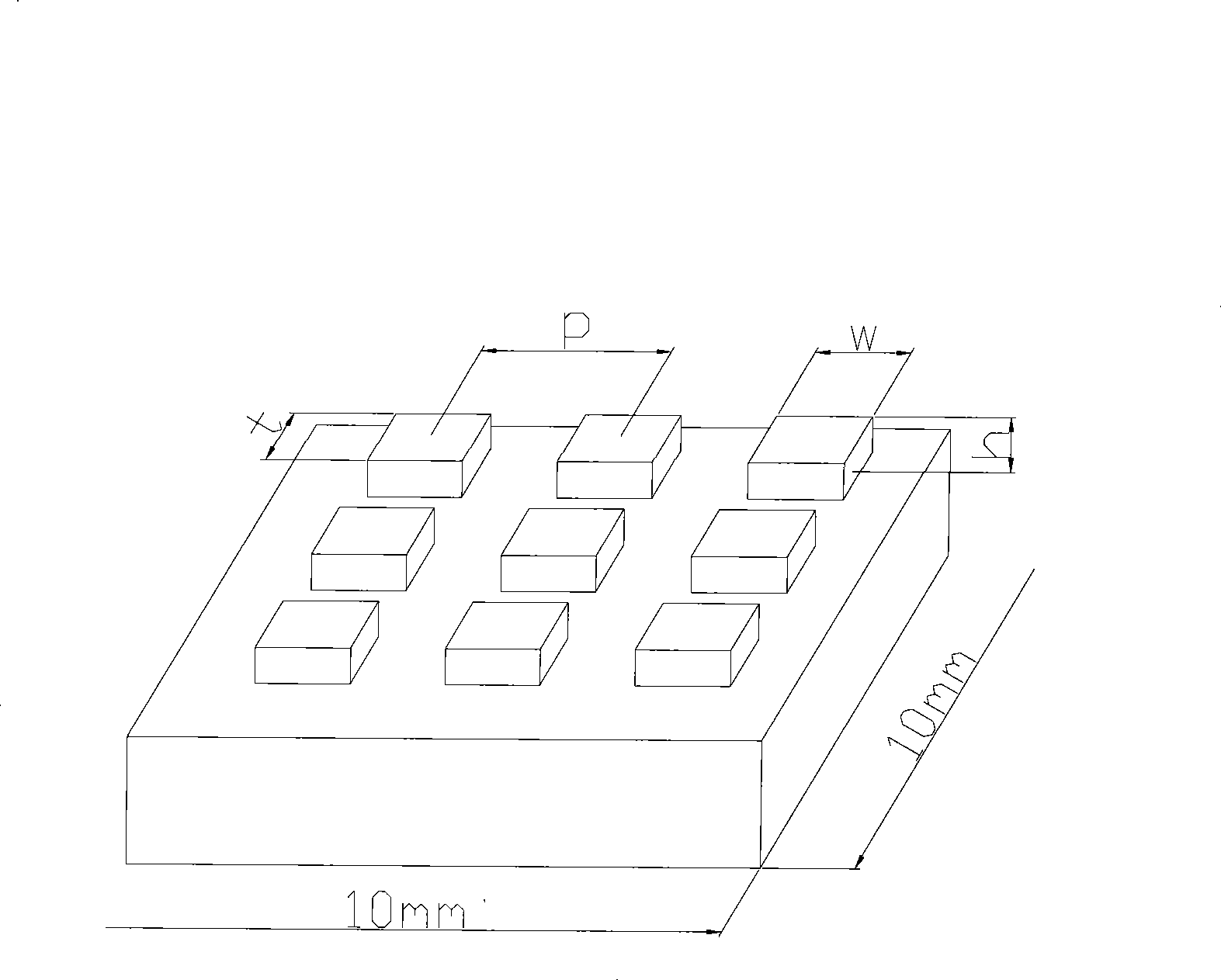Patents
Literature
60 results about "Bubble nucleation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Bubble nucleation. In the theoretical physics of the false vacuum, the system moves to a lower energy state – either the true vacuum, or another, lower energy vacuum – through a process known as bubble nucleation. In this, instanton effects cause a bubble to appear in which fields have their true vacuum values inside.
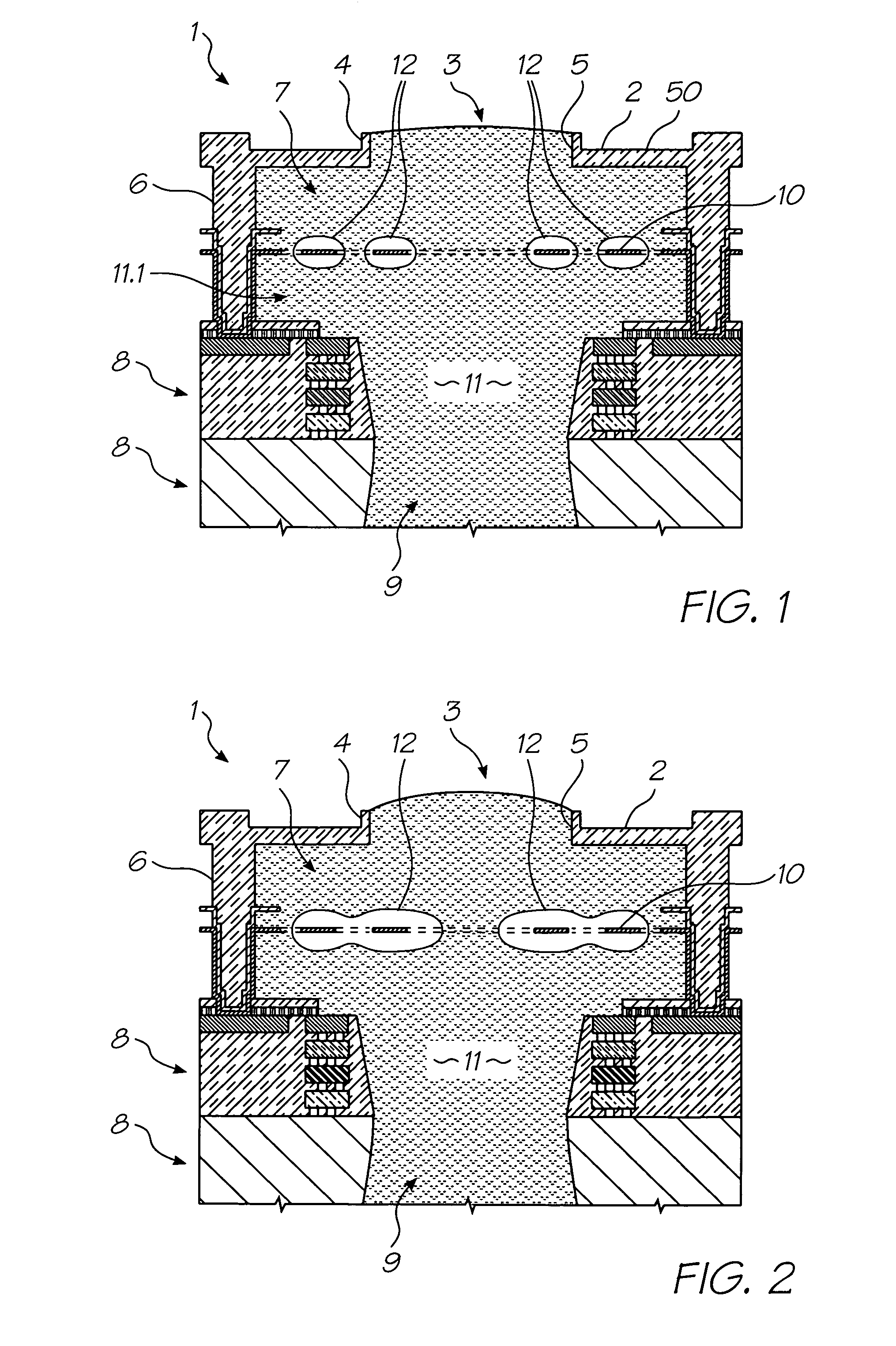
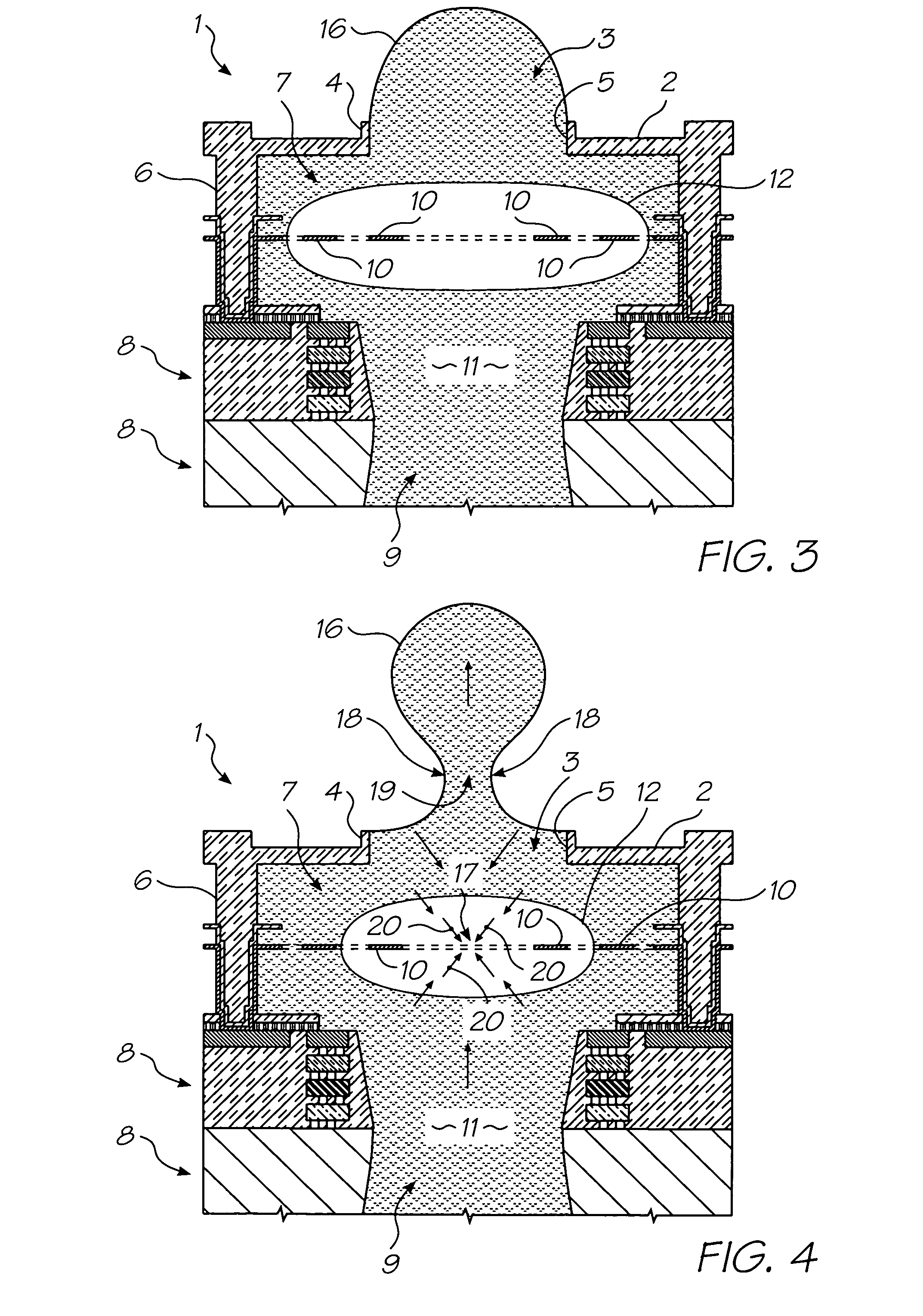
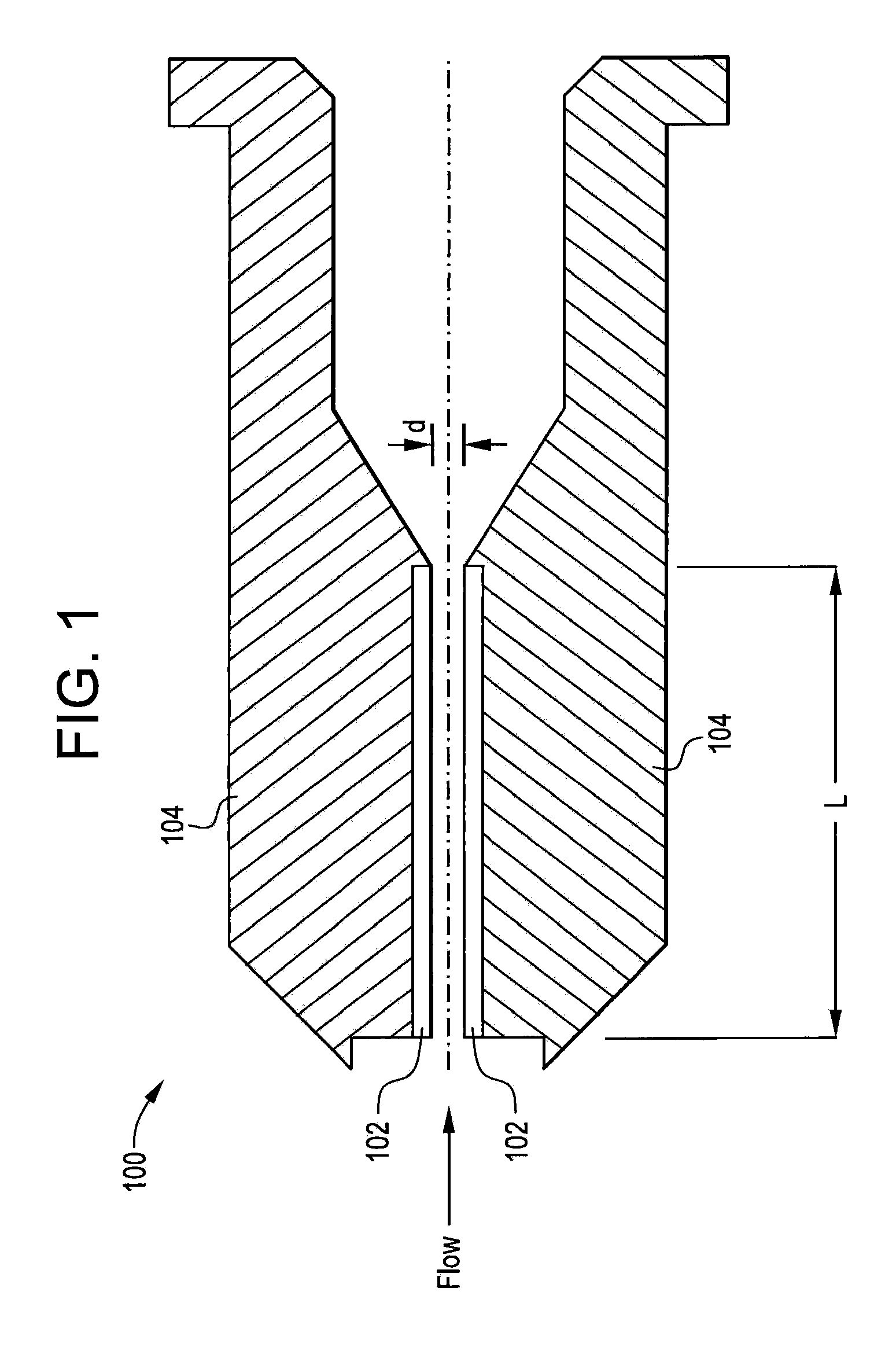
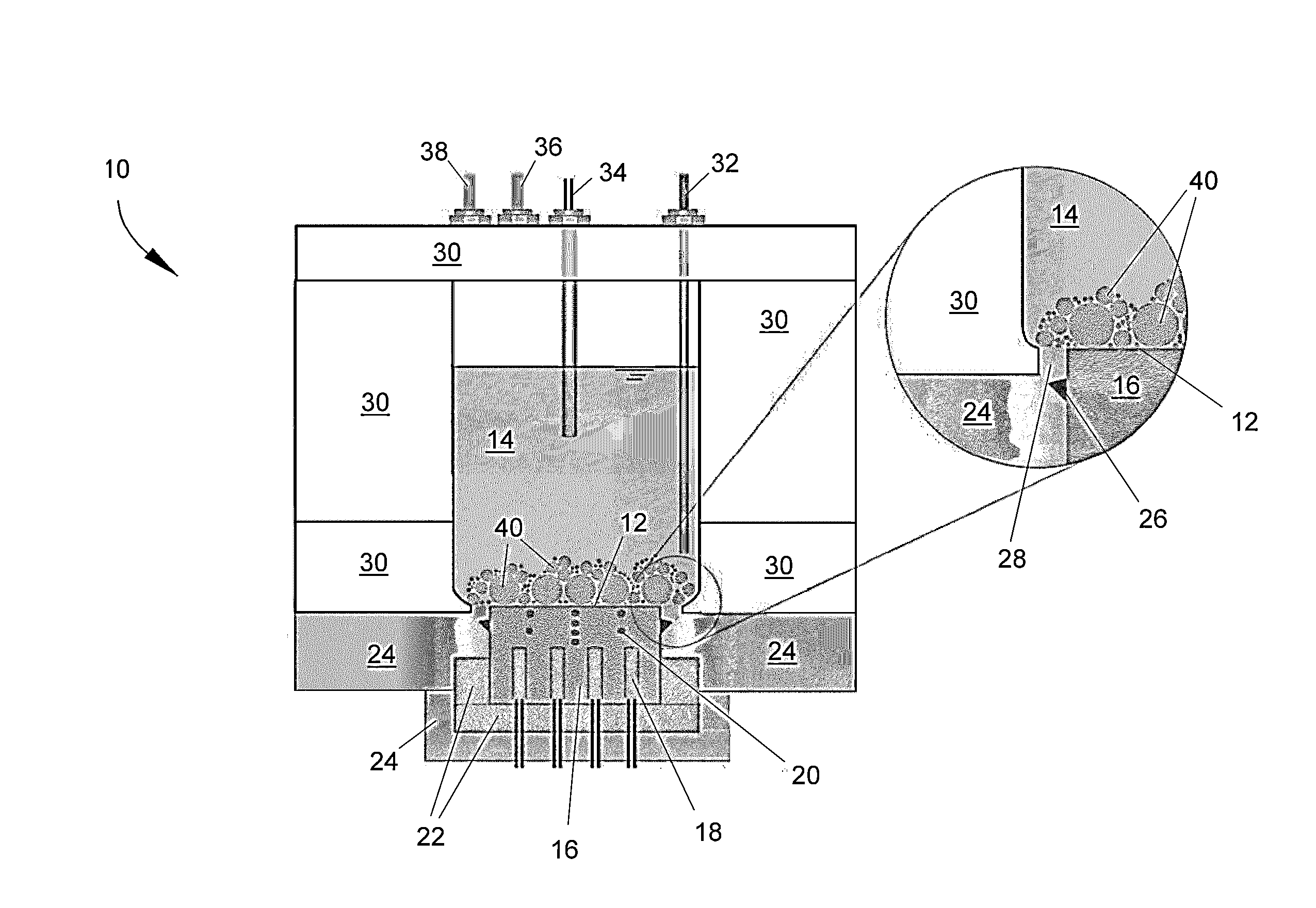
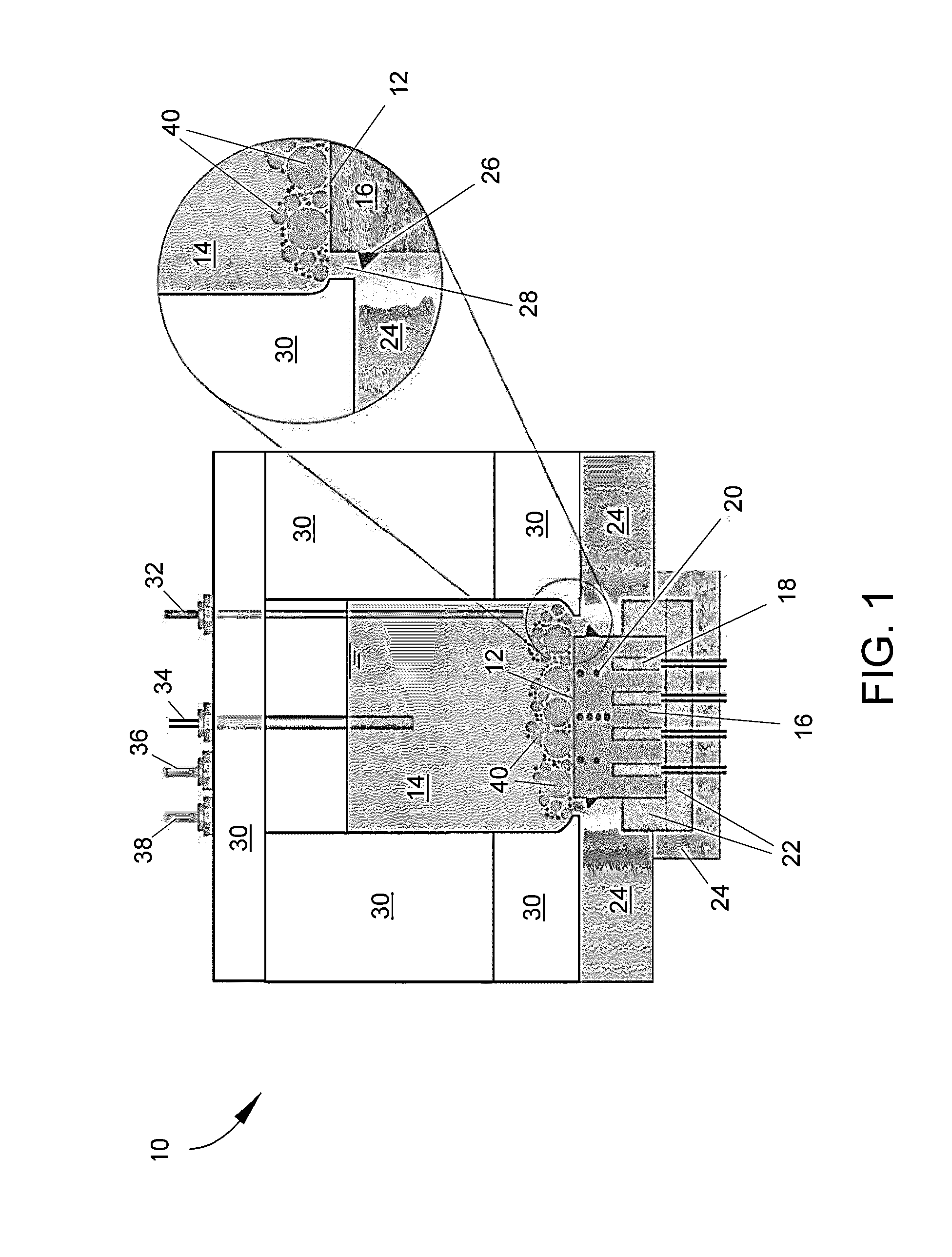
MEMS bubble generator
ActiveUS20060250453A1High material strengthHigh densityInking apparatusOther printing apparatusVapor bubbleSuperalloy
A MEMS vapor bubble generator with a chamber for holding liquid and a heater positioned in the chamber for heating the liquid above its bubble nucleation point to form a vapour bubble; wherein, the heater is formed from a superalloy.
Owner:SILVERBROOK RES PTY LTD
Low density edible animal chews and methods of making same
InactiveUS20160143320A1Low densitySmoother exterior surfaceBaking mixturesAnimal feeding stuffDental ProductLow density
Edible chews for pets have a low density (e.g. about 1.0 Kg / L or less) and a smooth exterior surface. One method by which the low density and the smooth exterior surface can be achieved uses a modified extrusion die to increase shear and restrict surface bubbles. Another method by which the low density and the smooth exterior surface can be achieved uses an extruder screw with a modified profile that holds a dough longer therein to create a whipping effect resulting in more bubble nucleation sites and hence a more uniform cellular matrix. The puffed (expanded) product was experimentally tested and provided better dental cleaning scores than a current unexpanded similarly formulated commercial dental product.
Owner:SOC DES PROD NESTLE SA
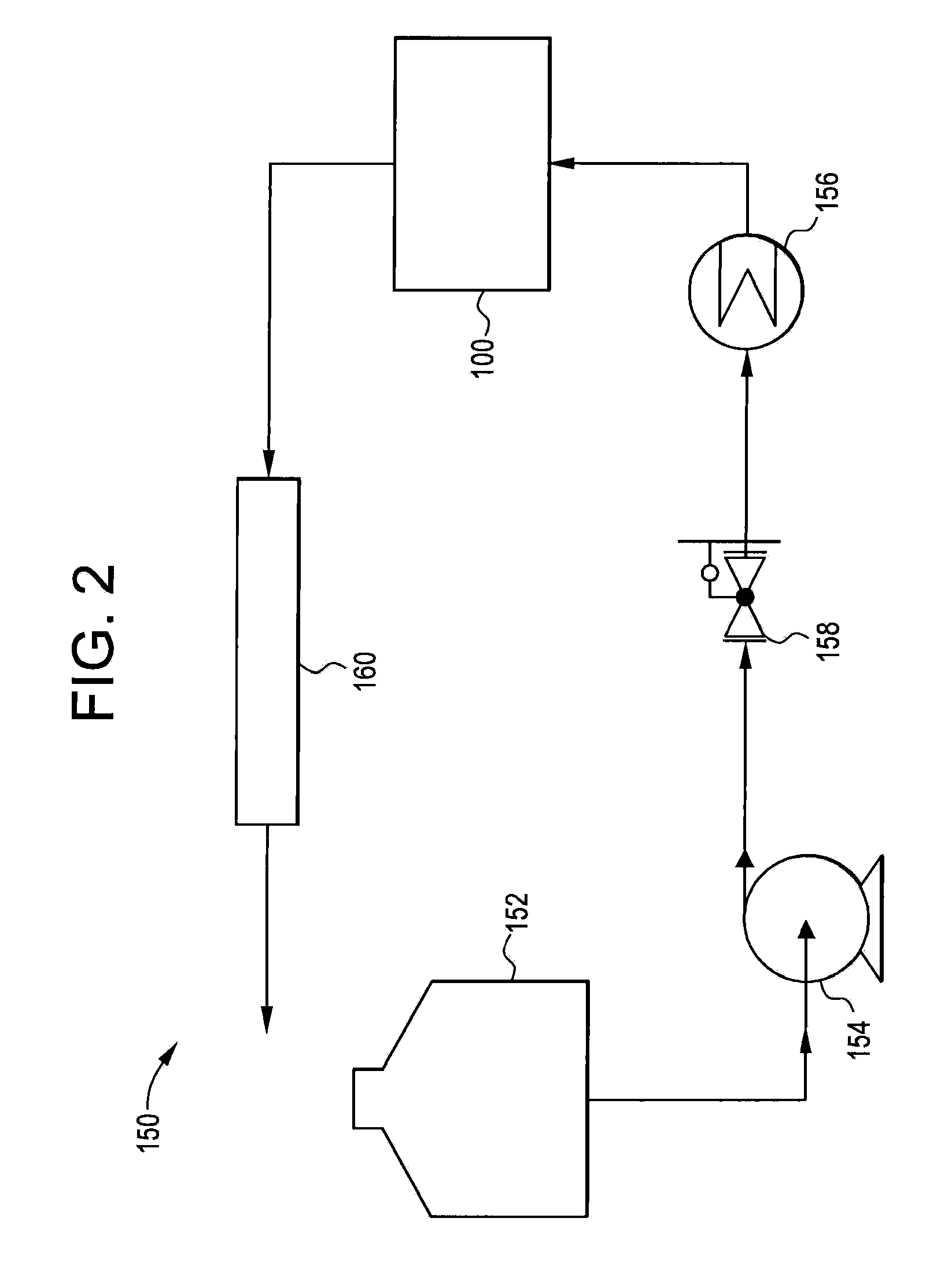
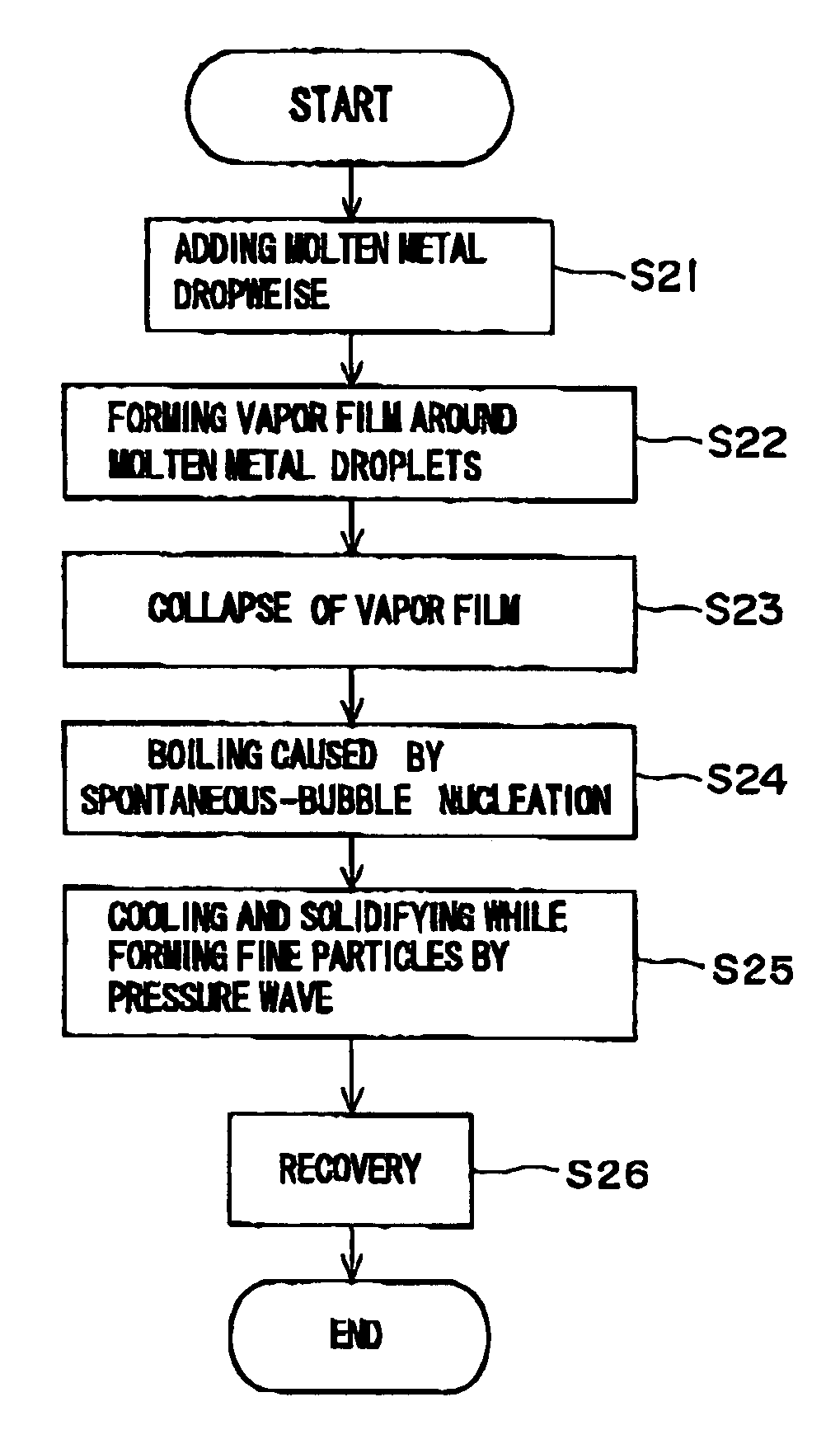
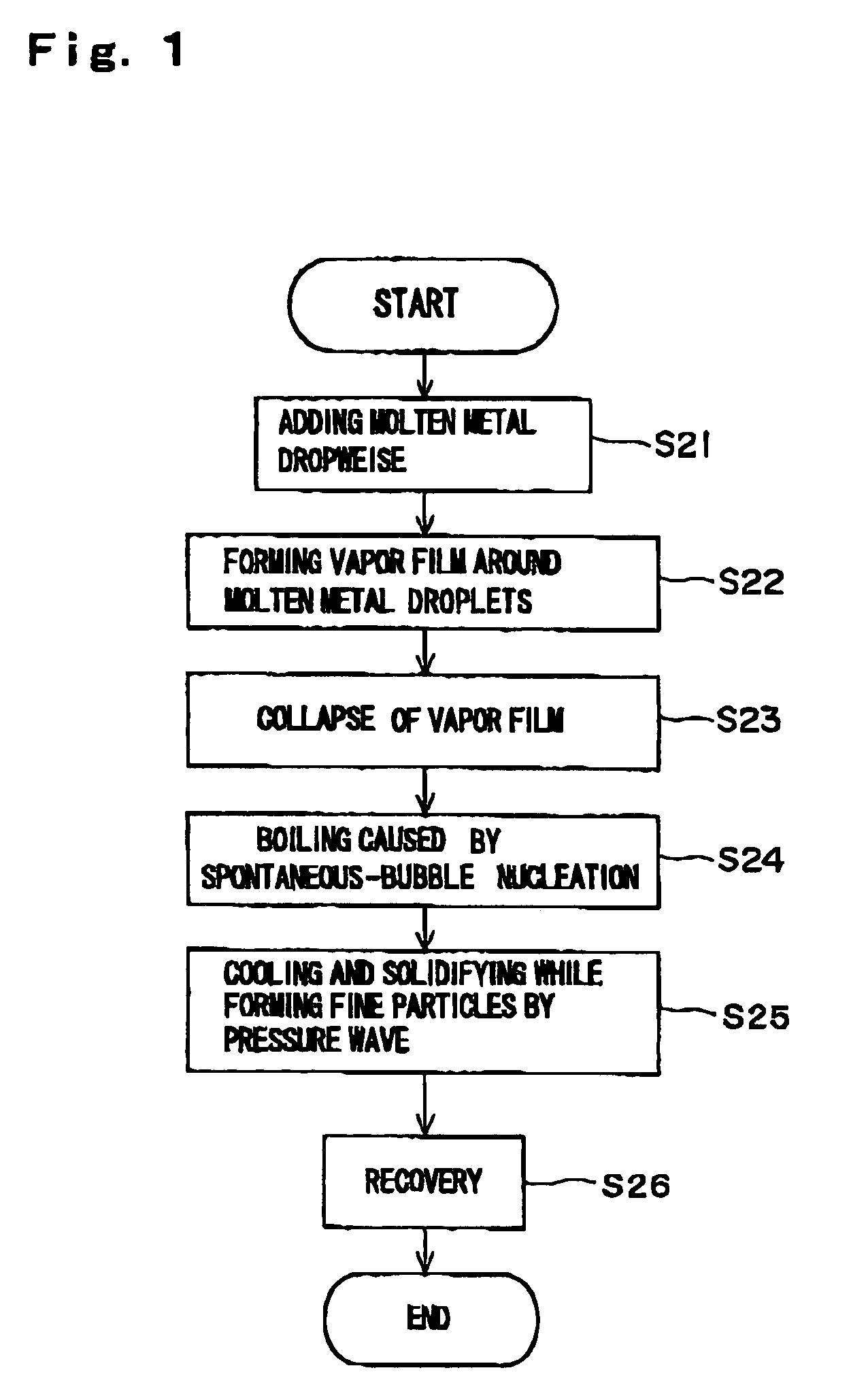
Method and apparatus for producing fine particles, and fine particles
InactiveUS6923842B2Effectively fragmentedIncrease surface areaAuxillary shaping apparatusMicrometerBubble nucleation
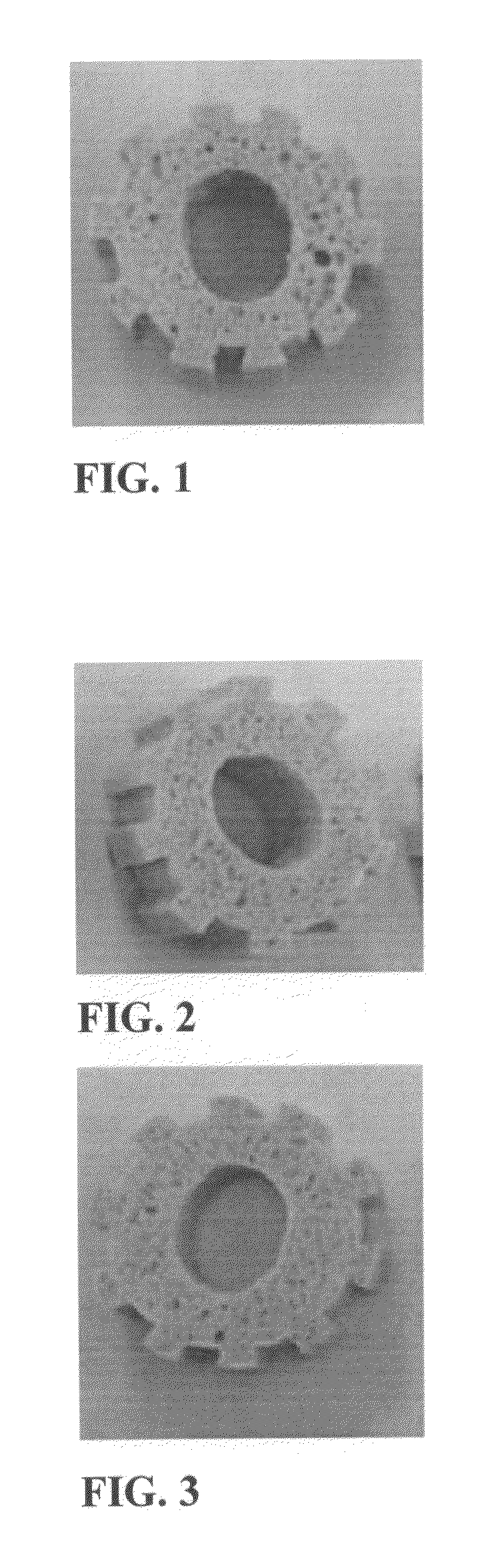
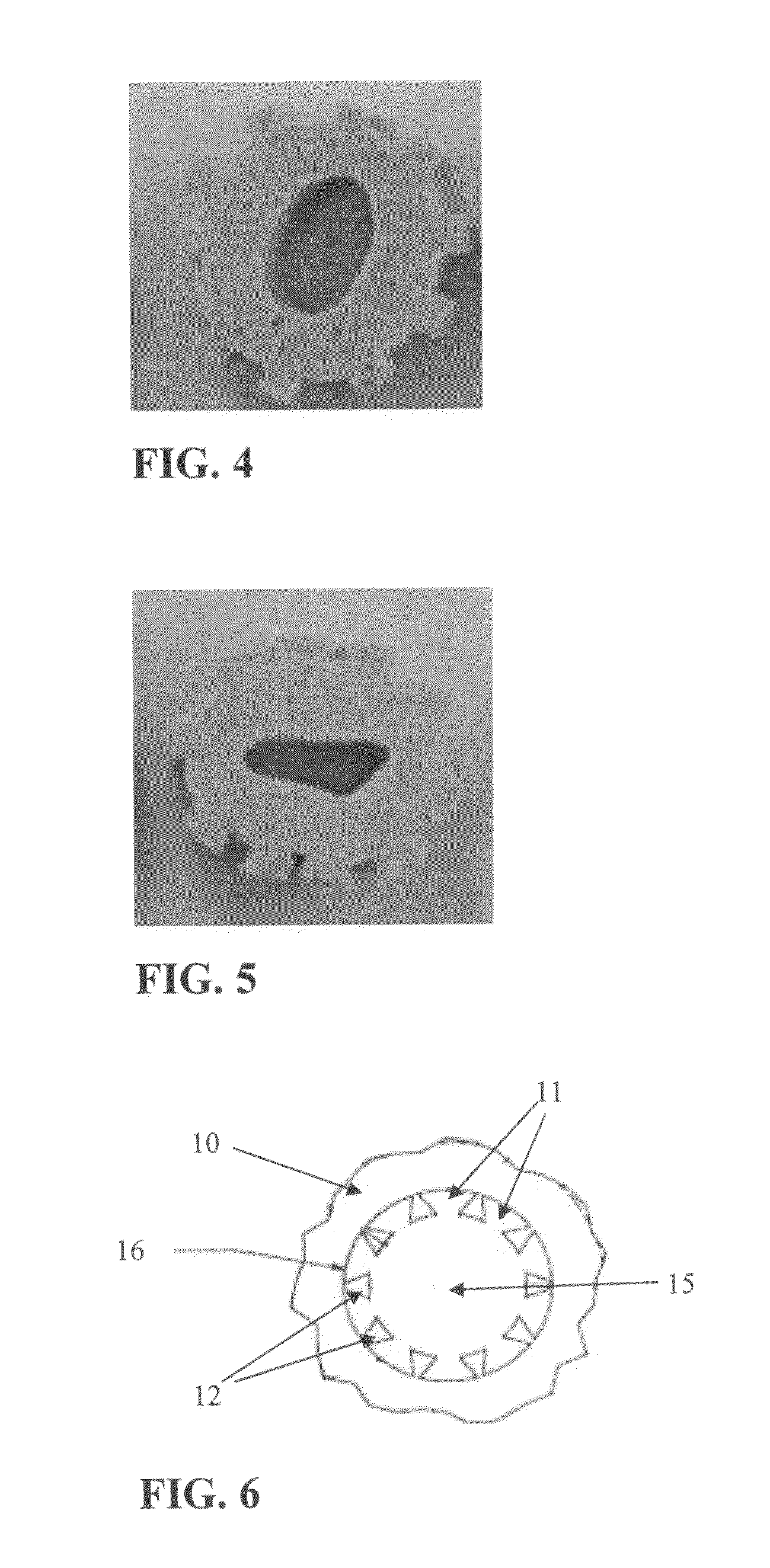
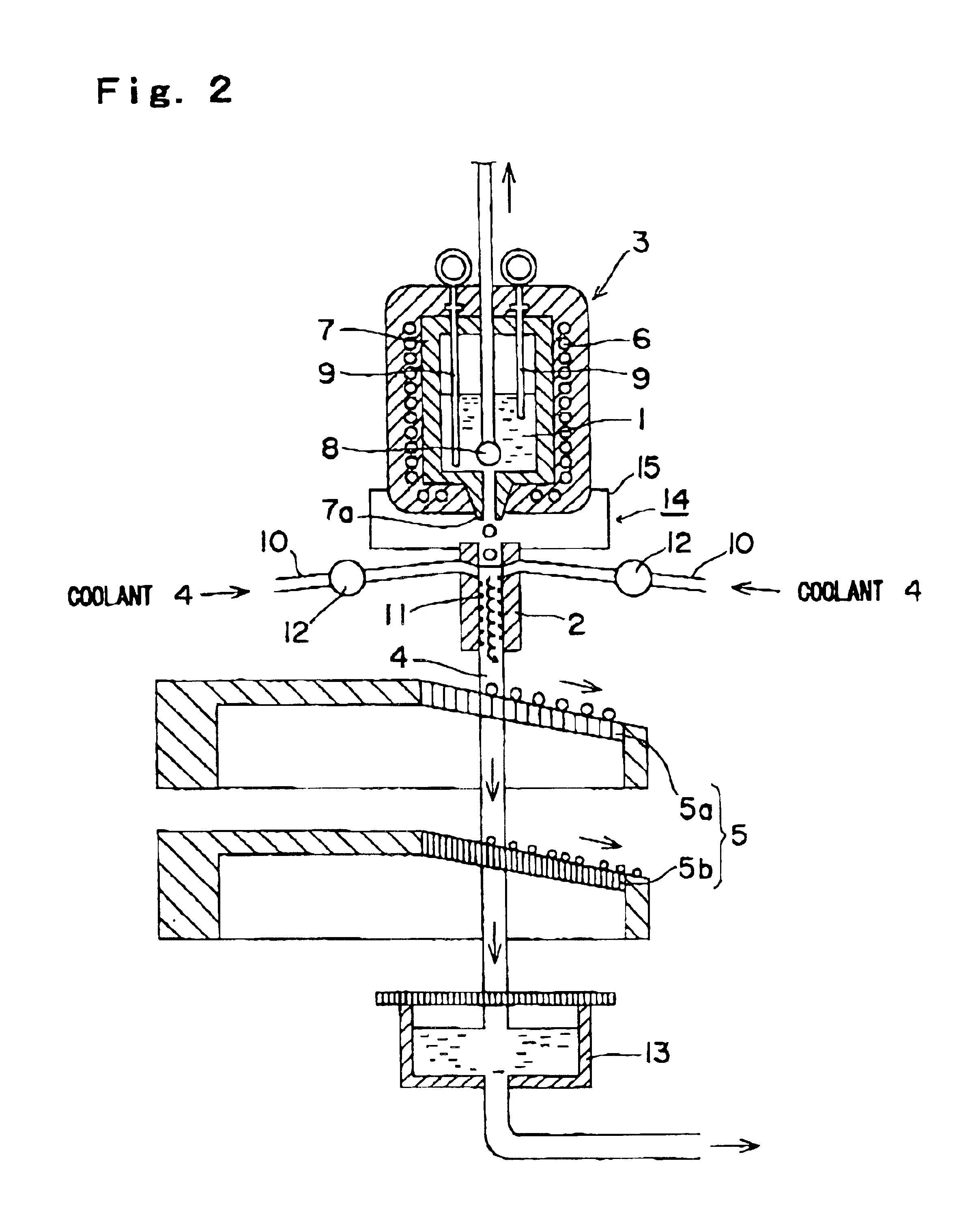
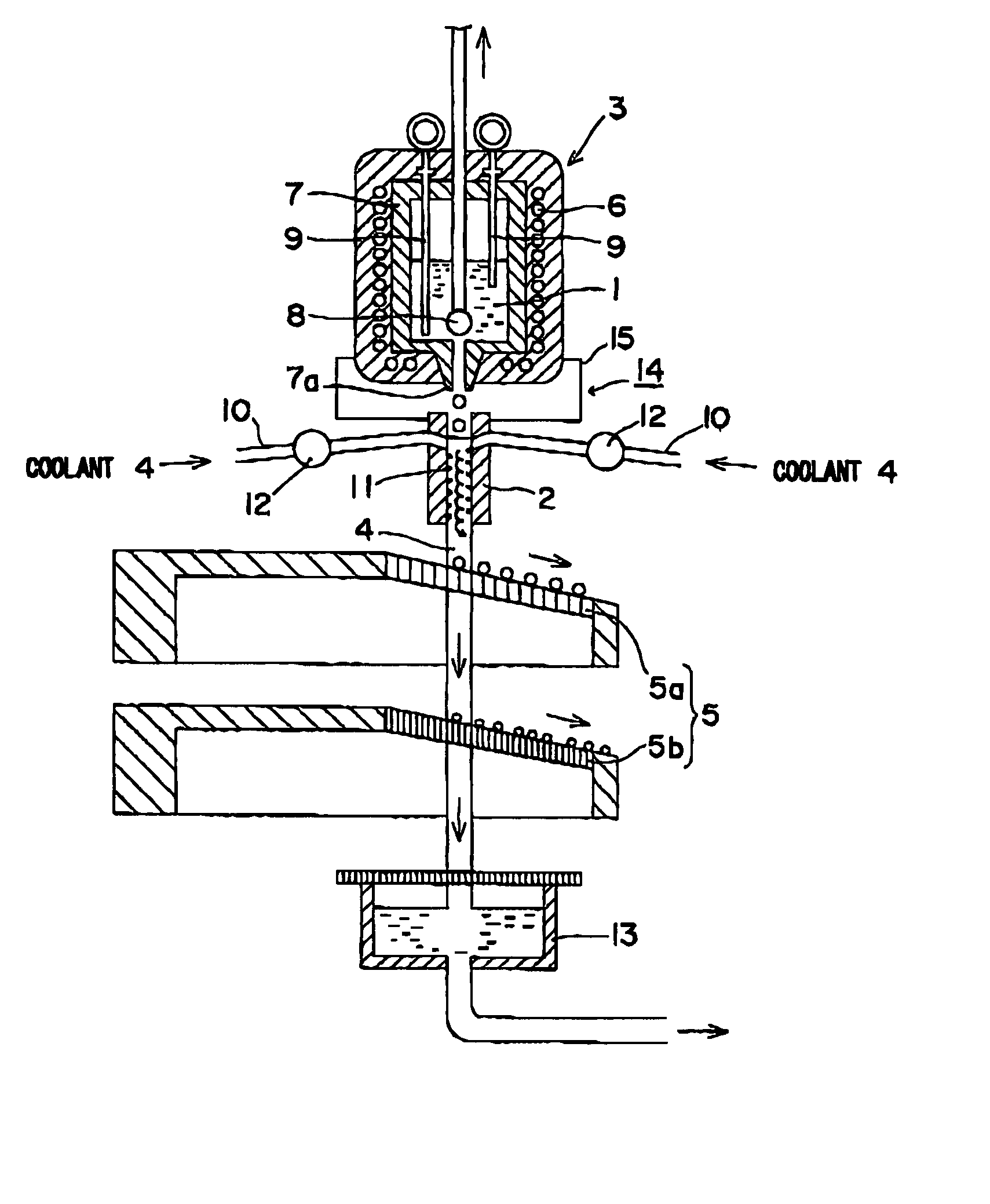
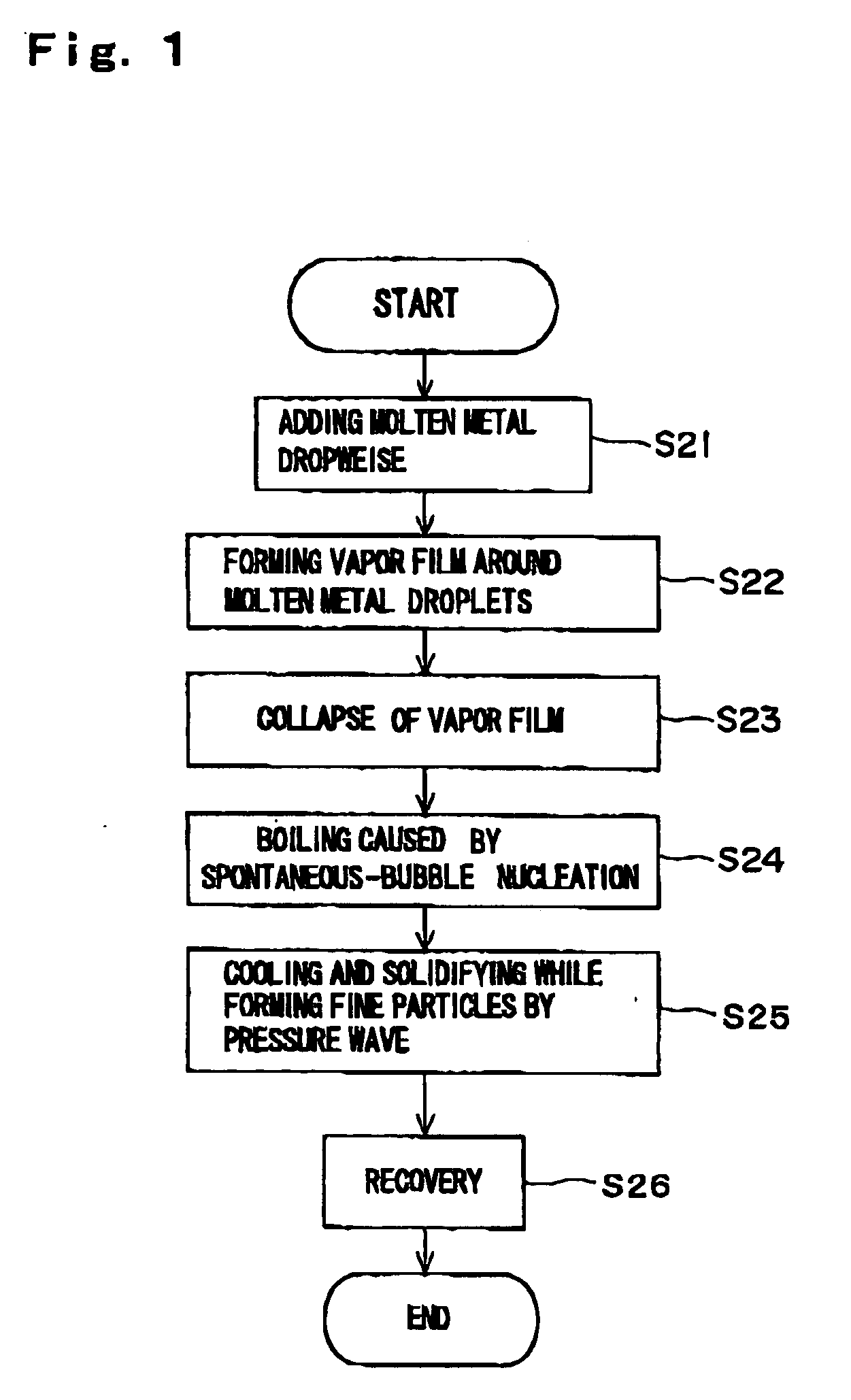
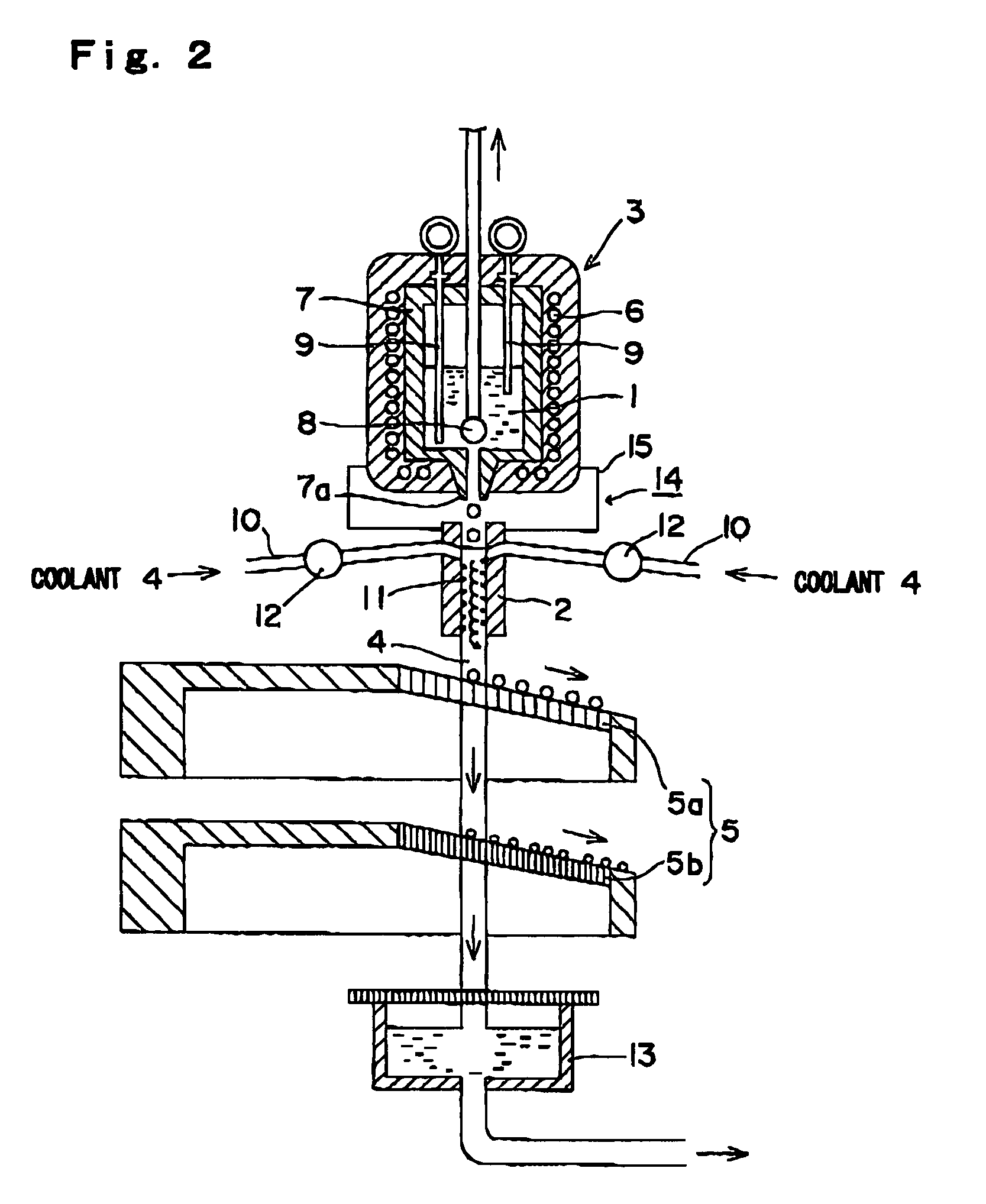
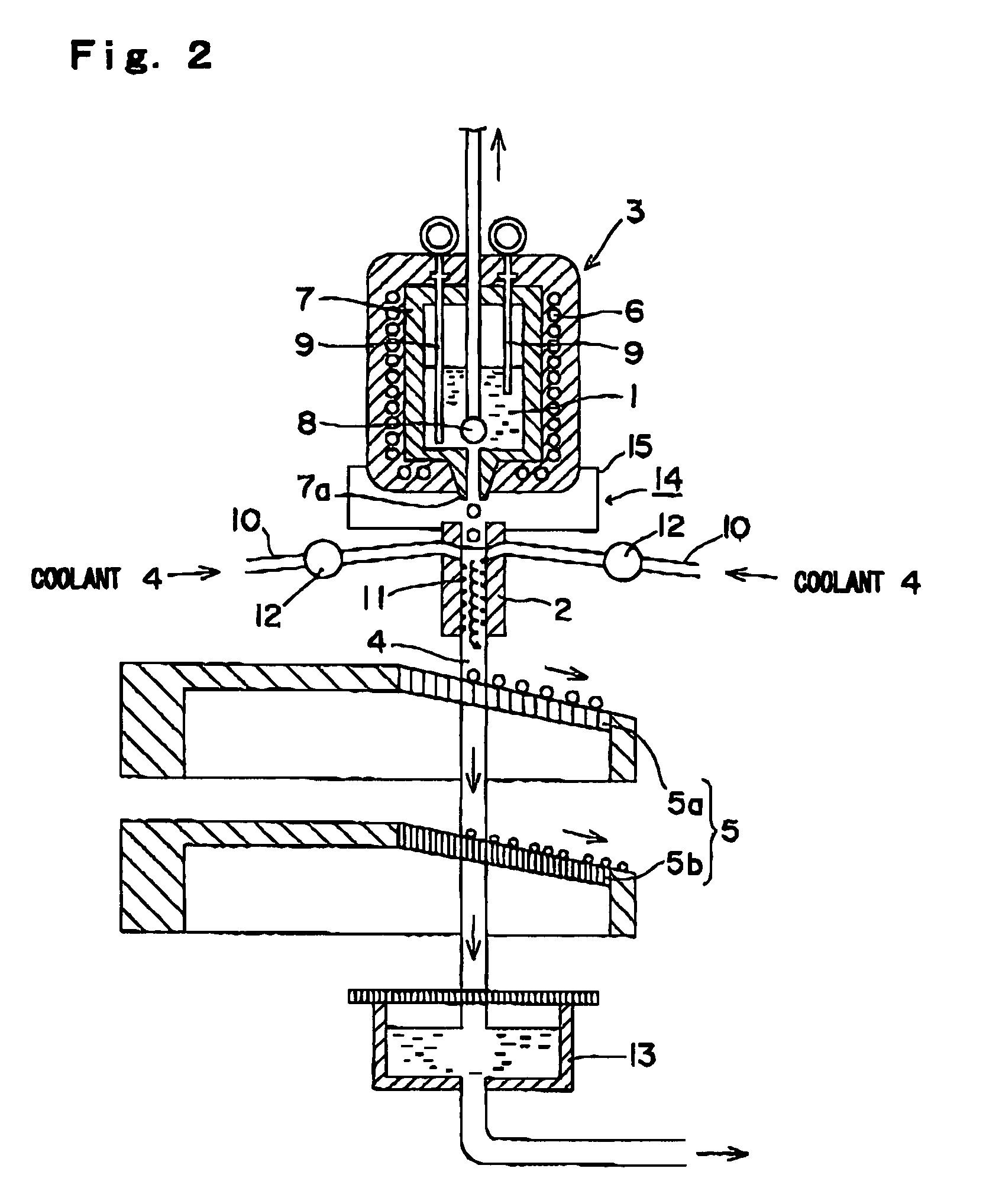
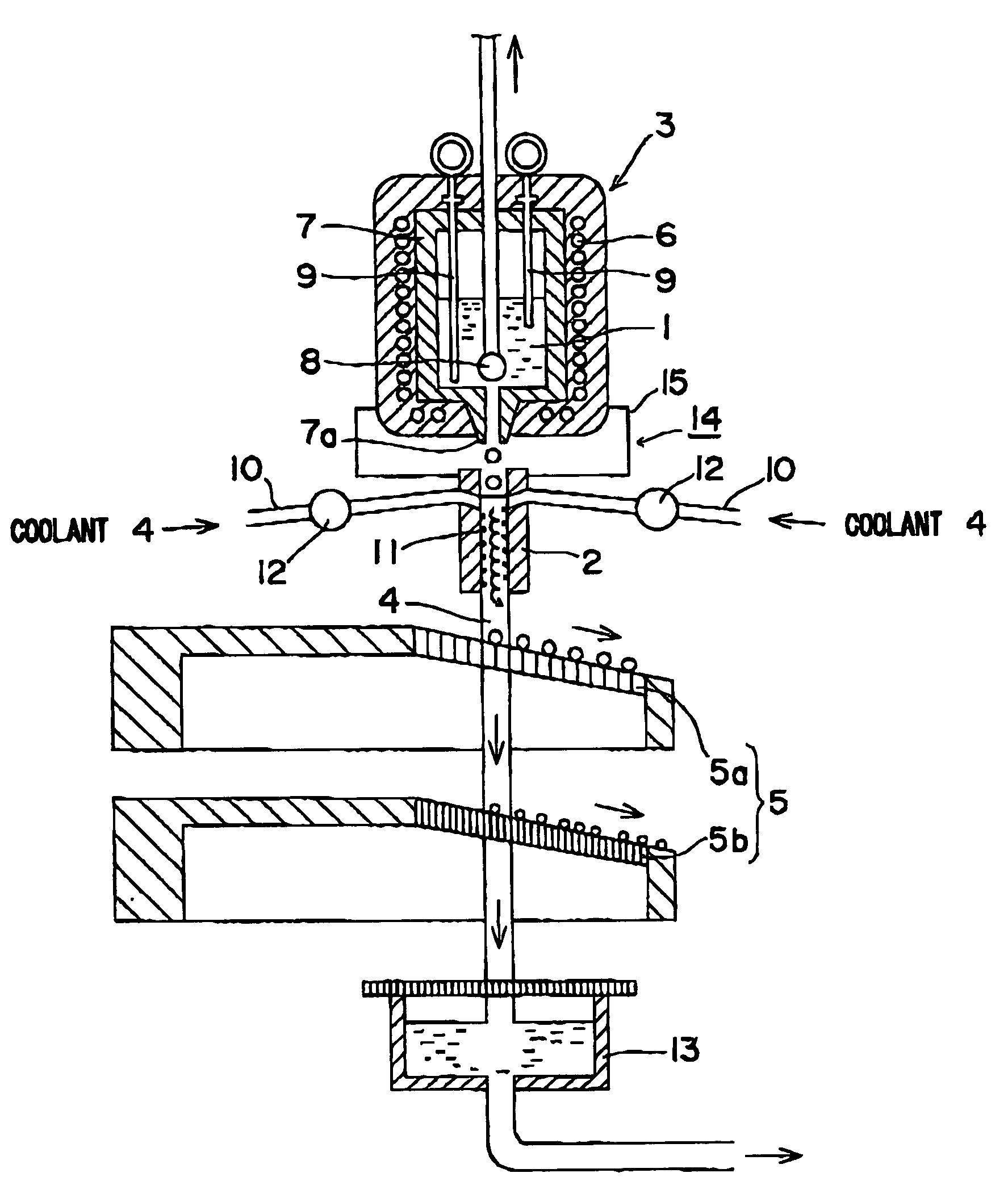
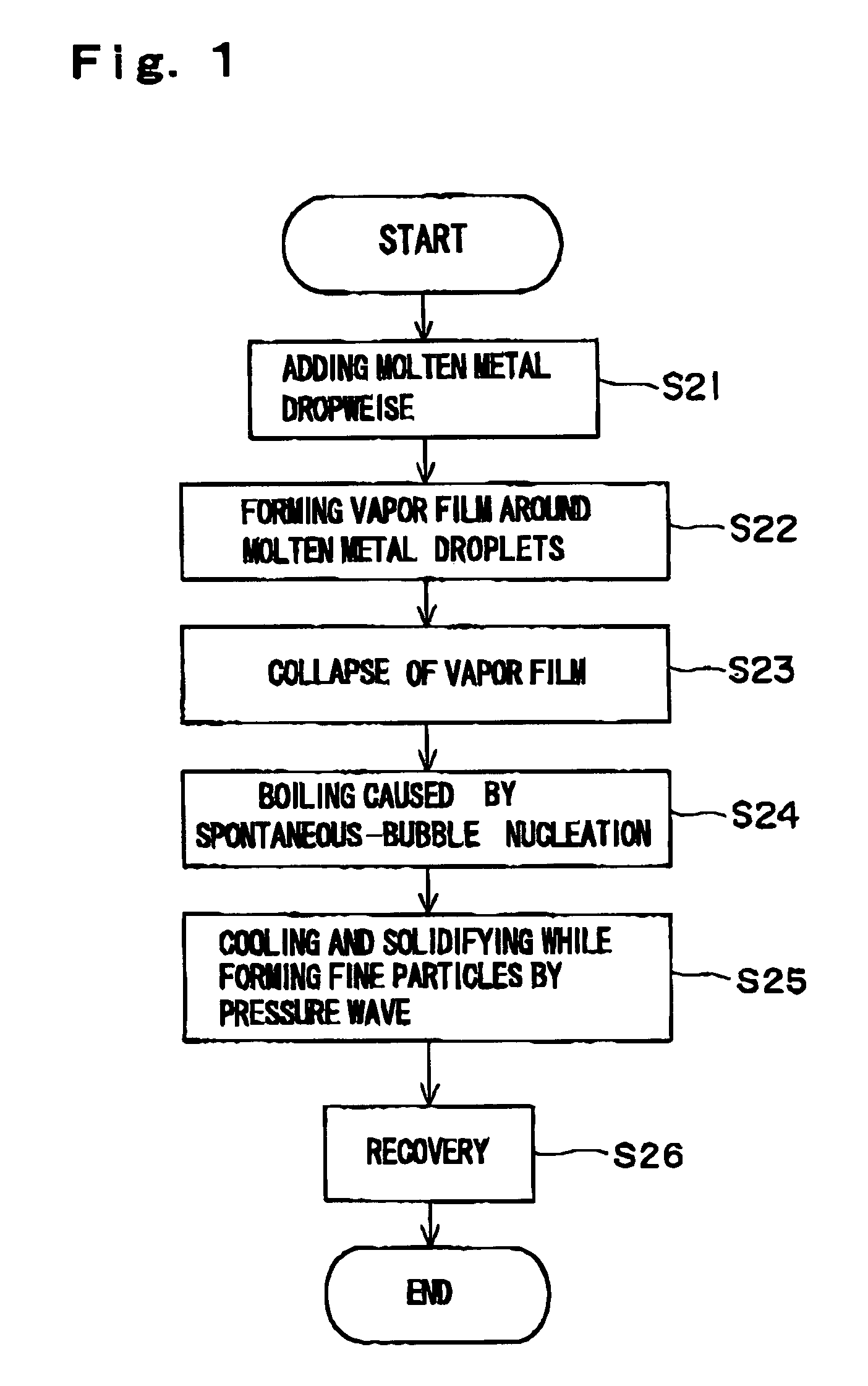
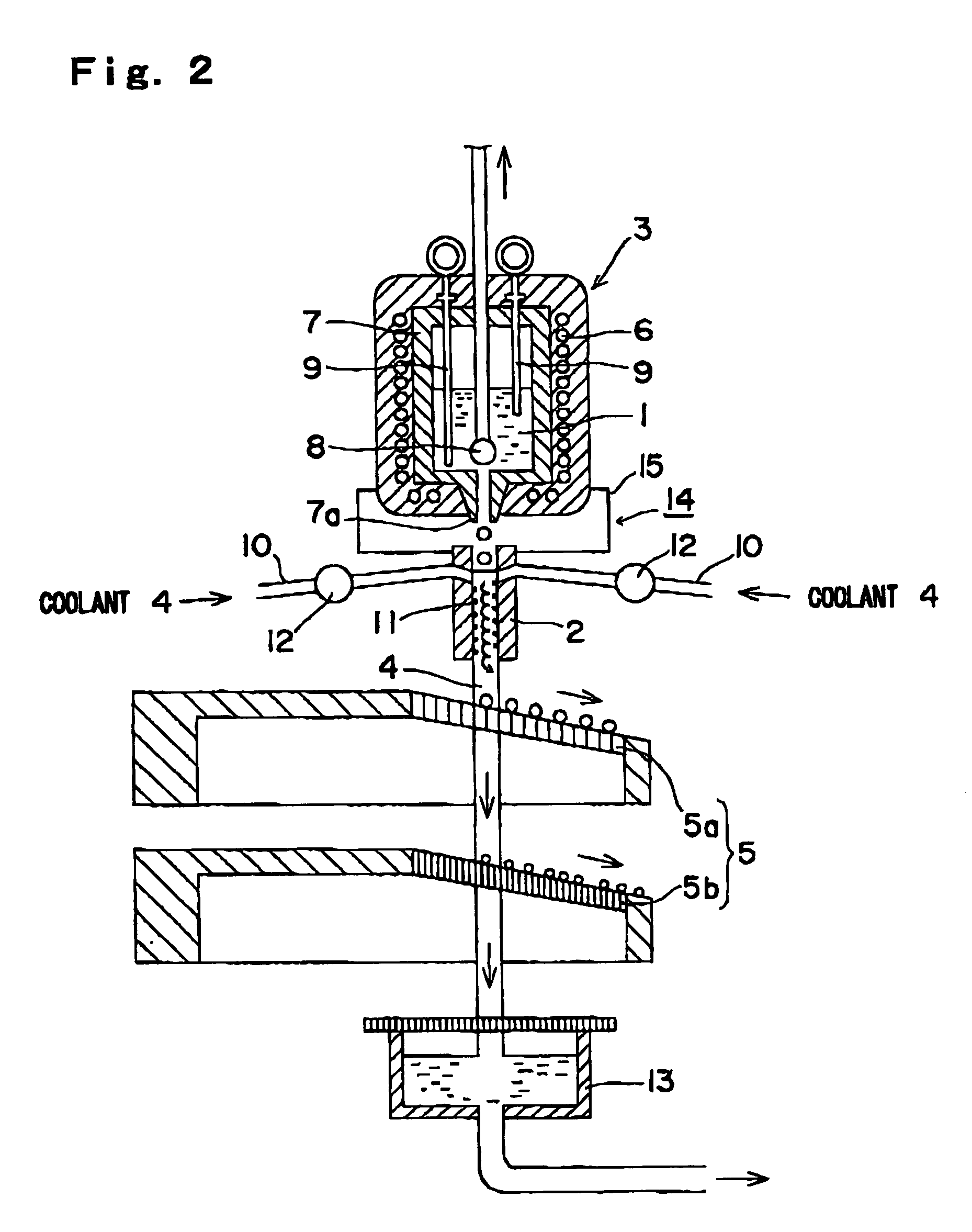
A method and apparatus are invented for producing fine particles, which can readily realize the formation of fine particles of sub-μm order to 100 micron order as well as fine particles of several micrometer which cannot be realized by a conventional method and apparatus available for producing fine particles, and a large quantity of fine particles having the desired particle diameter can be obtained with a high yield. A molten material (1), which is a molten raw material to be fragmented into fine particles, is supplied into a liquid coolant (4), boiling due to spontaneous-bubble nucleation is generated, and the molten material (1) is cooled and solidified while forming fine particles thereof by utilizing a pressure wave generated by this boiling. This production method is realized by apparatus comprising: material supplying means (3); a cooling section (2) which brings in the coolant (4) whose quantity is small and sufficient for cooling and solidifying the supplied molten material (1), and cools and solidifies the molten material (1) while forming fine particles thereof by utilizing a pressure wave generated by boiling due to spontaneous-bubble nucleation; and recovery means (5) for recovering fine particles from the coolant (4).
Owner:MITSUI MINING & SMELTING CO LTD
Boiling enhanced heat exchange structure of chips and fabrication method thereof
InactiveCN101447466AReduce thermal shockExtend your lifeSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesSputteringBubble nucleation
The invention relates to a high heat flux density boiling enhanced heat exchange technology, in particular to amicroelectronic chip high efficiency cooling technology with a high heat flux density, particularly the boiling enhanced heat exchange structure of chips and the fabrication method thereof, which is characterized in that a plurality of lug bosses with a column structure are corroded on the surface of a chip; a SiO2 layer is splashed on the surface of the chip with the lug bosses; and the SiO2 layer is corroded to form a porous structure. The boiling enhanced heat exchange structure of chips can provide sufficient bubble nucleation number and a larger effective heat exchange area under the circumstance of a lower wall surface superheat degree, thereby solving the problem that the thermal shock of the chip exists from incipient boiling to nucleate boiling, and meanwhile, improving critical heat flux density remarkably to ensure the effective heat exchange of a high heat flux density electronic device.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Method for preparing sandwich material PET foam for wind power generation blade
The invention relates to a method for preparing sandwich material PET foam for a wind power generation blade. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: feeding PET sheets into supercritical fluid under a high-pressure preheating environment, keeping the PET sheets for certain time, and then thermally treating the PET sheets by a quick pressure reduction method so as to reduce the solubility of gas in the polymer and initiate bubble nucleation and increment. Compared with the prior art, when the PET foam is prepared by using a supercritical CO2 fluid method, the CO2 has the characteristics of lower critical temperature, realization of supercritical operation nearby room temperature, low critical pressure, no-toxicity, combustion resistance, high-purity industrial product and the like. By using the method, the PET foam is used for replacing PVC foam, and the Balsa wood has low price and good effect.
Owner:SHANGHAI YUEKE COMPOSITE
Heavy oil reservoir dissolved gas drive numerical simulation method with bubble oil phenomenon
ActiveCN106156439AEnhanced overall recoveryHigh simulationClimate change adaptationSpecial data processing applicationsGas phaseMathematical model
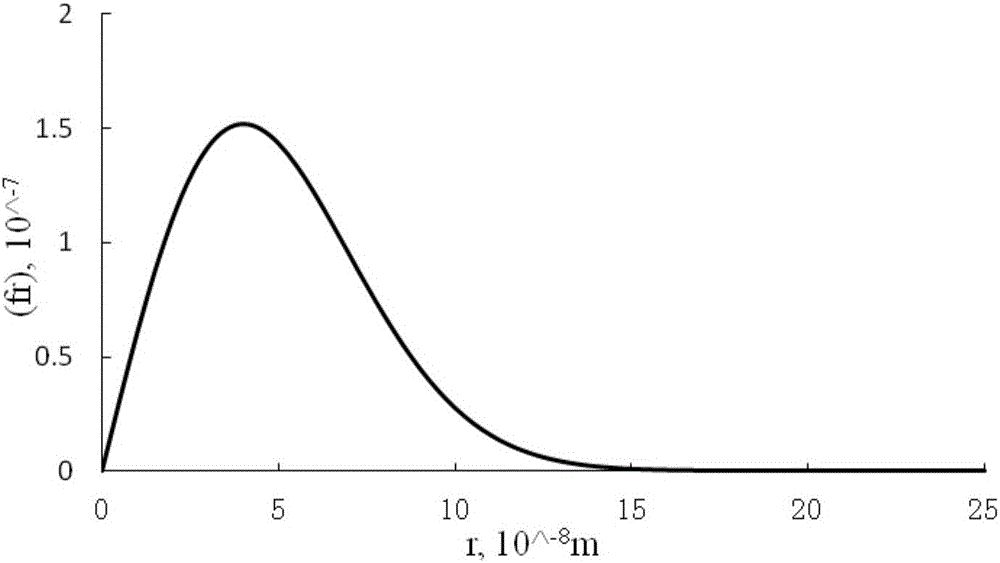
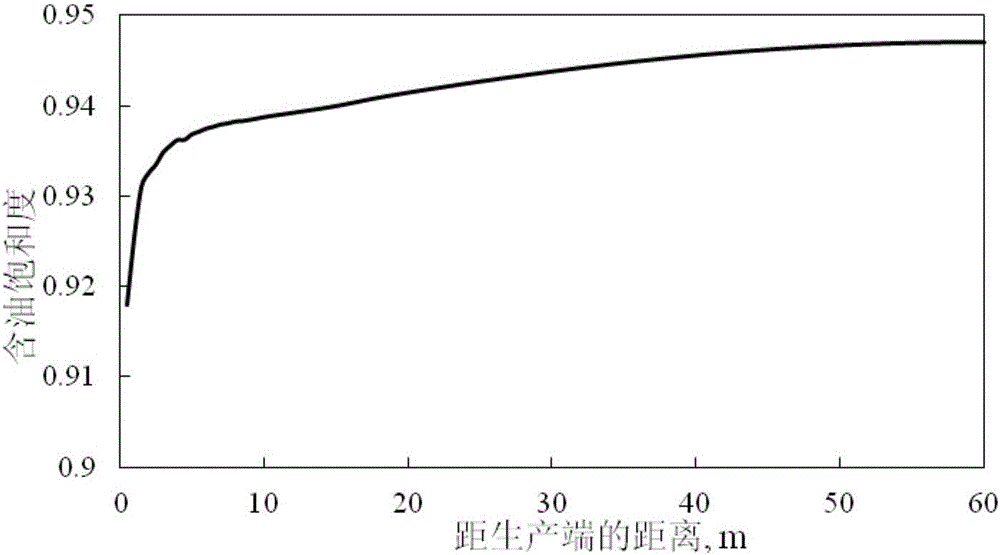
The invention provides a heavy oil reservoir dissolved gas drive numerical simulation method with a bubble oil phenomenon. The method comprises the following steps: in a microscopic view, establishing a mathematical model for describing a bubble nucleation and growth principle; on the basis, deducing a diffusion speed equation of gas from dissolved gas to bubbles; establishing a three-dimensional two-phase multi-component dissolved gas drive mathematical model; combining a finite difference method and an implicit pressure-explicit saturation (IMPES) method to solve; determining the saturation degree, the dissolved gas-oil ratio, the oil yield and the gas yield of oil reservoir pressure, an oil phase and a gas phase; and then, taking heavy oil reservoir dissolved gas drive experiments with the bubble oil phenomenon as evidences and determining uncertain parameters of the model through an experiment fitting method; and finally, revealing a development effect parameter influence principle through the fitted mode, understanding the bubble oil phenomenon, predicating the productivity of an oil field and formulating a development strategy to improve a heavy oil reservoir recovery ratio with the bubble oil phenomenon.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
Light-weight, high-toughness and low-water-absorption-ratio ultra high molecular weight polyethylene/nylon 6 micro-foaming composite material and preparation method thereof
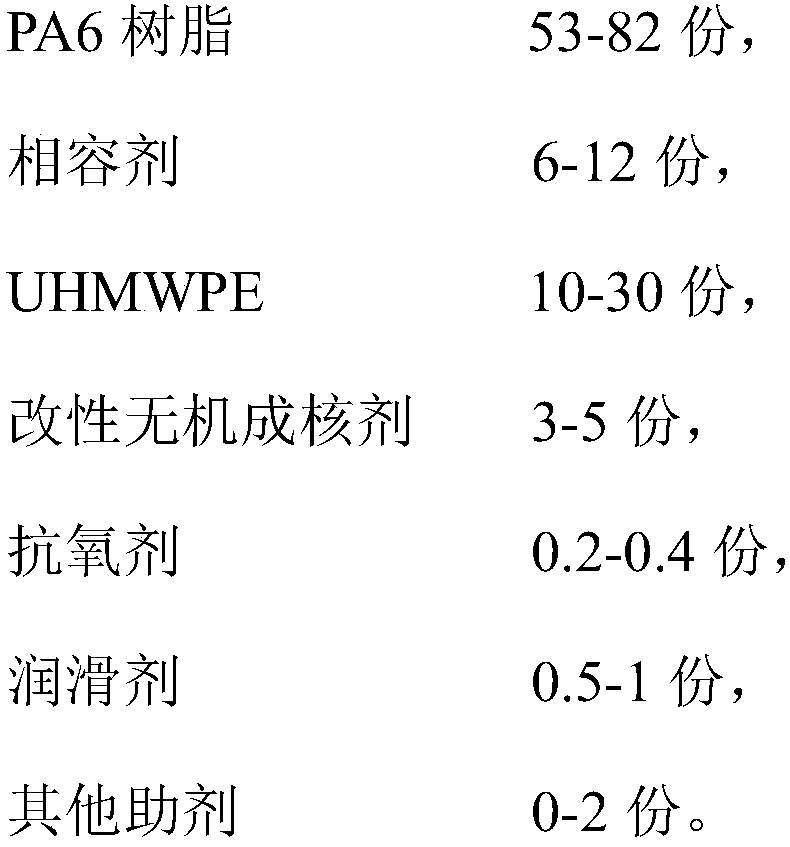
The invention discloses a light-weight, high-toughness and low-water-absorption-ratio ultra high molecular weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) / nylon 6 micro-foaming composite material and a preparation method thereof. The composite material is prepared from 97 to 99 weight percent of a polyamide composite material and 1 to 3 weight percent of a chemical foaming agent, wherein the polyamide composite material is prepared from the following components in parts by weight: 53 to 82 parts of PA6 (Polyamide 6), 6 to 12 parts of a compatilizer, 10 to 30 parts of UHMWPE, 3 to 5 parts of a modified inorganicnucleating agent, 0.2 to 0.4 part of an antioxidant, 0.5 to 1 part of a lubricant and 0 to 2 parts of other auxiliary agents. According to the light-weight, high-toughness and low-water-absorption-ratio ultra high molecular weight polyethylene / nylon 6 micro-foaming composite material, HDPE (High-density Polyethylene)-g-GMA (Glycidyl Methacrylate) is used as an interface bulking agent so that the interface binding force between the UHMWPE and the PA6 is enhanced, the impact strength of the PA6 is improved and the water absorption ratio of the PA6 is reduced; meanwhile, three-phase chain sections are mutually entwisted so that the melt strength of the PA6 is improved; the modified inorganic nucleating agent is subjected to chemical grafting modification through KH550 and GMA and the heterogeneous nucleation effect is remarkable; a dense bubble nucleation point is formed and the micro-foaming material with dense, fine and smooth bubble pores is obtained; the material has the characteristics of light weight, high impact strength, low water absorption ratio, high wear resistance and the like; foaming is realized through direct injection molding and a technology is simple; the material is widely applied to a lightweight technology of automobiles, household appliances, electronics and electrical appliances and the like.
Owner:ORINKO NEW MATERIAL CO LTD
Controllable microscopic bubble nucleation in fluid polymer material production method and its apparatus
InactiveUS7264757B2Unevenness easilyEqually distributedDough homogenizationFrozen sweetsEngineeringHigh pressure
Owner:EVERFOCUS WORLDWIDE
Printhead heaters with small surface area
ActiveUS20050179741A1Small surface areaSignificant impact energy requiredInking apparatusEngineeringBubble nucleation
A thermal inkjet printhead with generally planar heater elements disposed in respective bubble forming chambers, whereby the area of each heater is less than 300 μm2. The heater area influences: 1. the energy required to heat the heater volume up to the fluid superheat limit; 2. the energy required to heat the protective coatings covering the heater to the superheat limit; 3. the heat that diffuses into the underlayer prior to bubble nucleation; and, 4. the heat that diffuses into the ink prior to bubble nucleation. Reducing the surface area of the heater reduces all of these terms and has a significant impact on the energy required to form a bubble and eject ink.
Owner:MEMJET TECH LTD +1
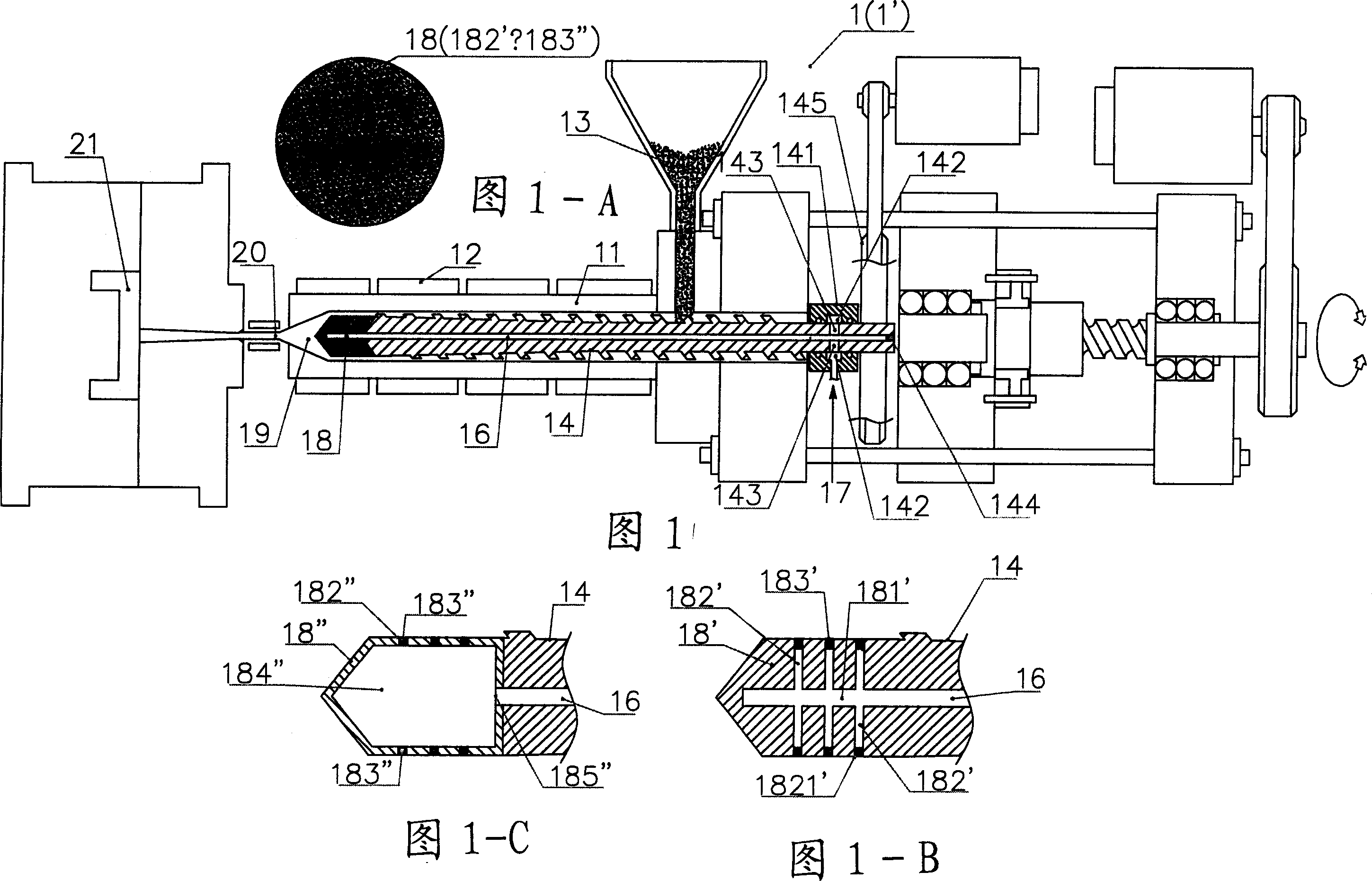
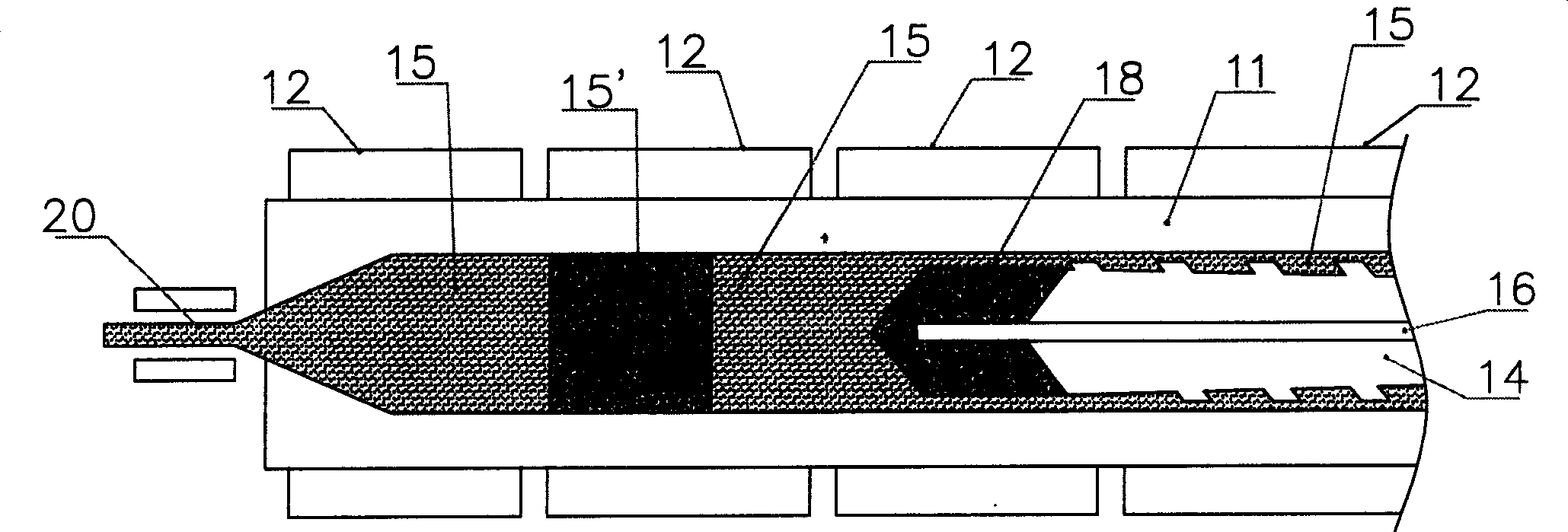
Method for controlling microscopic bubble nucleation in fluid polymer material production and its apparatus
InactiveCN1864981AEvenly dispersedClear connectionTransportation and packagingRotary stirring mixersMicrobubblesMolding machine
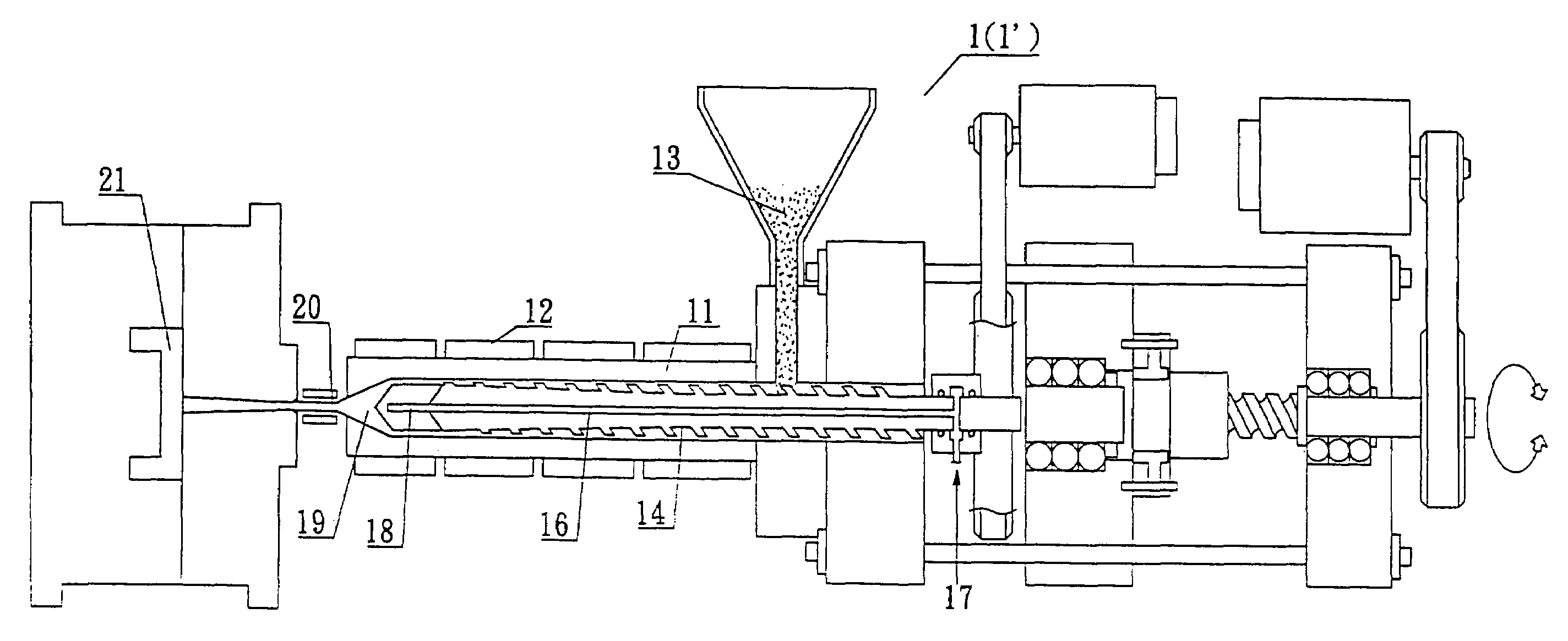
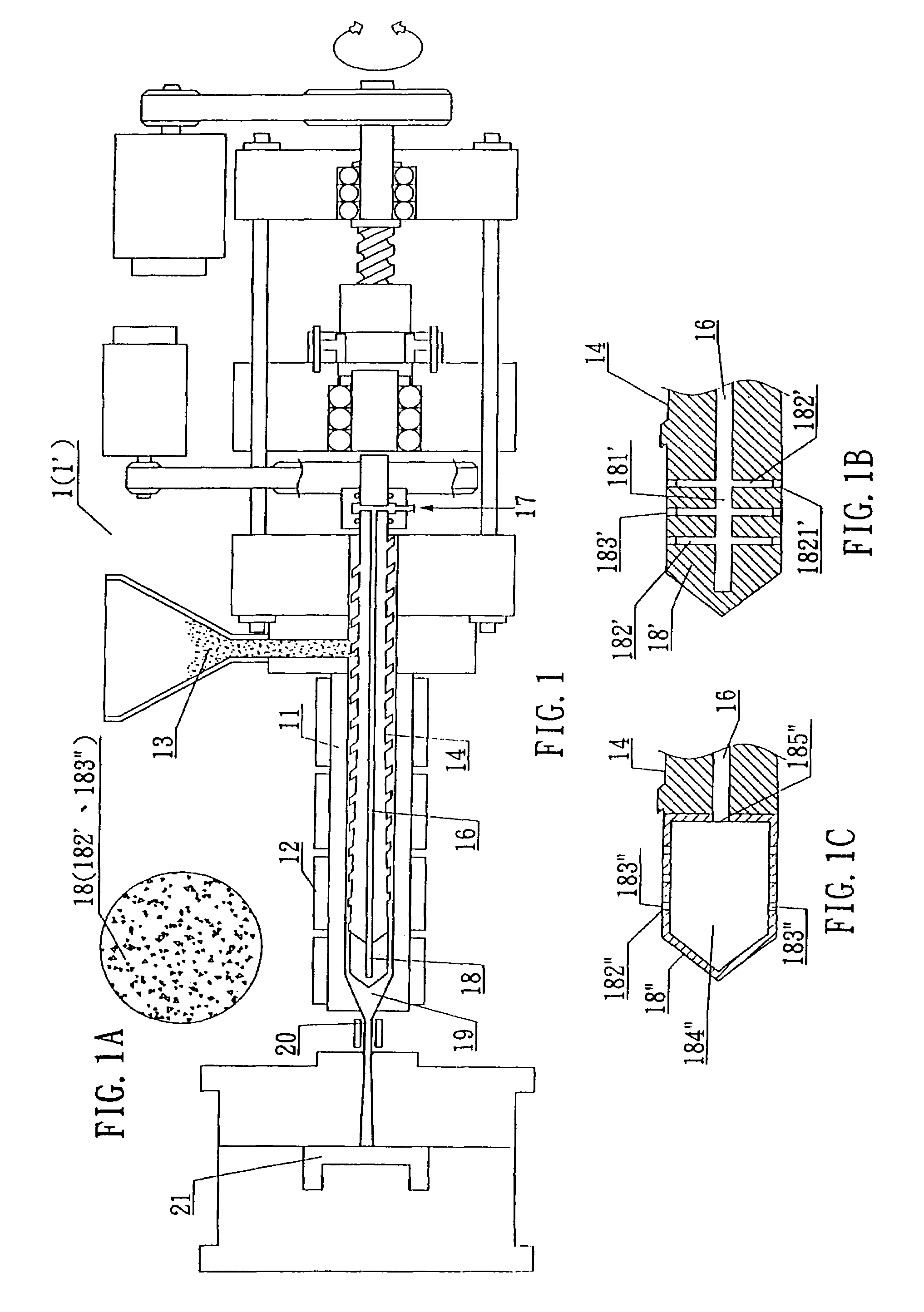
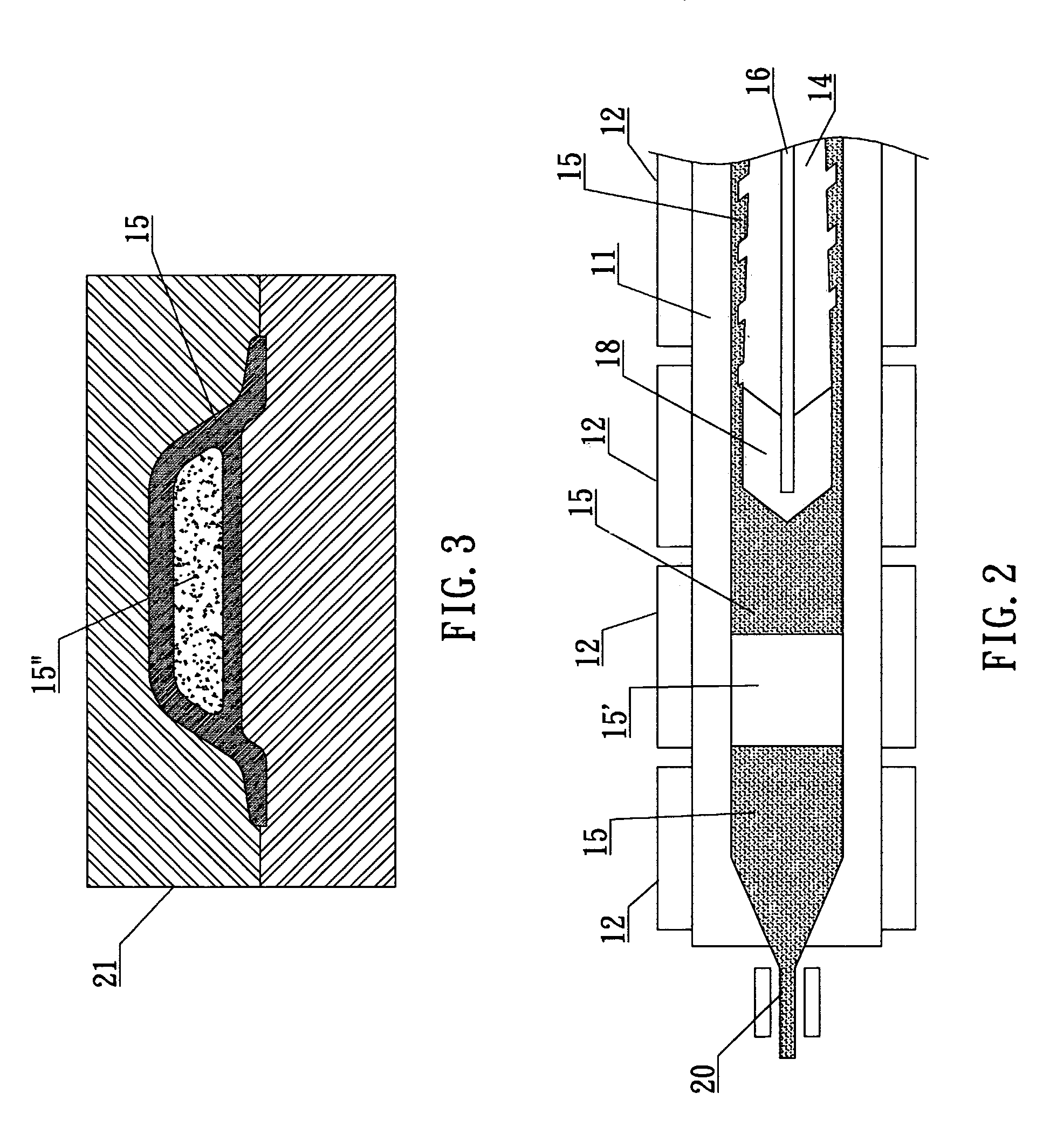
A method for controlling microscopic bubble nucleation in fluid polymer material production and its apparatus that utilizes a gas pipe (16) disposed in the conveyance screw shaft (14) of a conventional injection or extraction forming mechanism and, furthermore, a microbubble generating component (18) (such as a microscopic perforation vented metal head or a microscopic perforation ceramic head, etc.) installed at the front extremity of the conveyance screw shaft (14). At the rear extremity of the gas pipe (16), a pressurization pump or a high pressure gas storage tank is admitted from an air intake opening, enabling the gas to be indirectly heated by an electric heater (12) on the materials pipe (11). The high temperature gas is thereafter outputted from the microscopic perforations of the microbubble generating component (18) such that high temperature microscopic bubbles are directly admitted into the section of liquid polymer material which is then uniformly amalgamated by the conveyance screw shaft (14) and then deposited into a forming die (21). As a result, high pressure gas conveyance or termination is controllable; control is afforded as to whether each section of liquid polymer material is microbubble nucleated and amalgamated. The present invention thereby provides a microbubble nucleation production method in which the non-bubble nucleated is at the surface and the bubble nucleated is at the interior section when the liquid polymer material is poured into a forming die (21).
Owner:EVERFOCUS WORLDWIDE
Cavitation enhanced liquid atomization
A cavitation enhanced atomizing process comprises forming a flowing solution of the liquid to be atomized and a lower boiling cavitating liquid. This flowing solution is then contacted with a pressure reducing means, at a temperature below the bubble point of the cavitating liquid in the solution, to produce cavitation bubbles. These bubbles comprise cavitation liquid vapor and the bubble nucleation produces a two-phase fluid of the bubbles and liquid solution. The two-phase fluid is passed downstream into and through an atomizing means, such as an orifice, and into a lower pressure atomizing zone, in which the bubbles vaporize to form a spray of liquid droplets. The nucleated bubbles also grow in size as the so-formed two-phase fluid passes downstream to and through the atomizing means.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
Process for assisting in foaming of cross-linked polyolefin as well as ultrasonic treatment device for process
The invention discloses a process for assisting in foaming of cross-linked polyolefin as well as an ultrasonic treatment device for the process. The ultrasonic treatment device is configured in a common foaming furnace to ultrasonically treat a polyolefin foaming material which is just foamed but still in a molten state. Lots of small holes are formed in a polyolefin melt by high energy and strong cavitation effect of ultrasonic vibration, so that the free energy barrier for bubble nucleation is reduced, bubble formation is facilitated, the total quantity of bubbles is increased and the average diameter of bubbles is reduced. In addition, large bubbles can be broken into multiple small bubbles by strong ultrasonic vibration, and the small bubbles are re-surrounded by the polyolefin melt, so that the bubbles in the melt are more uniform, and the polyolefin material with densely and uniformly distributed air holes can be obtained.
Owner:SHANDONG TAISHAN JINRUN PLASTIC PRODS +1
Heat-dissipating component having stair-stepped coolant channels
ActiveUS7782616B1Improve cooling effectIncrease manufacturing costSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesCoolant flowSemiconductor chip
A heat-dissipating component including a heat-generating device such as a power semiconductor chip and a mounting structure is provided with coolant channels having a stair-stepped internal geometry that enhances cooling performance with both single-phase and two-phase cooling modes without unduly restricting coolant flow or significantly increasing manufacturing cost. The stair-stepped geometry enhances both single-phase and two-phase cooling modes by increasing the surface area of the channels, and further enhances the two-phase cooling mode by providing numerous high-quality bubble nucleation sites along the length of the channels. The stair-stepped channels are formed in the heat generating device and / or the mounting structure, and the stepped sidewalls may extend toward or away from the center of the channel.
Owner:DELPHI TECH IP LTD
Improved process for producing foamed aluminum by adopting ultrasonic melt-foaming method
InactiveCN104451230AImprove material performanceImprove mechanical propertiesMechanical crushingFoaming agent
The invention discloses an improved process for producing foamed aluminum by adopting an ultrasonic melt-foaming method. The process comprises the following steps: based on an ultrasonic cavitation effect and a mechanical crushing effect, adding a TiH2 foaming agent into an aluminum alloy melt, stirring, and simultaneously emitting ultrasonic waves into the aluminum alloy melt; fully dispersing TiH2 foaming agent particles by virtue of the ultrasonic waves, so that more bubble nucleation is generated and more fine bubbles are produced. Meanwhile, the formed bubbles are crushed by utilizing the ultrasonic cavitation effect, and more fine bubbles are formed, so that the aim of refining the foamed aluminum bubbles is achieved. In the heat insulation foaming process, the ultrasonic waves are continuously emitted into the aluminum alloy melt, and fine bubbles are maintained, so that the bubbles do not rapidly float upwards due to the action of the surface tension, and the mechanical property and density uniformity of the foamed aluminum are improved. Meanwhile, in the aluminum alloy solidification process, the aluminum alloy structure is refined by virtue of the action of the ultrasonic waves, and the performance of an aluminum alloy matrix is improved.
Owner:安徽省一鸣新材料科技有限公司
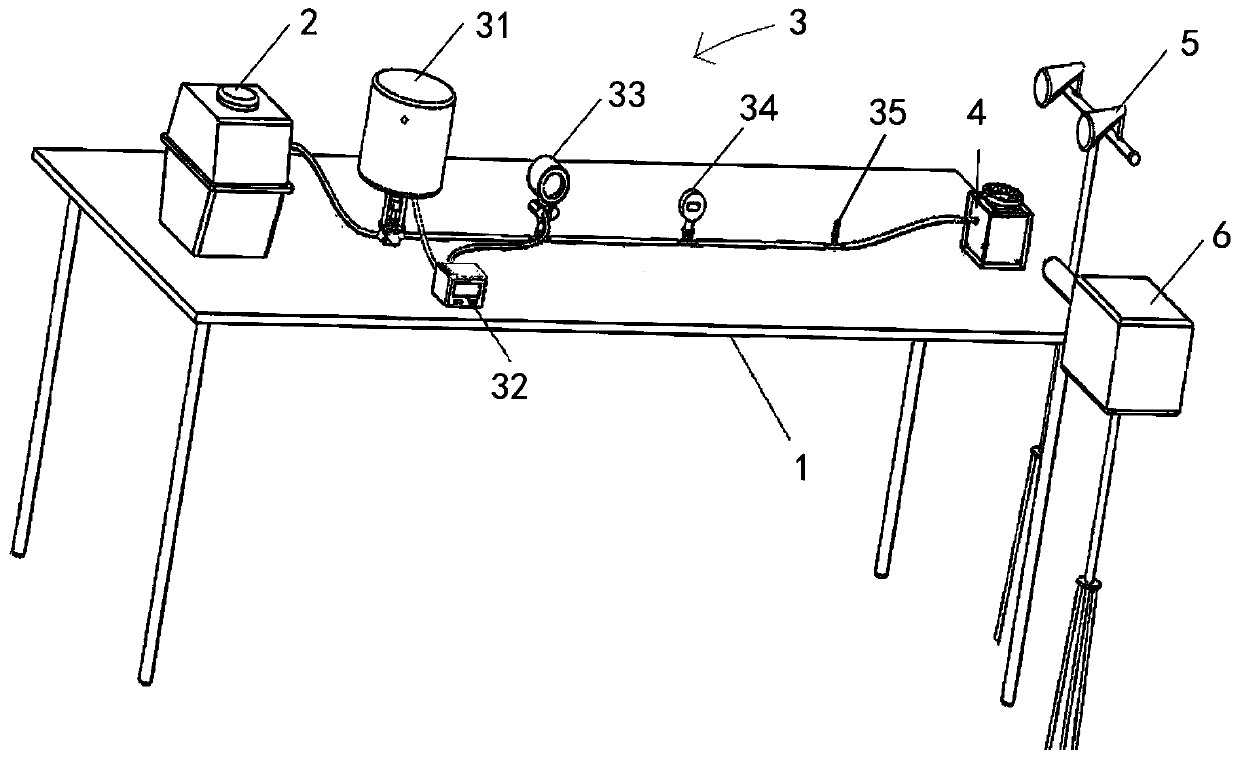
Mineral surface bubble nucleation and bubble growth process observation device and method
The invention discloses a mineral surface bubble nucleation and bubble growth process observation device and method. A vacuum pump, a pressure control assembly and a container are all arranged on a workbench. The light source supply assembly and a camera shooting assembly just face a cavity of the container, an air suction end of the vacuum pump is sequentially communicated with a pressure valve,a pressure sensor, a pressure gauge, a pressure release valve and the container so as to adjust the pressure in the cavity under the air suction effect of the vacuum pump, and therefore steam bubblescontrolled by diffusion or air bubbles caused by phase change are obtained. The interface bubbles prepared by the device and the method disclosed by the invention belong to heterogeneous bubble nucleation; steam bubbles or air bubbles are obtained; the pressure drop amplitude and the solution condition can be changed according to requirements, and then the properties, the number, the sizes and thecontact angles of mineral interface bubbles are selectively controlled such that the heterogeneous bubble nucleation and growth process on the mineral surface can be effectively researched, and the device and method have important guiding significance for the application of heterogeneous bubble nucleation in the mineral flotation field.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
Manufacturing method for microchannel heat exchange plate with multi-scale surface structure character
ActiveCN108362149AImprove heat transfer coefficientIncrease bubble nucleation pointIndirect heat exchangersMicro nanoMilling cutter
The invention discloses a manufacturing method for a microchannel heat exchange plate with a multi-scale surface structure character. Firstly, a multi-tooth saw web milling cutter combined cutter is used for machining array type microchannel structures with the micrometer scale character in metal base plates; then, smaller micro-nano surface structures with different structure shapes are machinedin the bottoms of microchannels in a laser machining manner, and then the array type microchannel structures and the micro-nano surface structures are packaged to sealing plates and cover plates, anda microchannel heat exchange plate is obtained. By utilization of the machining method, micro-nano composite structures are generated in the microchannels, bubble nucleation points can be effectivelyincreased, the effective heat exchange area is increased, a flow pattern structure is improved, and accordingly the purposes of enhancing boiling heat exchange and improving the microchannel heat transfer coefficient are achieved. Meanwhile, the machining method has the beneficial effects that the equipment requirement is low, the machining technology is simple, and the production cost is low. Themicrochannel array structure, with the multi-scale surface structure character, studied in the manufacturing method has wide application prospects in the electronic equipment heat dissipation field.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV +1
PE (Poly Ethylene) foaming material and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a PE (Poly Ethylene) foaming material and a preparation method of the PE foaming material. The PE foaming material comprises the following components in parts by weight: 60-80 parts of PE, 18-24 parts of composite foaming agent, 20-28 parts of EPDM (Ethylene-Propylene-Diene Monomer), 18-24 parts of glass fiber, 2-4 parts of PE wax, 2-4 parts of EPDM-g-MAH (Ethylene-Propylene-Diene Monomer grafted Maleic Anhydride) and 0.1-0.5 parts of antioxidant. In the PE foaming material, addition of ZnO can effectively facilitate decomposition of a foaming agent AC (Azodicarbonamide); an N atom of an AC azo group is provided with a lone pair electron and belongs to a lewis base substance, but Zn<2+> of ZnO can receive the lone pair electron and belongs to a lewis acid substance, so that combination of the N atom and Zn<2+> can easily facilitate decomposition of the foaming agent AC; nano CeO2 mainly exerts an effect of a nucleating agent, forms a liquid-solid interface between a melt and gas, and facilitates heterogeneous nucleation of bubbles, so that the activation energy of bubble nucleation and the nucleation number are reduced; and a fine and dense bubble structure with high closed porosity is finally formed.
Owner:ANHUI JIANGHUAI AUTOMOBILE GRP CORP LTD
Method and apparatus for producing amorphous metal
A method and apparatus are invented for producing an amorphous metal, which can readily realize amorphous metal fine particles of sub-micron order to 100 micron order including fine particles of several micrometer of a material from which an amorphous metal cannot be realized by conventional amorphous metal producing method and apparatus, with a high yield and an excellent extraction rate. A molten metal (1) is supplied into a liquid coolant (4), boiling due to spontaneous-bubble nucleation is generated, the molten metal (1) is rapidly cooled while forming fine particles thereof by utilizing a pressure wave generated by this boiling, thereby obtaining an amorphous metal. This production method is realized by apparatus comprising: material supplying means (3); a cooling section (2) which brings in the coolant (4) whose quantity is small and sufficient for cooling and solidifying the supplied molten metal (1), and rapidly cools the molten metal (1) while forming fine particles thereof by utilizing a pressure wave generated by boiling due to spontaneous-bubble nucleation, thereby obtaining amorphous fine particles; and recovery means (5) for recovering amorphous metal fine particles from the coolant (4).
Owner:MITSUI MINING & SMELTING CO LTD
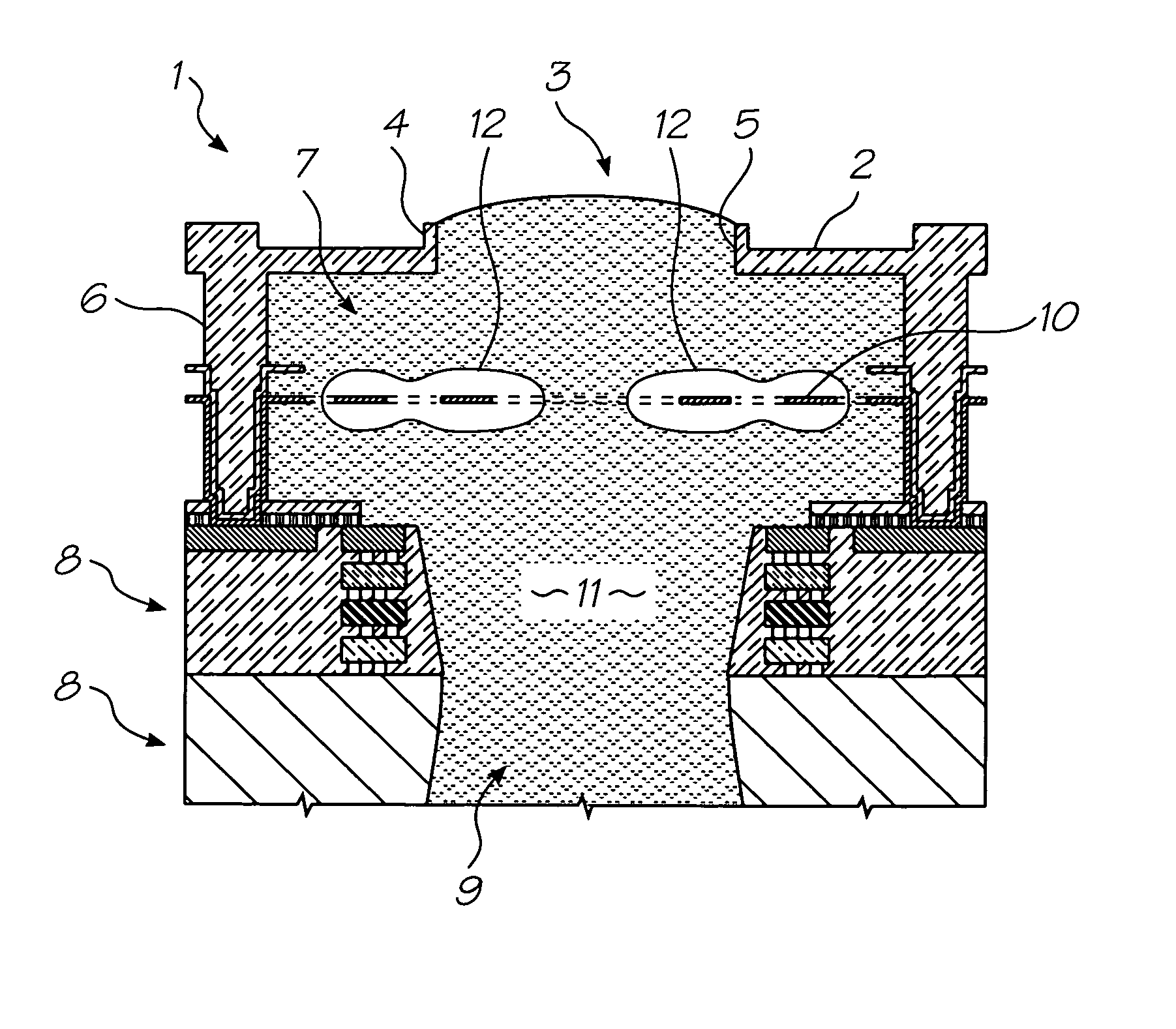
Surface Treatments And Coatings For Flash Atomization
A flash atomizer comprising a channel substrate configured to generate a vapor and form a two-phase flow of a fluid; and an enhanced surface disposed on the channel substrate and configured to change a temperature and a pressure required to form the vapor, wherein the enhanced surface texture comprises a plurality of active nucleation sites configured to promote heterogeneous bubble nucleation.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
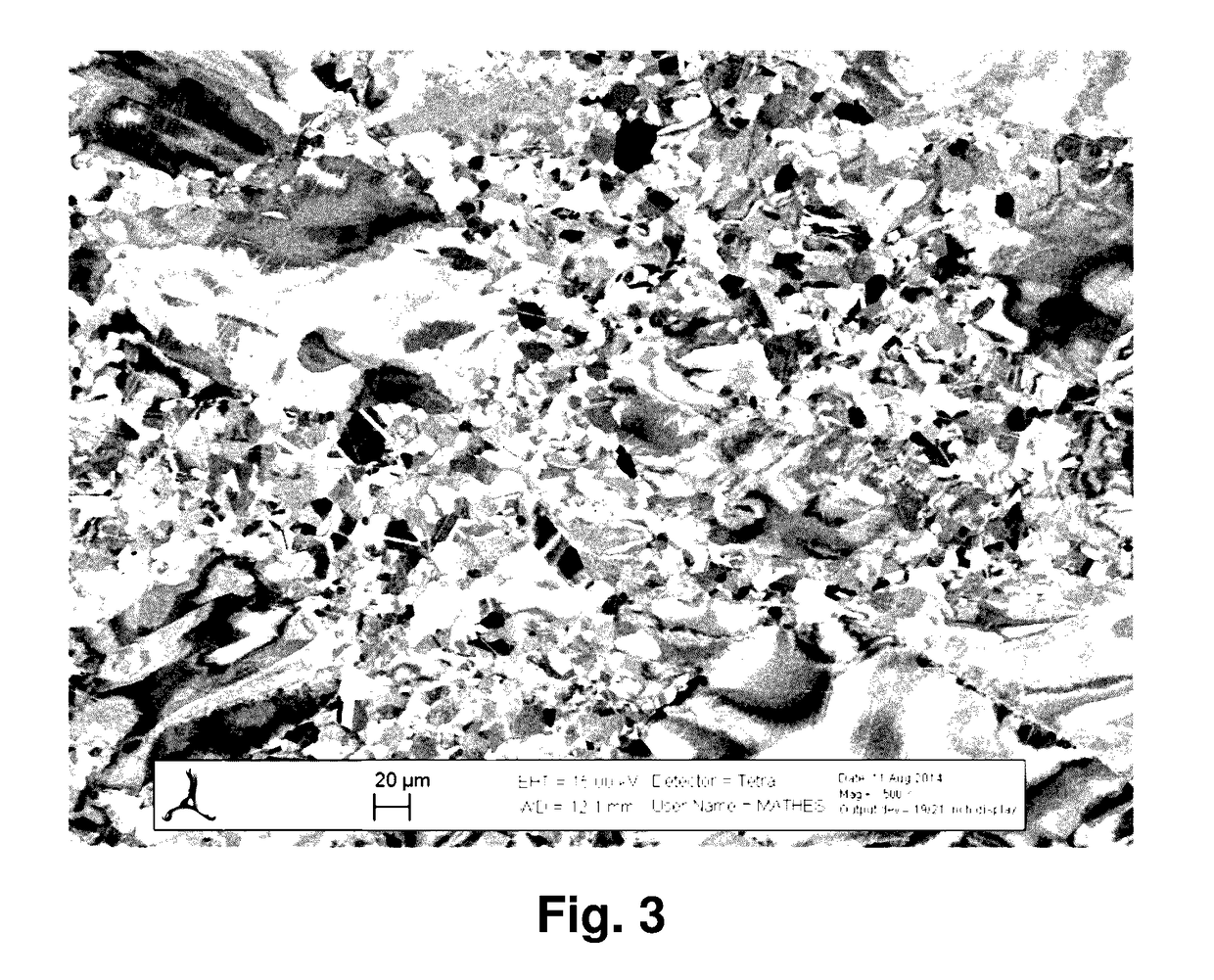
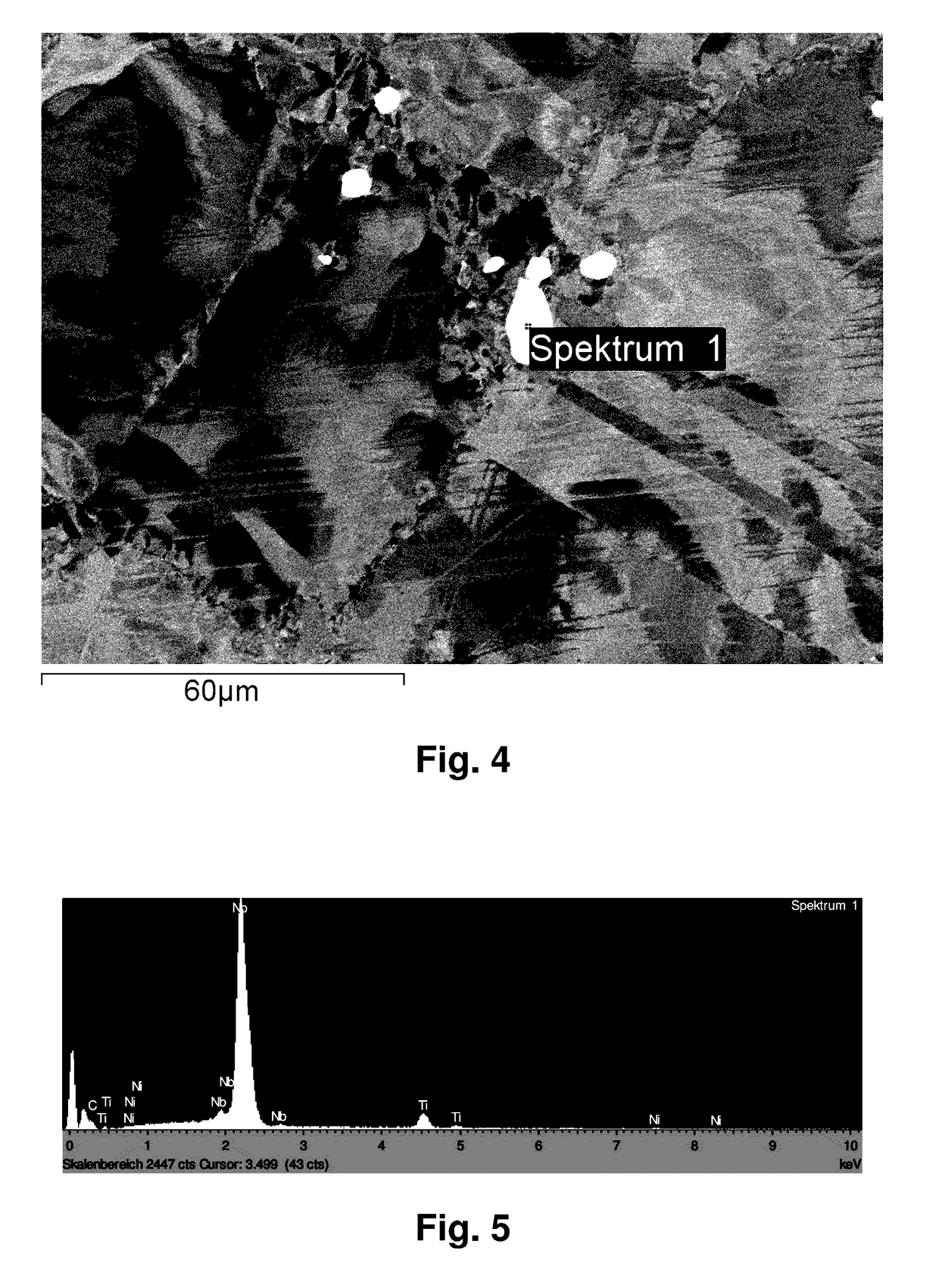
Processes for producing low nitrogen essentially nitride-free chromium and chromium plus niobium-containing nickel-based alloys and the resulting chromium and nickel-based alloys
Processes for producing low nitrogen, essentially nitride-free chromium or chromium plus niobium-containing nickel-based alloys include charging elements or compounds which do not dissolve appreciable amounts of nitrogen in the molten state to a refractory crucible within a vacuum induction furnace, melting said elements or compounds therein under reduced pressure, and effecting heterogeneous carbon-based bubble nucleation in a controlled manner. The processes also include, upon cessation of bubble formation, adding low nitrogen chromium or a low nitrogen chromium-containing master alloy with a nitrogen content of below 10 ppm to the melt, melting and distributing said added chromium or chromium-containing master alloy throughout the melt, bringing the resulting combined melt to a temperature and surrounding pressure to permit tapping, and tapping the resulting melt, directly or indirectly, to a metallic mold and allowing the melt to solidify and cool under reduced pressure.
Owner:CIA BRASILEIRA DE METALURGIA E MINERCAO
Low density edible animal chews and methods of making same
ActiveCN107105713AIncrease attractiveness/credibilityReduce heatAnimal feeding stuffAccessory food factorsDental ProductEngineering
Edible chews for pets have a low density (e.g. about 1.0 Kg / L or less) and a smooth exterior surface. One method by which the low density and the smooth exterior surface can be achieved uses a modified extrusion die to increase shear and restrict surface bubbles. Another method by which the low density and the smooth exterior surface can be achieved uses an extruder screw with a modified profile that holds a dough longer therein to create a whipping effect resulting in more bubble nucleation sites and hence a more uniform cellular matrix. The puffed (expanded) product was experimentally tested and provided better dental cleaning scores than a current unexpanded similarly formulated commercial dental product.
Owner:SOC DES PROD NESTLE SA
Preparation method of superconducting tape insulating coating
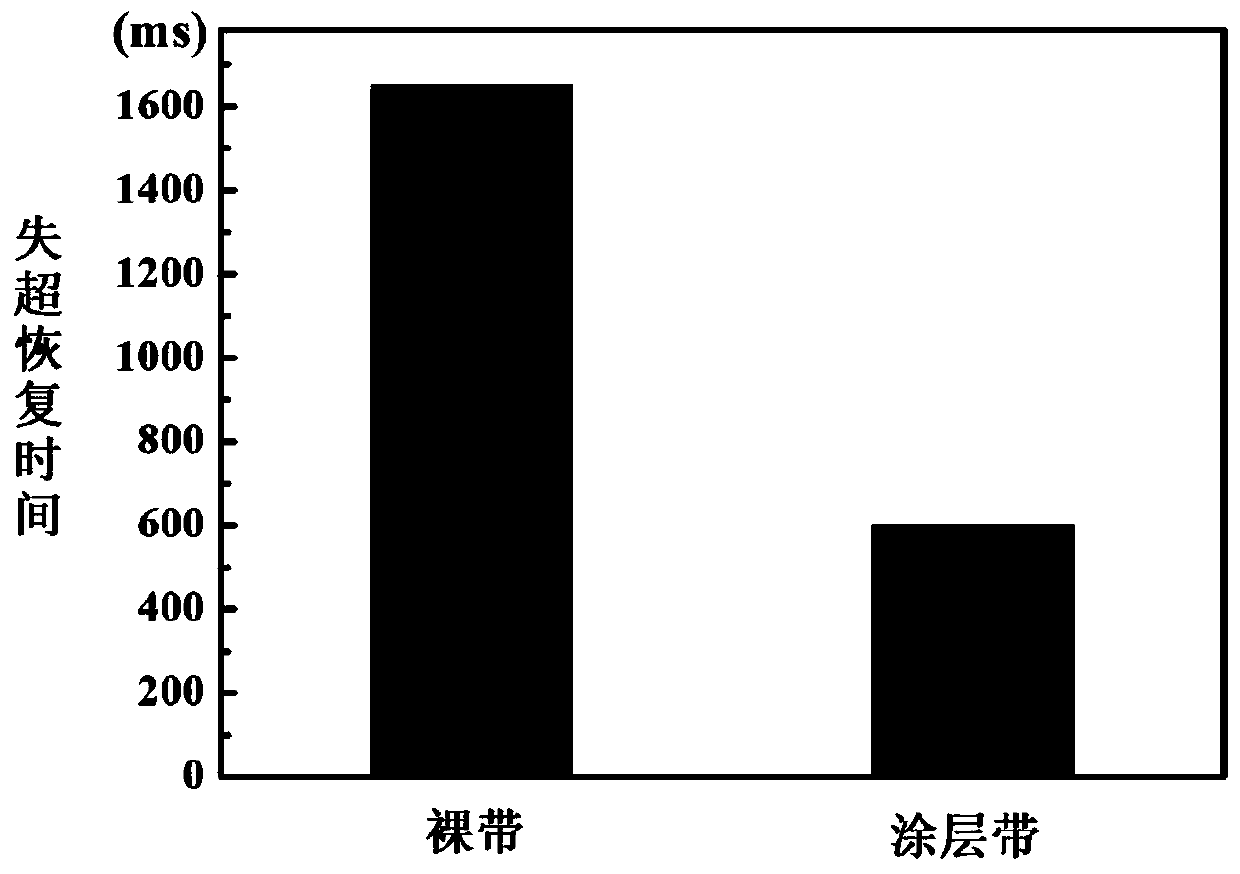
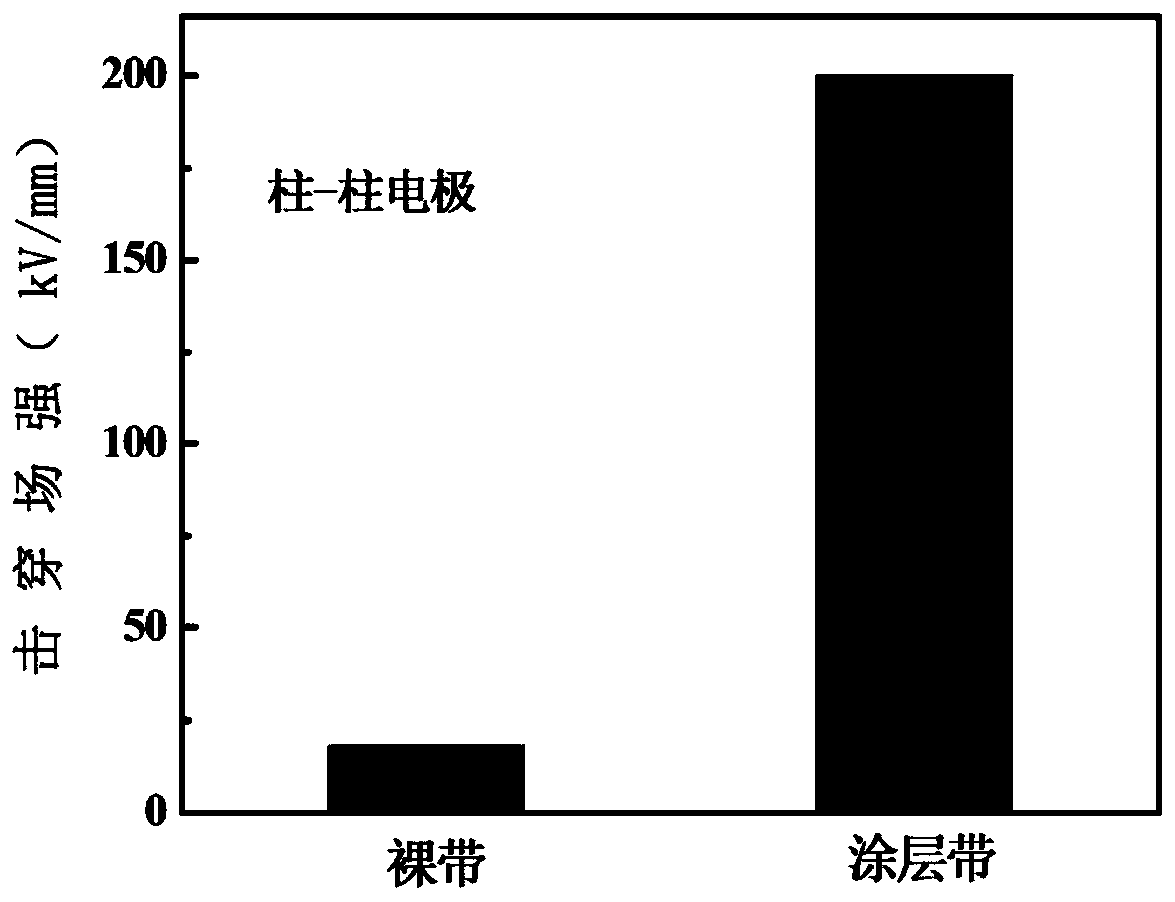
ActiveCN110452563AInhibition formationImprove heat transfer efficiencyCoatingsSpecial surfacesFreeze-dryingBoron nitride
The invention discloses a preparation method of a superconducting tape insulating coating. The insulating coating is boron nitride aerogel. The specific preparation method comprises the following steps: (1) preparation of boron nitride hydrosol; (2) preparation of a boron nitride hydrosol coating which coats the surface of a superconducting tape; and (3) preparation of a boron nitride aerogel coating on the surface of the superconducting tape. According to the scheme, the boron nitride aerogel with high heat conductivity and insulating characteristic is taken as a surface insulating coating, micropores in a porous structure of the aerogel are taken as bubble nucleation centers to inhibit formation of continuous large bubbles on the surface of the superconducting tape, and good heat transfer efficiency and stable insulating strength on the surface of the tape are maintained; the porous network structure of the boron nitride aerogel has high heat conductivity and insulating characteristic, rapid heat exchange between the superconducting tape and a liquid nitrogen medium can be realized, and quench recovery of the tape is accelerated; and a uniform insulating coating with the controllable thickness can be rapidly formed on the surface of the high-temperature superconducting tape through a repeated immersion-frictioning-freeze-drying process, and a technology is simple and easy toimplement.
Owner:SUZHOU NEW MATERIAL INST +1
Method for producing amorphous metal, method and apparatus for producing amorphous metal fine particles, and amorphous metal fine particles
A method and apparatus are invented for producing an amorphous metal, which can readily realize amorphous metal fine particles of sub-micron order to 100 micron order including fine particles of several micrometer of a material from which an amorphous metal cannot be realized by conventional amorphous metal producing method and apparatus, with a high yield and an excellent extraction rate. A molten metal (1) is supplied into a liquid coolant (4), boiling due to spontaneous-bubble nucleation is generated, the molten metal (1) is rapidly cooled while forming fine particles thereof by utilizing a pressure wave generated by this boiling, thereby obtaining an amorphous metal. This production method is realized by apparatus comprising: material supplying means (3); a cooling section (2) which brings in the coolant (4) whose quantity is small and sufficient for cooling and solidifying the supplied molten metal (1), and rapidly cools the molten metal (1) while forming fine particles thereof by utilizing a pressure wave generated by boiling due to spontaneous-bubble nucleation, thereby obtaining amorphous fine particles; and recovery means (5) for recovering amorphous metal fine particles from the coolant (4).
Owner:MITSUI MINING & SMELTING CO LTD
Novel principle and method for measuring diffusion coefficient of hydrogen in metal melt
The invention relates to a principle and method for measuring a diffusion coefficient of hydrogen nearby melting point temperature of a metal melt by utilizing solubility difference of the hydrogen in a metal liquid / solid phase and supersaturation conditions required by bubble nucleation. The method comprises the following steps of: by using a directional solidification device, melting metal in mixed gas of the hydrogen and argon at a certain pressure, so as to obtain an initial bubble-free layer with a certain thickness by utilizing directional hydrogen diffusion caused by the solubility difference of the hydrogen in the metal liquid / solid phase and the supersaturation conditions required by the bubble nucleation; combining the height of the bubble-free layer, the supersaturation conditions required by the nucleation and a nearly balance solidification principle of a single-phase alloy, so as to obtain the diffusion coefficient of the hydrogen nearby melting point temperature of the metal melt. The problems that the operation is complex and the diffusion coefficient of the hydrogen in a high-melting point metal melt is difficultly obtained by using the conventional method are solved, and the invention provides a principle and a method for simply and conveniently measuring the diffusion coefficient of the hydrogen nearby the melting point of the metal melt.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Beverage Container
ActiveUS20150217933A1Increase rangeEfficient use ofFruit and vegetables preservationLiquid materialNitrogenEngineering
A beverage container or package that includes an internal surface for promoting nitrogen bubble nucleation and growth. The surface incorporates a plurality of nanoscale structures, e.g. between 6 and 100 nanometres in size. Most preferably the structures are pits, greater than 15 nm in depth / height. Upon opening the container filled with a Nitrogen (and carbon dioxide) supersaturated beverage, a foaming effect occurs which provides a desirable head of fine bubbles when transferred to a drinking glass.
Owner:DIAGEO IRELAND UNLIMITED CO
Processes for producing low nitrogen essentially nitride-free chromium and chromium plus niobium-containing nickel-based alloys and the resulting chromium and nickel-based alloys
Processes for producing low nitrogen, essentially nitride-free chromium or chromium plus niobium-containing nickel-based alloys include charging elements or compounds which do not dissolve appreciable amounts of nitrogen in the molten state to a refractory crucible within a vacuum induction furnace, melting said elements or compounds therein under reduced pressure, and effecting heterogeneous carbon-based bubble nucleation in a controlled manner. The processes also include, upon cessation of bubble formation, adding low nitrogen chromium or a low nitrogen chromium-containing master alloy with a nitrogen content of below 10 ppm to the melt, melting and distributing said added chromium or chromium-containing master alloy throughout the melt, bringing the resulting combined melt to a temperature and surrounding pressure to permit tapping, and tapping the resulting melt, directly or indirectly, to a metallic mold and allowing the melt to solidify and cool under reduced pressure.
Owner:CIA BRASILEIRA DE METALURGIA E MINERCAO
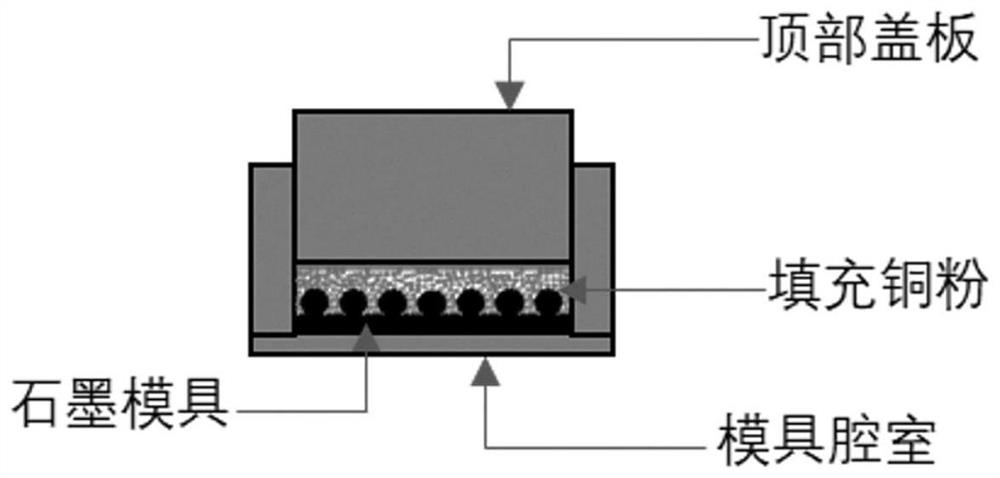
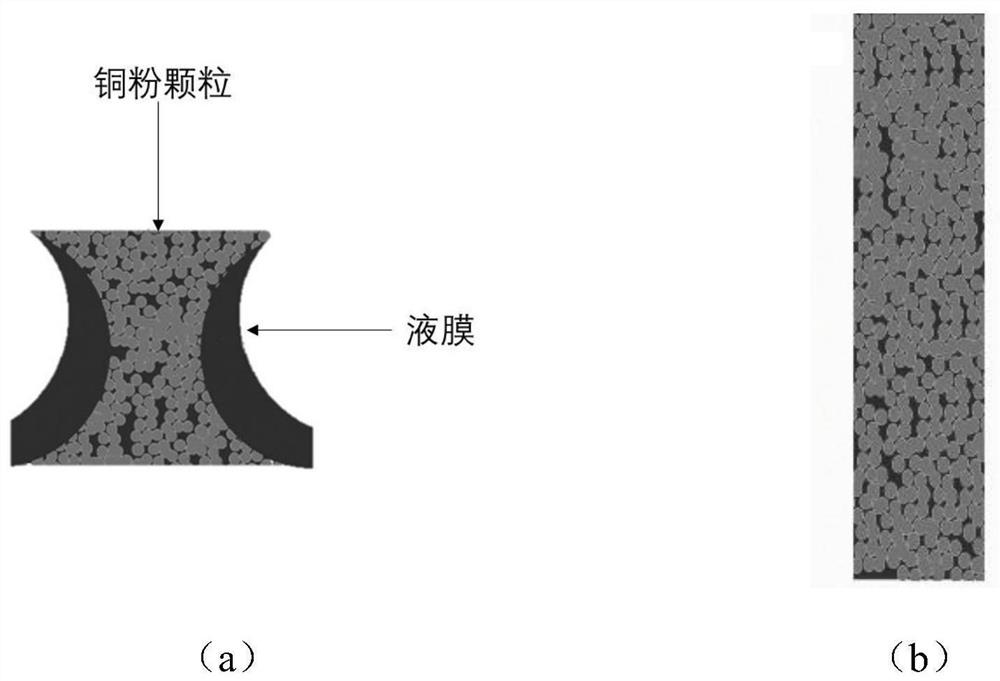
Composite microcavity porous curved-surface microchannel structure for liquid film boiling and preparation method thereof
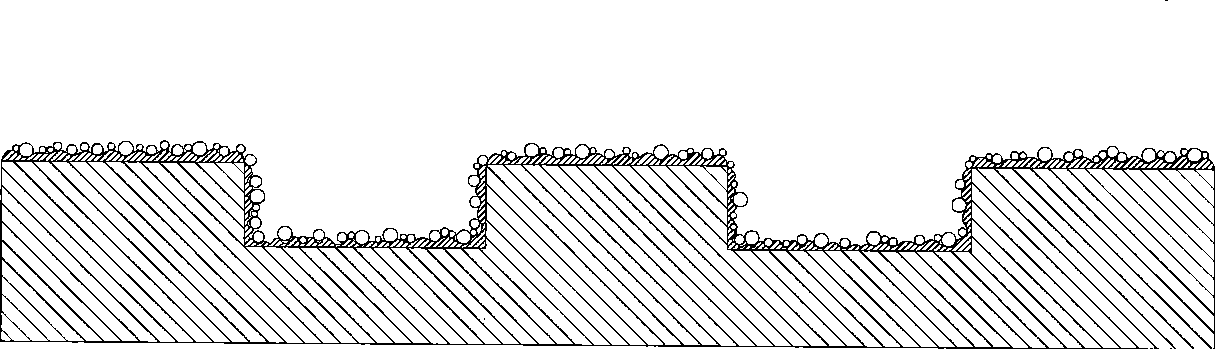
The invention provides a composite microcavity porous curved-surface microchannel structure for liquid film boiling and a preparation method thereof, and the preparation method comprises the following steps: carrying out compression molding on sodium chloride pore-forming agent particles and copper powder, or directly carrying out loose sintering on the copper powder, carrying out laying, combining, sintering, cleaning to remove the pore-forming agent, carrying out oxidation etching, and carrying out chemical cleaning to obtain the composite microcavity porous curved-surface microchannel structure. The composite micro-cavity porous curved surface micro-channel structure prepared by the preparation method disclosed by the invention is coupled with the advantages of high permeability between micro-columns and high capillary pressure between copper powder, and has good capillary performance; the micro-cavity structure on the surface of the copper powder increases the bubble nucleation density and the super-hydrophilic wettability and can delay CHF under high heat flux, the double-curved-surface structure design increases the pinning effect of liquid film spreading, the area of a thin liquid film near a three-phase contact line can be increased, and therefore the heat transfer area is increased, and the heat transfer performance is enhanced.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Method and apparatus for producing fine particles
InactiveUS20040224040A1Effectively fragmentedIncrease surface areaAuxillary shaping apparatusMicrometerBubble nucleation
A method and apparatus are invented for producing fine particles, which can readily realize the formation of fine particles of sub-m order to 100 micron order as well as fine particles of several micrometer which cannot be realized by a conventional method and apparatus available for producing fine particles, and a large quantity of fine particles having the desired particle diameter can be obtained with a high yield. A molten material (1), which is a molten raw material to be fragmented into fine particles, is supplied into a liquid coolant (4), boiling due to spontaneous-bubble nucleation is generated, and the molten material (1) is cooled and solidified while forming fine particles thereof by utilizing a pressure wave generated by this boiling. This production method is realized by apparatus comprising: material supplying means (3); a cooling section (2) which brings in the coolant (4) whose quantity is small and sufficient for cooling and solidifying the supplied molten material (1), and cools and solidifies the molten material (1) while forming fine particles thereof by utilizing a pressure wave generated by boiling due to spontaneous-bubble nucleation; and recovery means (5) for recovering fine particles from the coolant (4).
Owner:MITSUI MINING & SMELTING CO LTD
Free particle/porous medium composite enhanced boiling structure and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN110842202AAdd spoilersFast heat conductionHeat transfer modificationThermodynamicsPorous medium
The invention discloses a free particle / porous medium composite enhanced boiling structure. The structure comprises a substrate and a porous matrix structure formed on the surface of the substrate, aplurality of pore cavities are formed in the porous matrix structure, and free particles capable of moving in the pore cavity are dispersed in the pore cavity. When the free particle / porous medium composite enhanced boiling structure is prepared, metal particles are sintered to prepare a porous material matrix, the porous material matrix is drilled to form the pore cavity, and then the pore cavityis filled with free particles and sealed. The structure is based on the enhancing characteristics of nucleation activation in the boiling heat transfer process and liquid supply of a liquid absorbingcore to a nucleation site, bubbles are prevented from being mixed and the liquid backflow resistance is reduced by means of bubble nucleation and liquid supply partition. Meanwhile, the free particles collide with one another in the boiling process, so that heat transfer, microlayer evaporation and convective heat transfer in working fluid are enhanced, bubble nucleation is easy, the growth speedis high, the separation frequency is high, and therefore the enhanced boiling heat transfer is realized.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
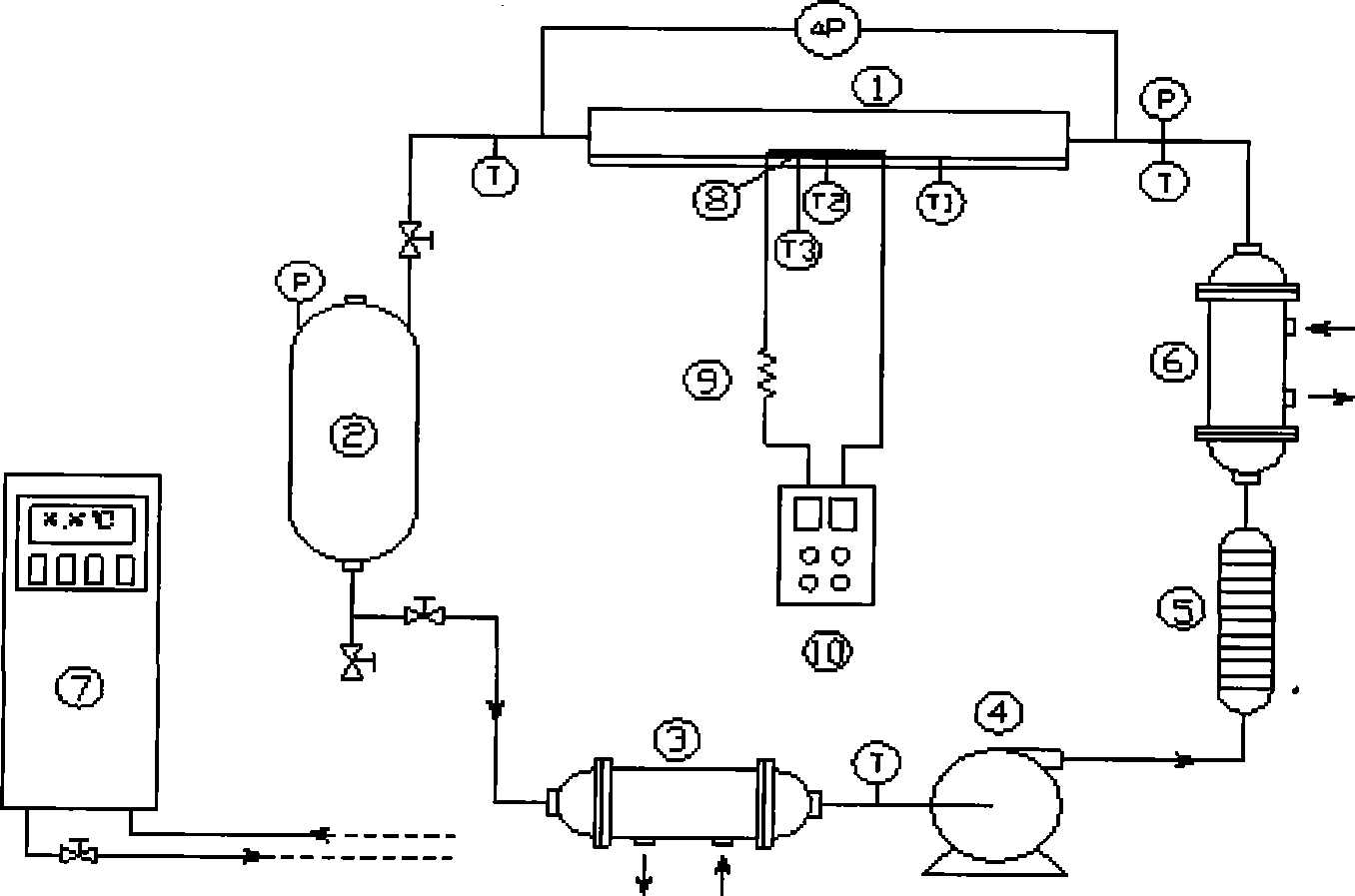
Apparatus and method for increasing boiling heat transfer therein
ActiveUS20150068712A1Enhanced boiling heat transferImprove heat transfer performanceCorrosion preventionCoatingsWorking fluidBoiling heat transfer
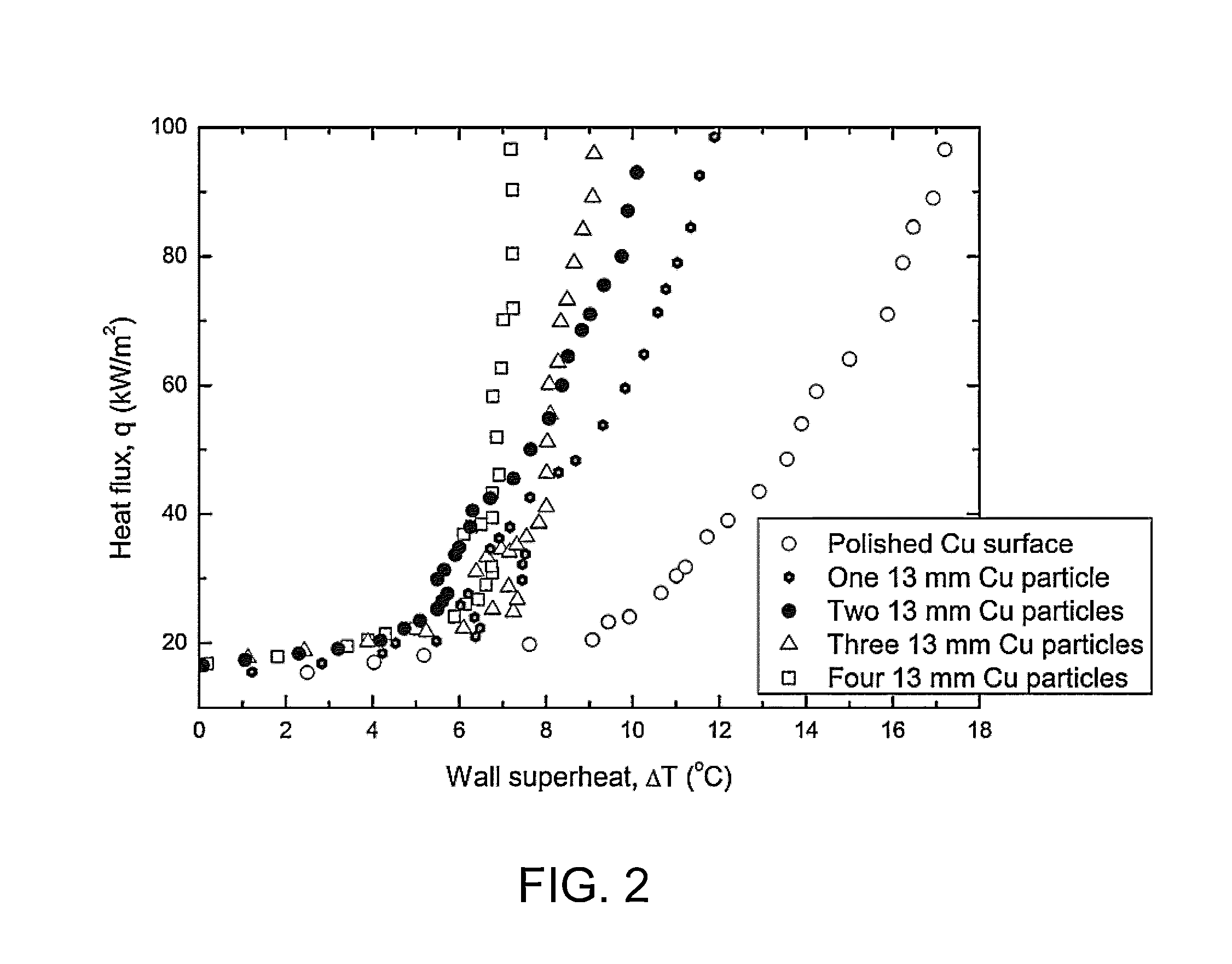
An apparatus and a method of enhancing boiling heat transfer therein capable of increasing both the critical heat flux and nucleate boiling heat transfer of a working fluid. The method includes placing free particles on a surface so as to define narrow corner gaps and cavities at interfaces between the particles and the surface and heating the surface while the surface is contacted by the working fluid to bring the working fluid to a boil, with the result that bubble nucleation is facilitated and nucleate boiling heat transfer from the surface is increased.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com