Method used for preparing FeS2 film and capable of controlling precursor grain size
A technology of grain size and precursor, applied in semiconductor devices, final product manufacturing, sustainable manufacturing/processing, etc., can solve problems such as inability to receive transmitted light from substrates, difficulty in controlling film quality, unfavorable promotion and use, etc., to achieve crystal The particle size can be easily controlled, improving the performance level of the film, and the effect of strong variability in area and shape
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
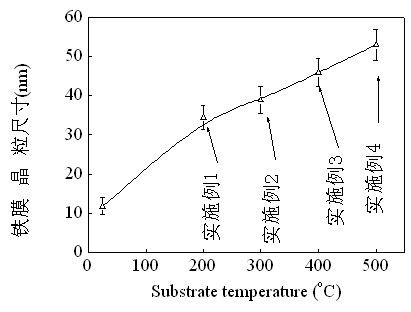
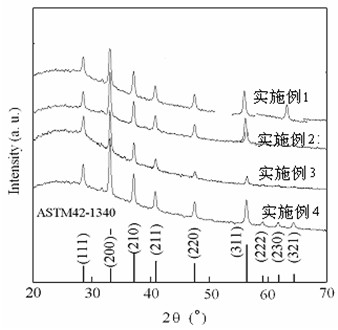
[0025] The coating substrate adopts an area of 26×76mm 2 The fully transparent glass slide was boiled in a saturated chromic acid solution for 15 minutes, rinsed with deionized water, then ultrasonically oscillated in acetone, absolute ethanol, and deionized water for 15 minutes, and finally dried at 200°C for 2 hours to obtain a crystal. Pure Fe films with a particle size of 30 nm.
[0026] The pure Fe film was sputtered in FJL-450 magnetron sputtering equipment, the substrate temperature was 200 ° C, and the temperature was kept for 0.5 h after sputtering to obtain a pure Fe film with a grain size of 30 nm and a thickness of 0.25 μm. The pure Fe membrane and the sulfur powder of the mass required to produce a nominal sulfur pressure of 80kPa at 400°C were packaged in a glass tube, and vacuumized and replaced with Ar gas 5 times before packaging. The packaged samples were vulcanized at 400°C for 40h.
Embodiment 2
[0028] The coating substrate adopts an area of 26×76mm 2 The fully transparent glass slides were boiled in saturated chromic acid solution for 15 minutes, rinsed with deionized water, then ultrasonically oscillated in acetone, absolute ethanol, and deionized water for 15 minutes, and finally dried at 200°C for 2 hours. Pure Fe film.
[0029] The pure Fe film was sputtered in FJL-450 magnetron sputtering equipment, the substrate temperature was 300 ° C, and the temperature was kept for 0.5 h after sputtering to obtain a pure Fe film with a grain size of 40 nm and a thickness of 0.28 μm. The pure Fe membrane and the sulfur powder of the mass required to produce a nominal sulfur pressure of 80kPa at 400°C were packaged in a glass tube, and vacuumized and replaced with Ar gas 5 times before packaging. The packaged samples were vulcanized at 450°C for 20h.
Embodiment 3
[0031] The coating substrate adopts an area of 26×76mm 2 The fully transparent glass slides were boiled in a saturated chromic acid solution for 15 minutes, rinsed with deionized water, then ultrasonically oscillated in acetone, absolute ethanol, and deionized water for 15 minutes, and finally dried at 200°C for 2 hours.
[0032]The pure Fe film was sputtered in FJL-450 magnetron sputtering equipment, the substrate temperature was 400 ° C, and the temperature was kept for 0.5 h after sputtering to obtain a pure Fe film with a grain size of 40 nm and a thickness of 0.30 μm. The pure Fe film and the sulfur powder of the mass required to produce a nominal sulfur pressure of 80kPa calculated at 400°C were packaged in a glass tube. Before packaging, the vacuum was evacuated and replaced with Ar gas 5 times. The packaged samples were vulcanized at 500°C for 10h.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com