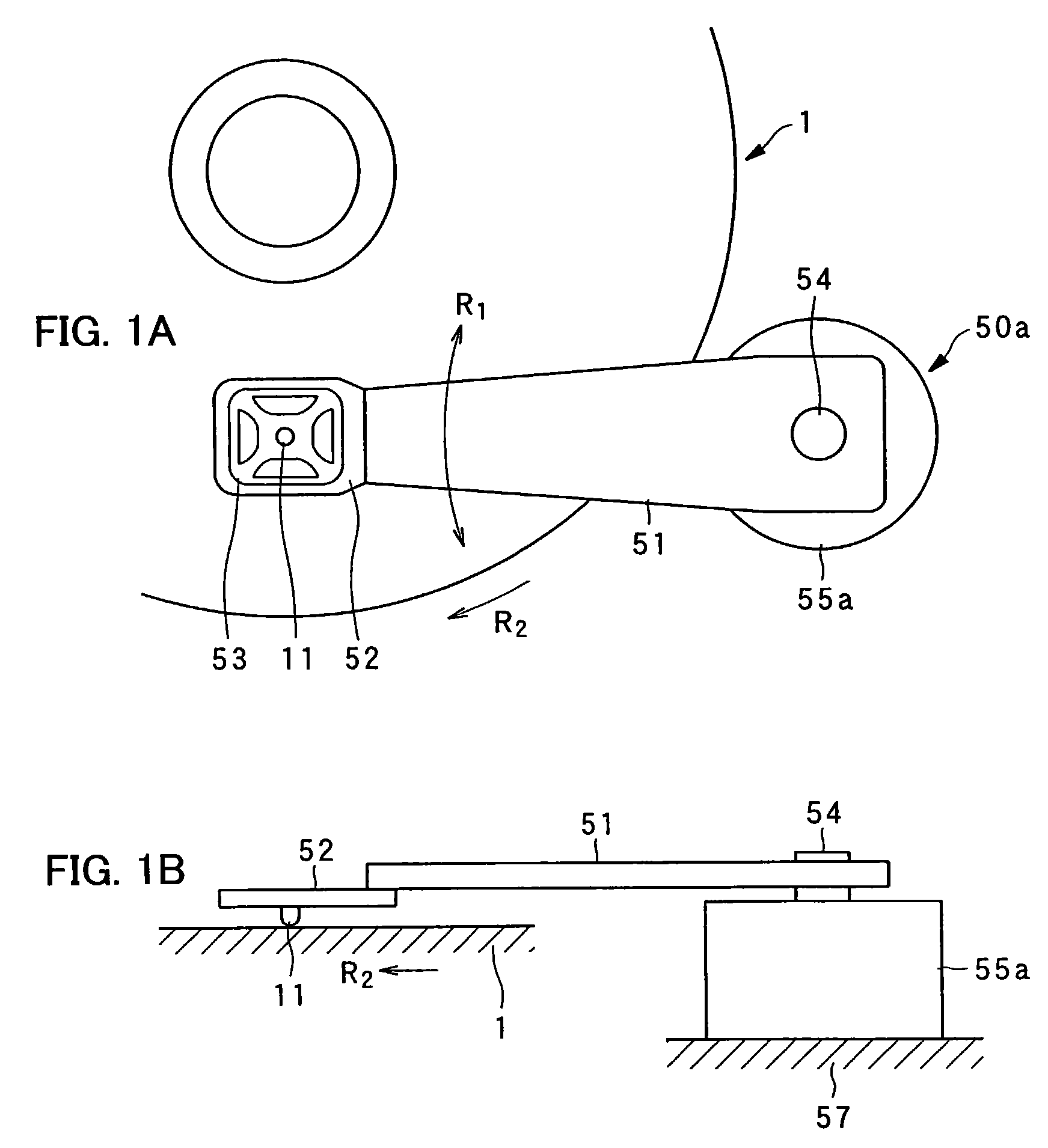
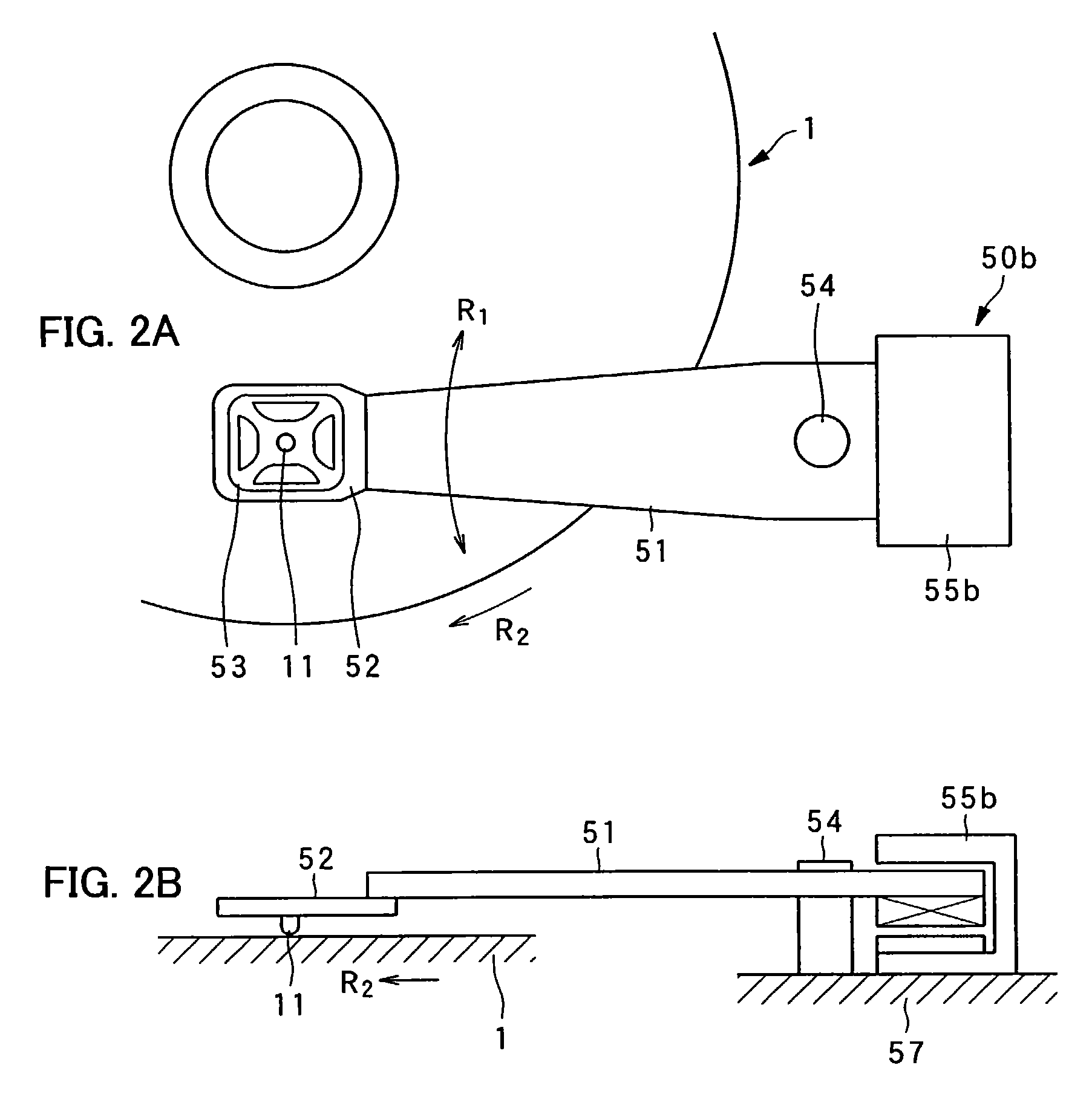
InactiveUS7221639B2Simple structureEasy to produceVariable capacitance carrier recordingNanoinformaticsEngineeringGimbal
An example pickup device is provided with: an arm; a gimbal holding device disposed on one end portion of the arm; a gimbal held by the gimbal holding device with a probe set in its center portion; and a motor of rotational type for rotating the arm around a rotating shaft. The probe, which is disposed on one end of the arm, is rotated in the radial direction of a dielectric recording medium by the rotation of the motor, causing accurate and quick tracking control and track access control.
Owner:PIONEER CORP +1
High density non-volatile memory device
InactiveUS7042755B1Suitable mechanical propertyPrevent charge leakageMaterial nanotechnologyNanoinformaticsFault toleranceChemical synthesis
This invention provides novel high density memory devices (FIG. 3) that are electrically addressable permitting effective reading and writing, that provide a high memory density (102), that provide a high degree of fault tolerance, and that are amenable to efficient chemical synthesis and chip fabrication. The devices arc intrinsically latchable, defect tolerant, and support destructive or non-destructive read cycles. In a preferred embodiment, the device comprises a fixed electrode electrically coupled to a storage medium having a multiplicity of different and distinguishable oxidation states wherein data is stored in said oxidation states by the addition or withdrawal of one or more electrons from said storage medium via the electrically coupled electrode.
Owner:NORTH CAROLINA STATE UNIV +1
Information recording/reading head
InactiveUS20040105373A1Electrostatic charge injection carrier recordingOptical head protectionBiomedical engineering
Owner:PIONEER CORP
Method of writing data on a storage device using a probe technique
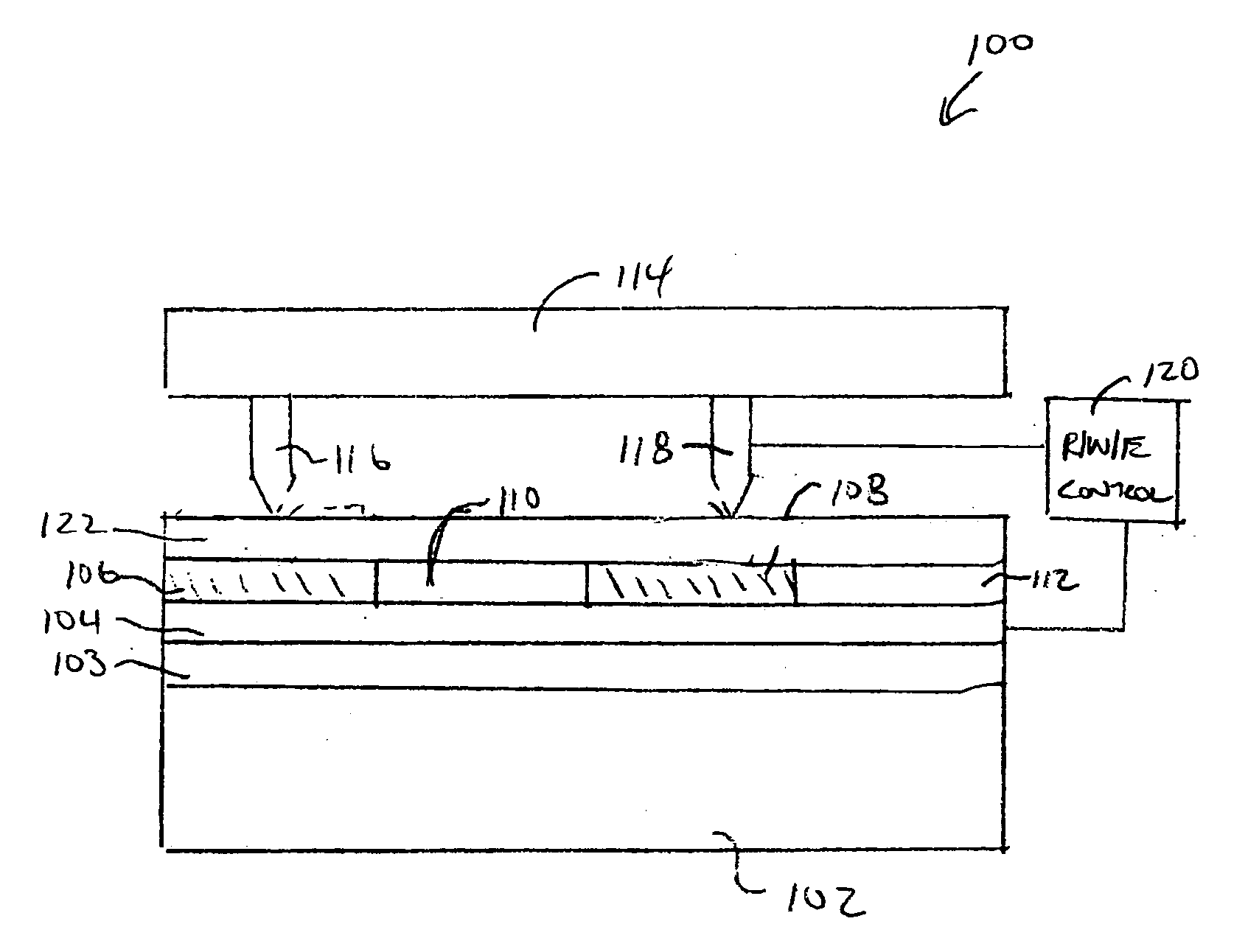
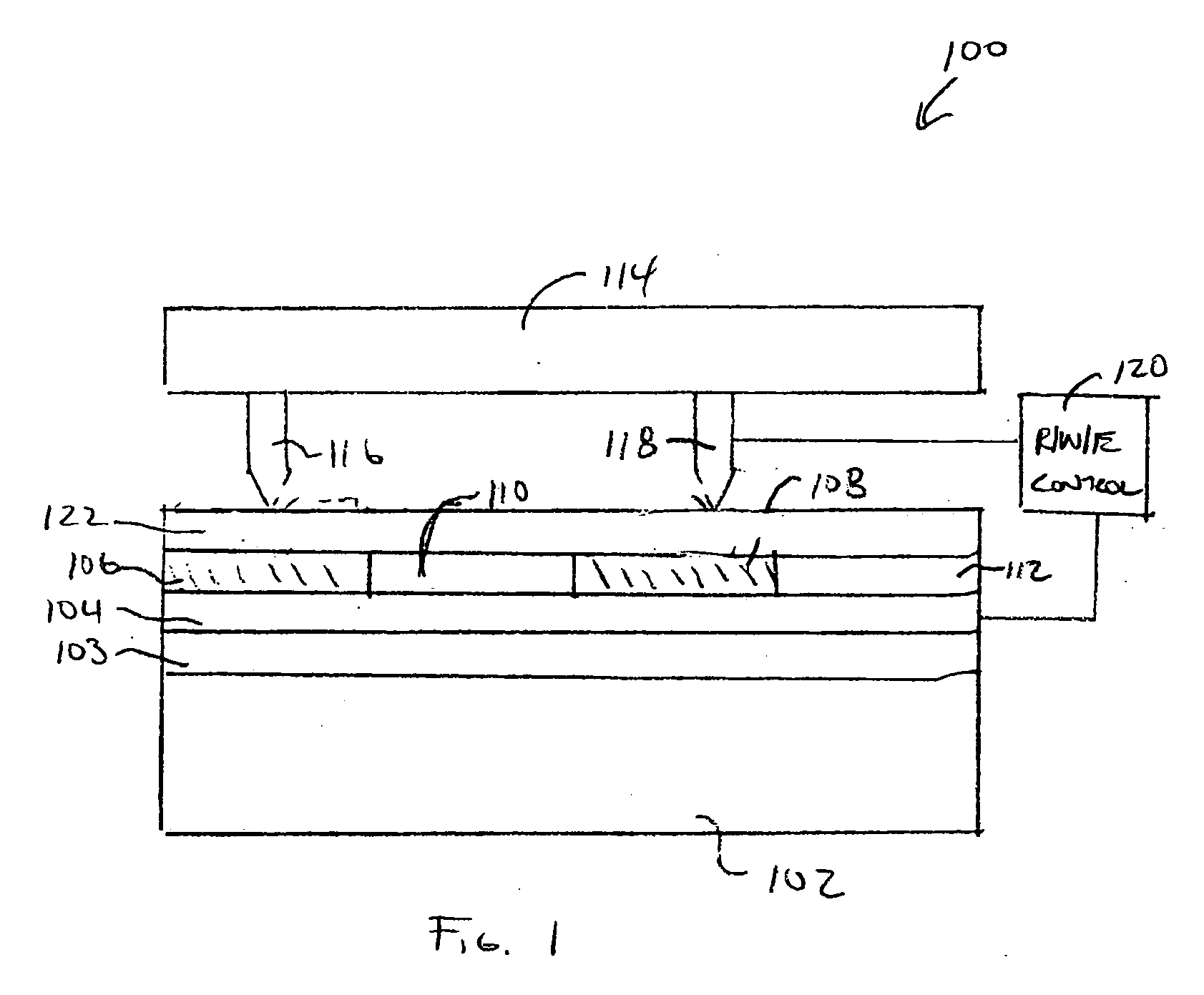
InactiveUS20050052984A1Low coercivityEfficient switchingCombination recordingNanoinformaticsElectrical resistance and conductanceEngineering
A method of writing data on a storage device using a probe technique. In the method of writing data on a memory device including a resistive probe used for reading and writing of data, a ferroelectric writing medium on which data is written by the resistive probe, and a lower electrode disposed on a bottom surface of the ferroelectric writing medium, heat and an electric field are applied simultaneously to a domain of the ferroelectric writing medium, on which the data will be written, by applying a voltage to the resistive probe and the lower electrode.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Projection having a micro-aperture, probe or multi-probe having such a projection and surface scanner, aligner or information processor comprising such a probe
InactiveUS6376833B2Decorative surface effectsMaterial analysis by optical meansSilicate glassPlastic materials
Owner:CANON KK
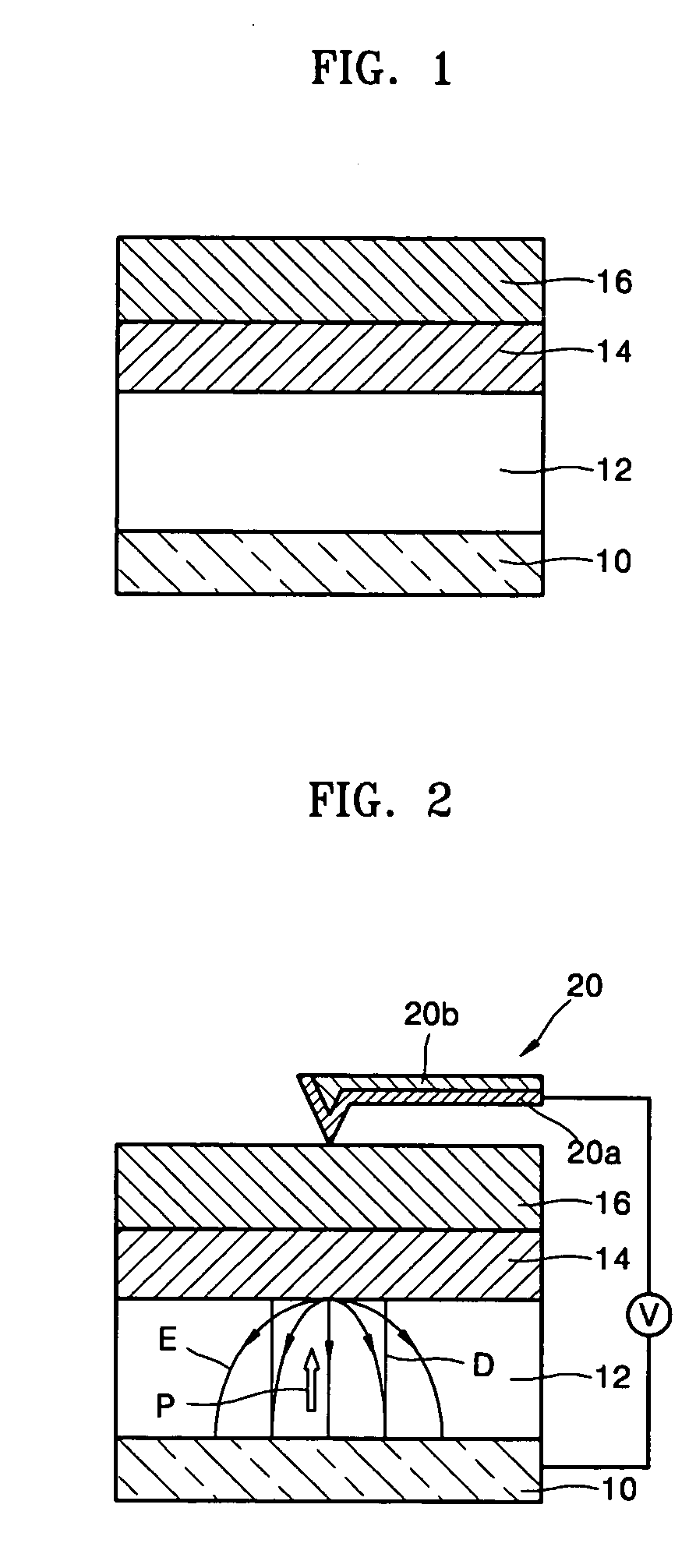
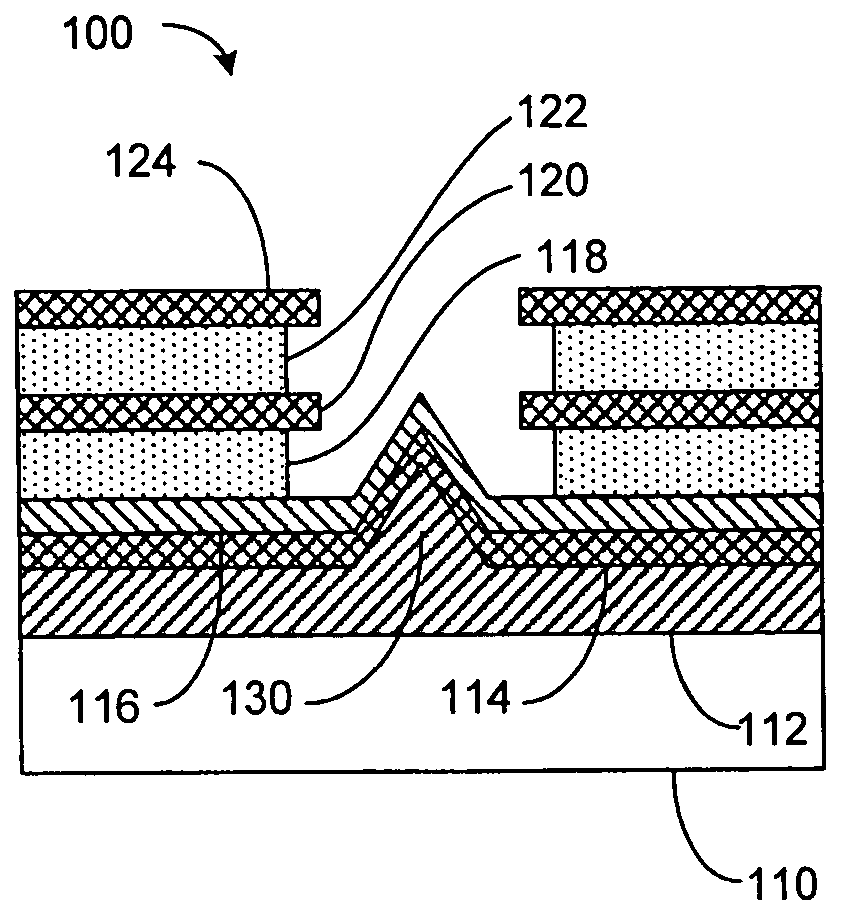
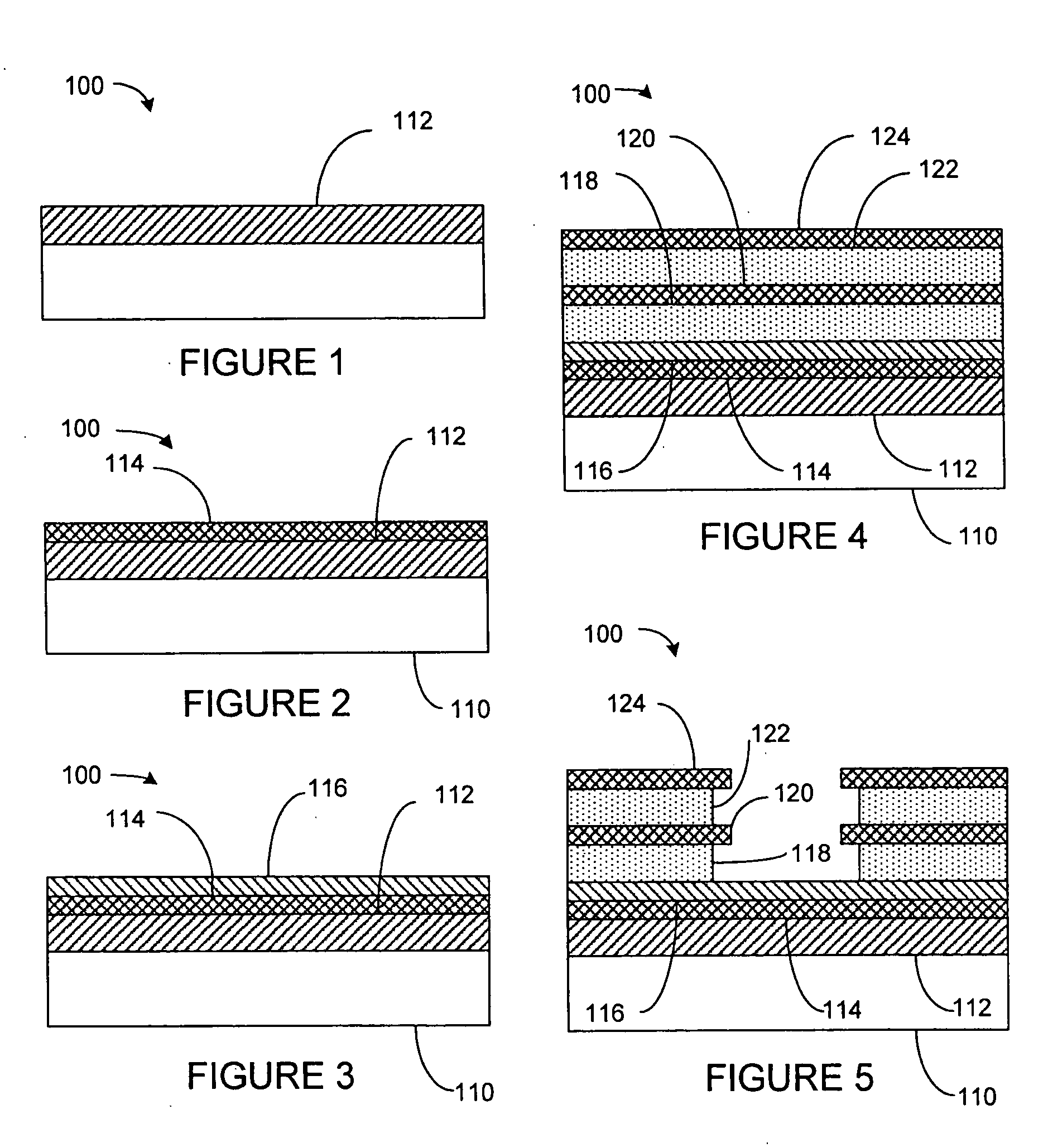
Recording medium comprising ferroelectric layer, nonvolatile memory device comprising recording medium, and methods of writing and reading data for the memory device
InactiveUS20050147018A1Little and no abrasionImprove reading speedNanoinformaticsMechanical record carriersComputer scienceSemiconductor
A recording medium including a ferroelectric layer, a nonvolatile memory device including the recording medium and methods of wiring and reading data in the memory device. The recording medium includes: a lower electrode; a ferroelectric layer to which data is recorded, formed on the lower electrode; a barrier layer formed on the ferroelectric layer; and a semiconductor layer formed on the barrier layer. The nonvolatile memory device includes a probe that reads and writes the data. Furthermore, in the method of writing data, a writing voltage is applied between the probe, which contacts the semiconductor layer, and the lower electrode and, in the method of reading data, a state of a remanent polarization of the ferroelectric layer is determined by applying a reading voltage between the probe and the semiconductor layer.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Electron emitter device for data storage applications and method of manufacture
InactiveUS20050029920A1Improve abilitiesLamp incadescent bodiesNanoinformaticsField emission deviceTitanium nitride
A field emission device, which among other things may be used within an ultra-high density storage system, is disclosed. The emitter device includes an emitter electrode, an extractor electrode, and a solid-state field controlled emitter that utilizes a Schottky metal-semiconductor junction or barrier. The Schottky metal-semiconductor barrier is formed on the emitter electrode and electrically couples with the extractor electrode such that when an electric potential is placed between the emitter electrode and the extractor electrode, a field emission of electrons is generated from an exposed surface of the semiconductor layer. Further, the Schottky metal may be selected from typical conducting layers such as platinum, gold, silver, or a conductive semiconductor layer that is able to provide a high electron pool at the barrier. The semiconductor layer placed on the Schottky metal is typically very weakly conductive of n-type and has a wide band gap in order to create conditions conducive to creating induced negative electron affinity at applied fields necessary to provide electron emission. One type of wide band-gap material can be selected from titanium dioxide or titanium nitride or other comparable materials.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com