Patents
Literature
95results about How to "Large gradient" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
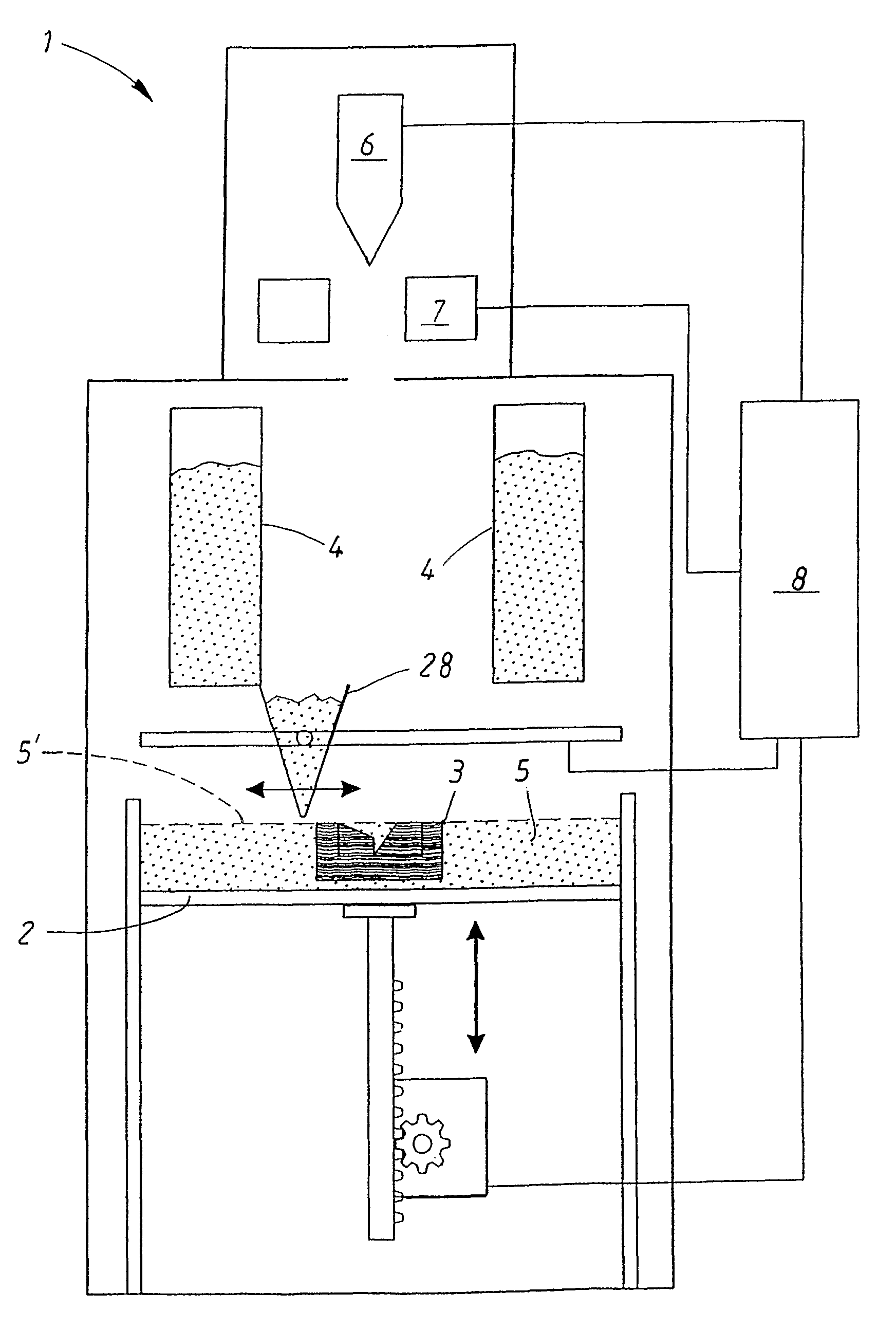
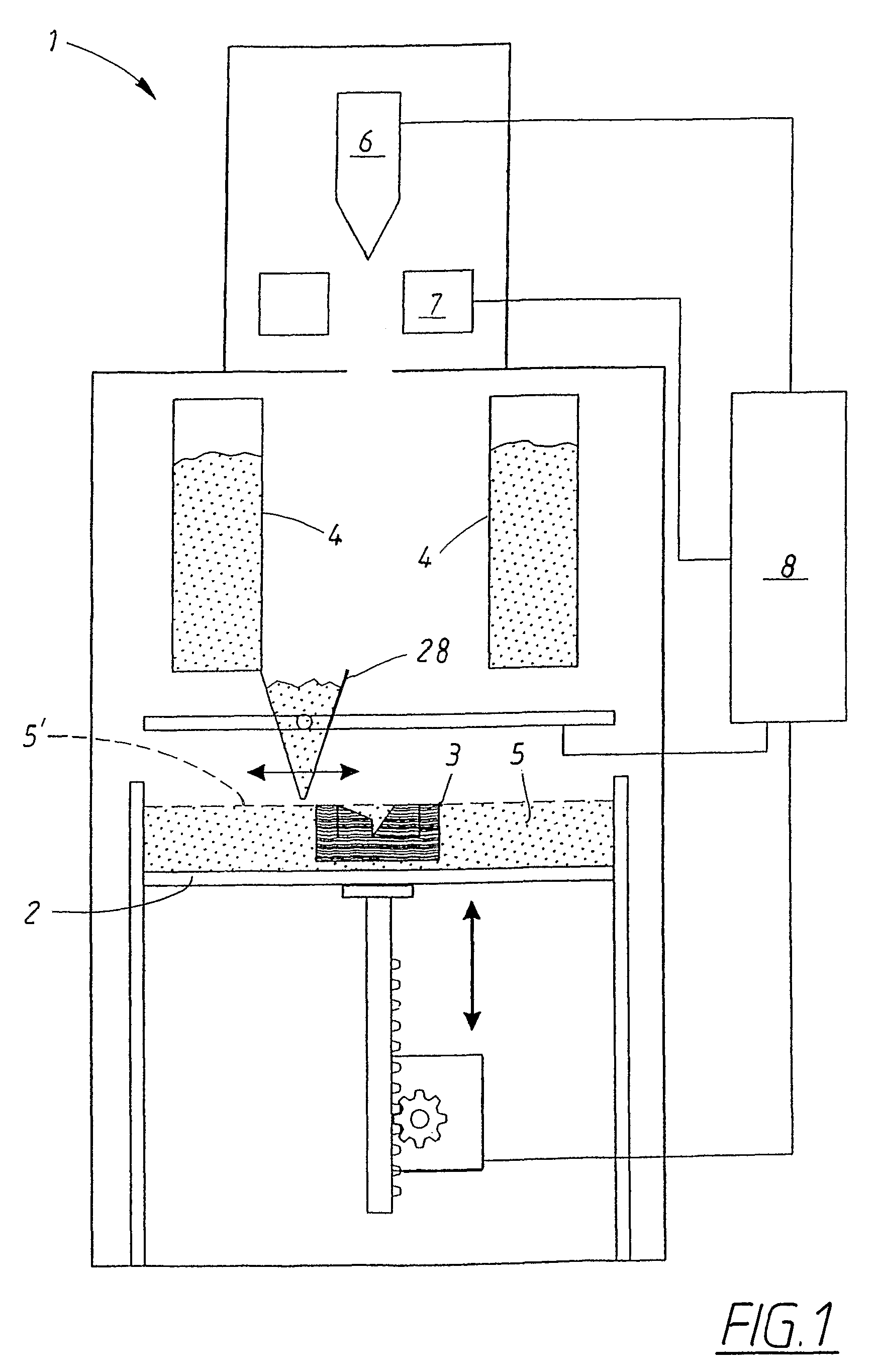
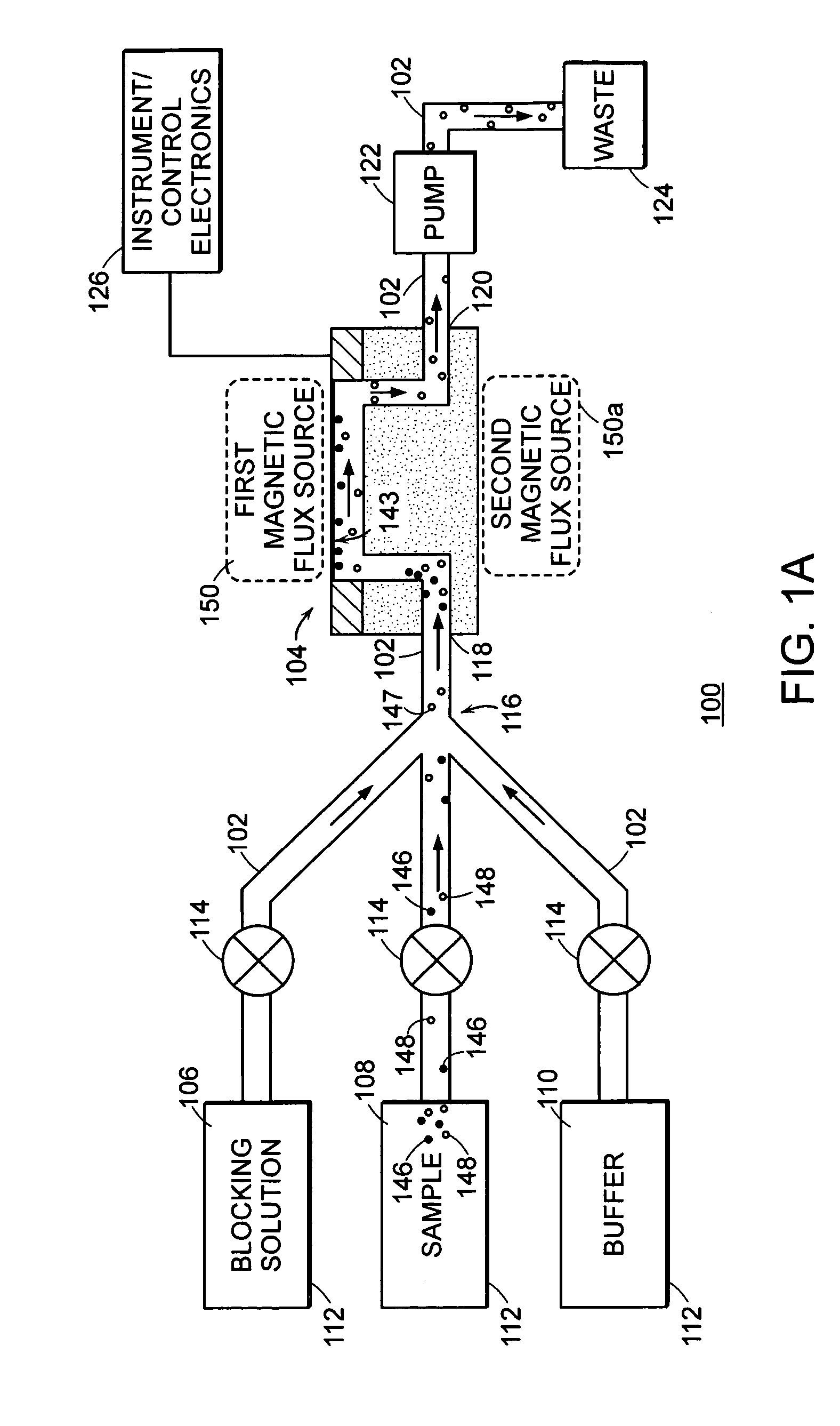
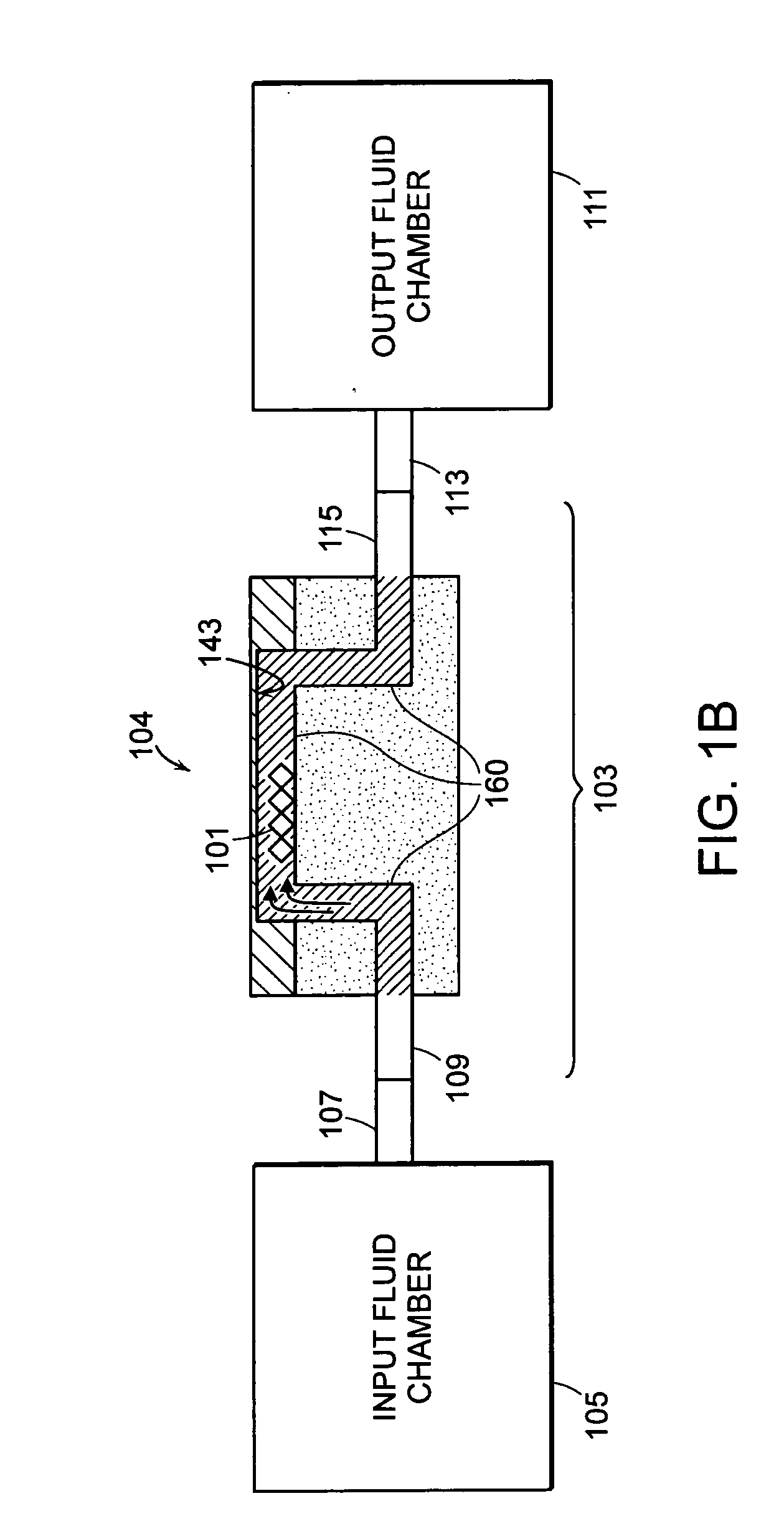
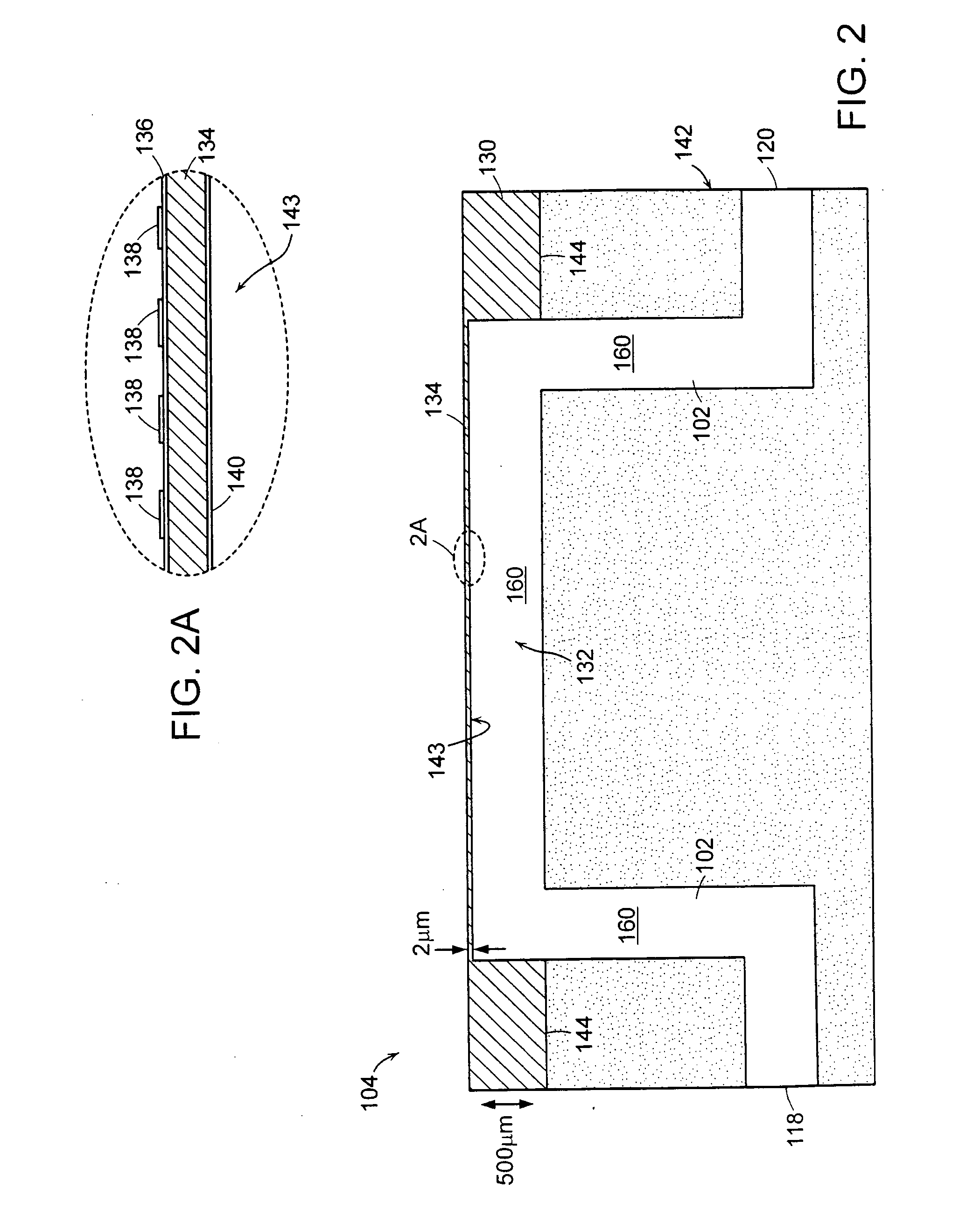
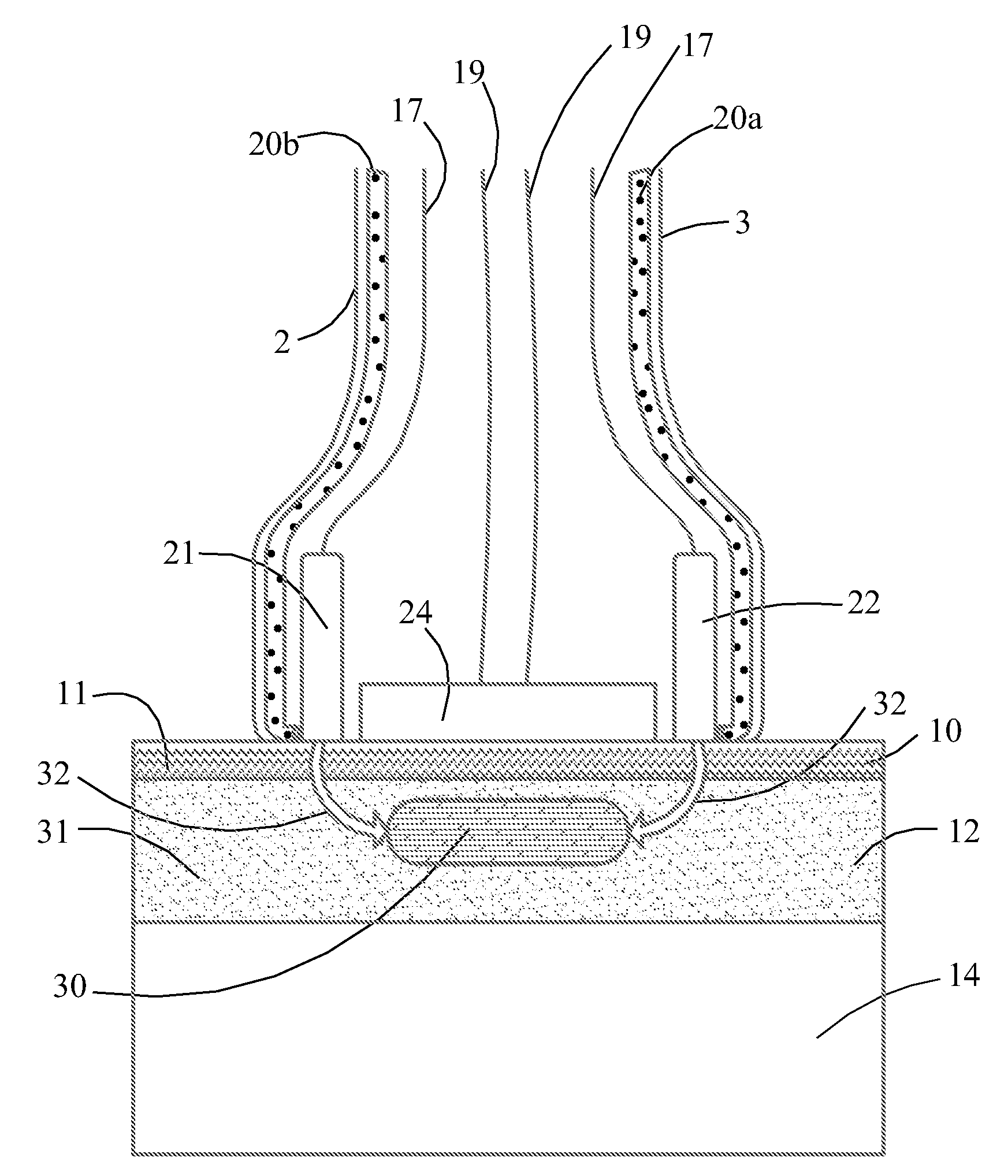
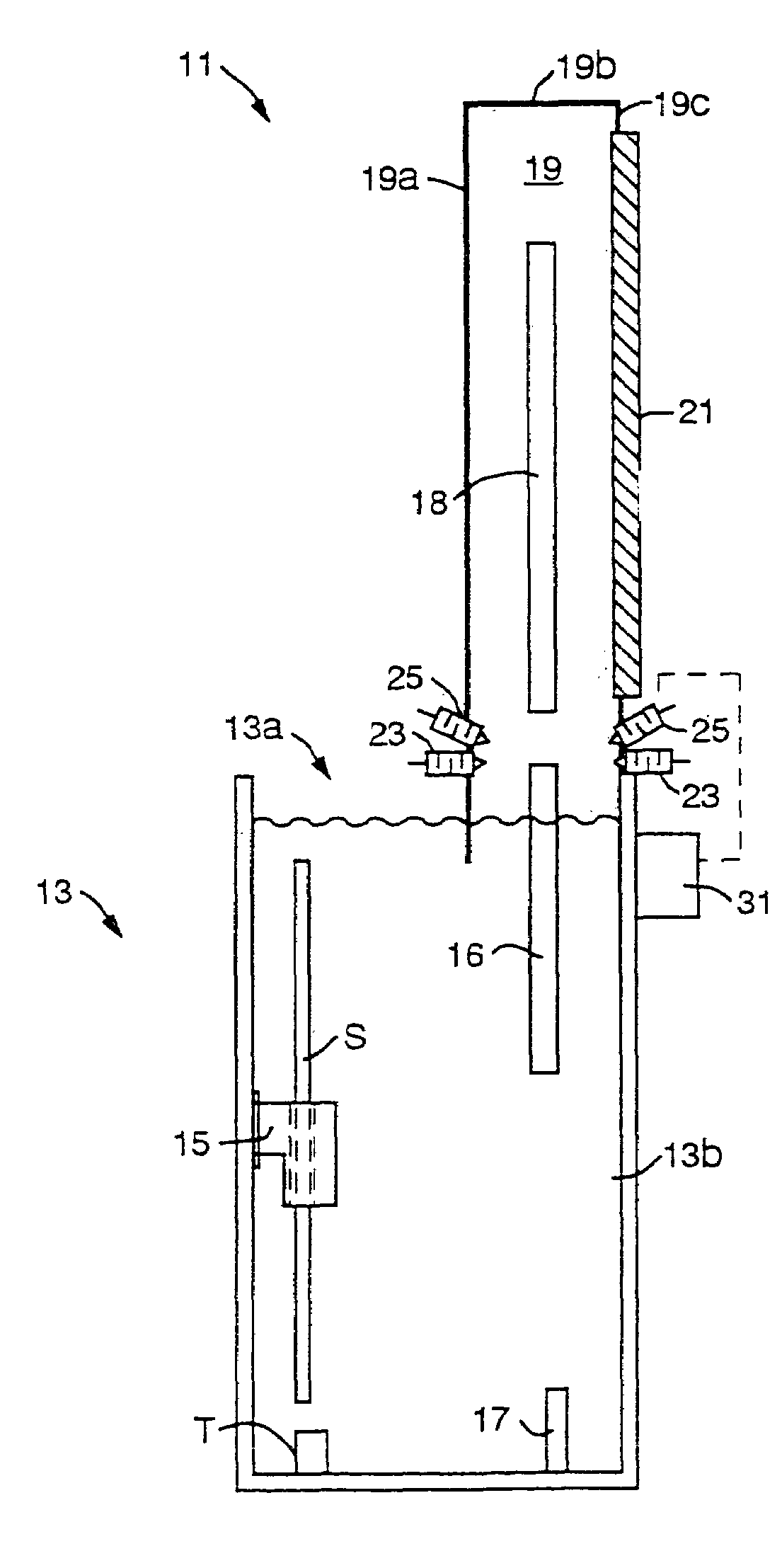
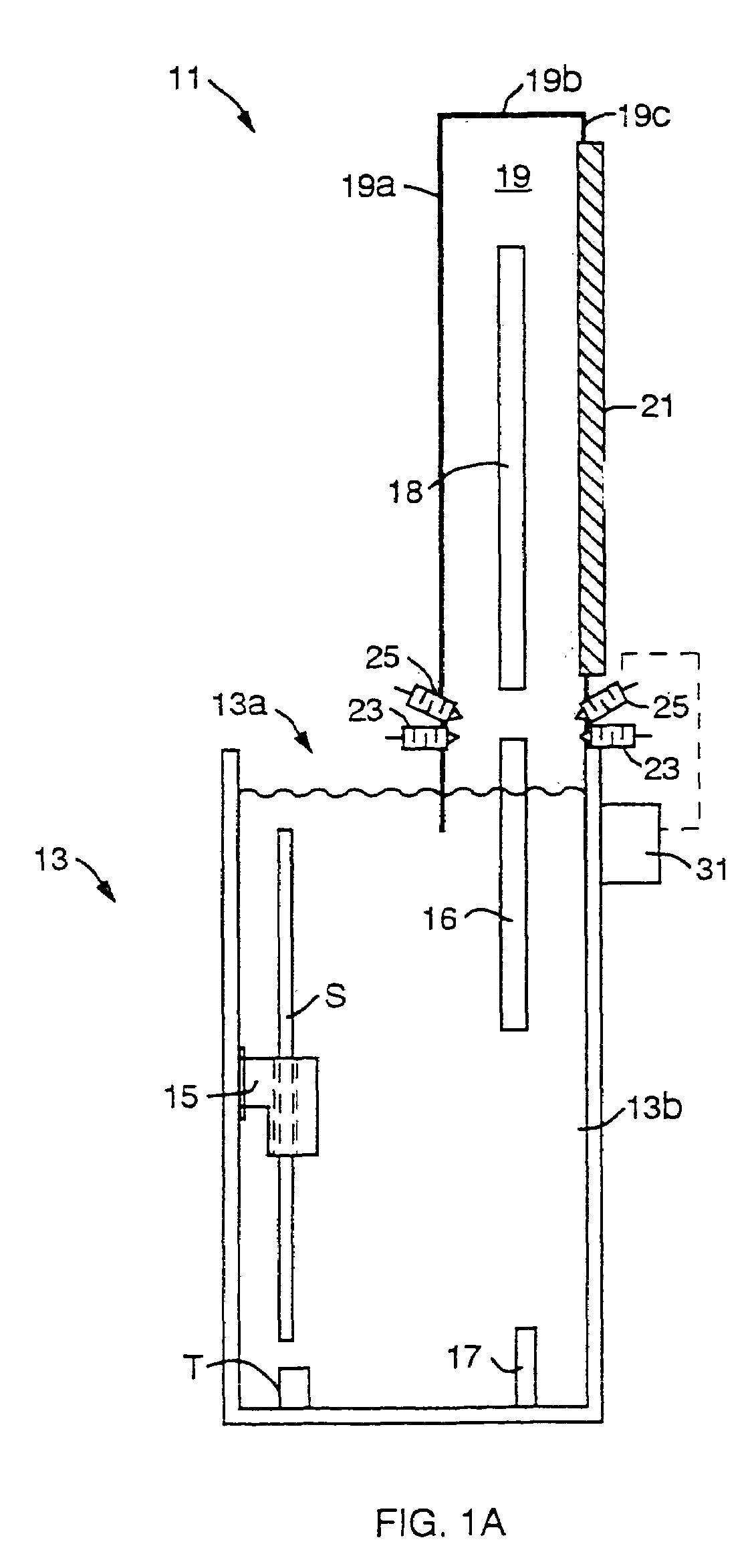
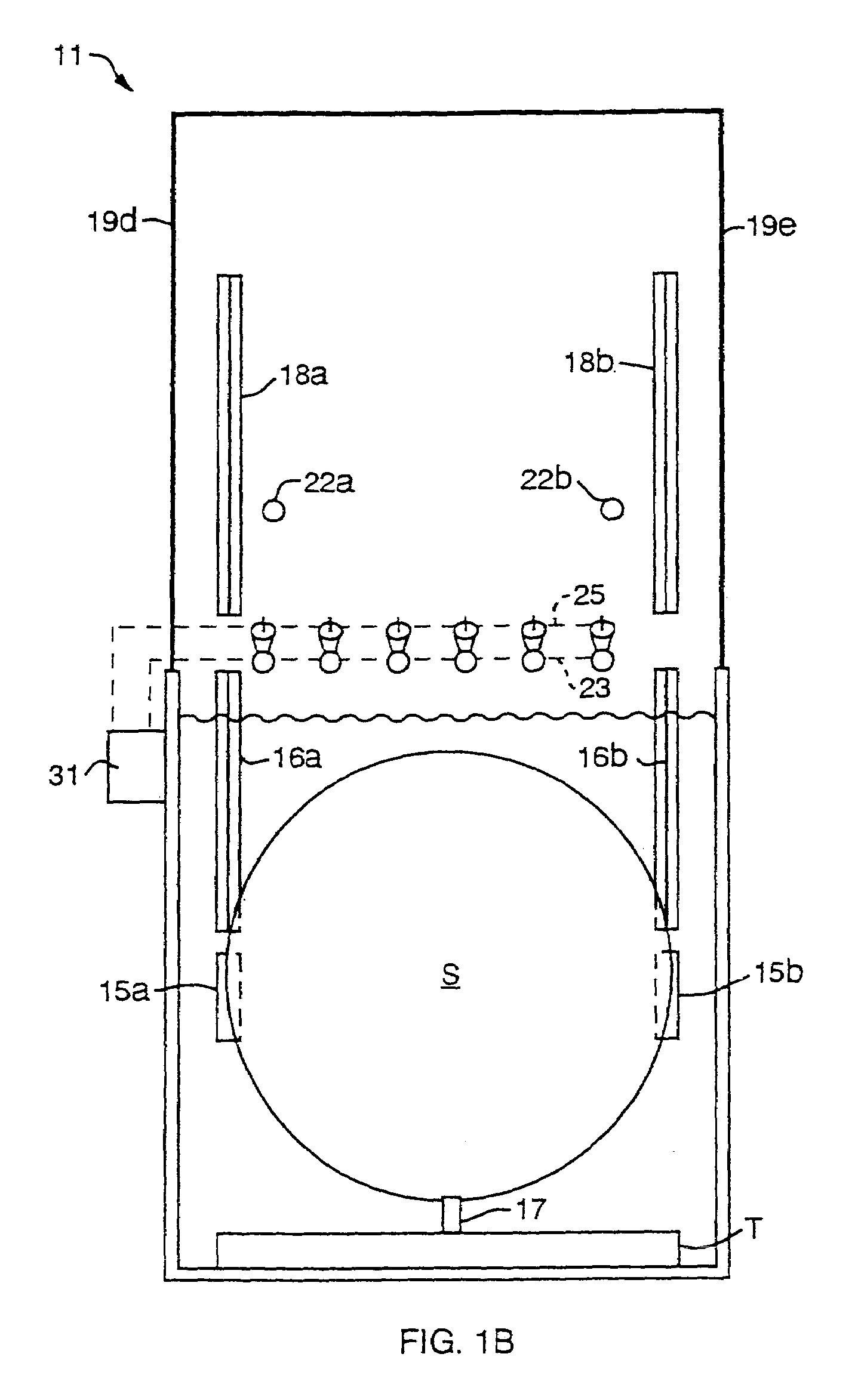
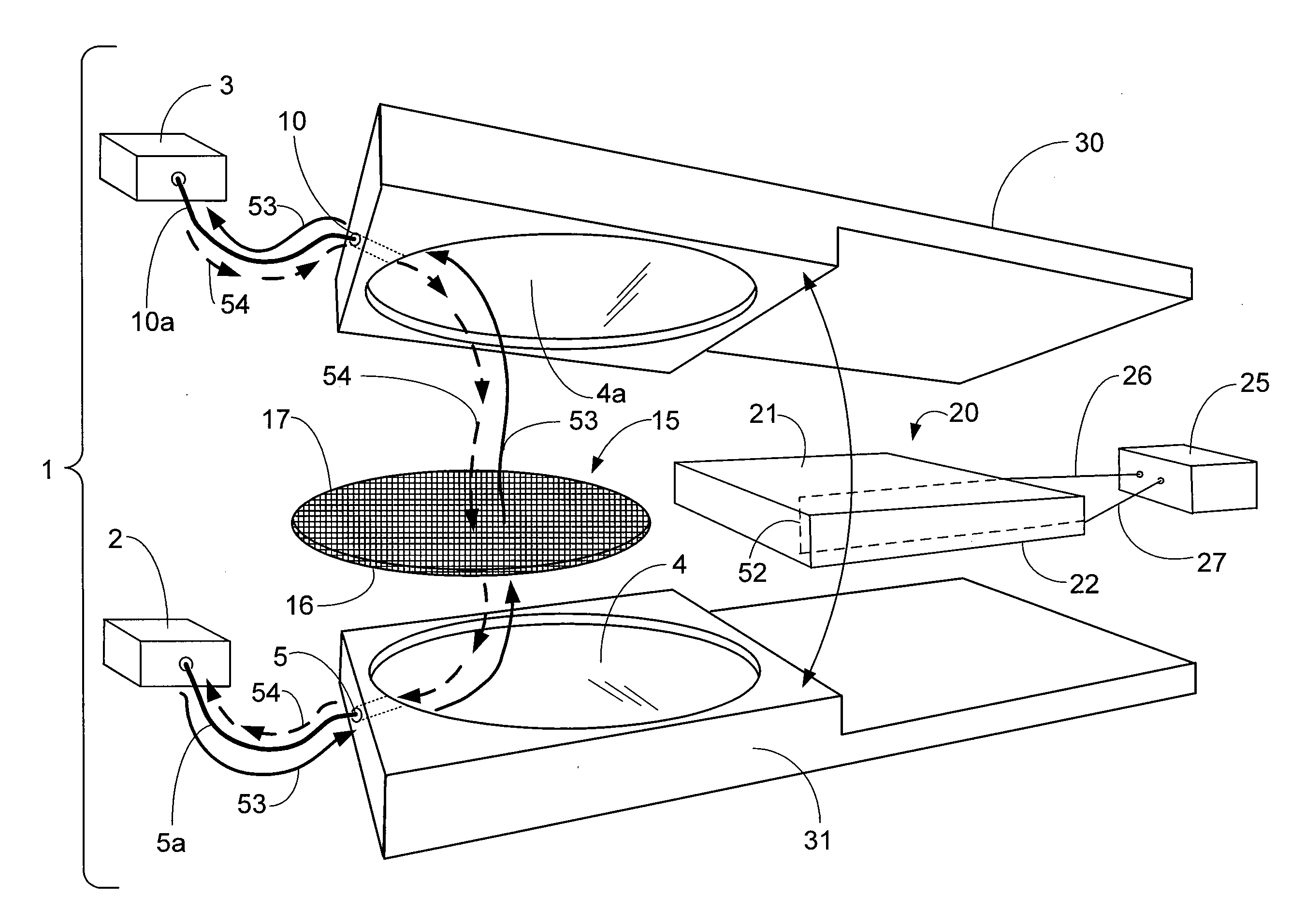
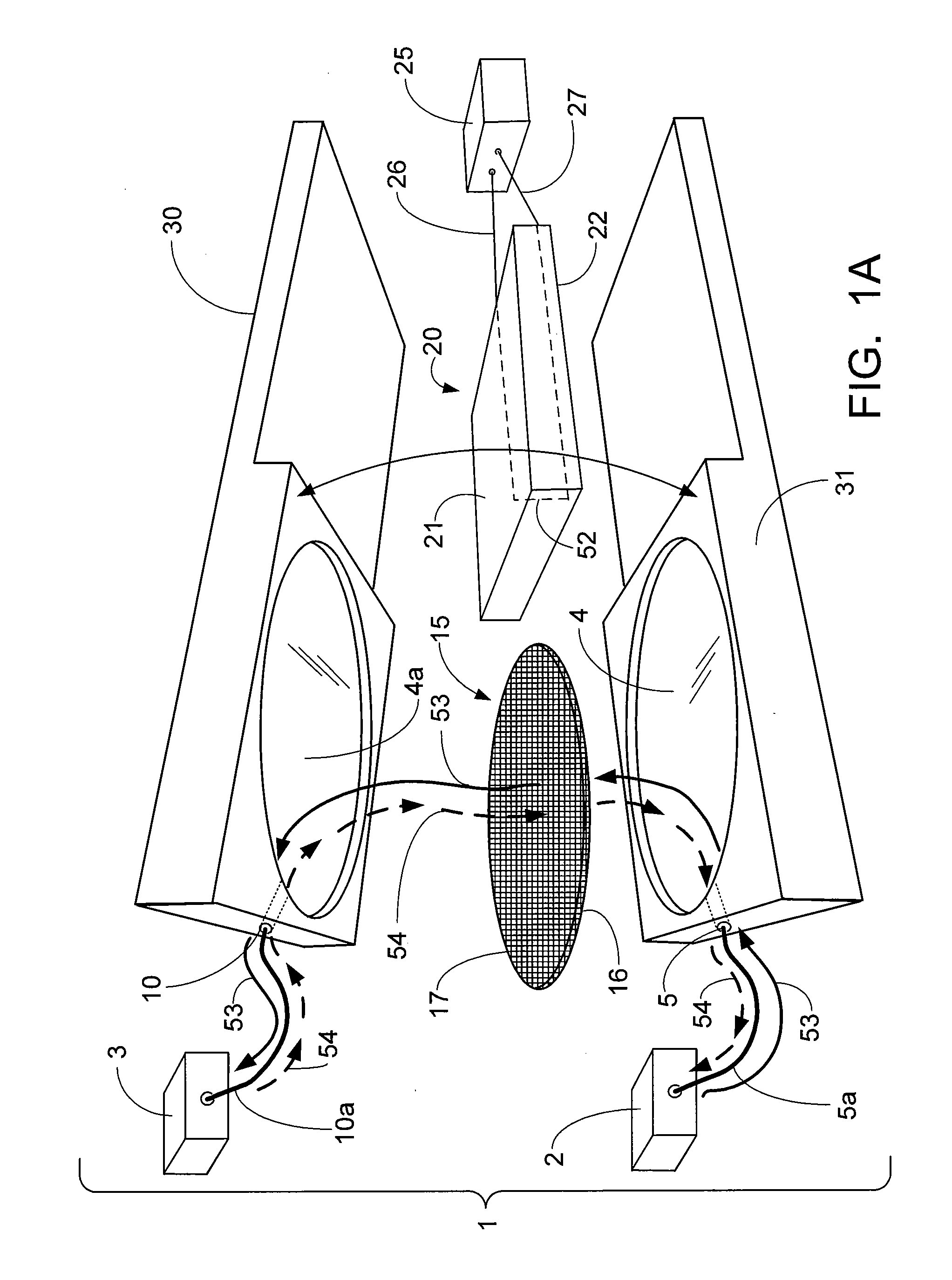
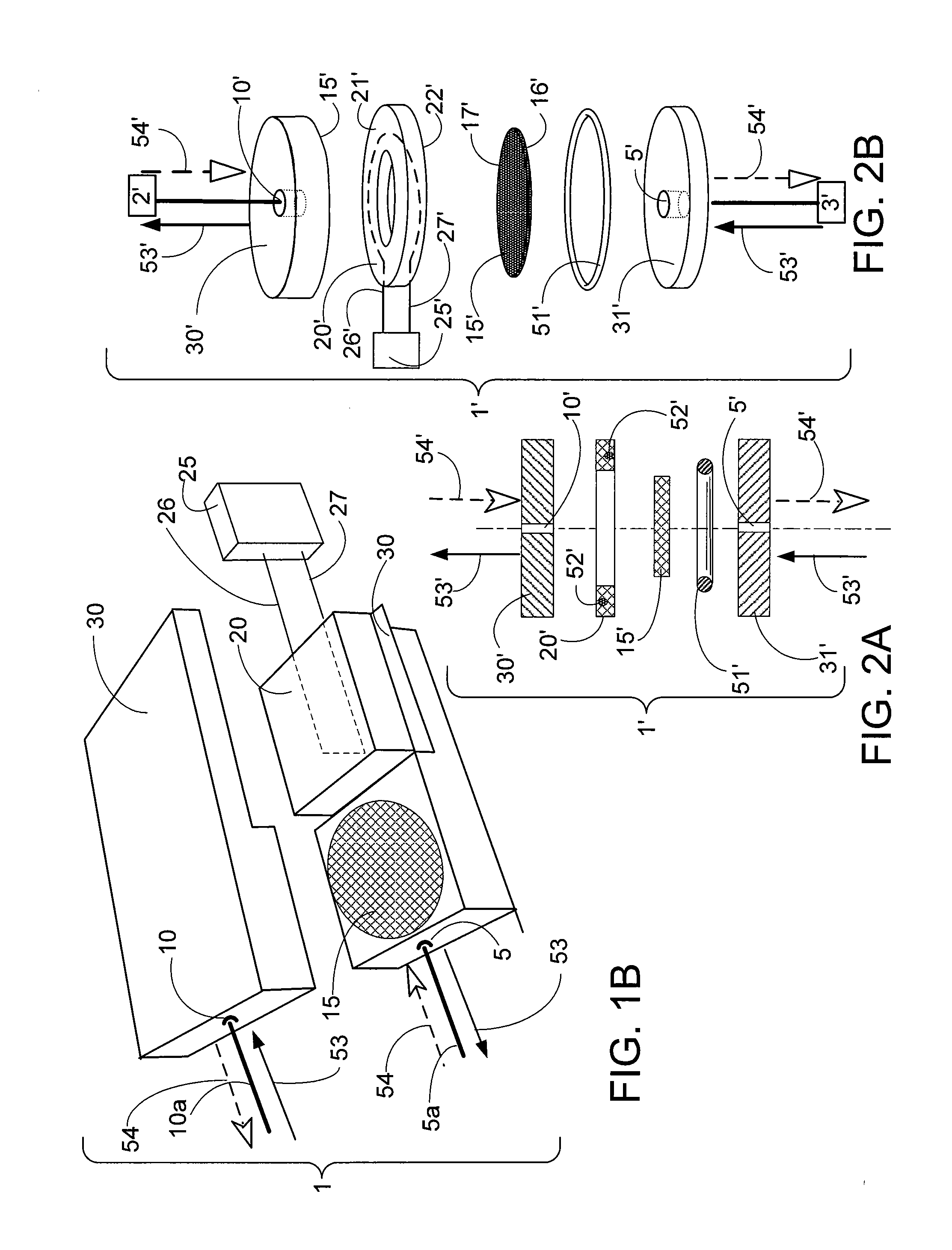
Method and device for producing three-dimensional objects
ActiveUS8187521B2Large gradientImprove conductivityElectric discharge tubesAuxillary shaping apparatusIrradiationHigh energy beam
A method for producing three-dimensional objects from a powder material which is capable of solidification by irradiation with a high-energy beam is disclosed. The method comprises homogeneously pre-heating the powder material by scanning with the high-energy beam along predetermined paths over a pre-heating area so that consecutive paths are separated by a minimum security distance which is adapted to prevent undesirable summation effects in the pre-heating area, and then solidifying the powder material by fusing together the powder material. Apparatus for producing such three-dimensional objects is also disclosed.
Owner:ARCAM AB
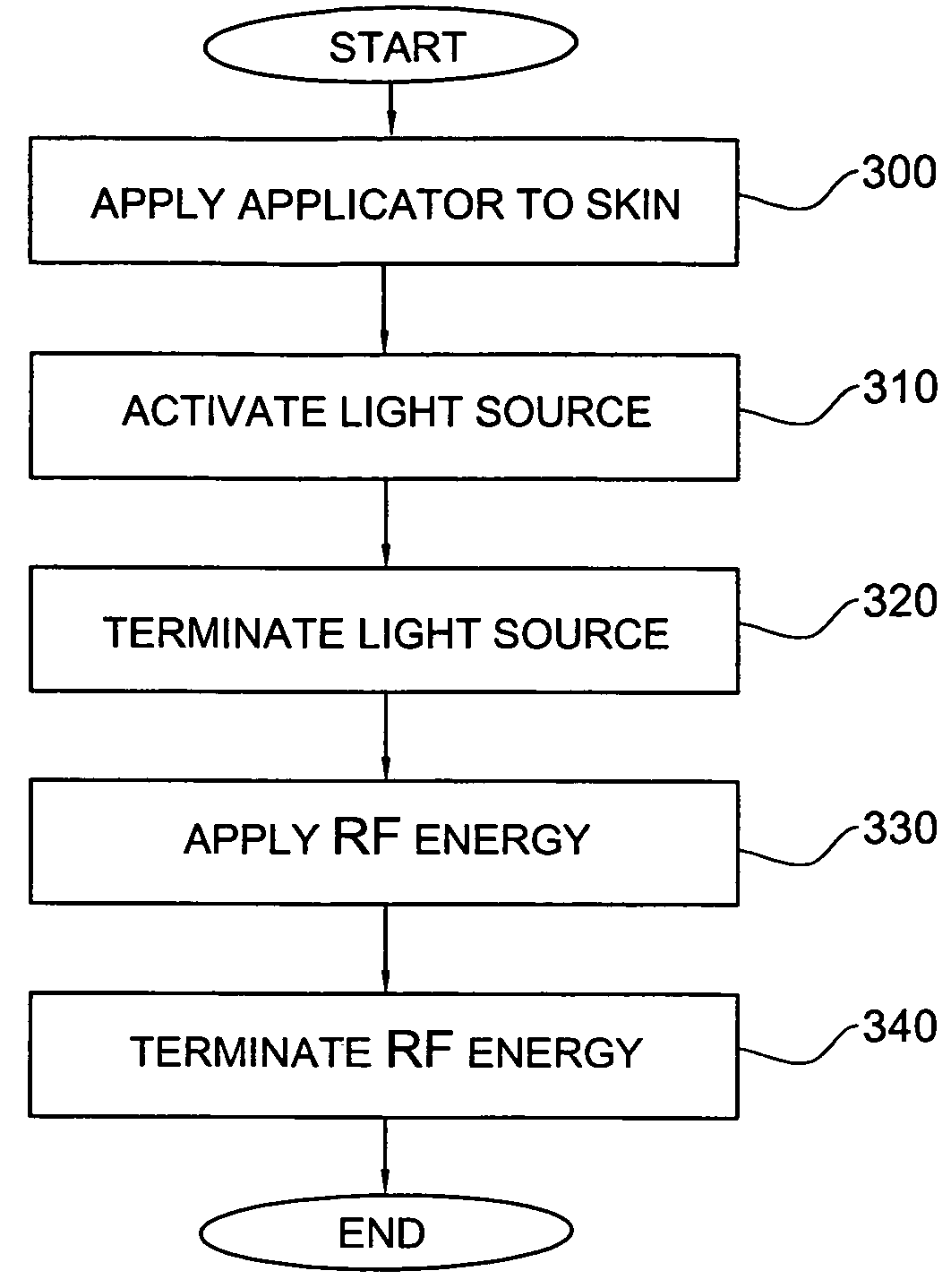
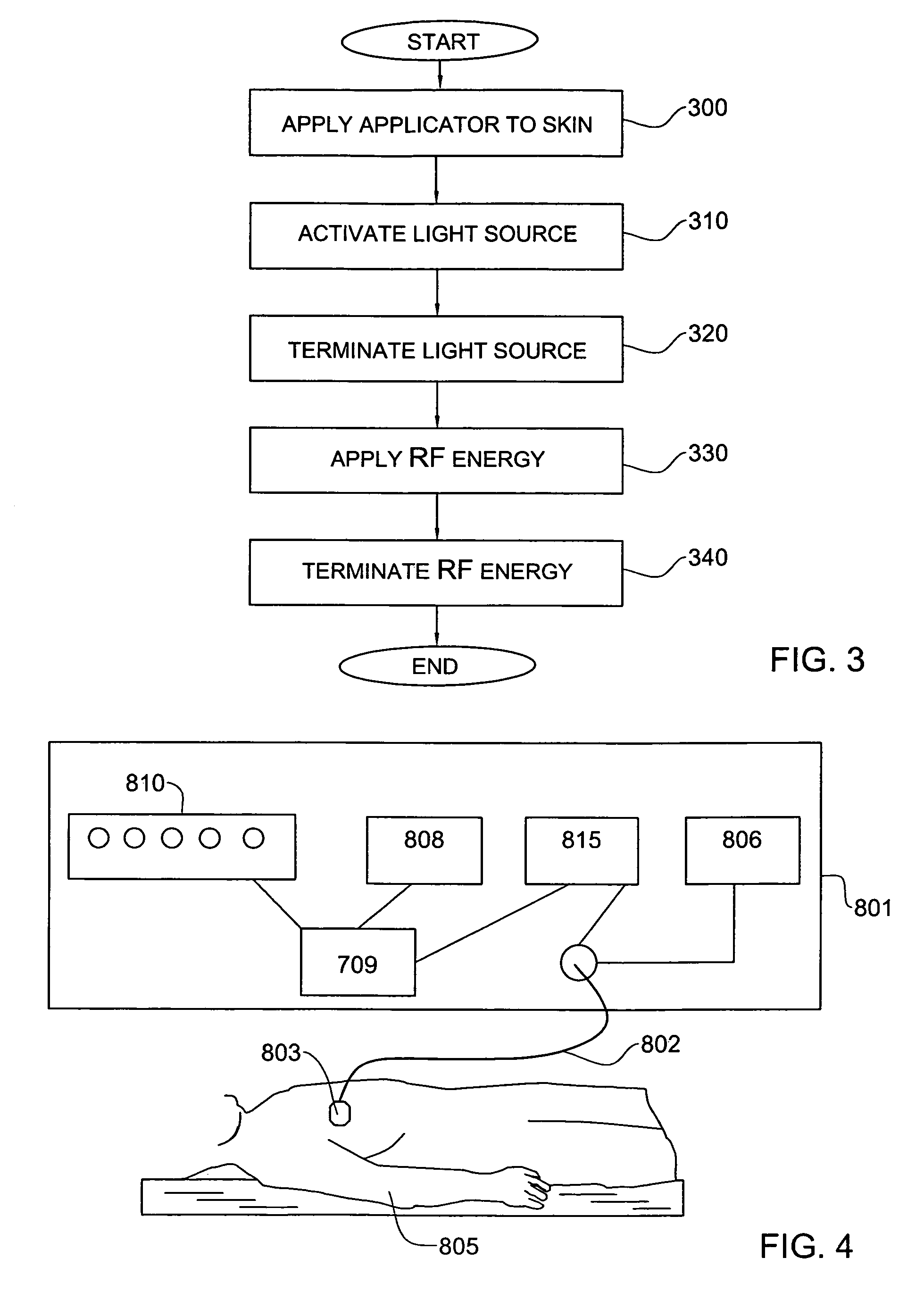
System and method for treating skin
InactiveUS7238183B2Increase choiceIncrease heatElectrotherapySurgical instruments for heatingTemperature differenceSkin tissue
System and method for treating a skin target. A temperature effector creates a temperature difference between the target and the skin tissue surrounding the target such that the target is at a higher temperature than the surrounding tissue by at least 5° C. One or more RF electrodes are attached to the skin and RF energy is applied.
Owner:SYNERON MEDICAL LTD
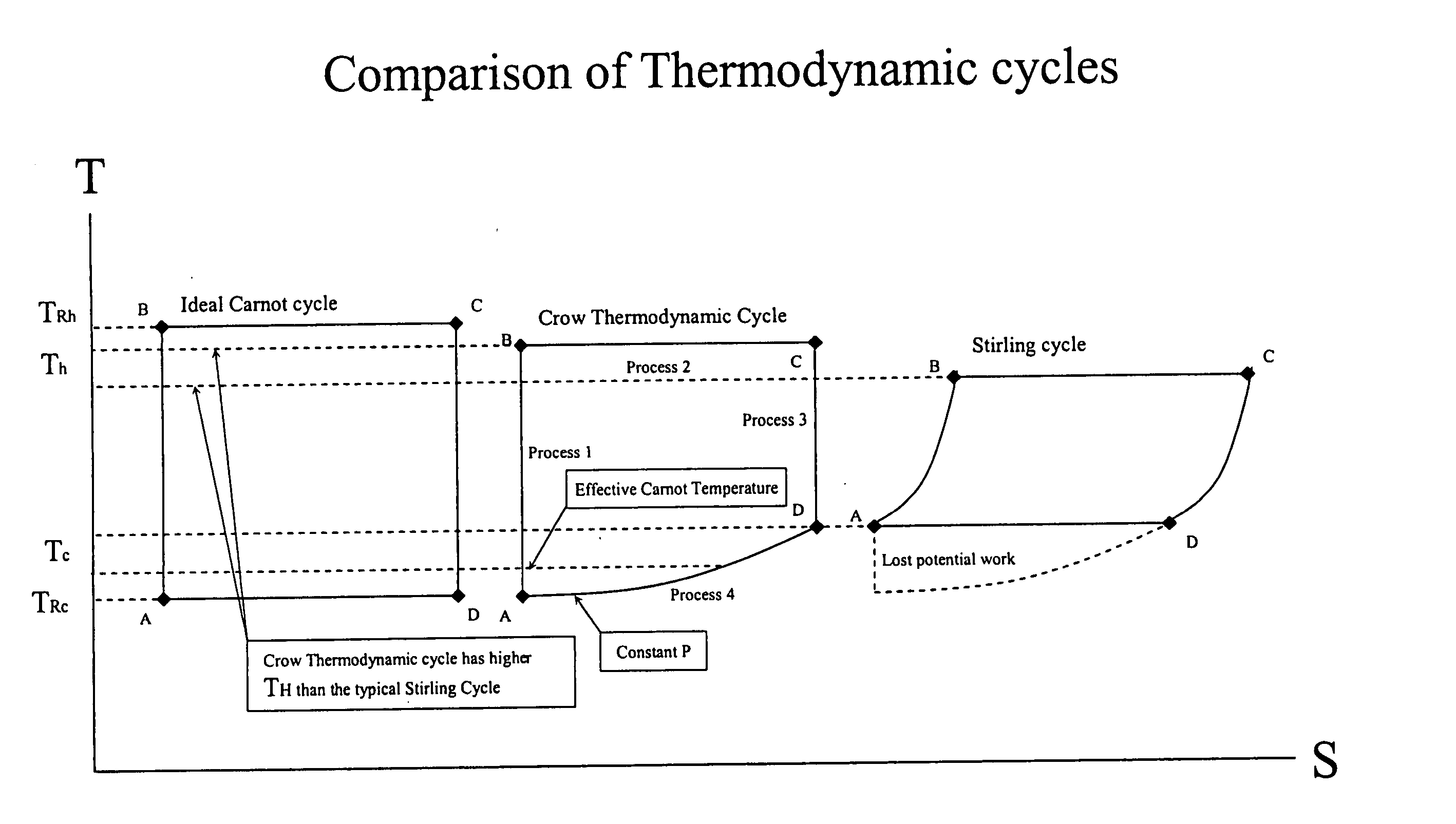
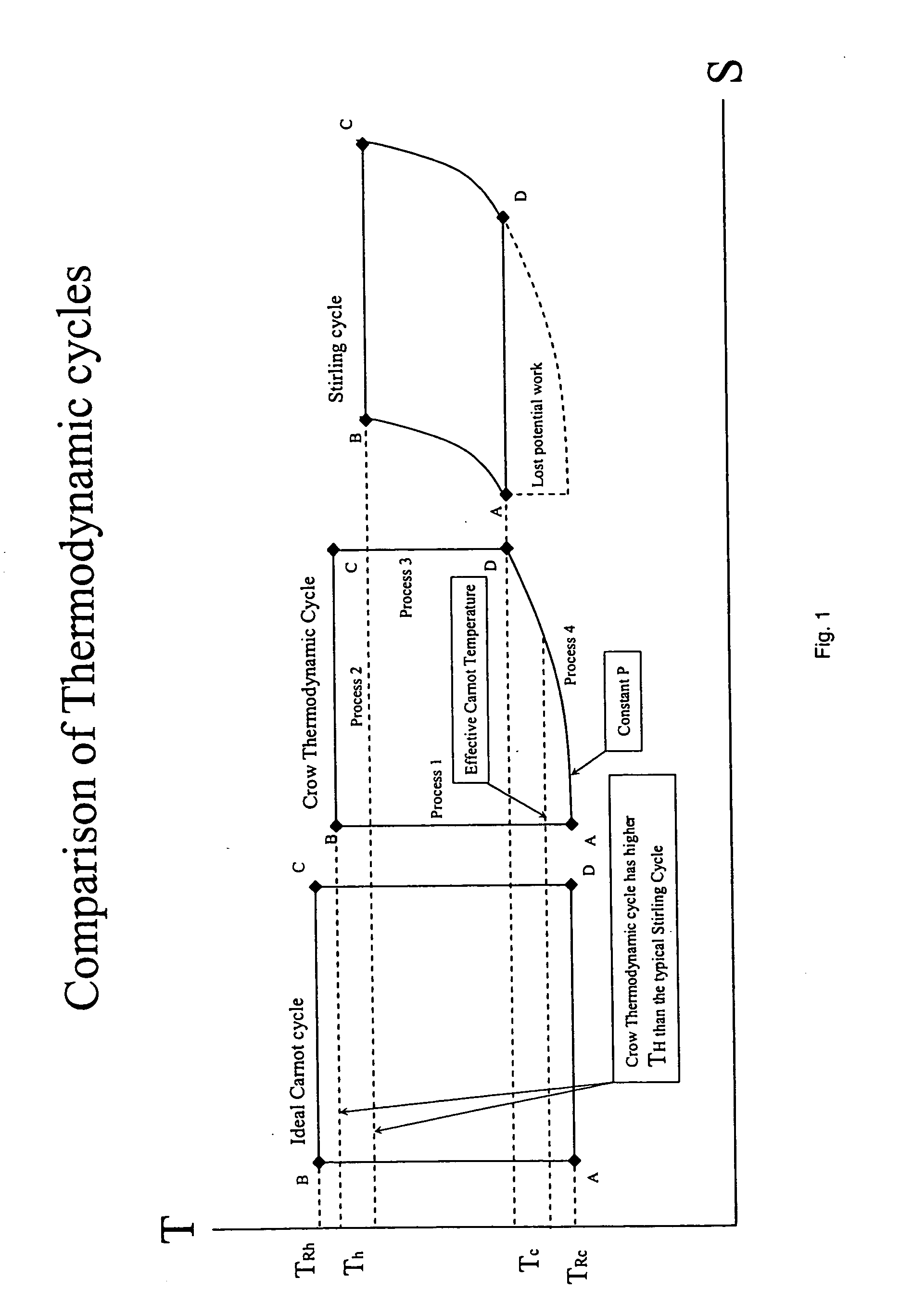
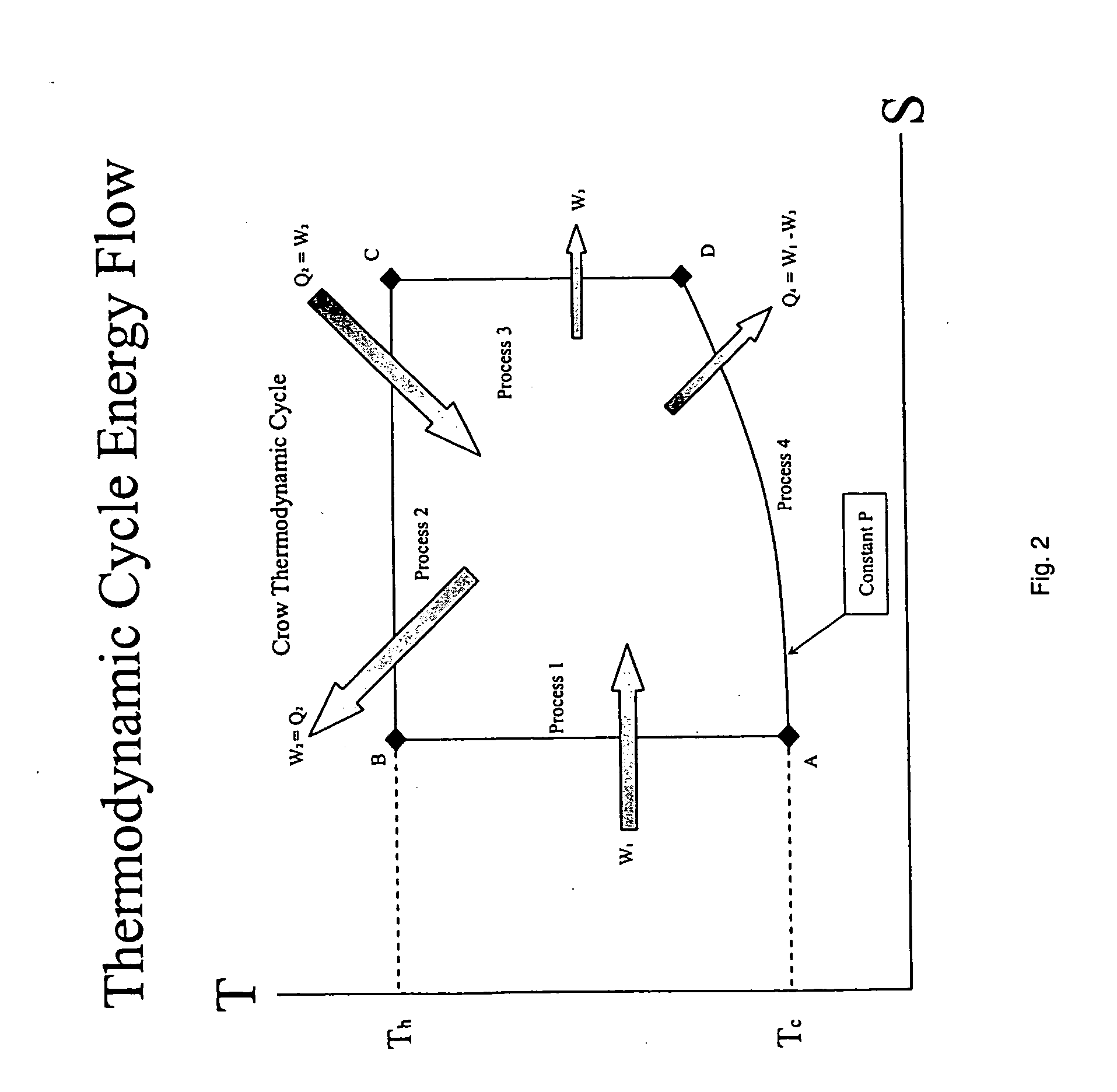
Method and apparatus for converting thermal energy to mechanical energy
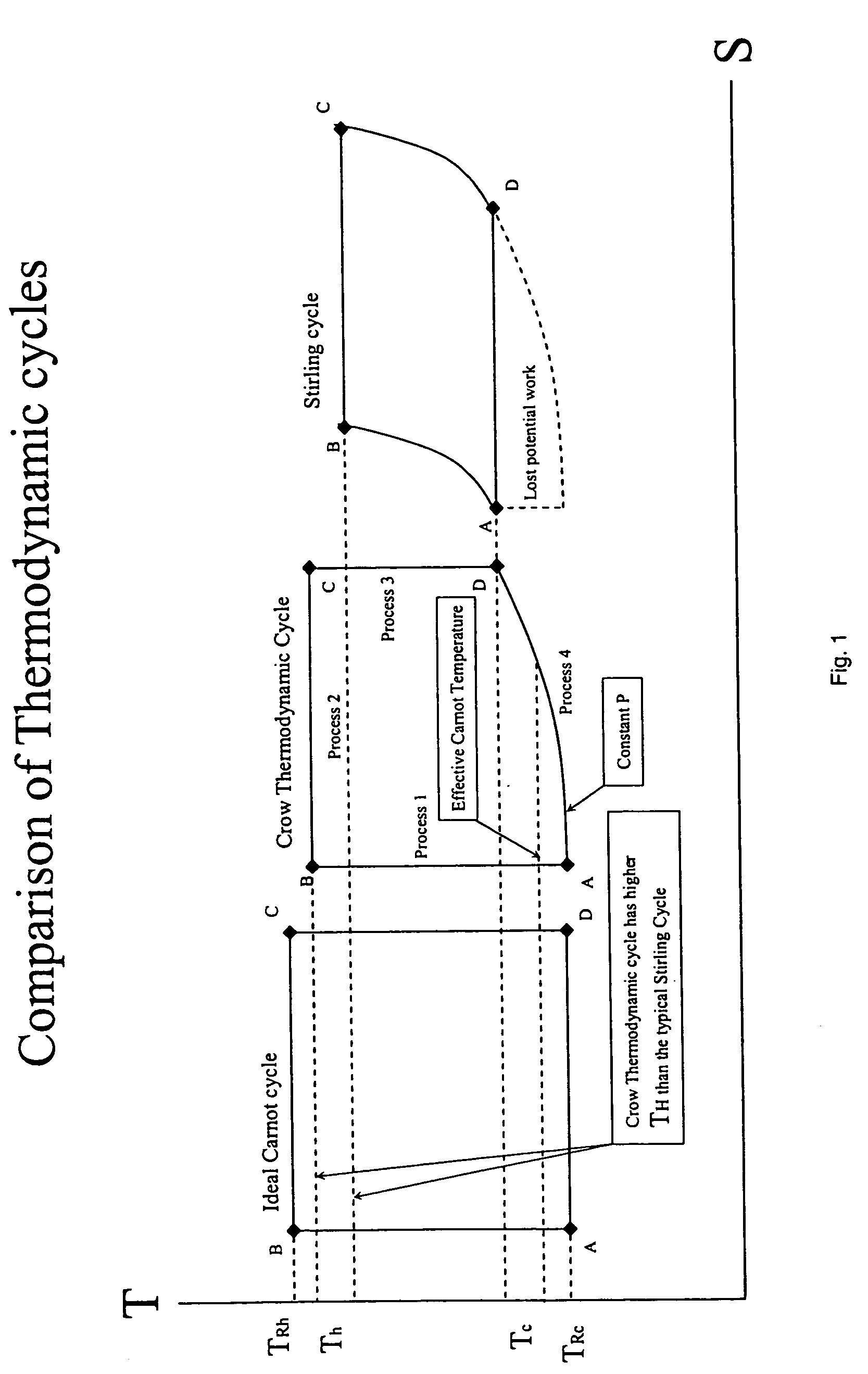
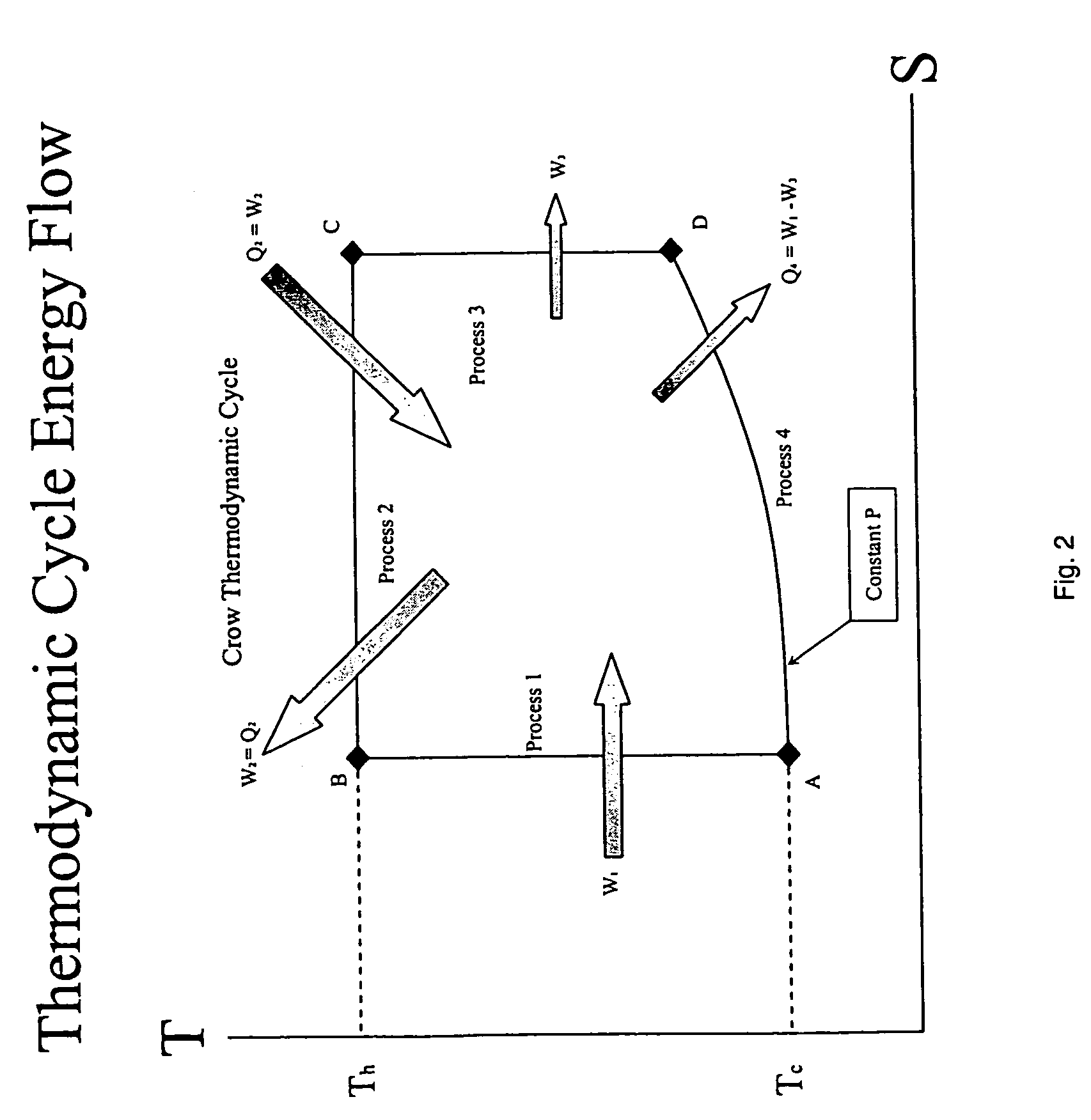
InactiveUS20060090467A1Improve efficiencyEfficient regenerationEricsson type enginesSteam engine plantsThermal energyWorking fluid
A method and apparatus for converting thermal energy to mechanical energy which can use a wide range of fuels and perform with a high efficiency. Operating on a little utilized thermodynamic cycle of isentropic compression, isothermal expansion, isentropic expansion and finally constant pressure cooling and contraction. The external heat engine utilizes a heat exchanger carrying heat from the external energy source to the working parts of the engine. Pistons and cylinders are activated by appropriate means to adiabatically compress the working fluid, for example ambient air, to transfer the entire mass of the air through the heat exchanger to accomplish isothermal expansion followed by adiabatic expansion and, finally, exhaust the air to ambient to allow for constant pressure cooling and contraction. Valve pistons in conjunction with the cylinders form valves that allow for the exchange of working fluid with ambient. Energy is added to the engine during isothermal expansion, whereby the energy of compression is added by a flywheel or other appropriate energy storage means, said flywheel stores energy recovered during adiabatic expansion. The thermodynamic cycle described and the engine embodiments disclosed, when run in reverse, perform as a heat pump or refrigeration device.
Owner:CROW DARBY
Methods and apparatus for detecting cardiac injury markers using an acoustic device
InactiveUS20060257945A1Improve the level ofAvoid delayBioreactor/fermenter combinationsMaterial nanotechnologyAnalyteResonant sensor
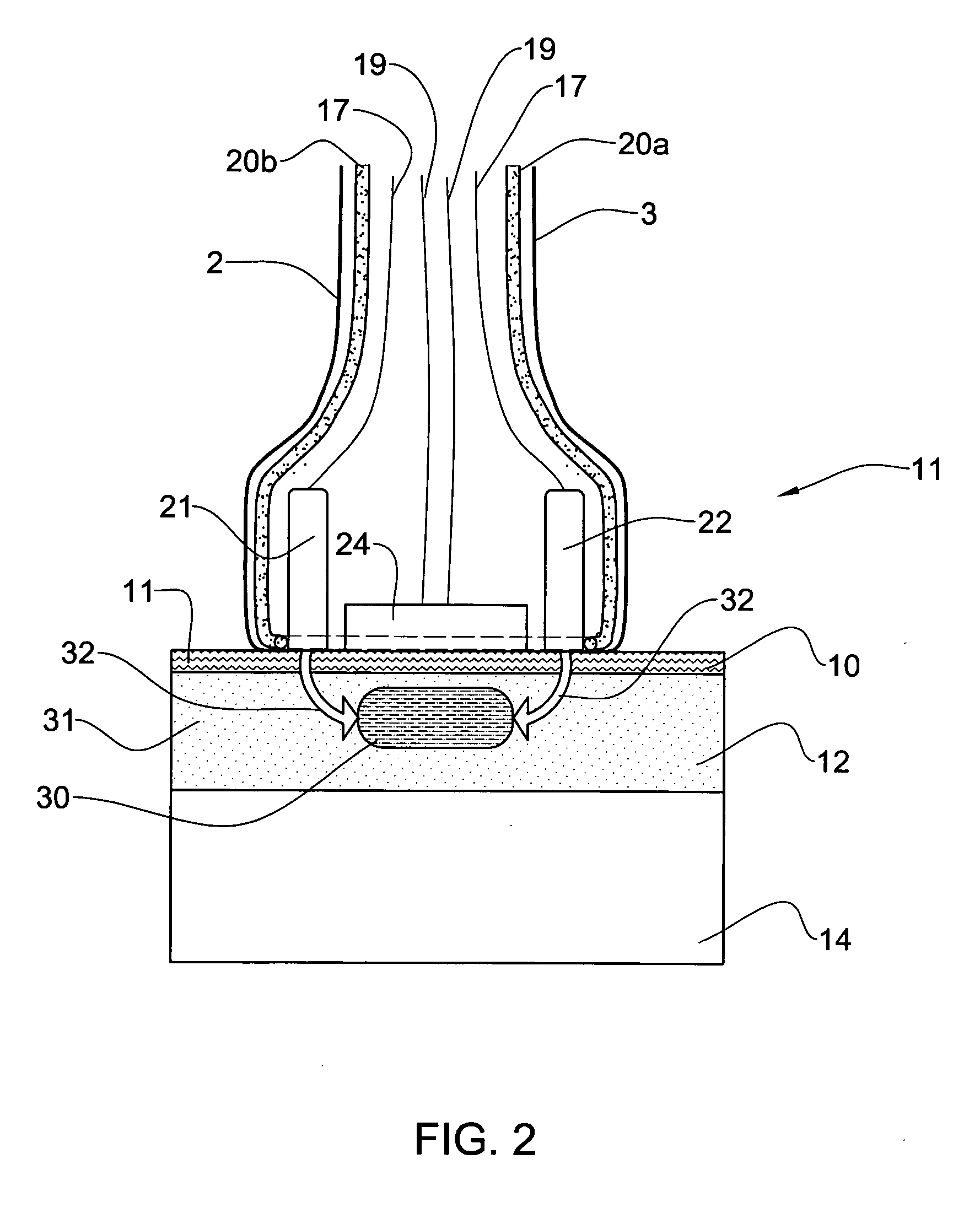
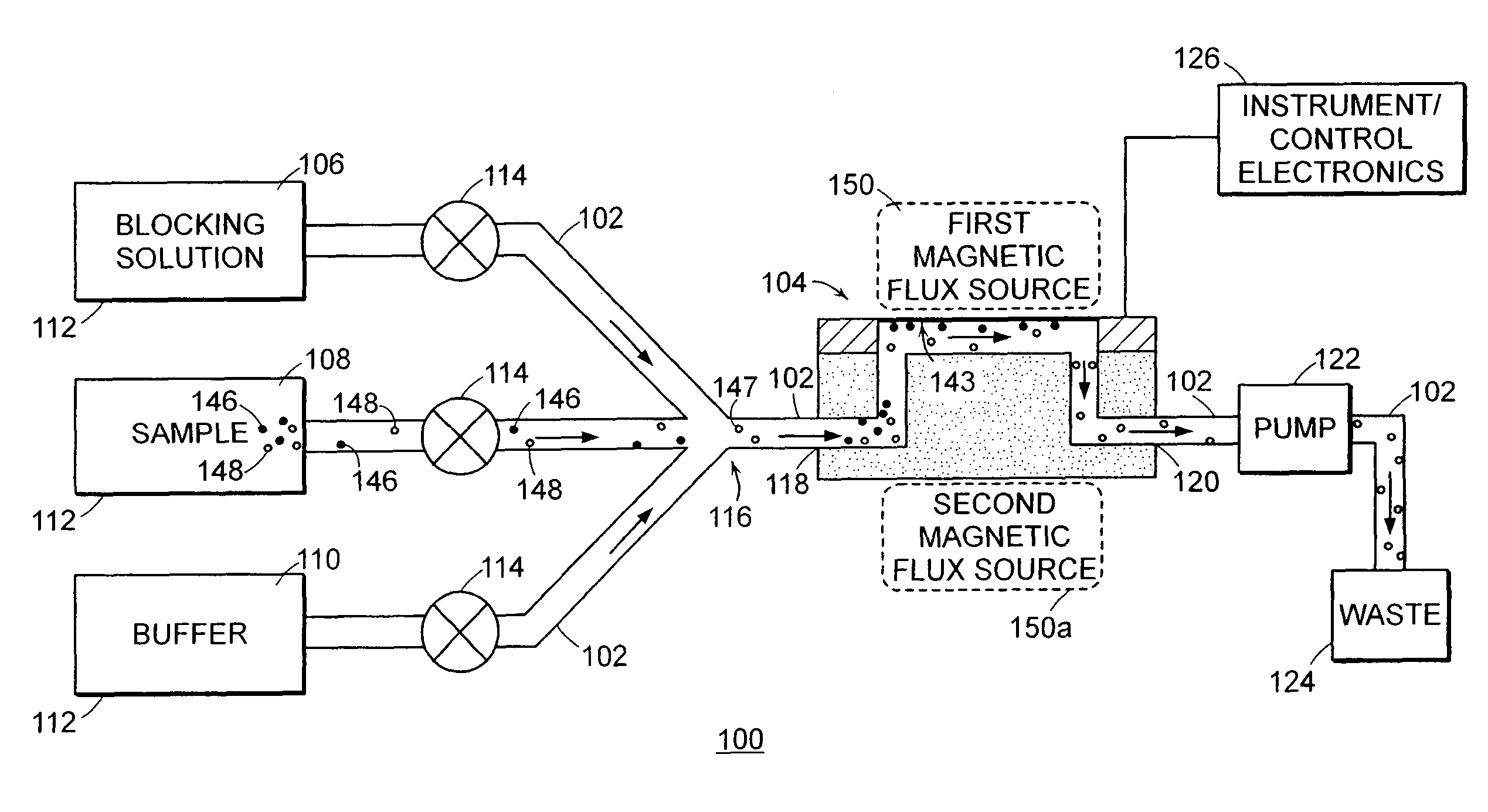
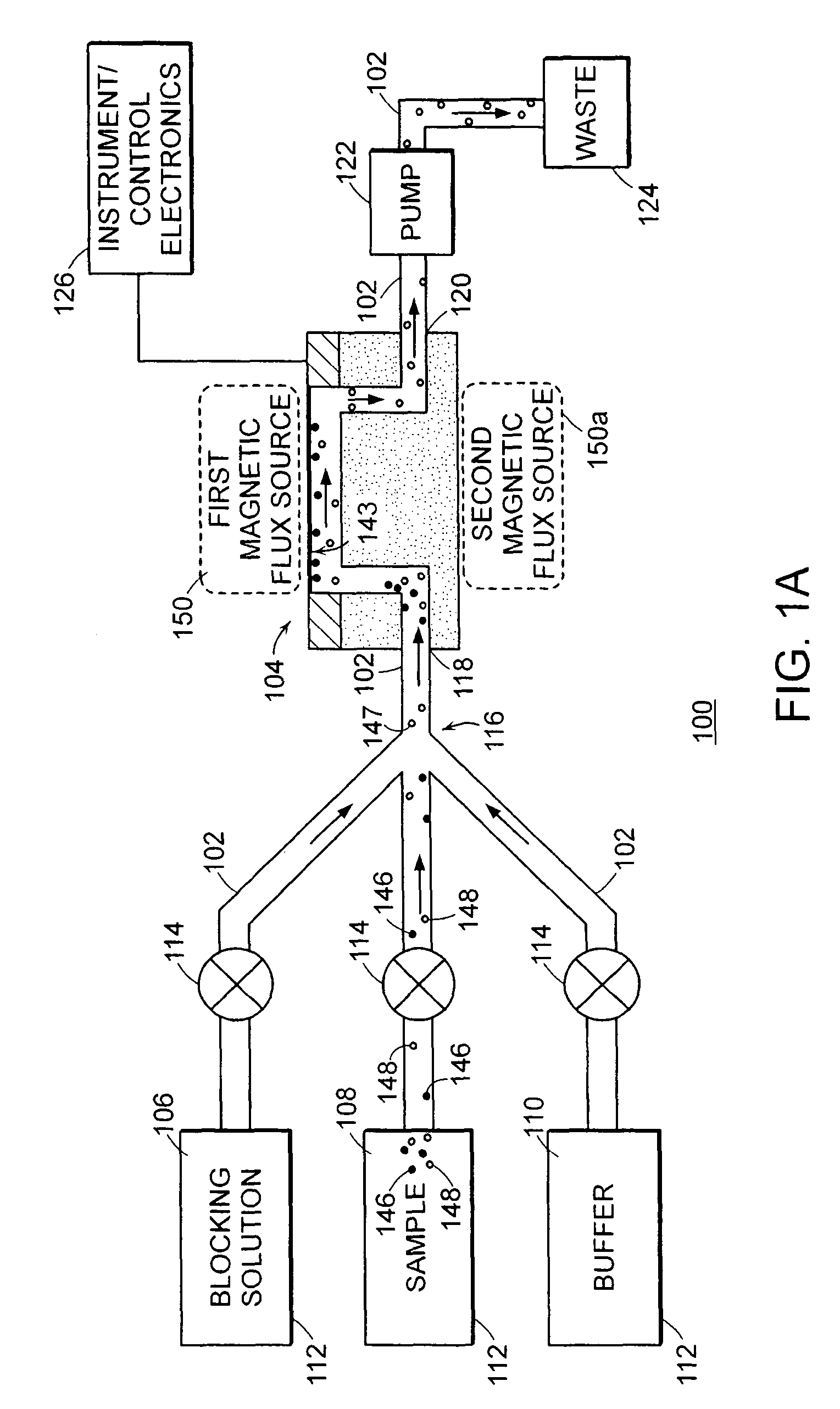
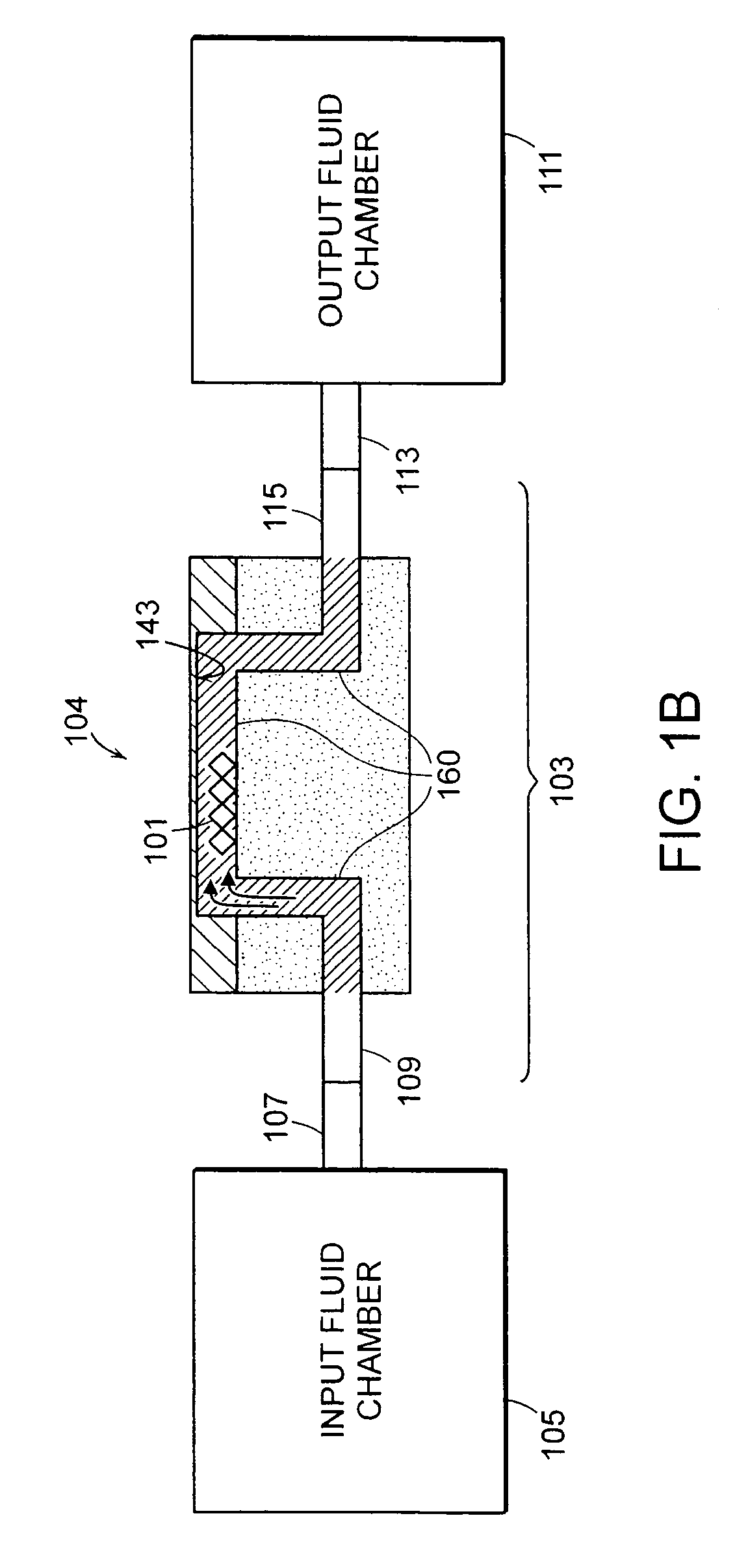
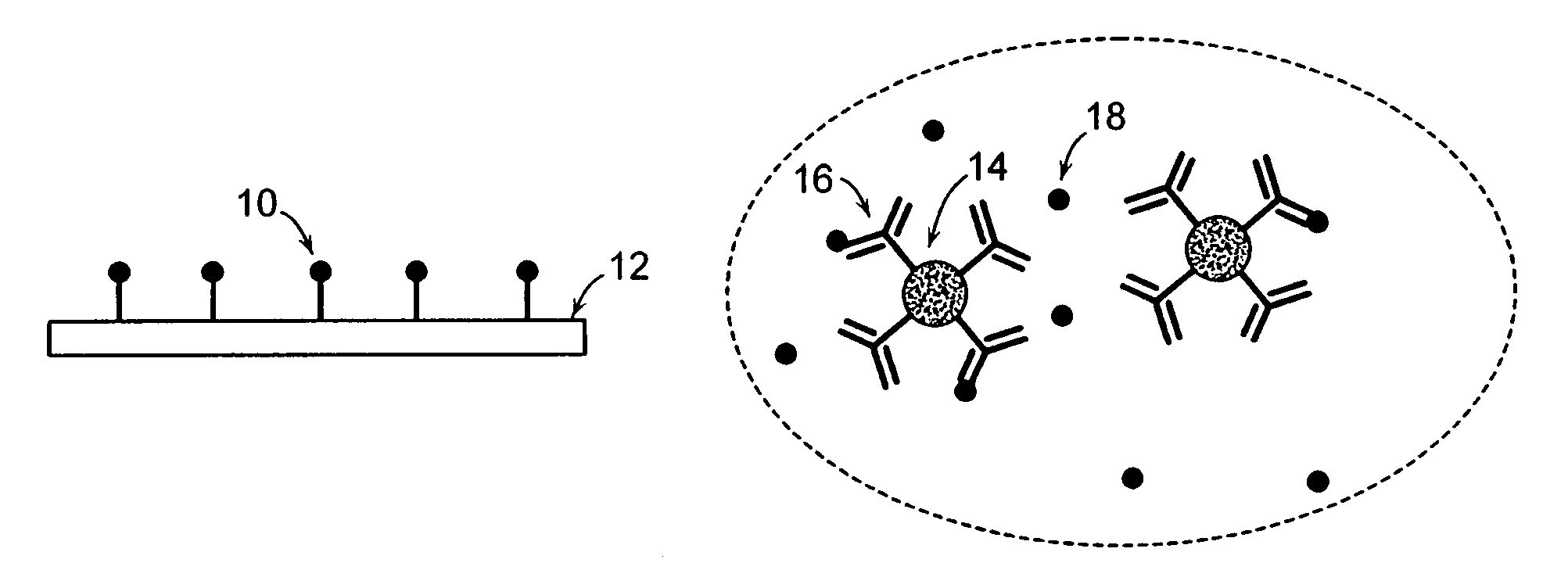
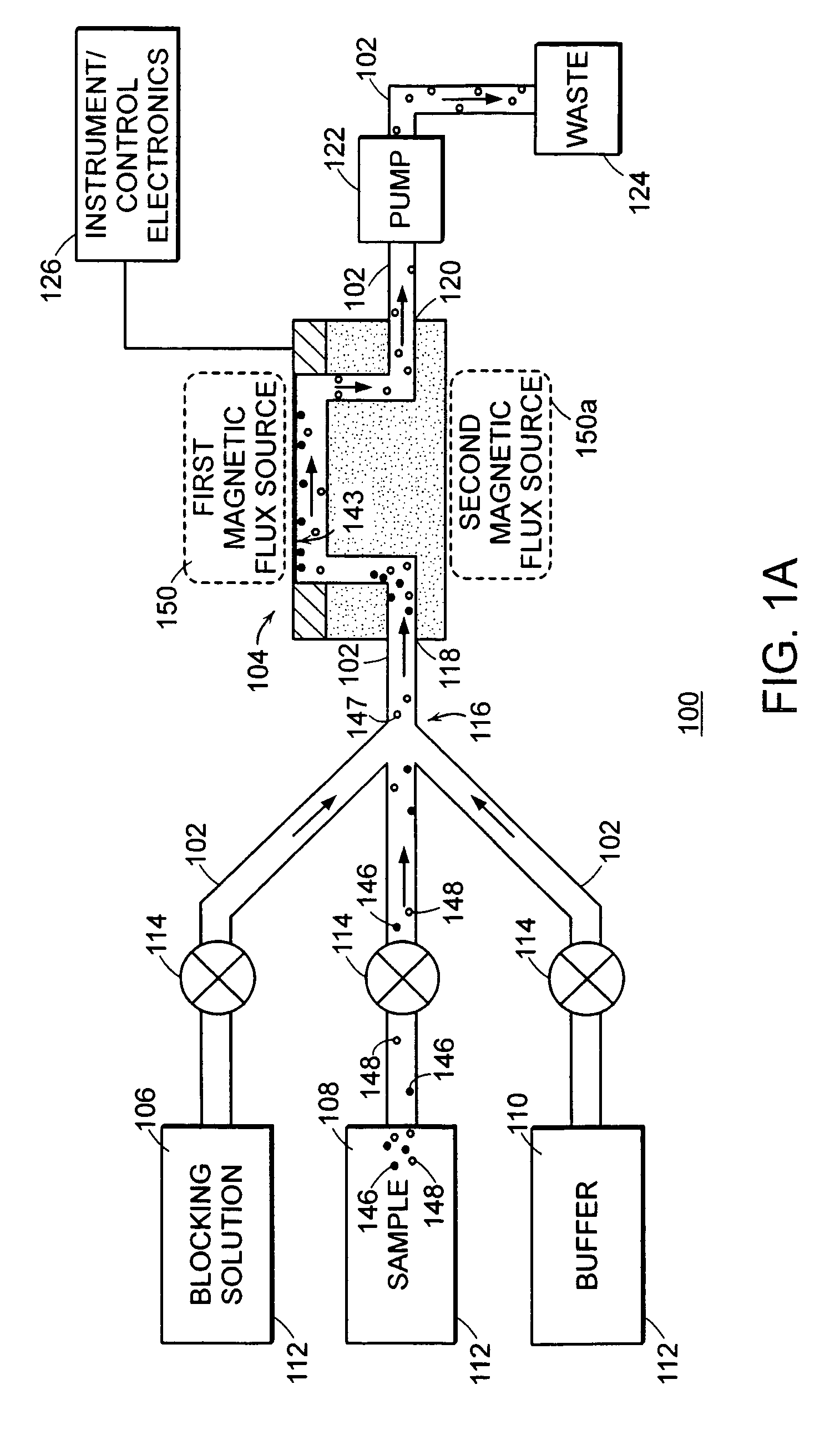
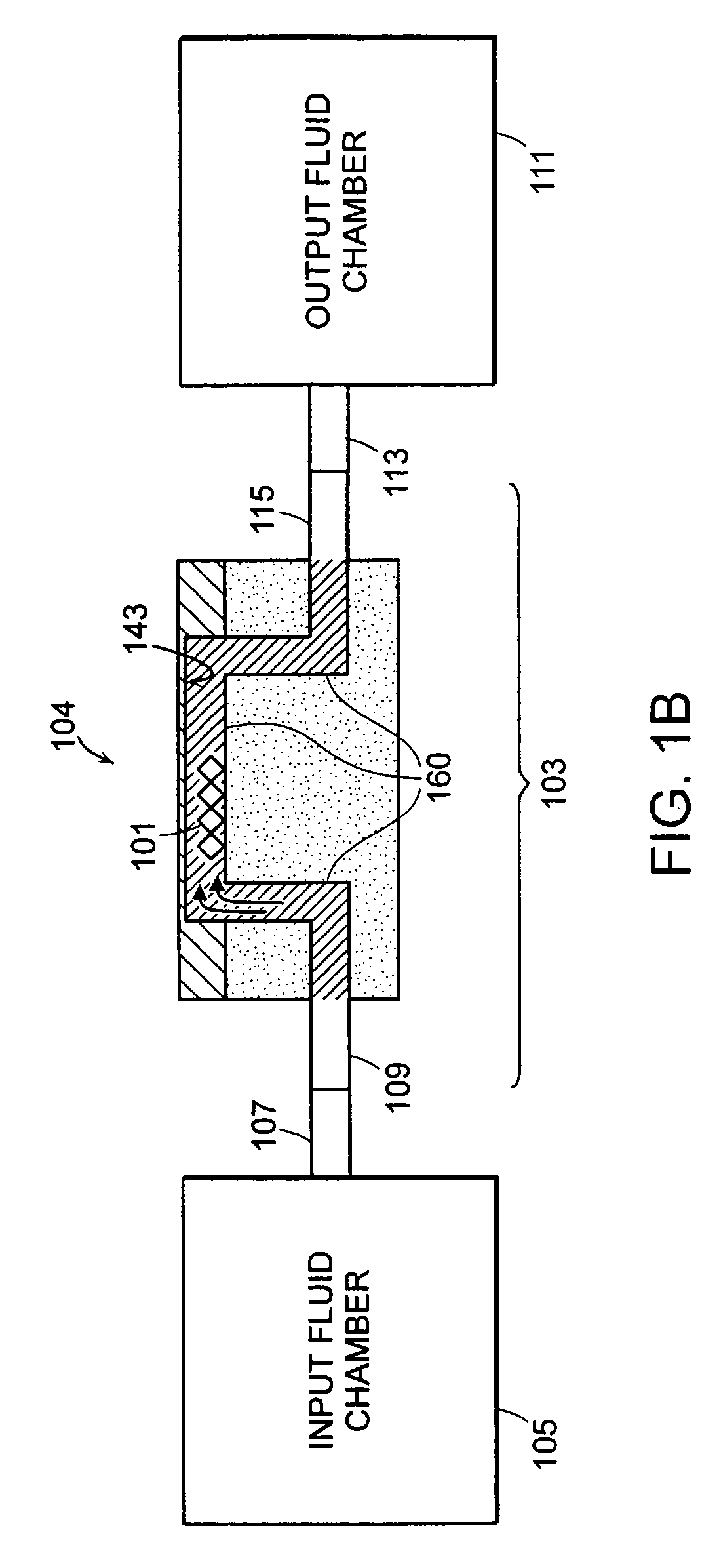
Methods for detecting cardiac injury by detecting one or more cardiac markers are provided. A plurality of particles, each of which is coated with a capture agent having an affinity for a cardiac marker, is combined with the sample to form a plurality of analyte-particle complexes. The system also includes a transport arrangement for transporting the sample to the sensor surface, and optionally a magnetic field inducing structure constructed and arranged to establish a magnetic field at and adjacent to the sensor surface. The resonant sensor produces a signal corresponding to an amount of analyte-particle complexes that are bound to the sensor surface.
Owner:BIOSCALE
Method and apparatus for treatment of skin using RF and ultrasound energies
ActiveUS7955262B2Improve conductivityNon-invasiveUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyFocus ultrasoundTransducer
Owner:SYNERON MEDICAL LTD
Method and apparatus for treatment of skin using RF and ultrasound energies
ActiveUS20070038156A1Improve conductivityNon-invasiveUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyFocus ultrasoundTransducer
A system and method for treating skin. The System comprises one or more ultrasound transducers and one or more pairs of RF electrodes. The ultrasound transducers are adapted to focus ultrasound energy at one or more focal volumes in the skin. The RF electrodes are adapted to deliver RF energy to the one or more focal volumes. The method comprises heating the skin to a first temperature at one or more focal volumes in the skin by focusing ultrasound energy at the one or more focal volumes. The focal regions are then heated to a second temperature, the second temperature being higher than the first temperature, by generating an RF current in a region of the skin containing the focal regions.
Owner:SYNERON MEDICAL LTD
Method and apparatus for analyzing bioprocess fluids
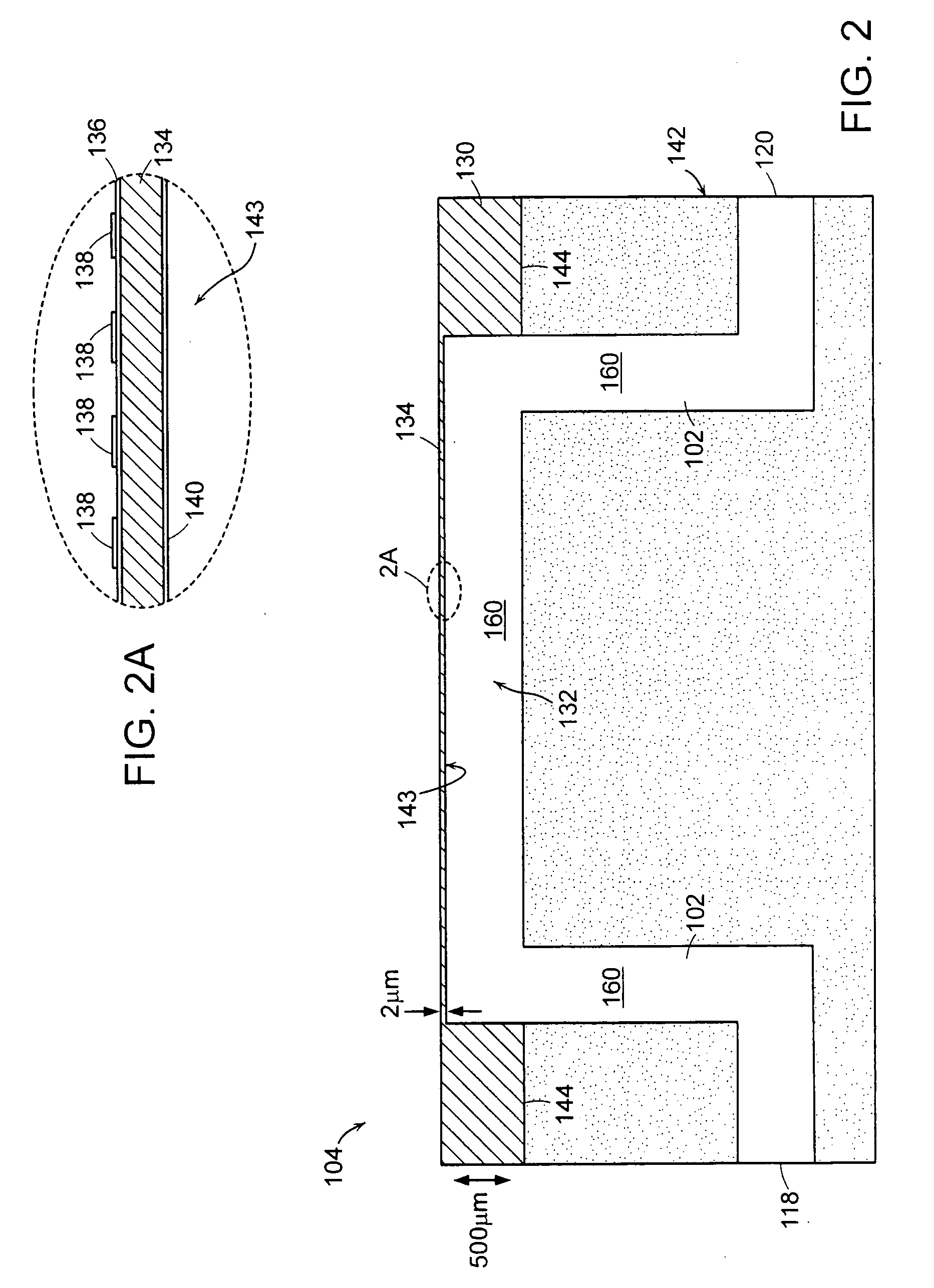
InactiveUS7749445B2High fractional captureLarge gradientMaterial nanotechnologyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsAnalyteResonant sensor
Methods and apparatus for analyzing bioprocess fluids are provided. A plurality of particles coated with a plurality of capture agents having an affinity for one or more biological markers is combined with bioprocess fluid to form a plurality of analyte-particle complexes. The system also includes a transport arrangement for transporting the sample to a sensor surface, and optionally a magnetic field inducing structure constructed and arranged to establish a magnetic field at and adjacent to the sensor surface. The resonant sensor produces a signal corresponding to an amount of analyte-particle complexes that are bound to the sensor surface.
Owner:BIOSCALE
Method and apparatus for separating fluid components
ActiveUS20060151384A1Minimal mixingReduced effectivenessRotary centrifugesLiquid displacementFluid compositionEngineering
A floating element for separating components of a physiological fluid comprises two parts that are relatively movable. The two parts define a prescribed volume between them when at their maximum separation, and one of the parts may be moved toward the other to express the fluid contained in the volume between the parts. The parts are made of materials having densities so that they assume a desired position in the fluid to allow selected components to be easily obtained are expressed.
Owner:GLOBUS MEDICAL INC
Bulk drying and the effects of inducing bubble nucleation
InactiveUS6884866B2Large gradientDecrease temperatureDrying solid materials without heatChemical/physical/physico-chemical stationary reactorsBiologyAir bubble
The present invention discloses apparatus and methods of inducing bubble nucleation to overcome problems commonly associated with preservation by foam formation. Specifically, the invention relates to methods of using bubble nucleation in foam formation to preserve sensitive biological materials. Preferred methods of inducing bubble nucleation include, mixing, chamber rotation, crystals, and ultrasound.
Owner:AVANT IMMUNOTHERAPEUTICS +1
Method and apparatus for analyzing bioprocess fluids
InactiveUS20070224700A1Low level of analyteLess timeBioreactor/fermenter combinationsMaterial nanotechnologyAnalyteResonant sensor
Owner:BIOSCALE
Method and apparatus for separating fluid components
ActiveUS7445125B2Reduced effectivenessReduce mixRotary centrifugesLiquid displacementEngineeringVolumetric Mass Density
A floating element for separating components of a physiological fluid comprises two parts that are relatively movable. The two parts define a prescribed volume between them when at their maximum separation, and one of the parts may be moved toward the other to express the fluid contained in the volume between the parts. The parts are made of materials having densities so that they assume a desired position in the fluid to allow selected components to be easily obtained are expressed.
Owner:GLOBUS MEDICAL INC
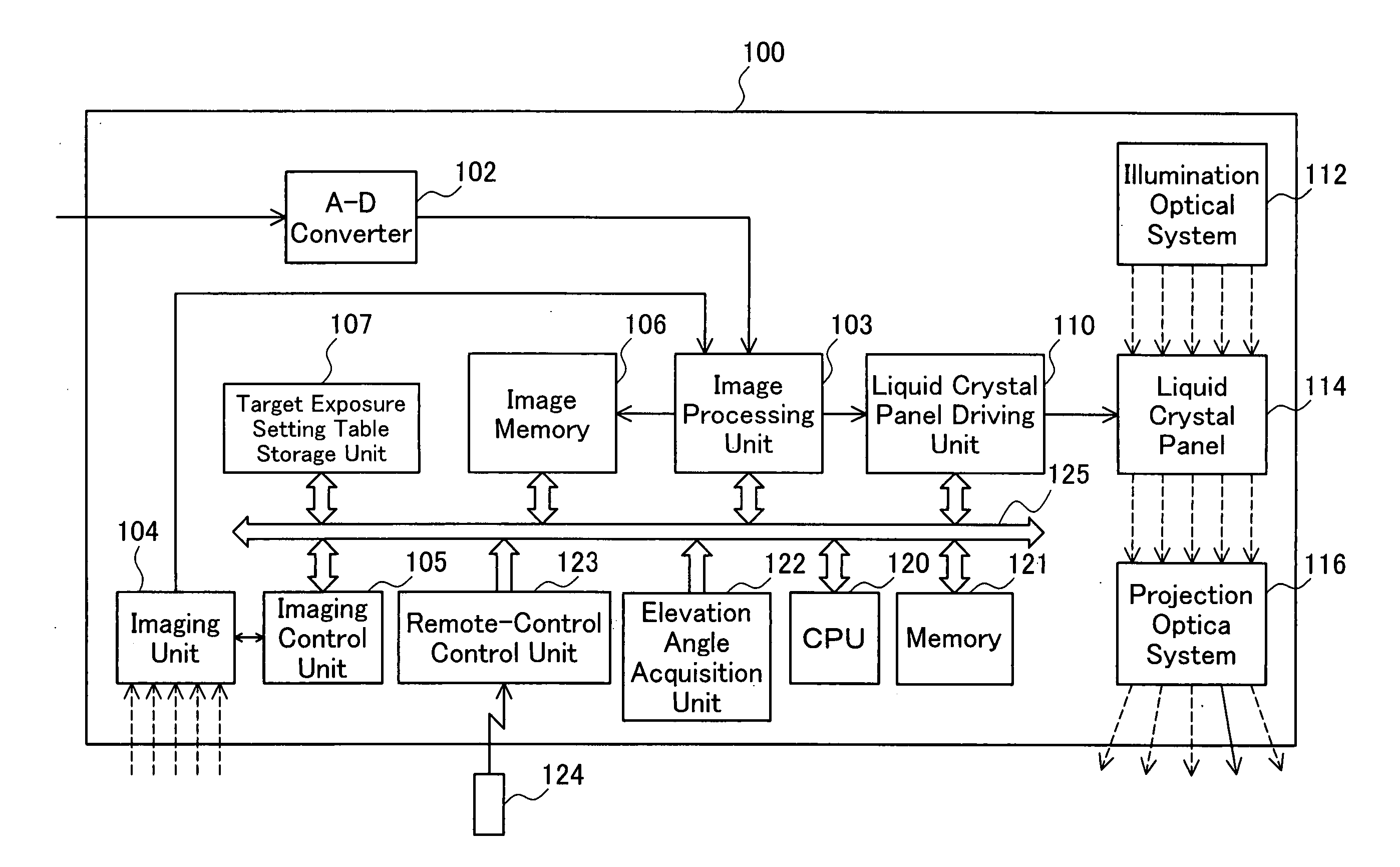
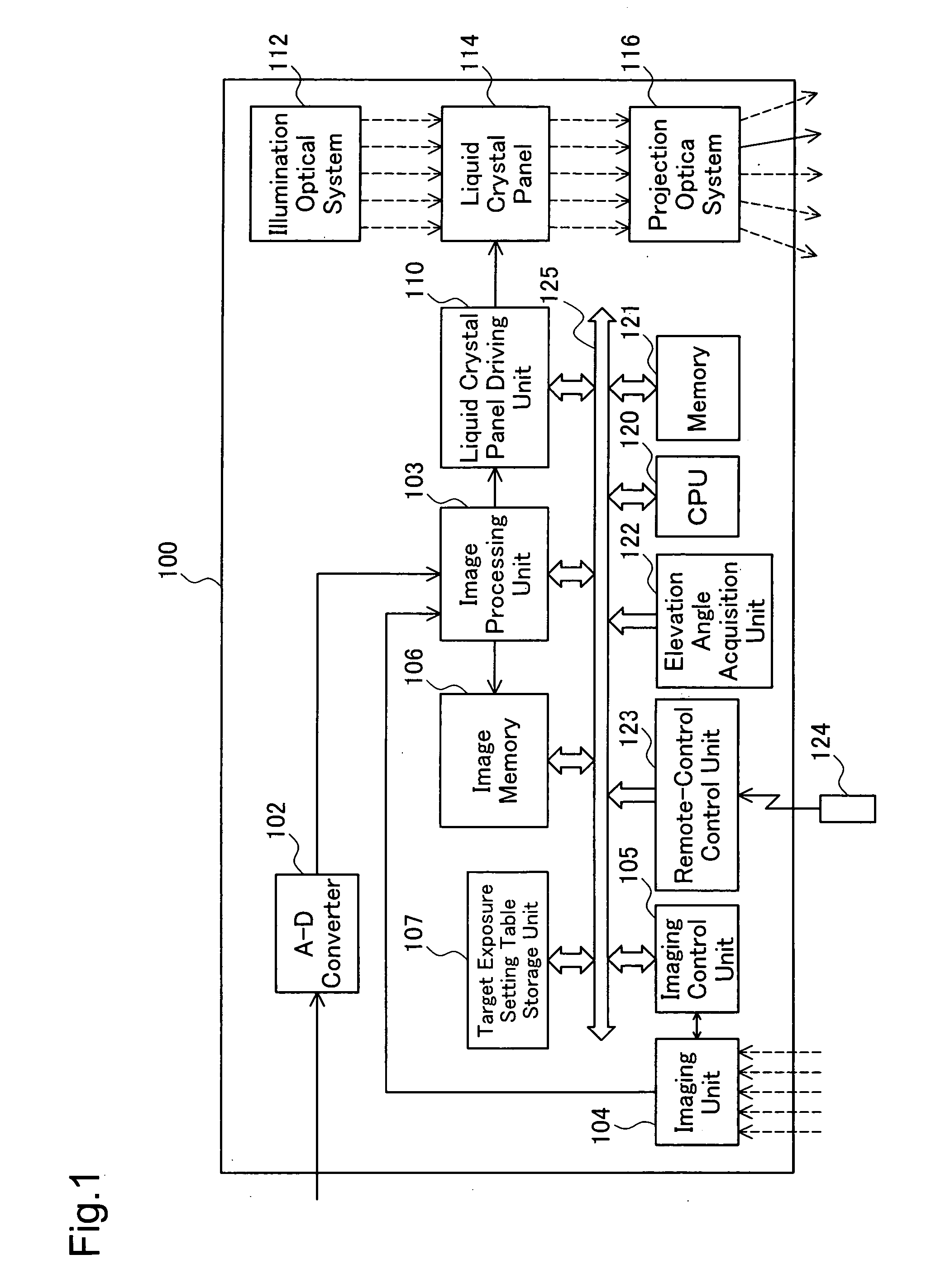
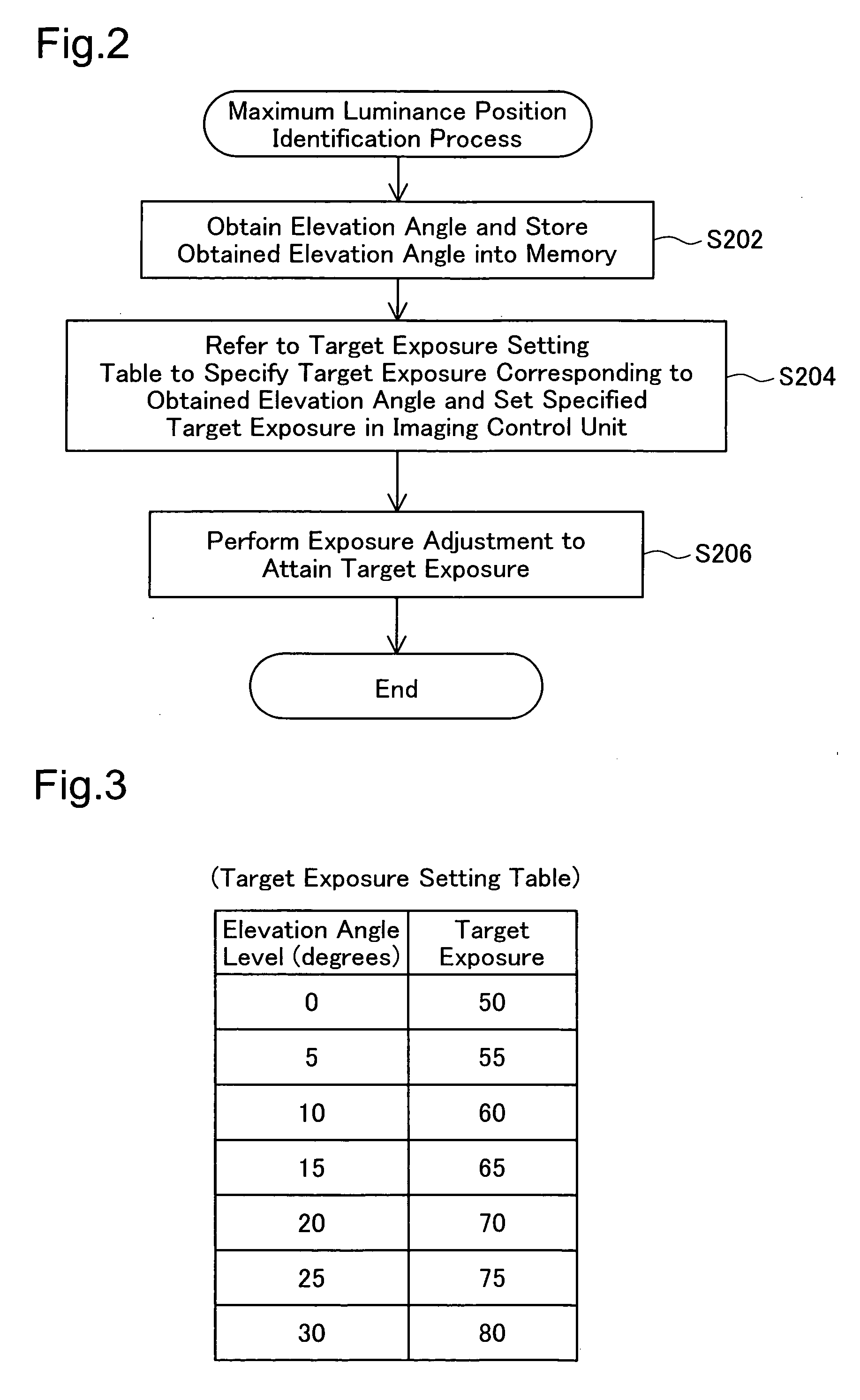
Projector and exposure adjustment method
InactiveUS20060176377A1Adequate and accurate keystone correctionEnsure identificationTelevision system detailsPrintersLightnessBrightness perception
A projector of the invention includes: an imaging structure that photographs an image projected on a projection object to take a photographed image; an imaging control module that performs exposure adjustment in the imaging structure to attain a preset target exposure; a control module that sets the target exposure in the imaging control module; an angle information acquisition module that obtains angle information representing an inclination of the projector to the projection object; and a storage unit that stores a map representing a variation in target exposure against the angle information. The control module controls the angle information acquisition module to obtain the angle information, refers to the map stored in the storage unit to specify a target exposure corresponding to the obtained angle information, and sets the specified target exposure in the imaging control module. Even in the state of elevation projection, this arrangement of the invention enables distinct identification of a maximum brightness position in the photographed image.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
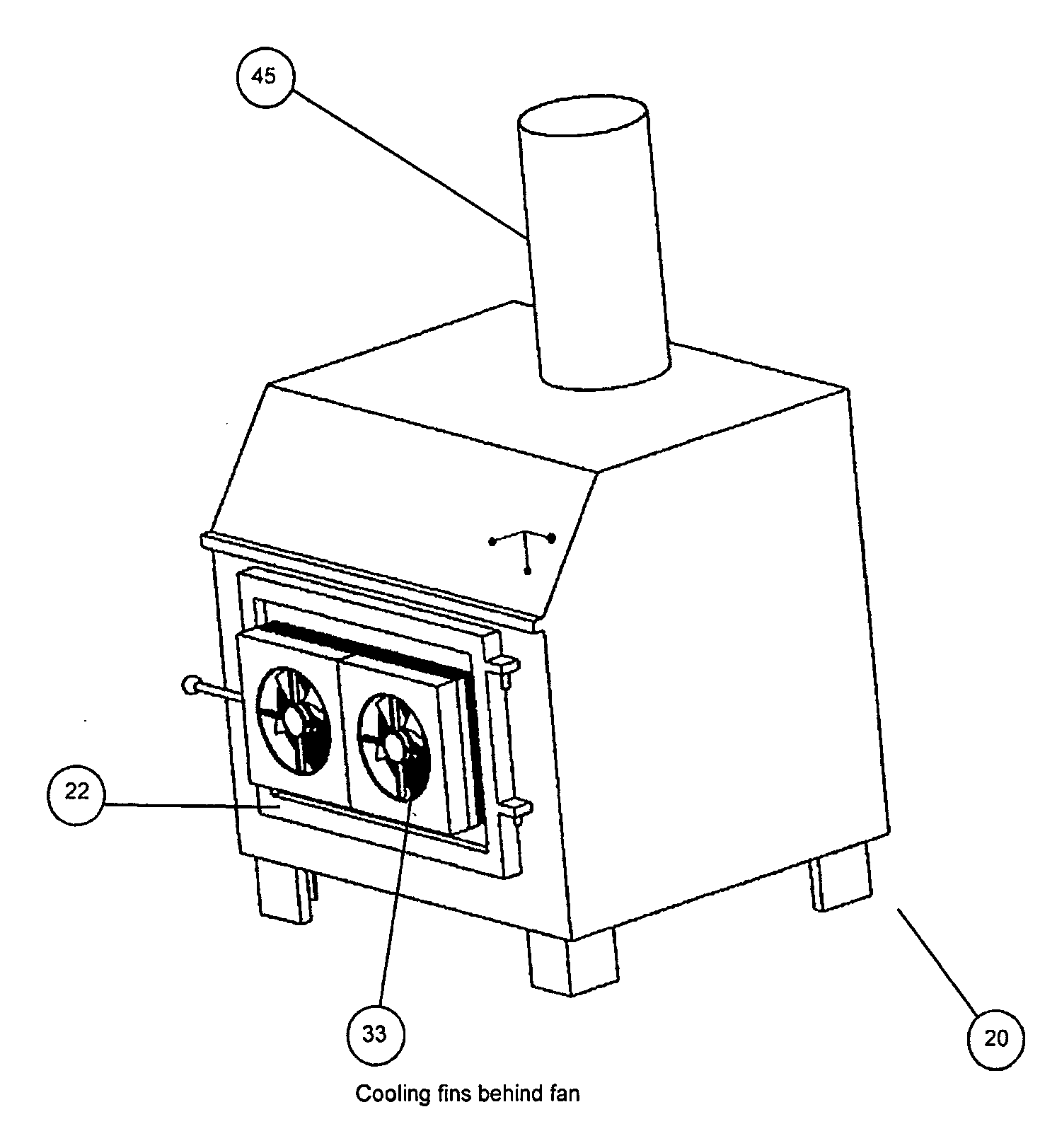
Thermo-electric generator for use with a stove
InactiveUS20080245352A1Efficient conversionLarge temperature gradientDomestic stoves or rangesThermoelectric device with peltier/seeback effectHeat sinkCoal
Disclosed is in combination, a stove and a thermoelectric generator, wherein the stove has a heating chamber and the generator has a hot side plate positioned in use within the heating chamber in a direct path of the heat therefrom. The generator may be incorporated with a door of the stove. Preferably, the generator has a cold side plate positioned in use to be exposed to ambient air close to the ground. The cold side plate may comprise cooling fins and the cooling fins may be positioned to be exposed to ambient air close to the ground. The generator may further comprise a protective mechanism to protect the generator from overheating, such as a grillwork guard or a shutter that closes to block the direct heat from the generator mechanism. The stove may be a wood stove or a coal stove. Generated power can be used to power cooling fans, charge an energy storage device and / or power external devices such as lights, fans or radios for example.
Owner:CAFRAMO
Method and apparatus for converting thermal energy to mechanical energy
InactiveUS7284372B2Improve efficiencyEfficient regenerationEricsson type enginesSteam engine plantsThermal energyExternal energy
A method and apparatus for converting thermal energy to mechanical energy which can use a wide range of fuels and perform with a high efficiency. Operating on a little utilized thermodynamic cycle of isentropic compression, isothermal expansion, isentropic expansion and finally constant pressure cooling and contraction. The external heat engine utilizes a heat exchanger carrying heat from the external energy source to the working parts of the engine. Pistons and cylinders are activated by appropriate means to adiabatically compress the working fluid, for example ambient air, to transfer the entire mass of the air through the heat exchanger to accomplish isothermal expansion followed by adiabatic expansion and, finally, exhaust the air to ambient to allow for constant pressure cooling and contraction. Valve pistons in conjunction with the cylinders form valves that allow for the exchange of working fluid with ambient. Energy is added to the engine during isothermal expansion, whereby the energy of compression is added by a flywheel or other appropriate energy storage means, said flywheel stores energy recovered during adiabatic expansion. The thermodynamic cycle described and the engine embodiments disclosed, when run in reverse, perform as a heat pump or refrigeration device.
Owner:CROW DARBY
Method and apparatus for detection of analyte using an acoustic device
InactiveUS7648844B2Easy to measureMaintain curative effectBioreactor/fermenter combinationsMaterial nanotechnologyAnalyteResonant sensor
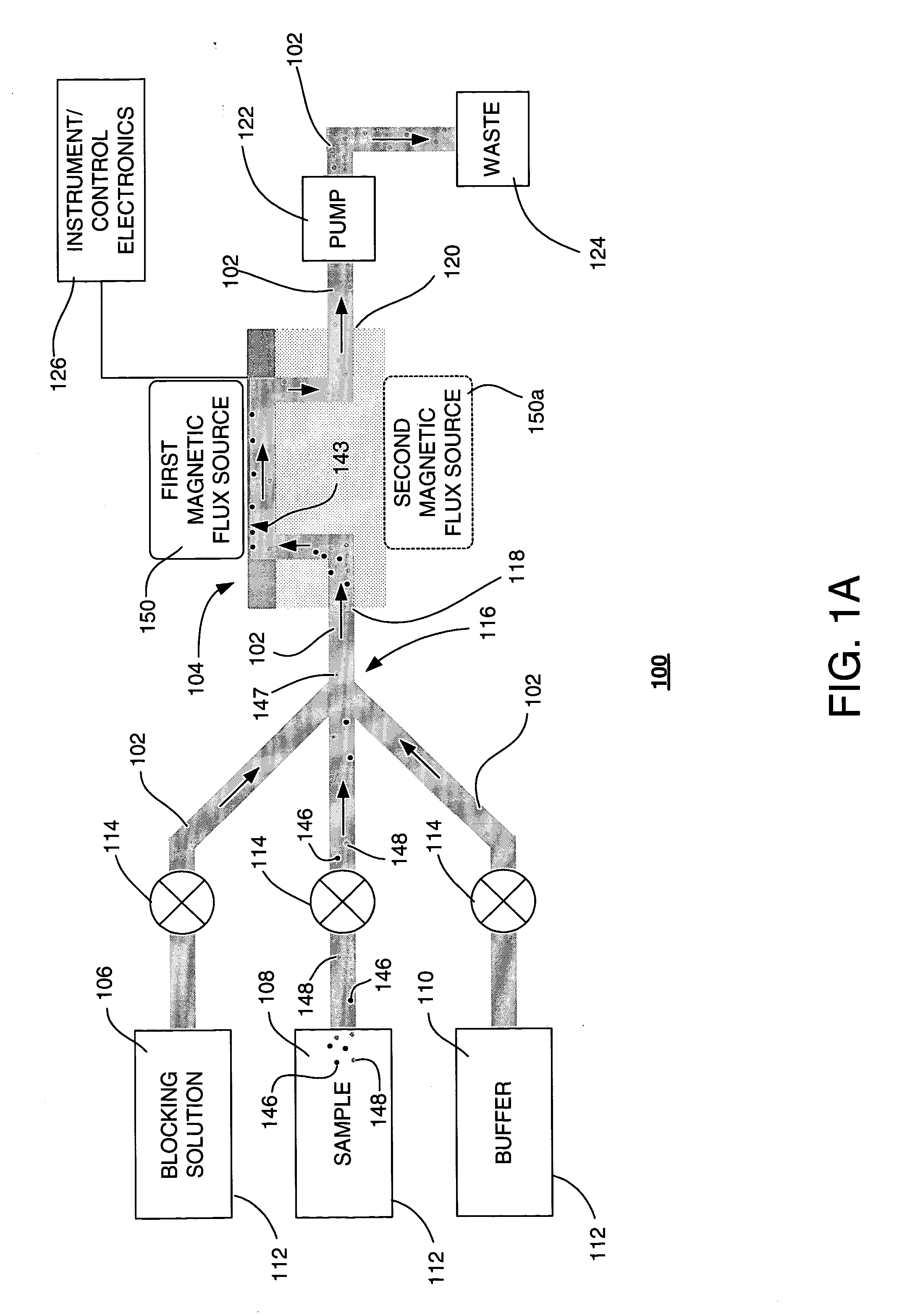
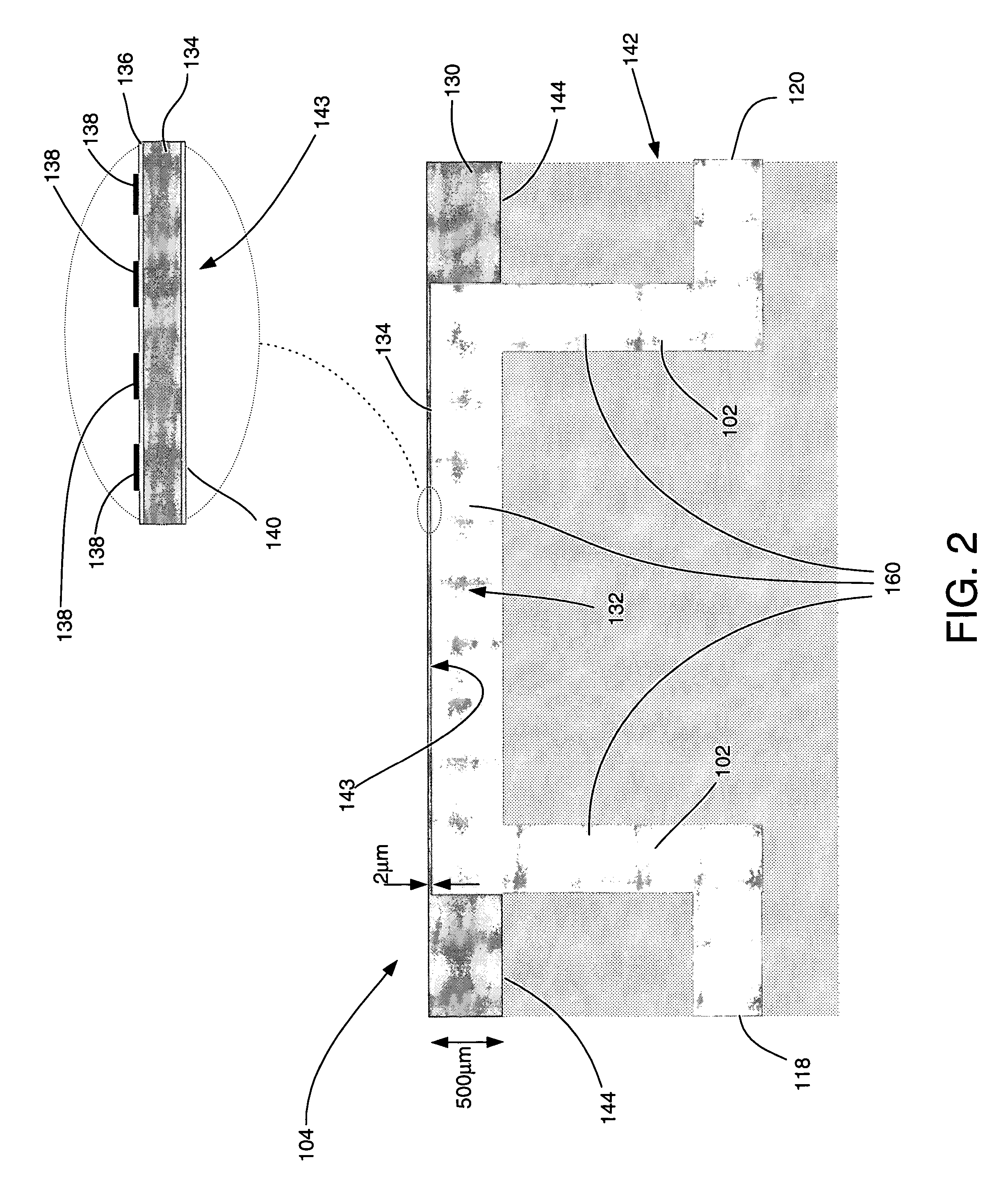
Methods for detecting analytes in a sample are provided. A plurality of particles, each of which is coated with a capture agent having an affinity for the analyte, is combined with the sample to form a plurality of analyte-particle complexes. The system also includes a transport arrangement for transporting the sample to the sensor surface, and a magnetic field inducing structure constructed and arranged to establish a magnetic field at and adjacent to the sensor surface. The resonant sensor produces a signal corresponding to an amount of analyte-particle complexes that are bound to the sensor surface.
Owner:BIOSCALE
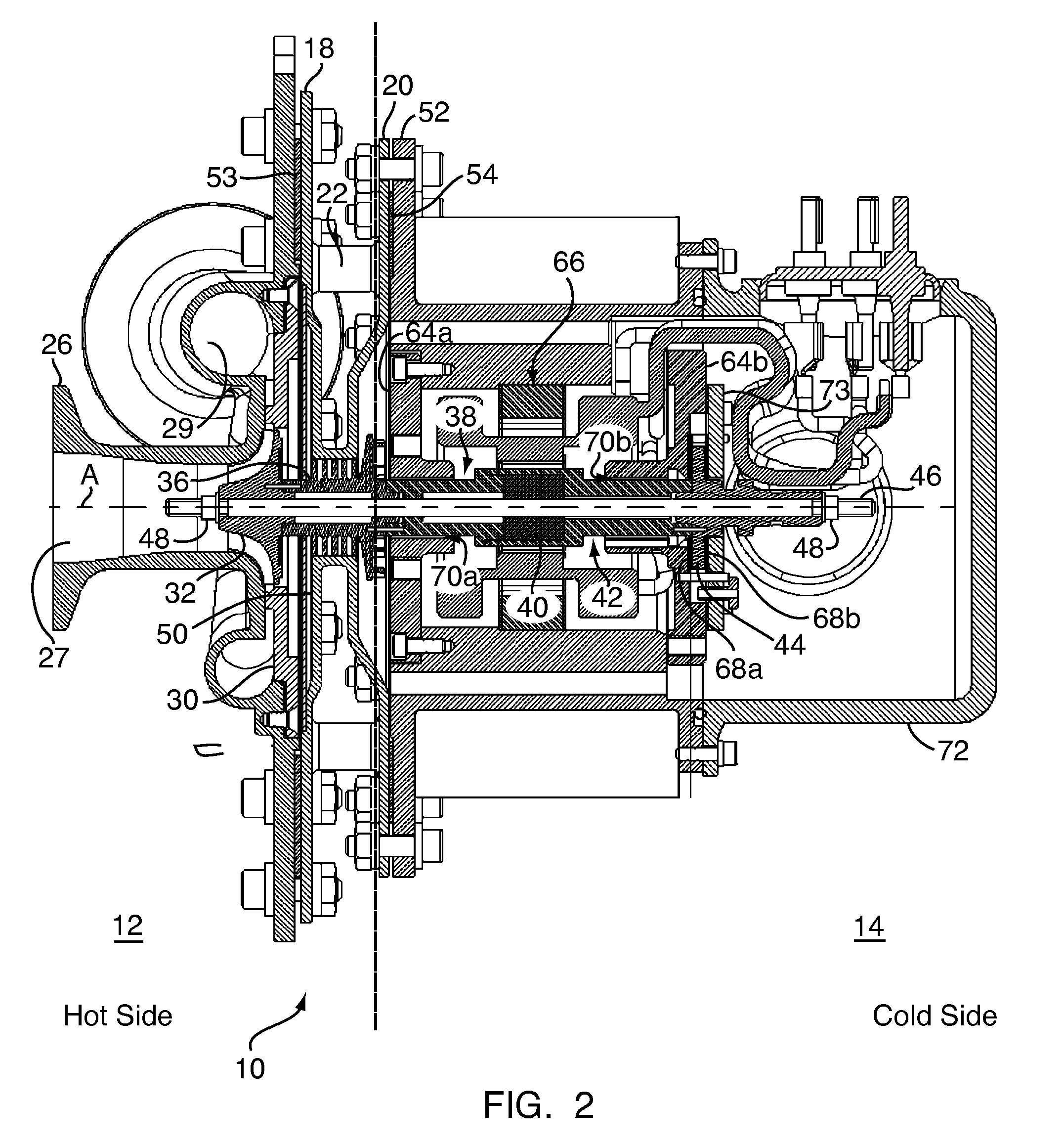
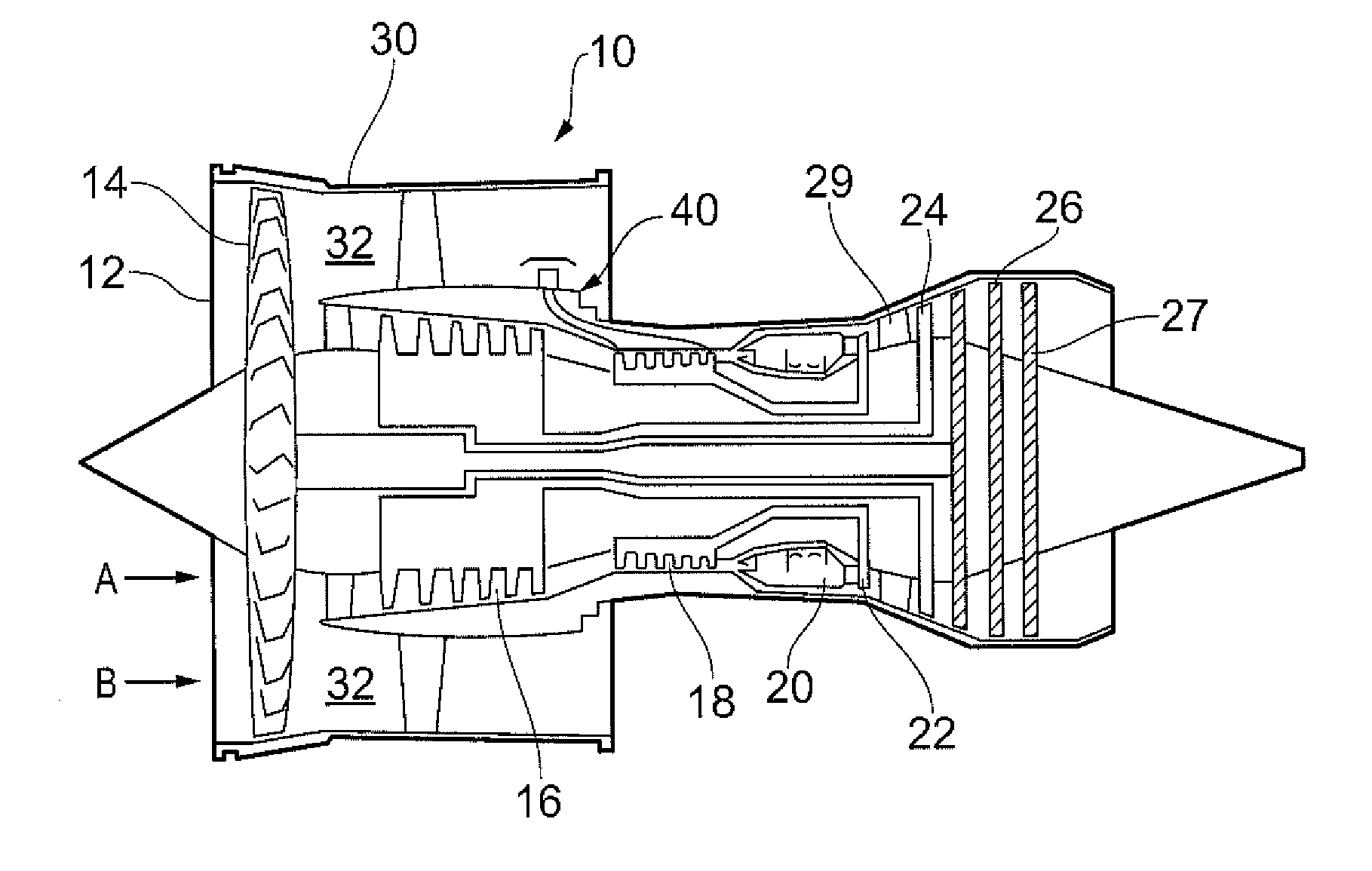
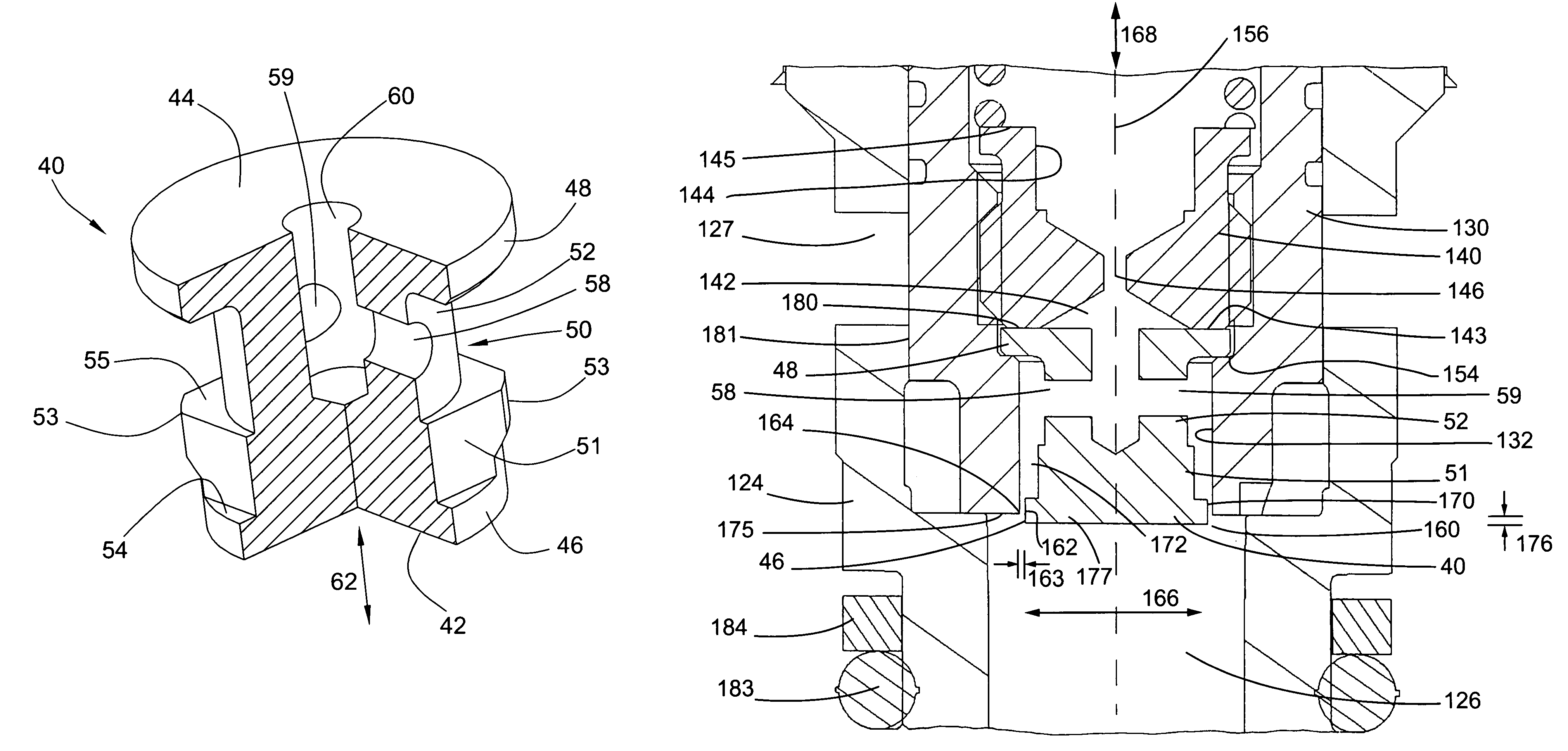
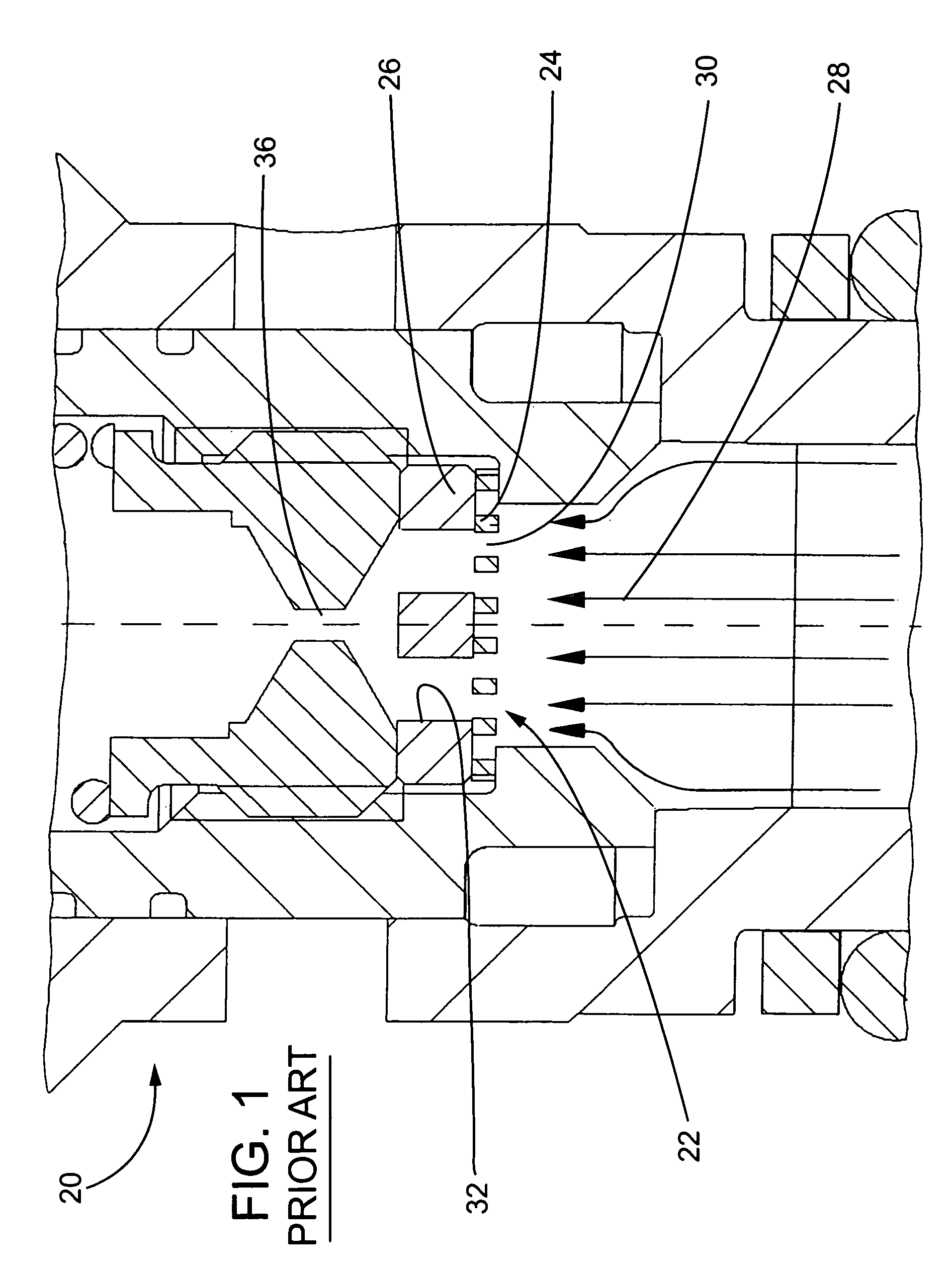
Heat exchange arrangement
ActiveUS20140341704A1Easy to controlEliminate and reduce thermally induced stressEngine fuctionsTurbine/propulsion engine coolingEngineeringGuide tube
A heat exchange arrangement for a gas turbine engine. The arrangement includes a first conduit for an engine component cooling fluid and a second conduit for a second fluid. The arrangement further includes a heat exchange portion in which fluids flowing through the first and second conduits are in a heat exchange relationship. A valve is provided, which is configured to moderate the mass flow rate of one of the fluids through the heat exchange portion. The arrangement includes divert valve in the first conduit which diverts flow to the second conduit as the flow in the second conduit is moderated to reduce thermal shock in the heat exchange portion.
Owner:ROLLS ROYCE PLC
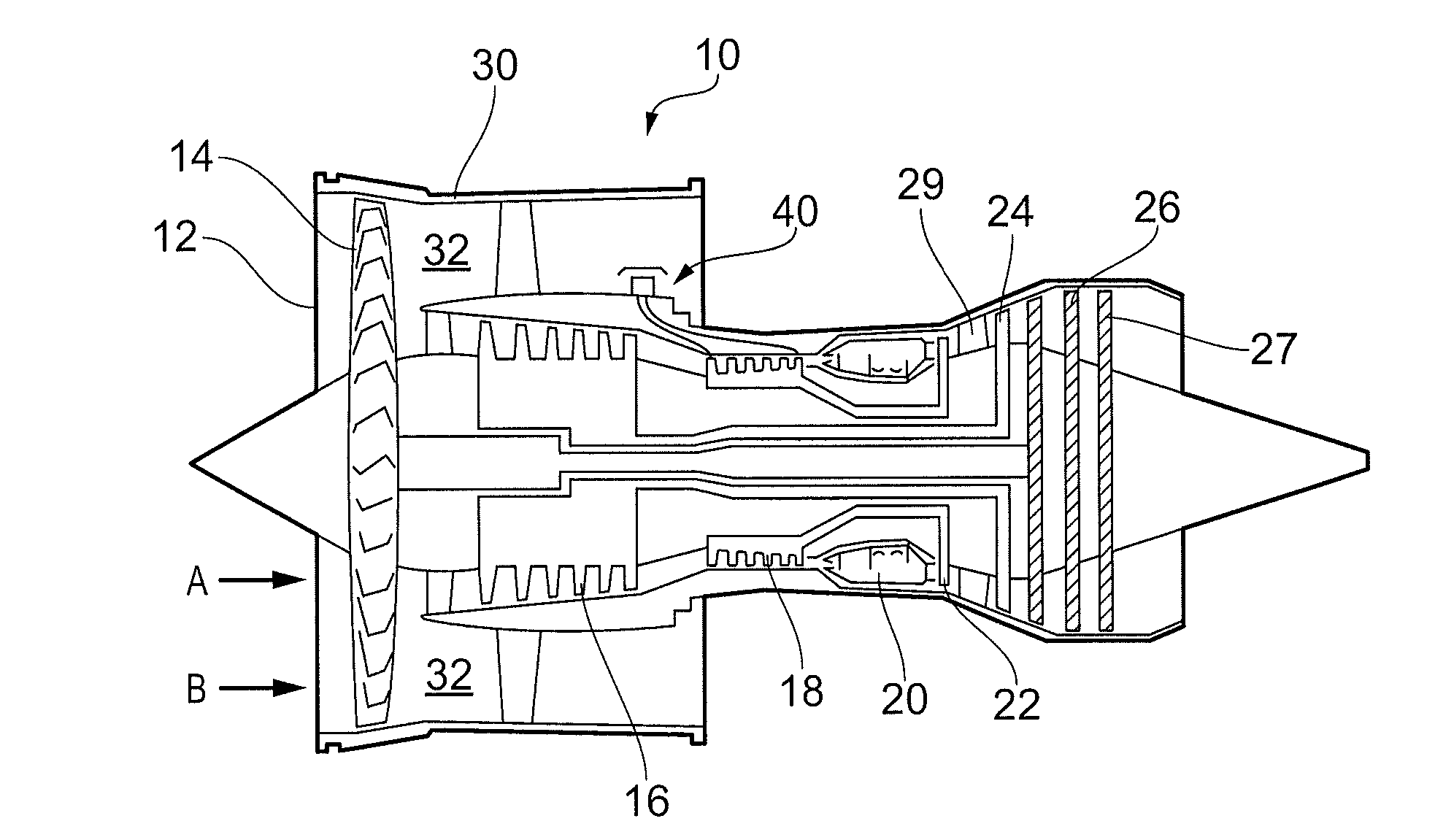
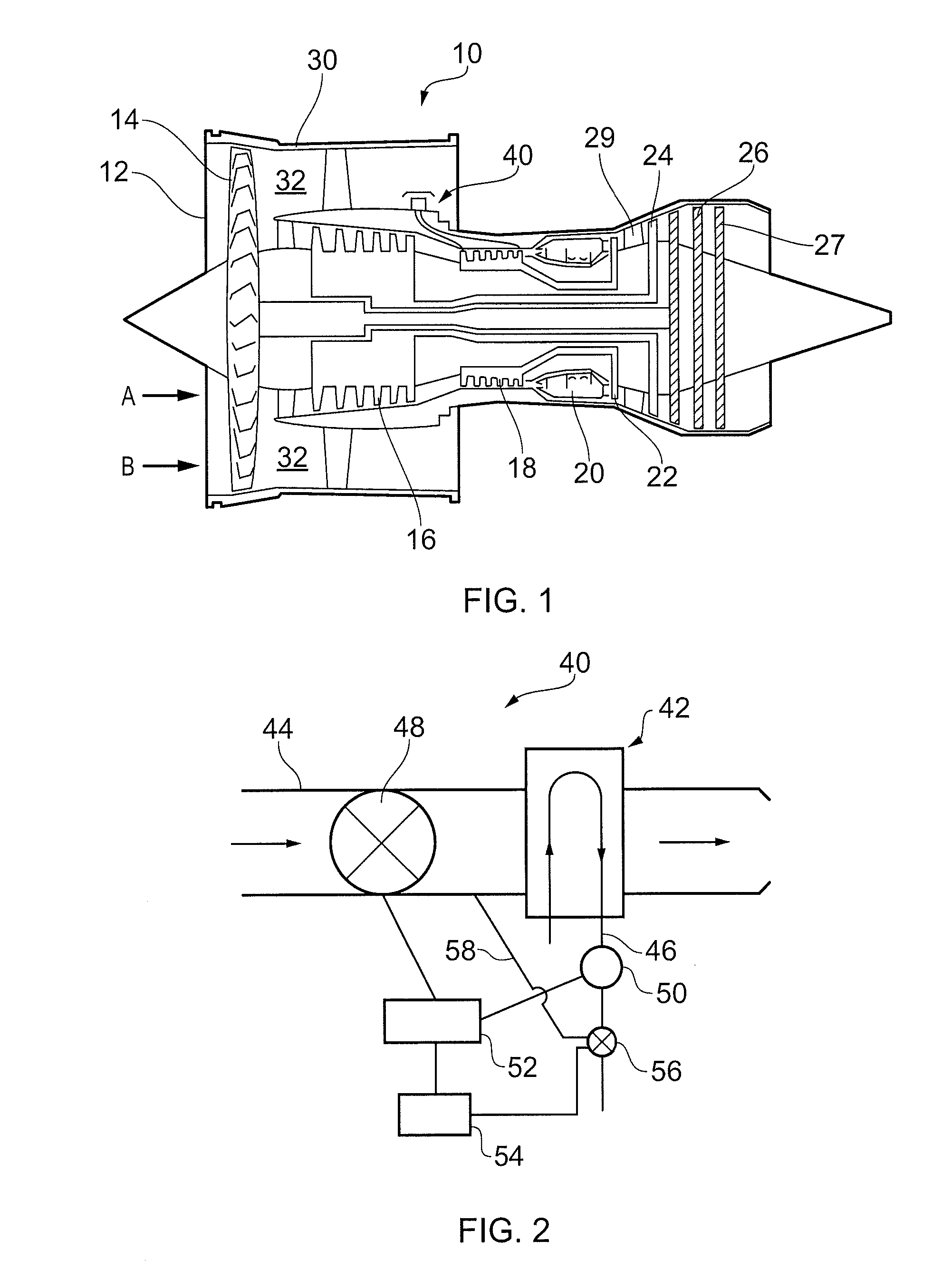
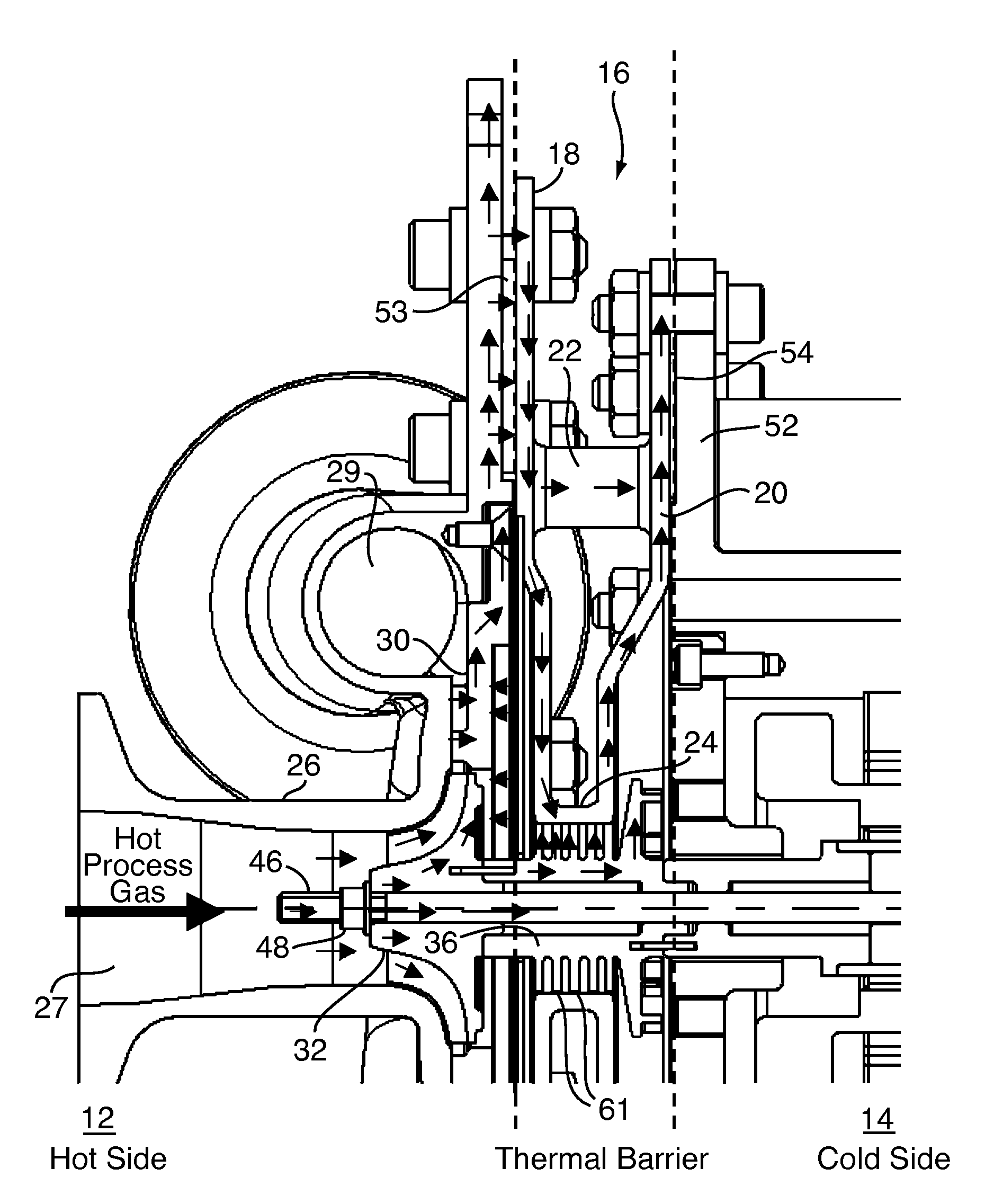
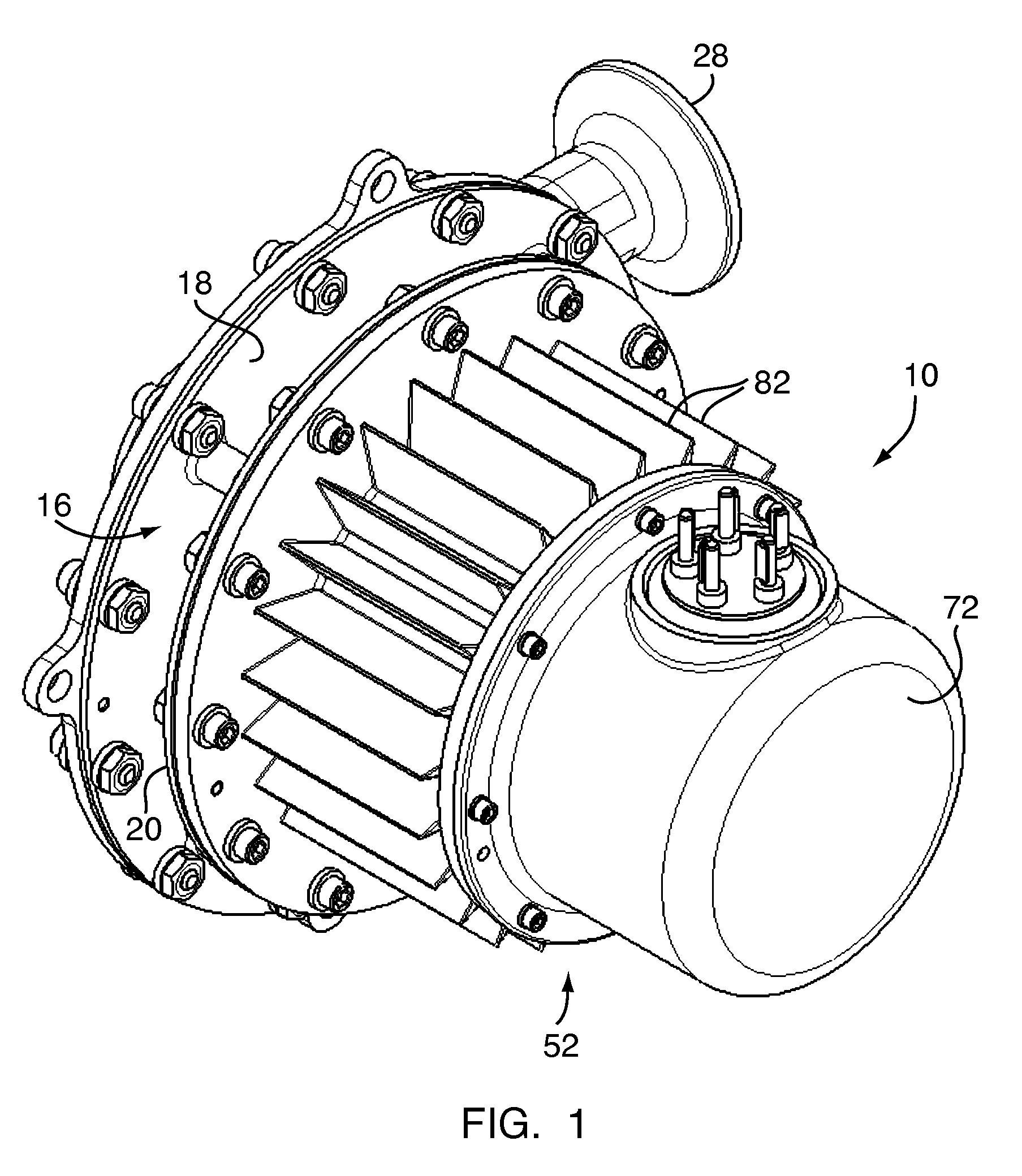
Foil gas bearing supported high temperature centrifugal blower and method for cooling thereof
InactiveUS20090087299A1Reduce heat transferHigh temperatureReaction enginesNon-positive displacement enginesImpellerEngineering
This invention provides a blower design capable of high temperature operation due to use of a self-sustaining cooling scheme through a sealed motor housing in which a cooling circuit can be created, and the use of a thermal barrier across which a temperature gradient may be formed. The thermal barrier may be formed by a thermal choke plate assembly positioned between a hot side and a cold side of the blower to dissipate heat conducted from the hot side. Alternatively, the thermal barrier may be formed by an internal fan ring provided with the blower's rotating assembly to dissipate heat conducted from the blower's impeller. The thermal choke plate assembly and the fan ring may further be used in combination to block heat transfer by all modes between a hot side and a cold side of the blower.
Owner:R & D DYNAMICS
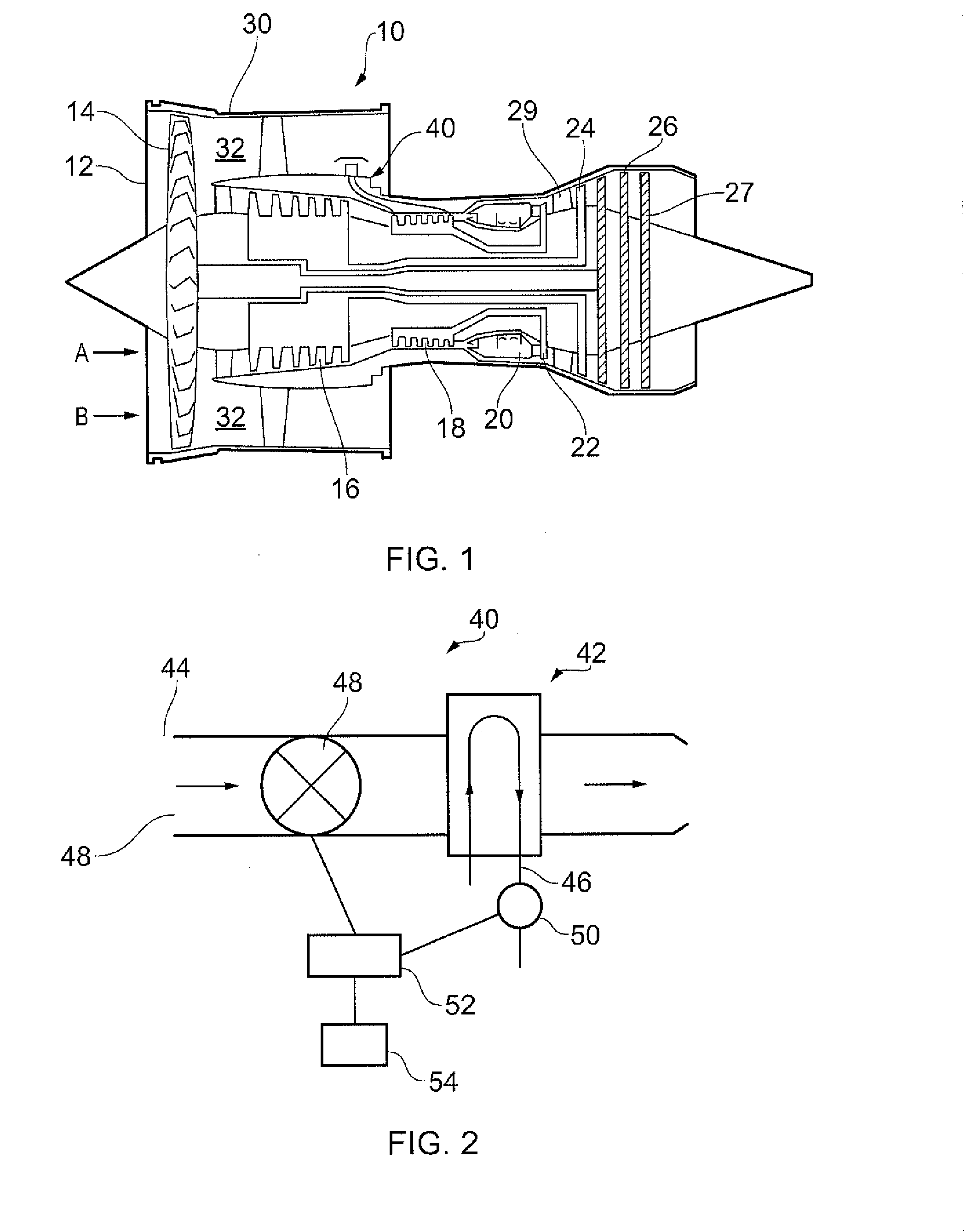
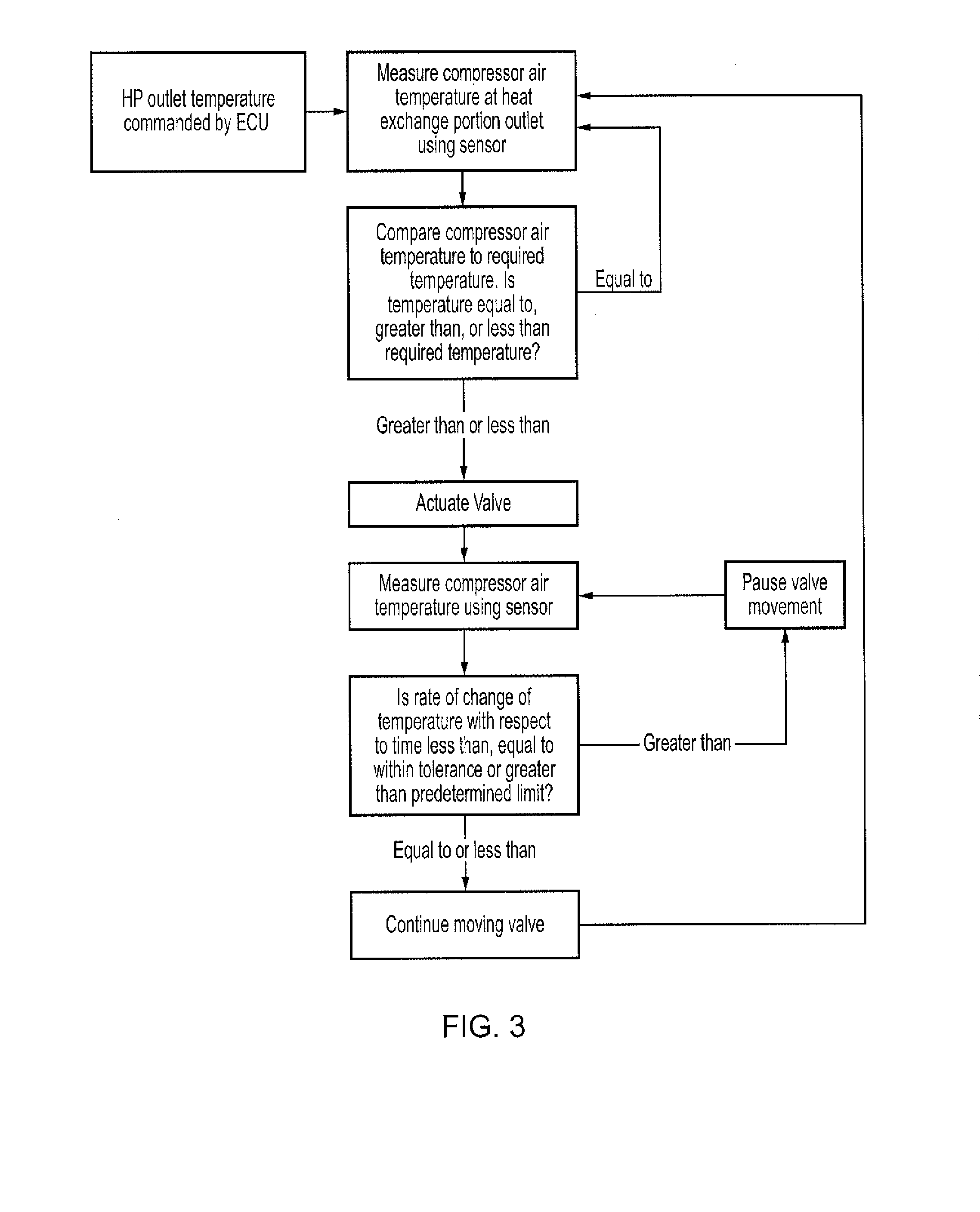
Heat exchange arrangement
InactiveUS20140131027A1Easy to controlEliminates and reduces thermally induced stressTemperatue controlGas turbine plantsEngineeringCooling fluid
A heat exchange arrangement (40) for a gas turbine engine (10). The arrangement (40) comprises a first conduit (46) for an engine component cooling fluid and a second conduit (44) for a second fluid. The arrangement further comprises a heat exchange portion (42) in which fluids flowing through the first and second conduits (46, 44) are in a heat exchange relationship. A valve 48 is provided, which is configured to moderate the mass flow rate of one of the fluids through the heat exchange portion (42). The arrangement comprises a temperature sensor (50) configured to sense a temperature of one of the fluids after said fluid has passed through the heat exchange portion (42) and a controller (52). The controller (52) is configured to control the valve (48) in response to a rate of change of the temperature with respect to time of the fluid sensed by the temperature sensor (50).
Owner:ROLLS ROYCE PLC
Apparatus for cleaning and drying substrates
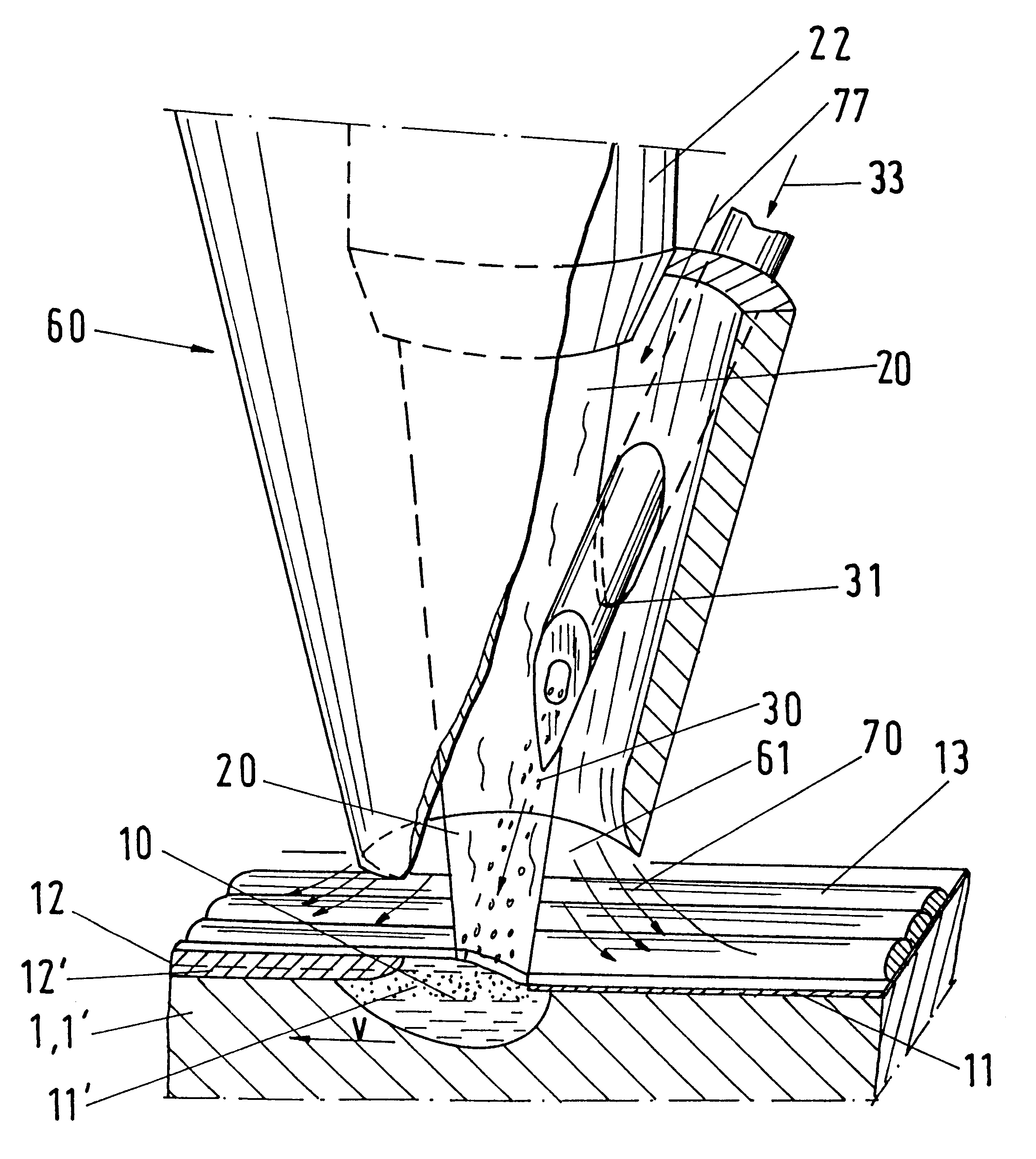
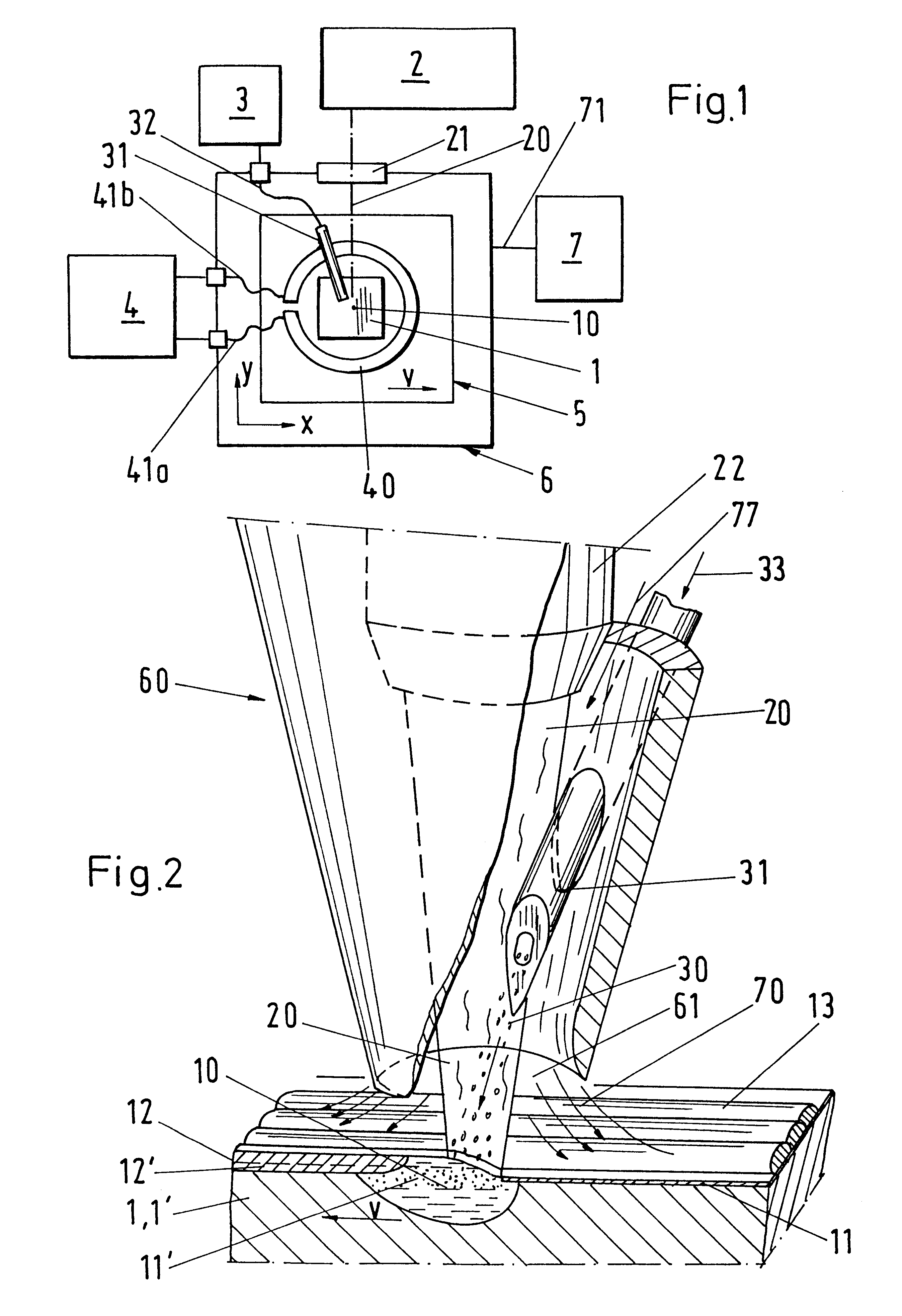
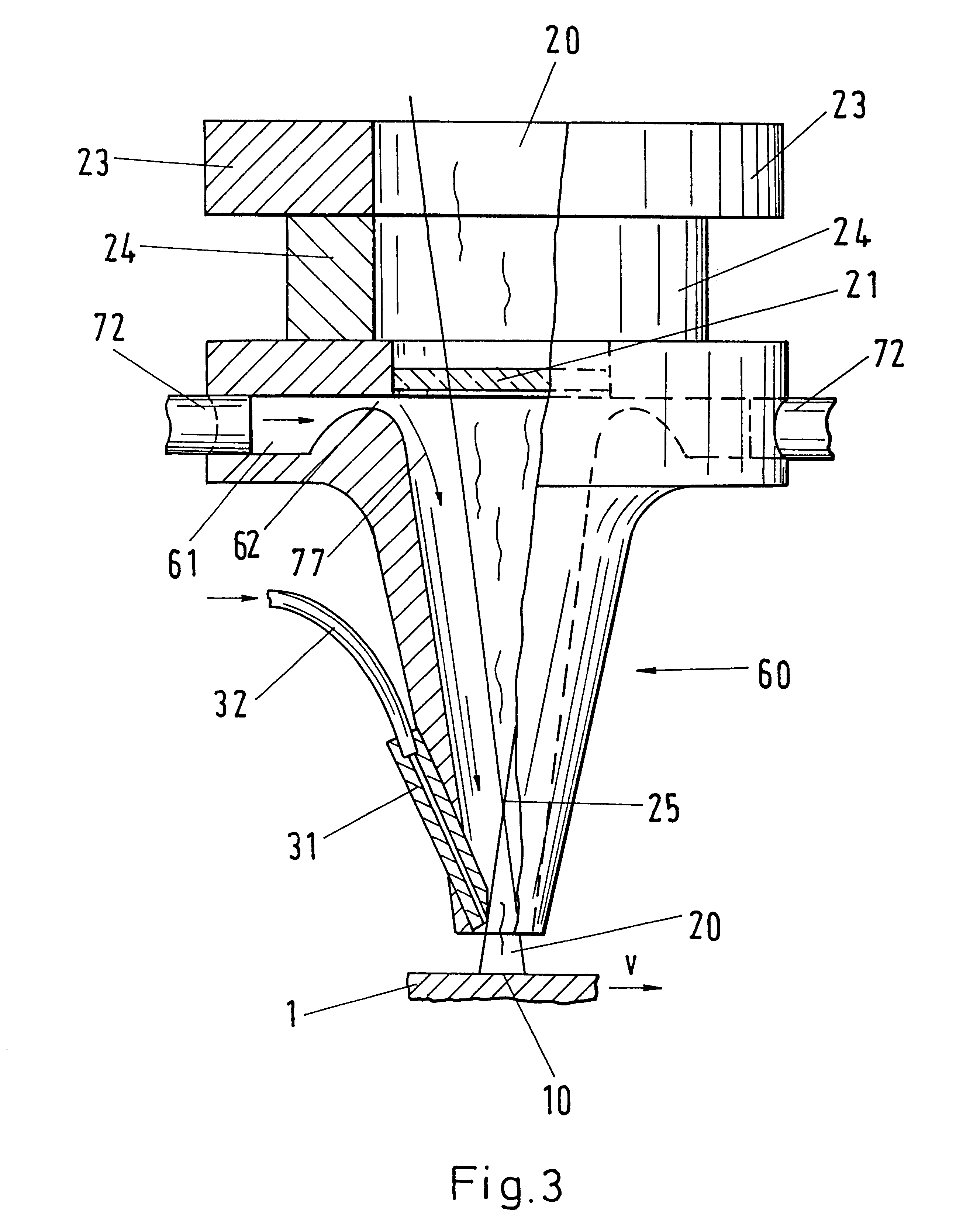
InactiveUS7252098B2Increase speedLarge gradientElectrostatic cleaningSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringMechanical engineering
A method and apparatus for cleaning, rinsing and Marangoni drying substrates is provided. A line of fluid is sprayed along a substrate surface forming an air / fluid interface line, and a line of drying vapor is supplied to the interface line to achieve Marangoni drying. Thus, a large portion of the substrate is simultaneously dried. A preferred apparatus employs a tank of cleaning and / or rinsing fluid. Above the tank fluid a source of rinsing fluid directs rinsing fluid to the surface of a substrate forming a meniscus on the substrate surface as the substrate is lifted from the cleaning fluid, and a drying vapor source directs drying vapor to the meniscus. The drying vapor lowers the surface tension of the meniscus, inducing a Marangoni flow of rinsing fluid from the substrate's surface, and thereby drying the substrate. The cleaning fluid tank has a substrate receiving and cleaning portion and a substrate rinsing portion. The rinsing fluid source and the drying vapor source are enclosed by a drying enclosure above the rinsing portion of the tank. Thus, substrate loading, cleaning, rinsing, drying and unloading are performed with at least partial overlap in time.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
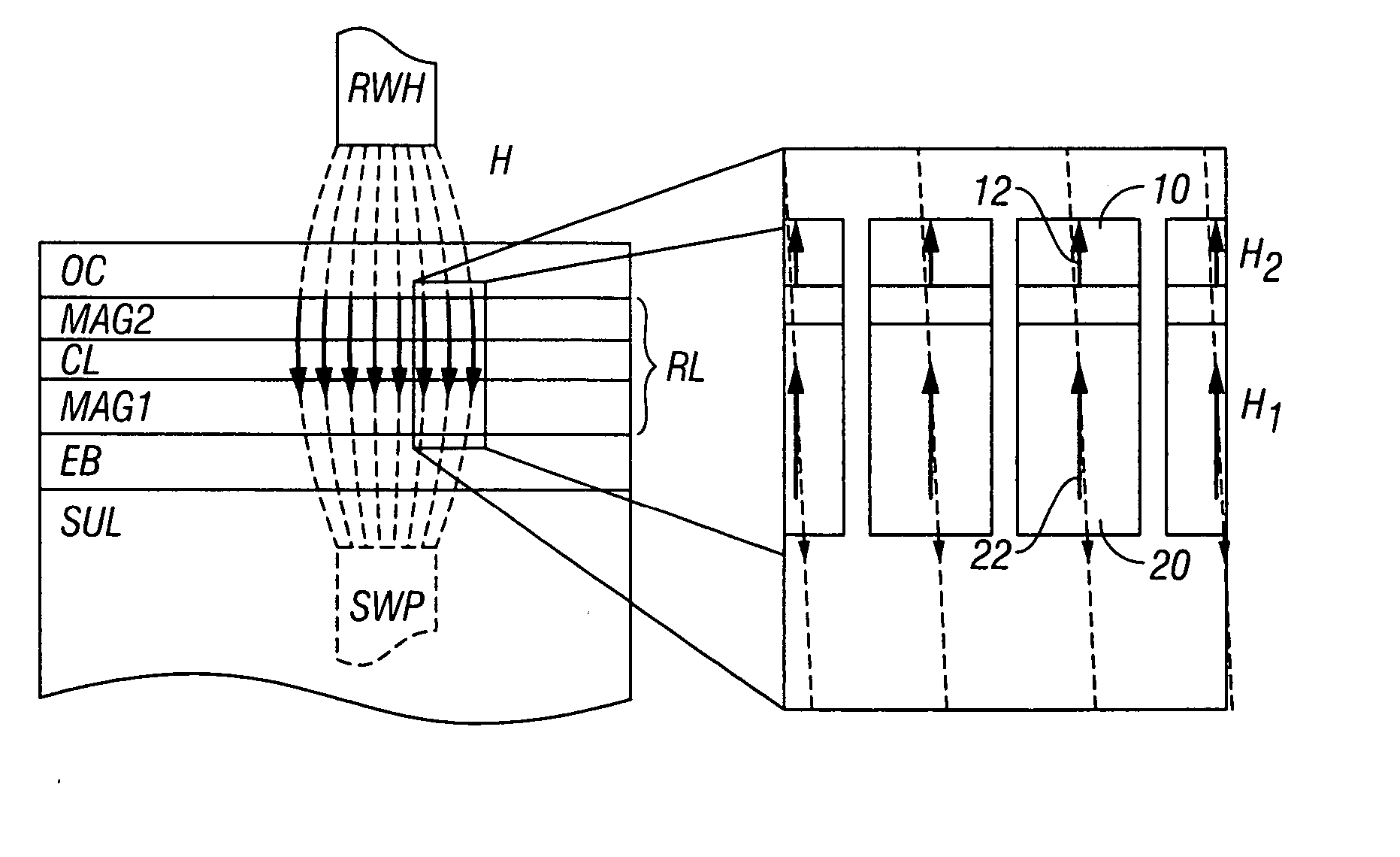
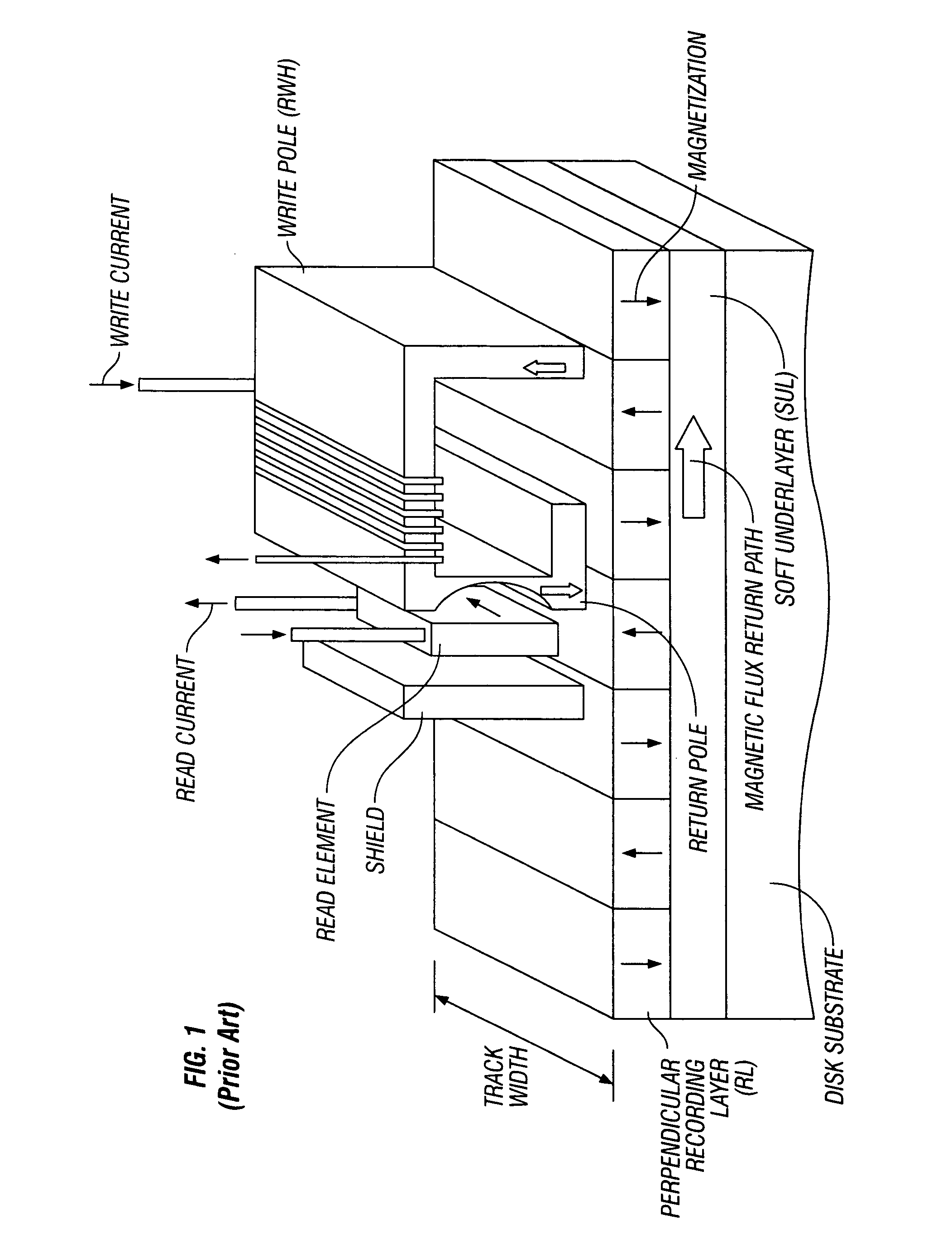
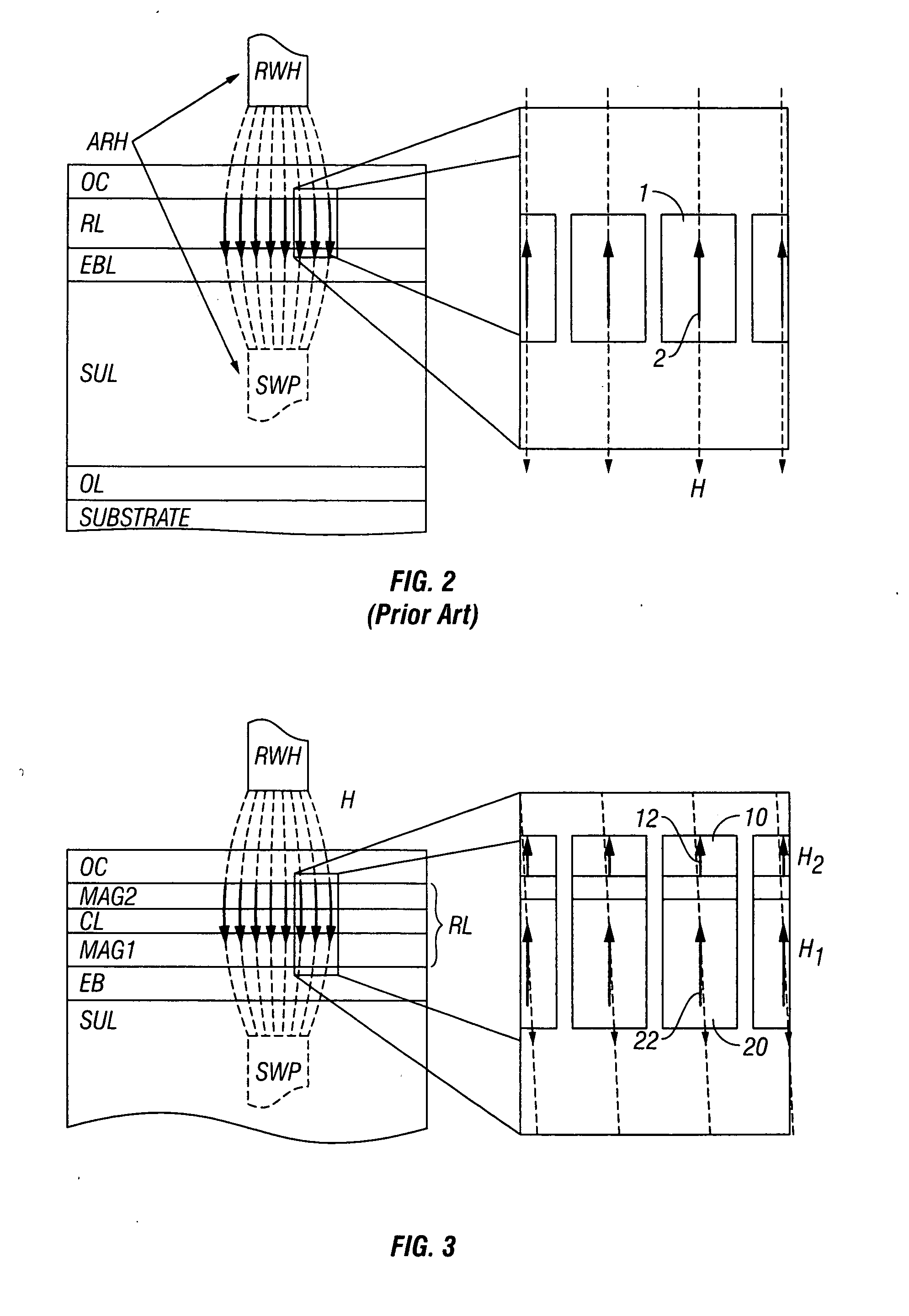
Perpendicular magnetic recording medium with multiple exchange-coupled magnetic layers having substantially similar anisotropy fields
InactiveUS20070212574A1Field strength decreaseLarge gradientRecord information storageDisk carriersNuclear magnetic resonanceMagnetic layer
A perpendicular magnetic recording medium has an “exchange-spring” type magnetic recording layer (RL) formed of two ferromagnetic layers with substantially similar anisotropy fields that are ferromagnetically exchange-coupled by a nonmagnetic or weakly ferromagnetic coupling layer. Because the write head produces a larger magnetic field and larger field gradient at the upper portion of the RL, while the field strength decreases further inside the RL, the upper ferromagnetic layer can have a high anisotropy field. The high field and field gradient near the top of the RL, where the upper ferromagnetic layer is located, reverses the magnetization of the upper ferromagnetic layer, which then assists in the magnetization reversal of the lower ferromagnetic layer. Because both ferromagnetic layers in this exchange-spring type RL have a high anisotropy field, the thermal stability of the medium is not compromised. The medium shows improved writability, i.e., a low switching field, as well as lower intrinsic media noise, over a medium with a conventional single-layer RL.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Desiccant regeneration
An aircraft fuel tank ventilation system, comprising a desiccative dehumidifying device including a desiccant medium disposed in flow communication between a vent open to the atmosphere and a fuel tank, and a microwave energy transmitter for energizing liquid water in the desiccant medium to facilitate regeneration of the medium. Also, a method of regenerating a desiccant medium of a dehumidifying device of an aircraft fuel tank ventilation system, the method comprising directing air through the desiccant medium, and transmitting microwave energy into the desiccant medium for energizing liquid water in the desiccant medium to facilitate regeneration of the medium.)
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS LTD
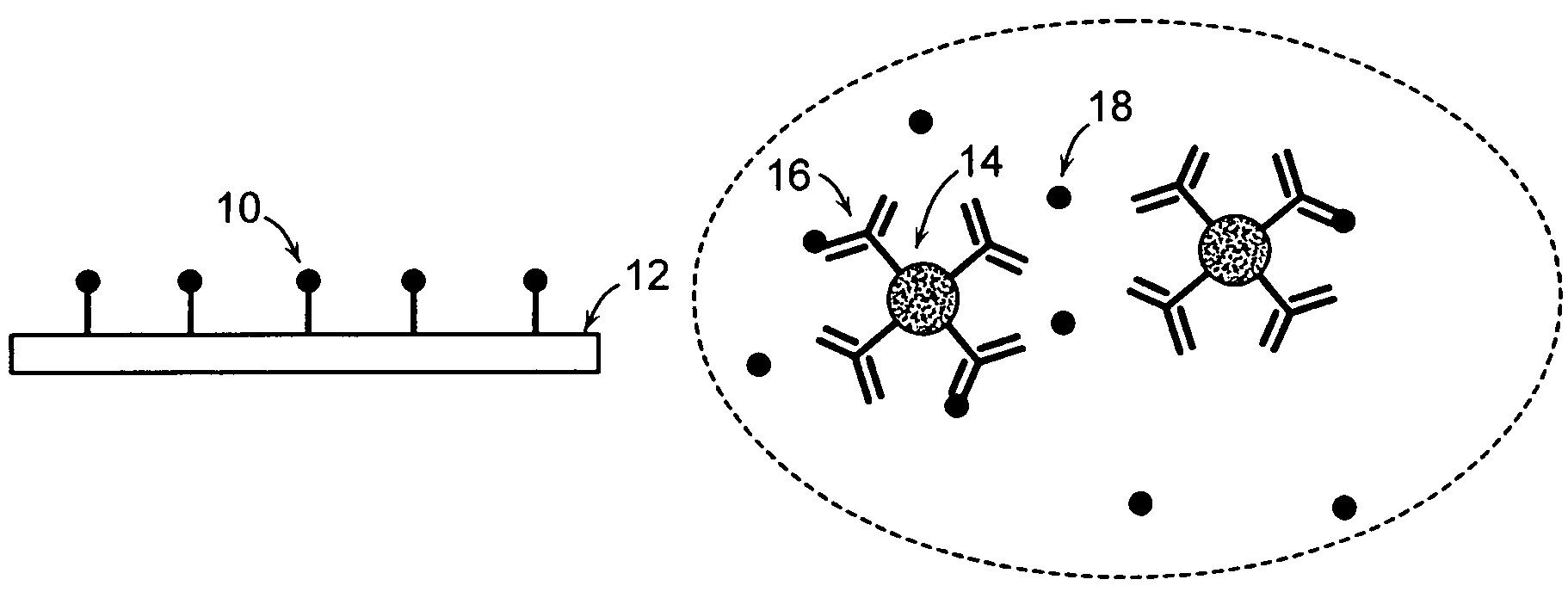
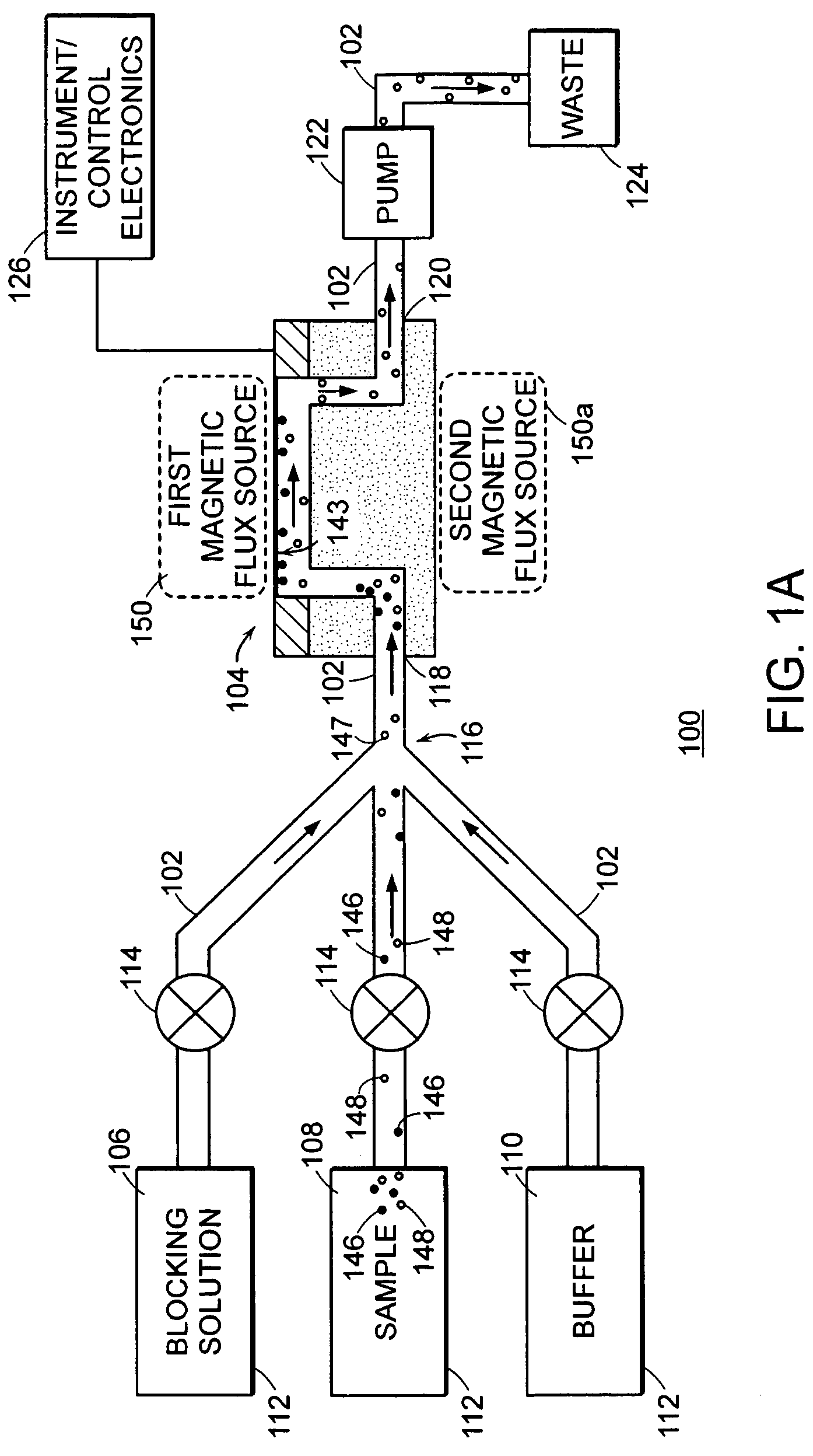
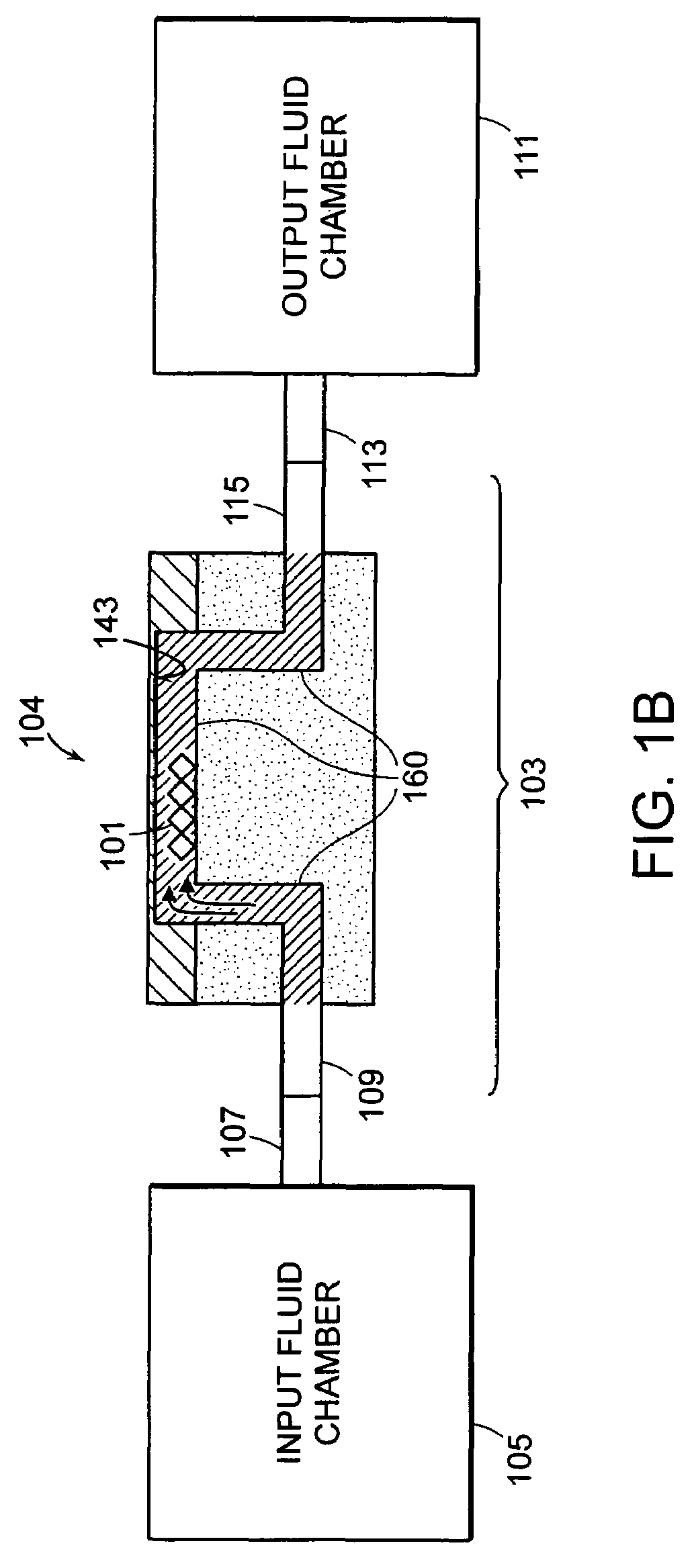
Method and apparatus for detection of analyte using a flexural plate wave device and magnetic particles
ActiveUS20060286685A1High fractional captureLarge gradientBioreactor/fermenter combinationsMaterial nanotechnologyAnalyteResonant sensor
A system for detecting an analyte in a sample includes a resonant sensor that has a sensor surface coated with the capture agent. A plurality of magnetic particles, each of which is coated with a capture agent having an affinity for the analyte, is combined with the sample to form a plurality of analyte-particle complexes. The system also includes a transport arrangement for transporting the sample to the sensor surface, and a magnetic field inducing structure constructed and arranged to establish a magnetic field at and adjacent to the sensor surface. The resonant sensor produces a signal corresponding to an amount of analyte-particle complexes that are bound to the sensor surface.
Owner:BIOSCALE
Method for making a perpendicular magnetic recording write head with a self aligned stitched write shield
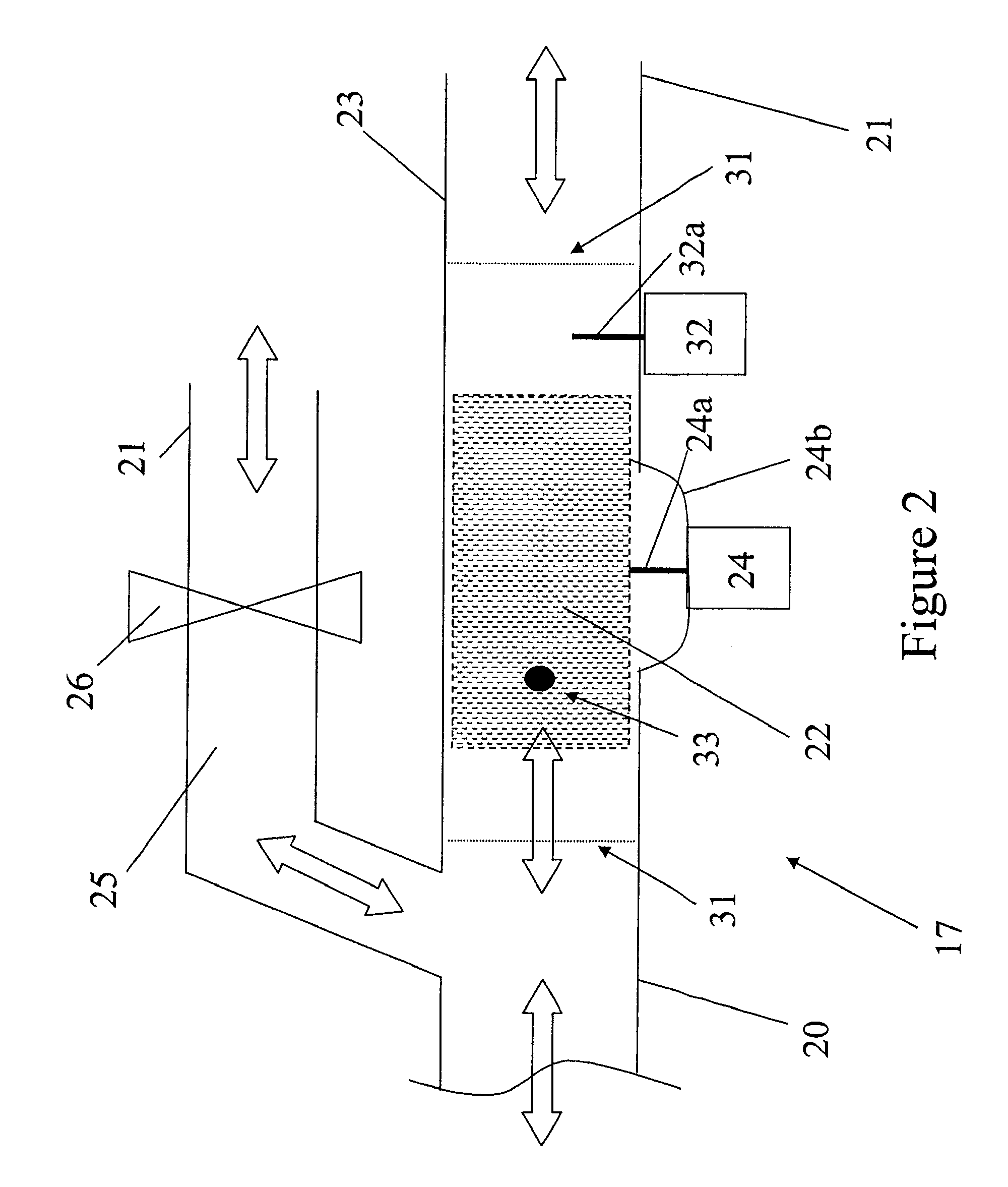
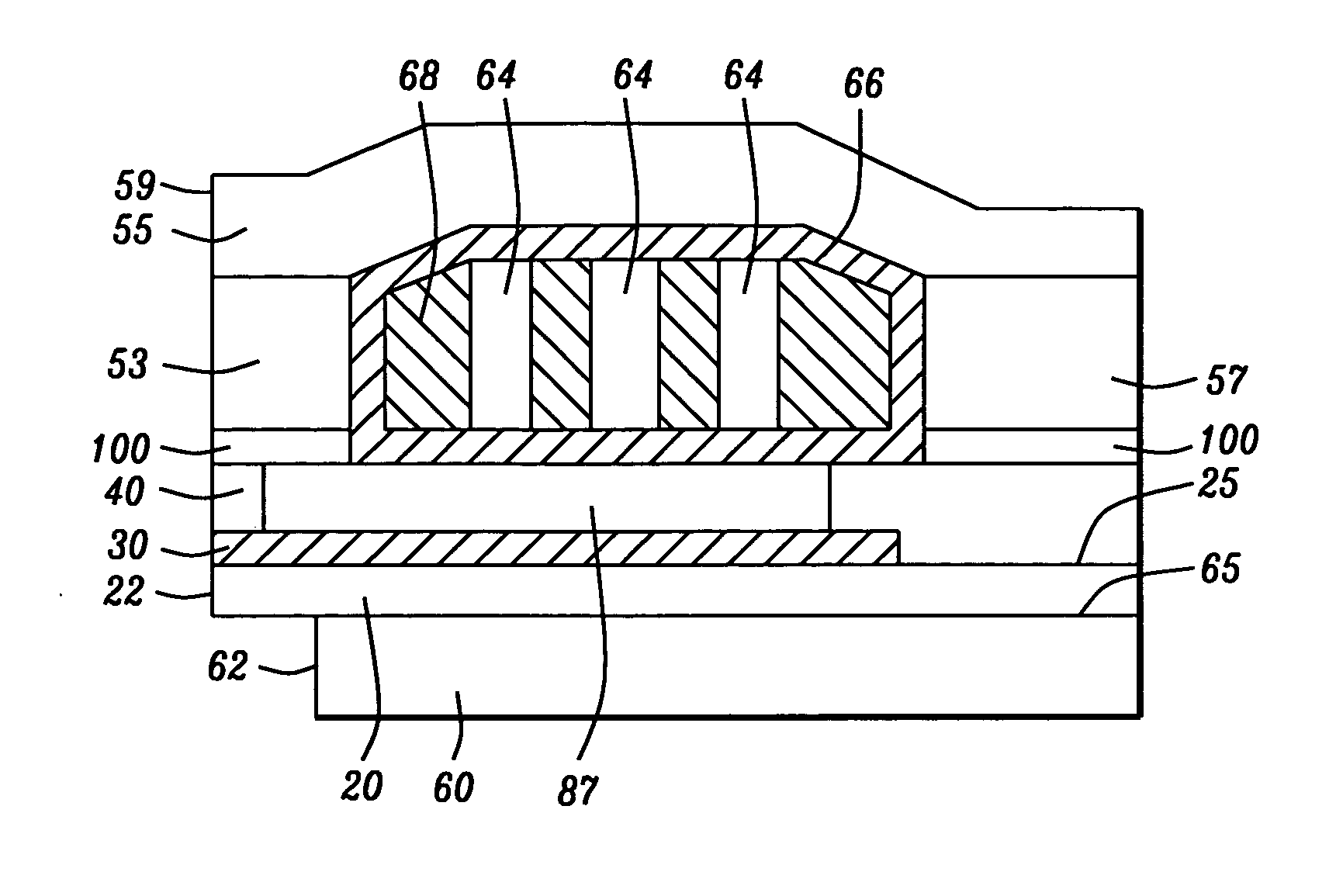
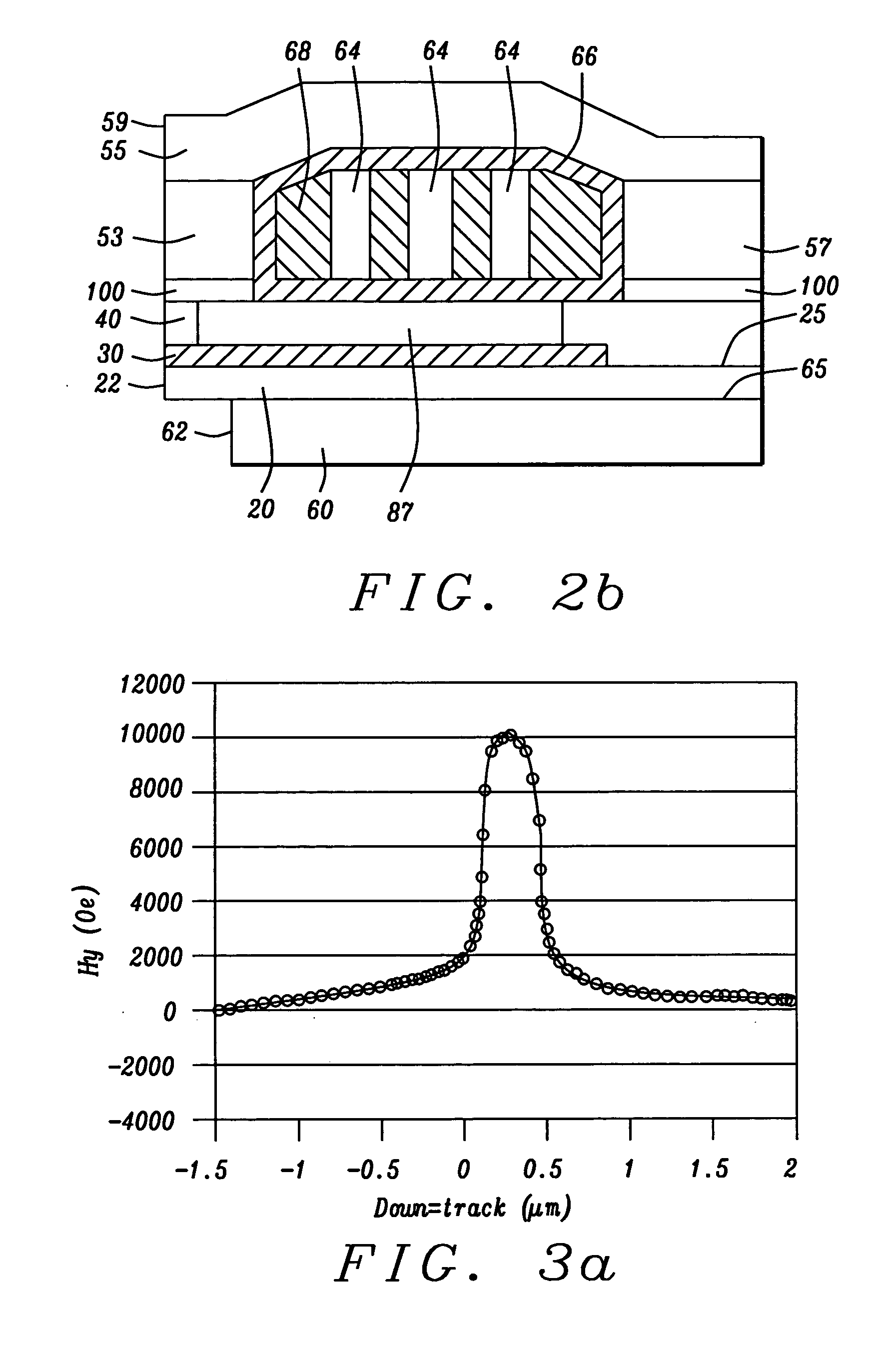
InactiveUS20050259356A1Large gradientShorten the trackConstruction of head windingsHeads using thin filmsVertical gradientEngineering
A perpendicular magnetic recording (PMR) head with single or double coil layers has a small write shield stitched onto a main write shield. The stitched shield allows the main write pole to produce a vertical write field with sharp vertical gradients that is reduced on both sides of the write pole so that adjacent track erasures are eliminated. From a fabrication point of view, both the main pole and the stitched shield are defined and formed using a single photolithographic process, a trim mask and CMP lapping process so that the main shield can be stitched onto a self-aligned main pole and stitched shield.
Owner:HEADWAY TECH INC
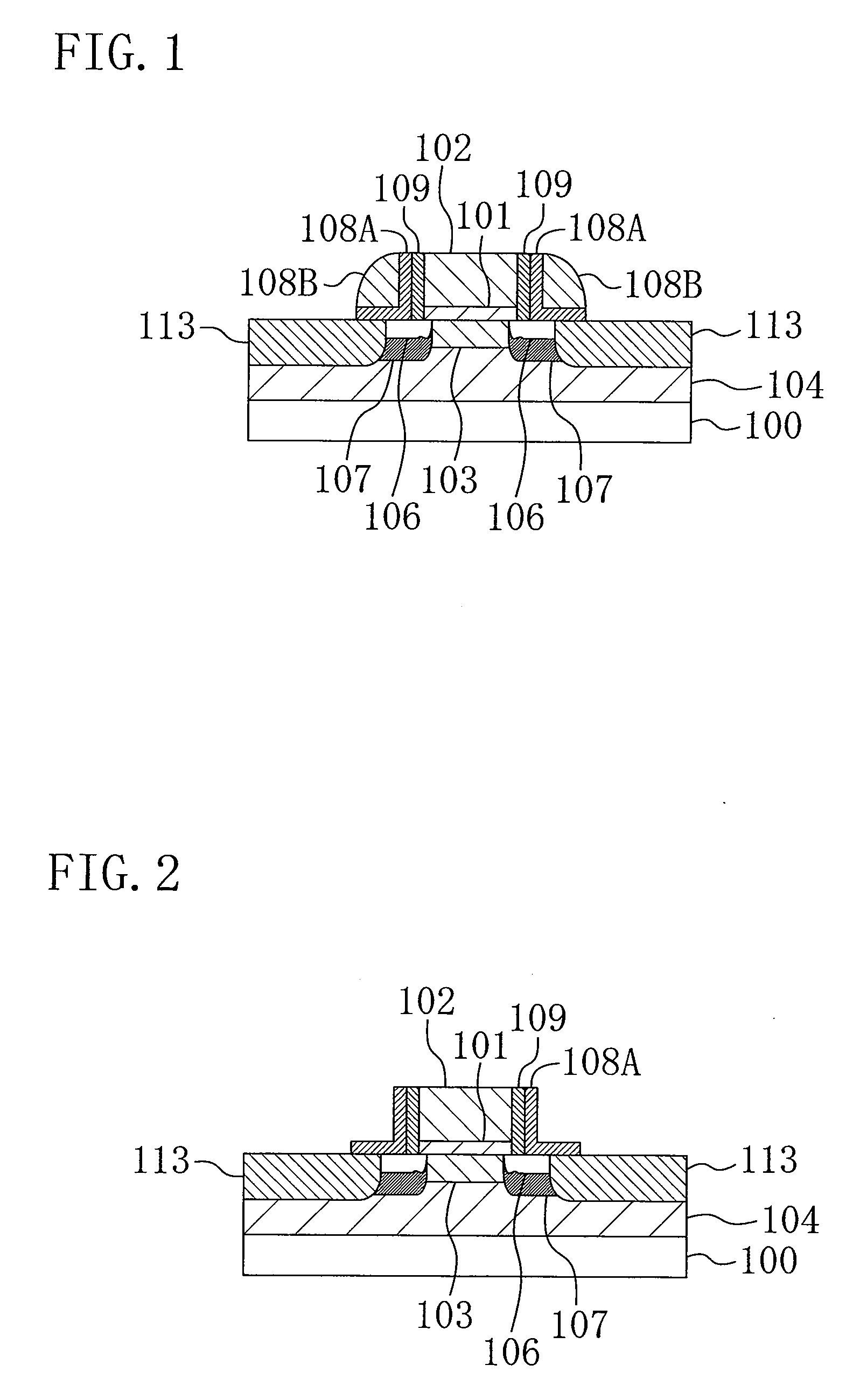
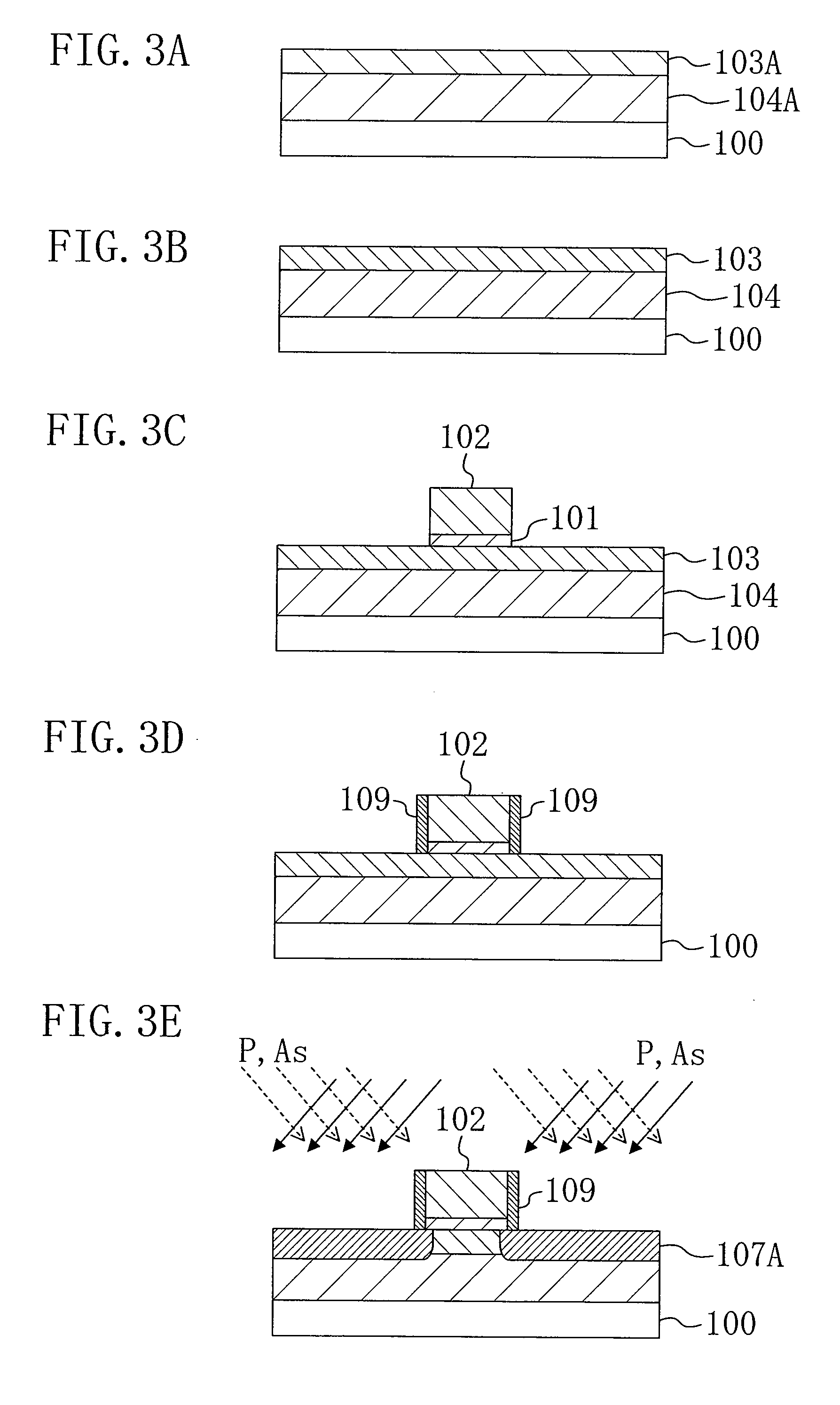
Semiconductor device and method of fabrication
ActiveUS20090278209A1Improve driving abilityLower resistanceTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDiffusion layerImpurity
A semiconductor device includes a gate electrode provided on a semiconductor region with a gate insulating film being interposed therebetween, extension diffusion layers provided in regions on both sides of the gate electrode of the semiconductor region, a first-conductivity type first impurity being diffused in the extension diffusion layers, and source and drain diffusion layers provided in regions farther outside than the respective extension diffusion layers of the semiconductor region and having junction depths deeper than the respective extension diffusion layers. At least one of the extension diffusion layers on both sides of the gate electrode contains carbon.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Method and apparatus for detection of analyte using an acoustic device
InactiveUS20090148857A1Easy to measureMaintain curative effectMaterial nanotechnologyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsAnalyteResonant sensor
Methods for detecting analytes in a sample are provided. A plurality of particles, each of which is coated with a capture agent having an affinity for the analyte, is combined with the sample to form a plurality of analyte-particle complexes. The system also includes a transport arrangement for transporting the sample to the sensor surface, and a magnetic field inducing structure constructed and arranged to establish a magnetic field at and adjacent to the sensor surface. The resonant sensor produces a signal corresponding to an amount of analyte-particle complexes that are bound to the sensor surface.
Owner:BIOSCALE
Method and apparatus for therapeutic drug monitoring using an acoustic device
InactiveUS7611908B2Easy to measureMaintain curative effectMaterial nanotechnologyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsMedicineResonant sensor
Methods for therapeutic drug monitoring are provided. A plurality of particles, each of which is coated with a capture agent capable of binding a therapeutic drug of choice is combined with the sample to form a plurality of therapeutic drug-particle complexes. The system also includes a transport arrangement for transporting the sample and / or particles to the sensor surface, and optionally a magnetic field inducing structure constructed and arranged to establish a magnetic field at and adjacent to the sensor surface. The resonant sensor produces a signal corresponding to an amount of therapeutic drug-particle complexes that are bound to the sensor surface.
Owner:BIOSCALE
Thermally driven knudsen pump
ActiveUS20120207625A1Improved thermal isolationIncreases gas flow impedanceFlexible member pumpsPressure pumpsThermoelectric materialsElectrical polarity
The present invention relates to thermally driven pumps. More specifically, one embodiment of the present invention relates to the use of a thermoelectric material to create a thermally driven, bi-directional pump, such as a micro pump, with no moving parts using the thermal transpiration effect (a Knudsen pump). One embodiment of the thermally driven pump of the present invention utilizes a thermoelectric material to assist with the thermal transpiration process resulting in a substantially symmetrical, bidirectional pump. A thermoelectric module is used to induce a temperature gradient across a nanoporous article having at least one nanochannel thus creating fluid flow via thermal transpiration across the nanochannel. The use of the thermoelectric module eliminates the need for a heat sink thereby making the pump substantially symmetrical and enabling bidirectional flow which is accomplished by reversing the polarity of the power supply to the thermoelectric module resulting in reversing the direction of heat transfer.A second embodiment of the thermally driven pump of the present invention comprises a uni-directional, pneumatic, micro fluidic, Knudsen pump which can be integrated into a lab-on-chip device and is configured to pump liquids. The Knudsen pump of the second embodiment is generally comprised of a channel system comprised of a nanochannel and a shallow channel embedded in a bottom substrate and capable of alignment in series with other channels within a lab-on-chip substrate. The nanochannel and shallow channel are both covered by a second substrate comprised of material conducive to finalize creation of the Knudsen channels. A heater is also included within the nanochannel to induce gas flow by thermal transpiration which pneumatically moves liquid through the channels of a lab-on-chip.
Owner:UNIV OF LOUISVILLE RES FOUND INC
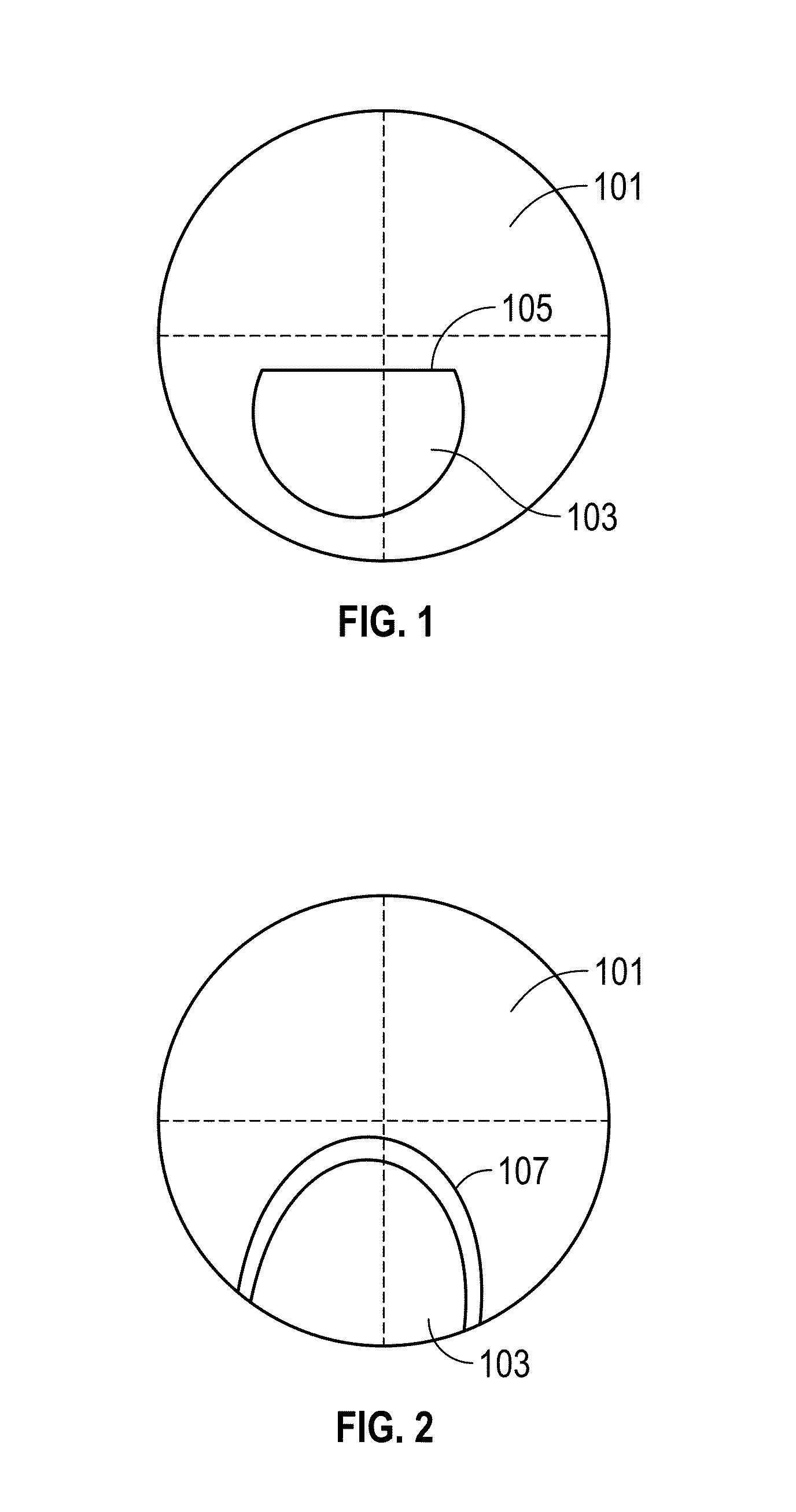
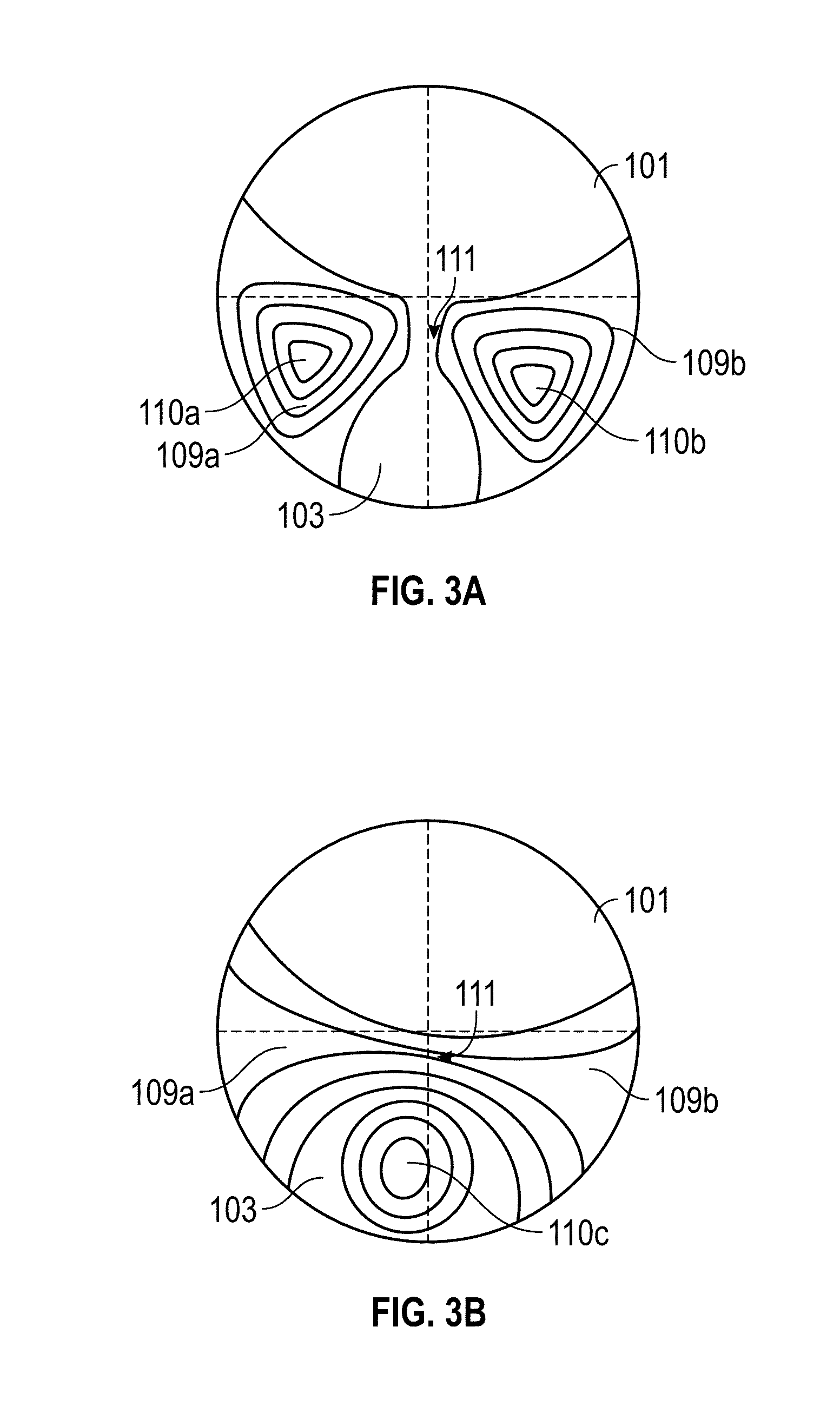
Quasi progressive lenses for eyewear
InactiveUS20150253587A1Reduce visual qualityStrengthening of residual cylinder powerOptical partsLensUses eyeglassesMultifocal lenses
Various embodiments disclose a quasi progressive lens including a first optical zone capable of providing distance vision, a second optical zone capable of providing near vision and a transition zone connecting the first and second optical zones. Physical dimensions (e.g., length and width) of the transition zone are adjusted to increase the size of the second optical zone in comparison to progressive lenses and to reduce residual cylinder power and aberrations along the convergence path in comparison to bifocal lenses.
Owner:SHAMIR OPTICAL IND LTD
Self-cleaning filter
ActiveUS7137406B2Effective and durable filterLimited spaceOperating means/releasing devices for valvesDispersed particle filtrationEngineeringSelf cleaning
Owner:US BANK N A
Method for the production of a ceramic layer on a metallic base material
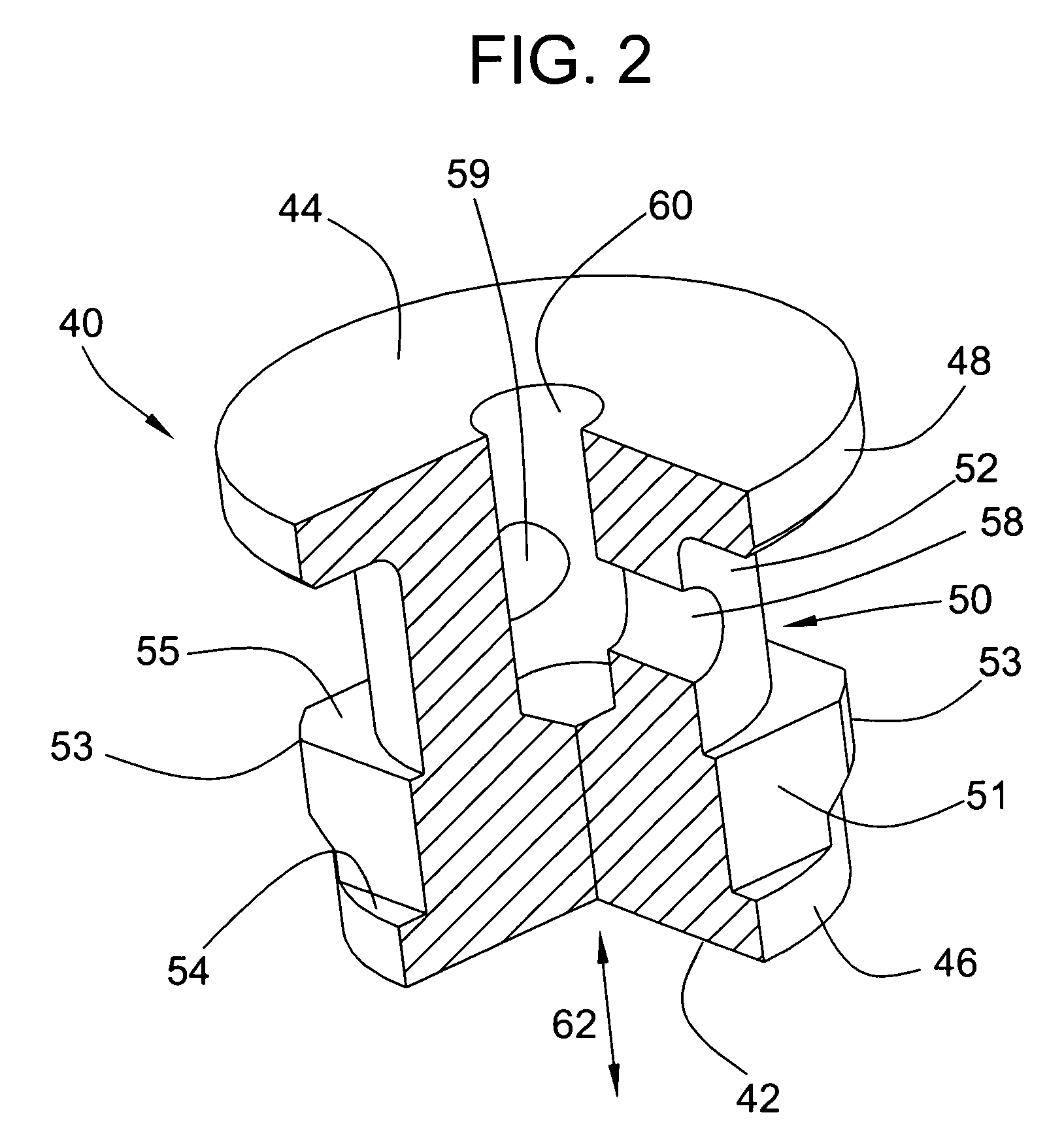
InactiveUS6221175B1Low residual tensionLayer thicknessVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingCeramic coatingAlloy
The method for the production of a ceramic layer on a metallic base material combines the following measures: The base material is preheated. Ceramic coating material is applied to a locally melted surface region of the base material. The coating material is therein likewise melted. A metallurgical bonding zone is provided using an additive material which reacts with the coating material and which is additionally applied to the base material as an adhesion producing layer or is added to the base material as a component of the alloy.
Owner:SULZER INNOTEC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com