Patents
Literature
67 results about "Out of plane motion" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
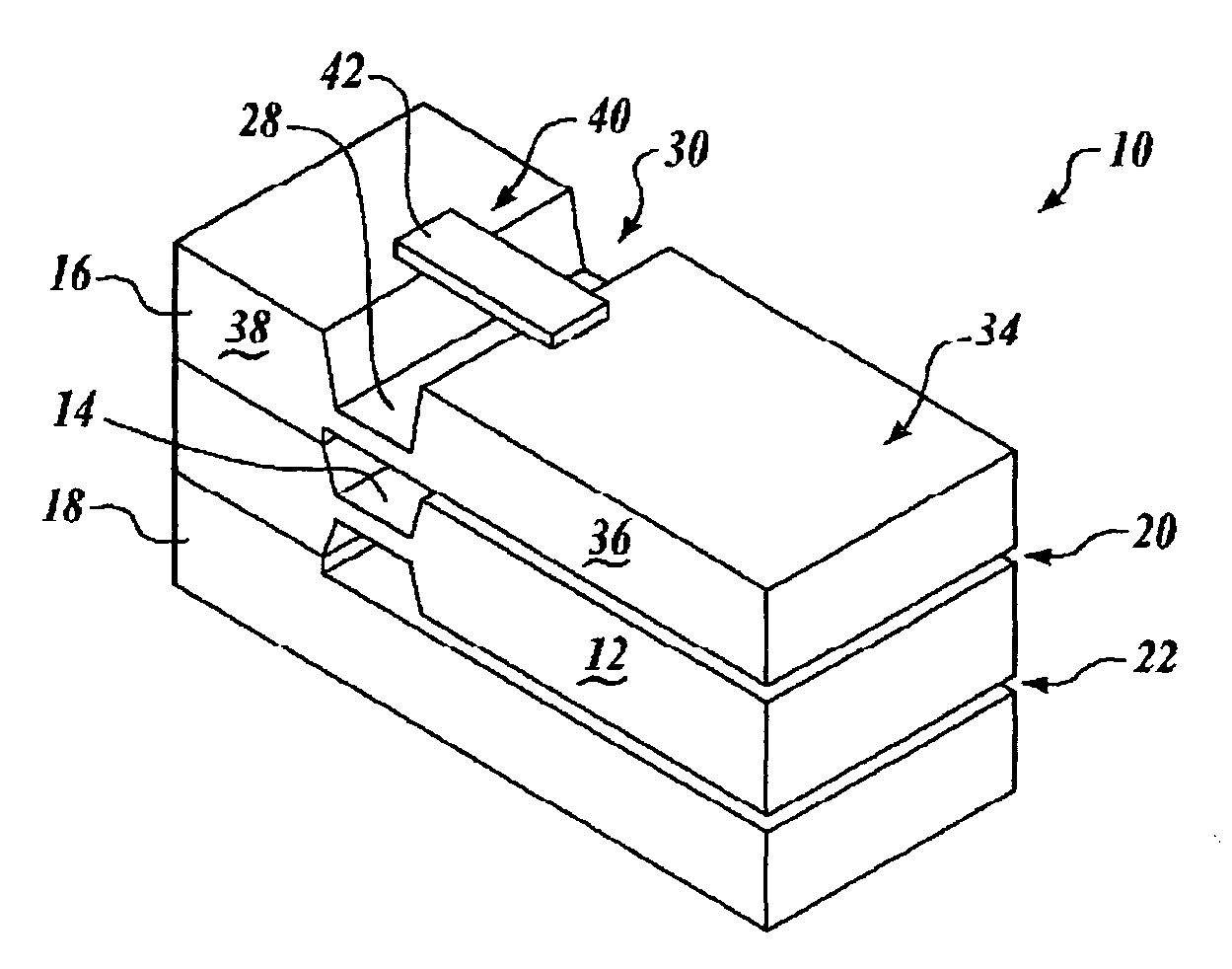
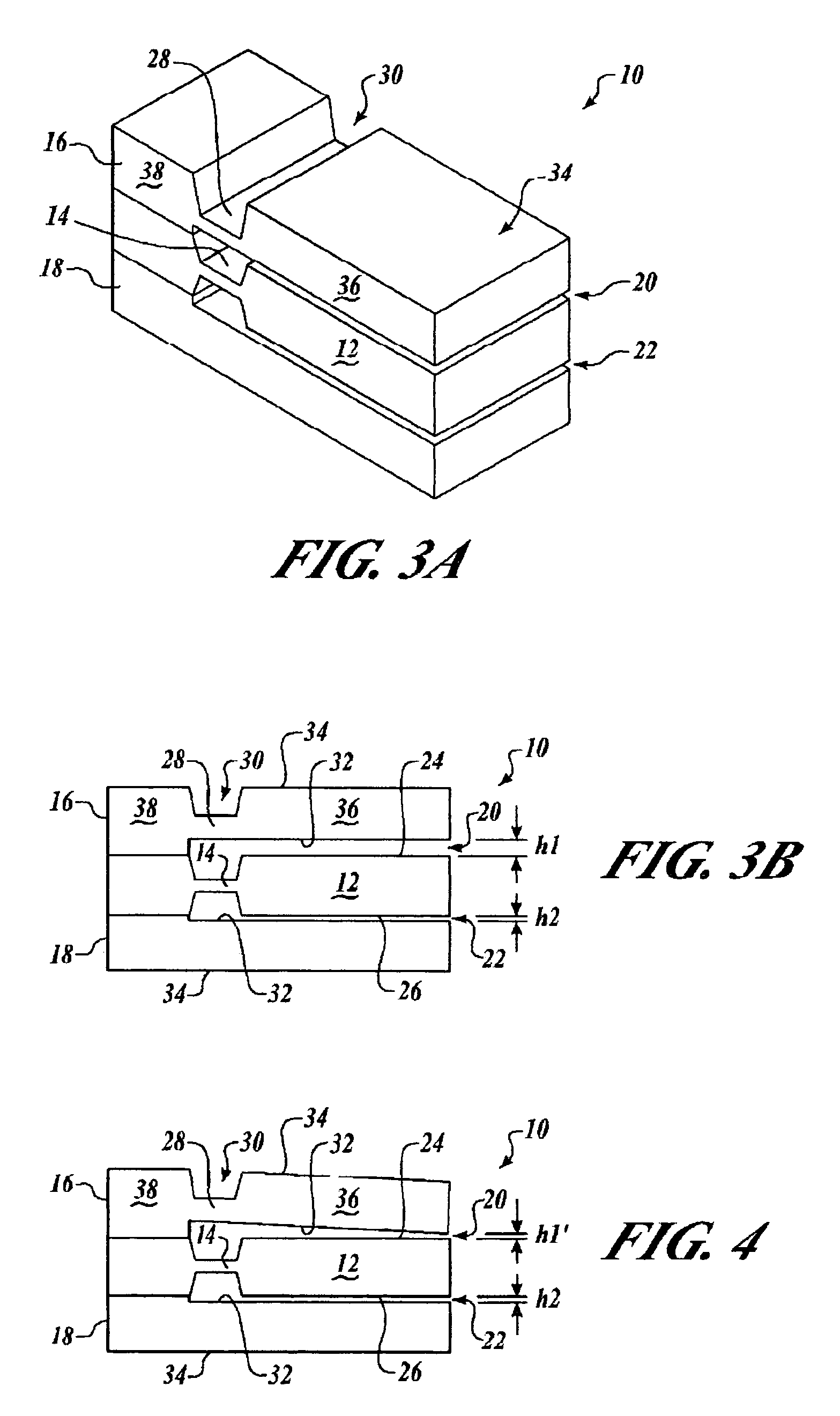
Method and apparatus for micro electro-mechanical systems and their manufacture
InactiveUS20020127760A1Less driving voltageSemiconductor electrostatic transducersSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOut of plane motionActuator
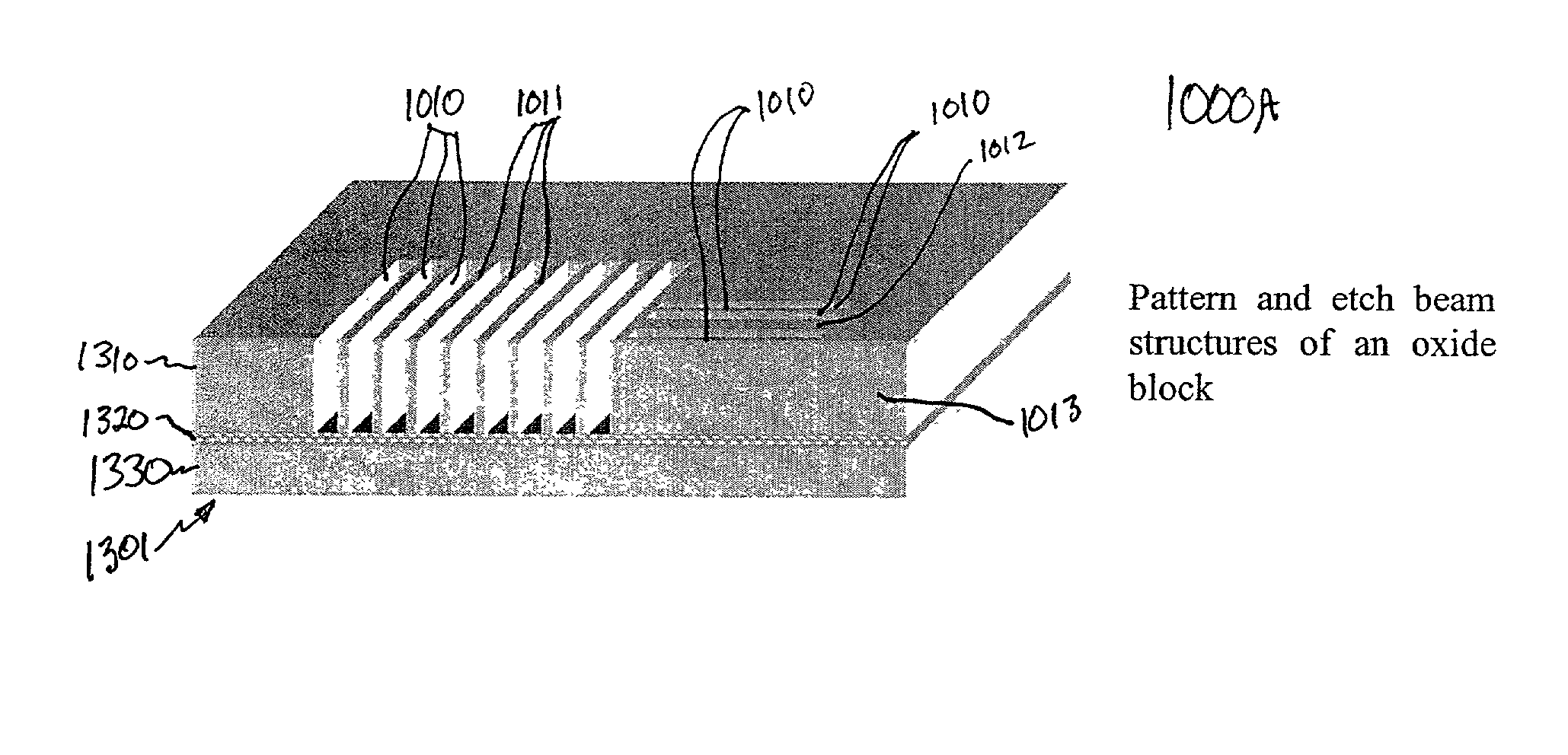
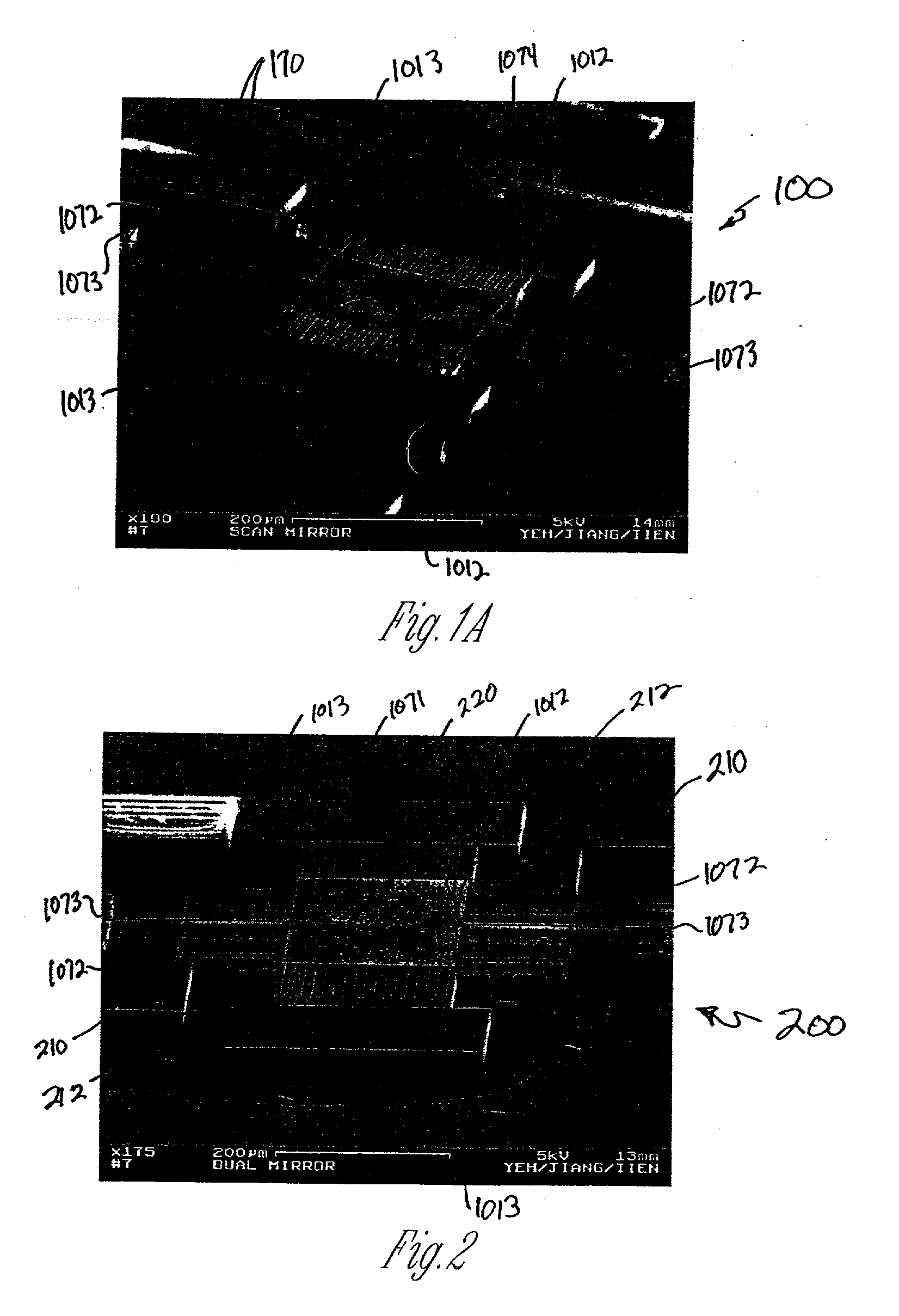
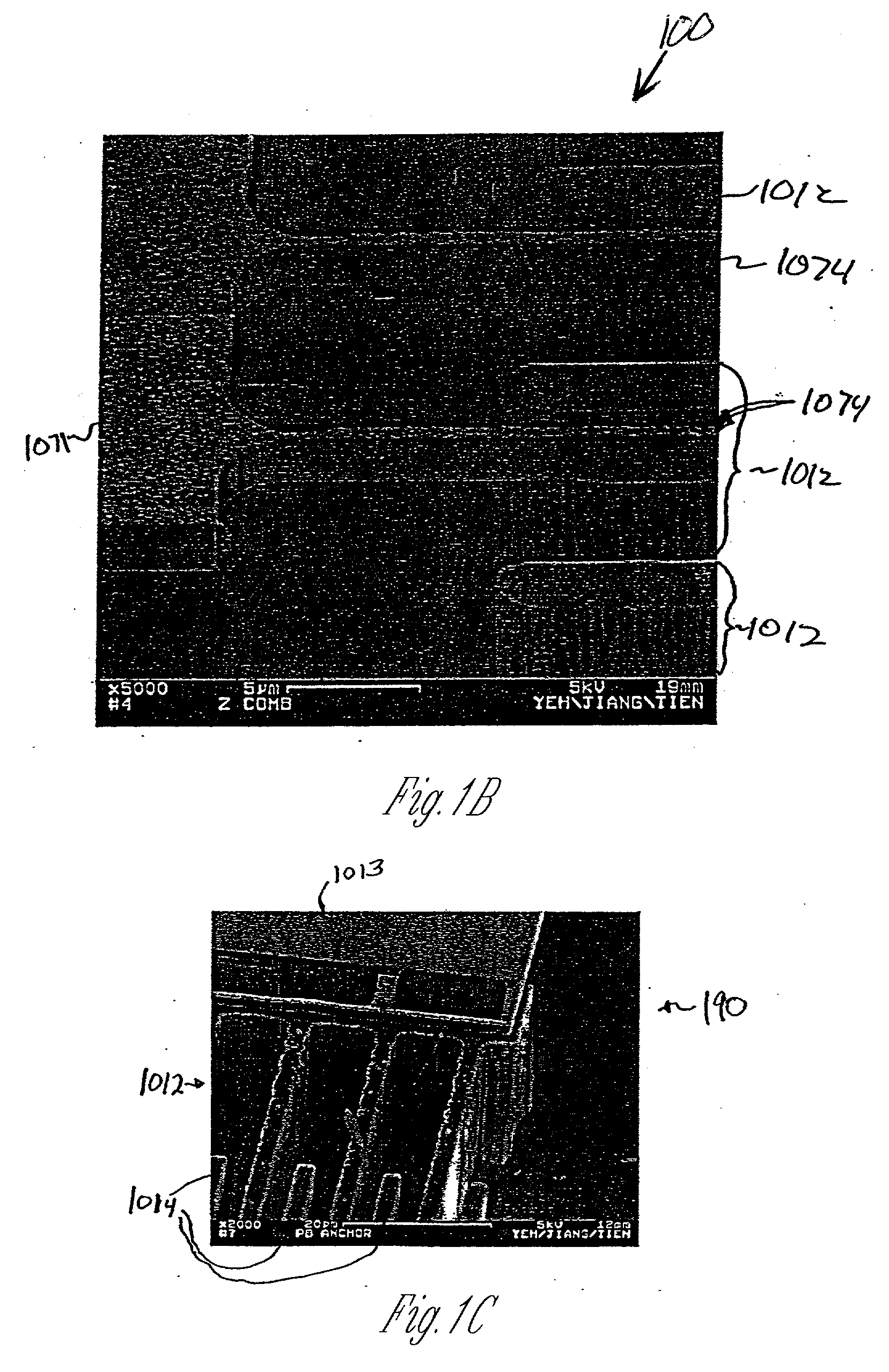
The present invention provides a fabrication process that integrates high-aspect-ratio silicon structures with polysilicon surface micromachined structures. In some embodiments the process includes forming an oxide block by etching a plurality of trenches to leave a plurality of vertical-walled silicon structures standing on the substrate, thermally and substantially completely oxidizing the vertical-walled silicon structures, and substantially filling spaces between the oxidized vertical-walled silicon structures with an oxide of silicon to form the oxide block. The process retains not only the high-aspect-ratio silicon structures possible with deep reactive ion etching (DRIE) but also the design flexibility of polysilicon surface micromachining. Using this process, polysilicon platforms have been fabricated, which are actuated by high-aspect-ratio combdrives for many applications such as x-y-z stages and scanning devices. The actuators include an asymmetric combdrive that actuates in torsional / out-of-plane motions, and a high-aspect-ratio combdrive that drives in translational motion.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
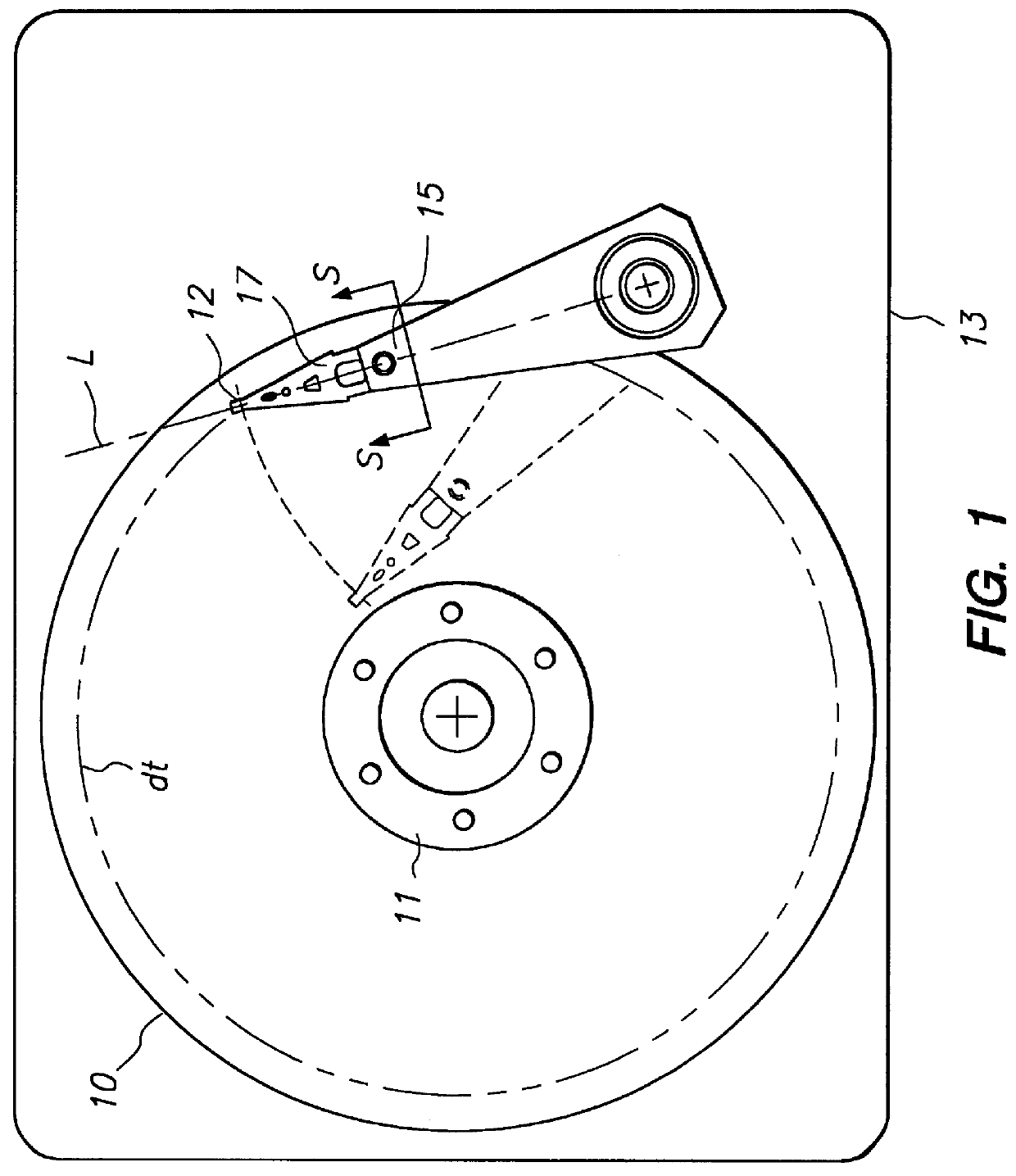
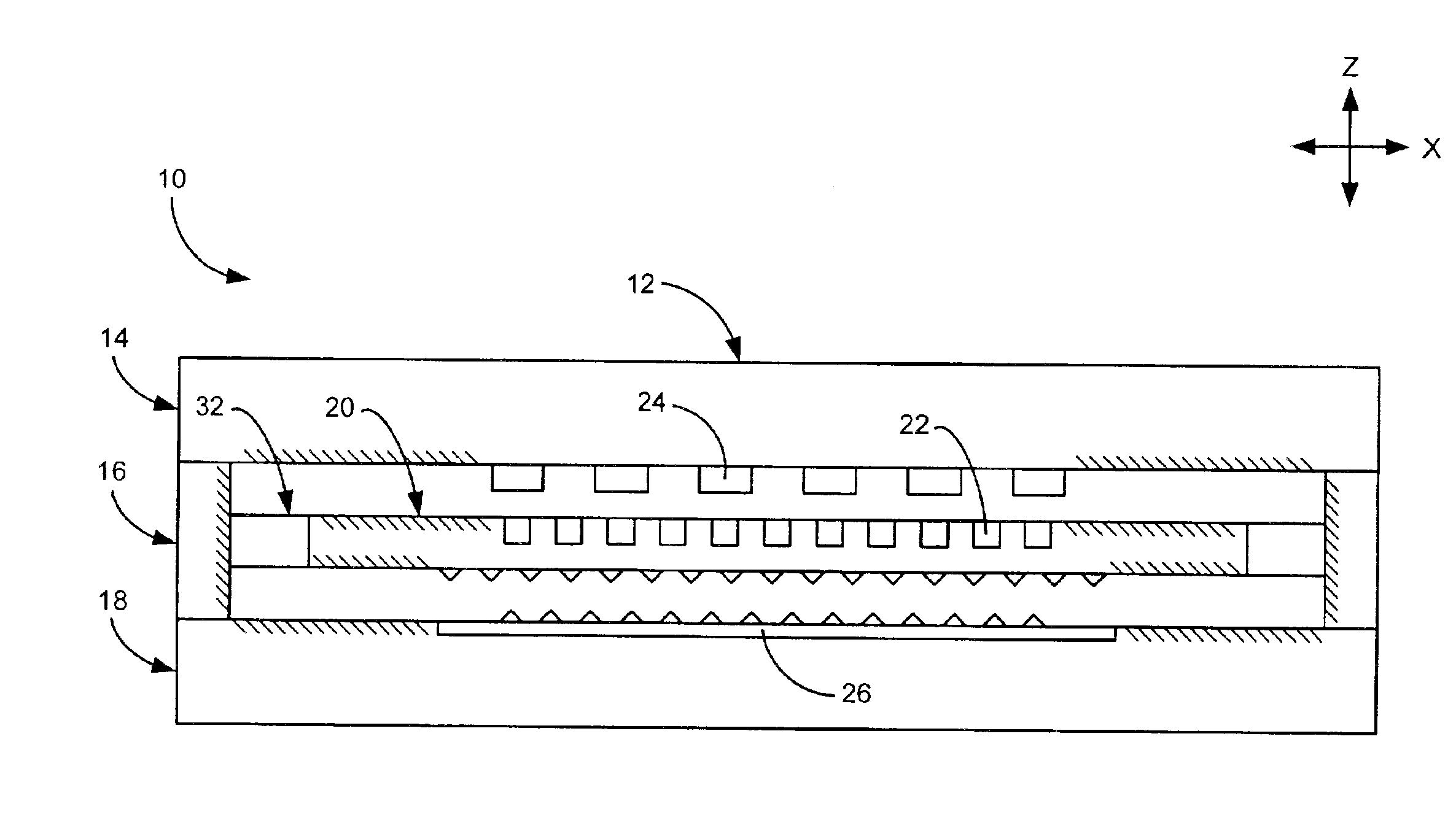
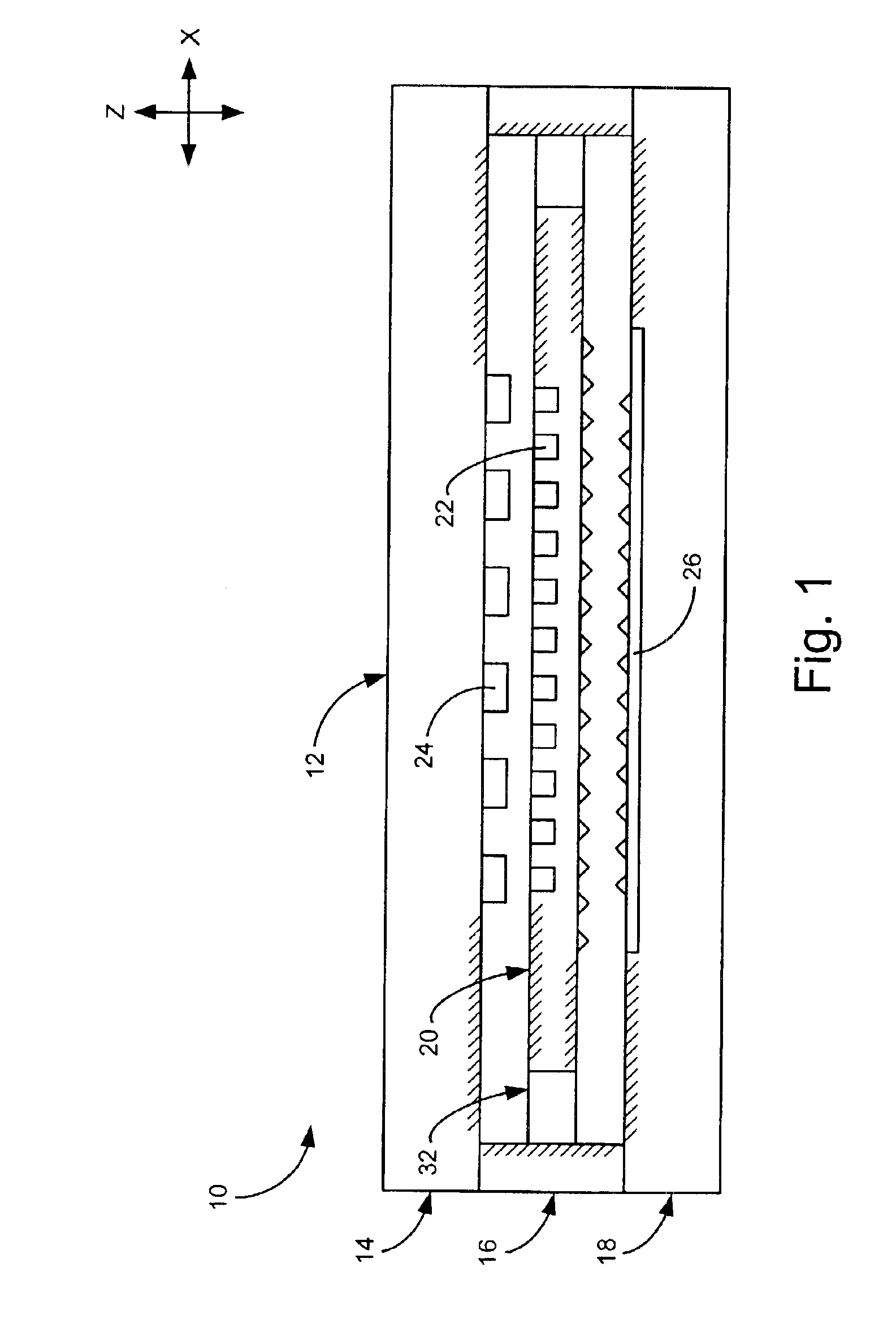
Roll-biased head suspension for reduced track misregistration
InactiveUS6088192ADecreased TMRReduce TMR otherwiseCarrier indicating/warning arrangementsRecord information storageHard disc driveOut of plane motion
Owner:MAXTOR
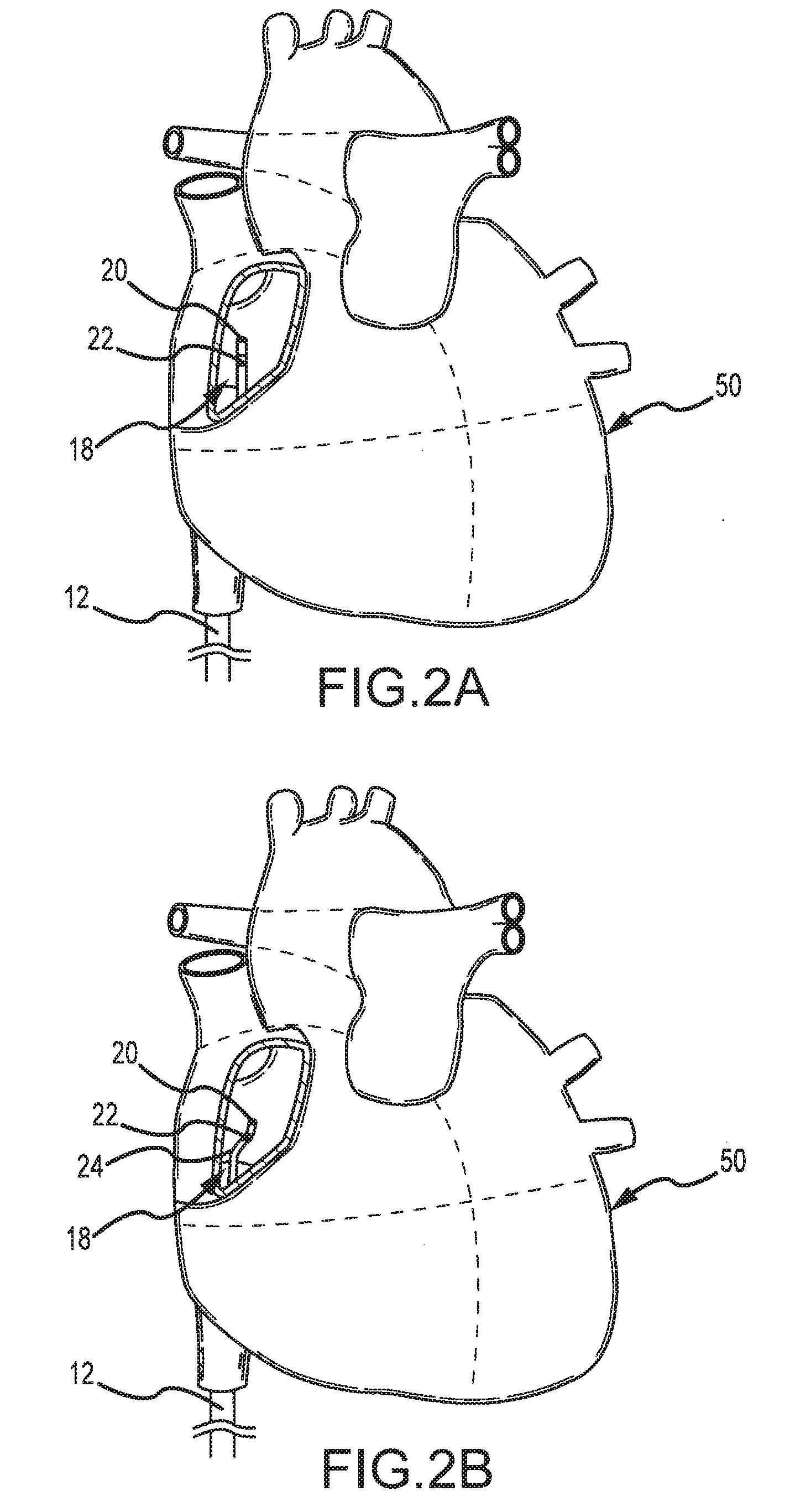
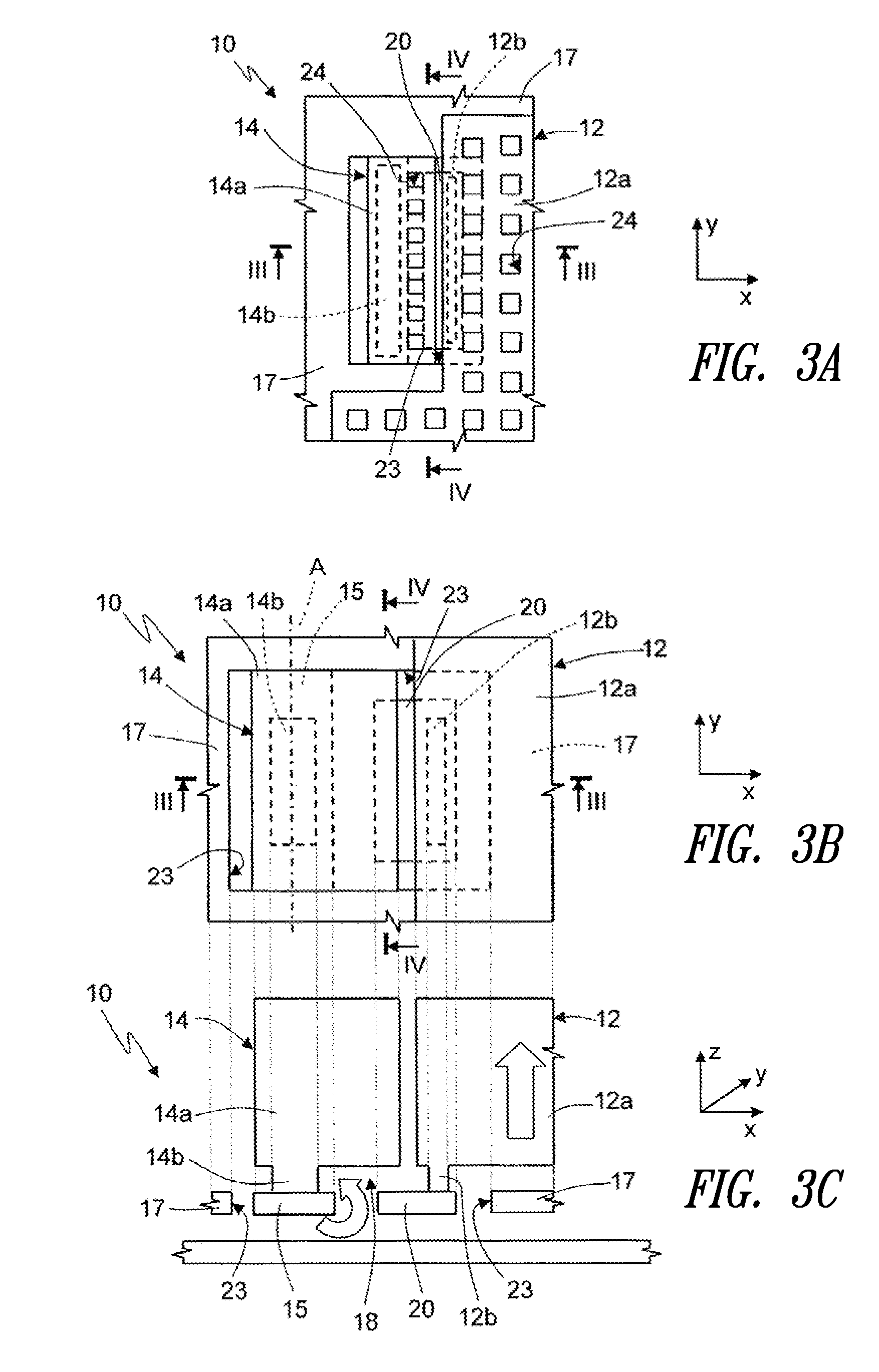
Deflectable catheter with distal deflectable segment
ActiveUS7985215B2Enhance and maximize sizeElectrocardiographyCatheterOut of plane motionProximal point
A guidable, or steerable, or deflectable catheter is provided that includes a proximal portion and a distal portion for insertion into a body cavity. A selectively deflectable segment having an anisotropic bending stiffness for deflection in individual planes is incorporated into the distal portion of the catheter shaft. Upon actuation of pull wires, the distal deflectable segment may be deflected to move / sweep the distal catheter tip through a sweeping plane. The anisotropic bending stiffness of the distal deflectable segment permits in-plane movement of the distal catheter tip in the sweeping plane while resisting any out-of-plane movements. In one arrangement, stiffening elements are selectively disposed within the distal deflectable segment such that the out-of-plane bending stiffness is largely increased and greater than the in-plane bending stiffness for deflection in the sweeping plane. In another arrangement, the cross section of a distal deflectable segment is altered to produce anisotropic area inertias of moment about its centroidal axes, and thus anisotropic bending stiffnesses.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
Robust and accurate freehand 3D ultrasound
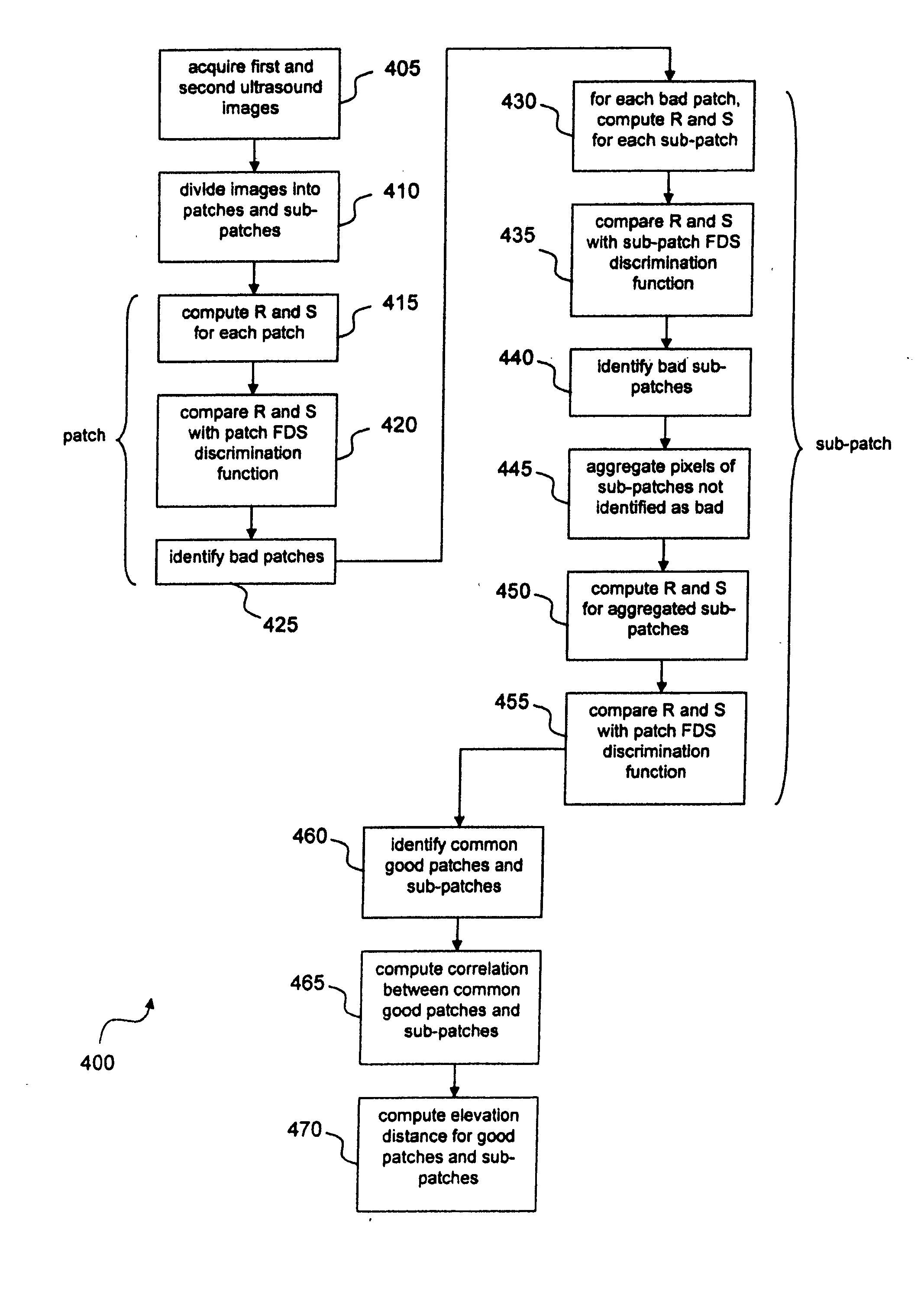
ActiveUS20100198068A1Improves ultrasound probe calibrationRobust ultrasound image registrationUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementCorrelation coefficientVein
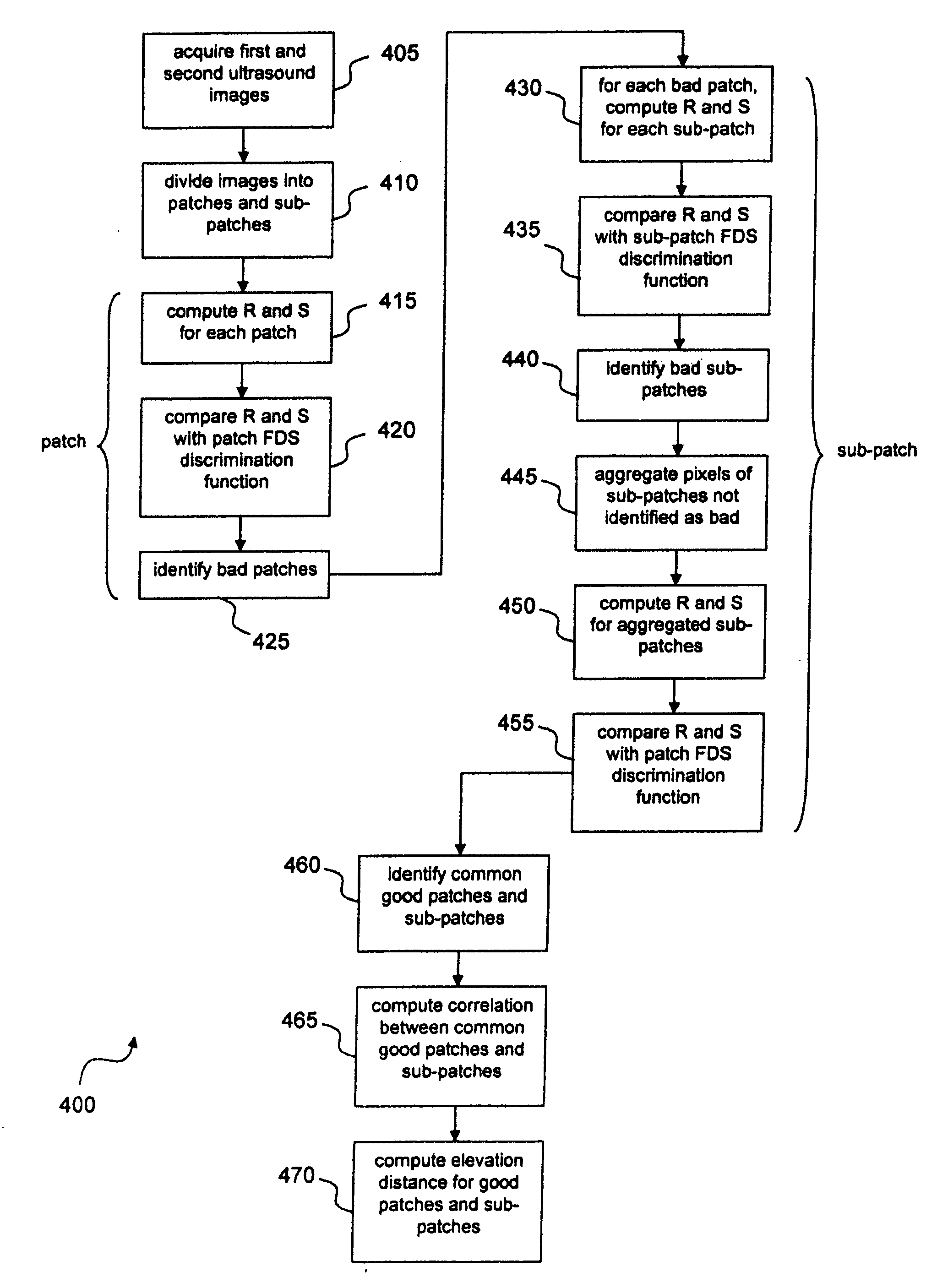
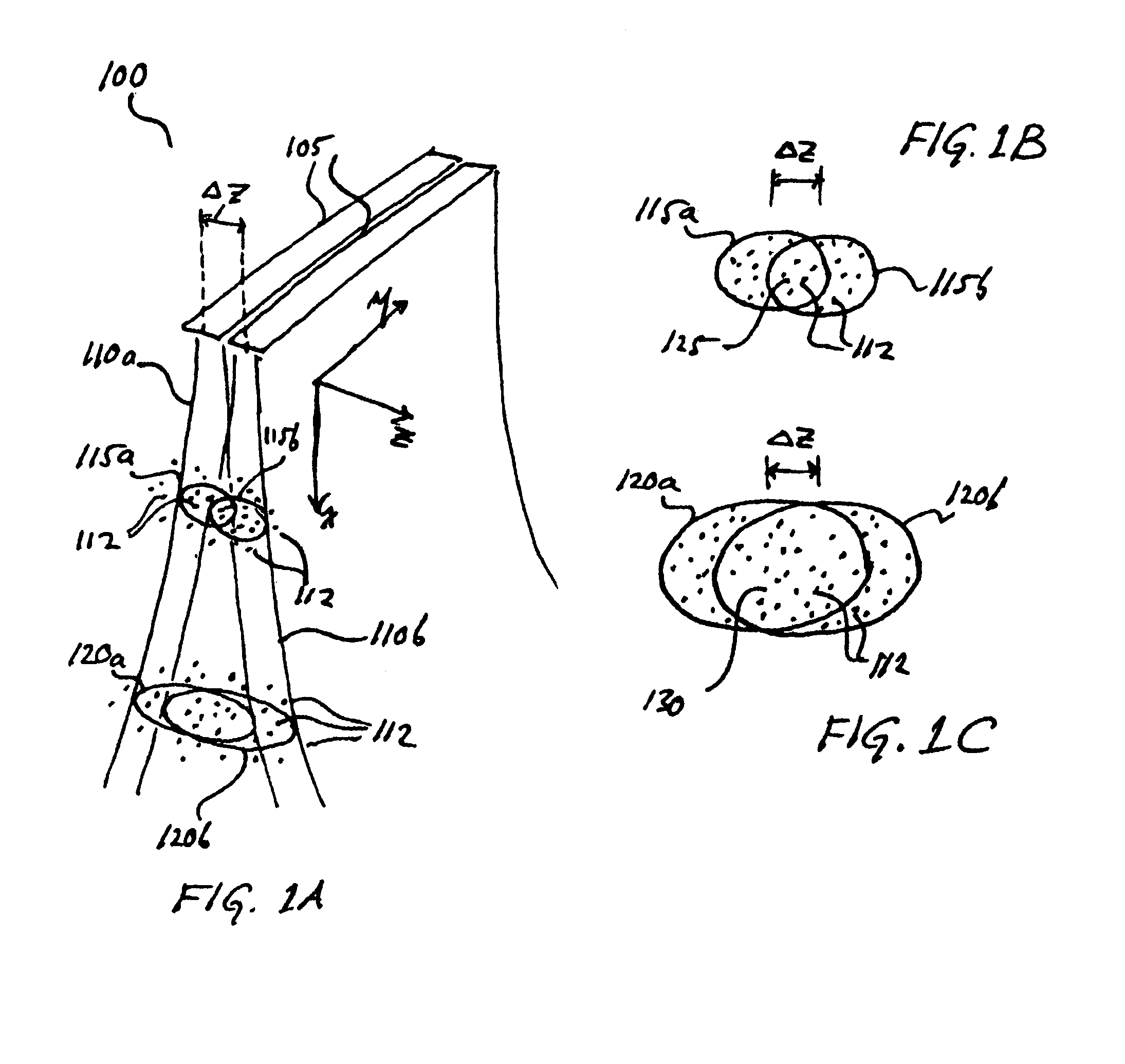
Disclosed is a system and method for computing out of plane motion between two ultrasound images. The method identifies regions of fully developed speckle that are common to the two images, computes a correlation coefficient corresponding to the two fully developed speckle image regions, and then computing an elevation distance corresponding to the correlation coefficient. The method exploits the measurable and characterizable relation between inter-image correlation and elevation distance, which may be determined from fully developed speckle regions. The method also identifies regions within the ultrasound images related to structure (e.g., vein or bone), and disregards these regions.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Movable micro-electromechanical device
InactiveUS6882019B2Permit some movementPrevent movementCarriage/perambulator accessoriesAcceleration measurement using interia forcesOut of plane motionEngineering
A movable system, such as a computer storage device, having a frame, a mover configured to move relative to the frame, and a mechanical suspension operatively coupled between the frame and mover. The mechanical suspension is configured to permit planar movement of the mover while substantially preventing out-of-plane movement, and includes a first flexure configured to flex in response to movement of the mover in a first direction relative to the frame, and a second flexure configured to flex in response to relative movement occurring in a second direction.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
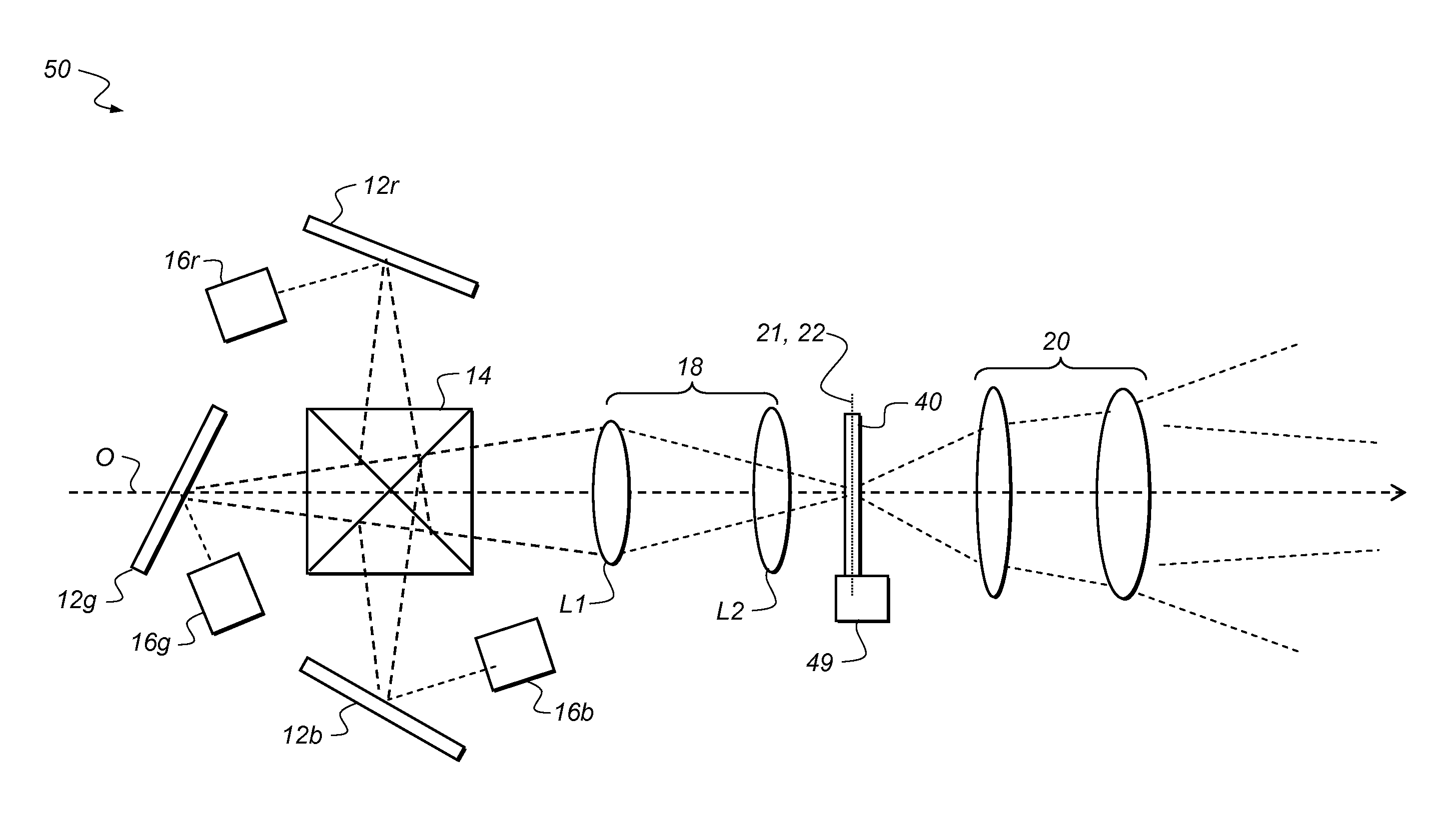
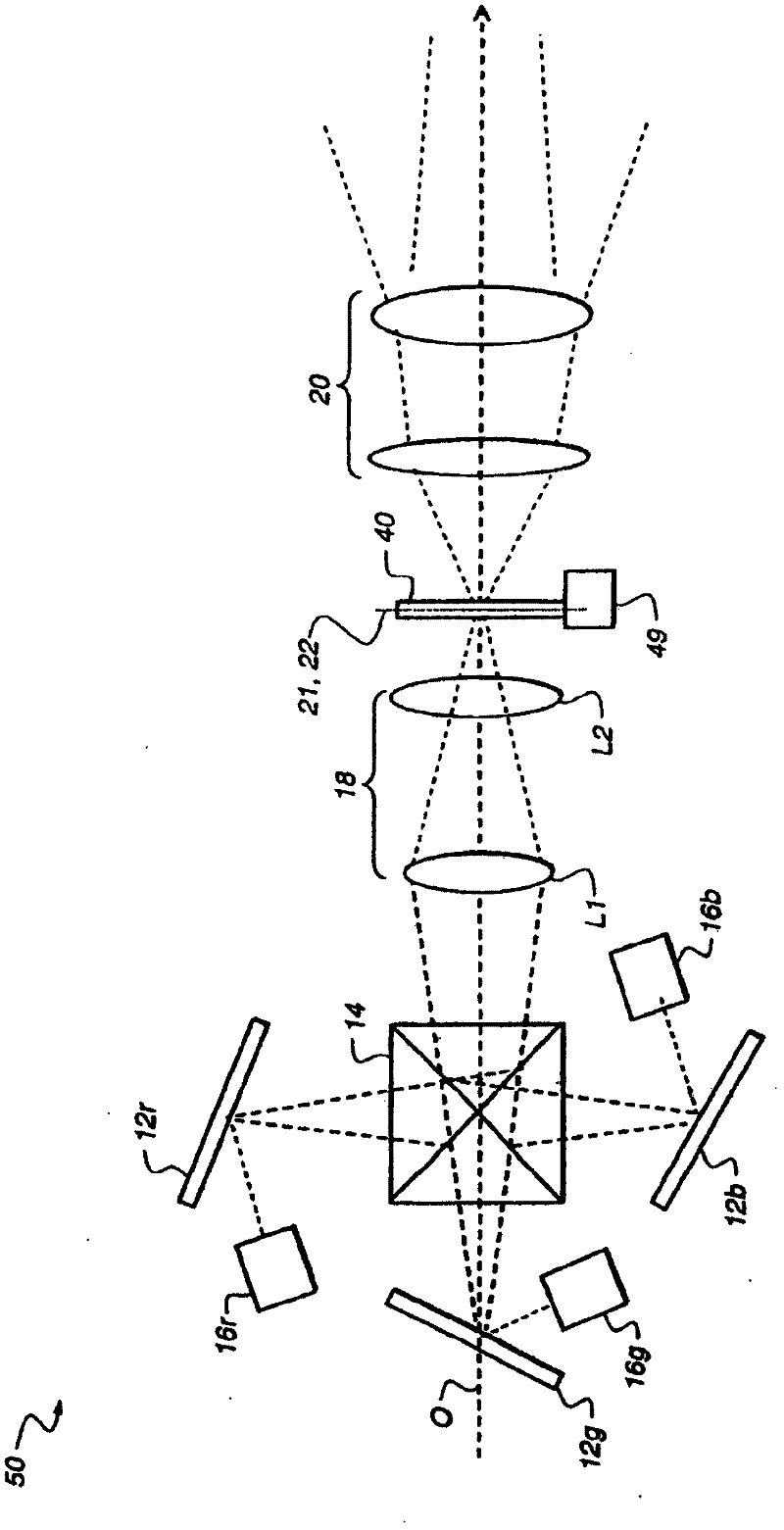
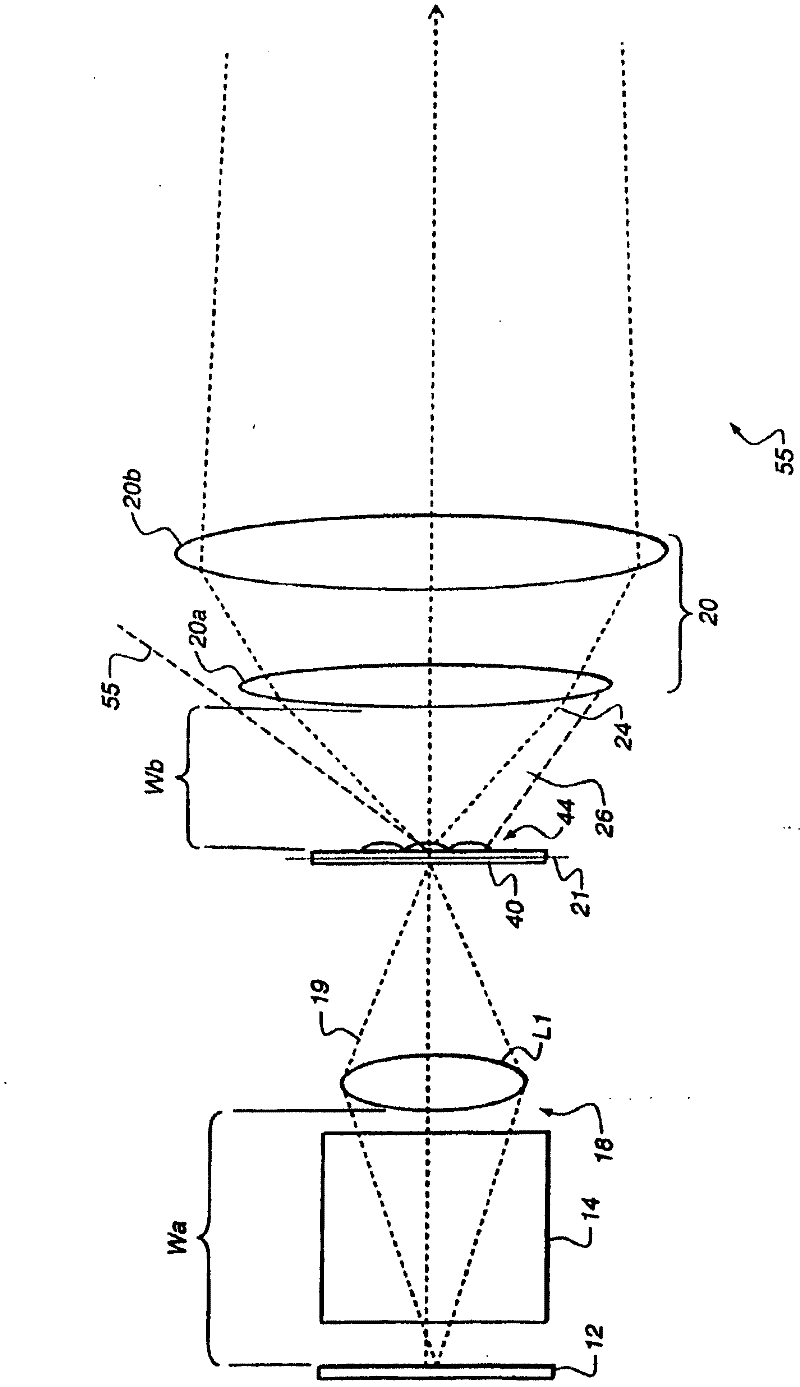
Out-of-plane motion of speckle reduction element
ActiveUS8366281B2Increase brightnessProjector focusing arrangementDiffusing elementsOut of plane motionIntermediate image
In a coherent light projection system including an image forming system, a relay system, a speckle reduction element, and a projection subsystem, the relay system can have a first f-number, and the projection subsystem can have a second f-number less than the first f-number. The relay system can have a first working distance, and the projection subsystem can have a second working distance less than the first working distance. The image forming system can project an initial image having a first size, and an intermediate image can have a second size greater than or equal to the first size. The speckle reduction element can have a curved surface through which the intermediate image is transferred. The speckle reduction element can include a lenslet arrangement formed on a surface thereof. The speckle reduction element can be moved in a direction parallel to an optical axis of the speckle reduction element.
Owner:IMAX THEATERS INT
Planar microelectromechanical device having a stopper structure for out-of-plane movements
ActiveUS8124895B2Acceleration measurement using interia forcesElectric switchesOut of plane motionEngineering
A microelectromechanical device has a mobile mass that undergoes a movement, in particular a spurious movement, in a first direction in response to an external event; the device moreover has a stopper structure configured so as to stop said spurious movement. In particular, a stopper element is fixedly coupled to the mobile mass and is configured so as to abut against a stopper mass in response to the spurious movement, thereby stopping it. In detail, the stopper element is arranged on the opposite side of the stopper mass with respect to a direction of the spurious movement, protrudes from the space occupied by the mobile mass and extends in the space occupied by the stopper mass, in the first direction.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
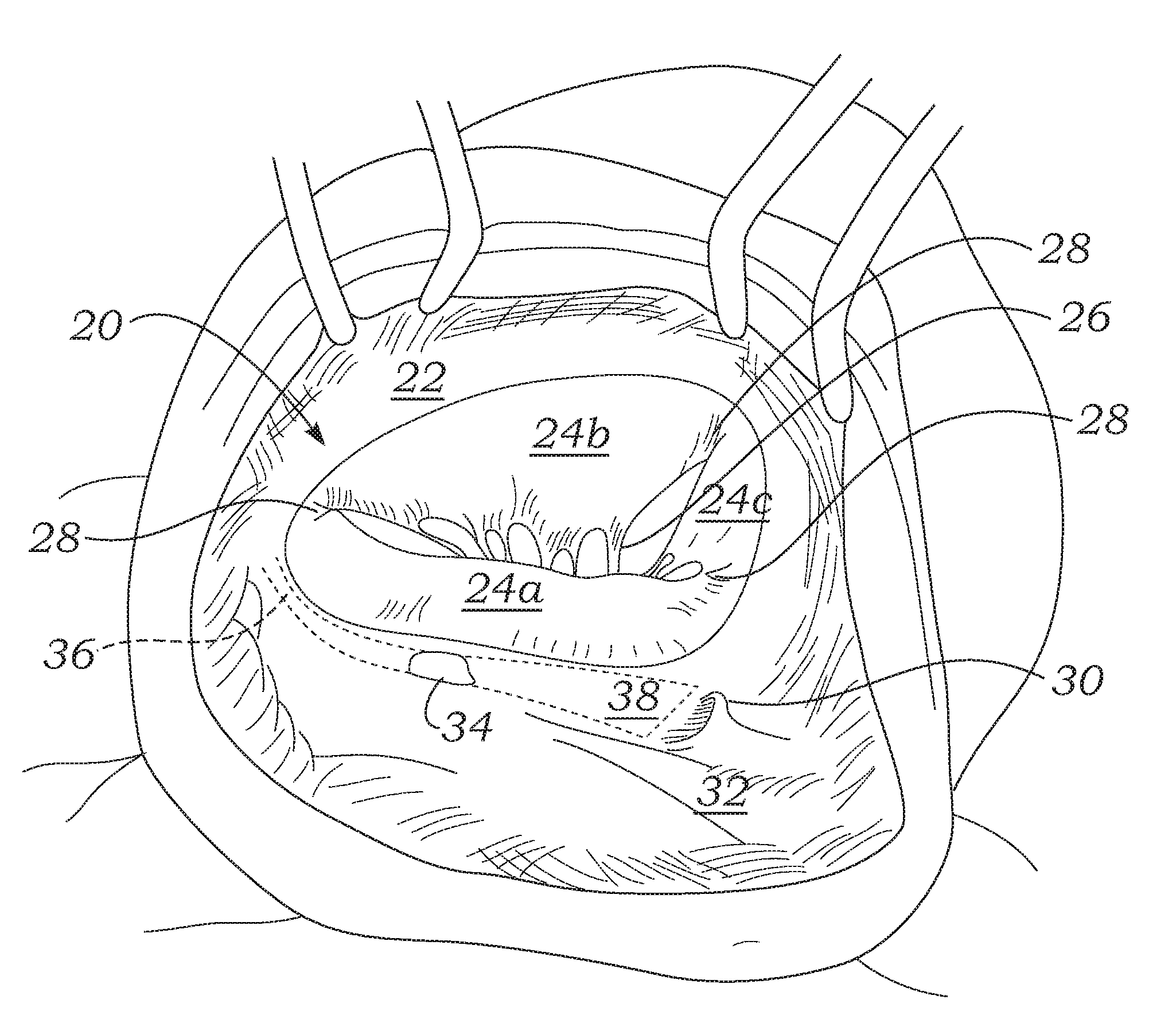
Physiologic tricuspid annuloplasty ring
ActiveUS20120071970A1Reduce constraintsReduce morbidityAnnuloplasty ringsTubular organ implantsAnatomical structuresOut of plane motion
A prosthetic tricuspid remodeling annuloplasty ring for use in tricuspid valve repairs to provide annular support after reconstructive valve surgery. The ring maintains an optimal annular dimension to prevent excessive dilatation of the natural valve annulus while adapting to the dynamic motion of the tricuspid annulus during the cardiac cycle. An exemplary ring features a waveform contour and may be constructed of a titanium core having a varying cross-section for selective flexibility for good Z-axis or out-of plane movement. The “waveform” contour and selective flexibility of the different segments of this ring are designed to adapt to the complex motion of the annulus. This reduces the stress on the anatomical structures and therefore minimizes the risk of arrhythmia and ring dehiscence.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Microelectromechanical device with motion limiters
ActiveUS20150241216A1Acceleration measurement using interia forcesSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsElement spaceOut of plane motion
A microelectromechanical device that comprises a first structural layer, and a movable mass suspended to a primary out-of plane motion relative the first structural layer. A cantilever motion limiter structure is etched into the movable mass, and a first stopper element is arranged on the first structural layer, opposite to the cantilever motion limiter structure. Improved mechanical robustness is achieved with optimal use of element space.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
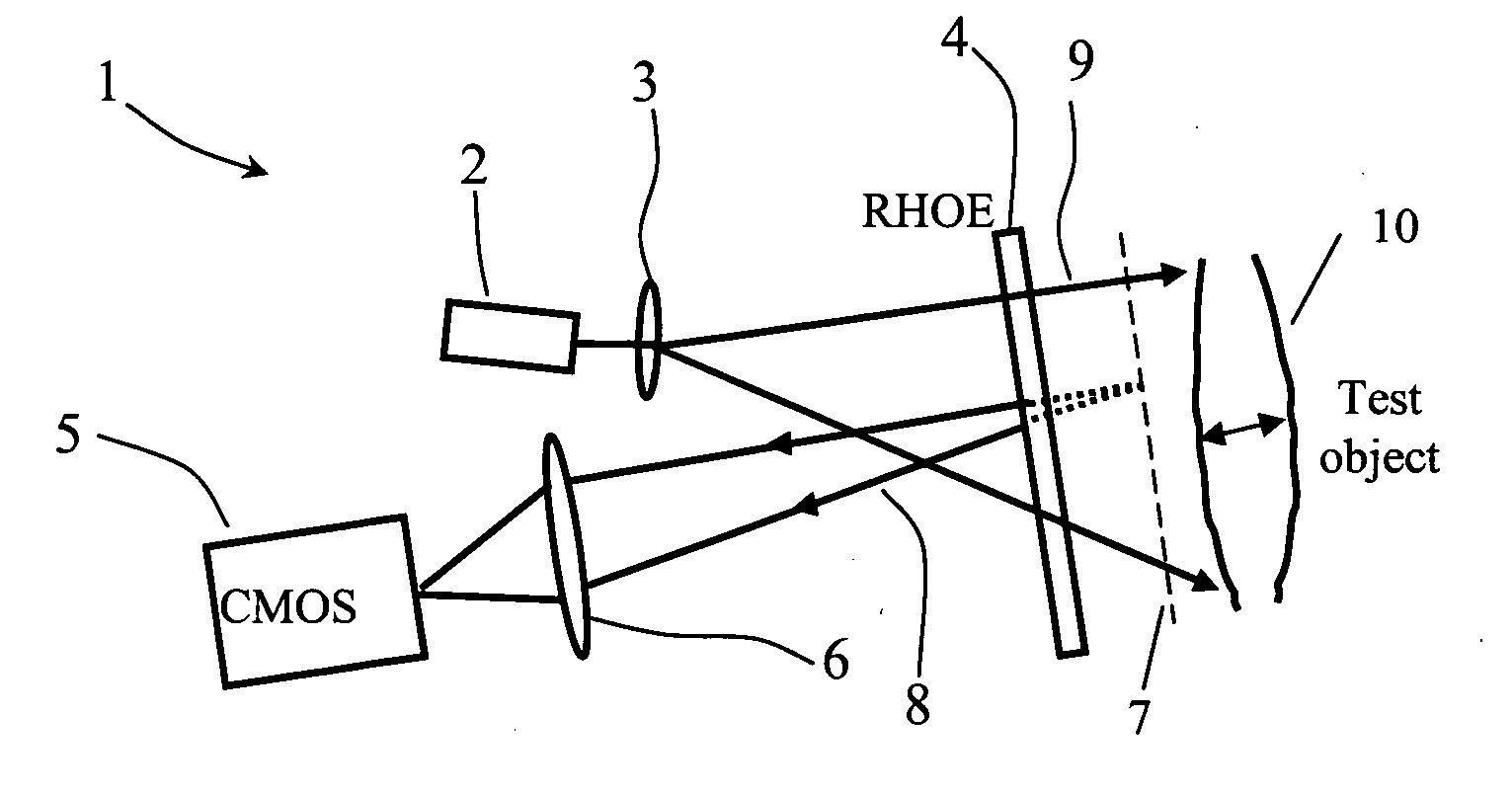
Multipoint laser doppler vibrometer
InactiveUS20100281986A1Subsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementWithdrawing sample devicesIn planeCMOS
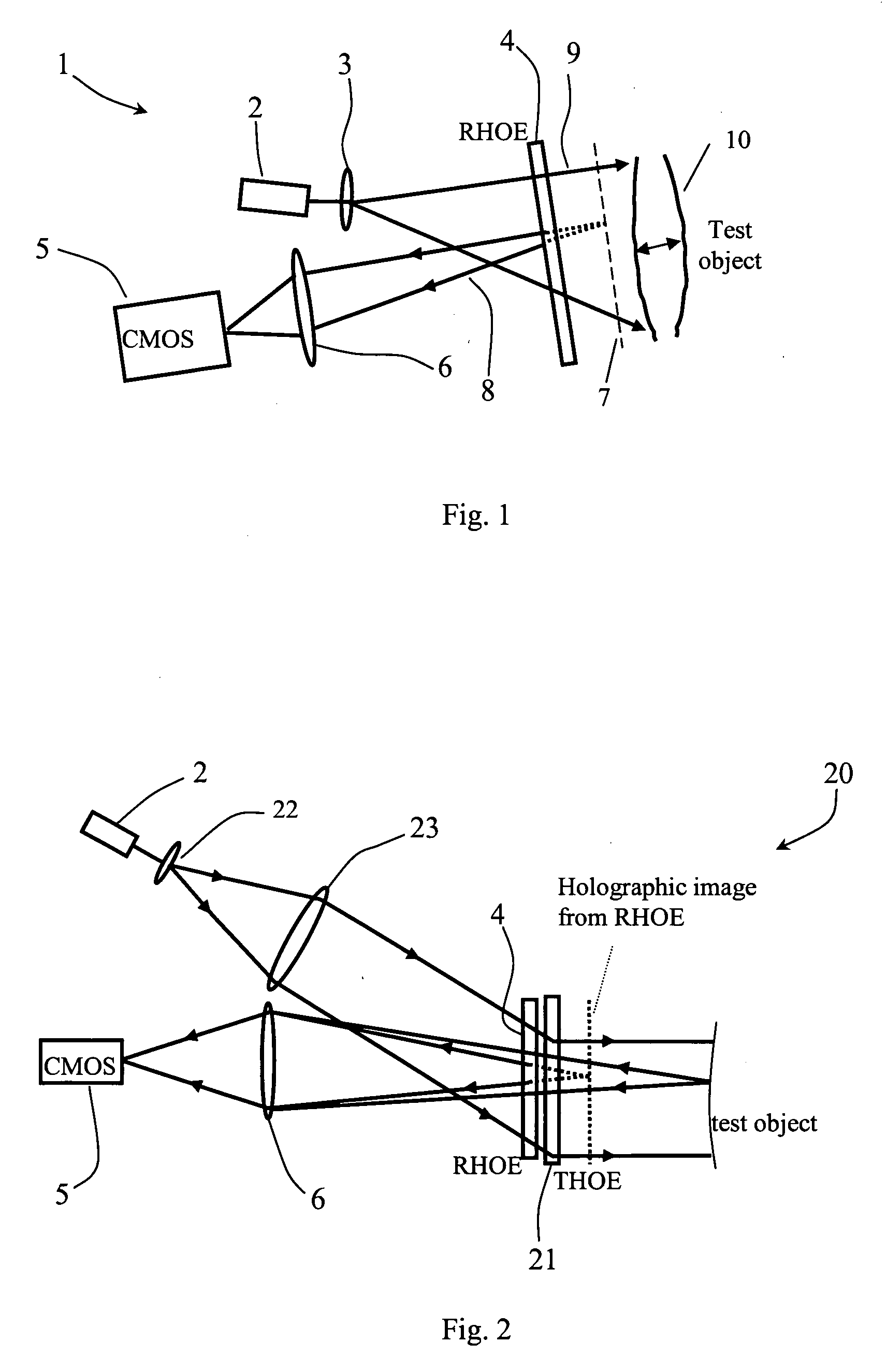
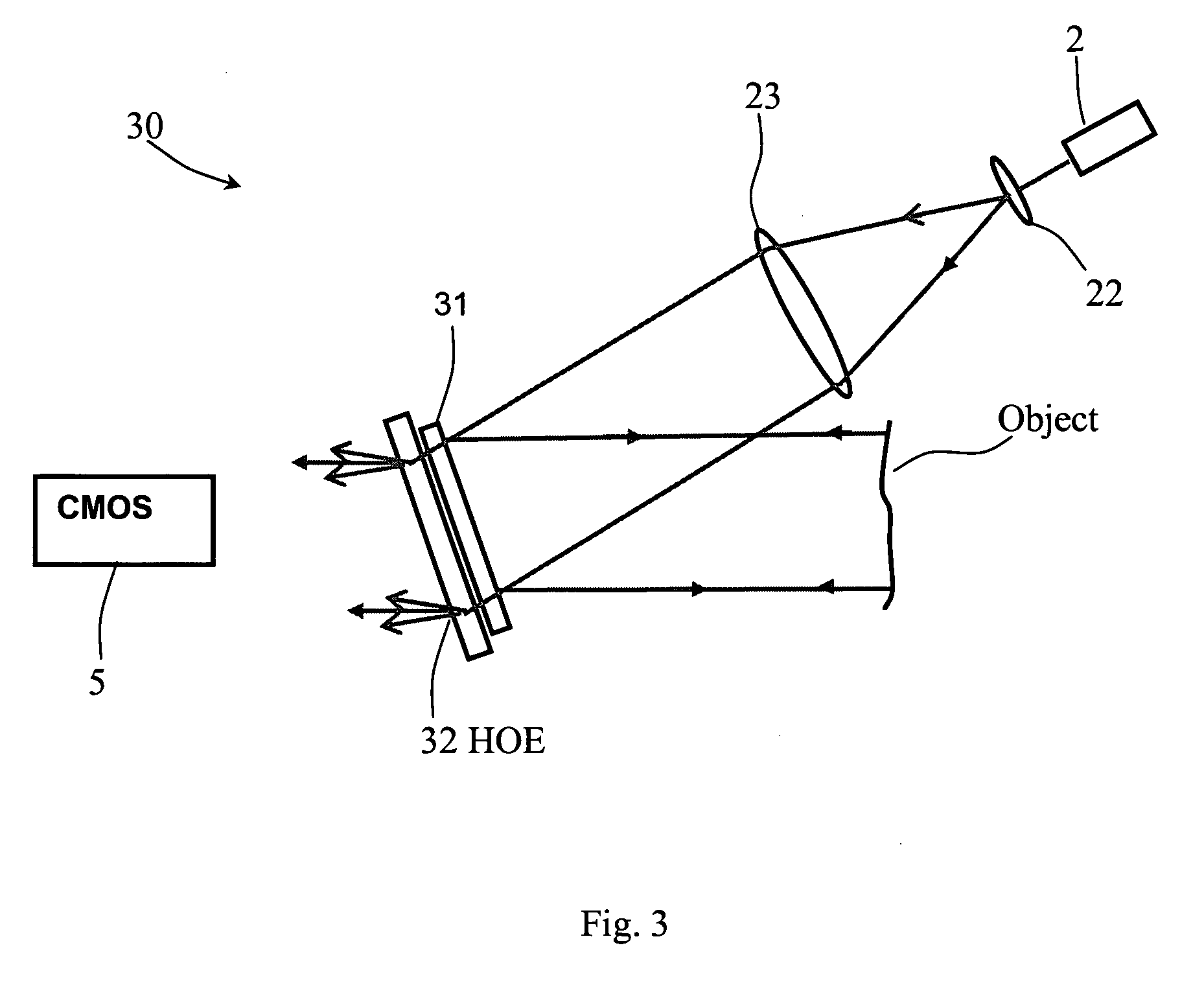
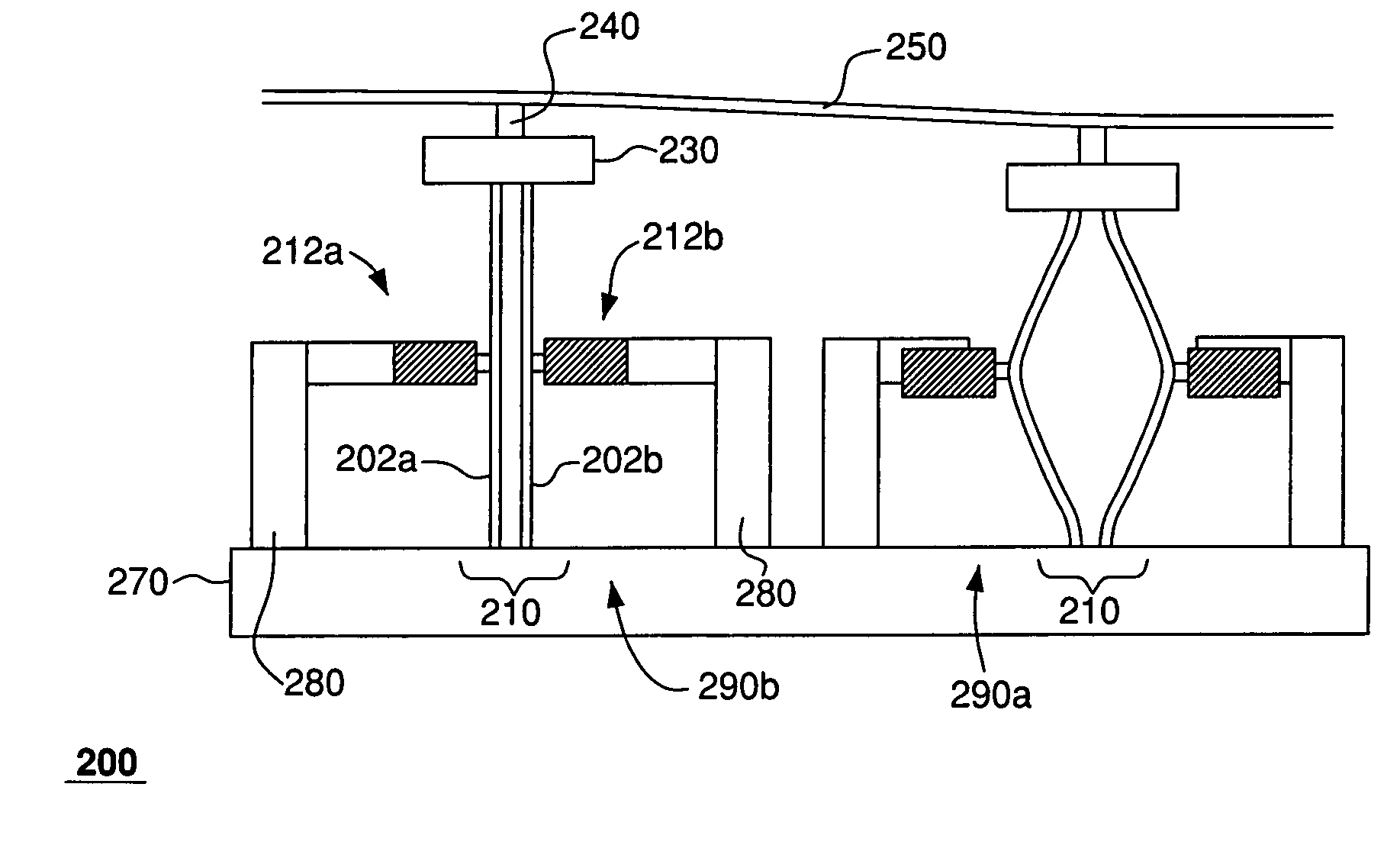
A multipoint laser Doppler vibrometer system (1) comprises a laser diode (2), beam expanding lens (3), a holographic optical element (HOE, 4) and a CMOS camera (5) receiving reflected light via optics (6). The HOE (4) is a hologram of a flat diffusely reflecting surface. Some light (8) is diffracted by the recorded hologram in the HOE (4) to provide a reference beam of light that is directed back towards the camera (5). Apart from some absorption the remaining light (9) continues onwards to illuminate the object The light that is reflected and scattered from the object (10) passes efficiently through the HOE (4) and interferes with the reference light (8) that is holographically reconstructed by the HOE (4) and subsequently detected by the camera (5). The beam from the laser diode (2) is divergent, which means that the sensitivity vector varies across the field of view. Thus the system is sensitive to both in-plane and out-of-plane motion of the object to an extent that depends on position of the object points. An alternative system (20) has two emission lenses (22, 23). The HOE (21) either redirects light already collimated by the lens combination (22, 23) or both redirects and collimates uncollimated light in such a way as to illuminate the object along the normal to its surface.
Owner:DUBLIN INST OF TECH +2
MEMS actuator for piston and tilt motion
ActiveUS6995895B2Alleviates stringent precision requirementElectrostatic generators/motorsOptical elementsIn planeOut of plane motion
A MEMS device having a spring structure formed by two flexible beams attached between a substrate and a movable bar. When non-end sections of the beams are pulled in opposite directions, the beam ends attached to the movable bar pull that bar toward the substrate, thereby transforming in-plane motion of the non-end sections into out-of-plane motion of the movable bar. When the non-end sections are displaced symmetrically, the movable bar translates toward the substrate. Alternatively, when the non-end sections are displaced non-symmetrically, the movable bar rotates with respect to the substrate. In one embodiment, each flexible beam is attached to a comb-shaped portion of a motion actuator, which has two such portions, each portion interleaved with the other portion and adapted to move with respect to the substrate and that other portion. When a voltage differential is applied between the portions, they move substantially parallel to the substrate, thereby deforming the beams and translating / rotating the movable bar.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC +1
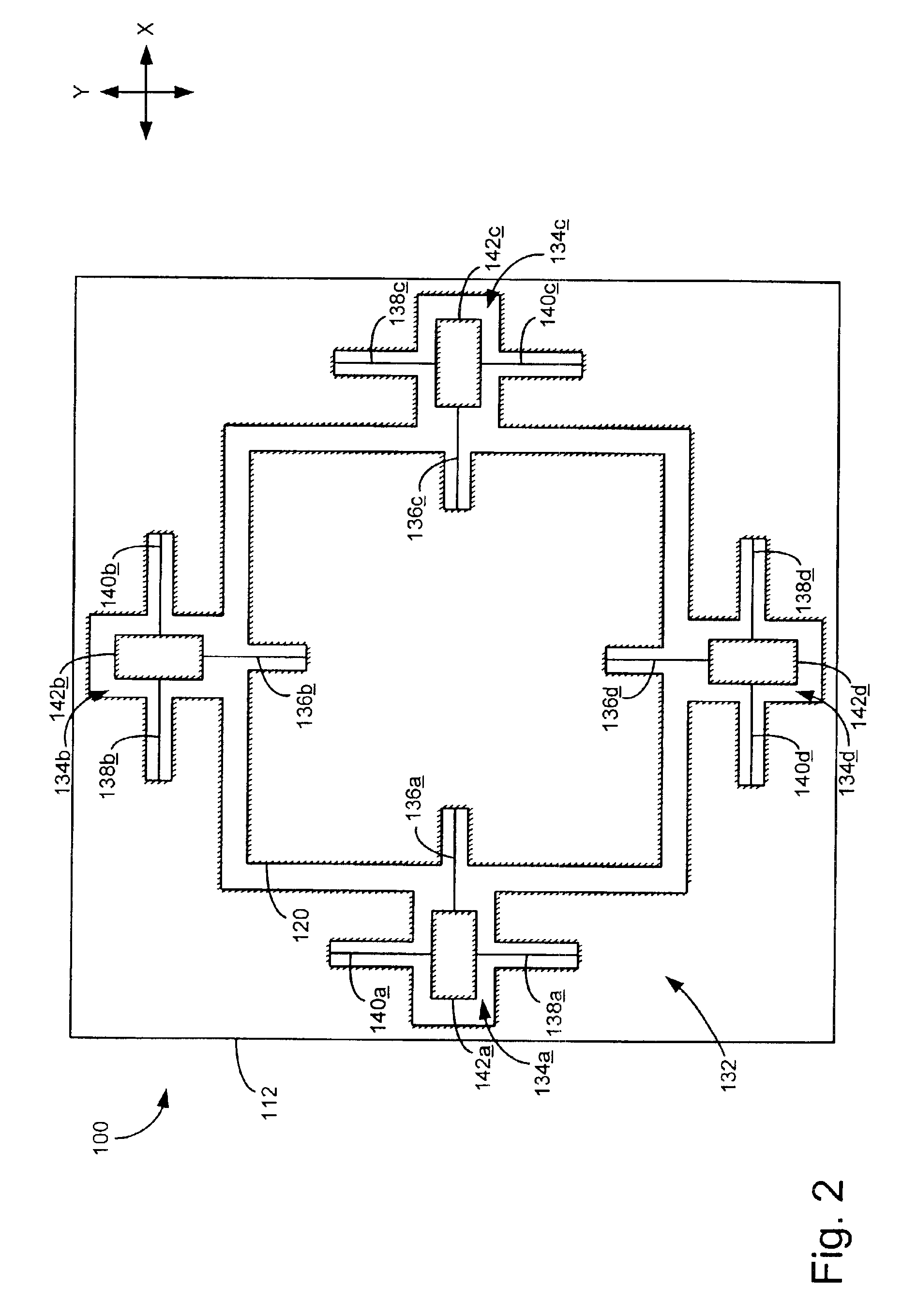
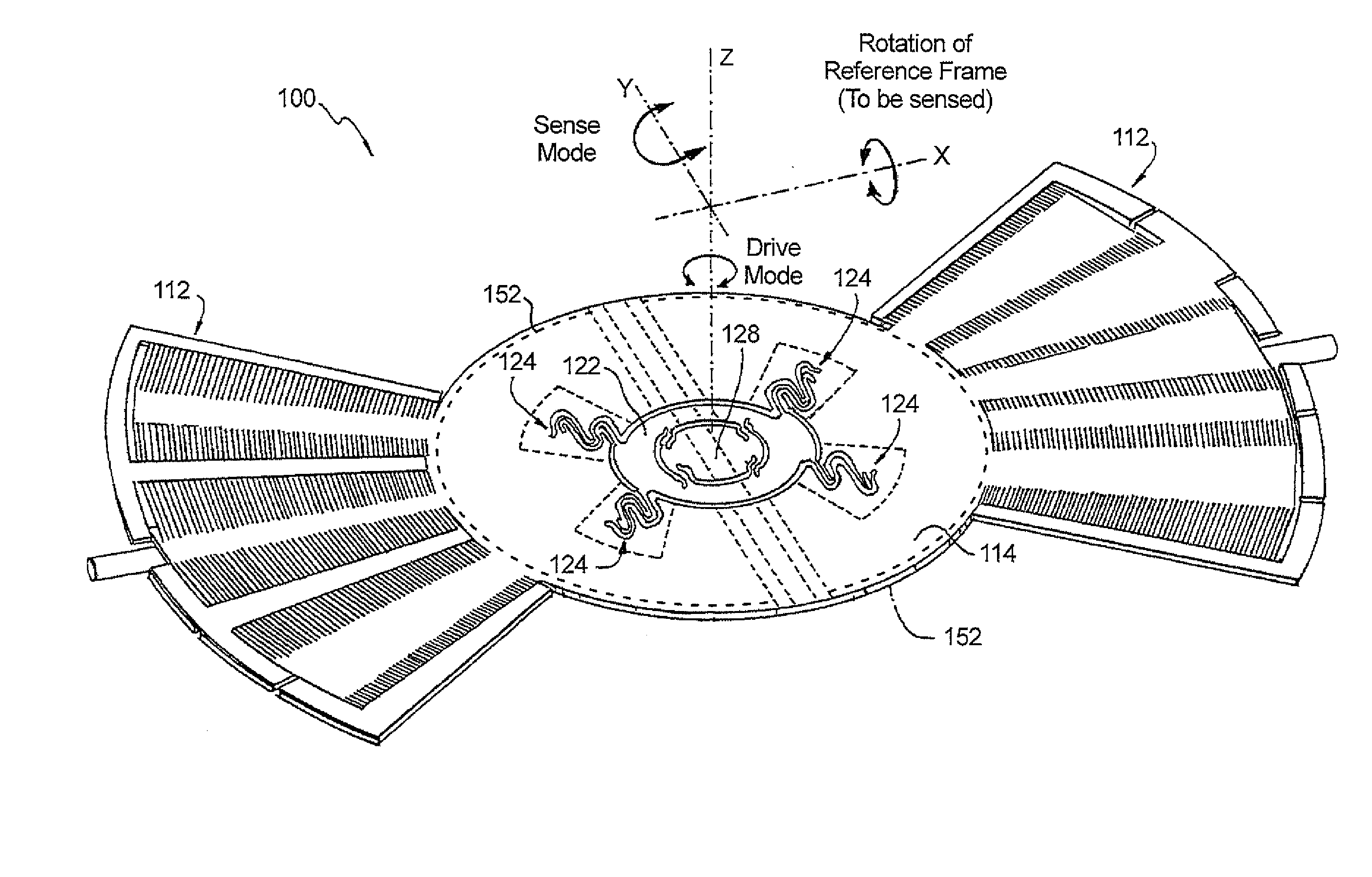
MEMS gyros with quadrature reducing springs
ActiveUS8539832B2Constant widthReduce sensitivityAcceleration measurement using interia forcesSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsOut of plane motionEngineering
Spring set configurations that include an advantageous combination of spring geometries are disclosed. Spring elements having curved and straight sections, orientation of spring element anchor points with respect to the common radius, orientation of spring element segments with respect to a specific axis, balance of the length of spring elements about the common radius, and mass balance about the common radius can be used to mitigate unwanted out of plane motion. The spring set provides planar motion while reducing undesired out of plane motion making MEMS devices substantially insensitive to the process-induced etch angle variations of the spring elements. The spring set can be used in a MEMS gyro device which maintains the desired resonant modes and consistently low quadrature error even with process variations in manufacturing causing undesirable etch angles.
Owner:ROSEMOUNT AEROSPACE
Manipulation of magnetic or magnetizable objects using magnetophoresis and dielectrophoresis
ActiveUS8409415B2Avoid stickingReduce the numberSludge treatmentElectrostatic separatorsIn planeElectrical conductor
Owner:KATHOLIEKE UNIV LEUVEN +1
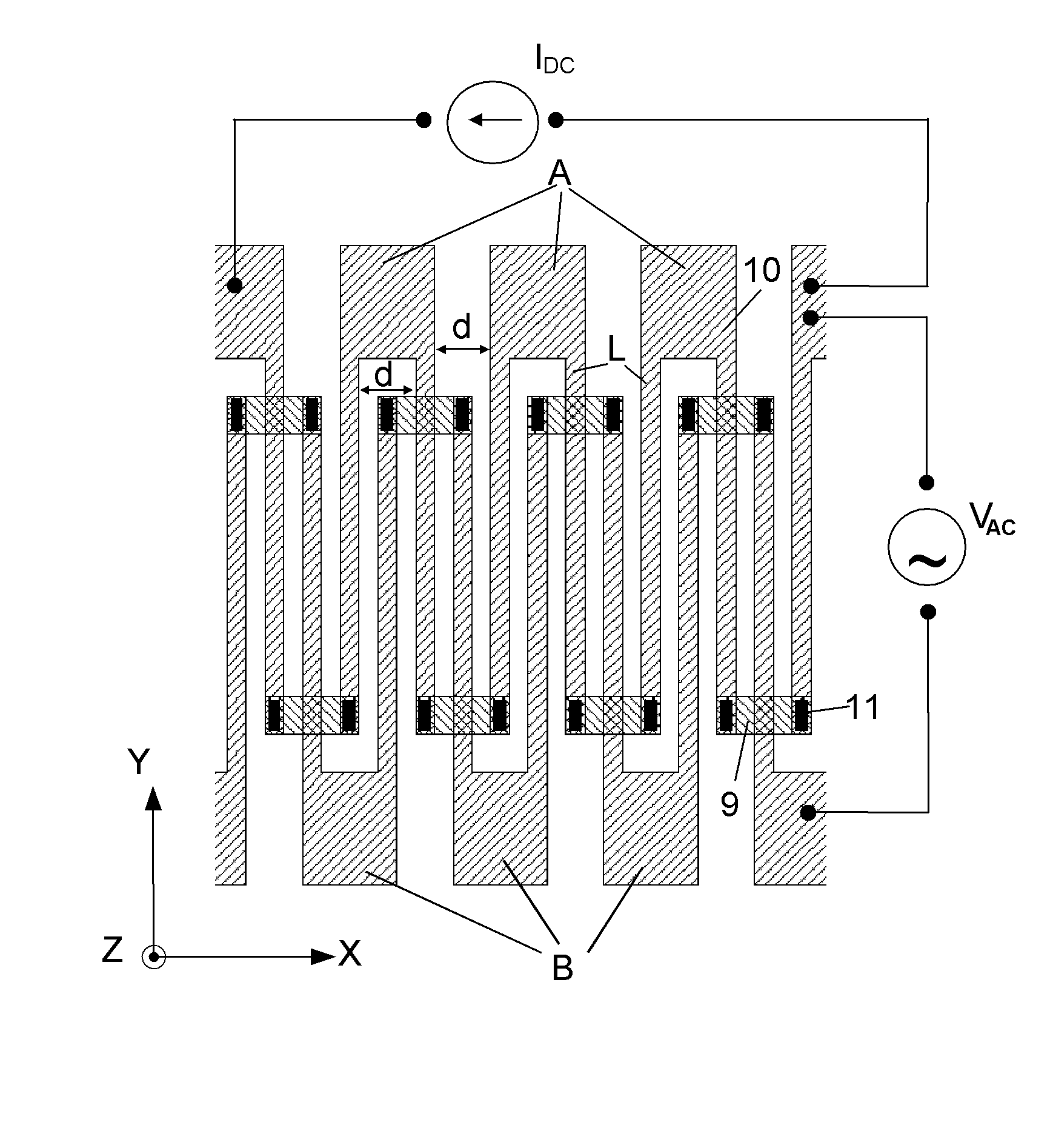
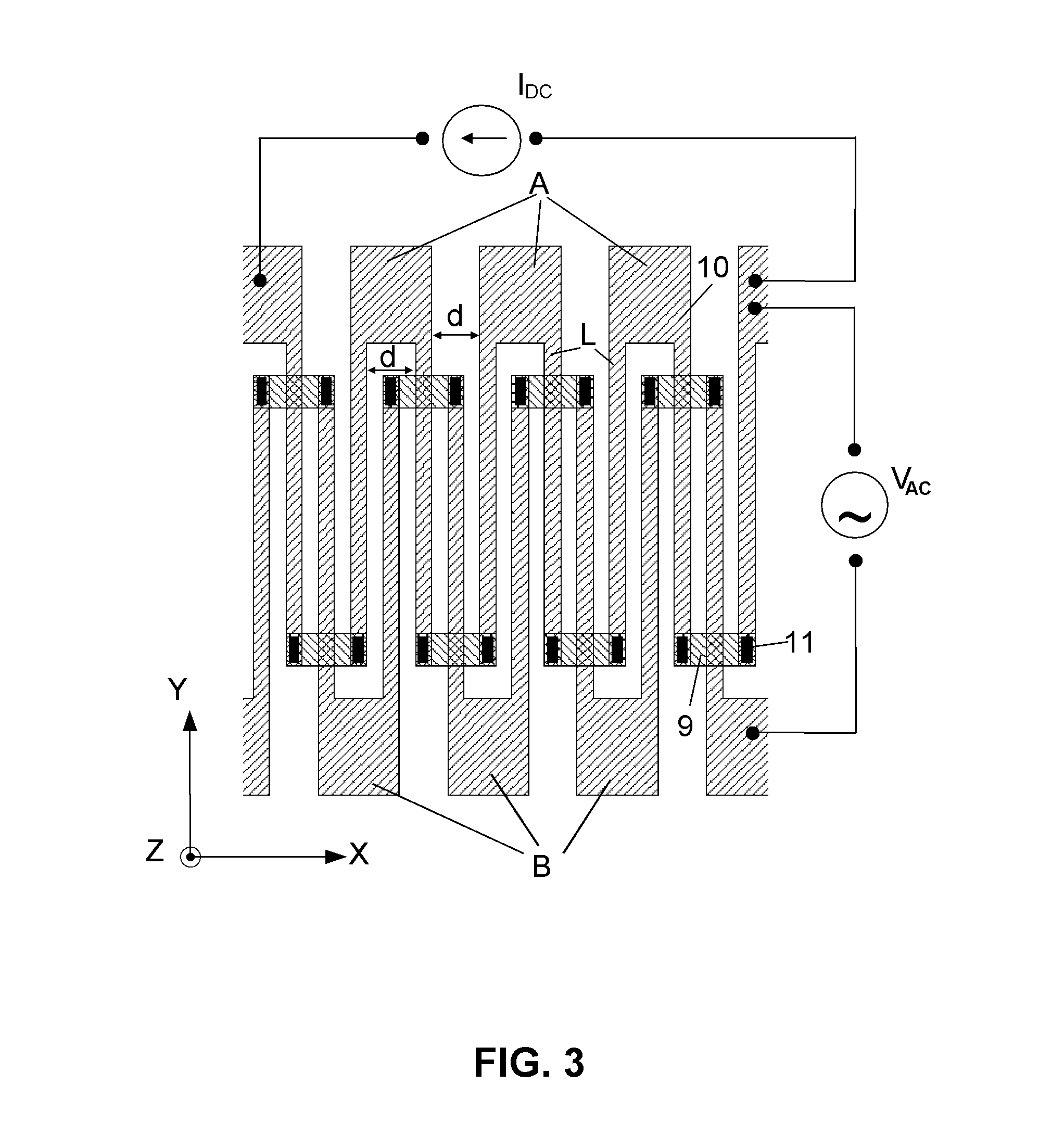
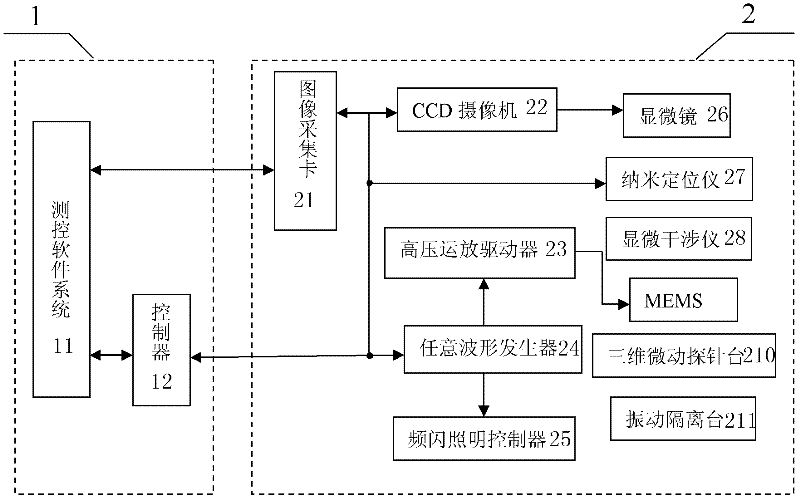
Device for detecting in-plane error in micro/nano device out-of-plane motion test and compensating method
InactiveCN102506710ASmall amount of calculationEasy to useUsing optical meansIn planeOut of plane motion
The invention discloses a device for detecting an in-plane error in a micro / nano device out-of-plane motion test and a compensating method. The device has a control and image processing unit and a phase shift micro interfering system which is connected with the control and image processing unit, wherein the phase shift micro interfering system comprises a vibration isolating table, a three-dimensional micro motion probe table, a tested micro / nano device, a micro interferometer, a nano positioning instrument and a microscope, which are arranged in turn, and a flash lighting controller, a high-pressure amplifier driver, an arbitrary waveform generator, a charged coupled device (CCD) camera, and an image acquisition card; the input end of the arbitrary waveform generator is connected with the control and image processing unit, and the output end of the arbitrary waveform generator is connected with the flash lighting controller and the high-pressure amplifier driver; the CCD camera is connected with a microscope; and the image acquisition card is connected with the control and image processing unit and the CCD camera respectively. The method comprises: acquiring the motion image of the tested micro / nano device; testing in-plane displacement; testing out-of-plane motion; and performing two-phase unwrapping of a time axis and a spatial axis. The invention is easy to use with high reliability.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
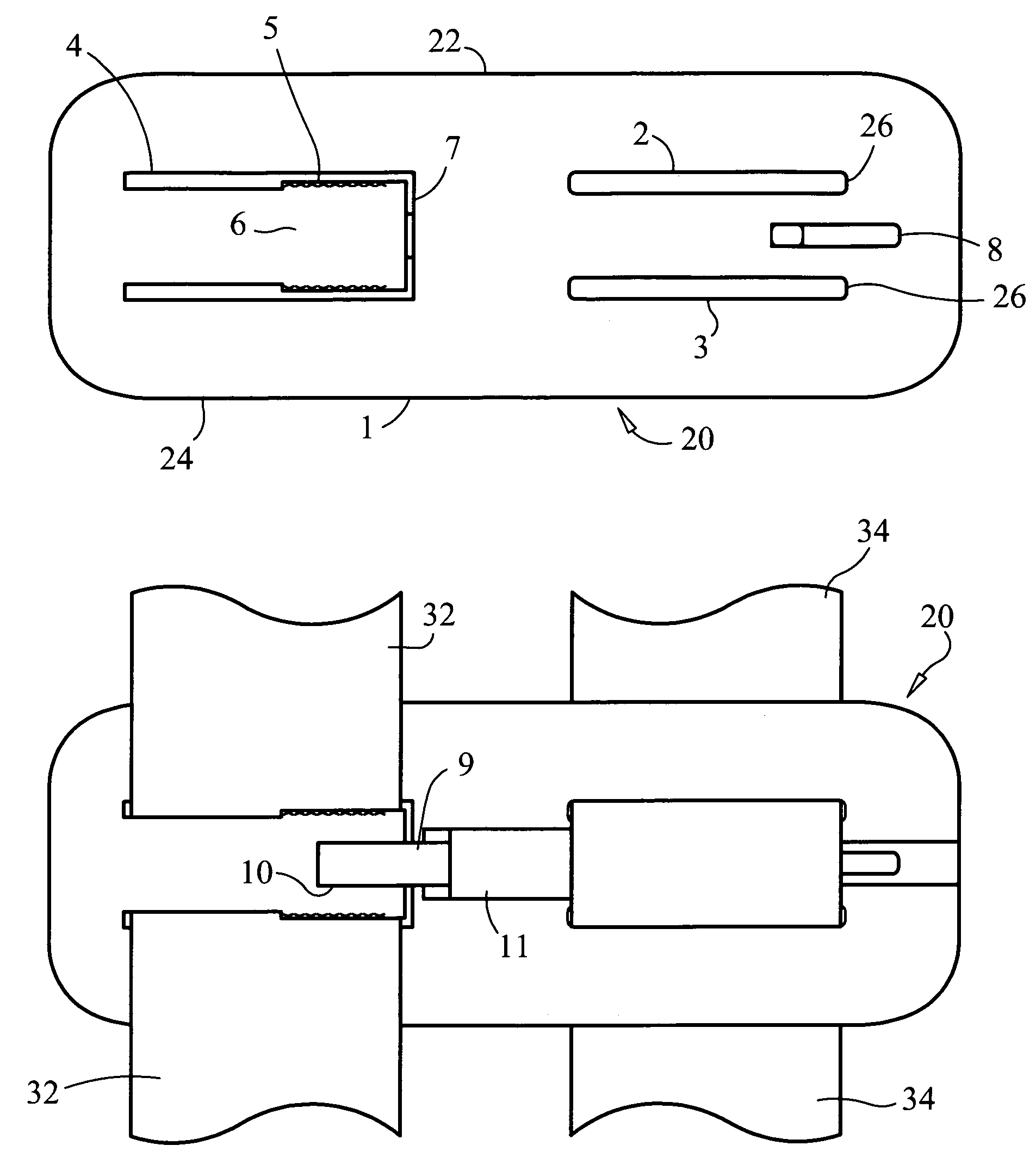
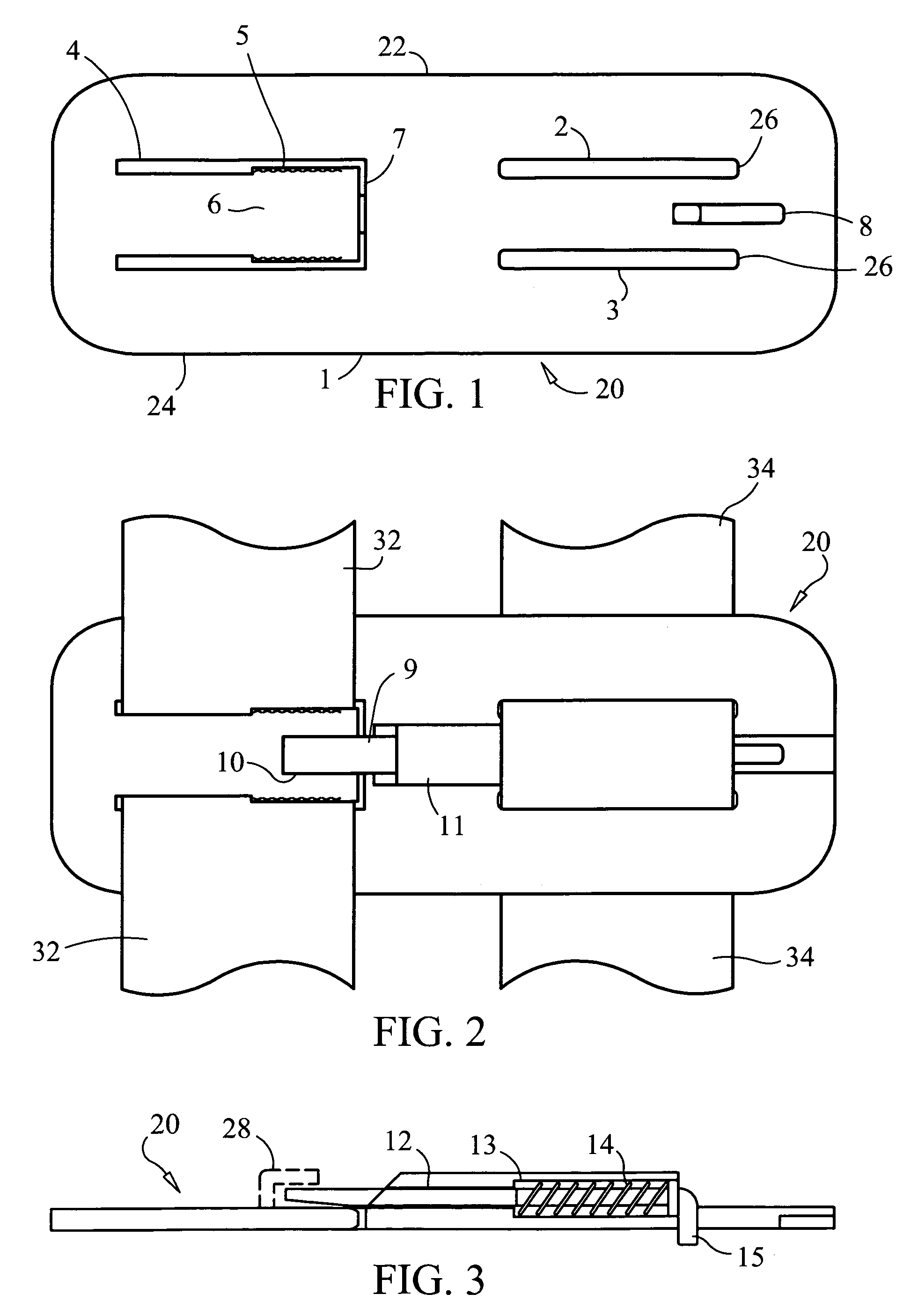
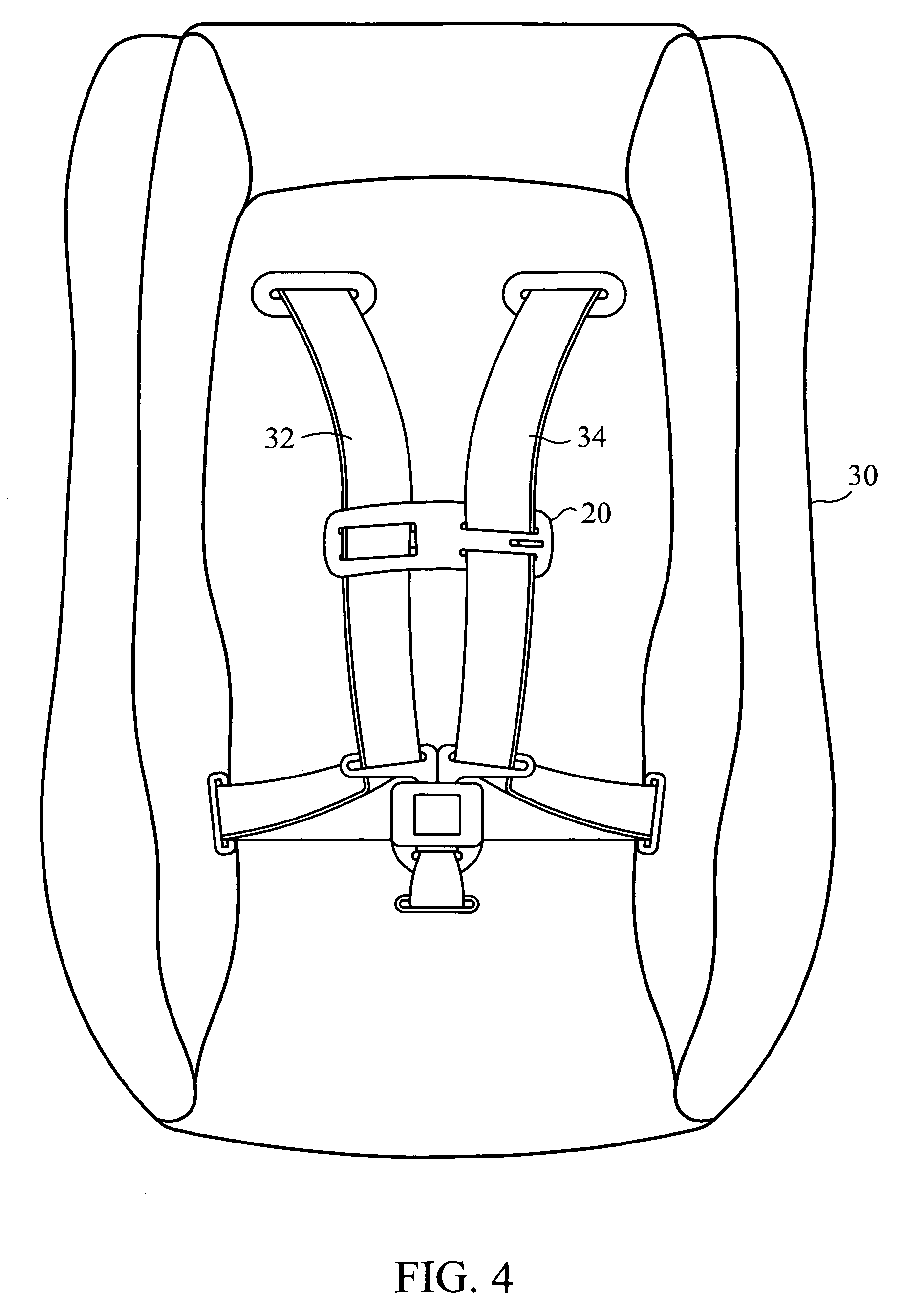
Shoulder belt clip for child safety seats and child carriers
InactiveUS7144086B1Prevent disengagementPrevent slippingSnap fastenersVehicle seatsOut of plane motionRight shoulder
A shoulder belt clip for restraining a child in a child safety seats or carrier. In a preferred embodiment, the shoulder belt clip is comprised of a plate made of flexible material and with two horizontal slots arranged in parallel on one side and a U-shaped opening on the other. The two straight slots maintain attachment to, but allow the clip to slide vertically on, the webbing that runs over the left shoulder of the child. The U-shaped opening forms a tab that admits entry of the webbing that runs over the right shoulder of the child and holds it until release is desired by the parent. A narrowing of the U-shaped opening causes compression of the webbing between the tab and the opening and thereby prevents slippage of the clip vertically on the webbing that runs over the left shoulder of the child. A lock comprised of a spring-loaded slider is fixed between and parallel to the two straight slots blocks the out-of-plane motion of the tab in the direction that would release the webbing, and also by its positioning prevents sliding the webbing laterally out the open end of the U-shaped opening. When release is desired by the parent, the lock slider is pushed back against the force of the spring and the flexible tab is pushed out-of-plane with respect to the body of the clip. This allows quick release of the webbing that runs over the right shoulder of the child.
Owner:HARCOURT JOHN A +1
Micromechanical hair flow velocity sensor based on weak coupling resonators, and running method thereof
PendingCN109975577AAchieving Dual Axis SensitivityImprove work performanceTelevision system detailsPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesIn planeOut of plane motion
The invention discloses a micromechanical hair flow velocity sensor based on weak coupling resonators. Out-of-plane stereo hair is adhered at a geometric center of a middle layer micro-silicon sensor,a structure of the middle layer micro-silicon sensor is composed of a mass block base, four same weak coupling resonator groups and four same out-of-plane motorial inhibition elastic structures; foursame weak coupling resonator groups are symmetrically arranged an upper direction, a lower direction, a left direction and a right direction of the mass block base; the weak coupling resonator groupsare connected with the mass block base through input straight girders of secondary force amplification levers; four same out-of-plane motorial inhibition elastic structures are symmetrically distributed at a left upper direction, a right upper direction a right lower direction and a left lower direction of the mass block base, and the out-of-plane motorial inhibition elastic structures are connected with the mass block base through the out-of-plane motorial inhibition elastic U-shaped girders. By arranging the weak coupling resonator groups and the out-of-plane motorial inhibition elastic structures in a symmetric structure, the biaxial sensitivity of in-plane flow velocity is realized.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Planar microelectromechanical device having a stopper structure for out-of-plane movements
ActiveUS20090194397A1Acceleration measurement using interia forcesElectric switchesOut of plane motionEngineering
A microelectromechanical device has a mobile mass that undergoes a movement, in particular a spurious movement, in a first direction in response to an external event; the device moreover has a stopper structure configured so as to stop said spurious movement. In particular, a stopper element is fixedly coupled to the mobile mass and is configured so as to abut against a stopper mass in response to the spurious movement, thereby stopping it. In detail, the stopper element is arranged on the opposite side of the stopper mass with respect to a direction of the spurious movement, protrudes from the space occupied by the mobile mass and extends in the space occupied by the stopper mass, in the first direction.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
Comb tooth capacitor of micromachine
InactiveCN102064021AStatic force will not be generatedSolving Cross-Axis Sensitivity IssuesTelevision system detailsImpedence networksCapacitanceGyroscope
The invention provides a comb tooth capacitor of a micromachine, and relates to the field of micro-electronic machines. The capacitor comprises a fixed comb tooth electrode and a movable comb tooth electrode, wherein the fixed comb tooth electrode and the movable comb tooth electrode overlapped to form a decoupling comb tooth capacitor; and when the movable comb tooth electrode and the fixed combtooth electrode oppositely carry out out-of-plane motion under the action of external force, the capacitance for the comb tooth capacitor of the micromachine does not changed. The comb tooth capacitor of the capacitor is low in cost and simple in structure, can effectively solve the problem of mode coupling for an actuator of a micromachine gyroscope and the problem of intersecting axle sensitivity of the micromachine gyroscope and an acceleration transducer.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
MEMS actuator for piston and tilt motion
ActiveUS20050174624A1Alleviates stringent precision requirementElectrostatic generators/motorsOptical elementsIn planeOut of plane motion
A MEMS device having a spring structure formed by two flexible beams attached between a substrate and a movable bar. When non-end sections of the beams are pulled in opposite directions, the beam ends attached to the movable bar pull that bar toward the substrate, thereby transforming in-plane motion of the non-end sections into out-of-plane motion of the movable bar. When the non-end sections are displaced symmetrically, the movable bar translates toward the substrate. Alternatively, when the non-end sections are displaced non-symmetrically, the movable bar rotates with respect to the substrate. In one embodiment, each flexible beam is attached to a comb-shaped portion of a motion actuator, which has two such portions, each portion interleaved with the other portion and adapted to move with respect to the substrate and that other portion. When a voltage differential is applied between the portions, they move substantially parallel to the substrate, thereby deforming the beams and translating / rotating the movable bar.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC +1
Accelerometer having adjustable damping
InactiveUS7392685B2Acceleration measurement using interia forcesTesting/calibration of speed/acceleration/shock measurement devicesOut of plane motionEngineering
An apparatus and method for an accelerometer mechanism having a proof mass that is suspended for out-of-plane motion between first and second damping plates, wherein at least one of the first and second damping plates is movable between first and second positions relative to the proof mass under the control of a position control structure that is coupled to the movable damping plate for positioning the damping plate in the second position relative to the proof mass.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Use of standoffs to protect atomic resolution storage mover for out-of-plane motion
InactiveUS20020171326A1Piezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesSnap-action arrangementsOut of plane motionImage resolution
A micro-machined actuator for use in, among other things, sensors and data storage devices. The actuator includes a stator wafer and a micro-mover positioned adjacent to the stator wafer. Between the stator wafer and the micro-mover are electrodes that are set to specified voltages and that emanate electric fields that position the micro-mover relative to the stator wafer. Also between stator wafer and the micro-mover are bumpers that prevent the electrodes from coming into contact with each other.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Device for transforming an out-of-plane movement into an in-plane movement, and/or vice-versa
ActiveUS20160195893A1Piezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesPiezoelectric/electrostrictive devicesOut of plane motionEngineering
An actuator comprising two devices each comprising an out-of-plane deformable element, said deformable element comprising a first fixed end anchored on a substrate and a second free end relative to the substrate, said device also comprising means to guide the second free end in in-plane translation along a first direction, the first deformable element being capable of deforming out-of-plane through application of a stimulus so that the second free end draws close to the first fixed end following in-plane translational movement. The actuator also comprises an element mobile in rotation about an axis orthogonal to the plane and mechanically linked to the free ends of the deformable elements, and a translationally mobile element mechanically linked to the rotationally mobile element.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
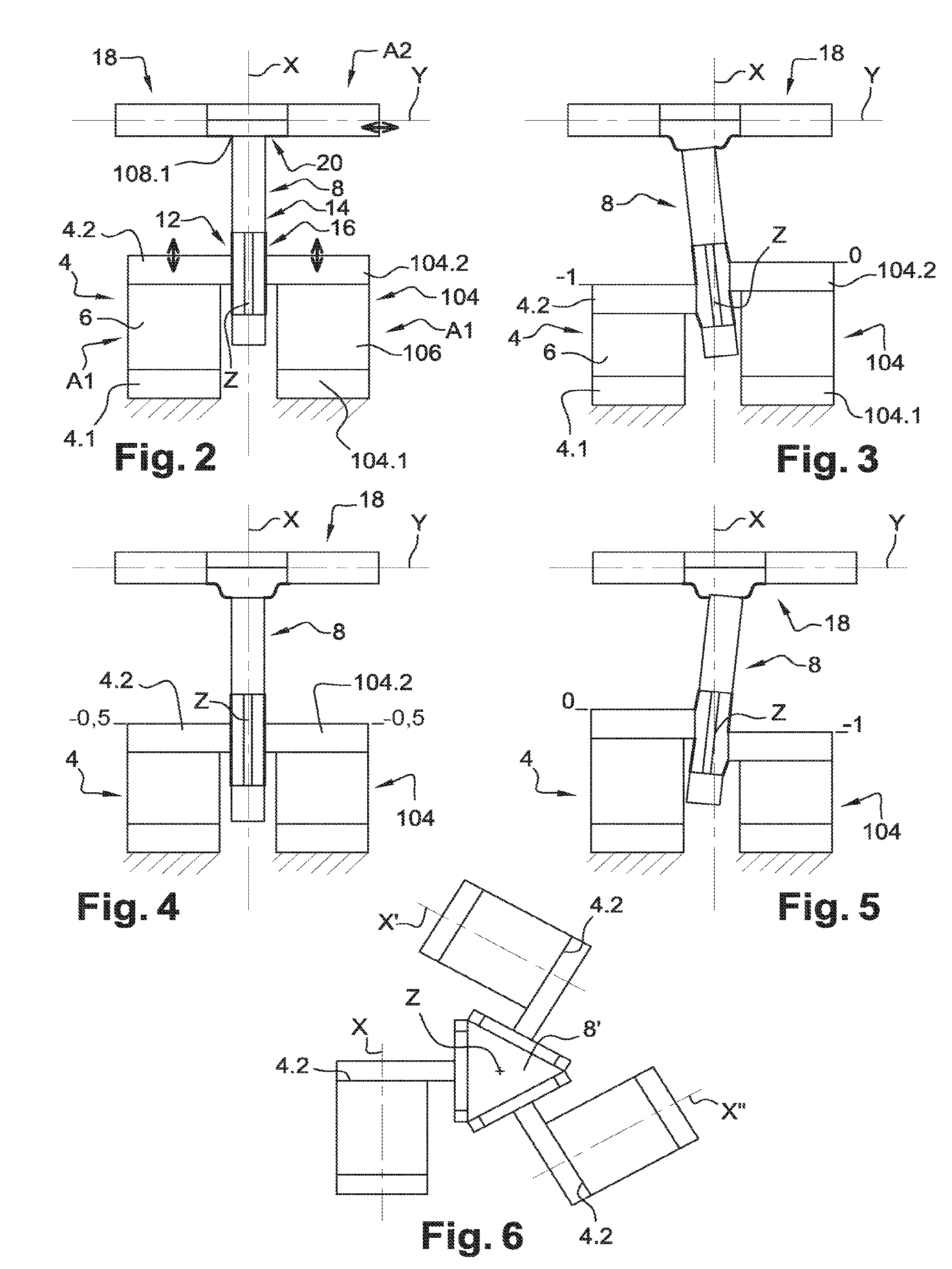
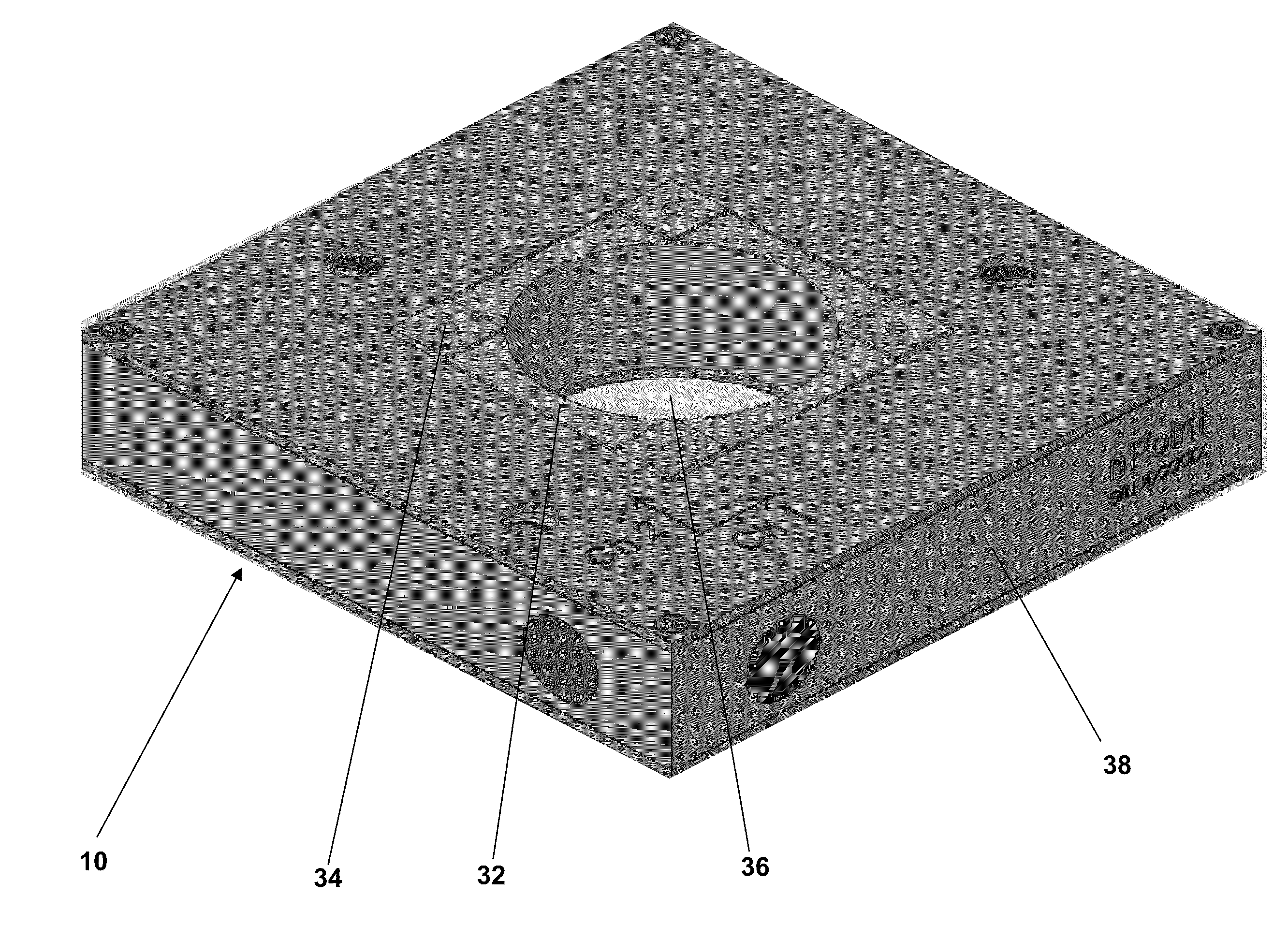
Active scanner bow compensator
ActiveUS20100117565A1Reduce relative motionDC motor speed/torque controlPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesAtomic force microscopyOut of plane motion
An active scanner bow compensator for use with a scanner is described. The scanner includes a moveable scanning platform supported within a frame. The active scanner bow compensator supports the scanner and includes a frame of reference, sensors, and an actuator. The sensors detect out-of-plane motion of the scanning platform relative to the frame of reference, and the actuators compensate for the out-of-plane motion by adjusting the orientation of the frame relative to the frame of reference. The active scanner bow compensator may be used in atomic force microscopy applications.
Owner:NPOINT
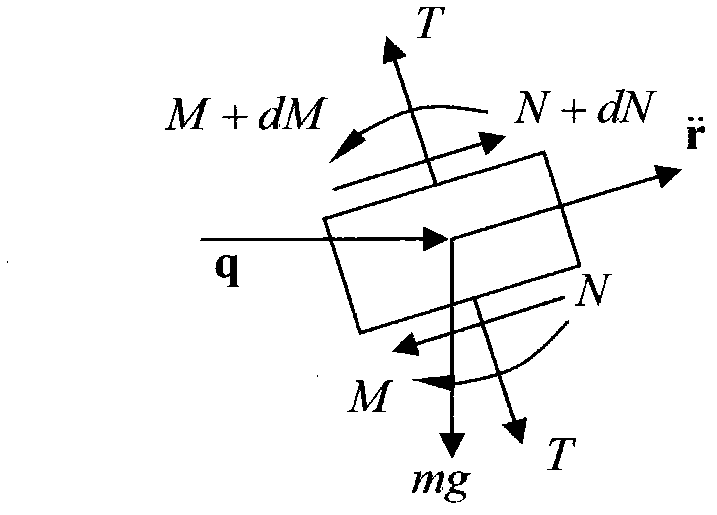
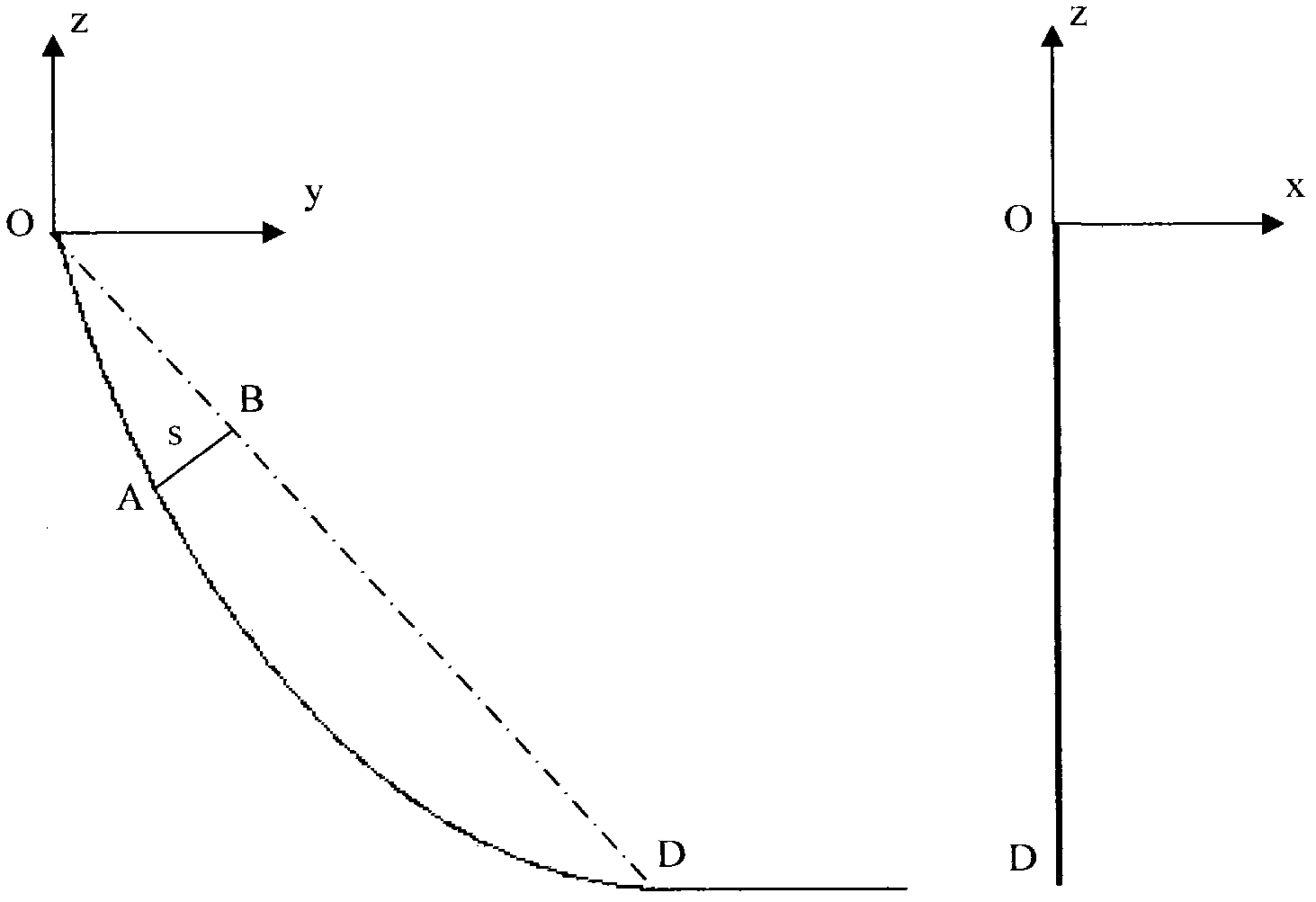
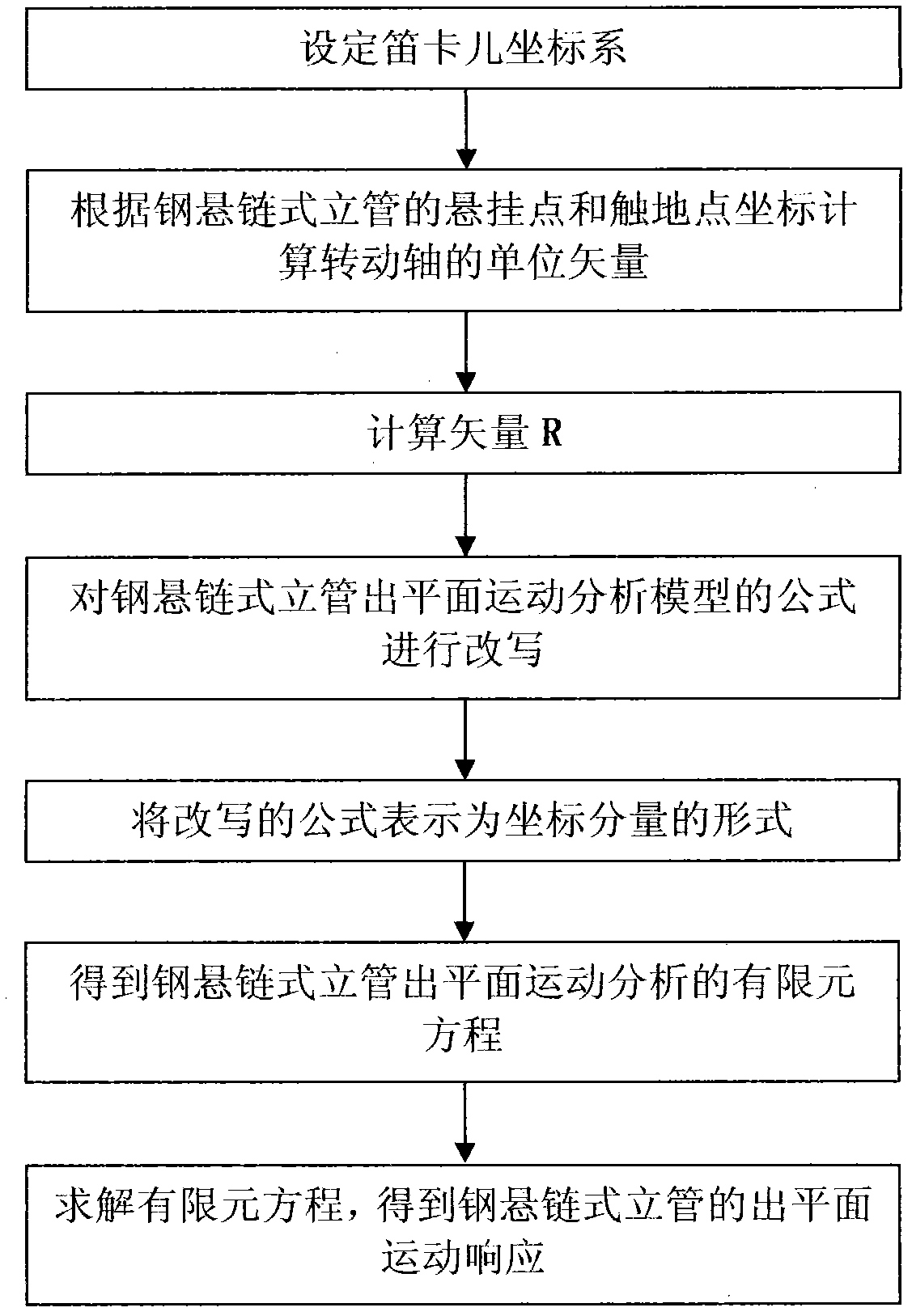
Method for analyzing out-of-plane motion of steel catenary riser
InactiveCN102354333AAdd rigid body rotationCompatible with exercise statusSpecial data processing applicationsOut of plane motionEngineering
The invention relates to a research method for marine deepwater risers, and particularly relates to a method for analyzing the out-of-plane motion of a steel catenary riser. By using the method disclosed by the invention, an improvement on the existing technique for analyzing the out-of-plane motion of a steel catenary riser is performed, the rigid body motion of the out-of-plane motion of a steel catenary riser is taken into consideration, an analytical mode of the out-of-plane motion of a steel catenary riser is built, and the rigid body rotation of the out-of-plane motion of a steel catenary riser is added, so that the analysis on the out-of-plane motion of a steel catenary riser is more consonant with an actual motion state.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
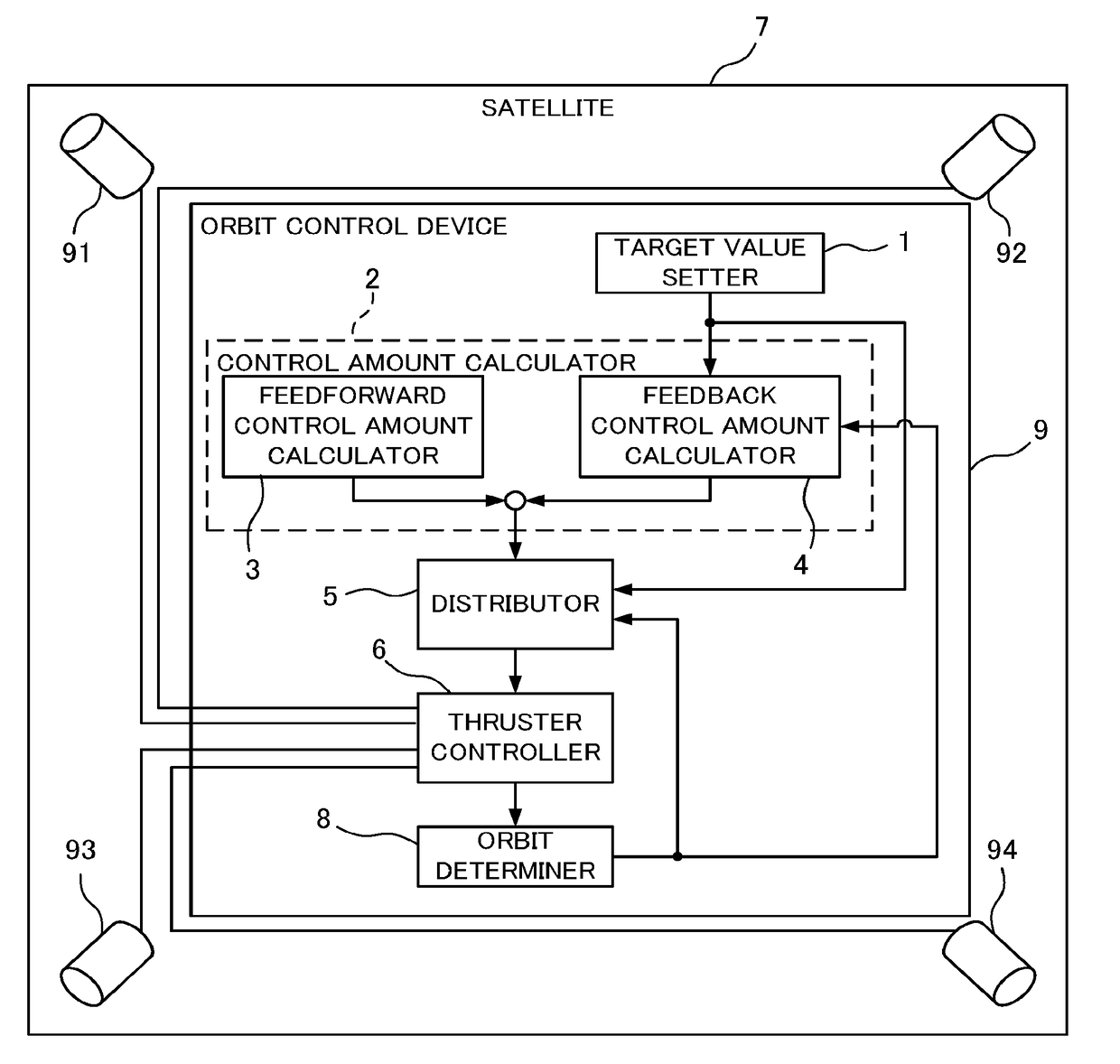
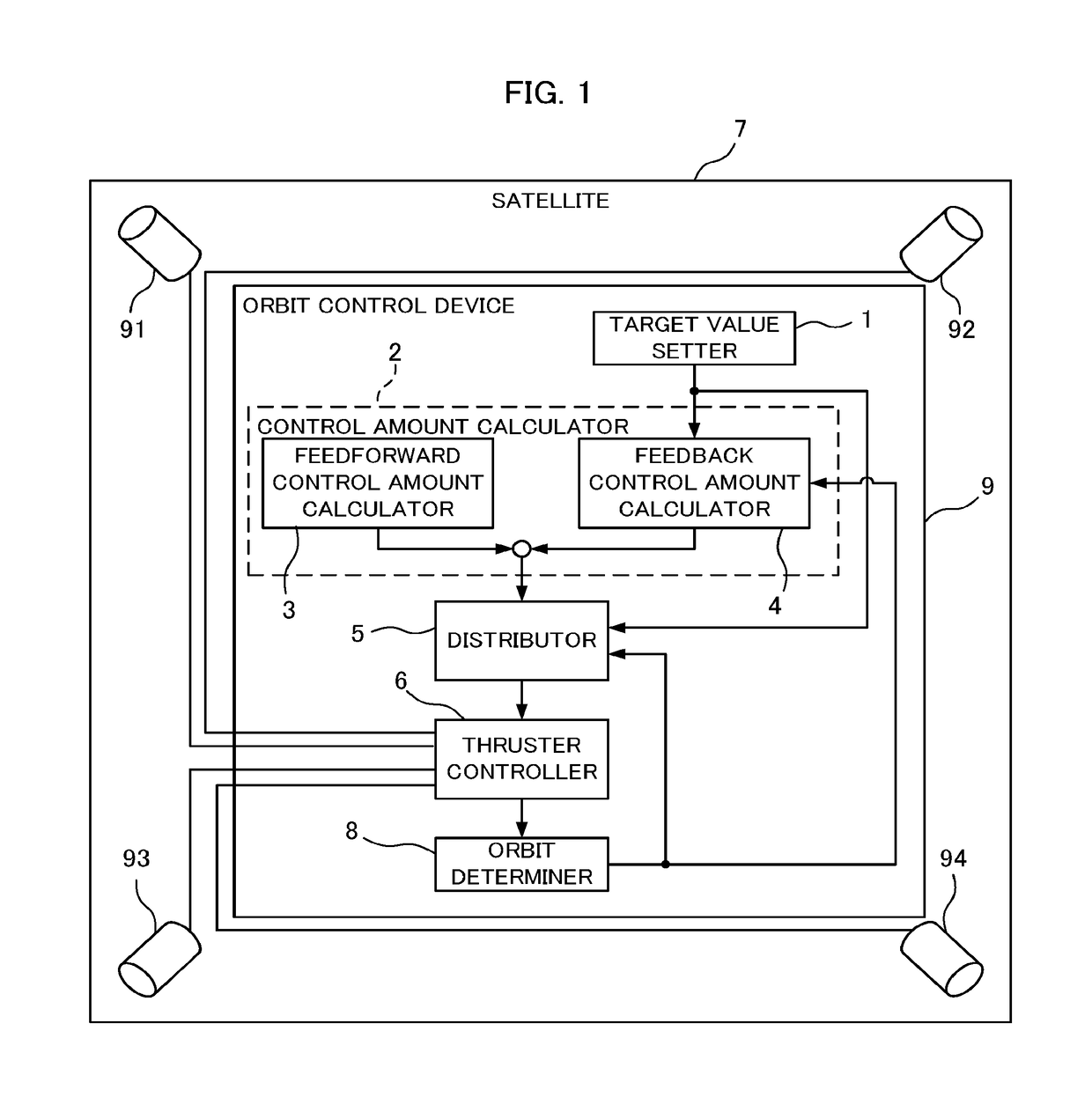
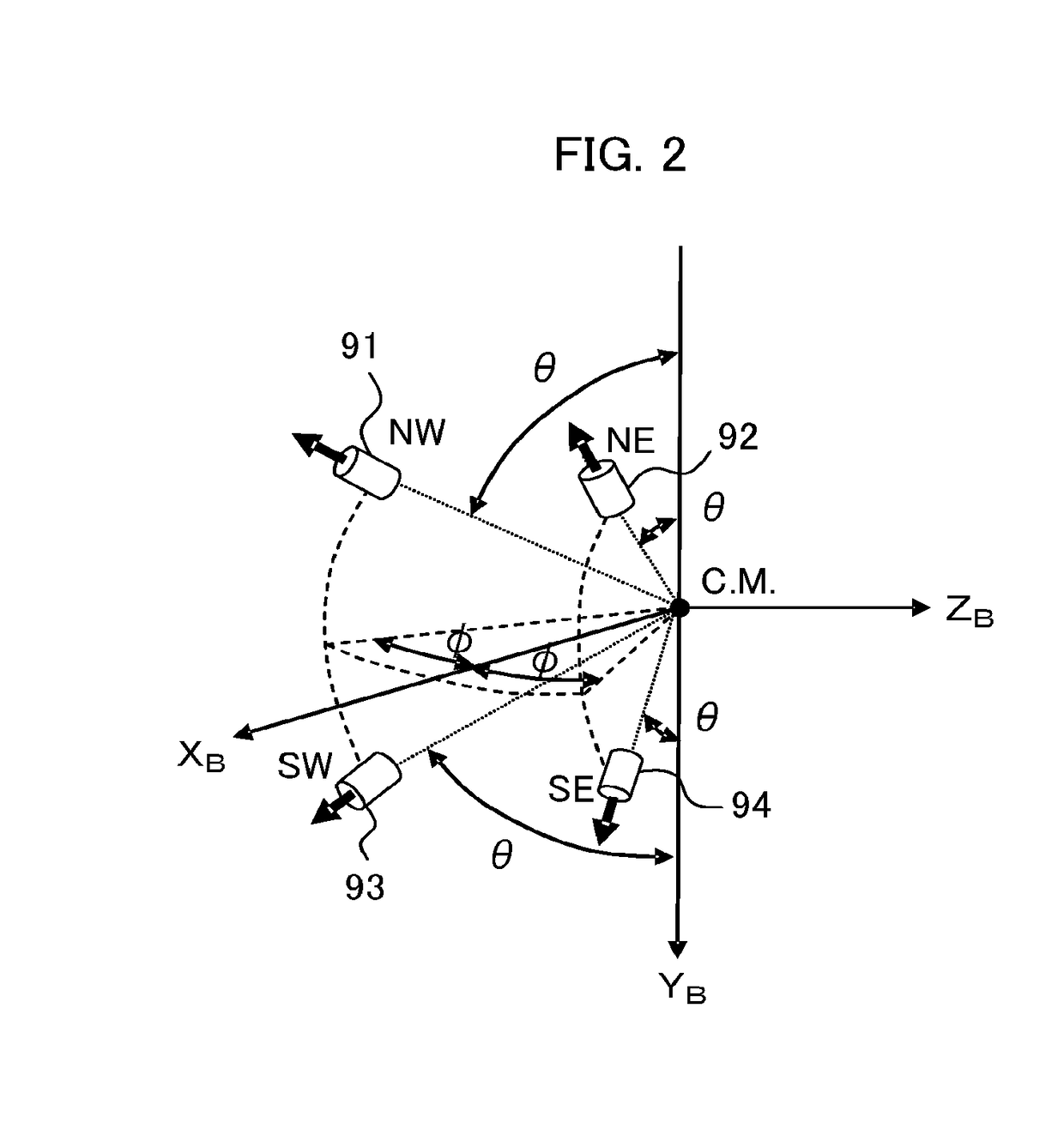
Orbit control device and satellite
A satellite comprises thrusters disposed with the firing directions each facing away from the mass center of satellite and different from each other. A control amount calculator calculates control amounts of the mean orbital elements from the mean orbital elements and the temporal change rates of the mean orbital elements set by an orbit determiner, and the target values. A distributor calculates firing timings and firing amounts of the thrusters for realizing the control amounts of the mean orbital elements by expressing a motion of satellite with orbital elements, solving an equation taking into account coupling of an out-of-plane motion and an in-plane motion due to thruster disposition angles and thruster firing amounts at multiple times, and combining one or more thruster firings controlling mainly an out-of-the-orbit-plane direction and one or more thruster firings controlling mainly an in-the-orbit-plane direction.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
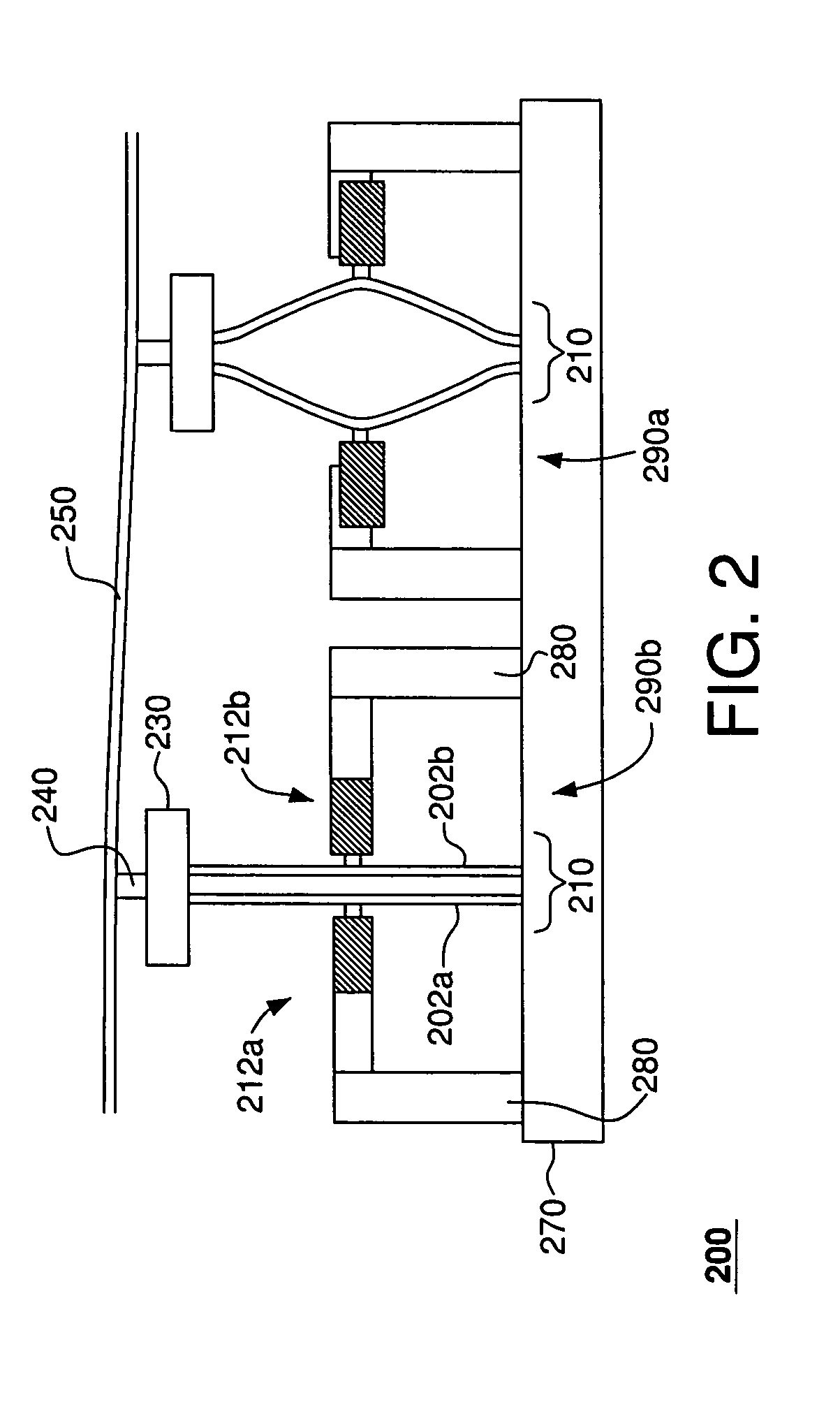
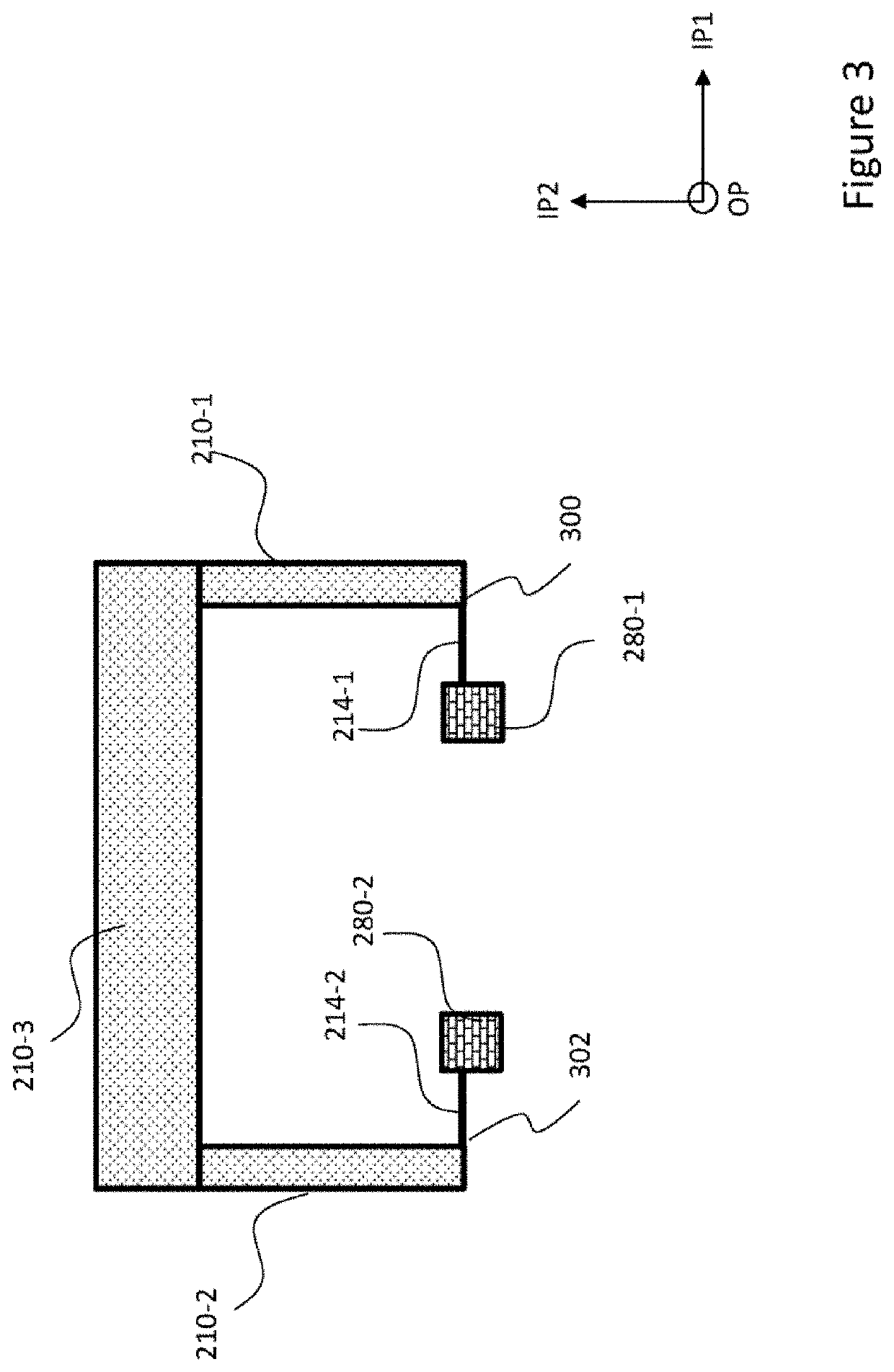
Microelectromechanical device for out-of-plane motion detection
The disclosure relates to a microelectromechanical device where the device structure includes a rotating mass structure and a linear mass structure. The rotating mass structure is formed of two rotating mass parts elastically coupled to the support through one or more springs that enable rotary motion of each of the rotating mass parts about respective rotary axes that extend parallel to each other along a first in-plane direction (IP1). The linear mass structure includes at least one elongate rigid body that extends in a second in-plane direction (IP2). One end of the linear mass structure is coupled to the first rotating mass part and the other end of the linear mass structure is coupled to the second rotating mass part such that rotary motions of the first and second masses result into linear motion of the linear mass structure in the out-of-plane direction (OP).
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Robust and accurate freehand 3D ultrasound
ActiveUS8559685B2Improves ultrasound probe calibrationRobust registration of imageUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementCorrelation coefficientVein
Disclosed is a system and method for computing out of plane motion between two ultrasound images. The method identifies regions of fully developed speckle that are common to the two images, computes a correlation coefficient corresponding to the two fully developed speckle image regions, and then computing an elevation distance corresponding to the correlation coefficient. The method exploits the measurable and characterizable relation between inter-image correlation and elevation distance, which may be determined from fully developed speckle regions. The method also identifies regions within the ultrasound images related to structure (e.g., vein or bone), and disregards these regions.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
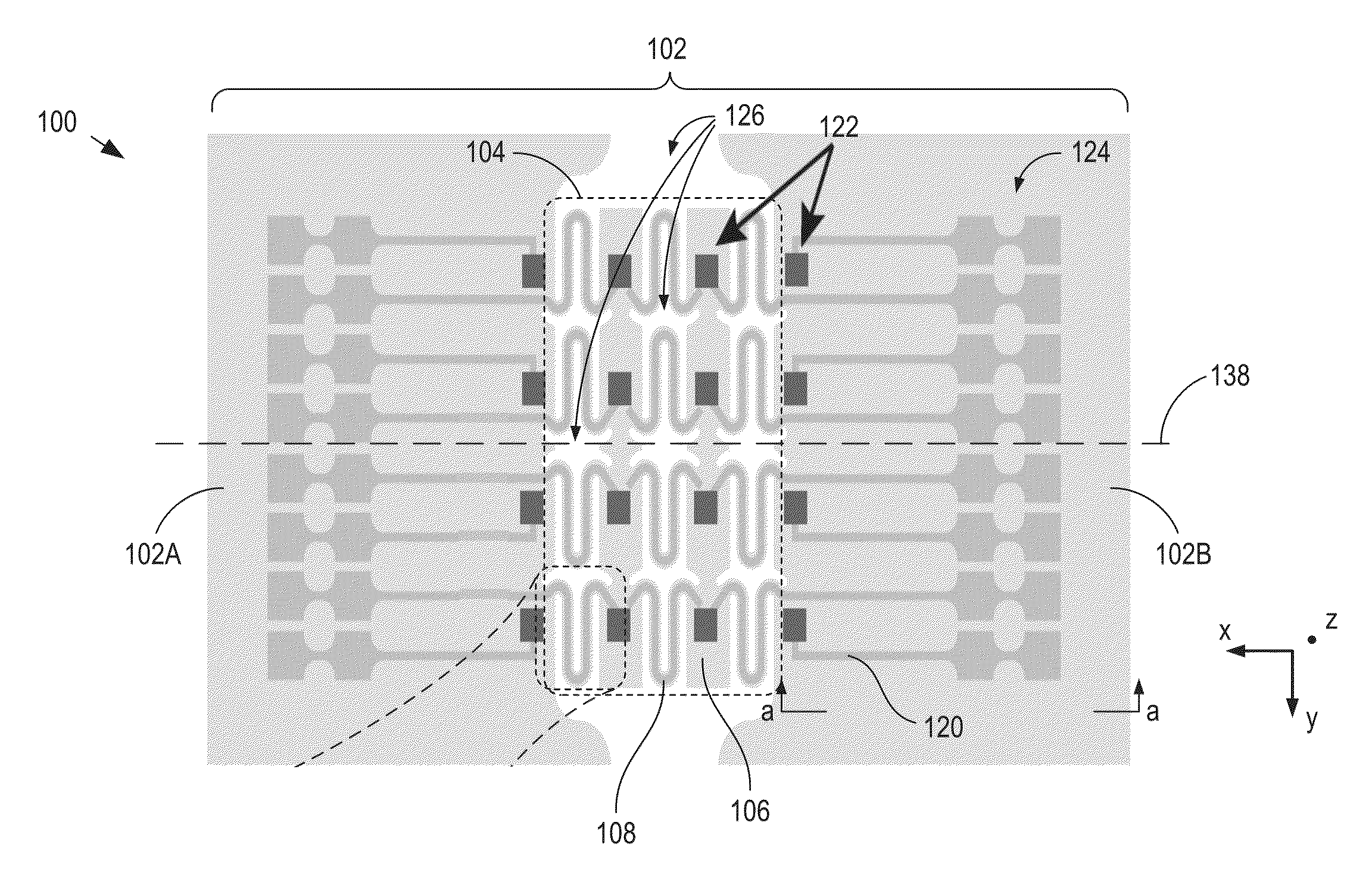
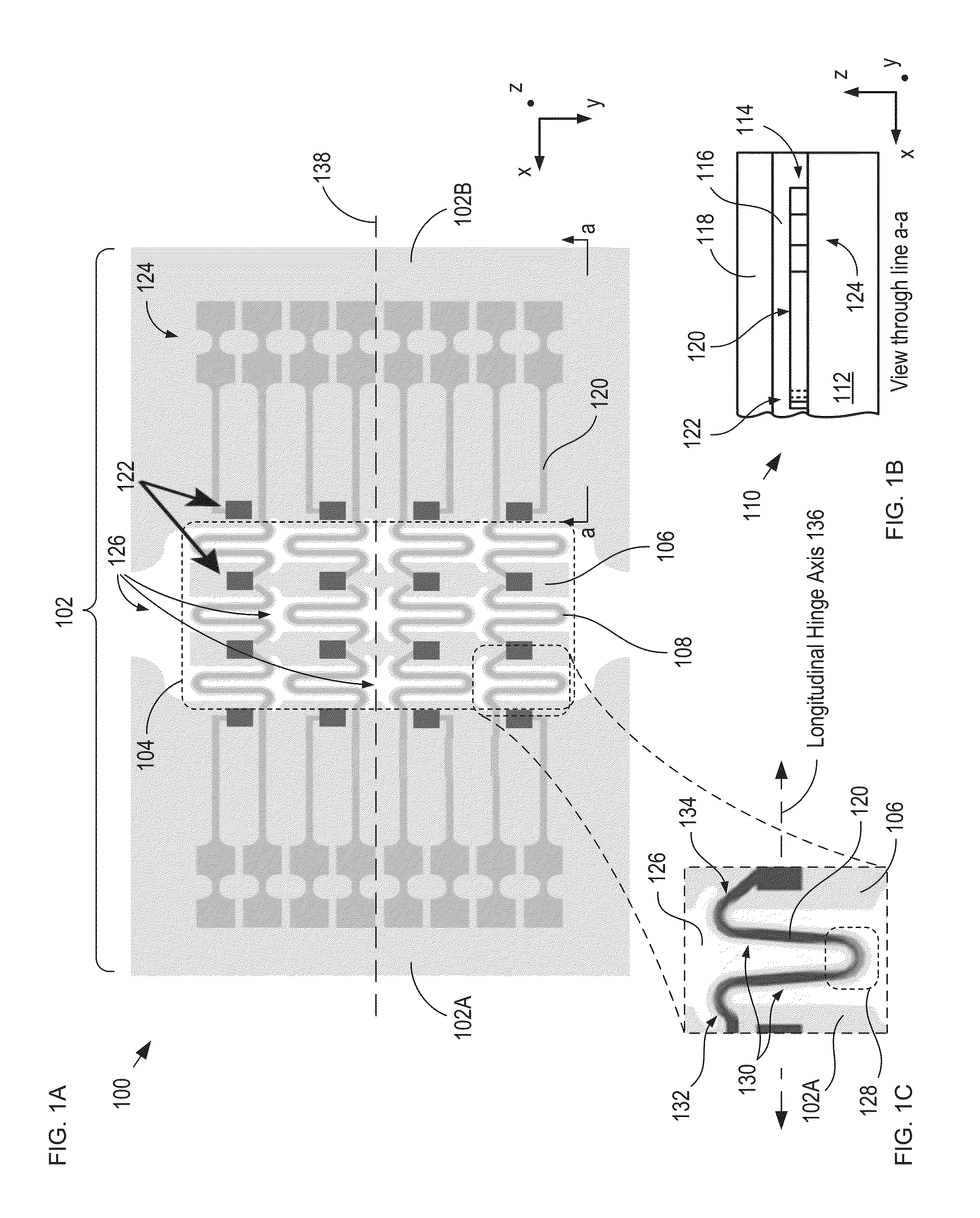
Mechanical connection for a MEMS and NEMS device for measuring a variation in pressure, and device comprising such a mechanical connection
ActiveUS11337016B2Increase capacityAvoid deformationPiezoelectric/electrostrictive microphonesFluid pressure measurement by electric/magnetic elementsRotational axisOut of plane motion
A mechanical connection is provided for a microelectromechanical and / or nanoelectromechanical device for measuring a variation in pressure. The device includes a fixed component extending in a main plane, a mobile component to move or deform in an out-of-plane direction under effect of a variation in pressure, and a detector of movement or deformation having at least one mobile element. The mechanical connection includes: a lever arm; a first connection connecting the mobile component to a first end of the lever arm, the first connection transmitting out-of-plane movement of the mobile component to the first end of the lever arm while allowing out-of-plane rotation of the lever arm about a direction of rotation; a second connection connected to the second end of the lever arm to allow mainly an out-of-plane rotation of the lever arm about an axis of rotation extending in the direction of rotation; a third connection connecting the lever arm to the detector at a given distance from the axis of rotation in the out-of-plane direction, the third connection being designed to convert the rotation of the lever arm about the axis of rotation into a translation in the plane of the at least one mobile element in a direction of translation.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Optical laser projection system with speckle reduction element configured for out-of-plane motion
InactiveCN102483523AReduce movementIncrease brightnessDiffusing elementsProjectorsIntermediate imageOut of plane motion
In a coherent light projection system including an image forming system (12), a relay system (18), a speckle reduction element (40), and a projection subsystem (20), the relay system can have a first f-number, and the projection subsystem can have a second f-number less than the first f-number. The relay system can have a first working distance, and the projection subsystem can have a second working distance less than the first working distance. The image forming system can project an initial image having a first size, and an intermediate image (22) can have a second size greater than or equal to the first size. The speckle reduction element can have a curved surface through which the intermediate image is transferred. The speckle reduction element can include a lenslet arrangement formed on a surface thereof. The speckle reduction element can be moved in a direction parallel to an optical axis of the speckle reduction element.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
In-plane-strain-actuated out-of-plane actuator
InactiveUS20160158933A1Improve adhesionSuitable adhesionMicromanipulatorFlexible microstructural devicesElectricityOut of plane motion
A micromechanical device capable of providing out-of-plane motion and force generation in response to an in-plane strain applied to the device is provided. Embodiments of the present invention comprise one or more islands that are operatively coupled with one or more hinges. The hinges are operative for inducing rotation of the islands when a lateral strain is applied to the structure. In some embodiments, the hinges are also electrically conductive such that they enable electrical communication between the one or more islands and devices external to the structure. Some embodiments of the present invention are particularly well suited for use in biological applications. Some devices in accordance with the present invention are fabricated using conventional planar processes, such as flex-circuit fabrication techniques.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com