Film grain simulation method
a film grain and simulation method technology, applied in the field of simulating film grain, can solve the problems of cineon® application not yielding good performance for many high-speed films, film grain simulation fails to achieve adequate fidelity when images, and motion picture films typically contain image-dependent nois
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
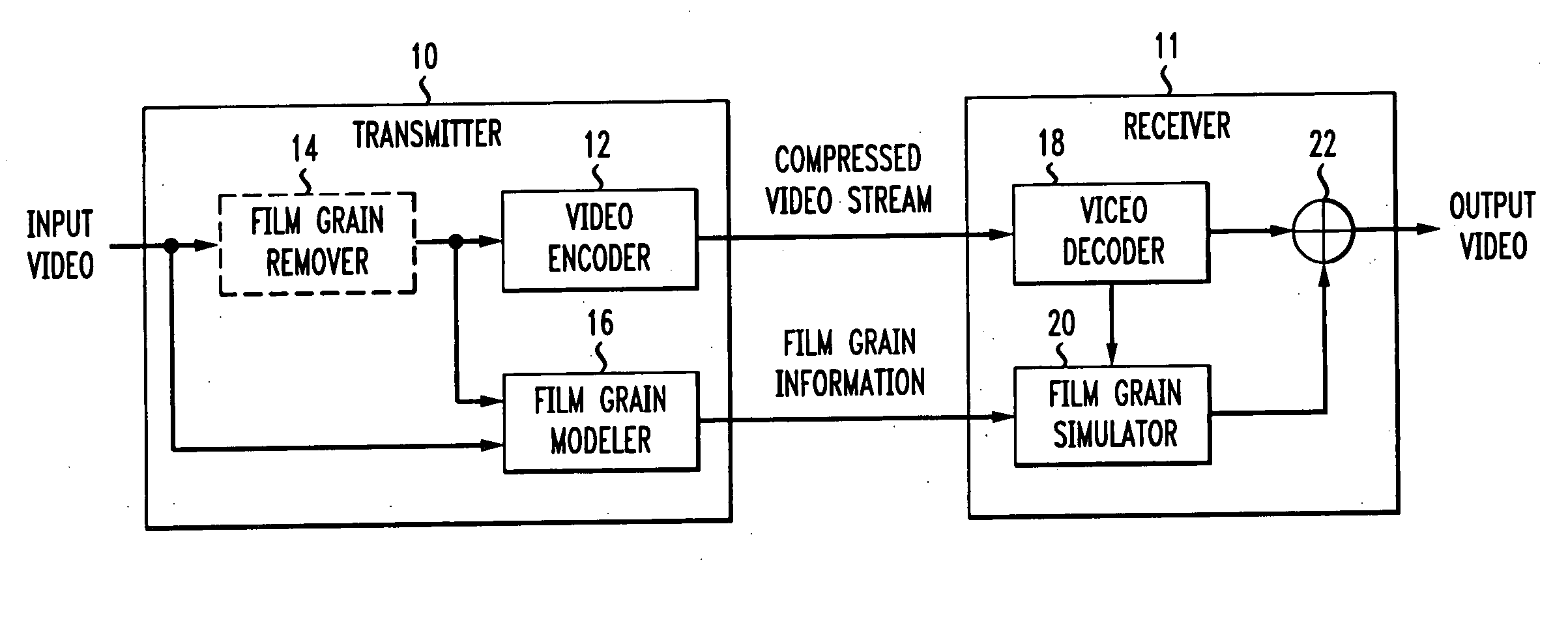
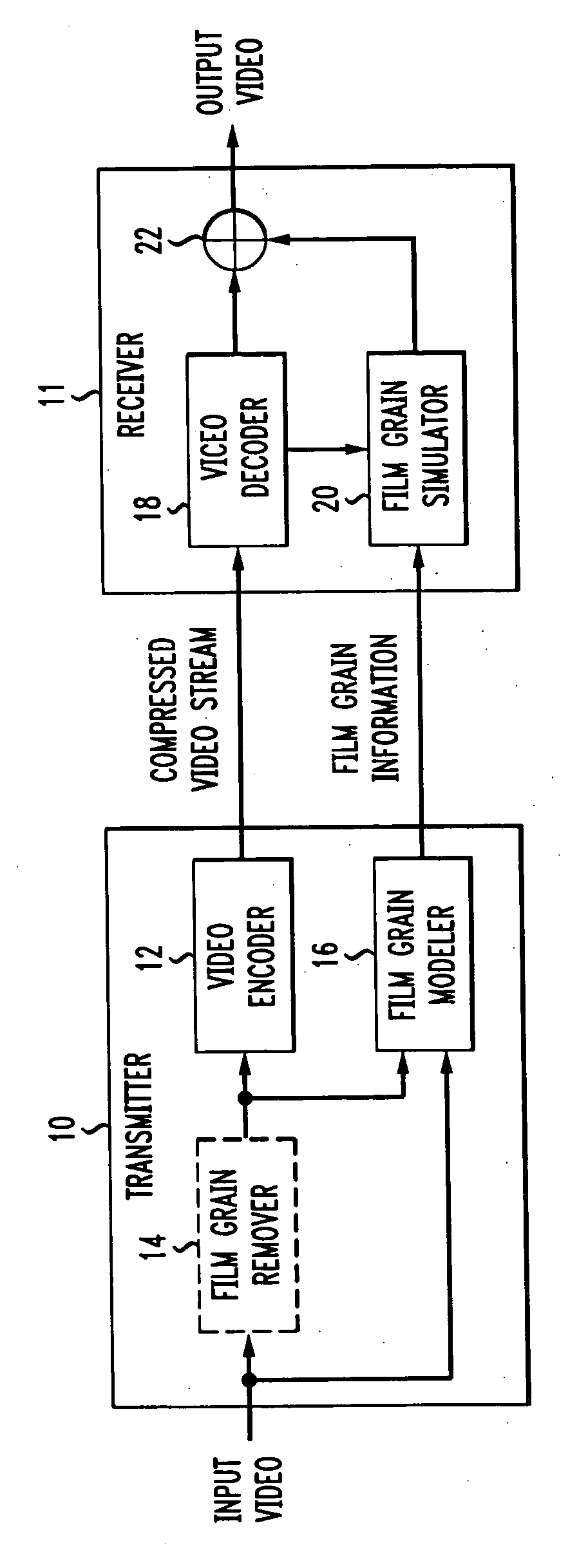
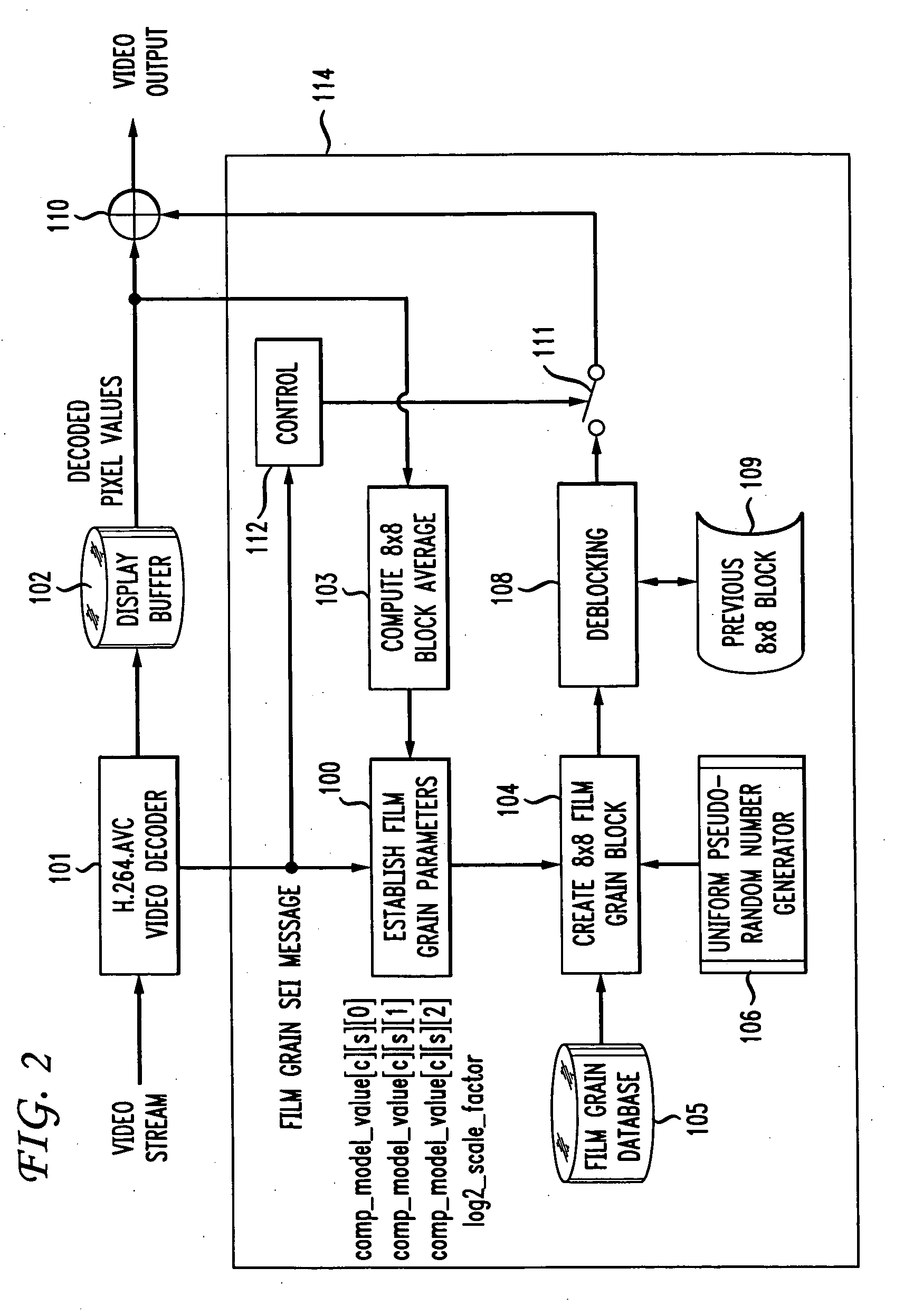
[0015] To understand the technique of the present principles for simulating a bit-accurate film grain pattern comprised of individual film grain blocks, a brief overview of film grain simulation will prove helpful. FIG. 1 depicts a block schematic diagram of a transmitter 10, which receives an input video signal and, in turn, generates a compressed video stream at its output. In addition, the transmitter 10 also generates information indicative of the film grain (if any) present in the sample. In practice, the transmitter 10 could comprises part of a head-end array of a cable television system, or other such system that distributes compressed video to one or more downstream receivers 11, only one of which is shown in FIG. 1. The transmitter 10 could also take the form of encoder that presents media like DVDs. The receiver 11 decodes the coded video stream and simulates film grain in accordance with the film grain information and decoded video, both received from the transmitter 10 o...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com