Assessment method for optimal installation configuration of inertial measurement unit with two-frequency mechanically-dithered laser gyroscopes
A technology of inertial measurement unit and machine-shaking laser gyro, which is applied in the field of guidance and control and inertial navigation, can solve the problems of reduced reliability, reduced precision, and easy-to-interference circuits, so as to improve the accuracy and reliability of use, prolong the service life, highly operable effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
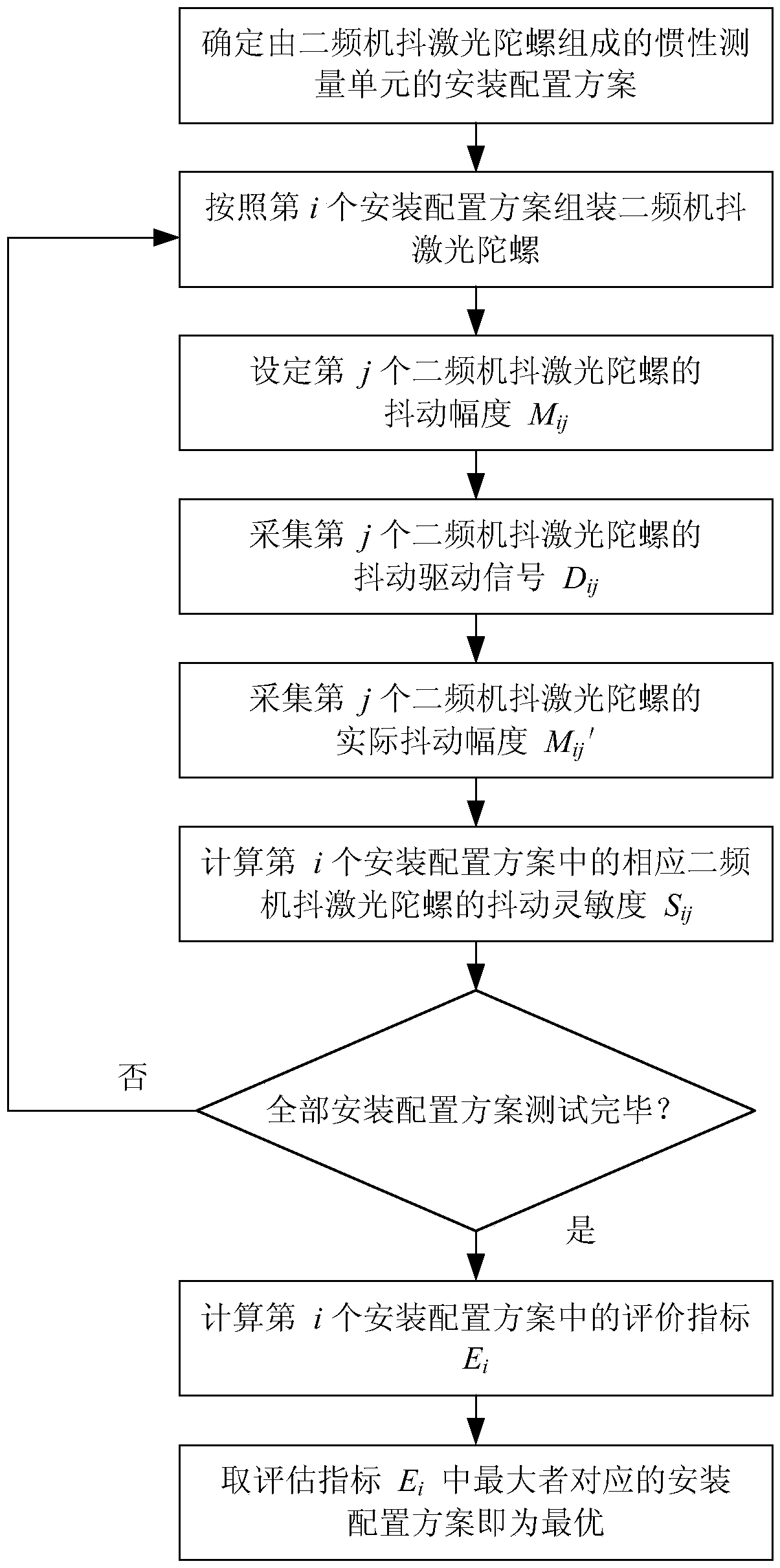
[0039] The specific implementation scheme adopted for realizing the object of the invention is:
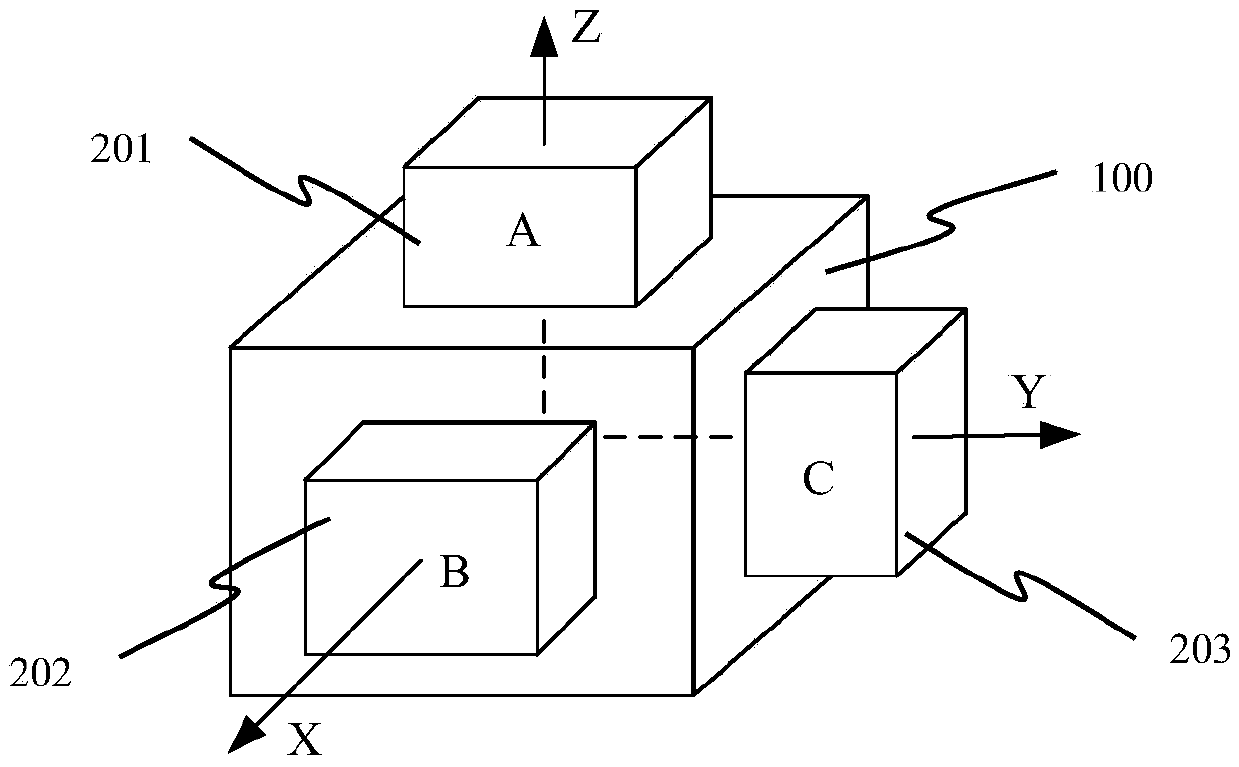
[0040] As an example, consider the design of an orthogonally mounted IMU such as figure 2 As shown, there are three orthogonal mounting surfaces on the mounting base 100 in the inertial measurement unit, and the normal directions of the mounting surfaces are respectively defined as X, Y, and Z directions. The models are defined as A, B, and C types according to the level of the natural frequency of the jitter. figure 2 It is an installation configuration scheme: Type A two-frequency machine-shaking laser gyro 201 is installed in the Z direction of the installation base 100, B-type two-frequency machine-shaking laser gyro 202 is installed in the X direction of the installation base 100, and C-type two-frequency machine The dithering laser gyro 203 is installed in the Y direction of the installation base 100 . ,
[0041] Step 1. Define three installation orientations as X, Y, a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com