Method for electrochemical plating on semiconductor wafers
a technology of conductive films and semiconductor wafers, applied in the direction of basic electric elements, electrical apparatus, semiconductor devices, etc., can solve the problems of step-like discontinuity in the applied current waveform, prevelant interconnections comprising copper, etc., to improve overall film quality, uniform and continuous grain structure, and reduce thermal stresses within the film
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
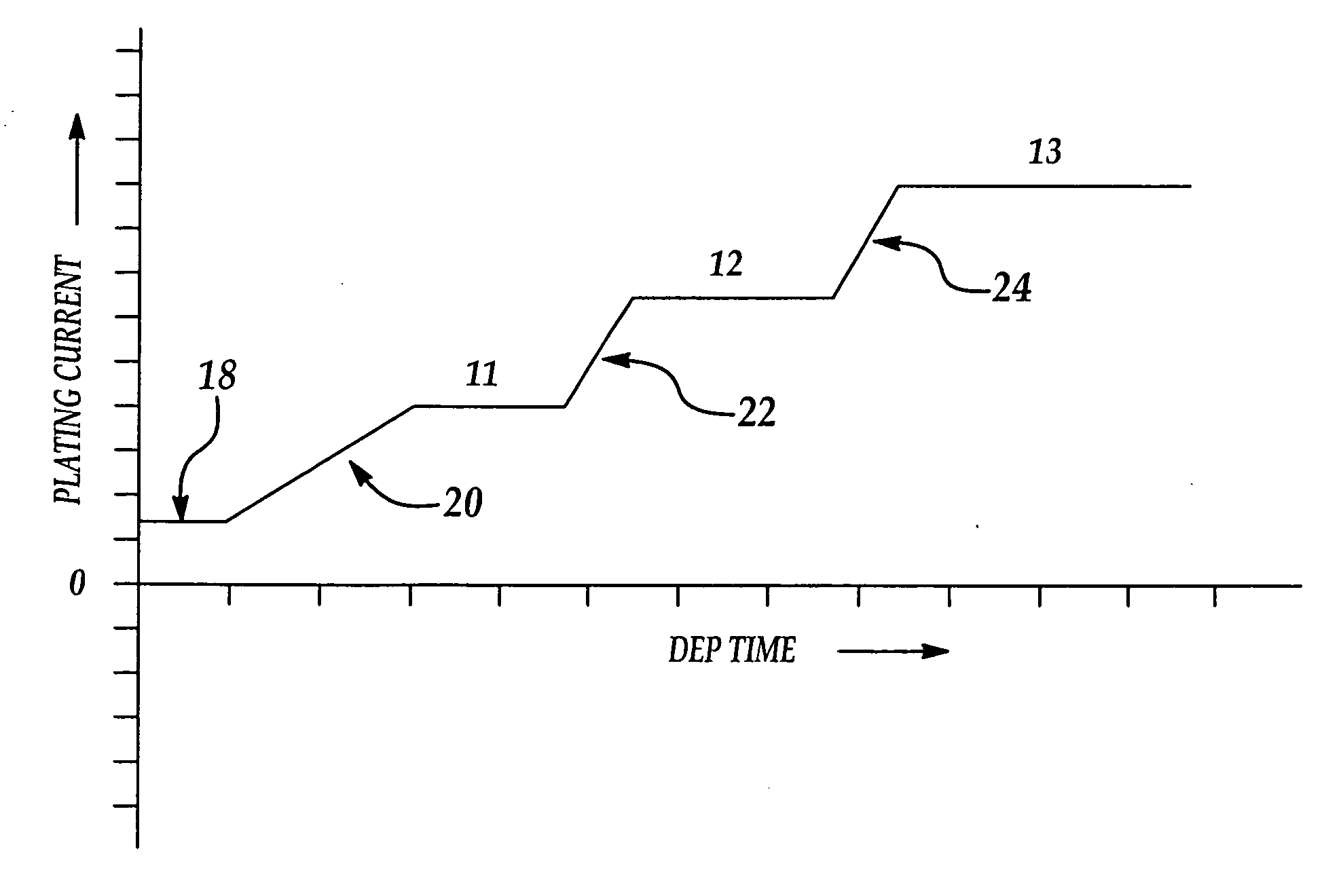
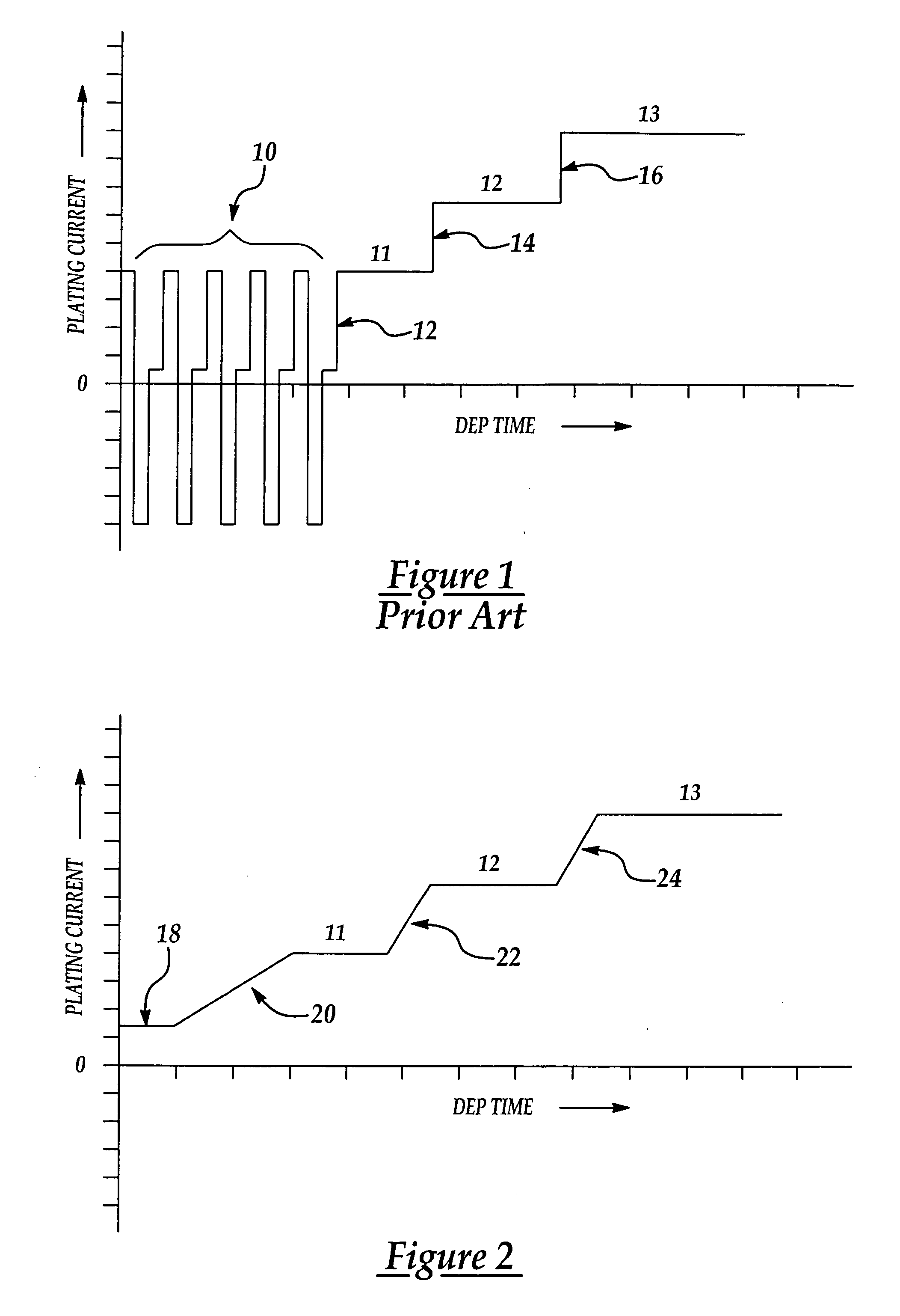
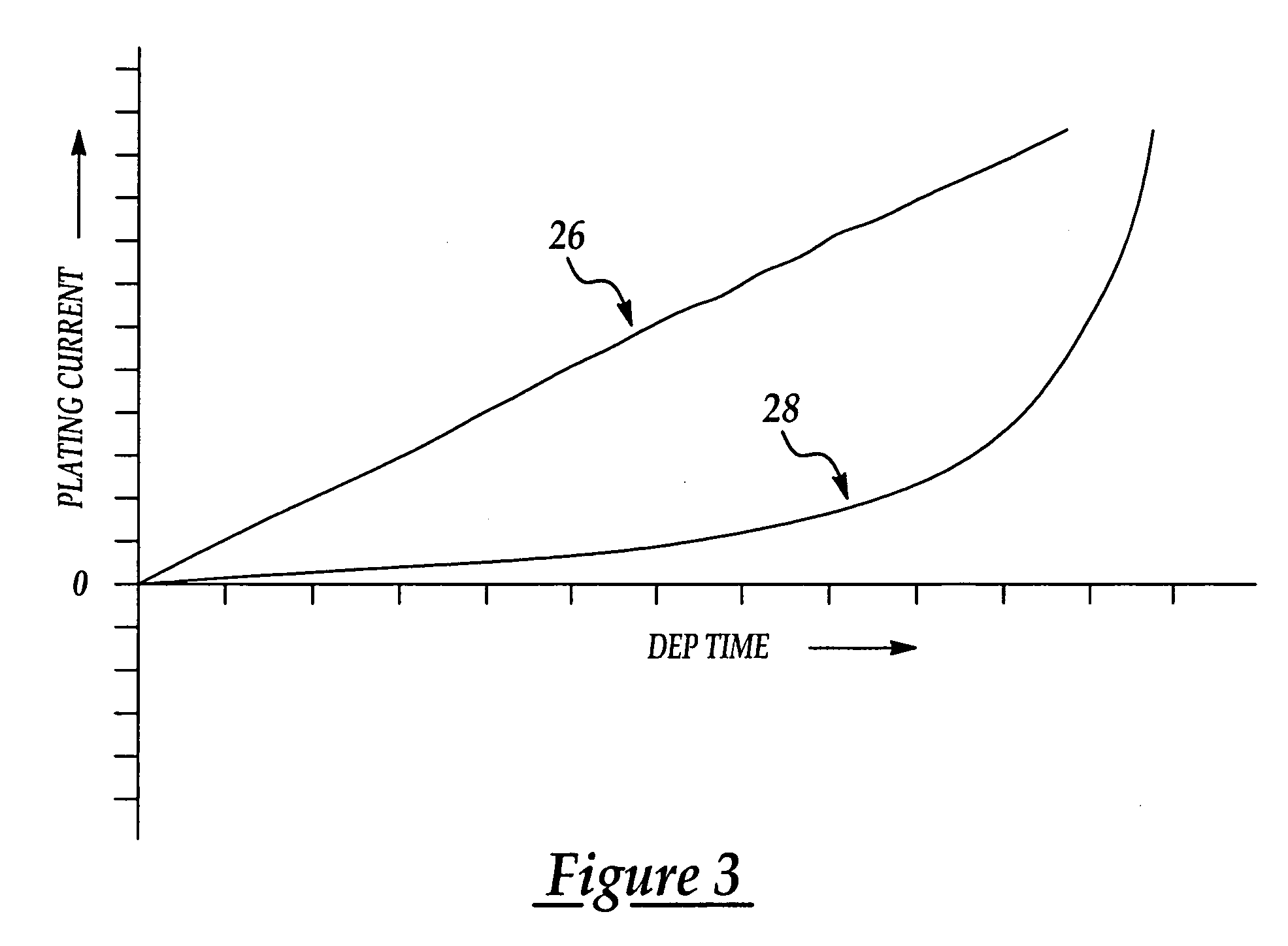
[0014] Referring first to FIG. 1, a typical process for electroplating copper on a semiconductor wafer began with depositing a barrier layer of a material such as tantalum nitride by means of sputtering. Next, a seed layer of copper is applied over the barrier layer using, for example, atomic layer deposition techniques. The seed layer of copper is applied to assure good electrical contact and adhesion of subsequent layers of copper. The seed layer of copper may be between 100 and 1000 angstroms, for example. Copper electroplating is then performed using a conventional electroplating apparatus which includes a vessel (not shown) containing an aqueous solution of CuSO4 and H2SO4, in the presence of various additives and leveling agents. The wafer is held by flexibly mounted gripping fingers (not shown) on the bottom of a spinning clam shell support which rotates the wafer while submerged within the plating bath. The wafer is electrically connected to a power source and acts as a cath...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com