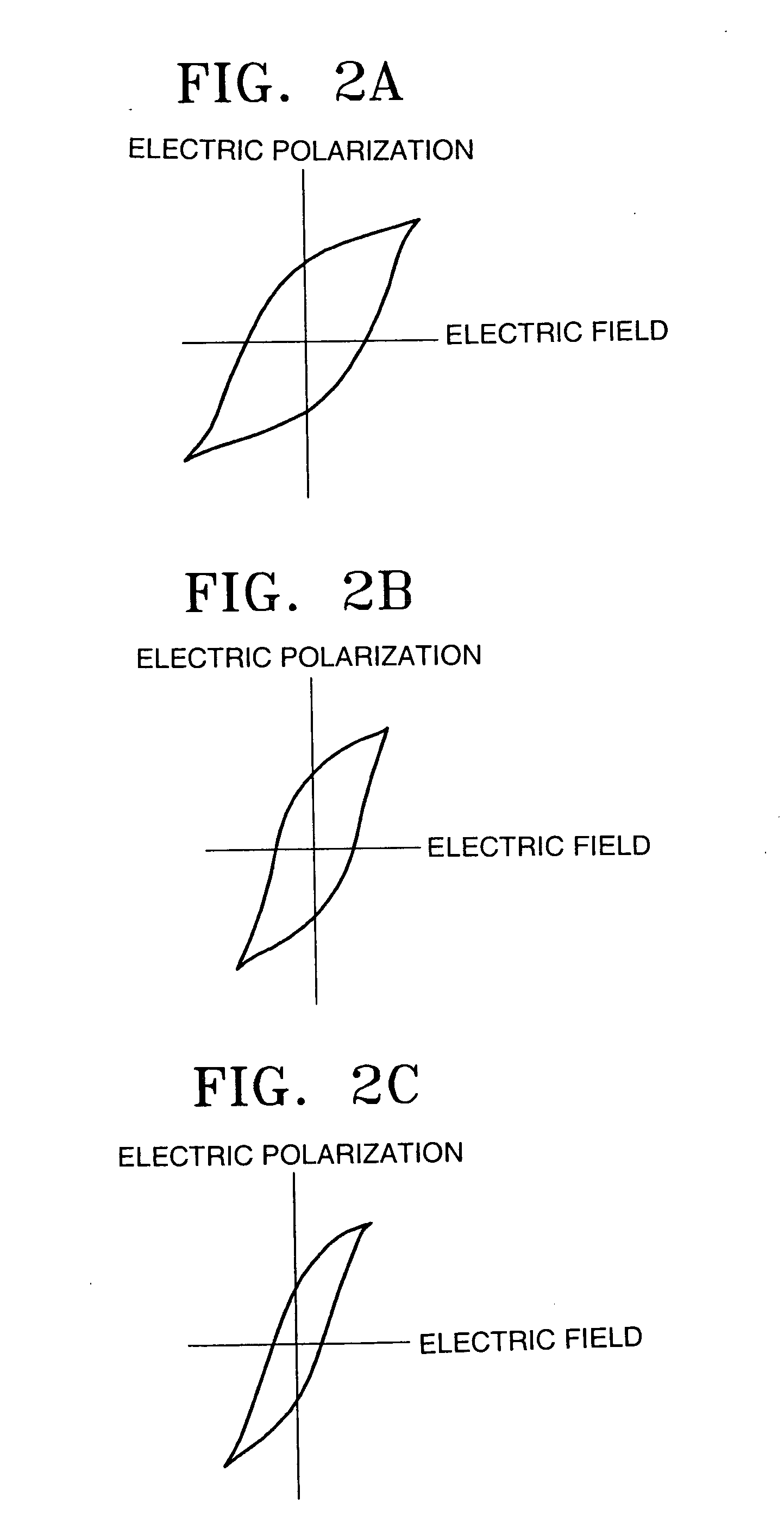
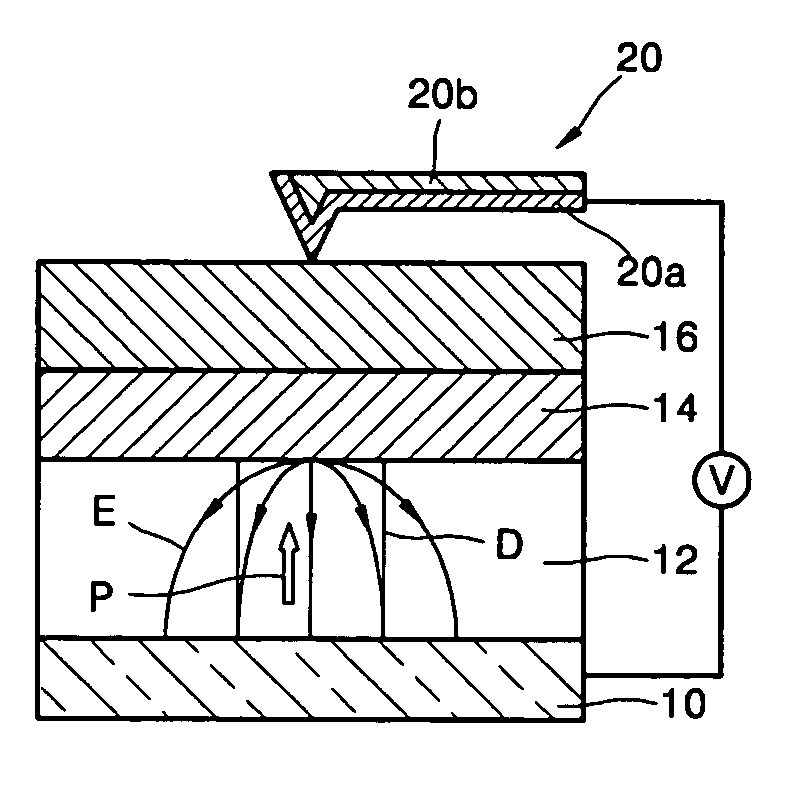
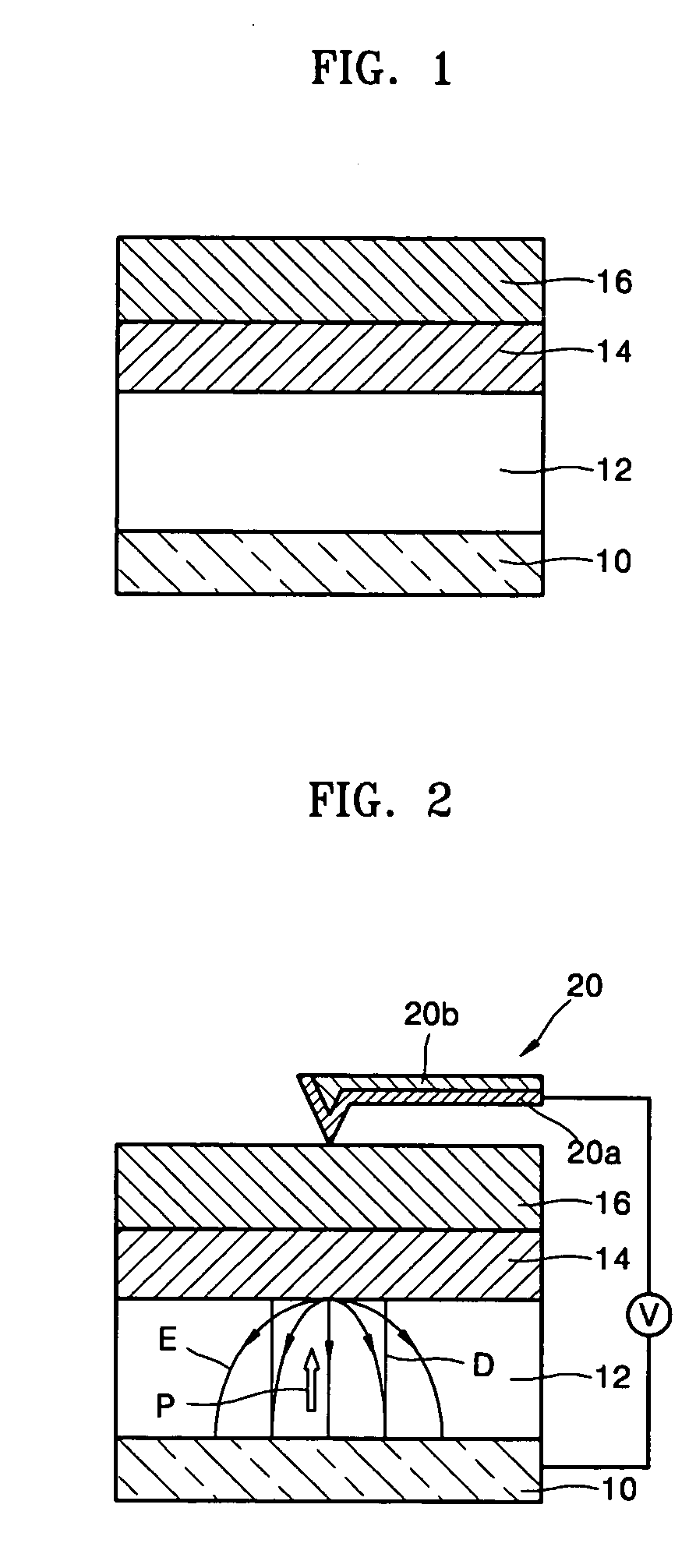
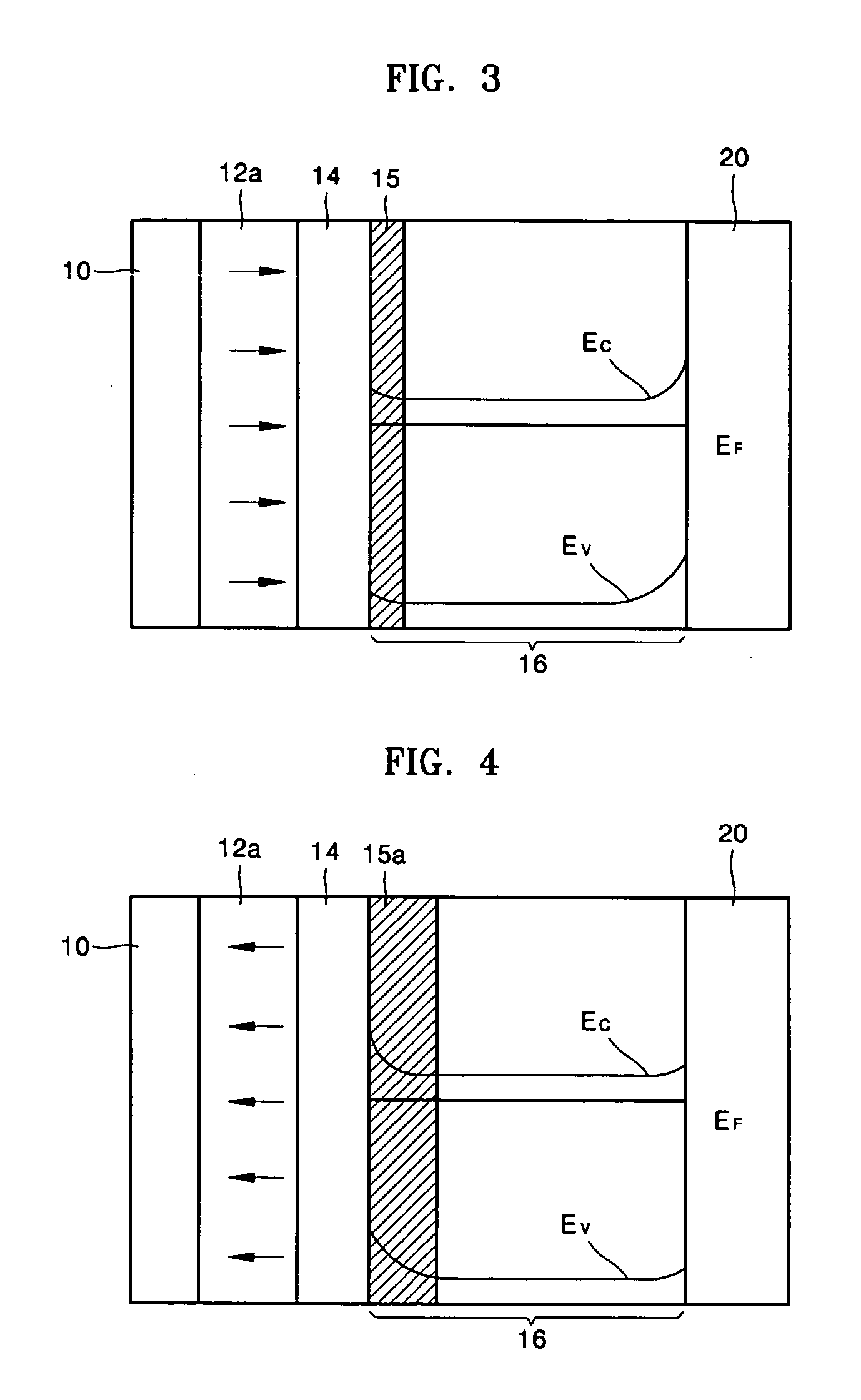
Patents
Literature
222results about "Ferroelectric carrier recording" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
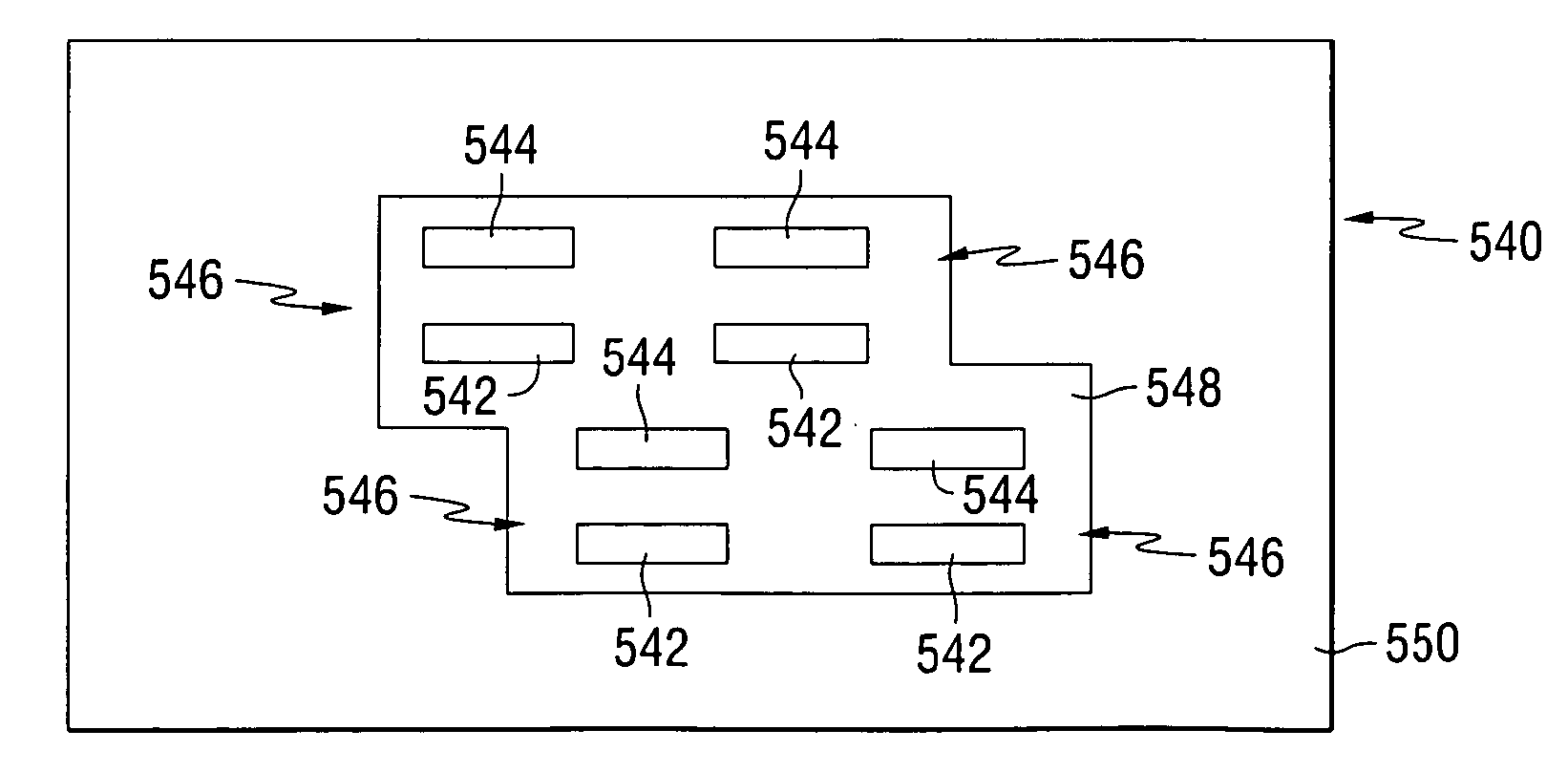
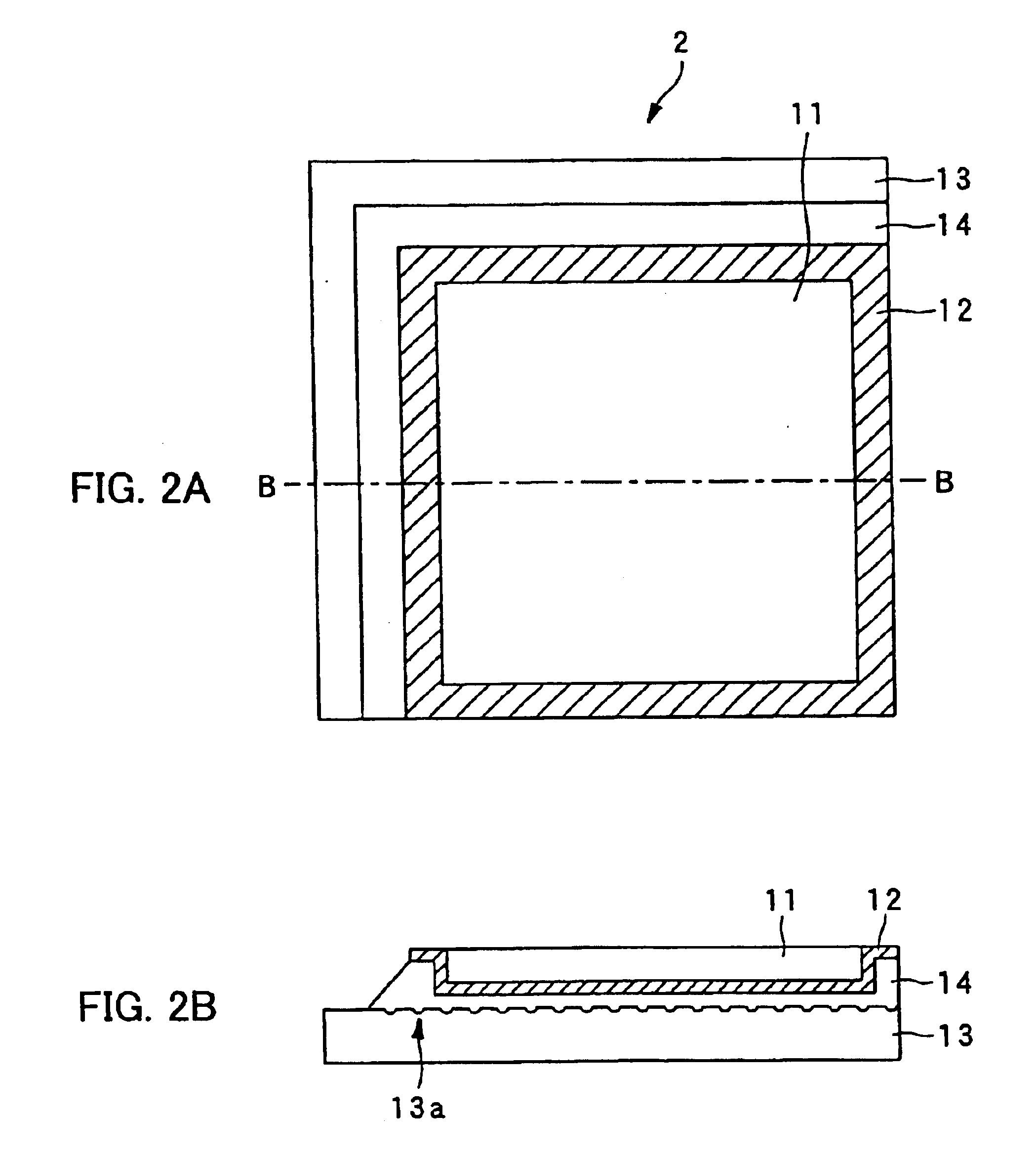
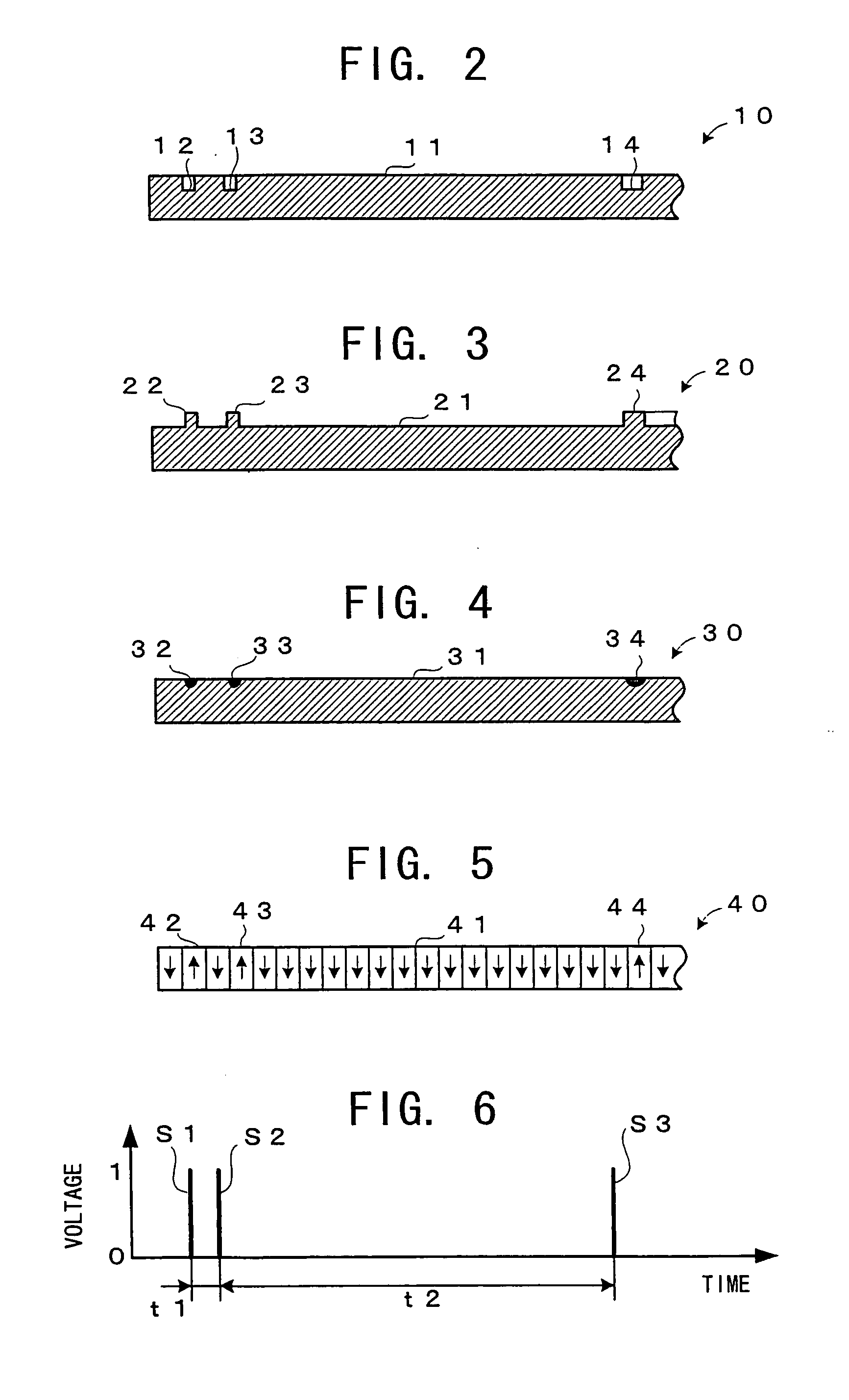
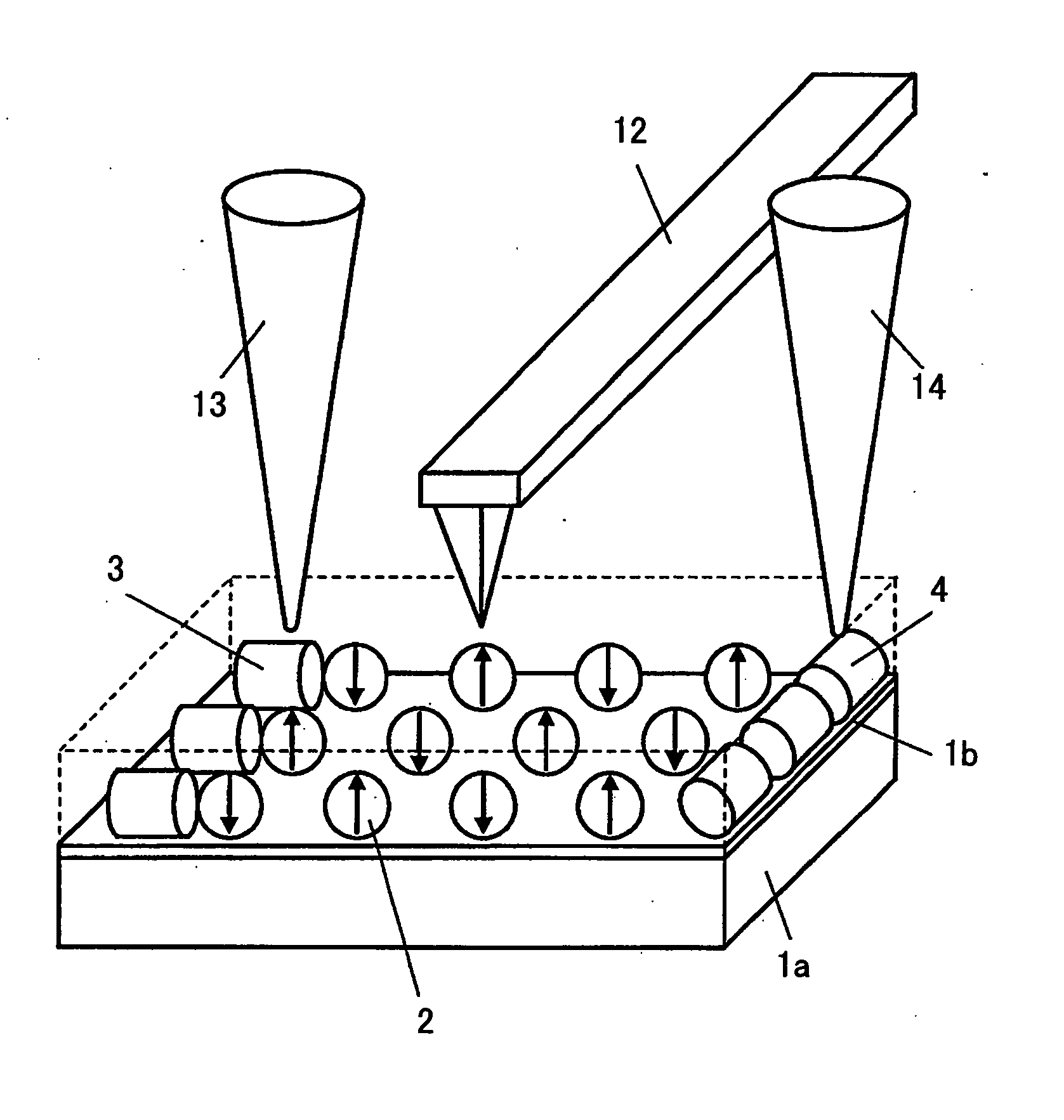
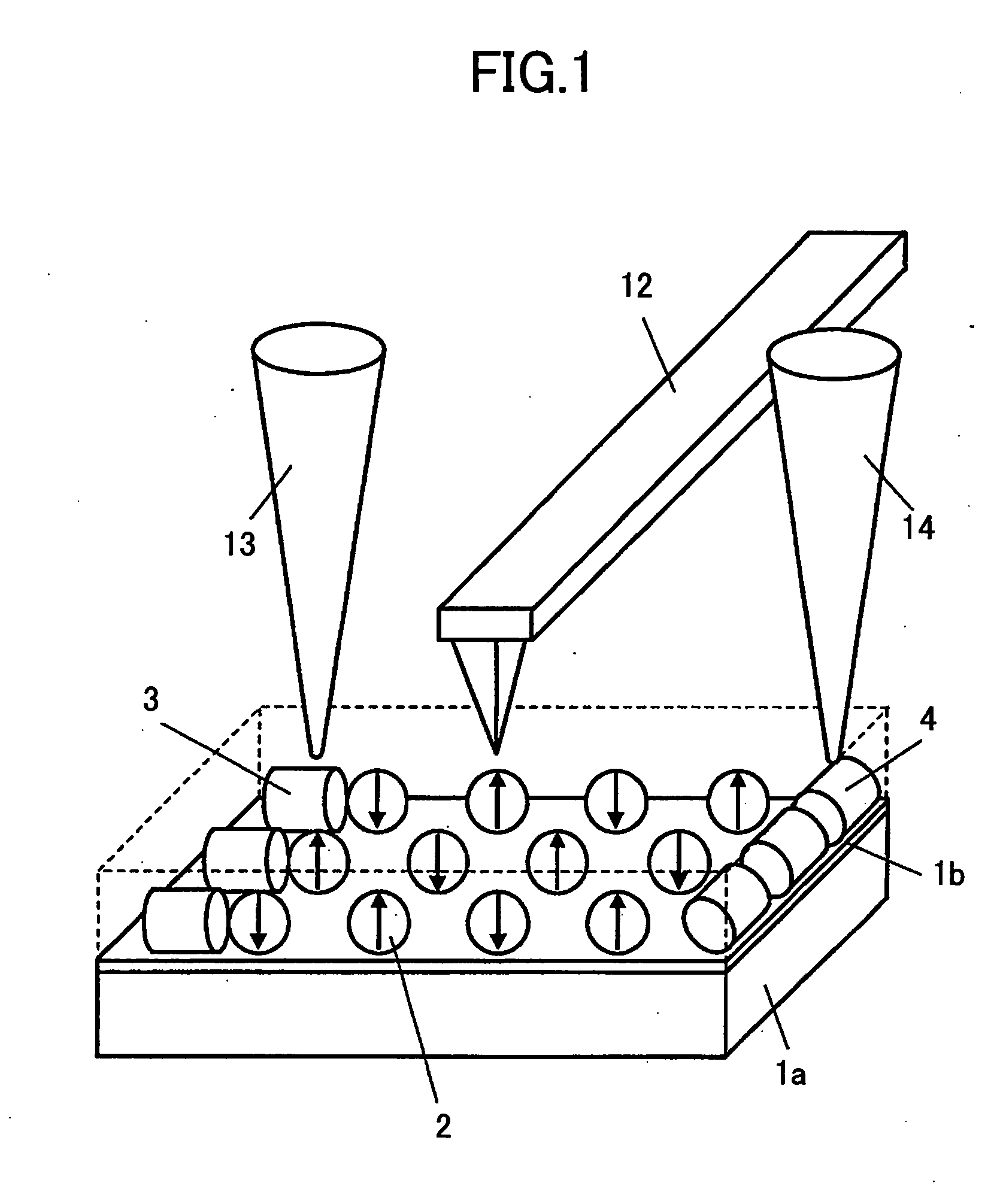
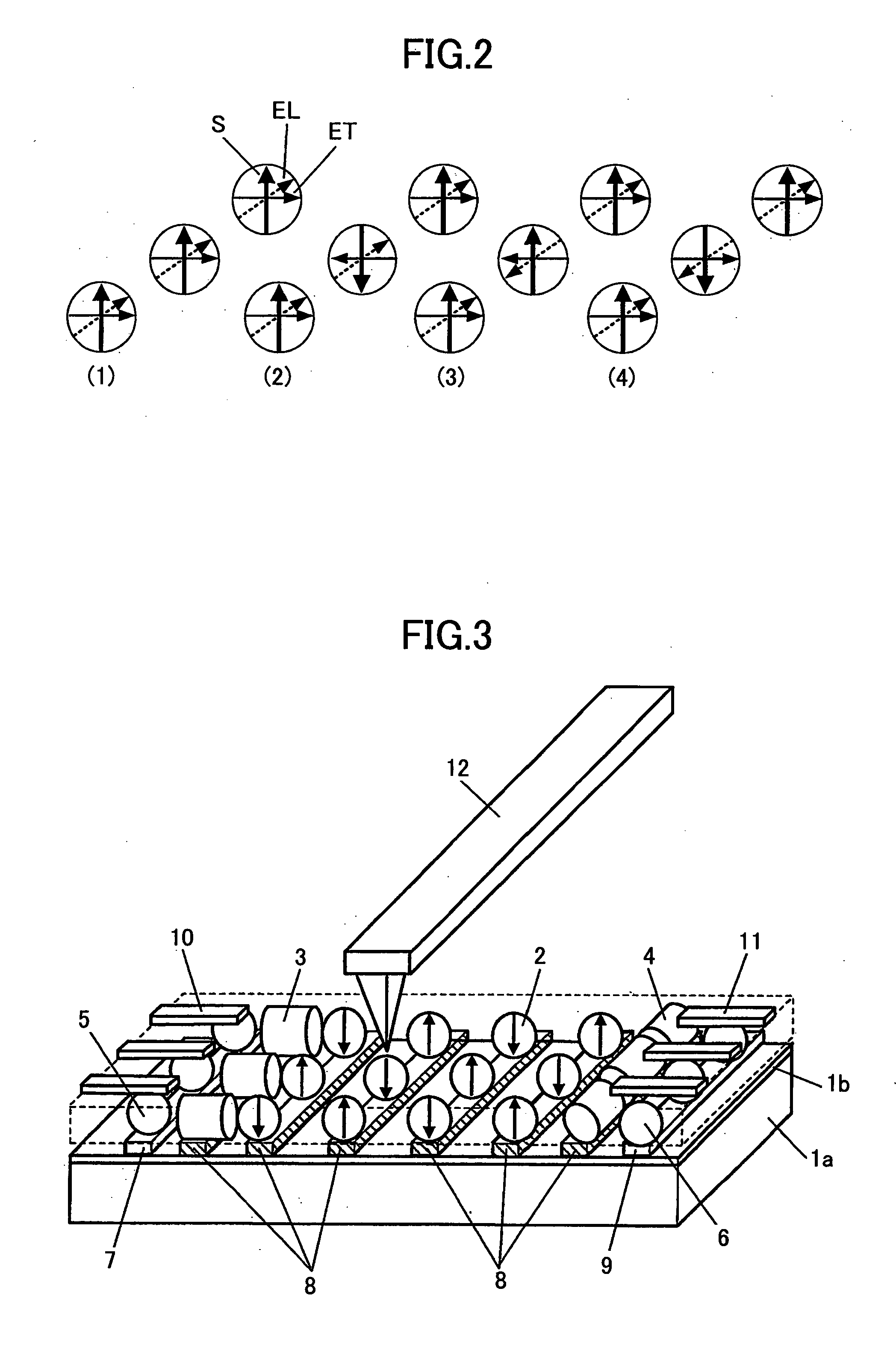
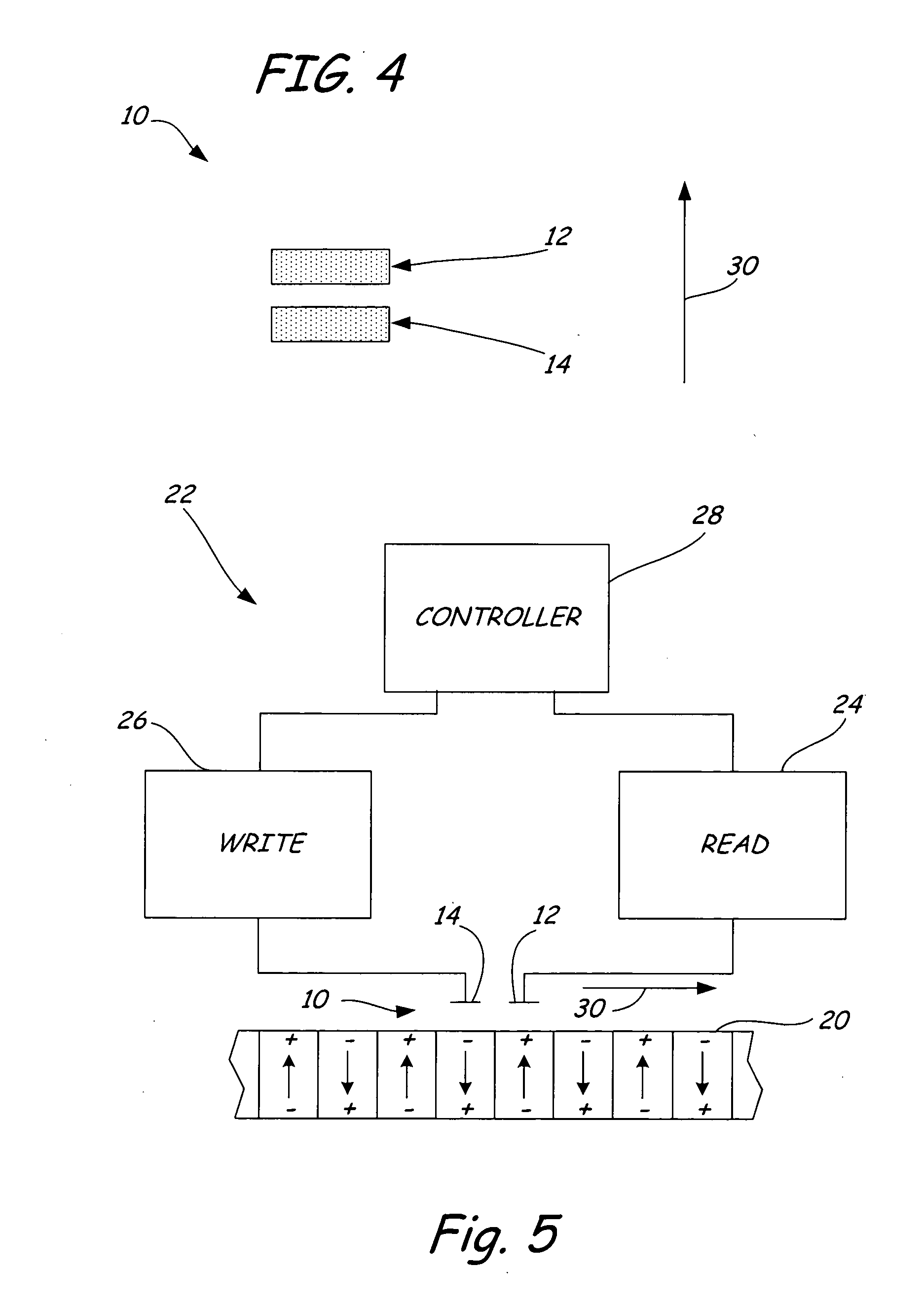
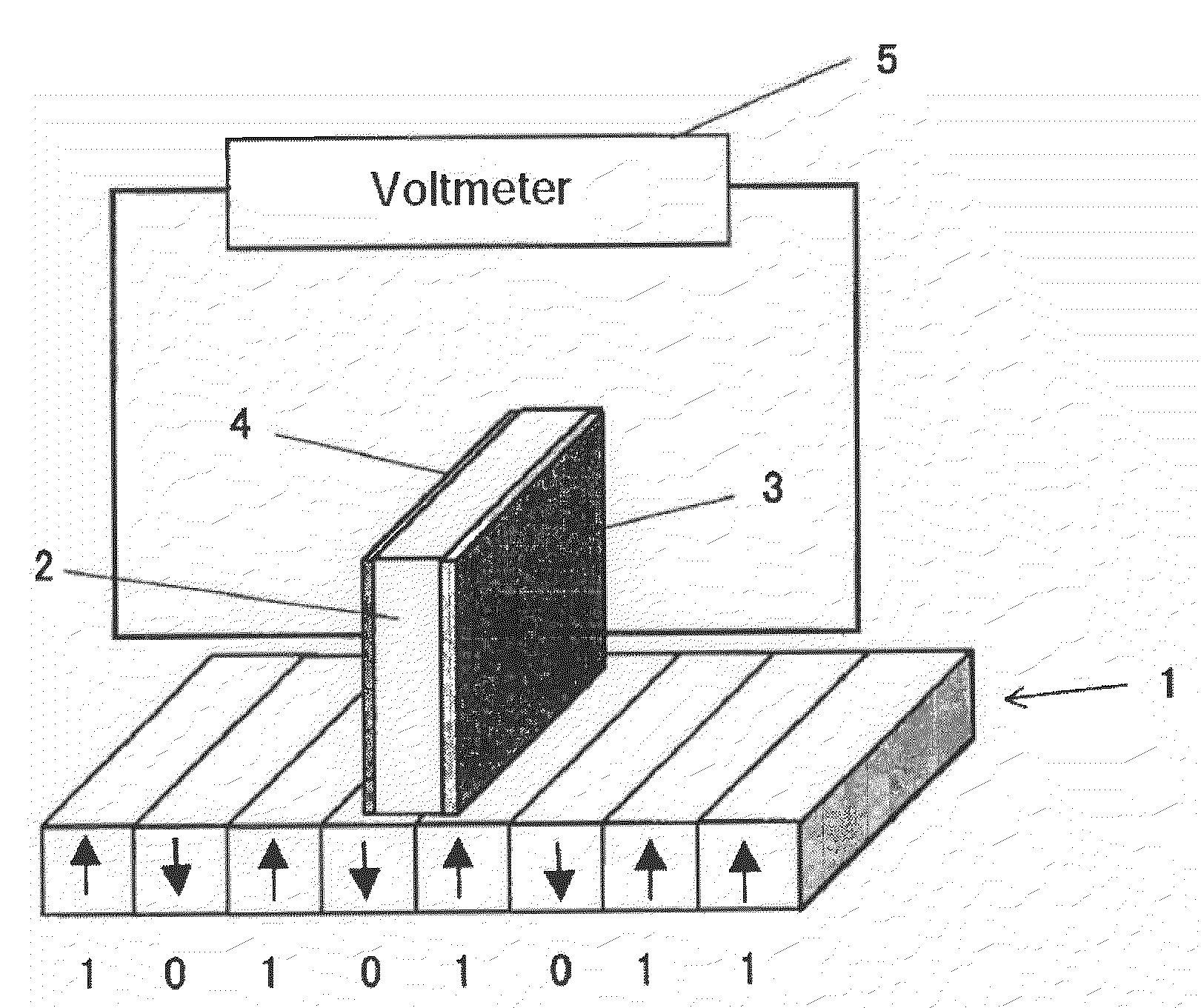
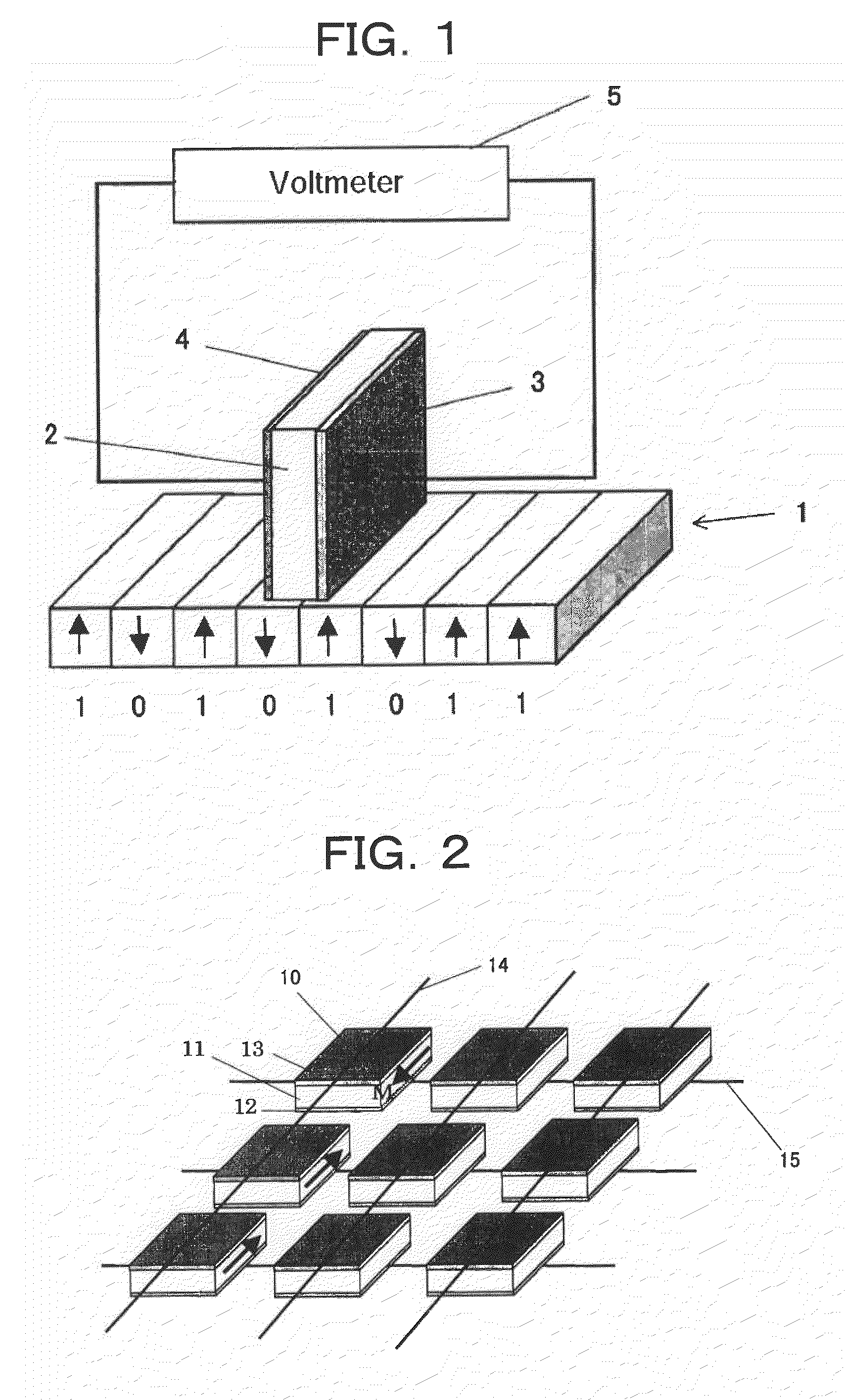
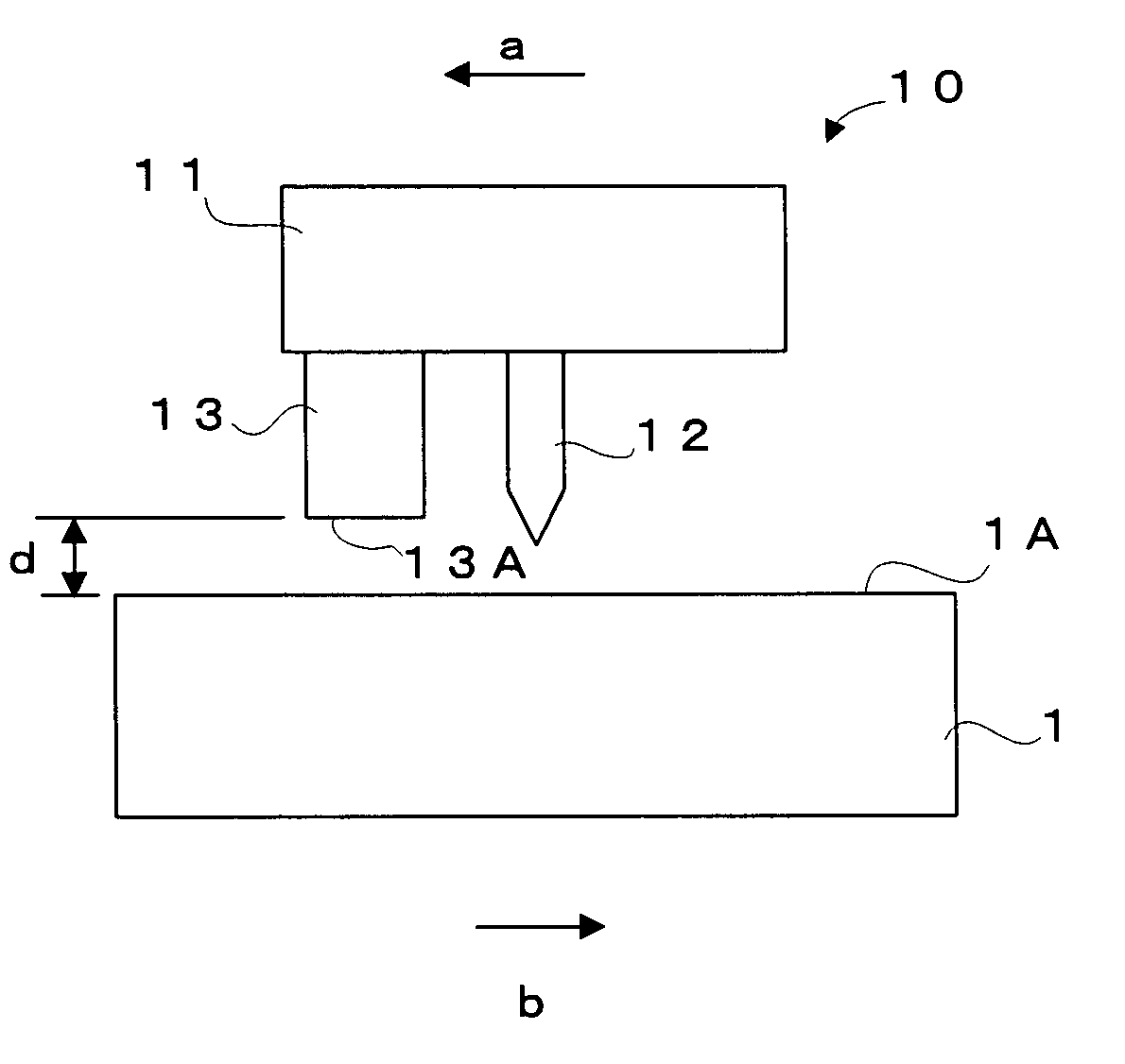
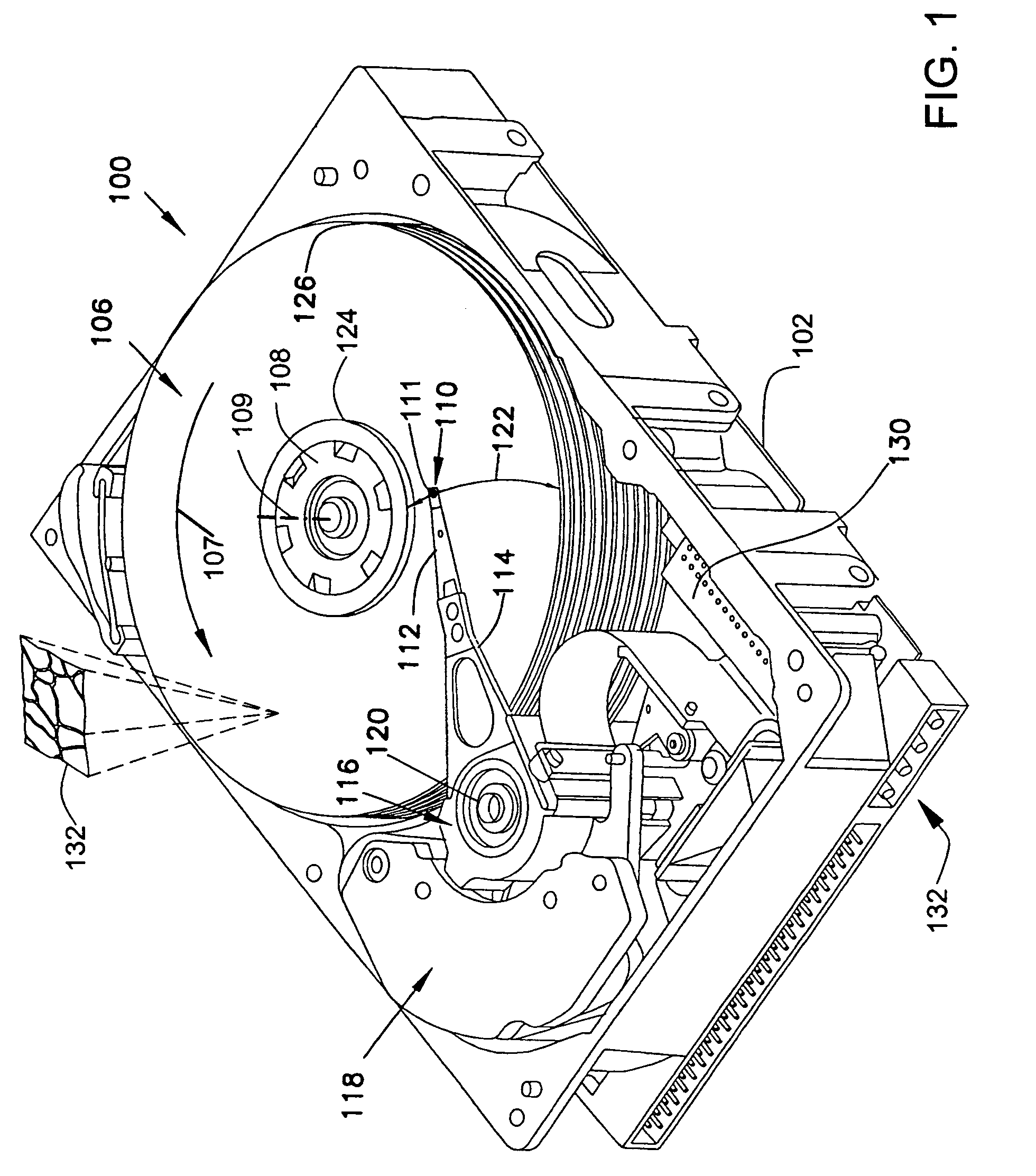
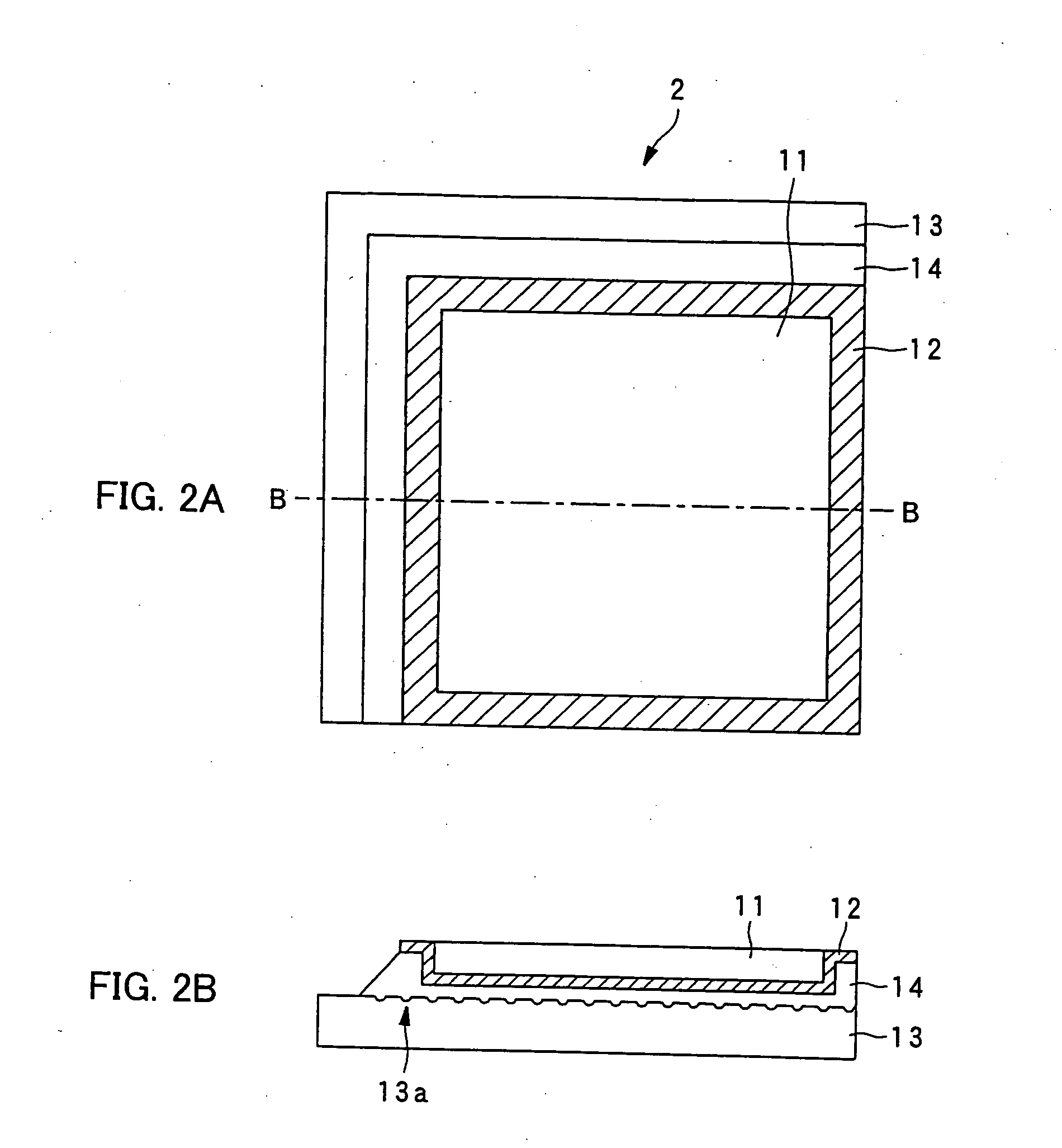
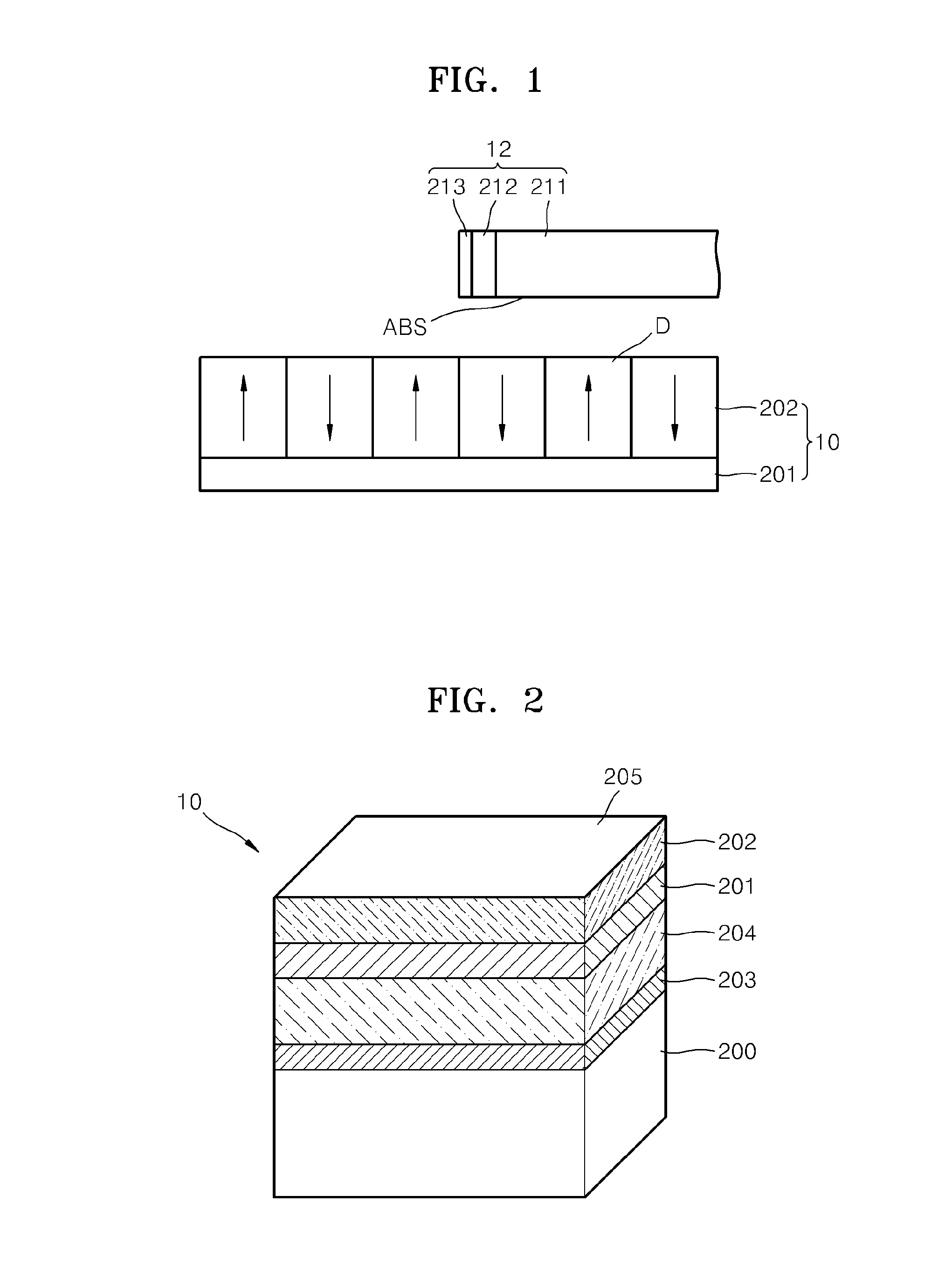
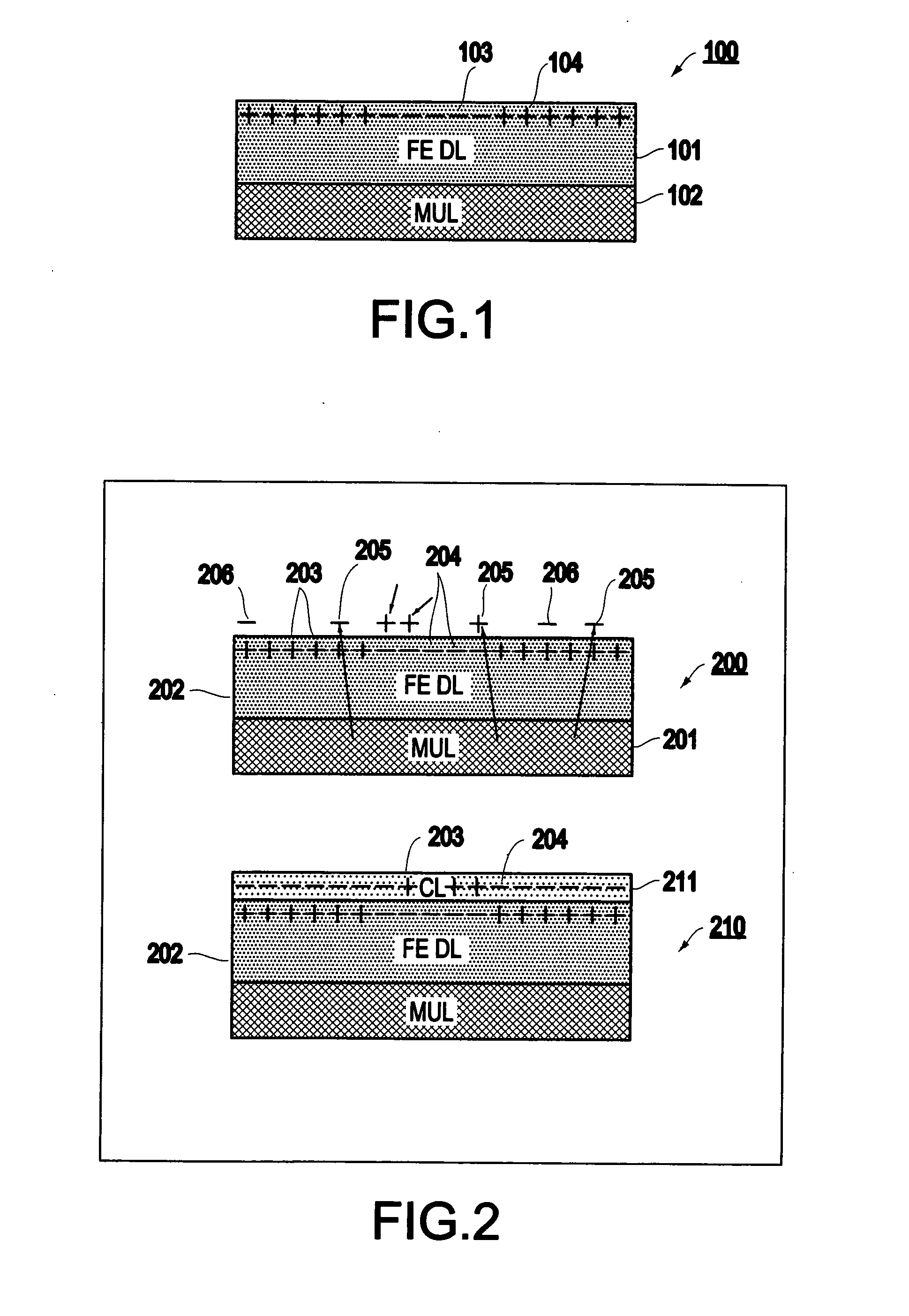
Ferroelectric probe storage apparatus
InactiveUS20060023606A1Ferroelectric carrier recordingRecord information storageTransducerEngineering
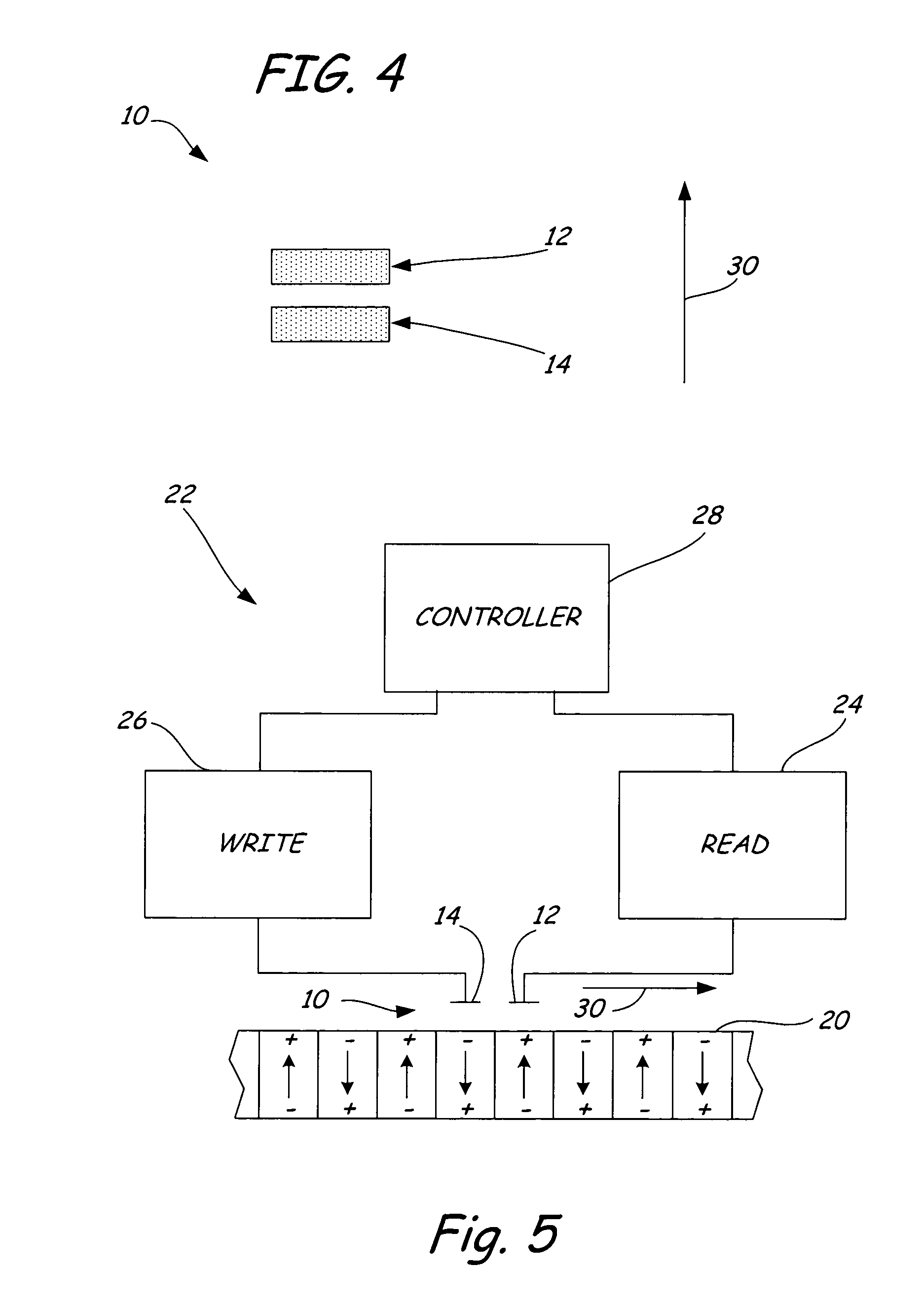
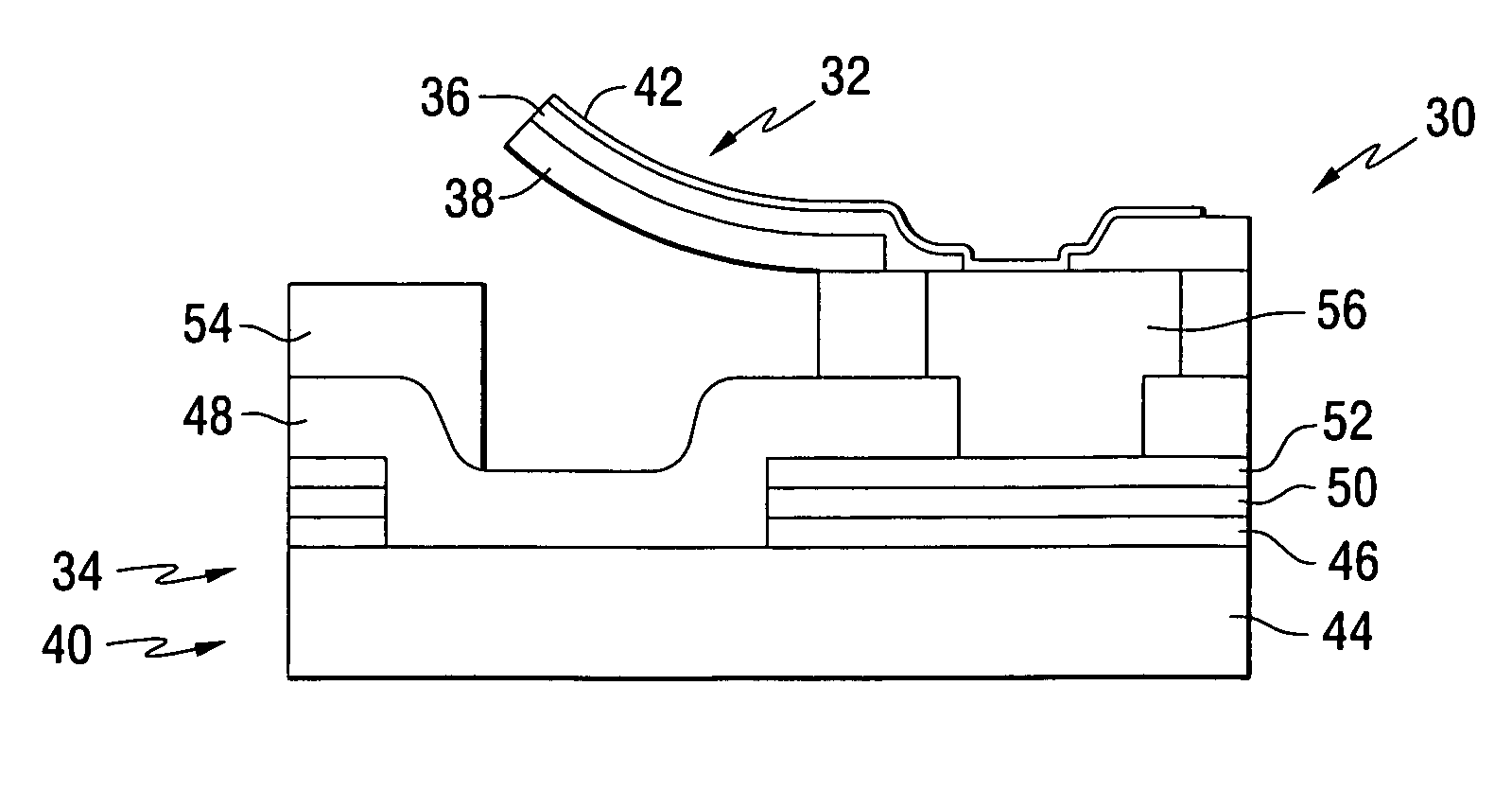
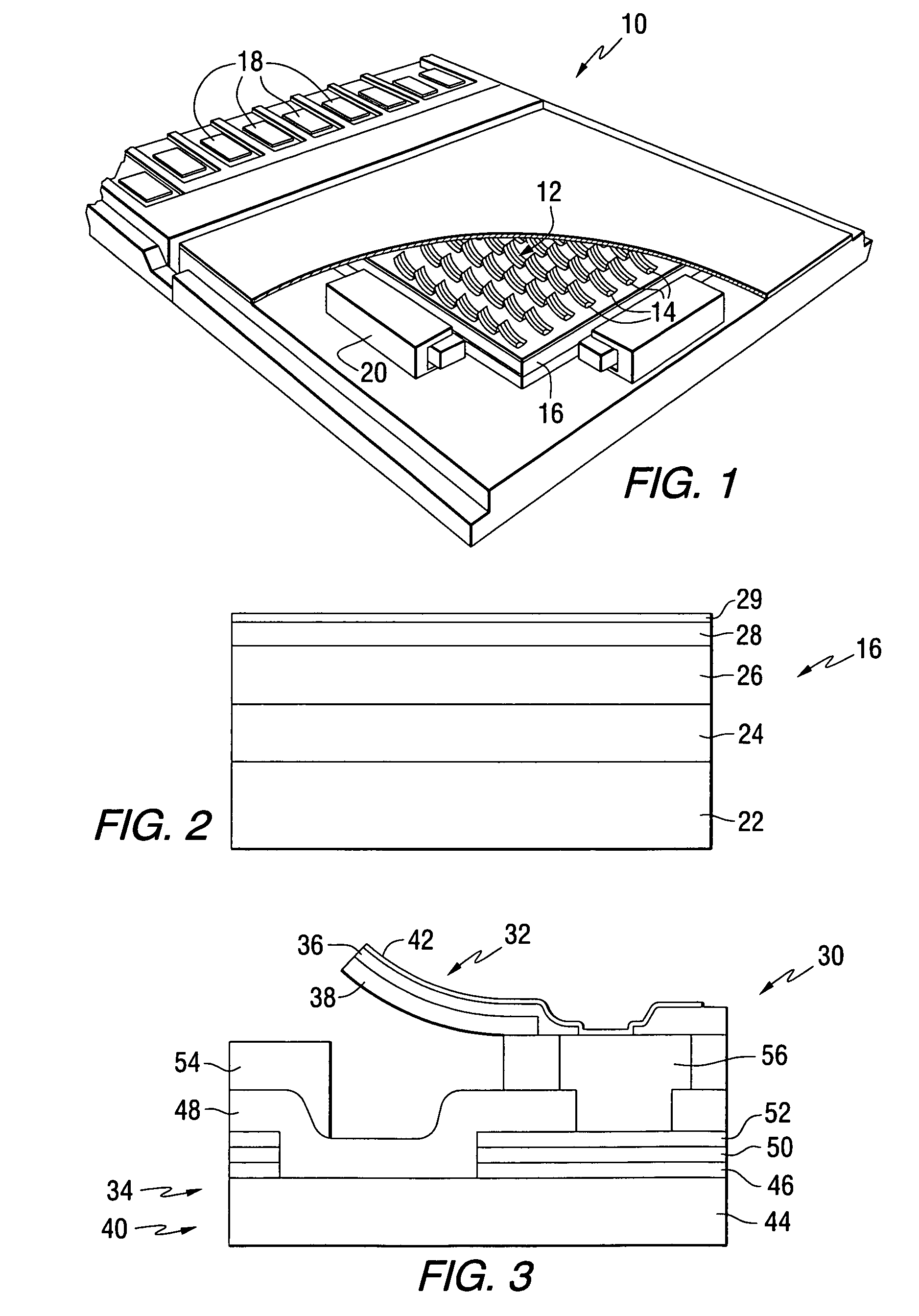
An apparatus comprises a ferroelectric storage medium, and a transducer for reading data from the ferroelectric storage medium and for writing data to the ferroelectric storage medium, wherein the transducer includes a substrate and a probe coupled to the substrate, wherein the probe includes a conductive element and a bilayer structure causing the probe to bend toward the ferroelectric storage medium.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
Two-parts ferroelectric RAM
InactiveUS6025618AEasy to manufactureEasy constructionPrinted circuit assemblingSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsElectrical connectionData recording
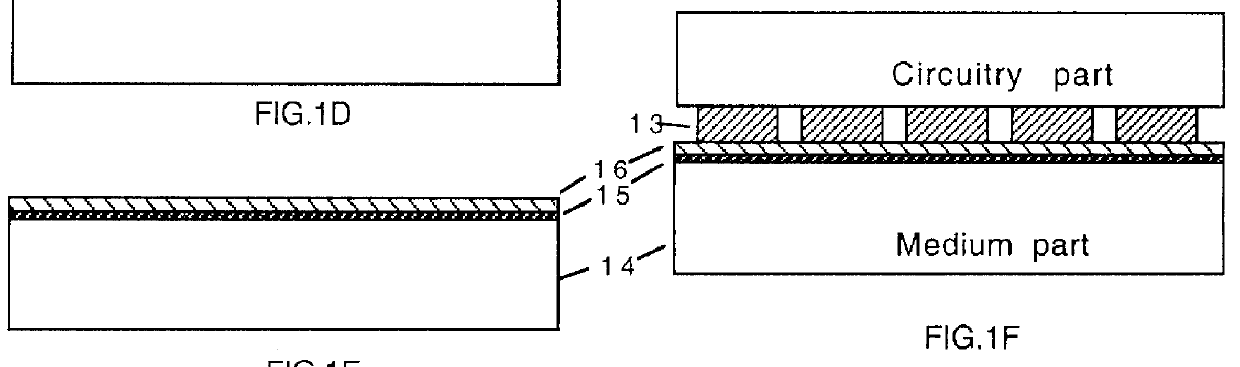
A method of fabricating a complex IC in two parts and making the electrical connections between them afterwards is described. By this method, a ferroelectric RAM is fabricated in two parts, where the first part has an array of unit cells each of those has a transistor or a group of transistors serving the purpose of selecting one address for data recording and has an array of electrically conductive pads facing upward, protruding out from the surface of the first part, where the second part consists of a data-recording layer on another substrate. The data-recording layer consists of ferroelectric material and is pressed on the first part during data writing and reading.
Owner:CHEN ZHI QUAN
Dielectric recording medium, and method of and apparatus for producing the same
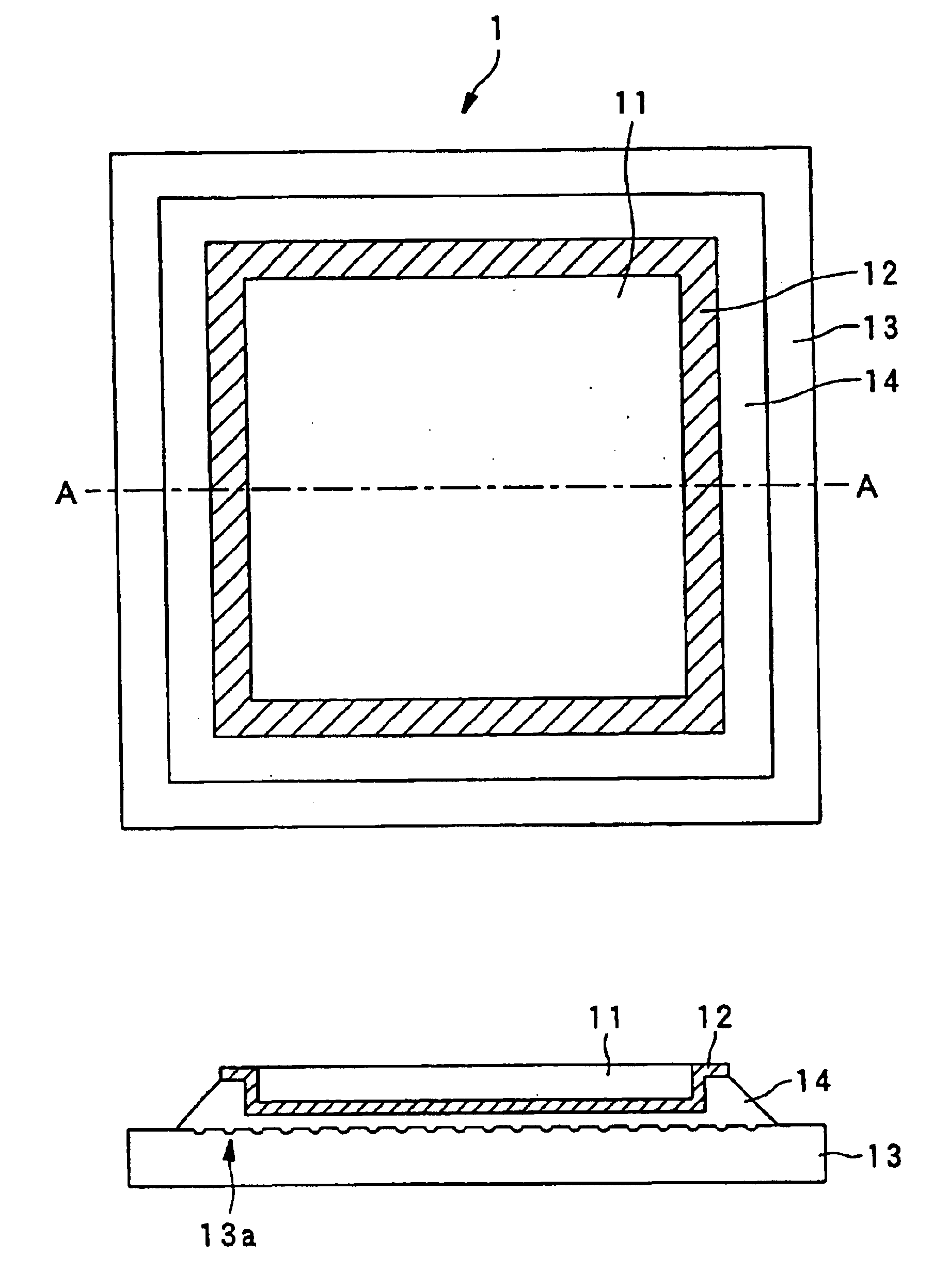
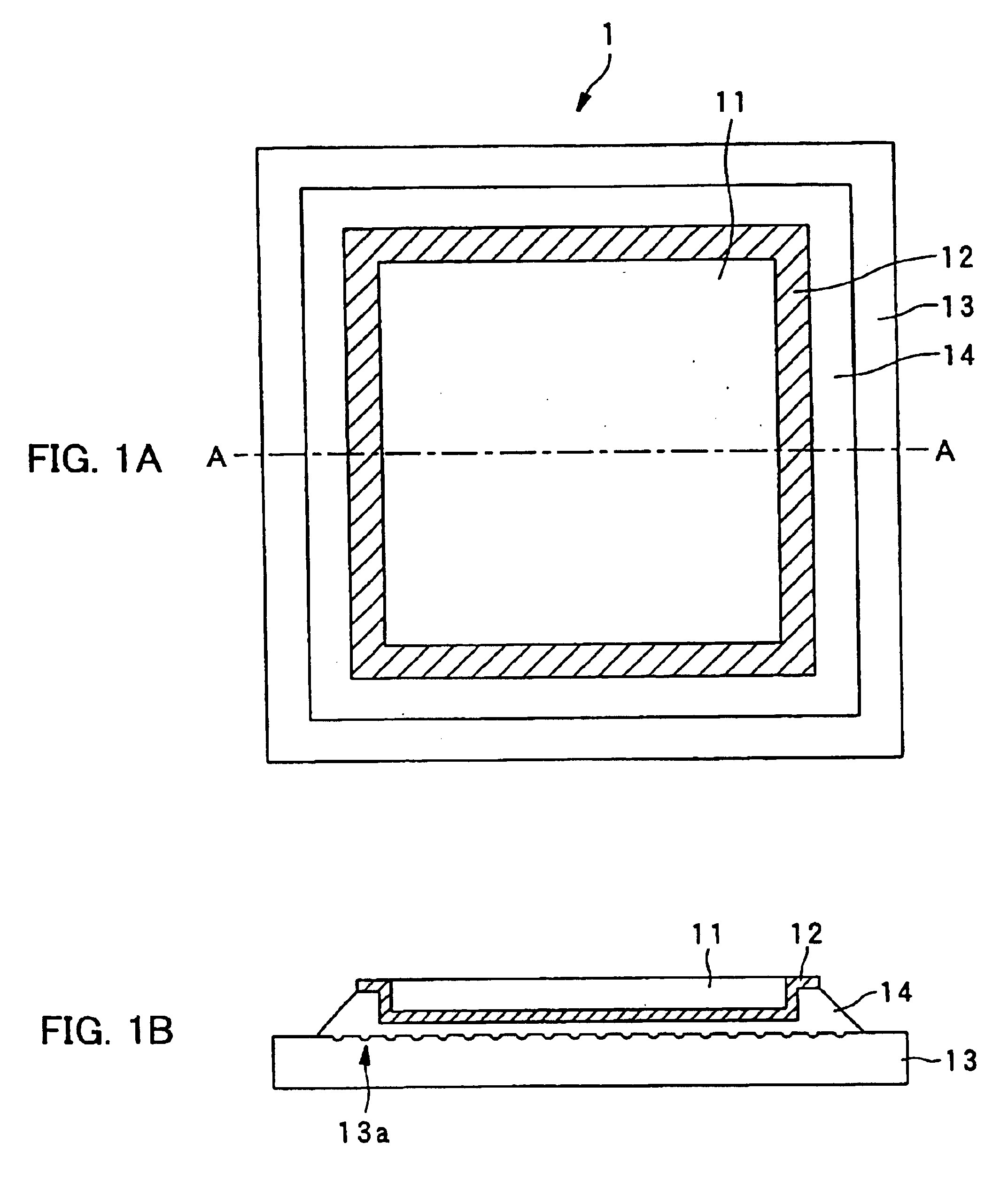
InactiveUS6841220B2Remove electric charge on the recording surface rapidlyImprove abilitiesNanoinformaticsFerroelectric carrier recordingSingle crystalOptoelectronics
The dielectric recording medium is provided with a dielectric material, a conductive thin film, and a substrate. The conductive thin film and the substrate are bonded by a resin adhesive. The dielectric material is constructed of a ferroelectric single crystal having a uniform thickness, and its one surface is used for a recording and / or reproducing surface, on the order of mm on a side and about 5000 Å thick. The conductive thin film, about 1000 to 2000 Å thick, is placed on a surrounding portion and a back surface of the recording and / or reproducing surface of the dielectric material. The substrate is intended to preserve the thin dielectric material and maintain the planarity, and concave portions are formed on the adhesive surface. The concave portions absorb excessive resin adhesive when the dielectric material is bonded onto the substrate, which makes the adhesive surface uniform and flat.
Owner:PIONEER CORP +1
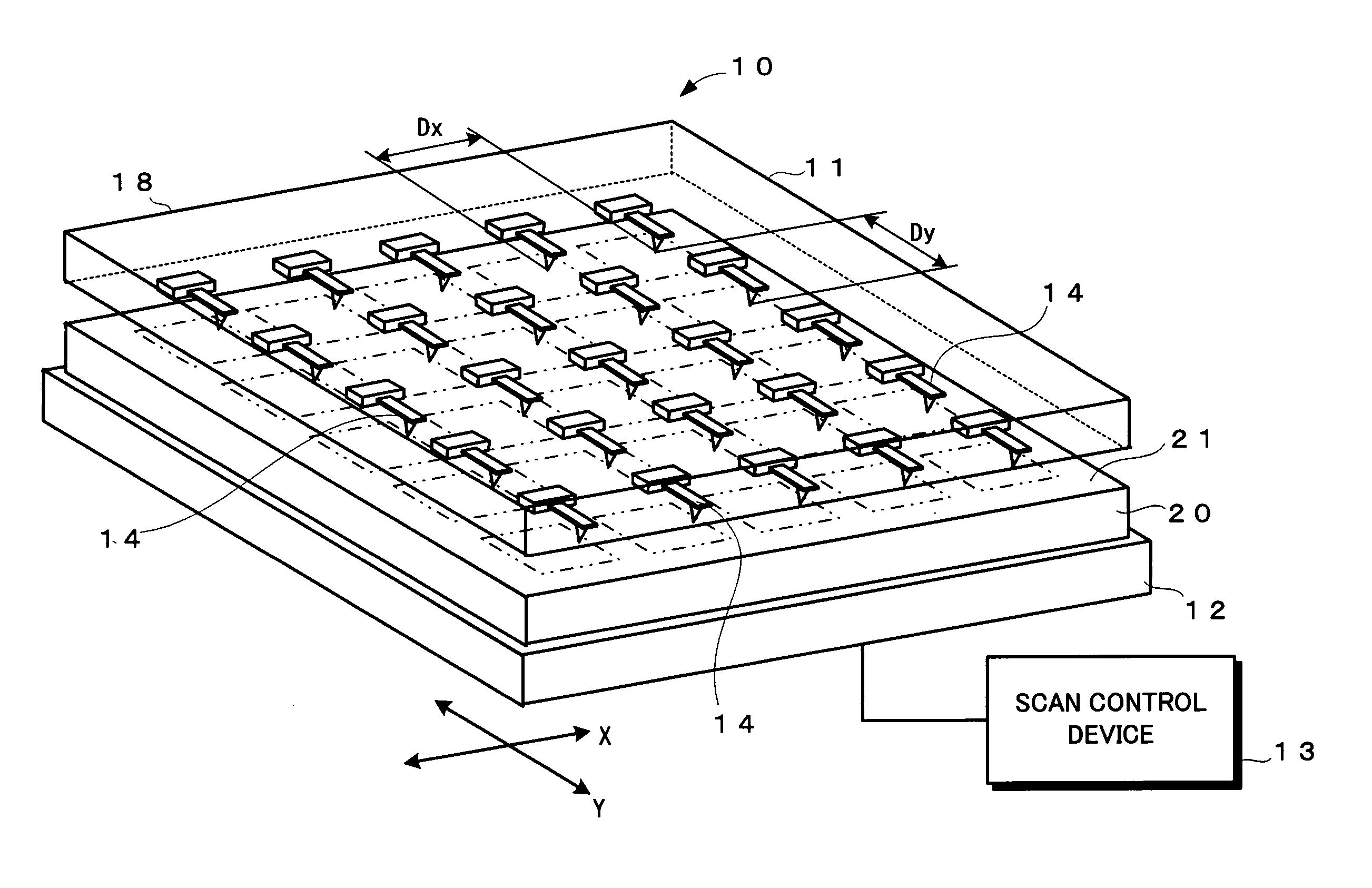
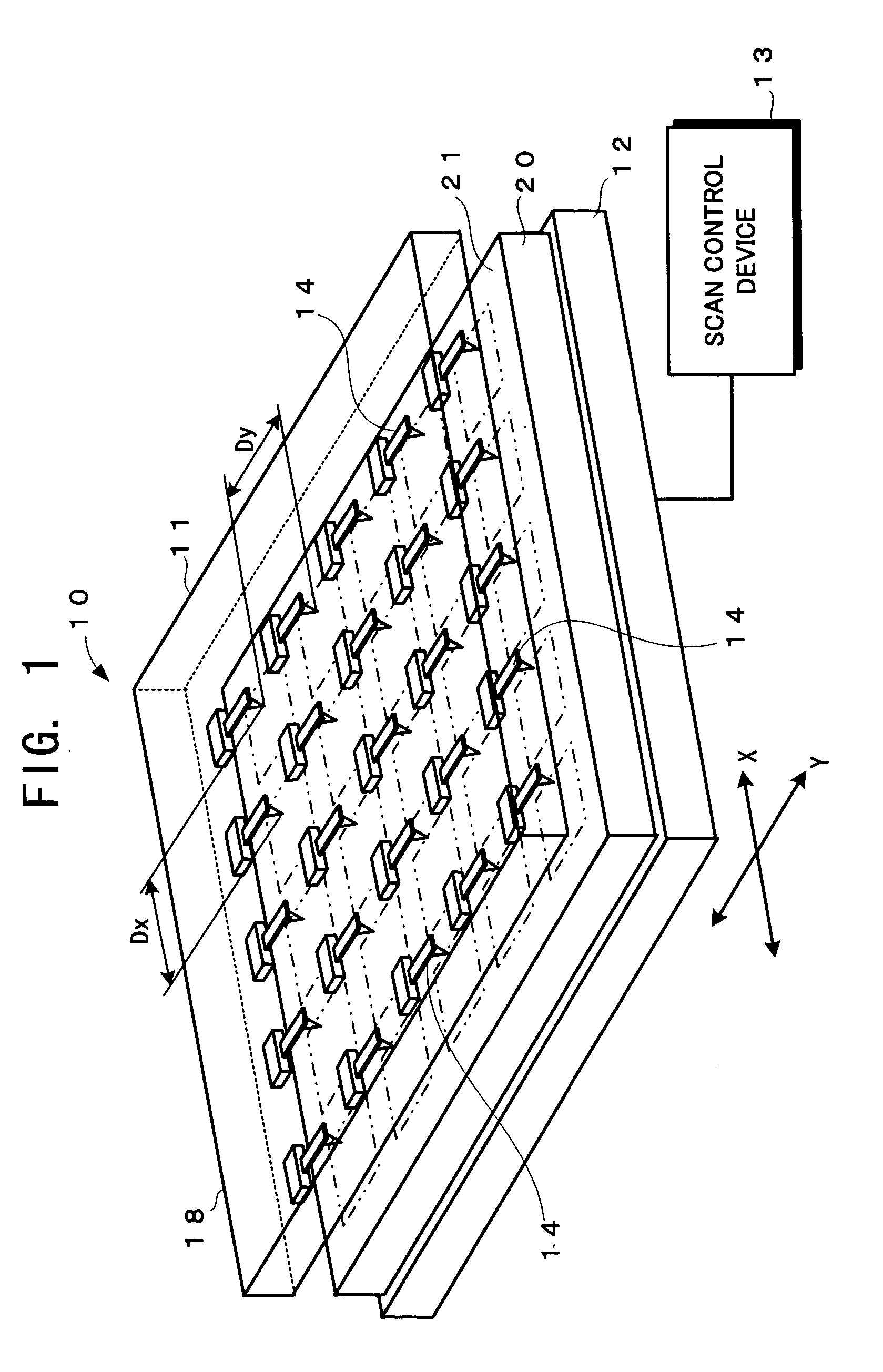
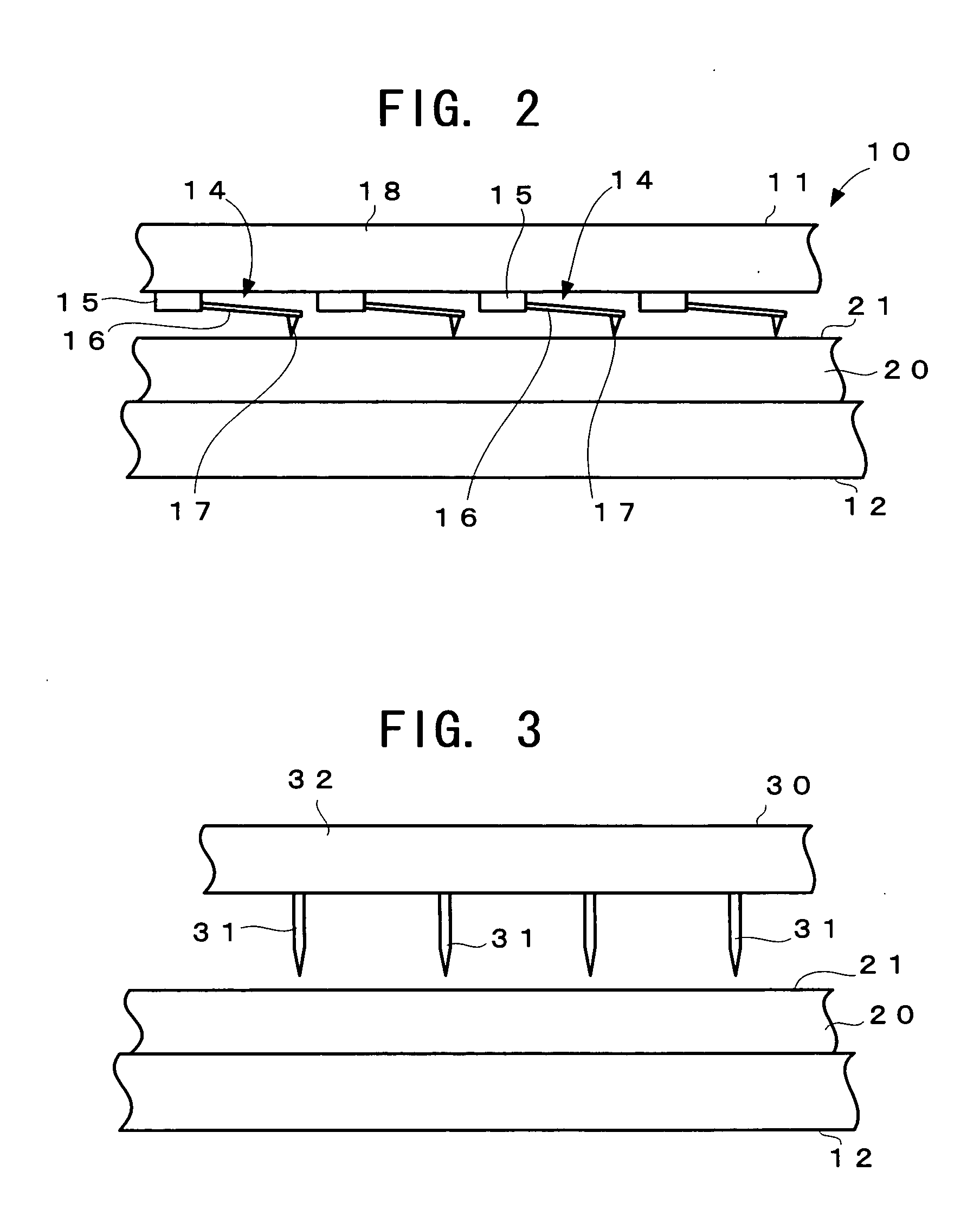
Information recording/reproducing apparatus and recording medium
InactiveUS20050099895A1Scan accuratelyReliable recordCombination recordingNanoinformaticsDisplacement controlComputer science
The scan range of each probe of a probe array is increased so that two or more recording areas formed on a recording surface of a recording medium can be scanned by using one probe. Moreover, displacement control information is recorded in advance between the recording areas which are mutually adjacent on the recording surface of the recording medium. On the basis of the displacement control information, the displacement of the probes are stabilized at a constant speed, and then the recording areas are scanned.
Owner:PIONEER CORP
Dielectric recording medium, and method of and apparatus for producing the same
InactiveUS7065033B2Facilitates probe tracingNanoinformaticsFerroelectric carrier recordingElectricityEngineering
A dielectric recording medium is provided with three layers of: a dielectric material, an electric conductor, and a substrate, and has a groove on the recording surface of the dielectric material. The groove is provided with one or a plurality of grooves. When a voltage is applied to a probe, the dielectric material just under the probe is polarized depending on an electric field generated between the electric conductor and the probe, which allows recording. Moreover, the groove facilitates the probe tracking since the probe scans along this groove.
Owner:PIONEER CORP +1
Recording/reproducing head, method of producing the same, and recording apparatus and reproducing apparatus
InactiveUS20050122886A1Easily and efficiently producedRecord data with stabilityElectrostatic charge injection carrier recordingVariable capacitance carrier recordingComputer hardwareHead parts
A recording / reproducing head for performing at least one of a record operation of recording information onto a dielectric recording medium and a reproduction operation of reproducing the information from the dielectric recording medium, the recording / reproducing head provided with: a support member which extends in a longitudinal direction of the recording / reproducing head; and a projection portion which is mounted on the support member such that a tip of the projection portion faces the dielectric recording medium, the projection portion having a ridge-line on the tip, the projection portion being capable of contacting the dielectric recording medium at one point on the ridge-line.
Owner:PIONEER CORP
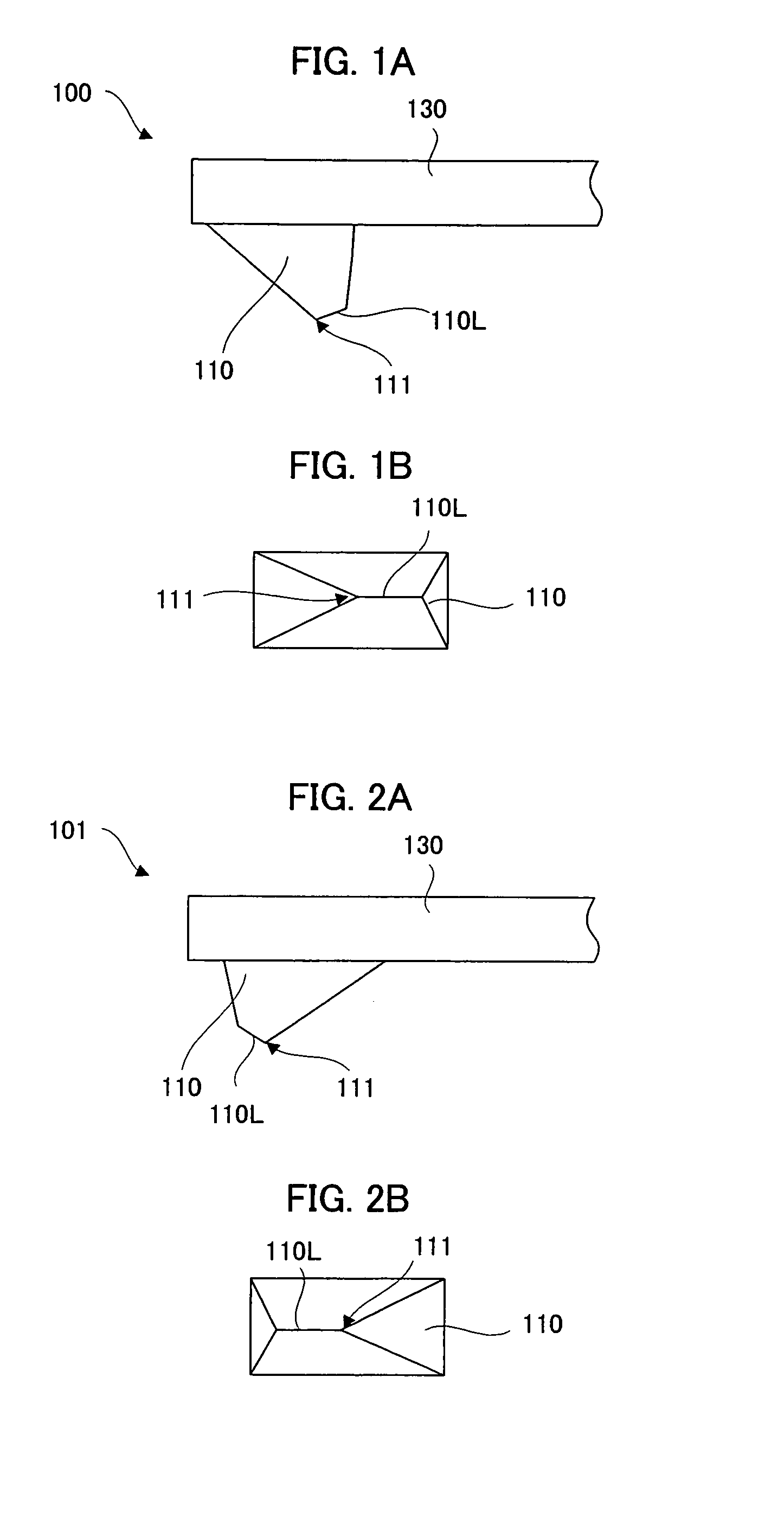
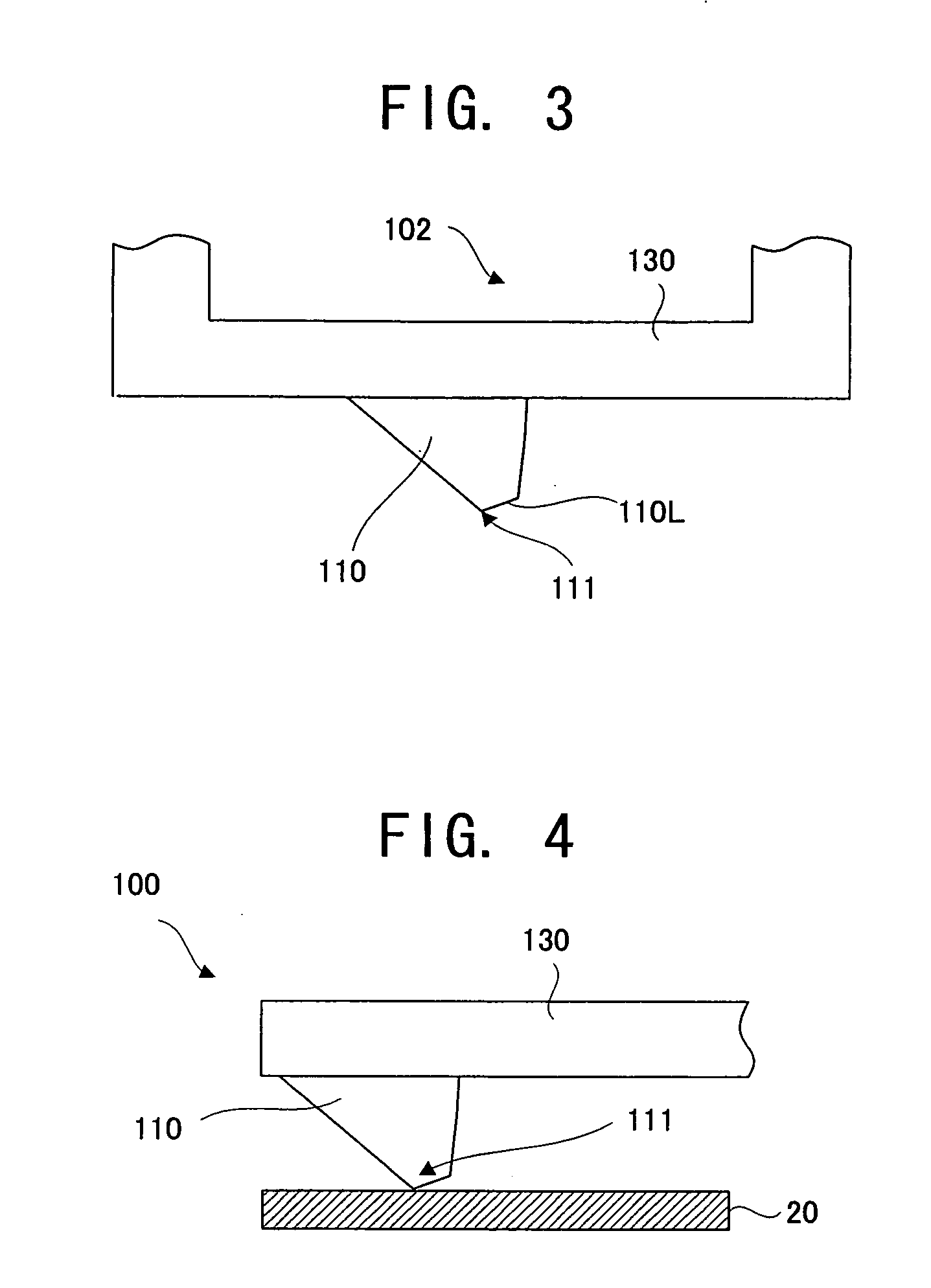
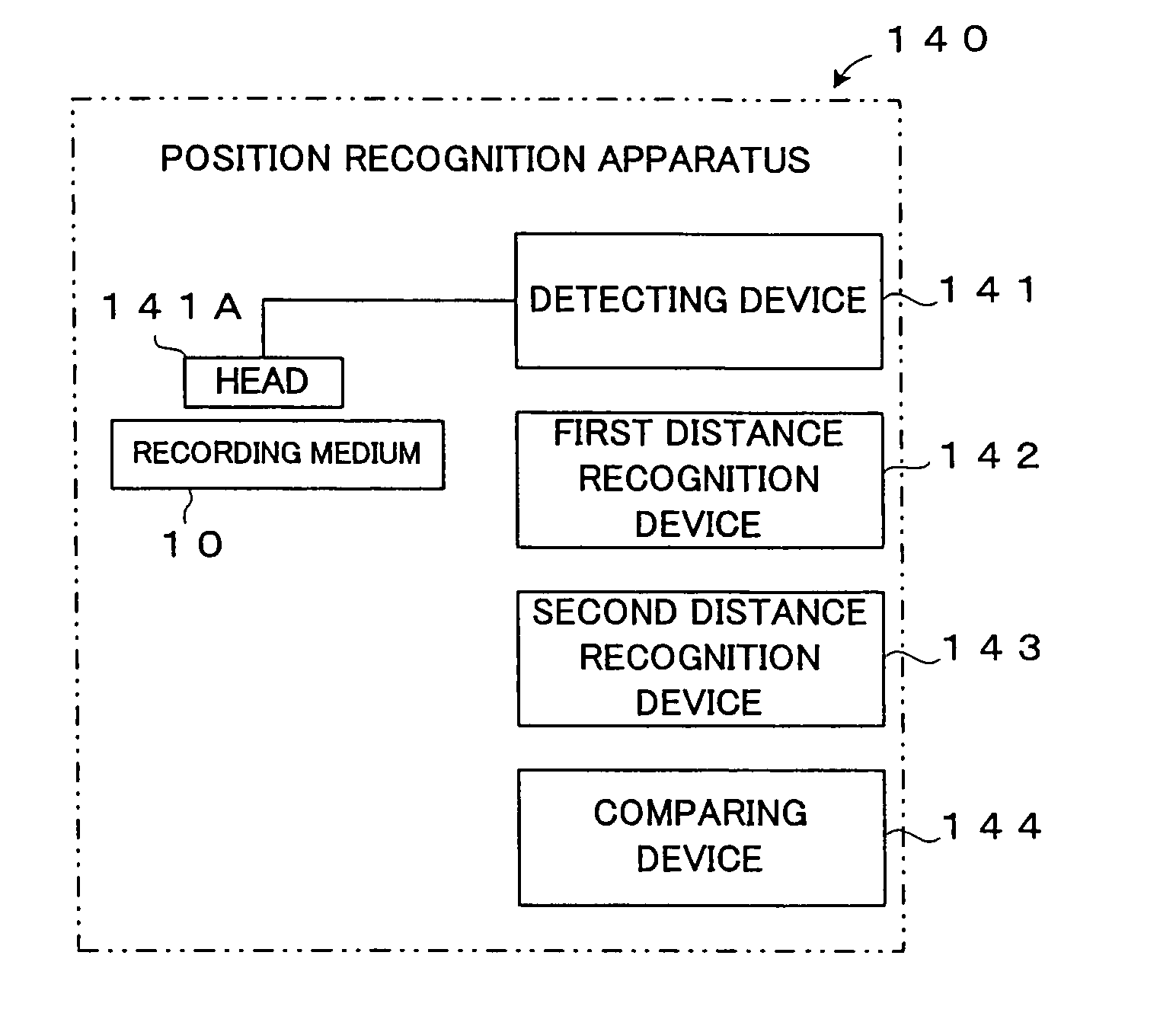
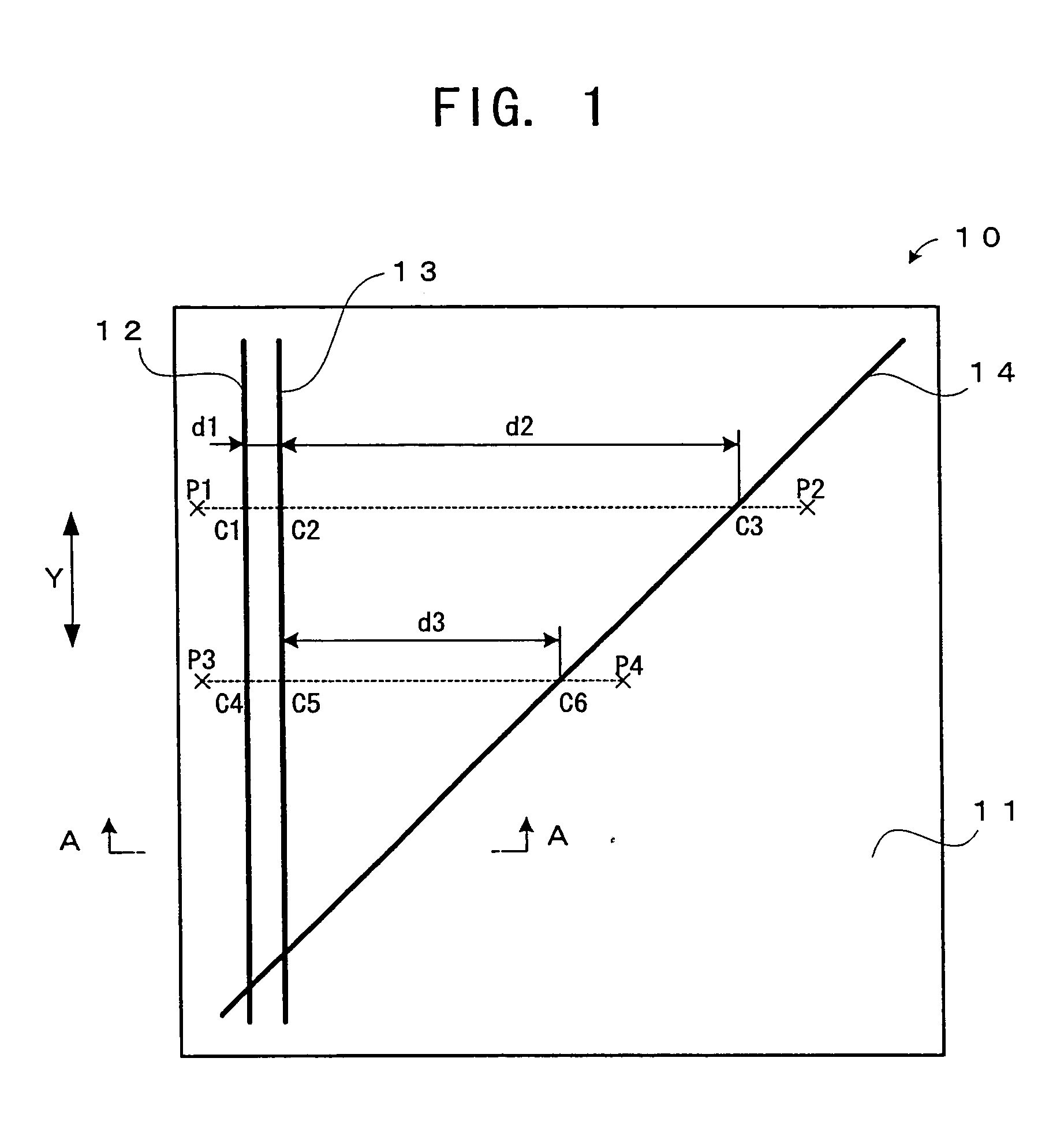
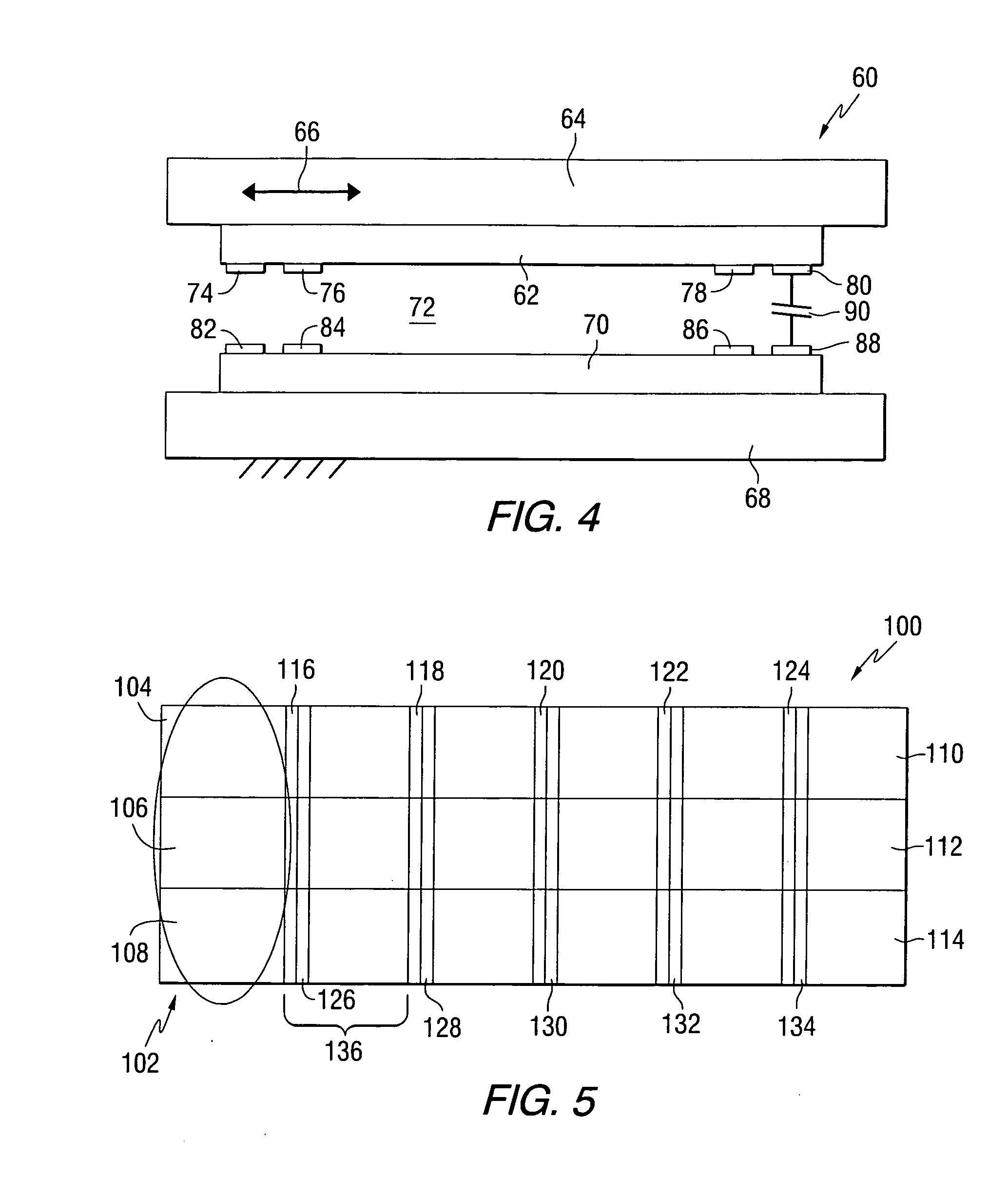
Recording medium having position recognition structure, and position recognition apparatus and method
InactiveUS20050047288A1Accurate identificationShorten the length of timeFilamentary/web record carriersNanoinformaticsComputer graphics (images)Scan line
Position information is formed on a recording surface 11 of a recording medium 10. The position information is constructed from first line segments, which are parallel to each other, and a second line segment, which crosses the first line segments. On the basis of a distance between (i) an intersection C1 of one of the first line segment and a scan line and (ii) an intersection C2 of another of the first line segments and the scan line, the intersection C2 and an intersection C3 of the second line segment and the scan line are measured or calculated. By this, a position of a head in a Y direction is recognized.
Owner:PIONEER CORP
Information recording apparatus and information recording method, information reproducing method and fade-in memory
InactiveUS20070230233A1High resolutionImproving recording density and accessibilityCombination recordingRadiation pyrometryLight emitting devicePhysics
An information recording apparatus comprises a plurality of fine particles forming an array on a plane in close proximity of each other, each of the plural particles including a ferromagnetic metal, a light-emitting device for exciting a near-field light, and a photo-electric conversion element for detecting a near-field light traveled along the fine particles.
Owner:RICOH KK +1
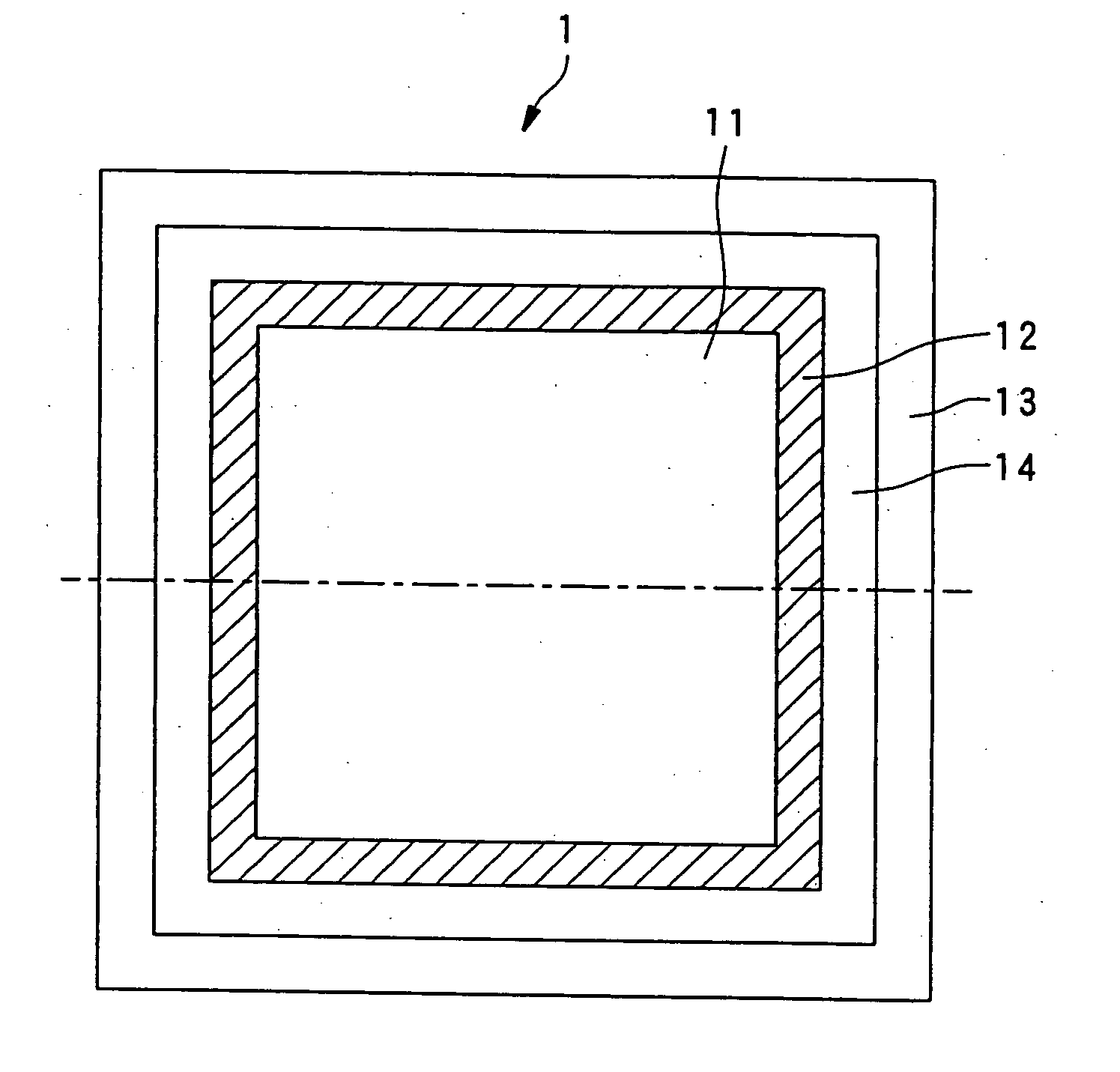
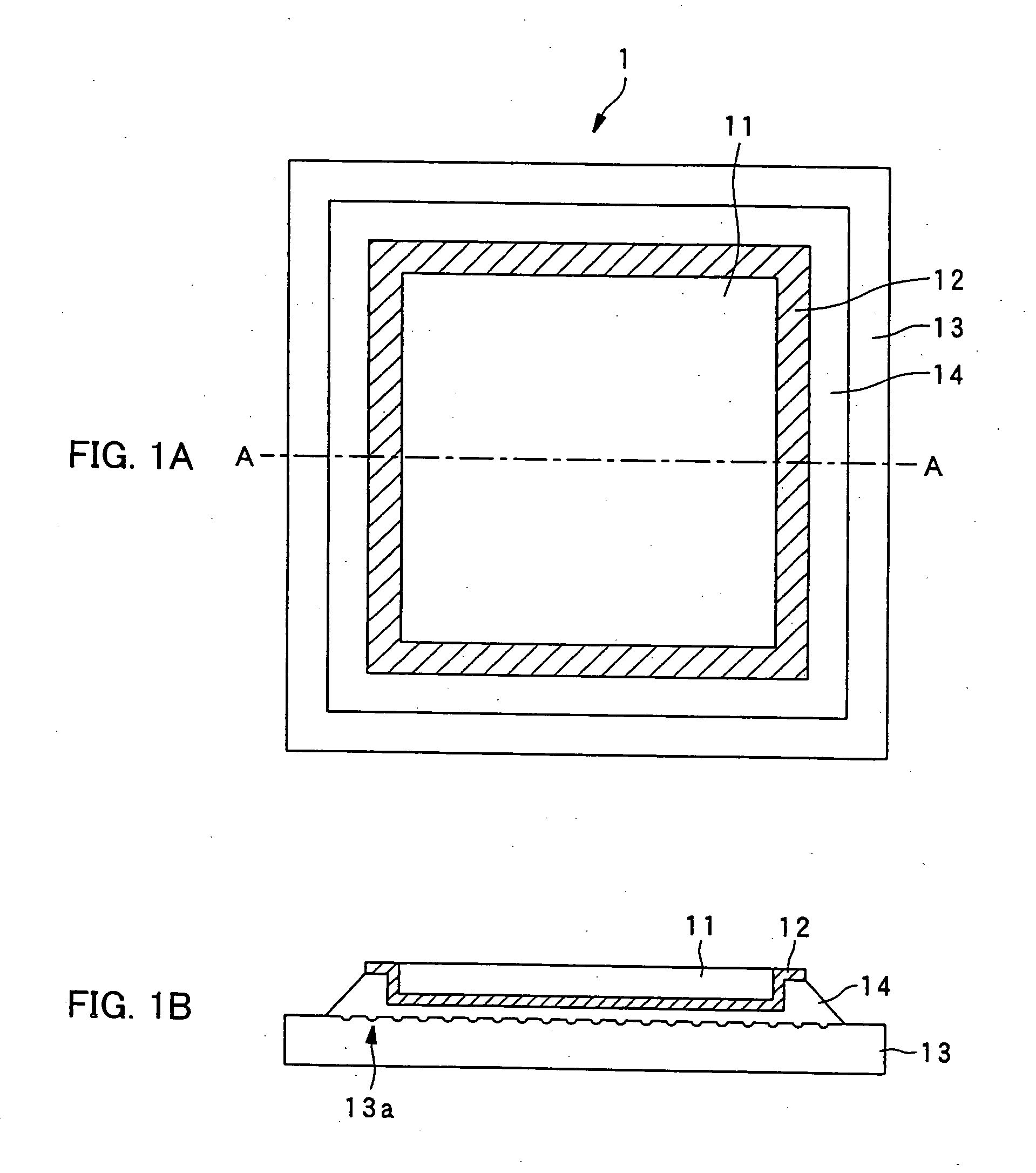
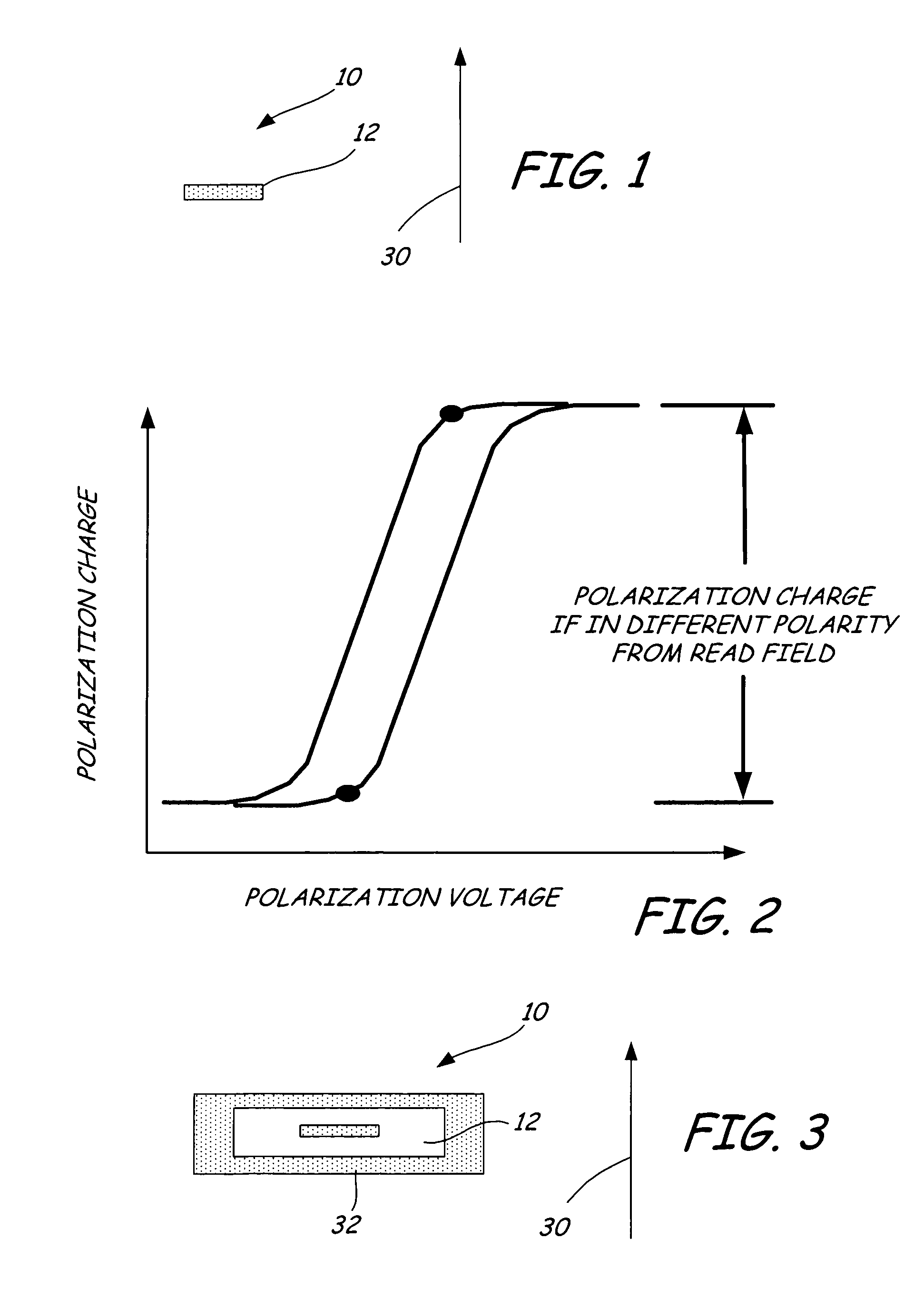
Record condition extraction system and method of dielectric recording medium, and information recording apparatus
InactiveUS6912193B2High-density and stable microdomainHigh-density and stableNanoinformaticsFerroelectric carrier recordingMeasurement deviceOutput device
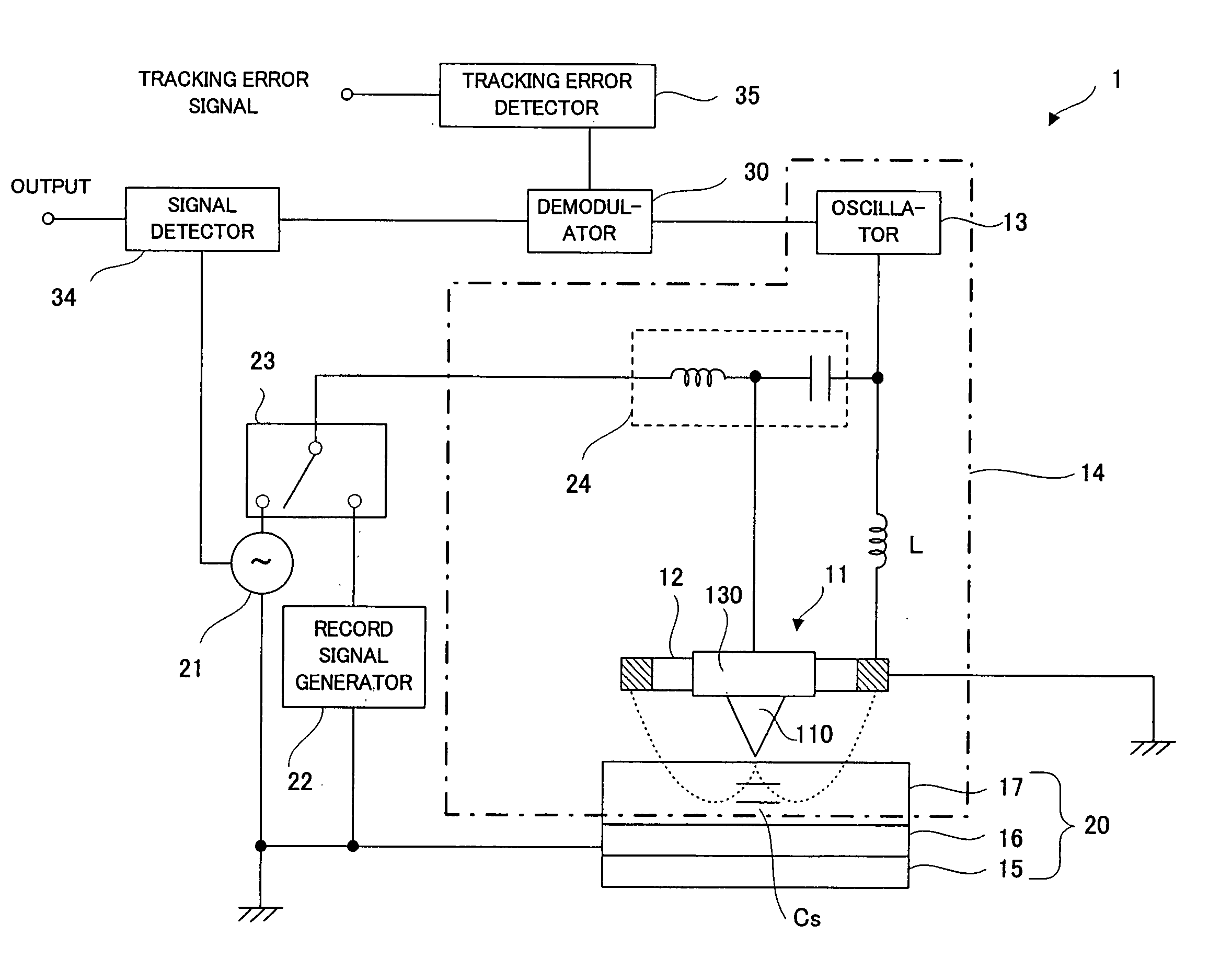
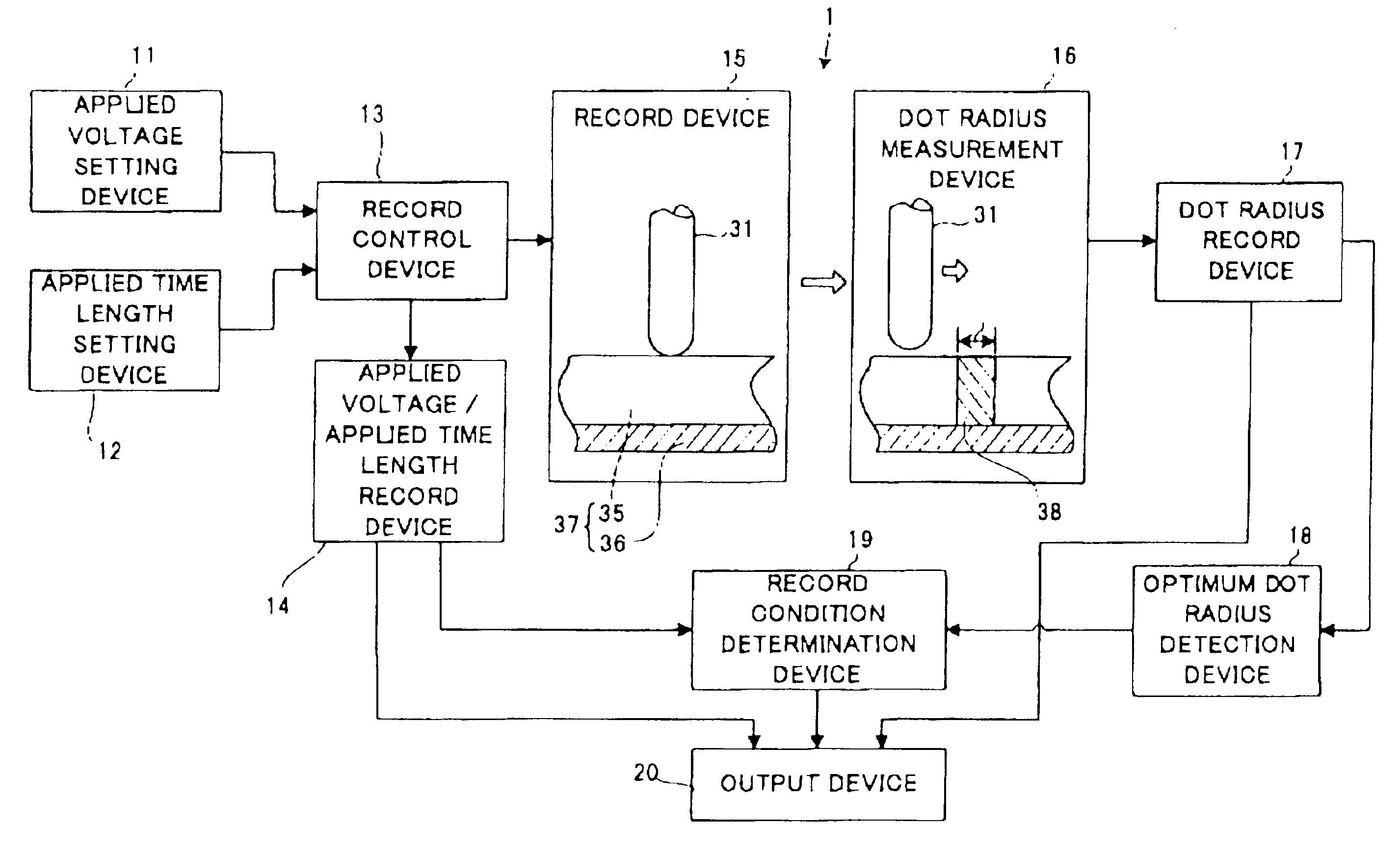
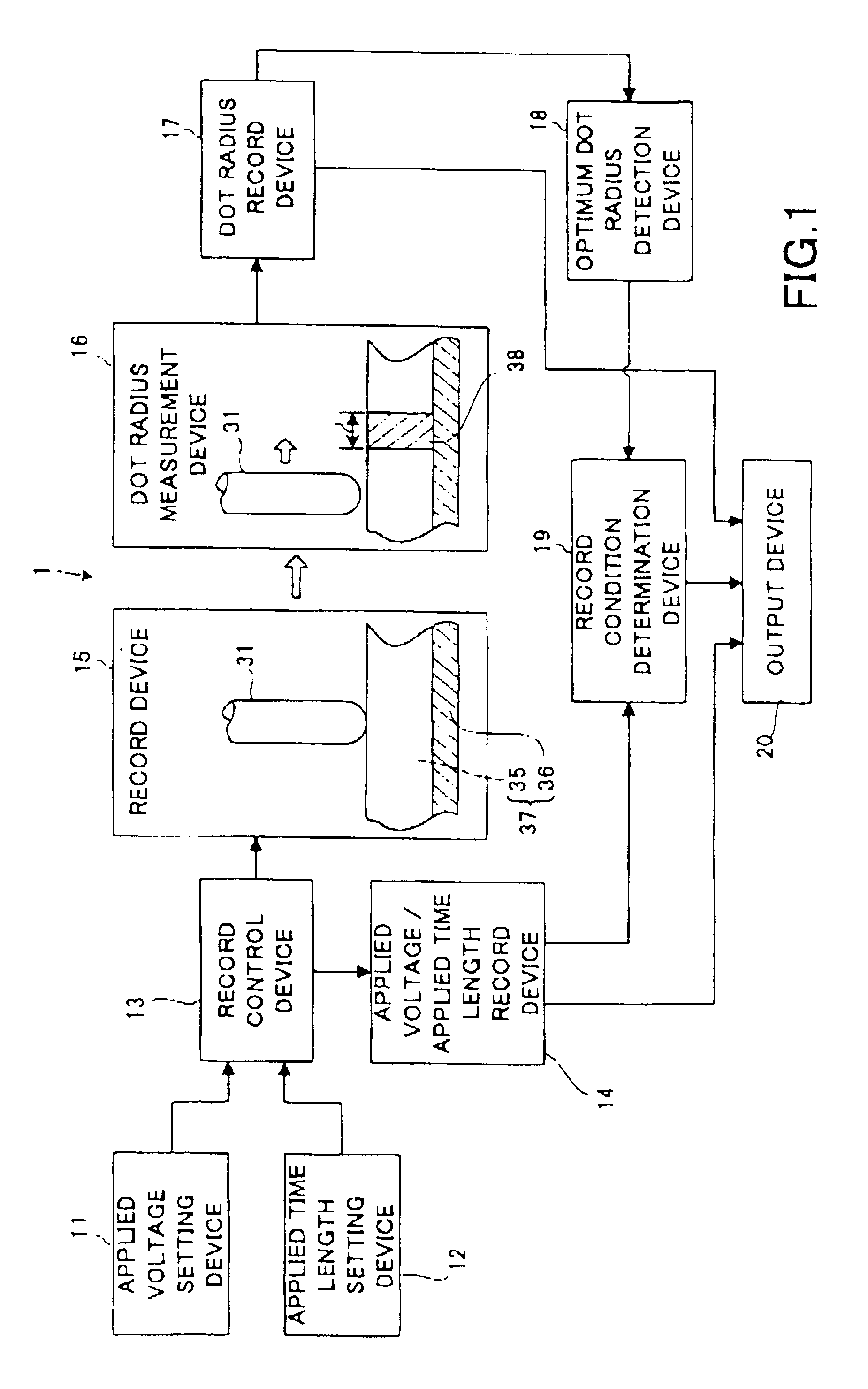
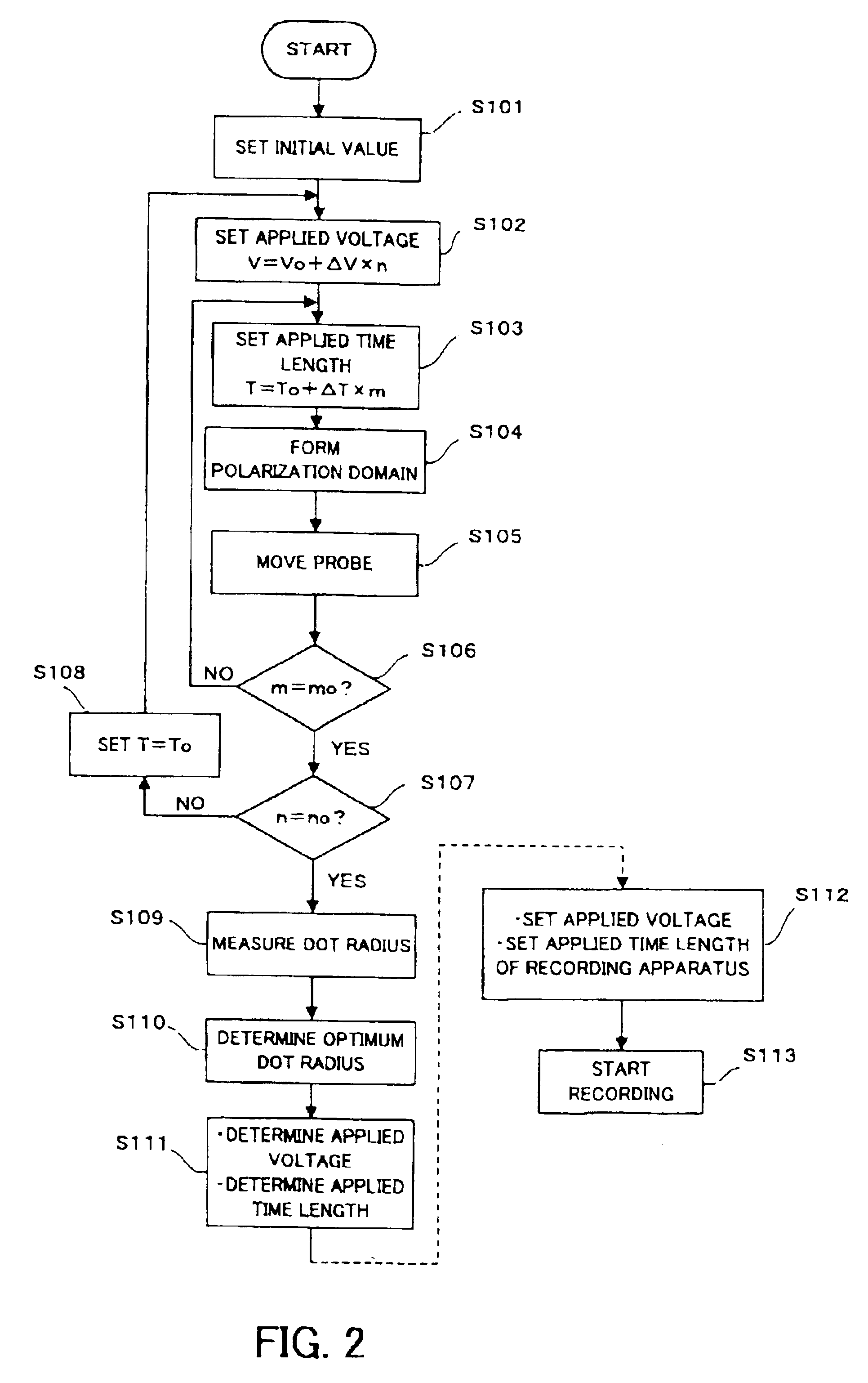
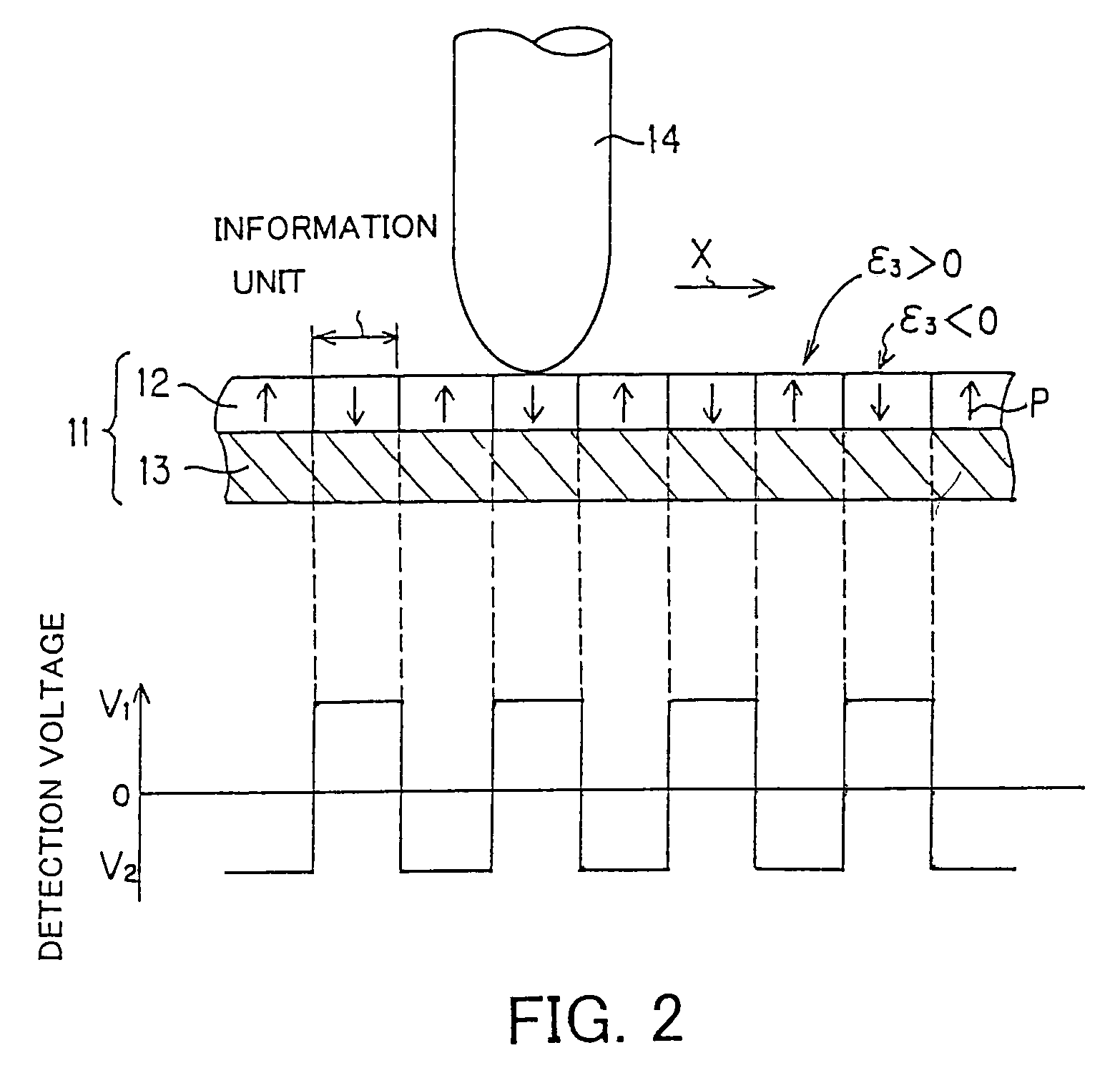
The record condition extraction system (1) of a dielectric recording medium is intended to obtain an applied voltage and an applied time length to be recorded when recording information in the dielectric recording medium. The record condition extraction system (1) is provided with: an applied voltage setting device (11); an applied time length setting device (12); a record control device (13); an applied voltage / applied time length record device (14); a record device (15); a dot radius measurement device (16); a dot radius record device (17); an optimum dot radius detection device (18); a record condition determination device (19); and an output device (20). The applied voltage setting device (11) and the applied time length setting device (12) set a voltage and a time applied to a probe (31) of the record device (15), respectively. The dot radius of a polarization domain 38, which is recorded at the record device (15), is measured at the dot radius measurement device (16), and the optimum polarization domain (38) is obtained at the optimum dot radius detection device (18). The applied voltage and the applied time length which have formed the polarization domain (38) are extracted as an optimum record condition.
Owner:YASUO CHO +1
Apparatus for recording information in and/or reproducing information from a ferroelectric recording medium
InactiveUS7149180B2Increase ratingsImprove signal-to-noise ratioVariable capacitance carrier recordingNanoinformaticsPhysicsInternal zone
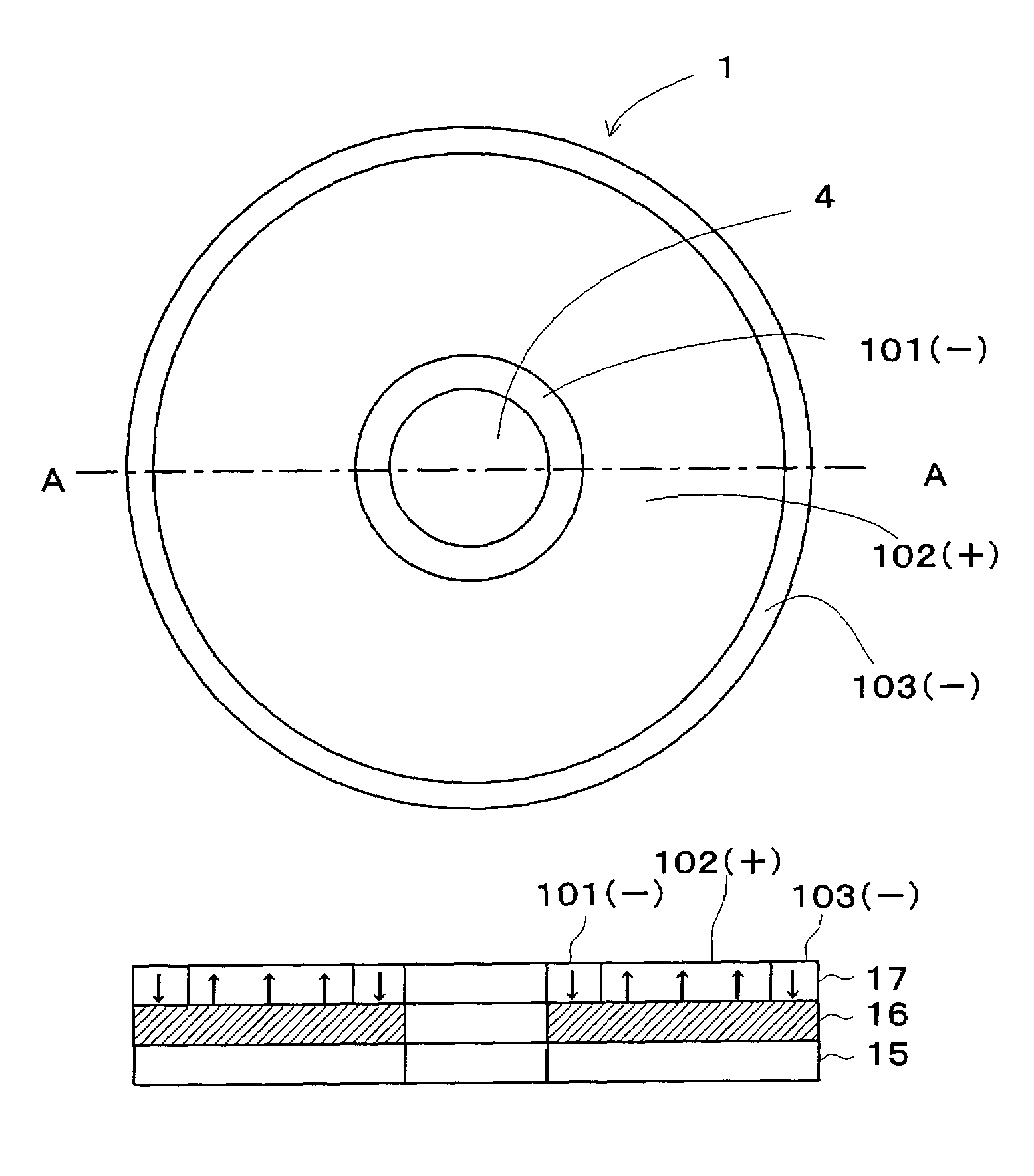
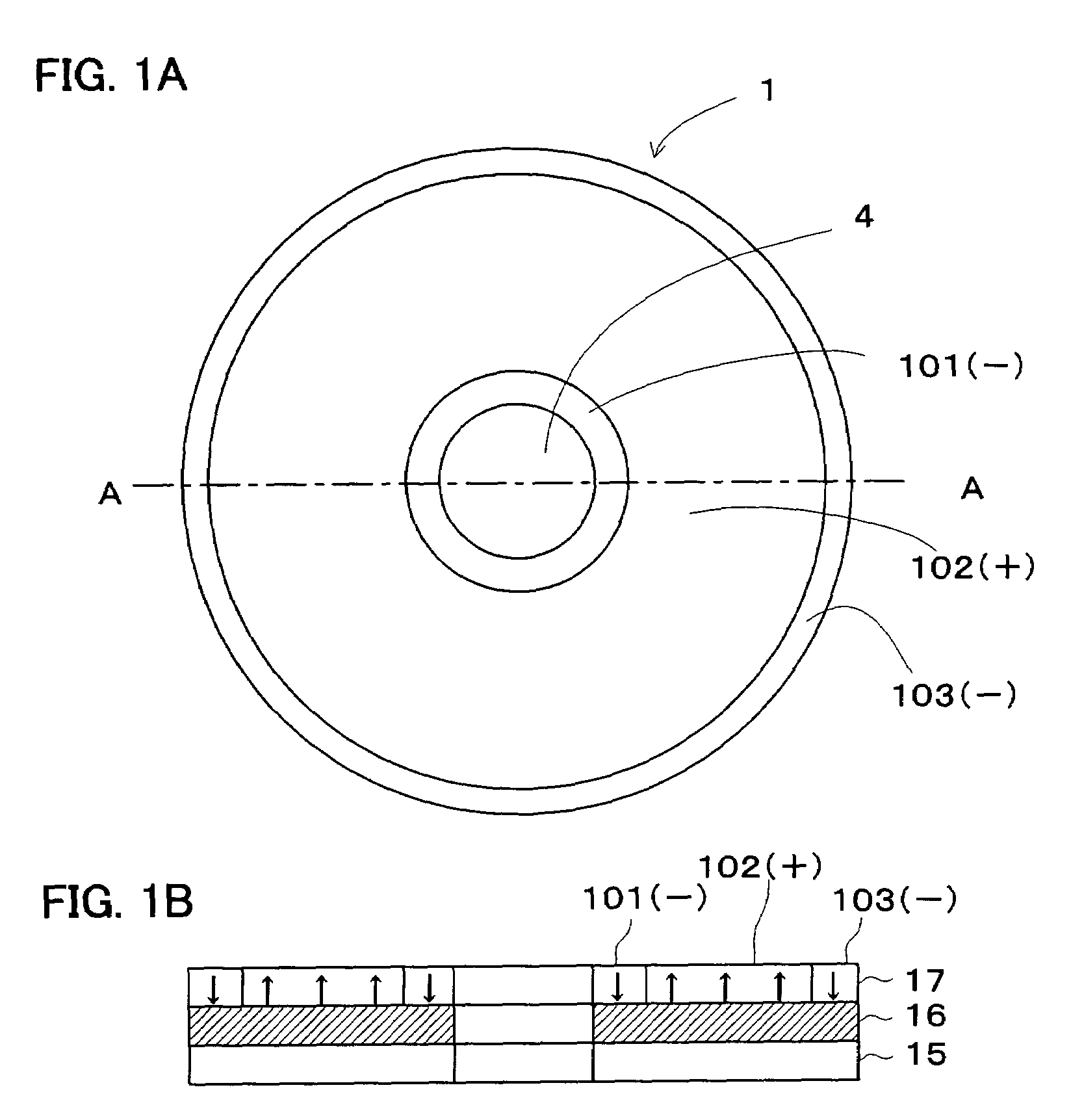
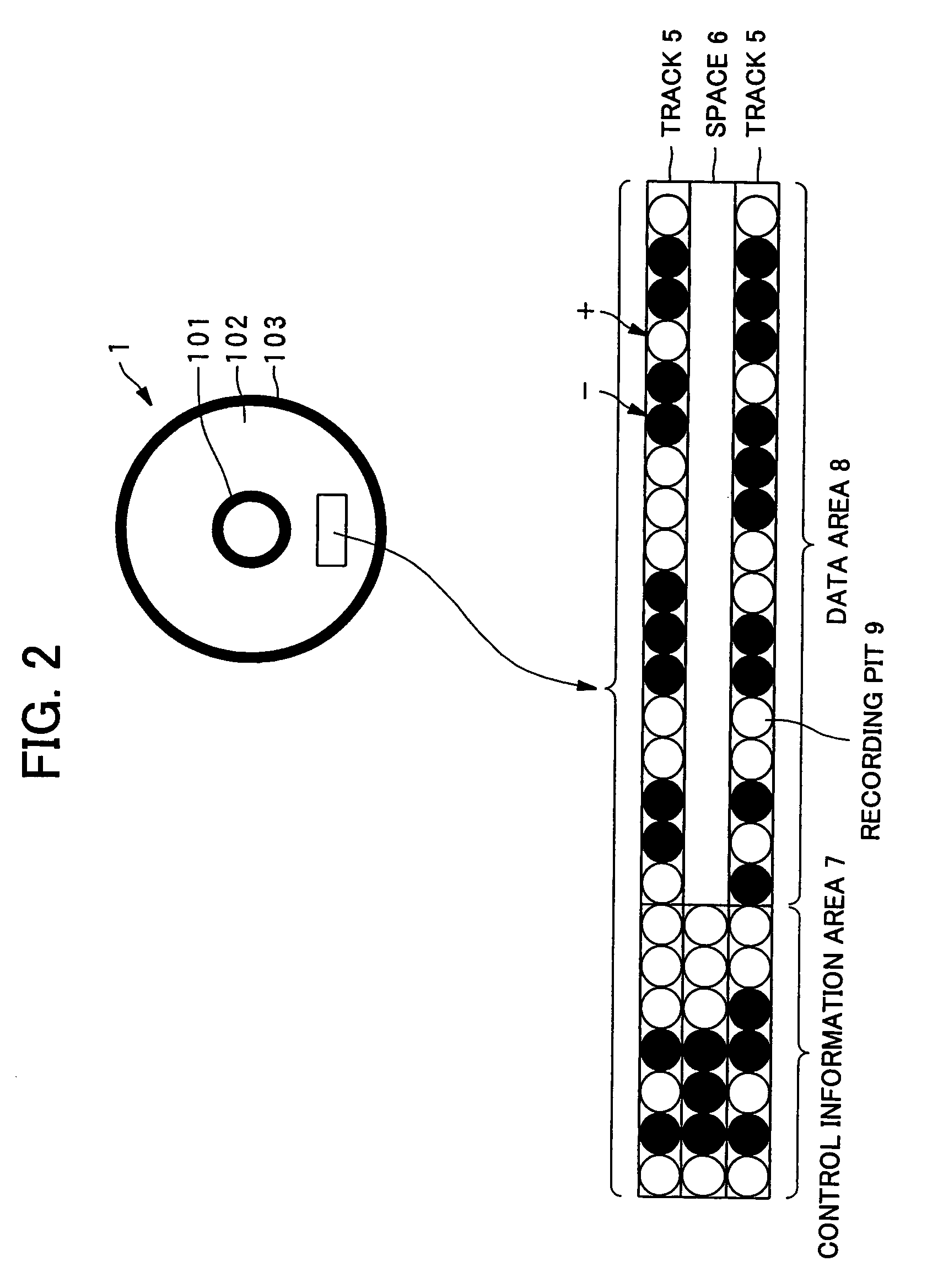
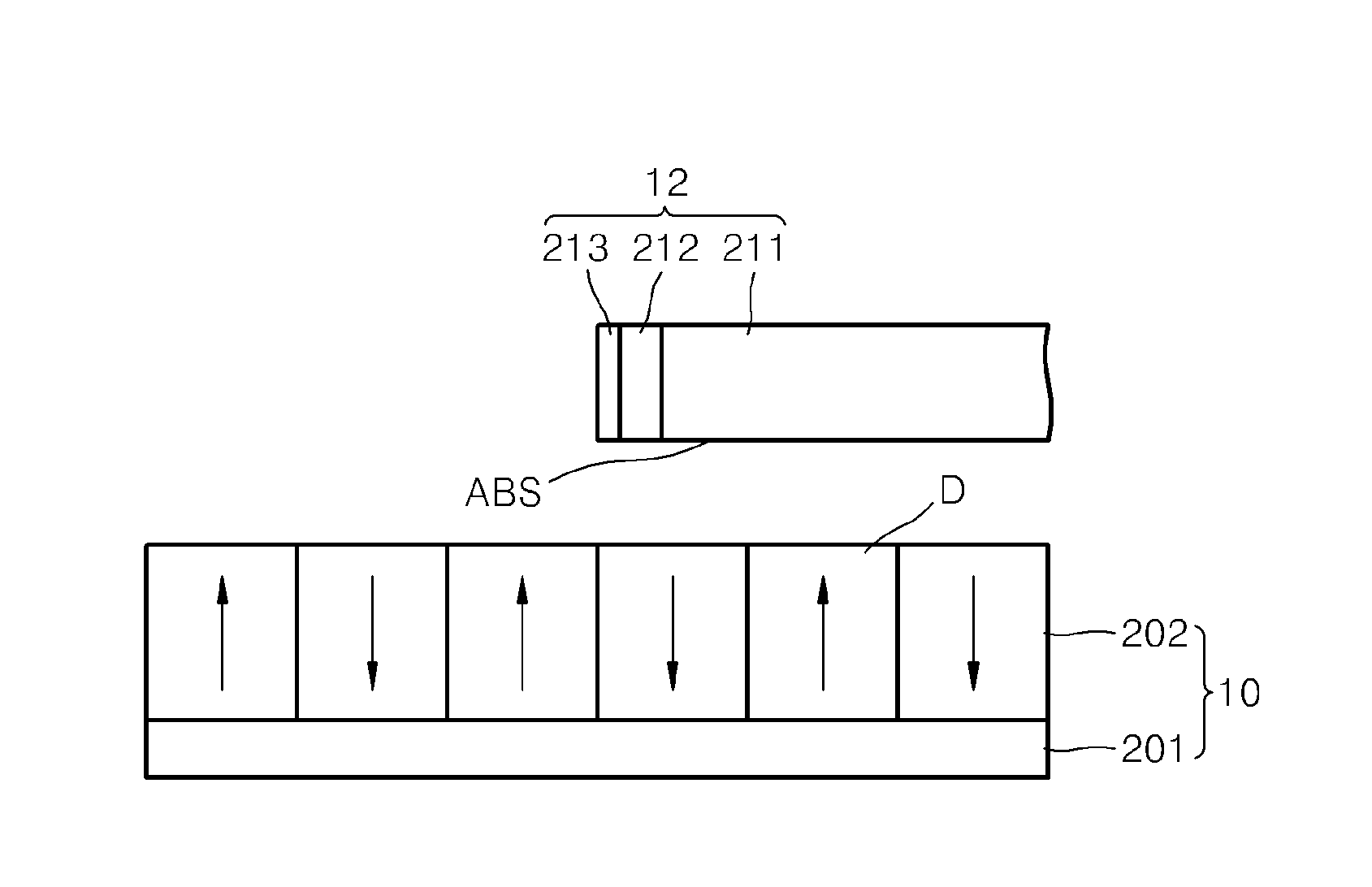
A dielectric recording medium in a disc form is provided with: a center hole; an inner area; a recording area; and an outer area, arranged concentrically from the inside in this order. The inner area, the recording area, and the outer area contain a uniform and flat dielectric material and are polarized with the polarization direction of the recording area opposite to that of the inner area and the outer area in their initial condition. The recording area in which data is recorded has tracks and spaces, each of which is between two of the tracks, and is provided with areas in which control information about the recording / reproducing is recorded, in the track and the space.
Owner:PIONEER CORP +1
Ferroelectric layer with domains stabilized by strain
ActiveUS20090155931A1Polycrystalline material growthFerroelectric carrier recordingRoom temperatureCritical thickness
The present invention describes a method including: providing a substrate; forming an underlying layer over the substrate; heating the substrate; forming a ferroelectric layer over the underlying layer, the ferroelectric layer having a thickness below a critical thickness, the underlying layer having a smaller lattice constant than the ferroelectric layer; cooling the substrate to room temperature; and inducing a compressive strain in the ferroelectric layer.
Owner:INTEL CORP
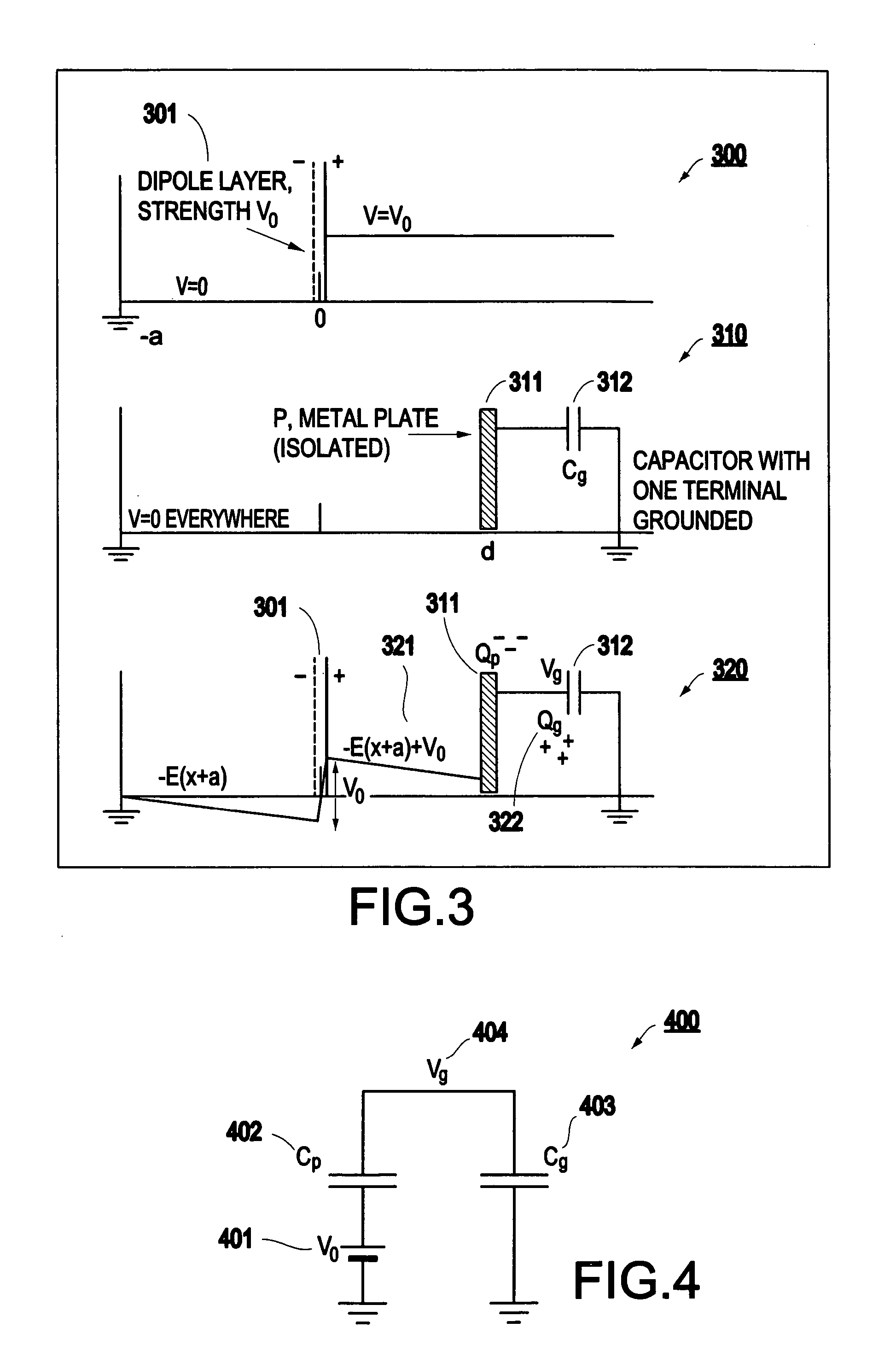
Information storage apparatus using semiconductor probe
InactiveUS6854648B2Increase speedSimple compositionElectrostatic charge injection carrier recordingNanoinformaticsEngineeringP–n junction
An information storage apparatus includes a recording medium and a head. The recording medium has an electrode layer, a ferroelectric film that is stacked on the electrode layer, and a semiconductor layer that is stacked on the ferroelectric film. The head has a semiconductor probe for forming a dielectric polarization on the ferroelectric film to record information and reproducing information from the dielectric polarizations on the ferroelectric film by making a p-n junction with the recording medium. Thus, it is possible to manufacture a small-sized information storage apparatus which is capable of repeatedly recording and reproducing information at a high speed.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Nanoscale Wire-Based Data Storage
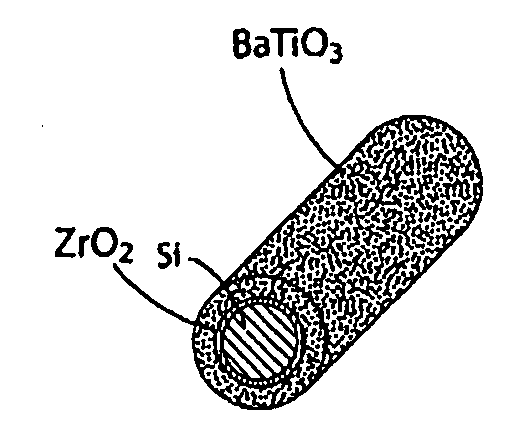
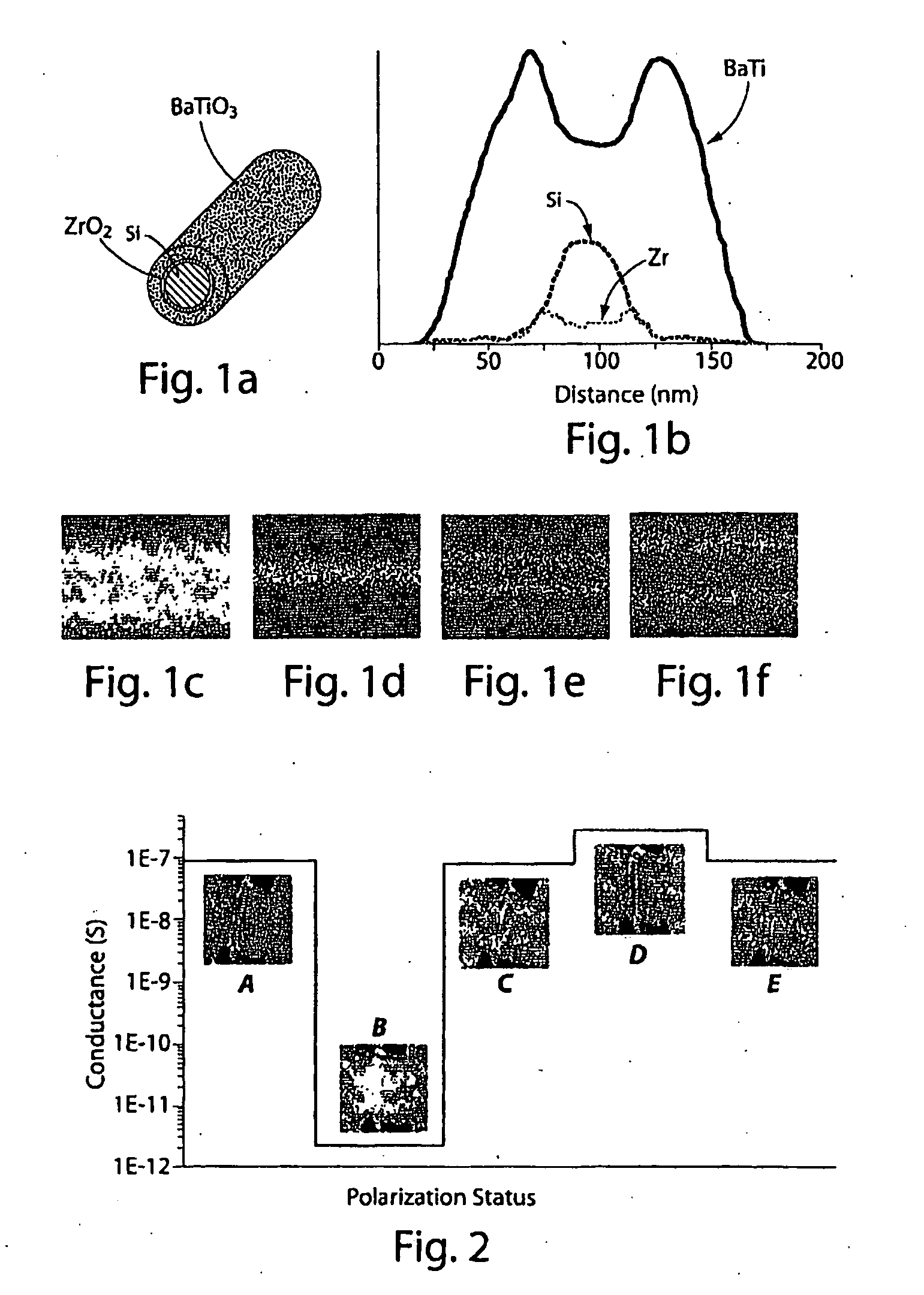
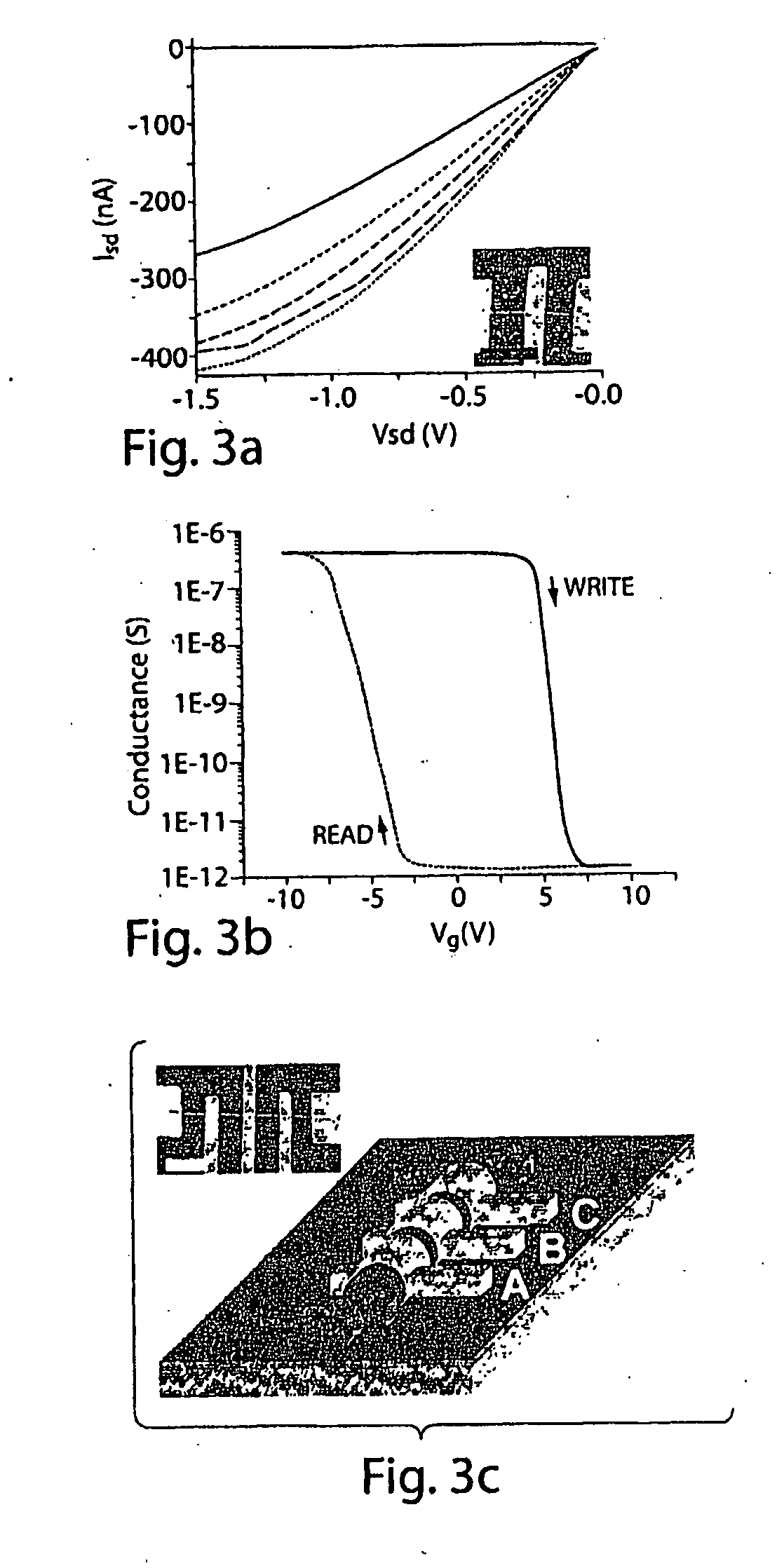
The present invention generally relates to nanotechnology and submicroelectronic devices that can be used in circuitry and, in some cases, to nanoscale wires and other nanostructures able to encode data. One aspect of the invention provides a nanoscale wire or other nanostructure having a region that is electrically-polarizable, for example, a nanoscale wire may comprise a core and an electrically-polarizable shell. In some cases, the electrically-polarizable region is able to retain its polarization state in the absence of an external electric field. All, or only a portion, of the electricallypolarizable region may be polarized, for example, to encode one or more bits of data. In one set of embodiments, the electrically-polarizable region comprises a functional oxide or a ferroelectric oxide material, for example, BaTiO3, lead zirconium titanate, or the like. In some embodiments, the nanoscale wire (or other nanostructure) may further comprise other materials, for example, a separation region separating the electricallypolarizable region from other regions of the nanoscale wire. For example, in a nanoscale wire, one or more intermediate shells may separate the core from the electricallypolarizable shell.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
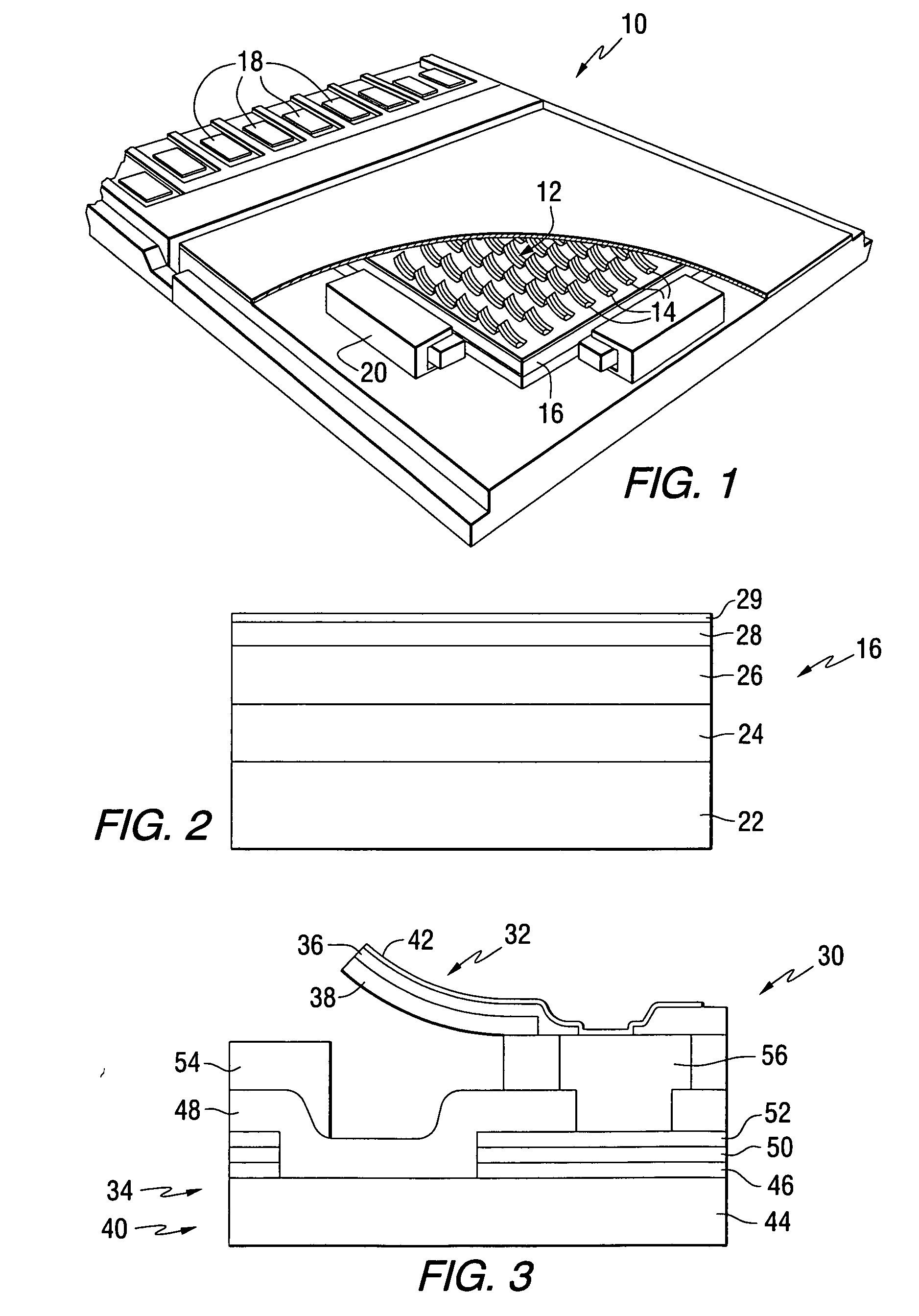
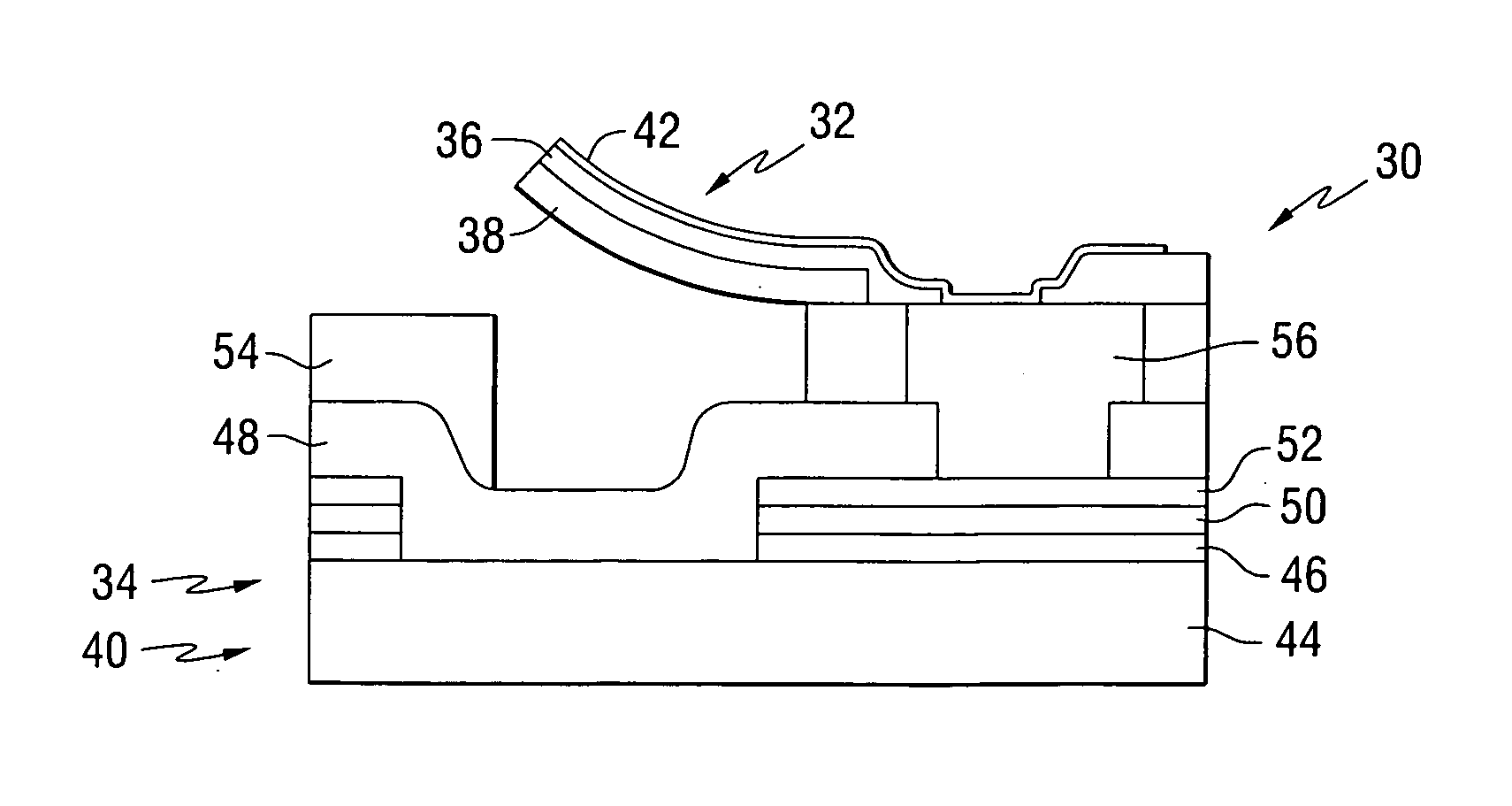
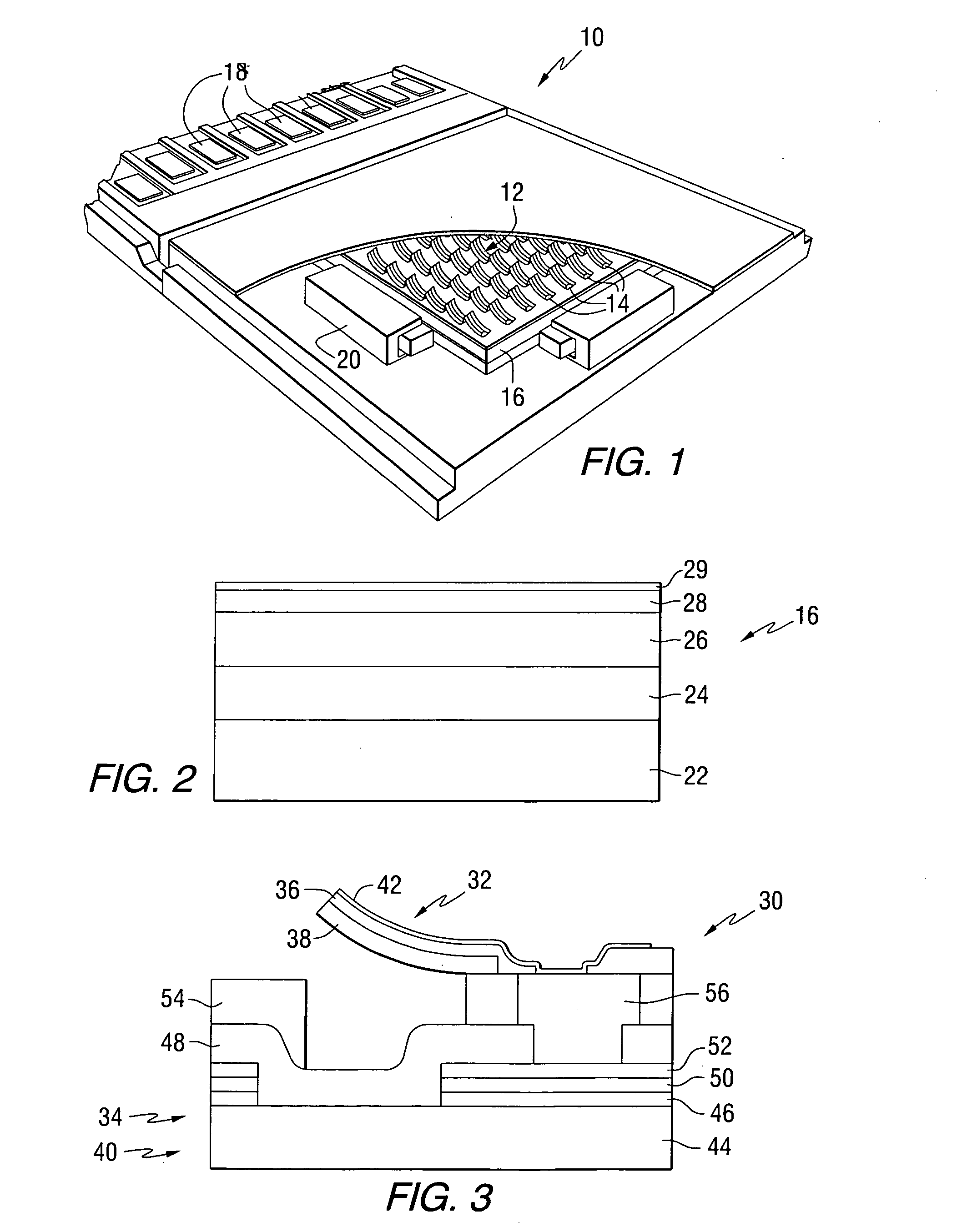
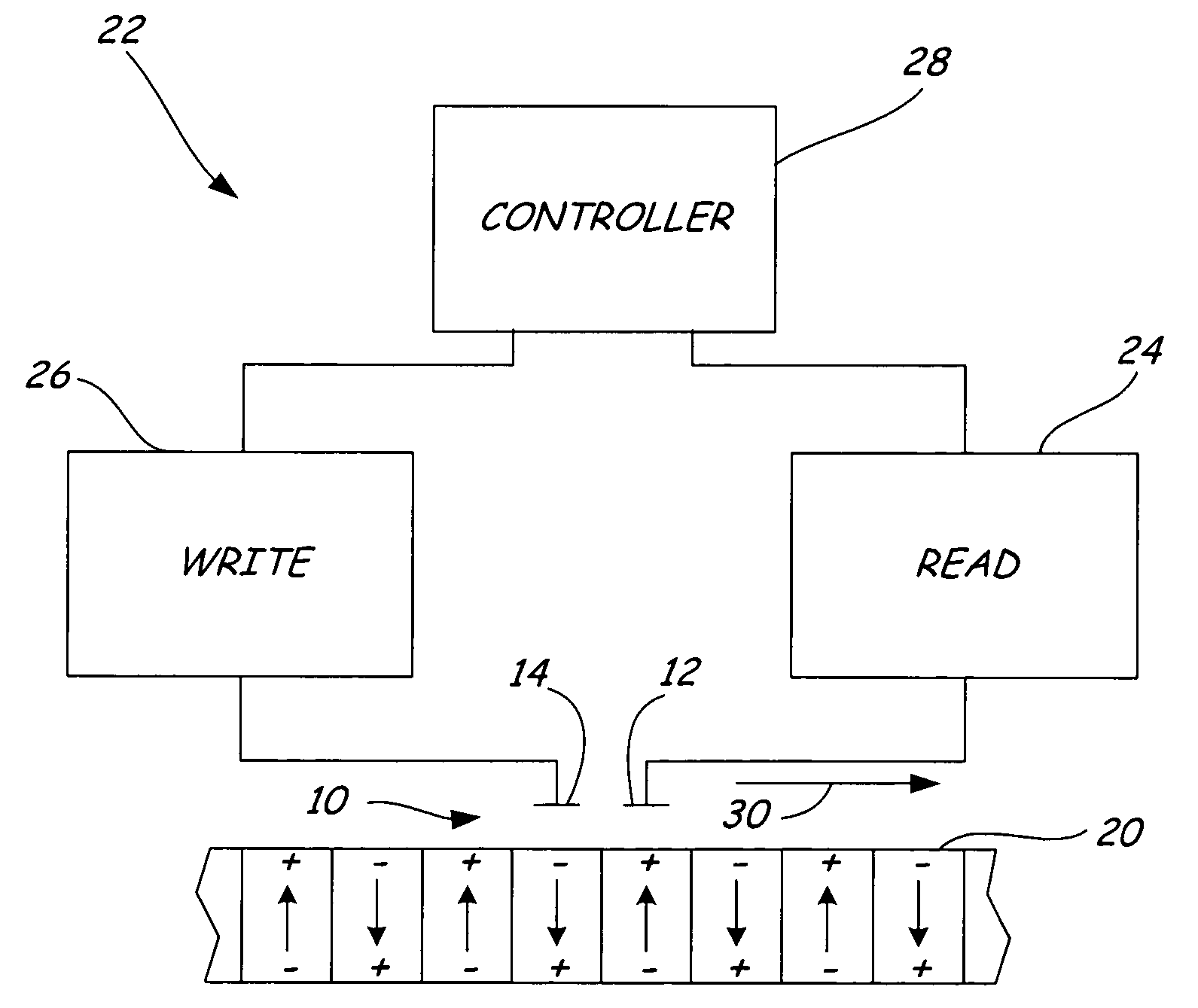
Transducers for ferroelectric storage medium
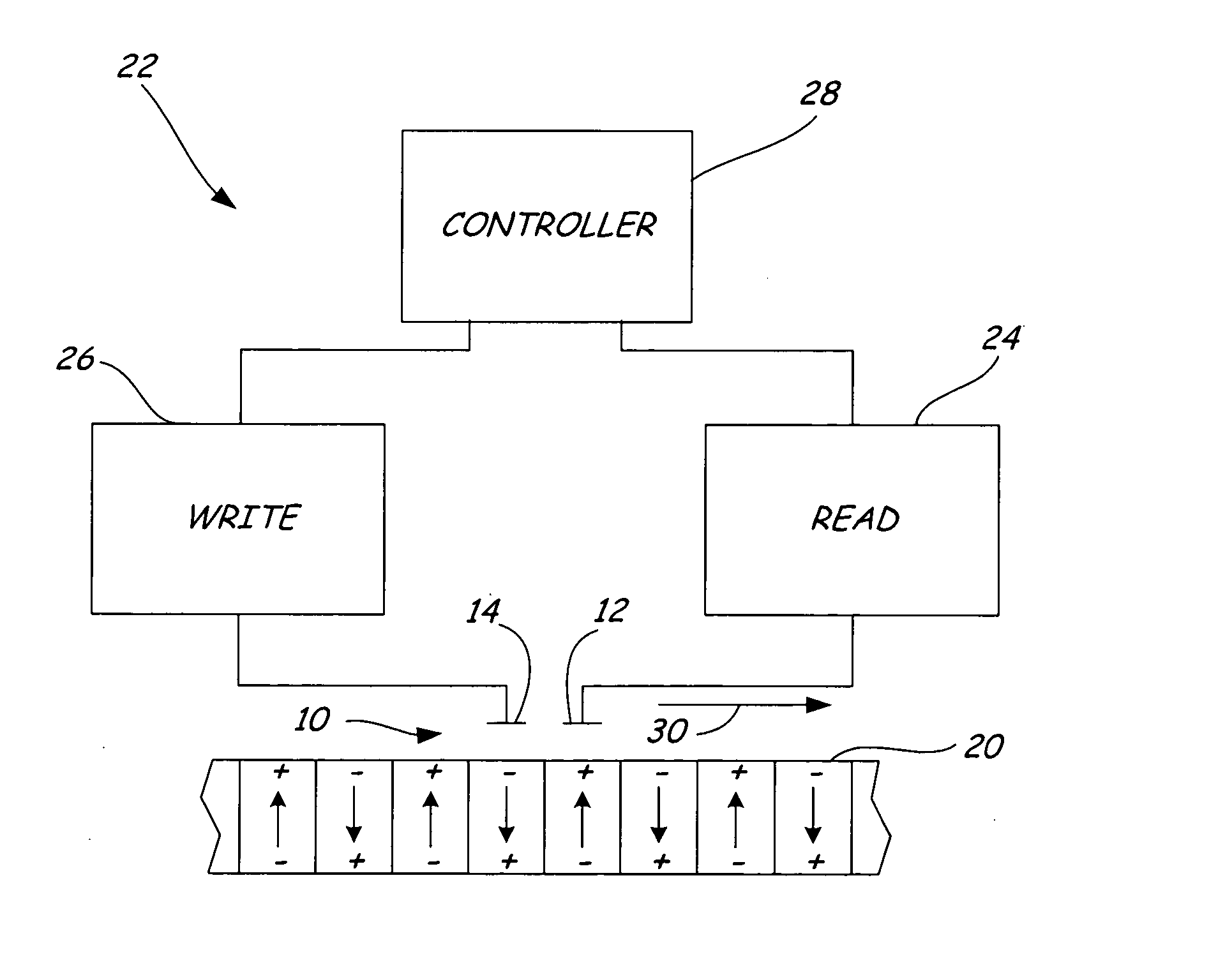
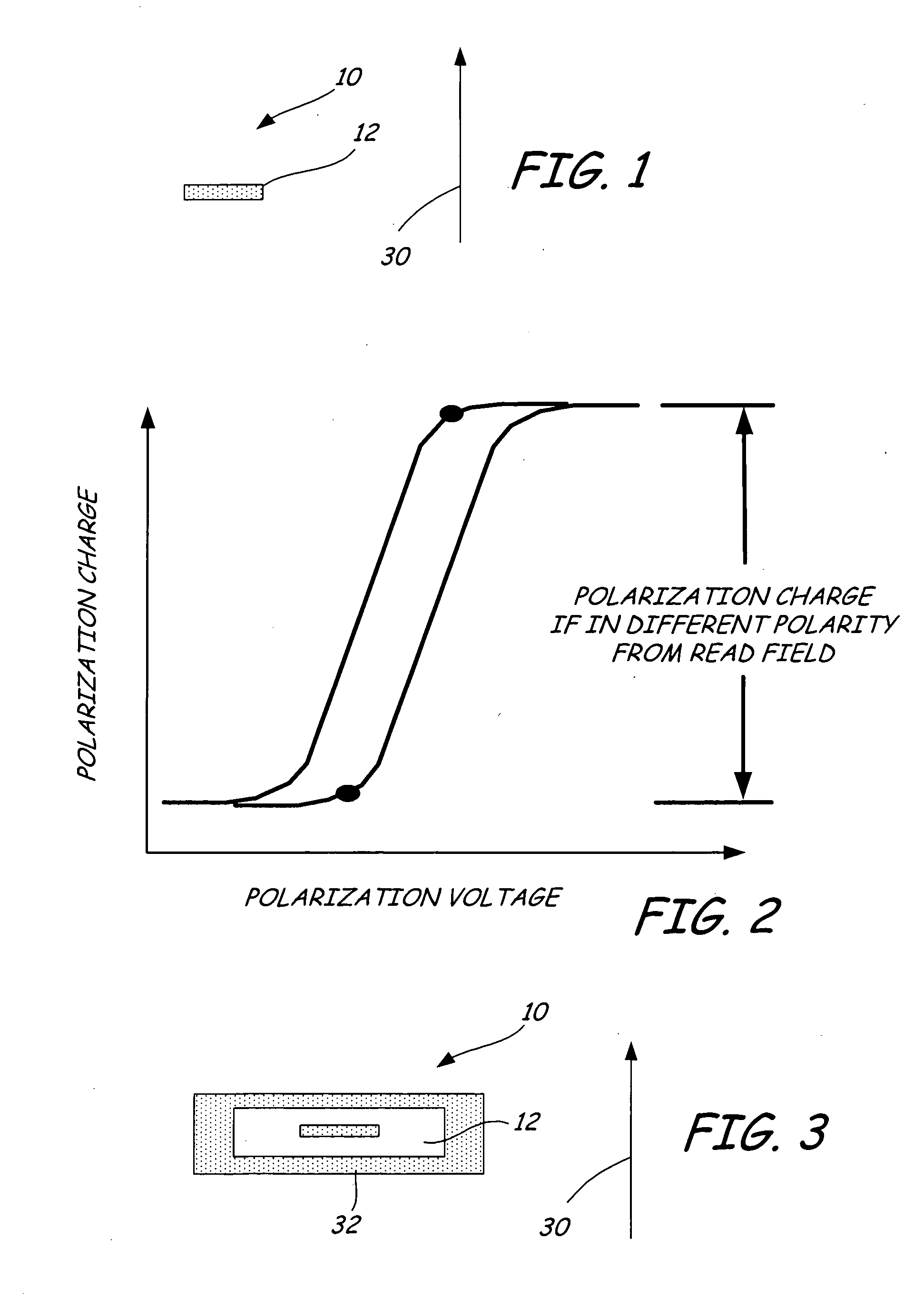
A ferroelectric transducer for use with a ferroelectric storage medium includes a read electrode. The read electrode emits a current when a polarity orientation of the read electrode is opposite a polarity orientation of a ferroelectric domain on the storage medium.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
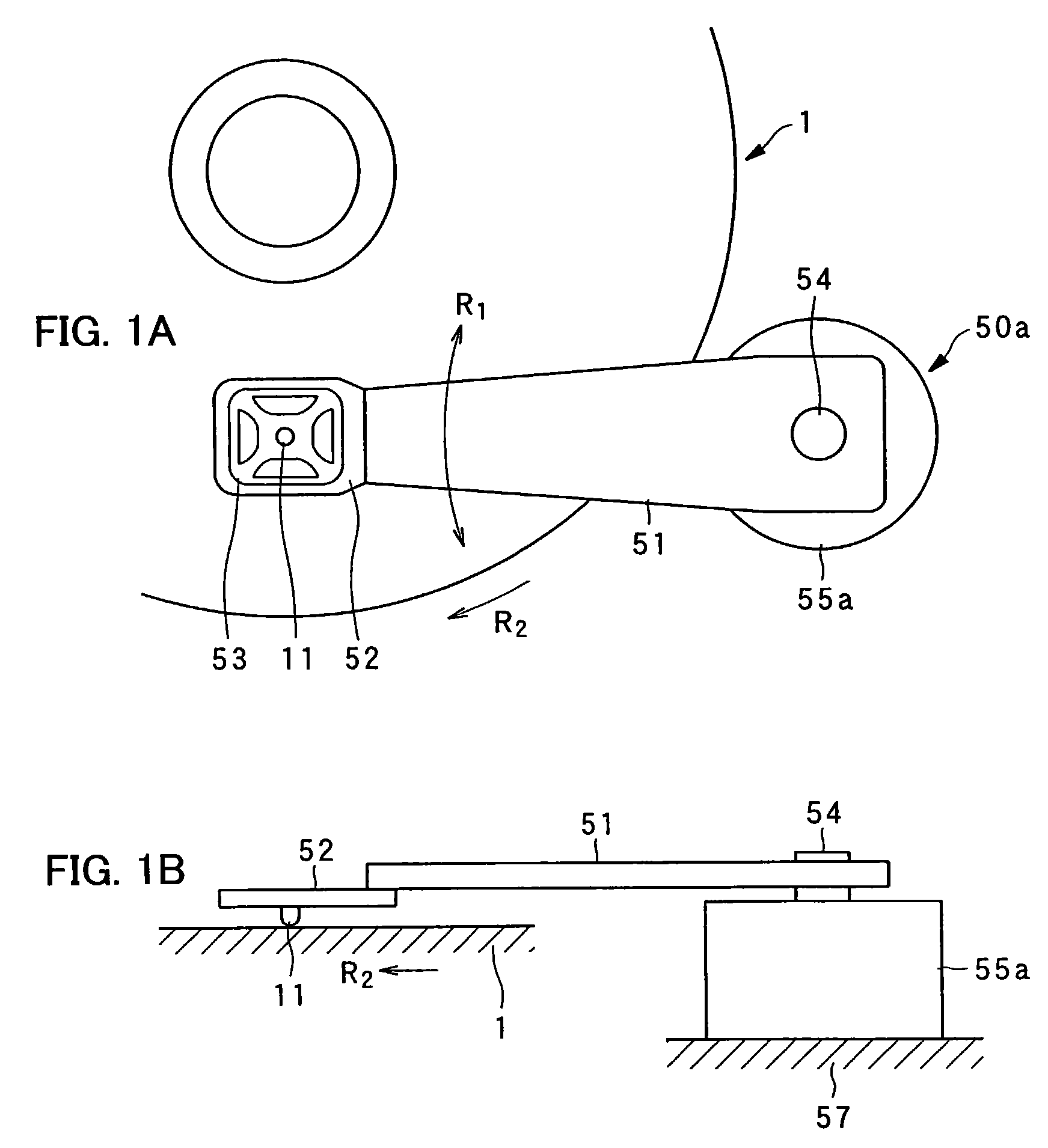
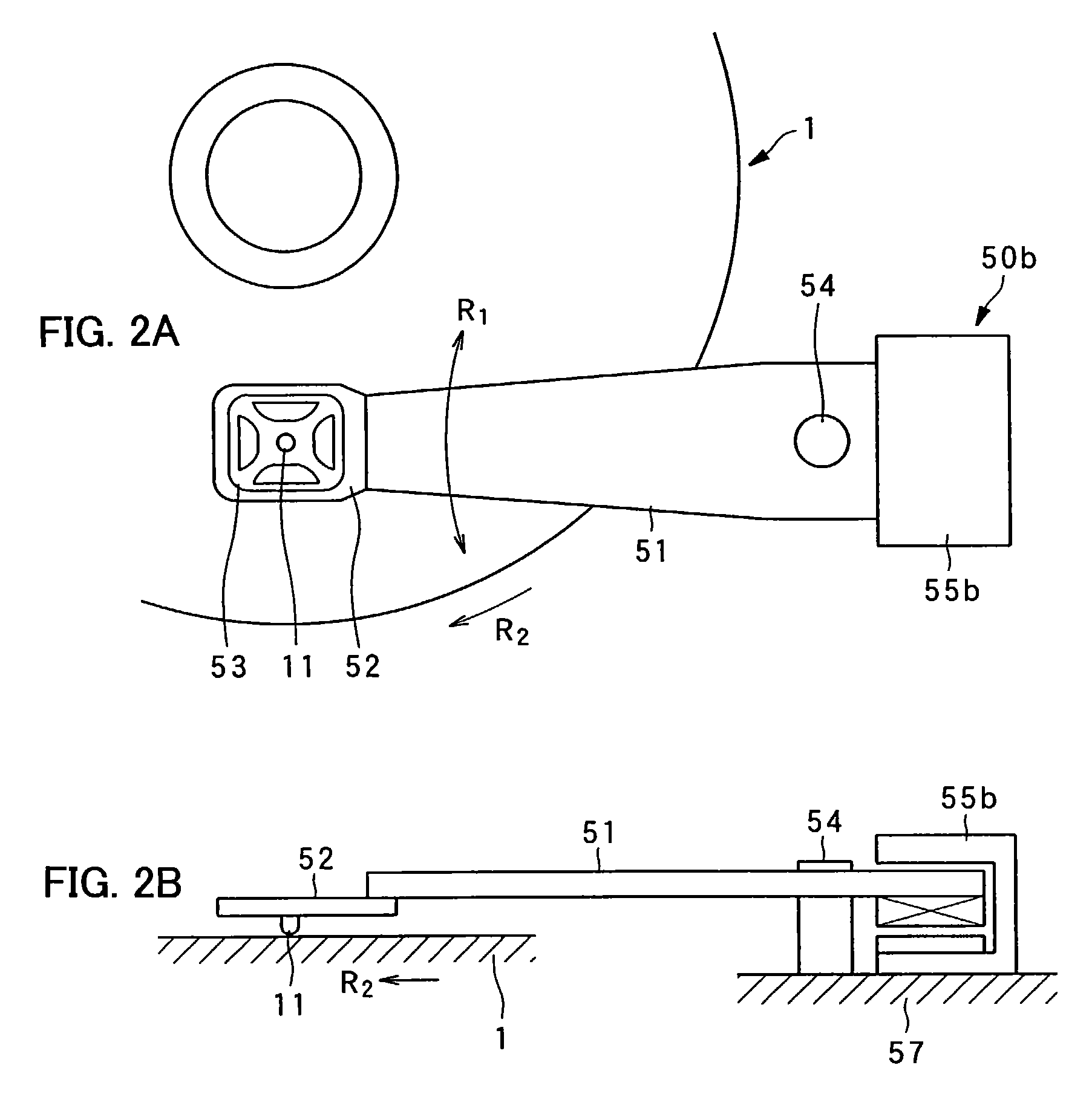
Pickup device
InactiveUS7221639B2Simple structureEasy to produceVariable capacitance carrier recordingNanoinformaticsEngineeringGimbal
An example pickup device is provided with: an arm; a gimbal holding device disposed on one end portion of the arm; a gimbal held by the gimbal holding device with a probe set in its center portion; and a motor of rotational type for rotating the arm around a rotating shaft. The probe, which is disposed on one end of the arm, is rotated in the radial direction of a dielectric recording medium by the rotation of the motor, causing accurate and quick tracking control and track access control.
Owner:PIONEER CORP +1
Multiferroic element
InactiveUS20090196818A1Simple structureSolid-state devicesGalvano-magnetic material selectionMagnetizationMultiferroics
A multiferroic element having a simple structure in which orientation of electric polarization or magnetization of a solid state material can be controlled by applying a magnetic field or an electric field, respectively. By applying an external magnetic field to a multiferroic solid state material that exhibits ferroelectricity and ferromagnetism having a spin structure such that the orientation of spin is rotating along the outside surface of a cone (apex angle alpha at the top of the cone is in a range of 0<alpha<=90 degrees), an electric polarization with orientation substantially perpendicular to the direction of the externally applied magnetic field can be controlled. Meanwhile, by applying an external electric field to the multiferroic solid state material, a magnetization with an orientation substantially perpendicular to the direction of the externally applied electric field can be controlled.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP +1
Information recording/reading head
InactiveUS20040105373A1Electrostatic charge injection carrier recordingOptical head protectionBiomedical engineering
Owner:PIONEER CORP
Method of writing data on a storage device using a probe technique
InactiveUS20050052984A1Low coercivityEfficient switchingCombination recordingNanoinformaticsElectrical resistance and conductanceEngineering
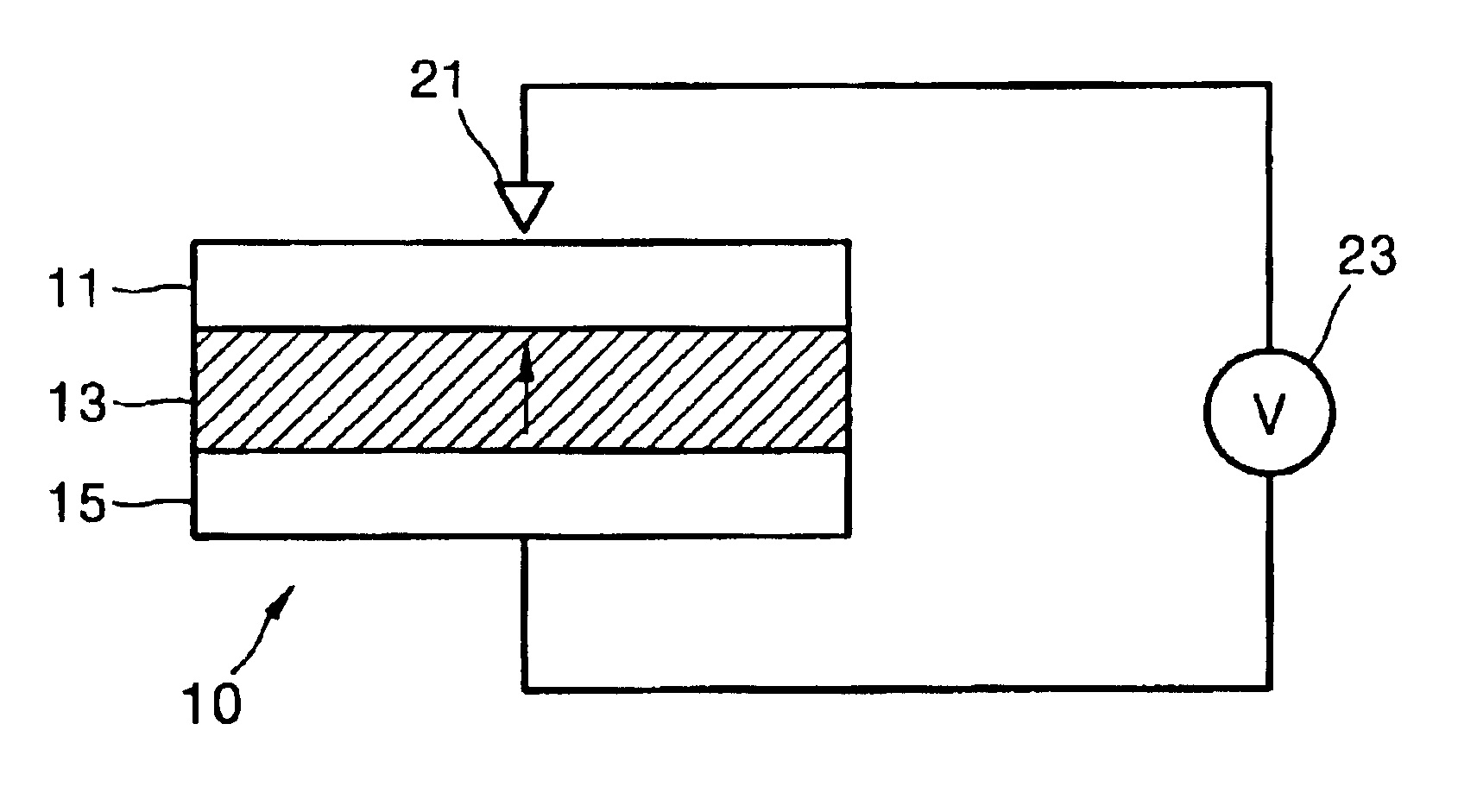
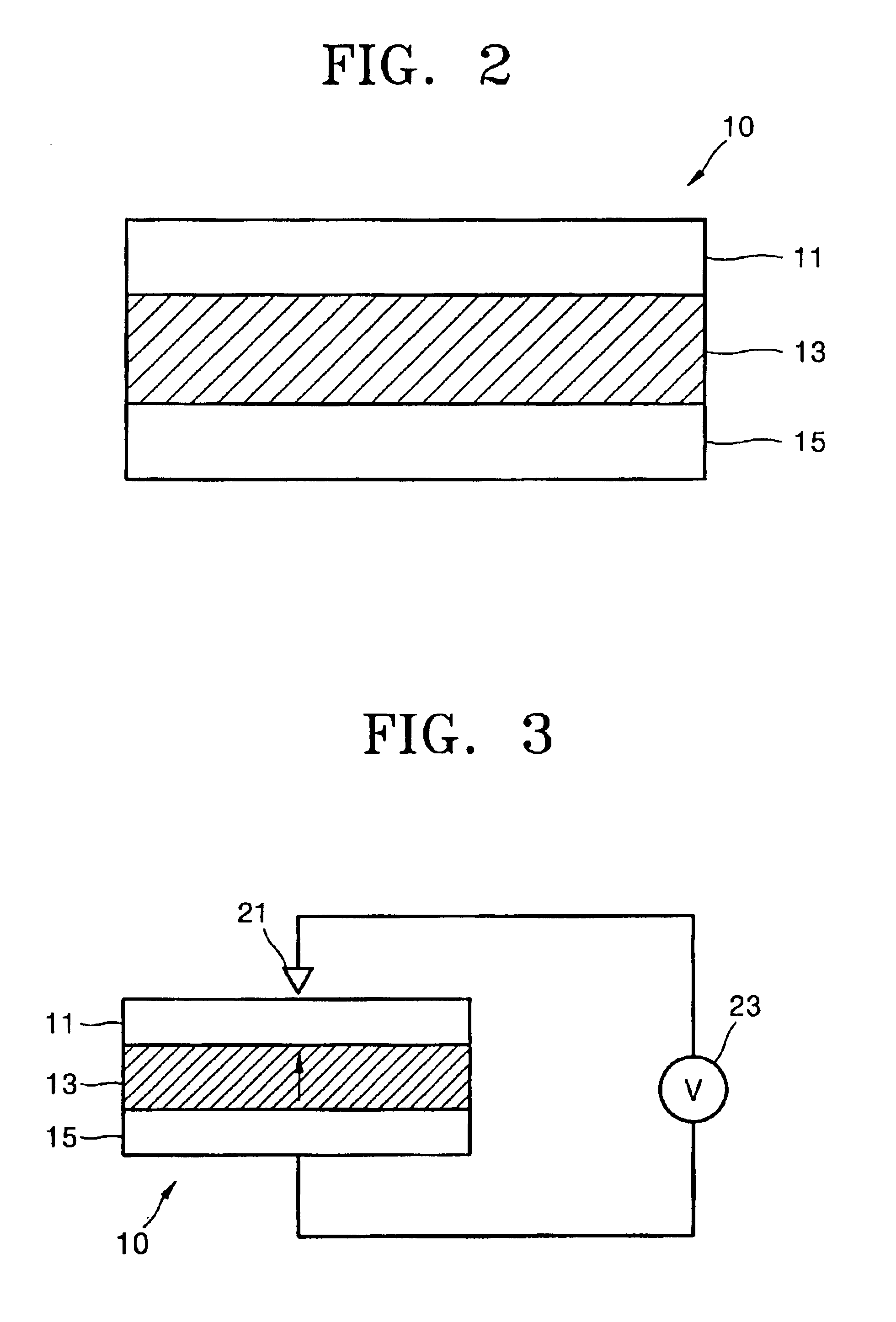
A method of writing data on a storage device using a probe technique. In the method of writing data on a memory device including a resistive probe used for reading and writing of data, a ferroelectric writing medium on which data is written by the resistive probe, and a lower electrode disposed on a bottom surface of the ferroelectric writing medium, heat and an electric field are applied simultaneously to a domain of the ferroelectric writing medium, on which the data will be written, by applying a voltage to the resistive probe and the lower electrode.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Recording medium comprising ferroelectric layer, nonvolatile memory device comprising recording medium, and methods of writing and reading data for the memory device
InactiveUS20050147018A1Little and no abrasionImprove reading speedNanoinformaticsMechanical record carriersComputer scienceSemiconductor
A recording medium including a ferroelectric layer, a nonvolatile memory device including the recording medium and methods of wiring and reading data in the memory device. The recording medium includes: a lower electrode; a ferroelectric layer to which data is recorded, formed on the lower electrode; a barrier layer formed on the ferroelectric layer; and a semiconductor layer formed on the barrier layer. The nonvolatile memory device includes a probe that reads and writes the data. Furthermore, in the method of writing data, a writing voltage is applied between the probe, which contacts the semiconductor layer, and the lower electrode and, in the method of reading data, a state of a remanent polarization of the ferroelectric layer is determined by applying a reading voltage between the probe and the semiconductor layer.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Information recording/reading head
InactiveUS7212484B2Improve accuracyEnhanced informationElectrostatic charge injection carrier recordingOptical head protectionBiomedical engineering
Owner:PIONEER CORP
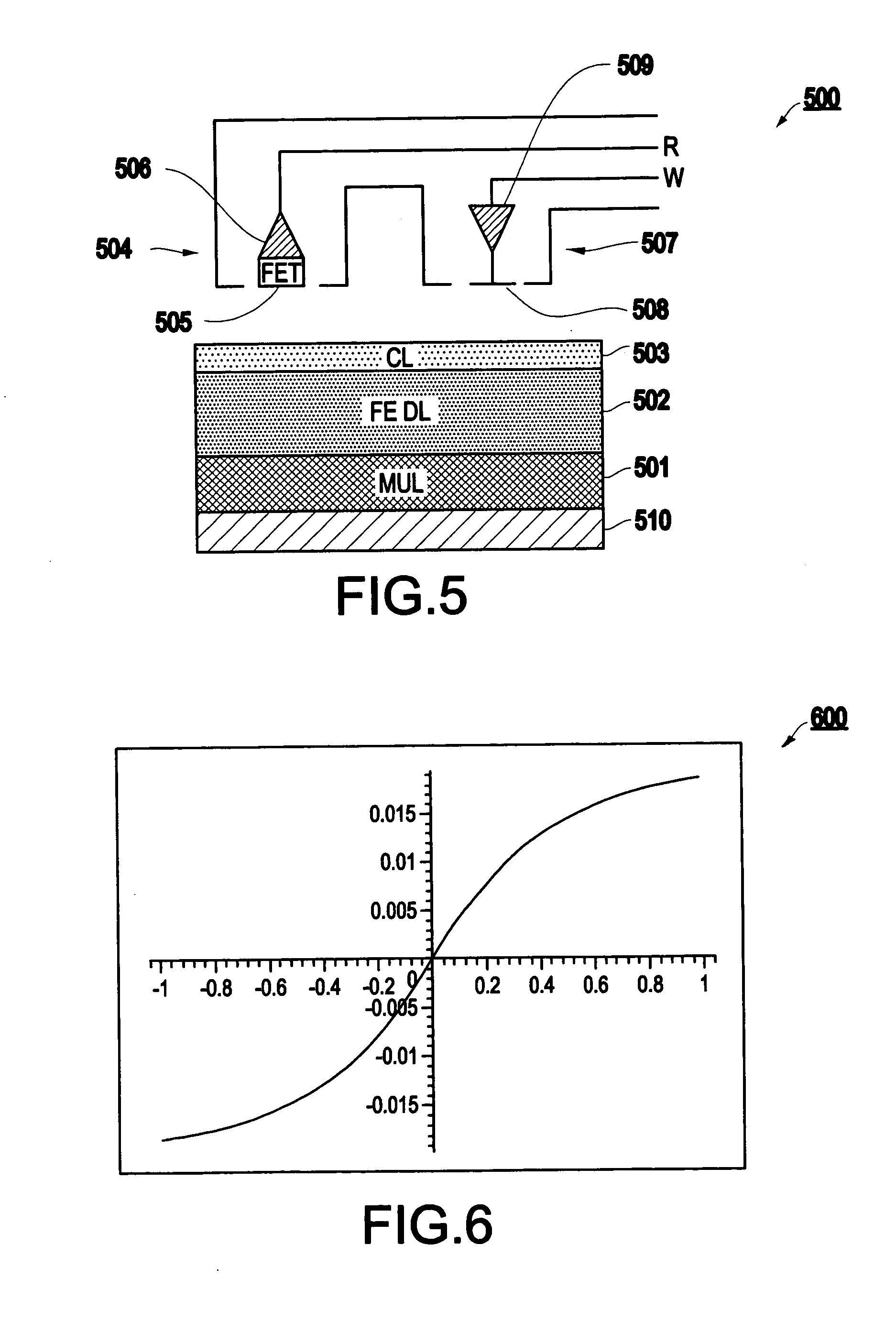
Memory array having a layer with electrical conductivity anisotropy
InactiveUS7026676B2TransistorVariable resistance carrier recordingComputational physicsContact region
A memory array includes a memory layer that has hysteretic domains with domain axes extending between first and second memory layer surfaces. A conductive layer on the first memory layer surface has anisotropically increased electrical conductivity in a thickness direction. A movable conductive probe has a contact area on the conductive layer and moves to access a selected hysteretic domain.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
Dielectric recording medium, and method of and apparatus for producing the same
InactiveUS20050098532A1Remove electric charge on the recording surface rapidlyImprove abilitiesDecorative surface effectsNanoinformaticsSingle crystalResin adhesive
The dielectric recording medium is provided with a dielectric material, a conductive thin film, and a substrate. The conductive thin film and the substrate are bonded by a resin adhesive. The dielectric material is constructed of a ferroelectric single crystal having a uniform thickness, and its one surface is used for a recording and / or reproducing surface, on the order of mm on a side and about 5000 Å thick. The conductive thin film, about 1000 to 2000 Å thick, is placed on a surrounding portion and a back surface of the recording and / or reproducing surface of the dielectric material. The substrate is intended to preserve the thin dielectric material and maintain the planarity, and concave portions are formed on the adhesive surface. The concave portions absorb excessive resin adhesive when the dielectric material is bonded onto the substrate, which makes the adhesive surface uniform and flat.
Owner:PIONEER CORP +1
Elevated electrodes for probe position sensing
InactiveUS20080089211A1Reduce frictionIncrease capacitanceNanoinformaticsFerroelectric carrier recordingEngineeringBiomedical engineering
An apparatus comprises a storage medium, a head substrate, wherein the storage medium and the head substrate are separated by a gap, a plurality of electrodes separated from each other, and a support structure positioned in the gap for supporting some of the electrodes. An apparatus comprising a storage medium, a head substrate, wherein the storage medium and the head substrate are separated by a gap, a plurality of posts positioned in the gap, a layer of low friction material positioned on one end of each of the posts, is also described.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
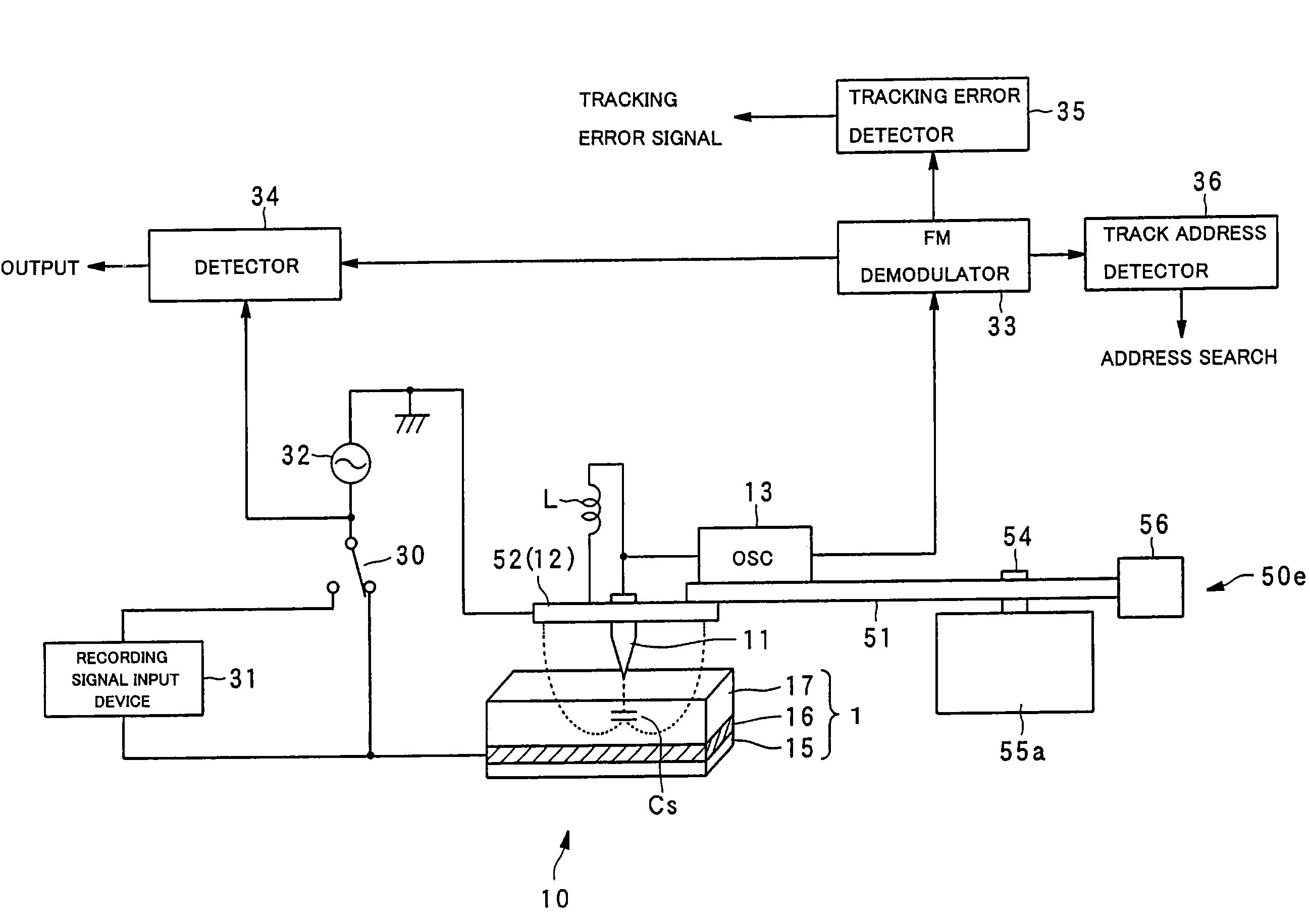
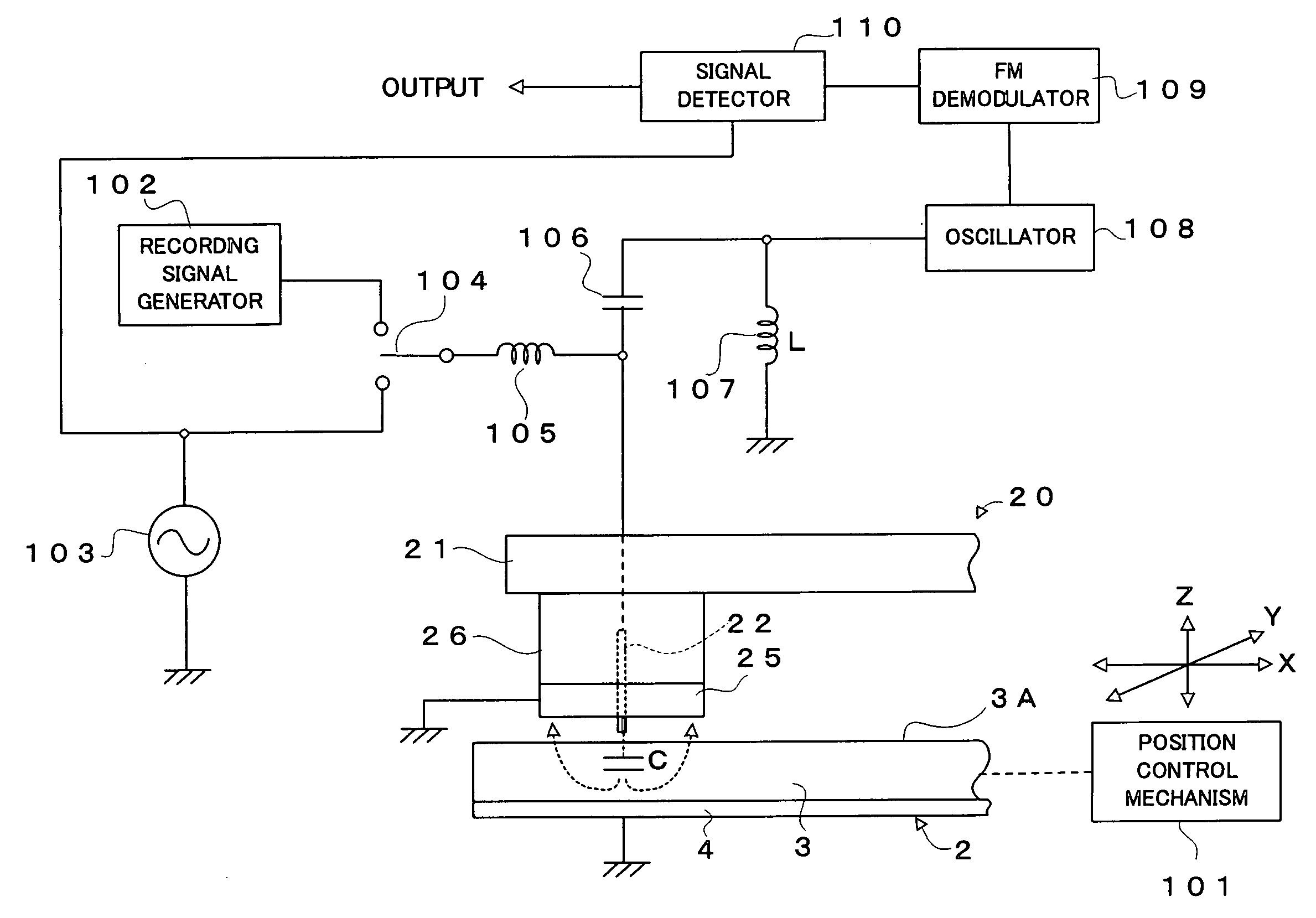
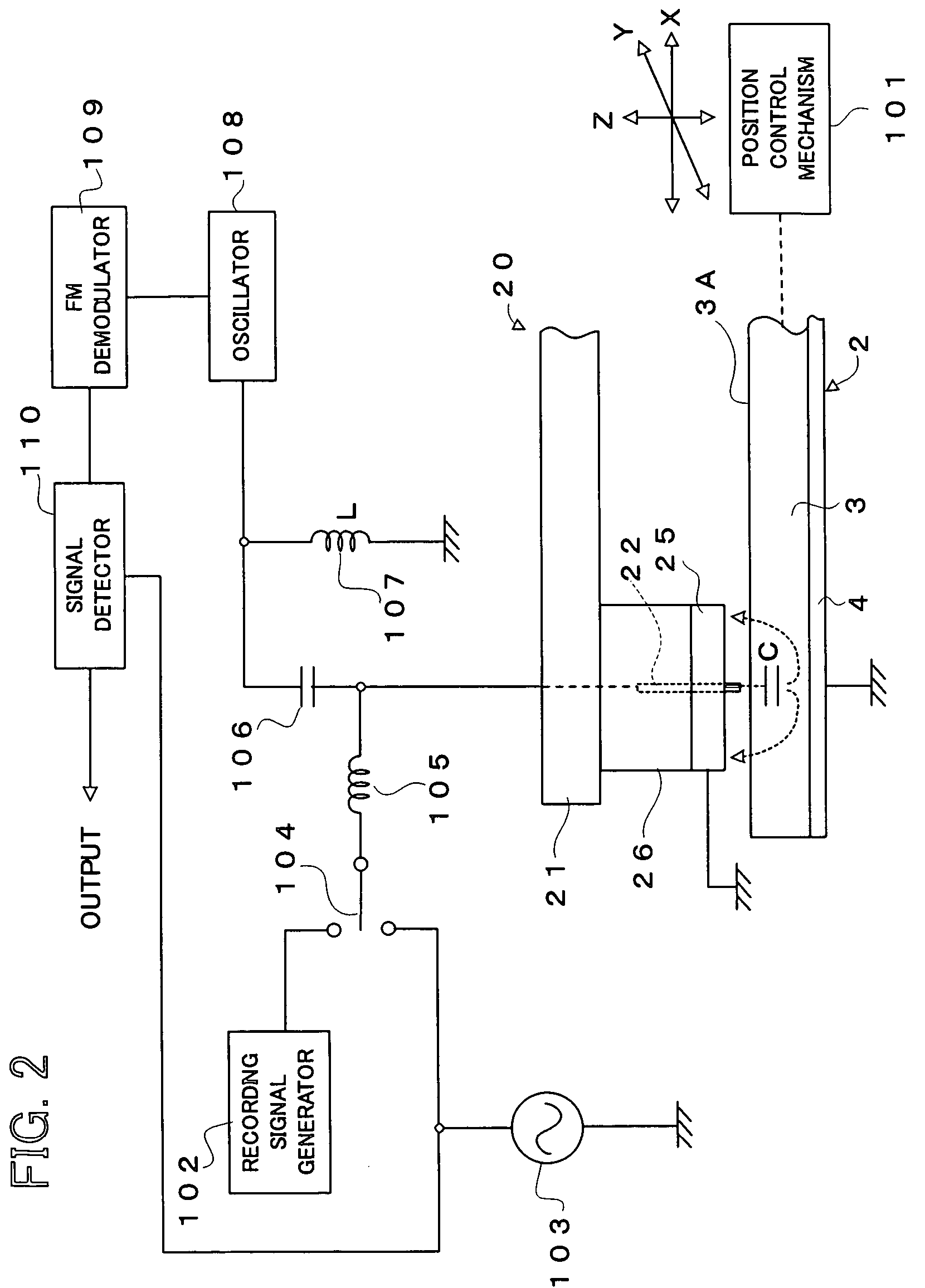
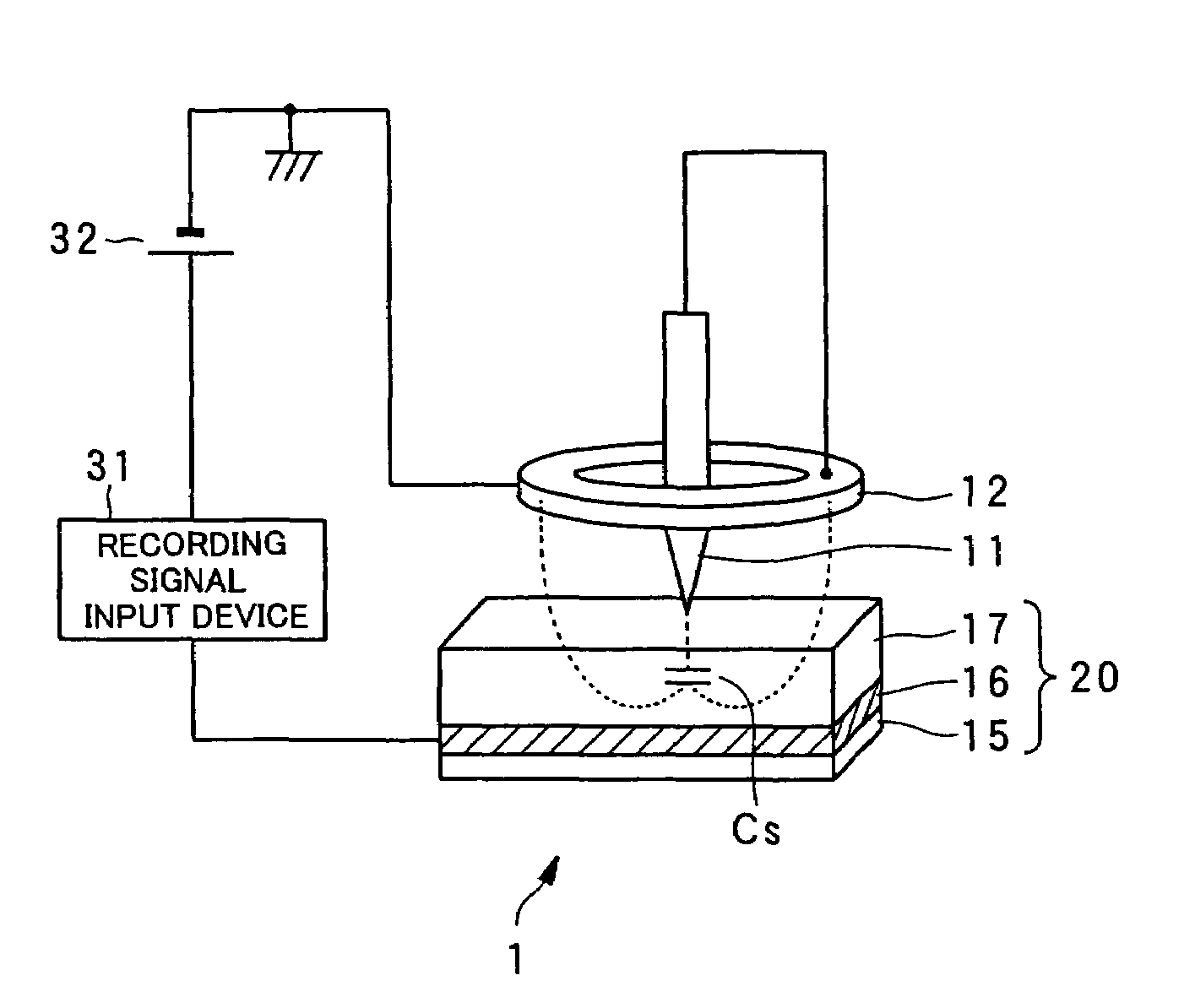
Dielectric information apparatus, tape-like medium recording/reproducing apparatus and disc-like medium recording/reproducing apparatus
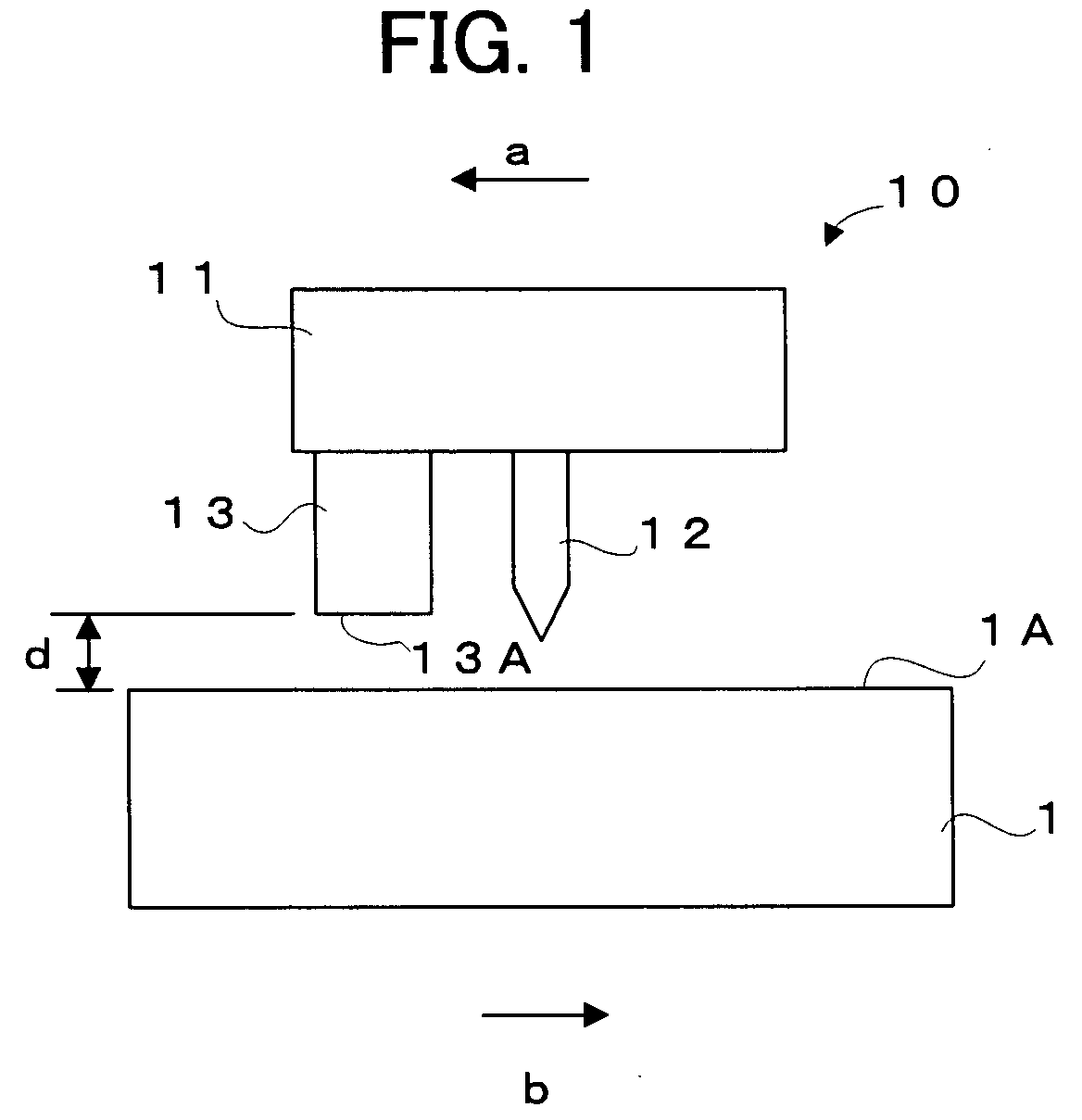
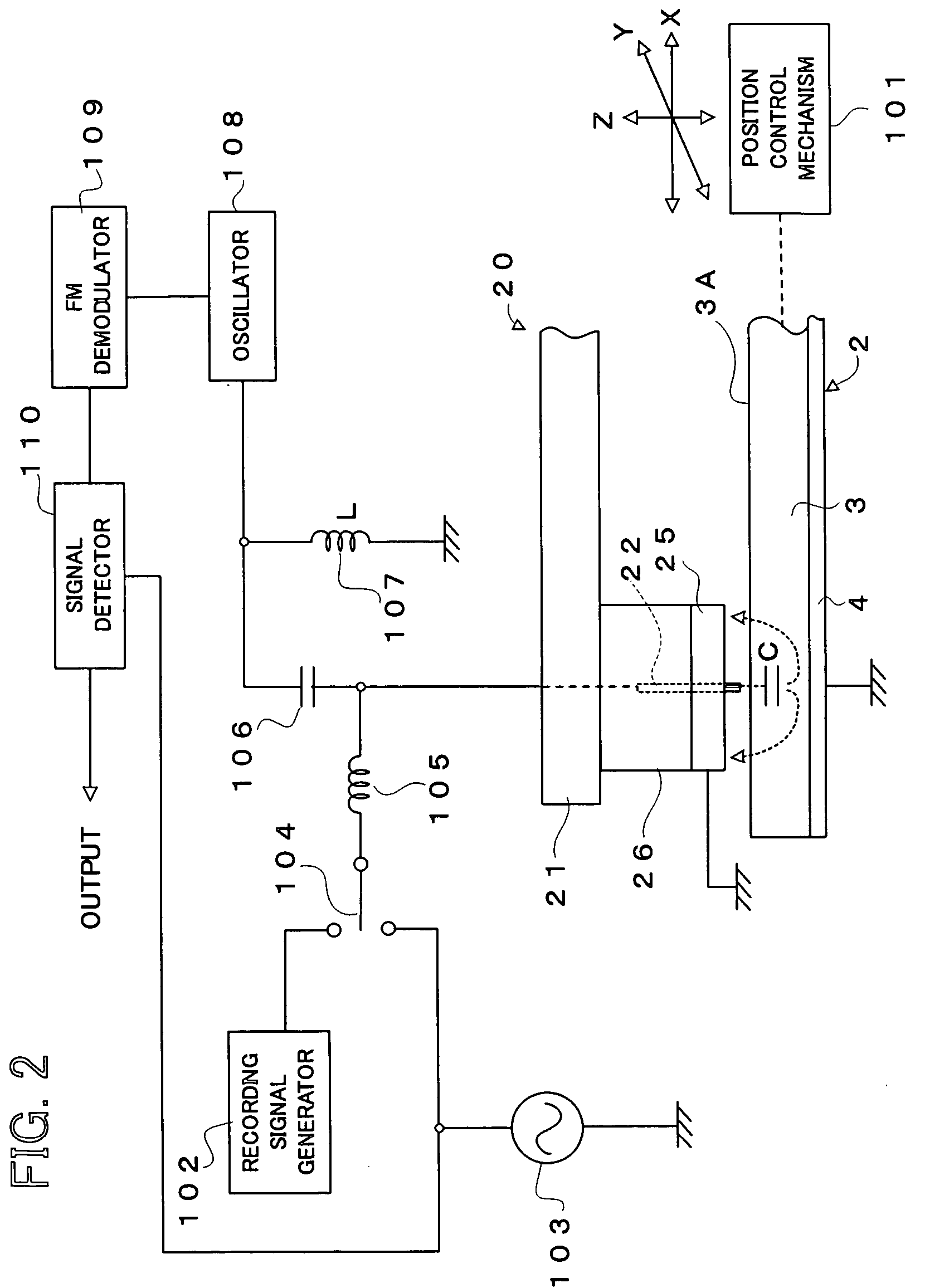
InactiveUS7242661B2Improve signal-to-noise ratioLarge circuit structureElectrostatic charge injection carrier recordingElectron beam carrier recordingElectricityCapacitance
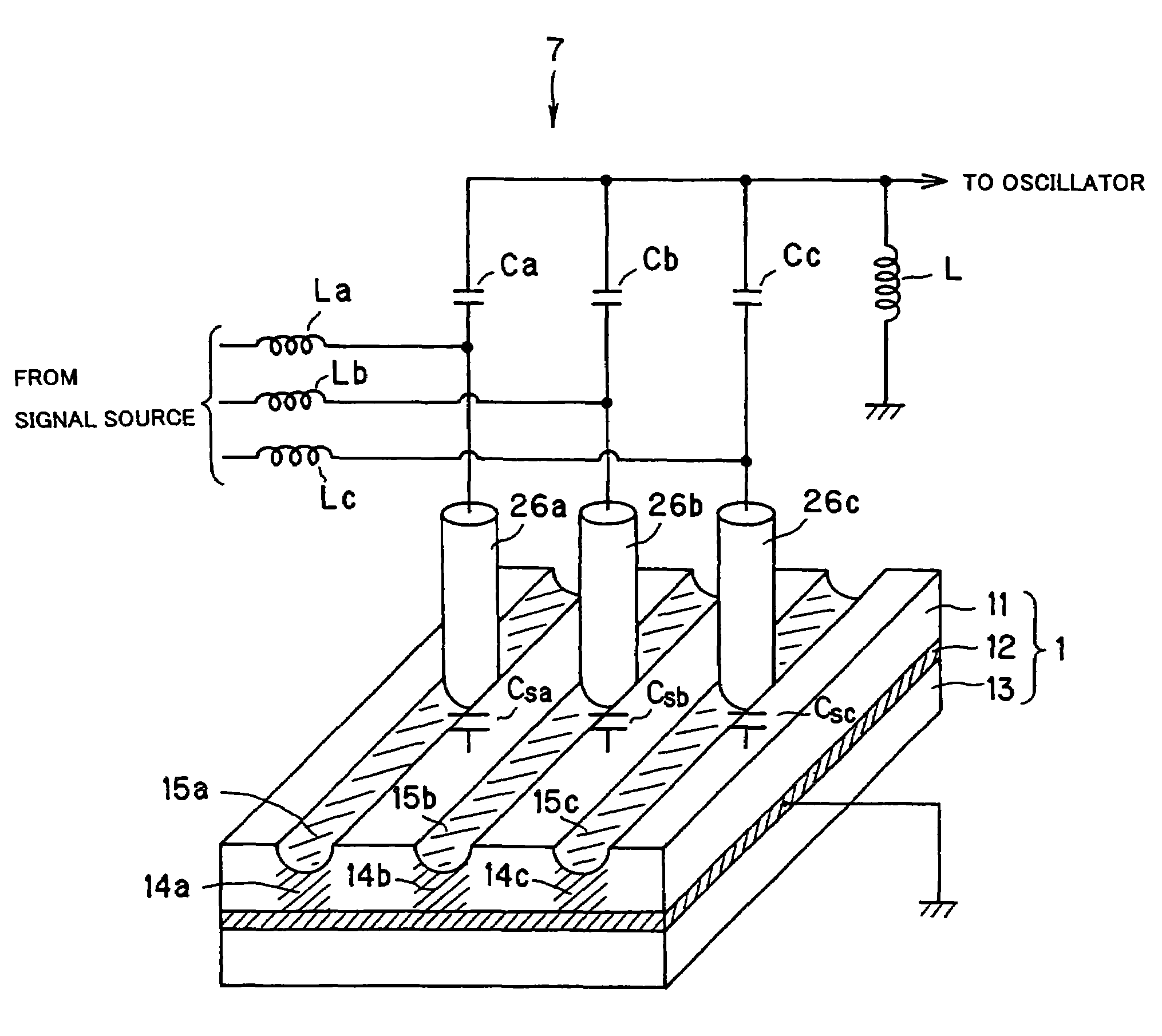
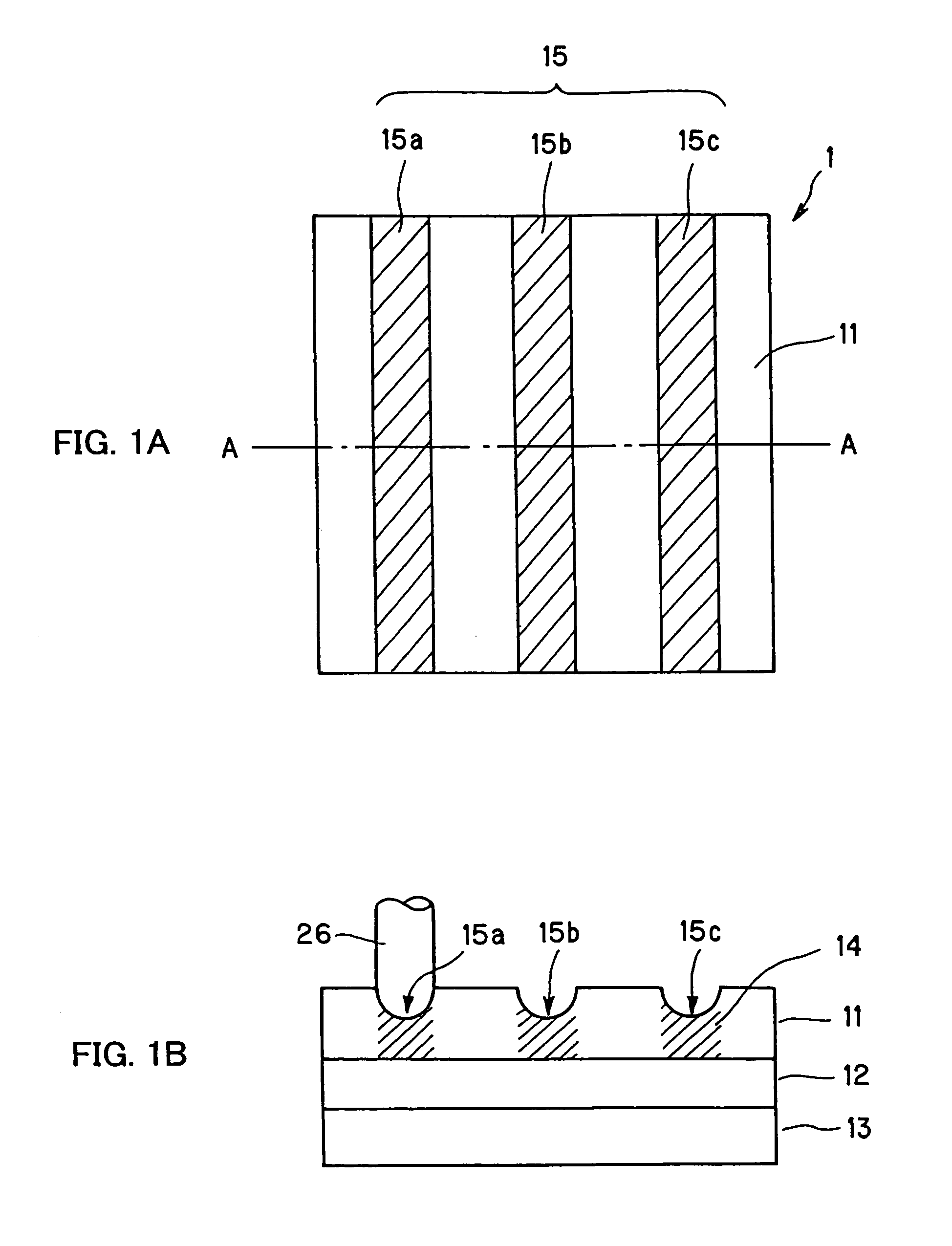
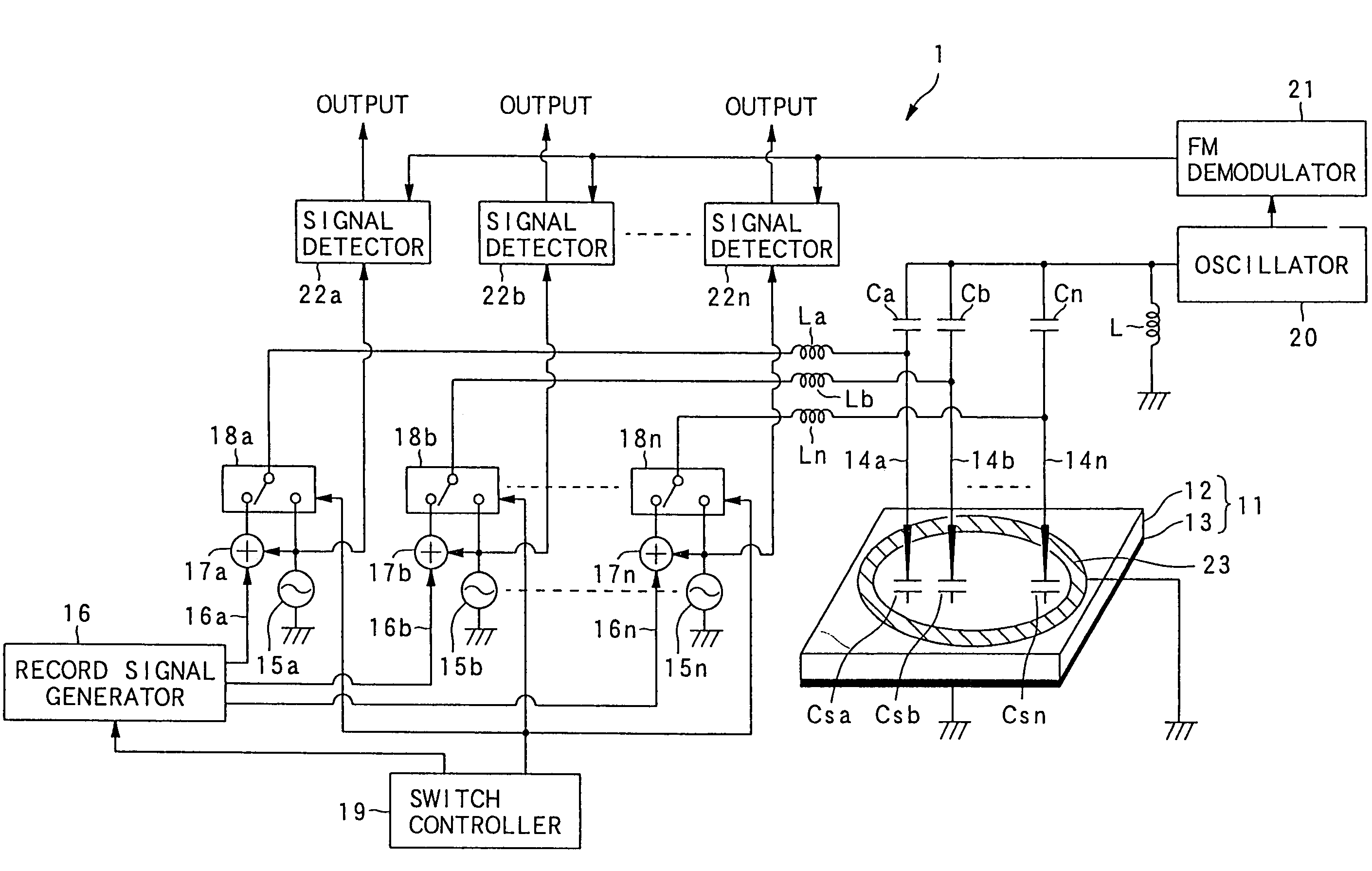
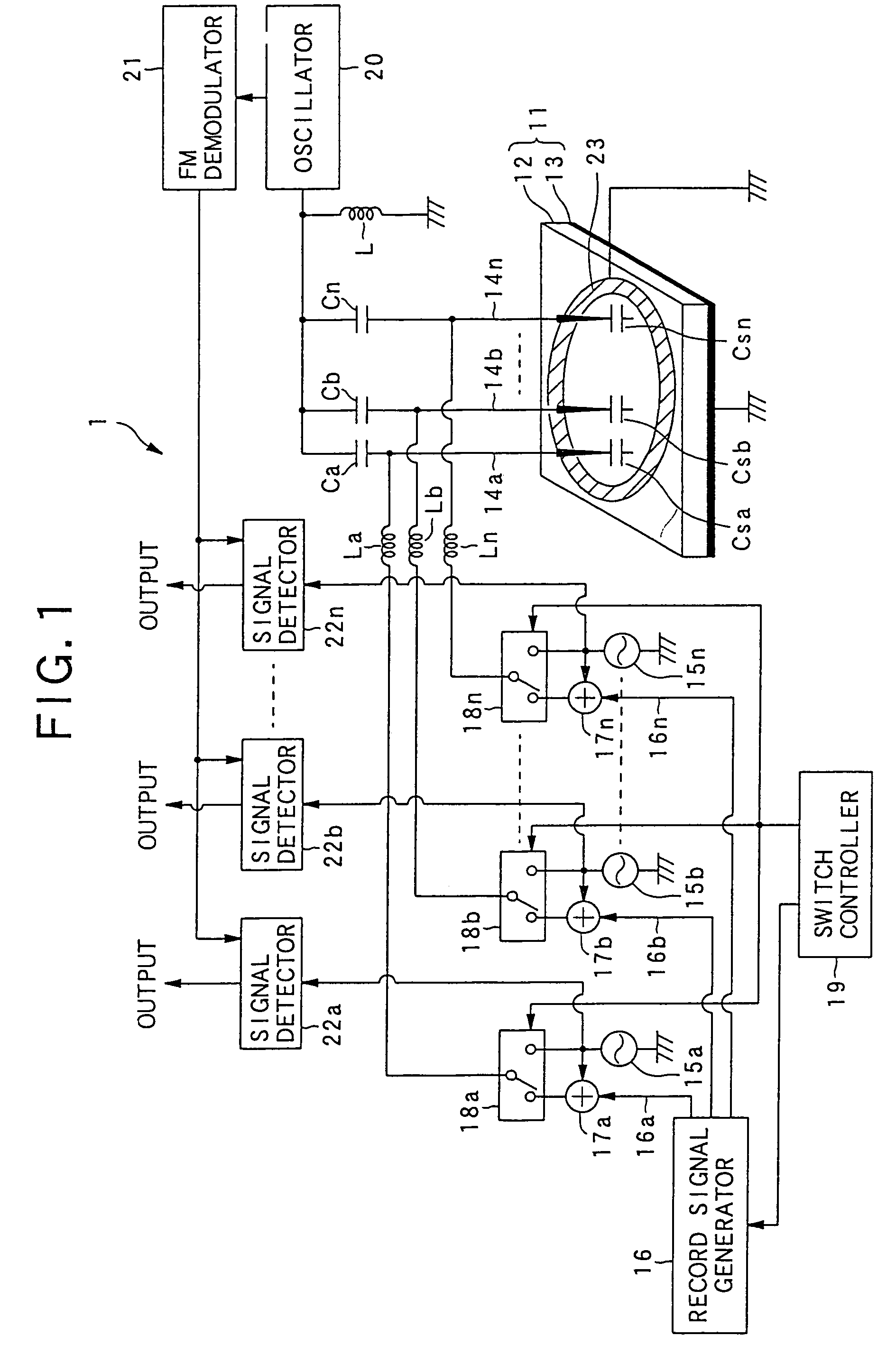
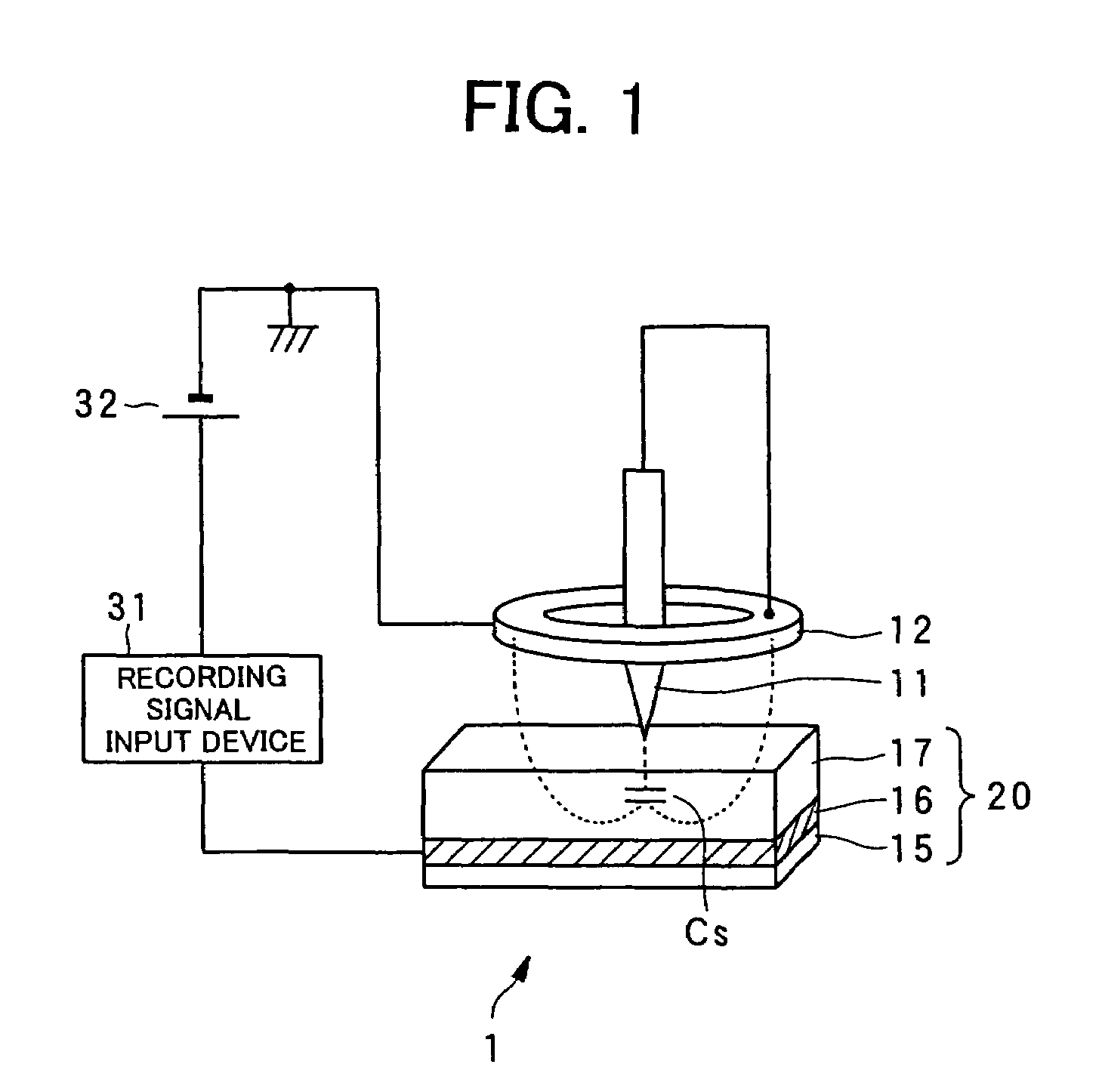
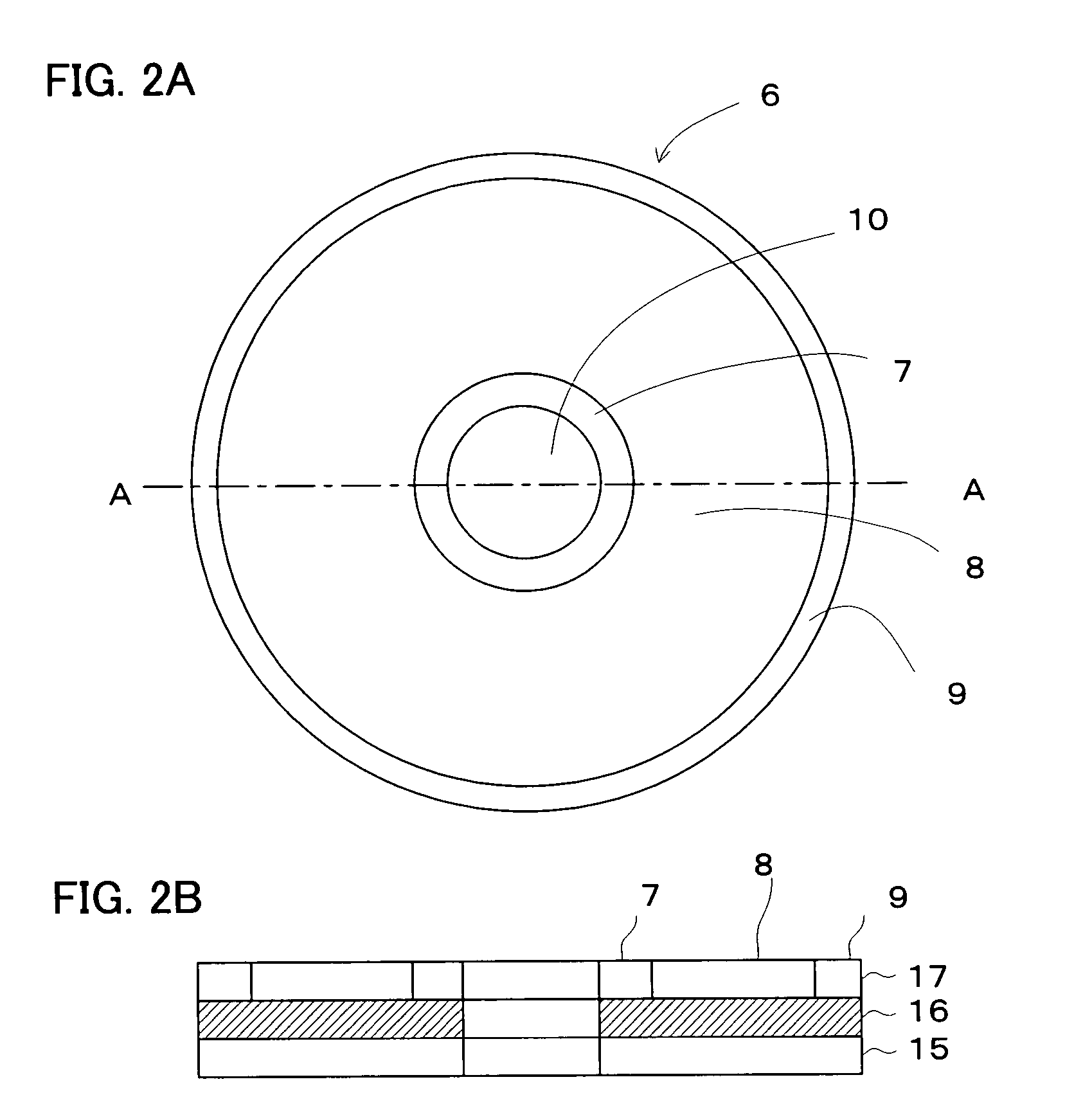
An example dielectric information apparatus is provided with a plurality of electrodes for recording information in a small area of a dielectric substance and an earthed electrode. The electrodes are placed such that the dielectric substance is sandwiched therebetween. The dielectric information apparatus reads out the information recorded in the small area of a dielectric thin film by applying alternating current signals to the first electrodes. The polarization direction of the small area and the direction of an applied electric field decide the dielectric constant of the small area, and the oscillation frequency of an oscillator is determined by a capacitance Cs corresponding to the dielectric constant. An oscillation signal of the oscillator is demodulated at an FM demodulator, and the information is detected from the demodulated signal at a signal detector. When recording, record signals are applied to the first electrodes, and the polarization direction is set to correspond to the record signals.
Owner:PIONEER CORP +1
Information storage medium using ferroelectric, method of manufacturing the same, and information storage apparatus including the same
InactiveUS20090168238A1Avoid damageDifferent record carrier formsBalustradesEngineeringAmorphous Crystals
Provided is an information storage medium using a ferroelectric, including a substrate having an amorphous crystal structure, an electrode layer formed on the substrate, and a ferroelectric layer in a (001) direction formed on the electrode layer.
Owner:POHANG UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
Transducers for ferroelectric storage medium
InactiveUS7397624B2Disposition/mounting of recording headsDriving/moving recording headsTransducerElectrical polarity
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
Short circuit reduction in a ferroelectric memory cell comprising a stack of layers arranged on a flexible substrate
ActiveUS20140210026A1Short numberSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesElectrodeShort circuit
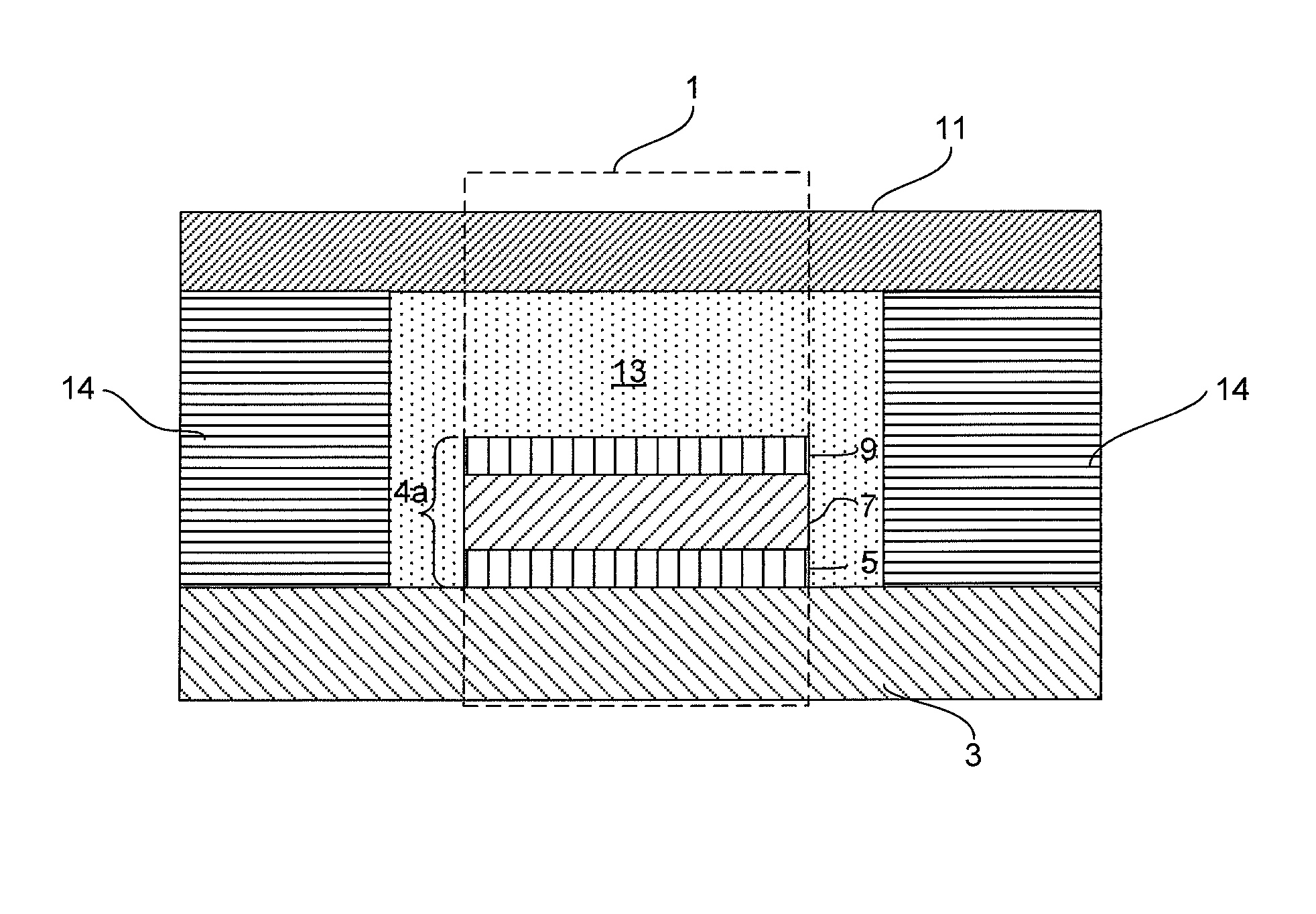
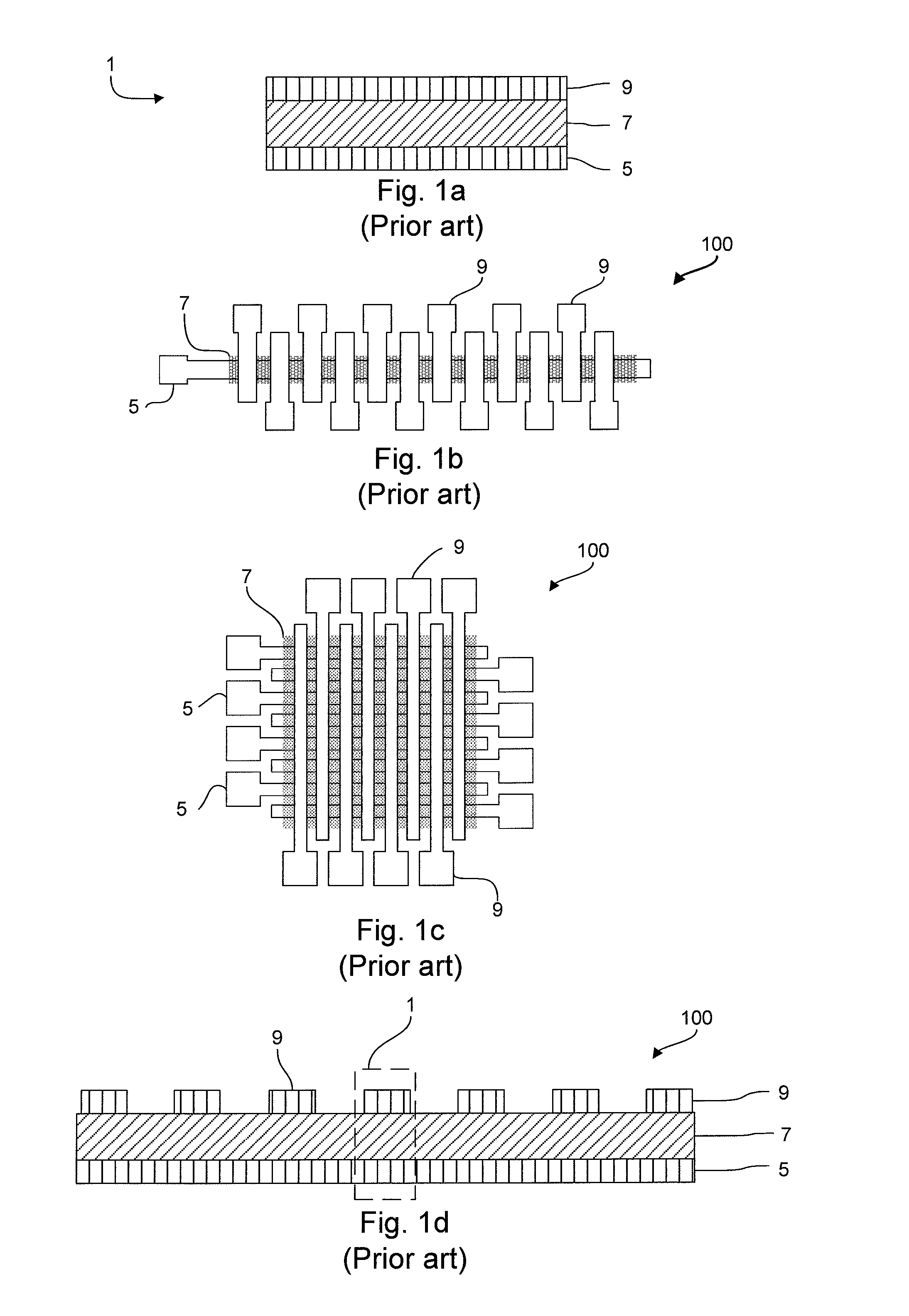
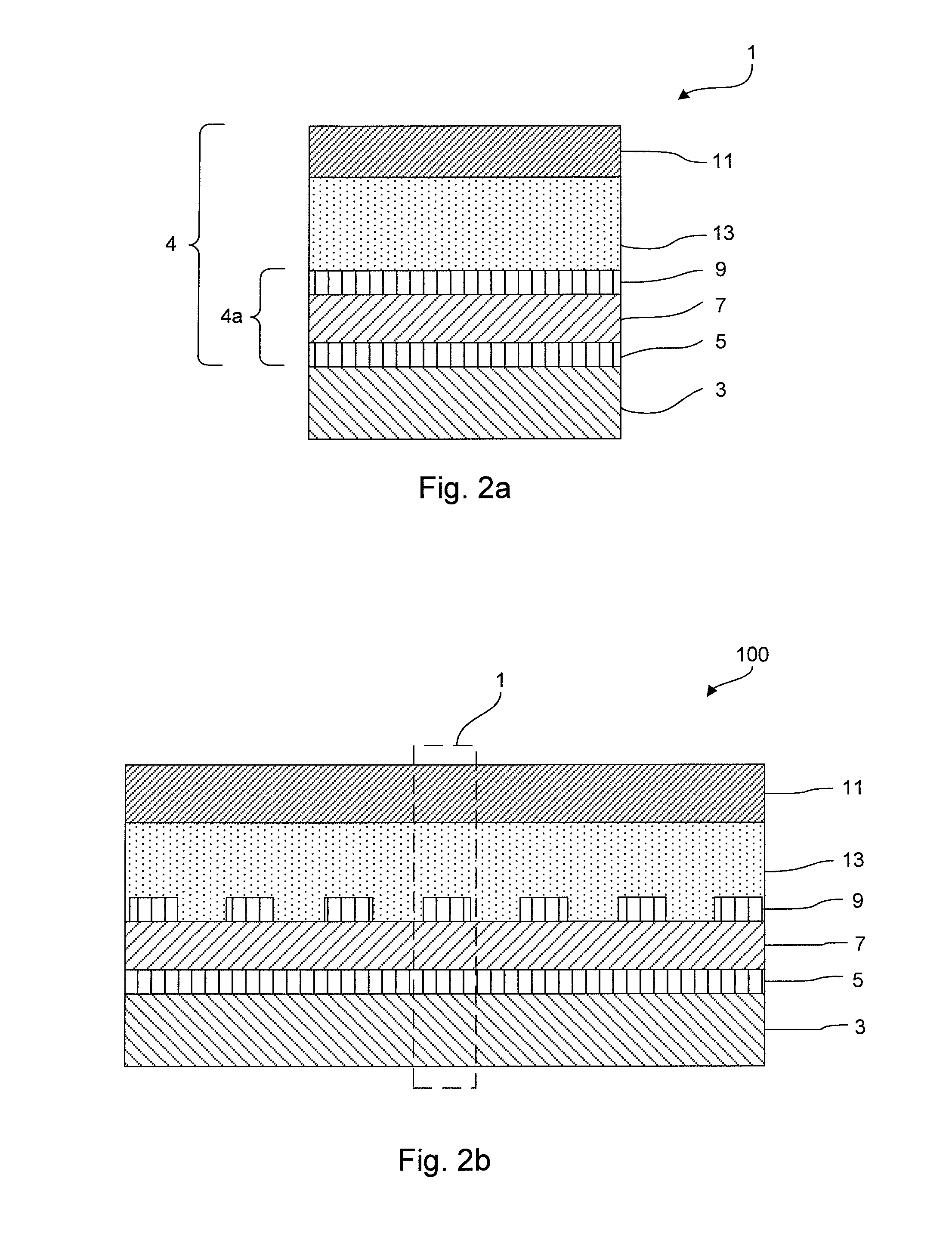
A ferroelectric memory cell (1) and a memory device (100) comprising one or more such cells (1). The ferroelectric memory cell comprises a stack (4) of layers arranged on a flexible substrate (3). Said stack comprises an electrically active part (4a) and a protective layer (11) for protecting the electrically active part against scratches and abrasion. Said electrically active part comprises a bottom electrode layer (5) and a top electrode layer (9) and at least one ferroelectric memory material layer (7) between said electrodes. The stack further comprises a buffer layer (13) arranged between the top electrode layer (9) and the protective layer (11). The buffer layer (13) is adapted for at least partially absorbing a lateral dimensional change (ΔL) occurring in the protective layer (11) and thus preventing said dimensional change (ΔL) from being transferred to the electrically active part (4a), thereby reducing the risk of short circuit to occur between the electrodes.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Method and structure for ultra-high density, high data rate ferroelectric storage disk technology using stabilization by a surface conducting layer
InactiveUS20050095389A1Reliable ultra-high density storageImprove accessibilityLayered productsFerroelectric carrier recordingUltra high densityHigh data rate
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Dielectric recording apparatus, dielectric reproducing apparatus, and dielectric recording / reproducing apparatus
InactiveUS7227830B2Small and inexpensiveVariable capacitance carrier recordingNanoinformaticsCapacitanceData recording
A dielectric recording / reproducing apparatus is provided with: a probe for applying an electric field to a dielectric material; a return electrode for returning the high frequency electric field for data reproduction; an inductor placed between the probe and the return electrode; an oscillator which oscillates at a resonance frequency determined according to the inductor and a capacitance formed in the dielectric material just under the probe; a switch for switching circuit connections depending on whether data recording is performed and data reproducing is performed; a recording signal input device for converting data to be recorded to generate a recording signal; a direct current voltage generation device for generating a direct current bias voltage to be applied to the dielectric material; a frequency-amplitude demodulator for demodulating an oscillation signal of the oscillator having the frequency that is changed depending on the capacitance owned by the dielectric material just under the probe; and a signal detector for detecting data from the demodulated signal.
Owner:CHO YASUO +1
Ferroelectric probe storage apparatus
An apparatus comprises a ferroelectric storage medium, and a transducer for reading data from the ferroelectric storage medium and for writing data to the ferroelectric storage medium, wherein the transducer includes a substrate and a probe coupled to the substrate, wherein the probe includes a conductive element and a bilayer structure causing the probe to bend toward the ferroelectric storage medium.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com