Method of writing data on a storage device using a probe technique
a data and storage device technology, applied in the field of writing data, can solve the problems of spm, the inability of the solid-state memory device to function as a high-density data writing device, and the inability to obtain a hard disk with a higher writing density, so as to achieve low coercive field, high coercive field, and low voltage
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0037] The present invention will now be described more fully with reference to the accompanying drawings, in which an exemplary embodiment of the invention is shown. In the drawings, the thicknesses of layers or regions may be exaggerated for clarity.
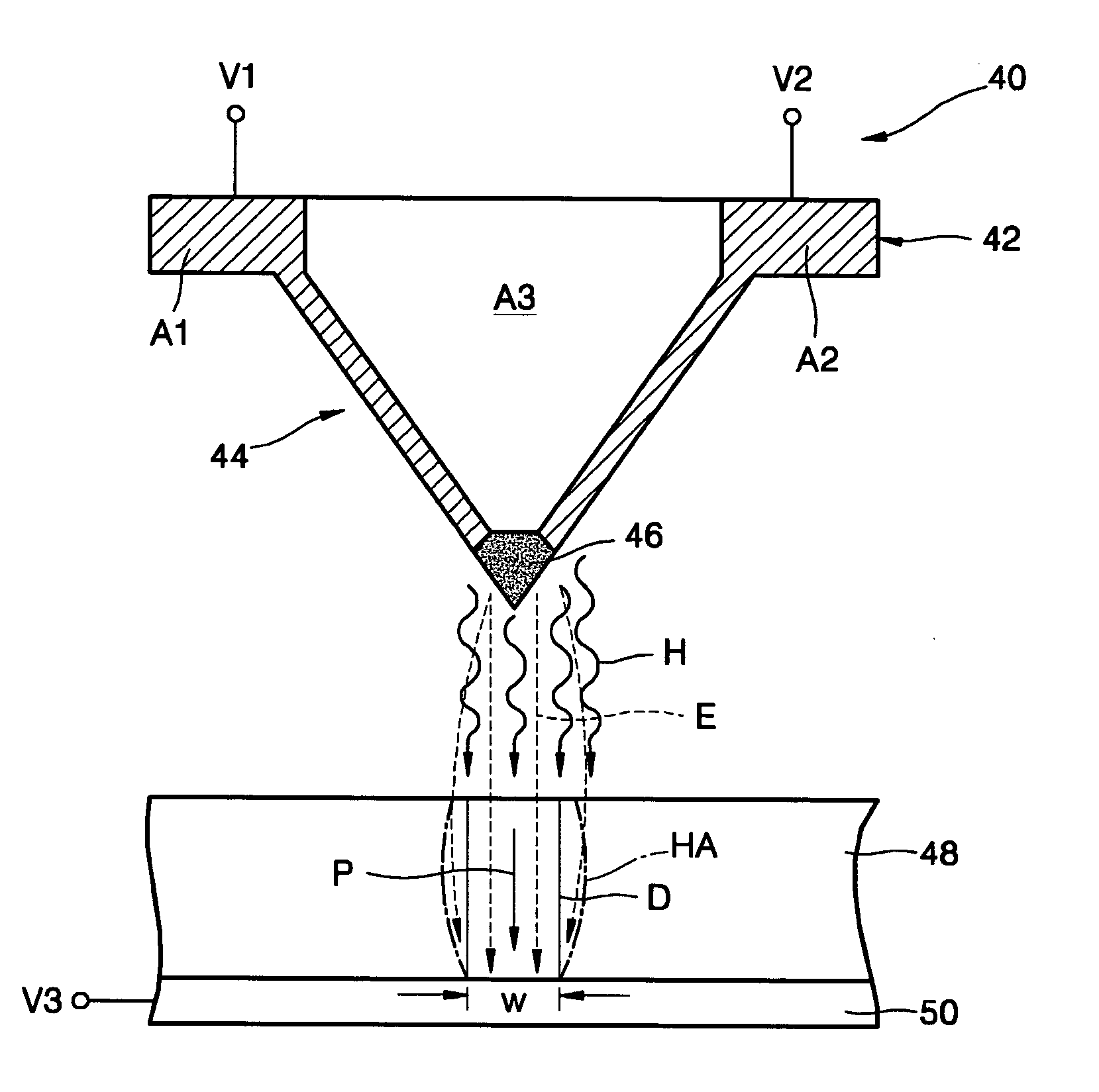
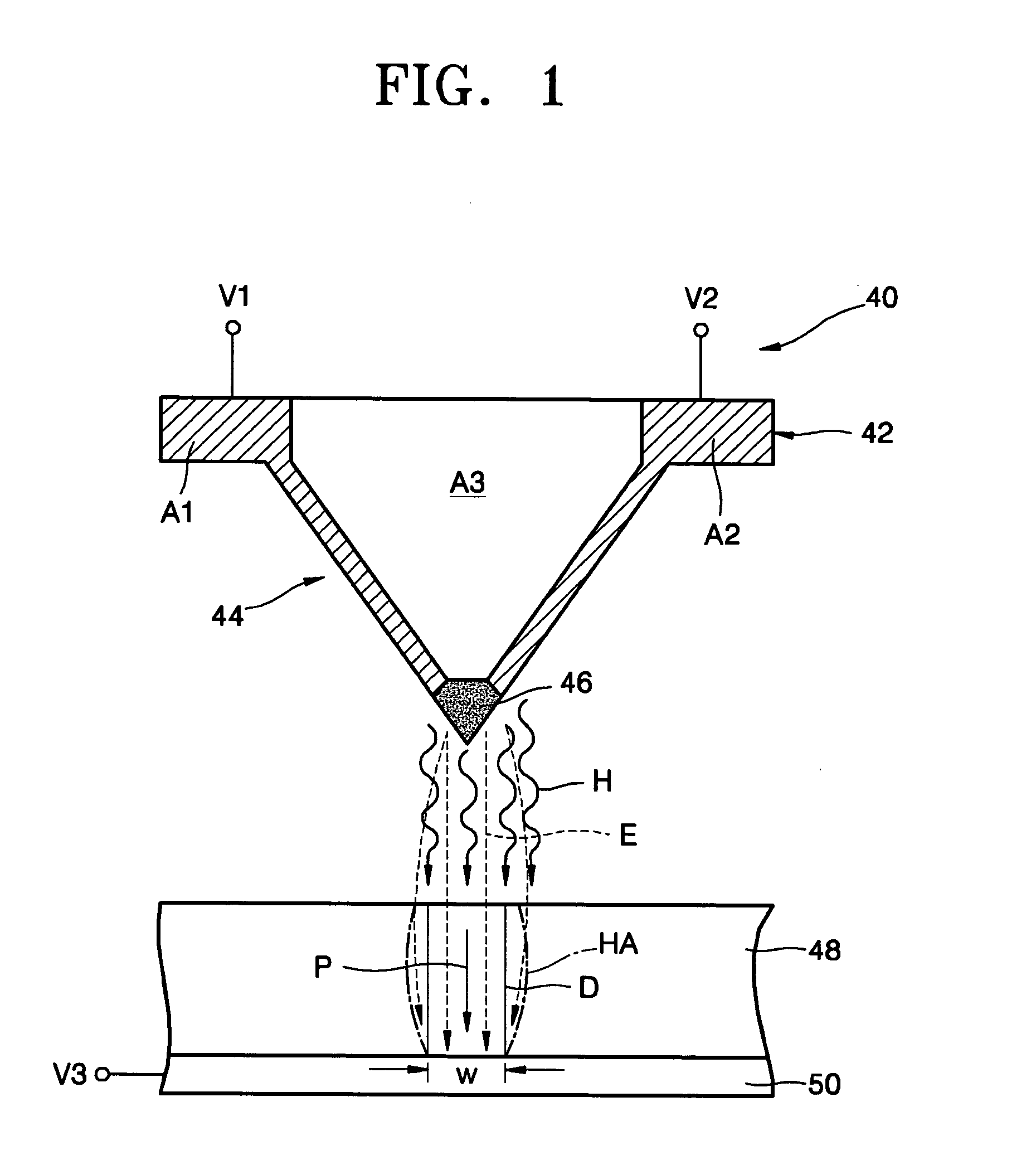
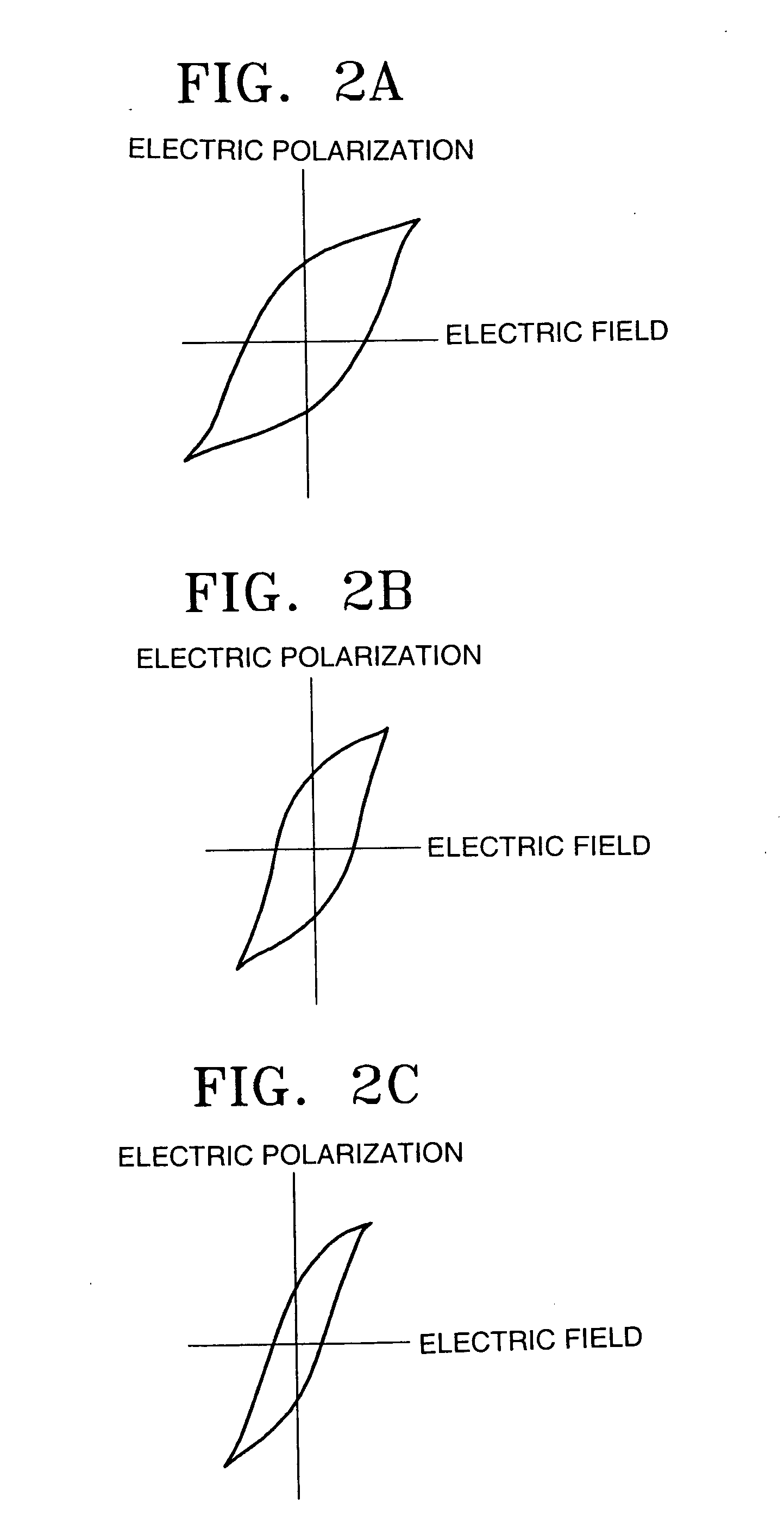
[0038] Referring to FIG. 1, reference numeral 48 denotes a ferroelectric layer used as a data writing medium. Although the ferroelectric layer 48 is preferably a PZT layer, it is possible to use other ferroelectric layers, for example, a BaTiO3 (BTO) layer, a triglycine sulfate (TGS) layer, or a triglycine selenate (TGSe) layer. A lower electrode 50 is disposed on a bottom surface of the ferroelectric layer 48. To write data, a third voltage V3 is applied to the lower electrode 50. A probe 40 is disposed above the ferroelectric layer 48. The probe 40 is positioned at the end of a cantilever (not shown) connected to a power supplier (not shown). The probe 40 comprises a flat panel portion 42, which is connected to the cantilever, and a...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| resistance | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com