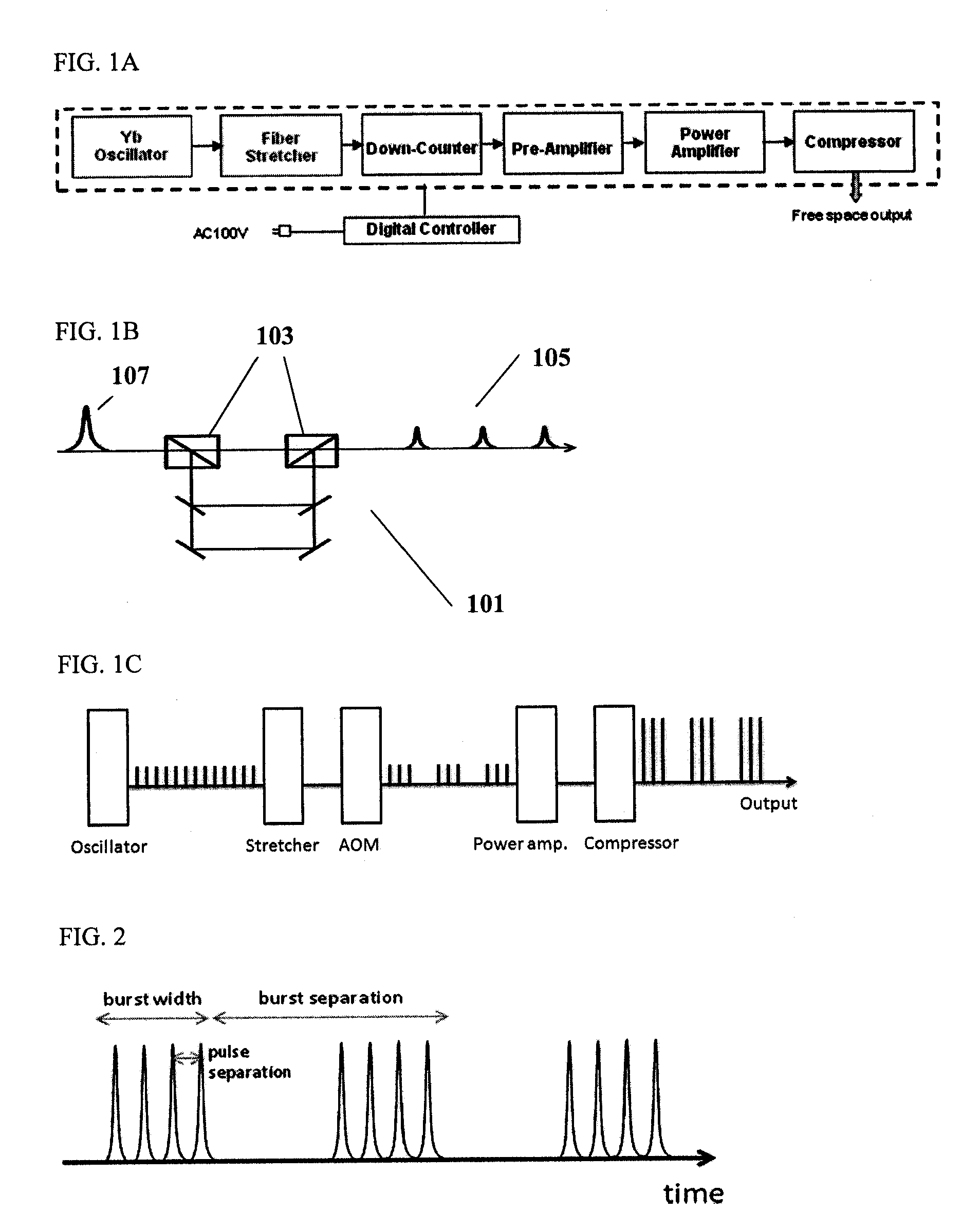
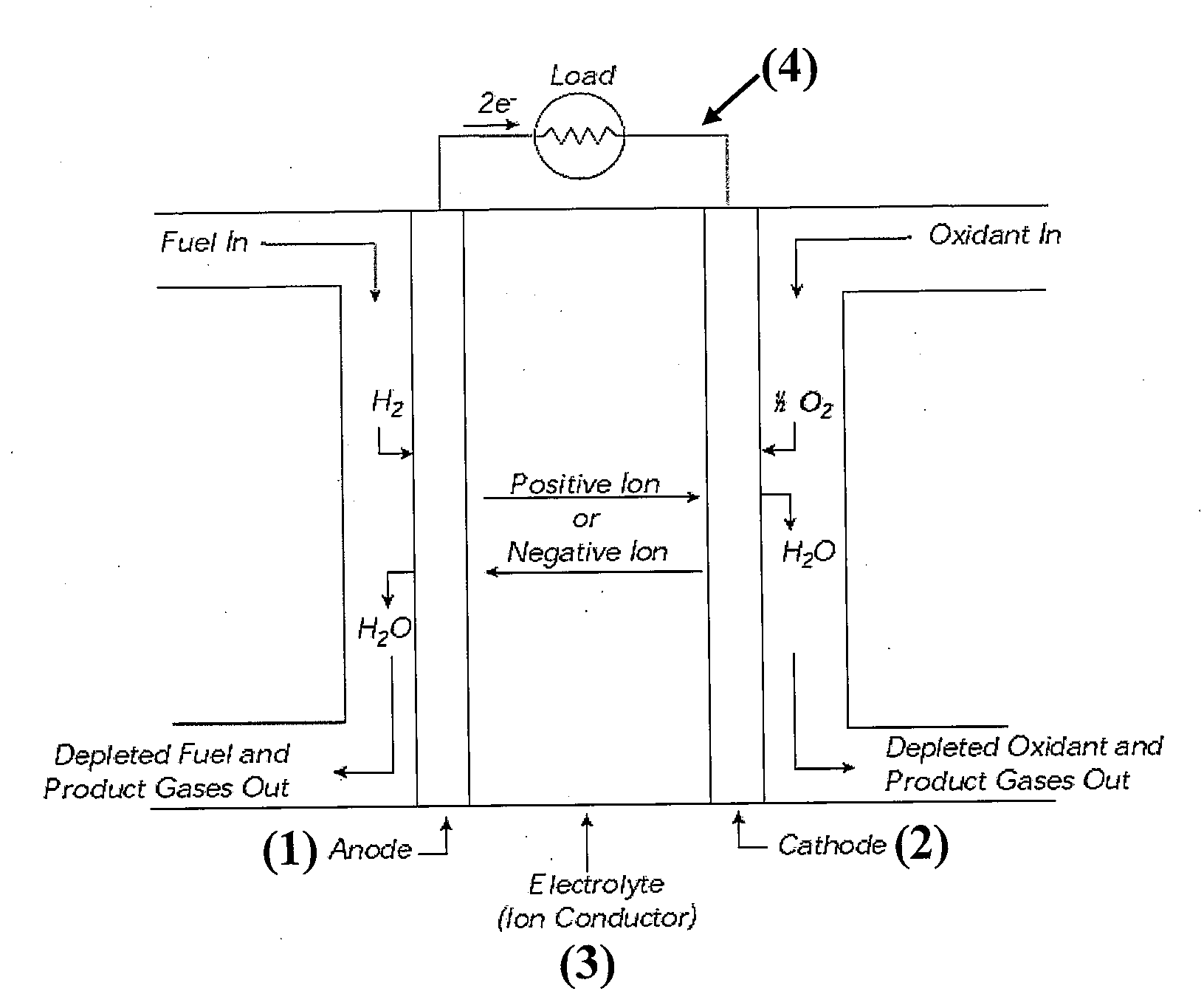
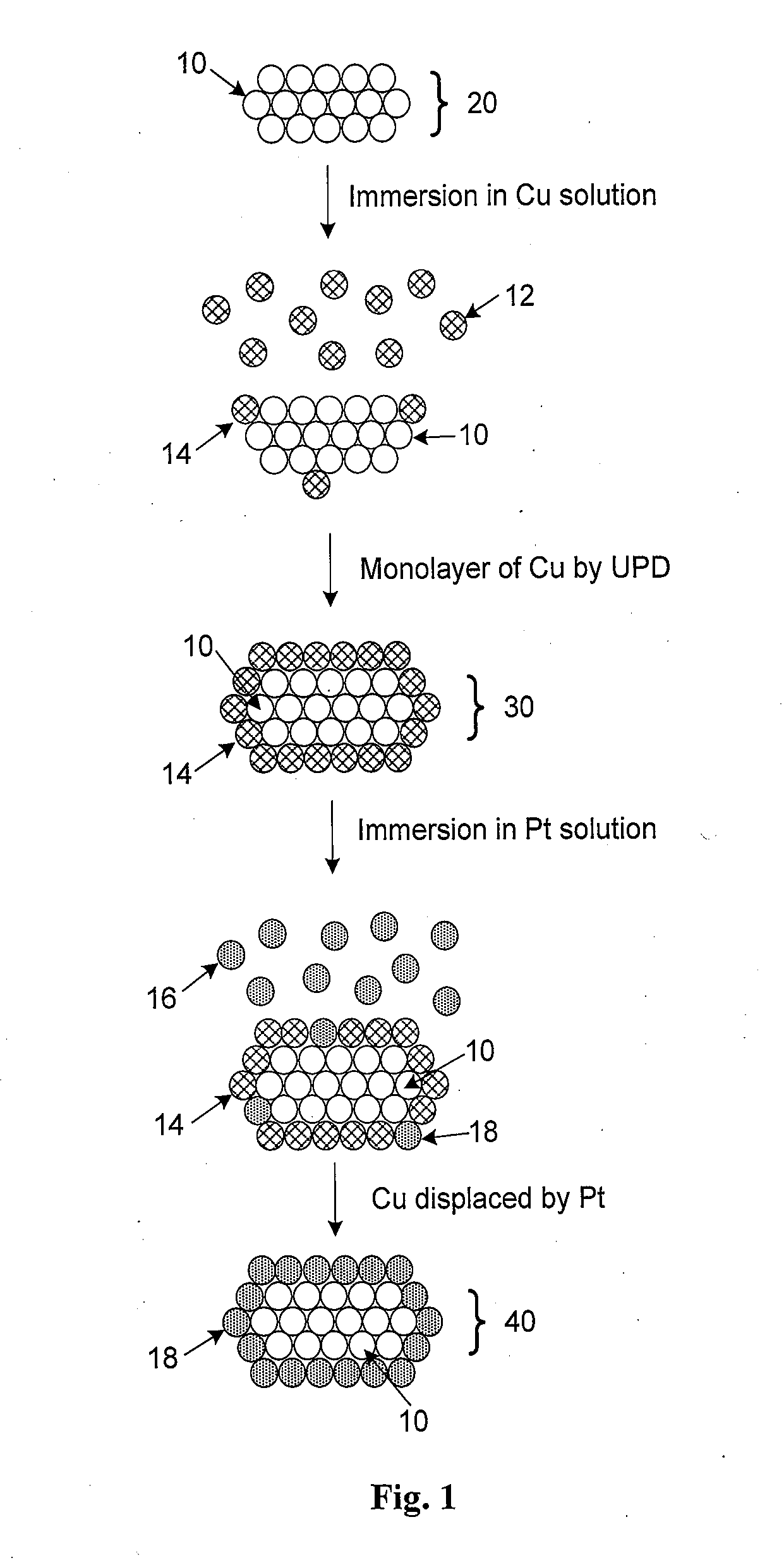
Patents
Literature
1385 results about "Sheet film" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
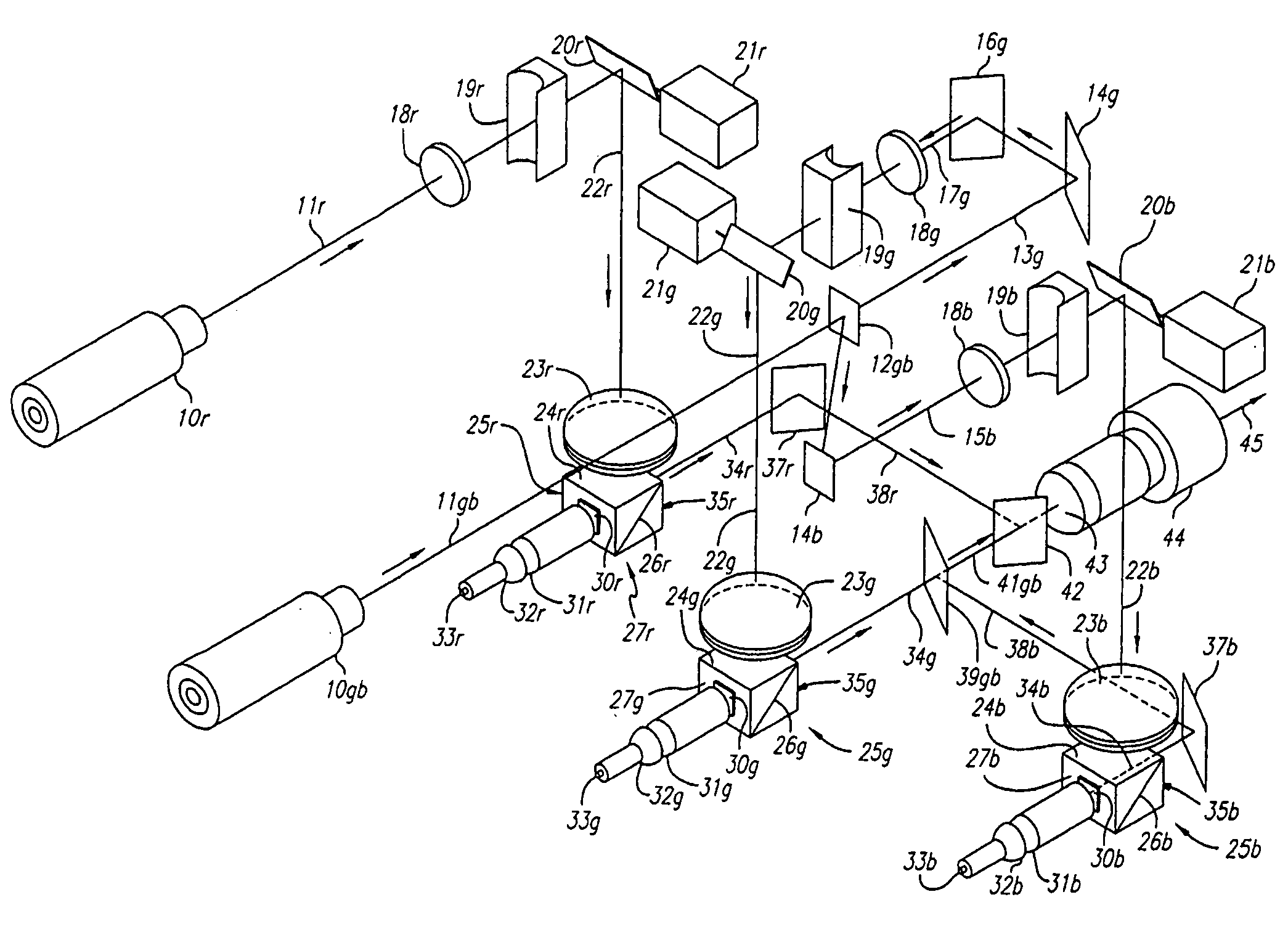
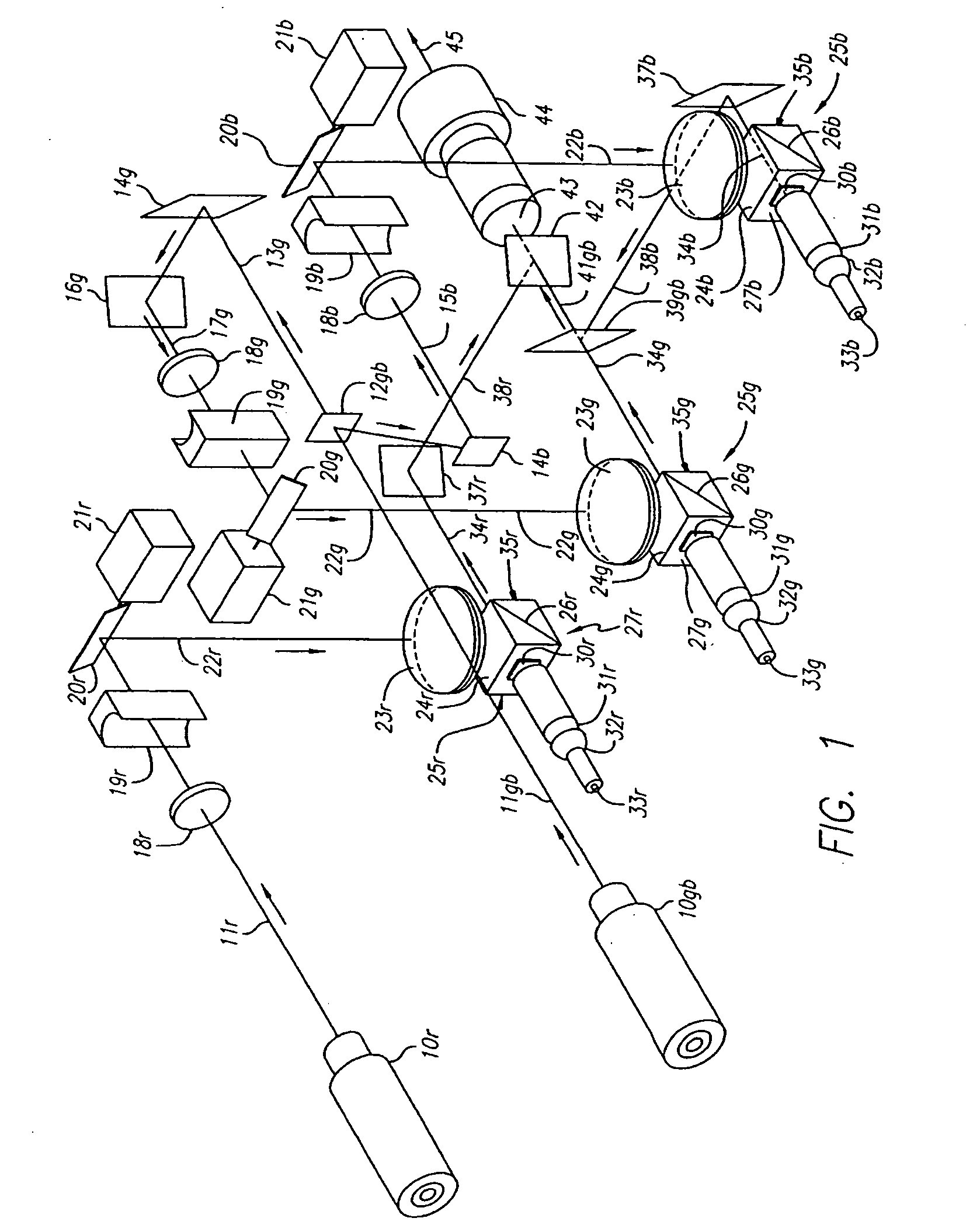
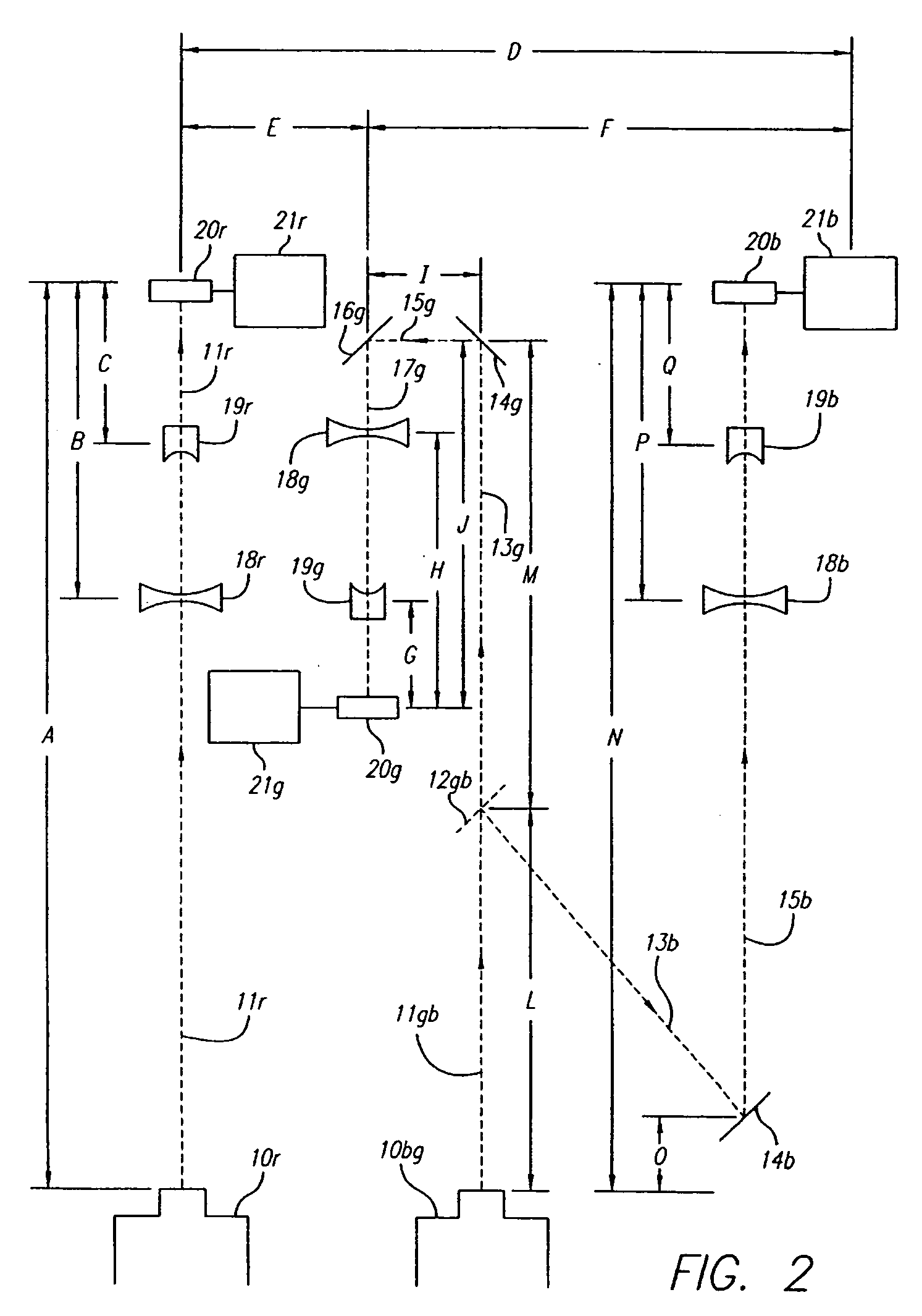
Sheet film is large format and medium format photographic film supplied on individual sheets of acetate or polyester film base rather than rolls. Sheet film was initially supplied as an alternative to glass plates. The most popular size measures 4×5 inches; smaller and larger sizes including the gigantic 20×24 inches have been made and many are still available today.
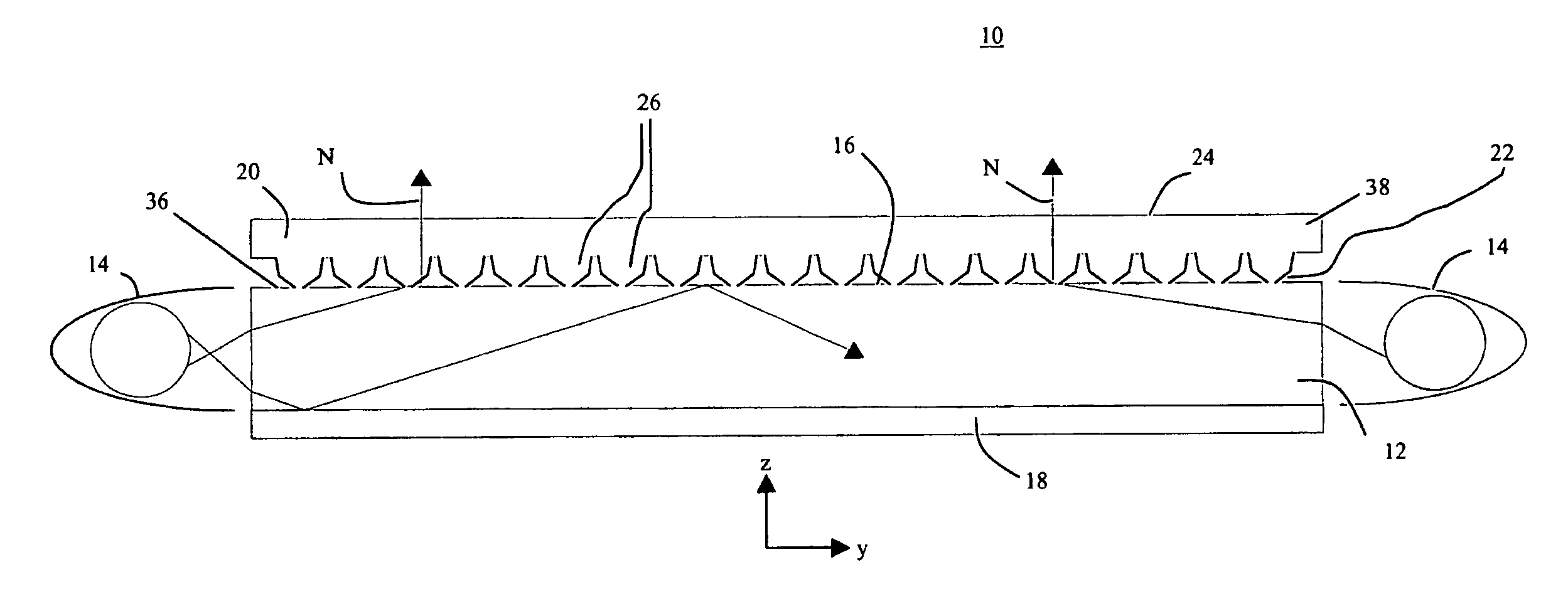
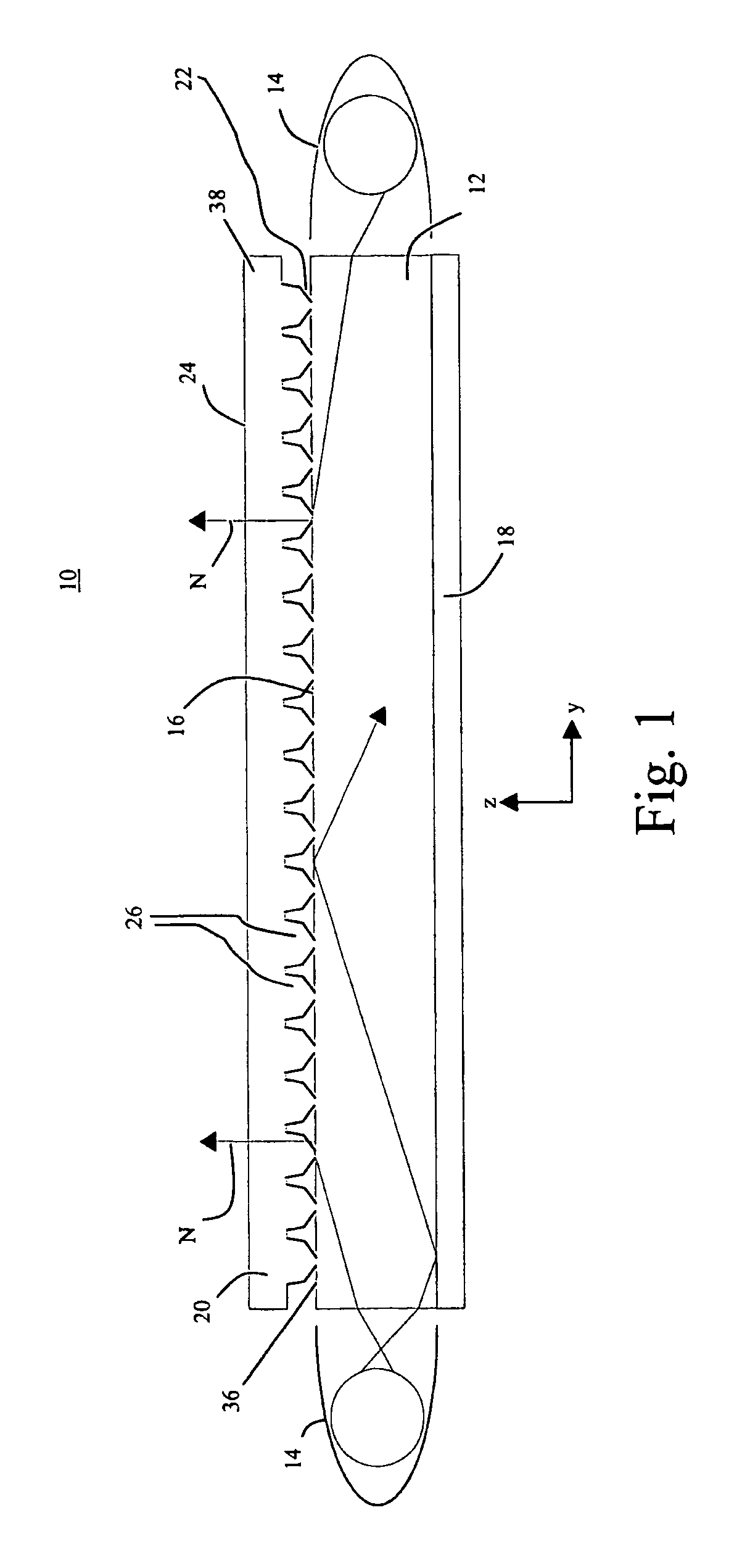
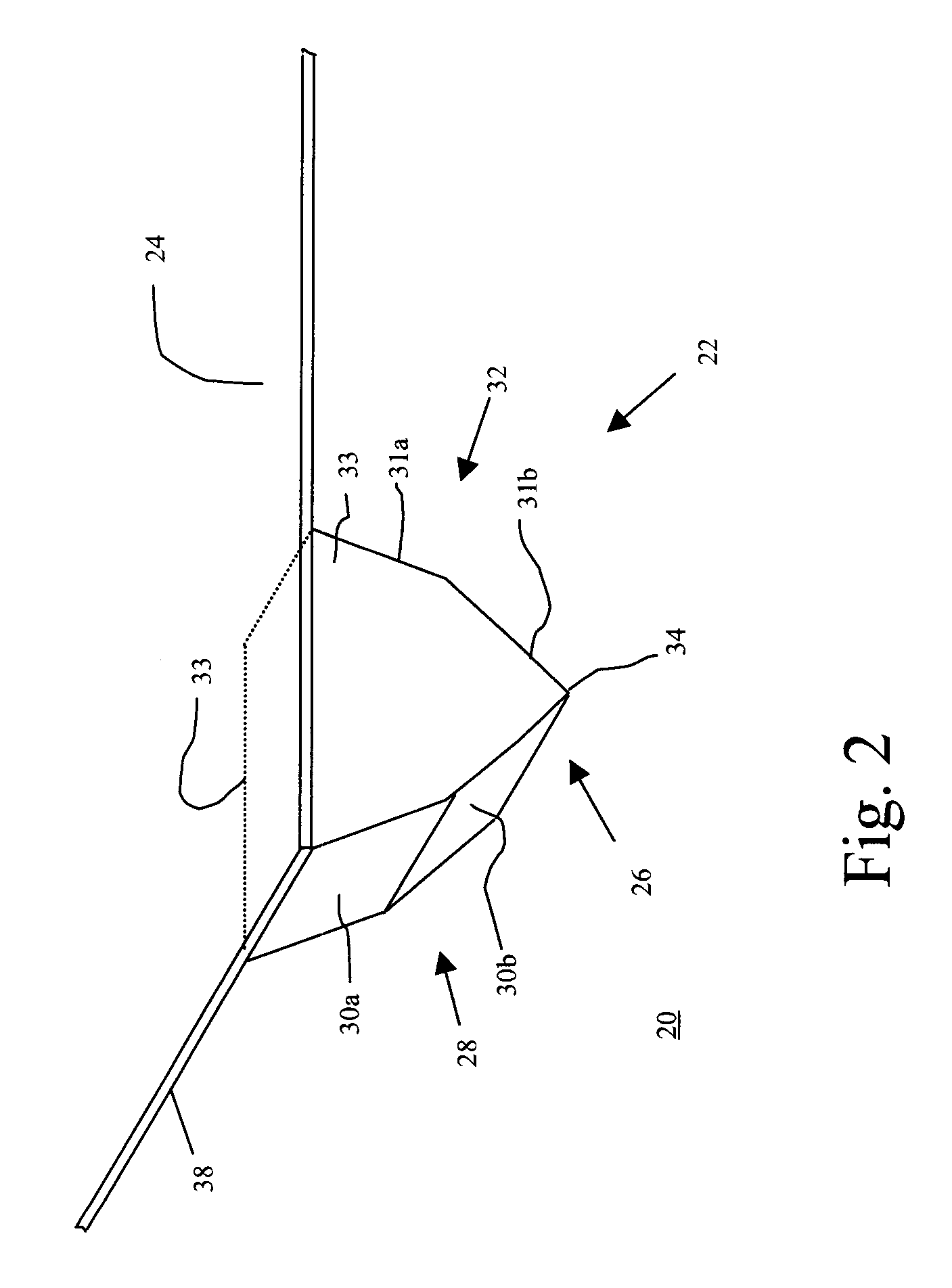
Apertured film
InactiveUS20050064136A1Increase in sizeFlatten filmButtonsLayered productsSheet filmLinear relationship
An apertured film web is disclosed. The web comprises a plurality of first regions having a first molecular orientation and a plurality of second regions having a second molecular orientation, the first and second regions being in an alternating and contiguous generally linear relationship in a first direction, the second molecular orientation being generally orthogonal to the first direction, and wherein the second region comprises openings defining apertures therein.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
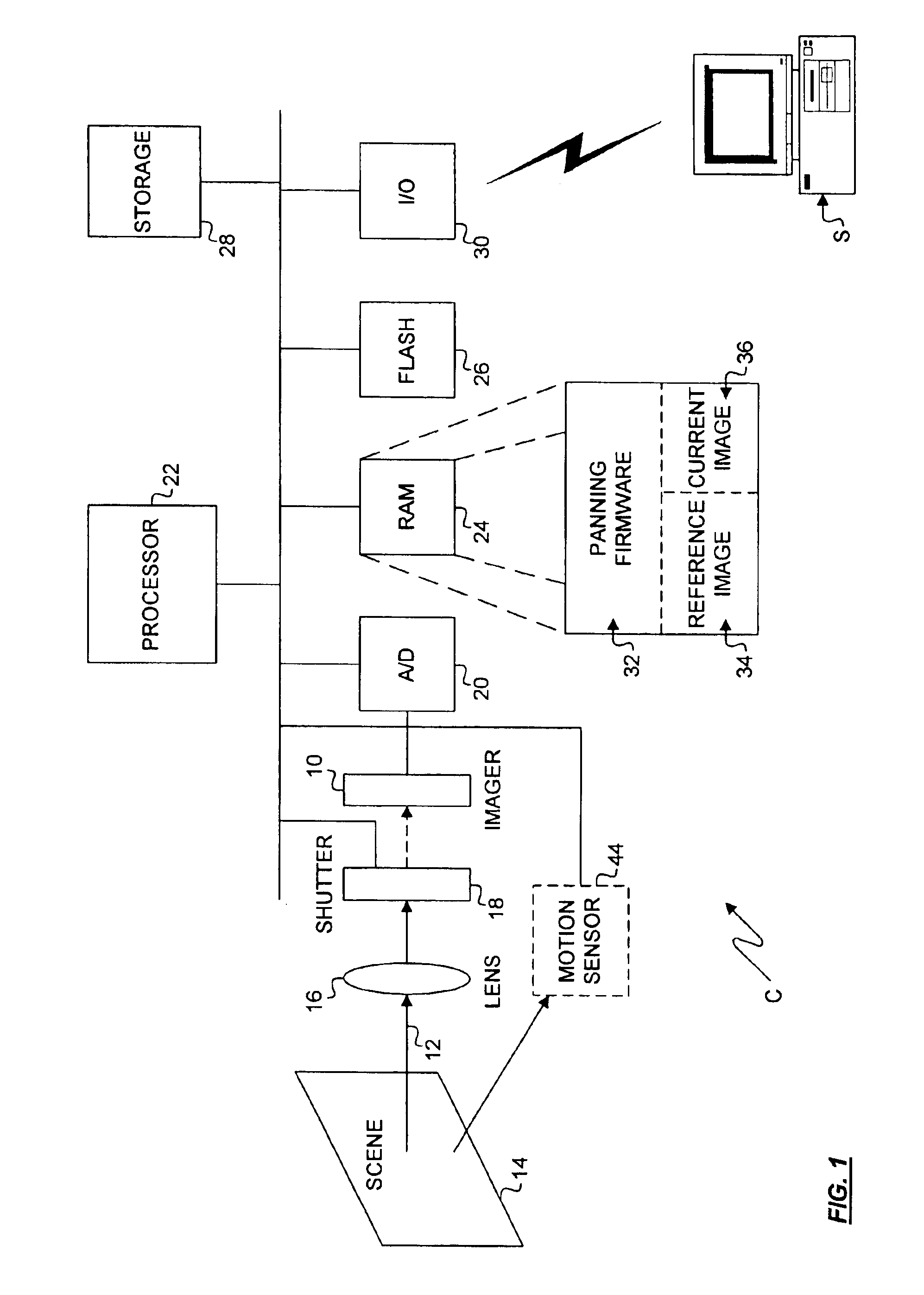
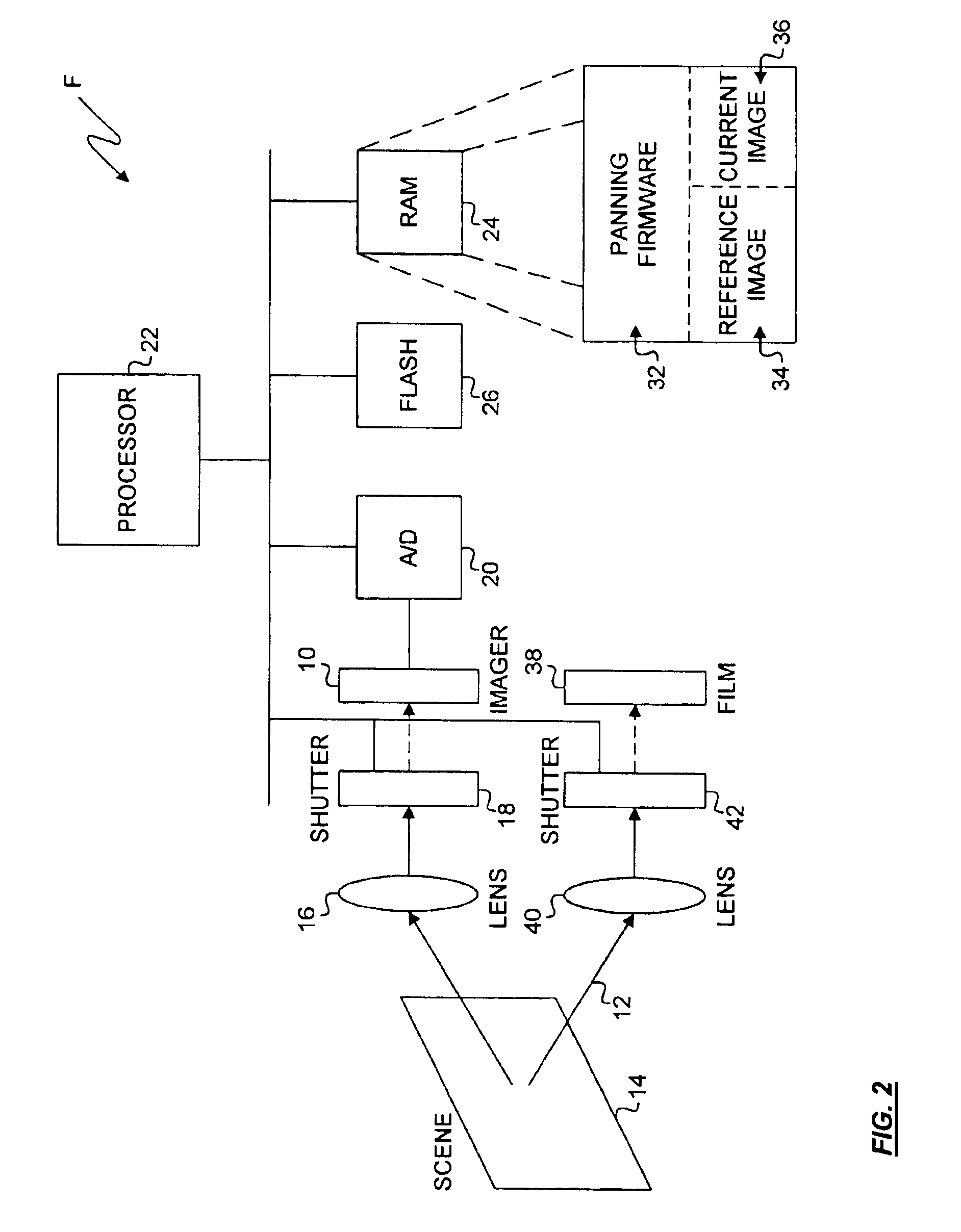
Method and apparatus for automatically capturing a plurality of images during a pan
A camera for automatically triggering a plurality of exposures during a pan based on a measure of camera displacement. During a pan, the camera regularly acquires images to compare a recently acquired image to a reference image. If the recently acquired image is optimally overlapped with the reference image, an exposure is triggered. In a digital camera, the images may be acquired with the native imager. In a film-based camera, or as an alternative embodiment for the digital camera, a sensor may be used to measure displacement. A series of images comprising a pan may be stored in the camera, or alternatively, each subsequent image may be stitched to a previous image to create a single panoramic image.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
X-ray labeling tape
A marking tape for transferring information written thereon to a film when the film is exposed to x-rays. The tape is a laminate of an upper film, a radiopaque emulsion, and a lower film. The top surface of the upper film is partially coated with a writable ink, and the ink coating positioned directly over the radiopaque emulsion. Pressure exerted by the user while writing on the ink surface causes the underlying emulsion to part. When the marking tape is affixed to a film cassette, x-rays penetrate the marking tape in those areas where the emulsion has been parted, the underlying film is exposed, and the information entered on the marking tape is thereby transferred to the film. The marking tape can be made in different sizes and radiopacities that can be distinguished by color-coding the writable surface.
Owner:DESENA DANFORTH
Imaging system
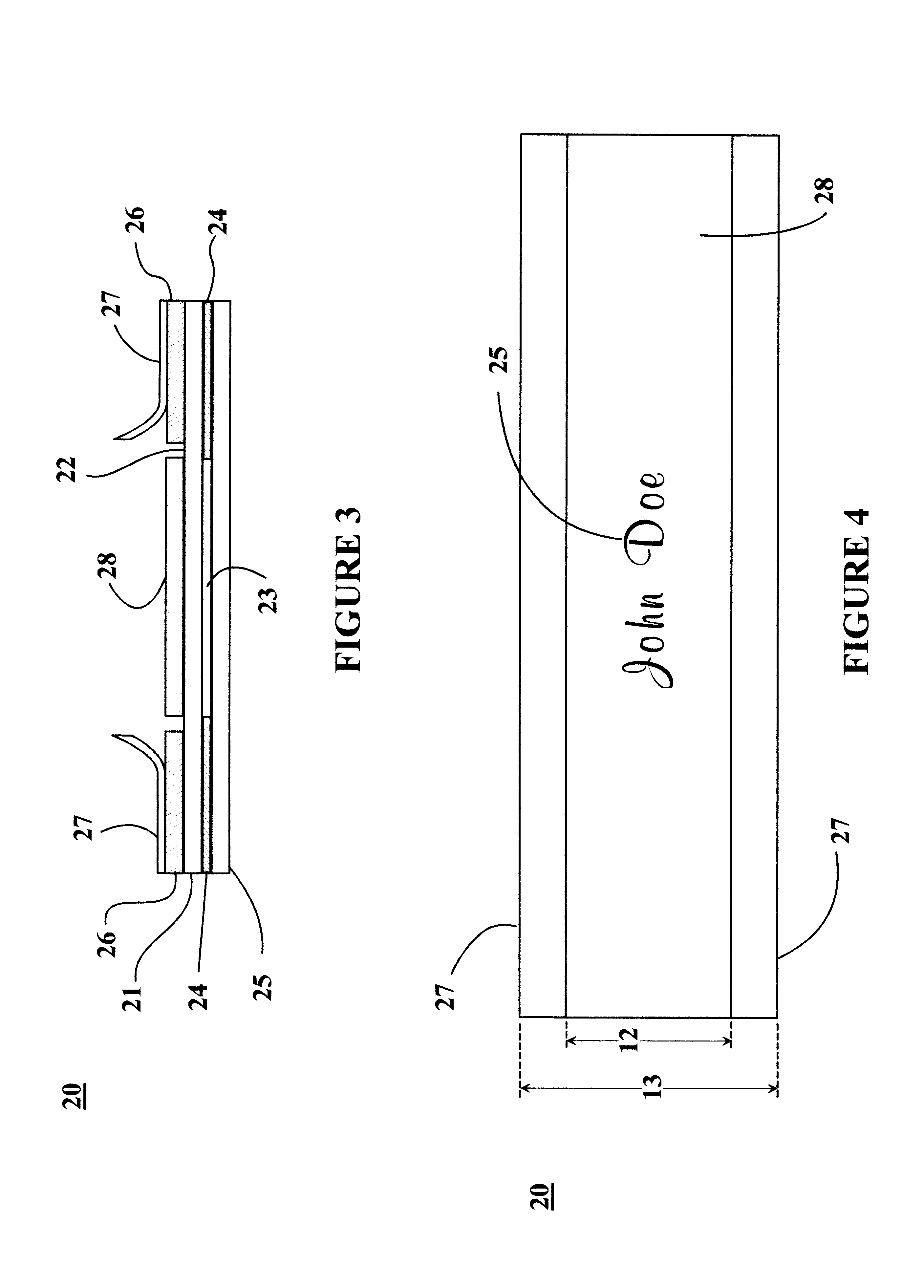
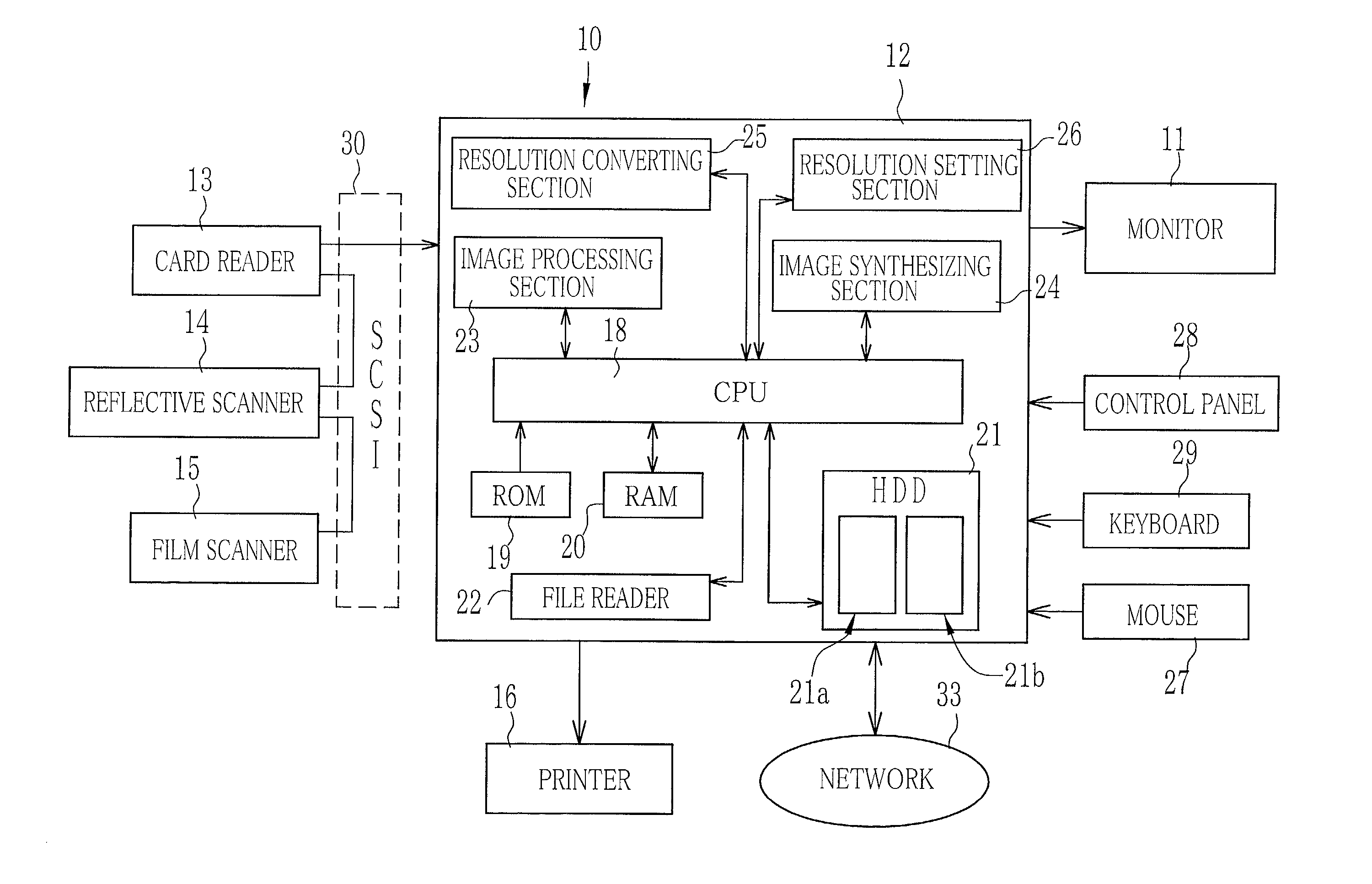
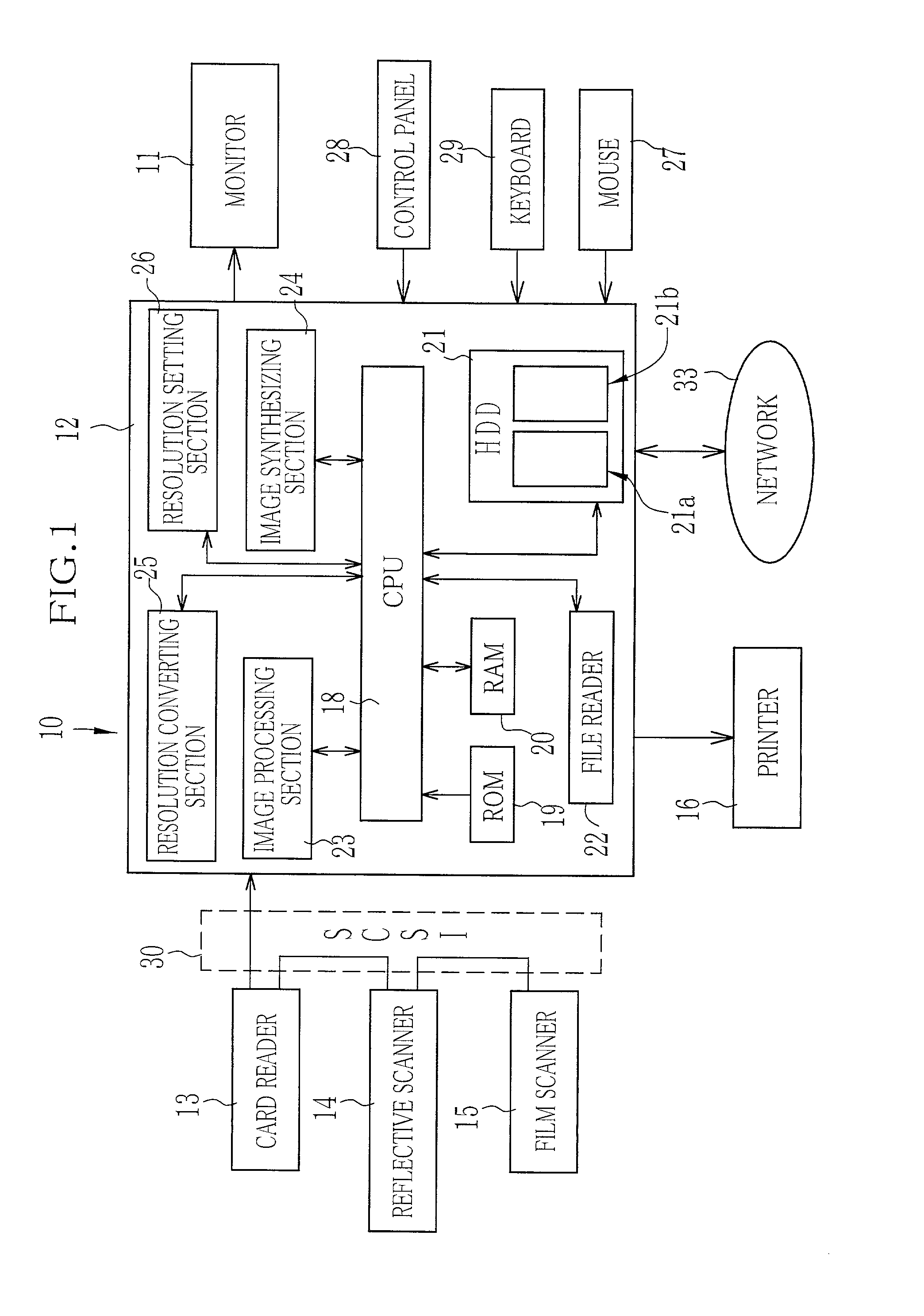
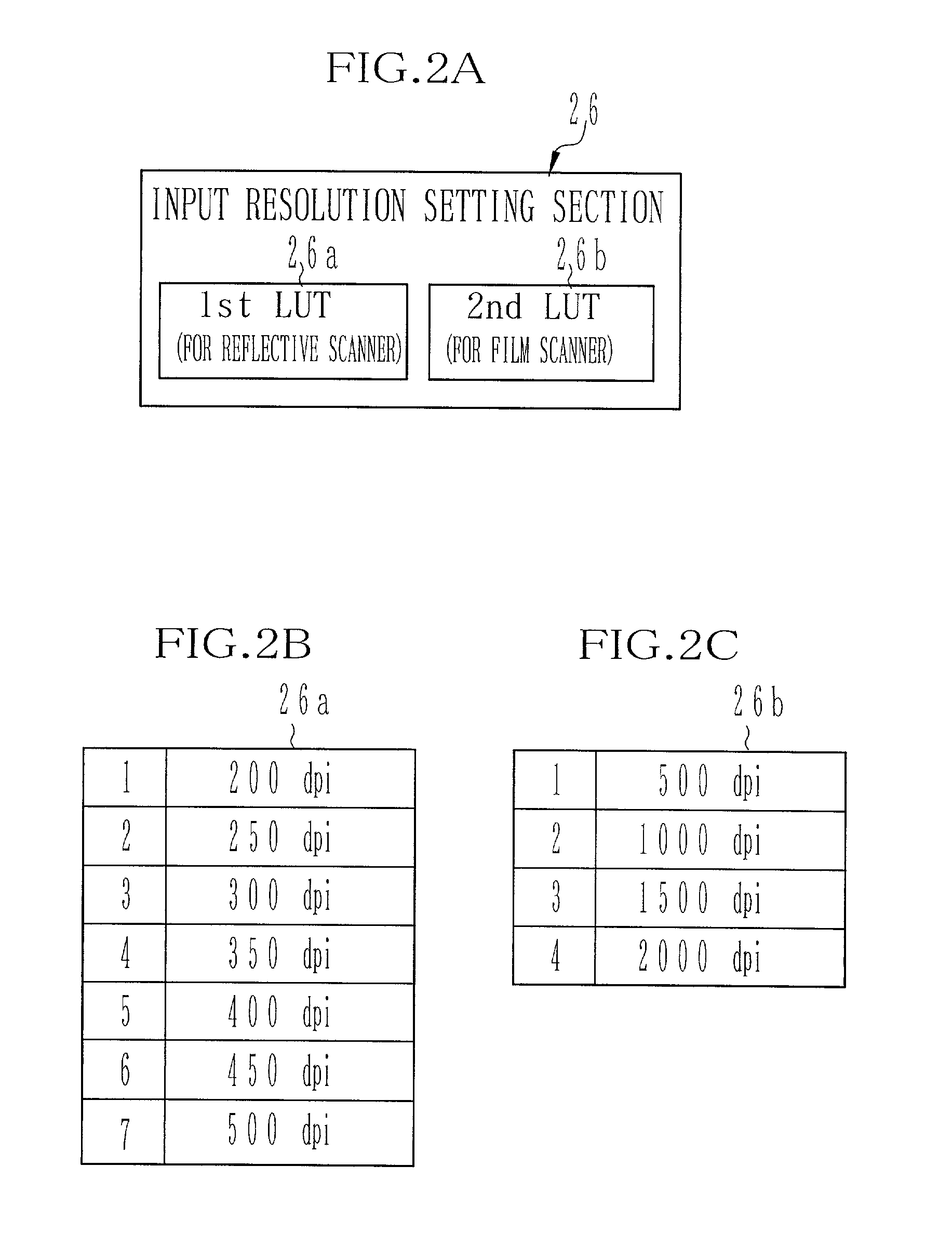
An imaging device (10) has a card reader (13), a reflective scanner (14) and a film scanner (15). The scanners has a pre-scanning mode of a low resolution and a fine scanning mode of a higher resolution. A preview image is displayed on the basis of image data taken from an original image through the scanner in the pre-scanning mode, and a cropping area of the original is designated on the preview image. An input resolution setting section (26) automatically sets the higher resolution for the fine scanning in accordance with the original size of the cropping area, a print size of the cropping area, and an output resolution of a printer (16). Based on image data taken at the higher resolution from the cropping area of the original image, the printer prints out an image.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP +1
Illumination apparatus and film
InactiveUS20070223252A1Easy to manufactureLow costOptical light guidesReflectorsTotal internal reflectionLight guide
An illumination apparatus comprises:(a) at least one light source;(b) a light guide for accepting light from the at least one light source and for guiding the light using total internal reflection, the light guide having a top surface;(c) a light extracting film having an input surface optically coupled with the top surface and an output surface for providing light,wherein the input surface comprises a plurality of features which are optically coupled to the top surface of the light guide, each feature having:(i) a first side comprising two or more planar segments; and(ii) a second side comprising two or more planar segments, andwherein the first and second sides intersect at an apex.
Owner:SKC HAAS DISPLAY FILMS CO LTD
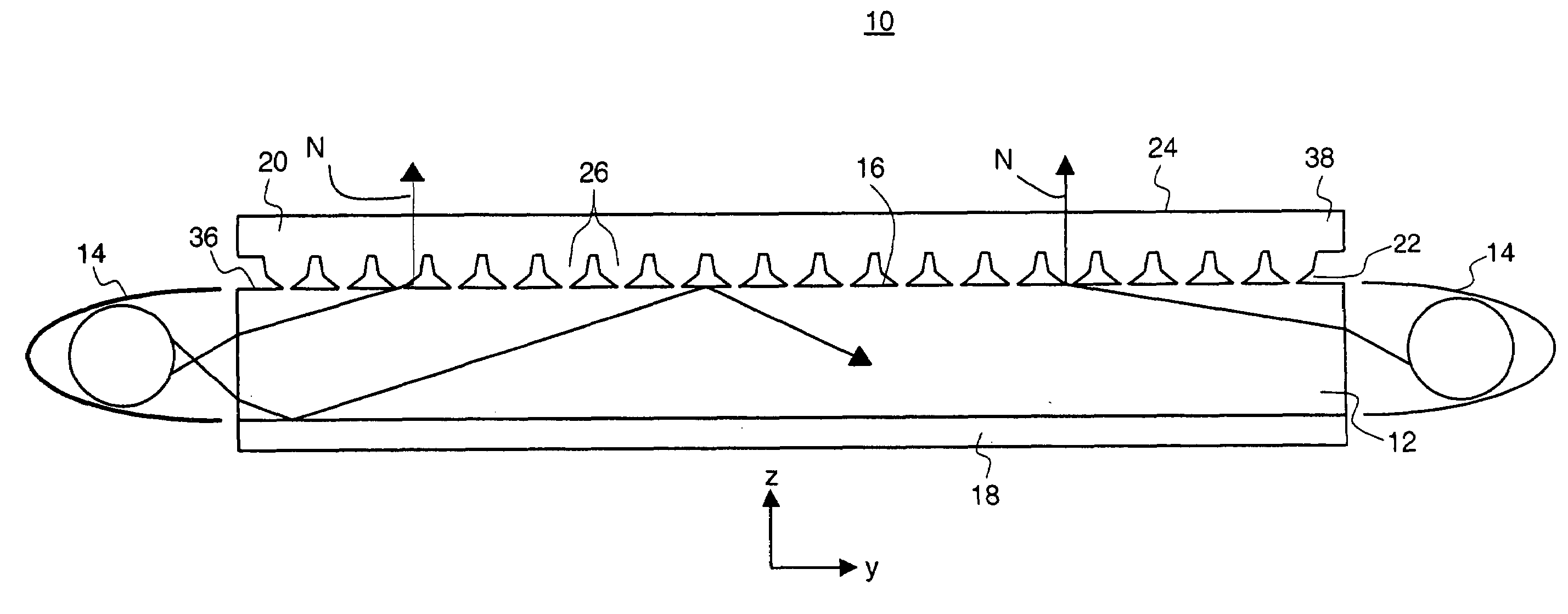
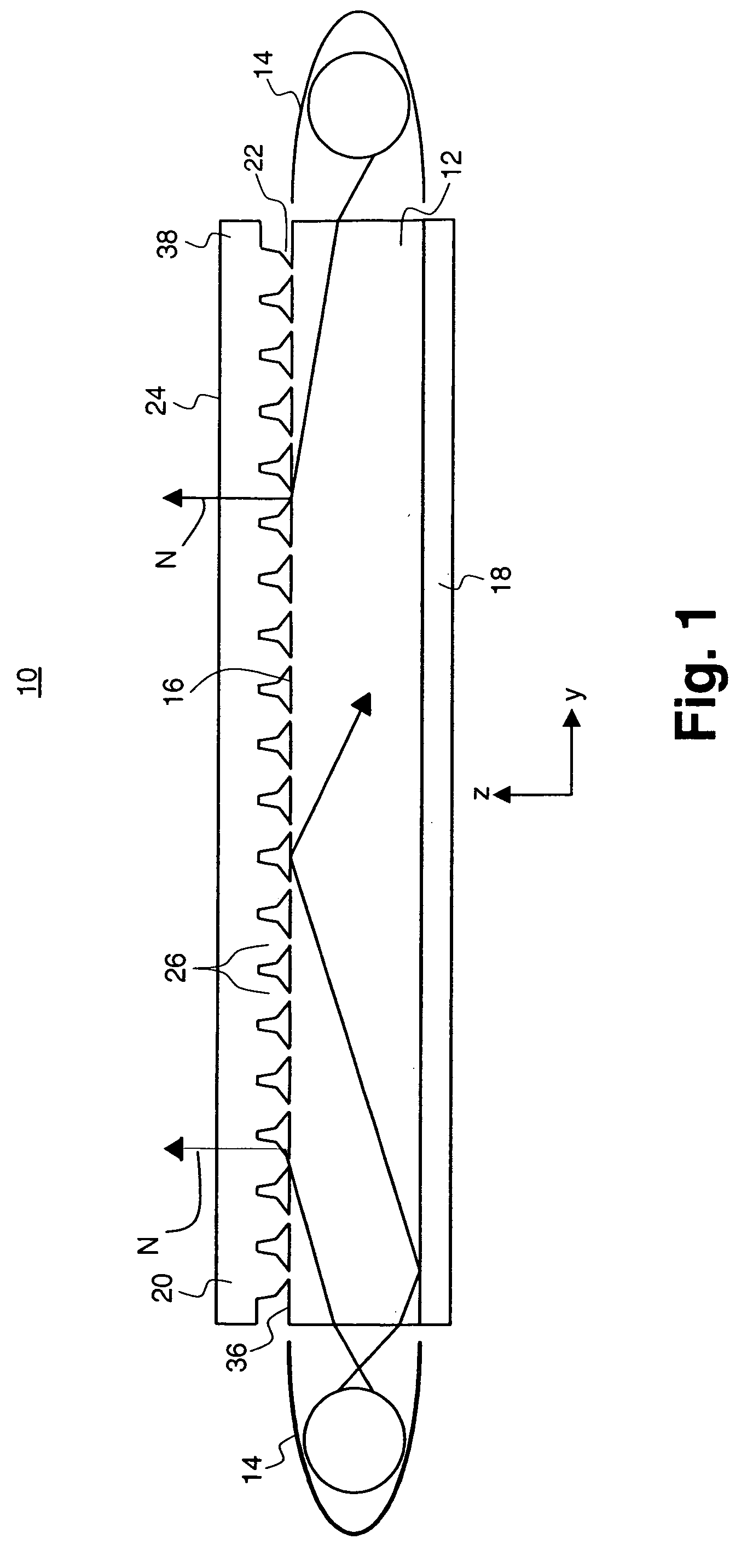
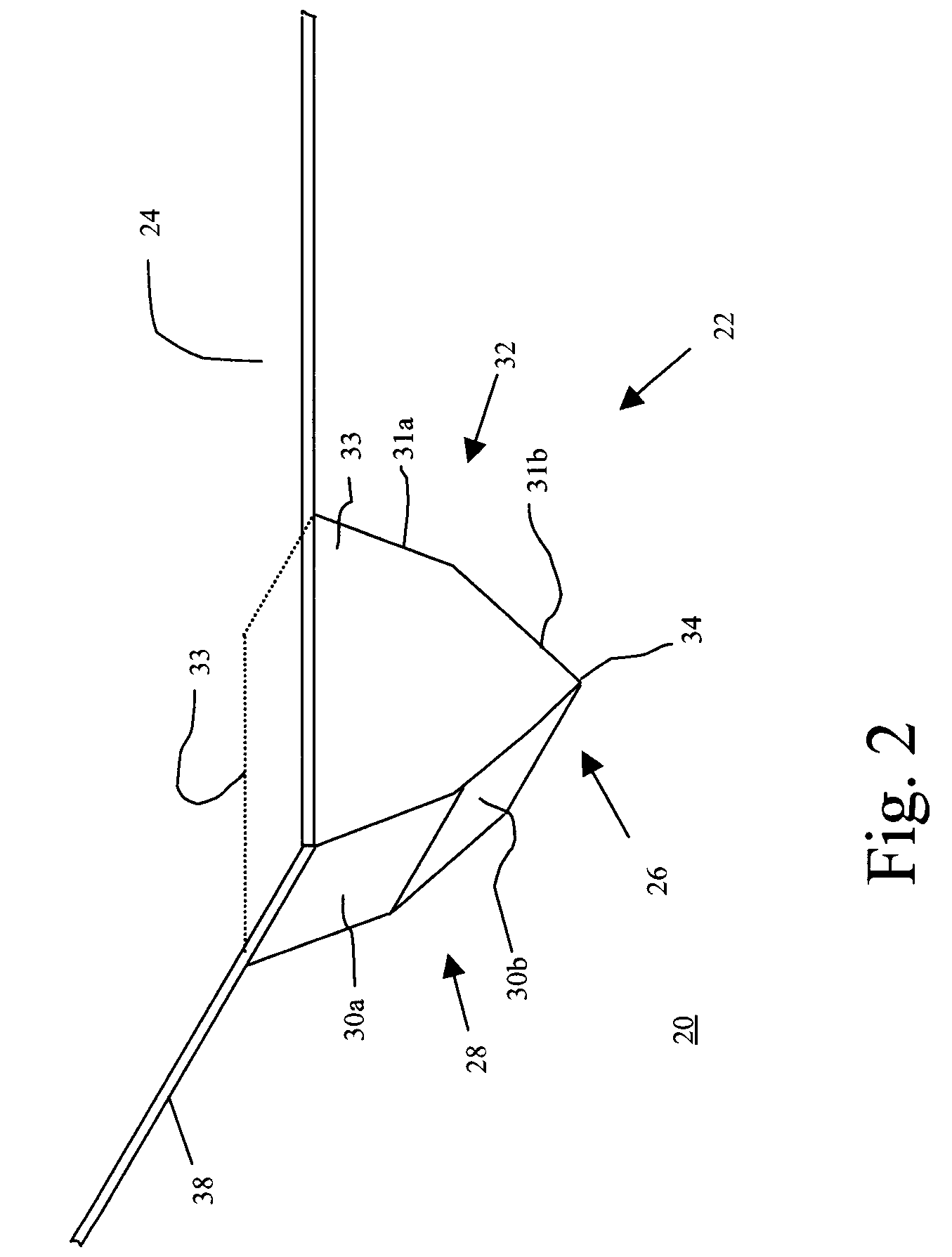
Film type apparatus for providing haptic feedback and touch screen including the same
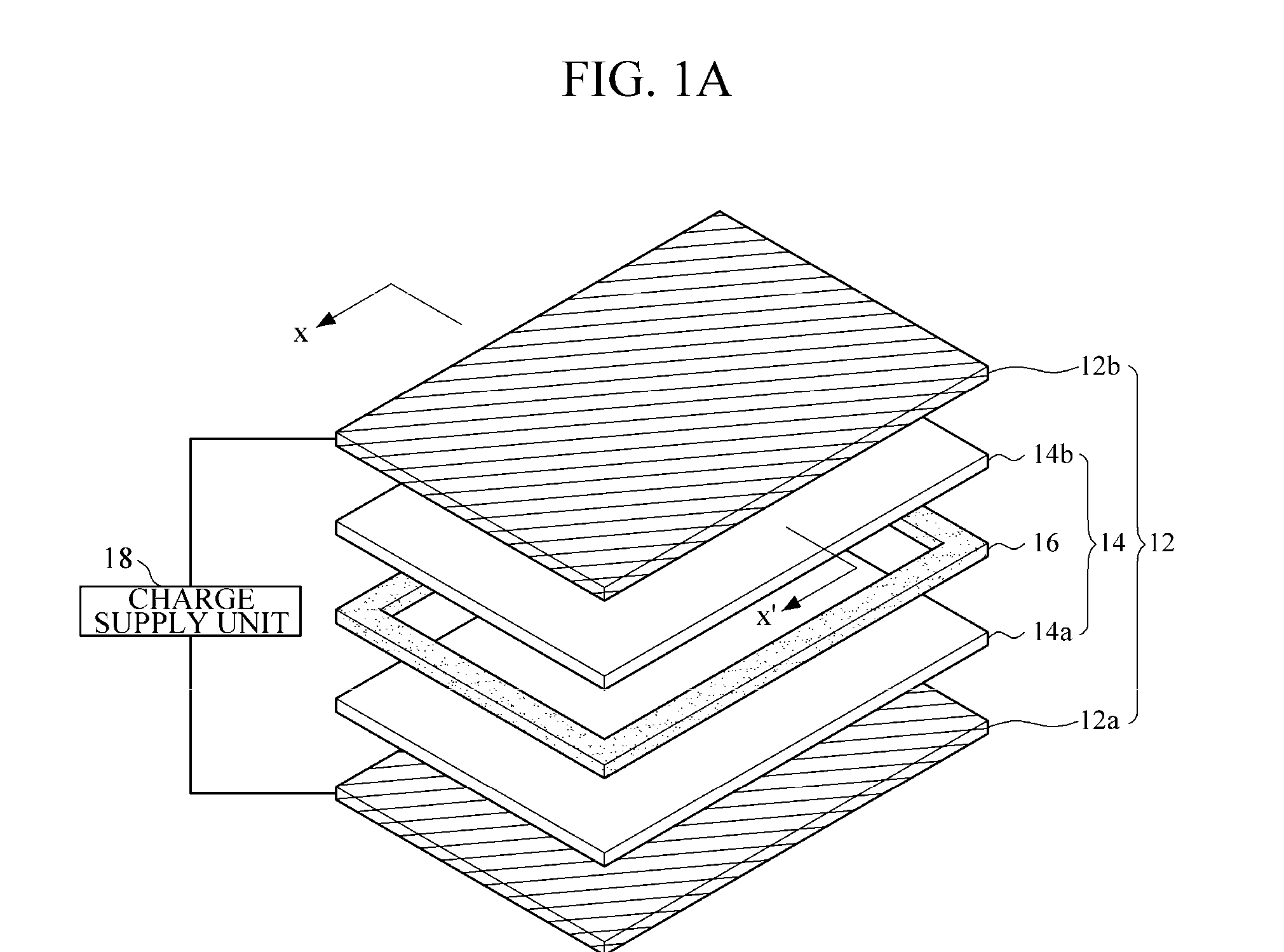
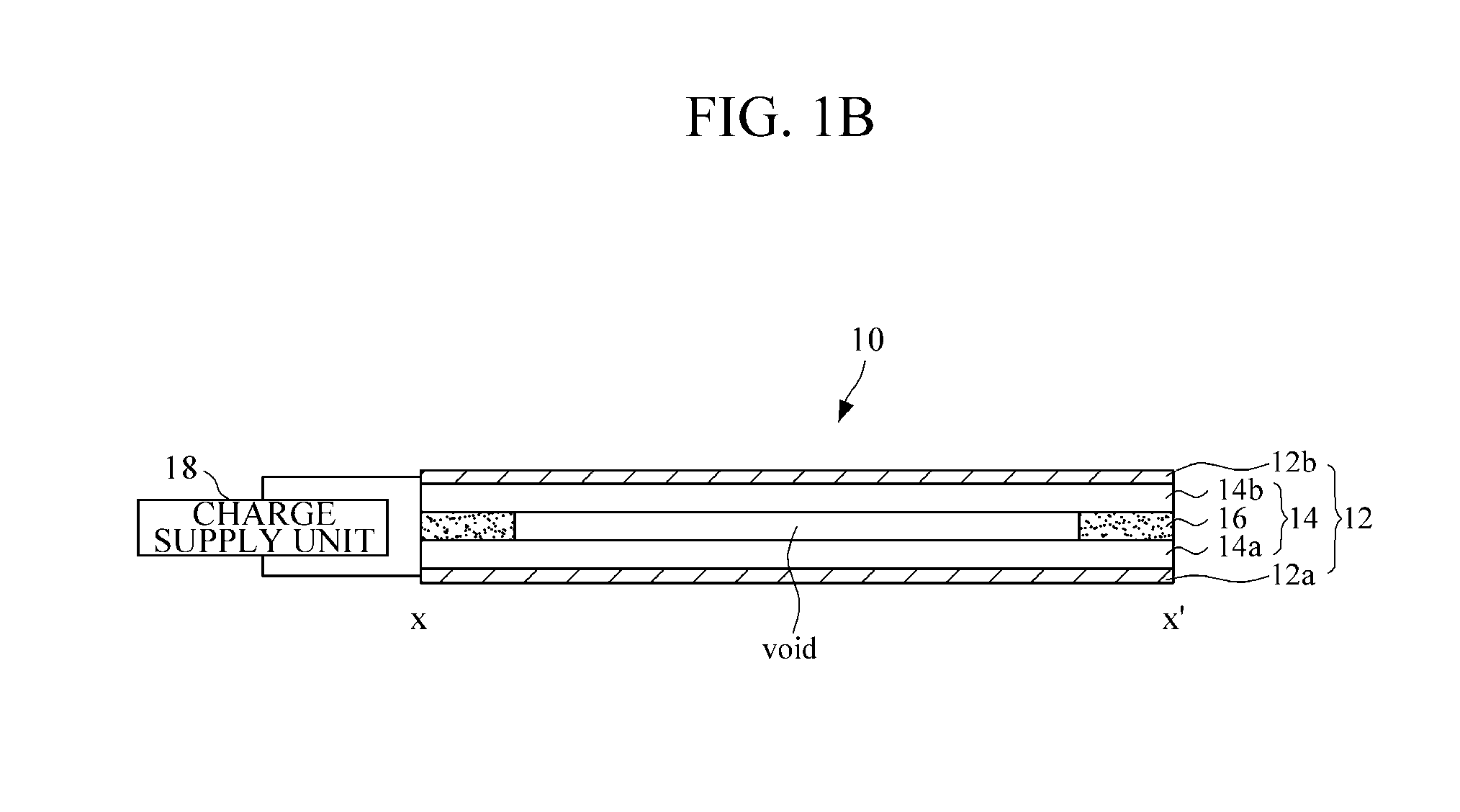
InactiveUS20120306790A1Small volumeThin thicknessElectronic switchingInput/output processes for data processingCapacitanceSheet film
A film type apparatus for providing haptic feedback and a touch screen including the same are provided. In the film type apparatus, a plurality of unit haptic feedback providing apparatuses are arranged in an array. Each of the unit haptic feedback providing apparatuses includes a lower electrode, a lower charge capacitive member disposed on the lower electrode, an upper charge capacitive member disposed apart from the lower charge capacitive member, a spacer disposed between the lower and upper charge capacitive members to separate the lower and upper charge capacitive members, an upper electrode disposed on the upper charge capacitive member, and a charge supply unit connected to the lower and upper electrodes to supply electric charge.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
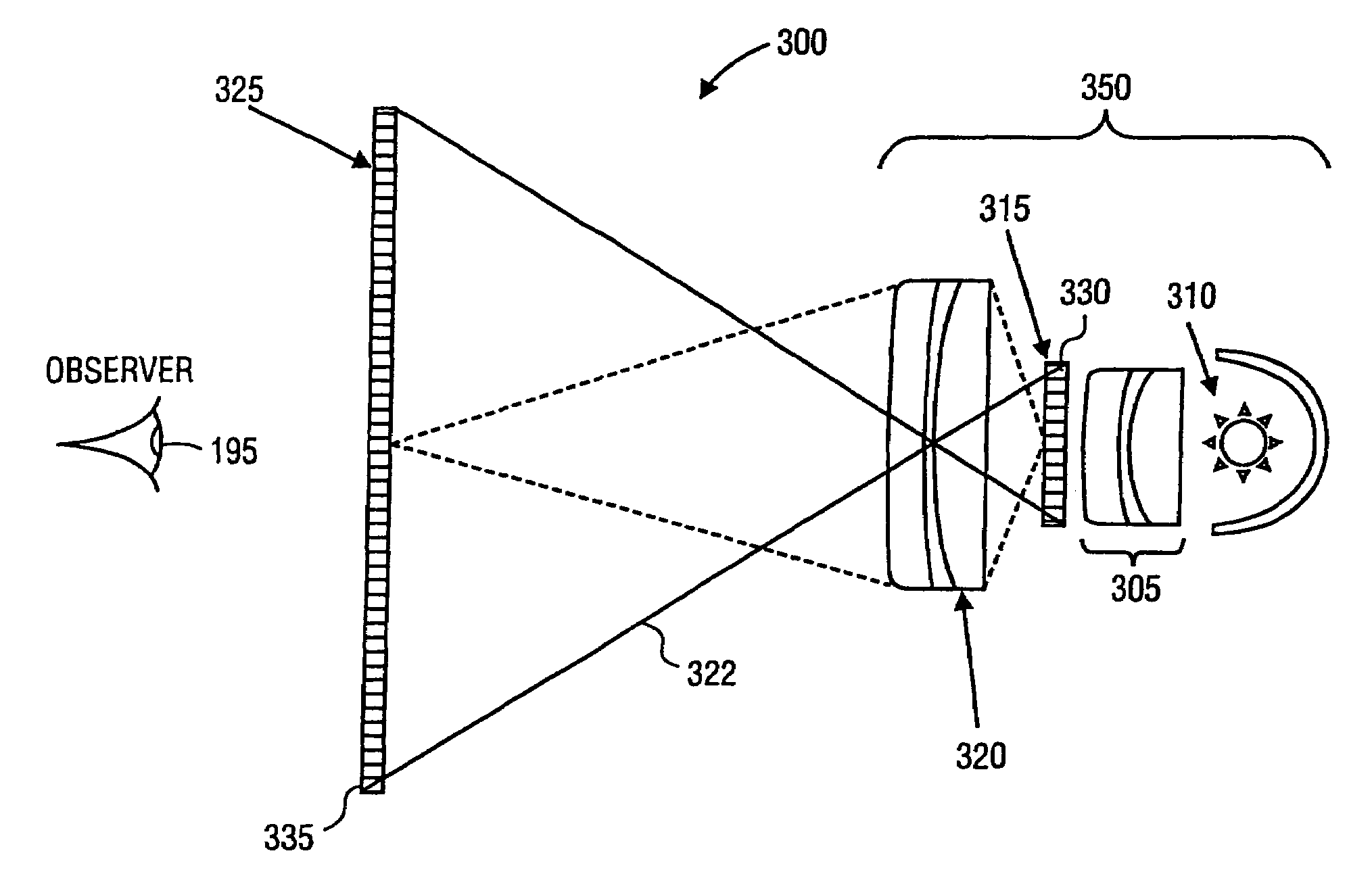
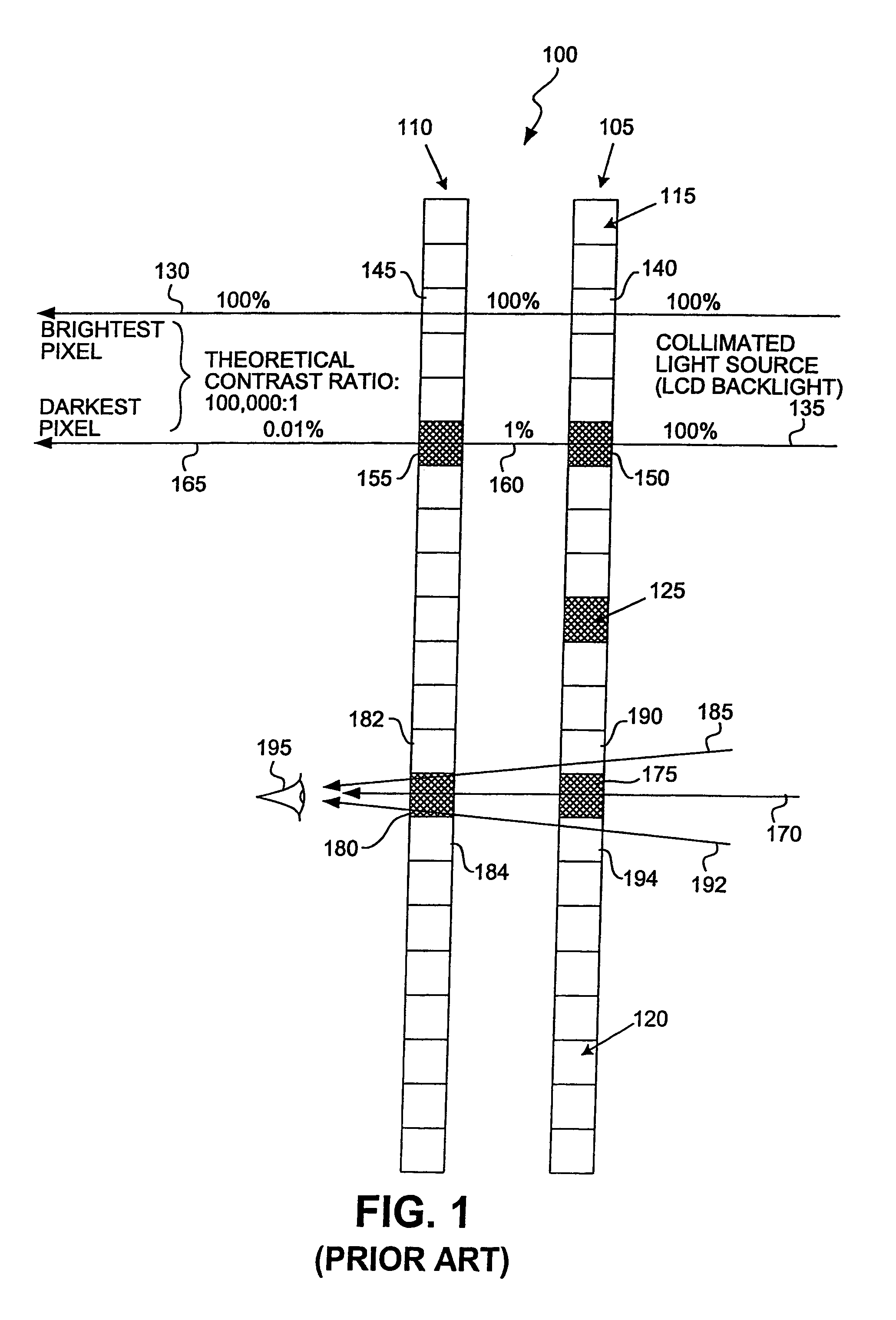
Dual-stage high-contrast electronic image display
InactiveUS7002533B2Lower ratioSimple and inexpensive methodTelevision system detailsColor television detailsDual stageSheet film
Electronic displays are provided which can reproduce image data with high contrast ratios and a gray scale range comparable to conventional X-ray film viewed on a light box. One such display includes a rear low-resolution LCD or DLP display which projects an image onto a high-resolution LCD display. In such embodiments, the mechanical and optical registration between the two displays is not critical. Therefore, modulation transfer function and distortion of the projection optics are not critical. Accordingly, the brightness of the inventive display can be maximized with high power lamps and high aperture projection optics. Because the display has a high dynamic range, the need for dynamic range compression algorithms is reduced.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
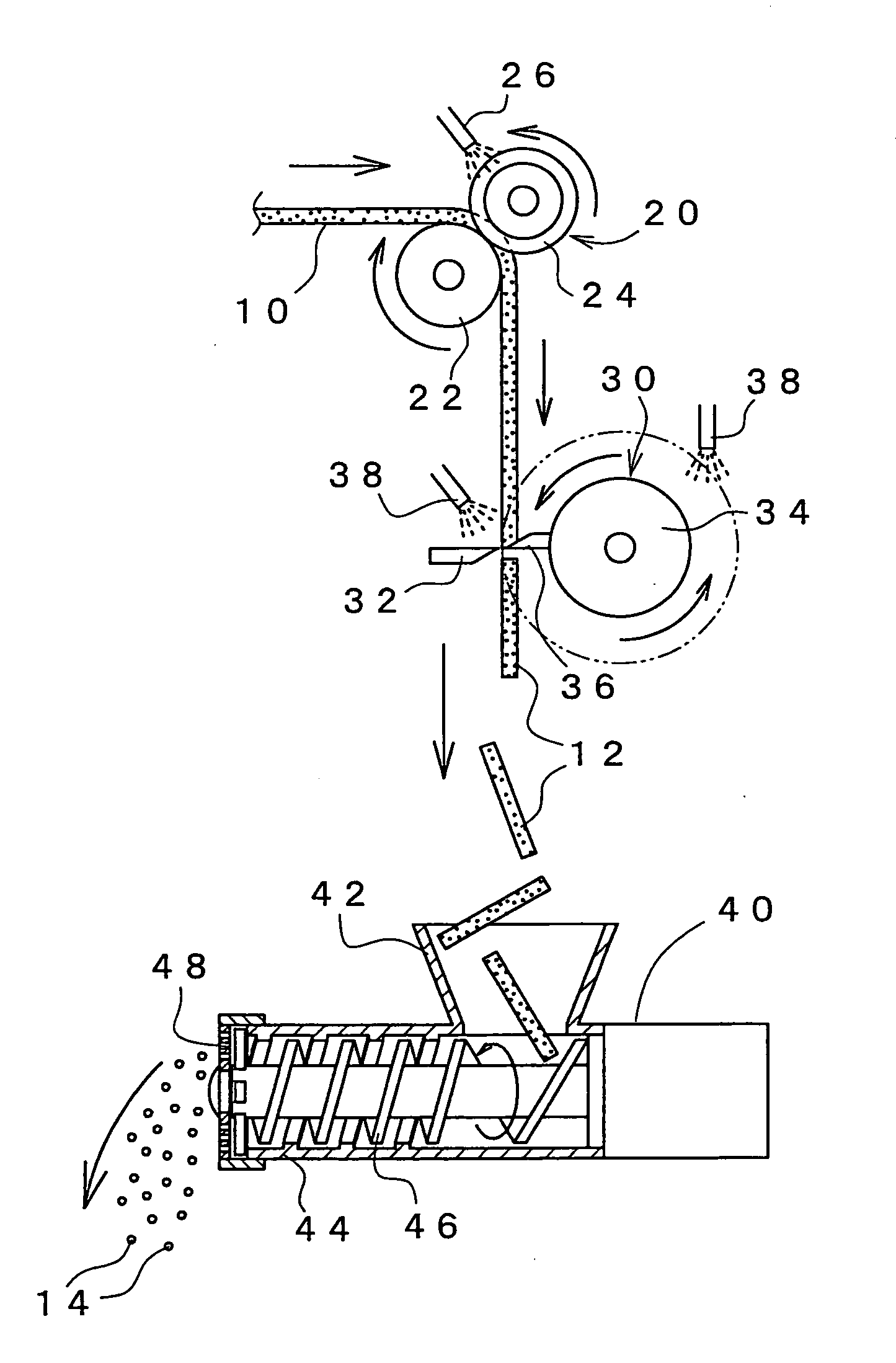
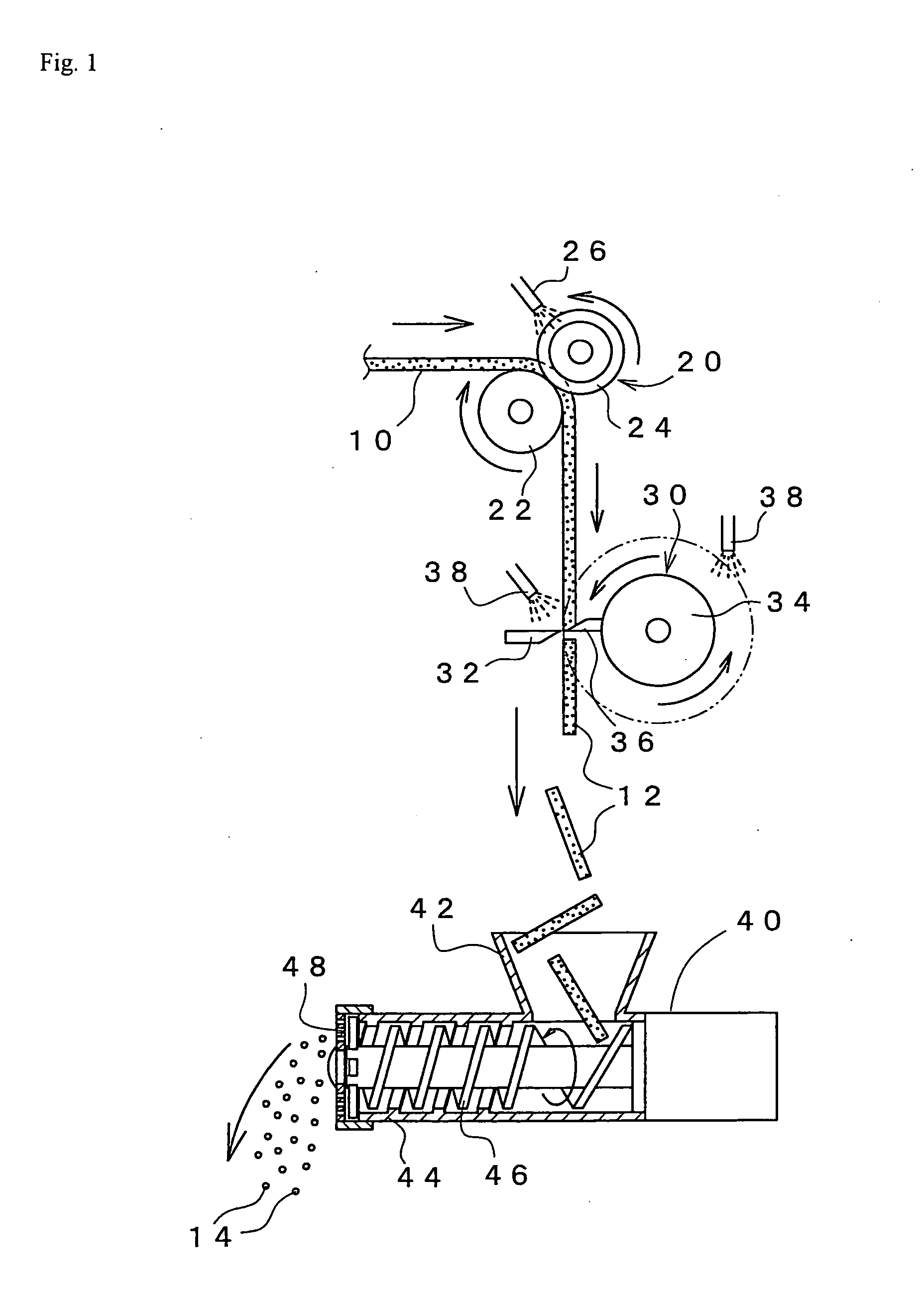
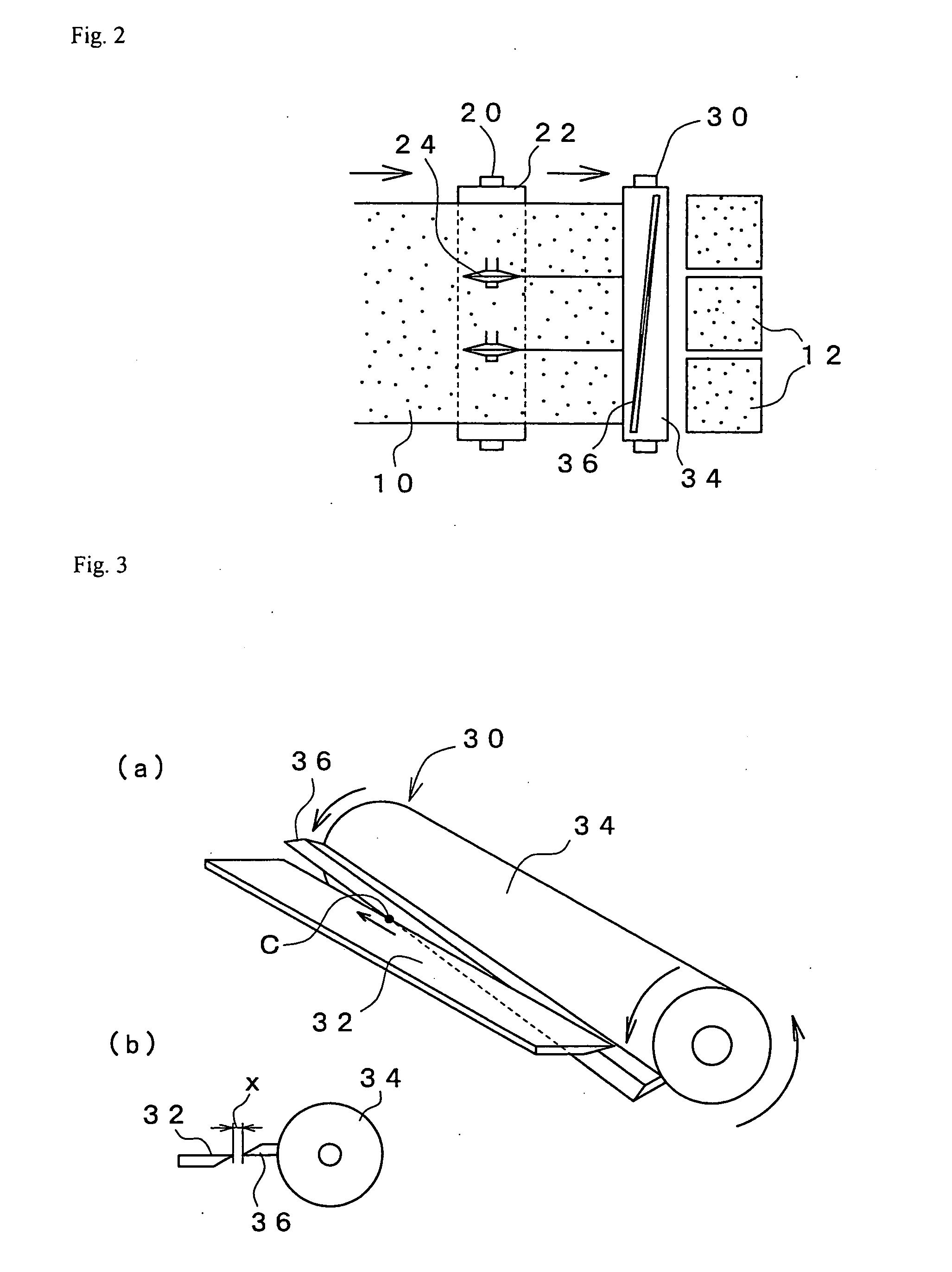
Method for dispensing a predetermined amount of film relative to load girth
The present invention provides a method and apparatus for dispensing a predetermined fixed amount of pre-stretched film based upon load girth. A non-rotating ring carries a belt. A film dispenser is mounted on a rotating ring, and the rotating ring includes a pulley that connects to the belt. Based upon the girth of the load to be wrapped, an amount of pre-stretched film to be dispensed for each revolution made by the rotating ring is determined. Good wrapping performance in terms of load containment (wrap force) and optimum film use is obtained by dispensing a length of pre-stretched film that is between approximately 100% and approximately 130% of load girth. Once the amount of film to be dispensed per revolution is determined, a mechanical ratio of ring drive to final pre-stretch surface speed (i.e., number of pre-stretch roller revolution / ring rotation) can be set. Thus, for each revolution of the rotating ring and dispenser, a predetermined fixed amount of film is dispensed and wrapped around the load.
Owner:LANTECH COM
Antisoiling hardcoat
InactiveUS6841190B2Easy to storeImprove the immunityTelevision system detailsCathode-ray/electron-beam tube vessels/containersSheet filmPerfluoropolyether
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Two Side Cut Reseal With Pressure Sensitive Adhesive and the Method for Making Same
InactiveUS20100111453A1Prevent premature deterioration of qualityAvoid damageCapsDecorative coversSheet filmHermetic packaging
Two side cut reseal with pressure sensitive adhesive. A flexible package having a reseal integrated within the opposite layers of its film is constructed using existing vertical form fill and seal packaging machines. The invention involves a single sheet of flexible packaging film web having at least three layers. In a preferred embodiment, the reseal is comprised of two offsetting score lines on interior and exterior sides of the film and spaced apart by 0.5 to 1 inch. The scoring creates lines of weakness, which define an opening in the package. Upon opening, a pressure sensitive adhesive layer, which is pattern applied in between the offsetting score lines, is exposed from an interior side of the film. The adhesive releasably adheres the inner and outer layers of the film back together once separated by a consumer.
Owner:FRITO LAY NORTH AMERICA INC
Multi-layered film window system
InactiveUS7281561B2Improve reflectivityReduce transmissionShutters/ movable grillesLight protection screensControl systemSheet film
A high R-rating window assembly storing multiple, reciprocating reflective flexible film layers in a sealed housing between rigid (e.g. glazed) layers. The glazed layers are separated on the order of 3 to 5-inches and are secured to low thermal conductivity framework pieces. The framework is capped with a motorized roller and film housing and the assembly is evacuated and filled with a desiccated, inert dry gas. Several plastic, reflective coated films are supported under tension in planar parallel relation between the glazing layers from the motorized roller and several guide rollers and guide tracks. Location sensors responsive to indicia on the films identify film position. Temperature sensors monitor ambient, internal and user set thermal conditions to control film exposure. The films are operable via a room control system and window controllers to define open, closed and partial exposure conditions. Alternative control functions may control film exposure in relation to room occupancy.
Owner:ANDERSON DONALD +1
Halogen-free resin composition and copper clad laminate and printed circuit board applying the same
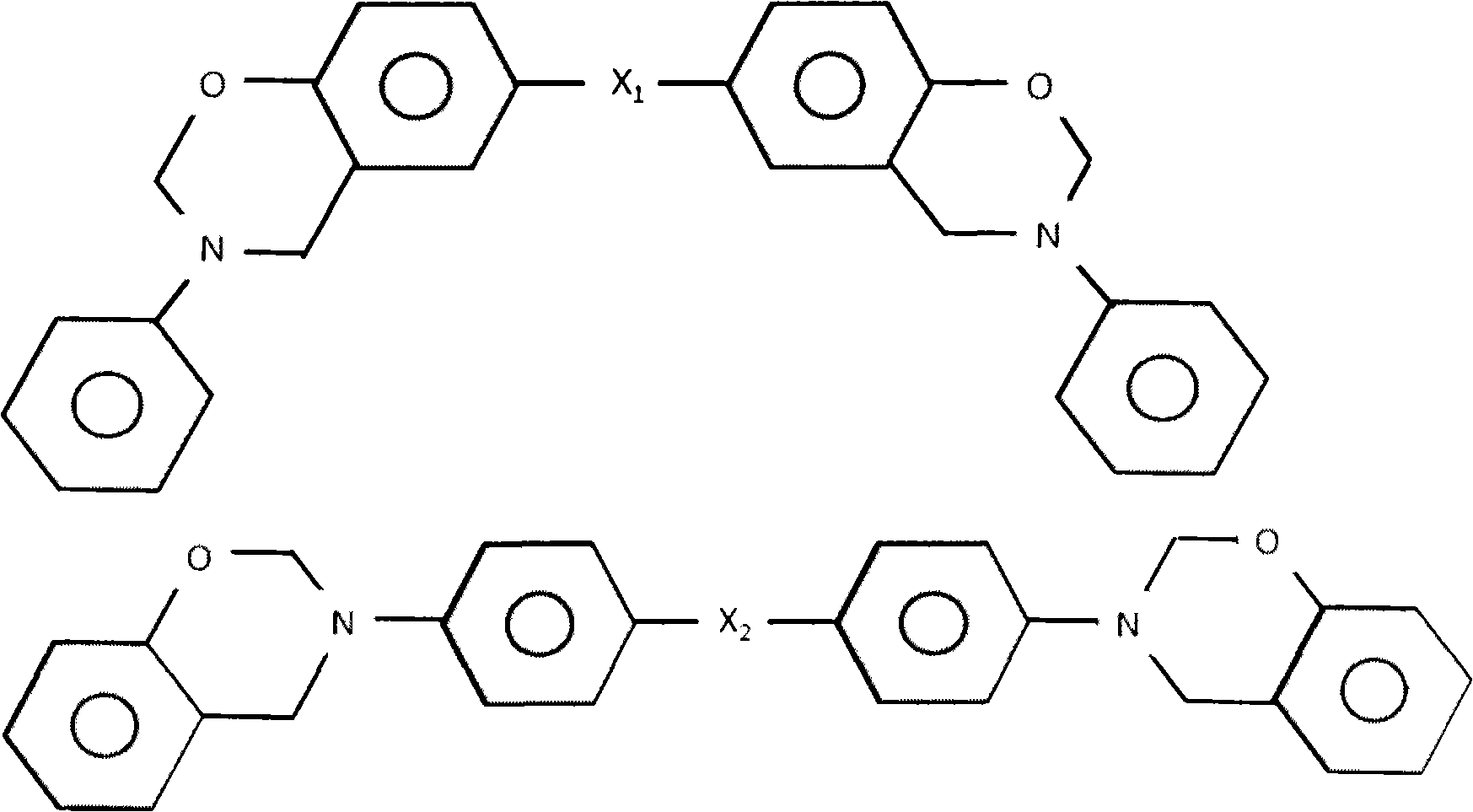
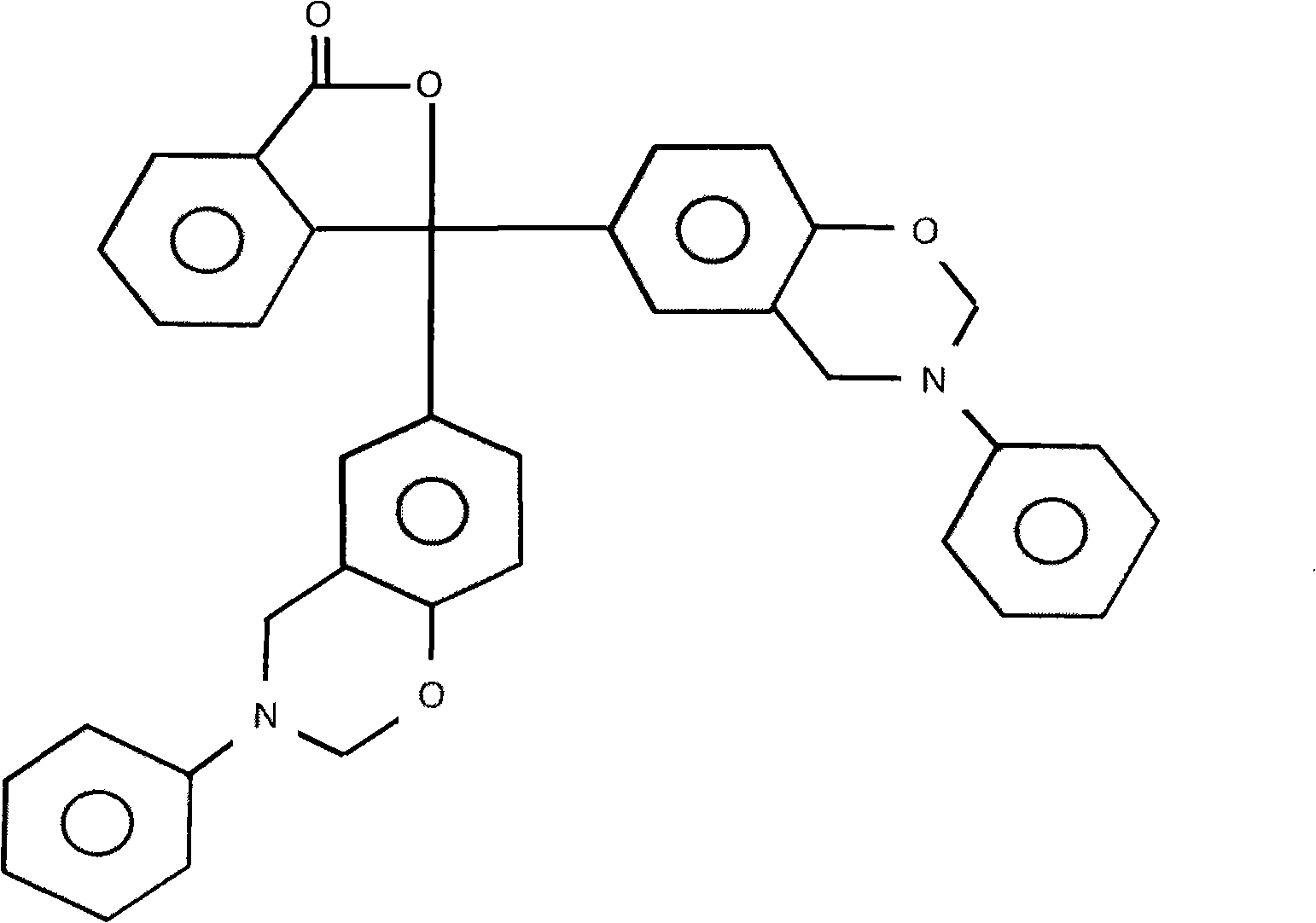
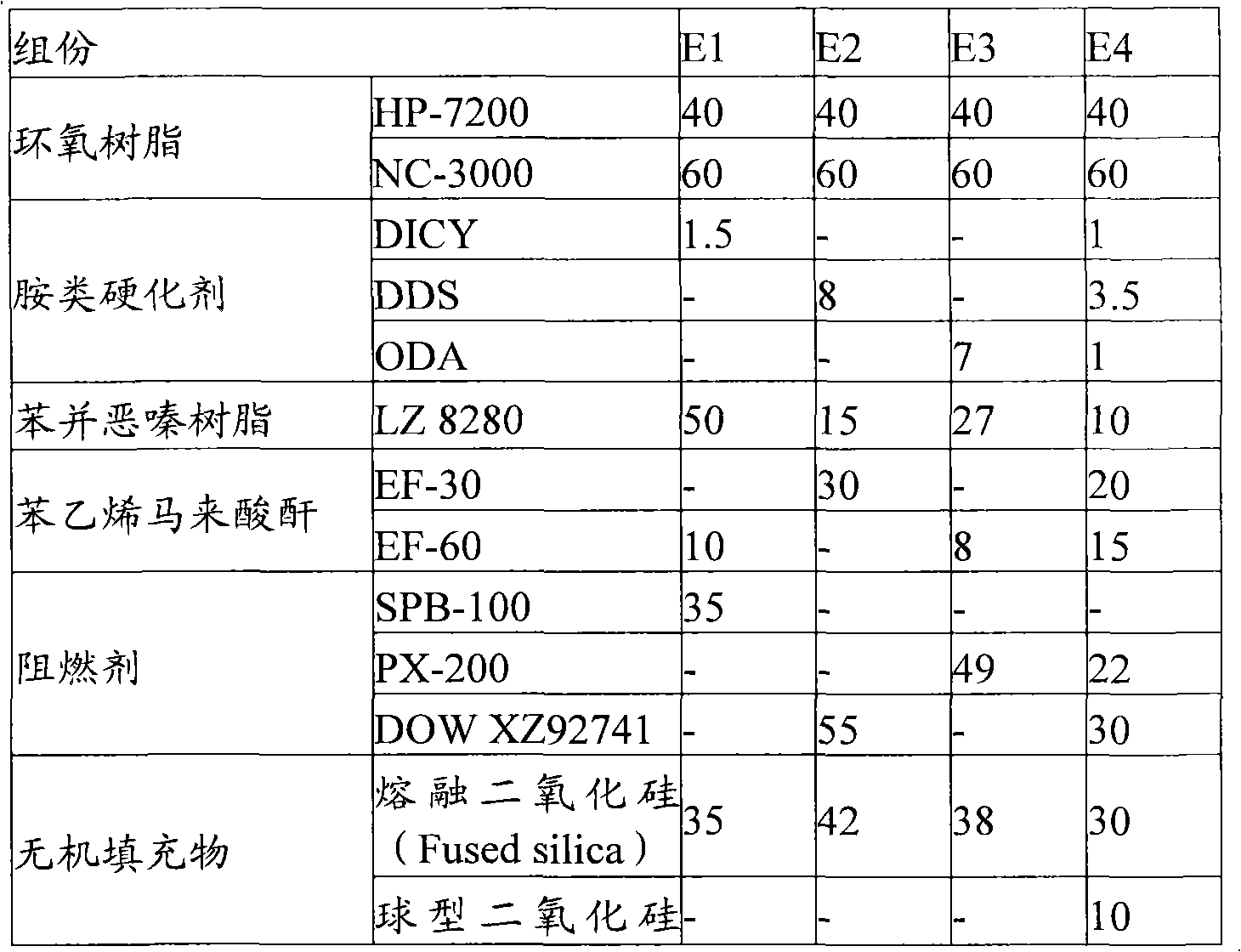
ActiveCN103131131ALow dielectric propertiesLow heat resistanceCircuit susbtrate materialsEpoxySheet film
The invention provides halogen-free resin composition, and a copper clad laminate and a printed circuit board applying the halogen-free resin composition. The halogen-free resin composition comprises, by weight, (A) 100 parts of epoxy resin, (B) 1 part -100 parts of benzoxazine resin, (C) 1part -100 parts of styrene maleic anhydride, (D) 0.5 part -30 parts of amine curing agents, and (E) 5-150 parts of halogen-free flame retardants. By means of the specified constituents and ration, the halogen-free resin composition achieves the purposes of low dielectric constant, low dielectric loss, high heat resistance, and high flame resistance, can be manufactured into semi-solidified rubber pieces or resin films, and then achieves the purposes of being applied to the copper clad laminate and the printed circuit board.
Owner:ELITE MATERIAL
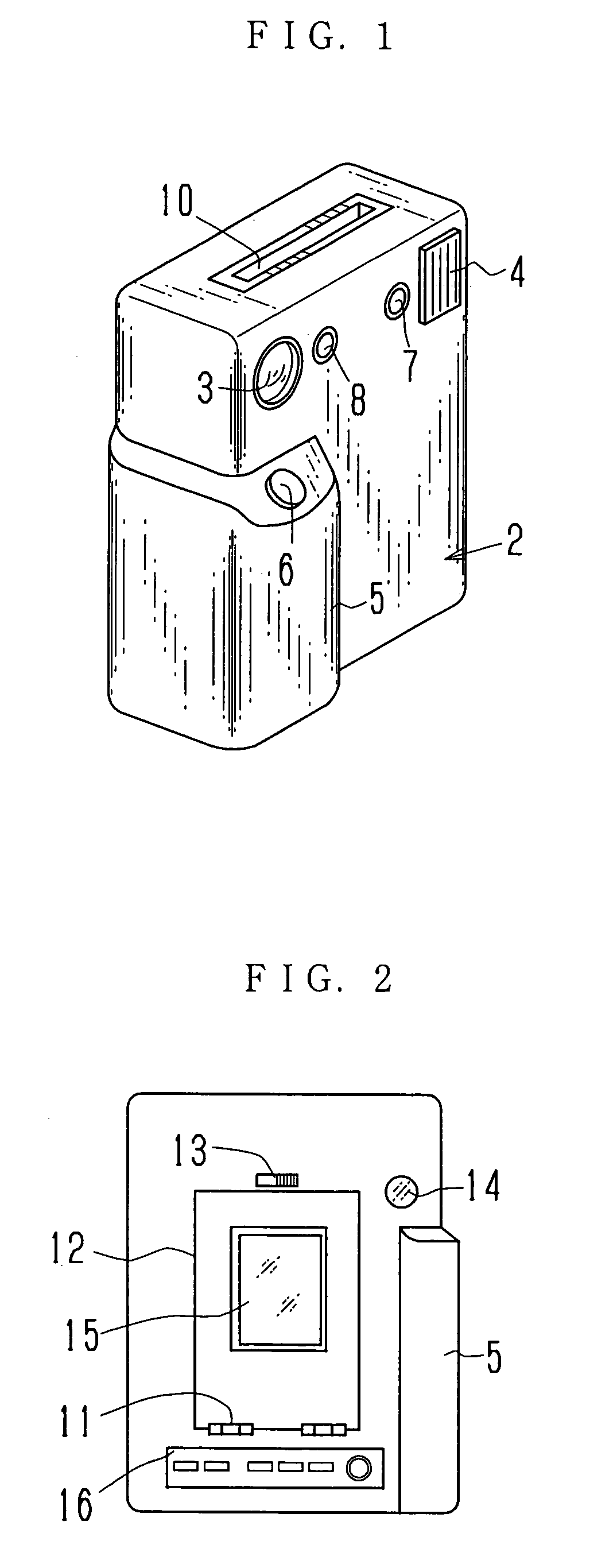
Electronic still camera, instant printer and instant film
InactiveUS6963359B1Reduce electric powerElectrical construction can be simpleTelevision system detailsColor television detailsSheet filmLight beam
Image data obtained through an image sensor is written in a memory. When printing an image, a printing head is driven in accordance with the image data read out from the memory in a line sequential fashion, and is synchronously moved in a sub scan direction, thereby exposing the instant film line by line. The image appears on the exposed instant film as a developing solution is developed by developing rollers while the instant film is advanced out through the developing rollers. Alternatively, the printing head is driven synchronously with the instant film being advanced. Thereby an image is printed at one sub scanning without the need for moving the printing head. The printing head is provided with an array of three color light emitting elements, and three color light beams are simultaneously projected onto the instant film. The electronic still camera is automatically set in an imaging mode when a power switch is turned on, and is switched to a display mode or a print mode as soon as a display mode key or a print mode key is operated. After being switched to the display mode, the electronic still camera is quickly switched to the imaging mode if only a shutter release button is operated.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP +1
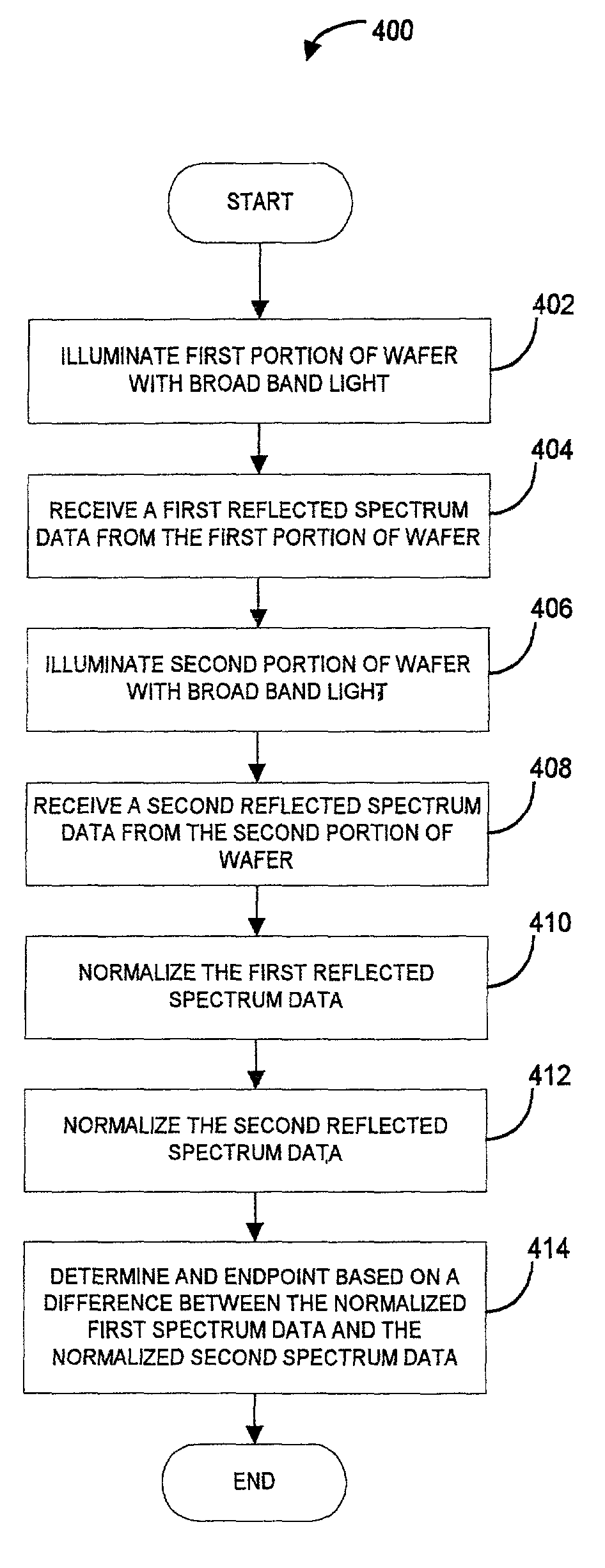
System and method of broad band optical end point detection for film change indication
A system and method for detecting an endpoint during a chemical mechanical polishing process is disclosed that includes illuminating a first portion of a surface of a wafer with a first broad beam of light. A first reflected spectrum data is received. The first reflected spectrum of data corresponds to a first spectra of light reflected from the first illuminated portion of the surface of the wafer. A second portion of the surface of the wafer with a second broad beam of light. A second reflected spectrum data is received. The second reflected spectrum of data corresponds to a second spectra of light reflected from the second illuminated portion of the surface of the wafer. The first reflected spectrum data is normalized and the second reflected spectrum data is normalized. An endpoint is determined based on a difference between the normalized first spectrum data and the normalized second spectrum data.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
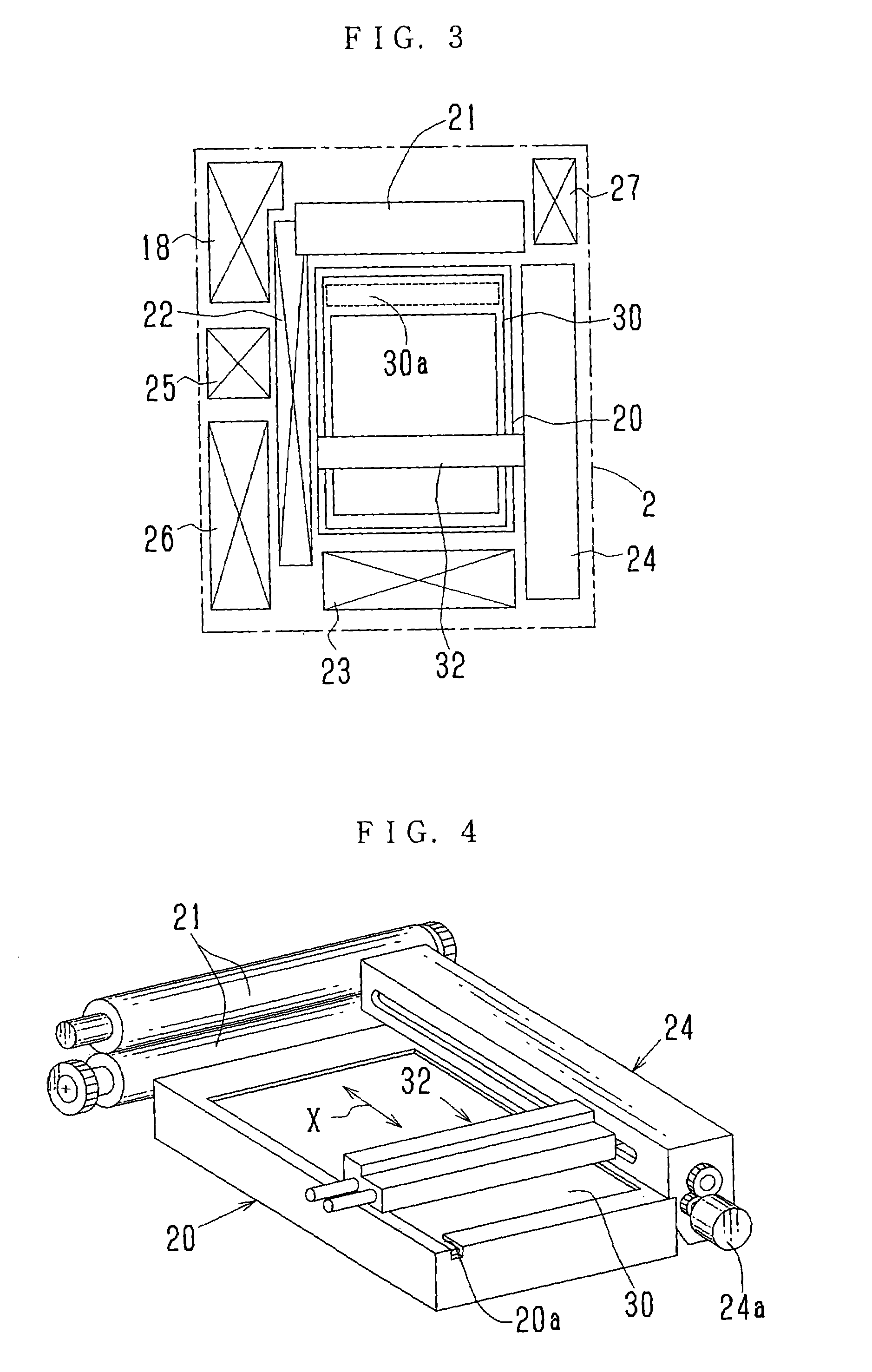
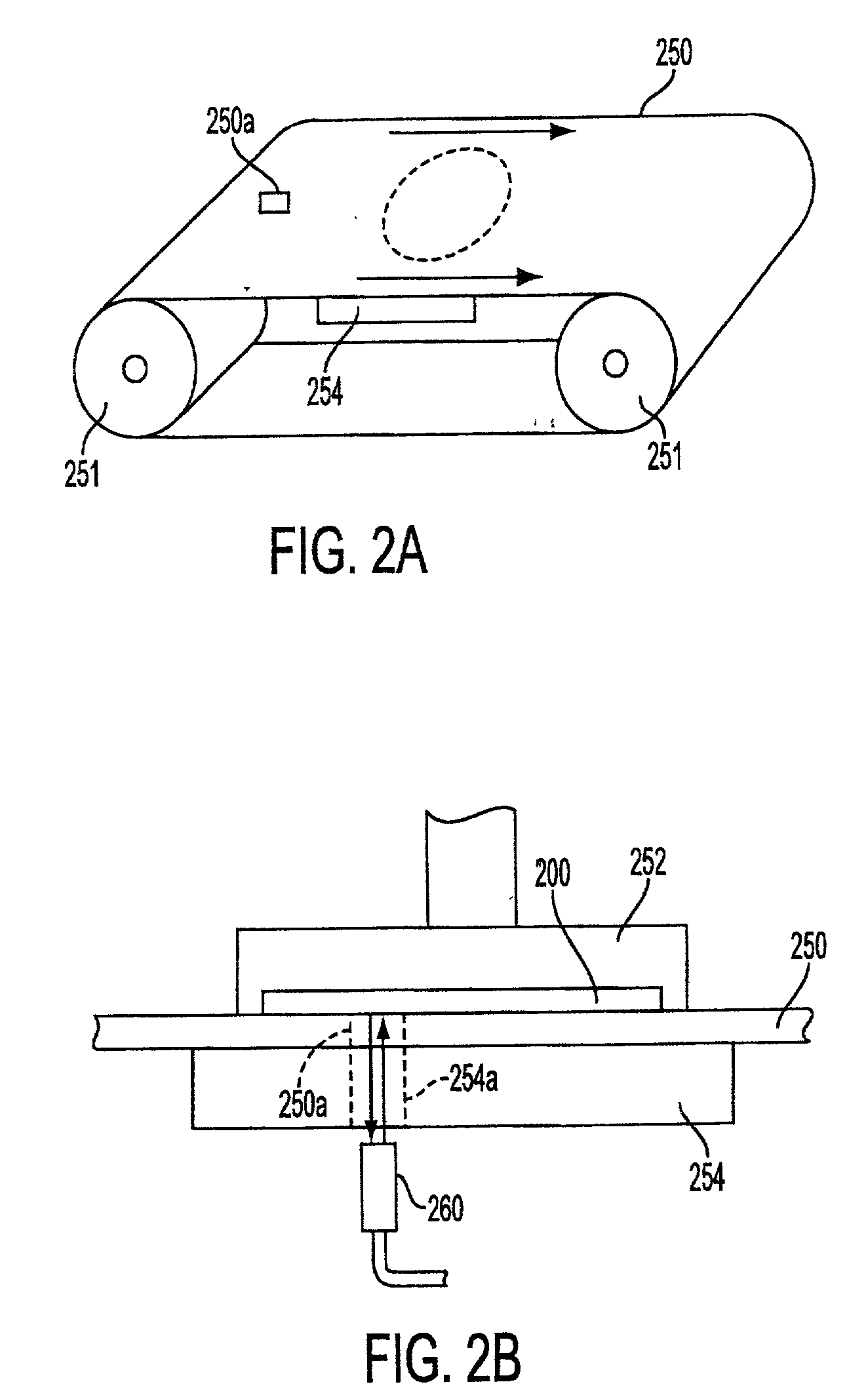
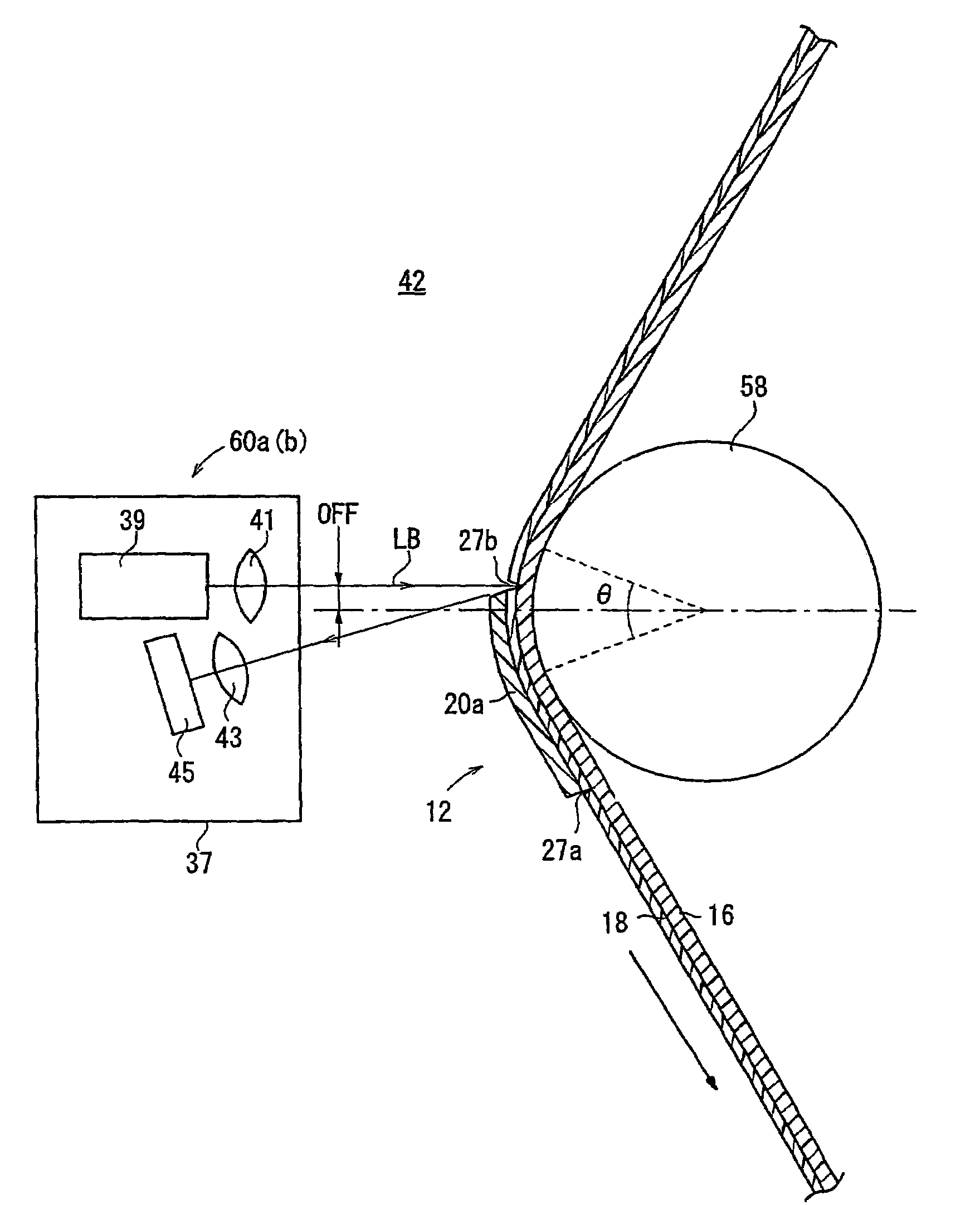
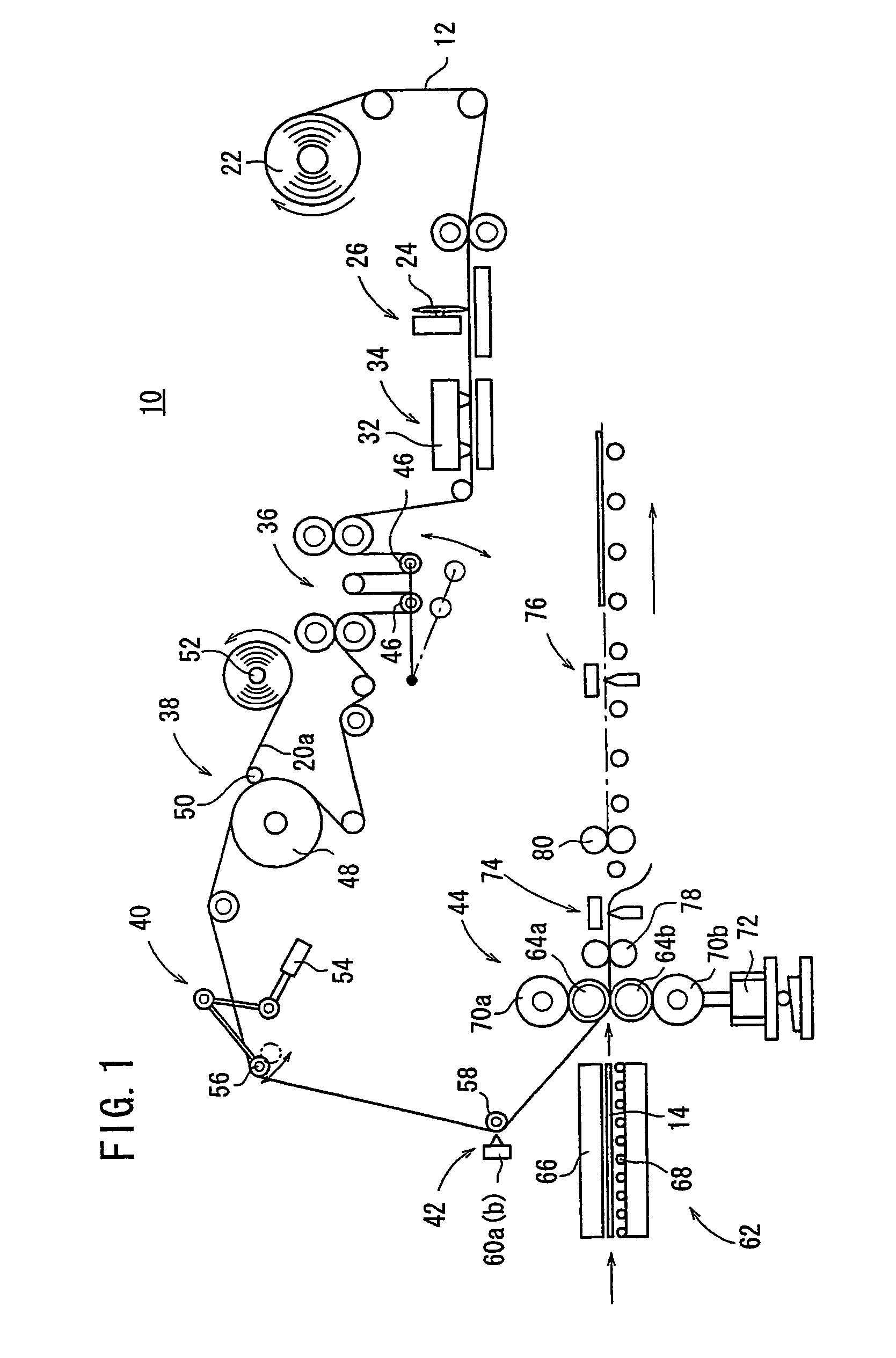
Detecting device and laminated body manufacturing apparatus employing such detecting device
InactiveUS7534989B2Simple and inexpensive structureReliable detectionInvestigating moving sheetsCounting objects on conveyorsSheet filmManufactured apparatus
A laser beam emitted from a laser diode of each of detectors is applied to a partly cut region of a photosensitive sheet film which is spread toward the detectors by a film bending roller. Part of the laser beam which is reflected from the partly cut region is detected by an amount-of-light sensor. The laser beam that is applied to a surface of the photosensitive sheet film other than the partly cut region is reflected outside of a light-detecting area of the amount-of light sensor, and is not detected by the amount-of-light sensor.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Illumination apparatus and film
InactiveUS7452120B2Easy to manufactureLow costElectric lightingOptical light guidesTotal internal reflectionLight guide
An illumination apparatus comprises:(a) at least one light source;(b) a light guide for accepting light from the at least one light source and for guiding the light using total internal reflection, the light guide having a top surface;(c) a light extracting film having an input surface optically coupled with the top surface and an output surface for providing light,wherein the input surface comprises a plurality of features which are optically coupled to the top surface of the light guide, such features having:(i) a first side comprising two or more planar segments; and(ii) a second side comprising two or more planar segments, andwherein either the length of at least some of the features is less than the width of the film or the first and second sides intersect at an apex.
Owner:SKC HAAS DISPLAY FILMS CO LTD
High shielding effect information leakage preventing glass
InactiveCN1482853AContainment leakImprove visibilityMagnetic/electric field screeningScreening apparatusHuman bodySheet film
The invention discloses a glass for prevention of information leakage which comprises glass, metal mesh and polycarbonate film, wherein two layers of polycarbonate films are arranged on each side of the metal mesh, a layer of glass is adhered on the outboard of the polycarbonate film by thermal compression bonding to form a unitary. The invention can effectively prevent information leakage, and diminishes the possible injury by the electromagnetic wave to the human body. íí
Owner:北京安方电磁屏蔽技术开发中心
Halogen-free resin composition as well as copper foil substrate and printed circuit board applying same
ActiveCN103013110AWith flame retardant functionWon't happenCircuit susbtrate materialsSheet filmCopper foil
The invention provides a halogen-free resin composition which comprises (A) 100 parts of cyanate ester resin, (B) 5-50 parts of styrene maleic anhydride, (C), 5-100 parts of polyphenyl ether resin, (D) 5-100 parts of maleimide resin, (E) 10-150 parts of nitrogenous compound, and (F) 10-1000 parts of inorganic filler. As the composition comprises components in special proportion, the halogen-free resin composition is low in dielectric constant, low in dielectric loss, high in heat resistance and high in flame resistance. The halogen-free resin composition can be prepared as a semi-cured film or a resin film, so that the composition can be applied to a copper foil substrate and a printed circuit board.
Owner:ELITE MATERIAL
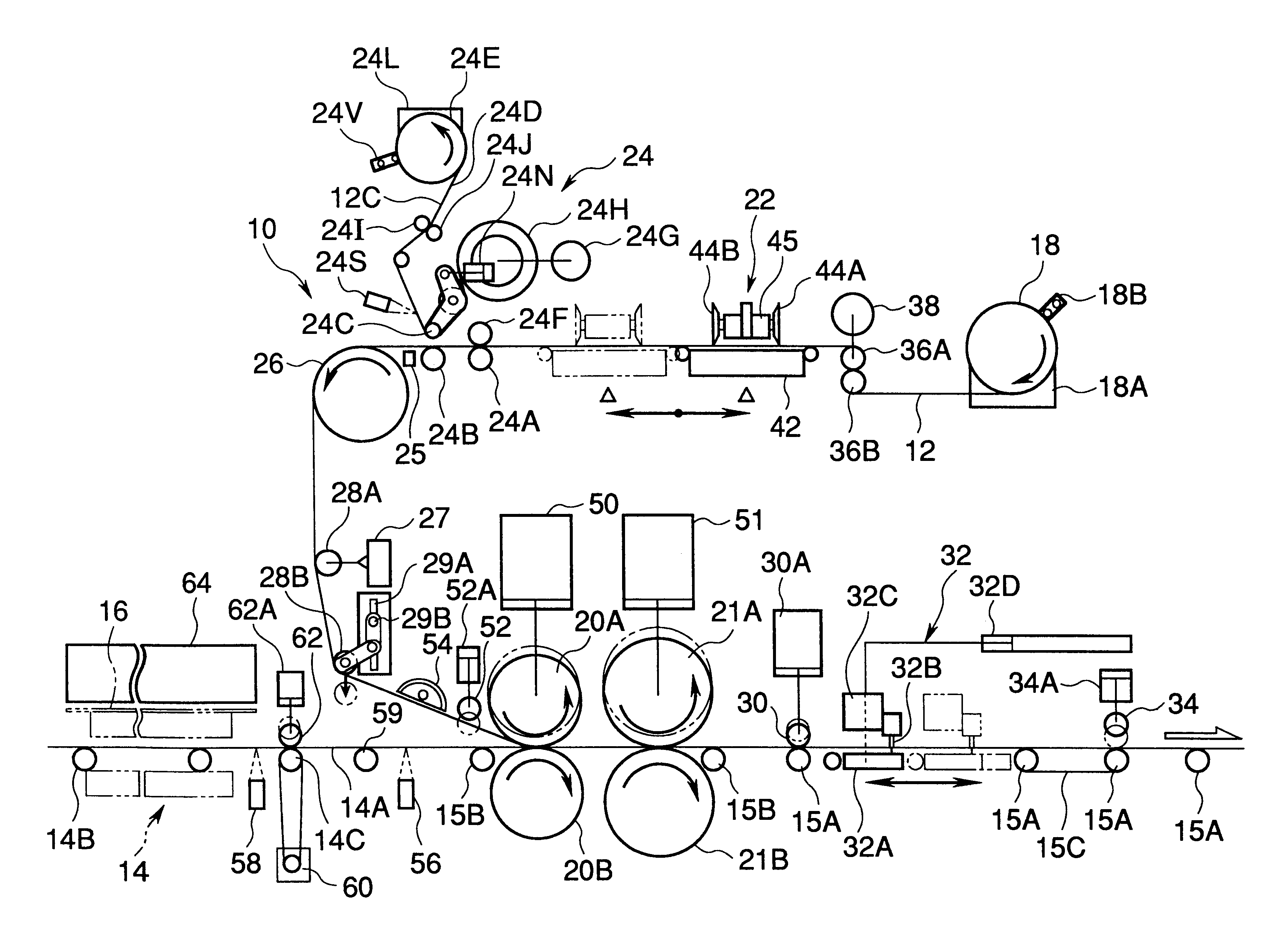
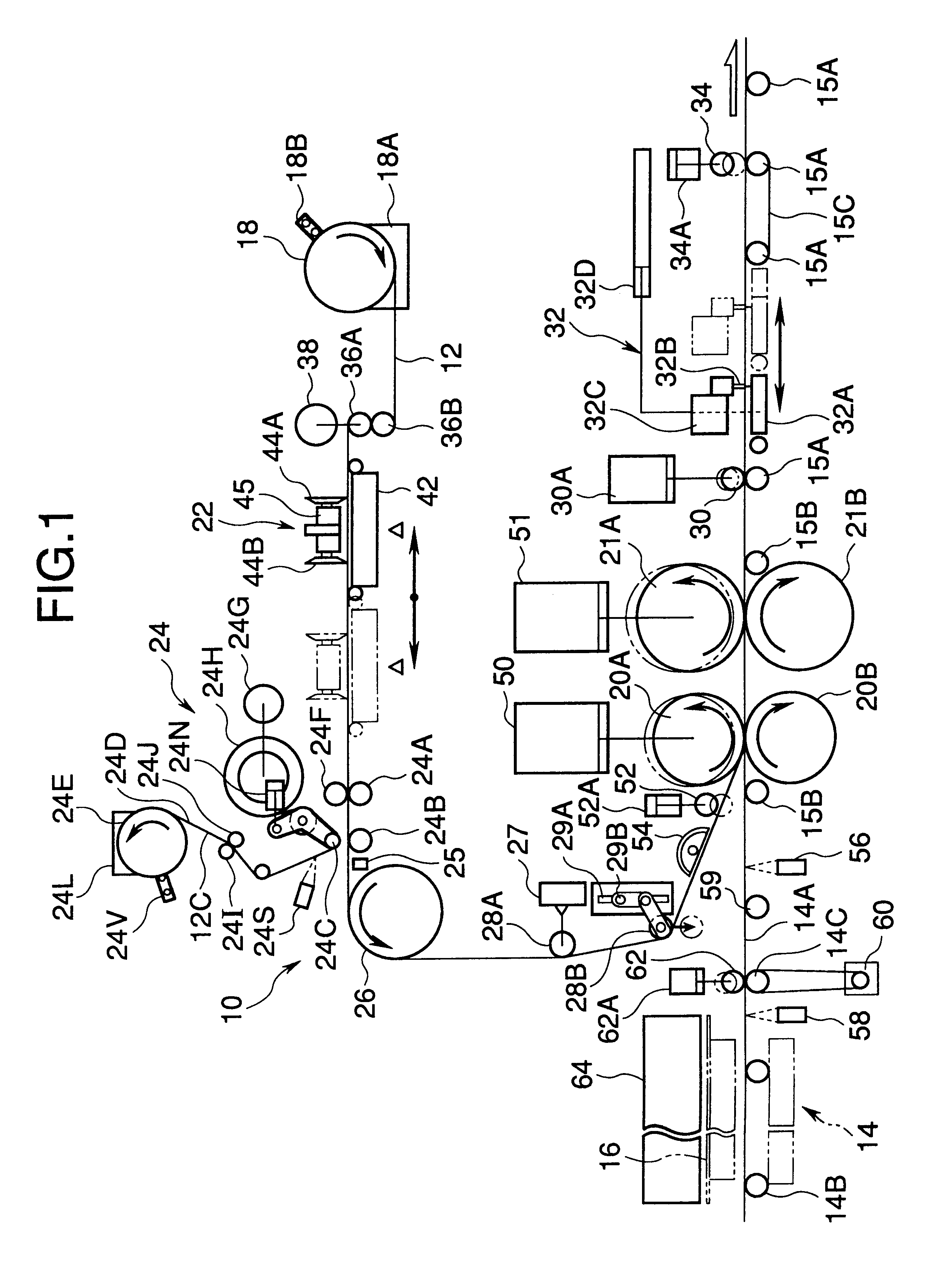
Production managing method for photo film production
InactiveUS20030025027A1Improve product qualityProne to defectPhotosensitive materialsMachines/enginesSheet filmEngineering
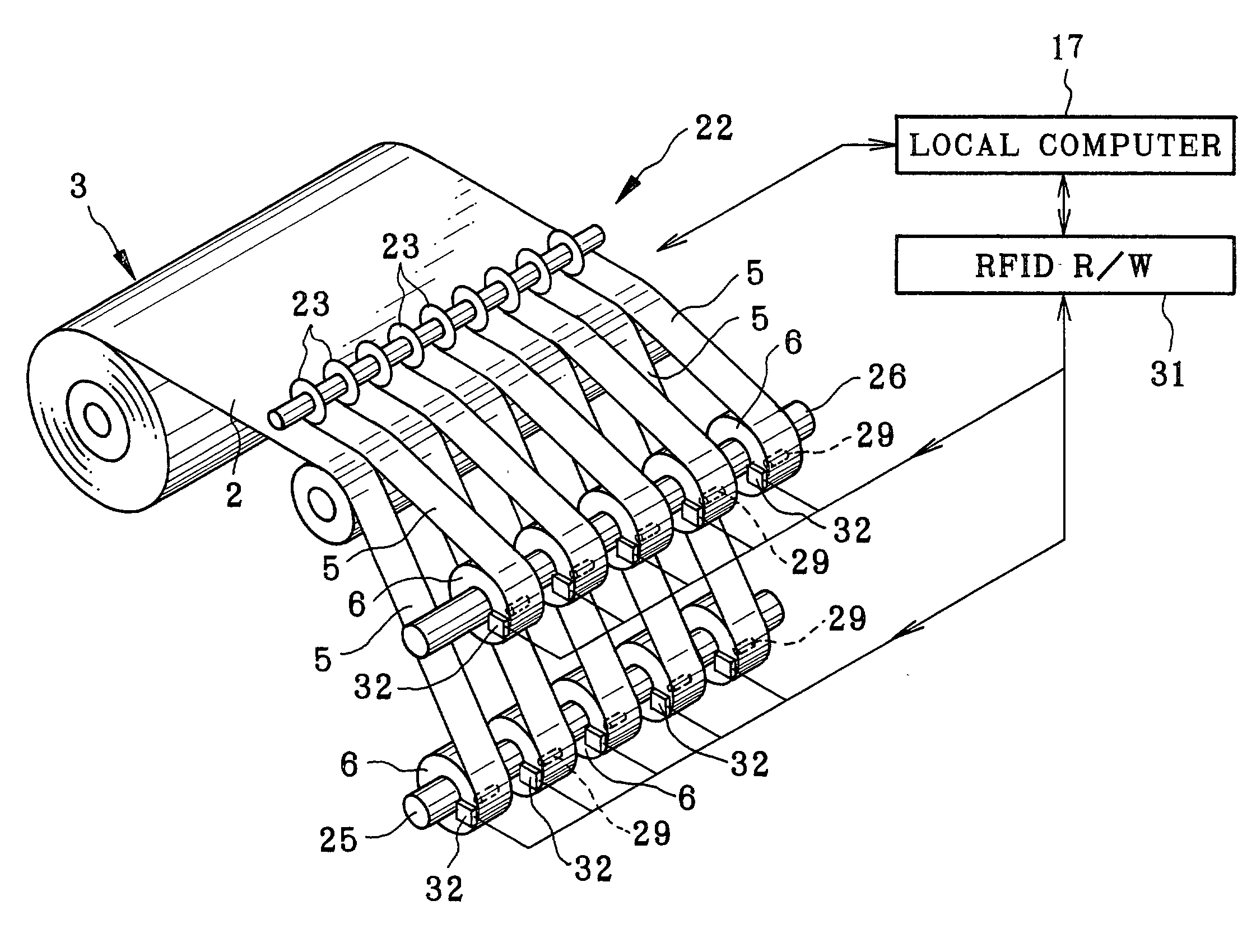
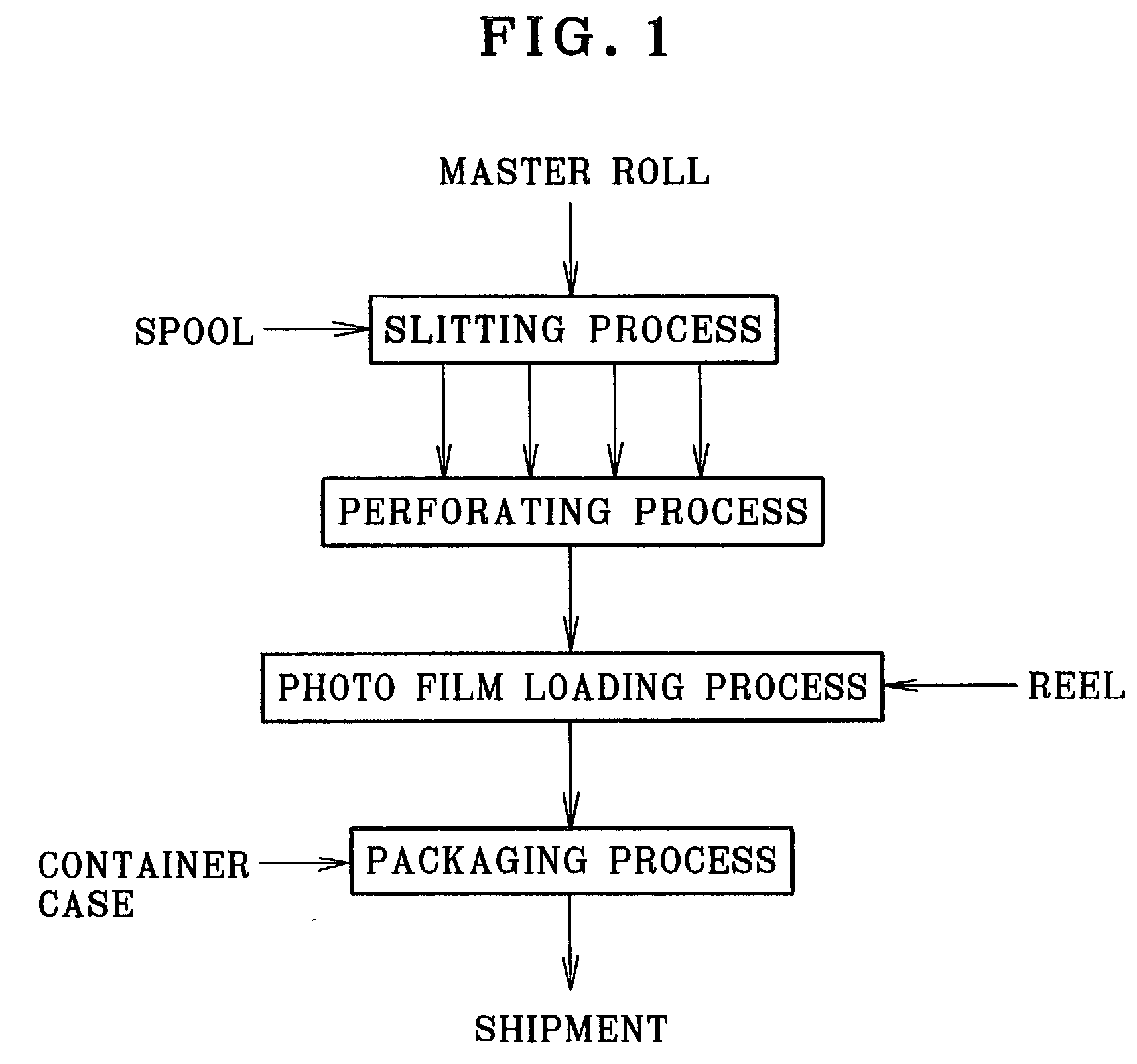
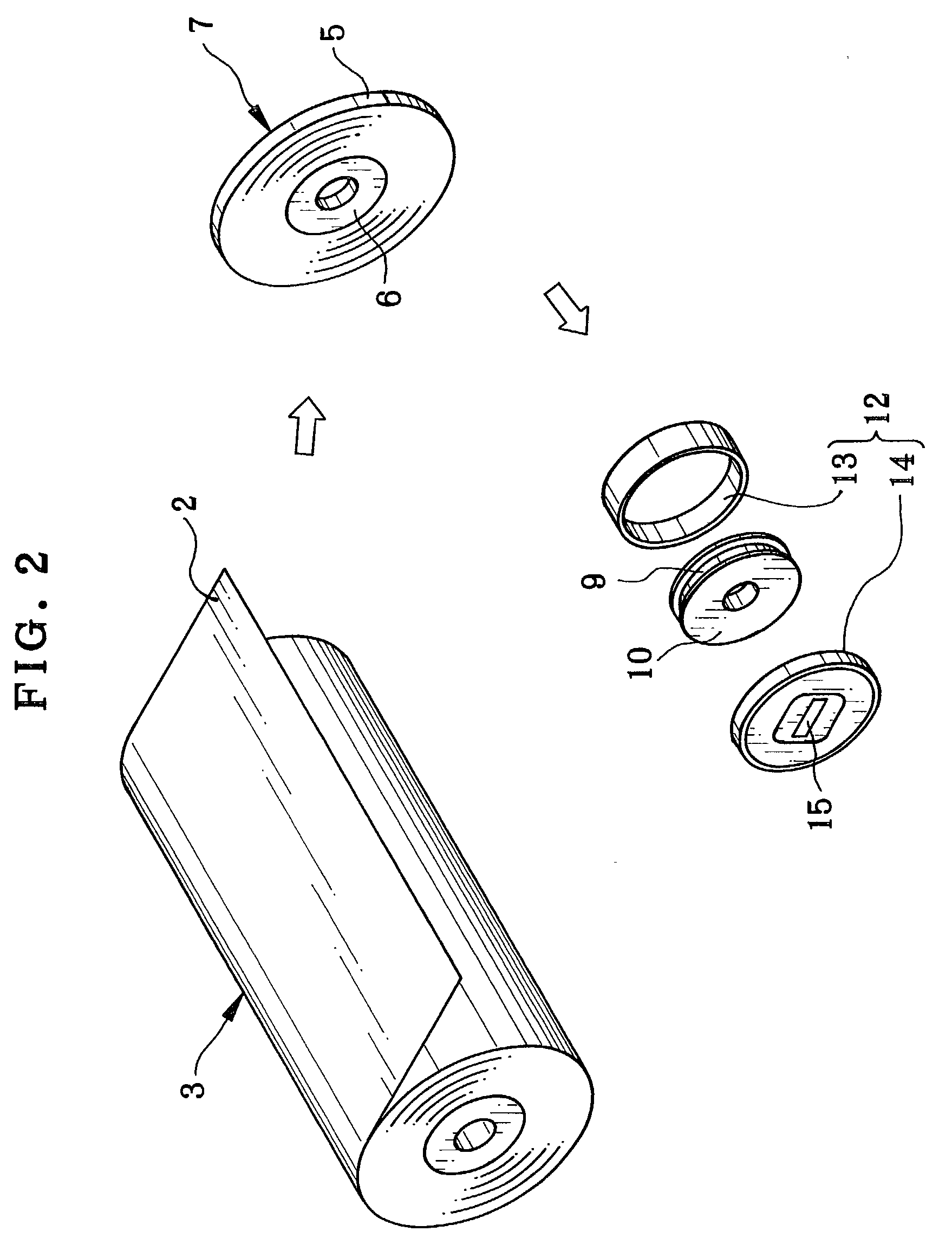
A production managing method for production of motion picture photo film is provided. At first, film web is slitted to produce continuous photo film having a predetermined width. Production managing information is written to an RFID (radio frequency identification) tag, and includes a roll number and slitting number, which are related to the film web and the continuous photo film. The continuous photo film is cut to produce motion picture photo film. The production managing information is stored in association with the motion picture photo film. The motion picture photo film is checked. If the motion picture photo film has a defect, the production managing information may be referred to for detecting a portion of the film web or the continuous photo film from which the defect derives. Other motion picture photo films with a defect will be traced.
Owner:FUJIFILM HLDG CORP +1
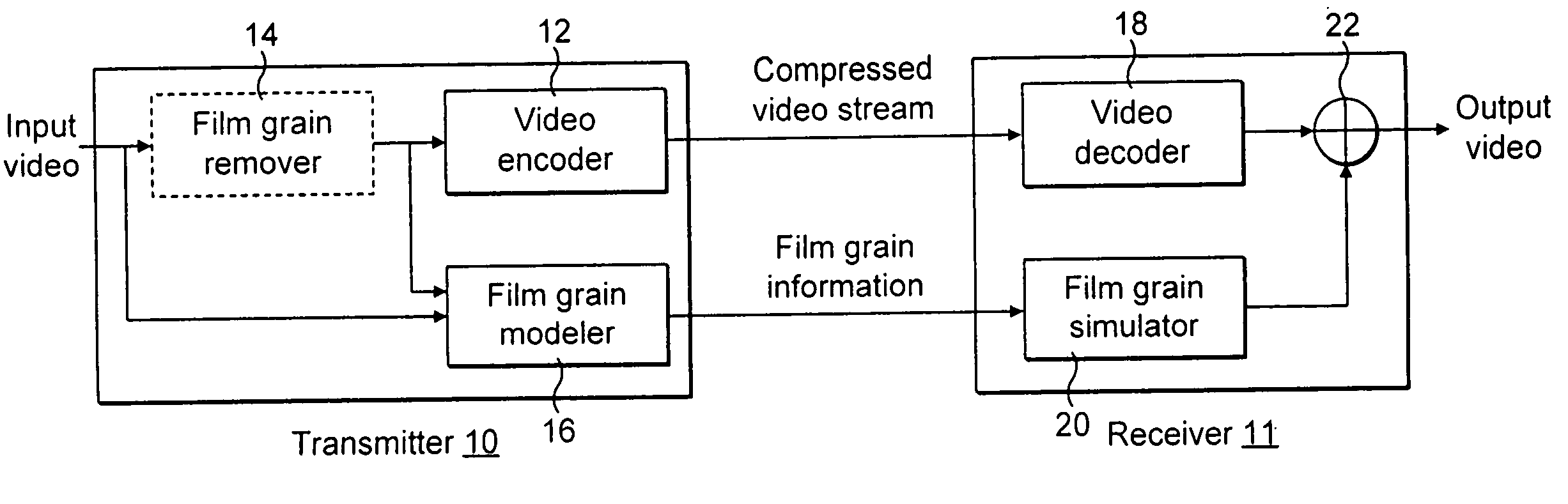
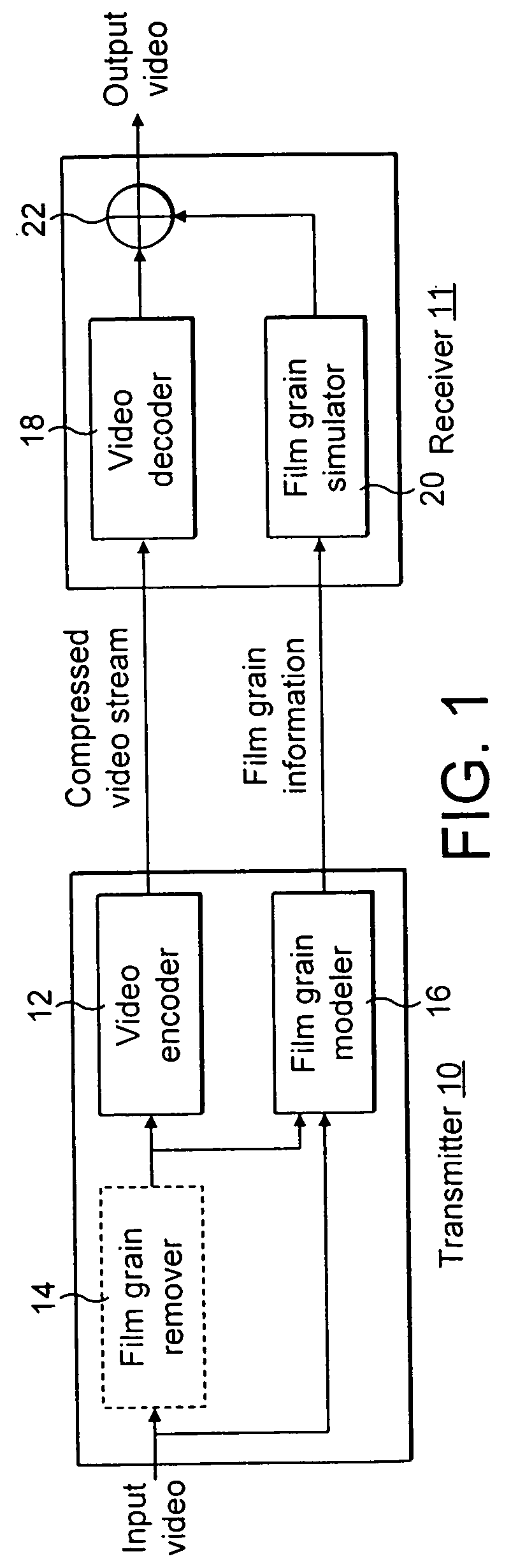
Digital film grain
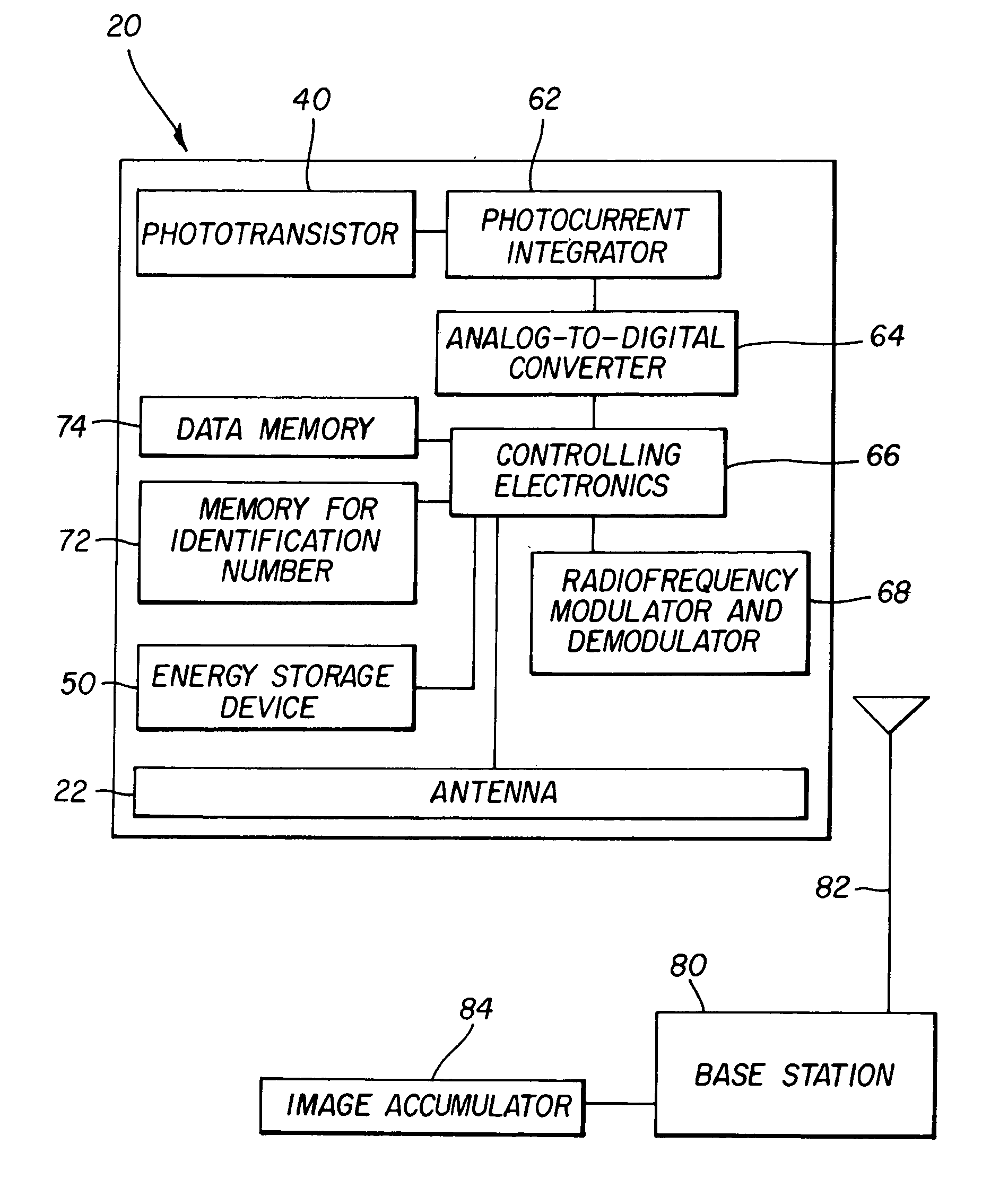
ActiveUS7015479B2Reduce lossesReduces and prevents signalTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesSheet filmRadiation flux
A digital film grain (20) comprises a phototransistor (40) which produces an electrical signal having a strength which is related to an input radiation flux. A transponder receives commands and power from a base station (80) and transmits information quantifying the radiation observed by that digital film grain. An image accumulator (84) connected to the base station (80) assembles an image from the profile of radiation reported by a distribution of digital film grains correlated to the locations of those grains.
Owner:CARESTREAM HEALTH INC
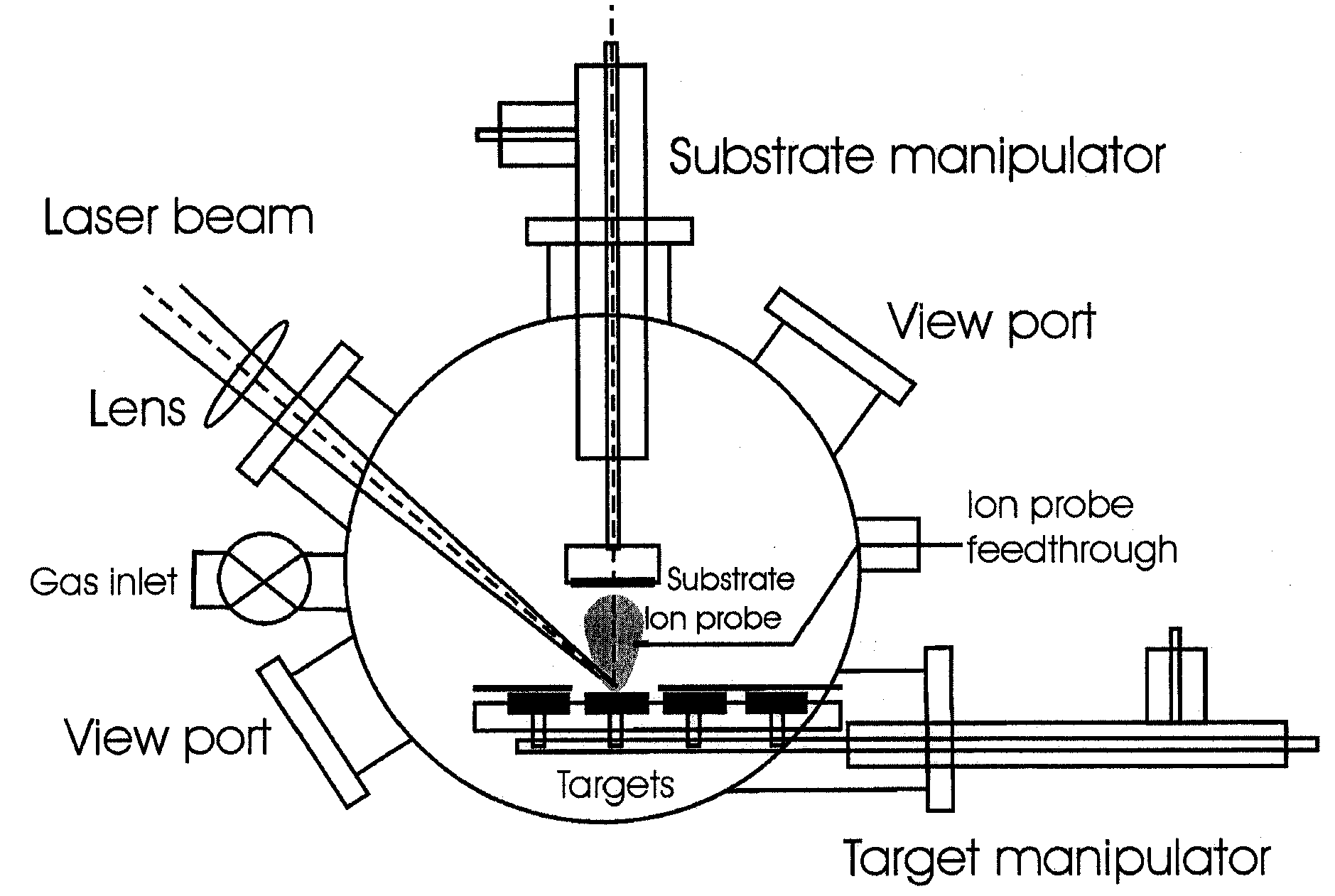
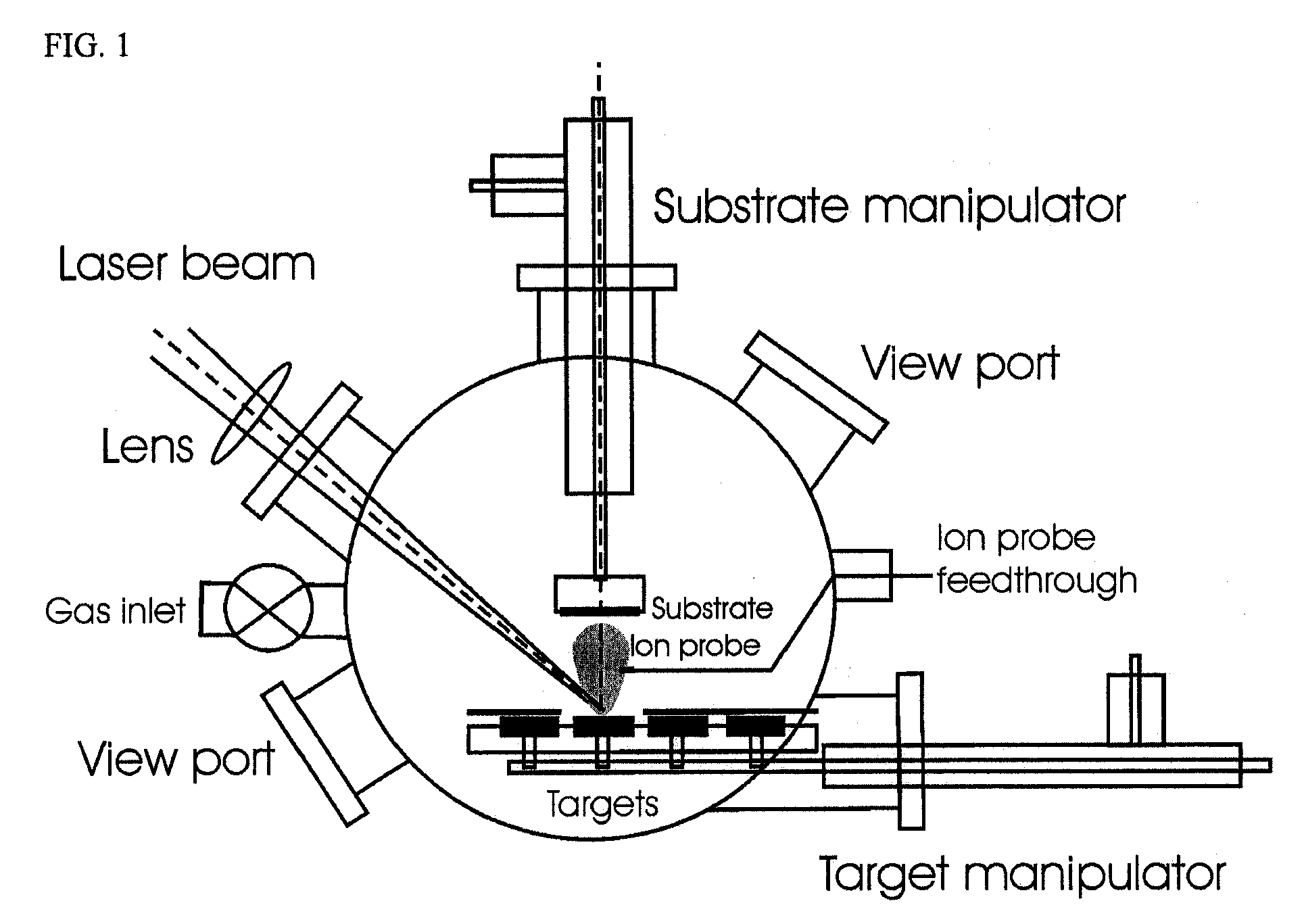
Method For Fabricating Thin Films
InactiveUS20090246530A1Small particle sizeEasily realizedLiquid surface applicatorsElectric discharge heatingSheet filmAlloy
A method of pulsed laser deposition (PLD) capable of continuously tuning formed-film morphology from that of a nanoparticle aggregate to a smooth thin film free of particles and droplets. The materials that can be synthesized using various embodiments of the invention include, but are not limited to, metals, alloys, metal oxides, and semiconductors. In various embodiments a ‘burst’ mode of ultrashort pulsed laser ablation and deposition is provided. Tuning of the film morphology is achieved by controlling the burst-mode parameters such as the number of pulses and the time-spacing between the pulses within each burst, the burst repetition rate, and the laser fluence. The system includes an ultrashort pulsed laser, an optical system for delivering a focused onto the target surface with an appropriate energy density, and a vacuum chamber in which the target and the substrate are installed and background gases and their pressures are appropriately adjusted.
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
Electrocatalyst Synthesized by Depositing a Contiguous Metal Adlayer on Transition Metal Nanostructures
InactiveUS20100099012A1Minimizes Pt loadingMaximizingActive material electrodesSolid electrolyte fuel cellsNanowireSheet film
Transition metal nanostructures coated with a contiguous, conformal submonolayer-to-multilayer noble metal film and their method of manufacture are described. The manufacturing process involves the initial formation of suitably sized transition metal or alloy nanostructures which may be nanorods, nanobars, or nanowires. A monolayer of a non-noble metal is deposited onto the surface of the nanostructures by underpotential deposition. This is followed by the galvanic displacement of the non-noble metal by a second metal to yield a conformal coating of a monolayer of the second metal on the surface of the nanostructures. The replacement of atoms of the first metal by atoms of the second metal is an irreversible and spontaneous redox reaction which involves the replacement of a non noble metal by a more noble metal. The process can be controlled and repeated to obtain the desired film coverage. The resulting coated nanostructures provide heightened catalytic activity and can be used as high-performance electrodes in fuel cells.
Owner:BROOKHAVEN NAT LAB +1
Increased contrast overhead projection films
InactiveUS6848795B2Increase contrastGood colorAutomatic/semiautomatic turning machinesLayered productsSheet filmPolymer
Disclosed is a projection media comprising a transparent polymer layer with random light diffusing elements and having a Tg of less than 75° C.
Owner:ROHM & HAAS DENMARK FINANCE
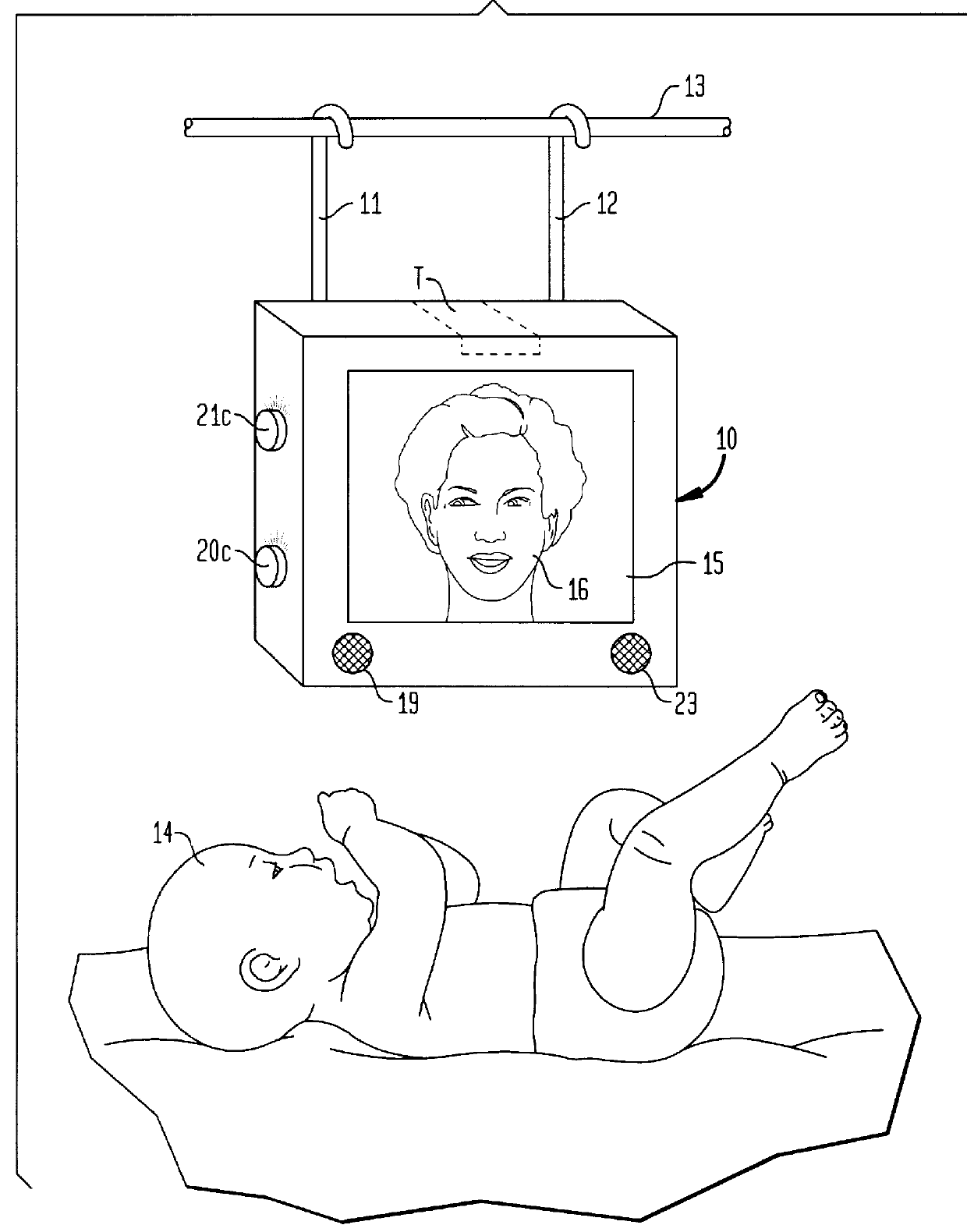
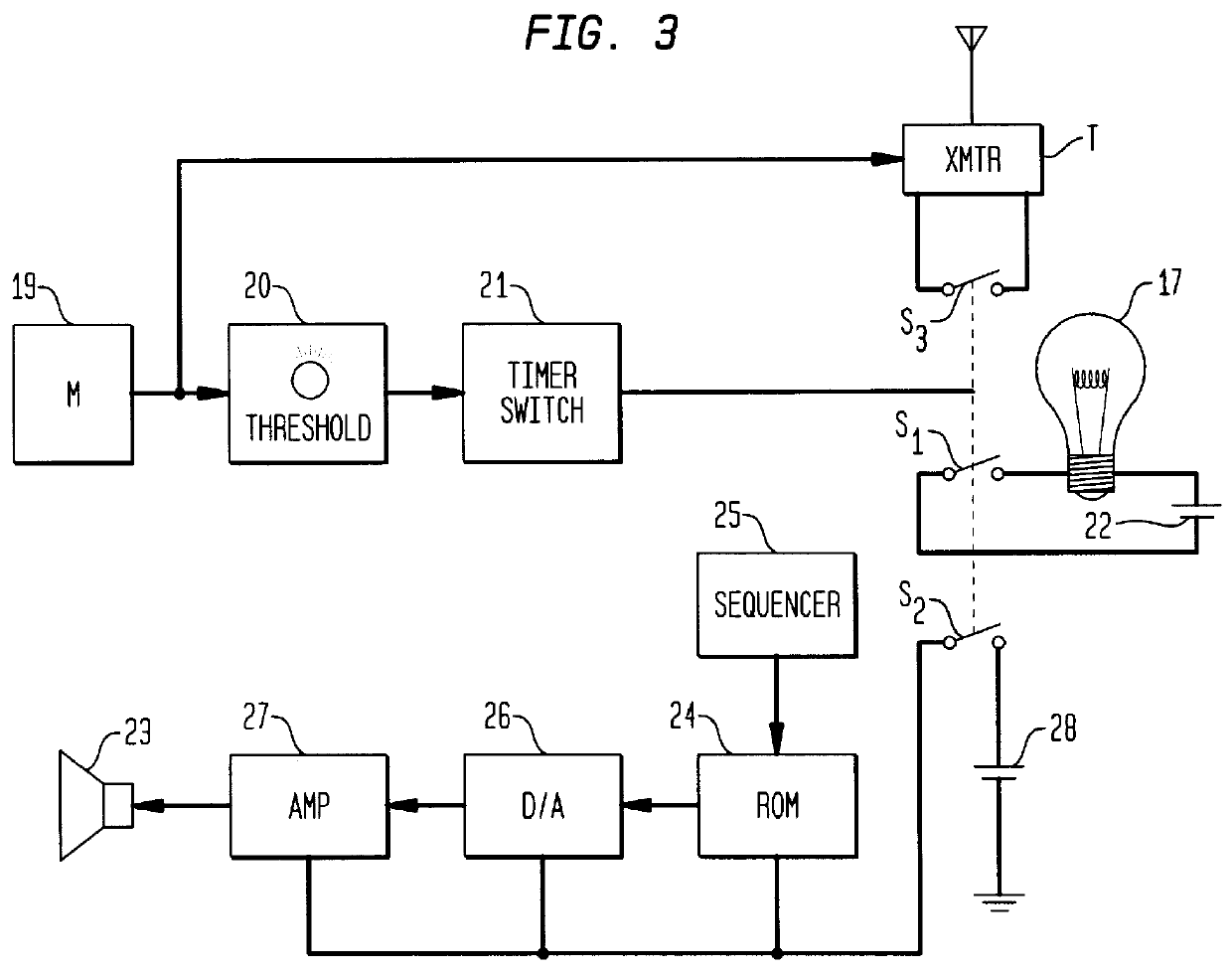
Combined monitor and light box assembly
A combined monitor and light box assembly installable in a crib enclosure occupied by an infant. The assembly which is interactive with the infant includes a light box on whose front face is mounted a semi-reflective mirror behind which is a film transparency having a photographic image of the infant's mother. When a light bulb in the box is energized to illuminate the transparency, the image of the mother becomes visible to the infant through the mirror which is then effectively transparent. Associated with the light box is a sound-activated switching device connected between the bulb and a power source. The switching device, when activated by crying sounds emanating from the infant, remains activated for a predetermined period to energize the bulb and illuminate the transparency. Also associated with the light box is a record playback unit having stored therein a voice message recorded by the mother addressed to her infant, the unit being rendered operative only when the bulb is energized. Hence when the infant cries, it is then presented with an image of its mother and hears her comforting message, as a consequence of which the infant is induced to stop crying. The monitor which is operative only after the switch is activated, radio-transmits the crying sounds then emanating from the infant to a receiver that can be heard by the mother.
Owner:SPECTOR DONALD
Process for production of hydrogel particles and process for cutting of high-concentration hydrogel sheet
ActiveUS20050046069A1Quality improvementImprove performanceFilament/thread formingMetal working apparatusHigh concentrationSolid component
An object of the present invention is to make it possible that: a high-concentration hydrogel sheet, which is suitable for production of high-performance water-absorbent resin particles, is cut efficiently without involving the adhesion to such as cutting-blades; and the subsequent disintegration operation is also successfully carried out; and hydrogel particles excellent in the quality and performances are efficiently produced. As a means of achieving this object, the process according to the present invention for production of hydrogel particles is a process for production of the hydrogel particles 14 from a high-concentration hydrogel sheet 10 and comprises: a step (a) of cutting a continuous sheet 10 of a crosslinked high-concentration hydrogel polymer of 50 to 80 weight % in solid component concentration every 10 to 100 cm lengthwise of the continuous sheet 10 while running it lengthwise, thereby obtaining cut pieces 12; and a step (b) of continuously supplying the cut pieces 12 (obtained from the step (a)) to a continuous disintegrator 40 to continuously carry out disintegration and discharge under conditions where the supply amount of the cut pieces 12 and the disintegrating and discharging abilities of the continuous disintegrator 40 satisfy (supply amount)≦(disintegrating and discharging abilities), thereby obtaining the hydrogel particles 14.
Owner:NIPPON SHOKUBAI CO LTD
Laser projection apparatus with liquid-crystal light valves and scanning reading beam
InactiveUS20050057727A1Image contrast superiorHigh resolutionProjectorsPicture reproducers using projection devicesBeam splitterLiquid crystal light valve
Laser lines at 635 nm or longer (ideally 647 nm) are preferred for red, giving energy-efficient, bright, rapid-motion images with rich, full film-comparable colors. Green and blue lines are used too—and cyan retained for best color mixing, an extra light-power boost, and aid in speckle suppression. Speckle is suppressed through beam-path displacement—by deflecting the beam during projection, thereby avoiding both absorption and diffusion of the beam while preserving pseudocollimation (noncrossing rays). The latter in turn is important to infinite sharpness. Path displacement is achieved by scanning the beam on the liquid-crystal valves (LCLVs), which also provides several enhancements—in energy efficiency, brightness, contrast, beam uniformity (by suppressing both laser-mode ripple and artifacts), and convenient beam-turning to transfer the beam between apparatus tiers. Preferably deflection is performed by a mirror mounted on a galvanometer or motor for rotary oscillation; images are written incrementally on successive portions of the LCLV control stage (either optical or electronic) while the laser “reading beam” is synchronized on the output stage. The beam is shaped, with very little energy loss to masking, into a shallow cross-section which is shifted on the viewing screen as well as the LCLVs. Beam-splitter / analyzer cubes are preferred over polarizing sheets. Spatial modulation provided by an LCLV and maintained by pseudocollimation enables imaging on irregular projection media with portions at distinctly differing distances from the projector—including domes, sculptures, monuments, buildings; waterfalls, sprays, fog, clouds, ice; scrims and other stage structures; trees and other foliage; land and rock surfaces; and even assemblages of living creatures including people.
Owner:TROYER DIANE
Mask film to form relief images and method of use
ActiveUS20080305407A1Good reverse line depthEnhance the imageRadiation applicationsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSheet filmImage transfer
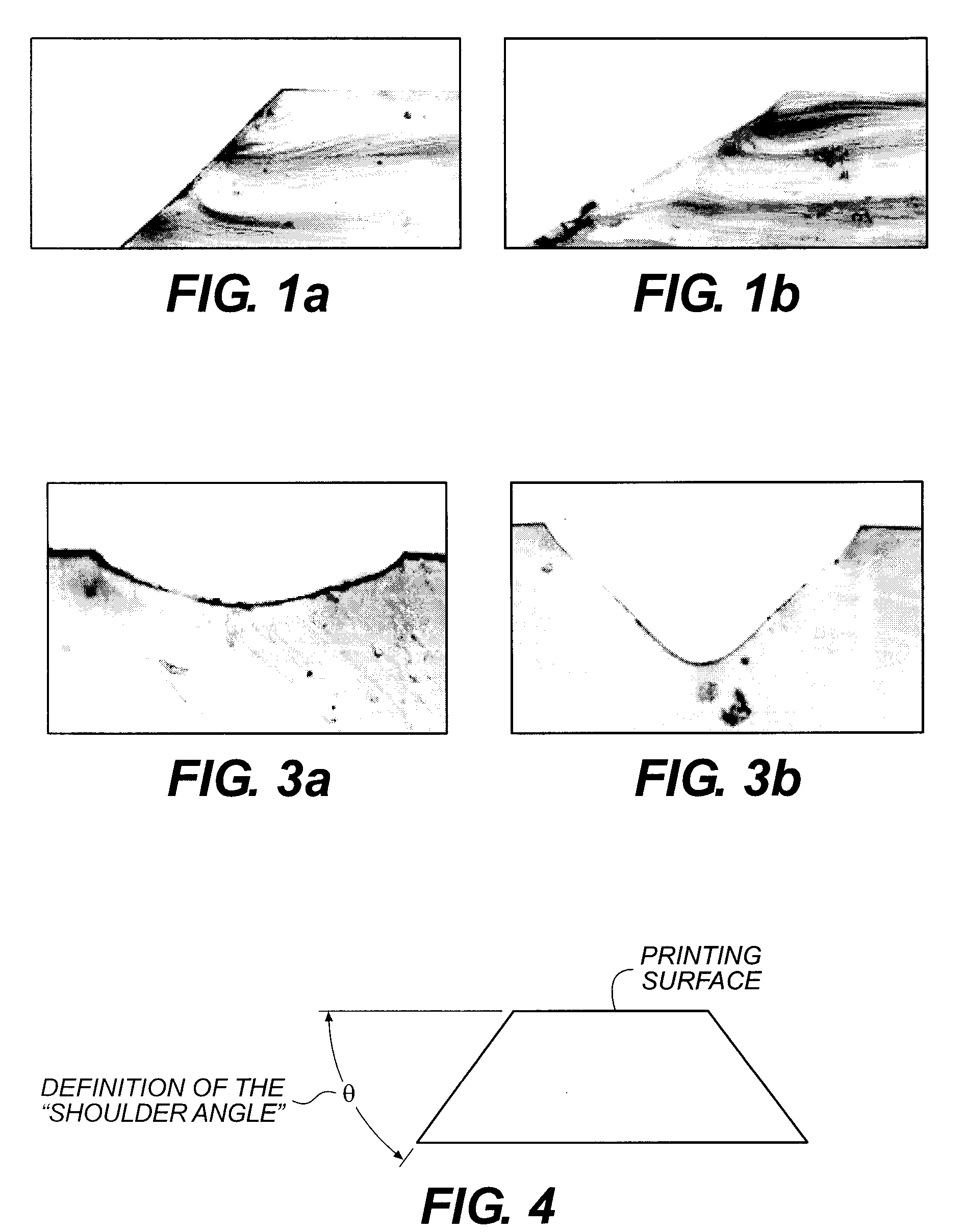
A mask-forming film has a transparent layer between the imageable layer and the carrier sheet, which transparent layer has a refractive index that is lower (by at least 0.04) than that of the carrier sheet or any immediately adjacent layer between it and the carrier sheet. This lower refractive index layer modifies the path of incident radiation during mask image transfer so as to provide steeper shoulder angles in the relief image solid areas.
Owner:MIRACLON CORP
Manufacturing method for manual patch of heat insulating layer of filament winding engine shell
The invention discloses a manufacturing method for a manual patch of a heat insulating layer of a filament winding engine shell. By controlling the preparation environment of the manual patch, an appropriate adhesive is selected, a multilayer patching method is adopted to reduce the film thickness of a single-layer manual patch and patch size, then a fiber yarn is used for preloading pressure, and the heat insulating layer is repaired to increase the internal mass and shape structure size of the heat insulating layer after curing, thus manufacturing the manual patch. The manufacturing method solves the problems of high film hardness, poor self-adhesion and mutual viscosity, and high patching difficulty of an EPDM material, the thickness of the heat insulating layer meets the design requirements, and an EPDM anatomical layer is compact and smoothly passes engine ground test assessment for a few times.
Owner:航天科工火箭技术有限公司
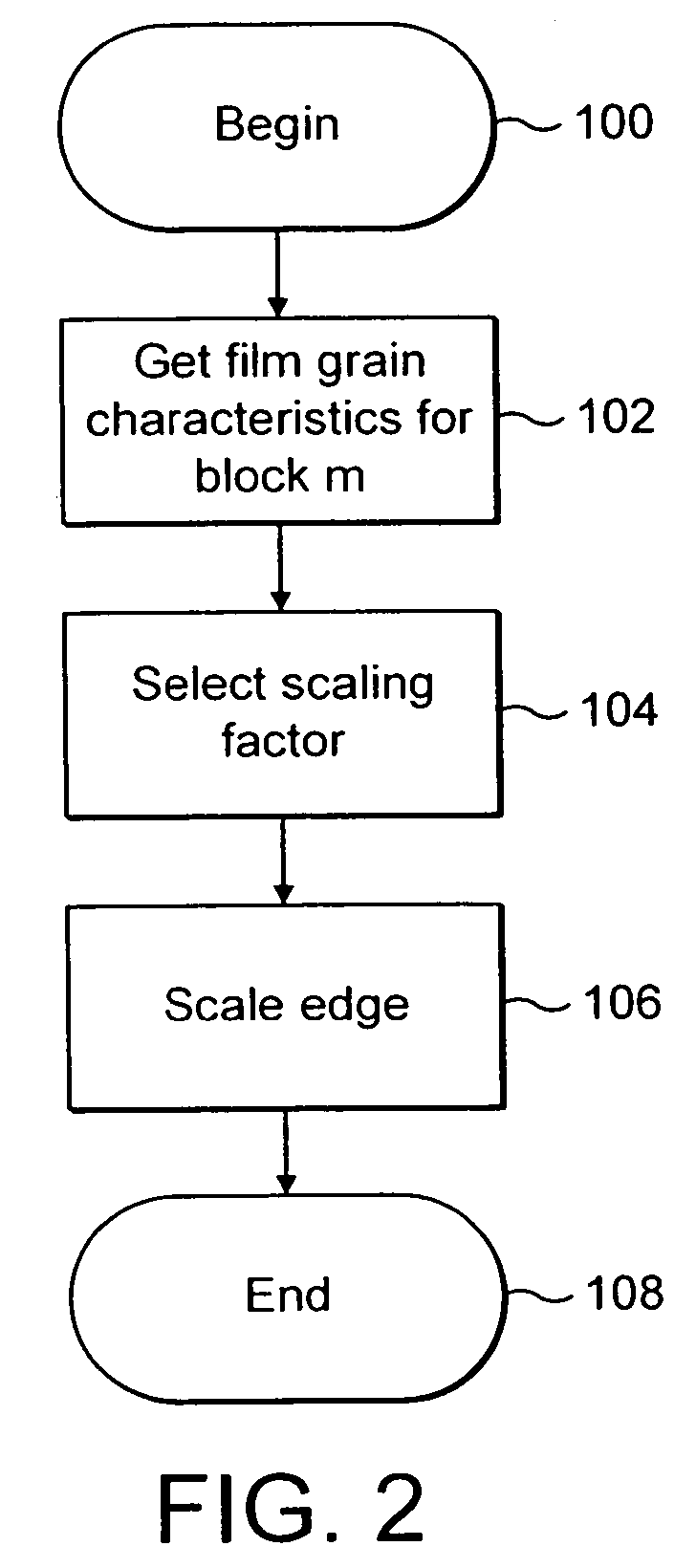
Technique for adaptive de-blocking of block-based film grain patterns
Reduction in the blockiness of a simulated film grain block can be achieved either by the use of adaptive downscaling or adaptive deblocking filtering to adjust the intensity of the pixels at the block edge in accordance with at least one film grain block parameter, such as film grain size, intensity and texture. Performing such adaptive downscaling or adaptive deblocking filtering achieves improved performance at lower computational cost by avoiding modification of film grain block pixels in lesser affected areas.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL VC HLDG INC
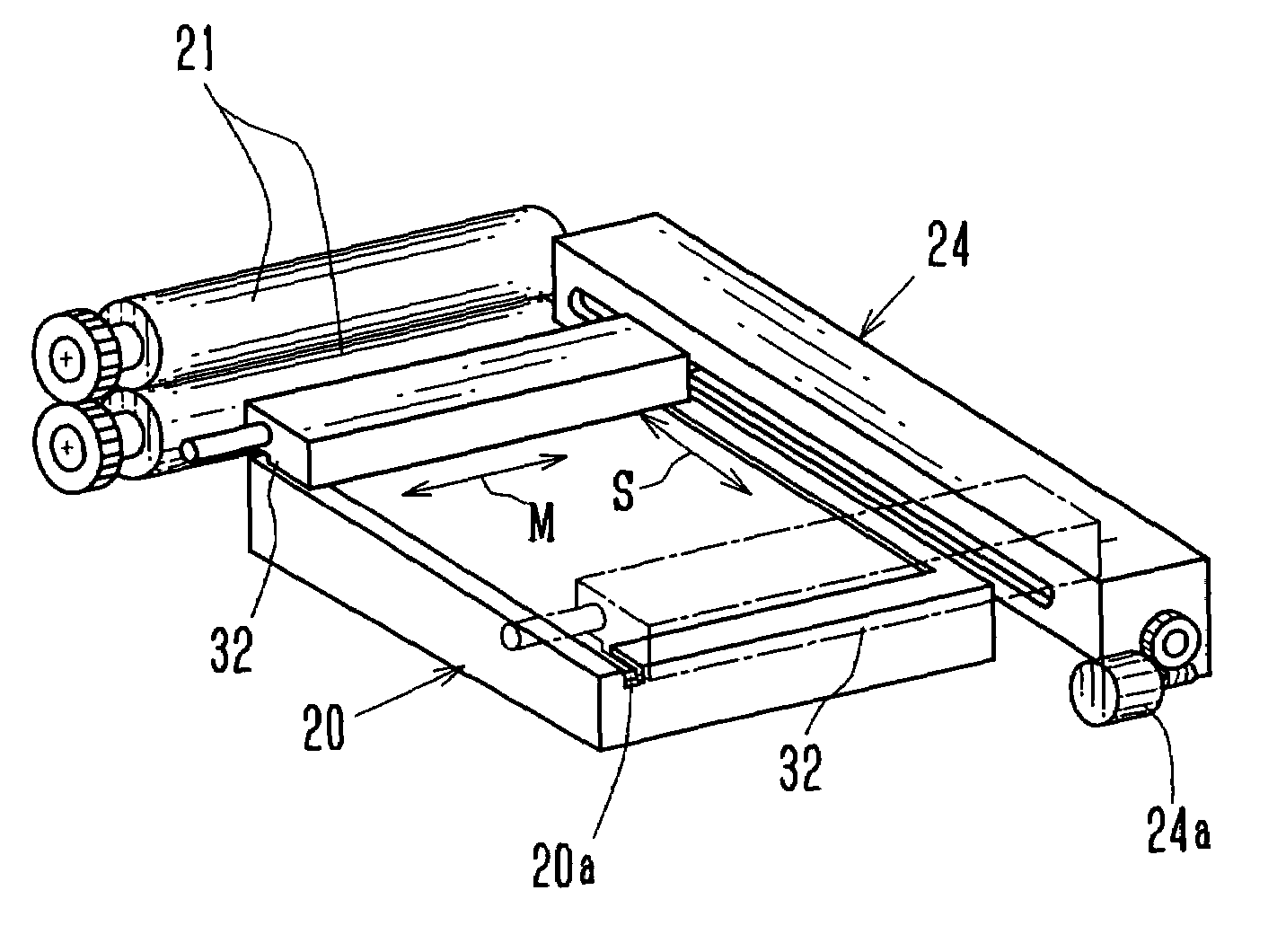
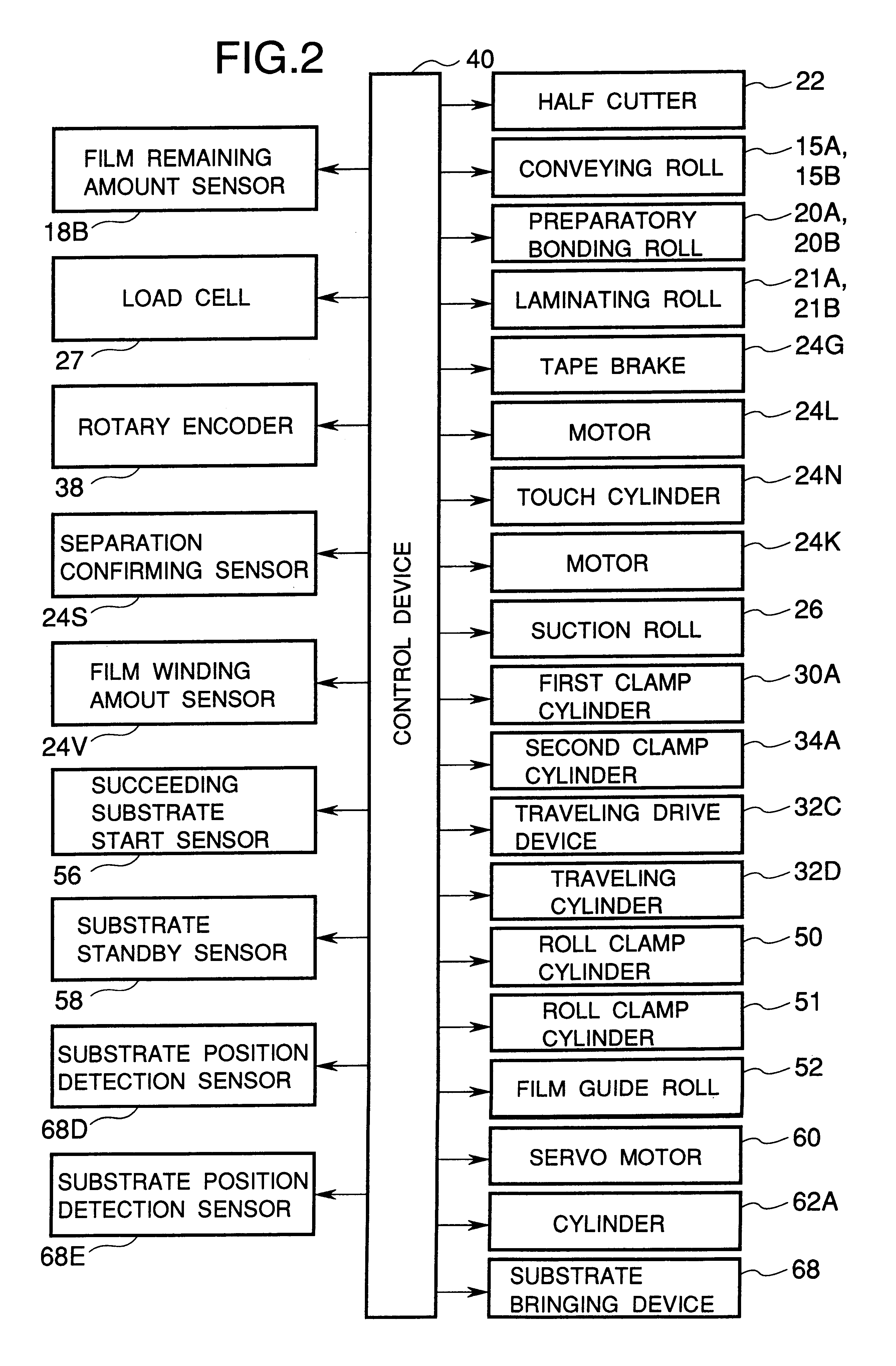
Film applying apparatus
InactiveUS6176286B1Small rangeSecure bondingMechanical working/deformationLamination ancillary operationsSheet filmEngineering
A film applying apparatus 10 is provided with preparatory bonding rolls 20A, 20B and laminating rolls 21A, 21B, and a laminated film 12 wound out from a film roll 18 and a substrate 16 conveyed by a substrate conveying device 14 pass between these rolls and pressure bonding is performed. Diameter of the preparatory bonding rolls 20A, 20B is made smaller than diameter of the laminating rolls 21A, 21B and range of elastic deformable area S1 at the roll surface at grasping starting of the substrate and the laminated film 12 by the preparatory bonding rolls 20A, 20B is made small thereby range of generating, air holding or the like is limited to small.
Owner:SOMAR CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com