Patents
Literature
56results about How to "Impeding determination" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
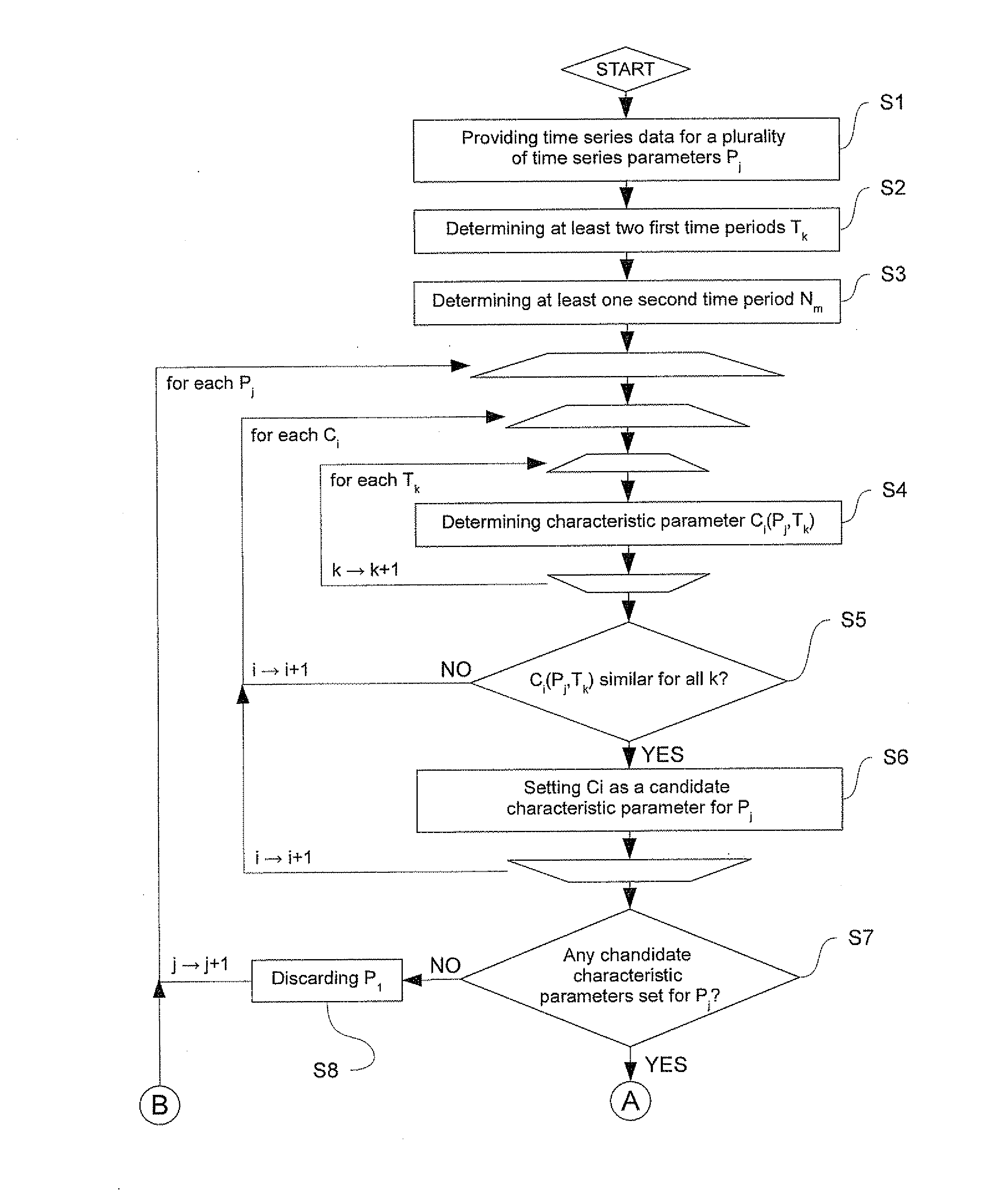
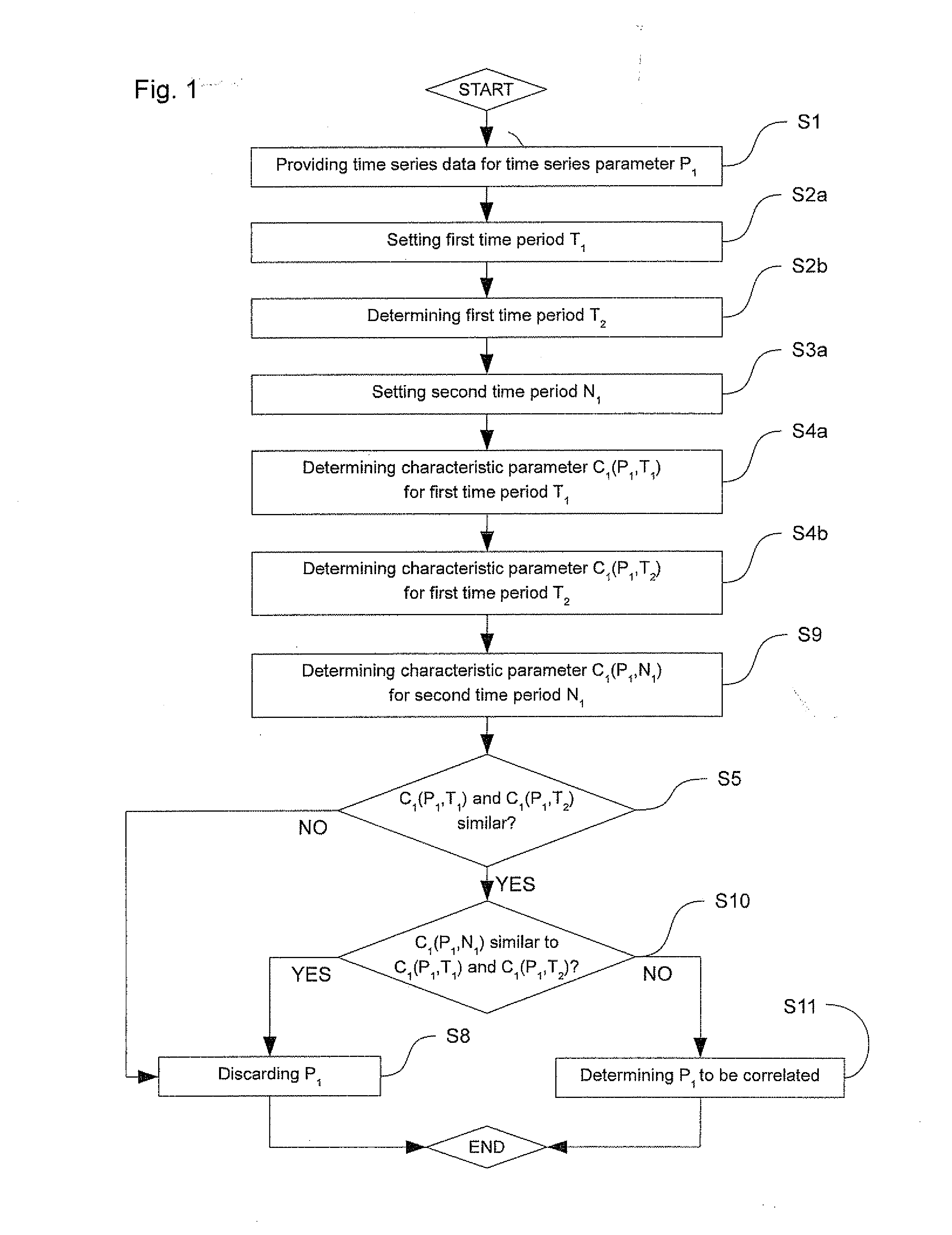
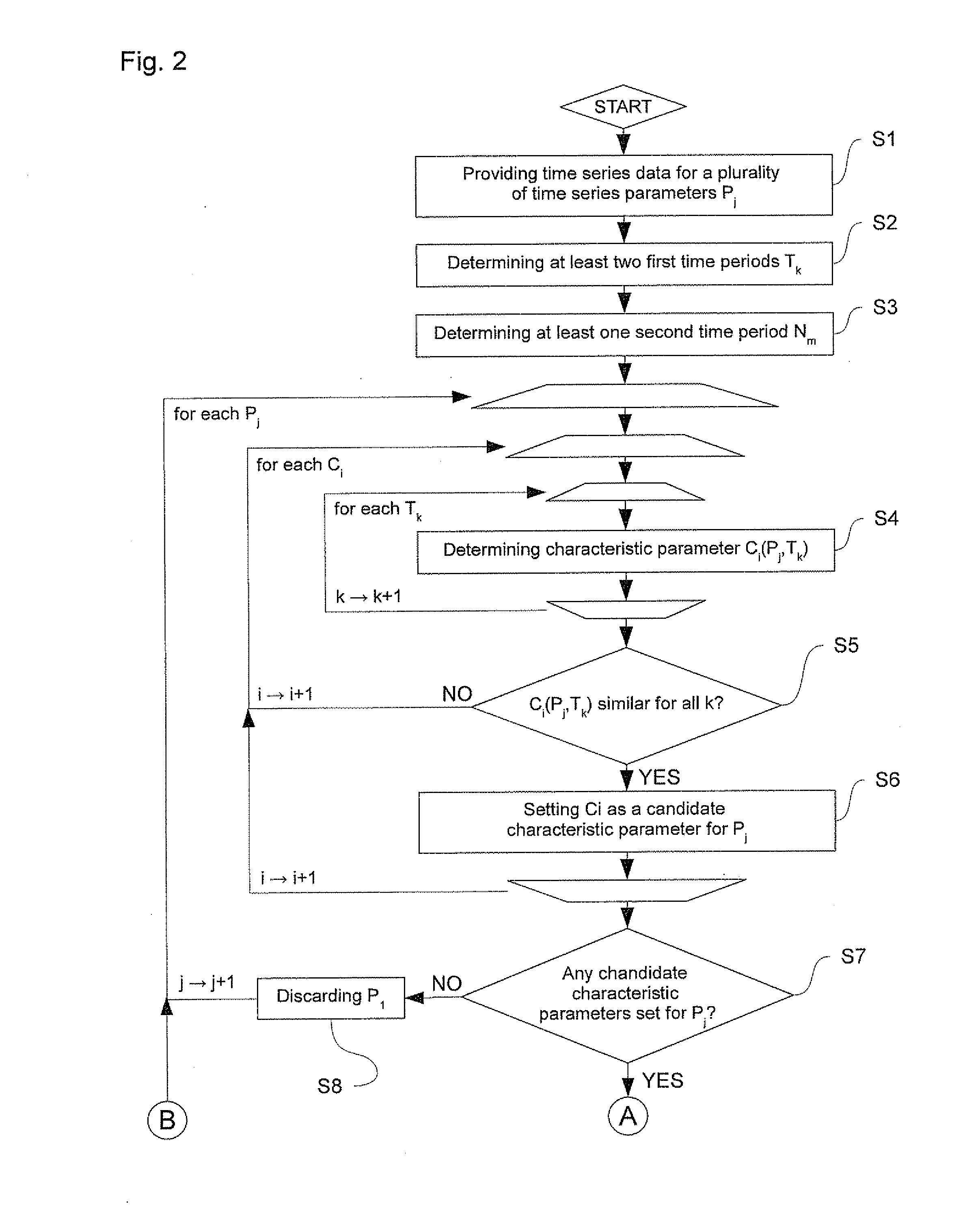
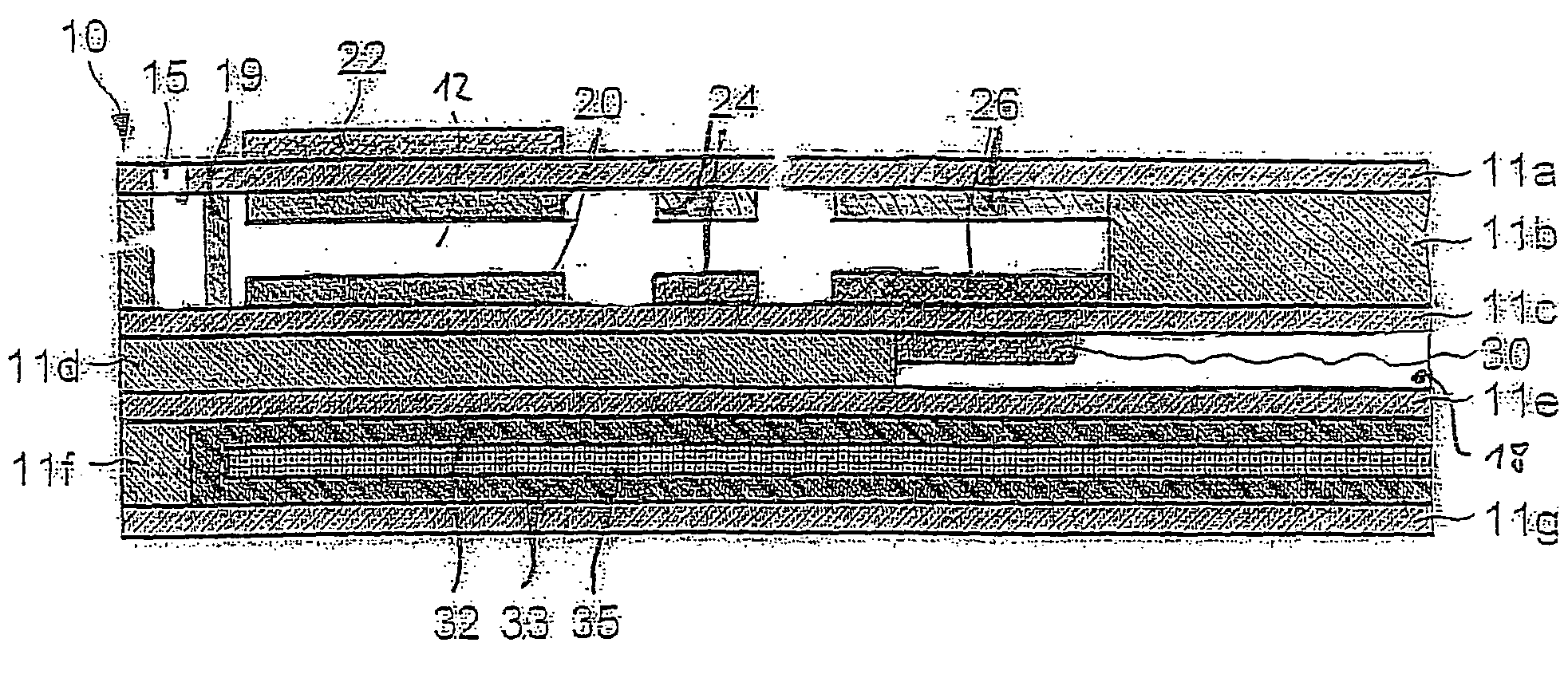
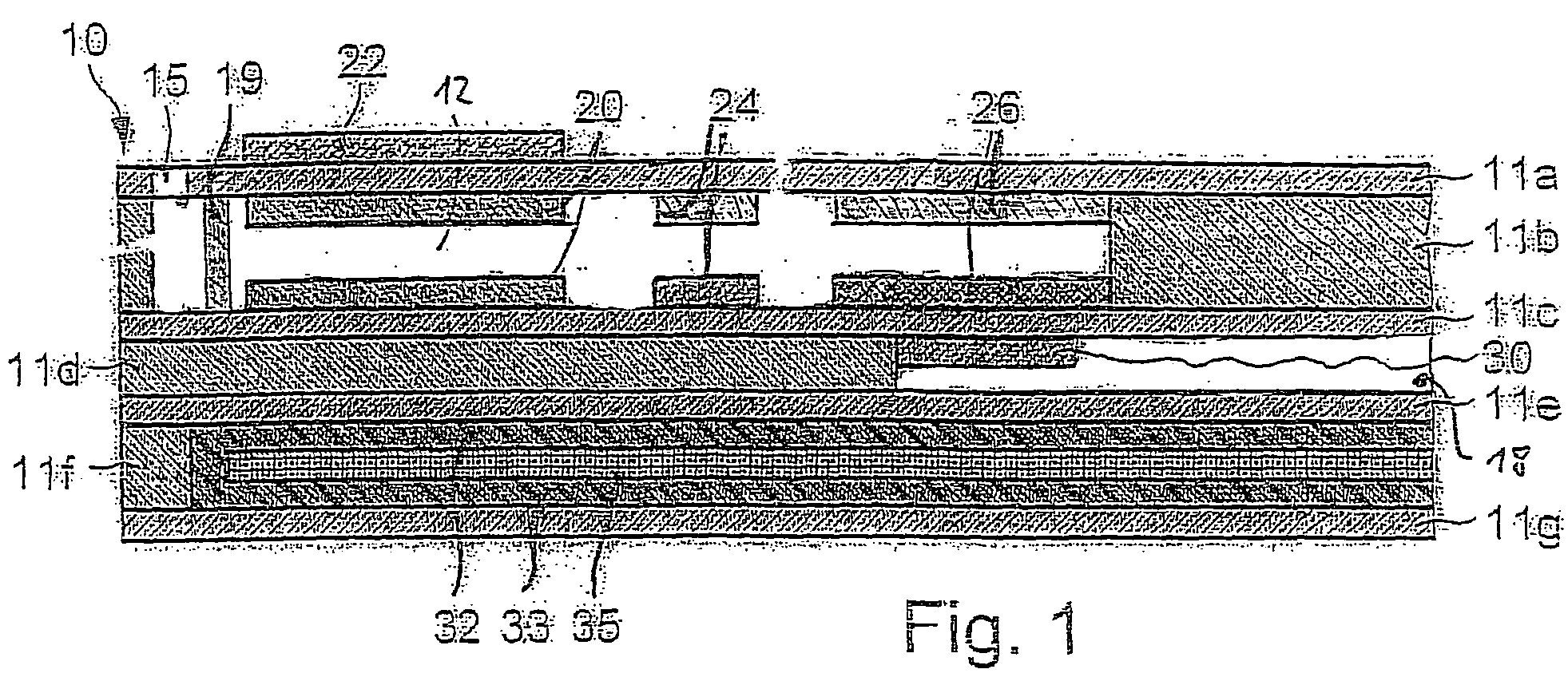
Method and apparatus for analyzing time series data
ActiveUS20110035188A1Improve accuracyReliable methodTime indicationSynchronous motors for clocksState dependentTime segment
The present invention relates to a method and an apparatus for determining which one or more time series parameters of a plurality of time series parameters relating to operation of a system are correlated with a first operation state of the system. According to the invention, the method comprises providing time series data including data relating to a time series of each of the plurality of time series parameters; determining at least two first time periods, wherein the system is in the first operation state during the at least two first time periods; determining at least one second time period, wherein the system is in a second operation state during the at least one second time period; determining, for each respective time series parameter of the plurality of time series parameters, a first characteristic parameter relating to a first characteristic of the time series of the respective time series parameter for each of the at least two first time periods and the at least one second time period; and determining which one or more time series parameters of the plurality of time series parameters relating to the operation of the system are correlated with the first operation state of the system by determining, for each respective time series parameter of the plurality of time series parameters, whether or not the respective time series parameter is correlated with the first operation state of the system based on the first characteristic parameters of the respective time series parameter determined for each of the at least two first time periods and the at least one second time period.
Owner:EUROPEAN SPACE AGENCY
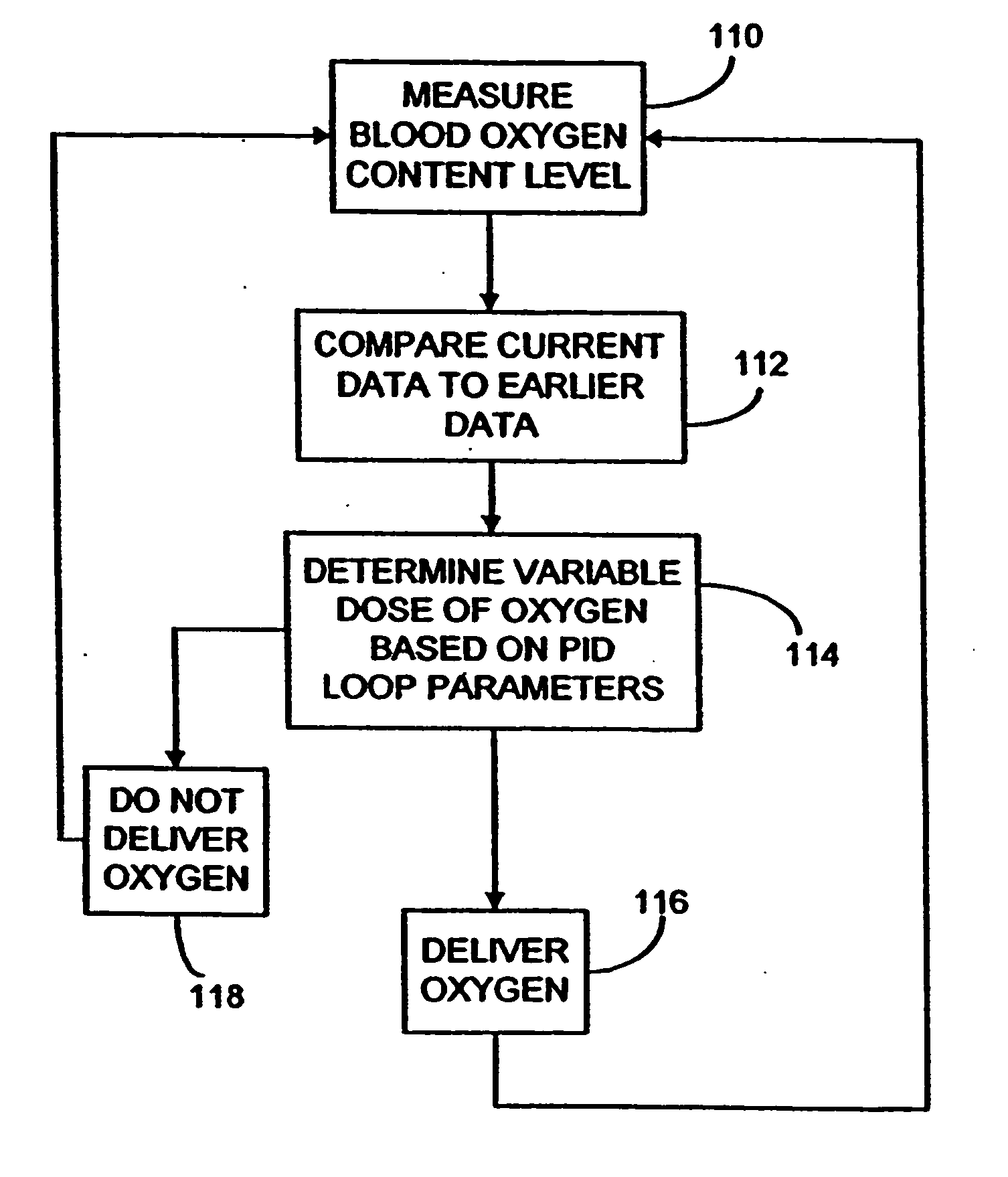
Control of respiratory oxygen delivery
InactiveUS20060213519A1Improve accuracyImprove system accuracyOperating means/releasing devices for valvesRespiratory masksDuring expirationExhalation
Methods and systems for supplying respiratory oxygen to users when the users are inhaling are disclosed. The methods and systems may rely on delivery devices that are selectively placed in fluid communication with either a respiration sensor or a source of oxygen. The methods and systems may actively monitor for exhalations, as well as monitor for oxygen in the oxygen source. The respiration sensor may preferably be a flow sensor.
Owner:MINNESOTA INNOVATIVE TECH & INSTR MITI
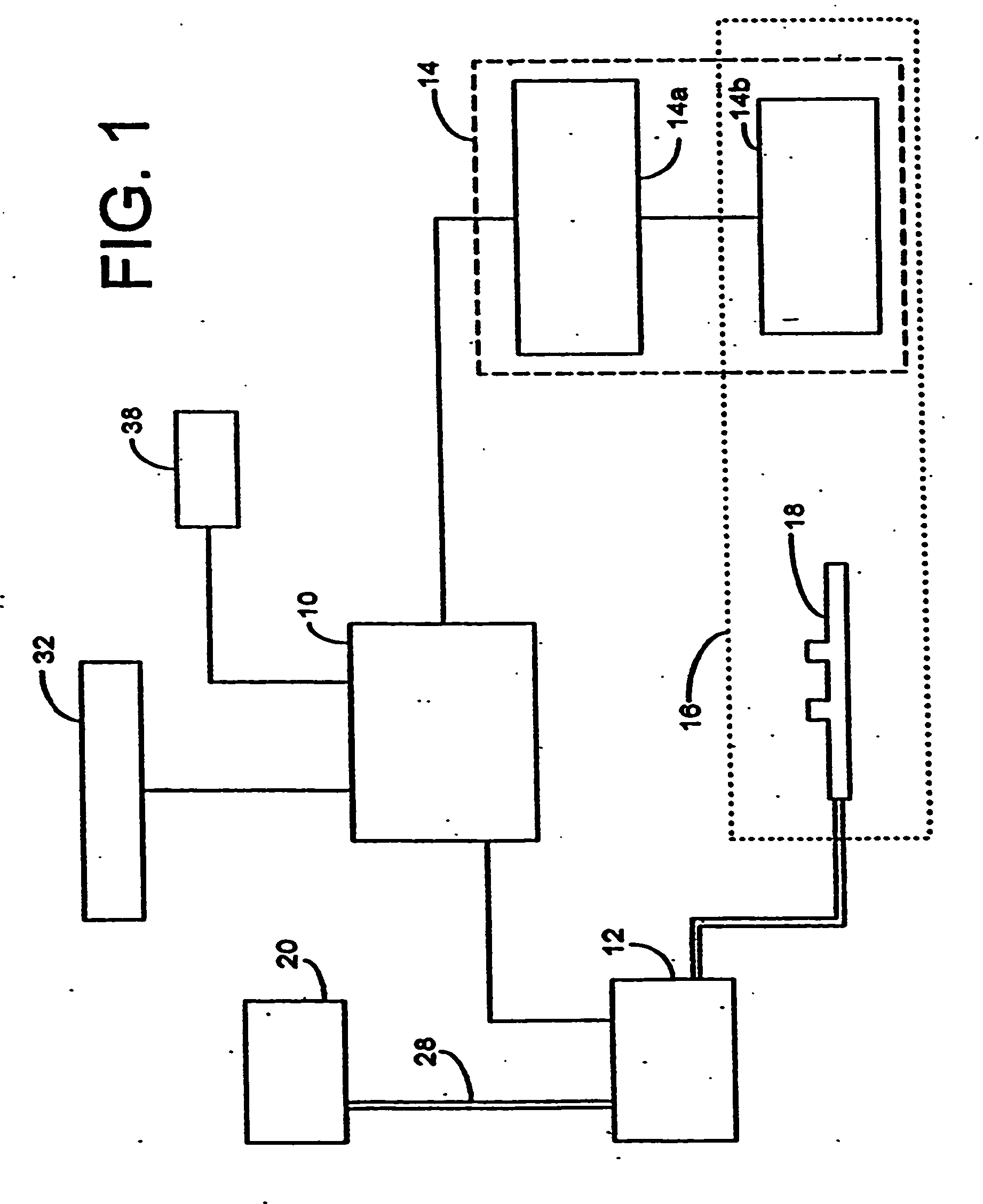
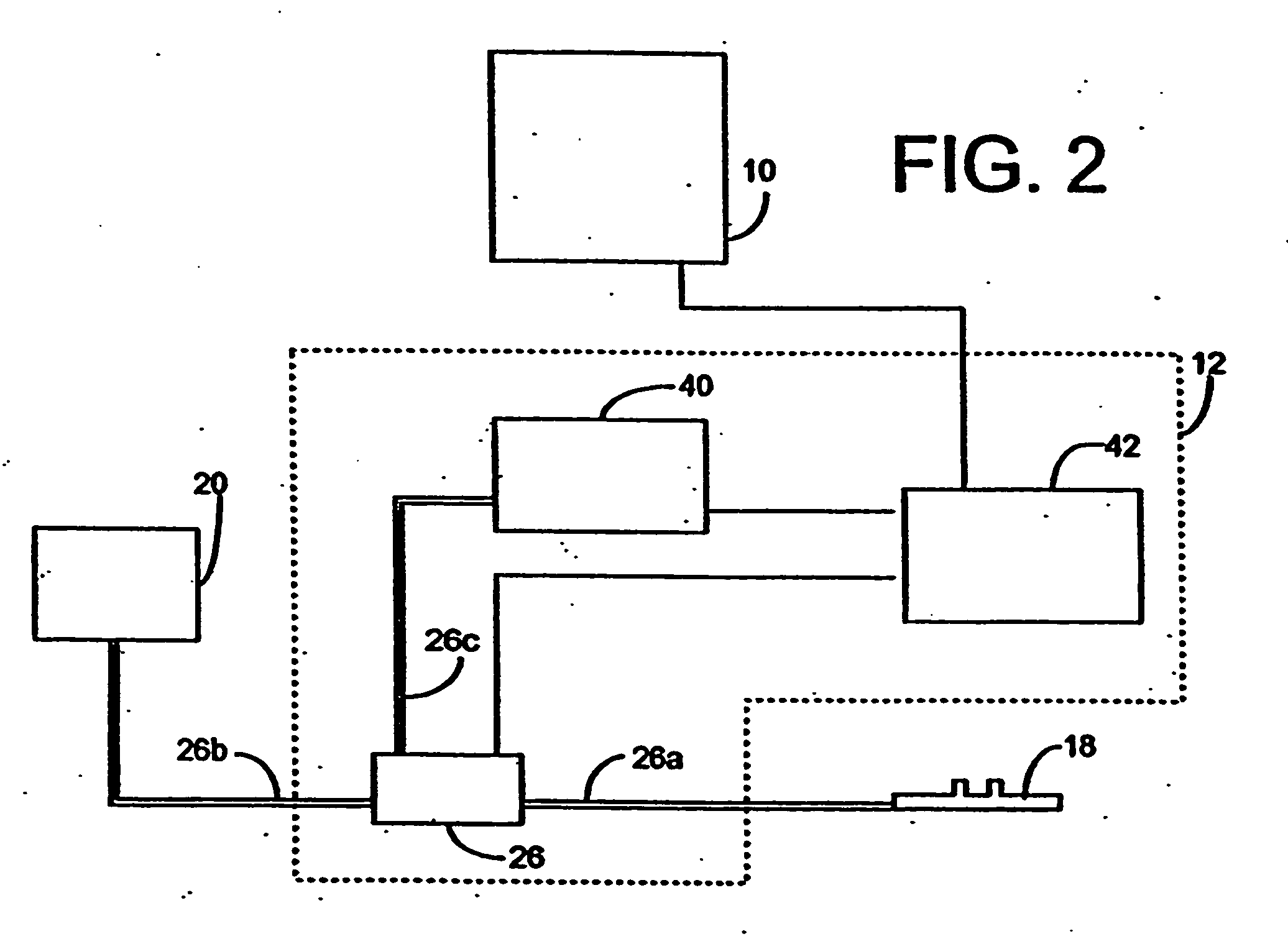
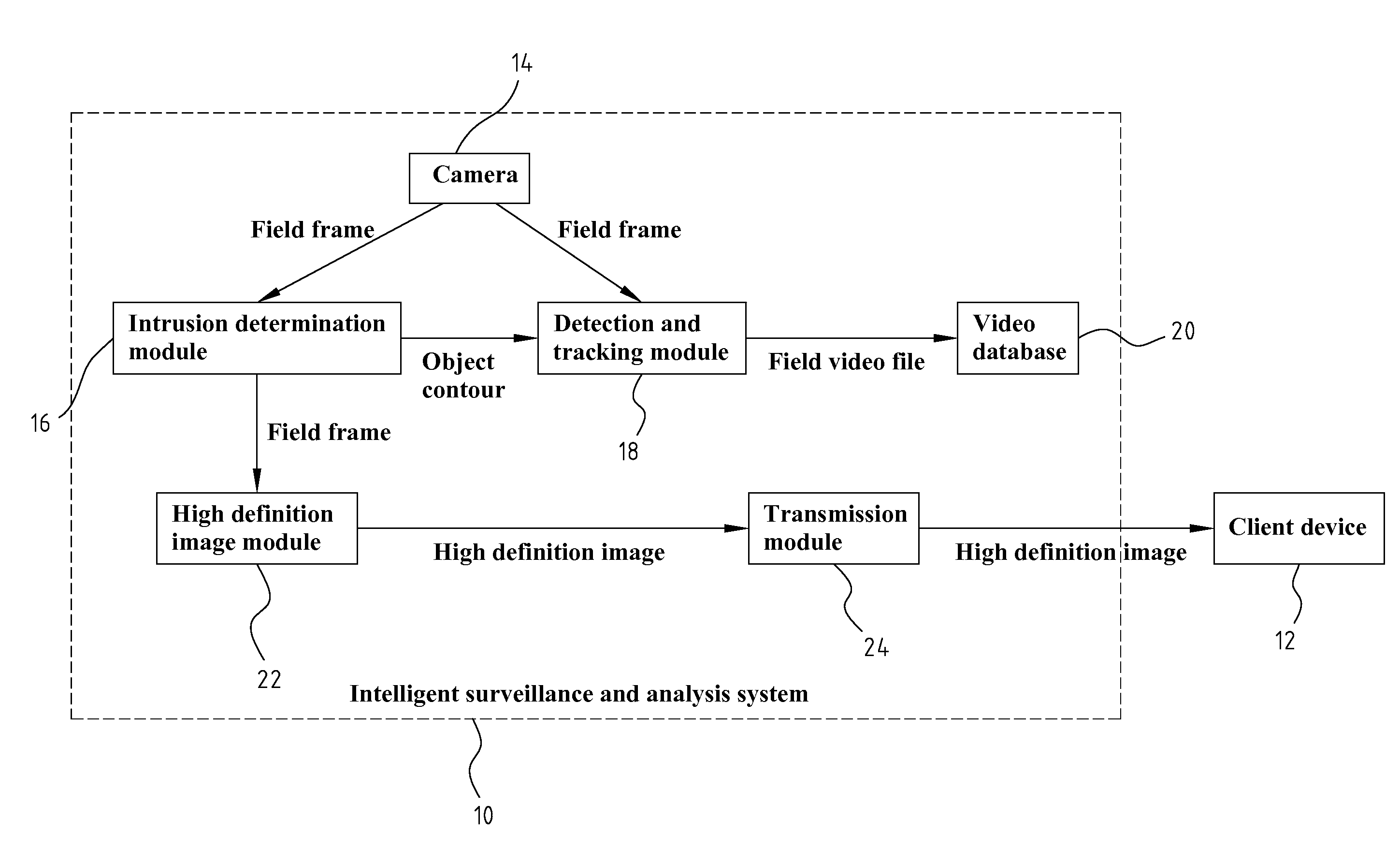
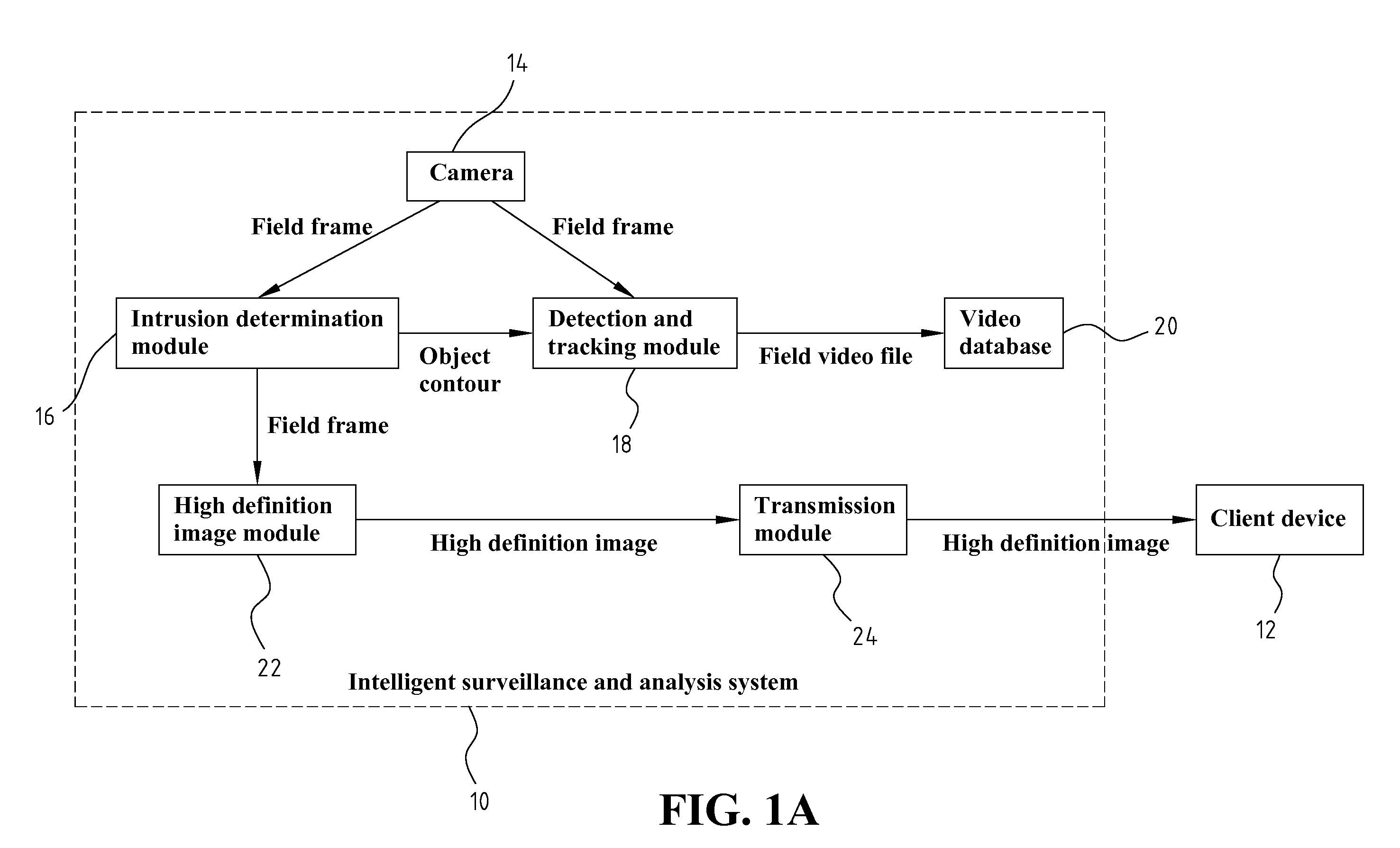
System And Method Of Intelligent Surveillance And Analysis
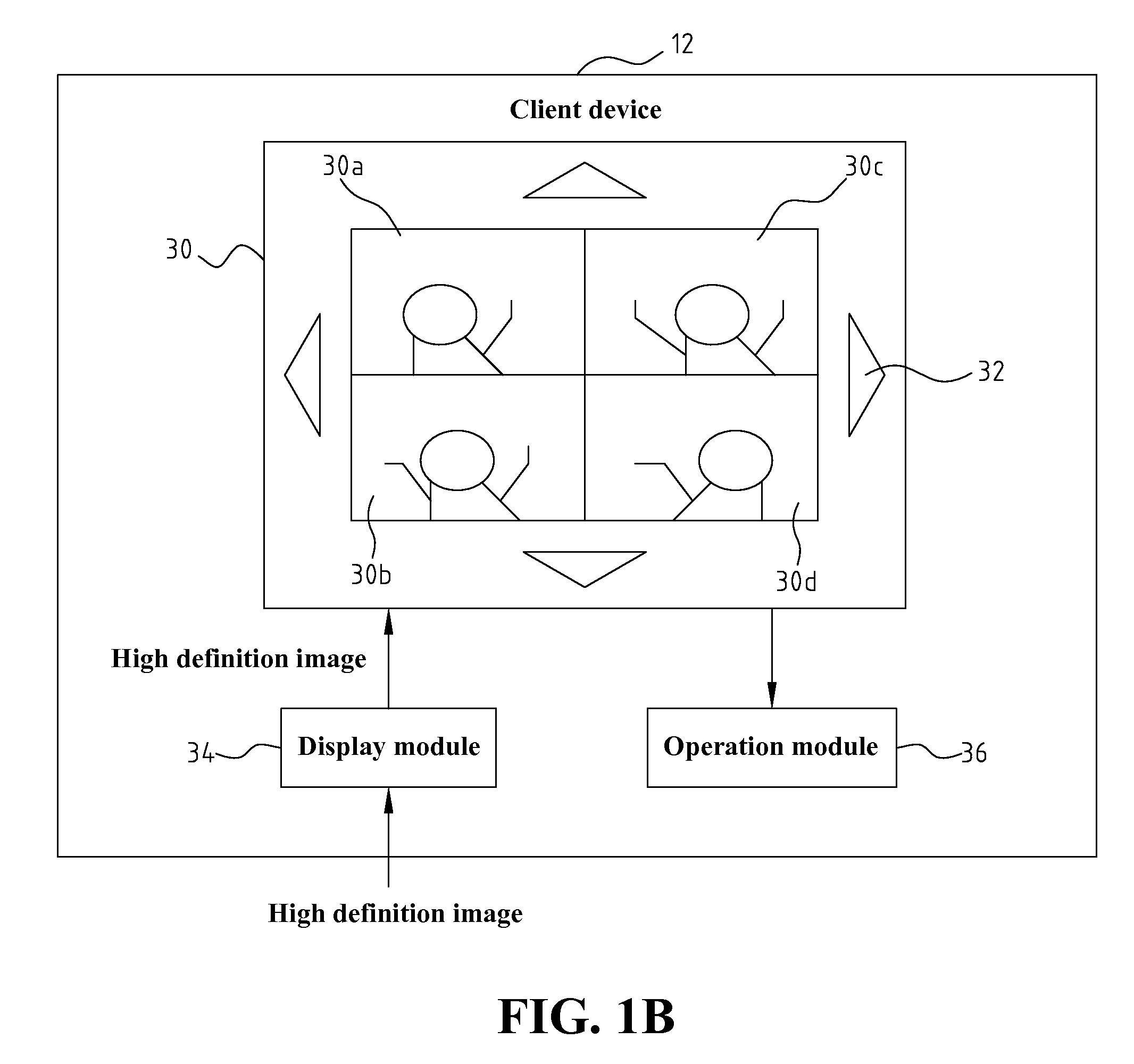
InactiveUS20080252722A1Impeding determinationReduce bandwidth loadCharacter and pattern recognitionColor television detailsHigh bandwidthSmart surveillance
System and method of intelligent surveillance and analysis mainly used for monitoring whether a field has an intrusion object (such as a thief), and instantly providing video or image of the suspected intruder to approved relevant individual (such as the house owner) for further confirmation of the presence of the intrusion object (such as thief); therefore, the wrongful determination by the computer is avoided. The aforementioned system includes, first the determination and extraction of the contour of the suspected intrusion object, then the continuous tracking of the suspected intrusion object according to the contour, continue capturing of images using the camera, and then storing these captured video temporarily, and finally notifying the house owner using the highest definition image of the video which occupies a lesser amount of bandwidth through various communication channels once the presence of thief is determined; the video is downloaded using higher bandwidth, and is played.
Owner:NAT CHIAO TUNG UNIV
Signal measurement and processing method and apparatus
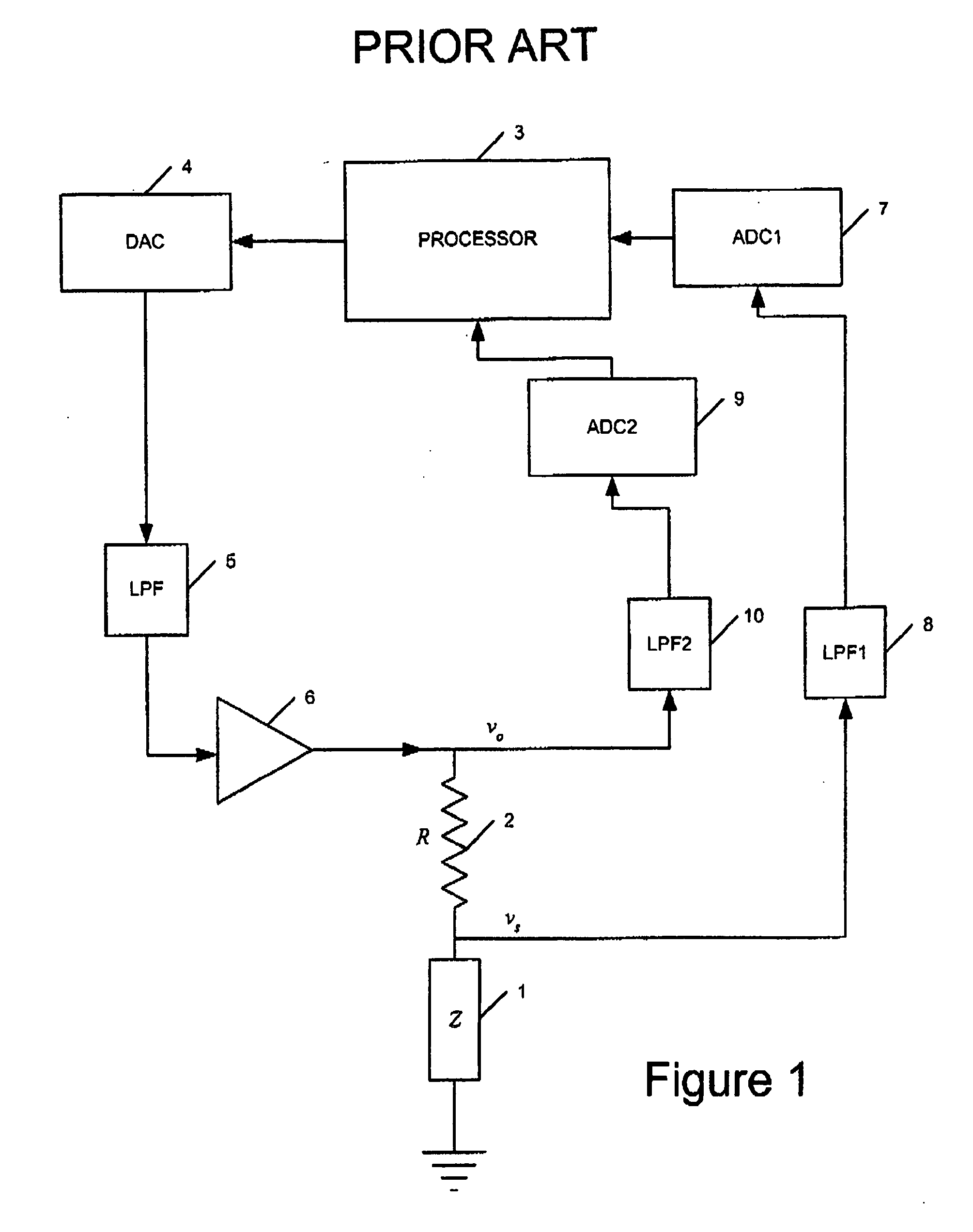
ActiveUS20050192765A1Accurate measurementImprove noise levelFrequency-division multiplex detailsEmergency protective circuit arrangementsElectrical impedanceElectric signal
Apparatus for generating an output dependent upon the impedance or at least one component of the impedance of a device comprises a load component having a known impedance or component thereof for connection in series with said device; a measurement channel for measuring voltages; a switch arrangement connected to said measurement channel for switching the measurement channel to sequentially measure a first voltage on a first side of said load component and a second voltage on a second side of said load component or a voltage difference across said load component; a processing arrangement connected to said measurement channel for processing the sequentially measured voltages to generate an output dependent upon said impedance or at least one component of the impedance of said device; and a signal generating arrangement for generating an electrical signal for application to the series connected load component and device.
Owner:ULTRA PCS LTD
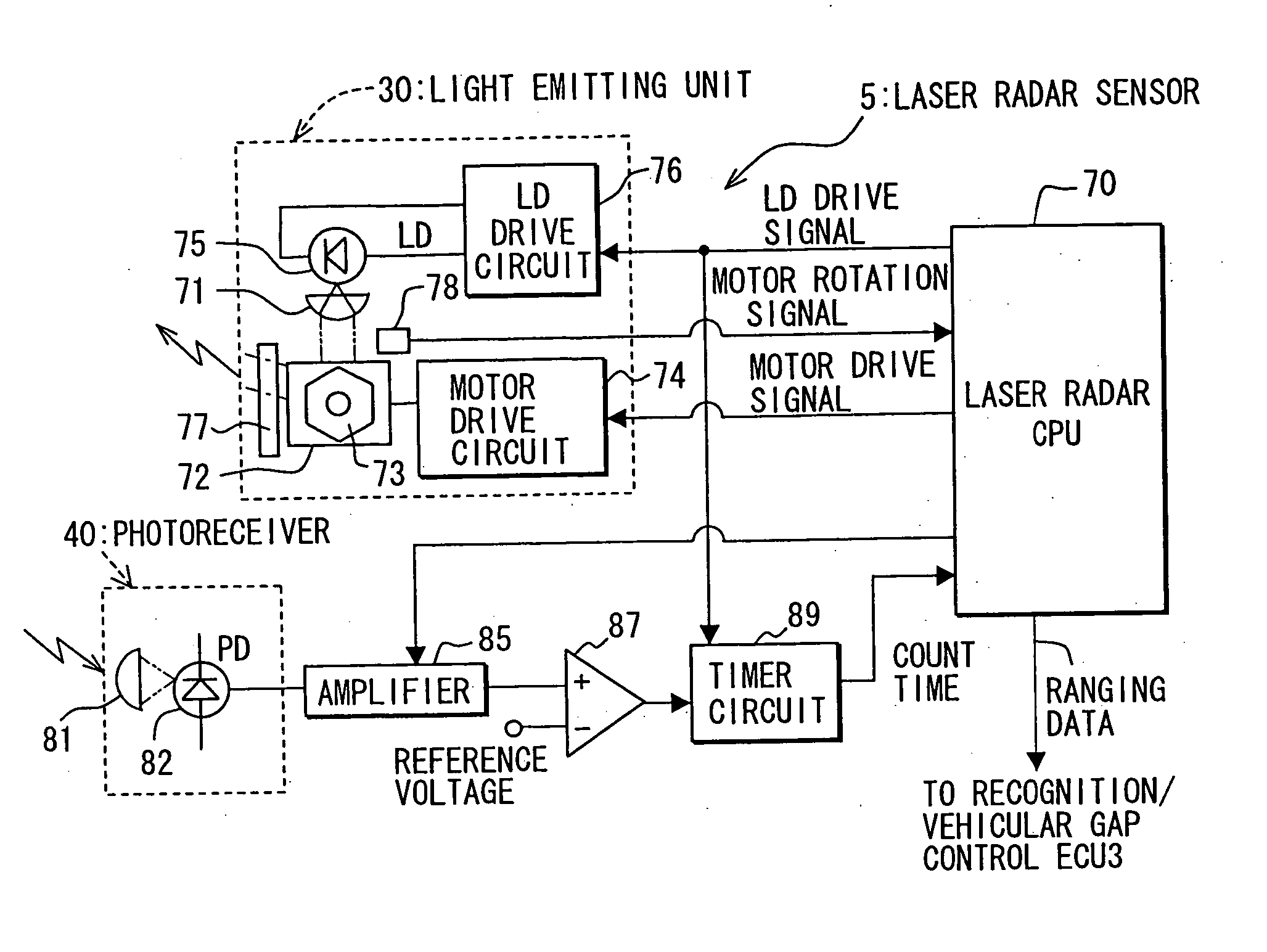
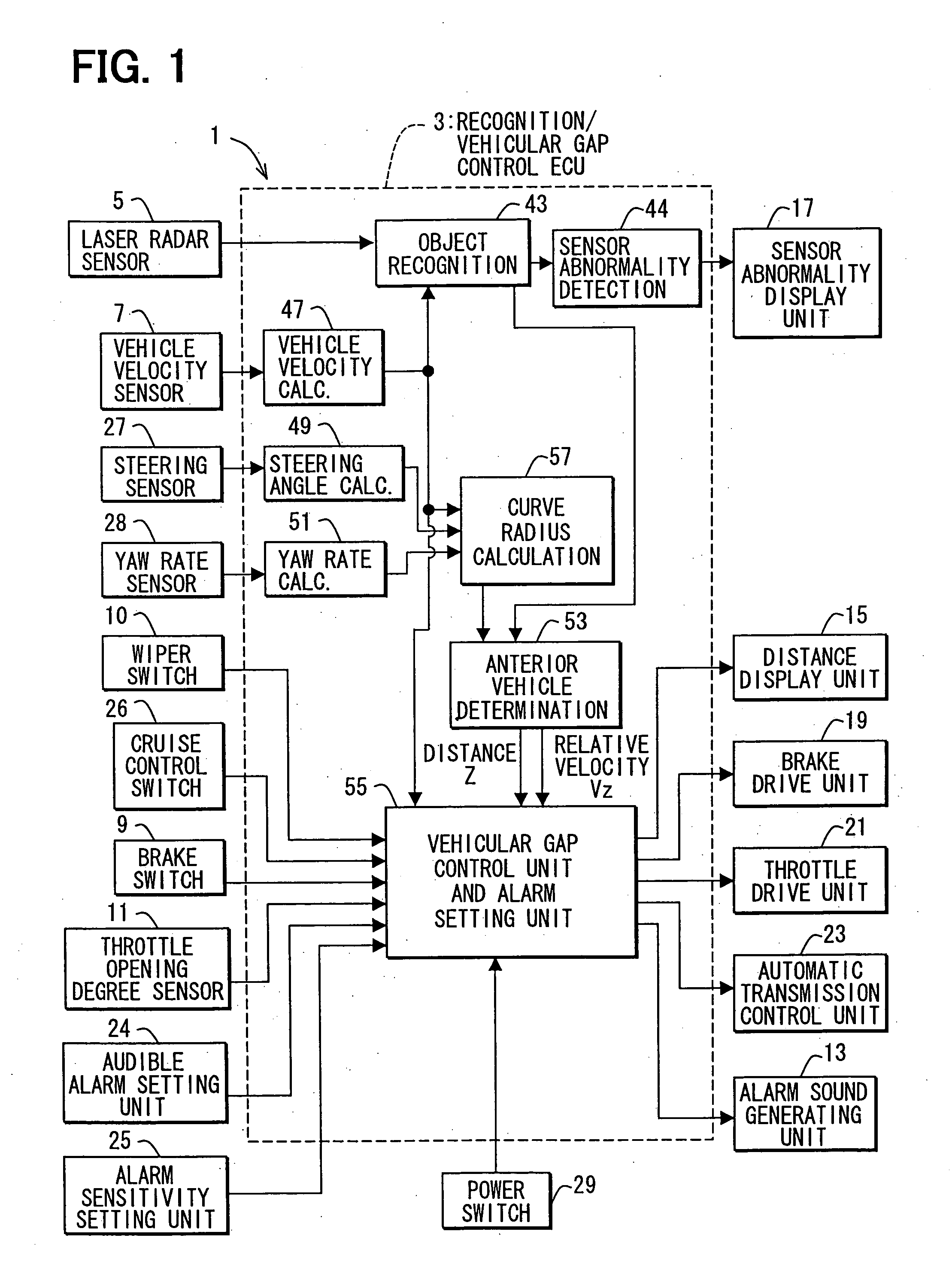
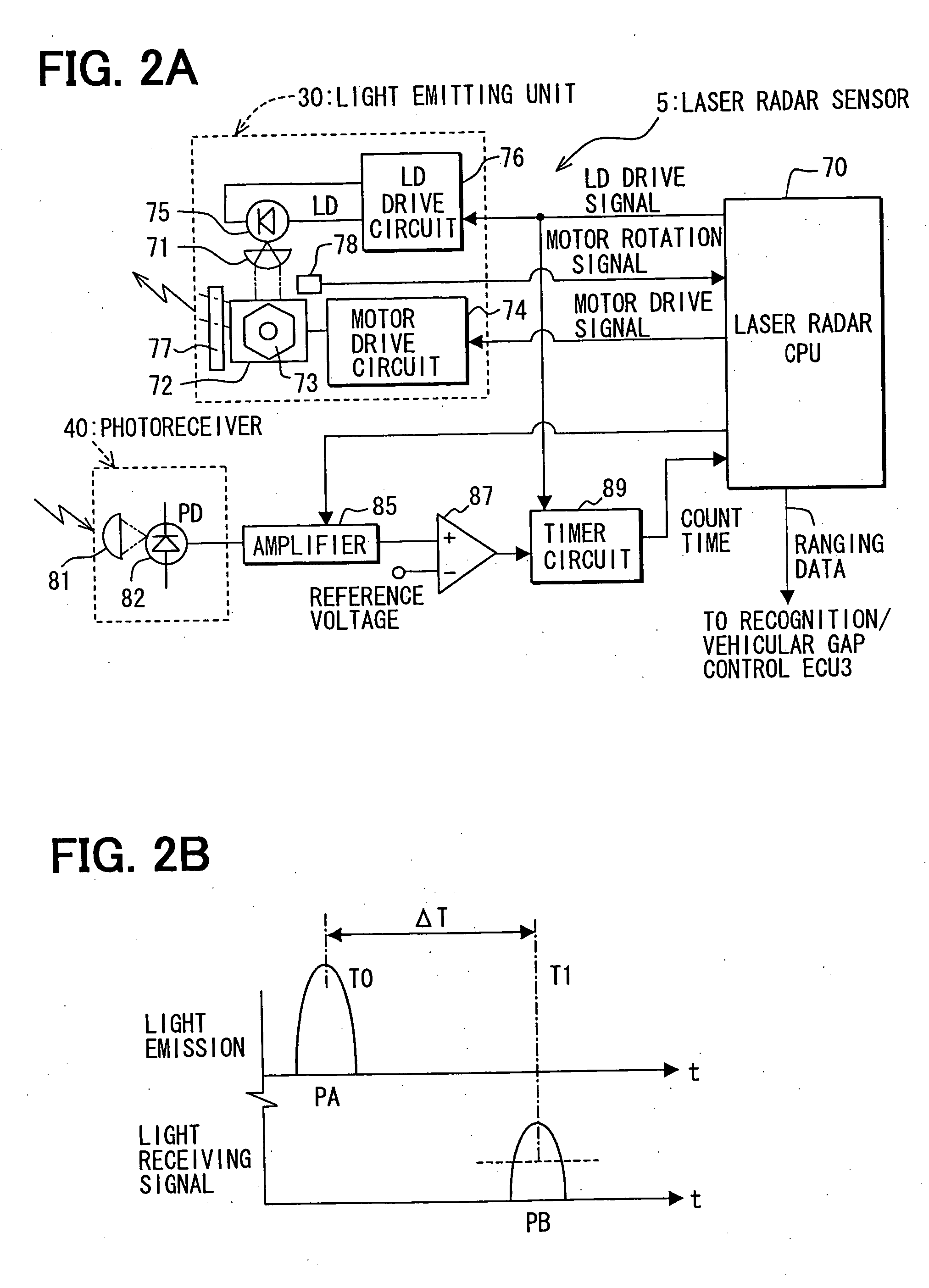
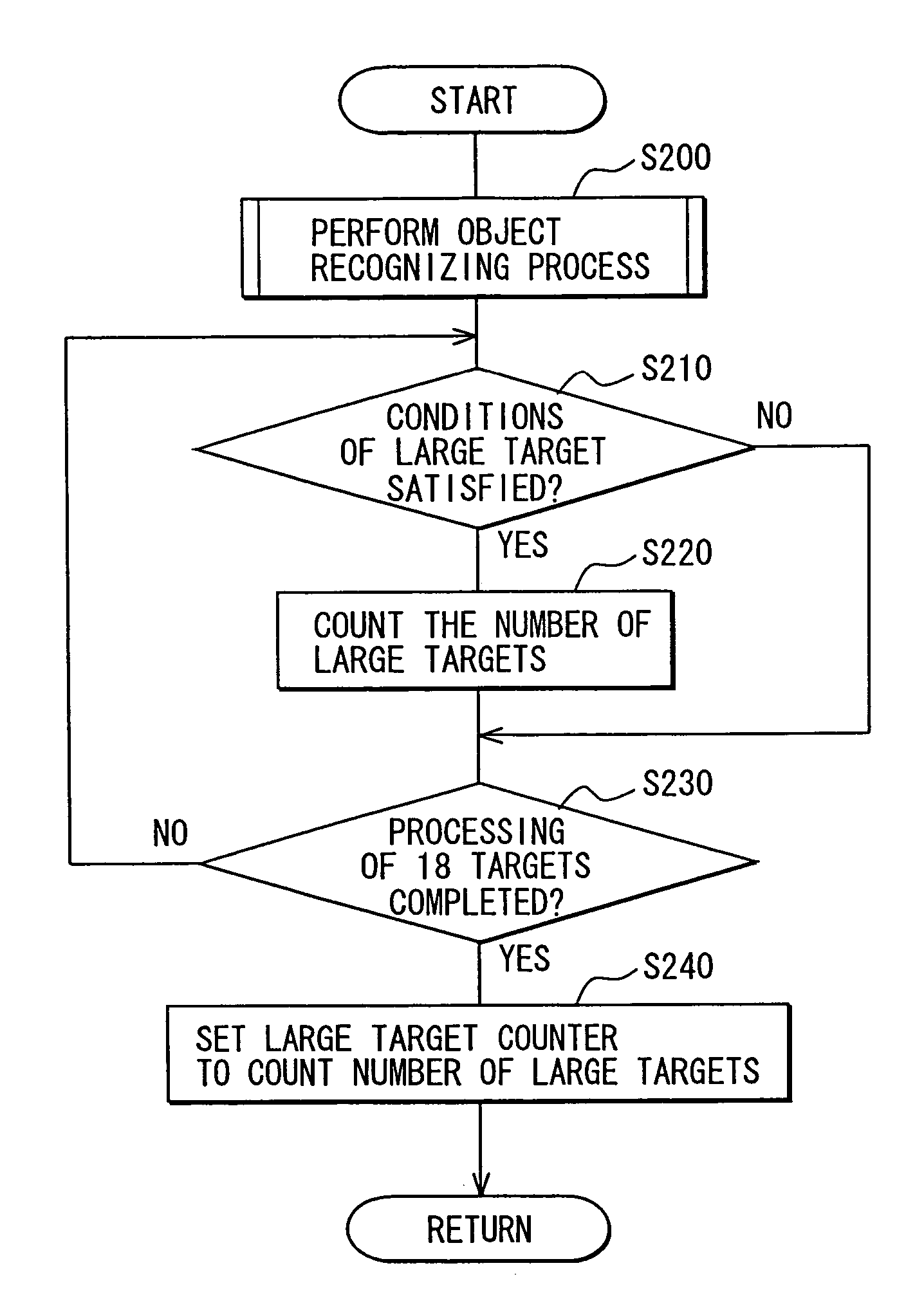
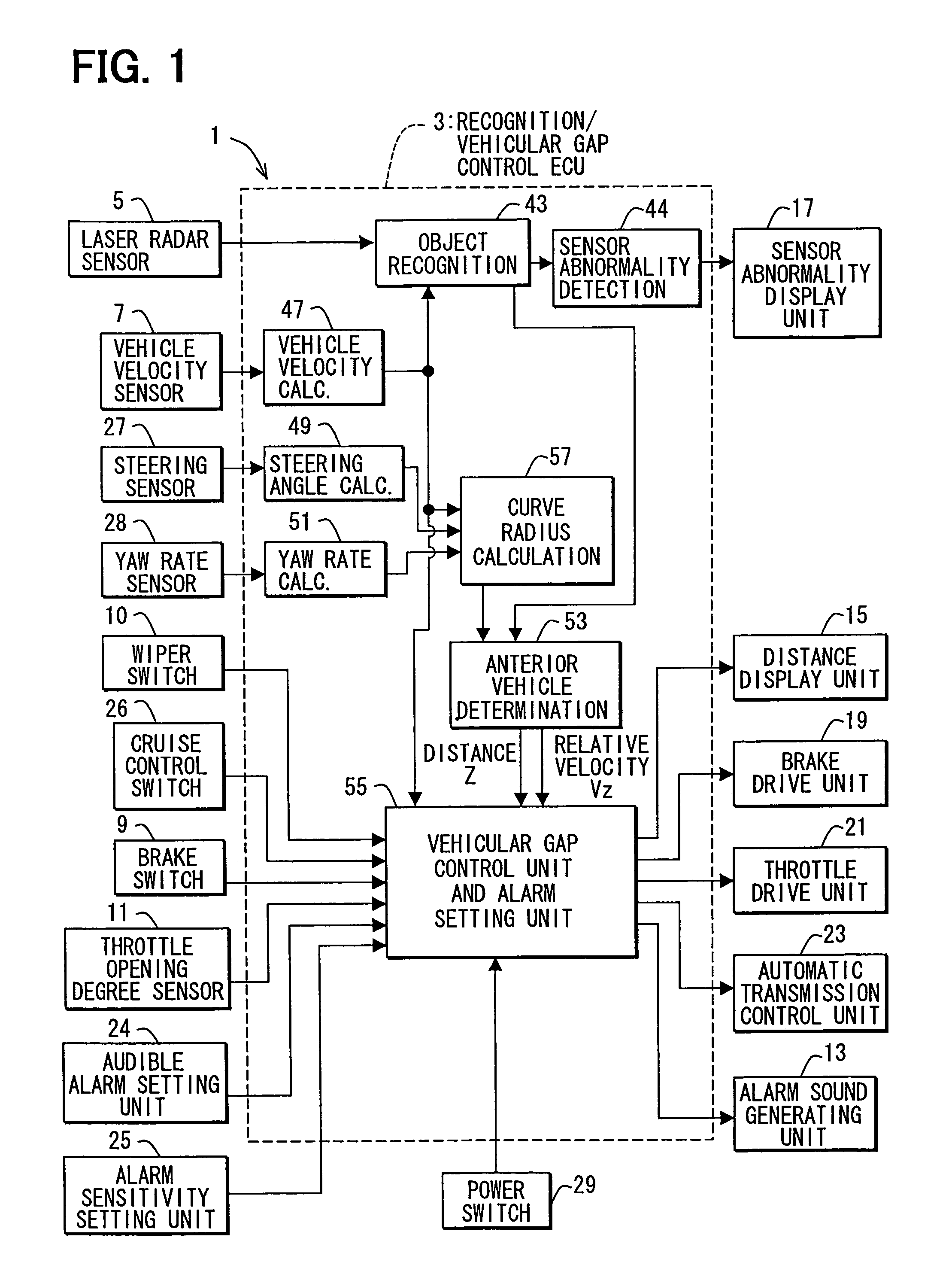
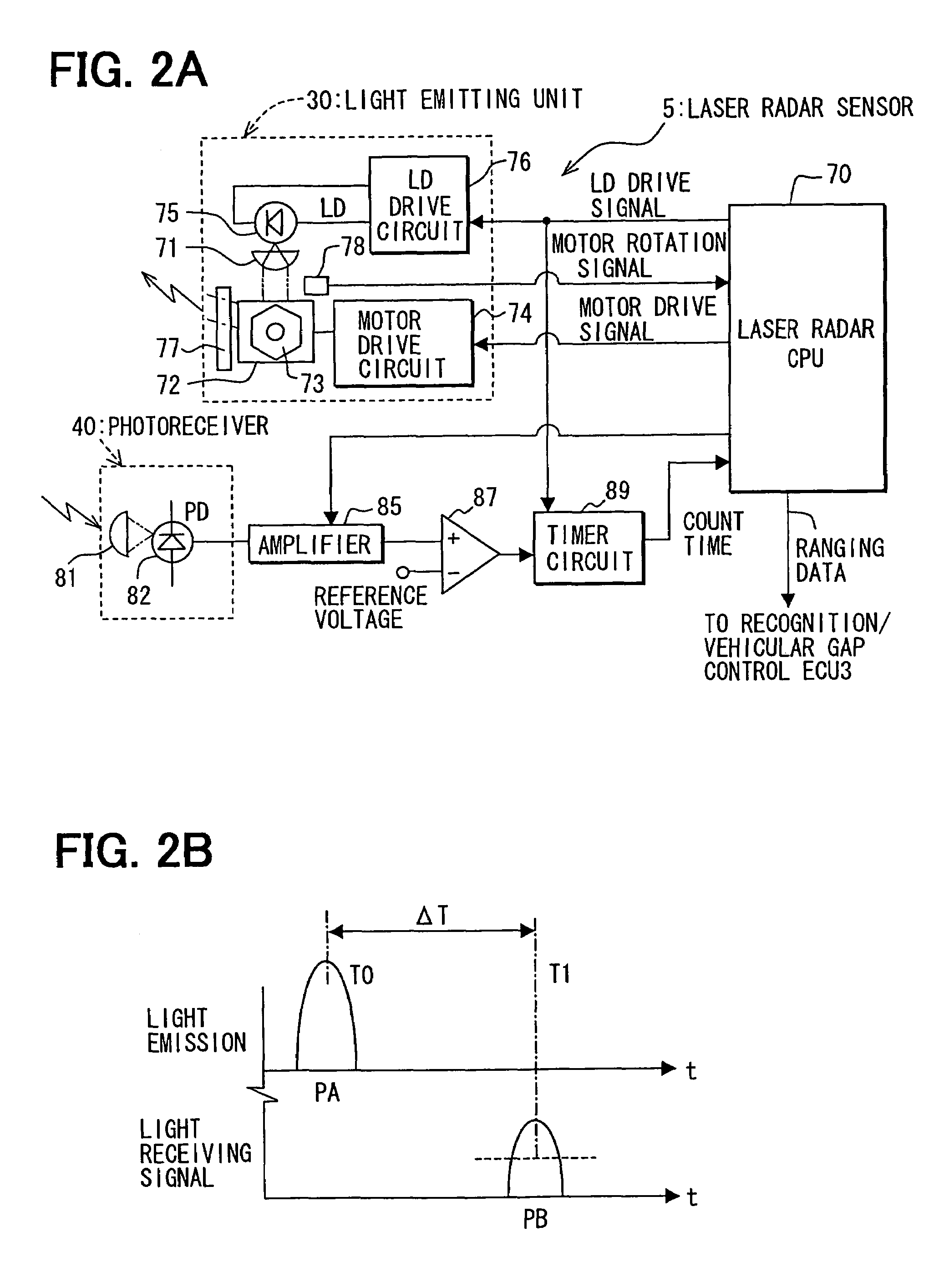
Object recognition system for vehicle
ActiveUS20050225744A1Accurate detectionSafe travelOptical rangefindersPedestrian/occupant safety arrangementSize determinationIdentification device
Owner:DENSO CORP
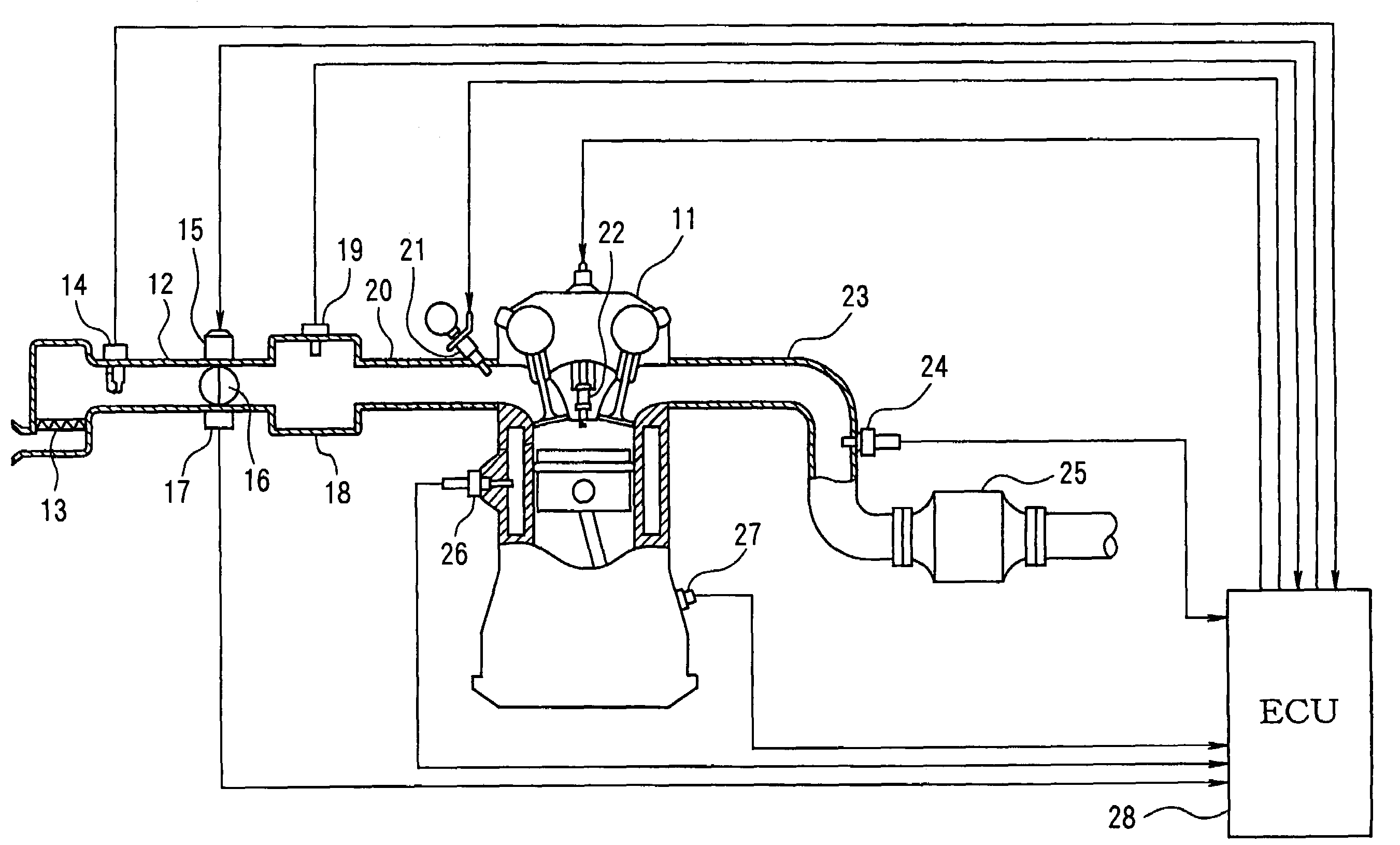
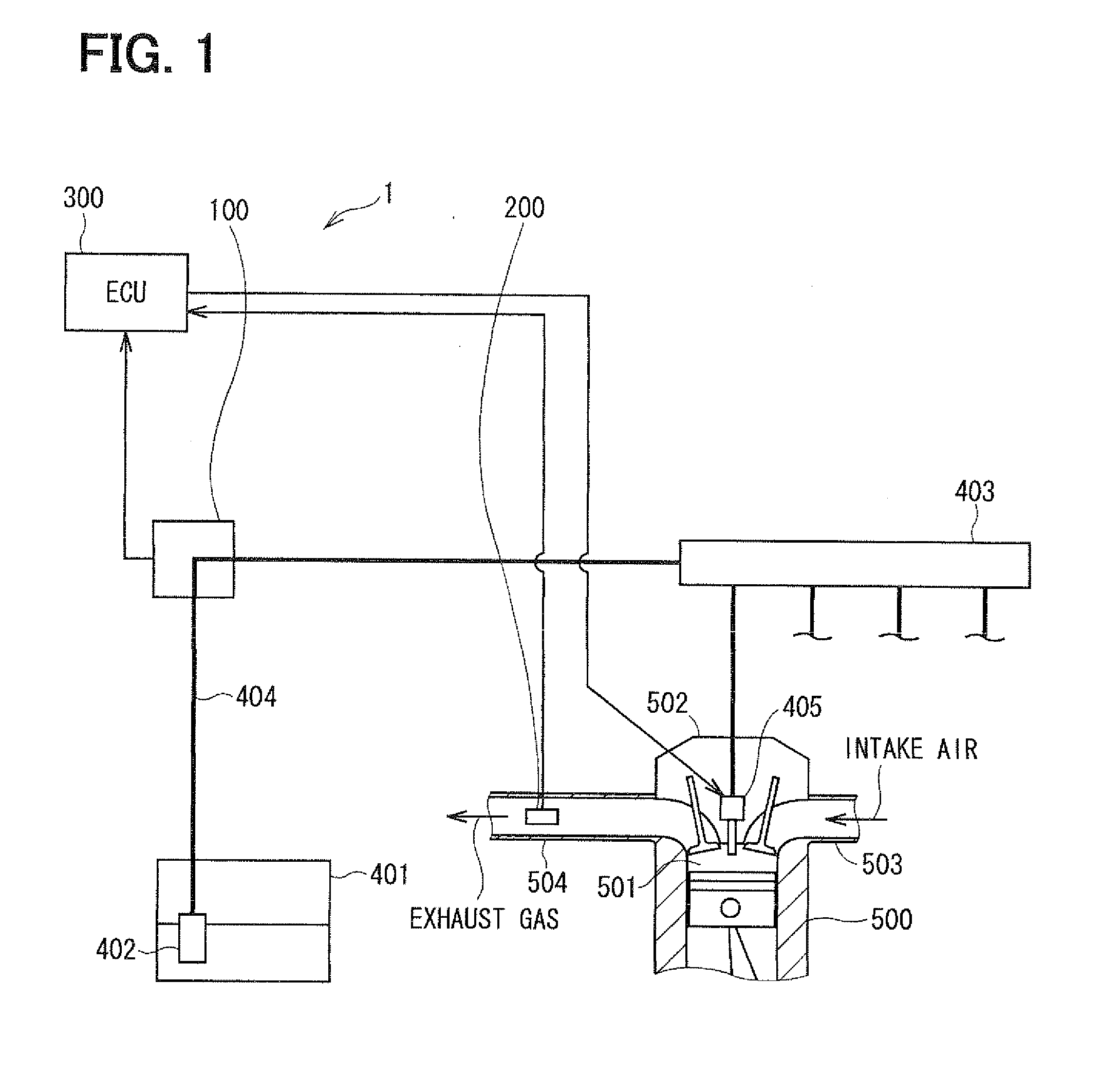
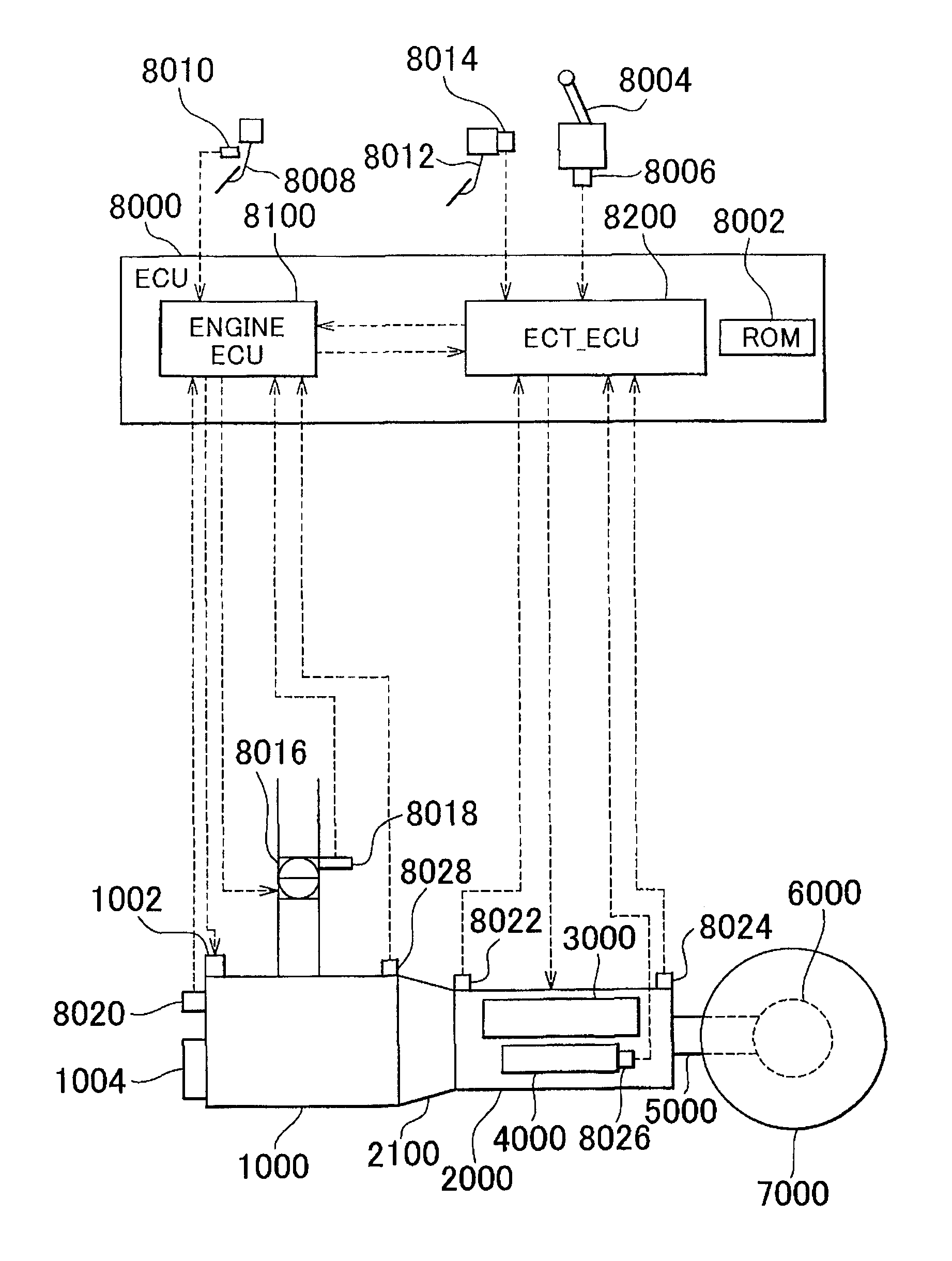
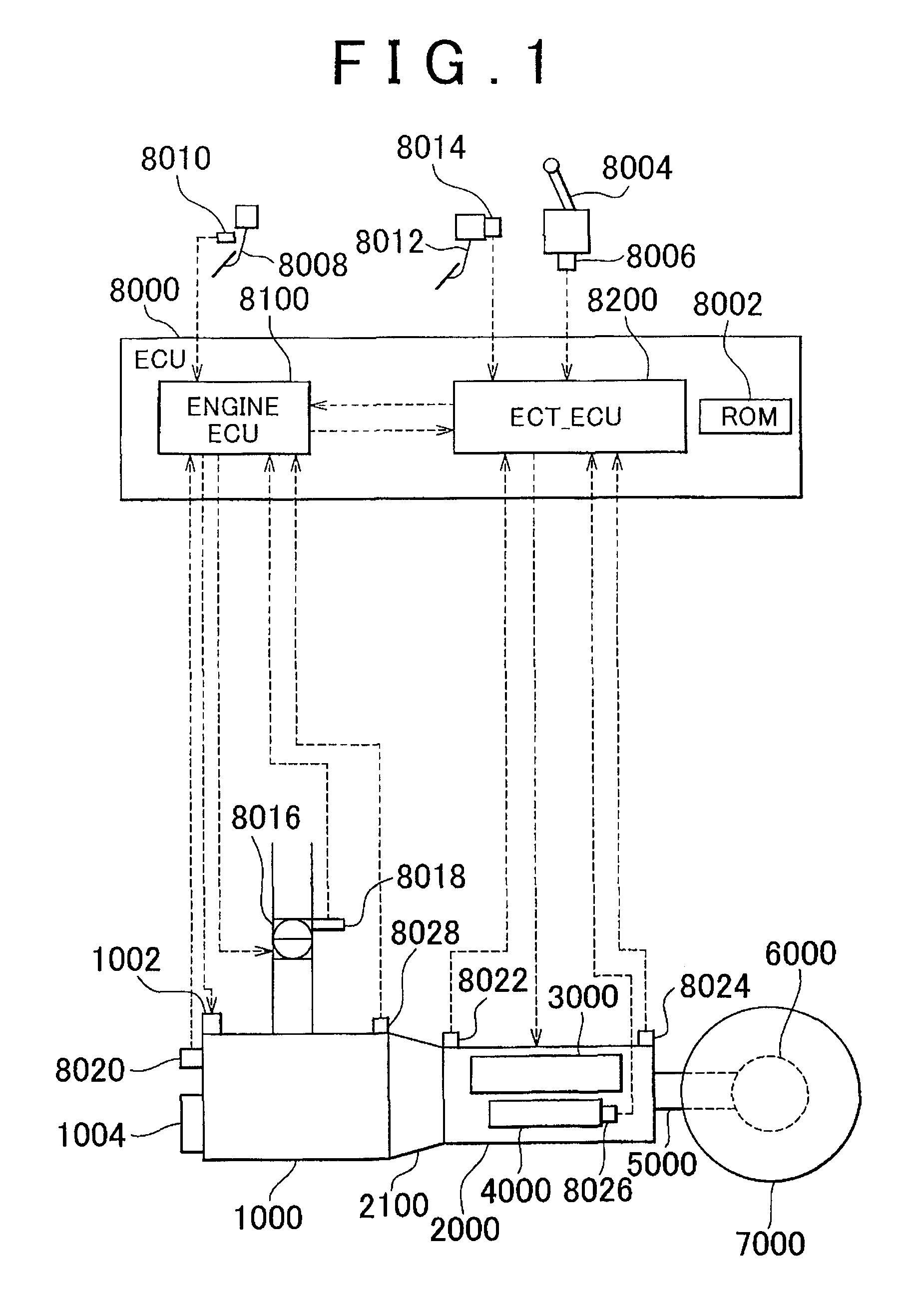
Air-fuel ratio controller for internal combustion engine and diagnosis apparatus for intake sensors
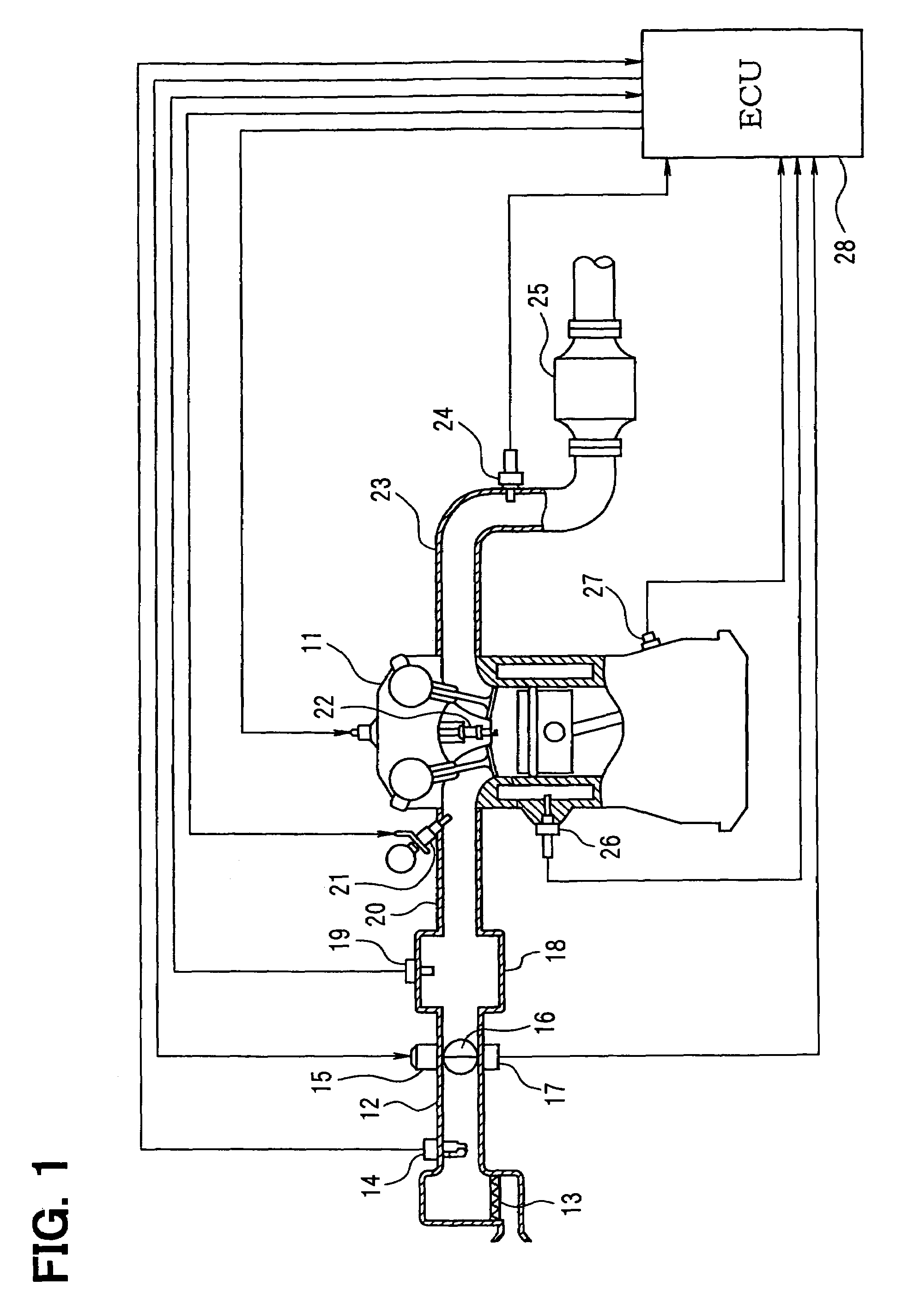
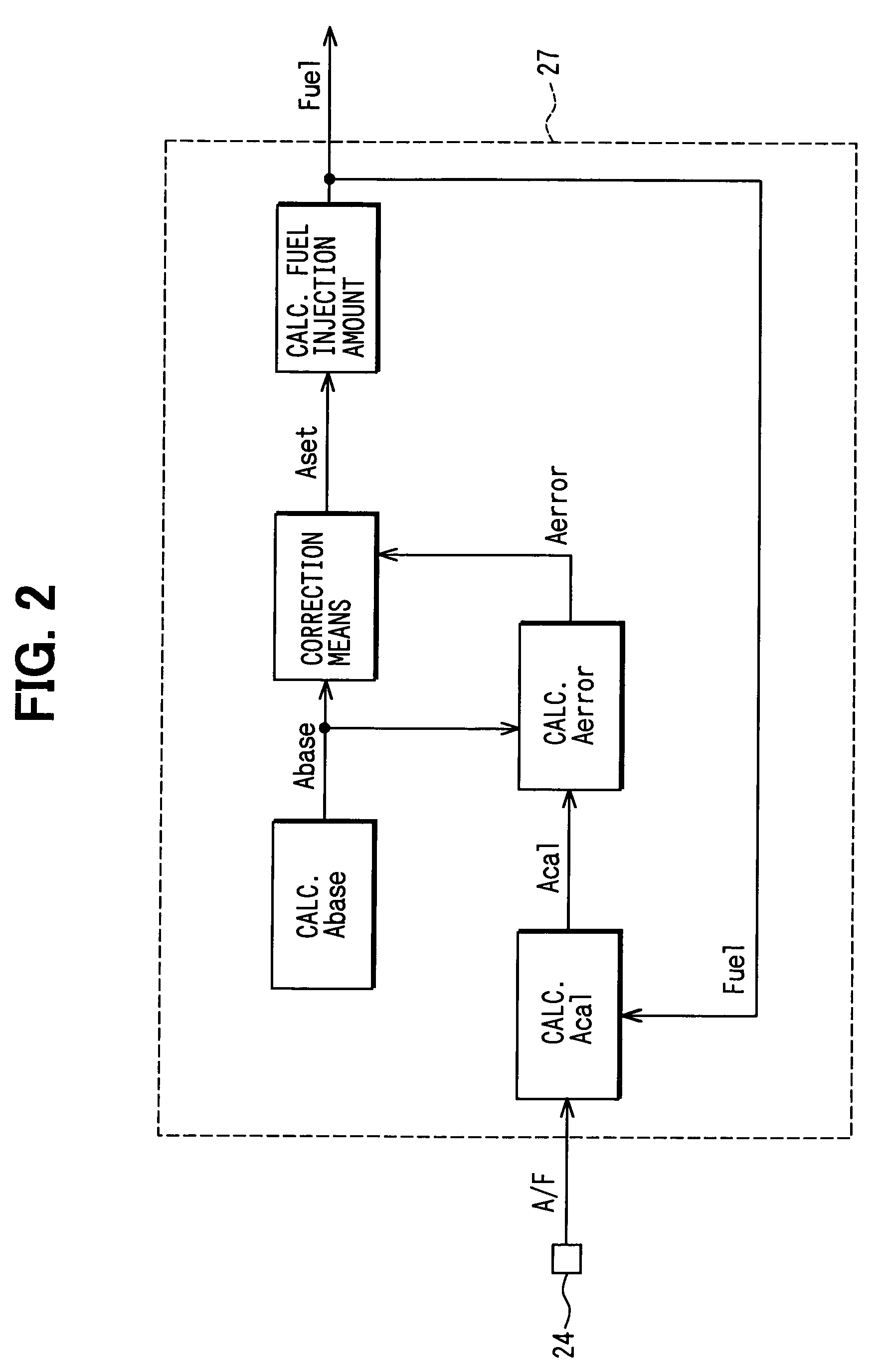
InactiveUS7273046B2Improve accuracyLimited robustnessElectrical controlEngine testingLow-pass filterExternal combustion engine
A computer calculates an estimated cylinder-intake-air amount based on outputs from an airflow meter and a throttle position sensor, and then calculates a reference cylinder-intake-air amount based on an air-fuel ratio in an exhaust gas and fuel injection amount. An error of the estimated cylinder-intake-air amount is calculated by comparing the reference cylinder-intake-air amount with an estimated cylinder-intake-air amount base value. The error is low-pass filtered. The estimated cylinder-intake-air amount base value is corrected to obtain the final estimated cylinder-intake-air amount.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Method and apparatus for evaluating possible 3-way call events
ActiveUS8050393B2Impeding determinationEfficient responseGraded-service arrangementsCalled number recording/indicationTelephone networkTelephony
The likelihood that a called party to a telephone call has forwarded the call to another party, or has conferenced the call to include another party is estimated by requiring that the called party supply a first signal, illustratively a first DTMF signal, later requiring that the called party provide a second signal, illustratively the same DTMF signal provided by the first signal, and comparing characteristics of said first and second signals as received at a telephone network node.
Owner:CONFINEMENT TELEPHONY TECH +1
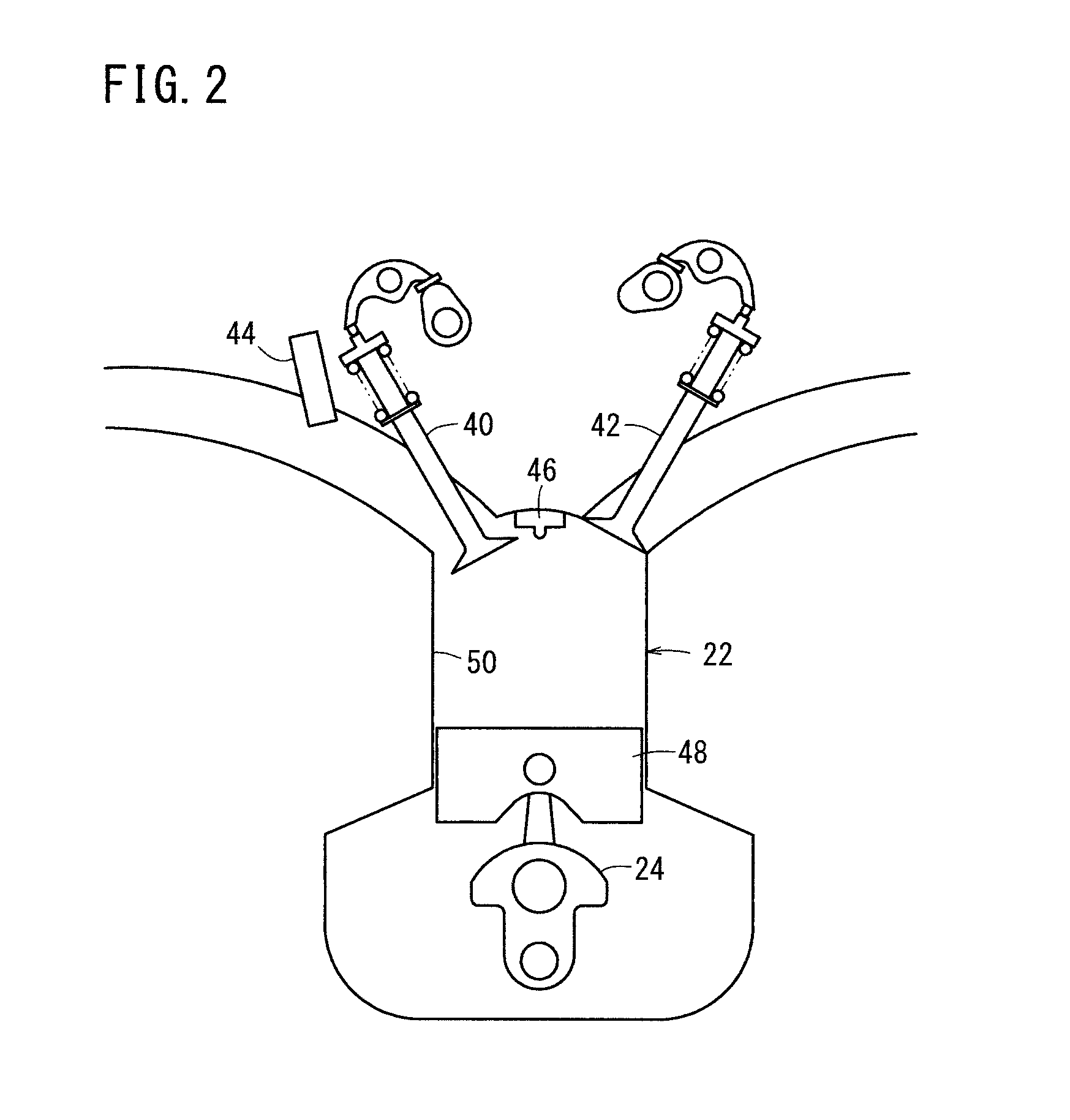
Anti-drunk driving apparatus for vehicle
InactiveUS7891456B2Impeding determinationPrevent counterfeitingElectric devicesPerson identificationAlcohol drinkDrunk driving
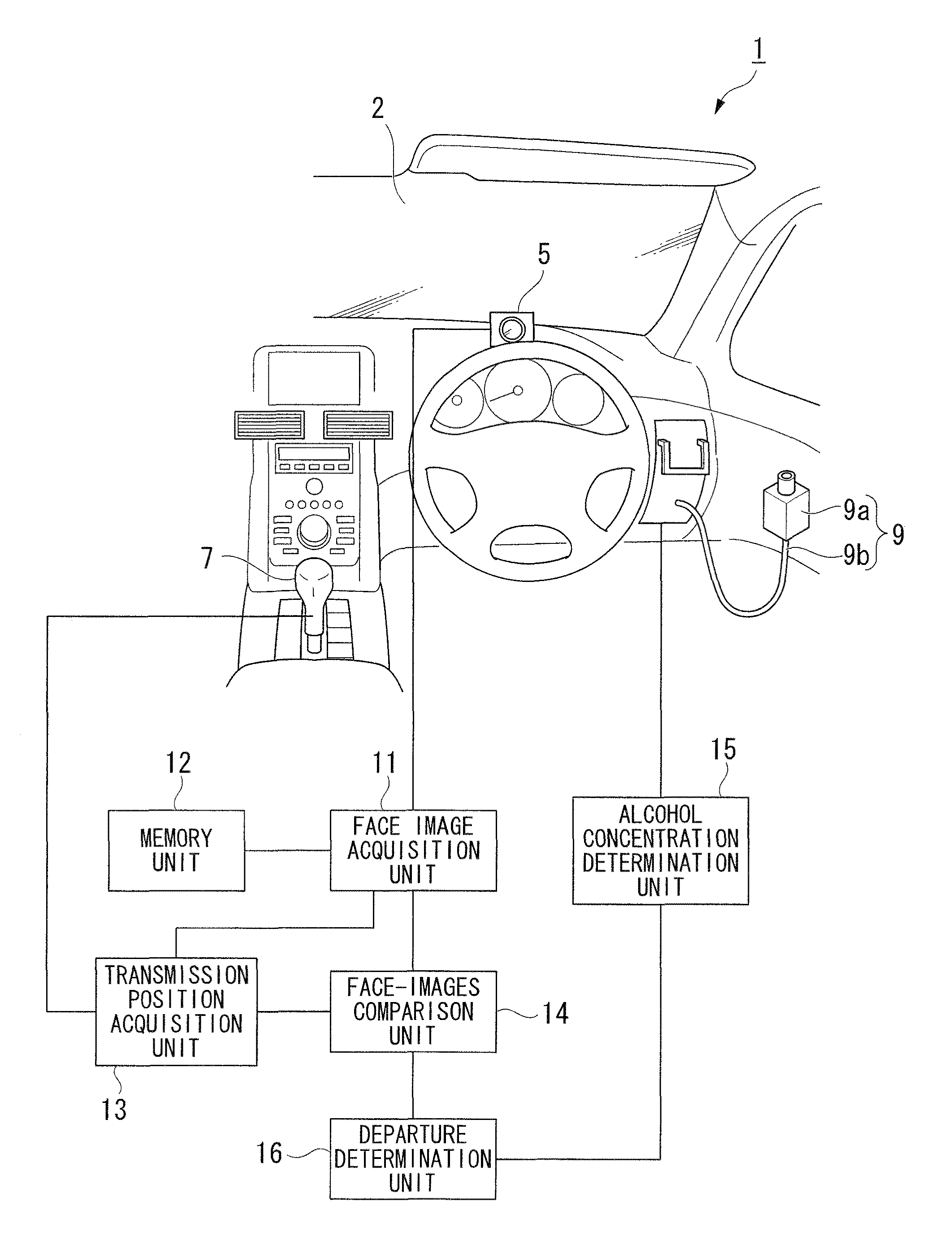
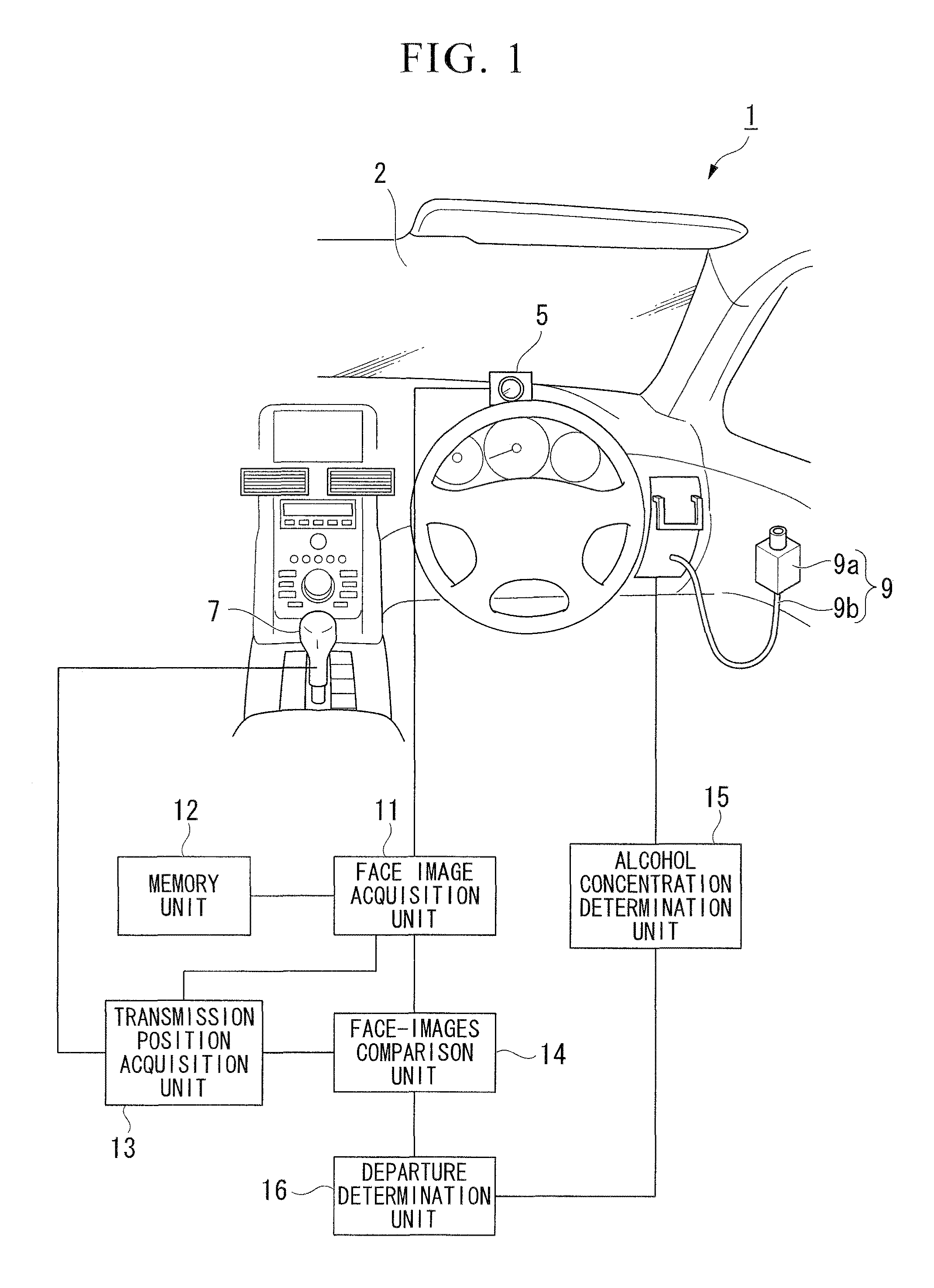
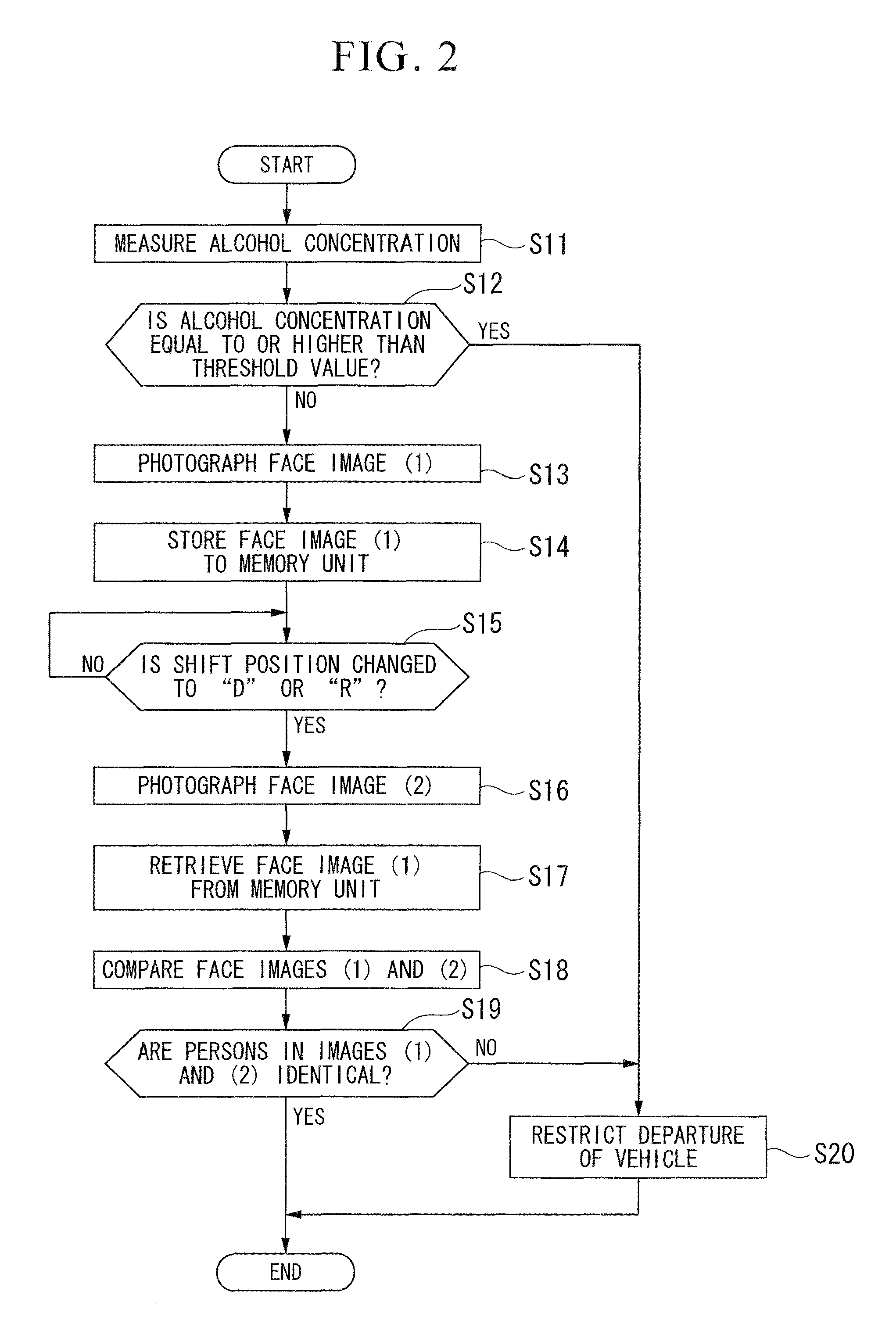
An anti-drunk driving apparatus for a vehicle including: an alcohol drinking determination device which determines whether or not a first person seated in a driver's seat is drunk; a driving restriction device which restricts driving of the vehicle in a case where it is determined that the first person seated in the driver's seat is drunk by the alcohol drinking determination device; a driving intention presumption device which presumes whether or not a second person seated in the driver's seat has an intention to drive; a photograph device which photographs the faces of the first and second persons; and a person identification device which determines whether or not the first and second persons are the same by comparing their faces in images, wherein if it is determined that the first and the second persons are not the same, the driving restriction device restricts driving of the vehicle.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Control device and control method for internal combustion engine
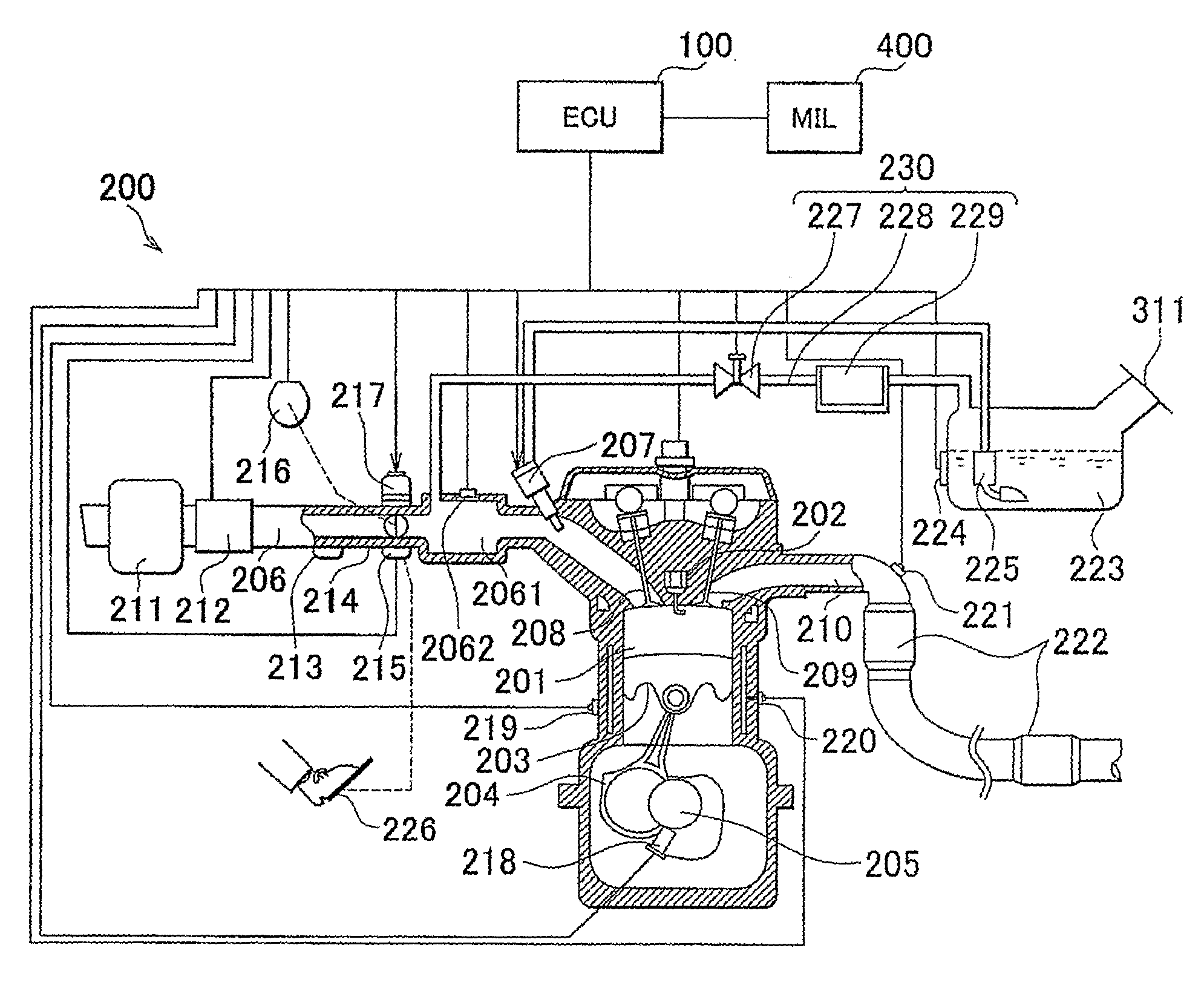
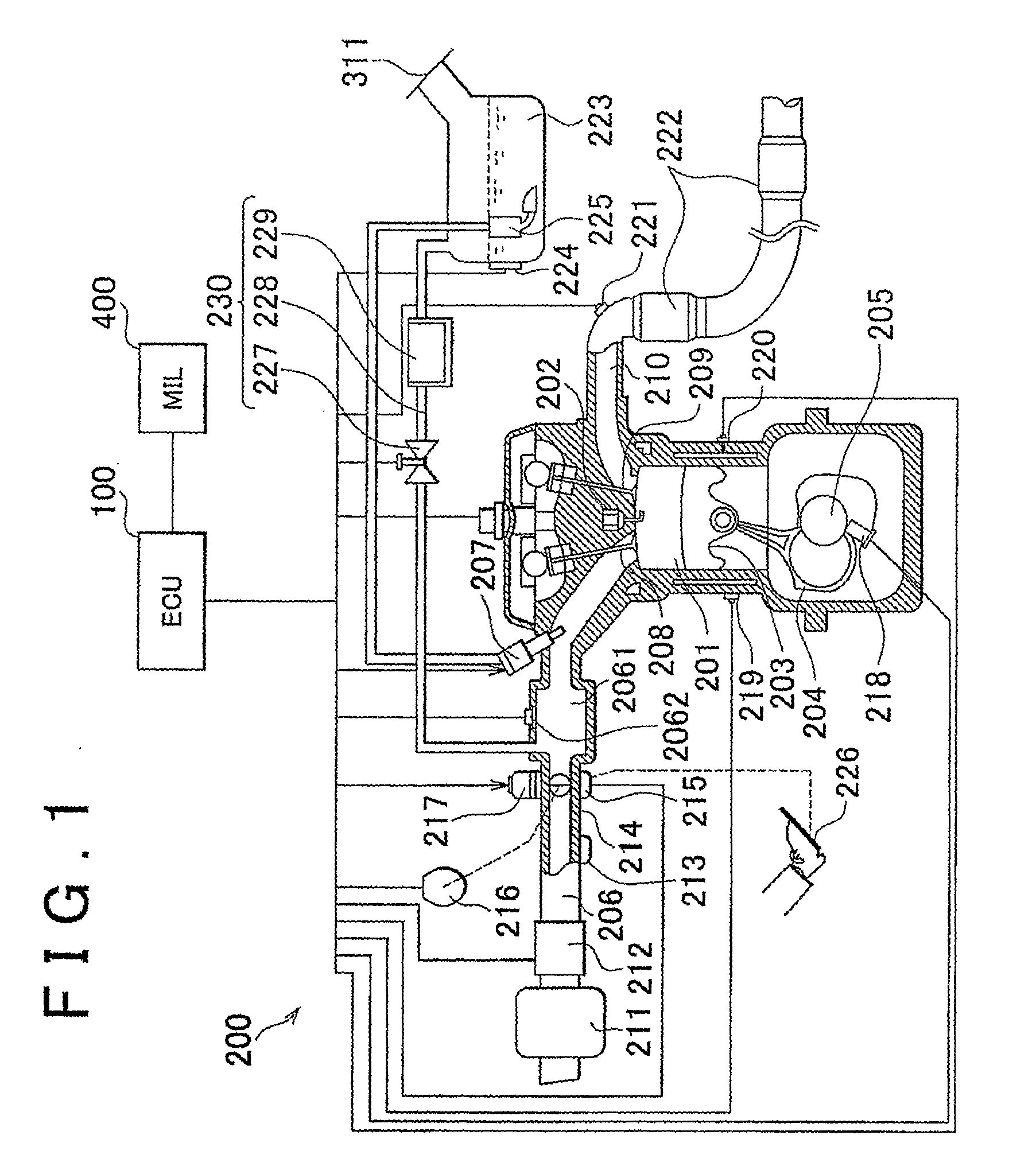
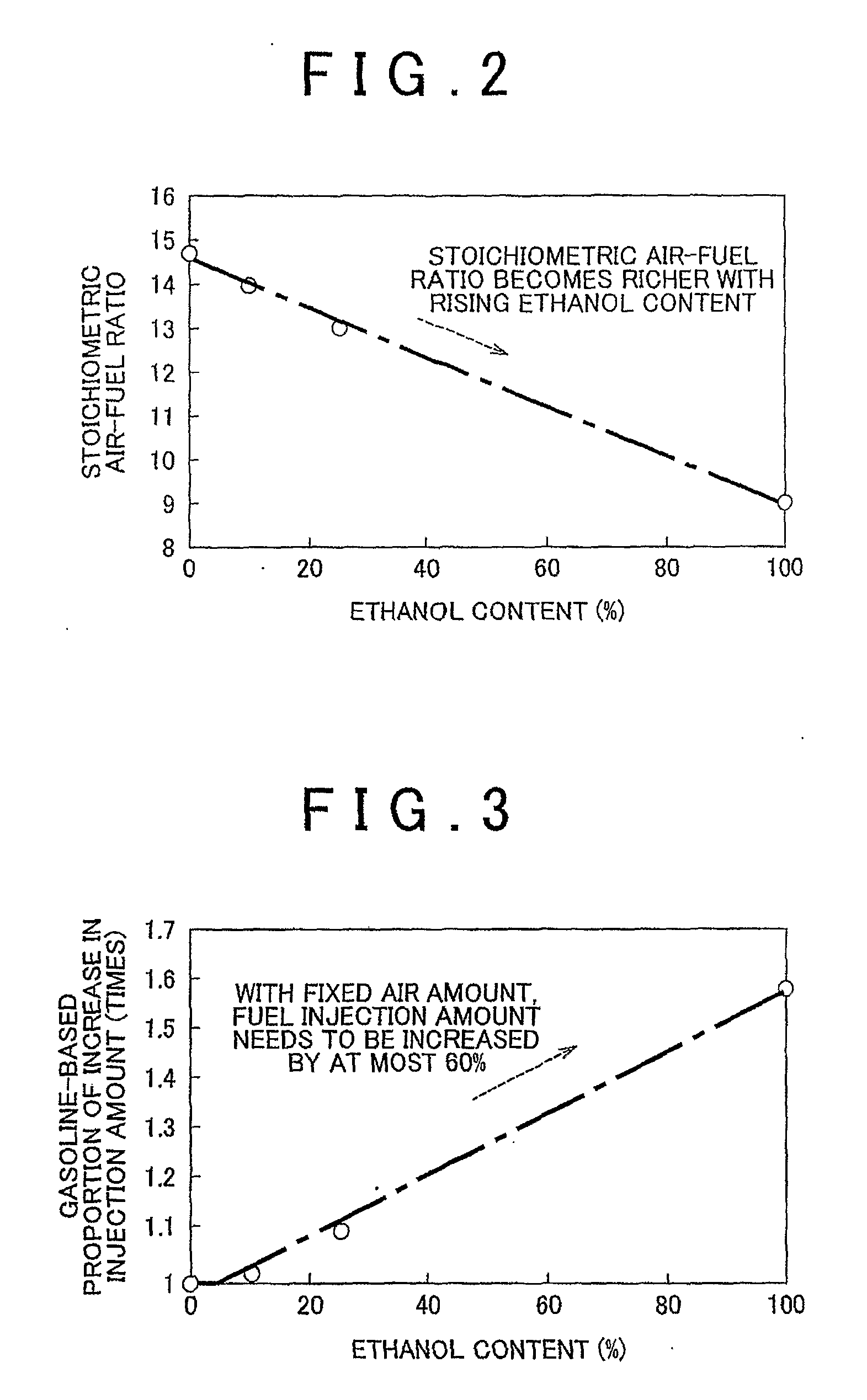
InactiveUS20100031941A1Impeding determinationSimple and easy fashionElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesGasolineEngineering
A control device and control method for an internal combustion engine capable of using a gasoline and alcohol blend as fuel. The control device includes: an air-fuel ratio correction device that performs an air-fuel ratio feedback correction process calculating an air-fuel ratio feedback correction amount for compensating for a divergence between a target value and an actually measured value of an air-fuel ratio of the engine; an air-fuel ratio learning device that performs an air-fuel ratio learning process calculating an air-fuel ratio learned value for converging the calculated air-fuel ratio feedback correction amount into a predetermined range from a predetermined correction reference amount; and an alcohol determination device that makes an alcohol determination that a concentration of the alcohol blended is greater than a predetermined concentration if a deviation of the calculated air-fuel ratio learned value being greater than a predetermined threshold value continues longer than a predetermined period.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
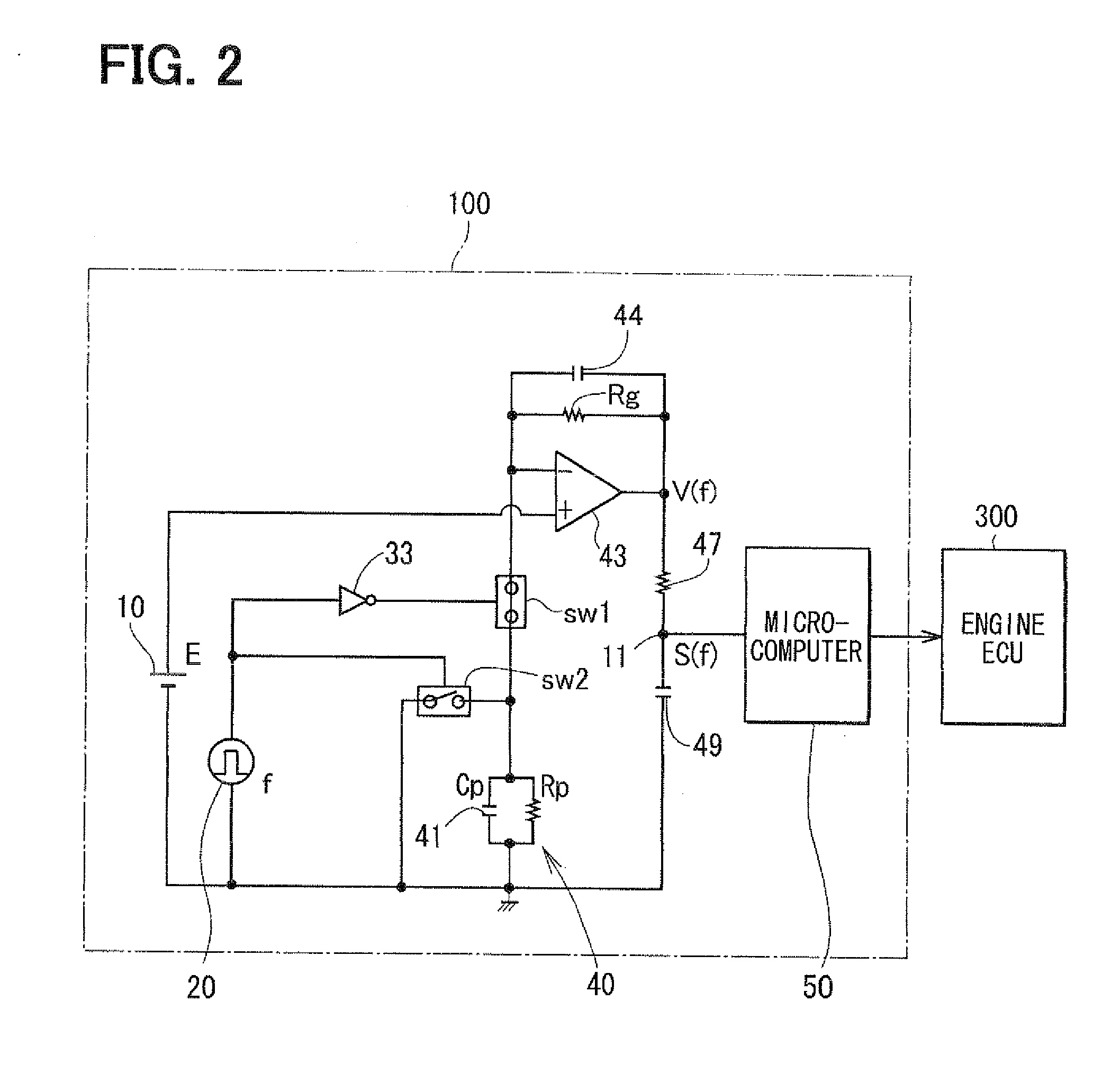
Liquid concentration measuring device
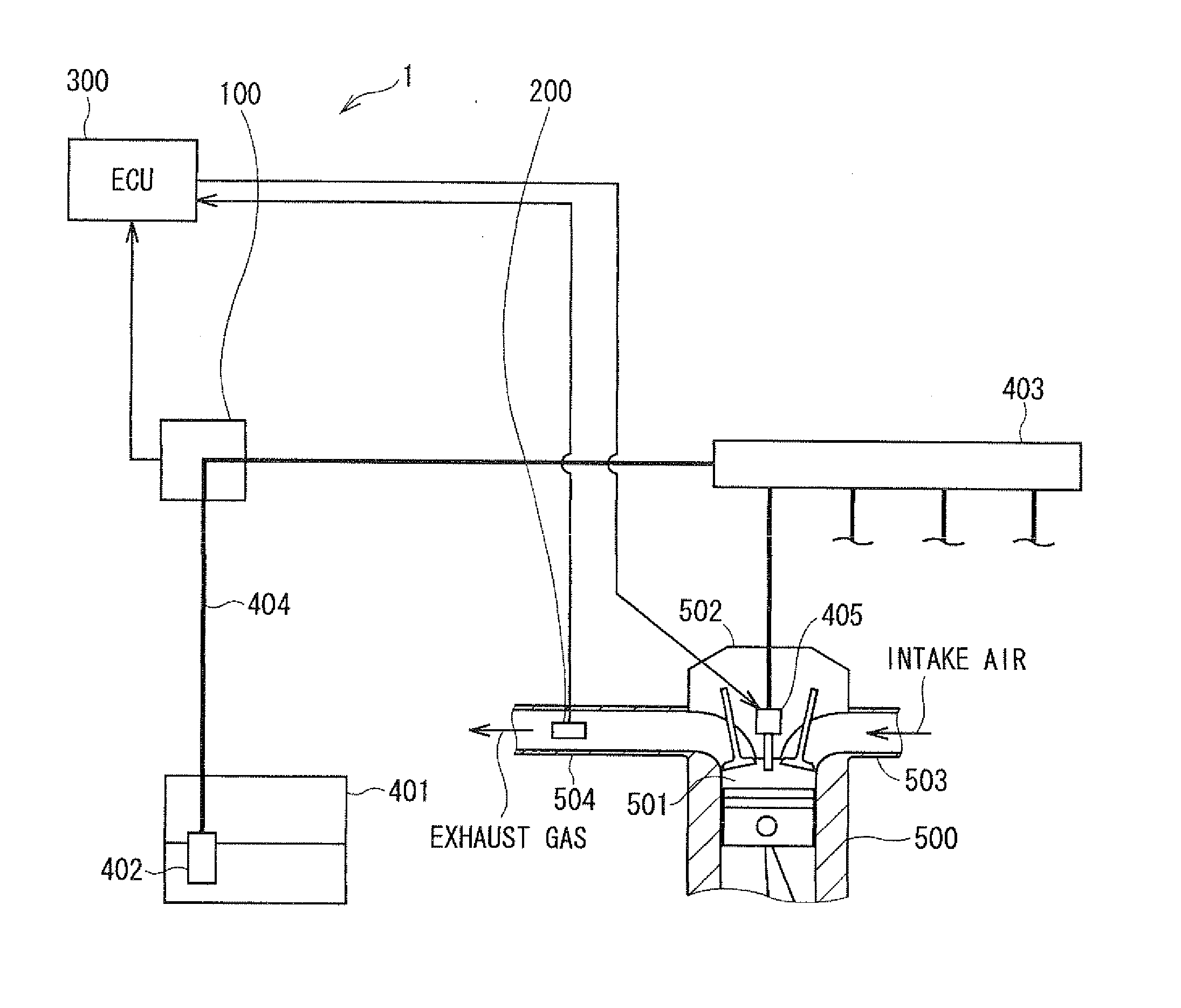
InactiveUS20100263647A1Avoid exceptionWide rangeElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesMicrocomputerAlcohol
A microcomputer of an alcohol concentration sensor reads a first measurement value corresponding to a first frequency and reads a second measurement value corresponding to a second frequency. The microcomputer calculates a difference between the first and second measurement values. The microcomputer performs stuck failure abnormality determination when a state where the difference between the measurement values is equal to or smaller than a predetermined value continues. The microcomputer outputs a PWM signal of a specific frequency, which is different from a frequency in a case of a normality, to an engine ECU. Thus, a failure of the alcohol concentration sensor can be surely determined.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Formation of an emergency lane
InactiveUS20150321698A1Impeding determinationSteering initiationsDigital data processing detailsAuthorizationControl theory
A supportive method for a driver of a first motor vehicle includes steps of scanning the surroundings of the first motor vehicle, of determining an action instruction to the driver of the first motor vehicle, in order to avoid getting in the way of a second motor vehicle having special authorization, of comparing the action instruction with further motor vehicles in the area of the first motor vehicle and of an outputting of the action instruction to the driver of the first motor vehicle.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
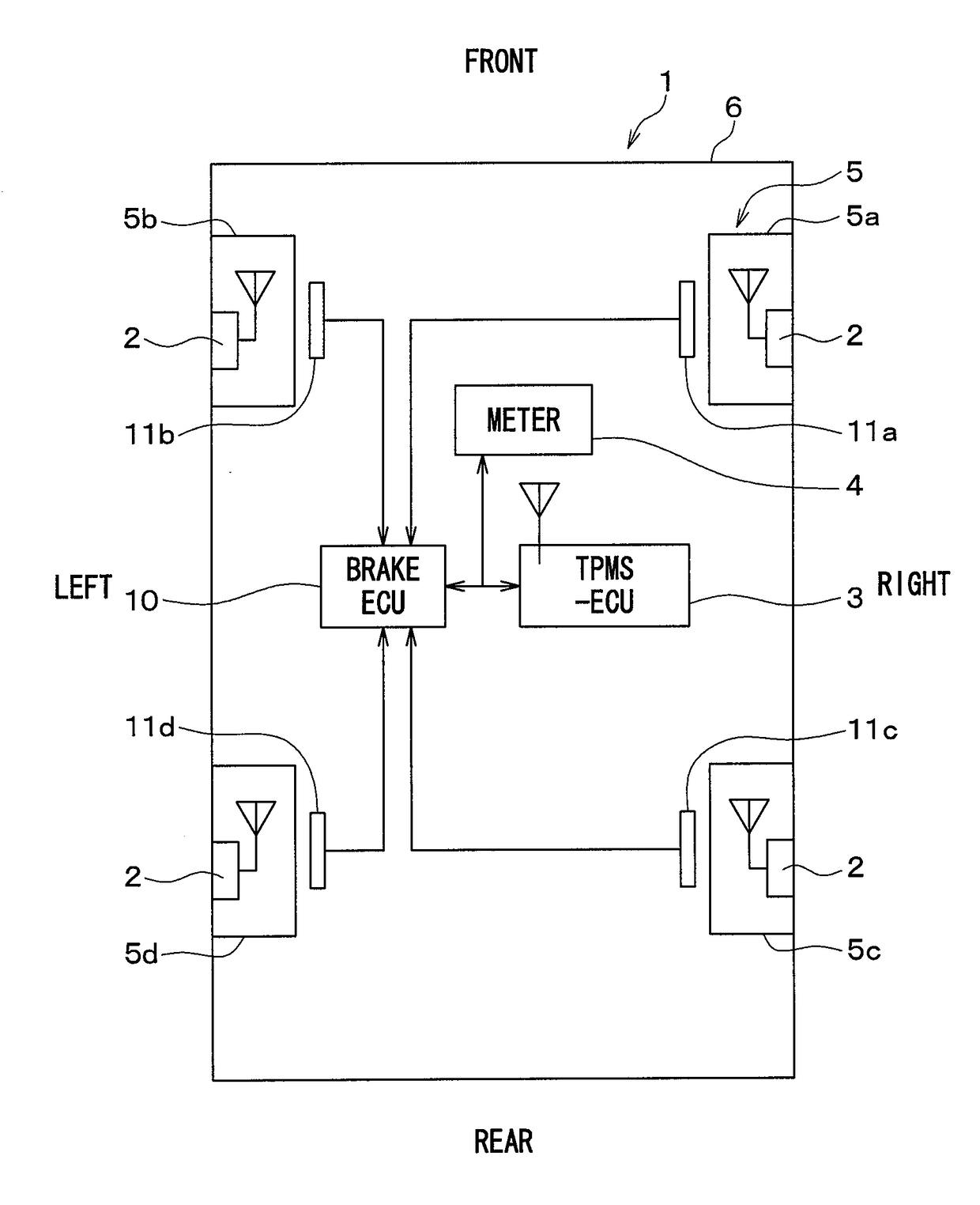
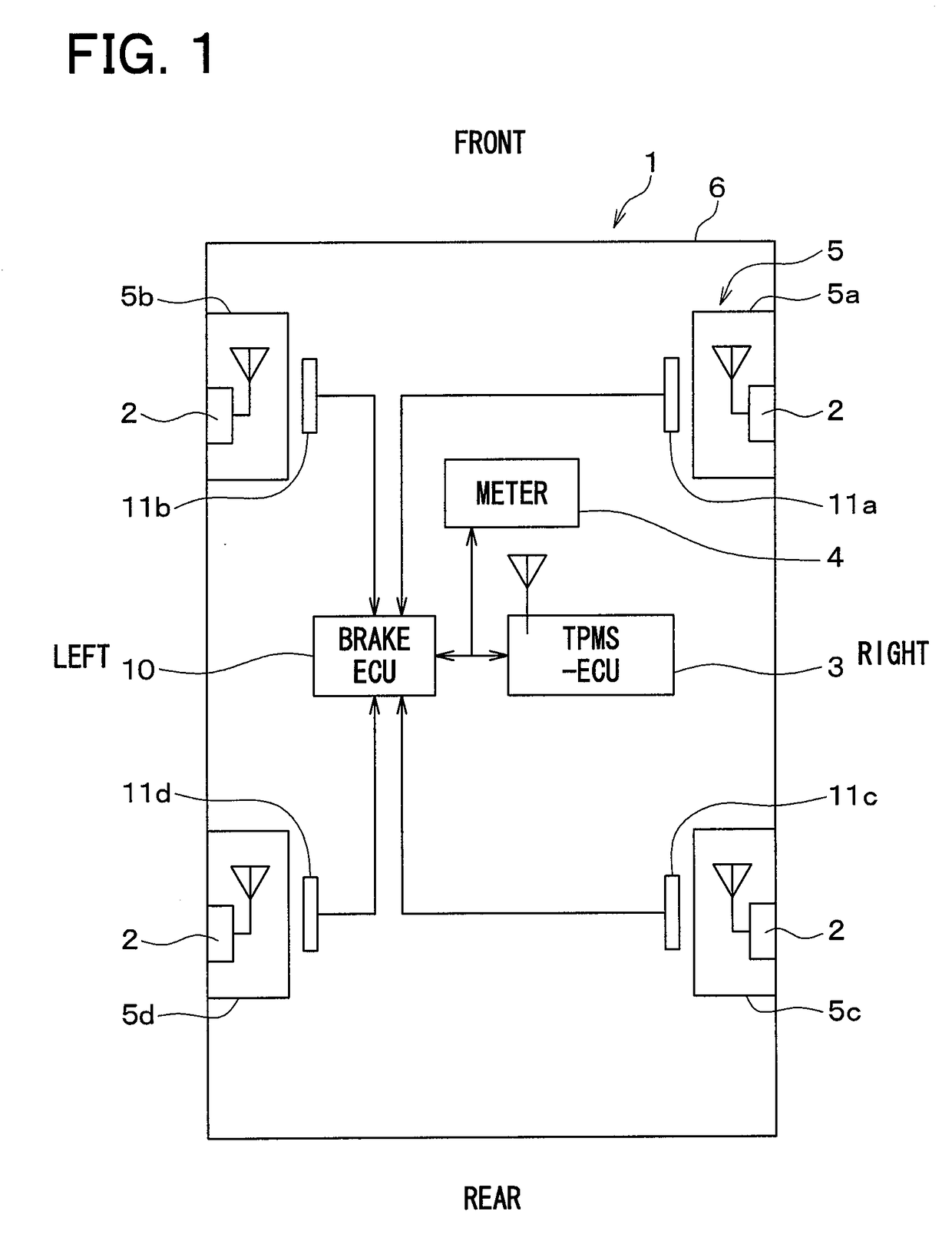
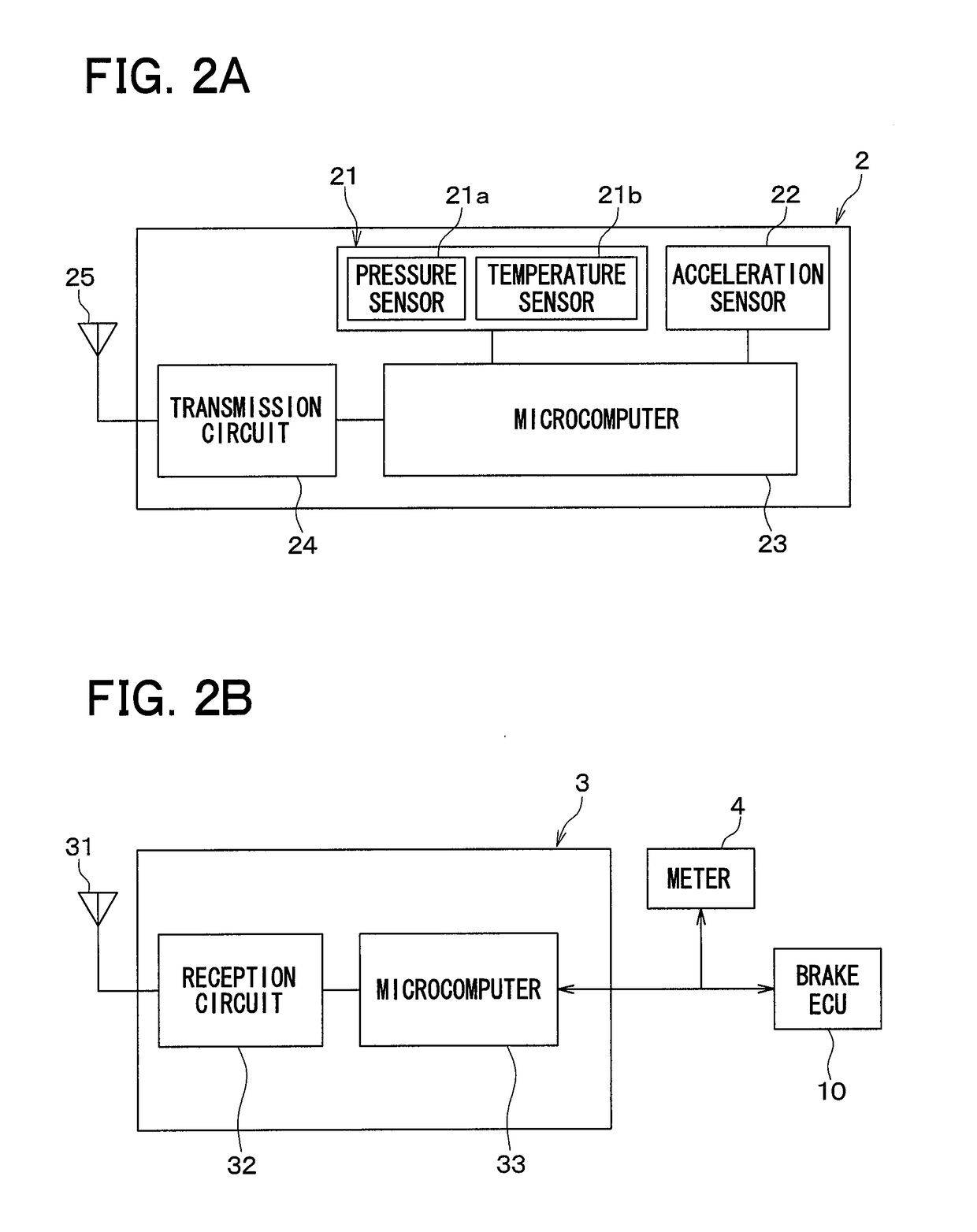
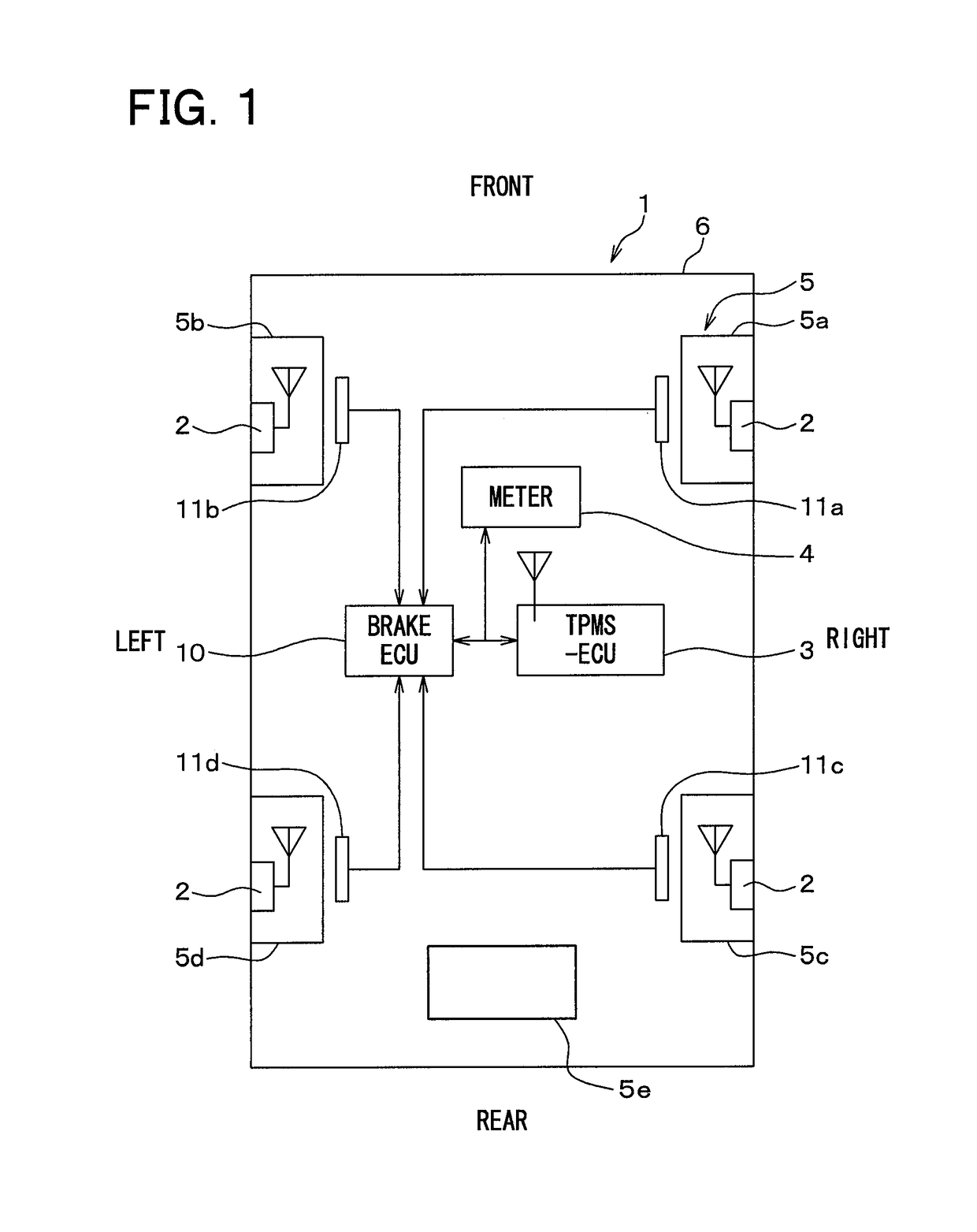
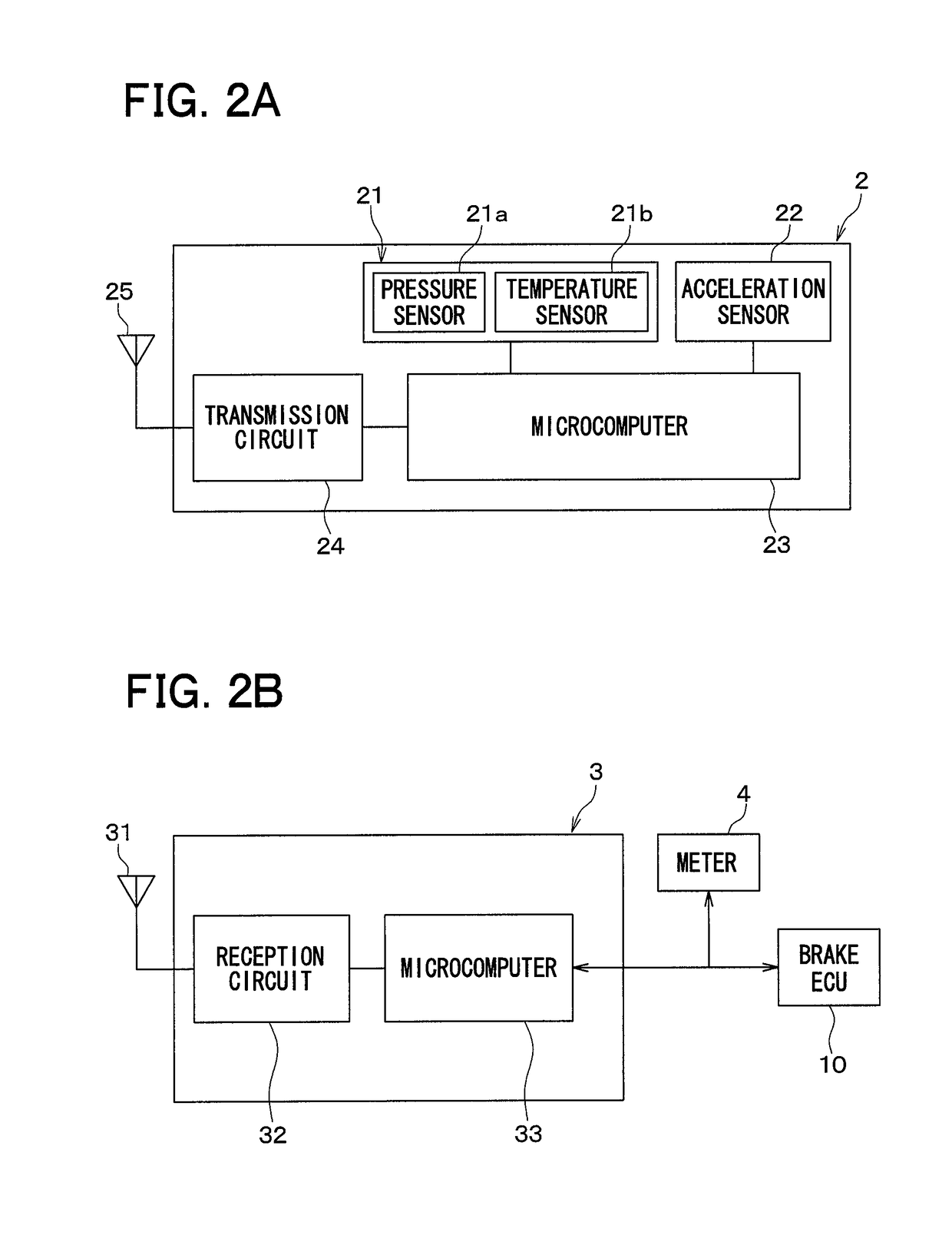
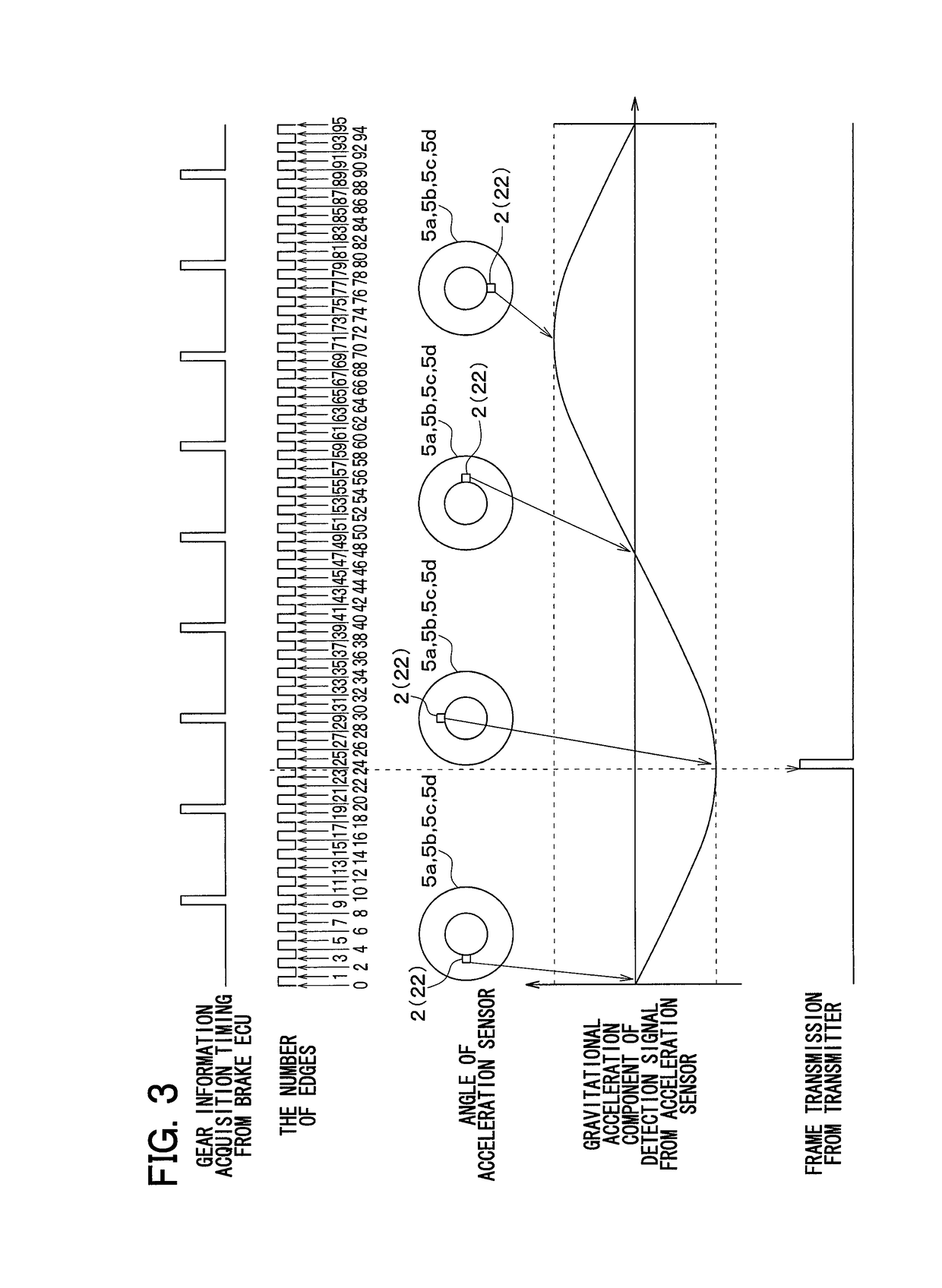
Wheel position detection device and tire-pressure detection system equipped with same
InactiveUS20180134102A1Prevent determinationIncrease the number ofAcceleration measurementTyre measurementsEngineeringTire pressure
A wheel position detection device includes: a transmitter in each wheel of a vehicle having a first control unit for transmitting a frame with ID and an acceleration sensor; and a receiver on a vehicle body, including a second control unit for registering the ID in association with the wheel. The first control unit detects a wheel speed, and stores data of the acceleration sensor in the frame. The second control unit includes: a first determination device that determines a condition that the acceleration sensor is not in an on-state; a candidate registration device that registers a candidate of the ID of a spare wheel when the condition is satisfied; a second determination device that determines a travel history of the vehicle; and a registration device that identifies the ID of the spare wheel when the travel history is present, and registers the ID in association with the spare wheel.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Method and apparatus for evaluating possible 3-way call events
ActiveUS20090067604A1Efficient responseImpeding determinationSpecial service for subscribersGraded-service arrangementsTelephone networkTelephone call
The likelihood that a called party to a telephone call has forwarded the call to another party, or has conferenced the call to include another party is estimated by requiring that the called party supply a first signal, illustratively a first DTMF signal, later requiring that the called party provide a second signal, illustratively the same DTMF signal provided by the first signal, and comparing characteristics of said first and second signals as received at a telephone network node.
Owner:CONFINEMENT TELEPHONY TECH +1
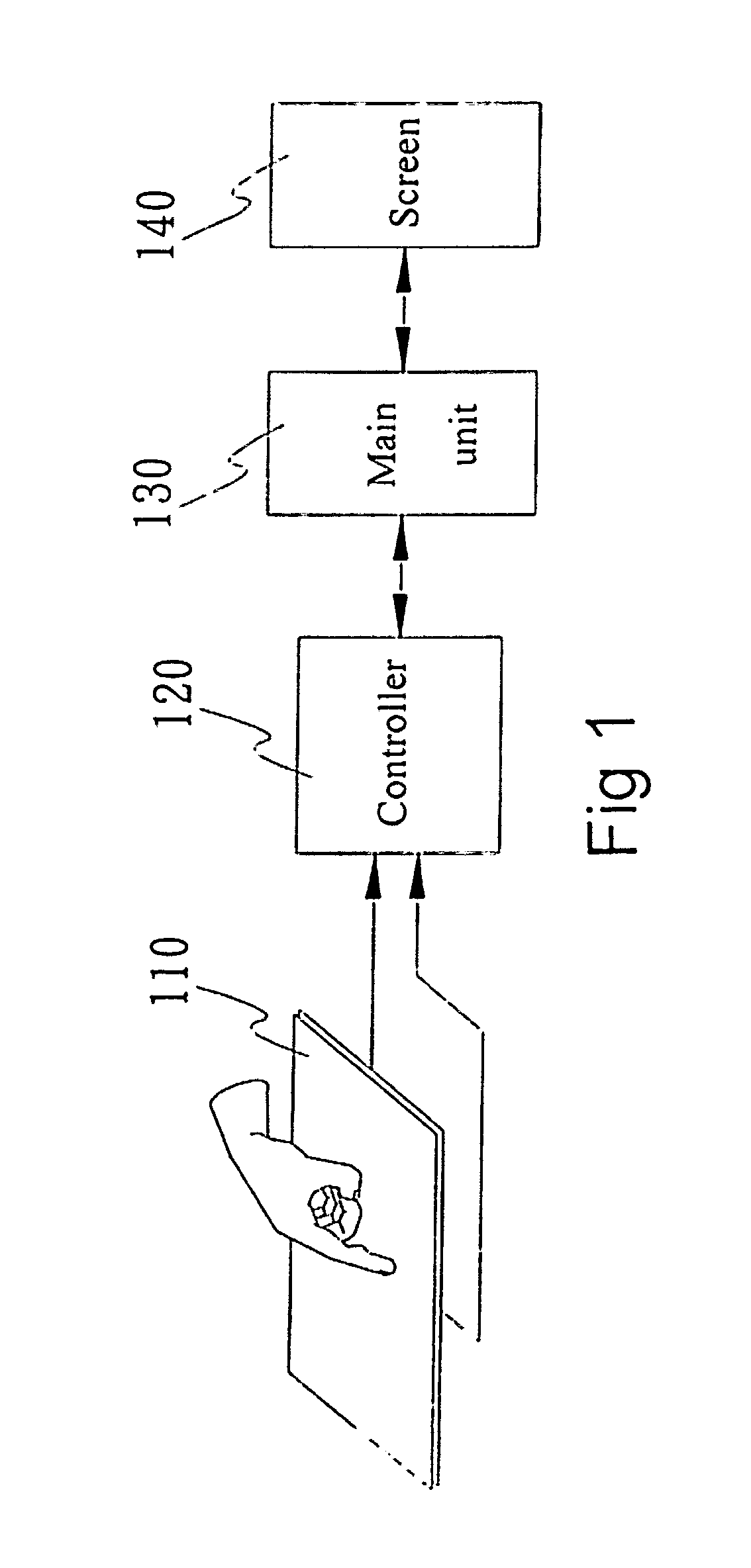
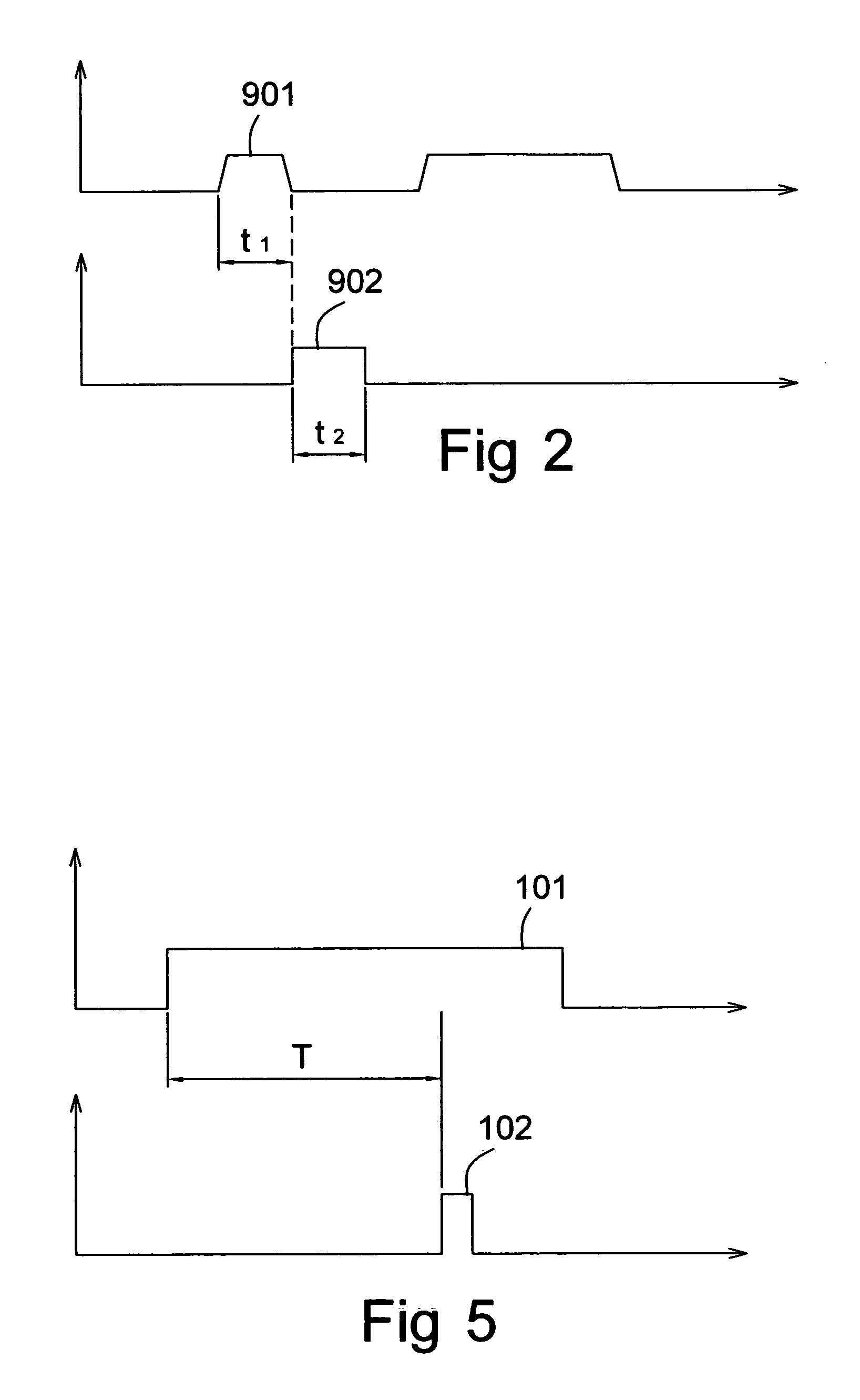
Touch control method of single tap and control module thereof
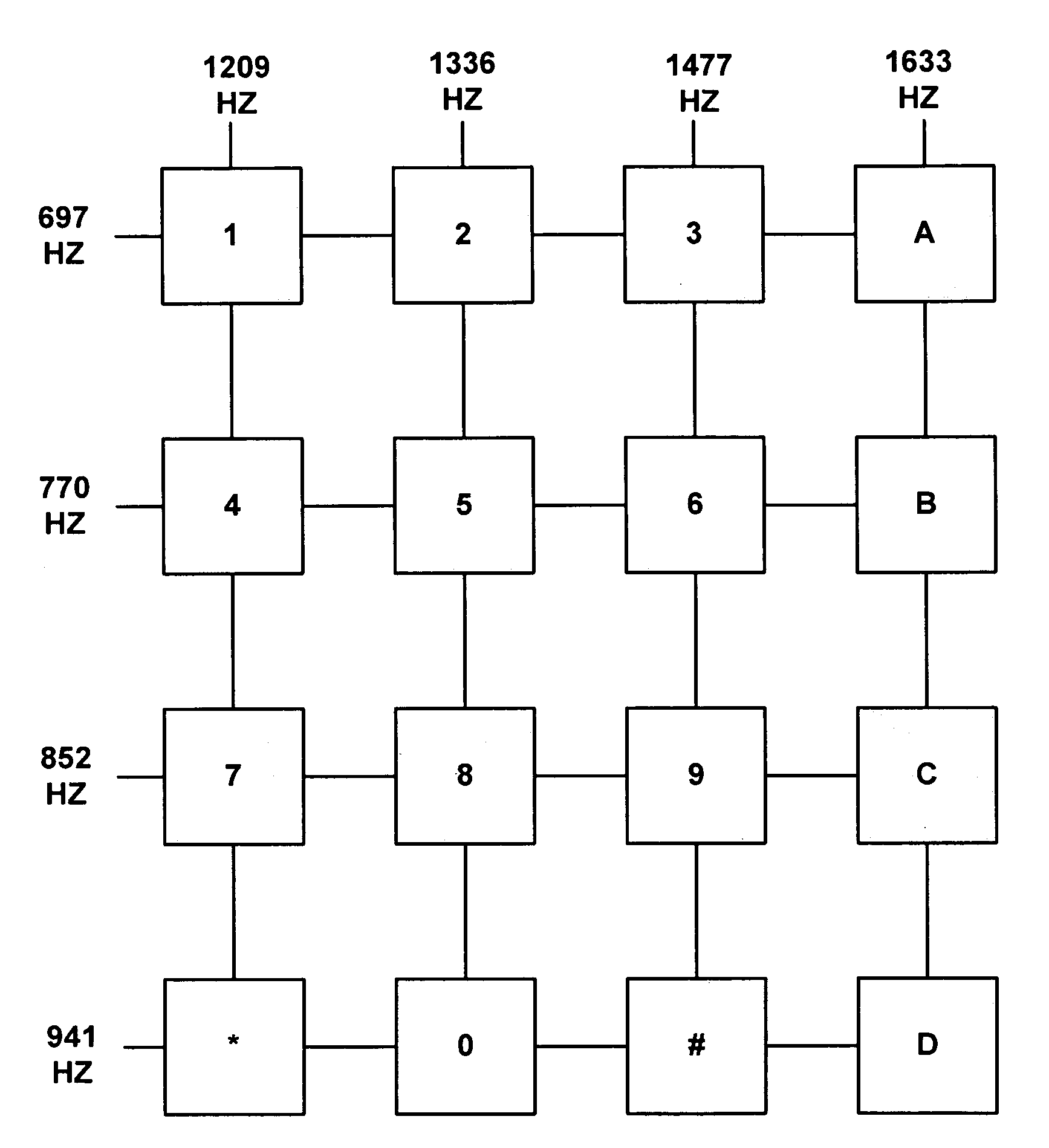
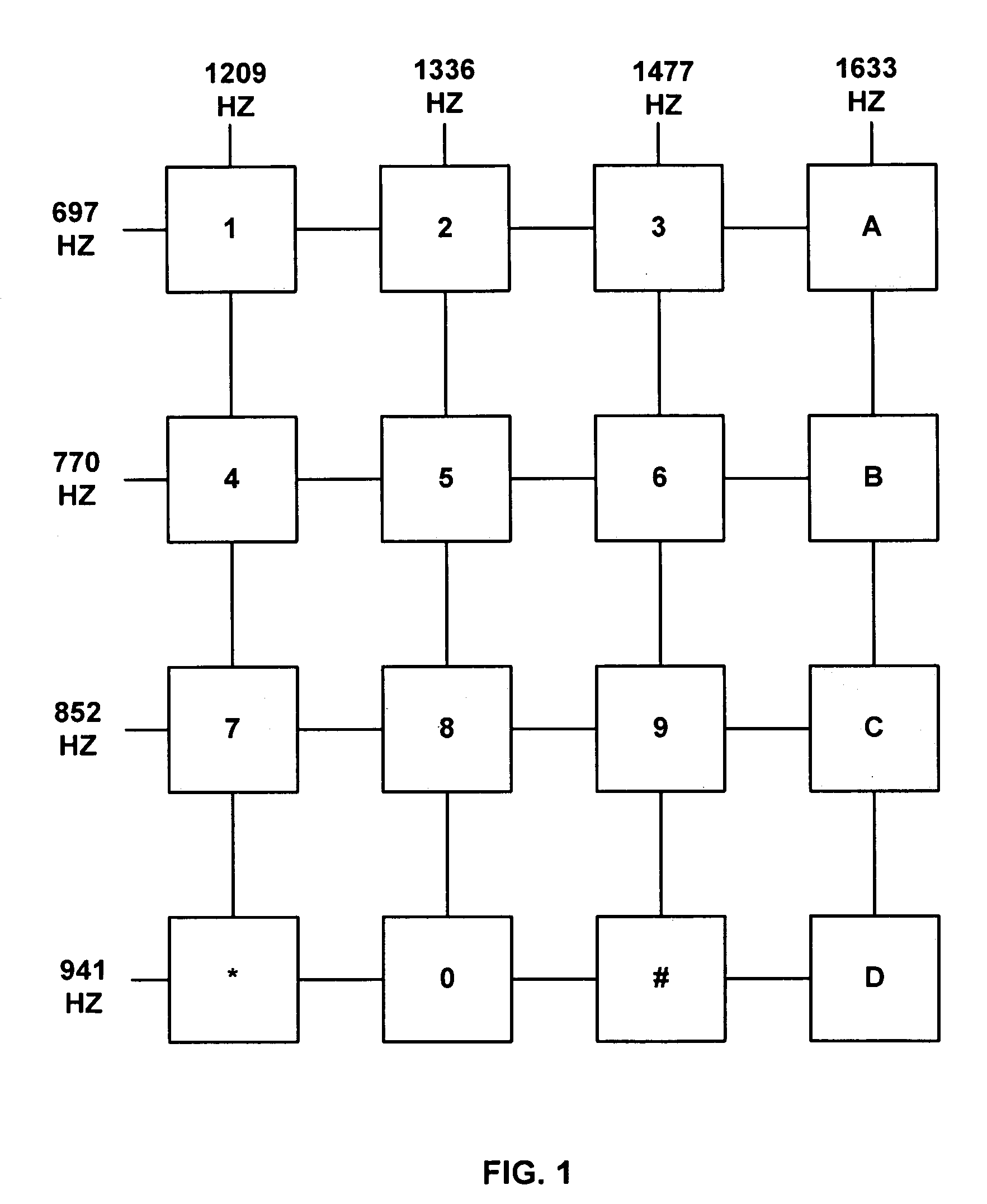
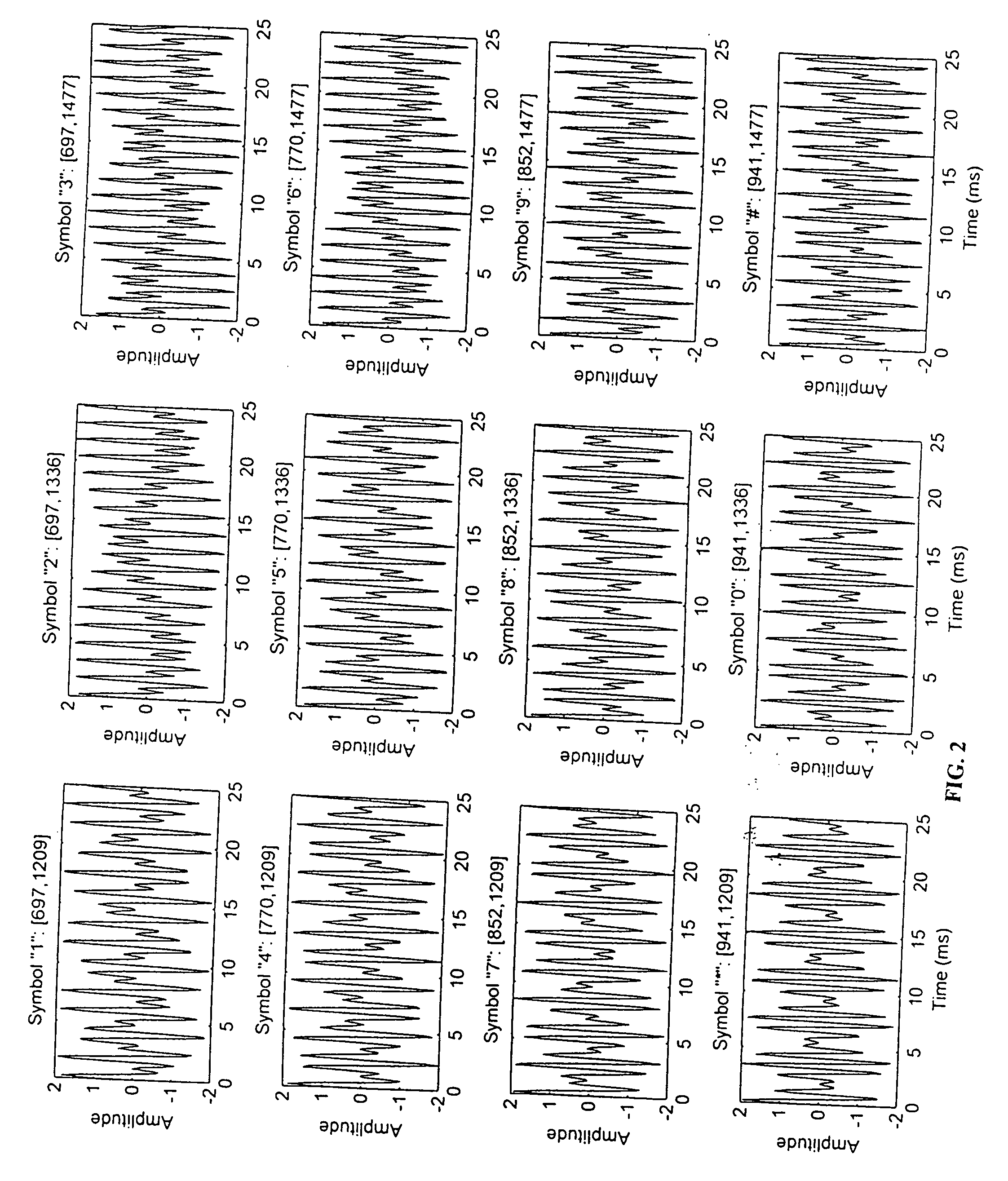
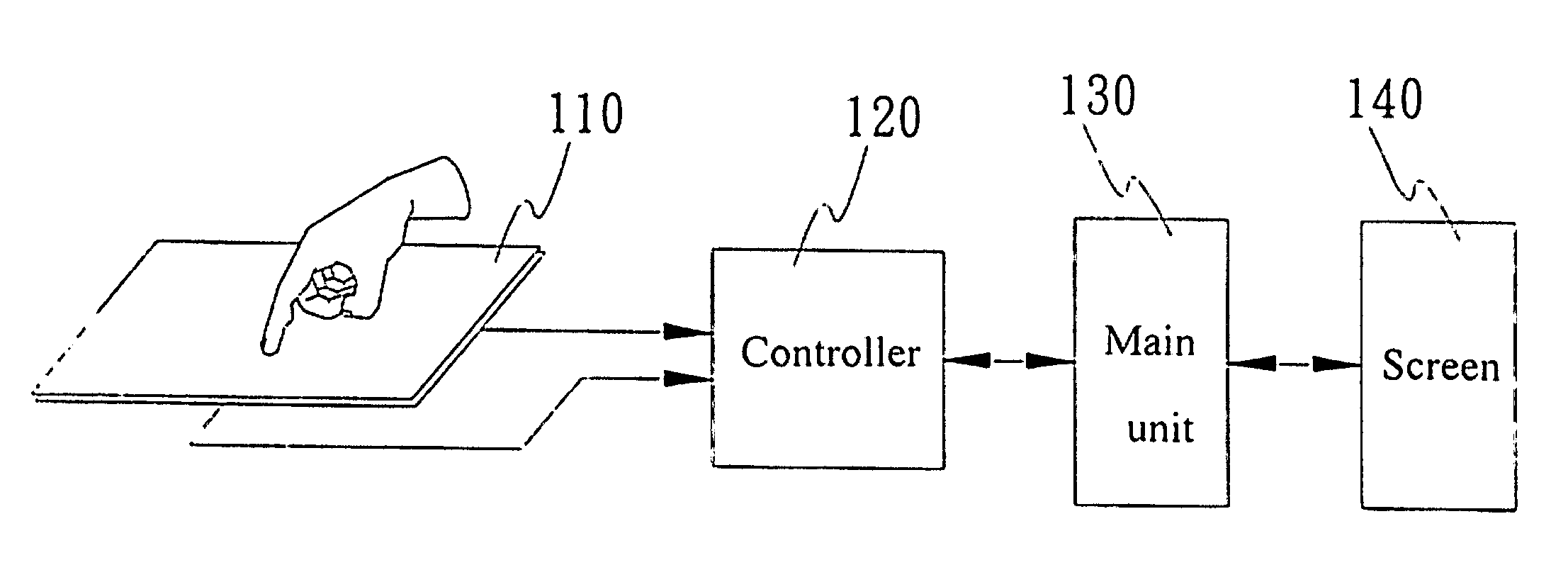
InactiveUS20060007175A1Avoid errors of judgmentImpeding determinationCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingStart timeControl signal
A touch control method of single tap, which identifies a touch of an object on a touch device by way of a control module of the touch device and a control signal being generated corresponding to the touch for being used by a main unit to perform subsequent control functions with reference time being set up in the control module, includes detecting a touch created by the object on the touch device and starting time counting once the touch occurs, keeping detecting and recording time duration of the object staying on the touch device and outputting a control signal representing the touch for being used by the main unit in case of only an effective touch having been detected within the reference time. The touch is determined as an effective touch by way of the object staying on the touch control device exceeding the reference time so that the object is not necessary to be apart from the touch control device immediately with less effort.
Owner:SENTELIC TECH CO LTD
Control device and control method for vehicle
InactiveUS20080058158A1Preventing unnecessary controlAvoid controlDigital data processing detailsGearing controlDriver/operatorAutomatic transmission
An ECU for a vehicle equipped with an automatic transmission includes a detection unit that detects a position of a transmission selection member manipulated by a driver; a determination unit that determines whether a gear step is abnormal when a preset time has elapsed after the transmission selection member is shifted from a drive position to a neutral position. The ECU further includes a control unit that controls the automatic transmission such that if the transmission selection member is shifted from the neutral position to the drive position when the gear step has been determined to be abnormal, a shock generated by the engagement of the frictional engagement elements is reduced.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
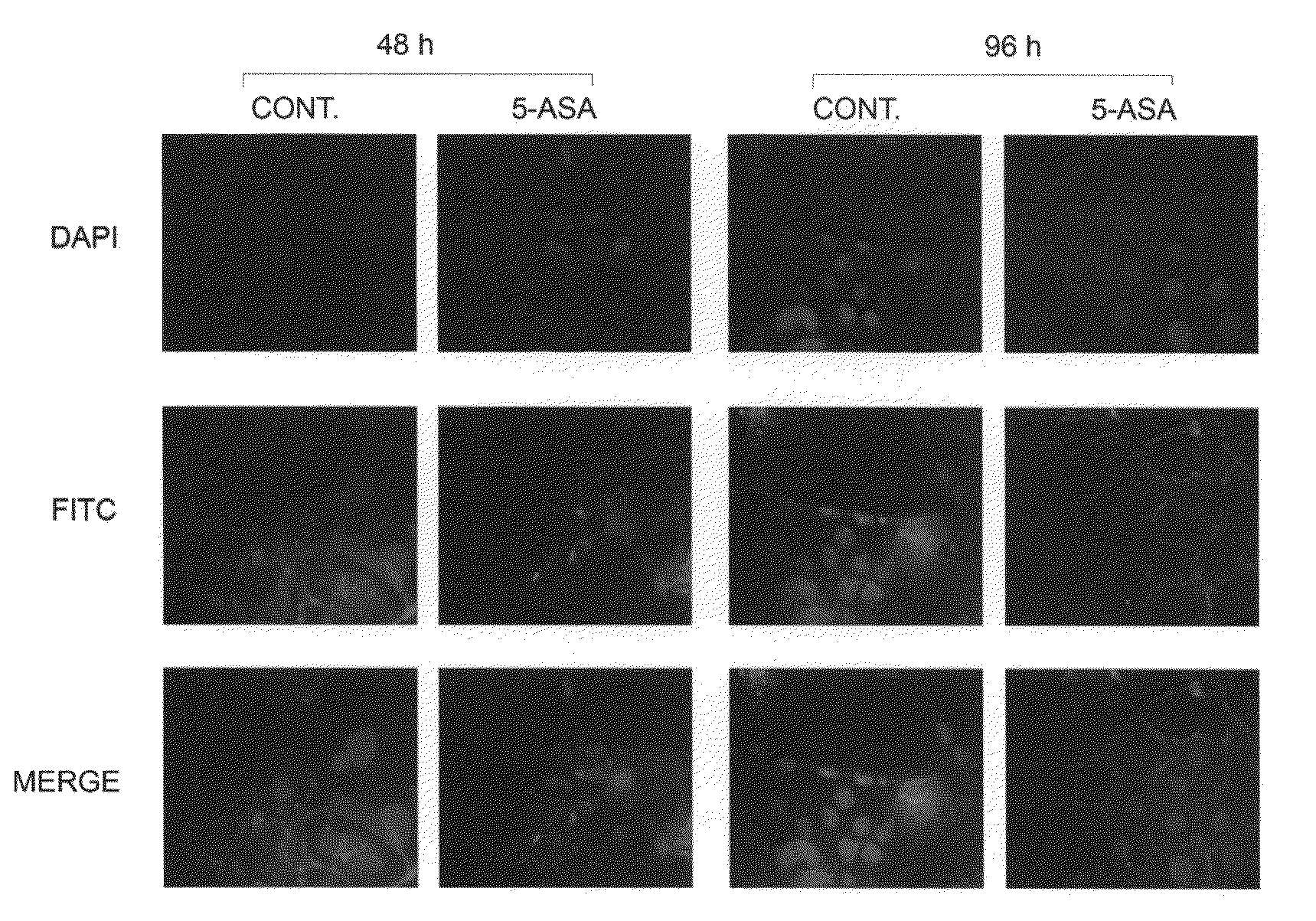
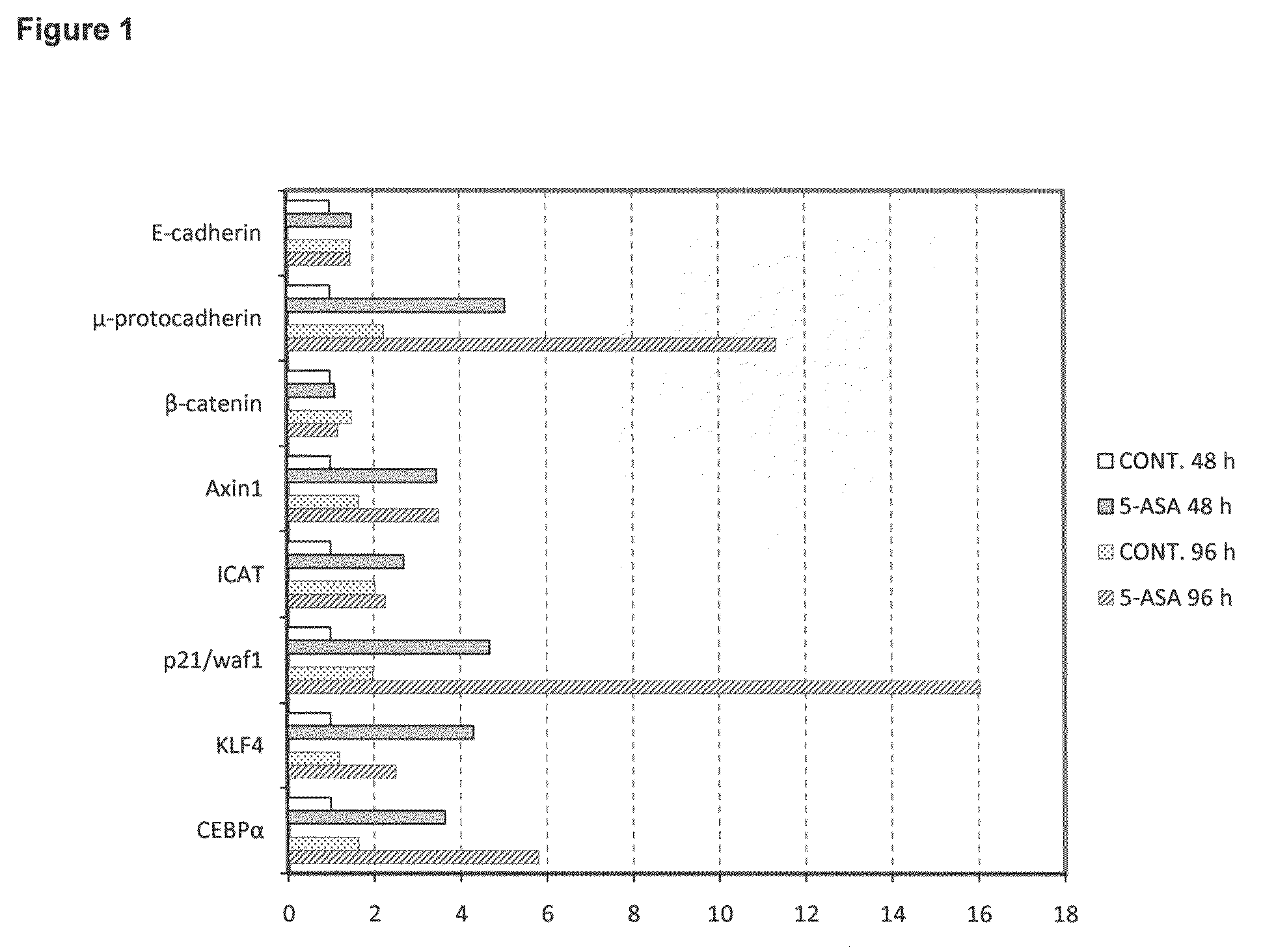
Determination of 5-ASA efficacy in CRC prevention and/or treatment by gene expression analysis
ActiveUS20100261174A1Preventing and treating CRCEffective preventionMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisBeta-cateninAXIN1
A method is disclosed for the determination of 5-ASA efficacy in preventing and / or treating CRC in a mammalian, which comprises the analysis of the inhibition of the β-catenin pathway in presence of 5-ASA. More in details, the method comprises measuring the expression of at least one gene involved in the regulation of the β-catenin signalling pathway, such as μ-protocadherin, E-cadherin, β-catenin, Axin1, ICAT, p21waf-1 and the expression of onco-suppressor genes, such as KLF4 and CEBPα. Gene expression can be measured in accordance to the methods commonly available in the art such as QRT-PCR and immunohistochemistry.
Owner:SOFAR SPA
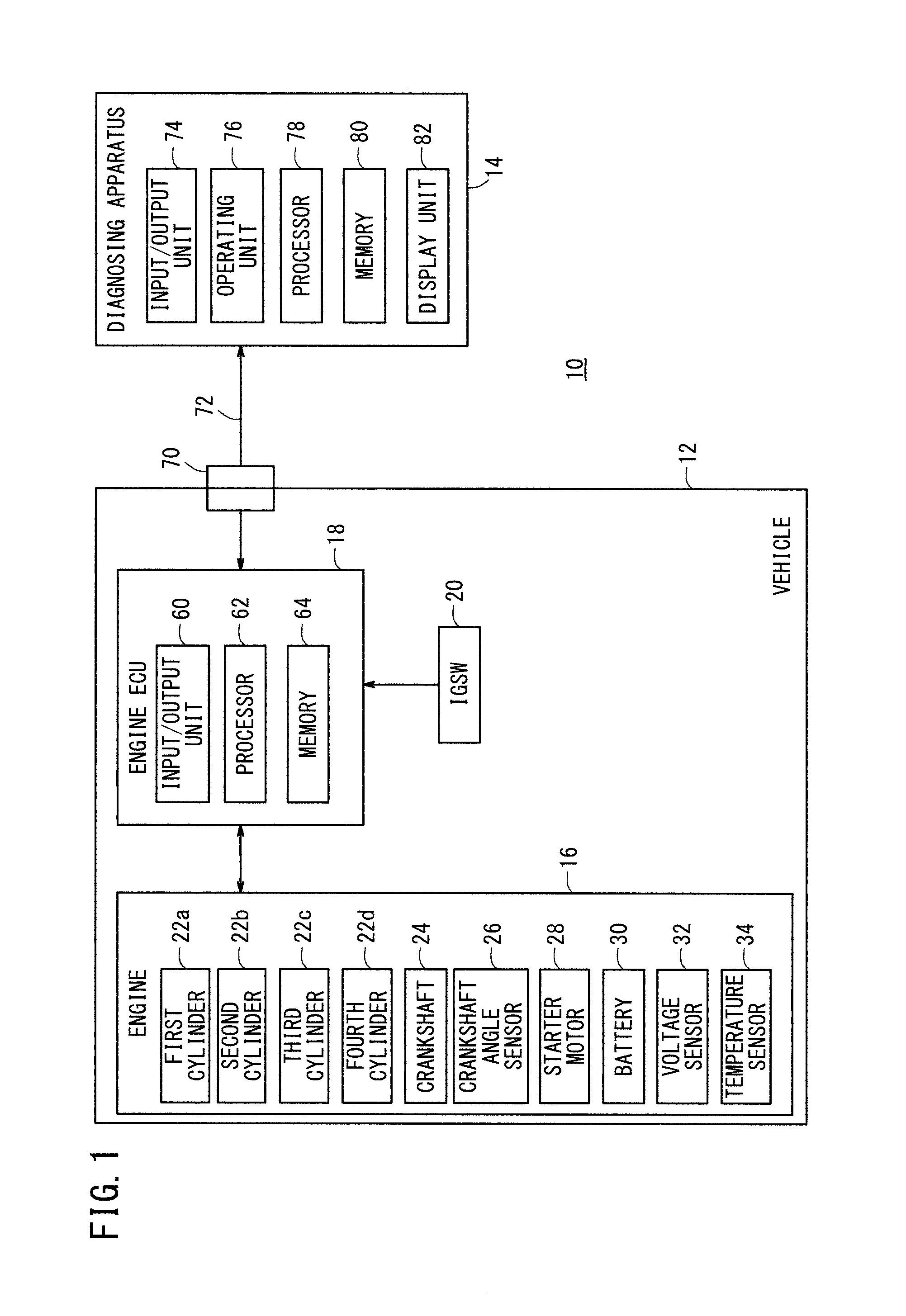
Method and apparatus for diagnosing engine fault
ActiveUS20140007664A1Increase efficiencyAccurately determineInternal-combustion engine testingElectrical controlAngular velocityCrankshaft
According to a method and an apparatus of the present invention for diagnosing a fault of an engine, a cranking rotation state is created by rotating a crank shaft while explosions in each cylinder are stopped; a variation of angular velocity of the crank shaft is detected for each cylinder in the cranking rotation state; a cylinder the compression pressure of which is insufficient is detected based on the variation; and if a cylinder indicated as a misfiring cylinder by a fault code is the same as the cylinder detected as being insufficient in compression pressure in the cranking rotation state, the cylinder is specified.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
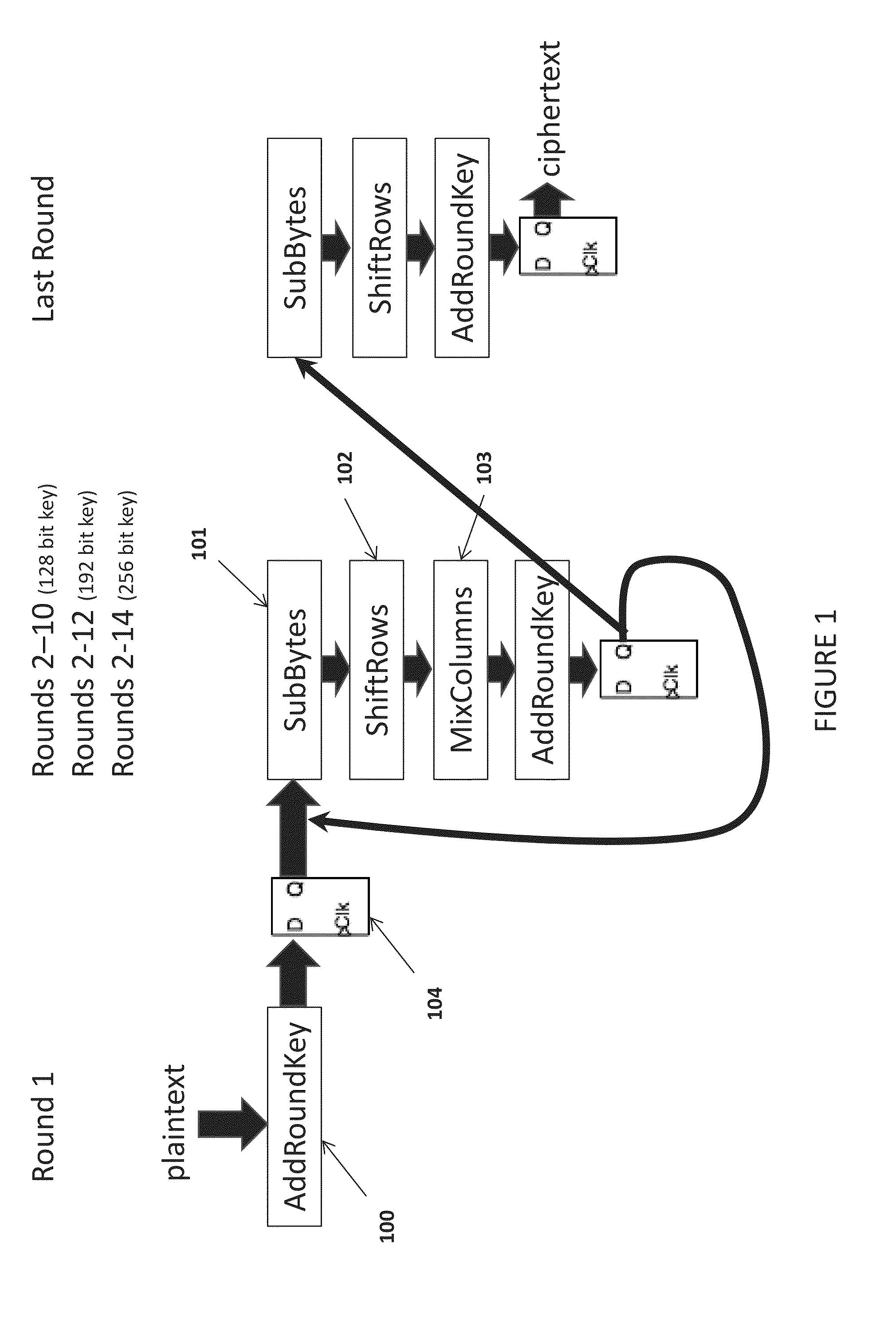
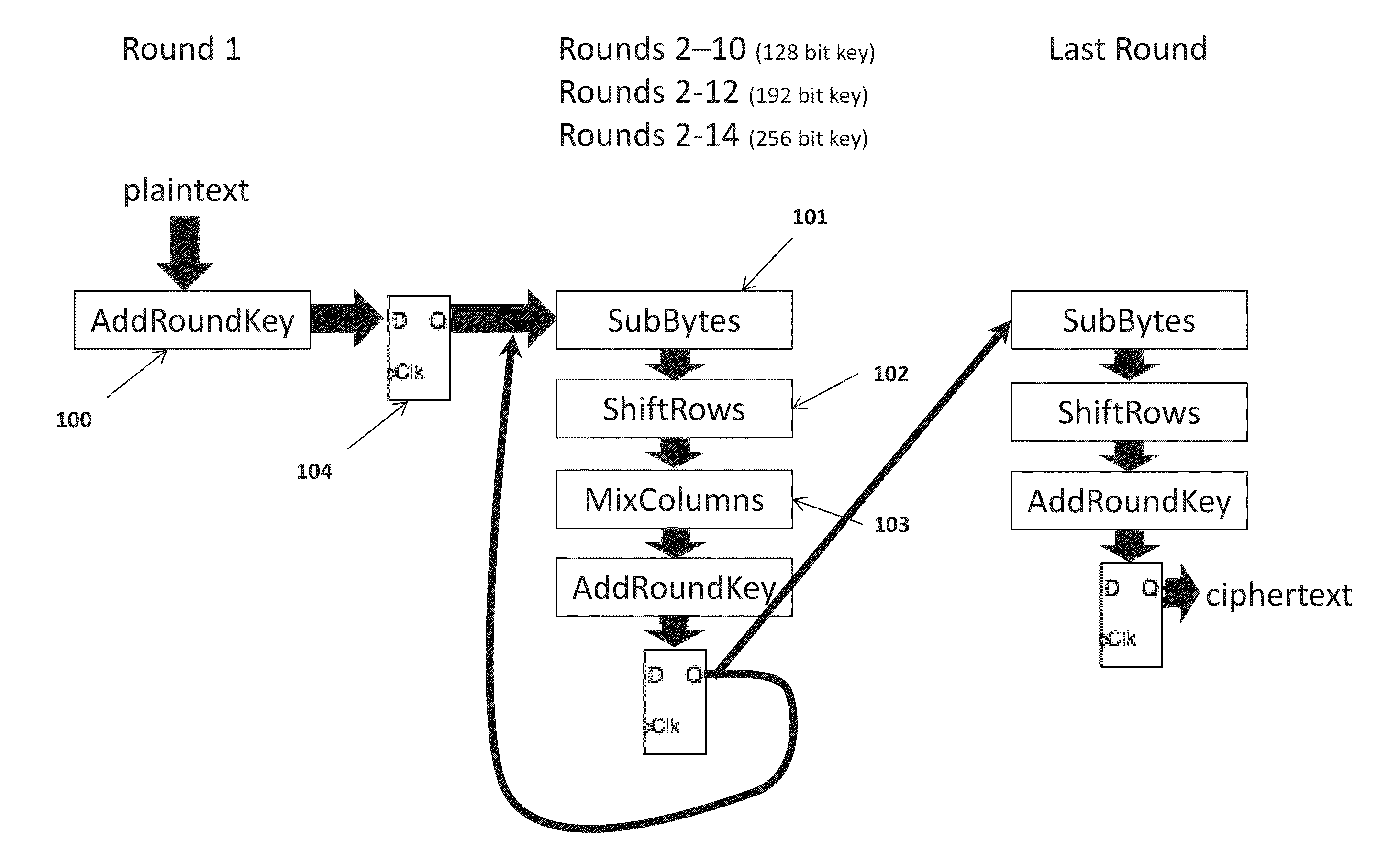
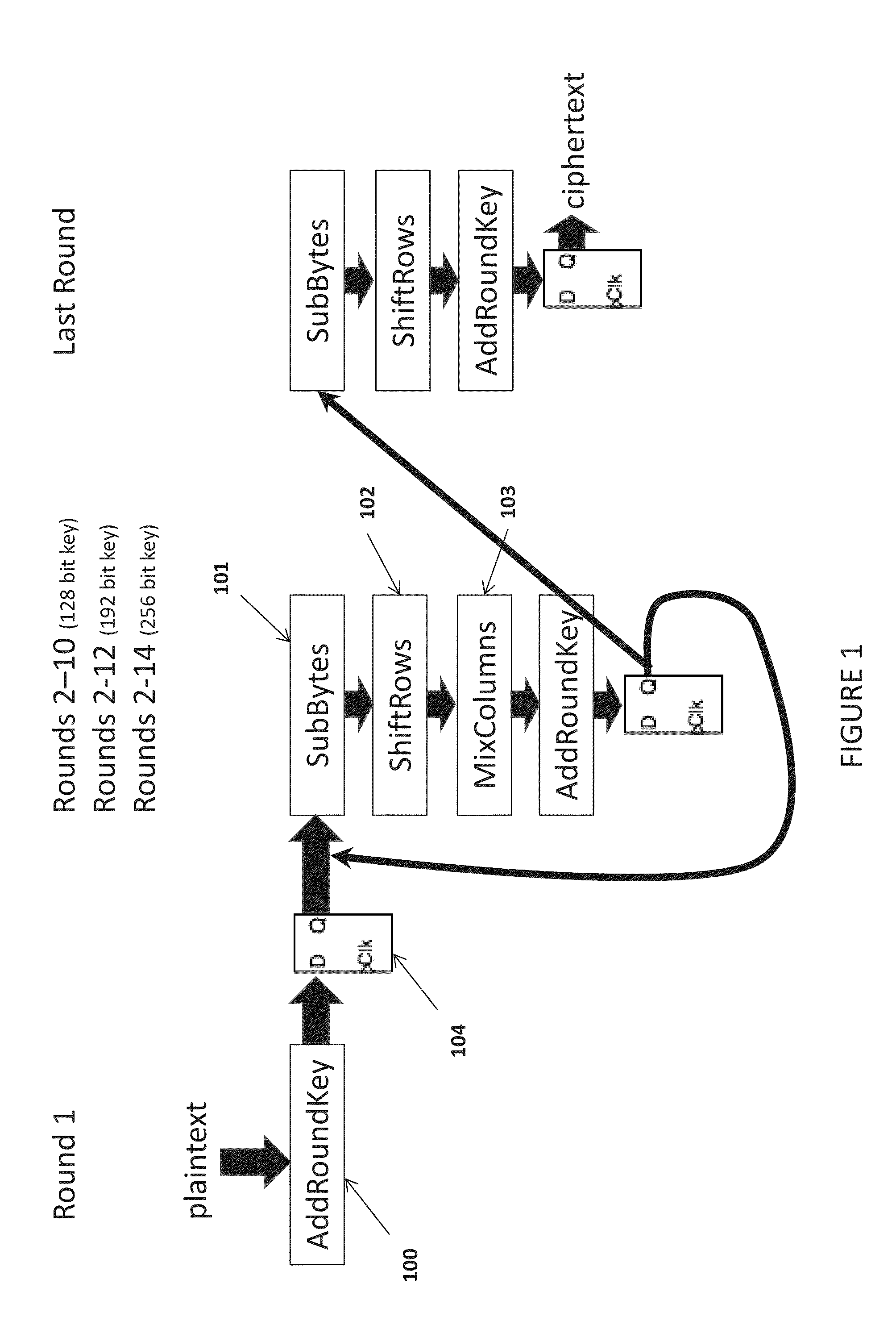
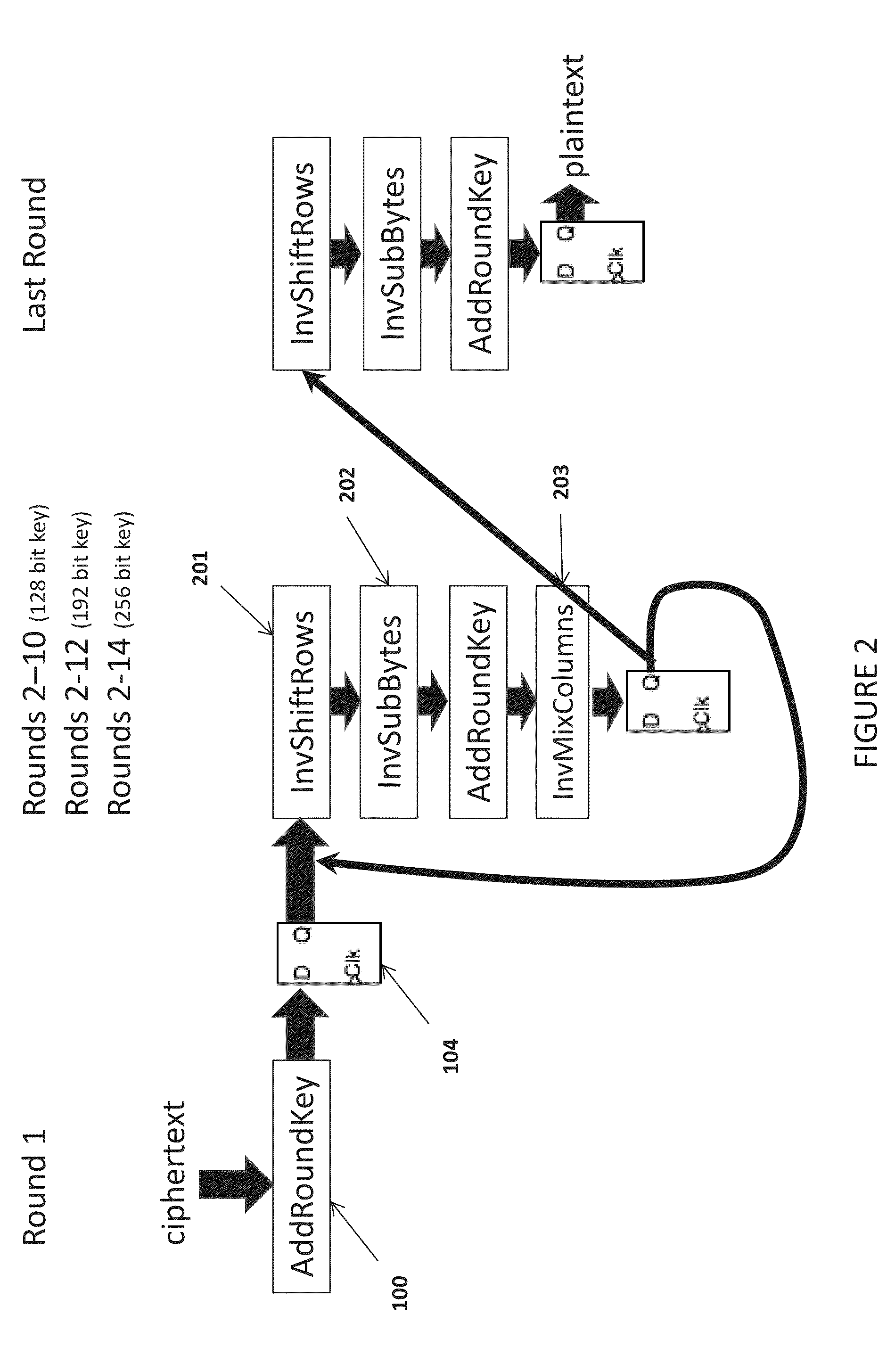
Apparatus and method to prevent side channel power attacks in advanced encryption standard using floating point operation
ActiveUS20140321639A1Avoid problemsImpeding determinationPublic key for secure communicationSecret communicationChannel powerComputer hardware
Apparatus and method for obscuring round 1 power consumption of hardware implementation of the AES algorithm. By simultaneously executing a processor floating point operation while executing round 1 of the AES algorithm power consumption of the AddRoundKey transformation is obscured. This prevents the opportunity to determine the AES key value during a side channel power attack.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESETNED BY THE SEC OF THE AIR FORCE
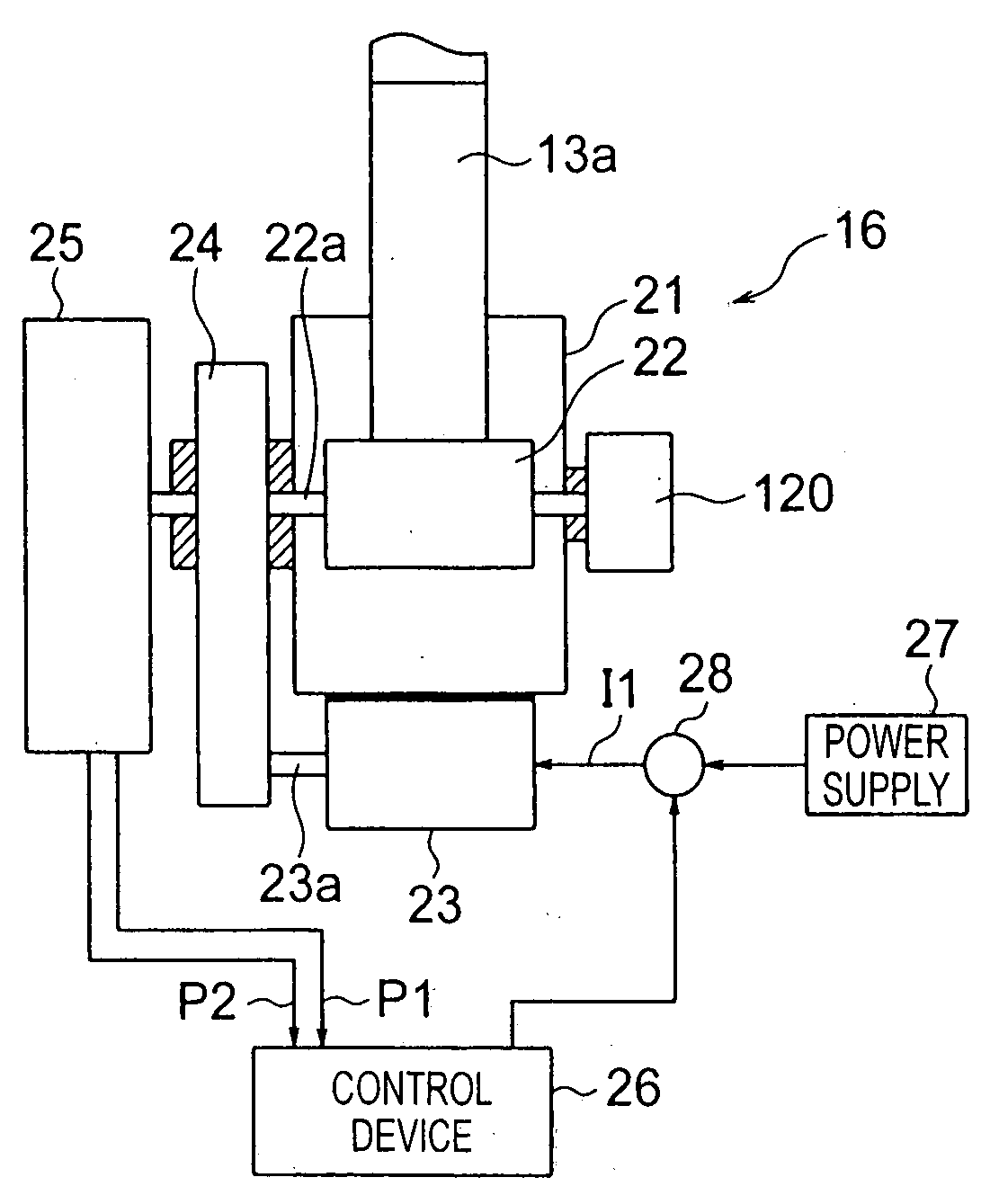
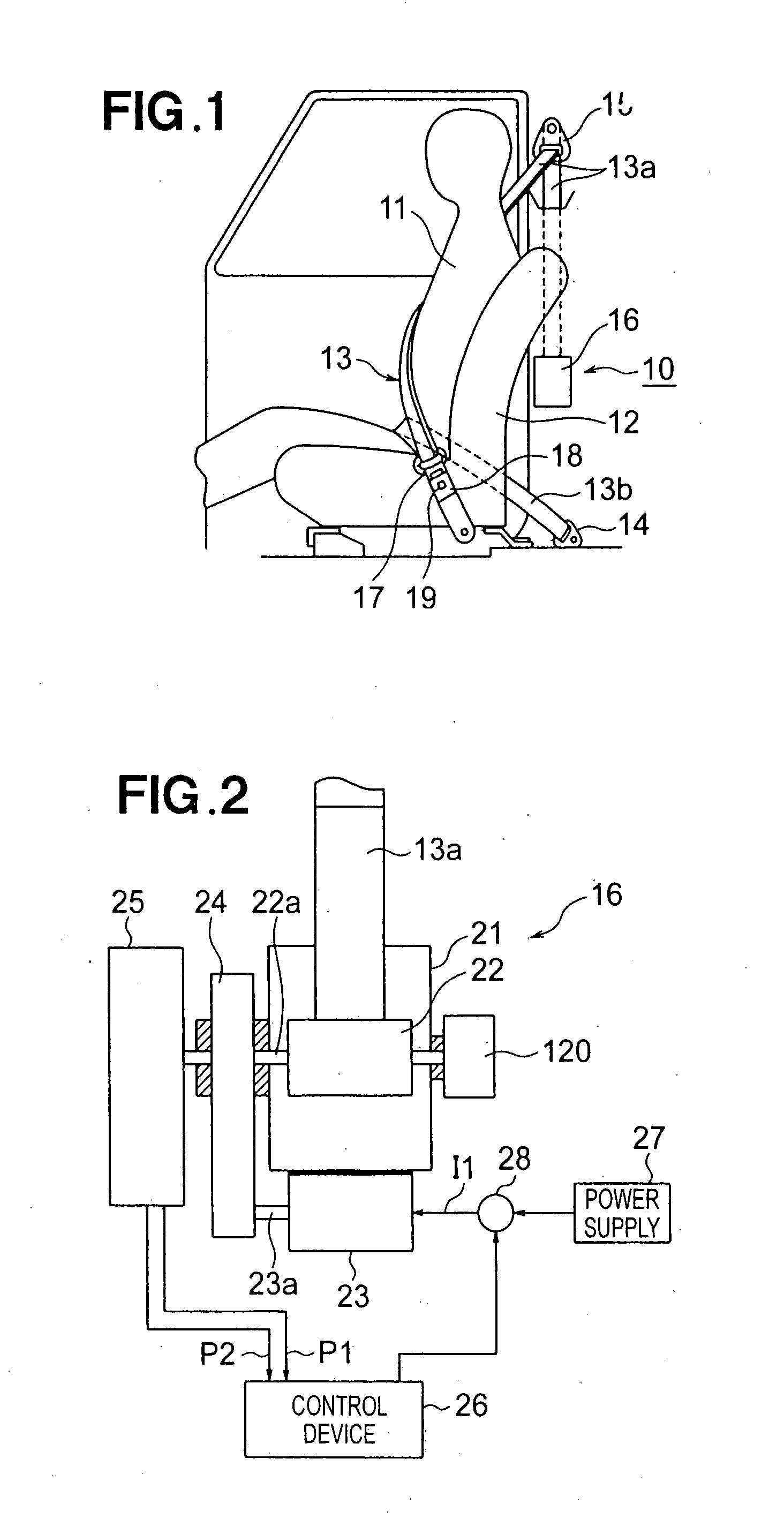
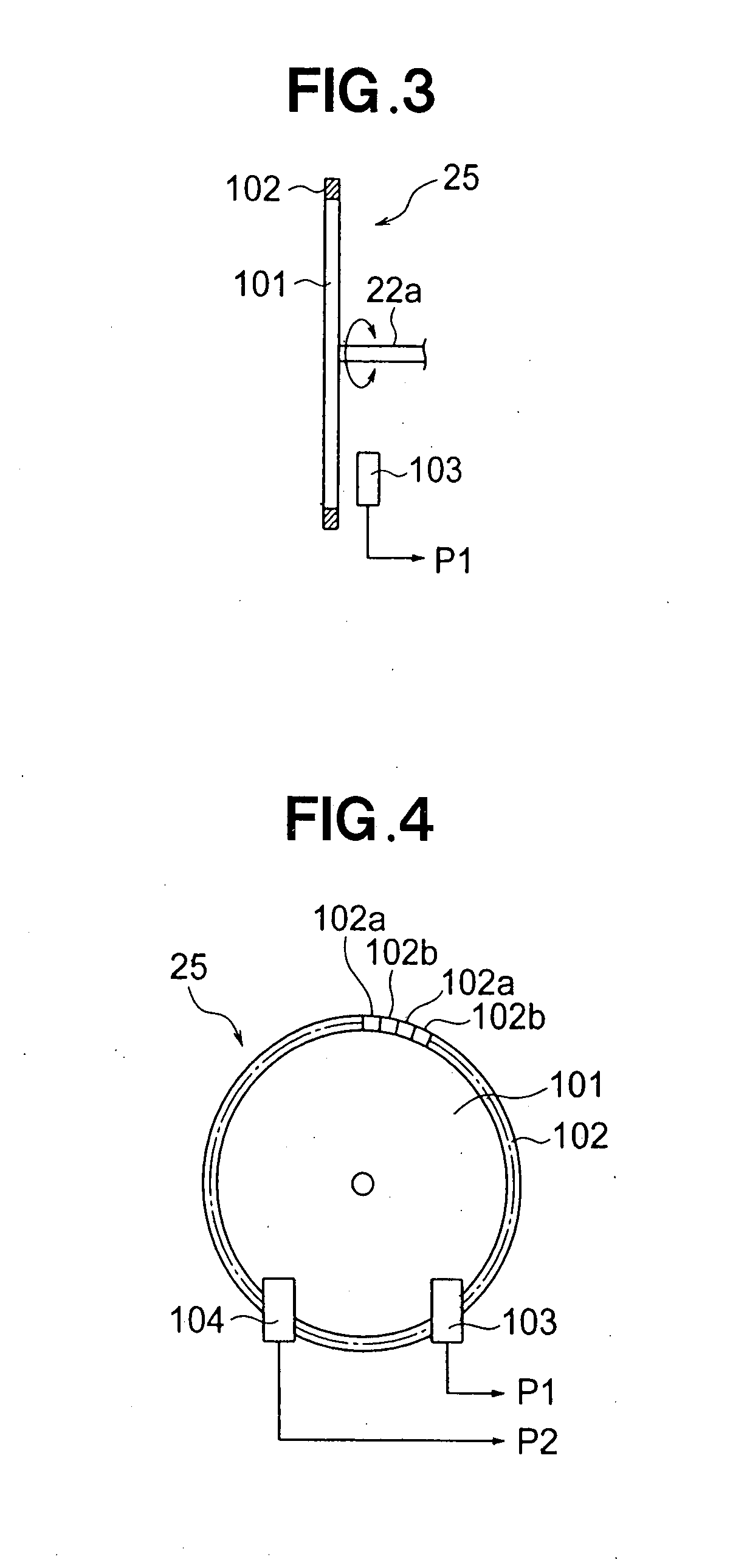
Vehicle seat belt apparatus
ActiveUS20070284868A1Eliminate unnecessary operationGrow fastElectric signal transmission systemsBelt retractorsSeat beltEngineering
Vehicle seat belt apparatus includes: a belt reel; a motor for driving the belt reel to take up a belt; a rotation detection section for detecting rotation of the belt reel; and a failure determination section for determining, on the basis of a detection signal output from the rotation detection section, whether or not the rotation detection section is currently in a failed state. The rotation detection section includes Hall ICs for generating first and second pulse signals that have characteristics such that temporal relationship between the first and second pulse signals is reversed in accordance with the rotating direction of the belt reel.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
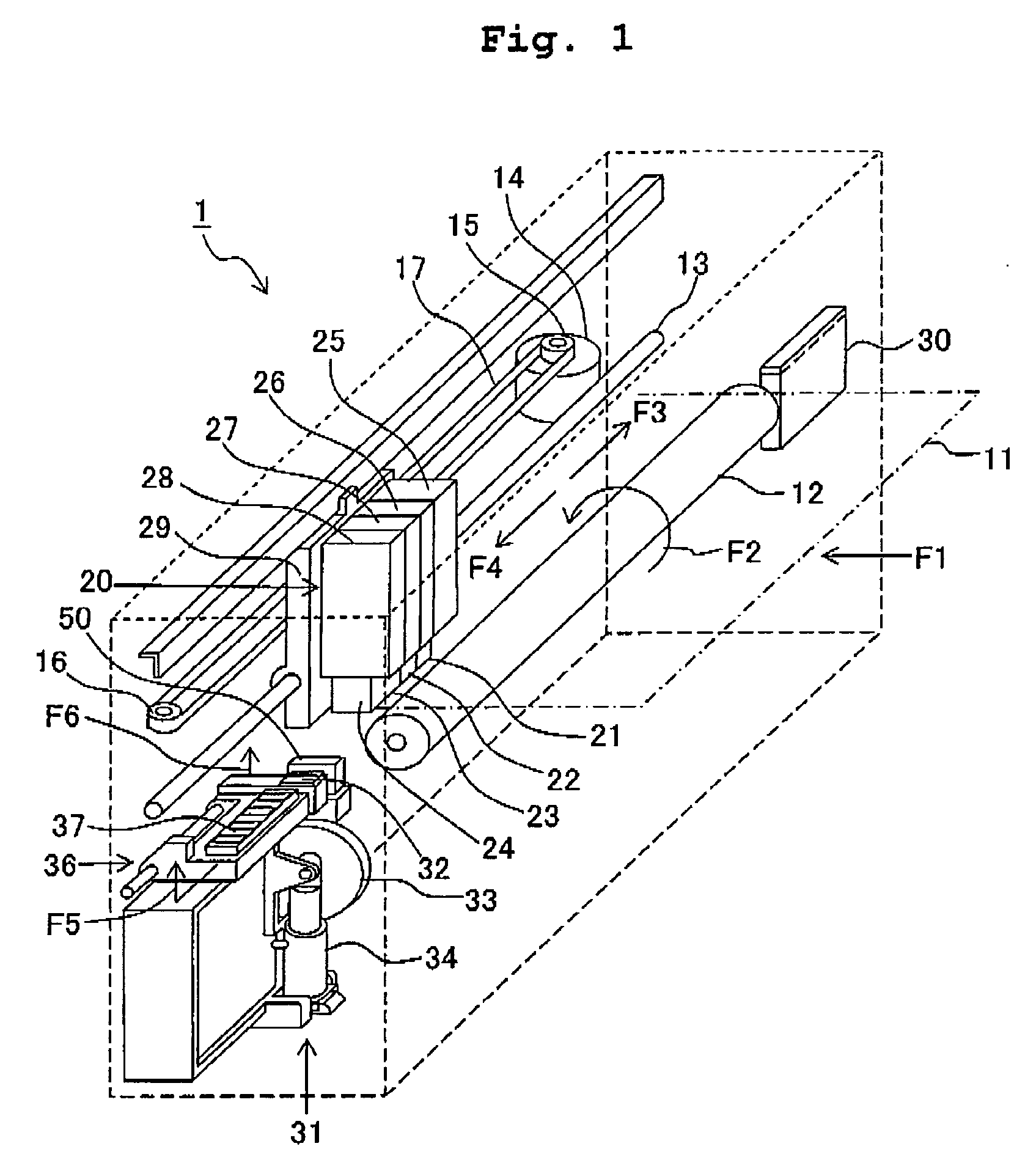
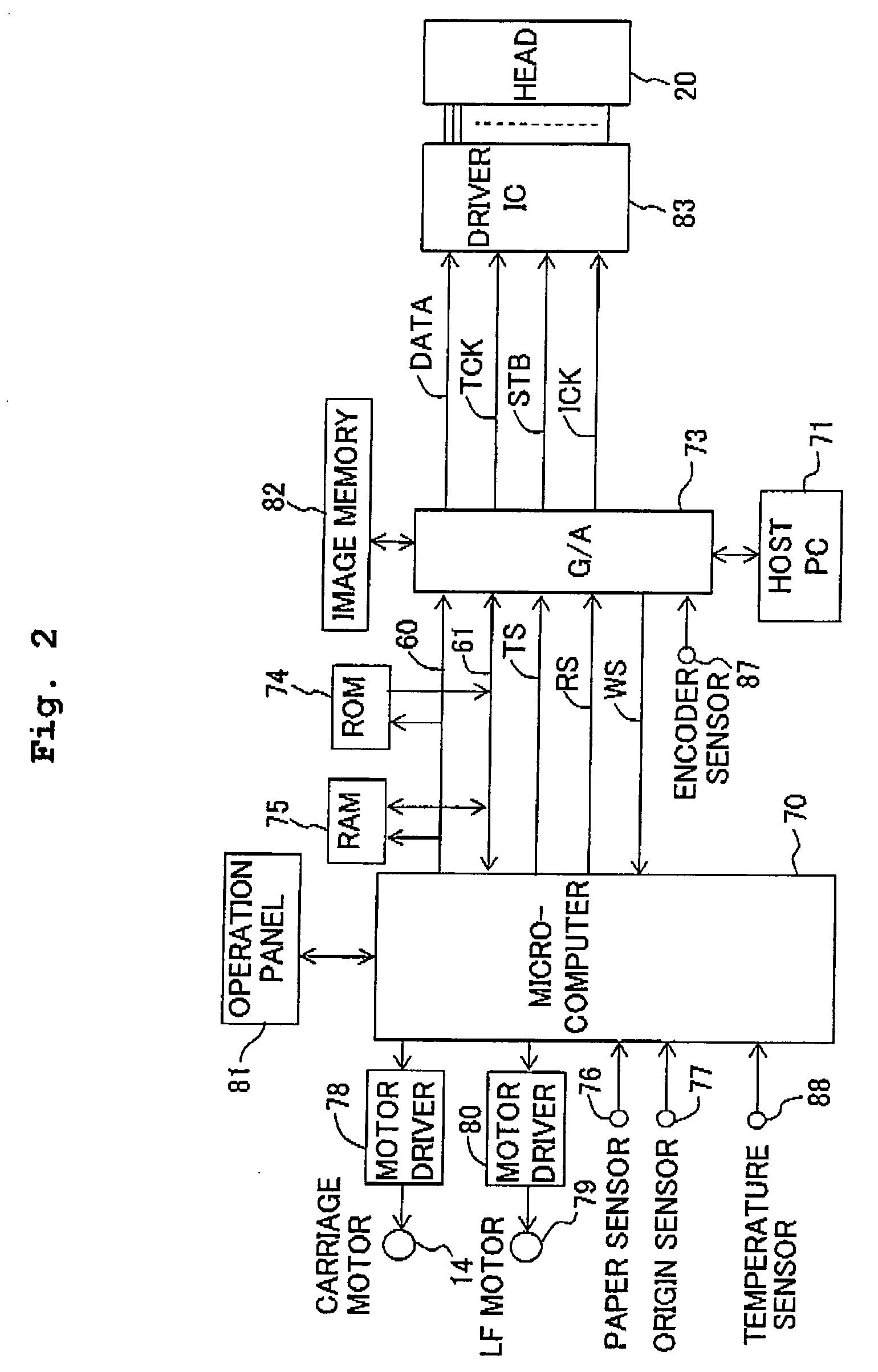
Ink-jet recording apparatus and recording method
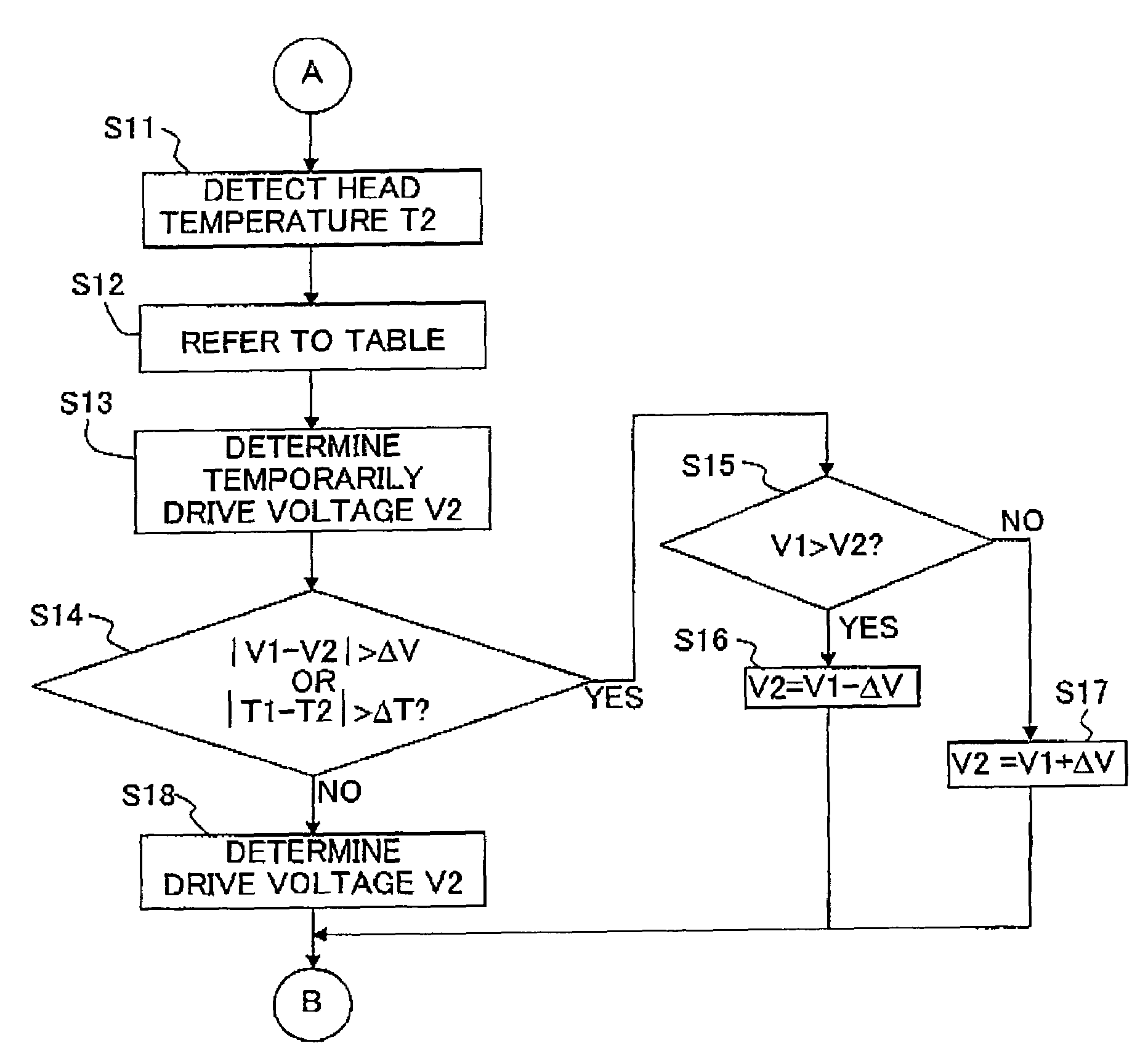
ActiveUS20070109344A1Satisfactory recording qualityQuality improvementOther printing apparatusVoltmeterEngineering
An ink-jet recording apparatus detects a temperature of an ink-jet head, and reads, from a table of set drive voltages, a drive voltage corresponding to that head temperature. The read drive voltage is determined to be a drive voltage V1 to be used in a recording for this time. Further, when the scanning number “n” of the ink-jet head has reached a value “m”, a drive voltage V2 to be used for next time is temporarily determined, based on the head temperature. When |V1−V2| is greater than a value ΔV, a voltage obtained by making a correcting, by an amount of ΔV, to the drive voltage V1 is determined to be the drive voltage V2 to be used next time. Therefore, even when the ink temperature is changed during the recording, it is possible to improve the recording quality.
Owner:BROTHER KOGYO KK
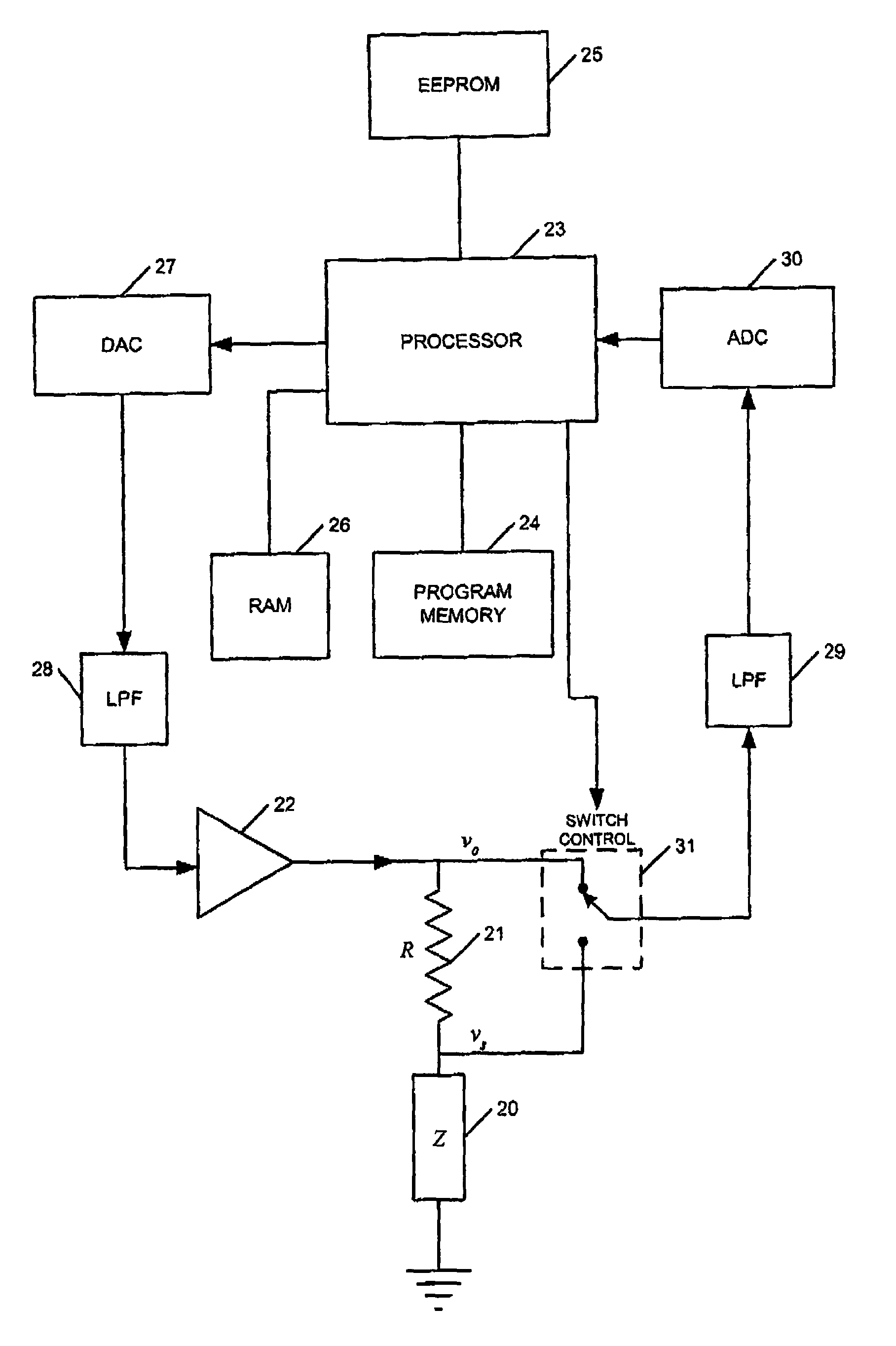
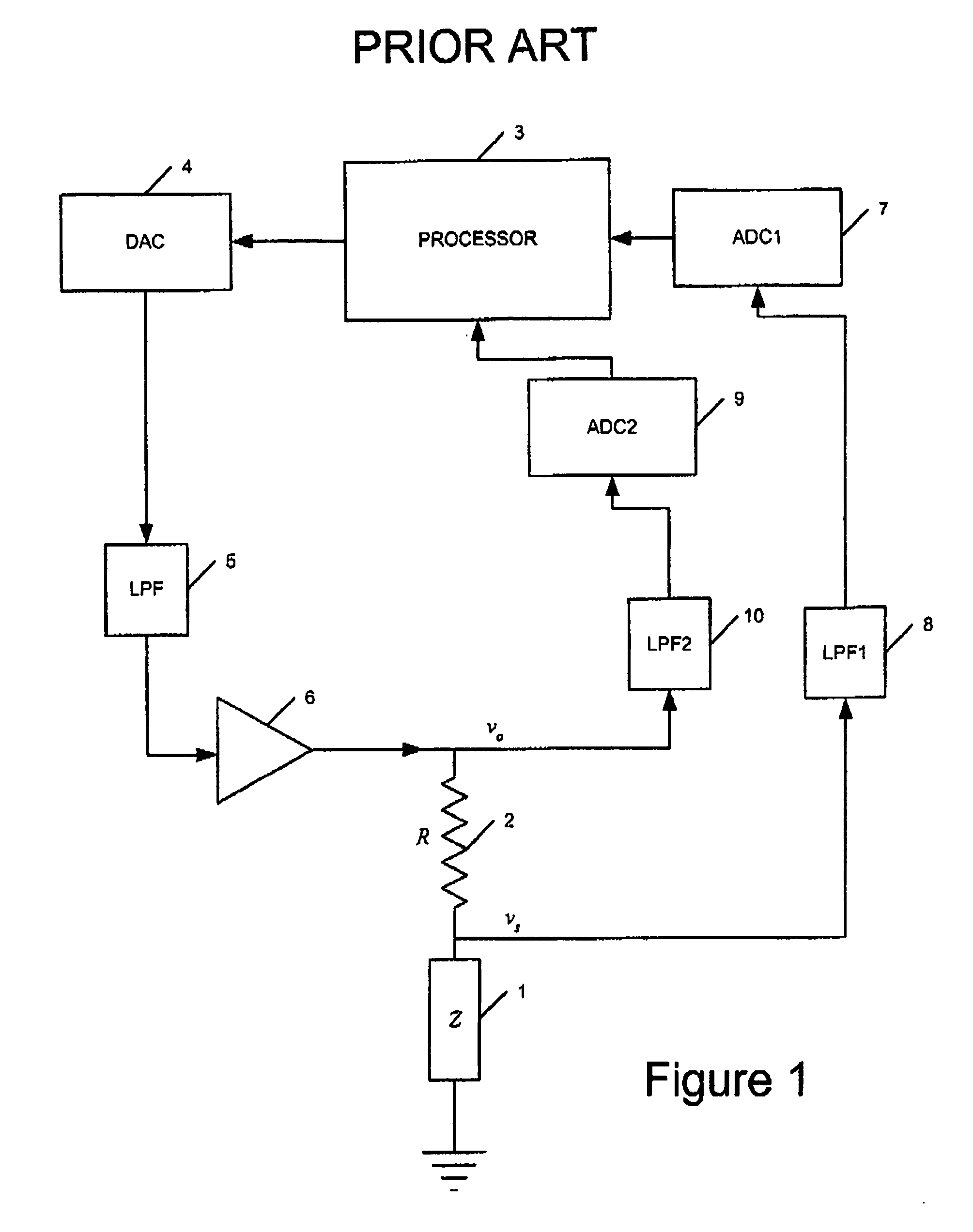
Signal measurement and processing method and apparatus
ActiveUS7548819B2Avoid the needProvide stability and required level of accuracyFrequency-division multiplex detailsEmergency protective circuit arrangementsEngineeringElectrical impedance
Apparatus for generating an output dependent upon the impedance or at least one component of the impedance of a device includes a load component having a known impedance or component thereof for connection in series with the device; a measurement channel for measuring voltages; a switch arrangement connected to the measurement channel for switching the measurement channel to sequentially measure a first voltage on a first side of the load component and a second voltage on a second side of the load component or a voltage difference across the load component; a processing arrangement connected to the measurement channel for processing the sequentially measured voltages to generate an output dependent upon the impedance or at least one component of the impedance of the device; and a signal generating arrangement for generating an electrical signal for application to the series connected load component and device.
Owner:ULTRA PCS LTD
Wire abnormality detecting device
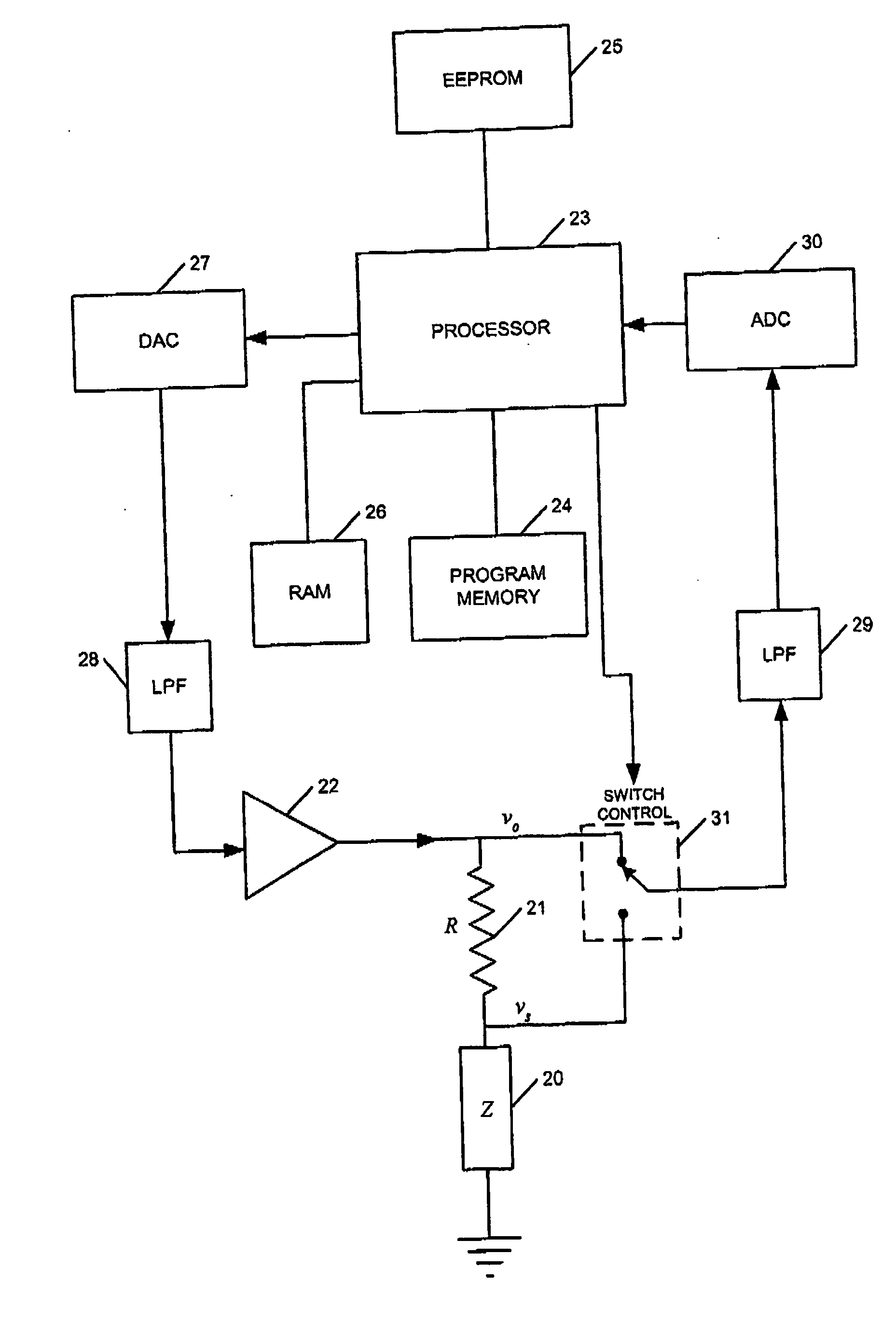
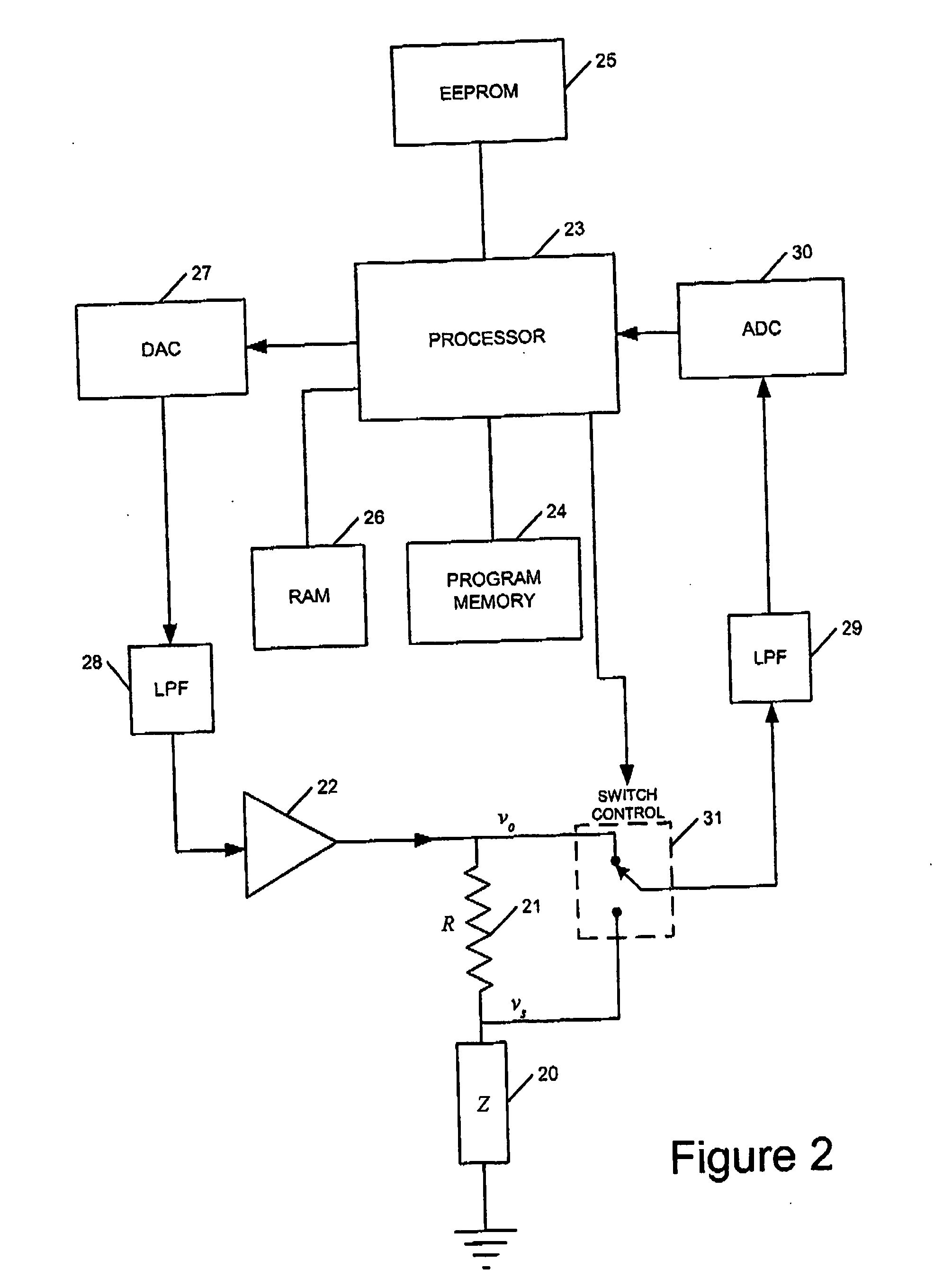
InactiveUS7701224B2Accurate measurementImpeding determinationShort-circuit testingTesting electric installations on transportAnomaly detectionResistor
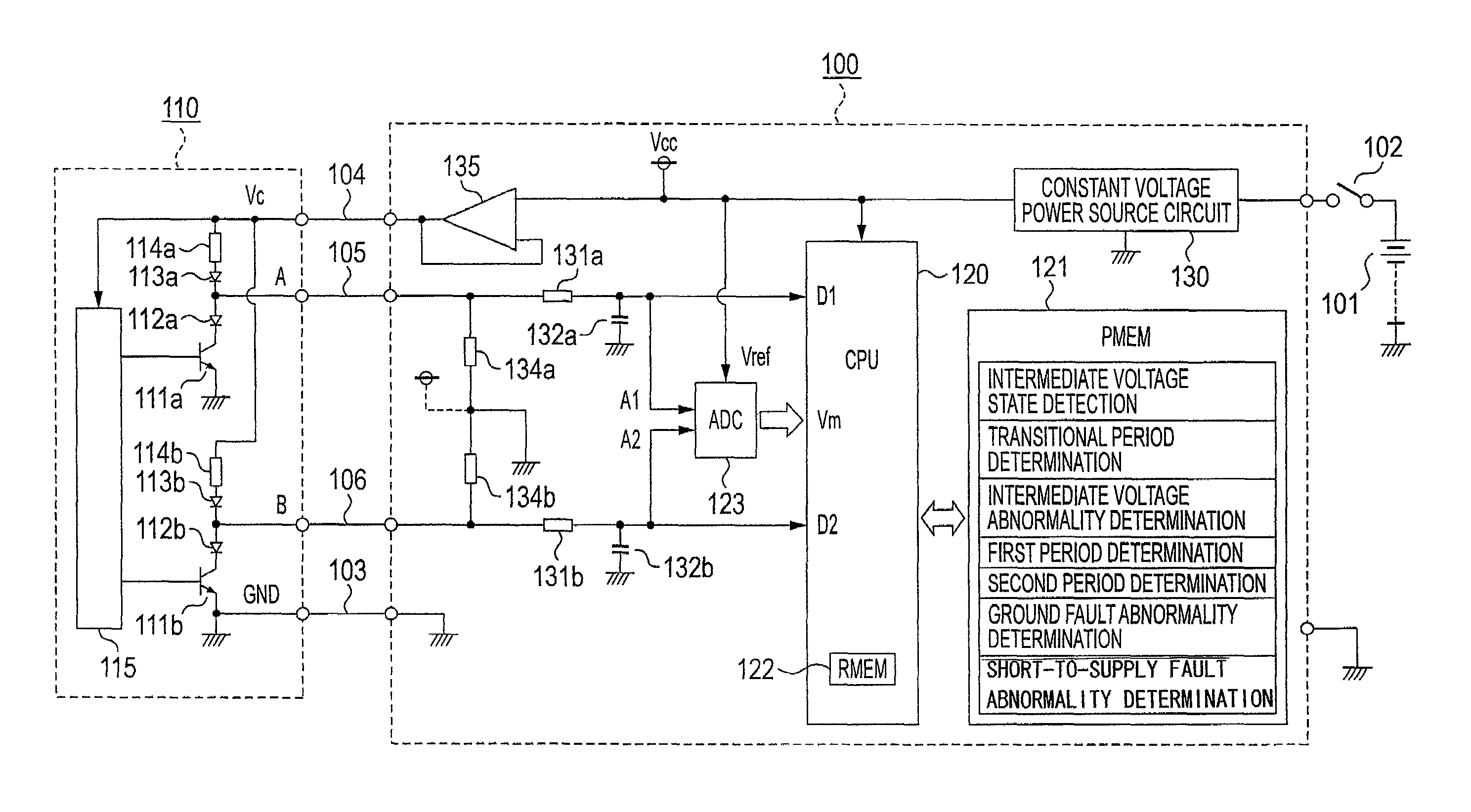
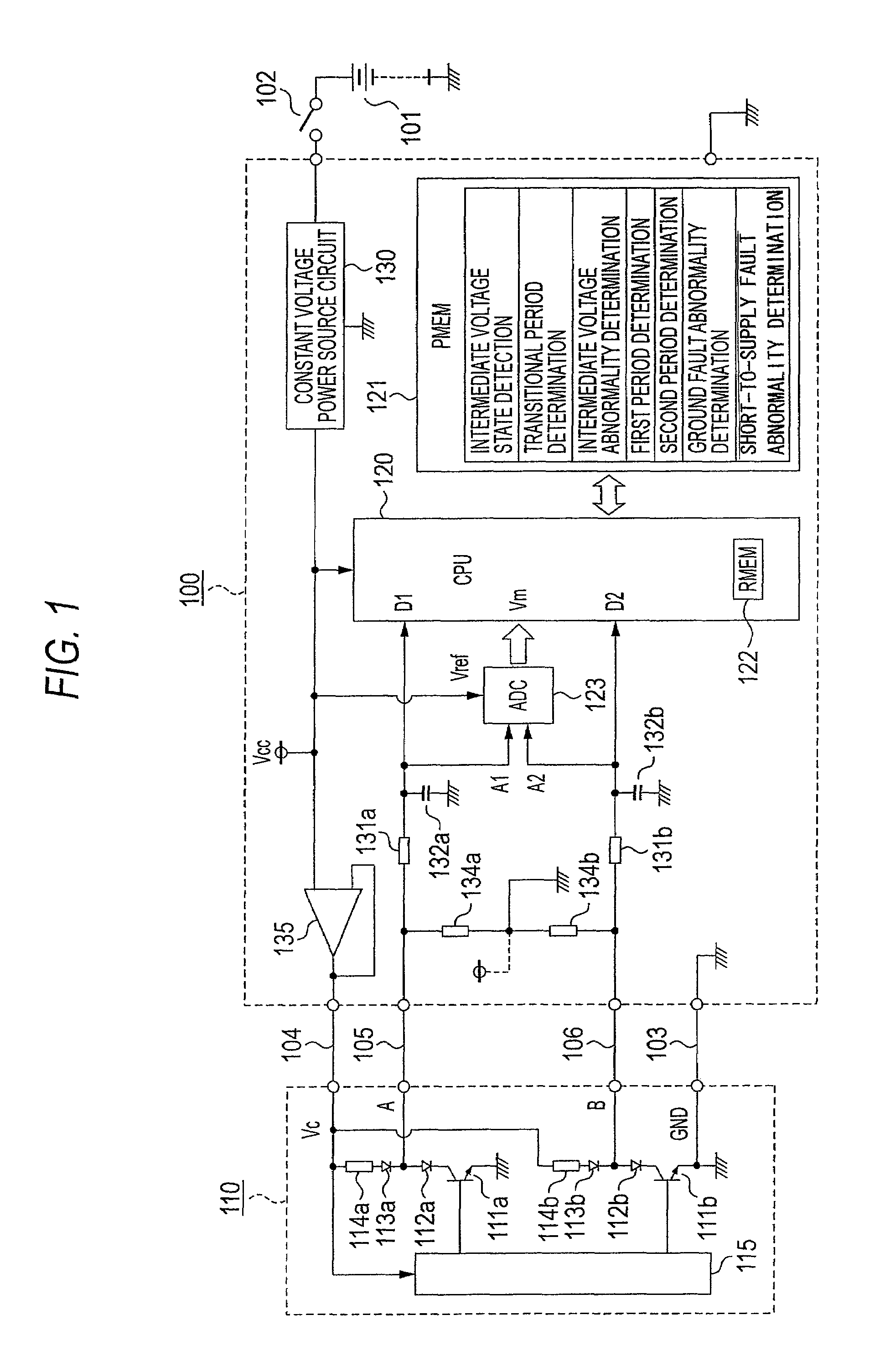
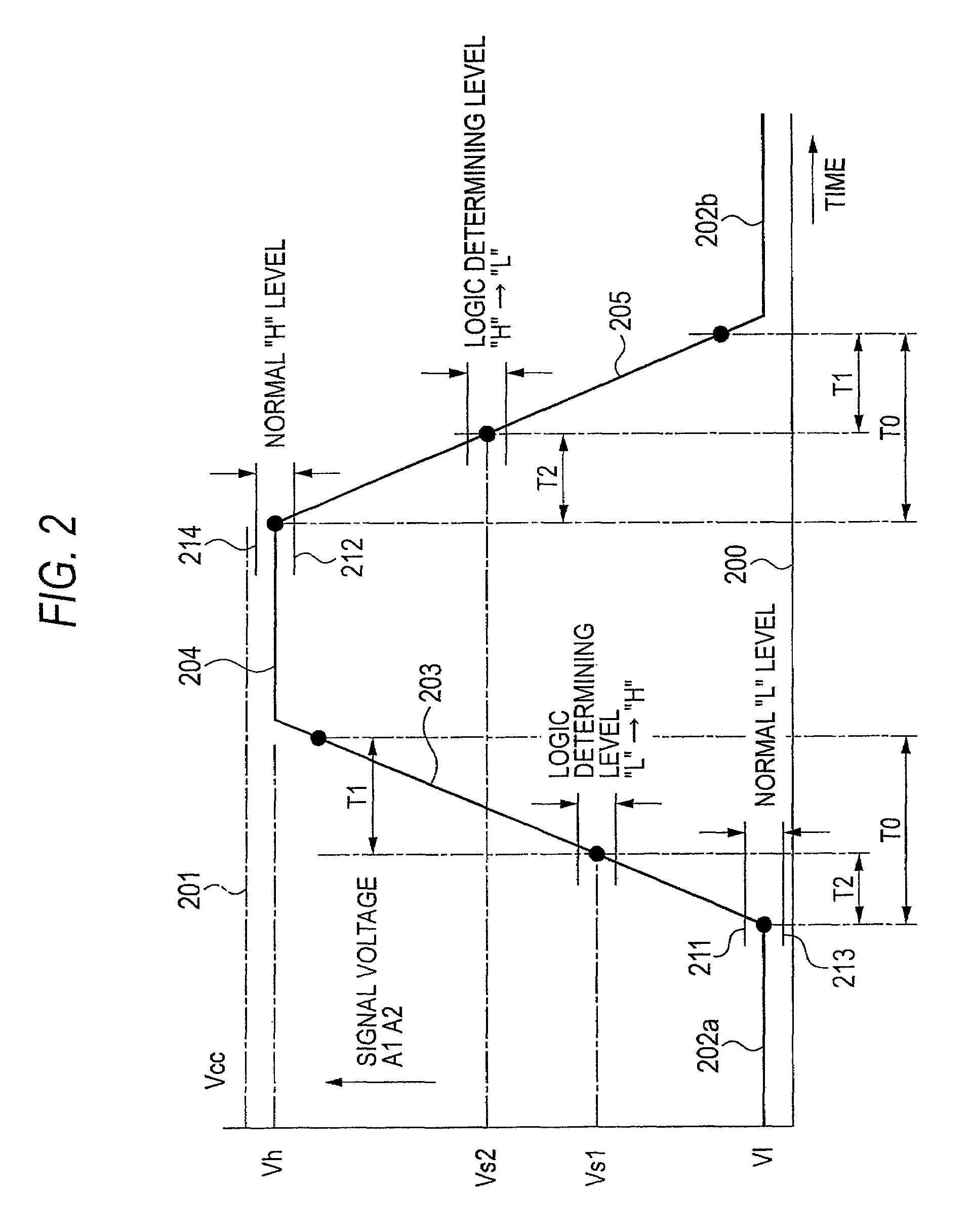
A sensor switch 111a connected to a constant voltage Vc via a breeder resistor 114a and dropper diodes 112a and 113a is connected to a microprocessor 120 that configures a wire abnormality detecting device 100, and the electric potential of the connection point between the dropper diodes 112a and 113a is inputted to the microprocessor 120 as a switch logic signal D1 via a signal wire 105 and a series resistor 131a. The signal voltage level of the switch logic signal D1 is inputted to the microprocessor 120 via an AD converter 123, and the microprocessor 120 cooperates with a program memory 121 to perform a determination of whether or not the signal voltage is in an abnormal intermediate voltage state. However, during a transitional period when the switch logic signal is changing between high and low, mistaken determination is prevented by avoiding abnormality determination.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Method and sensor element for determining a gas in a gas mixture
InactiveUS7763154B2Accurate measurementImpeding determinationWeather/light/corrosion resistanceVolume/mass flow measurementCombustionHydrogen
A method and a sensor element are provided for determining the concentration of an oxidizable gas in a gas mixture, e.g., in exhaust gases of internal combustion engines. Within the sensor element of a gas sensor, nitrogen oxides, hydrogen, and / or carbon monoxide contained in the gas mixture are at least partially removed in an initial step. In a further step, the concentration of the gas to be detected in the gas mixture freed of nitrogen oxides, carbon monoxide and / or hydrogen is ascertained.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
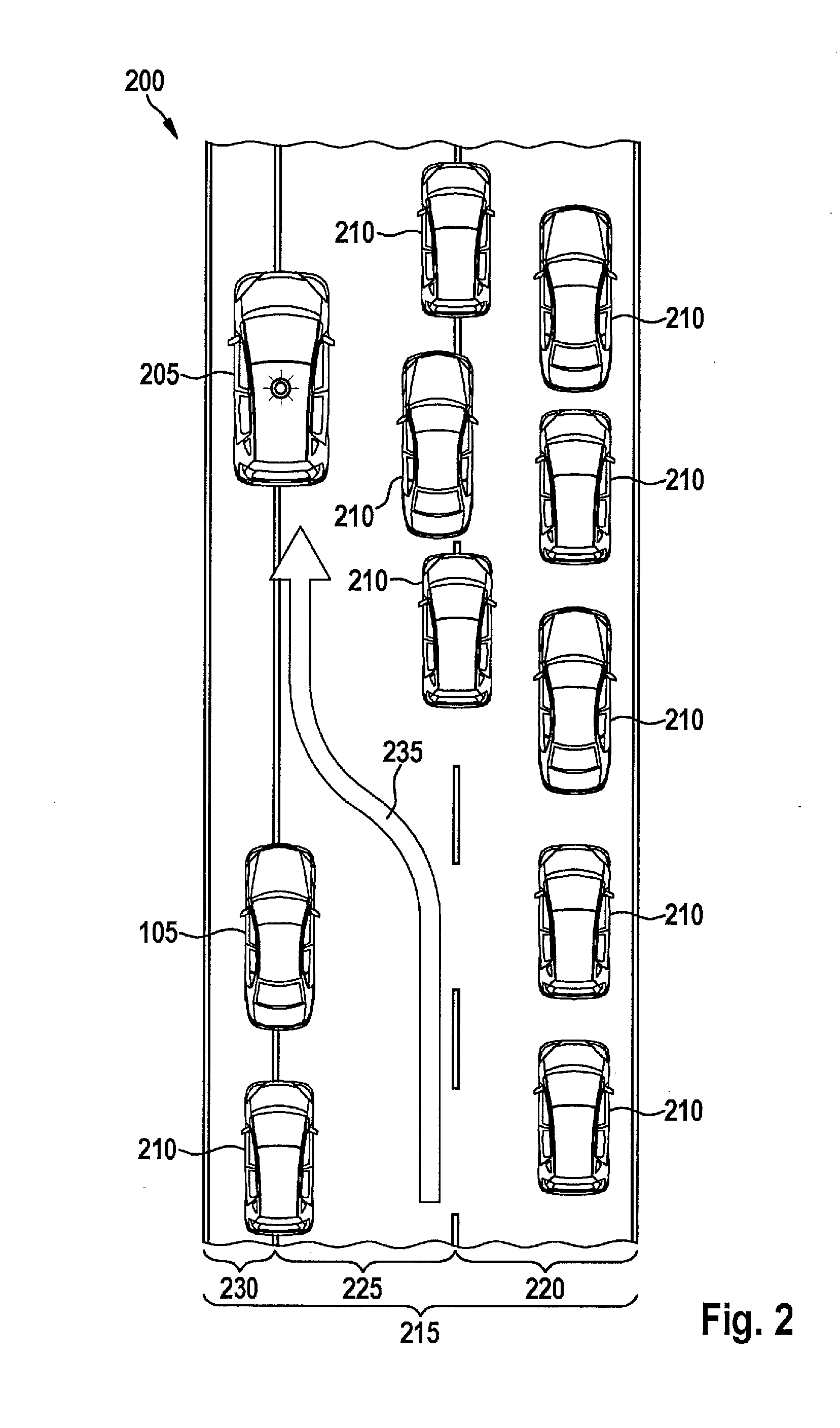
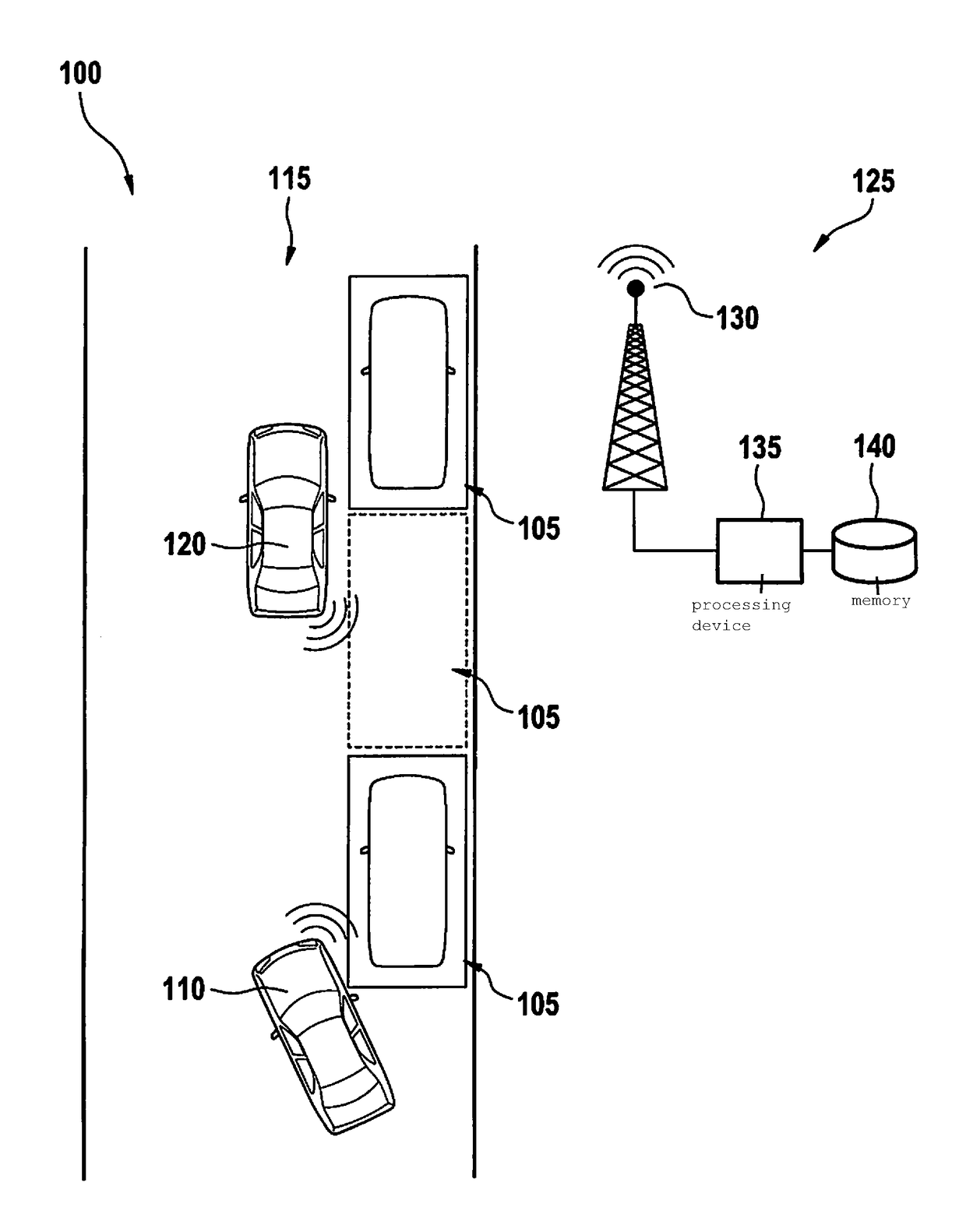
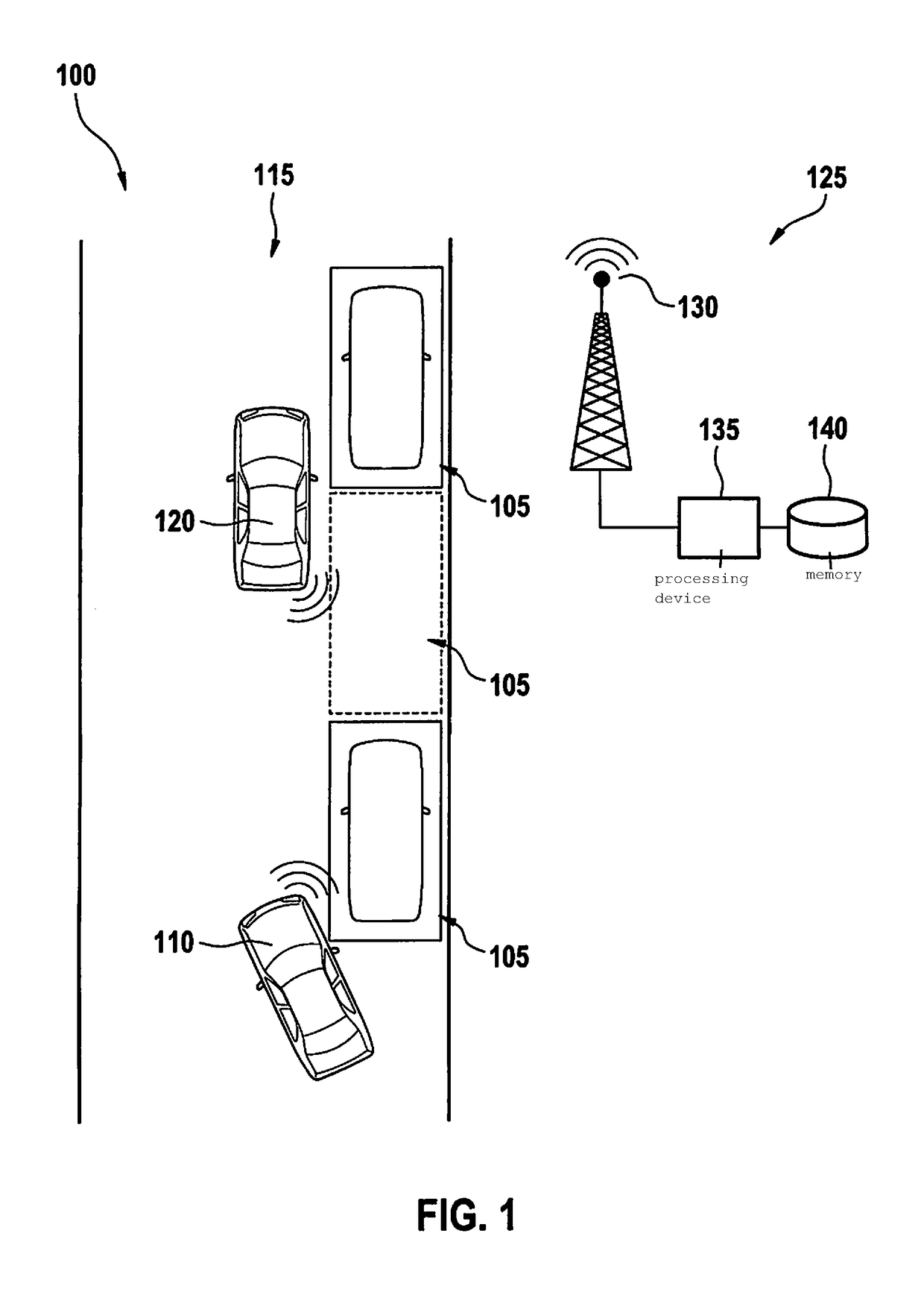
Determining an unoccupied street parking space
ActiveUS10026316B2Easy to shareSuppressing reportingIndication of parksing free spacesOptical signallingParking spaceMotor vehicle crash
A street parking space for a first motor vehicle is located within a predefined area. A method for determining an unoccupied street parking space includes steps of scanning environmental data of a second motor vehicle in the predefined area; determining an item of information regarding an unoccupied parking space in the area of the second motor vehicle on the basis of the environmental data; and reporting the item of information to a central instance. The central instance determines a demand for reports in the area on the basis of received information from a plurality of second motor vehicles, and suppresses further reports from a second motor vehicle as a function of the demand.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Wheel position detection device and tire-pressure detection system equipped with same
InactiveUS10214060B2Increase the number ofPrecise positioningAcceleration measurementTyre measurementsEngineeringTransmitter
A wheel position detection device includes: a transmitter in each wheel of a vehicle having a first control unit for transmitting a frame with ID and an acceleration sensor; and a receiver on a vehicle body, including a second control unit for registering the ID in association with the wheel. The first control unit detects a wheel speed, and stores data of the acceleration sensor in the frame. The second control unit includes: a first determination device that determines a condition that the acceleration sensor is not in an on-state; a candidate registration device that registers a candidate of the ID of a spare wheel when the condition is satisfied; a second determination device that determines a travel history of the vehicle; and a registration device that identifies the ID of the spare wheel when the travel history is present, and registers the ID in association with the spare wheel.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Object recognition system for vehicle
ActiveUS7468791B2Accurate detectionSafe travelOptical radiation measurementDigital data processing detailsSize determinationIdentification device
Owner:DENSO CORP
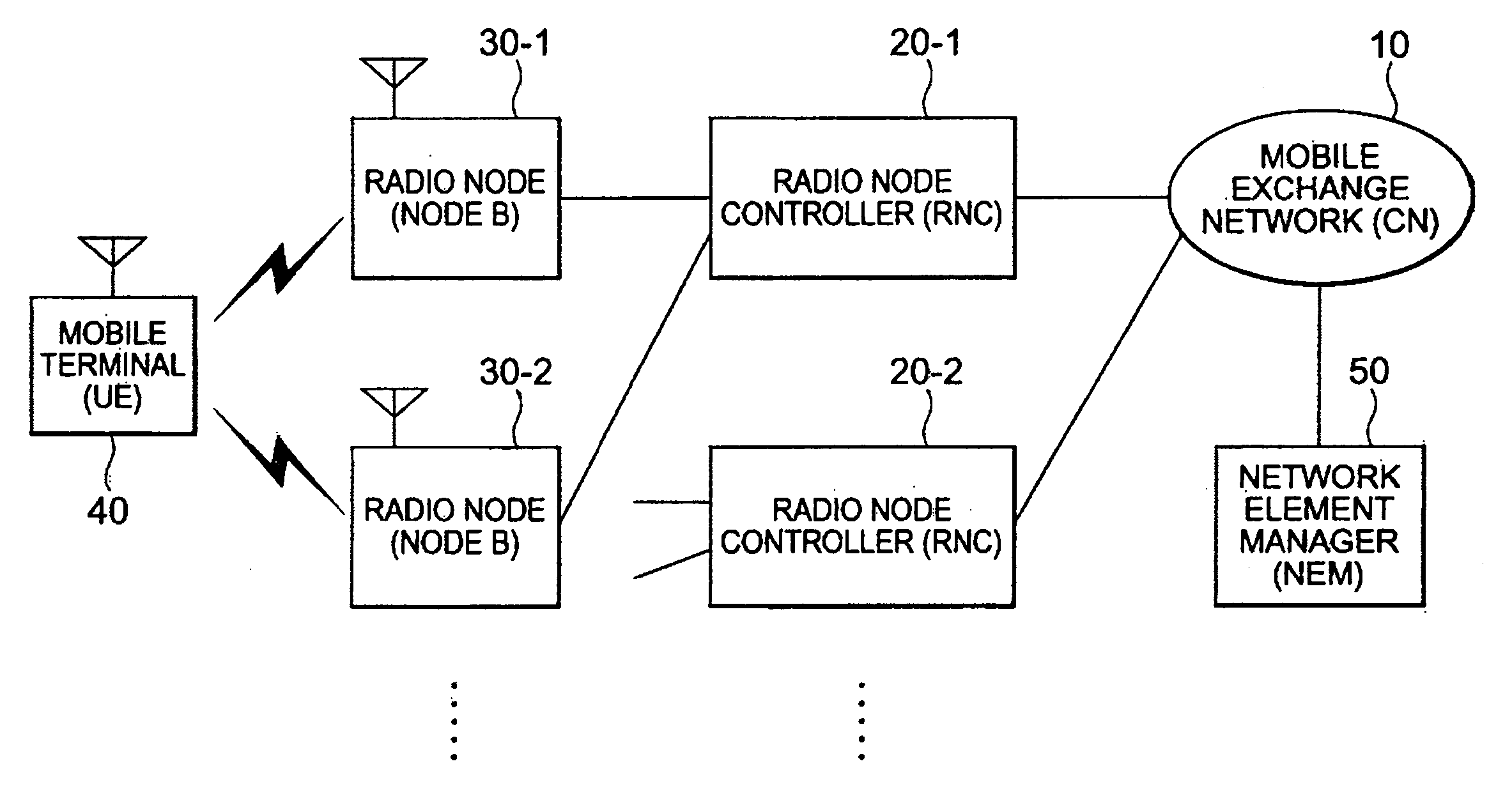
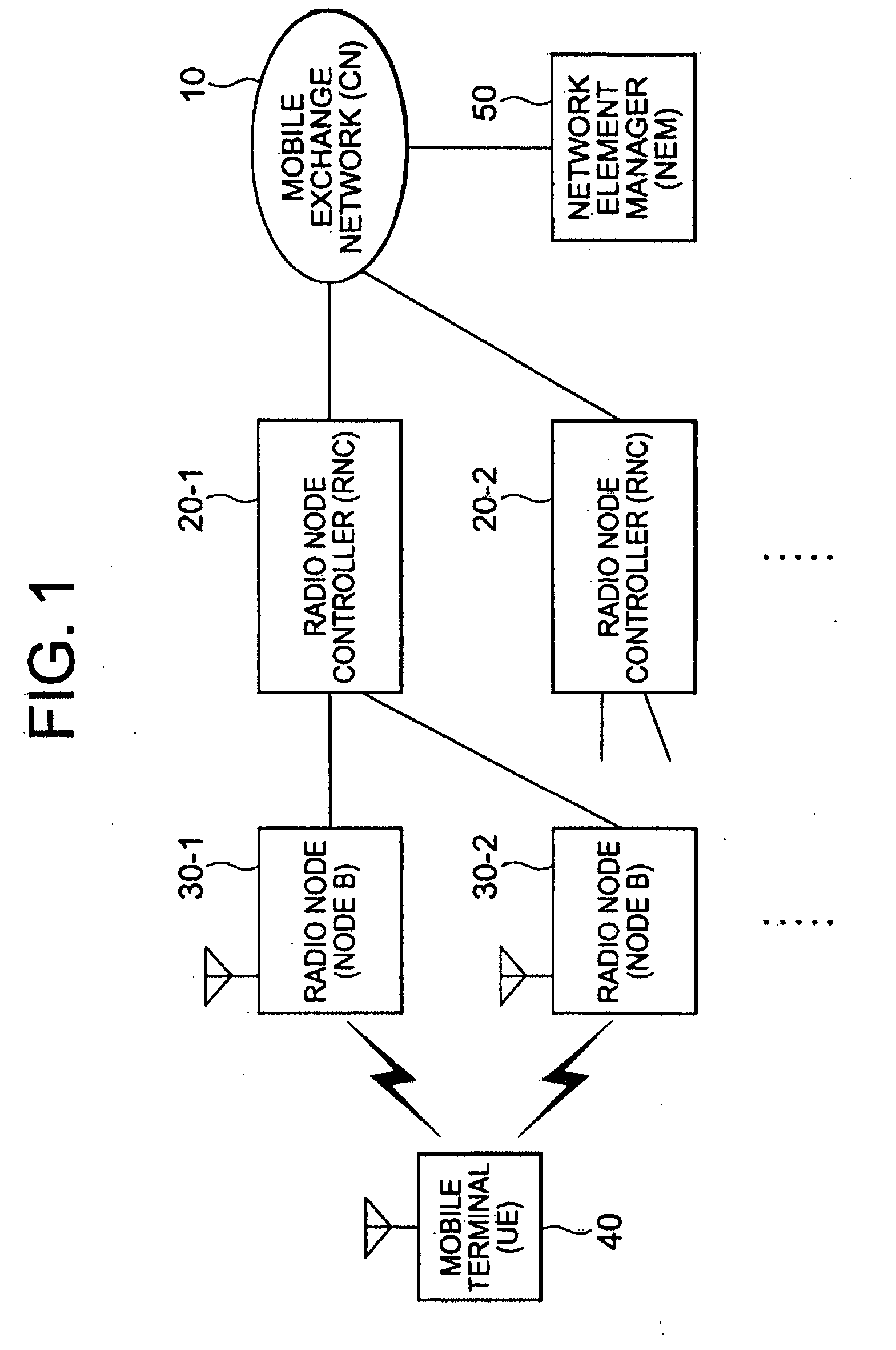
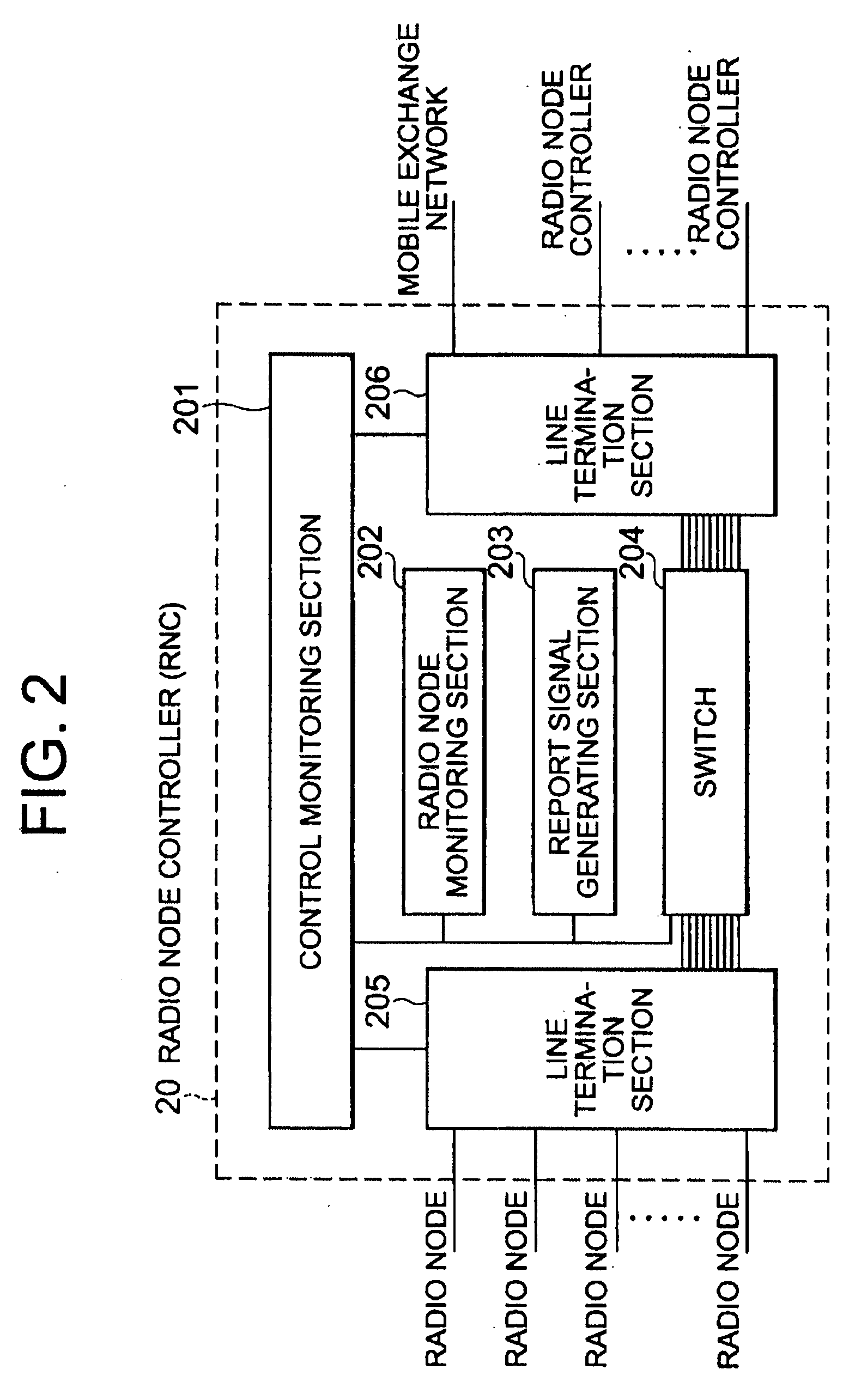
Mobile communication system
InactiveUS20040224673A1Increase freedomAvoid loadNetwork traffic/resource managementSpecial service for subscribersTelecommunicationsMobile communication systems
To provide a mobile communication system which can distribute area information from a radio Node to a mobile terminal in a unit of cell. A mobile communication system comprising: a radio Node having a plurality of cells; host apparatus connected to the radio Node so as to be able to communicate information with the radio Node; and a mobile terminal receiving information distributed from the radio Node, wherein area information different for each cell is distributed from the radio Node to the mobile terminals 40 existing in the cell included in the radio Node, the area information is transmitted, together with control information including type information added according to a content of the area information, from the host apparatus to the radio Node, and the cell to be distributed with the information is determined based on the type information.
Owner:RPX CORP
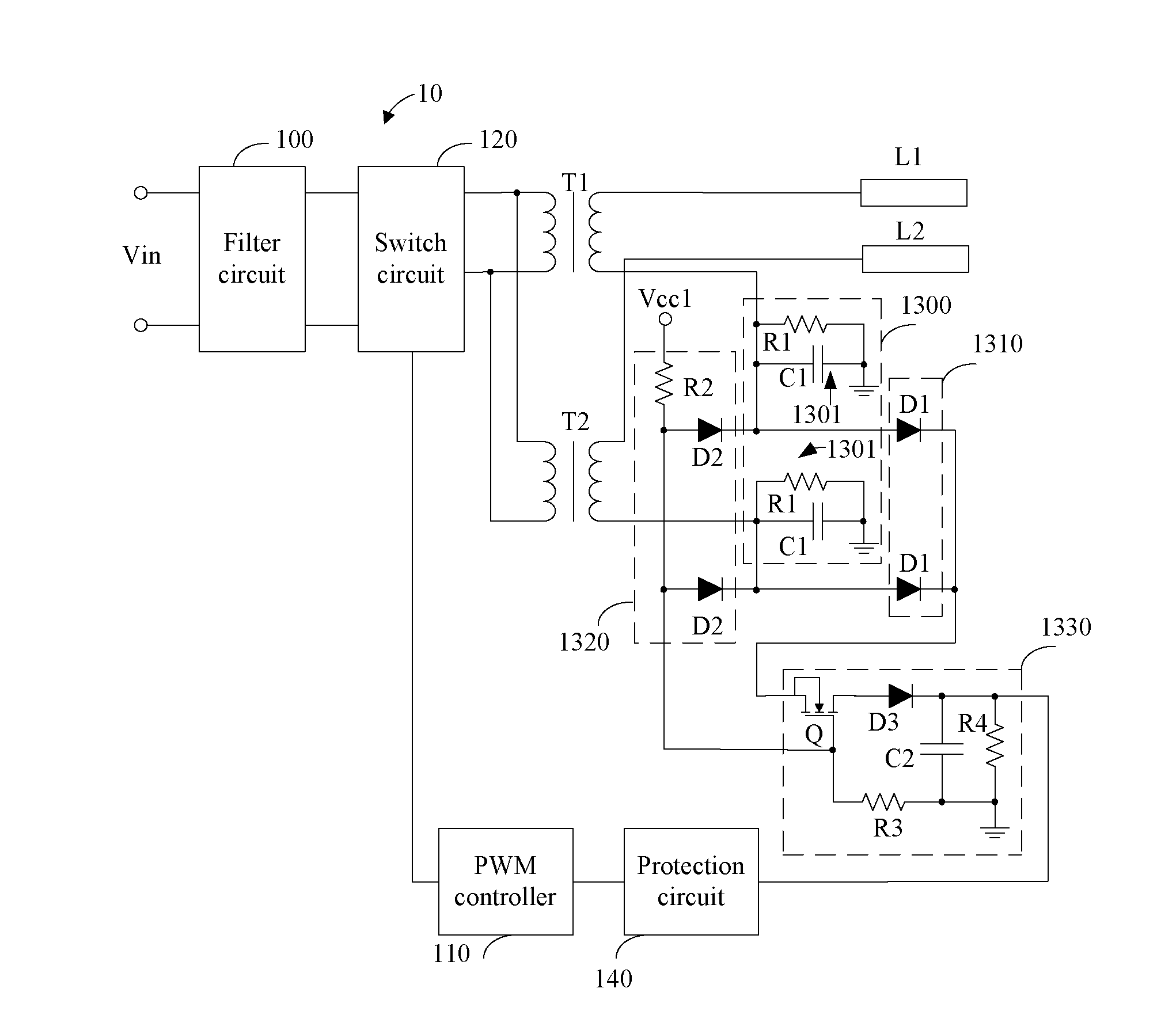
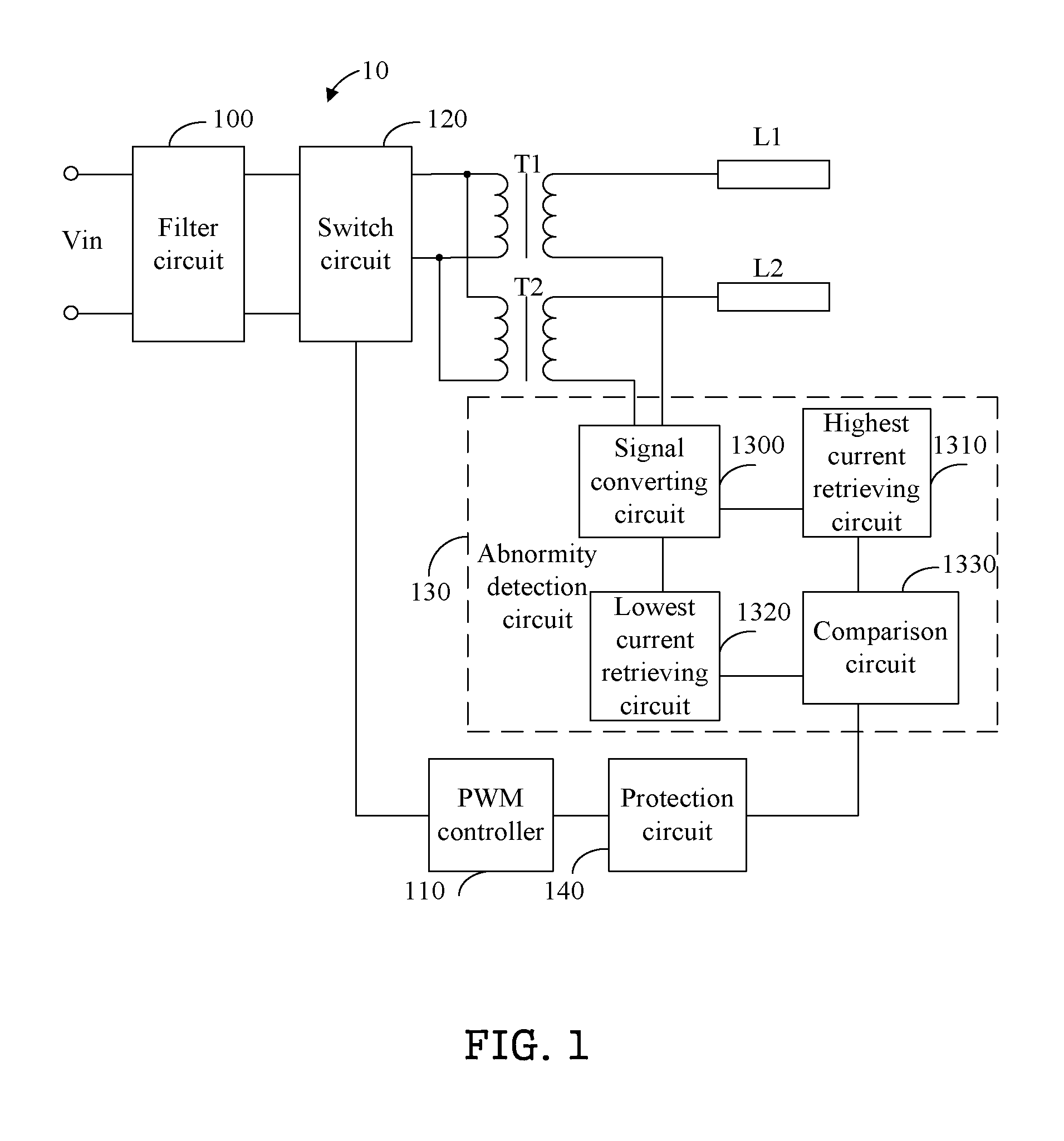
Multi-lamp driving system
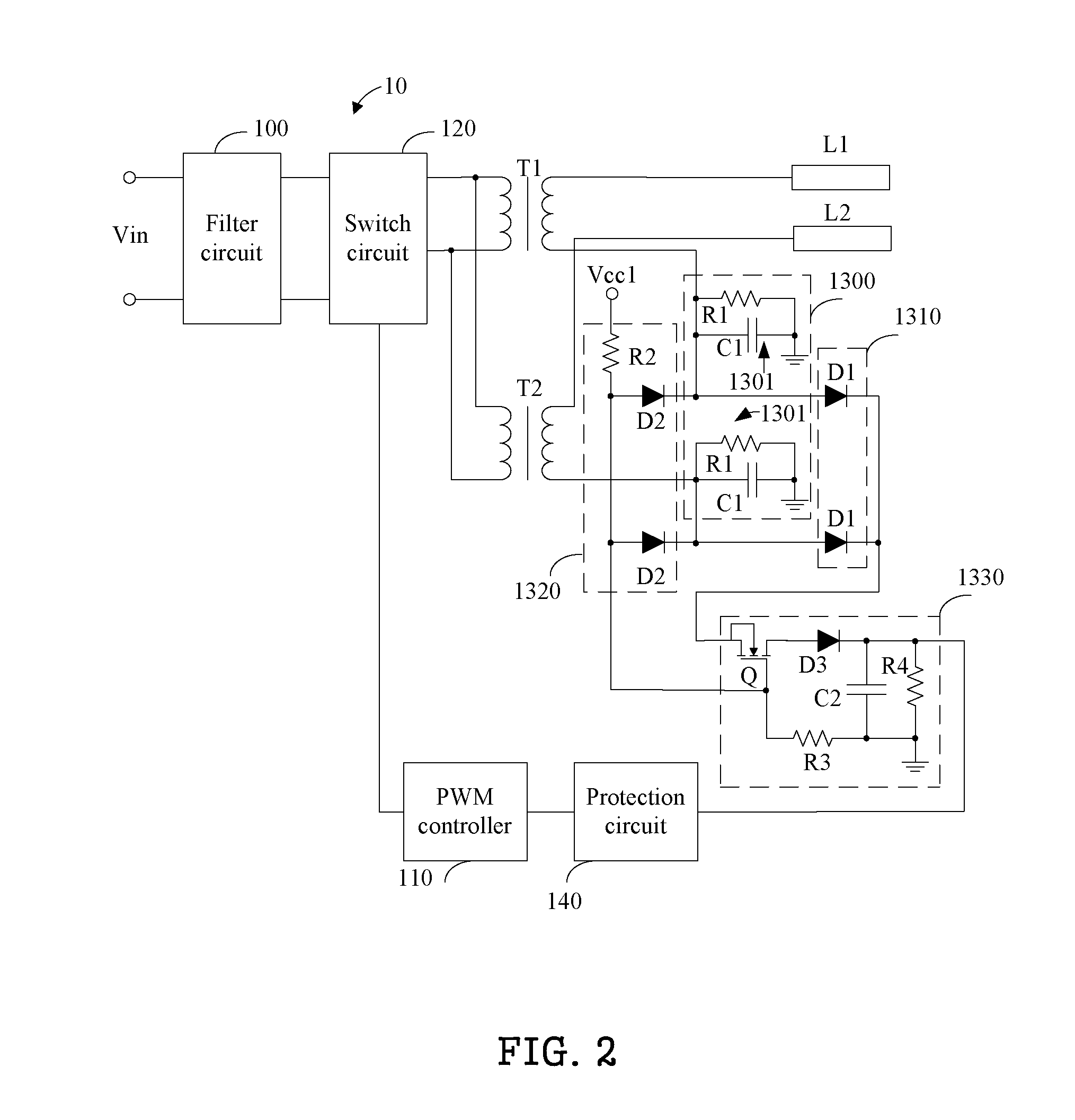
InactiveUS20120187866A1Impeding determinationElectrical apparatusElectric light circuit arrangementLow voltageTransformer
A multi-lamp driving system includes a filter circuit, a switch circuit, a pulse width modulation (PWM) controller, a protection circuit, transformers, and an abnormity detection circuit. Primary windings of the transformers are connected to the switch circuit in parallel, and high voltage terminals of secondary windings of the transformers are connected to lamps respectively. The abnormity detection circuit converts current signals flowing through the lamps into voltage signals, and retrieves highest and lowest voltage signals corresponding to highest and lowest current signal respectively. Then the abnormity detection circuit determines if a difference between the highest voltage signal and the lowest voltage signal exceeds a predetermined value, and generates a trigger signal if the difference between the highest and lowest voltage signals exceeds the predetermined value. The protection circuit receives the trigger signal, and controls the PWM controller to stop outputting PWM signals to the switch circuit.
Owner:AMPOWER TECH CO LTD
Ink-jet recording apparatus and recording method for realizing satisfactory recording even when ink temperature is suddenly changed
An ink-jet recording apparatus detects a temperature of an ink-jet head, and reads, from a table of set drive voltages, a drive voltage corresponding to that head temperature. The read drive voltage is determined to be a drive voltage V1 to be used in a recording for this time. Further, when the scanning number “n” of the ink-jet head has reached a value “m”, a drive voltage V2 to be used for next time is temporarily determined, based on the head temperature. When |V1−V2| is greater than a value ΔV, a voltage obtained by making a correcting, by an amount of ΔV, to the drive voltage V1 is determined to be the drive voltage V2 to be used next time. Therefore, even when the ink temperature is changed during the recording, it is possible to improve the recording quality.
Owner:BROTHER KOGYO KK
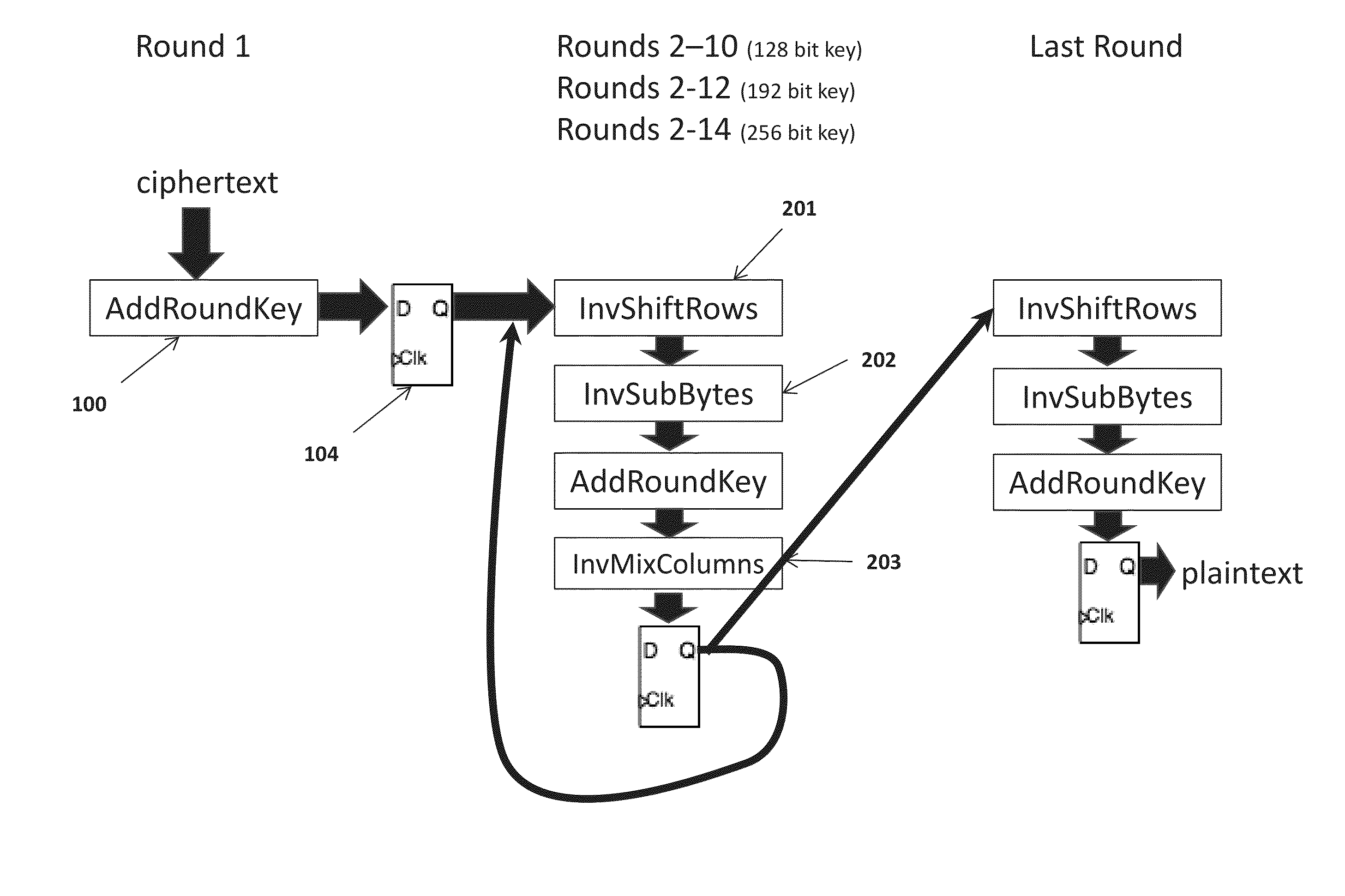
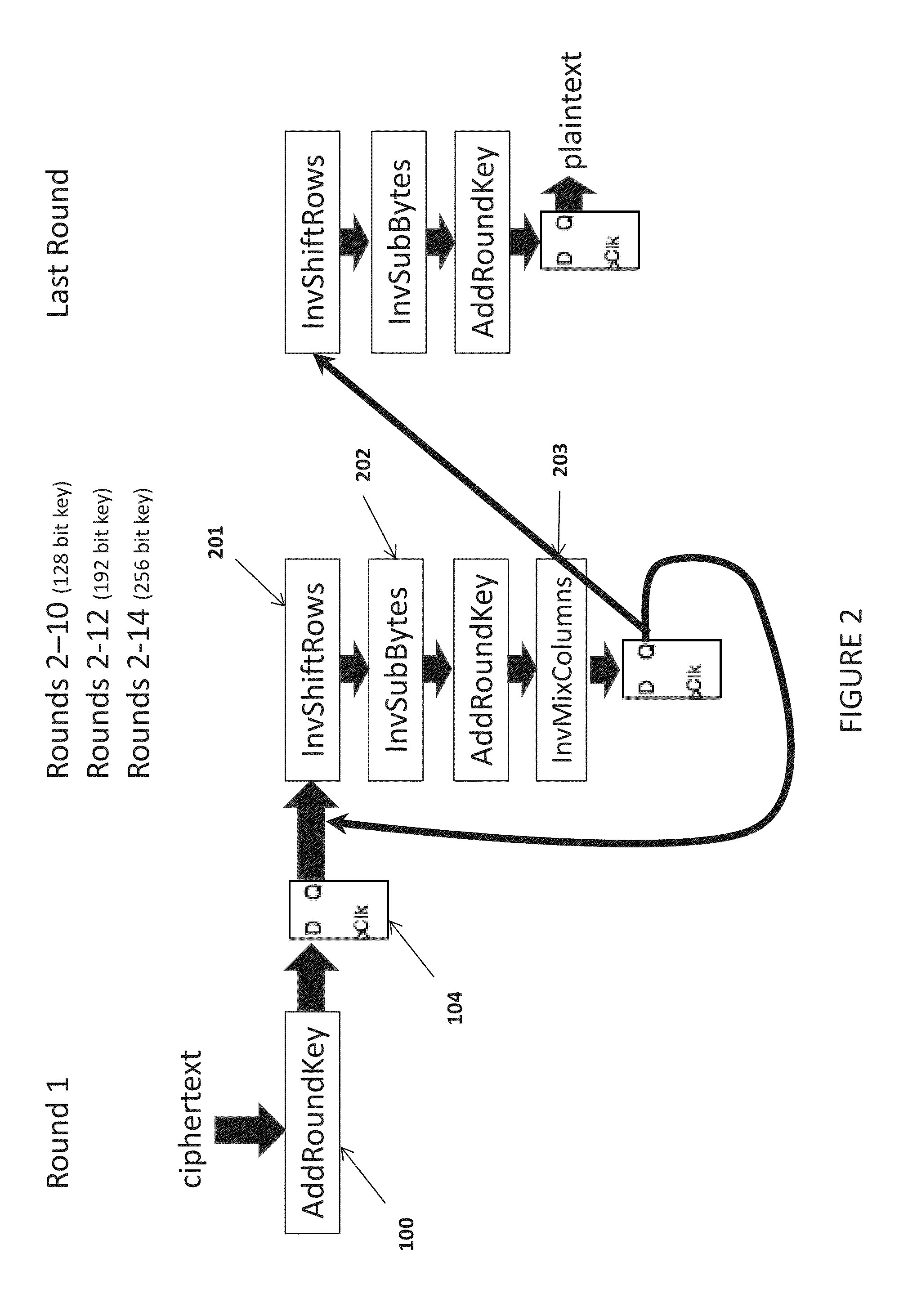
Apparatus and method to prevent side channel power attacks in advanced encryption standard
ActiveUS20140321638A1Avoid problemsImpeding determinationEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesSecret communicationChannel powerComputer hardware
Apparatus and method for obscuring round 1 power consumption of hardware implementation of the Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) algorithm. Additional hardware circuitry will provide consistent power consumption during round 1 of the AES algorithm. This prevents the opportunity to determine the AES key value during a side channel power attack.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESETNED BY THE SEC OF THE AIR FORCE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com