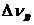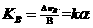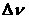Method for reducing square two-frequency laser gyroscope magnetic sensitivity
A laser gyro and magnetic sensitivity technology, applied in Sagnac effect gyroscopes, measuring devices, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of cavity deformation, difficulty and no error, and achieve the effect of reducing magnetic sensitivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment 1
[0049] figure 1 It is a schematic diagram of a square two-frequency laser gyro with coils installed on the gyro cavity proposed by the present invention, which includes two plane mirrors 1, 2 and two optical path length control mirrors 3, 4 and is composed of the four mirrors Ring resonator, winding holes 5, 6 processed beside the gain area of the ring resonator, coils 7, 8 wound on the gain area, gyro difference frequency signal output part 9, gyro light intensity signal output part 10, The optical path length control mirrors 3 and 4 can not only translate back and forth under the control of the path length control unit, but also can be deflected under the drive of the angle control unit, that is, they can not only translate back and forth to control the optical path length, but also angularly deflect. Controls the direction of the light path.
[0050] When the external magnetic field is figure 1 The square two-frequency laser gyro shown is in an unknown random rotation...
specific Embodiment 2
[0062] figure 2 It is a schematic diagram of a square two-frequency laser gyro with coils installed outside the gyro cavity proposed by the present invention, which includes two plane mirrors 11, 12 and two optical path length control mirrors 13, 14, and the four mirrors form a ring shape Resonant cavity, gyro difference frequency signal output part 15, gyro light intensity signal output part 16, coils 17, 18 placed outside the gyro cavity for generating magnetic field.
[0063] The coils 17 and 18 are installed in the gyroscope together with the gyro cavity. When the alternating magnetic field method is used in the first embodiment, an alternating current is first applied to the coils 17 and 18, and an alternating current is applied to the coils 17 and 18 through relevant technical means such as detection or spectrum analysis. Distinguish changes with frequency ω in size, the closed-loop measurement and control method is adopted, and the gyro is continuously obtained. I...
specific Embodiment 3
[0068] In the test room of the square two-frequency laser gyro before leaving the factory, the figure 2 The shown coil is installed in the square two-frequency laser gyro outside the gyro cavity, and the method and method adopted in the second embodiment are used to obtain the optimal control parameters of the control voltage of the pitch direction on a group of optical path length control mirrors 13 and 14; Subsequently, only the gyro block is installed in the gyroscope, and the open-loop measurement and control method is adopted, and the above method is used to measure a set of control voltage parameters of the pitch angle of the optical path length control mirror with the minimum magnetic sensitivity of the gyro, and use it as the implementation. In the example of the normal working parameters of the gyro, the optical path length control mirror of the gyro has been controlling the optical path of the gyro with this group of parameters.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com