Patents
Literature
87 results about "Short wave radiation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Shortwave radiation (SW) is radiant energy with wavelengths in the visible (VIS), near-ultraviolet (UV), and near-infrared (NIR) spectra. There is no standard cut-off for the near-infrared range; therefore, the shortwave radiation range is also variously defined.
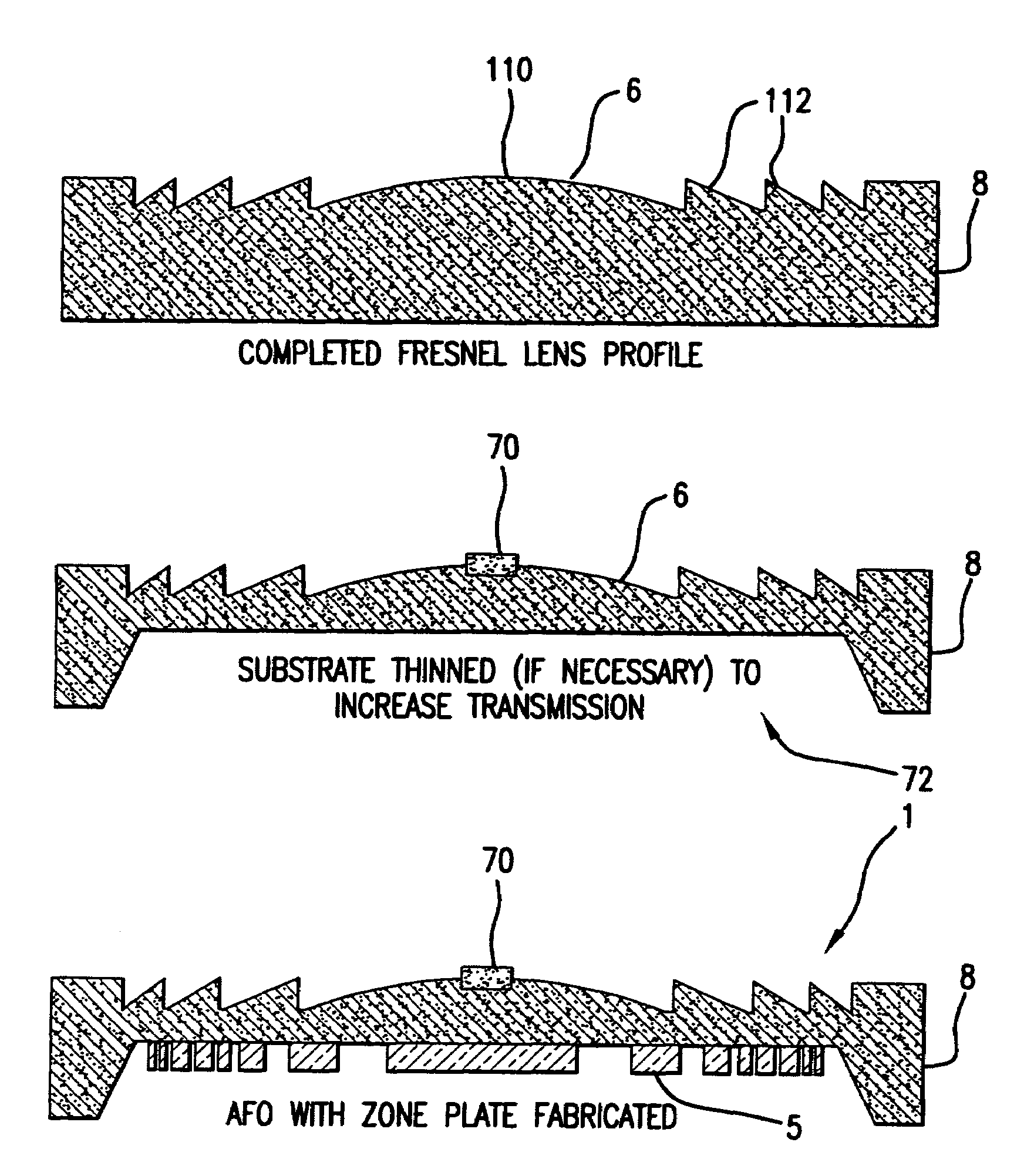
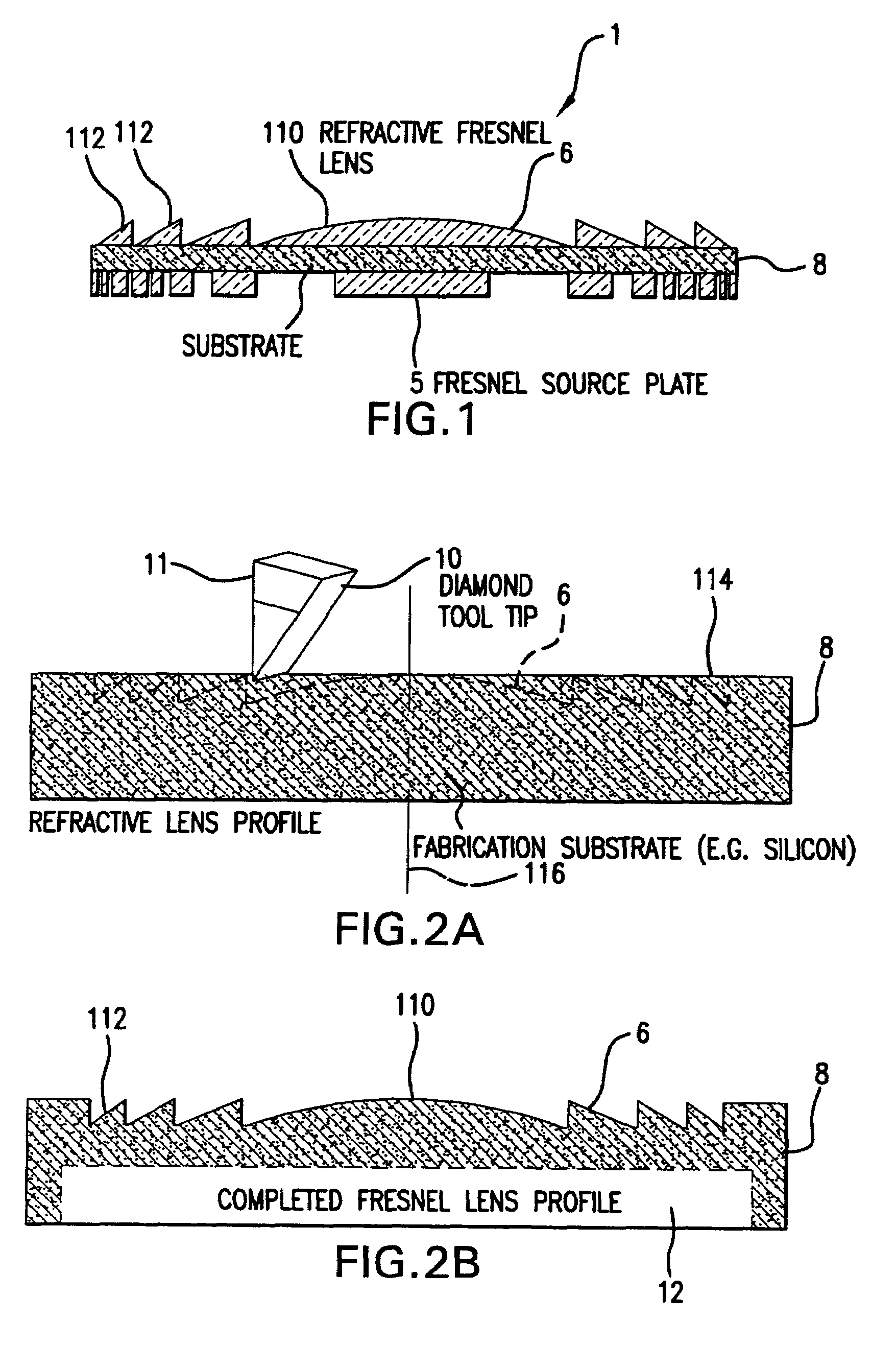
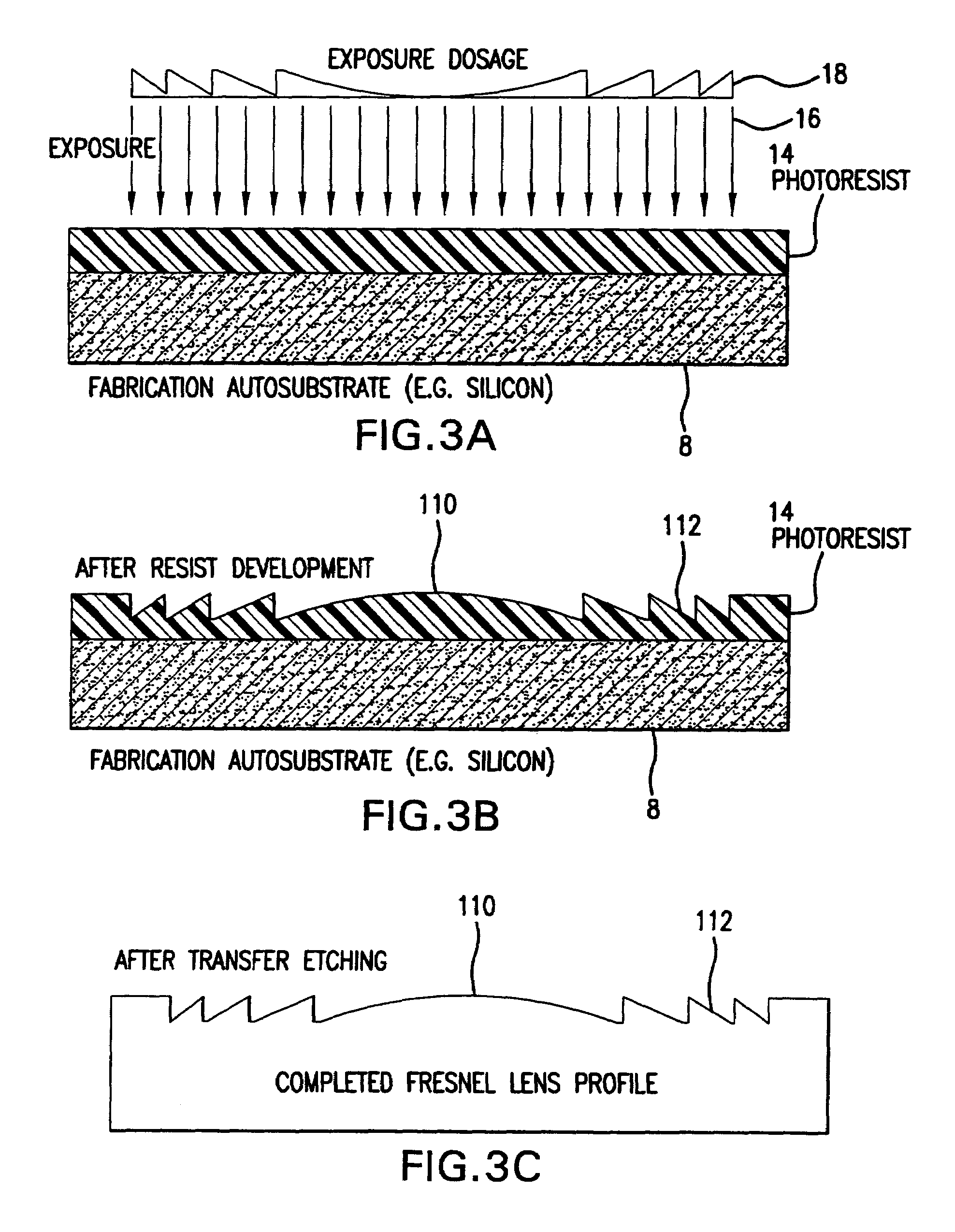
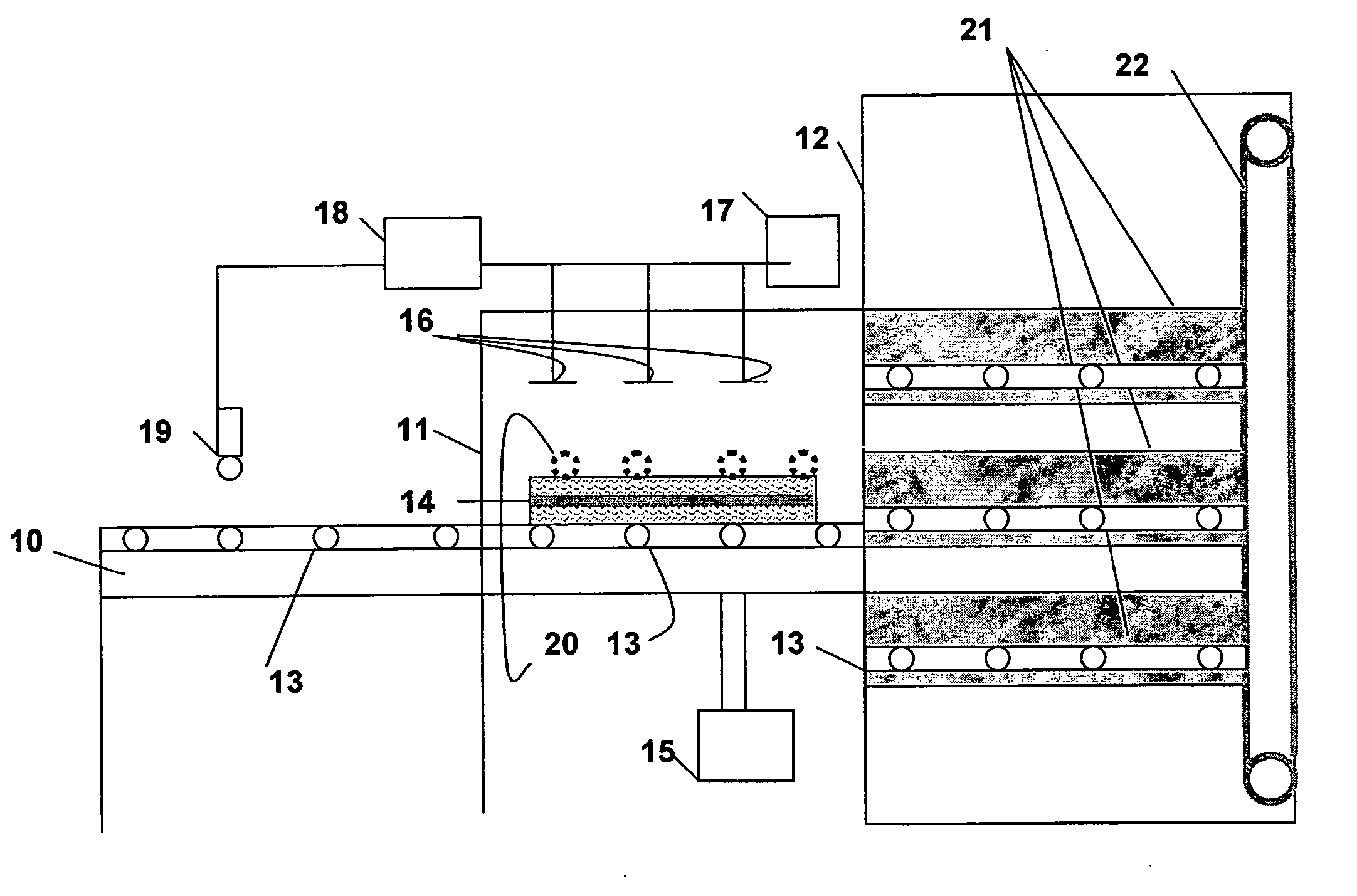
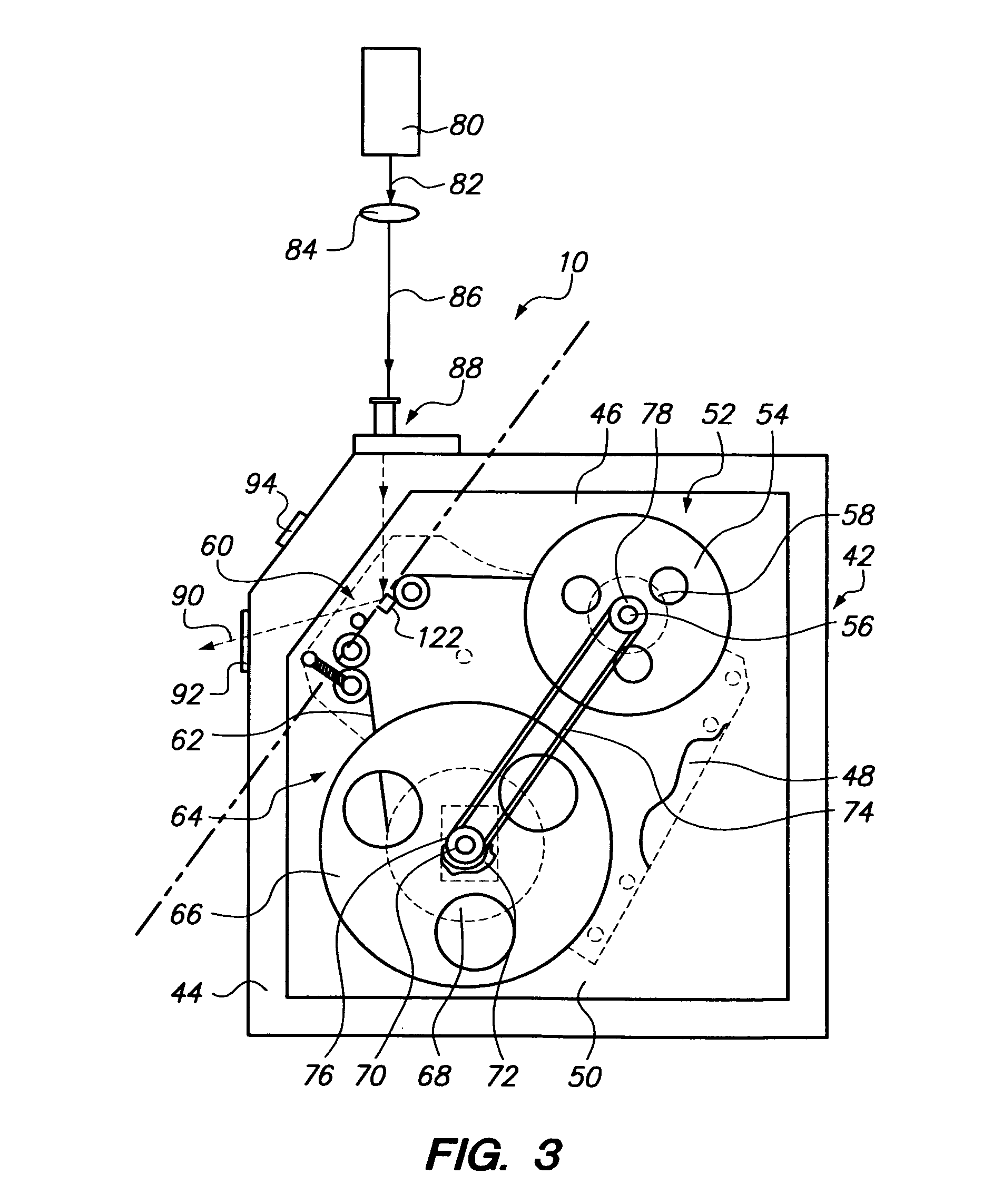
Fabrication methods for micro compounds optics
InactiveUS7365909B2Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesDiamond turningLithographic artist
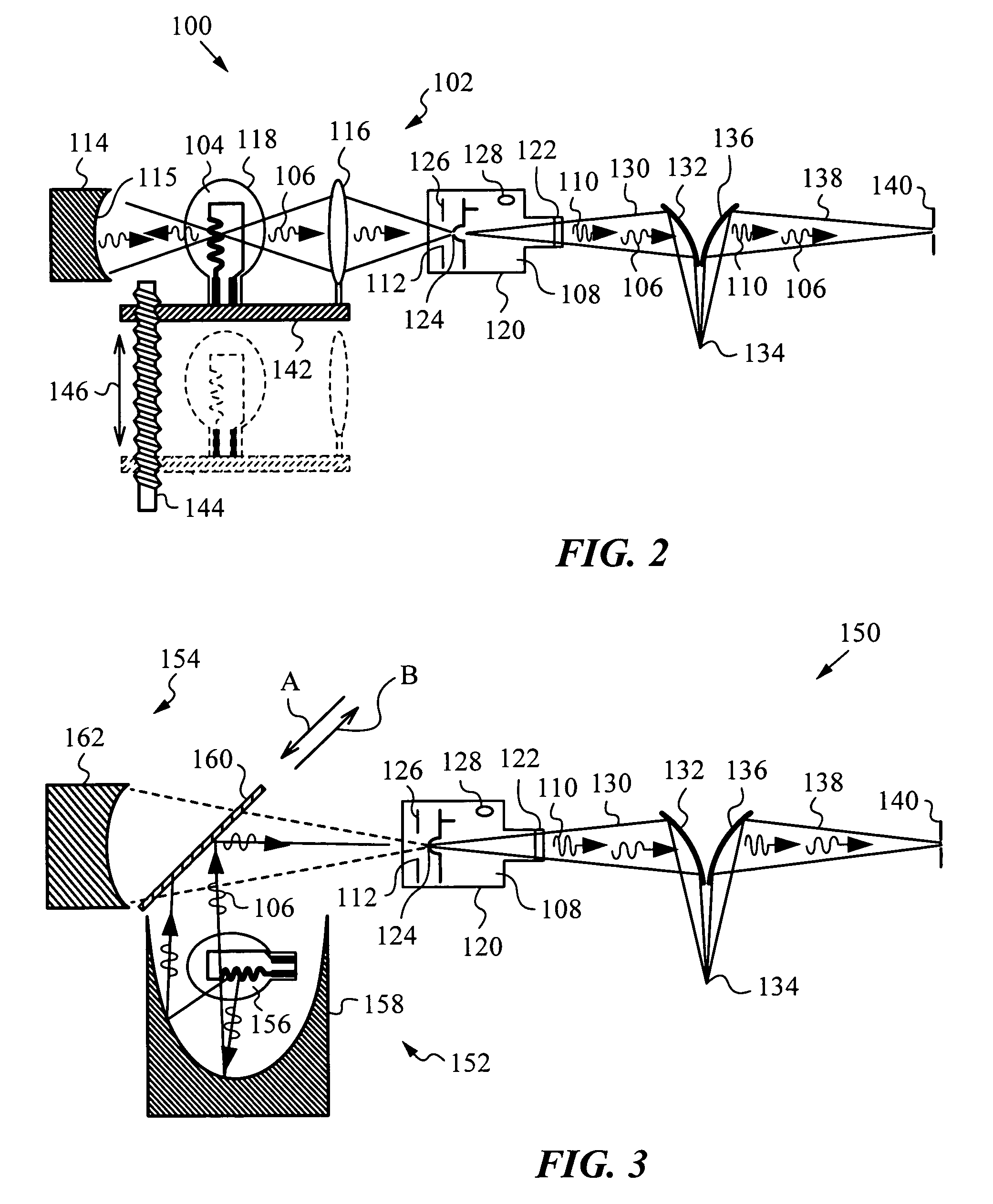
Methods for fabricating refractive element(s) and aligning the elements in a compound optic, typically to a zone plate element. The techniques are used for fabricating micro refractive, such as Fresnel, optics and compound optics including two or more optical elements for short wavelength radiation. One application is the fabrication of the Achromatic Fresnel Optic (AFO). Techniques for fabricating the refractive element generally include: 1) ultra-high precision mechanical machining, e.g,. diamond turning; 2) lithographic techniques including gray-scale lithography and multi-step lithographic processes; 3) high-energy beam machining, such as electron-beam, focused ion beam, laser, and plasma-beam machining; and 4) photo-induced chemical etching techniques. Also addressed are methods of aligning the two optical elements during fabrication and methods of maintaining the alignment during subsequent operation.
Owner:CARL ZEISS X RAY MICROSCOPY
Method and apparatus for laminating glass sheets
InactiveUS20070034317A1Improve efficiencyMechanical working/deformationLamination ancillary operationsProduction rateCooling chamber
The invention relates to a method and apparatus for laminating glass articles without using an autoclave. The sandwich structure to be laminated is placed in a controllable vacuum and subjected to short wave radiation with specified frequency and power. Pressure that is applied continuously during the heating and cooling is also specified for achieving an appropriate bond. An apparatus appropriate for realizing the invented process is also provided. The apparatus includes a loading table, furnace, and cooling chamber that are adjusted to and adjoined to each to other. These parts provide the necessary conditions for high-quality laminating simple and multi-sandwich structures with high production rate and efficiency. The apparatus is inexpensive and fits into the space of two glass article lengths.
Owner:GYROTRON TECH
Arrangement for the generation of intensive short-wave radiation based on a plasma
InactiveUS6995382B2Increased radiation outputHigh outputRadiation pyrometryRadiation/particle handlingSoft x rayPulse energy
The invention is directed to an arrangement for generating intensive radiation based on a plasma, particularly short-wavelength radiation from soft x-ray radiation to extreme ultraviolet (EUV) radiation. The object of the invention is to find a novel possibility for generating radiation generated from plasma in which the individual pulse energy coupled into the plasma and, therefore, the usable radiation output are appreciably increased while retaining the advantages of mass-limited targets. According to the invention, this object is met in that the target generator has a multiple-channel nozzle with a plurality of separate orifices, wherein the orifices generate a plurality of target jets, the excitation radiation for generating plasma being directed simultaneously portion by portion to the target jets.
Owner:XTREME TECH
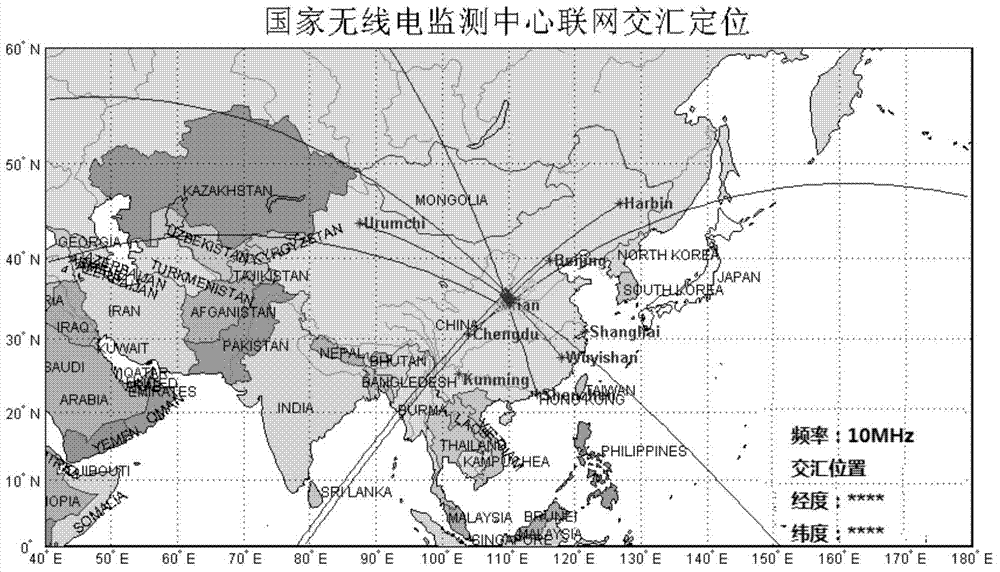
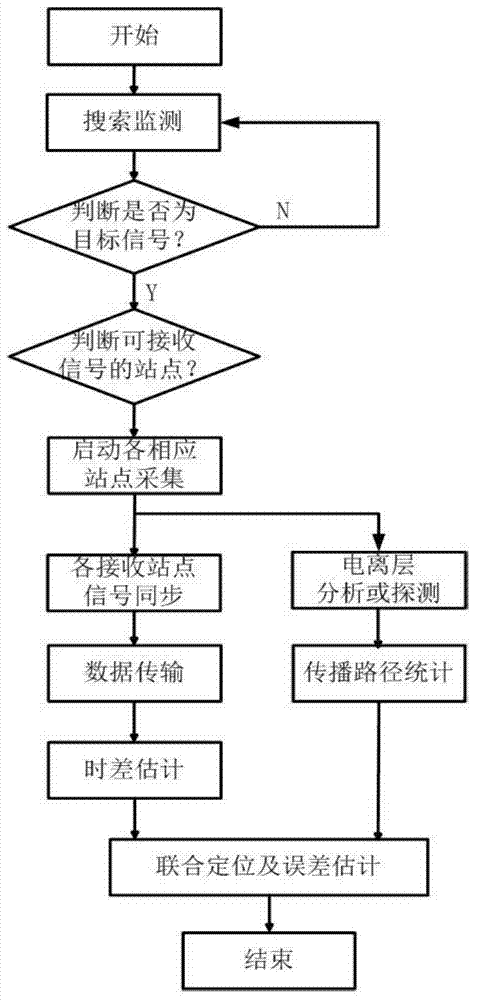
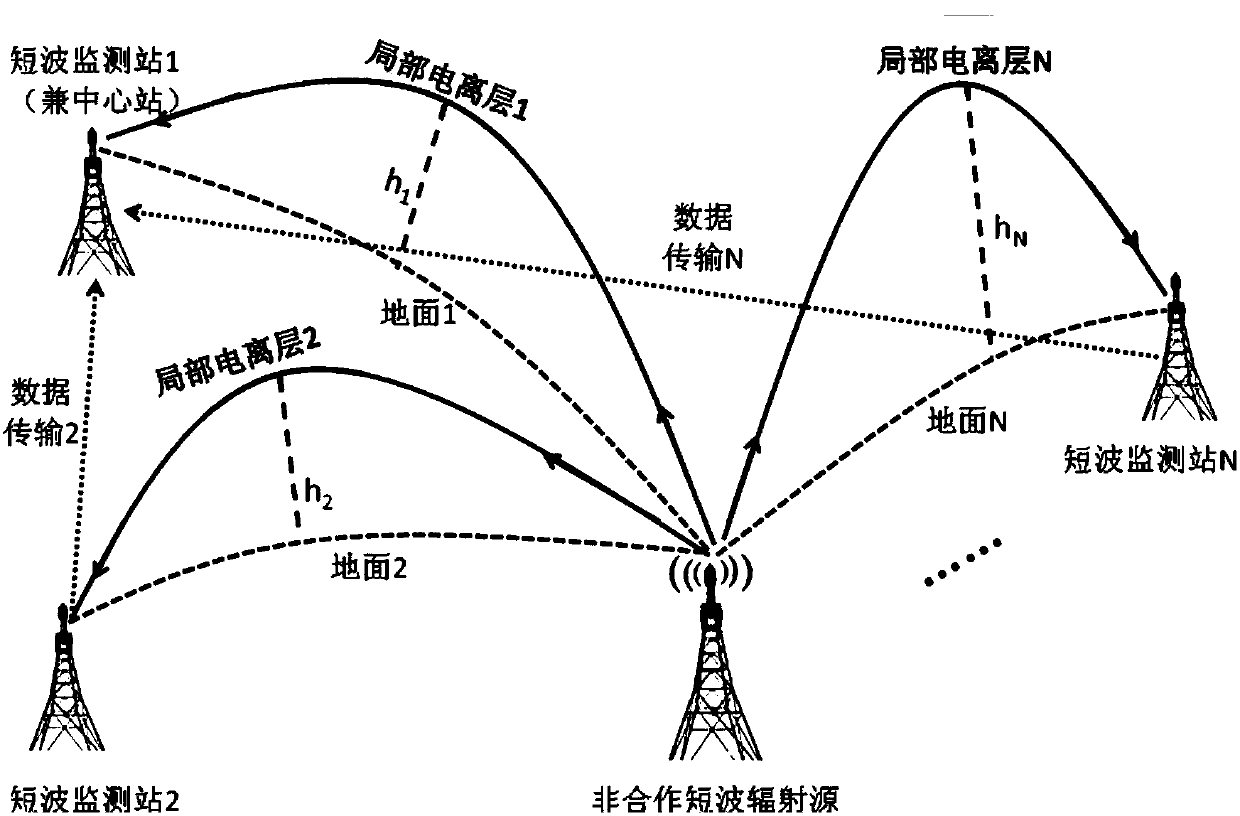
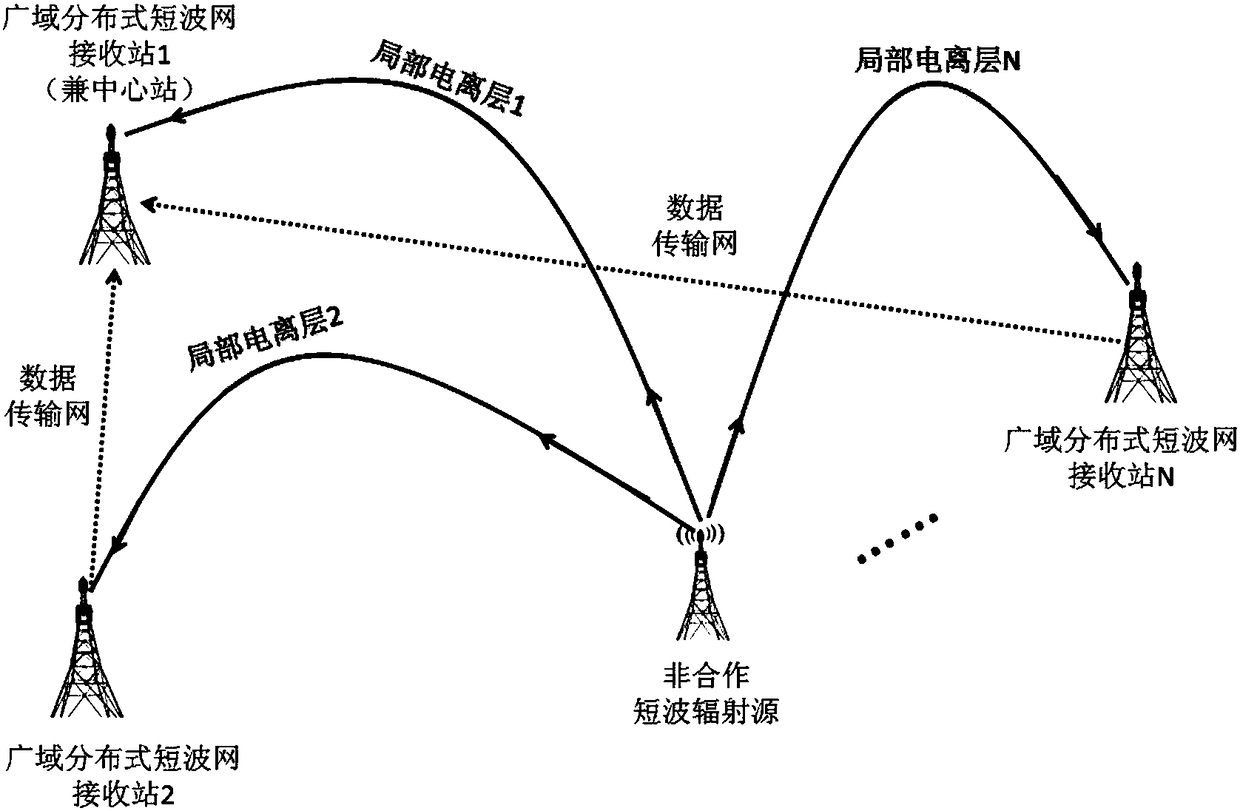
Ionospheric-reflection-based time difference of arrival positioning method for shortwave radiation source
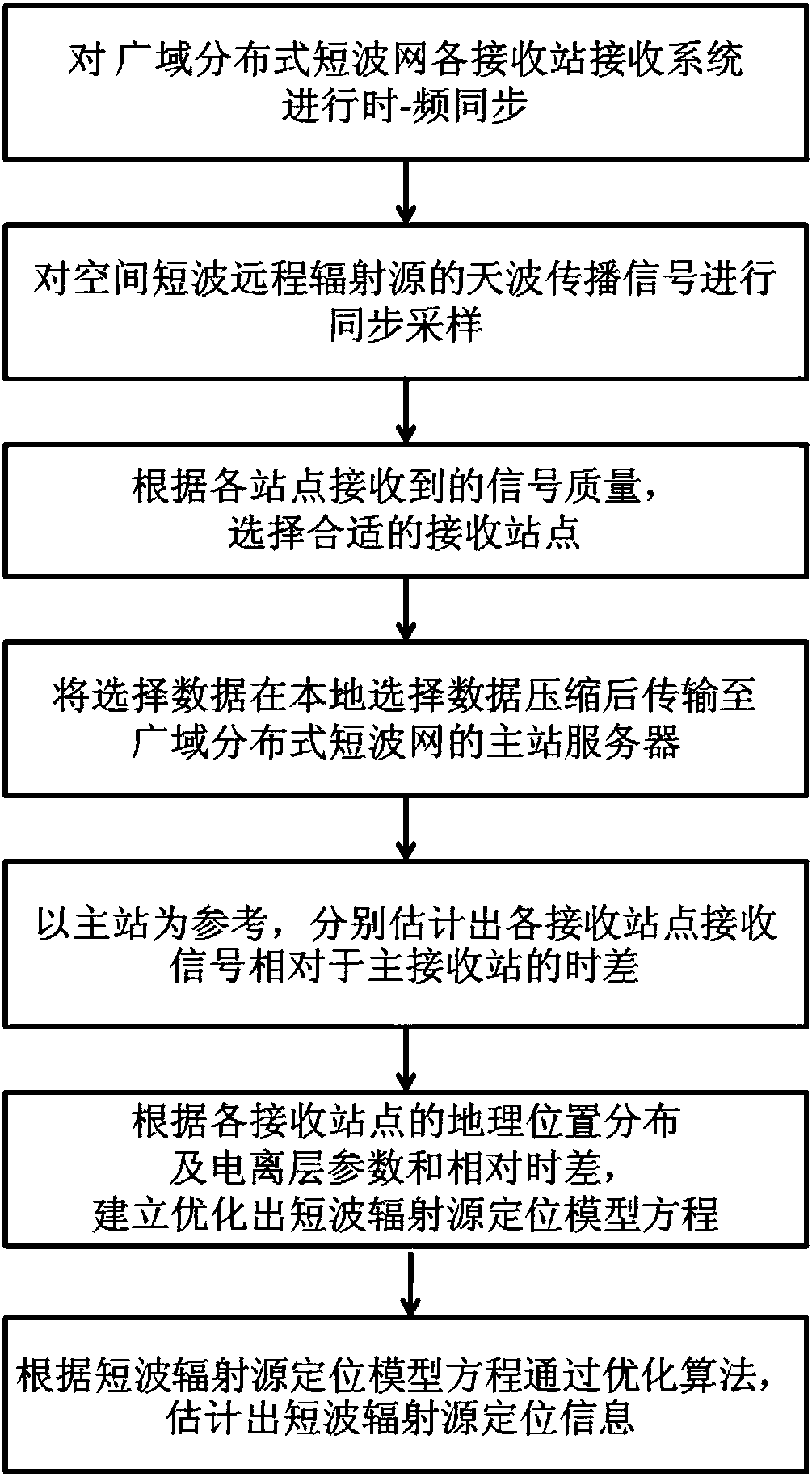
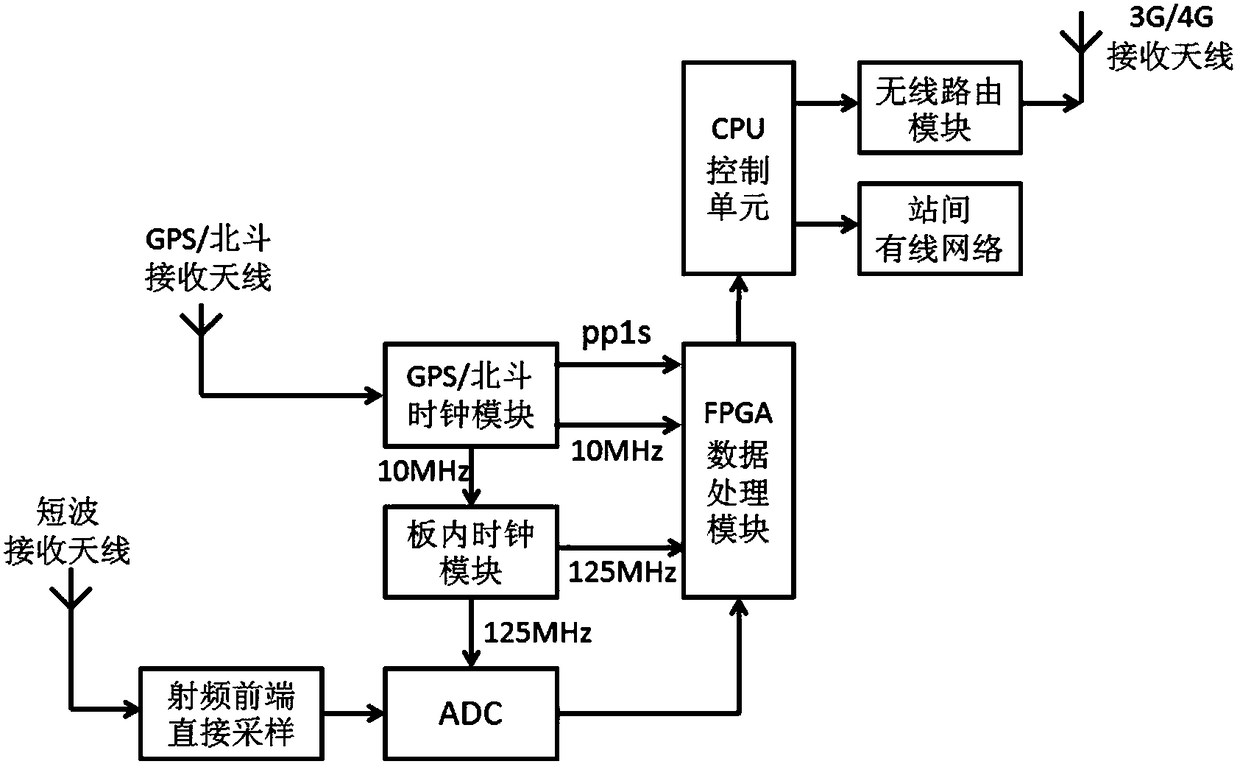
The invention discloses an ionospheric-reflection-based time difference of arrival positioning method for a shortwave radiation source, and belongs to the technical field of shortwave communication. The method comprises the following steps of selecting corresponding receiving sites to acquire found and monitored target signals; locally compressing the target signals, and transmitting the target signals to a master server; estimating propagation channels of the signals received by each receiving site, performing joint positioning error estimation in combination with each time difference of arrival, optimizing a positioning result according to the geographic position distribution of each receiving site and the variation amplitude of ionospheric parameters and the time differences of arrival, and giving a positioning error. According to the method, a conventional shortwave receiving antenna can be utilized, a large direction-finding antenna array is not required, the reflection influence of an ionospheric layer on shortwave sky wave signals is taken into full account, and the time differences of arrival of the signals at different receiving sites through different paths are used for positioning the shortwave radiation source; the method is disclosed according to actual needs, is particularly applied to regions where large antenna arrays cannot be erected, and is practically significant, and manpower and funds can be greatly saved.
Owner:国家无线电监测中心
Radiation source
InactiveUS20070152175A1Reduce decreaseElectric discharge tubesPhotomechanical apparatusLiquid metalExtreme ultraviolet
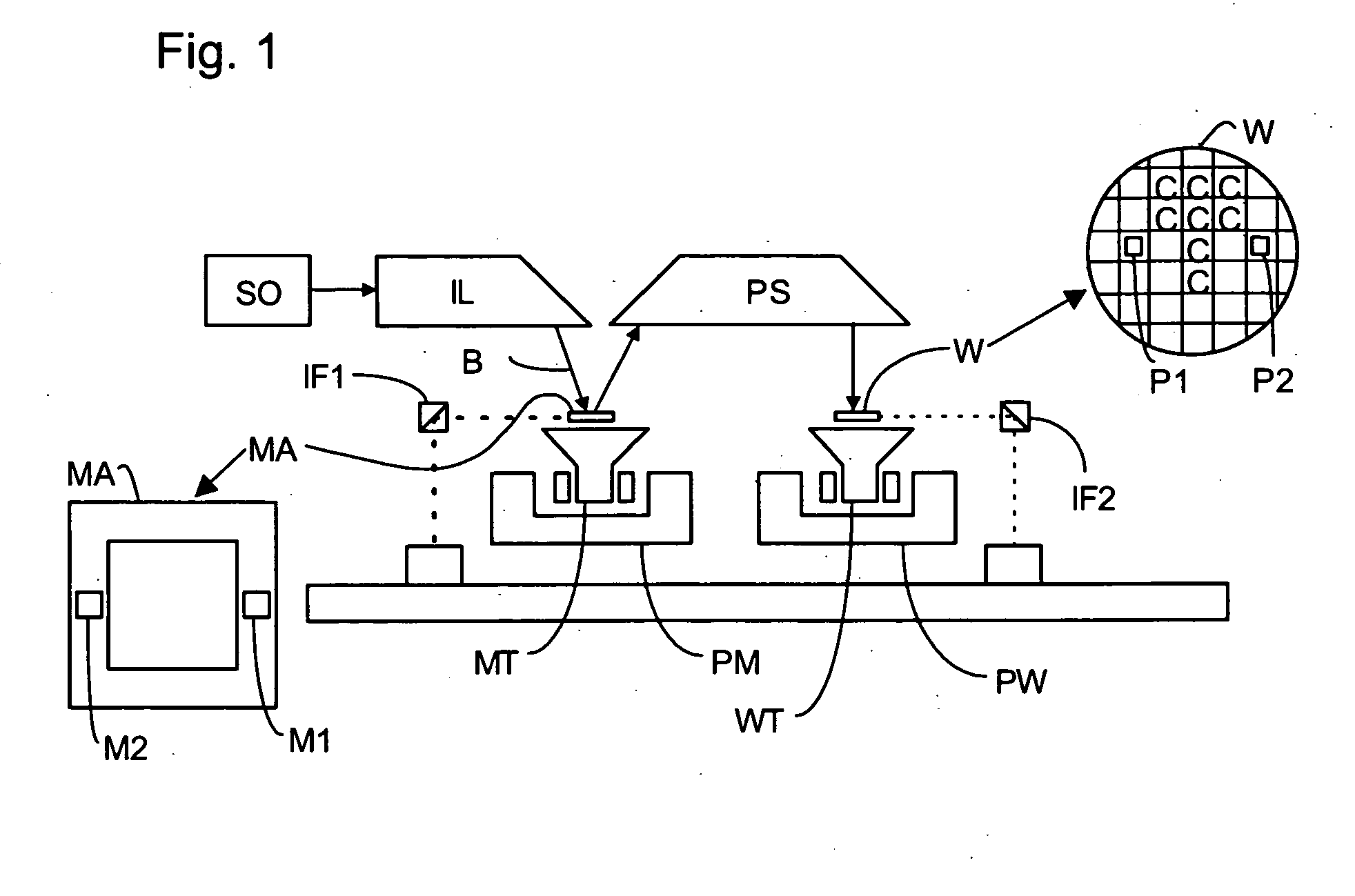
A radiation source generates short-wavelength radiation, such as extreme ultraviolet radiation, for use in lithography. Rotating electrodes are provided which dip into respective baths of liquid metal, for example, tin. An electrical discharge is produced between the electrodes to generate the radiation. Holes are provided in the electrodes and / or in a metal shielding plate around the electrodes to enable better pumping down to low pressure in the vicinity of the discharge to improve the conversion efficiency of the source. The holes in the electrodes improve cooling of the electrodes by causing stirring of the liquid metal, and by improving the thermal and electrical contact between the electrodes and the liquid metal. Improved electrical contact also reduces the time-constant of the discharge circuit, thereby further improving the conversion efficiency of the source.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Collector mirror for plasma-based, short-wavelength radiation sources
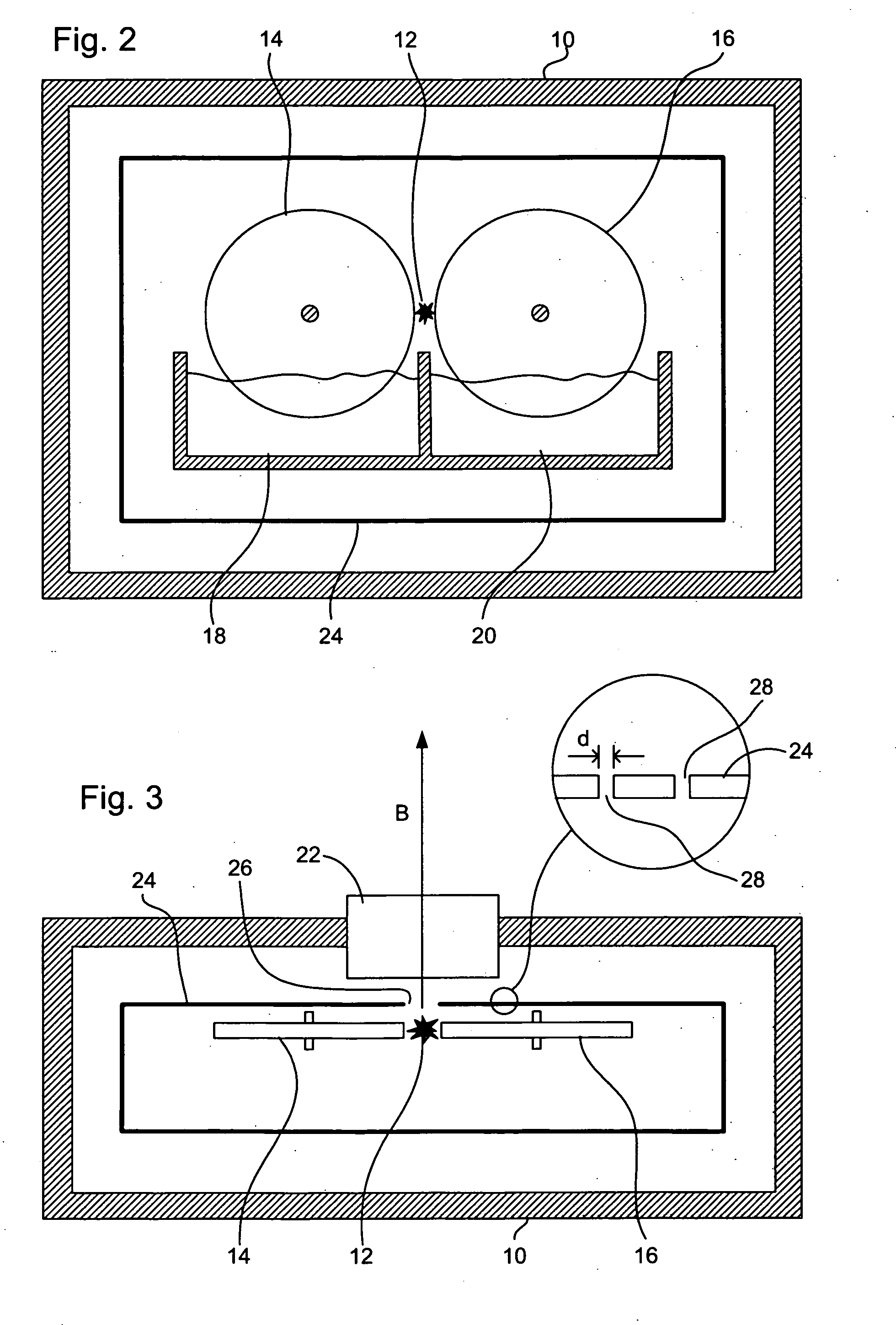
ActiveUS7329014B2Great expenditureImprove reflectivityMirrorsRadiation/particle handlingTransport mediumThermostat
The invention is directed to a collector mirror for short-wavelength radiation based on a plasma. It is the object of the invention to find a novel possibility for managing the temperature of a collector mirror for focusing short-wavelength radiation generated from a plasma which allows an efficient thermal connection to be produced between the optically active mirror surface and a thermostat system without the disadvantages relating to space requirements or high-precision manufacture of the collector mirror. This object is met, according to the invention, in that the collector mirror has a solid, rotationally symmetric substrate which comprises a material with high thermal conductivity of more than 50 W / mK and in which channels for cooling and temperature management are incorporated in the substrate so that a heat transport medium can flow through directly and for rapidly stabilizing the temperature of the optically active mirror surface. Heat of transient temperature spikes which occur in pulsed operation for plasma generation at the mirror surface and which temporarily exceed the temperature average by a multiple is quickly dissipated.
Owner:USHIO DENKI KK
Early detection of battery cell thermal event
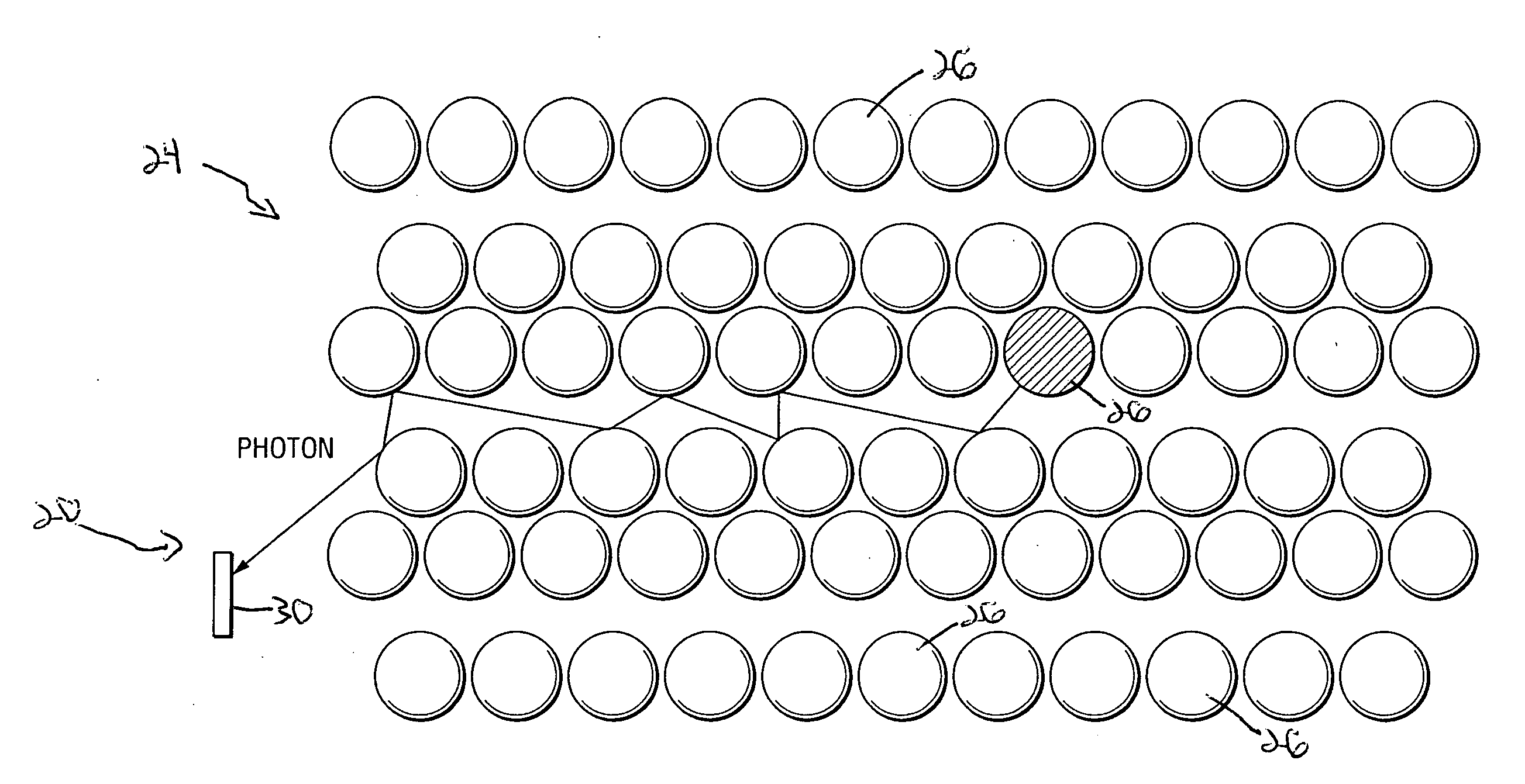
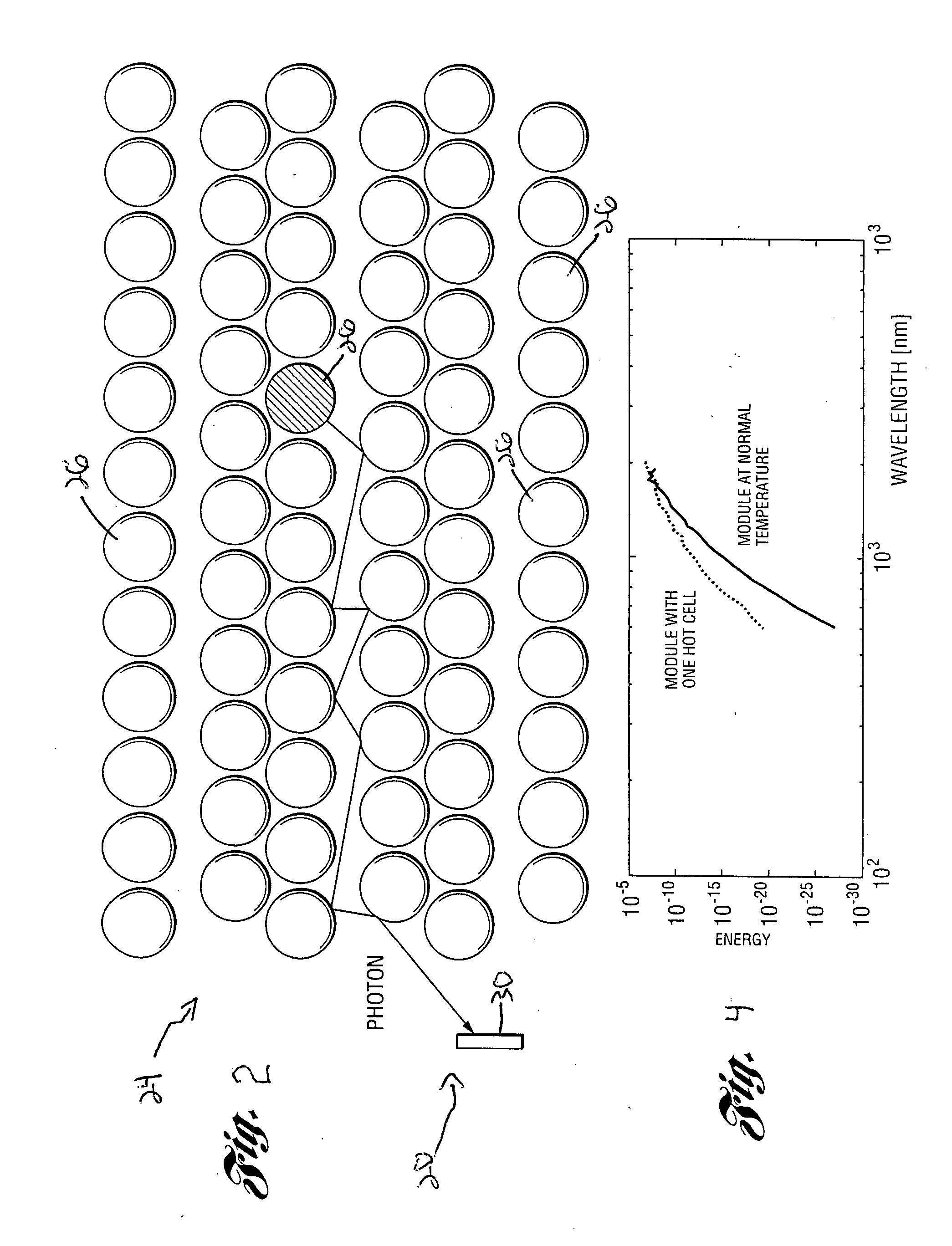
ActiveUS20080315839A1Early detectionReduce absorptionBatteries circuit arrangementsRadiation pyrometryControl systemElectric vehicle
A battery module for use in an electric vehicle is disclosed. The battery module includes a plurality of cells arranged in a predetermined pattern within the module. The battery module also includes an optical pyrometer arranged inside the module. The optical pyrometer is installed within the module after being tuned to detect a predetermined frequency or band of frequencies. The pyrometer will be used to detect an increase in short wave radiation density from one of the battery cells within the module wherein that battery cell has a temperature above a predetermined threshold. The optical pyrometer will be used to communicate an electric signal to a control system of the electric vehicle wherein that control system will implement a predetermined mitigation process to contain the thermal event of that one cell within the battery module.
Owner:TESLA INC
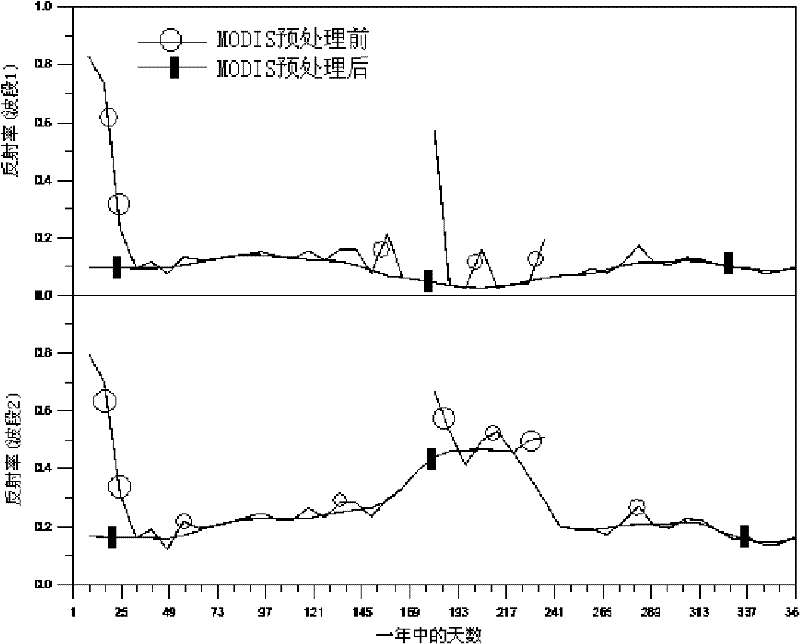
High-resolution vegetation productivity remote sensing estimation method based on downscaling
InactiveCN110276304AHigh precisionUniversalCharacter and pattern recognitionResourcesTerrainDownscaling
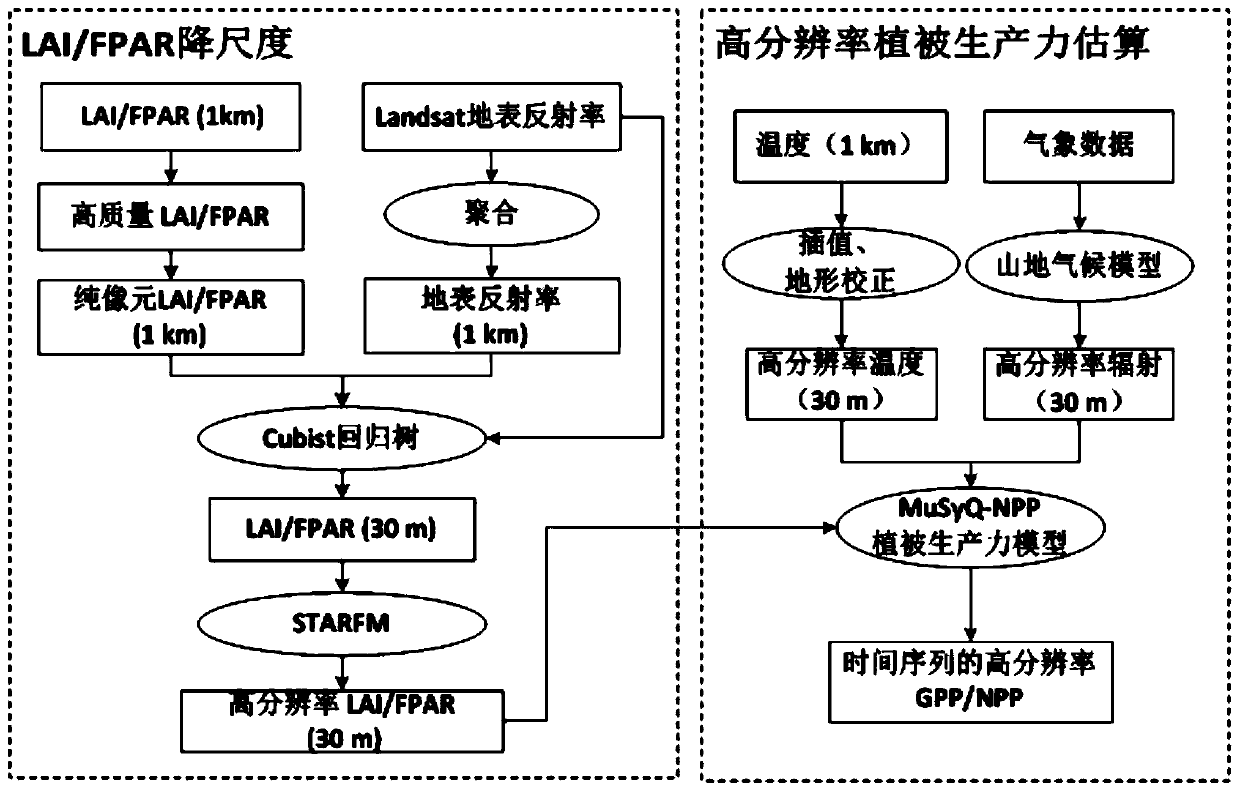
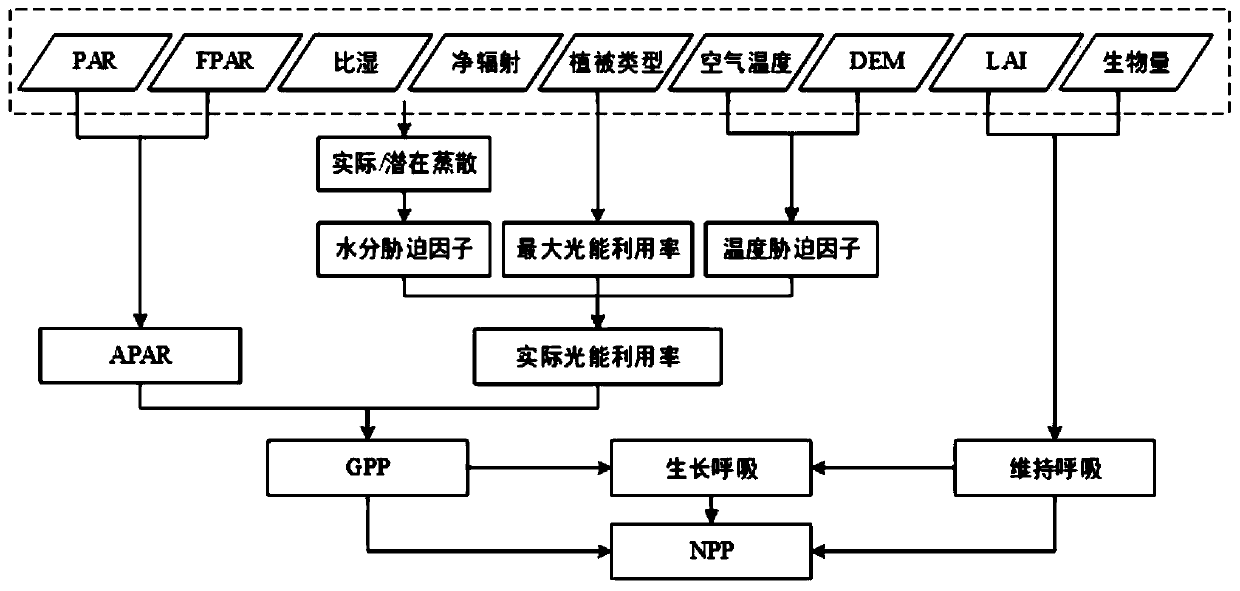
The invention provides a high-resolution vegetation productivity remote sensing estimation method based on downscaling. The high-resolution vegetation productivity remote sensing estimation method based on the downscaling comprises: carrying out downscaling on factors LAI / FPAR estimated by vegetation productivity, and obtaining high-resolution LAI / FPAR of a time sequence; performing spatial interpolation and terrain correction on the temperature to obtain a high-resolution temperature factor; simulating high-resolution solar short-wave radiation by using a mountainous microclimate model; inputting the downscaled high-resolution LAI / FPAR, the terrain-corrected high-resolution temperature factor and the solar short wave radiation data into a vegetation productivity model MuSyQ-NPP to obtain the high-resolution GPP / NPP of the continuous time sequence. The advantages of remote sensing data with different resolutions are fully exerted, the remote sensing data with high resolution and low resolution are fused, a technical scheme of a high-resolution vegetation productivity product with higher precision and stronger universality is constructed, and the problems that an existing vegetation productivity downscaling scheme is low in precision and insufficient in universality are solved.
Owner:BEIJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
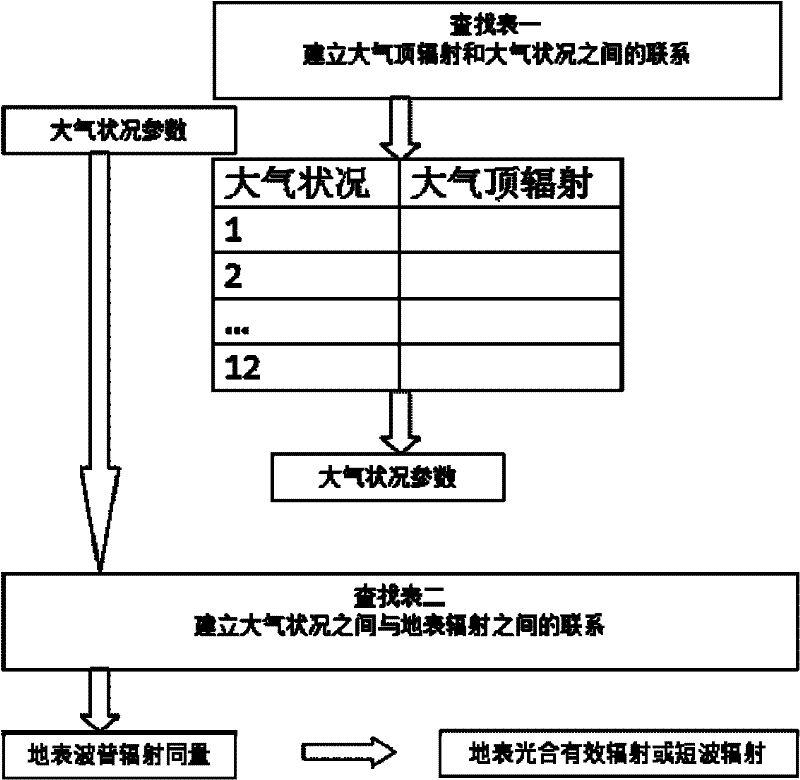
Inversion method and system of downlink shortwave radiation and photosynthetically active radiation data
InactiveCN102338869AImprove calculation accuracyHigh precisionWave based measurement systemsSpecial data processing applicationsSatellite dataAtmospheric sciences
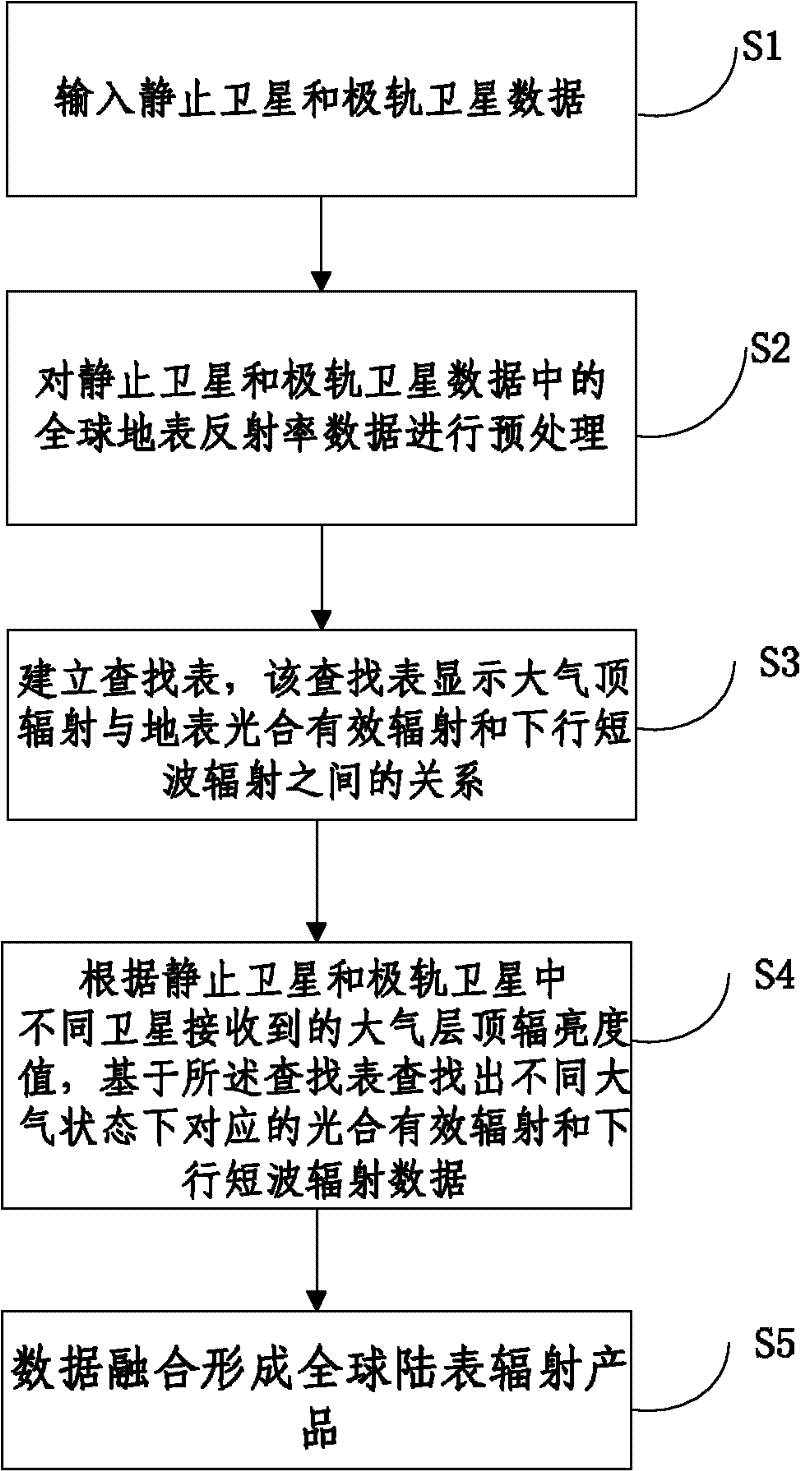
The invention relates to the technical field of satellite remote sensing and application and discloses an inversion method and system of downlink shortwave radiation and photosynthetically active radiation data. The method comprises the following steps of: (S1) inputting stationary satellite and polar orbital satellite data; (S2)pre-processing global surface reflectance data in the stationary satellite and polar orbital satellite data so as to remove the influence of the cloud on the ground reflectance; (S3) establishing a lookup table, wherein the lookup table displays the relationship between the extraterrestrial radiation and the surface photosynthetically active radiation and downlink shortwave radiation; (S4) on the basis of extraterrestrial radiation brightness values received by different satellites in the stationary satellite and polar orbital satellite, figuring out corresponding photosynthetically active radiation and downlink shortwave radiation under different atmospheric conditions according to the lookup table; and (S5) forming a global epicontinental radiation product according to data fusion. According to the invention, the calculation accuracy of the downlink shortwave radiation and photosynthetically active radiation data inversion is improved.
Owner:BEIJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
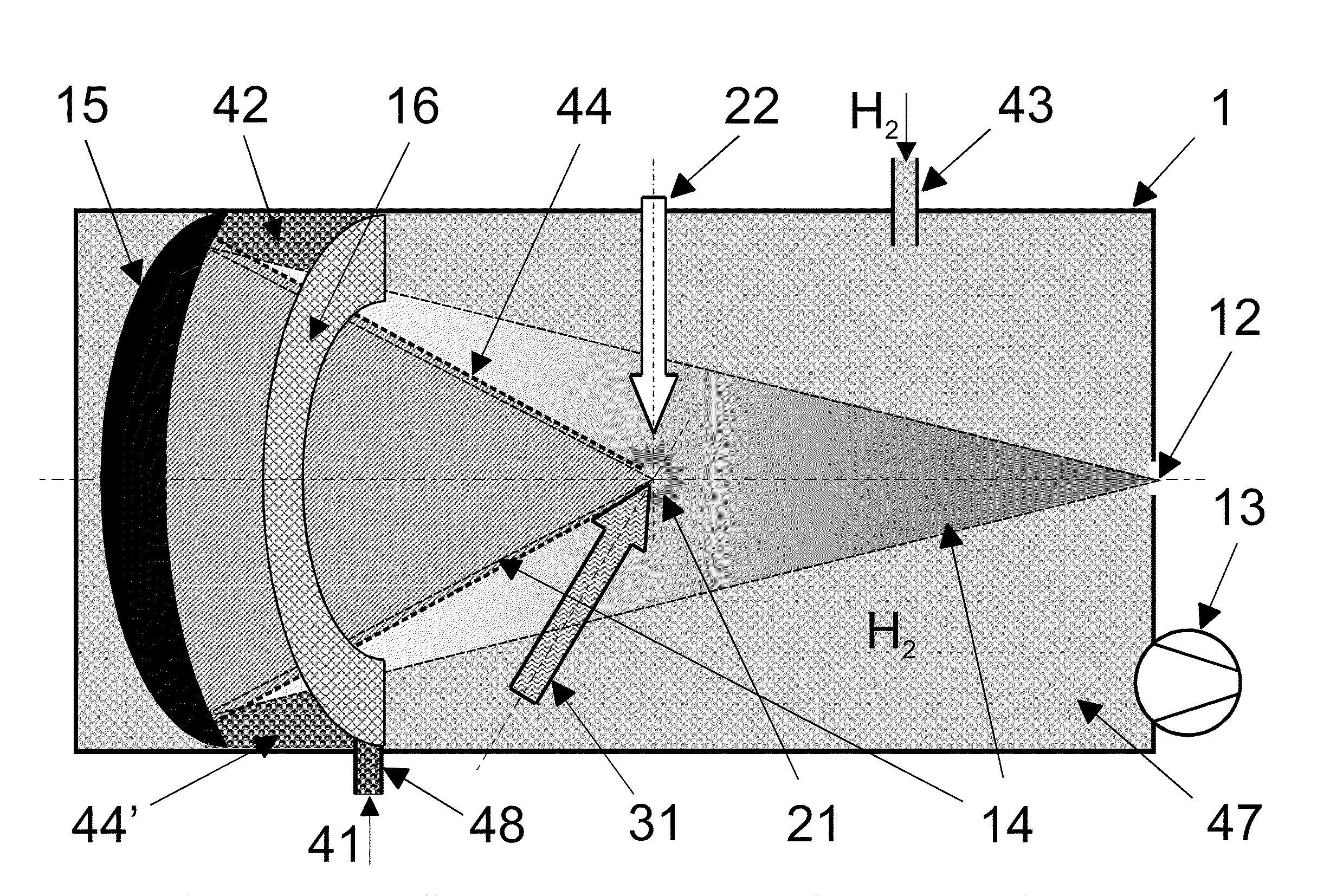
Method and arrangement for the operation of plasma-based short-wavelength radiation sources
InactiveUS20100078578A1Extensive debris mitigationLong life-timeRadiation pyrometryPhotomechanical apparatusHydrogenProduct gas
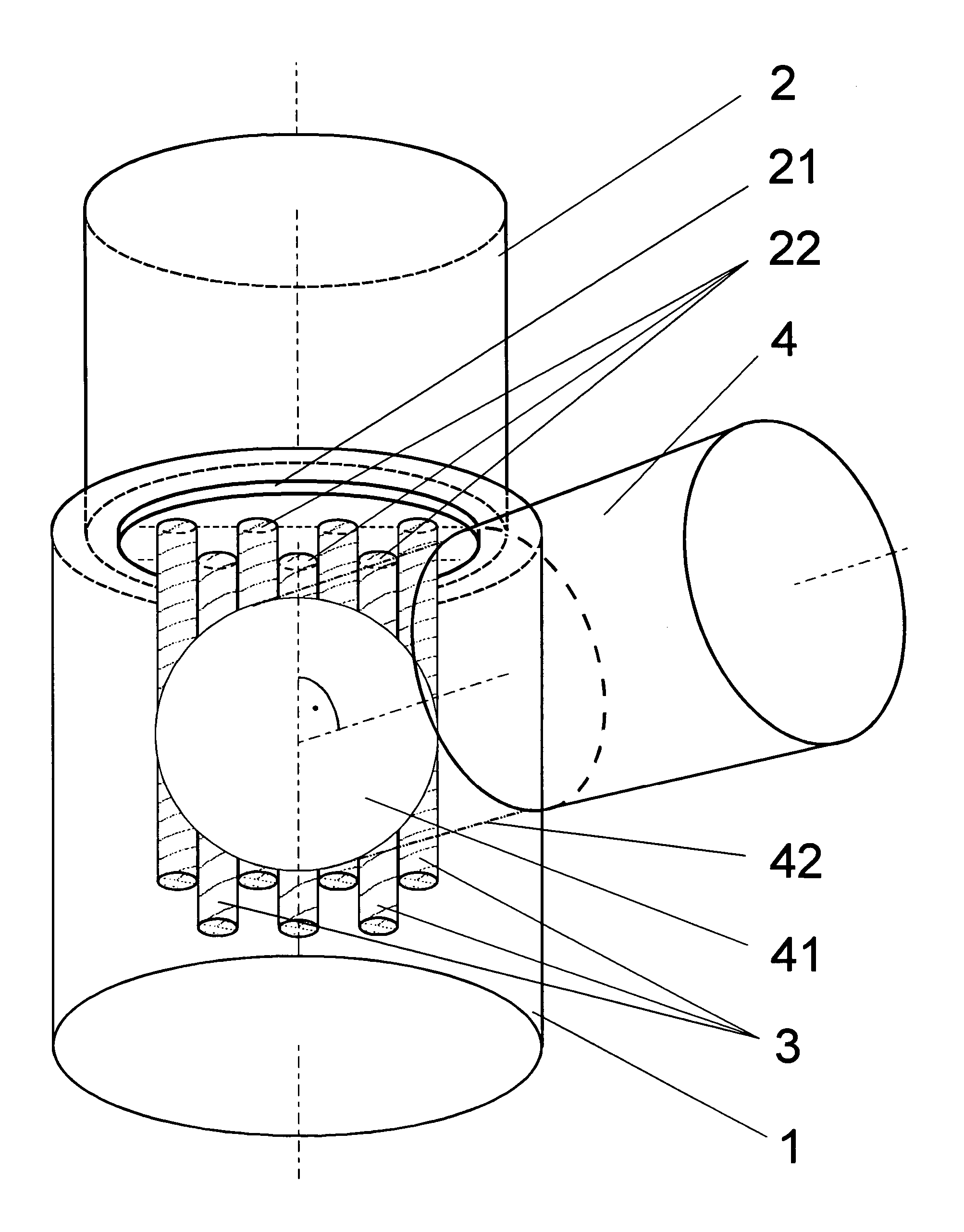
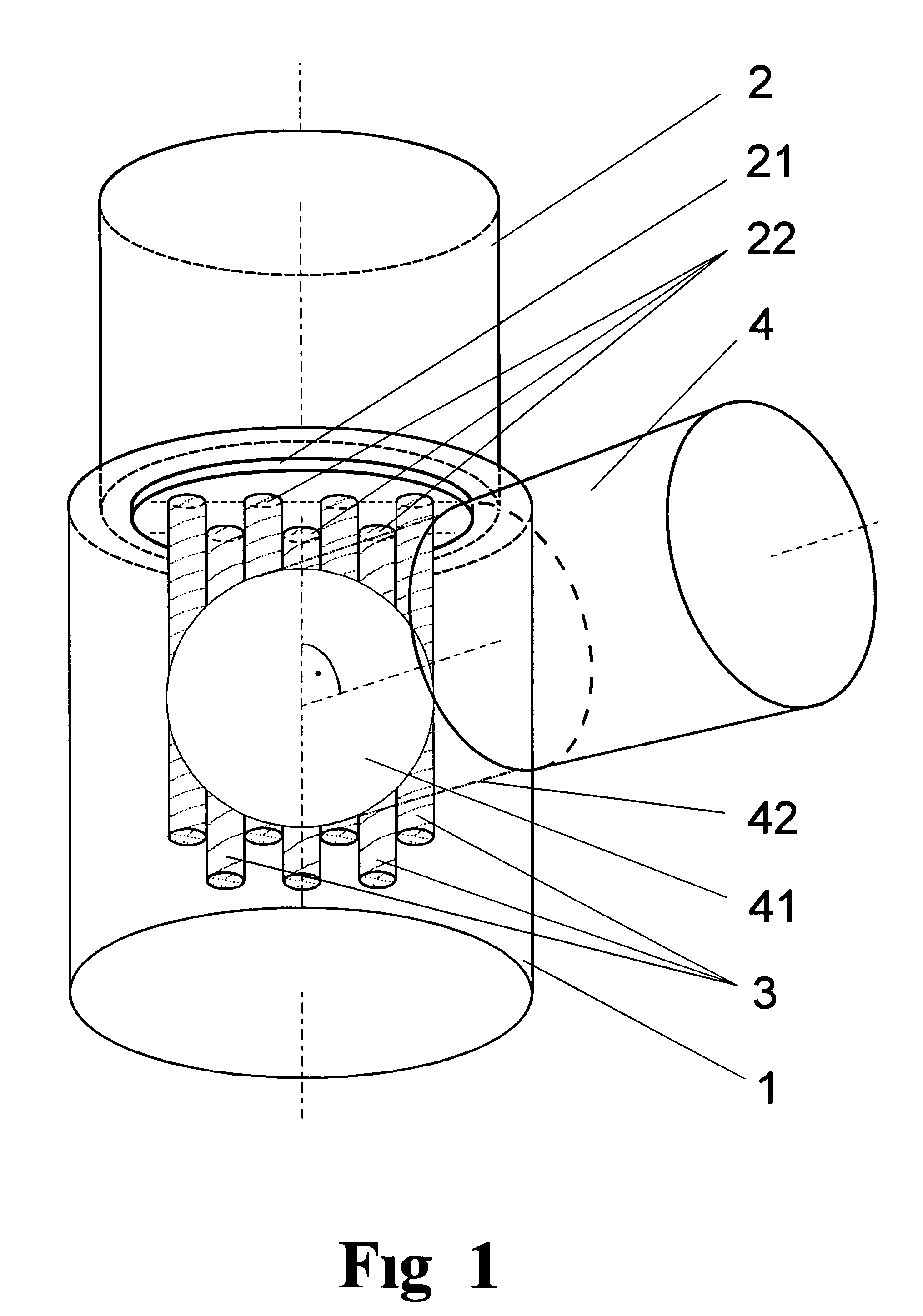
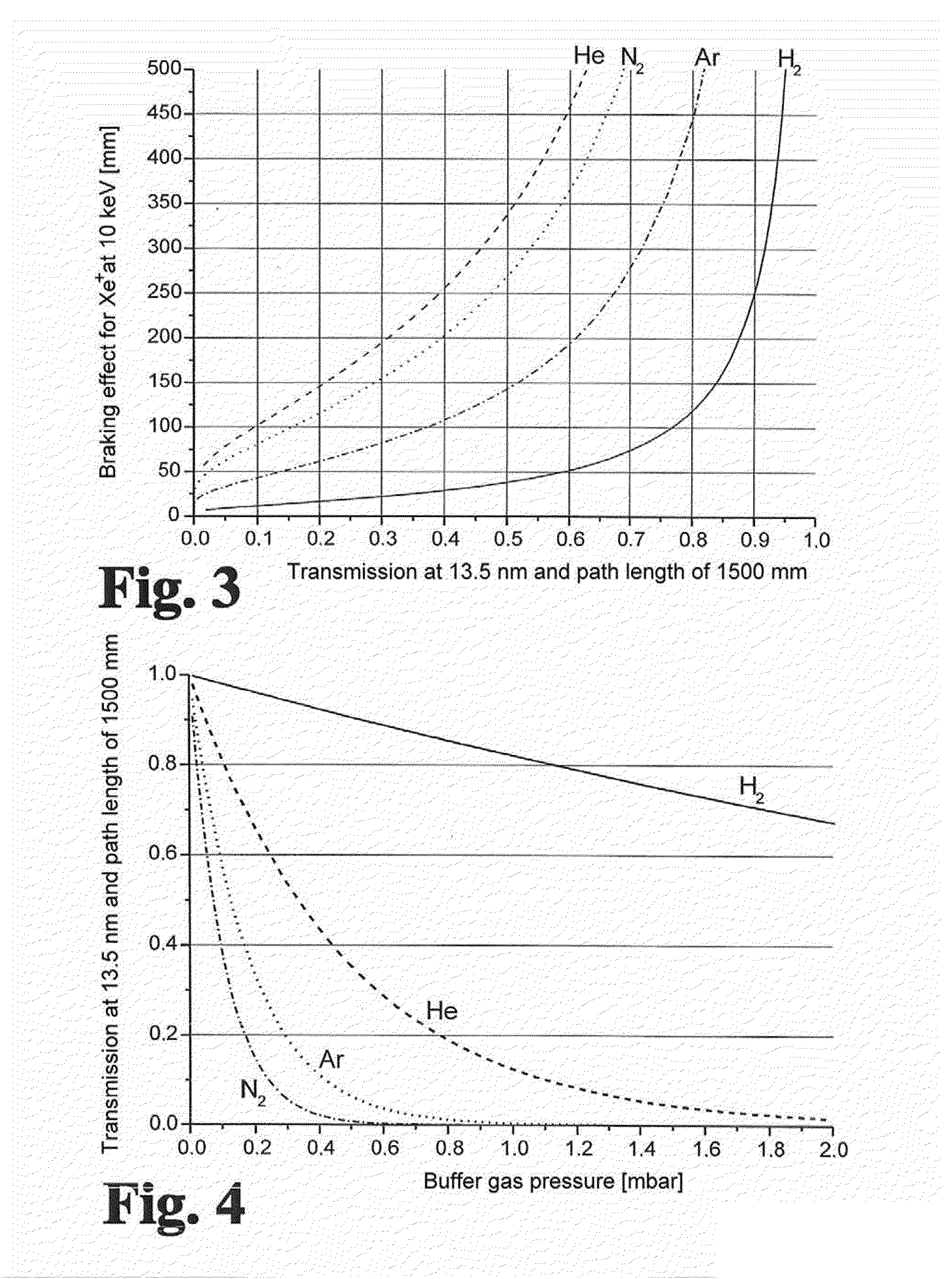
The invention is directed to a method for operating plasma-based short-wavelength radiation sources, particularly EUV radiation sources, having a long lifetime and to an arrangement for generating plasma-based short-wavelength radiation. It is the object of the invention to find a novel possibility for operating plasma-based short-wavelength radiation sources with a long lifetime which permits extensive debris mitigation without the main process of radiation generation being severely impaired through the use of buffer gas and without the need for substantial additional expenditure for generating partial pressure in a spatially narrowly limited manner. According to the invention, this object is met in that hydrogen gas as buffer gas (41) is introduced into the vacuum chamber (1) under a pressure such that a pressure-distance product in the range of 1 to 100 Pa·m is realized while taking into account the geometric radiation paths of the radiation emitted by the emitter plasma (21) within the buffer gas (41; 44), and the vacuum chamber (1) is continuously evacuated for adjusting a quasistatic pressure (42; 47) and for removing residual emitter material and buffer gas (41).
Owner:XTREME TECH
Photocatalyst material for absorbing full sunlight spectrum and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN107185565AIncrease profitRealize full spectrum utilizationPhysical/chemical process catalystsWater/sewage treatment by irradiationMicro nanoHigh energy
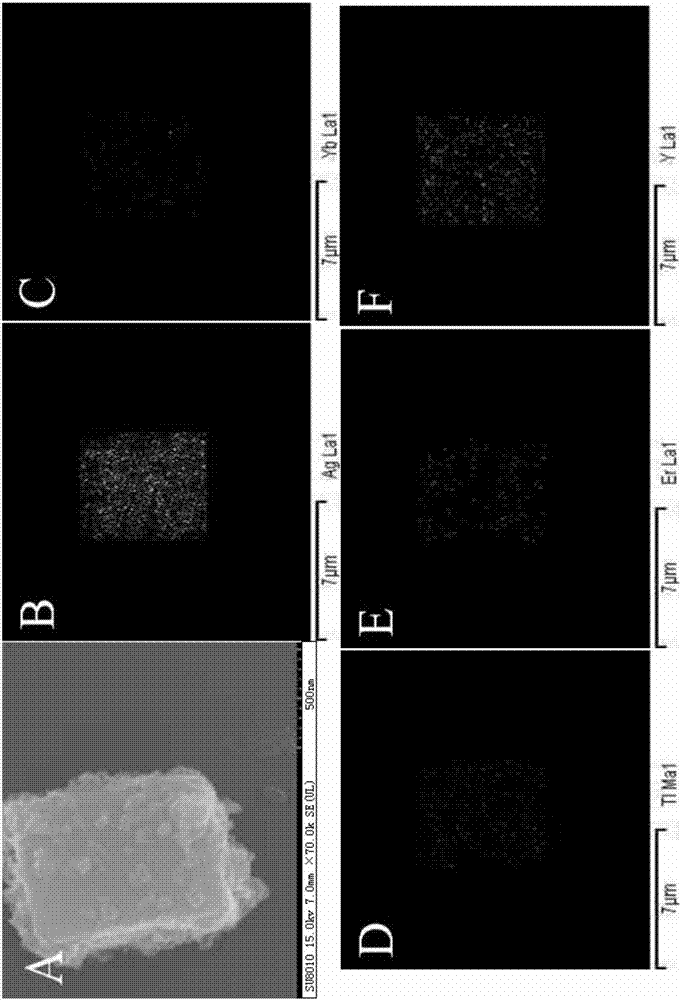
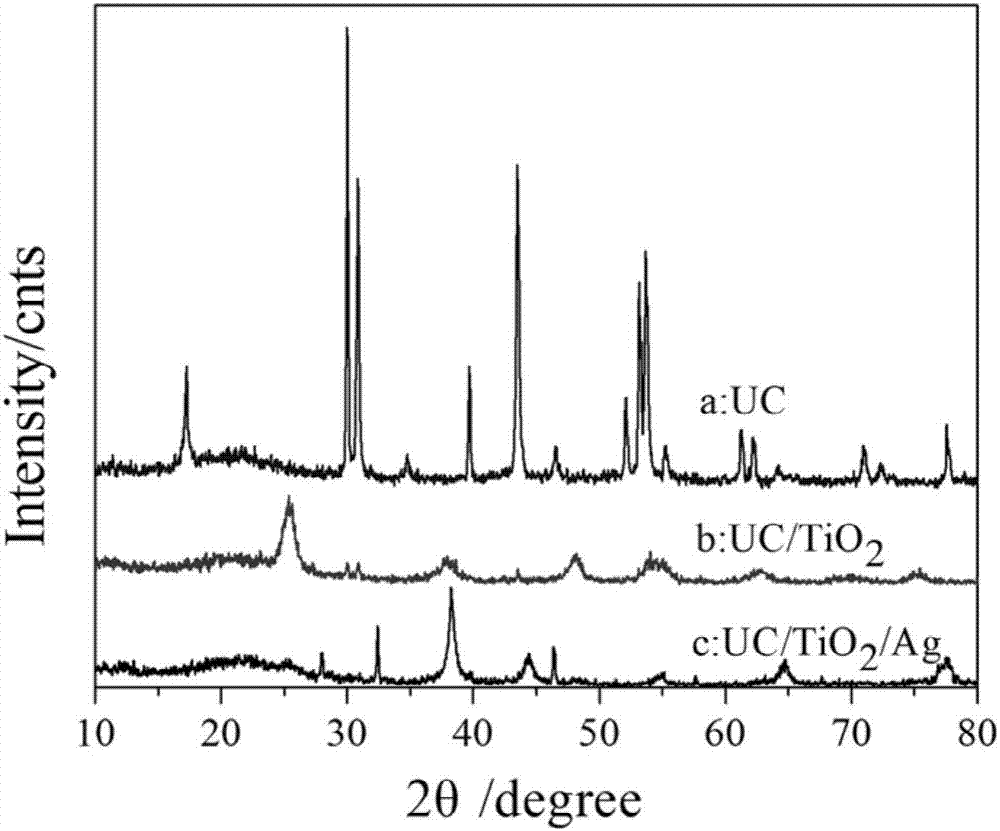
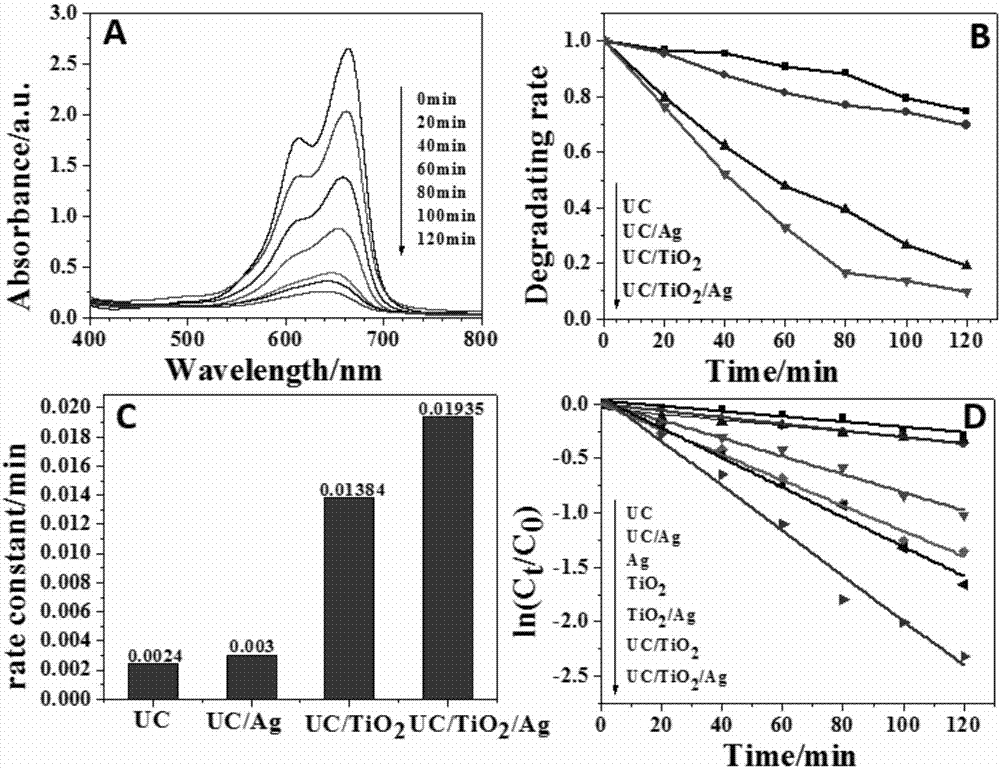
The invention provides a photocatalyst material for absorbing a full sunlight spectrum and a preparation method thereof and relates to the technical field of composite micro-nano materials. The material uses an upconversion material NaYF4: Yb,Er as a template, and the surface of the template is sequentially modified with TiO2 and Ag nanoparticles. Firstly, the upconversion material is obtained through hydro-thermal synthesis reaction, then is used as the template and is successively modified with the TiO2 and Ag nanoparticles through reduction reaction, and the UC / TiO2 / Ag composite micro-nano photocatalyst material is obtained. The photocatalyst material retains the advantage of efficiently absorbing ultraviolet and visible wavebands of high-energy excitation of a traditional photocatalyst material, meanwhile can also convert long-wave radiation of an infrared waveband in sunlight into visible waveband shortwave radiation which can be directly absorbed by the material, the sunlight utilization rate is further improved, full spectrum utilization of sunlight is achieved, and the photocatalyst material is hopeful to serve as a photocatalyst for sunlight-based efficient catalytic degradation of organic pollutants.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV
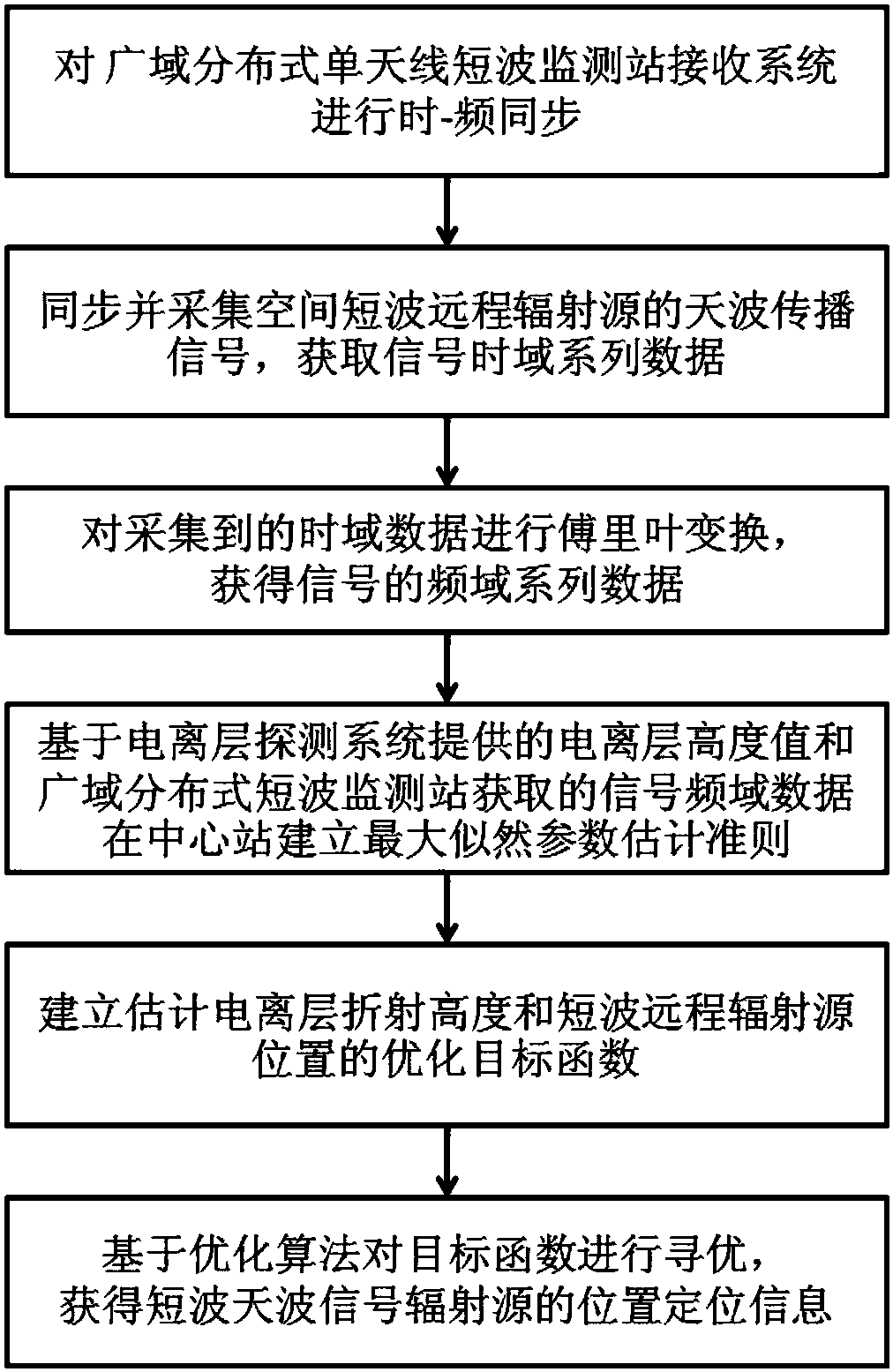
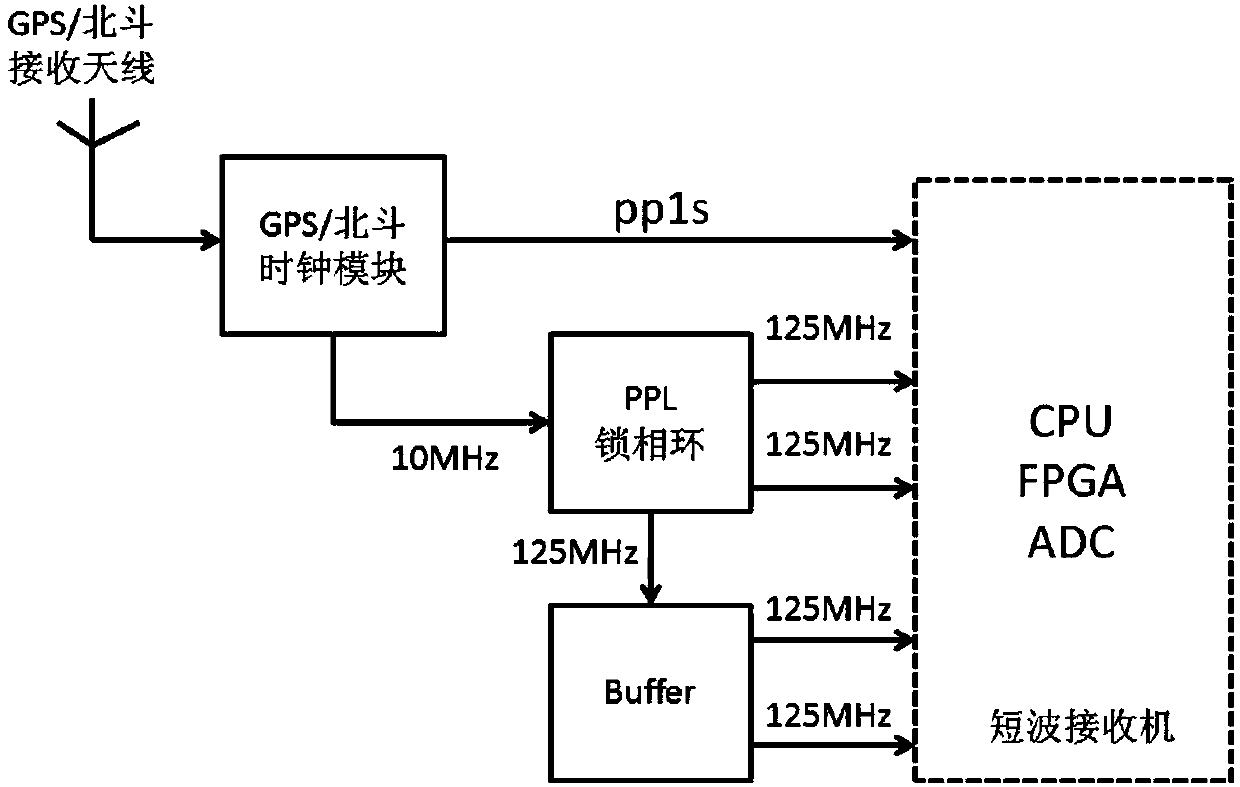
Short-wave remote radiation source one-step locating method based on wide-area distributed single-antenna receiving
ActiveCN108363037ASolve the problem of high precision positioningImprove performancePosition fixationSkywaveMathematical model
The invention relates to a short-wave remote radiation source one-step locating method based on wide-area distributed single-antenna receiving. The method comprises the steps: building a mathematic model of an arrival signal relative to a short-wave remote radiation source position function based on the short-wave antenna signal propagation principle; converting the wide-area distributed single-antenna received data into frequency domain data based on the technology of Fourier transform, and building a mathematic function model of the short-wave remote radiation source position and the heightof an ionized layer through an initial measured value of the height of the ionized layer and the maximum likelihood estimation criteria; finally obtaining the short-wave remote radiation source position information in a one-step mode based on the particle filtering or iteration optimization algorithms. According to the invention, there is no need of a large-scale array receiving station, and the method can achieve the high-precision one-step locating of the short-wave radiation source on the basis of a conventional wide-area distributes short-wave network through the single-channel receiving and algorithm software updating. The performances of the algorithms are reliable, and the method has great values in the fields of civil short-wave radio management and military short-wave radio detection.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Warm white light light-emitting diode (LED) and lithium matter fluorescent powder thereof
InactiveCN101694862AWell mixedGas discharge lamp usageLuminescent compositionsAluminateHeterojunction
The invention relates to a warm white light light-emitting diode (LED) and lithium matter fluorescent powder thereof, wherein the lithium matter fluorescent powder is used in the warm white light LED, adopts oxides of Ith and IIIth main group elements in a periodic table of elements as a matrix, and takes elements with transition in electron d layer and f layer as activation elements; the matrix of the fluorescent powder is formed by solid solutions of similar aluminates of lithium and yttrium, with the chemical formula of Li alpha (Gd1-xYx) 3AI5 plus alpha O12 plus 2 alpha: TR; and when the matrix is activated by short wave radiation, ion of the activation element can give off yellow orange light which is mixed with short wave radiation emitted by InGaN semiconductor heterojunction to form the warm white light. The warm white light LED uses the fluorescent powder to ensure that partial transmission can reach 15 to 30 percent of first-level blue light radiation of the InGaN semiconductor heterojunction, and 70 to 85 percent of the second orange-yellow radiation. In addition, the invention also discloses a preparation method of the fluorescent powder.
Owner:罗维鸿
Long wave pass infrared filter based on porous semiconductor material and the method of manufacturing the same
Scattering-type long wave pass filters for the infrared region of the spectrum offer high levels of suppression of the unwanted short-wave radiation, good levels of transmission of the desired long wave radiation combined with good control of the rejection edge position and shape and good mechanical stability of the filter layer. Such filters are well suited for the wide range of applications and can be used in various environments including cryogenic temperatures. Several methods of fabrication of such filters based on electrochemical etching of semiconductor materials in order to form porous layer are provided.
Owner:LAKE SHORE CRYOTRONICS INC
Non-cooperative short-wave radiation source wide-area distributed short-wave network single-antenna time difference positioning method
The invention relates to a non-cooperative short-wave radiation source wide-area distributed short-wave network single-antenna time difference positioning method. The method provided by the inventioncomprises the steps that a sky-wave propagation signal of a short-wave radiation source is collected, and a suitable receiving station is selected; the collected data are locally compressed and transmitted to a wide-area distributed short-wave network main station server; a main station is used as for reference to estimate the time difference of each receiving station relative to a main receivingstation; and finally, a positioning result is optimized according to the geographical distribution of each receiving station and the ionospheric height parameter and time difference. According to theinvention, the method is based on a single short-wave receiving antenna and a single-channel receiver of each station in the existing wide-area distributed short-wave network; short-wave radiation source positioning is realized by using the time difference generated by the short-wave sky-wave propagation signal which reaches each receiving station through different paths; rebuilding a large receiving station is not needed, which saves a lot of manpower and funds; and the method has important promotion and application values in both civil short-wave radio management and short-wave military technical investigation.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
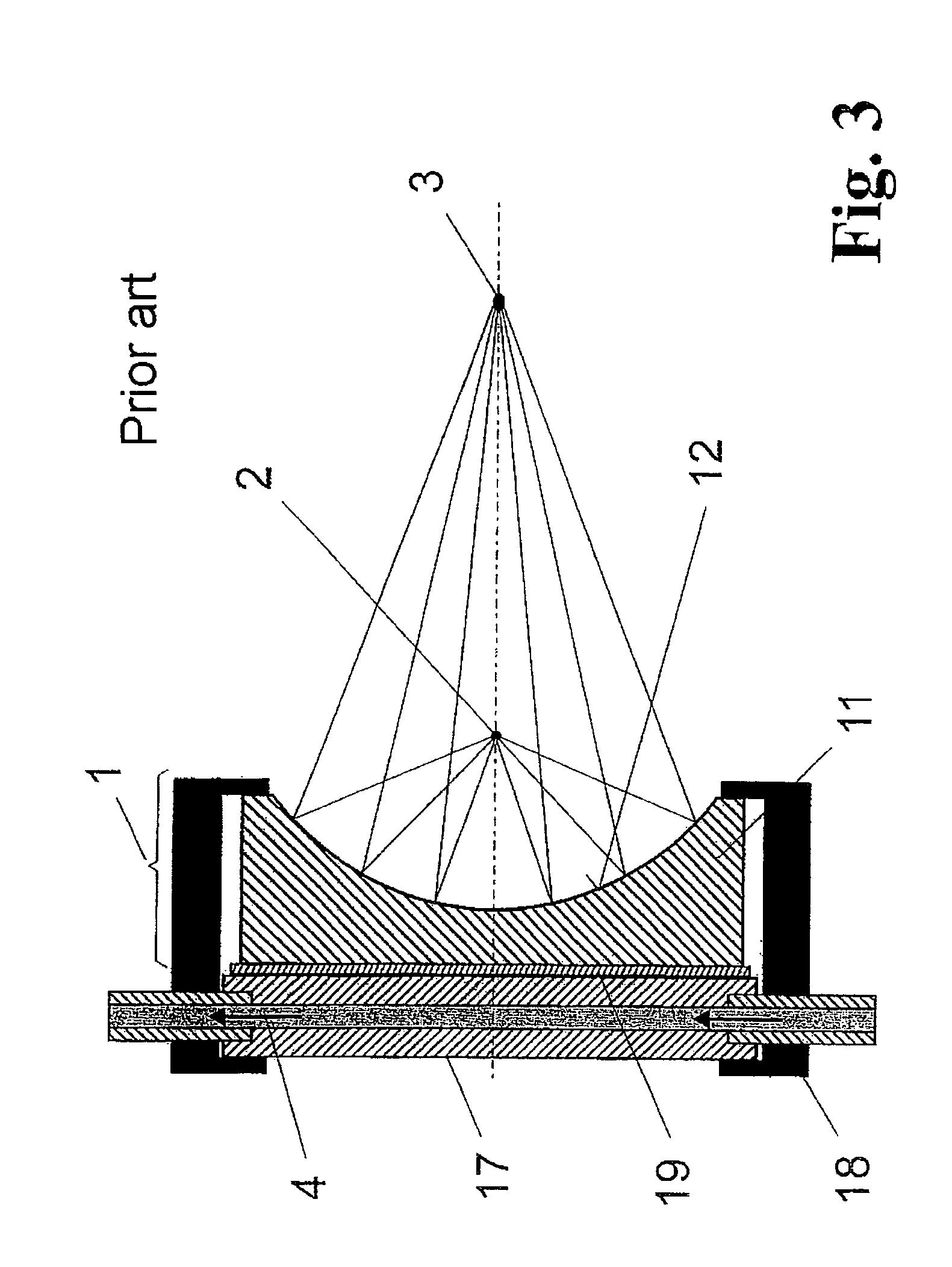
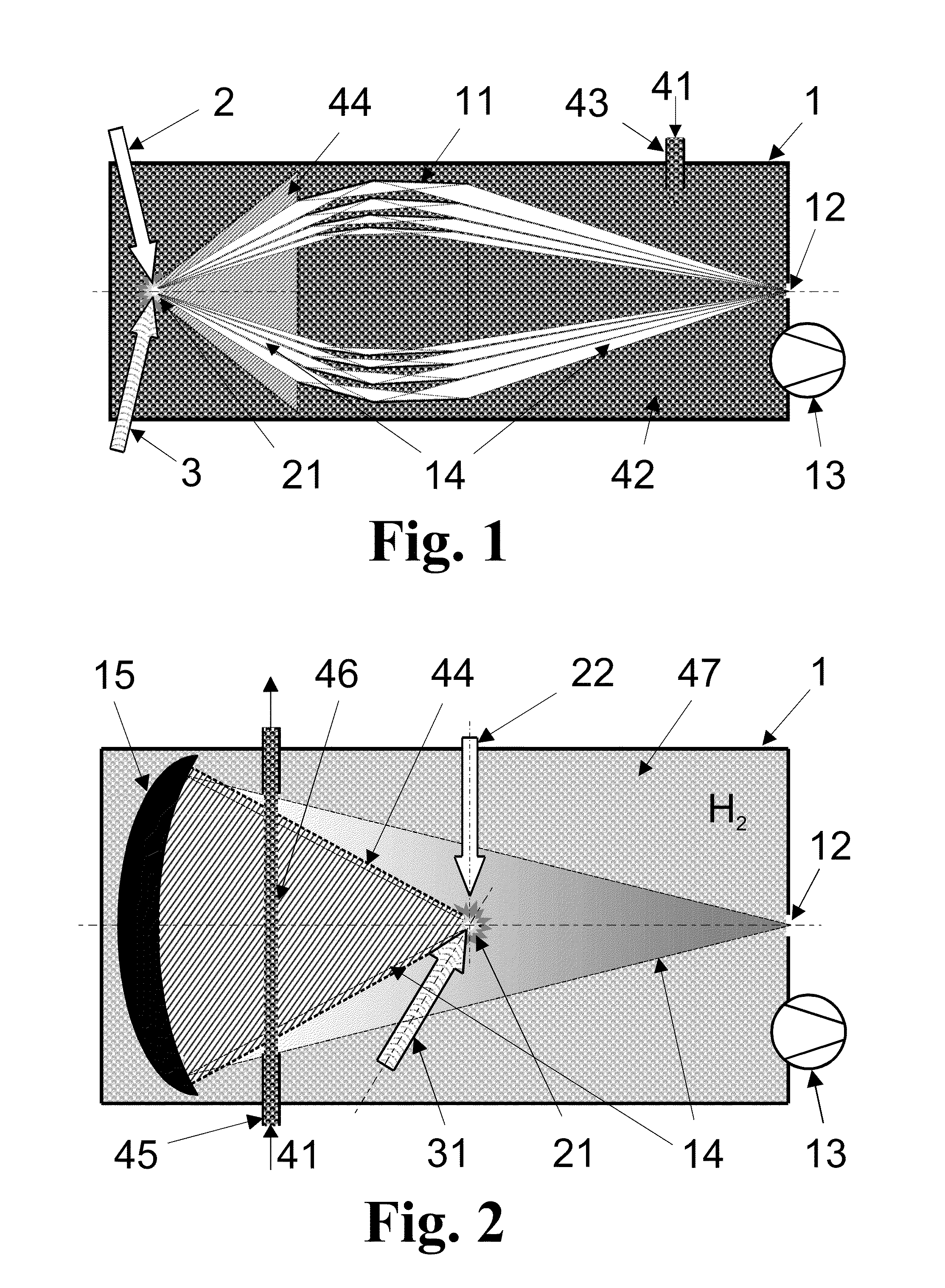
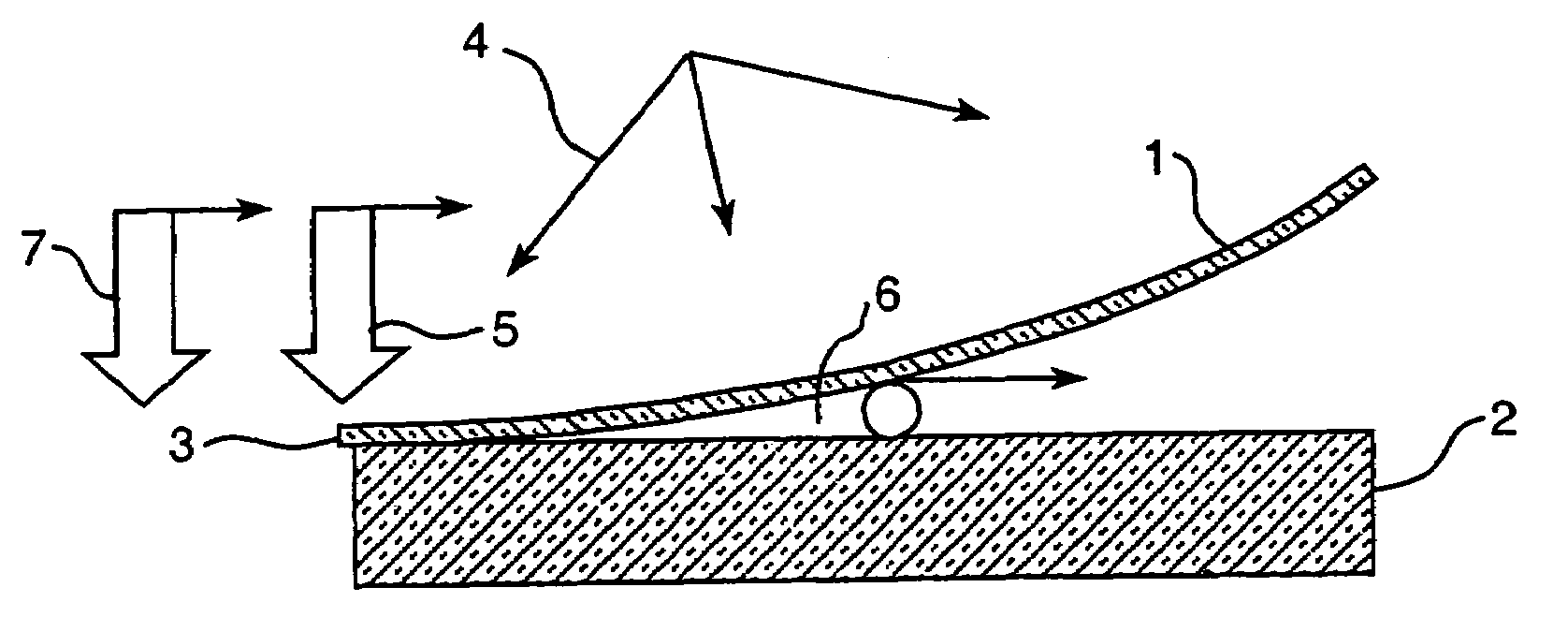
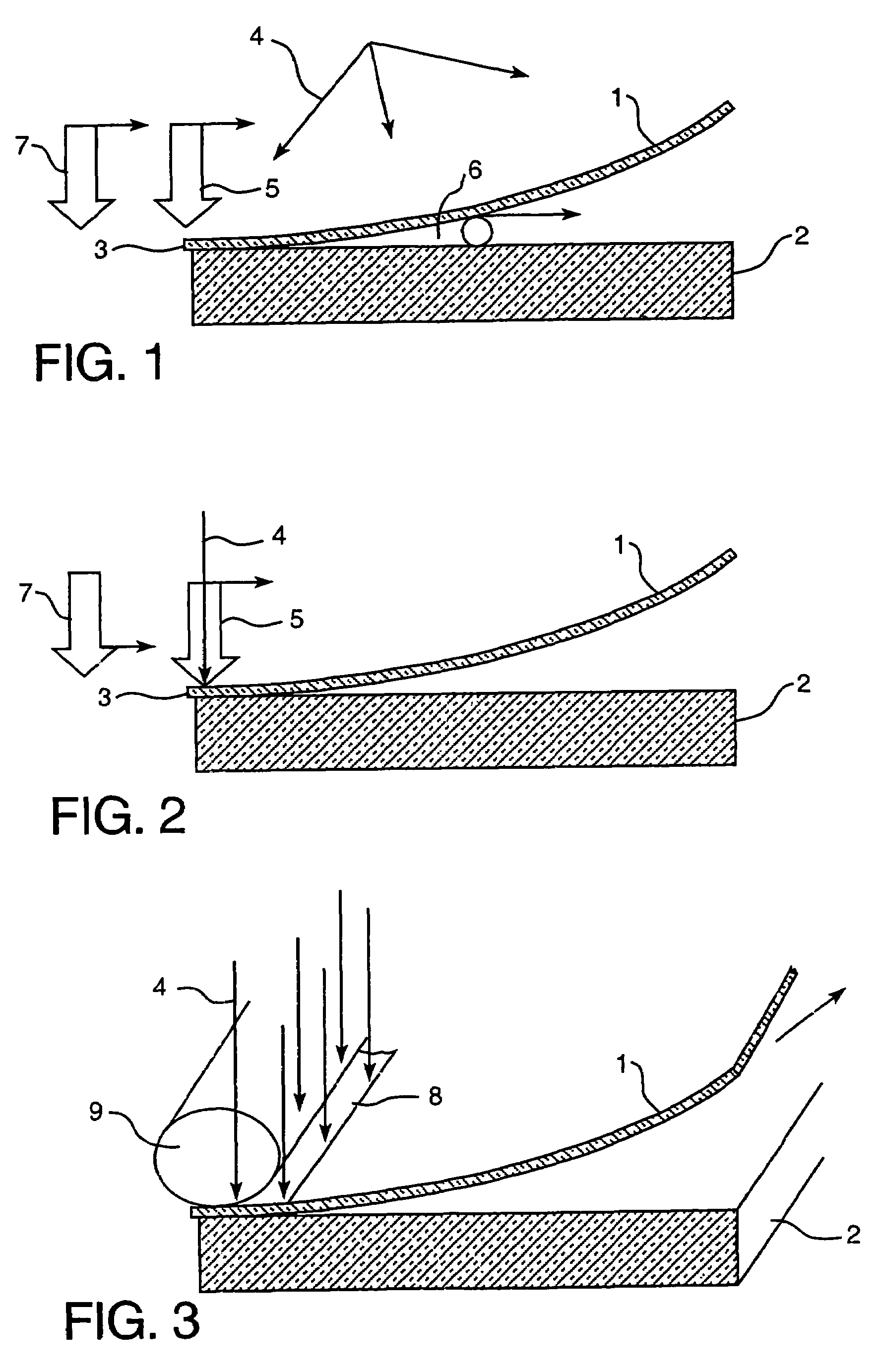
Apparatus for laminating glass sheets using short wave radiation
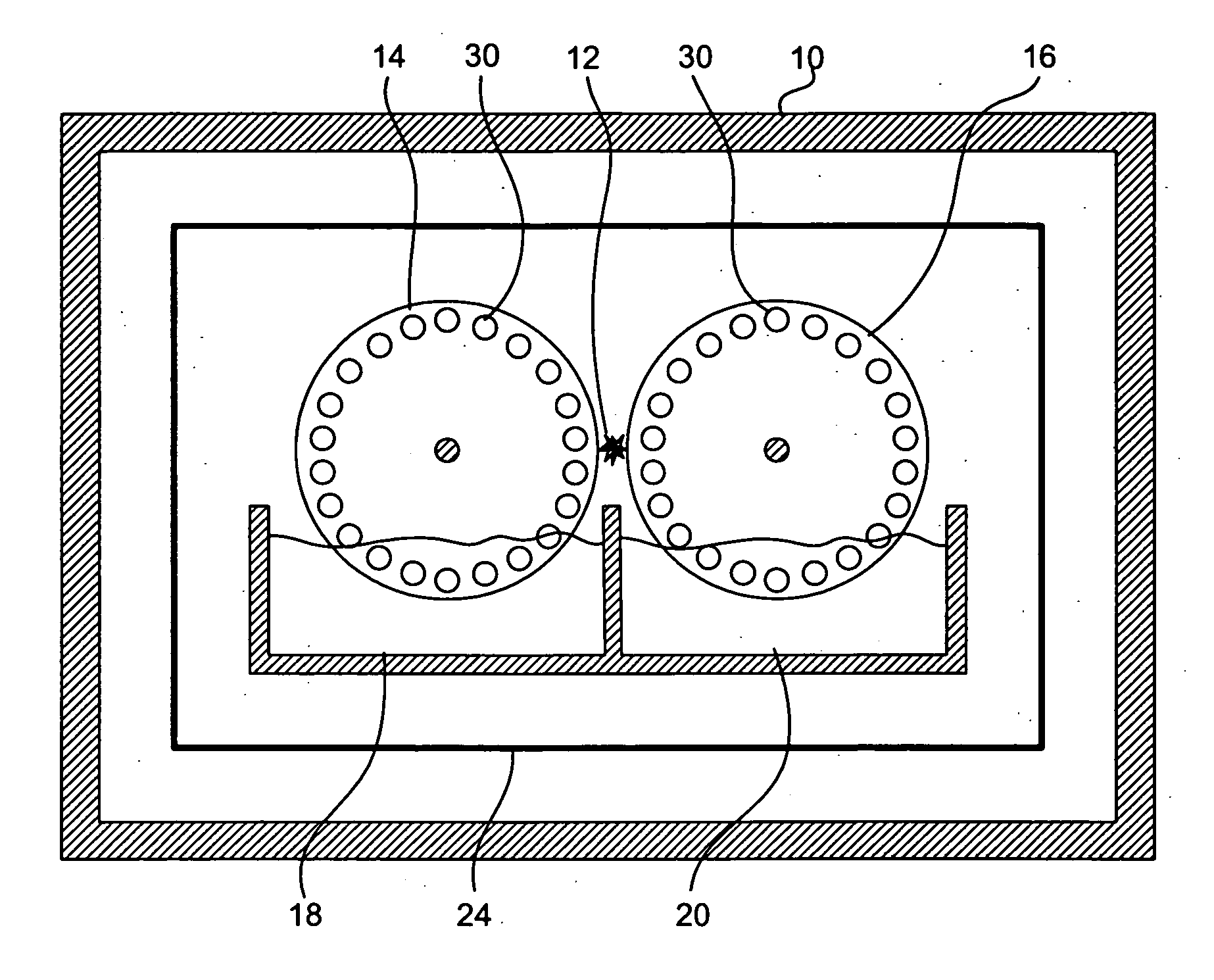
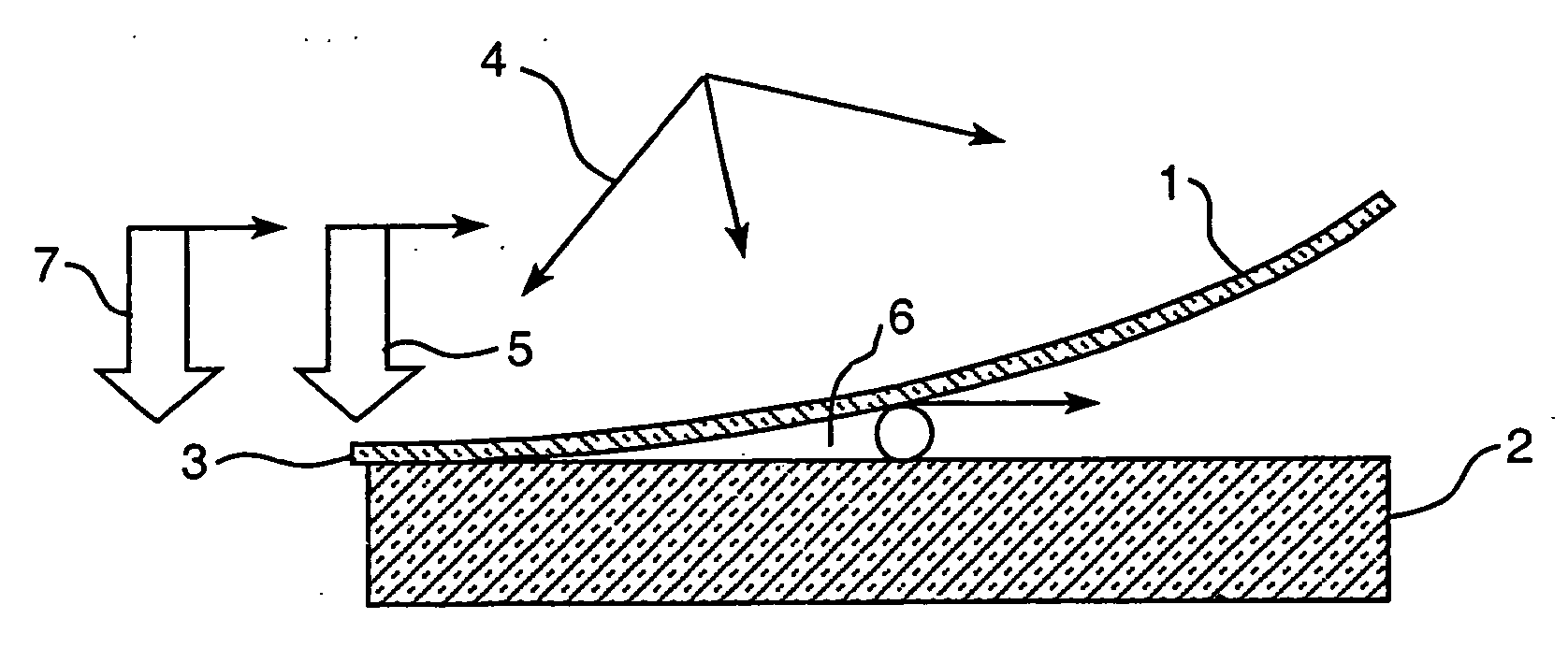
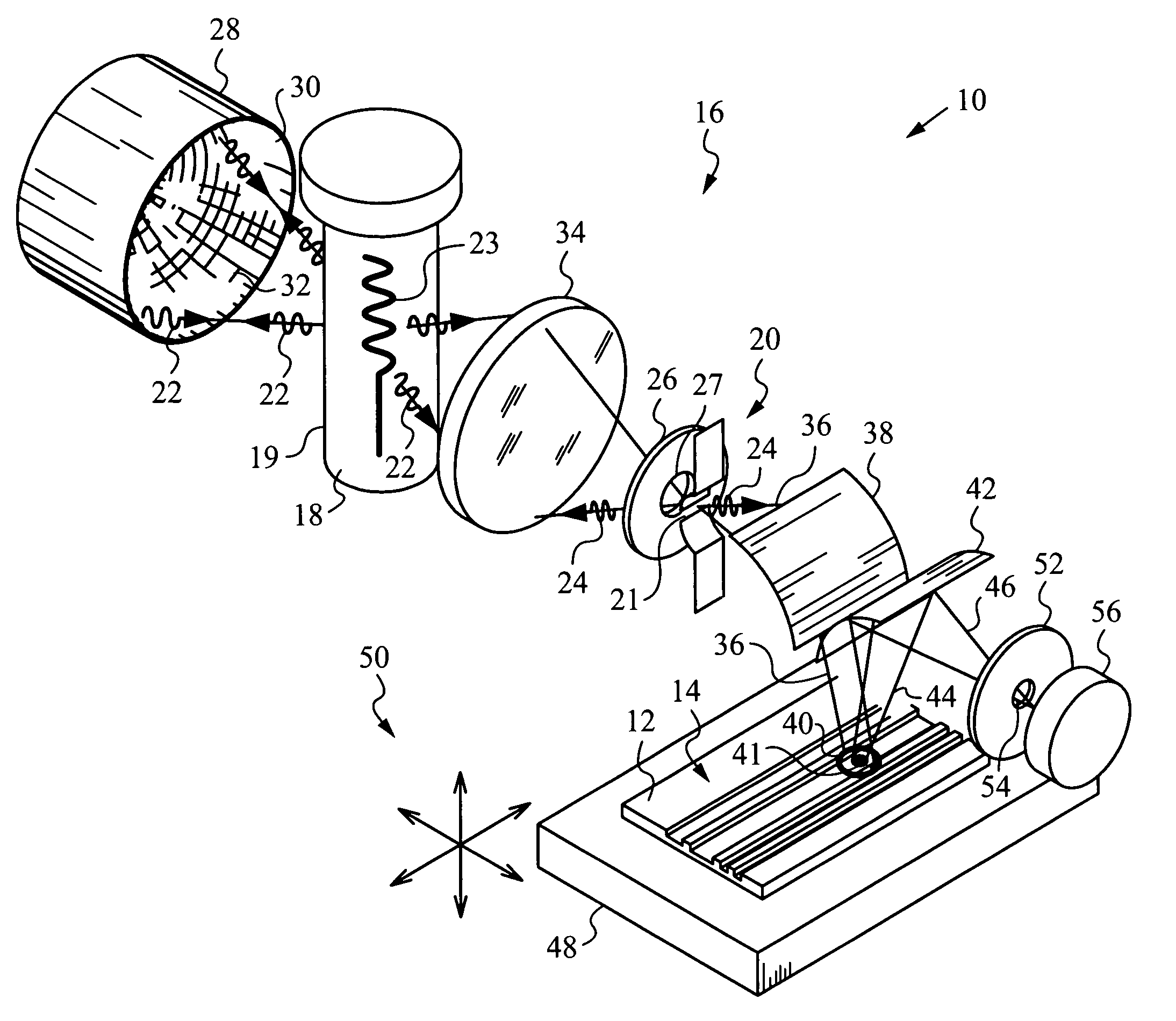
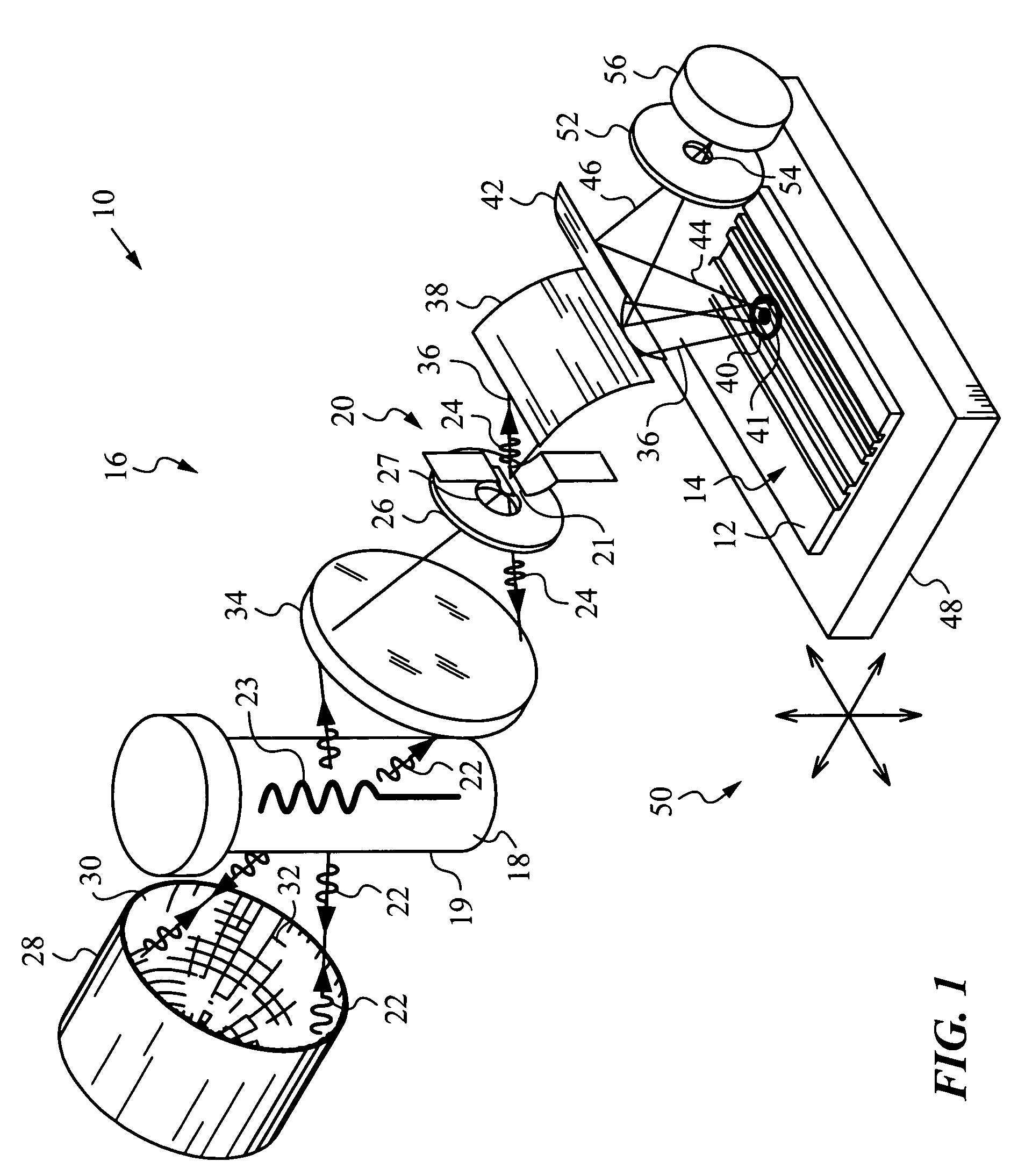
InactiveUS20060144522A1Increase chanceReduce energy consumptionLayered product treatmentLaminationEngineeringGlass sheet
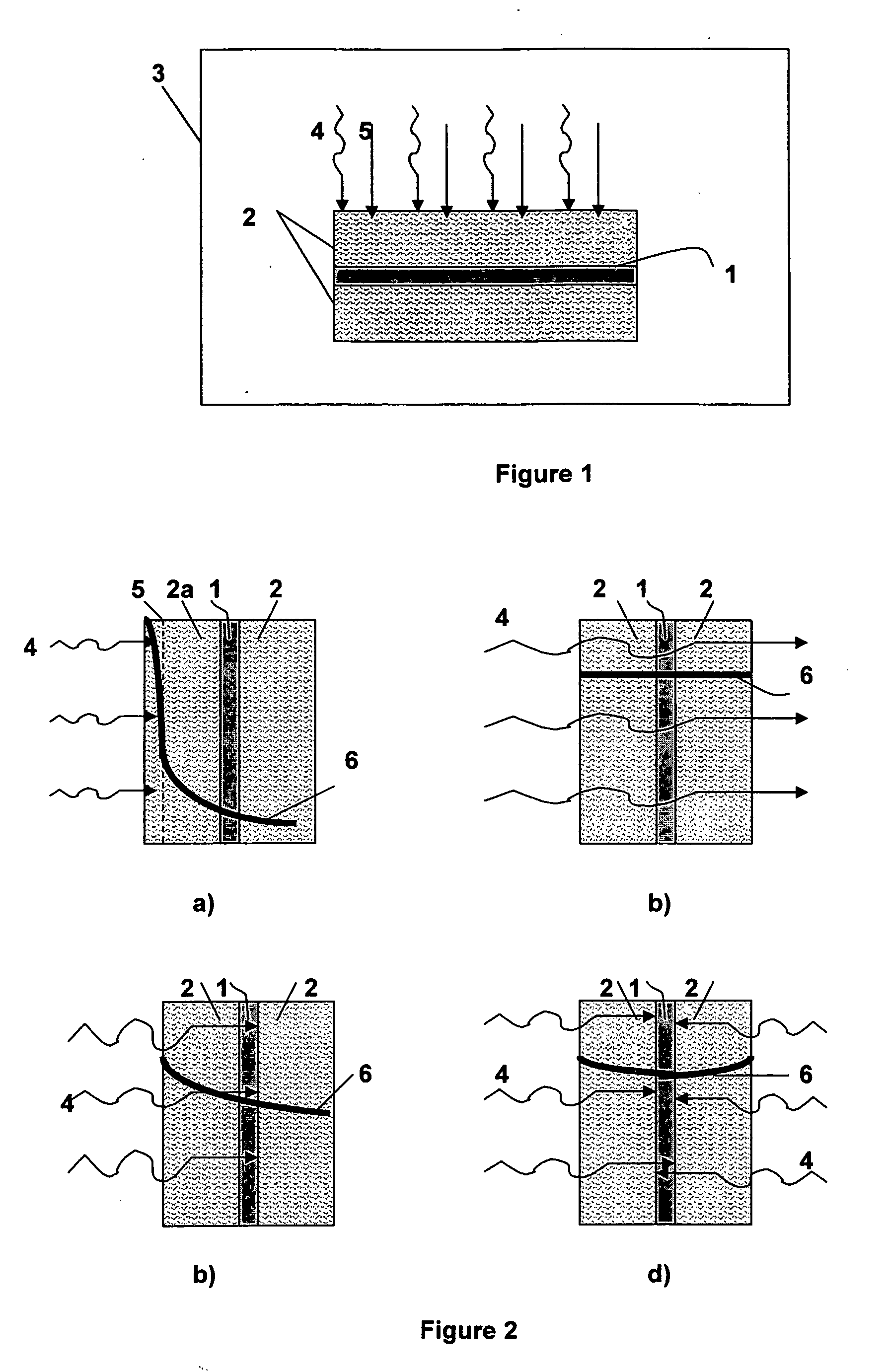
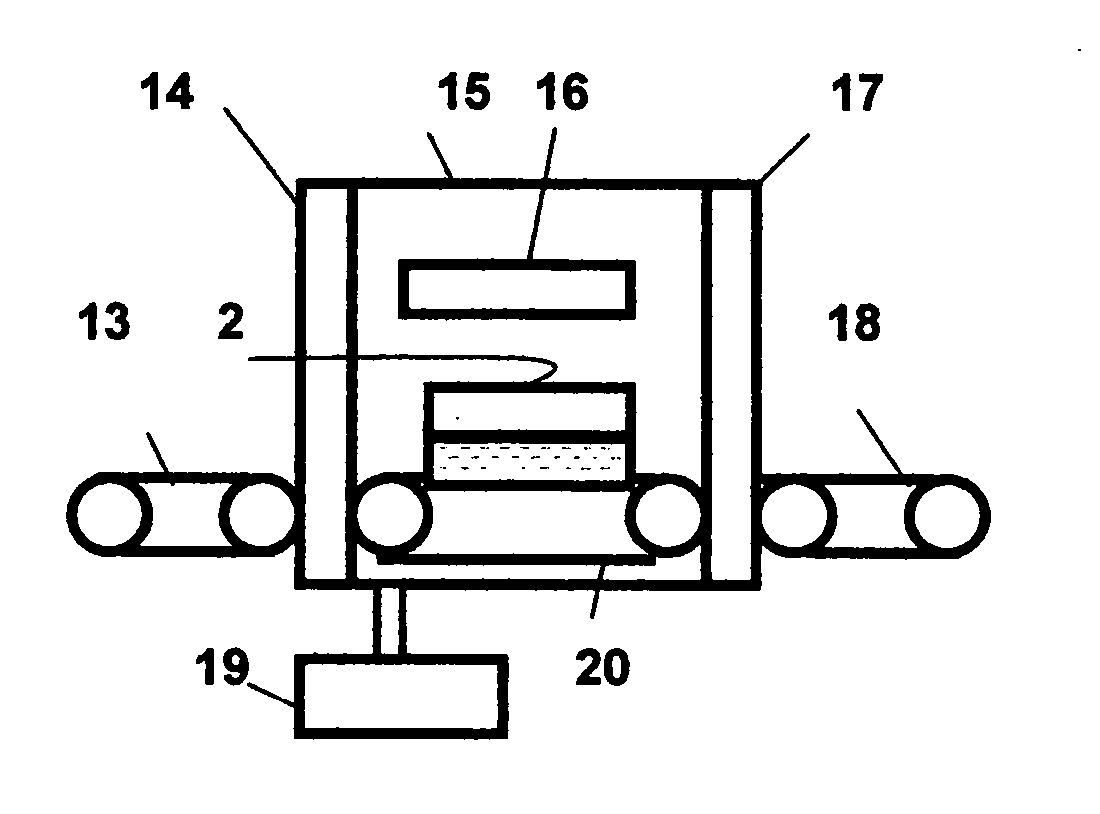
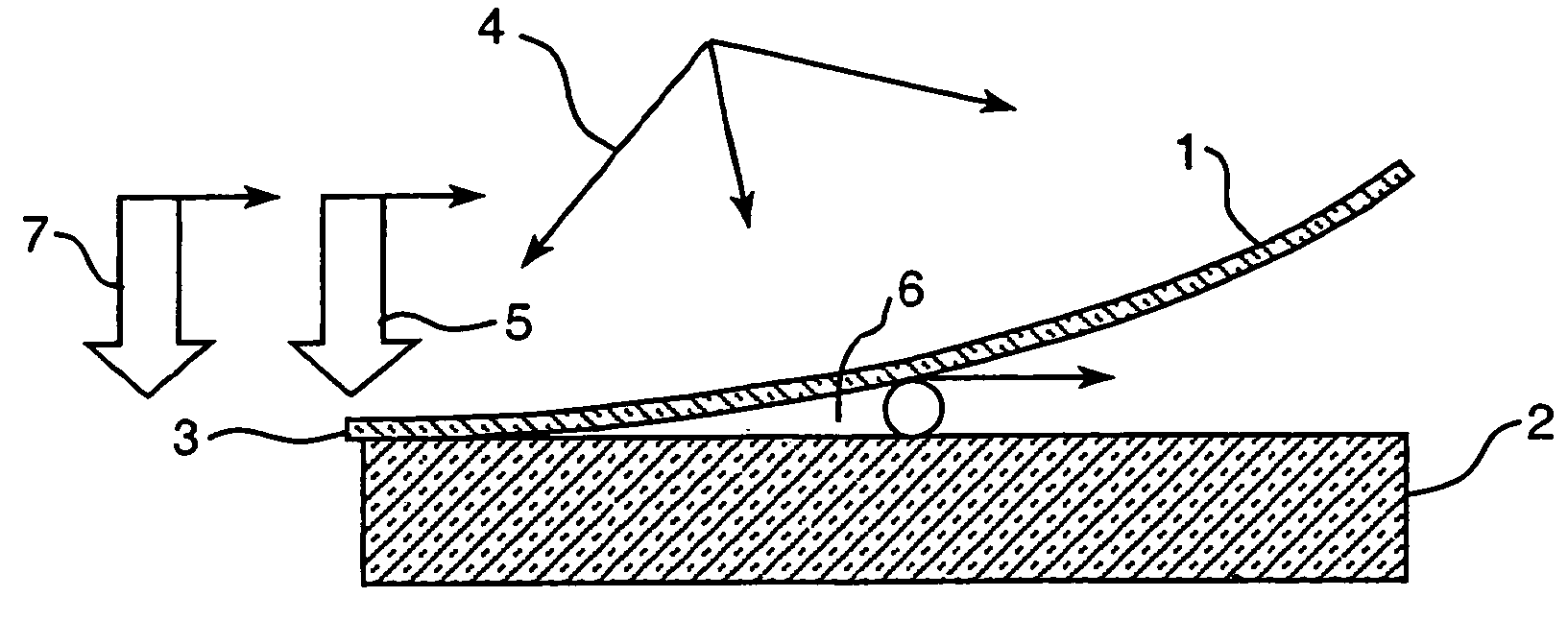
An apparatus for laminating glass sheets (2) with a laminating film (1). The apparatus includes a furnace (FIG. 6) including a vacuum chamber (15) having inlet and outlet vacuum locks (14, 17), a vacuum pump (19) connected to the chamber (15) for evacuating air therefrom and a through conveyor (20) for conveying glass sheets (2) from the inlet lock (14) to the outlet lock (17) and for positioning the sheets (2) with applied film (1) in the chamber (15) for heat treatment. Bonding heat is provided within the chamber (15) by a device (16 / 1, 2, 3) providing controllable distribution of short wave radiation (4) over selected areas (17) of the film (1) for bonding the film to one or more glass sheets (2). Incoming and outgoing bridge conveyors (13, 18) are provided respectively for the inlet and outlet vacuum locks (14, 17) for moving the glass sheets (2) into and out of the vacuum chamber (15).
Owner:GYROTRON TECH
High-brightness laser produced plasma source and methods for generating radiation and mitigating debris
ActiveUS20190166679A1Reduce decreaseExtended service lifeX-ray tube with very high currentX-ray apparatusDropletonLight beam
High-brightness LPP source and method for generating short-wavelength radiation which include a vacuum chamber (1) with an input window (6) for a laser beam (7) focused into the interaction zone (5), an output window (8) for the exit of the short-wavelength radiation beam (9); the rotating target assembly (3), having an annular groove (11); the target (4) as a layer of a molten metal formed by centrifugal force on the surface of the distal wall (13) of the annular groove (11) while the proximal wall (14) of the annular groove is designed to provide a line of sight between the interaction zone and both the input and output windows particularly during laser pulses. A method for mitigating debris particles comprises using an target orbital velocity high enough for the droplet fractions of the debris particles exiting the rotating target assembly not to be directed towards the input and output windows.
Owner:ISTEQ BV
Luminescent glass ceramic doped with multiple rare earth ions and capable of up and down-conversion to ultraviolet light and preparation method thereof
The invention provides luminescent glass ceramic doped with multiple rare earth ions and capable of up and down-conversion to ultraviolet light and a preparation method thereof; the glass ceramic is fluorosilicate glass ceramic doped with at least four rare earth ions, wherein on a basis of oxide, the molar content of the rare earth ions is 1% to 20% of the total amount of the glass ceramic; the glass ceramic can realize up conversion of infrared light and visible light into ultraviolet light, and also realize down conversion of short-wave radiation into ultraviolet light.
Owner:何森
Method for laminating glass sheets using short wave radiation
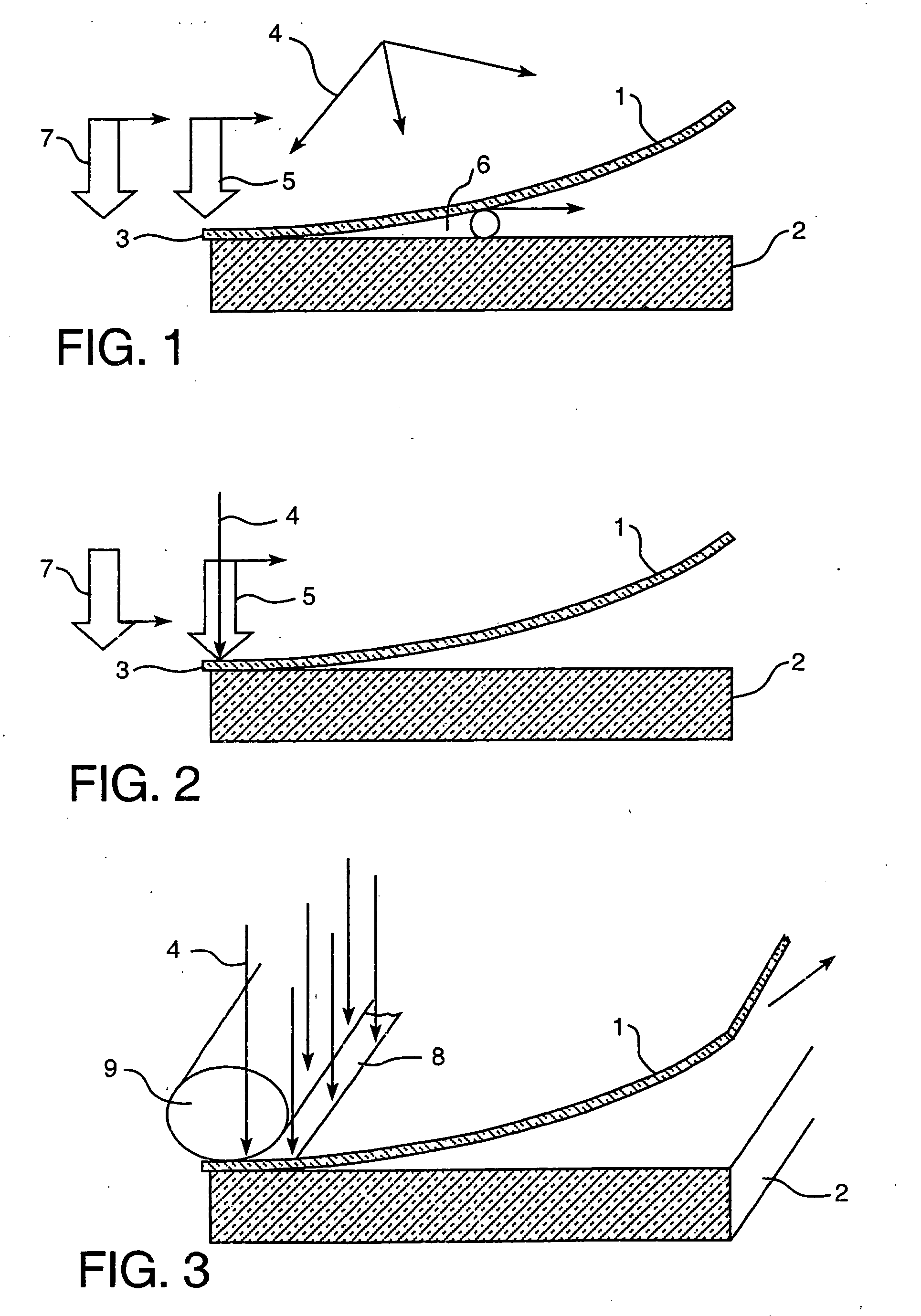
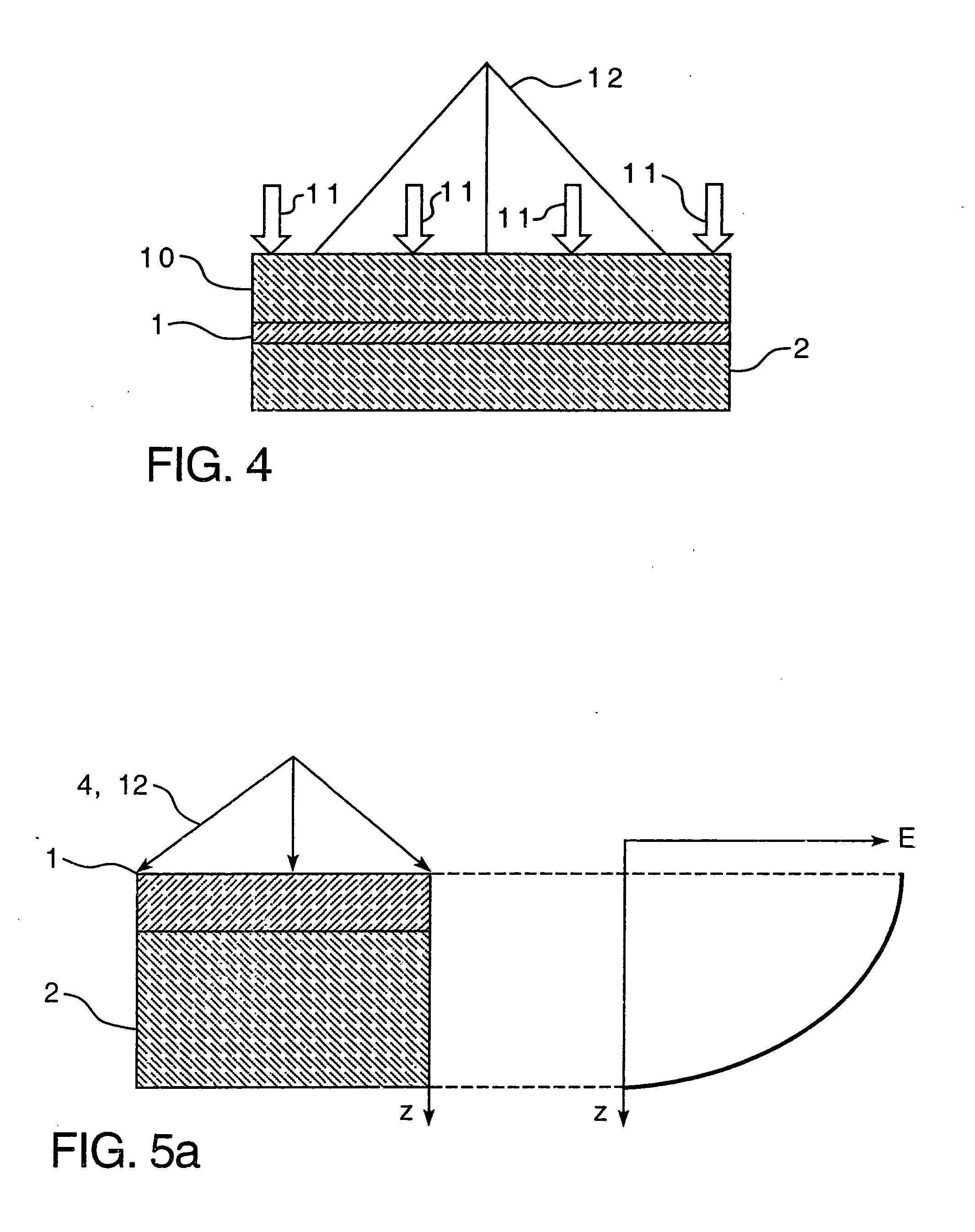
InactiveUS20060231190A1Improve bonding qualityAvoid surface damageLayered product treatmentLaminationEngineeringGlass sheet
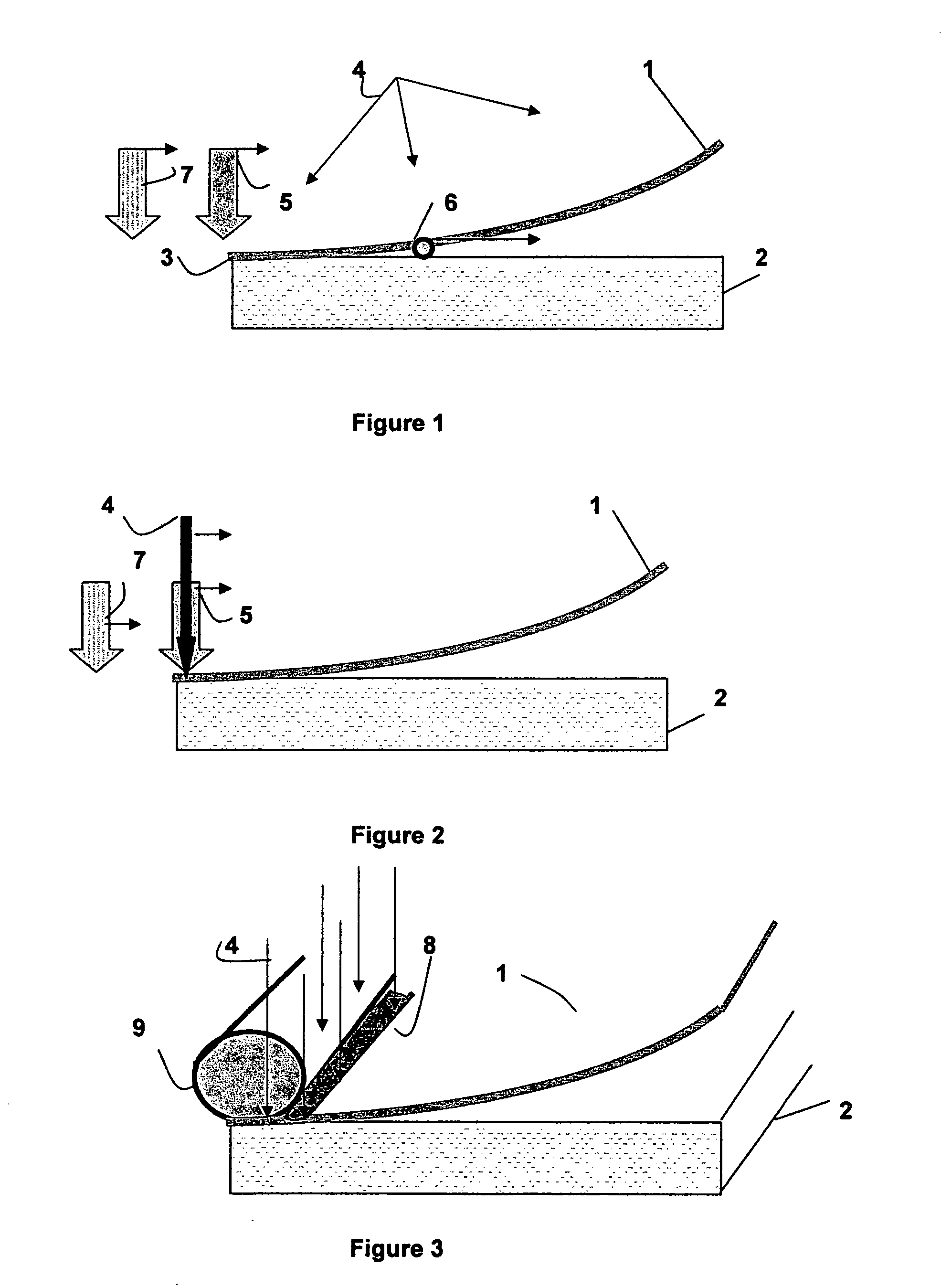
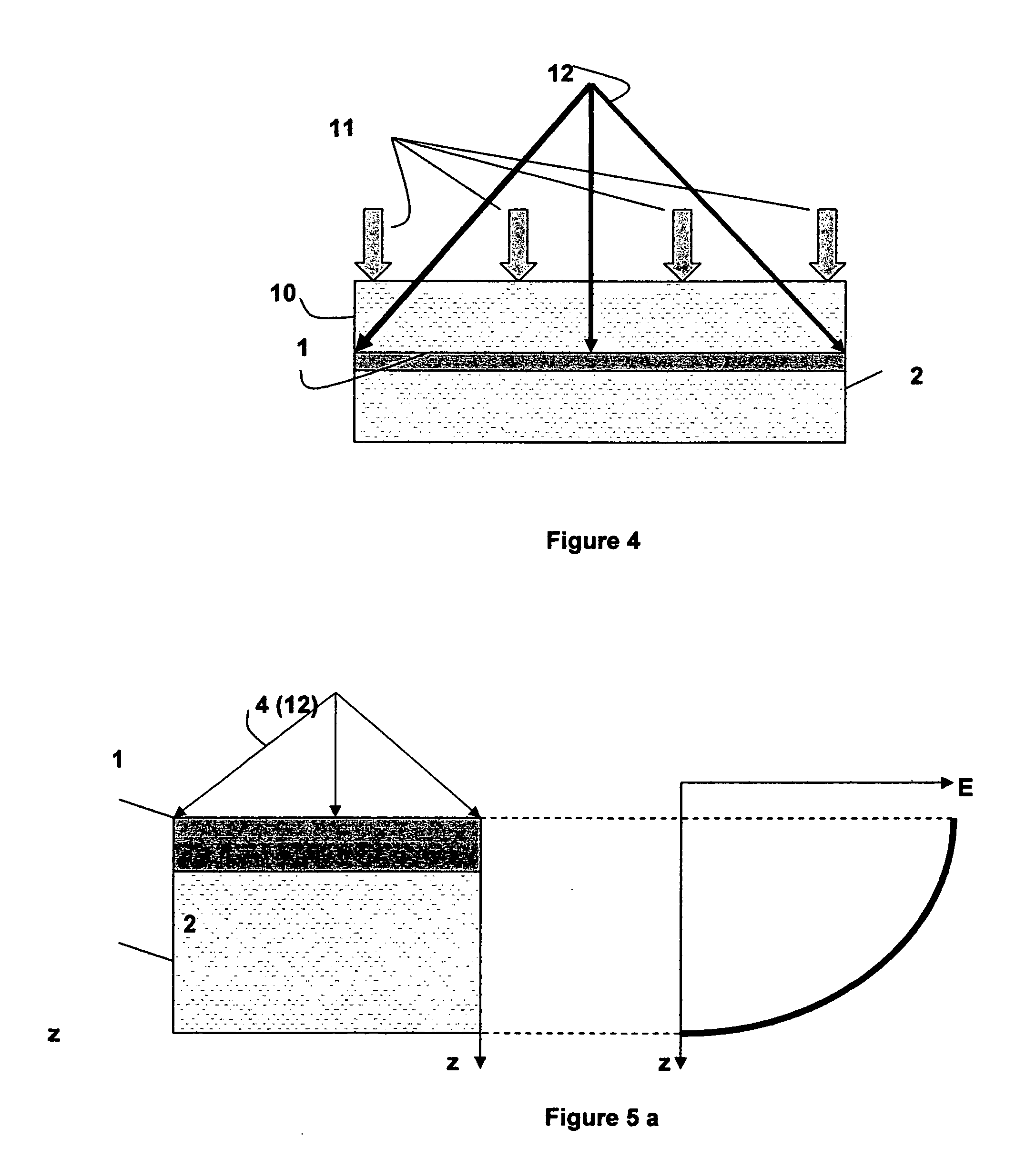
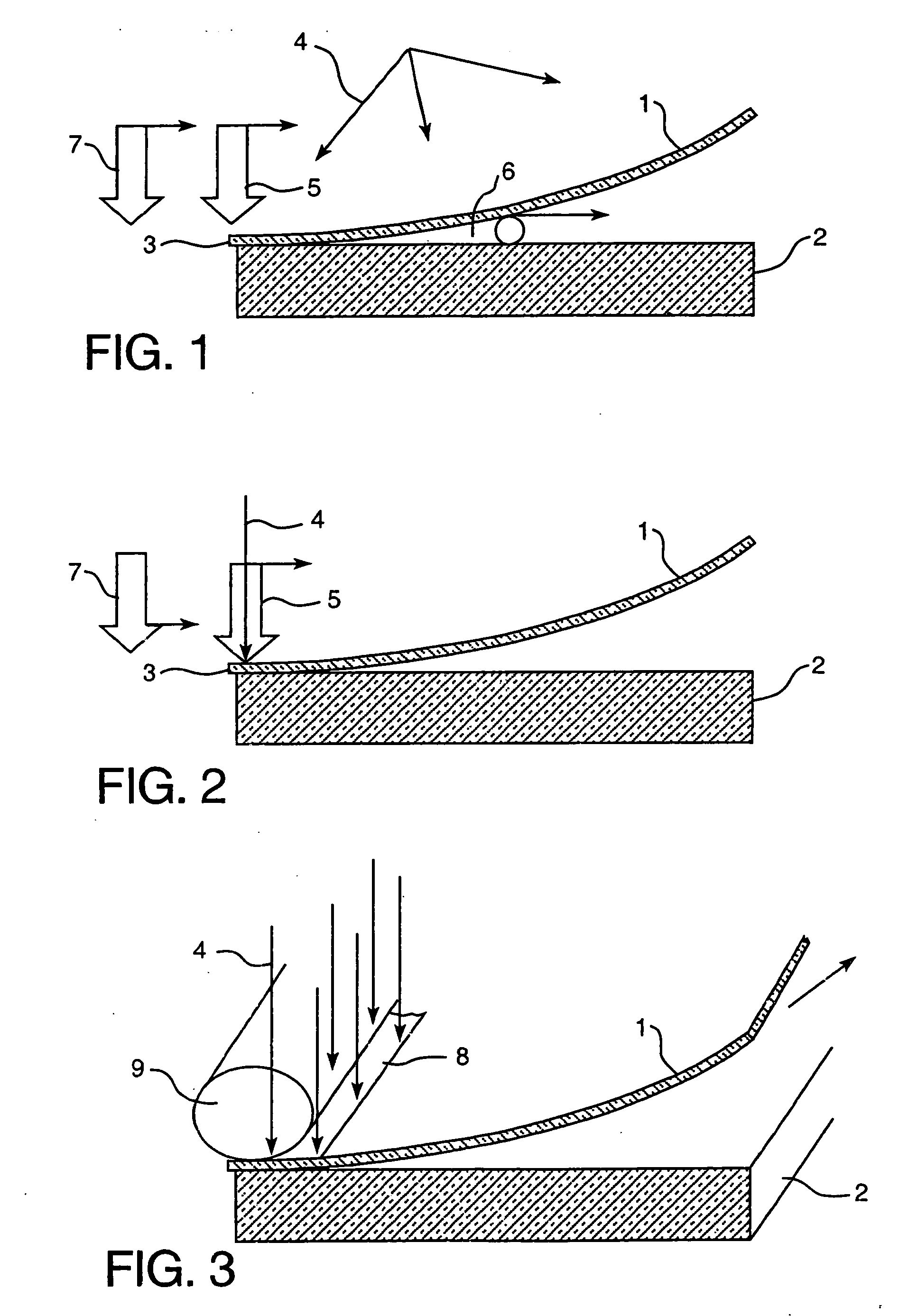
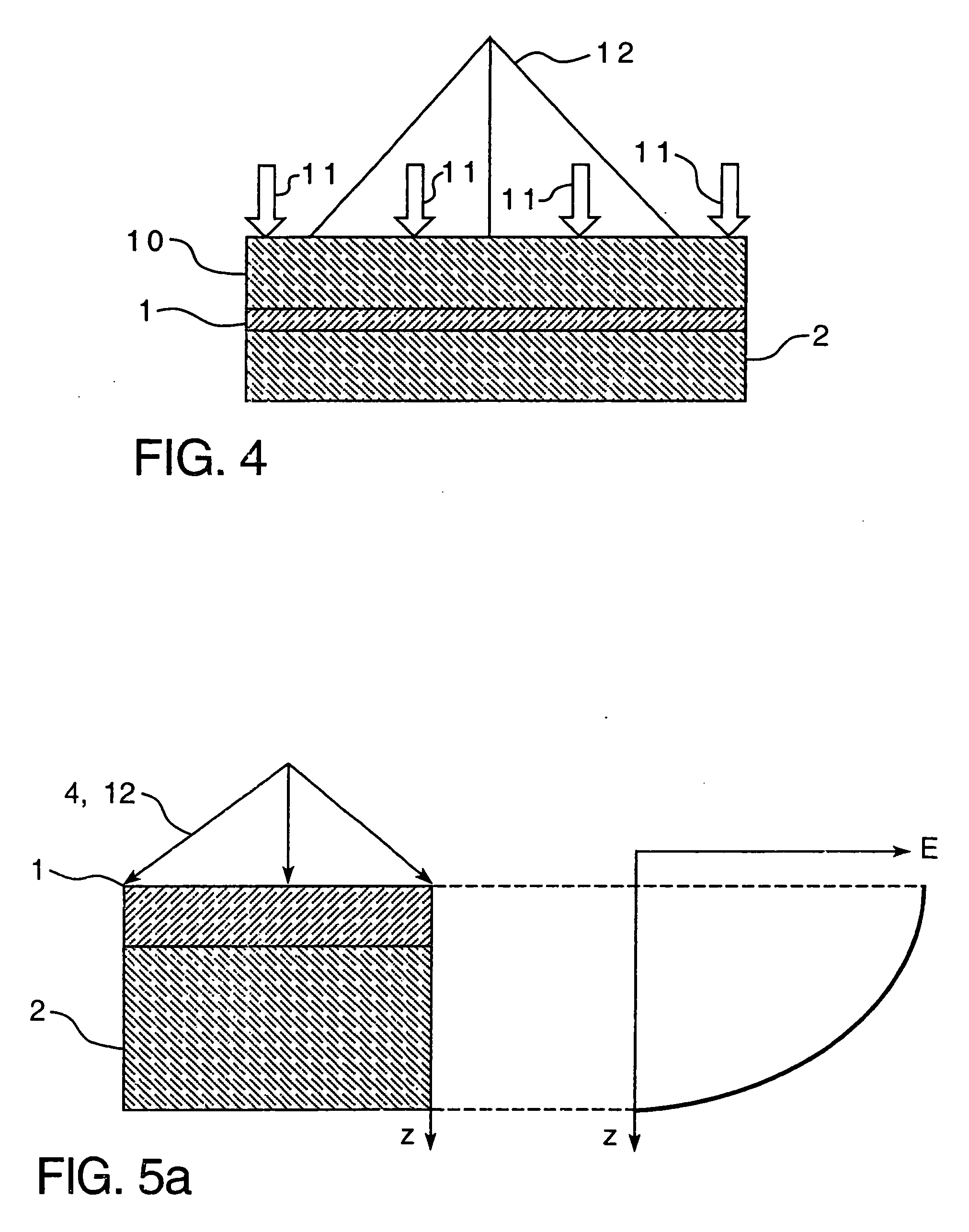
A method for laminating glass sheets wherein laminating film (1) is placed over one surface of a first glass sheet (2) and the film (1) is heated with short wave radiation (4) to a bonding temperature. Heated areas (8) of the film (1) are successively pressed to the glass sheet (2) in a continuous manner for purging air from between the film (1) and the first glass sheet (2) and for applying bonding pressure. The pressed film areas (8) are then cooled whereby an appropriate bond is attained between the film (1) and the first glass sheet (2). Thereafter the first glass sheet (2) with its bonded film is subjected to a partial vacuum and a second glass sheet (10) is positioned on the film (1) and the second glass sheet (10) is pressed (11) to the film (1). The film (1) is then reheated in selected areas with short wave radiation (12) to a bonding temperature and thereafter cooled whereby an appropriate bond is obtained between the selected film (1) areas and the second glass sheet (10) to provide a glass lamination.
Owner:GYROTRON TECH
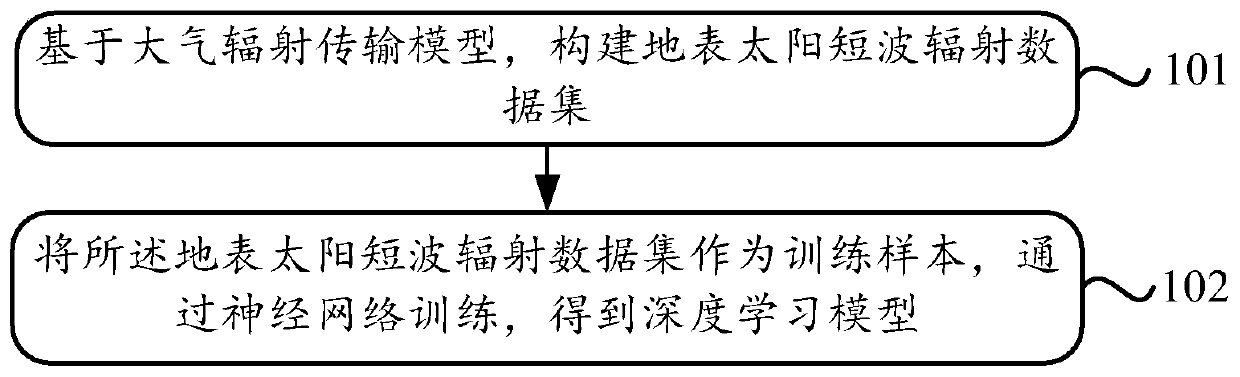
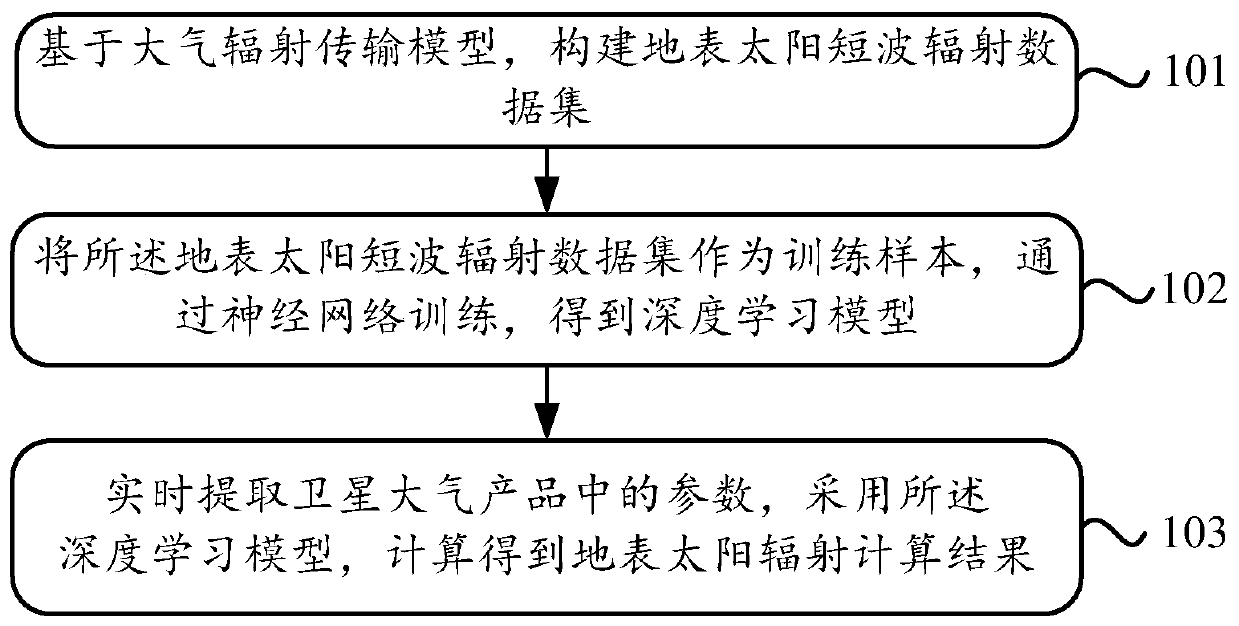
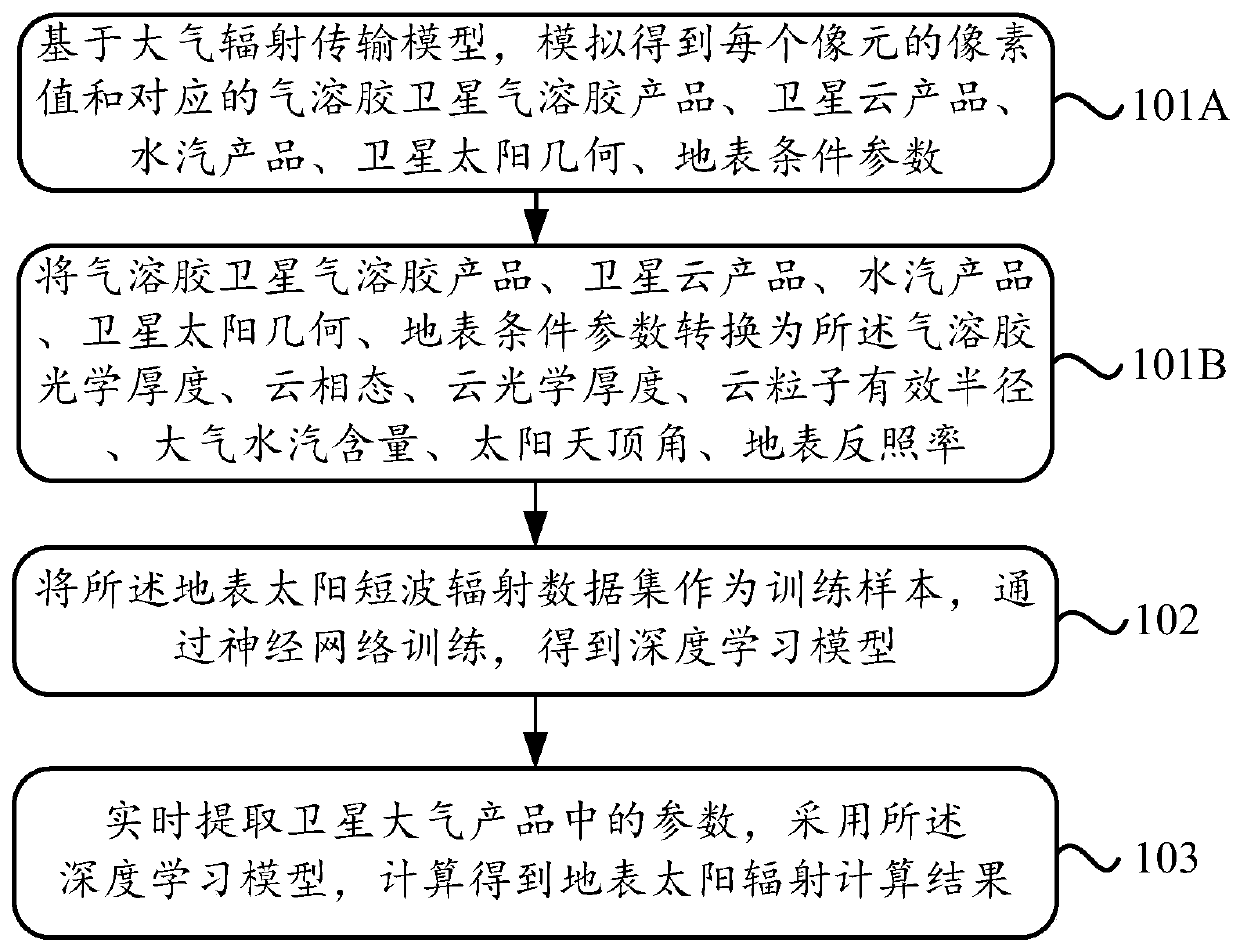
Surface solar radiation calculation method based on deep learning
InactiveCN110175375AQuick calculationFast computing powerDesign optimisation/simulationNeural architecturesNerve networkAtmospheric layer
The invention discloses a surface solar radiation calculation method based on deep learning which solves the problems that an existing method is long in calculation time and poor in universality and cannot be applied to cloud conditions. The method comprises the following steps of constructing an earth surface solar short wave radiation data set based on an atmospheric radiation transmission model; taking the surface solar short-wave radiation data set as a training sample; training through the neural networks to obtain a deep learning model, wherein the solar zenith angle, the aerosol opticalthickness, the atmospheric water vapor content, the cloud phase state, the cloud optical thickness, the cloud particle effective radius and the surface albedo are used as the neural network input layers, and the surface albedo, the surface downlink total solar radiation, the surface downlink direct solar radiation, the surface downlink diffused solar radiation and the atmospheric layer top upwardradiation are used as the neural network output layers. According to the method, the comprehensive, rapid and accurate calculation of the surface solar radiation is realized.
Owner:INST OF REMOTE SENSING & DIGITAL EARTH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
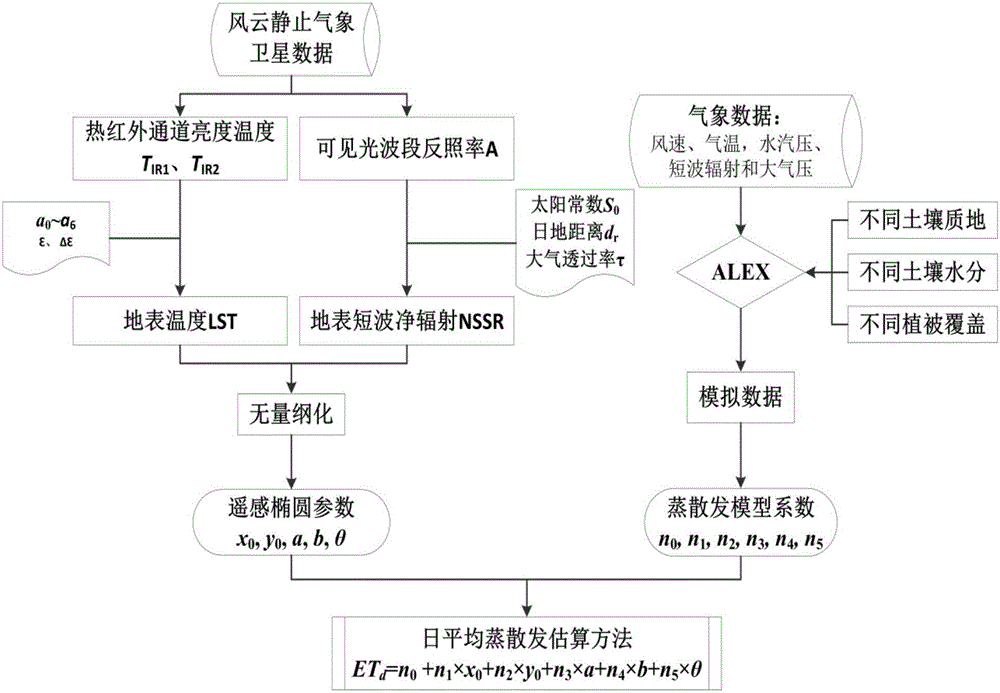
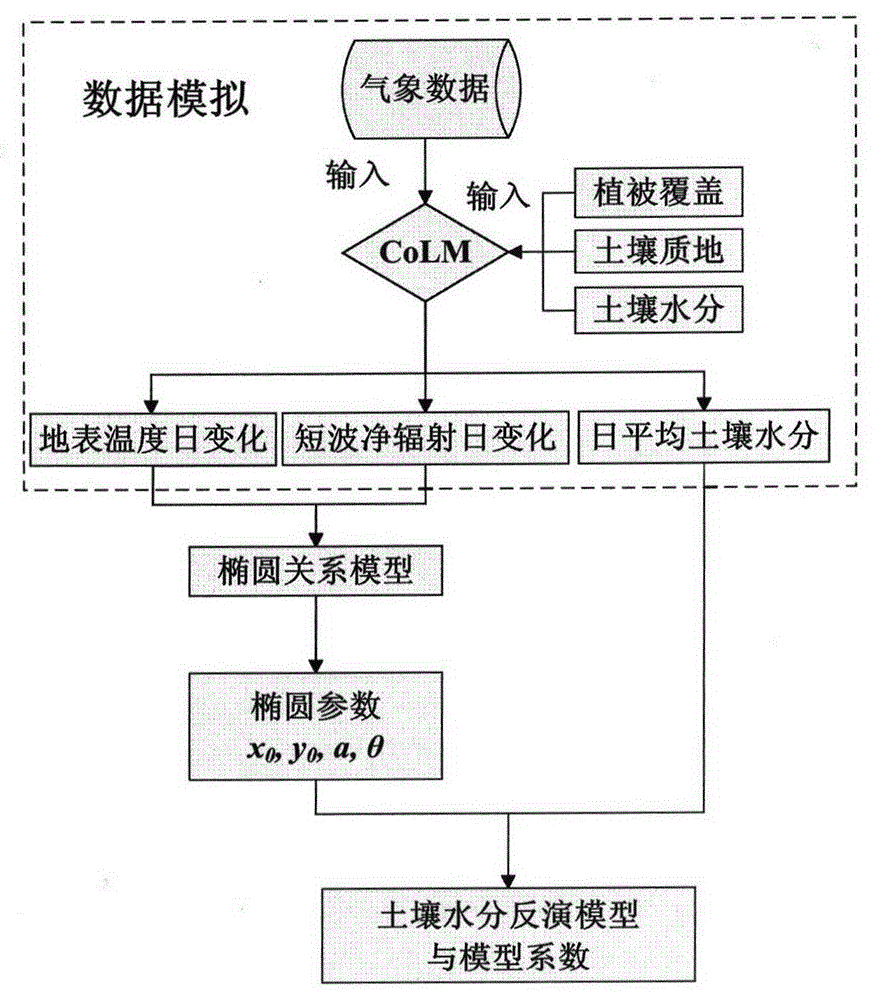
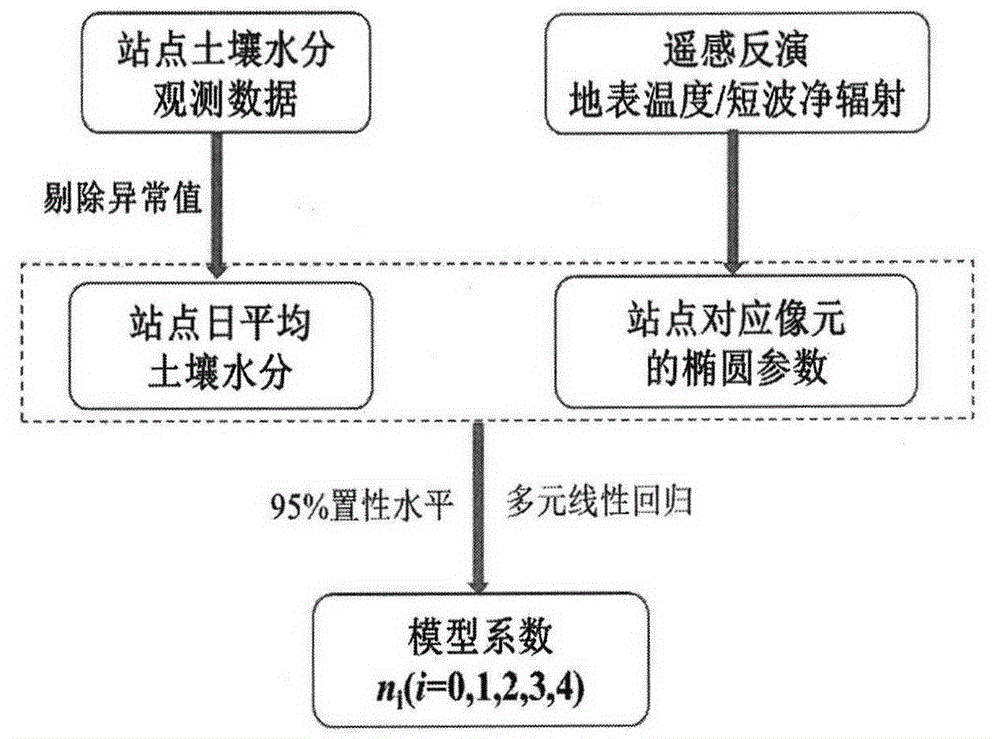
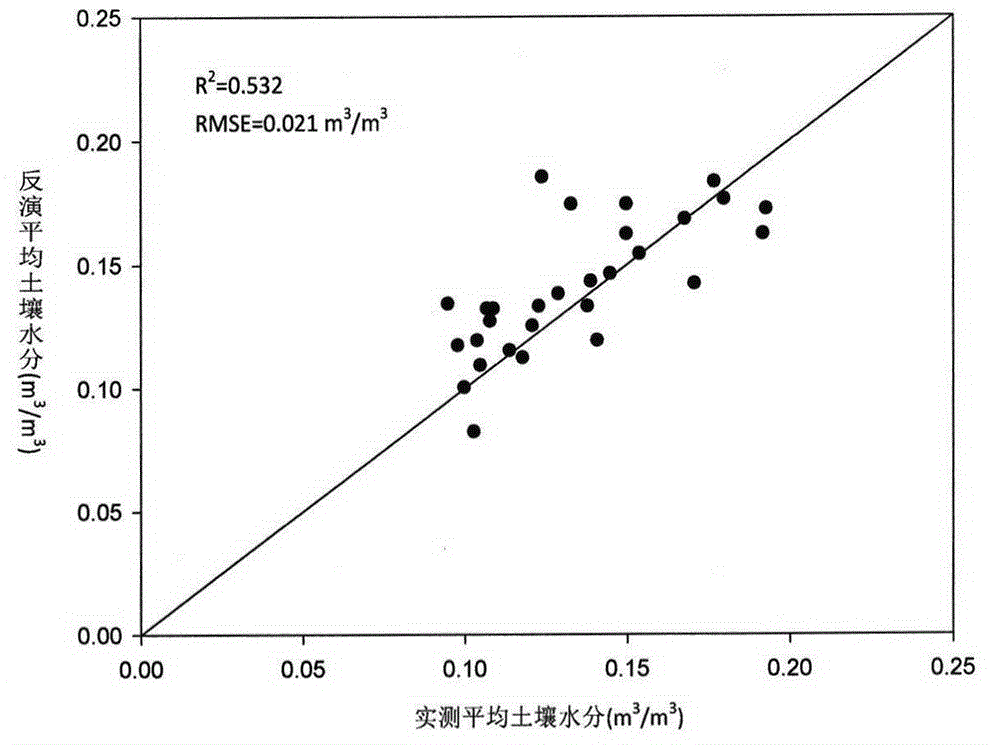
Method for evaluating daytime average evapotranspiration according to multi-temporal remote sensing data and meteorological data
ActiveCN105913149AReal-time key parametersReliable and accurate key parametersForecastingSpecial data processing applicationsSatellite dataEarth observation
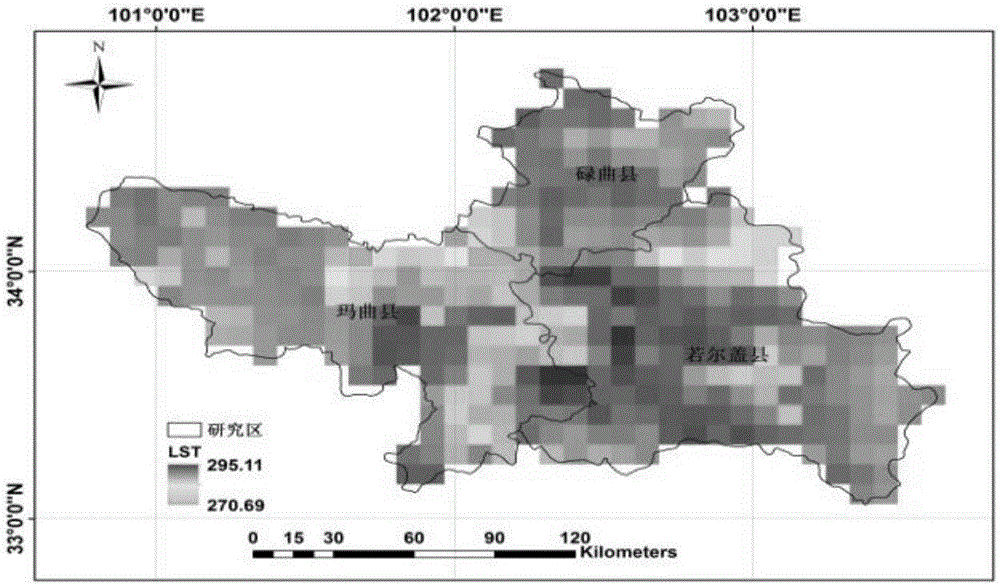
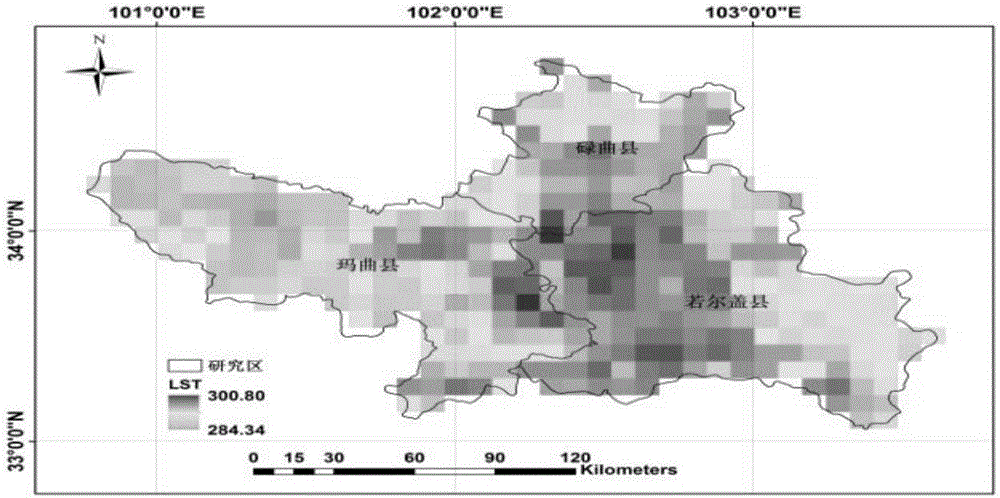
The invention discloses a method for evaluating daytime average evapotranspiration according to multi-temporal remote sensing data and meteorological data. The method comprises the following steps of calculating a remote sensing ellipse parameter through a land surface temperature (LST) and a net surface shortwave radiation (NSSR), calculating evapotranspiration model coefficients n0-n5 by means of ALEX model analog data; and estimating a daytime average evapotranspiration ETd by means of the remote sensing ellipse parameter and the evapotranspiration model coefficients n0-n5. According to the method of the invention, a multi-temporal earth observation advantage of a stationary meteorological satellite is sufficiently utilized. Through multi-temporal satellite data and meteorological data, the daytime average evapotranspiration is directly obtained. The method settles a problem that the daytime average evapotranspiration can be obtained through inversing instantaneous evapotranspiration and performing time scale expansion in prior art, and furthermore realizes direct estimation for the daytime average evapotranspiration based on FY-2 stationary meteorological satellite data.
Owner:INST OF AGRI RESOURCES & REGIONAL PLANNING CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
System and method for high intensity small spot optical metrology
ActiveUS7349103B1High strengthEasy to operateMaterial analysis by optical meansUsing optical meansBeam steeringOptical metrology
An apparatus and method for examining features of a sample with a broadband beam of light obtained from a long-wavelength source that may include two distinct emitters that emit a long-wavelength radiation and a short-wavelength source that emits a short-wavelength radiation. A passage is positioned between the sources and a reflective beam combining optics is provided for shaping the long-wavelength radiation to enter the short-wavelength source via the passage and also for shaping the short-wavelength radiation that exits through the passage and propagates toward the long-wavelength source. The reflective beam combining optics shape the short-wavelength radiation such that it re-enters the short-wavelength source via the passage and is combined with the long-wavelength radiation into the broadband beam that exits the short-wavelength source. A beam steering optics projects the broadband beam to a spot on the sample, and a scattered broadband radiation from the spot is intercepted and shaped to a broadband signal beam, which is passed through a sampling pinhole that passes a test portion of it on to a detector for optical examination; the test portion that is passed can correspond to a center portion of the spot.
Owner:N & K TECH
Method for laminating glass sheets using short wave radiation
InactiveUS20060113025A1Improve the heating effectImprove productivityLamination ancillary operationsLayered product treatmentEngineeringGlass sheet
A method for laminating glass sheets wherein laminating film (1) is placed over one surface of a first glass sheet (2) and the film (1) is heated with short wave radiation (4) to a bonding temperature. Heated areas (8) of the film (1) are successively pressed to the glass sheet (2) in a continuous manner for purging air from between the film (1) and the first glass sheet (2) and for applying bonding pressure. The pressed film areas (8) are then cooled whereby an appropriate bond is attained between the film (1) and the first glass sheet (2). Thereafter the first glass sheet (2) with its bonded film is subjected to a partial vacuum and a second glass sheet (10) is positioned on the film (1) and the second glass sheet (10) is pressed (11) to the film (1). The film (1) is then reheated in selected areas with short wave radiation (12) to a bonding temperature and thereafter cooled whereby an appropriate bond is obtained between the selected film (1) areas and the second glass sheet (10) to provide a glass lamination.
Owner:GYROTRON TECH
Method for laminating glass sheets using short wave radiation
InactiveUS7344613B2Increase chanceReduce energy consumptionLamination ancillary operationsLayered product treatmentEngineeringGlass sheet
A method for laminating glass sheets wherein laminating film (1) is placed over one surface of a first glass sheet (2) and the film (1) is heated with short wave radiation (4) to a bonding temperature. Heated areas (8) of the film (1) are successively pressed to the glass sheet (2) in a continuous manner for purging air from between the film (1) and the first glass sheet (2) and for applying bonding pressure. The pressed film areas (8) are then cooled whereby an appropriate bond is attained between the film (1) and the first glass sheet (2). Thereafter the first glass sheet (2) with its bonded film is subjected to a partial vacuum and a second glass sheet (10) is positioned on the film (1) and the second glass sheet (10) is pressed (11) to the film (1). The film (1) is then reheated in selected areas with short wave radiation (12) to a bonding temperature and thereafter cooled whereby an appropriate bond is obtained between the selected film (1) areas and the second glass sheet (10) to provide a glass lamination.
Owner:GYROTRON TECH
Early detection of battery cell thermal event
ActiveUS7939192B2Early detectionReduce absorptionCell temperature controlSecondary cells charging/dischargingControl systemEngineering
A battery module for use in an electric vehicle is disclosed. The battery module includes a plurality of cells arranged in a predetermined pattern within the module. The battery module also includes an optical pyrometer arranged inside the module. The optical pyrometer is installed within the module after being tuned to detect a predetermined frequency or band of frequencies. The pyrometer will be used to detect an increase in short wave radiation density from one of the battery cells within the module wherein that battery cell has a temperature above a predetermined threshold. The optical pyrometer will be used to communicate an electric signal to a control system of the electric vehicle wherein that control system will implement a predetermined mitigation process to contain the thermal event of that one cell within the battery module.
Owner:TESLA INC
Apparatus for generating shortwave radiation
ActiveUS8019046B1Maximize useEasy to operateX-ray tube electrodesX-ray tube with very high currentTarget surfaceMagnetic tape
An apparatus providing a source of shortwave electromagnetic radiation utilizing a tape having a first side and a second side and a laser beam focused and impinging on the first side of the tape. The apparatus utilizes a tape storage unit which delivers or feeds tape from the same. A base supports a first projecting element which contacts the second side of the tape emanating from the storage unit. A second projecting element supported by the base contacts the first side of the tape being fed from the tape storage unit. The portion of the tape between the first and second projecting elements constantly lies in a plane during the feeding of the tape and provides a target surface for a focused laser beam which generates shortwave radiation.
Owner:ERAN & JAN
Rat single-cage fixing device for electromagnetic exposure experiments
The invention discloses a rat single-cage fixing device for electromagnetic exposure experiments. The fixing device comprises a rat cage rack, two door control baffles and an adjusting baffle, wherein a cuboid cavity is defined in the rat cage rack, the two ends, in the length direction, of the cavity are open, and the rat cage rack is provided with an installation through hole communicated with the cavity; the two door control baffles can be movably connected with the two ends of the rat cage rack so as to open and close the two open ends of the cavity, and the door control baffles and the rat cage rack are provided with multiple vent holes making the cavity and the outside communicated; the adjusting baffle can be inserted in the installation through hole in a pluggable mode, and the cavity can be divided into two secondary cavities in the length direction of the cavity when the adjusting baffle is located in the installation through hole. The rat single-cage fixing device can not be limited by small radiation sources and narrow uniform fields, the radiation dosage precision can be improved to 25.45%, and animals can be conveniently put into the device. The device is successfully used in the biological effect research that high-frequency short-wave radiation causes rat brain injuries.
Owner:INST OF RADIATION MEDICINE ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI OF THE PLA
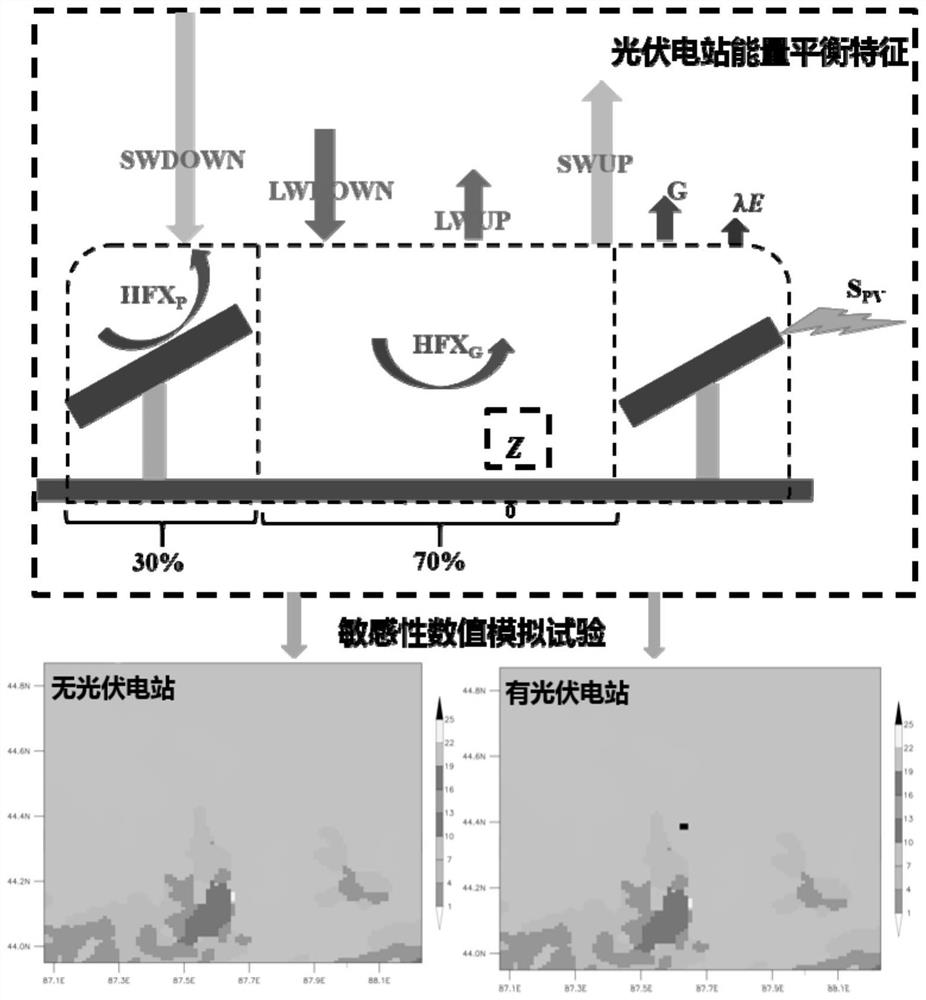
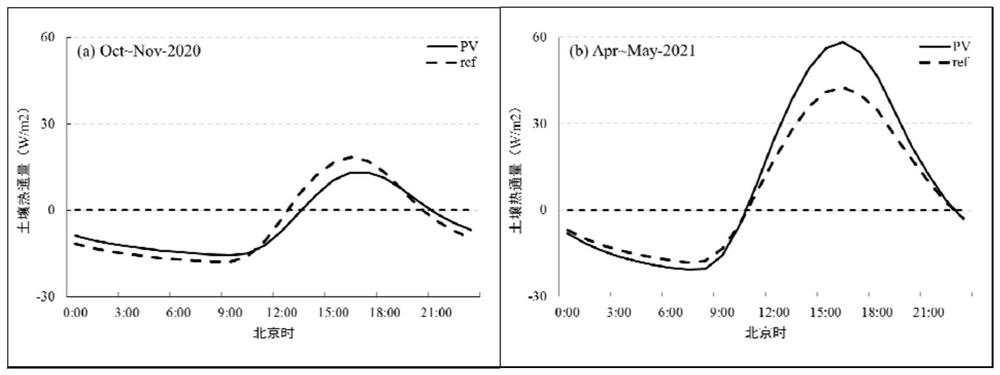
Mesoscale numerical simulation method for climate effect evaluation of onshore centralized photovoltaic power station
ActiveCN113987823ASolve the problem of objective quantitative evaluationReduce high dependencyData processing applicationsDesign optimisation/simulationHeat fluxEngineering
The invention discloses a mesoscale numerical simulation method for climate effect evaluation of an onshore centralized photovoltaic power station. The mesoscale numerical simulation method comprises the following steps of: preprocessing multisource meteorological observation data of the onshore centralized photovoltaic power station; performing surface short-wave radiation parameterization by using comprehensive albedo and photoelectric conversion efficiency; performing direct explicit numerical parameterization on heat-sensitive flux by using wind speed, air density and short-wave radiation; performing latent heat flux, soil heat flux and long-wave radiation parameterization by using a difference comparison method; carrying out parameterization on the dragging effect of a photovoltaic panel by utilizing dynamic roughness; and quantitatively evaluating the climate effect of the photovoltaic power station through a sensitivity numerical simulation test. According to the method, the objective quantitative evaluation problem of the climate influence of the large photovoltaic power station is solved; and the simulation method has relatively high universality. By adopting the method, post-evaluation can be carried out on the climate effect of the built photovoltaic power station, pre-evaluation can be carried out on the climate effect of the power station to be built, and a basis is provided for site selection and construction of a climate-friendly power station.
Owner:国家气候中心
Orthosilicate green phosphor for light emitting diode and preparation thereof
InactiveCN101475804AIncrease brightnessImprove performanceAlkaline-earth metal silicatesLuminescent compositionsHeterojunctionPhosphor
The invention relates to the field of radiation materials, in particular to orthosilicate fluorescent powder. Part of O<-2> in a silanoxide tetrahedron is replaced, the orthosilicate fluorescent powder has a P2nn crystal structure and gives off green radiation under the strong shortwave radiation excitation of InGaN heterojunction, wherein the maximum spectrum depends on the interrelation between the amount of Me<+2> or Ln<+2, 3> in a cation crystal lattice, and the intensity is determined by the amount of the atom O<-2> in the component which is replaced in the V, the VI and the VII families and is taken from the series of F, Cl, Br, I, S, Se, N and P. The orthosilicate fluorescent powder has two excitation wave zones of which the range is between 360 and 400 nanometers and between 450 and 490 nanometers, and the materials are used for establishing a bright and effective green LED by using a nitride heterojunction as a substrate.
Owner:罗维鸿 +1
Method for inverting topsoil volumetric water content by employing multi-temporal observation data of geostationary meteorological satellite
InactiveCN106291504ALow clay contentElectromagnetic wave reradiationICT adaptationData informationEarth surface
The invention discloses a method for inverting topsoil volumetric water content by employing multi-temporal observation data of a geostationary meteorological satellite. The method mainly includes: a soil moisture inversion model is built; the land surface temperature and net surface shortwave radiation are inverted in a quantification manner by employing the data of the geostationary meteorological satellite, dimensionless treatment is performed on the land surface temperature and the net surface shortwave radiation, ellipse fitting is performed on the multi-temporal land surface temperature and the net surface shortwave radiation, an ellipse parameter corresponding to each pixel is obtained, and the parameters are regarded as input data of the soil moisture inversion model; an acquisition method of model coefficients is obtained; and specific requirements of dimensionless treatment are imposed on the land surface temperature and the net surface shortwave radiation. According to the method, the problems caused by the lack of polar orbiting satellite data information of the conventional optical and thermal infrared remote sensing soil moisture inversion method are solved.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCIENCES +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com