Patents
Literature
371 results about "Replication method" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In science: Replication (scientific method), one of the main principles of the scientific method Replication (statistics), the repetition of a test or complete experiment Self-replication, the process in which something (a cell, virus, program) makes a copy of itself DNA replication, the process of copying a double-stranded DNA molecule.
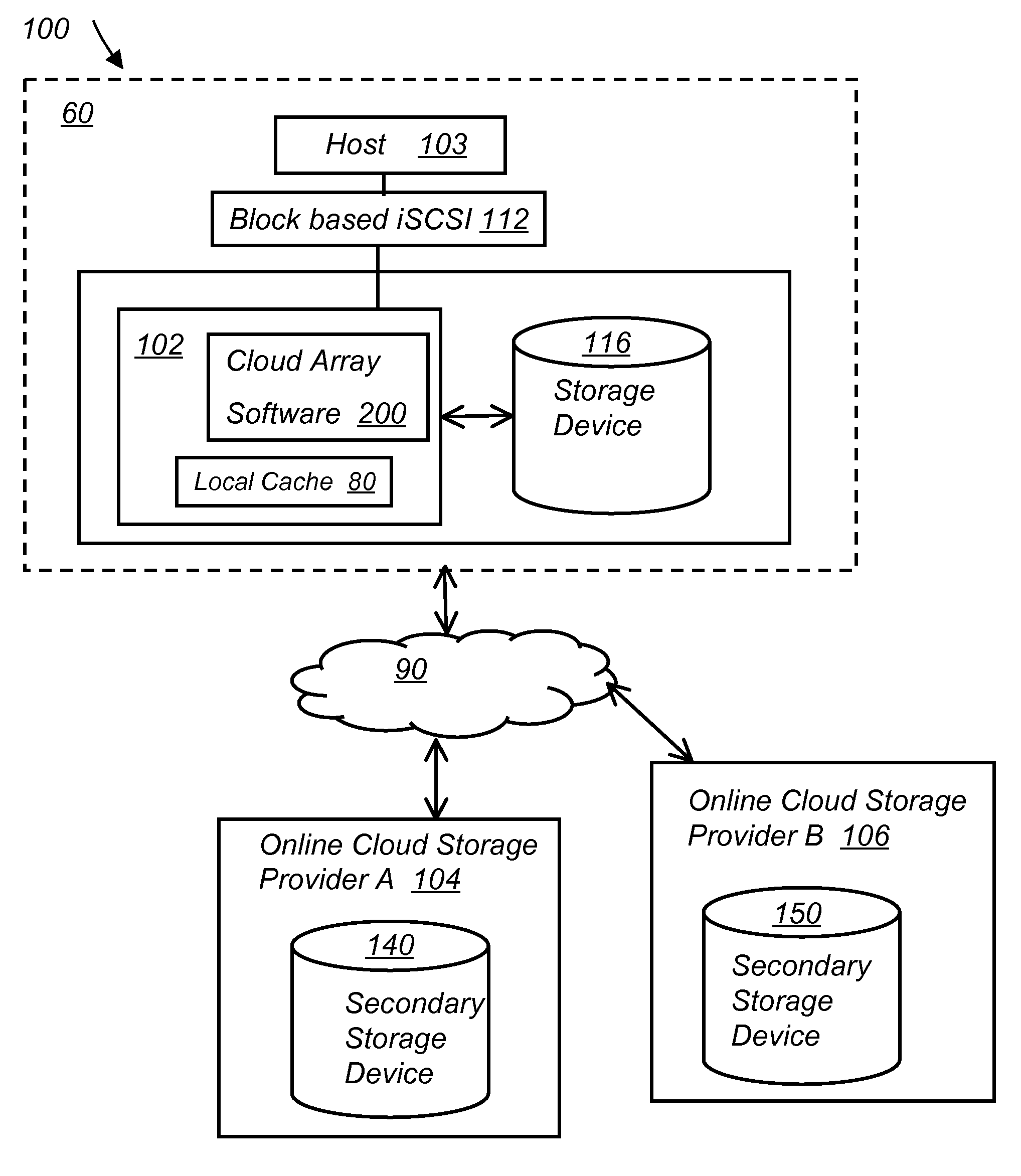
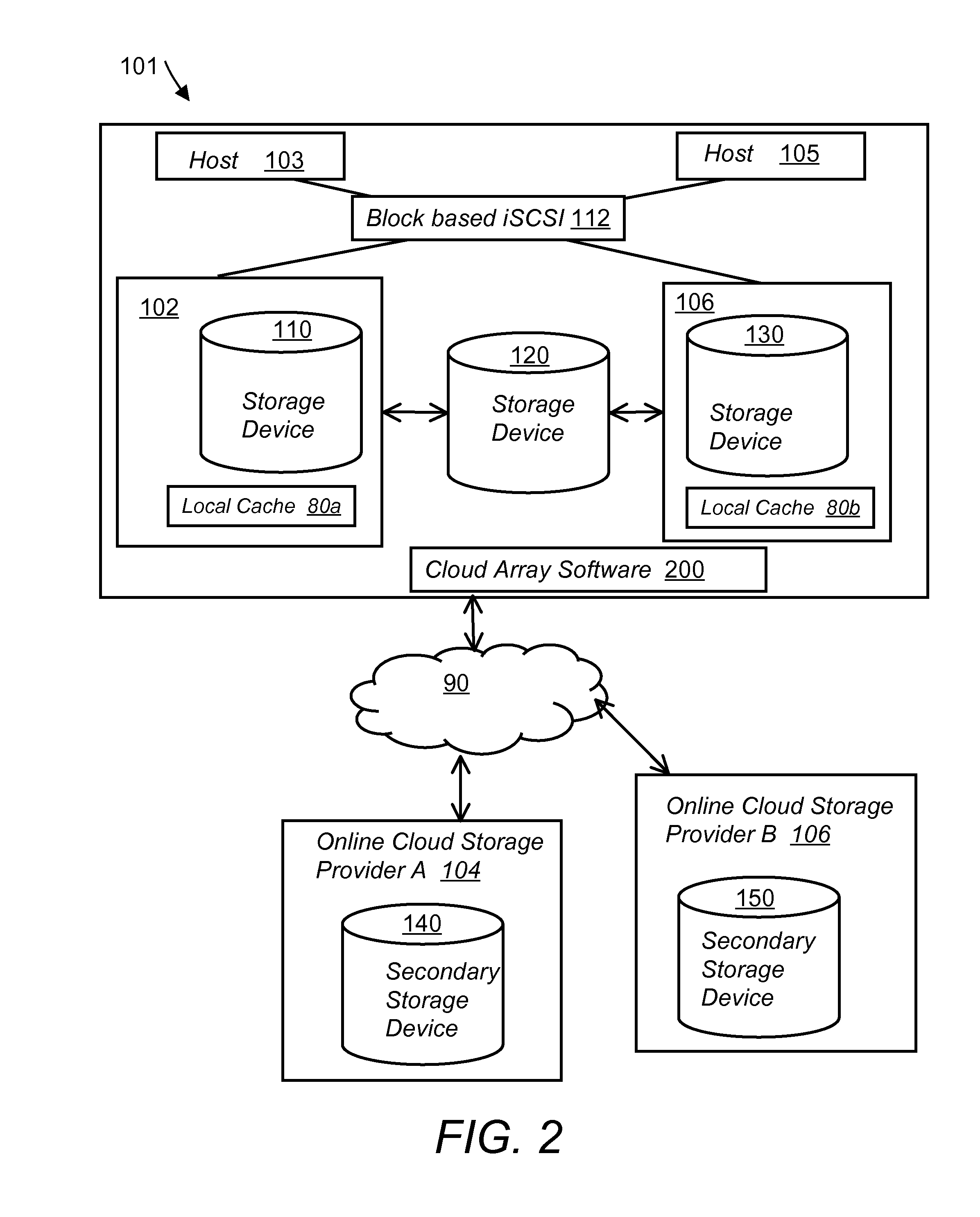
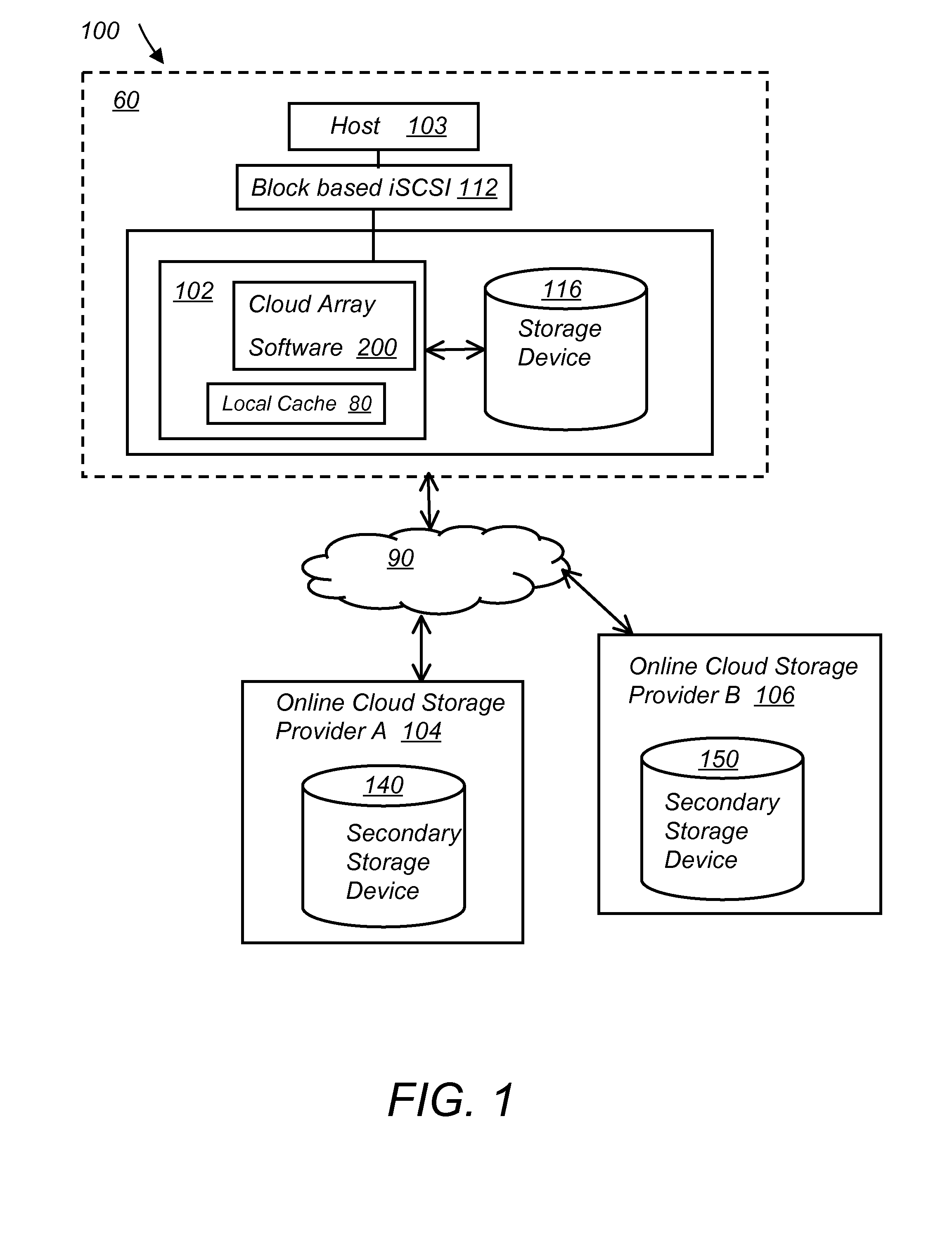
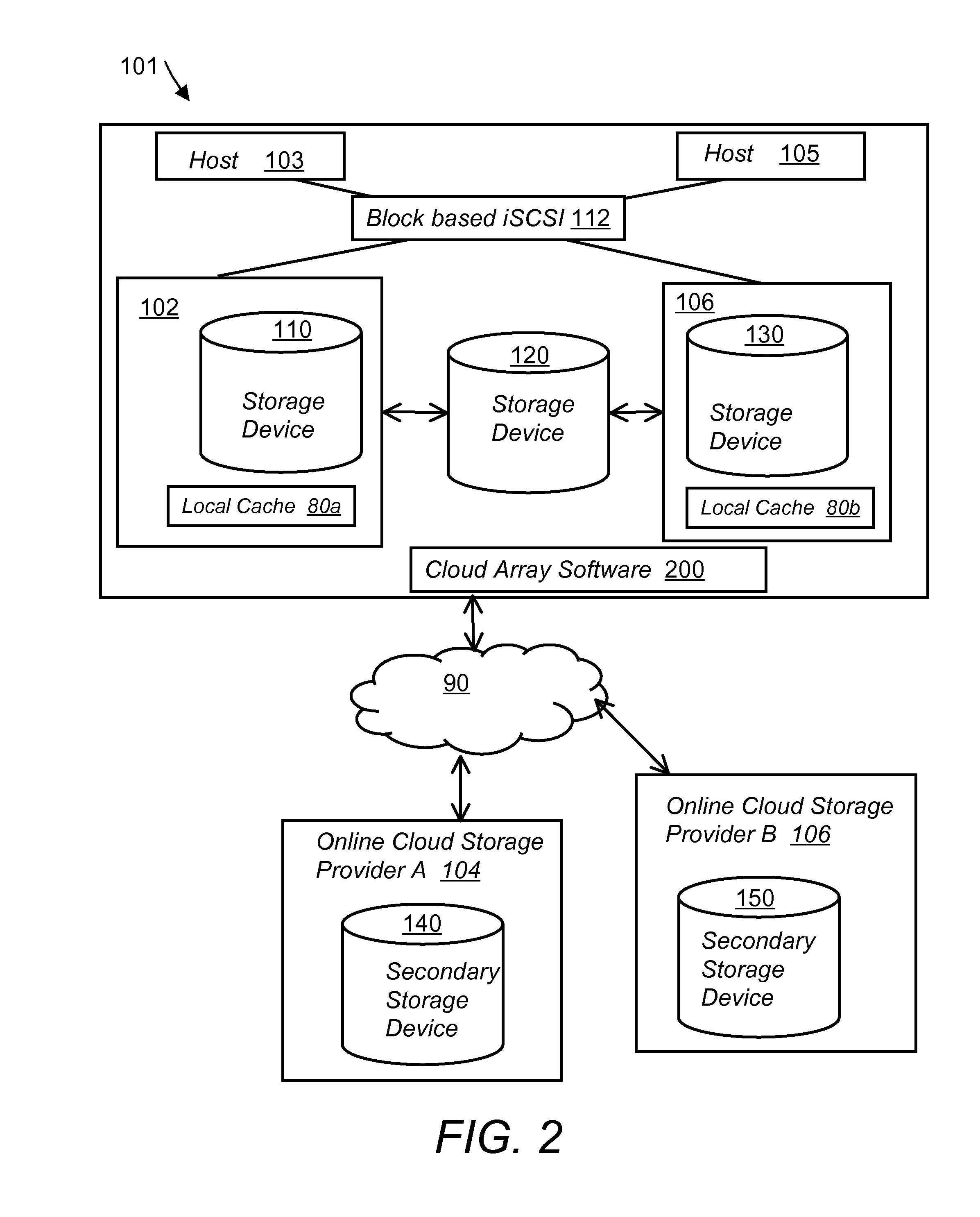
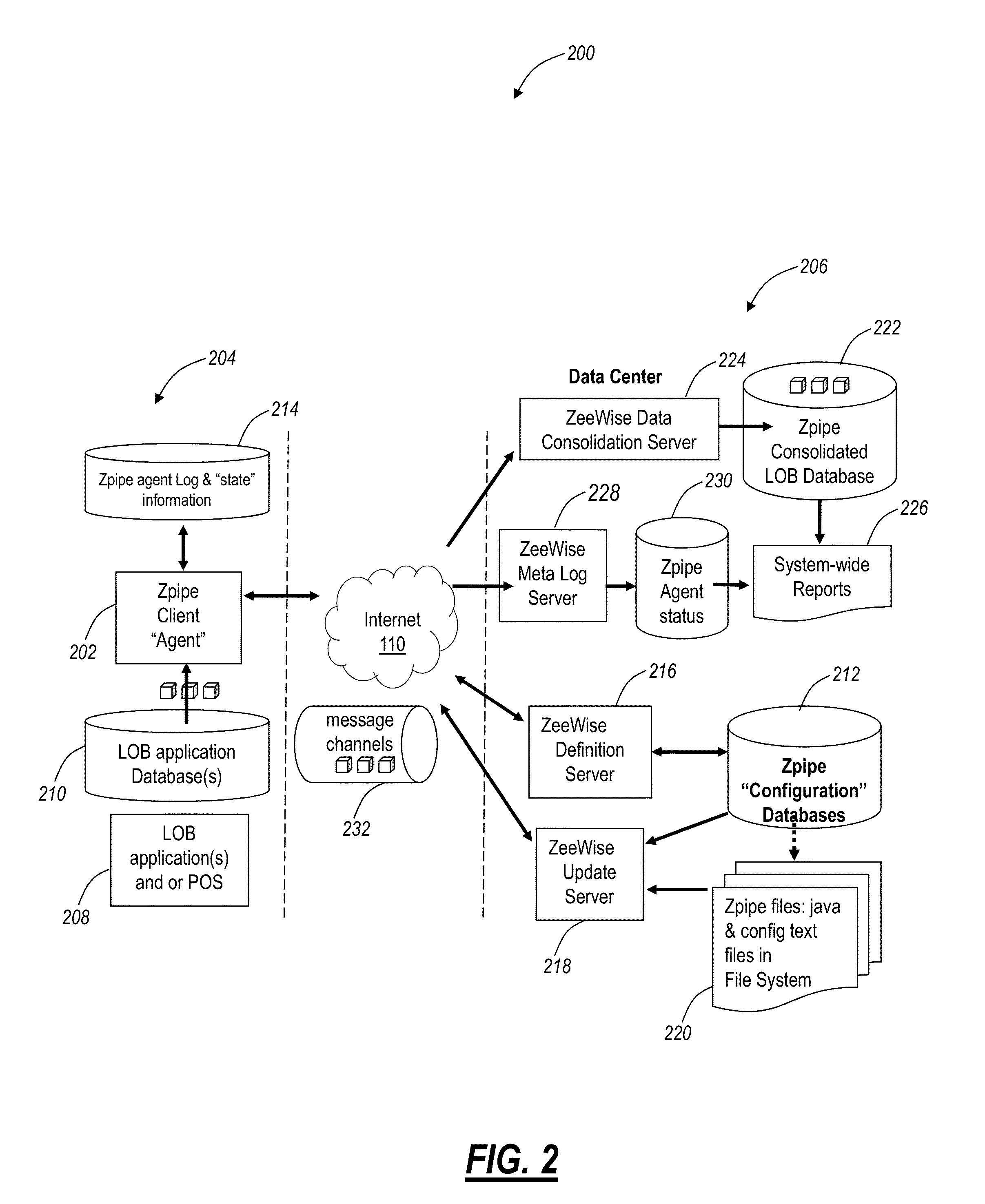
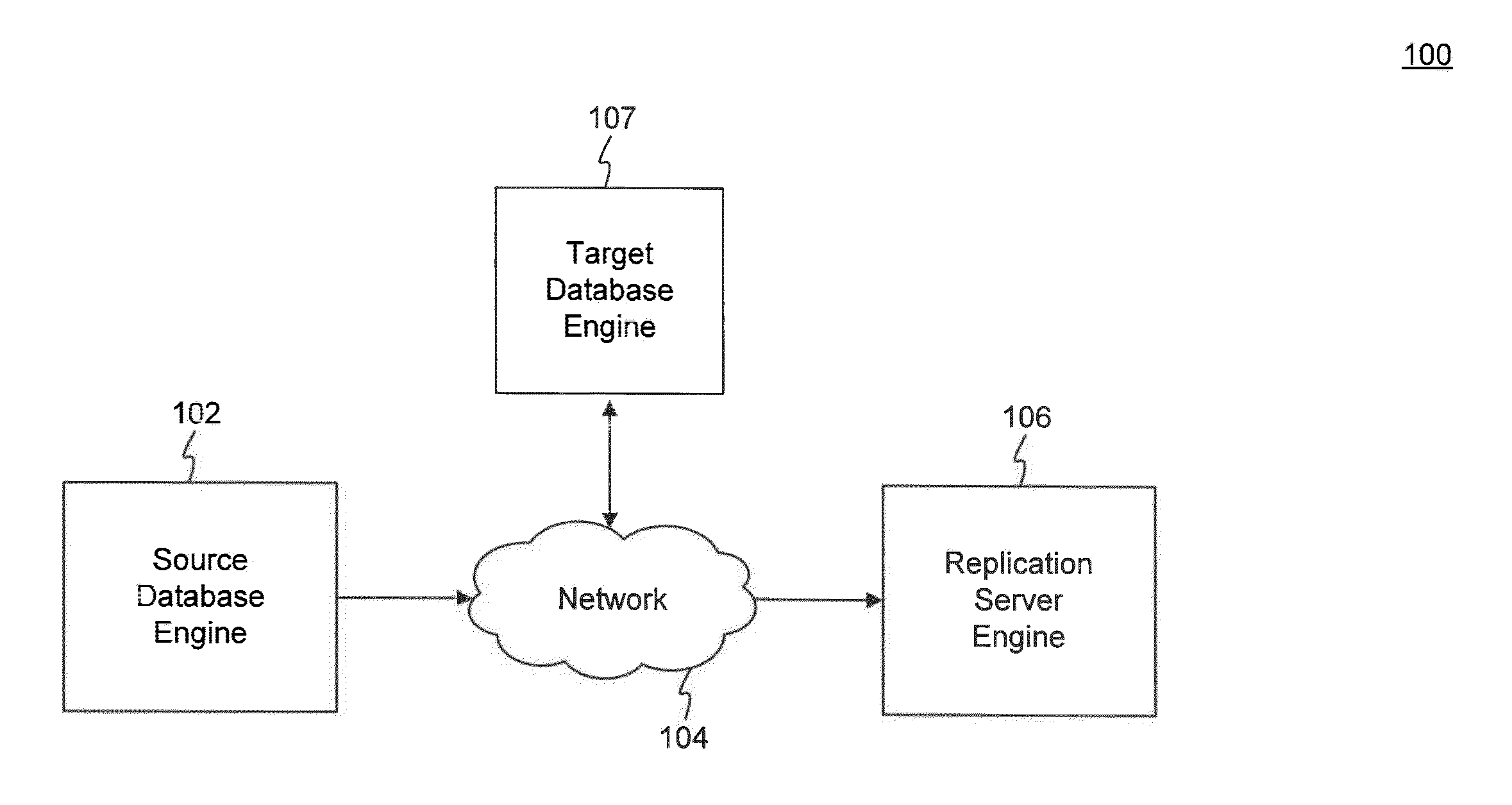
System and method for secure and reliable multi-cloud data replication
ActiveUS8762642B2Reduce the amount requiredReduce storage costsMemory architecture accessing/allocationUnauthorized memory use protectionReliable computingNetwork connection
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
System and method for secure and reliable multi-cloud data replication
ActiveUS20100199042A1Reduce the amount requiredReduce storage costsMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory loss protectionReliable computingReplication method
A multi-cloud data replication method includes providing a data replication cluster comprising at least a first host node and at least a first online storage cloud. The first host node is connected to the first online storage cloud via a network and comprises a server, a cloud array application and a local cache. The local cache comprises a buffer and a first storage volume comprising data cached in one or more buffer blocks of the local cache's buffer. Next, requesting authorization to perform cache flush of the cached first storage volume data to the first online storage cloud. Upon receiving approval of the authorization, encrypting the cached first storage volume data in each of the one or more buffer blocks with a data private key. Next, assigning metadata comprising at lest a unique identifier to each of the one or more buffer blocks and then encrypting the metadata with a metadata private key. Next, transmitting the one or more buffer blocks with the encrypted first storage volume data to the first online cloud storage. Next, creating a sequence of updates of the metadata, encrypting the sequence with the metadata private key and then transmitting the sequence of metadata updates to the first online storage cloud.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
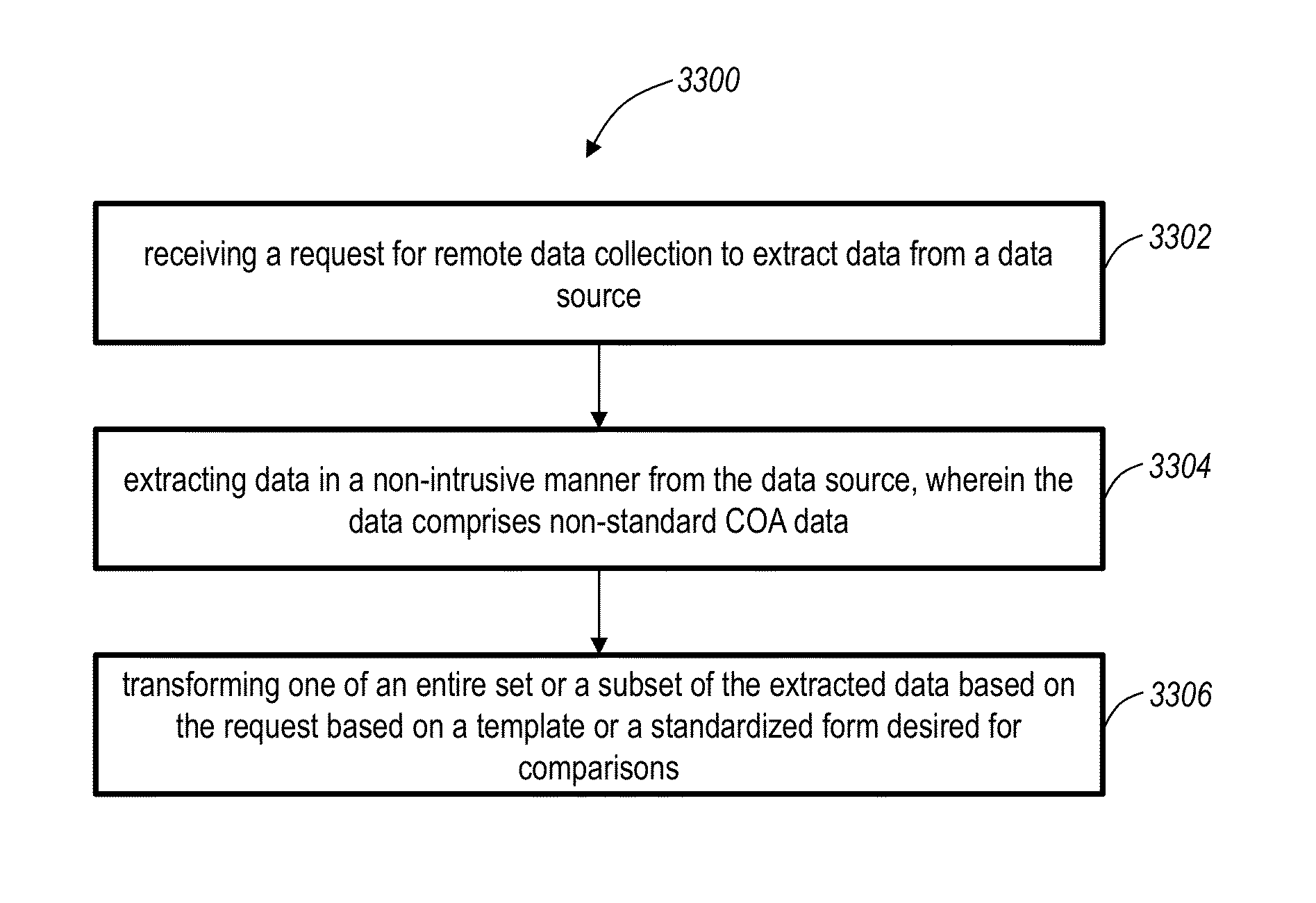
Systems and methods for collection and consolidation of heterogeneous remote business data using dynamic data handling
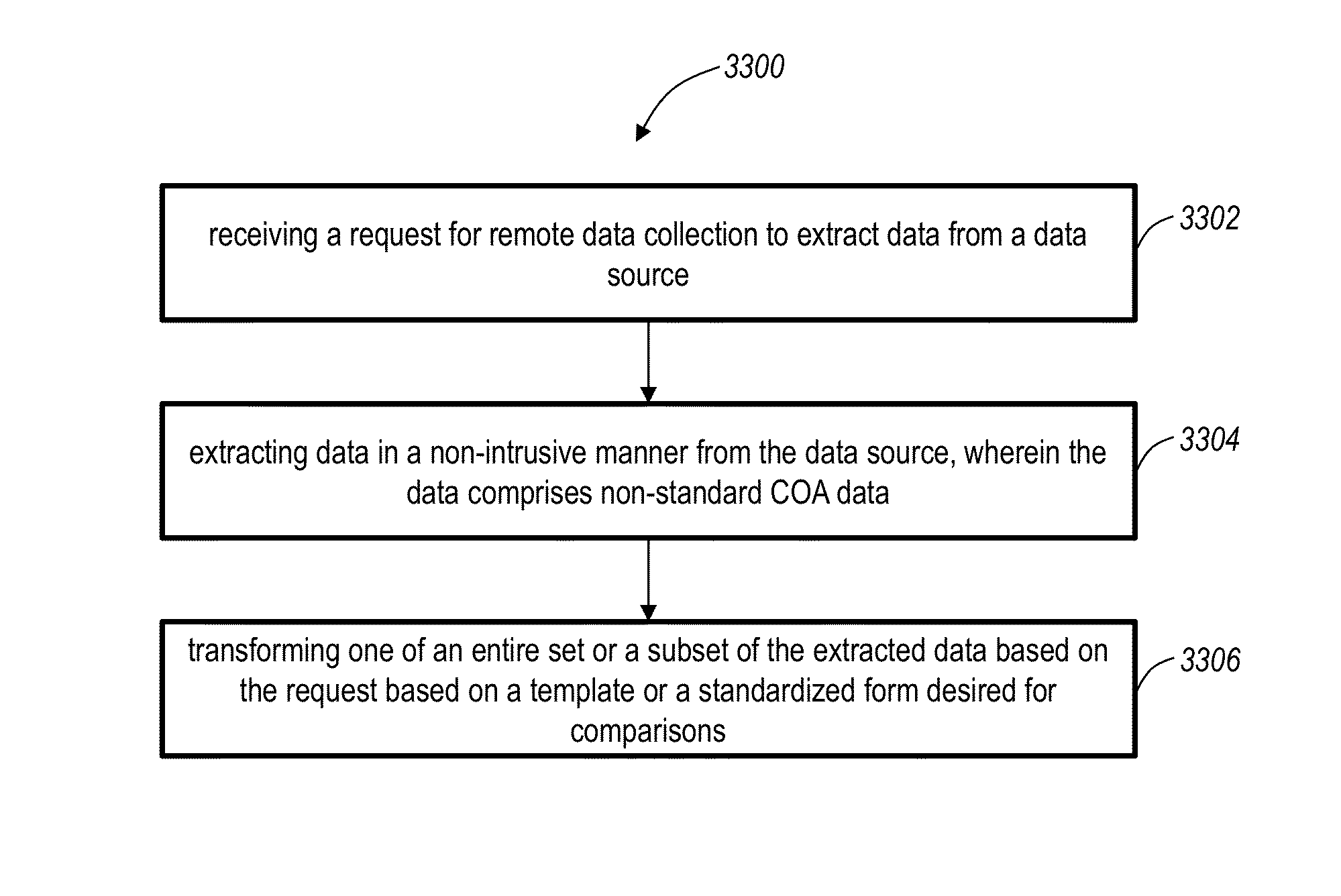
Remote data collection systems and methods retrieve data including financial, sales, marketing, operational and the like data from a plurality of databases and database types remotely over a network in an automated, platform-agnostic manner. An Extract Transform and Load (ETL) data replication method for Chart of Account (COA) standardization includes receiving a request for remote data collection to extract data from a data source; extracting data in a non-intrusive manner from the data source, wherein the data comprises non-standard COA data; and transforming one of an entire set or a subset of the extracted data based on the request based on a template or a standardized form desired for comparisons.
Owner:ZEEWISE
Graphene foam with three dimensional fully connected network and macroscopic quantity preparation method thereof
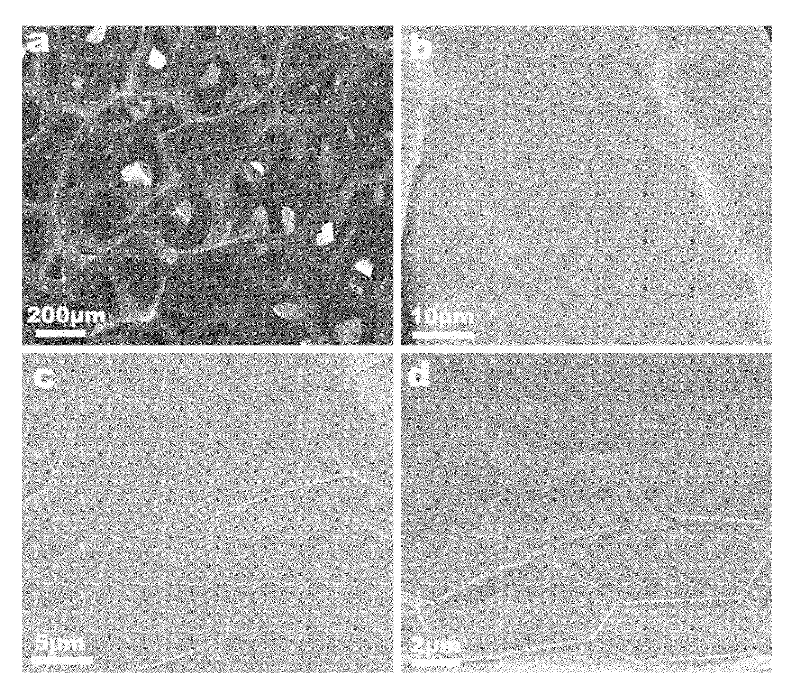
The invention relates to a graphene-based novel material and a chemical vapor deposition preparation technology thereof, in particular to graphene foam with a three dimensional fully connected network and a macroscopic quantity preparation method thereof. The method is suitable for a mass preparation of the graphene foam with high qualities. Three dimensional connected graphene can grow by catalytic cracking of carbon source gases on the surface of a three dimensional porous metal through the chemical vapor deposition technology, and a porous foam-shaped graphene three dimensional macroscopic body can be obtained after a porous metal base is removed by dissolving subsequently. According to the graphene foam with the three dimensional fully connected network and the macroscopic quantity preparation method thereof, a simple template replication method is used for preparing the three dimensional connected graphene macroscopic body, and the method has the advantages that the operation is simple and convenient, the rate of production is high, and the adjustment and control of the structure are easy. The graphene foam forms the fully connected network in a seamless connection mode, has a low density, a high porosity and specific surface area and excellent capabilities of charge conduction and heat conduction and establishes a foundation for applications of graphene in fields of electric conduction, thermally conductive composite materials, electromagnetic shielding, wave absorbing, catalysis, sensing and energy storage materials and the like.
Owner:INST OF METAL RESEARCH - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
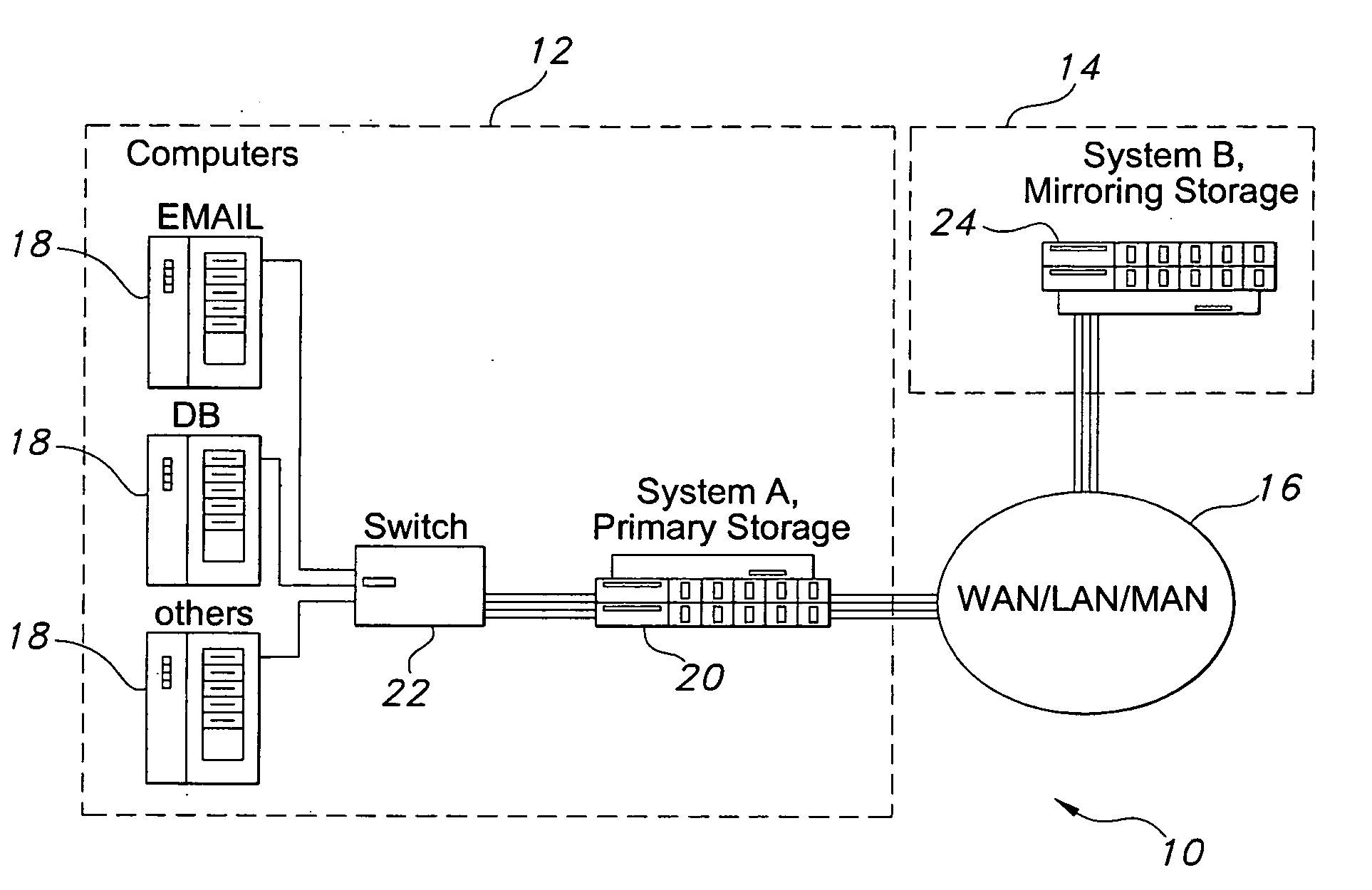
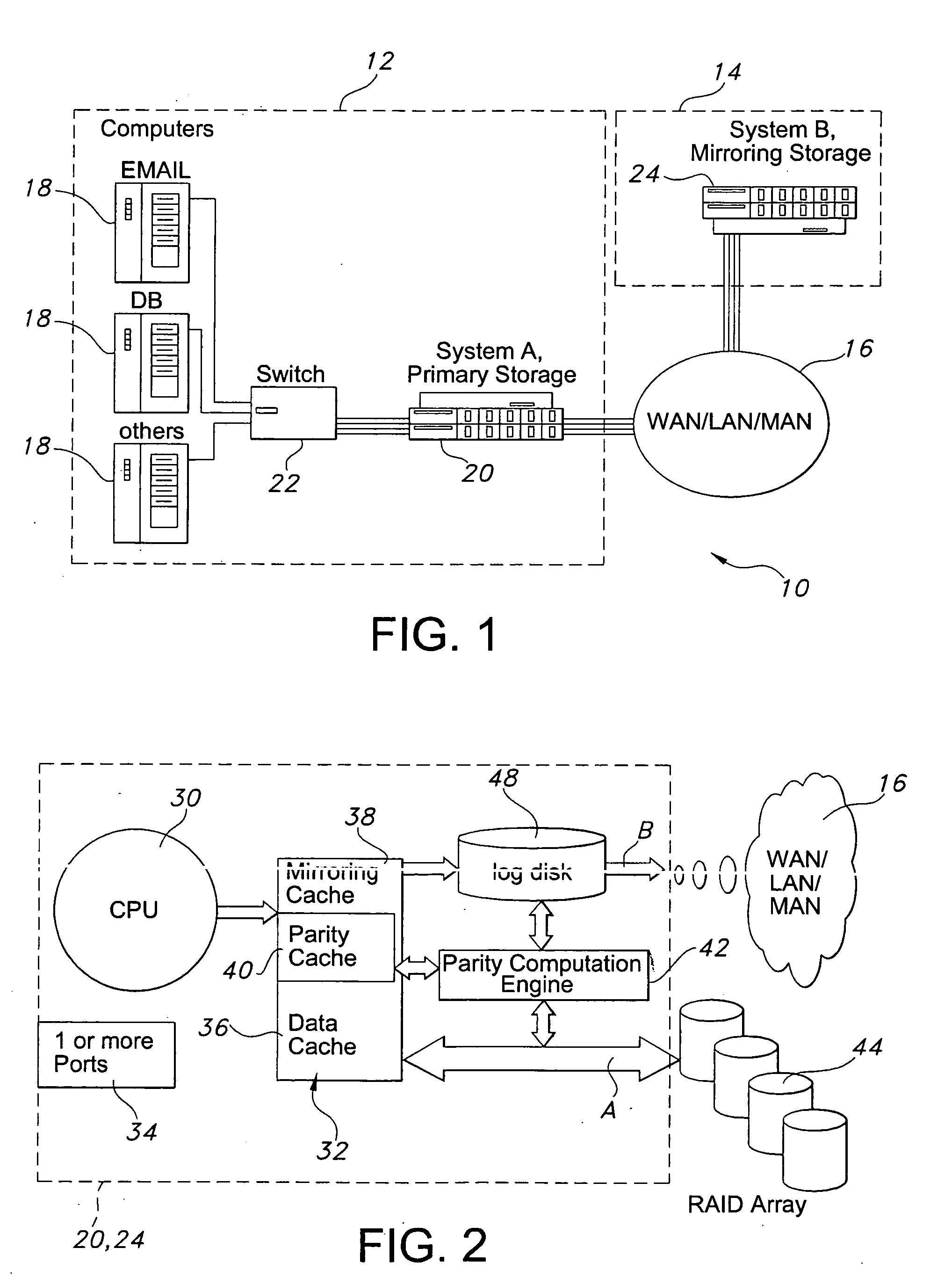
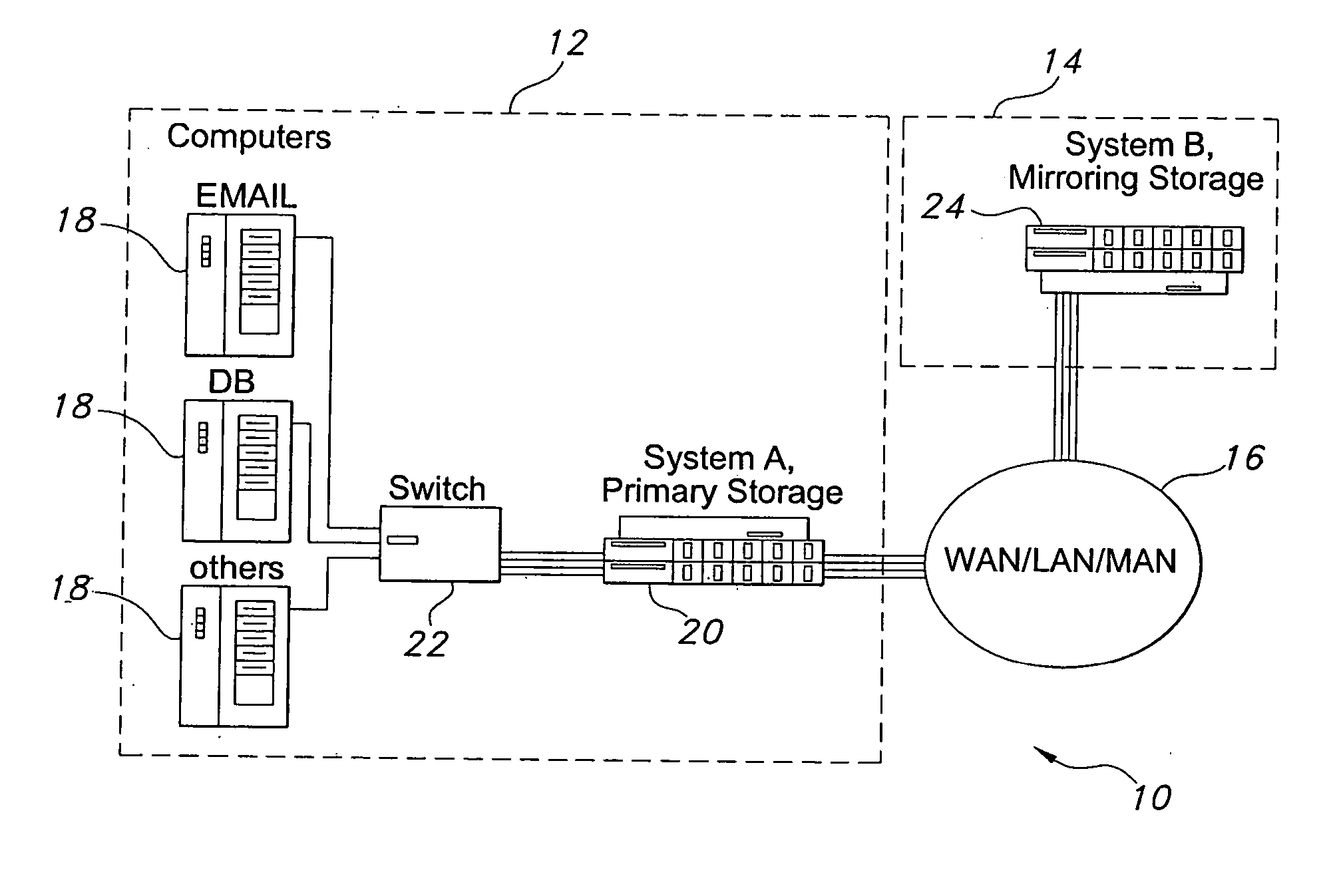
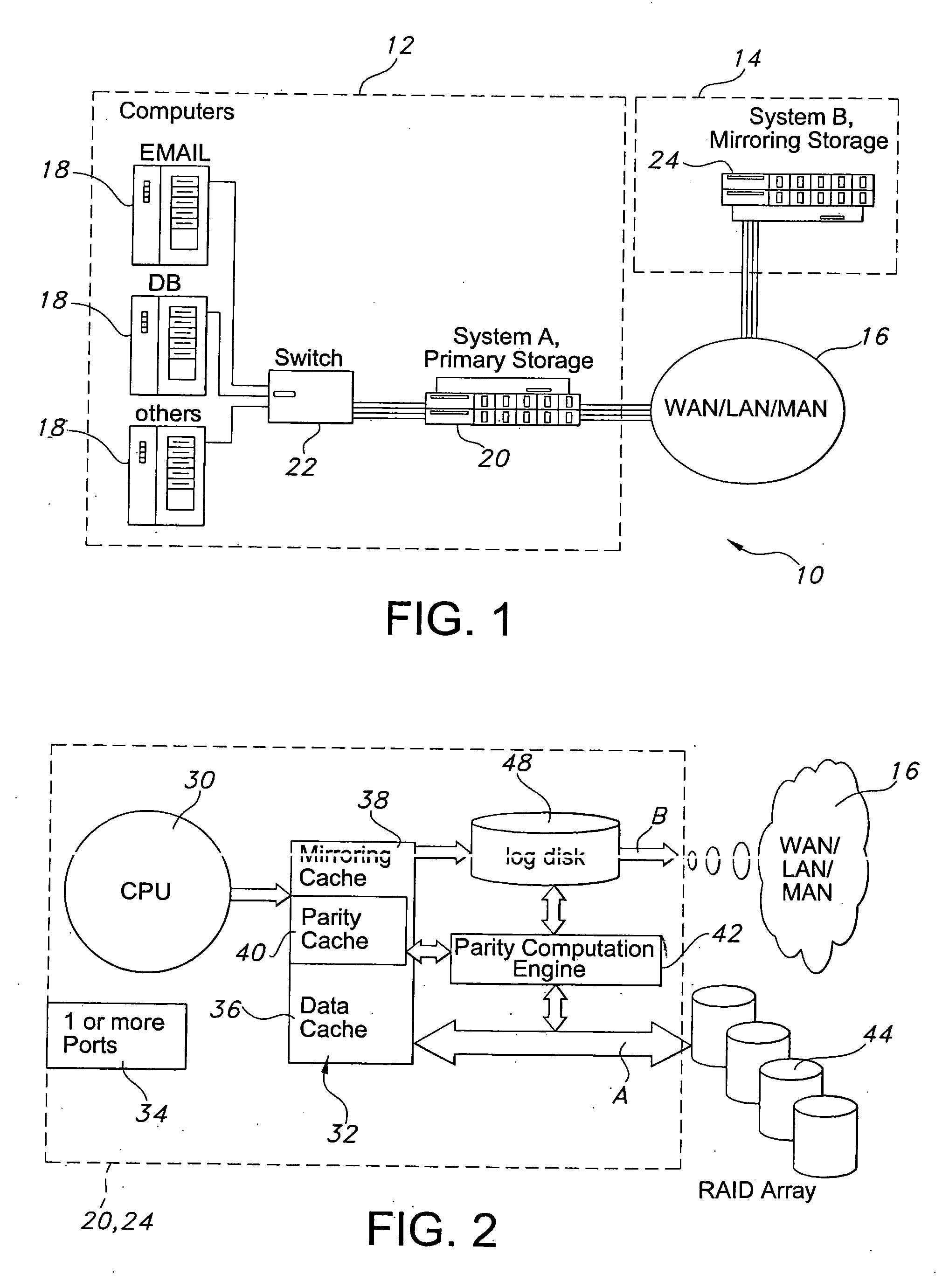
Data replication method over a limited bandwidth network by mirroring parities
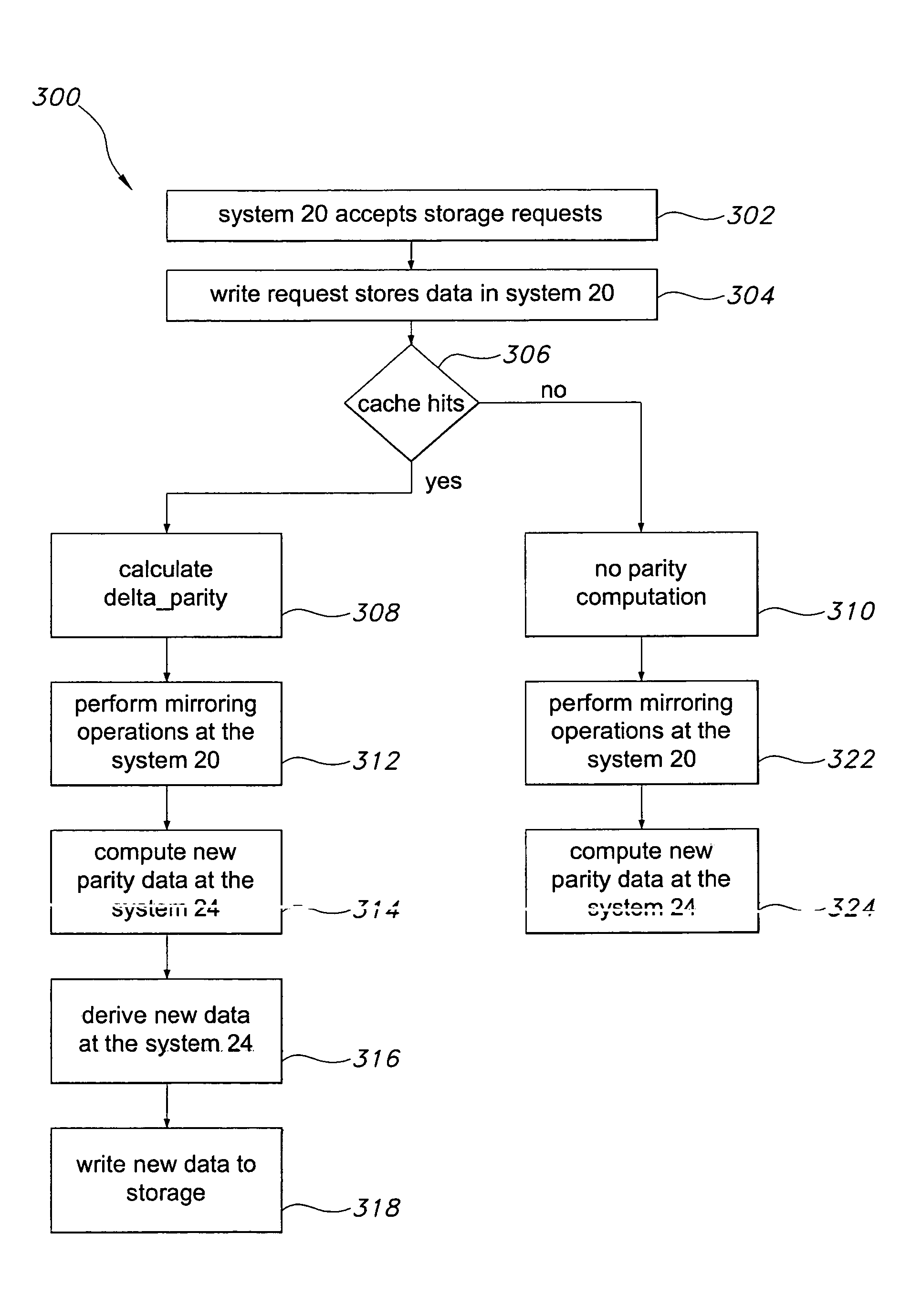
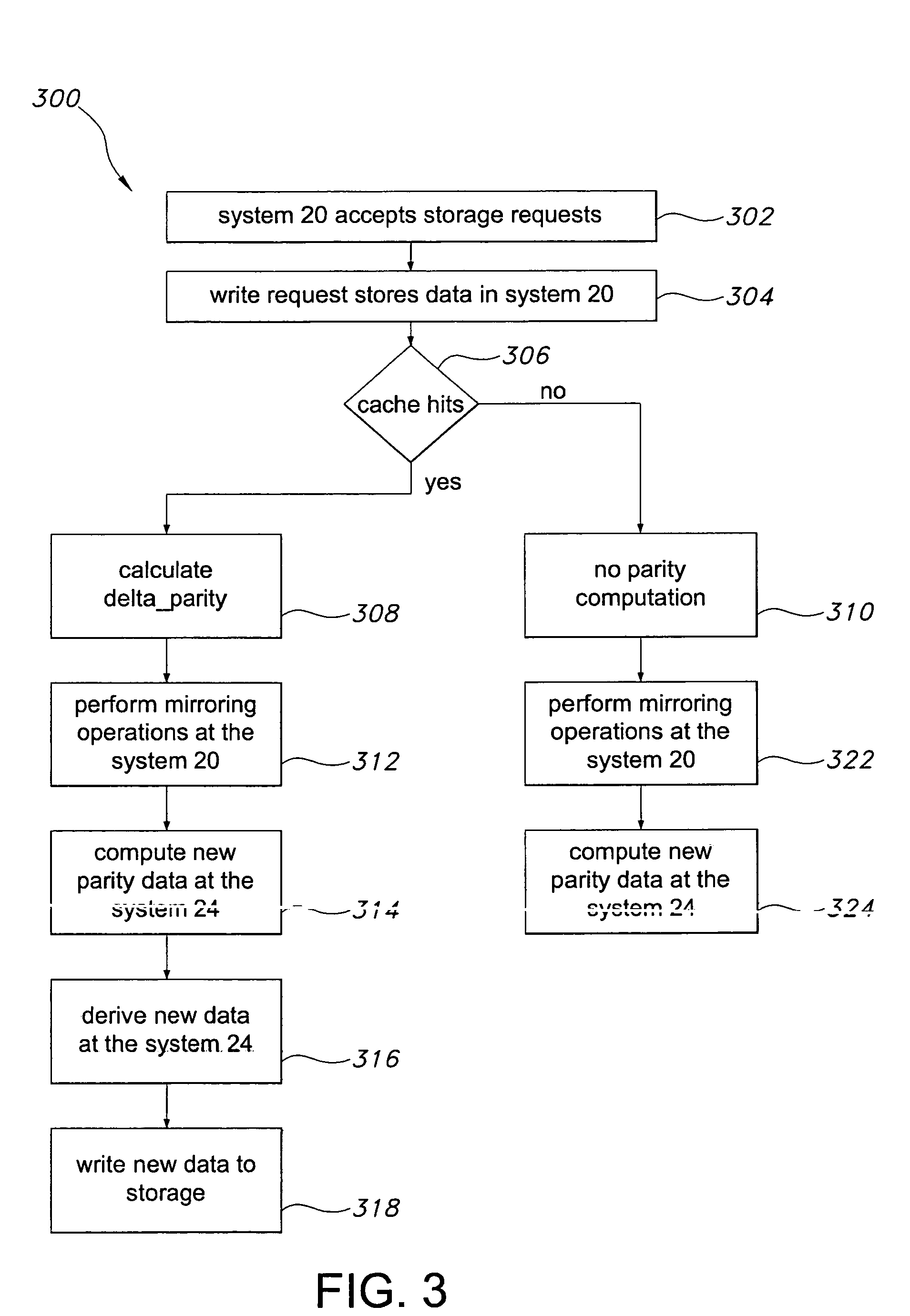
A method dramatically reduces the amount of data to be stored and transferred in a networked storage system. Preferably, the network storage system provides continued data protection through mirroring / replication, disk-to-disk backup, data archiving for future retrieval, and Information Lifecycle management (ILM). The idea is to leverage the parity computation that exists in RAID systems. By caching, transferring, and storing data parity or delta bytes of changes on a block as opposed to data block itself, substantial data reduction is possible without using sophisticated compression algorithms at the production side to minimize performance impacts upon production servers. Data can be computed using the parity / delta and previously existing data at mirror side, replication side, backup storage, or at retrieval time upon events such as failures or ILM operations.
Owner:ZOLL CIRCULATION +1
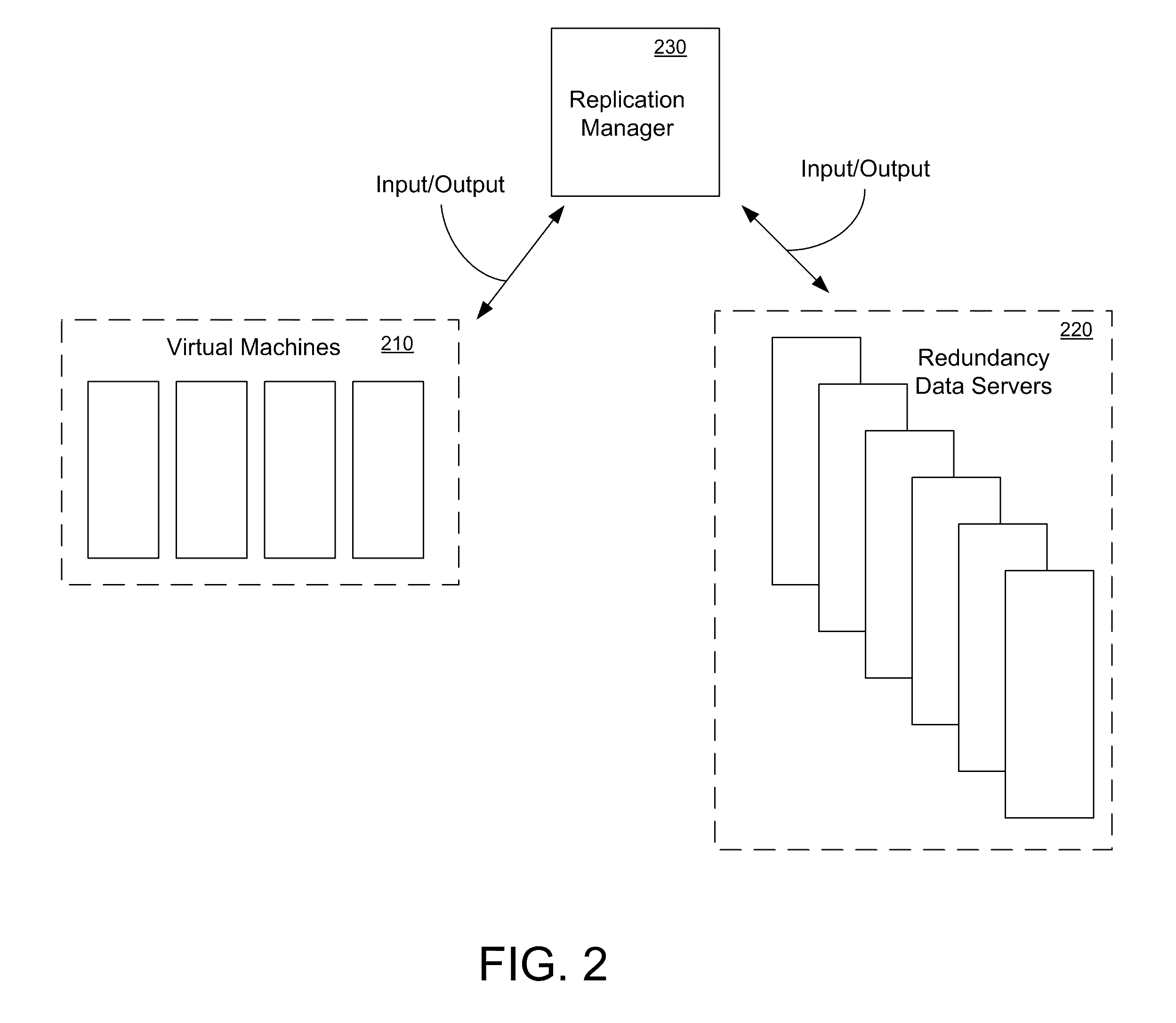
Virtual machine aware replication method and system
ActiveUS20120016840A1Efficient and highly available and highly scalable processEfficient, highly available, and highly scalableDigital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsVirtual file systemReplication method
A method for replicating a virtual file system of a virtual machine. The method includes accessing a host file system usage map of a host machine that indicates active blocks out of a plurality of blocks of the host file system, and accessing a virtual file system usage map of a virtual machine that indicates active blocks out of a plurality of blocks of the virtual file system. A merged usage map is generated from information of the host file system usage map and the virtual file system usage map that identifies active blocks of the host file system associated with the virtual file system. The virtual file system is then replicated at a replication destination in accordance with the merged usage map.
Owner:VERITAS TECH
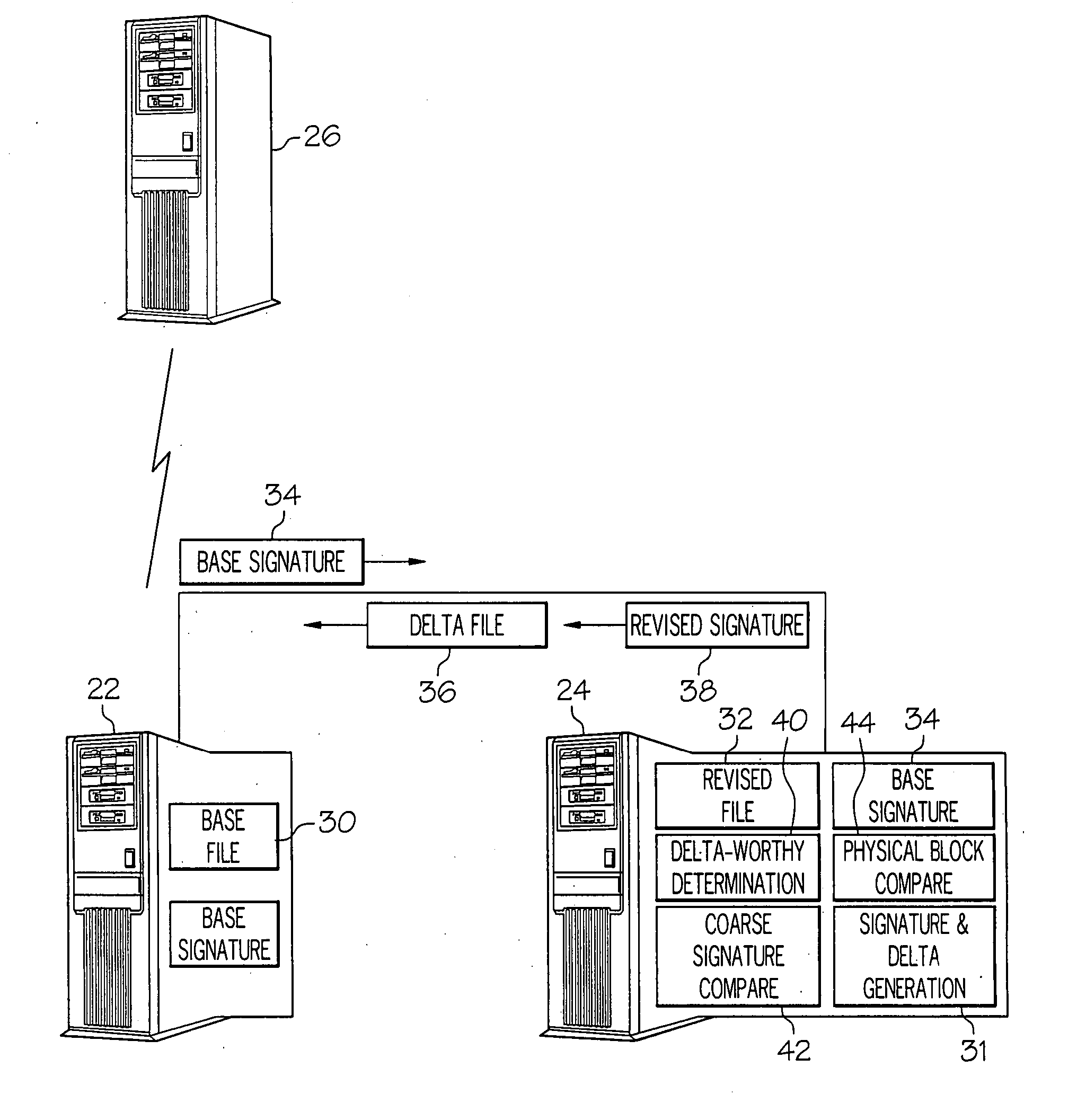
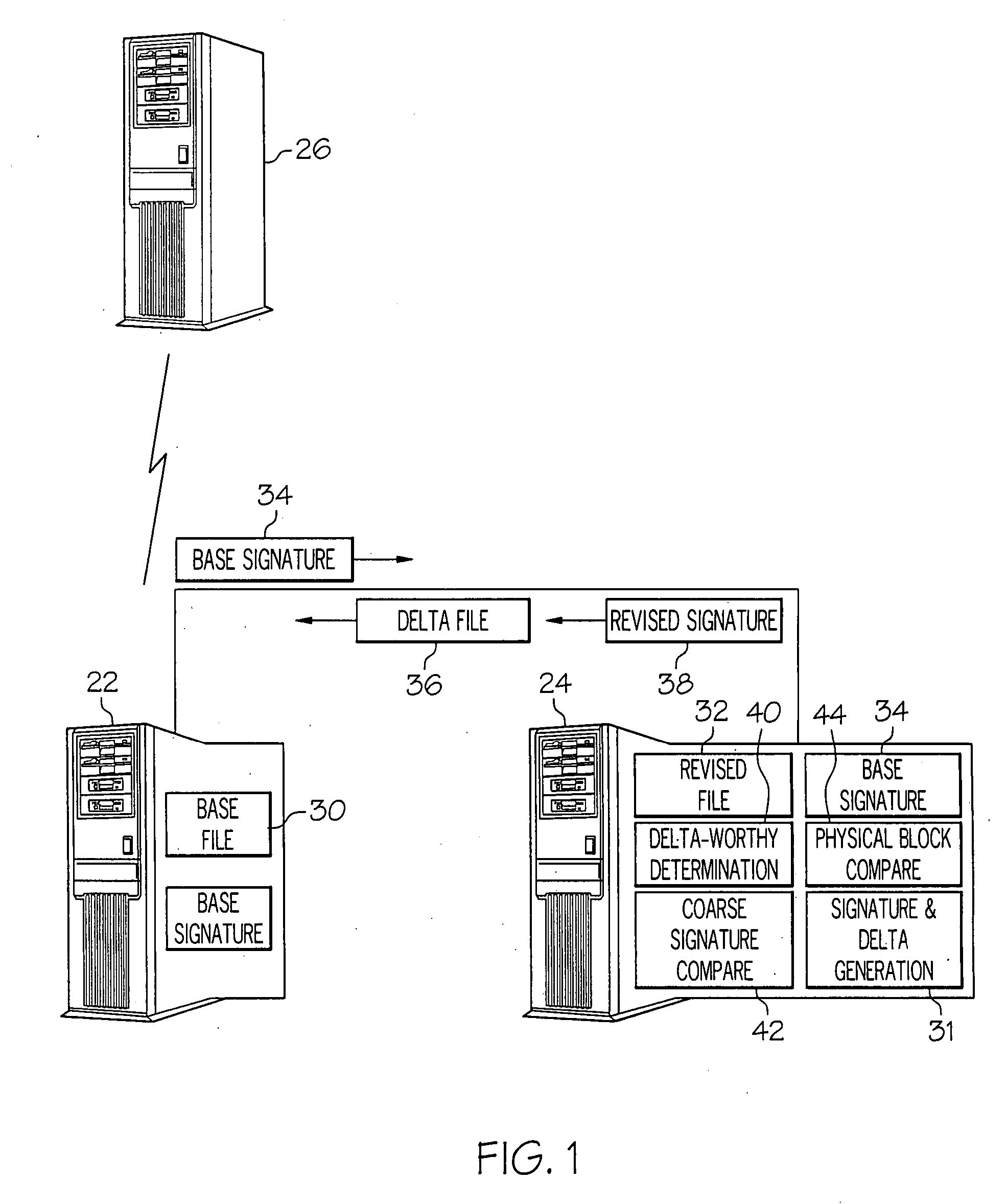
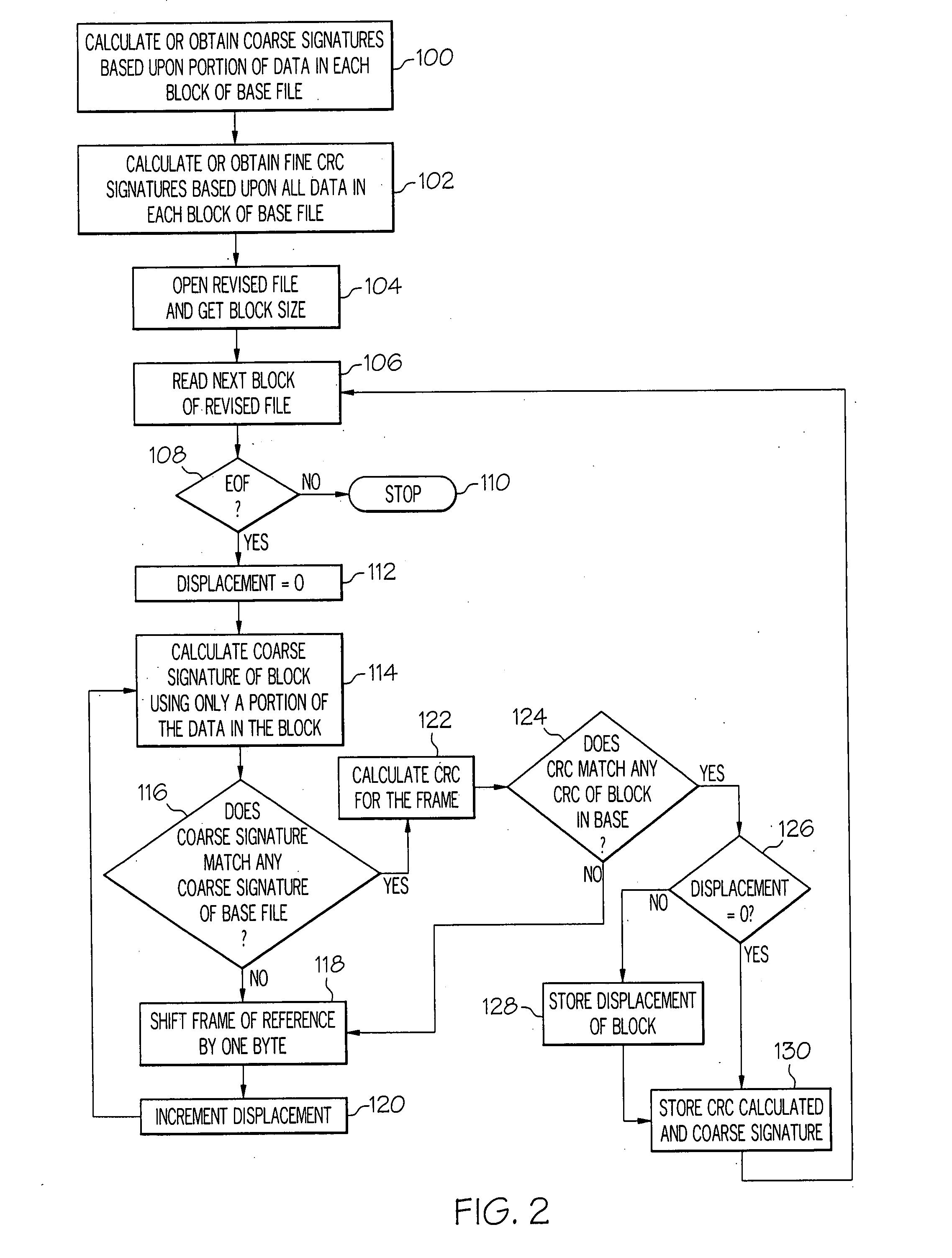
Methods and systems for file replication utilizing differences between versions of files
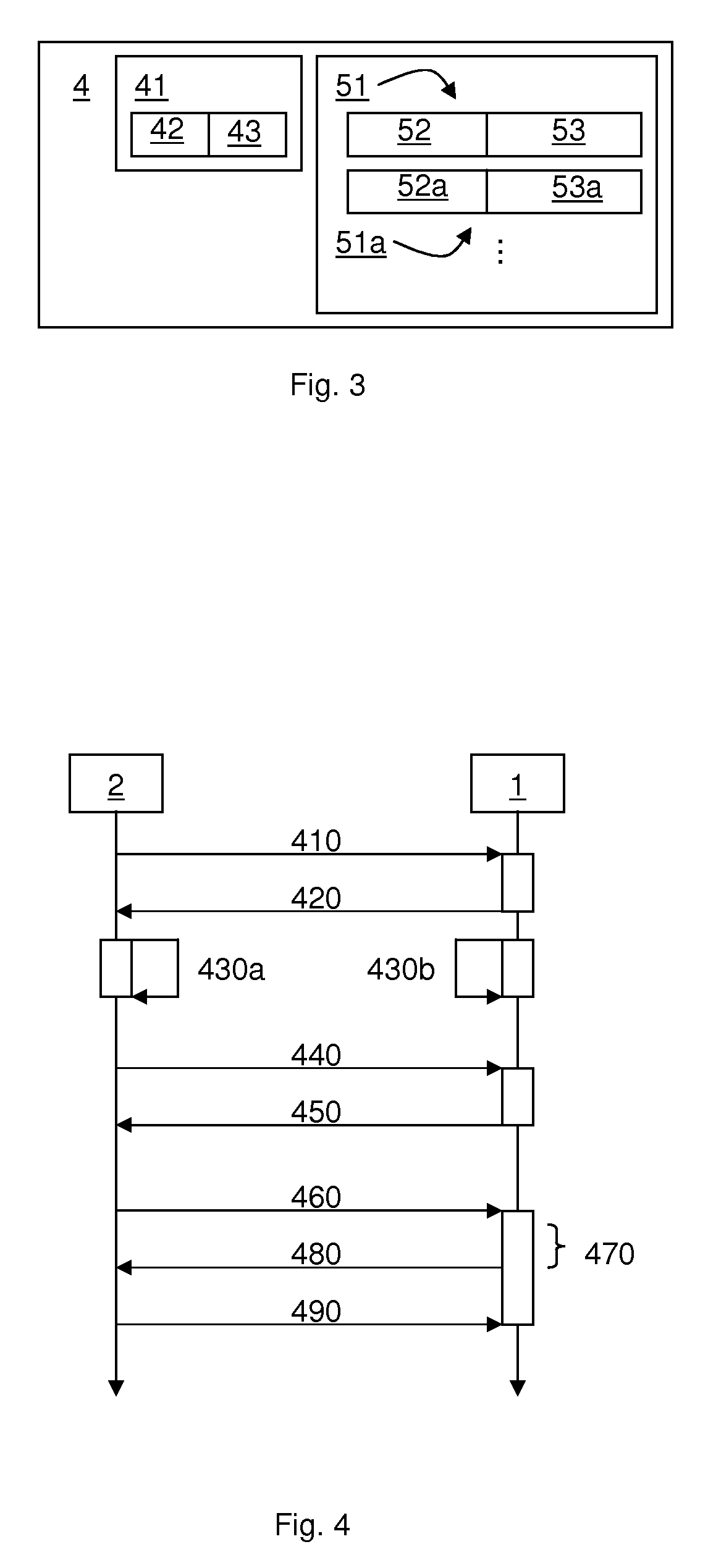
ActiveUS20070288533A1Block completeData processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsFile replicationComputer hardware
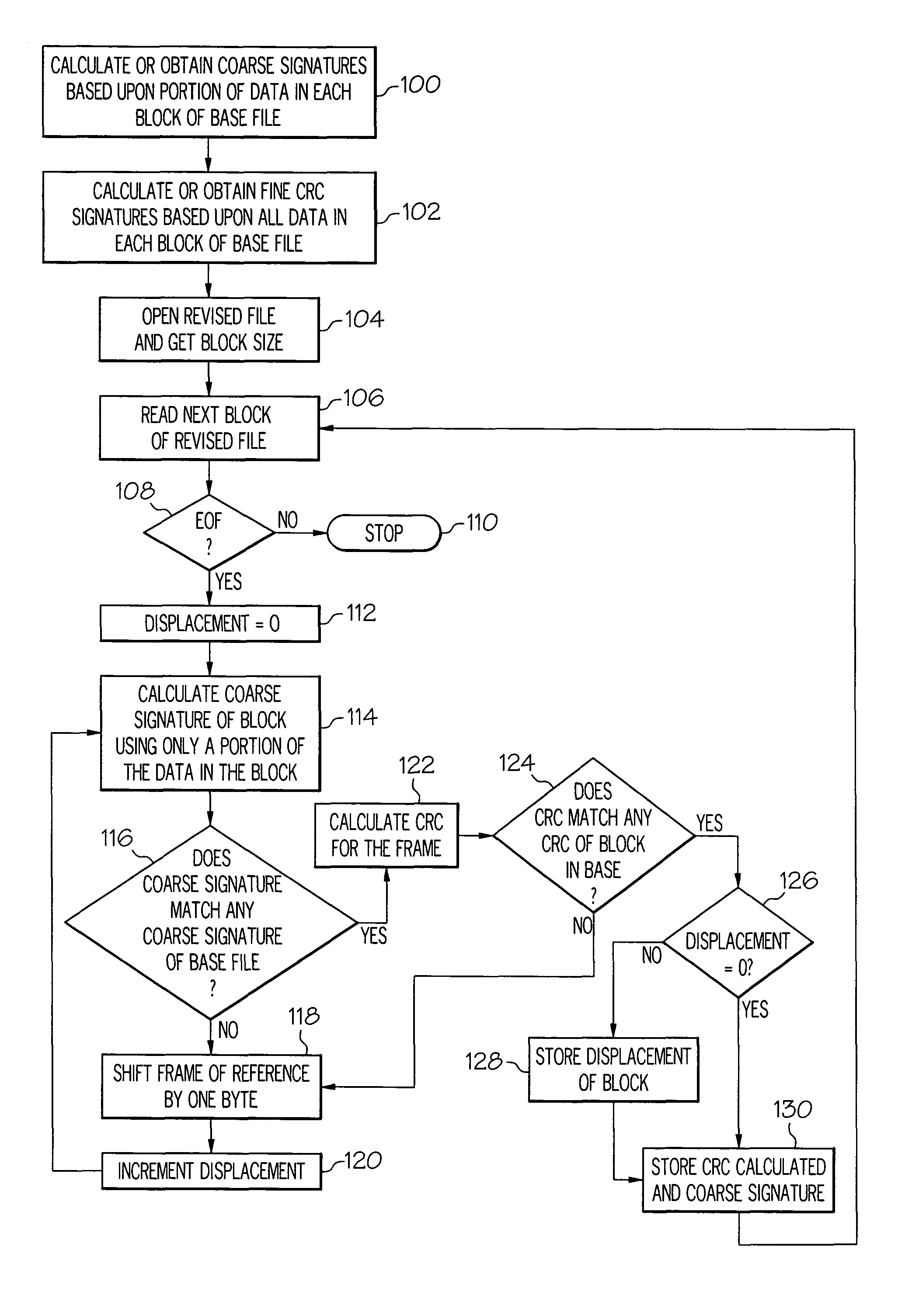
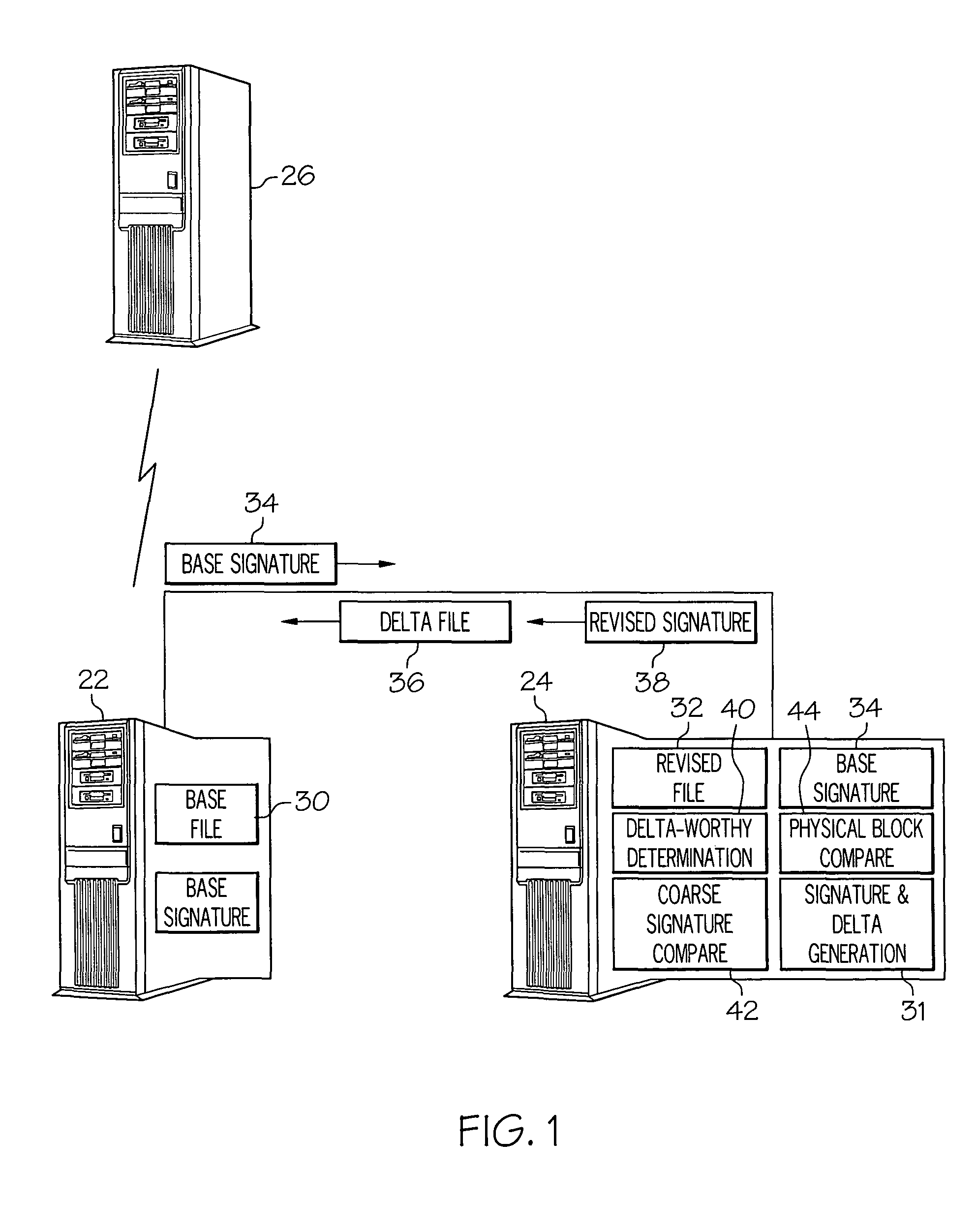
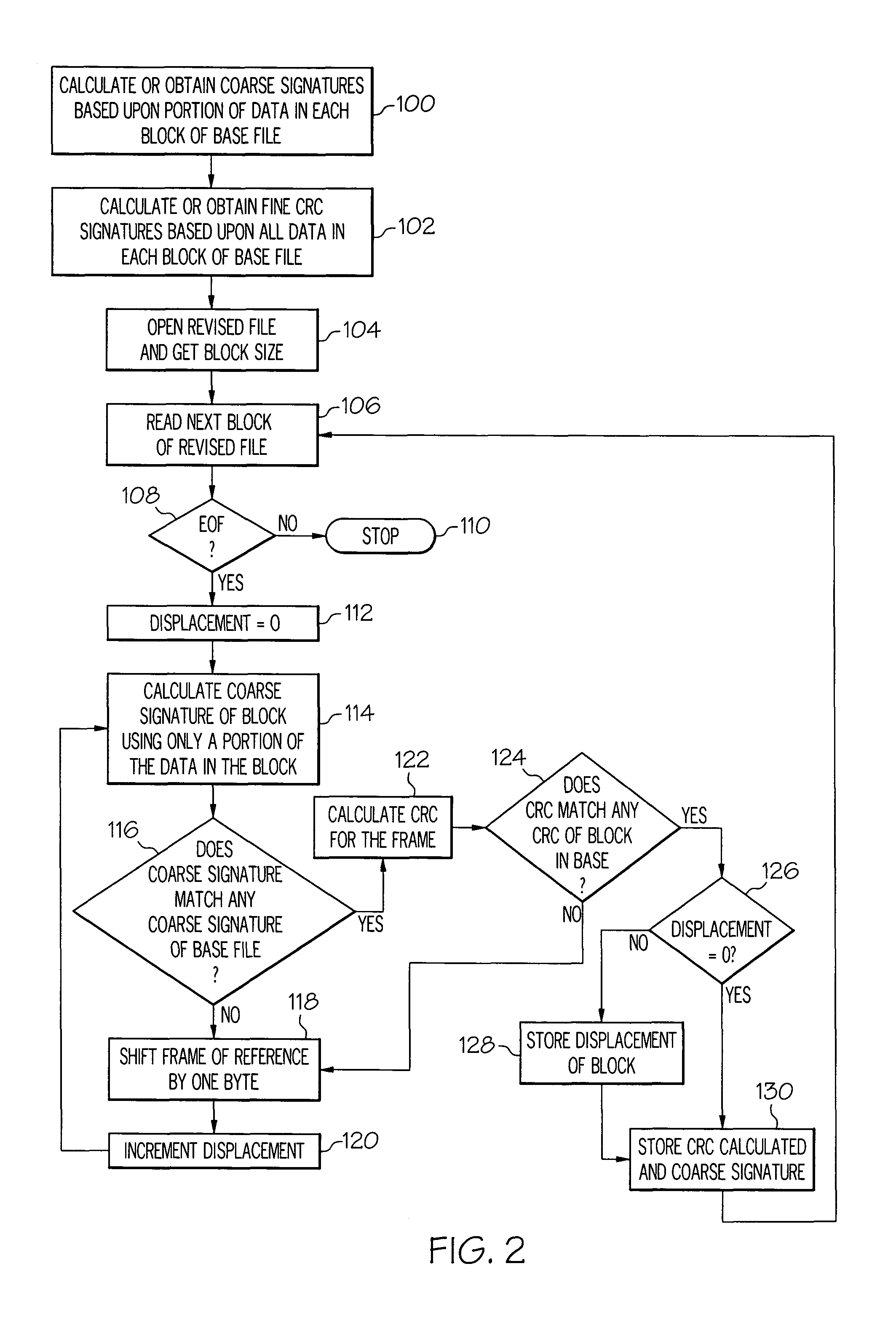
Methods and systems for efficient file replication are provided. In some embodiments, one or more coarse signatures for blocks in a base file are compared with those coarse signatures for blocks of a revised file, until a match is found. A fine signature is then generated for the matching block of the revised file and compared to a fine signature of the base file. Thus, fine signatures are not computed unless a coarse signature match has been found, thereby minimizing unneeded time-consuming fine signature calculations. Methods are also provided for determining whether to initiate a delta file generation algorithm, or whether to utilize a more efficient replication method, based upon system and / or file parameters. In accordance with additional embodiments, the lengths of valid data on physical blocks are obtained from physical block mappings for the files, and these lengths and mappings are utilized for delta file generation, to minimize unnecessary signature computations.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
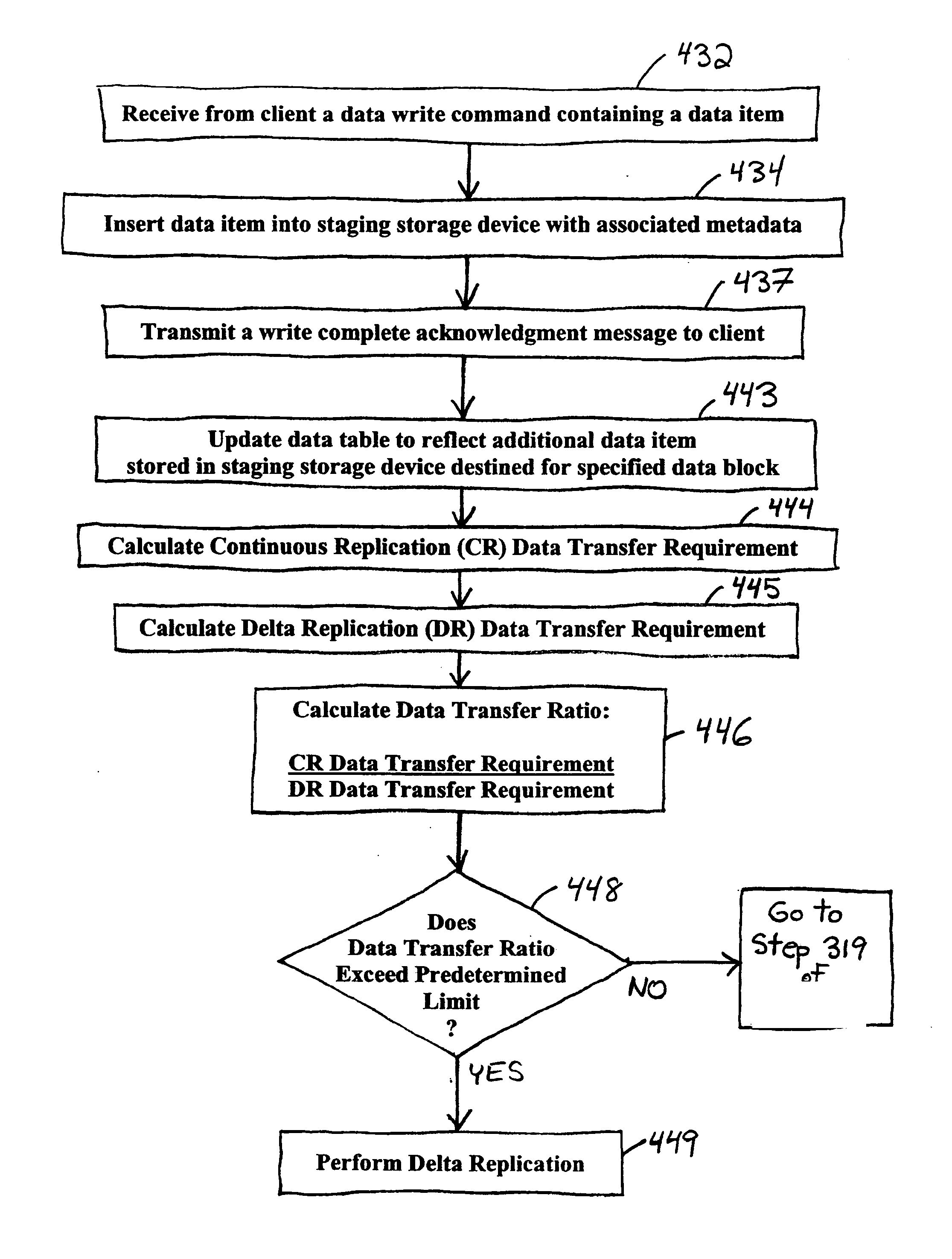
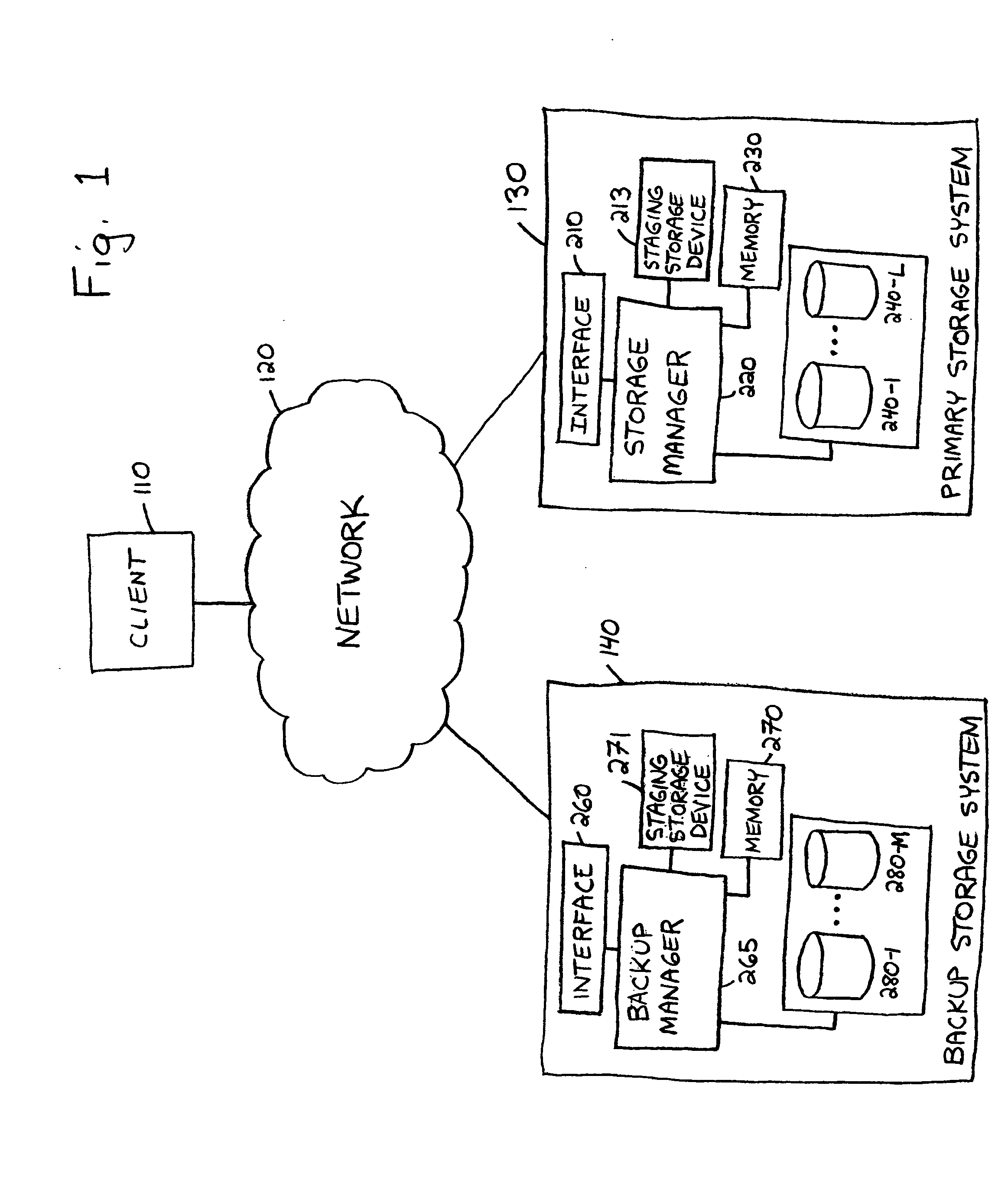
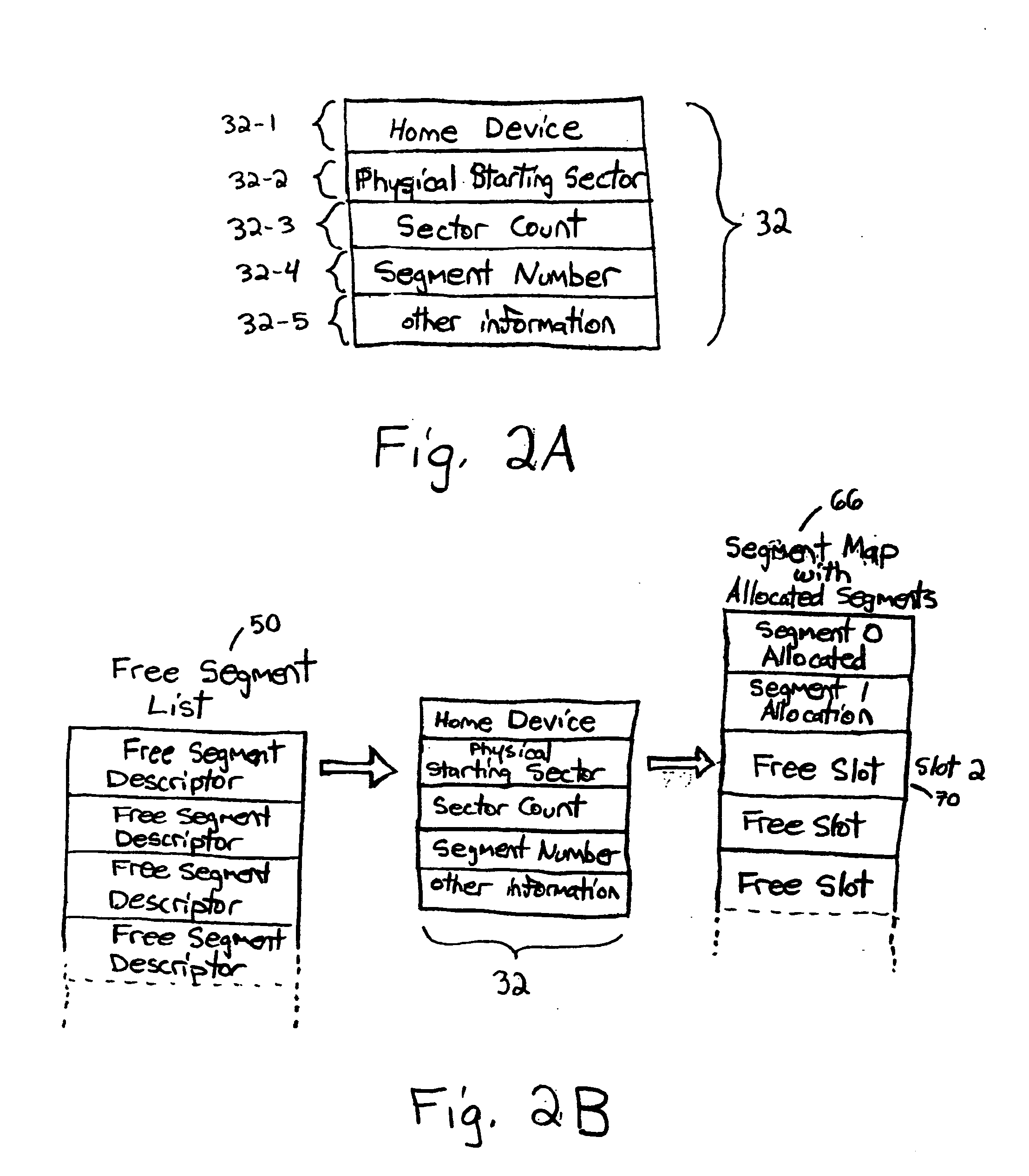
Method and system for storing data
ActiveUS20050172092A1Level of redundancyData processing applicationsDigital computer detailsReplication methodOperation mode
Data is stored by utilizing a first operating mode and a second operating mode. In one embodiment, in the first operating mode, a continuous replication method is utilized to store data on a primary storage system and to generate a backup version of the data on a backup storage system. While data is being stored in accordance with the first operating mode, one or more activities performed by the data storage system(s) are monitored. As long as the monitored activity or activities display a first status, the first operating mode is maintained. If the monitored activity or activities display a change in status, the first operating mode is suspended, and data is stored pursuant to the second operating mode. In one embodiment, in the second operating mode, a delta replication method is utilized to store data on the primary storage system and to back up the data on the backup storage system.
Owner:FALCONSTOR
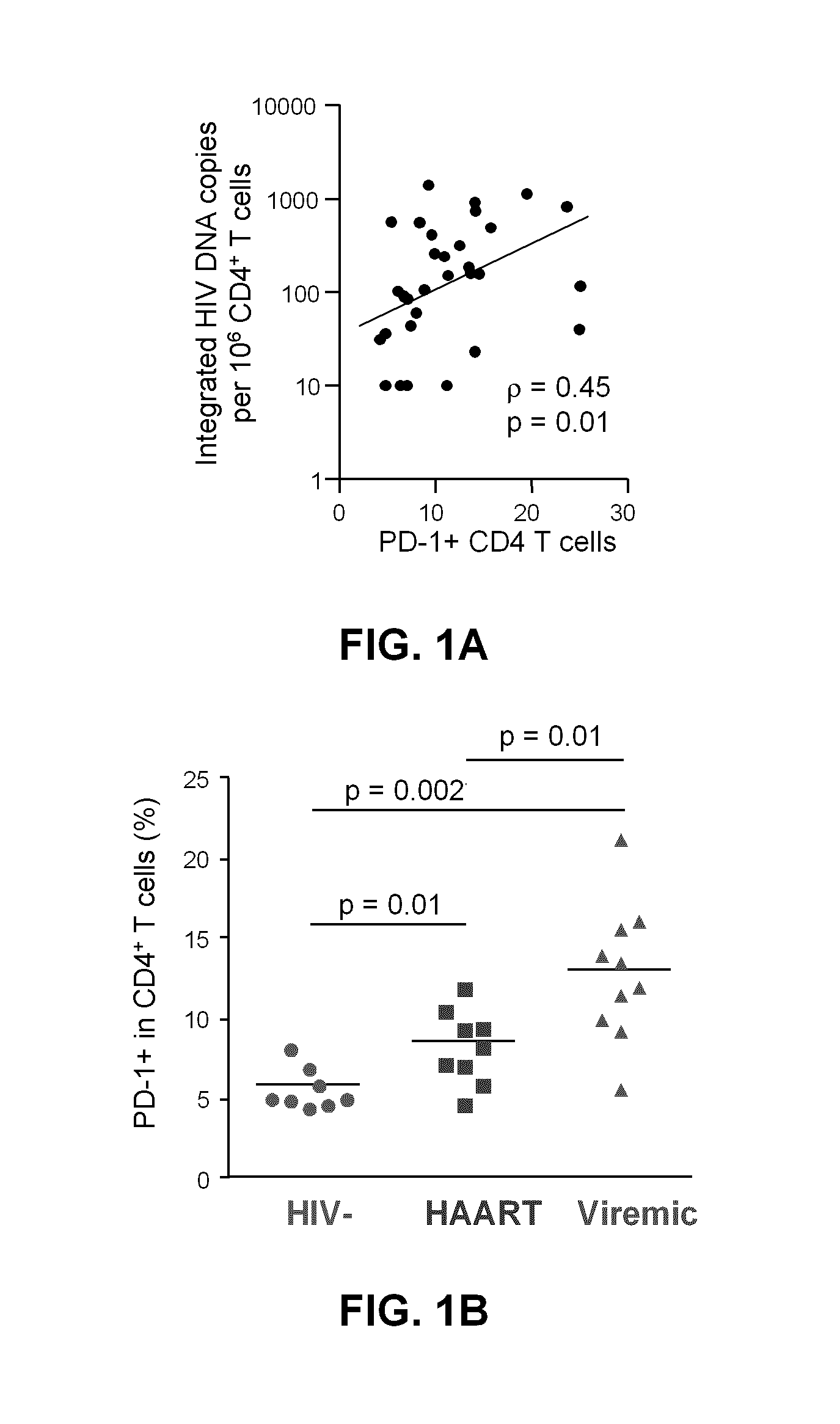
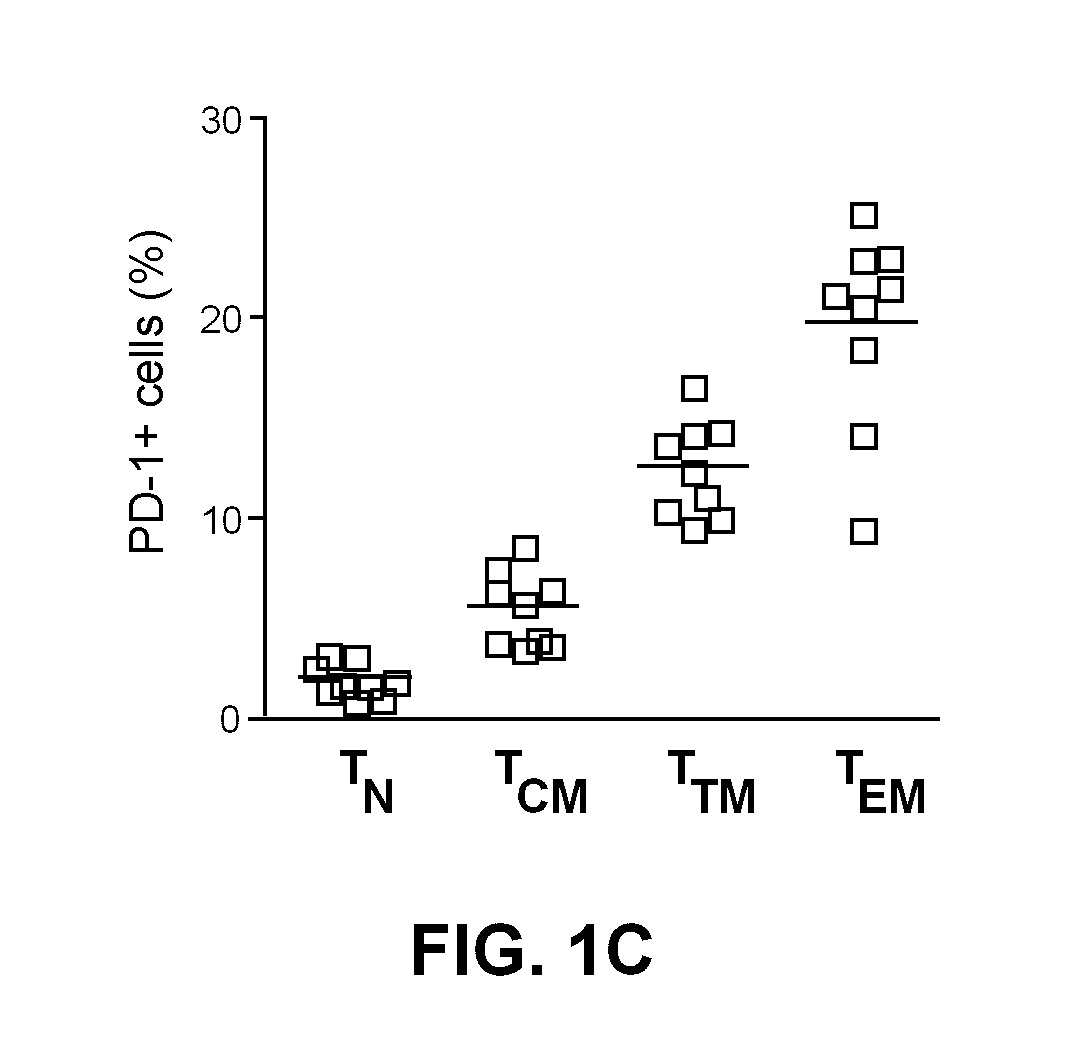
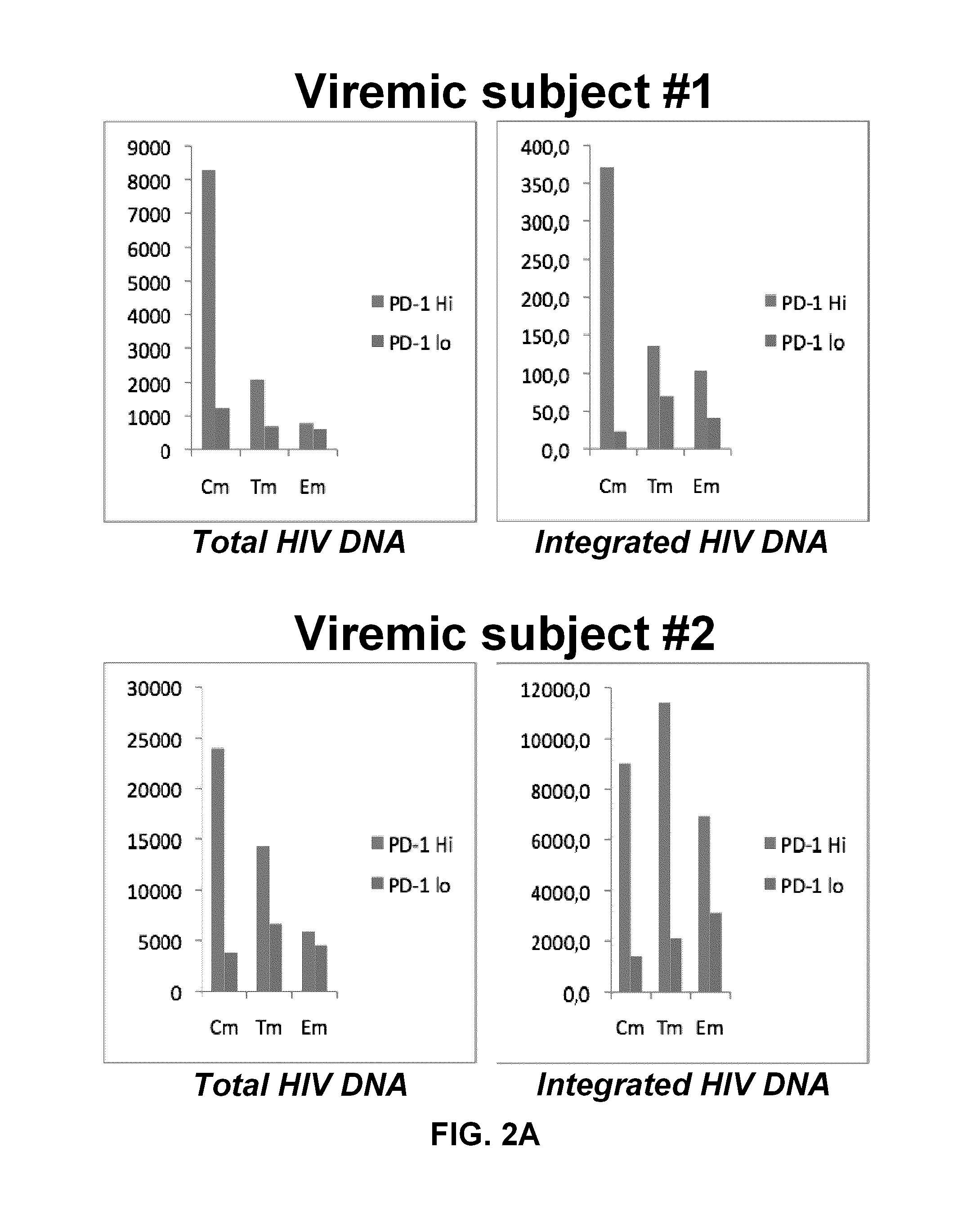
Pd-1 modulation and uses thereof for modulating HIV replication
InactiveUS20130202623A1Reduce in quantityPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsReplication methodHuman immunodeficiency virus (HIV)
Owner:OREGON HEALTH & SCI UNIV
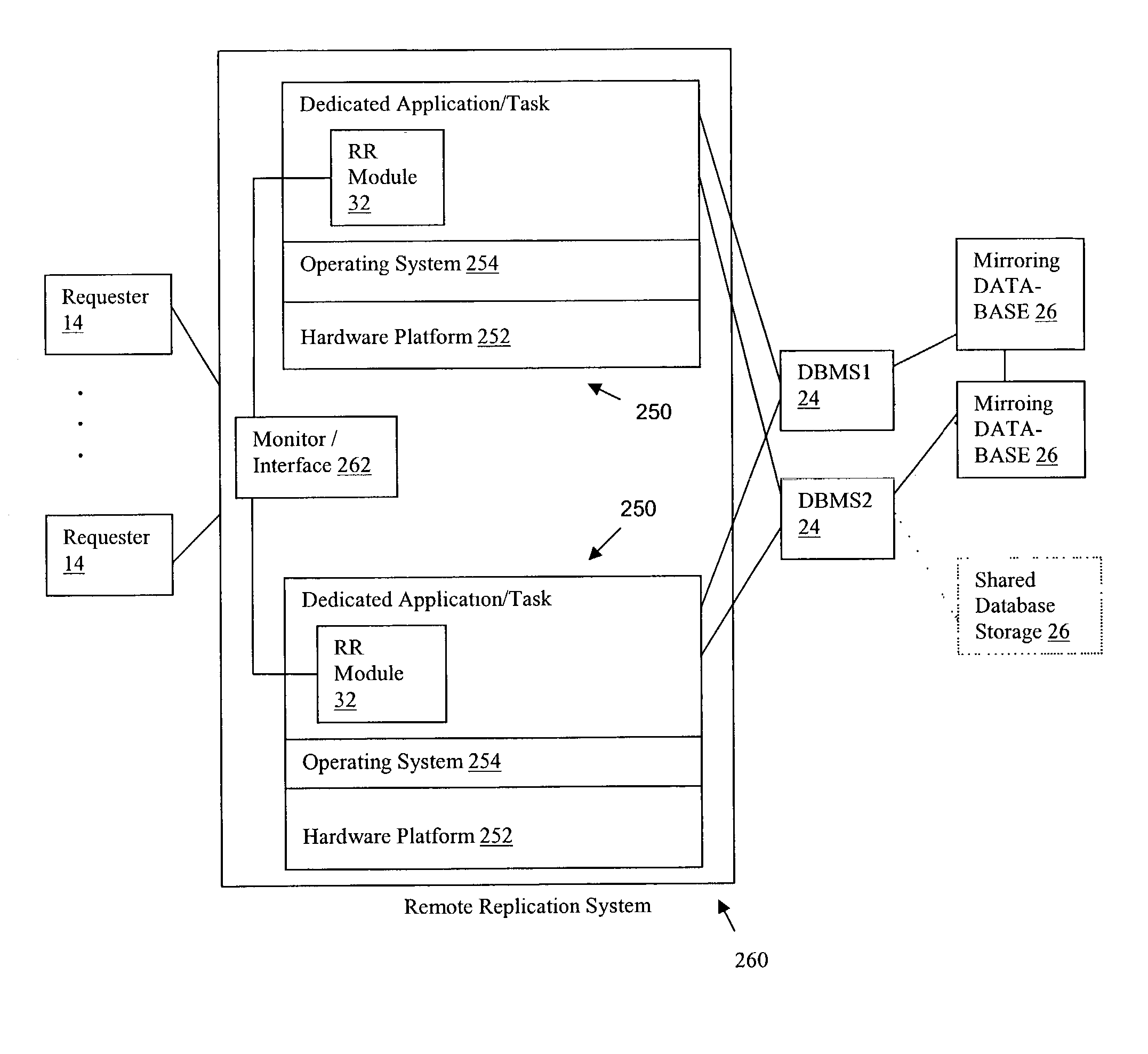
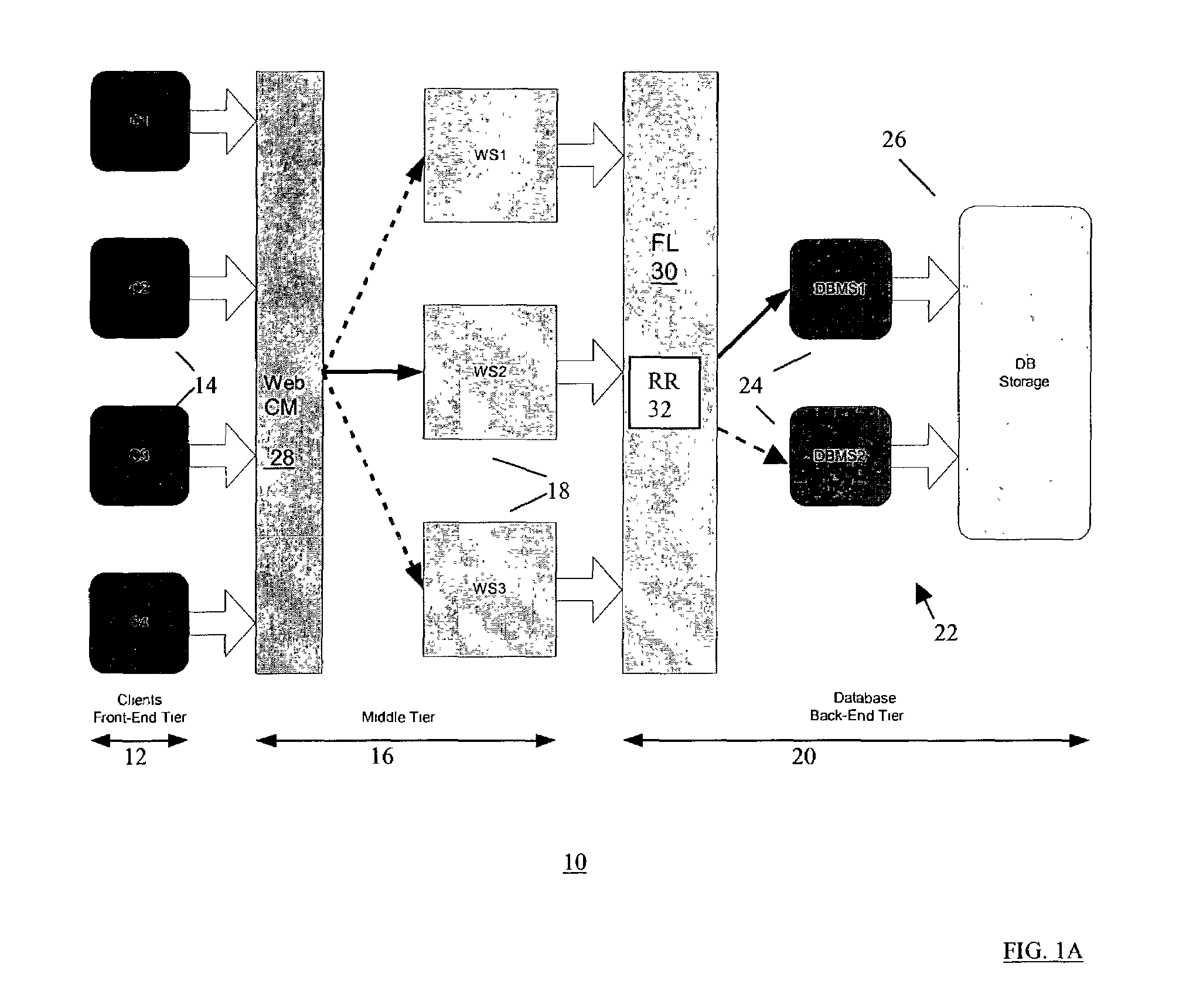
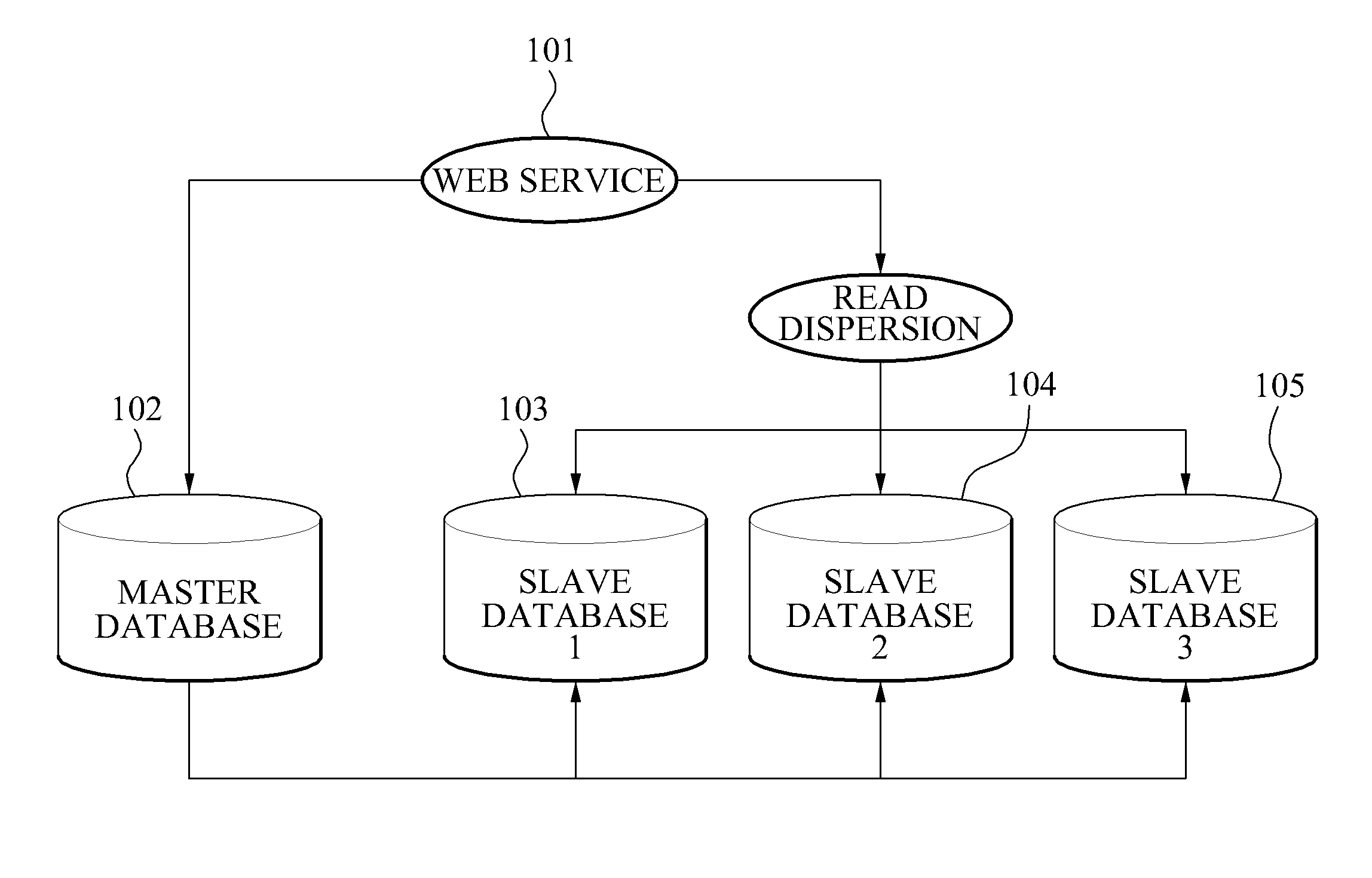
Database remote replication for back-end tier of multi-tier computer systems
InactiveUS7370064B2Reduce disadvantagesMaximize server efficiencyDigital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsReplication methodDatabase server
A replication method and system for a computer system having multiple database servers for at least one database, wherein database servers are provided with a unified view of the data content. The method includes the steps of establishing connections to said multiple database servers for communicating with said database servers; distinguishing between read and update query requests; and assigning queries to respective ones of said multiple database servers to preserve the consistency of the respective unified view of data of said multiple database servers in case of receiving update queries. Assigning each new query includes the steps of distinguishing between read and update queries, determining possible assignments of that new query to one or more of said multiple database servers, each said possible update query assignment to one of said multiple database servers being based on a transaction-based replication scheme to preserve the unified view data of said multiple database servers; and assigning that new query to one of said multiple database servers as a function of said possible assignments of that new query, to preserve respective unified view of data of said multiple database servers.
Owner:YOUSEFIZADEH HOMAYOUN
Data replication method over a limited bandwidth network by mirroring parities
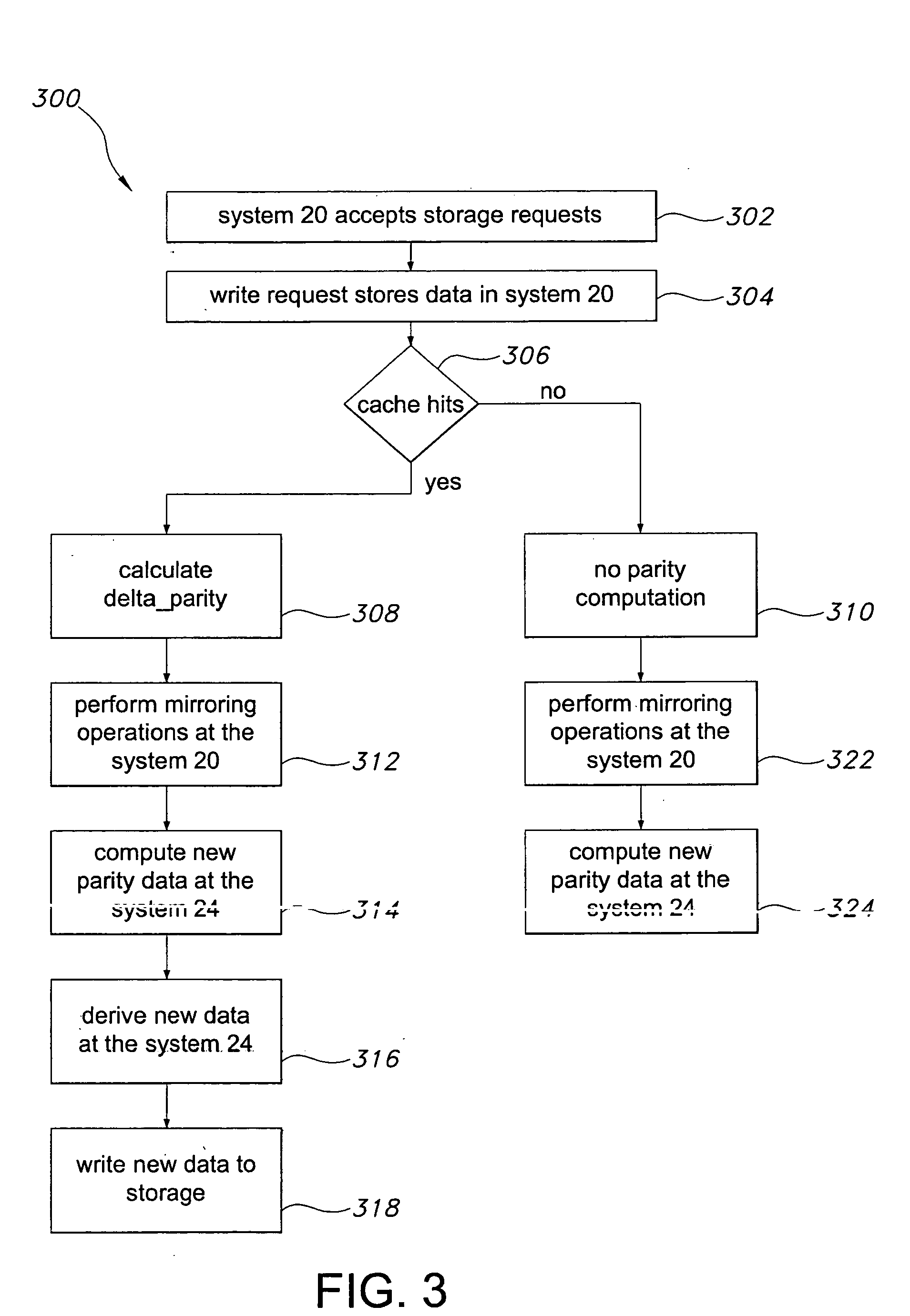
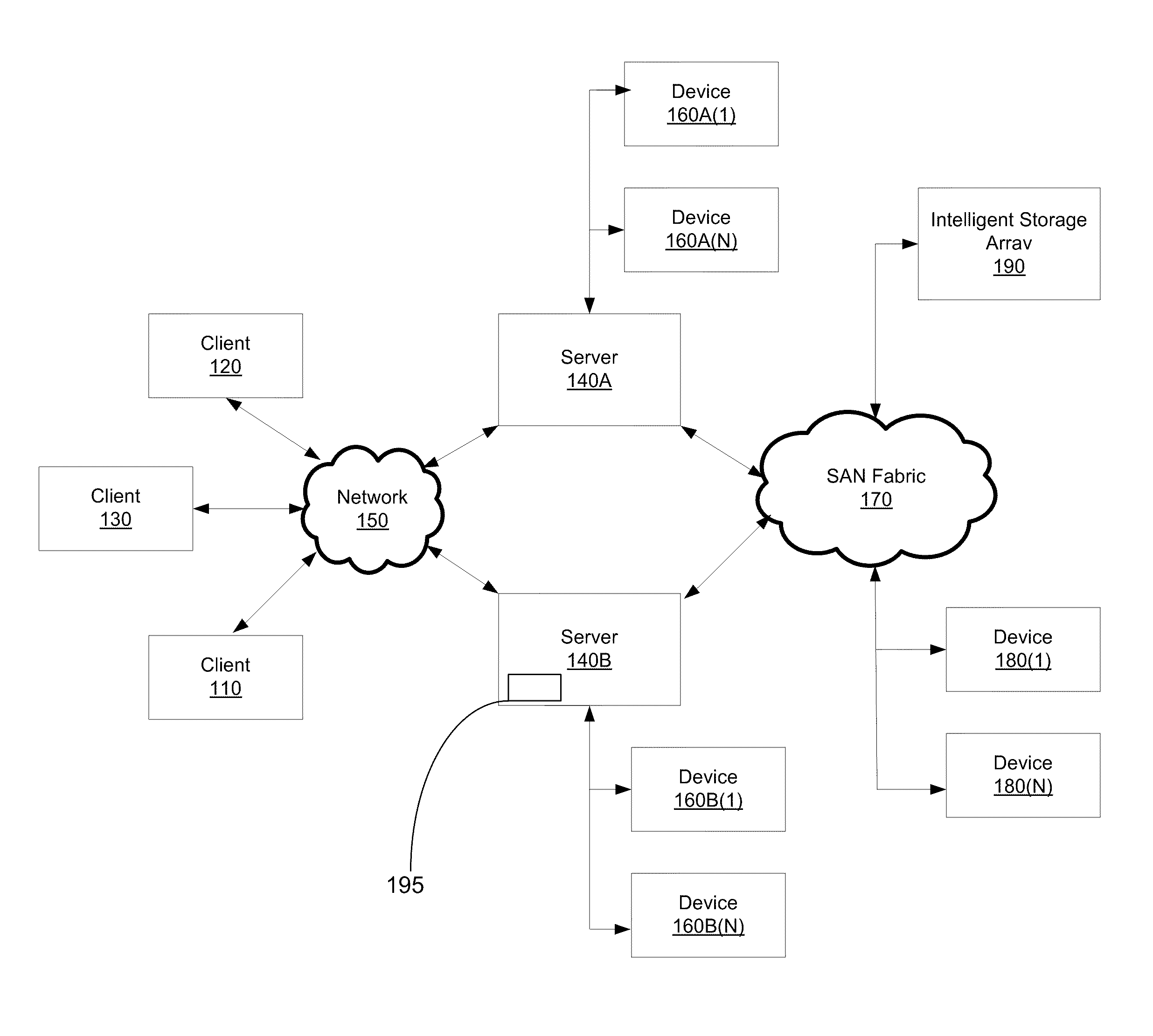
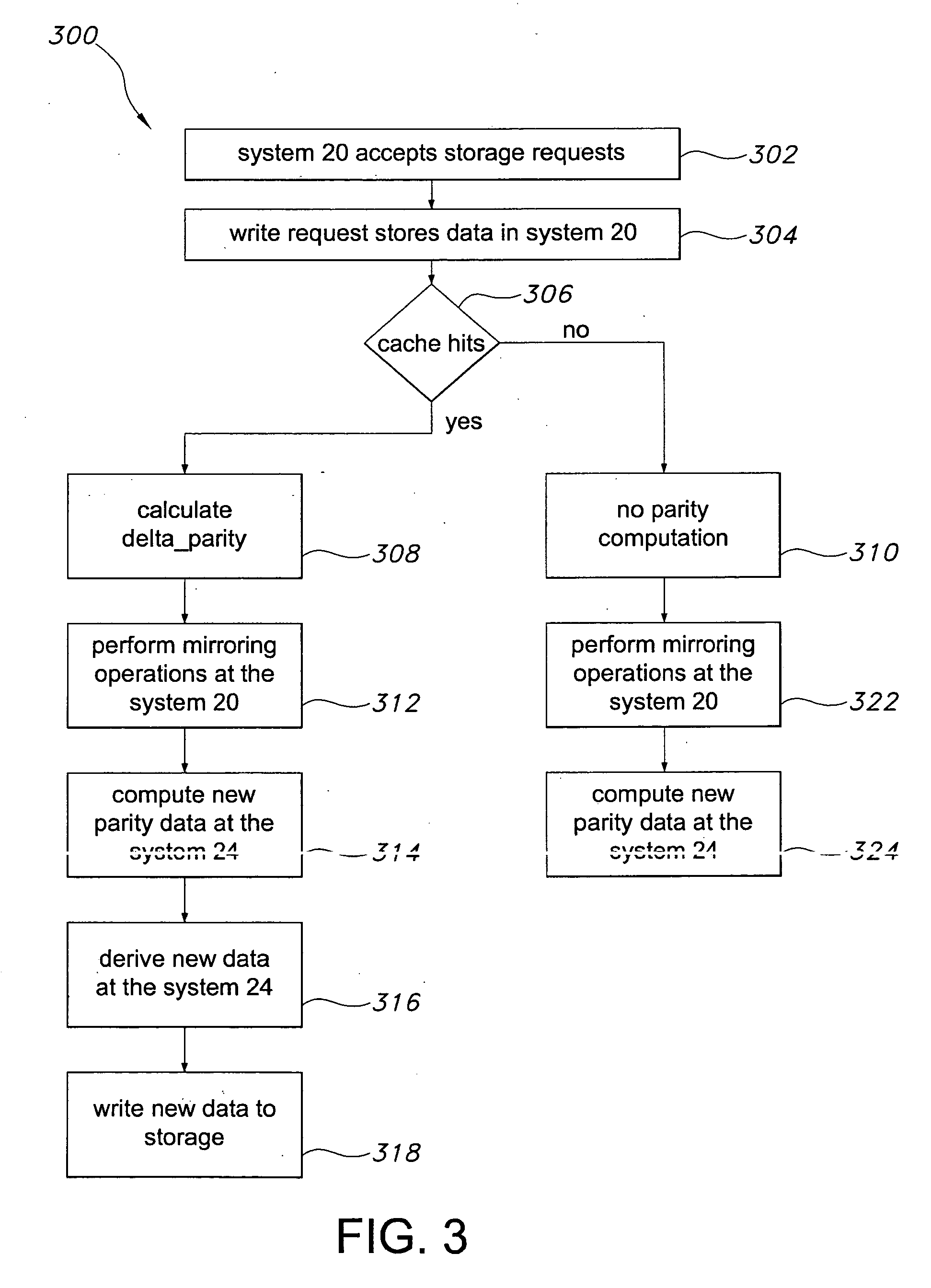
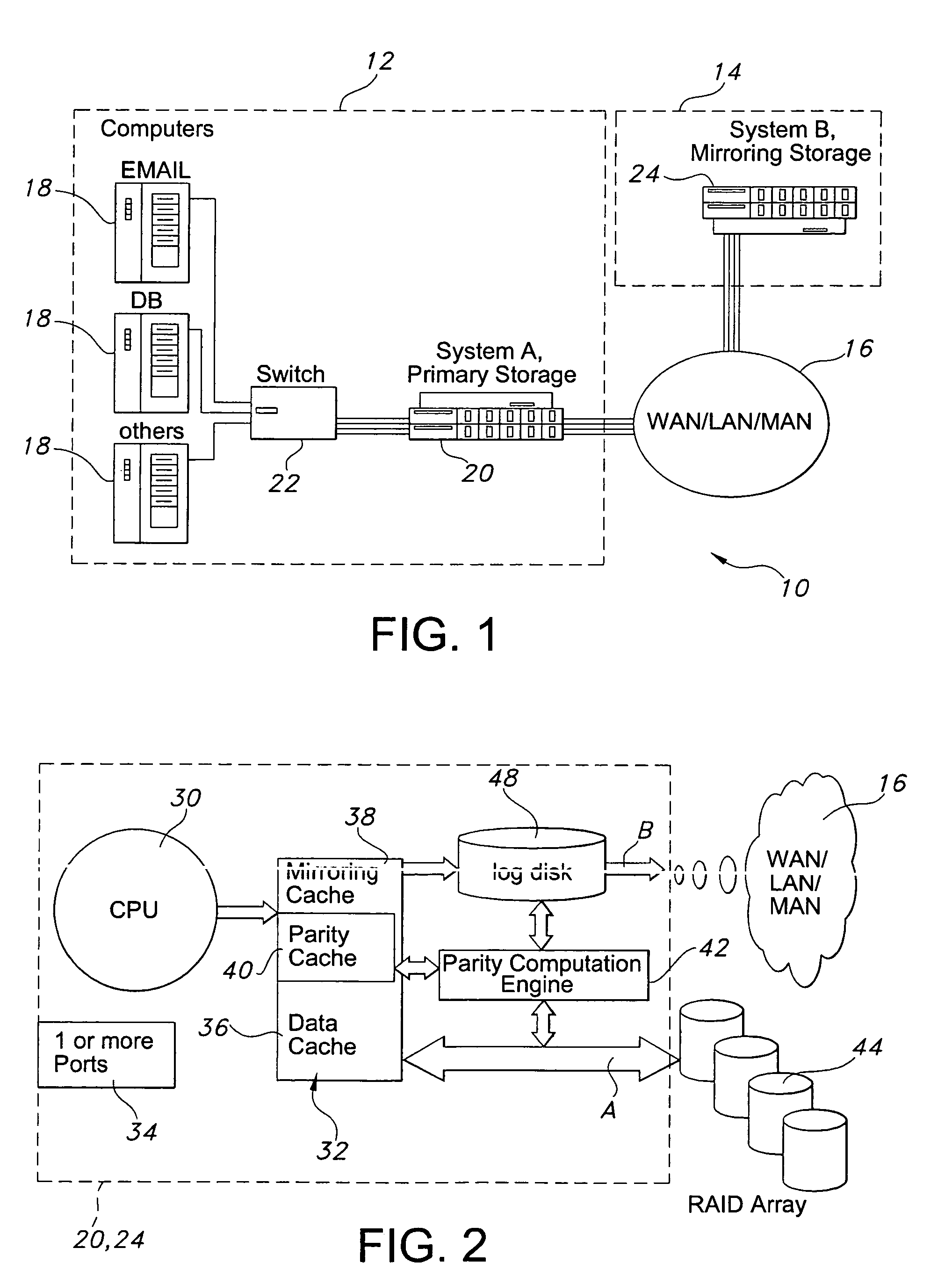
InactiveUS20060036904A1Easy to useReduce the amount requiredError detection/correctionRAIDNetwork connection
A storage architecture provides efficient remote mirroring of data in RAID storage or like to a remote storage through a network connection. The storage architecture mirrors only a delta_parity. A parity cache keeps the delta_parity of each data block until the block is mirrored to the remote site. Whenever network bandwidth is available, the parity cache performs a cache operation to mirror the delta_parity to the remote site. If a cache miss occurs, i.e. the delta_parity is not found in the parity cache, computation of the data parity creates the delta_parity. For RAID architectures, reading old data and old parity is a necessary step of computing new parity for every write operation. Thus, no additional operation is needed to compute the delta_parity for mirroring. At the remote site, the delta_parity is used to generate the new parity and the new data using the old data and parity and, in turn, WAN traffic is substantially reduced.
Owner:GEMINI STORAGE
Platform independent replication
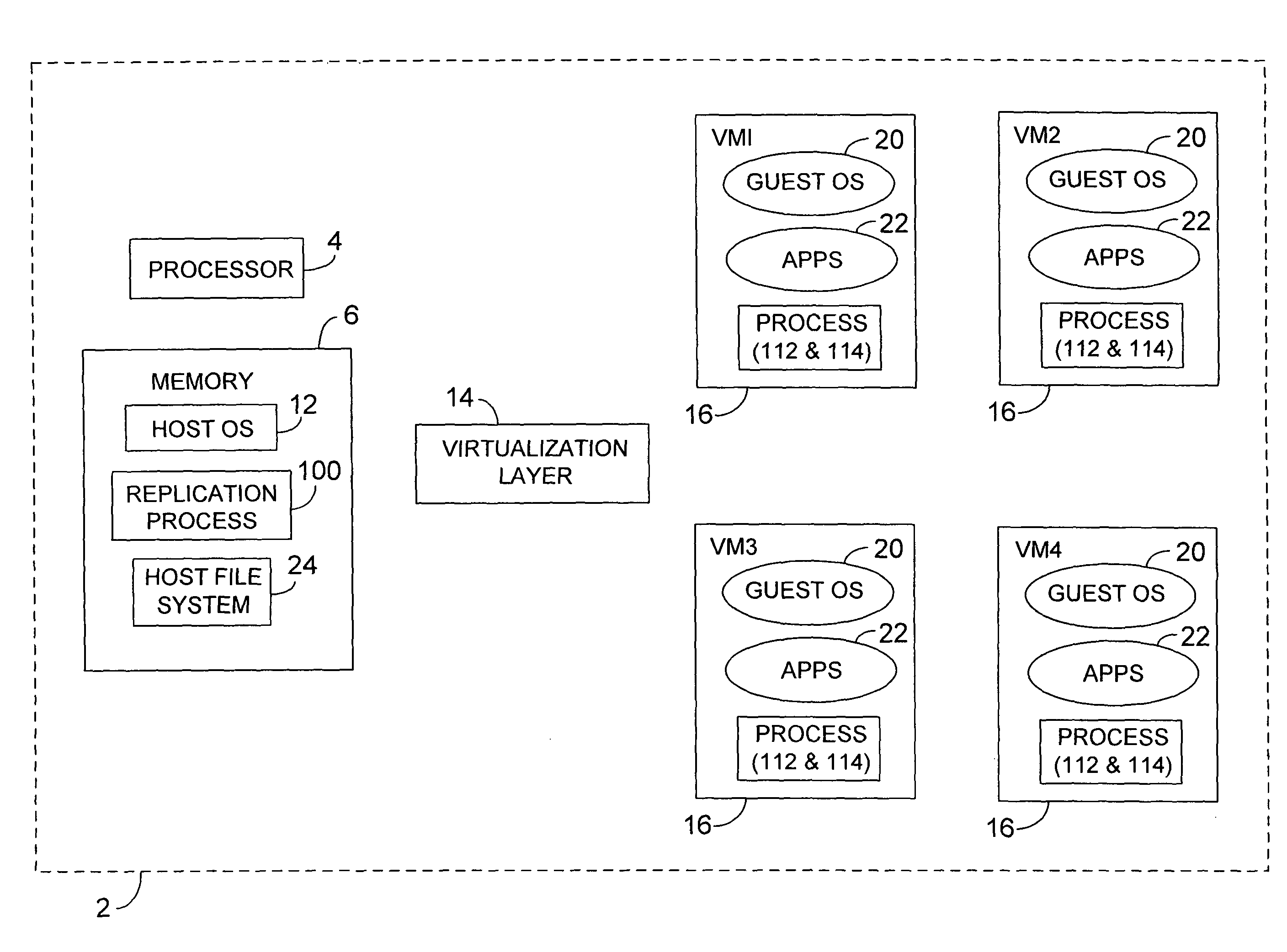
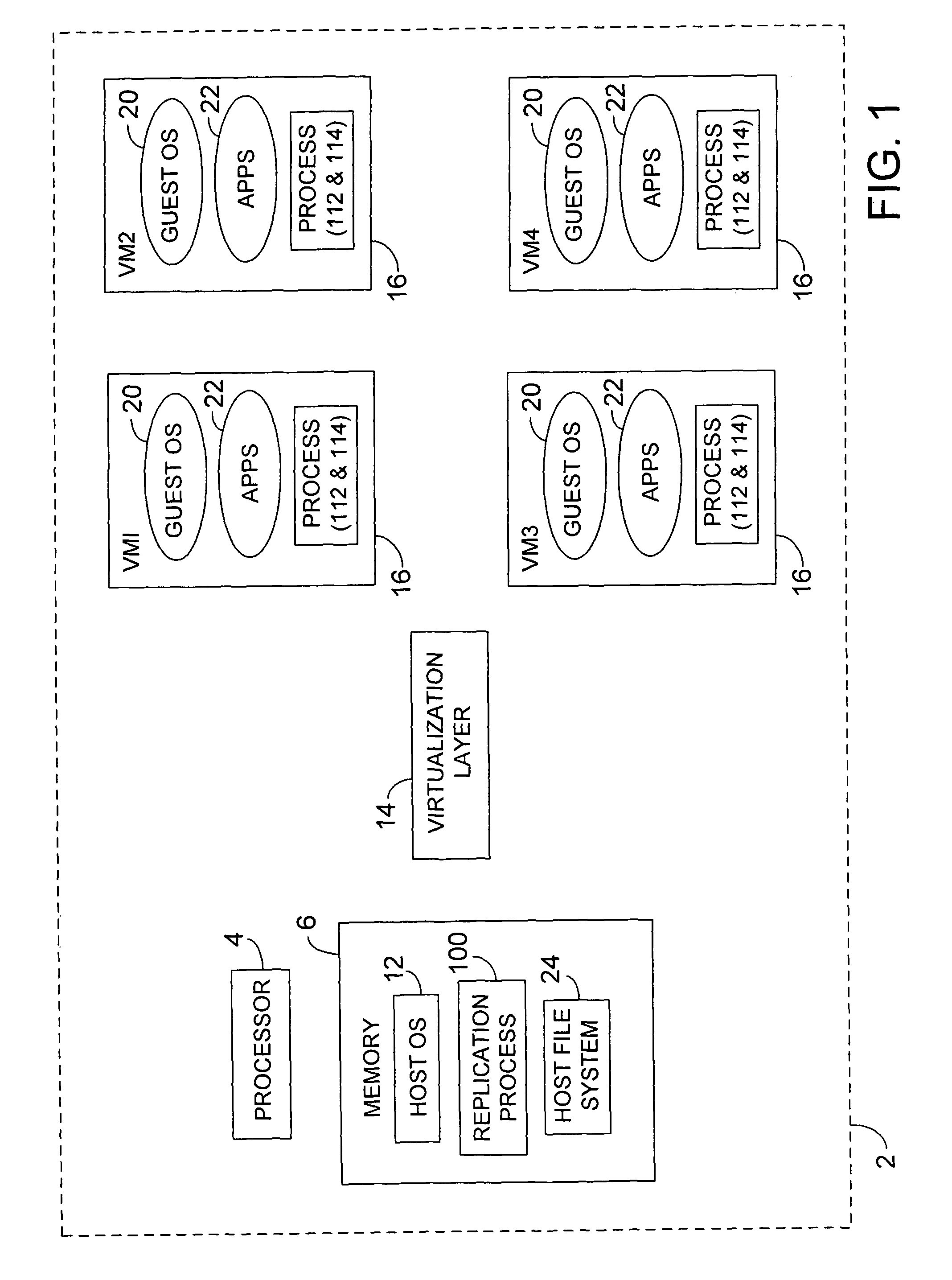
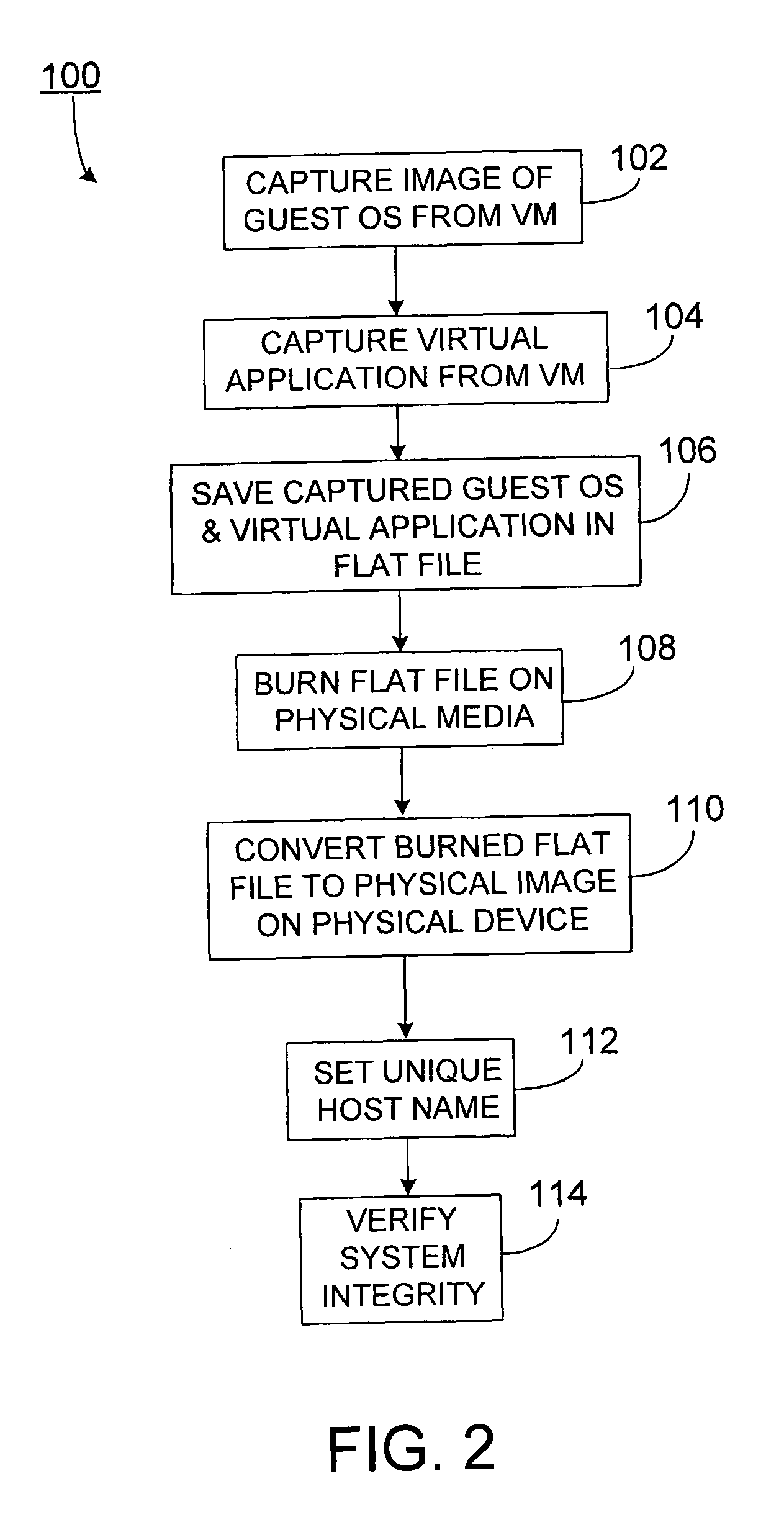
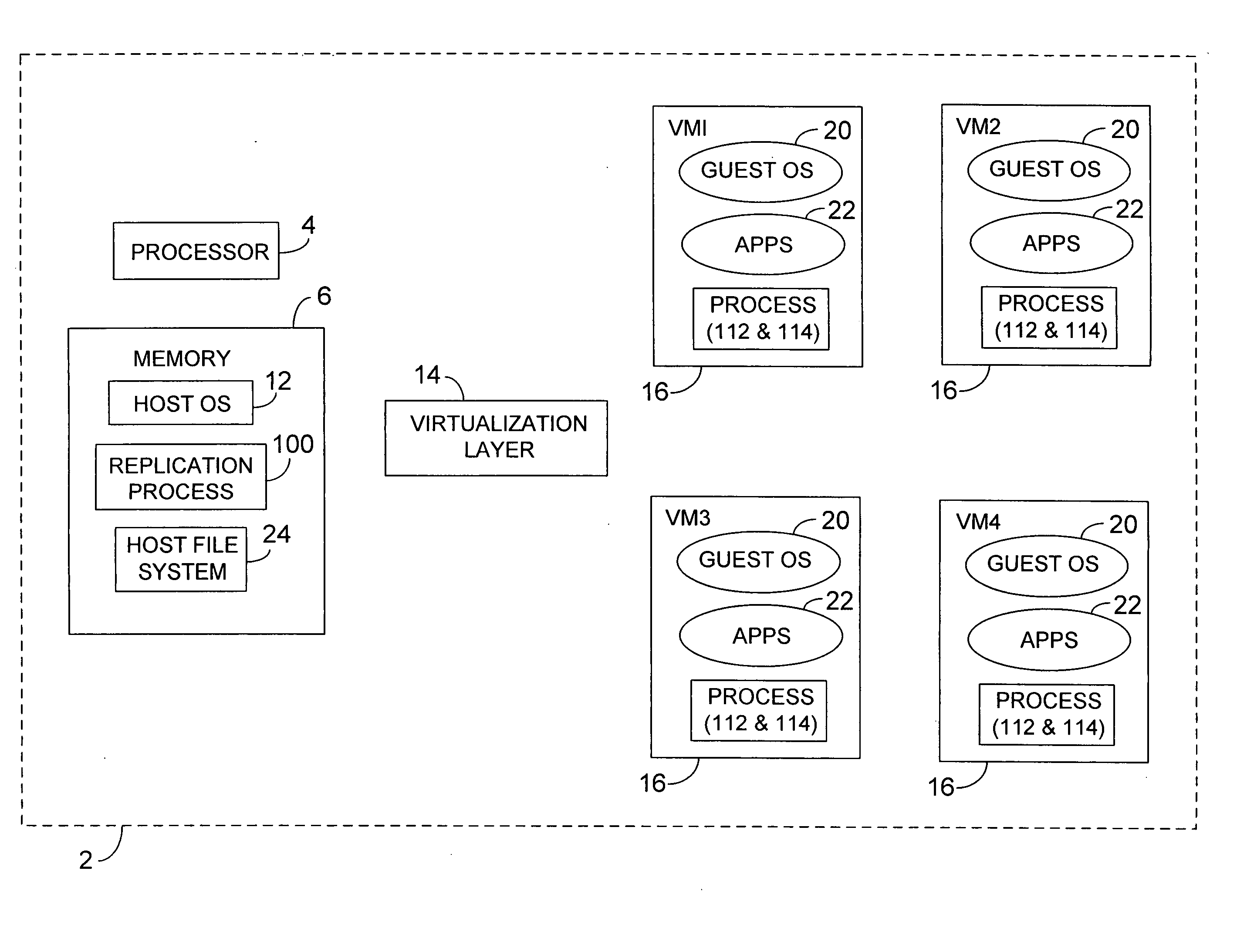
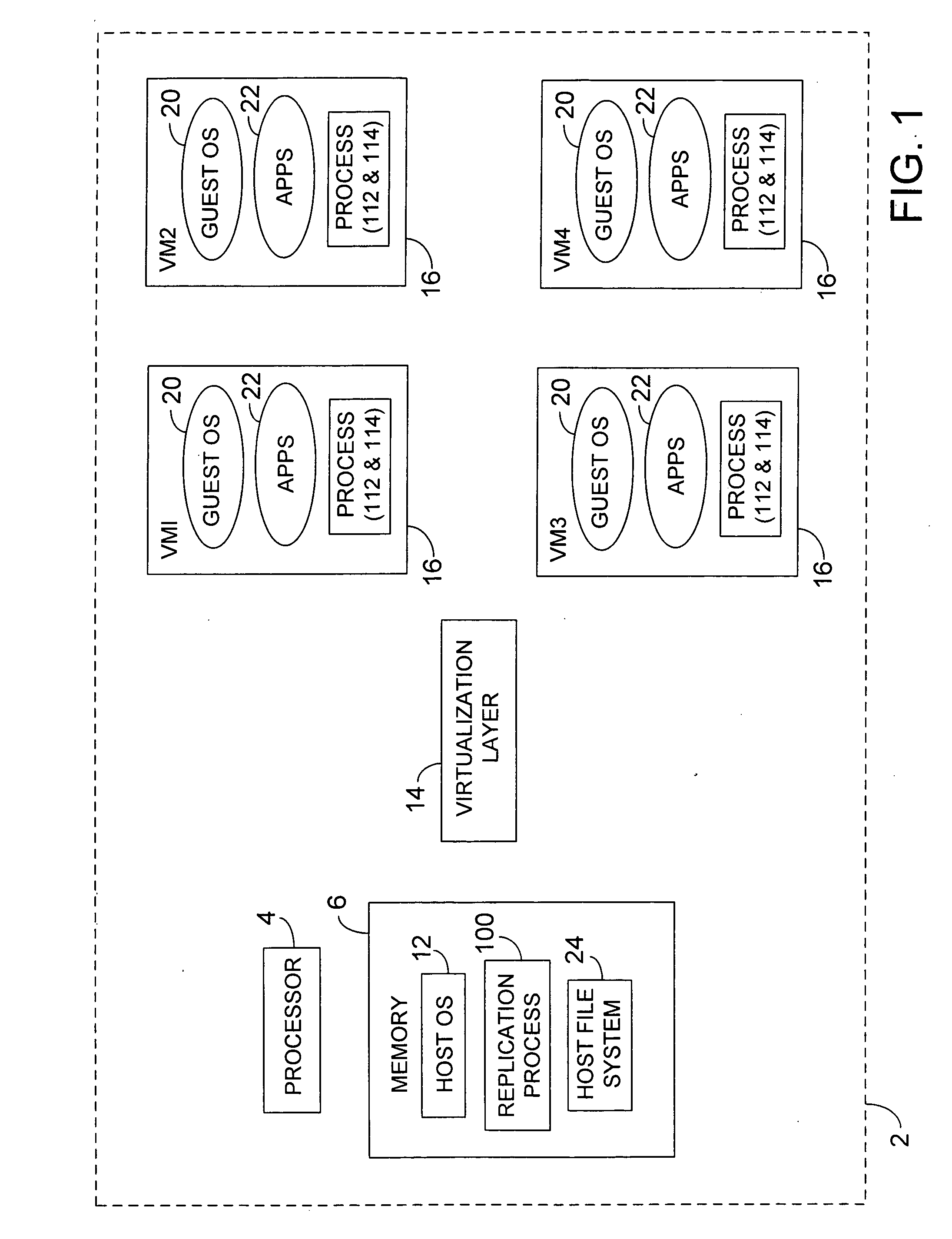
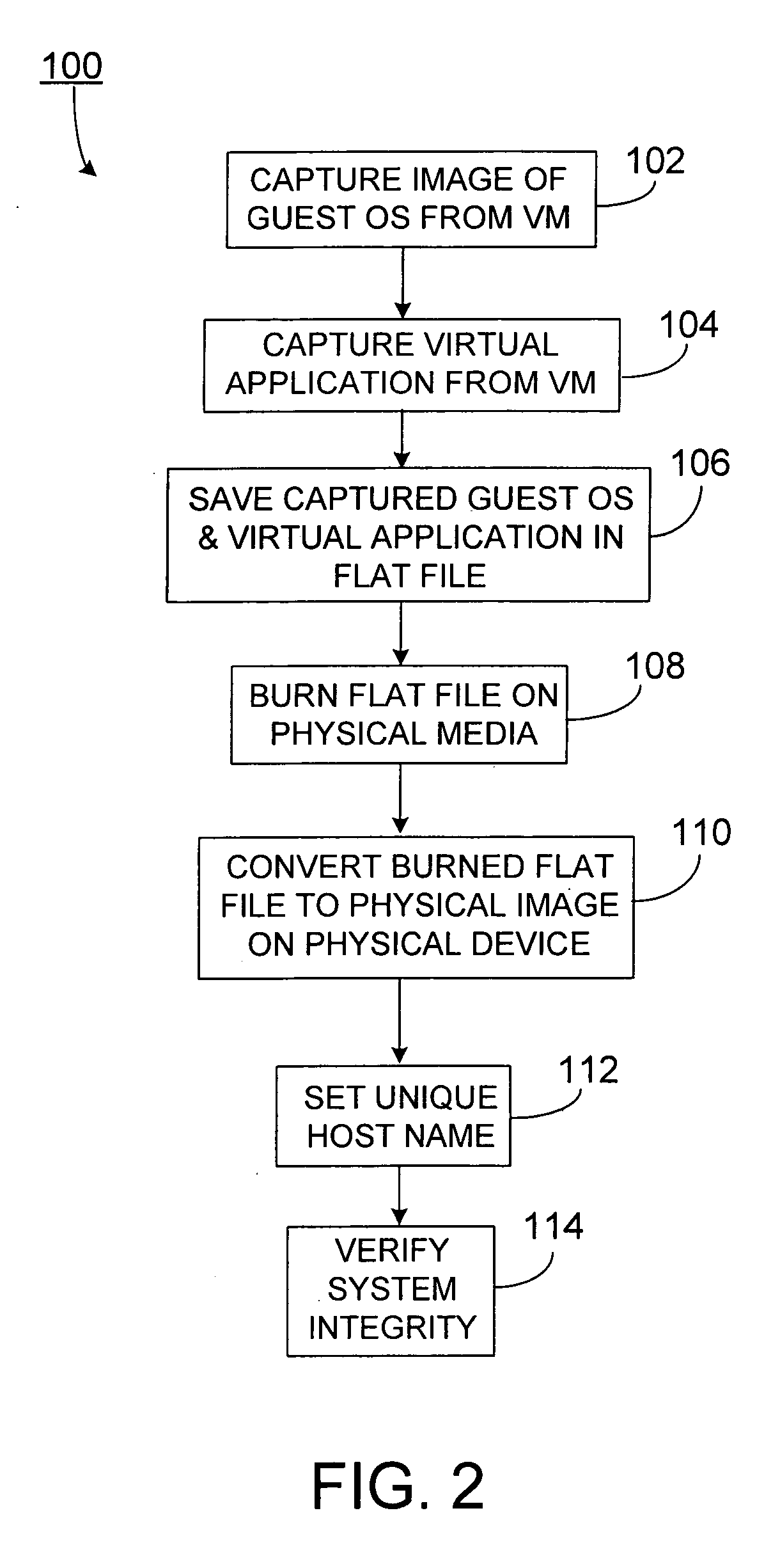
ActiveUS7725893B2Fast supplyReduce complexitySoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationMemory systemsVirtualizationOperational system
Methods and apparatus, including computer program products, for platform independent replication. Methods can include capturing a virtualized software application residing on a virtual machine, capturing a guest operating system residing on the virtual machine, and storing the captured virtualized software application including the guest operating system as a virtualization image in a flat file on a physical computing device.
Owner:SAP AG
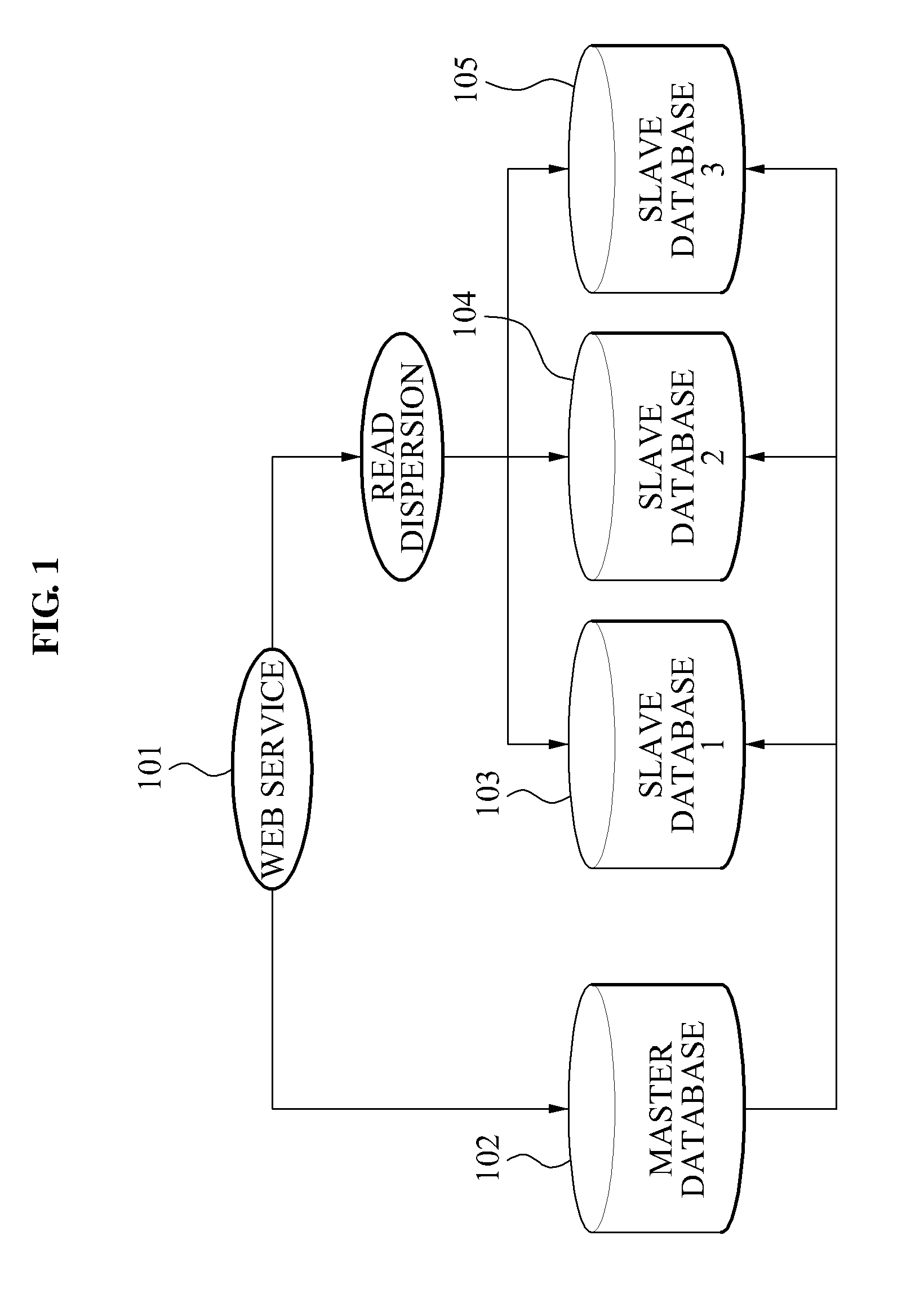
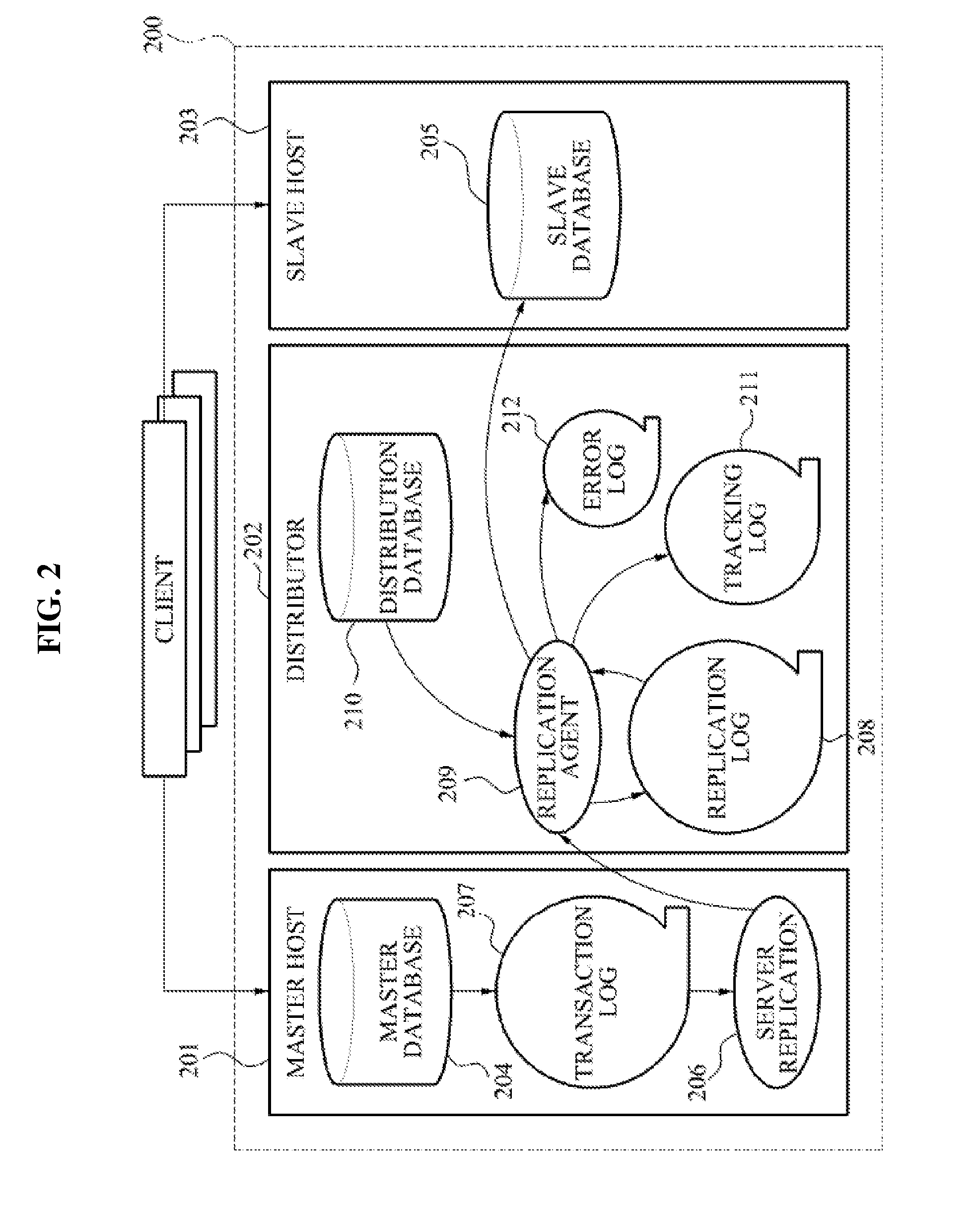
Data replication method and system for database management system
ActiveUS8874512B2Respond effectivelyQuick collectionDigital data processing detailsDatabase distribution/replicationReplication methodTransaction log
Disclosed is a data replication method in a Database Management System (DBMS). The data replication method includes generating a replication log through a transaction log of a master database to thereby transmit the generated replication log to a distributor, determining a slave host distributing the replication log to thereby distribute the replication log to the corresponding slave host, and reflecting the replication log in a slave database.
Owner:NAVER CORP
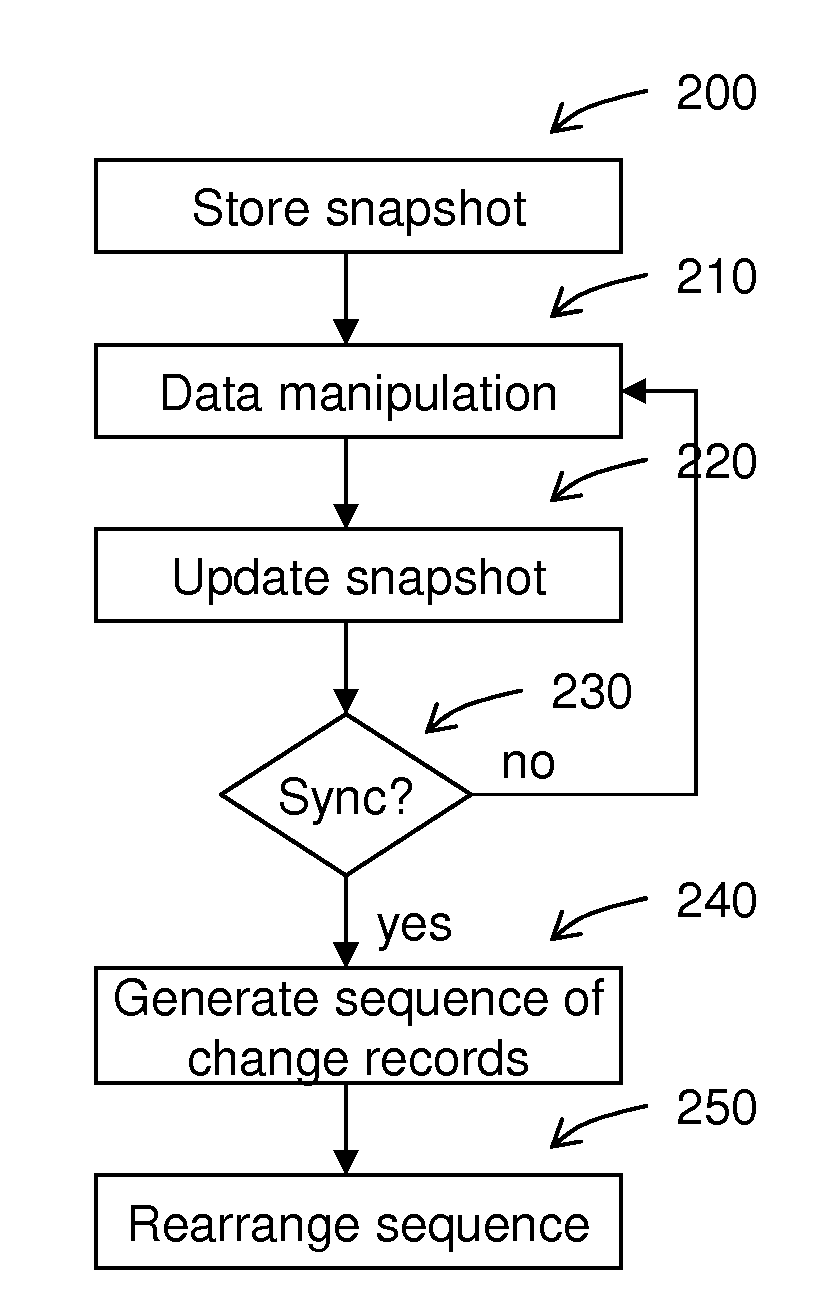
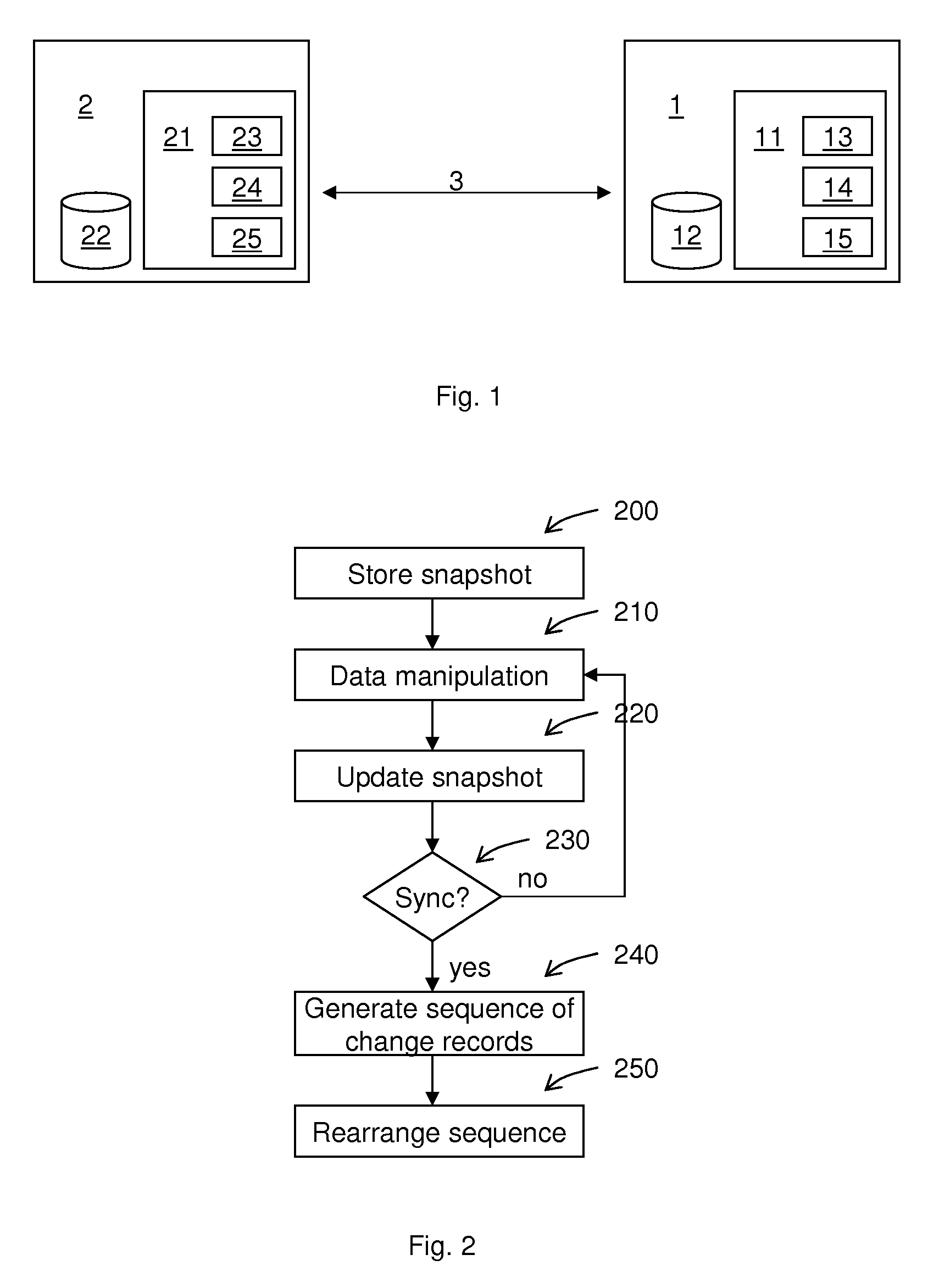
Database replication method and system
InactiveUS20070255763A1Reliable trackingReduce capacityDigital data information retrievalSpecial data processing applicationsReplication methodComputerized system
A database replication method comprises storing a database snapshot to determine changes applied to at least one first database system component; generating a sequence of change records using the database snapshot, and rearranging the sequence of change records to reflect referential dependencies, and a database computer system, data processing program, and computer program product therefor.
Owner:IBM CORP
Methods and systems for file replication utilizing differences between versions of files
ActiveUS7320009B1Data processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsFile replicationComputer hardware
Methods and systems for efficient file replication are provided. In some embodiments, one or more coarse signatures for blocks in a base file are compared with those coarse signatures for blocks of a revised file, until a match is found. A fine signature is then generated for the matching block of the revised file and compared to a fine signature of the base file. Thus, fine signatures are not computed unless a coarse signature match has been found, thereby minimizing unneeded time-consuming fine signature calculations. Methods are also provided for determining whether to initiate a delta file generation algorithm, or whether to utilize a more efficient replication method, based upon system and / or file parameters. In accordance with additional embodiments, the lengths of valid data on physical blocks are obtained from physical block mappings for the files, and these lengths and mappings are utilized for delta file generation, to minimize unnecessary signature computations.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Data replication method over a limited bandwidth network by mirroring parities
InactiveUS7457980B2Reduce the amount requiredReduce data volumeError detection/correctionRAIDReplication method
A method dramatically reduces the amount of data to be stored and transferred in a networked storage system. Preferably, the network storage system provides continued data protection through mirroring / replication, disk-to-disk backup, data archiving for future retrieval, and Information Lifecycle management (ILM). The idea is to leverage the parity computation that exists in RAID systems. By caching, transferring, and storing data parity or delta bytes of changes on a block as opposed to data block itself, substantial data reduction is possible without using sophisticated compression algorithms at the production side to minimize performance impacts upon production servers. Data can be computed using the parity / delta and previously existing data at mirror side, replication side, backup storage, or at retrieval time upon events such as failures or ILM operations.
Owner:ZOLL CIRCULATION +1
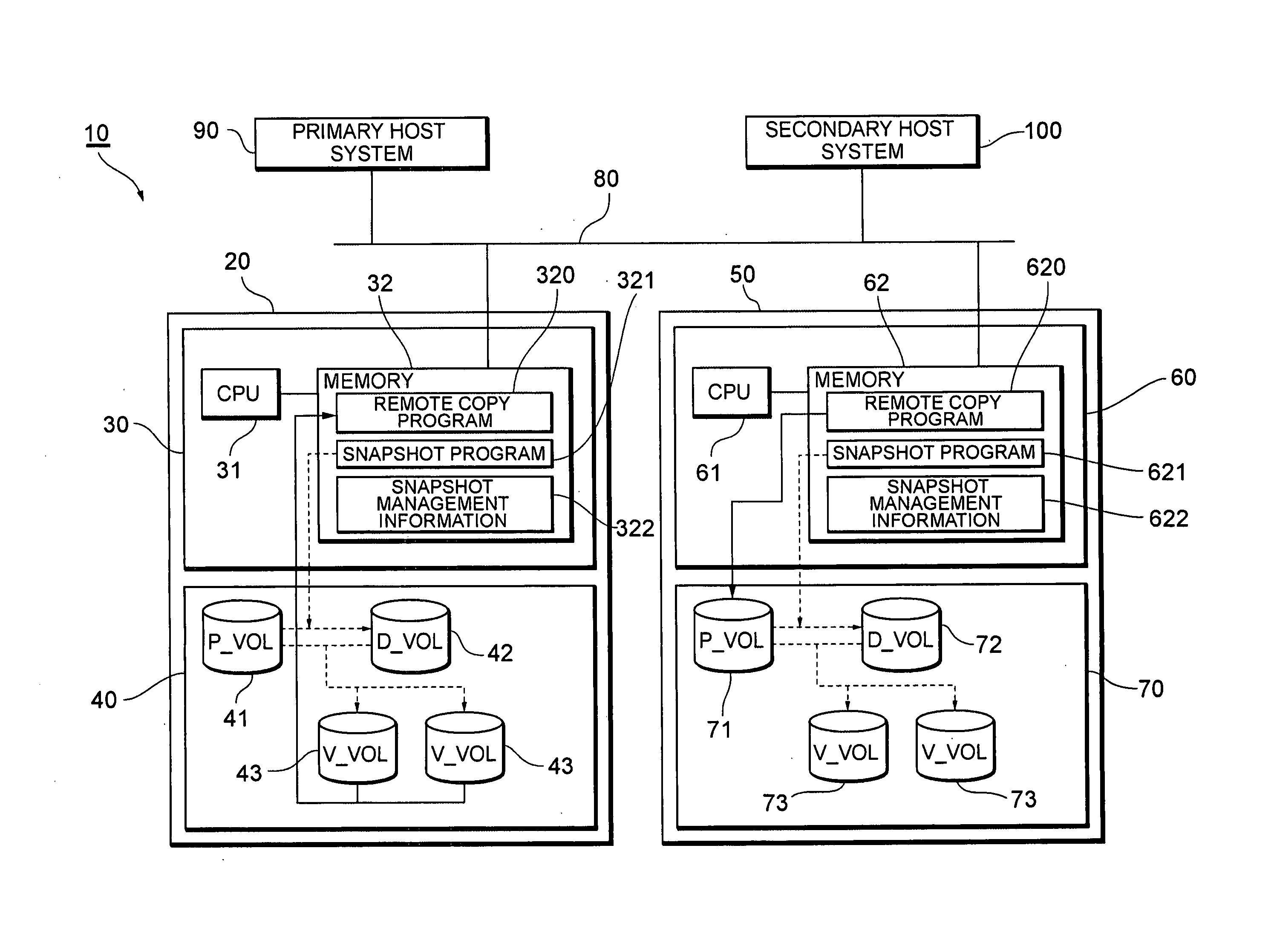
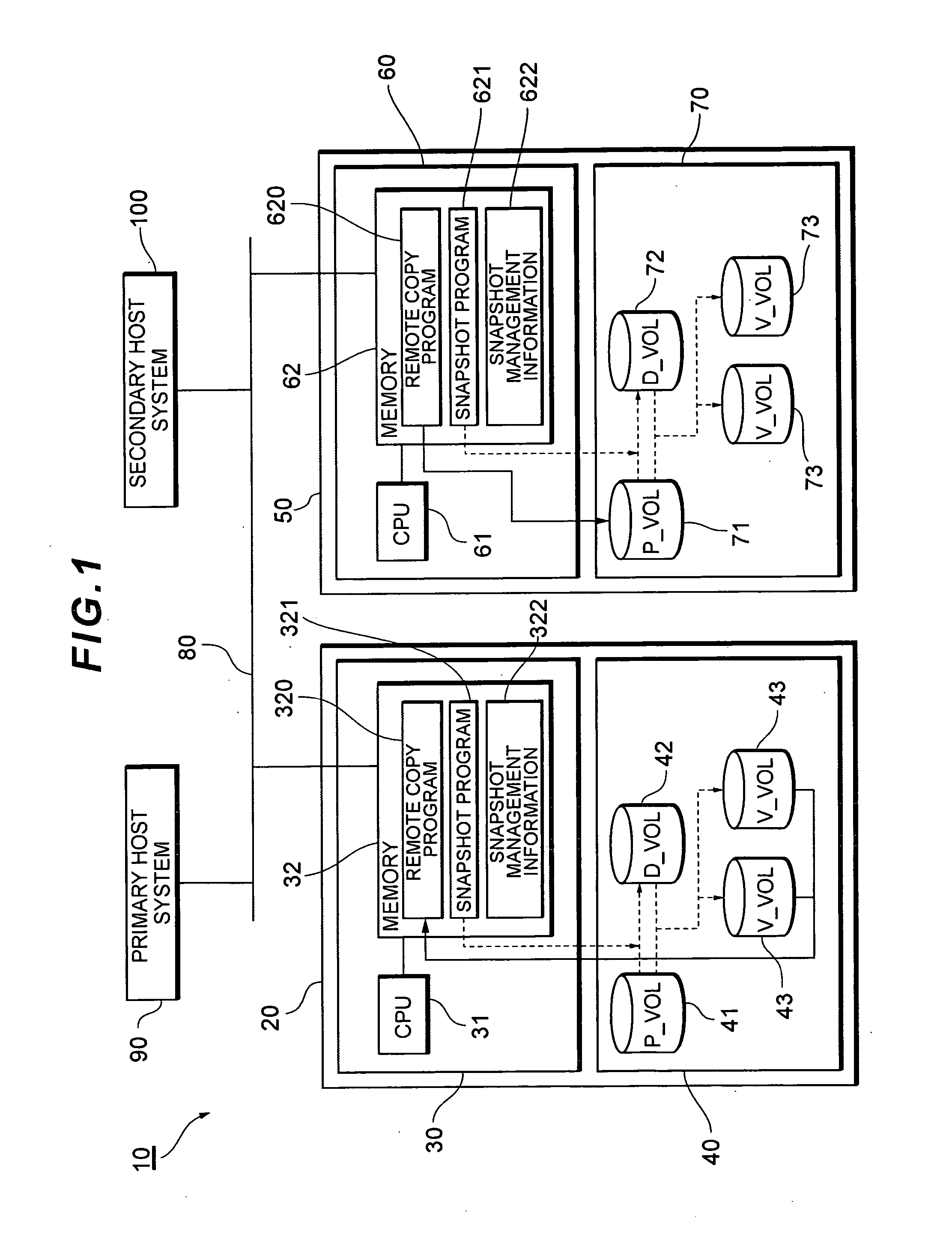
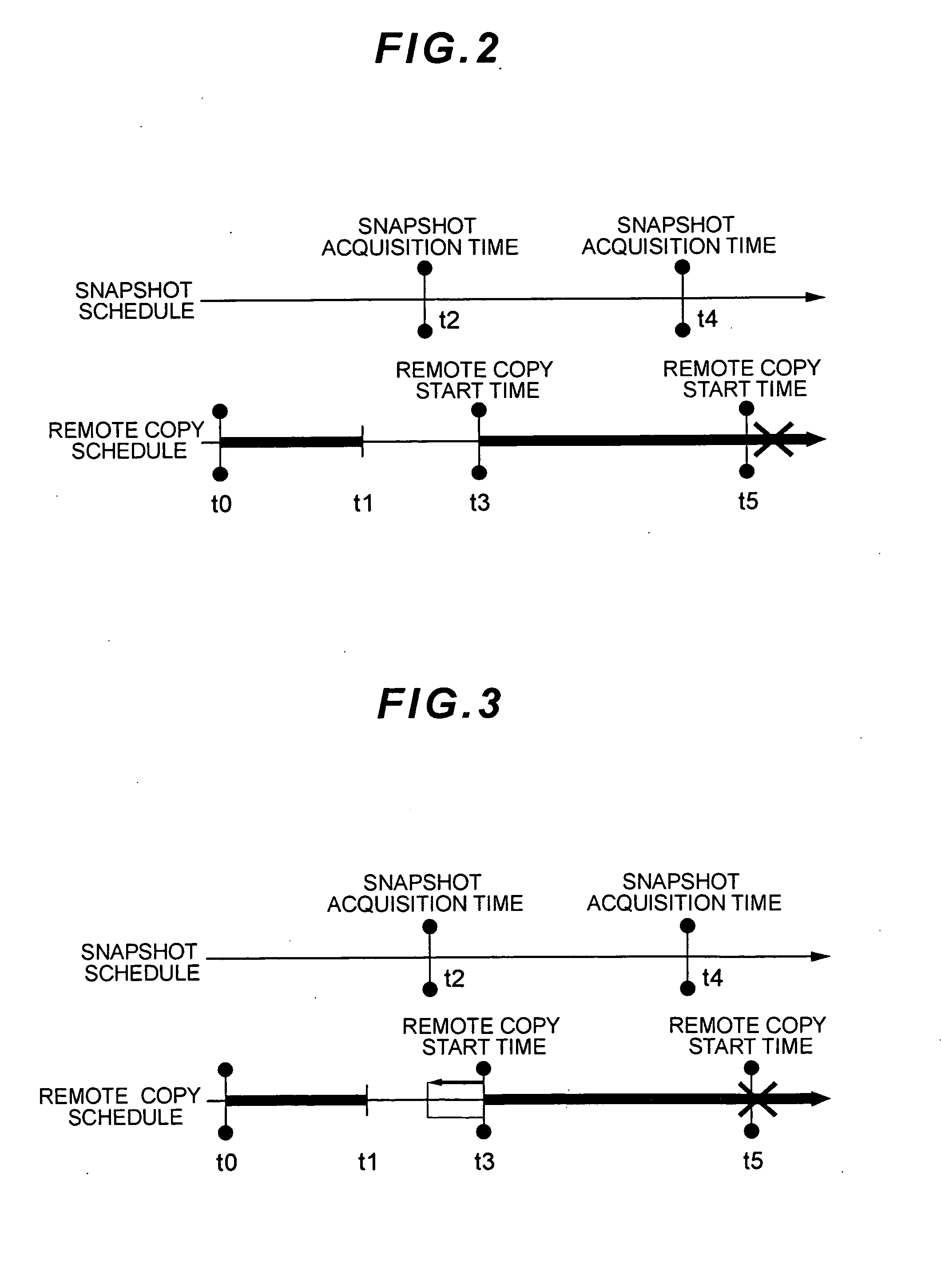
NAS system and remote copy method
InactiveUS20070168404A1Digital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsStart timeAcquisition time
The present invention remote copies difference data for snapshots in an appropriate manner. A NAS system having one or more file systems for storing data, a snapshot producing section for producing snapshots for the file systems based on a pre-scheduled snapshot acquisition time, a remote copy section for remote copying difference data for the snapshots based on pre-scheduled remote copy start times, and a scheduling section for re-scheduling the time of one or more of an Nth snapshot acquisition time, an Nth remote copy start time, and an (N+1)th remote copy start time, in such a manner that remote copying starting at the Nth remote copy start time finishes by the (N+1)th remote copy start time.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Intelligent replication method
InactiveUS6973464B1Data processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalFile replicationReplication method
A replication method supports file replication across a plurality of file servers by tracking the changes to the local volume on the storage system. Each change is then ranked according to a number of criteria. Each criterion is weighted, and an overall ranking is determined for each change. The changes are then ordered according to their ranks, and each change is transmitted to remote storage systems for remote duplication of the change.
Owner:MICRO FOCUS SOFTWARE INC
Methods, apparatus and computer programs for data replication
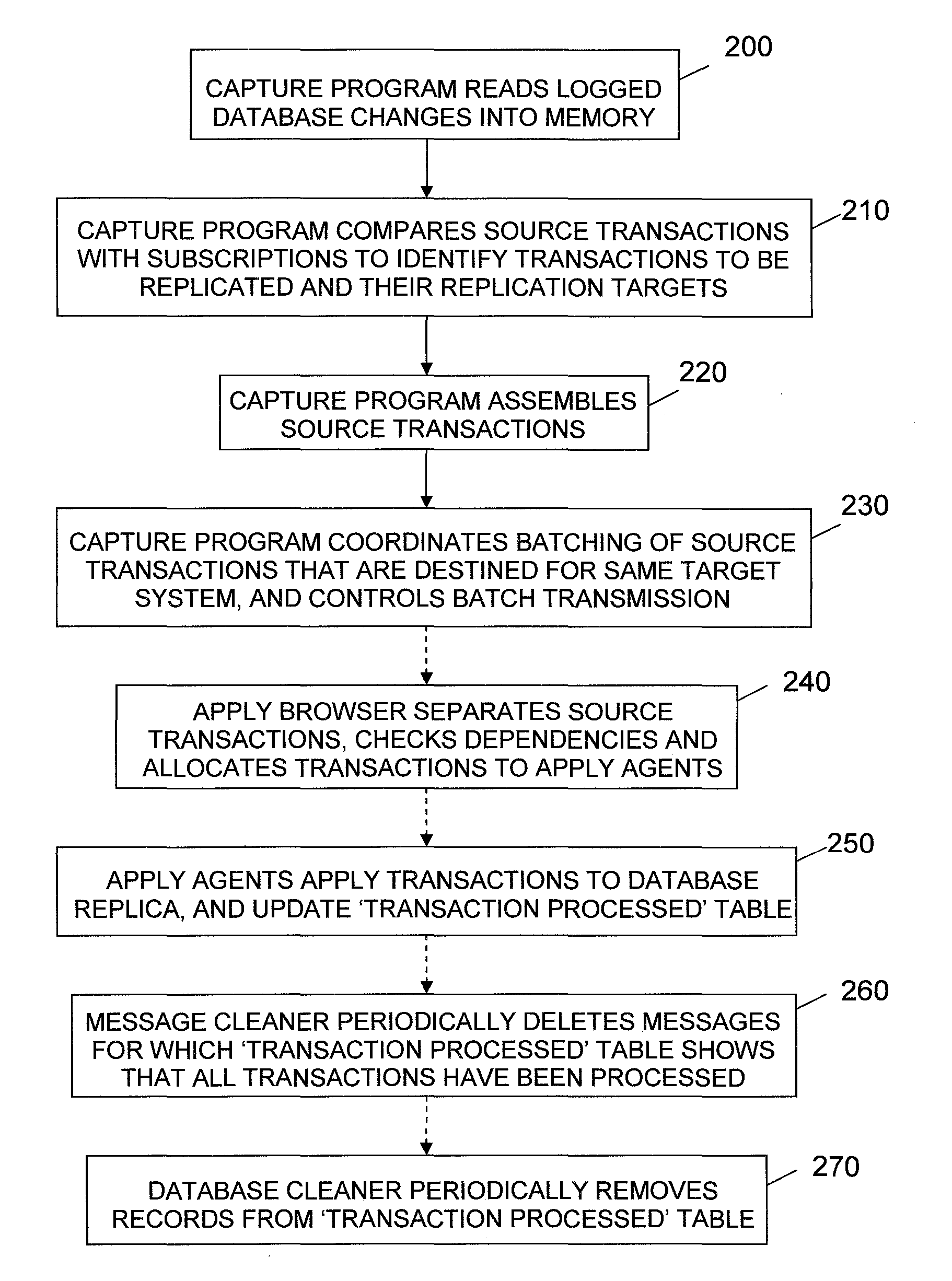
InactiveUS20080098044A1Facilitates efficient one-phase commit of apply operationImprove data transfer efficiencyDigital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsBatch processingReplication method
Methods, apparatus and computer programs are provided for data replication, such as for replicating a database or updating a cache. Source database change transactions are captured and batched together for efficient data transfer. On receipt at a target replica system, the batch of transactions within a message is separated and separate apply transactions corresponding to the source transactions are performed in parallel. A ‘transaction processed’ table is updated to reflect apply processing for each apply transaction. This table provides a confirmation of the status of each transaction that can be used during recovery processing to prevent re-apply of an apply transaction. The table can also be used to determine when it is safe to delete an incoming message from persistent storage on the target system, and to facilitate one-phase commit processing.
Owner:IBM CORP
Data copy method
InactiveUS20030101318A1Input/output to record carriersMemory systemsReplication methodTheoretical computer science
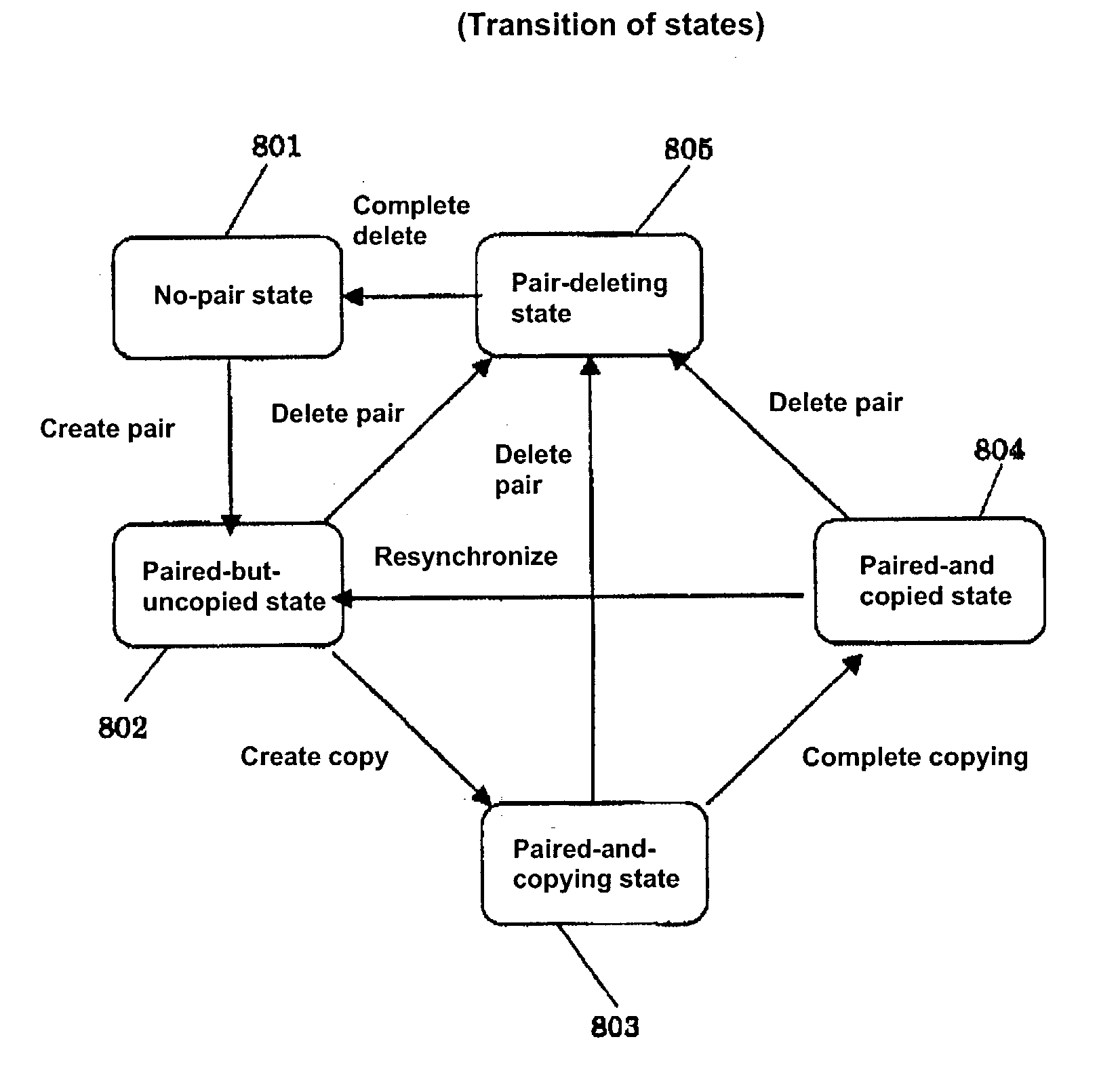
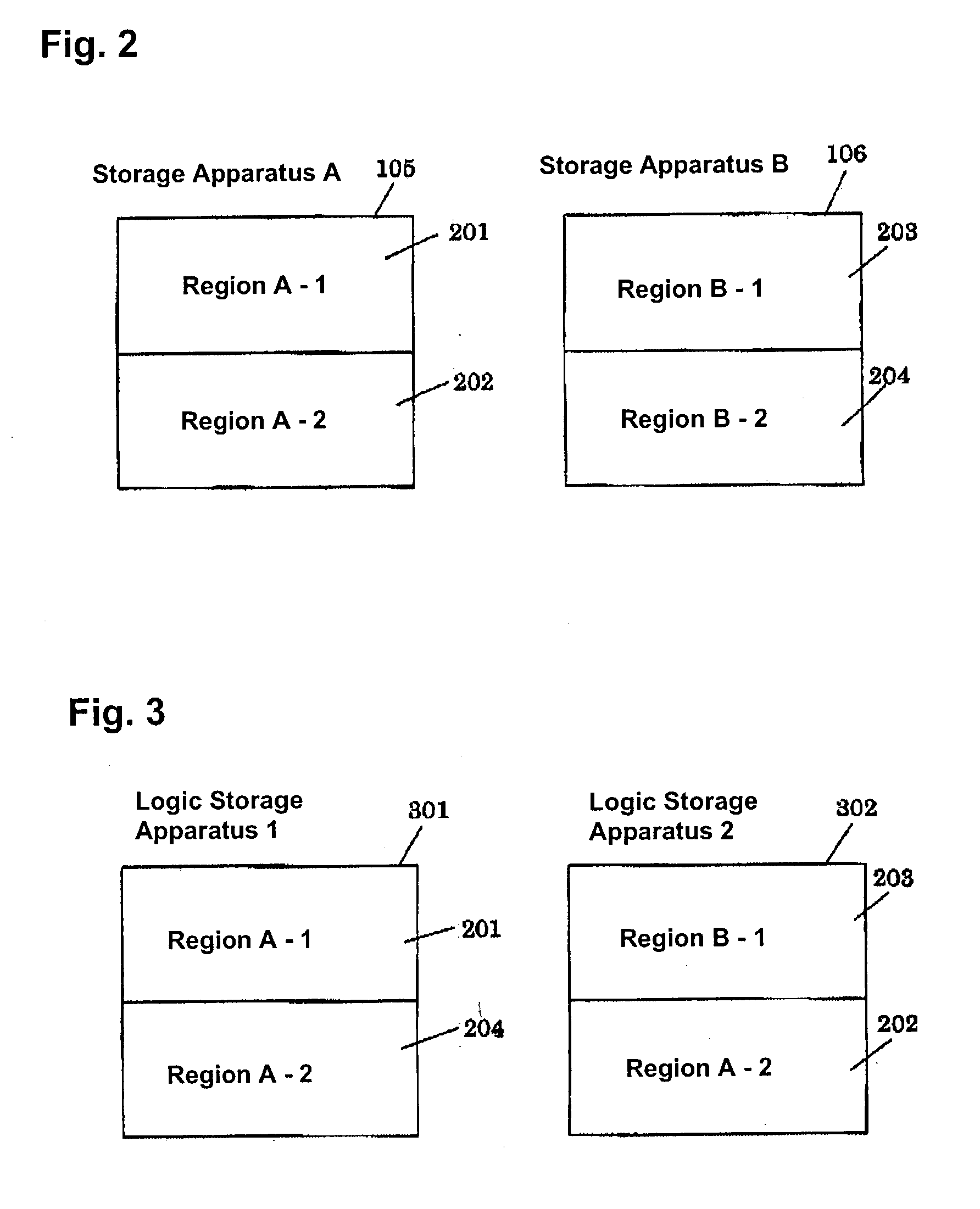
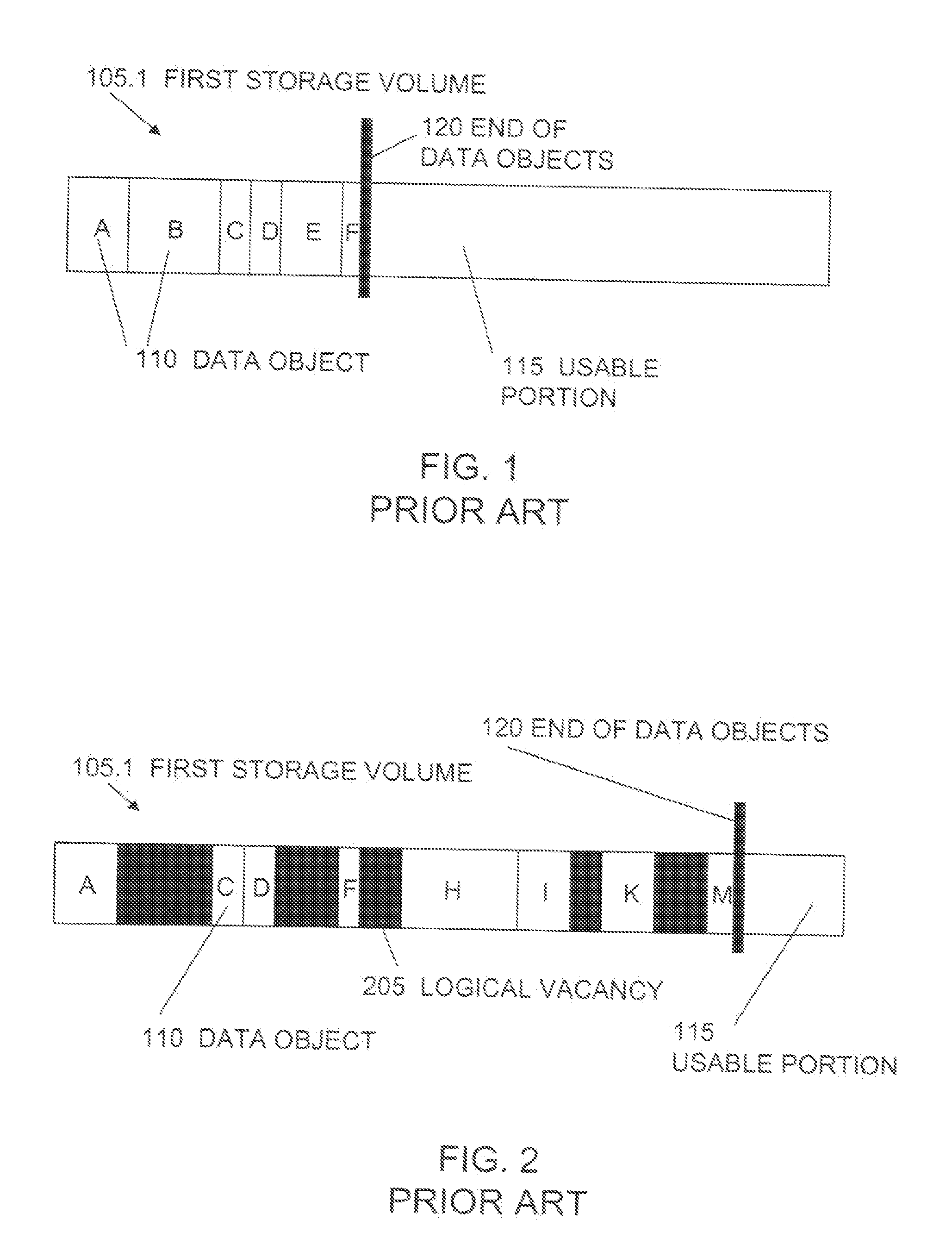
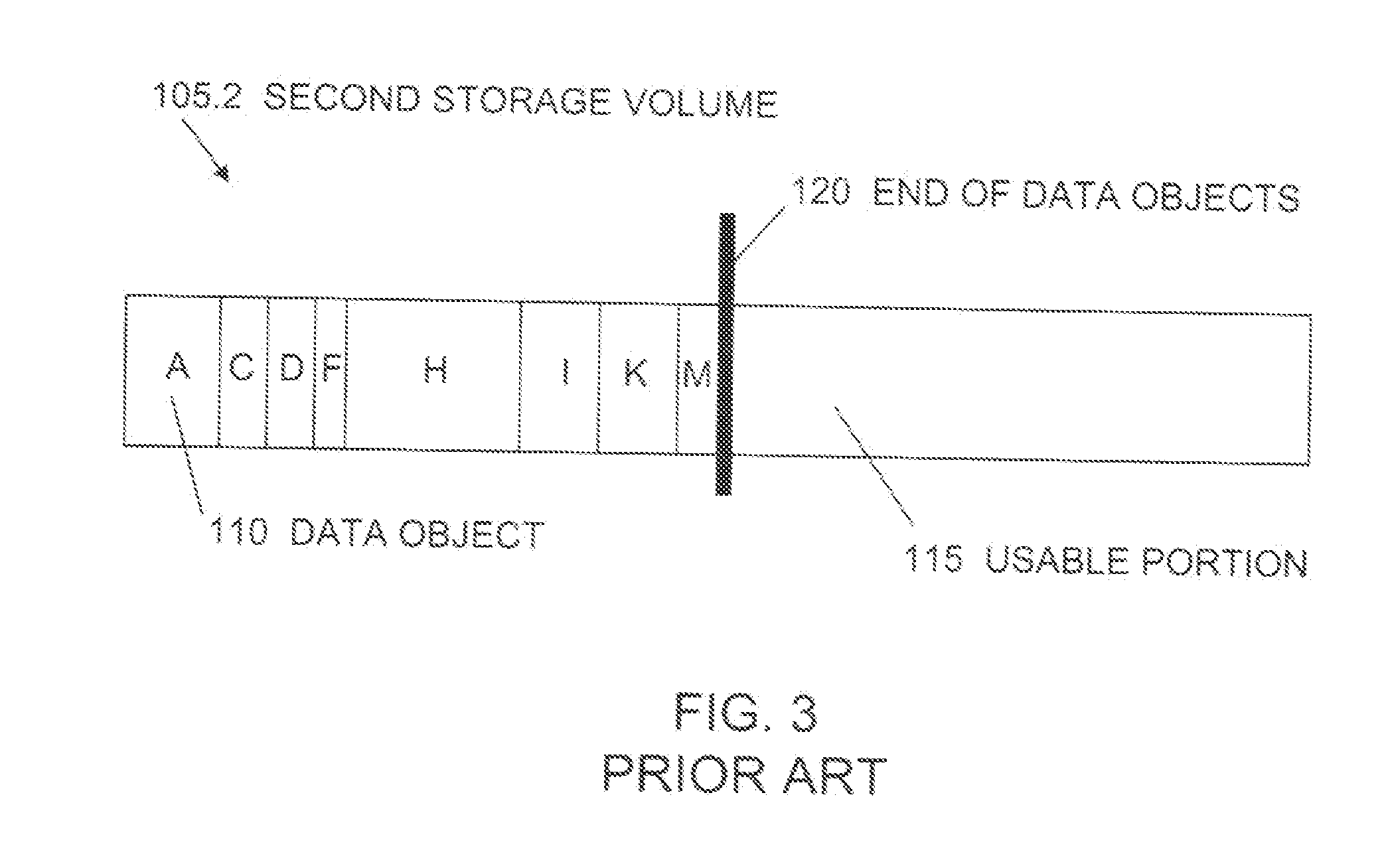
A data copy method for a disk sub system that is equipped with a first storage apparatus including a first logic storage apparatus divided into a first region and a second region and a second storage apparatus including a second logic storage apparatus divided into a first region and a second region, the first logic storage apparatus and the second logic storage apparatus connecting to a host apparatus, wherein data on the first logic storage apparatus is copied to the second logic storage apparatus by an instruction from the host apparatus. With the data copy method, the second logic storage apparatus is designated as a copy destination for copying data of the first logic storage apparatus, the second region of the first logic storage apparatus and the second region of the second logic storage apparatus are switched with one another, and data stored in the first region and the second region within the first storage apparatus are copied to the first region and the second region within the second storage apparatus.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Platform independent replication
ActiveUS20060248527A1Fast supplyReduce system complexitySoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationMemory systemsVirtualizationOperational system
Methods and apparatus, including computer program products, for platform independent replication. Methods can include capturing a virtualized software application residing on a virtual machine, capturing a guest operating system residing on the virtual machine, and storing the captured virtualized software application including the guest operating system as a virtualization image in a flat file on a physical computing device.
Owner:SAP AG
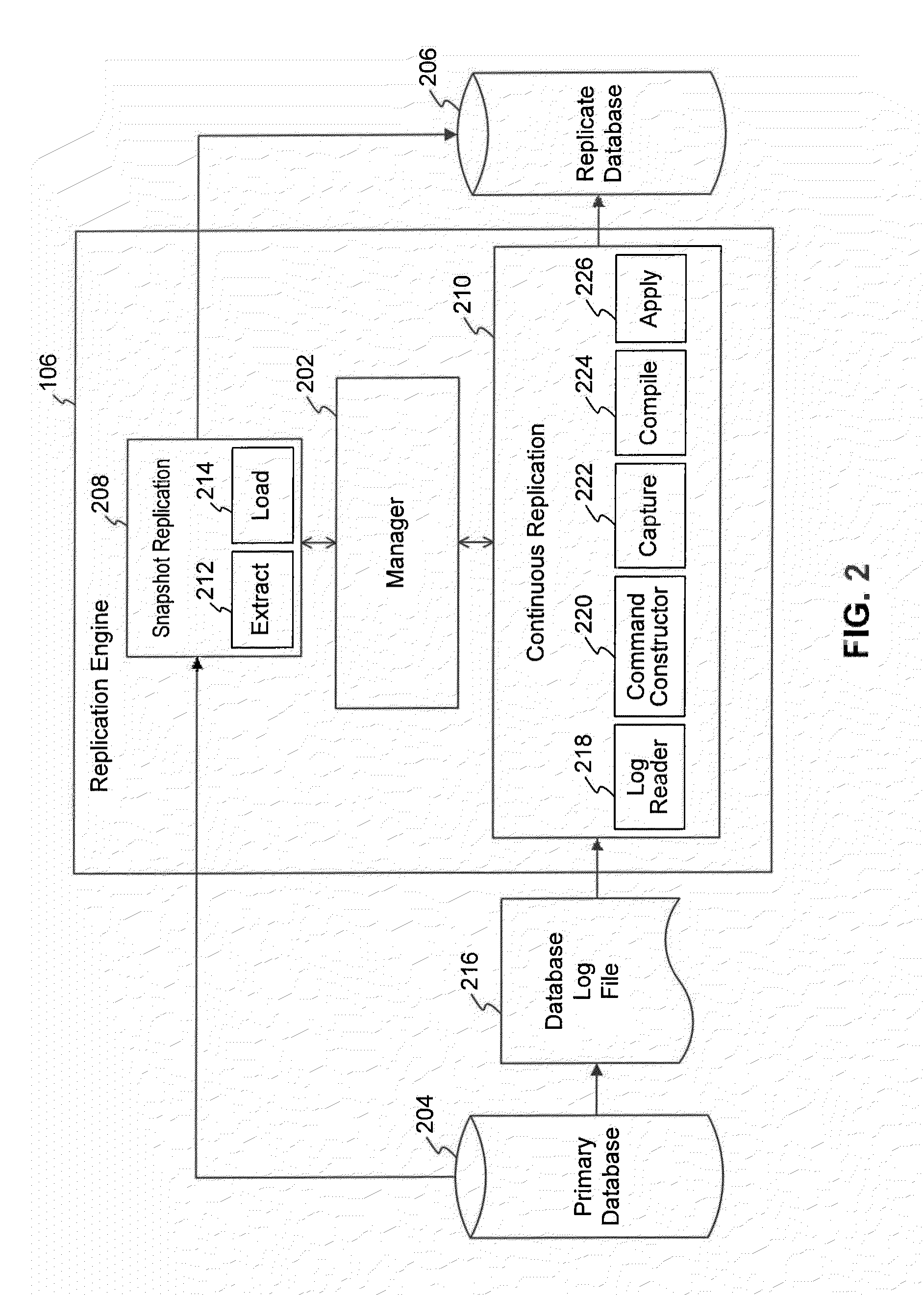
Database system providing improved methods for data replication
ActiveUS8121978B2Simple methodDigital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsReplication methodTransaction log
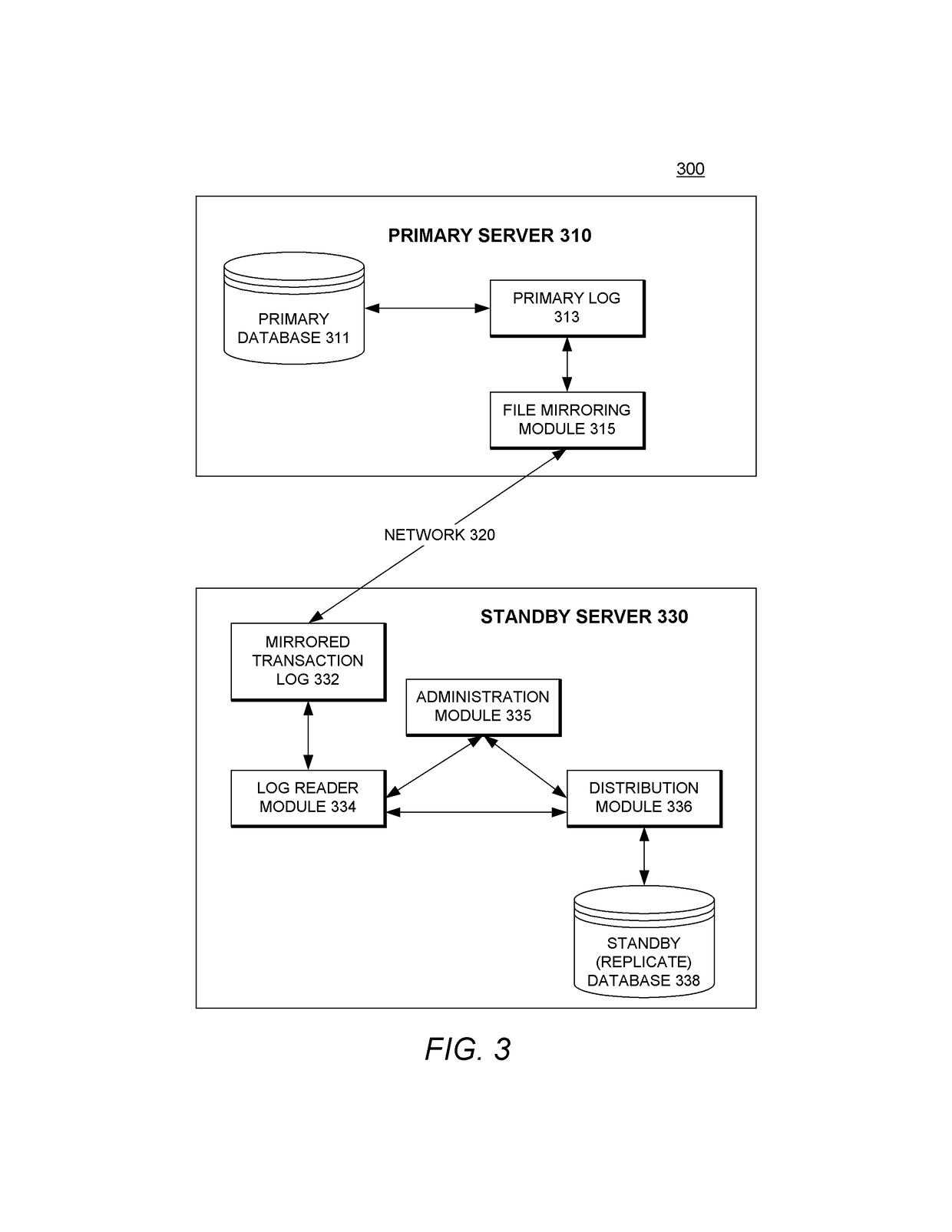
A system providing improved methods for data replication is described. A method for replicating a transaction from a primary database to a replicate database while the replicate database remains available for use comprises: recording information about a transaction being performed at a primary database in a transaction log; synchronously copying the information about the transaction in the transaction log to a mirrored transaction log; generating a reconstructed transaction based on the information about the transaction copied to the mirrored transaction log; and applying the reconstructed transaction at the replicate database while the replicate database remains available for use.
Owner:SYBASE INC
Sequential Media Reclamation and Replication
InactiveUS20080243860A1Input/output to record carriersDigital data processing detailsReplication methodParallel computing
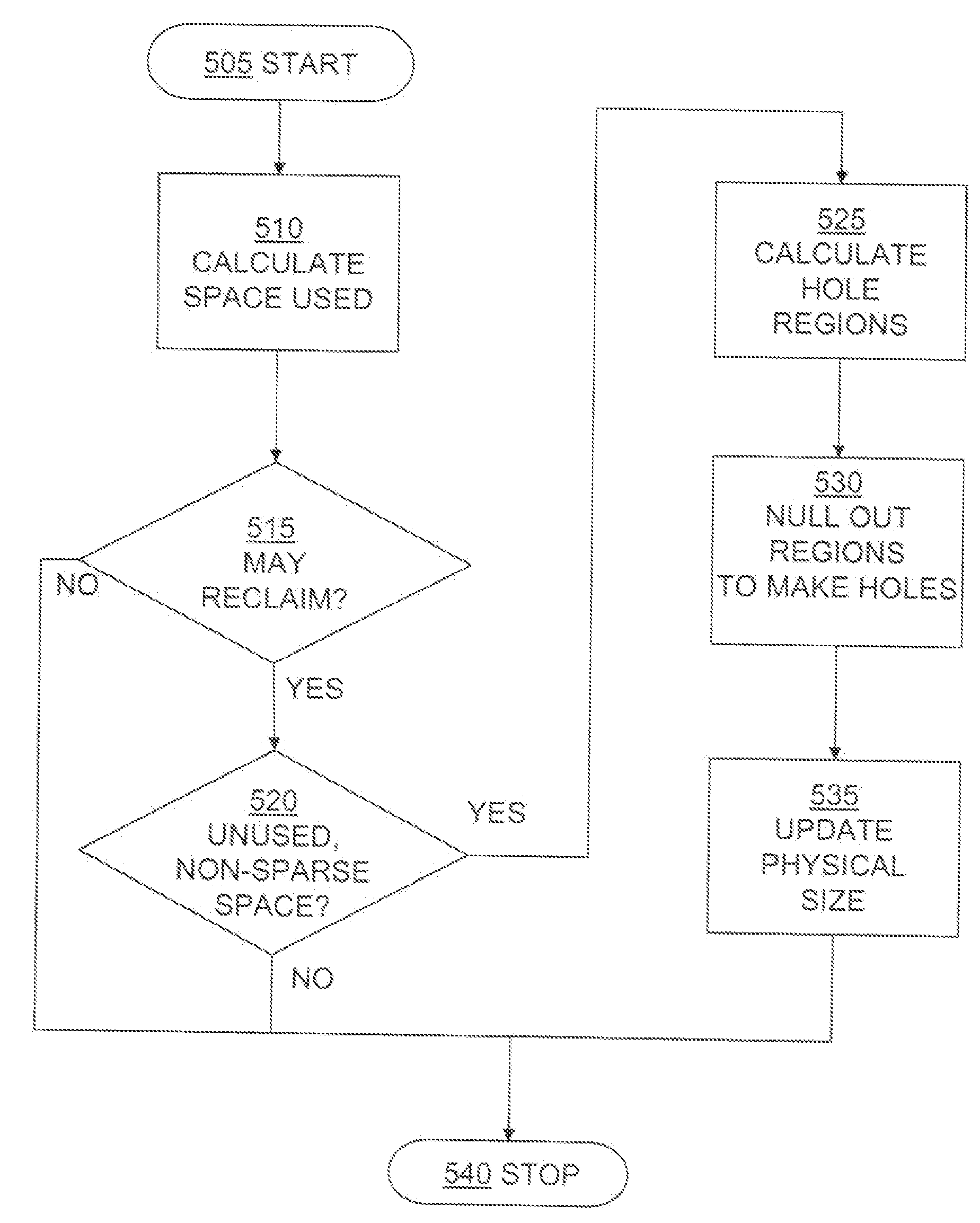
Sequential media reclamation is usually performed after portions of a sequential access volume's data are no longer needed and the unused portion of the volume exceeds a threshold. Improved sequential media reclamation is provided by using a sequential access disk volume (for example, a volume of a virtual tape library (VTL)) embodied as a sparse file. Reclamation of objects stored in the volume is accomplished by nulling out regions of the sparse file that contain the objects that are no longer needed. A replication method is also provided in which information about the objects stored in the sparse file (such as offset and length) is used during replication to enable the correct portions of a target volume (embodied as a sparse file) to be nulled out to match a source volume (also embodied as a sparse file).
Owner:IBM CORP
Medicinal anoectochilus Formosan tissue culture one-step seedling establishment fast replication method
InactiveCN101213942APromote growthCultivating equipmentsHorticulture methodsAnoectochilus roxburghiiCulture mediums
The invention discloses a rapid propagation method of culturing medical anoectochilus roxburghii tissue through which seedling is formed in only one step. The invention mainly consists of the flowing steps: firstly, culture medium is prepared by three steps of preparation, prepackaging and sterilization; secondly, explant is treated and inoculated, which step has two conditions: when a natural growth plant is used as an explant, the step consists of three steps of cleaning, sterilizing and inoculation, and when a tissue culture sterilized seedling is used as an explant, the sterilized inoculation is directly carried out; thirdly, cultivation; and fourthly, transplantation. The invention uses the middle stem of an anoectochilus roxburghii plant, which is produced by subculture, as an explant. A stem section which contains a stem node is inoculated on culture medium under sterile condition. The results show that after the optimum culture medium is cultured for four months, the average seedling number of each explant is 4.8; the average net increased number of the leaves of each plant is 3.6; the average increased root number is 2.5 and the average net increased fresh weight is 525.6mg. The growing condition of the tissue culture seedling is quite good after being transplanted to substrate. The survival rate of plants achieves to above 95 percent after three months. The invention can greatly shorten the tissue culture seedling time of anoectochilus roxburghii, significantly improve the culture efficiency and reduce the seedling cost. The invention can be used as an important method of producing anoectochilus roxburghii seedlings.
Owner:浙江省中药研究所有限公司
Systems and methods for collection and consolidation of heterogeneous remote business data using dynamic data handling
Remote data collection systems and methods retrieve data including financial, sales, marketing, operational and the like data from a plurality of databases and database types remotely over a network in an automated, platform-agnostic manner. An Extract Transform and Load (ETL) data replication method for Chart of Account (COA) standardization includes receiving a request for remote data collection to extract data from a data source; extracting data in a non-intrusive manner from the data source, wherein the data comprises non-standard COA data; and transforming one of an entire set or a subset of the extracted data based on the request based on a template or a standardized form desired for comparisons.
Owner:ZEEWISE
Computer system, remote copy method and first computer
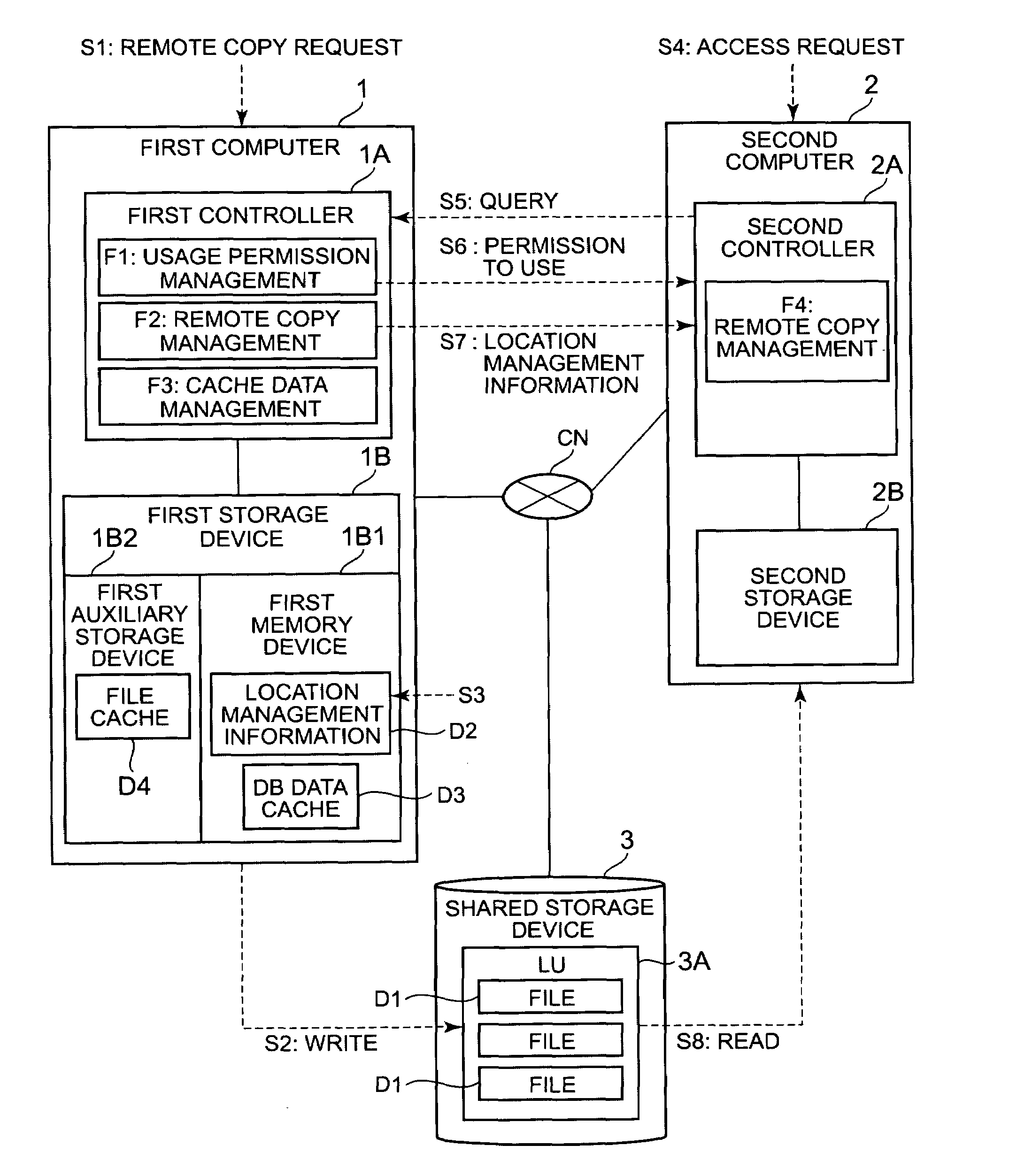
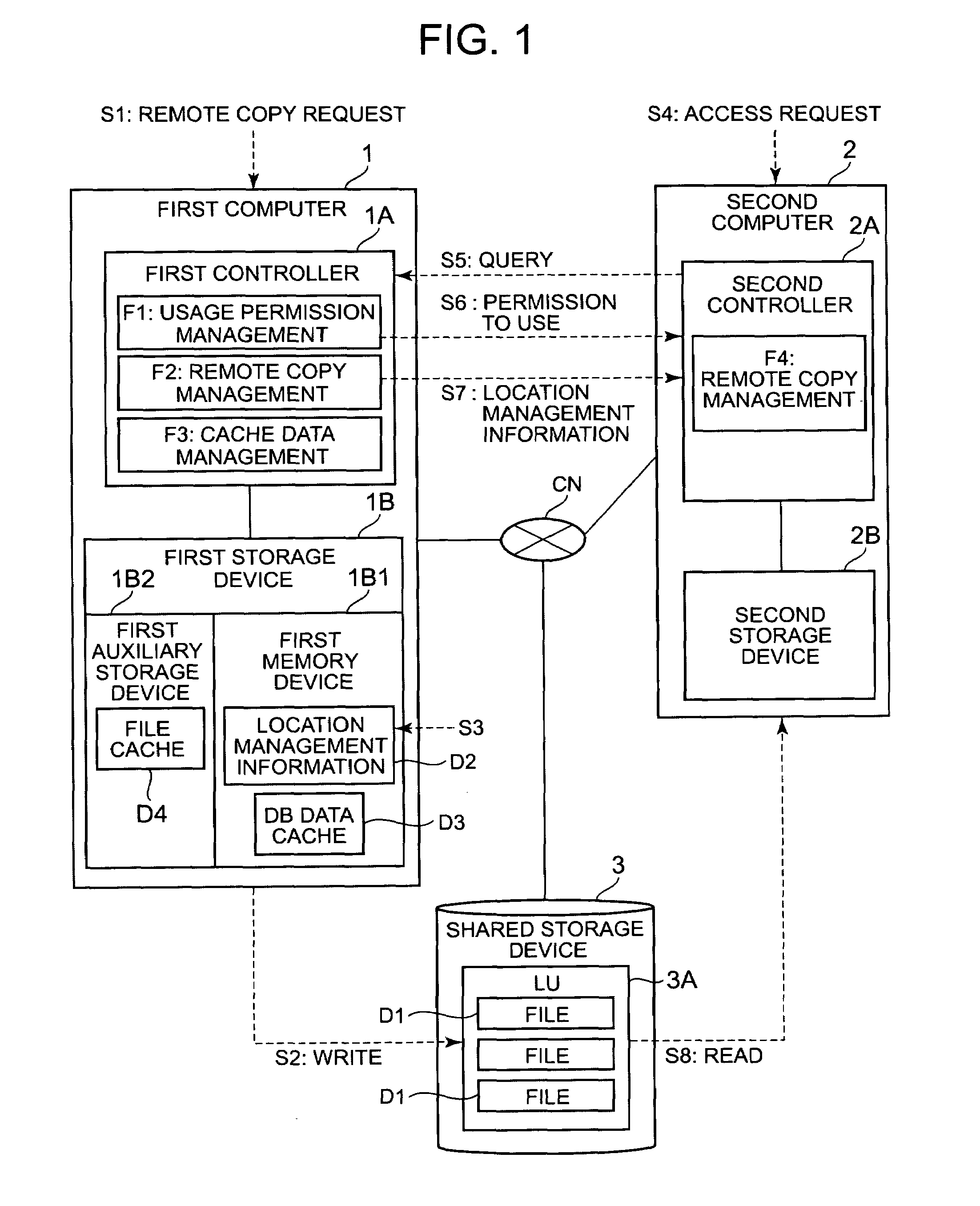
InactiveUS20090193207A1Preventing response performanceImprove responsivenessMemory loss protectionDigital computer detailsReplication methodComputerized system
In a computer system of the present invention, the logical volume of a network storage device can be exclusively shared by a plurality of computers. A first computer, upon receiving a remote copy request, writes a remote copy target file to a logical volume inside a shared storage device, and stores location management information showing the write-destination or the like of the file in a memory device. A second computer, upon receiving an access request, acquires the logical volume lock from the first computer. The second computer mounts the logical volume, and executes the desired processing. Furthermore, the second computer reads out the file from the logical volume based on the location management information.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
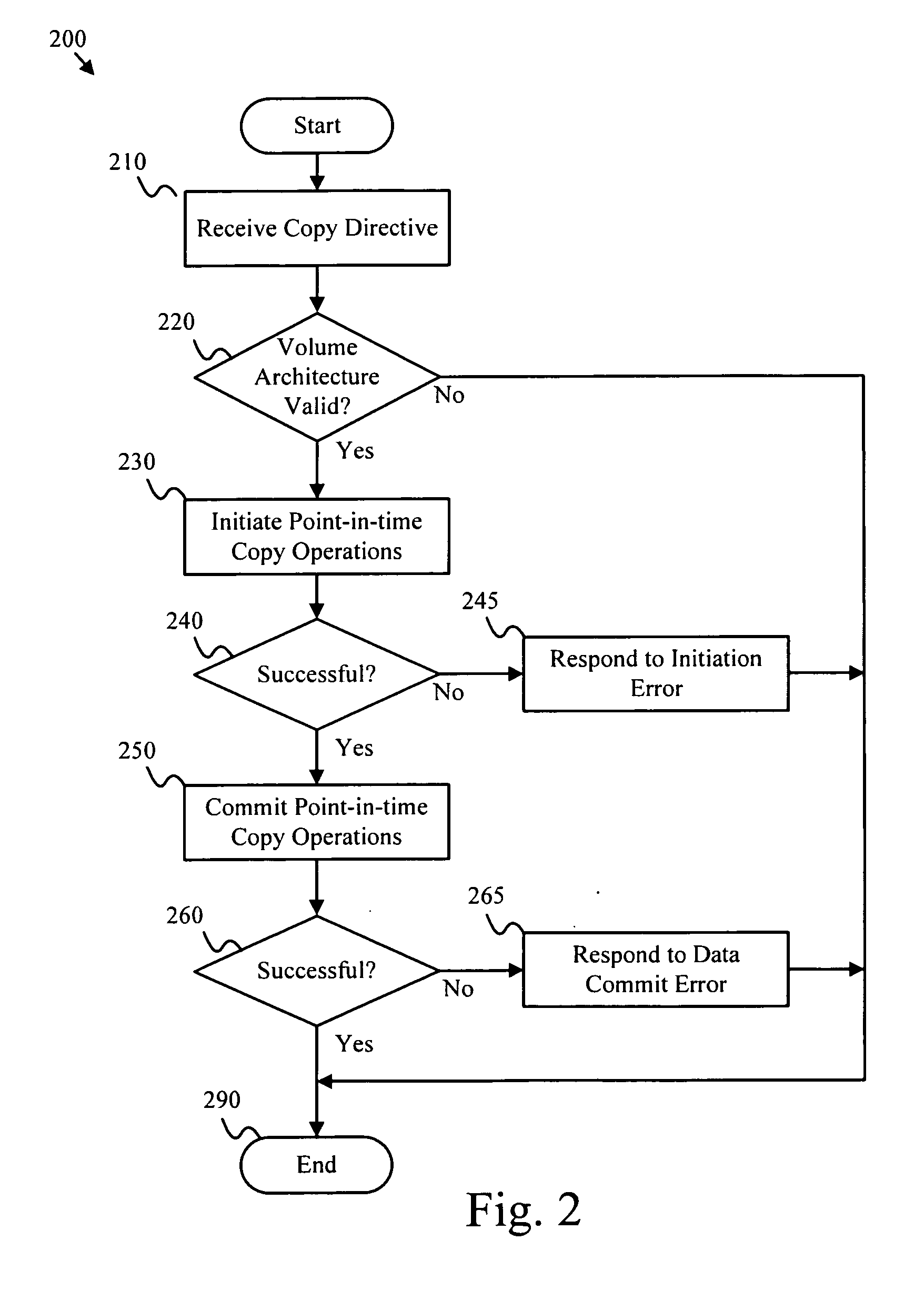
Point-in-time data replication method apparatus and system
InactiveUS20060182020A1Reduce complexityDigital data information retrievalError preventionData integrityData set
An apparatus, system, and method are disclosed for replicating point-in-time copies of local data to a remote site. The present invention mirrors point-in-time copy directives on the local data store to initiate a point-in-time copy operation on the remote copy of the local data, thereby efficiently providing remote access to a point-in-time copy of a dataset. Data integrity is ensured by committing local and remote point-in-time copy operations subsequent to successful initiation of both local and remote point-in-time copy operations. The present invention also, in one embodiment, rolls back a point-in-time copy operation in response to a failure to replicate the copy operation.
Owner:IBM CORP
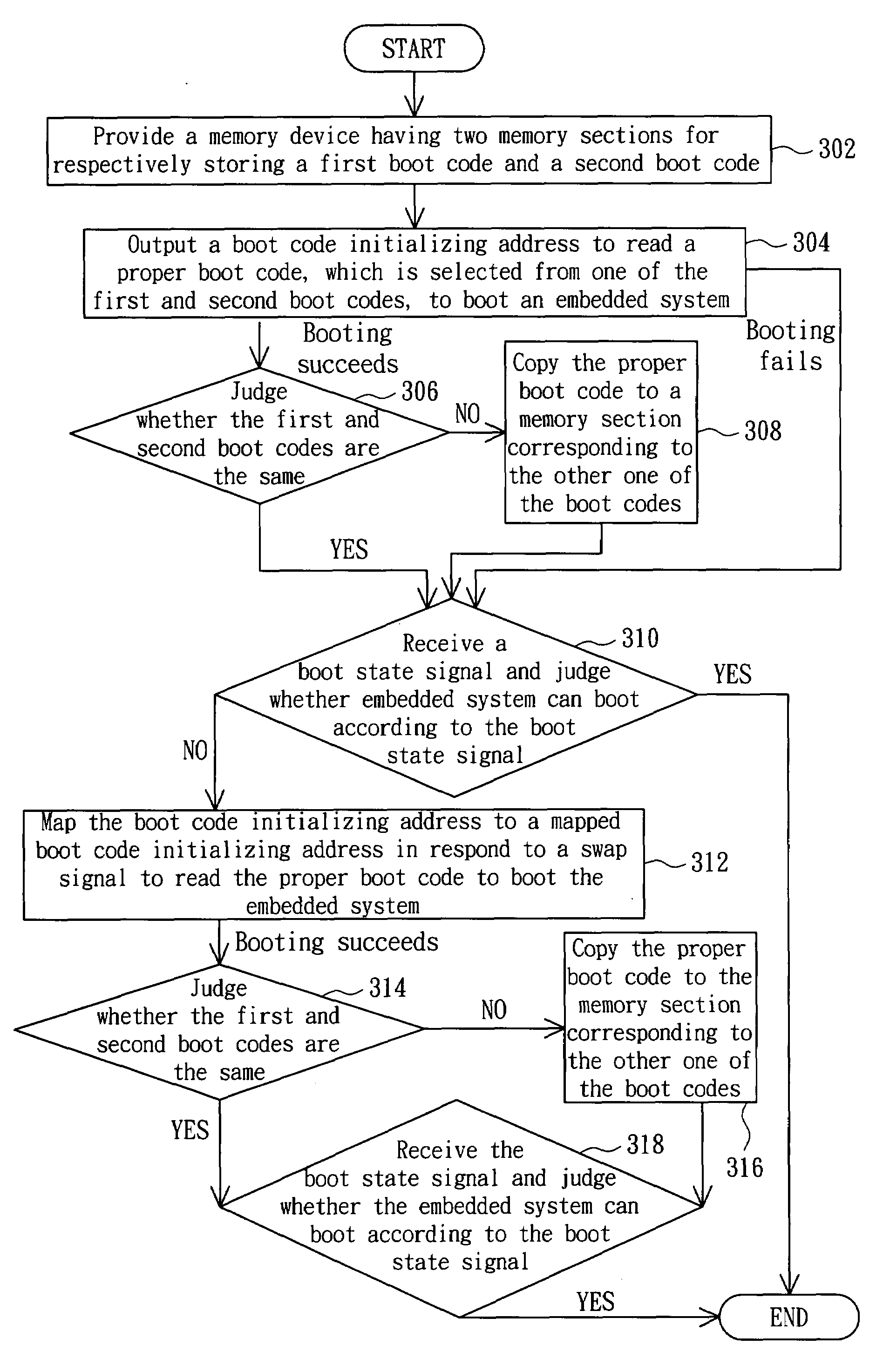
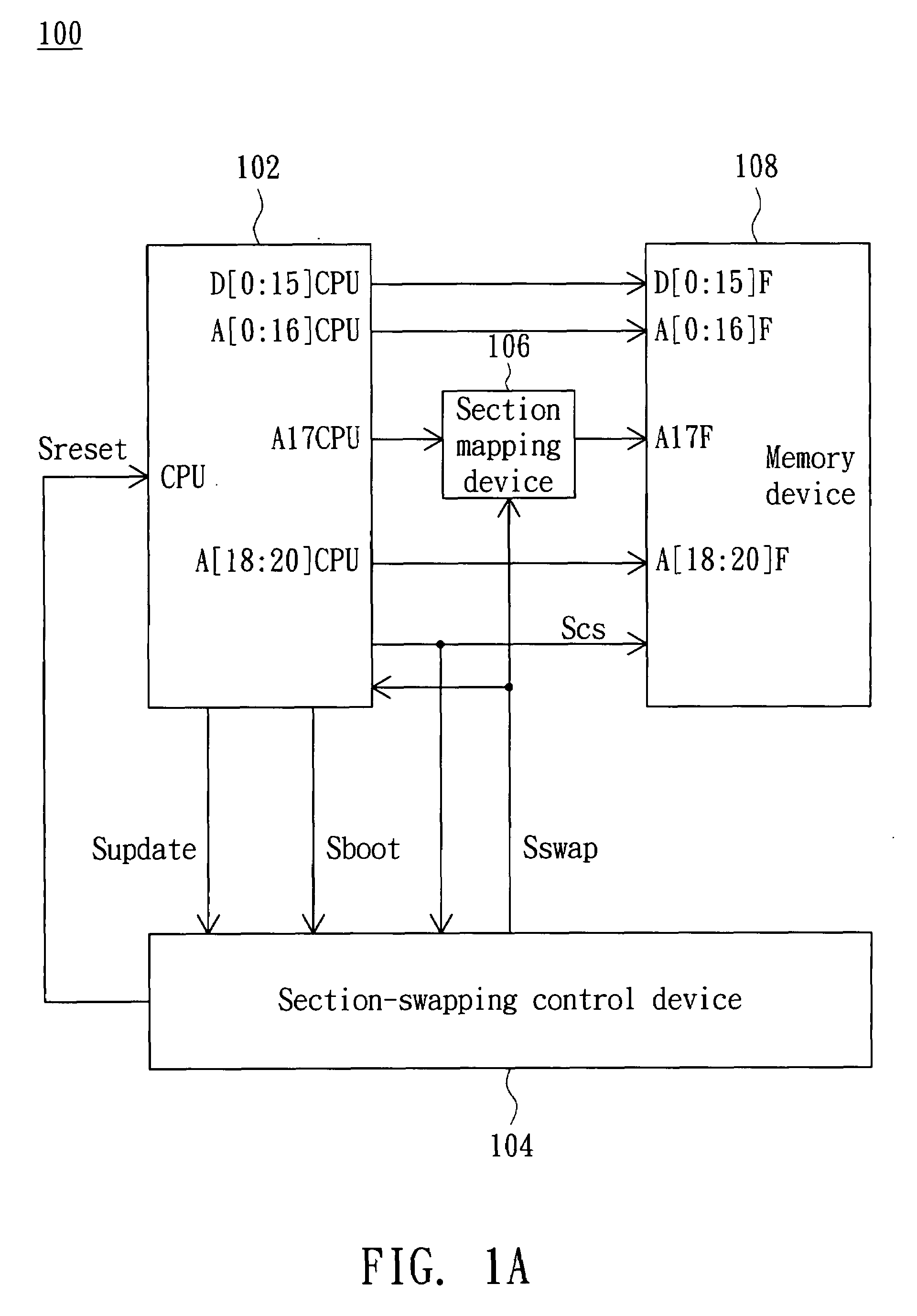
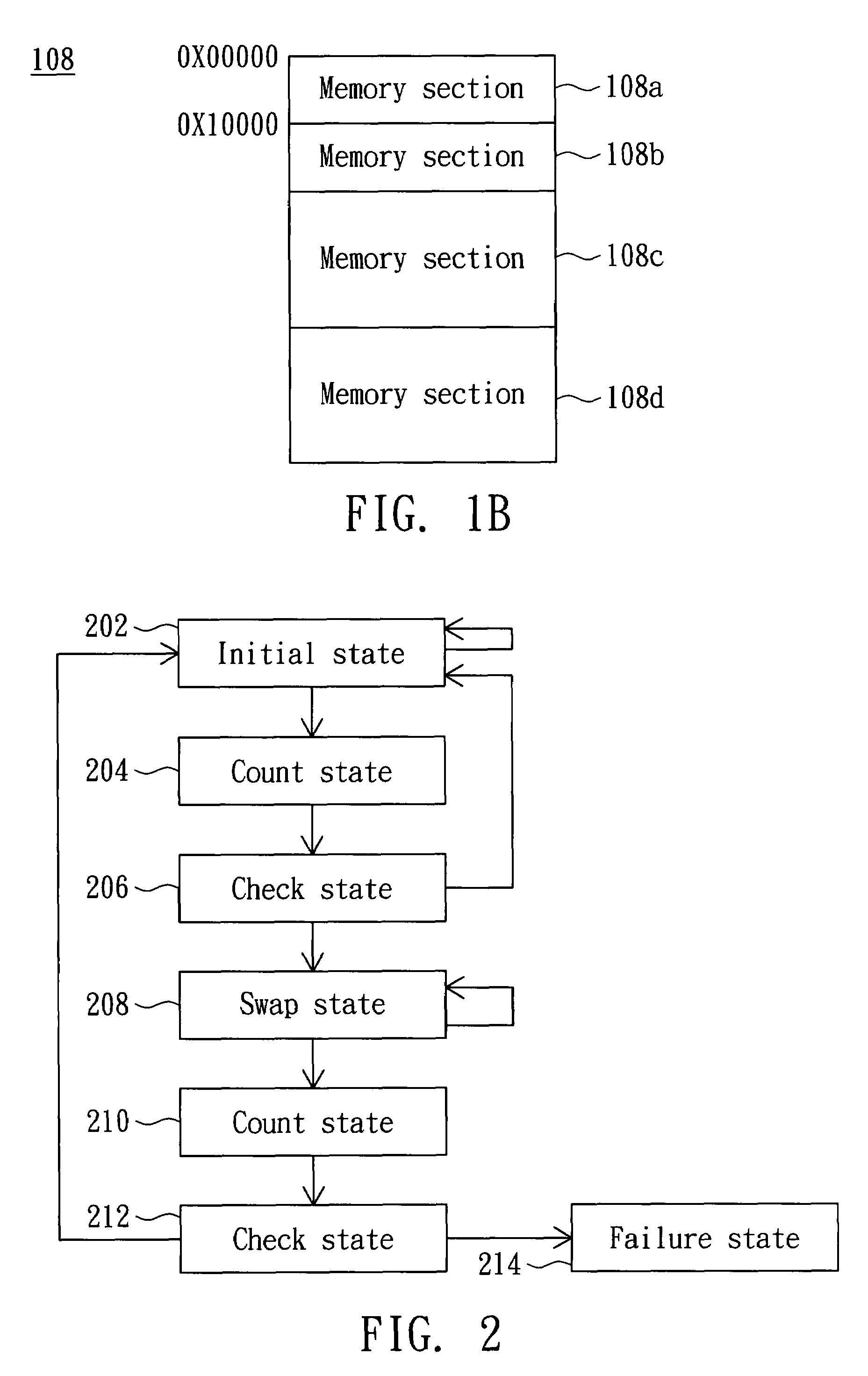
Embedded system and boot code auto-copy method thereof
InactiveUS20080040596A1Solve the real problemDigital computer detailsBootstrappingReplication methodControl equipment
An embedded system includes a CPU, a section-swapping control device, a memory device and a section mapping device. The CPU has a boot code initializing address. The section-swapping control device detects a boot condition of the CPU and thus outputs a swap signal. The memory device includes a first memory section and a second memory section for respectively storing a first boot code and a second boot code. The section mapping device is coupled to the CPU and the memory device. The section mapping device receives the swap signal and thus maps the boot code initializing address to an initial bit address of one of the first and second memory sections such that the CPU is booted according to one of the first and second boot codes.
Owner:QUANTA COMPUTER INC
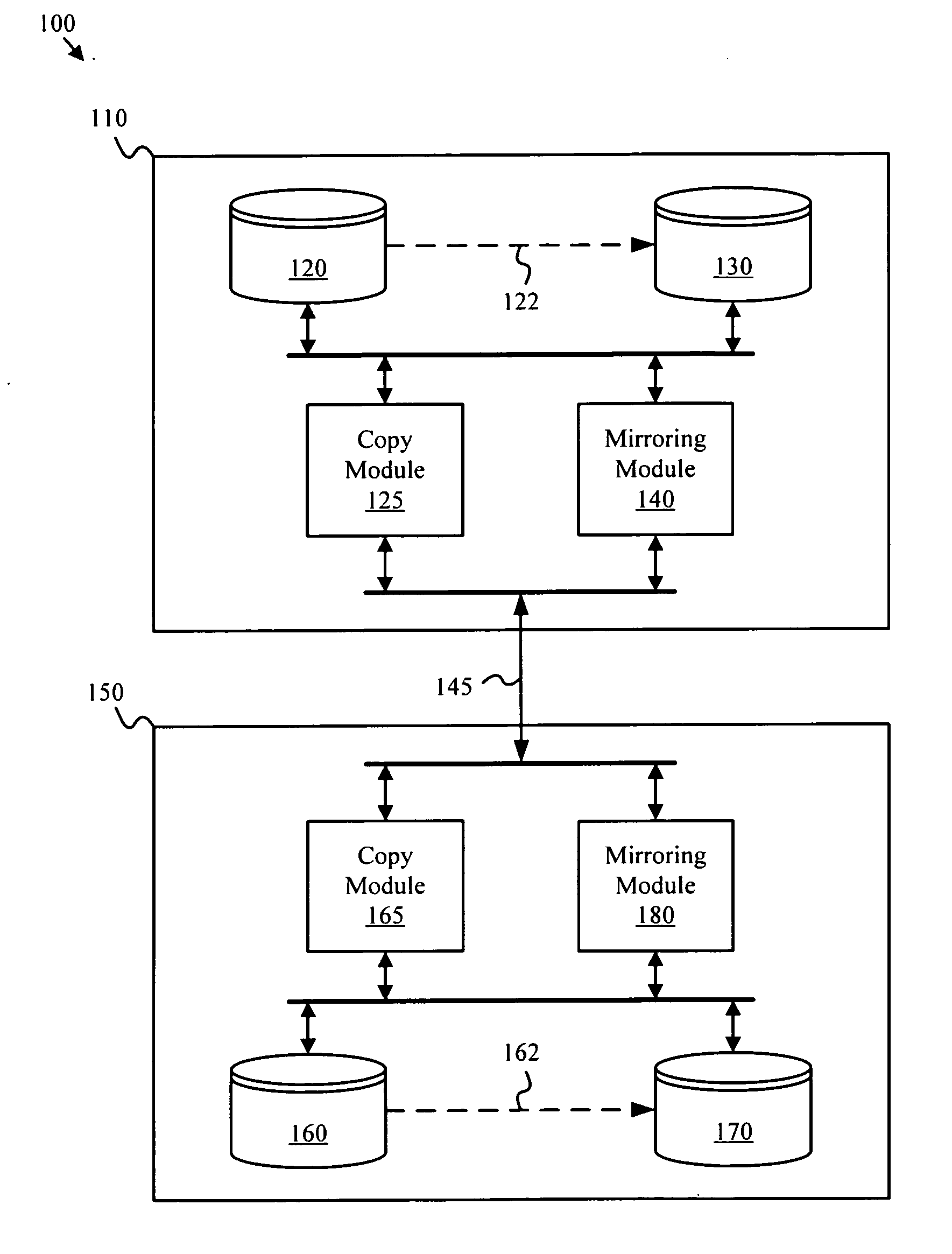
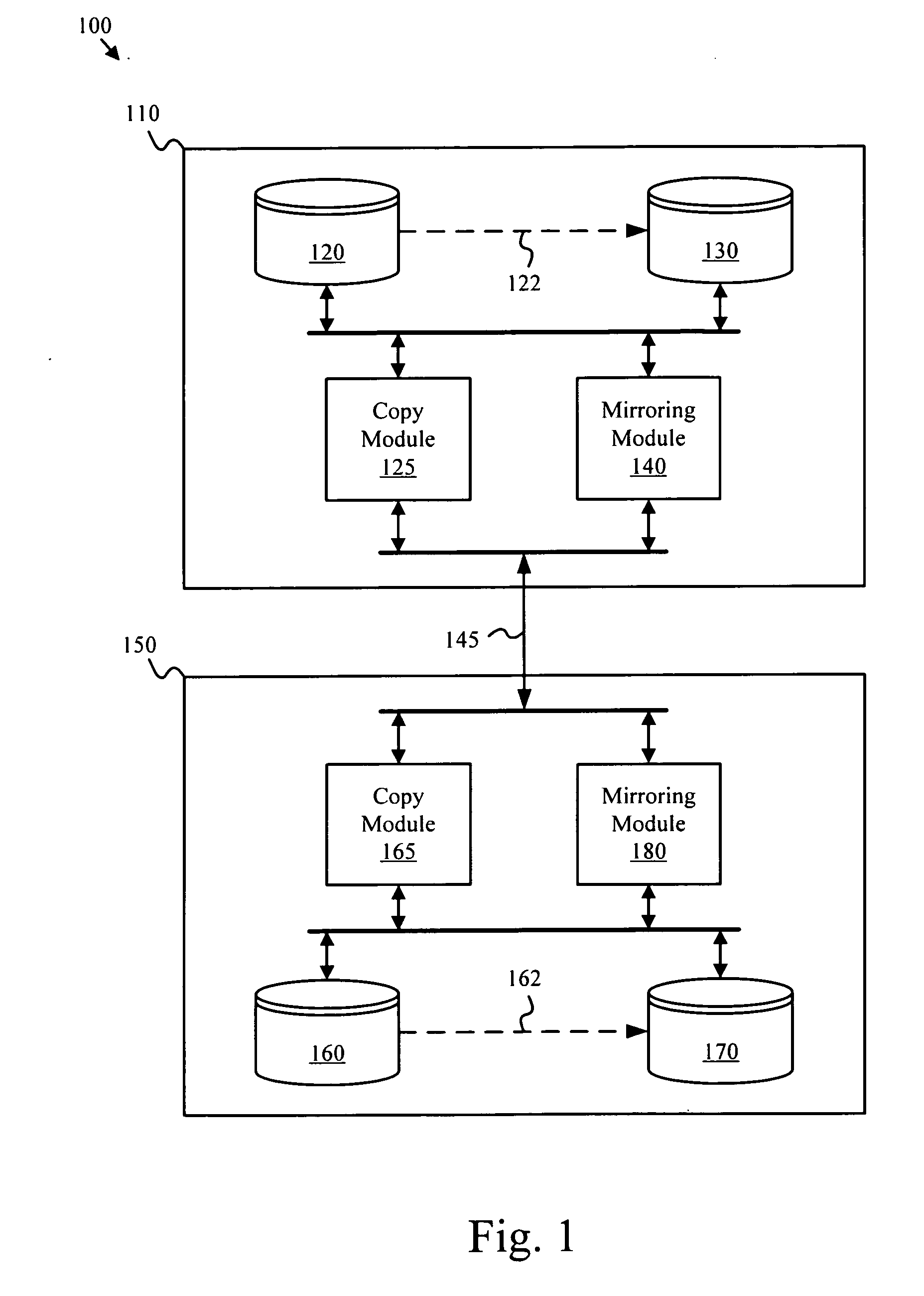
Hybrid data replication
ActiveUS20130159249A1Good flexibilityNegatively impacting performanceDigital data processing detailsError detection/correctionReplication methodData mining
System, method, computer program product embodiments and combinations and sub-combinations thereof for hybrid data replication are described. Aspects include identifying a type of database data replication, the type including a combination of replication approaches, and managing replication based on the identified type, including coordinated switching from one replication approach to another automatically with transactional consistency maintained among source and target databases.
Owner:SYBASE INC
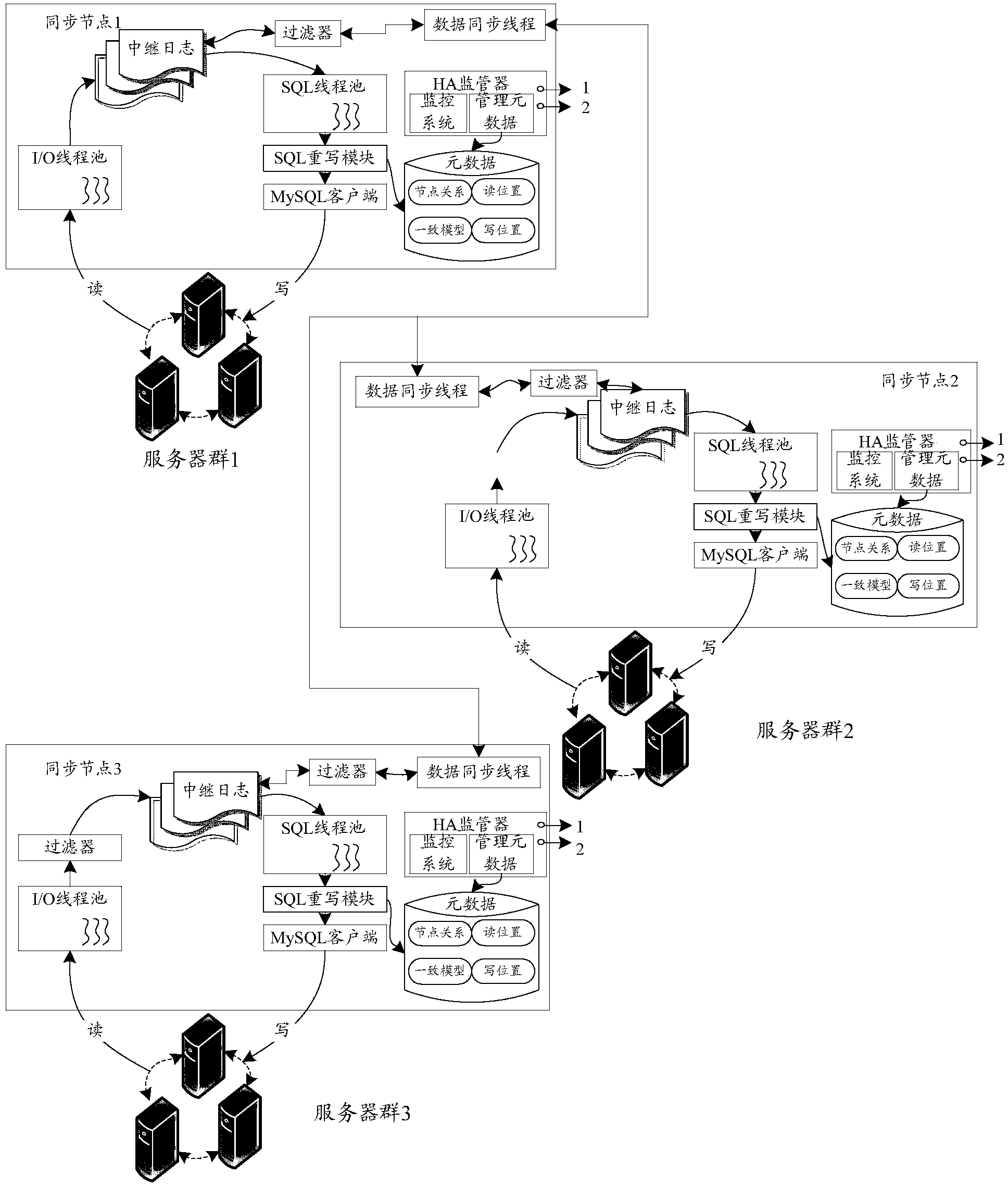
Data replication method and device
ActiveCN103560906AImplement data replicationImprove fault toleranceData switching networksTraffic capacityFault tolerance
The invention discloses a data replication method and device and belongs to the field of data processing. The method comprises the steps that log events with updated data recorded are obtained from one or more servers from a local replication group; the obtained log events are stored in relay logs in the local replication group; the version number of each relay log of the local replication group is updated, relay logs of the other replication groups and the version number of each relay log of the other replication groups are obtained, and log events with updated data recorded are obtained from one or more servers from the other replication groups and stored in the relay logs of the other replication groups; according to the version number of each relay log, relay logs are selected from the relay logs of the local replication group and from the relay logs of the other replication groups according to the version number of each relay log, and the data of one or more servers of the local replication group are updated according to the selected relay logs. The data replication method and device can reduce transmission frequency of the log events and network flow, and achieves high availability and high fault tolerance of the data and services.
Owner:珠海多玩信息技术有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com