Patents
Literature
47 results about "Ring laser gyroscope" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
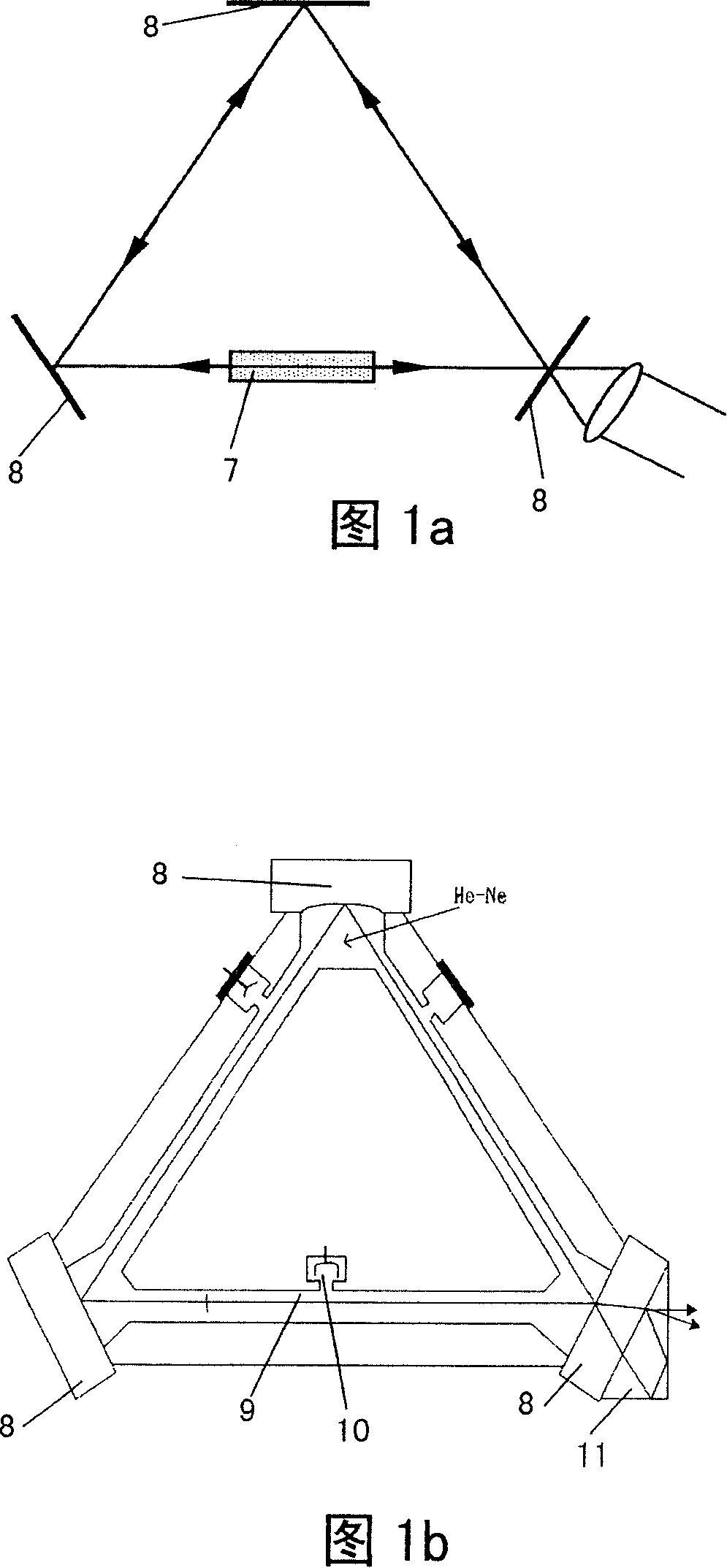
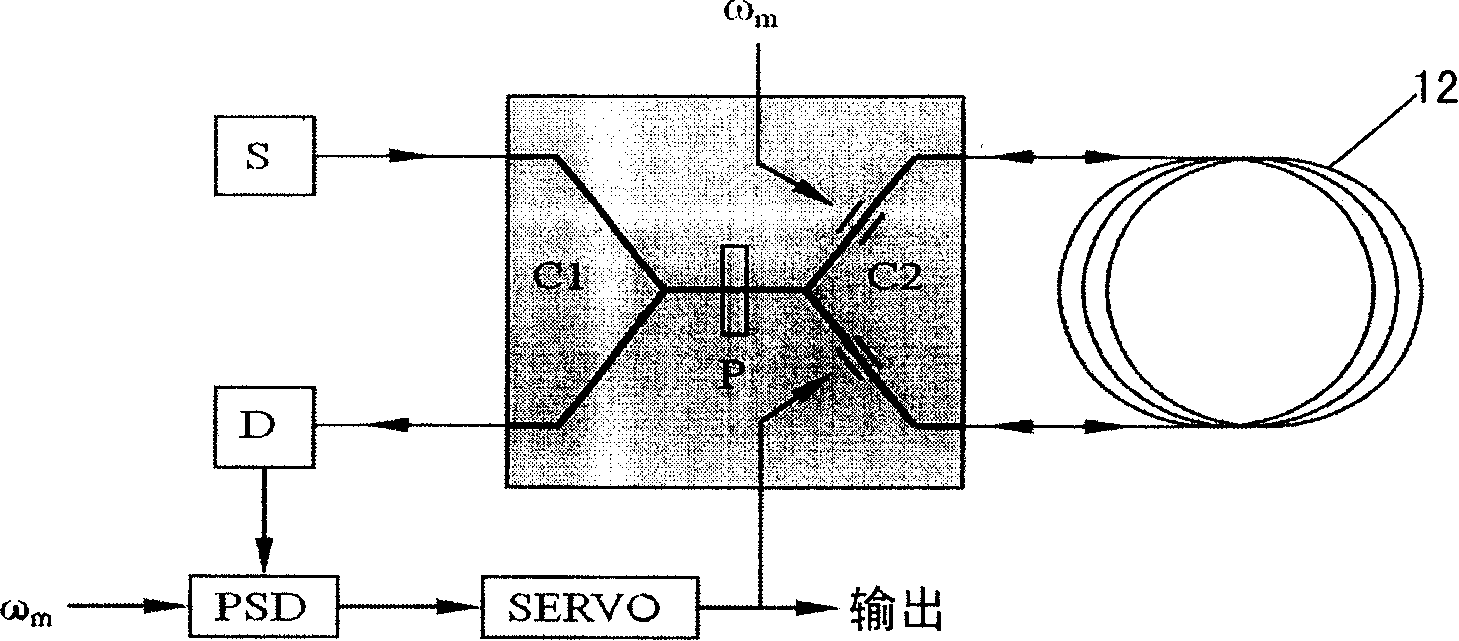
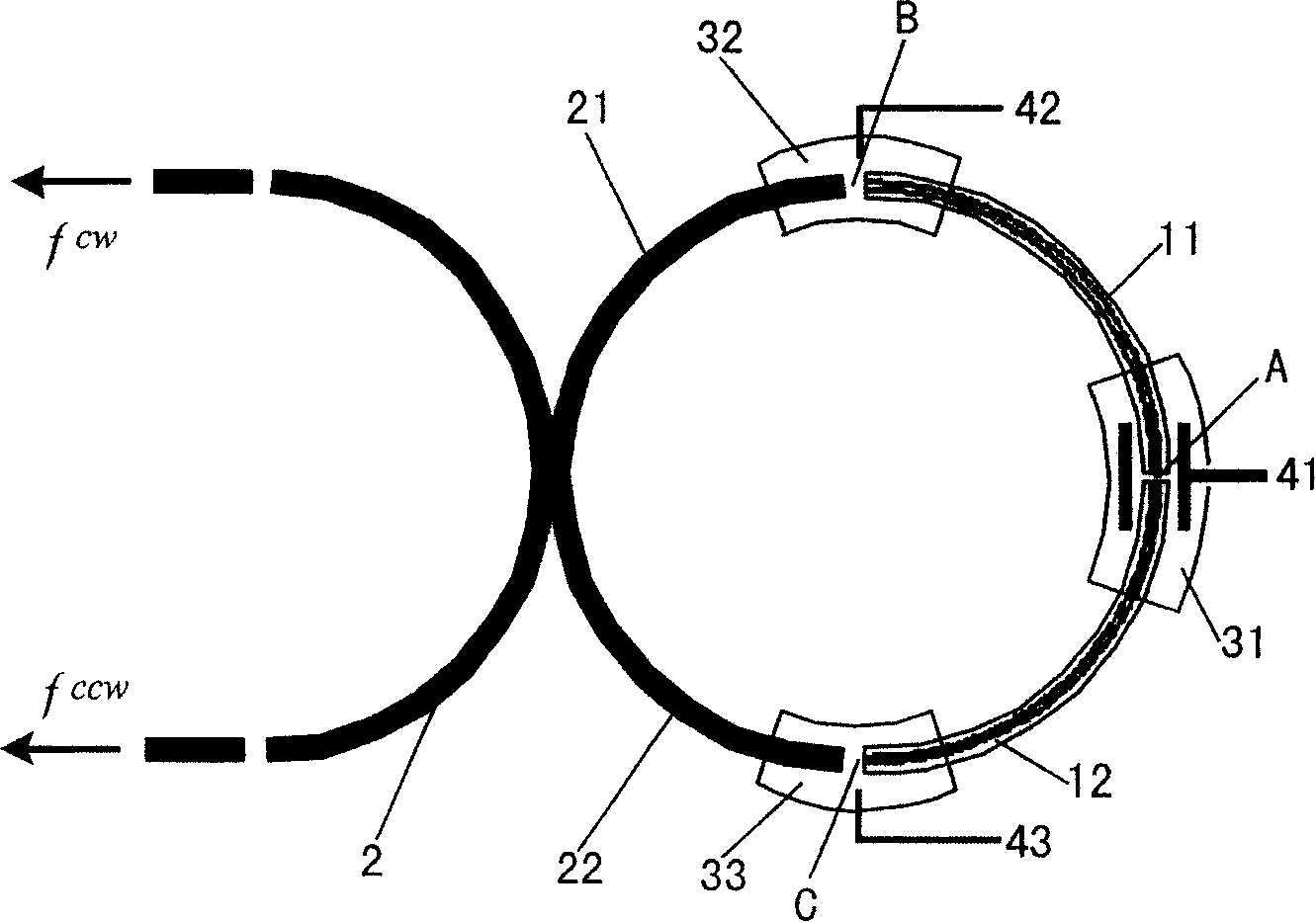
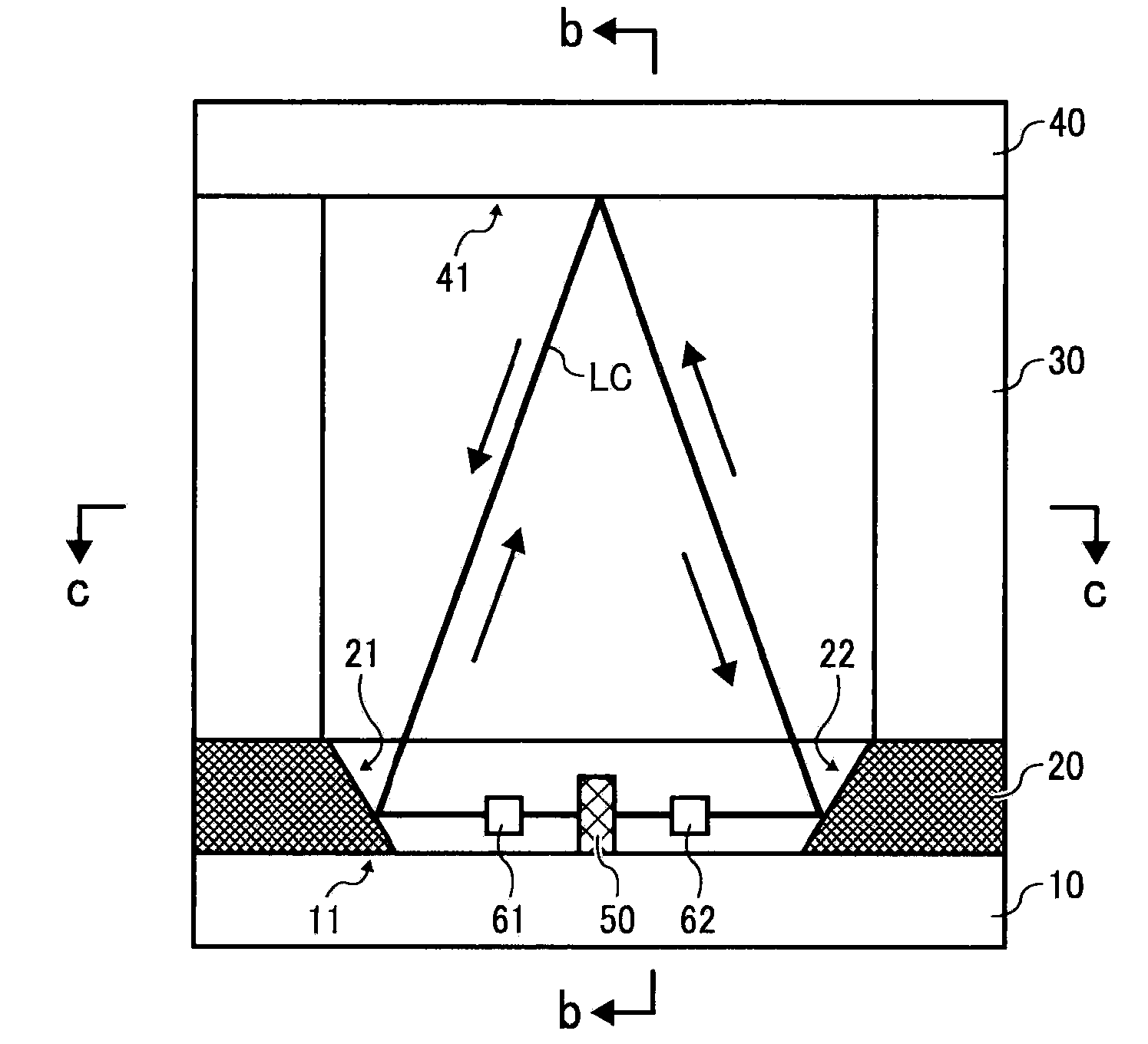
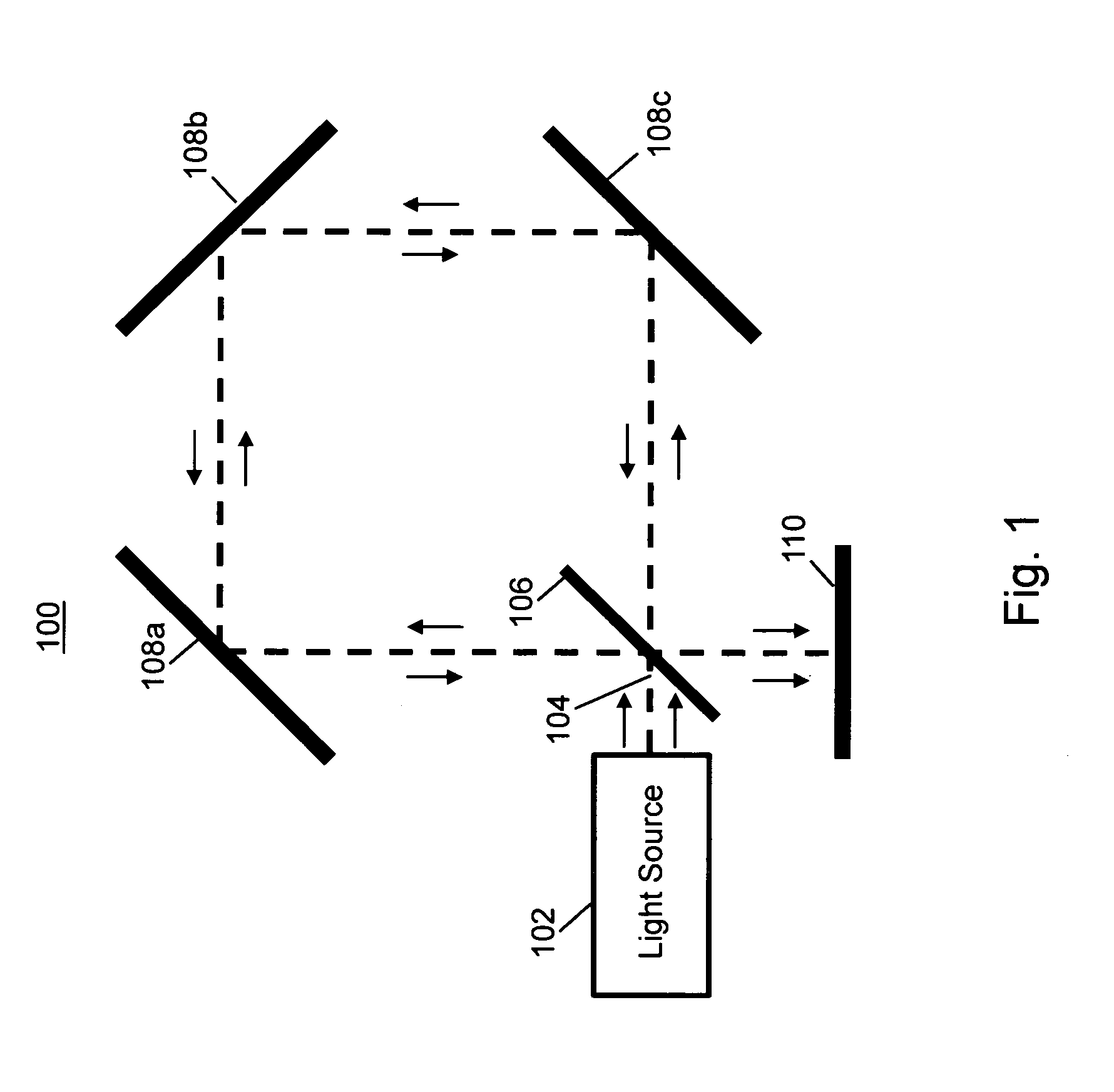
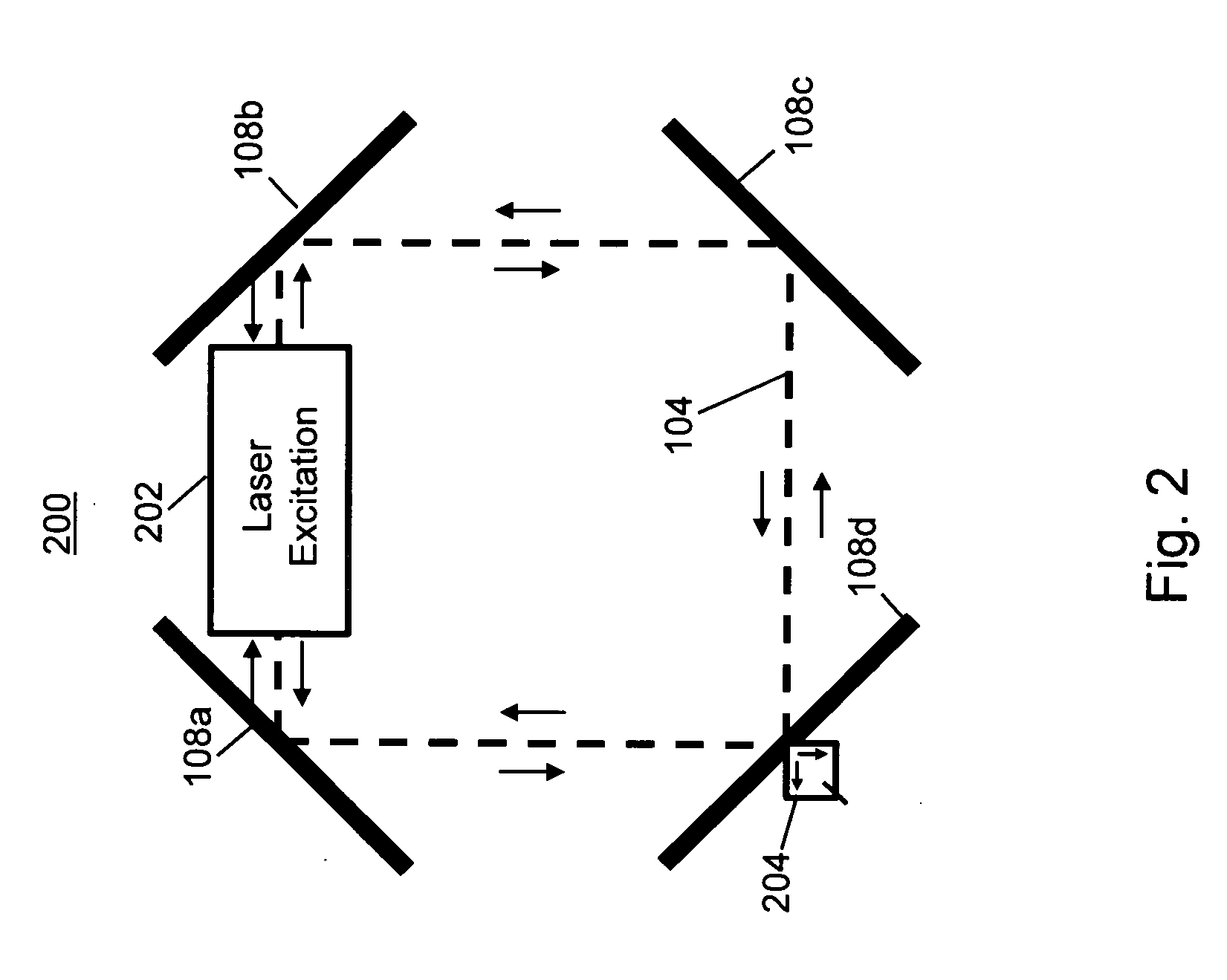
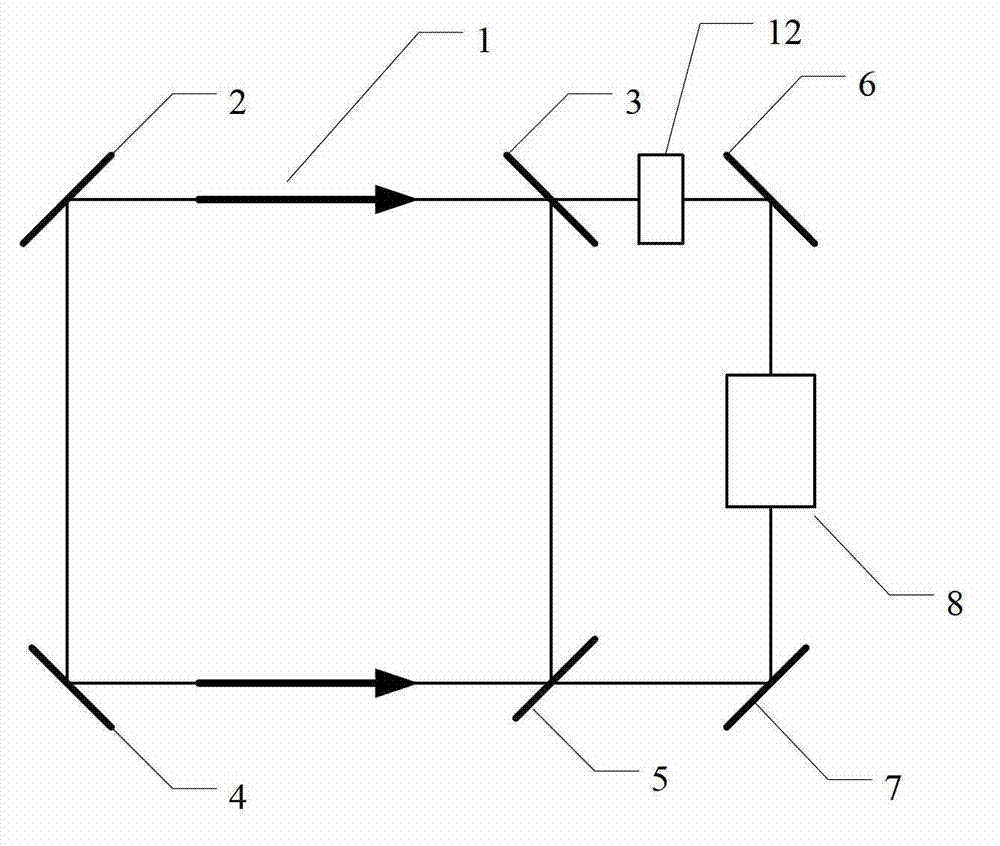
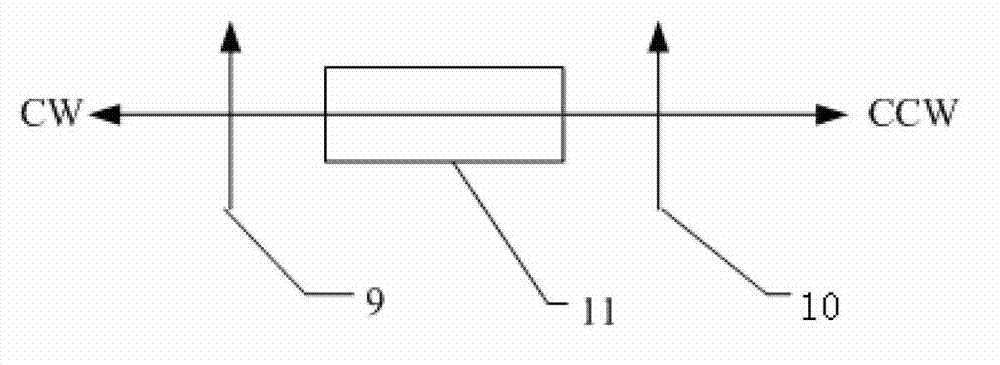
A ring laser gyroscope (RLG) consists of a ring laser having two independent counter-propagating resonant modes over the same path; the difference in the frequencies is used to detect rotation. It operates on the principle of the Sagnac effect which shifts the nulls of the internal standing wave pattern in response to angular rotation. Interference between the counter-propagating beams, observed externally, results in motion of the standing wave pattern, and thus indicates rotation.
Use of multiple masks to control uniformity in coating deposition
The uniformity of individual layers of multiple coating materials deposited on a substrate in a vacuum deposition process (such as for manufacturing mirrors for use in ring laser gyroscopes) is improved by an apparatus and method that include changing the masks placed in front of the substrate upon which the coating materials are to be deposited. Separate masks are tuned for each particular coating material to compensate for the unique plume shape of the material, and provide a uniform deposition of that particular coating material. Each mask is positioned in front of the substrate when the material for which the mask has been tuned is being deposited. The masks are changed when the coating material is changed, without venting the chamber.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
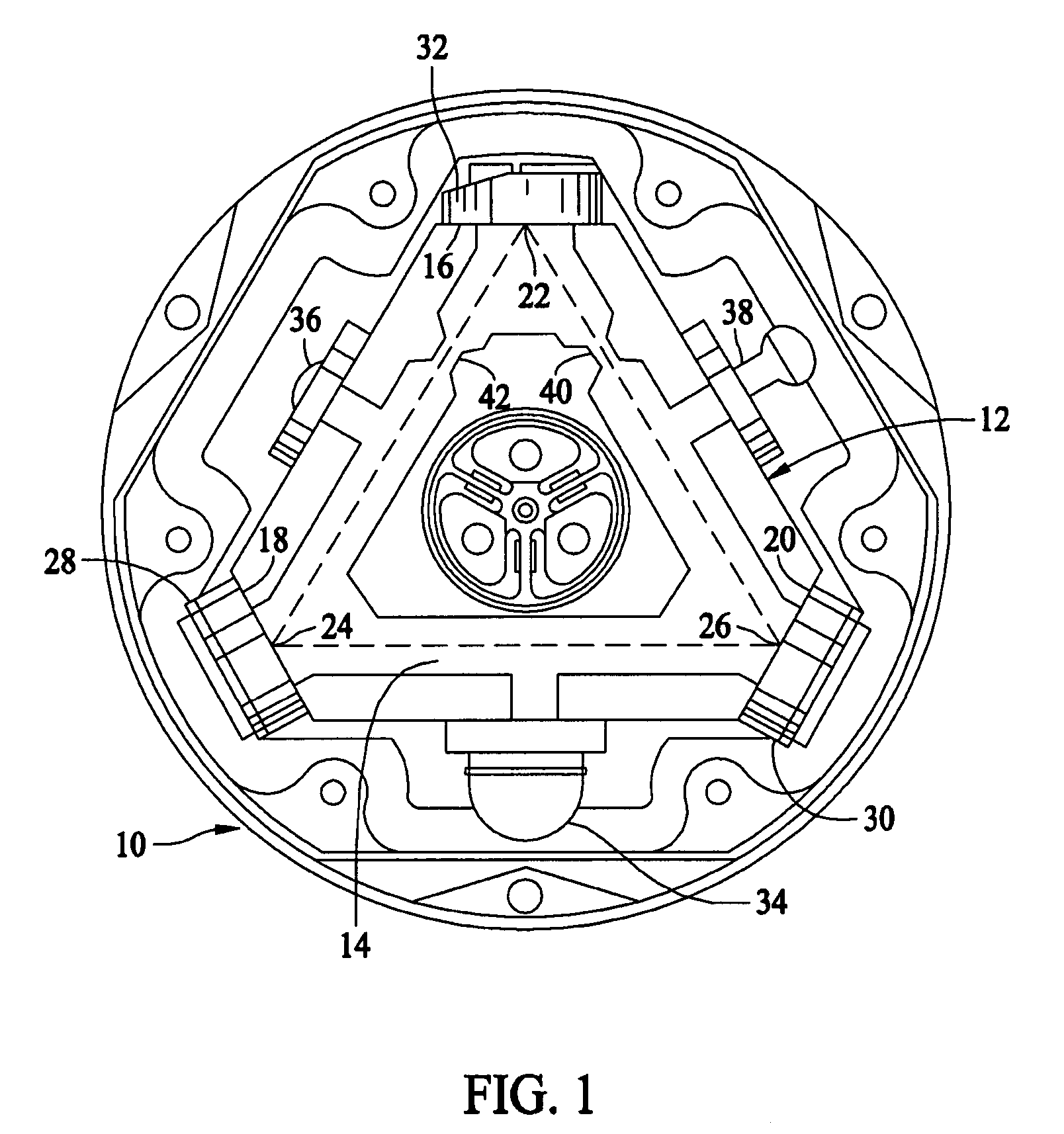
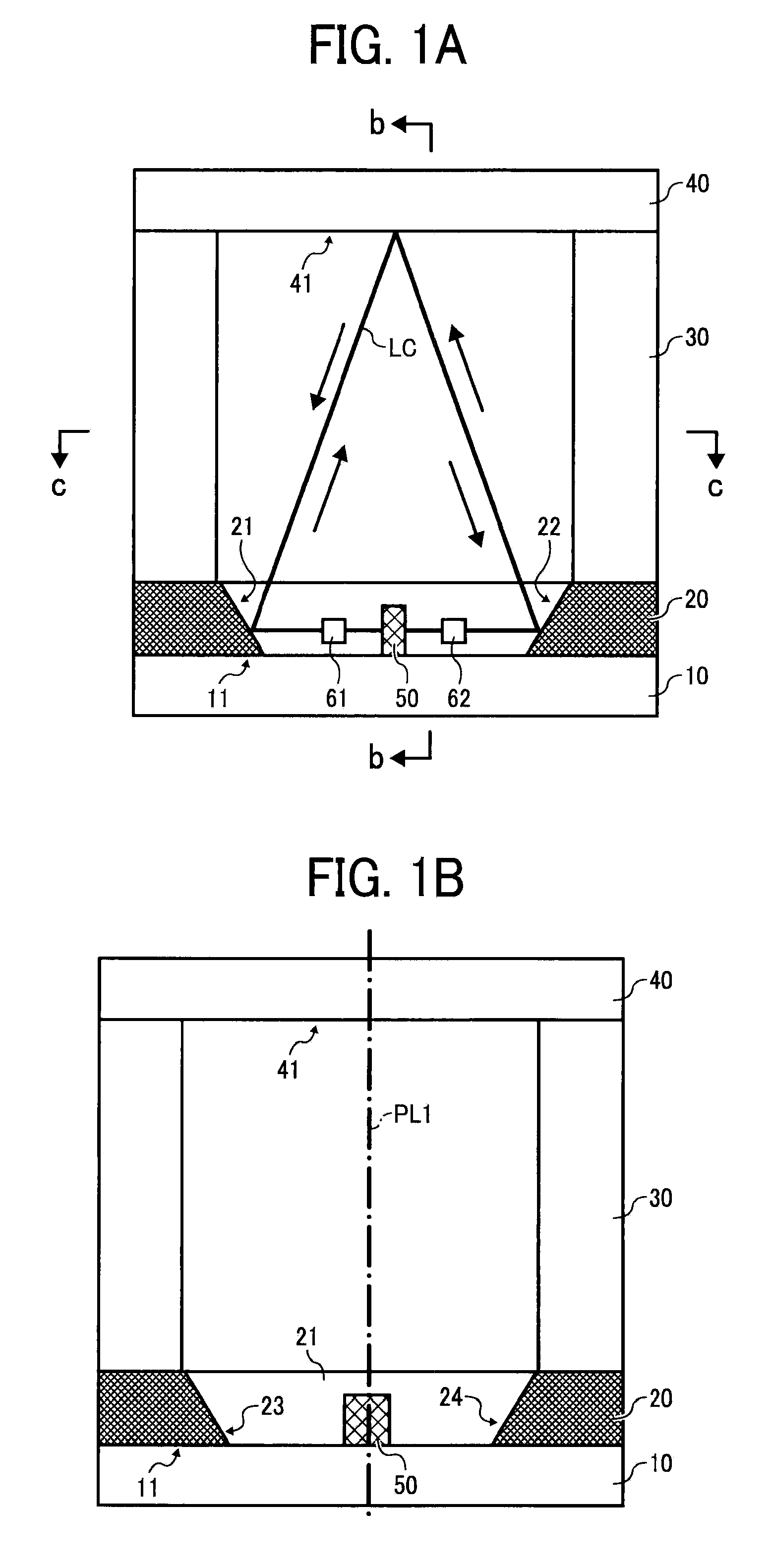
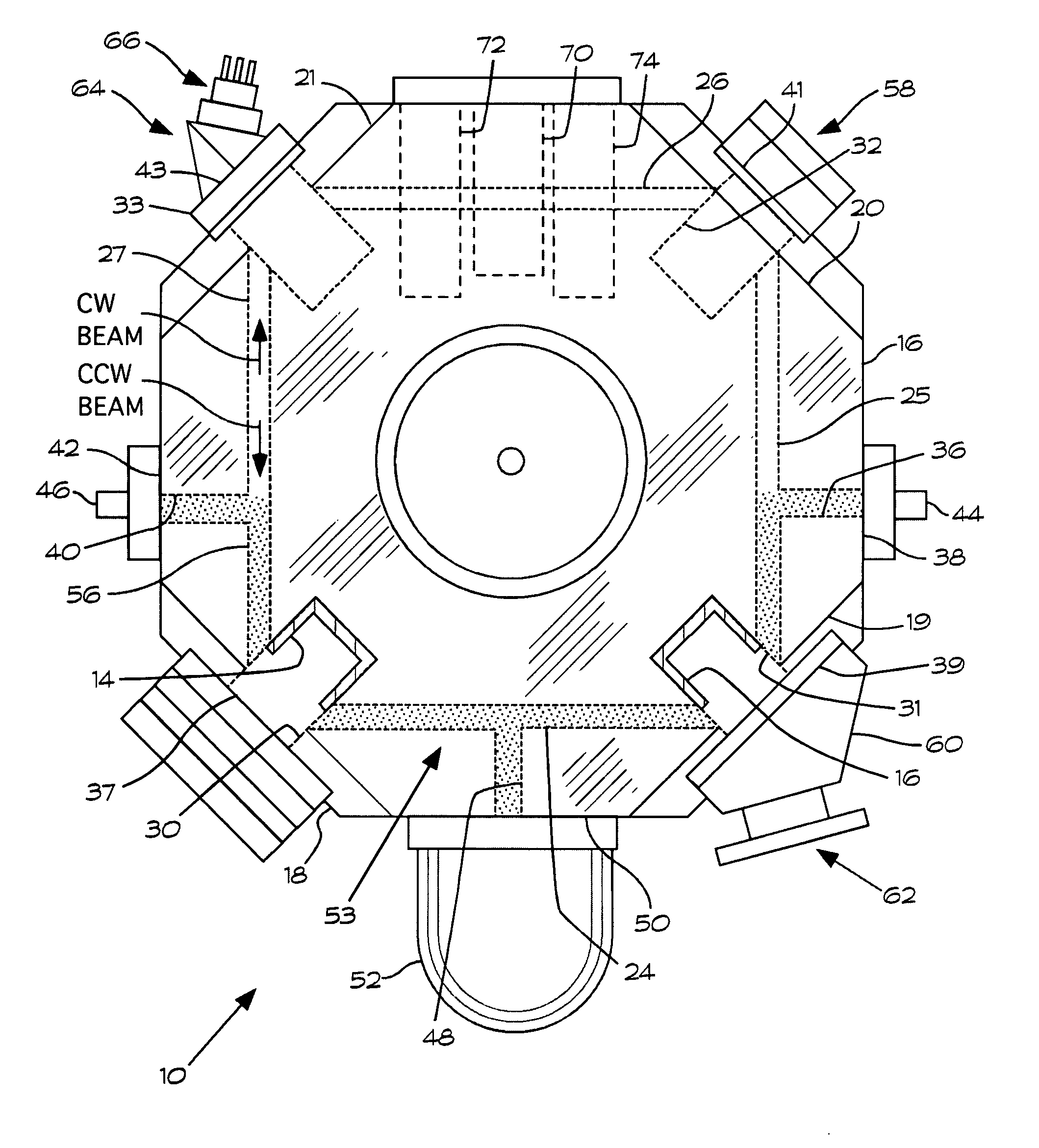
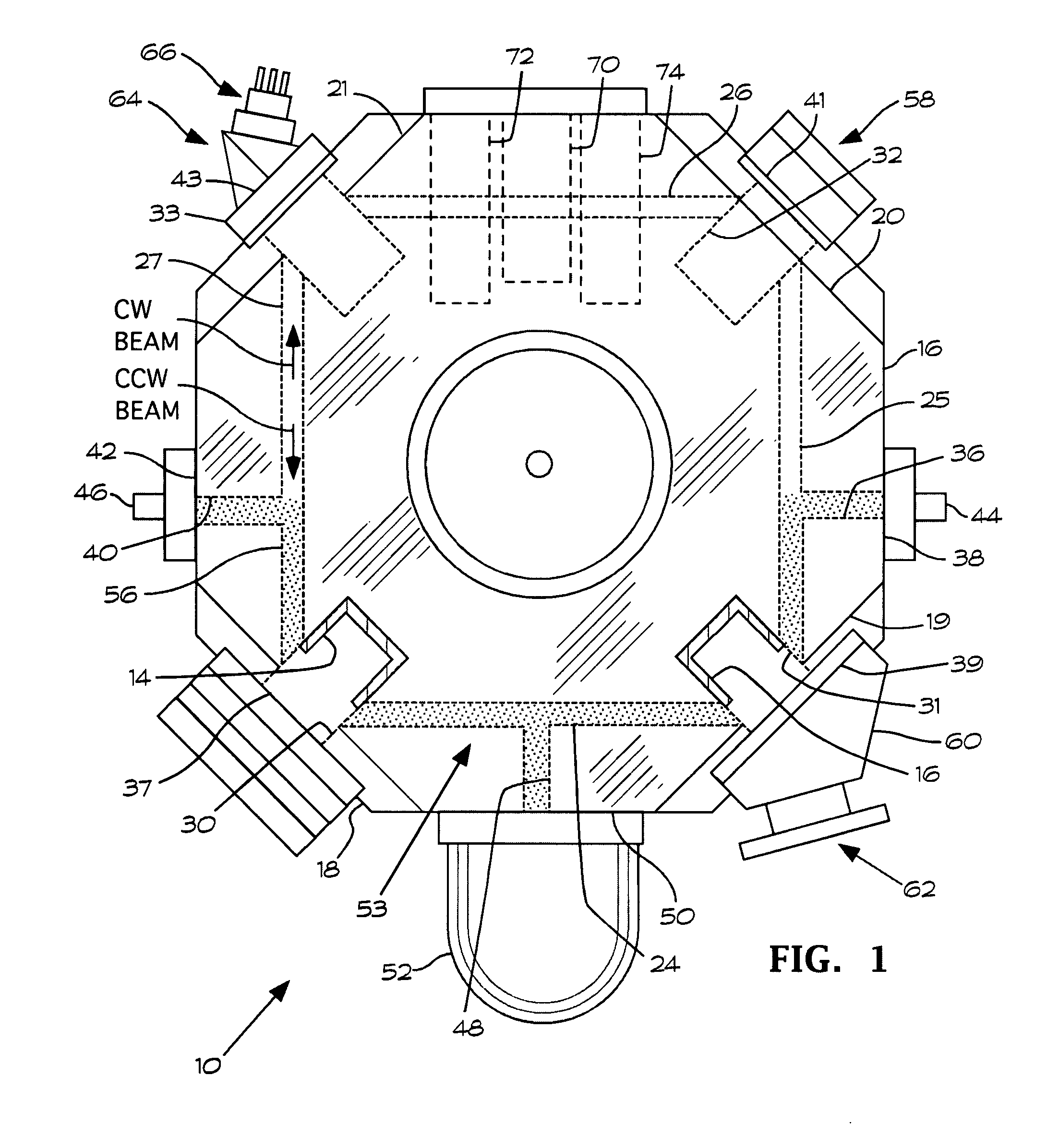
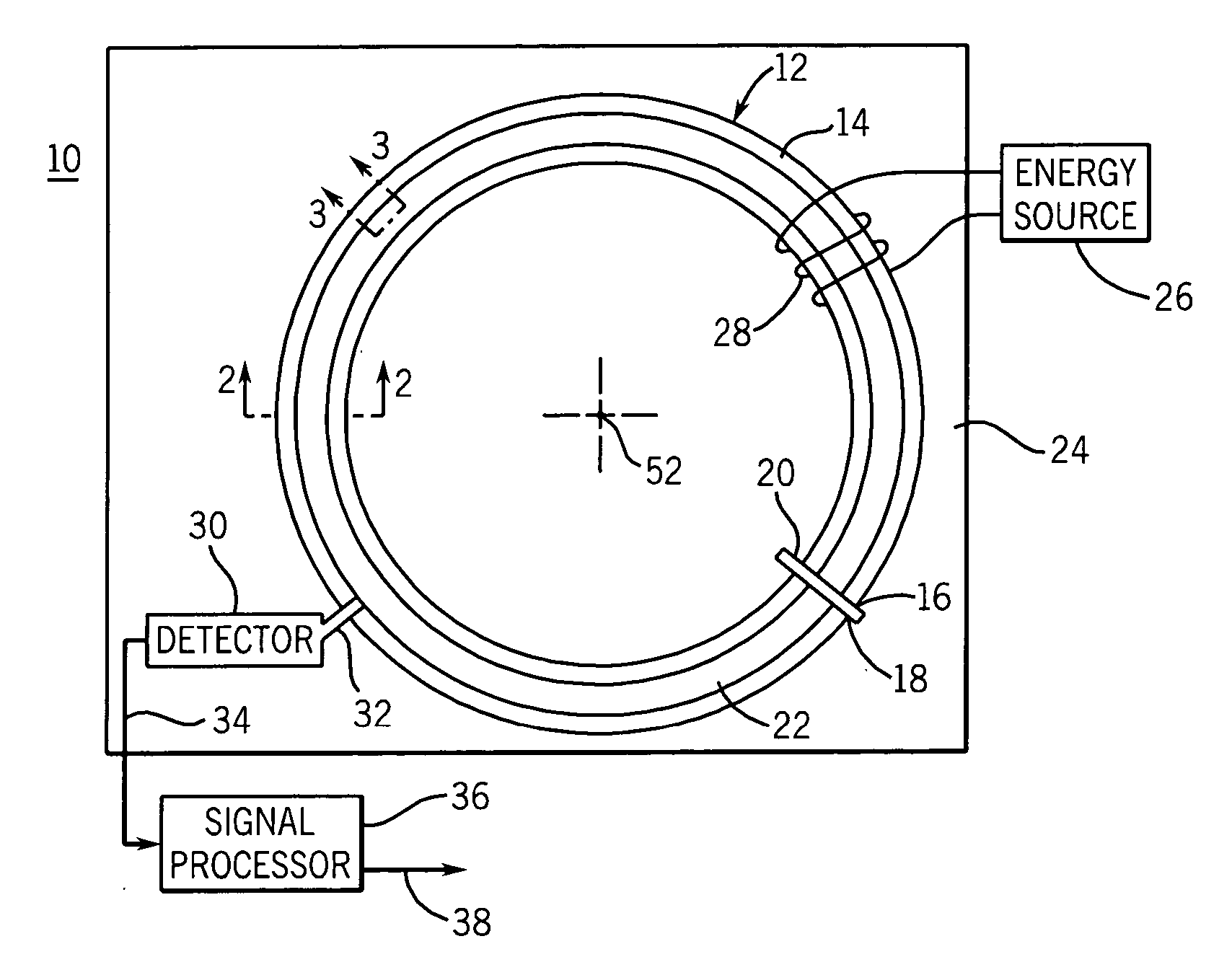
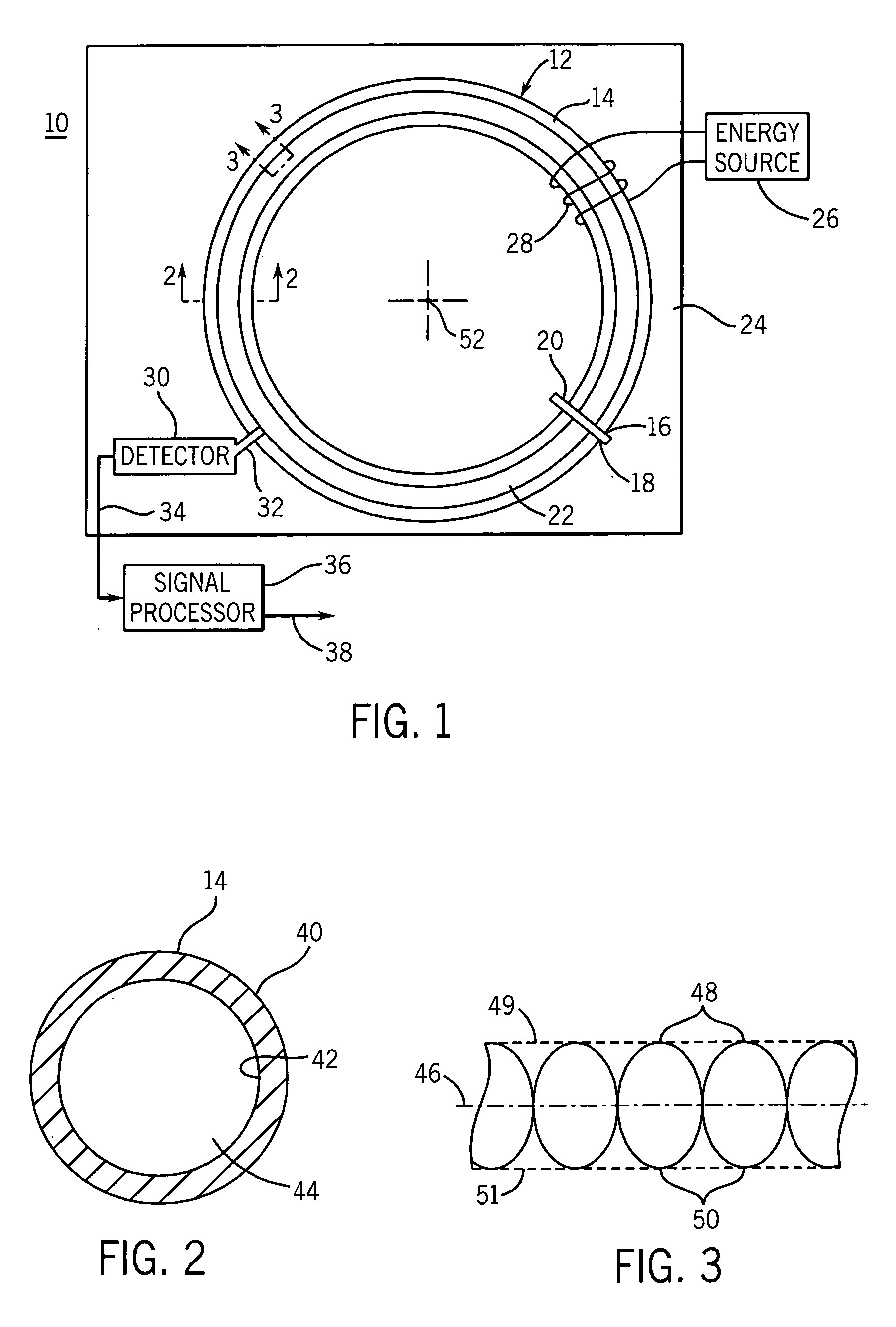
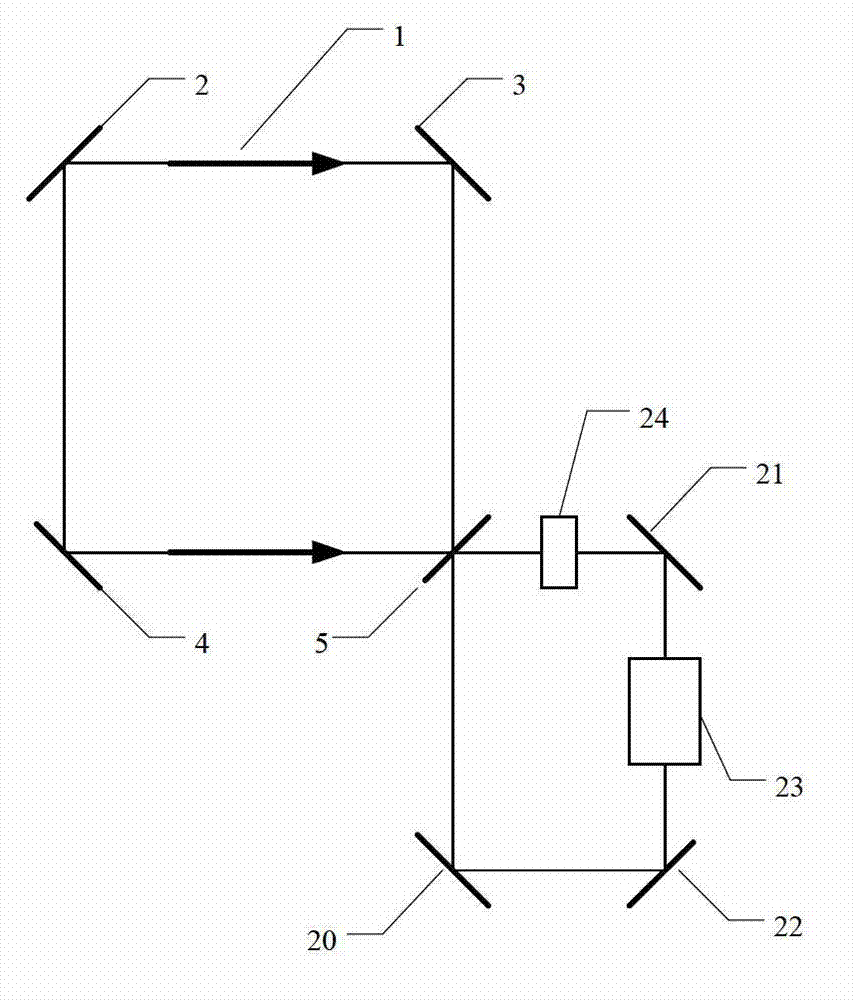
Single sensor ring laser gyroscope
InactiveUS7330269B2Speed measurement using gyroscopic effectsSagnac effect gyrometersPath lengthControl signal
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
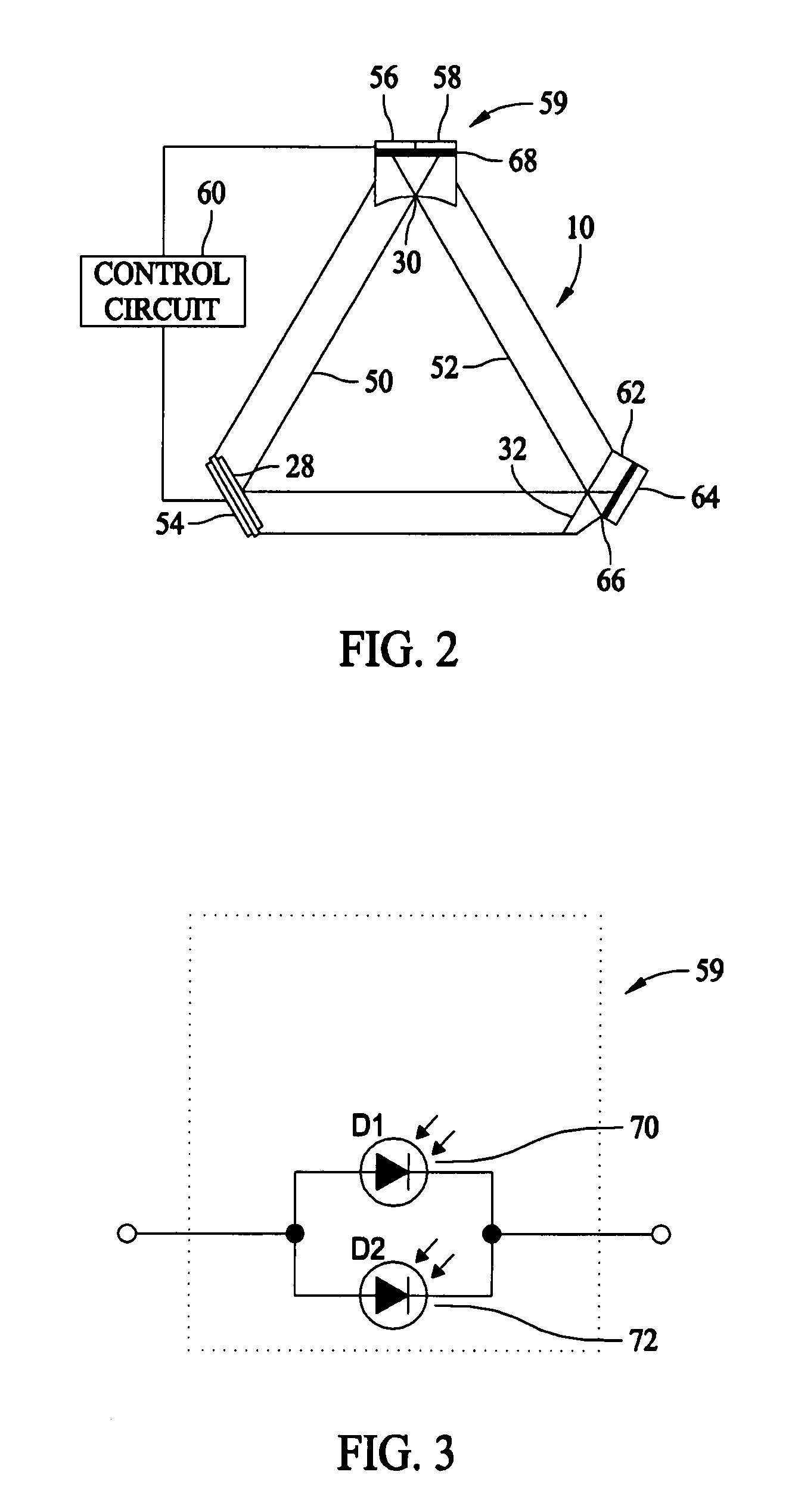
Ring laser gyroscope that does not require mirrors
ActiveUS7245381B2Speed measurement using gyroscopic effectsSagnac effect gyrometersFiberRing laser gyroscope
In an embodiment of a ring laser gyroscope, a hollow bandgap fiber is filled with a gas or material that will generate laser beams within the fiber upon being excited by an energy source. A detector coupled to the fiber detects a standing wave pattern within the fiber, wherein changes in the detected standing wave pattern indicates a corresponding change in the orientation of the fiber.
Owner:LITTON SYST INC +1
Optical fibre gas laser and optical fiber type ring laser gyroscope possessing the laser
ActiveCN101165977AGood zoom effectSimple structureExcitation process/apparatusSagnac effect gyrometersFiber couplerRobotic systems
Owner:THE HONG KONG POLYTECHNIC UNIV
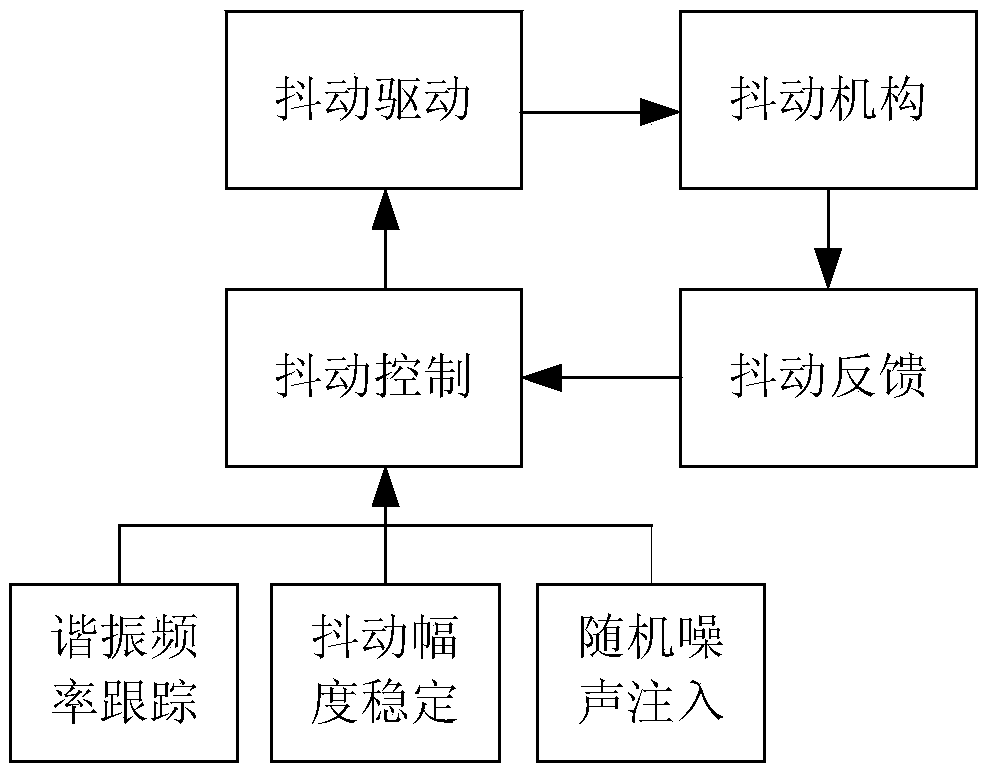
Active vibration damping control method for mechanically dithered ring laser gyroscope
InactiveCN105547274ANo change in dimensionsSeamless replacementSagnac effect gyrometersElectricityRing laser gyroscope
The invention relates to an active vibration damping control method for a mechanically dithered ring laser gyroscope. In the bottom space of an installation housing provided with a mechanically dithered ring laser gyroscope, N equally spaced damping weight spokes are arranged between a central base and an external wall of the installation housing, and the N weight spokes are in rotational symmetry about the center of the central base; both sides of each vibration damping weight spoke are provided with piezoelectric ceramic sheets, wherein one is used for detecting a dither signal generated by a mechanical dither device of the mechanically dithered ring laser gyroscope and then inputting the signal to a processor; and the processor outputs an active damping driving signal voltage and loads the voltage onto the remaining 2N-1 piezoelectric ceramics. The method simplifies the complex process of actual parameter adjustment, shortens the setup time of active vibration damping and improves the control precision.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
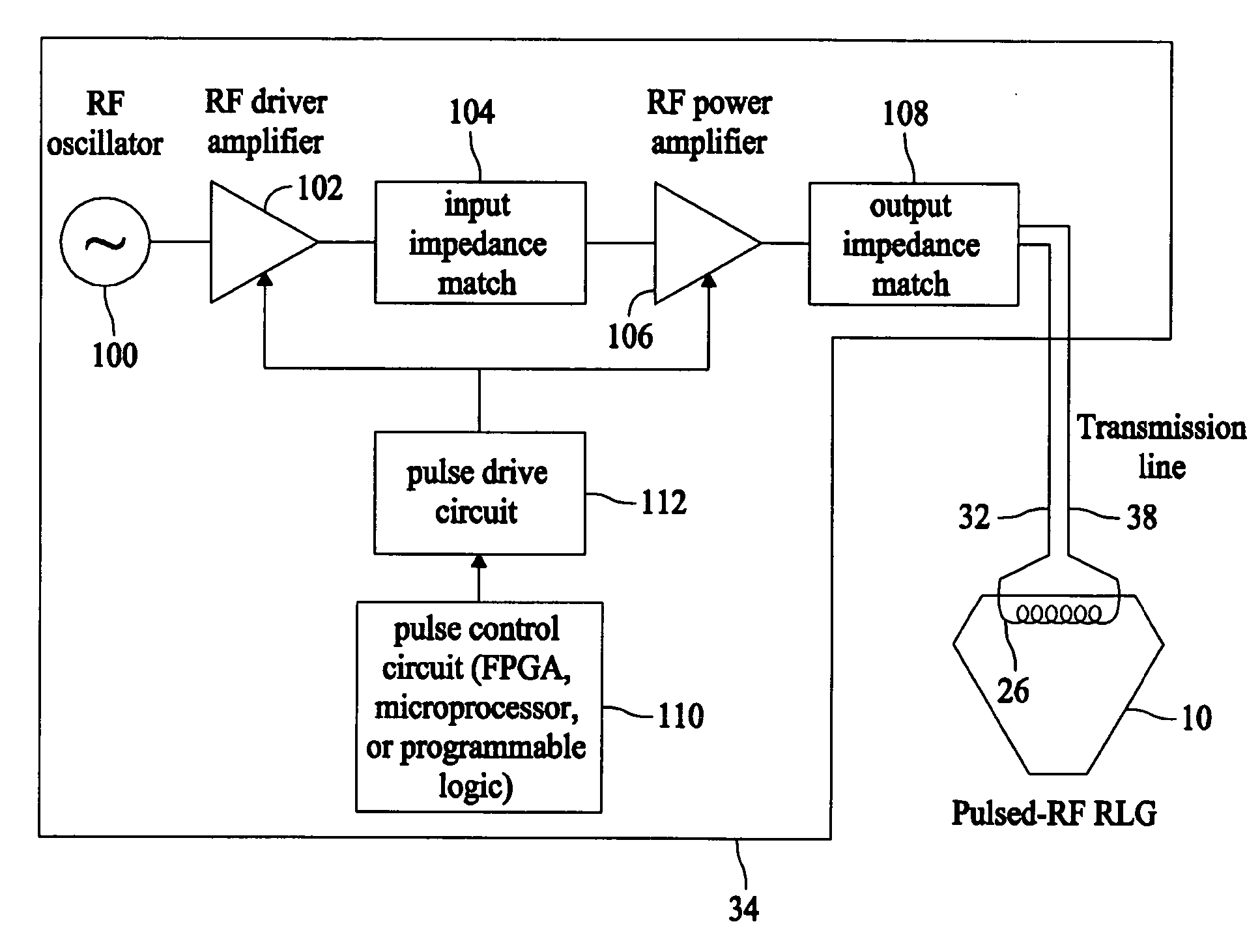
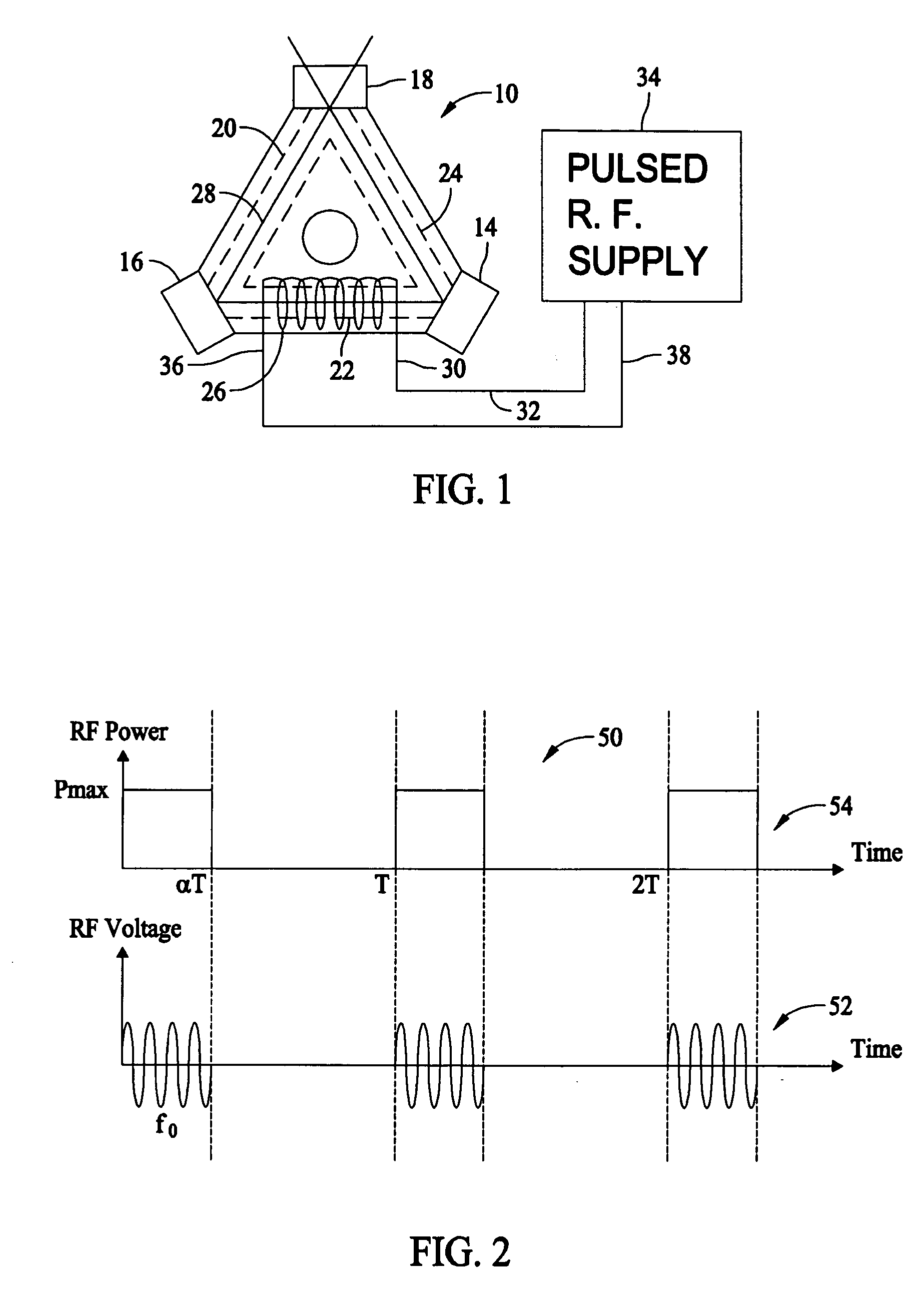
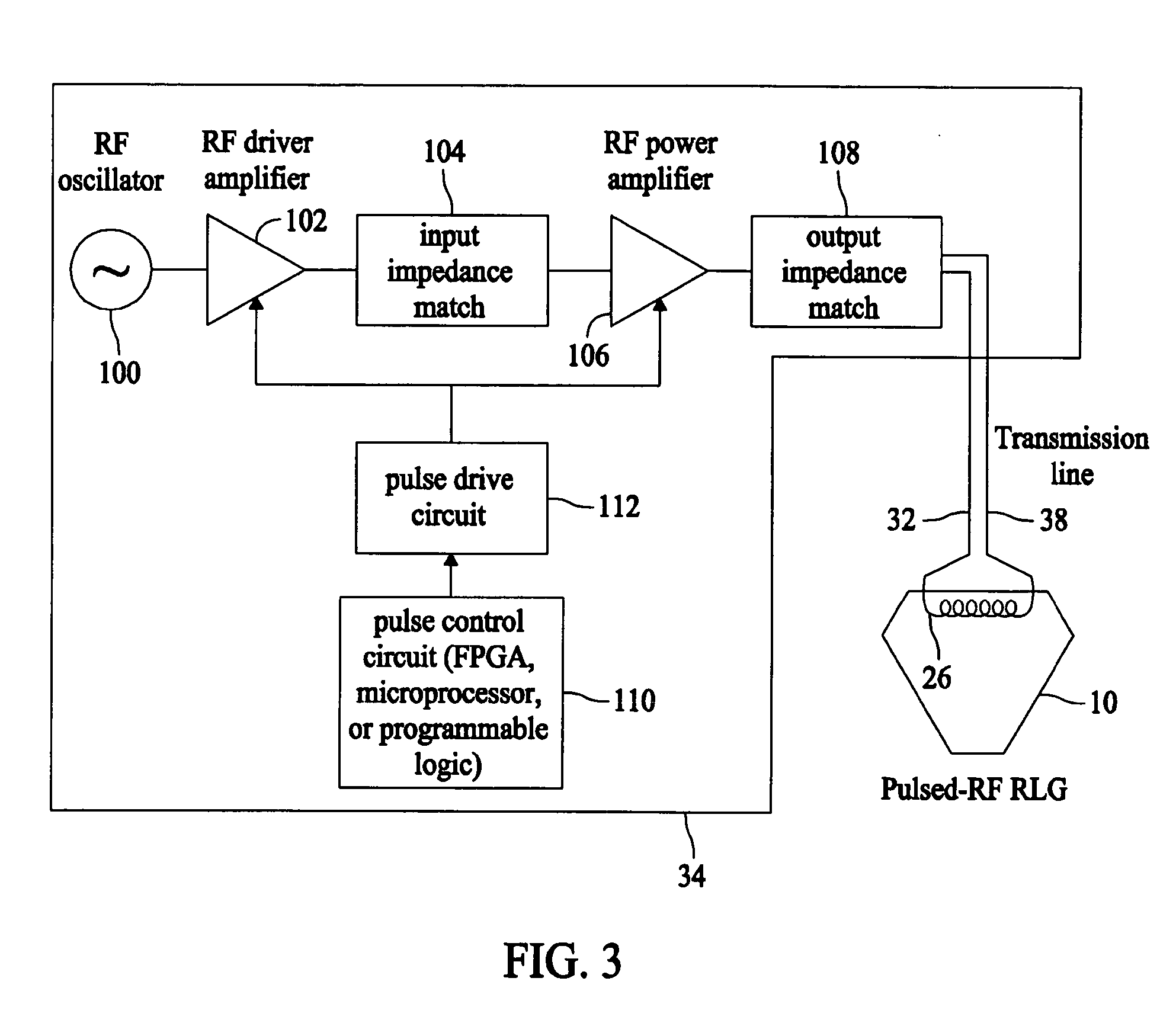
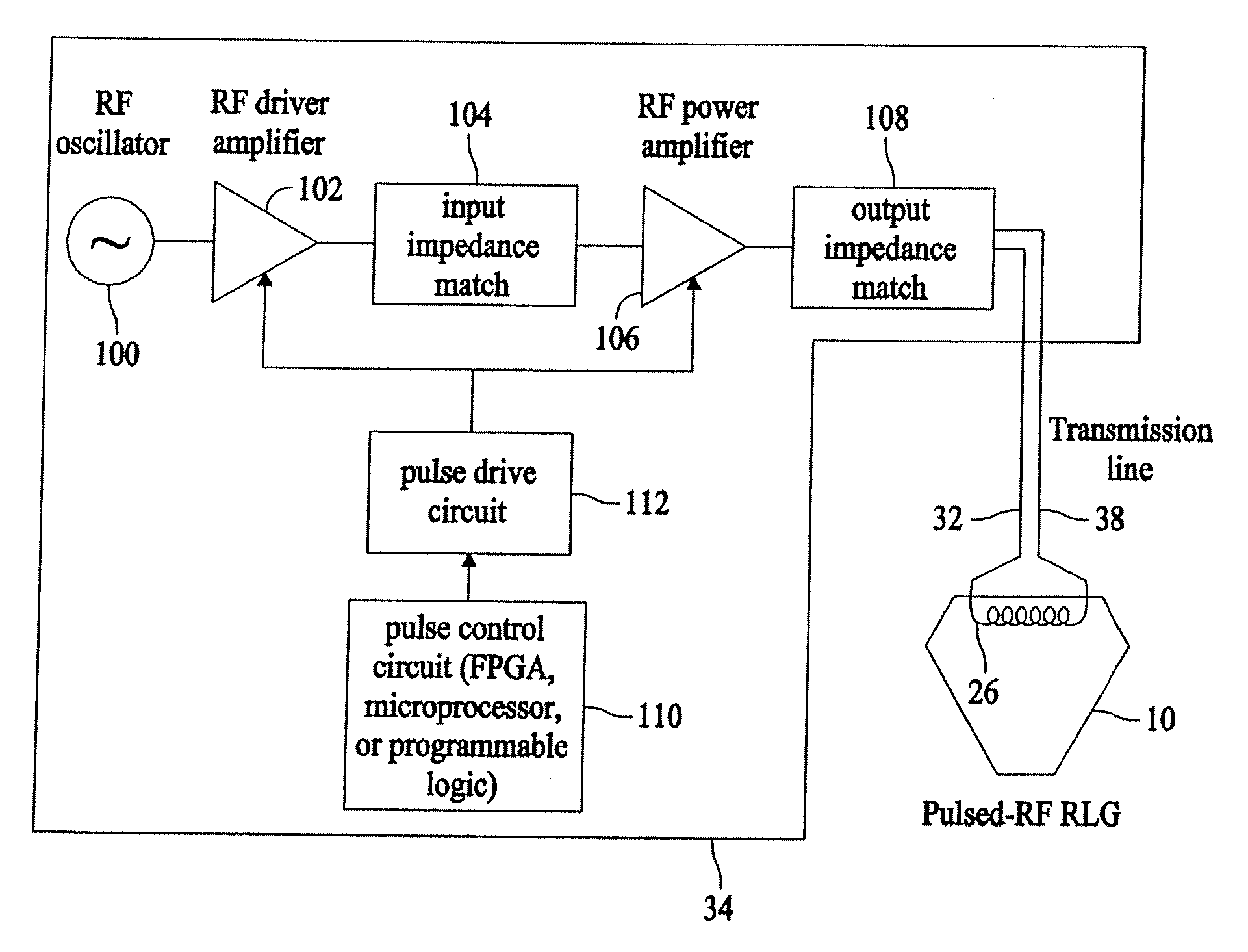
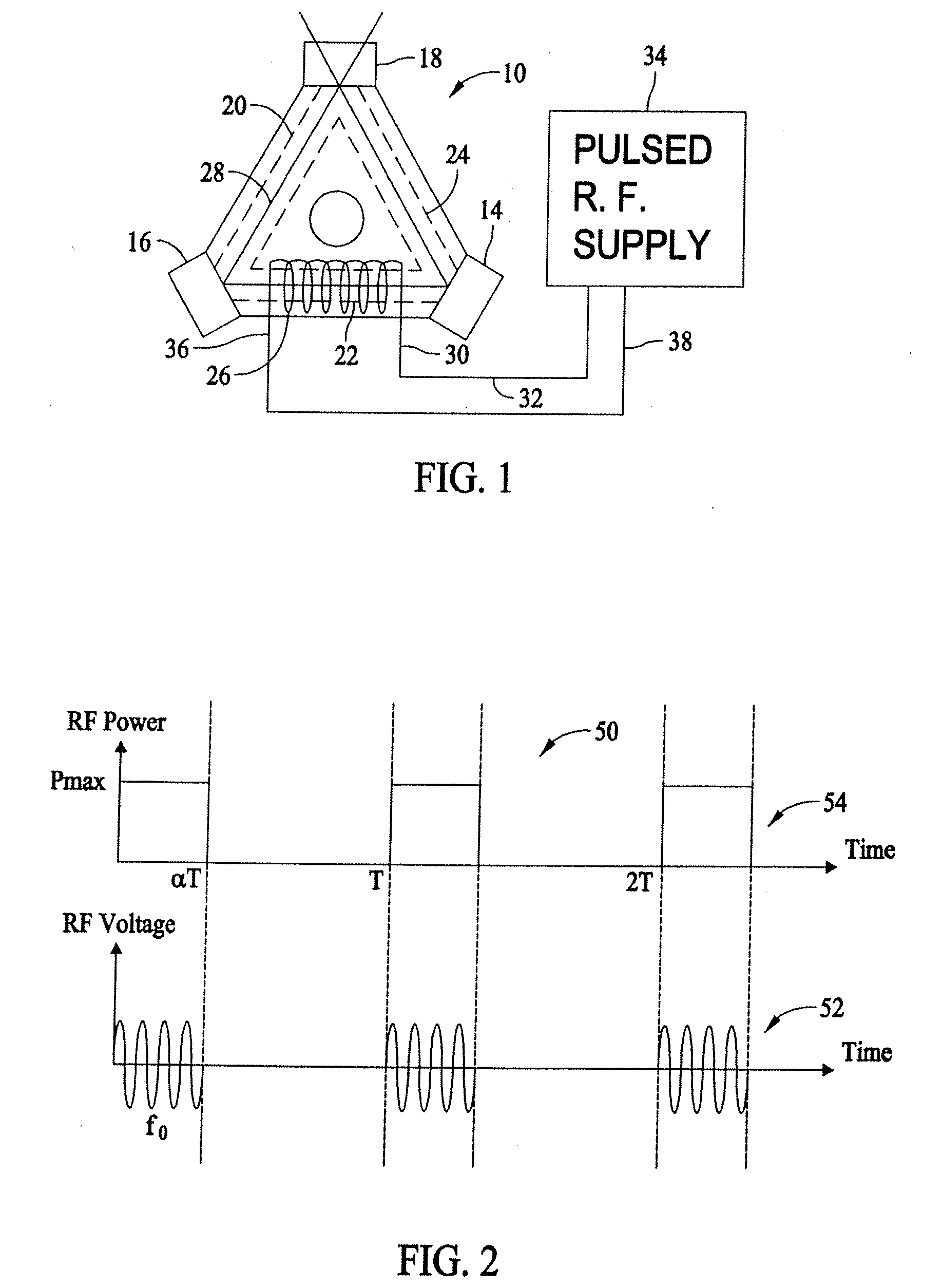
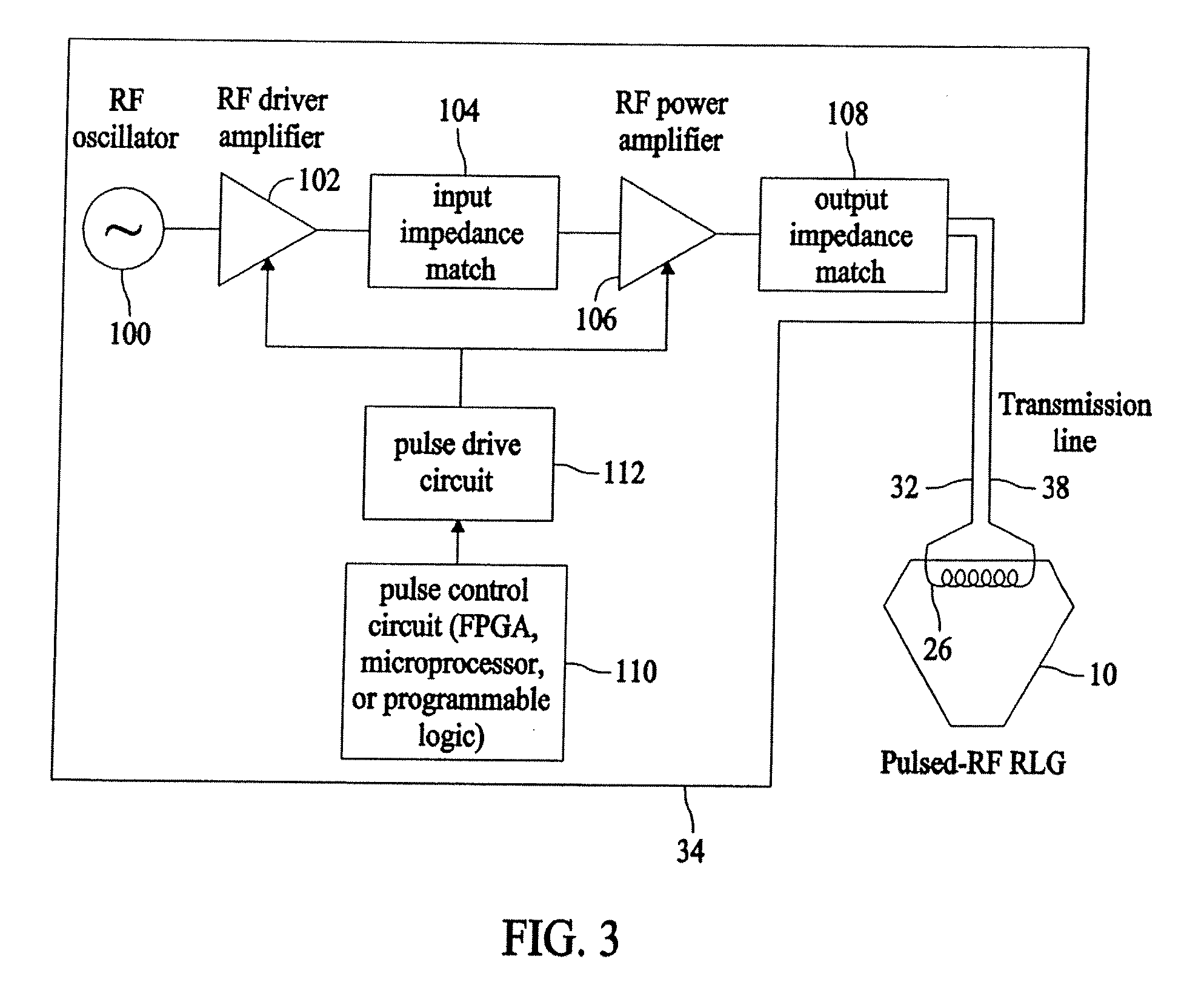
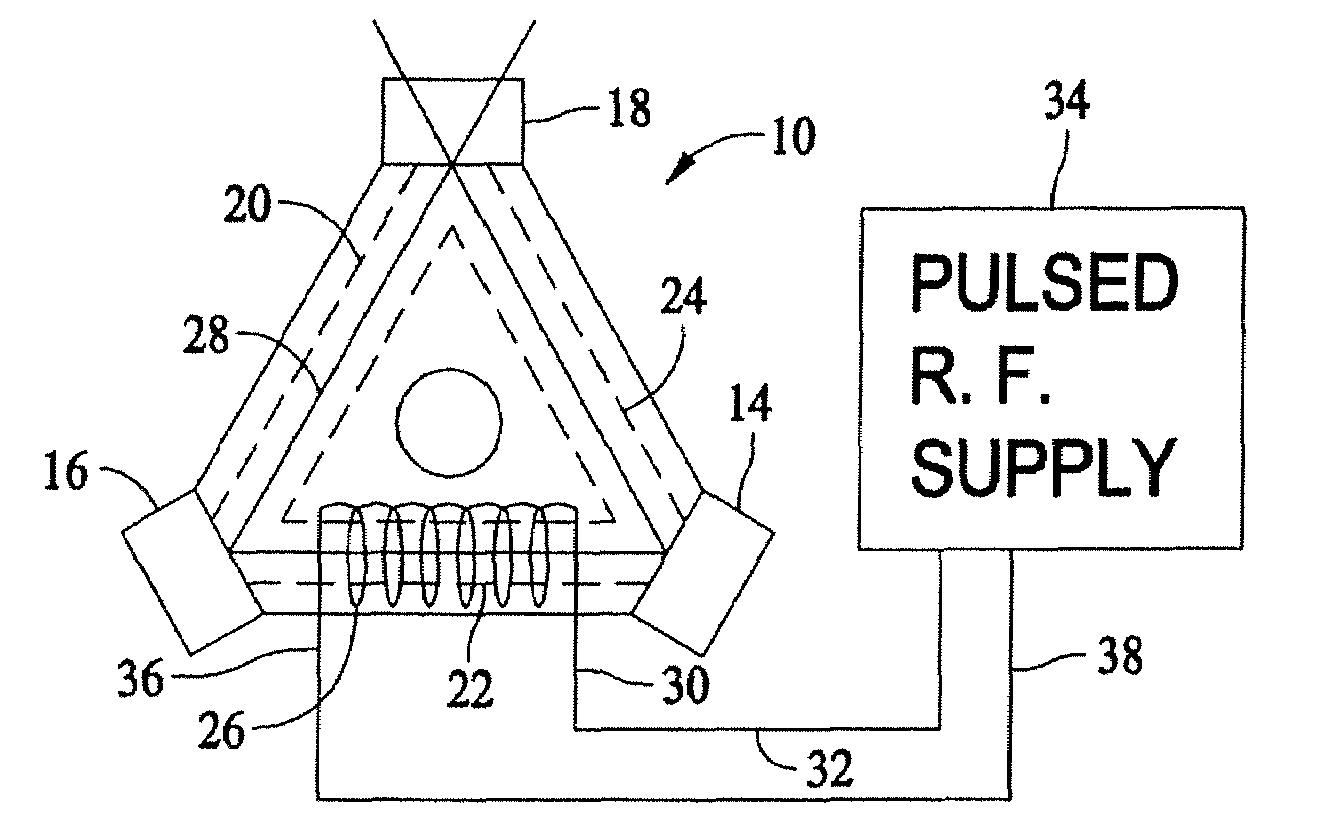
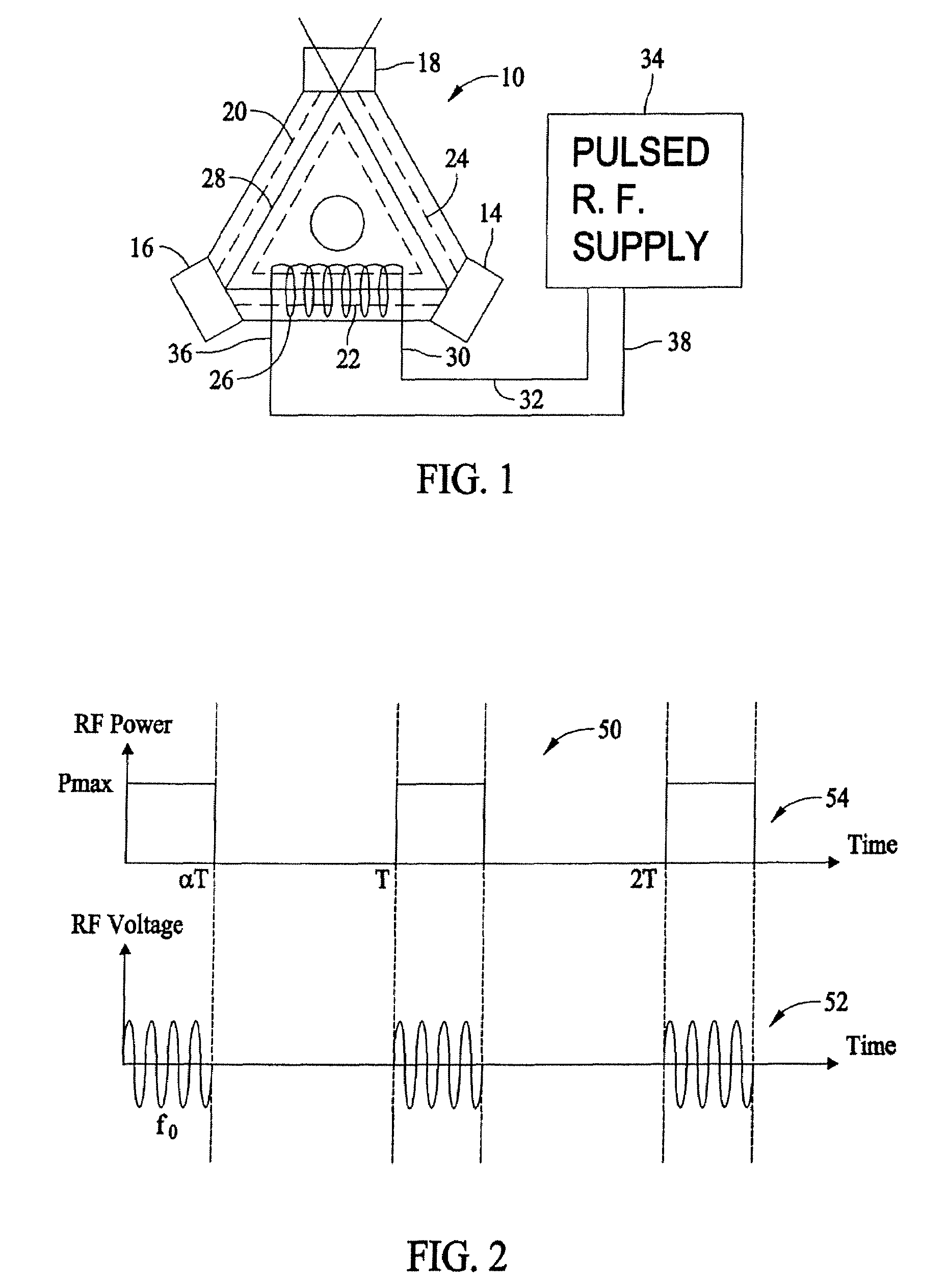
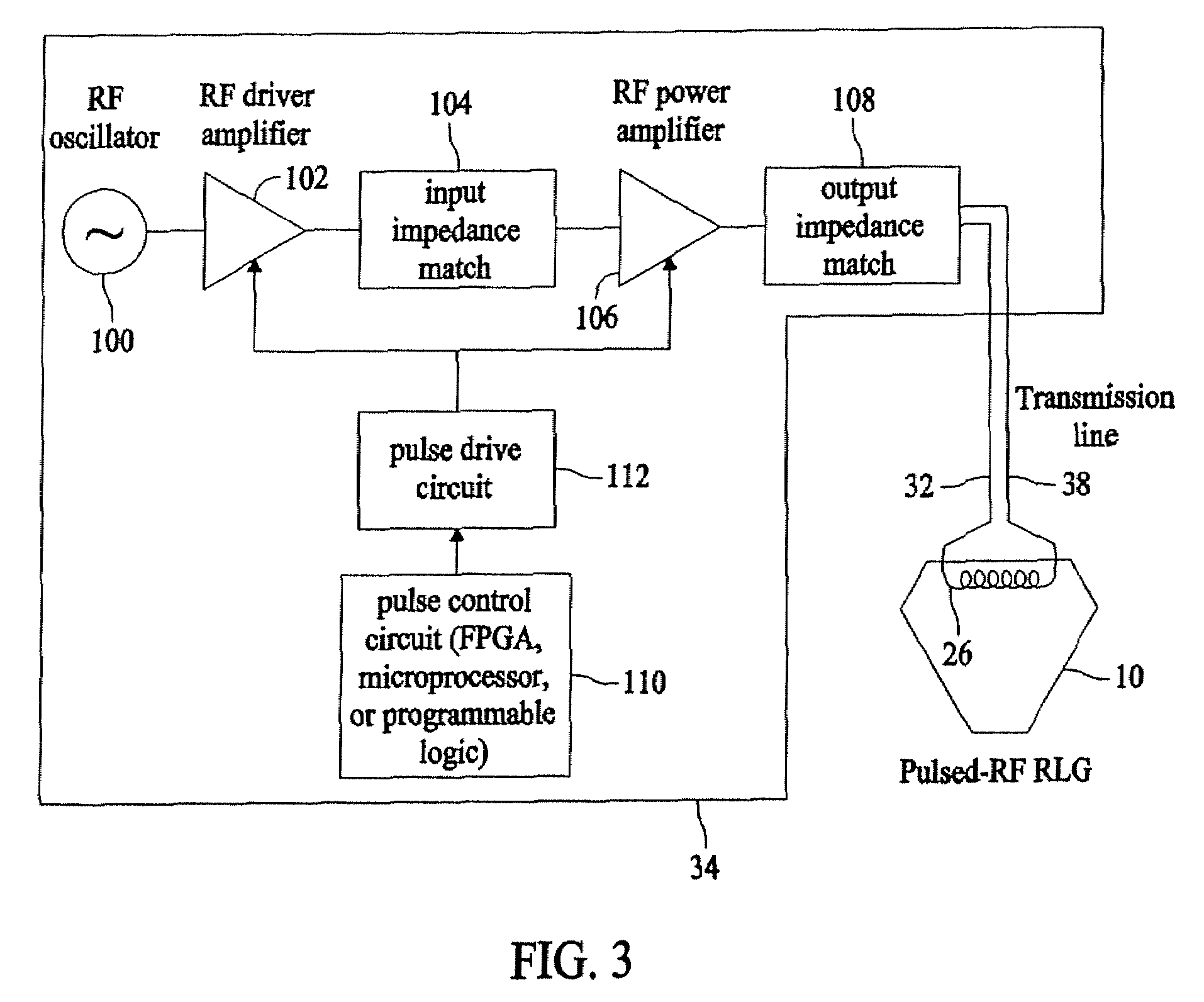
Systems and methods for utilizing pulsed radio frequencies in a ring laser gyroscope
InactiveUS20060165146A1Laser detailsSagnac effect gyrometersRadio frequency energyRing laser gyroscope
A ring laser gyroscope is described which includes a gyroscope block, a radio frequency transmitting device, and a radio frequency energy source. The a gyroscope block has at least one discharge bore containing a gain medium, and the radio frequency transmitting device is located within the gyroscope block in proximity to at least one discharge bore and located so as to encompass the discharge bore. The radio frequency energy source is configured to apply a pulsed radio frequency signal to the transmitting device.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
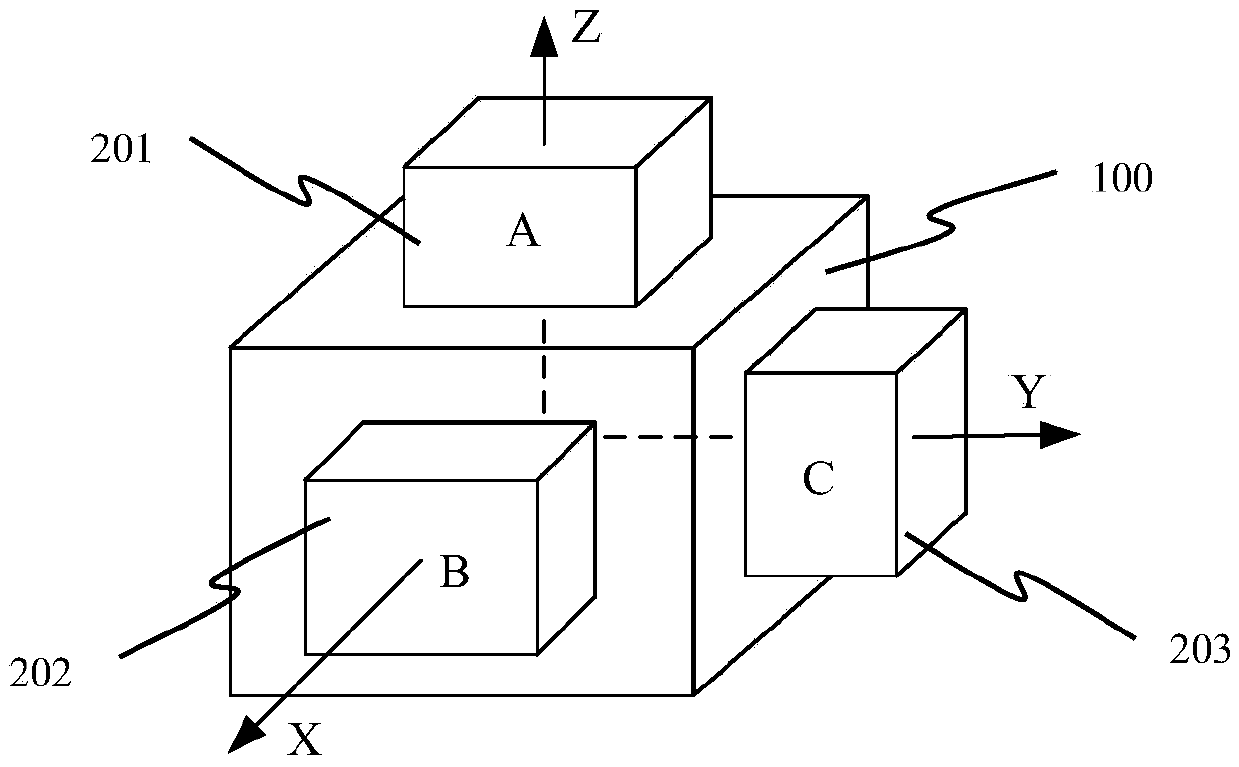
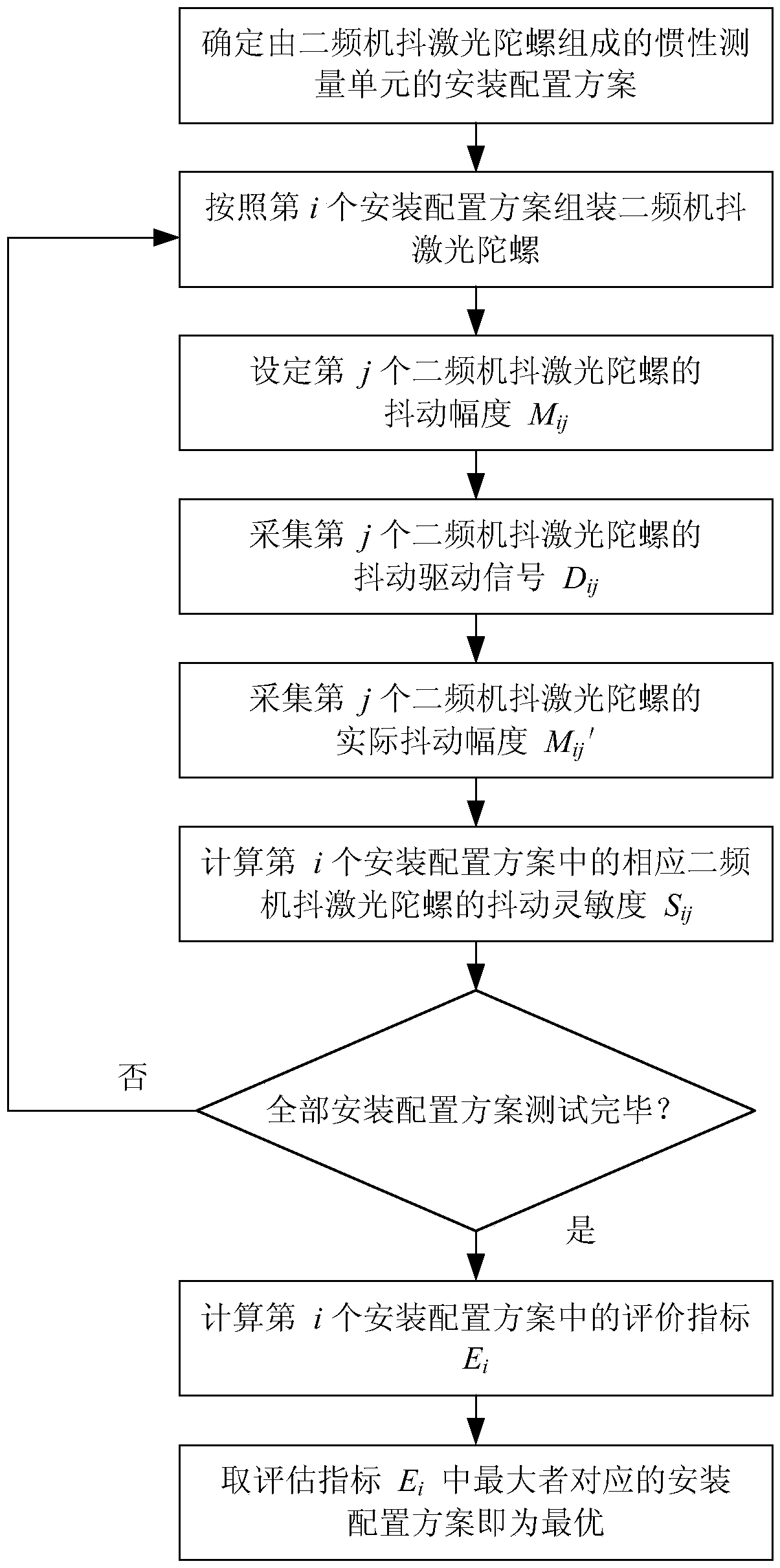
Assessment method for optimal installation configuration of inertial measurement unit with two-frequency mechanically-dithered laser gyroscopes
ActiveCN105547294AMeasuring Jitter SensitivityEasy to measureNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsSagnac effect gyrometersRing laser gyroscopeMarine navigation
The invention discloses a dithering sensitivity-based assessment method for the dithering sensitivities of two-frequency mechanically-dithered laser gyroscopes, and belongs to the field of inertial navigation, guidance and control. The method comprises the steps that 1, the target dithering amplitudes of the two-frequency mechanically-dithered laser gyroscopes are set; 2, the driving voltage of the two-frequency mechanically-dithered laser gyroscopes is collected; 3, the actual dithering amplitudes of the two-frequency mechanically-dithered laser gyroscopes are collected; 4, the dithering sensitivities of the two-frequency mechanically-dithered laser gyroscopes installed on an inertial measurement unit under the different installation configurations are calculated; 5, the dithering sensitivities of the two-frequency mechanically-dithered laser gyroscopes under the different configurations are compared, and then the optimal installation configuration scheme of the inertial measurement unit with the two-frequency mechanically-dithered laser gyroscopes is obtained. When the method is used for designing the inertial measurement unit composed of the two-frequency mechanically-dithered laser gyroscopes, the configuration scheme with the most suitable dithering frequency and installation positions is selected, it is guaranteed that the inertial measurement unit can work in the best state, the using precision of the two-frequency mechanically-dithered laser gyroscopes is improved, and the service life of the two-frequency mechanically-dithered laser gyroscopes is prolonged.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Light path circuit apparatus and ring laser gyro
InactiveUS20090021744A1Low costEasily perform angular velocity detectionSagnac effect gyrometersSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsRing laser gyroscopeRing laser
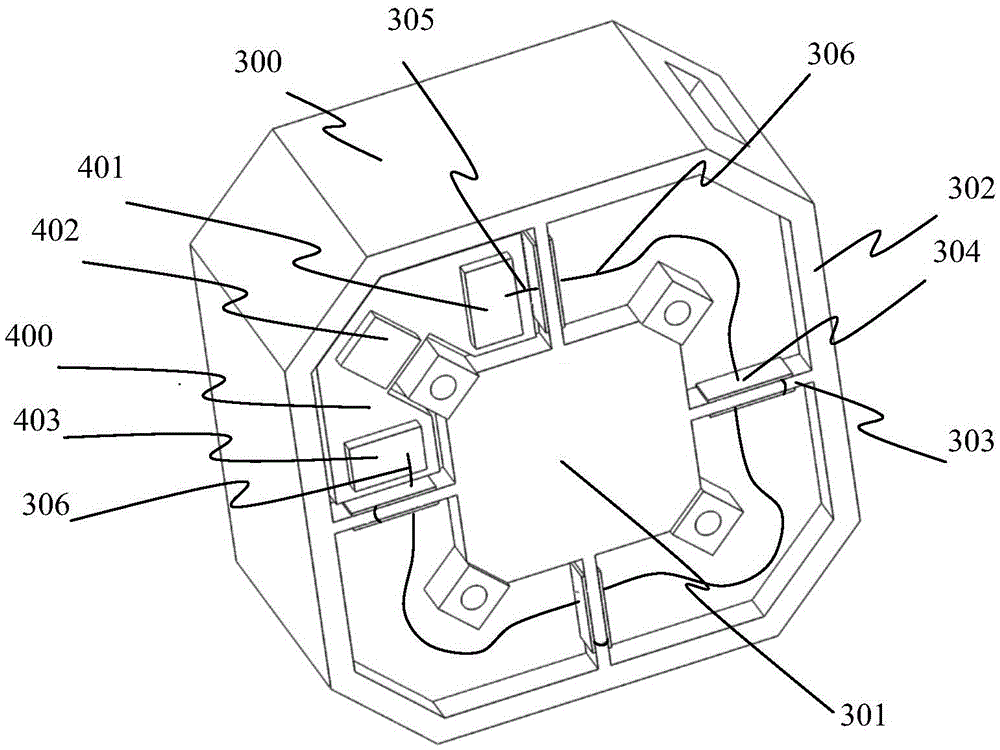
A light path circuit apparatus suited for a small sized ring laser gyro, includes a base having a standard plane, one or more substrates laminated parallel against the standard plane in a direction orthogonal to the standard plane, a light source, wherein on the base and / or the one or more substrates, 3 or more reflective surfaces, having normal lines within a prescribed one plane orthogonal to the standard plane, are constituted parallel or with tilt by a prescribed angle to the standard plane, the light source is disposed to emit light within the prescribed one plane, and the light emitted from the light source circulates within the one plane in a forward and backward direction by three or more reflective surfaces and constitutes a light path circuit that laser oscillates.
Owner:RICOH KK
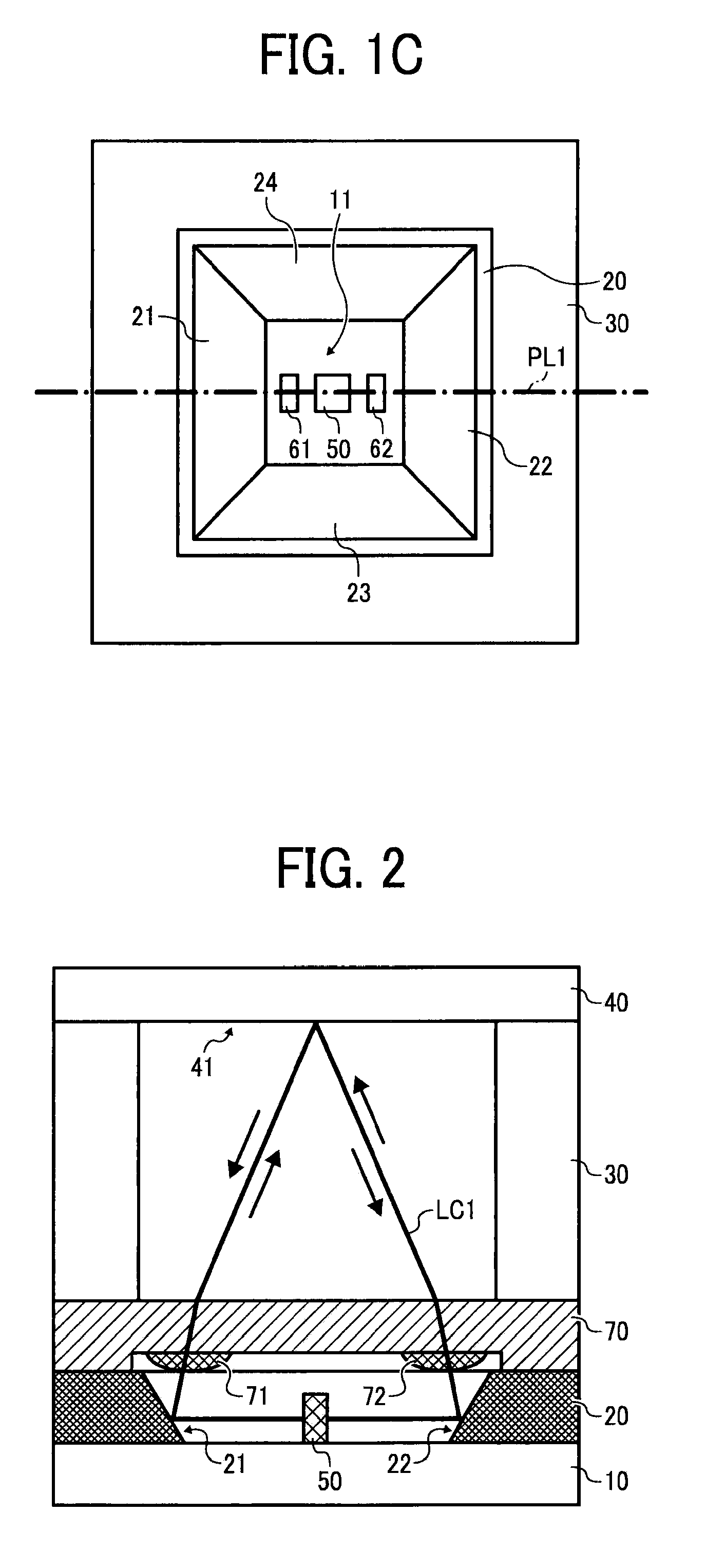
Low-laser loss parameter comprehensive measurement device for high reflector
InactiveCN101839803AFlexible designAdd measurement functionTesting optical propertiesAngle of incidenceRing laser gyroscope
The invention relates to a low-laser loss parameter comprehensive measurement device for a high reflector. In the process of developing a high-performance laser gyro, a high reflector in an annular cavity is required to have very low scattering, transmission and back scattering loss; and in an annular laser gyro, loss generated by all elements of a laser cavity is the main reason for the locking of the annular laser gyro. The low-laser loss parameter comprehensive measuring device for the high reflector, which is provided by the invention, comprises a light source assembly and an integrating sphere which are arranged on an optical platform, wherein the light source assembly is provided with a wave plate and an attenuating plate, and the integrating sphere is provided with a photomultiplier, a transmission measurement component A, an integral scattering measurement component B and a back scattering measurement component C. The invention realizes the measurement of integral scattered power, transmissivity and back scattered power on the same device, improves the measurement function of the device, reduces the measurement cost, and can automatically change an incidence angle by rotating a sample in the measurement; and in addition, all the three measurements can obtain two-dimension measured value distribution map of the sample.
Owner:XIAN TECH UNIV
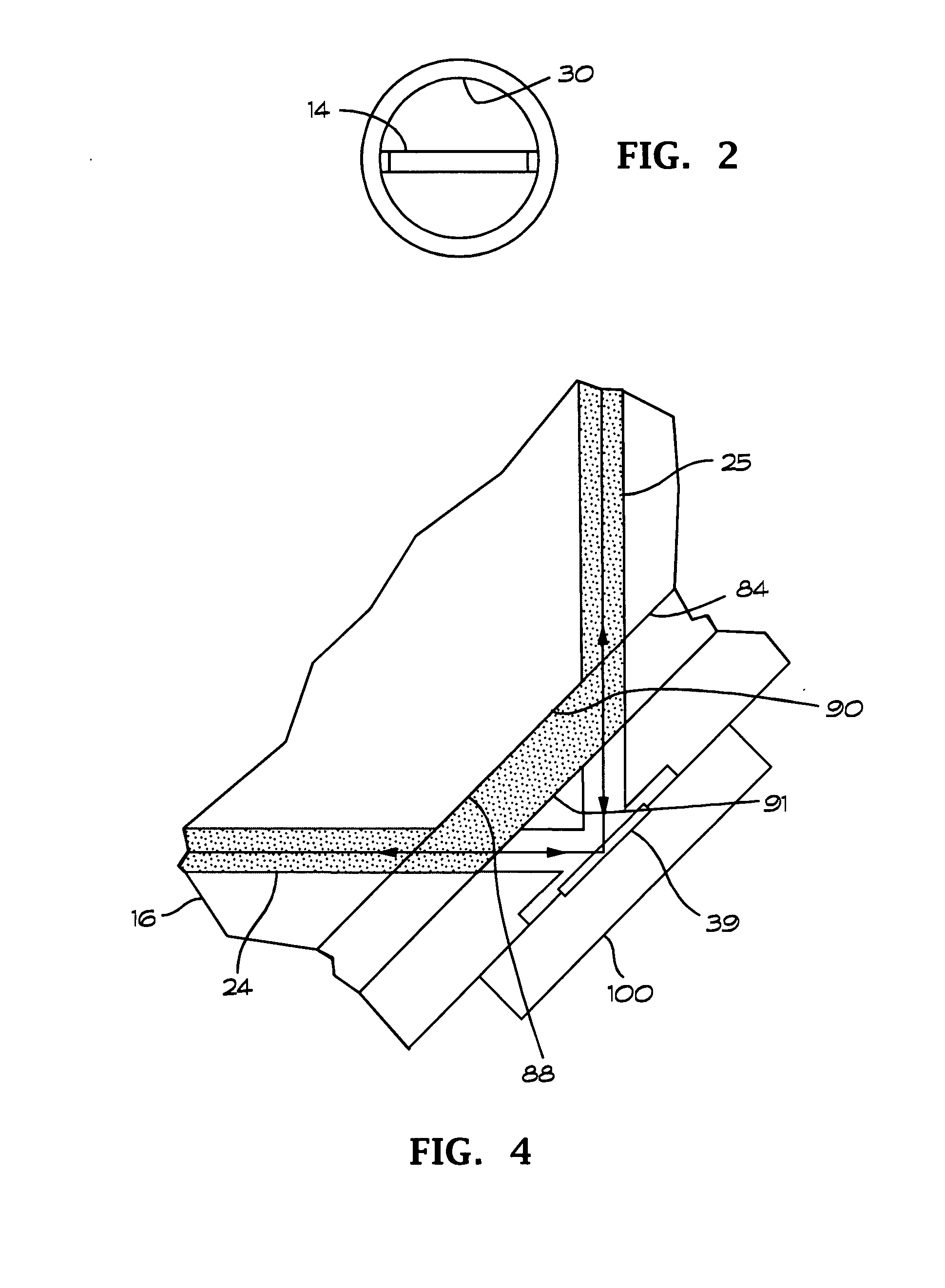
Plasma shunting apparatus and method for ring laser gyroscope
ActiveUS20080304052A1Reduce exposureInexpensiveLaser detailsSagnac effect gyrometersElectrical conductorRing laser gyroscope
A ring laser gyroscope includes a first plasma shunt arranged to prevent the plasma from contacting a first mirror in the gain region and a second plasma shunt arranged to prevent the plasma from contacting a second mirror in the gain region. The first and second plasma shunts may comprise electrical conductors located in the respective mirror wells and arranged such that contact between the plasma and the electrical conductors quenches the plasma in the mirror wells and produces electrical currents that travels across the mirror wells. The electrical conductors may be formed as metallized strips arranged to extend across the mirror wells, or they may be formed from metal wires. The plasma shunts may alternatively comprise diversion passages formed in the frame and arranged such that the plasma fills the diversion passages and bypasses the mirrors.
Owner:LITTON SYST INC
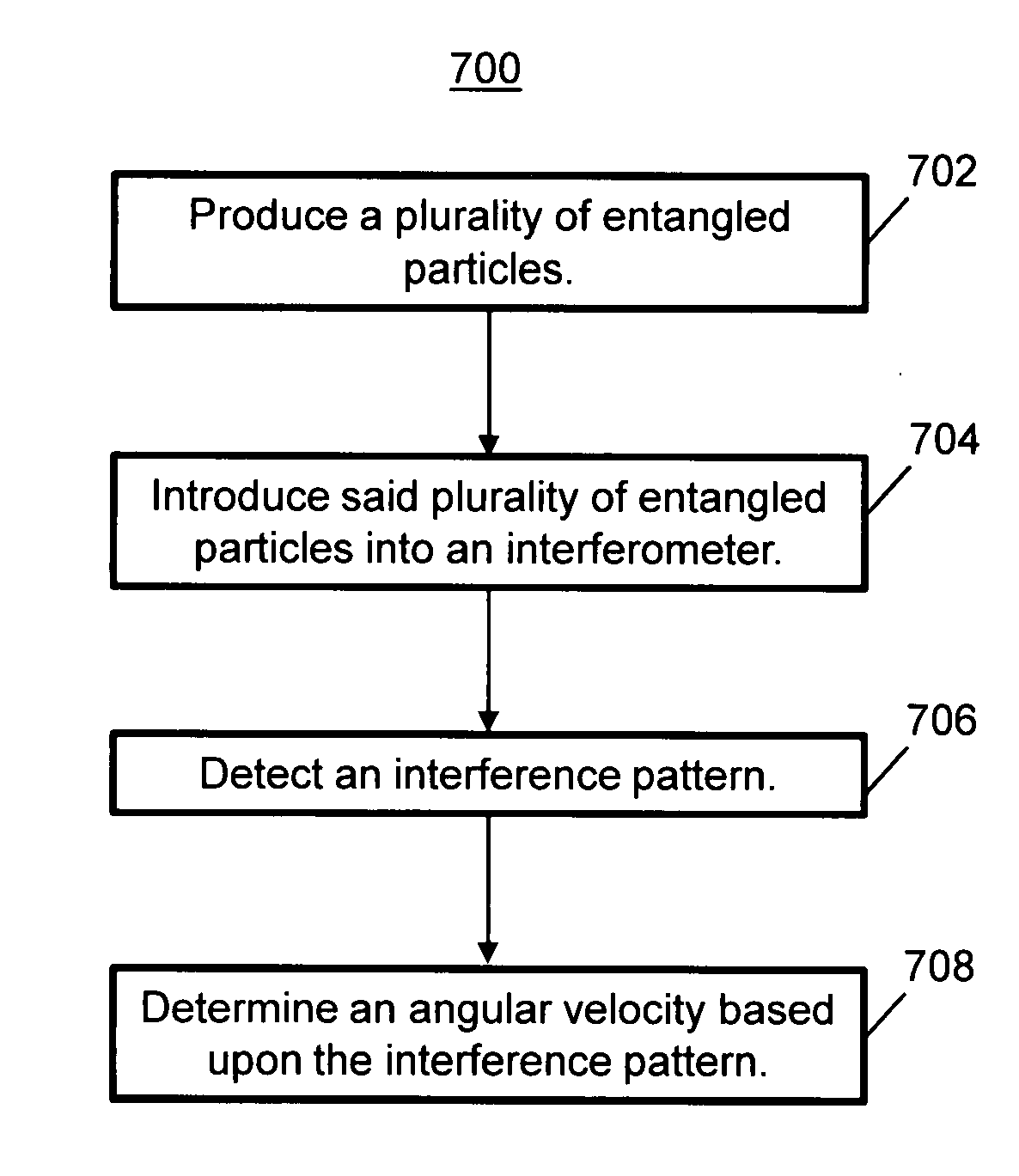
System and method for improving the resolution of an optical fiber gyroscope and a ring laser gyroscope
InactiveUS20080285046A1High resolutionSagnac effect gyrometersSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsImage resolutionAngular velocity
A system and method for improving the resolution of an optical fiber gyroscope and a ring laser gyroscope is provided. Entangled photons are introduced into an interferometer of a gyroscope. One or more detectors detect an interference pattern used to determine the angular velocity of a platform. The interference pattern may be a spatial and / or temporal interference pattern. The detectors may count the sub-wavelength interferometer fringes that indicate the direction and degree of angular rotation about the central axis of the apparatus. The detectors may measure a beat frequency.
Owner:FULLERTON LARRY W
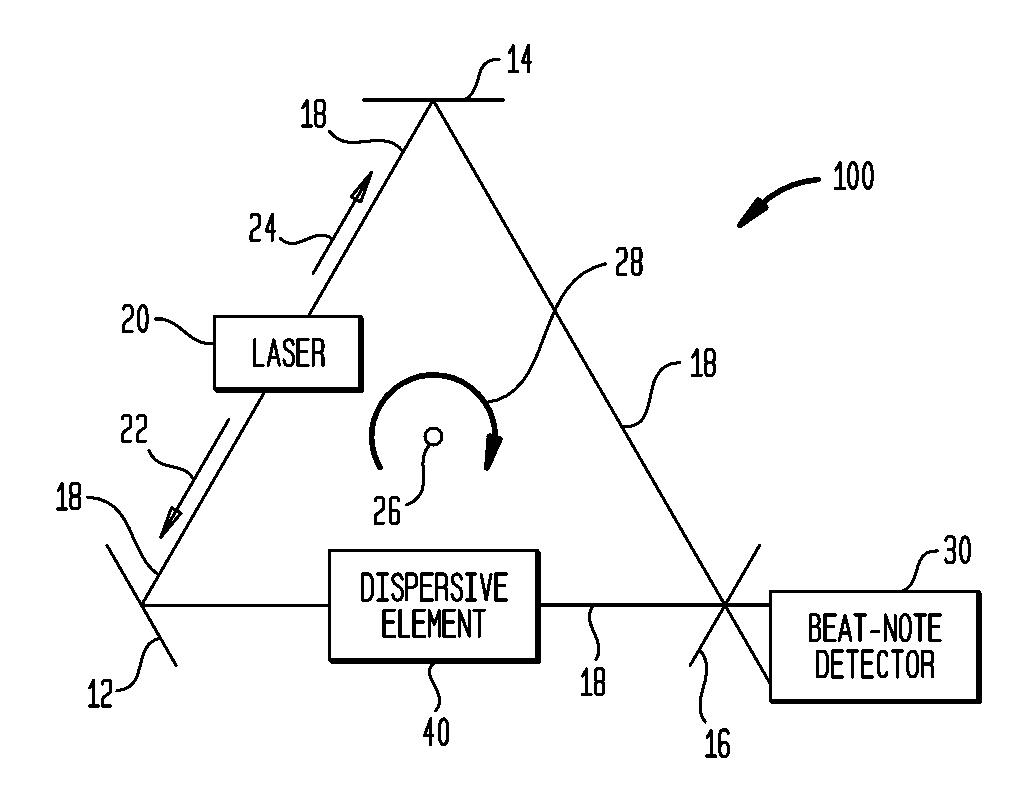
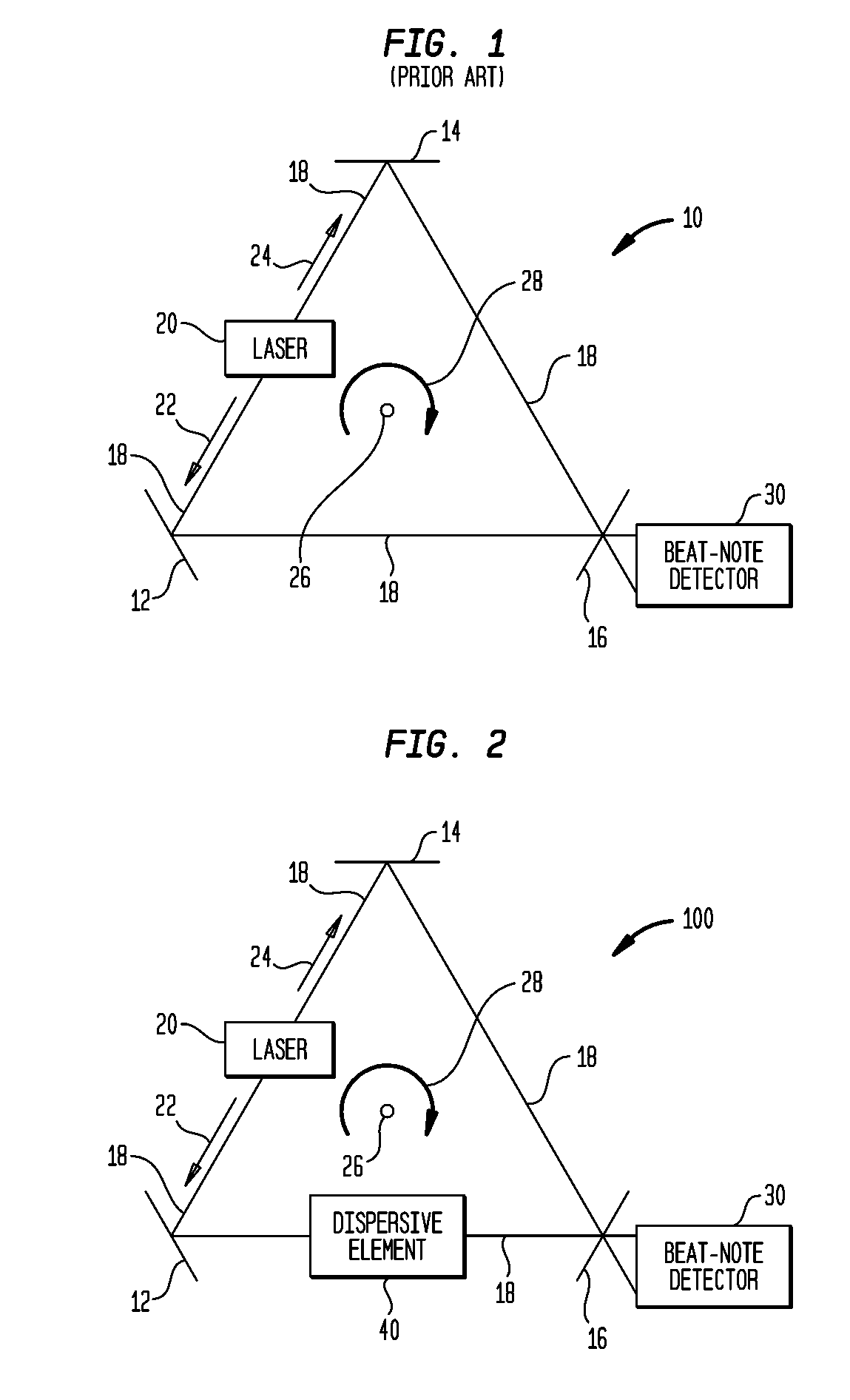
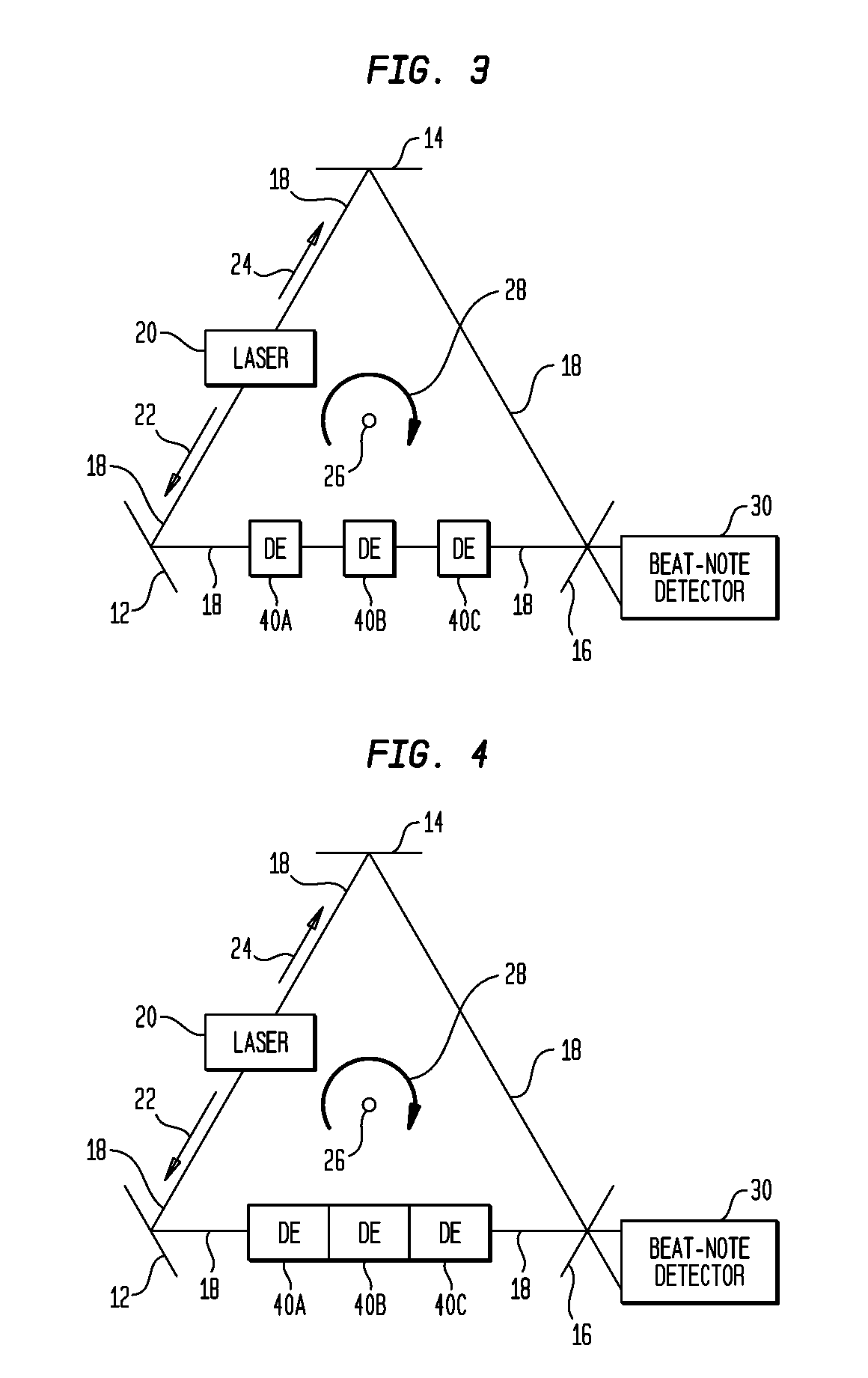
Ring-laser gyroscope system using dispersive element(s)
InactiveUS7804600B1Increase rotation speedReduce speedLaser detailsSagnac effect gyrometersRefractive indexRing laser gyroscope
A ring-laser gyroscope system includes a ring-laser gyroscope (RLG) and at least one dispersive element optically coupled to the RLG's ring-shaped optical path. Each dispersive element has a resonant frequency that is approximately equal to the RLG's lasing frequency. A group index of refraction defined collectively by the dispersive element(s) has (i) a real portion that is greater than zero and less than one, and (ii) an imaginary portion that is less than zero.
Owner:NASA
Ring laser gyroscope that does not require mirrors
ActiveUS20060132788A1Speed measurement using gyroscopic effectsSagnac effect gyrometersFiberClassical mechanics
In an embodiment of a ring laser gyroscope, a hollow bandgap fiber is filled with a gas or material that will generate laser beams within the fiber upon being excited by an energy source. A detector coupled to the fiber detects a standing wave pattern within the fiber, wherein changes in the detected standing wave pattern indicates a corresponding change in the orientation of the fiber.
Owner:LITTON SYST INC +1
Laser gyroscope offset frequency method based on external cavity feedback
InactiveCN103033178AReduce complexityEliminate mechanical noiseSagnac effect gyrometersPath lengthPhase difference
The invention relates to a laser gyroscope offset frequency method based on external cavity feedback. The method particularly comprises the following steps of: establishing a feedback external cavity outside a laser gyroscope cavity, and reflecting clockwise beams into a laser resonant cavity; and arranging a nonreciprocal optical device in an external cavity light path, so that feedback light waves of clockwise and anticlockwise light waves have phase difference, and frequency offset is established between the clockwise and anticlockwise light waves of the laser gyroscope. A path length modulation part is arranged in the feedback external cavity light path, and the external cavity light path is modulated, so that the frequency offset of the laser gyroscope is modulated, and an effect similar to mechanical dither is obtained. A modulation signal in a laser gyroscope reading device is filtered by employing a filtering technology, so that an angular velocity signal of laser gyroscope measurement is obtained. According to the method, mechanical noise is not generated, and extremely high modulation frequency can be adopted, so that a response speed of the laser gyroscope is increased.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Laser mirror for a ring laser gyroscope
InactiveUS20080137706A1Optical resonator shape and constructionGyroscopes/turn-sensitive devicesOptical coatingRing laser gyroscope
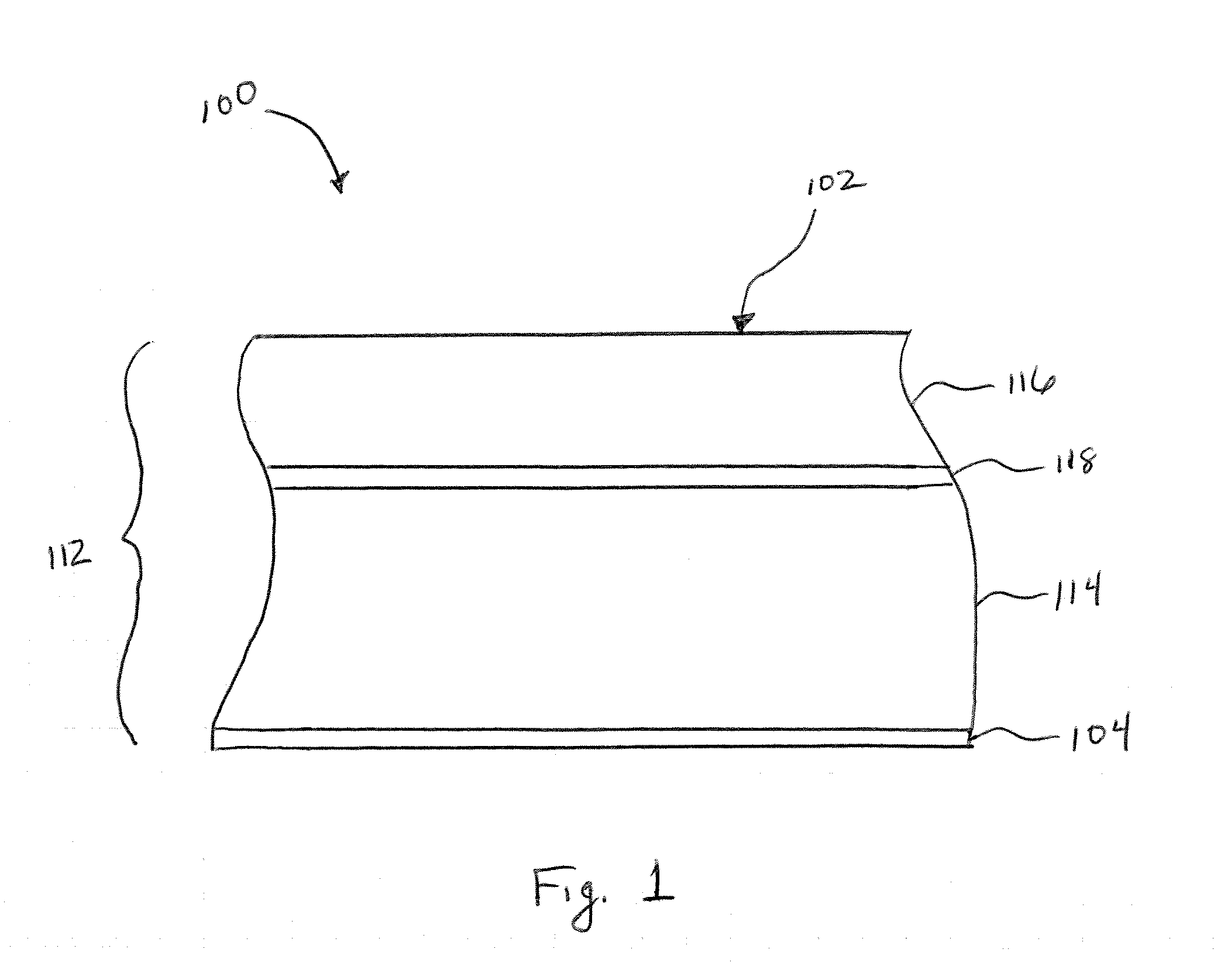
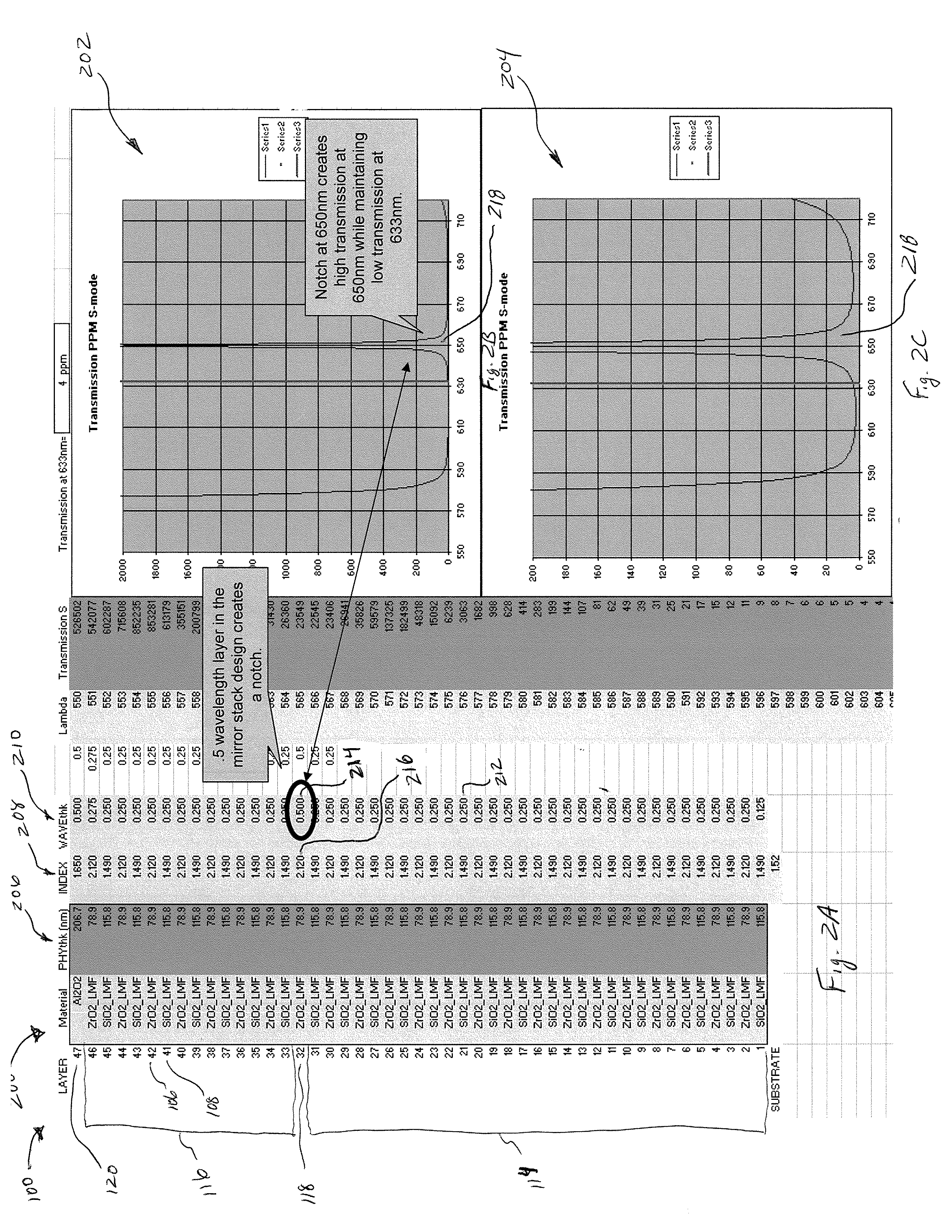
A laser mirror for a ring laser gyroscope (RLG) includes an intermediate optical coating, positioned within approximately a mid portion of the laser mirror for improving the performance of the RLG, and specifically for improving the reflectance of at least one wavelength emission. The properties of the intermediate optical coating and its placement within the laser mirror results in a good reflection of a first predetermined wavelength emission wavelength, for example a 633 nanometer wavelength emission, and a poor reflection of a second predetermined wavelength emission, for example a 650 nanometer wavelength emission. In one embodiment, the intermediate optical coating includes a half-wave or a multiple half-wave thickness and is made from Zirconium Oxide.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Method for reducing square two-frequency laser gyroscope magnetic sensitivity
ActiveCN103424111AReduce magnetic susceptibilityReduce non-coplanar anglesSagnac effect gyrometersPath lengthResonance
The invention discloses a method for reducing square two-frequency laser gyroscope magnetic sensitivity. The method includes the steps that a, at least two adjacent light path long control mirrors are installed in four reflectors on a square two-frequency laser gyroscope; b, an external magnetic field is initiatively applied to the laser gyroscope in a normal work state, and gyroscope difference frequency change caused by application of the external magnetic field is detected; c, angles of pitch of the two light path long control mirrors are controlled so as to adjust coplane degrees of a resonance light path of a gyroscope resonance cavity, the gyroscope difference frequency change caused by the external magnetic field is made to be the smallest and the state is kept finally. Compared with the prior art, the method is characterized in that path length control mirrors commonly used in the square two-frequency laser gyroscope in the prior art are replaced by light path long control mirrors, the angle control function of the control mirrors is utilized, gyroscope difference frequency signals serve as detection objects directly, non-coplanar angles of the resonance light path are reduced through adjustment, and therefore the purpose of reducing the square two-frequency laser gyroscope magnetic sensitivity can be achieved.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Systems and methods for utilizing pulsed radio frequencies in a ring laser gyroscope
ActiveUS20080089381A1Laser detailsSagnac effect gyrometersRadio frequency signalRing laser gyroscope
Ring laser gyroscope that includes a gyroscope block, a radio frequency transmitting device, and a radio frequency energy source. The gyroscope block has at least one discharge bore containing a gain medium, and the radio frequency transmitting device is located within the gyroscope block in proximity to at least one discharge bore and located so as to encompass the discharge bore. The radio frequency energy source is configured to apply a pulsed radio frequency signal to the transmitting device.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Method and apparatus for pavement cross-slope measurement
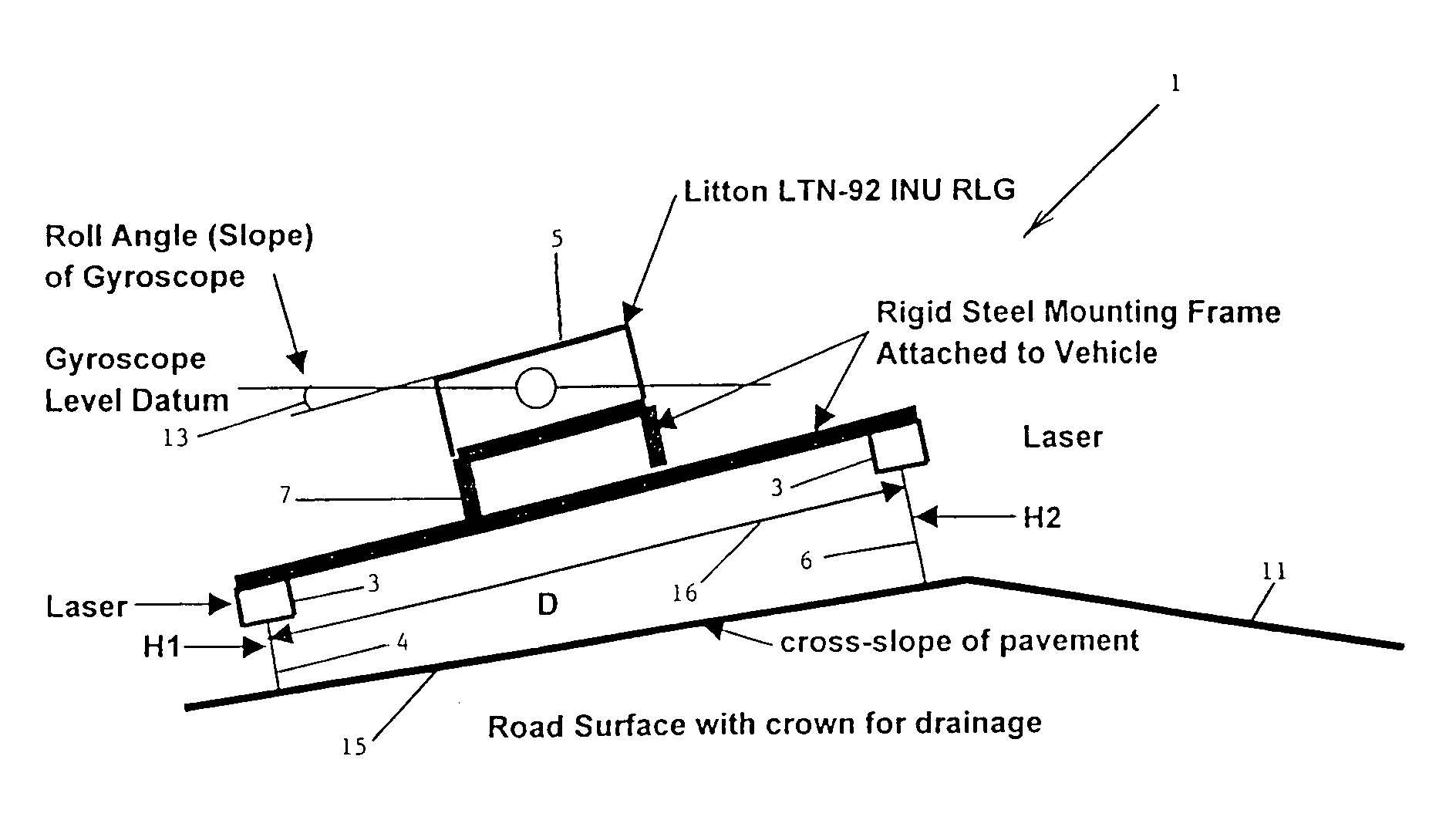
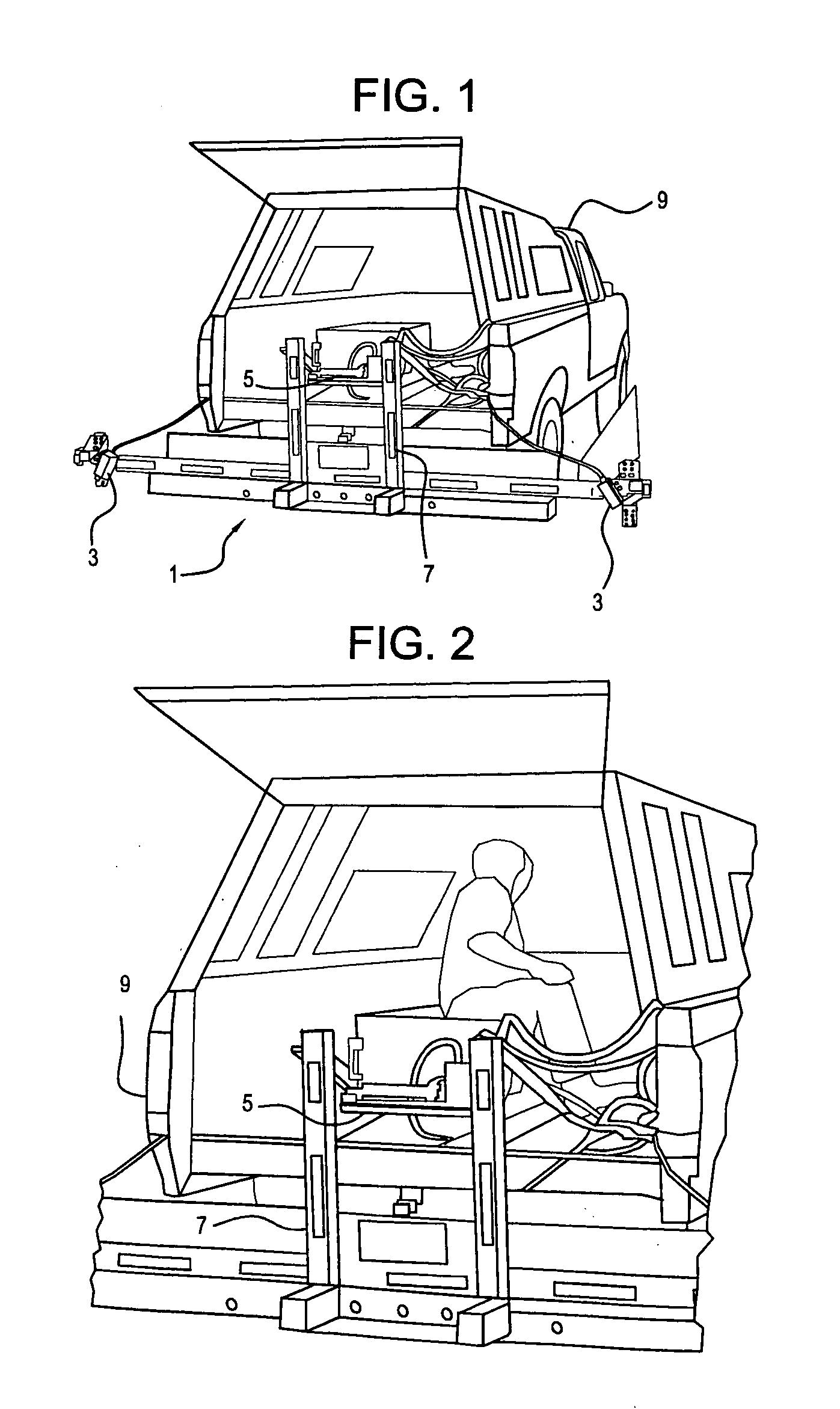
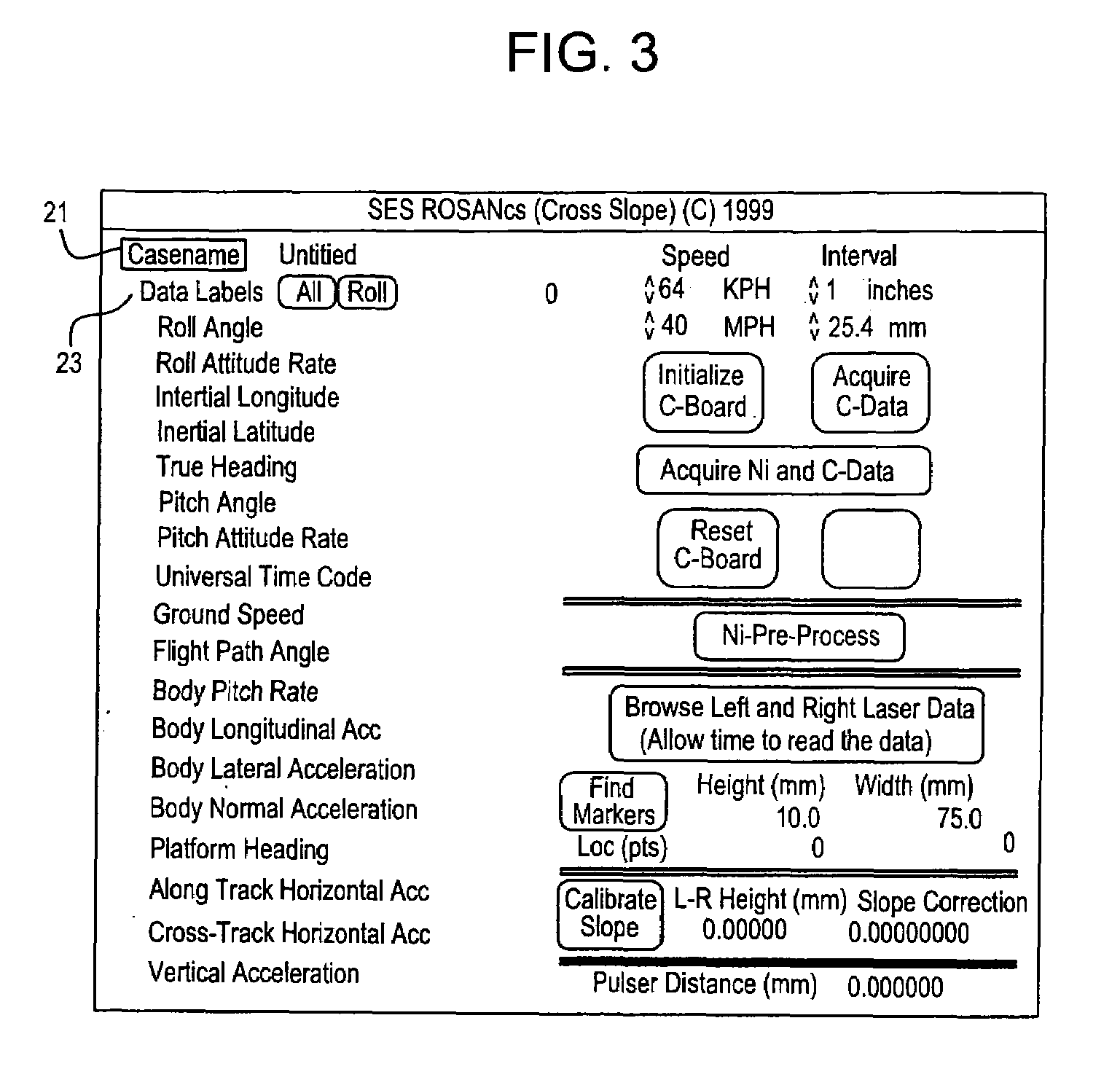
InactiveUS7142952B2Reduce riskLess-costly to performInstruments for road network navigationAnalogue computers for trafficMeasurement deviceRing laser gyroscope
Pavement cross-slope is measured at highway speeds by mounting a ring-laser gyroscope on a vehicle and measuring deviation of the transverse slope of the vehicle. Precise laser distance measuring devices are mounted transversely with respect to the vehicle at significantly distant points to measure vehicle roll by measuring displacement of the laser distance measuring units from the pavement. The difference between at rest measurements of the laser distance measuring devices, the dynamic measurements produced by those devices and the relation of the dynamic measurement to the distance between the measurements provides the exact value of vehicle roll with respect to the pavement. That exact value of vehicle roll is compared with the ring gyro angular measurement to produce a precise measurement of pavement slope. A positional device is mounted on the vehicle for determining the position of the vehicle on the roadway. A computer is mounted on the vehicle and a recording device is mounted on the vehicle to record the precise slope of the roadway at the precise position on the pavement being measured.
Owner:MEKEMSON JAMES R +1
Systems and methods for utilizing pulsed radio frequencies in a ring laser gyroscope
ActiveUS7697587B2Laser detailsSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsRadio frequency signalRing laser gyroscope
Ring laser gyroscope that includes a gyroscope block, a radio frequency transmitting device, and a radio frequency energy source. The gyroscope block has at least one discharge bore containing a gain medium, and the radio frequency transmitting device is located within the gyroscope block in proximity to at least one discharge bore and located so as to encompass the discharge bore. The radio frequency energy source is configured to apply a pulsed radio frequency signal to the transmitting device.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
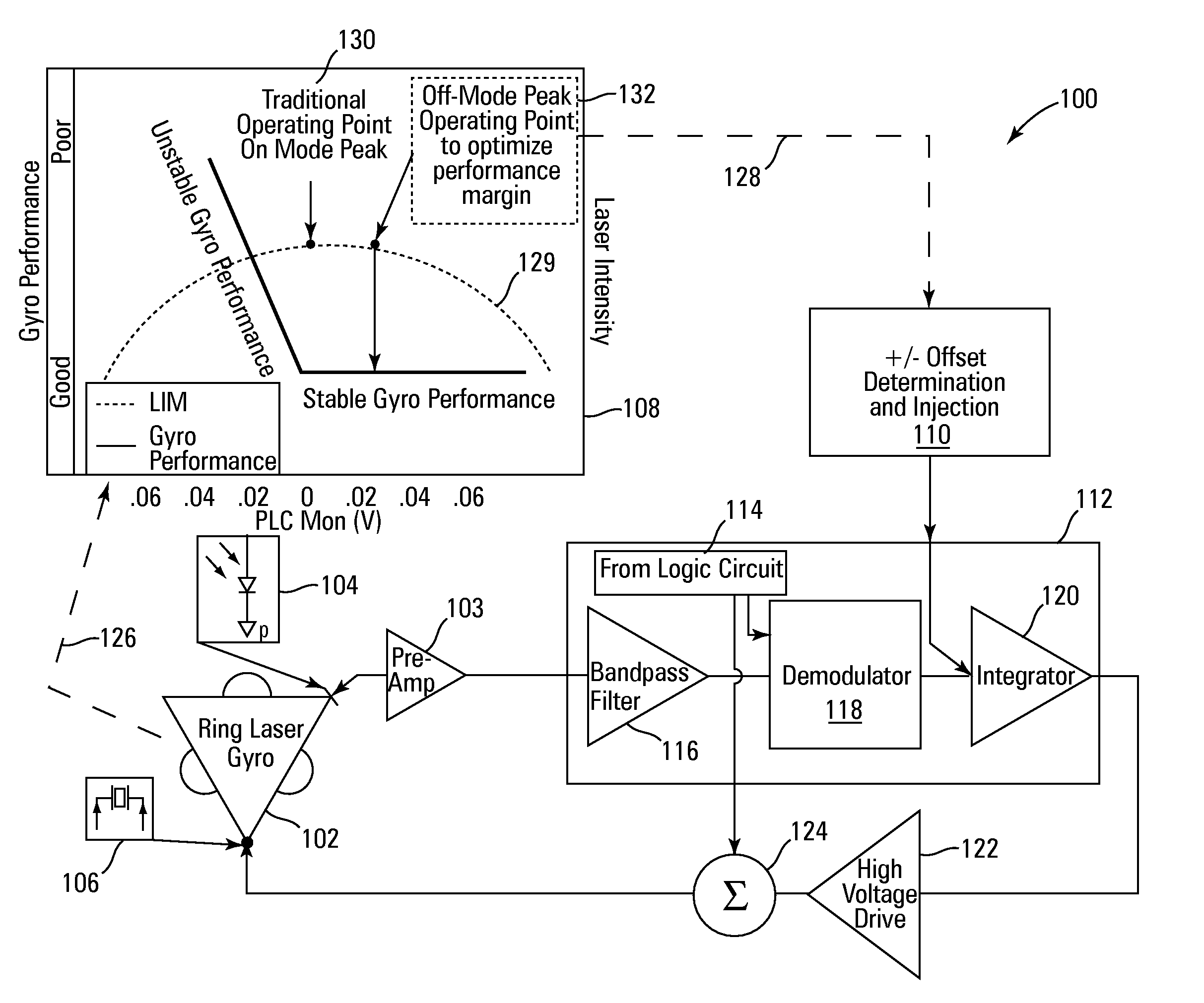
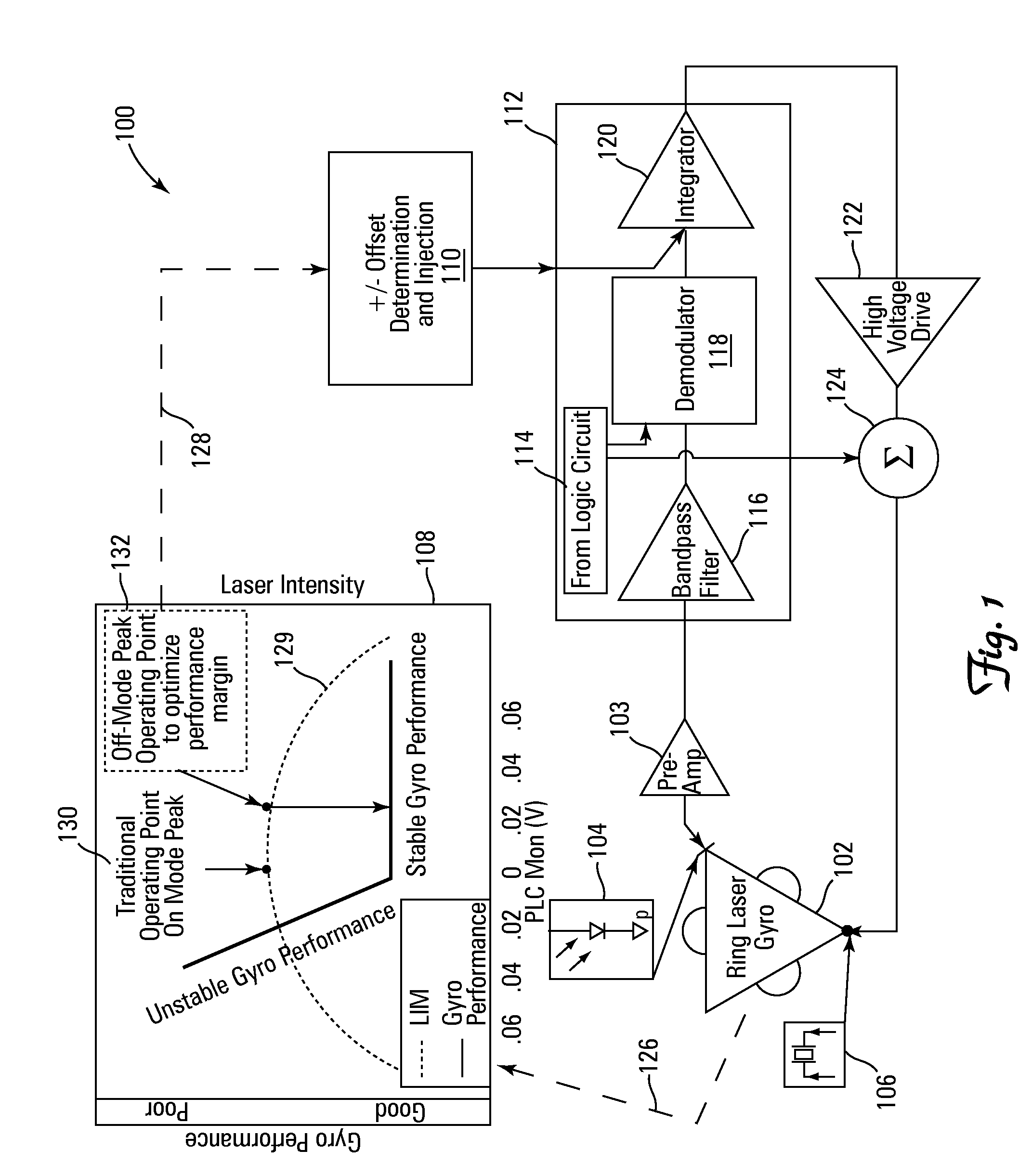
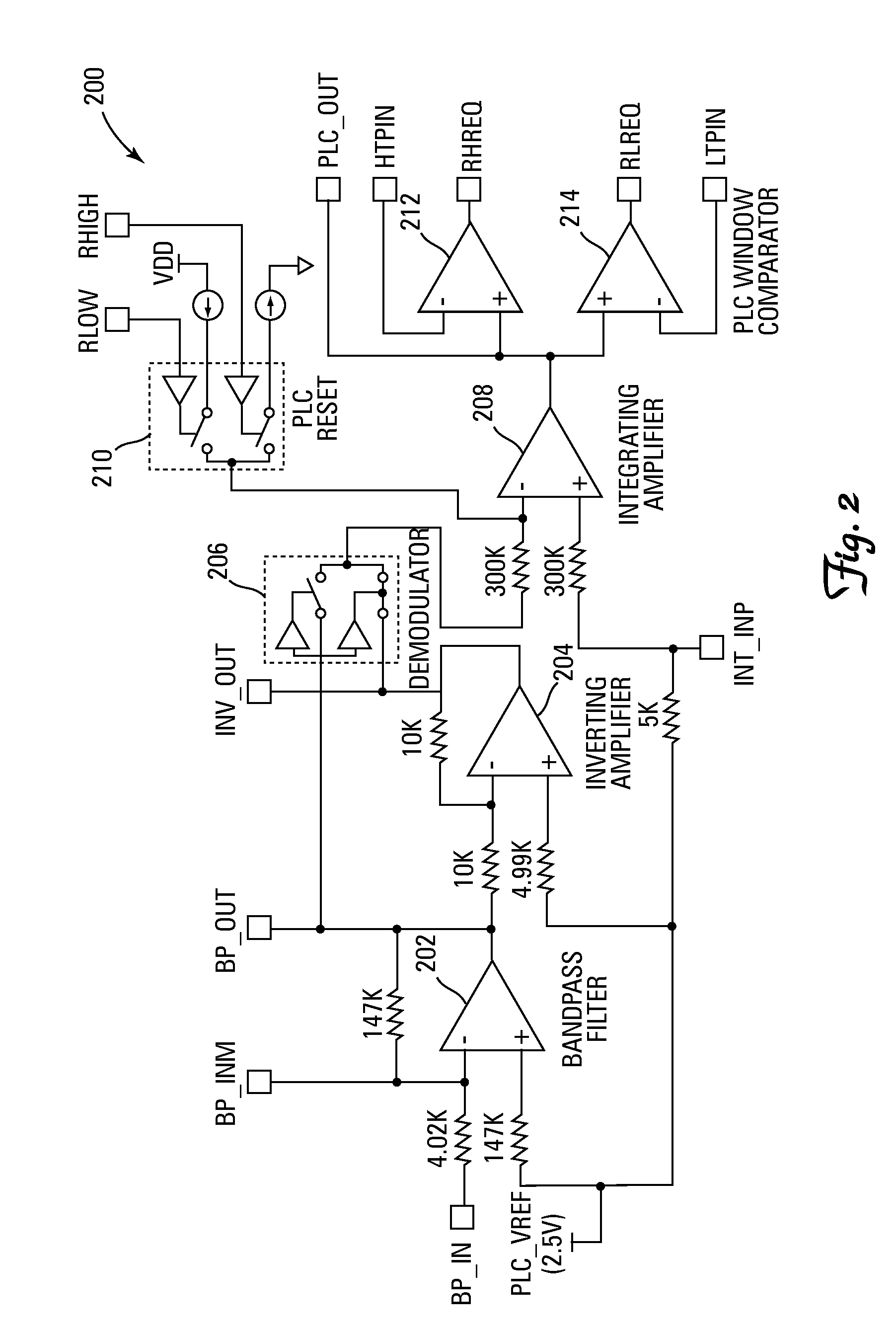
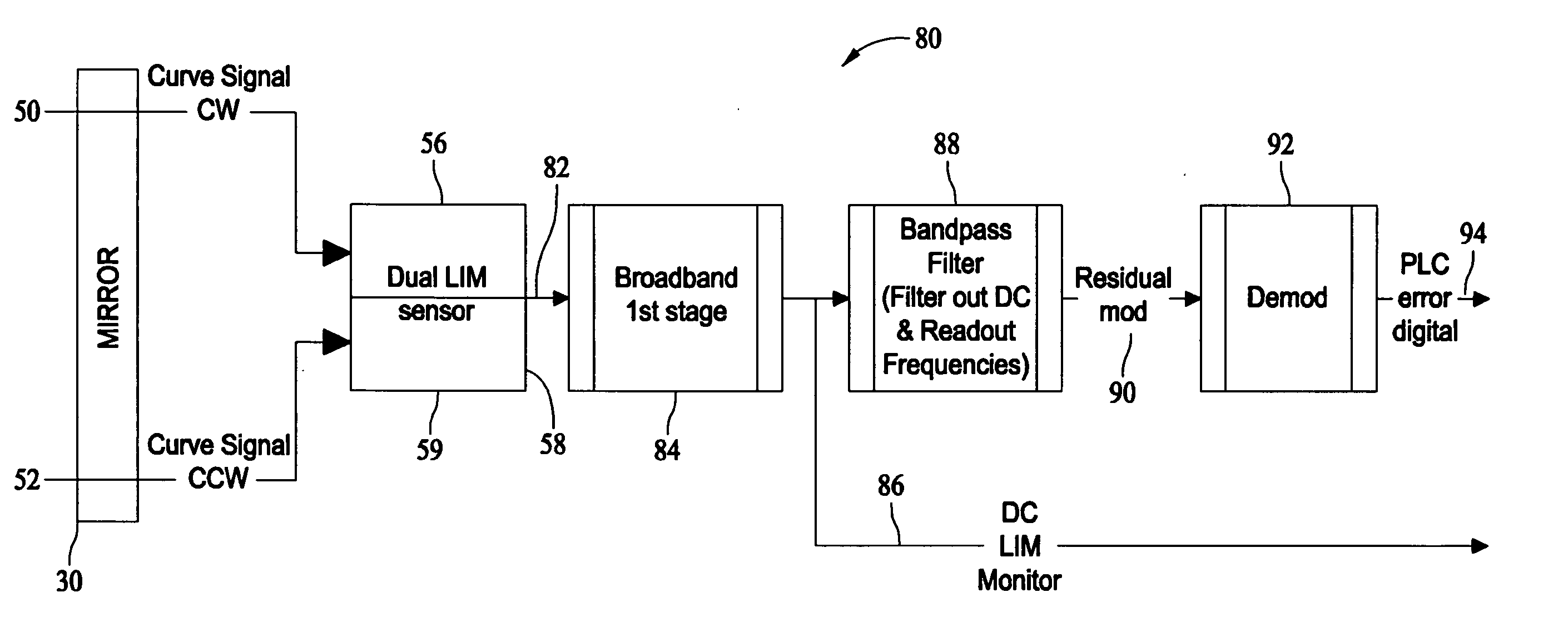
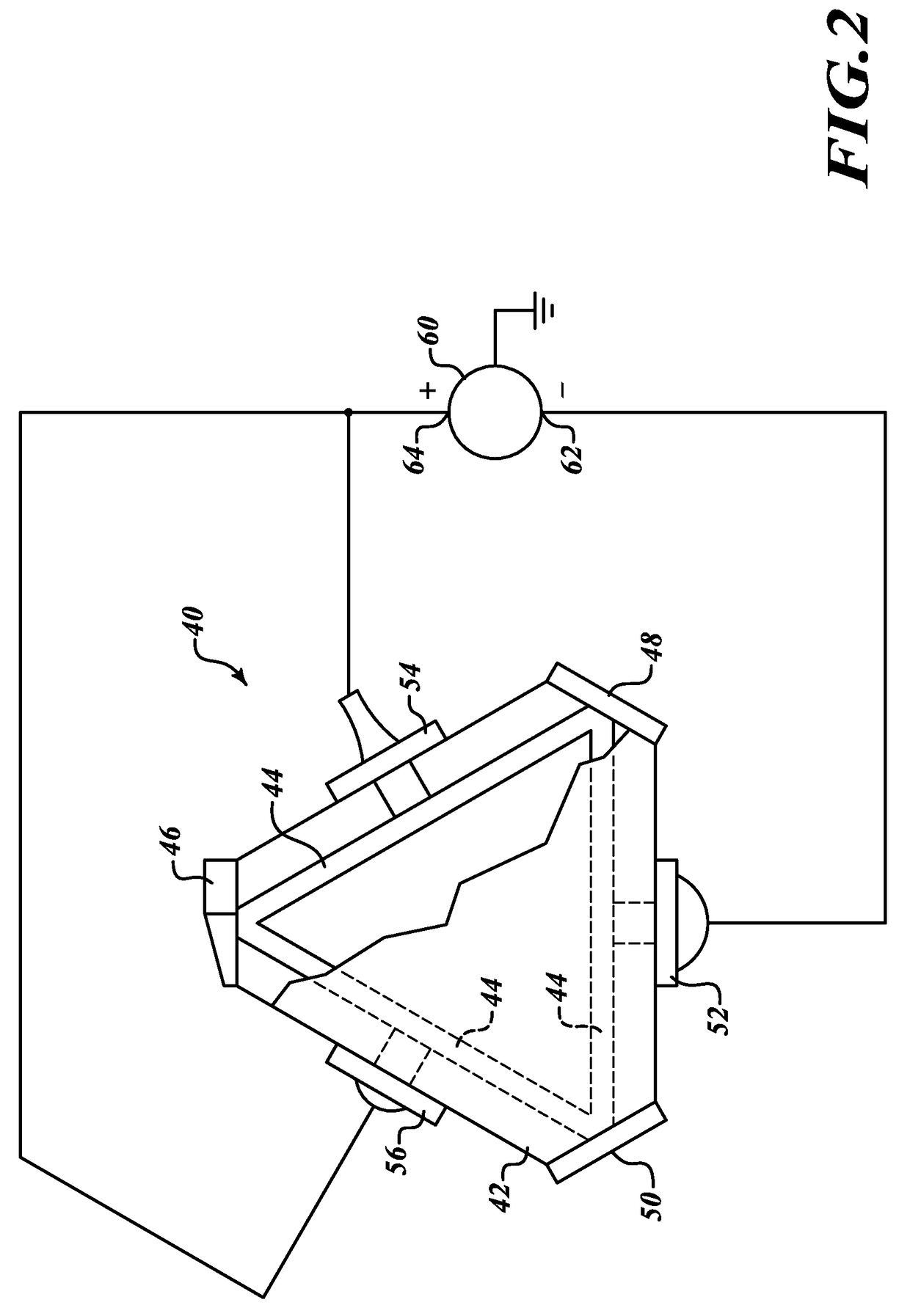
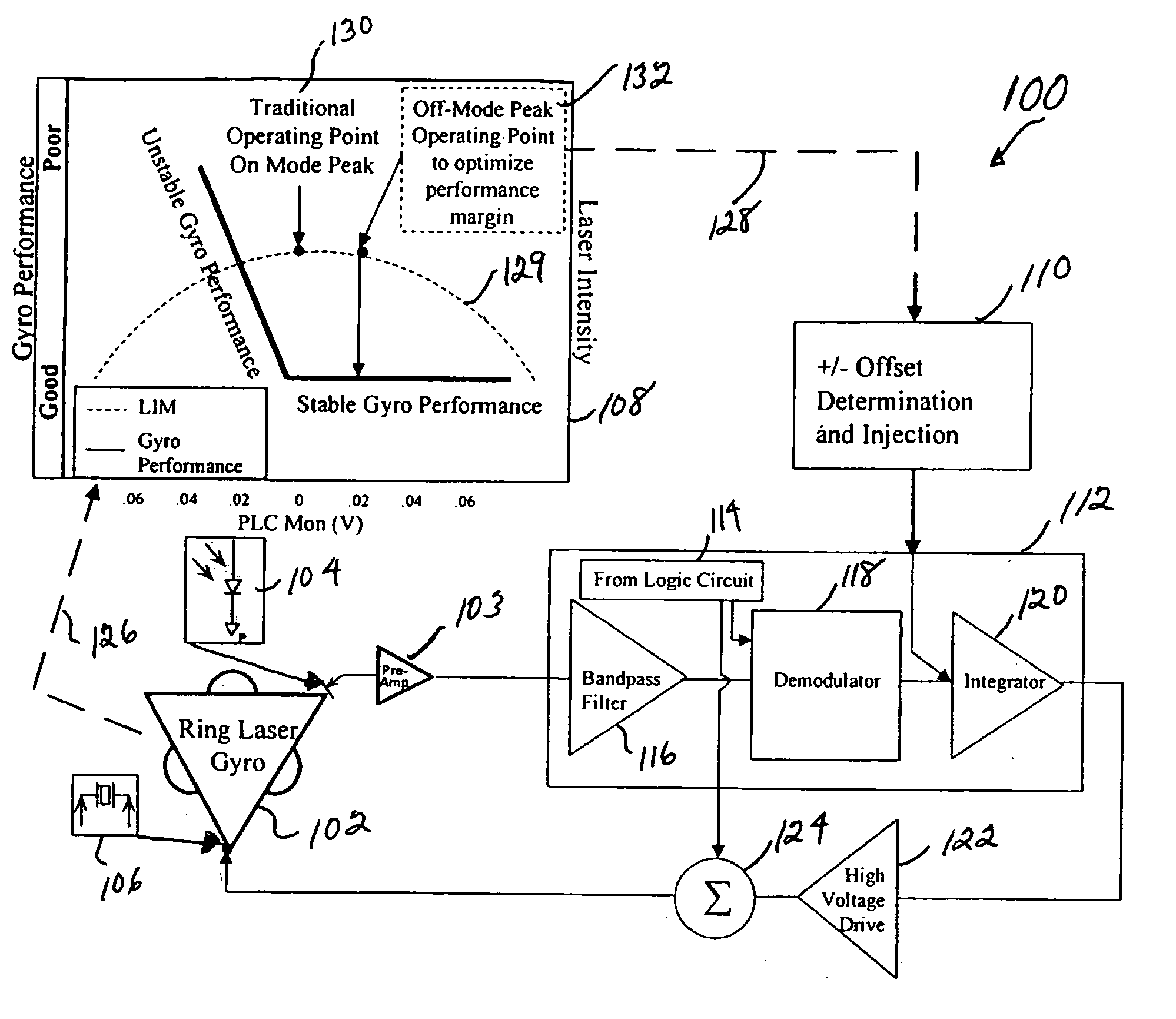
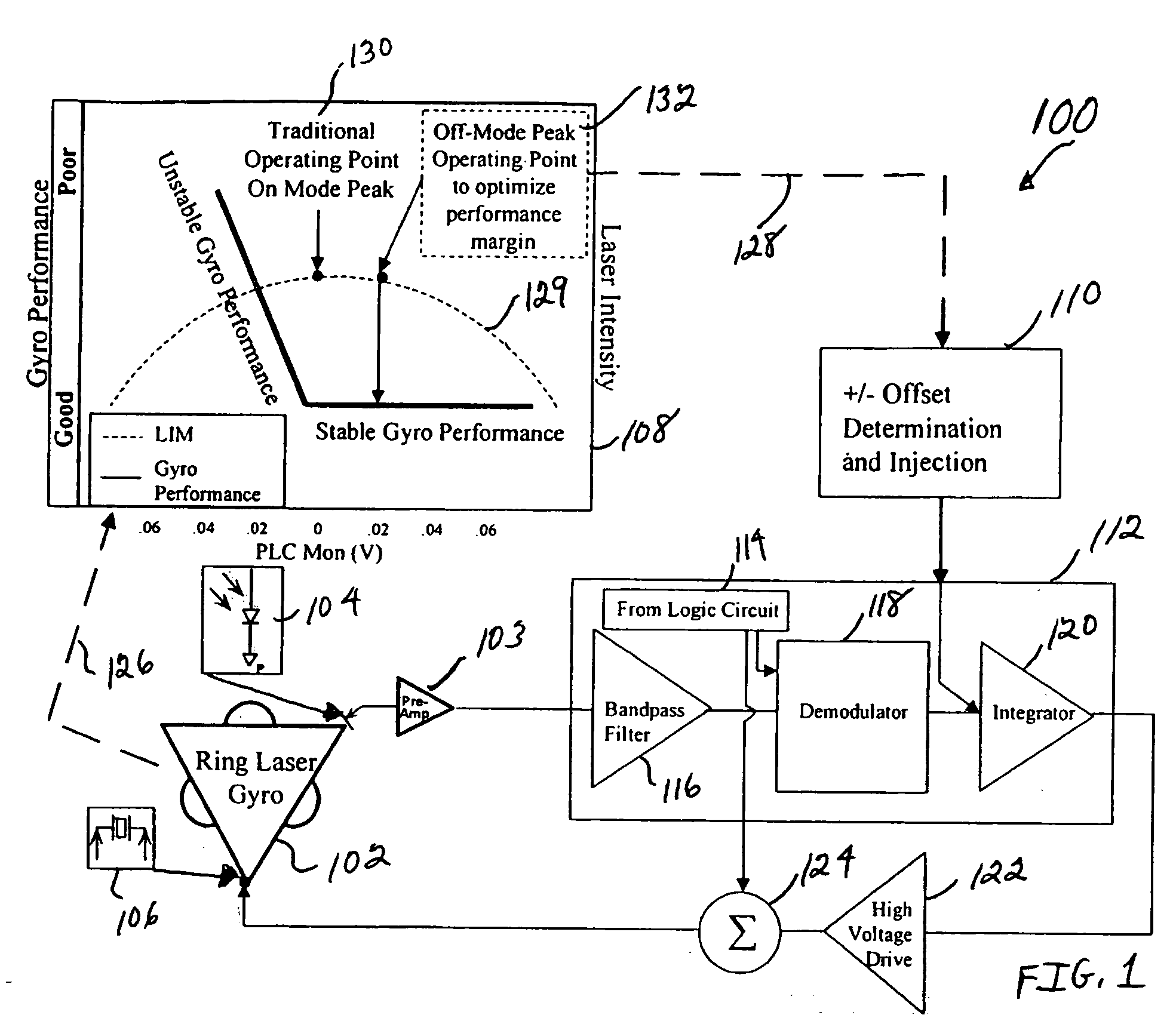
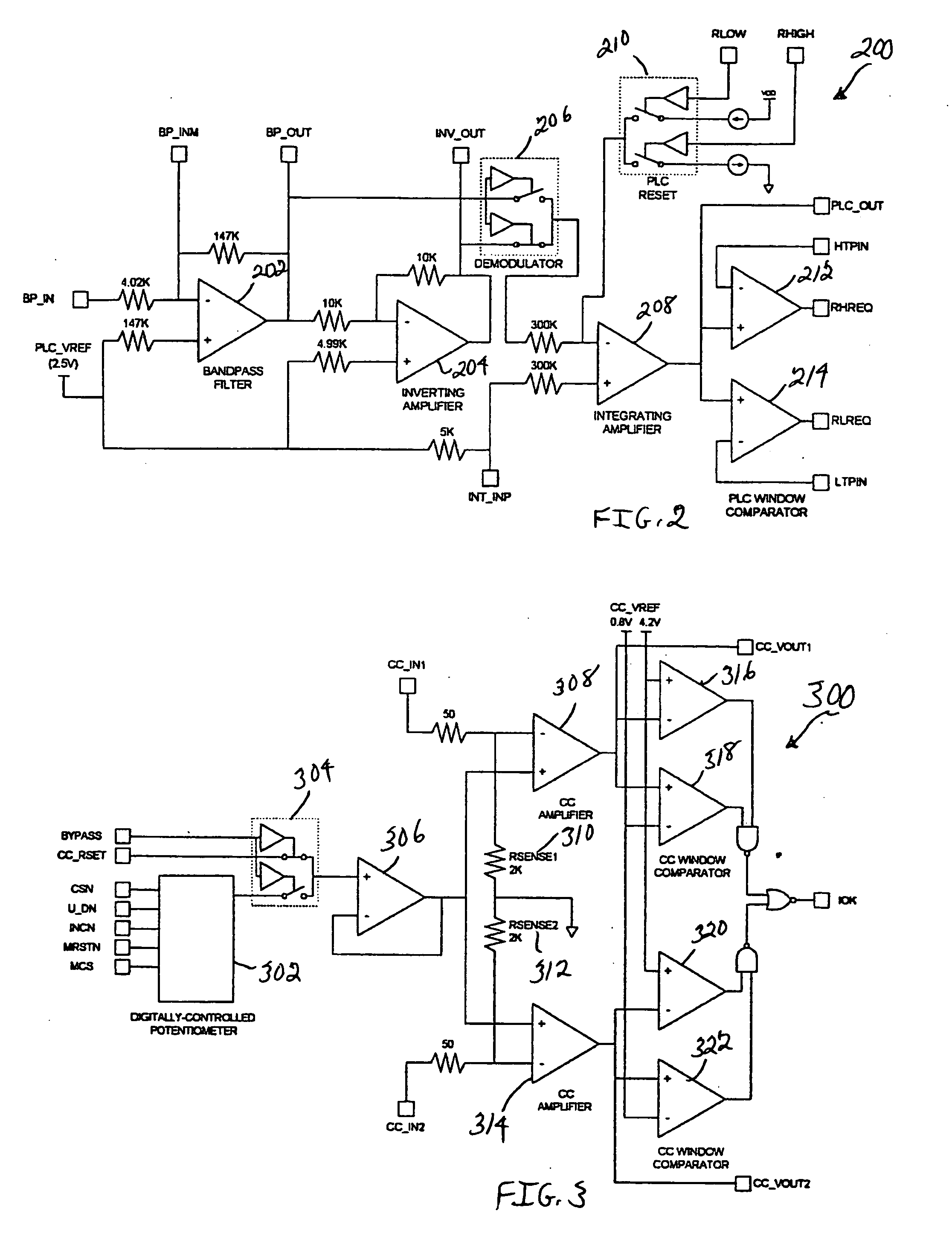
System, circuit and method for off-mode-peak operation of ring laser gyroscopes
InactiveUS7271915B2Avoid exciting the undesirable transverse modesSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsSagnac effect gyrometersOperating pointRing laser gyroscope
A system, circuit and method are disclosed for operating a Ring Laser Gyroscope (RLG) off-mode-peak to avoid exciting undesirable transverse modes. An alternate PLC operating point can be used to bias the optical path length of the RLG to an appropriate side of an ideal integer number of wavelengths, and thus avoid exciting the undesirable transverse modes. Although this alternate PLC operating point is not perfect with respect to establishing an integer number of wavelengths, this operation provides acceptable performance of the RLG's (in particular, short length path RLG's), and acceptable margin can be established relative to variations in the PLC set points involved.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
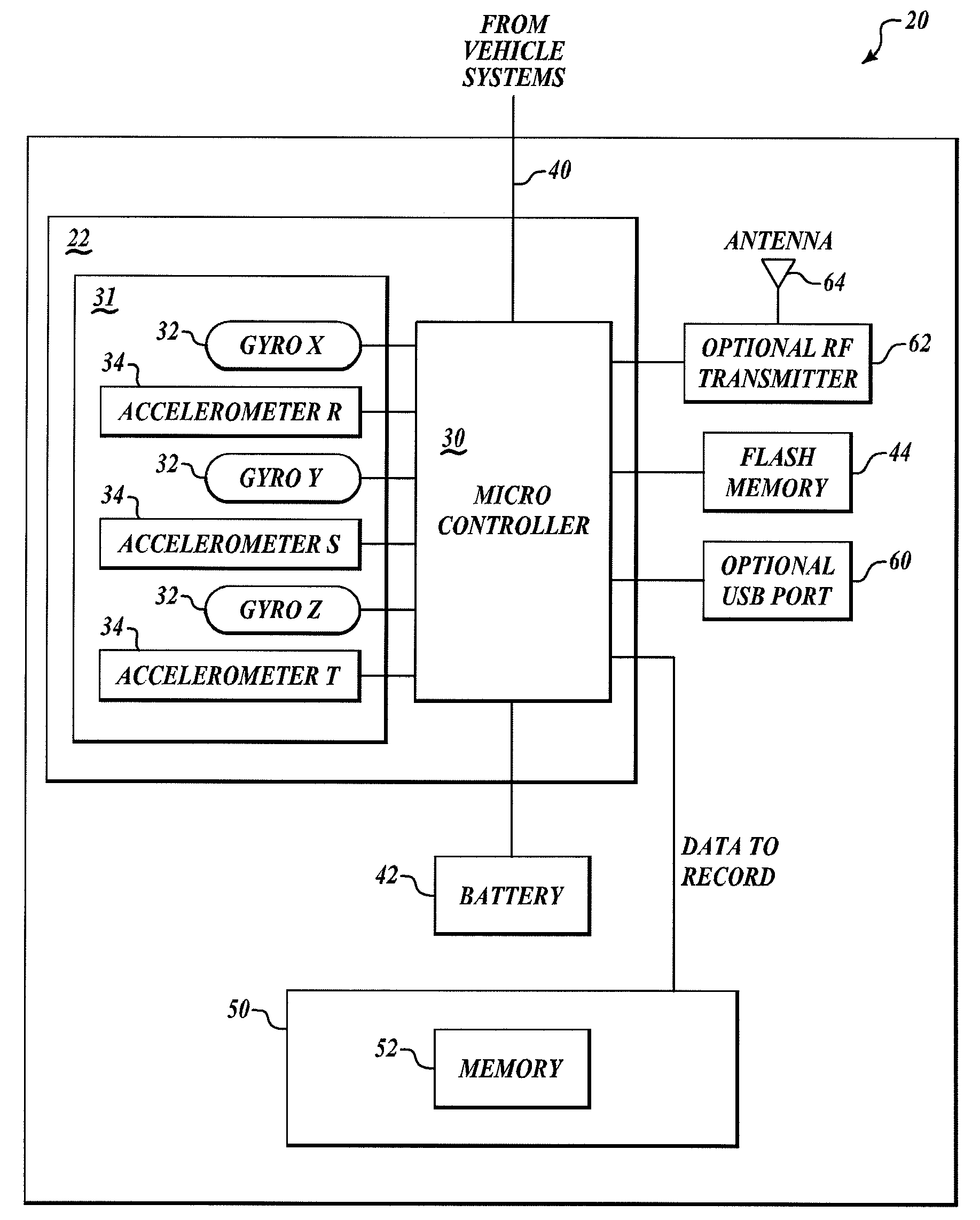
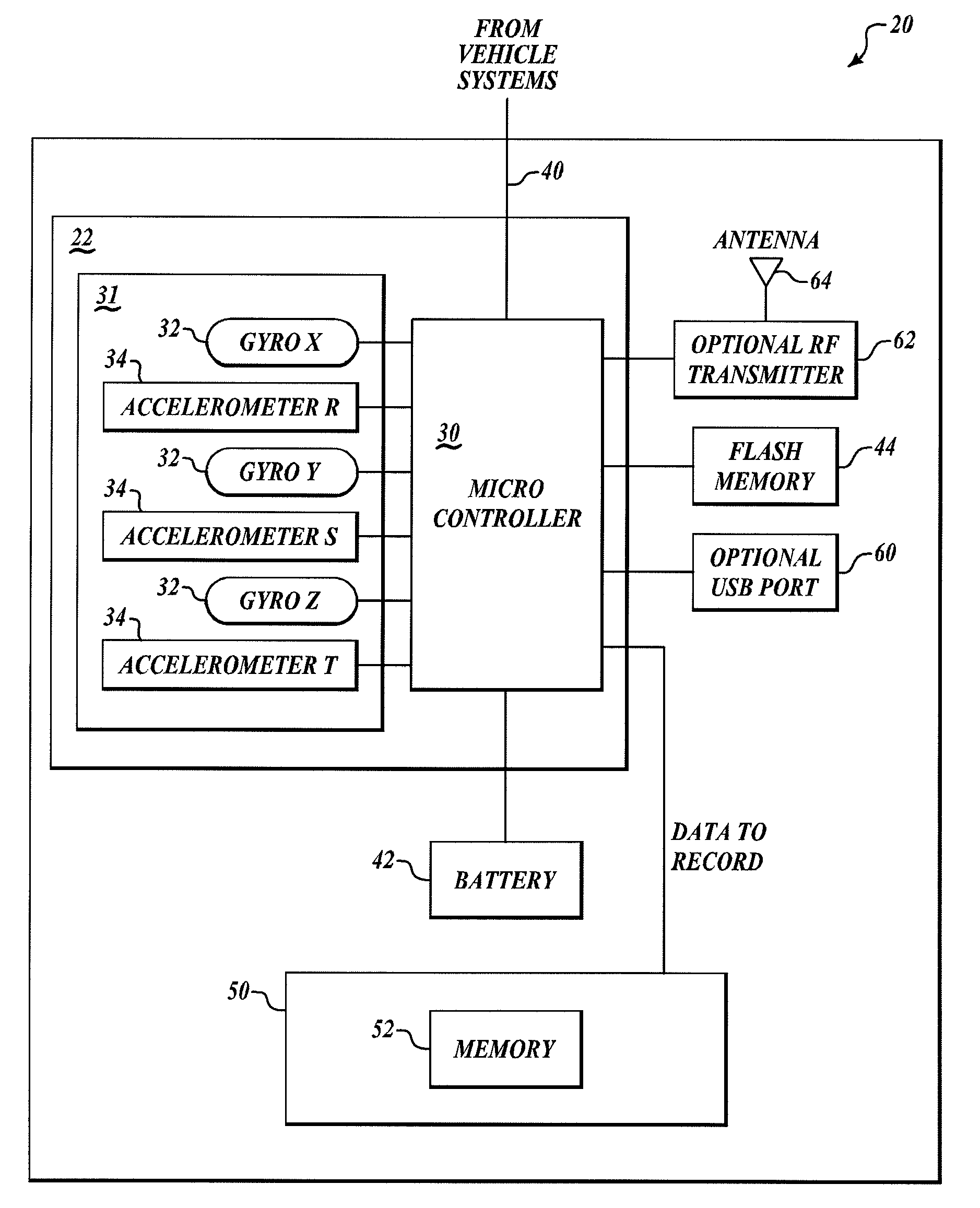
Data recorder
InactiveUS20080249680A1Vehicle testingRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesMicrocontrollerRing laser gyroscope
Systems and methods for recording information in a vehicle data recorder device. The vehicle data recorder device includes an inertial measurement unit (IMU), a crash survivable unit having memory, and a microcontroller in data communication with the IMU and the memory. The microcontroller receives angular rate information and acceleration information from the IMU and stores the received angular rate information and acceleration information in the memory. The IMU includes two or more MEMS gyroscopes or ring laser gyroscopes. In one example, the microcontroller stores angular rate information and acceleration information in the memory until a threshold event has occurred. The threshold event includes at least one of the angular rate information or acceleration information indicating zero with respect to a rotating earth coordinate frame for a predetermined period of time.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
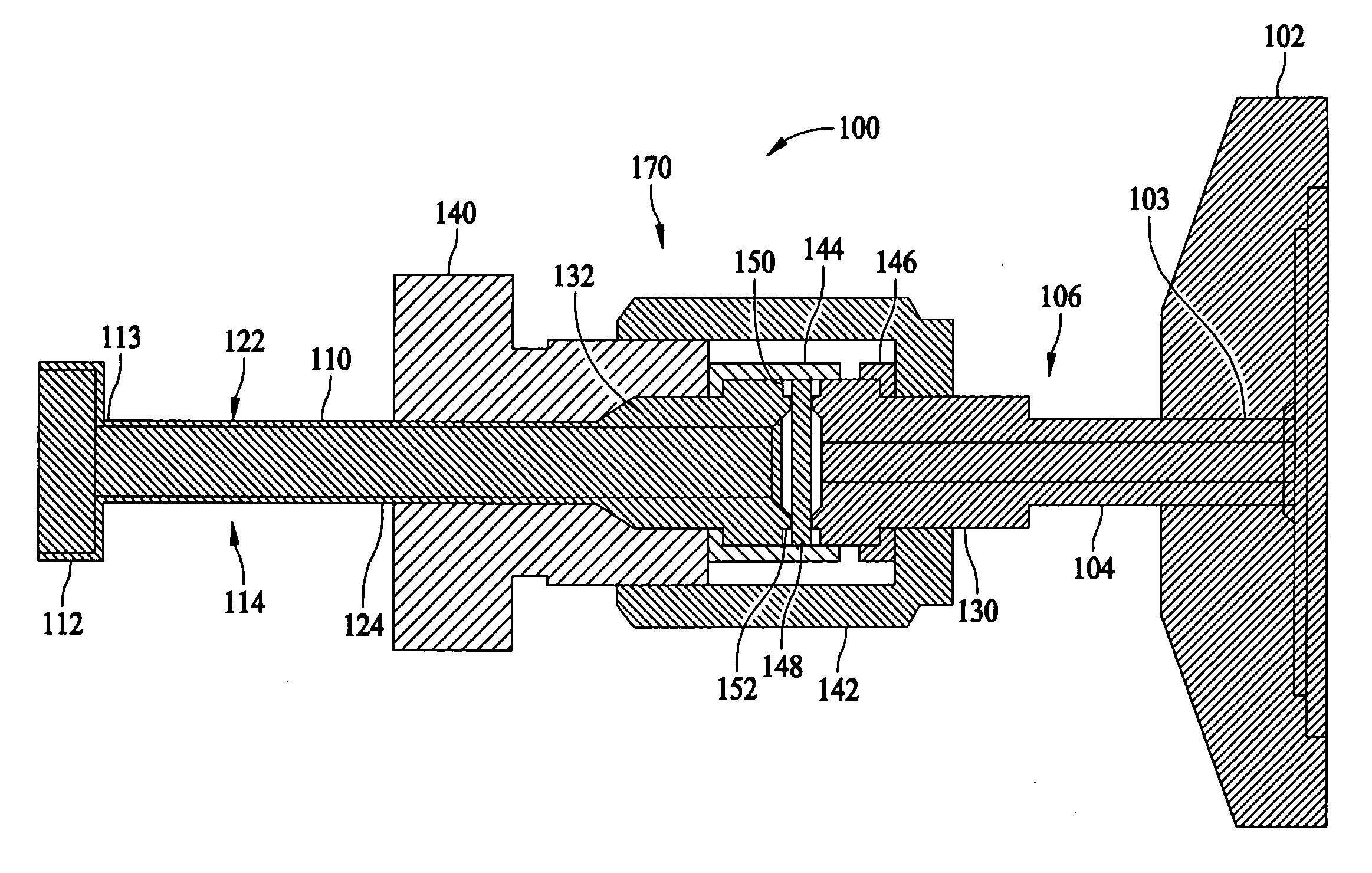
Fill tube-flange assembly for ring laser gyroscope block
InactiveUS20080012325A1Fluid pressure sealed jointsJoints with sealing surfacesRing laser gyroscopeEngineering
A fill tube and flange assembly for fabrication of ring laser gyroscope blocks is described. The assembly includes a flange assembly, a fill tube assembly, and a compression interface. The flange assembly includes a flange tube and a fluid port at a first end of the flange assembly tube. The fill tube assembly includes a fill tube and a laser block engaging portion at a first end of the fill tube. The compression interface is configured to couple second ends of the fill tube and the flange assembly tube.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
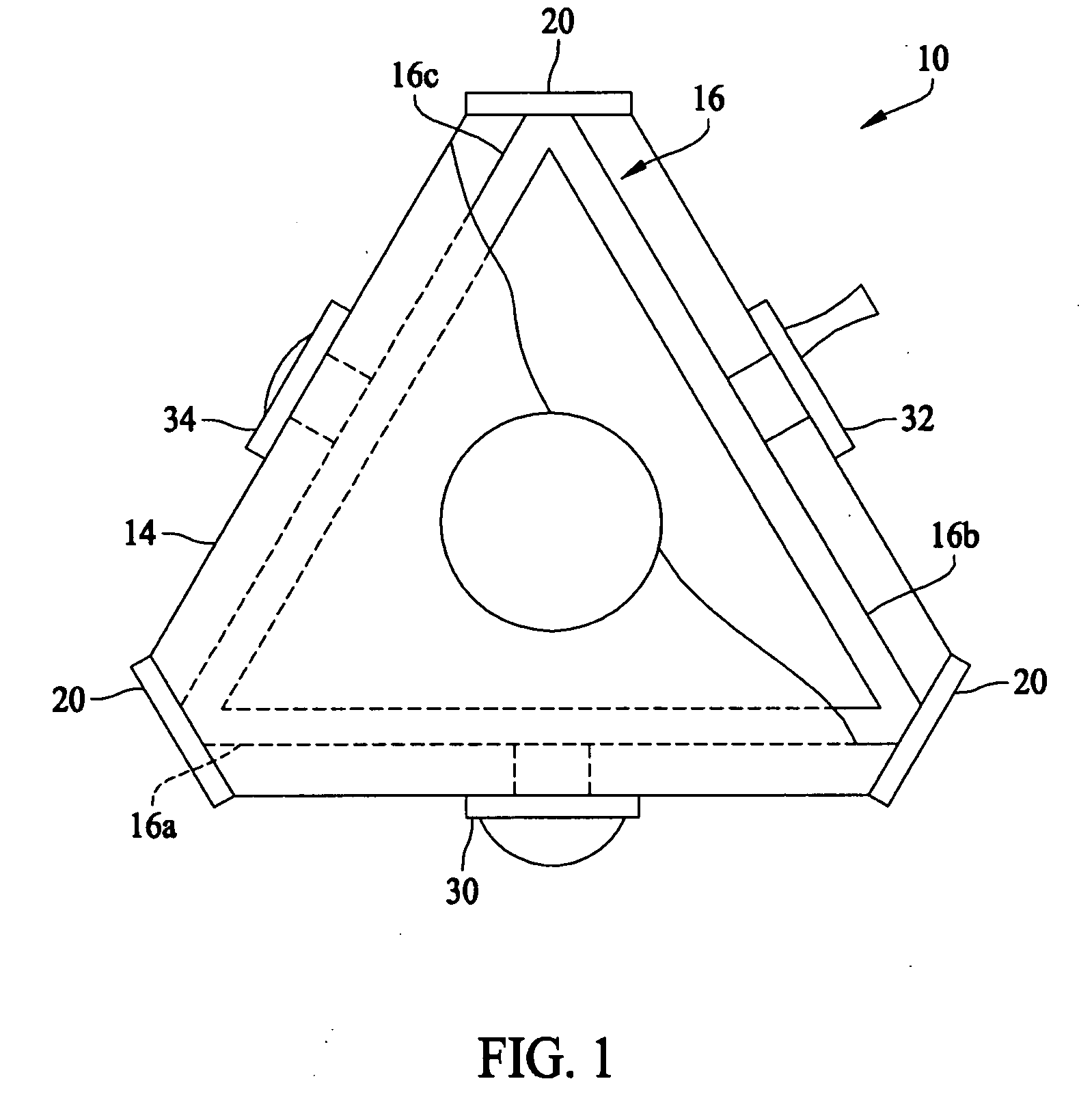
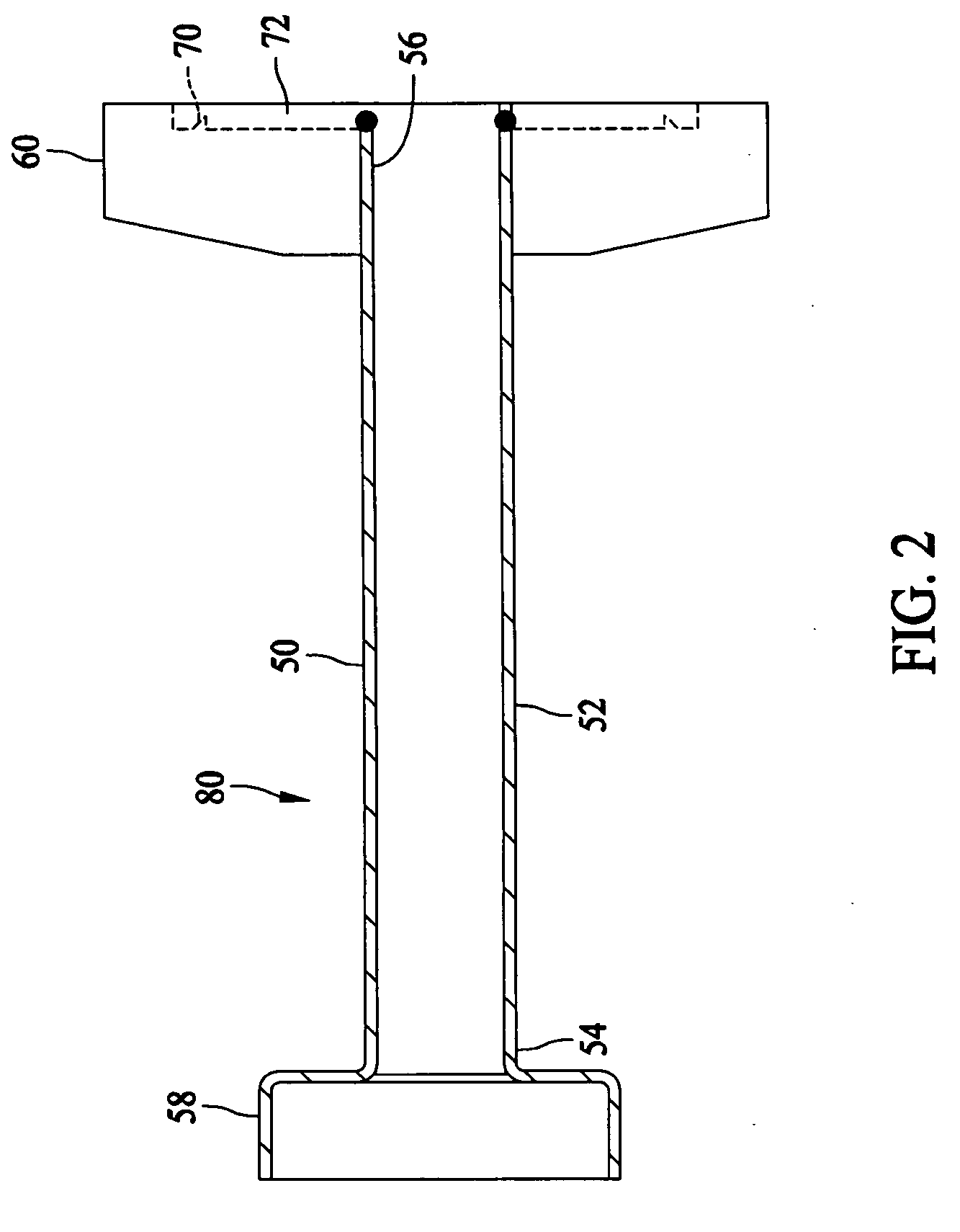
Single sensor ring laser gyroscope
InactiveUS20060164650A1Speed measurement using gyroscopic effectsSagnac effect gyrometersPath lengthControl signal
A ring laser gyroscope is described which includes a laser cavity configured to provide an optical laser path for a pair of counter-propagating laser beams, an optical sensor configured to receive a portion of the energy from the counter-propagating laser beams, and a unit configured to receive outputs from the optical sensor. The unit is configured to utilize the output to generate at least a residual path length control signal, a laser intensity monitor signal, and readout signals.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
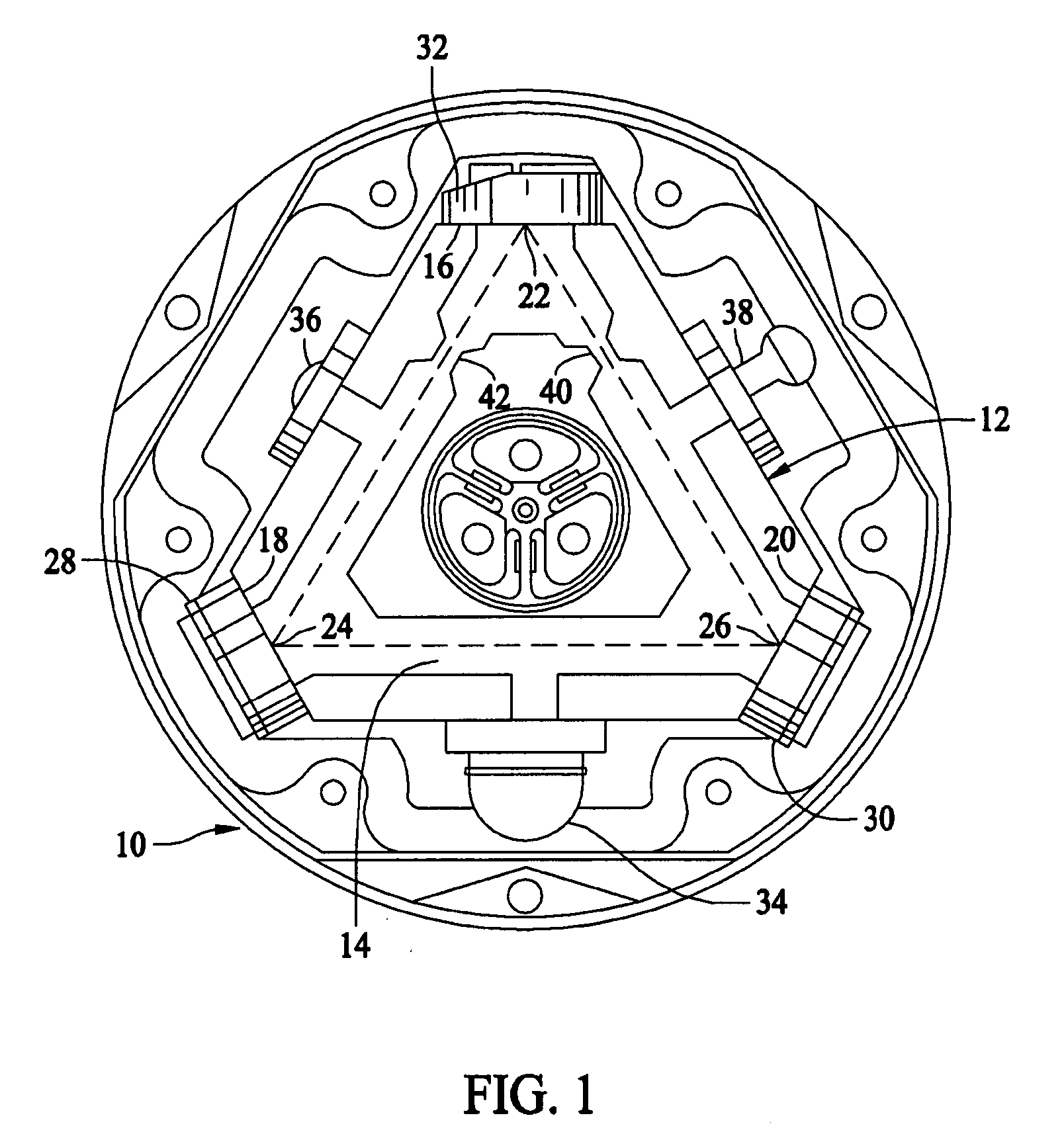
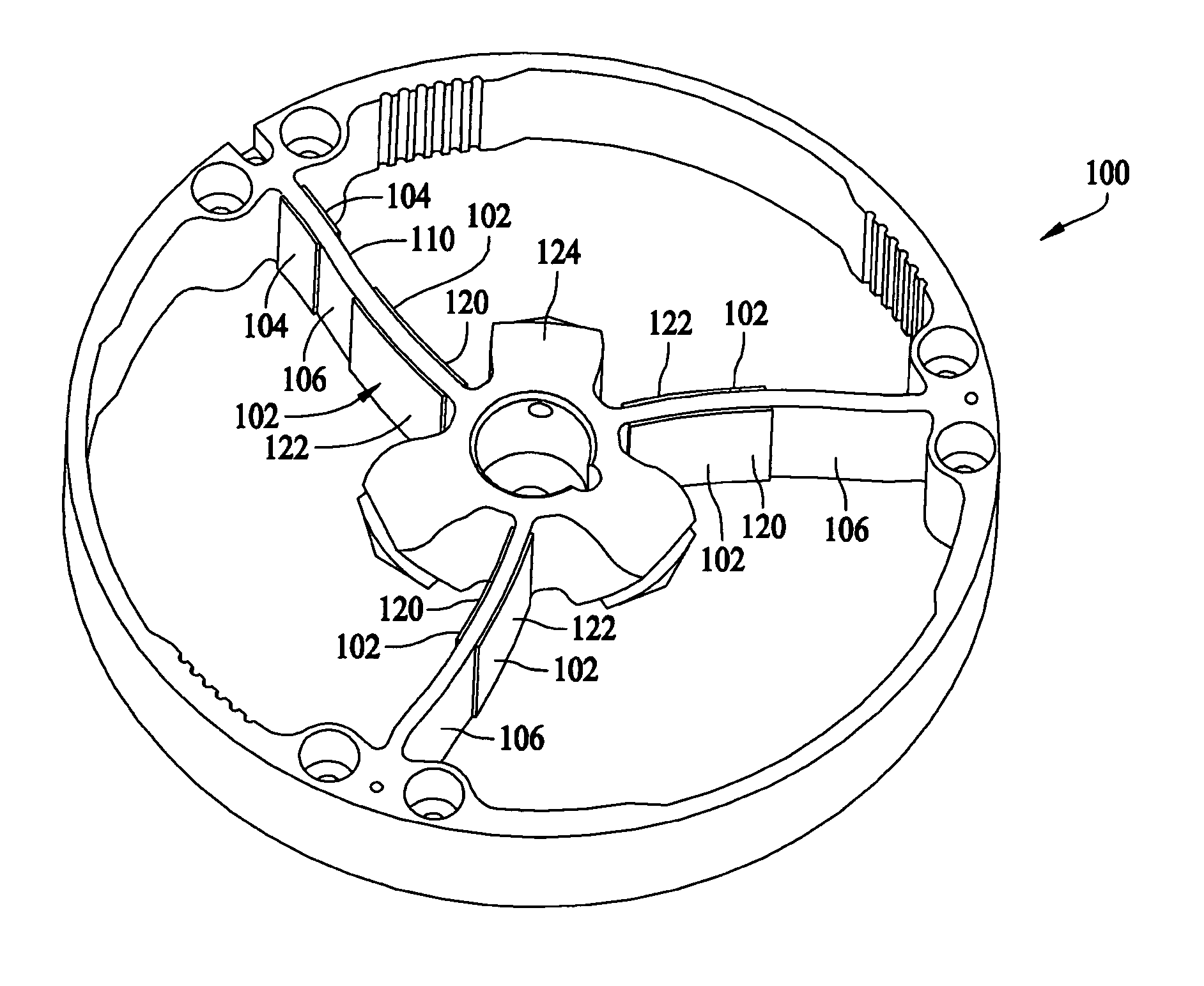
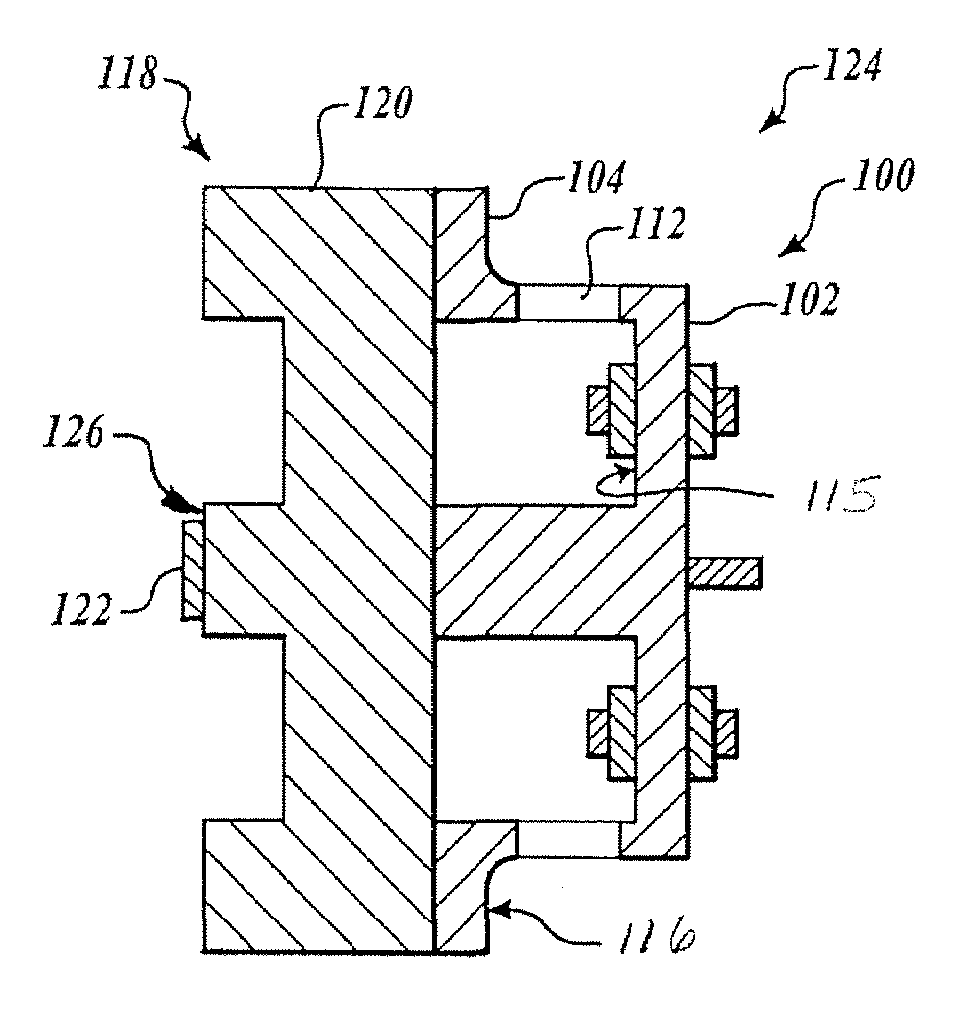
Baseplate for a ring laser gyroscope
ActiveUS20080079948A1Improved distortion characteristicsEvenly distributedSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsSagnac effect gyrometersElectricityPath length
A path length control driver for a ring laser gyroscope includes a baseplate, a number of piezoelectric elements, and electrodes. The baseplate includes openings selectively sized and located on the baseplate for reducing distortion thereof during thermal or other mechanical loading. The baseplate includes a central hub extending from a central portion of an actuator plate, which comprises an annular diaphragm member. The baseplate further includes an outer rim or sidewall coupled to the actuator plate and a baseplate flange extending from the sidewall. In one embodiment, a portion of the baseplate flange is attached to a mirror transducer substrate assembly. The mirror transducer substrate assembly includes a reflective device, such as a mirror, and a transducer block. The transducer block includes an optical contact surface onto which the mirror is affixed. The piezoelectric elements are employed to achieve a desired amount of movement of the baseplate, which in turn induces micro-movements or micro-adjustments of the mirror.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Orthogonal-mode laser gyroscope
ActiveUS10180325B2Reduce and eliminate couplingAvoid interferenceSagnac effect gyrometersFiberClosed loop
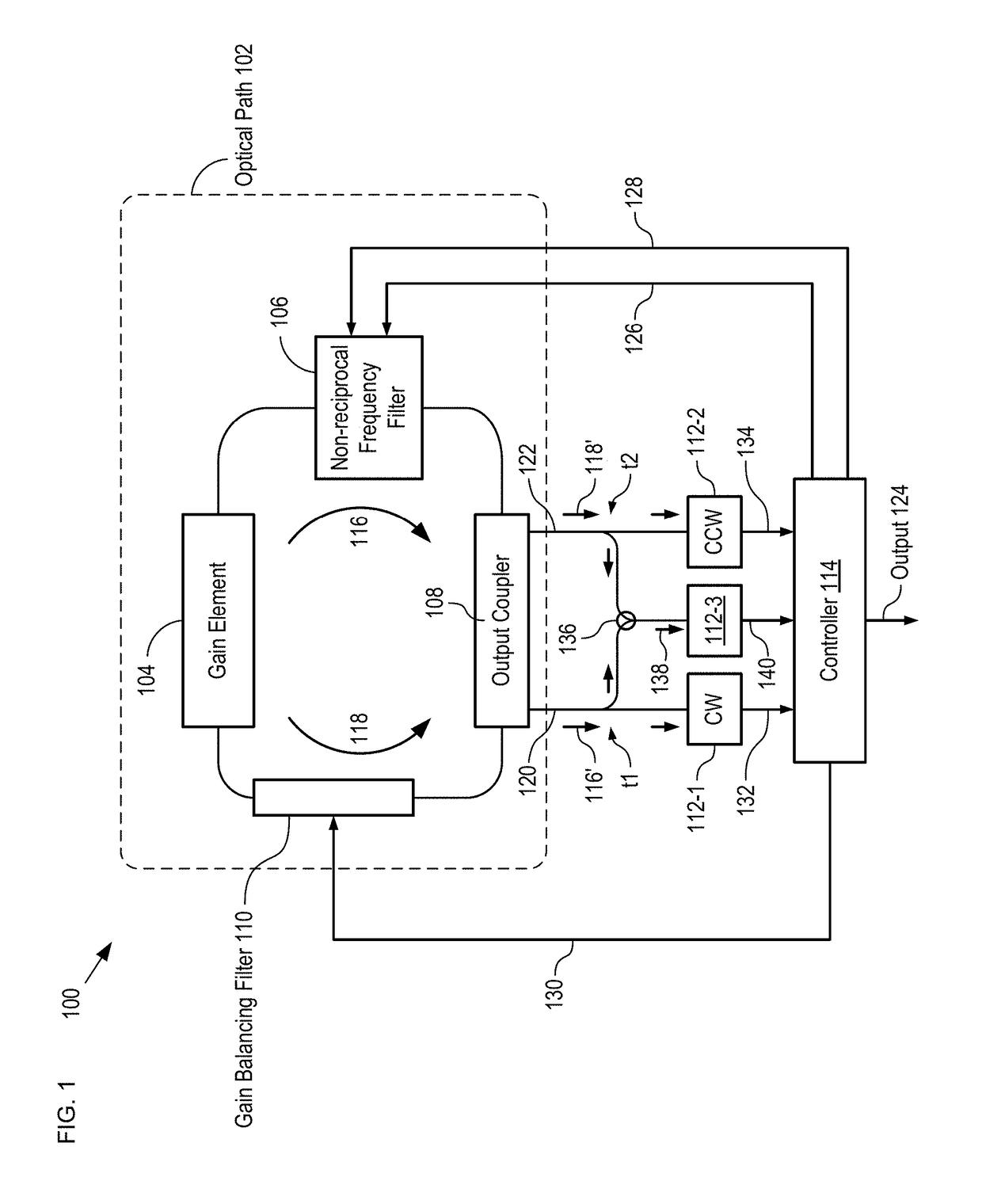
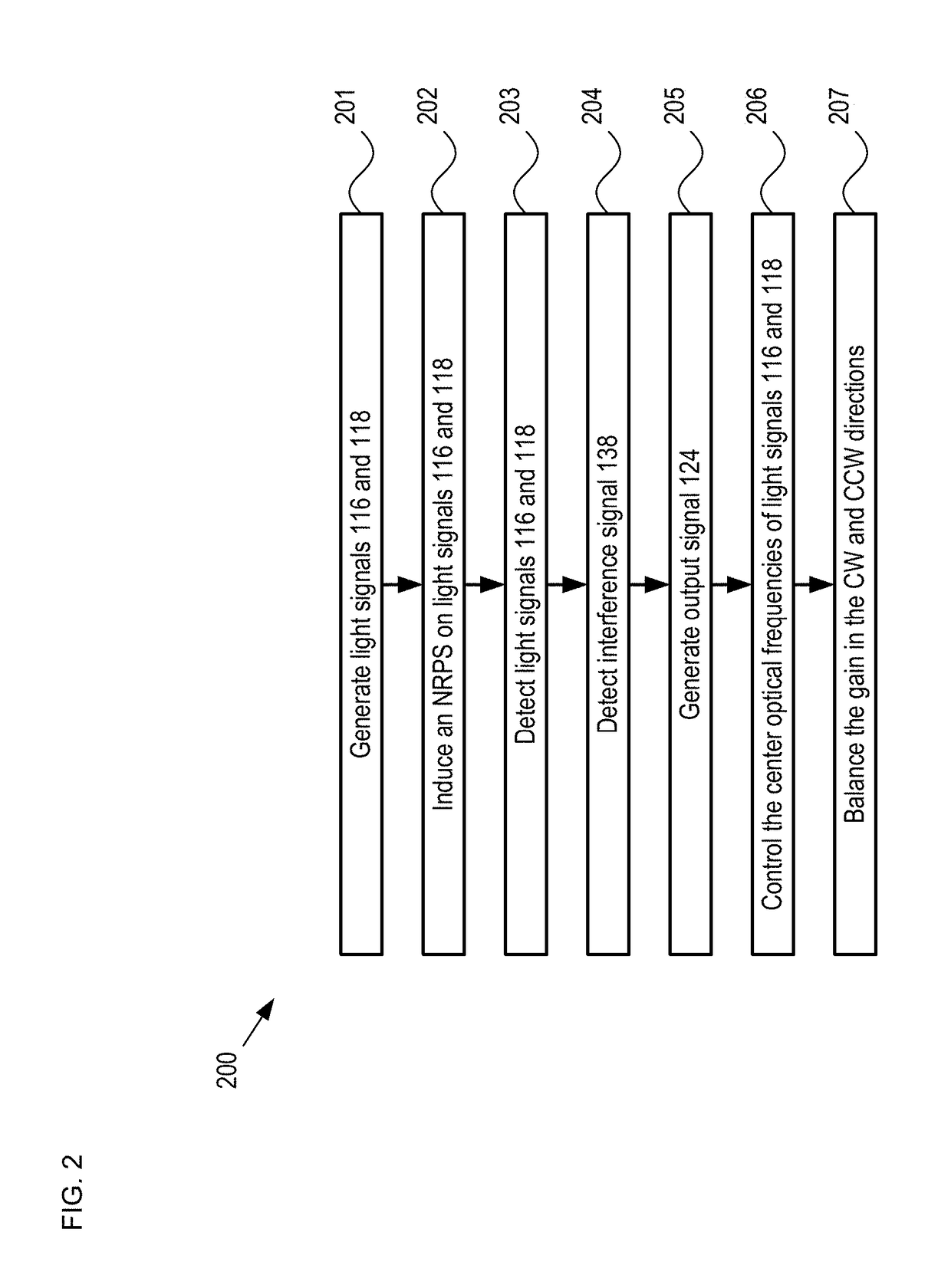
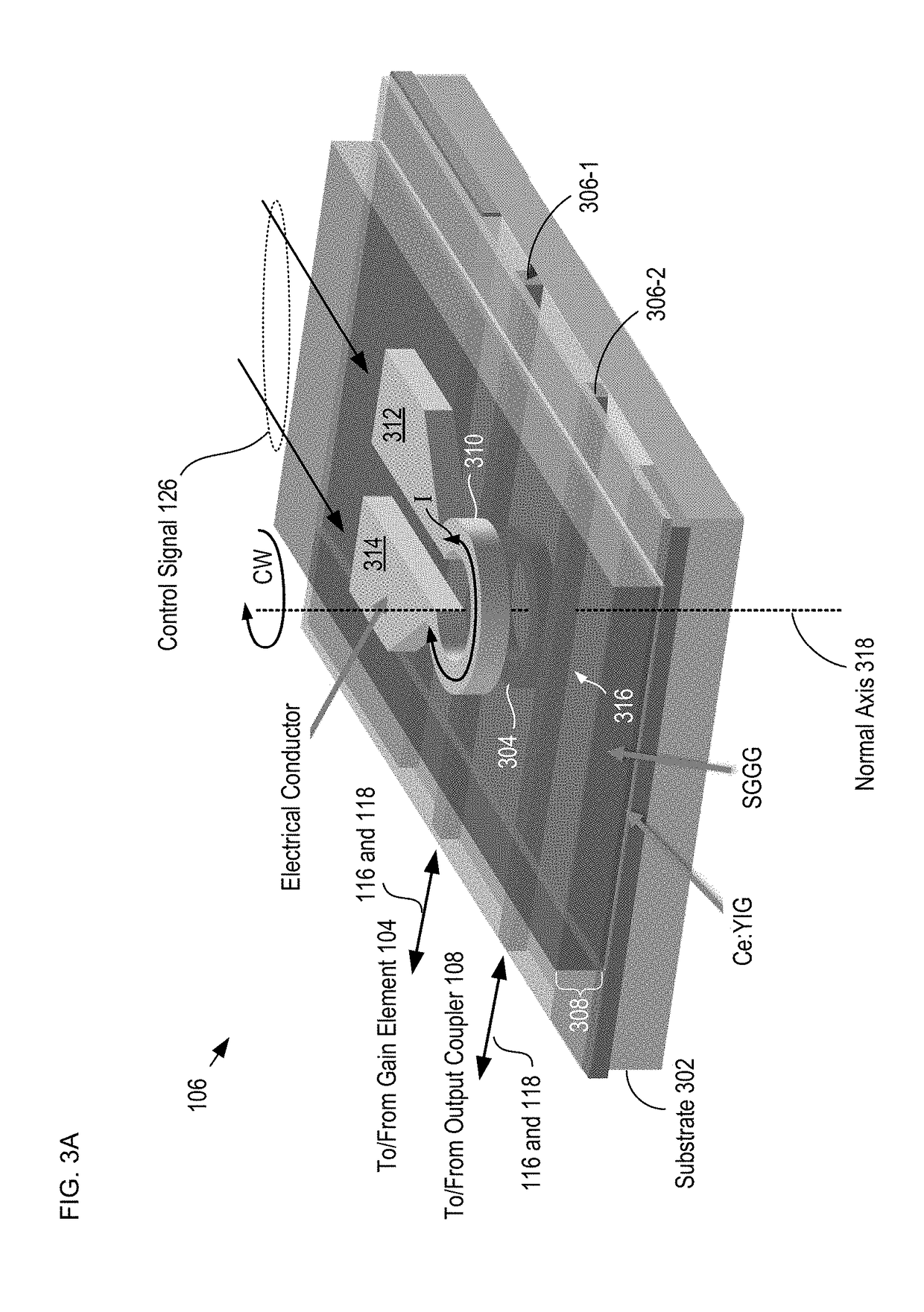
A fiber-optic gyroscope is disclosed, wherein the fiber-optic gyroscope has counter-propagating light signals in a closed-loop optical path, and where the light signals are characterized by an orthogonality that mitigates optical coupling between them. In some embodiments, the orthogonality is a difference in frequency of the two signals. In some embodiments, the orthogonality is a difference in the polarizations of the two signals. The orthogonality is imparted on the light signals by a non-reciprocal element that is optically coupled with the optical path. In some embodiments, a gain-balancing filter is also included to ensure that the loop gain for each light signal is substantially equal to one. In some embodiments, the light signals are provided by a gain element that is characterized by inhomogeneous broadening.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Enhanced scale factor ring laser gyroscope
InactiveUS7907284B2Improve rotational sensitivityImprove scaleLaser detailsSagnac effect gyrometersSpinsRing laser gyroscope
An embodiment of the invention enhances the rotation sensitivity and decreases the dead band width of a standard HeNe ring laser gyroscope (RLG), with the highest enhancement at low rotation rates. The addition of a gas with nuclear spin to the traditional HeNe gain medium is used to create the intracavity gain medium with an anomalous dispersive quality and thus enhanced rotation sensitivity.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
System, circuit and method for off-mode-peak operation of ring laser gyroscopes
InactiveUS20060176489A1Avoid exciting the undesirable transverse modesSagnac effect gyrometersSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsOperating pointPath length
A system, circuit and method are disclosed for operating an RLG off-mode-peak to avoid exciting undesirable transverse modes. An alternate PLC operating point can be used to bias the optical path length of the RLG to an appropriate side of an ideal integer number of wavelengths, and thus avoid exciting the undesirable transverse modes. Although this alternate PLC operating point is not perfect with respect to establishing an integer number of wavelengths, this operation provides acceptable performance of the RLG's (in particular, short length path RLG's), and acceptable margin can be established relative to variations in the PLC set points involved. For example, a PLC loop can be used to dither about this operating point as a discriminate to allow closed loop control of the path length. Also, a PSSD control architecture can be used to establish and maintain a requisite path length over relatively wide variations in operating temperature. Specifically, a small offset error can be injected into a conventional PSSD loop for an RLG, which causes the loop to converge on a pre-selected operating point that is on one side of a conventional convergence point. The magnitude and polarity characteristics of this operating point offset can be determined for each RLG, or such characteristics can be consistently used for a family of RLG's.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
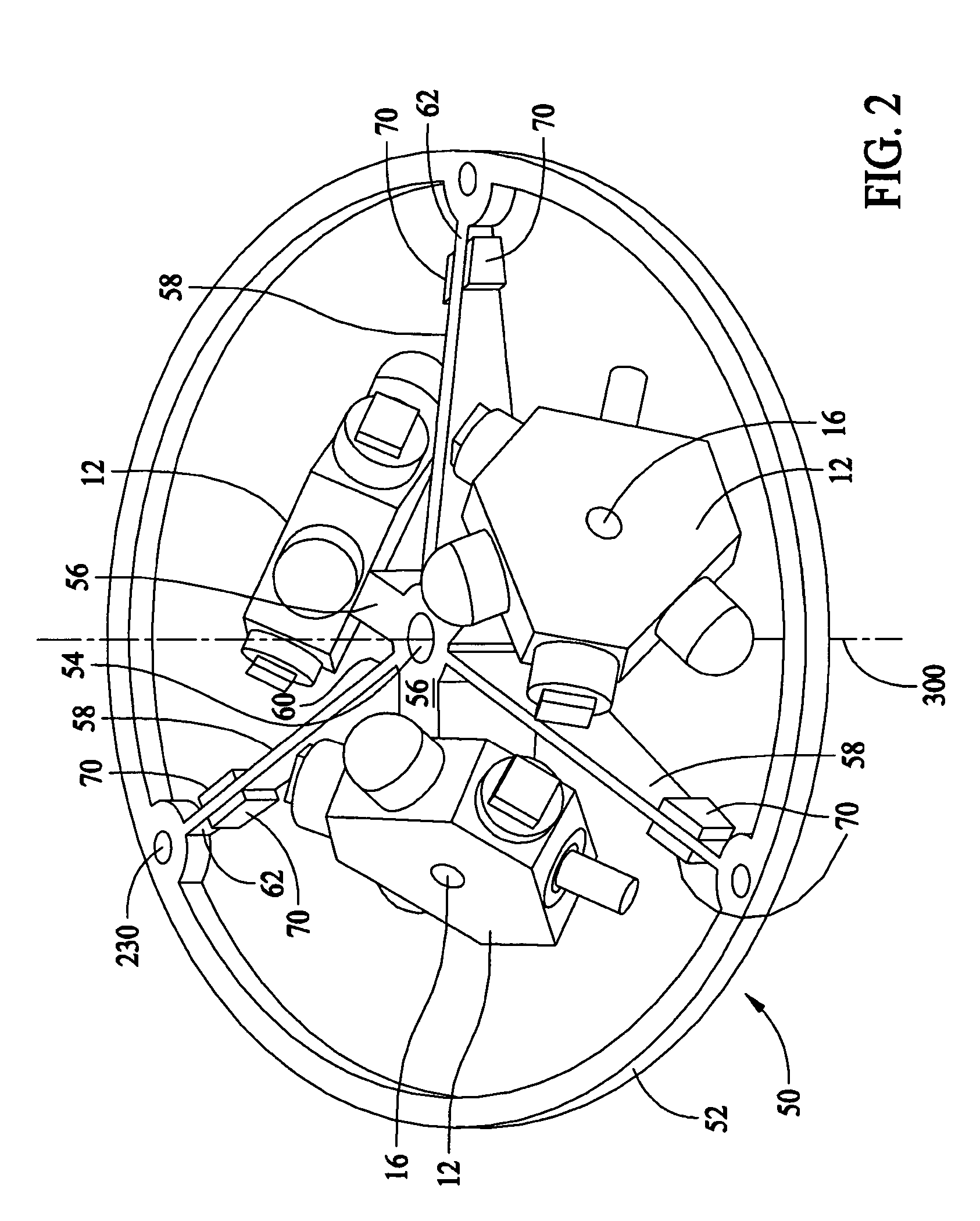
Dither motor having integrated drive and pickoff transducers
InactiveUS7375816B2Speed measurement using gyroscopic effectsSagnac effect gyrometersElectrical connectionRing laser gyroscope
A ring laser gyroscope is described that includes at least one laser gyroscope block and a dither motor, where the gyroscope blocks are configured to engage the dither motor. The dither motor has an outer ring, a hub section, at least one radially extending reed extending between the outer ring and the hub section, and at least one piezoelectric transducer attached the reed. The piezoelectric transducer includes a common piezo-ceramic having a contiguous void line that allows for a separate electrical connection to be made to electrode surfaces on each side of the void line.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Baseplate for a ring laser gyroscope
ActiveUS7535574B2Reduce the amount of distortionEvenly distributedSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsSagnac effect gyrometersElectricityPath length
A path length control driver for a ring laser gyroscope includes a baseplate, a number of piezoelectric elements, and electrodes. The baseplate includes openings selectively sized and located on the baseplate for reducing distortion thereof during thermal or other mechanical loading. The baseplate includes a central hub extending from a central portion of an actuator plate, which comprises an annular diaphragm member. The baseplate further includes an outer rim or sidewall coupled to the actuator plate and a baseplate flange extending from the sidewall. In one embodiment, a portion of the baseplate flange is attached to a mirror transducer substrate assembly. The mirror transducer substrate assembly includes a reflective device, such as a mirror, and a transducer block. The transducer block includes an optical contact surface onto which the mirror is affixed. The piezoelectric elements are employed to achieve a desired amount of movement of the baseplate, which in turn induces micro-movements or micro-adjustments of the mirror.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
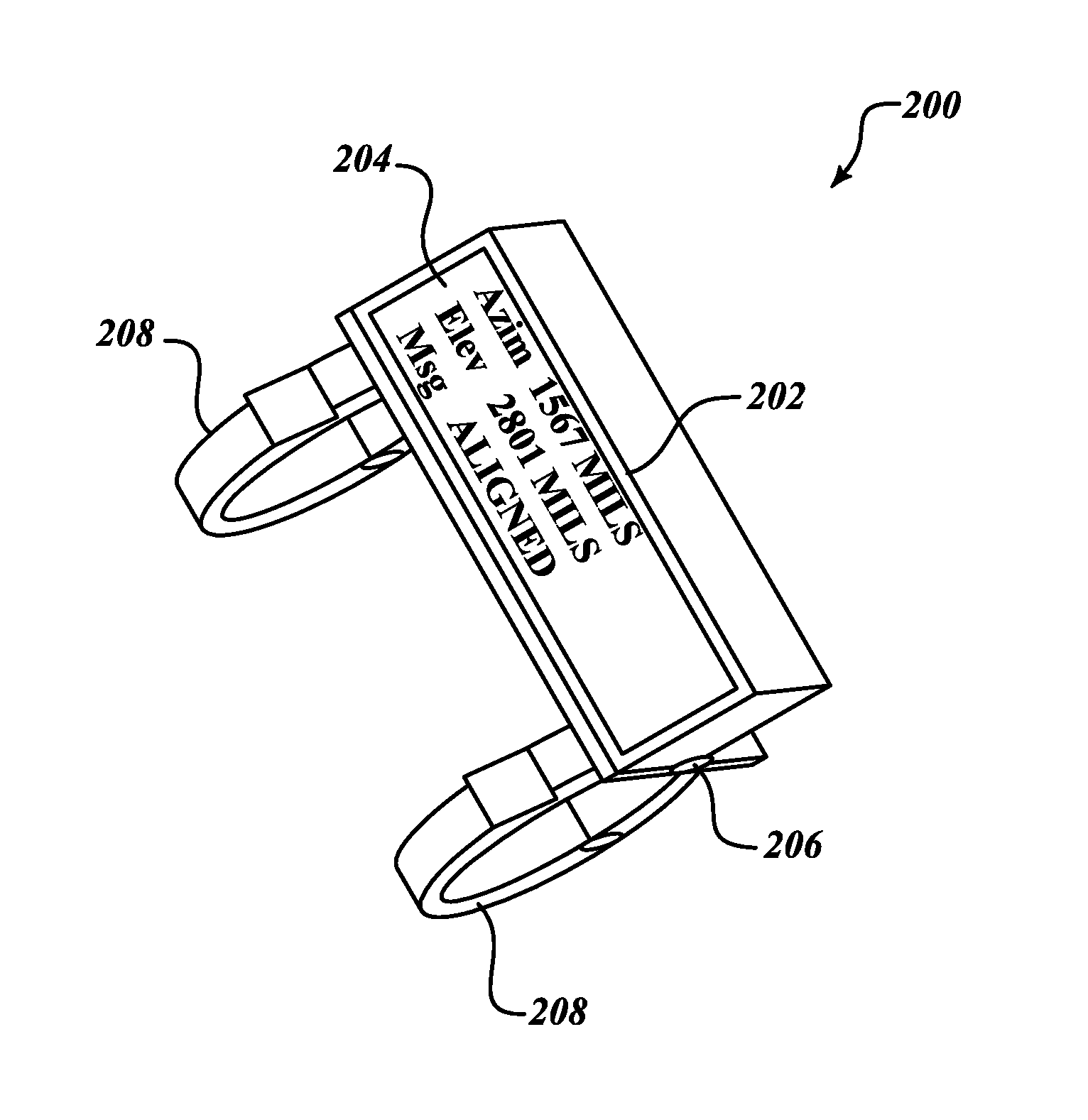
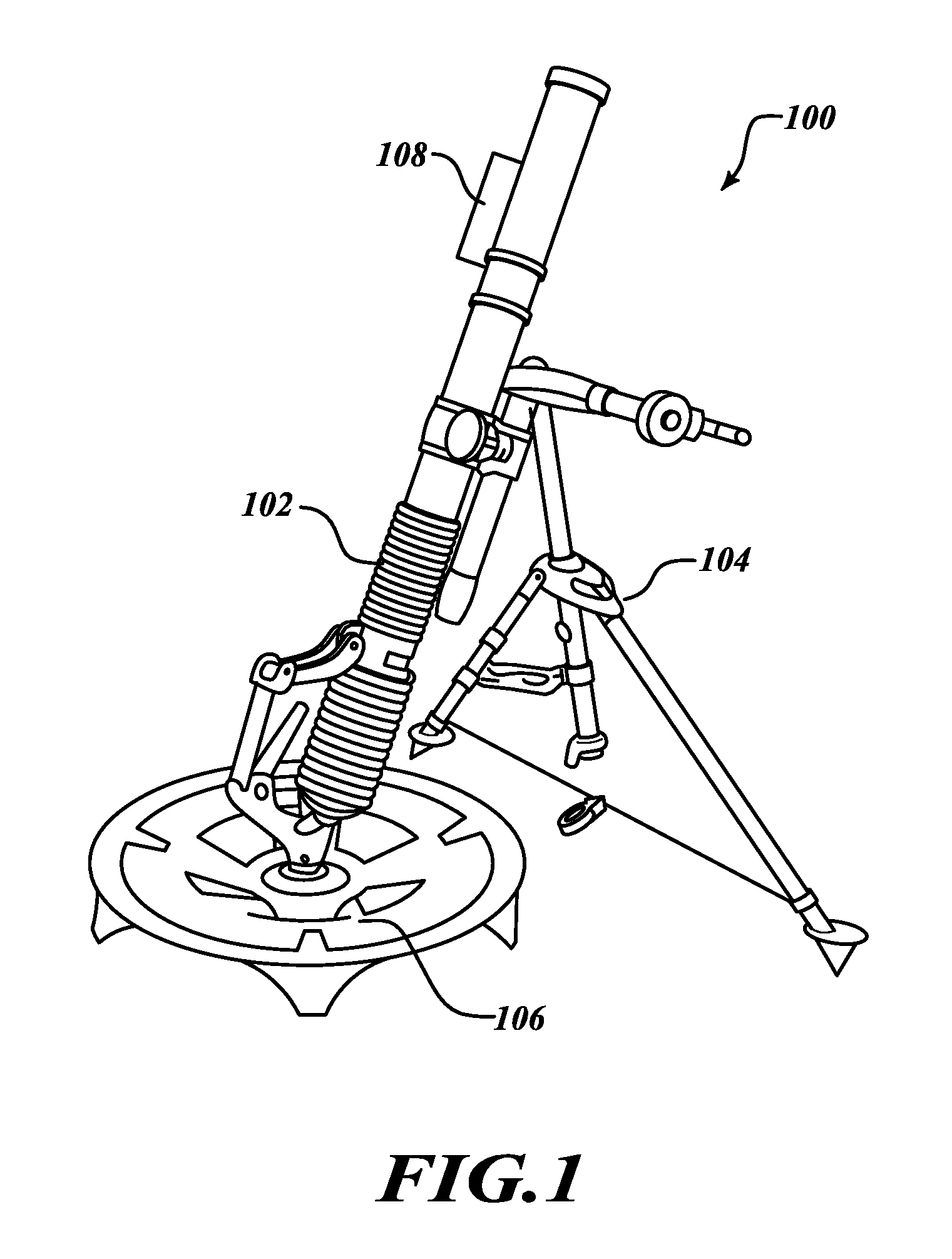
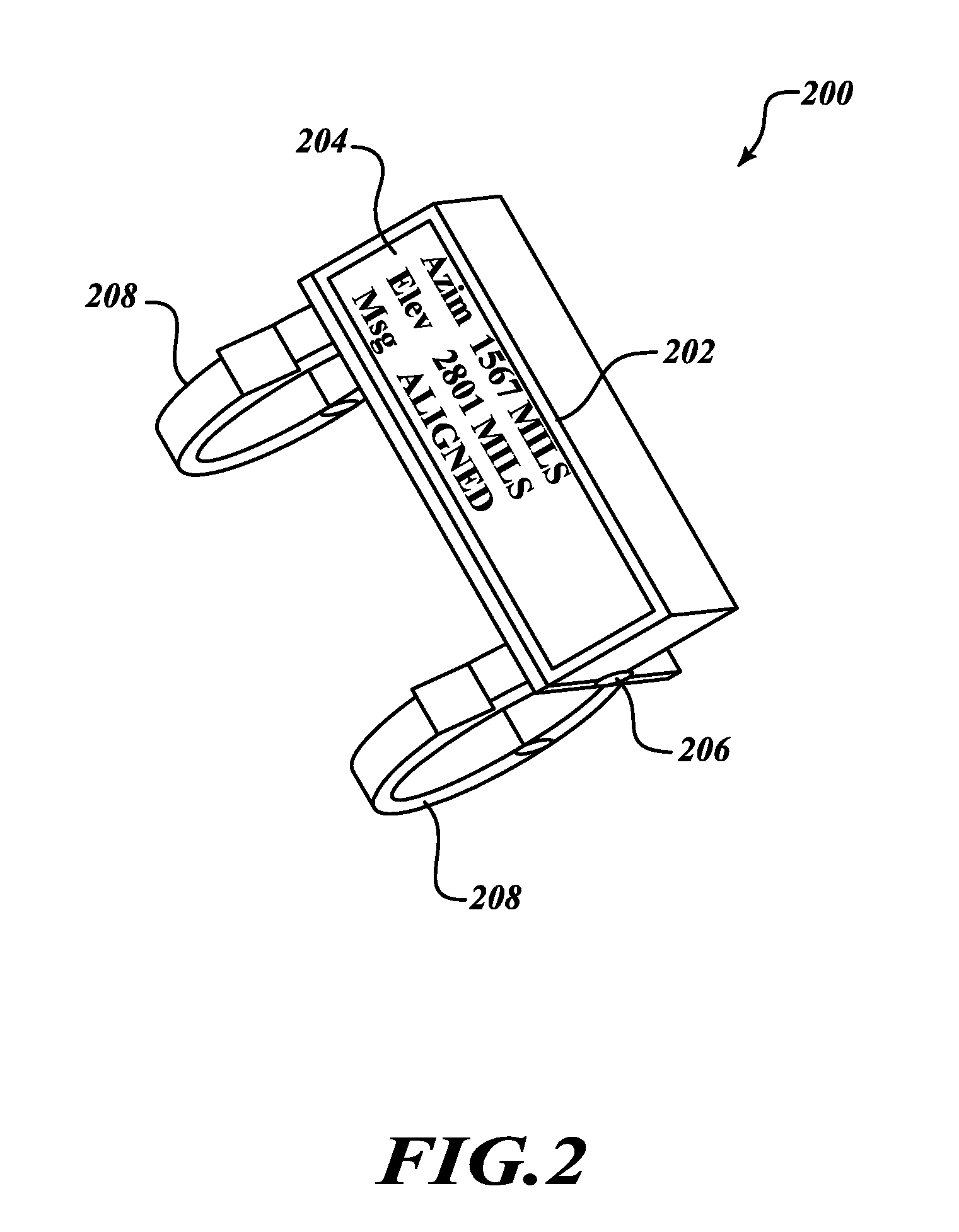
Systems and methods for a lightweight north-finder
Systems and methods for a lightweight north-finder. A method of using a north-finder includes a tube configured to fire munitions secured to a base in preparation of firing operations. A north-finder coupled to a tube in order to determine an azimuth and elevation. The north-finder is rotated ninety degrees about an axis parallel to the tube in order to confirm the determined azimuth and elevation. The determined azimuth and elevation is displayed to a user. A system of using a north-finder includes a tube configured to fire munitions secured to a base. A north-finder mount coupled to the tube having a north-finder is configured to determine an azimuth and elevation. The north-finder includes a ring laser gyro, an accelerometer, and an inertial measurement unit, wherein, when the north-finder is rotated ninety degrees about an axis parallel to the tube, azimuth and elevation values are confirmed.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com