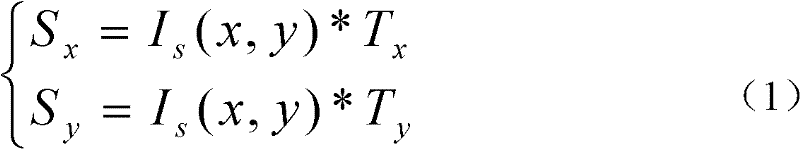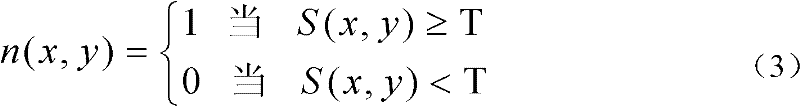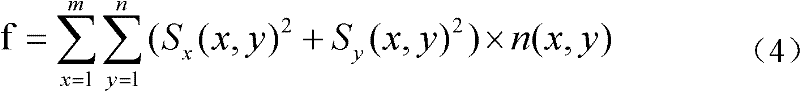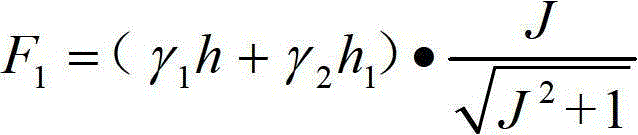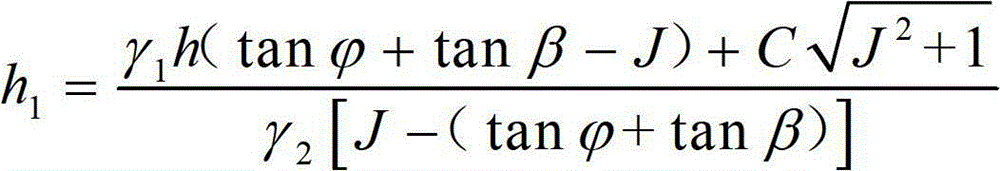Patents
Literature
182 results about "Vertical gradient" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Vertical Gradient. Water levels in nested well clusters (wells located closely together) indicate upward or downward flow in aquifers or flow between adjacent geologic units. Flow is governed by Darcy's Law: where q is the Darcy flux (volume of water per unit area per unit time) and K is the hydraulic conductivity.
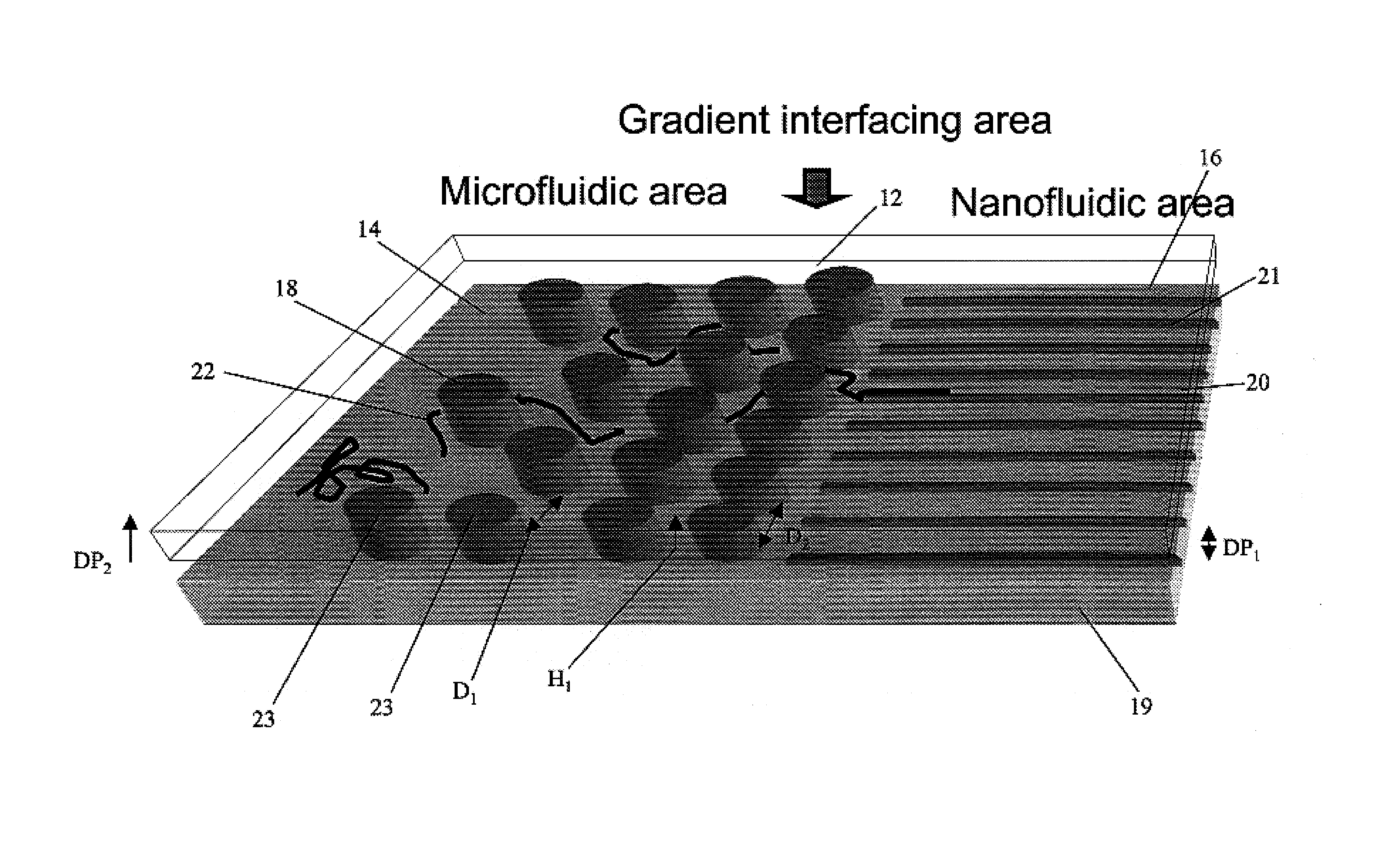
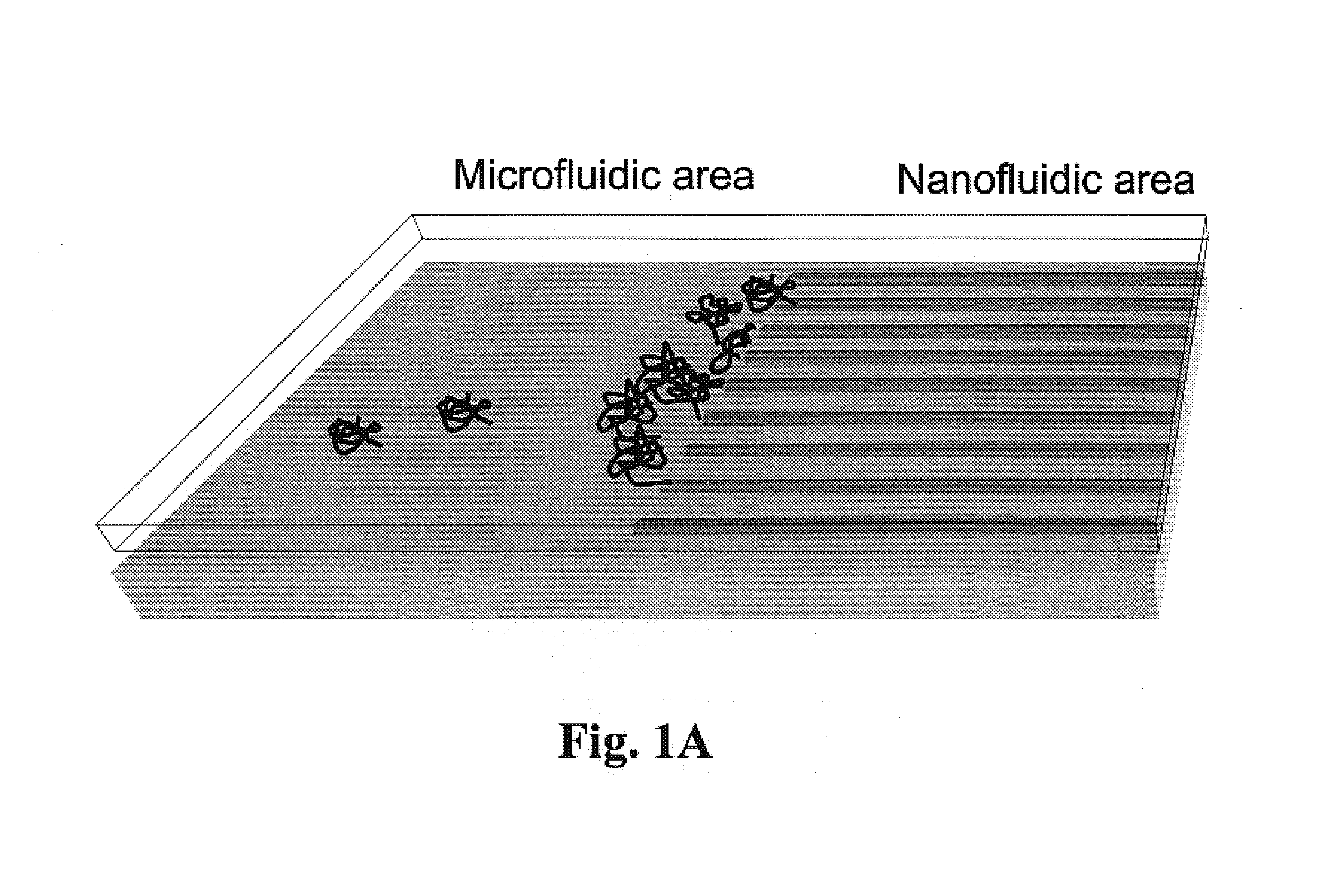
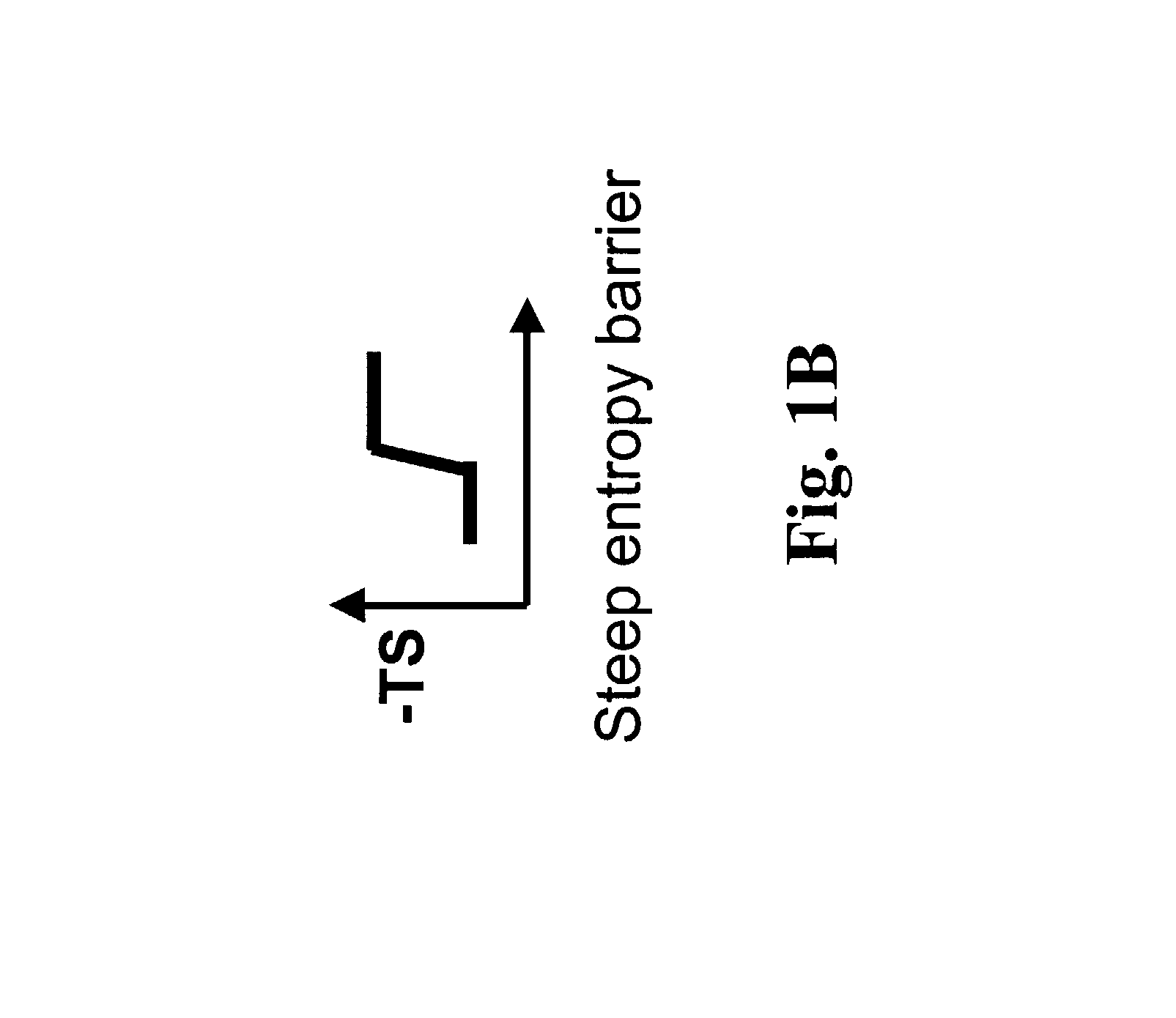
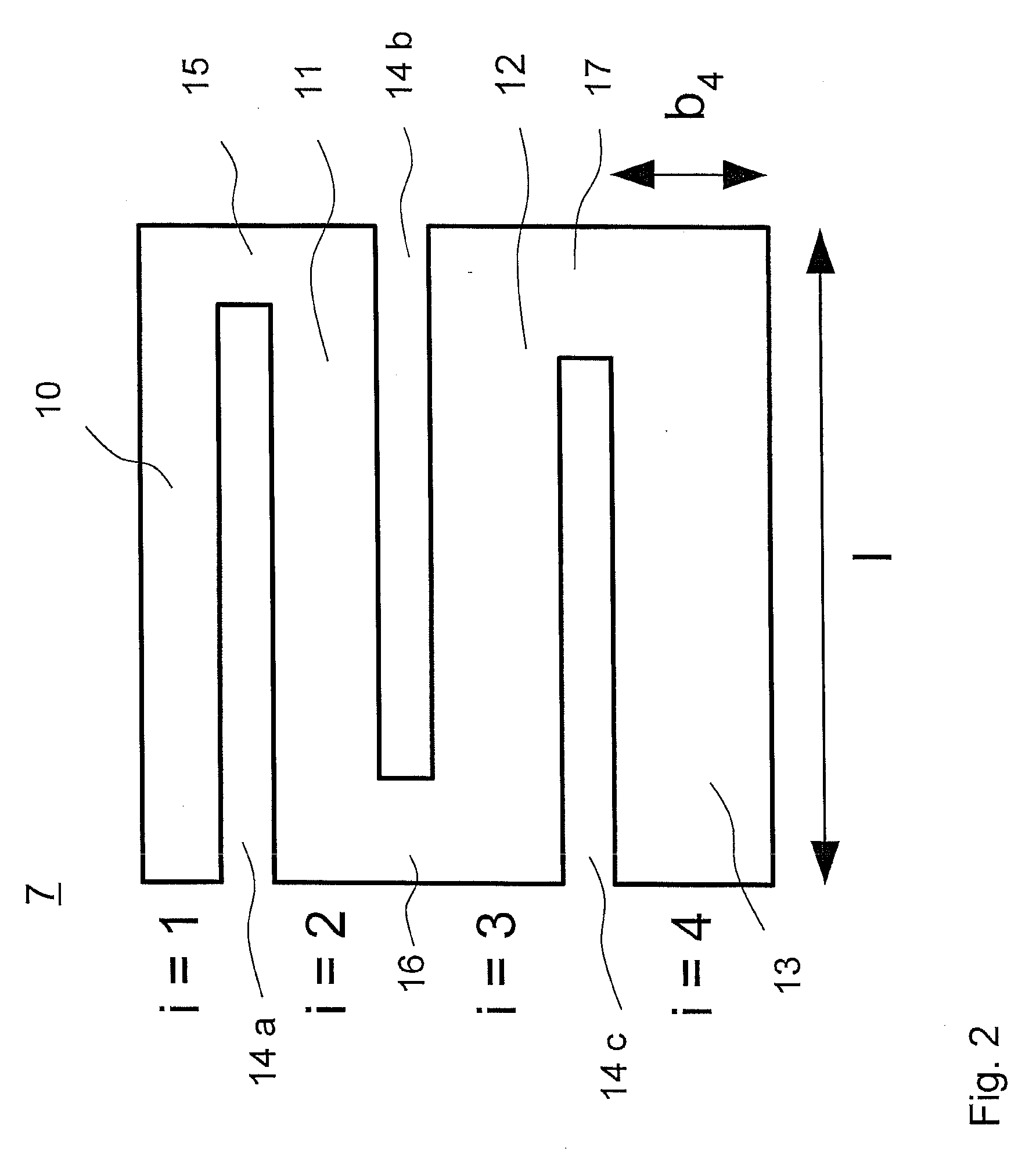
Gradient structures interfacing microfluidics and nanofluidics, methods for fabrication and uses thereof
ActiveUS7217562B2Improve throughputReduces the local entropic barrierMaterial nanotechnologyNanostructure manufactureVertical gradientMicrofluidics
The present invention relates to a device for interfacing nanofluidic and microfluidic components suitable for use in performing high throughput macromolecular analysis. Diffraction gradient lithography (DGL) is used to form a gradient interface between a microfluidic area and a nanofluidic area. The gradient interface area reduces the local entropic barrier to nanochannels formed in the nanofluidic area. In one embodiment, the gradient interface area is formed of lateral spatial gradient structures for narrowing the cross section of a value from the micron to the nanometer length scale. In another embodiment, the gradient interface area is formed of a vertical sloped gradient structure. Additionally, the gradient structure can provide both a lateral and vertical gradient.
Owner:PRINCETON UNIV
Method for producing monocrystalline metal or semi-metal bodies
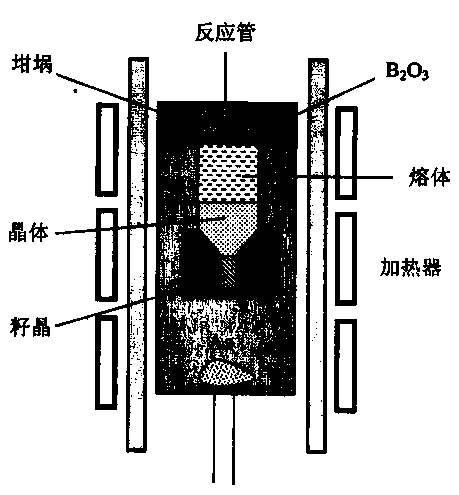
InactiveUS20090047203A1Cheap methodCost effective productionPolycrystalline material growthSiliconVertical gradientCrucible
Owner:SCHOTT AG
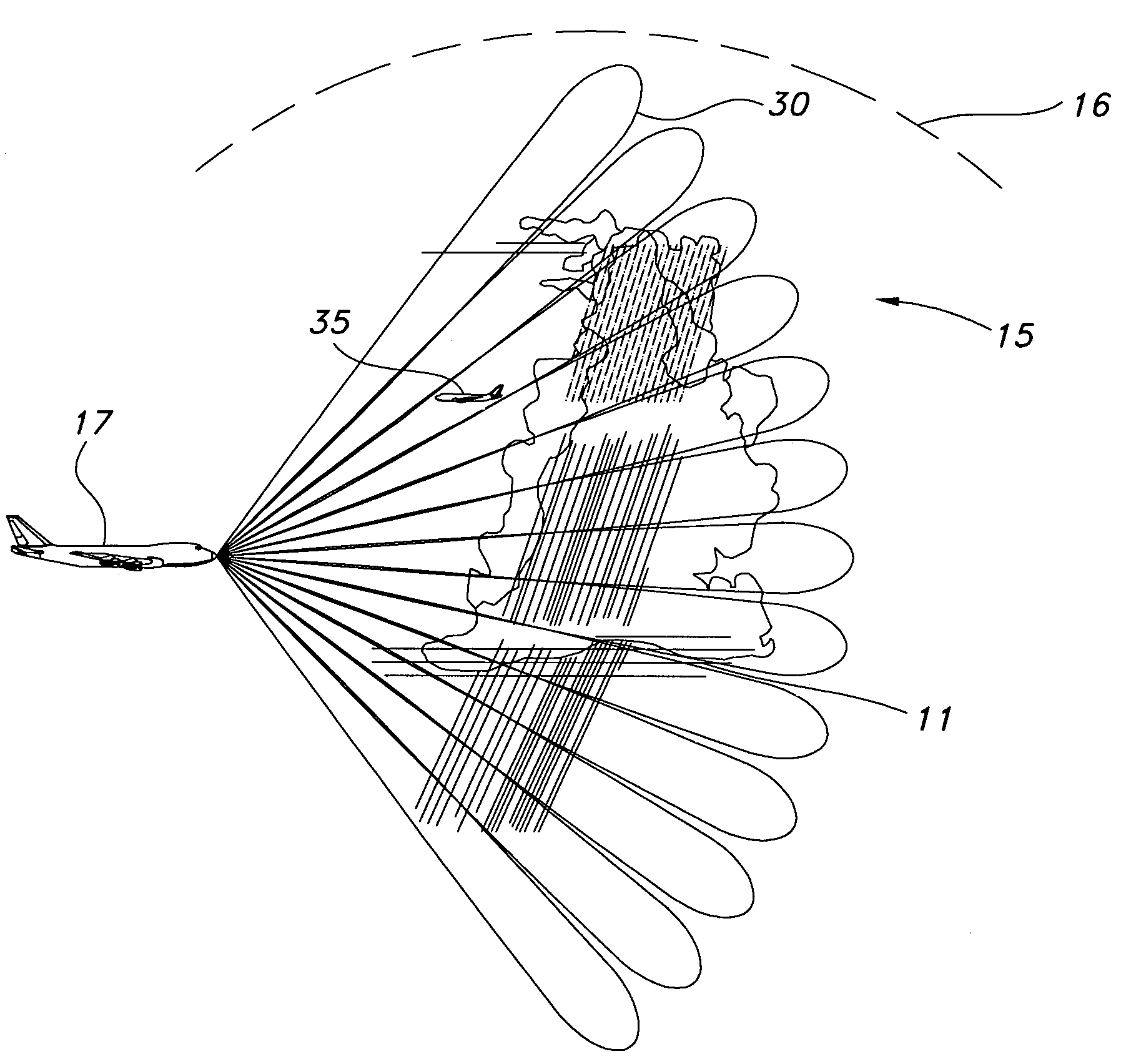
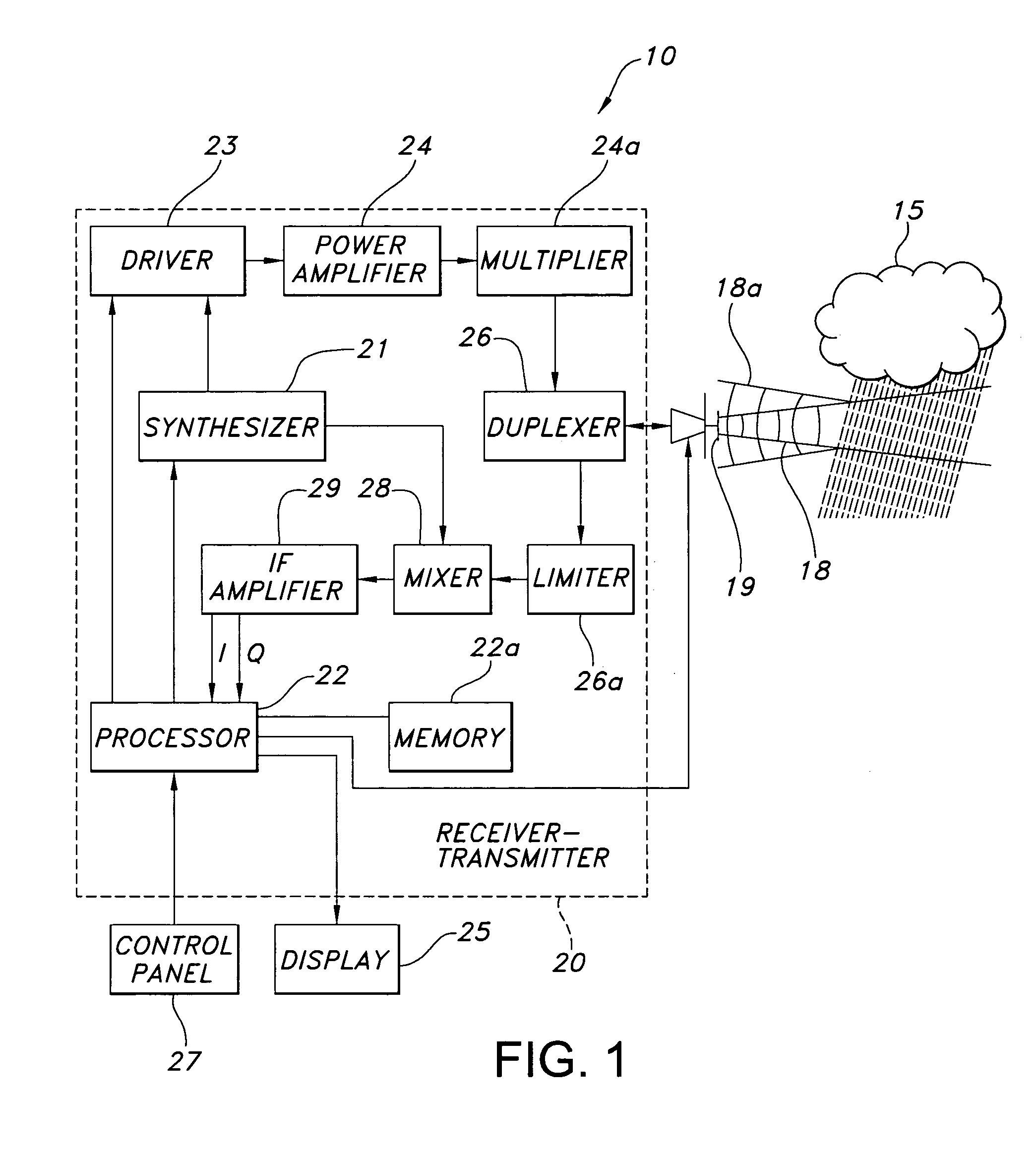
Removal of spurious aircraft detections on weather radar
ActiveUS7417578B1Improve performanceAvoid confusionRadio wave reradiation/reflectionICT adaptationDoppler velocitySpectral width
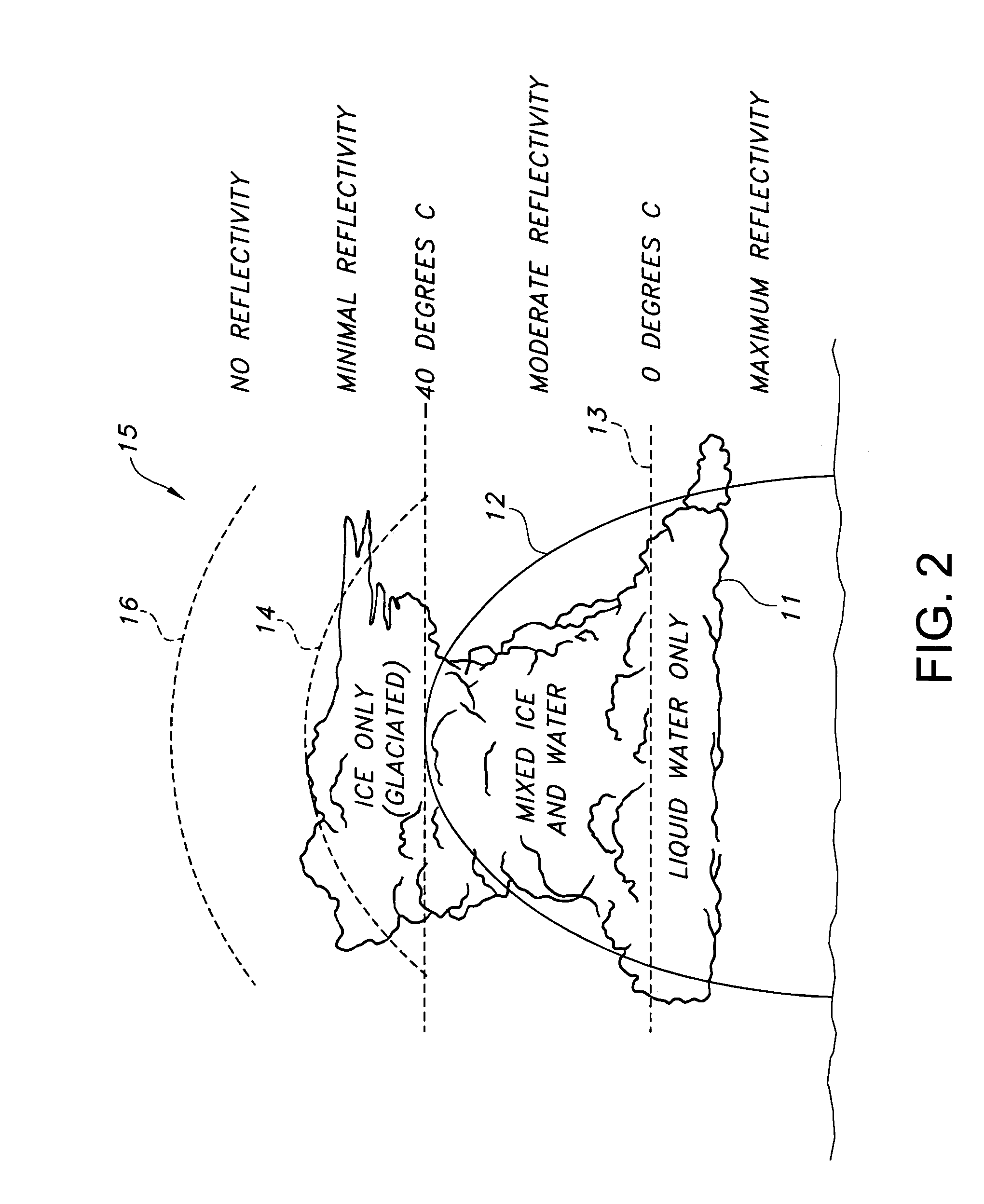
A weather radar detects and removes spurious aircraft from a weather radar display by using one of the methods of differentiating radar return length, estimating a vertical gradient of reflectivity, tracking radar returns into regions that are eliminated from the weather display to provide differentiation, tracking areas of radar returns that allow detection and removal of the spurious aircraft in relative geometries, differentiating Doppler velocity, and differentiating spectral width. The methods may be used individually or in combination to improve performance.
Owner:ROCKWELL COLLINS INC
Edge detection based on variable-length codes of block coded video
ActiveUS7054367B2Television system detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesVariable-length codePattern recognition
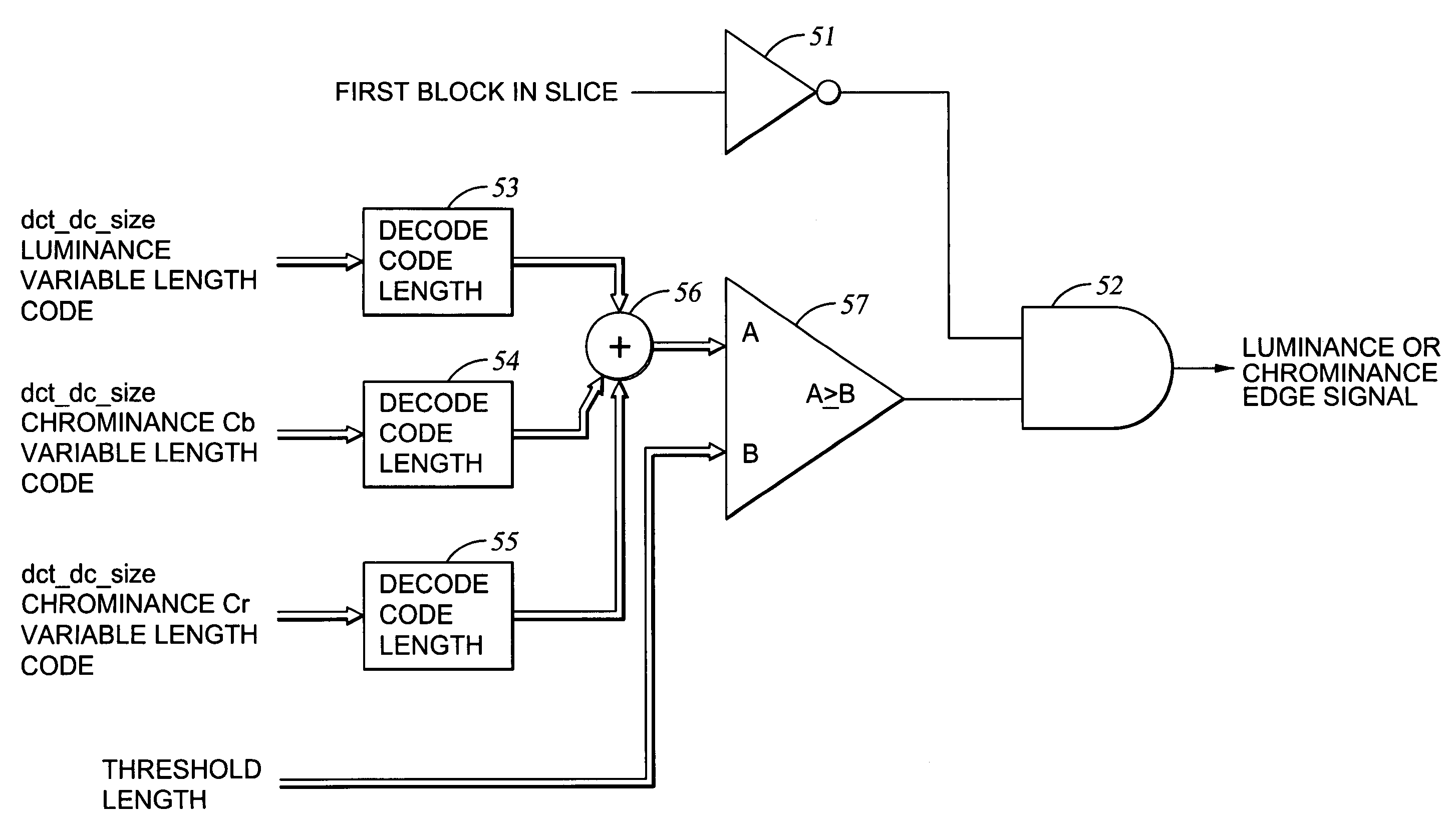
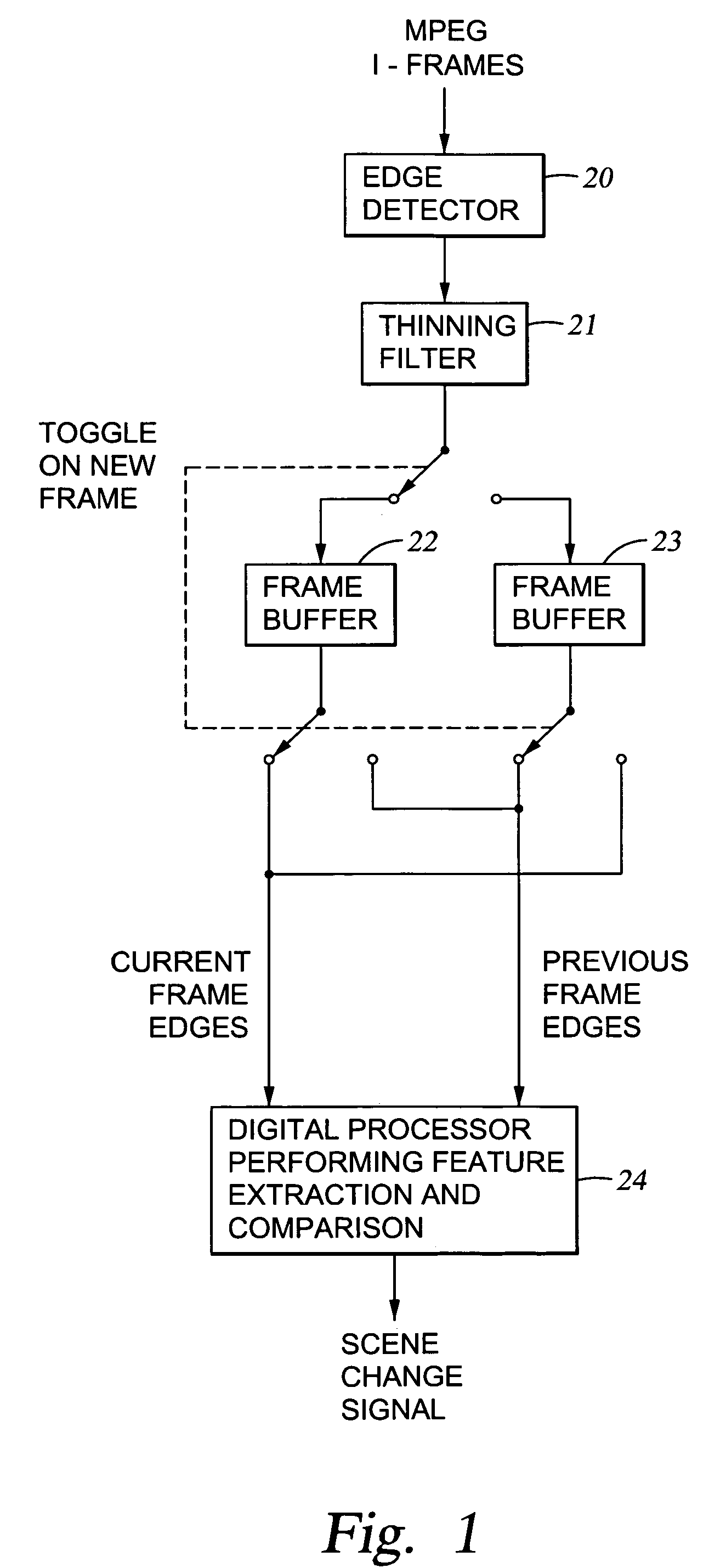
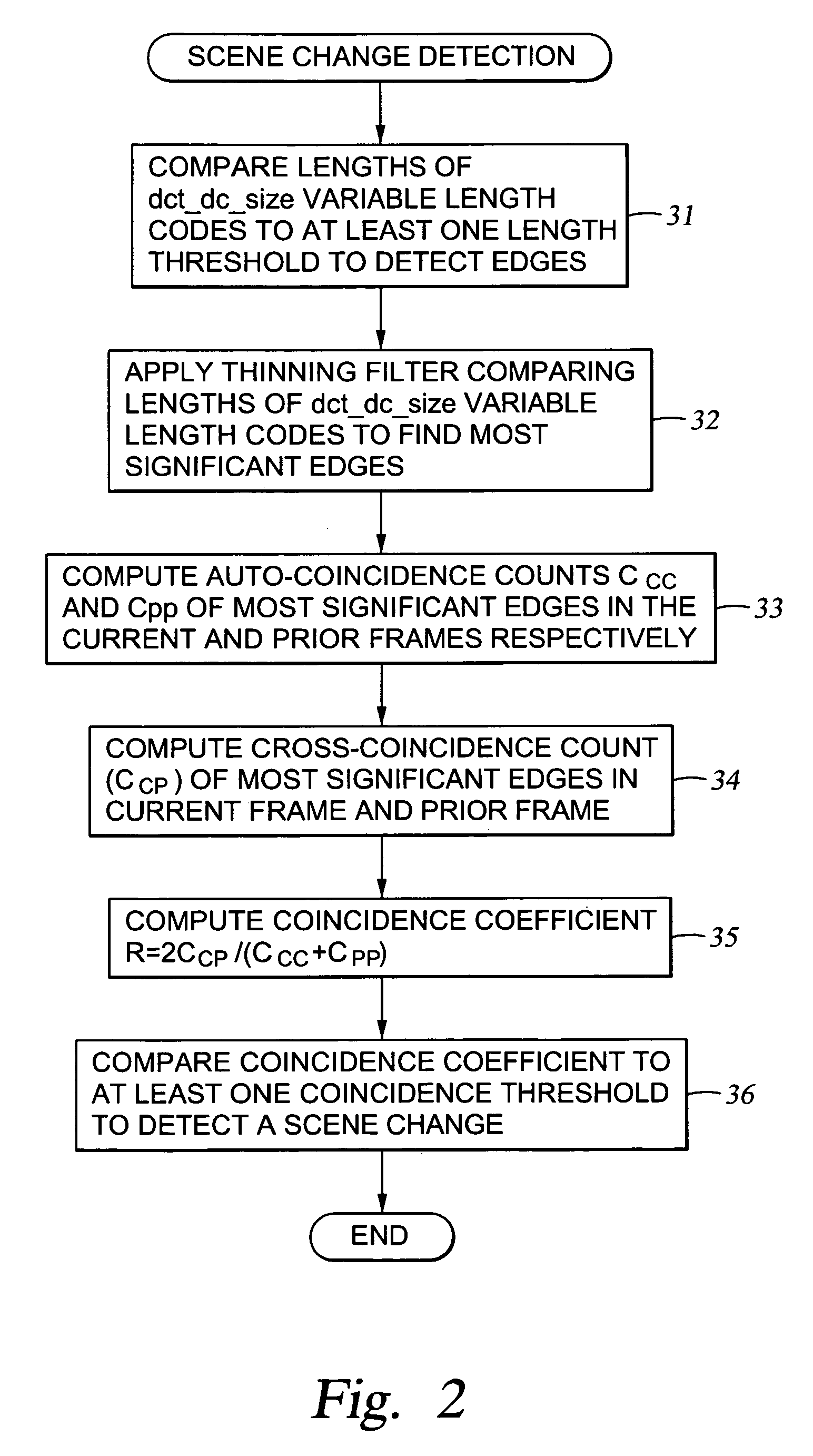
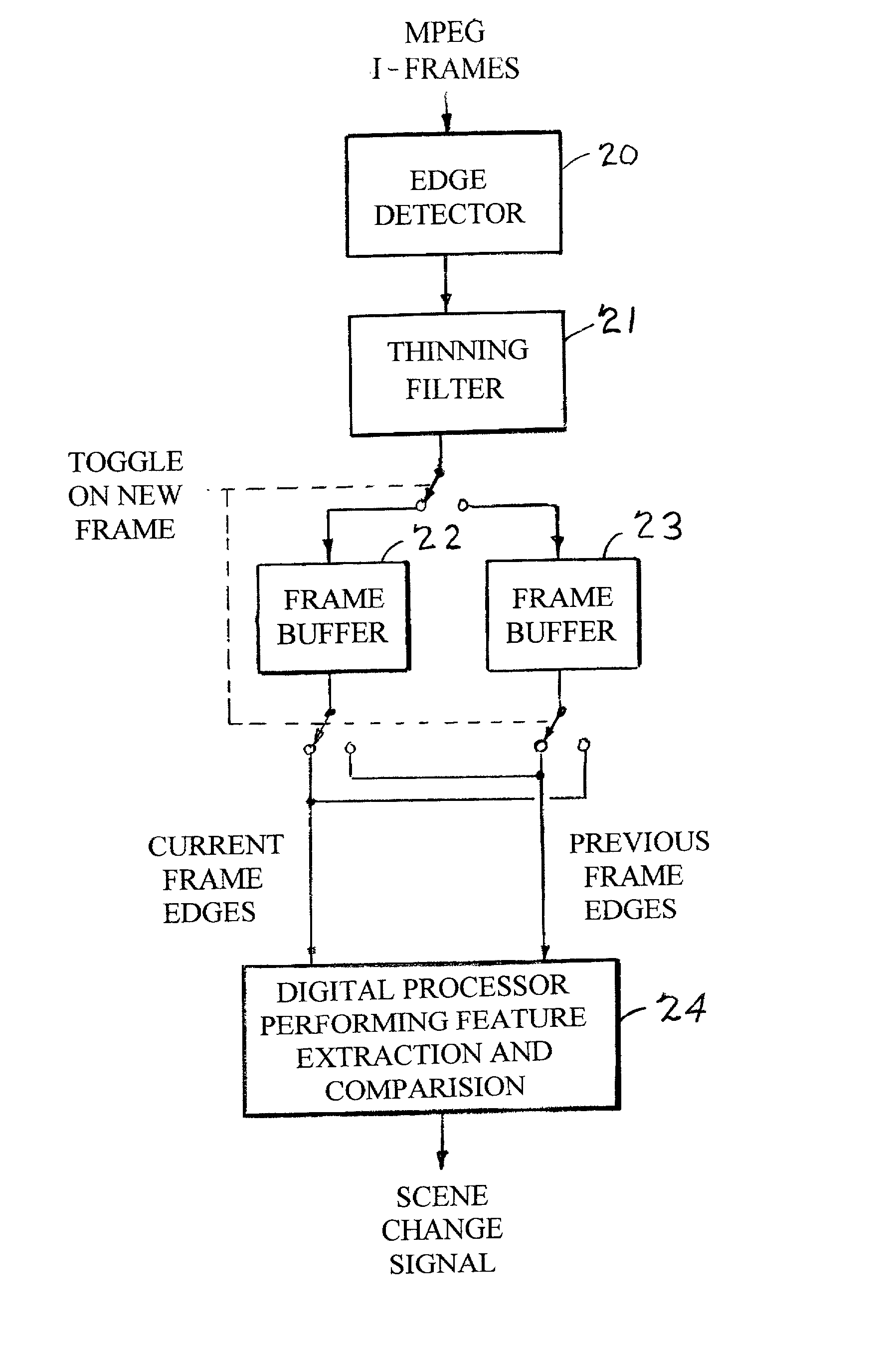
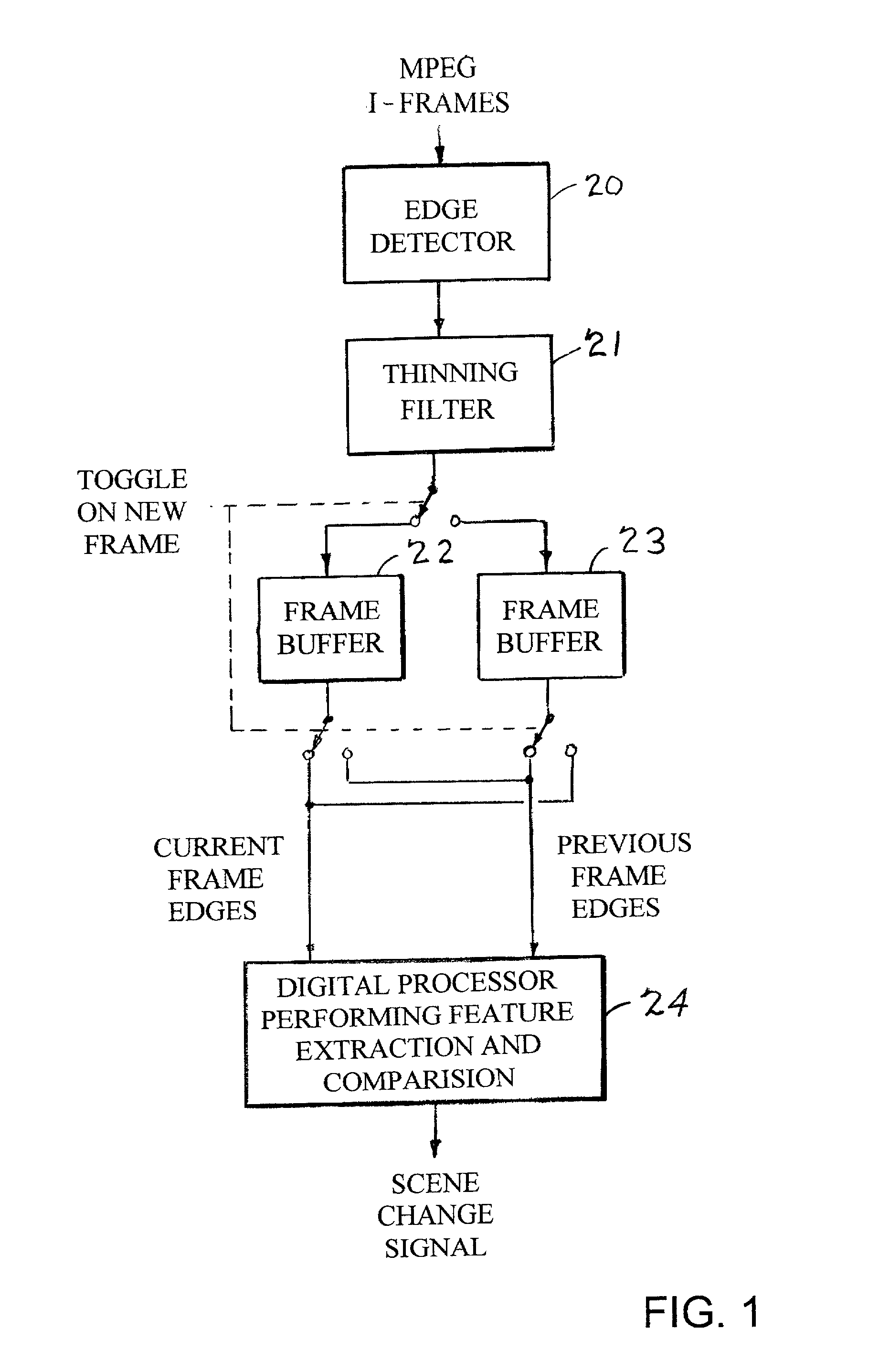
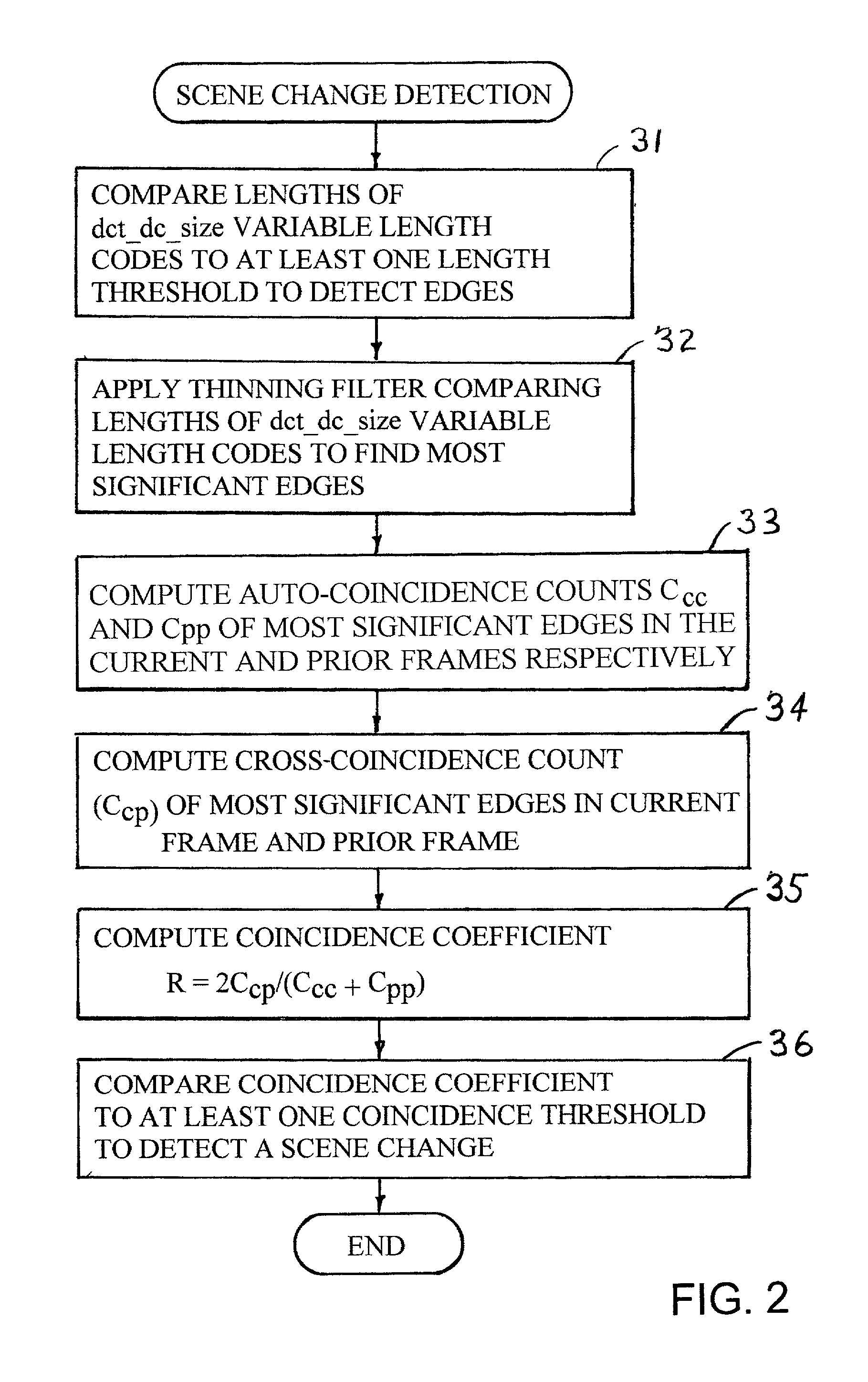
Edges are detected in block coded video by a threshold comparison upon the lengths of variable-length codes used for encoding the differential DC coefficients of the pixel blocks. A thinning filter compares the code lengths of the differential DC coefficients of adjacent blocks in order to retain the edge indications of more significant edges and to exclude the edge indications of less significant edges. The edge indications can be split into substantially independent channels for luminance or chrominance, for edges having positive or negative horizontal gradient components, and for edges having positive or negative vertical gradient components. The edge indications for successive frames in an MPEG sequence are compared to each other in various ways in order to detect scene changes.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
Analytical cartridge with fluid flow control
ActiveUS20100009430A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsPorous substrateAnalyte
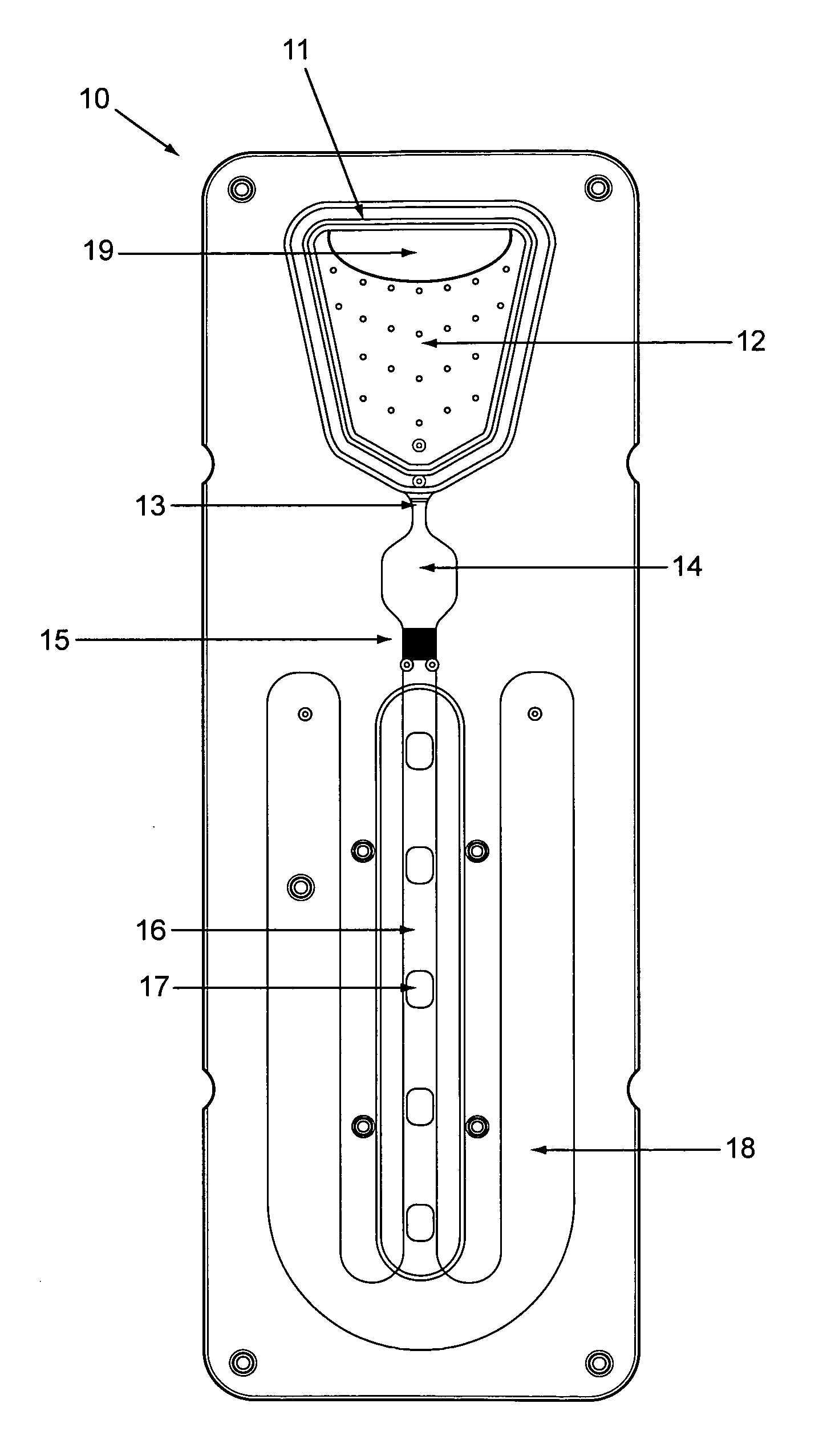
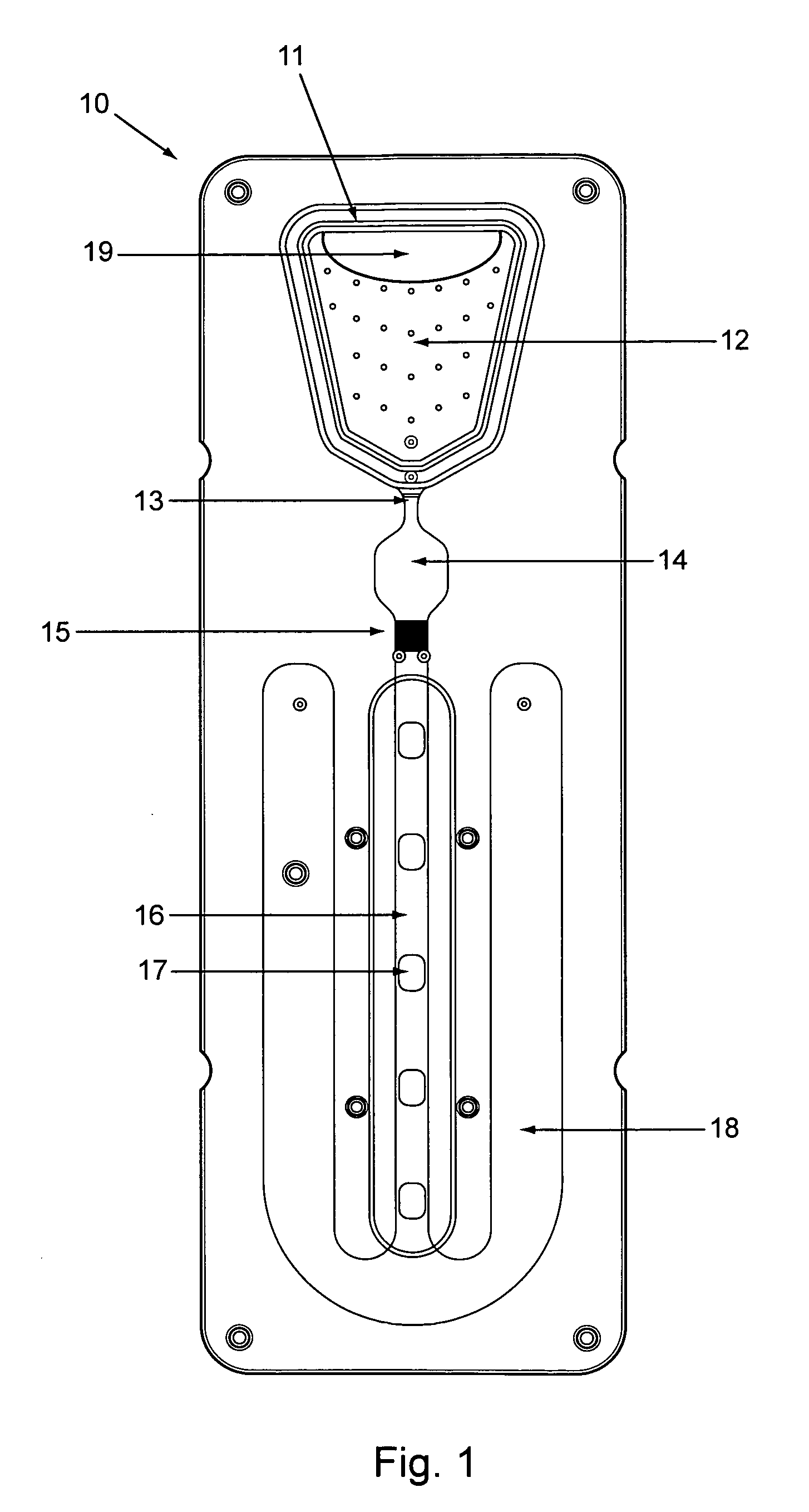
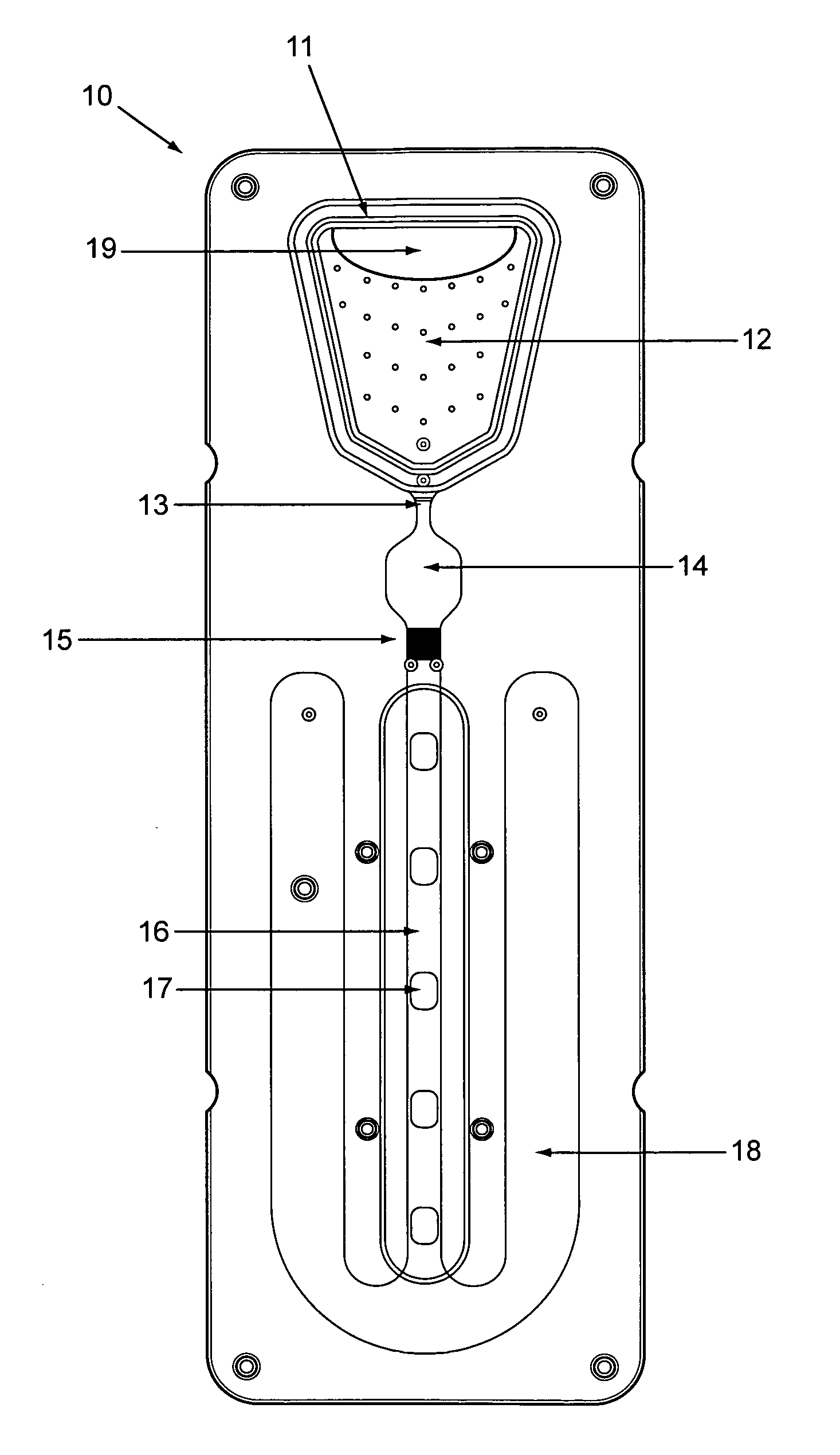
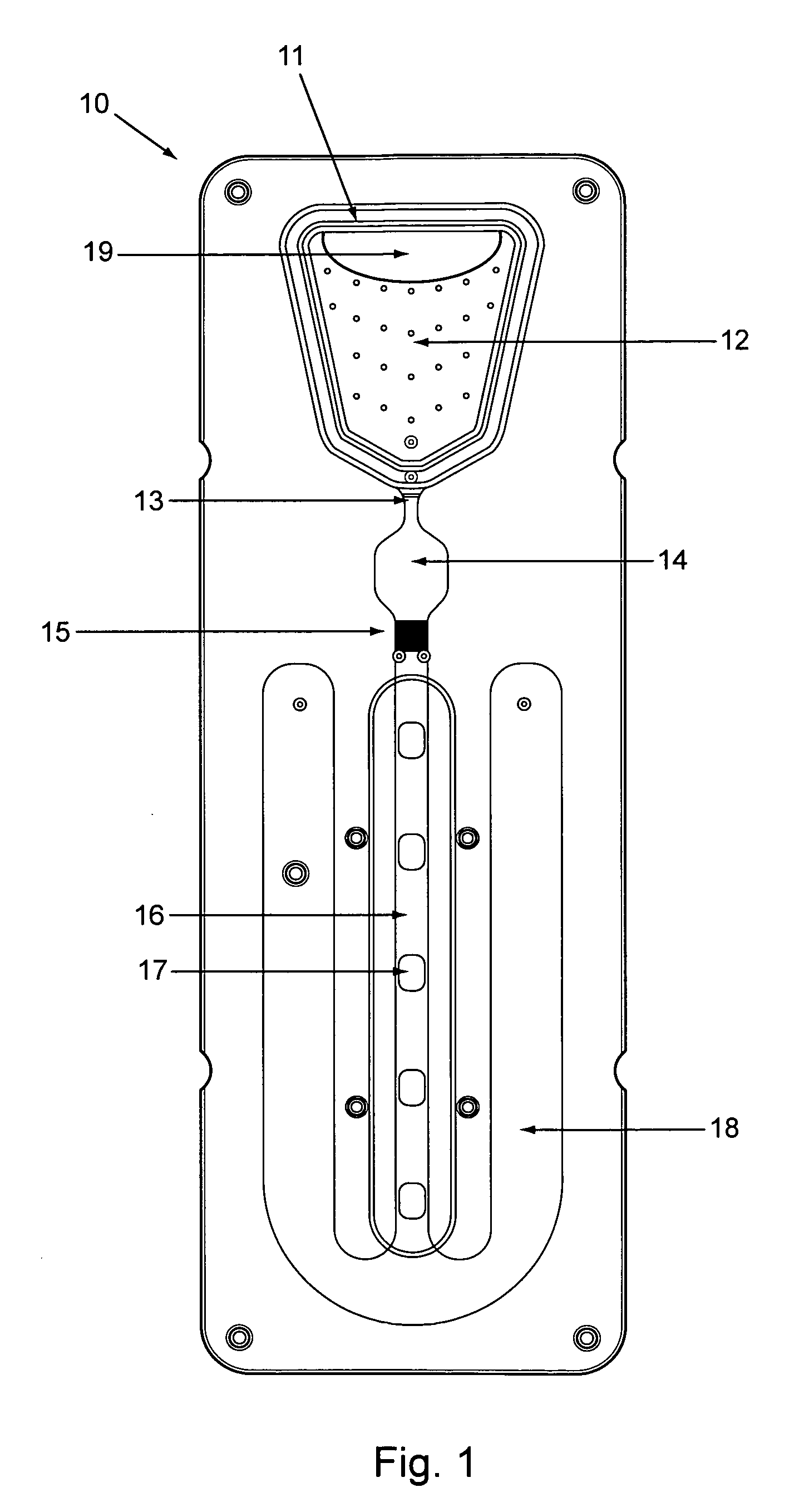
Analytical cartridges, systems and methods of processing a sample for analysis using capillary flows. Vertical gradient sample filtration provides filtrate to an incubation chamber for a time controlled by a flow modulator at the outlet of the incubation chamber. The flow modulator can include a serpentine capillary flow path without side walls. Incubated filtrate can flow from the incubation chamber to a detection channel after a predetermined time. The detection chamber can include one or more analytical regions in a porous substrate for detection of two or more analytes on the same cartridge from the same sample.
Owner:MICROPOINT BIOTECHNOLOGIES CO LTD
Edge detection based on variable-length codes of block coded video
ActiveUS20030142750A1Television system detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesVariable-length codePattern recognition
Edges are detected in block coded video by a threshold comparison upon the lengths of variable-length codes used for encoding the differential DC coefficients of the pixel blocks. A thinning filter compares the code lengths of the differential DC coefficients of adjacent blocks in order to retain the edge indications of more significant edges and to exclude the edge indications of less significant edges. The edge indications can be split into substantially independent channels for luminance or chrominance, for edges having positive or negative horizontal gradient components, and for edges having positive or negative vertical gradient components. The edge indications for successive frames in an MPEG sequence are compared to each other in various ways in order to detect scene changes.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
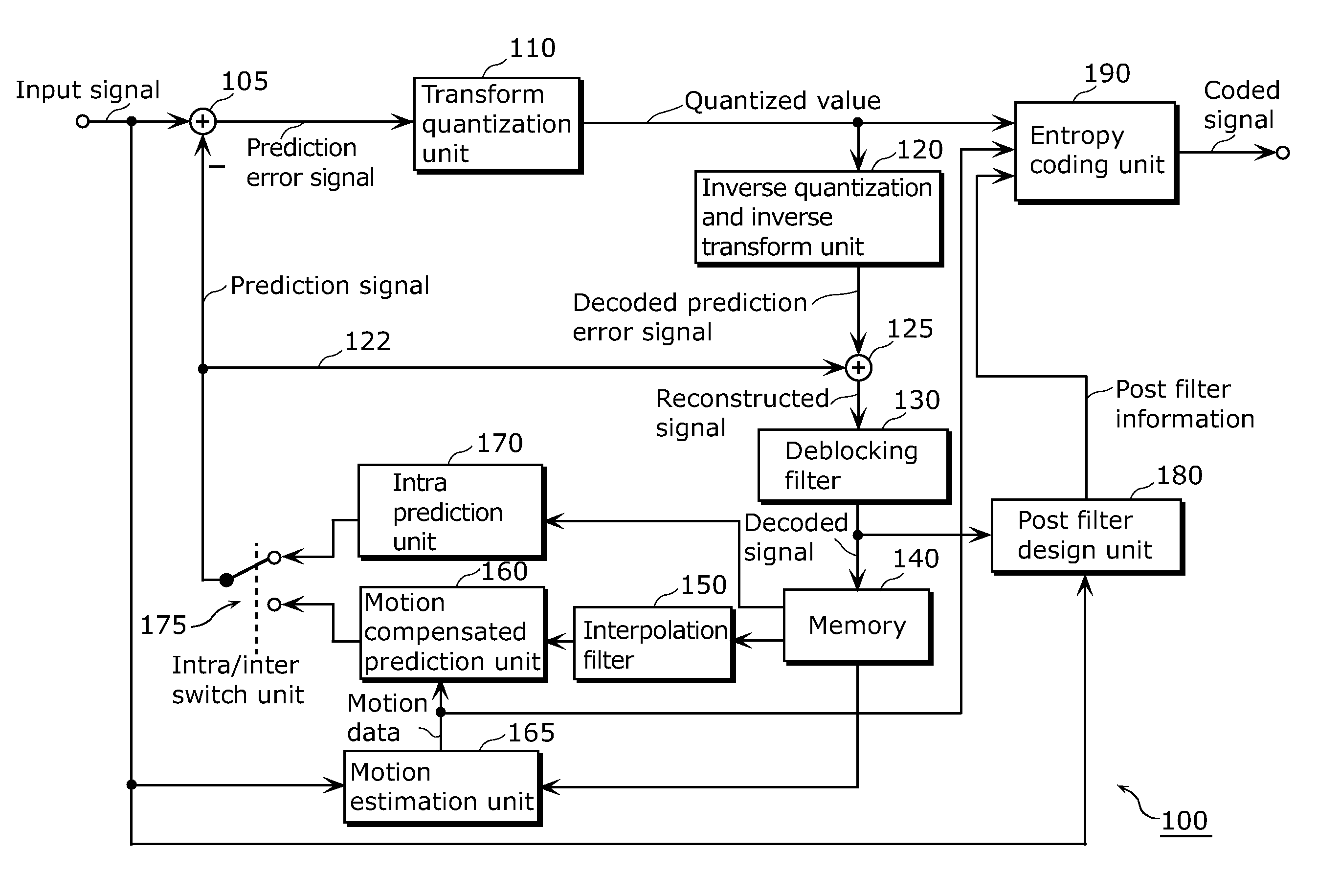
Video Coder Providing Implicit Coefficient Prediction and Scan Adaptation for Image Coding and Intra Coding of Video
InactiveUS20110075739A1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionVertical gradientAlgorithm
A predictive video coder performs gradient prediction based on previous blocks of image data. For a new block of image data, the prediction determines a horizontal gradient and a vertical gradient from a block diagonally above the new block (vertically above a previous horizontally adjacent block). Based on these gradients, the encoder predicts image information based on image information of either the horizontally adjacent block or a block vertically adjacent to the new block. The encoder determines a residual that is transmitted in an output bitstream. The decoder performs the identical gradient prediction and predicts image information without need for overhead information. The decoder computes the actual information based on the predicted information and the residual from the bitstream.
Owner:AT&T INTPROP I L P
Crystal growing device and method
InactiveCN101555620AAfter-treatment apparatusPolycrystalline material growthVertical gradientCrucible
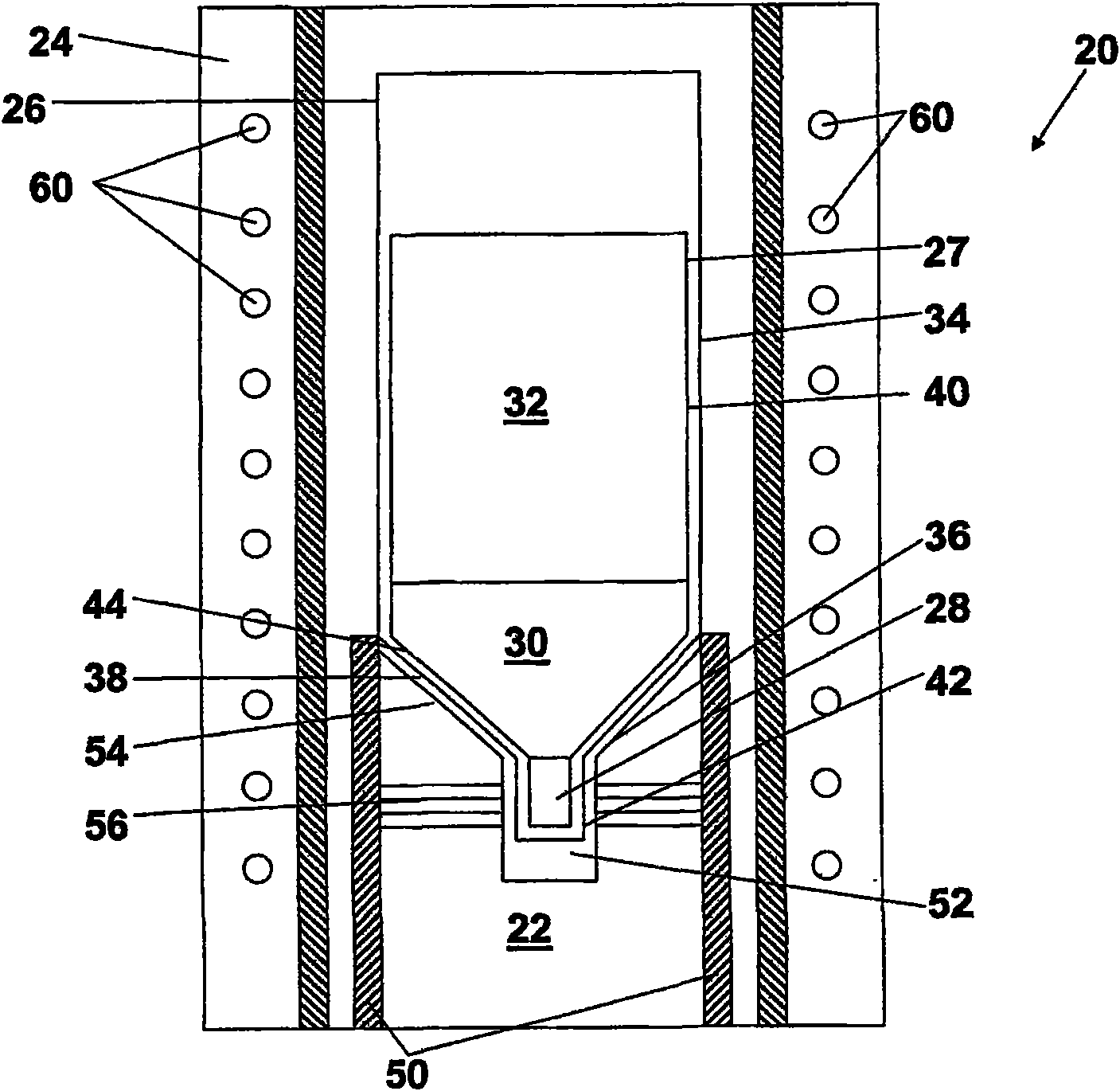
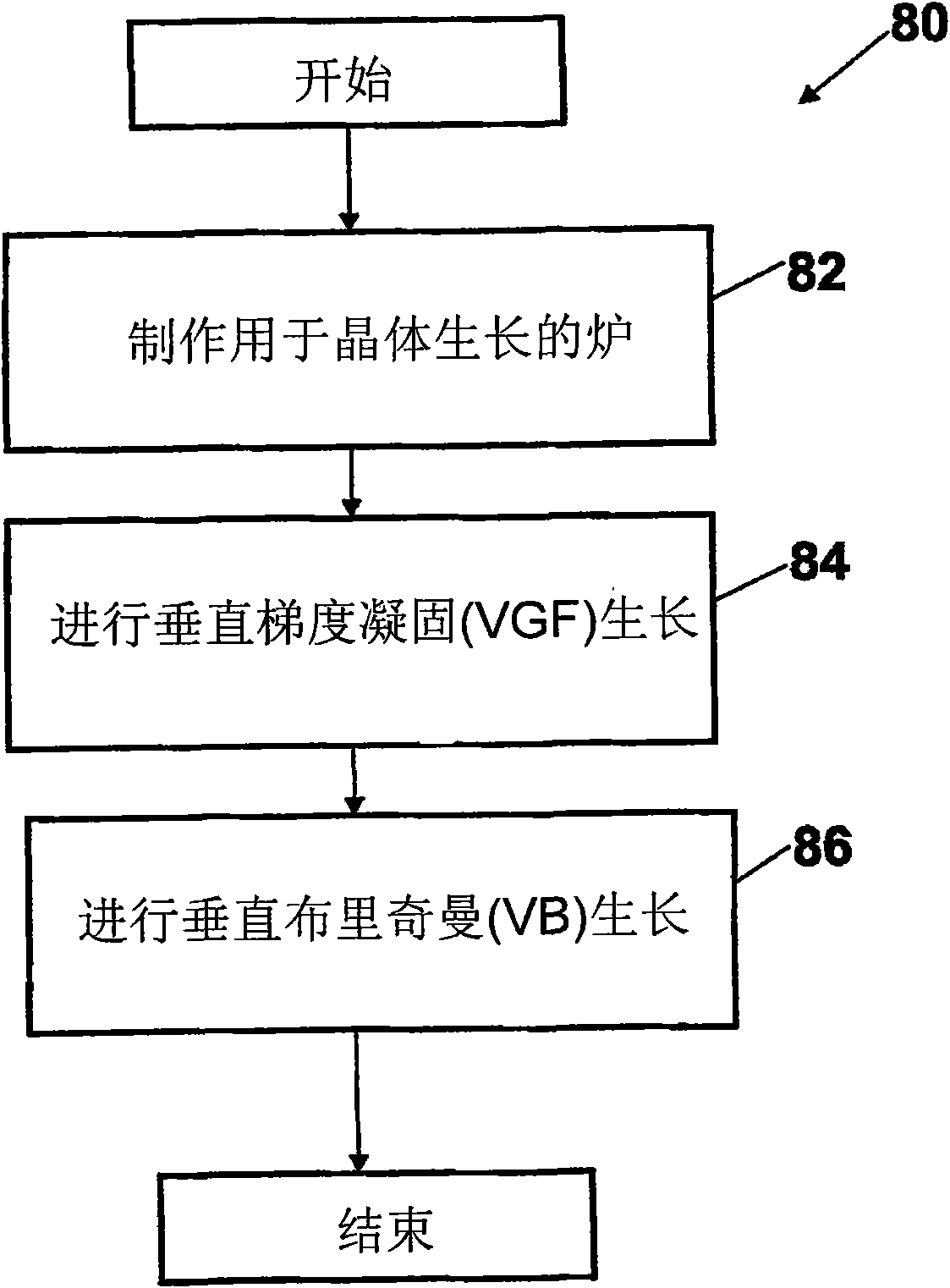
The invention discloses a system and a method using VGF and VB growing technology to carry out crystal growth to reduce body inlaid crystal. In a demonstration embodiment, an ampoule bottle containing a raw material is inserted into a furnace with a heating resource, and a vertical gradient solidifying technology is used for crystal growth, wherein the crystallizing temperature gradient can move corresponding to the crystal and / or the furnace to melt the raw material and convert the raw material into monocrystal compound; and a vertical Bridgman technology is used for crystal growth on a crucible, wherein the ampoule bottle / heating source can relatively move to continuously melt the raw material and convert the raw material into monocrystal compound.
Owner:AXT INC +1
Analytical cartridge with fluid flow control
Owner:MICROPOINT BIOTECHNOLOGIES CO LTD
Vidicon definition detection method based on definition test card
The invention discloses a vidicon definition detection method based on a definition test card, comprising the following steps of: 1) selecting a video definition test card, selecting vidicons with different definition grades, shooting an image of the definition test card, and measuring a definition function value of the definition test card, wherein the specific processes are as follows: 1.1) detecting a horizontal gradient, a vertical gradient and a total gradient of the image; 1.2) carrying out threshold value process; 1.3) calculating definition evaluation function values; 1.4) carrying out normalization process, and storing the obtained definition function value of the image shot by the vidicons with different definition grades and the definition grades of the vidicons into a database; 2) shooting a picture of the definition test card by a vidicon to be detected, calculating the definition function value of the picture, comparing the obtained definition function value with the definition function value of the image stored in the database, and selecting the most approximate numerical value as the definition grade of the vidicon to be detected. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of convenience, rapidness and good reliability.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
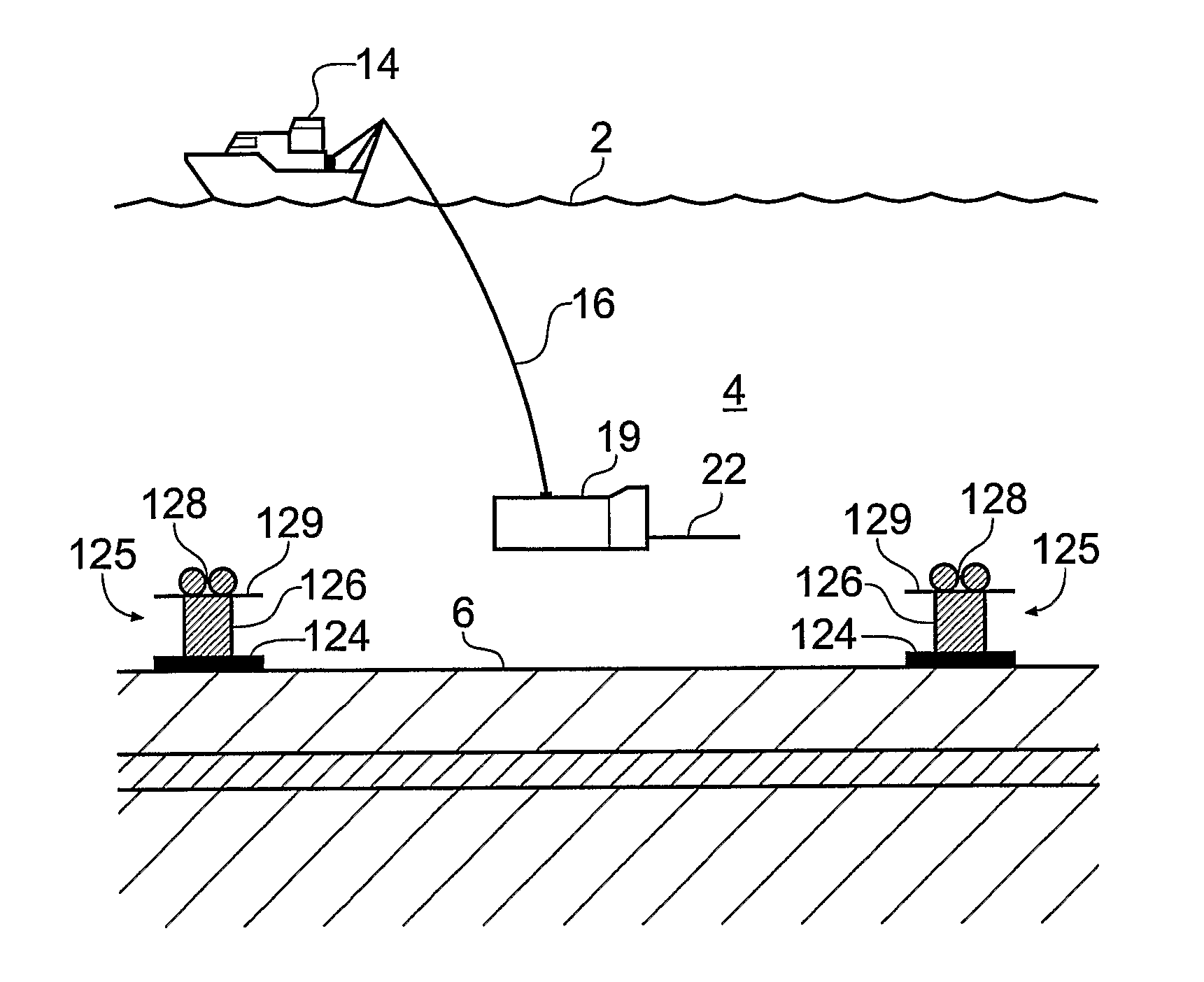
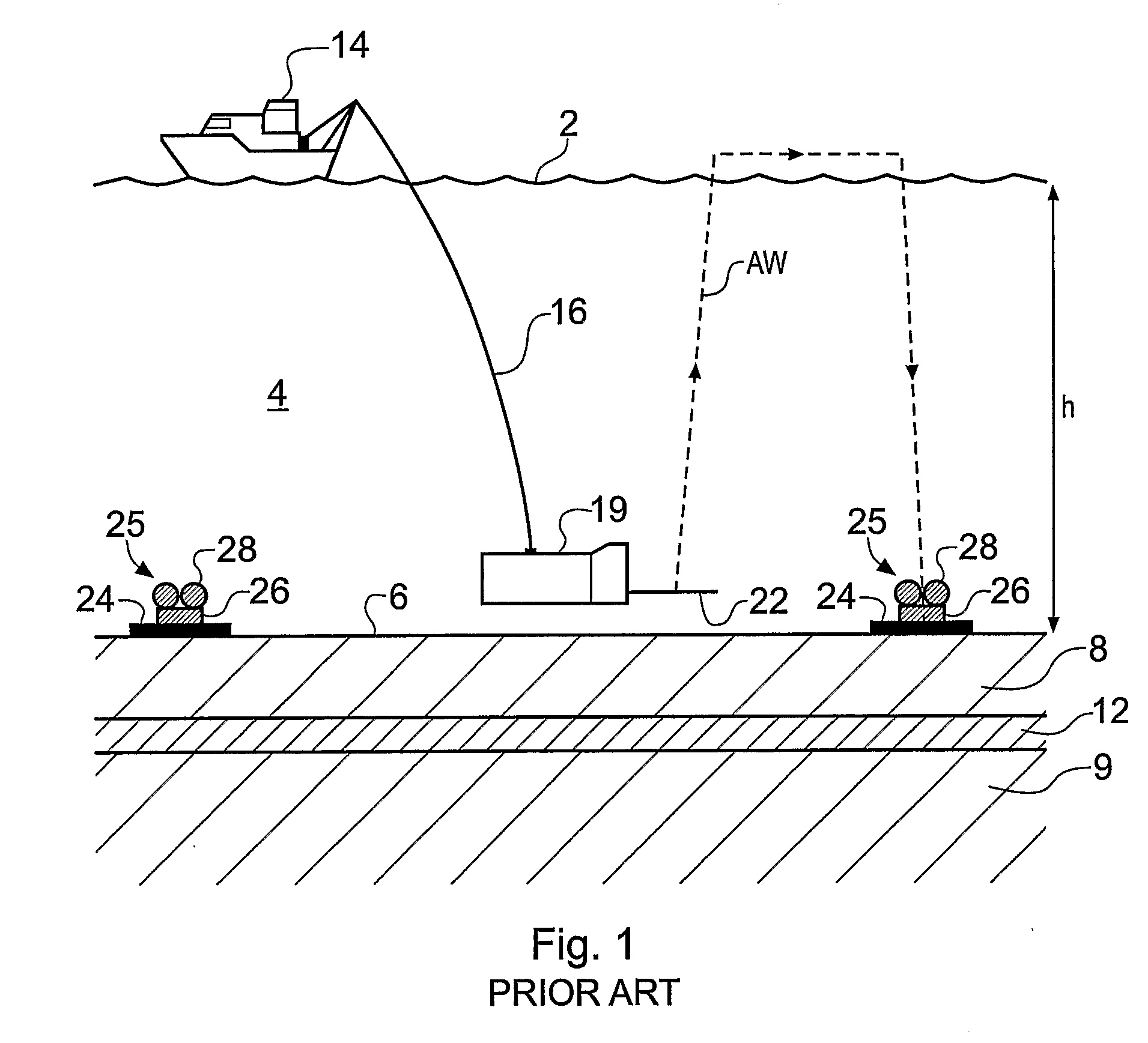
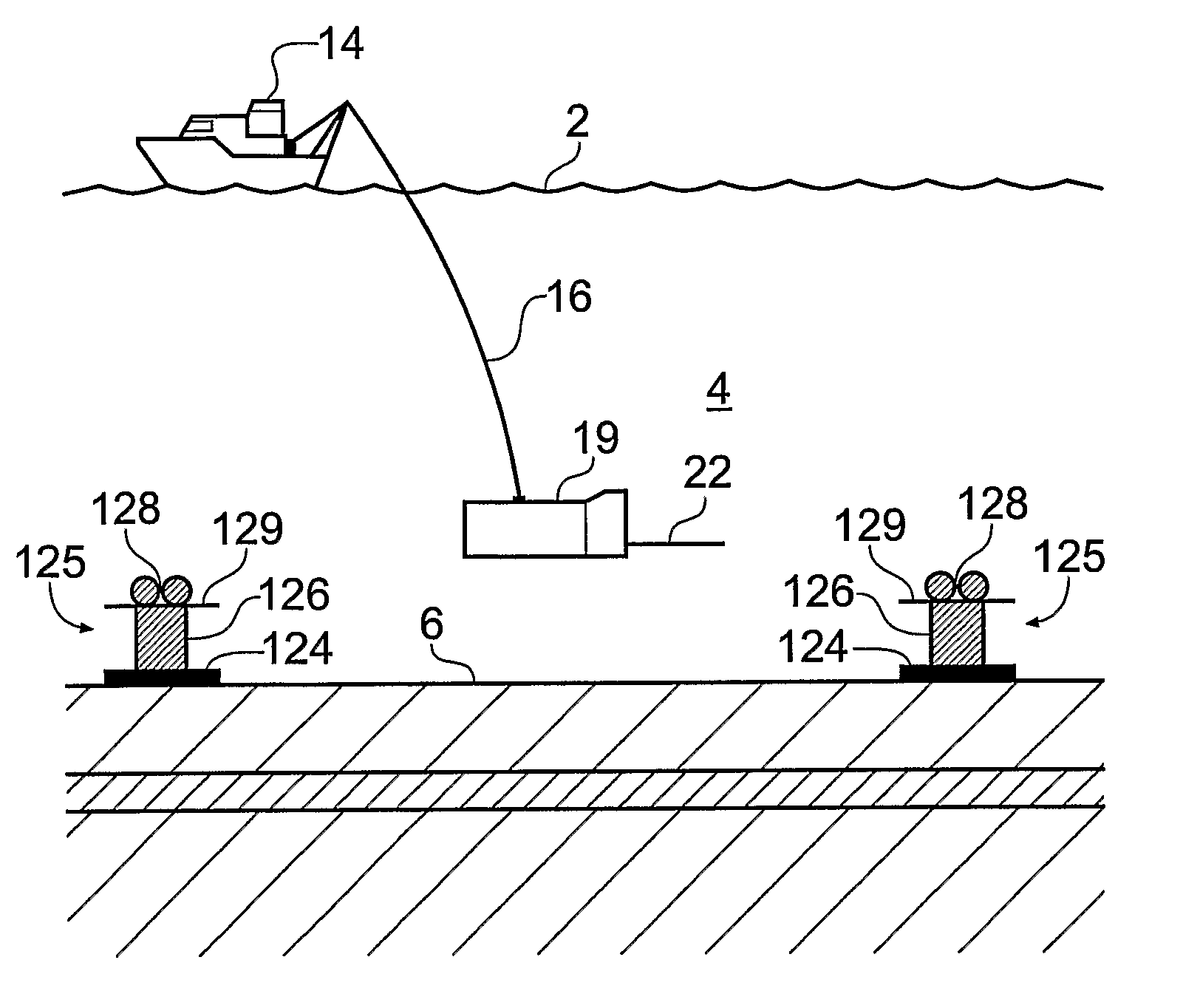
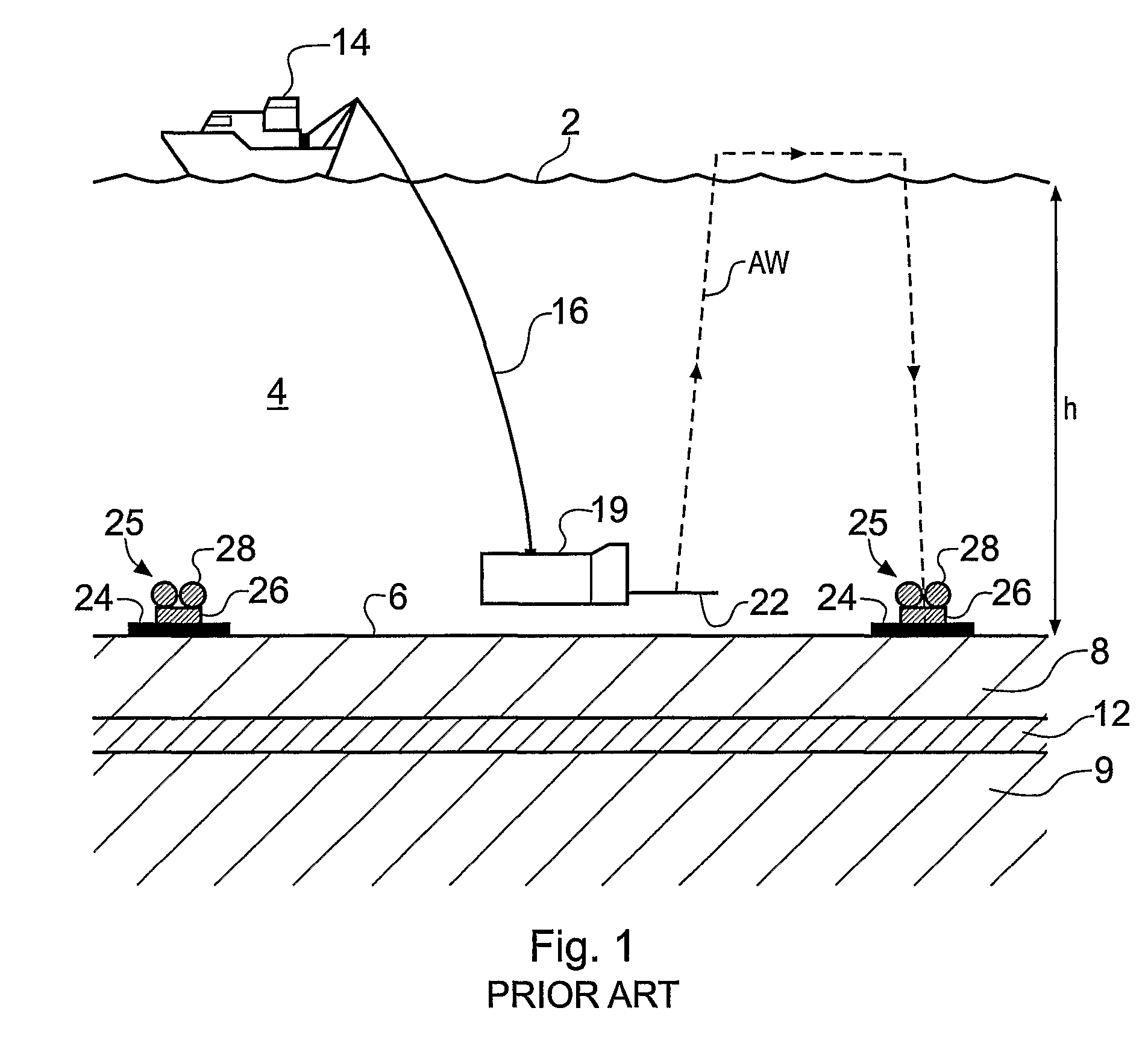
Electromagnetic Surveying for Resistive or Conductive Bodies
ActiveUS20070288211A1Reduce analysisSuitable for collectionElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSurveyHydrocotyle bowlesioidesTransmitter
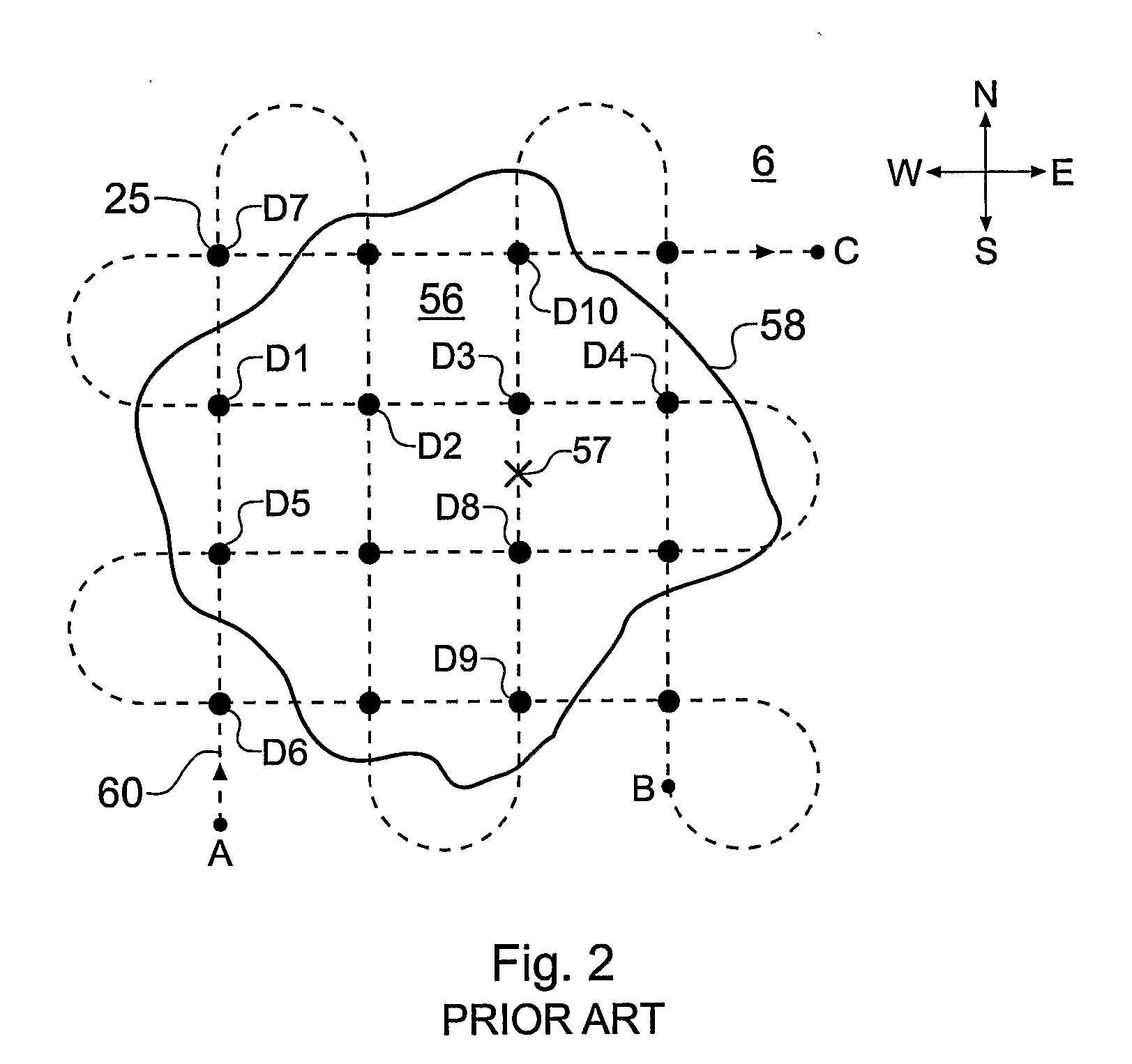
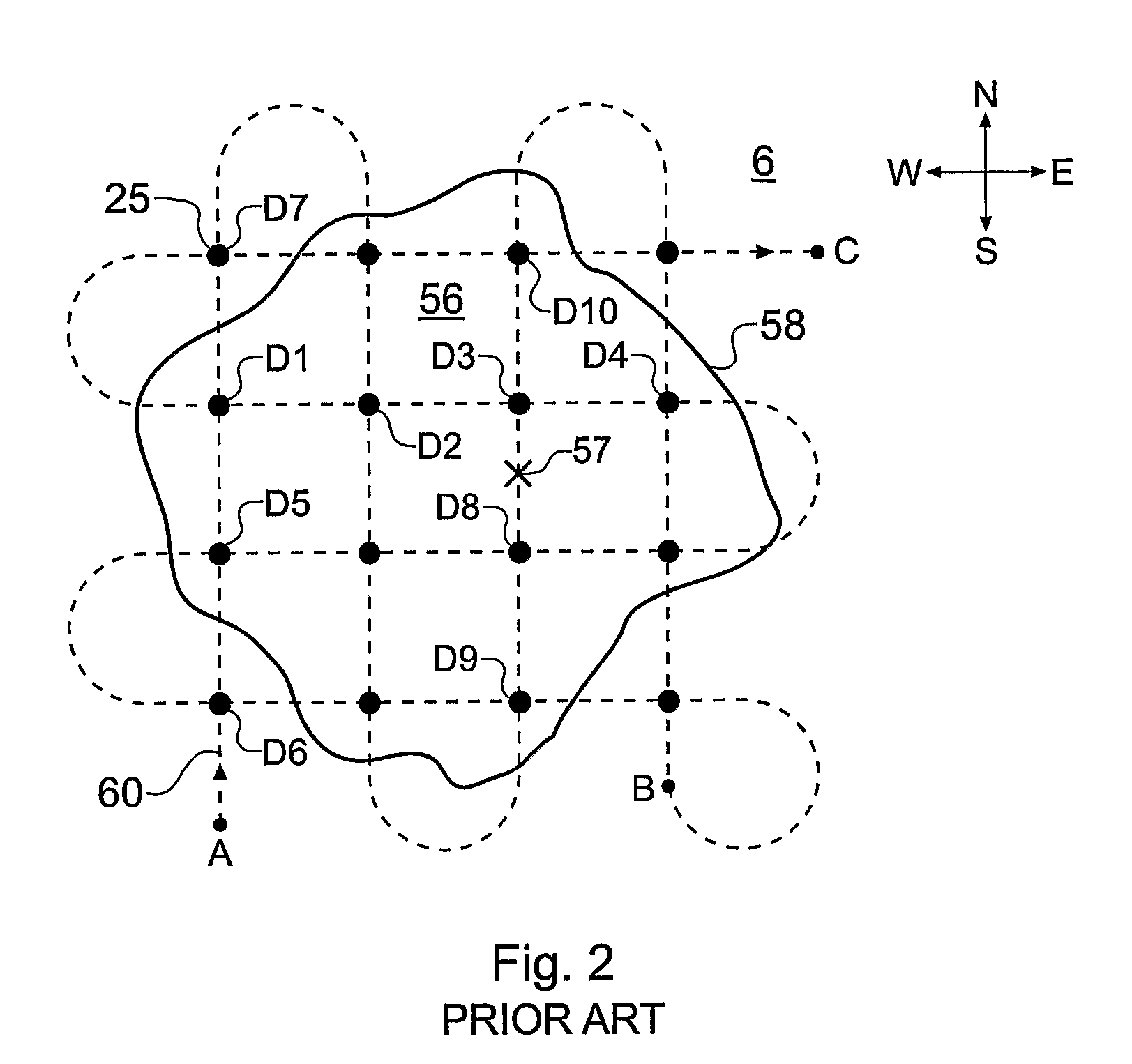
A method of analysing electromagnetic survey data from an area of seafloor (6) that is thought or known to contain a conductive or resistive body, such as a subterranean hydrocarbon reservoir (12), is described. The method includes providing electric field data and magnetic field data, for example magnetic flux density, obtained by at least one receiver (25) from a horizontal electric dipole (HED) transmitter (22) and determining a vertical gradient in the electric field data. The vertical gradient in the electric field data and the magnetic field data are then combined to generate combined response data. The combined response data is compared with background data specific to the area being surveyed to obtain difference data sensitive to the presence of a subterranean hydrocarbon reservoir. Because the combined response data are relatively insensitive to the transverse electric (TE) mode component of the transmitted signal, the method allows hydrocarbon reservoirs to be detected in shallow water where the TE mode component interacting with the air would otherwise dominate. Furthermore, because there is no mixing between the TE and transverse magnetic (TM) modes in the combined response data, data from all possible transmitter and receiver orientations may be used. The background data may be provided by magneto-telluric surveying, controlled source electromagnetic surveying or from direct geophysical measurement.
Owner:PGS GEOPHYSICAL AS
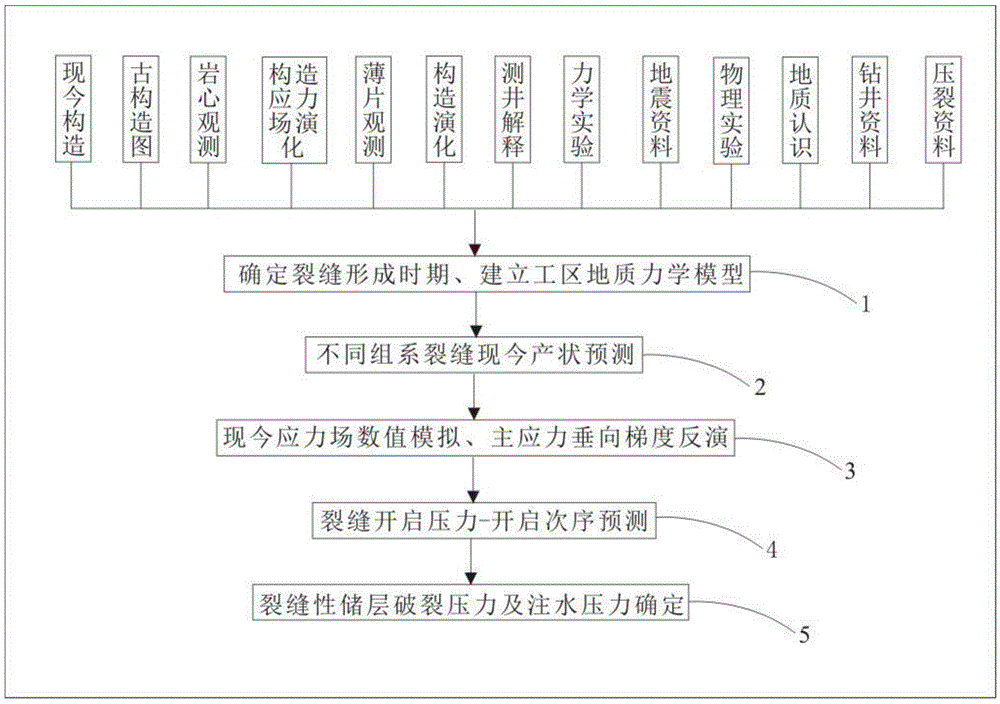
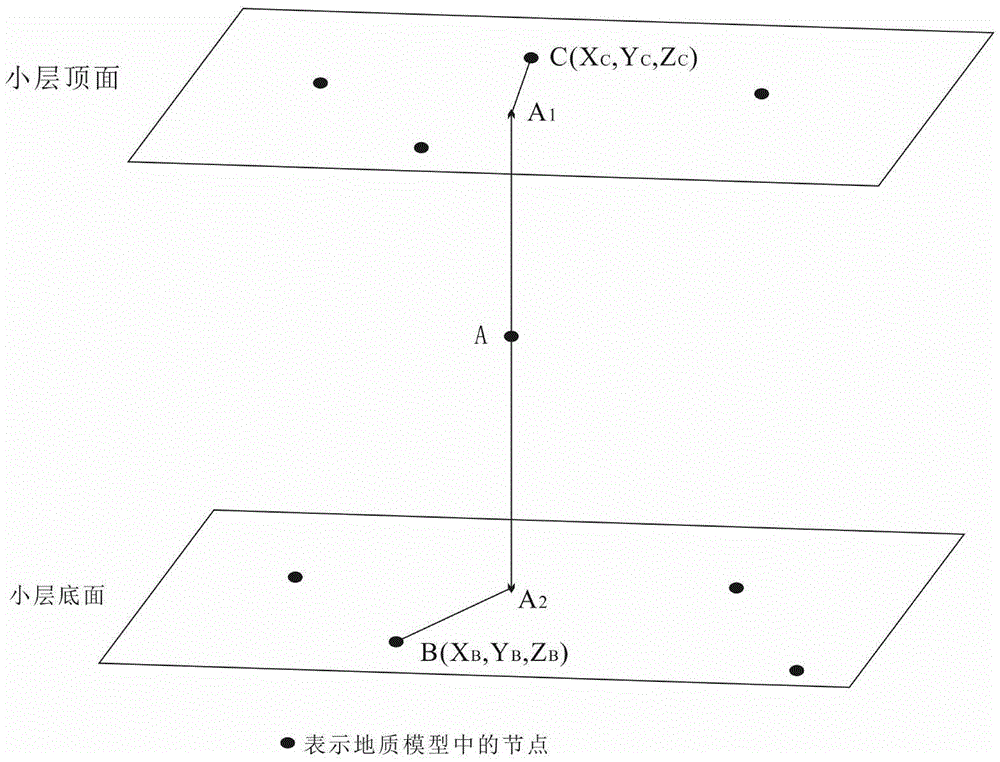
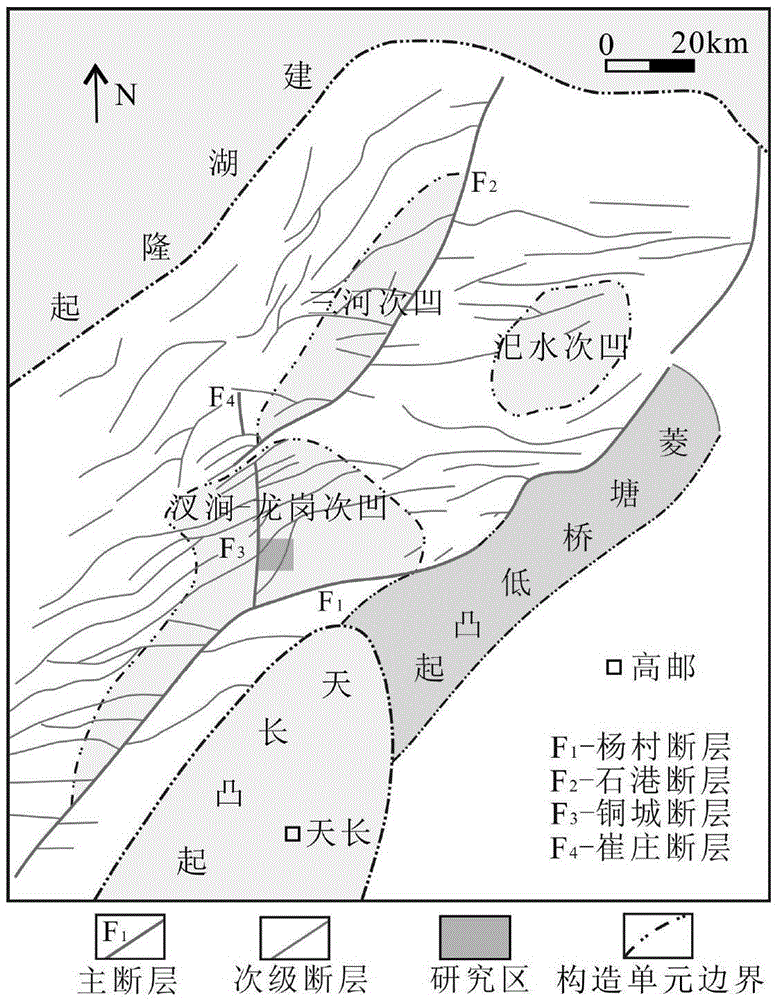
Method for forecasting opening pressure, opening sequence and water injection pressure of reservoir fissure
InactiveCN105672971AHigh utility valueReduce forecasting costsFluid removalPrincipal stressVertical gradient
The invention relates to the field of exploration and development of oil and gas fields, in particular to a method for forecasting the opening pressure, the opening sequence and the water injection pressure of a reservoir fissure. According to the method, a geomechanical model is determined through geological data, physical experiments and the like, and on the basis of paleo-stress-field numerical simulation, by means of the rock fracturing criterion and the ancient-and-modern rock-mechanics layer evolution characteristics, the present occurrence of different group fissures is forecasted; on the basis of present-stress-field numerical simulation, the work-area rock-mechanics layer distribution regularities are combined, principal-stress vertical gradients of different nodes are obtained with the rock-mechanics layer-top-bottom-face point searching method, ground stress information and fissure information are synthesized, inversion forecast of the opening pressure, the opening sequence and the water injection pressure of the fissure is achieved. The method is composed of strict mathematical algorithm derivation, after corresponding geological information is digitized, the corresponding calculation procedure can be developed with computer programming languages, forecast cost is low, and operability is high.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
Spatial prediction method, image decoding method, and image coding method
ActiveUS20130028530A1Reduce complexityIncreased complexityCharacter and pattern recognitionDigital video signal modificationDecoding methodsVertical gradient
A spatial prediction method capable of reducing the complexity of spatial prediction includes: detecting an edge (E) overlapping the current block by obtaining a horizontal gradient (Gy) and a vertical gradient (Gx) between pixels within a block adjacent to the current block; calculating an integer slope of the edge; determining, for each pixel position within the current block, a sub-pel position being an intersection between (i) a line that has the integer slope and passes through the pixel position and (ii) a boundary of the adjacent block; and predicting, for each pixel position, a pixel value at the pixel position based on a pixel value interpolated in the sub-pel position, wherein the boundary of the adjacent block is a row or a column that is the closest to the current block, among rows or columns of pixels included in the adjacent block.
Owner:SUN PATENT TRUST
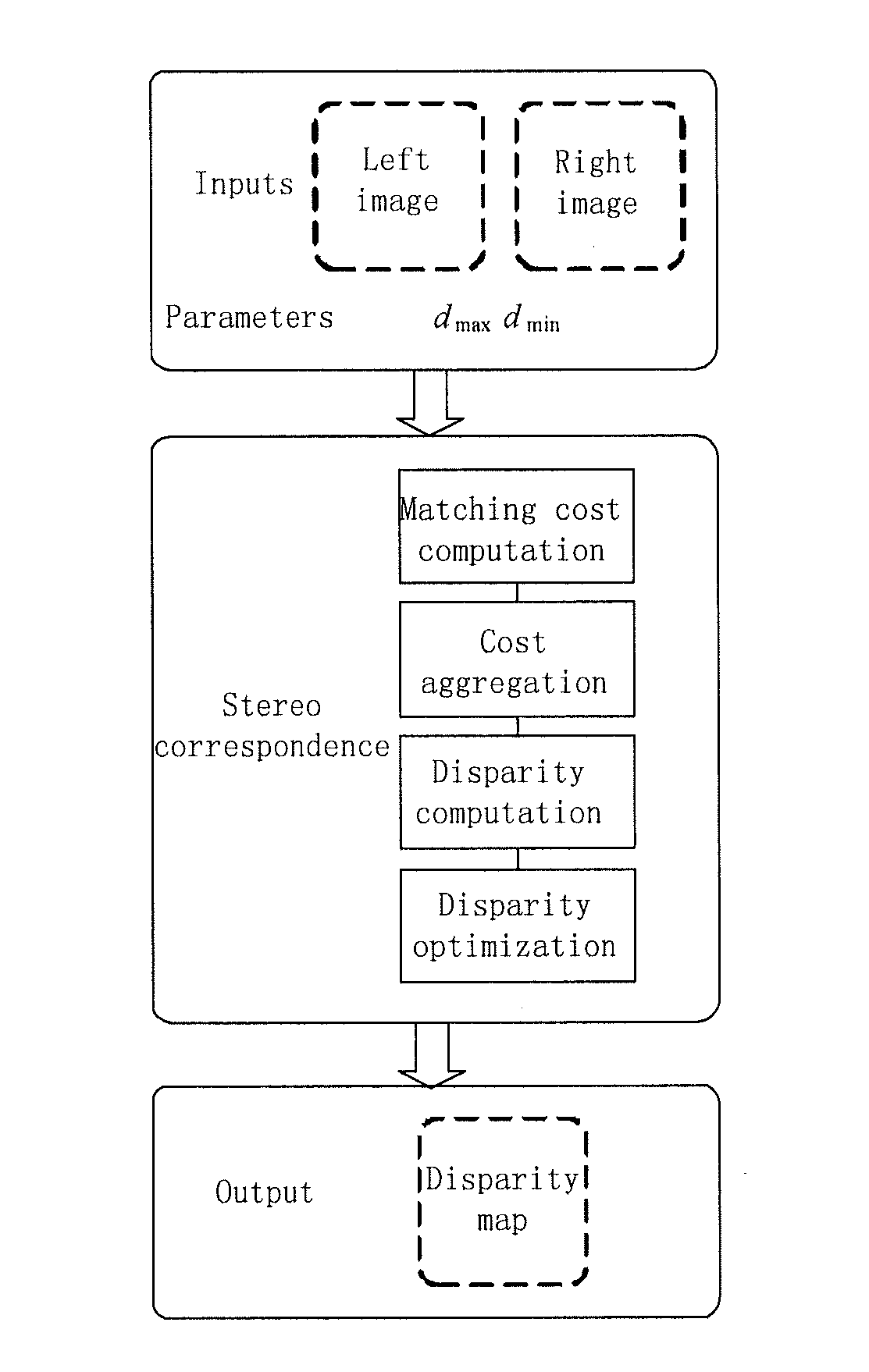
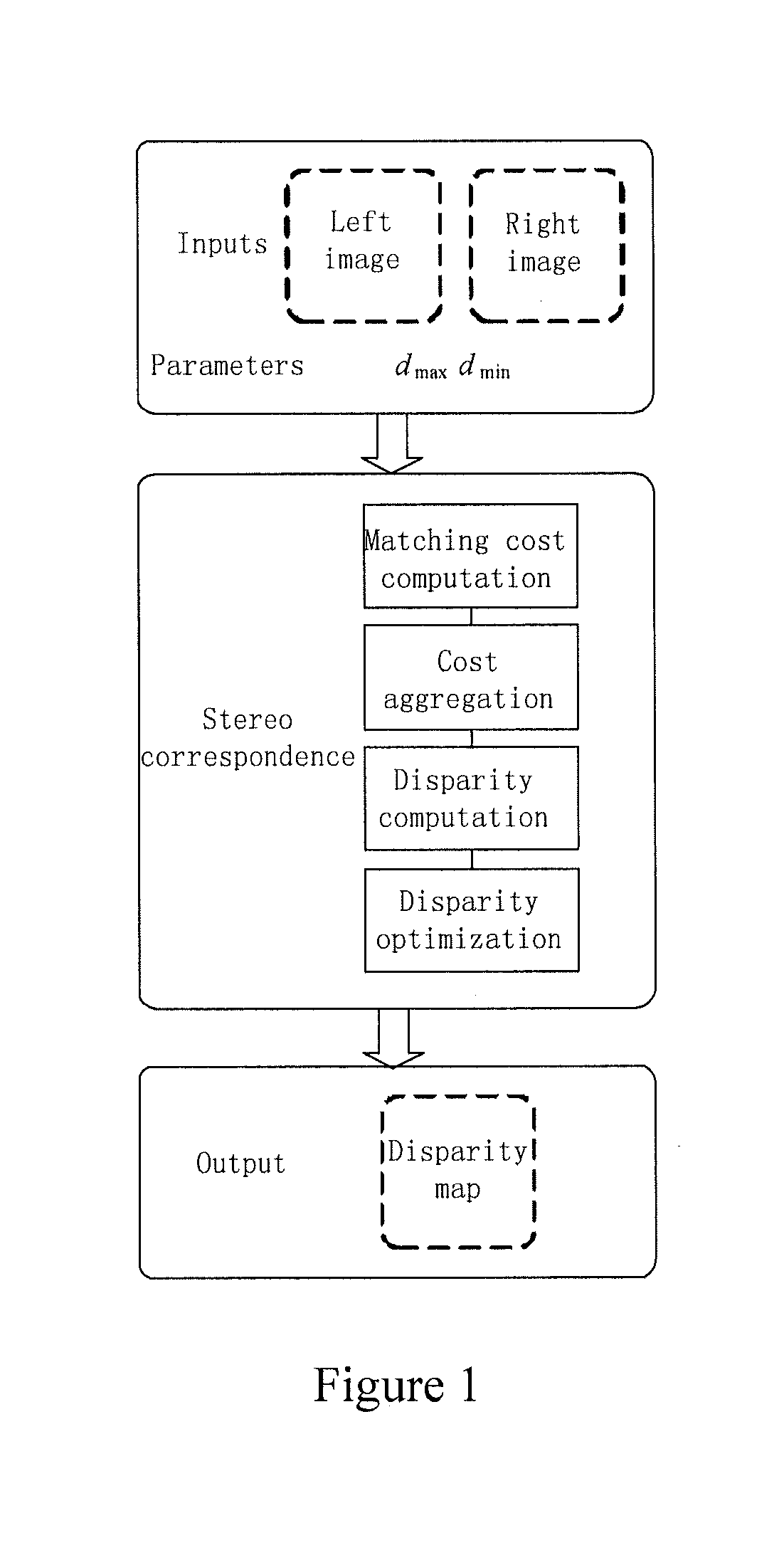
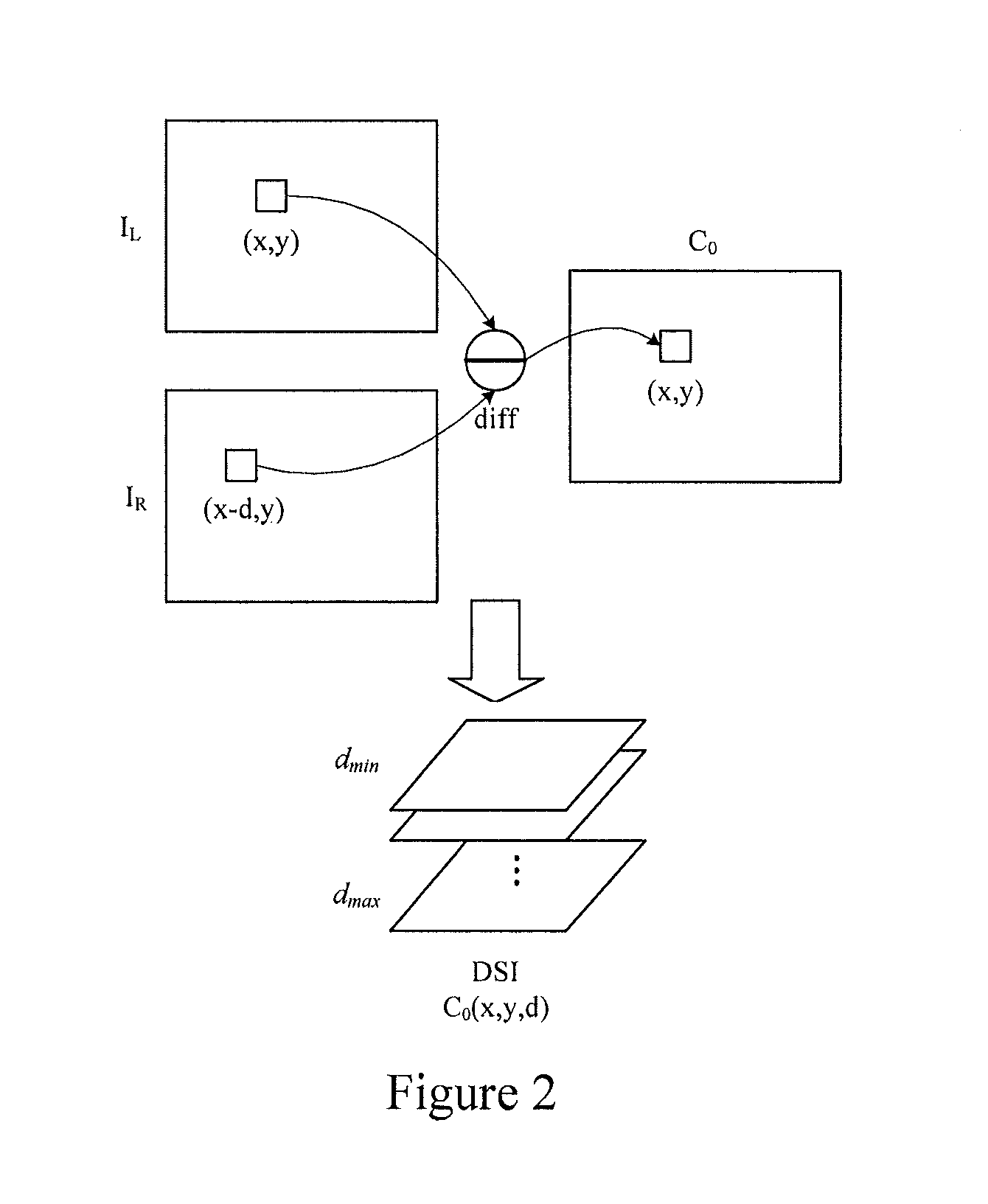
Method and system for stereo correspondence
A method and system for stereo correspondence. The method for stereo correspondence includes a matching cost computation step, a cost aggregation step, a disparity computation step, and a disparity optimization step. The matching cost computation step acquires a left disparity space image and a right disparity space image by using horizontal gradients and vertical gradients of intensities of all component channels of every pixel in a left image and a right image. Utilizing the invention, accurate disparity maps may be acquired quickly.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Device and method for the production of monocrystalline or multicrystalline materials, in particular multicrystalline silicon
InactiveUS20070266931A1Cheap productionAfter-treatment apparatusPolycrystalline material growthElectrical conductorSingle crystal
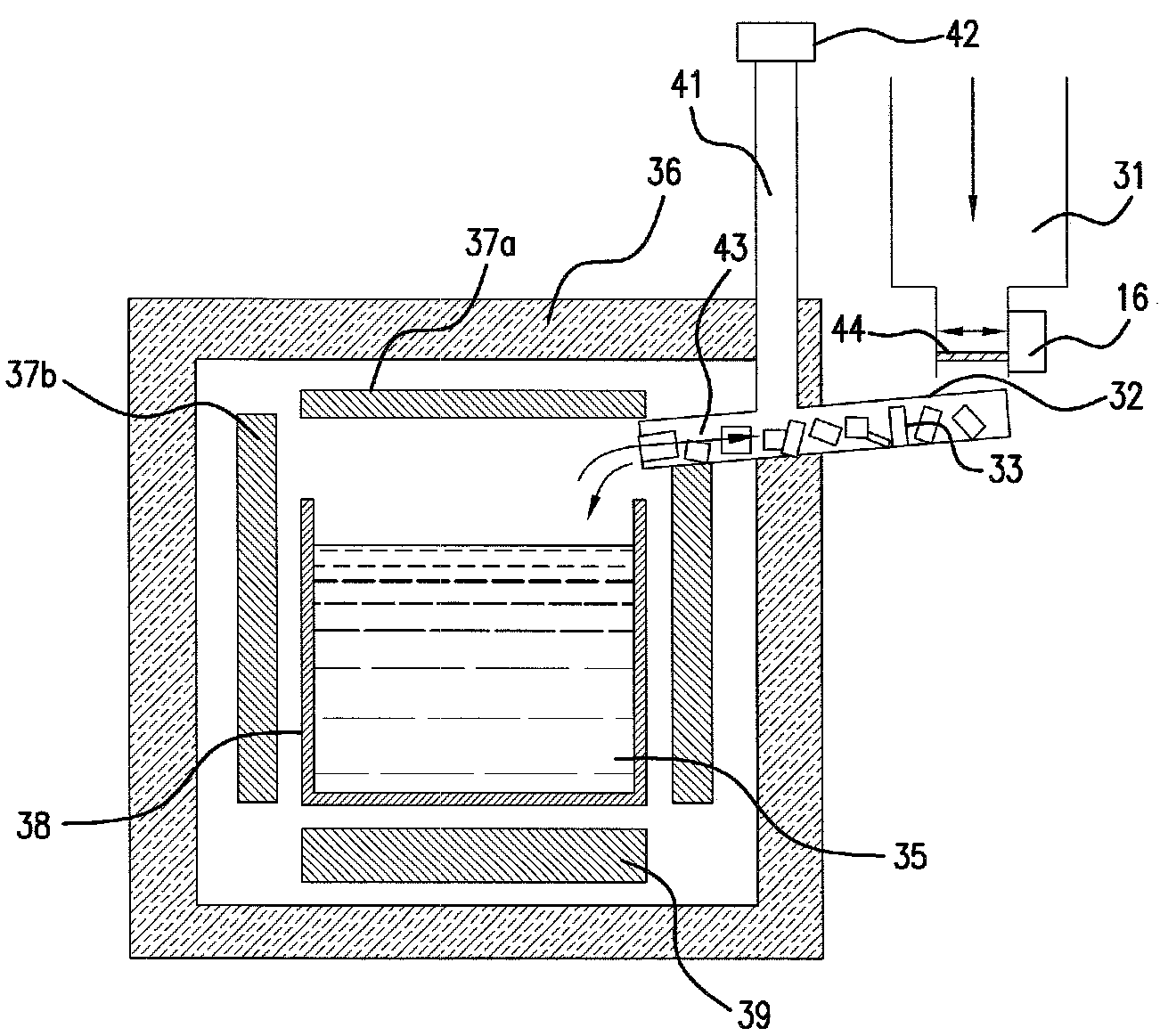
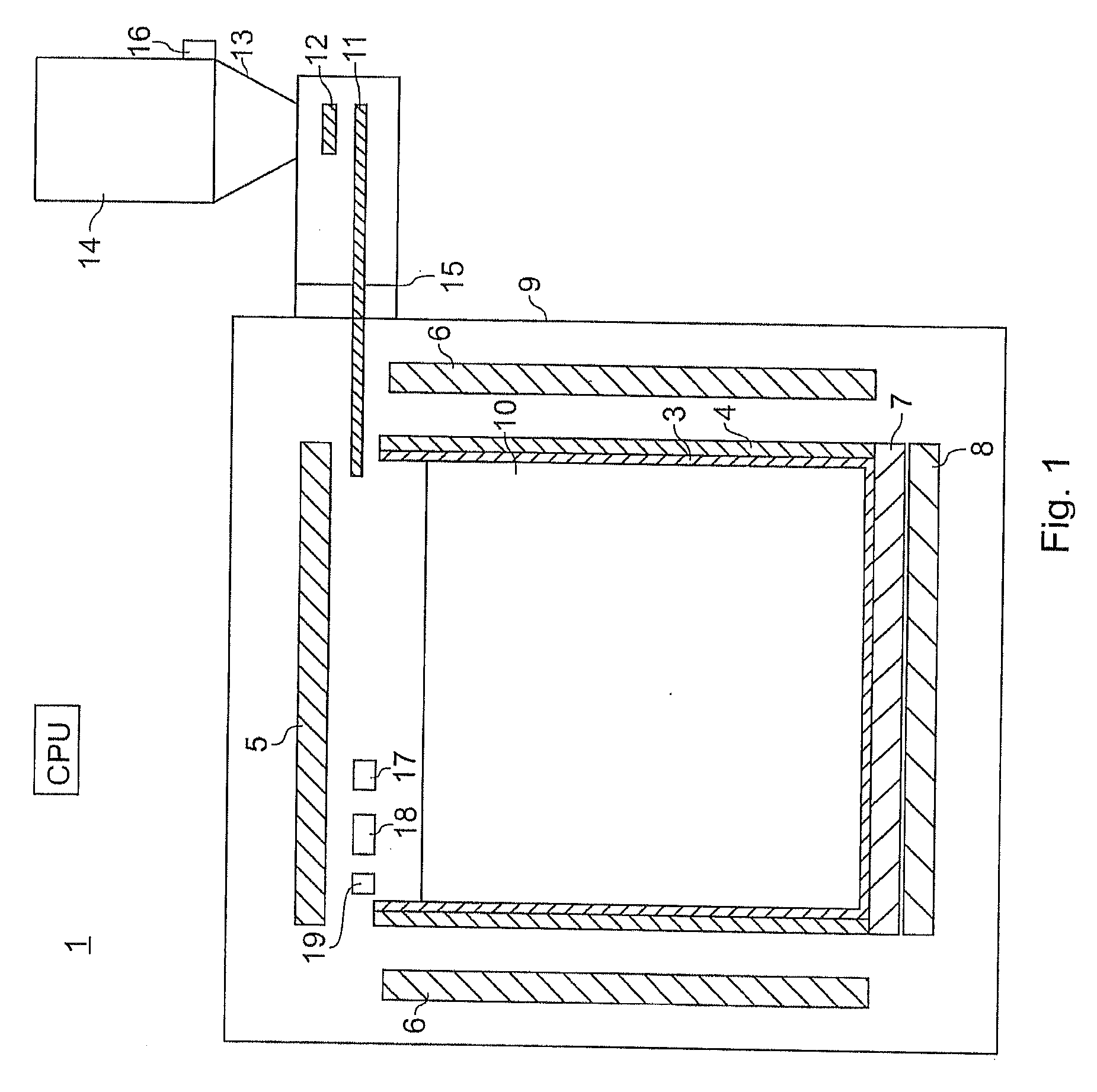
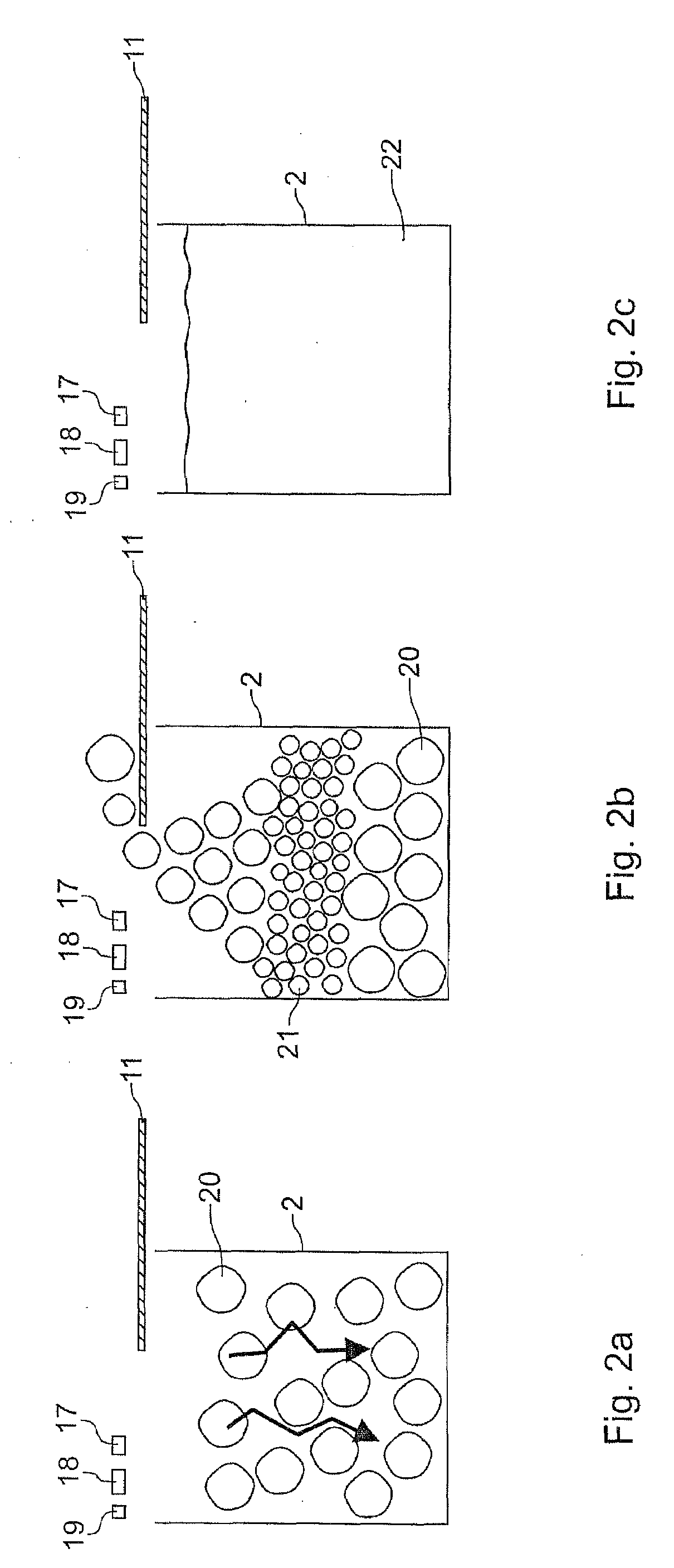
The invention relates to a device and a method for the production of monocrystalline or multicrystalline materials using the vertical-gradient-freeze method, in particular silicon for applications in photovoltaics. According to the invention a low amount of wastage is achieved in that the cross section of the crucible is polygonal, in particular rectangular or square-shaped. Disposed around the circumference of the crucible there is a flat or planar heating element, in particular a jacket heater, which generates an inhomogeneous temperature profile. This corresponds to the temperature gradient formed in the centre of the crucible. The heat output of the flat heating element decreases going from the top end to the bottom end of the crucible. The flat heating element comprises a plurality of parallel heating webs, extending in a vertical or horizontal meandering course. The heat output from the webs is set by varying the conductor cross section. To avoid local overheating in corner areas of the crucible, constrictions of the cross section are provided at inversion zones of the meandering courses of the webs. The flat heating element can be formed from a plurality of interconnected individual segments.
Owner:SCHOTT AG
Gallium arsenide polycrystal non-liquid seal synthesizing method and apparatus
InactiveCN101498047AReduce lossAvoid contaminationPolycrystalline material growthSingle crystal growth detailsBridgman methodSynthesis methods
The invention discloses a GaAs polycrystal and liquid seal-free synthesis method and a GaAs polycrystal and liquid seal-free synthesis device. The method is based on the liquid seal-free synthesis of GaAs polycrystals and positions crystallization by a vertical Bridgman method so that synthetized cylindrical GaAs polycrystals do not comprise gallium groups and arsenic groups and are extremely uniformly distributed so as to directly satisfy the requirements of the vertical Bridgman method or the vertical gradient freezing method for the growth of GaAs single crystals. The device comprises a synthesis furnace and a graphite system, wherein the graphite system comprises an insulation unit, a heating unit, a synthesis unit and a motion unit capable of enabling the synthesis unit to lift and rotate. The synthetized GaAs polycrystals synthesized by the method of the invention reach a stoichiometric proportion at the level of a horizontal Bridgman method and avoid staining a Si impurity. Compared with a boric oxide liquid seal synthesis method, the synthesis method avoids staining a boron impurity.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRONICS TECH GRP NO 46 RES INST +1
Method for making a perpendicular magnetic recording write head with a self aligned stitched write shield
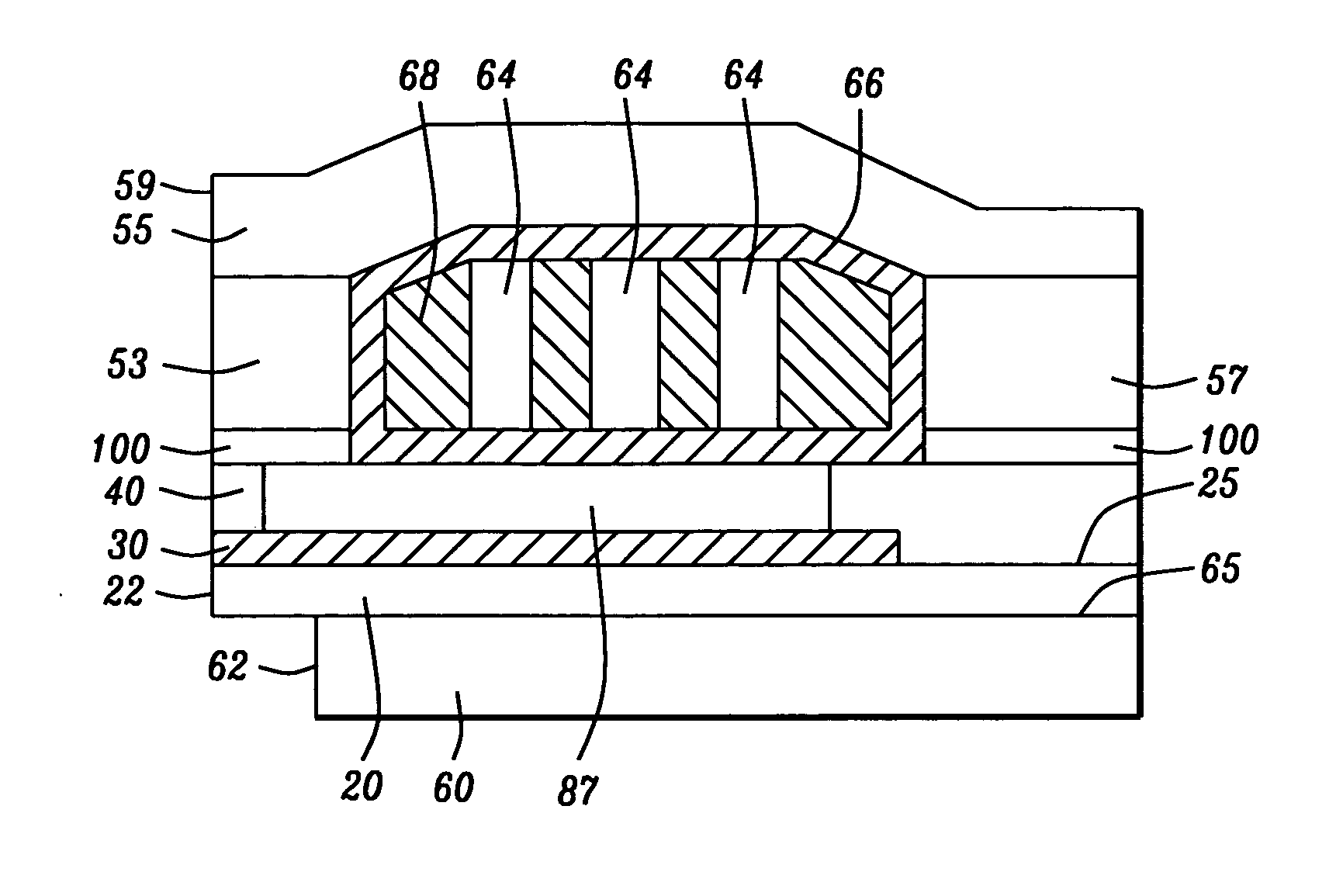
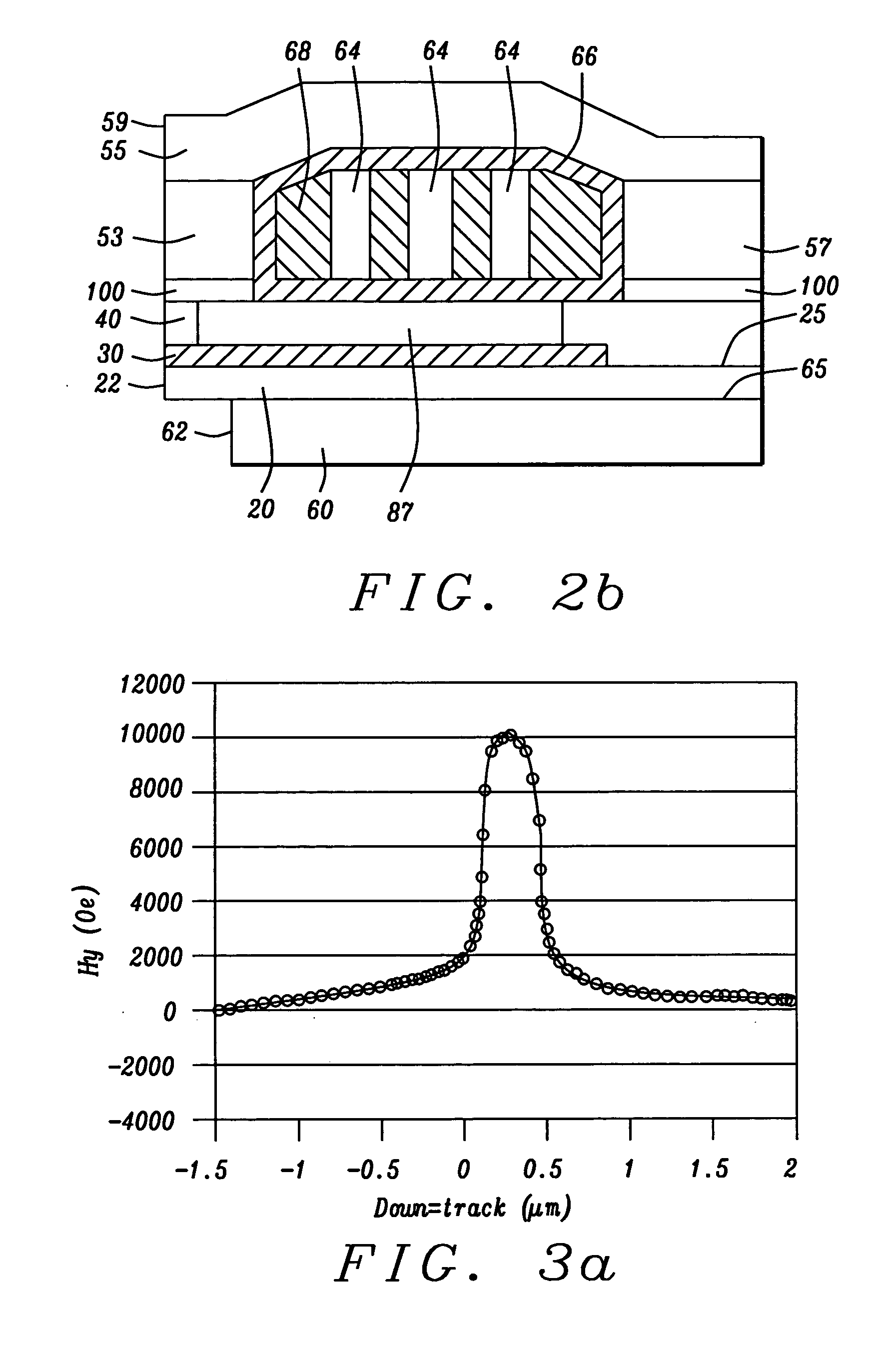
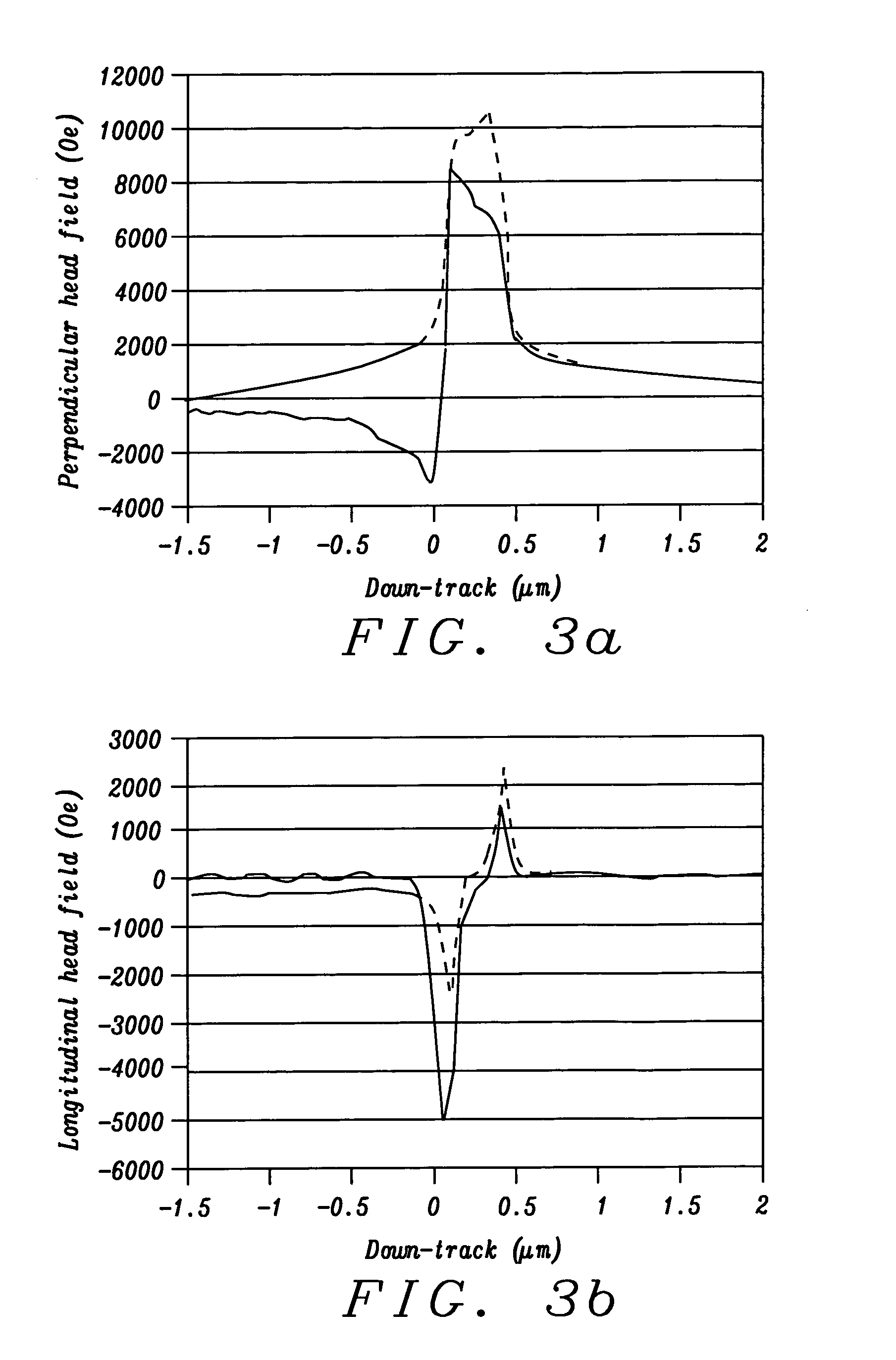
InactiveUS20050259356A1Large gradientShorten the trackConstruction of head windingsHeads using thin filmsVertical gradientEngineering
A perpendicular magnetic recording (PMR) head with single or double coil layers has a small write shield stitched onto a main write shield. The stitched shield allows the main write pole to produce a vertical write field with sharp vertical gradients that is reduced on both sides of the write pole so that adjacent track erasures are eliminated. From a fabrication point of view, both the main pole and the stitched shield are defined and formed using a single photolithographic process, a trim mask and CMP lapping process so that the main shield can be stitched onto a self-aligned main pole and stitched shield.
Owner:HEADWAY TECH INC
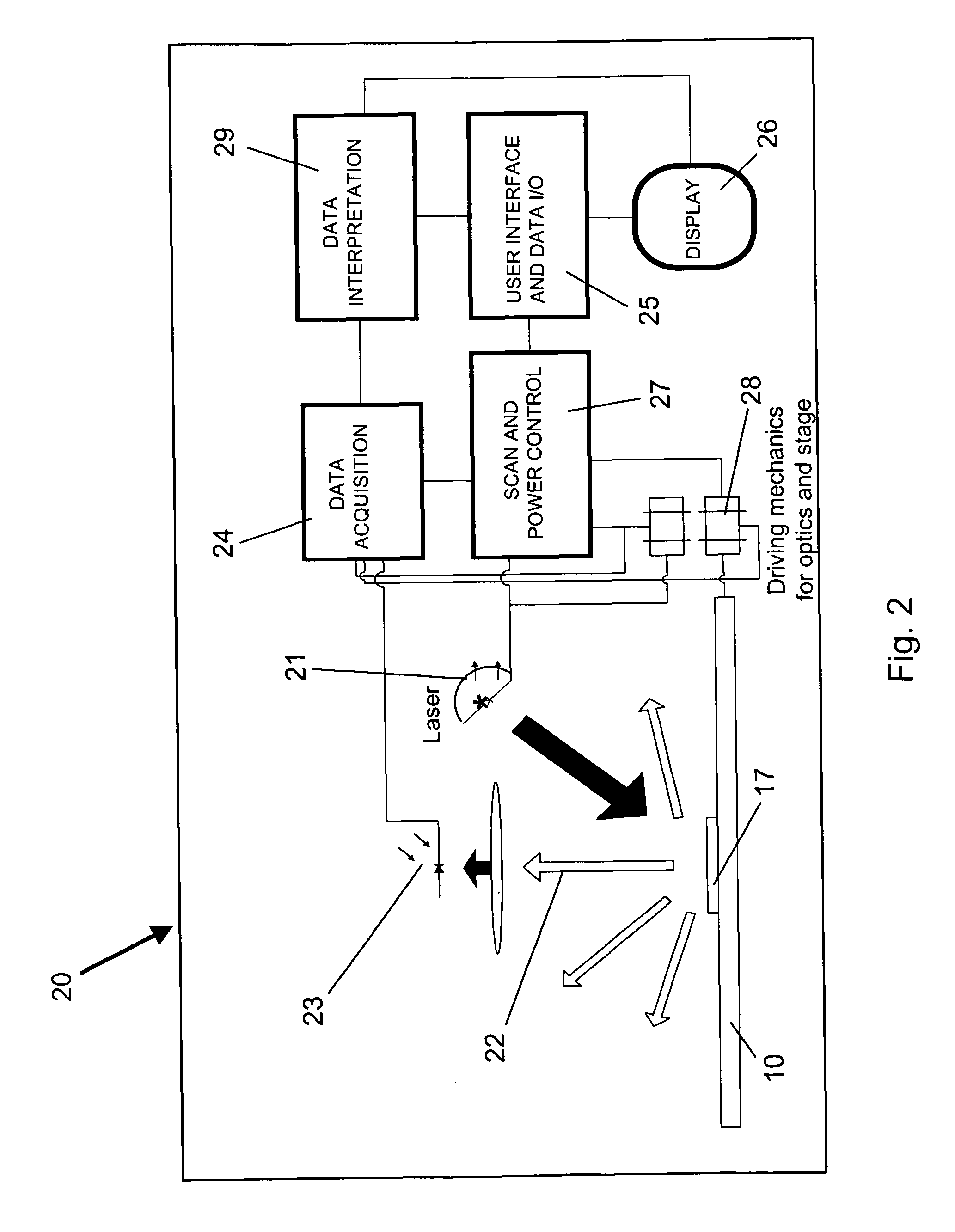
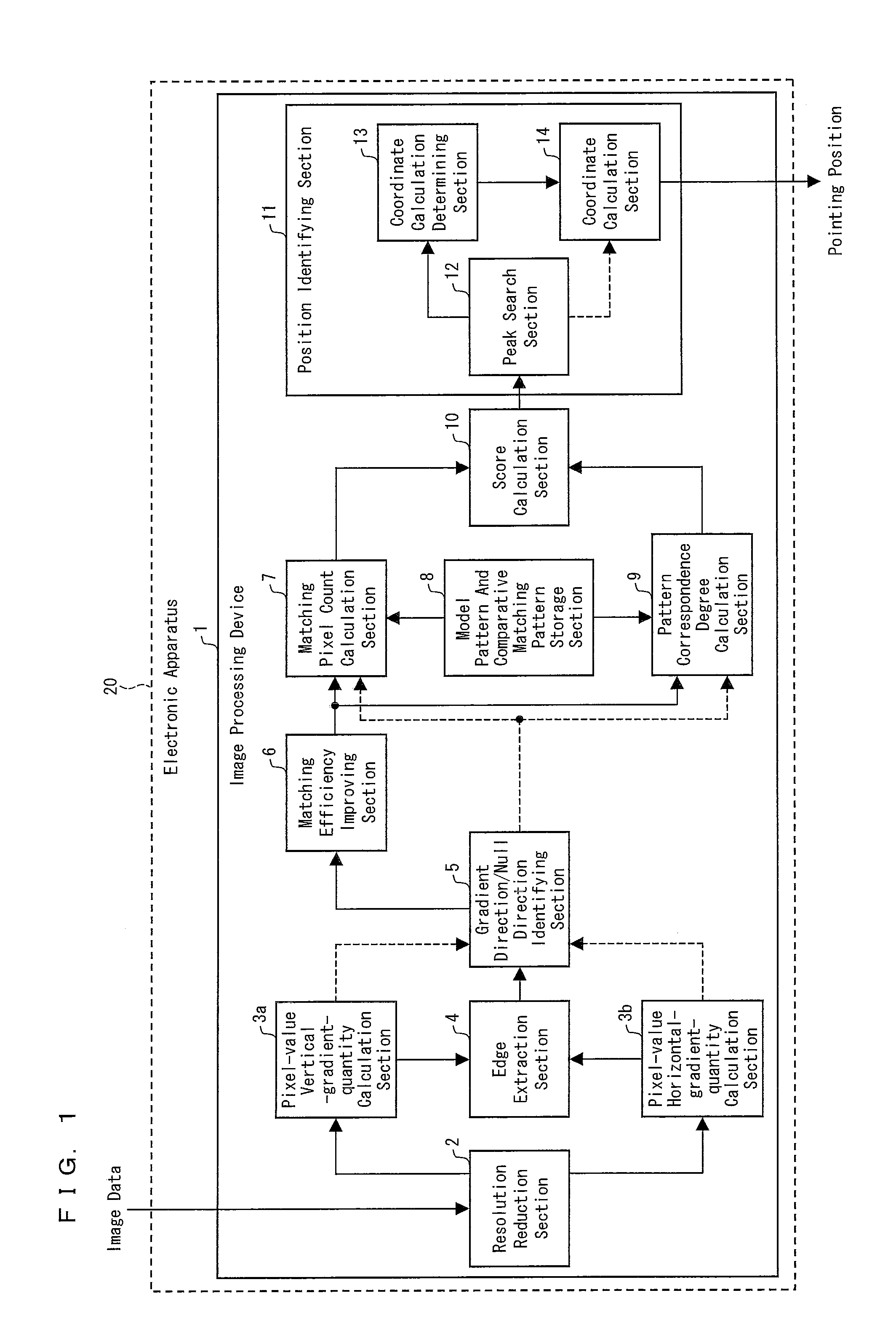
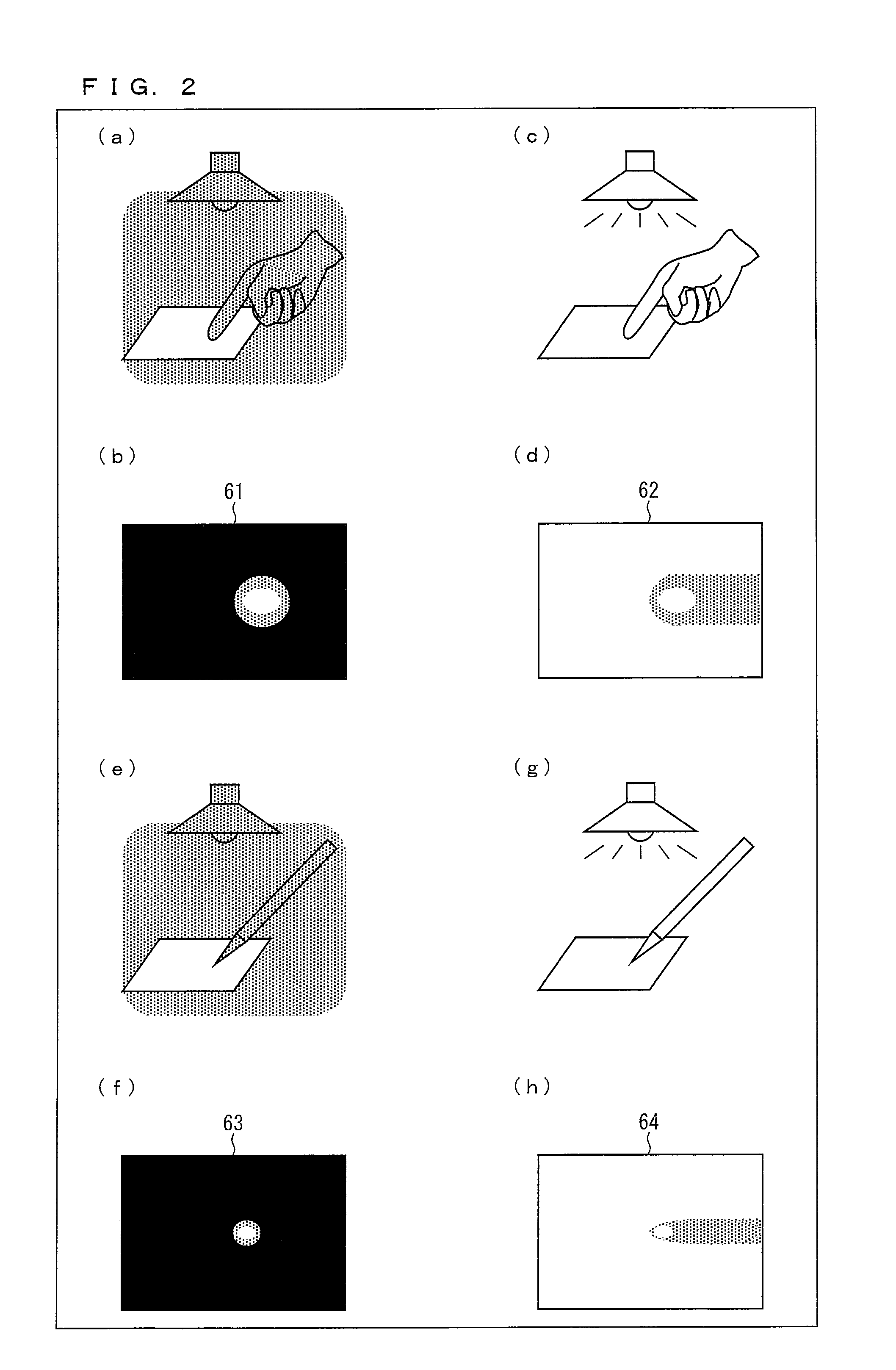
Image processing device, control program, computer-readable storage medium, electronic apparatus, and image processing device control method
InactiveUS20100142830A1Small memoryShort processing timeImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionImaging processingVertical gradient
The invention includes: a pixel-value vertical-gradient-quantity calculation section (3a) and a pixel-value horizontal-gradient-quantity calculation section (3b) for calculating, for each pixel in image data, a vertical-direction gradient quantity (Sy) and a horizontal-direction gradient quantity (Sx) for a pixel value; a gradient direction / null direction identifying section (5) for identifying, for each pixel, either a gradient direction or null direction from the vertical-direction gradient quantity (Sy) and the horizontal-direction gradient quantity (Sx); a score calculation section (10) for calculating an correspondence degree from a number of pixels for which a gradient direction contained in the matching region matches a gradient direction contained in the model pattern and a pattern correspondence degree which is a degree of similarity of a matching pattern between the gradient direction for each pixel in the matching region and the gradient direction for each pixel in the model pattern to a comparative matching pattern; and a position identifying section (11) for identifying the position in the captured image pointed at with the image capture object from a position of a target pixel for which the correspondence degree is a maximum.
Owner:SHARP KK
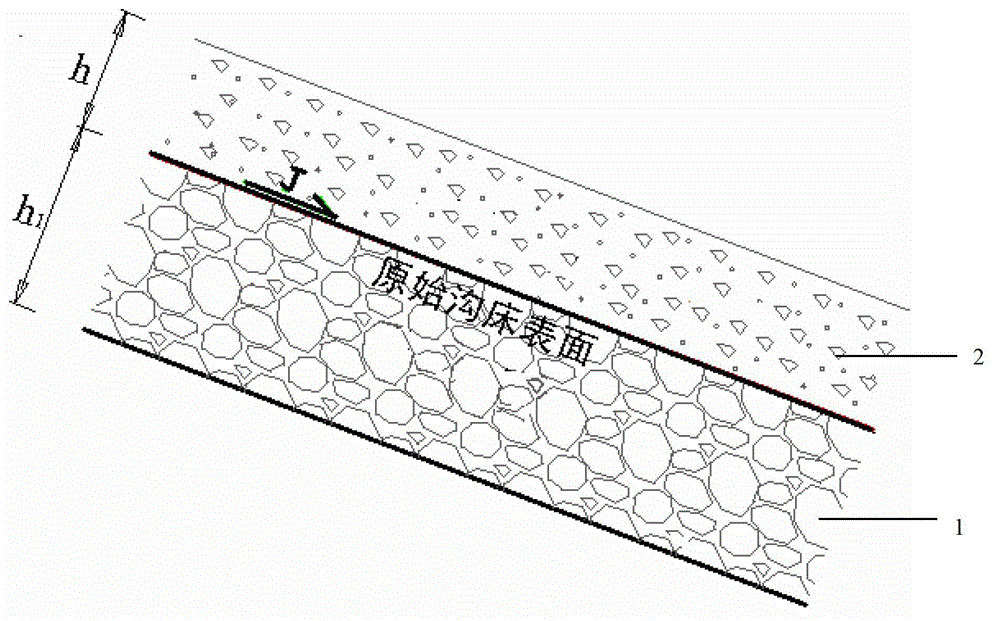
Method for measuring maximum scour depth of viscous debris flow gully bed and application thereof
ActiveCN102943450AIncrease resistance to movementAvoid destructionHydraulic engineering apparatusVertical gradientPrevention project
The invention discloses a method for measuring the maximum scour depth of a viscous debris flow gully bed and the application thereof. The method comprises the following steps: weight Gamma1, depth h and a dynamic friction angle Beta of a viscous debris flow body, weight Gamma2, an internal frictional angle Phi and a viscosity coefficient C of cumulus deposits of an original gully bed, and vertical gradient J of the gully channel are determined by means of survey, measurement and sampling of the debris flow gully, testing of debris flow characteristic parameters and the like; and the obtained parameters are substituted into a calculation formula to obtain the maximum scour depth of the viscous debris flow gully bed. The method is applicable to the design of foundation embedded depth in a viscous debris flow prevention project, and the obtained maximum scour depth of the viscous debris flow gully bed serves as the minimum foundation embedded depth in the prevention project. Compared with the prior art, as the method is based on rigorous theory derivation, the maximum scour depth of the viscous debris flow gully bed can be reasonably determined, and references on the design of the foundation embedded depth in the prevention project are provided; and the method is high in result accuracy and can meet the requirements of the practical project.
Owner:INST OF MOUNTAIN HAZARDS & ENVIRONMENT CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Human eye positioning method and device and human eye region positioning method and device
ActiveCN104050448AEliminate distractionsGood effectCharacter and pattern recognitionState of artVertical gradient
The invention discloses a human eye positioning method and device which are used for solving the problem that in the prior art, human eye positioning can not be conducted on a low-resolution face image. The invention further provides a human eye region positioning method and device which are used for solving the problem that in the prior art, human eye region positioning is poor in robustness with interference from glasses and eyebrows. The human eye region positioning method comprises the steps that a left eye region and a right eye region of a face grayscale image are determined; according to horizontal grayscale integral projection, vertical grayscale integral projection, horizontal gradient integral projection and vertical gradient integral projection of the obtained left eye region, the position of the center of a left eyeball in the left eye region is determined; according to horizontal grayscale integral projection, vertical grayscale integral projection, horizontal gradient integral projection and vertical gradient integral projection of the obtained right eye region, the position of the center of a right eyeball in the right eye region is determined.
Owner:HISENSE VISUAL TECH CO LTD
Growing method and growing device for indium phosphide single crystal
ActiveCN104911690AReduce dosageSimple processPolycrystalline material growthFrom frozen solutionsDopantVertical gradient
The invention provides a growing method for an indium phosphide single crystal. The method comprises the following steps: using a vertical gradient freeze method for heating indium phosphide seed, indium phosphide polycrystal, diboron trioxide and red phosphorus, and growing crystals to obtain the indium phosphide single crystal, wherein the red phosphorus takes up 0.05-0.1% of the total mass of the indium phosphide polycrystal, the diboron trioxide and the red phosphorus. By the provided growing method, the indium phosphide single crystal with substantially lower dislocation density can be obtained without adding dopant such as ferrum or sulfur, thereby simplifying the technology and saving the cost; moreover, the few red phosphorus (only one tenth of the dosage of the red phosphorus in the prior art) is used in the preparation method, thereby reducing the danger during the production. It is shown by experiments that the average dislocation density of the indium phosphide single crystal obtained by the provided growing method is 2000-4000 / cm2, with the local dislocation density being less than 500 / cm2. The invention further provides a growing device of the indium phosphide single crystal.
Owner:威科赛乐微电子股份有限公司
Stitched shielded pole structure for a perpendicular magnetic recording write head
InactiveUS7221539B2Reduces unwanted side writing and adjacentReduce Flux LeakageManufacture head surfaceHeads using thin filmsLeading edgeVertical gradient
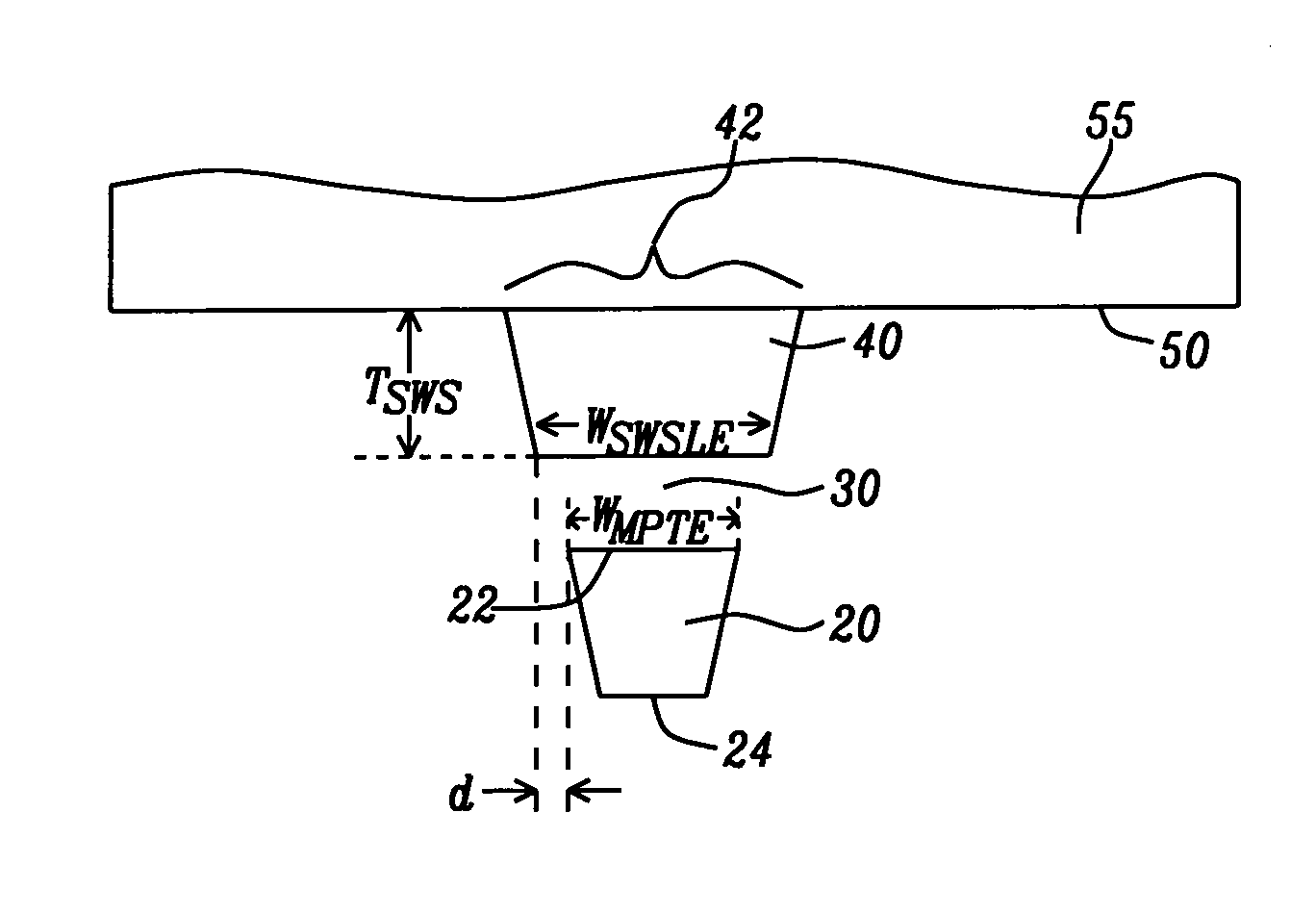
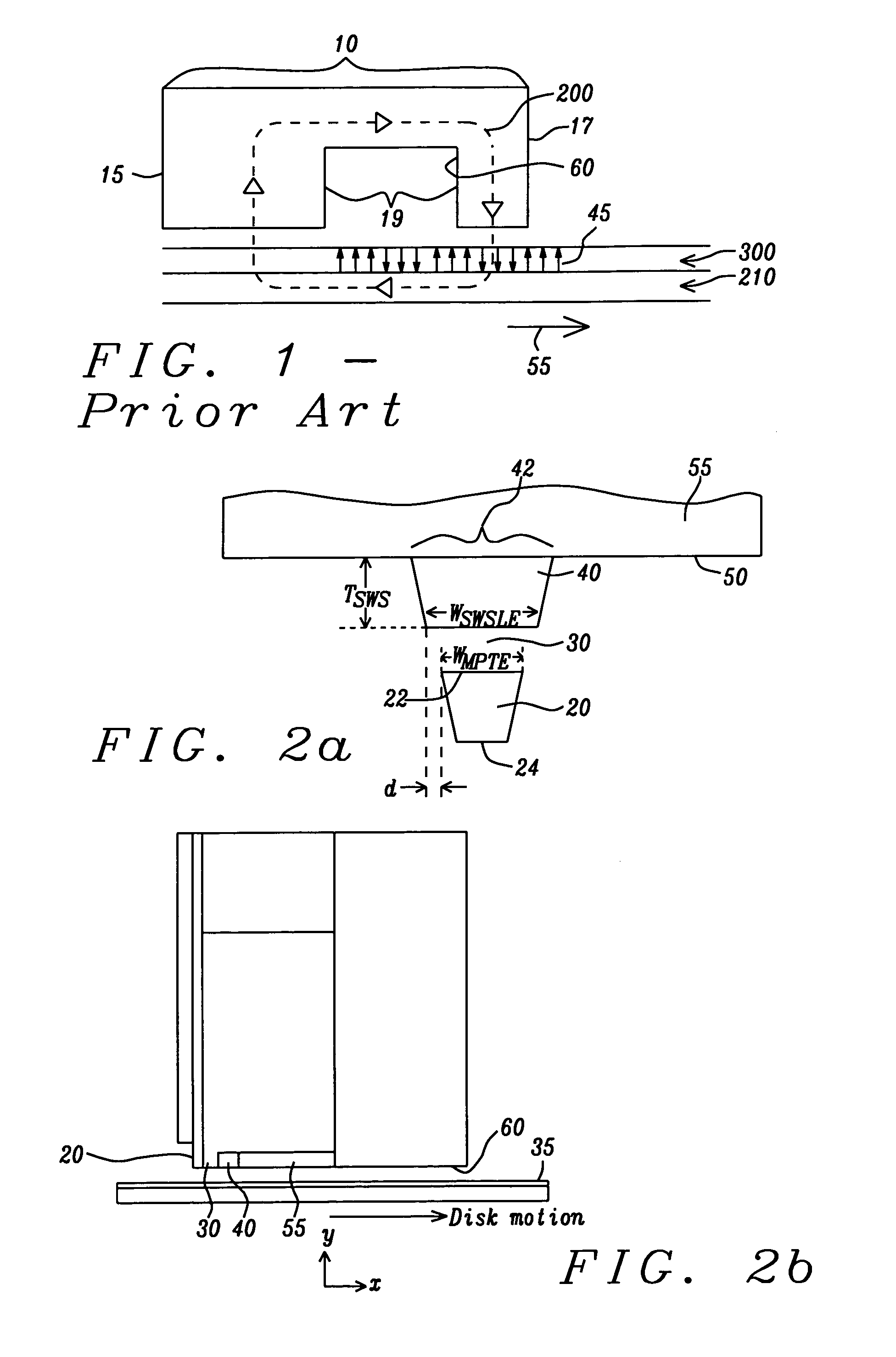
A PMR write head has a stitched shield formation which results in a strong perpendicular write field with sharp vertical gradients. The shape of the stitched shield is determined by two design parameters, d=½(WSWSLE−WMPTE), and TSWS, where WSWSLE is the width of the leading edge of the stitched shield in the ABS plane, WMPTE is the width of the trailing edge of the main magnetic pole in the ABS plane and TSWS is the thickness of the stitched shield. By a proper choice of these parameters, the write field of the head is sharply limited in the cross-track direction, so that adjacent track erasures are eliminated.
Owner:HEADWAY TECH INC
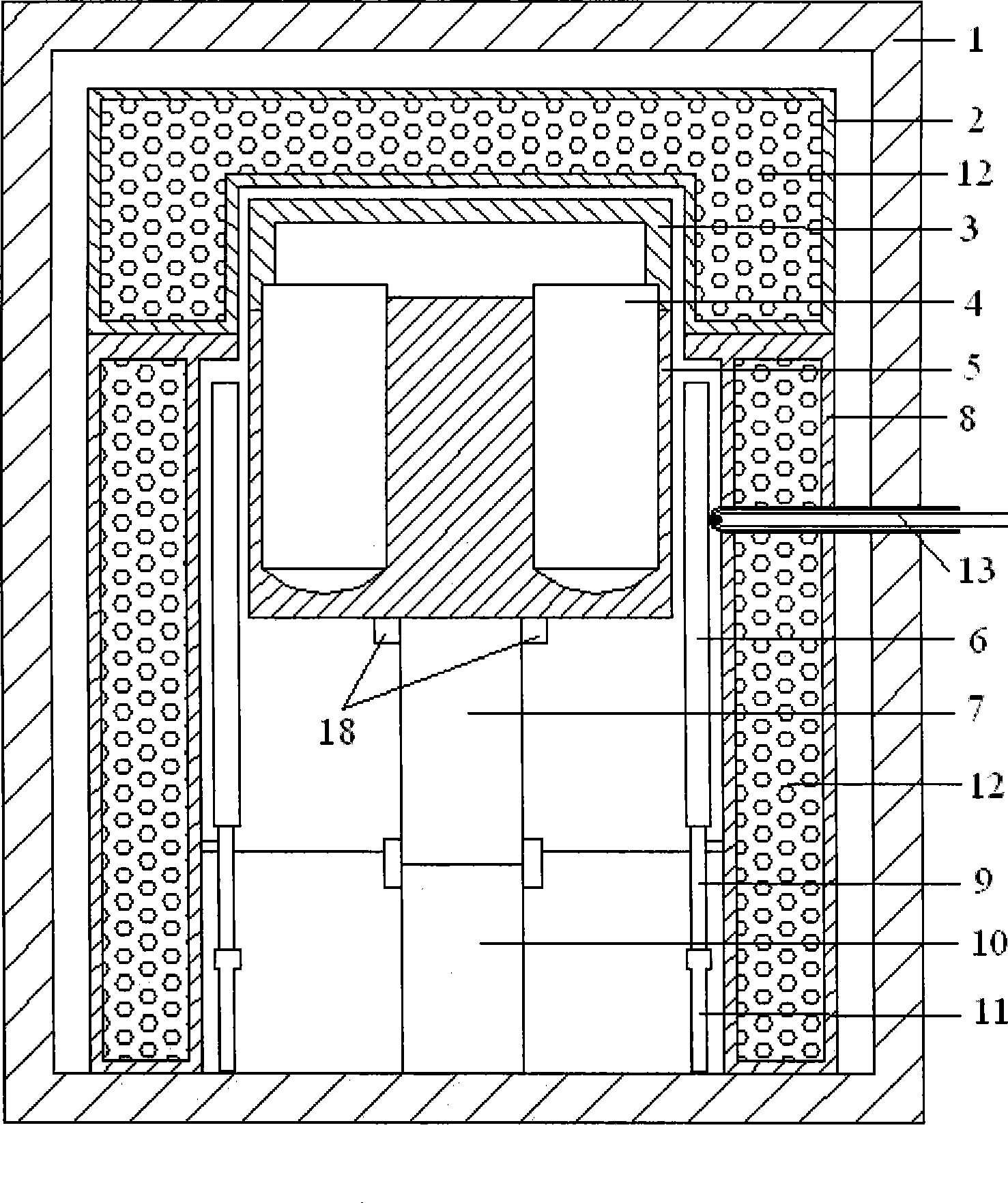
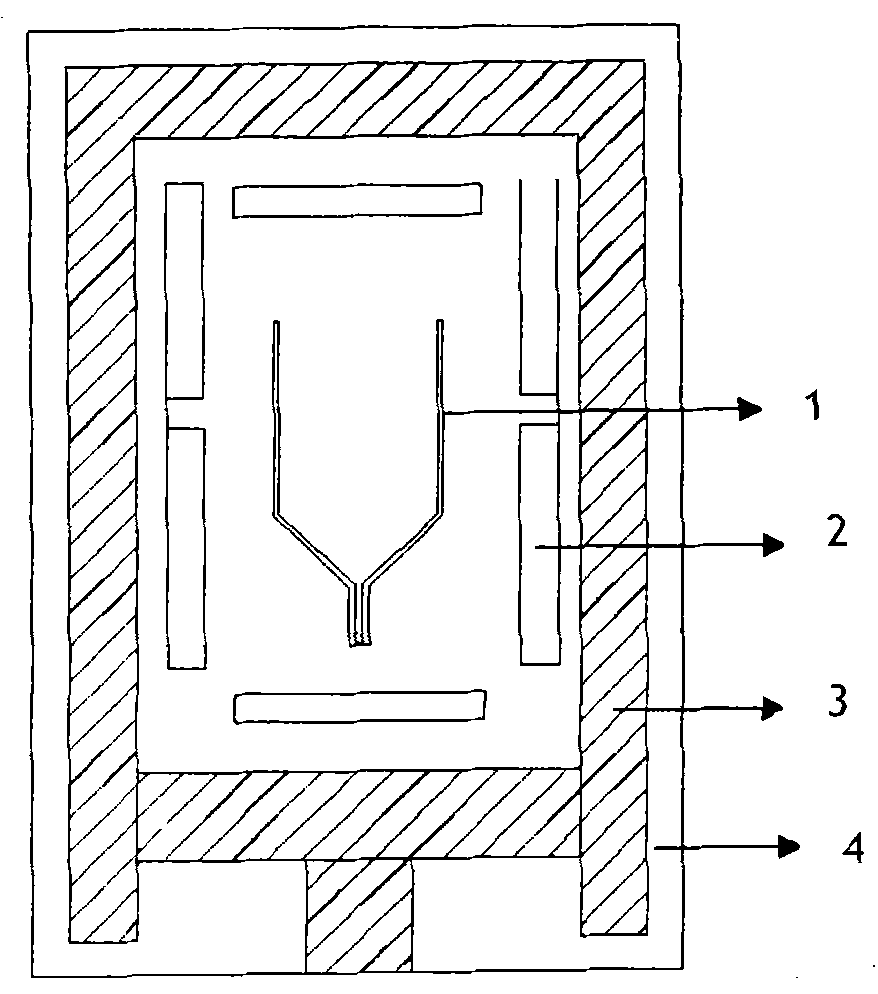
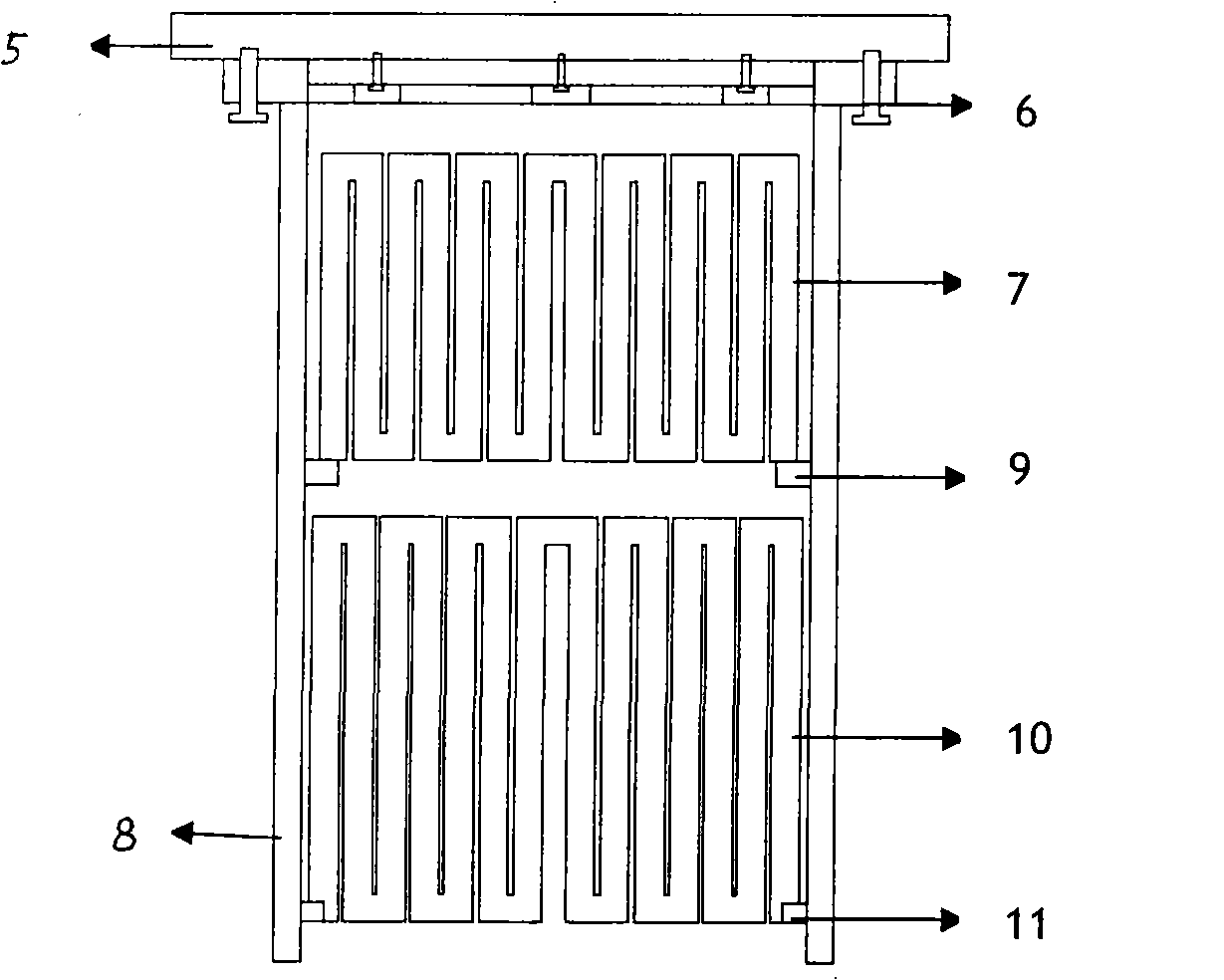
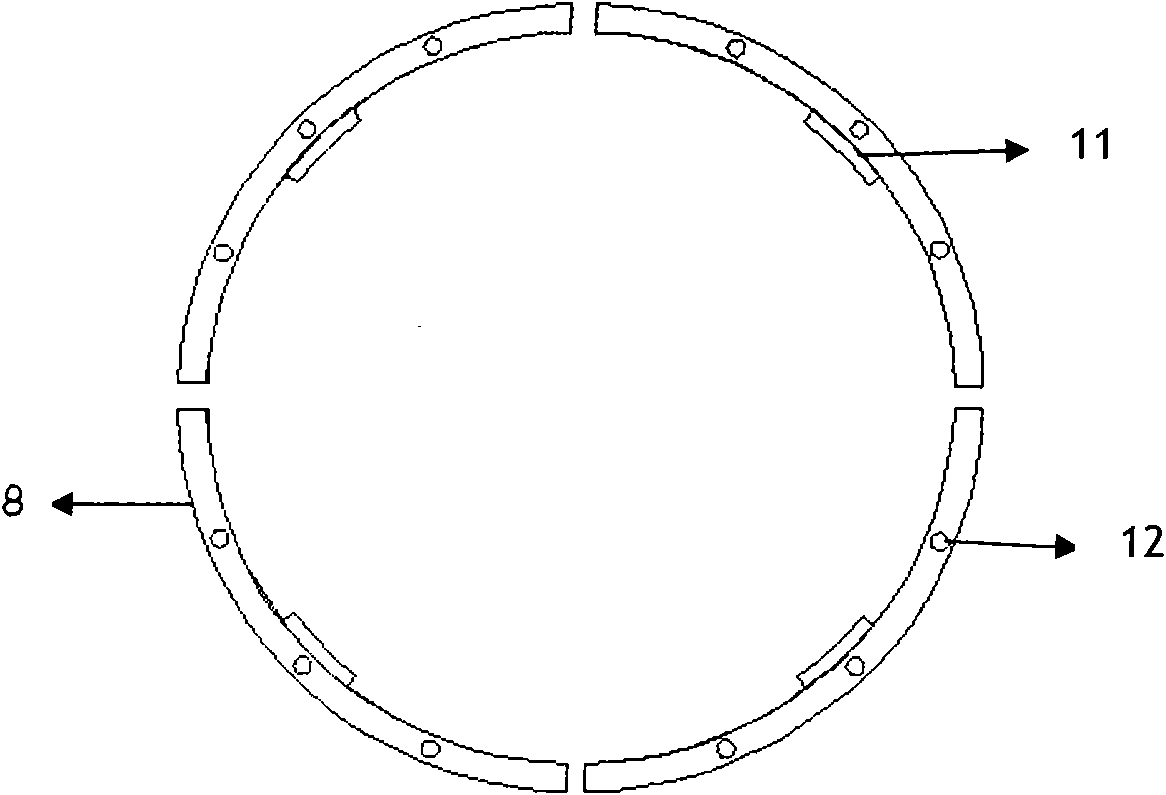
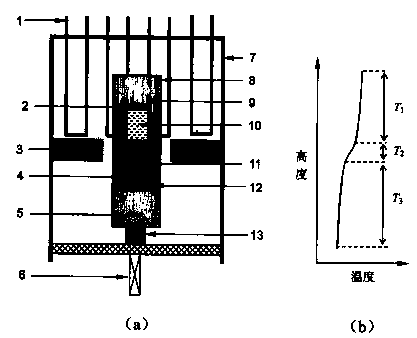
Multi-stage side heater in vertical gradient freezing crystal growing furnace
InactiveCN102108543AImprove utilization efficiencyGood symmetryFrom frozen solutionsThermal energyGraphite electrode
The invention discloses a multi-stage side heater in a vertical gradient freezing crystal growing furnace. The multi-stage side heater comprises a graphite sleeve, and an upper heater and a lower heater positioned in the graphite sleeve, wherein the upper heater in the graphite sleeve is connected with a graphite electrode fixed on an upper furnace cover plate, and is connected with the graphite sleeve through boron nitride; or the upper heater is supported by a graphite block, and the graphite sleeve is connected with an electrode fixed on the upper furnace cover plate; the lower heater is arranged in the graphite sleeve and is supported by a graphite block; and the graphite sleeve is connected with the electrode fixed on the upper furnace cover plate, and is fixed on the upper furnace cover plate through a screw. The invention has the advantages that: a suspended side heating system can entirely move upwards together with a furnace cover, and is entirely detached, and an insulating layer outside the heating system is not needed to be detached, so equipment maintenance, material loading and material taking are greatly facilitated; and a long plate electrode is adopted, a complete graphite cylinder is formed outside the side heating system, and the graphite cylinder can absorb, reradiate and reflect heat of the heater, so the heat utilization ratio is improved, and a thermal field has higher symmetry and stability.
Owner:GENERAL RESEARCH INSTITUTE FOR NONFERROUS METALS BEIJNG +1
Method for magnetic resonance quick imaging
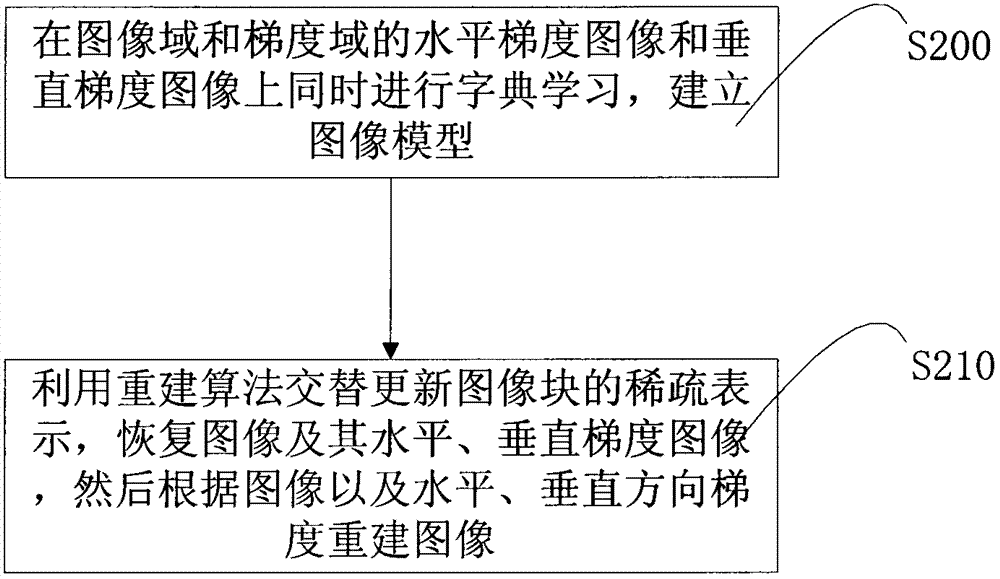
ActiveCN103049923AOvercoming the block effectAccurate reconstruction2D-image generationPattern recognitionAdaptive learning
The invention belongs to the technical field of image processing, and particularly relates to a method for magnetic resonance quick imaging. The method for the magnetic resonance quick imaging comprises the following steps of step A, carrying out dictionary studying on a horizontal gradient image and a vertical gradient image of an image gradient domain, and establishing an image model; and step B, alternately updating the sparse expression of image blocks by a remodeling algorithm, restoring the horizontal gradient and the vertical gradient, and remodeling images on the horizontal gradient and the vertical gradient. The method for the magnetic resonance quick imaging, provided by the embodiment of the invention, has the advantages that through the introduction of the self-adaptive dictionary studying, the block effect of the target image caused by the fixed finite difference conversion is overcome, and the images with more complicated structures can be processed, so as to more precisely remodel; and after being processed, the gradient images are more sparse than the original images, so more accuracy and robustness of the dictionary studying are realized, the images can be expressed more sparsely, the fidelity is higher, and more details can be restored.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH
Image processing device and method, program, and recording medium
InactiveUS20090136146A1Useful in detectionAccurate detectionTelevision system detailsImage analysisImaging processingVertical gradient
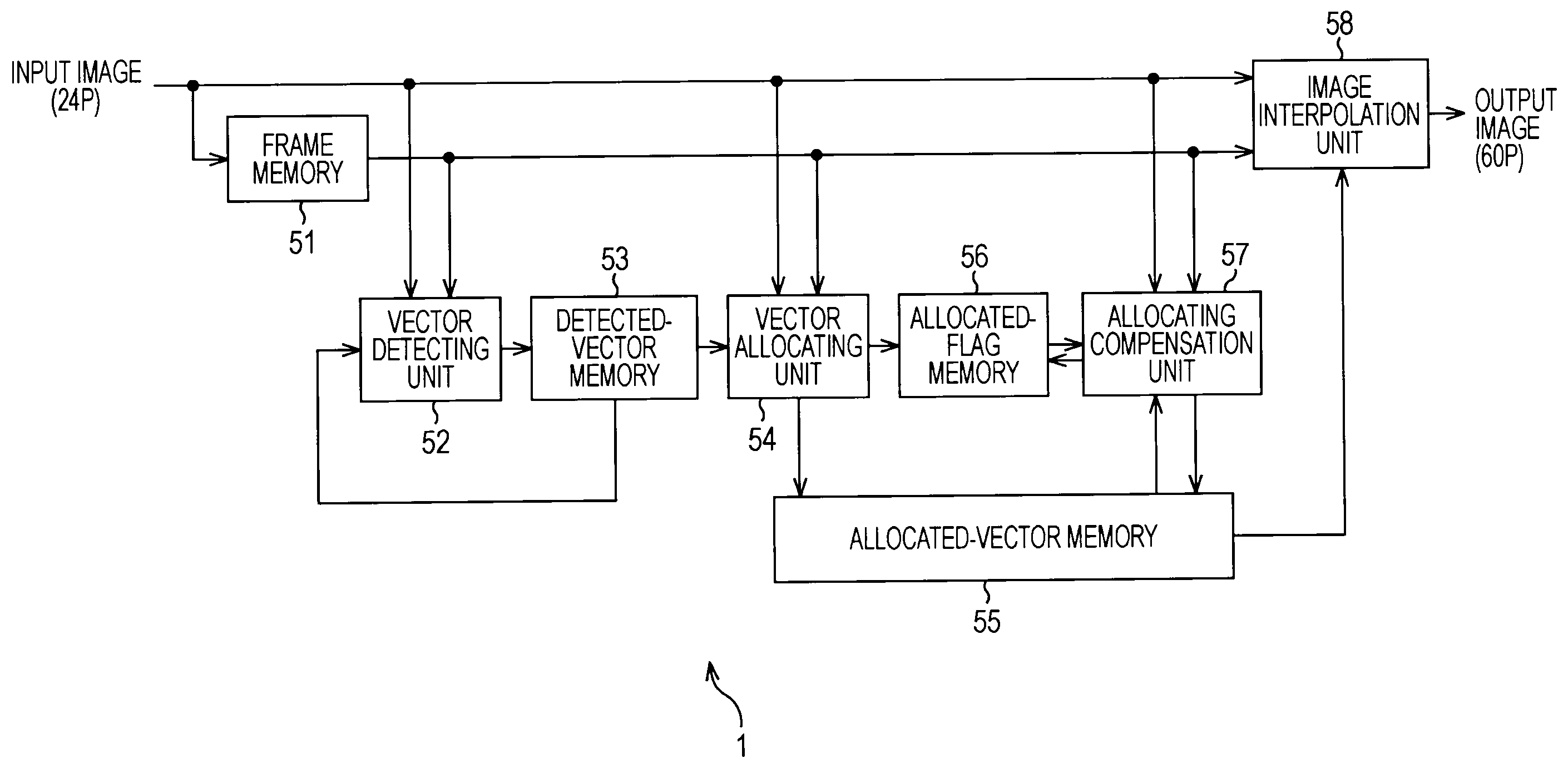
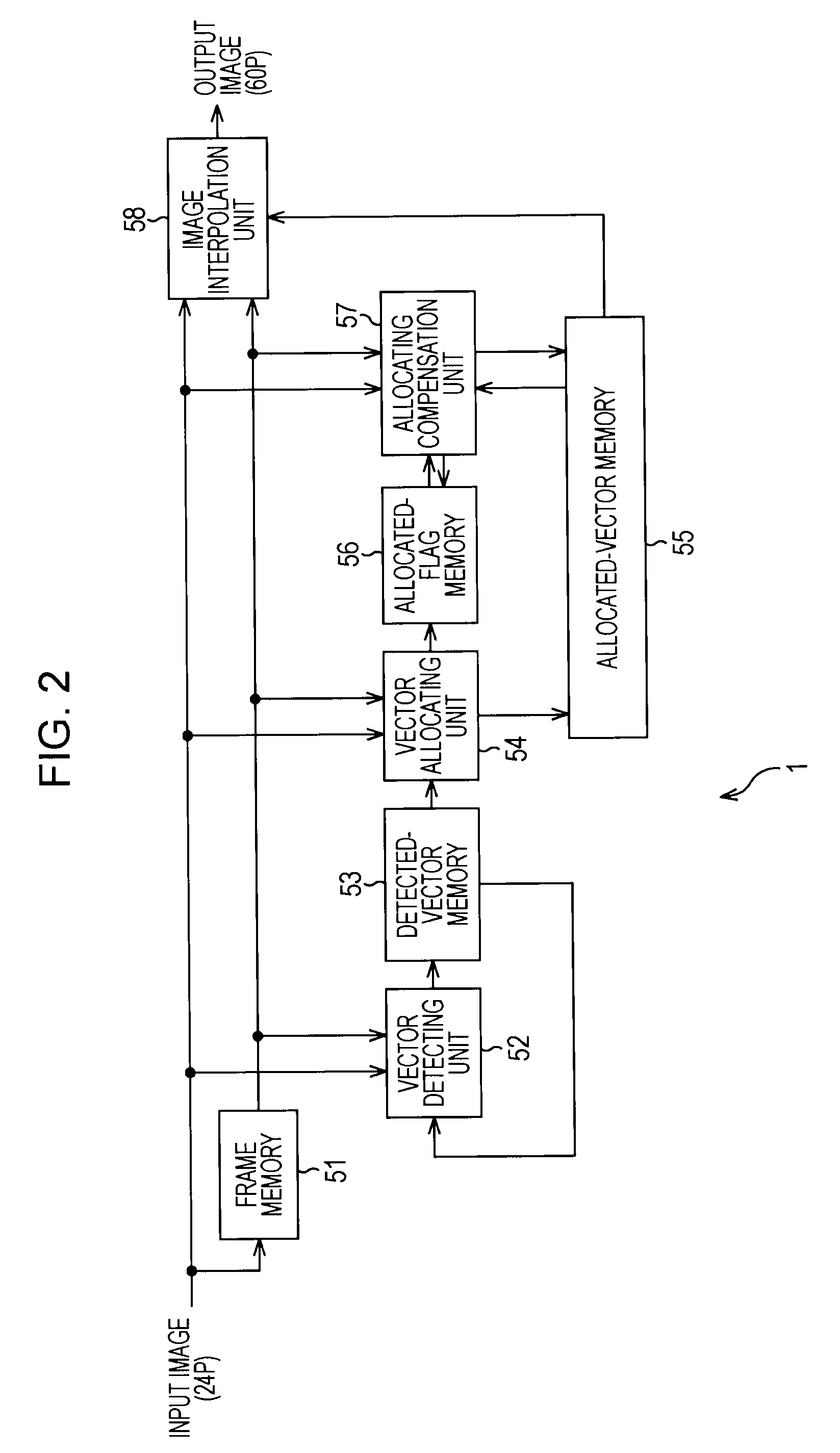
The present invention relates to an image processing device and method, a program, and a recording medium whereby the detection precision of a motion vector by the gradient method can be further improved. A counter value computing unit 451 acquires the number of valid pixels, the number of pixels having no gradient in the horizontal direction, and the number of pixels having no gradient in the vertical direction from a valid pixel number counter 441, a no-horizontal-gradient counter 442, and a no-vertical-gradient counter 443, computes the ratio between valid pixels within a computation block and one-sided gradient pixels among the valid pixels, and controls the value of a flag which a flag setting unit 452 sets in accordance with the computation results. The flag setting unit 452 sets the value of a gradient flag, and outputs the gradient flag to the subsequent stage. At the subsequent stage, gradient method computation and vector evaluation processing are executed based on the gradient flag. The present invention can be applied to a signal processing device for performing frame frequency conversion processing from a 24P signal to a 60P signal.
Owner:SONY CORP
Method for analyzing temperature gradient effect of flat steel box girder of long-span steel bridge
InactiveCN102243671AAnalysis method is simpleSpecial data processing applicationsVertical gradientMetallurgy
The invention discloses a method for analyzing a temperature gradient effect of a flat steel box girder of a long-span steel bridge. The structure of a steel box girder is a hexagonal flat steel box girder. The method comprises the following steps of: analyzing the sectional temperature gradient distribution of the steel box girder; acquiring a gradient curve of piecewise linear change of the maximum temperature along a vertical direction; and analyzing influence of temperature on stress and deformation of the steel box girder. The method is applicable to orthotropic flat steel box girders with or without a footway flange plate. The sectional temperature gradient distribution, the vertical gradient curve and a formula, which are acquired according to the method, are accordant with the distribution of sectional temperatures of the structure of the flat steel box girder at a sunlight temperature difference. By applied temperature gradient distribution which is acquired according to the method, the influence of temperature on stress and deformation can be analyzed. The research of the method is aided financially by national science and technology supporting planning projects 2009BAG15B03.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV +1
Improved gradient freeze GaAs single crystal growing method
InactiveCN103789835APolycrystalline material growthFrom frozen solutionsBridgman methodVertical gradient
The invention provides an improved gradient freeze GaAs single crystal growing method. According to the method, a traditional vertical gradient freeze (VGF) or vertical Bridgman (VB) crystal growing device is improved. The improved gradient freeze GaAs single crystal growing method is characterized in that a heating system is installed at the top of a crystal growing furnace and heating elements are a set of series-connection U-shaped silicomolybdic bars. The distribution curve of temperatures in a furnace body is formed through a heat insulation plate. GaAs raw materials are molten in a high-temperature area above the heat insulation plate and melt grows in a crystallizing mode in a temperature gradient area formed by the heat insulation plate. Obtained crystals are moved to the space below the heat insulation plate through a descending device, and high-temperature in-situ annealing is conducted to release thermal stress. GaAs single crystals grown by the adoption of the technology have the advantages of being low in dislocation, large in size, small in thermal stress and the like.
Owner:KUNSHAN DINGJING GALLIUM CRYSTAL MATERIAL
Electromagnetic surveying for resistive or conductive bodies
ActiveUS8099239B2Reduce analysisSuitable for collectionWater resource assessmentSpecial data processing applicationsOcean bottomElectric field
A method of analyzing electromagnetic survey data from an area of seafloor (6) that is thought or known to contain a conductive or resistive body, such as a subterranean hydrocarbon reservoir (12), is described. The method includes providing electric field data and magnetic field data, for example magnetic flux density, obtained by at least one receiver (25) from a horizontal electric dipole (HED) transmitter (22) and determining a vertical gradient in the electric field data. The vertical gradient in the electric field data and the magnetic field data are then combined to generate combined response data. The combined response data is compared with background data specific to the area being surveyed to obtain difference data sensitive to the presence of a subterranean hydrocarbon reservoir. Because the combined response data are relatively insensitive to the transverse electric (TE) mode component of the transmitted signal, the method allows hydrocarbon reservoirs to be detected in shallow water where the TE mode component interacting with the air would otherwise dominate. Furthermore, because there is no mixing between the TE and transverse magnetic (TM) modes in the combined response data, data from all possible transmitter and receiver orientations may be used. The background data may be provided by magneto-telluric surveying, controlled source electromagnetic surveying or from direct geophysical measurement.
Owner:PGS GEOPHYSICAL AS
Method for analyzing dip in seismic data volumes
InactiveUS6850864B2Mechanical area measurementsDigital computer detailsVertical gradientData location
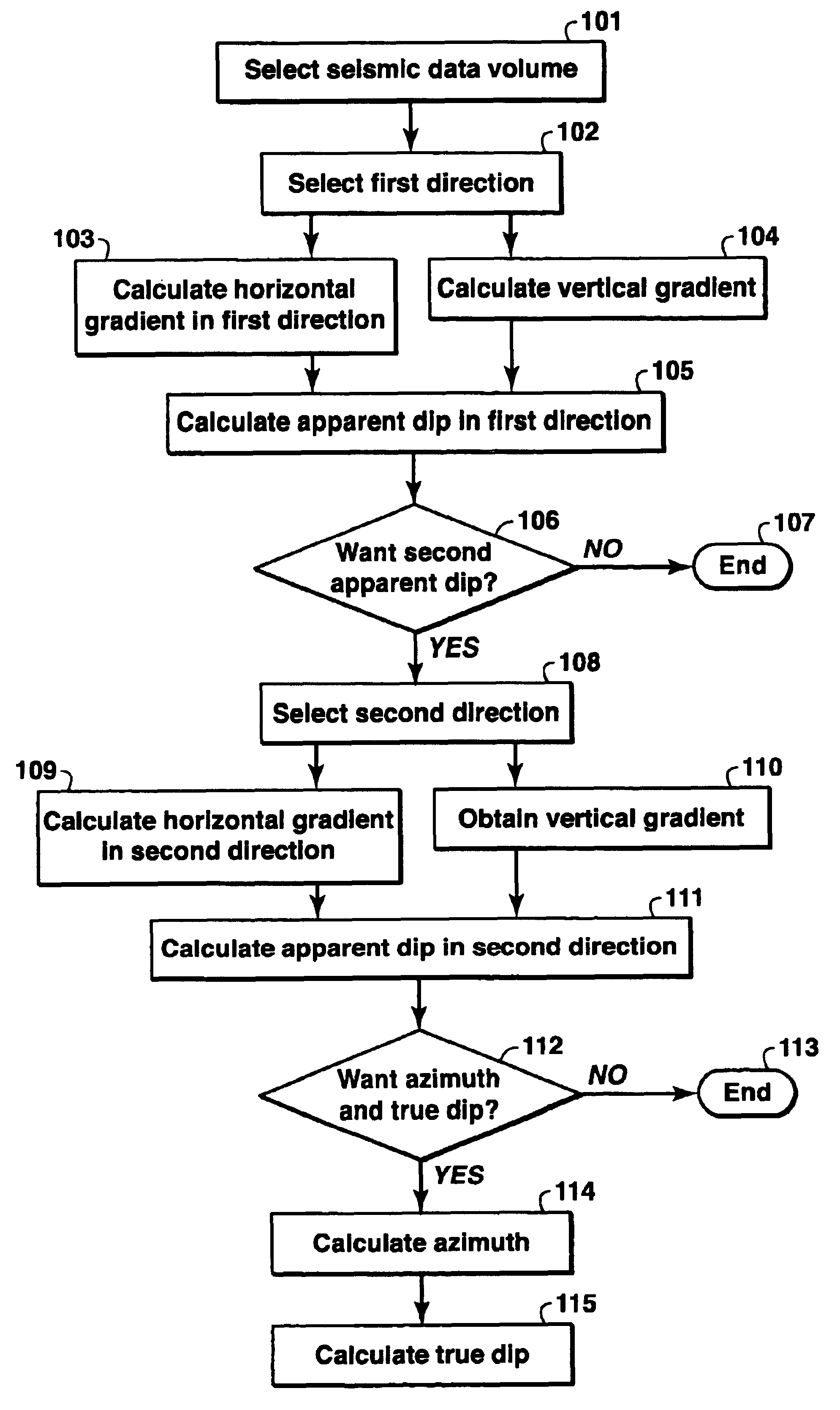
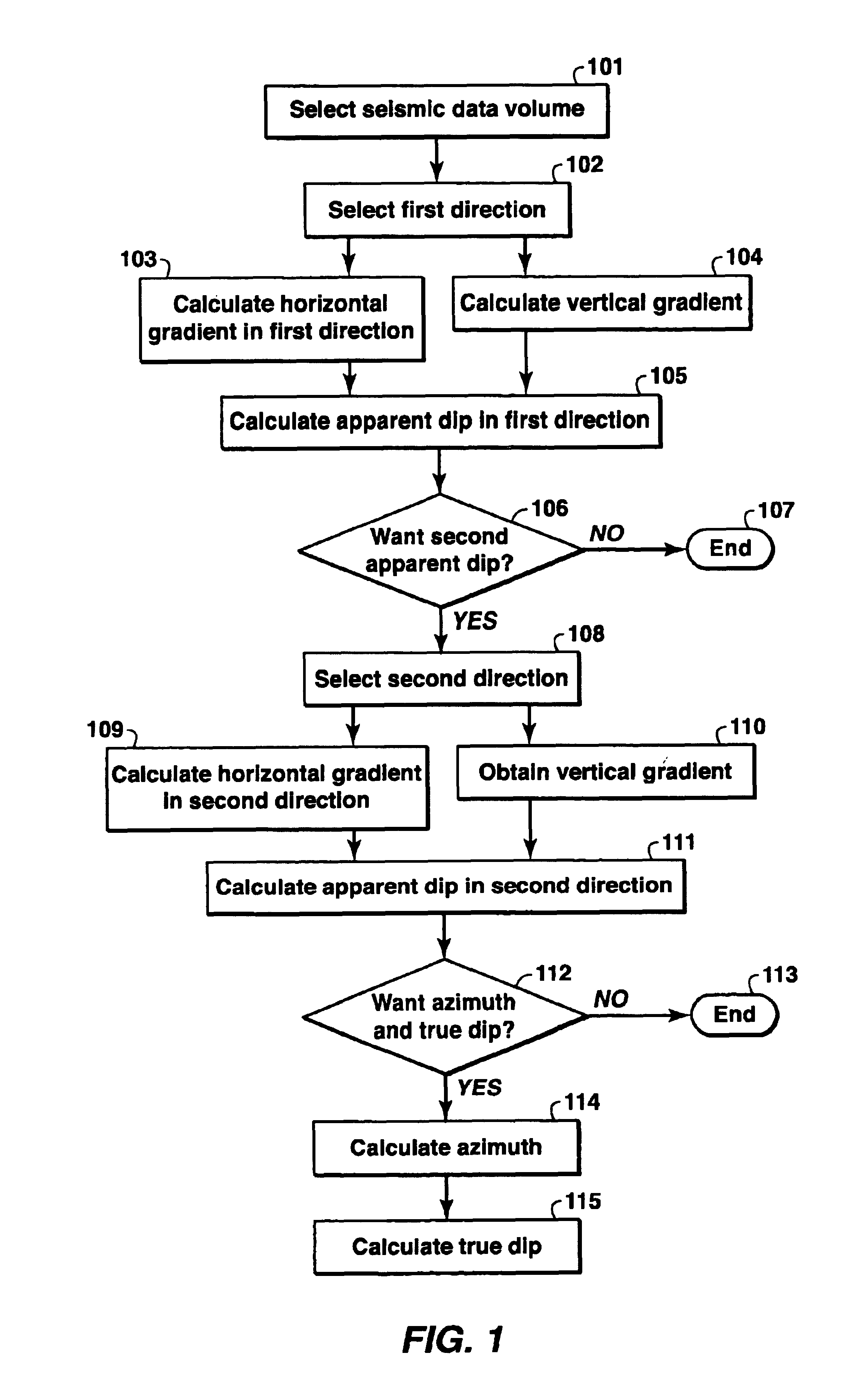
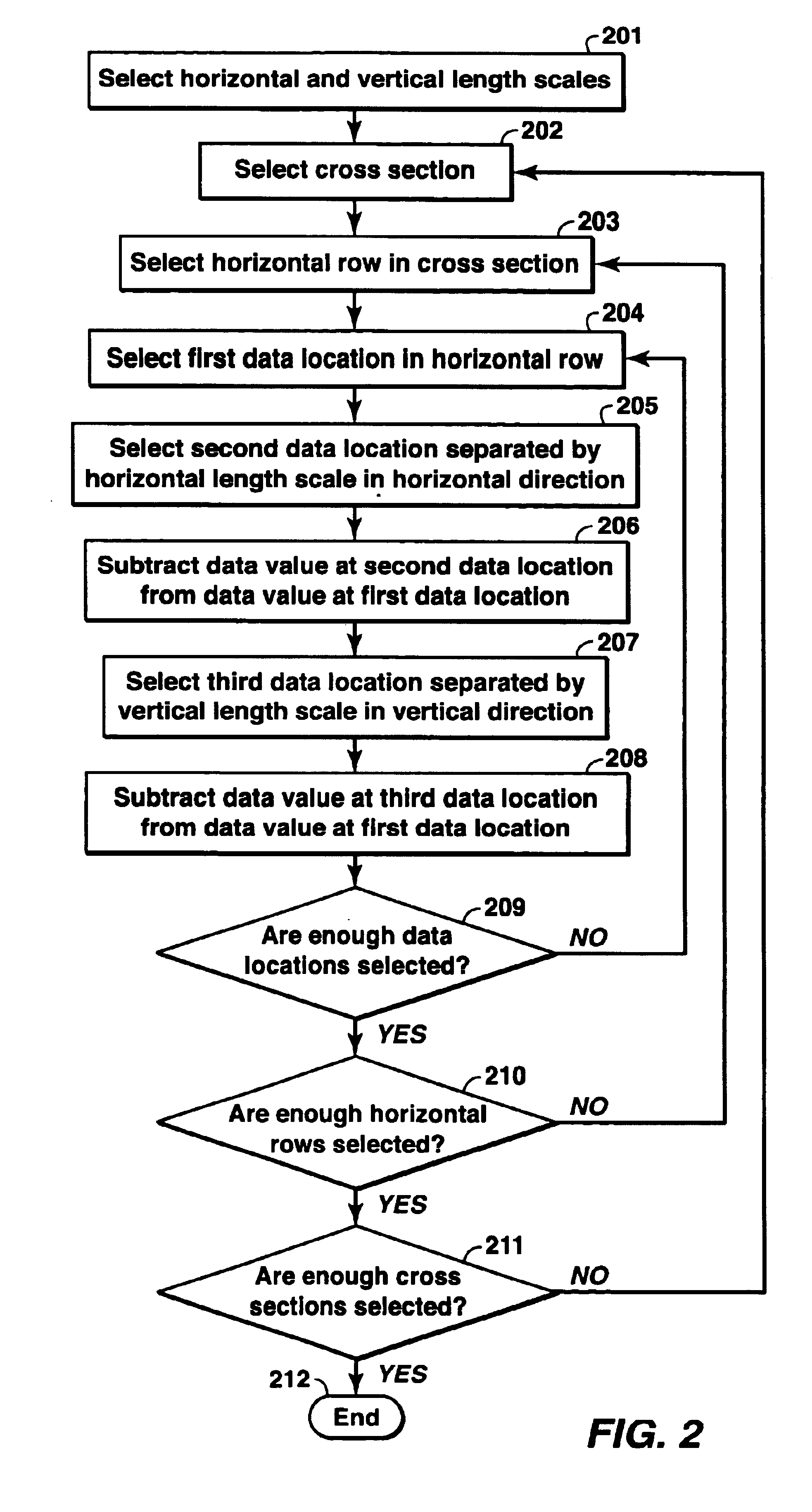
A method of analyzing dip in a seismic data volume in which a horizontal gradient is calculated in a first direction in the seismic data volume. A vertical gradient is calculated at data locations in the seismic data volume corresponding to the locations at which the horizontal gradient was calculated. Dip is calculated in the first direction from the horizontal gradient in the first direction and the vertical gradient. Repetition of the process for the entire seismic data volume results in a dip volume.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL UPSTREAM RES CO
Method for producing a monocrystalline or polycrystalline semiconductore material
ActiveUS20090158993A1High filling levelShort melting timeAfter-treatment apparatusPolycrystalline material growthVertical gradientCrucible
The invention relates to a method for producing a monocrystalline or polycrystalline semiconductor material by way of directional solidification, wherein lumpy semiconductor raw material is introduced into a melting crucible and melted therein and directionally solidified, in particular using the vertical gradient freeze method.In order to prevent contamination and damage, the semiconductor raw material is melted from the upper end of the melting crucible. The molten material trickles downward, so that semiconductor raw material which has not yet melted gradually slumps in the melting crucible. In this case, the additional semiconductor raw material is replenished to the melting crucible from above onto a zone of semiconductor raw material which has not yet melted or is not completely melted, in order at least partly to compensate for a volumetric shrinkage of the semiconductor raw material and to increase the filling level of the crucible.In order to reduce the melting-on time and to influence the thermal conditions in the system as little as possible, the semiconductor raw material to be replenished is heated by the purposeful introduction of heat to a temperature below the melting temperature of the semiconductor raw material and introduced into the container in the heated state.
Owner:SCHOTT AG
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com