Patents
Literature
84results about How to "Lower read latency" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
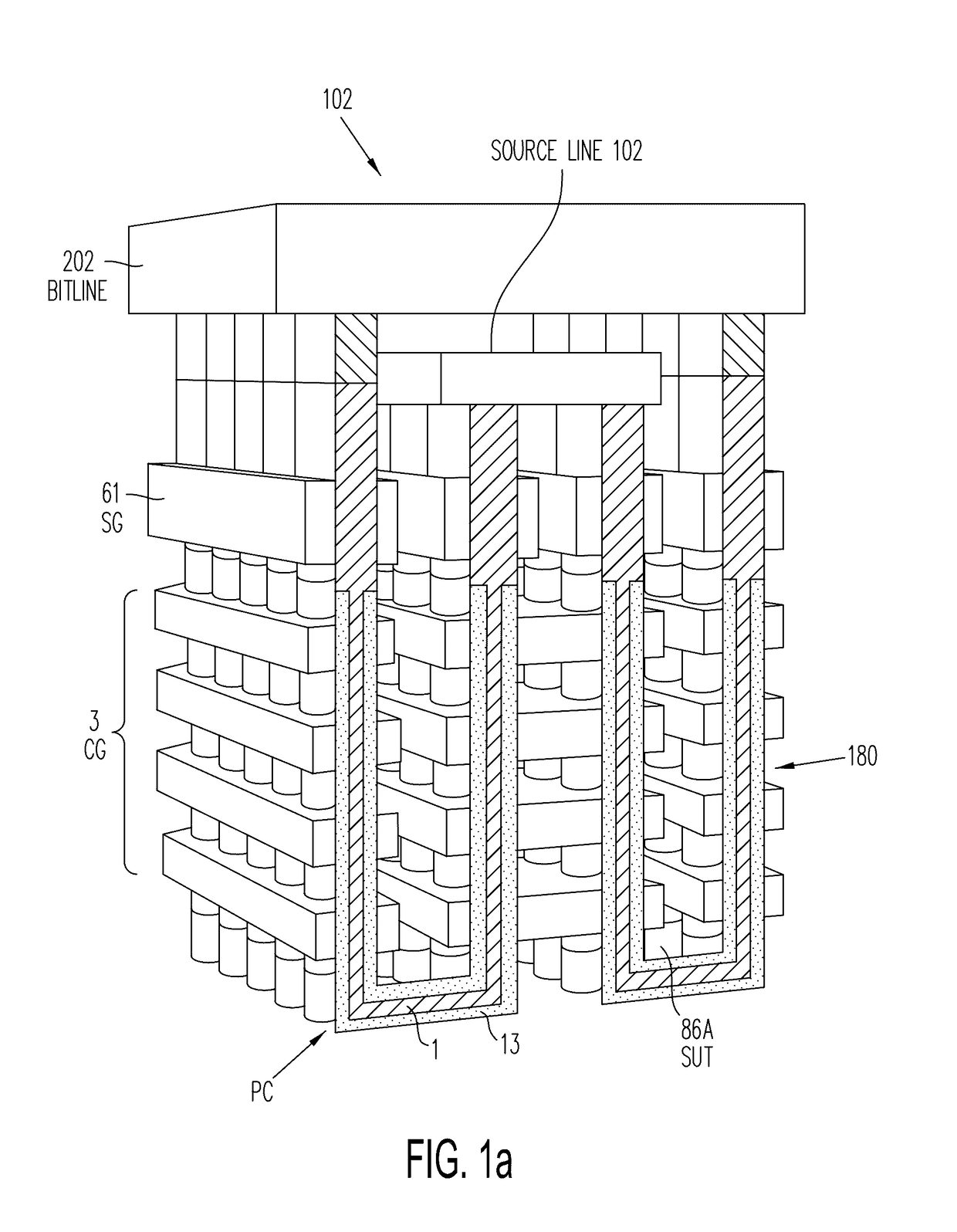
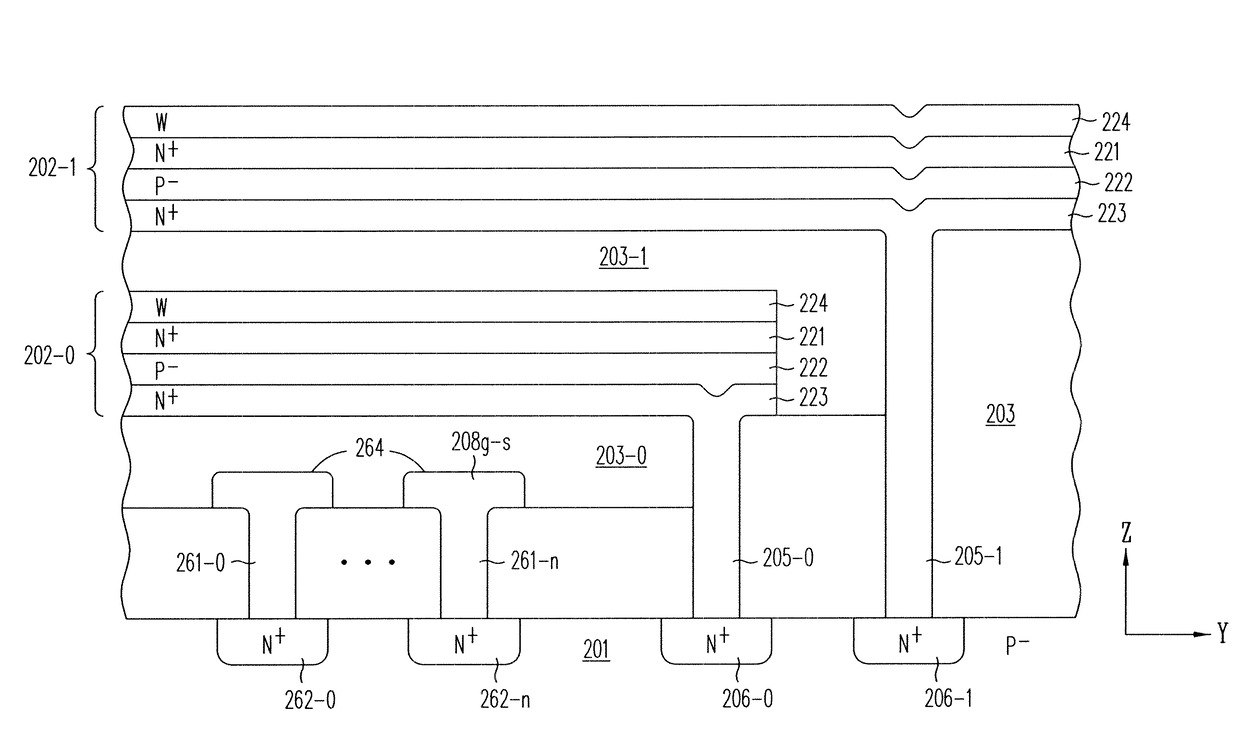
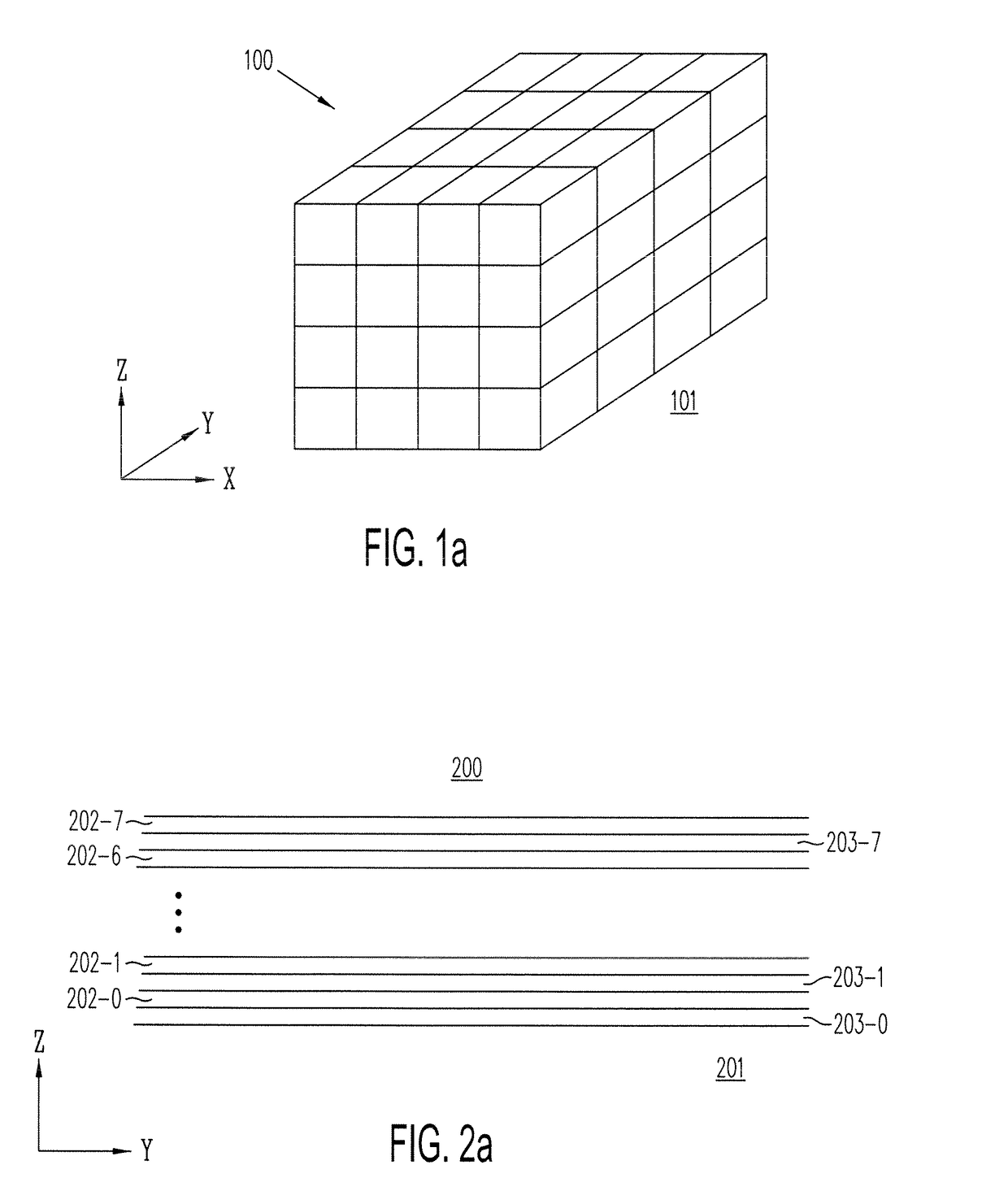
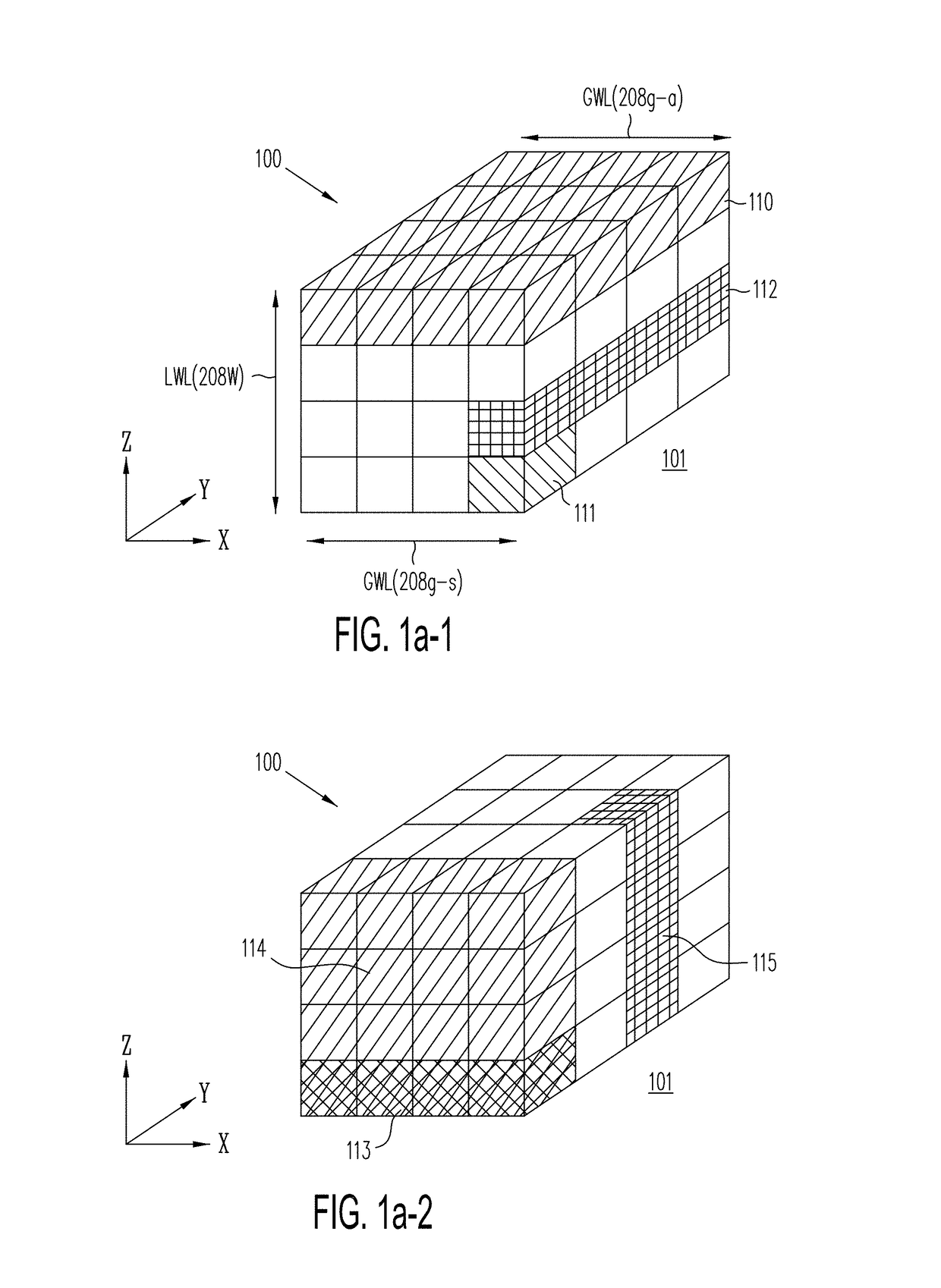
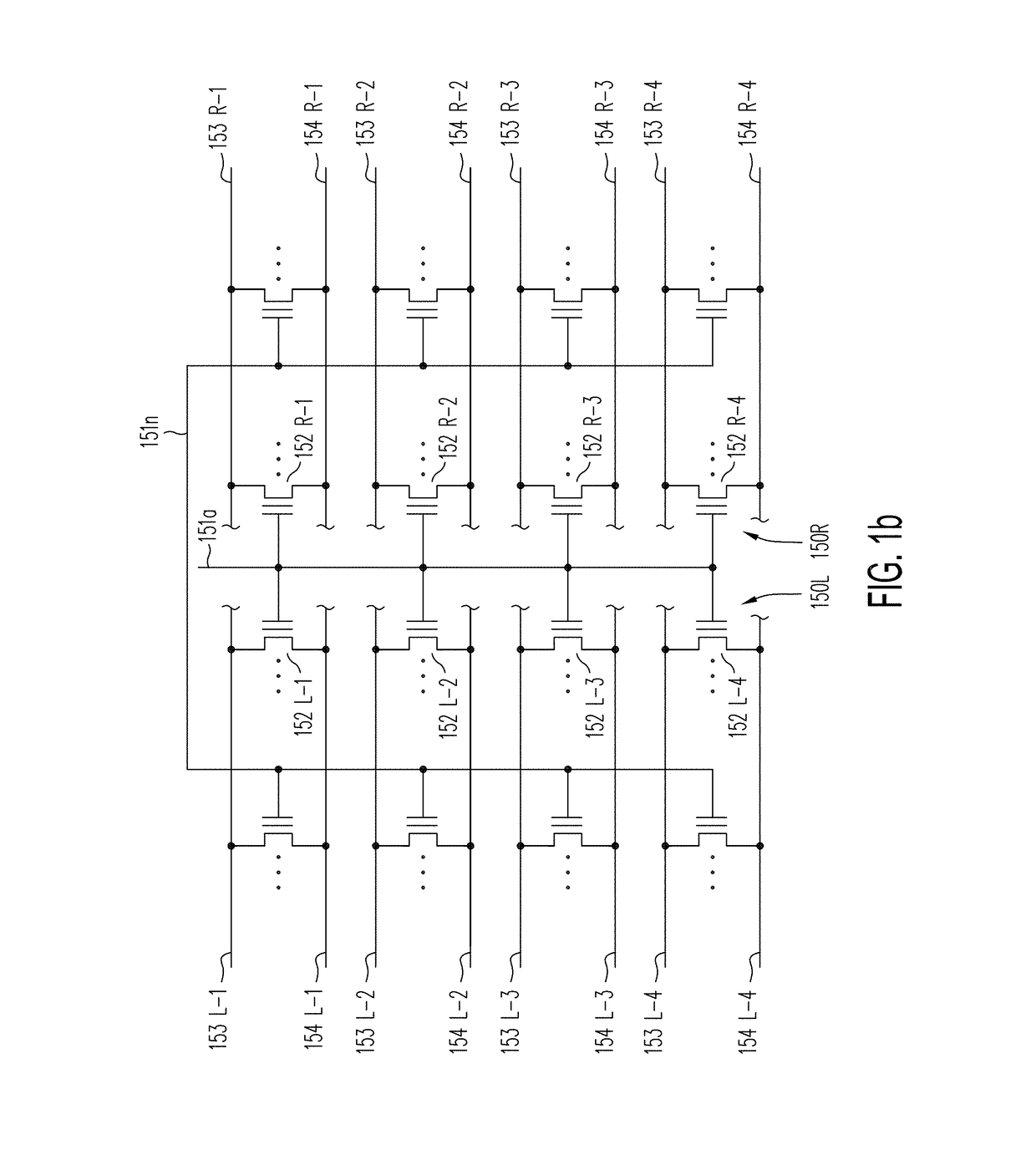
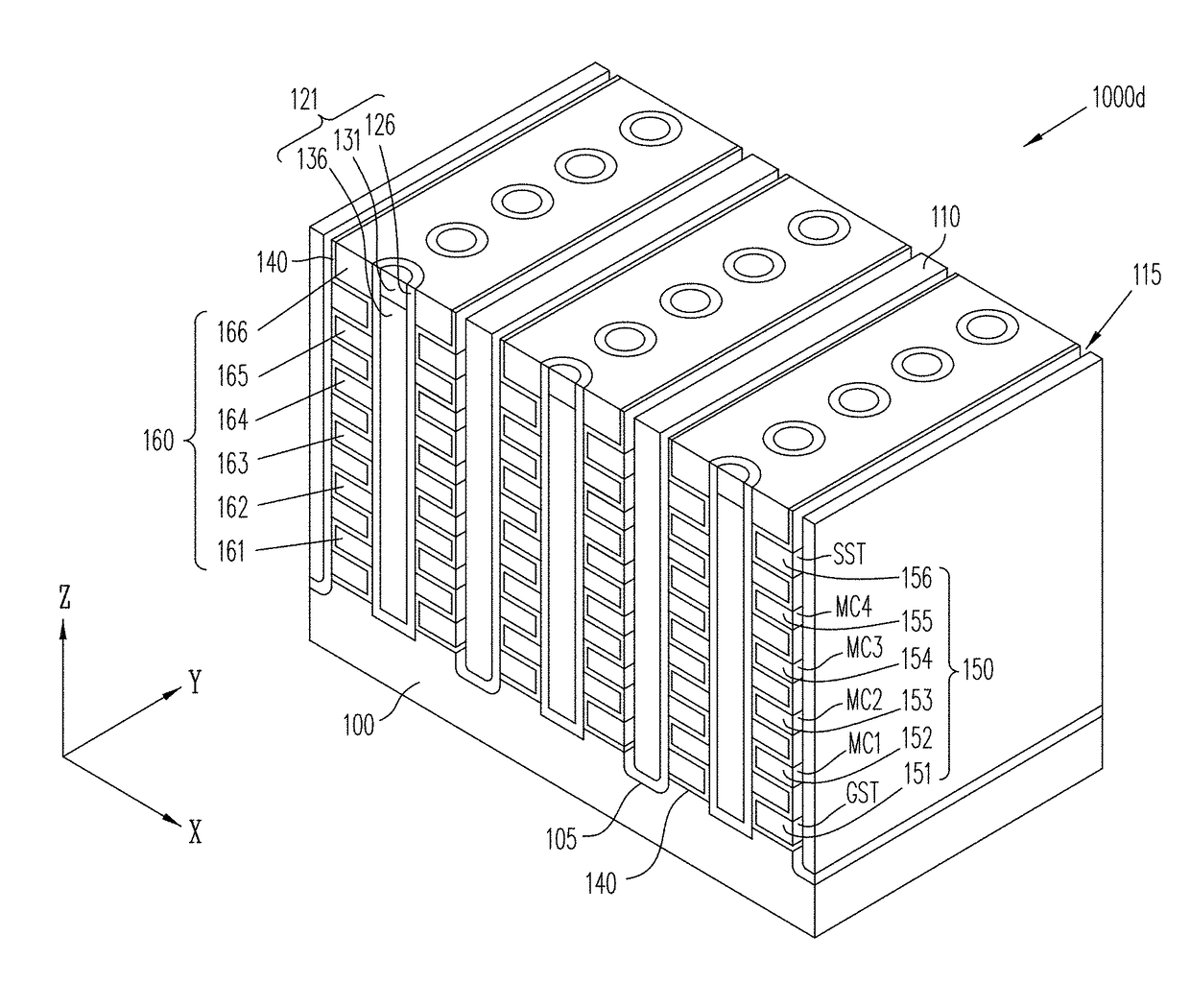
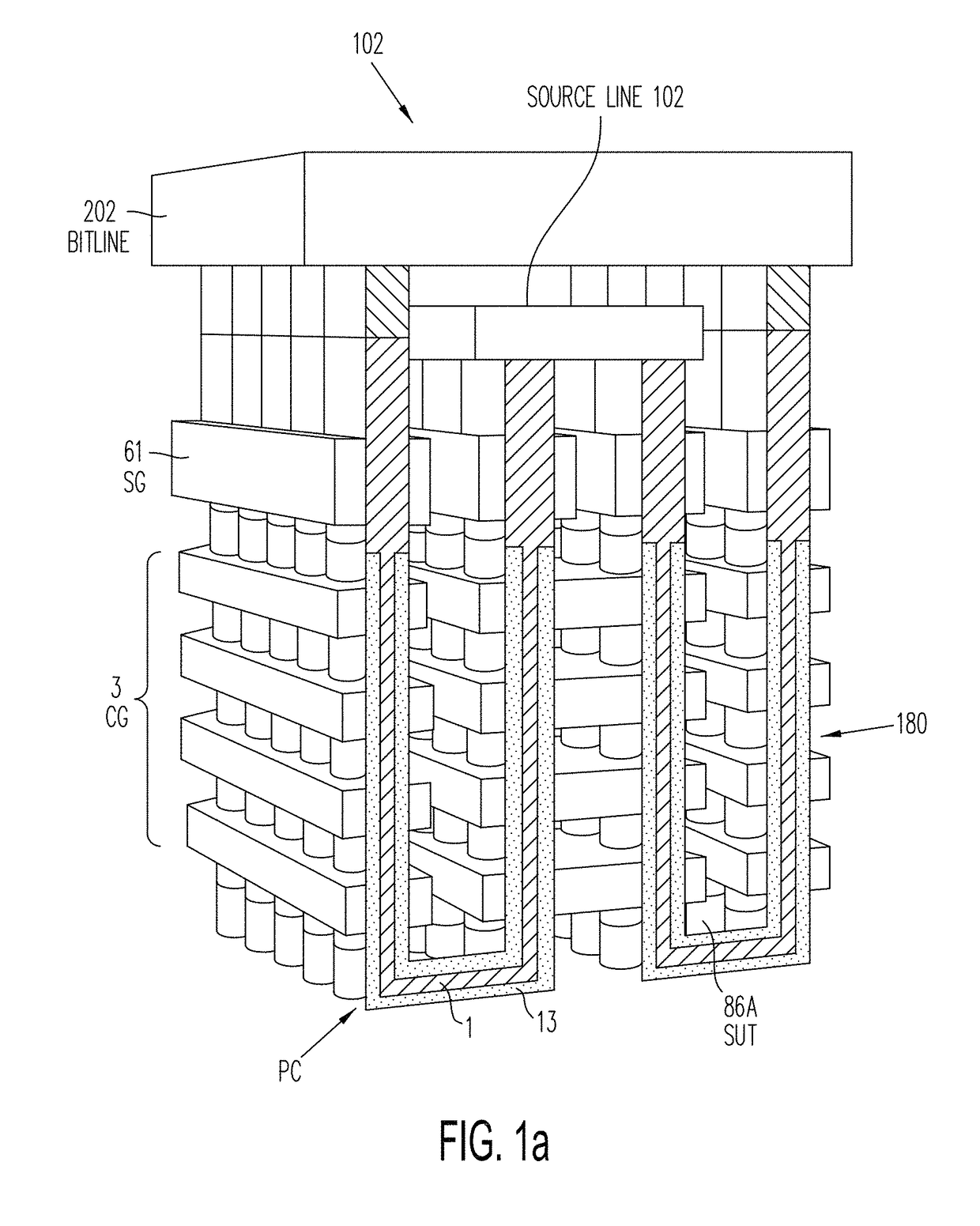
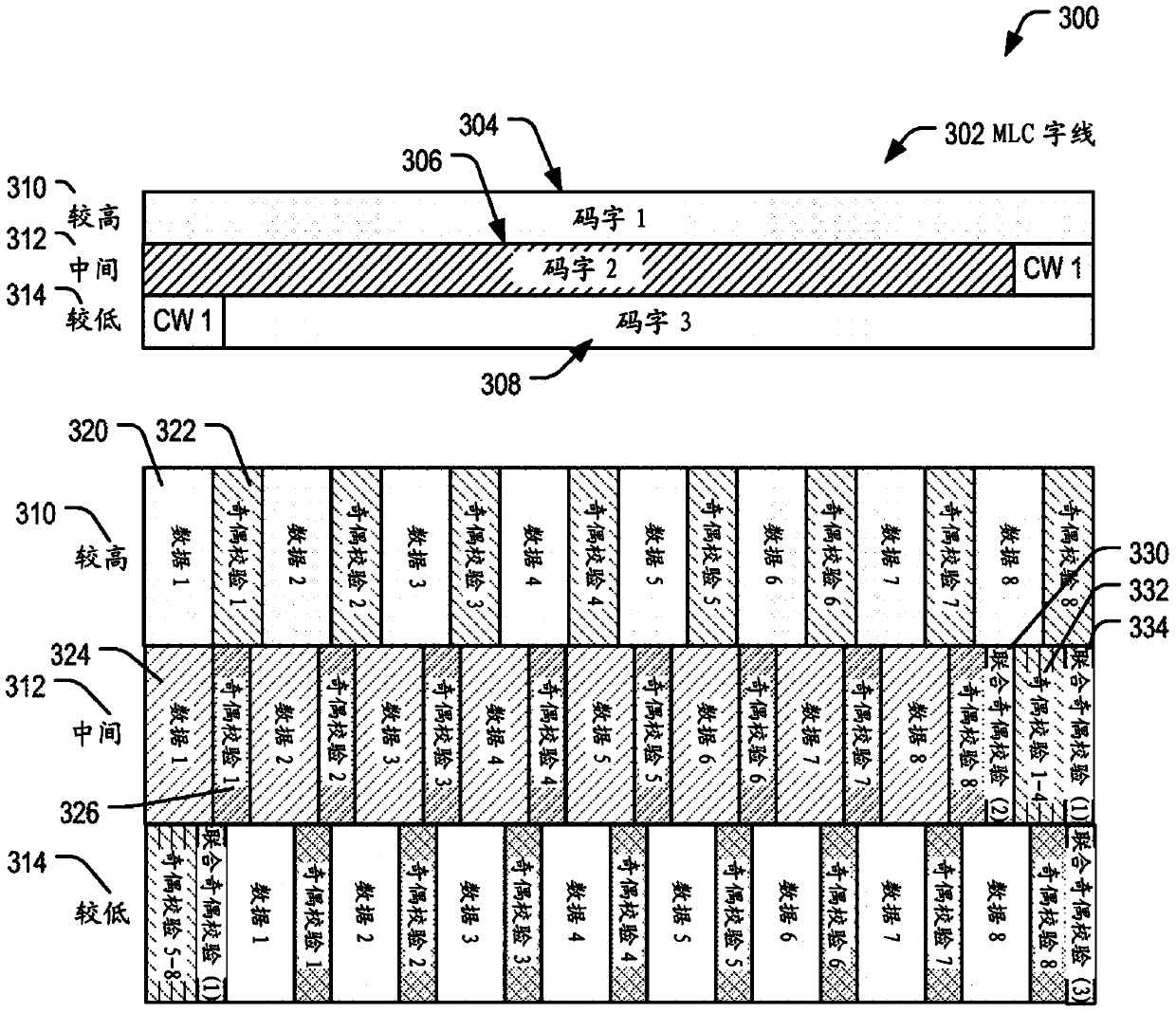
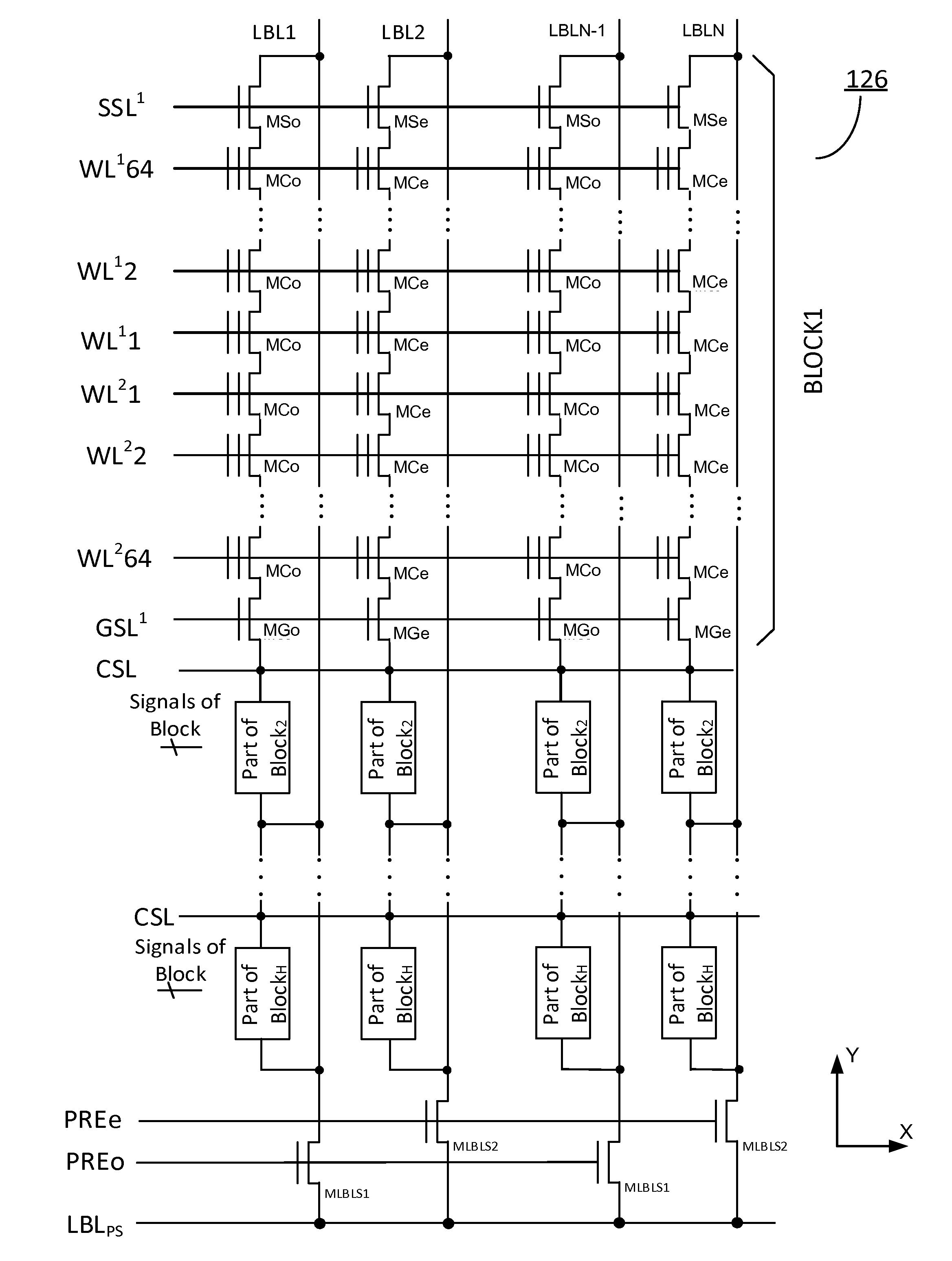
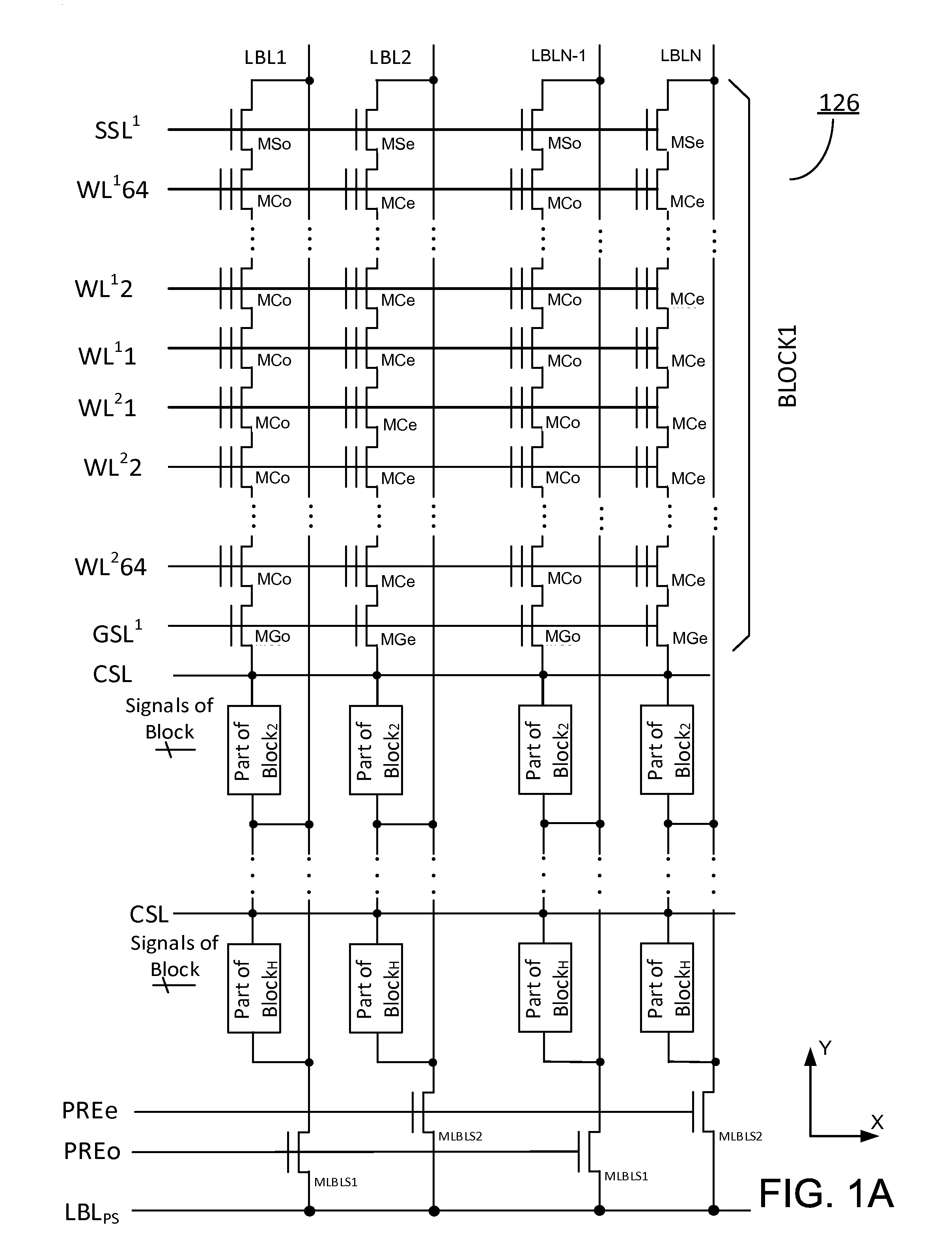
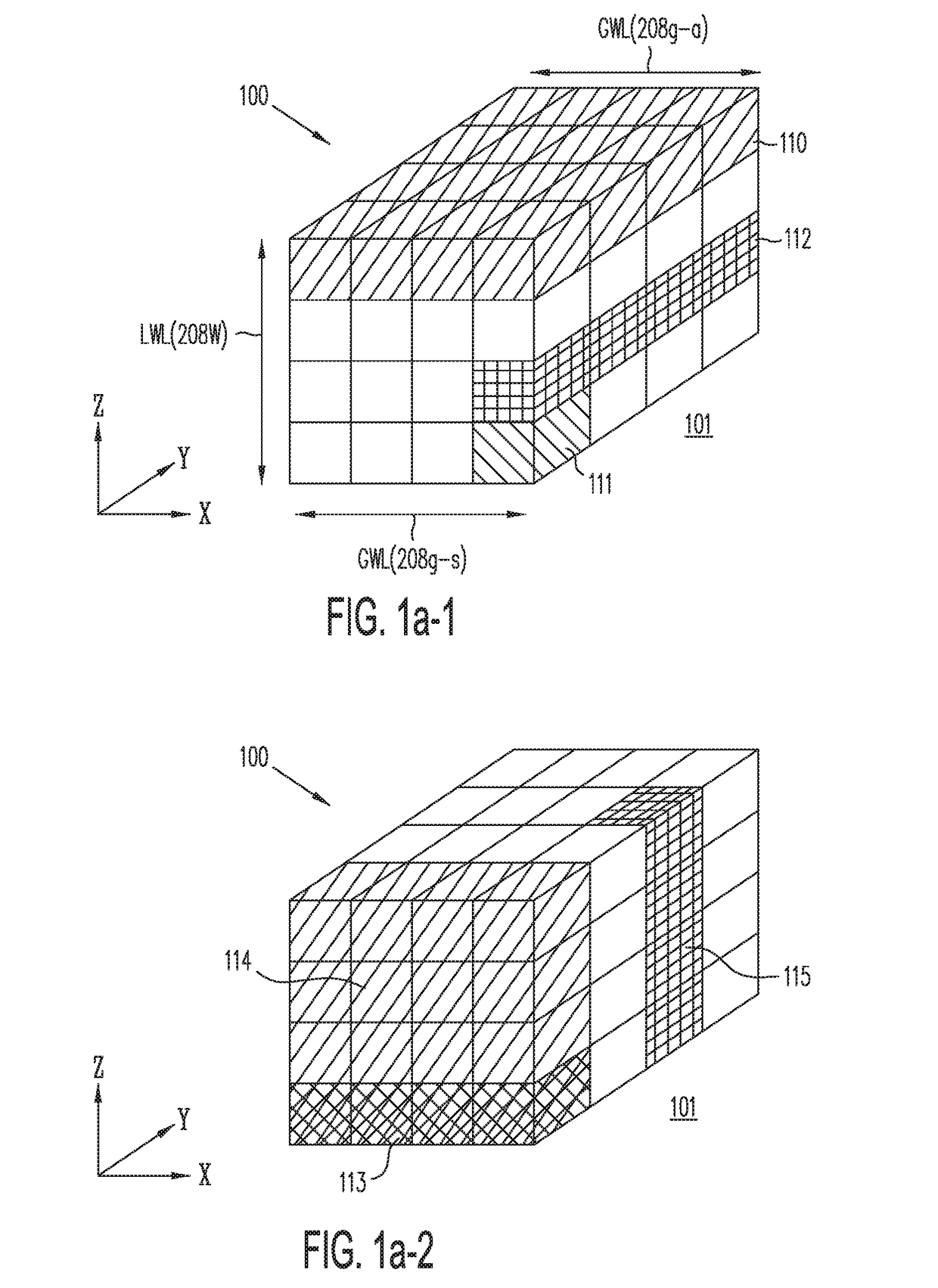
Three-dimensional vertical nor flash thin film transistor strings
ActiveUS20170148517A1Less resistanceFaster senseTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsEngineeringPolycrystalline silicon
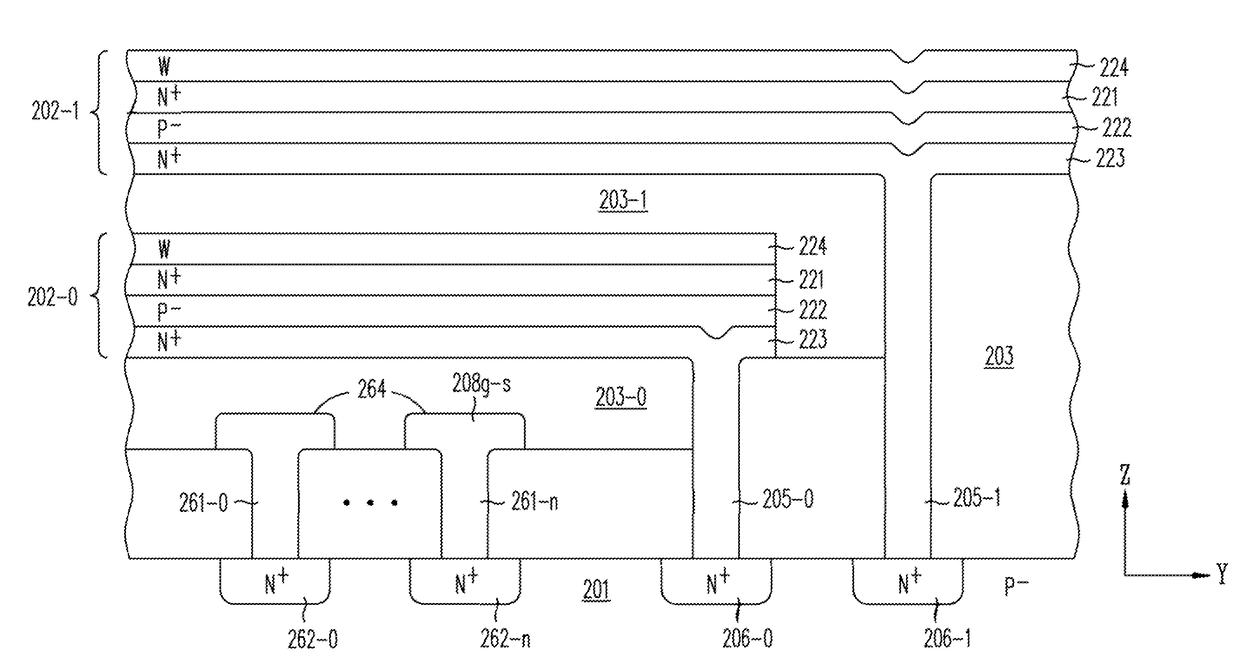
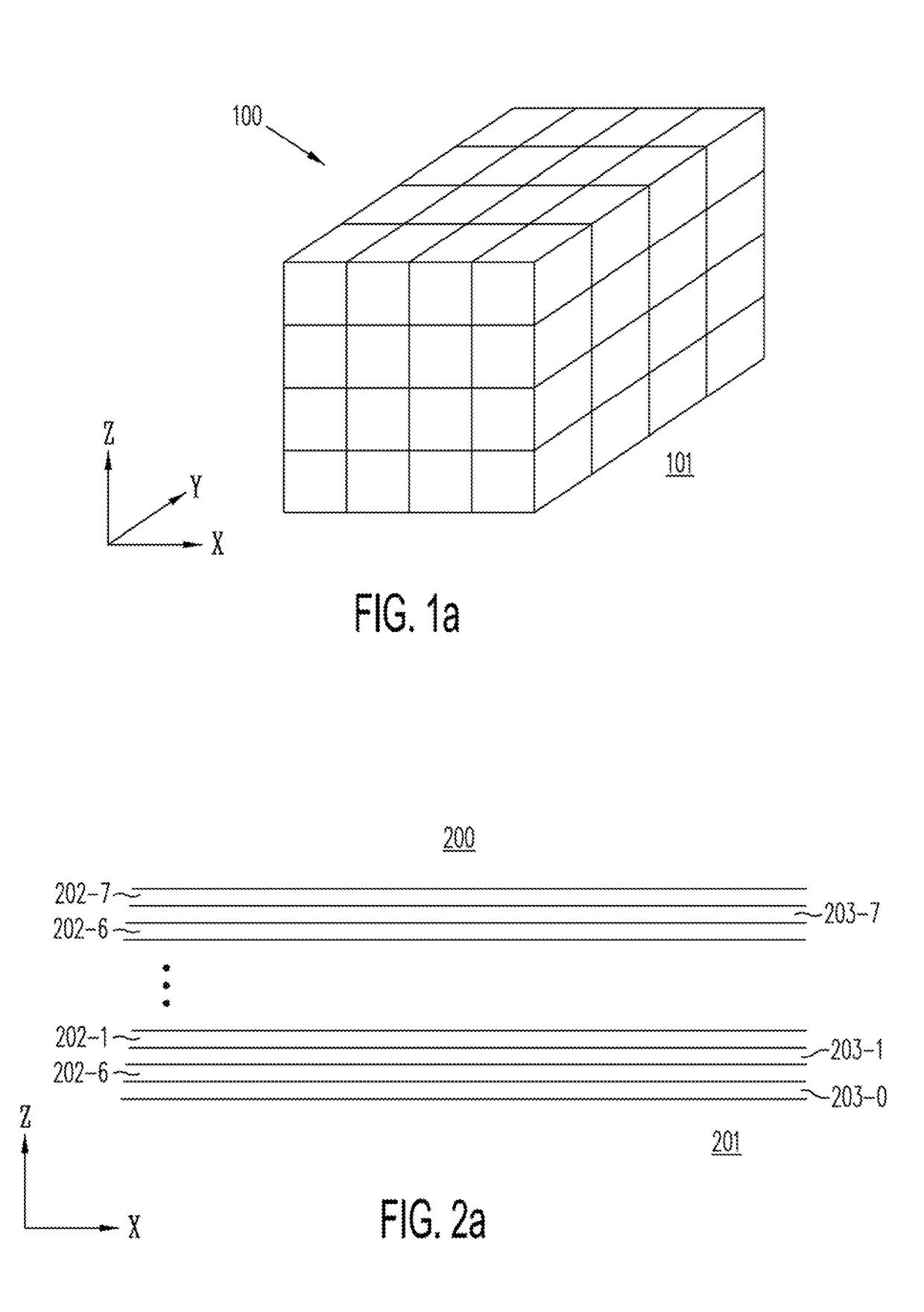
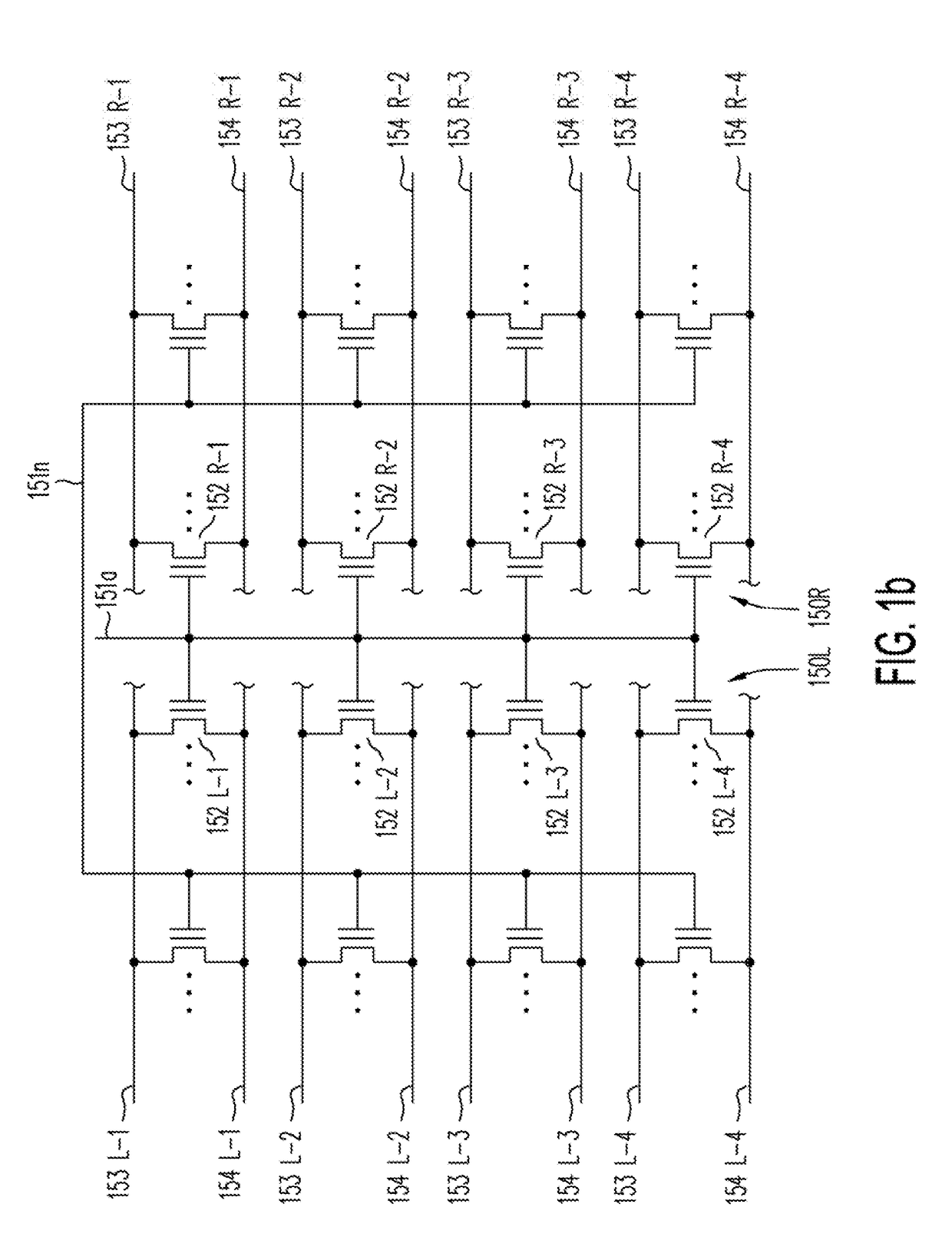
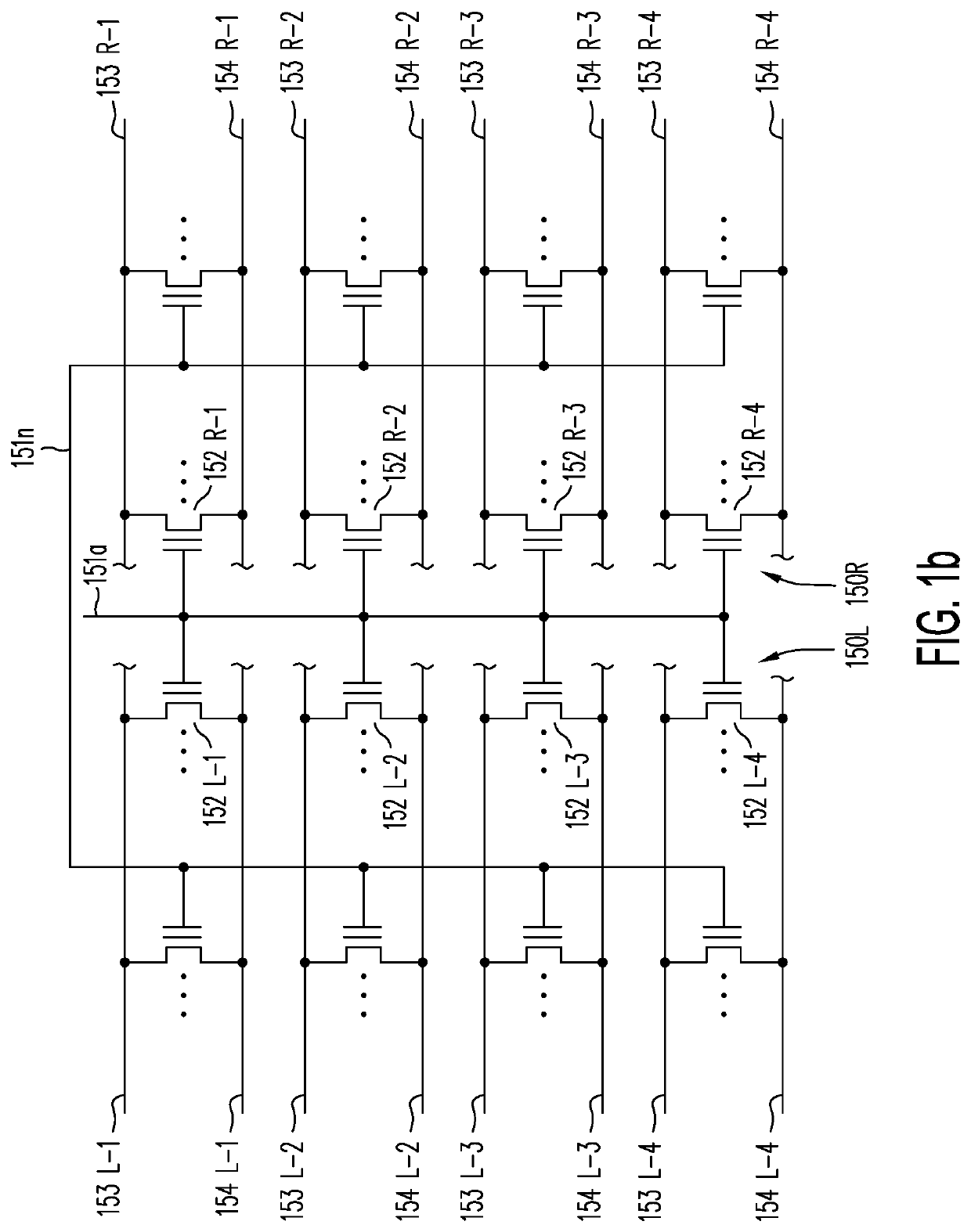
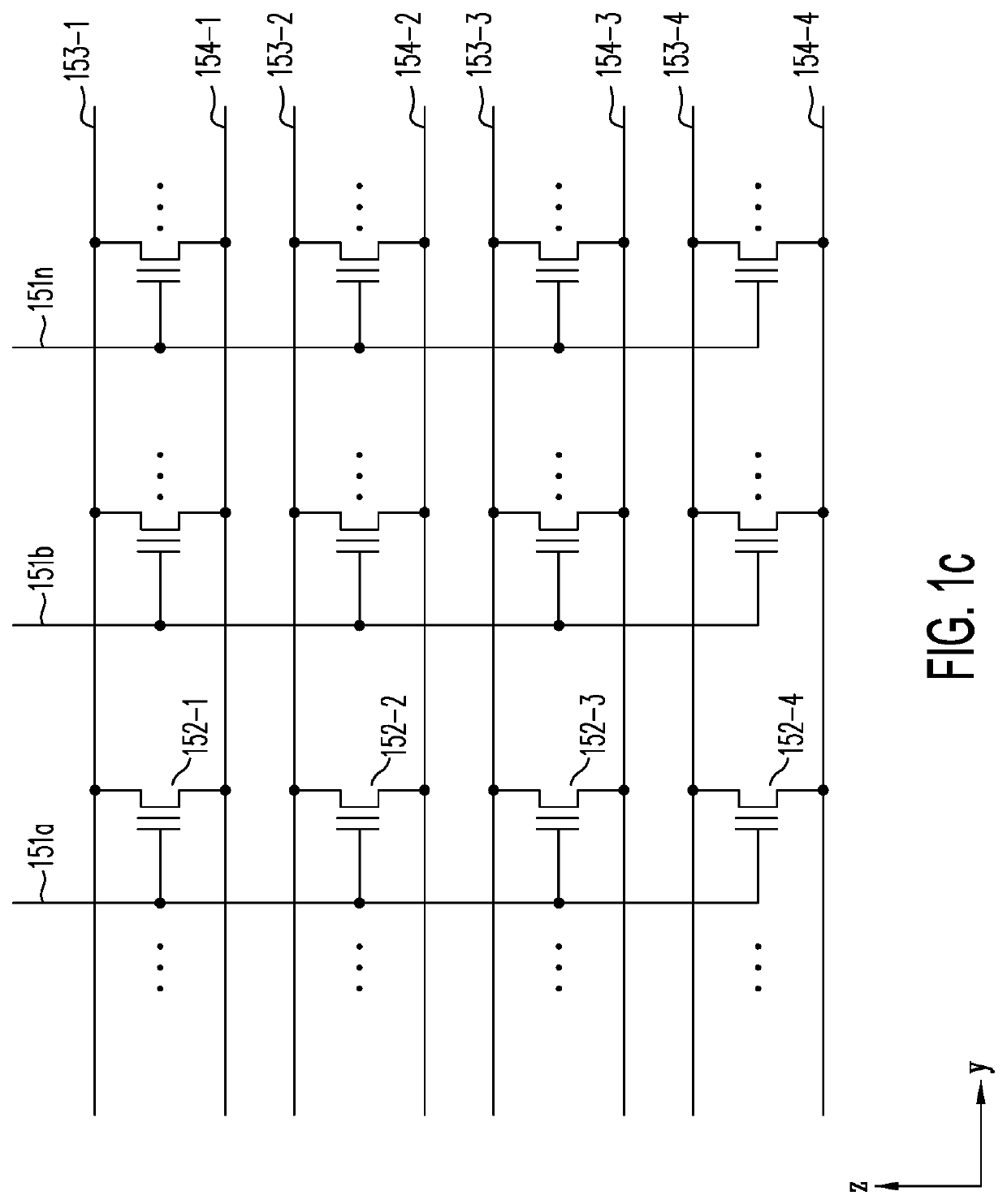
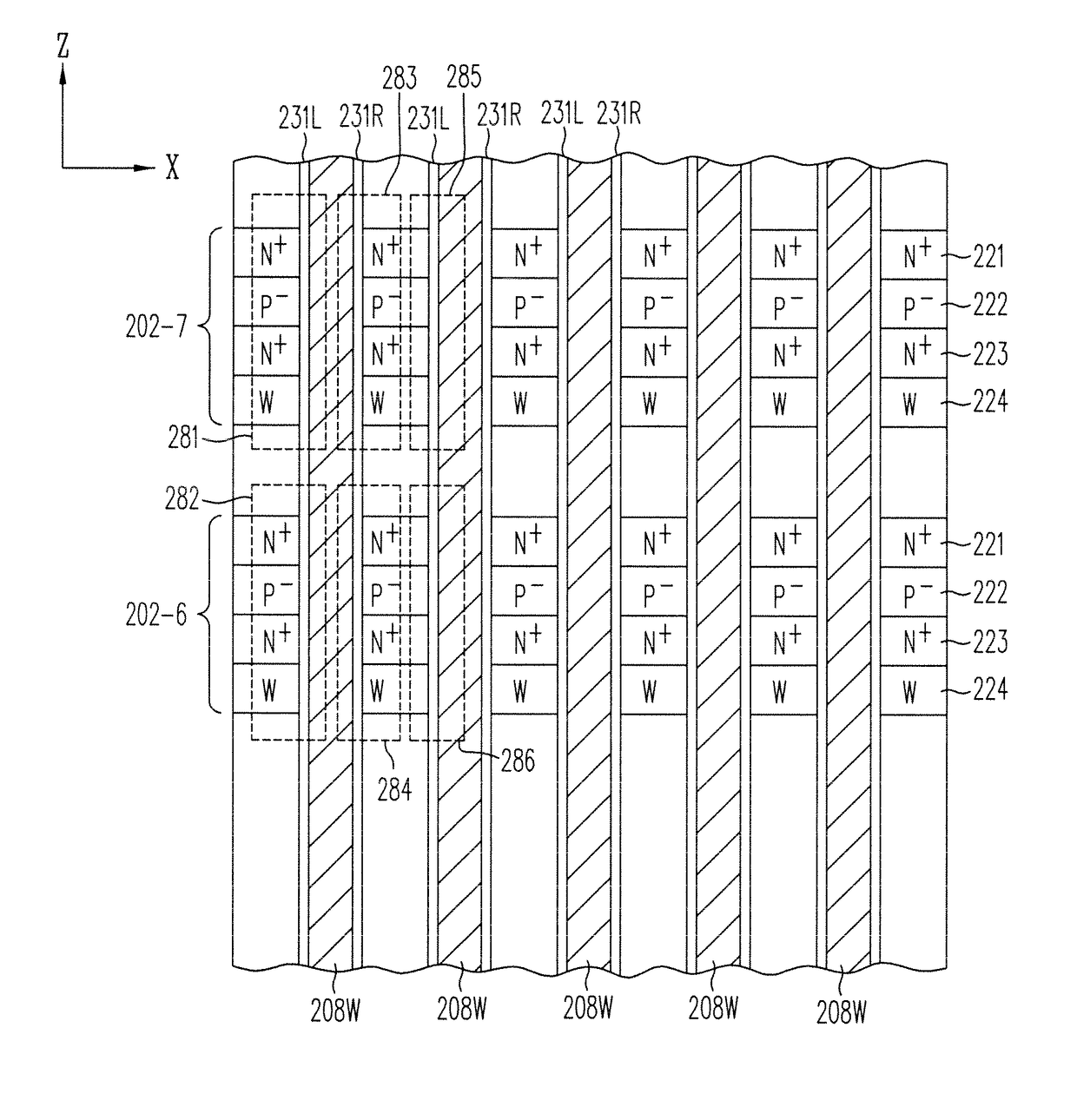
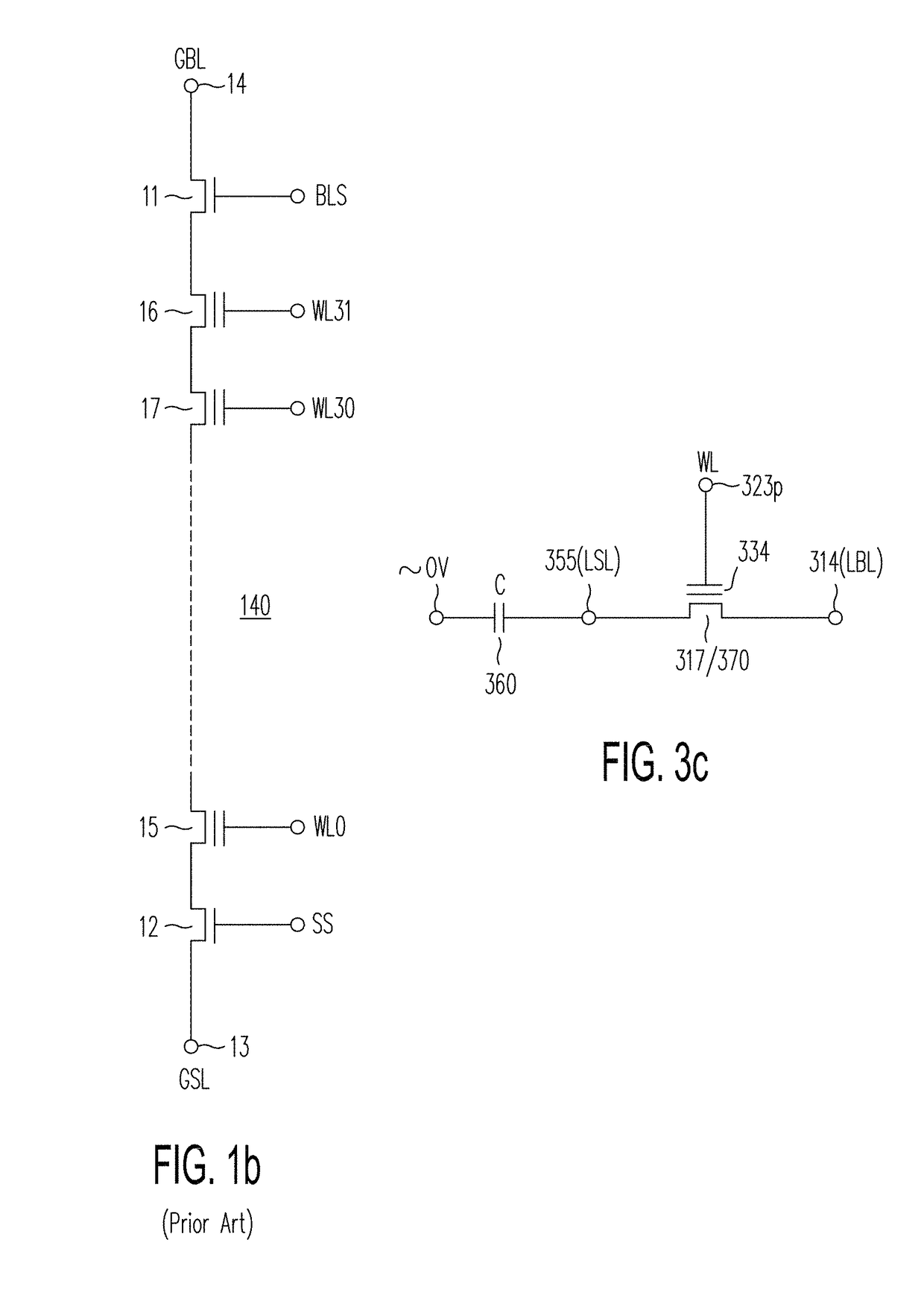
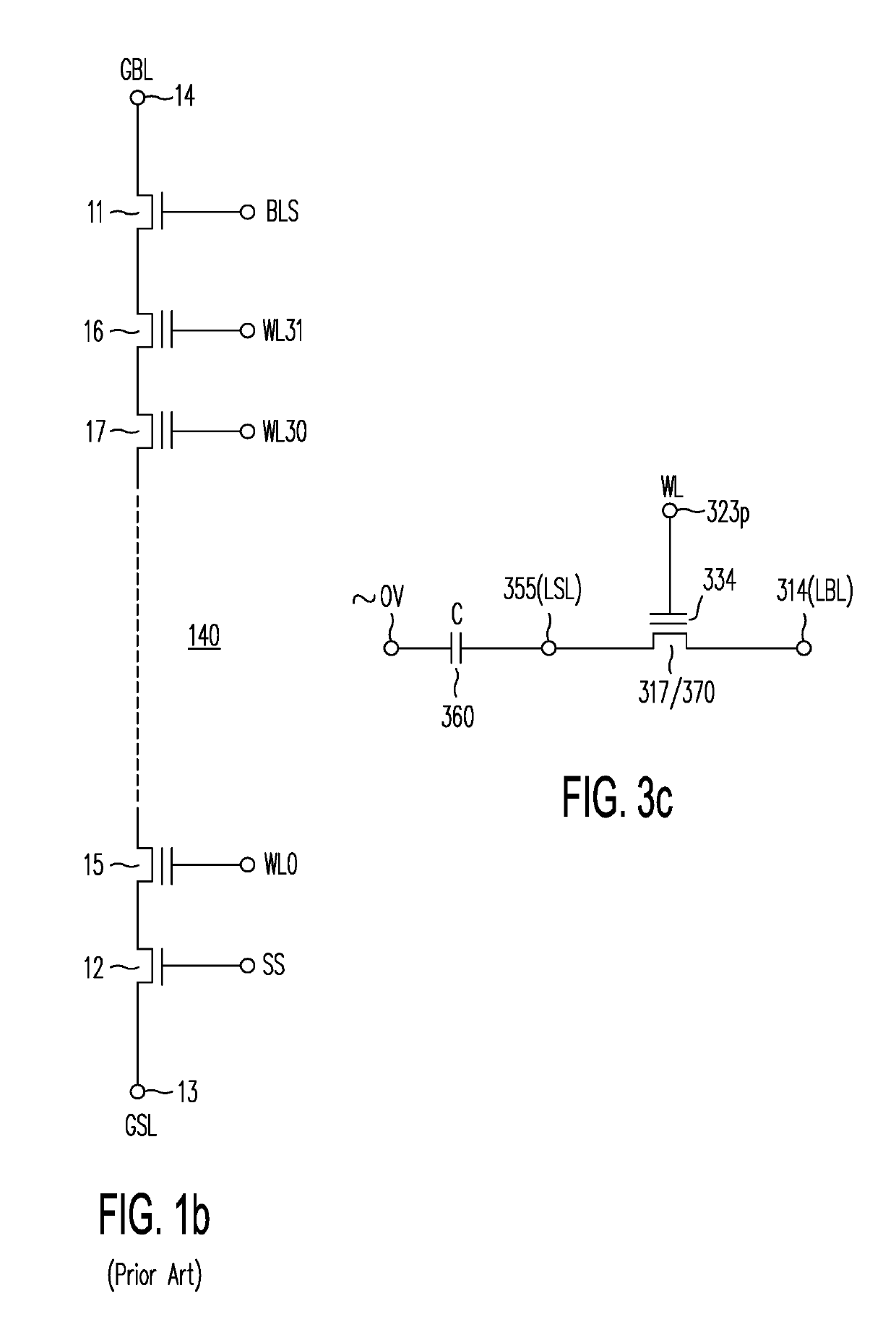
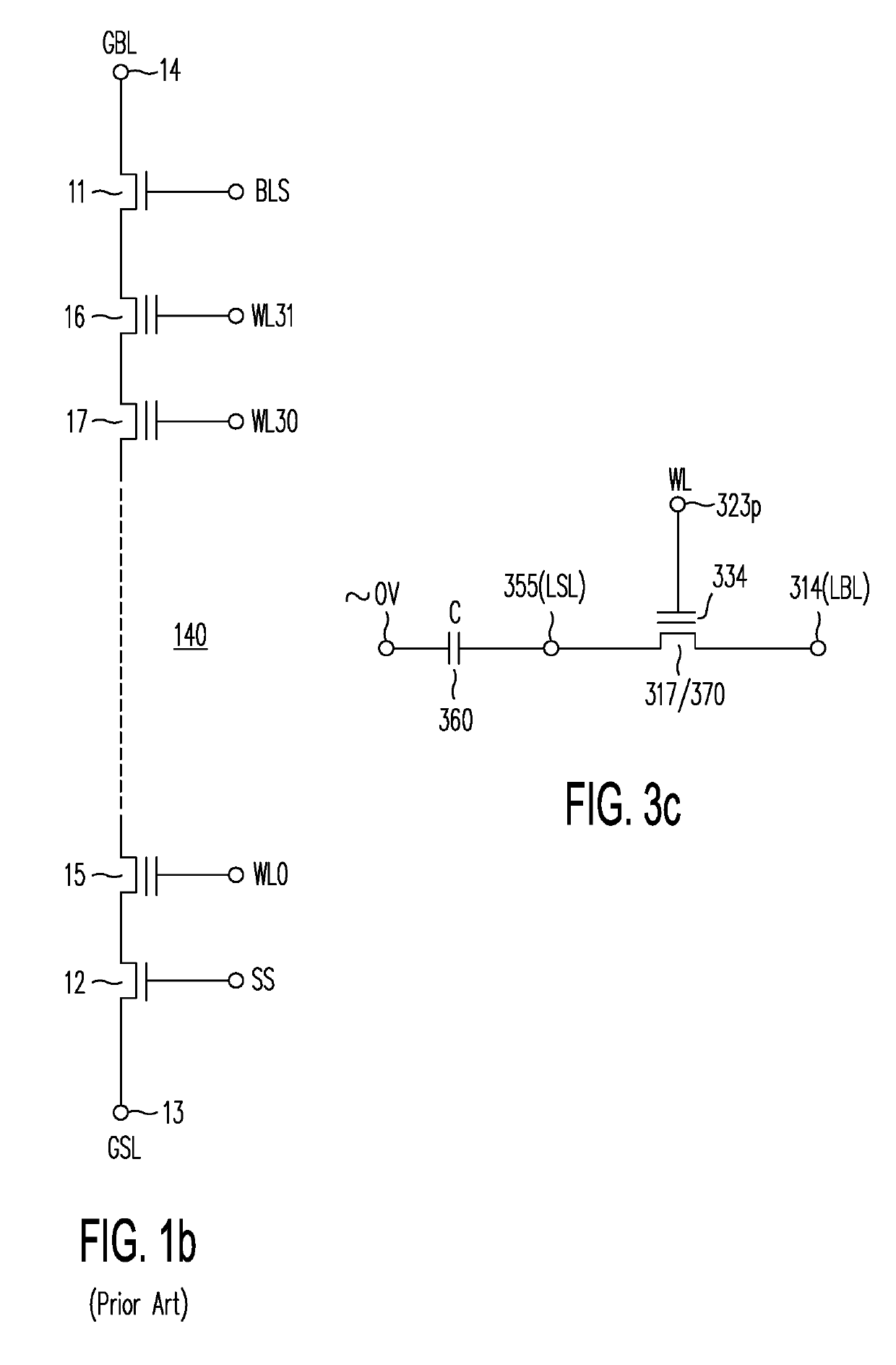
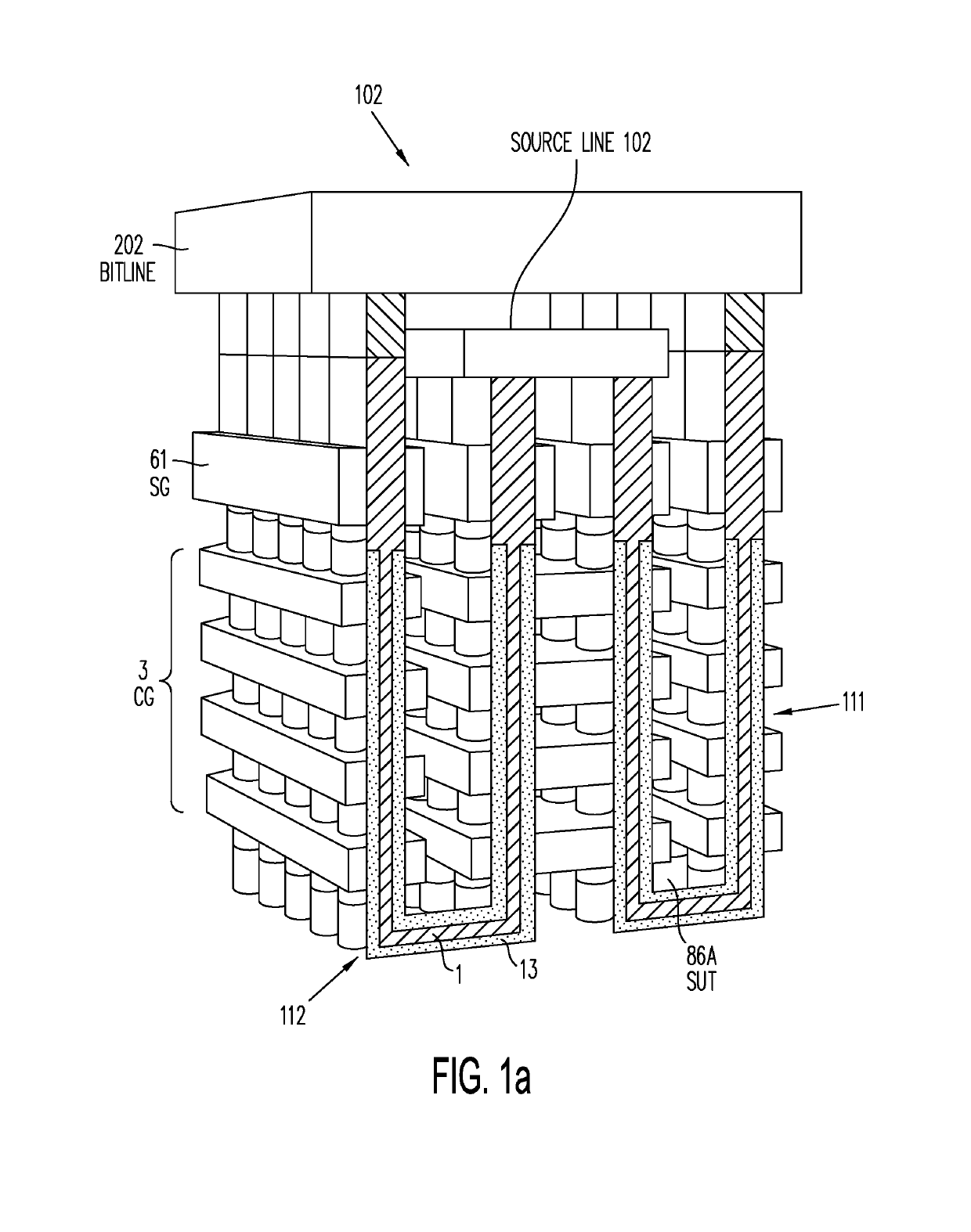
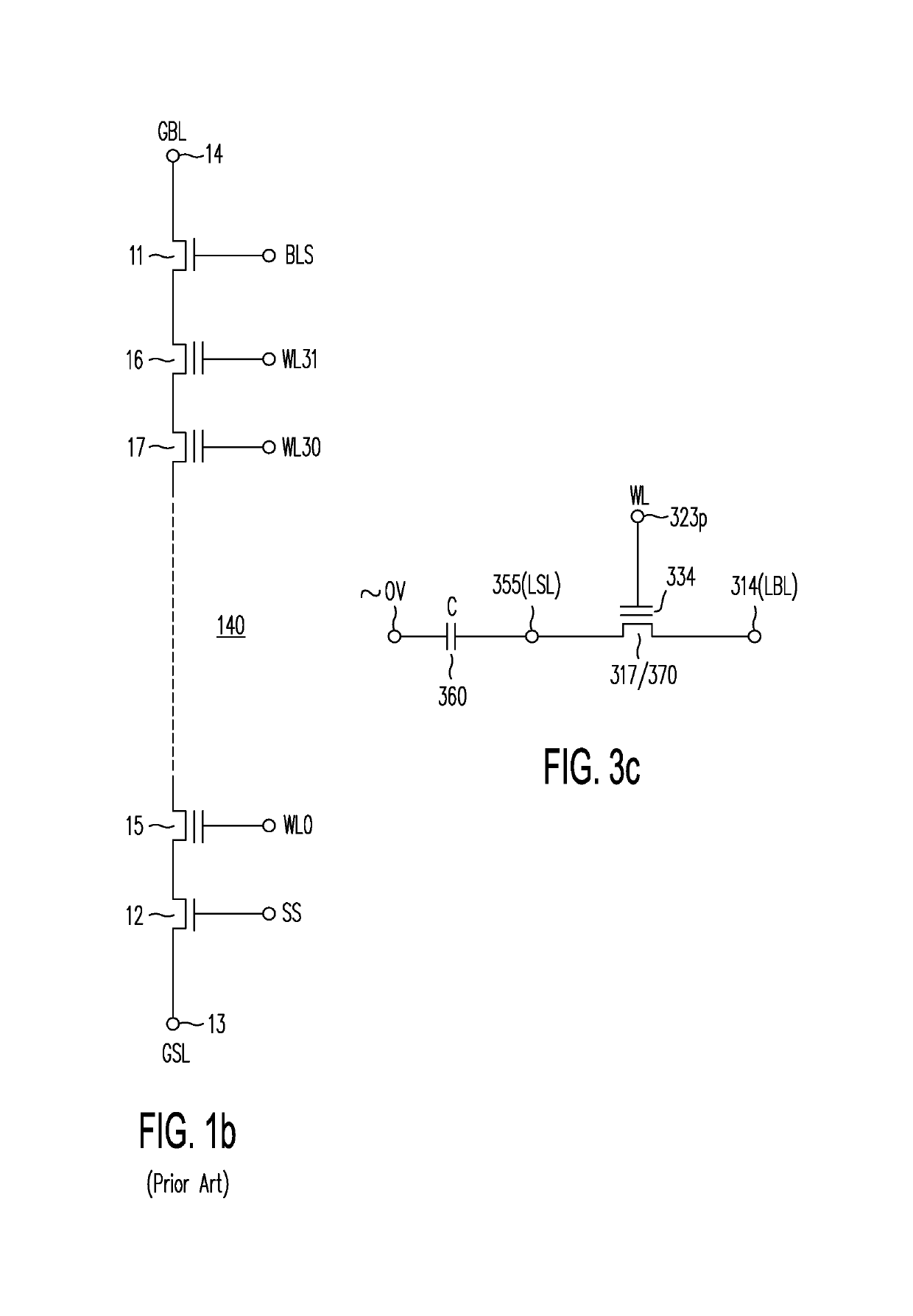
A memory structure, includes (a) active columns of polysilicon formed above a semiconductor substrate, each active column extending vertically from the substrate and including a first heavily doped region, a second heavily doped region, and one or more lightly doped regions each adjacent both the first and second heavily doped region, wherein the active columns are arranged in a two-dimensional array extending in second and third directions parallel to the planar surface of the semiconductor substrate; (b) charge-trapping material provided over one or more surfaces of each active column; and (c) conductors each extending lengthwise along the third direction. The active columns, the charge-trapping material and the conductors together form a plurality of thin film transistors, with each thin film transistor formed by one of the conductors, a portion of the lightly doped region of an active column, the charge-trapping material between the portion of the lightly doped region and the conductor, and the first and second heavily doped regions. The thin film transistors associated with each active column are organized into one or more vertical NOR strings.
Owner:SUNRISE MEMORY CORP
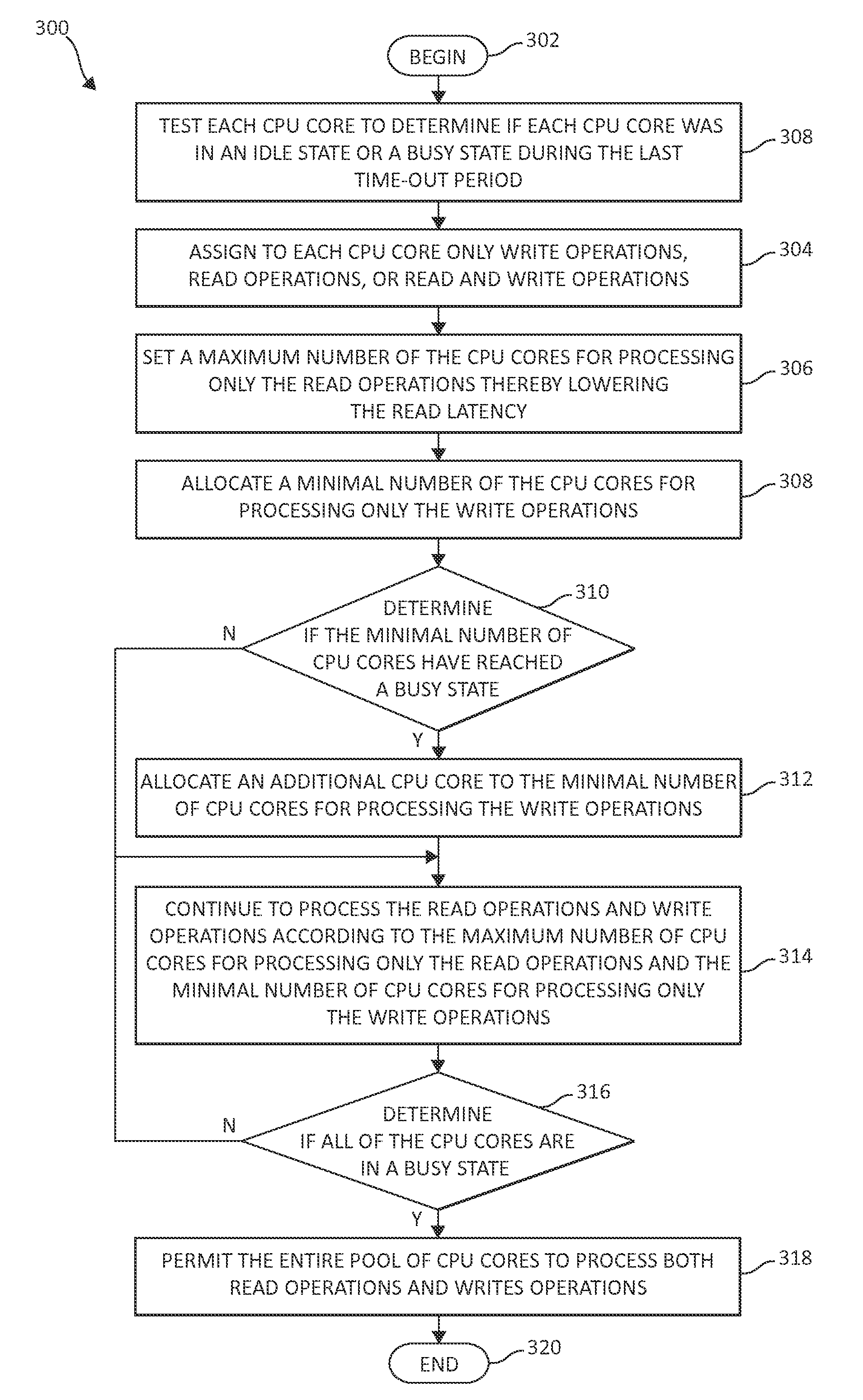
Reducing read latency using a pool of processing cores
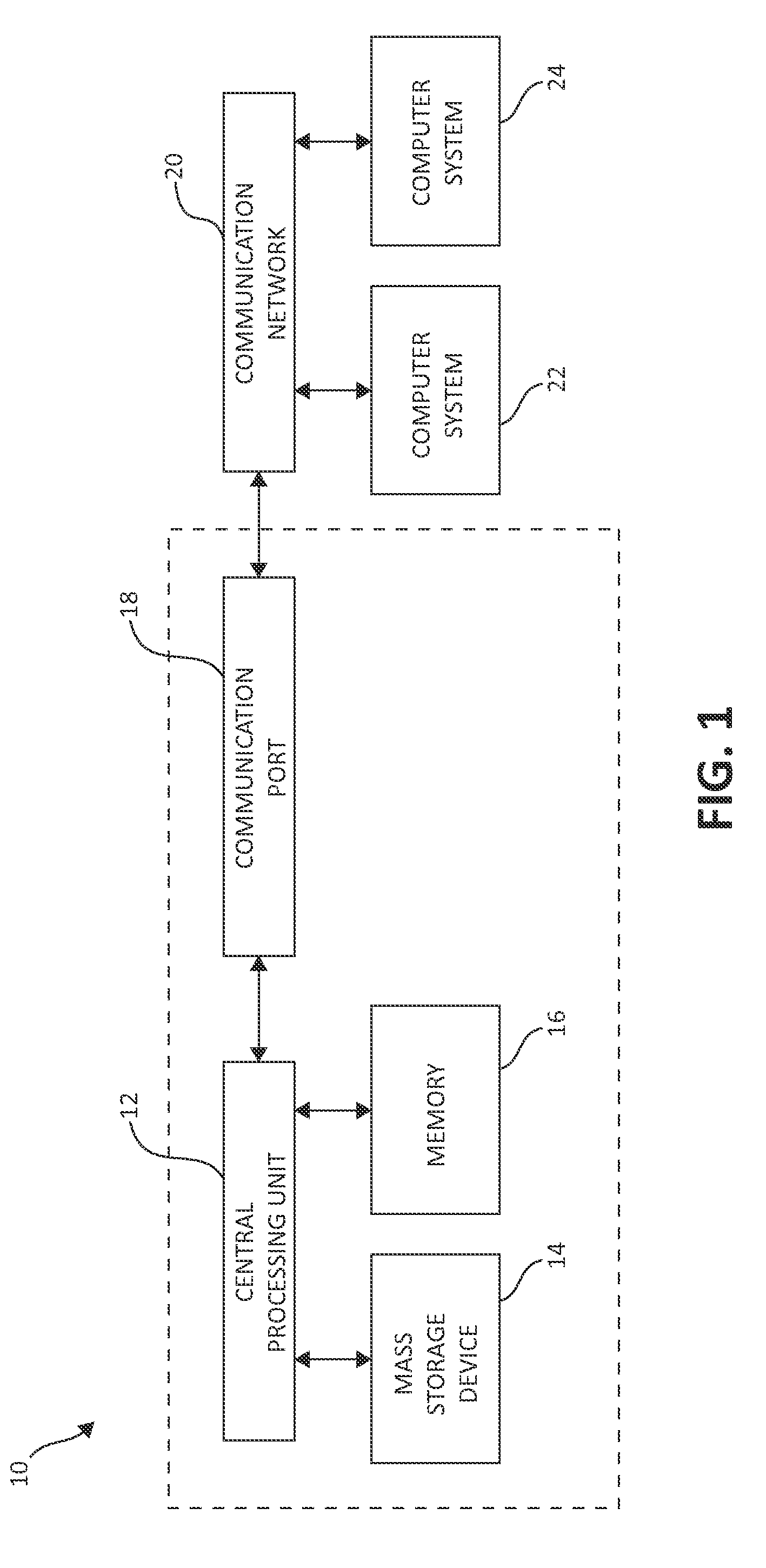
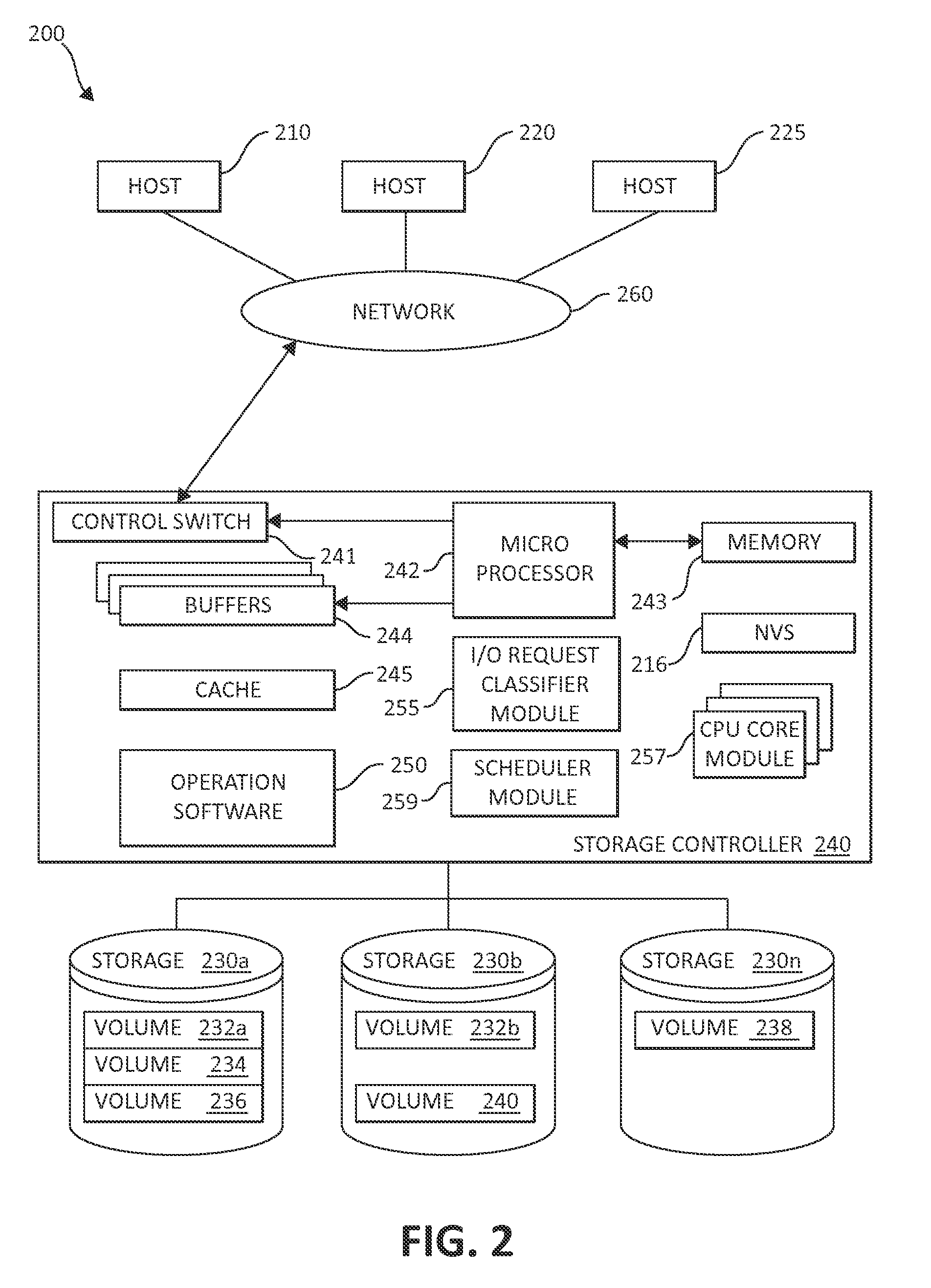
ActiveUS8930633B2Avoid read latencyLower read latencyInput/output to record carriersHardware monitoringProcessing coreComputer science
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
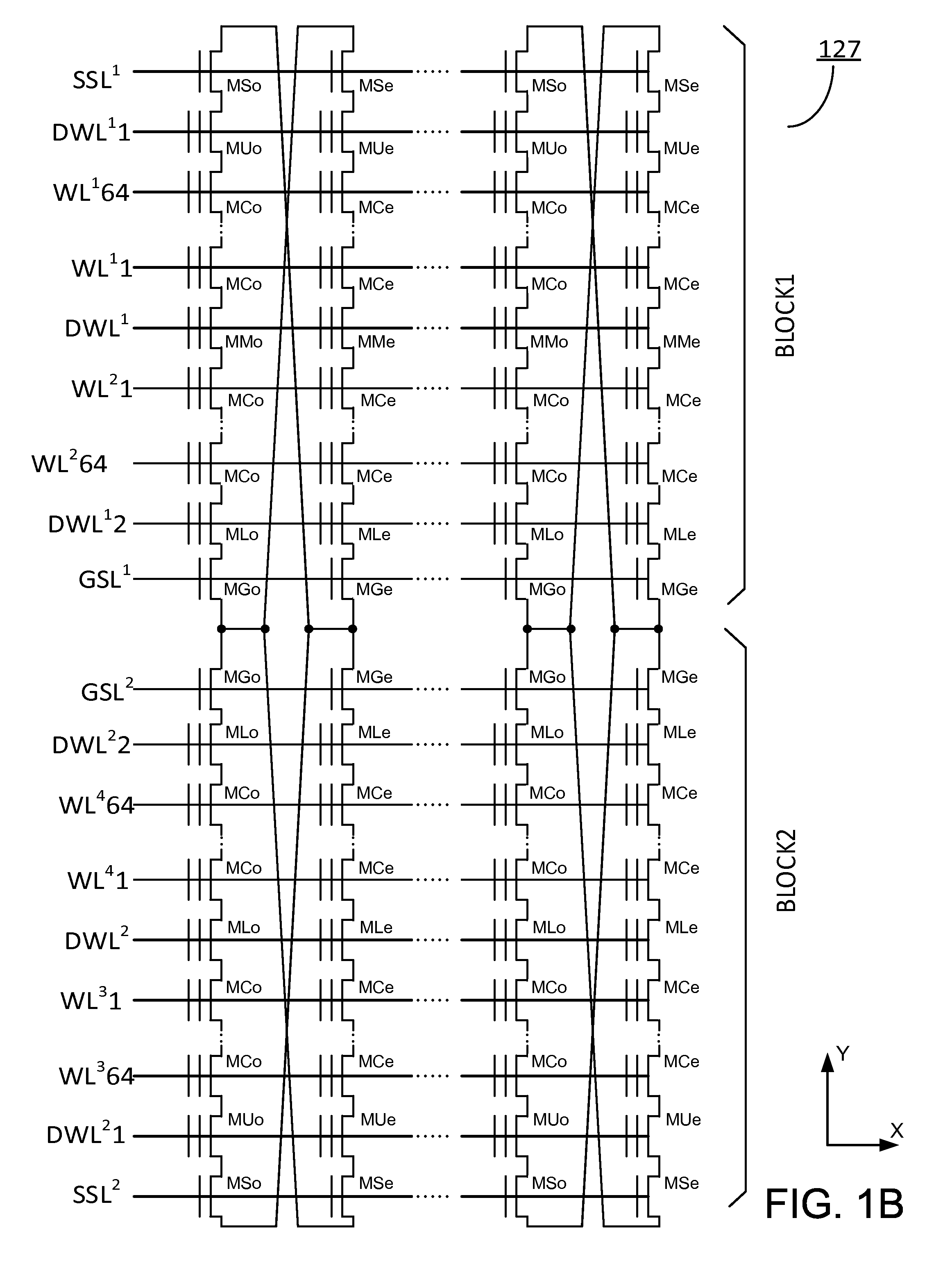
Multi-gate nor flash thin-film transistor strings arranged in stacked horizontal active strips with vertical control gates
ActiveUS20180090219A1High densityLower read latencySolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesEngineeringVertical control
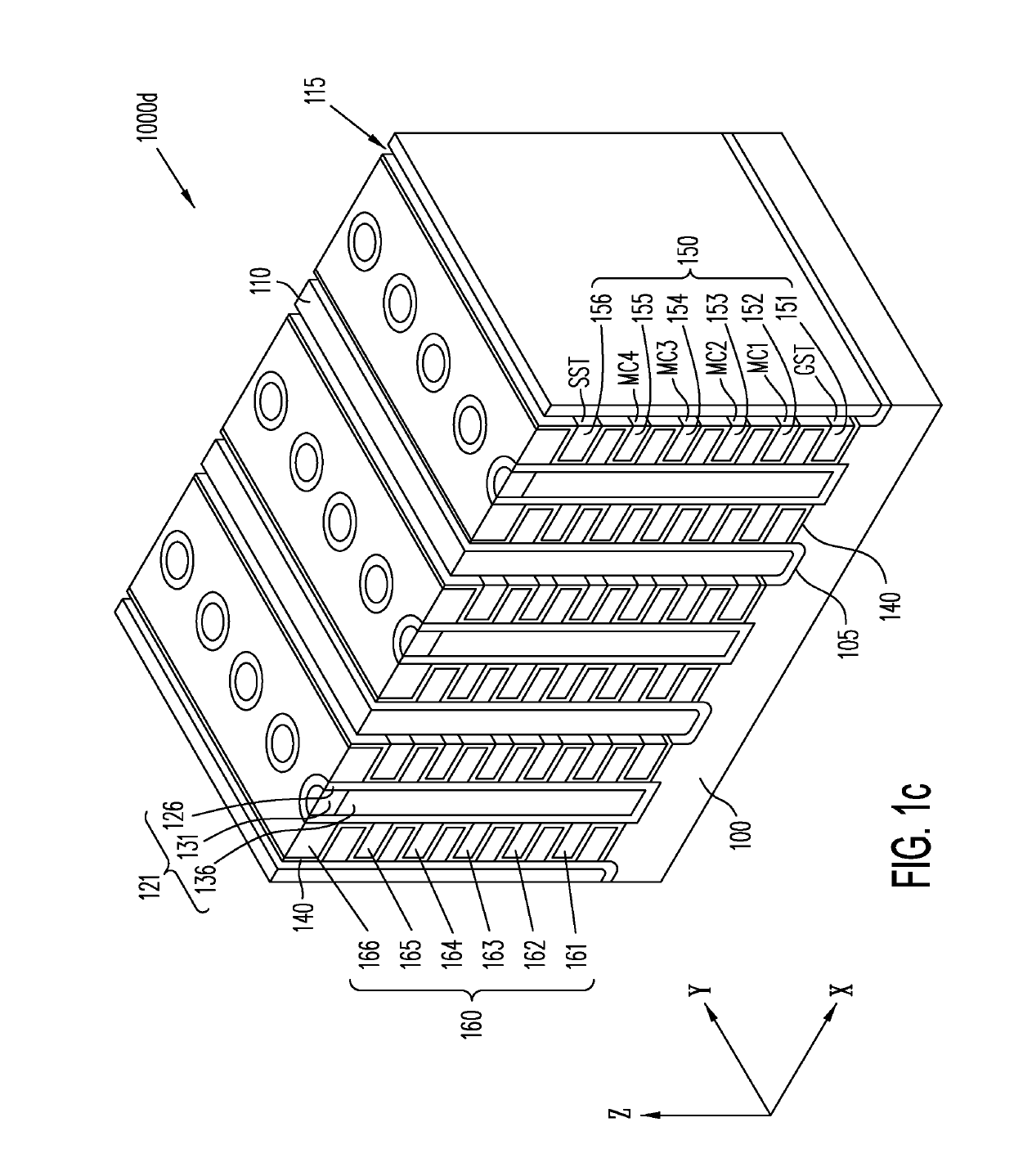
Multi-gate NOR flash thin-film transistor (TFT) string arrays (“multi-gate NOR string arrays”) are organized as stacks of horizontal active strips running parallel to the surface of a silicon substrate, with the TFTs in each stack being controlled by vertical local word-lines provided along one or both sidewalls of the stack of active strips. Each active strip includes at least a channel layer formed between two shared source or drain layers. Data storage in the TFTs of an active strip is provided by charge-storage elements provided between the active strip and the control gates provided by the adjacent local word-lines. Each active strip may provide TFTs that belong to one or two NOR strings, depending on whether one or both sides of the active strip are used.
Owner:SUNRISE MEMORY CORP
Implementing logic function and generating analog signals using nor memory strings
ActiveUS20200227123A1High densityLower read latencyTransistorSolid-state devicesTheoretical computer scienceEngineering
NOR memory strings may be used for implementations of logic functions involving many Boolean variables, or to generate analog signals whose magnitudes are each representative of the bit values of many Boolean variables. The advantage of using NOR memory strings in these manners is that the logic function or analog signal generation may be accomplished within one simultaneous read operation on the NOR memory strings.
Owner:SUNRISE MEMORY CORP
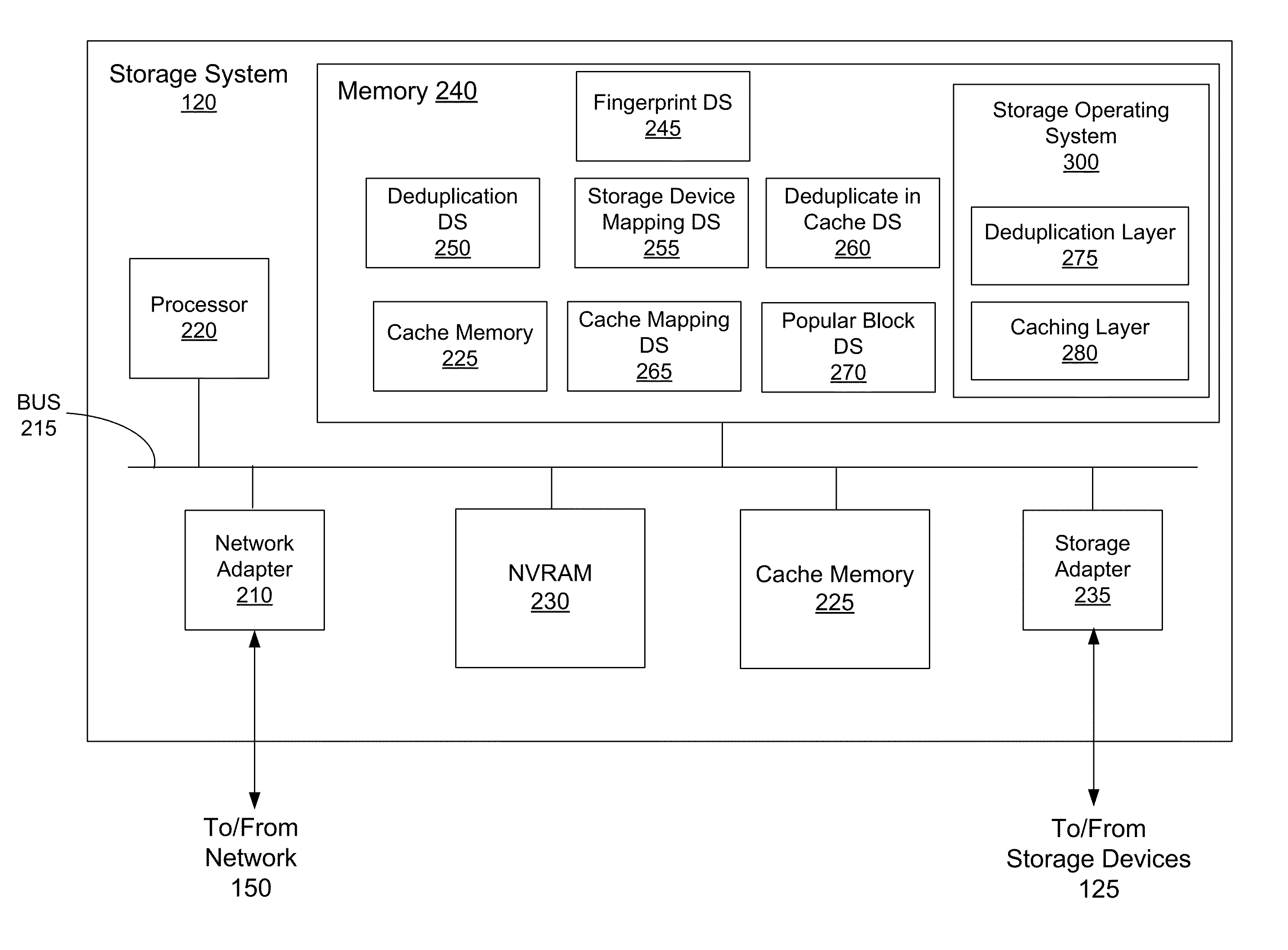
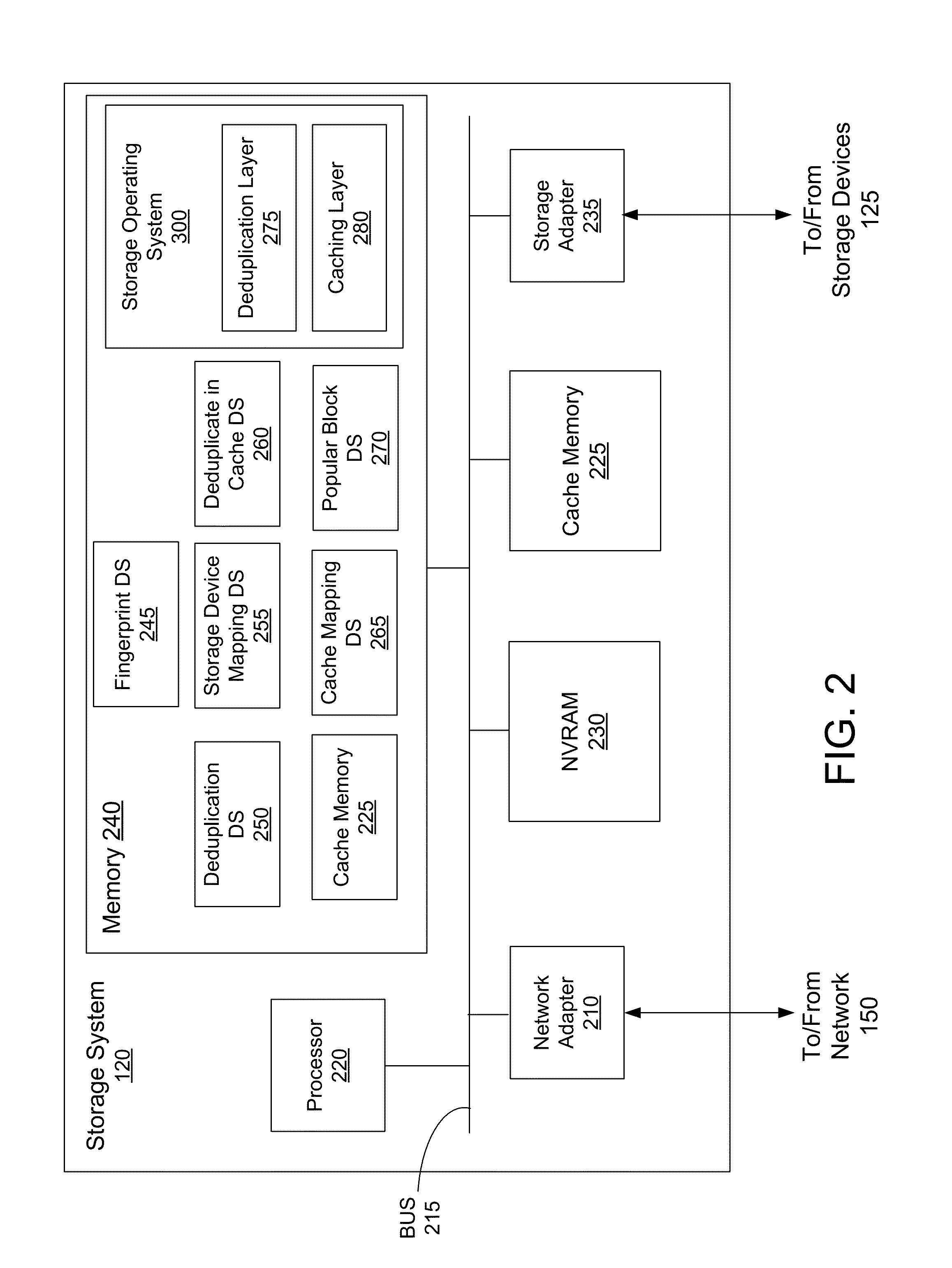
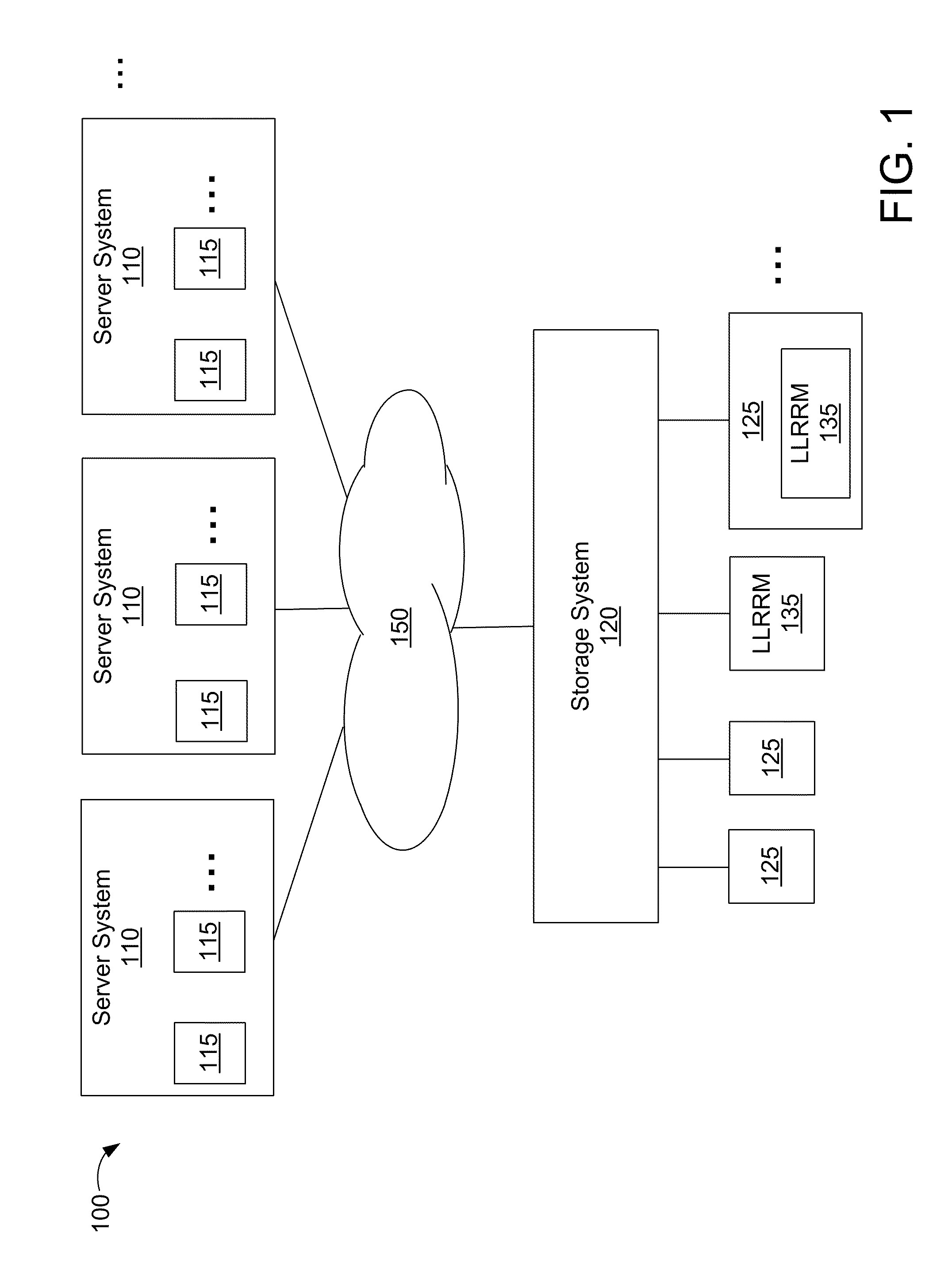
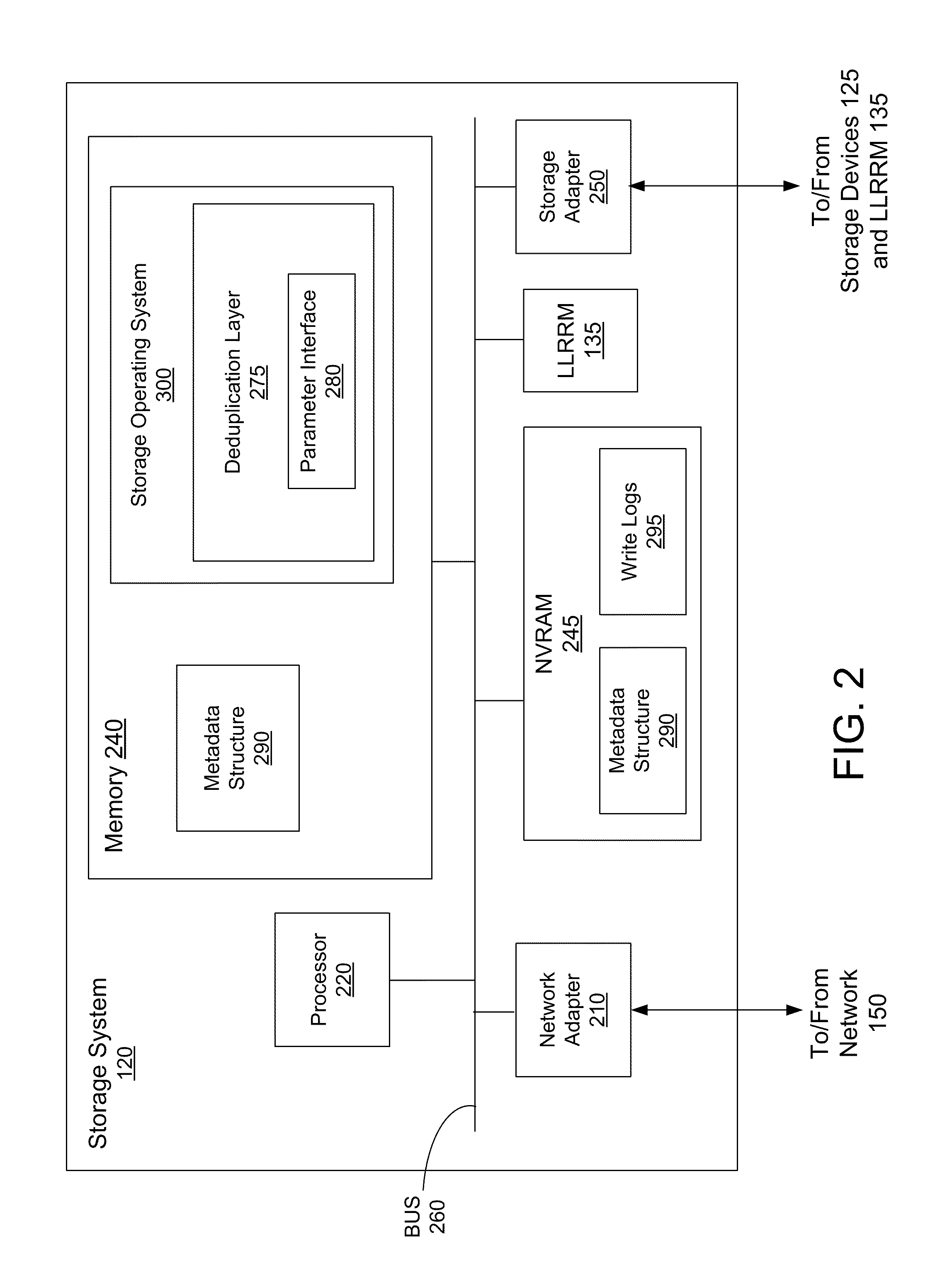
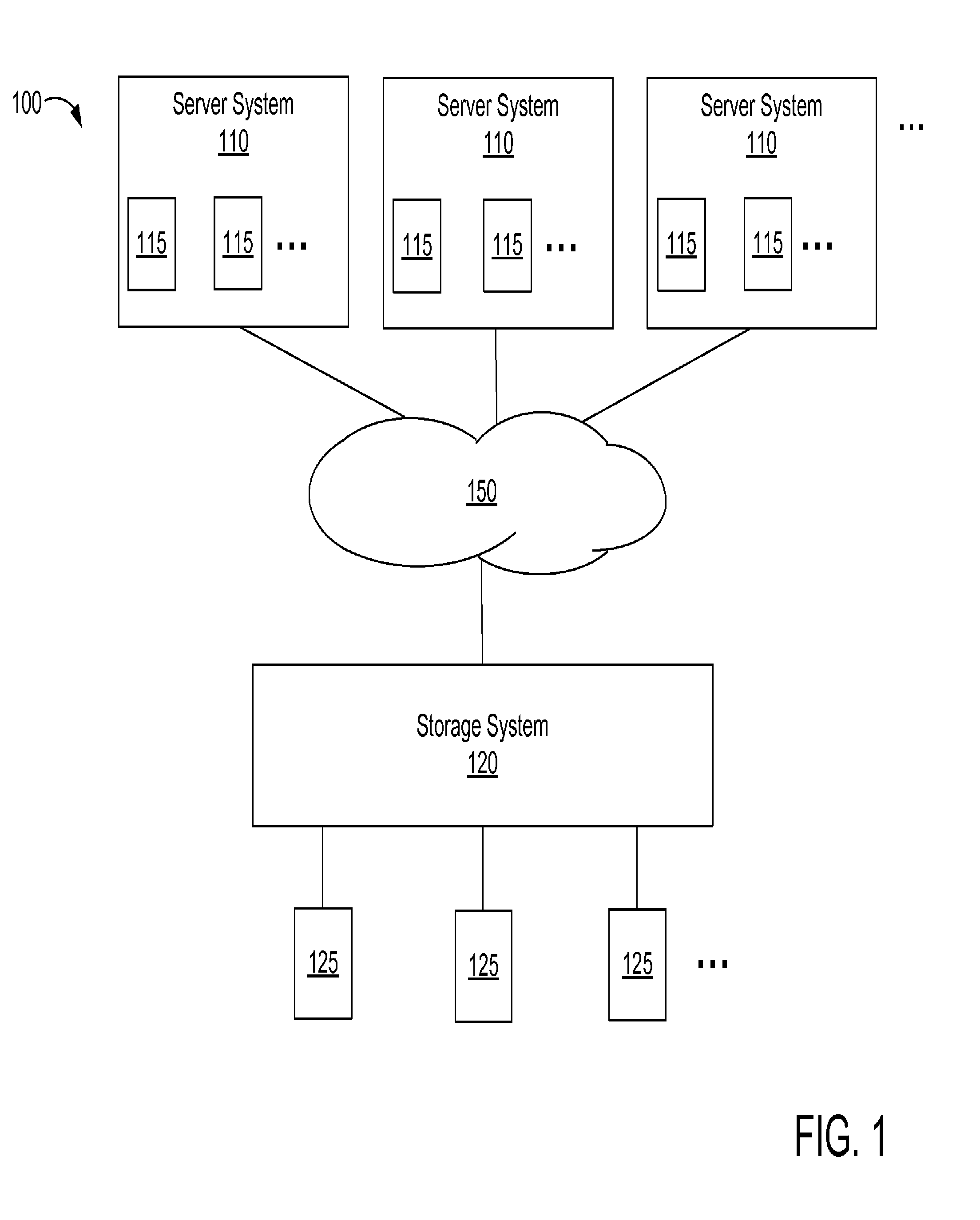
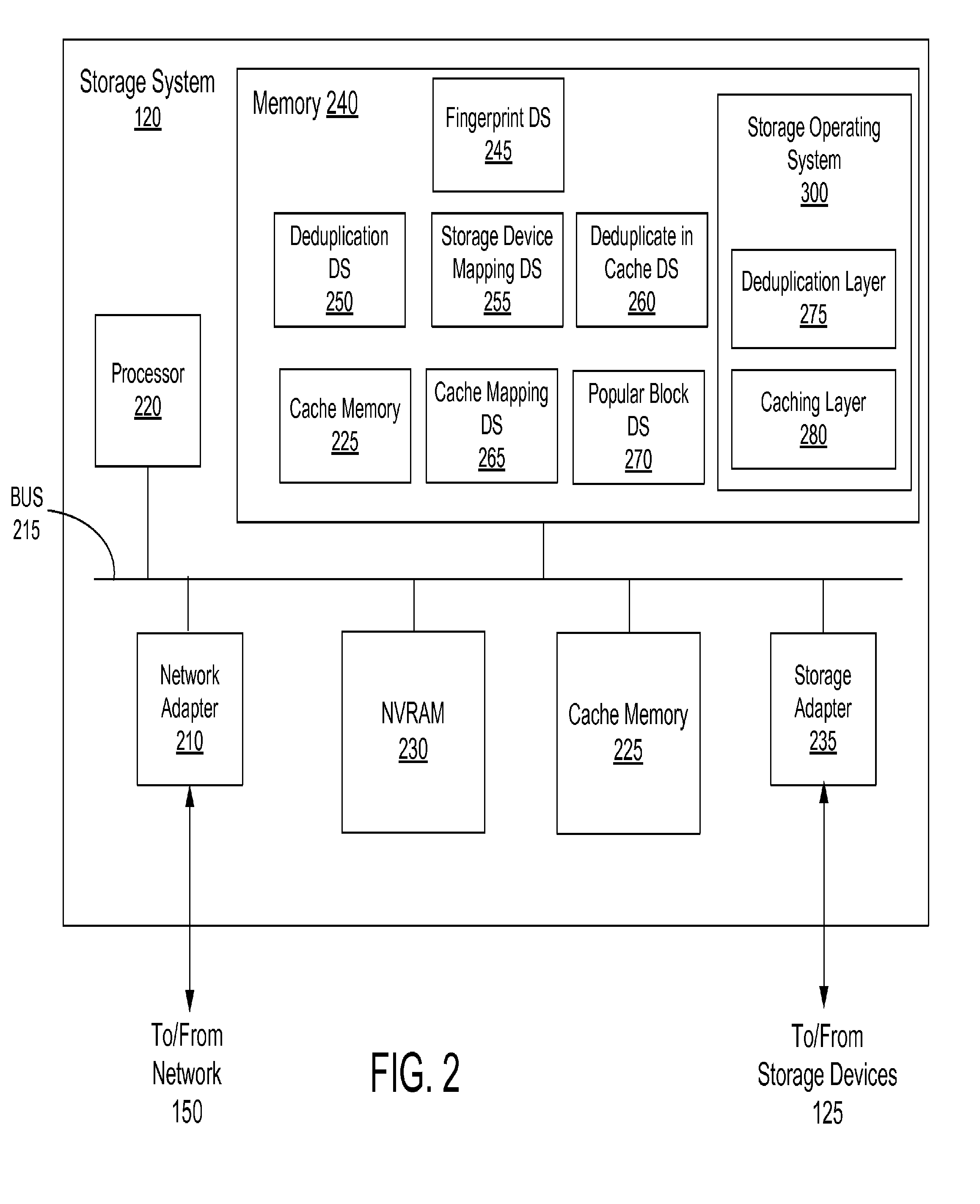
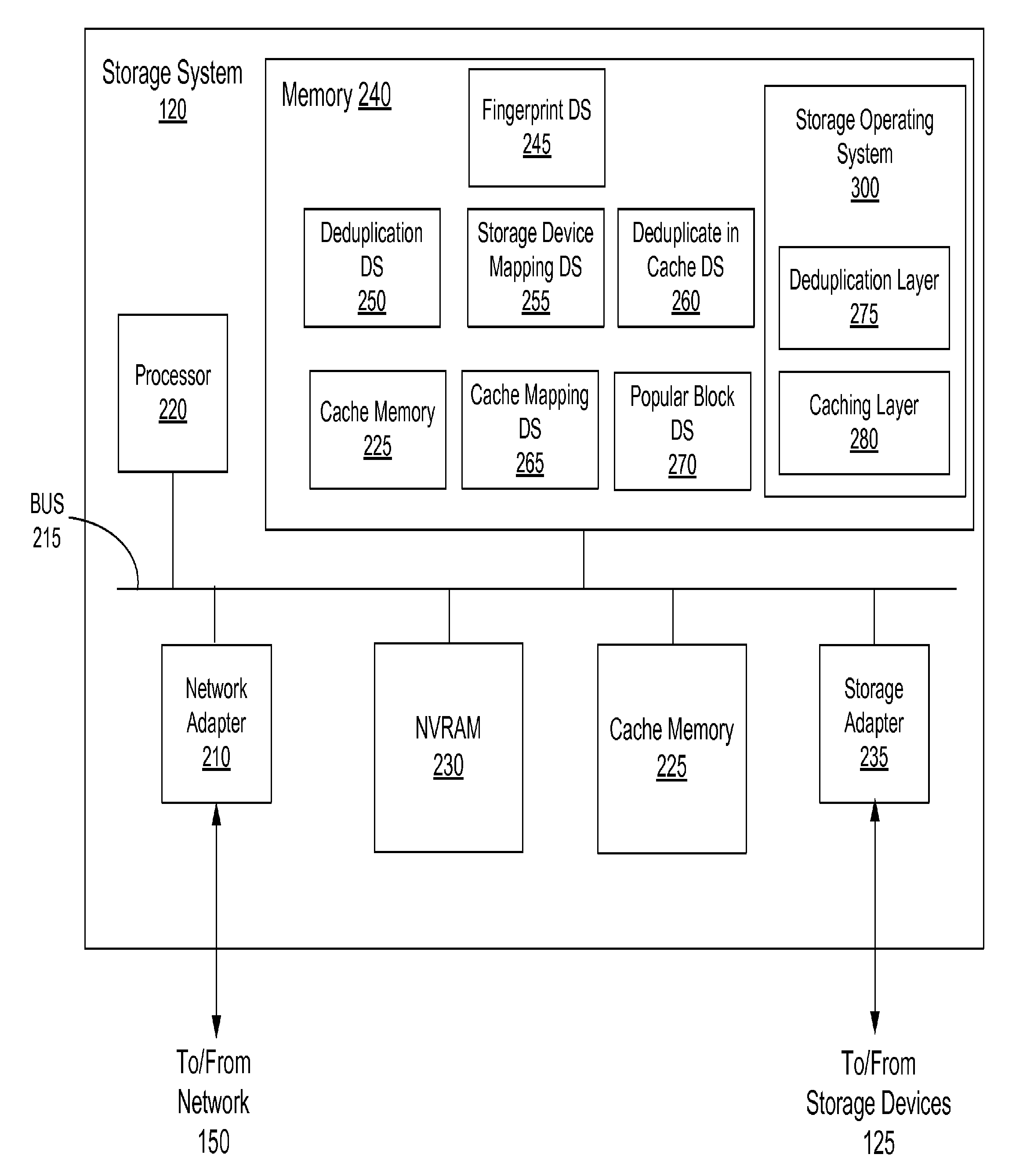
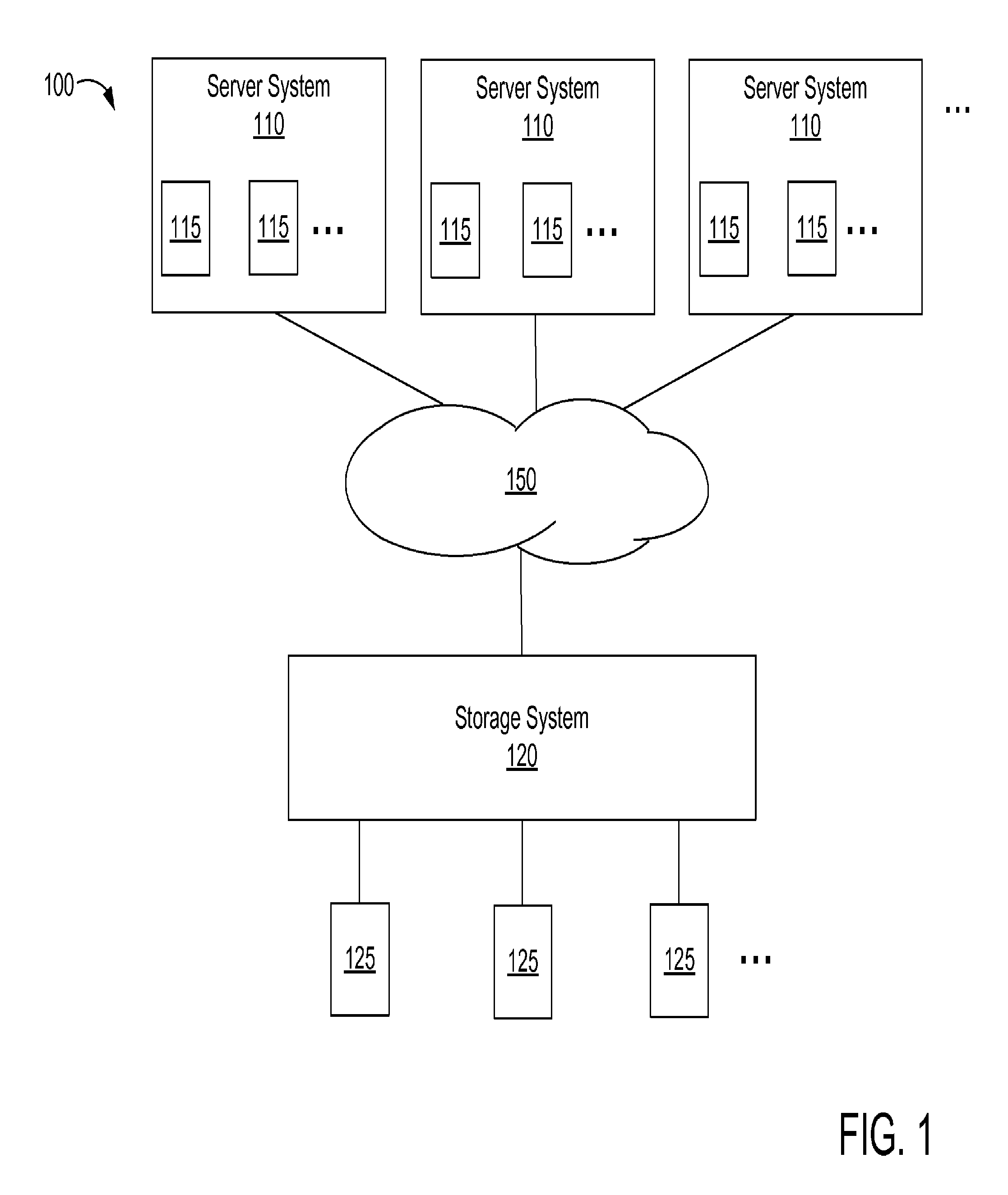
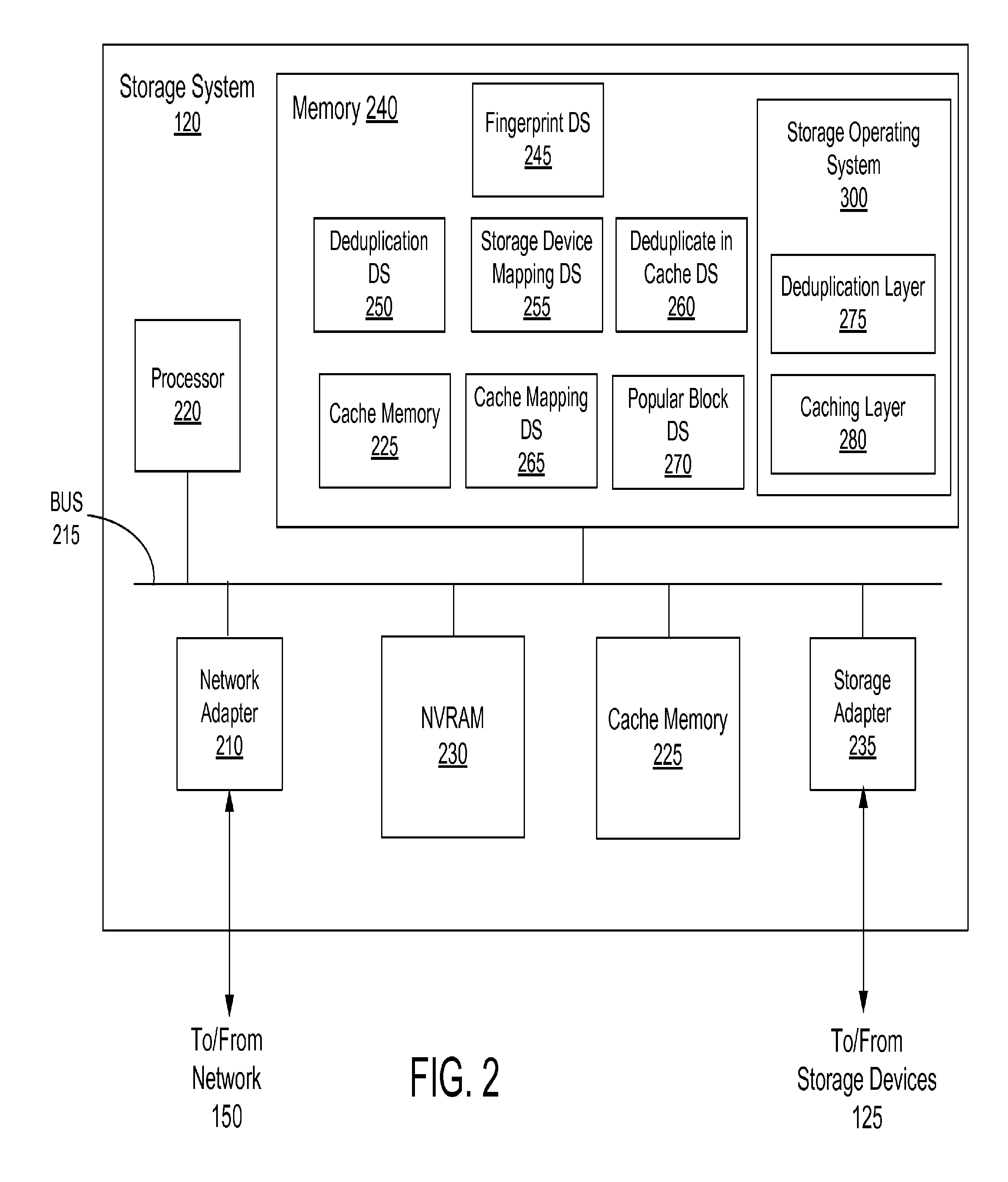
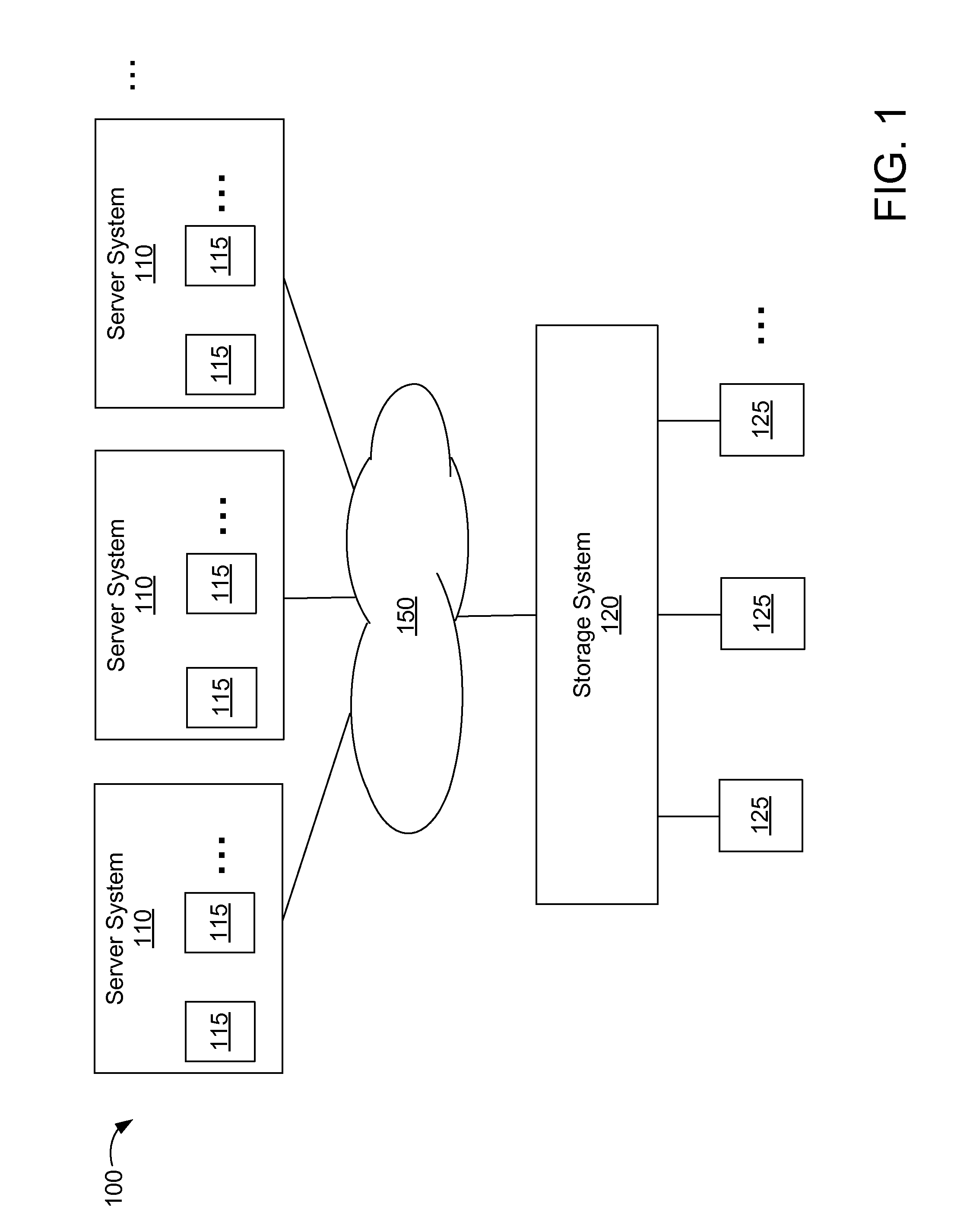
Deduplication of data blocks on storage devices
ActiveUS8732403B1Save on storageHigh trafficMemory adressing/allocation/relocationInput/output processes for data processingOperational systemData deduplication
A storage system comprises a cache for caching data blocks and storage devices for storing blocks. A storage operating system may deduplicate sets of redundant blocks on the storage devices based on a deduplication requirement. Blocks in cache are typically deduplicated based on the deduplication on the storage devices. Sets of redundant blocks that have not met the deduplication requirement for storage devices and have not been deduplicated on the storage devices and cache are targeted for further deduplication processing. Sets of redundant blocks may be further deduplicated based on their popularity (number of accesses) in cache. If a set of redundant blocks in cache is determined to have a combined number of accesses being greater than a predetermined threshold number of accesses, the set of redundant blocks is determined to be “popular.” Popular sets of redundant blocks are selected for deduplication in cache and the storage devices.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
Multi-gate nor flash thin-film transistor strings arranged in stacked horizontal active strips with vertical control gates
ActiveUS20170092370A1Improve storage densityLower read latencySolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesEngineeringVertical control
Multi-gate NOR flash thin-film transistor (TFT) string arrays (“multi-gate NOR string arrays”) are organized as stacks of horizontal active strips running parallel to the surface of a silicon substrate, with the TFTs in each stack being controlled by vertical local word-lines provided along one or both sidewalls of the stack of active strips. Each active strip includes at least a channel layer formed between two shared source or drain layers. Data storage in the TFTs of an active strip is provided by charge-storage elements provided between the active strip and the control gates provided by the adjacent local word-lines. Each active strip may provide TFTs that belong to one or two NOR strings, depending on whether one or both sides of the active strip are used.
Owner:SUNRISE MEMORY CORP
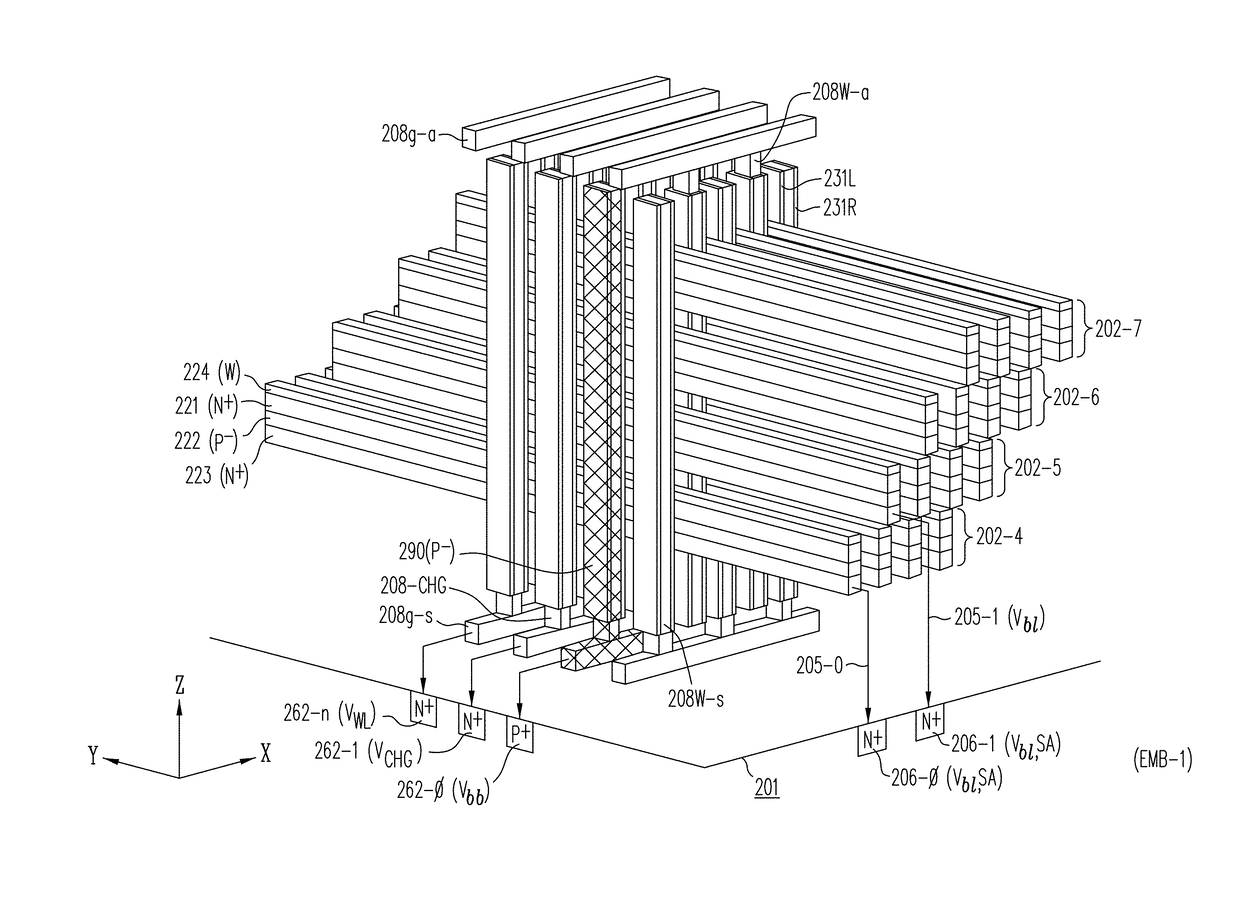
Capacitive-coupled non-volatile thin-film transistor NOR strings in three-dimensional arrays
ActiveUS10121553B2High densityLower read latencyTransistorSolid-state devicesCapacitive couplingParasitic capacitance
Owner:SUNRISE MEMORY CORP
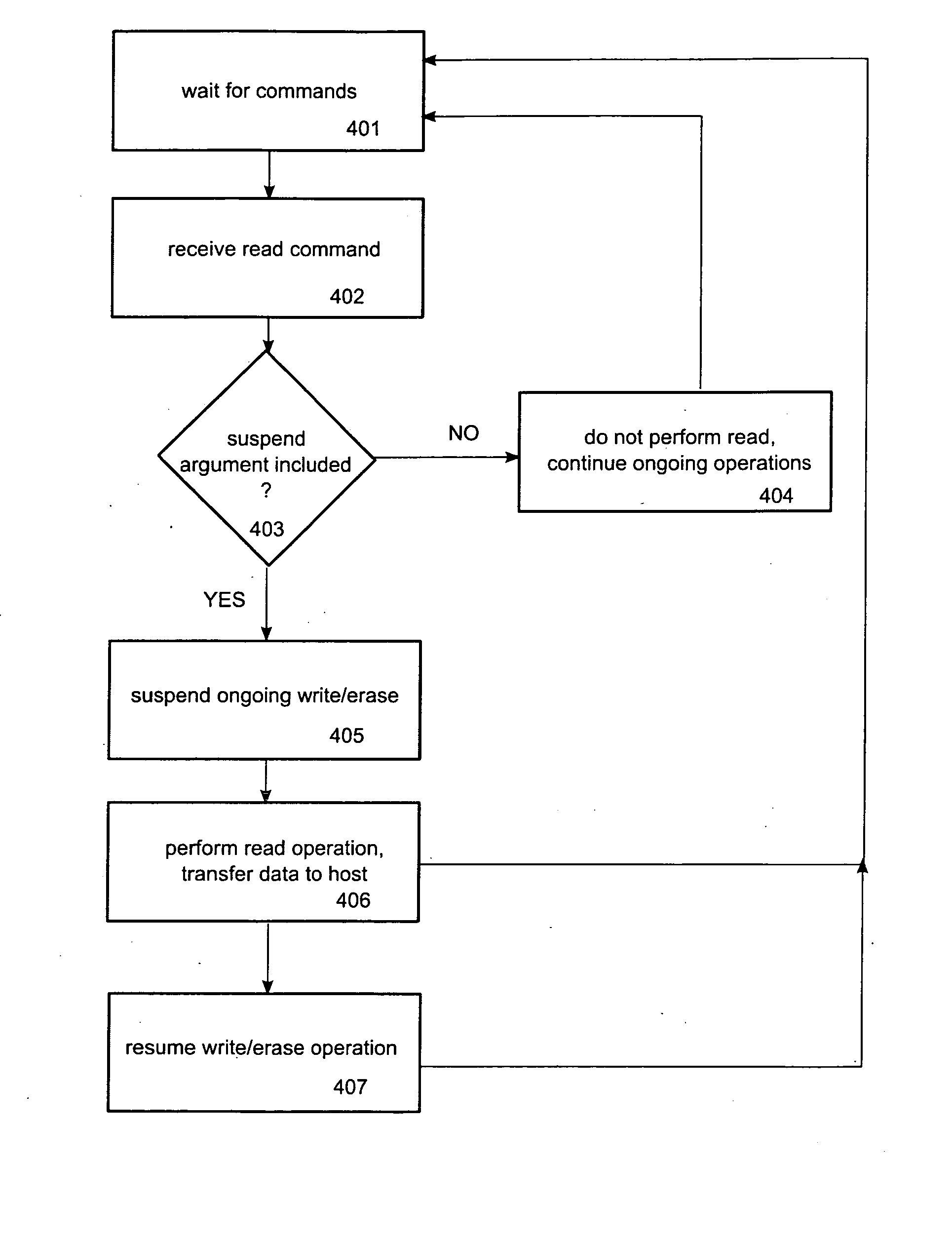
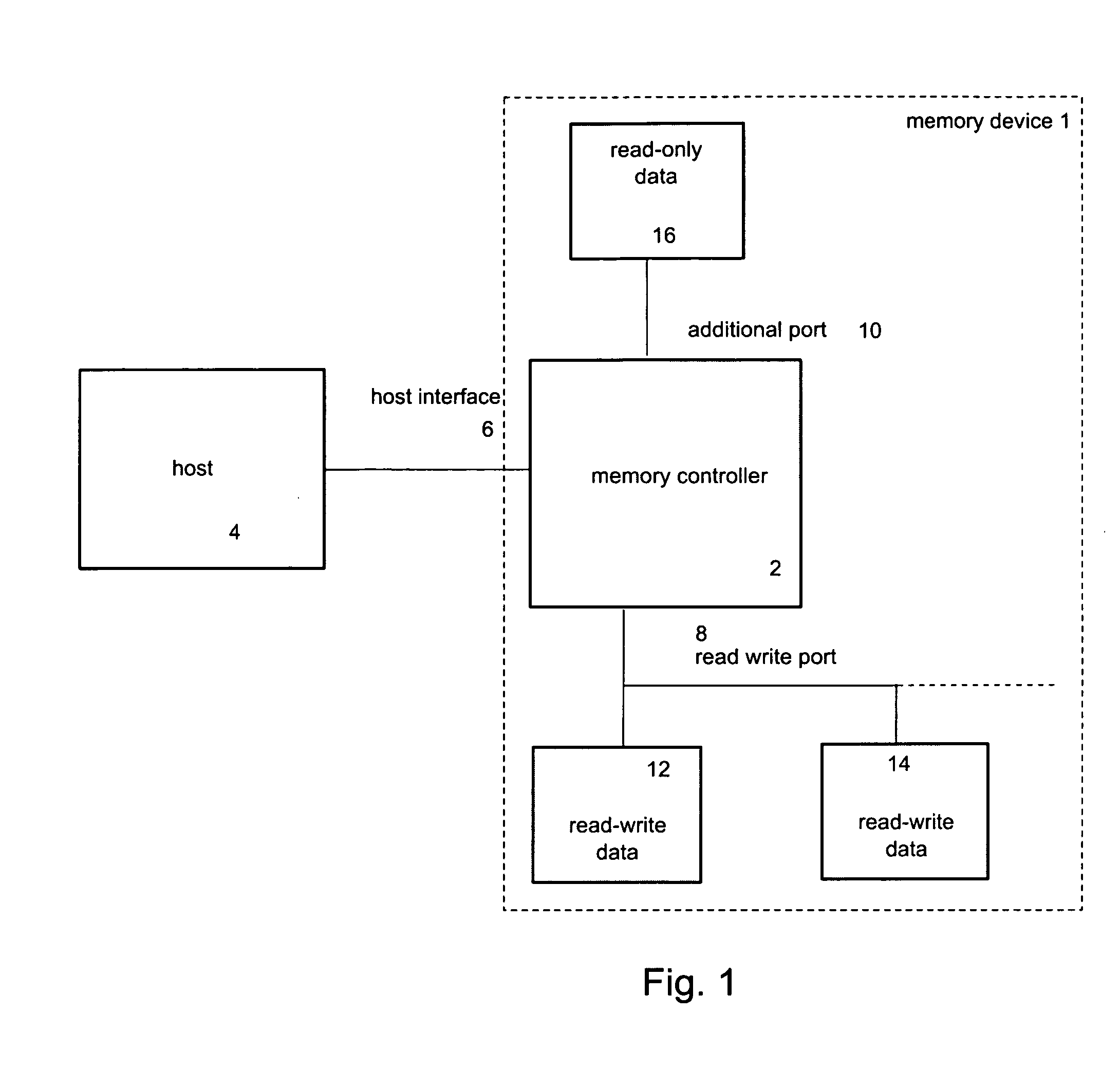
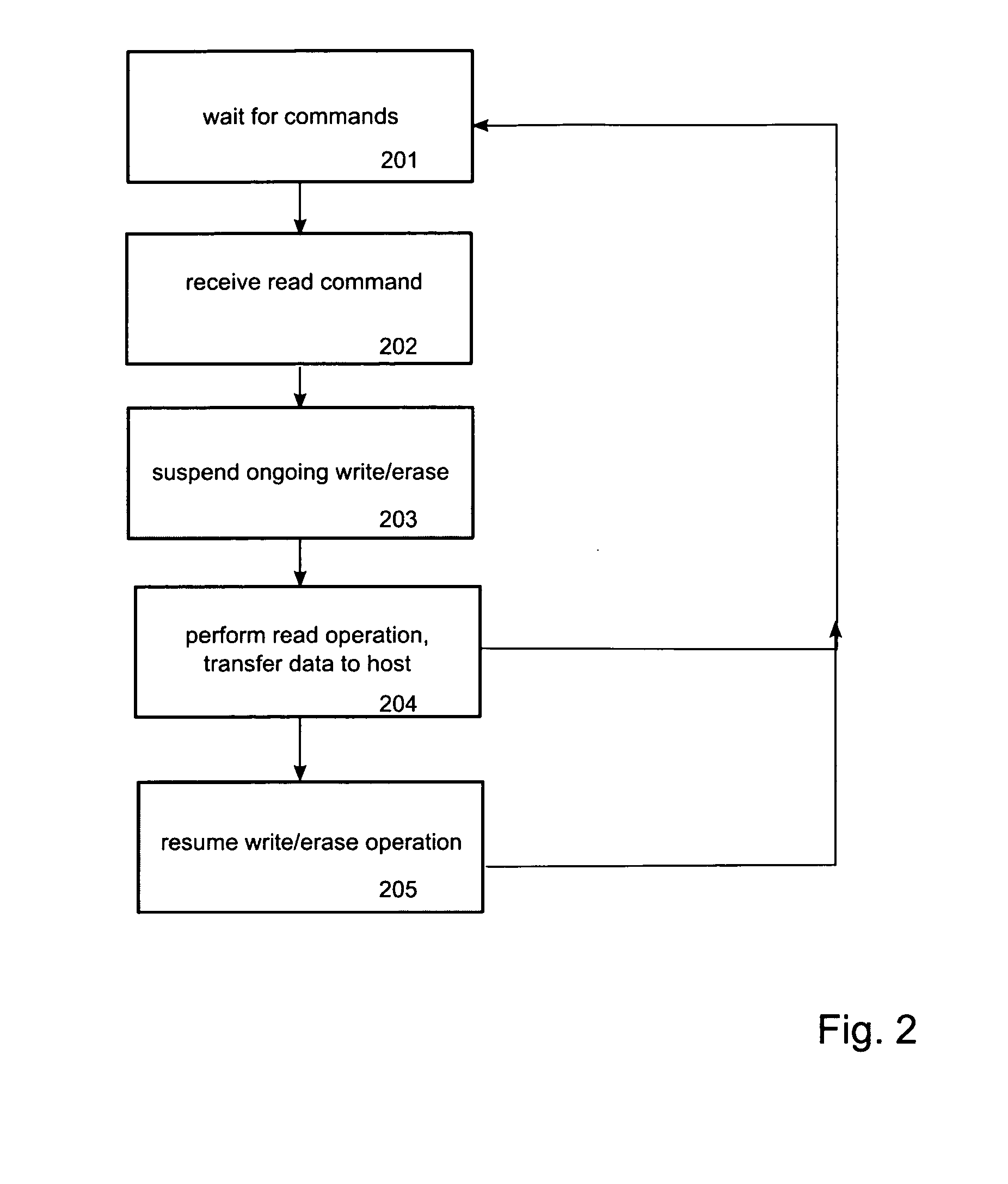
Method and device for reduced read latency of non-volatile memory
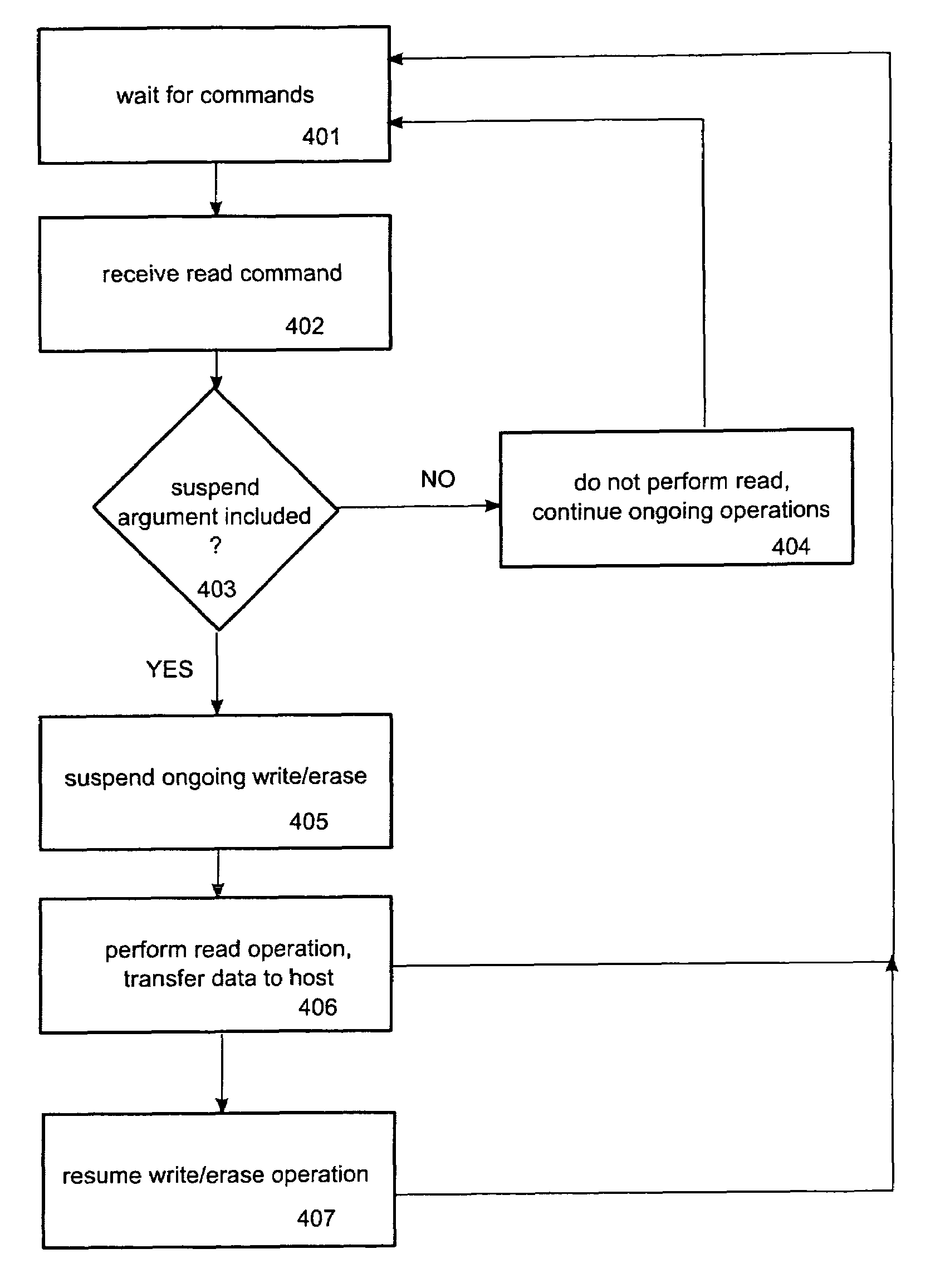
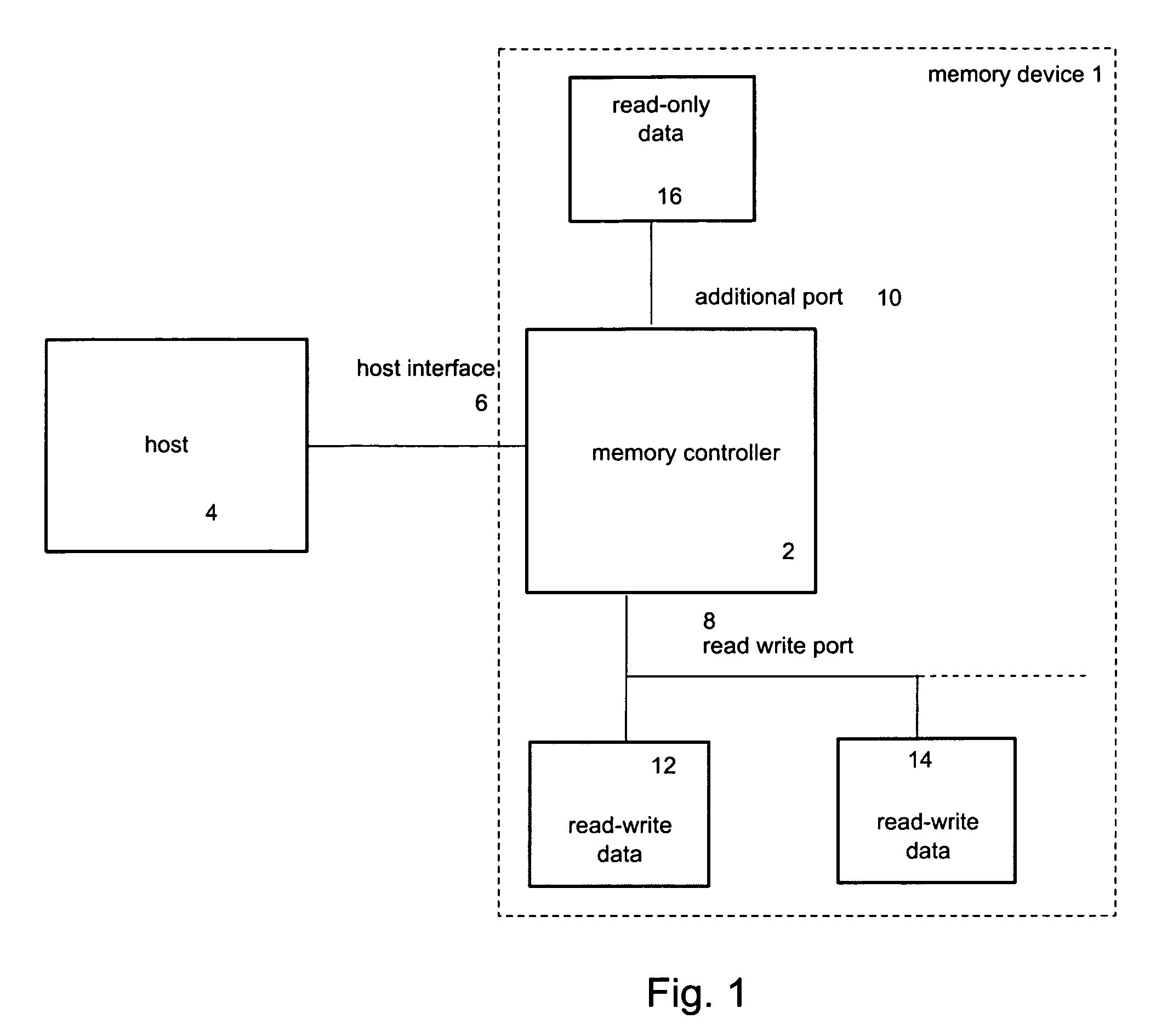
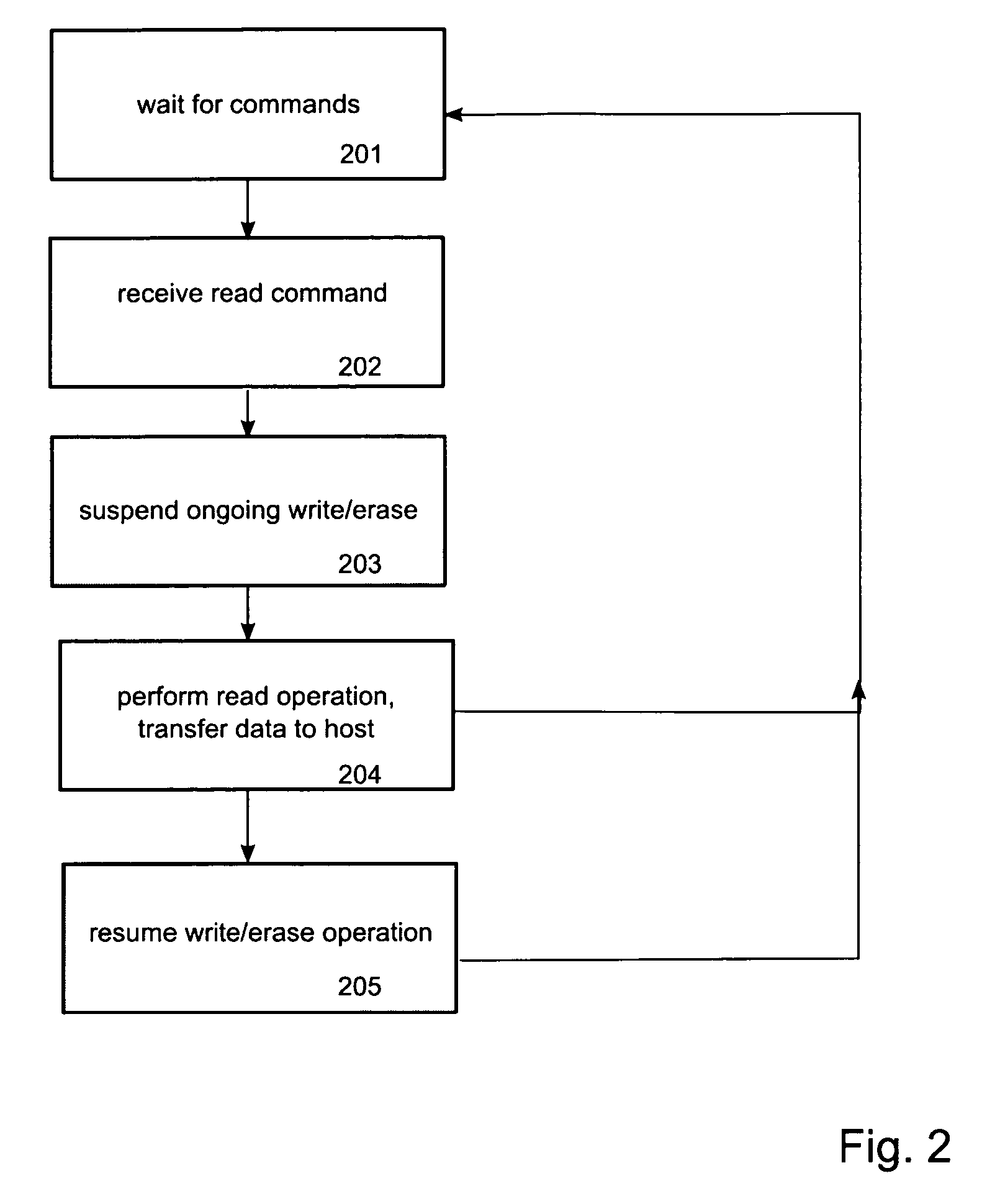
ActiveUS20070239926A1Lower read latencyRead-only memoriesDigital storageControl memoryMemory controller
Systems, apparatuses and methods for controlling access operations in a memory device that may include a memory controller(s) and memory. Commands, registers and / or other mechanisms may be defined to be supported by the memory device, where such commands, registers, and / or other mechanisms facilitate the control of read and write / erase operations to allow these operations to be performed simultaneously. Thus, a write and / or erase operation may be initiated on a first memory, a read operation initiated by a set of commands on a second memory, wherein the read and write / erase operations are performed substantially at the same time.
Owner:MEMORY TECHNOLOGIES LLC
Multi-gate NOR flash thin-film transistor strings arranged in stacked horizontal active strips with vertical control gates
ActiveUS9892800B2High densityLower read latencySolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesEngineeringVertical control
Multi-gate NOR flash thin-film transistor (TFT) string arrays (“multi-gate NOR string arrays”) are organized as stacks of horizontal active strips running parallel to the surface of a silicon substrate, with the TFTs in each stack being controlled by vertical local word-lines provided along one or both sidewalls of the stack of active strips. Each active strip includes at least a channel layer formed between two shared source or drain layers. Data storage in the TFTs of an active strip is provided by charge-storage elements provided between the active strip and the control gates provided by the adjacent local word-lines. Each active strip may provide TFTs that belong to one or two NOR strings, depending on whether one or both sides of the active strip are used.
Owner:SUNRISE MEMORY CORP
Deduplication of Data on Disk Devices Using Low-Latency Random Read Memory
ActiveUS20110131390A1Lower latencyLower read latencyMemory adressing/allocation/relocationFile access structuresLatency (engineering)Memory deduplication
Deduplication of data using a low-latency random read memory (LLRRM) is described herein. Upon receiving a block, if a matching block stored on a disk device is found, the received block is deduplicated by producing an index to the address location of the matching block. In some embodiments, a matching block having a predetermined threshold number of associated indexes that reference the matching block is transferred to LLRRM, the threshold number being one or greater. Associated indexes may be modified to reflect the new address location in LLRRM. Deduplication may be performed using a mapping mechanism containing mappings of deduplicated blocks to matching blocks, the mappings being used for performing read requests. Deduplication described herein may reduce read latency as LLRRM has relatively low latency in performing random read requests relative to disk devices.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
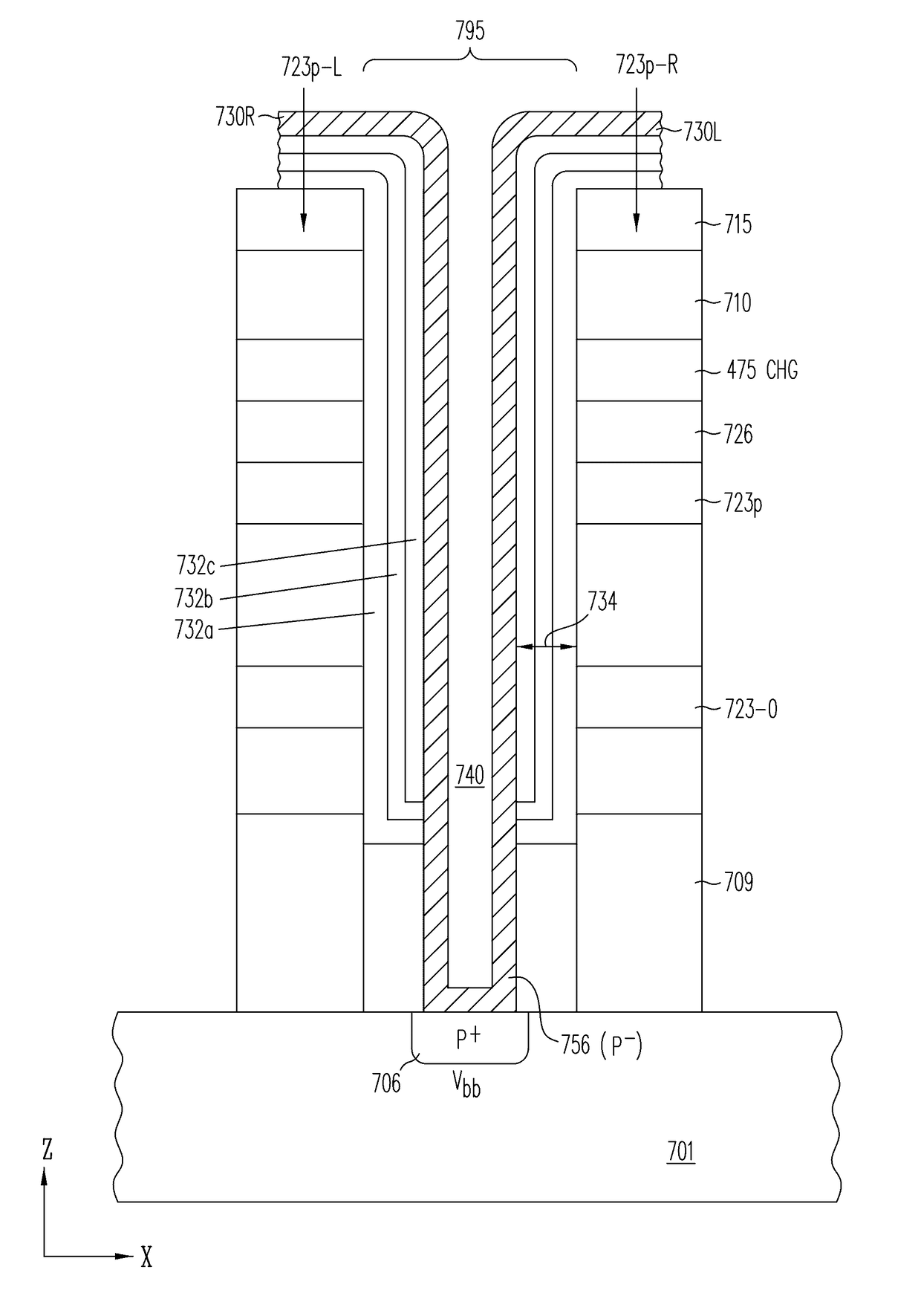
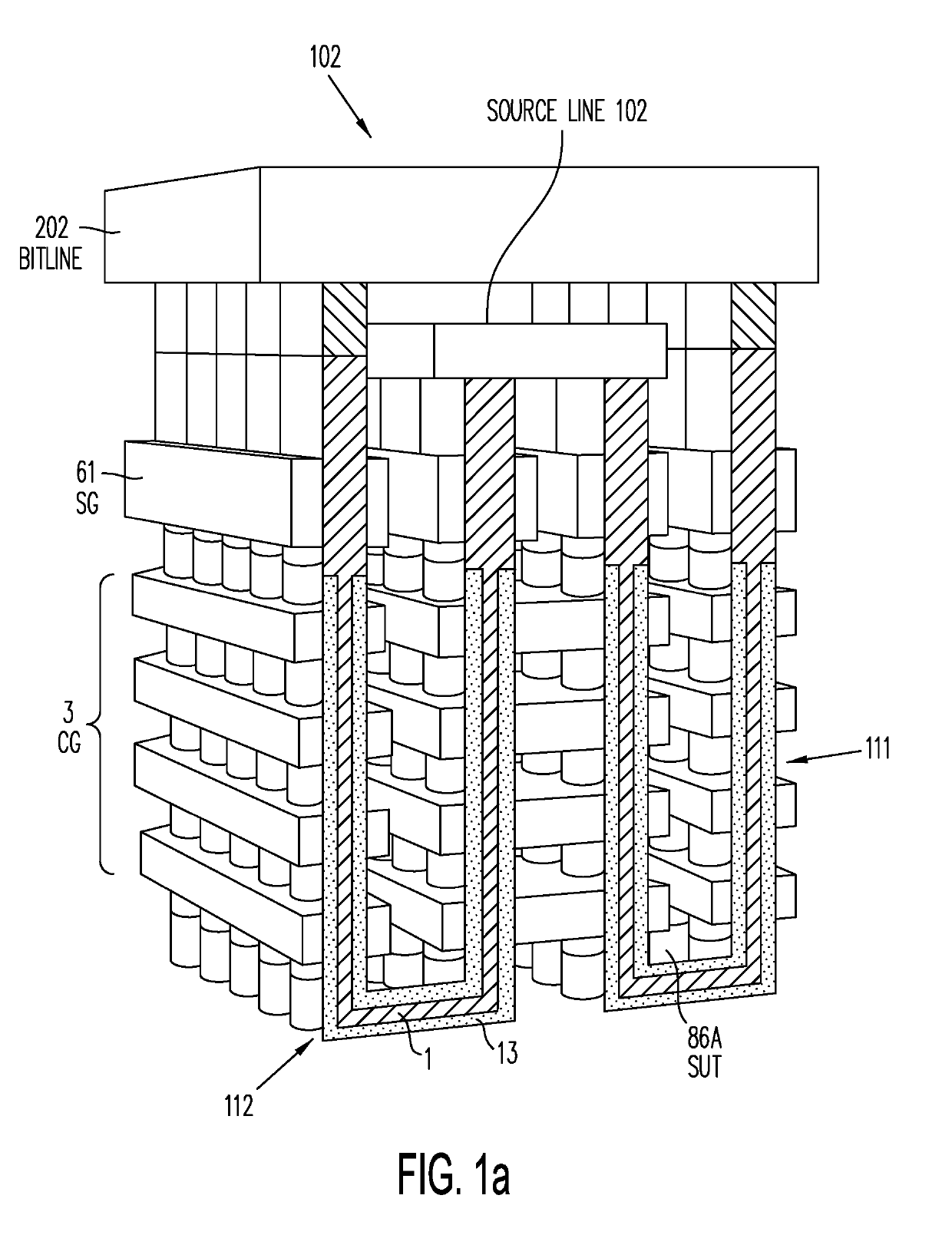
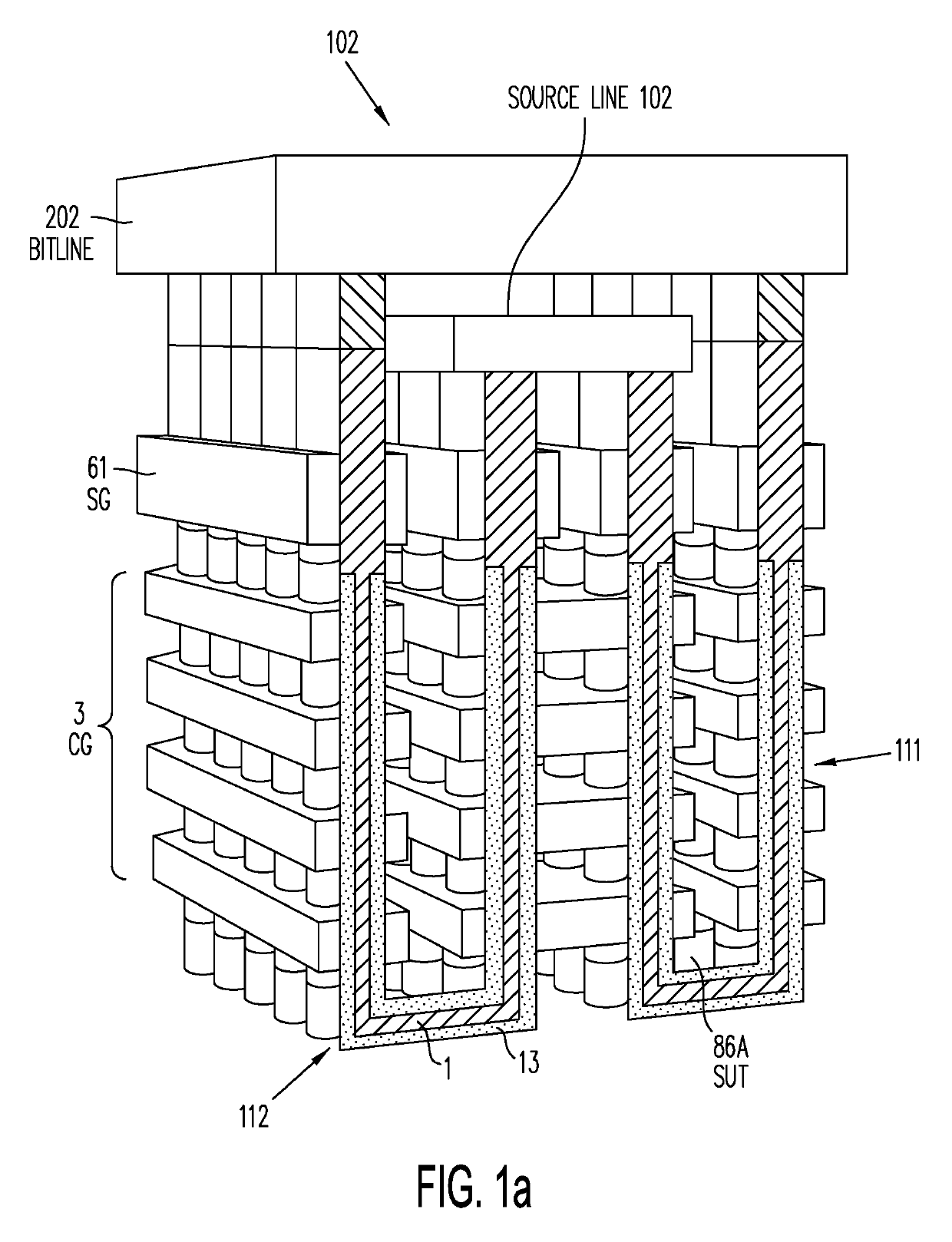
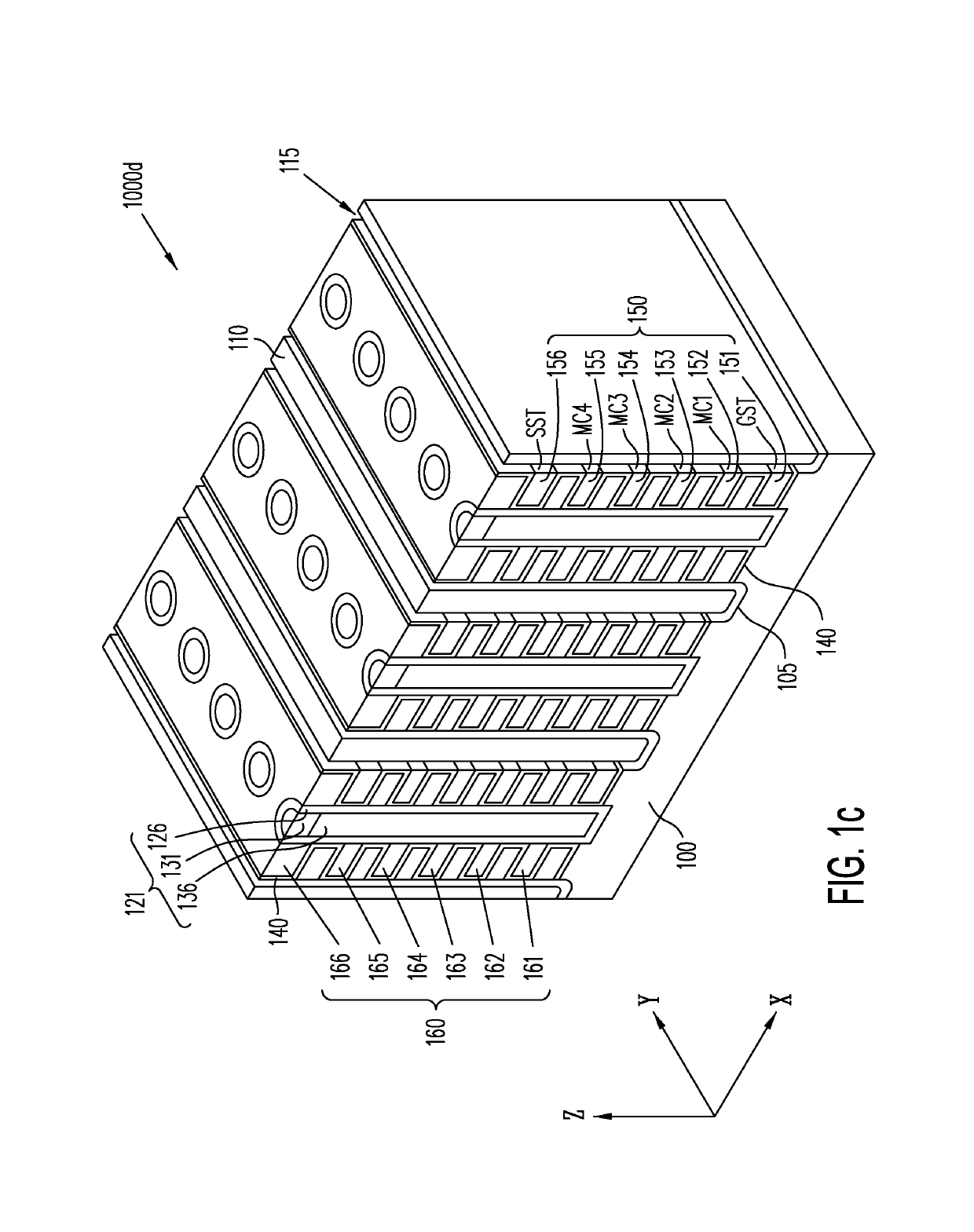
Three-dimensional vertical NOR flash thin film transistor strings
ActiveUS9842651B2Lower resistanceFast sensingTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsElectrical conductorThin membrane
A memory structure, includes (a) active columns of polysilicon formed above a semiconductor substrate, each active column extending vertically from the substrate and including a first heavily doped region, a second heavily doped region, and one or more lightly doped regions each adjacent both the first and second heavily doped region, wherein the active columns are arranged in a two-dimensional array extending in second and third directions parallel to the planar surface of the semiconductor substrate; (b) charge-trapping material provided over one or more surfaces of each active column; and (c) conductors each extending lengthwise along the third direction. The active columns, the charge-trapping material and the conductors together form a plurality of thin film transistors, with each thin film transistor formed by one of the conductors, a portion of the lightly doped region of an active column, the charge-trapping material between the portion of the lightly doped region and the conductor, and the first and second heavily doped regions. The thin film transistors associated with each active column are organized into one or more vertical NOR strings.
Owner:SUNRISE MEMORY CORP
Three-dimensional vertical NOR Flash Thin-Film Transistor Strings
ActiveUS20190319044A1Lower read latencyReduce sensitivityTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsAudio power amplifierEngineering
A memory structure, includes active columns of polysilicon formed above a semiconductor substrate, each active column includes one or more vertical NOR strings, with each NOR string having thin-film storage transistors sharing a local source line and a local bit line, the local bit line is connected by one segment of a segmented global bit line to a sense amplifier provided in the semiconductor substrate.
Owner:SUNRISE MEMORY CORP
Three-dimensional vertical NOR Flash Thin-Film Transistor Strings
ActiveUS20190244971A1Lower read latencyReduce sensitivityTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSemiconductorSense amplifier
A memory structure, includes active columns of polysilicon formed above a semiconductor substrate, each active column includes one or more vertical NOR strings, with each NOR string having thin-film storage transistors sharing a local source line and a local bit line, the local bit line is connected by one segment of a segmented global bit line to a sense amplifier provided in the semiconductor substrate.
Owner:SUNRISE MEMORY CORP
Three-dimensional vertical NOR flash thin-film transistor strings
ActiveUS10381378B1Lower resistanceFast sensingTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsBit lineAudio power amplifier
A memory structure, includes active columns of polysilicon formed above a semiconductor substrate, each active column includes one or more vertical NOR strings, with each NOR string having thin-film storage transistors sharing a local source line and a local bit line, the local bit line is connected by one segment of a segmented global bit line to a sense amplifier provided in the semiconductor substrate.
Owner:SUNRISE MEMORY CORP
Three-dimensional vertical NOR flash thin-film transistor strings
ActiveUS10475812B2Lower resistanceFast sensingTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsBit lineAudio power amplifier
Owner:SUNRISE MEMORY CORP
Method and device for reduced read latency of non-volatile memory
Systems, apparatuses and methods for controlling access operations in a memory device that may include a memory controller(s) and memory. Commands, registers and / or other mechanisms may be defined to be supported by the memory device, where such commands, registers, and / or other mechanisms facilitate the control of read and write / erase operations to allow these operations to be performed simultaneously. Thus, a write and / or erase operation may be initiated on a first memory, a read operation initiated by a set of commands on a second memory, wherein the read and write / erase operations are performed substantially at the same time.
Owner:MEMORY TECHNOLOGIES LLC
Magnetic disk cache system based on solid-state disk
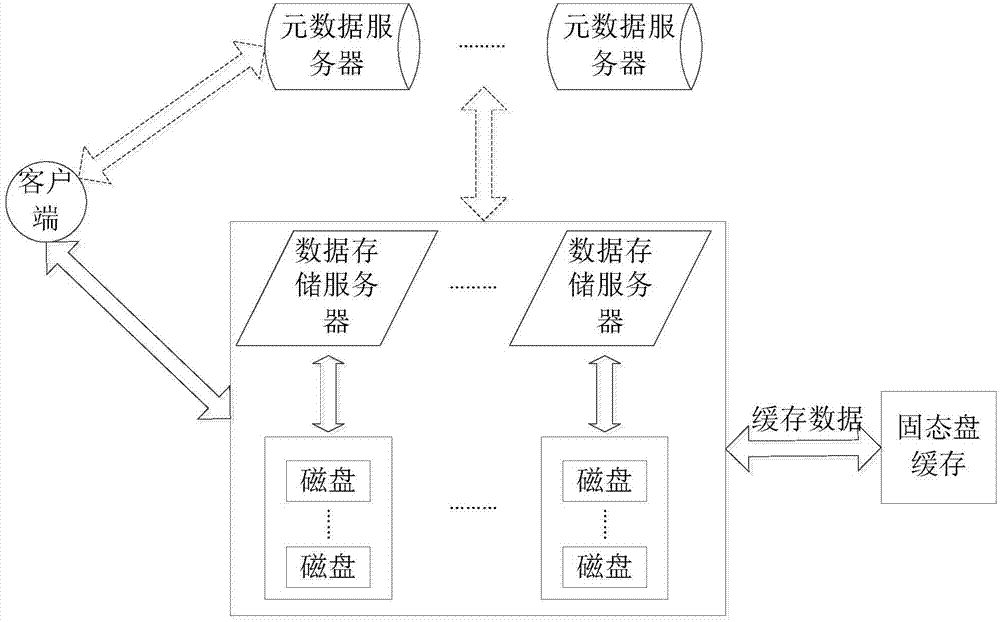
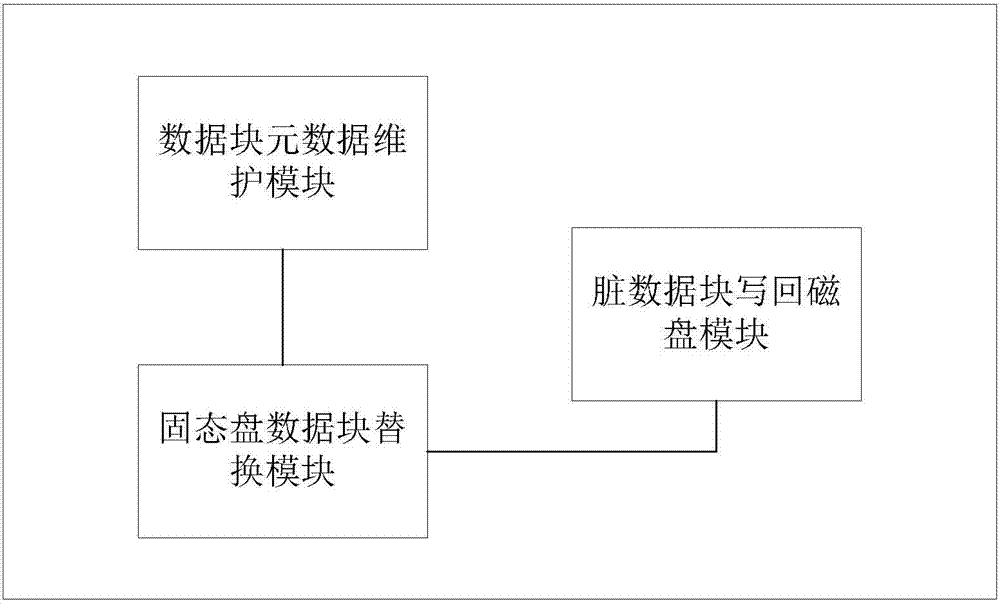
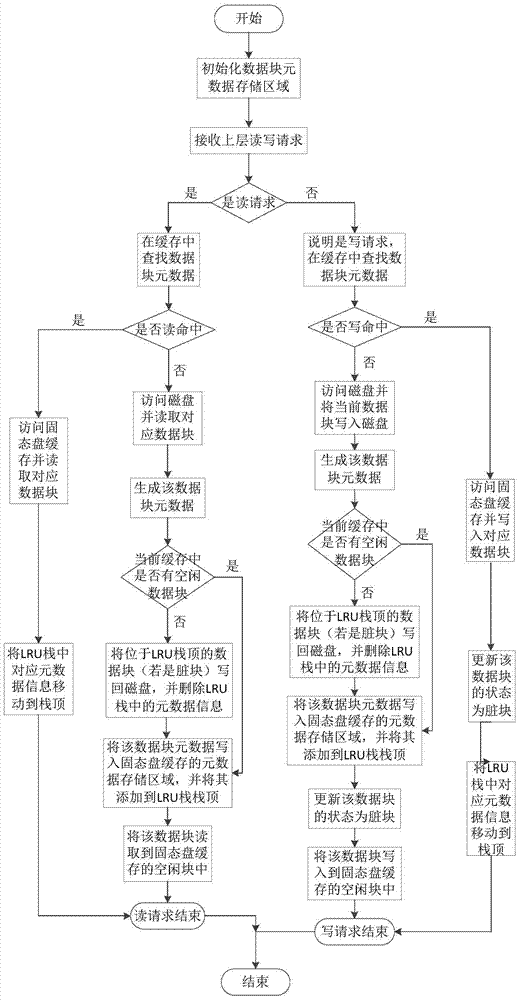
ActiveCN103885728AImprove read and write performanceLower read latencyInput/output to record carriersMemory adressing/allocation/relocationMagnetic disksDirty data
The invention discloses a magnetic disk cache system based on a solid-state disk and belongs to the technical field of cache systems in computer data storage systems. The magnetic disk cache system based on the solid-state disk comprises a data block metadata maintenance module, a solid-state disk data replacement module and a dirty data block writing-back disk module. According to the magnetic disk cache system based on the solid-state disk, the reading and writing performance of disk data in a large-scale storage environment is improved through the solid-state disk, and the data block reading and writing hit rate and the cache space utilization rate are high; meanwhile, it is guaranteed that data blocks cached under the condition that a computer is restarted due to faults can not be lost easily, the cold-to-hot convergence time of solid-state disk equipment is shortened, and the problems that according to a computer data storage system in the prior art, the cache space is limited, cached data can be lost easily, and the cache space can not be fully utilized can be solved.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Deduplication of data blocks on storage devices
ActiveUS20140325147A1Save on storageHigh trafficInput/output to record carriersMemory adressing/allocation/relocationOperational systemData deduplication
A storage system comprises a cache for caching data blocks and storage devices for storing blocks. A storage operating system may deduplicate sets of redundant blocks on the storage devices based on a deduplication requirement. Blocks in cache are typically deduplicated based on the deduplication on the storage devices. Sets of redundant blocks that have not met the deduplication requirement for storage devices and have not been deduplicated on the storage devices and cache are targeted for further deduplication processing. Sets of redundant blocks may be further deduplicated based on their popularity (number of accesses) in cache. If a set of redundant blocks in cache is determined to have a combined number of accesses being greater than a predetermined threshold number of accesses, the set of redundant blocks is determined to be “popular.” Popular sets of redundant blocks are selected for deduplication in cache and the storage devices.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
Systems and methods of storing data
ActiveCN103827833AEqual reliabilityImprove reliabilityRead-only memoriesDigital storageData systemComputer science
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Realizing a storage system
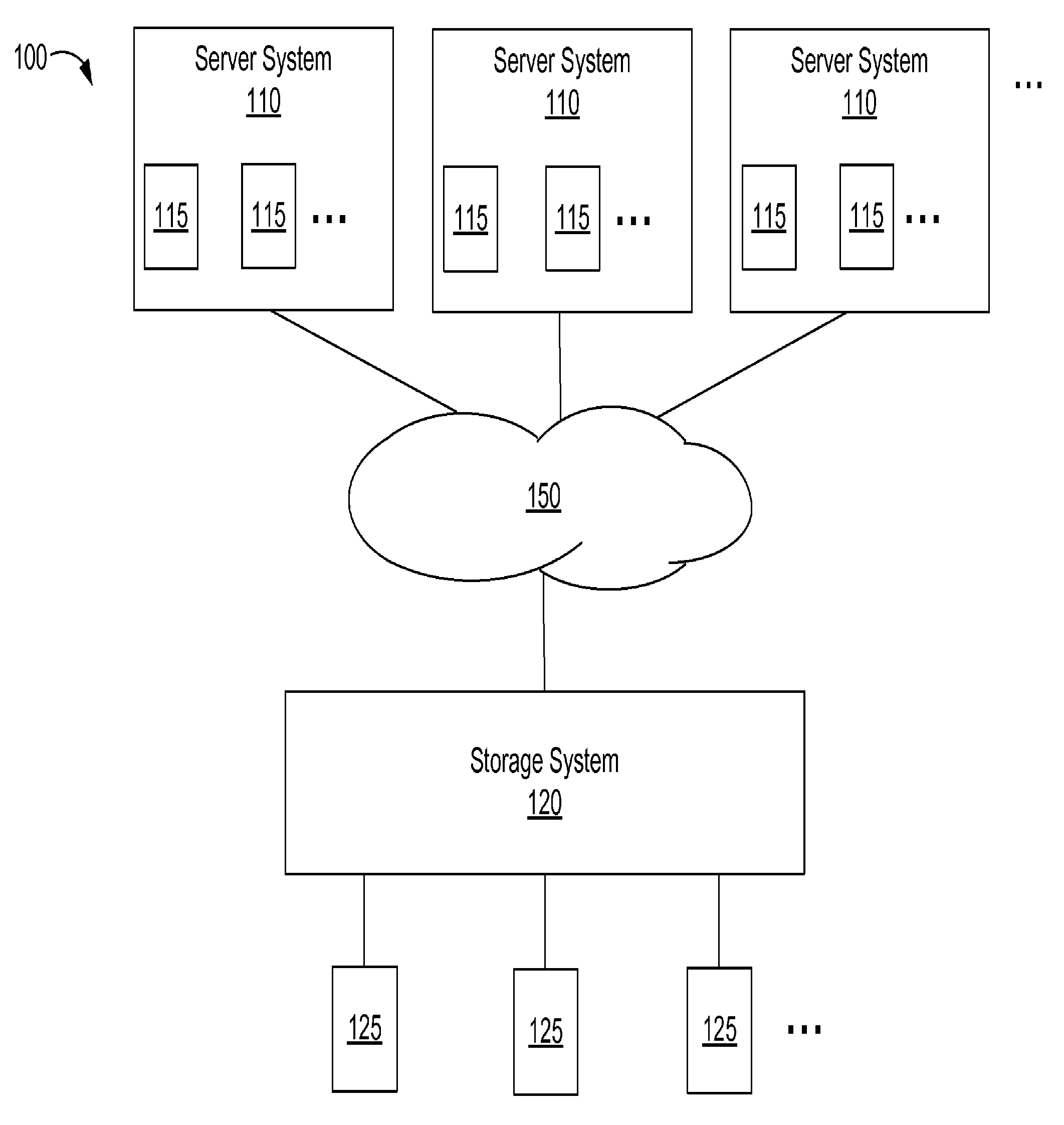
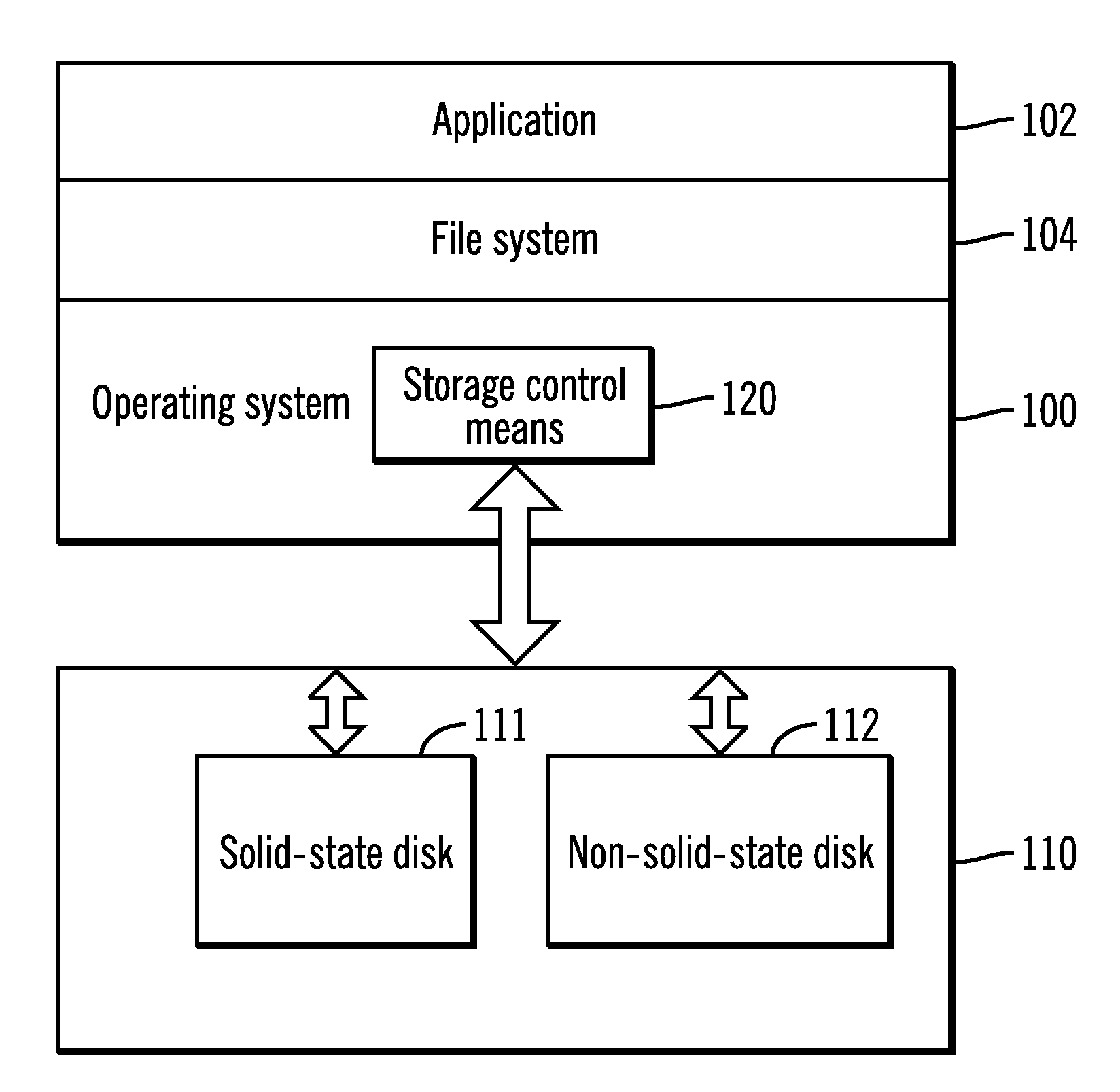
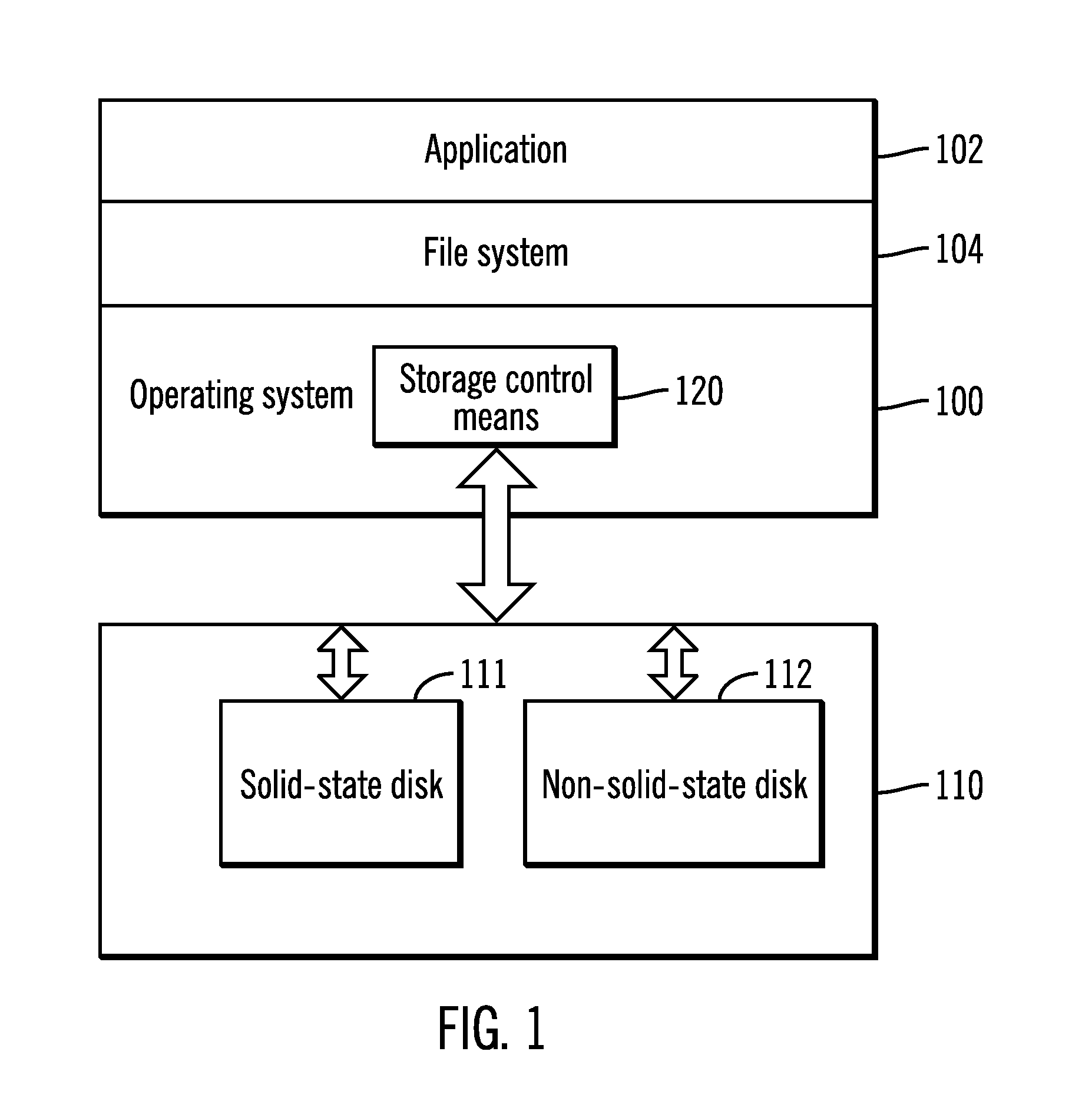
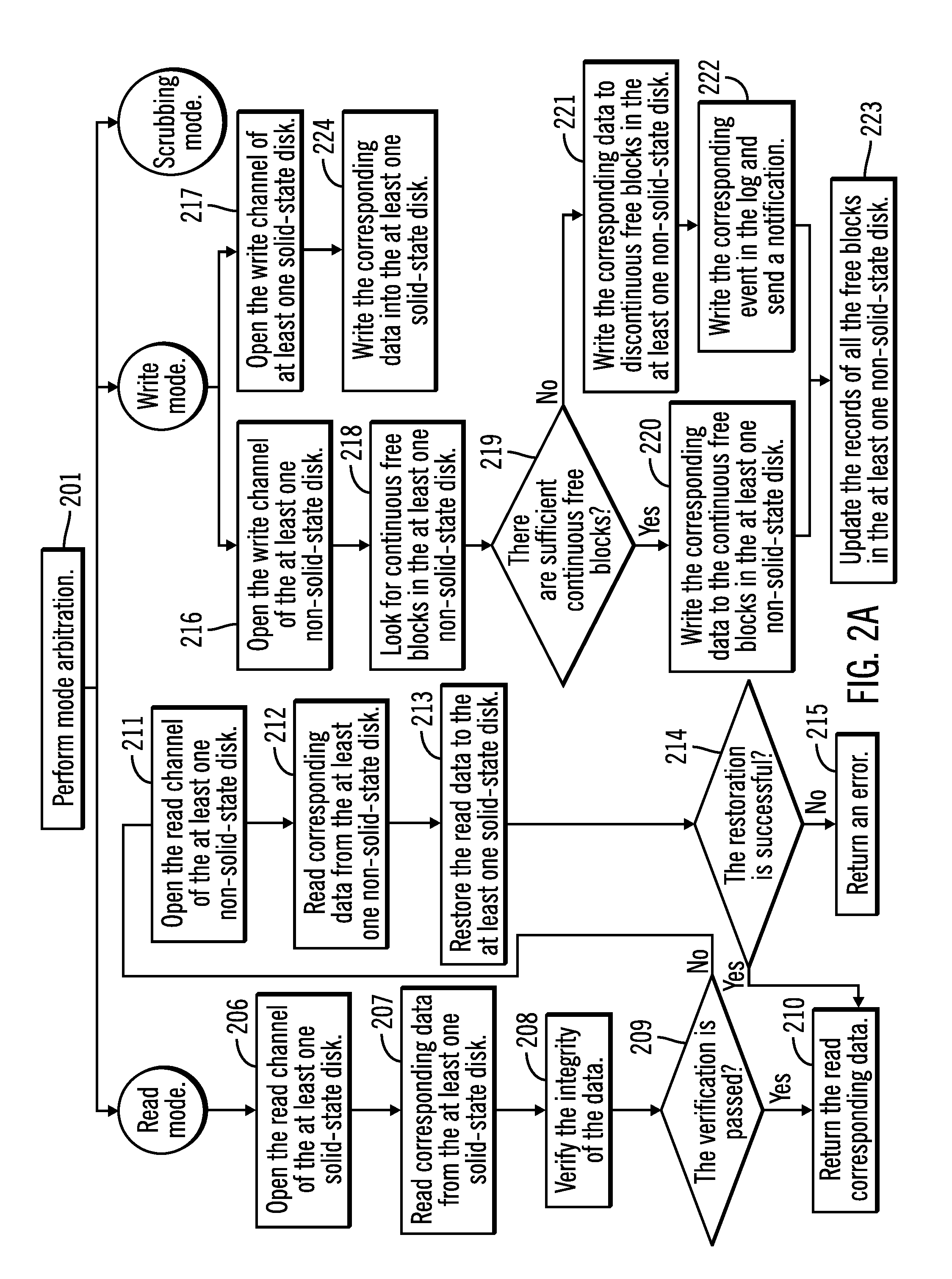
ActiveUS20110320709A1Lower read latencyReduce adverse effectsMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationSolid-stateDisk array
A storage system and a method for realizing a storage system is disclosed, the storage system comprising: a disk array comprising at least one solid state disk and at least one non-solid state disk; and a storage control means configured to: in response to entering a scrubbing mode, scan and move data blocks in the at least one non-solid state disk in the disk array to form more continuous free blocks. The storage system of the present invention has good read and write performances, higher data reliability and availability, and lower cost.
Owner:IBM CORP
Self-timed slc NAND pipeline and concurrent program without verification
ActiveUS20160093384A1Program latency reducedLower read latencyRead-only memoriesDigital storageParallel computingRandom choice
A hierarchical-GBL / LBL NAND array with a plurality of LG and MG groups in either orthogonal BL / CSL scheme or parallel BL / SL scheme including a plurality of block-decoders with a shared self-timed delay control circuit and a plurality of fully-shielding dynamic CACHE registers made of 2 local broken metal lines within the array and DRAM-like SA is provided. Each DCR capacitor is flexibly expandable by connecting multiple CLGs made by the local broken metal lines of the LGs to form a CMG of a larger MG. Based on the NAND array, multiple randomly selected WLs in multiple random blocks within multiple random LGs within one MG can be selected on basis of one WL per block per LG for performing an ABL pipeline and concurrent SLC program without verification, and on basis of one WL per block per MG for performing an ABL-like or HBL pipeline and concurrent SLC read.
Owner:APLUS FLASH TECH
Caching and deduplication of data blocks in cache memory
ActiveUS20140289476A1Save on storageHigh trafficMemory architecture accessing/allocationError detection/correctionOperational systemParallel computing
A storage system comprises a cache for caching data blocks and storage devices for storing blocks. A storage operating system may deduplicate sets of redundant blocks on the storage devices based on a deduplication requirement. Blocks in cache are typically deduplicated based on the deduplication on the storage devices. Sets of redundant blocks that have not met the deduplication requirement for storage devices and have not been deduplicated on the storage devices and cache are targeted for further deduplication processing. Sets of redundant blocks may be further deduplicated based on their popularity (number of accesses) in cache. If a set of redundant blocks in cache is determined to have a combined number of accesses being greater than a predetermined threshold number of accesses, the set of redundant blocks is determined to be “popular.” Popular sets of redundant blocks are selected for deduplication in cache and the storage devices.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
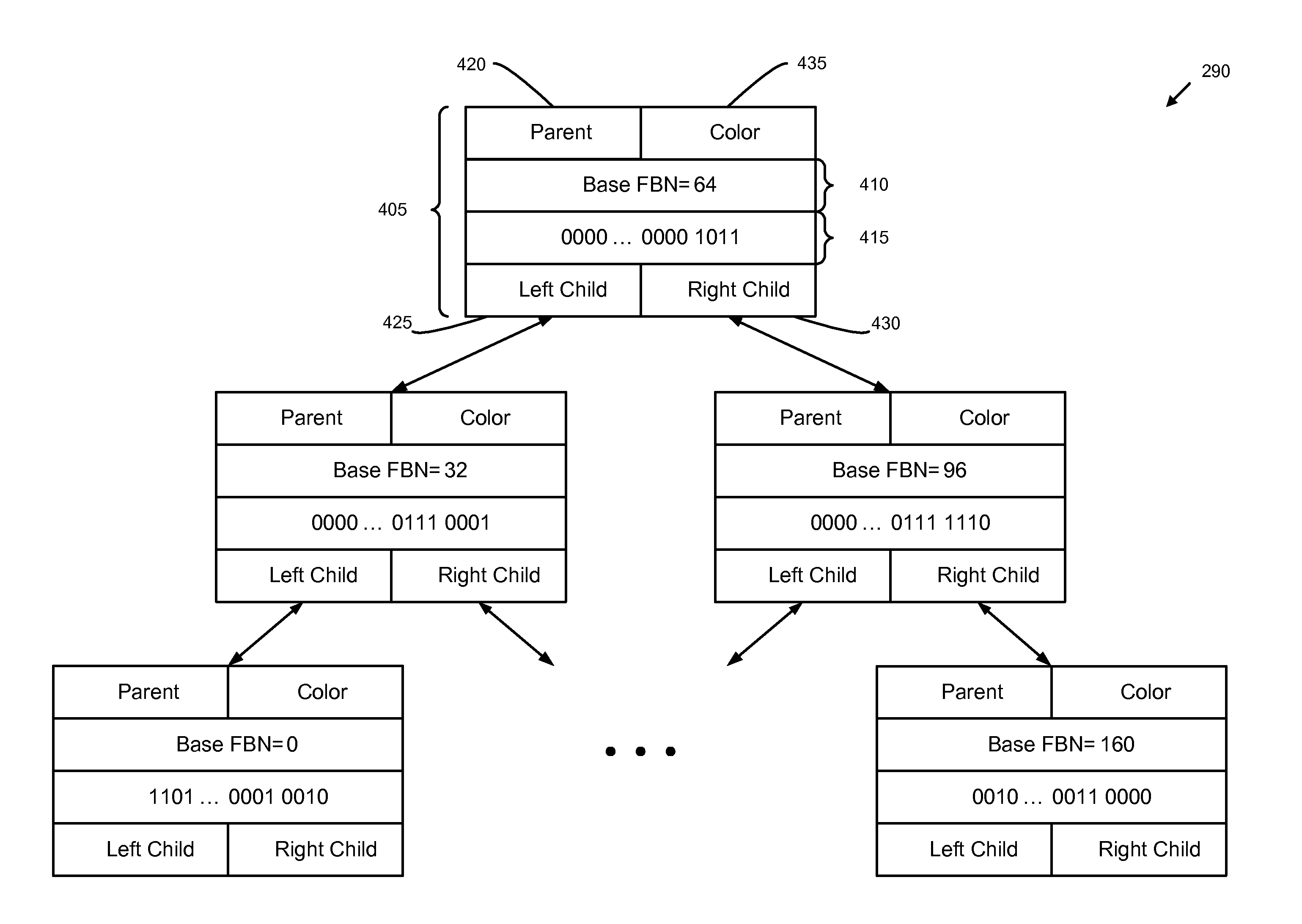
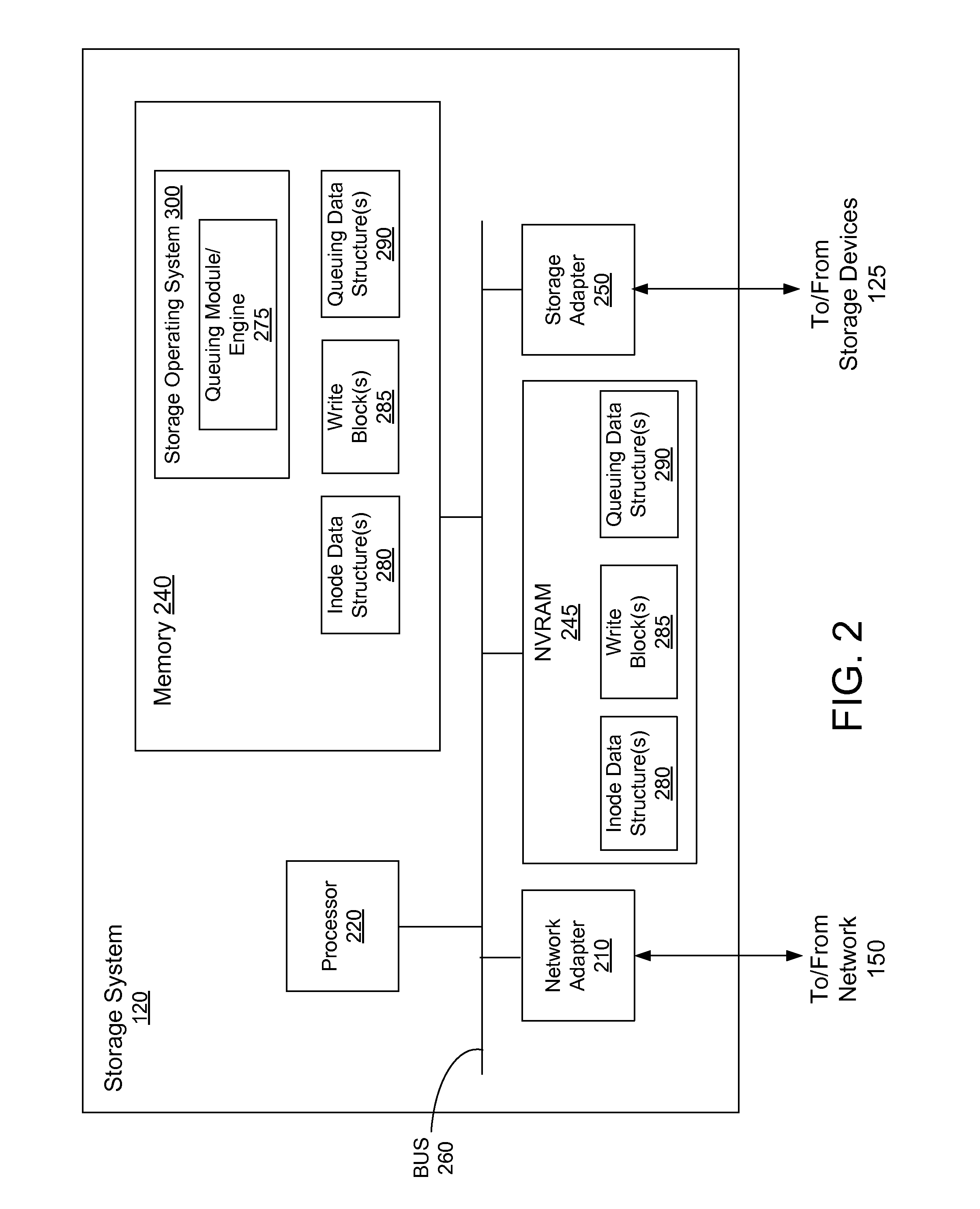
Queuing received write blocks for reducing file fragmentation
ActiveUS8806143B1Reduce file fragmentationLower read latencyDigital data information retrievalInput/output to record carriersTheoretical computer scienceSingle node
A method and apparatus for queuing FBNs of received write blocks for a file to a queuing data structure for assigning LBNs to the FBNs is described herein. A queuing data structure may comprise a modified binary search tree, such as a modified red-black search tree. Each node of a queuing data structure may comprise a base field for storing a base FBN and a range field for storing a range value comprising X bits. The range field of a single node may represent a range of two or more FBNs (“FBN range”), the FBN range being based on the base FBN. Each FBN in the FBN range may have a corresponding bit in the range field, the base FBN corresponding to a “base bit” in the range field. The value of the corresponding bit in the range field may indicate whether the FBN has been received.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
Capacitive-Coupled Non-Volatile Thin-Film Transistor Strings in Three Dimensional Arrays
ActiveUS20190006015A1High densityLower read latencyTransistorSolid-state devicesCapacitive couplingParasitic capacitance
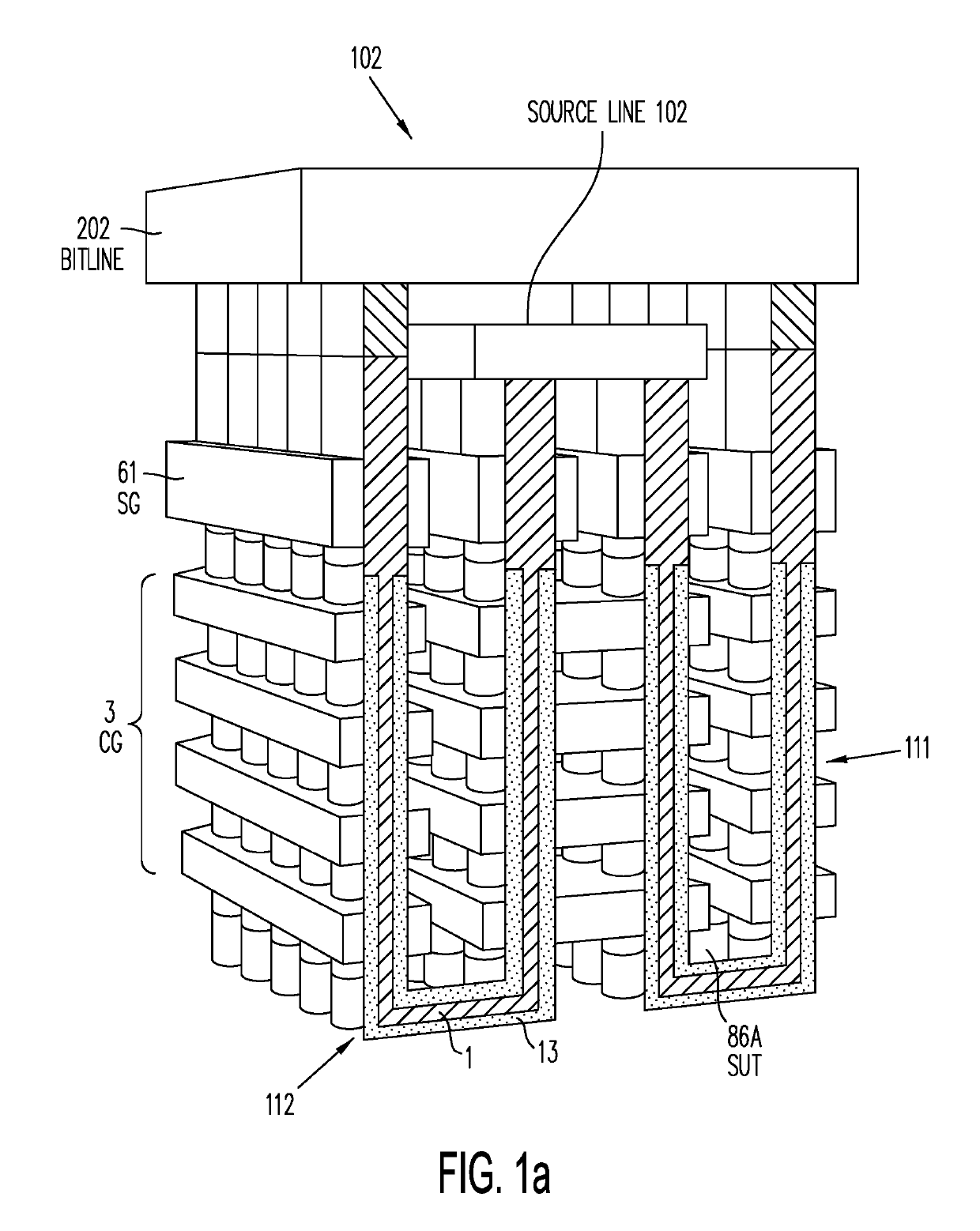
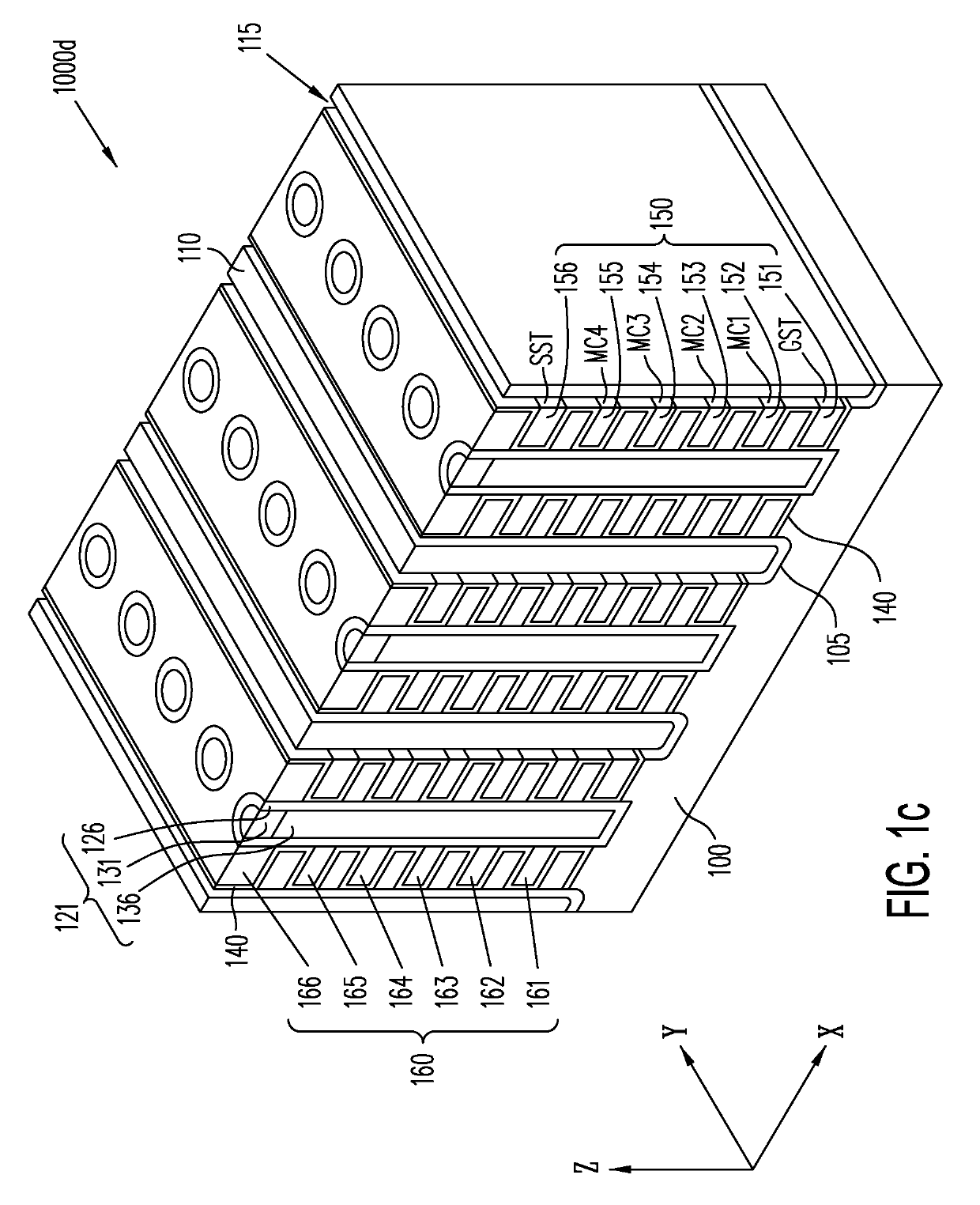
Multi-gate NOR flash thin-film transistor (TFT) string arrays are organized as three dimensional stacks of active strips. Each active strip includes a shared source sublayer and a shared drain sublayer that is connected to substrate circuits. Data storage in the active strip is provided by charge-storage elements between the active strip and a multiplicity of control gates provided by adjacent local word-lines. The parasitic capacitance of each active strip is used to eliminate hard-wire ground connection to the shared source making it a semi-floating, or virtual source. Pre-charge voltages temporarily supplied from the substrate through a single port per active strip provide the appropriate voltages on the source and drain required during read, program, program-inhibit and erase operations. TFTs on multiple active strips can be pre-charged separately and then read, programmed or erased together in a massively parallel operation.
Owner:SUNRISE MEMORY CORP
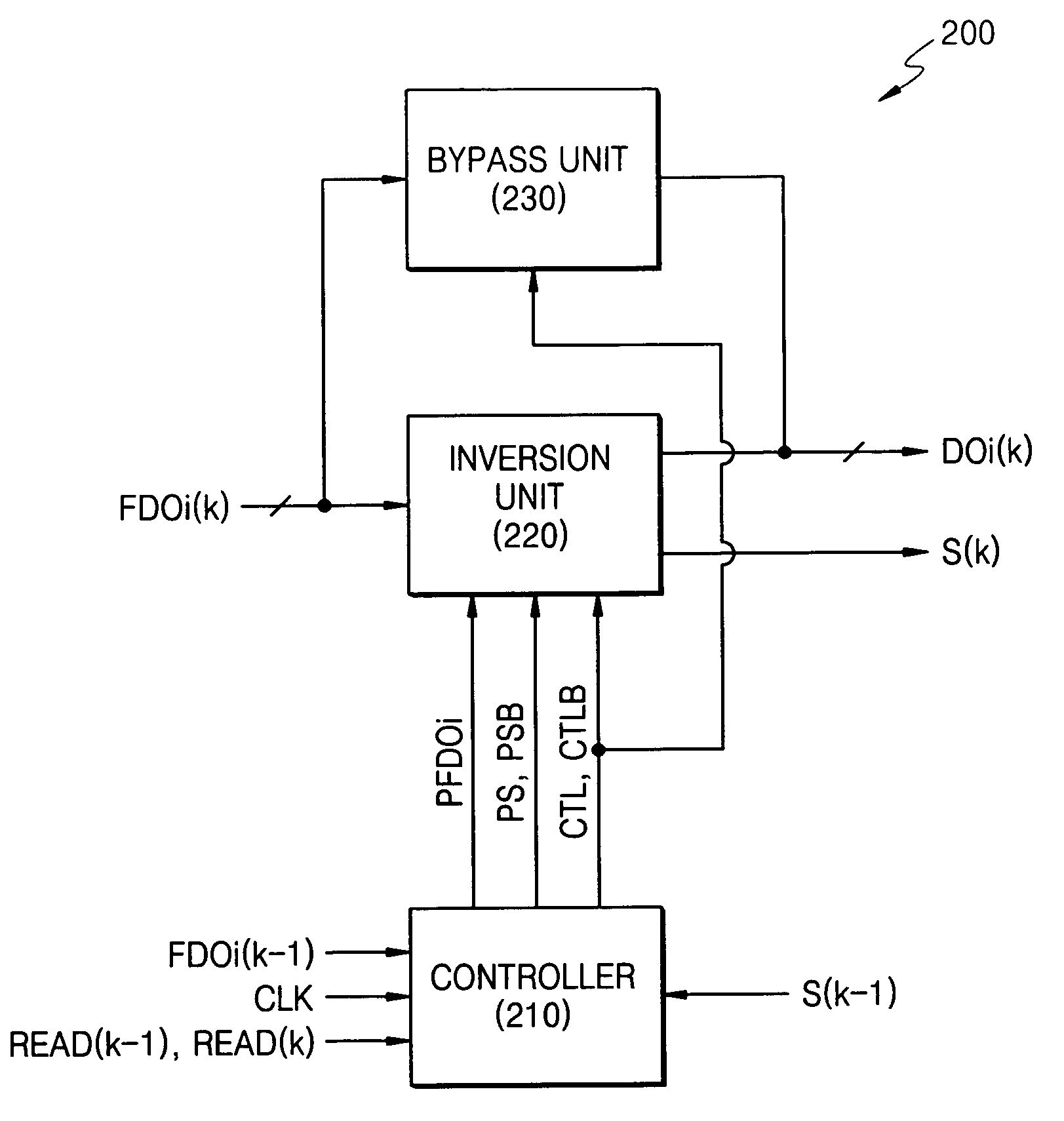
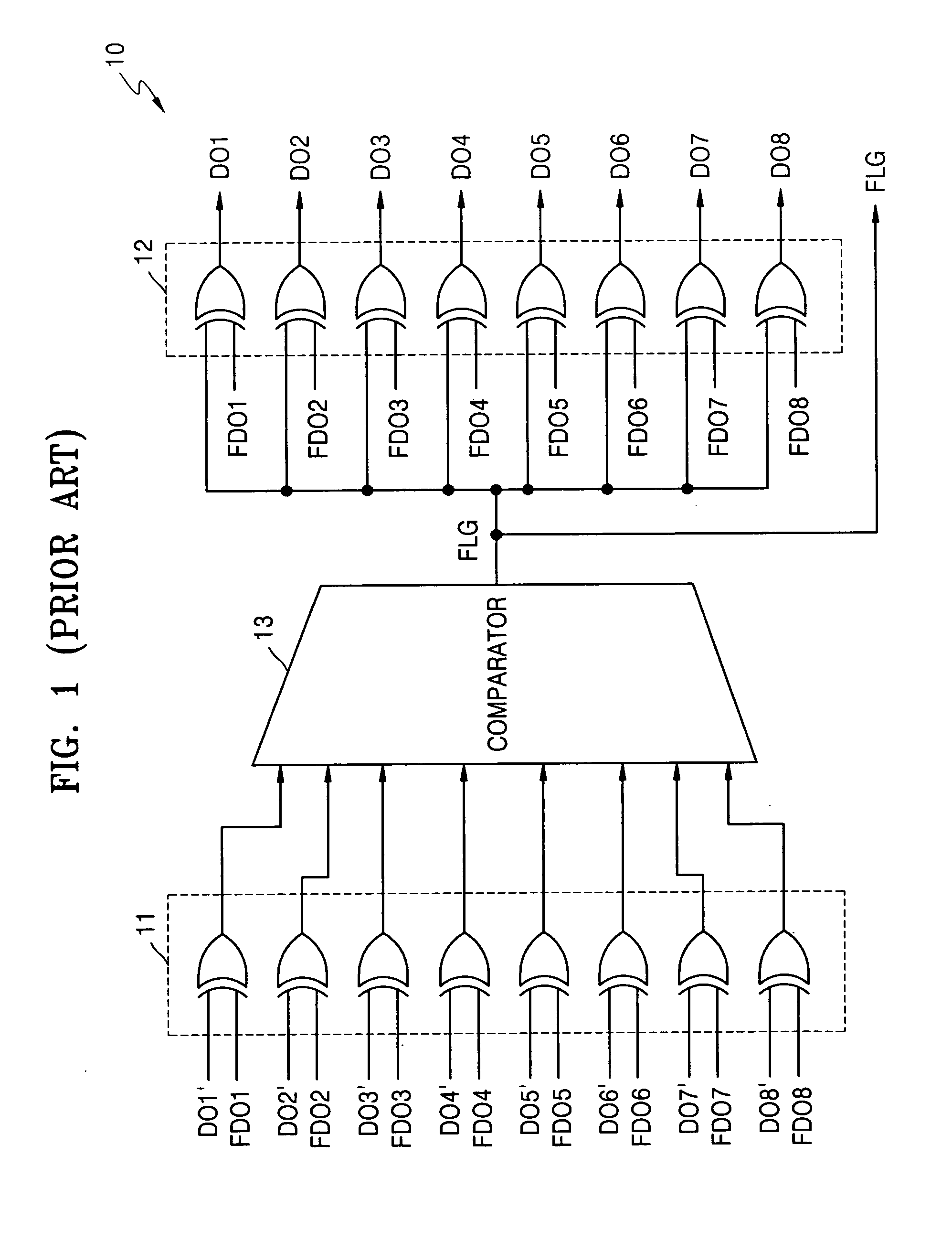
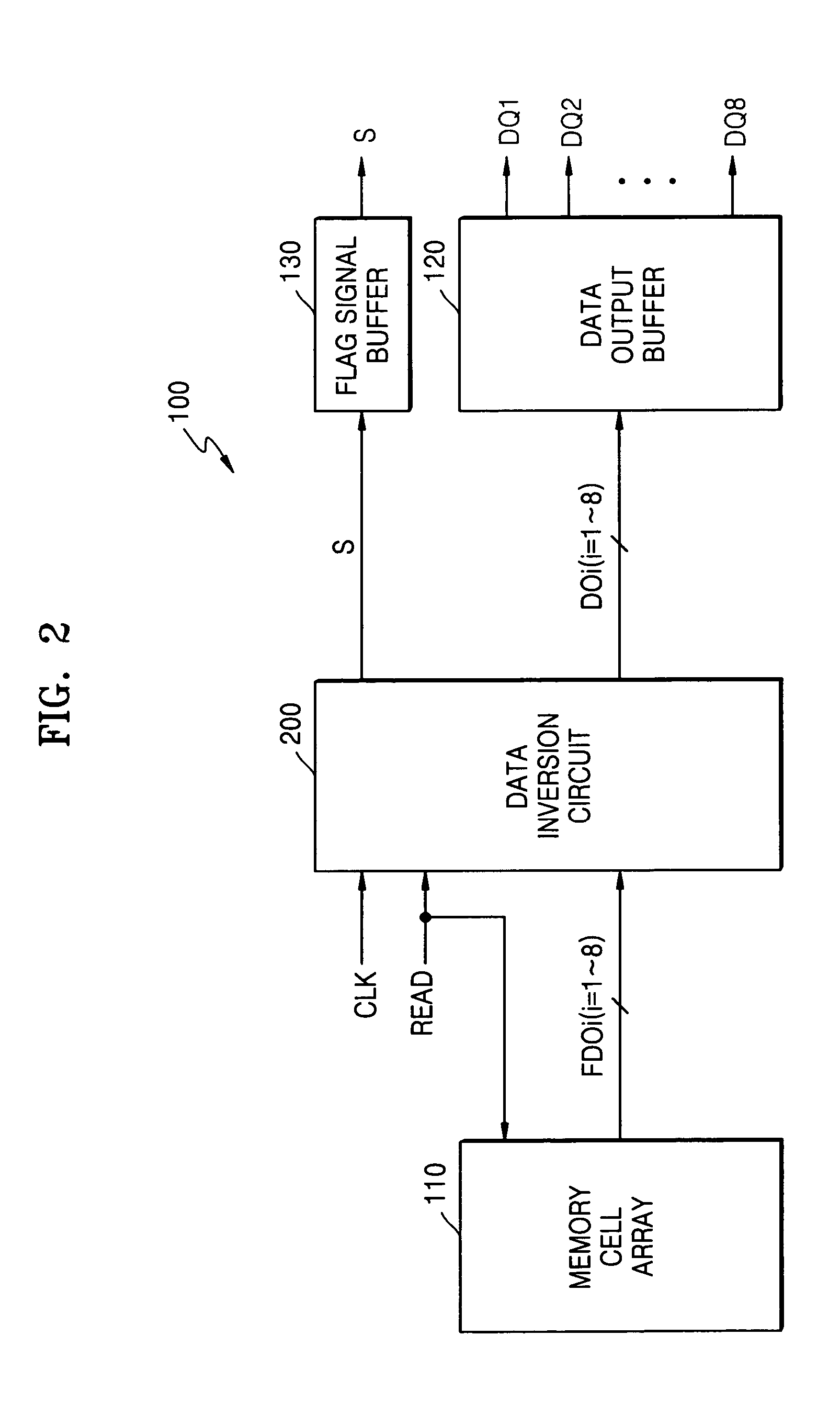
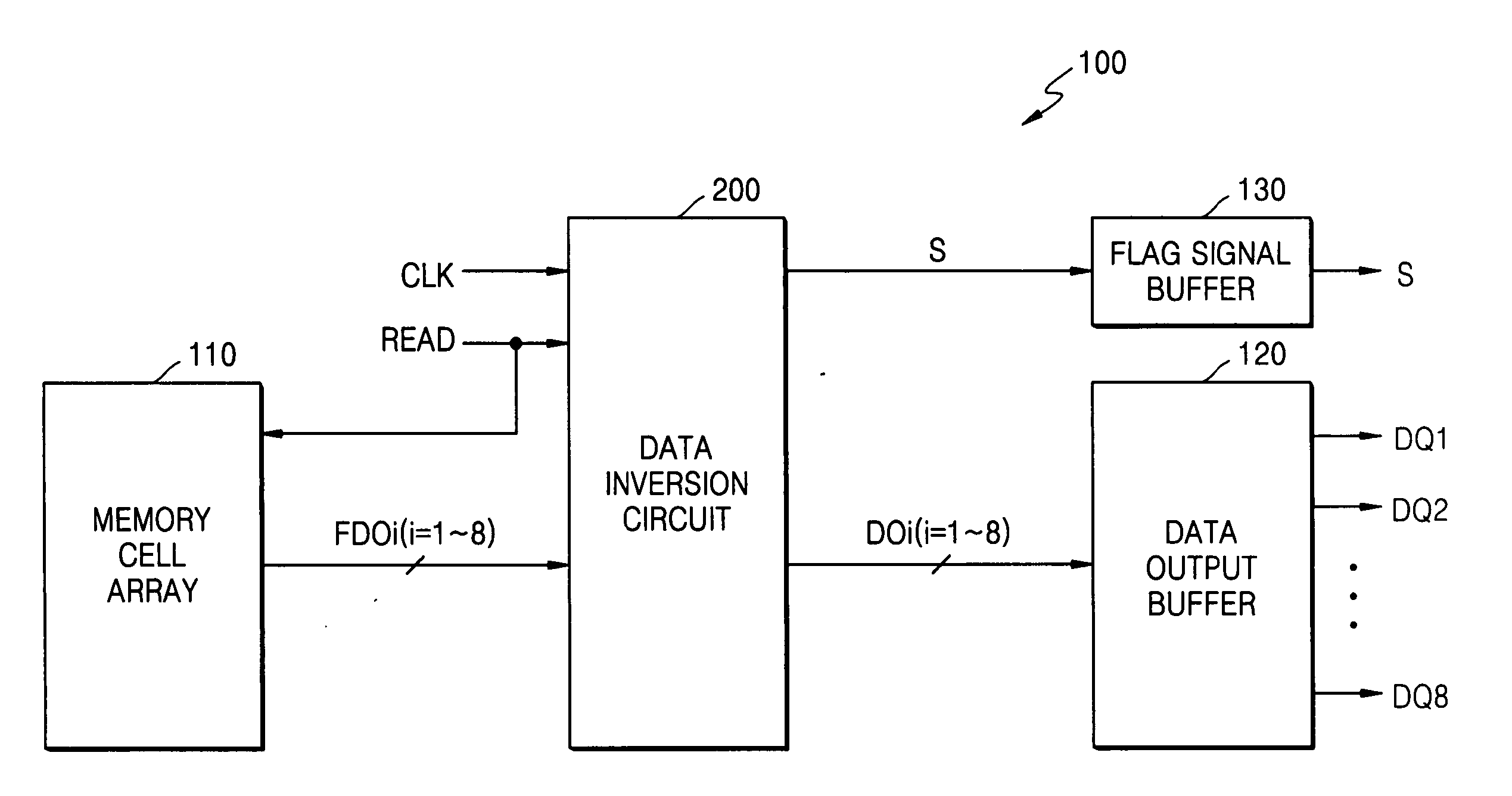
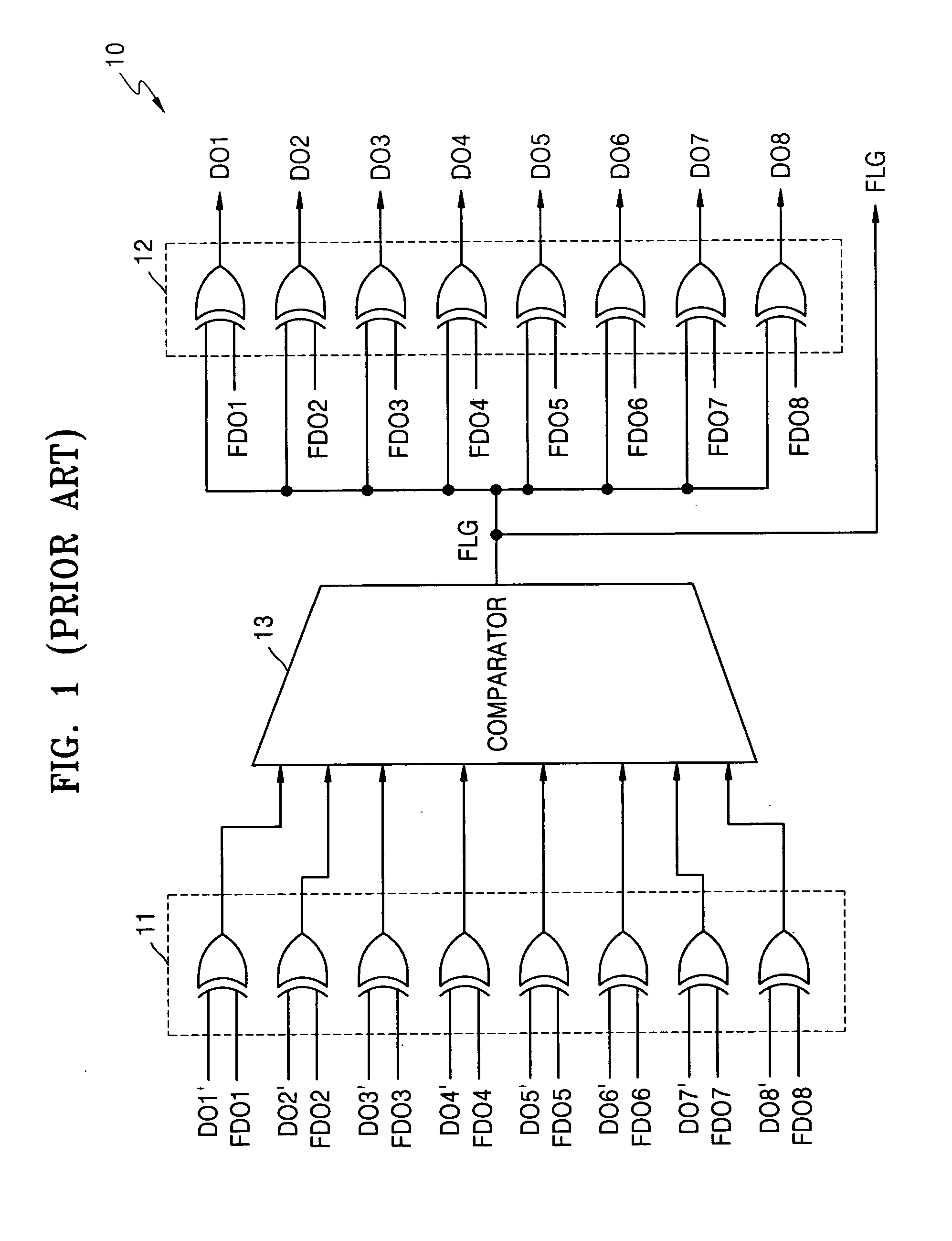
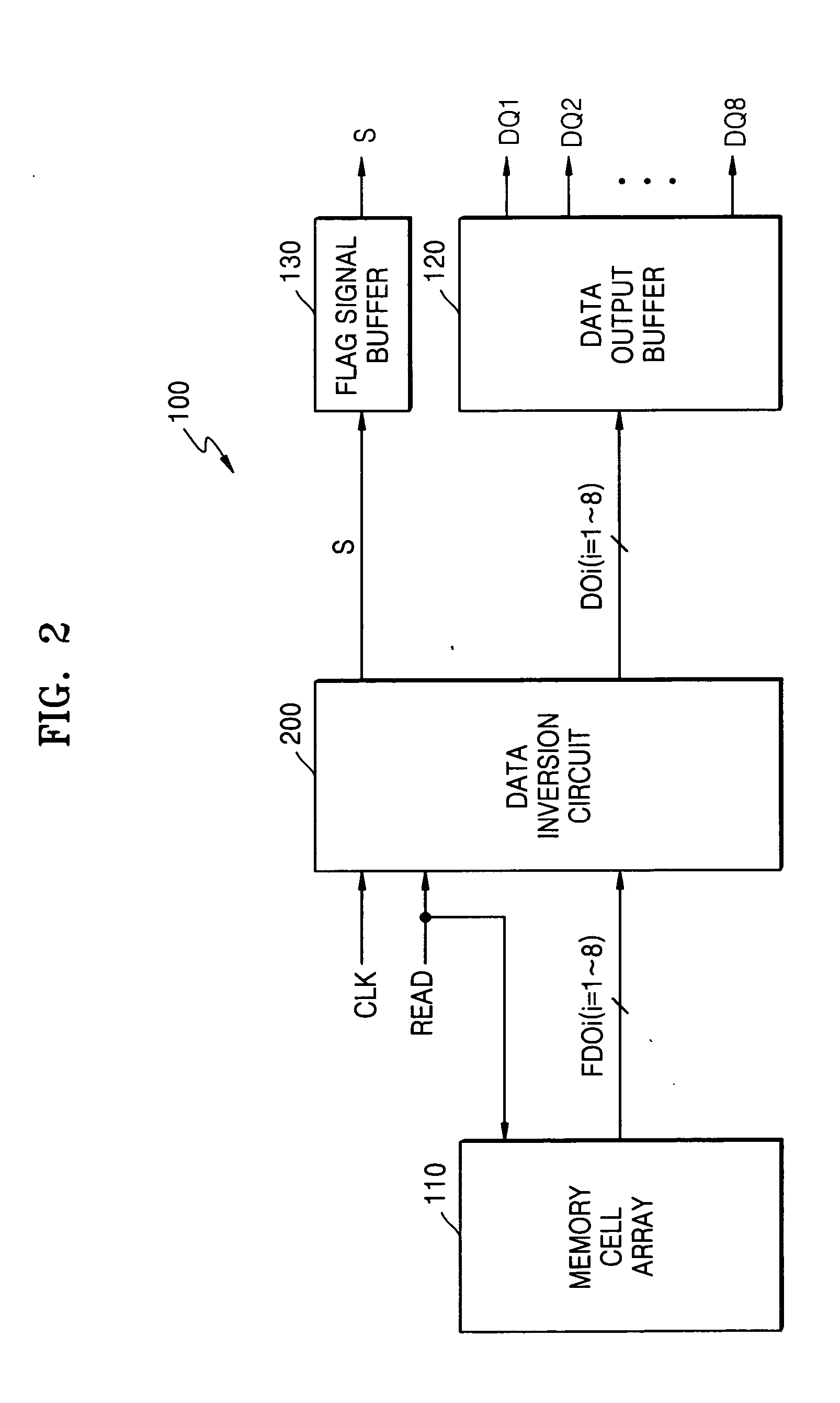
Data inversion circuits having a bypass mode of operation and methods of operating the same
InactiveUS7142021B2Lower read latencyReduce noiseExclusive-OR circuitsComputation using non-contact making devicesOperation modeIntegrated circuit
An integrated circuit device includes a data inversion circuit configured to support an inversion mode of operation. The inversion mode of operation inverts selected ones of a plurality of N-bit words received in consecutive sequence at inputs thereof. The data inversion circuit is further configured to support a bypass mode of operation. The bypass mode of operation disables inversion of a second one of the plurality of N-bit words when a delay between receipt of the second one of the plurality of N-bit words and receipt of an immediately preceding first one of the plurality of N-bit words is greater than a predetermined time interval. Related methods are also discussed.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method and device for controlling data parallelly reading and writing of internal memory in decoding device
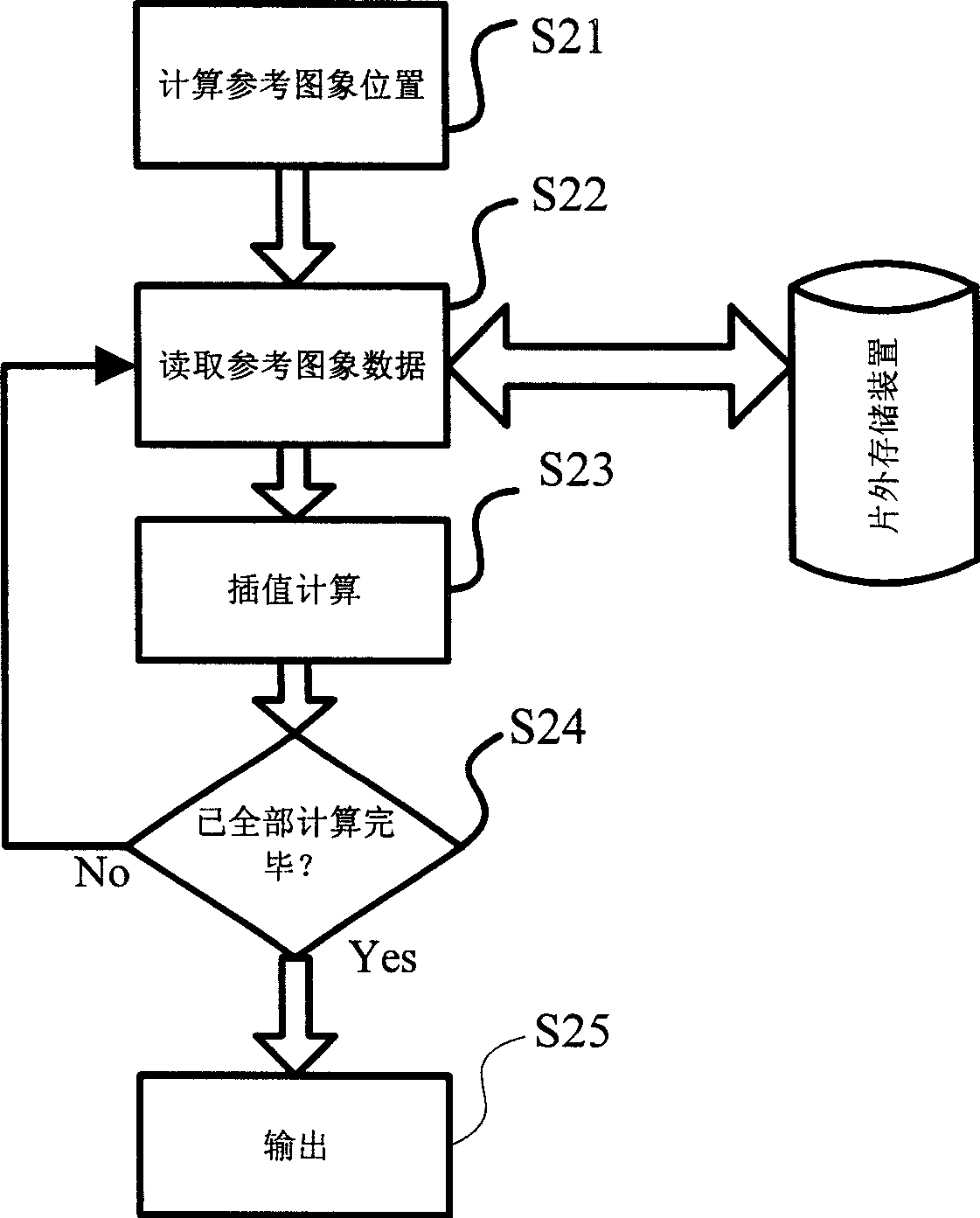
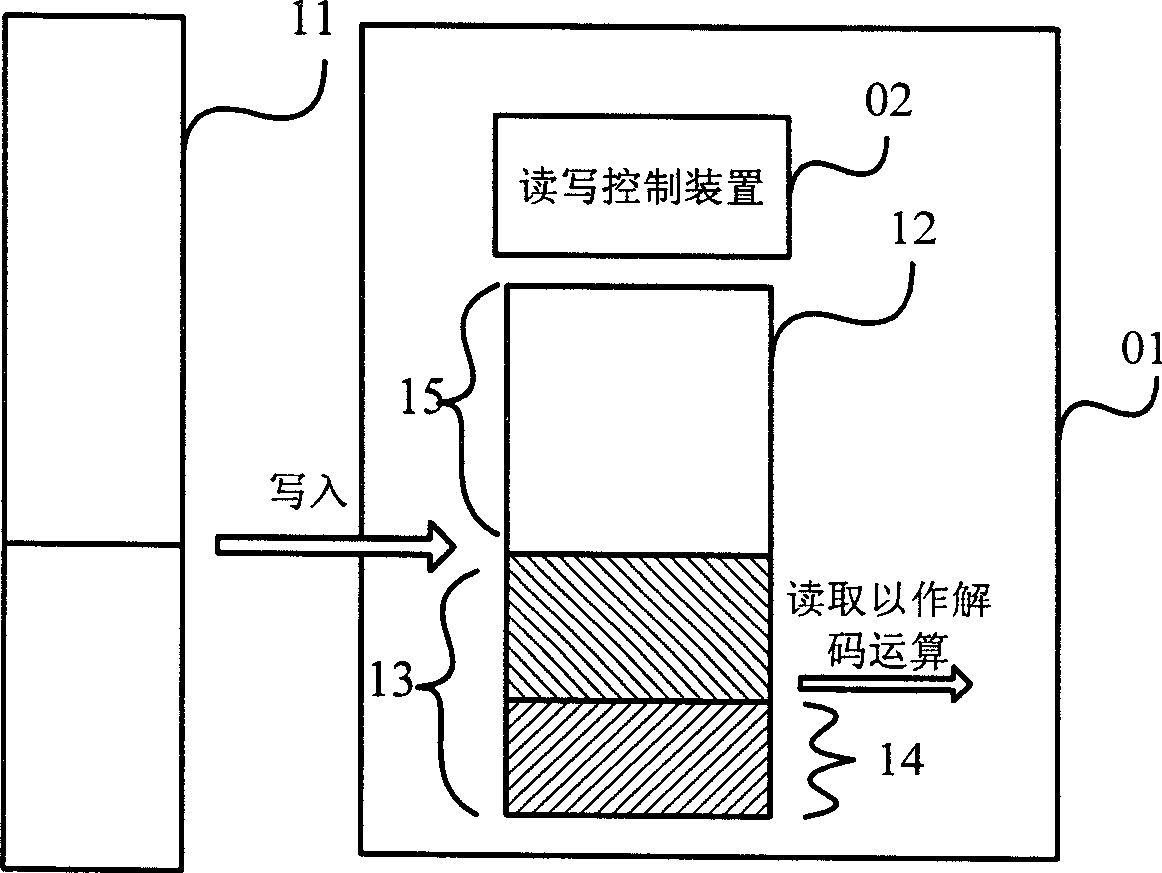
InactiveCN101399977AReduce sizeLower read latencyTelevision systemsDigital video signal modificationCapacitanceInternal memory
The existing movement compensation video frequency decoding scheme based on macroblock tandemly reads external data and reads saved data for interpolation, and results in relatively large capacitance of on-chip storage device configured in video frequency decoding device and drop of decoding speed. The invention provides a method for controlling to write external data in on-chip storage device in parallel and for on-chip storage device reading the accessible data for decoding algorithm, its device capable of reducing capacitance and decoding time of on-chip storage device.
Owner:CHIPNUTS TECH INC
Method for reading and writing solid-state disk and solid-state disk thereof
InactiveCN103425439AExtended service lifeImprove experienceInput/output to record carriersThe InternetSolid-state drive
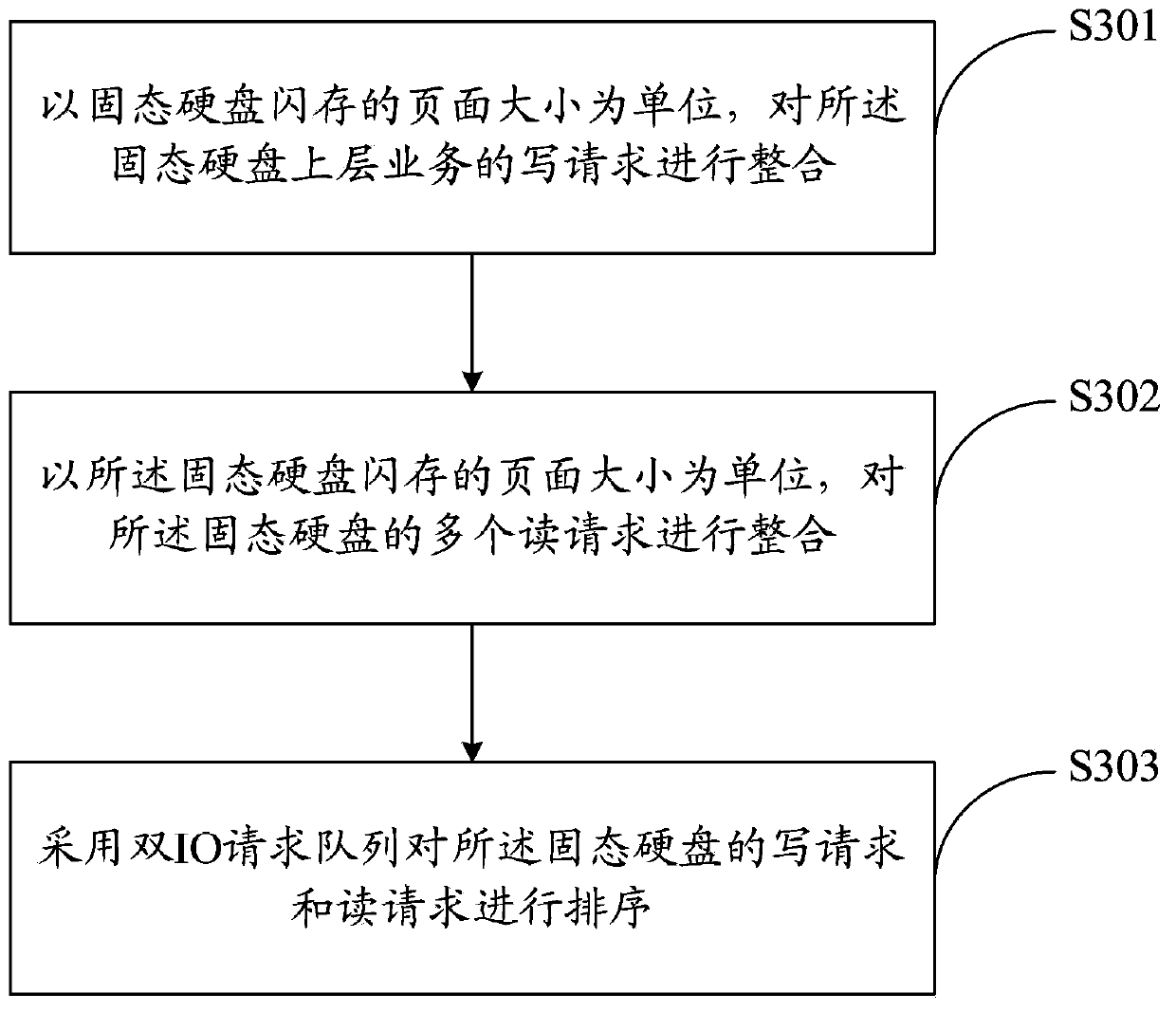
The invention belongs to the technical field of solid-state disks, and provides a method for reading and writing a solid-state disk and the solid-state disk of the method. In order to achieve the aims, the invention provides the method for reading and writing the solid-state disk. The method comprises the following steps: A, using the page size of flash memory of the solid-state disk to integrate write requests of an upper-layer service on the solid-state disk, B, using the page size of the flash memory of the solid-state disk to integrate a plurality of read requests of the solid-state disk, and C, adopting an IO request queue to rank the write requests and the read requests of the solid-state disk. Therefore, according to the method for reading and writing the solid-state disk and the solid-state disk of the method, the application of the solid-state disk in the Internet is optimized, and the use efficiency of the solid-state disk is improved.
Owner:RAMAXEL TECH SHENZHEN
Method of operating storage device
ActiveUS20190362796A1Reduce power consumptionLower read latencySolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesStorage cellVoltage reference
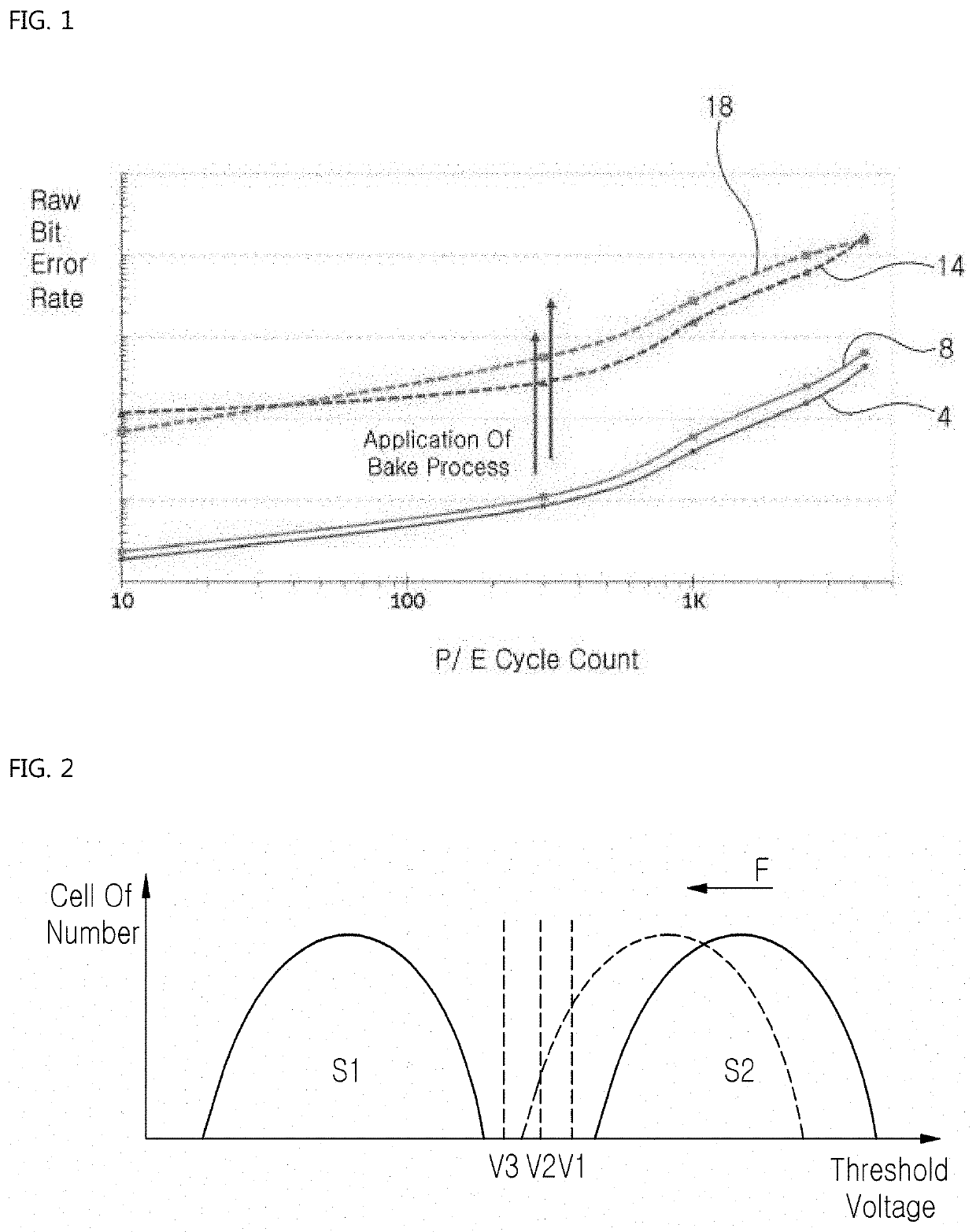
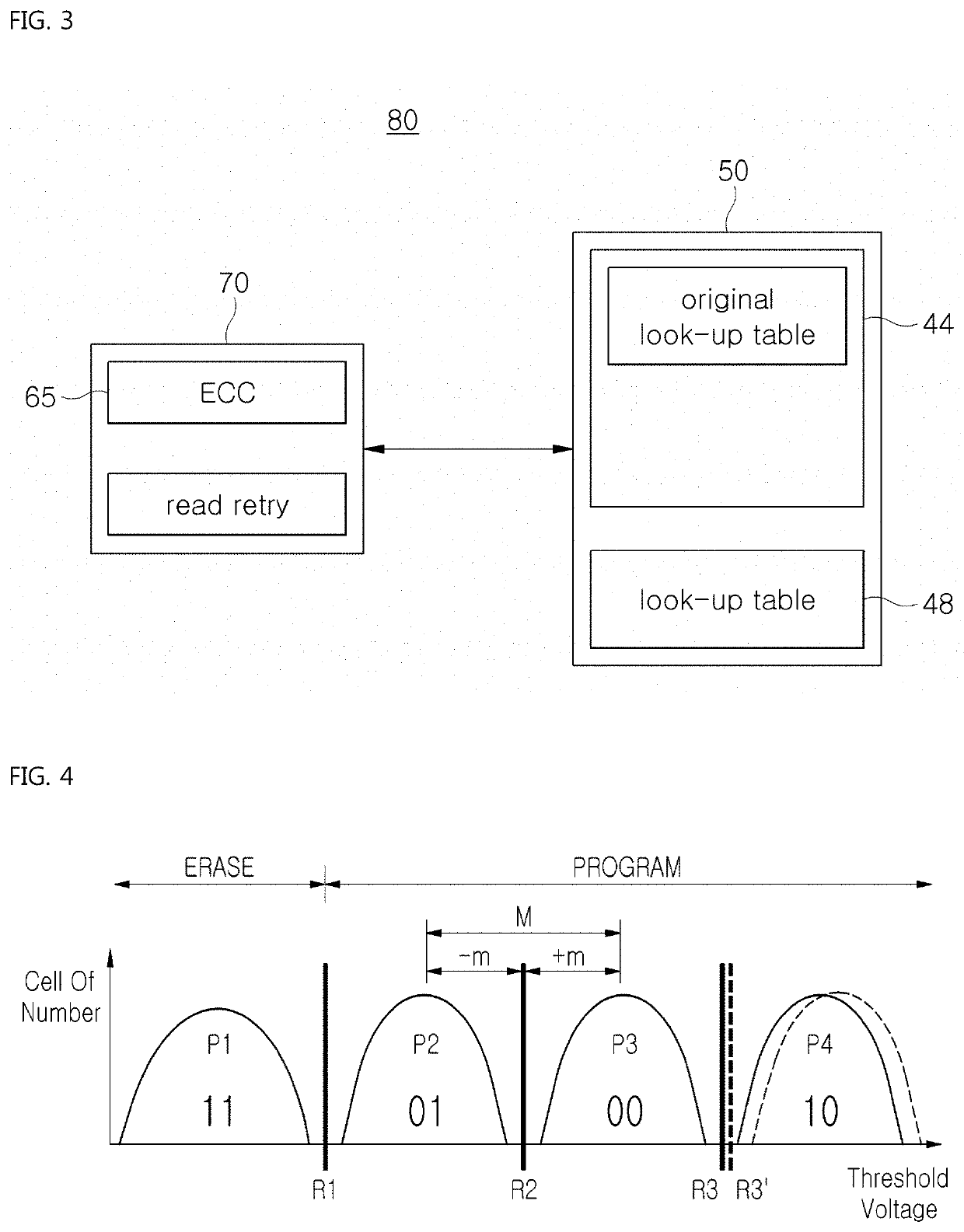
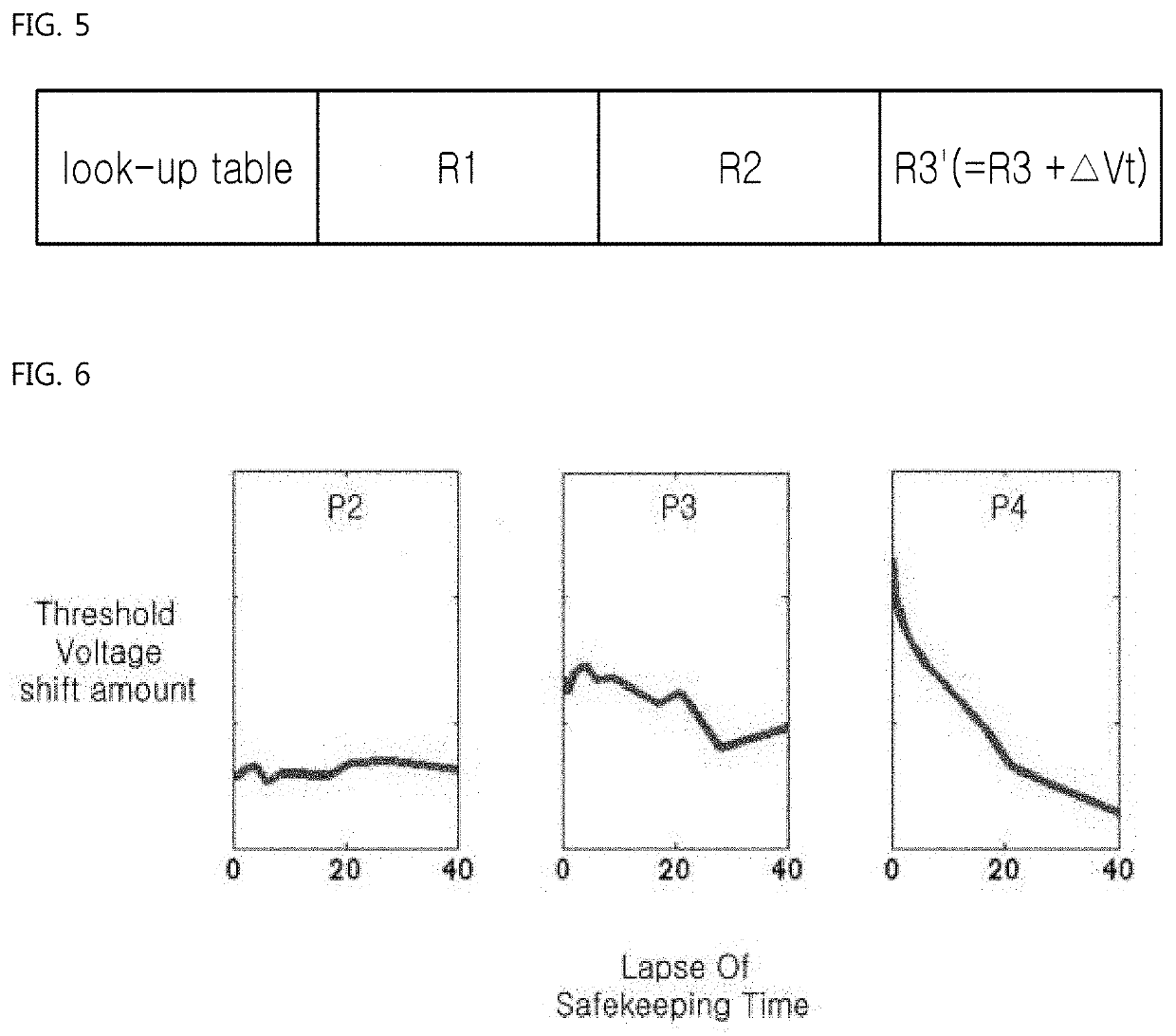
Disclosed is a method of operating a storage device including a NAND flash memory including memory cells grouped into blocks, each block being divided into pages. According to the method, a controller in the storage device loads, onto a memory region, a look-up table containing first read reference voltage sets corresponding to respective retention degradation stages of the NAND flash memory and second read reference voltages sets corresponding to respective pages which vary in terms of the threshold voltages. Subsequently, the controller performs a read operation on the memory cells on a per-block basis by using the first read reference voltage set corresponding to a current retention degradation stage, the second read reference voltage set corresponding to a current page, or both, until all of the memory cells in a current block are correctly read.
Owner:ESSENCORE LTD +1
Data inversion circuits having a bypass mode of operation and methods of operating the same
InactiveUS20050127945A1Reduce simultaneous switching noiseLower read latencyExclusive-OR circuitsComputation using non-contact making devicesEngineeringOperation mode
An integrated circuit device includes a data inversion circuit configured to support an inversion mode of operation. The inversion mode of operation inverts selected ones of a plurality of N-bit words received in consecutive sequence at inputs thereof. The data inversion circuit is further configured to support a bypass mode of operation. The bypass mode of operation disables inversion of a second one of the plurality of N-bit words when a delay between receipt of the second one of the plurality of N-bit words and receipt of an immediately preceding first one of the plurality of N-bit words is greater than a predetermined time interval. Related methods are also discussed.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Solid state disk data reading and writing method and solid state disk
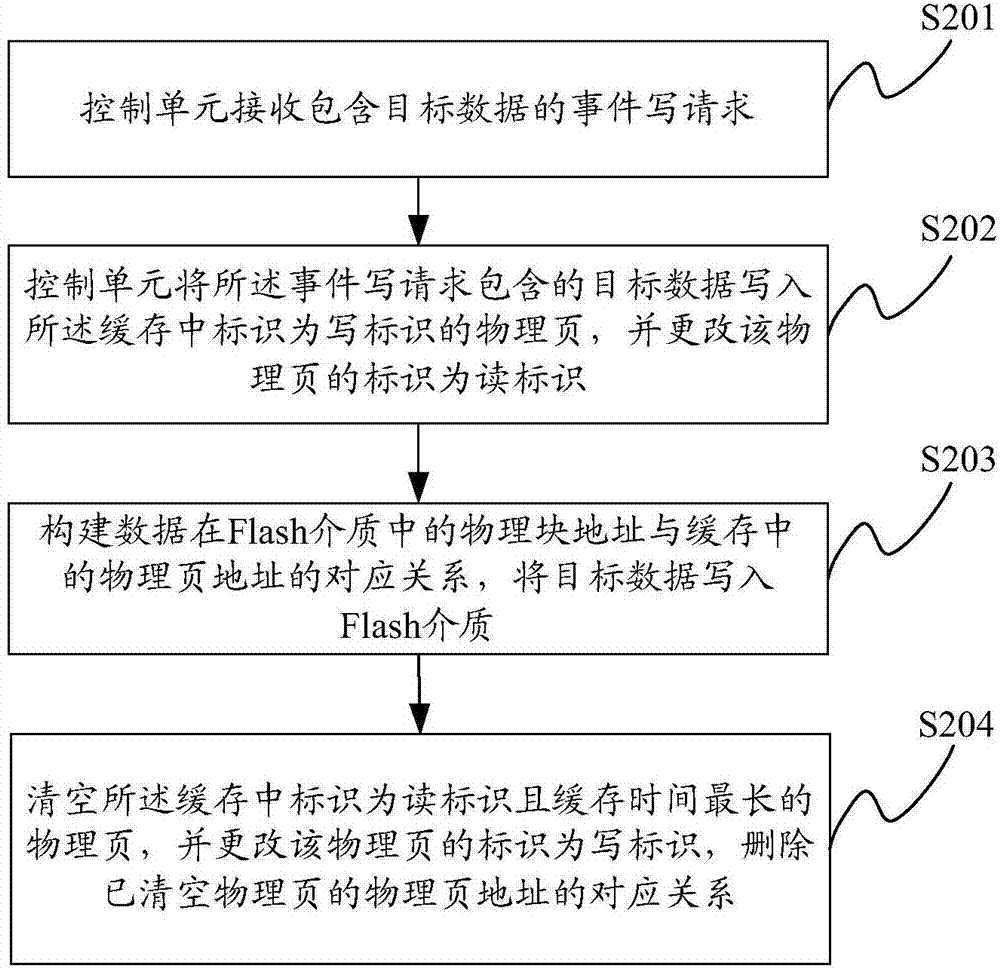
ActiveCN107273306AGuaranteed accuracyHigh speedMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationSolid-state driveLogical address
The invention provides a solid state disk data reading and writing method and a solid state disk. The method comprises the steps that an event reading request including a logic block address of target data is received; a physical block address corresponding to the logic block address in a Flash medium is looked up; the difference value of a current physical block address and the physical block address is calculated; if the difference value is greater than the number of instable physical pages in the Flash medium, the target data is read from the Flash medium based on the physical block address; if the difference value is not greater than the number of the instable physical pages in the Flash medium, the target data is read from a cache based on the physical block address, wherein data in the instable physical pages is backed up in the cache. The data reading accuracy is improved on the basis that the handling difficulty in the reading process is not increased.
Owner:SUZHOU LANGCHAO INTELLIGENT TECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com