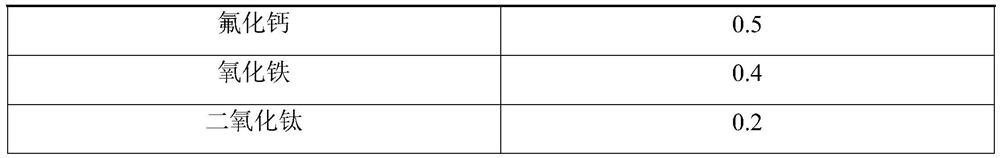
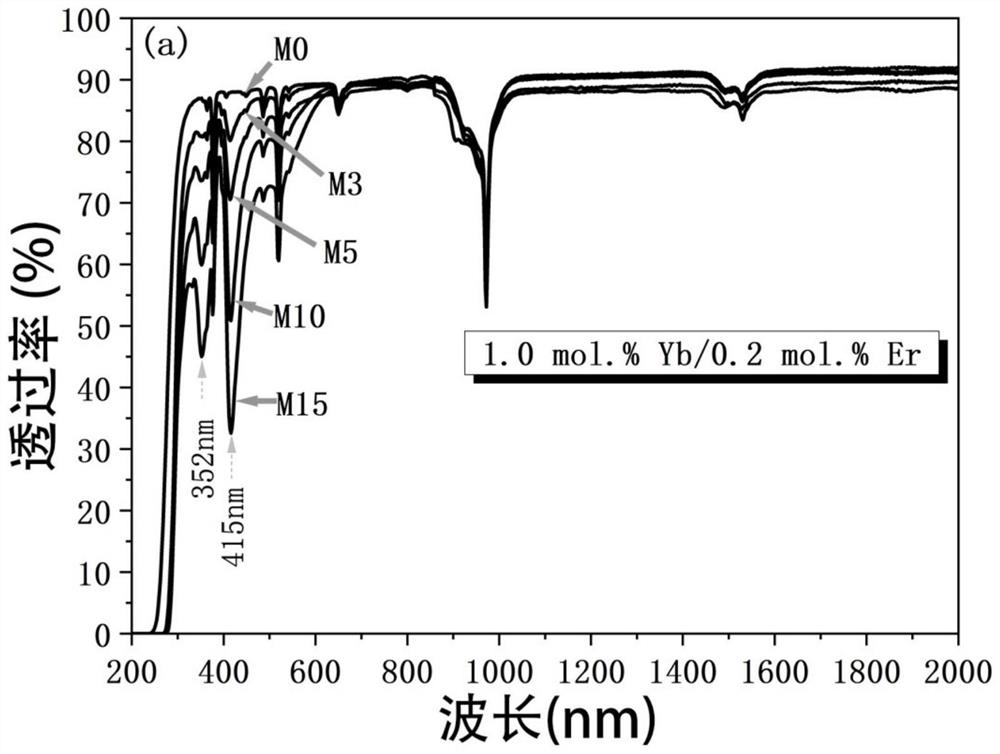
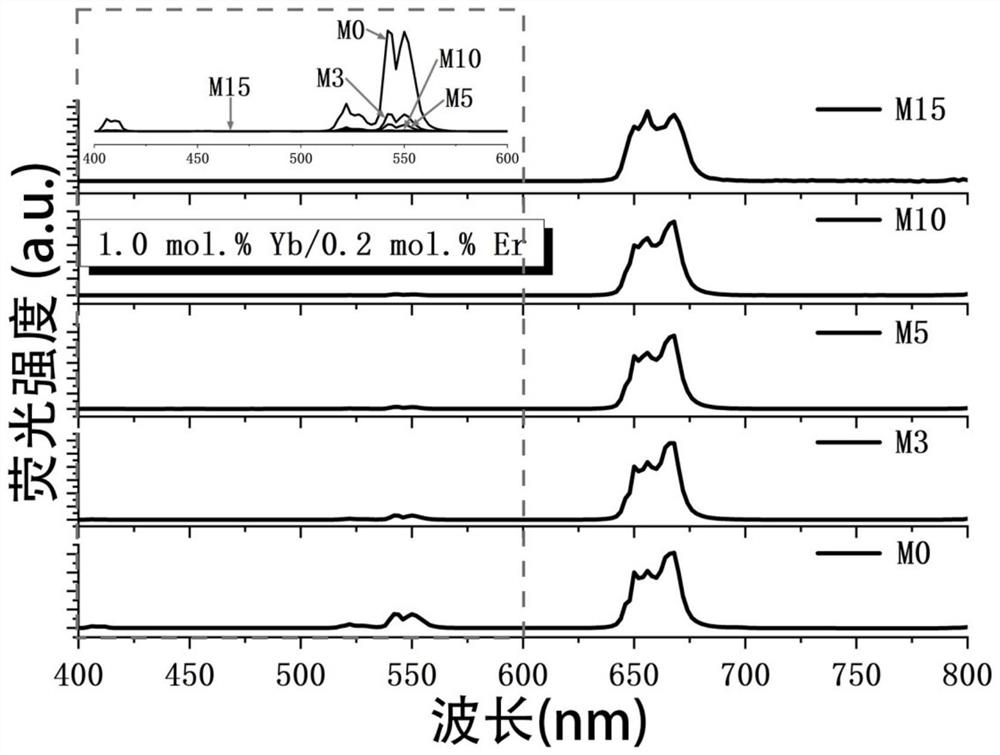
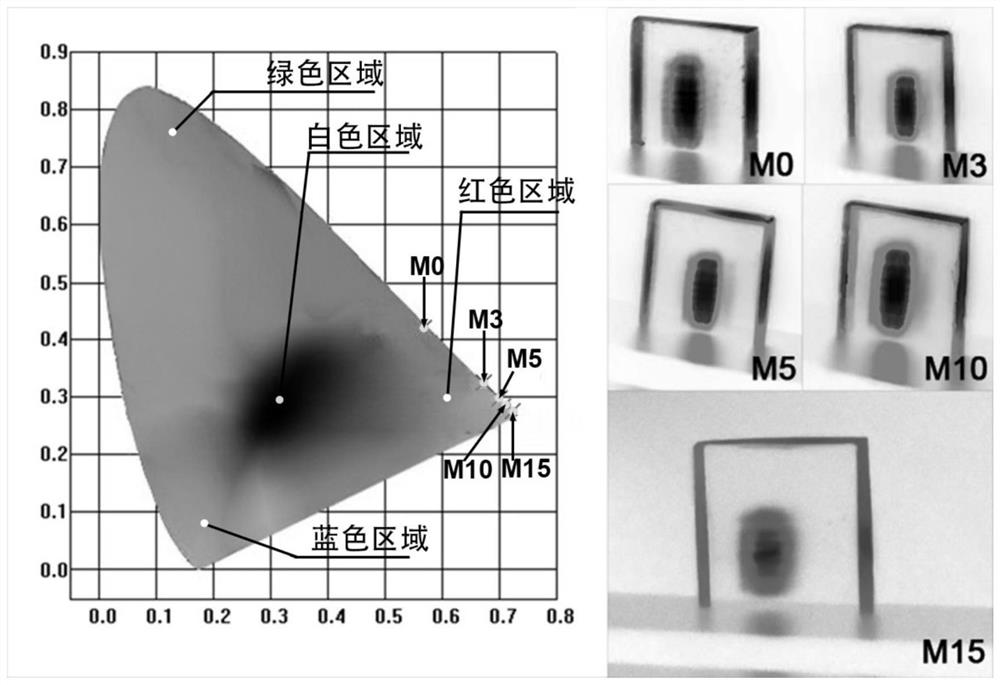
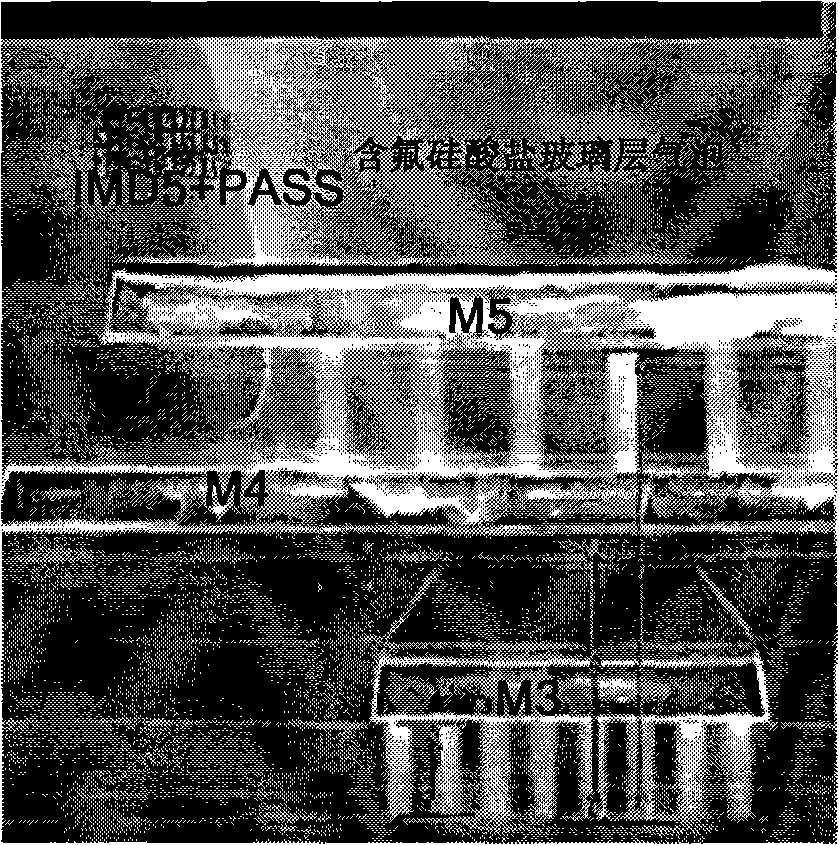Patents
Literature
39 results about "Fluorosilicate glass" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Fluorosilicate glass (FSG) is a glass material composed primarily of fluorine, silicon and oxygen. It has a number of uses in industry and manufacturing, especially in semiconductor fabrication where it forms an insulating dielectric. The related fluorosilicate glass-ceramics have good mechanical and chemical properties.
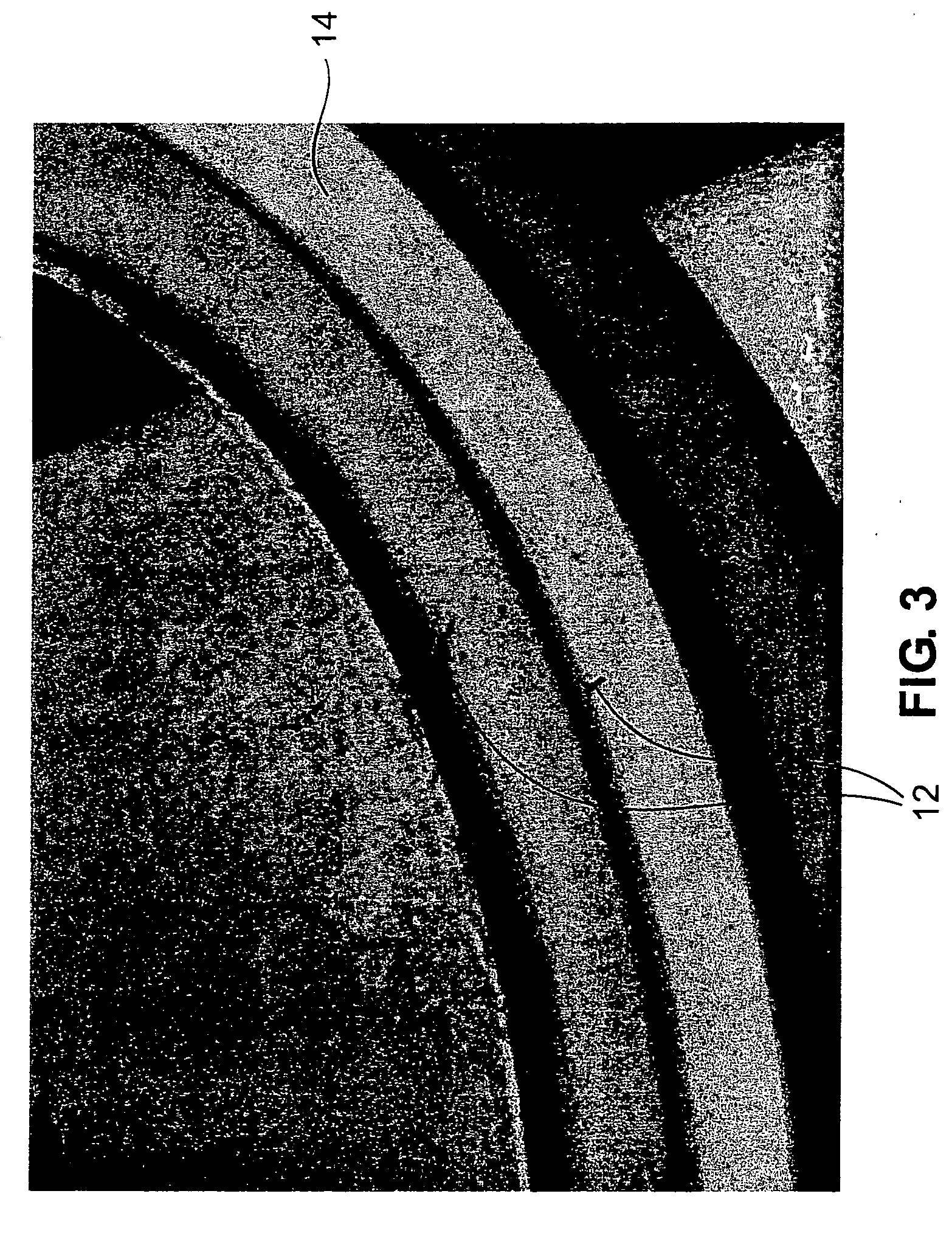
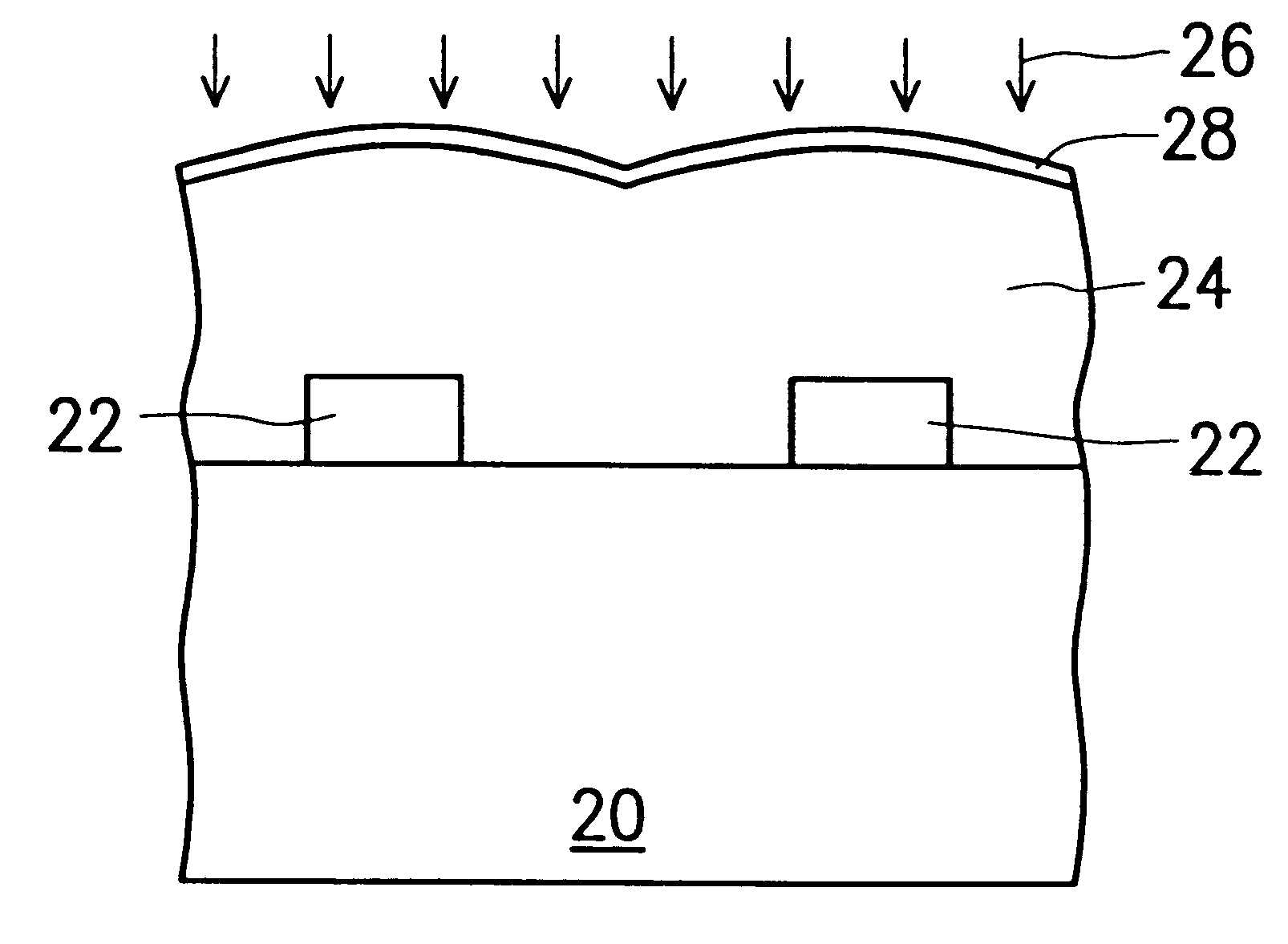
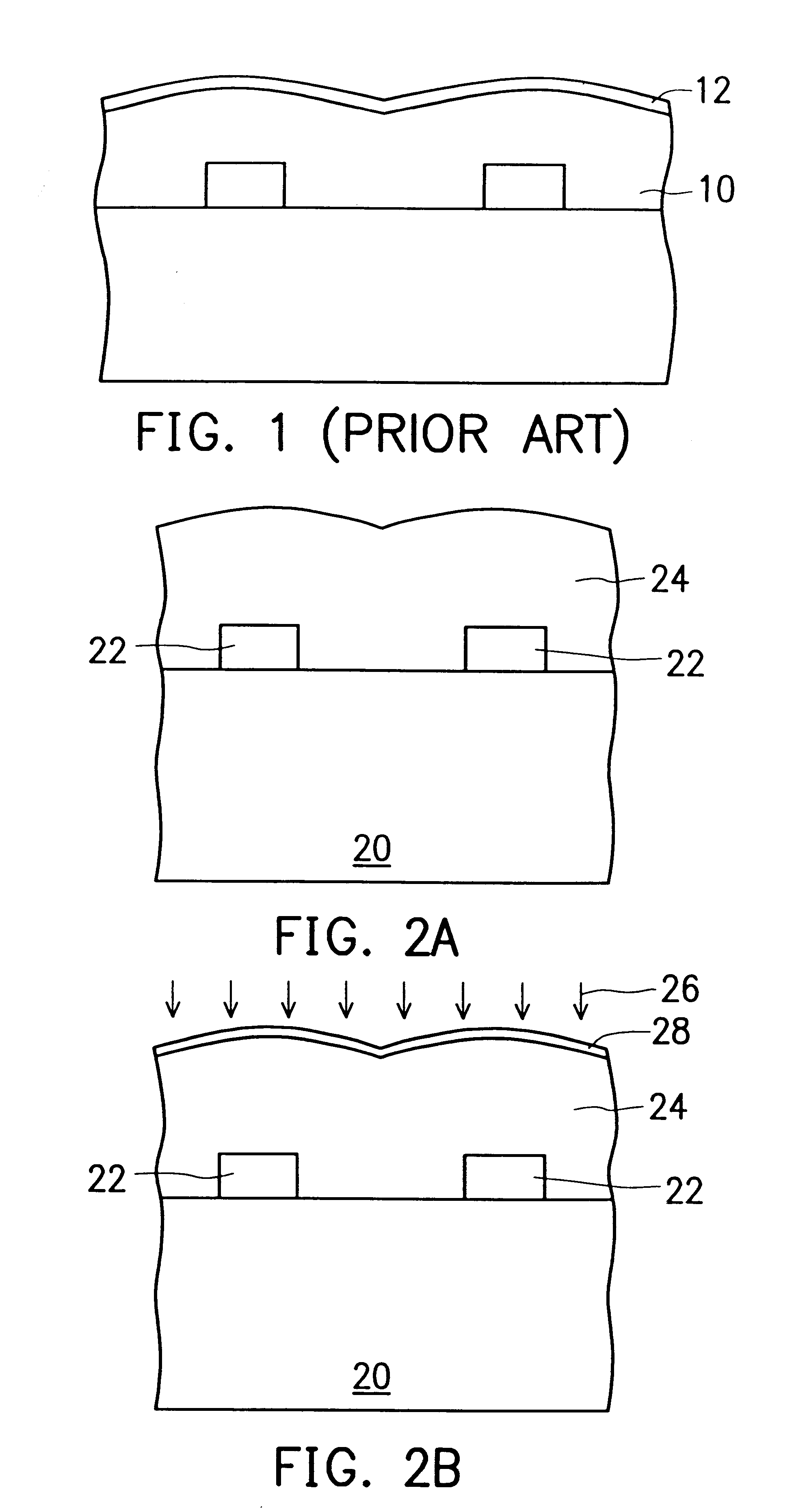
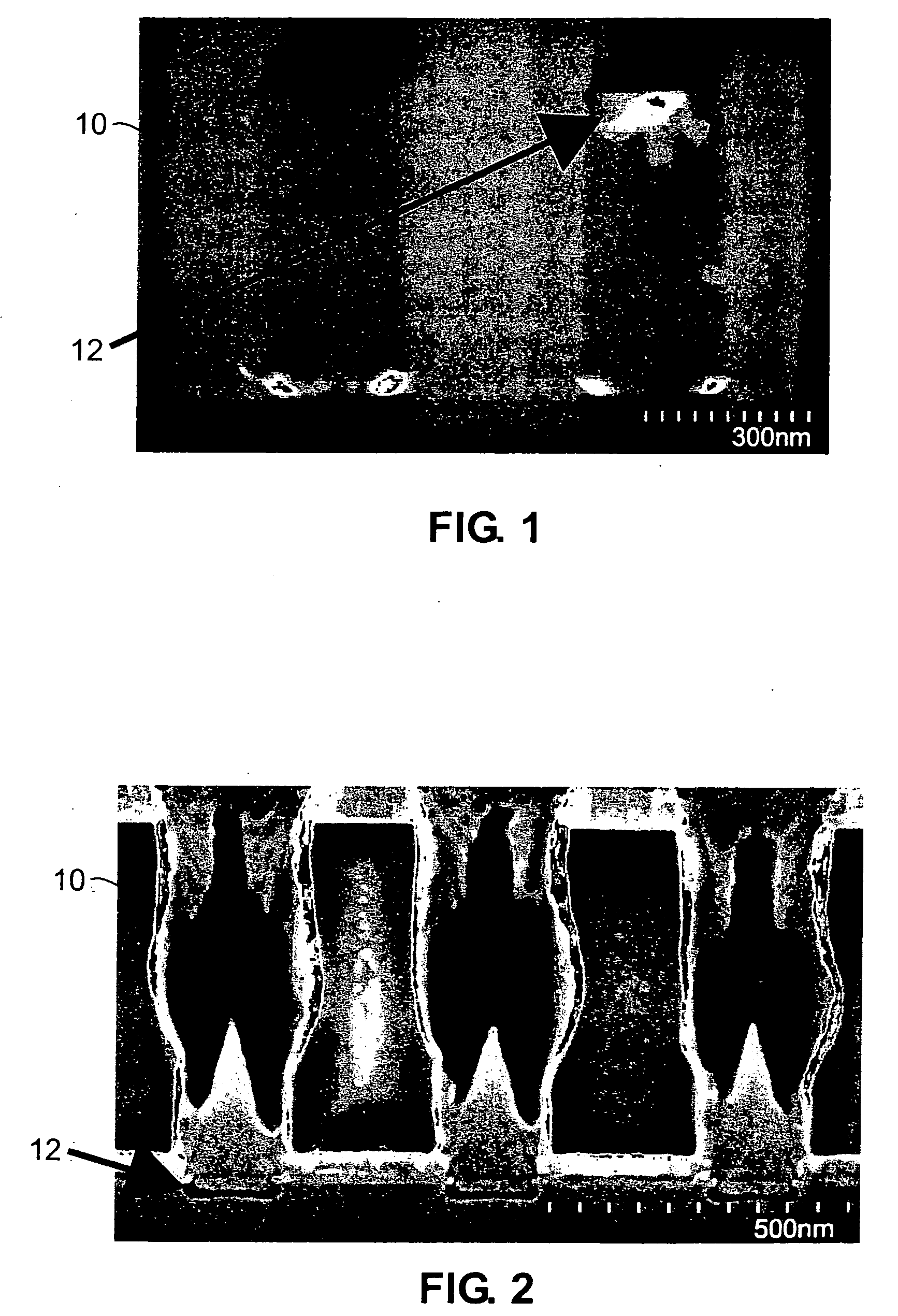
Method of forming fluorosilicate glass (FSG) layers with moisture-resistant capability
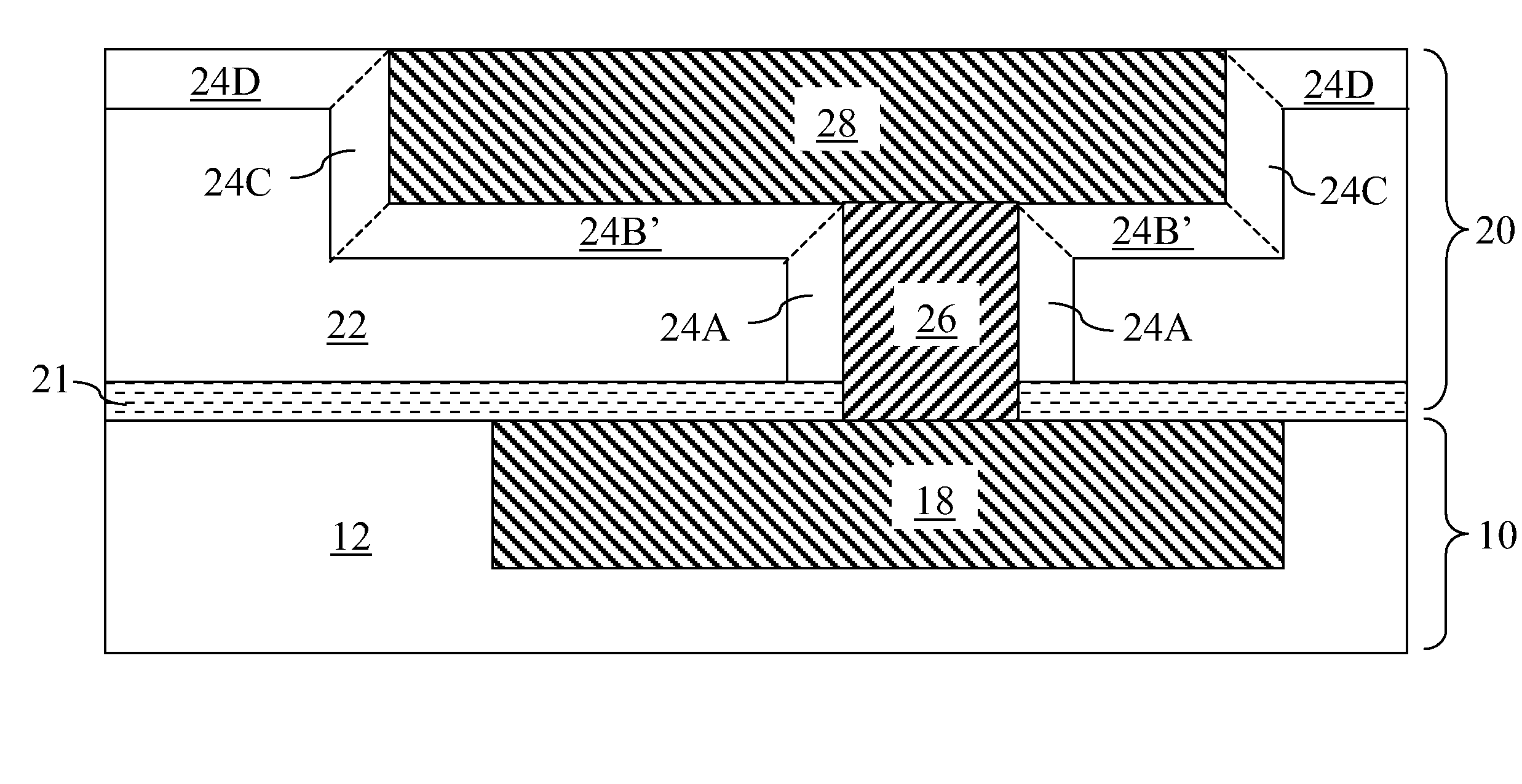
InactiveUS6284677B1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingFluorosilicate glassSilicate glass
A method is provided for forming fluorosilicate glass (FSG) layers that serve as inter-metal dielectric (IMD) layers in a semiconductor wafer with a high moisture-resistant capability. In particular, the method can nonetheless allow the resultant semiconductor circuit to have a low RC delay. The method includes the step of subjecting the FSG layer to a plasma treatment so as to form a moisture-resistant layer over the FSG layer. In the plasma treatment, the ionized gas of ammonia is used as the plasma. As a result of this plasma treatment, a layer of nitrogen-containing compound having a high moisture-resistant property is formed over the FSG layer, which serves as a moisture-resistant layer that can protect the FSG layer from absorbing moistures.
Owner:UNITED MICROELECTRONICS CORP
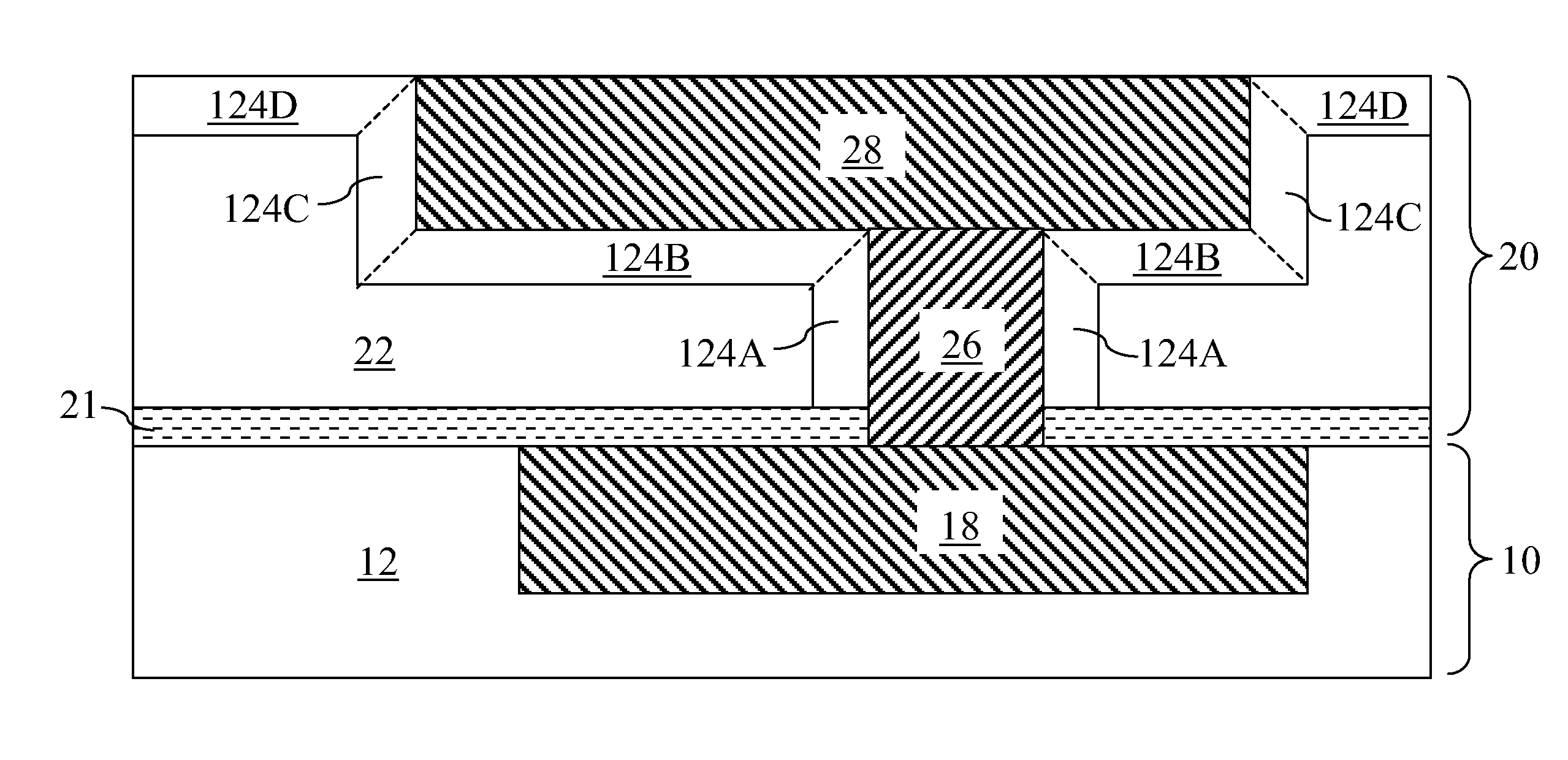
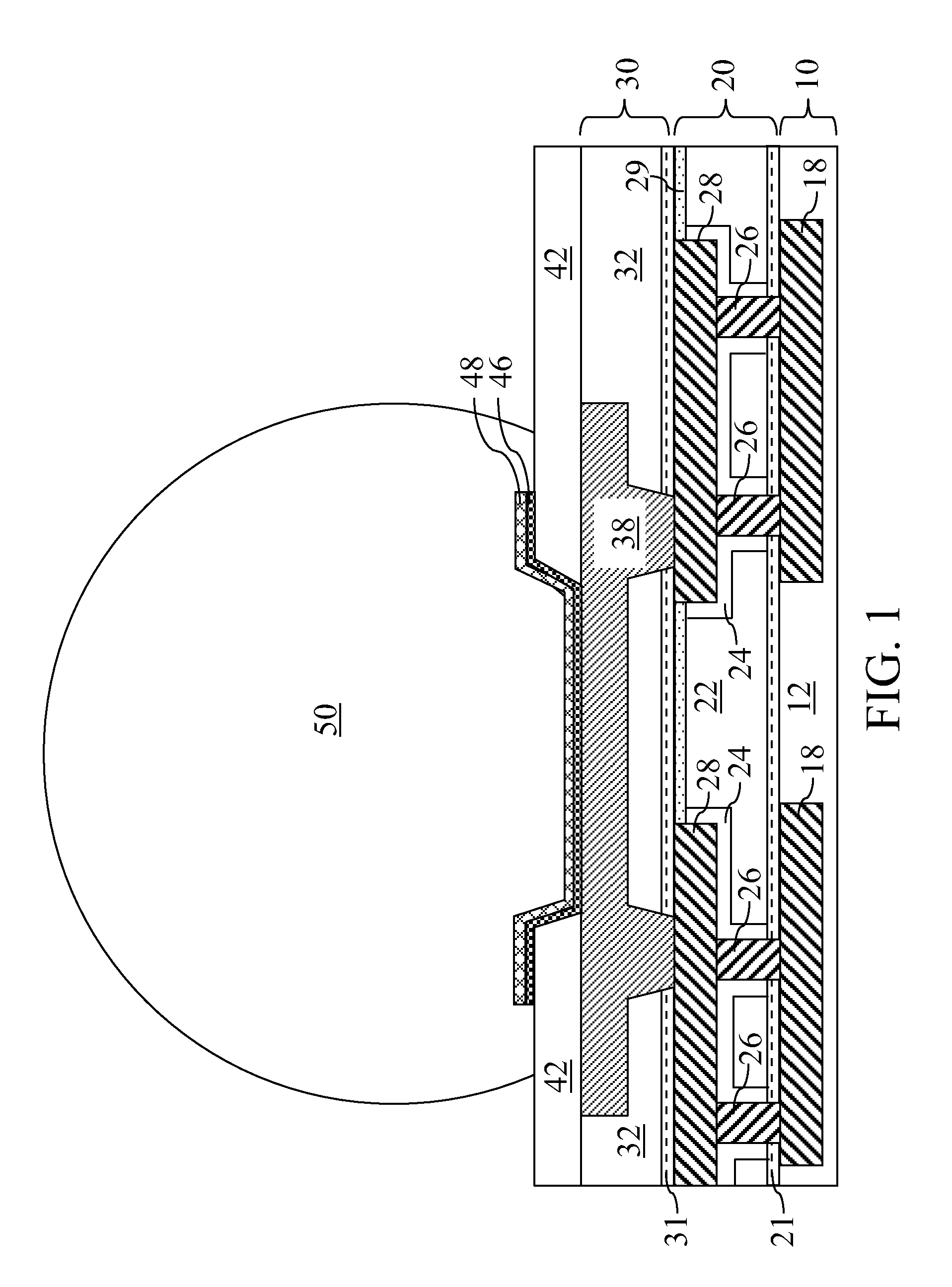
Fluorine depleted adhesion layer for metal interconnect structure
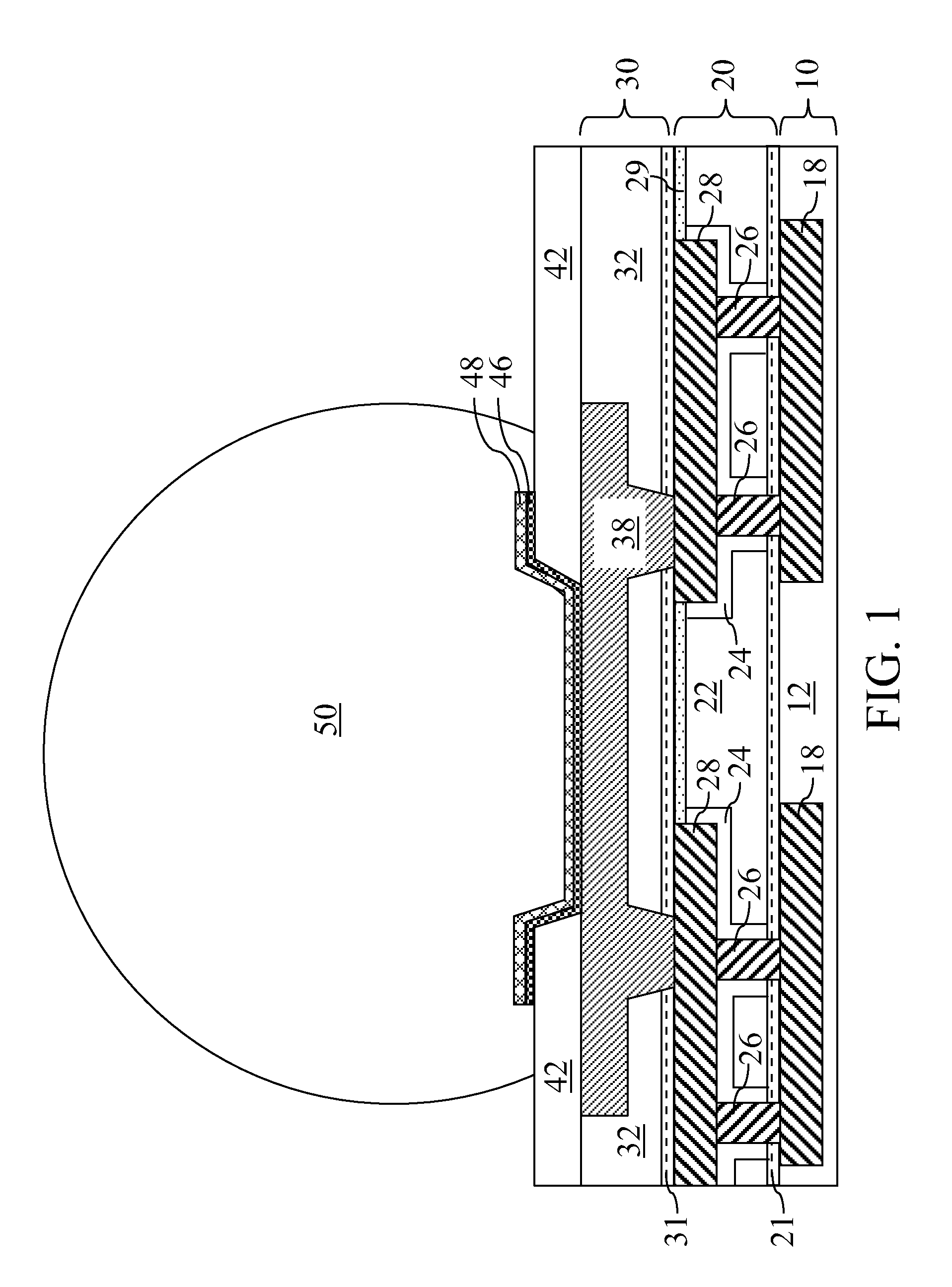
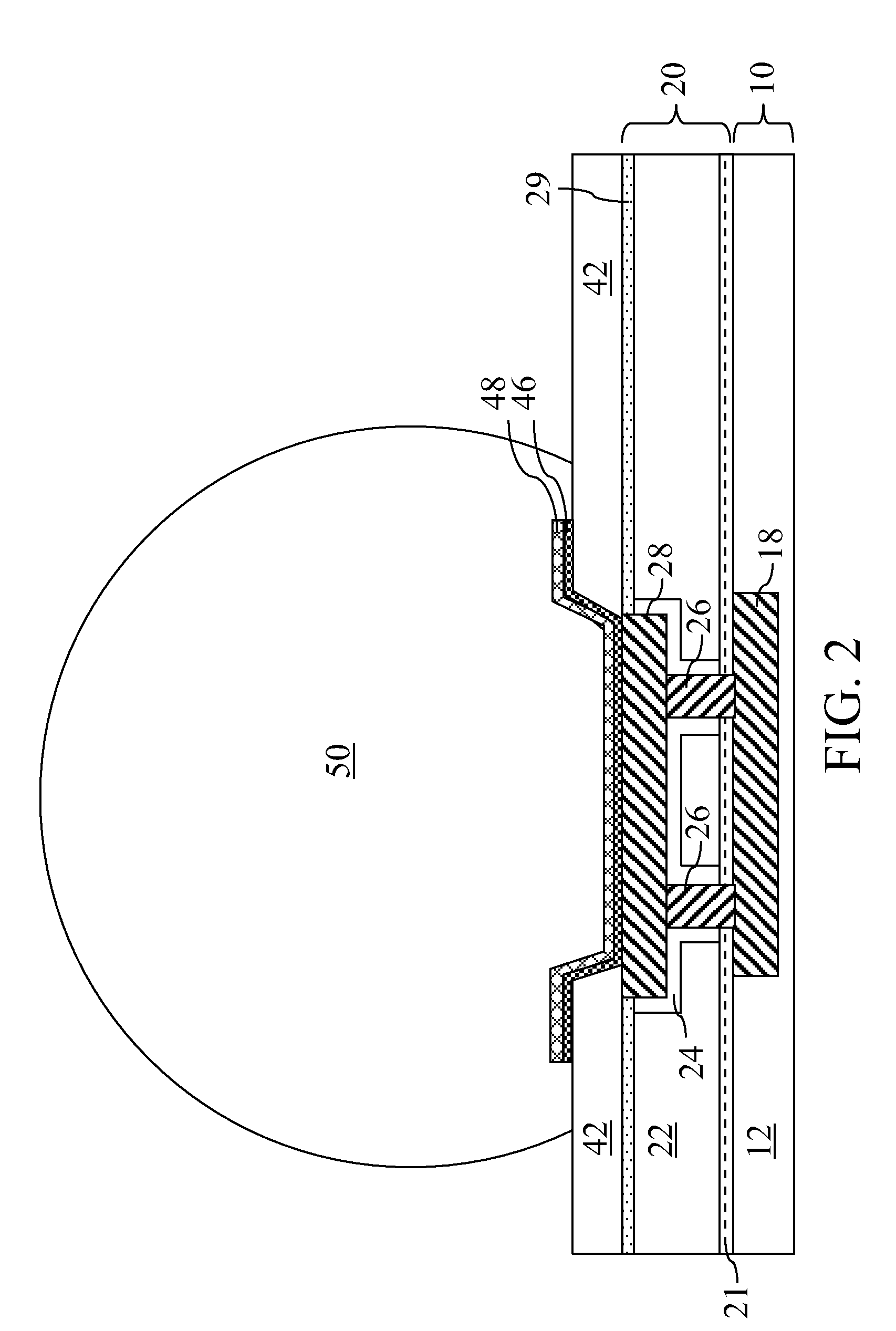
ActiveUS20090212439A1Improve adhesionIncrease resistanceSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesHigh resistanceState of art
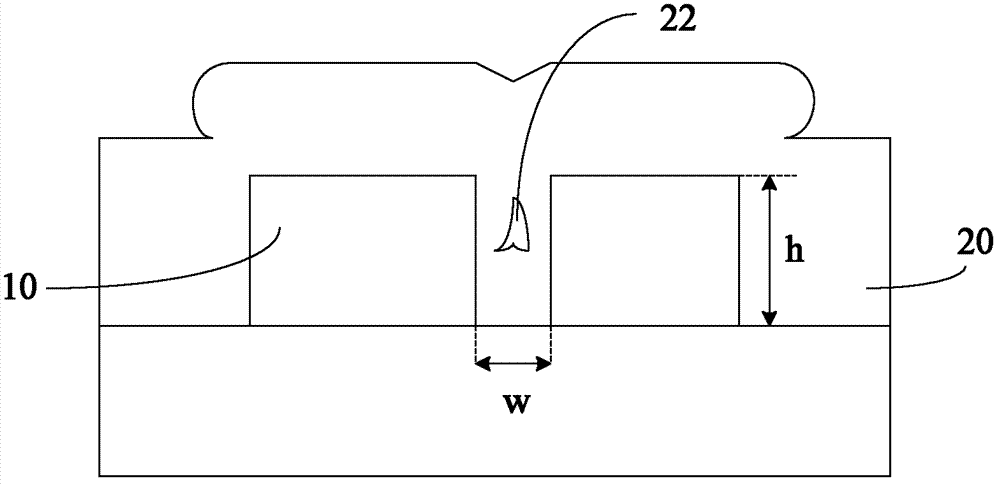
A line trough and a via cavity are formed within a dielectric layer comprising a fluorosilicate glass (FSG) layer. A fluorine depleted adhesion layer is formed within the line trough and the via cavity either by a plasma treatment that removes fluorine from exposed surfaces of the FSG layer, or by deposition of a substantially fluorine-free dielectric layer. Metal is deposited within the line trough and the via cavity to form a metal line and a metal via. The fluorine depleted adhesion layer provides enhanced adhesion to the metal line compared with prior art structures in which a metal line directly contacts a FSG layer. The enhanced adhesion of metal with an underlying dielectric layer provides higher resistance to delamination for a semiconductor package employing lead-free C4 balls on a metal interconnect structure.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Complementary replacement of material
InactiveUS7399709B1Increase contrastMinimized roughnessDecorative surface effectsSolid-state devicesResistResolution enhancement technologies
An image reversal method is described that removes the etch resistance requirement from a resist. A high resolution resist pattern comprised of islands, lines, or trenches is formed with a large process window by exposing through one or more masks including phase edge masks and optionally with resolution enhancement techniques. A complementary material replacement (CMR) layer comprised of an organic polymer or material such as fluorosilicate glass which has a lower etch rate than the resist is coated over the resist pattern. CMR and resist layers are etched simultaneously to provide an image reversed pattern in the CMR layer which is etch transferred into a substrate. The method avoids edge roughness like bird's beak defects in the etched pattern and is useful for applications including forming contact holes in dielectric layers, forming polysilicon gates, and forming trenches in a damascene process. It is also valuable for direct write methods where an image reversal scheme is desired.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Method of forming an electrical isolation associated with a wiring level on a semiconductor wafer
InactiveUS20070090531A1Reduce impactSimple processSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesGas phaseFluorosilicate glass
A method of forming a wiring level and an electrical isolation associated with the wiring level on a surface of a semiconductor wafer comprises the steps of providing the semiconductor wafer having said surface, forming a plurality of electrically conductive wiring lines upon said surface, each of the wiring lines having a spacing with respect to neighboring one of the wiring lines, depositing a first layer of amorphous carbon upon the wiring lines by means of non-conformal plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition (PECVD), such that air-filled voids formed below the first layer within the spacings between neighboring wiring lines. Alternatively, OSG (organo-silicon glass) or FSG (fluorine doped silicon glass) may be deposited to yield air-filled voids within the spacings. According to an embodiment, the carbon, OSG or FSG layers are used as an IMD-layer (line-to-line isolation), added by a further layer of a dielectric material, which then serves as an ILD-layer (level-to-level isolation).
Owner:OFFENBERG DIRK +3
Semiconductor device contamination reduction in a fluorinated oxide deposition process
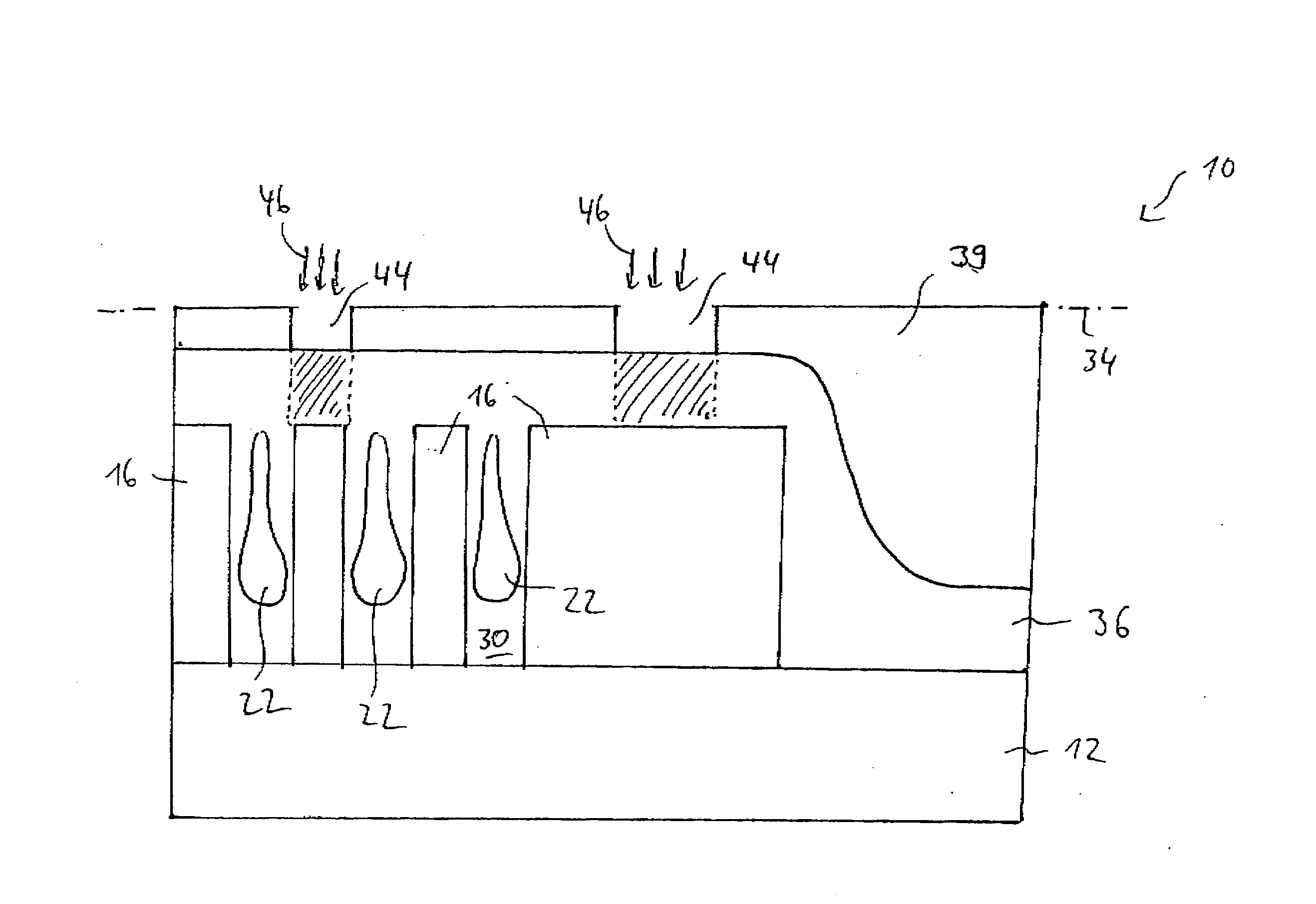
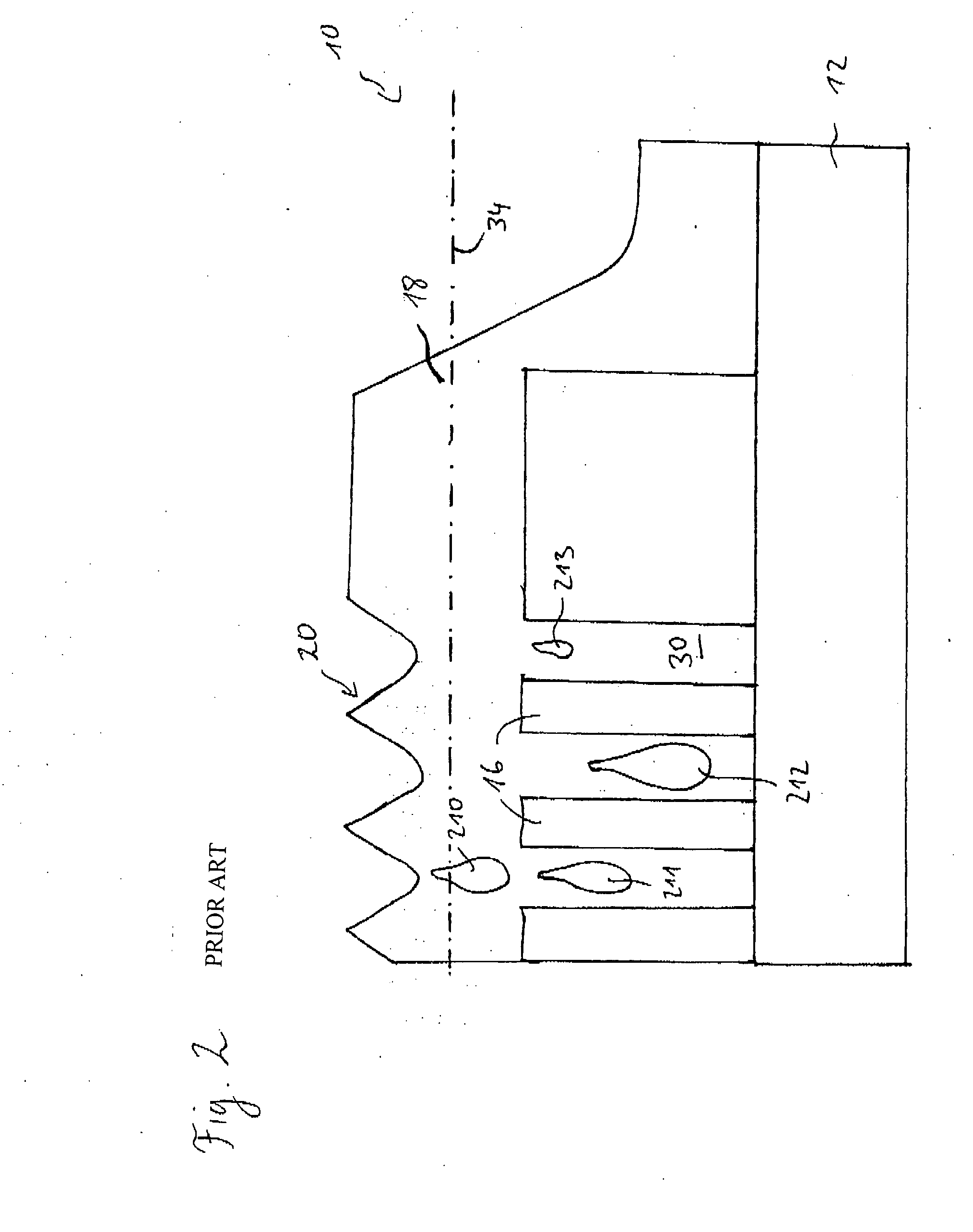
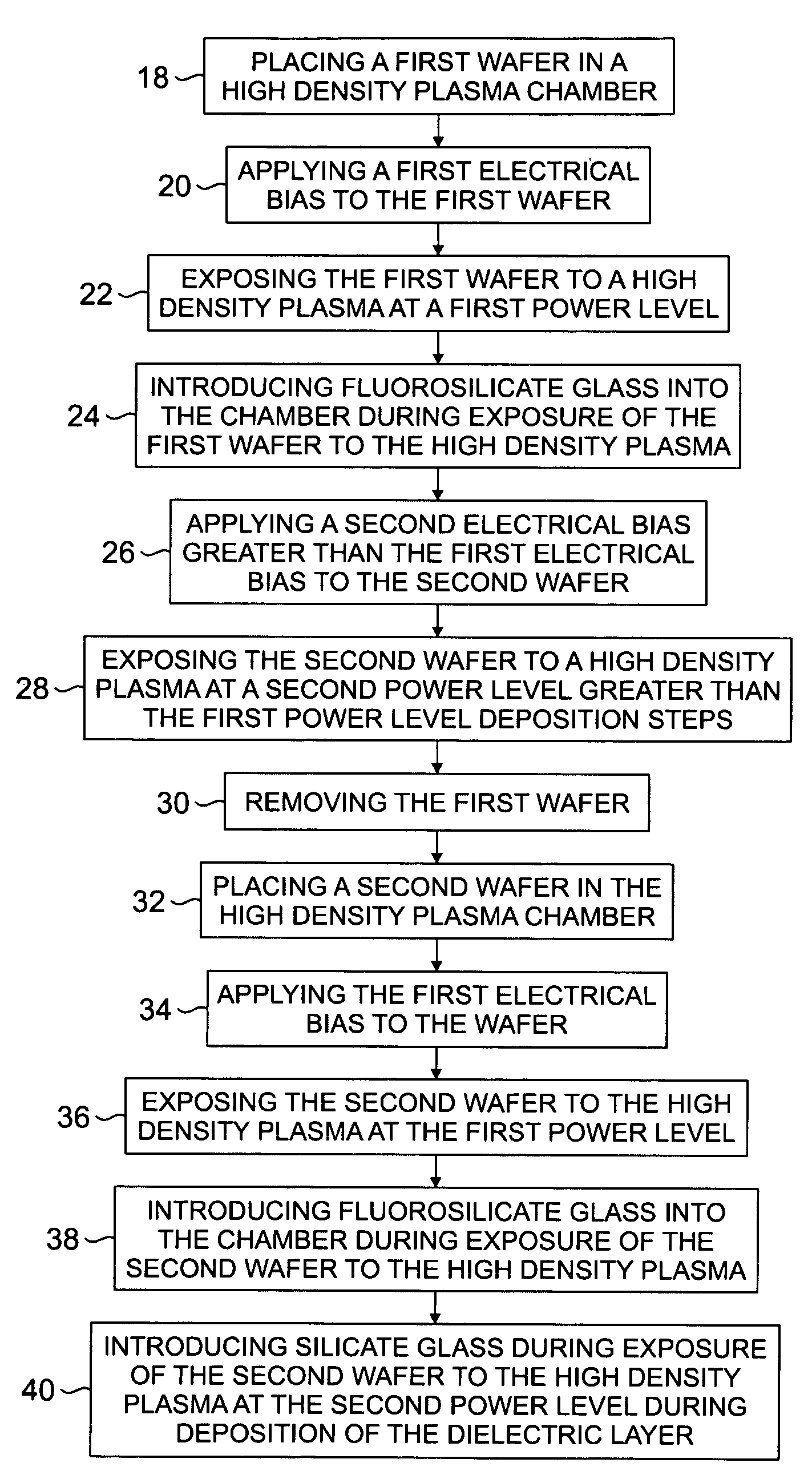
InactiveUS20050191863A1Liquid surface applicatorsVacuum evaporation coatingHigh densityDevice material
A method for improving throughput in a semiconductor wafer deposition process in a high density plasma chamber includes processing a first wafer in the high density plasma chamber using a process that includes high power sufficient to burn fluorosilicate glass residue in the chamber. The method further includes removing the first wafer and processing additional wafers using the same process without cleaning the chamber between wafers.
Owner:AGERE SYST INC
Luminescent glass ceramic doped with multiple rare earth ions and capable of up and down-conversion to ultraviolet light and preparation method thereof
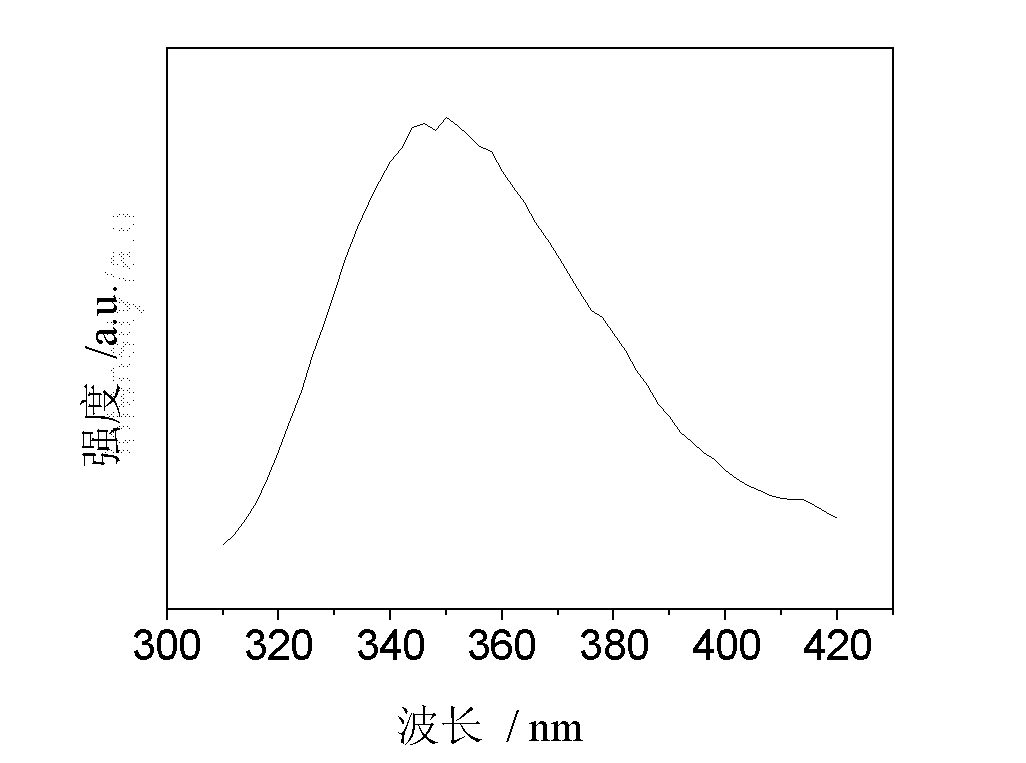
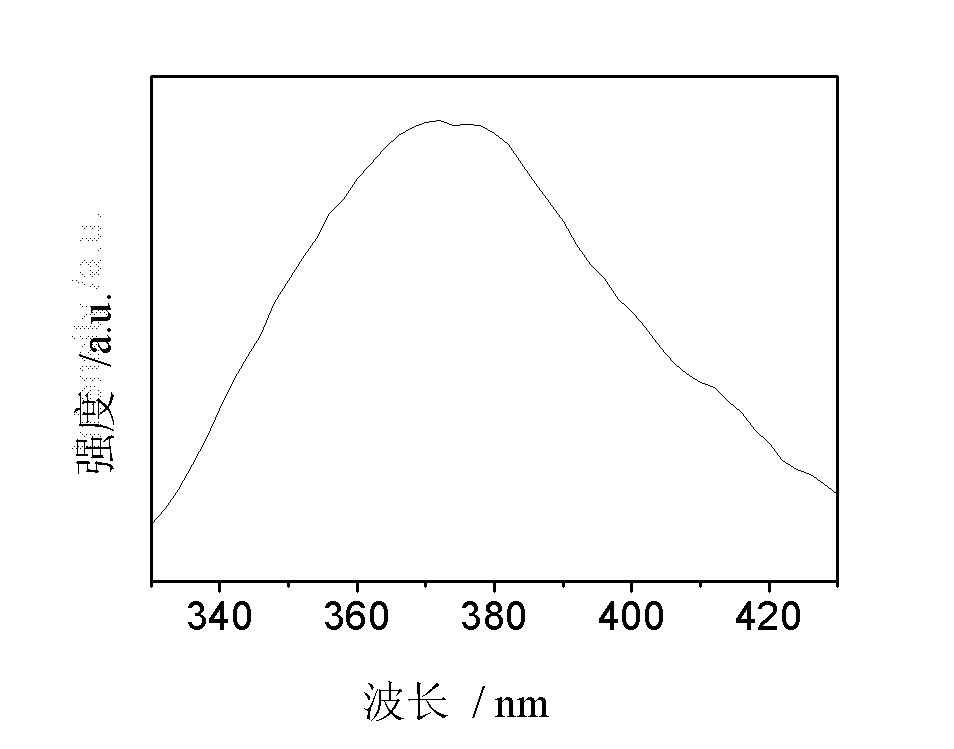
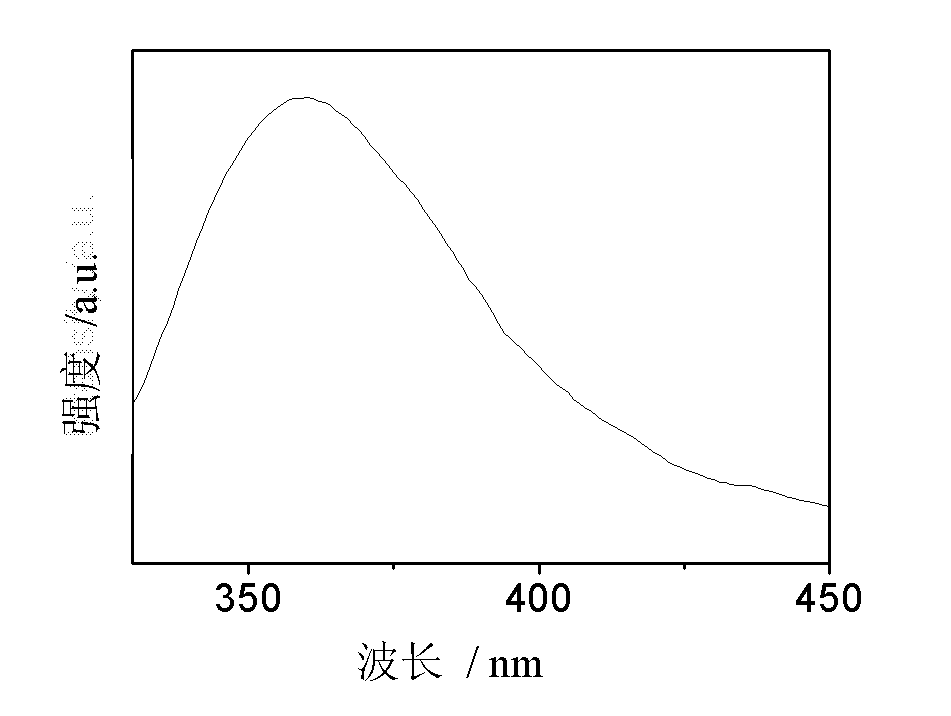
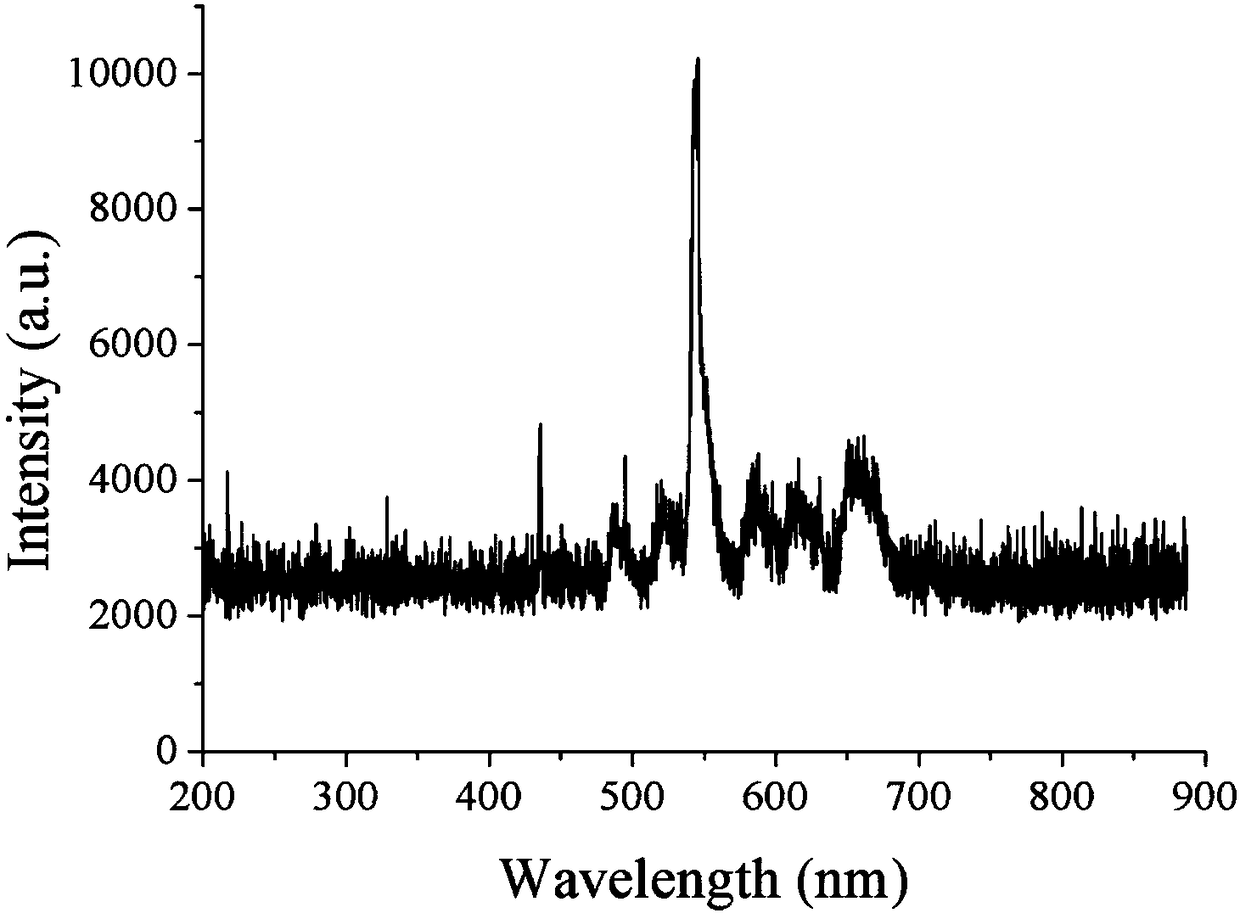
The invention provides luminescent glass ceramic doped with multiple rare earth ions and capable of up and down-conversion to ultraviolet light and a preparation method thereof; the glass ceramic is fluorosilicate glass ceramic doped with at least four rare earth ions, wherein on a basis of oxide, the molar content of the rare earth ions is 1% to 20% of the total amount of the glass ceramic; the glass ceramic can realize up conversion of infrared light and visible light into ultraviolet light, and also realize down conversion of short-wave radiation into ultraviolet light.
Owner:何森
Method for preventing fluorine diffusion in manufacturing process of fluorine-silicon glass
InactiveCN1844003APrevent proliferationReduce surface fluorine concentrationFluorosilicate glassSilicon
The invention relates to a fluorine nonproliferation method in the manufacturing technique using fluosilicic glass, after finishing manufacturing Damascus wire structure, disposing fluosilicic glass dielectric with plasma for 1-5 times, reducing surface fluorine concentration of fluosilicic glass low dielectric materials, then depositing protective covering suppressing fluorine diffusion, finally, etching bottom barrier layer, completing Damascus structure.
Owner:SHANGHAI INTEGRATED CIRCUIT RES & DEV CENT +1
Preparation method of microsphere cavity laser based on ultra-strong up-conversion multi-component glass material
InactiveCN108258571ALower the thresholdQuickly skip the crystallization temperatureActive medium shape and constructionLine widthMicrosphere
The invention relates to a method for preparing a microsphere cavity laser based on ultra-strong up-conversion multi-component glass material, and belongs to the technical field of microsphere cavitylasers. The method comprises the preparation of Yb-Er ion co-doped multi-component fluorosilicate glass and Yb-Er ion co-doped glass microspheres. And the prepared microspheres are packaged by a laser. The Preparation method of microsphere cavity laser based on ultra-strong up-conversion multi-component glass material combines the ultra-high up-conversion quantum efficiency of Yb-Er ions in the fluorosilicate glass with the high quality factor of the glass microspheres, and solves the problems of uncontrollable crystallization in the development process of the prior-conversion optical fiber laser and the over-high pumping threshold value. According to the invention, the pumping light intensity is greatly enhanced through optical path coupling, resonance of the whispering wall mode is realized in Yb-Er co-doped fluorine silicate microspheres, and finally laser output with narrow line width is realized. The method is simple in preparation process, belongs to the wave band with the smallest transmission loss in seawater, can be used for naval equipment, and solves the problem of detection of underwater targets and marine communication.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
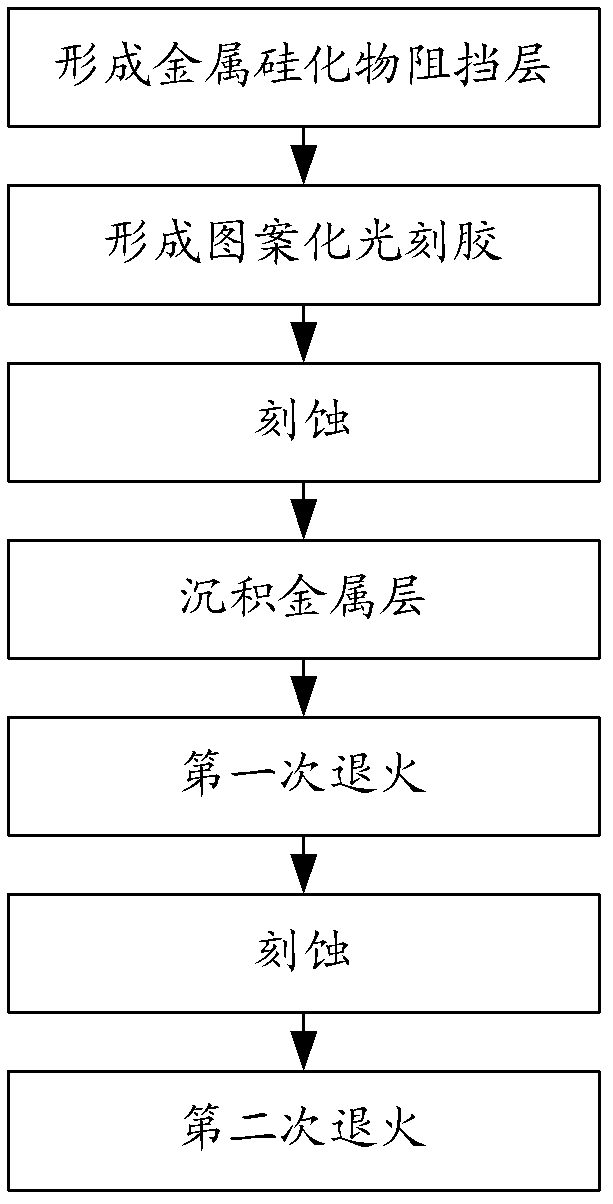
Method for forming metal silicide
InactiveCN102832112AIncrease contentSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesSalicideFluorosilicate glass
The invention provides a method for forming metal silicide. Before a metal silicide block layer is formed, a layer of silicofluoride glass film is deposited on a silicon substrate to be as a buffer layer. Fluorine element in the silicofluoride glass film can spread into the silicon substrate. Introduction of the fluorine element can restrain the metal from suddenly entering the silicon substrate together in an initial stage when the metal silicide is formed, and can fix the metal element which has already spread into the silicon substrate, thereby reducing defects.
Owner:SEMICON MFG INT (SHANGHAI) CORP
Fluorine depleted adhesion layer for metal interconnect structure
ActiveUS8039964B2Improve adhesionIncrease resistanceSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesHigh resistanceState of art
A line trough and a via cavity are formed within a dielectric layer comprising a fluorosilicate glass (FSG) layer. A fluorine depleted adhesion layer is formed within the line trough and the via cavity either by a plasma treatment that removes fluorine from exposed surfaces of the FSG layer, or by deposition of a substantially fluorine-free dielectric layer. Metal is deposited within the line trough and the via cavity to form a metal line and a metal via. The fluorine depleted adhesion layer provides enhanced adhesion to the metal line compared with prior art structures in which a metal line directly contacts a FSG layer. The enhanced adhesion of metal with an underlying dielectric layer provides higher resistance to delamination for a semiconductor package employing lead-free C4 balls on a metal interconnect structure.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
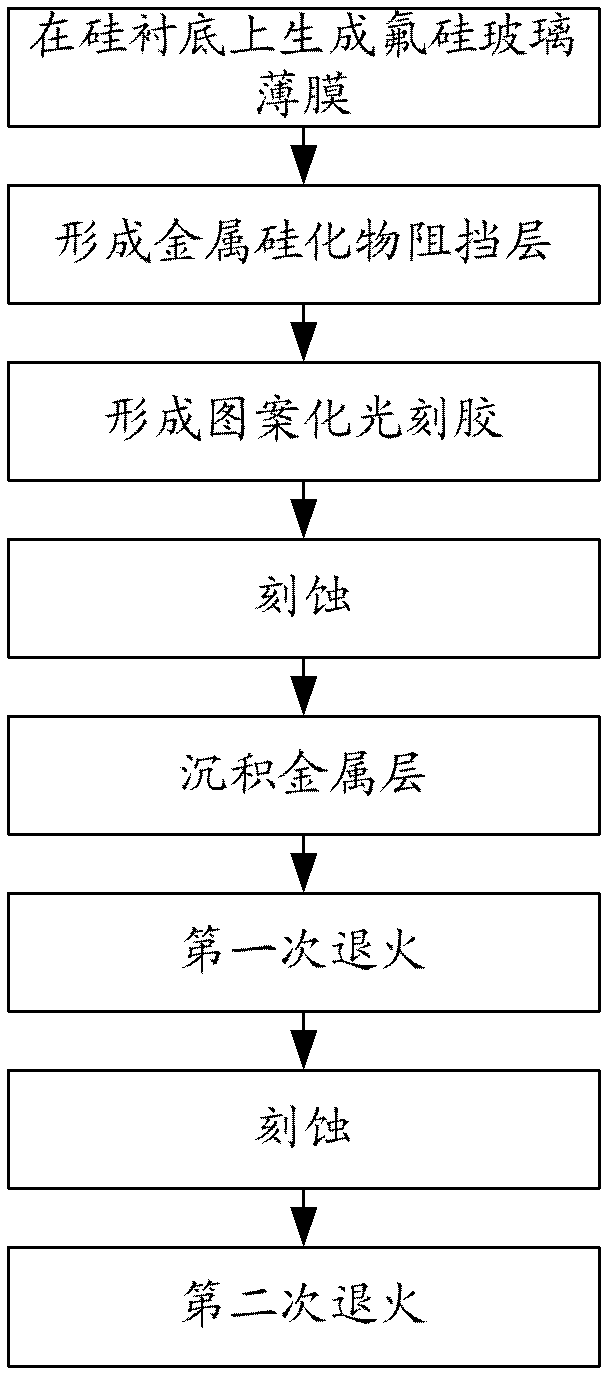
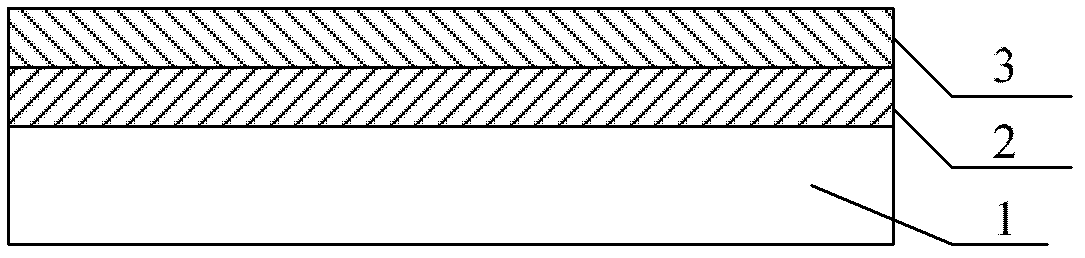
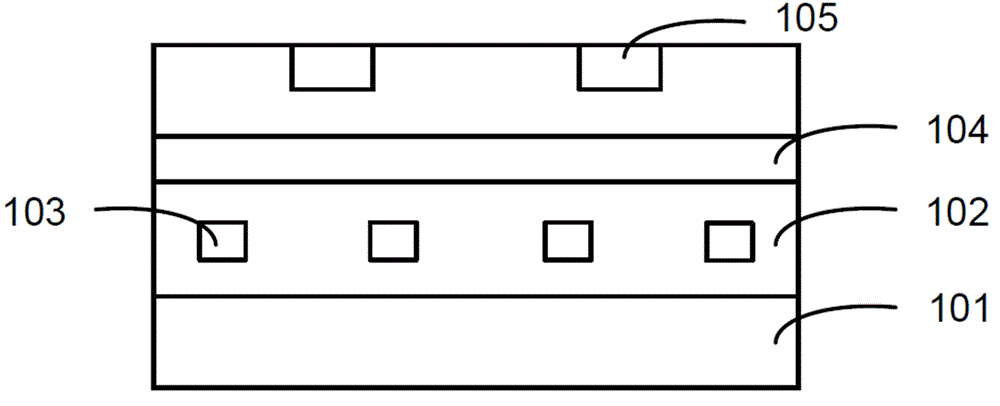
Silicon-on-insulator device and intermetallic dielectric layer structure thereof and manufacturing method
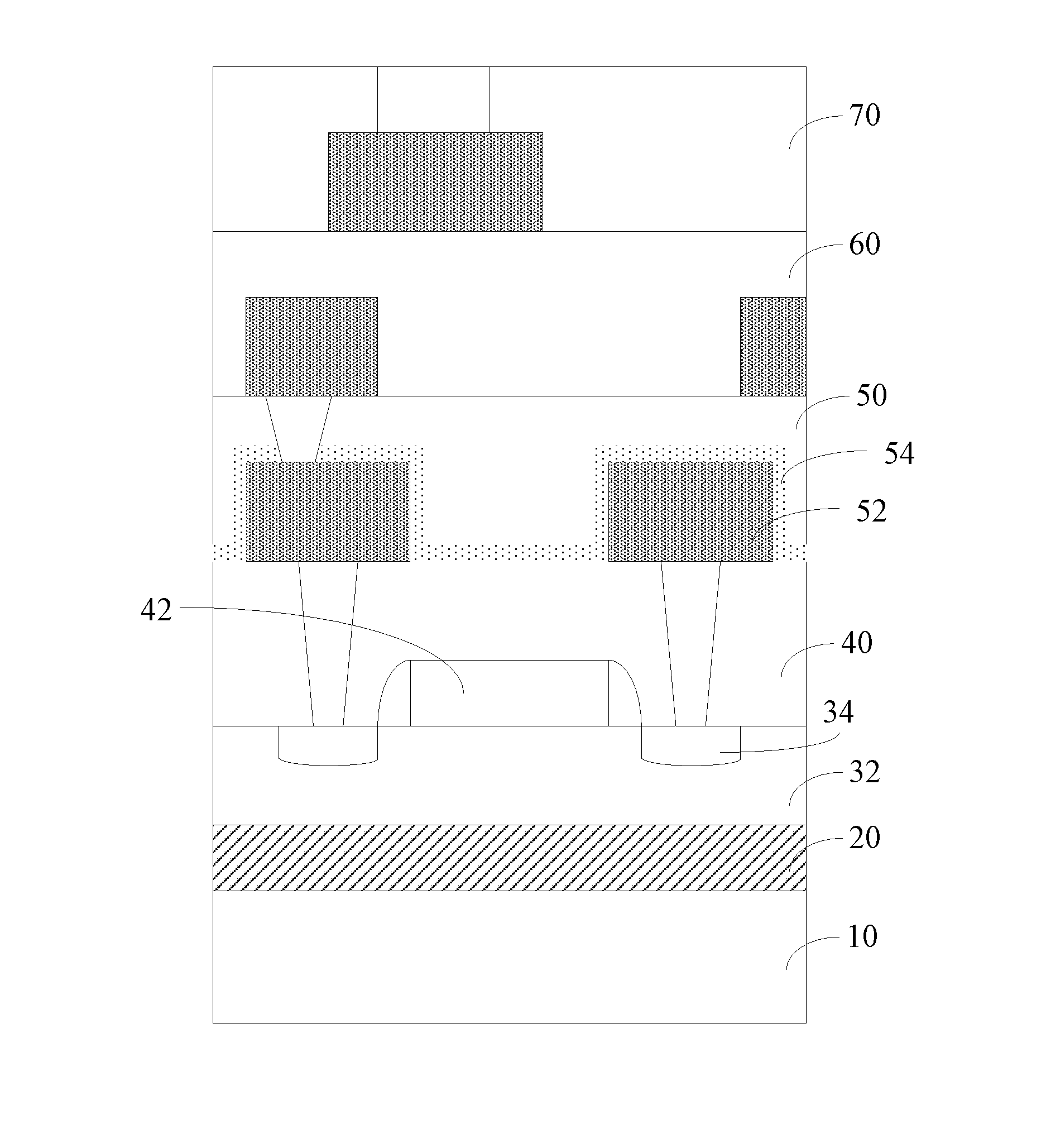
ActiveUS20170011957A1Improve performanceAvoid damageSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesIntegrity assessmentMetal interconnect
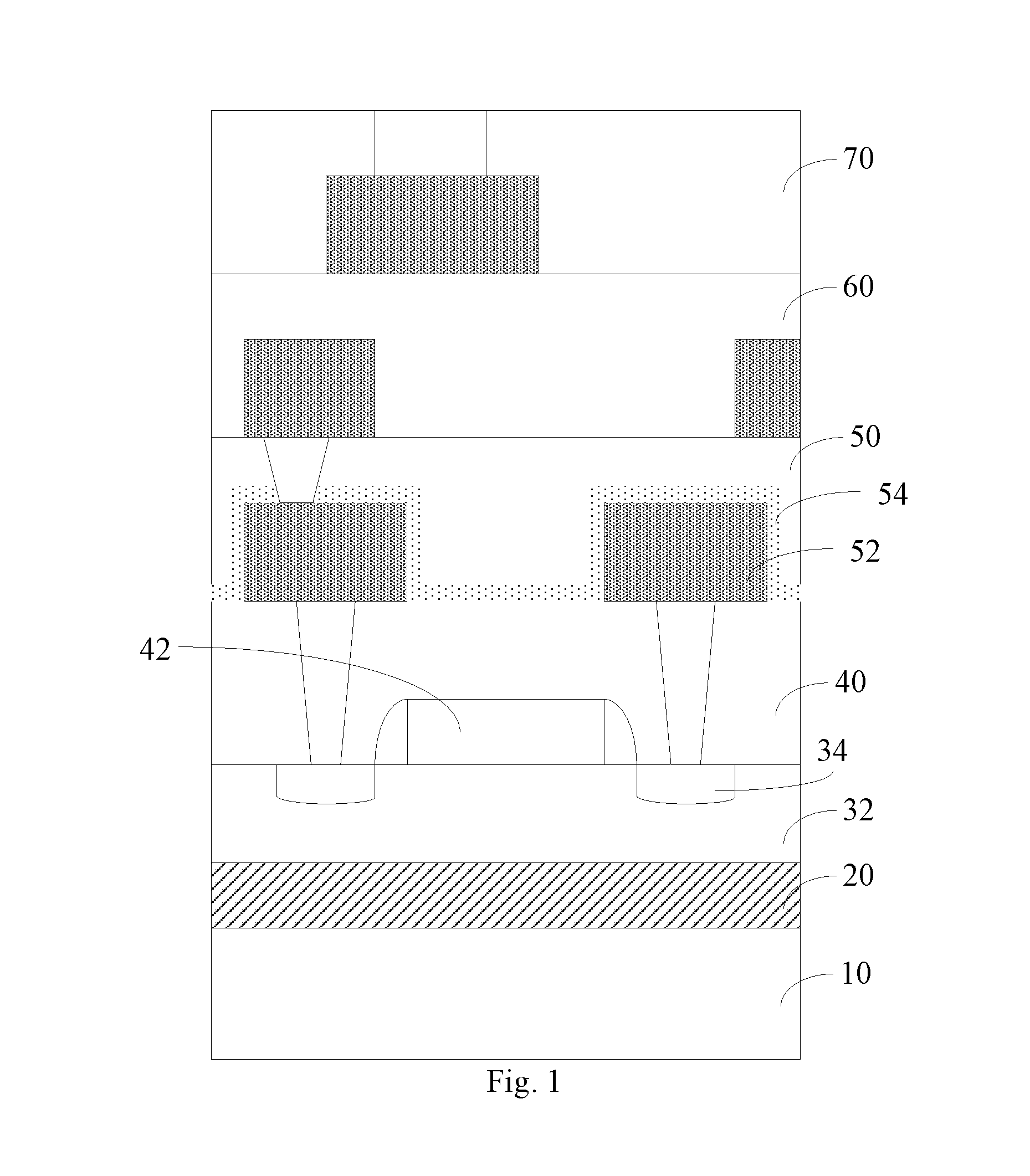
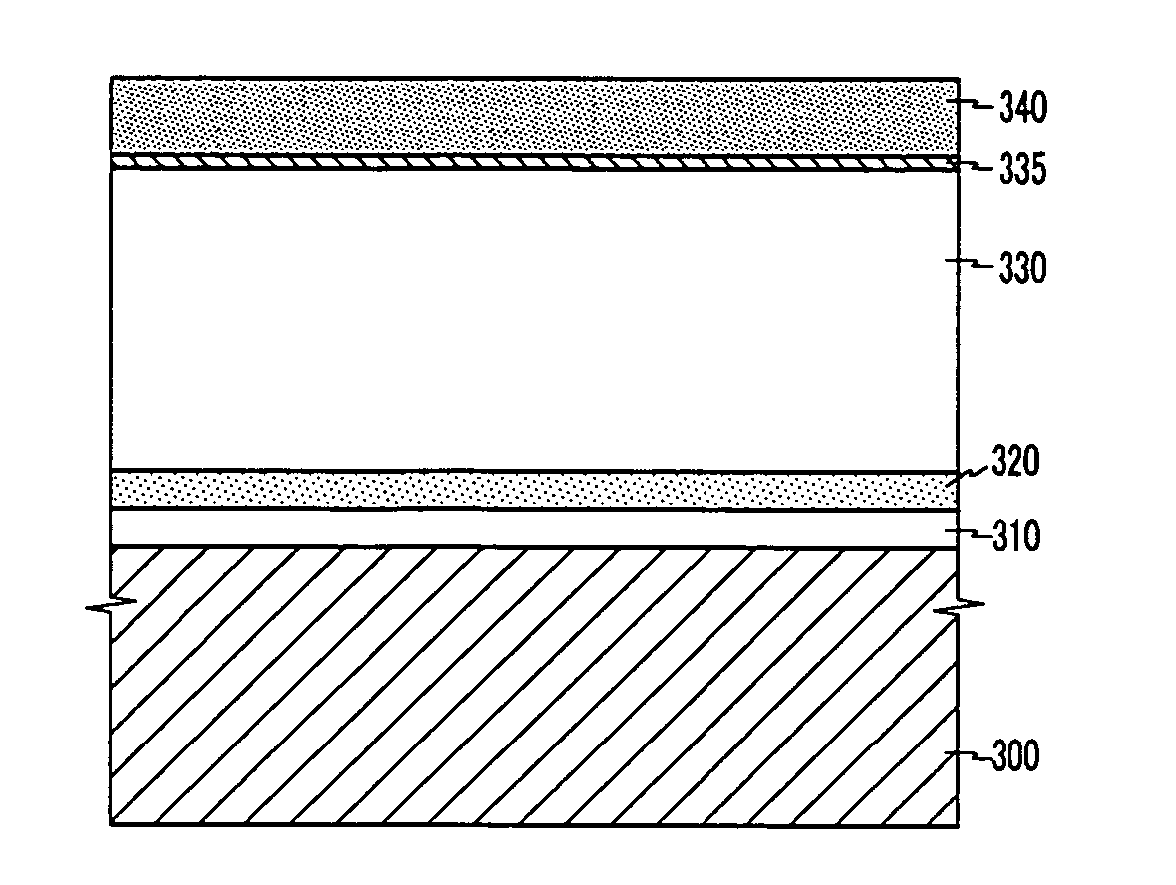
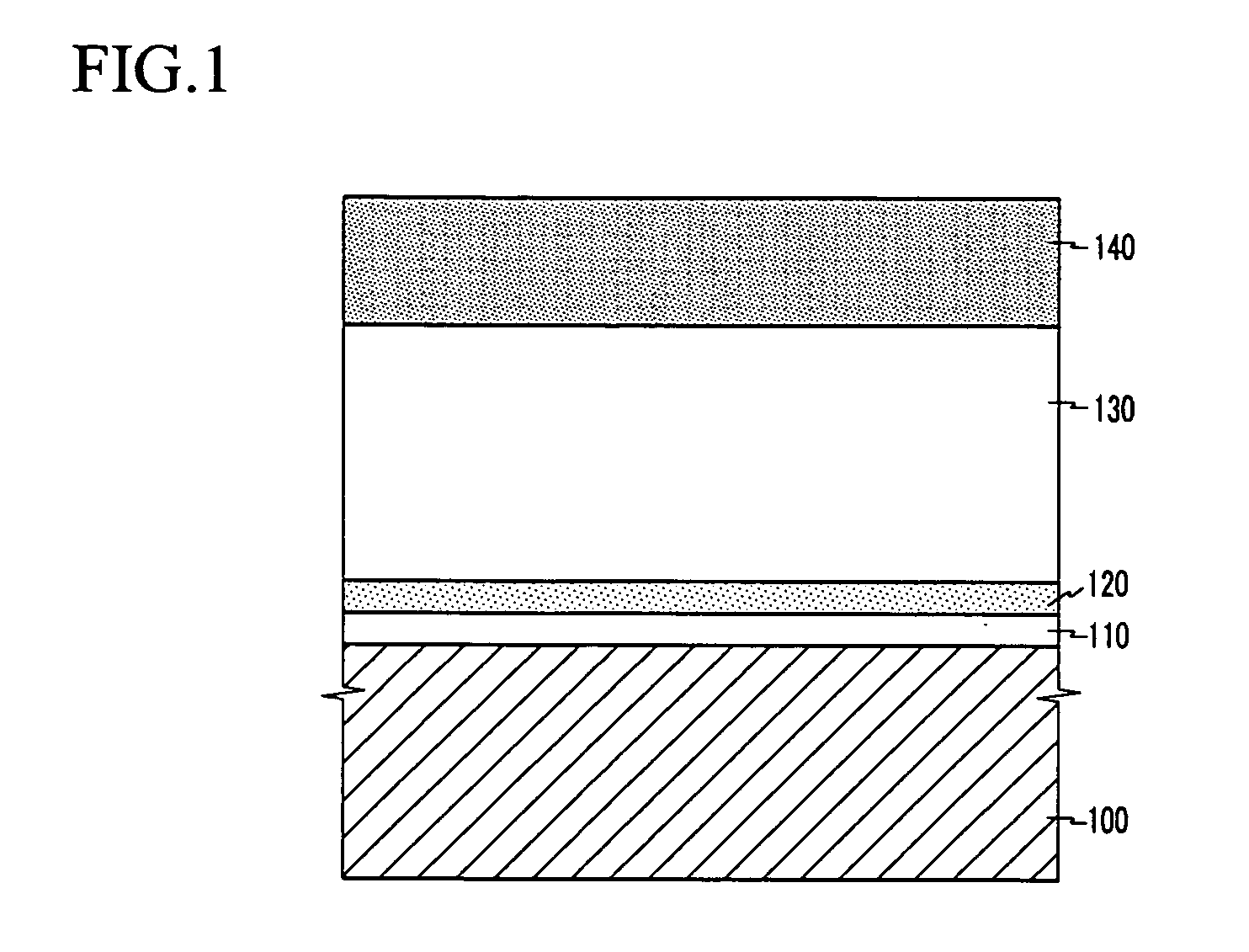
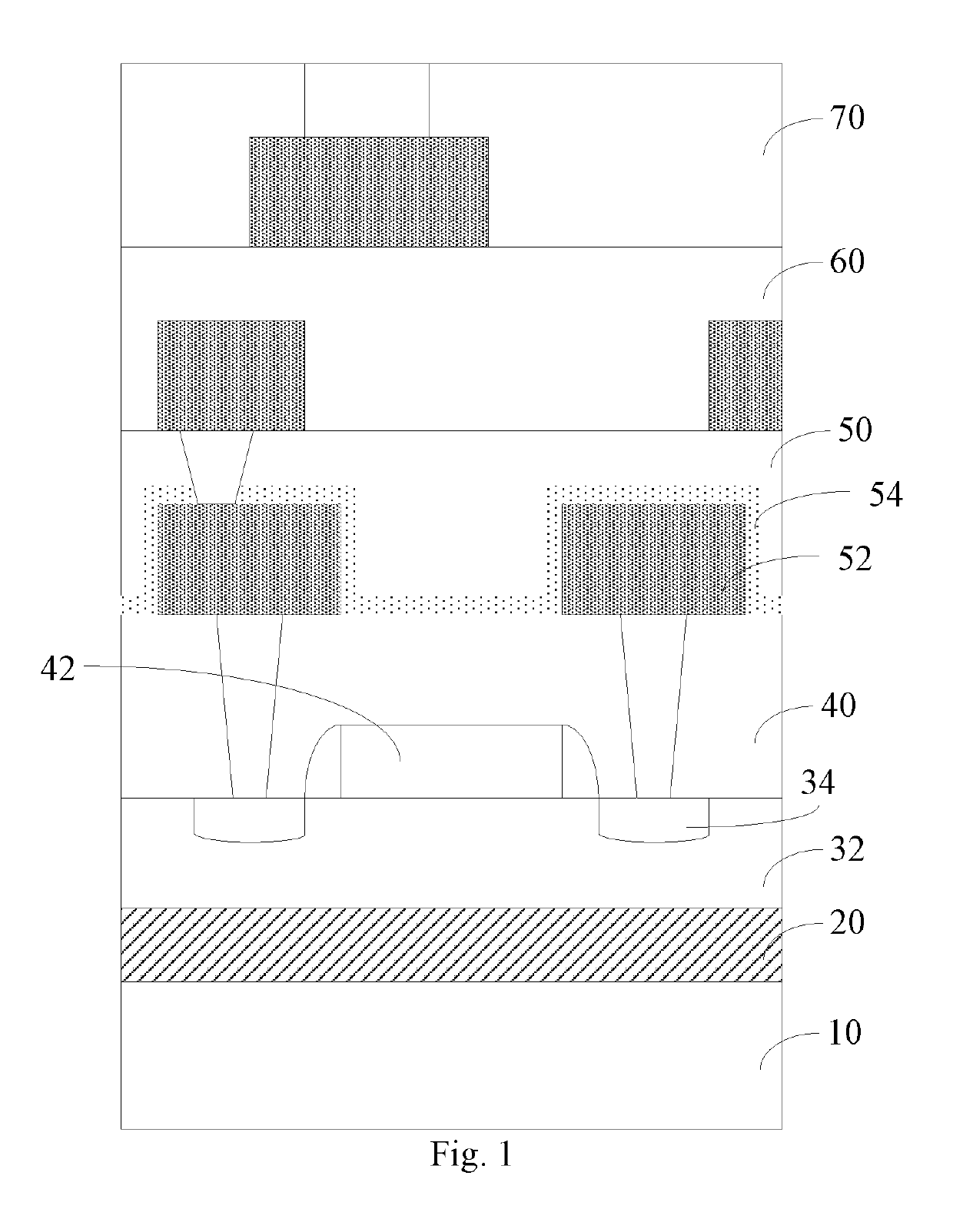
Provided is an intermetallic dielectric layer structure of a silicon-on-insulator device, comprising a silicon-rich oxide layer (54) covering a metal interconnect, a fluorine-silicon glass layer on the silicon-rich oxide layer, and a non-doped silicate glass layer on the fluorine-silicon glass layer; the thickness of the silicon-rich oxide layer (54) is 700 angstroms ±10%; the silicon-rich oxide layer having a greater thickness captures movable ions on an unsaturated bond, such that it is difficult for the movable ions to pass through the silicon-rich oxide layer, thus blocking the movable ions. The present invention has good performance in an integrity evaluation of the gate oxide layer, and avoids damage to the device caused by the aggregation of movable ions at an interface. Also provided are a silicon-on-insulator device and a method of manufacturing the intermetallic dielectric layer of the silicon-on-insulator device.
Owner:CSMC TECH FAB2 CO LTD
Process for effectively controlling air bubble producing in forming process of fluorine-containing silex glass interlayer medium layer
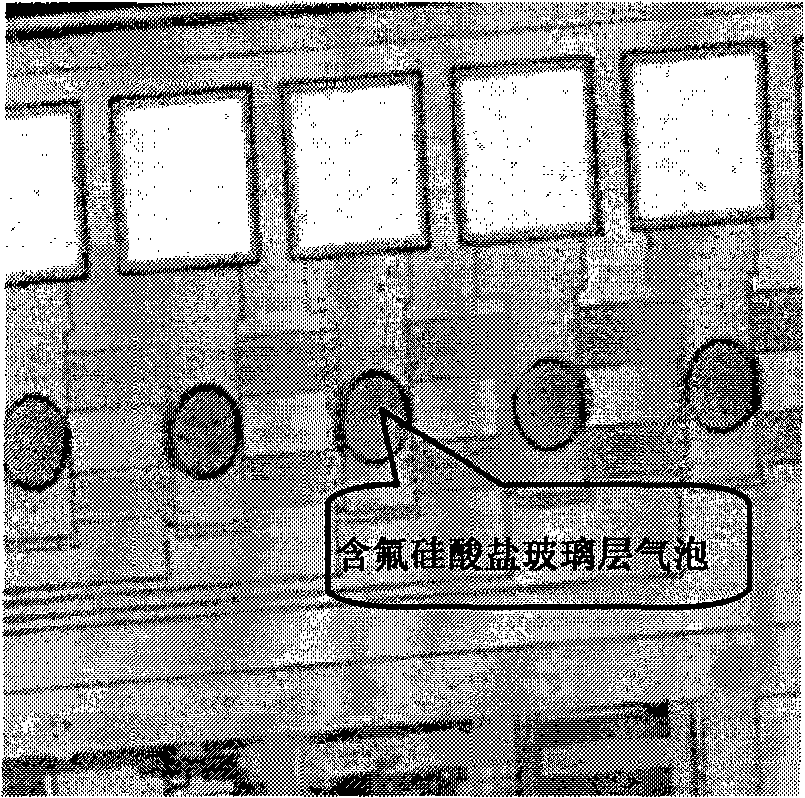
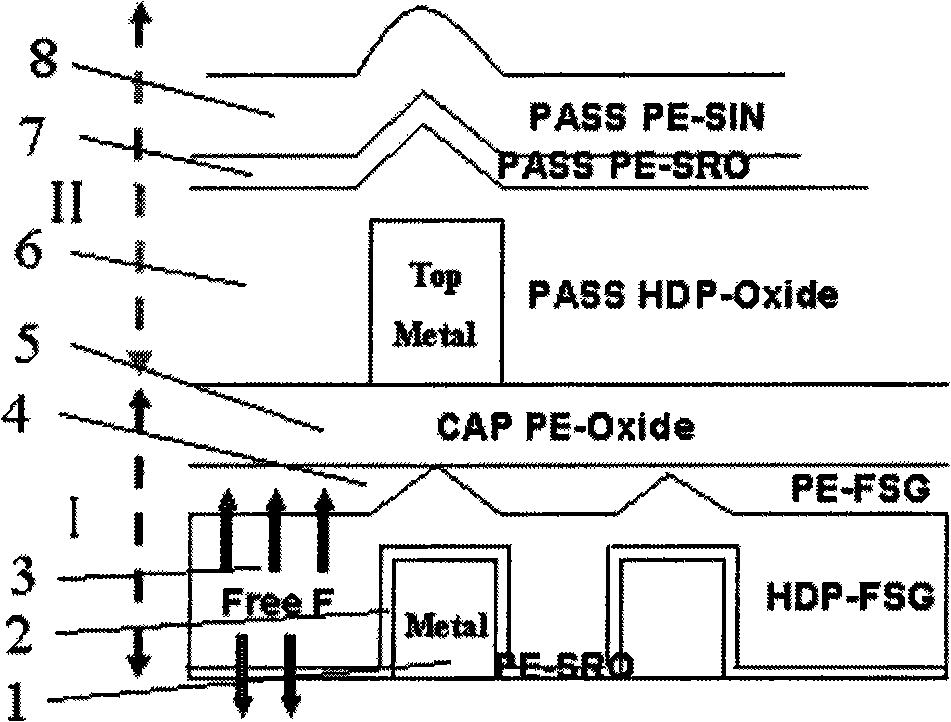
InactiveCN101289284ASemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGlass/slag layered productsFluorosilicate glassEngineering
According to a method of the invention that air bubble is effectively controlled to be produced in the formation of an inter-layer medium layer of fluorine-contained silicon glass, a final inter-layer medium layer (I) with three-layer structure is formed and an HDP-SRO layer (9) is formed on a formed PE-Oxide medium layer of a capacitor before a final protection layer (II) with three-layer structure is formed, which causes the existing final protection layer (II) formed with three-layer structure to become a final protection layer (III) with fourth-layer structure by adding the HDP-SRO layer (9), thus preventing fluorine ions from escaping from the inter-layer medium layer of the fluorine-contained silicon glass and improving the product percent of pass.
Owner:SEMICON MFG INT (SHANGHAI) CORP
Forming method of metal inter-lamination dielectric layer and metal inter-lamination dielectric layer
ActiveCN103094194APrevent spreading outGuaranteed filling qualitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesFluorosilicate glassFluoride
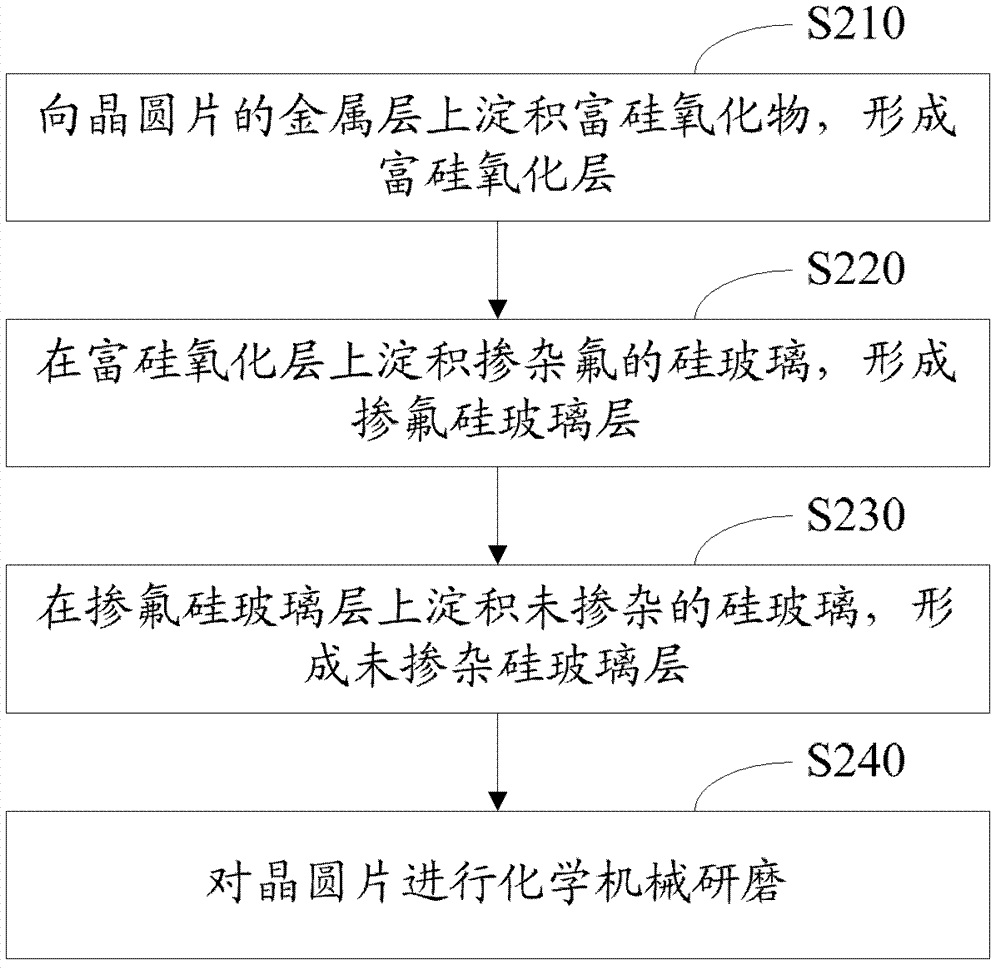
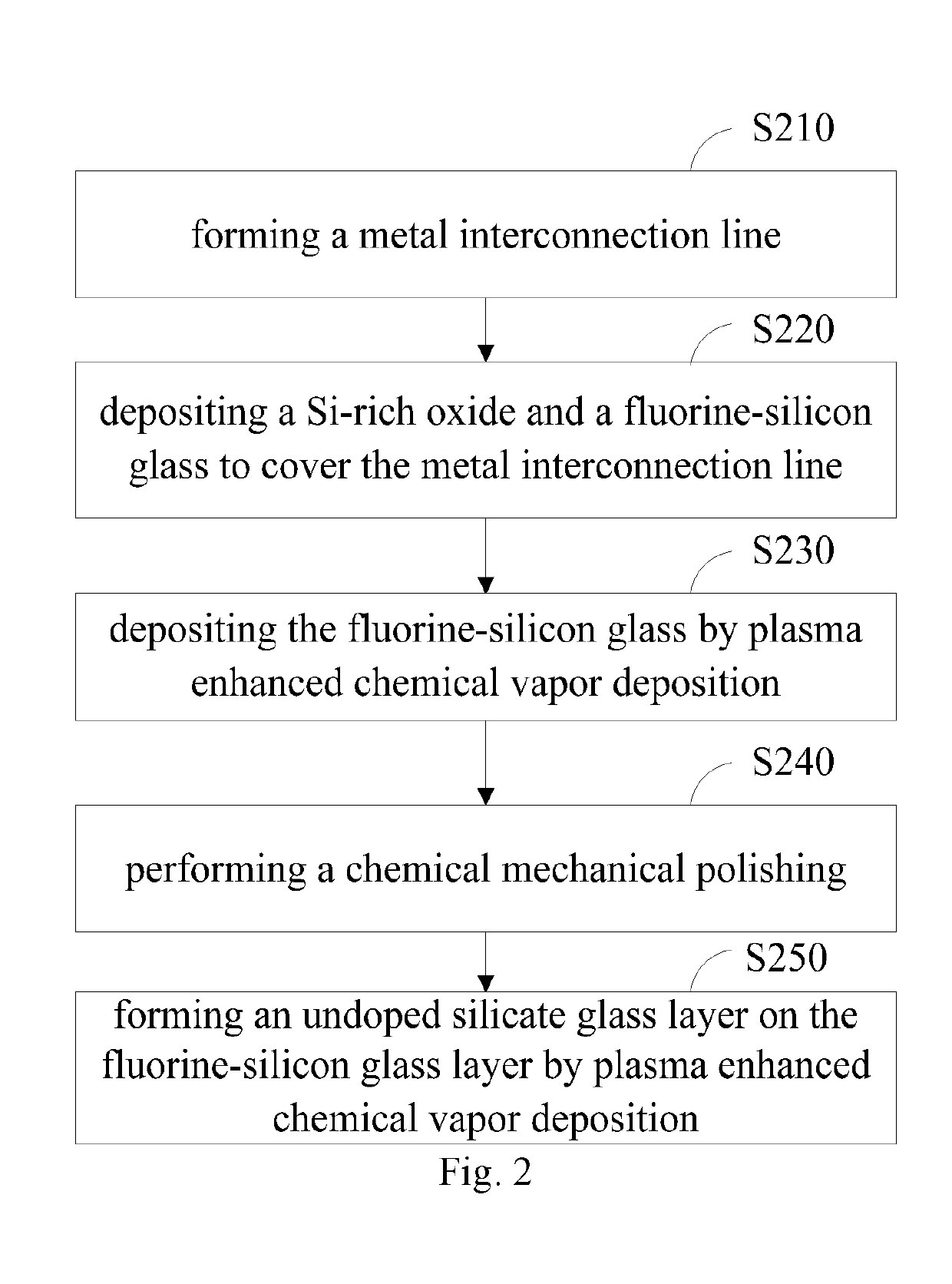
The invention relates to a forming method of a metal inter-lamination dielectric layer and further relates to the metal inter-lamination dielectric layer. The forming method of the metal inter-lamination dielectric layer comprises the following steps: step A, a silicon rich oxide is deposited on a metal layer of a wafer to form a silicon rich oxidation layer; step B, silicon glass with fluoride doped is deposited on the silicon rich oxidation layer to form a fluoride-doped silicon glass layer; step C, silicon glass which is of non-fluoride-doped is deposited on the fluoride-doped silicon glass layer to form a non- fluoride-doped silicon glass layer; and step D, the non-fluoride-doped silicon glass layer is formed by one side of the non-doped silicon glass layer and chemical mechanical lapping is conducted on the one side of the non-doped silicon glass layer. The fluoride-doped silicon glass is filled on the bottom of IMD (Inter-metal dielectric) and is good in filling performance, and meanwhile, non- fluoride-doped silicon glass is used as a blocking layer of the fluoride-doped silicon glass layer to prevent the fluoride from spreading. Filling quality is guaranteed, and meanwhile, required processes are less, cost is saved, and work efficiency is improved.
Owner:CSMC TECH FAB2 CO LTD
Inter-metal dielectric of semiconductor device and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveUS20060141785A1Improve mobilityPrevent peelingSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesFluorosilicate glassCopper
An exemplary manufacturing method of an inter-metal dielectric of a semiconductor device according to an embodiment of the present invention includes forming a first silicon-rich oxide (SRO) layer on a silicon substrate provided with or otherwise having a copper line layer therein, forming a plasma enhanced fluorosilicate glass (PEFSG) layer on the first SRO layer, plasma-treating the PEFSG layer, and forming a second SRO layer on the plasma-treated PEFSG layer. According to the present invention, the thickness of the second SRO layer of the inter-metal dielectric can be reduced. Consequently, process cost can be reduced, and the total thickness of the inter-metal dielectric can be reduced so as to lower the dielectric constant thereof, reduce the aspect ratio of any via holes that are subsequently formed in the inter-metal dielectric, and potentially increase the yield as a result of the reduced via hole aspect ratio.
Owner:DONGBU ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Self hardening glass carbomer composition
InactiveCN1809329AHigh hardnessReduce sensitivityImpression capsSurgical adhesivesFluorosilicate saltAcid water
The present invention relates to a self hardening glass carbomer composition obtainable by treating a fluorosilicate glass powder with: (a) a poly(dialkylsiloxane) having terminal hydroxyl groups, wherein the alkyl groups contain 1 to 4 carbon atoms, (b) an aqueous acid solution, and (c) separating the treated fluorosilicate glass powder from the aqueous acid solution. The glass carbomer compositions according to the invention have for example good toughness and strength and excellent fluoride release, In addition, the glass carbomer compositions according to the invention do not show shrinkage or expansion, an essential property for providing fillings for cavities having high strength and long durability. Moreover, the glass carbomer composition according to the present invention has a lower sensitivity towards abrasion and wear, a greater stiffness, a smoother surface, a better colourfastness, a better adherence to e.g. bone tissue and a lower water sensitivity.
Owner:健康玻璃基金会
Self hardening glass carbomer composition
InactiveUS20060217455A1Improve toughnessHigh strengthImpression capsSurgical adhesivesFluoride releaseHydroxy compound
The present invention relates to a self hardening glass carbomer composition obtainable by treating a fluorosilicate glass powder with: (a) a poly(dialkylsiloxane) having terminal hydroxyl groups, wherein the alkyl groups contain 1 to 4 carbon atoms, (b) an aqueous acid solution, and (c) separating the treated fluorosilicate glass powder from the aqueous acid solution. The glass carbomer compositions according to the invention have for example good toughness and strength and excellent fluoride release, In addition, the glass carbomer compositions according to the invention do not show shrinkage or expansion, an essential property for providing fillings for cavities having high strength and long durability. Moreover, the glass carbomer composition according to the present invention has a lower sensitivity towards abrasion and wear, a greater stiffness, a smoother surface, a better colourfastness, a better adherence to e.g. bone tissue and a lower water sensitivity.
Owner:STICHTING GLASS FOR HEALTH
Hard mask laminated structure and fabrication method thereof
ActiveCN104112698AAvoid it happening againImprove stabilitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingFluorosilicate glassDeposition process
The invention provides a hard mask laminated structure and a fabrication method thereof. The hard mask laminated structure comprises: a low-kappa medium hard film layer which is bonded onto the surface of a substrate; a fluorine and silicone glass layer which is bonded onto the surface of the low-kappa medium hard film layer; a metal hard film layer which is bonded onto the surface of the fluorine and silicone glass layer; and a shielding oxide layer which is bonded onto the surface of the metal hard film layer. According to the invention, the traditional tetraethoxysilane hard film layer HMTEOS is replaced with the fluorine and silicone glass layer, so the defect that the etching rate of the tetraethoxysilane hard film layer is slow compared with the low-kappa dielectric layer so as to form a overhanging structure can be overcome, and the generation of holes in the subsequent deposition process can be avoided, so that the deposition quality can be greatly improved, and the device stability and performance can be improved. According to the invention, the process is simple, so the structure and the method is suitable for being used in industry production.
Owner:SEMICON MFG INT (SHANGHAI) CORP
Silicon-on-insulator device and intermetallic dielectric layer structure thereof and manufacturing method
ActiveUS10276430B2Improve performanceAvoid damageSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesIntegrity assessmentMetal interconnect
Provided is an intermetallic dielectric layer structure of a silicon-on-insulator device, comprising a silicon-rich oxide layer (54) covering a metal interconnect, a fluorine-silicon glass layer on the silicon-rich oxide layer, and a non-doped silicate glass layer on the fluorine-silicon glass layer; the thickness of the silicon-rich oxide layer (54) is 700 angstroms .+-.10%; the silicon-rich oxide layer having a greater thickness captures movable ions on an unsaturated bond, such that it is difficult for the movable ions to pass through the silicon-rich oxide layer, thus blocking the movable ions. The present invention has good performance in an integrity evaluation of the gate oxide layer, and avoids damage to the device caused by the aggregation of movable ions at an interface. Also provided are a silicon-on-insulator device and a method of manufacturing the intermetallic dielectric layer of the silicon-on-insulator device.
Owner:CSMC TECH FAB2 CO LTD
Method for eliminating static electricity of metal conducting layer to complete etching
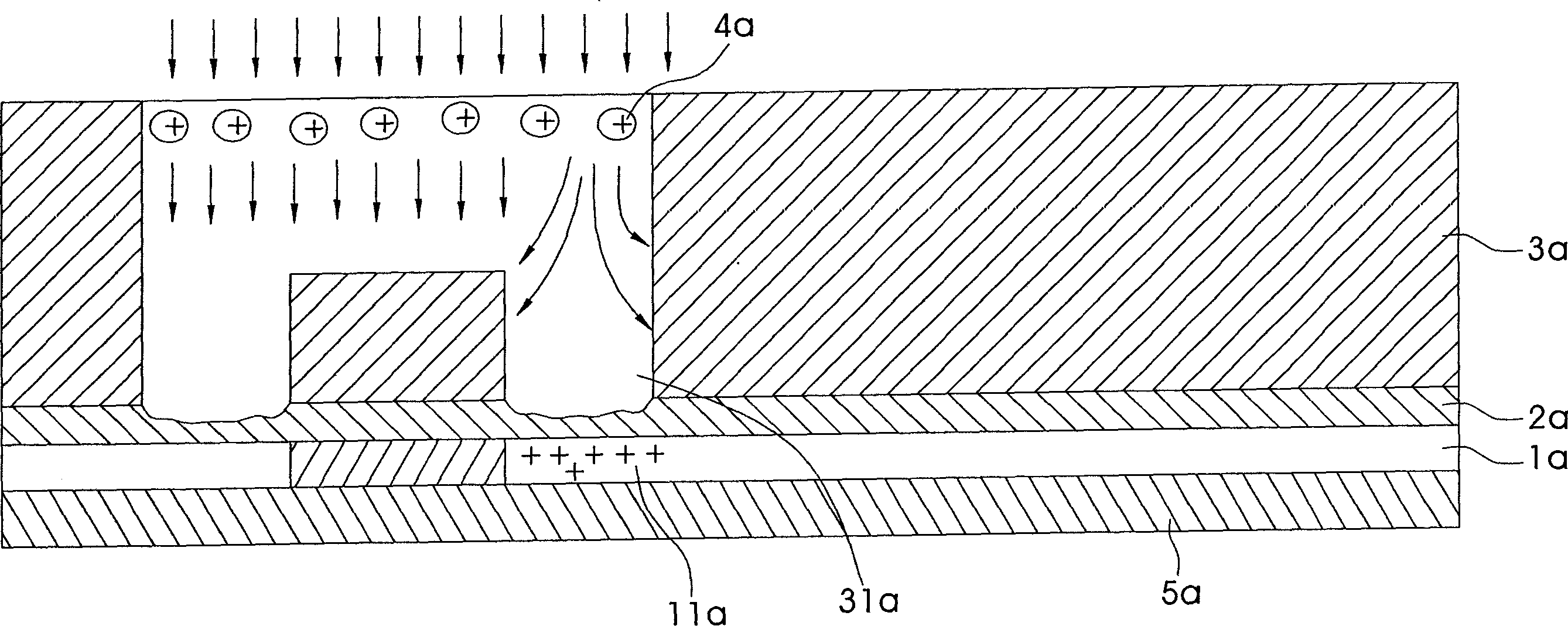
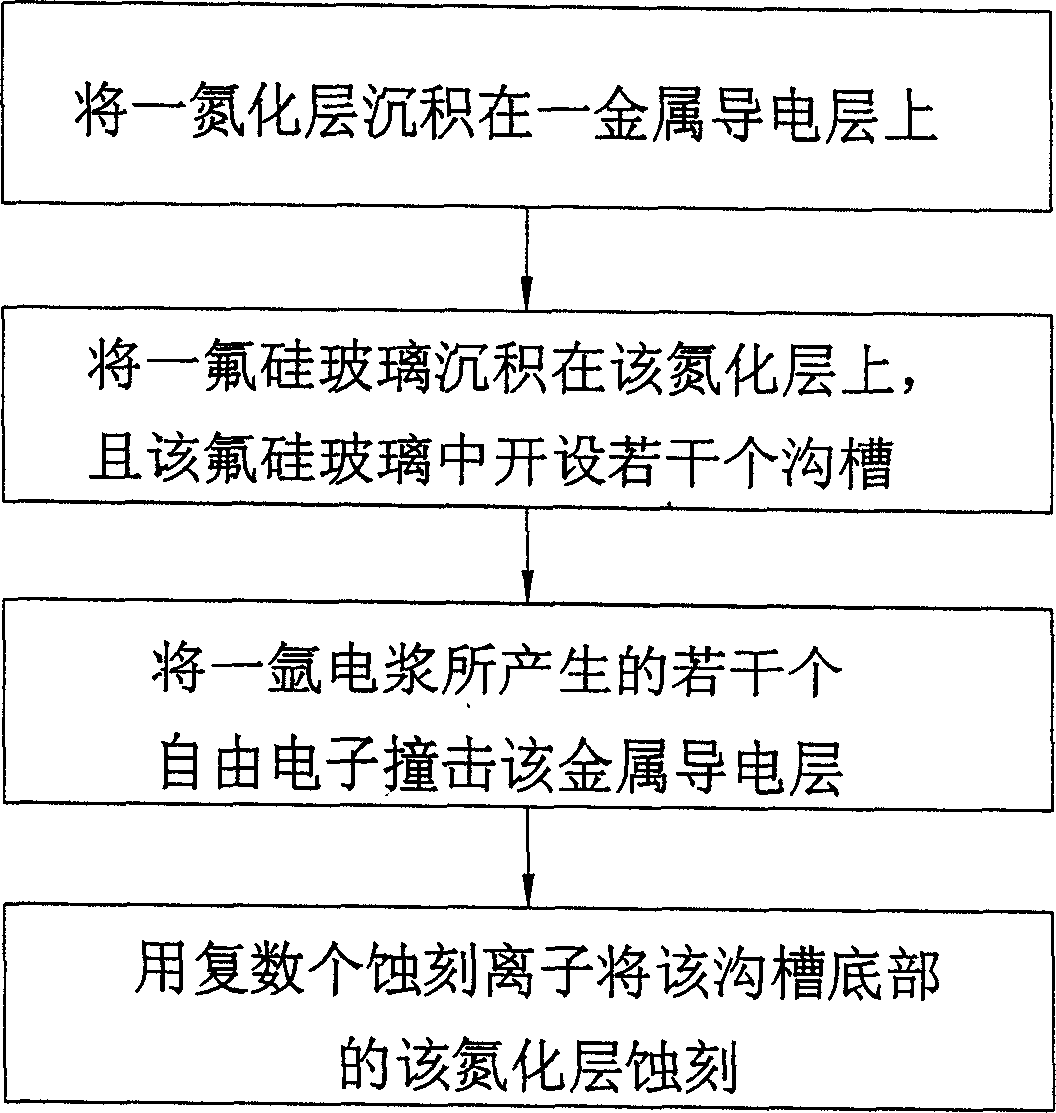
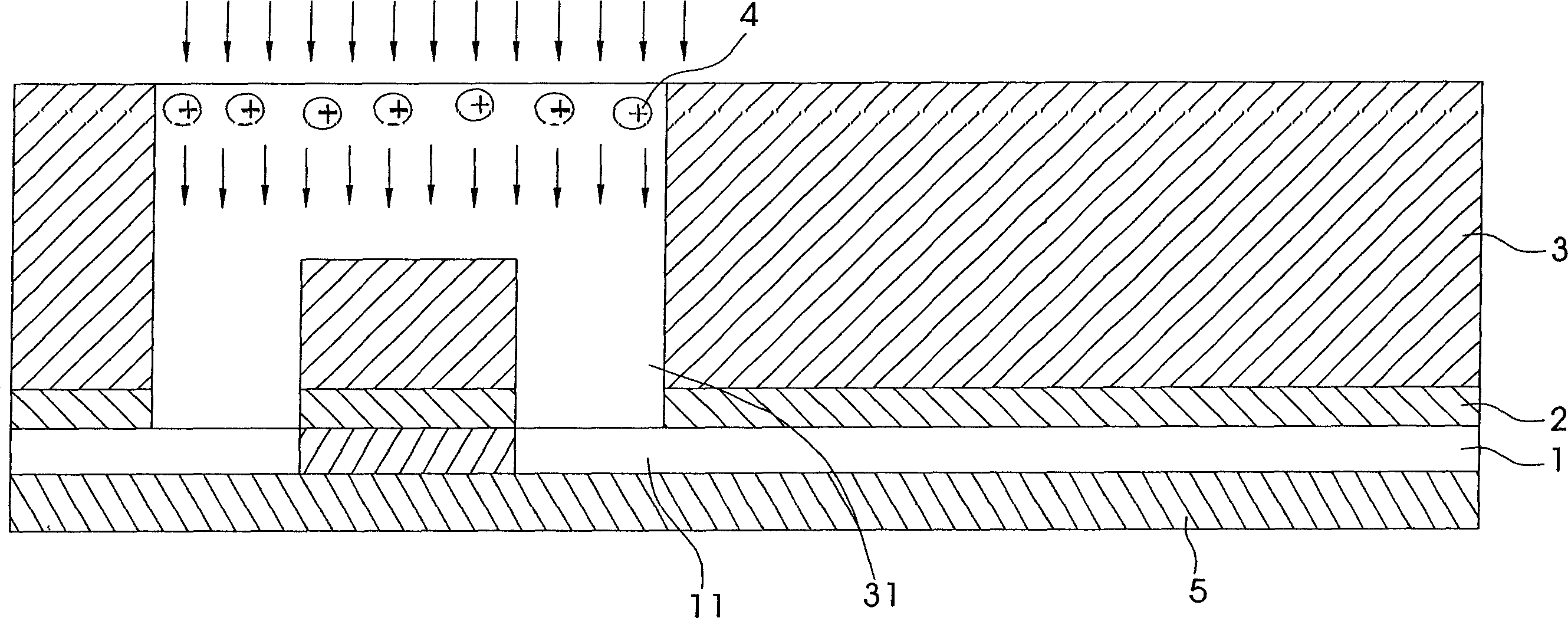
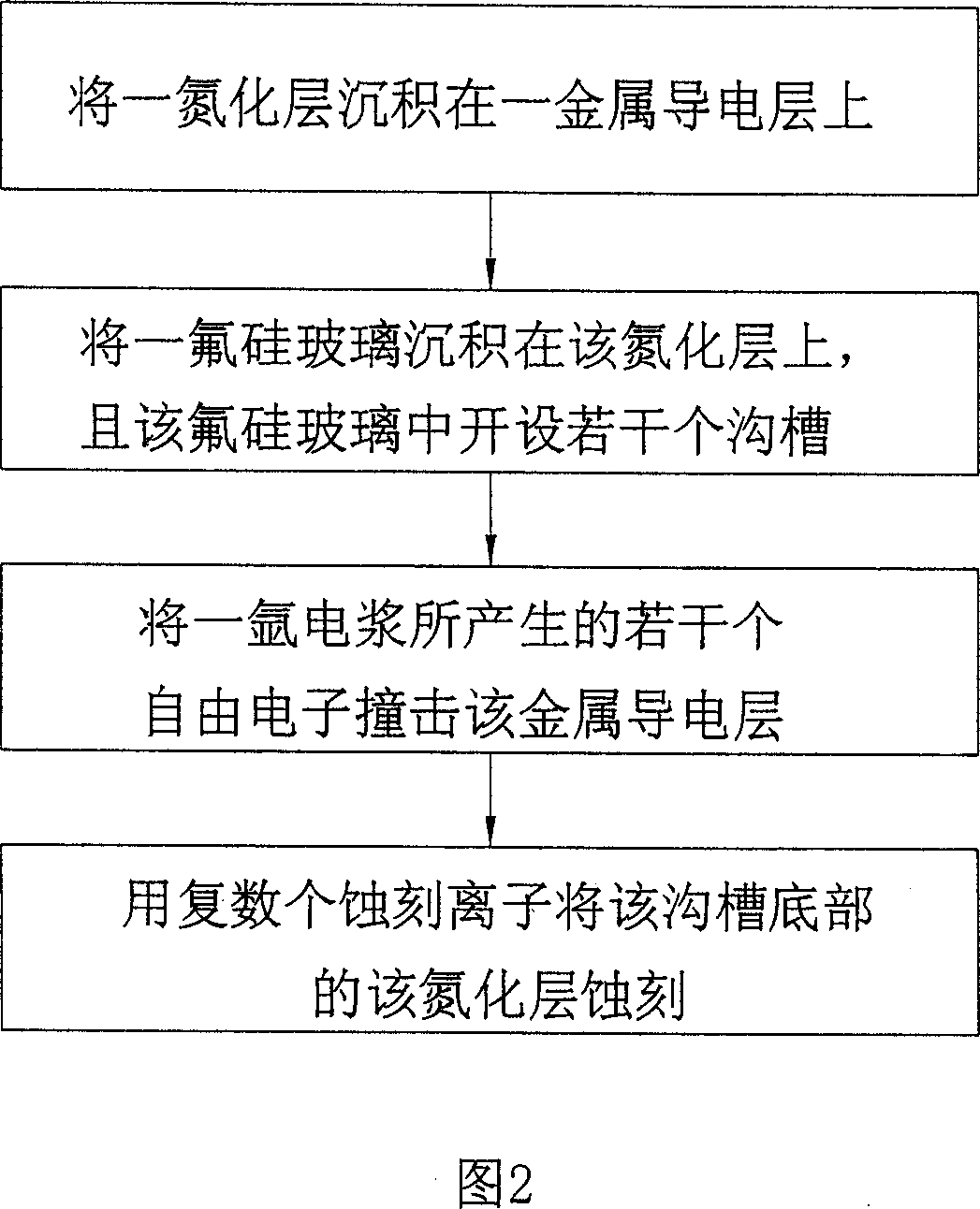
ActiveCN1635614ASolve the problem of incomplete etchingImprove yieldSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEtchingFluorosilicate glass
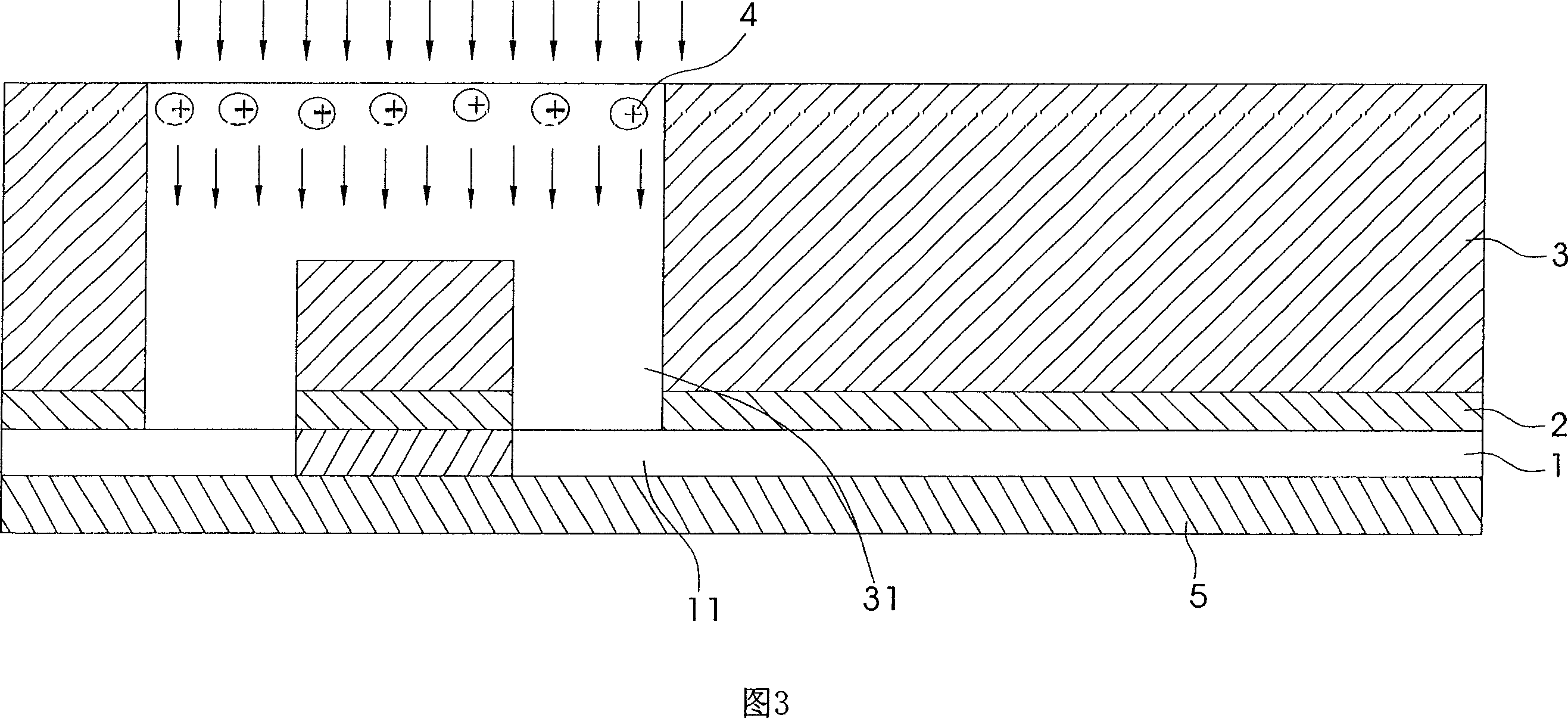
This invention relates to a method to remove metal conductive layer static complete etching, which comprises the following steps: a, depositing a metal conductive layer on the on nitrogen layer; b, depositing a fluorin and silicon glass on the nitrogen layer with several round holes and grooves opened; c, using the electric plasm with high gas pressure and low density generated free electrons impacting the metal conductive layer; d, etching the nitrogen layer on the round holes and groove bottom by several etching ions.
Owner:SEMICON MFG INT (SHANGHAI) CORP +1
Manufacturing method of semiconductor device
ActiveCN102815663BPerformance impactStructural solutionDecorative surface effectsChemical vapor deposition coatingCMOSRough surface
The invention discloses a manufacturing method for a semiconductor device. The method comprises the steps of providing a semiconductor substrate provided with a CMOS device therein, forming a fluorine silica glass layer on the upper surface of the semiconductor substrate; forming a silicon-rich material layer on the fluorine silica glass layer; and forming an MEMS device on the silicon-rich material layer. By forming the silicon-rich material layer after the manufacture of the CMOS device and before the manufacture of the MEMS device, problems that structural holes and rough surfaces which are resulted from bubbles formed by fluorine aggregation in a heat treatment process with a process temperature higher than 400 DEG C and relatively long heat-preservation time can be solved; and thus influences on subsequent processes and performances of the device can be prevented effectively.
Owner:SEMICON MFG INT (SHANGHAI) CORP
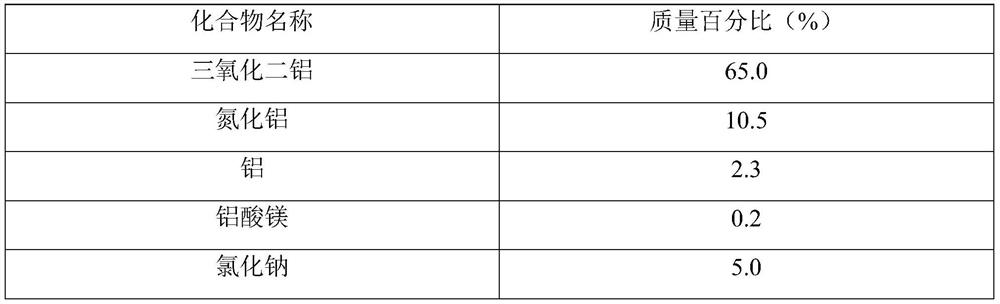
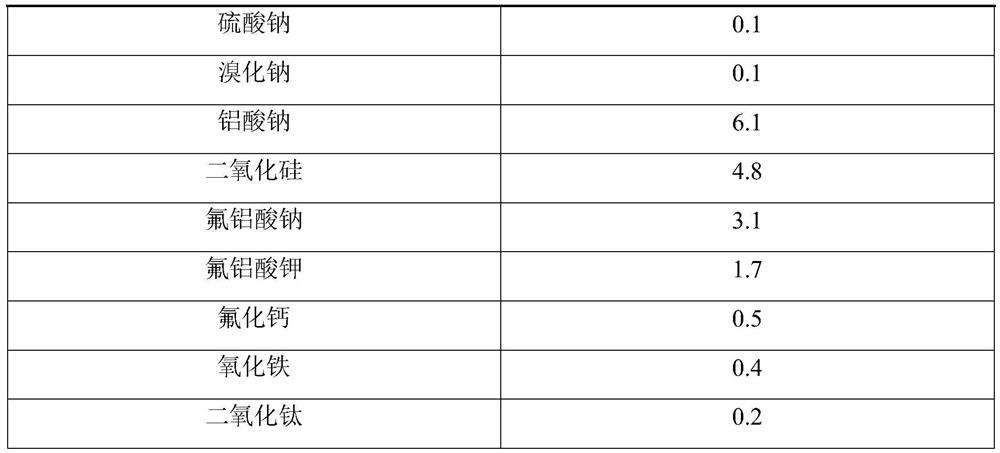
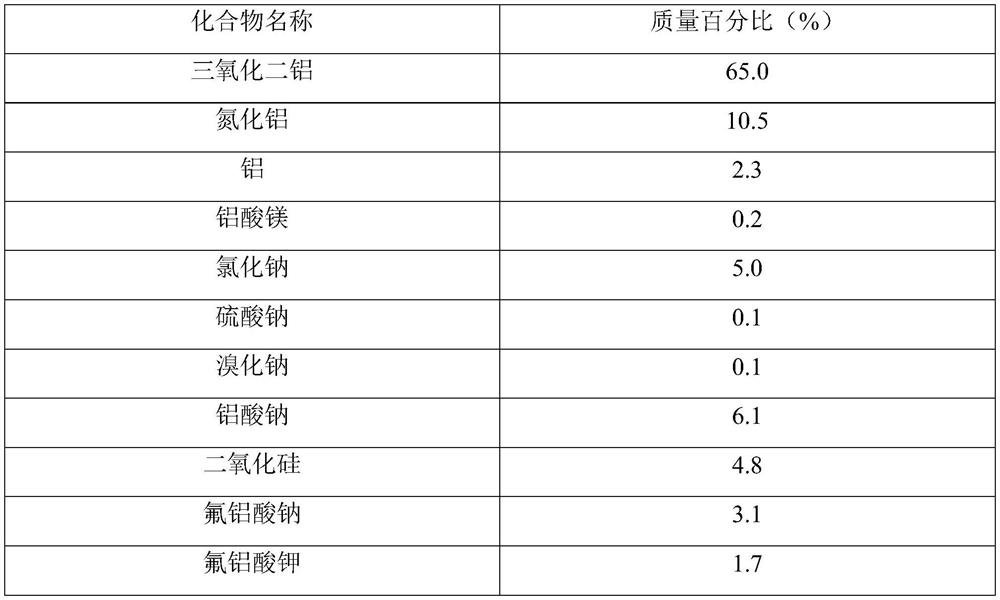
Sponge brick produced from aluminum ash and preparation process thereof
PendingCN114105612AEffective consumptionEfficient use ofCeramic materials productionCeramicwareSocial benefitsFluorosilicate salt
Owner:淄博天之润生态科技有限公司
Method for eliminating static electricity of metal conducting layer to complete etching
InactiveCN100345262CSolve the problem of incomplete etchingImprove yieldSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEtchingFluorosilicate glass
This invention relates to a method to remove metal conductive layer static complete etching, which comprises the following steps: a, depositing a metal conductive layer on the on nitrogen layer; b, depositing a fluorin and silicon glass on the nitrogen layer with several round holes and grooves opened; c, using the electric plasm with high gas pressure and low density generated free electrons impacting the metal conductive layer; d, etching the nitrogen layer on the round holes and groove bottom by several etching ions.
Owner:SEMICON MFG INT (SHANGHAI) CORP +1
A high numerical aperture all-solid-state fluorotellurite glass optical fiber, preparation method and application thereof
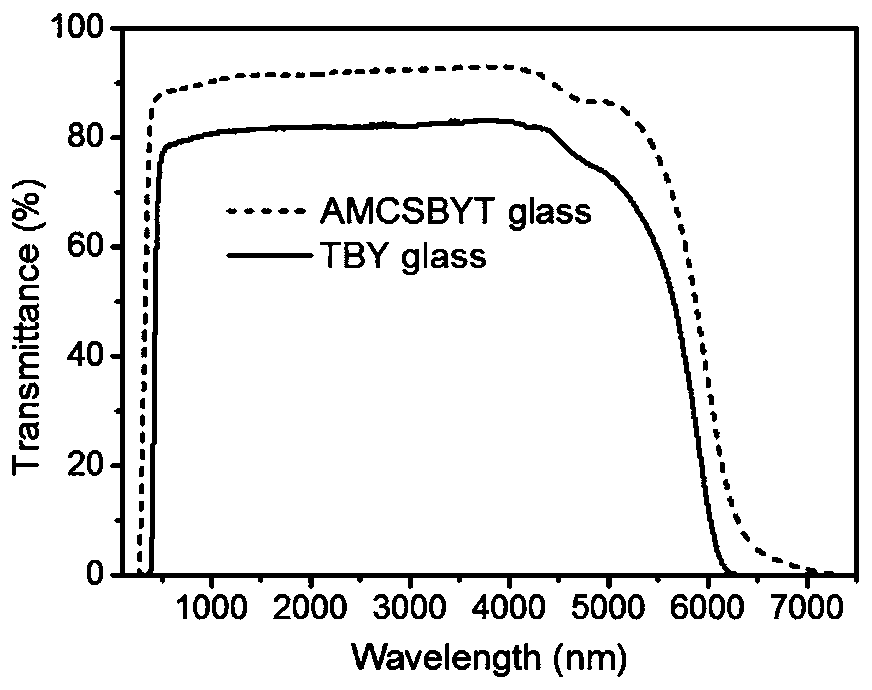
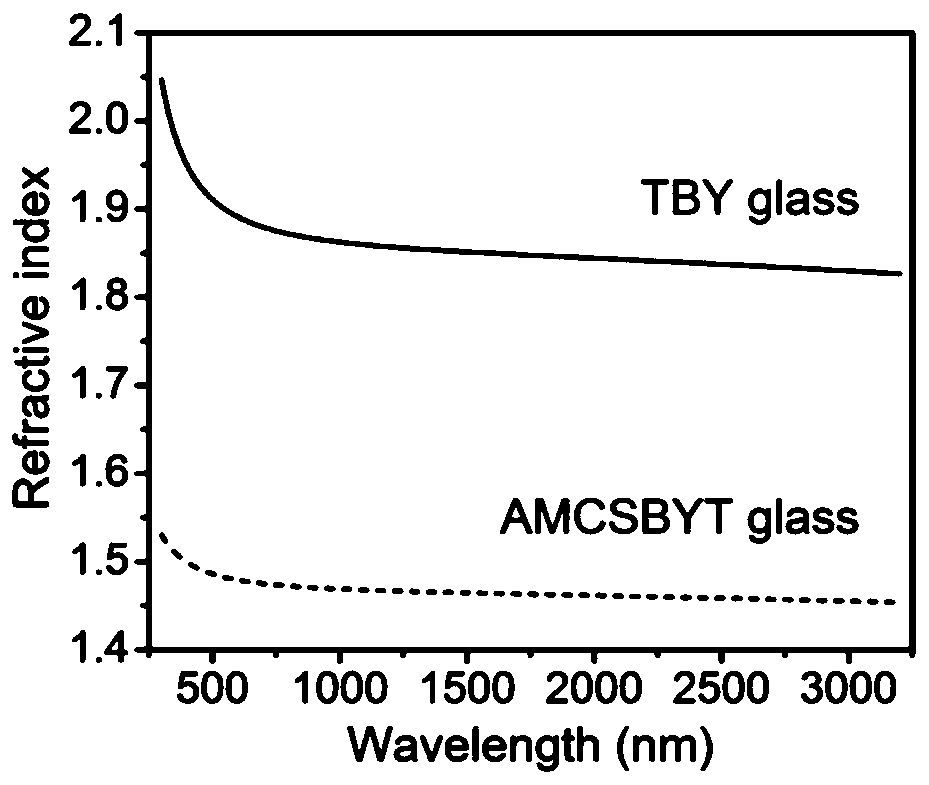
The invention discloses a high-numerical-aperture all-solid-state fluorotellurite glass optical fiber, as well as a preparation method and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of special glass optical fibers. The high-numerical-aperture all-solid-state fluorotellurite glass optical fiber comprises a fiber core and a cladding layer, wherein the fiber core is made of tellurium yttrium barium (TBY), the diameter of the fiber core is 0.5 to 100 microns, and the fiber core comprises TeO2, BaF2 and Y2O3; and the cladding layer is made of aluminum magnesium calcium strontium barium yttrium tellurium (AMCSBYT), the thickenss is 1 to 200 microns, and the cladding layer comprises AlF3, MgF2, CaF2, SrF2, BaF2, YF3 and TeO3. The matrix glass is molten in a glove box protected by nitrogen, so that the low hydroxyl content of the prepared glass sample is guaranteed, and the optical fiber is prepared with a rod tube method. The prepared optical fiber has relatively high numerical aperture and relatively low limited loss. The chromatic dispersion and the non-linearity of the optical fiber can be regulated and controlled on a large scale by changing the core diameter size of the optical fiber. The optical fiber serves as a non-linear medium, and an intermediate infrared super-continuous light source with spectral bandwidth coverage being 0.35 to 5.5 microns and output average power being tens of watts can be obtained.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
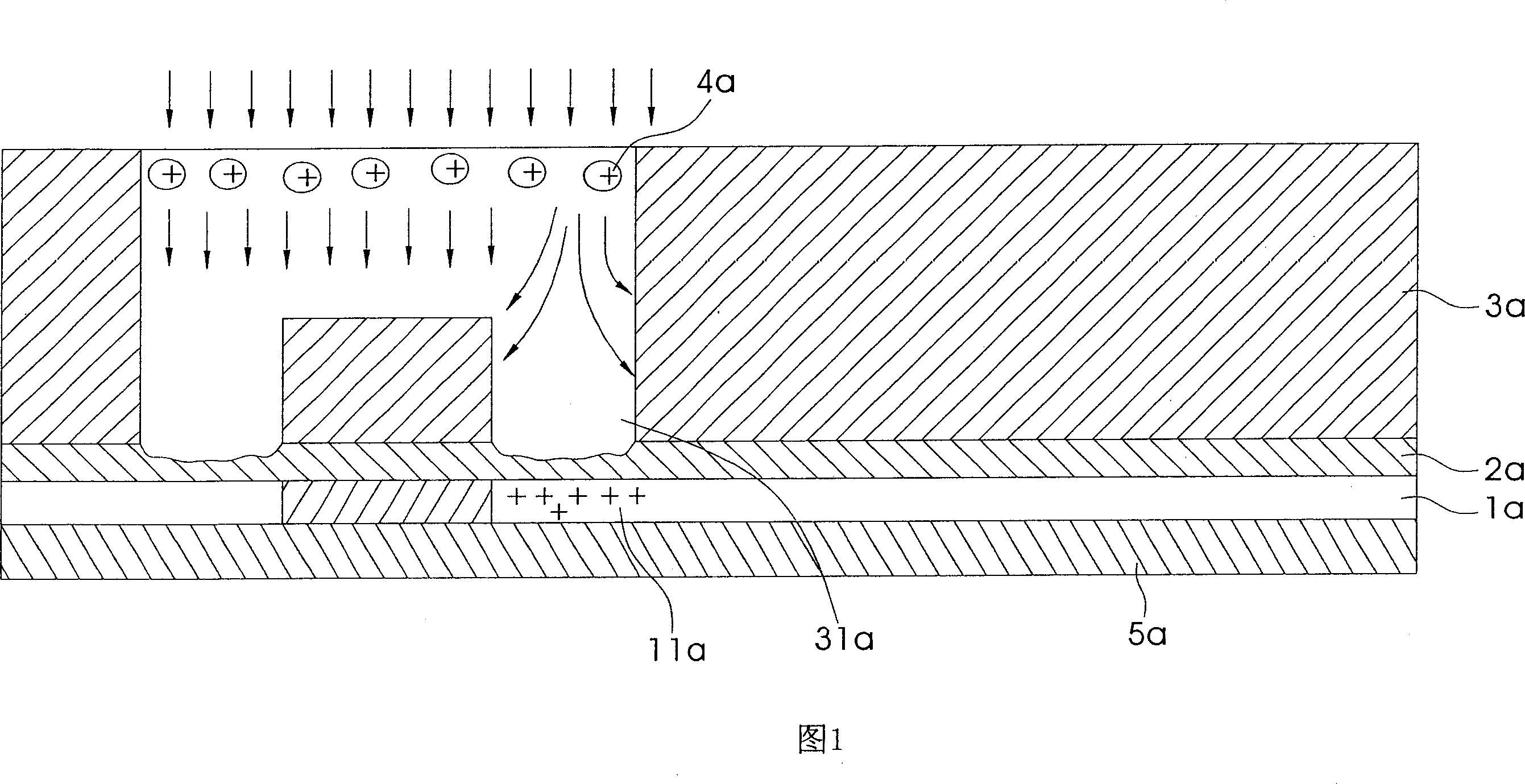
A method for suppressing crystal defects of fluorosilicate glass
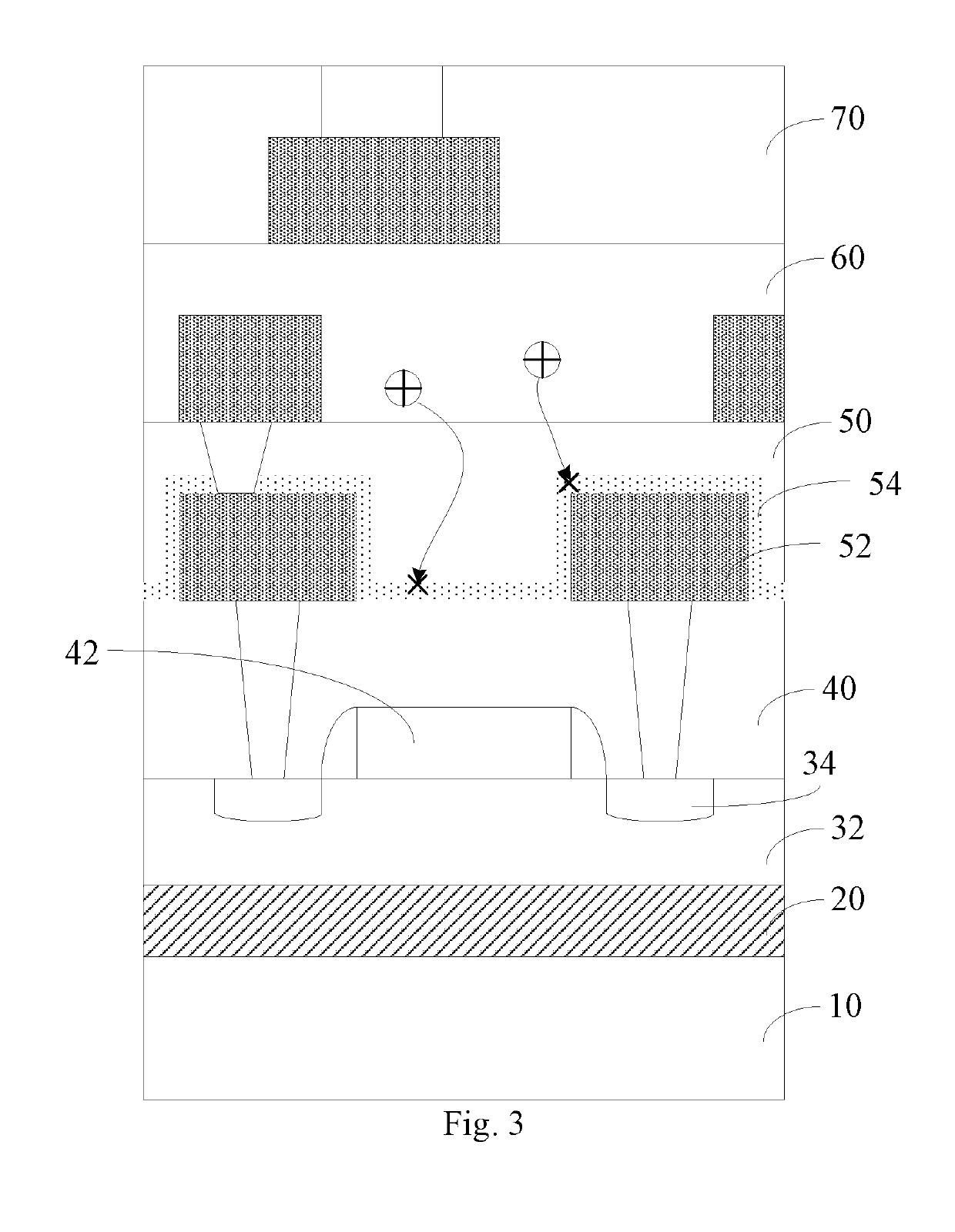
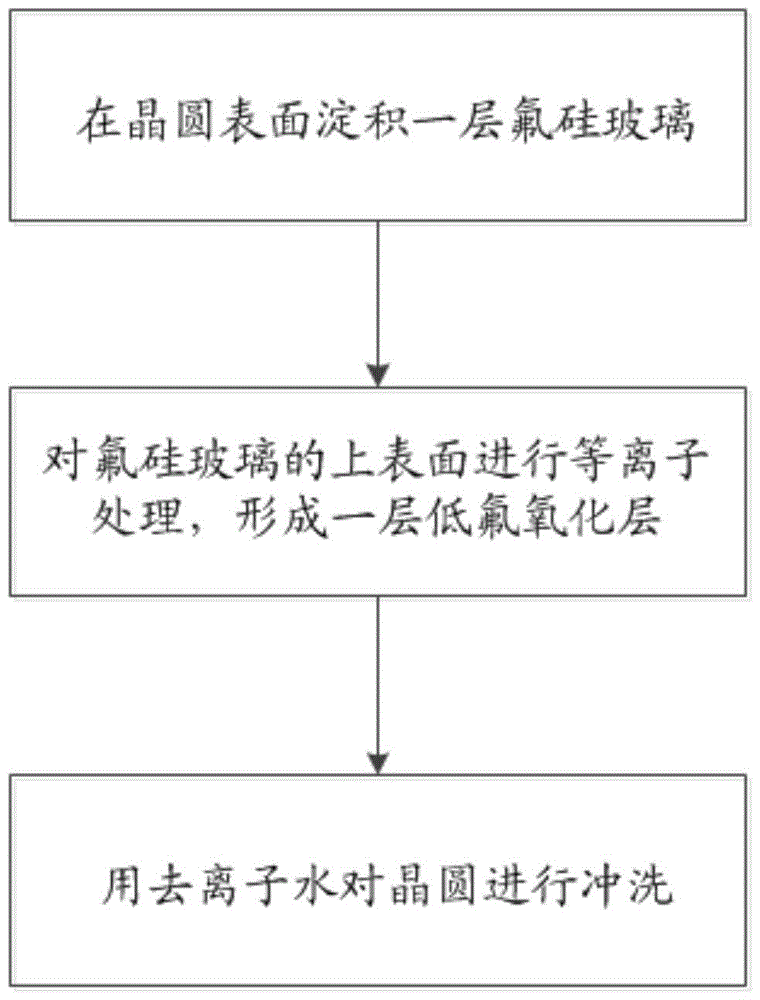
ActiveCN103871966BAvoid defectsImprove reliabilitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHydrofluoric acidFluorosilicate glass
A method for suppressing crystal defects of fluorosilicate glass, comprising the following steps: Step 1, depositing a layer of fluorosilicate glass on the surface of a wafer; Step 2, performing plasma treatment on the upper surface of the fluorosilicate glass to form a layer of low-fluorine oxide layer; Step 3, rinsing the wafer with deionized water; Step 1 and Step 2 are carried out in the same chemical vapor deposition reaction chamber. The beneficial effects of the present invention are: after the deposition of the fluorosilicate glass, plasma treatment is carried out in the same cavity to reduce the fluorine on the upper surface of the fluorosilicate glass, suppress its hydrophilicity, and prevent crystal defects, and at the same time use deionized water and a small amount of surface The fluorine reacts to form hydrofluoric acid, which is then washed out of the wafer, further consolidating the effect and improving the reliability of the device.
Owner:WUHAN XINXIN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Luminescent glass ceramic doped with multiple rare earth ions and capable of up and down-conversion to ultraviolet light and preparation method thereof
The invention provides luminescent glass ceramic doped with multiple rare earth ions and capable of up and down-conversion to ultraviolet light and a preparation method thereof; the glass ceramic is fluorosilicate glass ceramic doped with at least four rare earth ions, wherein on a basis of oxide, the molar content of the rare earth ions is 1% to 20% of the total amount of the glass ceramic; the glass ceramic can realize up conversion of infrared light and visible light into ultraviolet light, and also realize down conversion of short-wave radiation into ultraviolet light.
Owner:何森
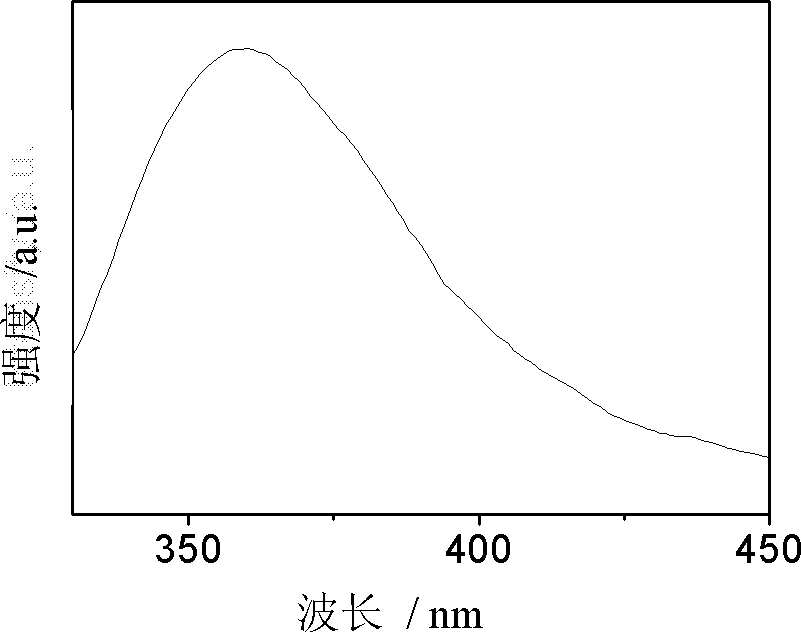
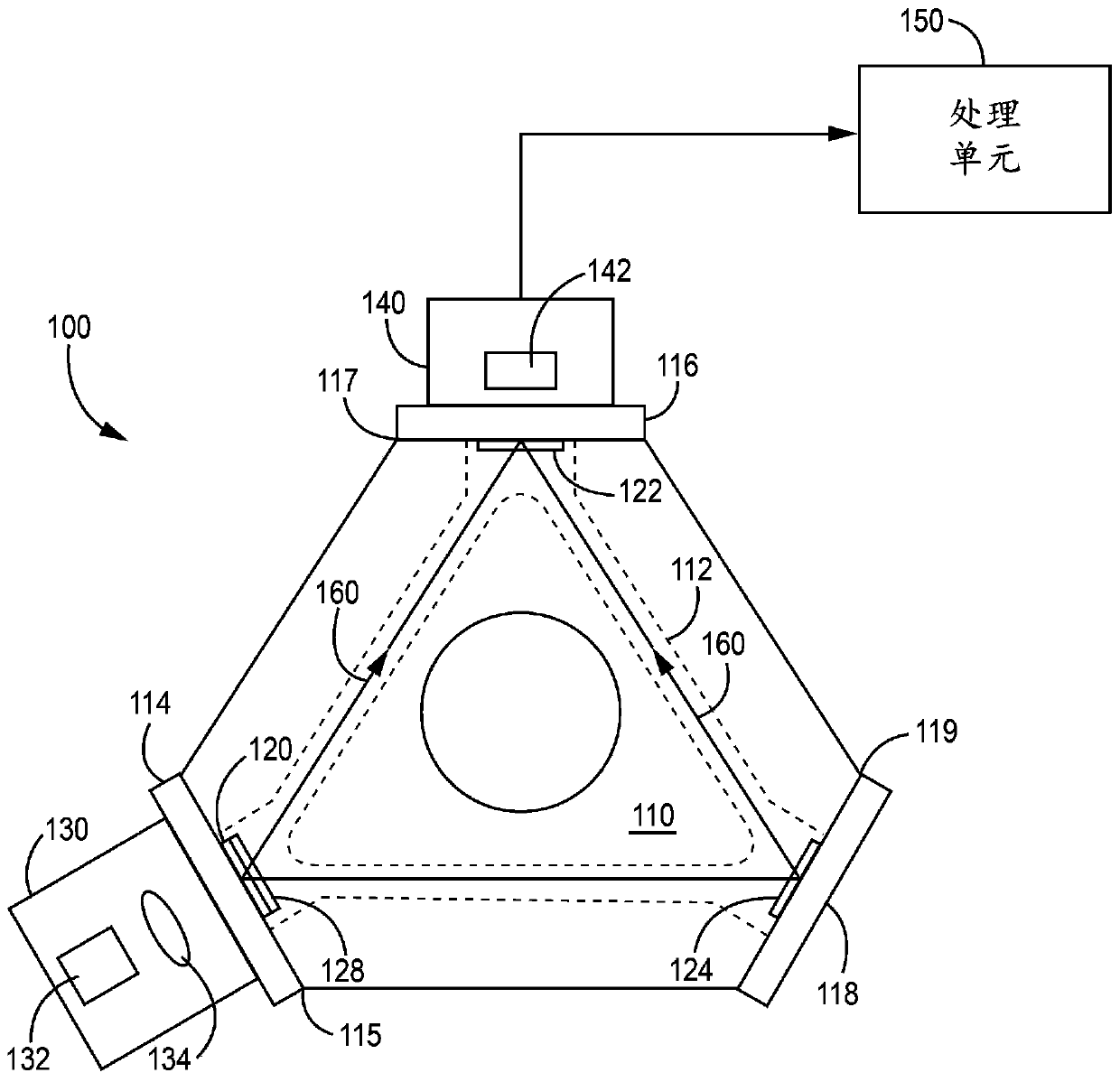
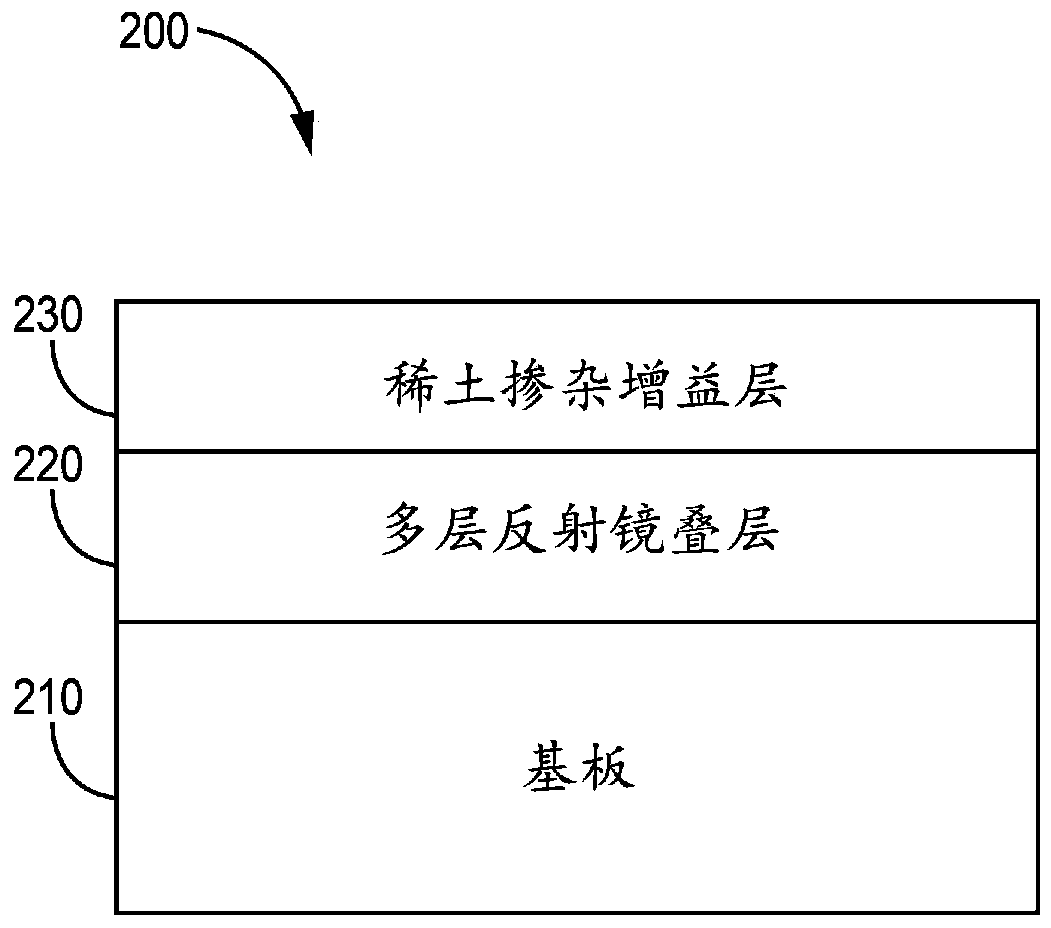
Solid state ring laser gyroscope using rare-earth gain dopants in glassy hosts
The invention discloses a solid state ring laser gyroscope using rare-earth gain dopants in glassy hosts. The invention provides a solid state ring laser gyroscope which comprises a laser block including a resonant ring cavity having an optical closed loop pathway; a plurality of mirror structures mounted on the block and including respective multilayer mirrors that reflect light beams around theclosed loop pathway; and a pump laser assembly in optical communication with the closed loop pathway through one of the mirror structures. One or more of the multilayer mirrors includes a rare-earth doped gain layer operative to produce bidirectional optical amplification of counter-propagating light beams in the closed loop pathway. In some embodiments, the gain layer comprises a rare-earth dopant other than neodymium that is doped into a glassy host material comprising titania, tantalum oxide, alumina, zirconia, silicate glass, phosphate glass, tellurite glass, fluorosilicate glass, or non-oxide glass. Alternatively, the gain layer can comprise a neodymium dopant that is doped into a glassy host material other than silica.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Refractory brick produced from aluminum ash and preparation process thereof
PendingCN114014675AEffective consumptionEfficient use ofCeramic materials productionClaywaresSocial benefitsFluorosilicate salt
The invention belongs to the technical field of building materials, and particularly relates to a refractory brick produced from aluminum ash and a preparation process thereof. The refractory brick produced from the aluminum ash is prepared by taking the aluminum ash as a main raw material and adding a high-temperature binding agent and a forming binding agent as auxiliary materials. According to the invention, the aluminum ash in the electrolytic aluminum industry can be effectively consumed, on one hand, the problem of environment-friendly discharged waste disposal of electrolytic aluminum enterprises is solved, on the other hand, efficient utilization of resources is realized, on the other hand, a refractory material product with a good market prospect is provided, and the economic benefit, the environment-friendly benefit and the social benefit are very remarkable; meanwhile, the problem of fluorine pollution of the aluminum ash can be well solved, fluorine and aluminum-silicon-calcium in the aluminum ash form fluorosilicate glass with stable chemical properties at high temperature, and fluorine is not dissolved out any more.
Owner:淄博天之润生态科技有限公司
Special optical glass with pure red luminous properties and its preparation method and application
ActiveCN113105113BImprove luminous efficiencyGuaranteed a high degree of transparencyGlass furnace apparatusThermometers using physical/chemical changesChemical compositionFluorosilicate glass
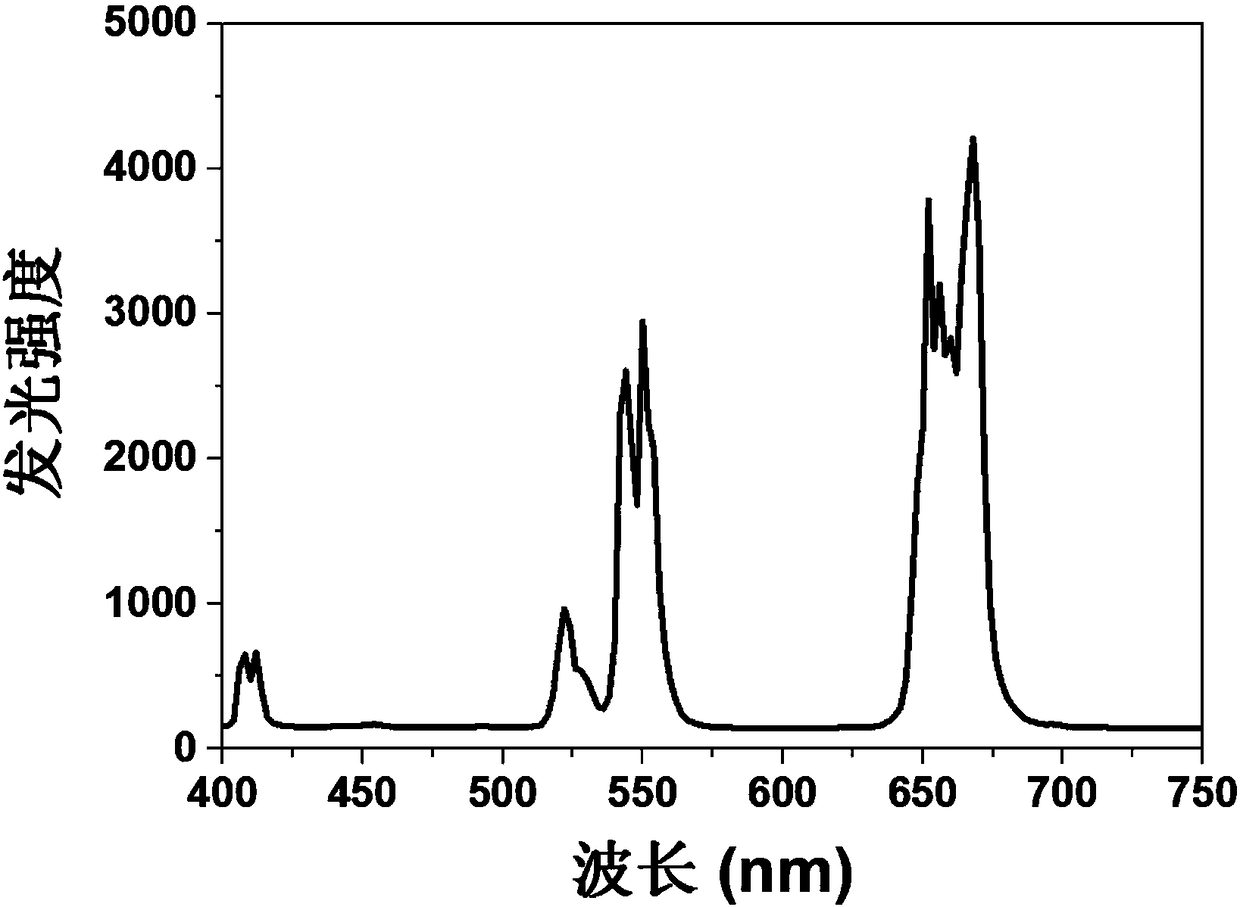
The invention discloses a special optical glass with pure red light emission characteristics, a preparation method and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of special optical glass materials. The special optical glass of the present invention includes a glass matrix, and a reducing agent and a rare earth fluoride doped externally on the basis of the glass matrix; the chemical composition of the glass matrix is: a SiO 2 ‑bZnF 2 ‑cZnCl 2 ‑dLiF‑eMnF 2 ; In the formula, a, b, c, d, e are molar ratio numbers, and its values are respectively: a is 40-50mol.%, b is 15-20mol.%, c is 10-15mol.%, d is 15mol.%, e is 0-15mol.%; the dosing amount of reducing agent is 0.05-3.0mol.%, and the dosing amount of rare earth fluoride is 0.1-2.0mol.%. The invention utilizes the characteristics of phase separation of fluorosilicate glass to regulate the performance of the glass from different dimensions, and finally obtains a special optical glass with good thermodynamic stability and high luminous efficiency. The special optical glass of the invention realizes the pure red light emission of rare earth ions, and can be applied to the fields of glass / optical fiber display, optical fiber temperature sensing, photodynamic therapy and the like.
Owner:TAISHAN UNIV
A kind of semiconductor device and its forming method
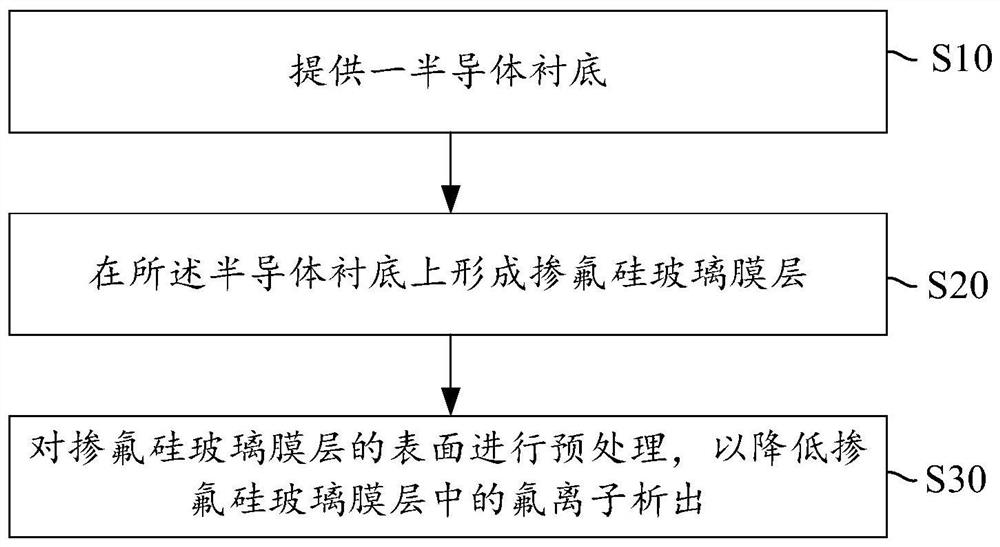
ActiveCN110556295BImprove reliabilityReduce precipitationSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDevice materialMaterials science
The present invention provides a semiconductor device and its forming method. The forming method of the semiconductor device comprises the following steps: providing a semiconductor substrate; forming a fluorine-doped silicon glass film layer on the semiconductor substrate; Pretreatment to reduce the precipitation of fluoride ions in the fluorine-doped silicon glass film layer. The present invention pretreats the surface of the fluorine-doped silicate glass film layer, so that the dangling bonds on the surface of the fluorine-doped silicate glass film layer are saturated with oxygen atoms in hydrogen peroxide, thereby passivating the surface of the fluorine-doped silicate glass film layer, and then The speed of fluorine ion precipitation in the fluorine-doped silicon glass film layer is reduced, so that the waiting time between the deposition of FSG, chemical mechanical polishing and the formation of the subsequent covering layer of the fluorine-doped silicon glass film layer does not need to be controlled. The crystal defects that appear improve the reliability of the device, and at the same time, also reduce the process of rework or cleaning, reduce the process time, and improve the process efficiency.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUAHONG GRACE SEMICON MFG CORP
Semiconductor device and forming method thereof
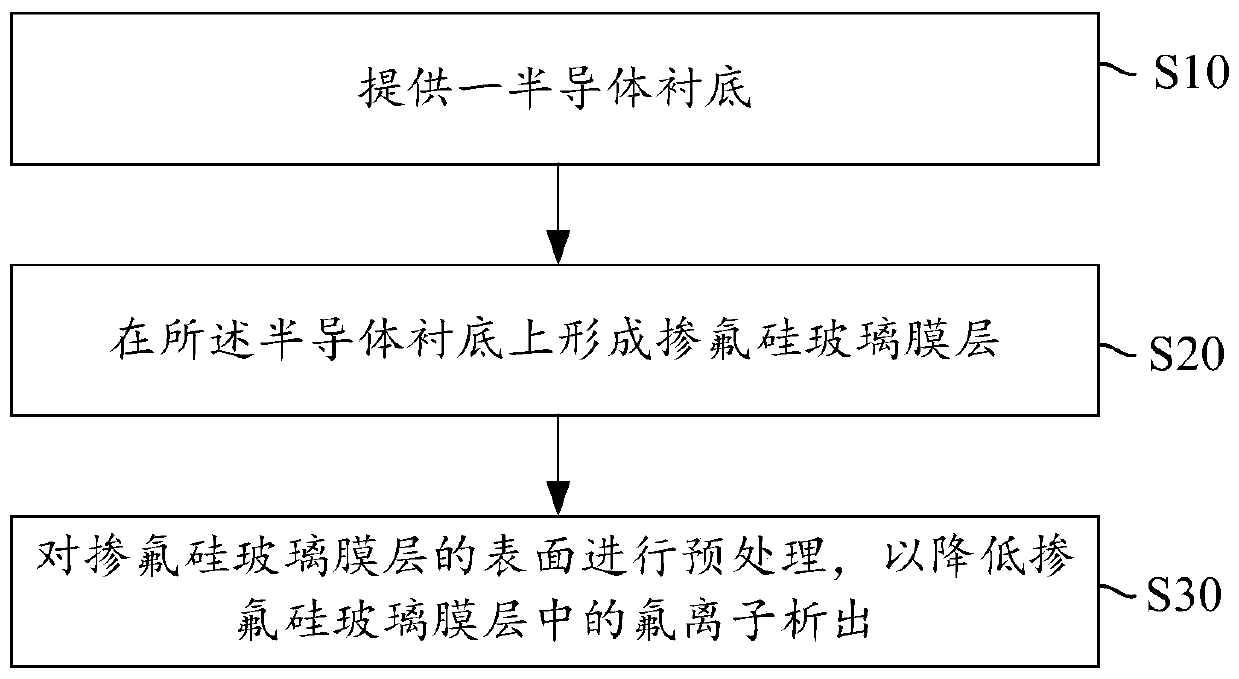
ActiveCN110556295AImprove reliabilityReduce precipitationSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectrical conductorCrystallographic defect
The invention provides a semiconductor device and a forming method thereof. The forming method of the semiconductor device comprises the steps of providing a semiconductor substrate; forming a fluorine-doped silica glass film layer on the semiconductor substrate; and carrying out pretreatment on the surface of the fluorine-doped silica glass film layer so as to reduce the precipitation of fluorineions in the fluorine-doped silica glass film layer. According to the invention, the surface of the fluorine-doped silica glass film layer is pretreated, so that dangling bonds on the surface of the fluorine-doped silica glass film layer are saturated by oxygen atoms in hydrogen peroxide, the surface of the fluorine-doped silica glass film layer is passivated, the precipitation speed of fluorine ions in the fluorine-doped silica glass film layer is reduced, and the waiting time of the fluorine-doped silica glass film layer among FSG deposition, chemical mechanical grinding and subsequent covering layer formation does not need to be controlled, so that the crystal defects are overcome, and the reliability of the device is improved. Meanwhile, the reworking or cleaning procedures are reduced, the process time is shortened, and the process efficiency is improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUAHONG GRACE SEMICON MFG CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com